Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
246 results about "Auto fluorescence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
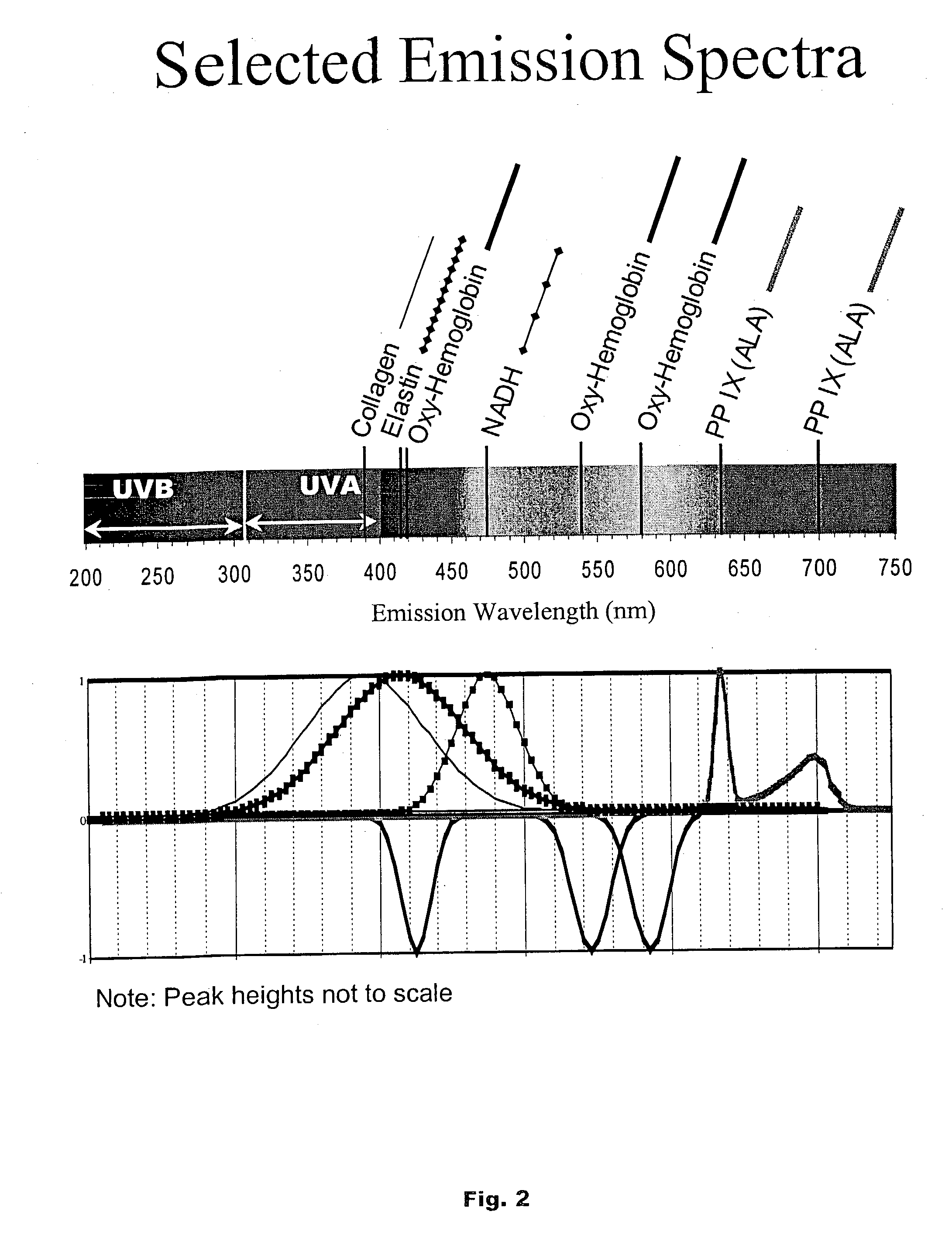
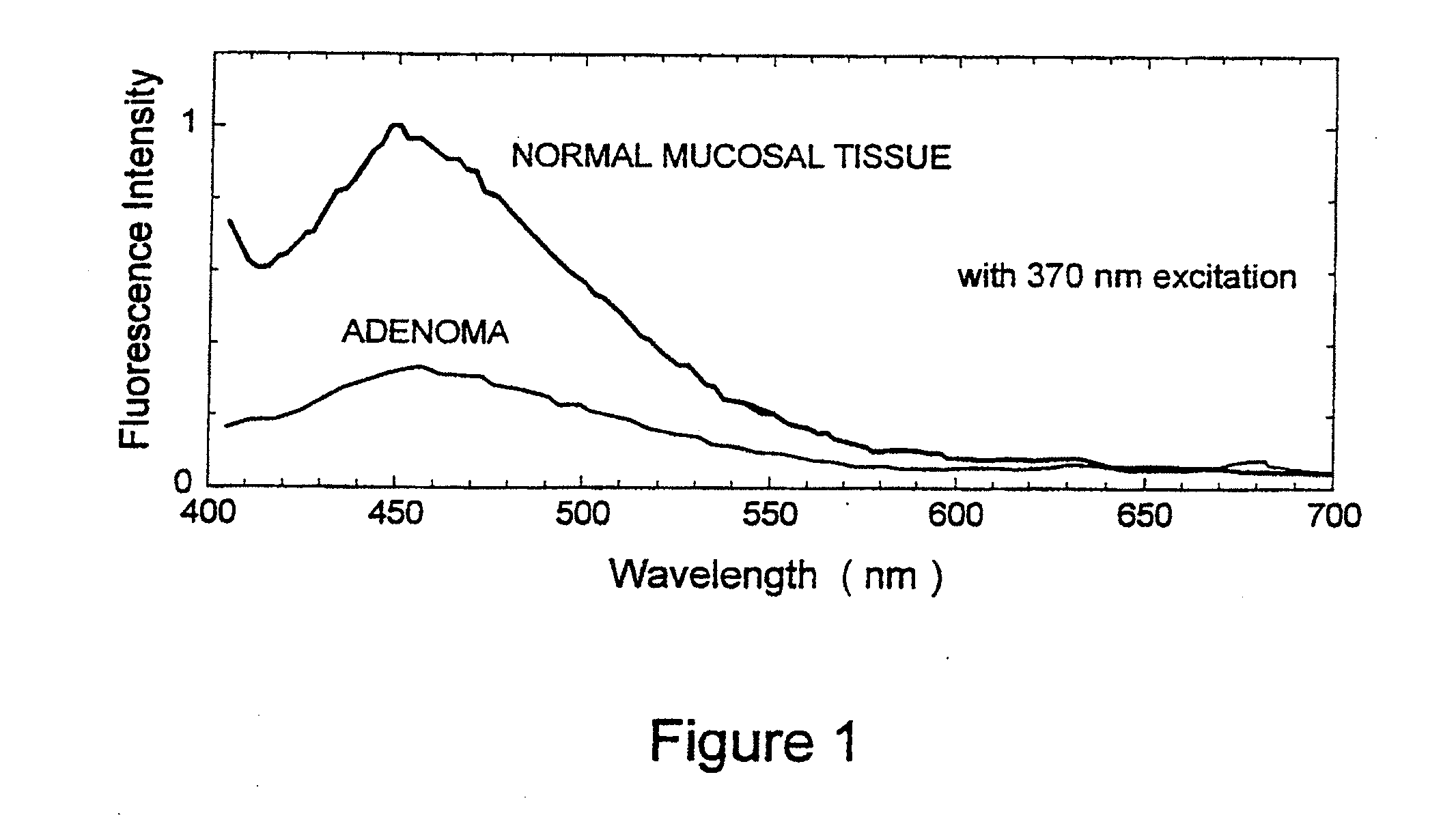
Auto-fluorescence is the natural emission of light by biological structures when they have absorbed light. The compounds like Collagen, and Riboflavin, including amino acids like tyrosine, tryptophan, phenylalanine emit the fluorescence signal. Auto-fluorescence increases with cell size.
Multivariate analysis of green to ultraviolet spectra of cell and tissue samples
InactiveUS20010034477A1Diagnostics using lightSpectrum investigationMultivariate classificationTissue sample
This invention relates to methods for processing in vivo skin auto-fluorescence spectra for determining blood glucose levels. The invention also relates to methods of classifying cells or tissue samples or quantifying a component of a cell or tissue using a multivariate classification or quantification model.
Owner:ARGOSE
Dual mode real-time screening and rapid full-area, selective-spectral, remote imaging and analysis device and process
InactiveUS20030158470A1Quick scanAvoid delayDiagnostics using spectroscopyEndoscopesSpectral bandsImaging processing
The invention provides a device and process for real-time screening of areas that can be identified as suspicious either through image segmentation utilizing image processing techniques or through treatment with an exogenous fluorescent marker that selectively localizes in abnormal areas. If screening detects a suspicious area, then the invention allows acquiring of autofluorescence images at multiple selected narrow differentiating spectral bands so that a "virtual biopsy" can be obtained to differentiate abnormal areas from normal areas based on differentiating portions of autofluorescence spectra. Full spatial information is collected, but autofluorescence data is collected only at the selected narrow spectral bands, avoiding the collection of full spectral data, so that the speed of analysis is increased.
Owner:STI MEDICAL SYST
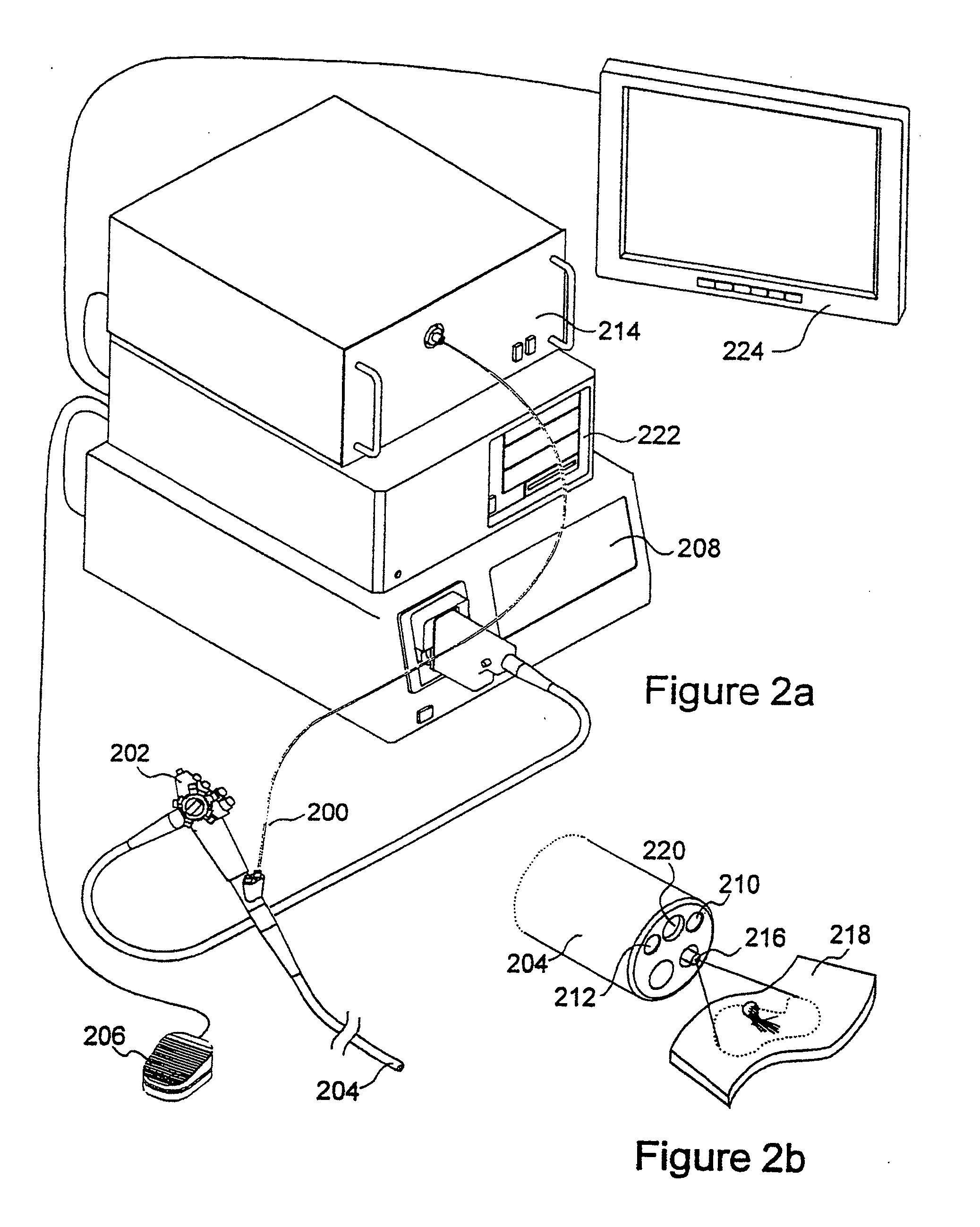
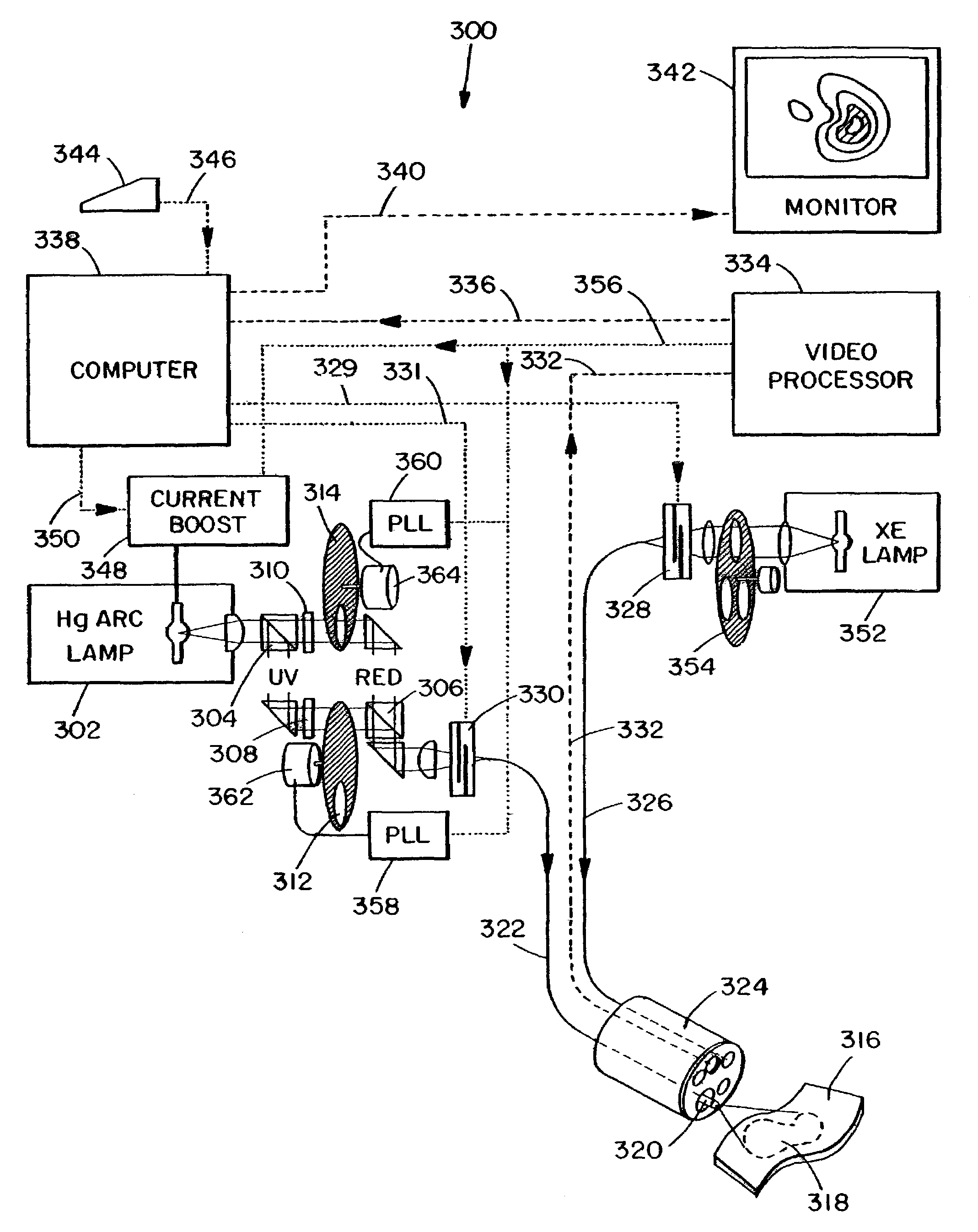
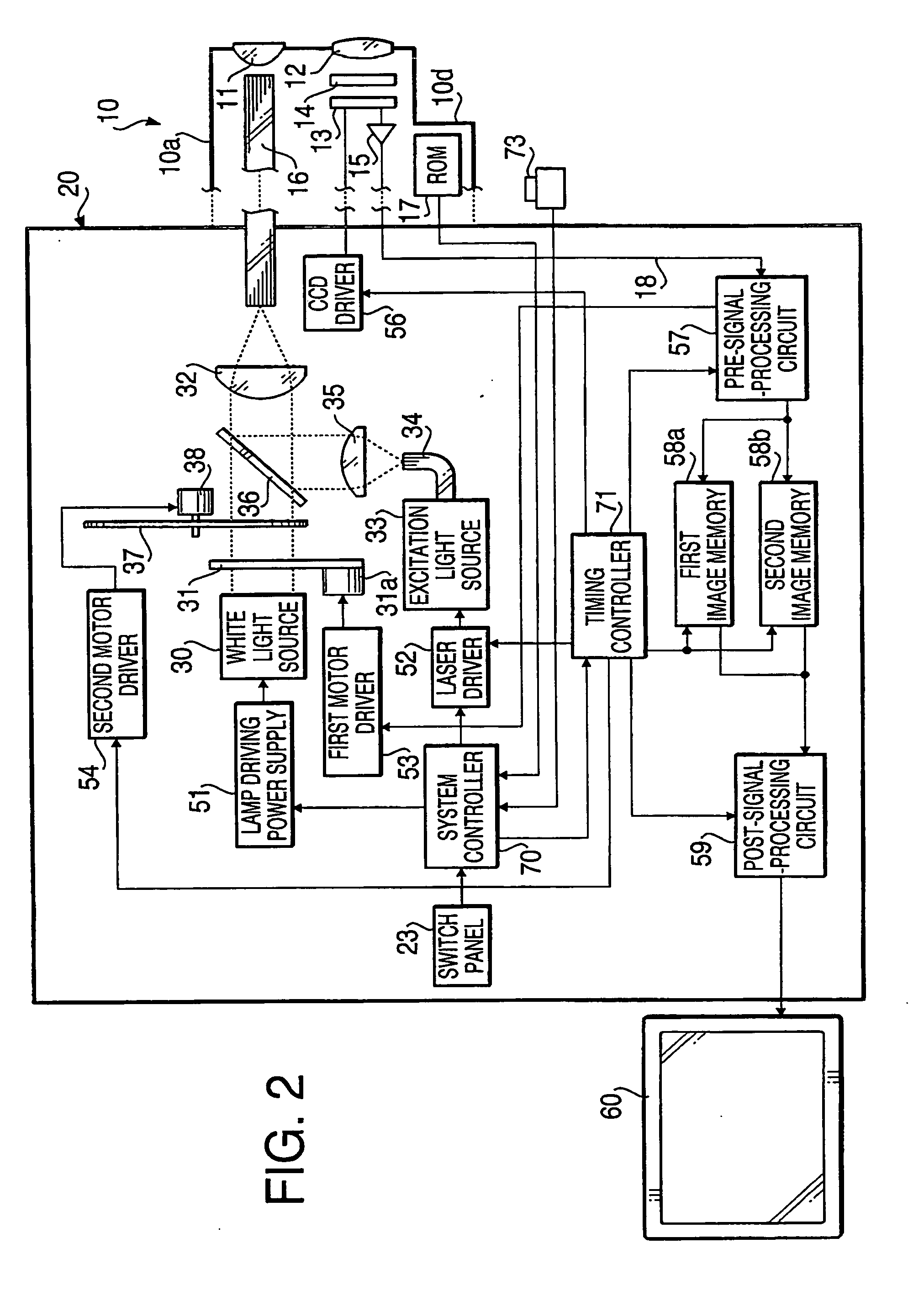
Autofluorescence imaging system for endoscopy
InactiveUS20110213252A1Improve featuresQuantitative precisionSurgeryEndoscopesColor imageUltraviolet lights
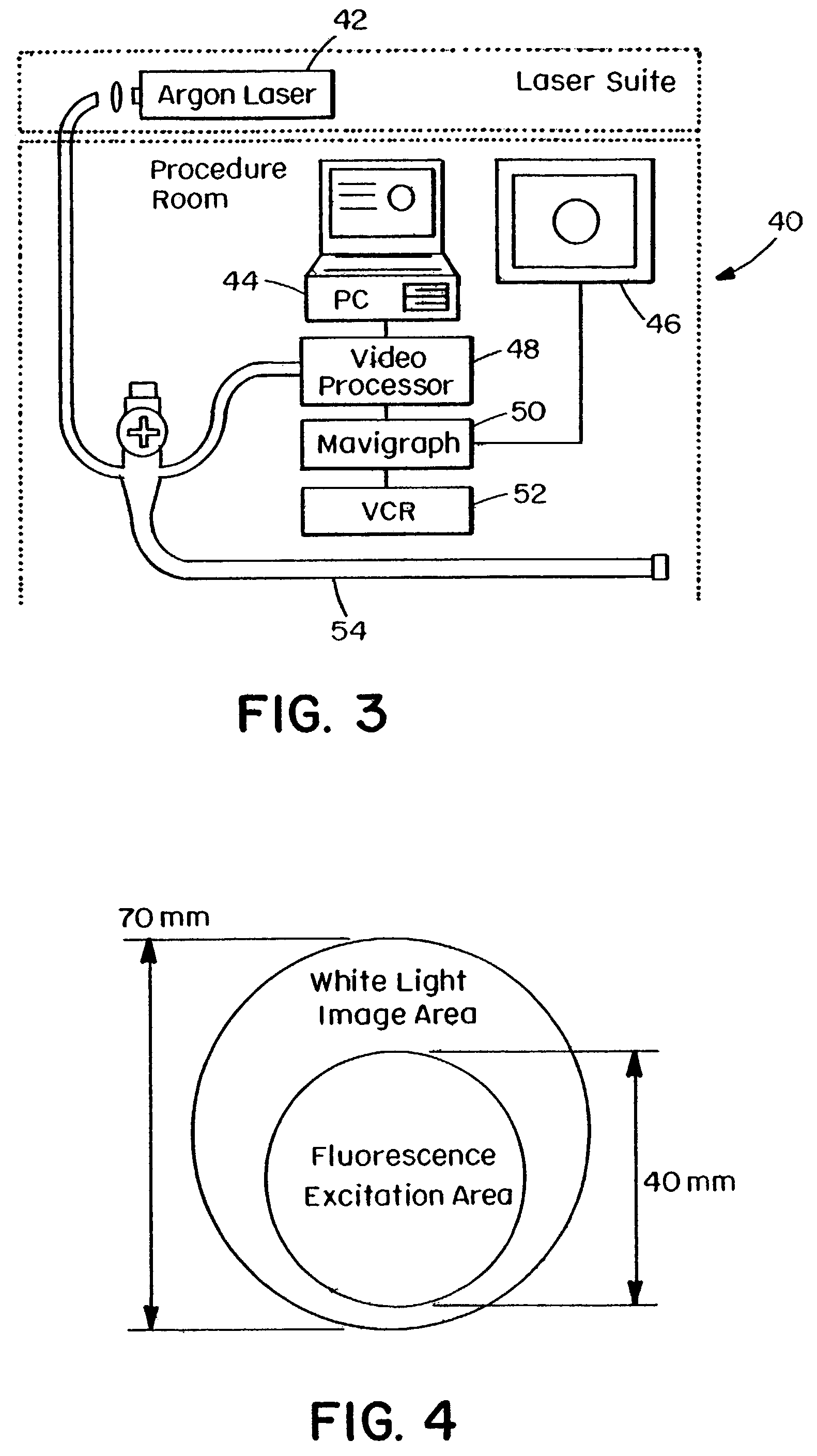
A system and method for imaging tissue autofluorescence through a video endoscope is described, comprising a light source capable of providing both ultraviolet light capable of inducing tissue autofluorescence and visible light which induces little or no autofluorescence, an optical system to deliver both wavelength bands to the tissue with the same apparent spatial and angular intensity distribution, a means for digitally acquiring the resulting, visible fluorescence and visible reflectance images using a single imaging detector at the distal tip of the endoscope and a means for digitally processing said images to generate a final, false-color image for display which indicates regions of tissue dysplasia. This system can either be added on to an existing video endoscope or integrated into its structure. The combined system can be electronically switched between normal white light imaging and fluorescence imaging.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Fluorescence imaging endoscope
InactiveUS7235045B2Simplify System DesignConvenient registrationRaman/scattering spectroscopySurgeryLaser lightReflectivity
An endoscope having an optical guide that is optically coupled to a first broadband light source and a second laser light source that emits light at a wavelength in a range of 350 nm to 420 nm. The endoscope has an image sensor at a distal end and collects a reflectance image including red, green and blue components with the image sensor in response to illumination by said broadband light source. The image sensor also collects an autofluorescence image having a blue component, a green component and a red component. A processor processes the fluorescence image by determining a ratio of the fluorescence image and the reflectance image to provide a processed fluorescence image.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
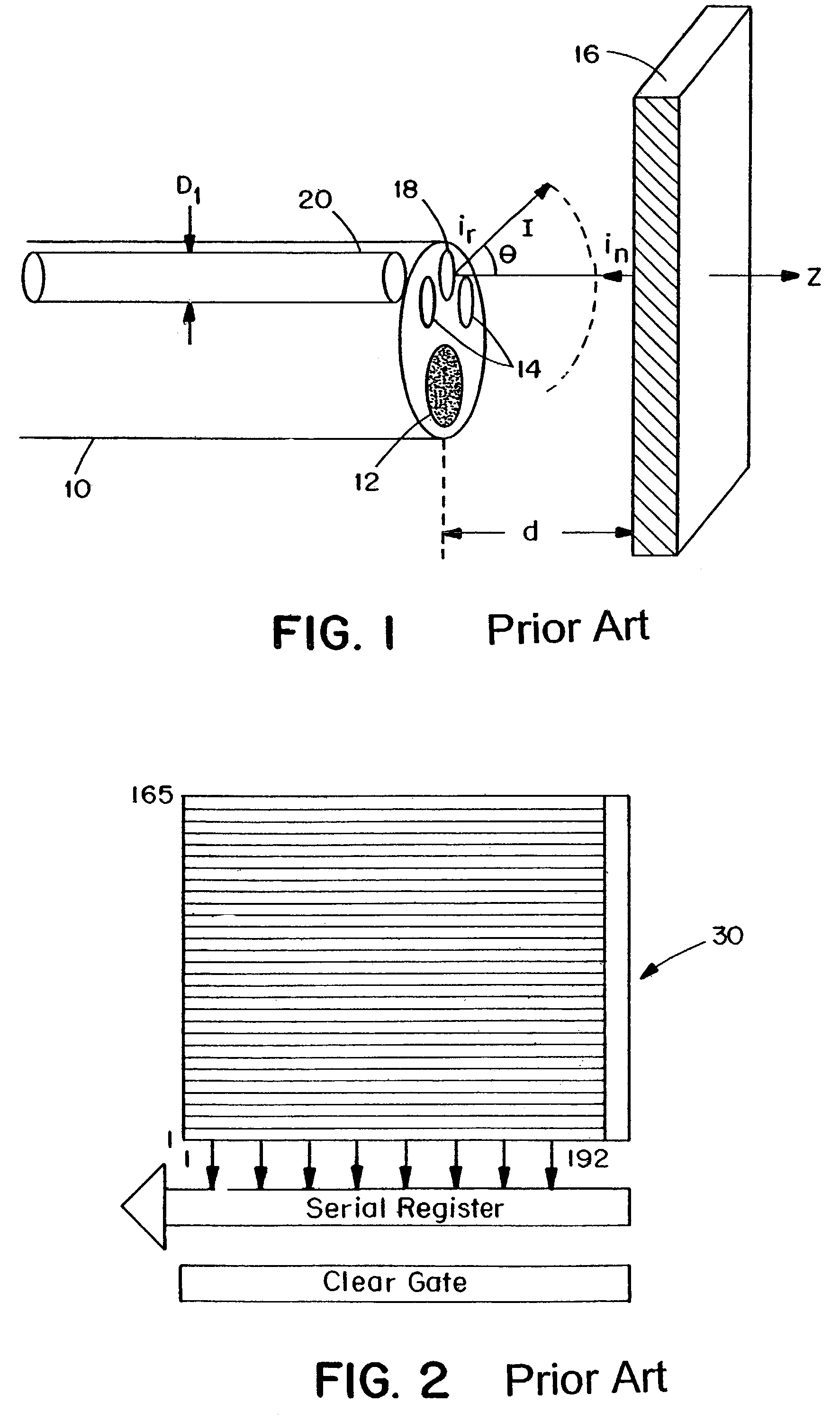
System and method for detecting and classifying biological particles
InactiveUS6885440B2Chemiluminescene/bioluminescenceScattering properties measurementsHarmonicBiological particles
A continuous wave laser excites a biological particle. Detection channels are created to detect light scattered by the biological particle, and to detect any auto-fluorescence emitted by the biological particle. Additional channels can also detect light emitted by auto-fluorescence of the biological particle when simultaneously excited by light at harmonics of the laser's fundamental wavelength. The biological particle is identified using Mie scattering and auto-fluorescence. Ratio-metric calculations generated by calculating ratios of detected peak heights or integrated pulse values in the channels provides additional information for identifying and classifying the biological particle. A warning or alert can be provided if the identified biological particle is a particle of interest.
Owner:UNKNOWN +1
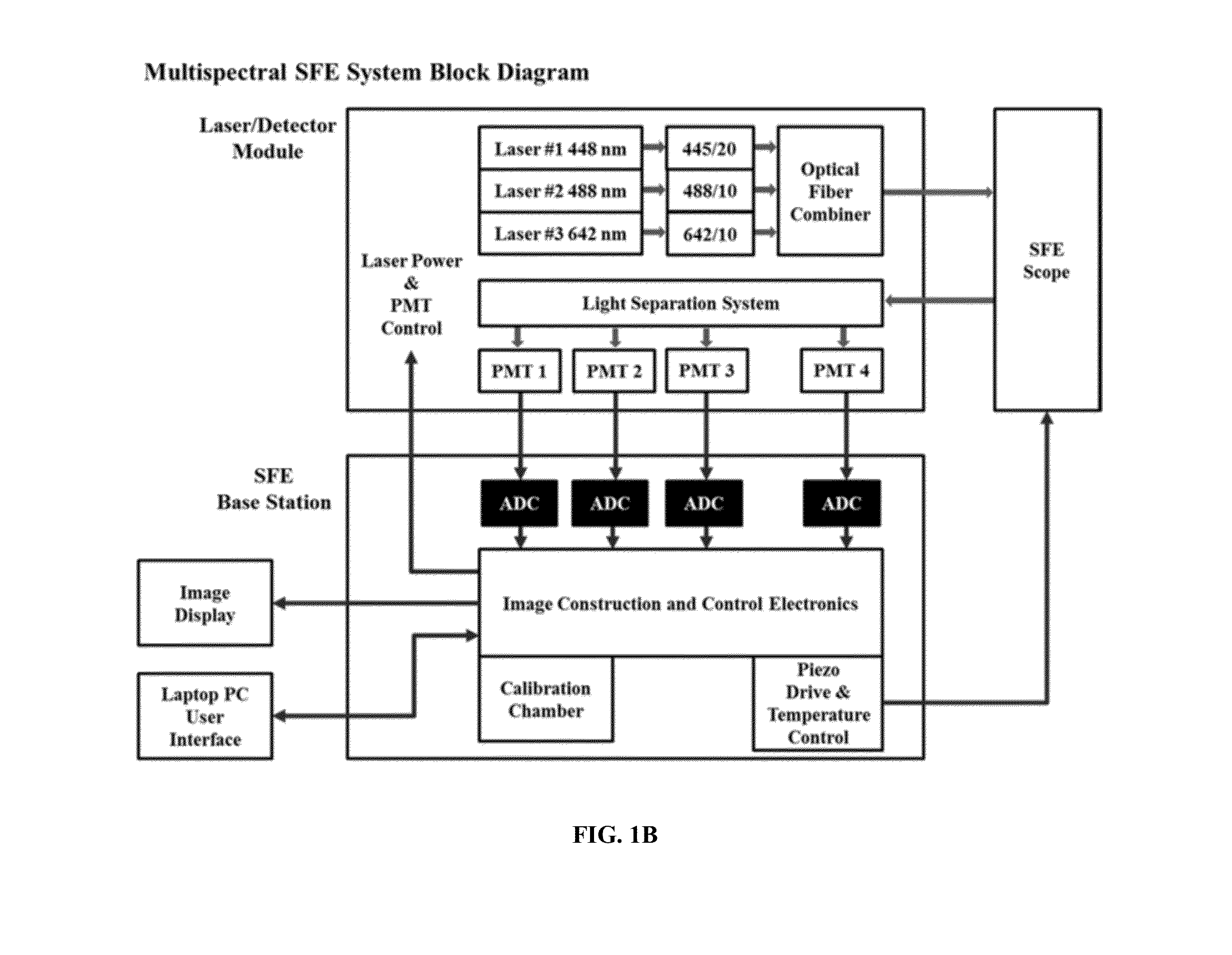
Multispectral wide-field endoscopic imaging of fluorescence
ActiveUS20150216398A1Decrease one or more undesirable effects of the interfering fluorescence signalReduce distractionsRaman/scattering spectroscopySurgeryWide fieldMultispectral image
Improved methods, systems and apparatus relating to wide field fluorescence and reflectance imaging are provided, including improved methods, systems and apparatus relating to removal of background signals such as autofluorescence and / or fluorophore emission cross-talk; distance compensation of fluorescent signals; and co-registration of multiple signals emitted from three dimensional tissues.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Fluorescence Detection
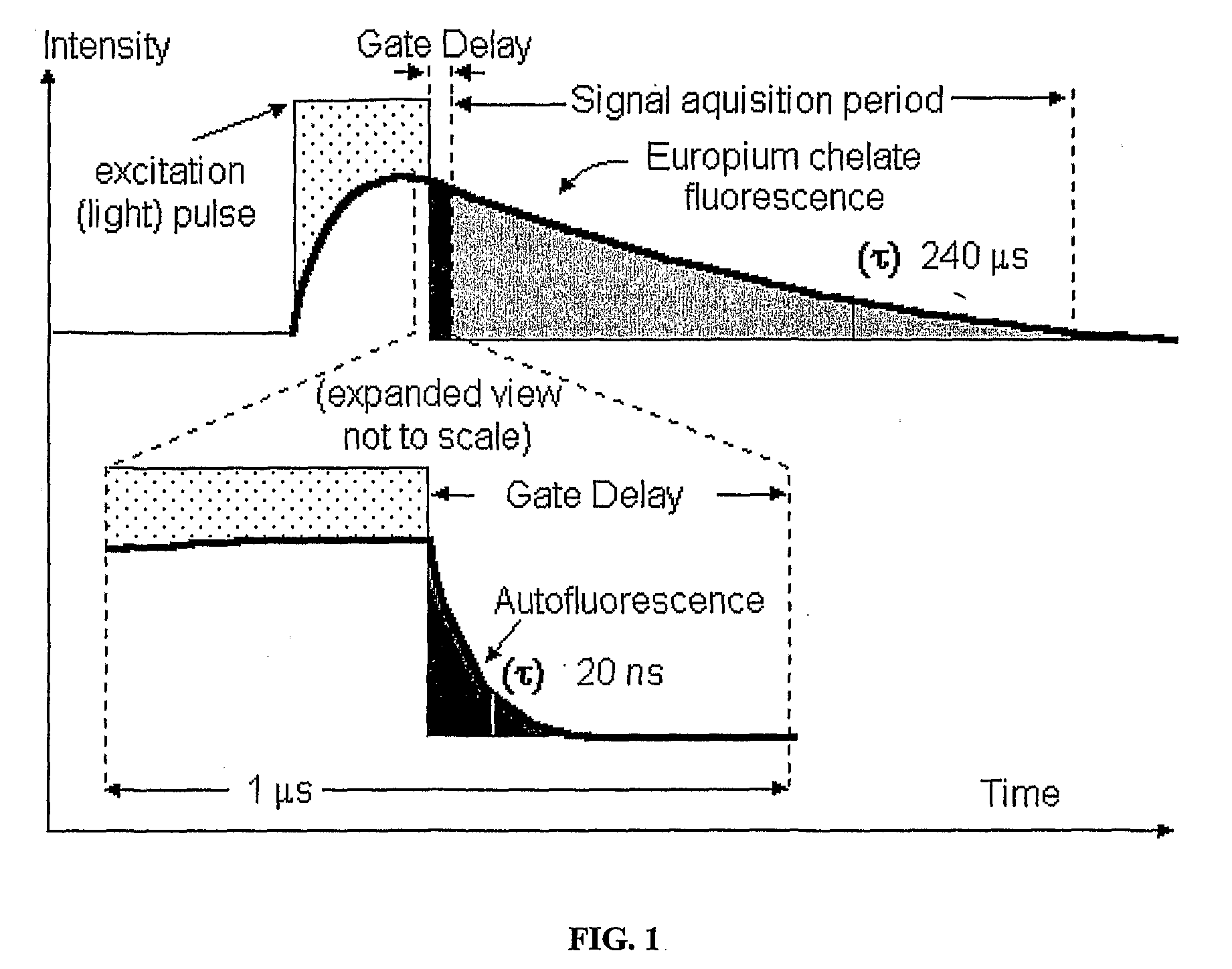
InactiveUS20080265177A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsUltravioletLight emission
A fluorescence detection system comprises a light source (22), dichroic mirror (32), excitation port (16), emission port (14), and a detector. The light source (22) is, for example, a pulsed ultraviolet LED, with a light emission that decays sufficiently rapidly to permit gated detection of fluorescence from a fluorescently-labelled species, at a time when it is distinguishable from autofluorescence. The detector is, for example, an electron multiplying CCD, with high gain on-chip amplification. A circuit (26) may be used to control a repeating cycle of (i) generation of a 20-200 microsecond UV. pulse; (ii) a gate delay of 1-5 microseconds; and (iii) a 10-800 microsecond detection period. This allows time-resolved-fluorescence-microscopy with real time or near real time operation.
Owner:MACQUARIE UNIV
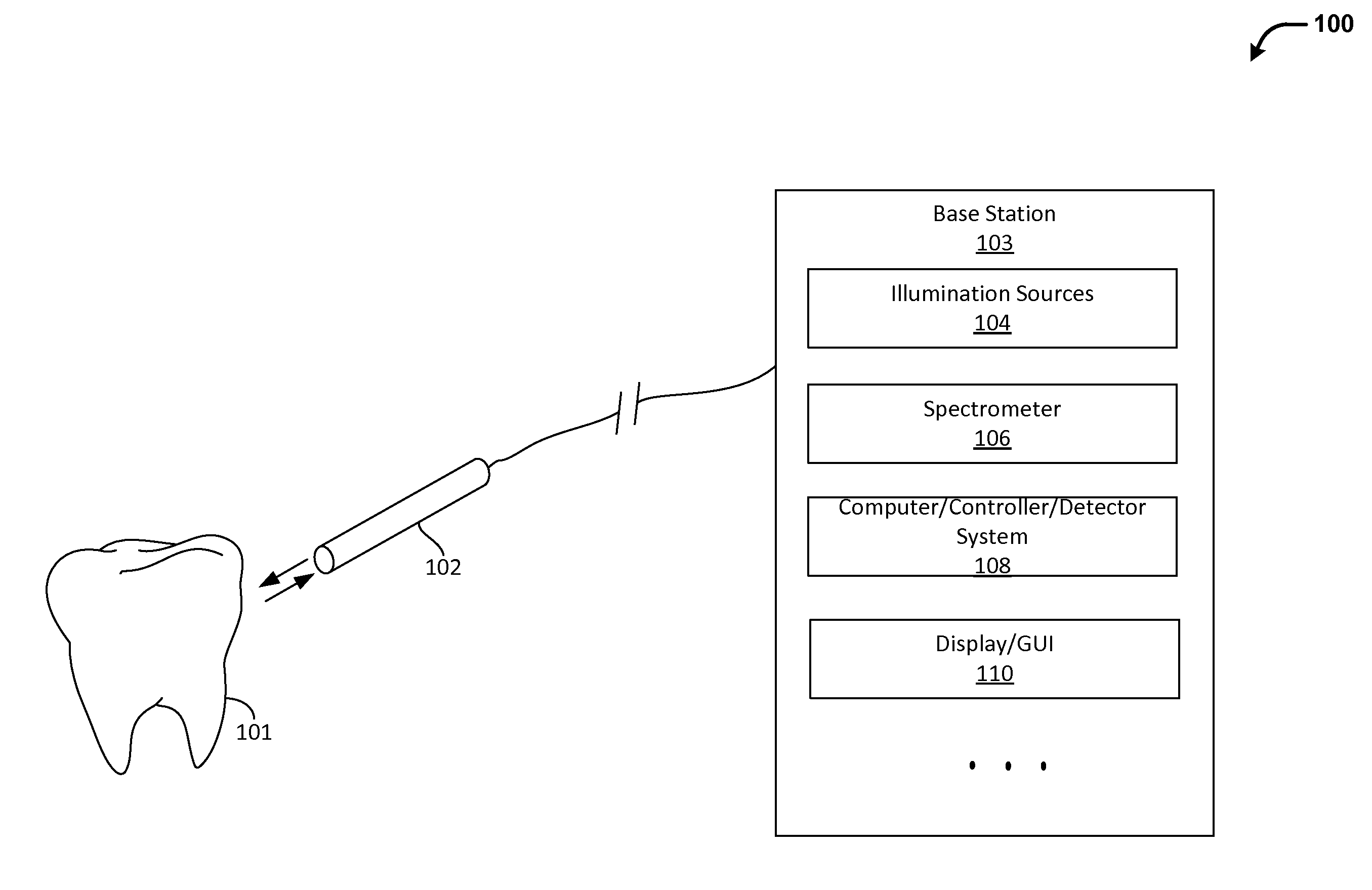
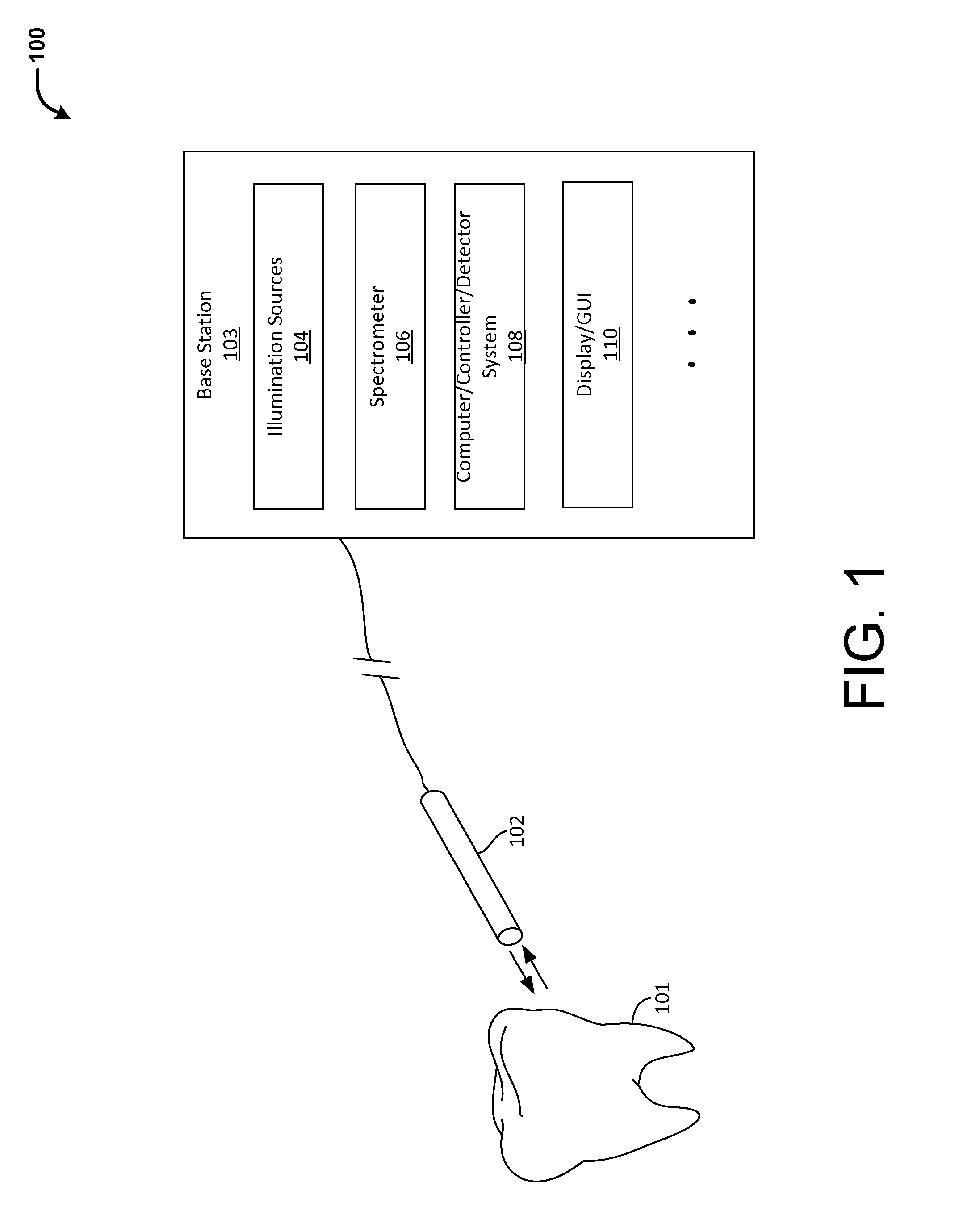
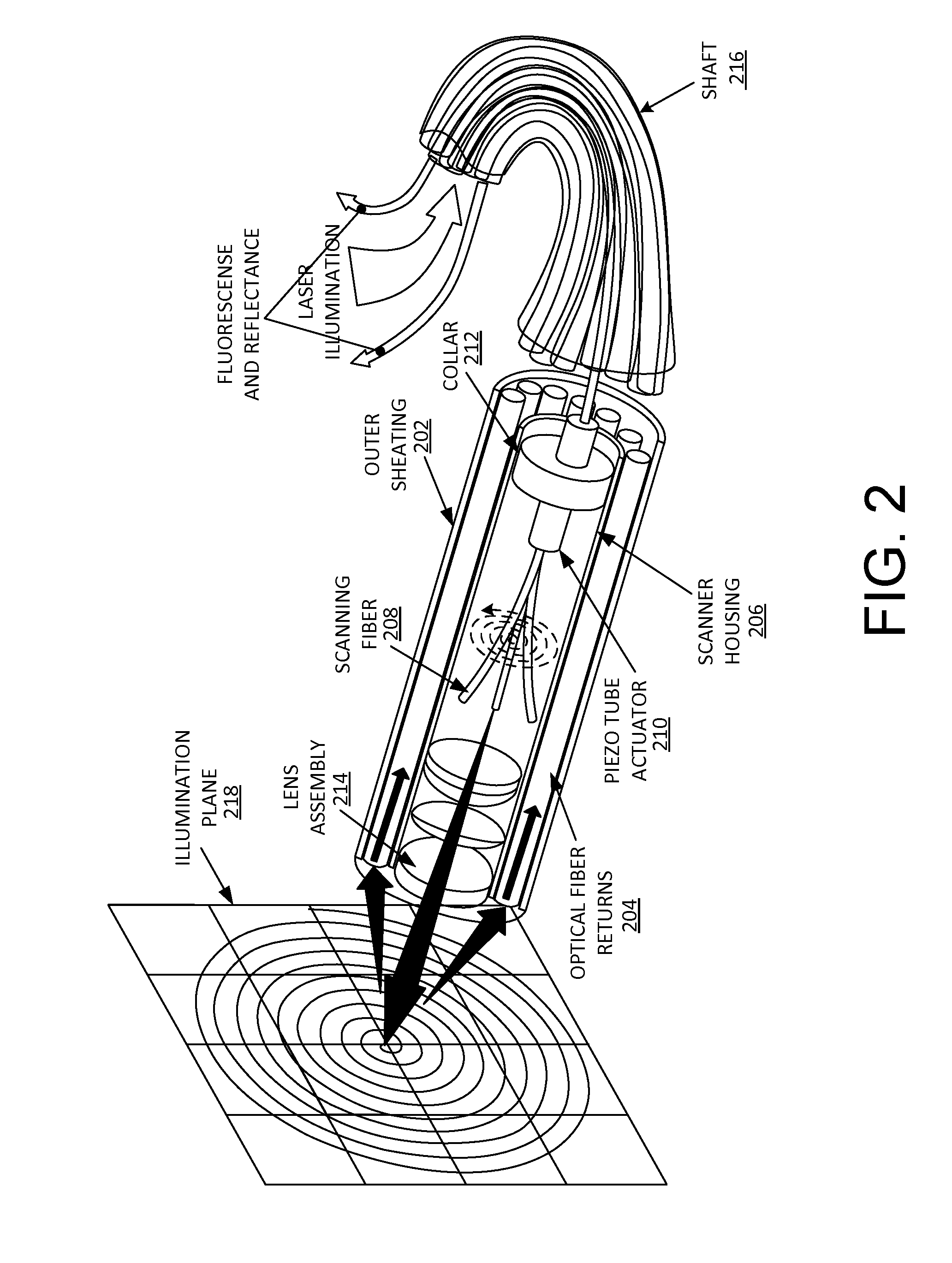
Dental demineralization detection, methods and systems
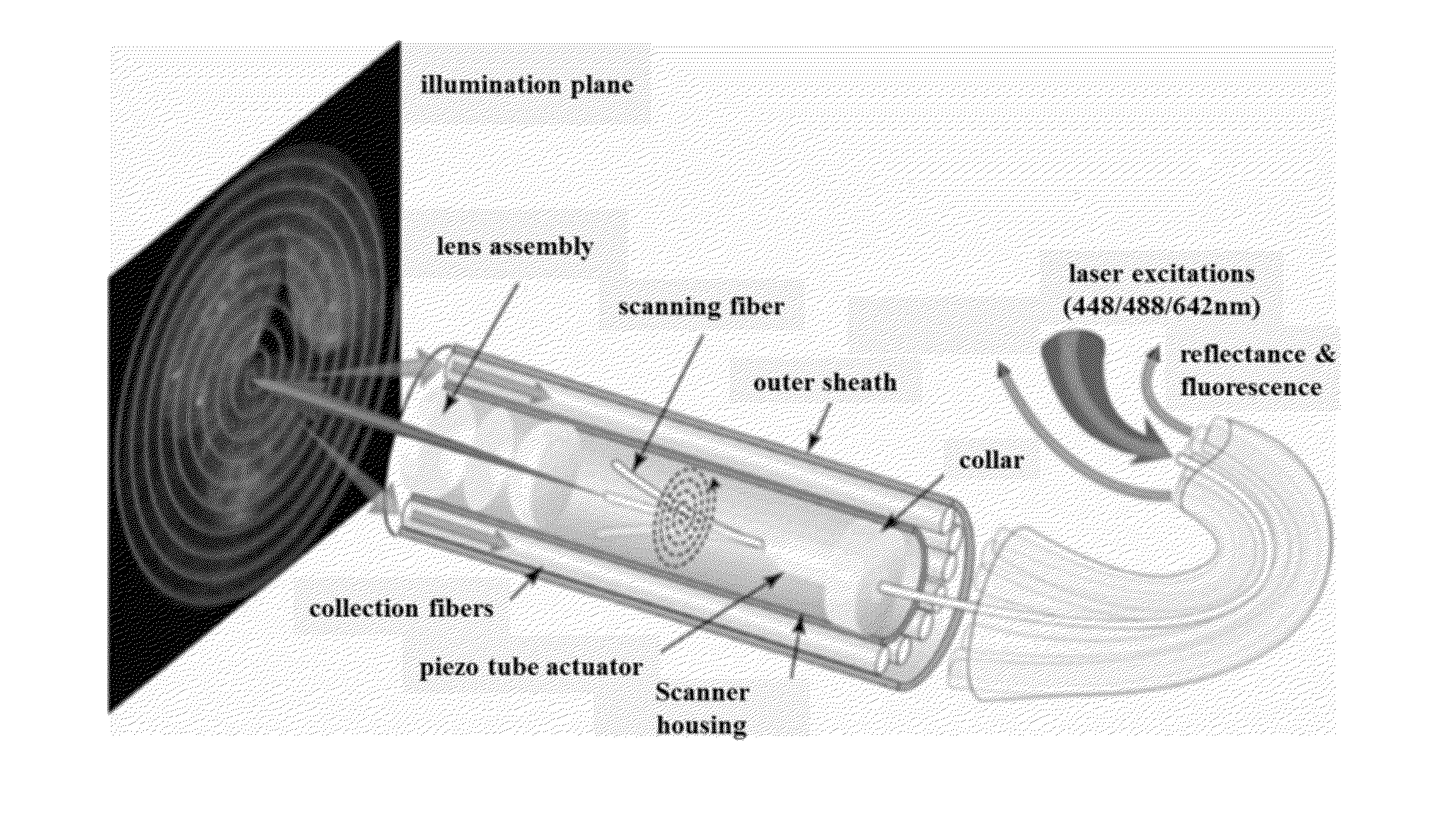
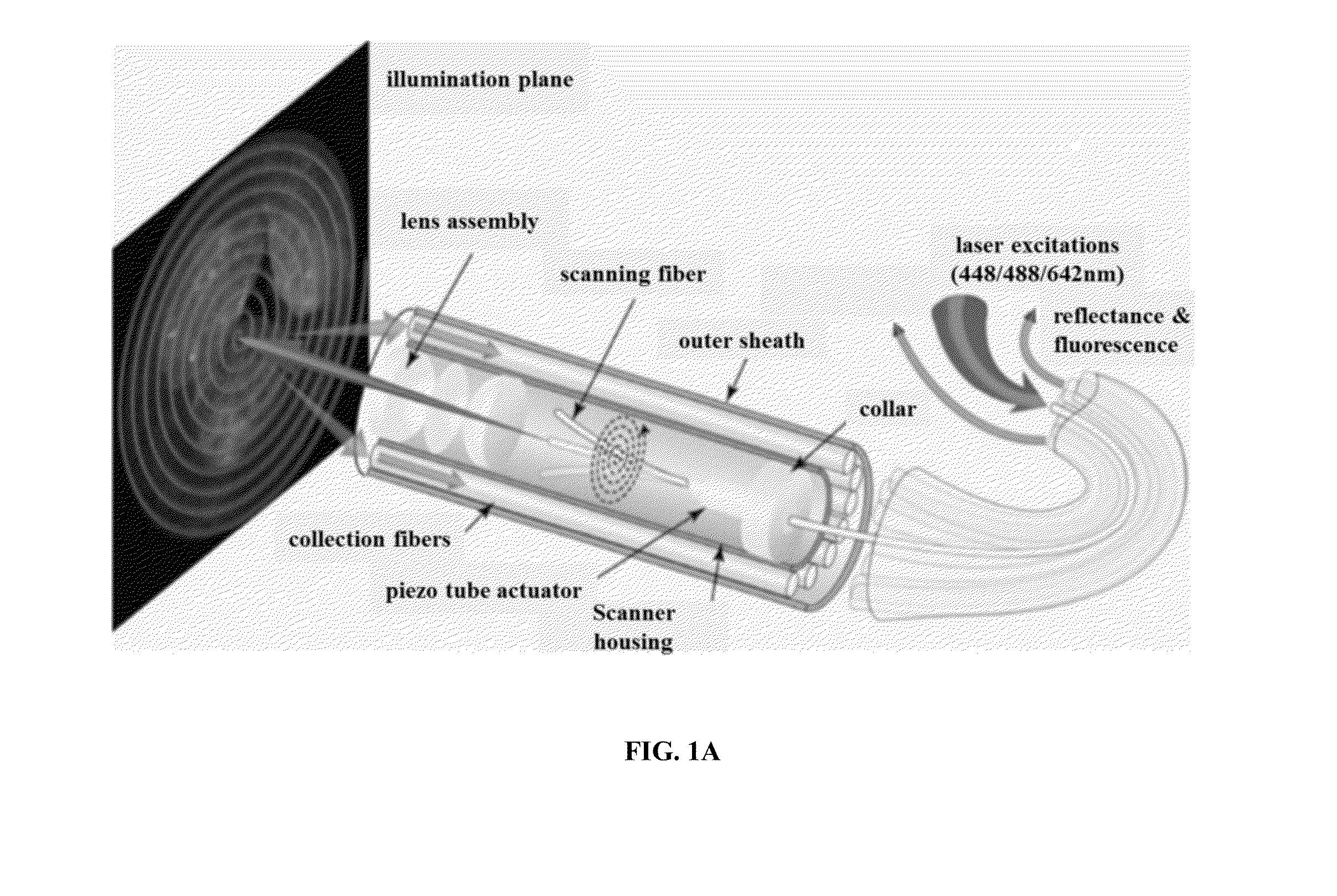
Methods and systems for detecting early stage dental caries and decays are provided. In particular, in an embodiment, laser-induced autofluorescence (AF) from multiple excitation wavelengths is obtained and analyzed. Endogenous fluorophores residing in the enamel naturally fluoresce when illuminated by wavelengths ranging from ultraviolet into the visible spectrum. The relative intensities of the AF emission changes between different excitation wavelengths when the enamel changes from healthy to demineralized. By taking a ratio of AF emission spectra integrals between different excitation wavelengths, a standard is created wherein changes in AF ratios within a tooth are quantified and serve as indicators of early stage enamel demineralization. The techniques described herein may be used in conjunction with a scanning fiber endoscope (SFE) to provide a reliable, safe and low-cost means for identifying dental caries or decays.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
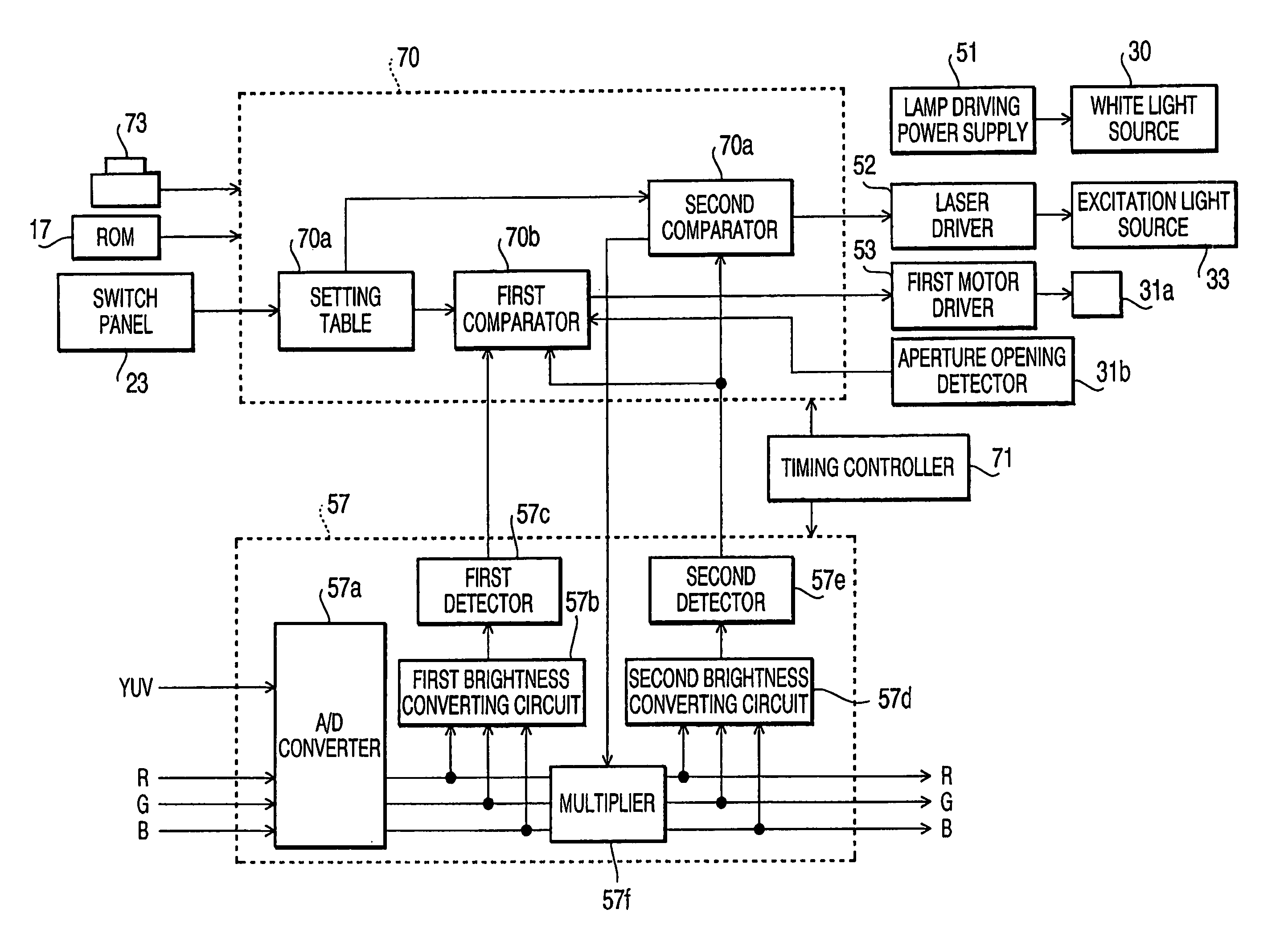
Electronic endoscope system for fluorescence observation
InactiveUS20060020169A1Reduce fatigueReduce brightness differenceSurgeryEndoscopesControl systemDisplay device
An electronic endoscope system, which is adapted to observe a fluorescence image of autofluorescence emitted from a body cavity wall irradiated with excitation light as well as a normal image of the body cavity wall illuminated with white light on a display device, includes a brightness control system configured to adjust brightness of at least one of the normal image and the fluorescence image to reduce brightness difference between the normal image and the fluorescence image to be displayed.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Electronic endoscope system for fluorescence observation
An electronic endoscope system, which is adapted to observe a fluorescence image of autofluorescence emitted from a body cavity wall irradiated with excitation light, includes a controller that controls a light source apparatus to alternately introduce either white light or excitation light into a light guide while taking a normal color image and the fluorescence image, and controls an image signal generating system to generate normal color image signals and fluorescence image signals. The controller further controls a display device to display a still fluorescence image in a first window defined on a displaying area thereof based on the fluorescence image signals which have been generated when a still image switch is turned ON during the time to take the fluorescence image, and simultaneously to display a moving normal color image in a second window defined on a displaying area thereof based on the normal color image signals generated every time the body cavity wall is intermittently illuminated with the white light, the first window being larger than the second window.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Method for detection and analysis of aromatic hydrocarbons from water
InactiveUS20100068821A1Easy to judgeBiological testingTesting organic contamination in waterAromatic hydrocarbonOrganic chemistry
Methods for analyzing aromatic hydrocarbons dissolved in water are discussed. The methods include providing a substrate coated with a thin film layer of a material, wherein the material has a high affinity for at least one aromatic hydrocarbon, the material is substantially optically transparent, and the material has near-zero auto fluorescence, inserting the coated substrate directly into an environmental location including water, waiting for an exposure time permitting at least one aromatic hydrocarbon to absorb into the thin film layer, retrieving the coated substrate from the environmental location, removing any non-absorbed matter from the coated substrate, and performing fluorescence analysis on the coated substrate to detect aromatic hydrocarbons present in the thin film layer. Also methods for analyzing aromatic hydrocarbons dissolved in water contained in coated vessels are provided.
Owner:DAKOTA TECH
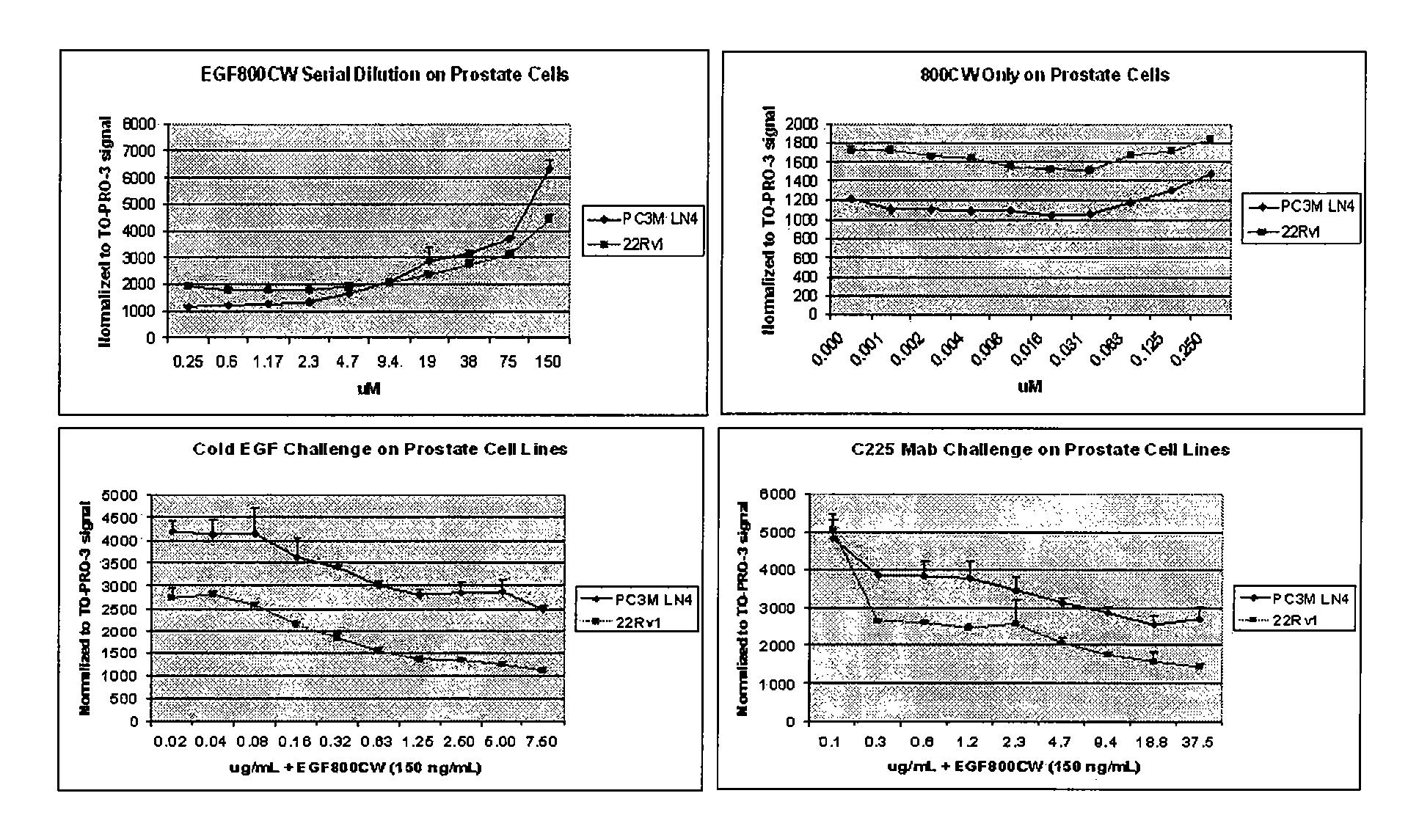
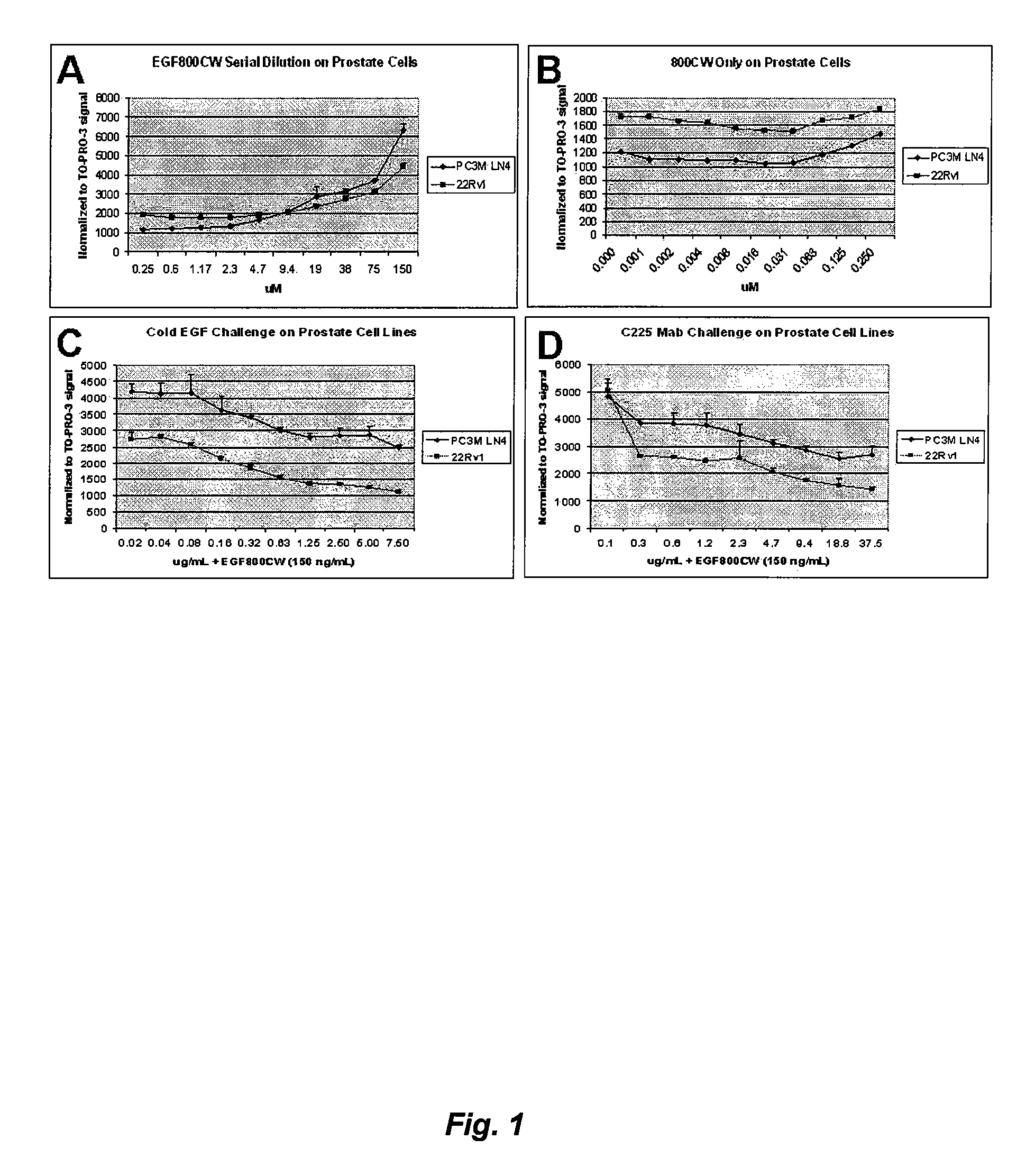
Optical fluorescent imaging
InactiveUS20060280688A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMethine/polymethine dyesAbnormal tissue growthNoninvasive imaging
Compounds and methods are disclosed that are useful for noninvasive imaging in the near-infrared (NIR) spectral range. The NIR is highly sensitive for tumor detection and tracking. The application discloses targeting a tumor-enriched cell surface receptor with a ligand-conjugated fluorescent probe, which specifically allows detection of the tumor relative to the negligible animal autofluorescence.
Owner:LI COR
Fluorescence detecting system
A fluorescence detecting system includes a stimulating light projector which projects onto an object part which has been dosed with a fluorescence agent first stimulating light in the exciting wavelength range of the fluorescence agent and second stimulating light which differs from the first stimulating light in the wavelength band and is in the exciting wavelength range of the auto-fluorescence material contained in the object part, and a fluorescence information obtainer which obtains the fluorescence from the fluorescence agent information based on the fluorescence from the fluorescence agent emitted from the object part in response to projection of the first stimulating light and the auto-fluorescence information based on the auto-fluorescence emitted from the object part in response to projection of the second stimulating light. The fluorescence agent is a fluorescence agent which does not emit fluorescence in response to projection of the second stimulating light.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Electronic endoscope system for fluorescence observation
An electronic endoscope system, which is adapted to observe a fluorescence image of autofluorescence emitted from a body cavity wall irradiated with excitation light, includes a controller that controls a light source apparatus to alternately introduce either white light or excitation light into a light guide while taking a normal color image and the fluorescence image, and controls an image signal generating system to generate normal color image signals and fluorescence image signals. The controller further controls a display device to display a still fluorescence image in a first window defined on a displaying area thereof based on the fluorescence image signals which have been generated when a still image switch is turned ON during the time to take the fluorescence image, and simultaneously to display a moving normal color image in a second window defined on a displaying area thereof based on the normal color image signals generated every time the body cavity wall is intermittently illuminated with the white light, the first window being larger than the second window.
Owner:HOYA CORP
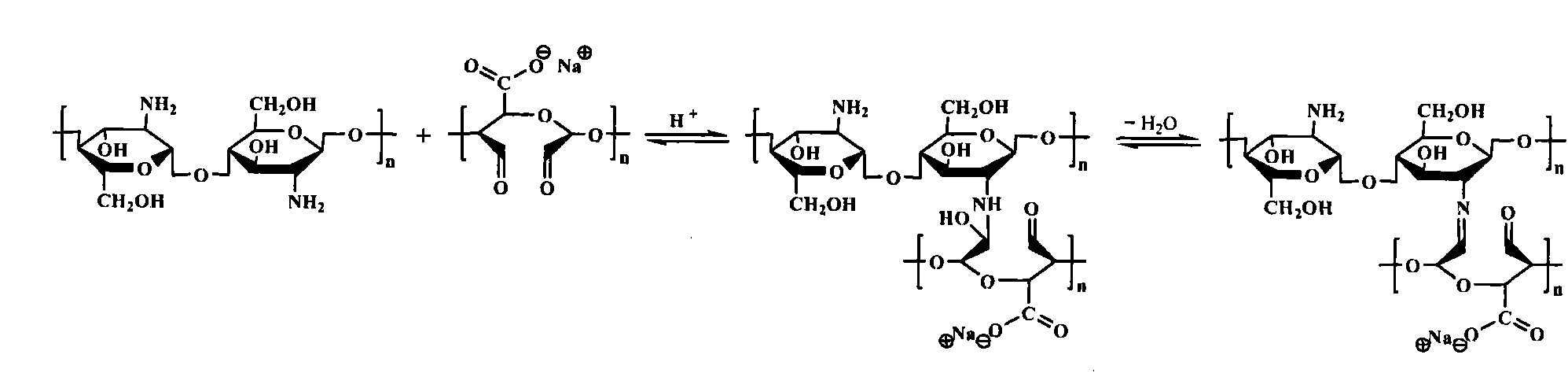
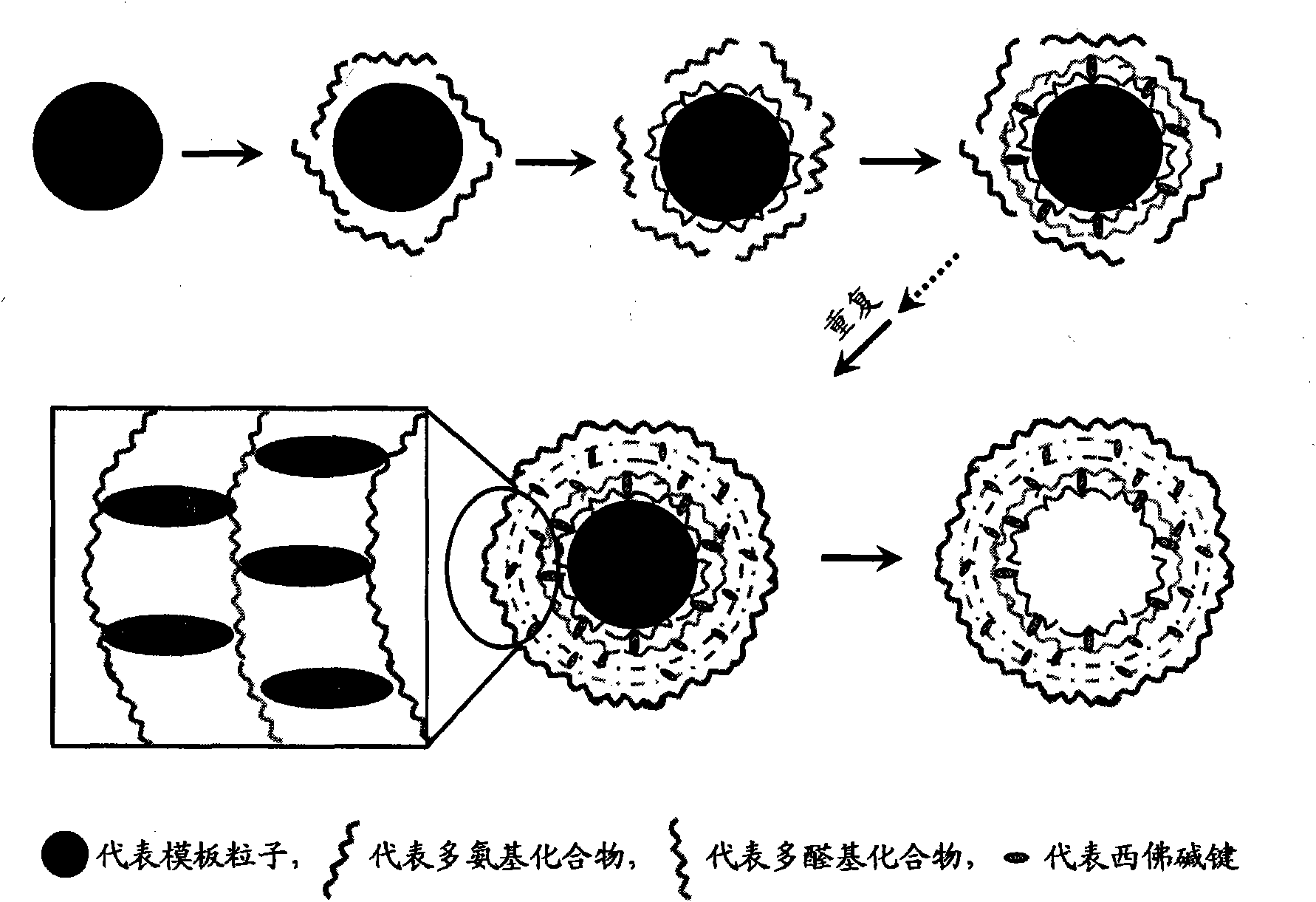
Layer-by-layer assembled microcapsule and its preparation method
ActiveCN102335575AImprove stabilityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMicroballoon preparationCross-linkBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to a biologically compatible microcapsule and its preparation method, especially a Schiff base bond based and layer-by-layer assembled biologically compatible microcapsule and its preparation method. The microcapsule is characterized in that the capsule wall consists of biologically compatible and biodegradable polysaccharides and derivatives thereof, and the Schiff base bond forms among the capsule wall components without employing additional cross linking agent. Compared with microcapsules prepared by traditional methods, the microcapsule obtained in the method has the advantages of good stability, biocompatibility, biodegradability, nontoxity, auto-fluorescence and pH responsive permeability, as well as no need for a cross linking agent.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods and compositions for the preparation and use of fixed-treated cell-lines and tissue in fluorescence in situ hybridization
InactiveUS6995020B2Easy to detectReduced autofluorescenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical treatmentTreated cell
This invention relates to methods for the detection of one or more mRNA transcripts in paraffin-embedded tissue by “mRNA liberation in fixed-treated tissue or ‘MLIFTT’”. This method includes treating the tissue with ammonia-ethanol and sodium borohydride combined with pressure cooking of the tissue. The chemical treatments reduce the tissue autofluorescence and the physical treatments overcome the interference created by the fixation-induced chemical bonds. The methods of the present invention can be utilized to identify a plurality of mRNA transcripts in a microarray format.
Owner:AUREON LAB INC +2
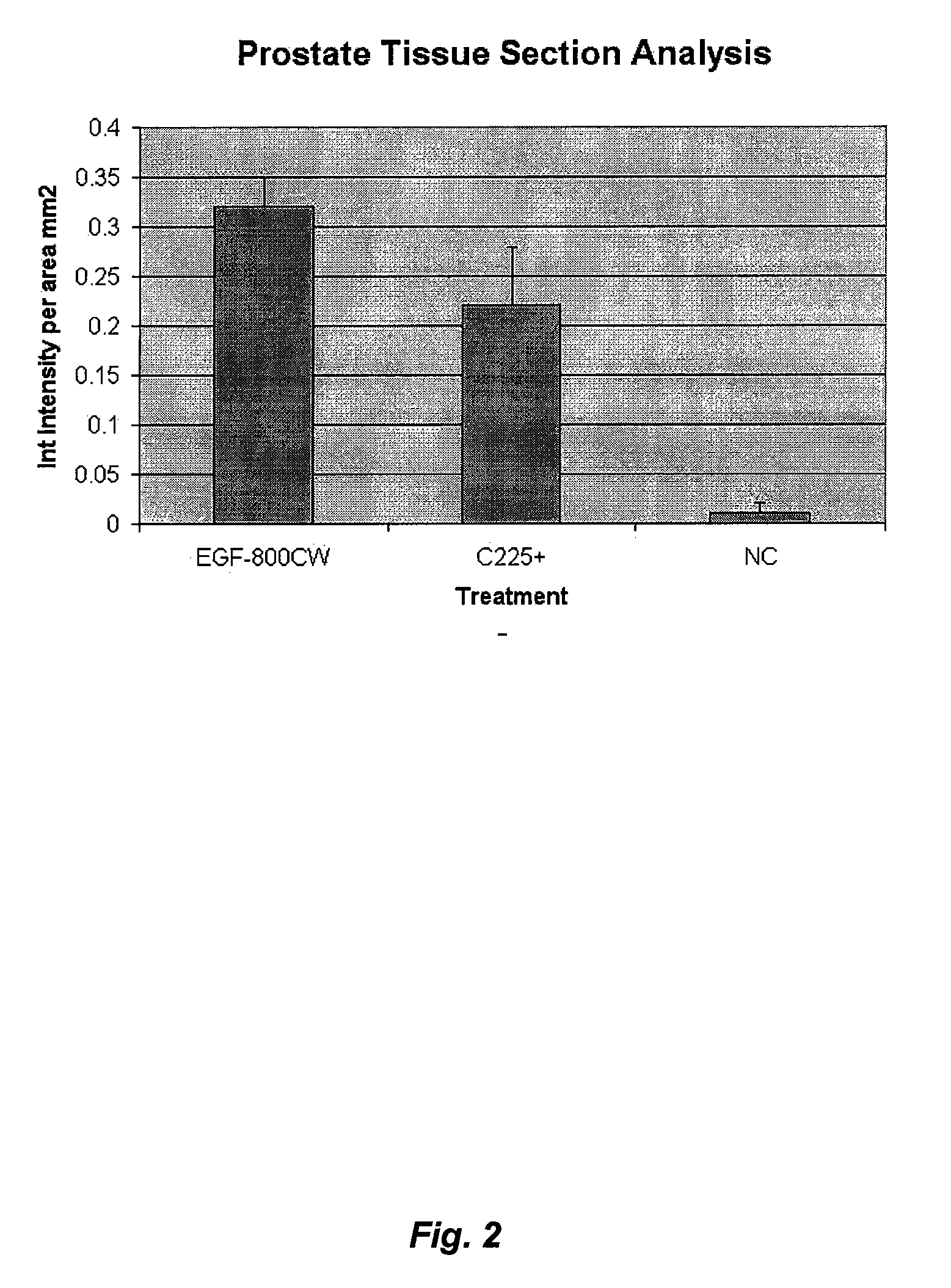
Method for Determining Effectiveness of Medicine Containing Antibody as Component
InactiveUS20130230866A1High sensitivityWide rangeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTissue stainingTreatment effect
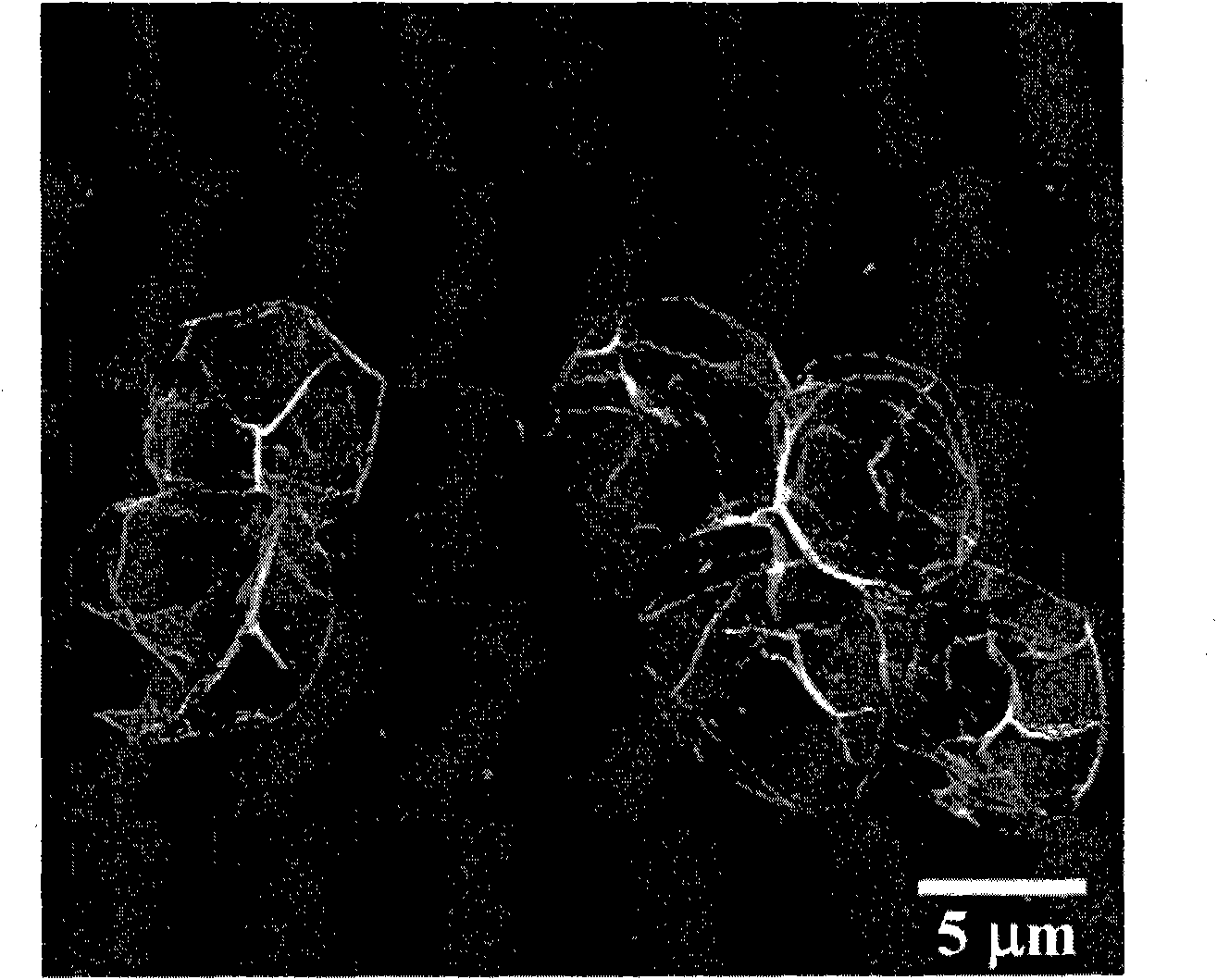
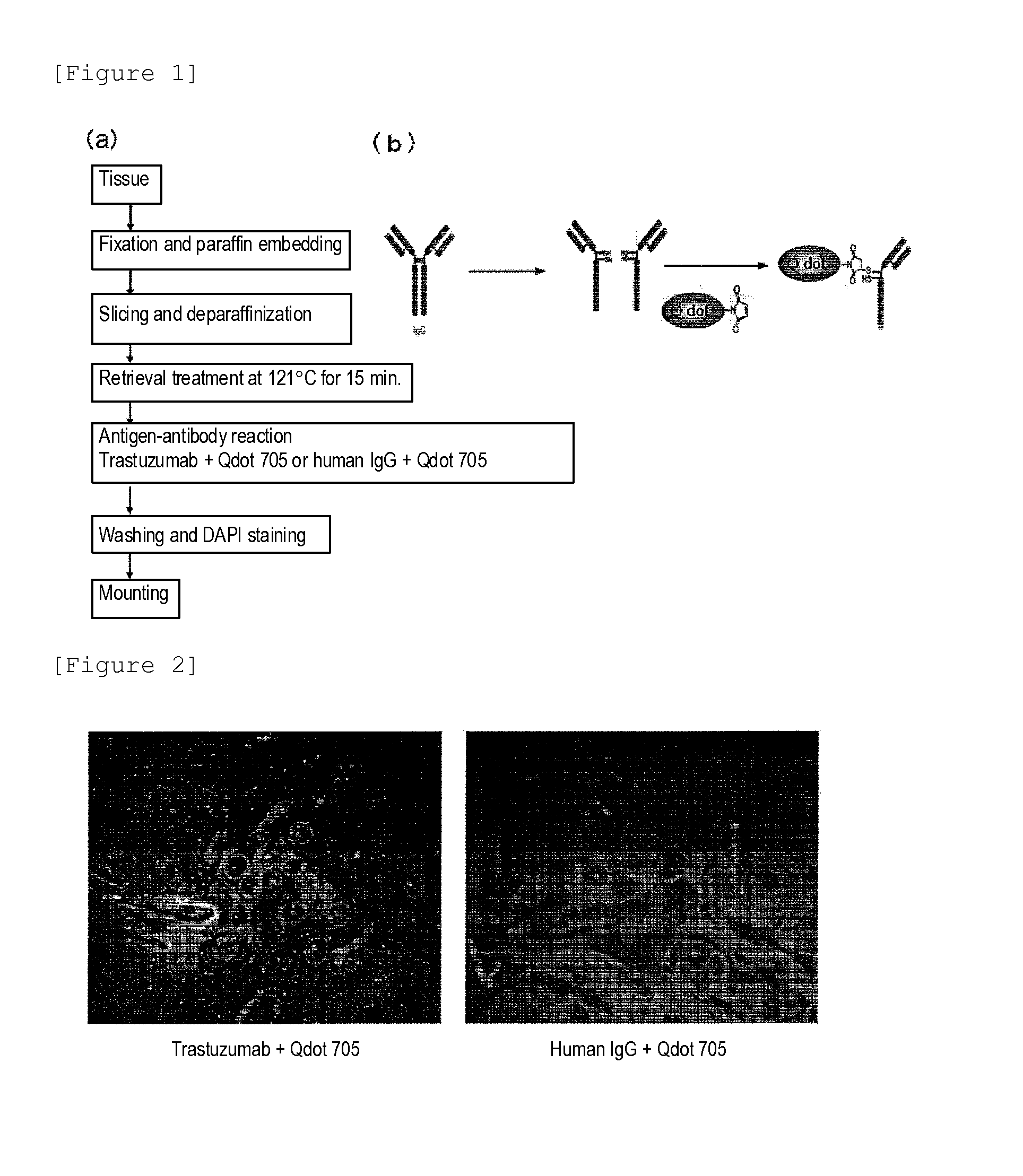
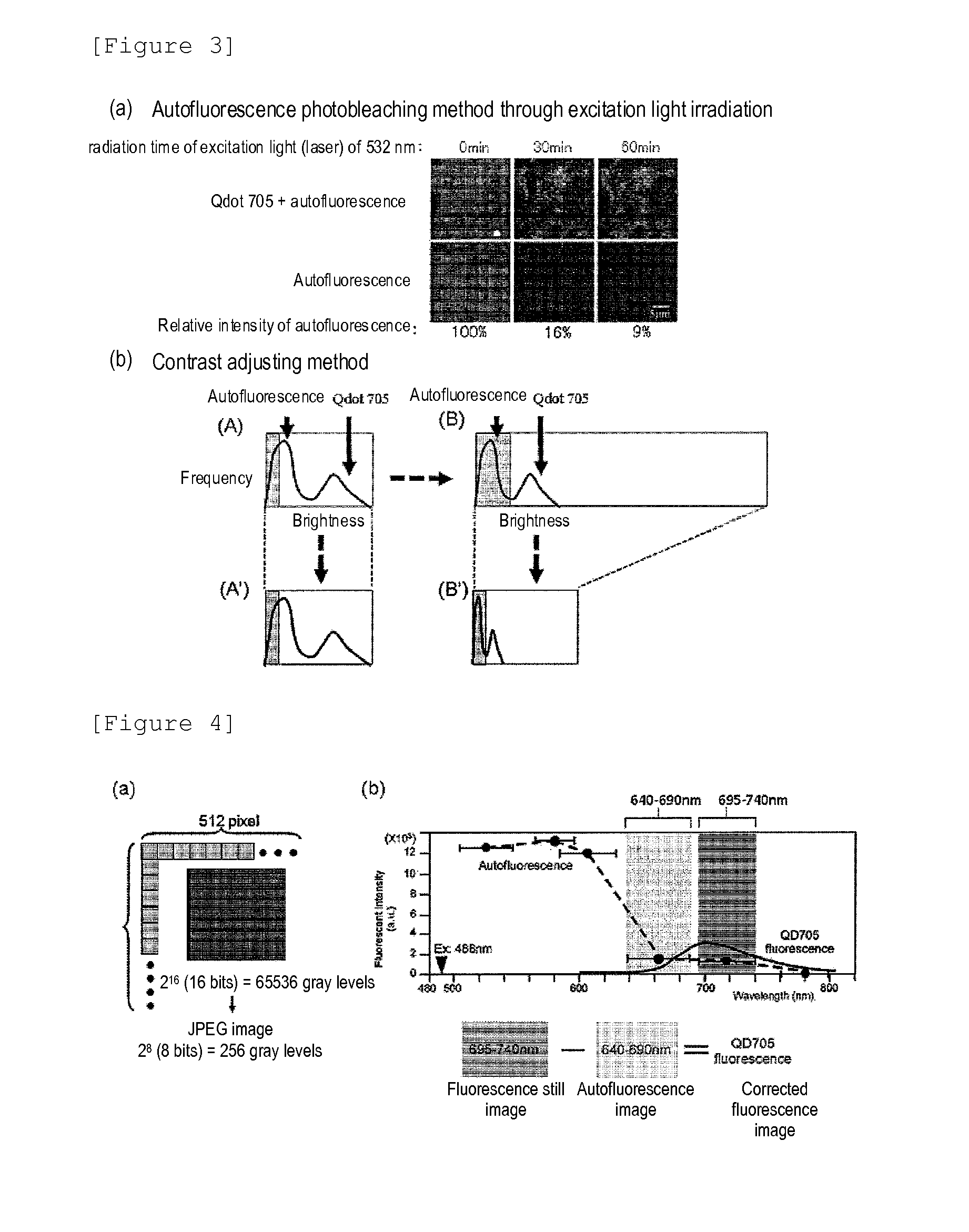
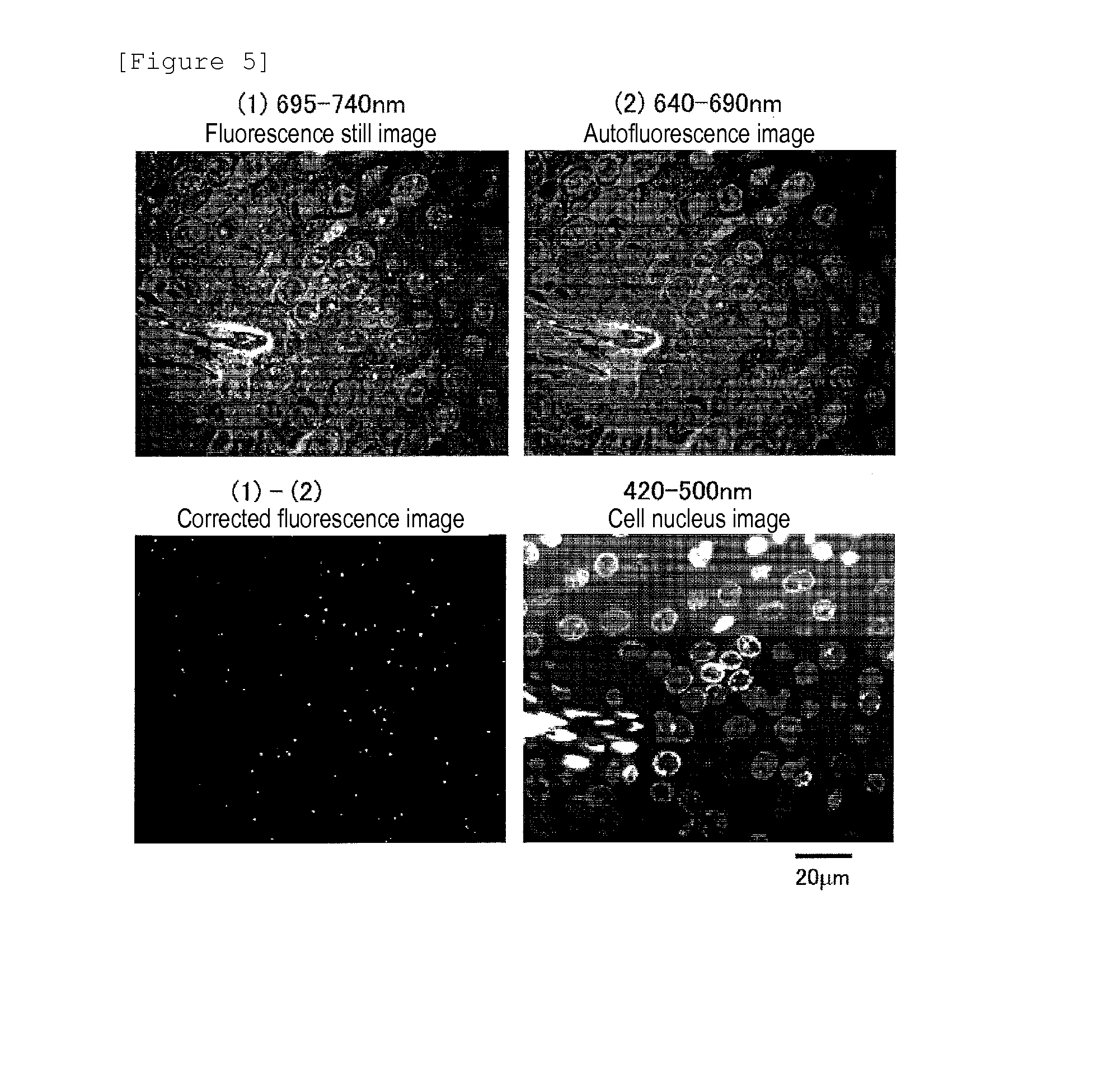
Protein recognized by an antibody used as an active ingredient of an antibody medicine such as trastuzumab or an antibody used for targeting a target site of an active ingredient is highly accurately quantitatively determined by employing a quantitative tissue staining method of biological tissues, thereby providing a method for determining therapeutic effectiveness of a medicine containing such an antibody as a component. The effectiveness of a medicine containing an antibody as a component is determined by employing a tissue staining method comprising the steps of: labeling the antibody in the medicine containing an antibody as a component with a fluorescent material and contacting the thus fluorescence-labeled antibody with a tissue sample; obtaining a fluorescence image by irradiating, with excitation light, a tissue site contacted with the antibody; obtaining an autofluorescence image in the same field of view and at the same focus as in the fluorescence image in a close region on a shorter wavelength side or a longer wavelength side of an acquisition wavelength region of fluorescence emitted by the fluorescent material; obtaining a corrected fluorescence image by performing image processing for removing fluorescence brightness of the autofluorescence image from fluorescence brightness of the fluorescence image; counting the number of cells in the tissue site contacted with the antibody; measuring average fluorescence brightness per fluorescent particle; and calculating the number of fluorescent particles per cell.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
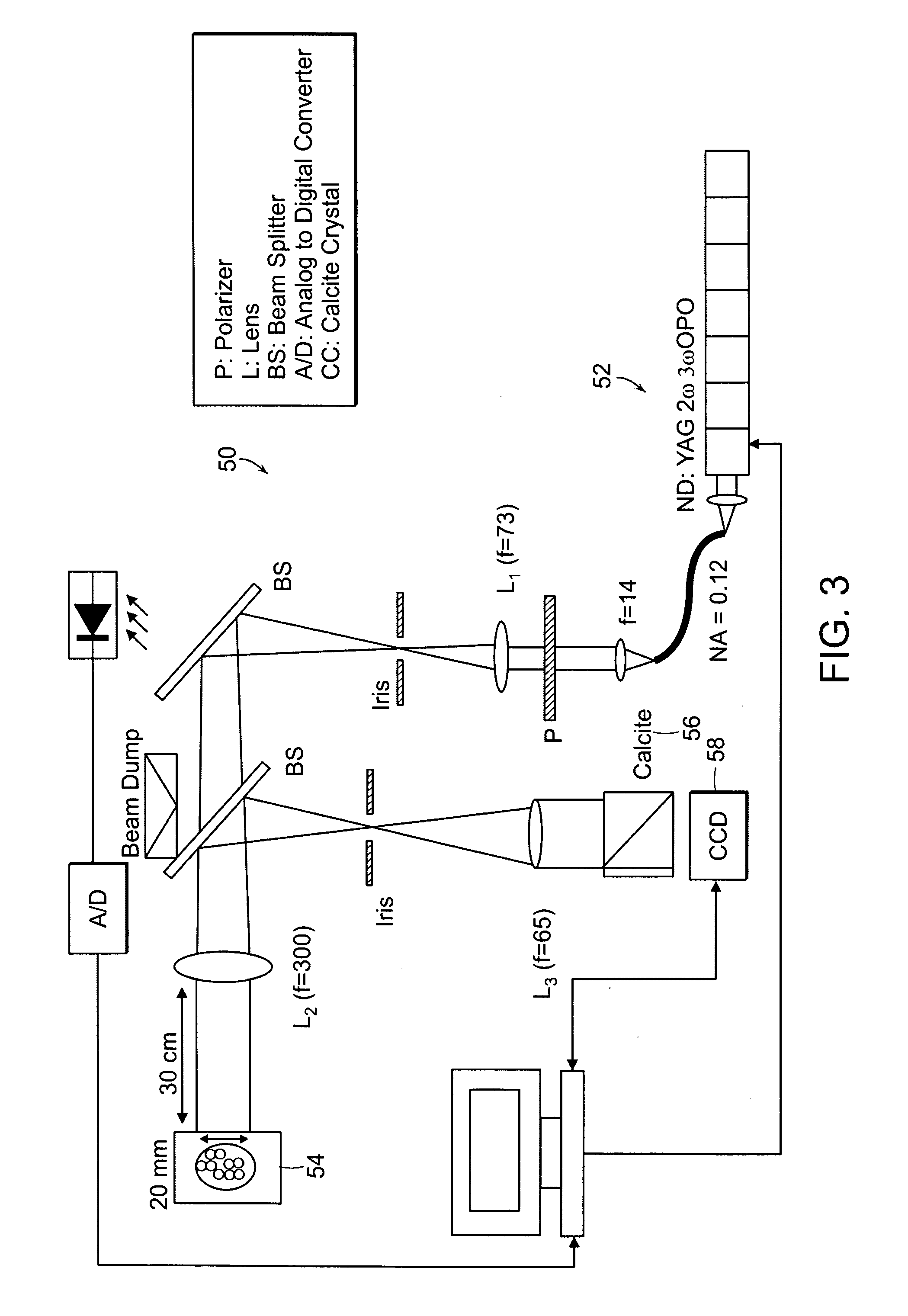
Harmonic generation microscopy
A harmonic generation microscopy employs a laser device that emits a laser beam having a predetermined wavelength that causes no autofluorescence in a biological sample and that, after excited, induces both the second and third harmonic waves. The laser beam is projected onto a sample and an observation beam from the sample is received. The observation beam is directed through a splitter to separate the second harmonic wave and the third harmonic wave both of which are then converted into corresponding electrical signals. The electrical signals are fed to a computer-based image processing equipment to form an image of the sample on the basis of the second and third harmonic waves.
Owner:NARIONAL TAIWAN UNIV
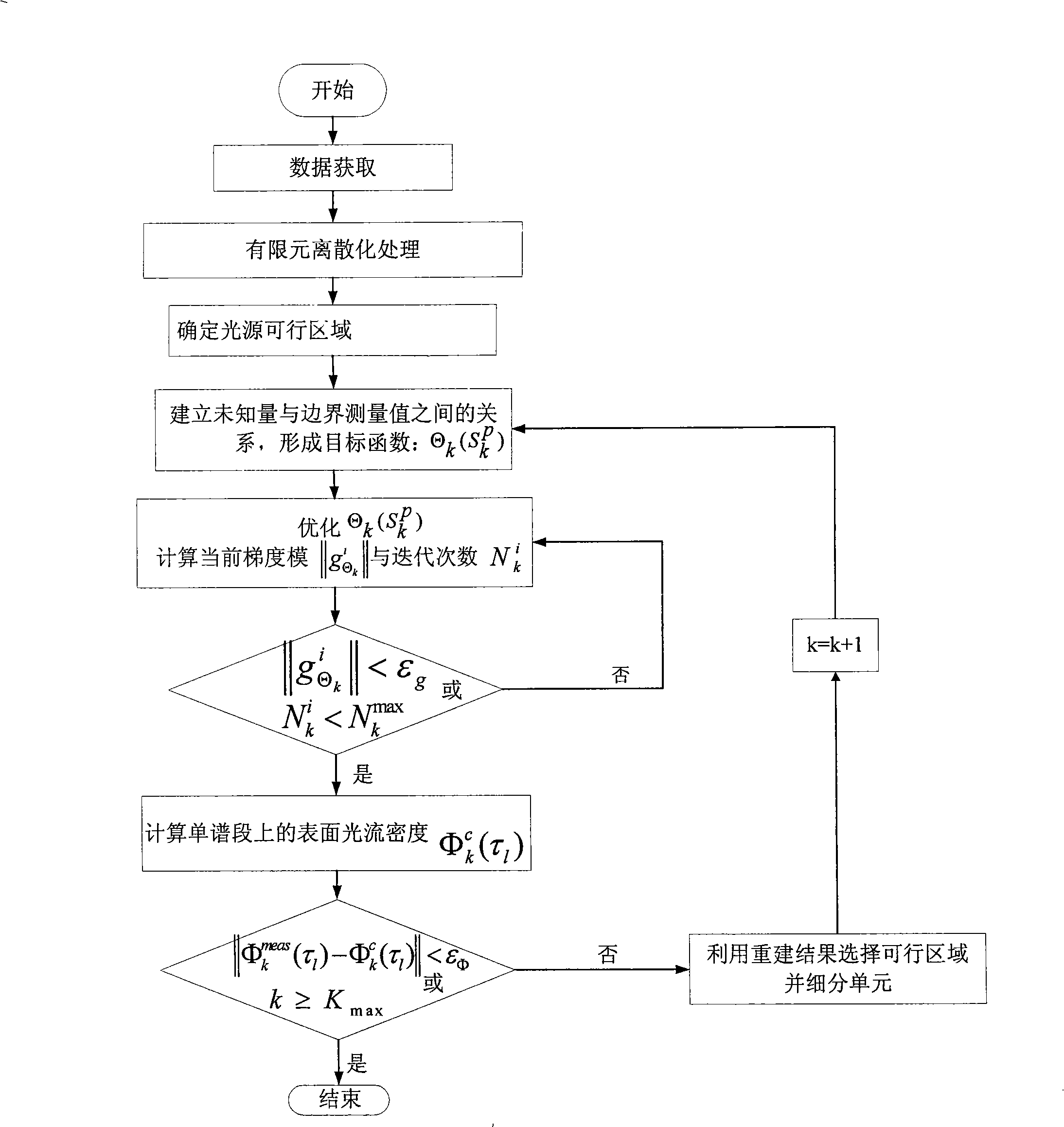
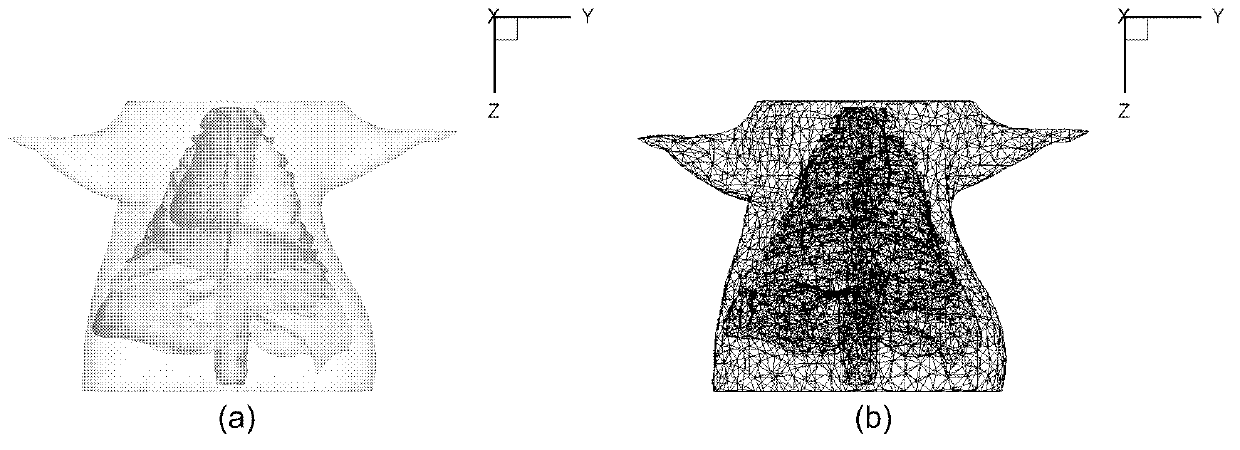
Multi-optical spectrum autofluorescence dislocation imaging reconstruction method based on single view
InactiveCN101342075ASolve inaccurateHigh speedDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsReconstruction methodData acquisition
The invention relates to a multi-spectrum auto fluorescence fault imaging reconstruction method based on single view, which belongs to the optical molecular imaging field. The method is based on the diffusivity equation model, considers the uneven characteristics of small animal body, and simultaneously also considers the spectrum and the practical application characteristics of the auto fluorescence light source. In order to achieve the purpose, the multi-spectrum auto fluorescence fault imaging reconstruction method based on single view comprises the flowing steps: firstly, data acquisition; secondly, the dispersing processing of finite element; thirdly, the optimization of the selection of the feasible light source zone; fourthly, the reconstruction of the light source. The method overcomes the defects that the reconstruction light source of the auto fluorescence fault imaging reconstruction method is inaccurate, the reconstruction speed is low, the real-time processing is not convenient, and error can exist during the multi-spectrum data acquisition.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
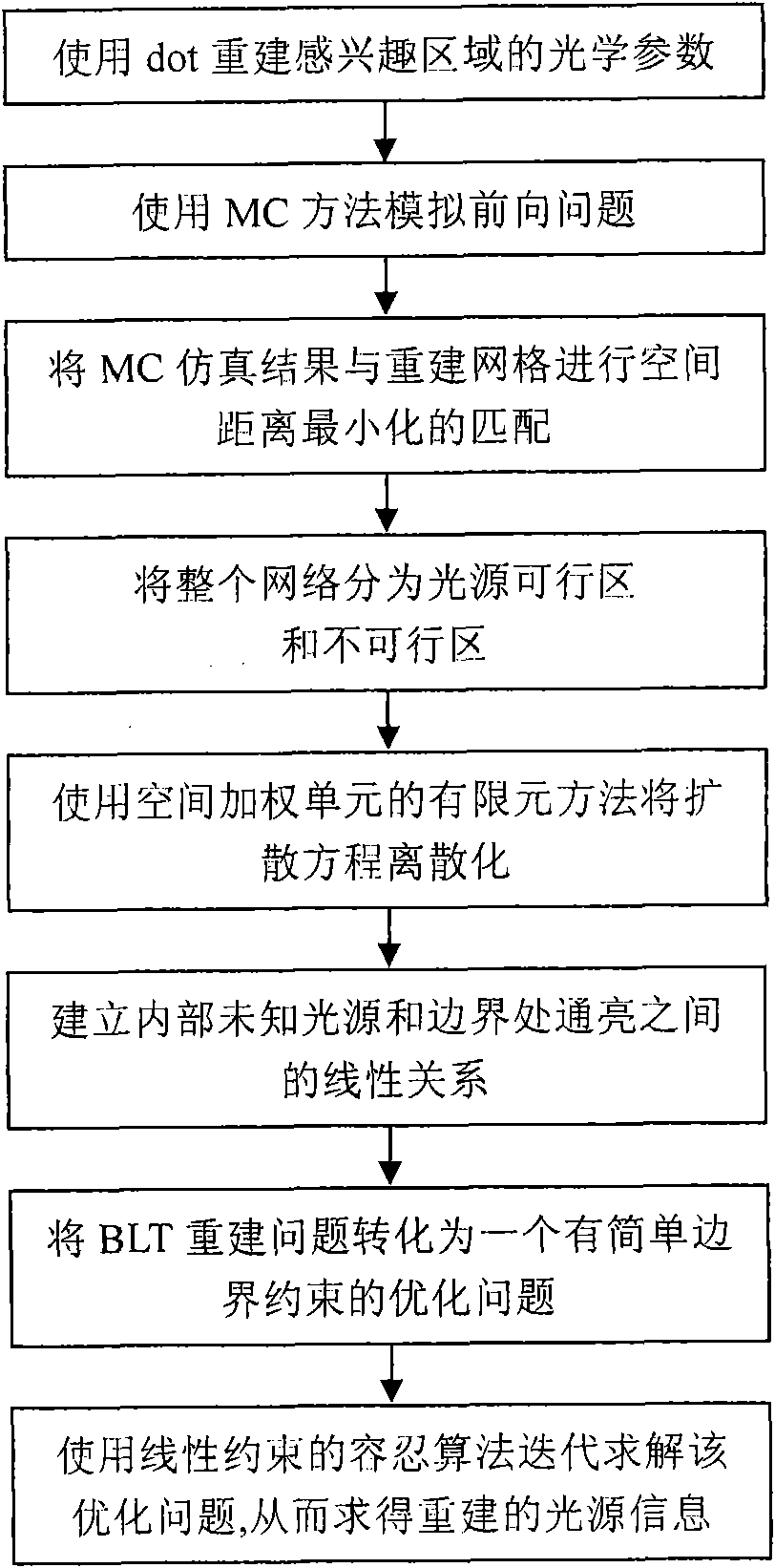
Finite-element reconstruction method for space weighting of auto-fluorescence imaging
InactiveCN101539518AHigh speedSolving Quantitative Reconstruction Problems2D-image generationDiagnostic recording/measuringNumerical stabilityOptical tomography
The invention puts forward a finite-element reconstruction method for space weighting of auto-fluorescence imaging. The method uses a diffuse optical tomography (DOT) technique to precisely reconstruct optical parameters of main biological tissue. The method limits a possible real light-source region, and divides a whole reconstruction region into a light-source possible region and a light-source impossible region so as to improve the numerical stability and effectiveness of reconstruction problems and reduce the ill-conditioned property of BLT reconstruction problems. In order to avoid famous 'Inverse Crime' problems, the method adopts a Monte Carlo (MC) random method to simulate the process of transmitting light in the biological tissue. Then the invention puts forward a finite-element method based on a space-weighting unit and adopts a tolerant algorithm for linear constrained optimization problems to reconstruct light-source information.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Luminescent, spherical, non-autofluorescent silica gel particles having variable emission intensities and frequencies
InactiveUS20050147974A1Detection sensitivityAvoid disadvantagesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementSilica gelAmount of substance
Spherical, transparent silica gel particles with a high luminescence that are produced through the encapsulation of one or more different luminescent substances in a silica gel matrix. By varying the concentration of the luminescent substances and through the encapsulation of substances with different emission frequencies, the particles can be used as multiplex coding and marker systems in bioanalytics and diagnostics.
Owner:MAGNAMEDICS
Device for photodynamic diagnosis or treatment
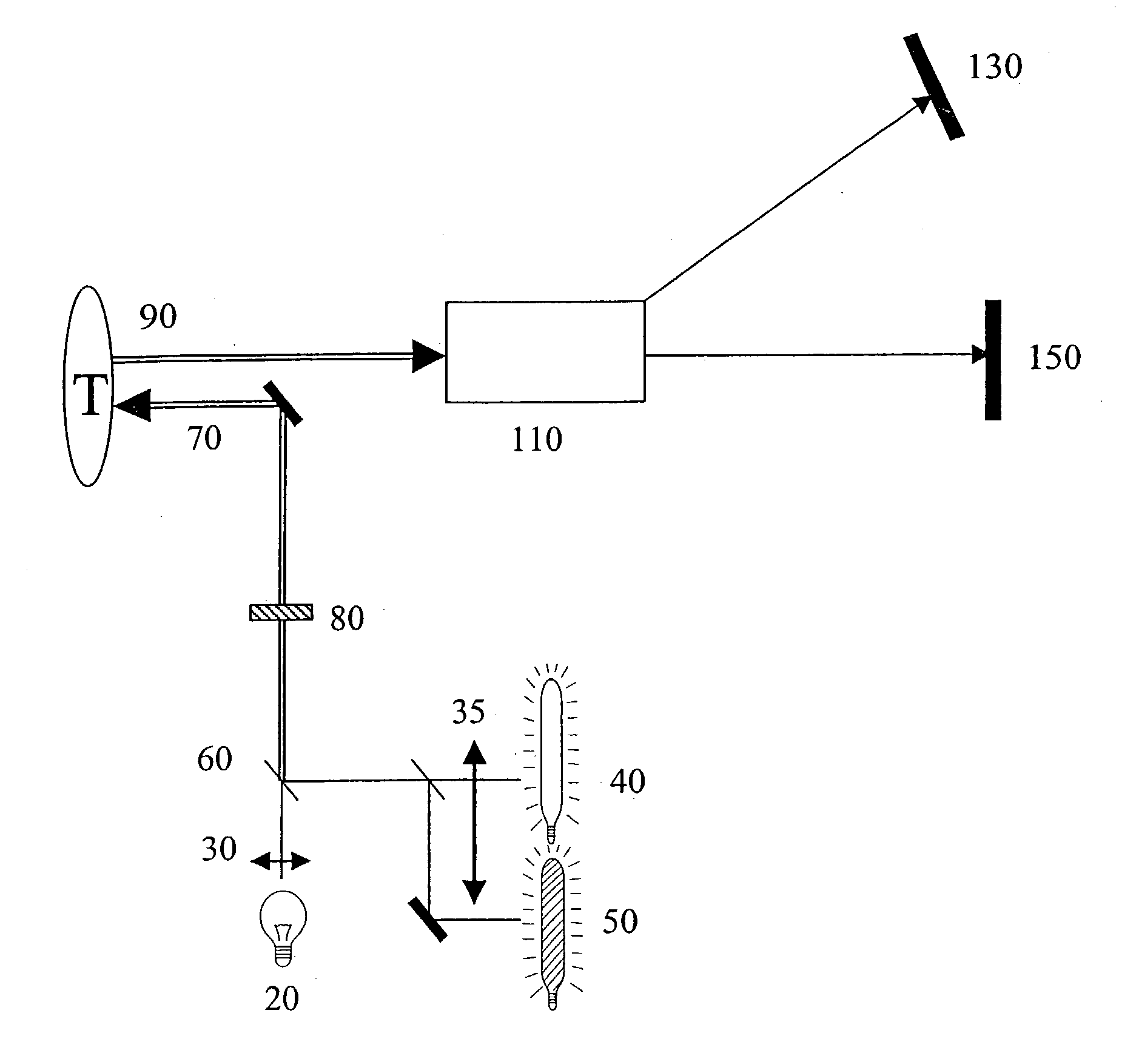
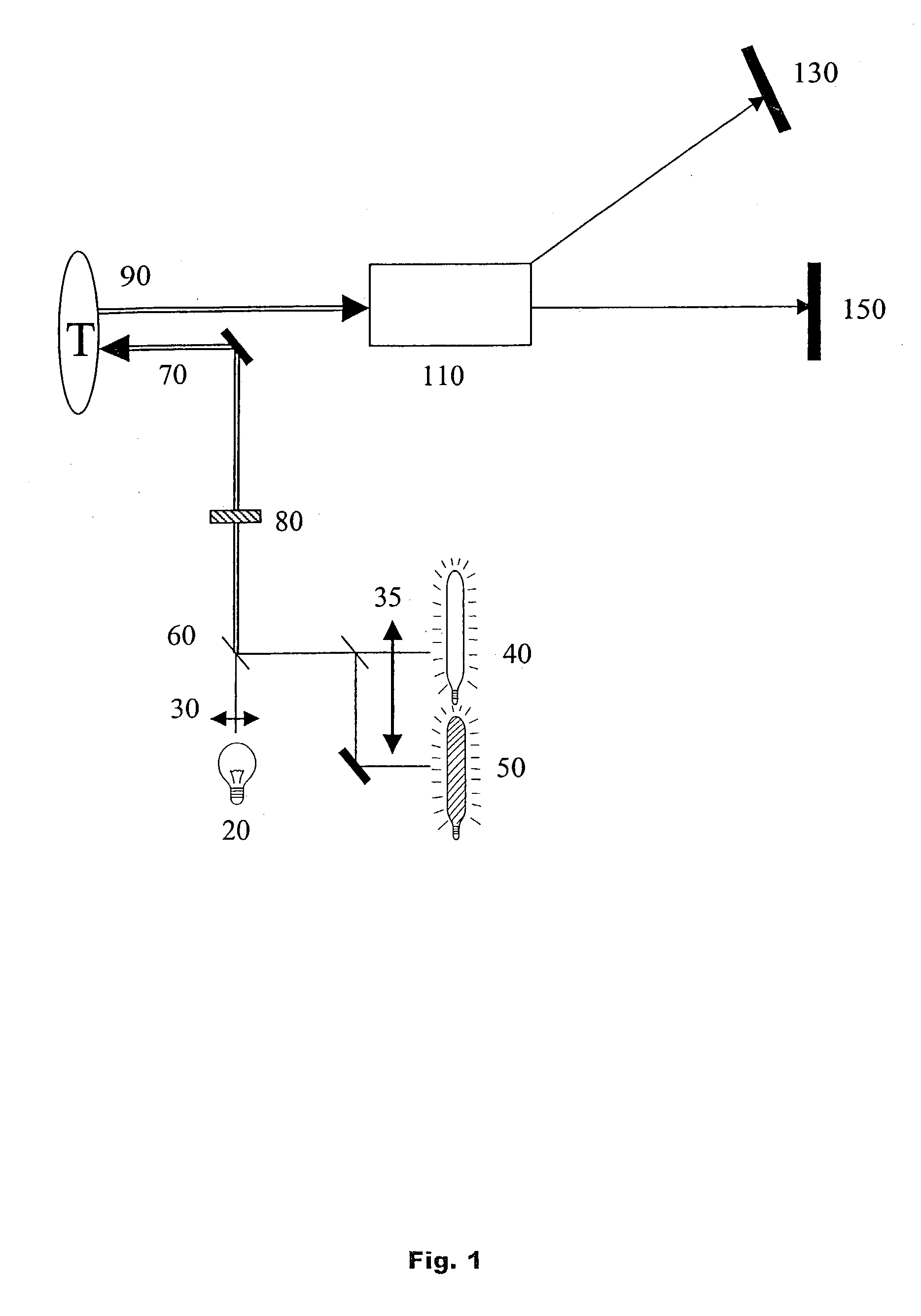
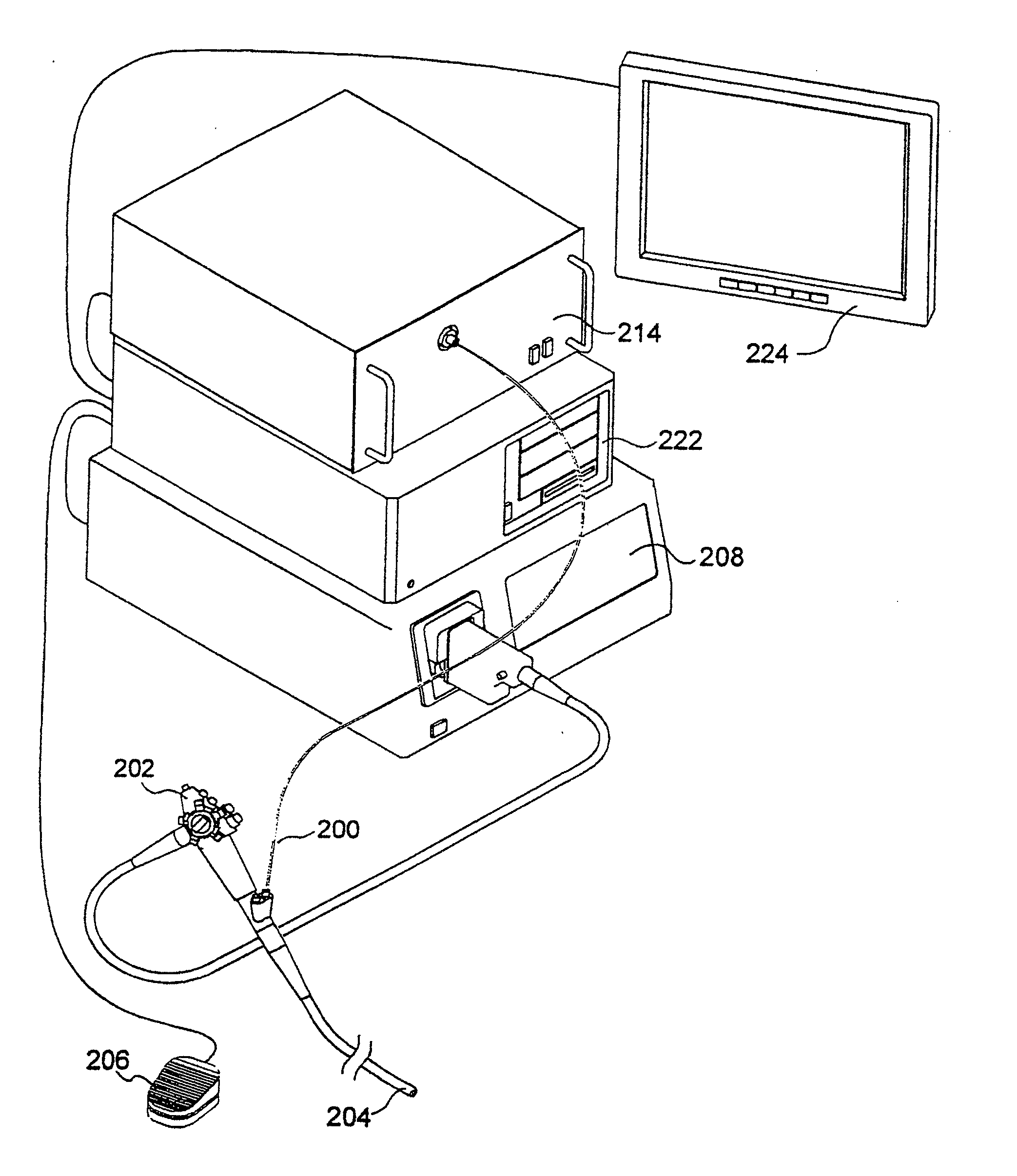
An endoscopic or microscopic apparatus for diagnosis by means of a light-induced reaction in biologic tissue "in vivo" which is created by a photo-amboceptor or by autofluorescence is provided. The inventive apparatus is characterized by the feature that at least one reference wavelength lambdar is provided which is longer by up to 2Deltalambda at maximum or smaller than the wavelength lambdas at the point of intersection.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
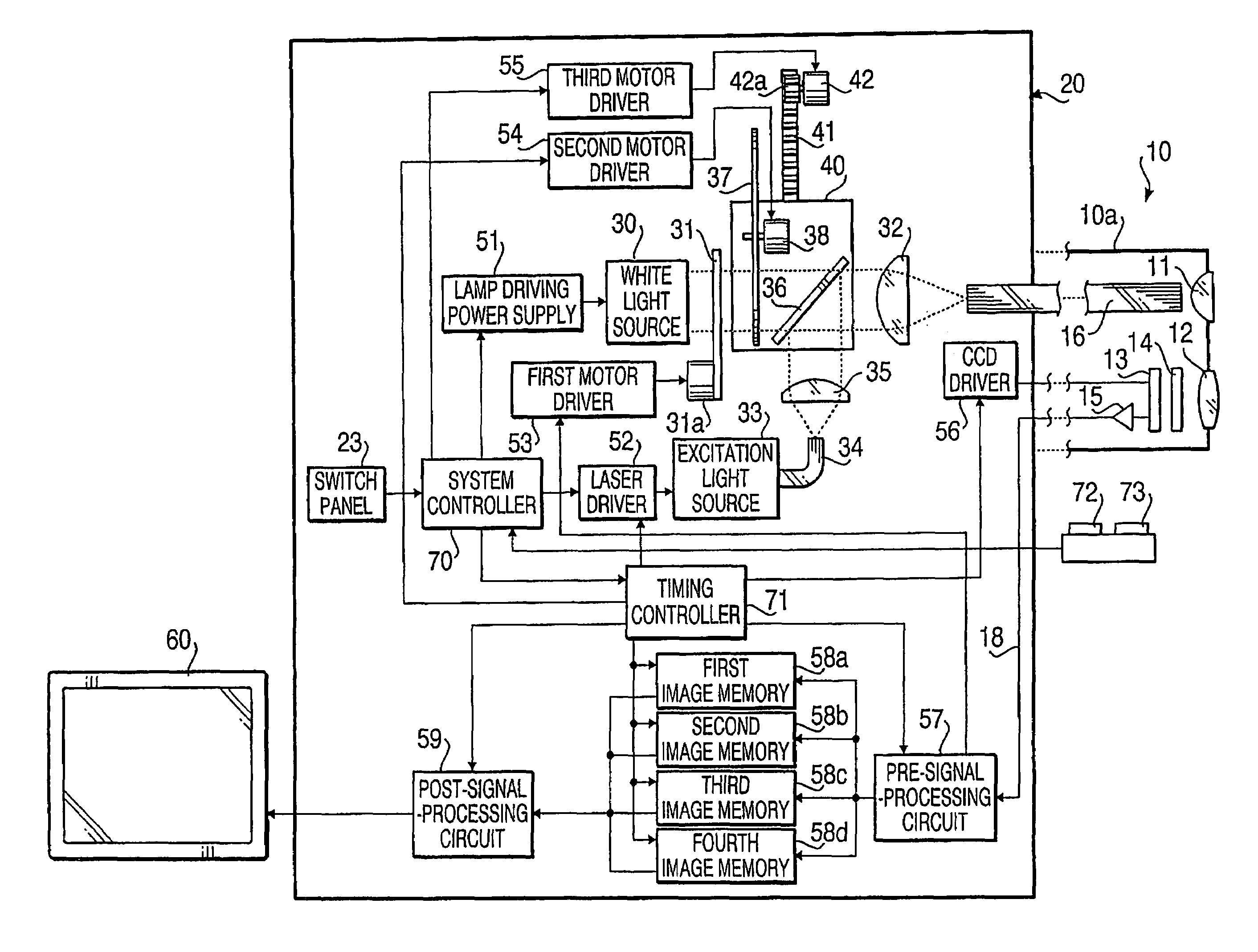
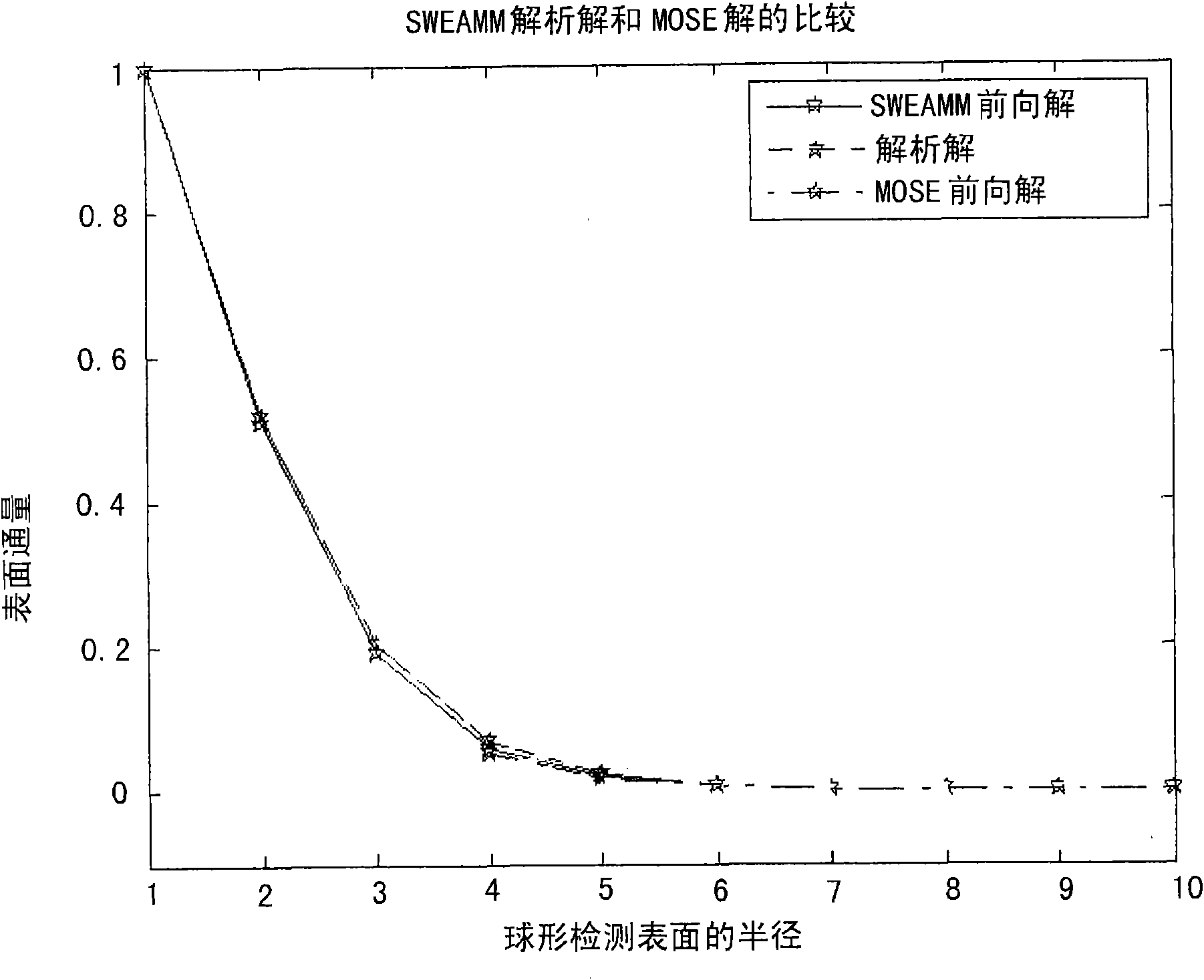
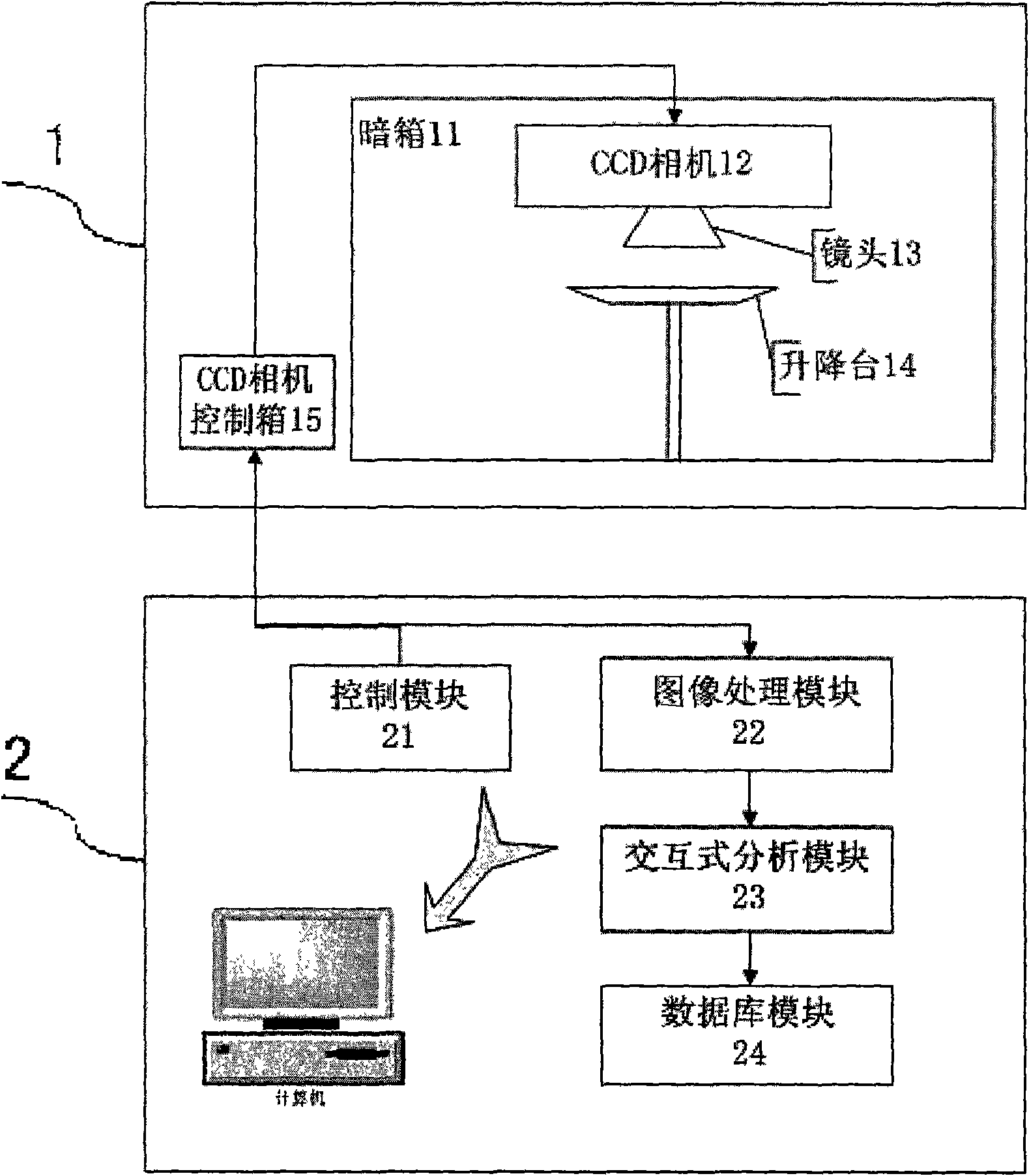
Auto-fluorescence molecule image system
ActiveCN101766476AAccurate analysisPrecise positioningImage analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringKnowledge FieldCcd camera
The invention belongs to an auto-fluorescence molecule image system which comprises a camera bellows, a CCD camera lens control module, an image processing module, an interactive analysis module and a database module. A system factor corrected by an integrating sphere can be converted into a photon density in an interesting area by the system through a pixel value. The system can work after a temperature value of the CCD camera is set and locked. Firstly, the light source in the camera bellows is opened to shoot an outline of a target object, then the light source is closed to capture a fluorescence signal which projects the outline of the detected object, and the signal is superposed with the outline image. User can choose the interesting area by using a selecting tool so as to acquire a photon density value for performing scientific research. The system of the invention can provide a database function for the user to conveniently manage the data and preview the images. The system of the invention has the advantages of reasonable structure, obvious function, convenient operation, low cost, wide application in the field of researching the small animals in non-invasive biologic experiment.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Color translating UV microscope
A color translating UV microscope for research and clinical applications involving imaging of living or dynamic samples in real time and providing several novel techniques for image creation, optical sectioning, dynamic motion tracking and contrast enhancement comprises a light source emitting UV light, and visible and IR light if desired. This light is directed to the condenser via a means of selecting monochromatic, bandpass, shortpass, longpass or notch limited light. The condenser can be a brightfield, darkfield, phase contrast or DIC. The slide is mounted in a stage capable of high speed movements in the X, Y and Z dimensions. The microscope uses broadband, narrowband or monochromat optimized objectives to direct the image of the sample to an image intensifier or UV sensitive video system. When an image intensifier is used it is either followed by a video camera, or in the simple version, by a synchronized set of filters which translate the image to a color image and deliver it to an eyepiece for viewing by the microscopist. Between the objective and the image intensifier there can be a selection of static or dynamic switchable filters. The video camera, if used, produces an image which is digitized by an image capture board in a computer. The image is then reassembled by an overlay process called color translation and the computer uses a combination of feedback from the information in the image and operator control to perform various tasks such as optical sectioning and three dimensional reconstruction, coordination of the monochromater while collecting multiple images sets called image planes, tracking dynamic sample elements in three space, control of the environment of the slide including electric, magnetic, acoustic, temperature, pressure and light levels, color filters and optics, control for microscope mode switching between transmitted, reflected, fluorescent, Raman, scanning, confocal, area limited, autofluorescent, acousto-optical and other modes.
Owner:1192062 ALBERTA
Methods and systems for analyzing fluorescent materials with reduced autofluorescence
InactiveUS20100167413A1Improve abilitiesLower Level RequirementsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical reactionNucleotide
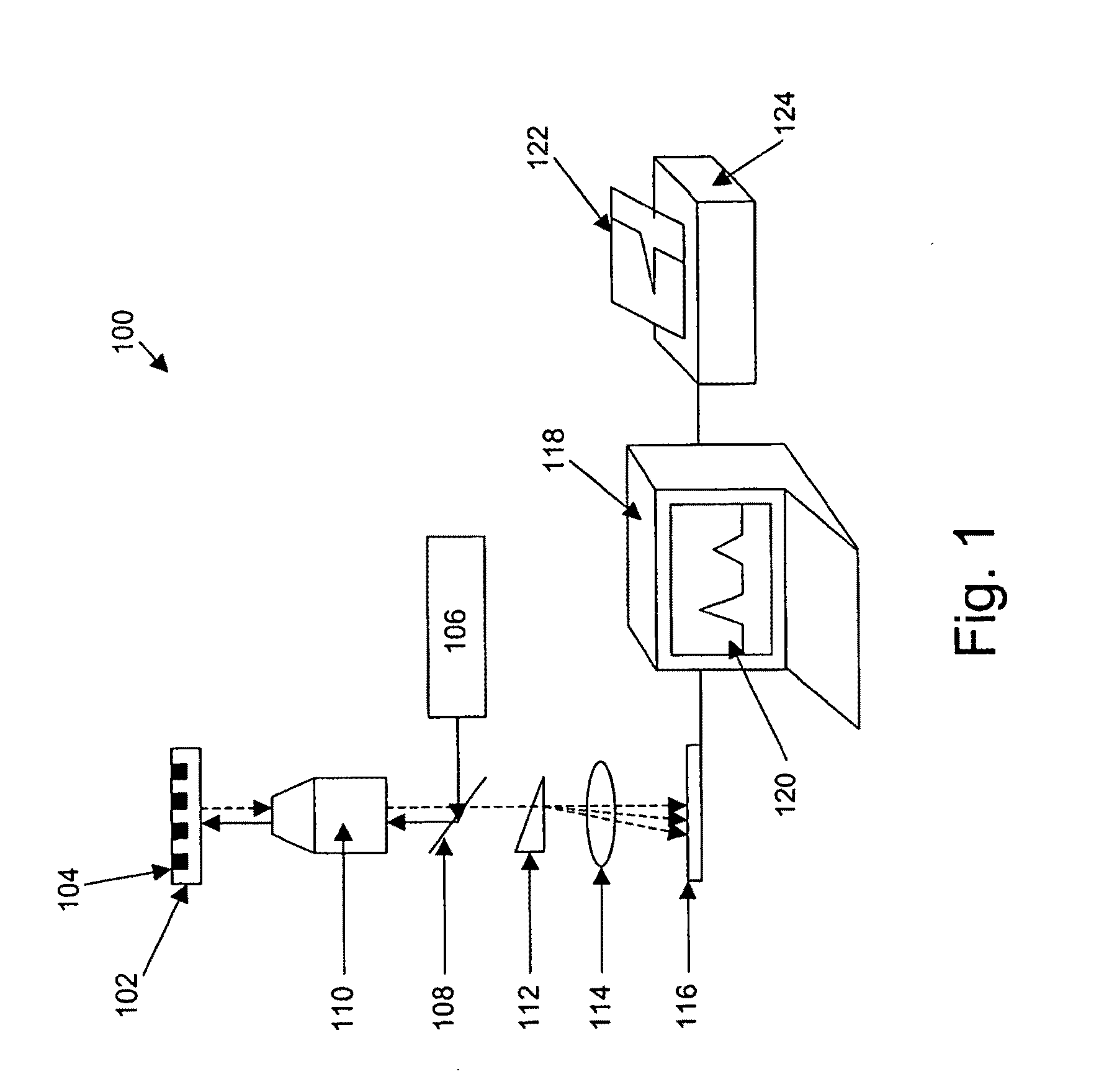
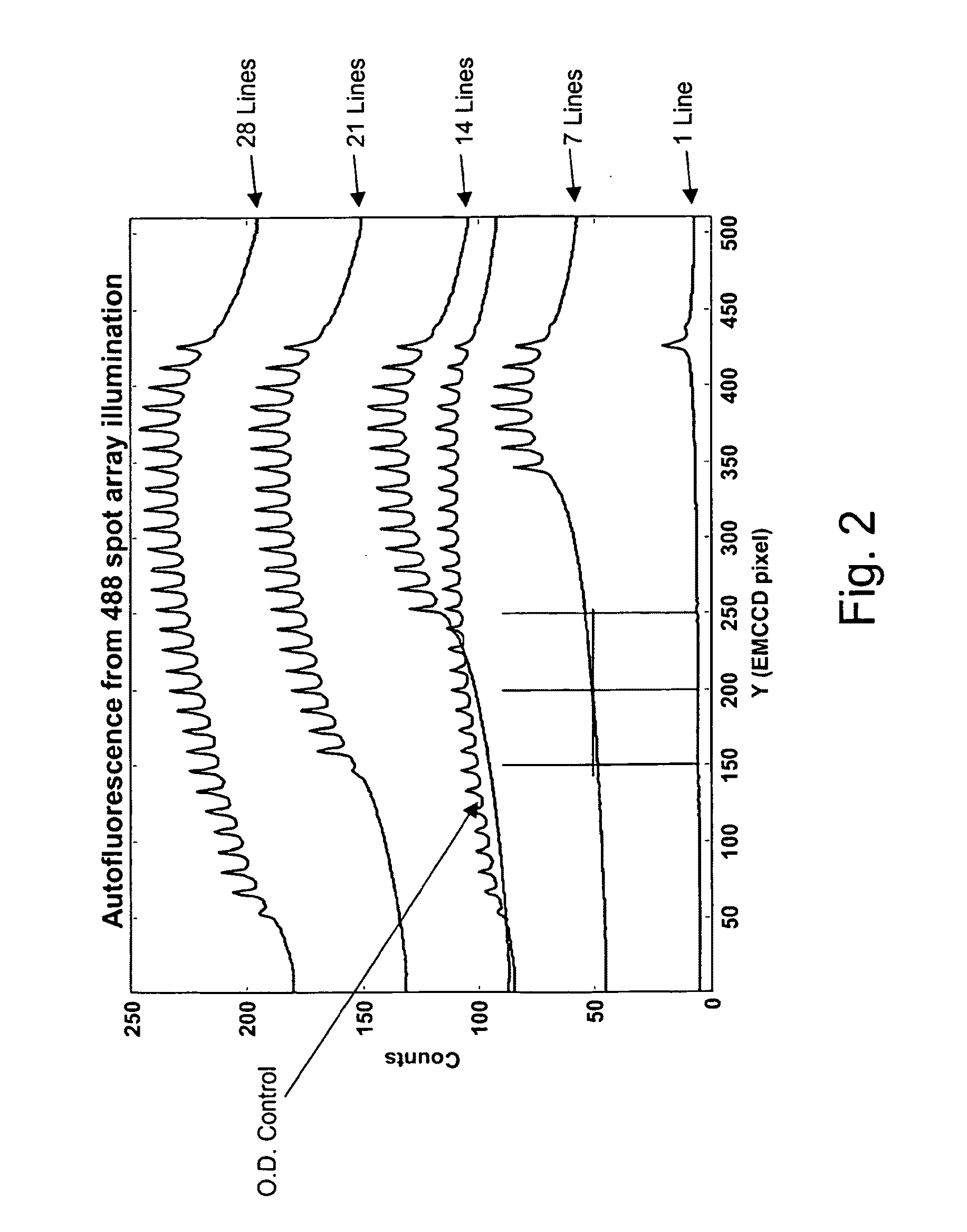
Mitigative and remedial approaches to reduction of autofluorescence background noise are applied in analytical systems that rely upon sensitive measurement of fluorescent signals from arrays of fluorescent signal sources. Such systems are for particular use in fluorescence based sequencing by incorporation systems that rely upon small numbers or individual fluorescent molecules in detecting incorporation of nucleotides in primer extension reactions. Systems and methods for analyzing highly multiplexed sample arrays using highly multiplexed, high-density optical systems to illuminate high-density sample arrays and / or provide detection and preferably confocal detection off signals emanating from such high-density arrays. Systems and methods are applied in a variety of different analytical operations, including analysis of biological and biochemical reactions, including nucleic acid synthesis and derivation of sequence information from such synthesis.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Harmonic generation microscopy
ActiveUS20050063041A1Eliminates photo-damageMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceLaser beamsMicroscopy
A harmonic generation microscopy employs a laser device that emits a laser beam having a predetermined wavelength that causes no autofluorescence in a biological sample and that, after excited, induces both the second and third harmonic waves. The laser beam is projected onto a sample and an observation beam from the sample is received. The observation beam is directed through a splitter to separate the second harmonic wave and the third harmonic wave both of which are then converted into corresponding electrical signals. The electrical signals are fed to a computer-based image processing equipment to form an image of the sample on the basis of the second and third harmonic waves.
Owner:NARIONAL TAIWAN UNIV
Tri modal spectroscopic imaging
InactiveUS20070167835A1High speedHigh sensitivityDiagnostics using lightSpectrum investigationMedicineReflectivity
The present invention relates to a spectroscopic imaging system using autofluorescence and reflectance images to diagnose tissue. A preferred embodiment of the invention uses a plurality of light sources to illuminate a tissue region to provide the fluorescence and reflectance images, respectively.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Spectroscopically enhanced imaging
InactiveUS20100069720A1Sufficiently dispersedAccurate measurementSurgeryDiagnostics using spectroscopyMedicineTrue positive rate
The present invention provides systems and methods for the spectroscopic determination of the physical characteristics of the tissue under observation by an autofluorescence or other endoscope without the requirement of contacting the tissue directly. The optical probe contained in the endoscope itself is passive and may be either built into the endoscope or positioned in a biopsy channel of same. The spectroscopic information, combined with other information provided by the endoscope such as total fluorescence, improves the sensitivity and specificity of the identification of precancerous or cancerous lesions.
Owner:NEWTON LAB
Auto-fluorescence tomography re-establishing method based on multiplier method
ActiveCN102988026AImprove robustnessAccurate and reliable light source distribution informationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSteep descentDescent direction
The invention discloses an auto-fluorescence tomography re-establishing method based on a multiplier method. The auto-fluorescence tomography re-establishing method based on the multiplier method comprises the following steps of: carrying out discretization by using a finite element method diffusion equation, and establishing an optimization problem model without constraint conditions based on a penalty term of an L1 norm; obtaining a dual model of the optimization problem model without constraint conditions; establishing an augmentation lagrange function of the dual model; simplifying the maximum function of the augmentation lagrange function; solving the maximum value of the augmentation lagrange function by using a truncated-Newton algorithm; upgrading the target vector by using the gradient of the augmentation lagrange function as the steepest descent direction of a target vector; upgrading a penalty vector; and calculating an objective function value J(w), calculating k=k+1 if the ratio of the norm of J(w)k-J(w)(k-1) to the norm of Pai m being not smaller than t0l is real, and jumping to the step S4, otherwise, ending the calculation, wherein t0l is the convergence efficiency threshold value of the target function. The auto-fluorescence tomography re-establishing method provided by the invention can quickly obtain accurate and reliable light source distribution information within a large image-forming region, so that other parameters except from the regularization parameter can realize self-adaptive adjustment for improving the image-forming robustness.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Flow type fluorescence microscopy imaging device and method
InactiveCN103308440ASolve tailingOvercoming the smearing problemIndividual particle analysisFluorescence/phosphorescenceTrailing phenomenonMicroscopy
The invention discloses a flow type fluorescence microscopy imaging device, in order to solve the problems of small focal depth of an imaging flow cytometer as well as trailing which occurs when a moving object is imaged. The imaging device has the following beneficial effects that (1) auto-fluorescence or non-auto-fluorescence of cells is excited by a light sheet source with the thickness near a diffraction limit, so that the problem of small focal depth of fluorescence microscopy imaging can be solved; (2) only the cells positioned within the range of focal depth are excited to emit fluorescence and a background of a fluorescence image can be lowered effectively, so that the sensitivity of a system can be enhanced effectively; (3) the cells perpendicularly pass through an excitation light source and are subjected to fluorescence imaging in a way that the imaging direction is parallel to the flowing direction of a sample, so that the trailing phenomenon can be well inhibited; (4) multiple cells are allowed to be detected simultaneously, so that the detection speed of the system can be increased.
Owner:香港浸会大学深圳研究院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com