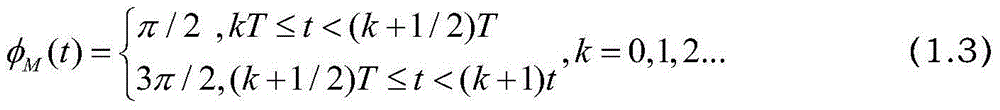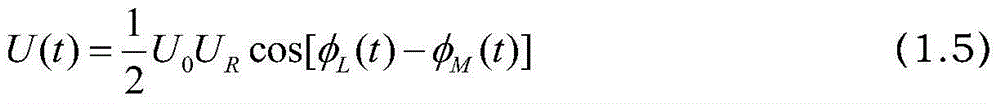Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
437 results about "Raman laser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A Raman laser is a specific type of laser in which the fundamental light-amplification mechanism is stimulated Raman scattering. In contrast, most "conventional" lasers (such as the ruby laser) rely on stimulated electronic transitions to amplify light.
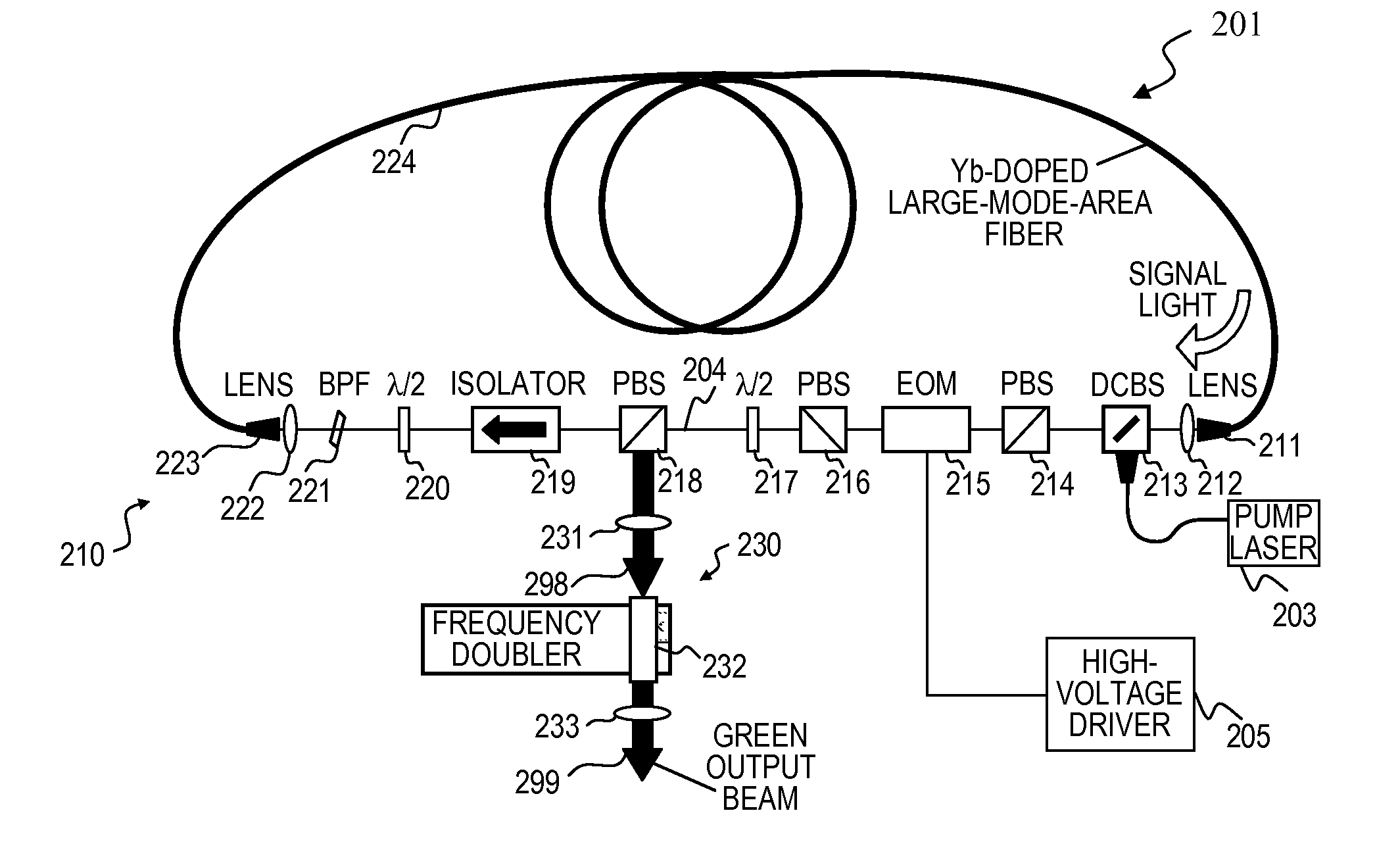
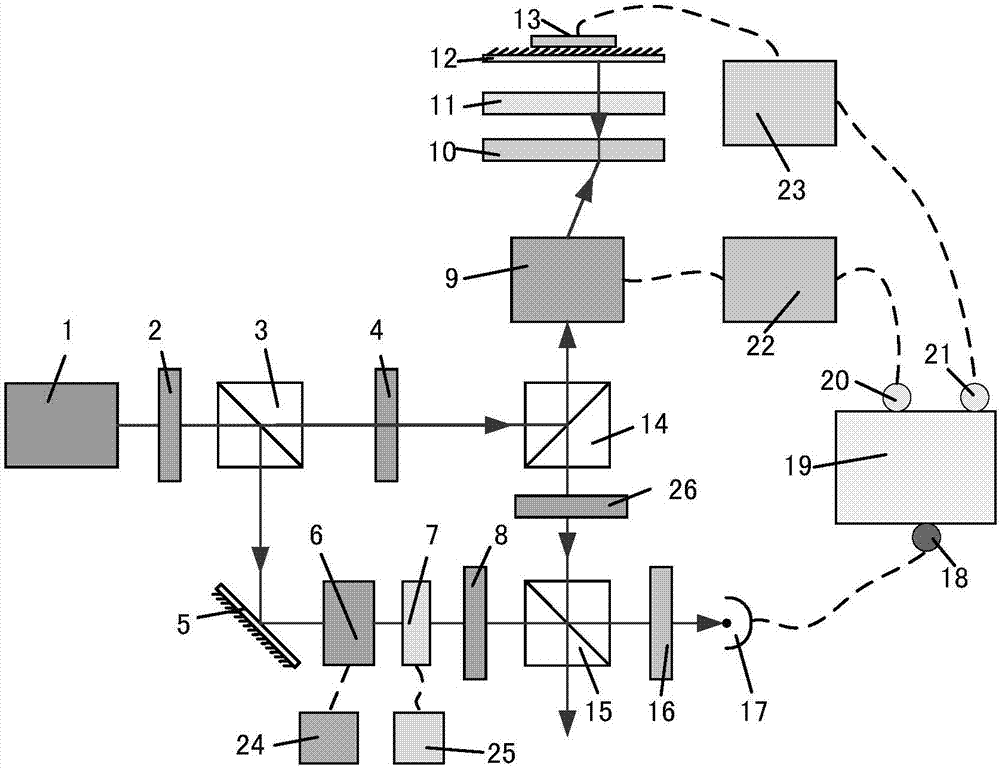
High power optical apparatus employing large-mode-area, multimode, gain-producing optical fibers
ActiveUS20080180787A1Promote absorptionIncrease brightnessExcitation process/apparatusCoupling light guidesFiberNanosecond
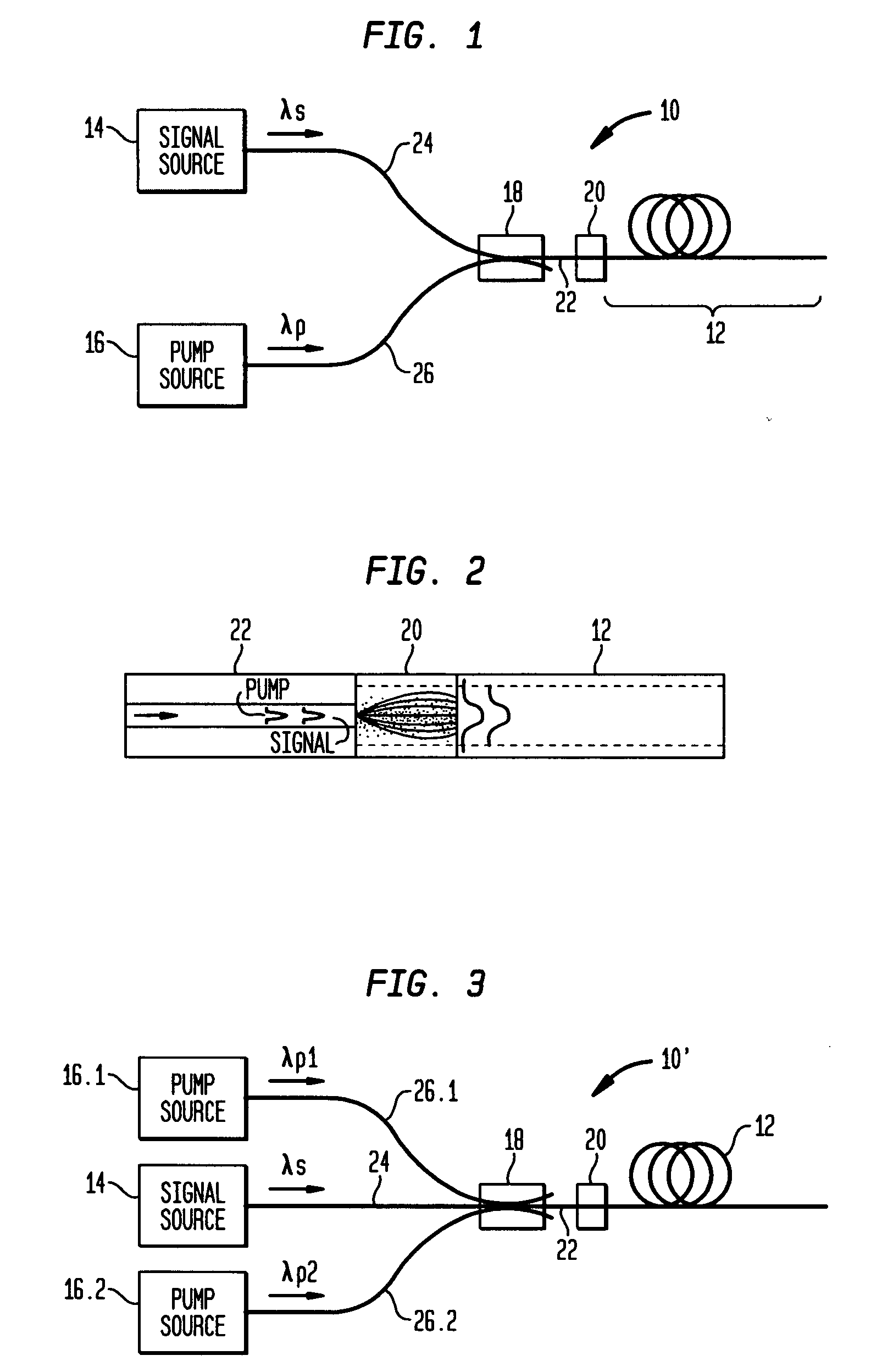
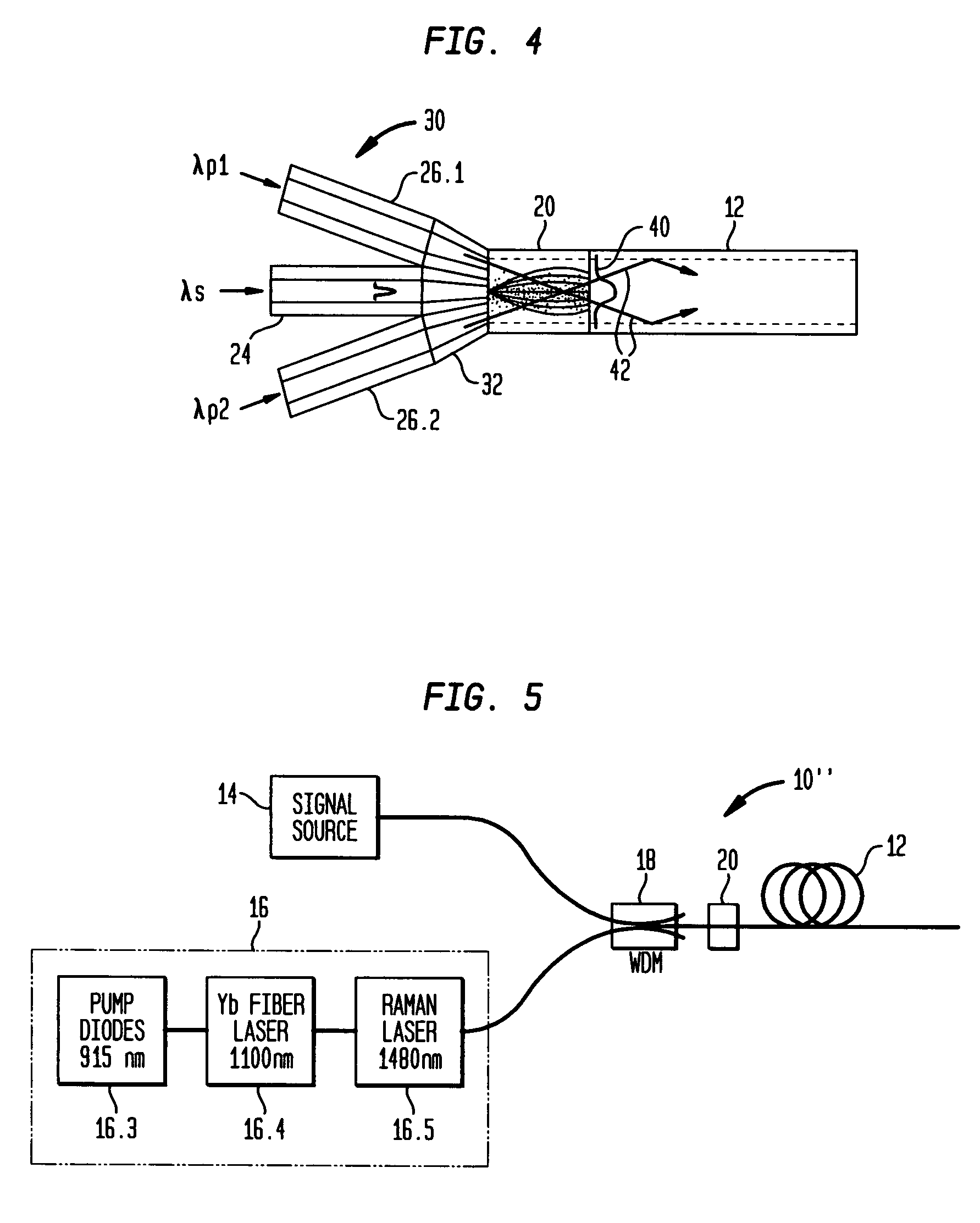
Optical apparatus includes a multimode, gain-producing fiber for providing gain to signal light propagating in the core of the fiber, and a pump source for providing pump light that is absorbed in the core, characterized in that (i) the pump source illustratively comprises a low brightness array of laser diodes and a converter for increasing the brightness of the pump light, (ii) the pump light is coupled directly into the core, and (iii) the area of the core exceeds approximately 350 μm2. In one embodiment, the signal light propagates in a single mode, and the pump light co-propagates in at least the same, single mode, both in a standard input fiber before entering the gain-producing fiber, and a mode expander is disposed between the input fiber and the gain-producing fiber. In another embodiment, multiple pumps are coupled into the core of the gain-producing fiber. The pumps may generate light of the same wavelength or of different wavelengths. In accordance with a particular embodiment of our invention, we have demonstrated amplification of nanosecond optical pulses at 1545 nm in a single clad Er-doped fiber having a core area of 875 μm2; the core was pumped by a high brightness Raman laser at 1480 nm; and the pulses had a record peak power of several hundred kW.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
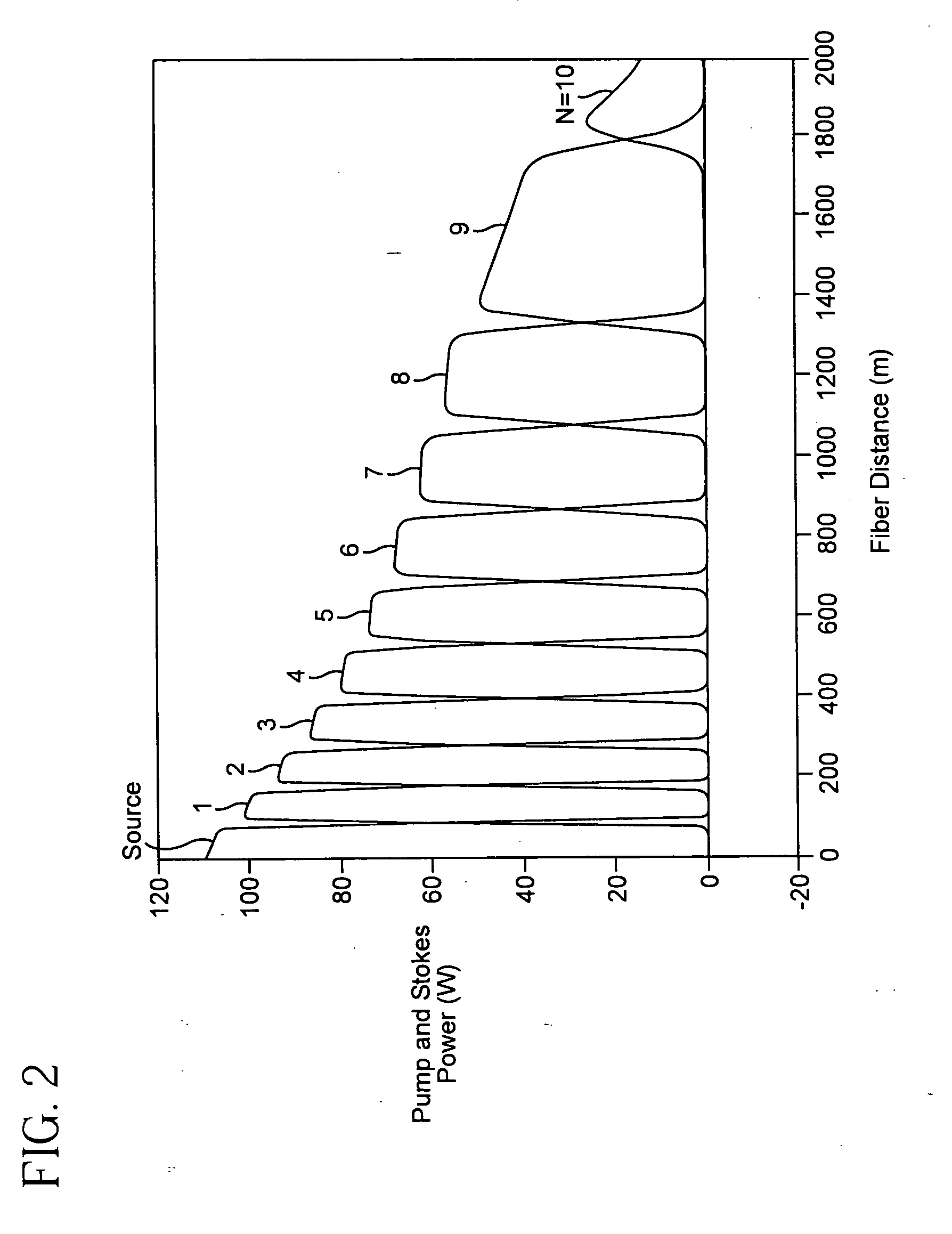
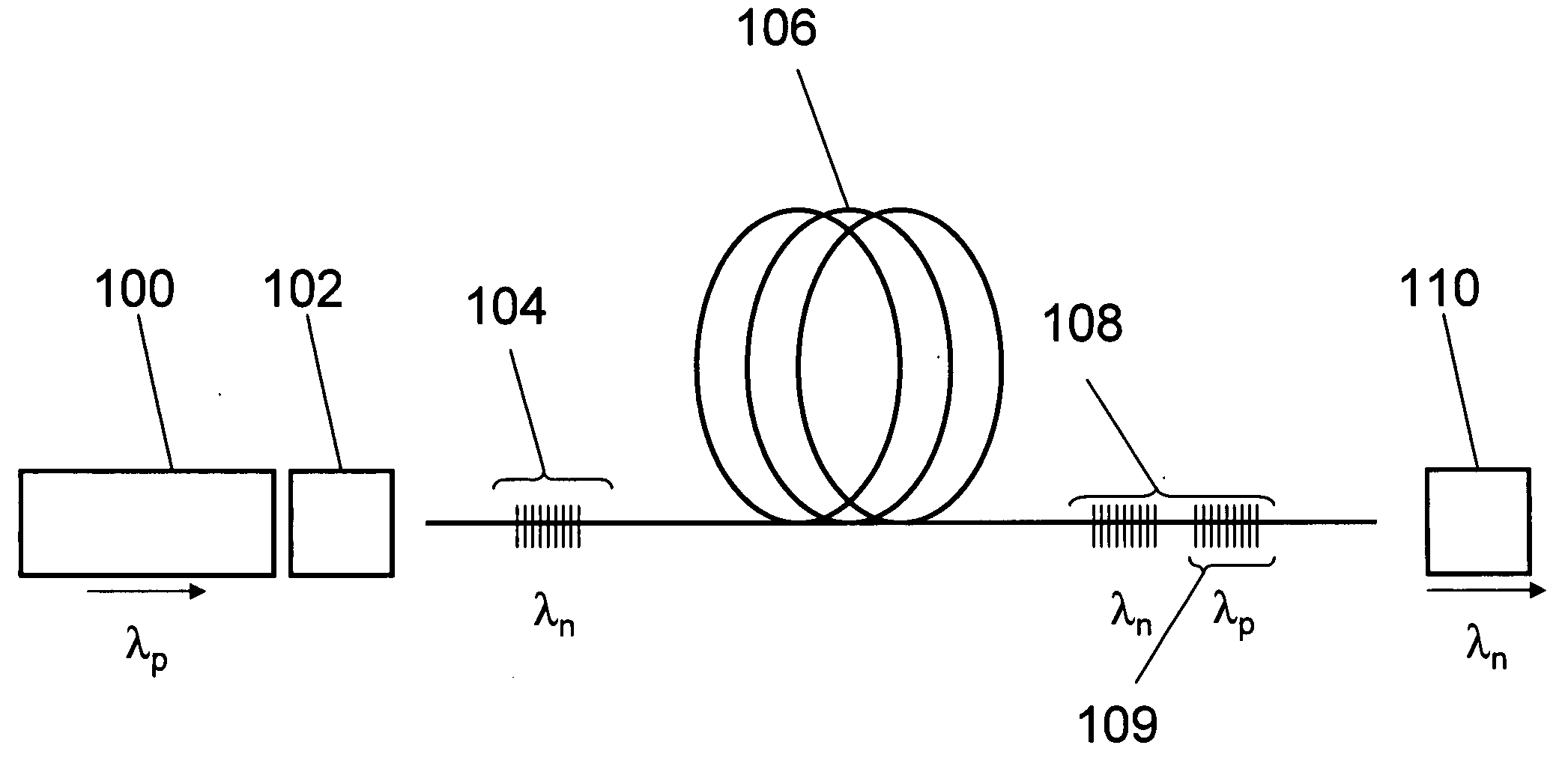
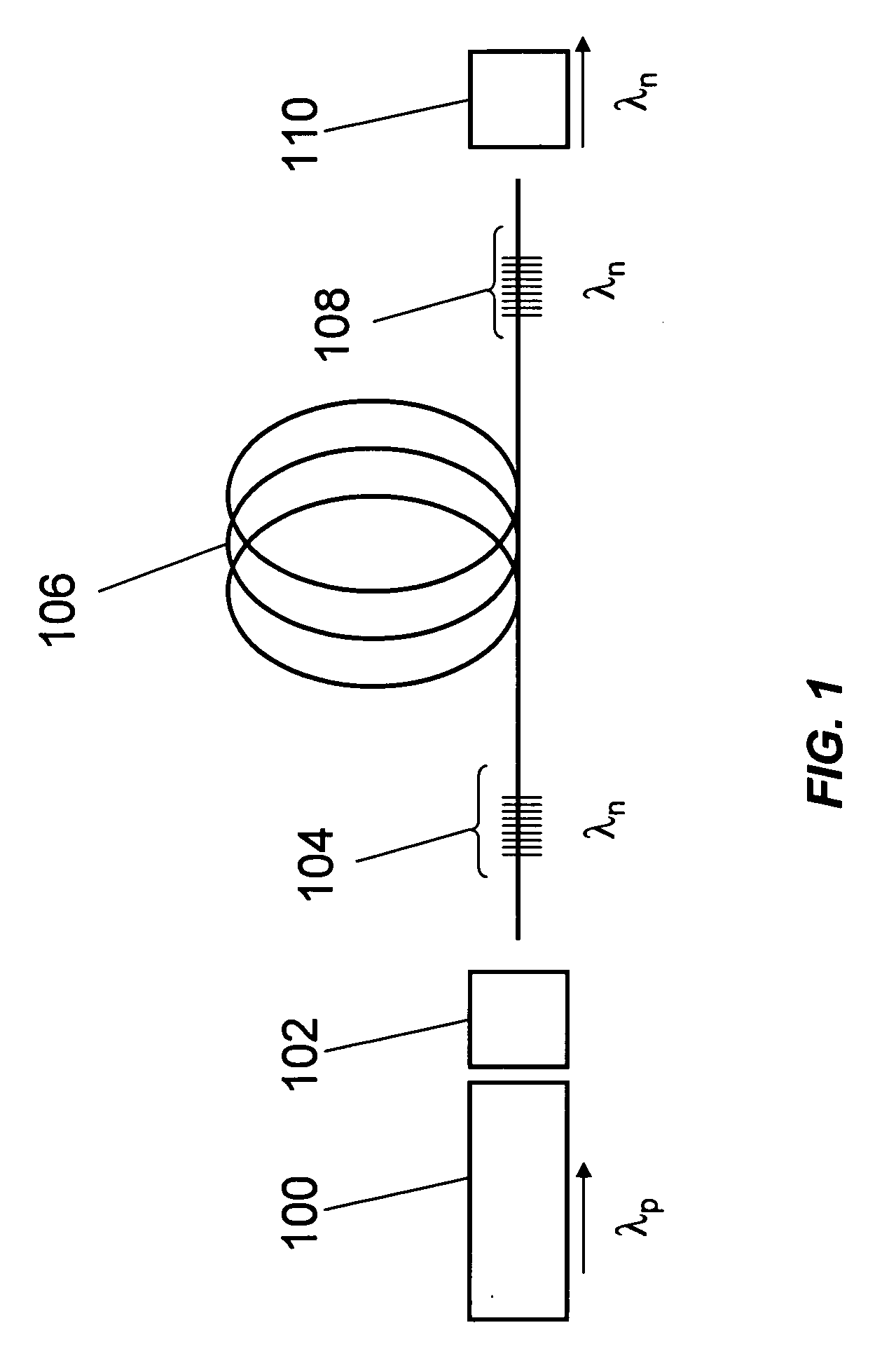
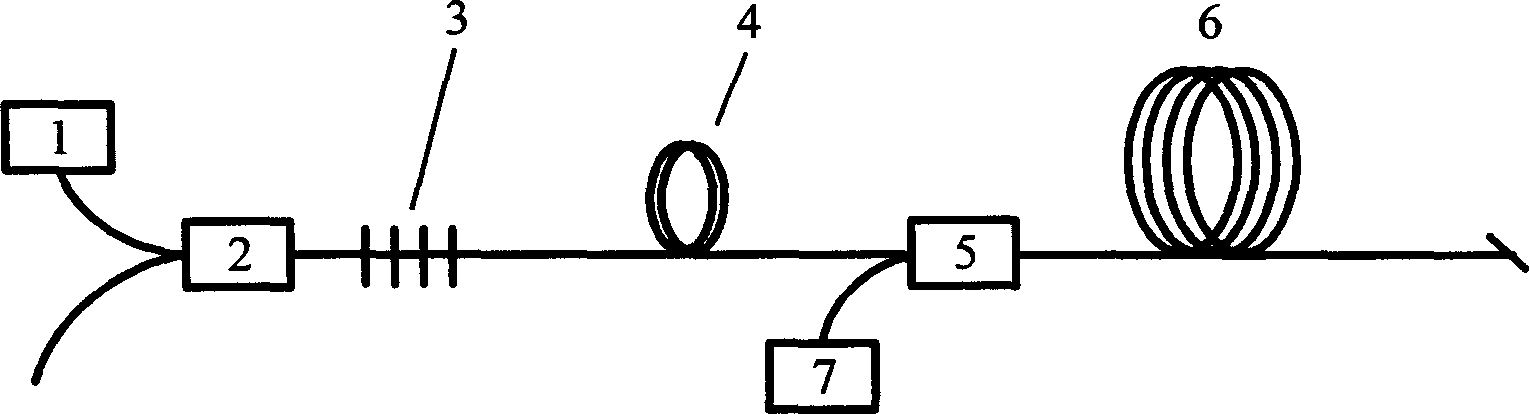
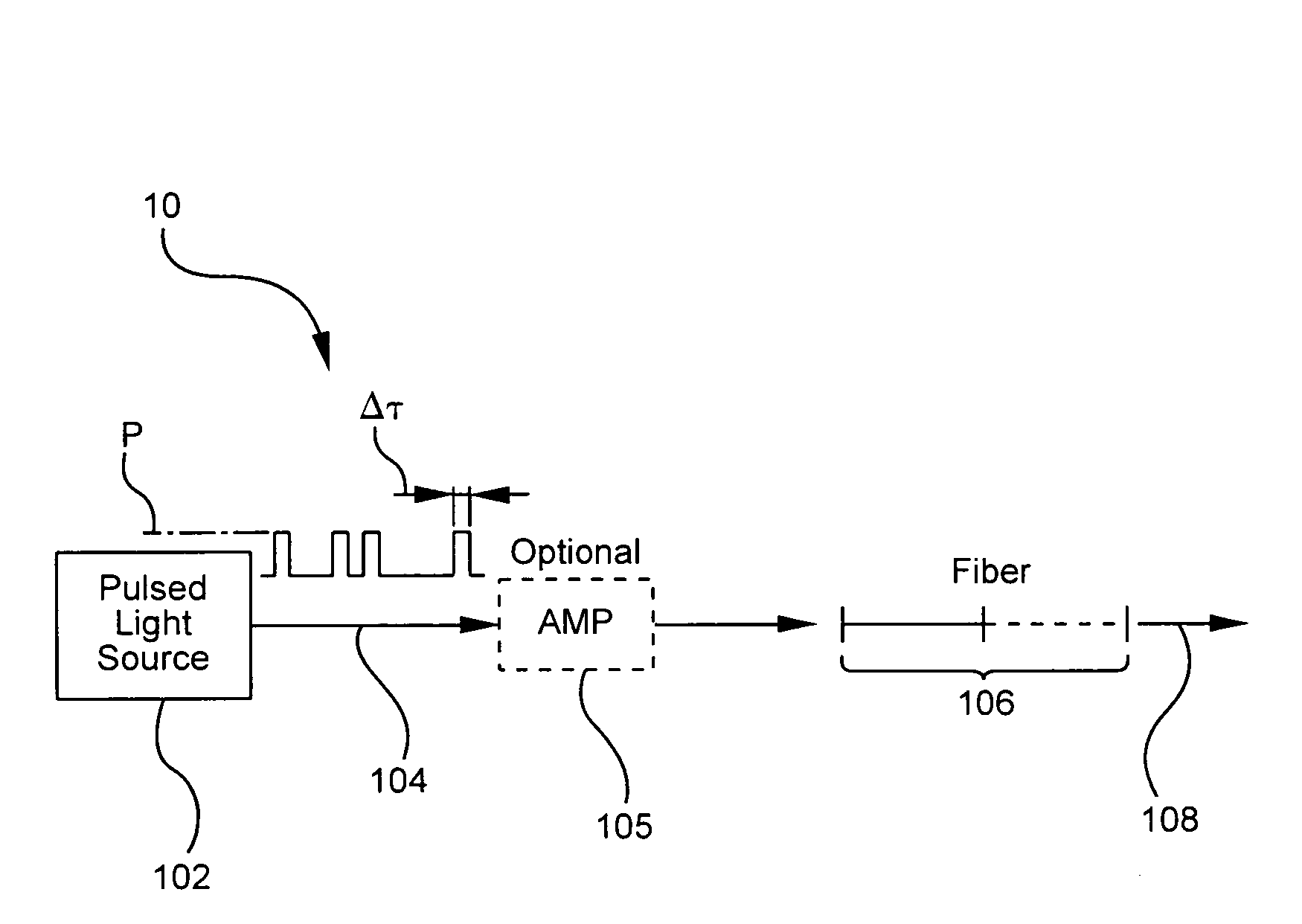
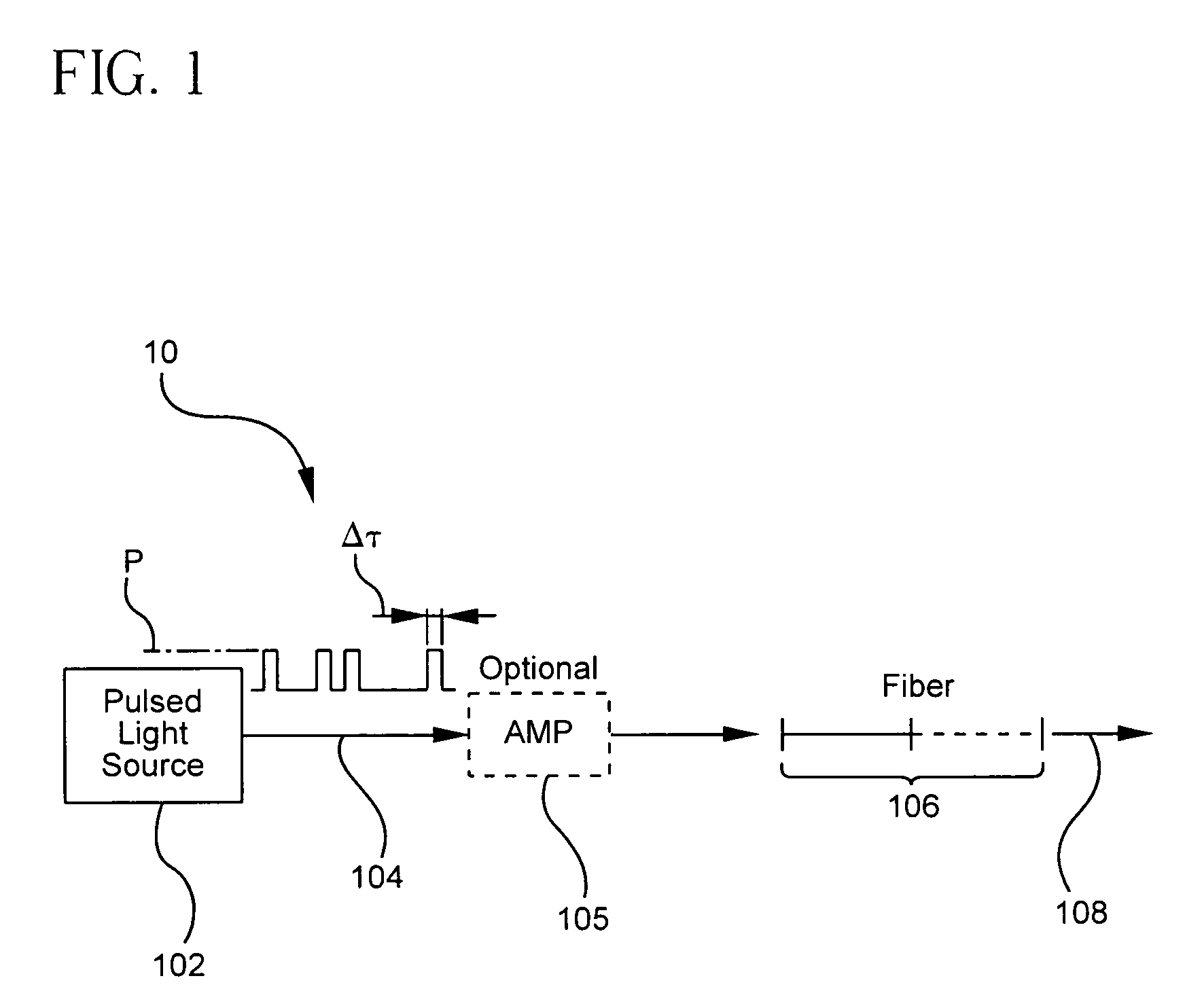
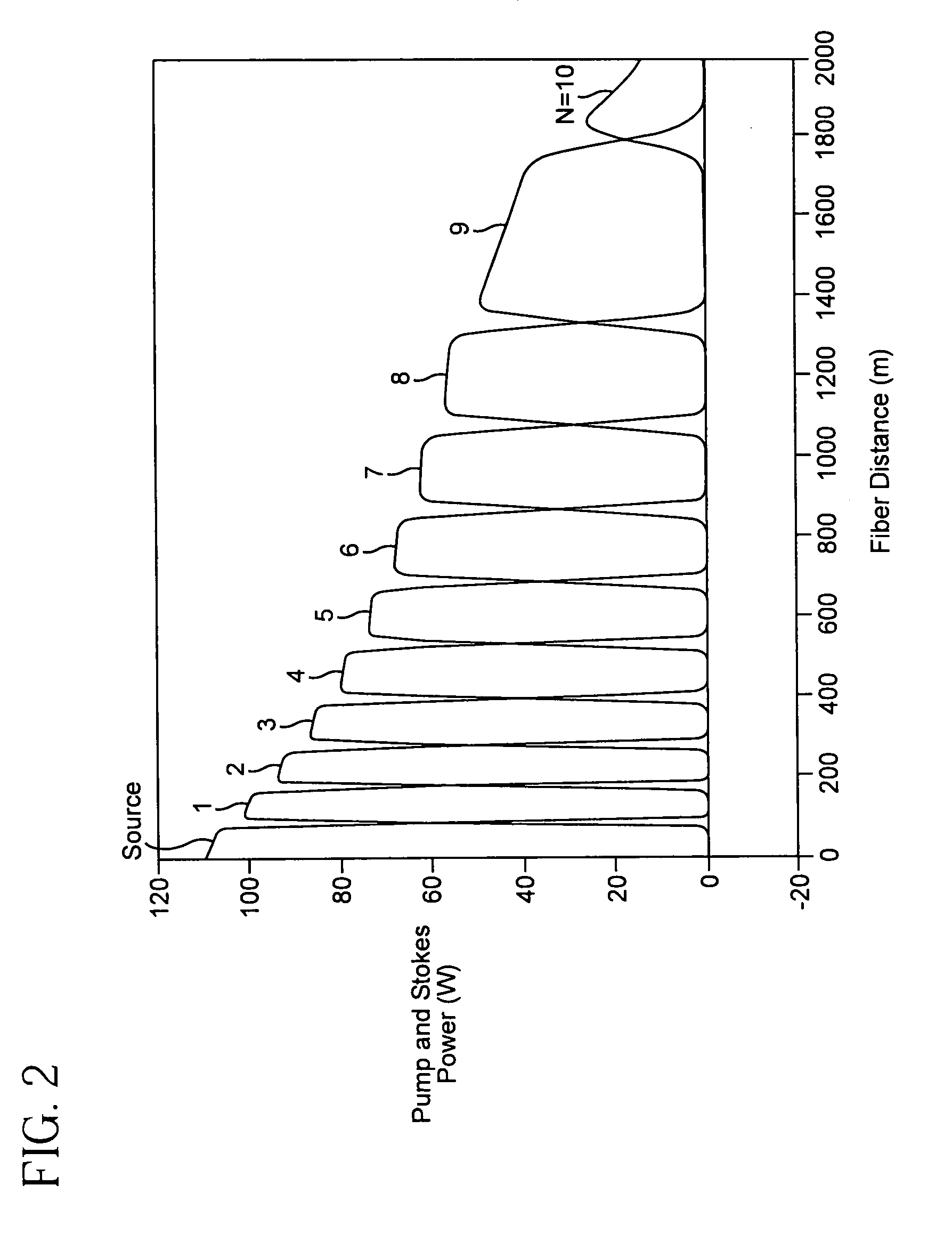
Pulsed cascaded raman laser
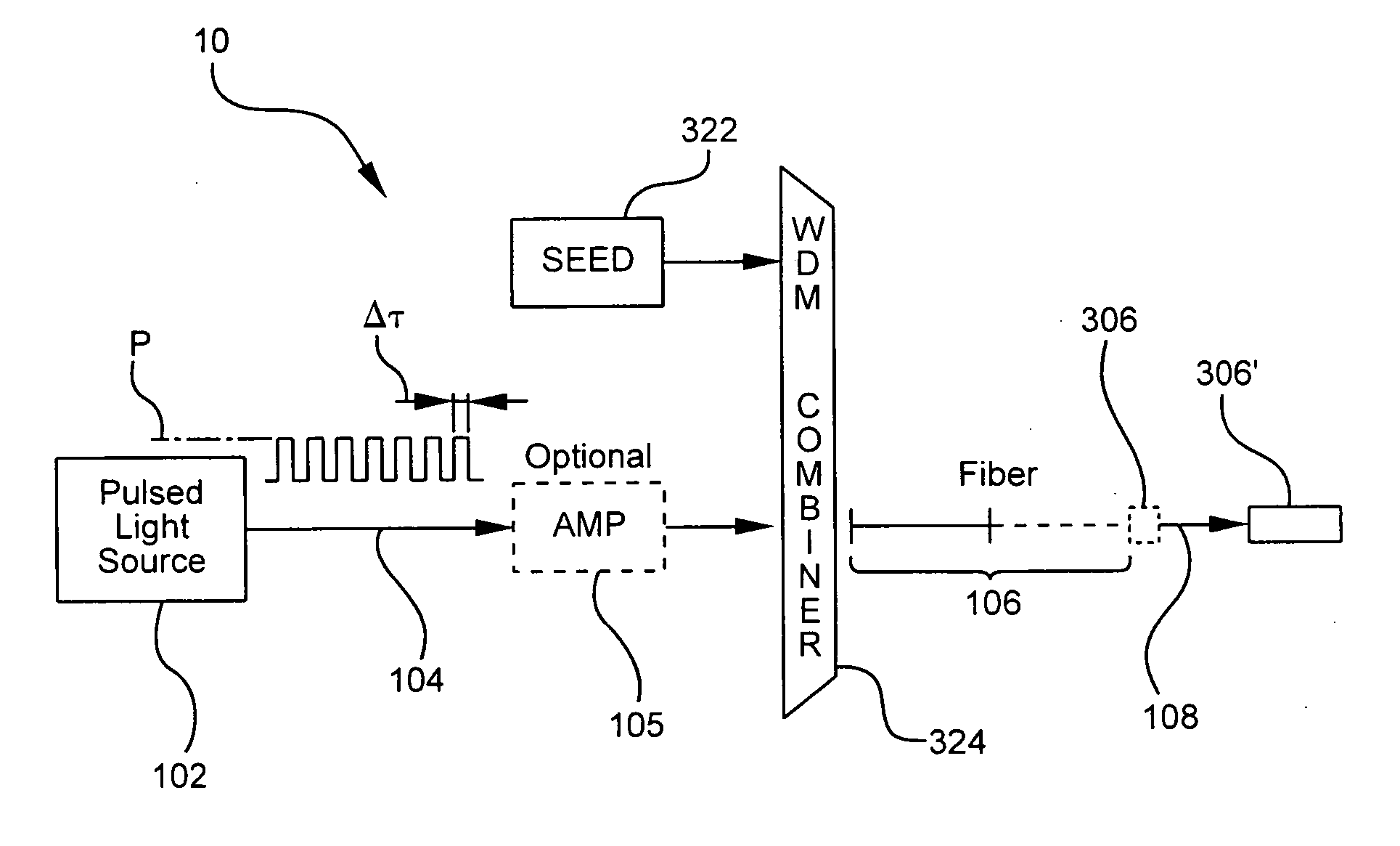
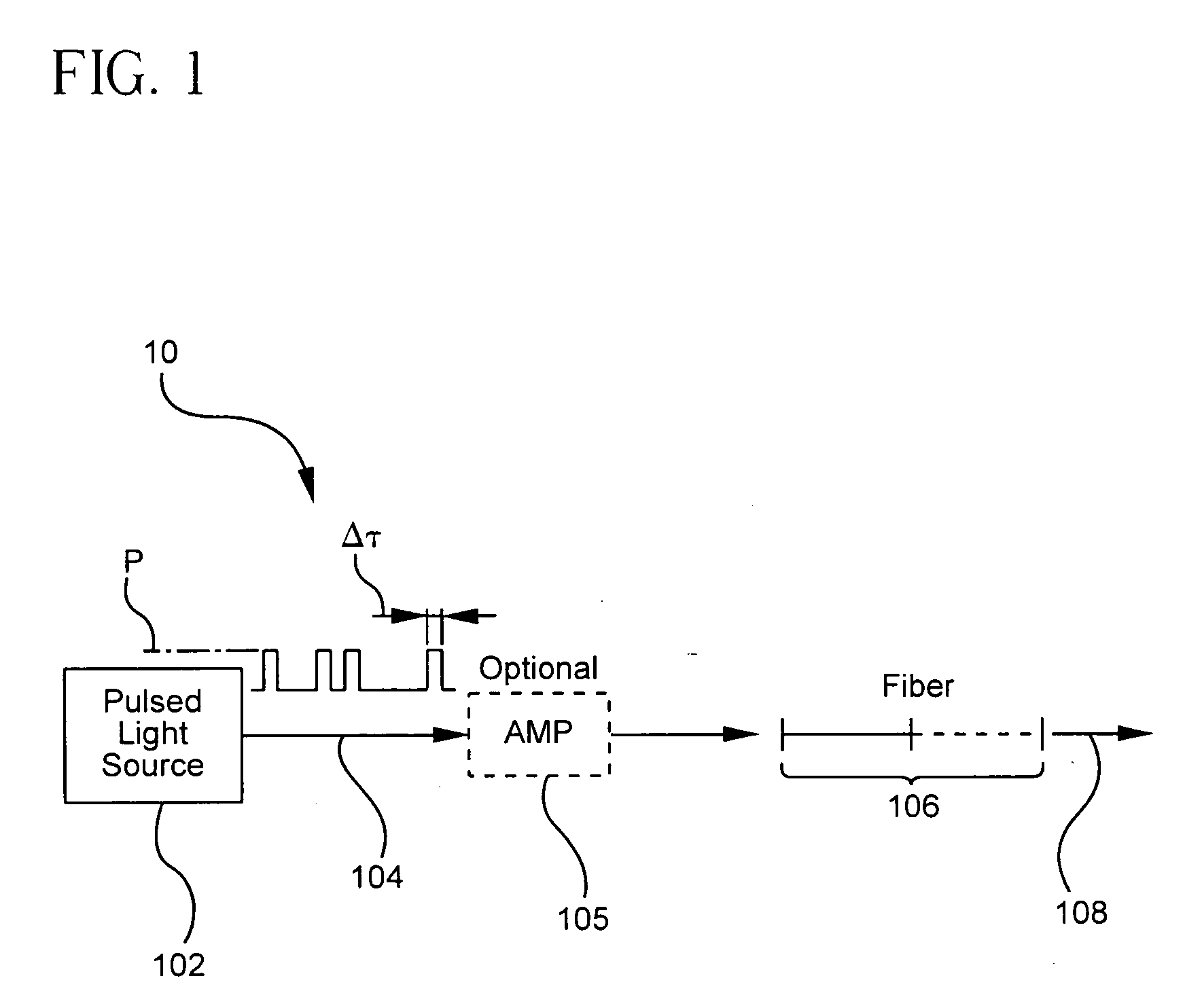
A pulsed cascaded Raman laser (10) includes a pulsed light source (102) for generating a pulsed light (104) having an optical spectrum centered at a source wavelength. A non-linear Raman conversion fiber (106) is coupled to the pulsed light source (102). The pulsed light (104) traverses the nonlinear Raman conversion fiber (106) and the source power at the source wavelength is converted to a power output of an output signal (108) having an output wavelength longer than the source wavelength by a cascaded Stimulated Raman Scattering process, such that most of the source power is converted to the power of the last Stokes order in a single pass through the non-linear Raman conversion fiber (106).
Owner:CORNING INC
Method and apparatus for generating high power visible and near-visible laser light
ActiveUS20090225793A1Efficient and reliableIncrease light outputLaser using scattering effectsSemiconductor lasersOptical radiationFiber
A multimode-fiber Raman laser includes a pump source configured to provide optical radiation centered at a pump wavelength and characterized by a spectral bandwidth greater than 100 MHz and an oscillator resonant at an emission wavelength greater than the pump wavelength. The oscillator includes an input coupler optically aligned with the pump source and a multimode optical fiber optically coupled to the input coupler. The multimode optical fiber includes an input section having a fiber Bragg grating, an intracavity section of a predetermined length optically coupled to the input section, and an output section having a fiber Bragg grating. The oscillator also includes an output coupler optically coupled to the multimode optical fiber and configured to provide a laser output at the emission wavelength.
Owner:RAM PHOTONICS IND LLC
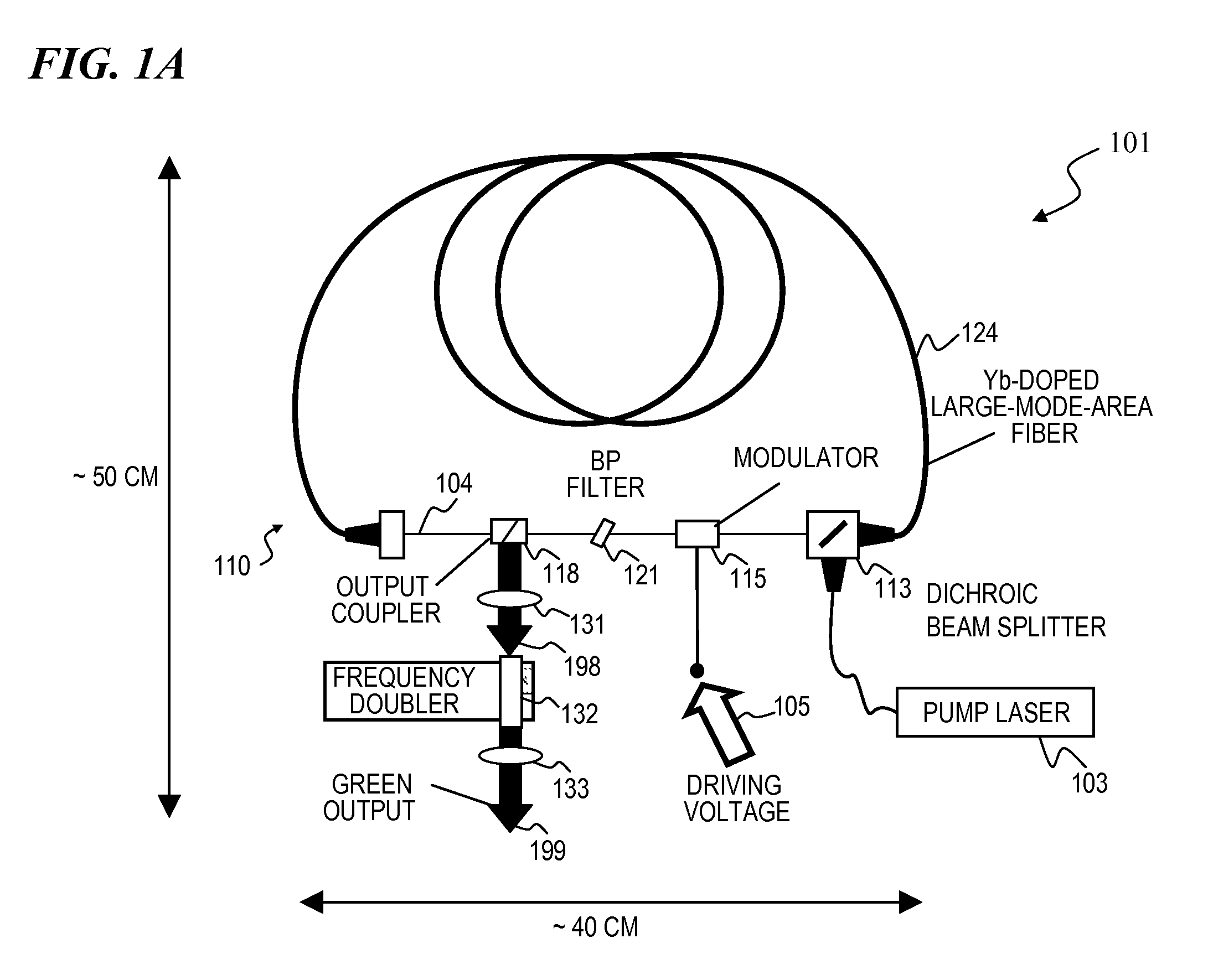
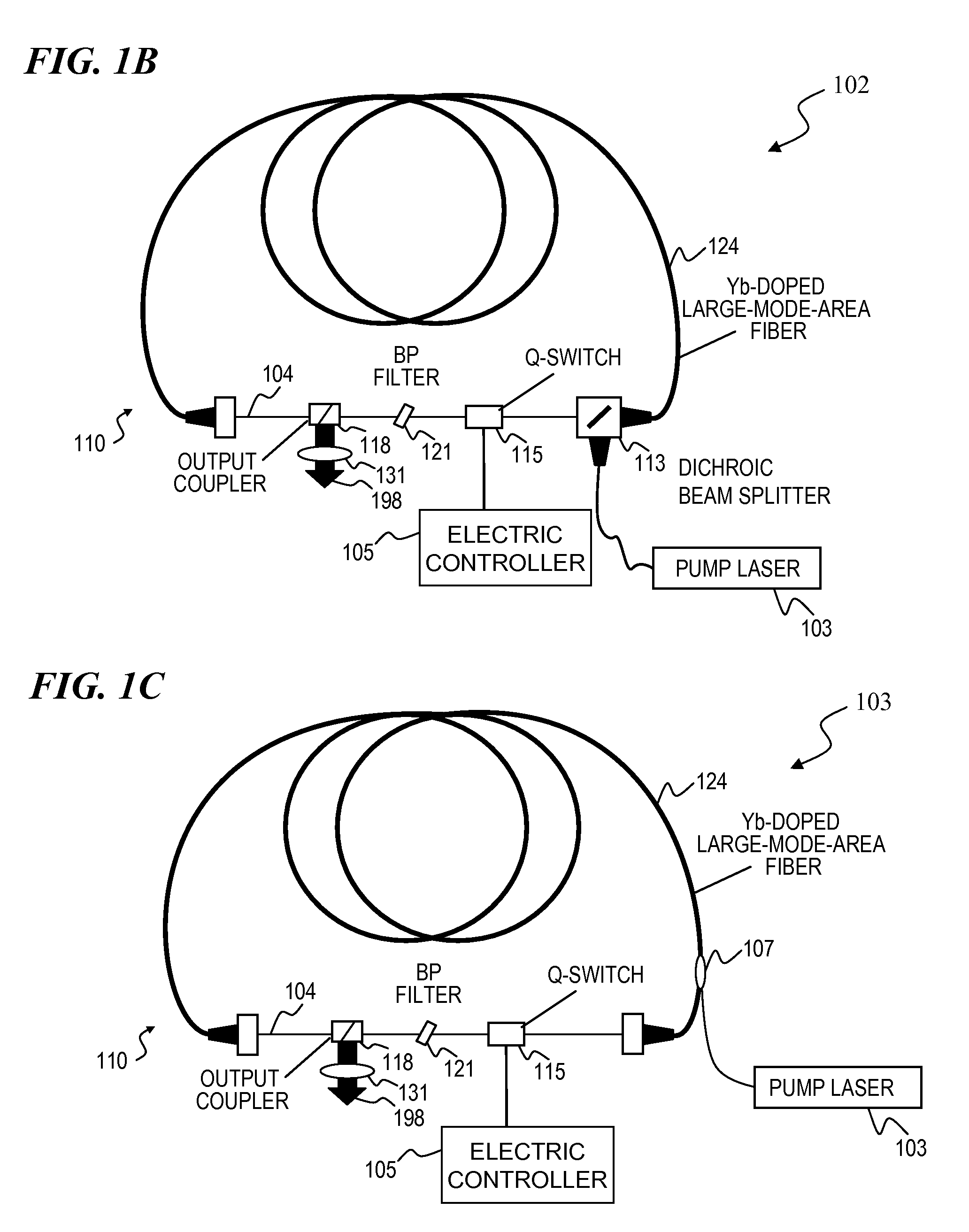
High-power, pulsed ring fiber oscillator and method
InactiveUS7876803B1Low costSmall footprintLaser using scattering effectsNon-linear opticsBand-pass filterUltraviolet
A ring laser includes a large-core rare-earth-doped fiber ring-connected with a free-space path having an electro-optic switch, output coupler, and intracavity band-pass filter to enforce lasing operation in narrow wavelength range. In some cavity-dumped modes, the laser is configured in a similar manner, except that an output coupler is omitted since the optical power is extracted from the laser cavity by the electro-optic switch itself. The same laser can be configured to operate in Q-switched and / or cavity-dumping modes as well as in hybrid modes (e.g., partial Q-switch, followed by cavity dumping, or even CW). In some embodiments, the laser can be used as, or inject laser light into, a regenerative solid-state amplifier, or a Raman laser, or can be also used to generate visible, ultra-violet, mid-infrared, and far-infrared (THz) radiation via nonlinear wavelength conversion processes. The various embodiments can use a power oscillator or seed-plus-amplifier MOPA configuration.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Combination inertial sensor based on multi-component atom interferometer and measurement method of combination inertial sensor
ActiveCN103837904ARealize synchronized measurementsHighly integratedAcceleration measurement using interia forcesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsEarthquake monitoringLaser light
The invention discloses a combination inertial sensor based on a multi-component atom interferometer and a measurement method of the combination inertial sensor, and relates to the technical field of inertial measurement through atom interference. The combination inertial sensor comprises a first inertial-moment-sensitive cold atom interferometer, a second inertial-moment-sensitive cold atom interferometer and a vacuum communication cavity, wherein the first inertial-moment-sensitive cold atom interferometer and the second inertial-moment-sensitive cold atom interferometer are the same in structure. The vacuum communication cavity is communicated with an atom interference area of the first inertial-moment-sensitive cold atom interferometer and an atom interference area of the second inertial-moment-sensitive cold atom interferometer in the horizontal direction. According to the measurement method, multi-frequency laser light is used for simultaneously and independently manipulating two types of alkali metal atoms in the same physical unit, wherein the acceleration and the gravity gradient of one type of alkali metal atoms are measured through a three-pulse pi / 2-pi-pi / 2 Raman laser sequence, and the rotating speed of the other type of alkali metal atoms is measured through a four-pulse pi / 2-pi-pi-pi / 2 Raman laser sequence. Synchronous measurement of a plurality of inertial moments is realized through a simplex physical device at the same time, and the combination inertial sensor based on the multi-component atom interferometer and the measurement method of the combination inertial sensor can play an important role in inertial navigation, resource exploration, earthquake monitoring, physical geographical research and other fields.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Solid state diamond Raman laser
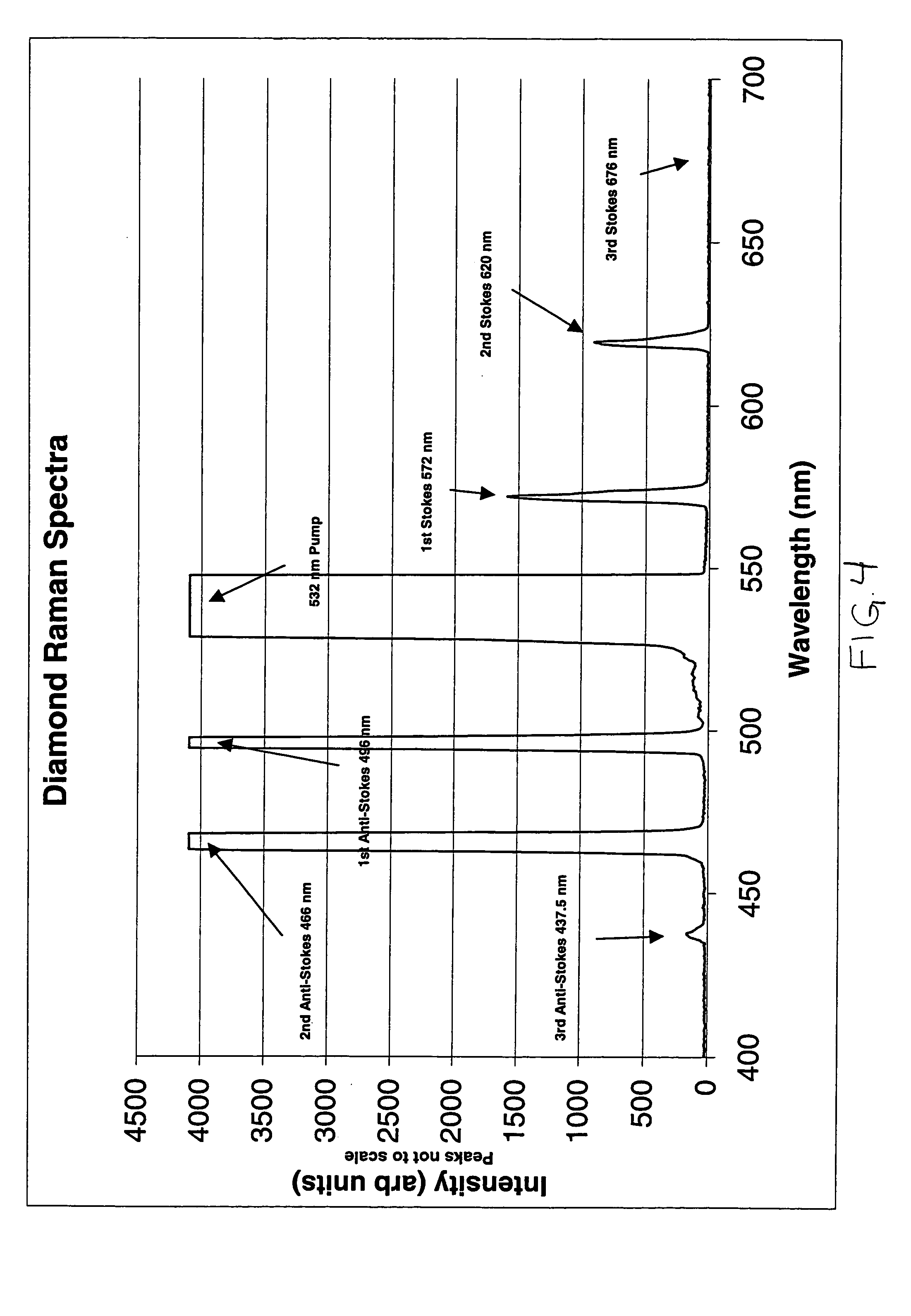
InactiveUS20050163169A1High power applicationLaser using scattering effectsActive medium materialStimulate raman scatteringSingle crystal
A solid state Raman laser includes a laser pump for producing a first radiation at a high power and at a first wavelength along an optical path, a solid Raman active medium in the optical path of the first radiation, the medium including single crystal diamond having a first surface and a second surface, where the first radiation at a high power produces stimulated Raman scattering in the medium and the medium generates a second radiation at a second wavelength, a first optical element in the optical path of the first radiation, wherein the first optical element allows the first wavelength to be transmitted and allows the second wavelength to be reflected, and a second optical element in the optical path of the first radiation, wherein the second optical element allows the first wavelength to be transmitted and allows the second wavelength to be reflected.
Owner:SPECTRA SYST CORP
Stable solid state raman laser and method of operating same
InactiveUS20040028090A1Effective approachLimited scalabilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionSolid massInstability
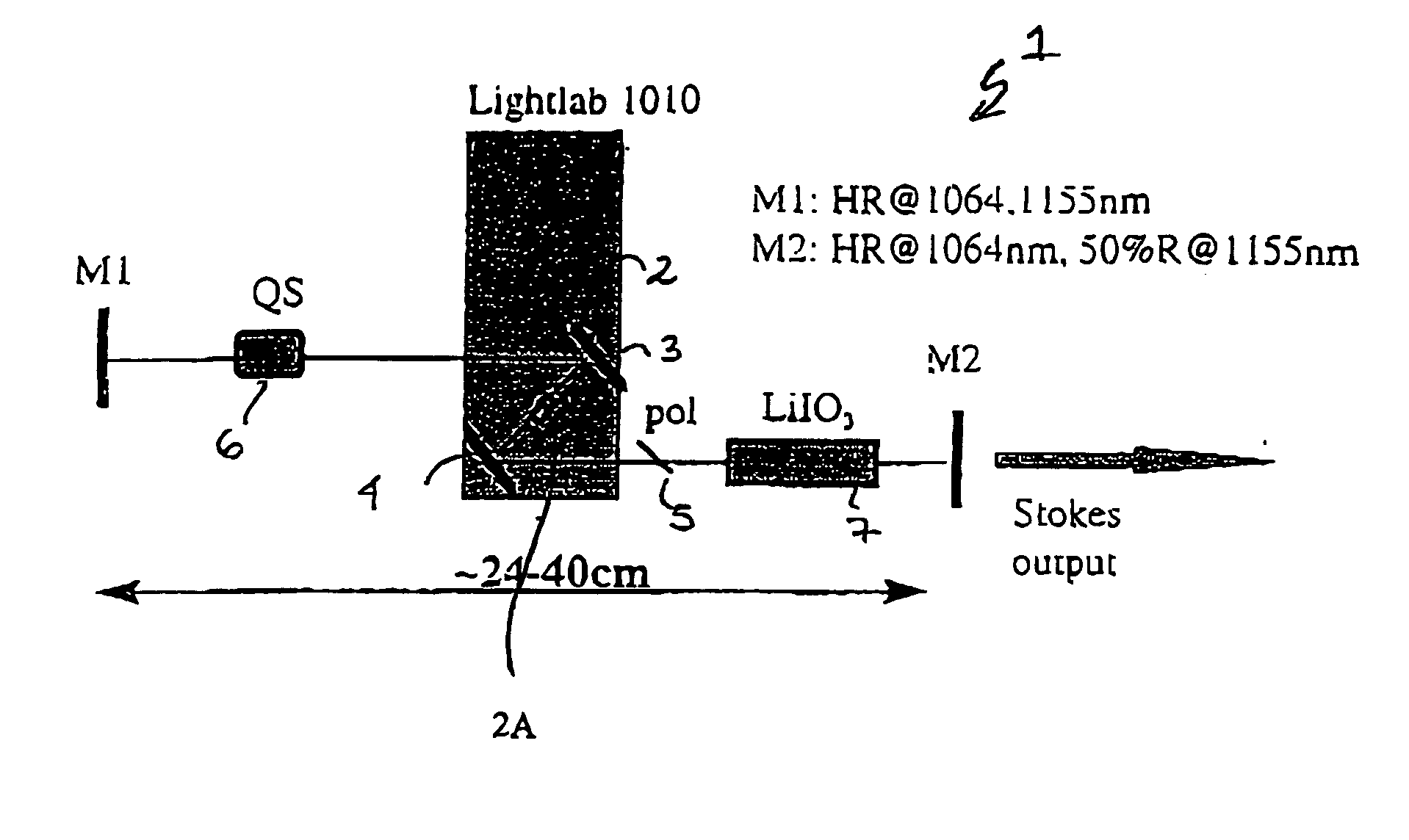
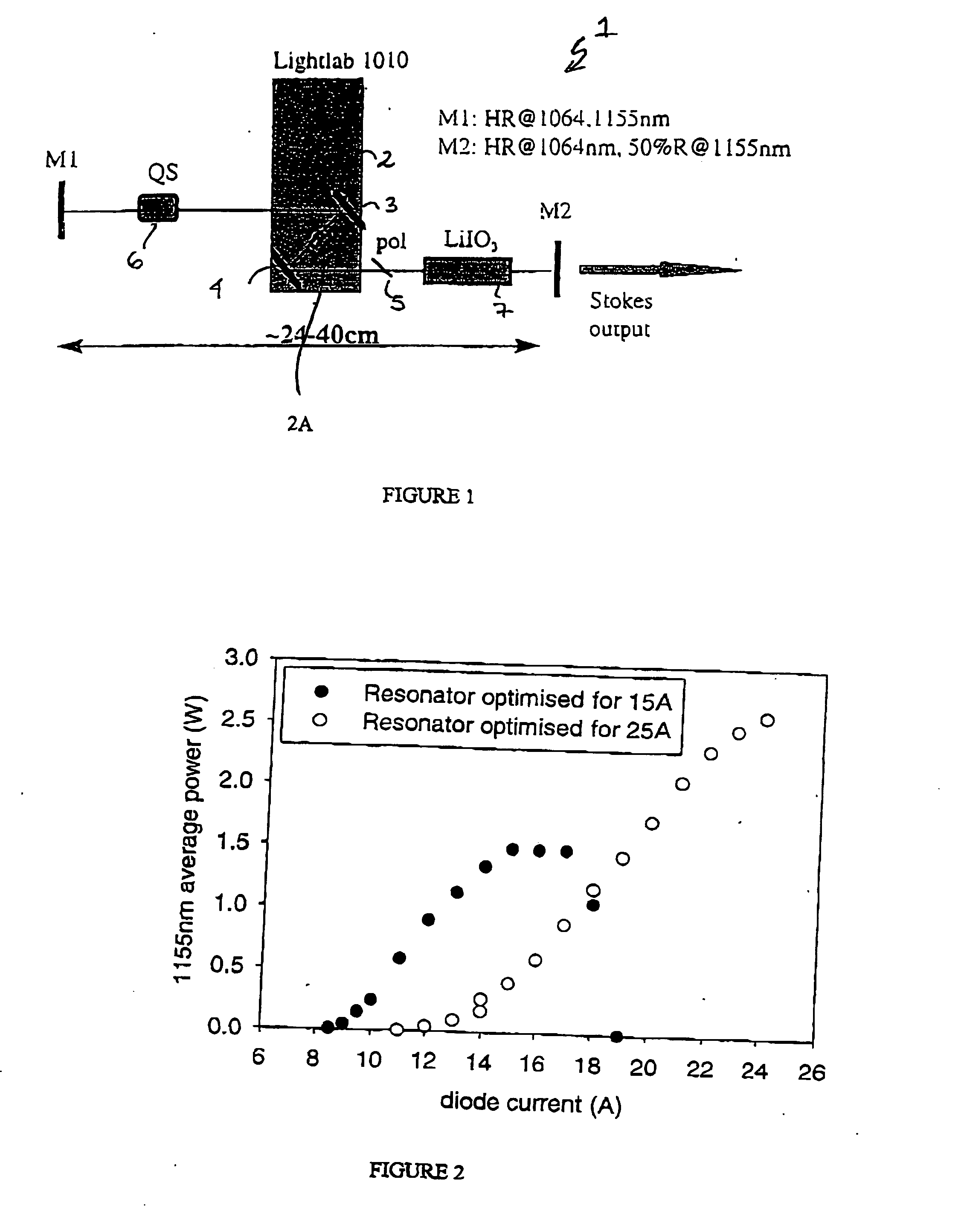
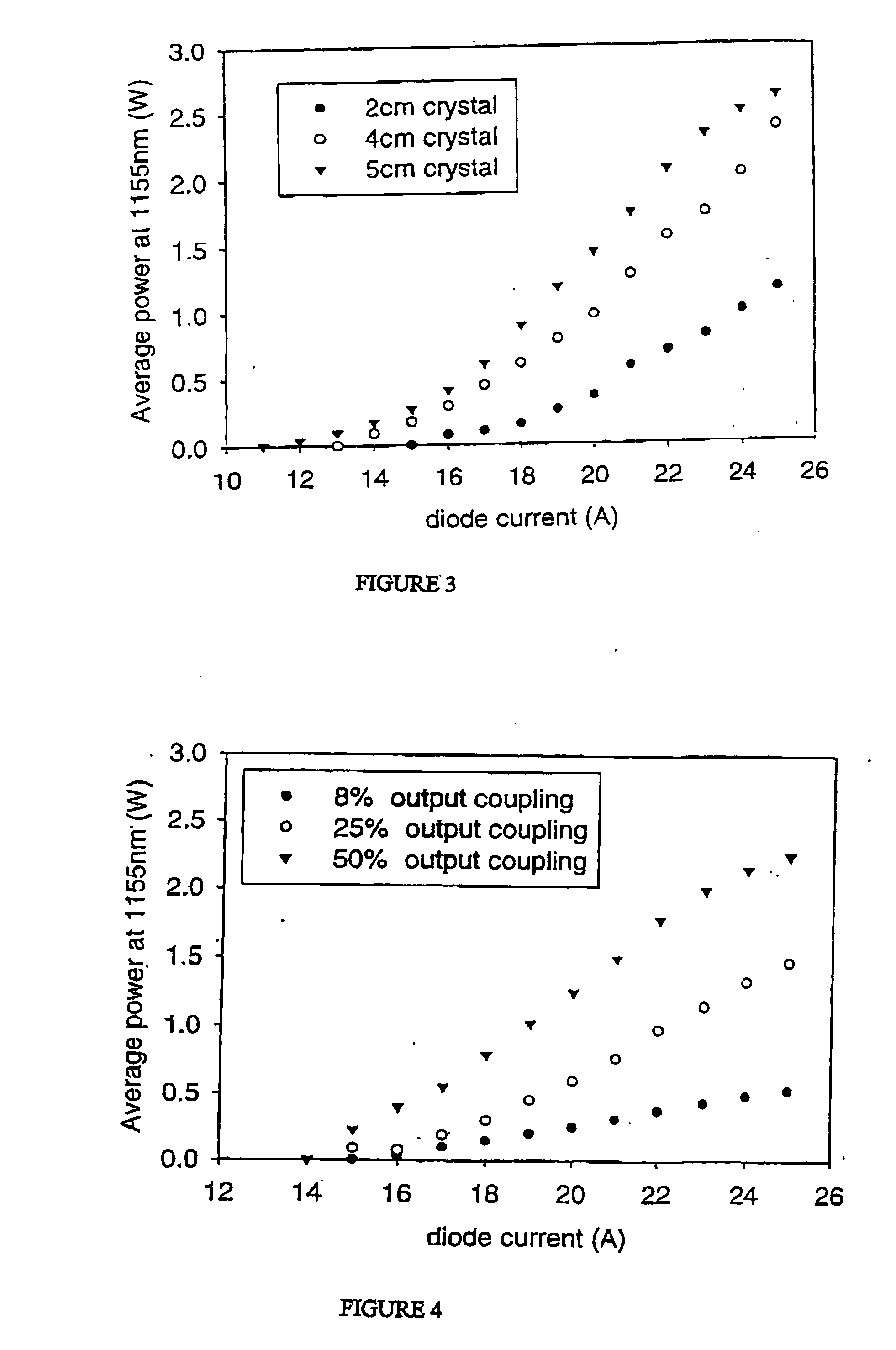
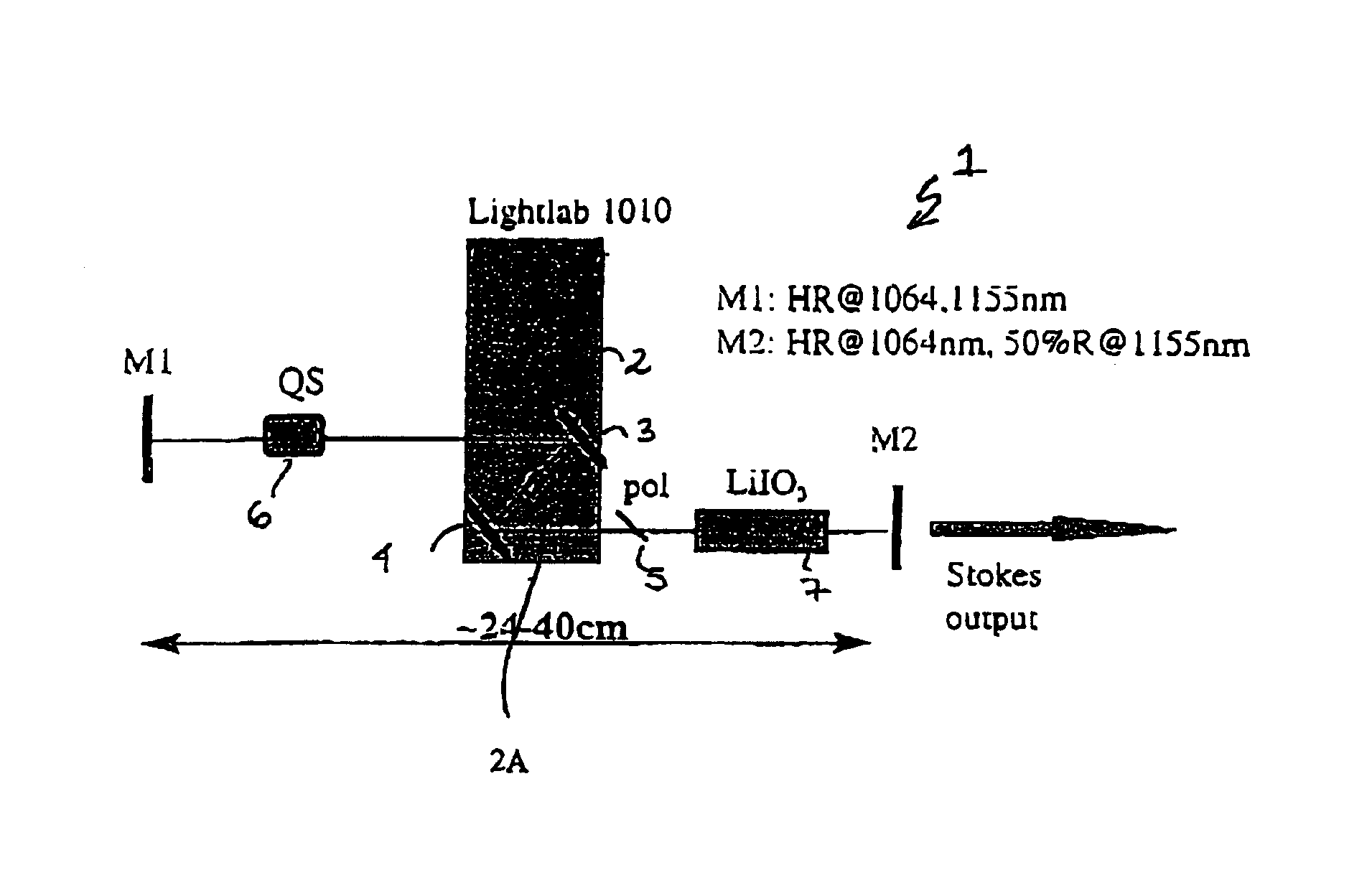
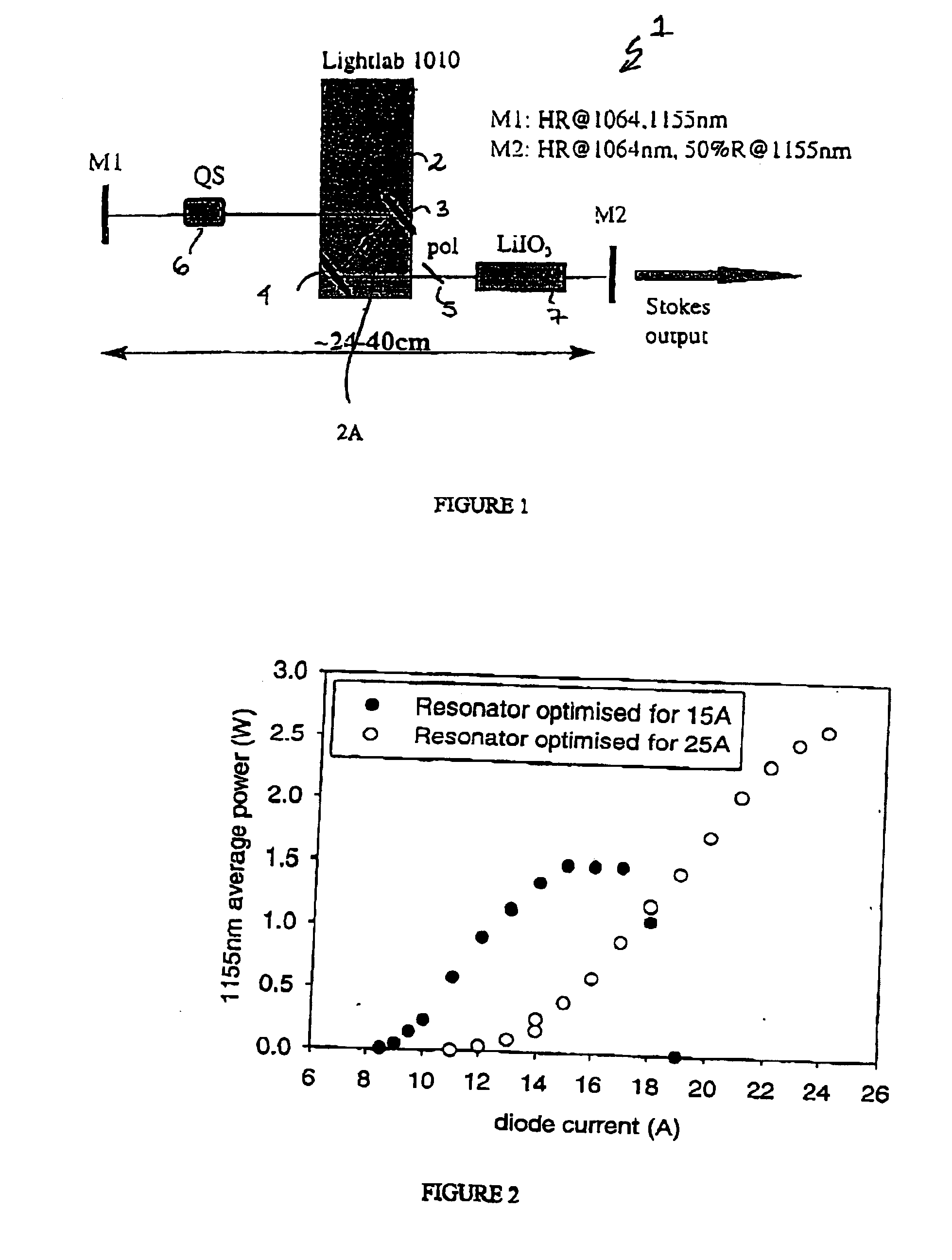
The present invention relates to a stable solid-state Raman laser (1), the solid-state Raman laser including: (a) a resonator cavity defined by at least two reflectors (M1 and M2), (b) a laser material (2A) located in the resonator cavity and capable of generating a cavity laser beam which propagates within the resonator cavity, (c) a solid Raman medium (7) located in the resonator cavity for shifting the frequency of the cavity laser beam to produce a Raman laser beam which propagates within the resonator cavity; and (d) an output coupler (M2) for coupling and outputting the Raman laser beam from the resonator cavity, wherein at least one parameter selected from the group consisting of (i) the position of the laser material (2A) relative to the position of the Raman medium (7) in the cavity, (ii) the length of the cavity and (iii) the curvature of at least one of the reflectors (M1 or M2), is selected such that changes in the focal lengths of both the laser material (2A) and the Raman medium (7) as a result of thermal effects in the laser material (2A) and the Raman medium (7) during operation of the laser do not substantially cause instability in the power of the output Raman laser beam. A method of maintaining stable operation of a solid state Raman laser is also described.
Owner:MACQUARIE UNIV
Single-wavelength four-Raman laser radar detection system and detection method
ActiveCN104880711AEfficient collectionEliminate the effects ofElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationRadar systemsData acquisition
The invention discloses a single-wavelength four-Raman laser radar detection system and a detection method. The system combines three laser radar technologies of atmospheric temperature measurement via pure-rotation Raman scattering, vapor measurement via vibration Raman scattering, and measurement of atmosphere aerosol optical characteristics via Raman Mie scattering and an inversion method. The laser radar system employs 355 nm single-wavelength pulse laser as a detection light source and a large-diameter optical reception telescope with high transmittance for measuring the wavelength to collect atmospheric back scattering light signals, four wavelength atmospheric Raman scattering light signals and Mie scattering echo light signals of 353 nm, 354 nm, 355 nm, 386 nm, and 407 nm are mutually separated via an angle separation method of color separation filters and interference filters by a following optical path, the above five-wavelength scattering light signals are gated via narrowband interference filters, photoelectric conversion of photomultipliers of the same type is accomplished, and data acquisition is accomplished by a five-channel data collector.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Novel optical fiber Brillouin light time domain analyzer
InactiveCN101324424AHigh gainAvoid difficultiesThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansBeam splitterFiber gratings
The invention discloses an optical fiber Brillouin optical time domain analyzer, which is made based on optical fiber broadband nonlinear light amplification effect and strain, temperature effect and optical light domain analysis principle of coherent amplified Brillouin scattering. The optical fiber Brillouin optical time domain analyzer comprises a narrowband single-frequency fiber laser, a fiber beam splitter, a pulse modulator, two optical fiber circulators, a heterodyne receiver, a digital signal processor, a fiber-grating filter, a monomode fiber and a continuous-operating fiber Raman pump laser. The continuous-operating high-power fiber Raman pump laser is used as the pump light source of the Brillouin optical time domain analyzer, which can overcome the difficulty in strictly locking the frequency of a detection laser and the pump laser of the Brillouin optical time domain analyzer; and boardband fiber nonlinear scattering amplification is used for substituting for narrowband Brillouin amplification to increase the gain of stimulated Brillouin scattering with back amplification, thus improving the S / N ratio of the system, increasing the measurement length, and improving the accuracy for simultaneous measurement of stain and temperature.
Owner:WEIHAI BEIYANG PHOTOELECTRIC INFORMATION TECH
Vertical gravity gradient measuring sensor based on atom interference effect
ActiveCN103472495ARealize synchronized measurementsCancellation noiseGravitational wave measurementAtomic groupUnit device
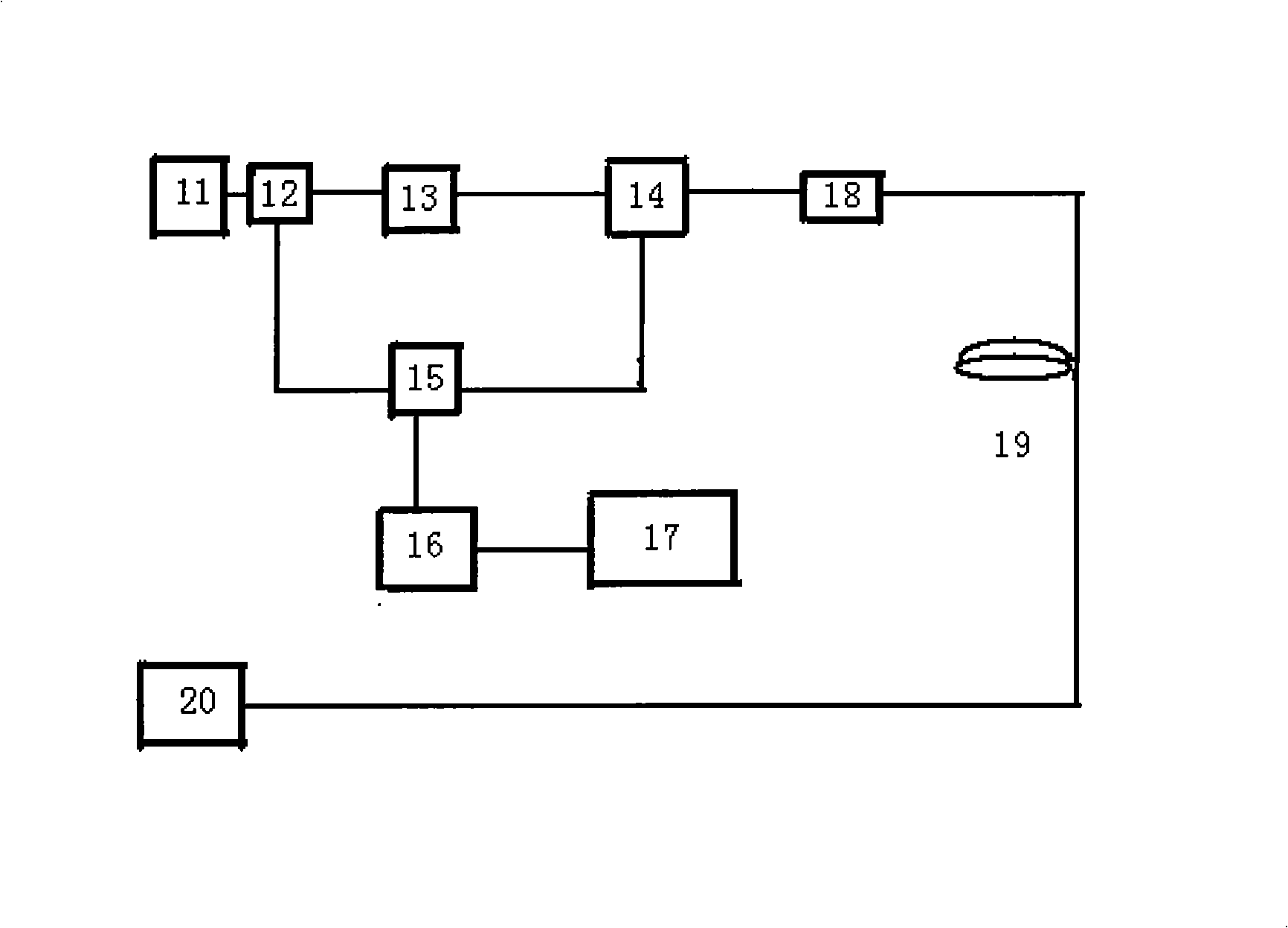
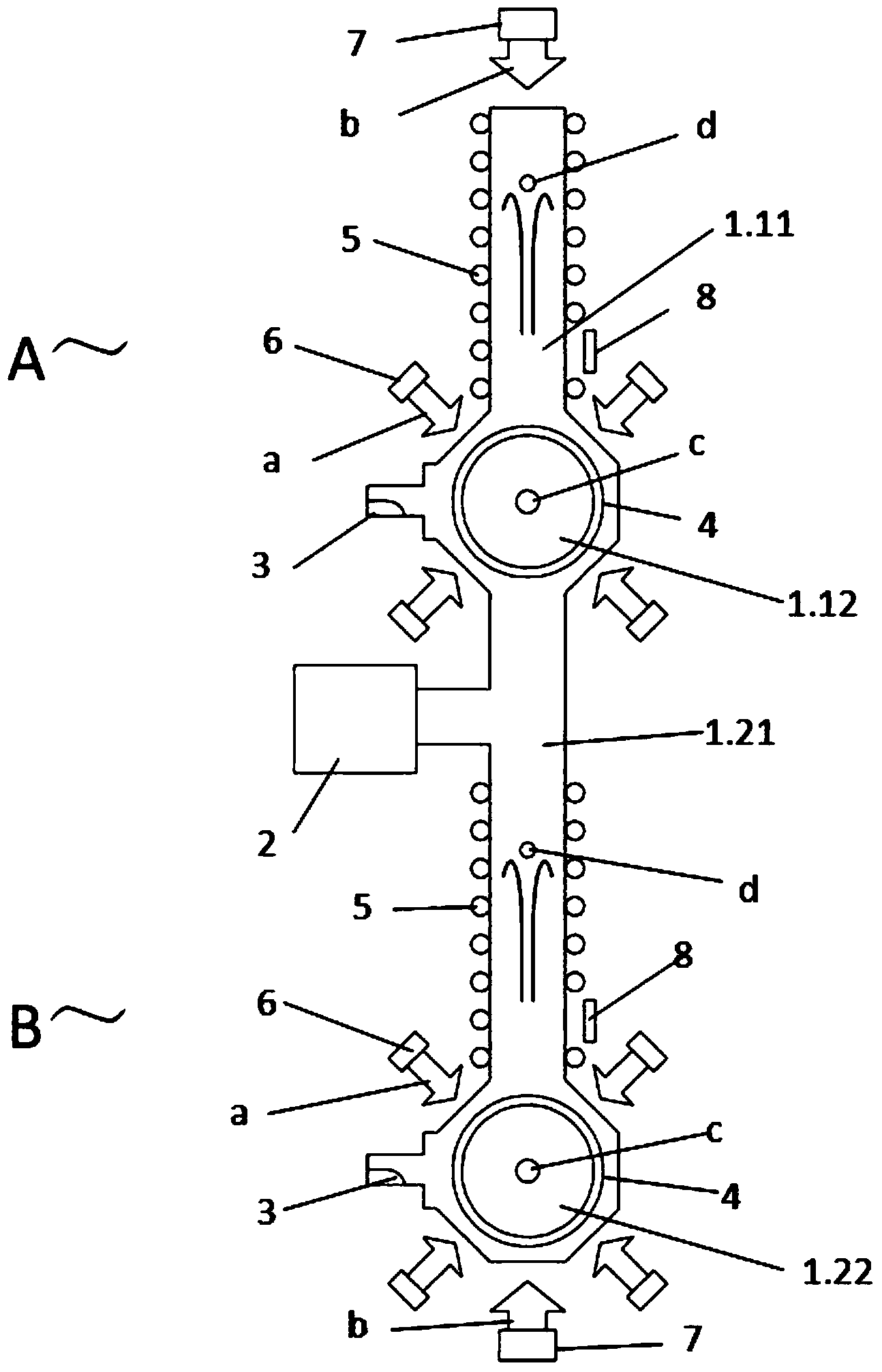
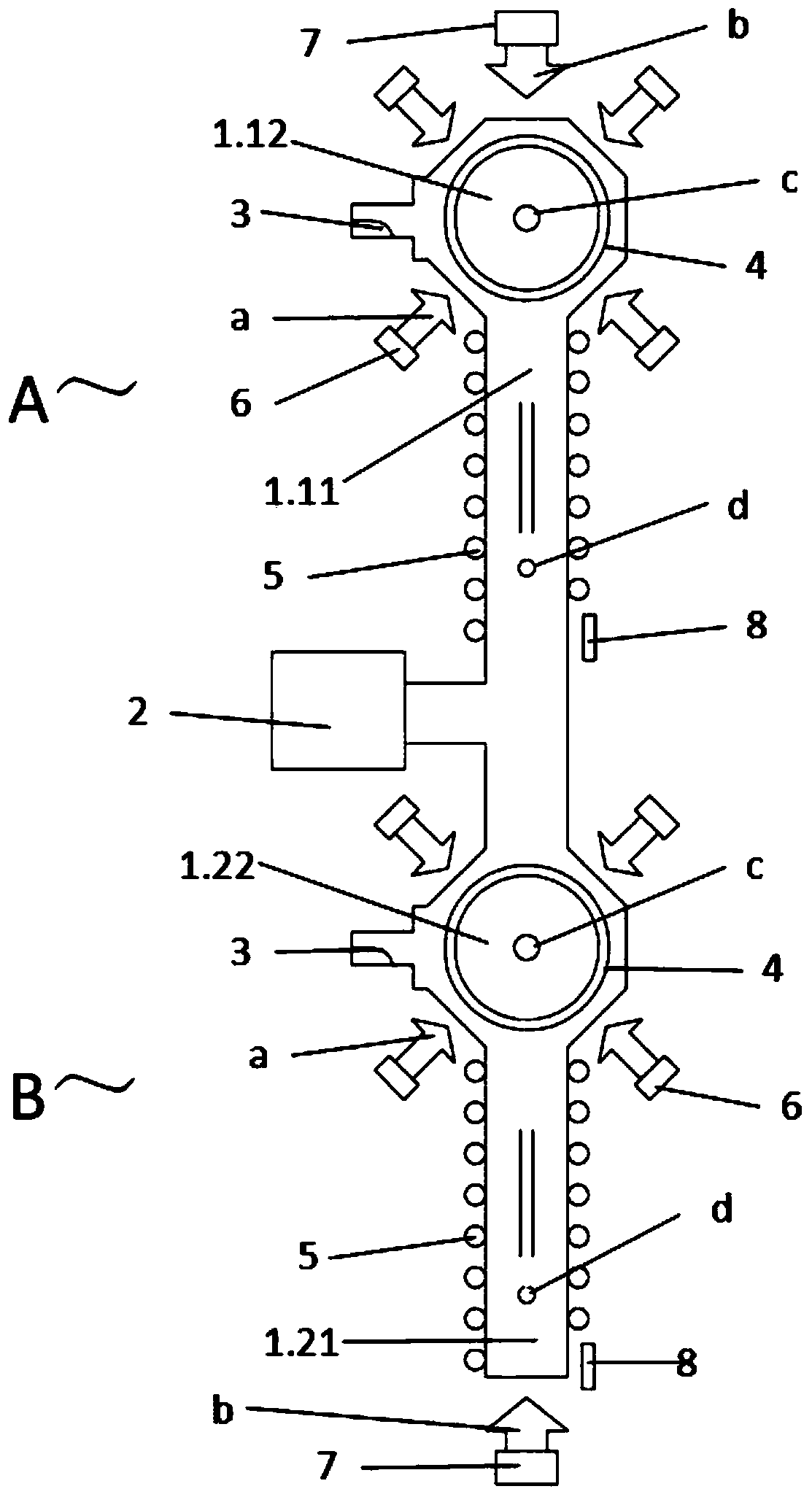
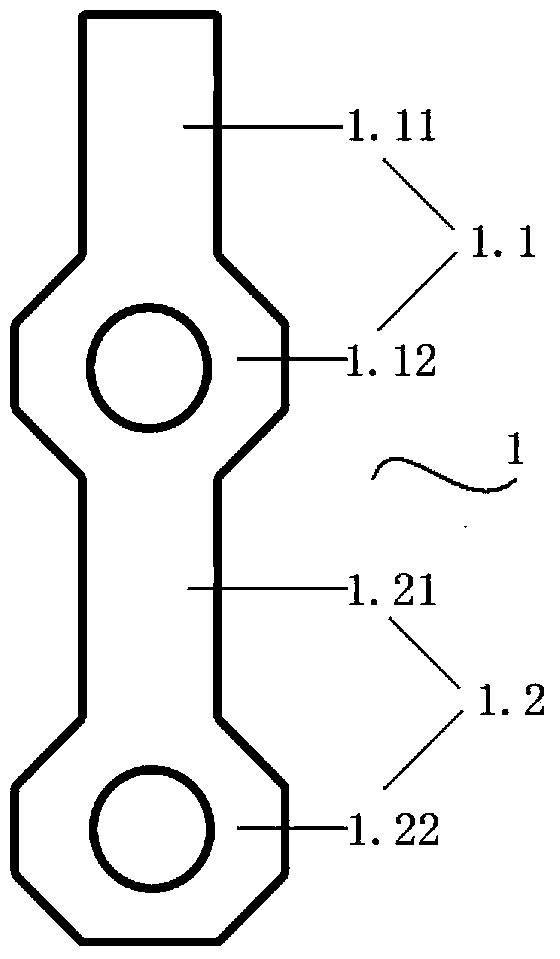
The invention discloses a vertical gravity gradient measuring sensor based on an atom interference effect, and belongs to the technical field of gravity surveying. The sensor comprises a first unit device (A) and a second unit device (B) of the same structures, and is characterized in that a first vacuum container (1.1) and a second vacuum container (1.2) are connected end to end in the mode that central axes are overlapped in the gravity direction to form a vacuum container (1), and the hollow part inside the first vacuum container (1.1) and the hollow part inside the second vacuum container (1.2) are communicated into a whole; two Raman laser beam emitters (7) are respectively arranged on the vacuum container (1) along the central axis of the gravity field direction, and the Raman laser beam emitters (7) carry out opposite emitting and point to the preparation regions of cold atomic groups (c), and the two unit devices share the pair of Raman laser beam emitters (7). The vertical gravity gradient measuring sensor enables noise and deviation from environment and Raman laser phase positions to be offset in a common-mode mode, and reduces the complexity, the size, the mass and the power consumption of a physical system.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Stable solid state raman laser and a method of operating same
InactiveUS6901084B2Avoid optical damageCavity stabilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionResonant cavitySolid mass
The present invention relates to a stable solid-state Raman laser, the solid-state Raman laser including a resonator cavity defined by at least two reflectors, a laser material located in the resonator cavity and capable of generating a cavity laser beam which propagates within the resonator cavity, a solid Raman medium located in the resonator cavity for shifting the frequency of the cavity laser beam to produce a Raman laser beam which propagates within the resonator cavity; and an output coupler for coupling and outputting the Raman laser beam from the resonator cavity, wherein at least one parameter selected from the group consisting of the position of the laser material relative to the position of the Raman medium in the cavity, the length of the cavity and the curvature of at least one of the reflectors, is selected such that changes in the focal lengths of both the laser material and the Raman medium as a result of thermal effects in the laser material and the Raman medium during operation of the laser do not substantially cause instability in the power of the output Raman laser beam. A method of maintaining stable operation of a solid state Raman laser is also described.
Owner:MACQUARIE UNIV
Mid to far infrared diamond raman laser systems and methods
ActiveUS20130043392A1Increased Raman gainMinimise absorption lossLaser using scattering effectsMaterial analysis by optical meansResonant cavityMicrometer
A mid- to far-infrared solid state Raman laser system comprising a resonator cavity comprising: an input reflector adapted to be highly transmissive for light with a first wavelength in the range of about 3 to about 7.5 micrometers for admitting the first beam to the resonator cavity; and an output reflector adapted to be partially transmissive for light with a second wave-length greater than about 5.5 micrometers for resonating the second wavelength in the resonator and for outputting an output beam, the input reflector further being adapted to be highly reflective at the second wavelength for resonating the second wave-length in the resonator; and a solid state diamond Raman material located in the resonator cavity for Raman shifting the pump beam and generating the second wavelength.
Owner:MACQUARIE UNIV
Ultrafast raman laser systems and methods of operation
InactiveUS20120263196A1Decrease length of resonatorShorten the lengthLaser using scattering effectsLight beamWavelength
A Raman laser system, the system comprising a resonator cavity comprising a plurality of reflectors, wherein at least one reflector is an output reflector adapted for outputting a pulsed output beam from the resonator cavity at a frequency corresponding to a Raman shifted frequency of the pump beam, wherein the output reflector is partially transmitting at the Raman-converted frequency; a solid state Raman-active medium located in the resonator cavity to be pumped by a pulsed pump beam having a pump repetition rate and for Raman-converting a pump pulse incident on the Raman-active medium to a resonating pulse at a Raman-converted frequency resonating in the resonator cavity; a resonator adjuster for adjusting the optical length of the resonator to match the round-trip time of the resonating Raman-converted pulse with the pump beam repetition rate such that the resonating pulse is coincident both temporally and spatially with a pump pulse in the Raman-active medium on each round trip, to Raman amplify the resonating pulse at the Raman-converted frequency in the Raman-active medium. Also a multiwavelength Raman laser system further comprising a dispersive element and a plurality of coupled resonator cavities. Also, methods for providing ultrafast pulsed Raman laser operation.
Owner:MACQUARIE UNIV
Method for acquiring complex refractive index of urban aerosol on basis of various ground-based remote sensing technologies
InactiveCN103175759AReduce mistakesImprove discriminationMaterial analysisAtmospheric layerExtinction
The invention relates to a method for acquiring a complex refractive index of urban aerosol on the basis of various ground-based remote sensing technologies. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring the extinction coefficient and the scattering extinction ratio of the aerosol through an inverse algorithm by virtue of Raman laser radar echo signals, and integrating the extinction coefficient of a certain route to acquire the optical thickness of the aerosol on the route; continuously correcting the extinction coefficient and the scattering extinction ratio by performing iterative alignment on an aerosol optical thickness of a whole atmospheric layer acquired via a sun photometer and the aerosol optical thickness acquired via a laser radar according to a Monte Carlo principle; then acquiring the particle size distribution of the aerosol via a particle spectrometer; and finally, acquiring the complex refractive index of the urban aerosol according to a mie-scattering model by virtue of the known scattering extinction ratio of the aerosol and the particle size distribution of the aerosol. According to the invention, the complex refractive index of the urban aerosol is acquired by the Raman laser radar, the sun photometer and the particle spectrometer, and the method has the advantages of small error, high discriminability and high universality.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Random-distribution feedback optical fiber laser
InactiveCN102354900AShorten the lengthIncrease output powerOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionRayleigh scatteringGrating
The invention relates to a random-distribution feedback optical fiber laser which can realize stable, space-irrelevant and continuous laser output, and belongs to the technical field of the optical fiber laser. The random-distribution feedback optical fiber laser comprises a pump laser, a wavelength division multiplexer, a fiber bragg grating, an Er-doped optical fiber, an optical fiber Raman laser and a long monomode optical fiber. The reflection effect of the fiber bragg grating is combined with the distributed Rayleigh scattering effect of the optical fiber to form a distributed random feedback optical resonant cavity; and the light is subjected to gain amplification by an Er-doped optical fiber and the stimulated Raman scattering effect. Compared with the random-distribution feedback optical fiber laser reported before, the threshold value of the pump laser and the length of the monomode optical fiber can be reduced, and the limitation on stimulated emission wavelength and the wavelength number by a Rayleigh gain peak is broken through, thereby realizing the purpose of tuning the laser wavelength. The random-distribution feedback optical fiber laser is suitable for fields, such as remote optical fiber sensing, remote communication and the like.
Owner:唐山市神州科贸有限公司
Light-emitting resonant structure driving raman laser
InactiveUS20070258492A1Laser using scattering effectsTransit-time tubesElectromagnetic radiationRaman laser
In a laser system, a set of substantially coherent electromagnetic radiation is applied as an input to a Raman laser. The Raman laser may be fabricated on the same integrated circuit as the source of the substantially coherent electromagnetic radiation or may be fabricated on a different integrated circuit as the source of the substantially coherent electromagnetic radiation.
Owner:ADVANCED PLASMONICS
Silica sol gel micro-laser on a substrate and method of fabrication
InactiveUS20050169331A1Laser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionLine widthErbium doping
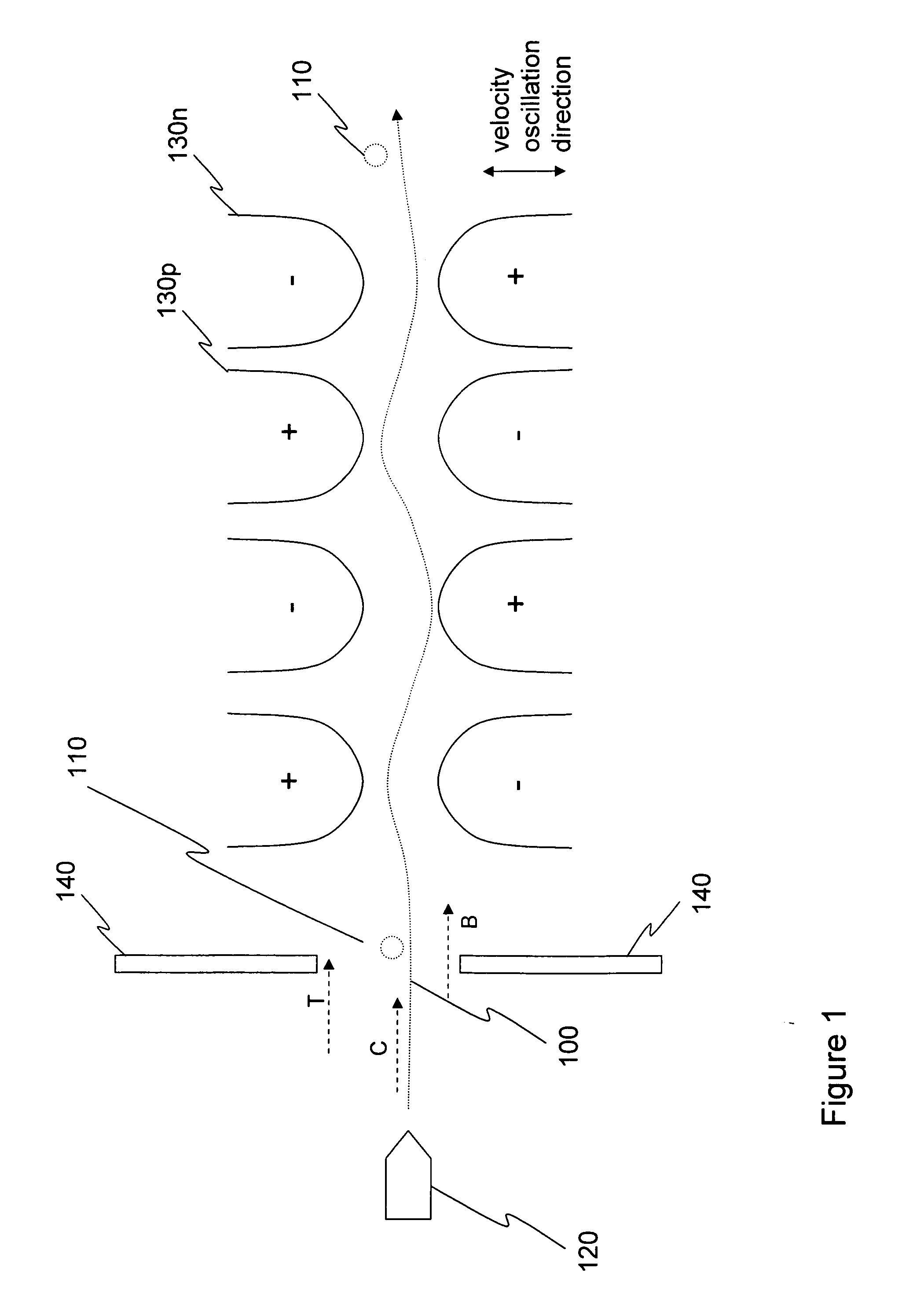
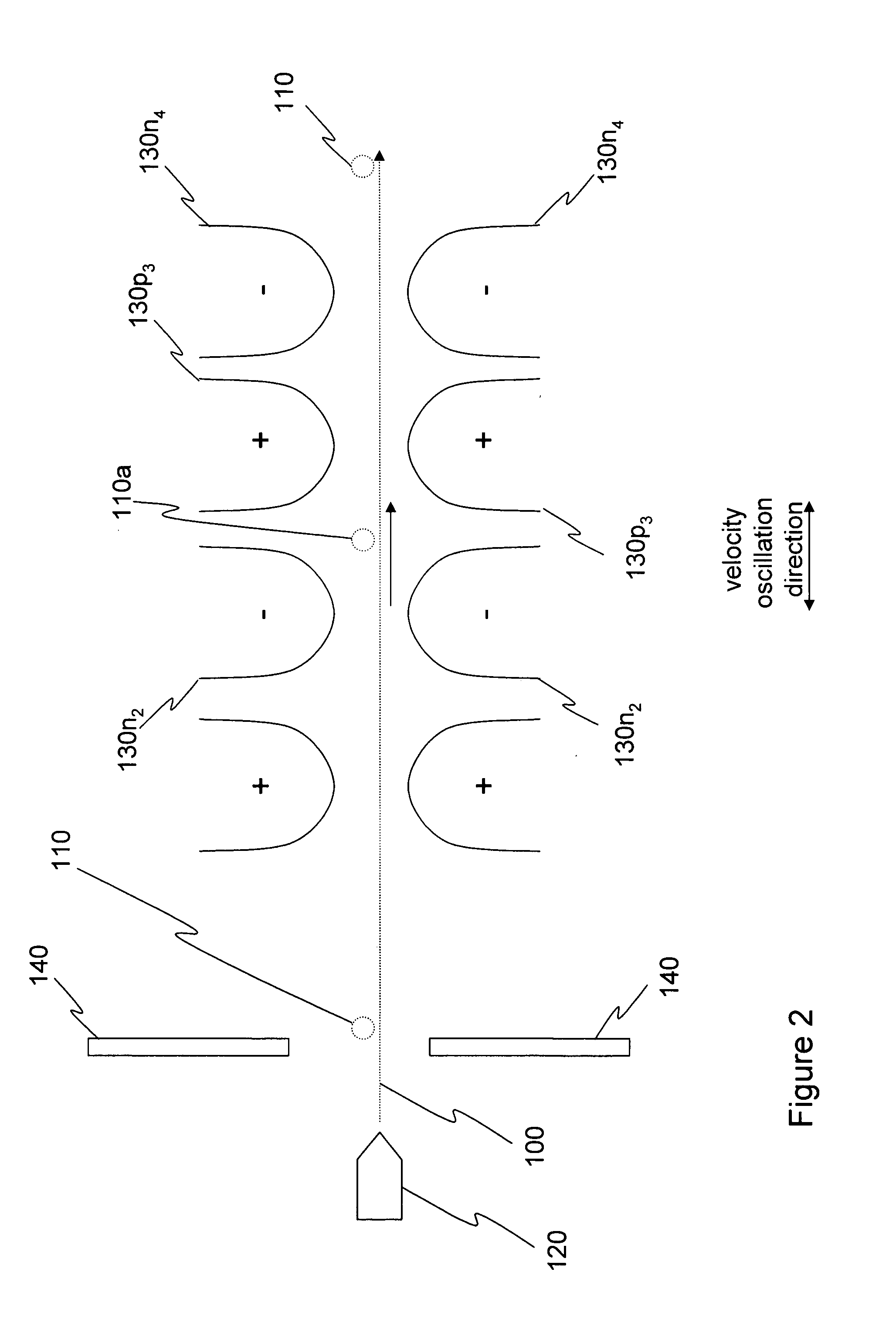
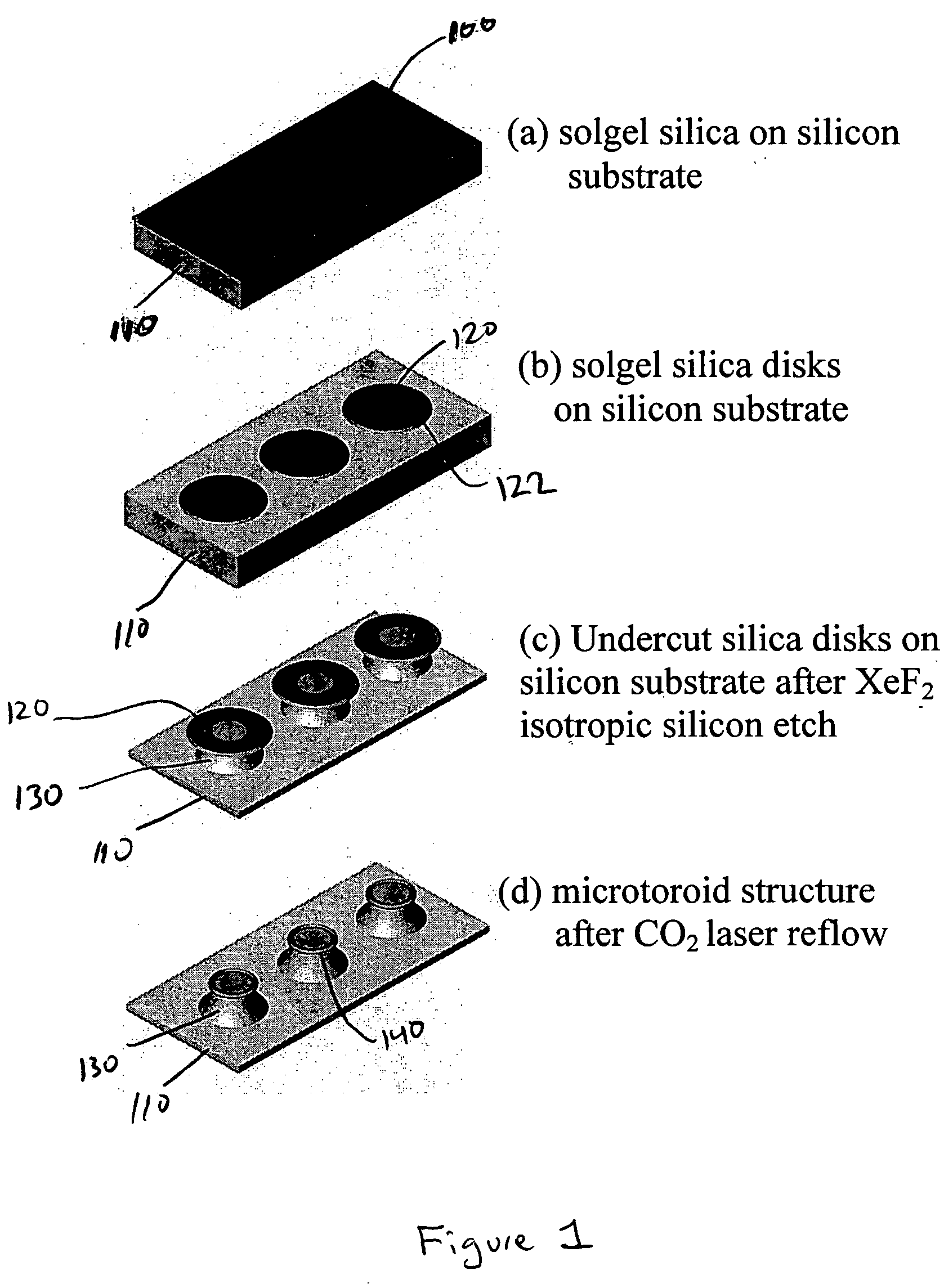
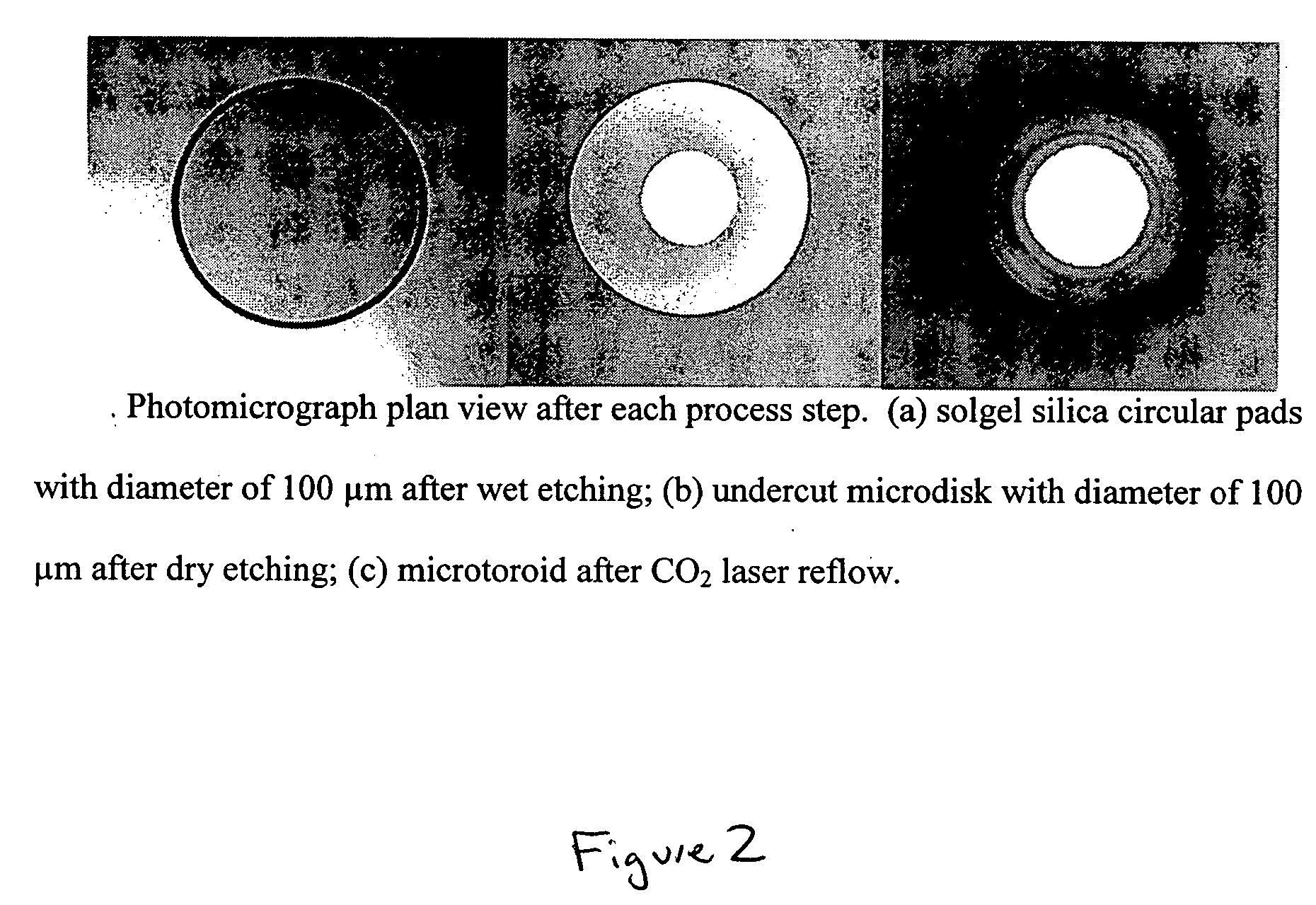
Silica sol gel micro-lasers and methods of fabricating micro-lasers on a chip or a wafer. A silica sol gel micro-laser includes a silica sol gel optical micro-cavity, a substrate, and a support member or pillar that extends between the micro-cavity and the substrate. An outer surface or periphery of the micro-cavity extends beyond a top of the sol gel support member or is overhanging with respect to the underlying support member. Optical energy travels along an inner surface of the silica sol gel micro-cavity. Undoped silica sol gel micro-cavities can be used for Raman lasers. Sol gel micro-cavities can be doped with, for example, erbium, and can be used for erbium-doped micro-lasers that have ultra narrow line widths, for example, less than 100 Hz. Undoped and doped silica sol gel micro-lasers can have Q factors greater than 107.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Sensor and method for measuring gravitational potential three-order differential quotient based on atom interference effect
ActiveCN103472494AOverall small sizeHigh measurement accuracyGravitational wave measurementStructure analysisPhase difference
The invention discloses a sensor and method for measuring a gravitational potential three-order differential quotient based on an atom interference effect, and relates to the technical field of cold atoms in atomic and molecular physical subjects. The sensor is composed of two cold atom interference devices, the central axes of two interference regions are overlapped, two vacuum containers are communicated into a whole in the direction of the central axes, and meanwhile a two-dimensional magneto-optical trap region is arranged. The measuring method is characterized in that the collecting process of a single set of original data points comprises the following steps that the two devices are used for emitting four synchronous faller cold atom groups, an initial state is prepared, synchronous correlation operations based on common Raman laser beams are carried out, and a final state is detected; the data processing process comprises the steps of converting n sets of original data points into n two-order phase difference data points and carrying out fitting processing. According to the system and the method, the influence of external interference and internal noise on measurement can be greatly restrained, and important significance is achieved for resource exploration, geologic structure analysis, physical geography study and other fields.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
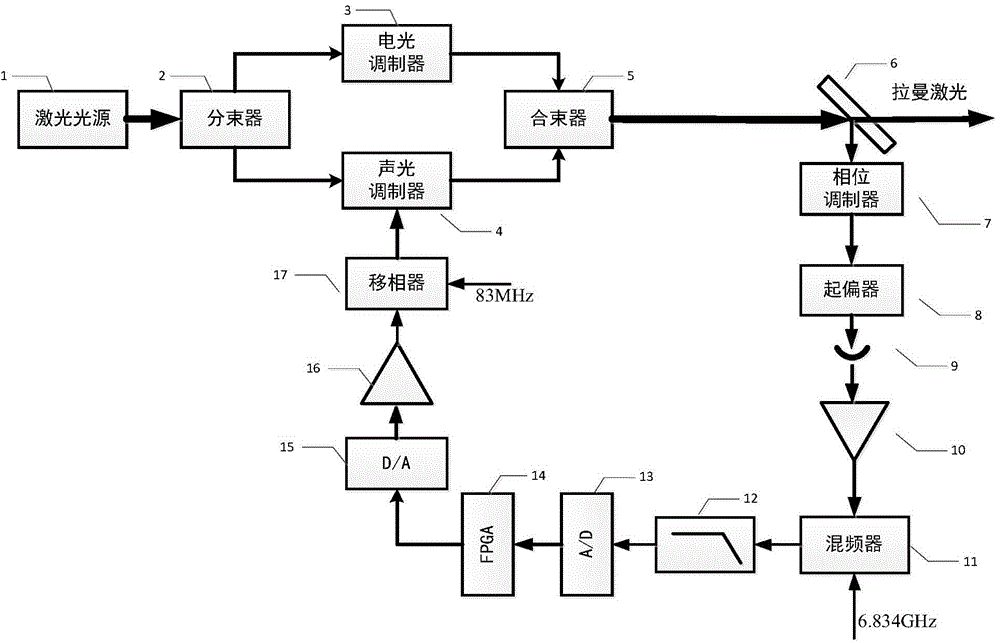
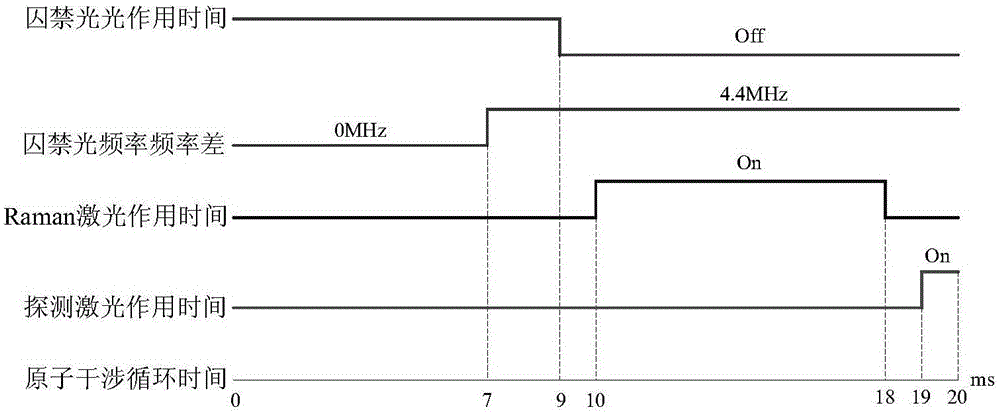
Automatic compensation device of phase noise of Raman laser system based on closed loop feedback and method thereof
InactiveCN104682187ARealize regulationAchieve compensationLaser using scattering effectsLow noisePhase noise
The invention discloses an automatic compensation device of a phase noise of a Raman laser system based on closed loop feedback and a method thereof. The device comprises a laser source, a beam splitter, an electrooptical modulator, an acoustic optical modulator, a beam combiner, a half-transparent half-reflecting mirror, a phase modulator, a polarizer, a photoelectric detector, a low noise microwave amplifier, a frequency mixer, a low pass filter, an analog-digital converter, an FPGA, a digital-to-analog converter, a low frequency amplifier and a phase shifter. The automatic compensation device and method provided by the invention are capable of automatically adjusting and compensating a phase difference in the Raman laser system and reducing the phase noise caused by the vibration of a light path of the Raman laser system. By adopting the circuit control mode, the advantages of integration, modularization and easy debugging of a control system are achieved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
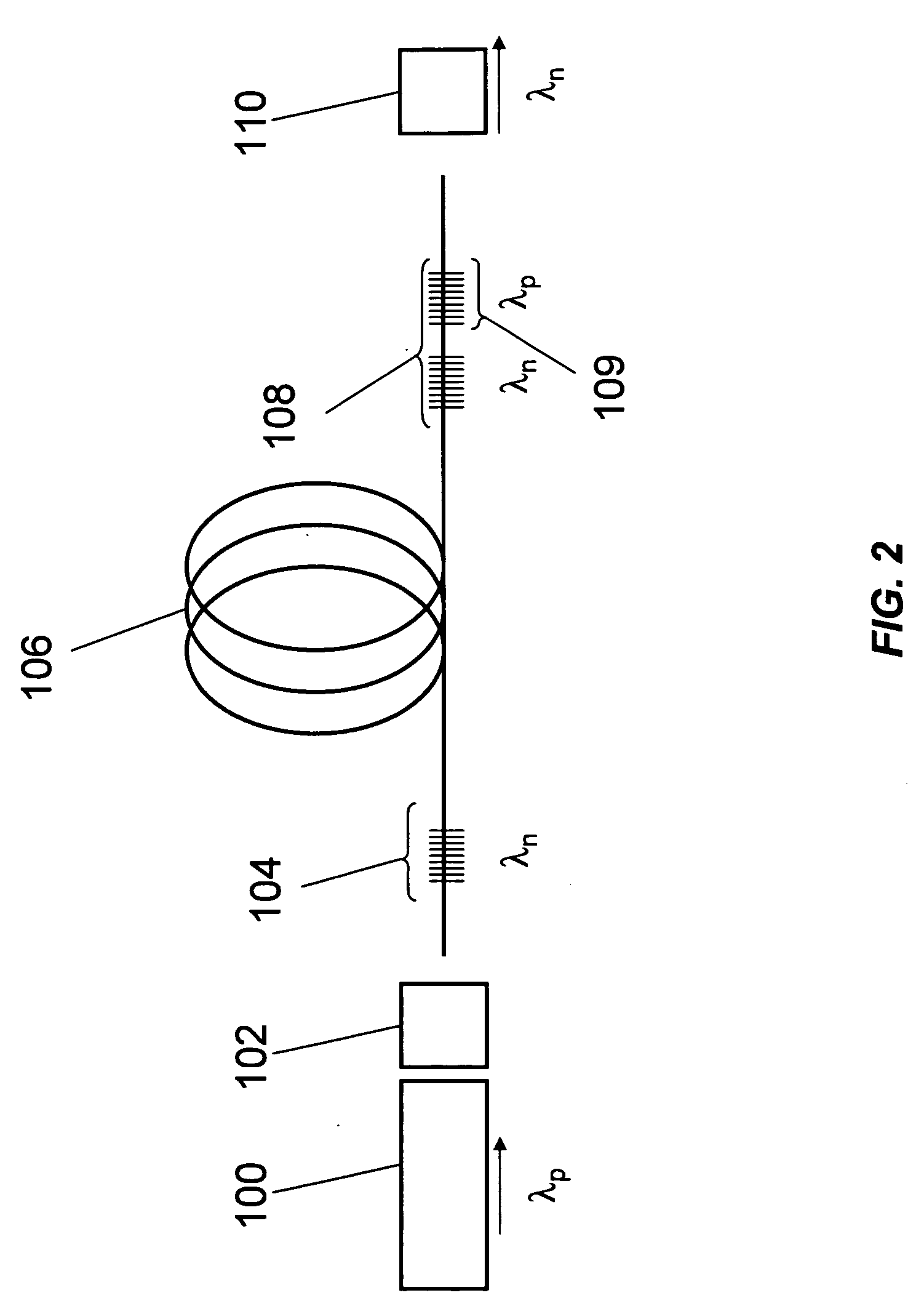
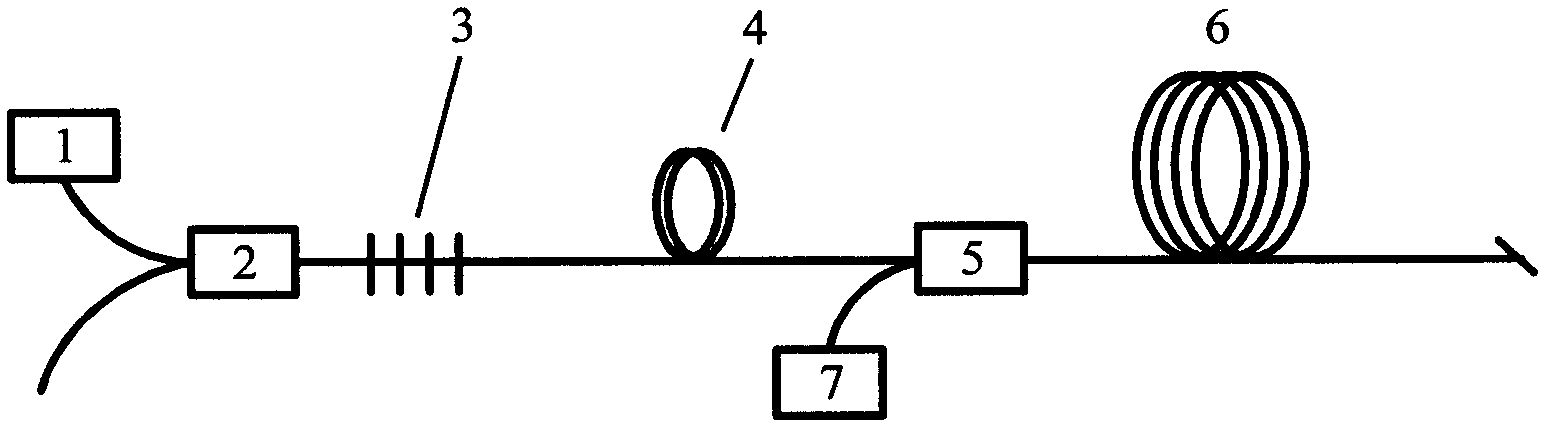
Pulsed cascaded Raman laser
A pulsed cascaded Raman laser (10) includes a pulsed light source (102) for generating a pulsed light (104) having an optical spectrum centered at a source wavelength. A non-linear Raman conversion fiber (106) is coupled to the pulsed light source (102). The pulsed light (104) traverses the nonlinear Raman conversion fiber (106) and the source power at the source wavelength is converted to a power output of an output signal (108) having an output wavelength longer than the source wavelength by a cascaded Stimulated Raman Scattering process, such that most of the source power is converted to the power of the last Stokes order in a single pass through the non-linear Raman conversion fiber (106).
Owner:CORNING INC
Optical fiber type tunable gas Raman laser light source based on hollow-core photonic crystal fiber
ActiveCN101764350ALower the thresholdFlexible wavelength selectionLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionHigh pressureHollow core
The invention discloses an optical fiber type tunable gas Raman laser light source based on hollow-core photonic crystal fiber, wherein a pulse-type tunable single mode Yb-doped fiber laser is used as the excitation source and is connected with one end of the hollow-core photonic crystal fiber filled with high pressure hydrogen (H2) through single mode fiber, and the other end of the hollow-core photonic crystal fiber is connected with the single mode fiber and is used as the output end. Compared with the traditional optical fiber laser, the invention has lower threshold, more flexible wavelength selection and wider spectral range, and can be used as an important means for expanding the wavelength of laser and can obtain the laser which can not be obtained by the conventional laser in some important wave bands.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
All optical fibre adjustable width continuous spectrum laser pump source for superflat wide-band Raman amplification
InactiveCN1477739AFlexible adjustmentAchieving Broadband Ultra-PlanarizationLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCircular cavityRaman laser
The present invention relates to an all-optical-fibre adjustable bandwidth continuous spectrum laser pump source (FBCSL) for ultraflat wideband Raman amplification, belonging to the field of high-speed wideband optical fibre communication technology. It adopts a high optical non-linear optical fibre (HNL-DSF) with approaching flat zero dispersion characteristics at Raman laser wavelength place as gain medium, and on the two ends of the above-mentioned HNL-DSF) a wideband reflector can be connected to form all the optical fibre Fabry-Perot (F-P) adjustable bandwidth continuous spectrum Raman laser or a wideband wavelength division multiplexing optical fibre coupler is connected to form all-optical-fibre circular cavity adjustable bandwidth continuous spectrum Raman laser.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
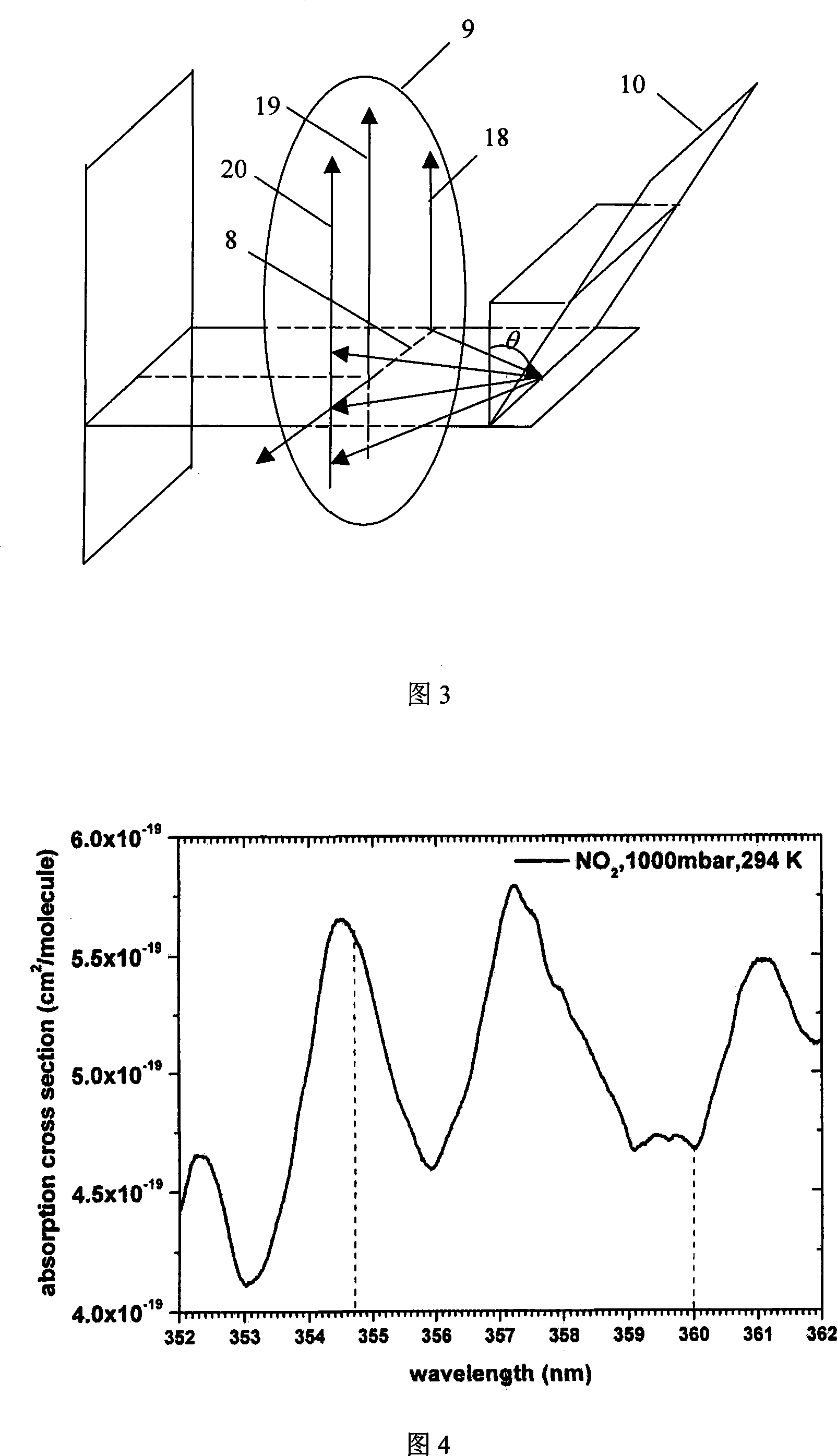
Laser radar for determining atmosphere NO2 concentration based on raman light source differential absorption method
InactiveCN101101261AHigh wavelength resolutionImprove signal-to-noise ratioRaman scatteringColor/spectral properties measurementsFiberData acquisition
The invention discloses a laser radar is based upon lame light source difference absorption process to test thickness of NO2 in the atmosphere, it includes lame light source, light incept and spectrum components, photo-detection and control transaction components, the characteristic is that the light incept and spectrum components accepts the scattered light from atmosphere backward by telescope tube of incept light, after coupling of light fiber, making the light to lay in the focal plane of lens, ripping into the raster by collimation lens, after section out the wave length of light 354.71nm and 360.00nm,recepted by the two emergent light fiber on the focal plane of lens. The raster is blazed grating, it has definite included angle with lens; the photo-detection and control transaction part includes microcomputer, data acquisition card, chronotron, enlarge shaping circuit, photomultiplier and photo-electricity probe. The invention has the beneficial purpose of easy structure, low cost, high diffraction efficiency, good flexibility, convenient using and vindicate etc.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
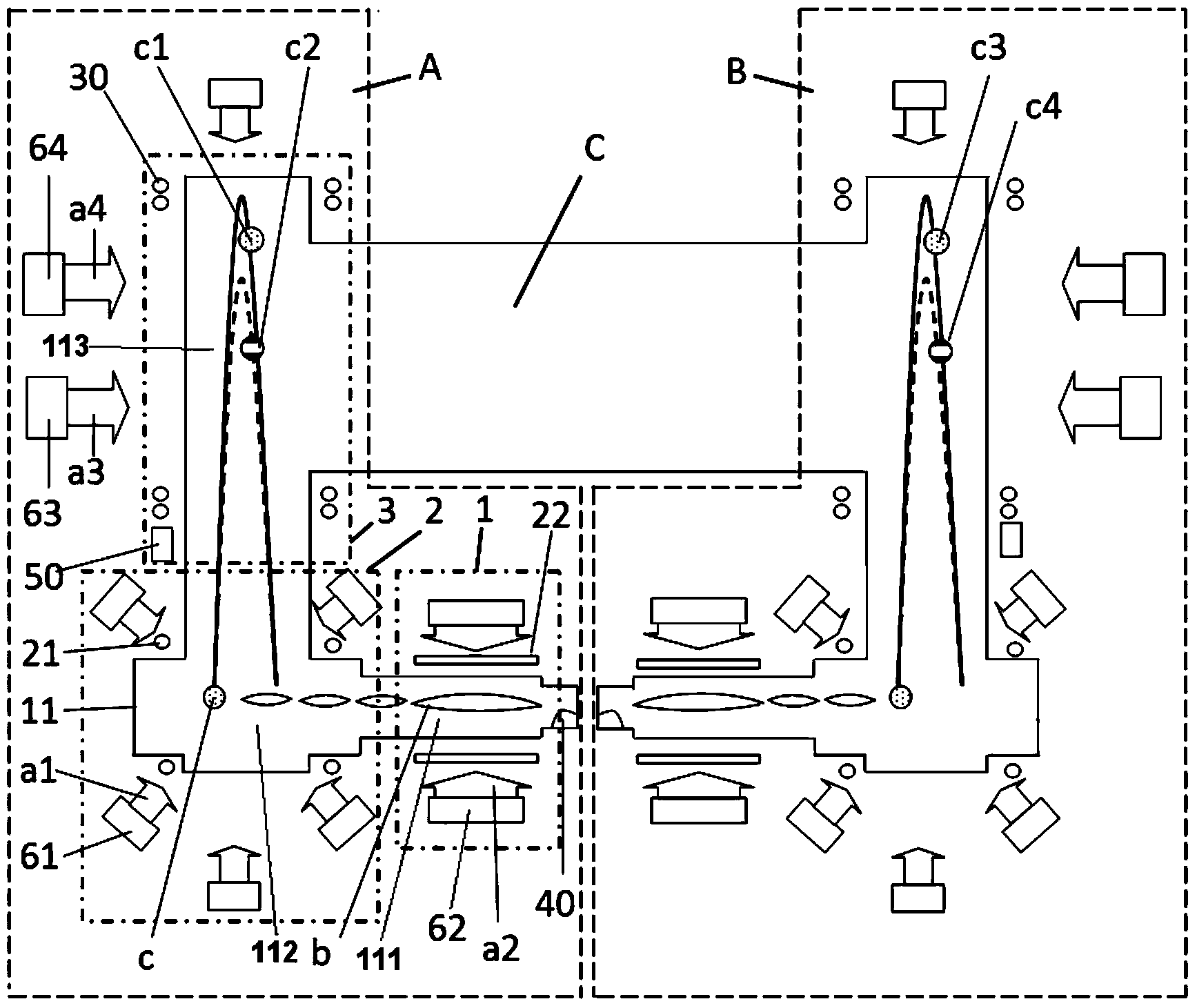
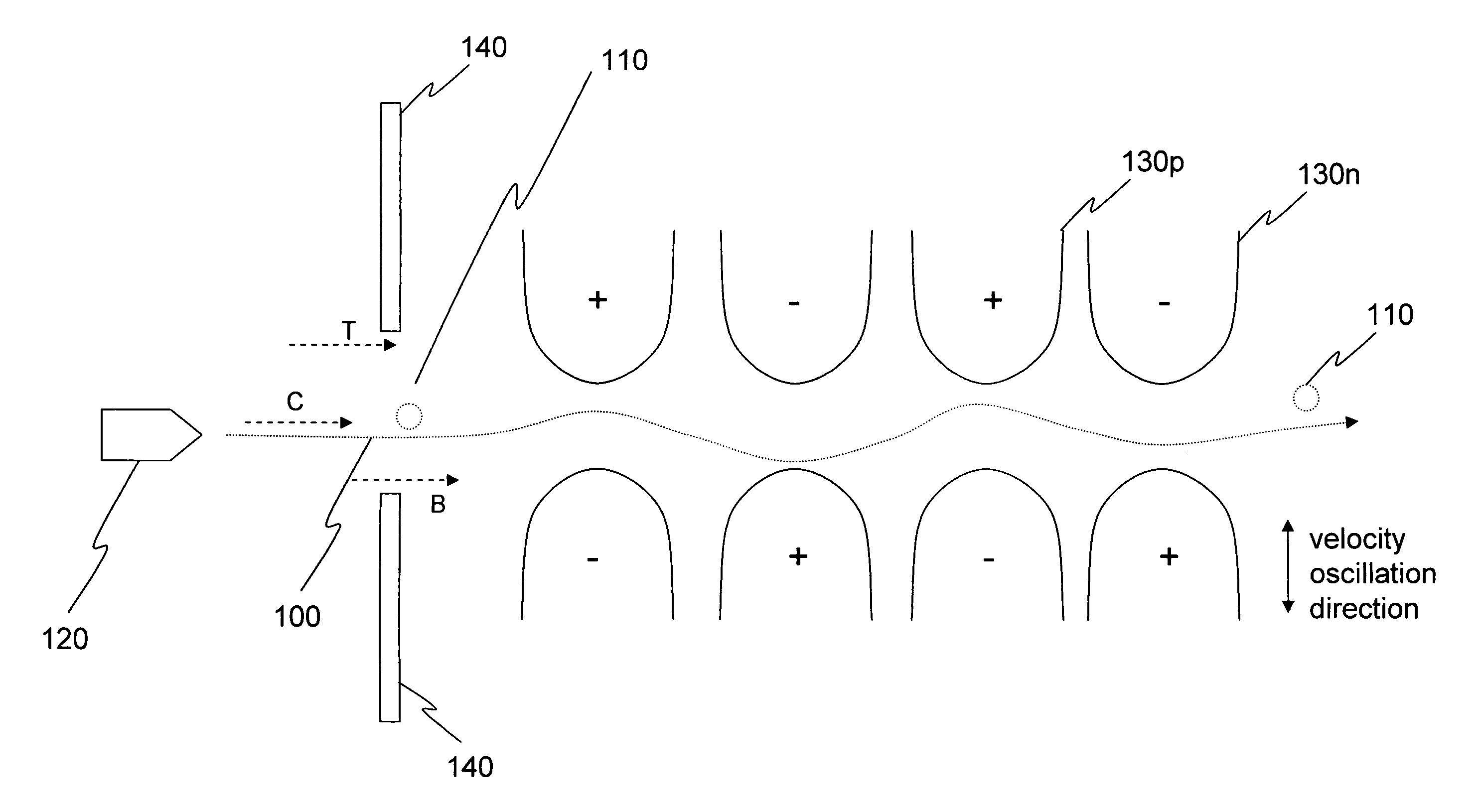
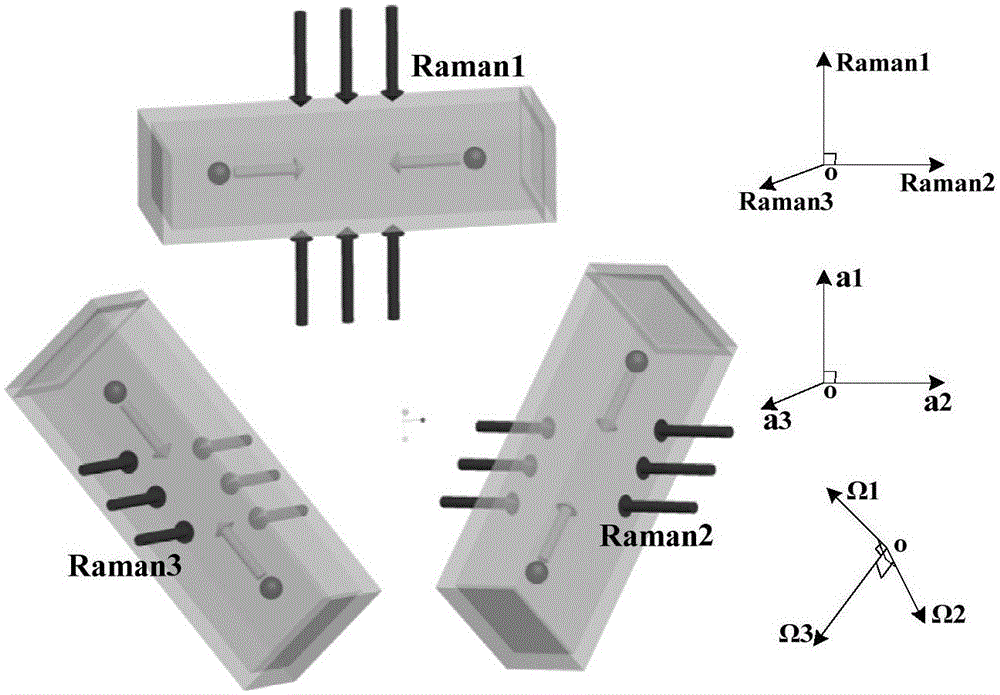
Cold atom interferometry principle-based inertia measuring device
ActiveCN105066991ASynchronization work statusNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsBeam splitterRubidium
The invention discloses a cold atom interferometry principle-based inertia measuring device. The cold atom interferometry principle-based inertia measuring device comprises three inertia measuring units, a Raman laser, and a light dividing device with adjustable splitting ratio; each inertia measuring unit comprises a single-mode narrow linewidth laser, an interferometic cavity, a optical fiber beam splitter, four acoustic optical modulators (AOM), and one electrooptical modulator (EOM); the interferometic cavities are filled with rubidium atomic vapor; Raman laser light send by the Raman laser can be divided into three beams of Raman laser light via the light dividing device with adjustable splitting ratio, and the three beams of Raman laser light are send to the three inertia measuring units; wherein the incidence directions of the three beams of Raman laser light are orthogonal to each other. According to the cold atom interferometry principle-based inertia measuring device, a reasonable structure scheme is adopted; three atom interferometers are arranged in a pyramid mode, so that sensitive acceleration directions of the atom interferometers are orthogonal to each other, and sensitive angular velocity directions are orthogonal to each other. One set of laser system is shared by the three atom interferometers, so that synchronization of atom interference process is realized, and the atom interferometer-based inertia measuring units are sensitive to inertial parameters with six degrees of freedom simultaneously.
Owner:NO 717 INST CHINA MARINE HEAVY IND GRP
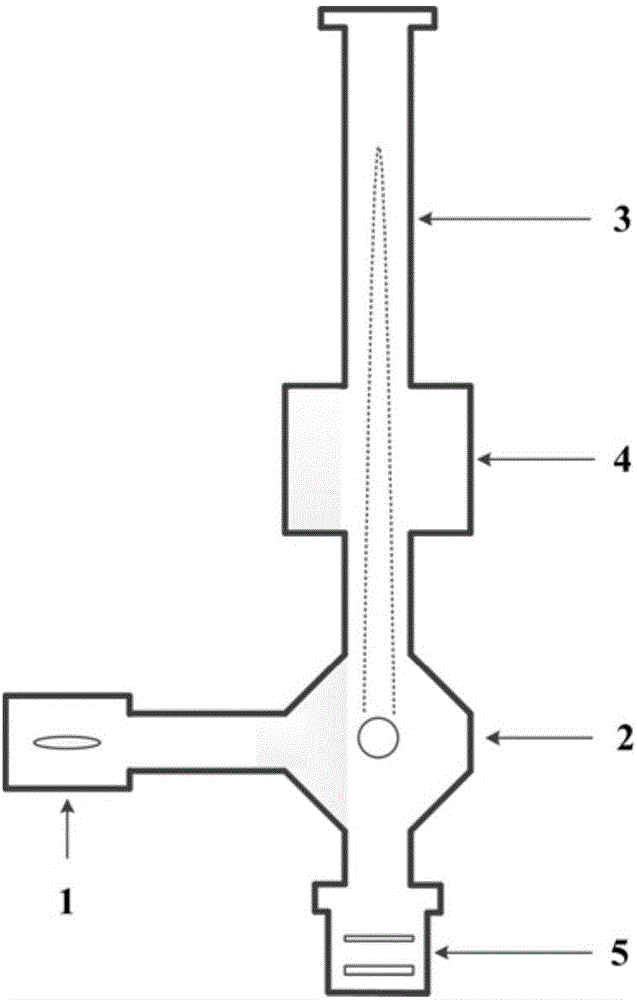
Vacuum device for atomic interference gravity measurement
ActiveCN106597561ASmall sizeLower the altitudeGravitational wave measurementMagneto-optical trapRaman laser
The invention provides a vacuum device for atomic interference gravity measurement, which comprises a two-dimensional magneto-optical trap component, a three-dimensional magneto-optical trap component, an interference component, a detection component and an optical component, wherein the two-dimensional magneto-optical trap is used for atom two-dimensional cooling; the three-dimensional magneto-optical trap component is a tetrakaidecahedron after eight vertex angles are cut from a cube for three-dimensional cooling for atoms after two-dimensional cooling and tossing cooled atoms; the interference component is a cylindrical hollow pipeline for Raman laser incidence; the interference component enables interference to happen to the atoms under mutual effects of stimulated Raman transition laser and tossed atoms; the detection component is cubic for detecting the transition probability of atoms after interference; and the optical component is used for reflecting the incident Raman laser, and together with incident laser, a stimulated Raman transition laser pair is formed. The device height is greatly reduced, the weight of the device is lessened, the device is more flexible, and the stability is greatly enhanced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Self-contained module for injecting signal into slave laser without any modifications or adaptations to it
A self-contained module injects seeds into a slave laser for applications such as single mode or multimode injection seeding, master oscillator power amplifiers, regenerative amplifiers, optical parametric oscillators, Raman lasers, and LIDAR systems. The injection source provides a continuous wavelength sweeping for master-slave resonance to replace conventional cavity length control of the slave laser and phase locking schemes. The inventive module can be operated remotely as a separate unit or be packaged as a subsystem in the injection seeding system. The salve can be used as it is. Modifications of the slave laser and / or additional efforts are not needed.
Owner:PAVILION INTEGRATION
Two-channel phase jitter inhibiting device and method for Raman laser system
ActiveCN107463007AAchieve independent controlPhase Noise SuppressionLaser using scattering effectsNon-linear opticsPrismPolarizer
The invention provides a two-channel phase jitter inhibiting device and a method for a Raman laser system. The device comprises a frequency stabilized laser, a 1 / 2 wave piece, a polarization splitting prism, a 45 degrees reflecting mirror, an electrooptical modulator, a Fabry-Perot interferometer, an acousto-optic modulator, a plano-convex lens, a 1 / 4 wave piece, a 0 degree reflecting mirror, a PZT, a polarizer, a pretreatment circuit, a control circuit based on FPGA, a D / A converter, a acousto-optic modulator driver, a PZT driver, an electrooptical modulator driver and a Fabry-Perot interferometer controller. The two-channel phase jitter inhibiting device and the method can realize the independent control of power and frequency of two lasers; a high-frequency feedback and a low-frequency feedback are utilized to inhibit the phase jitter of the Raman laser; compared with a single-channel phase feedback system, the requirement on the circuit system is reduced, and the stability of the phase feedback system is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
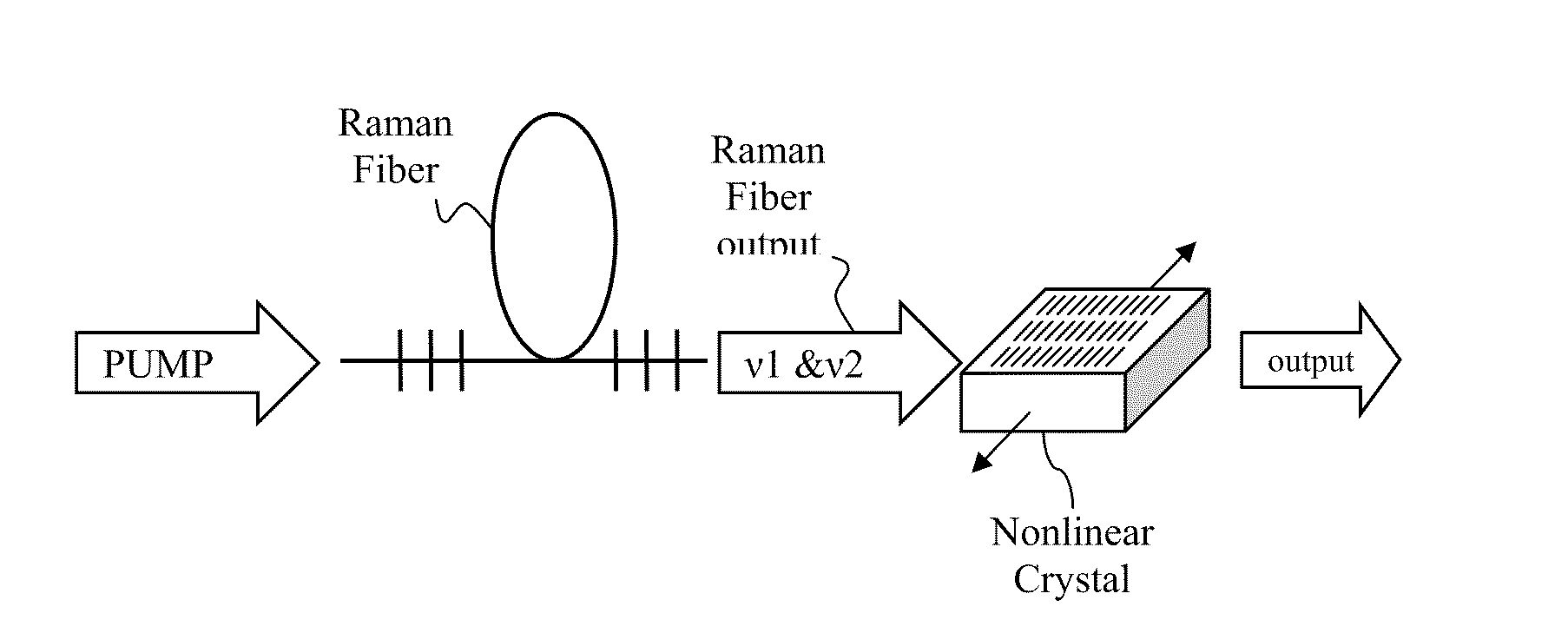
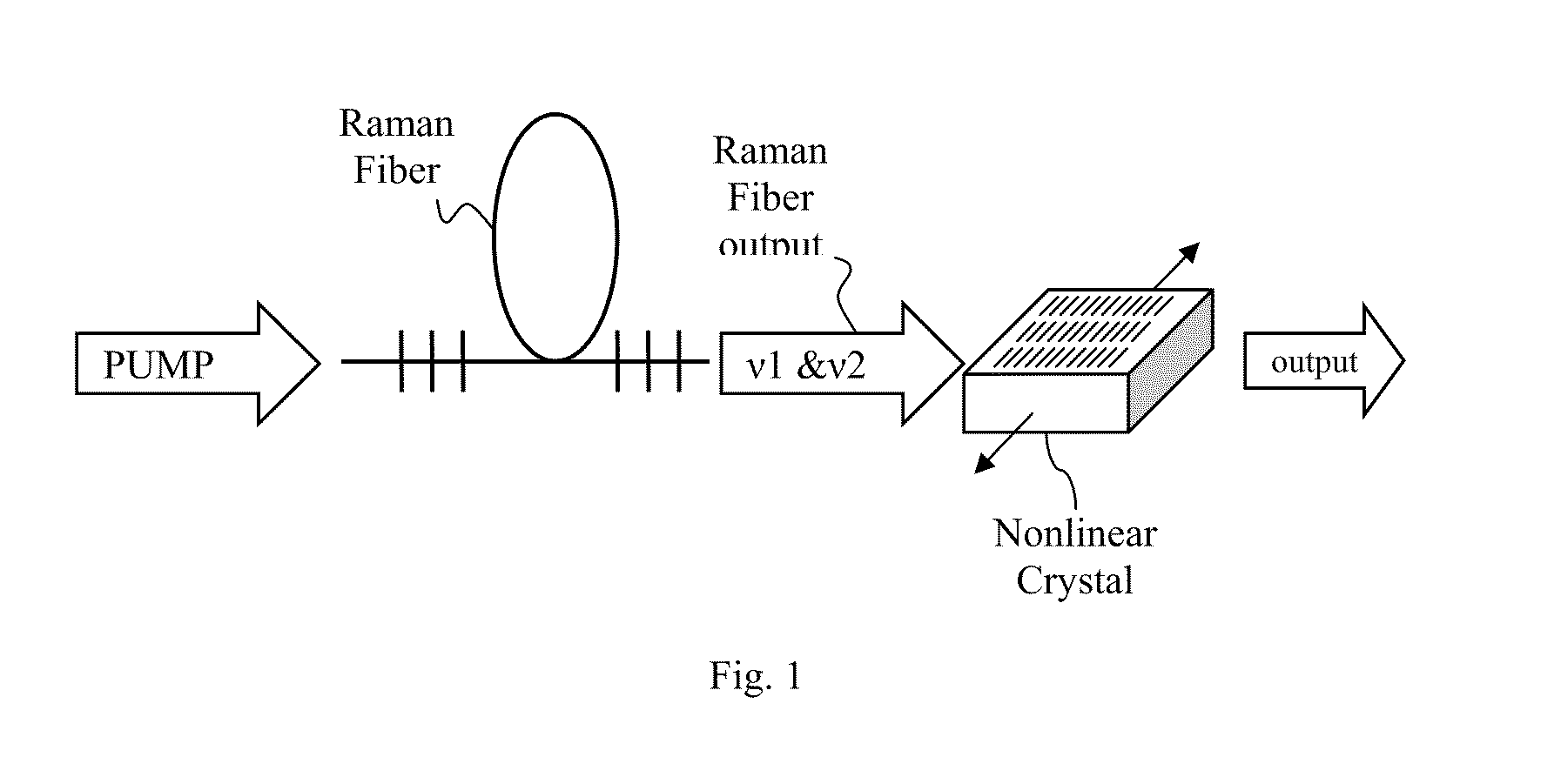
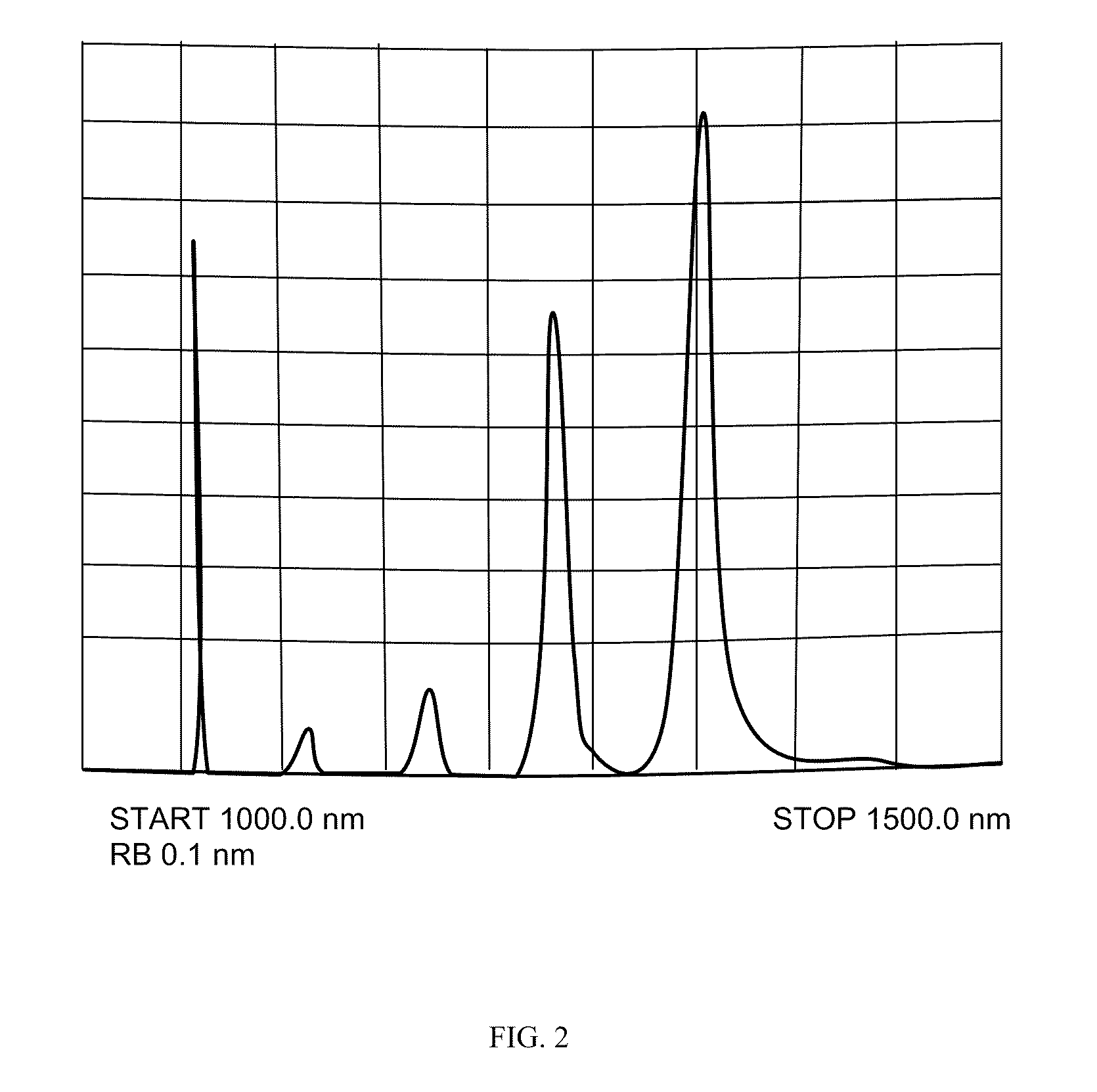
Multiple wavelength raman laser
A pulsed laser system may include a Raman fiber that is configured to act as multiple wavelength Raman laser. The fiber is configured to receive a pulsed input beam from an input source and convert the input beam to an output beam having narrow band outputs at first and second frequencies v1 and v2.
Owner:IPG PHOTONICS CORP
Mid-infrared cascade Raman fiber lasers
InactiveCN101582559AAvoid craft difficultiesAvoiding the difficulties of high-efficiency lasersLaser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionGratingMid infrared laser
The invention discloses a mid-infrared cascade Raman fiber lasers, which is characterized by comprising a doubly coated ZBLAN fluoride fiber that comprises the following components: 53mol. % of ZrF4, 20mol. % of BaF2, 4mol. % of LaF3, 4mol. % of AlF3 and 20mol. % of NaF. One end of the doubly coated ZBLAN fluoride fiber is connected with a high power fiber-doped pump laser, and a cavity resonator of Raman lasers is formed by a plurality of fiber Bragg grating pairs inscribed on two ends of the ZBLAN fiber. By using the stimulated Raman effect of ZBLAN fiber, the Stokes light in all phases generated by Raman frequency shift of pump light form resonance in the fiber Bragg grating pairs to finally realize output of mid-infrared laser. The invention has the advantages of simple and compact structure, high beam quality, high conversation rate, solves the problem that the traditional fiber laser is difficult to generate laser in mid-infrared section, and can be widely used in various fields such as military, medical treatment, environmental monitoring and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Wavelength converting system and method
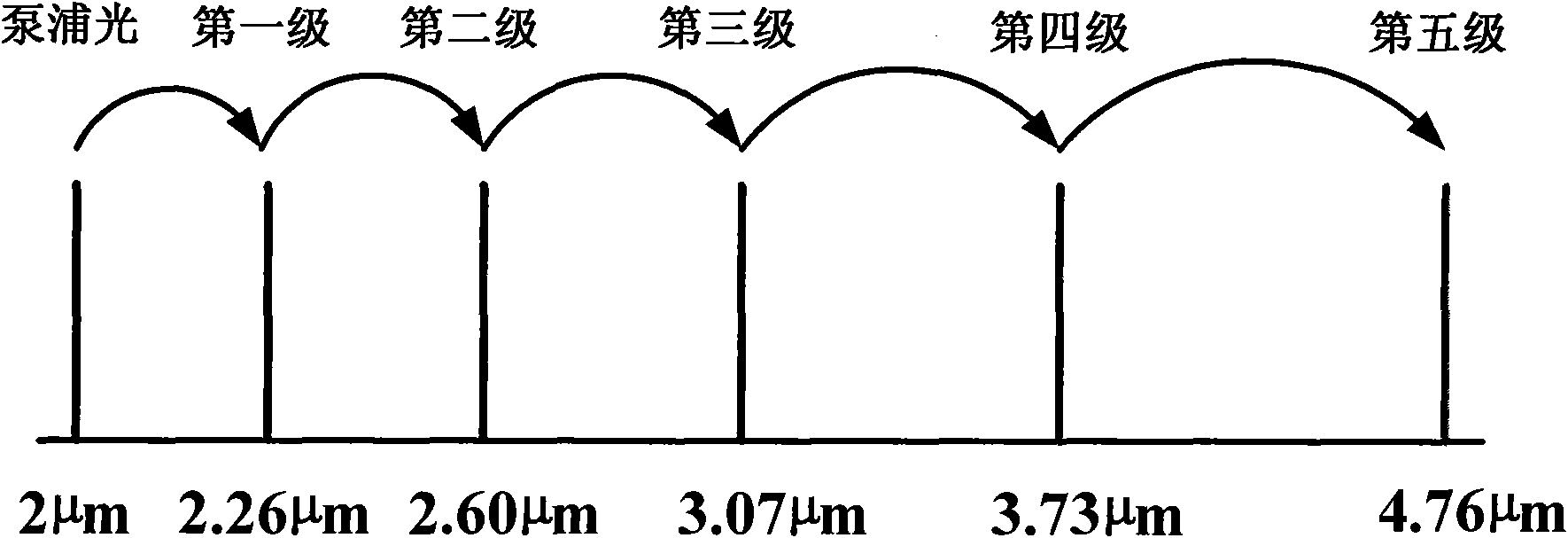
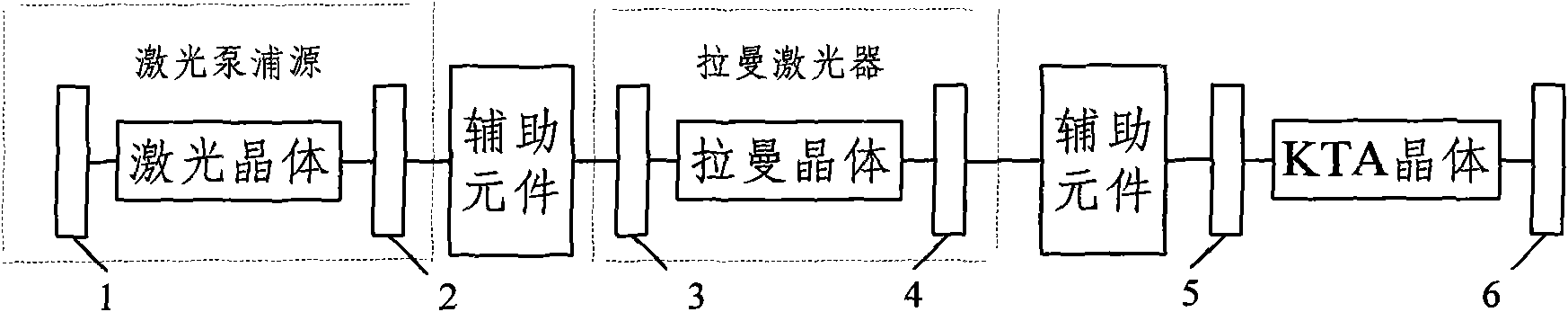
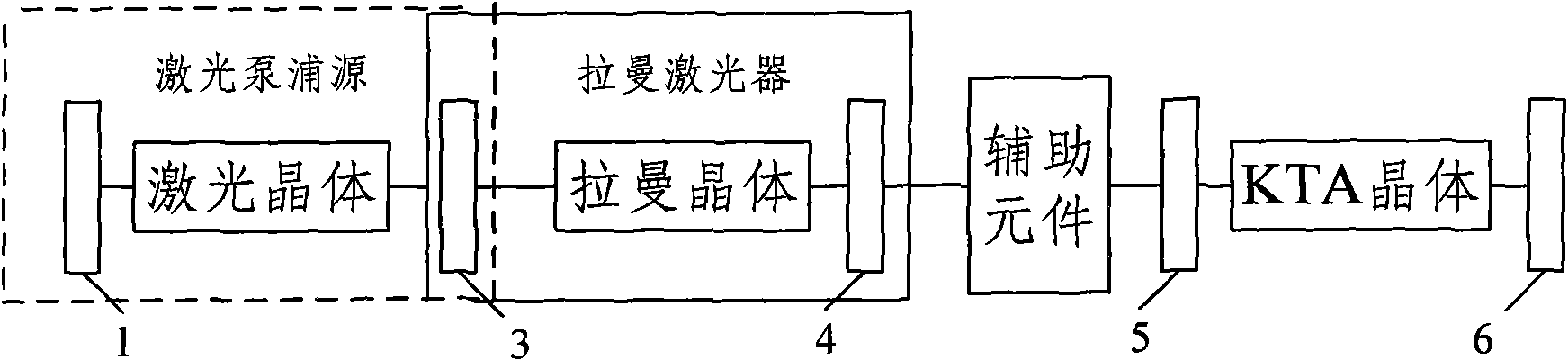
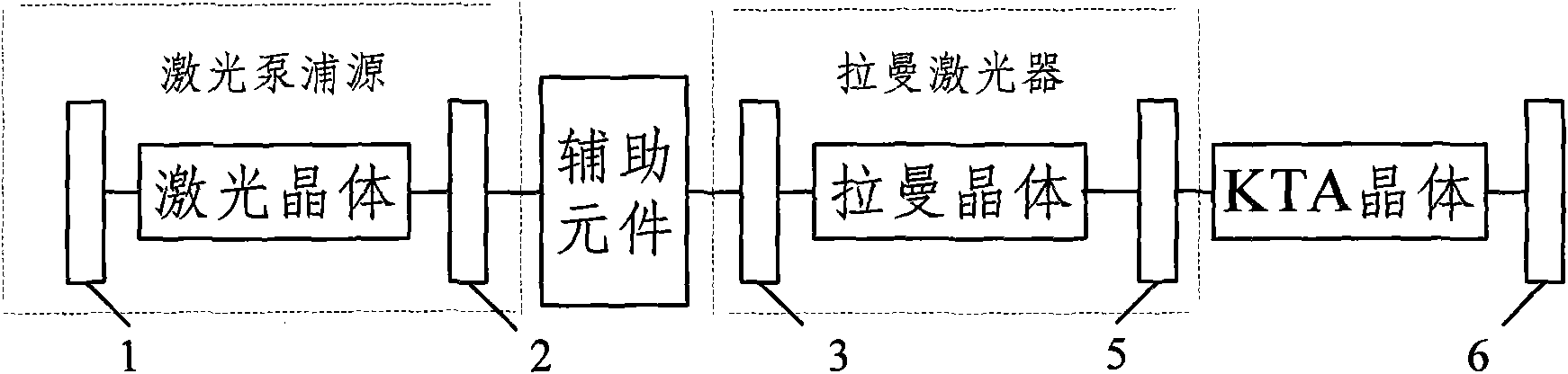
InactiveCN101895054ASimple designExtended Range of Laser Frequency VariationsLaser using scattering effectsLight demodulationLight beamLength wave
The invention relates to a wavelength converting system and a wavelength converting method. The system comprises a laser pumping source, a Raman laser and a KTA crystal which are cascaded, wherein the laser pumping source is used for generating pumping light and inputting the pumping light to the Raman laser; the Raman laser is used for performing Raman transform after receiving the pumping light and outputting laser to the KTA crystal; and the KTA crystal is used for performing an optical parameter conversion process by adopting a non-critical matching mode or a 90-degree critical matching mode after receiving the laser output by the Raman laser. The system and the method expand the laser frequency variation range of the crystal; the converting system is convenient to avoid the walk-off effect by using a larger effective nonlinear coefficient of the nonlinear crystal, simplifies the design of an optical parameter converter, and improves the conversion efficiency and stability; and the system has the advantages of compact structure, good beam quality and high efficiency.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com