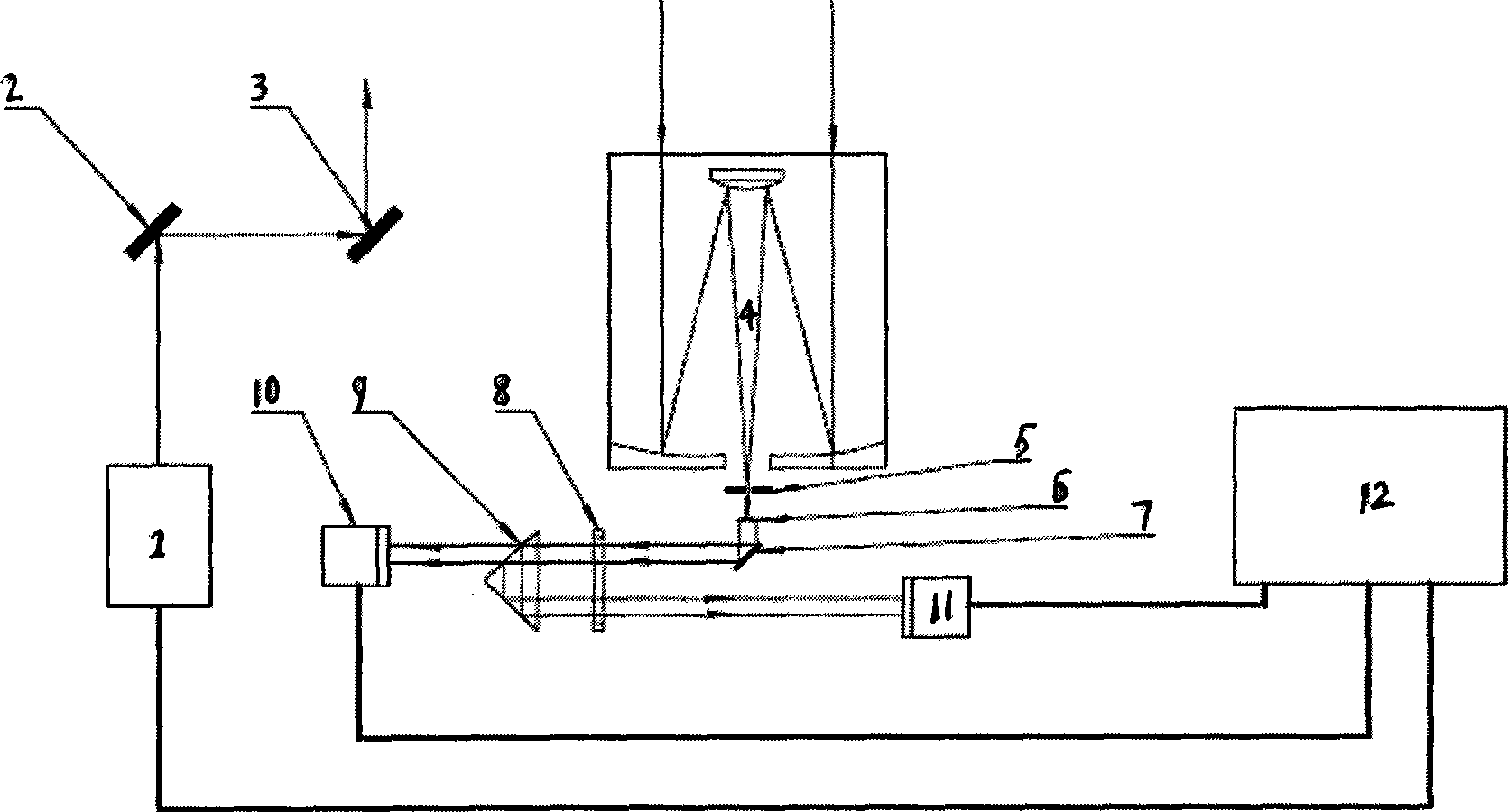
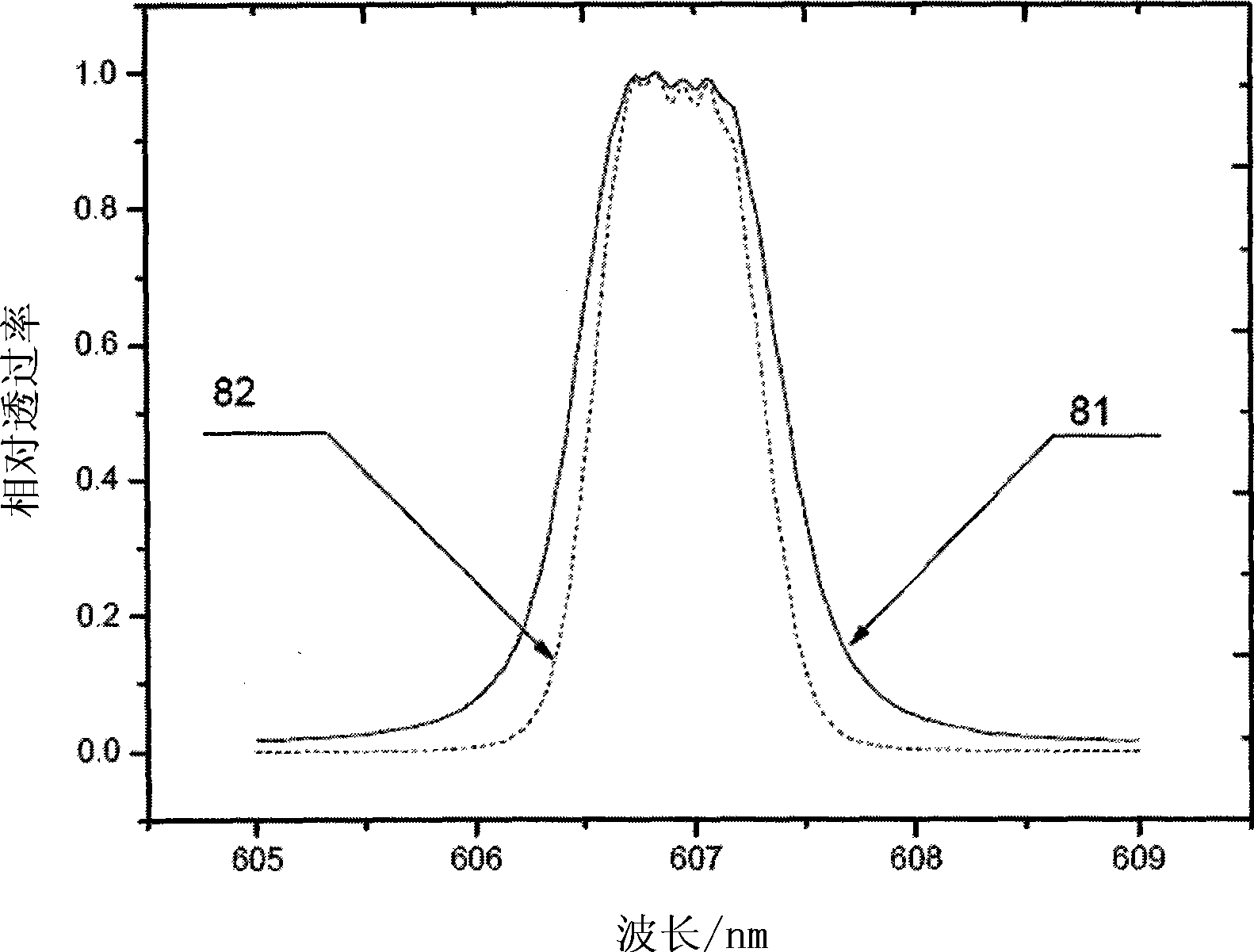
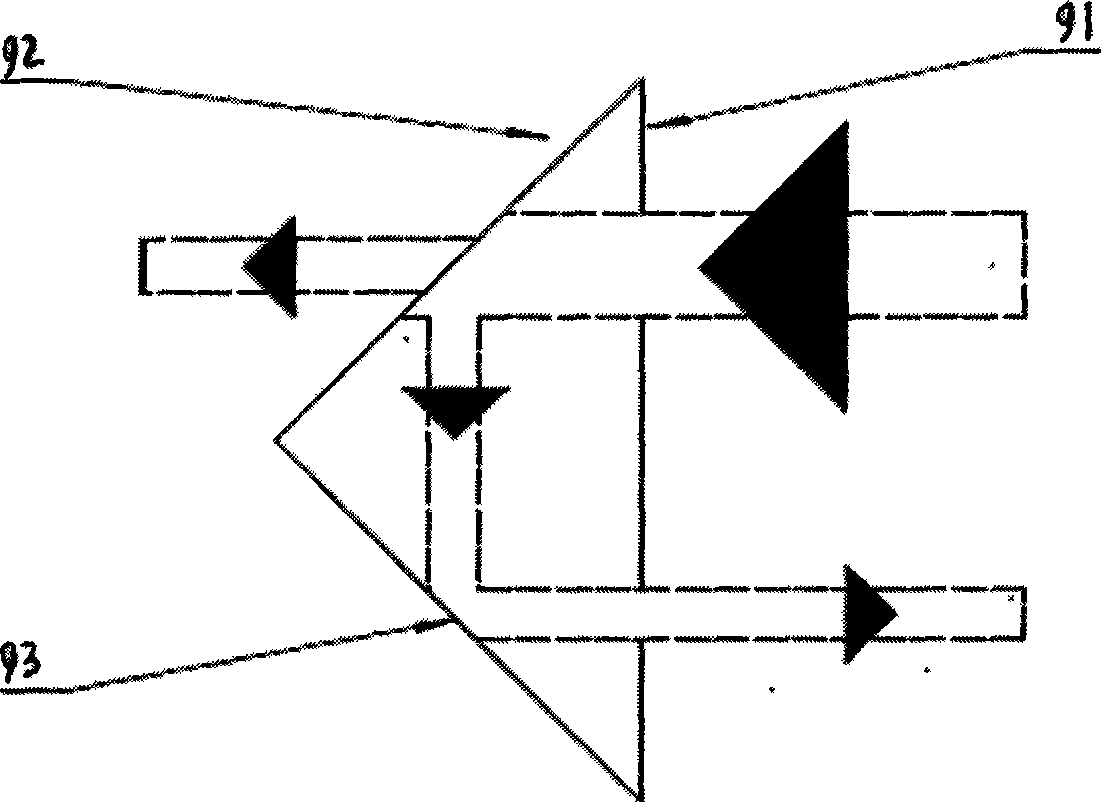
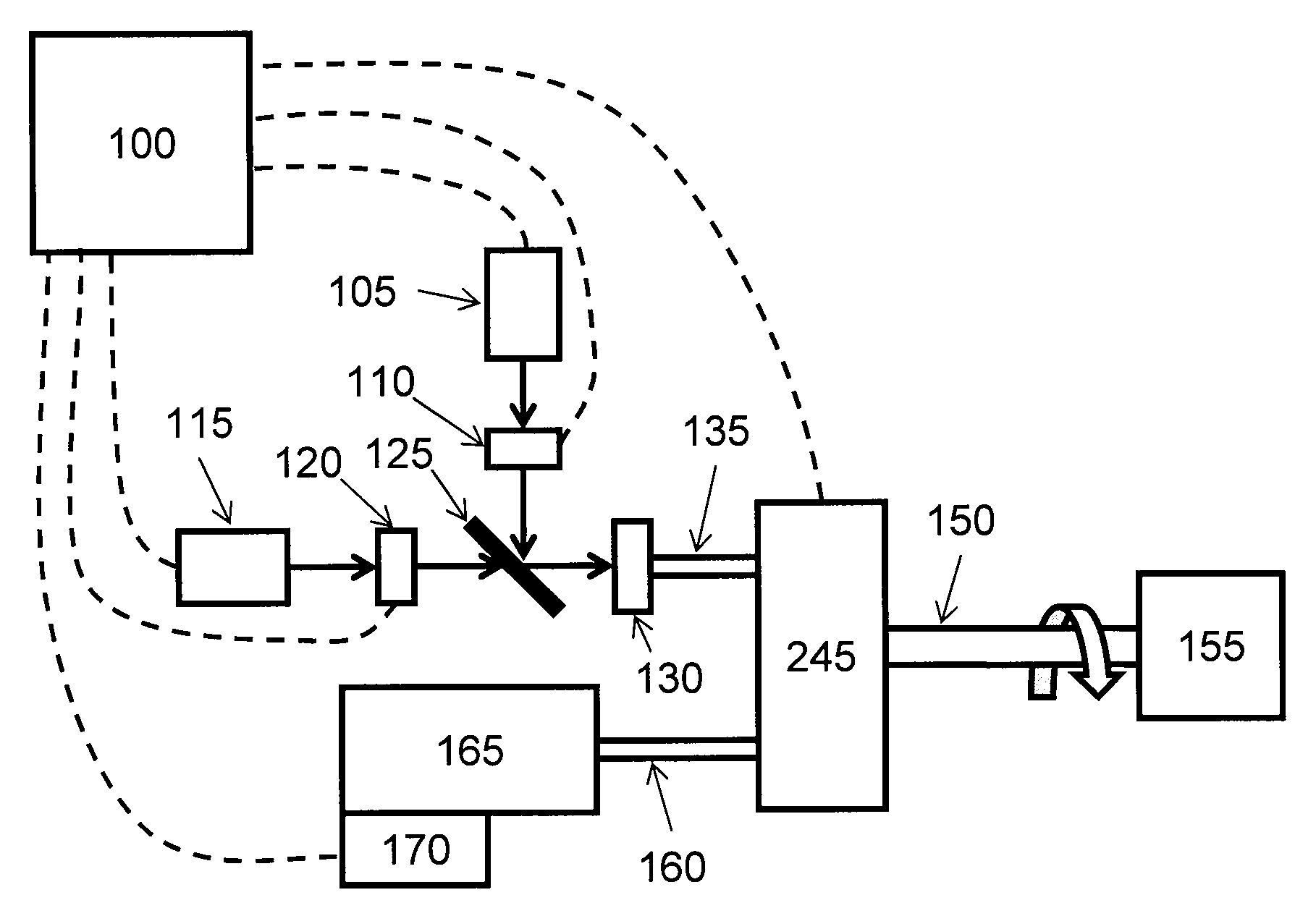
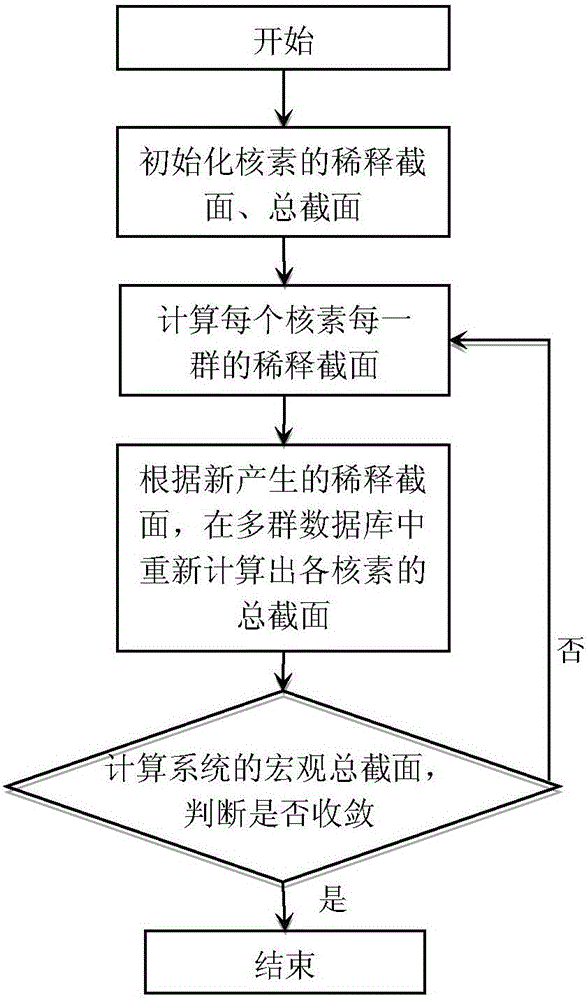
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
114 results about "Elastic scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Elastic scattering is a form of particle scattering in scattering theory, nuclear physics and particle physics. In this process, the kinetic energy of a particle is conserved in the center-of-mass frame, but its direction of propagation is modified (by interaction with other particles and/or potentials). Furthermore, while the particle's kinetic energy in the center-of-mass frame is constant, its energy in the lab frame is not. Generally, elastic scattering describes a process where the total kinetic energy of the system is conserved. During elastic scattering of high-energy subatomic particles, linear energy transfer (LET) takes place until the incident particle's energy and speed has been reduced to the same as its surroundings, at which point the particle is "stopped."
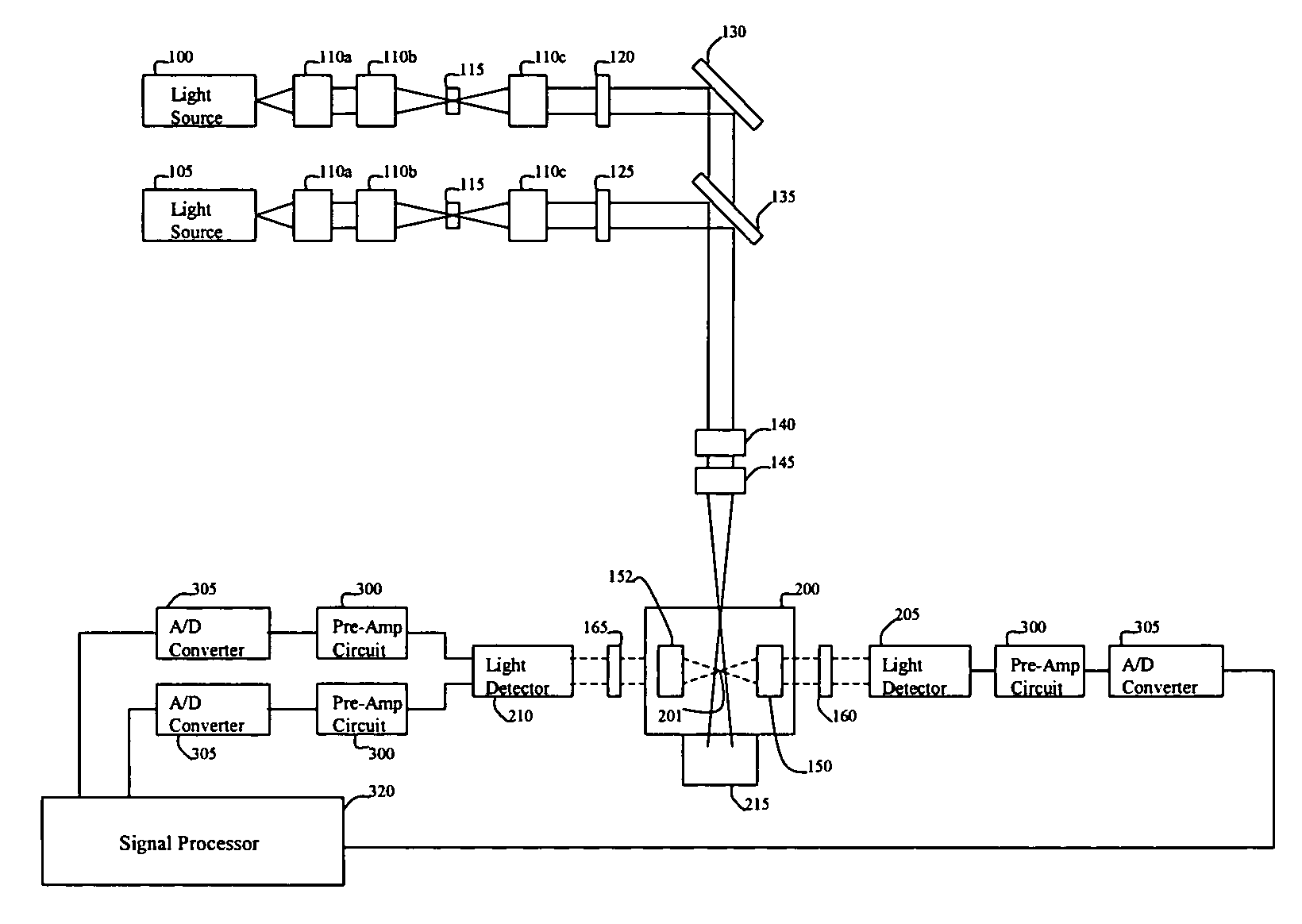
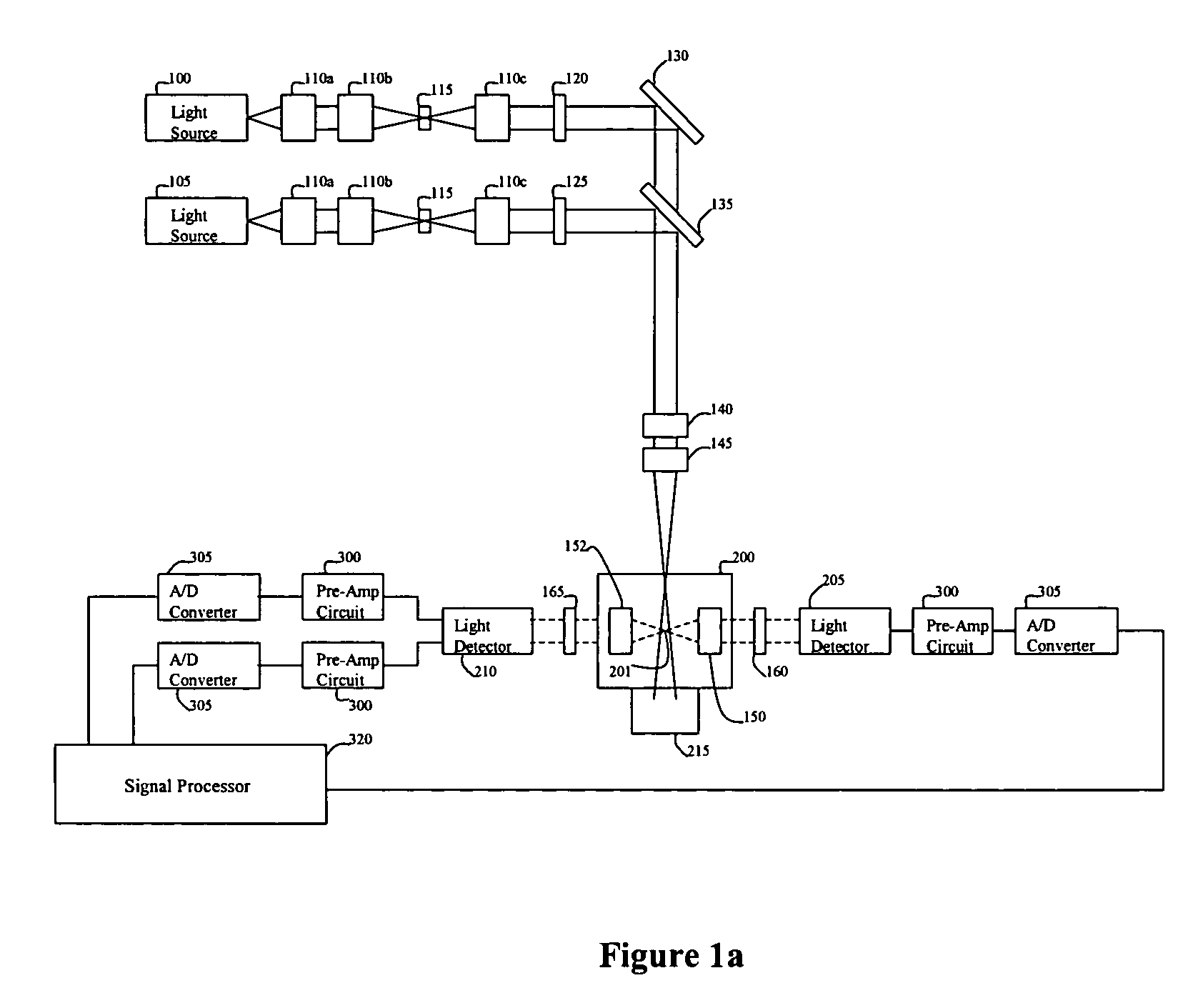
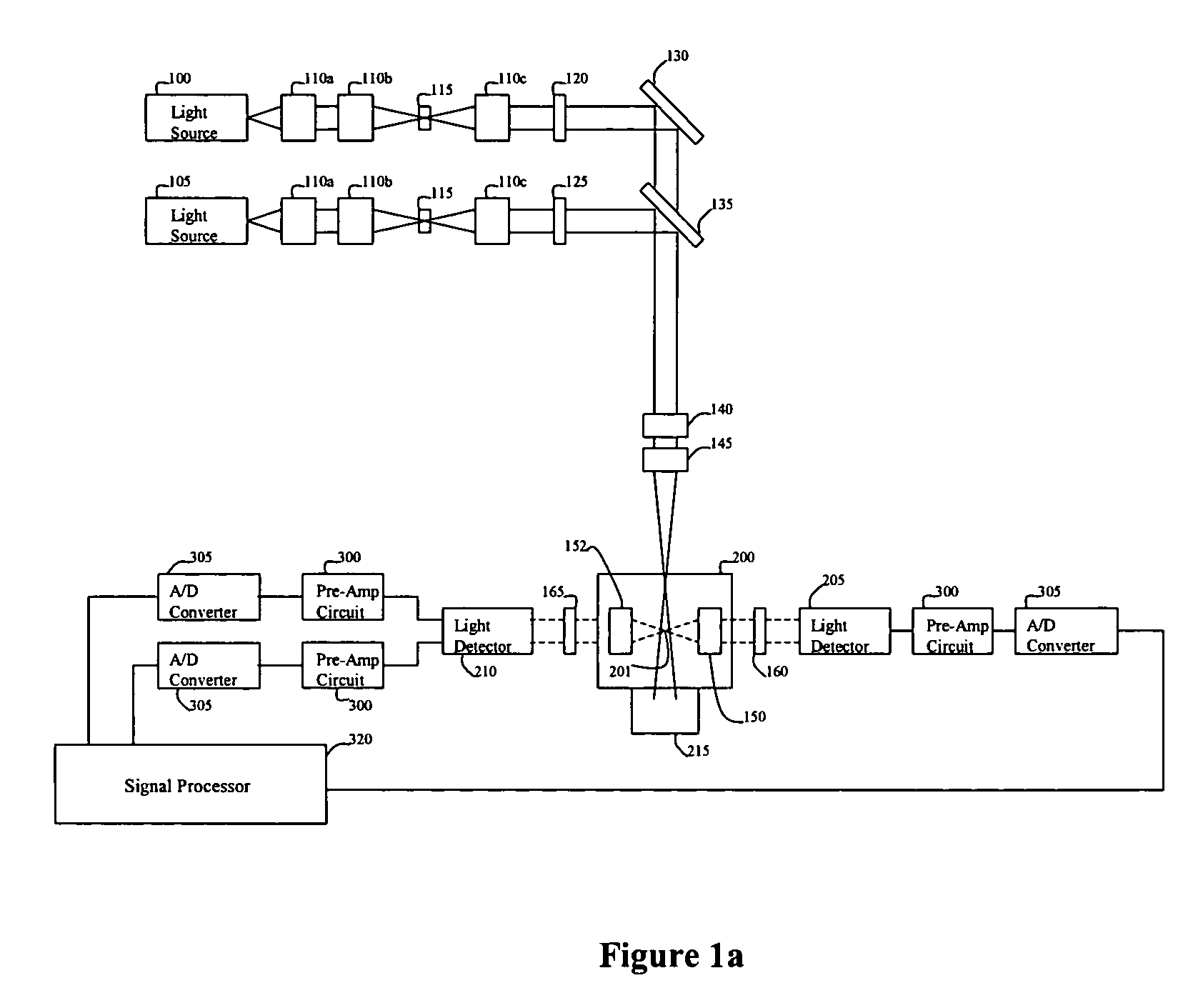
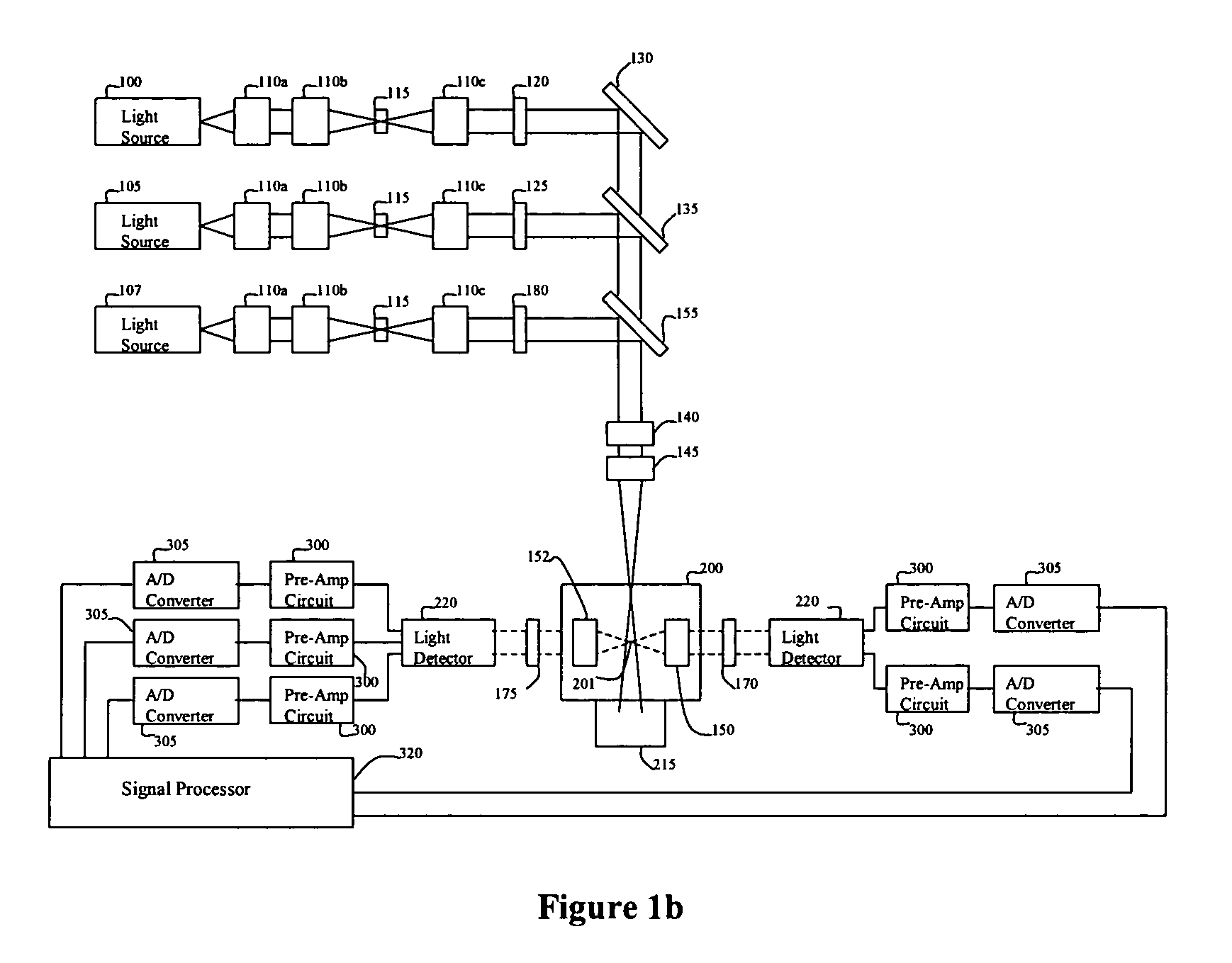
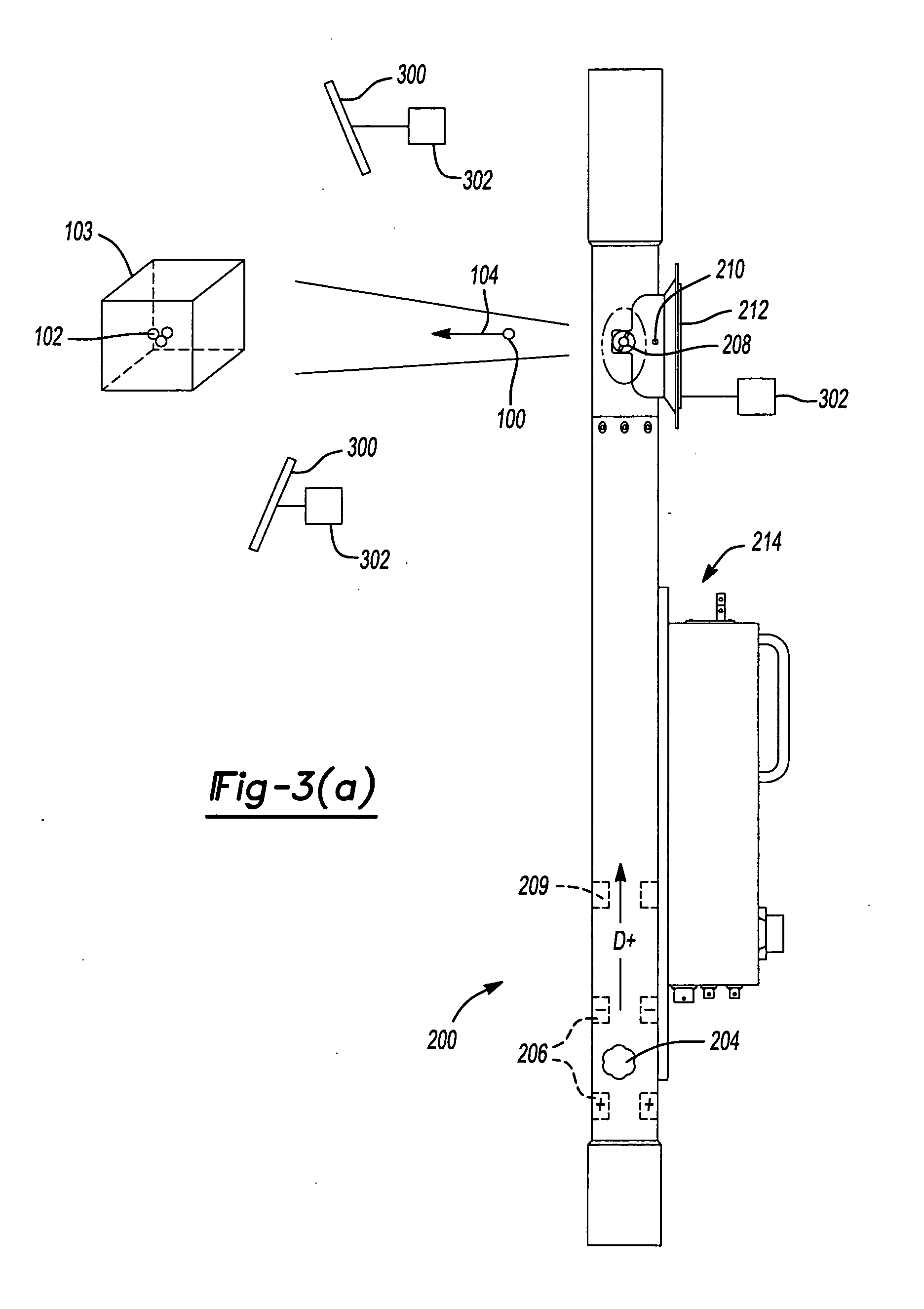
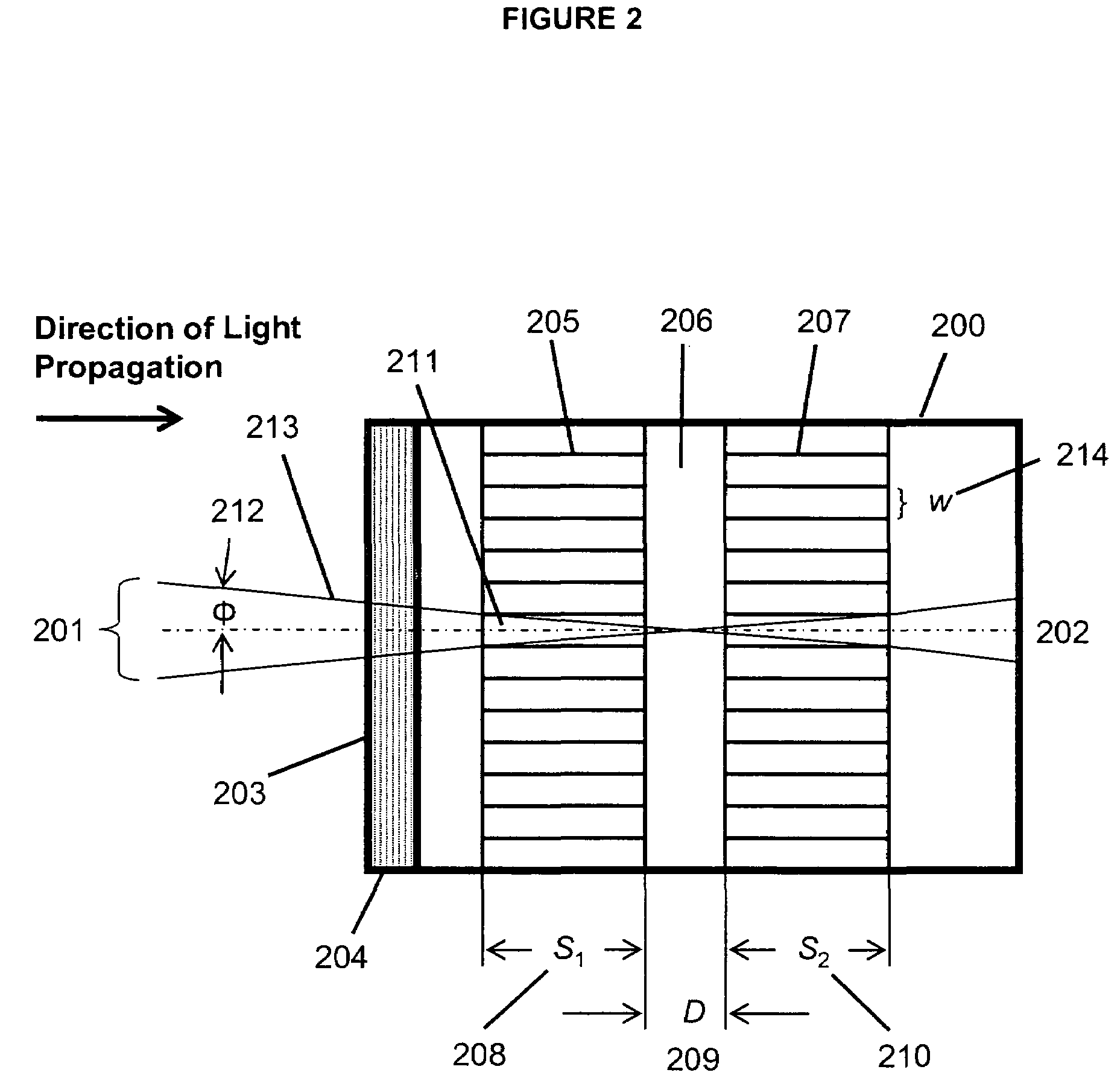
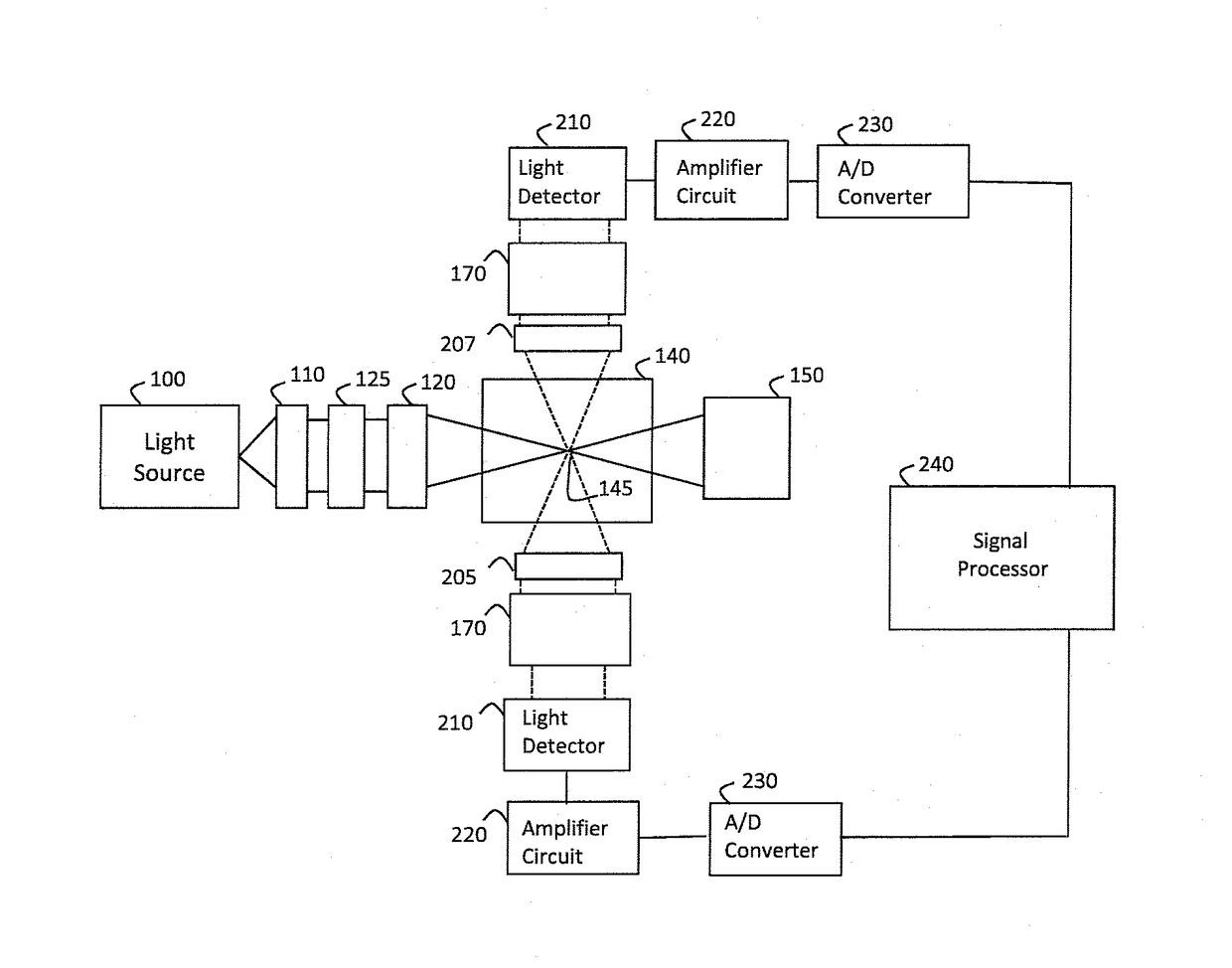
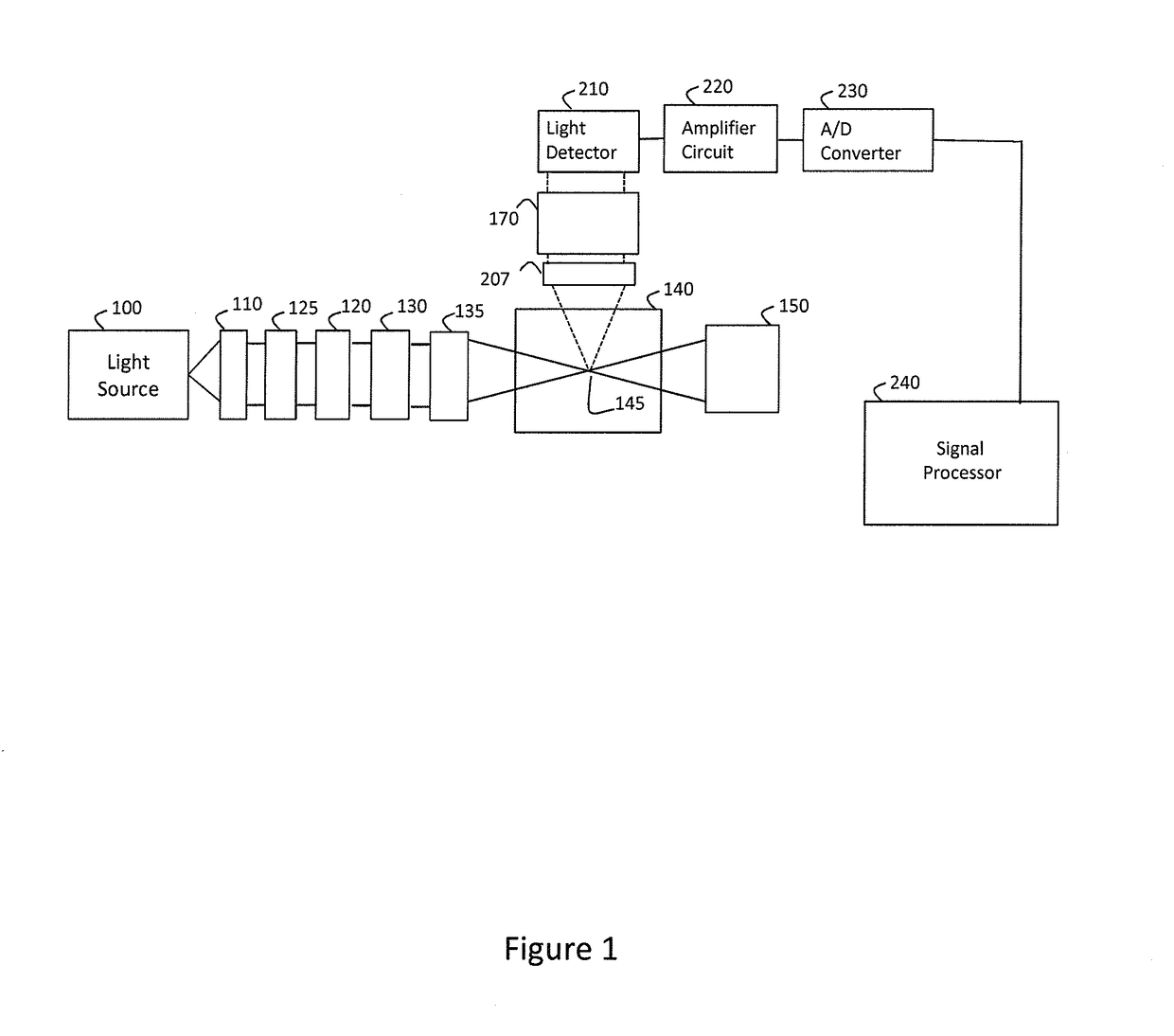
Multi-spectral optical method and system for detecting and classifying biological and non-biological particles
ActiveUS7106442B2Withdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansFluorescenceBiological particles
Enhanced methods, apparatuses and systems are disclosed for the real-time detection and classification of biological and non-biological particles by substantially simultaneously measuring a single particle's characteristics in terms of size and density, elastic scattering properties, and absorption and fluorescence.
Owner:FLIR DETECTION
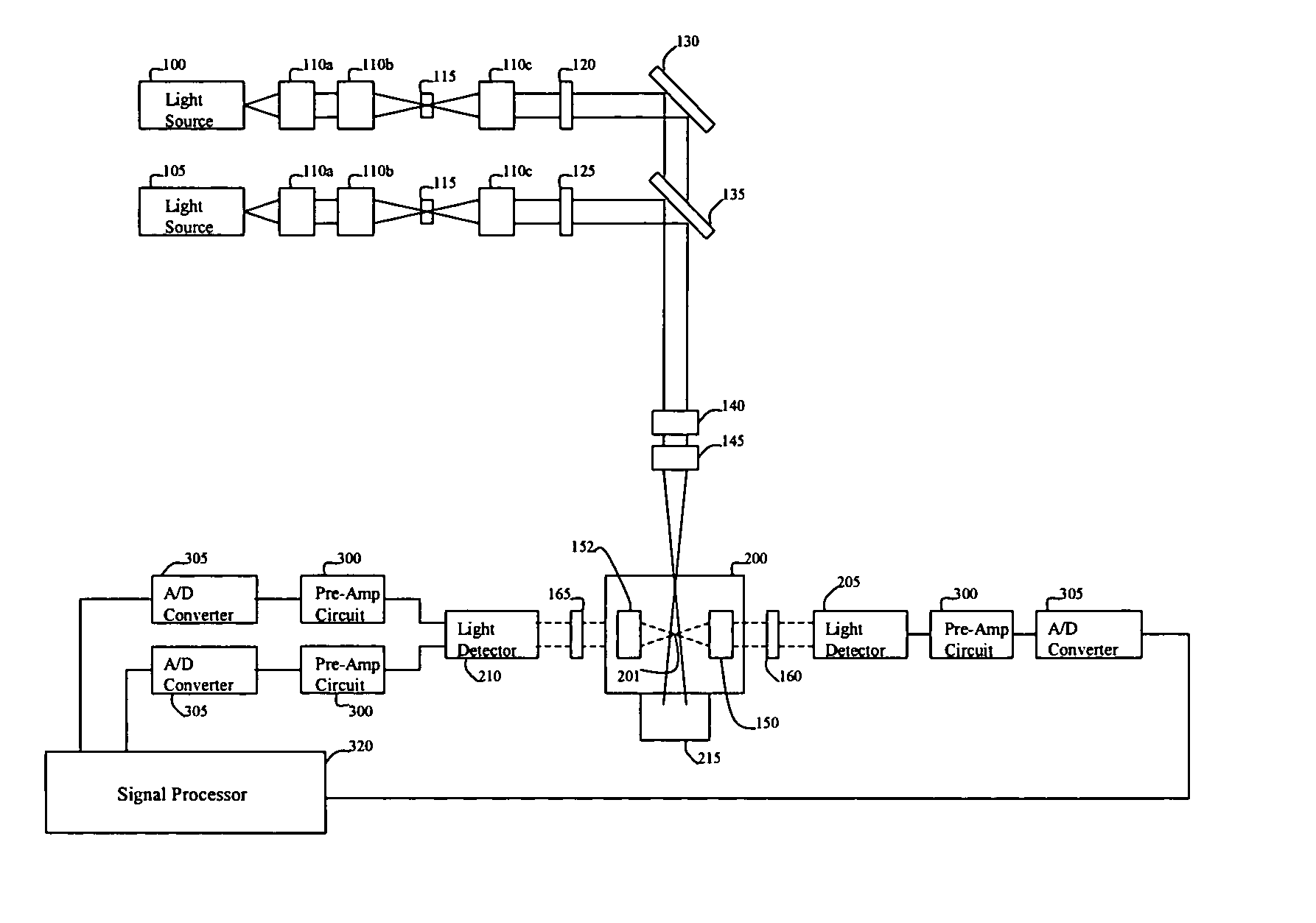
Multi-spectral optical method and system for detecting and classifying biological and non-biological particles
ActiveUS20050243307A1Easy to detectWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansFluorescenceBiological particles
Enhanced methods, apparatuses and systems are disclosed for the real-time detection and classification of biological and non-biological particles by substantially simultaneously measuring a single particle's characteristics in terms of size and density, elastic scattering properties, and absorption and fluorescence.
Owner:FLIR DETECTION
3-D imaging system
InactiveUS20050007448A1Color television detailsClosed circuit television systemsTime gatingInelastic scattering
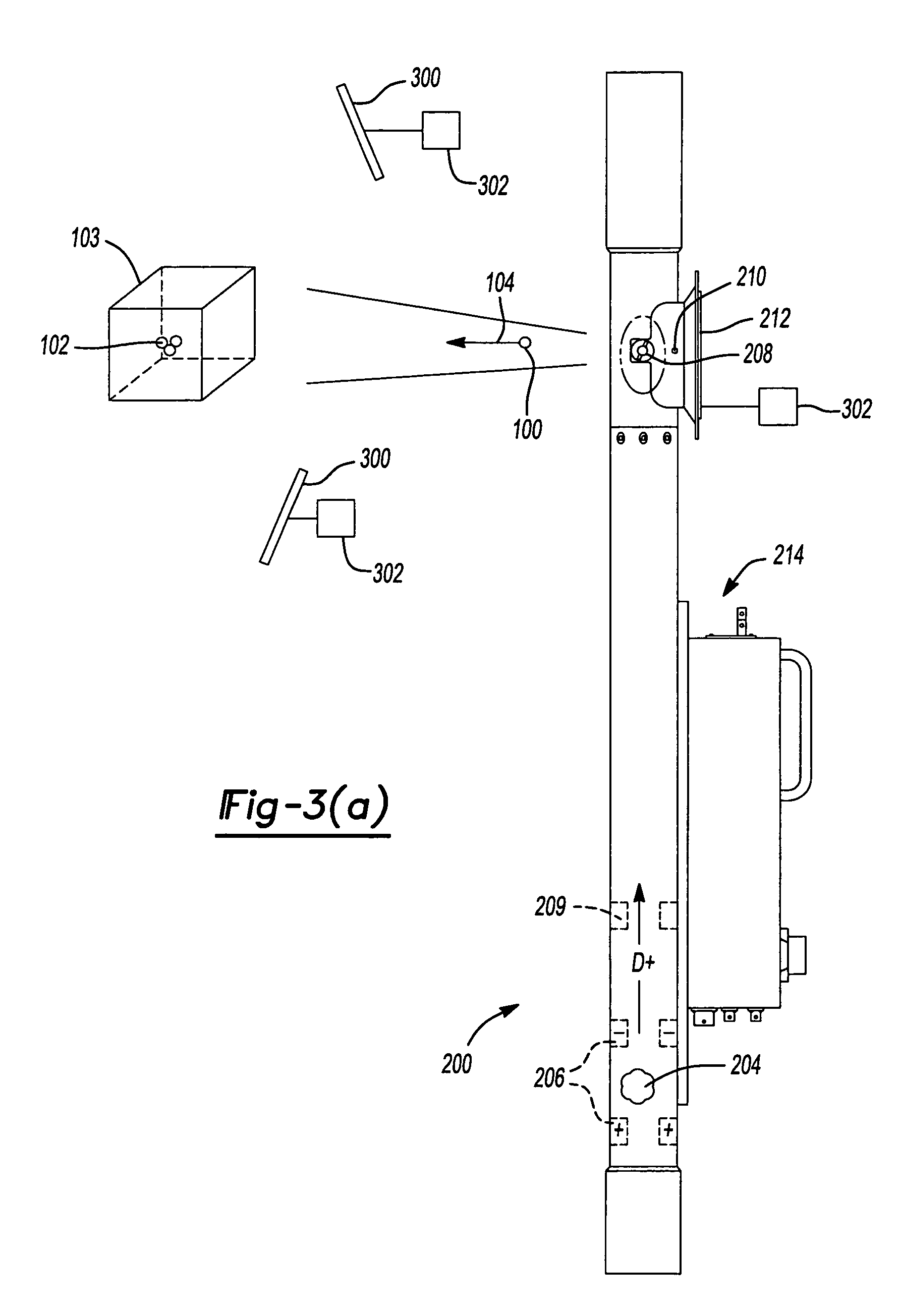
The invention is directed to a remote 3-D imaging system which uses a novel illumination source to establish the relationship of the image features to the system, which is displayed by virtue of calculations. In addition to static surfaces, moving surfaces may be studied and corrections due to turbidity and platform position are also easily compensated for. The instant system may also contain a plurality of sensing systems based on light, including traditional reflective or elastic scattering and novel fluorescent or non-elastic scattering still and video imaging systems, including time-gated systems.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
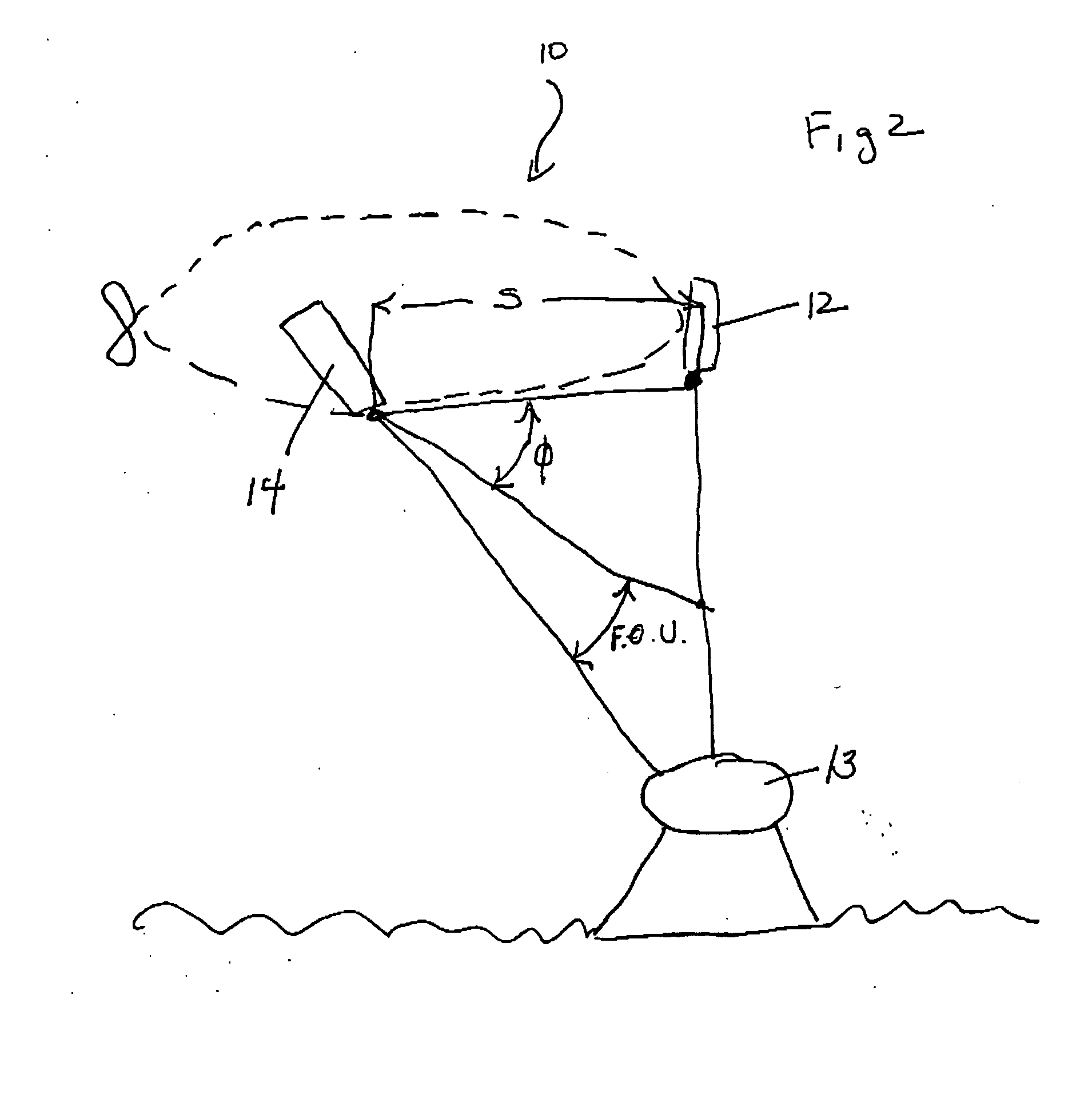
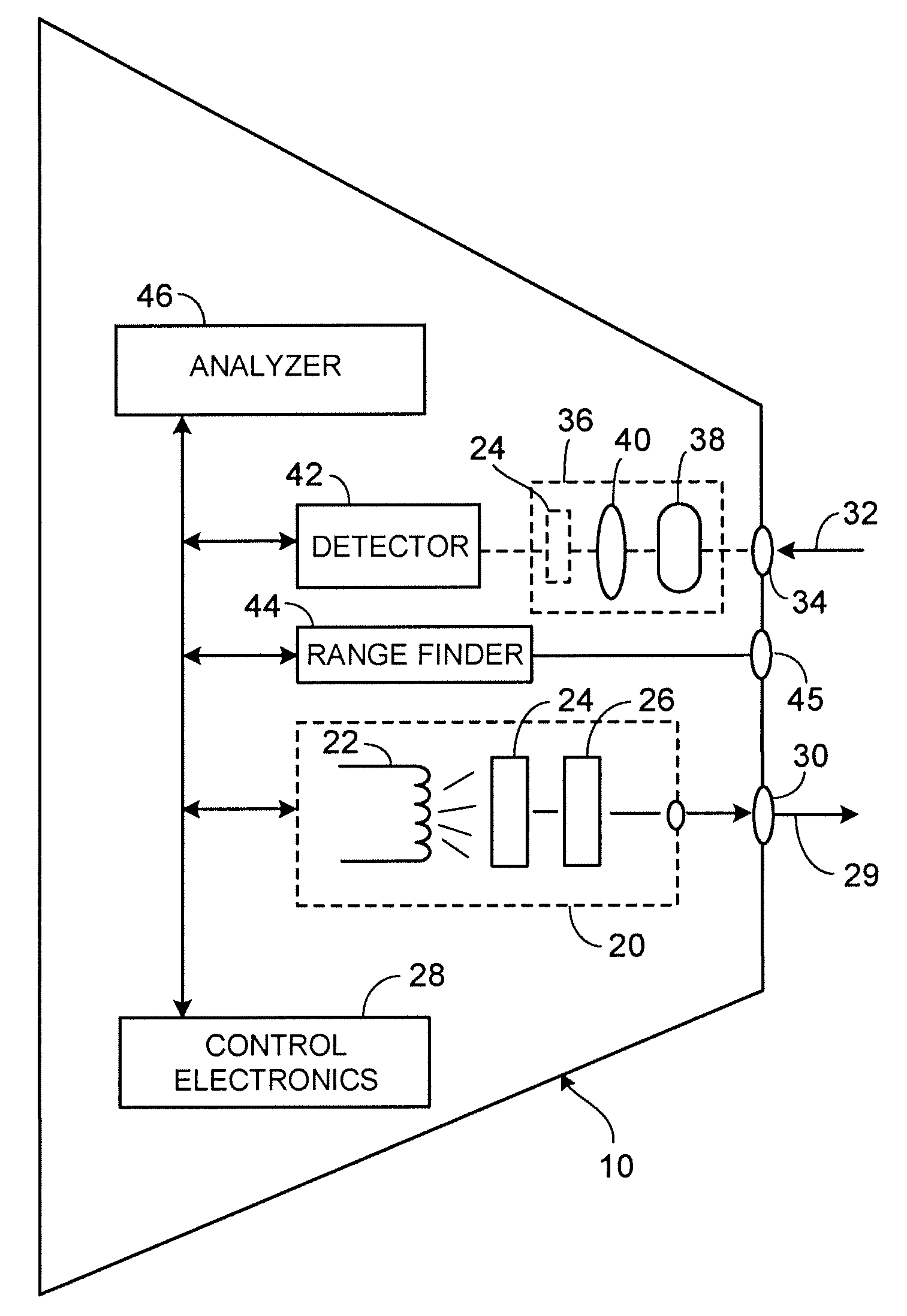
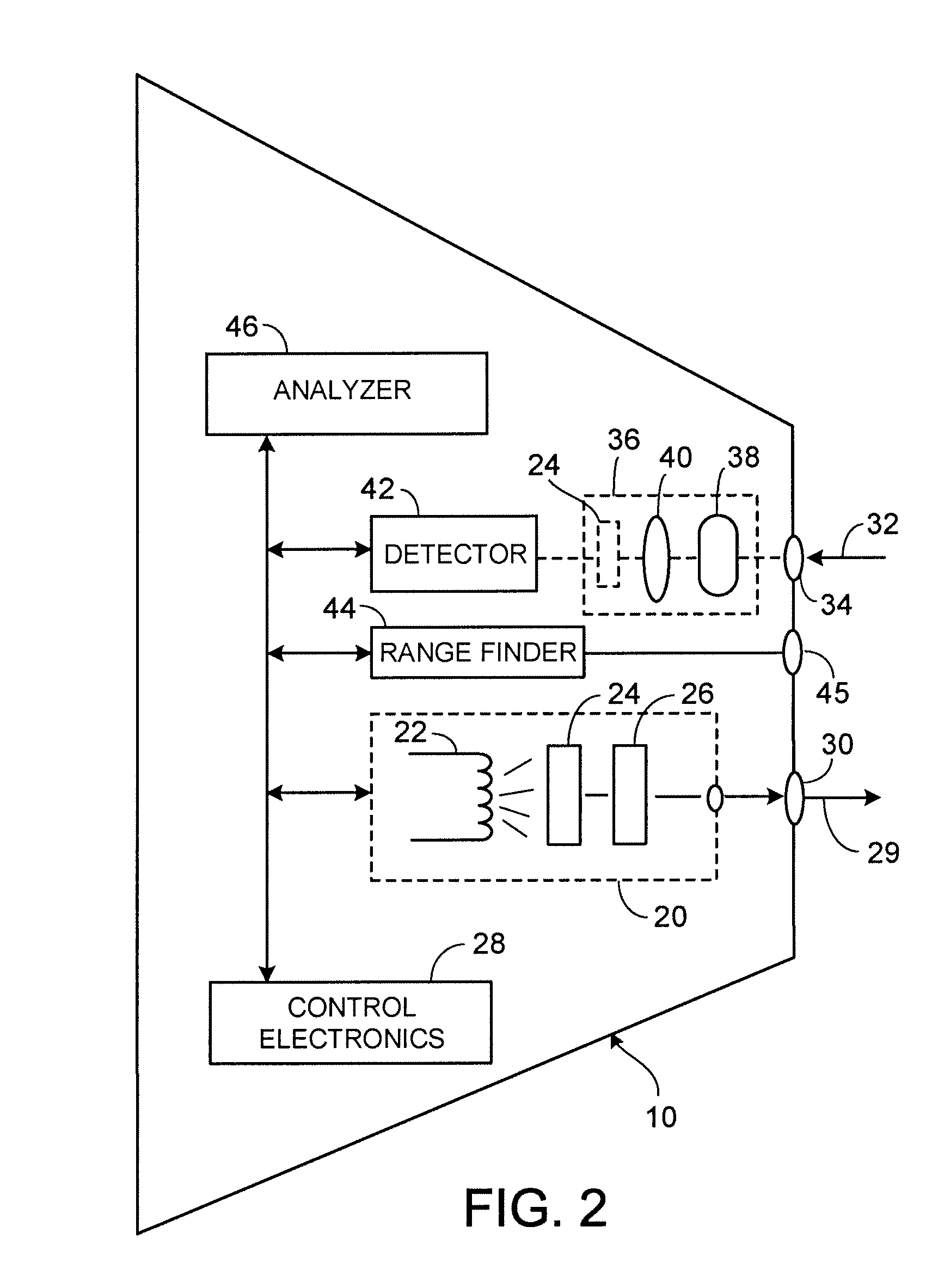
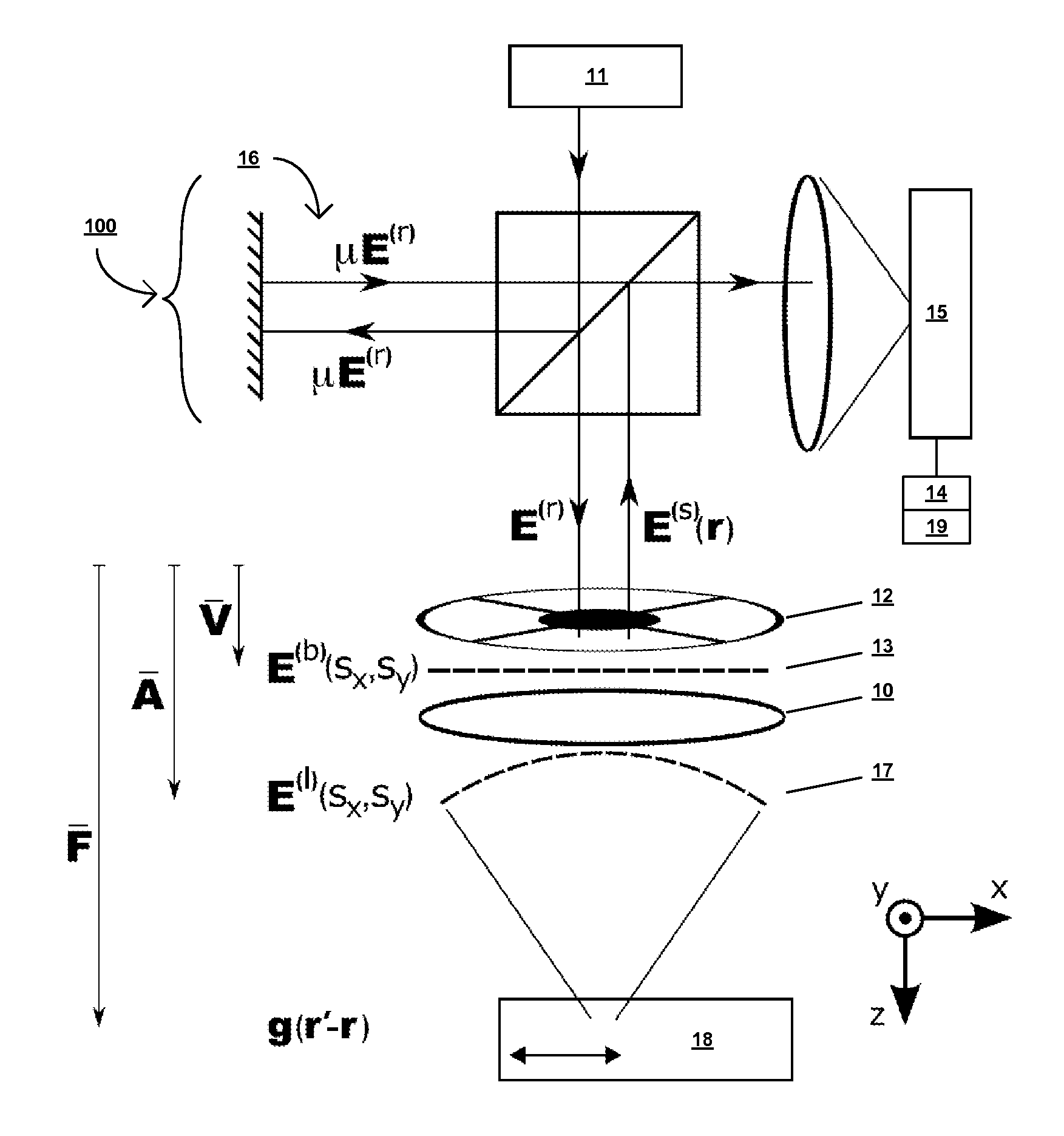
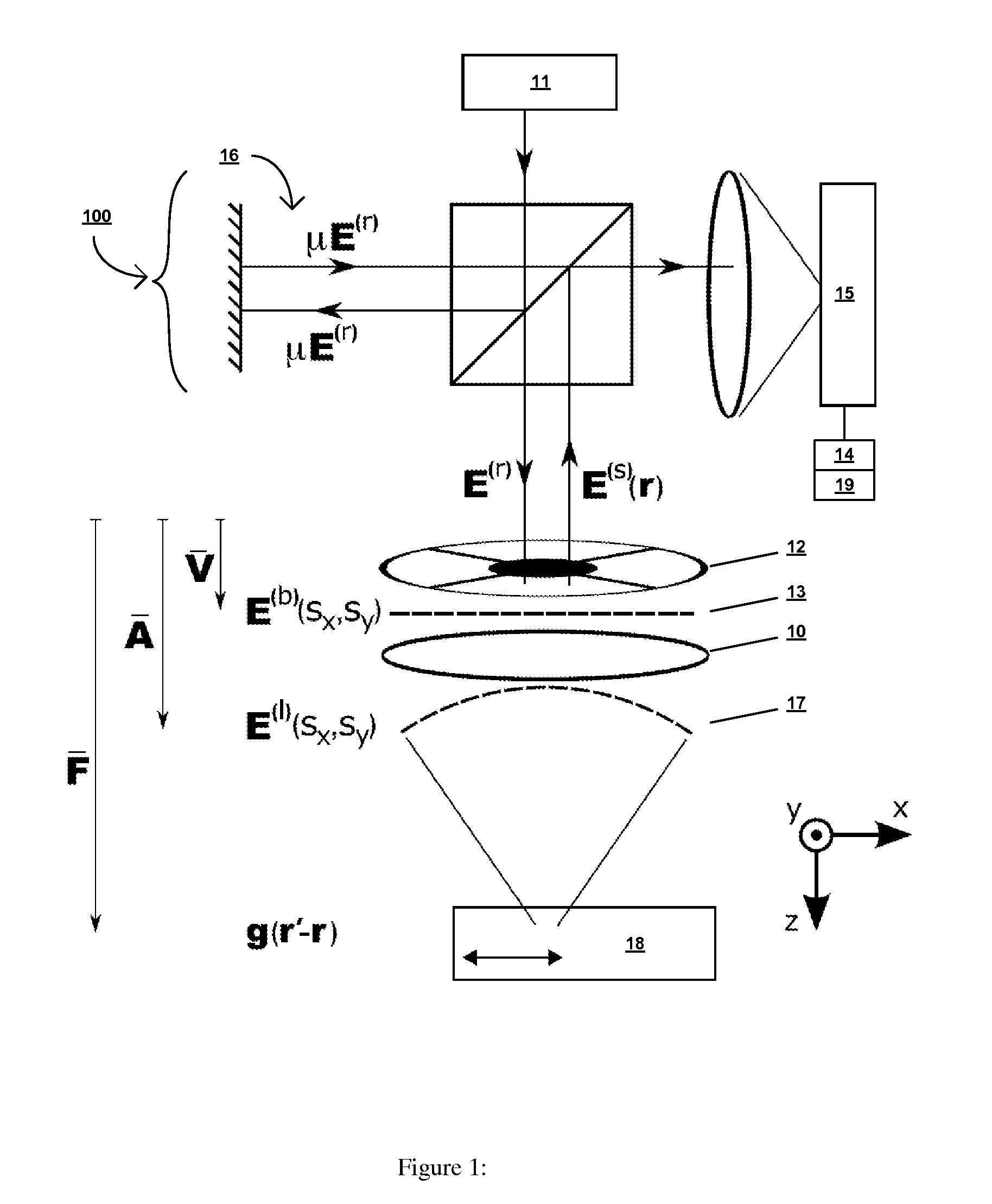
Imaging elastic scattering spectroscopy
ActiveUS7428048B1Early detectionDiagnostics using lightPolarisation-affecting propertiesSpectroscopyAbnormal cell
An apparatus for image elastic scattering spectroscopy is disclosed that is comprised of a light source for generating polarized light. Means are provided to convey the polarized light to a target. A collector receives light reflected from the target. A detector is responsive to the collector for generating images at both parallel and perpendicular polarizations for each of a plurality of wavelengths. A range finder detects a distance to the target. Control electronics control the image generation and the range finder. The apparatus may be configured to image areas on the surface of the body or configured so as to be inserted into various body cavities. Typically, the apparatus will be used in conjunction with an analyzer for analyzing the images for evidence of abnormal cells. Methods of gathering data and of screening for abnormal cells are also disclosed.
Owner:SPECTRAL MOLECULAR IMAGING
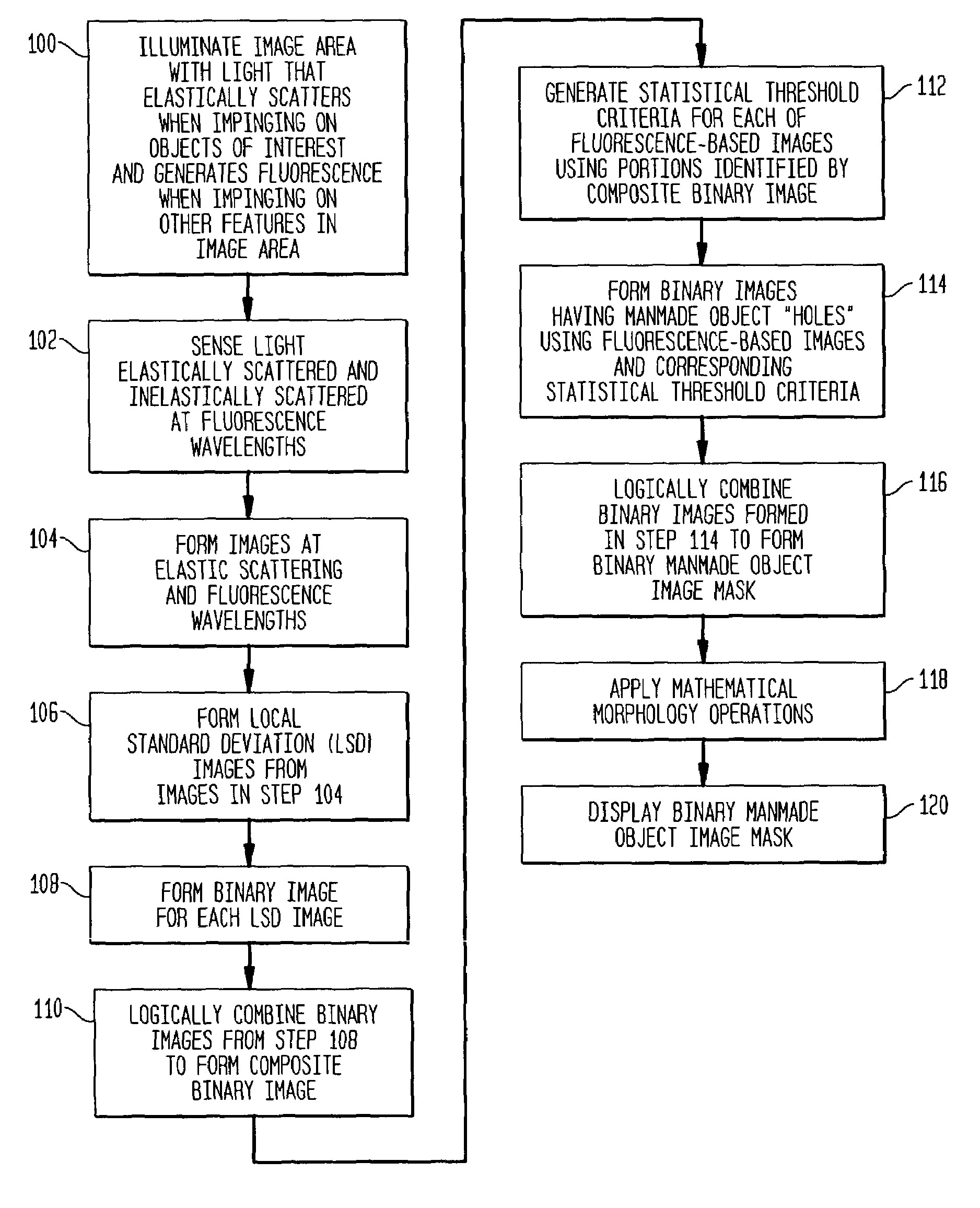
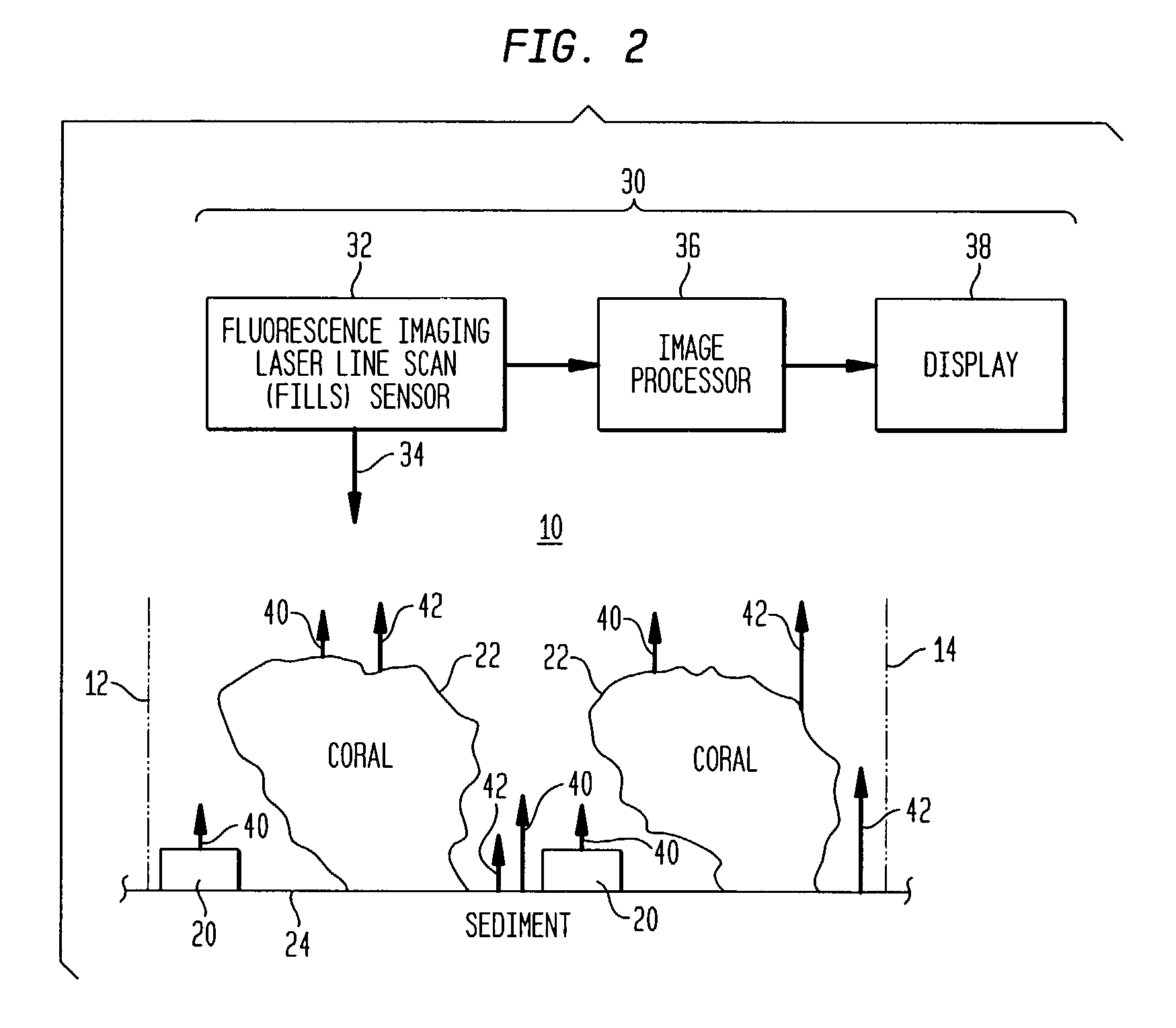
Method of generating images to aid in the detection of manmade objects in cluttered underwater environments
InactiveUS6970578B1Easy to detectCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsPattern recognitionFluorescence
An underwater image area is illuminated with light generating elastic scattering from manmade objects and naturally-occurring features, and fluorescence from naturally-occurring features. Local standard deviation (LSD) images are formed using the elastic scattered and fluorescent light. Elements of each LSD image are compared to threshold criteria to generate: i) first binary images having first image state portions indicating manmade objects and naturally-occurring features, and ii) second image state portions indicating background. The first binary images are logically combined generating a composite image mask. Statistical threshold criteria for each fluorescence-based image is generated using only portions identified by portions of the composite image mask indicating of background. Elements of each fluorescence-based image are compared to statistical threshold criteria to generate second binary images. At least two second binary images are logically combined to generate a binary manmade object image mask delineates between manmade objects and everything else.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
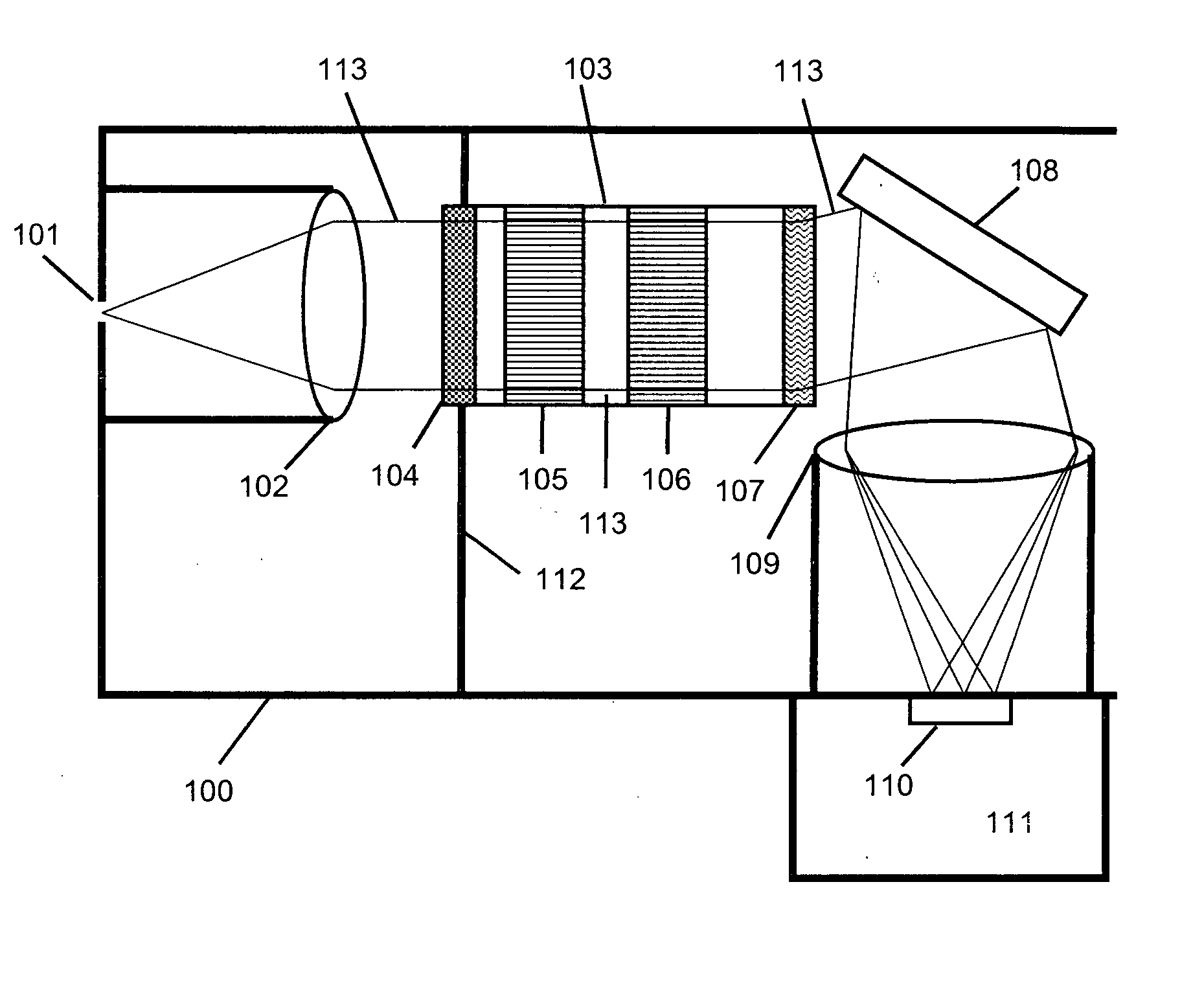
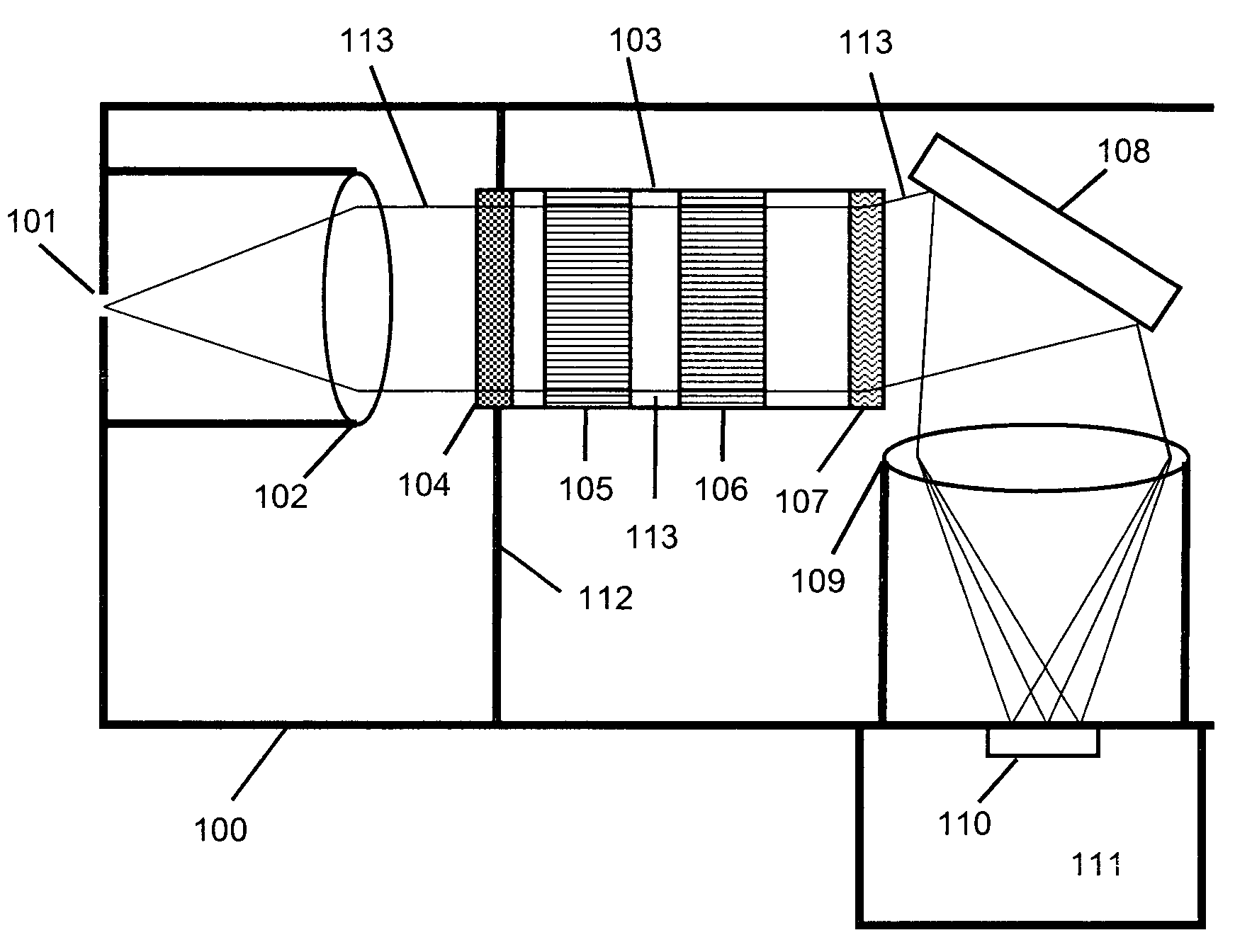
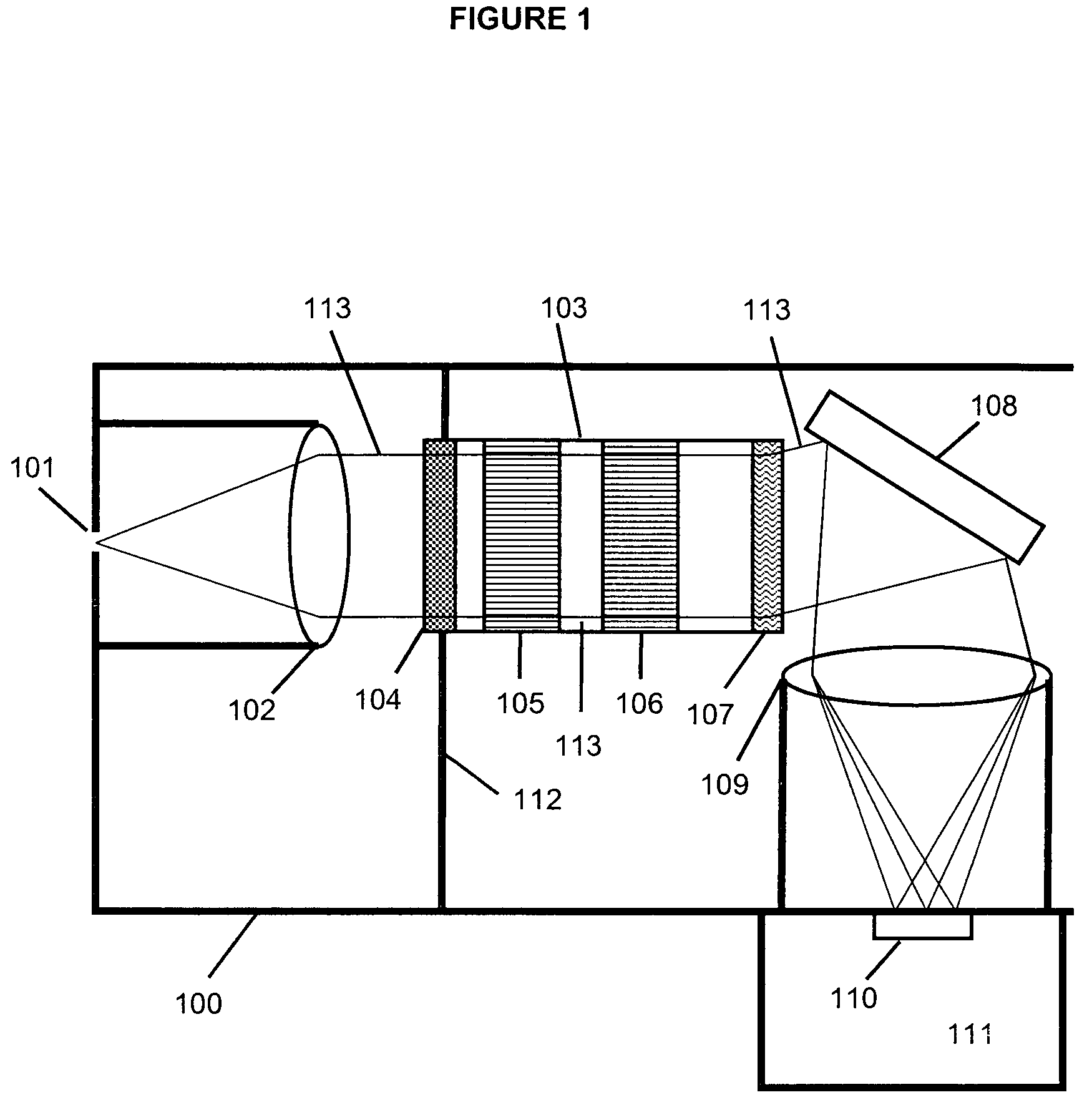
Compact and rugged imaging Raman spectrograph
InactiveUS20080030728A1Improve efficiencyEnhance optical throughputRadiation pyrometryAdditive manufacturing apparatusSpectrographSpectral filtering
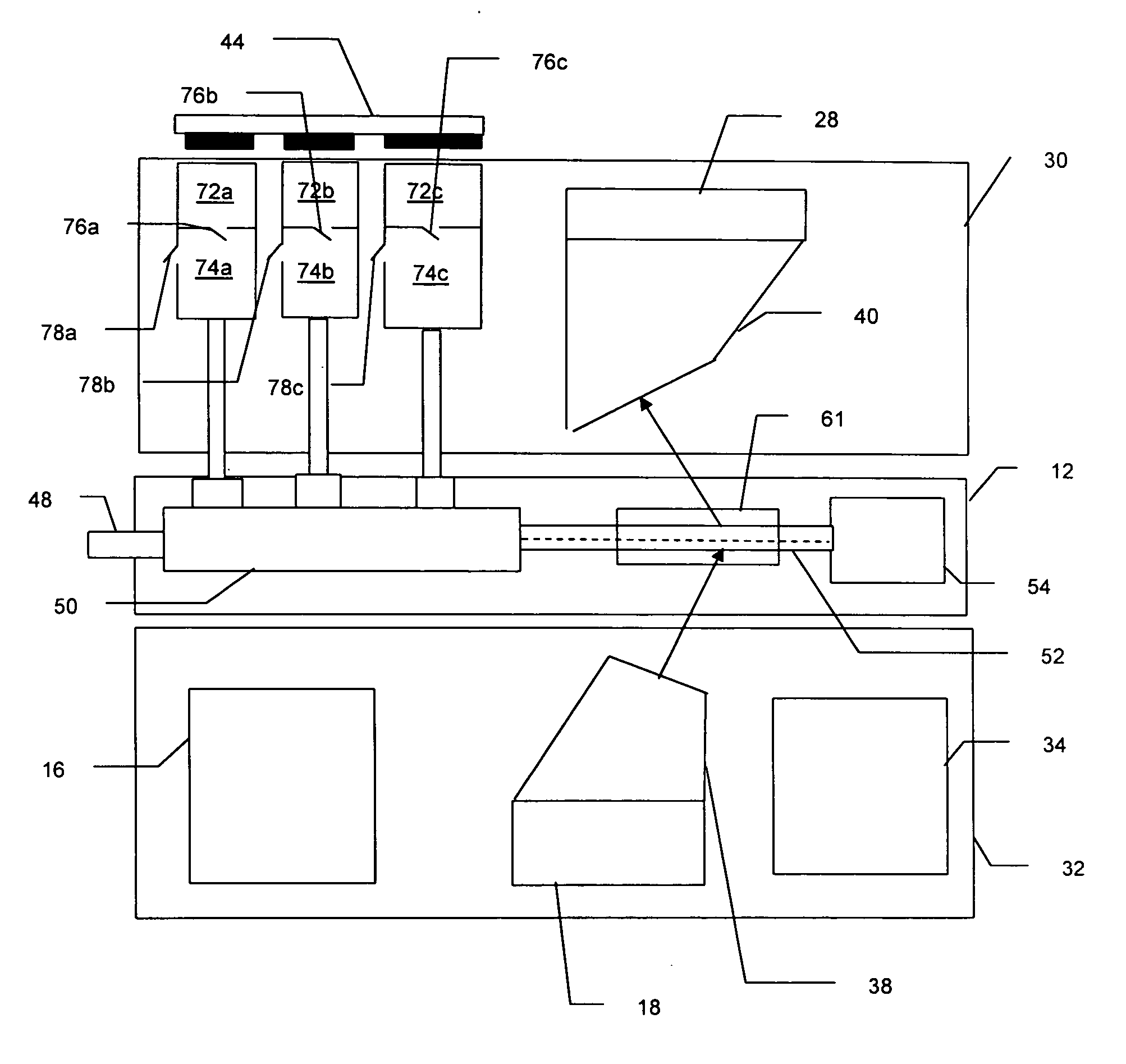
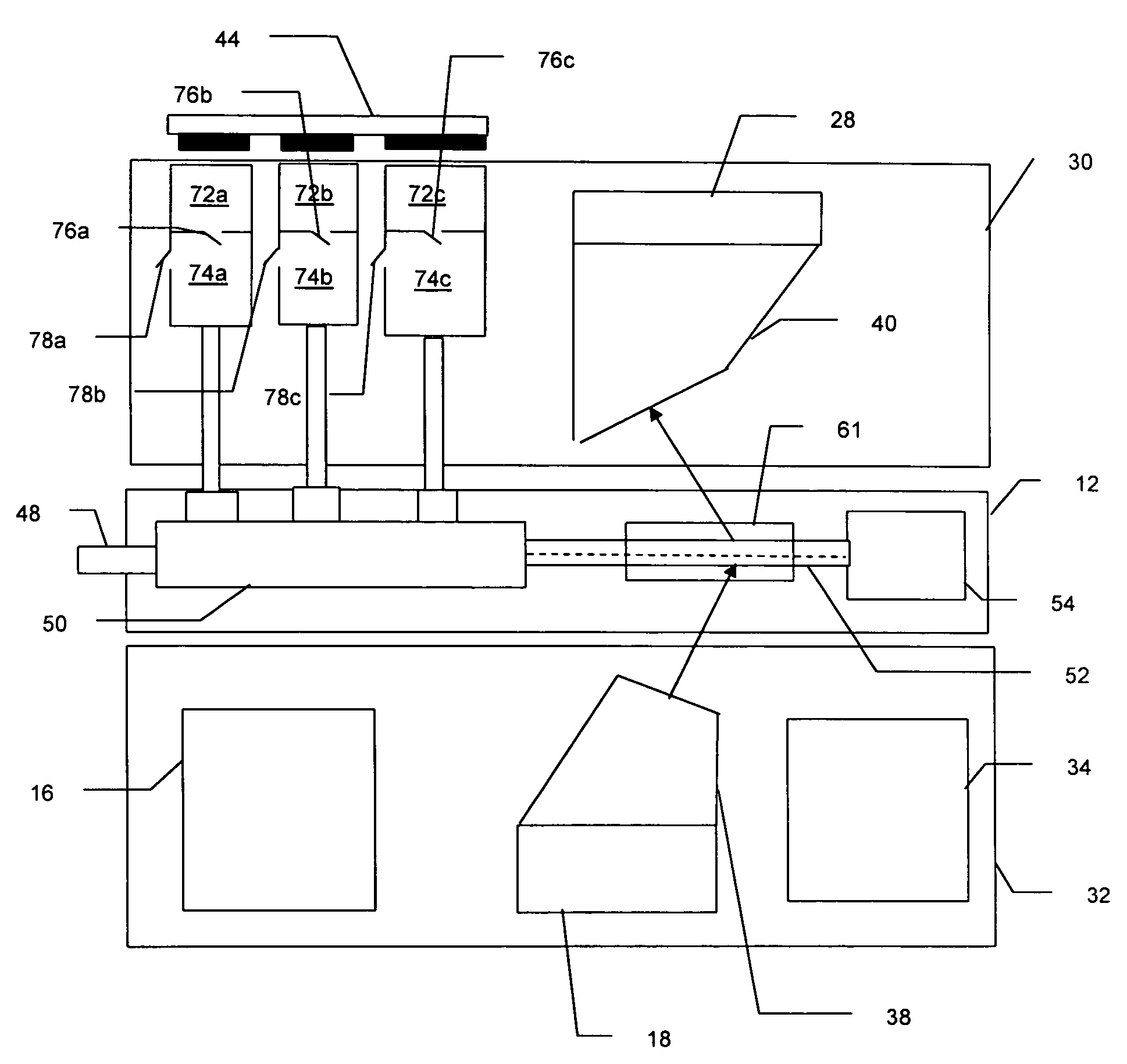
A compact and robust imaging Raman spectrograph has a collimating input lens assembly, a spectral filter assembly, a transmission diffraction grating, a focusing lens assembly, and a light detector. The spectral filter assembly is located between the two lenses and comprises a notch or long-pass filter optical interference filter, a plurality of optical channel plates for limiting the optical acceptance angle of the light passing the optical interference filter, and a transmission diffraction grating, all mounted in a single assembly. The spectral filter assembly permits a very high degree of elastically scattered light rejection and excellent stray-light reduction and management, while permitting a high level of optical throughput to maximize the signal of the weakly scattered Raman signal.
Owner:NGUYEN QUANG VIET
Neutron irradiative methods and systems
ActiveUS20080156997A1Capture cross-sectionHigh incidenceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron irradiationSignal characteristic
A neutron elastic scattering detector device for non-invasively detecting the presence of at least one predetermined element of an object of interest. The detector device comprises a neutron source that simultaneously outputs, at a creation time, a neutron in a first direction and an associated baseline particle in a second direction. The first direction is opposite of the second direction. The neutron can impinge upon the predetermined element of the object of interest and scatter therefrom in a third direction. A baseline particle detector system detects the baseline particle and outputs a baseline signal characteristic thereof. A neutron detector system detects the neutron and outputs a scattering signal in characteristic thereof. The processing unit analyzes the baseline signal and the scattering signal to determine the presence of the predetermined element.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
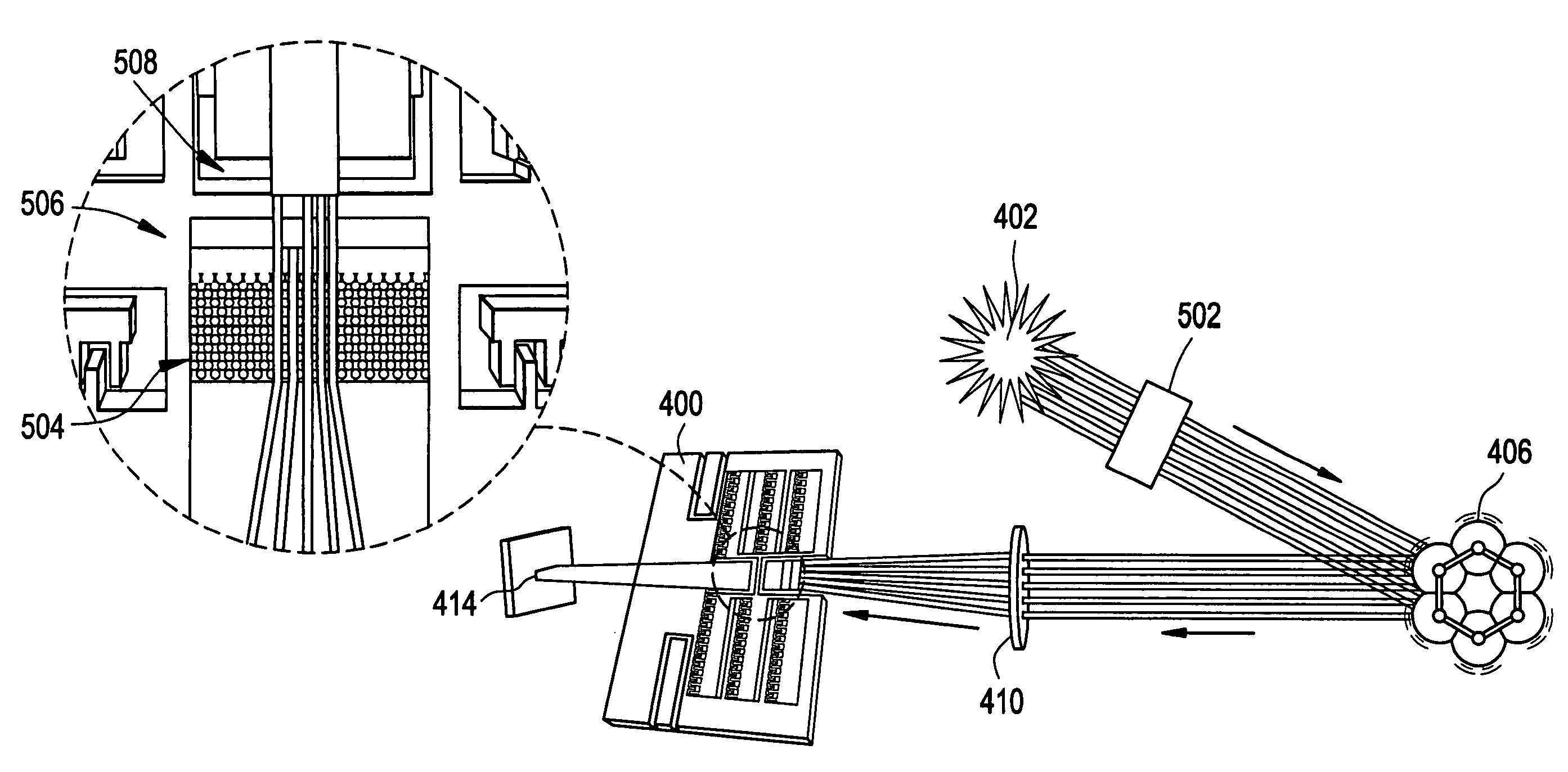
Flow cytometer apparatus for three dimensional diffraction imaging and related methods
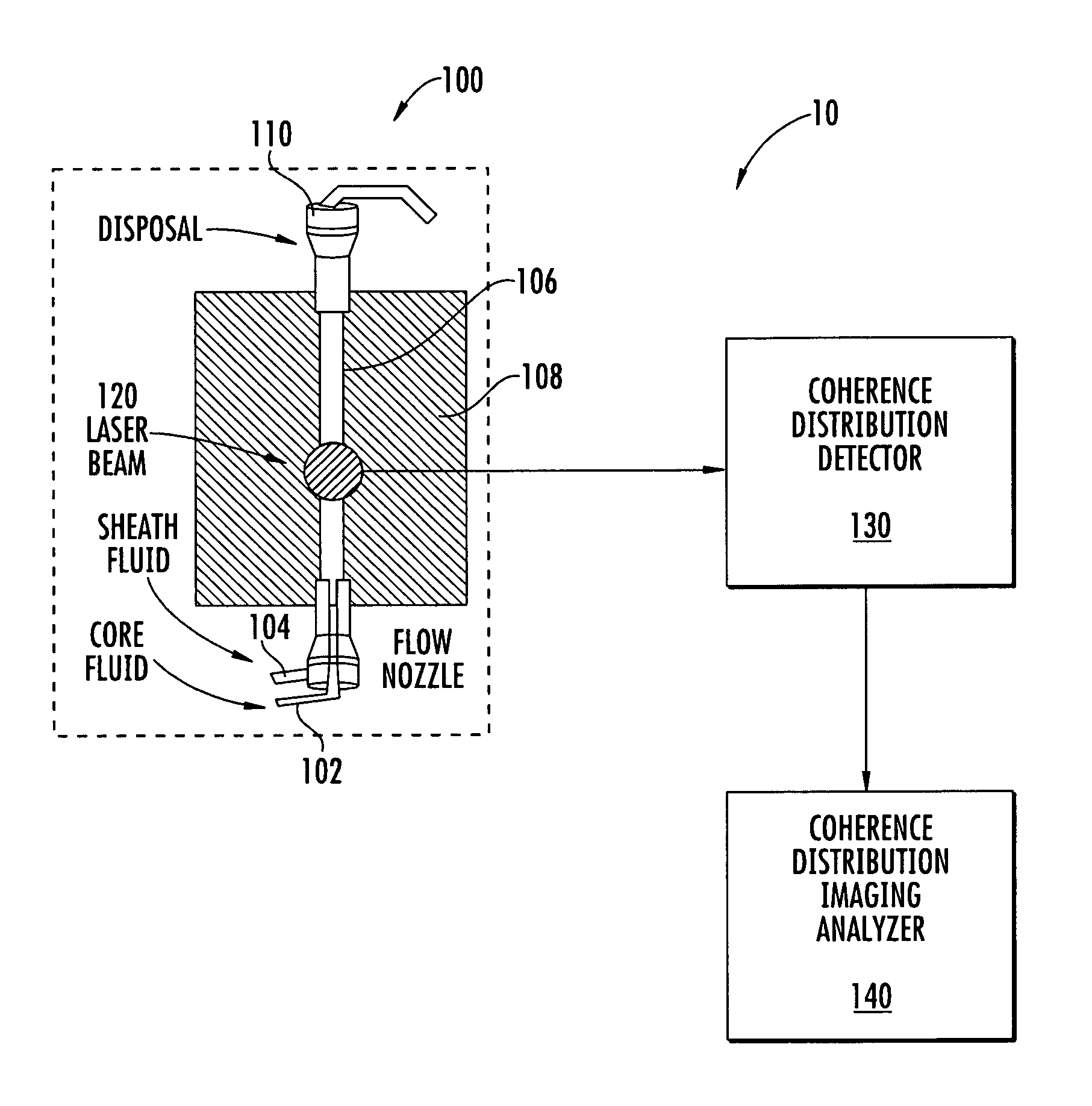
The invention relates to a flow cytometer system for detection of three dimensional diffraction image and a method program product. The system includes a fluid controller configured to form a hydrodynamically focused flow stream including an outer sheath fluid and an inner core fluid; a coherent light source configured to illuminate a particle in the inner core fluid; a detector configured to detect a spatially coherent distribution of elastically scattered light from the particle excited by the coherent light source; an analyzing module configured to extract a three-dimensional morphology parameter of the particle from a spatially coherent distribution of the elastically scattered light. The method includes forming the hydrodynamically focused flow stream including the outer sheath fluid and the inner core fluid; illuminating one particle in the inner core fluid with the coherent light source; elastically detecting scattered light from the particle that is excited by the coherent light source; and extracting a three-dimensional morphology parameter of the particle from a spatially coherent distribution of the elastically scattered light. According to the invention, it is possible to perform single-particle analysis to a polulation containing a plurality of particles in a multi-dimensional feature space.
Owner:EAST CAROLINA UNIVERISTY
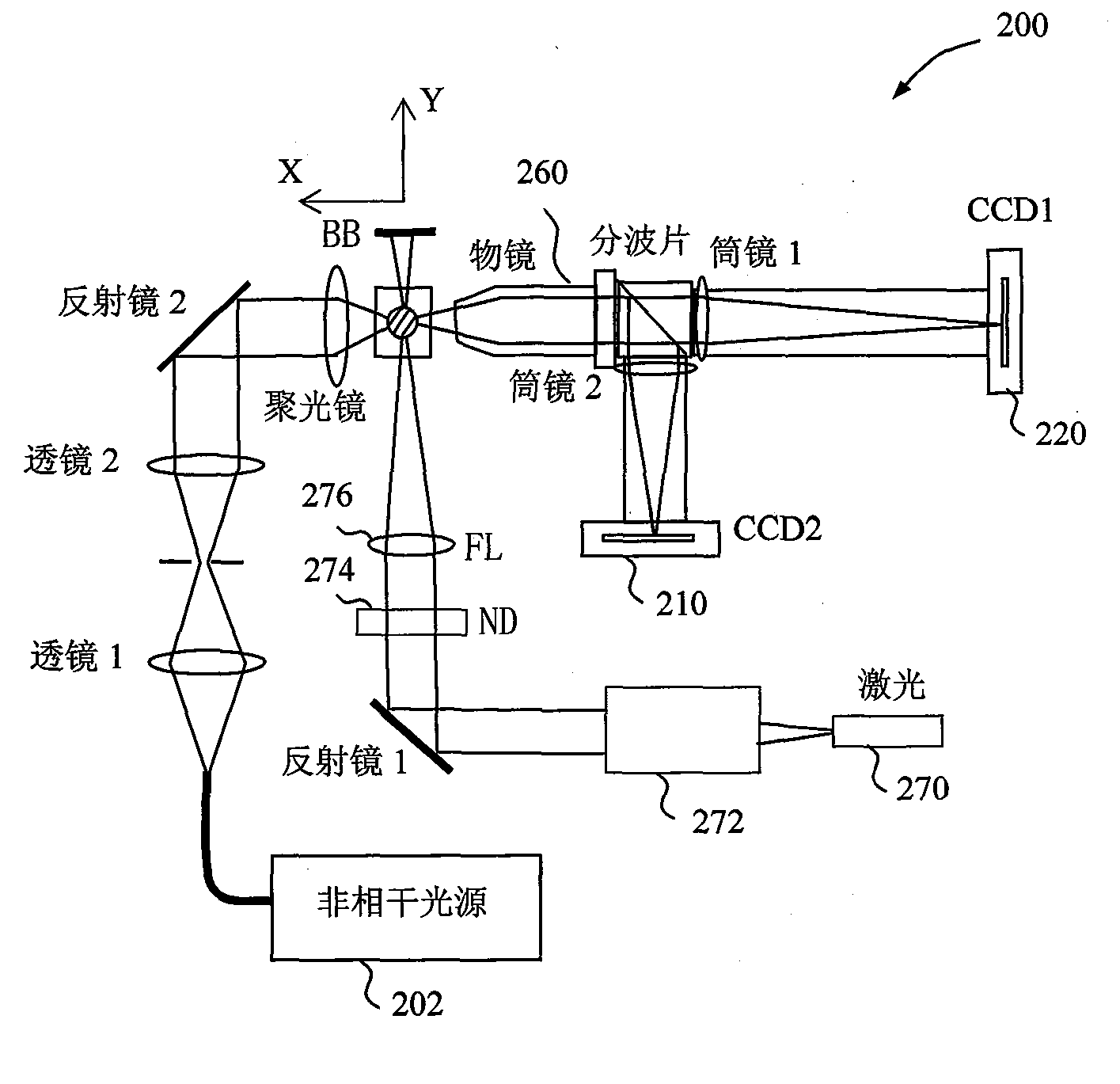
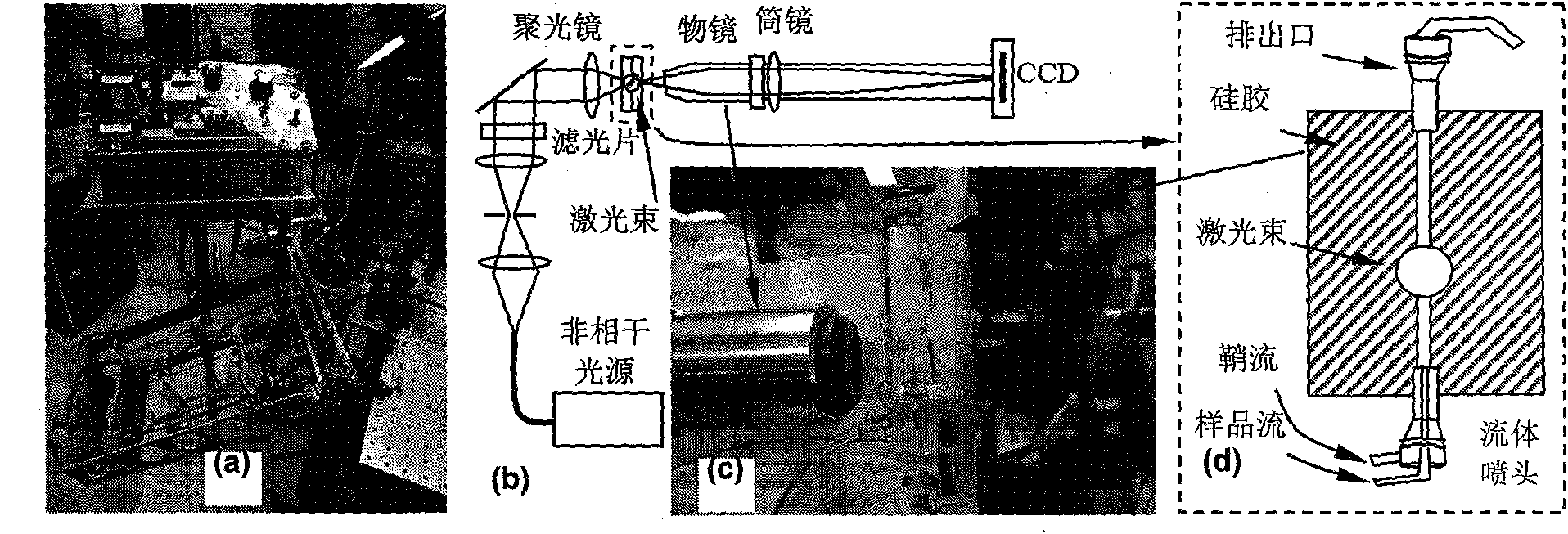
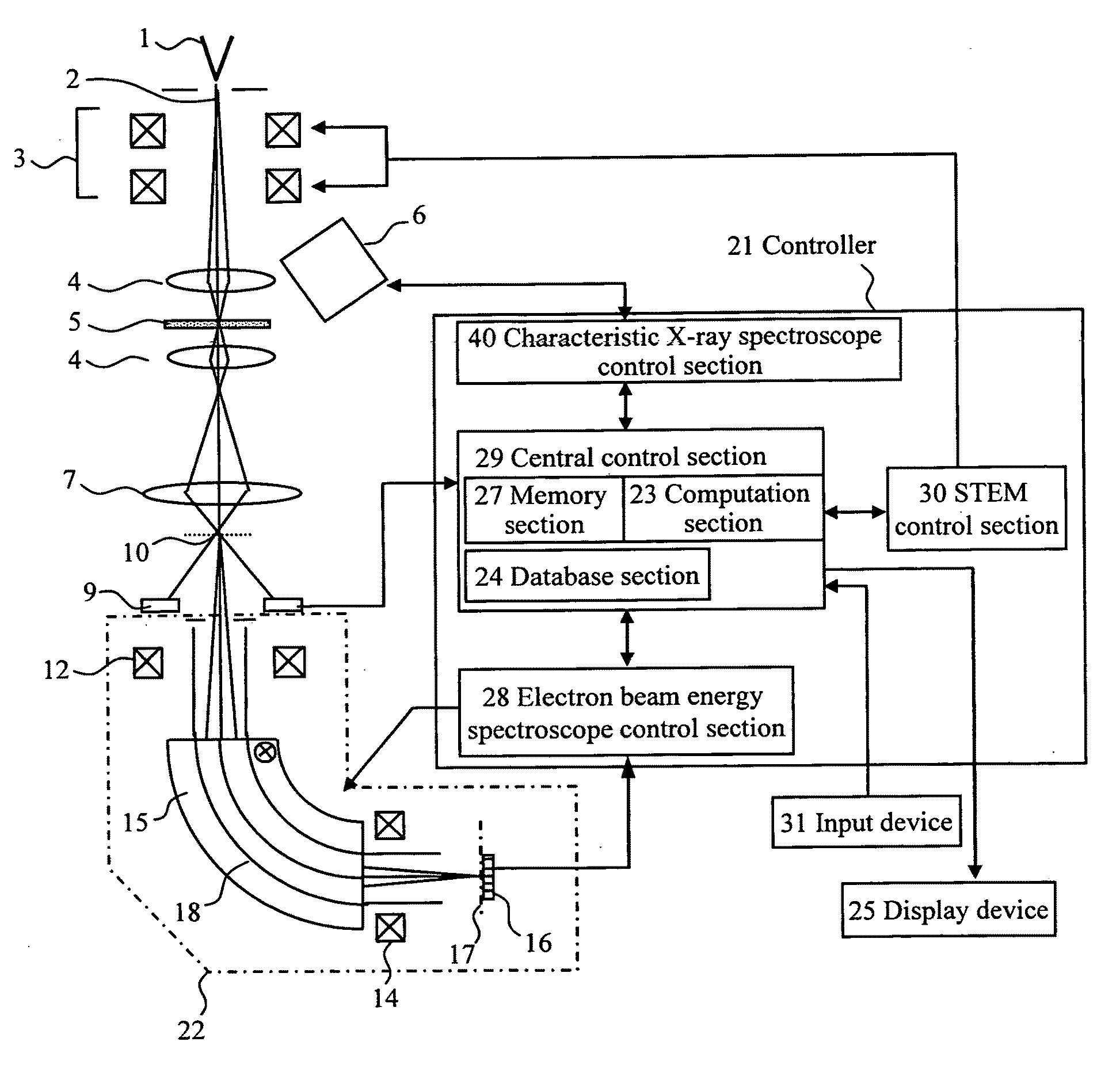
Electronic microscope apparatus
ActiveUS20090194691A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioImprove spatial resolutionThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationBeam energySpectroscopy
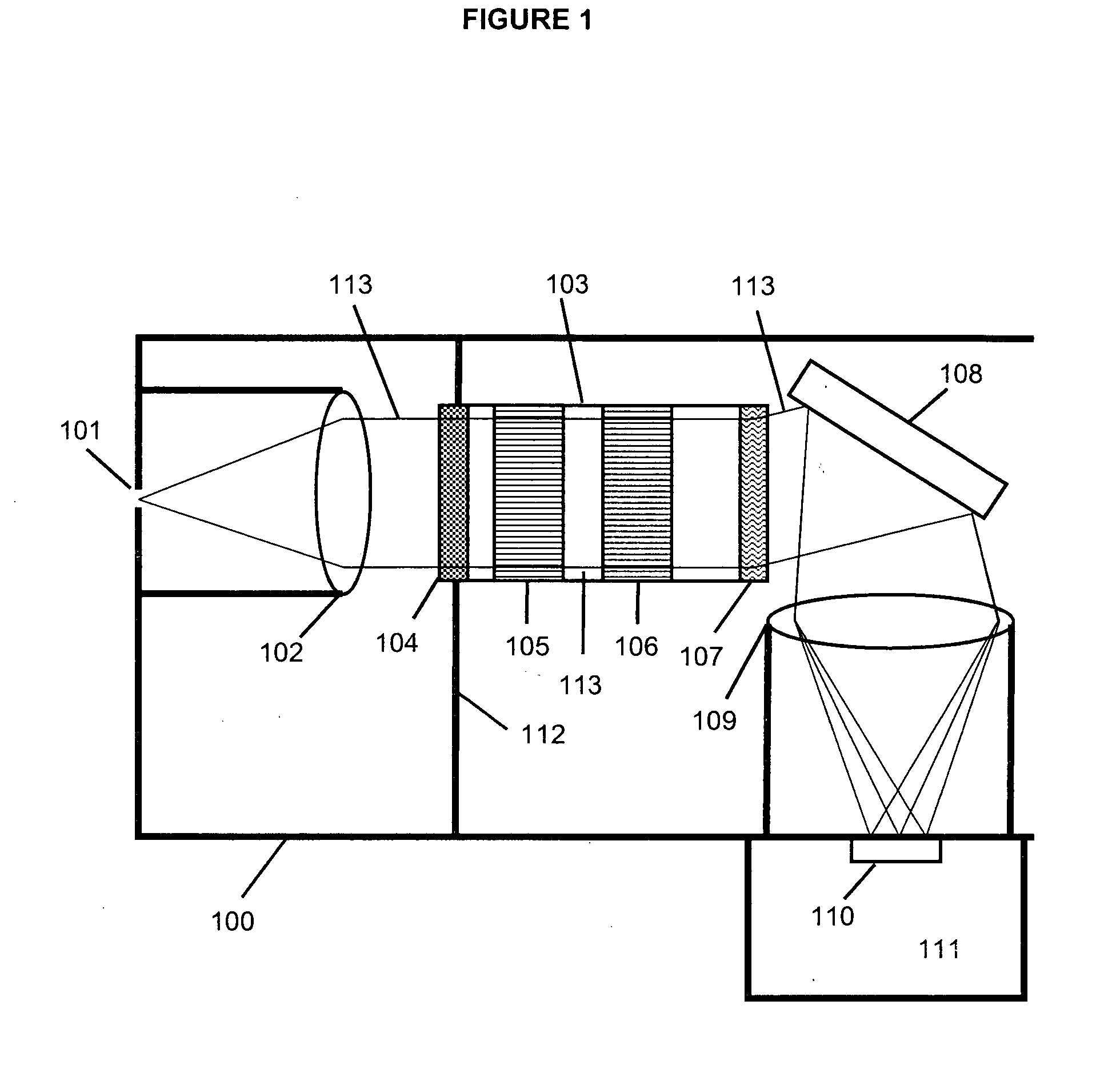
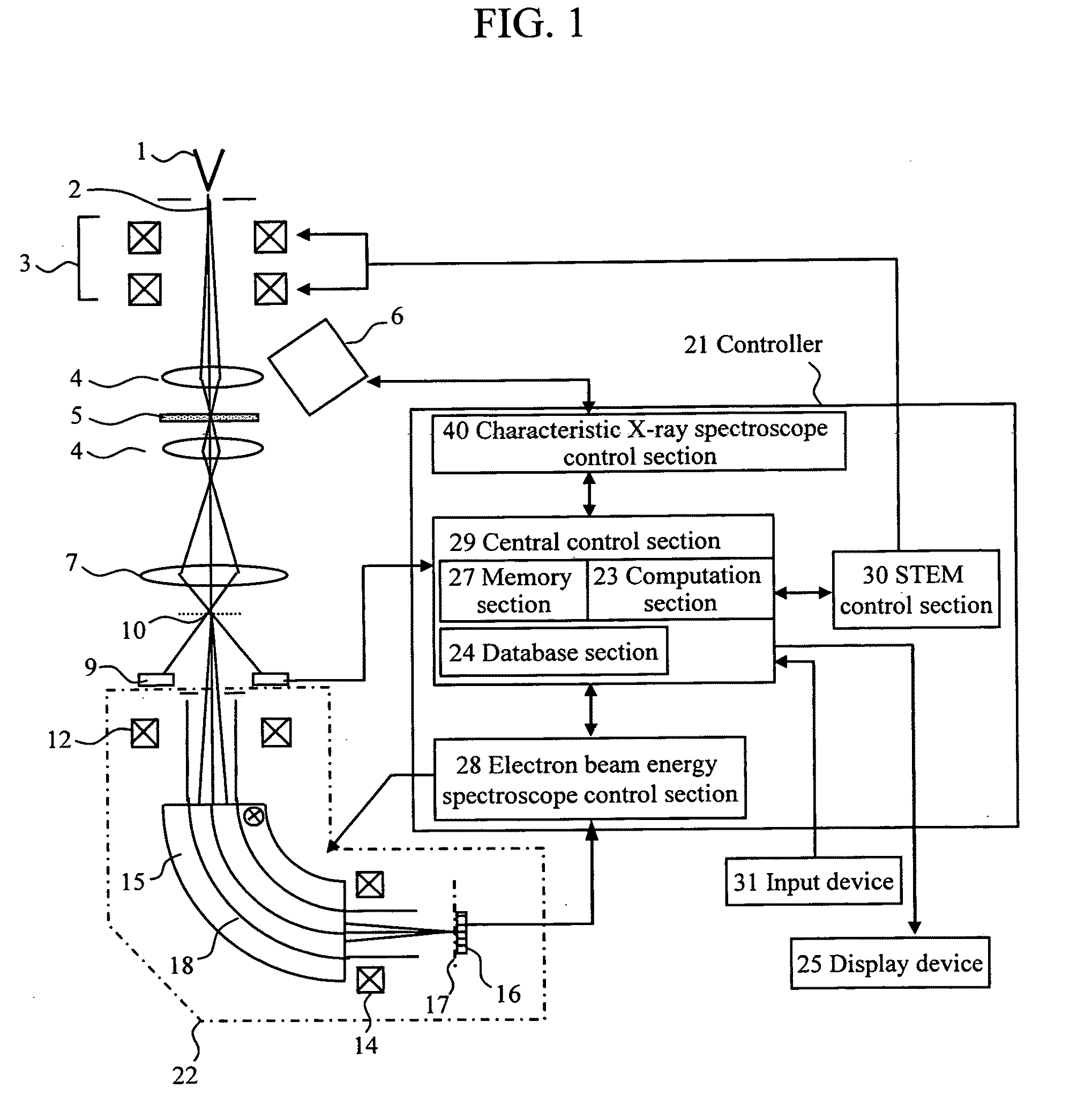
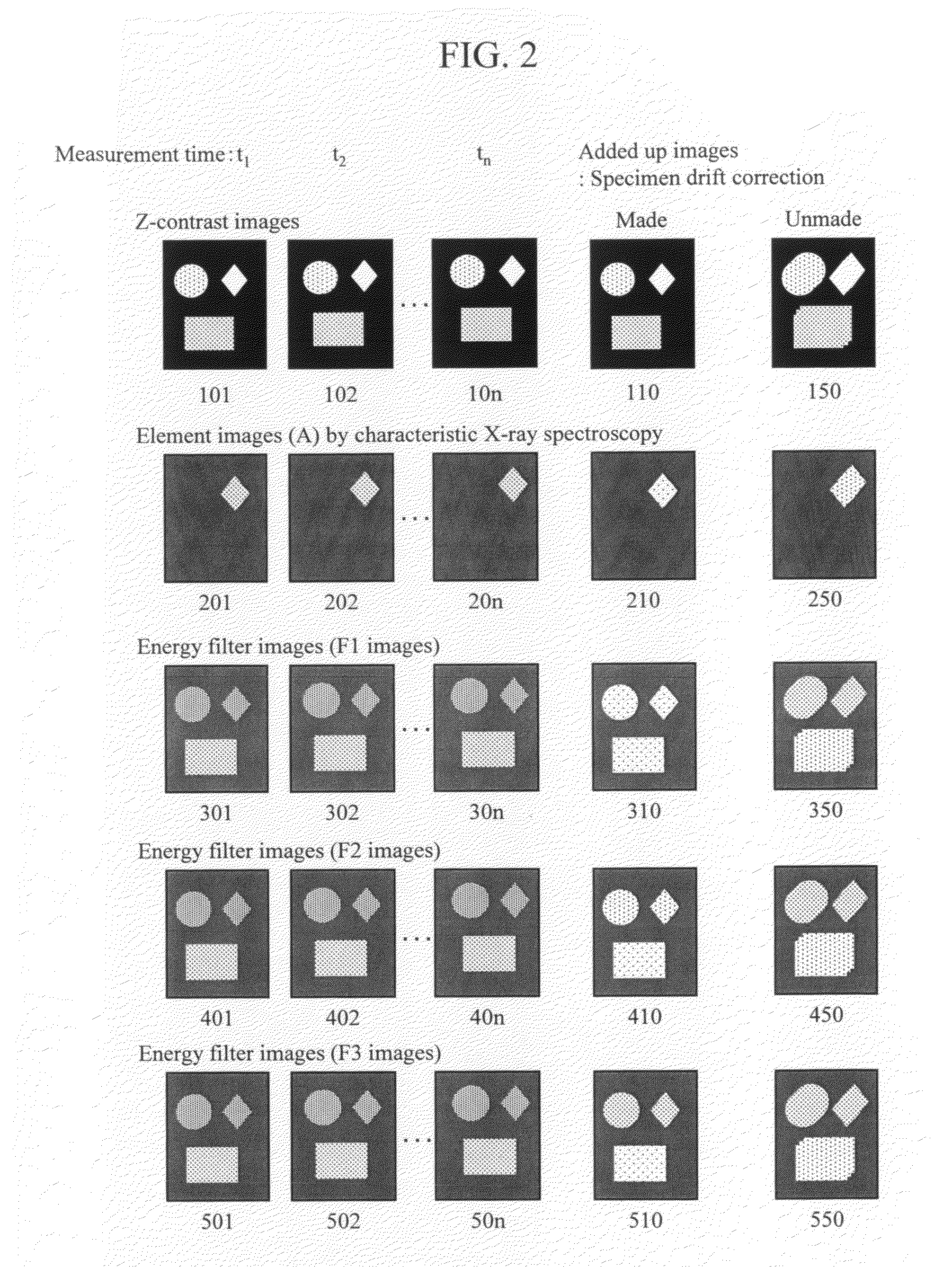
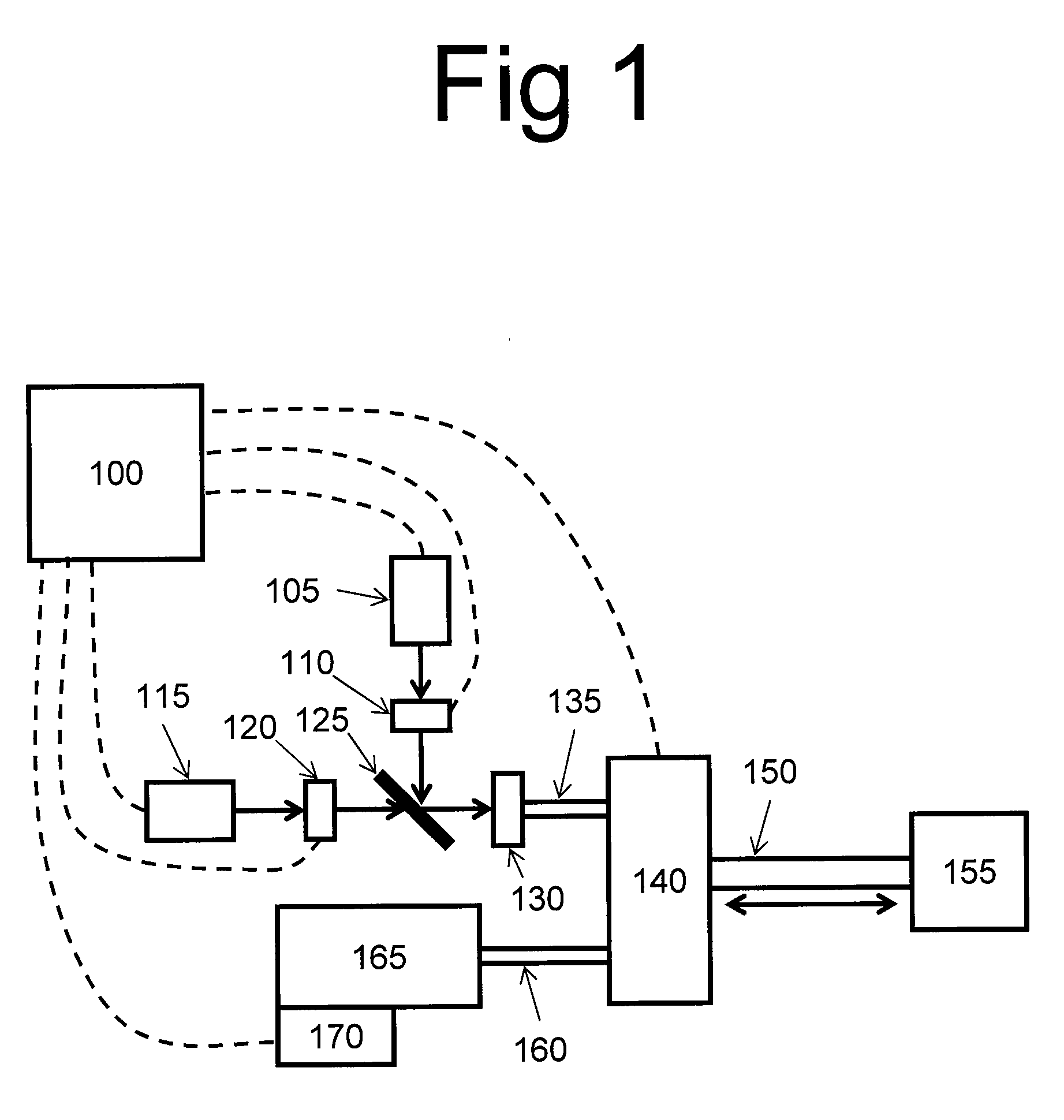
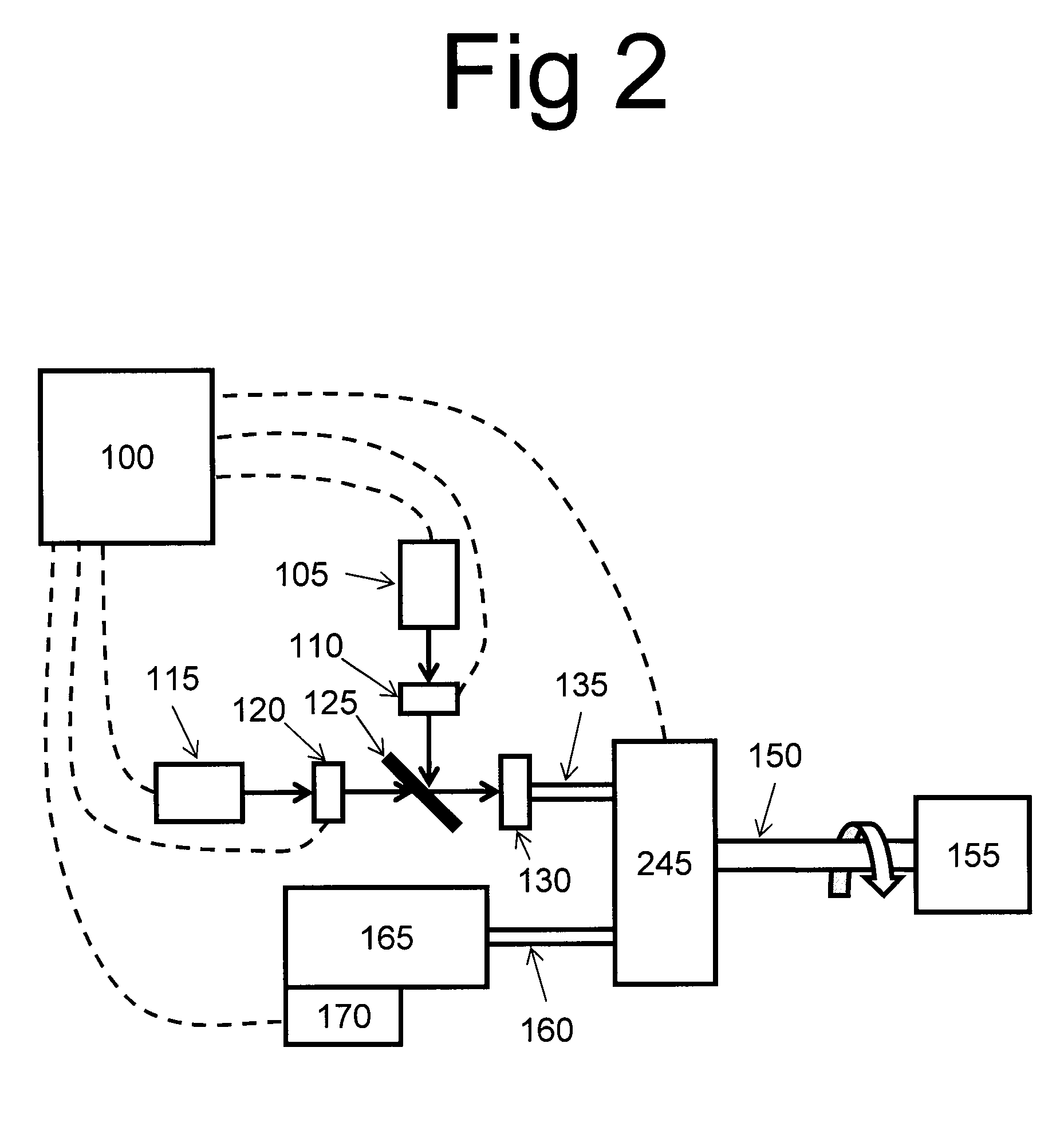
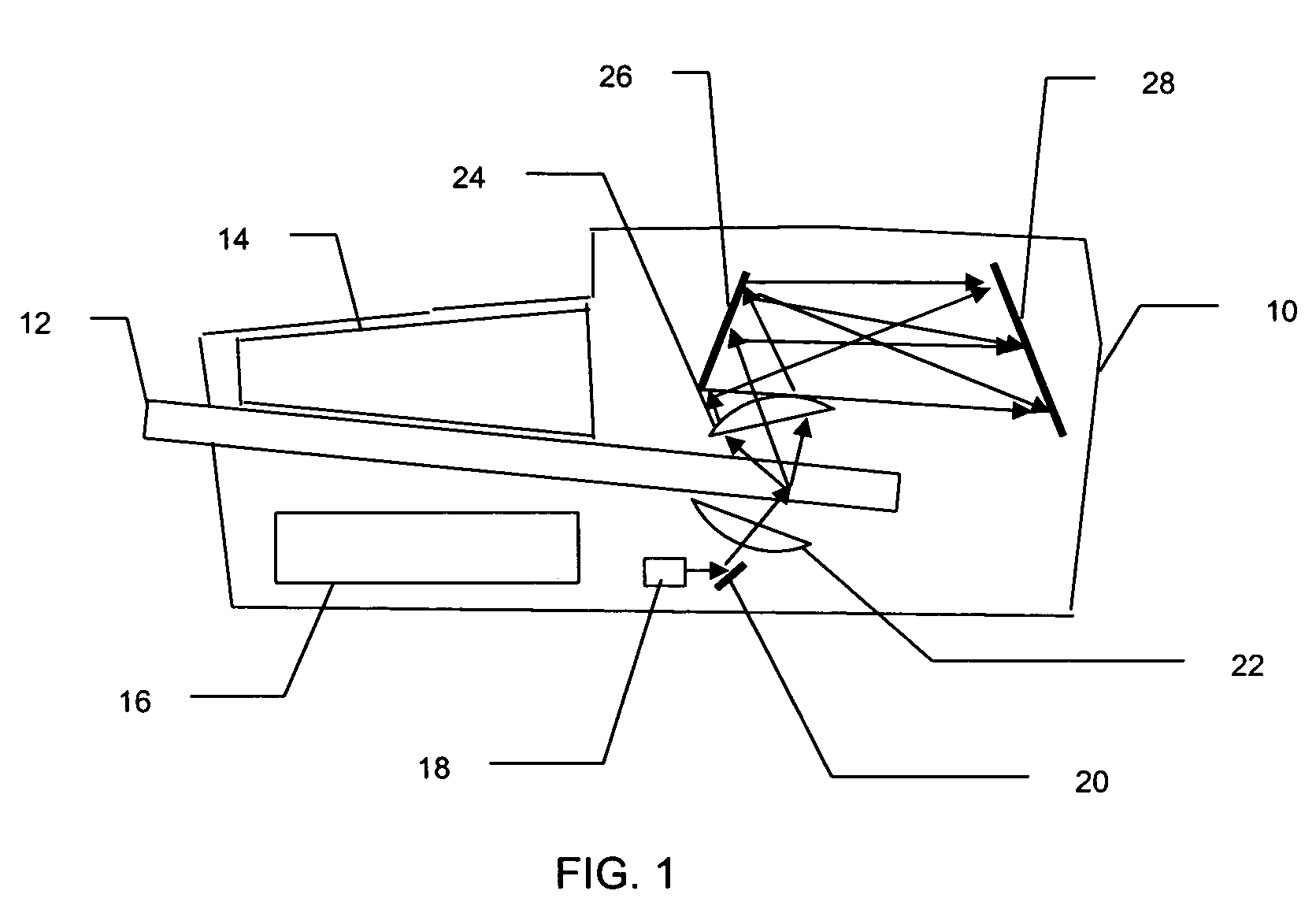
To enable measurement of an elastically scattered electron image, a characteristic-X-ray-based element image and an electron-beam-energy-spectroscopy-based element image with a high S / N and high spatial resolution in an electronic microscope having a function to produce an element image. Measurement of a characteristic X-ray signal and electron beam energy loss spectra or measurement of a plurality of energy filter signals including a core loss of an observed element is performed simultaneously and continuously with detection of elastically scattered electrons transmitted through a specimen to be analyzed, and element images based on characteristic X-rays and electron beam energy spectroscopy are added up while correcting a positional misalignment with respect to elastically scattered electron images continuously observed (see FIG. 1).
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Neutron irradiative methods and systems
ActiveUS7405409B2Fast analysisImprove personnel safetyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron irradiationSignal characteristic
A neutron elastic scattering detector device for non-invasively detecting the presence of at least one predetermined element of an object of interest. The detector device comprises a neutron source that simultaneously outputs, at a creation time, a neutron in a first direction and an associated baseline particle in a second direction. The first direction is opposite of the second direction. The neutron can impinge upon the predetermined element of the object of interest and scatter therefrom in a third direction. A baseline particle detector system detects the baseline particle and outputs a baseline signal characteristic thereof. A neutron detector system detects the neutron and outputs a scattering signal in characteristic thereof. The processing unit analyzes the baseline signal and the scattering signal to determine the presence of the predetermined element.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Localized surface plasmon resonance sensing system, appartatus, method thereof
ActiveUS20100128275A1Sensor smallEasy to set upScattering properties measurementsLaboratory glasswaresOpto electronicLocalized surface plasmon
A sensing system comprises a light source, an optical fiber, a plurality of noble metal nano-particles, a micro-fluidic module and a photo detector. The optical fiber couples an incident light. The plurality of noble metal nano-particles are disposed on a surface of the optical fiber to form a noble metal nano-particle submonolayer, the noble metal nano-particles are substantially separated from each adjacent noble metal nano-particles such that the conductivity of the noble metal nano-particle submonolayer is smaller than that of a metal film. The micro-fluidic module accommodates the optical fiber and a sample, and the sample is driven to contact with the noble metal nano-particles. The photo detector detects an emergent light from the optical fiber. When the incident light interacts with the noble metal nano-particles, a signal derived from localized surface plasmon resonance in form of attenuated light or elastic scattered light is outputted through the photo detector.
Owner:INSTANT NANOBIOSENSORS CO LTD
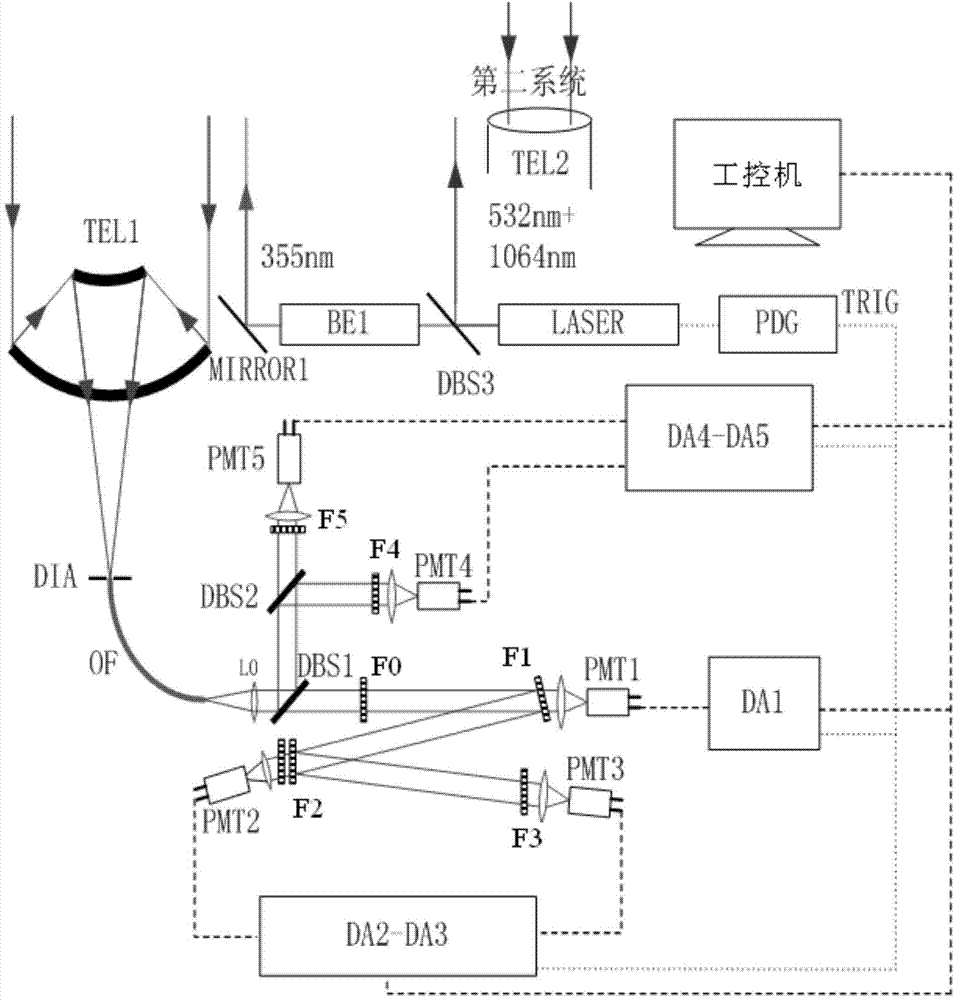
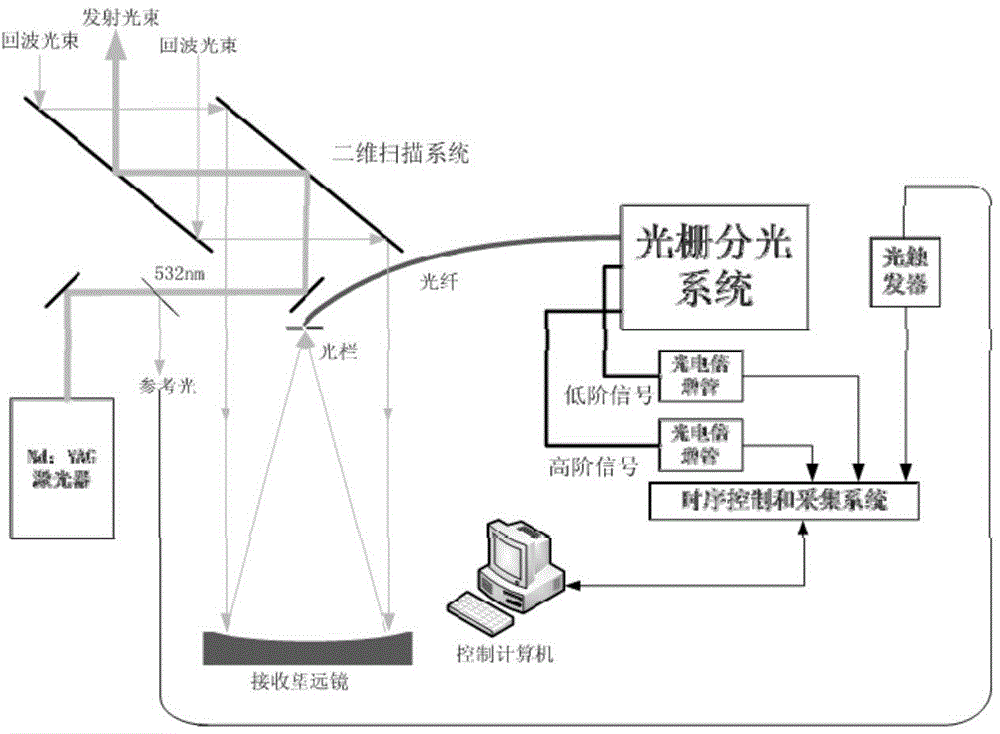
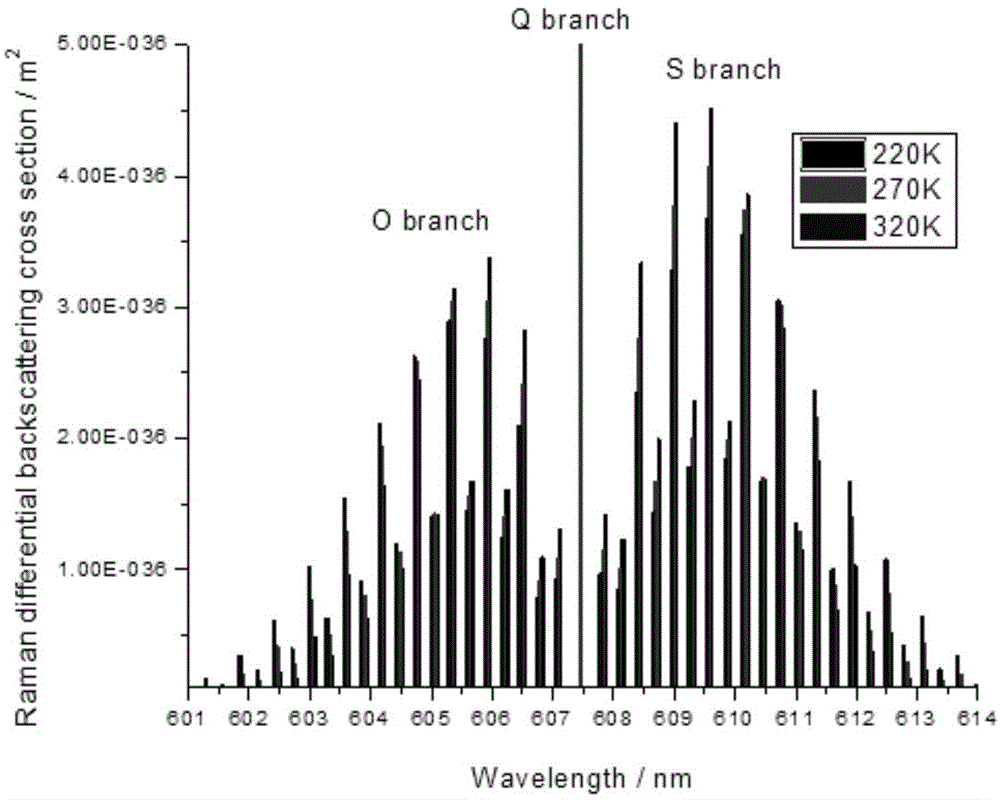
Vibration-rotational Raman-Mie scattering multi-wavelength laser radar system and working method thereof
ActiveCN103792544AExpand the detection rangeImprove detection accuracyScattering properties measurementsRaman scatteringRadar systemsWater vapor
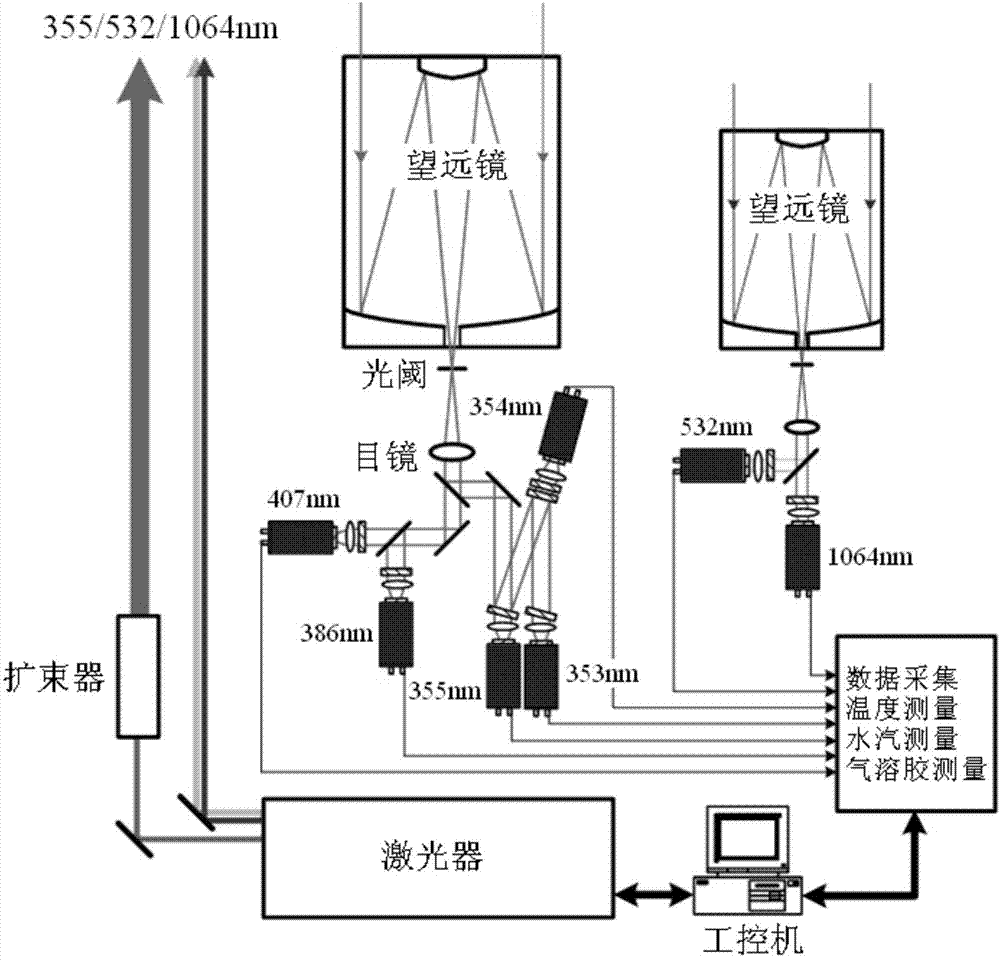
The invention discloses a vibration-rotational Raman-Mie scattering multi-wavelength laser radar system and a working method thereof. The system comprises a first system and a second system, wherein the first system works in an ultraviolet wave segment, the second system works in a visible infrared wave segment, and the first system and the second system both comprise laser emission units, optical receiving units, signal detection and data collecting units and control units. The laser emission units are used for emitting lasers to air, the optical receiving units are used for receiving back scattering echo signals of the air on the lasers emitted by the laser emission units, and conduct rotational Raman, vibration Raman and elastic scattering light splitting on the back scattering echo signals, the signal detection and data collecting units are used for obtaining parameter information of air temperature, water vapor, aerosol and cloud from the back scattering echo signals after light splitting, and the control units are used for controlling the laser emission units, the optical receiving units and the signal detection and data collecting units to run. The vibration-rotational Raman-Mie scattering multi-wavelength laser radar system and the working method of the system can achieve all-weather air comprehensive continuous automatic observation.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
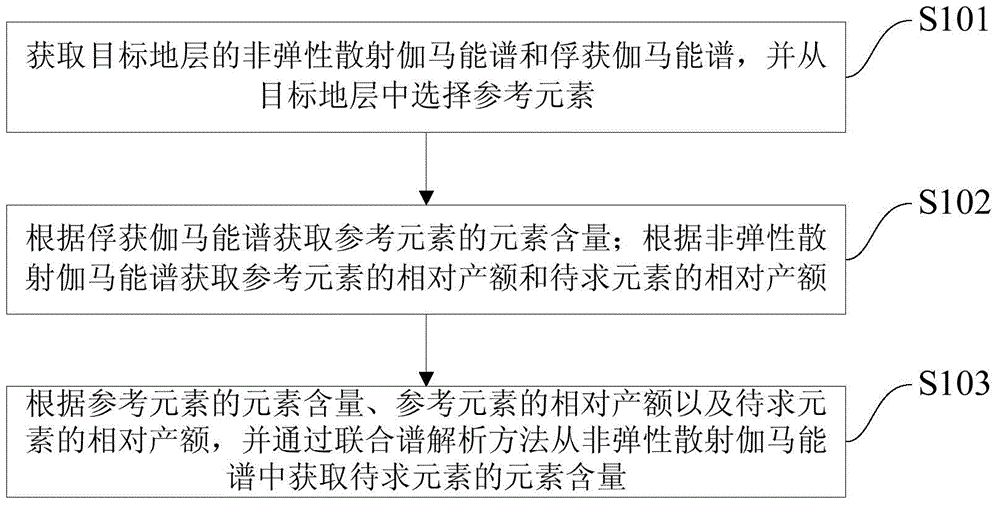
Inelastic scattering and capture gama-ray spectra combination analyzing method
The invention provides an inelastic scattering and capture gama-ray spectra combination analyzing method which includes the following steps: acquiring inelastic scattering gama-ray spectra and capture gama-ray spectra on a target stratum and selecting reference elements from the target stratum; acquiring the element content of the reference elements according to the capture gama-ray spectra; acquiring relative yield of the reference elements and the relative yield of the elements to be solved according to the inelastic scattering gama-ray spectra; acquiring the element content of the elements to be solved from the in elastic scattering gama-ray spectra according to the element content of the reference elements, the relative yield of the reference elements and the relative yield of the elements to be solved in a combination spectra analyzing method. By means of the method, the element content which is low in capture radiation reaction section and cannot be acquired from the capture gama-ray spectra can be obtained from the inelastic scattering gama-ray spetra.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Flow cytometer apparatus for three dimensional difraction imaging and related methods
ActiveUS9013692B2Scattering properties measurementsLuminescent dosimetersThree dimensional morphologyParticle physics
A flow cytometer assembly includes a fluid controller configured to form a hydrodynamically focused flow stream including an outer sheath fluid and an inner core fluid. A coherent light source is configured to illuminate a particle in the inner core fluid. A detector is configured to detect a spatially coherent distribution of elastically scattered light from the particle excited by the coherent light source. An analyzing module configured to extract a three-dimensional morphology parameter of the particle from a spatially coherent distribution of the elastically scattered light.
Owner:HU XIN HUA
Laser radar device for detecting atmospheric temperature based on vibration-rotation Raman spectrum
InactiveCN104793218AAvoid interferenceEasy detectionThermometers using physical/chemical changesElectromagnetic wave reradiationBeam splitterAtmospheric temperature
The invention discloses a laser radar device for detecting the atmospheric temperature based on a vibration-rotation Raman spectrum. After laser is emitted from a laser device, the light beam can be amplified and the diffusion angle can be compressed by using a beam expander, and finally the light beam is emitted to the atmosphere through a pointing mirror; atmospheric back scattering light is collected by using a telescope, subsequently passes through an aperture diaphragm, and is finally led into a subsequent optical system through an optical fiber; the outgoing light of the optical fiber is converted into collimated parallel light by using a collimating lens, and is subsequently divided into two paths of signals by using a beam splitter, one path of the signals passes through a low-order signal light filtering piece, and the other path of the signals passes through a high-order signal light filtering piece; the two paths of the signal light is converted into electric signals through a photomultiplier I and a photomultiplier II, and is subsequently acquired and stored by using an acquirer. The strength of a vibration-rotation Raman spectral line is related to the atmospheric temperature, and different from a pure rotation Raman spectral line which is in an interval of 1-3nm from an elastic scattered ray, a vibration Raman spectral line is in an interval of 70nm from the elastic scattered ray, so that interference of an elastic scattering signal can be effectively avoided by adopting the vibration Raman spectral line.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compact and rugged imaging Raman spectrograph
InactiveUS7548313B2Minimize impactImprove transmission efficiencyAdditive manufacturing apparatusRadiation pyrometrySpectrographSpectral filtering
A compact and robust imaging Raman spectrograph has a collimating input lens assembly, a spectral filter assembly, a transmission diffraction grating, a focusing lens assembly, and a light detector. The spectral filter assembly is located between the two lenses and comprises a notch or long-pass filter optical interference filter, a plurality of optical channel plates for limiting the optical acceptance angle of the light passing the optical interference filter, and a transmission diffraction grating, all mounted in a single assembly. The spectral filter assembly permits a very high degree of elastically scattered light rejection and excellent stray-light reduction and management, while permitting a high level of optical throughput to maximize the signal of the weakly scattered Raman signal.
Owner:NGUYEN QUANG VIET
Compact, hand-held raman spectrometer microsystem on a chip
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
Vibrating Raman lidar scattered light processing system and processing method
ActiveCN101477196AImprove signal-to-noise ratioSolution rangePrismsOptical filtersBandpass filteringPrism
The invention provides a vibration Raman laser radar scattering optical processing system based on a narrow bandpass filter and a reflex prism, and a processing method thereof. Aiming at two problems of a wide dynamic range of laser radar signal intensity and strong noise signal relative to a Raman scattering signal, the method and the system divide back scattering light into a high channel and a low channel for detecting and sufficiently utilize the narrow bandpass filter to improve the accuracy of temperature measurement and enlarge the range of the temperature measurement. An upper noise signal is relative weak, and can be fed into a photoelectric detection system for detecting through the narrow bandpass filter for once; and a lower noise signal is strong, the back scattering light of atmosphere passes through the same optical filter for twice by special optical technology, and spectrum of total transmittance is equivalent to squared spectrum of single transmittance so as to furthest suppress photonoise. After elastic scattering and background light of emission wavelength are compressed, under the condition of a multiplier tube is unsaturated, the echo intensity of the Raman scattering signal can be improved by increasing single pulse energy of emission laser, thereby achieving the aims of improving the accuracy of the temperature measurement and enlarging the range of the temperature measurement.
Owner:常熟紫金知识产权服务有限公司
Apparatus, computer-accessible medium and method for measuring chemical and/or molecular compositions of coronary atherosclerotic plaques in anatomical structures
InactiveUS20090073439A1Reduce absorptionReduce scatterDiagnostics using spectroscopyAnalogue computers for chemical processesInelastic scatteringAnatomical structures
Exemplary apparatus and method can be provided for controlling at least one electro-magnetic radiation. For example, it is possible to rotate and / or translate at least one optical waveguide. At least one of the optical waveguide(s) can receive a first radiation at a first wavelength and transmit the first radiation to at least one sample. Such optical waveguide and / or another optical waveguide may receive a second radiation at a second wavelength that is different from the first wavelength. For example, the second radiation may be produced based on an inelastic scattering of the first radiation. In addition, exemplary apparatus and method can be provided which can also be used to receive data associated with the second radiation, determine at least one characteristic of the at least one sample based on the data, and generate the image and / or the map of a portion of the arterial sample based on the at least one characteristic. Further, exemplary computer-accessible medium can be provided which includes a software arrangement thereon. When a processing arrangement executes the software arrangement, the processing arrangement is configured to modify at least one characteristic of an arrangement using certain procedures. These exemplary procedures include simulating at least one electro-magnetic radiation provided into and out of the arrangement, simulating an inelastic scattering radiation from at least one simulated sample, receiving the simulated inelastic scattering radiation into and out of the simulated arrangement, and determining a simulated characteristic of the simulated arrangement as a function of the simulated inelastic scattering radiation.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Raman detection based flow cytometer
InactiveUS20060103840A1Radiation pyrometryWithdrawing sample devicesInelastic scatteringParticle flow
A method and apparatus for enabling chemical identification of individual particles, cells of molecules by obtaining a Raman spectrum of a particle, cell or molecule as it flows past a sensing point in a flow cytometer. The particles, which may be cells or molecules, are associated with a suitable noble metal colloid or colloidal aggregate. Cellular particles may be associated with gold or silver colloidal particles by ultra-sonic sonification while in a sample preparation reservoir containing the gold or silver colloidal suspension. The colloid associated particles are then hydrodynamically focused into a single file by a fluid control module. The surface-enhance Raman Spectrum of individual particles are obtained by illuminating the particle with a laser as the particle flows past a sensing point and gathering the light that is non-elastically scattered (Raman scattered) by the particle. The surface-enhanced Raman spectrum is then analyzed to identify the particle.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Raman detection based flow cytometer
A method and apparatus for enabling chemical identification of individual particles, cells of molecules by obtaining a Raman spectrum of a particle, cell or molecule as it flows past a sensing point in a flow cytometer. The particles, which may be cells or molecules, are associated with a suitable noble metal colloid or colloidal aggregate. Cellular particles may be associated with gold or silver colloidal particles by ultra-sonic sonification while in a sample preparation reservoir containing the gold or silver colloidal suspension. The colloid associated particles are then hydrodynamically focused into a single file by a fluid control module. The surface-enhance Raman Spectrum of individual particles are obtained by illuminating the particle with a laser as the particle flows past a sensing point and gathering the light that is non-elastically scattered (Raman scattered) by the particle. The surface-enhanced Raman spectrum is then analyzed to identify the particle.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Backward elastic scattering spectral measurement analysis system and method for online detection of size distribution of small particles in suspension
InactiveCN106198325AClear Scattering AngleSimple structureParticle size analysisMultiple-scale analysisMilk products
The invention discloses a backward elastic scattering spectral measurement analysis system and method for online detection of size distribution of small particles in a suspension. A linear array fiber probe and an off-axis parabolic reflector are used to construct a multi-angle spectral measurement system, and a spectral analysis method based on wavelet multi-scale analysis is utilized to provide quick and accurate acquisition for the size distribution of particles. The method may be used for real-time monitoring of the production of standard particle, detection of oil-in-water pollutants, granularity detection for milk products, study on particle structure in biological cells and the like. The system is simple, and analytical results are accurate.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
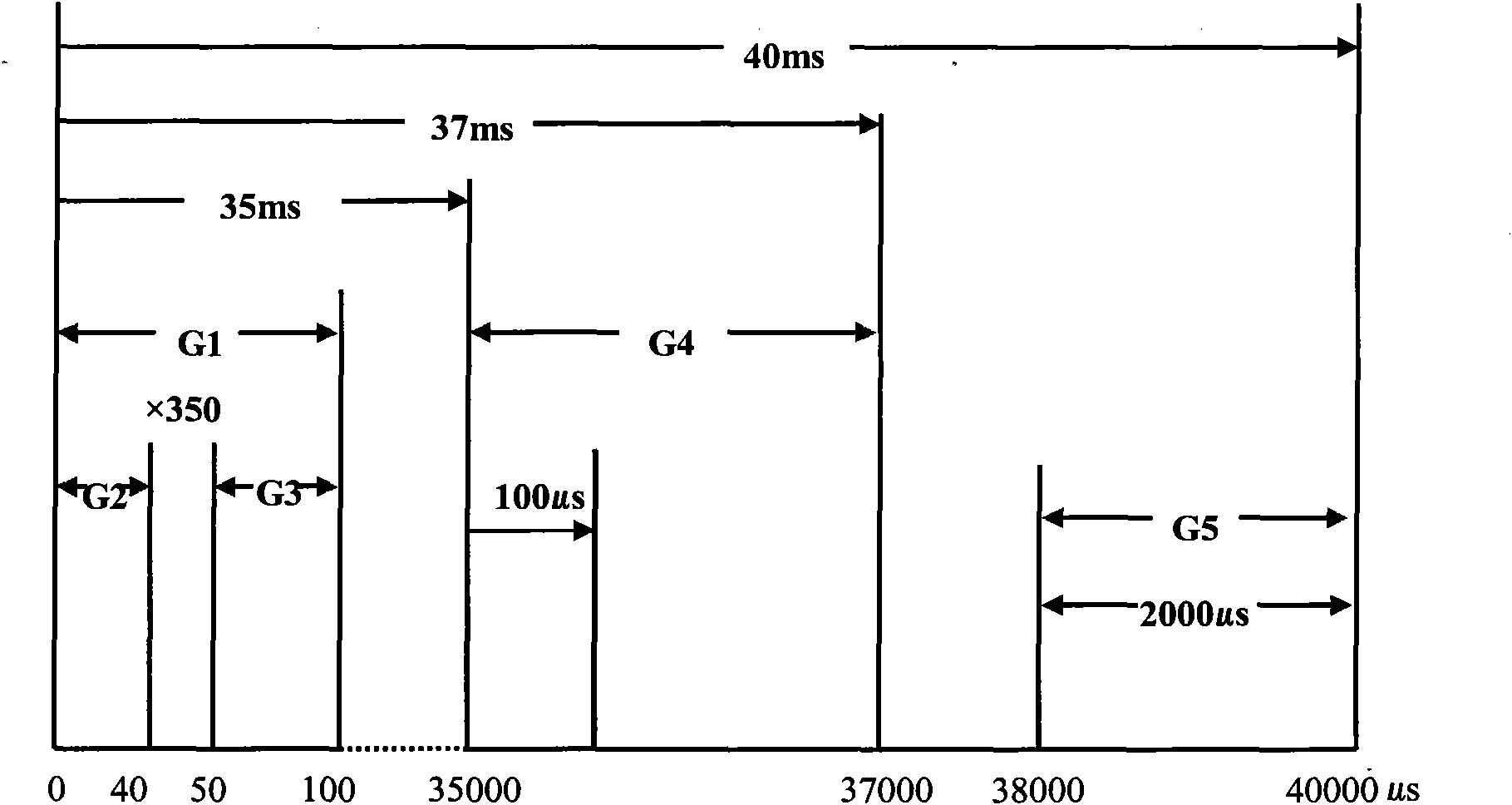
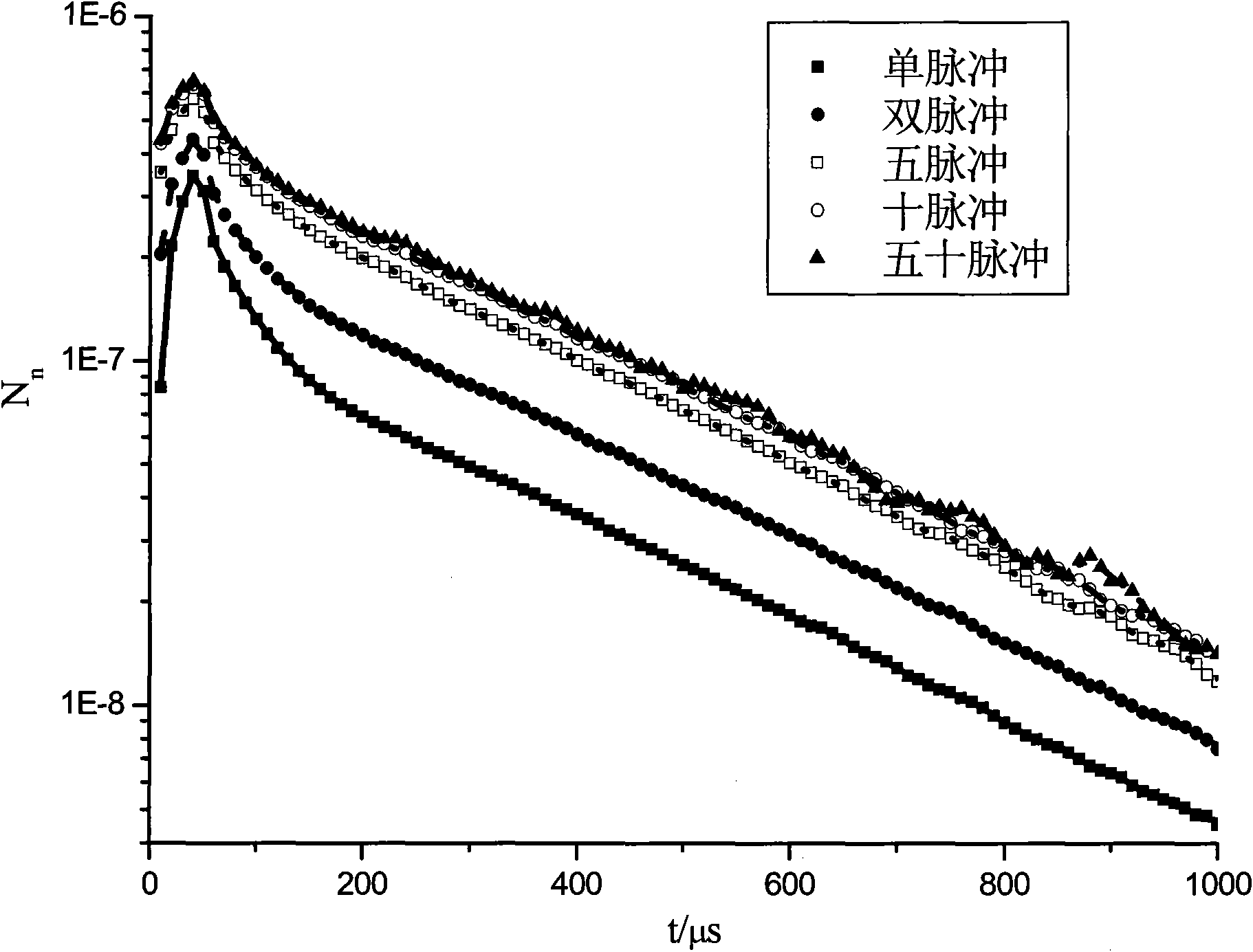
Time sequence design method for collecting double pulse neutron gamma spectrums
InactiveCN101915093ACount Statistical GuaranteeReduce uncertaintyBorehole/well accessoriesPorosityTime spectrum
The invention discloses a time sequence design method for collecting double pulse neutron gamma spectrums, which solves the technical problems that only a gamma energy spectrum or a gamma time spectrum can be collected in a down-hole process in the conventional pulse neutron saturation logging technique, the measurement of two physical parameters cannot be completed simultaneously, the saturation can be determined by means of other materials such as porosity and the like. A complete measurement period of the double pulse neutron gamma spectrums comprises three time slices: a C / O measurement time slice, a neutron service life measurement time slice and a background gamma energy spectrum measurement time slice, totally 40000 mus. By designing a double pulse emission and measurement time sequence, the inelastic dispersion can be measured by making use of the repeatedly emitted neutrons of a narrow pulse and the gamma energy spectrum can be seized, the gamma time spectrum can be also measured by making use of the emitted neutrons of a wide pulse, and as two parameters are obtained simultaneously in the same measurement at the same depth point, the uncertain factors are reduced, and the measurement accuracy is improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +2
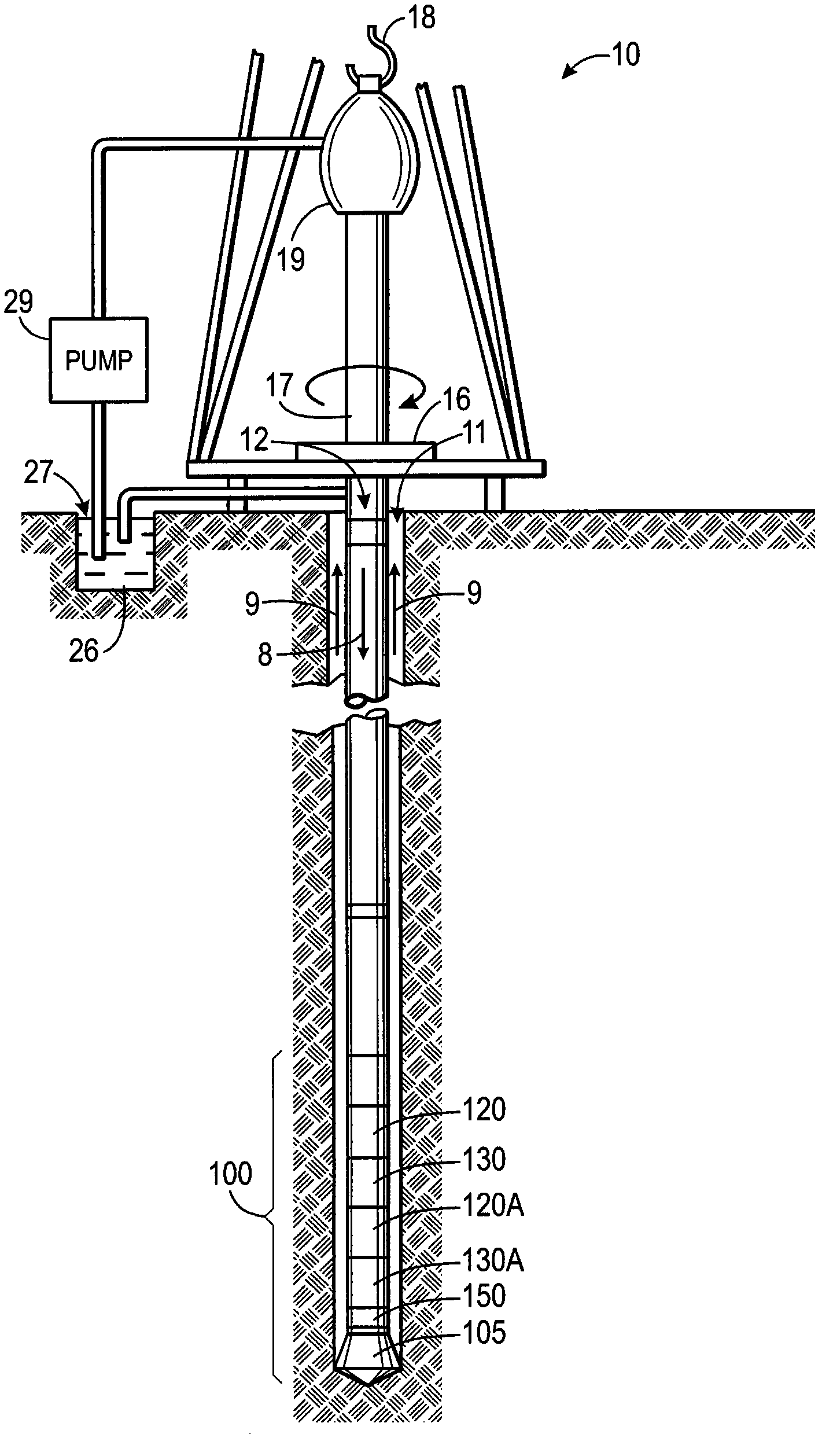
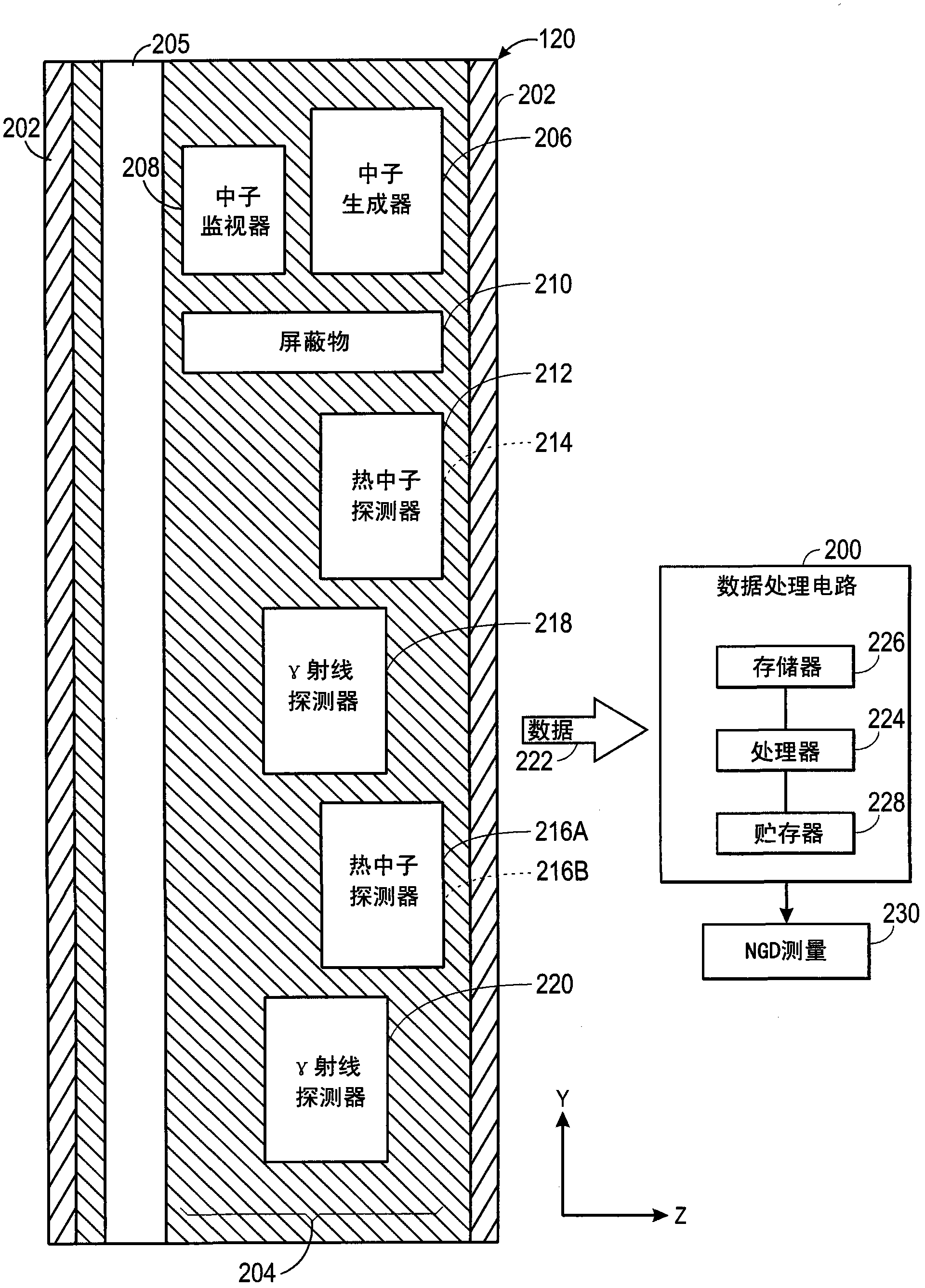
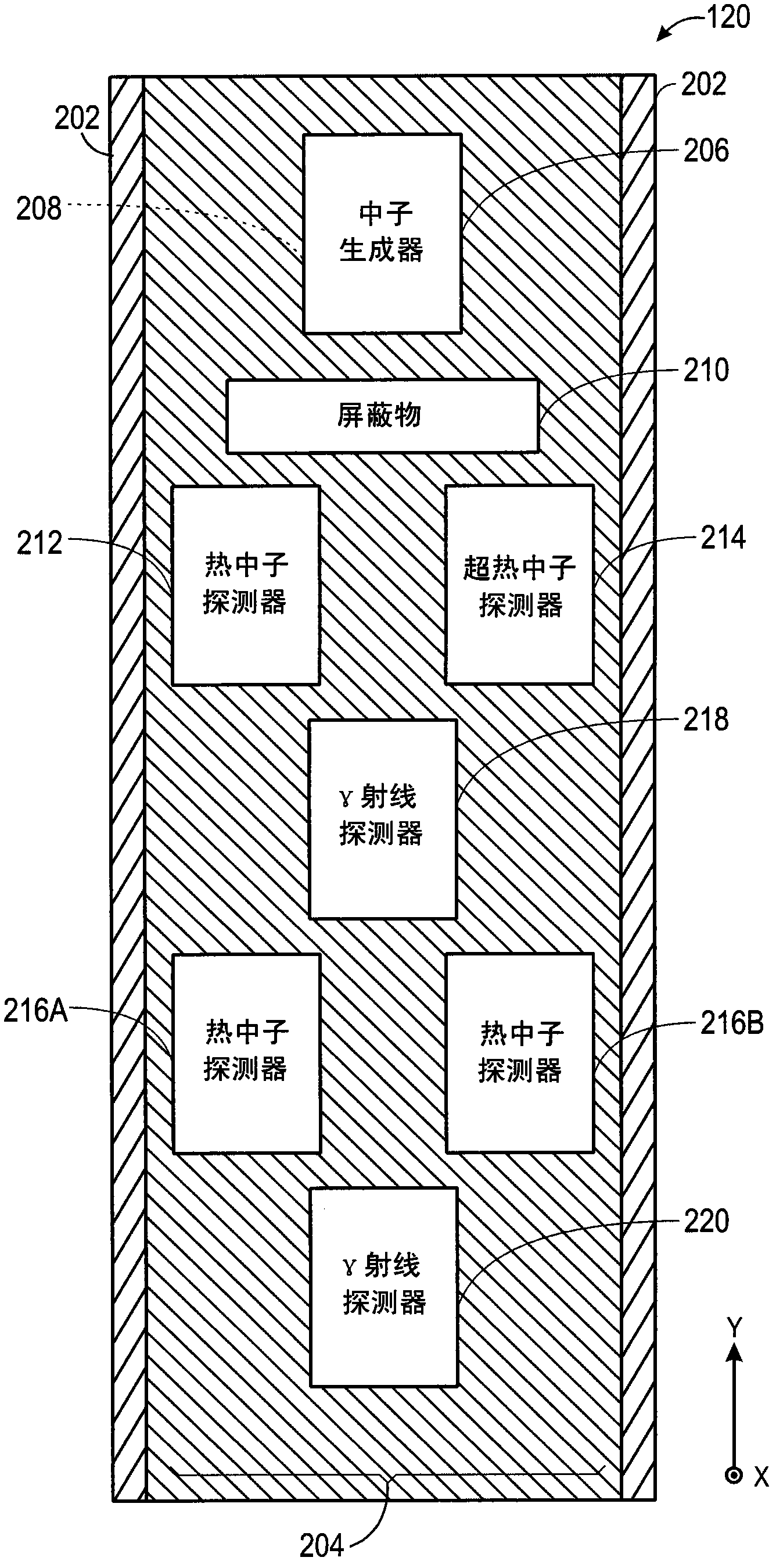
Correction for low porosity effects on neutron gamma density
InactiveCN102330552AAccurate measurementAccurate Neutron Gamma DensityBorehole/well accessoriesNuclear radiation detectionPorosityHydrogen index
Systems, methods, and devices are provided to determine an accurate neutron-gamma density (NGD) measurement for a broad range of formations, including low-hydrogen-index or low-porosity formations and formations with heavy elements. For example, such an NGD measurement may be obtained by emitting neutrons into a formation such that some of the neutrons inelastically scatter off elements of the formation and generate inelastic gamma rays. The neutrons and inelastic gamma rays that return to the downhole tool may be detected. Some characteristics of certain formations are believed to affect the fast neutron transport of the formations. Thus, if a formation has one or more of such characteristics, a correction may be applied to the count rate of neutrons, the count rate of inelastic gamma rays, or the neutron transport correction function, upon which the neutron-gamma density (NGD) may be determined.
Owner:PRAD RES & DEV LTD
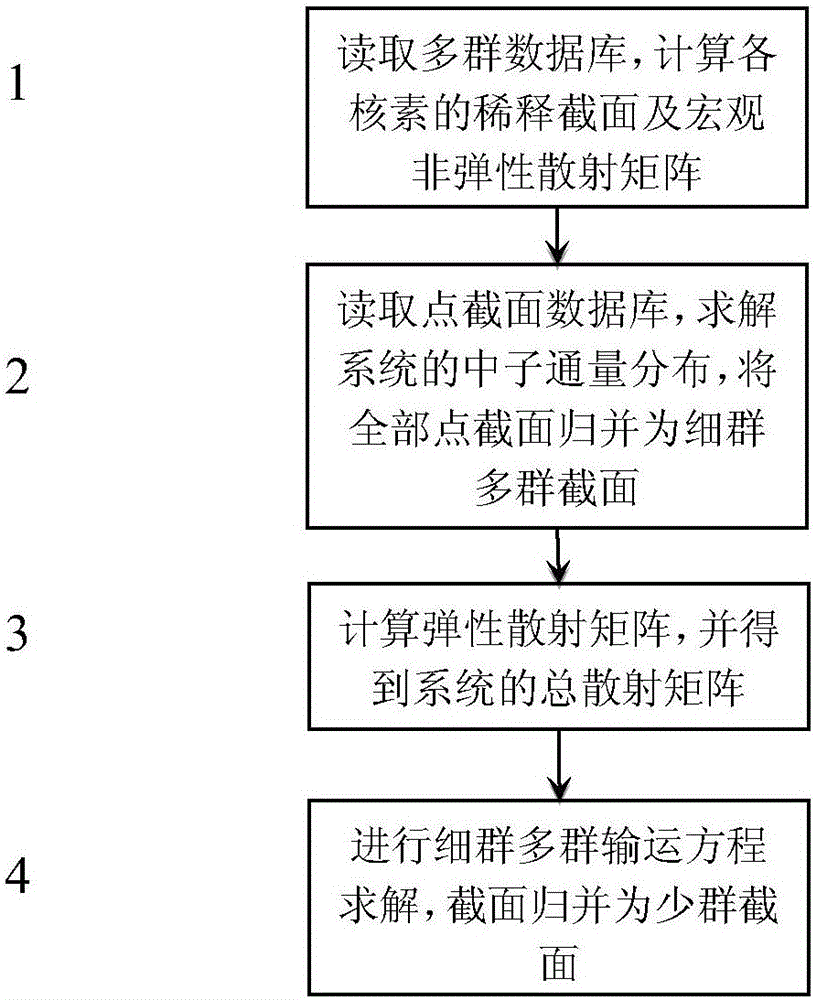
High-accuracy fast neutron reactor assembly few-group cross section obtaining method
InactiveCN106128518AFine-grained consideration of elastic scattering resonance effectsCareful consideration of resonance interference effectsNuclear energy generationFast fission reactorsReal systemsNeutron transport
Provided is a high-accuracy fast neutron reactor assembly few-group cross section obtaining method. The fine-group cross section of a fast neutron reactor assembly is calculated in the mode that point cross section data and multi-group data are combined, online calculation of an elastic scattering matrix is performed, a neutron transport equation is solved by using the fine-group cross section to obtain fine-group neutron-flux density, energy groups are merged on the basis, and accordingly few-group parameters of the fast reactor assembly are obtained. Due to the fact that the method directly uses the point cross section data, the elastic scattering resonance effect of a medium mass nuclide and the resonance interference effects of all nuclides are accurately considered. The neutron-flux density of a real system is adopted in the energy group merging process, and merging results are more accurate. The overall errors of fast reactor assembly few-group parameters calculated by adopting the method are within 1% compared with a reference value, and the method has higher accuracy.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
3-D imaging system with pre-test module
InactiveUS7796809B1Sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionColor television detailsInelastic scatteringFluorescence
A remote 3-D imaging system which uses a novel angular relationship to establish the relationship of the image features to the system, which is displayed by virtue of calculations. In addition to static surfaces, moving surfaces may be studied and corrections due to turbidity and platform position are also easily compensated for. A pre-test module is also included which predicts and has the ability to re-adjust the instrumentation to the test conditions as predicted by a hybrid Monte Carlo model. The instant system may also contain a plurality of sensing systems based on light, including traditional reflective or elastic scattering and novel fluorescent or non elastic scattering still and video imaging systems, including time-gated systems.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
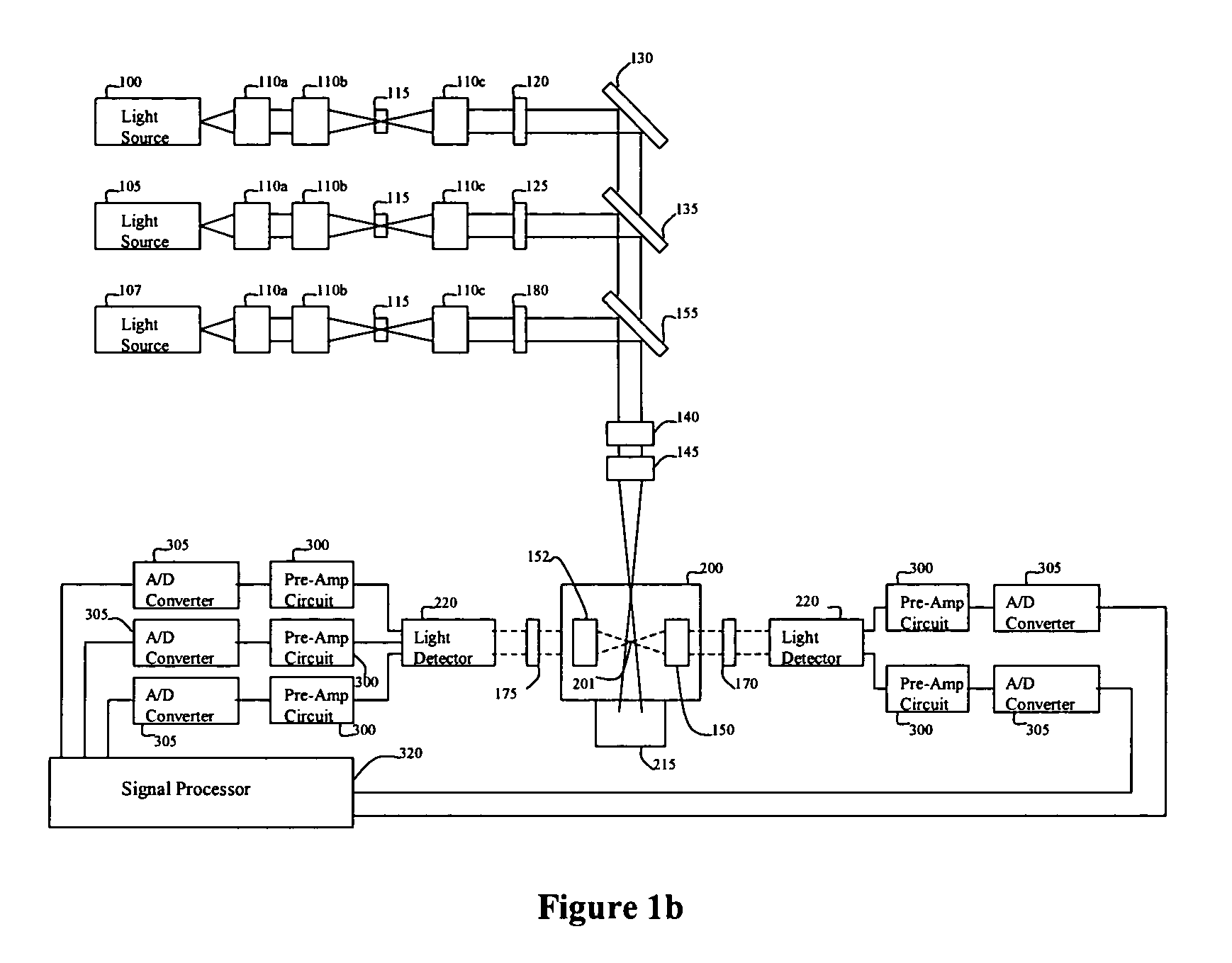
Realtime optical method and system for detecting and classifying biological and non-biological particles
ActiveUS20170315045A1Material analysis by optical meansBiological particle analysisRefractive indexParticle physics
Methods, apparatuses, and systems for detecting and classifying individual airborne biological and non-biological particles, in real time, based on particle size and polarized elastic scatter. Auto-fluorescence content may also be used along with particle size and polarized elastic scatter for further orthogonal classification. With polarized elastic scattering, the degree of linear or circular depolarization produced from particle morphology, refractive index, internal asymmetric structures and molecular optical activity can be used for classifying individual airborne particles. Alternatively, circular intensity differential scattering (CIDS) or linear intensity differential scattering (LIDS) can be used to discriminate individual particles.
Owner:HAMILTON ASSOCS
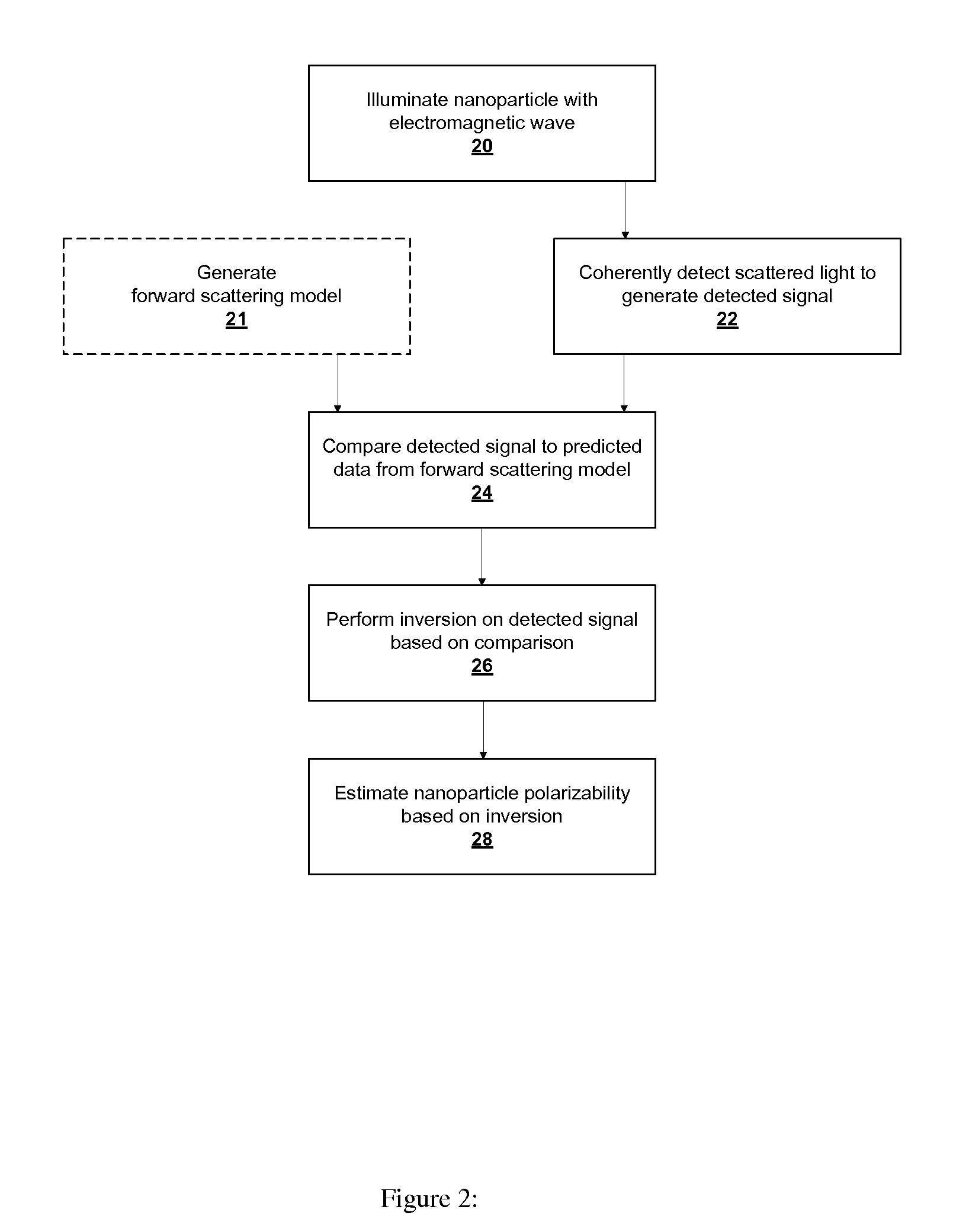
Robust Determination of the Anisotropic Polarizability of Nanoparticles Using Coherent Confocal Microscopy
ActiveUS20100067005A1Minimize cost functionPolarisation-affecting propertiesParticle size analysisImage estimationParticle physics
A coherent confocal microscope for fully characterizing the elastic scattering properties of a nanoparticle as a function of wavelength. Using a high numerical aperture lens, two-dimensional scanning and a simple vector beam shaper, the rank-2 polarizability tensor is estimated from a single confocal image. A computationally efficient data processing method is described and numerical simulations show that this algorithm is robust to noise and uncertainty in the focal plane position. The measurement of the polarizability removes the need for a priori assumptions regarding the nanoparticle shape.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
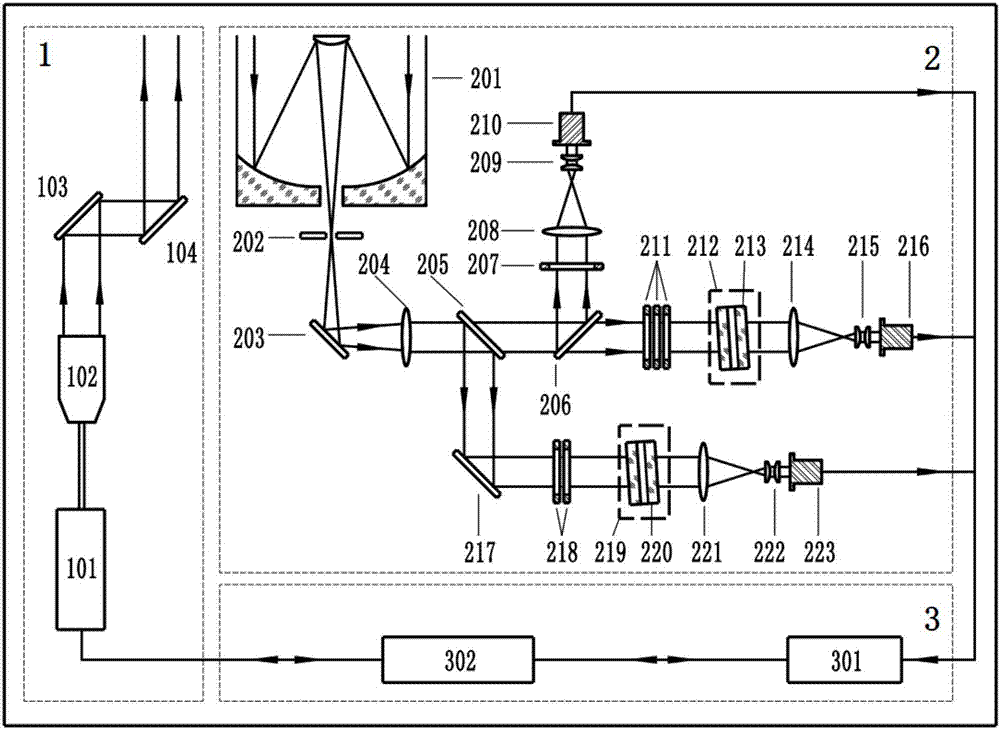
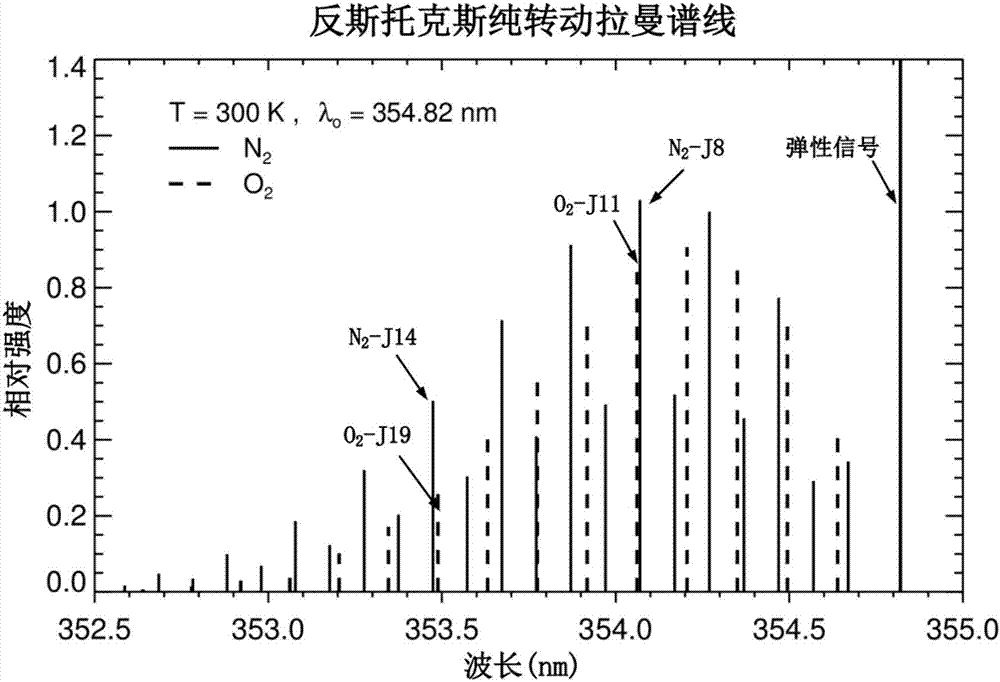
Ultraviolet quasi-single pure-rotation Raman spectrum extraction-based all-day temperature measurement laser radar
ActiveCN107024699AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove working environmentThermometers using physical/chemical changesElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadar systemsAtmospheric temperature
The present invention discloses an ultraviolet quasi-single pure-rotation Raman spectrum extraction-based all-day temperature measurement laser radar. The laser radar comprises a laser emitting unit, an optical receiving unit and a signal acquisition and control unit. The laser emitting unit emits the ultraviolet laser of 354. 82 nm in wavelength and the ultraviolet laser is adopted as a detection light source. The laser emitting unit sends a pulse laser beam to the atmosphere. The pulse laser beam and atmospheric particles interact to generate a series of discrete spectrum line scattering signals. The optical receiving unit receives the scattering signals through a telescope and then respectively and simultaneously extracts elastic scattering signals and quasi-single-branched anti-stoke pure-rotation Raman spectral line signals through three channels. The signal acquisition and control unit realizes the real-time acquisition and the inversion of signals, so that the normal and orderly operation of the entire laser radar system is ensured. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the signal-to-noise ratio of the system is enhanced, and the light-receiving path is optimized. The system stability is improved. The all-day detection of the atmospheric temperature, the aerosol space distribution and time evolution parameters is implemented.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Bio-photonic-scanning calibration method
InactiveUS20050197581A1Reliable radiant responseBetter signal to noise ratioDiagnostics using lightRaman scatteringPhotonicsIn vivo
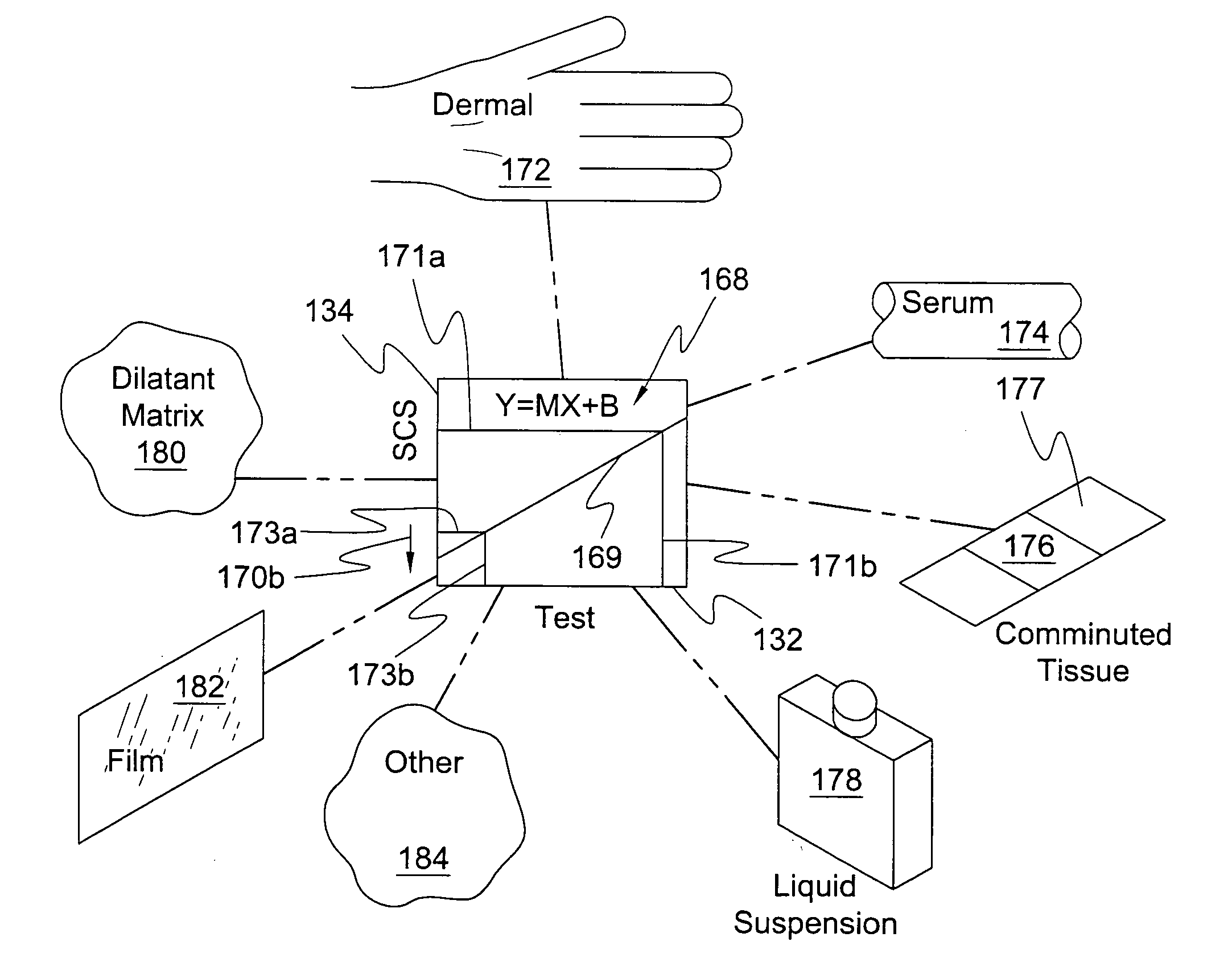
Methods, apparatus, and compositions calibrate a bio-photonic scanner detecting selected molecular structures of tissues, nondestructively, in vivo. The apparatus may include a processor, memory, and scanner. The scanner directs light nondestructively onto tissue in vivo, then receives back a radiant response through a system of mirrors and lenses back into the detector. Software for controlling the scanner and processing its output may be calibrated using a synthetic material to mimic the radiant response of tissue. Calibration may account for background fluorescence and elastic scattering, mimicking skin tissue materials having substantially no Raman scattering response of interest. Dopants may be added to the matrix of white scan material to mimic selected molecular structures in tissue. Matrix materials include a dilatant compound, and dopants include biological materials as well as K-type polarizing film and other materials.
Owner:NU SKIN INT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com