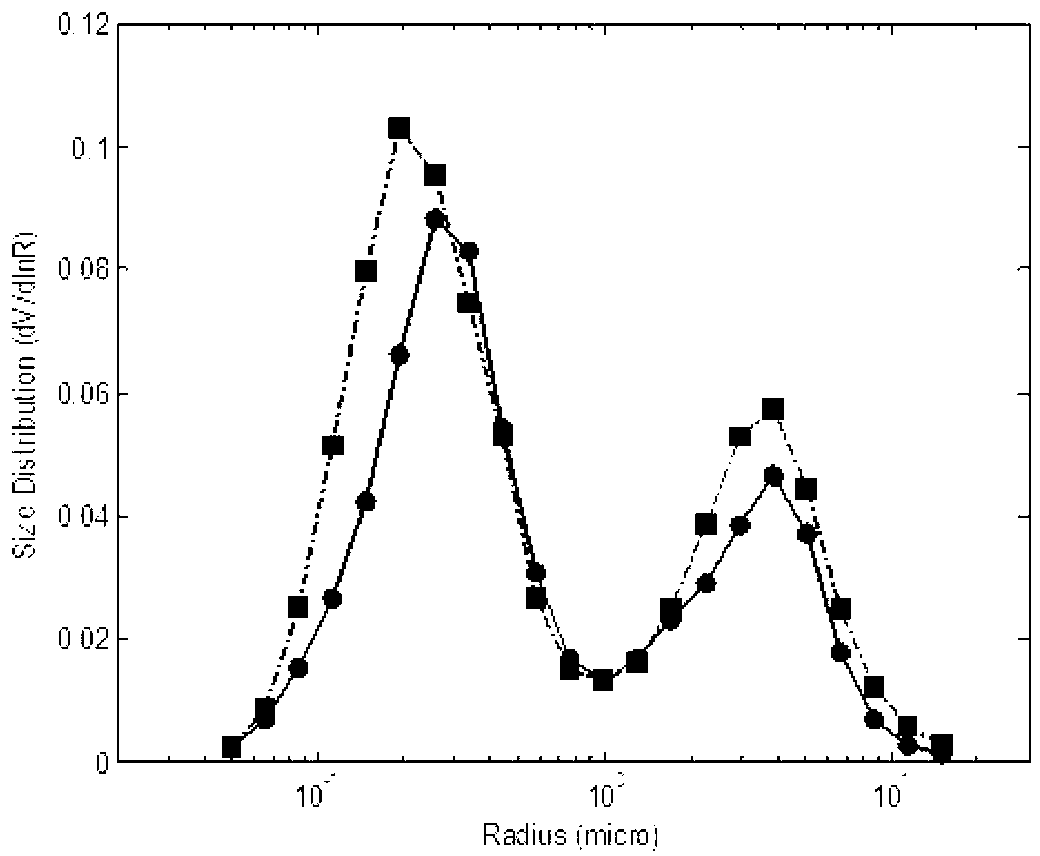
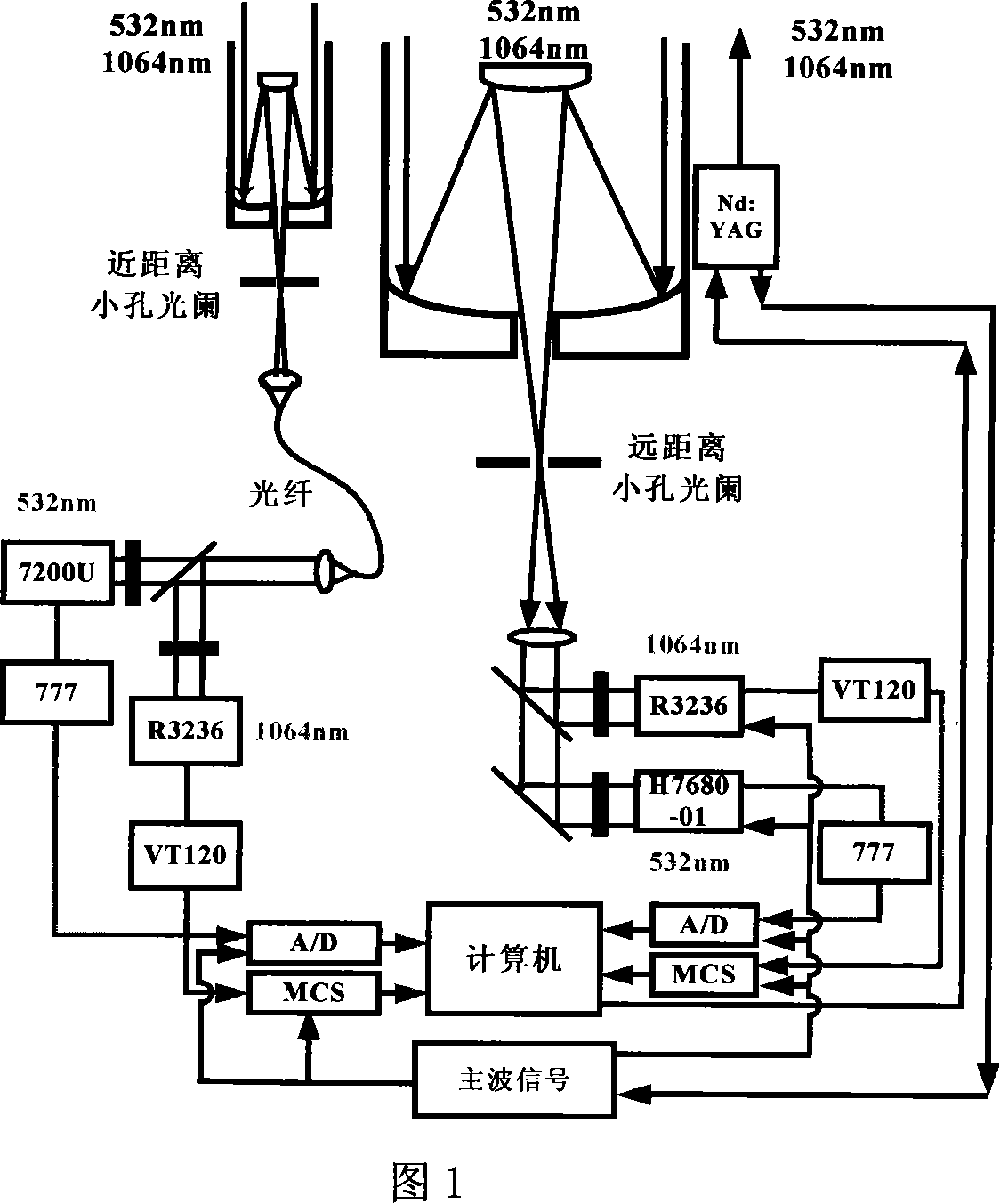
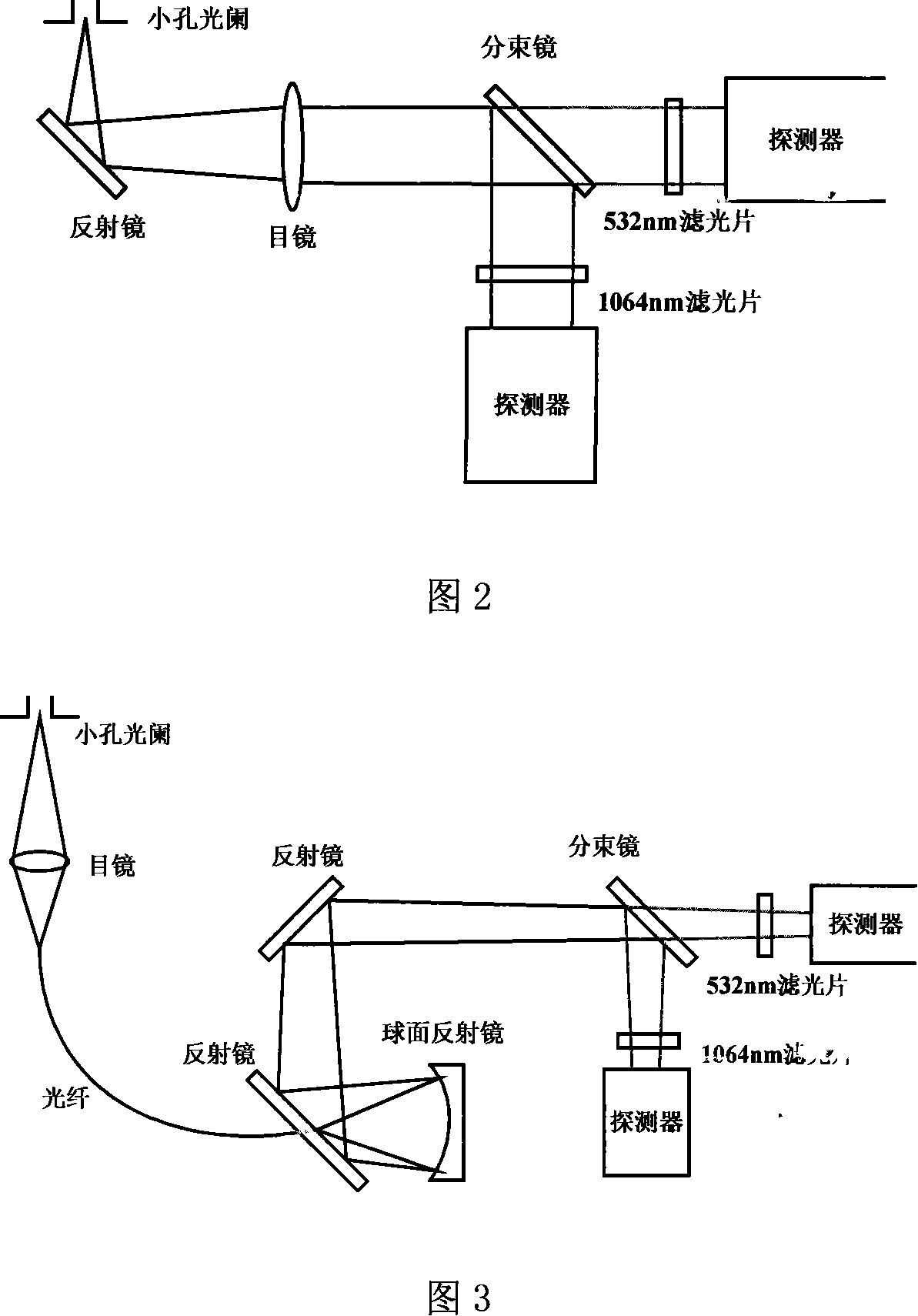
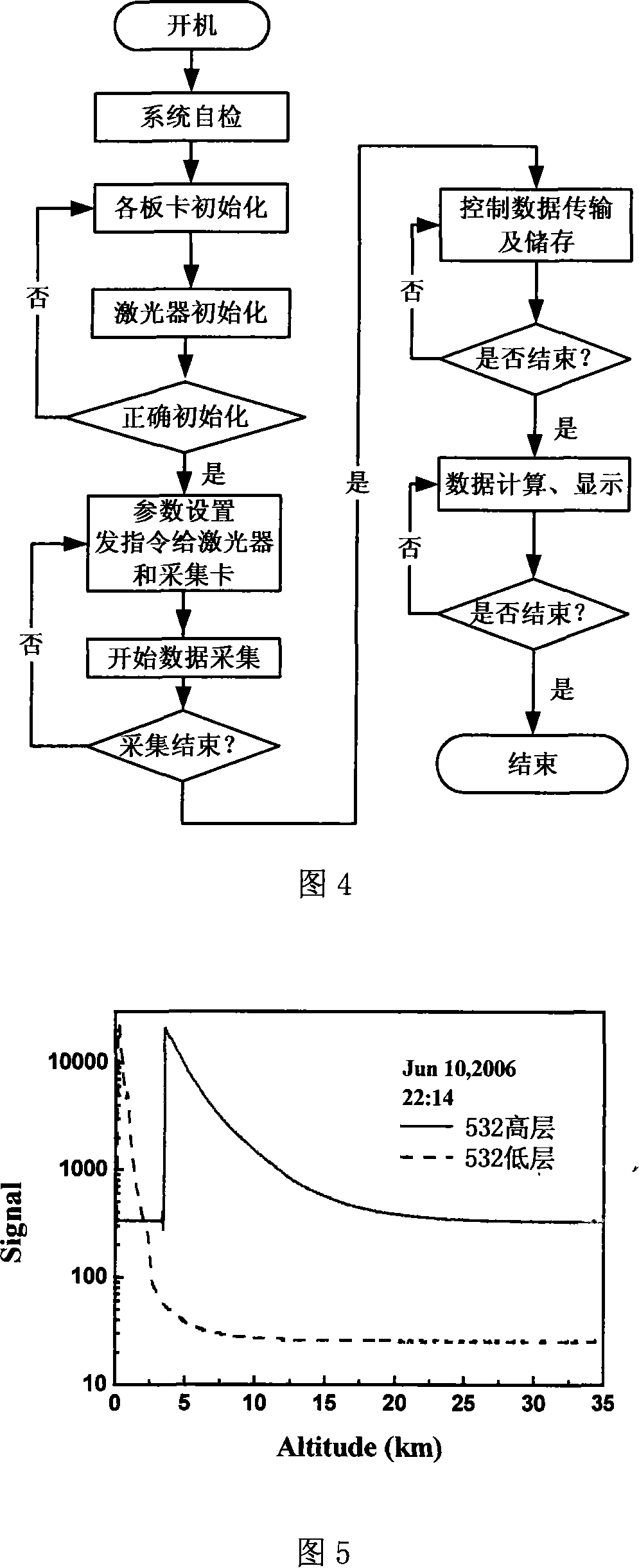
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
184 results about "Mie scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
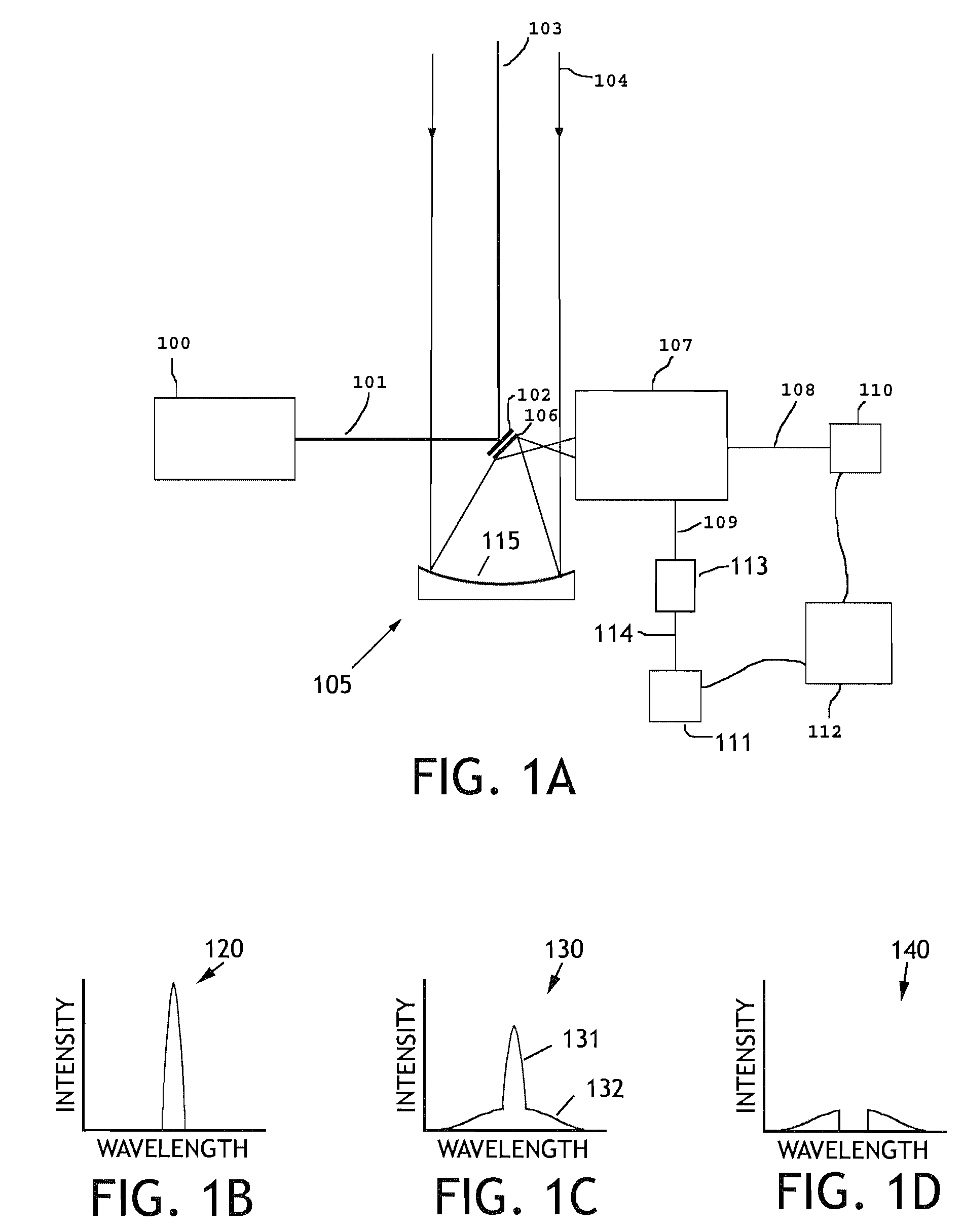
The Mie solution to Maxwell's equations (also known as the Lorenz–Mie solution, the Lorenz–Mie–Debye solution or Mie scattering) describes the scattering of an electromagnetic plane wave by a homogeneous sphere. The solution takes the form of an infinite series of spherical multipole partial waves. It is named after Gustav Mie.
System and method for detecting and classifying biological particles
InactiveUS6885440B2Chemiluminescene/bioluminescenceScattering properties measurementsHarmonicBiological particles
A continuous wave laser excites a biological particle. Detection channels are created to detect light scattered by the biological particle, and to detect any auto-fluorescence emitted by the biological particle. Additional channels can also detect light emitted by auto-fluorescence of the biological particle when simultaneously excited by light at harmonics of the laser's fundamental wavelength. The biological particle is identified using Mie scattering and auto-fluorescence. Ratio-metric calculations generated by calculating ratios of detected peak heights or integrated pulse values in the channels provides additional information for identifying and classifying the biological particle. A warning or alert can be provided if the identified biological particle is a particle of interest.
Owner:UNKNOWN +1
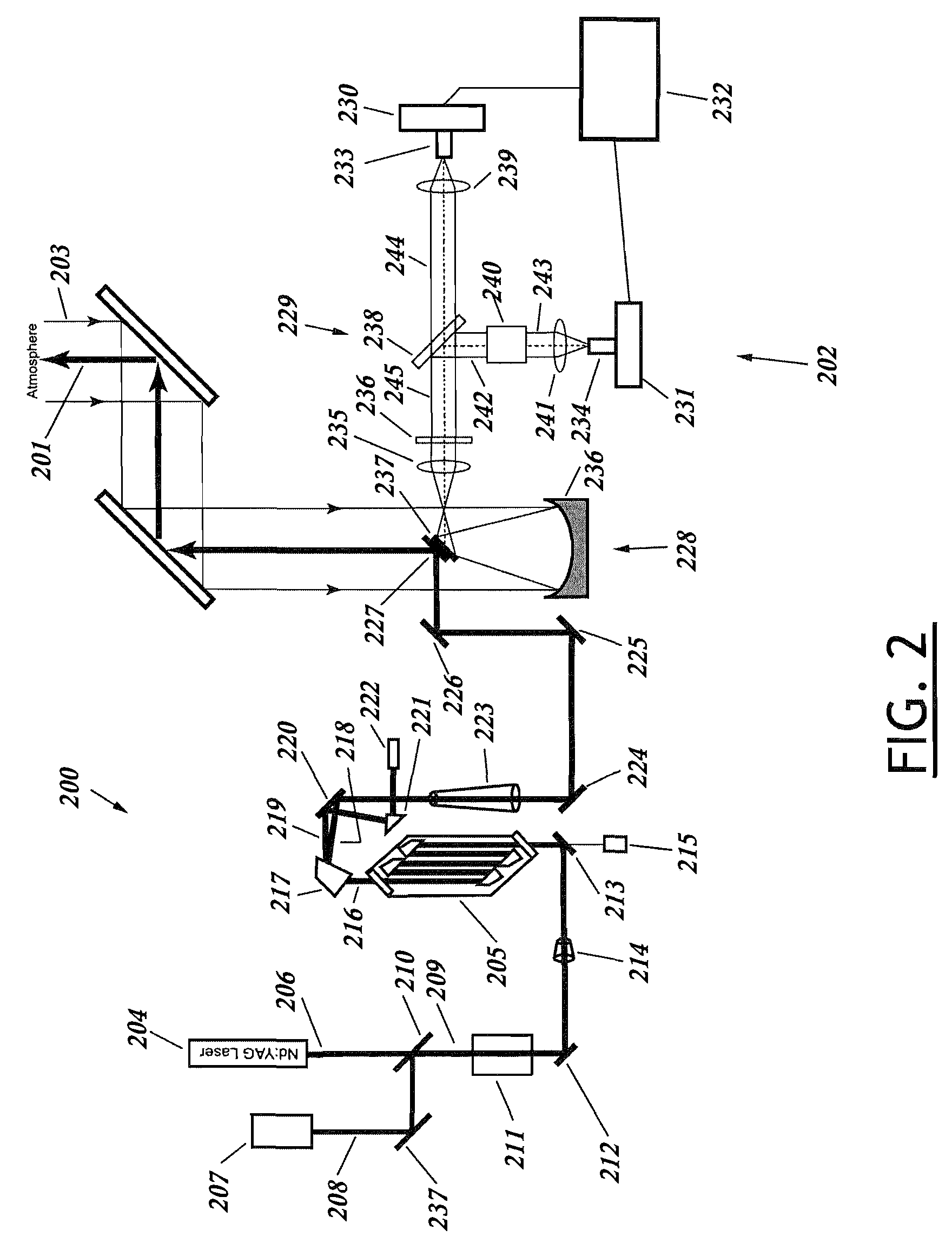
Lidar system for remote determination of calibrated, absolute aerosol backscatter coefficients
ActiveUS7656526B1Effort directedSafely and quickly and efficiently identifyRaman scatteringParticle size analysisBeam splitterAerosol backscatter
A lidar system capable of remotely identifying calibrated absolute aerosol backscatter coefficients of atmospheric aerosol particles by transmitting a beam of light and spectrally separating the intensity of Rayleigh and Mie backscattering is disclosed. The transmitter features high pulse energy to generate sufficient Rayleigh backscattering, enabling atmospheric scanning in a timely manner. The transmitter employs a seeded Nd:YAG laser and a seeded stimulated Raman scattering wavelength shifter to achieve narrow bandwidth, eye-safe laser pulses. The receiver employs a telescope, collimating lens, beam splitter, molecular absorption filter, focusing lenses, and avalanche photodiodes. Mie backscattering is blocked by the molecular absorption filter to provide a Rayleigh signal, which is used with knowledge of atmospheric density to calibrate the Mie signal. The system is intended for atmospheric research and aerosol monitoring applications where calibrated Mie scattering intensity is necessary to measure the optical depths of aerosol structures such as plumes, clouds, and layers.
Owner:UNIV FOR ATMOSPHERIC RES
Feedback mechanism for smart nozzles and nebulizers
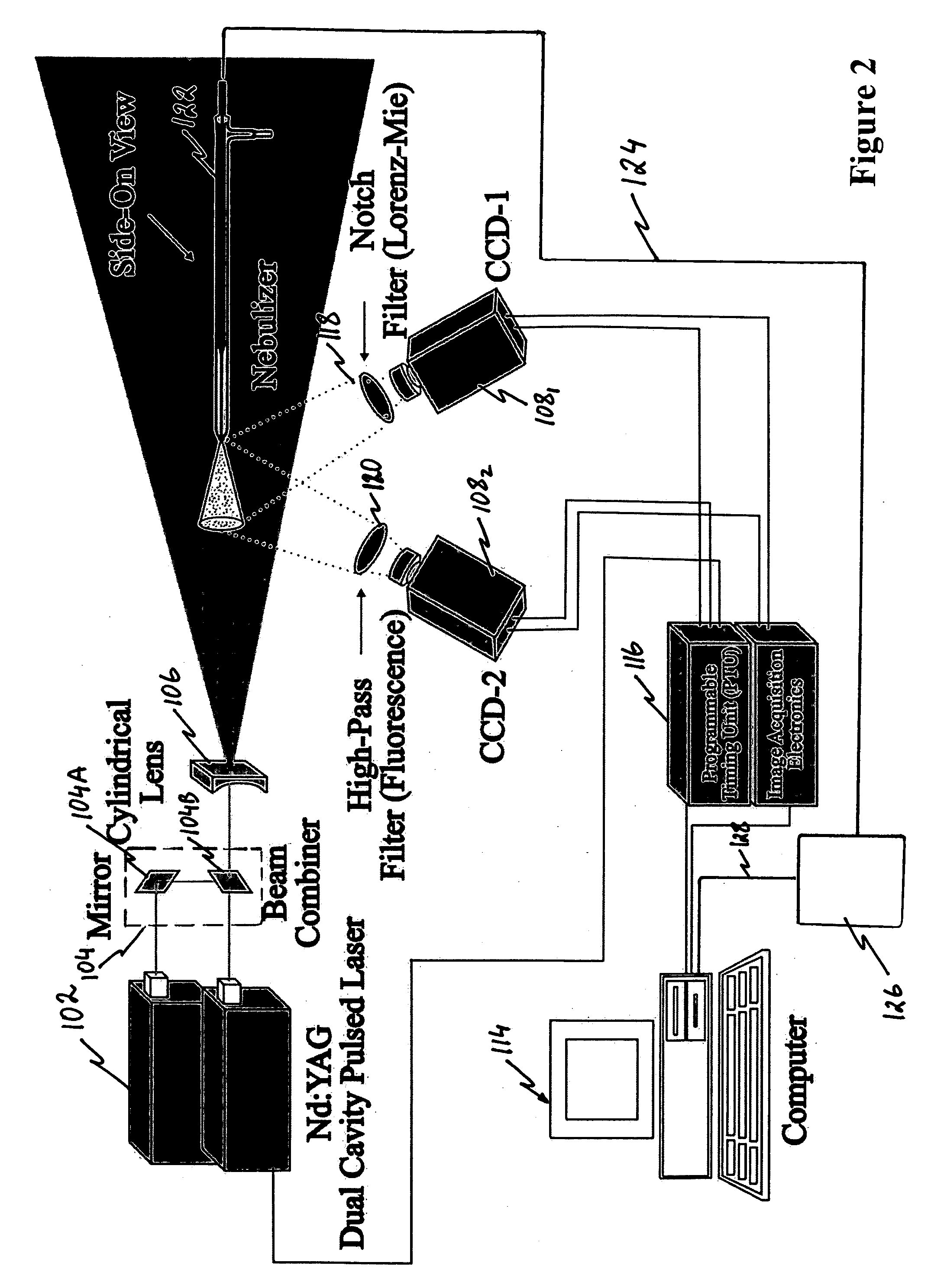
ActiveUS20070299561A1Reduce the amount requiredImprove performanceSelf-acting watering devicesWatering devicesFluorescenceLaser light
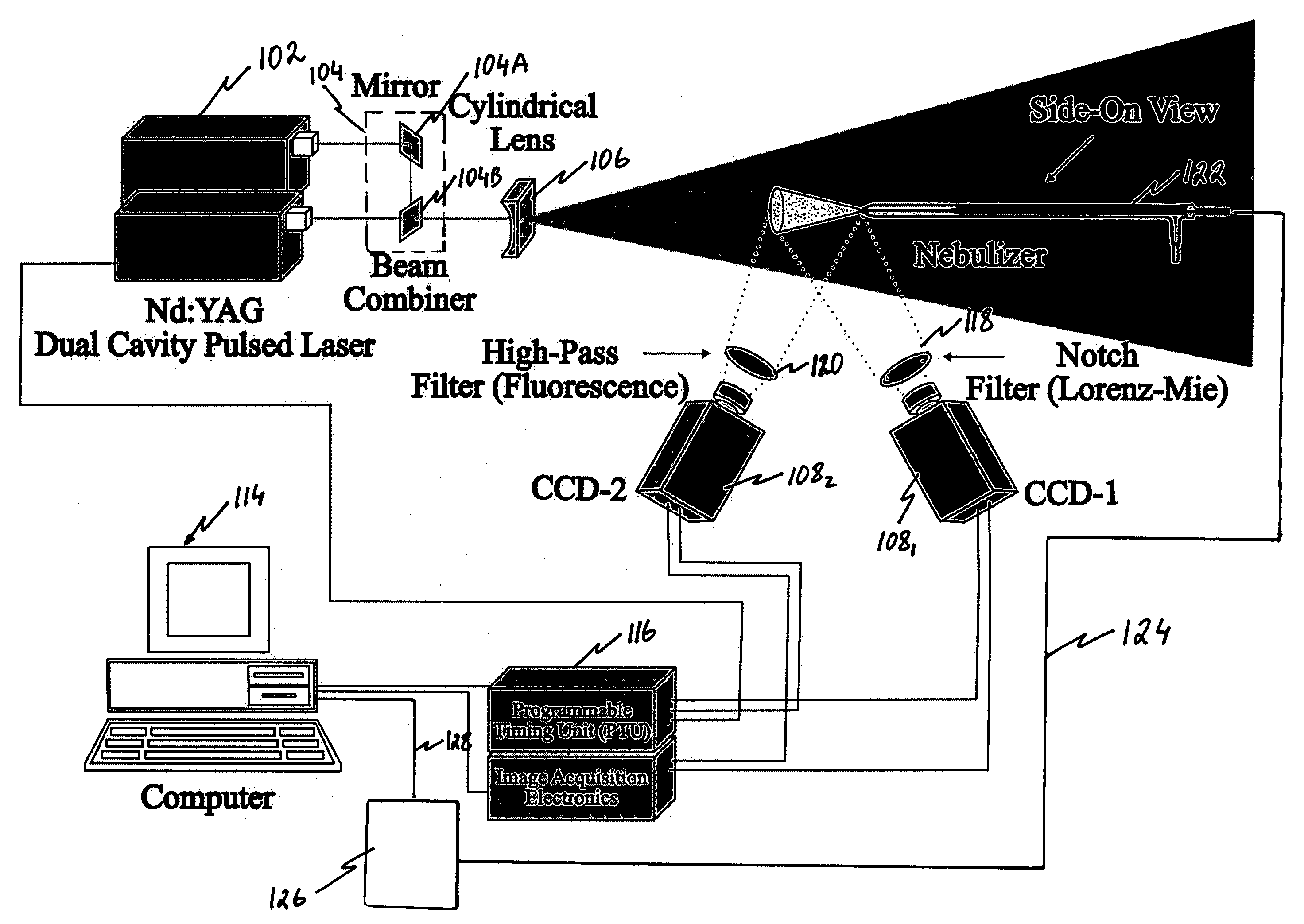
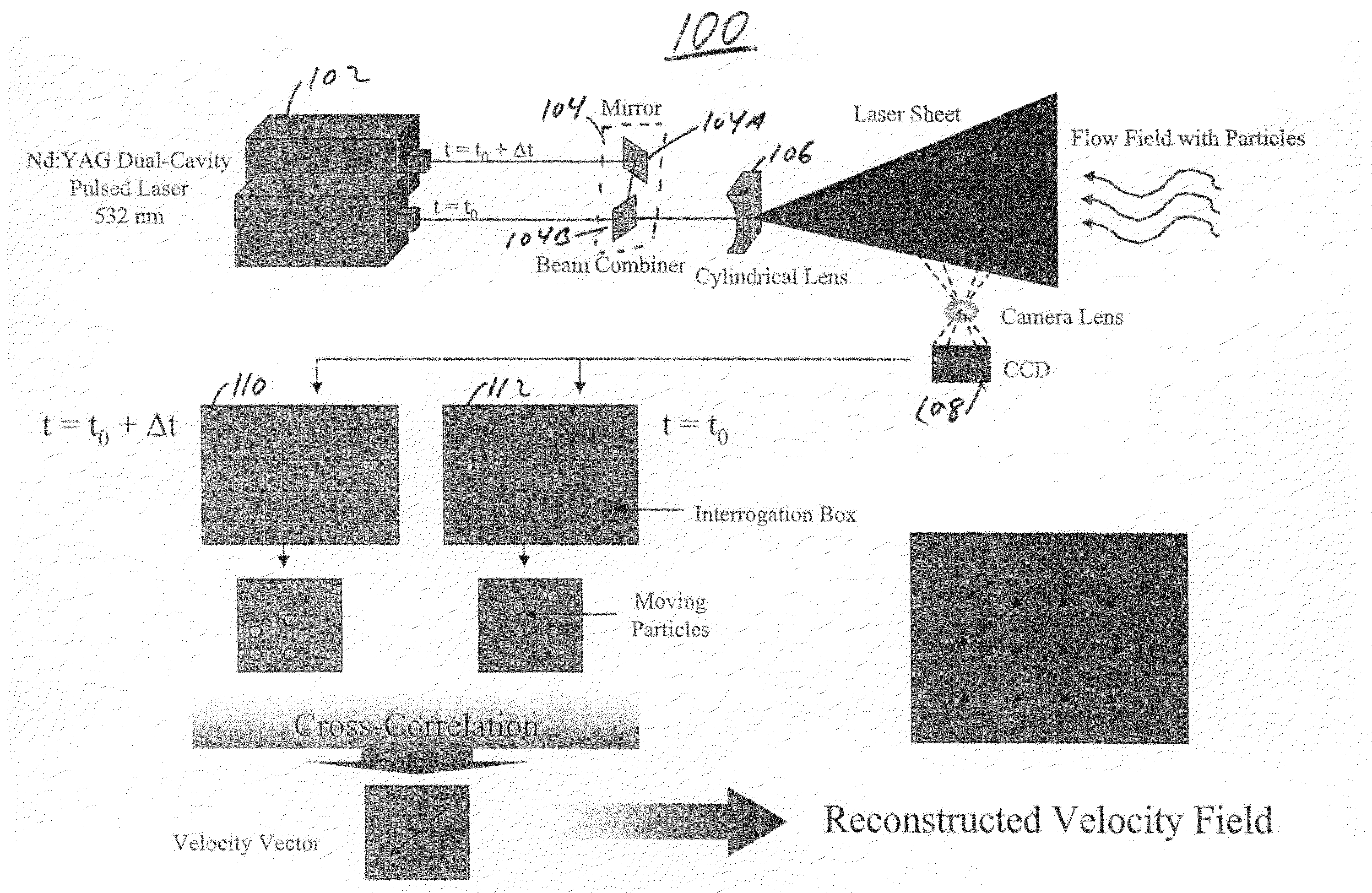
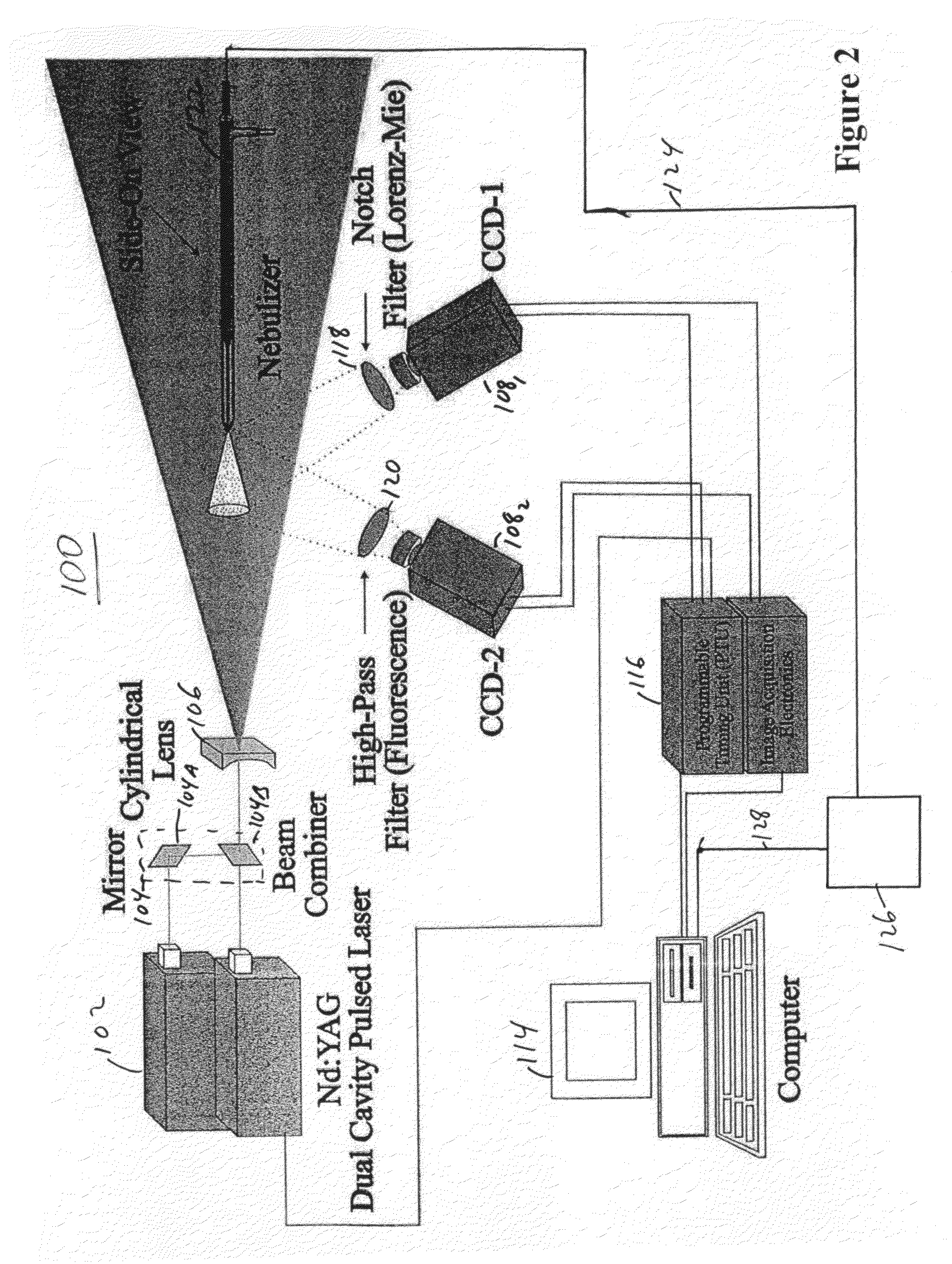
Nozzles and nebulizers that can be adjusted to produce an aerosol with optimum and reproducible quality based on the feedback information obtained using laser imaging techniques are provides. Two laser-based imaging techniques based on particle image velocimetry (PIV) and optical patternation are provided to map and contrast the size and velocity distributions for indirect and direct pneumatic nebulizations in plasma spectrometry. The flow field of droplets is illuminated by two pulses from a thin laser sheet with a known time difference. The scattering of the laser light from droplets is captured by a charge coupled device (CCD), providing two instantaneous images of the particles. Pointwise cross-correlation of the corresponding images yields a two-dimensional (2-D) velocity map of the aerosol velocity field. For droplet size distribution studies, the solution is doped with a fluorescent dye and both laser induced florescence (LIF) and Mie scattering images are captured simultaneously by two CCDs with the same field of view. The ratio of the LIF / Mie images provides relative droplet size information, which is then scaled by a point calibration method via a phase Doppler particle analyzer (PDPA). Two major outcomes are realized for three nebulization systems: 1) a direct injection high efficiency nebulizer (DIHEN); 2) a large-bore DIHEN (LB-DIHEN); and 3) a PFA microflow nebulizer with a PFA Scott-type spray chamber. First, the central region of the aerosol cone from the direct injection nebulizers and the nebulizer-spray chamber arrangement comprise fast (>13 m / s and >8 m / s, respectively) and fine (<10 μm and <5 μm, respectively) droplets as compared to slow (<4 m / s) and large (>25 μm) droplets in the fringes. Second, the spray chamber acts as a momentum separator, rather than a droplet size selector, as it removes droplets having larger sizes or velocities. Smart-tunable nebulizers may utilize the measured momentum as a feedback control for adjusting certain operation properties of the nebulizer, such as operating conditions and / or critical dimensions.
Optoelectronic device encapsulant
InactiveUS6356686B1Preventing interfering accumulationAvoid wear and tearCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideEpoxyParticulates
An optically clear encapsulant for optoelectronic packages exhibits a suitably high viscosity both to replace a silicon nitride passivation layer required on a VCSEL die and to fill a gap between the die and an optical coupler, preventing light signal degradation. The encapsulant exhibits optical transparency to light having a wavelength of about 850 nanometers (nm) with substantially no Mie scattering since particulate fillers are not required to modulate viscosity in the encapsulant. Also, the encapsulant further seals wire bonds between the die and a cable header to prevent abrasive wear. The gap-filling encapsulant is particularly suitable for use with vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) technology. The encapsulant includes prior to curing, a difunctional acrylate epoxy resin exhibiting pseudoplastic flow and a viscosity of greater than about 0.7x106 centipoise. Accordingly, a method of manufacturing an optical subassembly may eliminate a separate passivation step and instead fill the gap between the die and optical coupler with an optically clear encapsulant.
Owner:IBM CORP
Detection method and laser radar of Raman-Mie scattering laser atmospheric signal
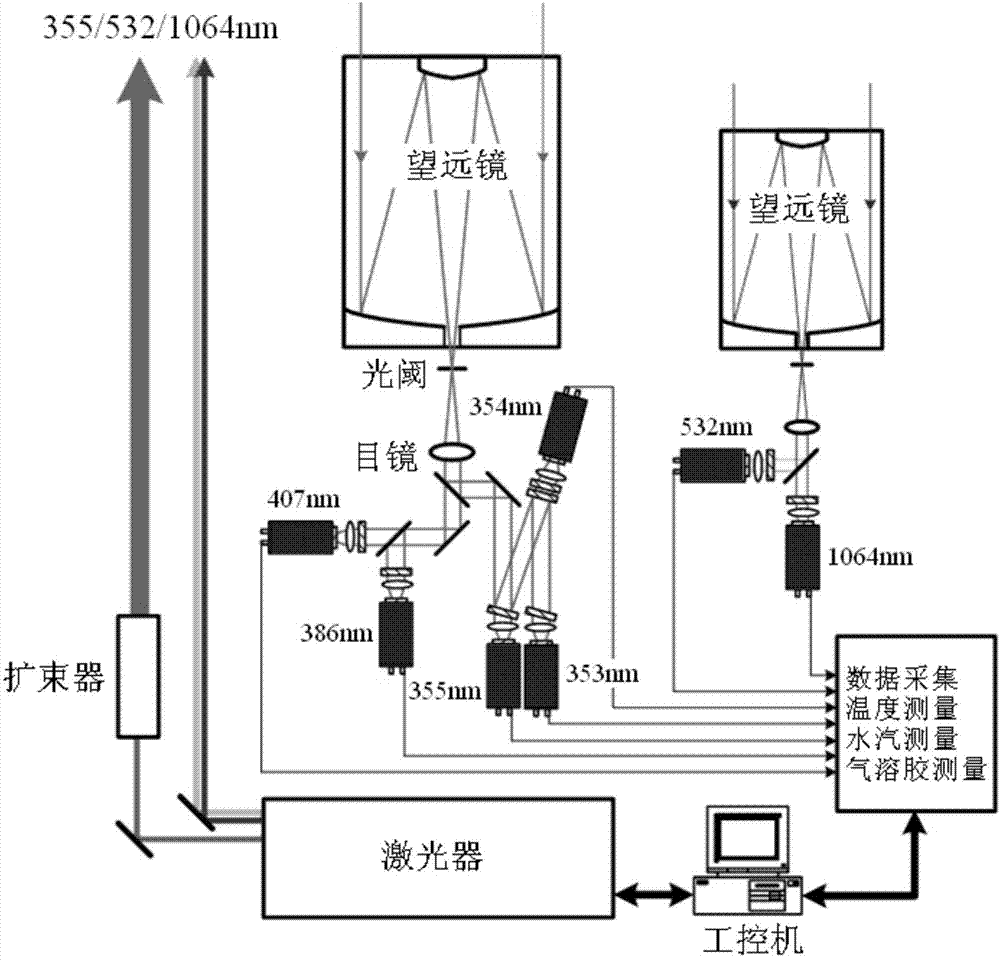
InactiveCN1657972ARealize continuous observationRealize measurementElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationEyepieceTropospheric aerosol
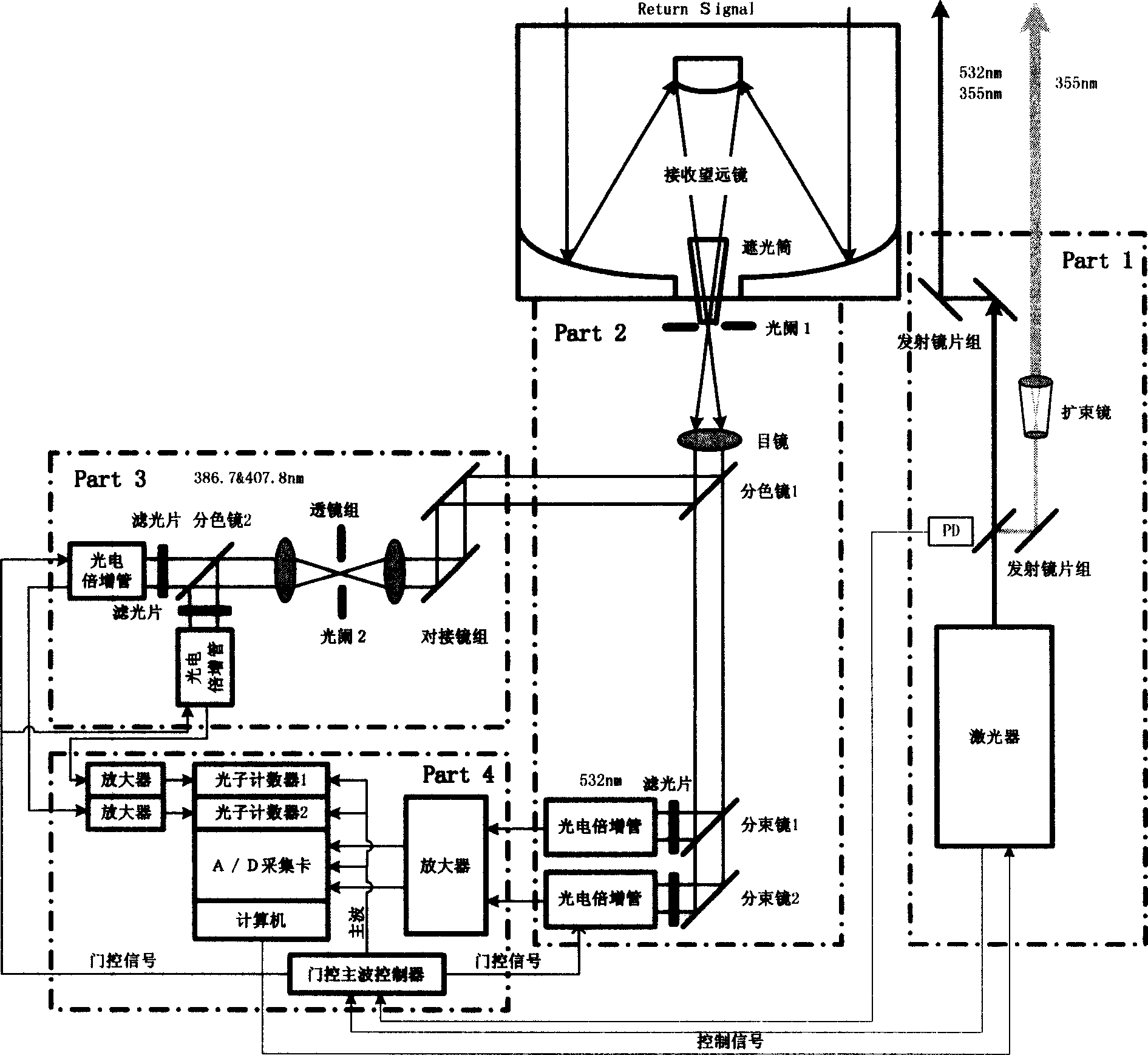
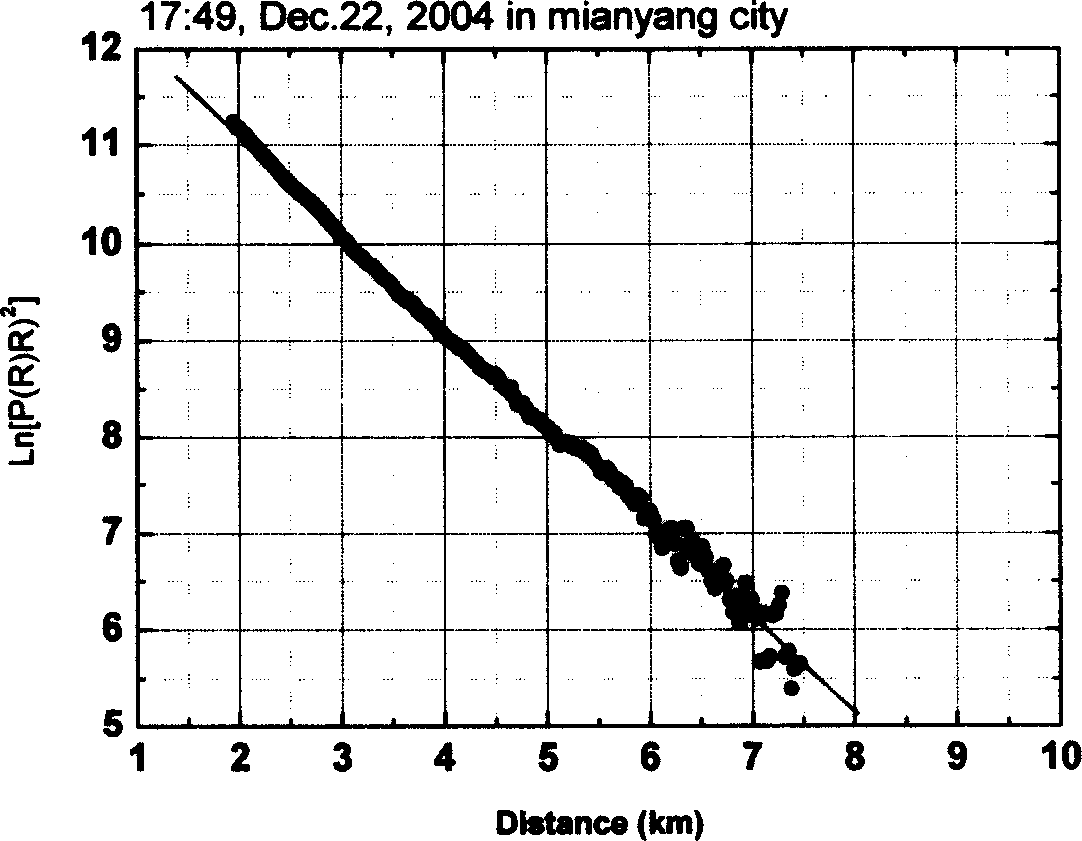
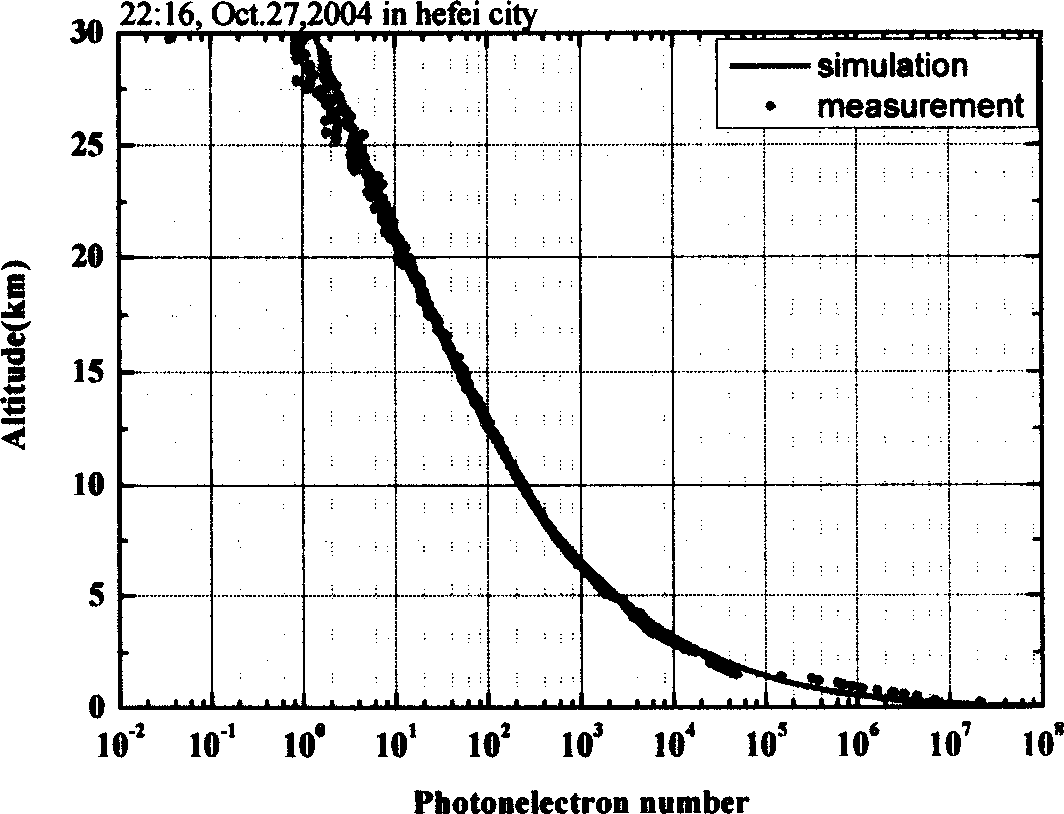
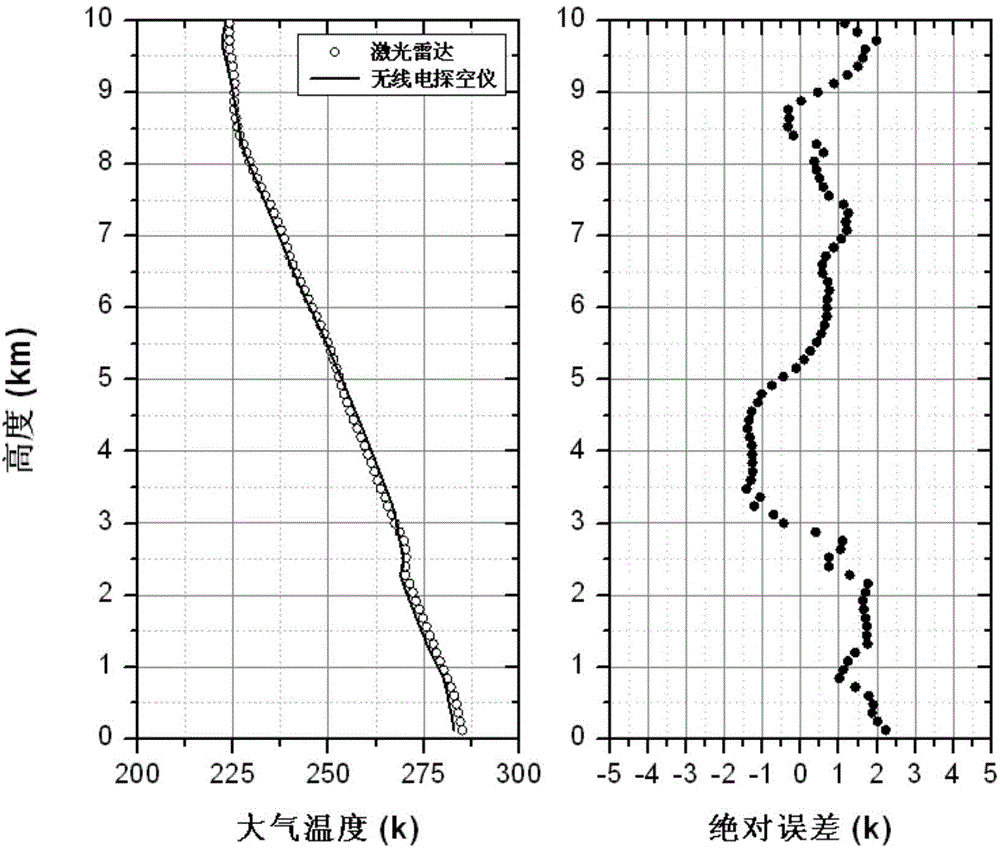
This invention is a detecting of Roman-Mie dispersion laser atmosphere signal and laser radar. It sets up the radar with the output of double-frequency 532nm and triple-frequency 355nm, launches the 532nm, 15% of the 35nm to the sky and 85% of the 355nm after diffusion, and the two optical paths parallel with the optical path of the receiving telescope, and simultaneously carry out the pitching motion with the receiving telescope; the receiving telescope backward dispersing light, the backward light gets into the telescope, then passes the glare tube, the adjusting field view stop and ocular glass, and the dichroic mirror process, and divides the 407nm, the 386nm and the 532nm scattered light into three beams, and the 532nm scattered light is divided into 15% and 85% beams, and the four beams are respectively received by the multiplier phototube, magnified by the magnifier and collect and process the data. It can detect the level visibility of the atmosphere, the aerosol of the whole troposphere and the vertical outline of winding cloud light eliminating system and the water and air mixture ratio from the ground to the lower part of the troposphere. The detecting error of the level visibility is 15%, the errors of the aerosol light eliminating modulus and the vertical outline of the water and air mixture are 20%.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Single-wavelength four-Raman laser radar detection system and detection method
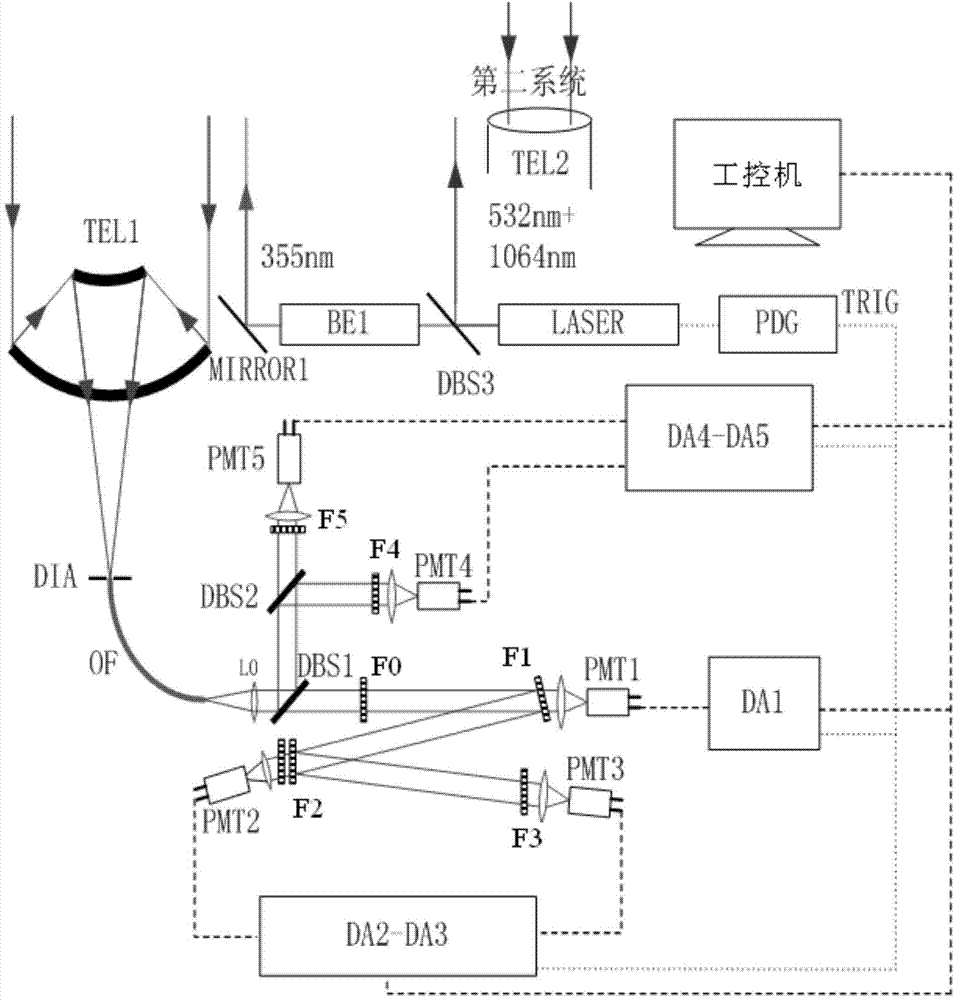
ActiveCN104880711AEfficient collectionEliminate the effects ofElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationRadar systemsData acquisition
The invention discloses a single-wavelength four-Raman laser radar detection system and a detection method. The system combines three laser radar technologies of atmospheric temperature measurement via pure-rotation Raman scattering, vapor measurement via vibration Raman scattering, and measurement of atmosphere aerosol optical characteristics via Raman Mie scattering and an inversion method. The laser radar system employs 355 nm single-wavelength pulse laser as a detection light source and a large-diameter optical reception telescope with high transmittance for measuring the wavelength to collect atmospheric back scattering light signals, four wavelength atmospheric Raman scattering light signals and Mie scattering echo light signals of 353 nm, 354 nm, 355 nm, 386 nm, and 407 nm are mutually separated via an angle separation method of color separation filters and interference filters by a following optical path, the above five-wavelength scattering light signals are gated via narrowband interference filters, photoelectric conversion of photomultipliers of the same type is accomplished, and data acquisition is accomplished by a five-channel data collector.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
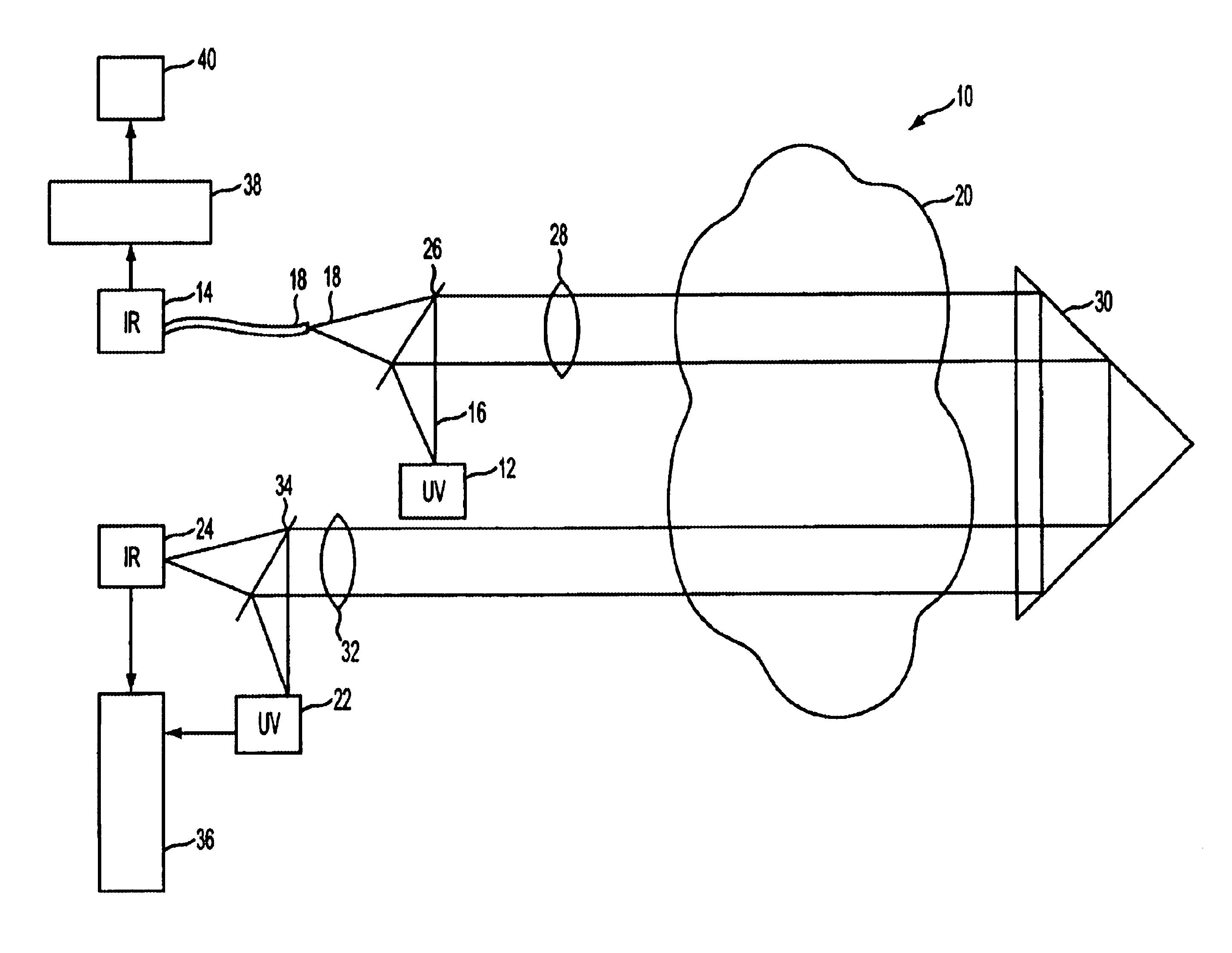
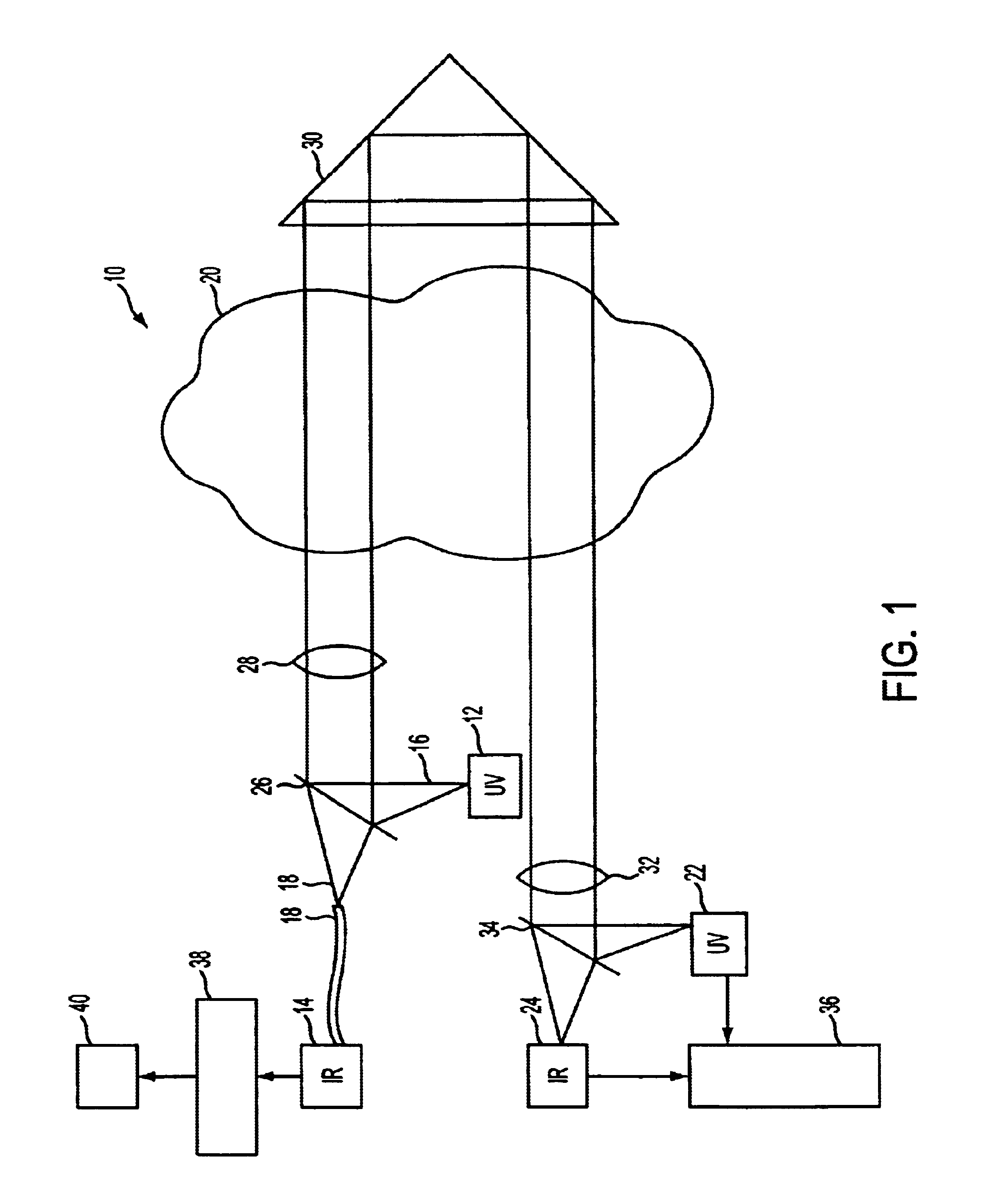
Method and apparatus for measuring particulates in vehicle emissions
InactiveUS6841778B1Accurate calculationRadiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsParticulatesCo2 absorption
A method and apparatus for measuring particulates in vehicle emissions. An ultraviolet light beam having a predetermined wavelength, and an infrared light beam having a predetermined wavelength are propagated through the exhaust plume of a vehicle that has passed on the road. The reduction in intensities of the light beams are measured. The reduction in intensity of the ultraviolet light is due to scattering of the light by particles in the exhaust. A portion of the reduction in intensity of the infrared light is due to absorption of the light by carbon dioxide in the exhaust and a portion of the reduction in intensity is due to the scattering of light by the particles in the exhaust. To distinguish between the two, a portion of the infrared light is run through a test cell with a known amount of carbon dioxide. The reduction in intensity is measured and compared with the reduction in intensity of the infrared light passing through the exhaust plume. As one measure of particulate content, the ratio of the particles in the exhaust whose diameter is greater than said predetermined wavelength of ultraviolet light to the density of the carbon dioxide in the exhaust plume is calculated. Another measure of particulate content is the ratio of the particles in the exhaust whose diameter is greater than said predetermined wavelength of infrared light to the density of the carbon dioxide in the exhaust plume. The average size of the particles is calculated from the ratio of the particles whose diameter is greater than the predetermined wavelength of ultraviolet light to the particles whose diameter is greater that the predetermined wavelength of infrared light is calculated. The average particle size is determined from the Mie efficiency using Mie scattering and absorption theory.
Owner:ENVIROTEST SYST HLDG CORP
Color filter based on silicon metasurfaces and nanostructured metal films and applications
The invention discloses a color filter based on silicon metasurfaces and nanostructured metal films and applications. The filter comprises a silicon substrate; the end surface of the silicon substrate is provided with silicon metasurfaces distributed in an array mode; the upper ends of the array-type silicon metasurfaces and the connection gap between the silicon substrate and the array-type silicon metasurfaces are provided with metal films based on nanostructures. As silicon has a relatively-high refractive index in a visible spectrum range, each silicon nano disc is equivalent to a nano resonator, and resonance of electric dipoles and magnetic dipoles caused by Mie scattering can be generated. At the wavelength of resonance, light stored in the silicon nano discs can be effectively coupled to the silicon substrate with the same high refractive index, and thus, reflection of light at the wavelength of resonance can be highly restrained. In the visible spectrum range, the structure which can effectively absorb light of a certain particular wavelength and reflect light of the remaining wavelengths can successfully filter a particularly color.
Owner:青岛志牛智能科技有限公司
Exhaust gas analyzing device and exhaust gas analyzing method
InactiveCN101346619AAccurately calculate concentrationAccurately calculate pressureScattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsParticulatesPhotodetector
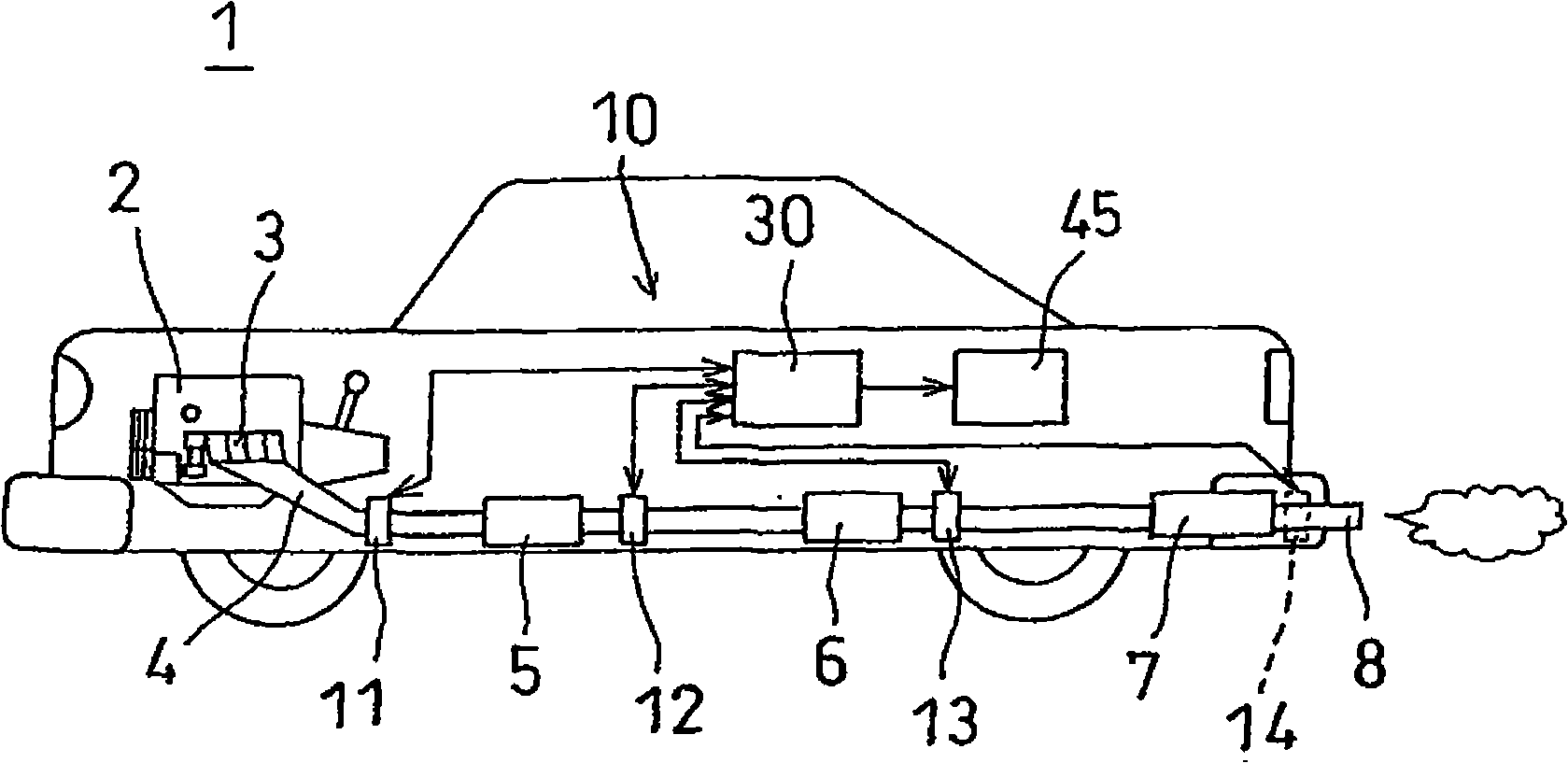
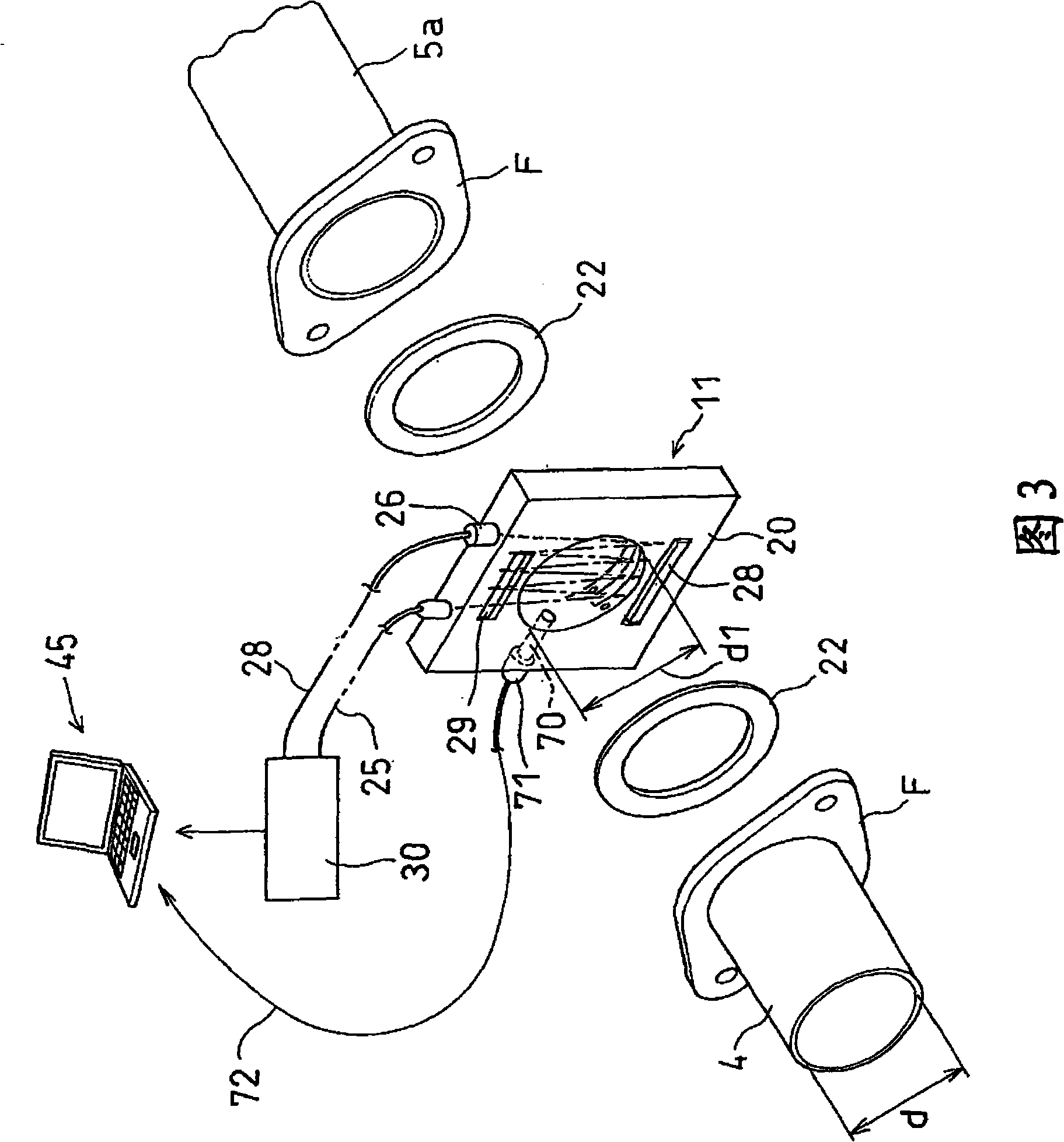
An exhaust gas analyzing device capable of measuring in real time the concentration of particulate materials contained in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine, comprising an exhaust gas passing hole (21) that admits exhaust gas exhausted from an internal combustion engine, an optical fiber (25) for applying a laser beam in a direction perpendicular to an exhaust gas flow running through this exhaust gas passing hole, a detector (26) receiving a laser beam after passed through exhaust gas, a photodetector (71) receiving Mie scattering light produced from particulate materials PM contained in exhaust gas by laser beam irradiation, and a personal computer (45) as a computing unit for computing the concentrations of components in exhaust gas based on light reception data on transmitted light intensity obtained from the detector (26) and also computing the concentrations of particulate materials contained in exhaust gas based on an actually measured data on scattering light intensity obtained from the photodetector (71); and an exhaust gas analyzing method.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Apparatus capable of simultaneously measuring diesel spray structure and combustion characteristic and method thereof
ActiveCN106404410AReduce radiation interferenceAchieve resolutionInternal-combustion engine testingDiesel sprayDiesel combustion
The invention belongs to the diesel spray and combustion visualization research field and discloses a measurement apparatus capable of simultaneously measuring a diesel spray structure and a combustion characteristic based on a laser diagnosis technology and a method thereof. In the past, test researches of a diesel spray characteristic and the combustion characteristic can not be performed simultaneously. In the invention, through using a Mie scattering technology of a laser and a laser induced fluorescence technology (OH-PLIF), the spray structure and the combustion characteristic during diesel combustion can be simultaneously measured and researched. The corresponding apparatus comprises a laser system, a constant volume combustion bomb system, a fuel oil supply system, a signal synchronization system and a signal acquisition system. The test apparatus can simultaneously carry out test researches of a liquid phase length of diesel spray and OH-PLIF distribution under a combustion condition, simultaneously can indicate a liquid phase area in a diesel combustion OH-PLIF distribution map and solves an interference problem of a liquid phase signal to a laser-induced fluorescence signal.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for acquiring complex refractive index of urban aerosol on basis of various ground-based remote sensing technologies
InactiveCN103175759AReduce mistakesImprove discriminationMaterial analysisAtmospheric layerExtinction
The invention relates to a method for acquiring a complex refractive index of urban aerosol on the basis of various ground-based remote sensing technologies. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring the extinction coefficient and the scattering extinction ratio of the aerosol through an inverse algorithm by virtue of Raman laser radar echo signals, and integrating the extinction coefficient of a certain route to acquire the optical thickness of the aerosol on the route; continuously correcting the extinction coefficient and the scattering extinction ratio by performing iterative alignment on an aerosol optical thickness of a whole atmospheric layer acquired via a sun photometer and the aerosol optical thickness acquired via a laser radar according to a Monte Carlo principle; then acquiring the particle size distribution of the aerosol via a particle spectrometer; and finally, acquiring the complex refractive index of the urban aerosol according to a mie-scattering model by virtue of the known scattering extinction ratio of the aerosol and the particle size distribution of the aerosol. According to the invention, the complex refractive index of the urban aerosol is acquired by the Raman laser radar, the sun photometer and the particle spectrometer, and the method has the advantages of small error, high discriminability and high universality.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Dualwavelength dual-field Mie scattering laser radar structure and its detecting method
InactiveCN101071171AShorten the timeCorrected overlap factorElectromagnetic wave reradiationNd:YAG laserWavelength
This invention discloses dual field view dual-wavelength laser radar scattering meters structure and detection methods, including laser launch unit echo signal receiver modules, the follow-up optical modules, signal detection and acquisition module and control unit; The laser launch unit using Nd: YAG laser, launching 532 nm and 1064 nm wavelength of the laser pulse at the same time and received by the diameters of 400 mm and 200 mm telescope. Two receiving optical telescope module are follow-up optical module. Optical signal from the follow-up optical module are received by the detection and acquisition module and control unit. atmospheric aerosol extinction coefficient of the vertical profile and continuous distribution, and extinction coefficient level of continuous distribution, can be analyzed through the various atmospheric aerosol optical parameters.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Spherical multifunctional constant volume bomb
ActiveCN103926196AEasy to processEasy to installMaterial analysis by optical meansPlanar laser-induced fluorescencePresent method
The invention discloses a spherical multifunctional constant volume bomb. The spherical multifunctional constant volume bomb comprises a body with a spherical shape and more than two window holes in the spherical body, wherein the axes of the window holes are intersected at the sphere center of the body; the area close to the sphere center is a hollow test area; a through hole pointing to the test area is reserved between the window holes. The spherical multifunctional constant volume bomb is simple in structure, convenient to machine, compact in structure and light in bomb body weight, and can bear high strength; the temperature field of the test area is uniform; all sealing pieces of a volume bomb adopt non-cooling sealing; the internal temperature and the pressure are easily controlled; continuous test at a high temperature and a high temperature can be realized; an optical system and an injector are arranged flexibly; the test range is wide; a plurality of test methods, such as planar laser-induced fluorescence, a laser absorption and scattering method, a Phase Doppler method, a schlieren method and Mie scattering, combination of various test methods and simultaneous measurement can be realized for spraying, evaporating, mixing, combusting, soot forming and the like; a testing optical circuit can be arranged at any angle; the spherical multifunctional constant volume bomb has universality.
Owner:平湖瓦爱乐发动机测试技术有限公司
Inversion method of aerogel vertical profile based on laser radar
ActiveCN110441777AImprove signal-to-noise ratioSmall fluctuationICT adaptationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAtmospheric sciencesMie scattering
The invention discloses an inversion method of an aerogel vertical profile based on a laser radar. An inversion model of the mass concentration and particle spectrum of the Mie scattering laser radaraerogel is established by combining the working principle of the Mie scattering laser radar and the radiation transmission process of the laser in the atmosphere; the near ground mass concentration ofthe aerogel can be directly inverted from an optical remote-sensing image after computing the aerogel optical thickness through the method disclosed by the invention. By constructing the bridge between the remote-sensing data and the ground monitoring data, the remote-sensing inversion precision is improved, and the bottleneck that the atmosphere remote-sensing can only inverse the aerogel upright concentration is overcome, and the aerogel near ground mass concentration can be obtained by directly inverting, thereby intuitionally evaluating the harm to the human health by the atmospheric pollution, and the significance for the atmosphere remote-sensing is particularly outstanding.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Rayleigh Doppler anemometry laser radar based on wide spectrum gated coherent detection
ActiveCN106886031AImplement detectionAchieve gatingElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationRayleigh scatteringDiscriminator
The present invention discloses a Rayleigh Doppler anemometry laser radar based on wide spectrum gated coherent detection. A band pass filter is used to filter an aerosol mie scattering signal in echo signal current, and a preamplifier is used to amplify a molecular Rayleigh scattering signal. An adjustable band pass filter is used to carry out scan filtering on the amplified Rayleigh signal in a range, and an electric scanning frequency discriminator structure is realized. According to the Rayleigh Doppler anemometry laser radar, the advantages of an amplification effect of a weak signal and a high detection complexity are used in the coherent detection, and the advantage of a small data processing calculation quantity in using a frequency discriminator to discriminate an echo signal in direction detection is used. A problem that a traditional coherent anemometry laser radar can not detect a molecular wide spectrum Rayleigh signal is solved, and the application of a coherent Doppler anemometry laser radar in temperature measurement and high altitude sounding is realized.
Owner:江苏光在科技有限公司
Device and method for measuring concentration of high-pressure combustion carbon black particles
InactiveCN102305757ALarge measuring rangeLower requirementParticle suspension analysisMeasurement deviceData acquisition
The invention discloses a device and a method for measuring the concentration of high-pressure combustion carbon black particles. The device for measuring the concentration of the high-pressure combustion carbon black particles comprises a laser, a first attenuator, a light path collimation component, a first polaroid, a high-pressure sample chamber, a second polaroid, a focusing lens, a first optical filter, a linear array charge coupled device (CCD) image sensor and a computer. In the method, lasers with different wavelengths are successively emitted by the laser and pass through the high-pressure sample chamber, and the concentration of particles to be measured is obtained by measuring the light intensity of transmission light which passes through the high-pressure sample chamber and light which is taken as a reference light path and does not pass through the high-pressure sample chamber according to a Mie scattering theory. By the method, the concentration can be measured conveniently and quickly; the method has low requirements on instruments and equipment, the process of data acquisition and processing is simple, and the measurement range is relatively wider; moreover, measurement results are accurate, and the method is high in speed and repeatability, and can be popularized and applied in the field of particle measurement.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Atmosphere fine particle spatial and temporal distribution Raman mie scattering laser radar surveying device
ActiveCN103616698AIncrease chromatic aberrationLarge deviation angleGas dispersion analysisElectromagnetic wave reradiationSystems designTemporal resolution
The invention discloses an atmosphere fine particle spatial and temporal distribution Raman mie scattering laser radar surveying device. The device works at the wavelengths of 532nm, 355nm and 387nm and is provided with four detection channels. A light source is an Nd: YAG solid laser. According to the transmitting optical design, a single multi-wavelength coupling transmitting telescope is used. According to the receiving optical system design, a receiving telescope which is high in efficiency and small in caliber is used. According to the subsequent optical design, a multi-channel subsequent optical system is used. Expansion is facilitated, and a high protection grade and the high electromagnetic-interference-resisting capability are achieved. Detection light for detecting the wavelength of 532nm and detection light for detecting the wavelength of 355nm share the same transmitting telescope. A transmitting optical system and a receiving optical system are coaxially designed, and the systems are provided with small detection dead zones and designed with 387nm wavelength nitrogen Raman detection channels. Detection of the laser radar ratio close to a ground layer can be achieved, the detection precision of the systems is ensured, and synchronous remote sensing detection on multiple parameters of atmosphere fine particles is achieved. The device can be launched into the atmosphere at any angle so as to achieve all-weather on-line detection on the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of the atmosphere fine particles. The device has the advantages of being high in detection precision, little in inversion error, high in spatial and temporal resolution and the like.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Inversion method of extinction coefficient of aerosol based on Raman-Mie scattering laser radar
ActiveCN109596594ARealize high-precision detectionOvercome limitationsScattering properties measurementsRaman scatteringBoundary valuesExtinction
The invention provides an inversion method for an extinction coefficient of an aerosol based on a Raman-Mie scattering laser radar, comprising the steps of: Step 1: obtaining an echo signal of a Ramanchannel in the Raman-Mie scattering laser radar, and determining an lidar ratio of the aerosol by Ansmann method, that is, obtaining the extinction coefficient and a backscattering coefficient of theaerosol by using Raman method; Step 2: obtaining an echo signal of a Mie channel in the Raman-Mie scattering laser radar, and inverting a distribution profile of the extinction coefficient of the aerosol based on Fernald method; and Step 3: correcting, based on an inversion result of the Raman method in step 1, key parameters required to invert the distribution profile of the extinction coefficient by using the Mie scattering method in step 2, that is, a boundary value of the extinction coefficient of the aerosol, thereby improving the inversion precision of the distribution profile of the extinction coefficient of the Mie scattering channel. According to the inversion method for the extinction coefficient of the aerosol based on the Raman-Mie scattering laser radar provided by the invention, high-precision detection of aerosols is achieved by combining the characteristics of Raman scattering and Mie scattering.
Owner:江苏光在科技有限公司
Method for differentiated investigation of diverse structures in preferably biological preparations
The invention relates to a method for examining different structures in preferably biological preparations in a differential manner, especially by means of confocal laser scanning microscopy. The method is characterized in that particles having a specific diameter and specific characteristics are assigned to the structures and in that said structures are detected by detecting the particles which have specifically bonded in or to the preparations. The detection process is carried out in an advantageous manner by marking the structures with metal particles with diameters of 10 nm to 1,500 nm and detecting Mie scattering or a plasmon signal.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Vibration-rotational Raman-Mie scattering multi-wavelength laser radar system and working method thereof
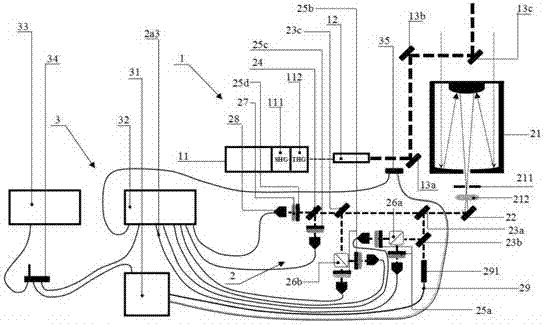
ActiveCN103792544AExpand the detection rangeImprove detection accuracyScattering properties measurementsRaman scatteringRadar systemsWater vapor
The invention discloses a vibration-rotational Raman-Mie scattering multi-wavelength laser radar system and a working method thereof. The system comprises a first system and a second system, wherein the first system works in an ultraviolet wave segment, the second system works in a visible infrared wave segment, and the first system and the second system both comprise laser emission units, optical receiving units, signal detection and data collecting units and control units. The laser emission units are used for emitting lasers to air, the optical receiving units are used for receiving back scattering echo signals of the air on the lasers emitted by the laser emission units, and conduct rotational Raman, vibration Raman and elastic scattering light splitting on the back scattering echo signals, the signal detection and data collecting units are used for obtaining parameter information of air temperature, water vapor, aerosol and cloud from the back scattering echo signals after light splitting, and the control units are used for controlling the laser emission units, the optical receiving units and the signal detection and data collecting units to run. The vibration-rotational Raman-Mie scattering multi-wavelength laser radar system and the working method of the system can achieve all-weather air comprehensive continuous automatic observation.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Multiband Raman-fluorescence laser radar system
A multiband Raman-fluorescence laser radar system comprises a laser emitting system, an echo signal receiving system and a signal collecting system, and can detect multiband polarized mie scattering signals, nitrogen and water vapor Raman scattering signals and 32-channel night atmosphere fluorescence signals at the same time. The laser emitting system can emit laser beams of 355nm, 532nm and 1064nm at the same time; the echo signal receiving system splits and filters echo signals to acquire polarized mie scattering signals of 355nm and 532nm and Raman scattering signals of 607nm and 660nm; the signal collecting system is connected with the echo signal receiving system, collects vertical and horizontal polarized mie scattering signals of 355nm and 532nm, nitrogen and water vapor Raman signals of 607nm and 660nm and night atmosphere weak fluorescence signals of 32-channel wavelength and combines detection of the night atmosphere weak fluorescence signals of 32-channel wavelength with detection of the polarized mie scattering signals of 355nm and 532nm and waveband of 607nm and 660nm to detect and study spatial and temporal distribution features and complex composition of bioaerosol, atmosphere water vapor spatial and temporal distribution, haze carcinogenic composition and generation and disappearance process.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
PM2.5 concentration monitoring method based on CCD back scattering
InactiveCN104316443ASimple calculationSufficient dataParticle suspension analysisParticulatesRadar imaging
The invention relates to a PM2.5 concentration monitoring method based on CCD back scattering. The method comprises the steps of imaging emitted laser beams on a CCD through scattering of atmospheric particulate matters according to a mie scattering principle and a CCD laser radar imaging principle, inputting the laser beams into a computer through a data wire, and acquiring corresponding data through picture catching software; performing matlab function fitting to obtain a corresponding model according to an echo scattering diagram acquired by the catching software, and inverting the concentration of PM2.5 from the measured data of the echo scattering diagram by the model. The method can be used for monitoring the PM2.5 concentration in a specific region in real time. By the adoption of a statistical reasoning mode, complicated data calculation is ingeniously avoided; the echo scattering diagram is statistically analyzed according to a telescope imaging principle and the mie scattering principle; furthermore, by the selection of the relation between the image brightness sum within a certain range and the PM2.5 mass concentration, the calculation is simplified.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Preparation method of high-purity and low-loss chalcogenide glass
InactiveCN103332851AImprove uniformityHigh purityGlass furnace apparatusChalcogenide glassPhotochemistry
The invention provides a preparation method of high-purity and low-loss chalcogenide glass, belonging to a preparation method of the chalcogenide glass. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: removing hydrocarbon impurity in the glass by taking ultra-dry gallium chloride as a purifying agent, and distilling and purifying the glass in combination with the conventional deoxidant, aluminum, magnesium or zirconium metal; placing glass mixture into a quartz ampoule to be sealed in by means of vacuum supply, founding the glass mixture in a vacuum ampoule, dynamically distilling the glass, and remelting the mixture after distilling; and effectively removing the hydrocarbon impurity in the glass by taking the ultra-dry gallium chloride as the purifying agent, so that the Mie scattering imperfection is hardly formed in the finally-obtained high-purity chalcogenide glass, and the low-loss homogeneous glass can be obtained. According to the high-purity chalcogenide glass synthesized by the preparation method provided by the invention, the minimum loss under the infrared transmission waveband is less than 0.3dB / m, and the corresponding loss of the absorption peak of the residual impurity is less than 8dB / m, so that the preparation method can be used in the field of an infrared glass optical element and an infrared optical fiber. The ultra-dry gallium chloride purifying agent can be easily obtained, and is lower in price; the carbon, hydrogen and oxygen impurities can be removed from the chalcogenide glass at high efficiency; the prepared chalcogenide glass is better in uniformity and less in light scattering.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Microbial detection apparatus and method
InactiveUS20120257192A1Easy to useEfficient measurementRaman/scattering spectroscopyScattering properties measurementsFluorescenceLight beam
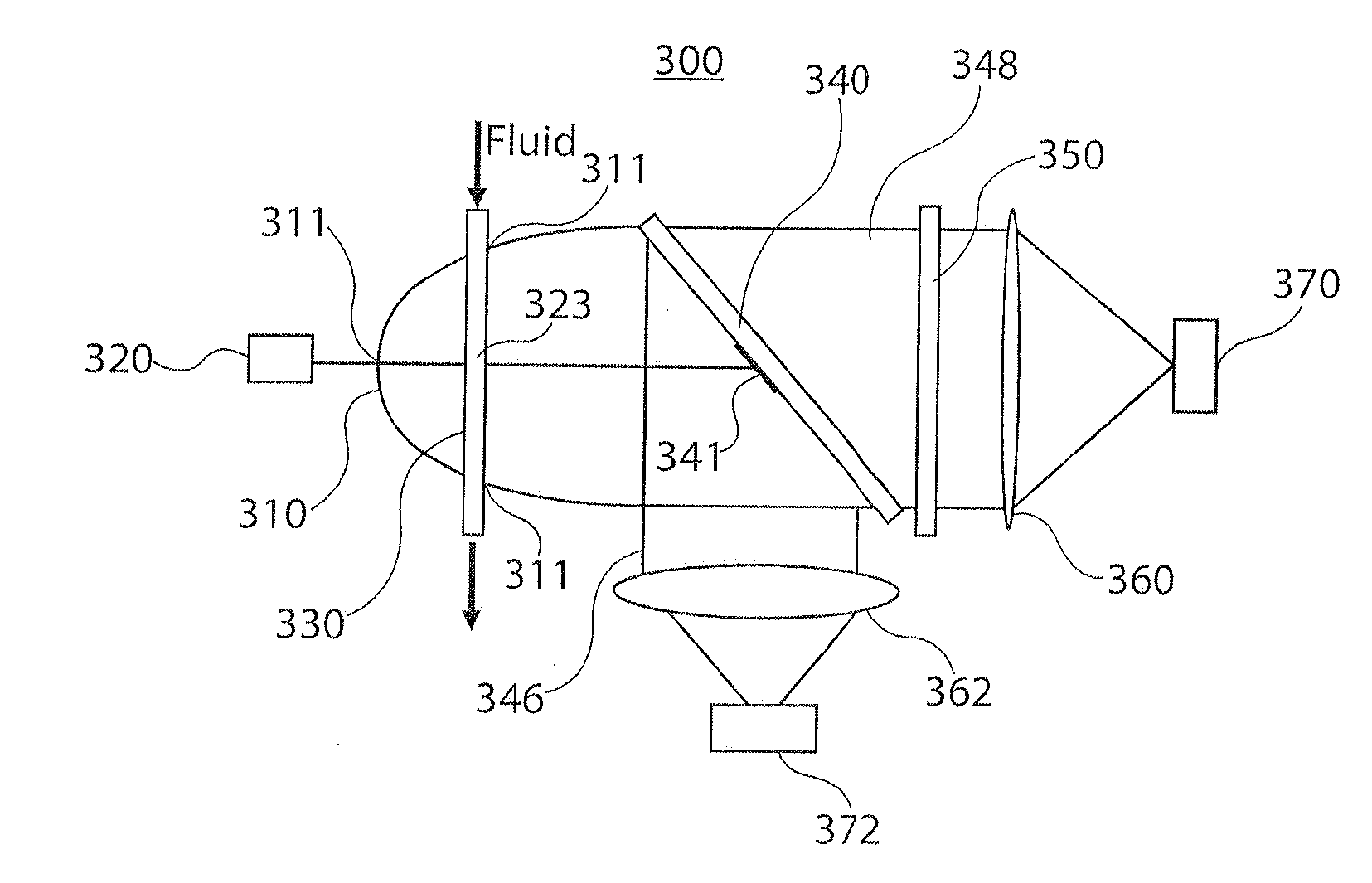
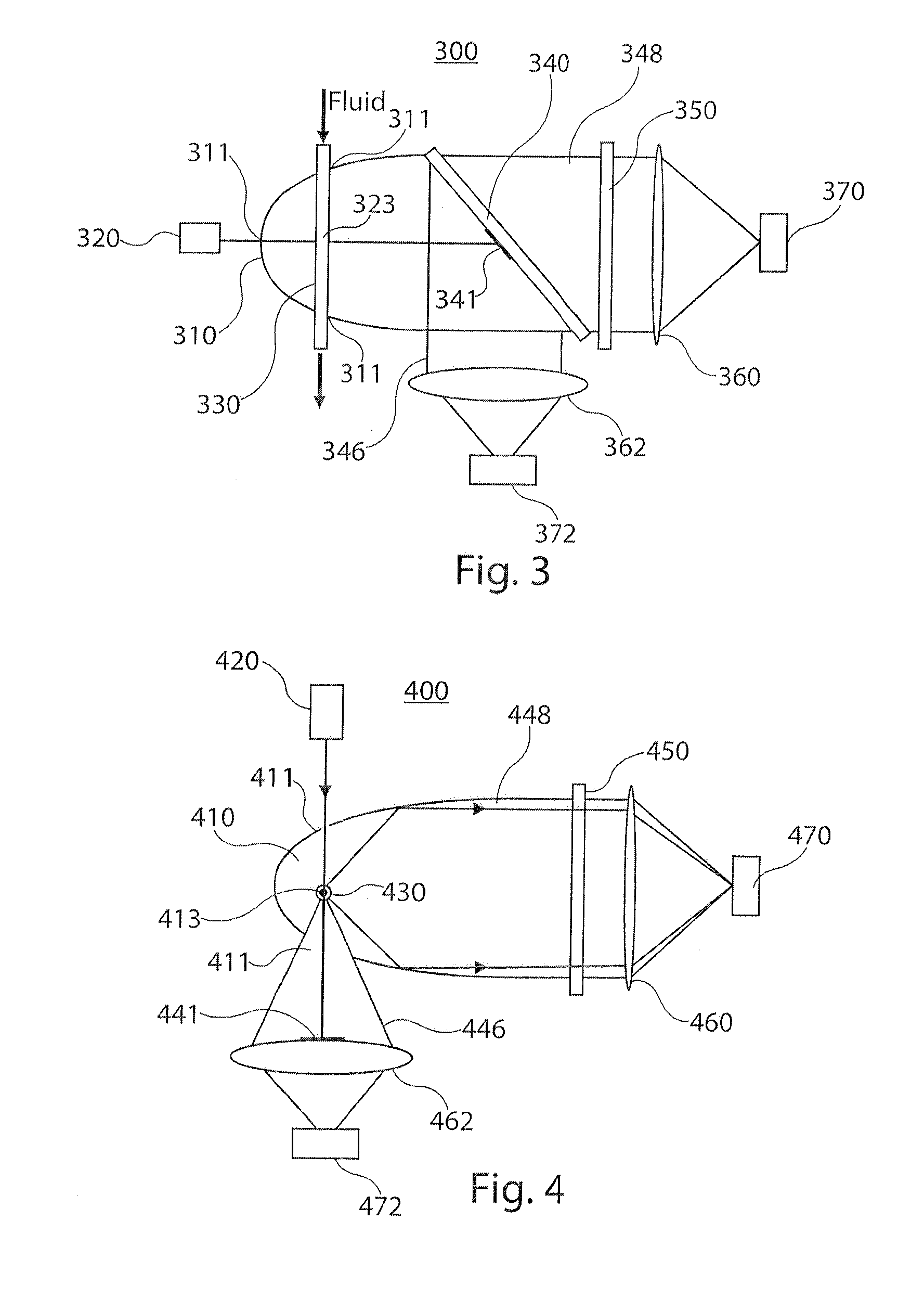
A microbial detection apparatus is provided. The apparatus includes a parabolic reflector. A light source is configured to direct a beam of light toward the focal point of the parabolic reflector. A fluid flow tube passes through the focal point of the parabolic reflector, such that the light beam path and the flow tube intersect at the focal point of the parabola. The fluid flow tube is configured to contain a flow of fluid. A first detector is included for detecting fluorescence light emitted from microbes within the fluid passing through the flow tube. A second detector is included for detecting Mie scattered light from particles within the fluid passing through the flow tube.
Owner:METTLER TOLEDO THORNTON
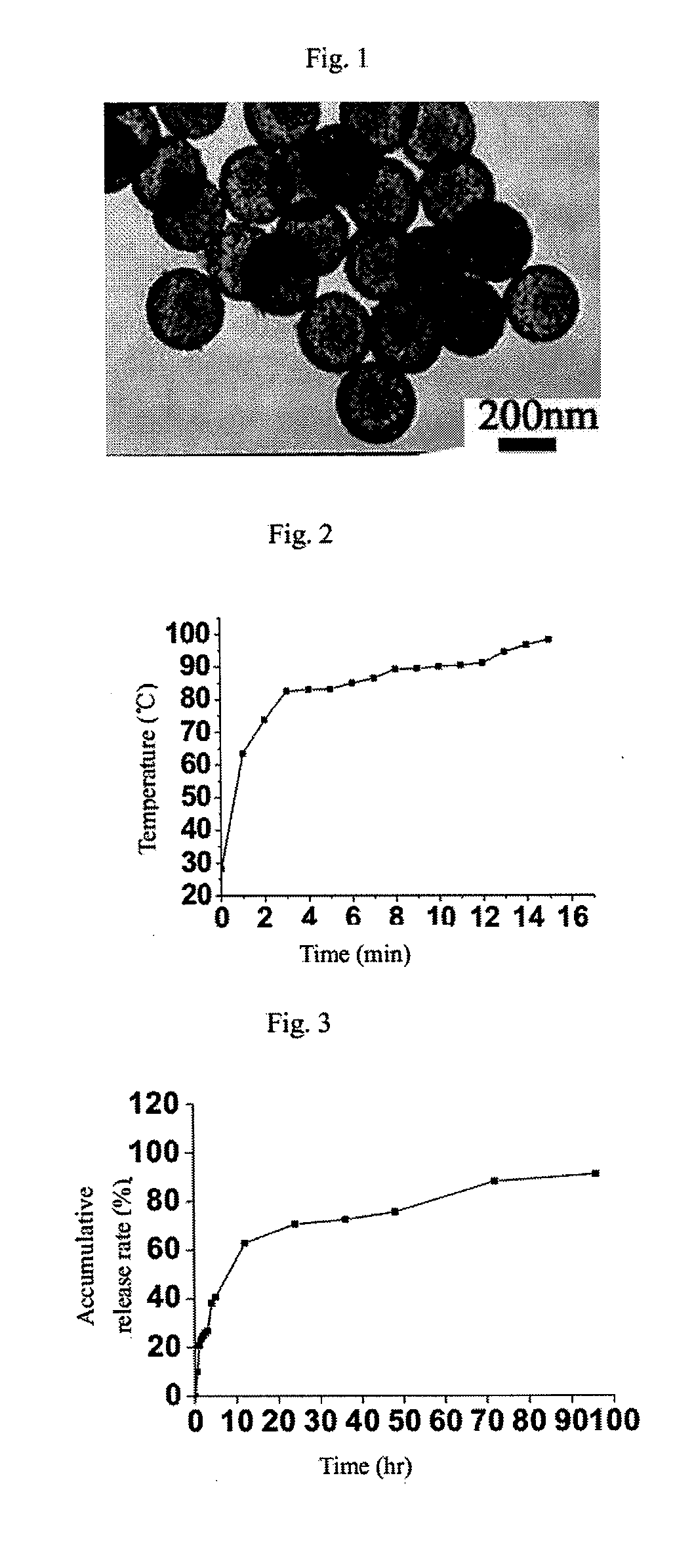
Hollow polymer sub-micron sphere coated with gold case, preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN101168597AFunctionalGood biocompatibilityPowder deliverySynthetic resin layered productsPolyelectrolytePolymer science
The invention belongs to the technical field of nanometer materials, in particular to a gold-shell-coated hollow polymer submicron sphere, a preparation method and application thereof. In the invention, polymer submicron spheres are used as templates, multi-layer coated polyelectrolytes are used as functional materials, and the surface is evenly coated with gold shells. The size of the hollow gold shell submicron sphere and the thickness of the gold shell can be controlled. At the same time, according to the Mie scattering theory, the gold-shell-coated hollow polymer submicron sphere can adjust its absorption in the near-infrared region, and can convert the light energy of the near-infrared laser into surrounding heat energy, which can be used as a heat-sensitive device for cancer treatment. material for killing malignant tumor cells. The material of the present invention can combine thermotherapy and sustained release of antineoplastic drugs and be used in cancer treatment.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Feedback mechanism for smart nozzles and nebulizers
ActiveUS7483767B2Enhancing signal level and precision and accuracyImprove accuracy and precisionSelf-acting watering devicesWatering devicesFluorescenceLaser light
Nozzles and nebulizers able to produce aerosol with optimum and reproducible quality based on feedback information obtained using laser imaging techniques. Two laser-based imaging techniques based on particle image velocimetry (PTV) and optical patternation map and contrast size and velocity distributions for indirect and direct pneumatic nebulizations in plasma spectrometry. Two pulses from thin laser sheet with known time difference illuminate droplets flow field. Charge coupled device (CCL)) captures scattering of laser light from droplets, providing two instantaneous particle images. Pointwise cross-correlation of corresponding images yields two-dimensional velocity map of aerosol velocity field. For droplet size distribution studies, solution is doped with fluorescent dye and both laser induced florescence (LIF) and Mie scattering images are captured simultaneously by two CCDs with the same field of view. Ratio of LIF / Mie images provides relative droplet size information, then scaled by point calibration method via phase Doppler particle analyzer.
Owner:GEORGE WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY
Hollow Mesoporous Silica Sphere Coated with Gold and Preparation Method Thereof and Use in Cancer Therapy
InactiveUS20110196285A1Easily connect tumor specific ligand folic acid tumorIncrease surface areaOrganic active ingredientsElectrotherapyControlled releaseLight energy
The present invention relates to the preparation method of a hollow mesoporous silica sphere coated with gold shell and its use in tumor therapy. In the present invention, the hollow mesoporous silica sphere is made as core and its surface is uniformly coated with the gold shell. The antitumor medicine is loaded in the hollow mesoporous silica sphere and the tumor specific targeting agent is coupled with the surface of the gold shell. The particle size of the hollow mesoporous silica sphere and the thickness of the gold shell are controllable. Based on the Mie Scattering Theory, the hollow mesoporous silica sphere coated with gold shell can adjust its absorption in near-infrared area and convert the light energy of infrared laser into peripheral heat which can kill the malignant tumor cells. The hollow mesoporous silica sphere can be used as a carrier for sustained / controlled release of therapeutic medicine, and the tumor specific targeting agent coupled with the surface of the gold shell can make the medicine have the function of targeting.
Owner:CHEN DONG +2
Process and apparatus for non-invasive, continuous in vivo measurement of hematocrit
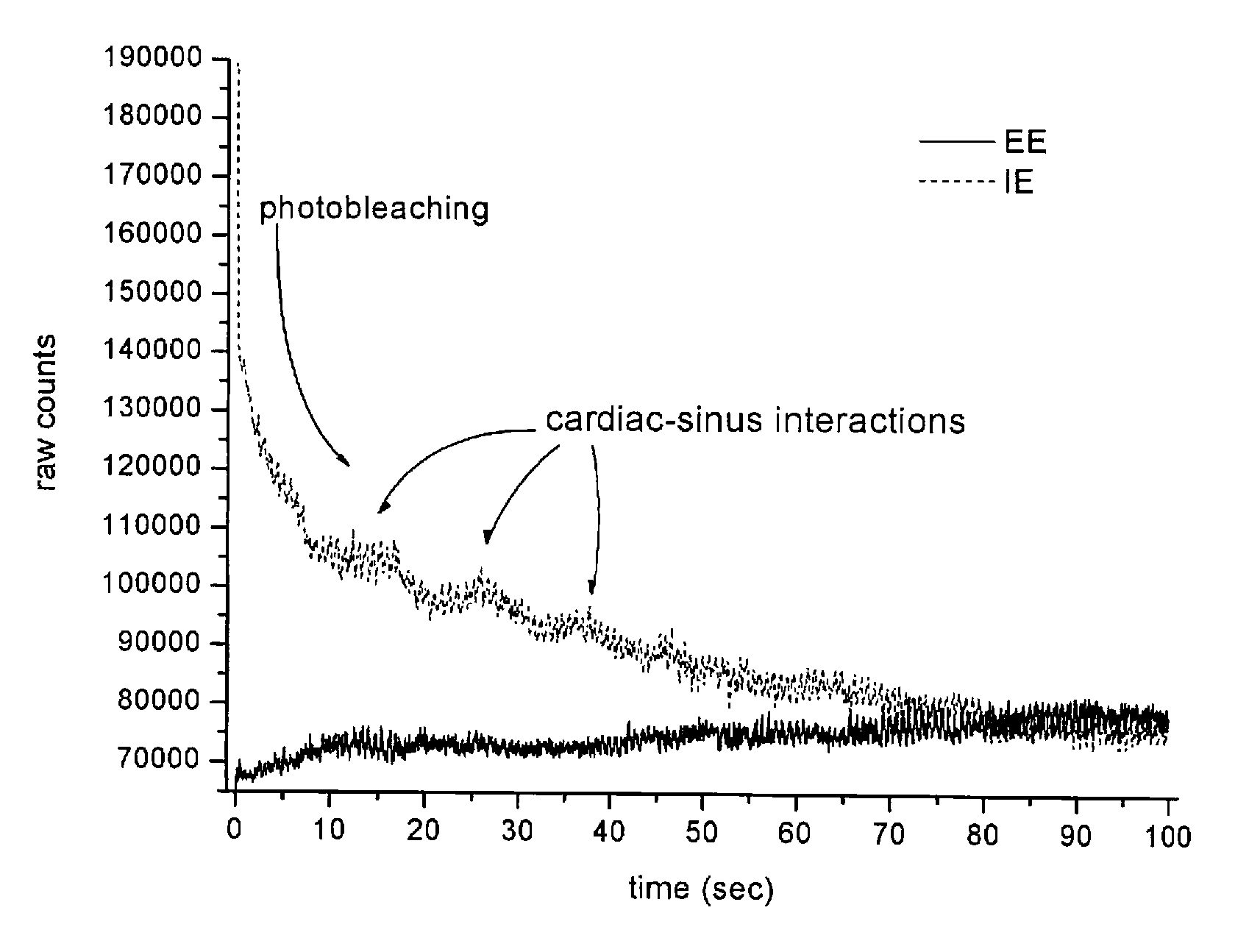
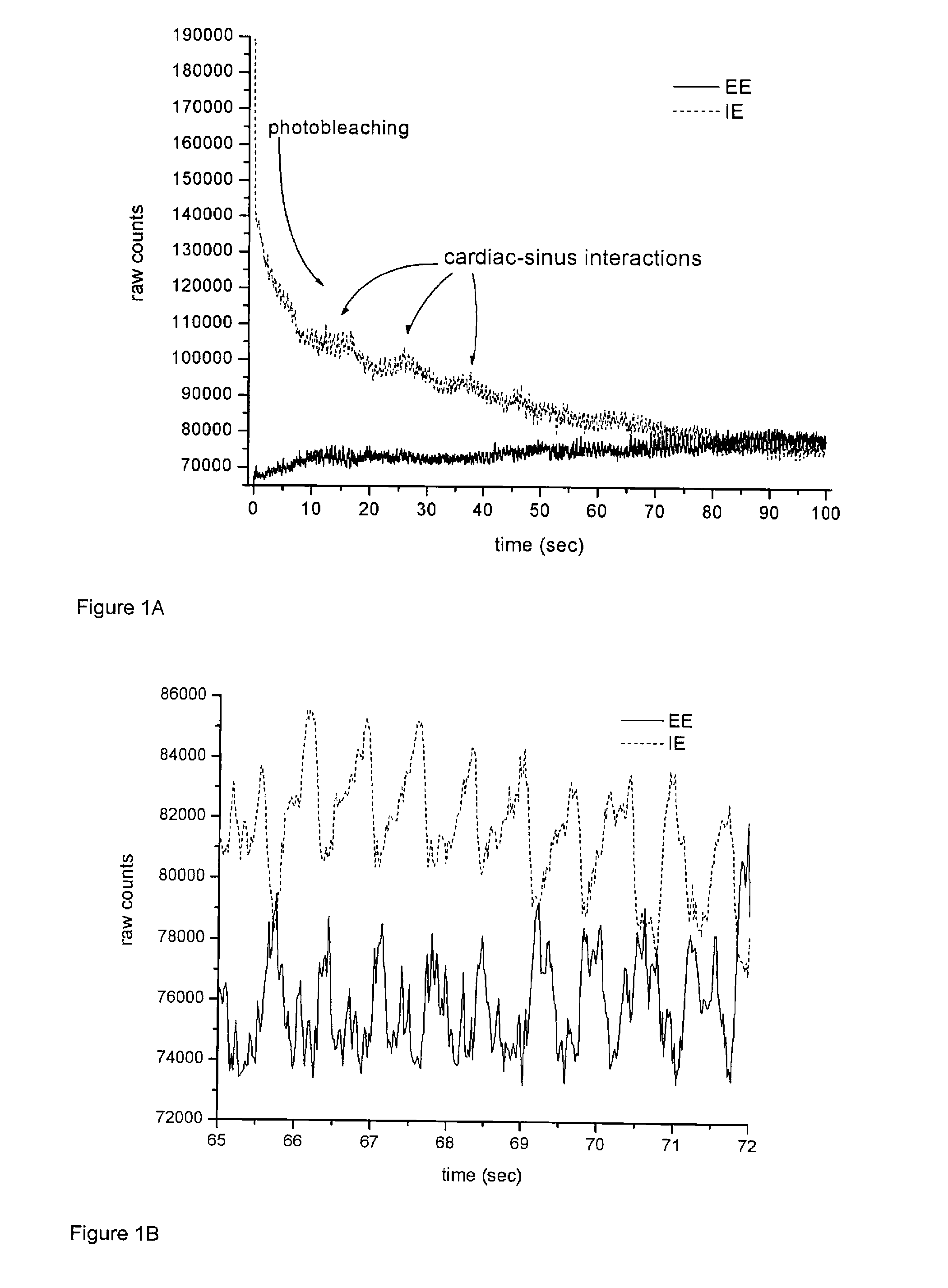
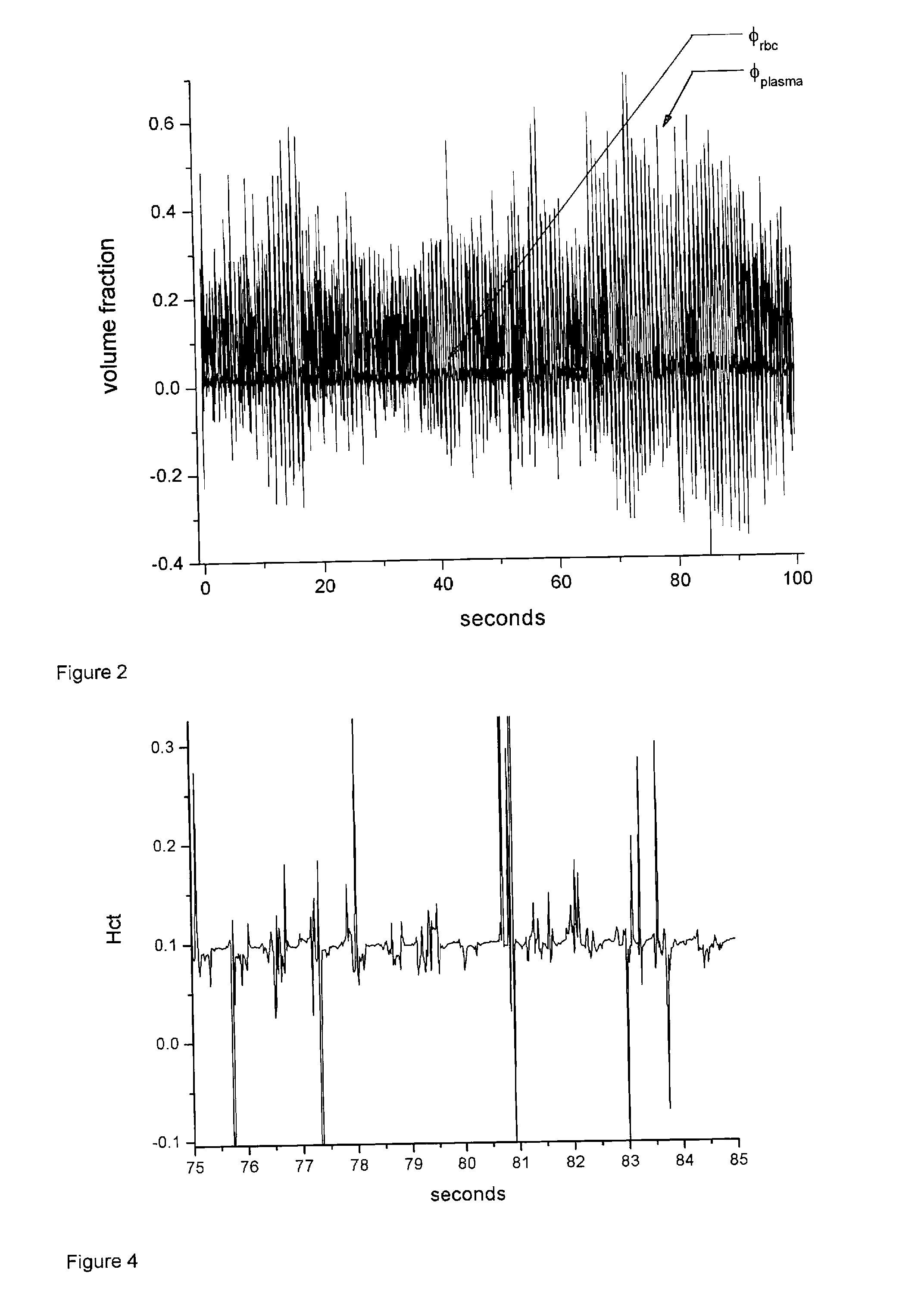
ActiveUS20110077496A1Minimize standard deviationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFluorescenceRelative Volume
The invention provides a method and apparatus obtaining a hematocrit from a sample of in vivo tissue. The method comprises irradiating the sample with a single incident wavelength on a sample of tissue, simultaneously measuring wavelength shifted (IE) and unshifted (EE) light emitted from the tissue, and determining a relative volume of light emitted from two phases, wherein the two phases comprise a first Rayleigh and Mie scattering and fluorescent phase associated with red blood cells, and a second, non-scattering phase associated with plasma. The hematocrit is calculated from the volume of light emitted by the first phase relative to the total volume of light emitted from the first and second phases.
Owner:LIGHTOUCH MEDICAL +1
Diffuser for LED light sources
InactiveUS20110042700A1Effective coolingSmall and lightPoint-like light sourceLighting heating/cooling arrangementsLight emissionMie scattering
An LED light source, which includes at least one LED, a panel between the LED and the light emission surface of the light source, and a filler material inside the panel containing a material to diffuse the light from the at least one LED by Mie scattering.
Owner:SWITCH BULB CO INC
Screen and projection system
InactiveCN101943851AReduce power consumptionGuaranteed qualityBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsLength waveProjection system
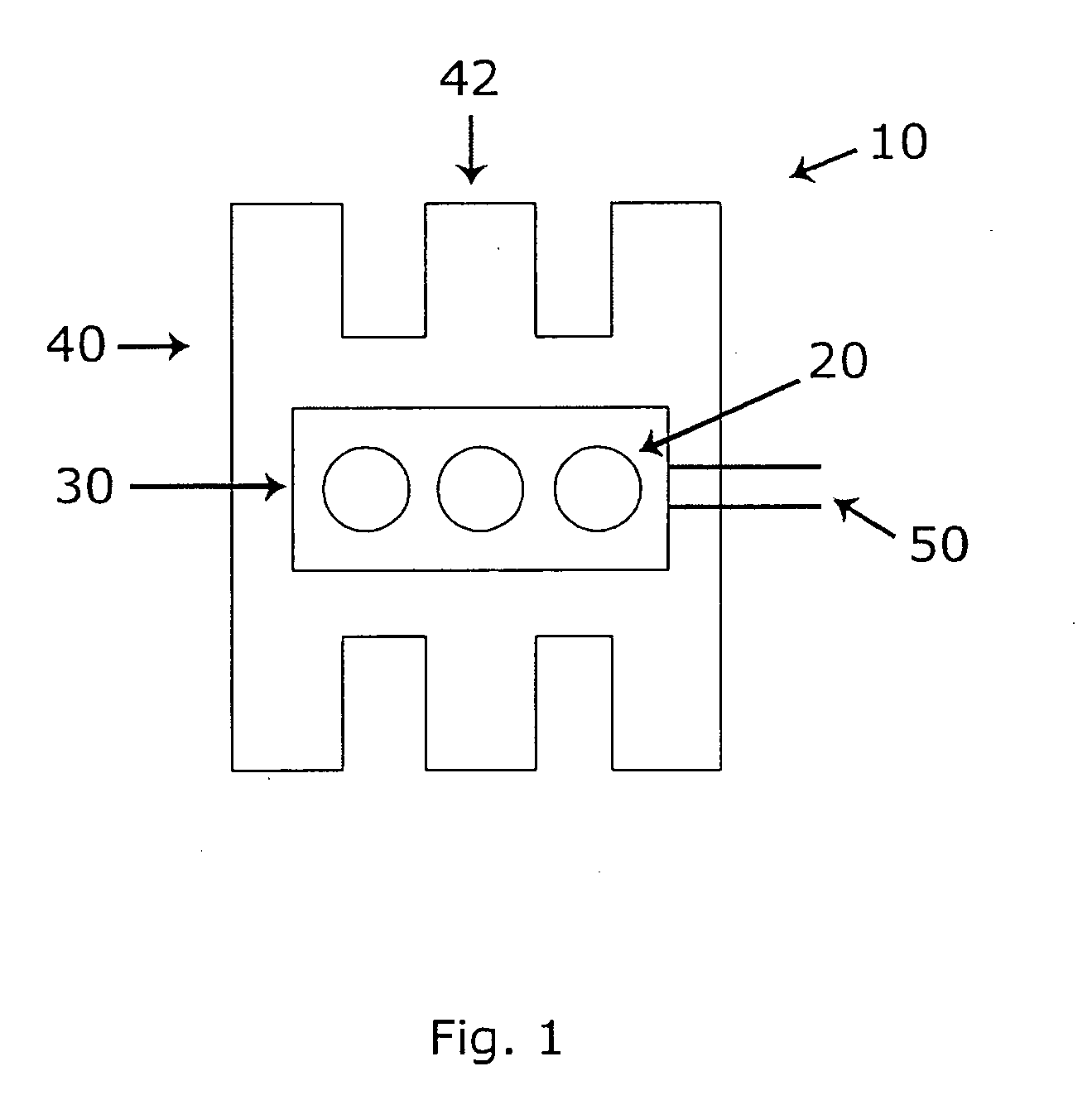
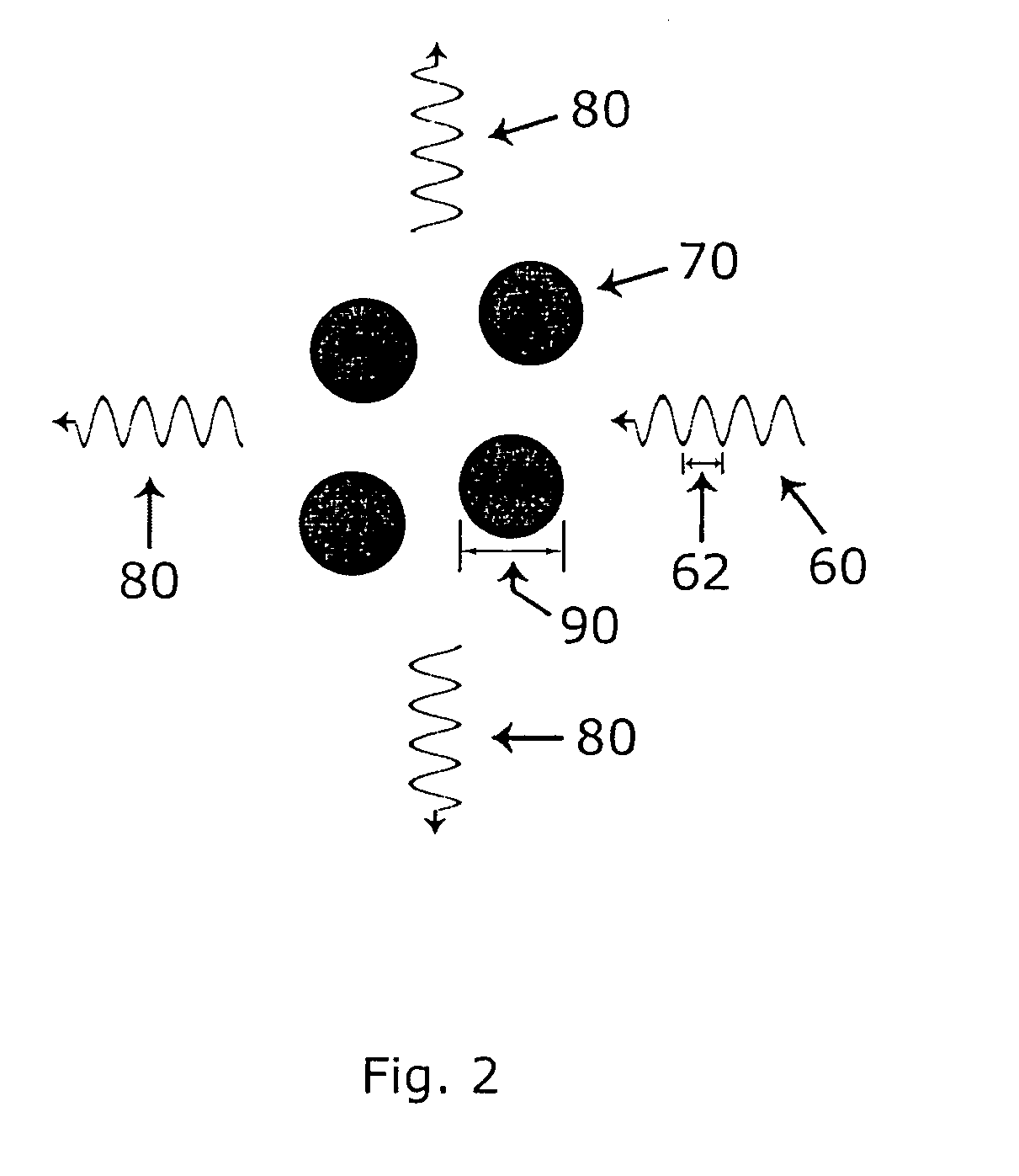
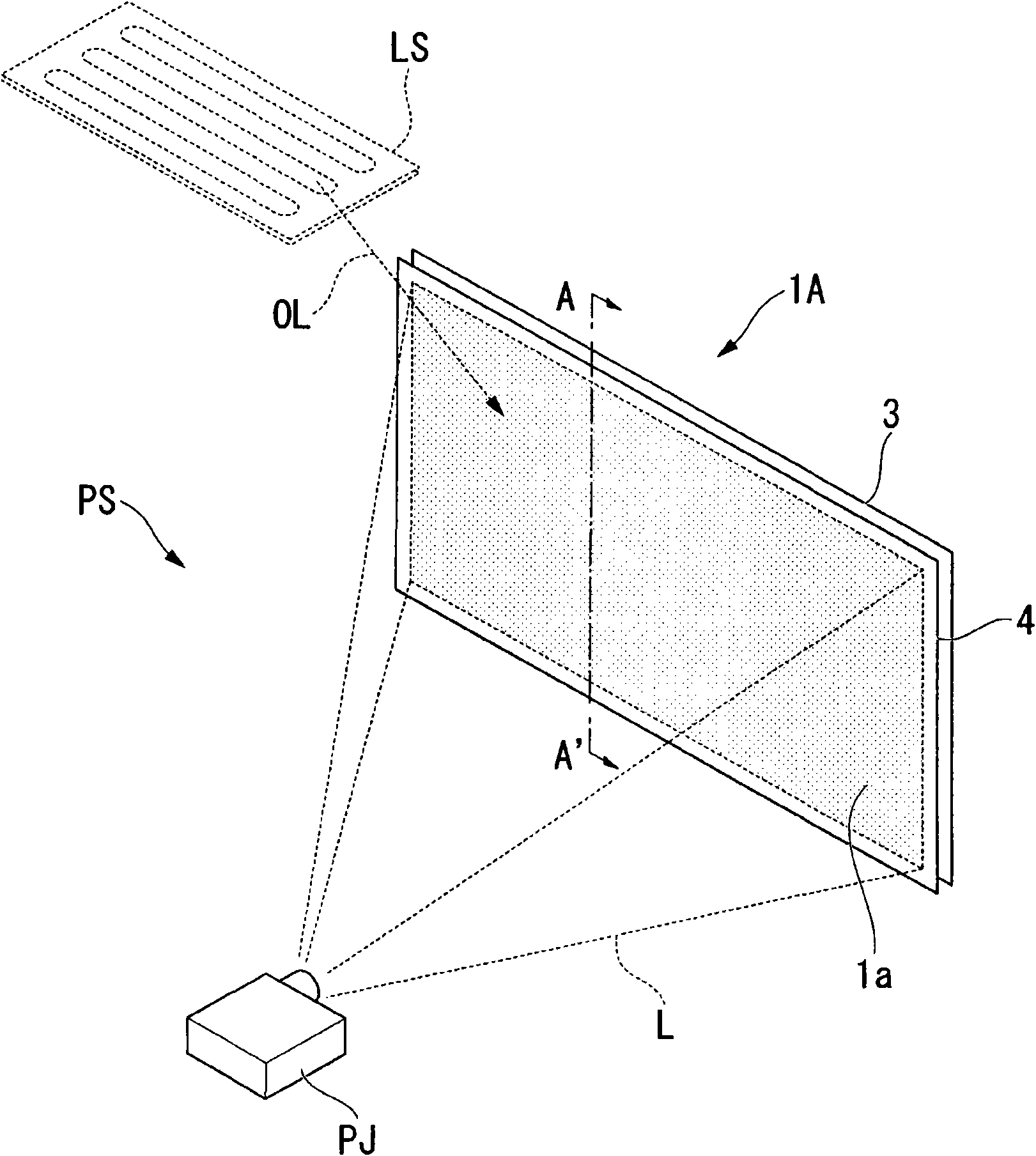
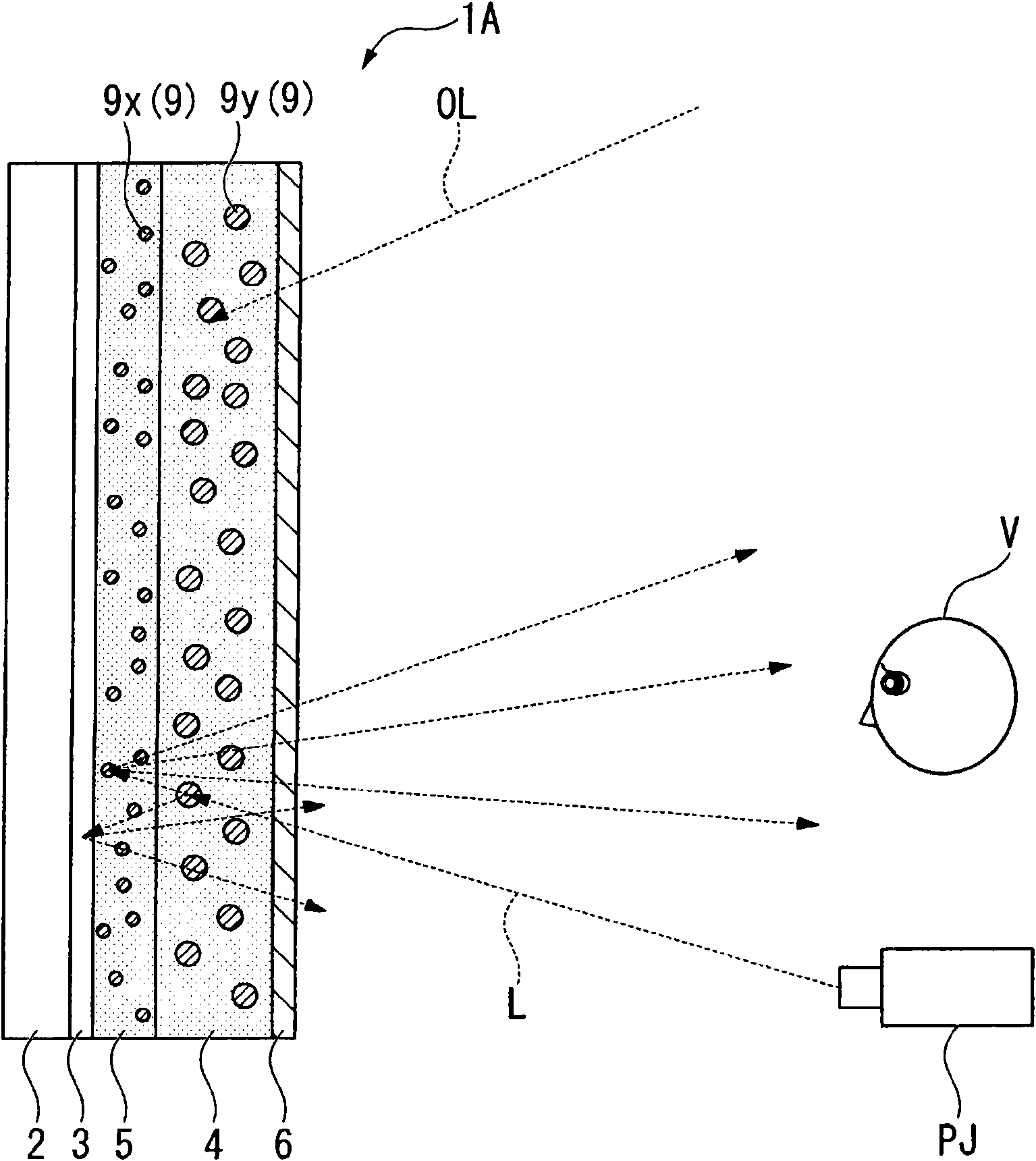
The invention aims at providing a screen and a projection system capable of reducing manufacture procedure and used for obtaining image with improved contrast ratio with lower cost. A screen includes: a substrate 2; and a first color material layer 4 disposed on one surface of the substrate 2, wherein the first color material layer 4 includes a first color material 9y adapted to absorb light with a part of wavelengths of an incident light, and the first color material 9y has a peak absorption wavelength in a visible light range, and a size of causing Mie scattering on the light in the visible light range.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com