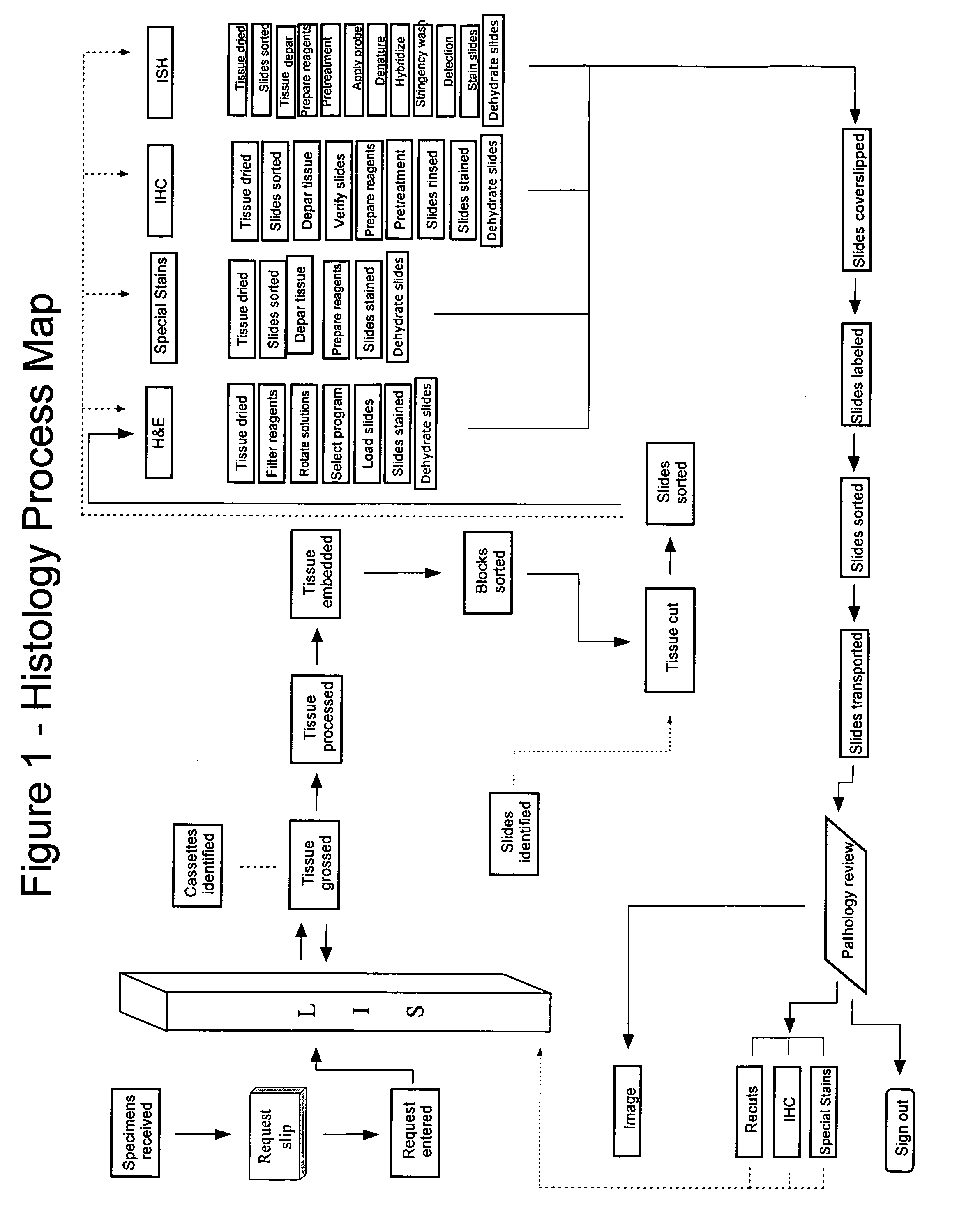
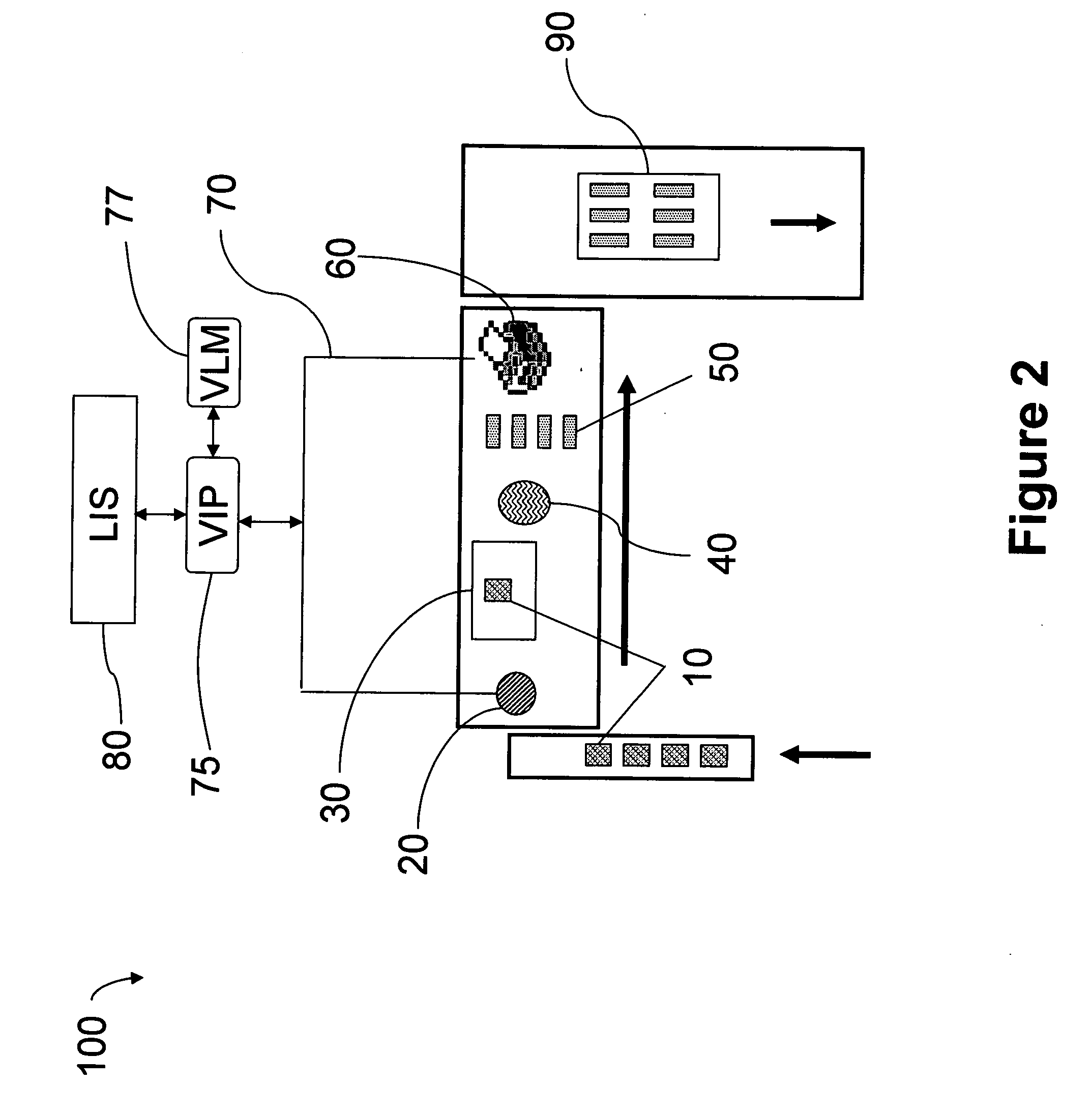
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
72 results about "Tissue staining" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
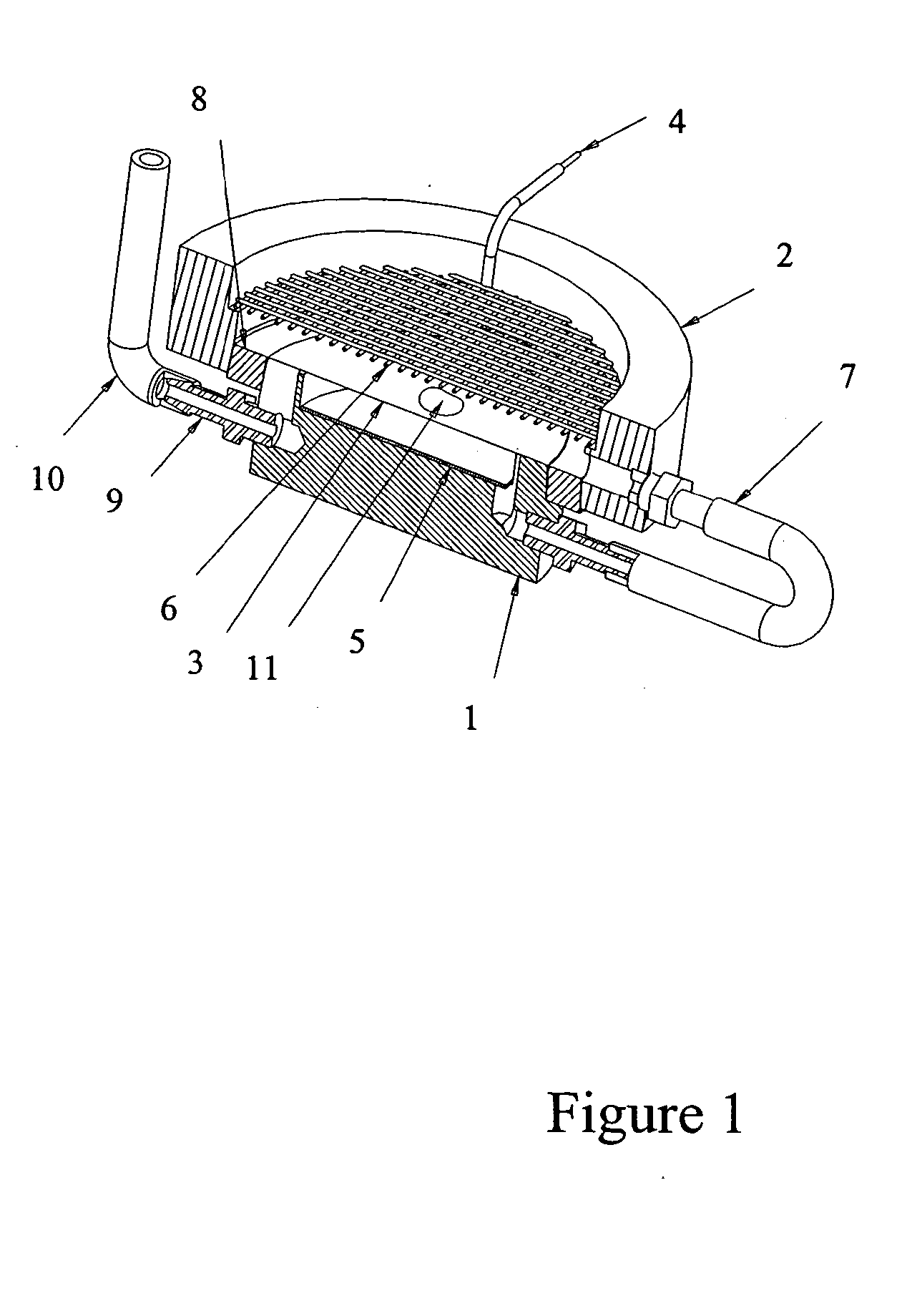
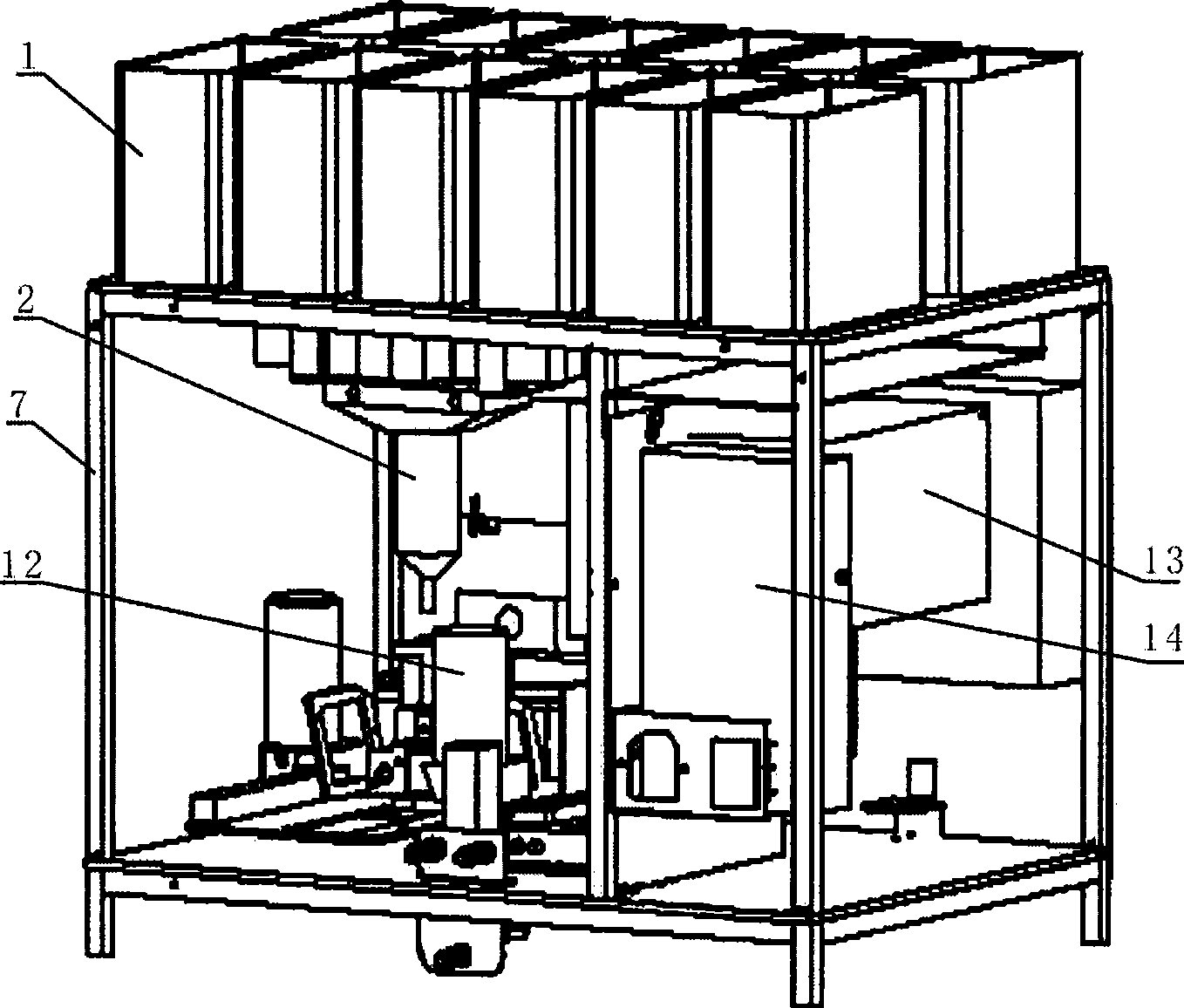
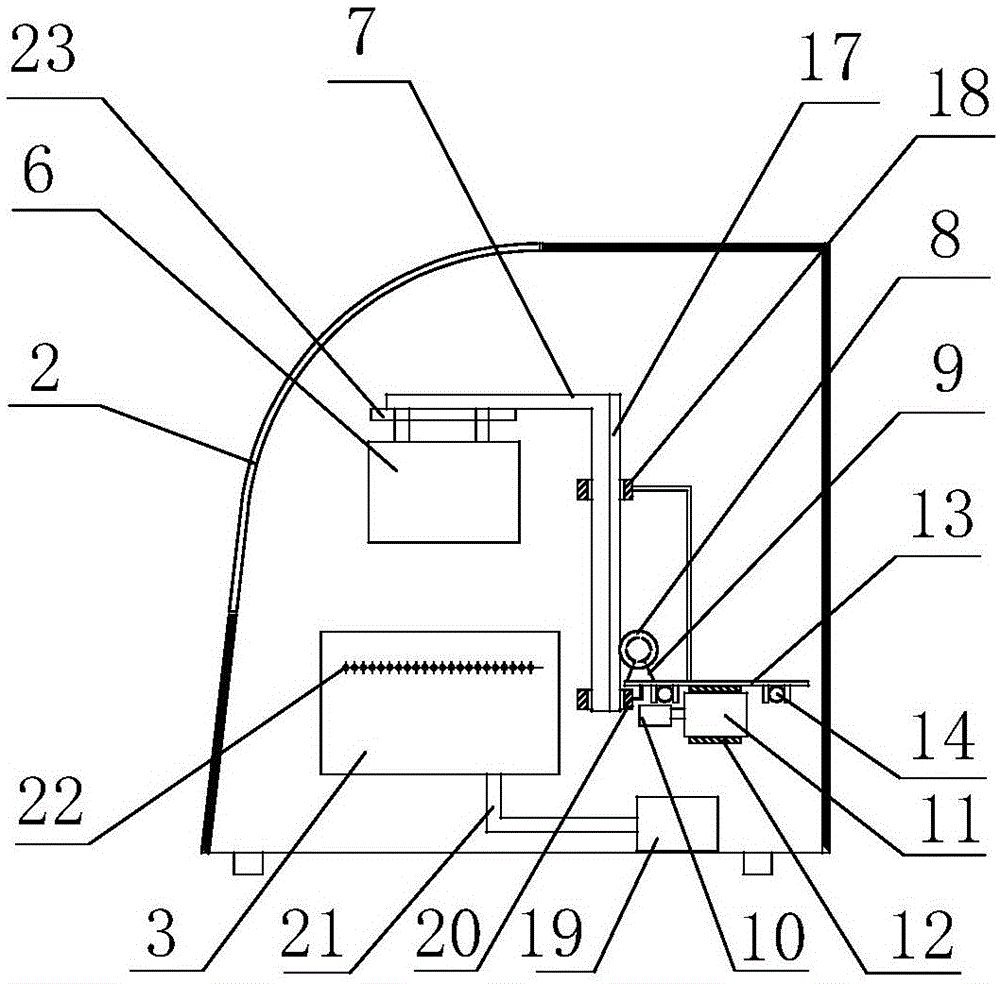
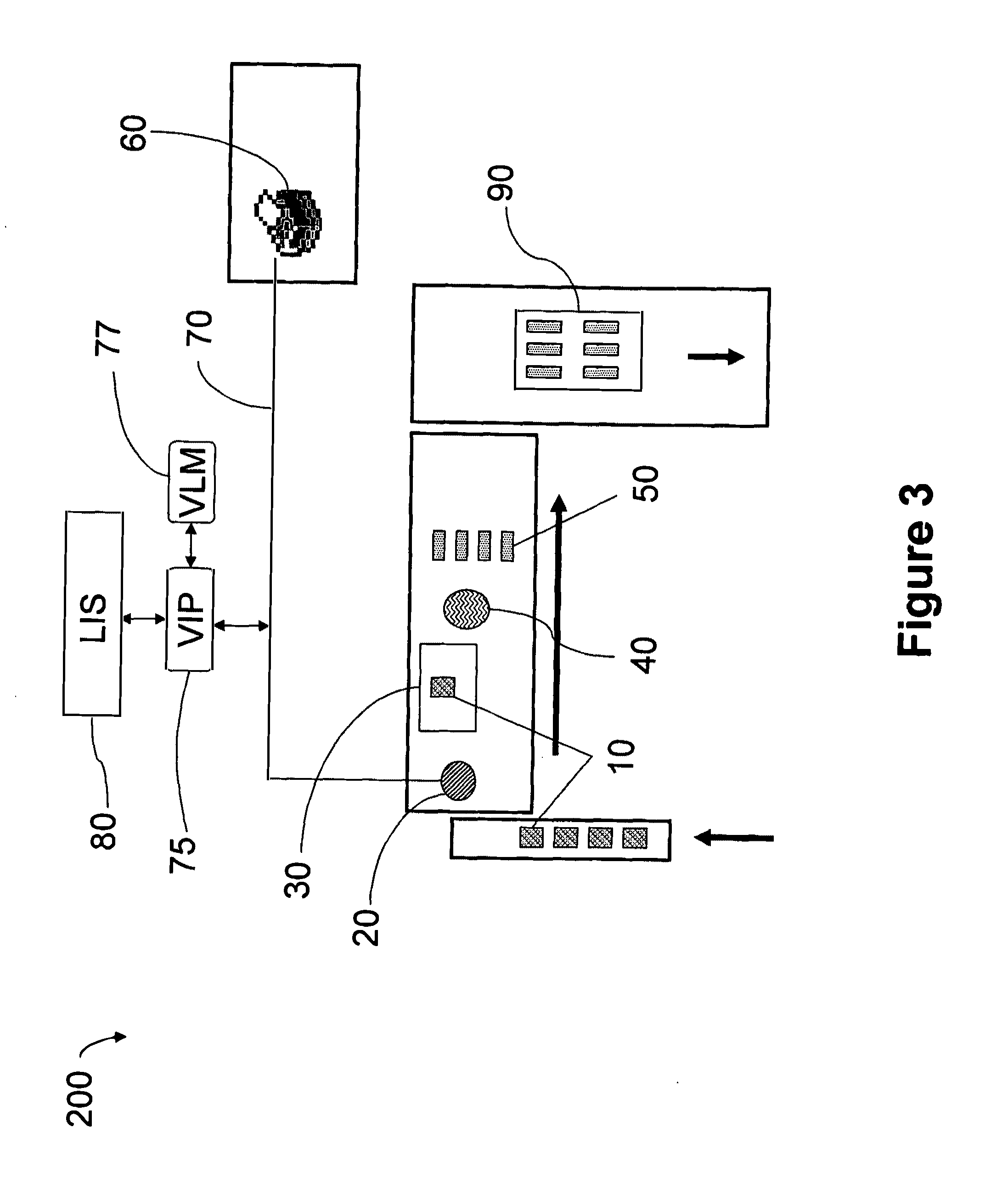
Automated tissue staining system and reagent container
InactiveUS6998270B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTissue stainingEngineering
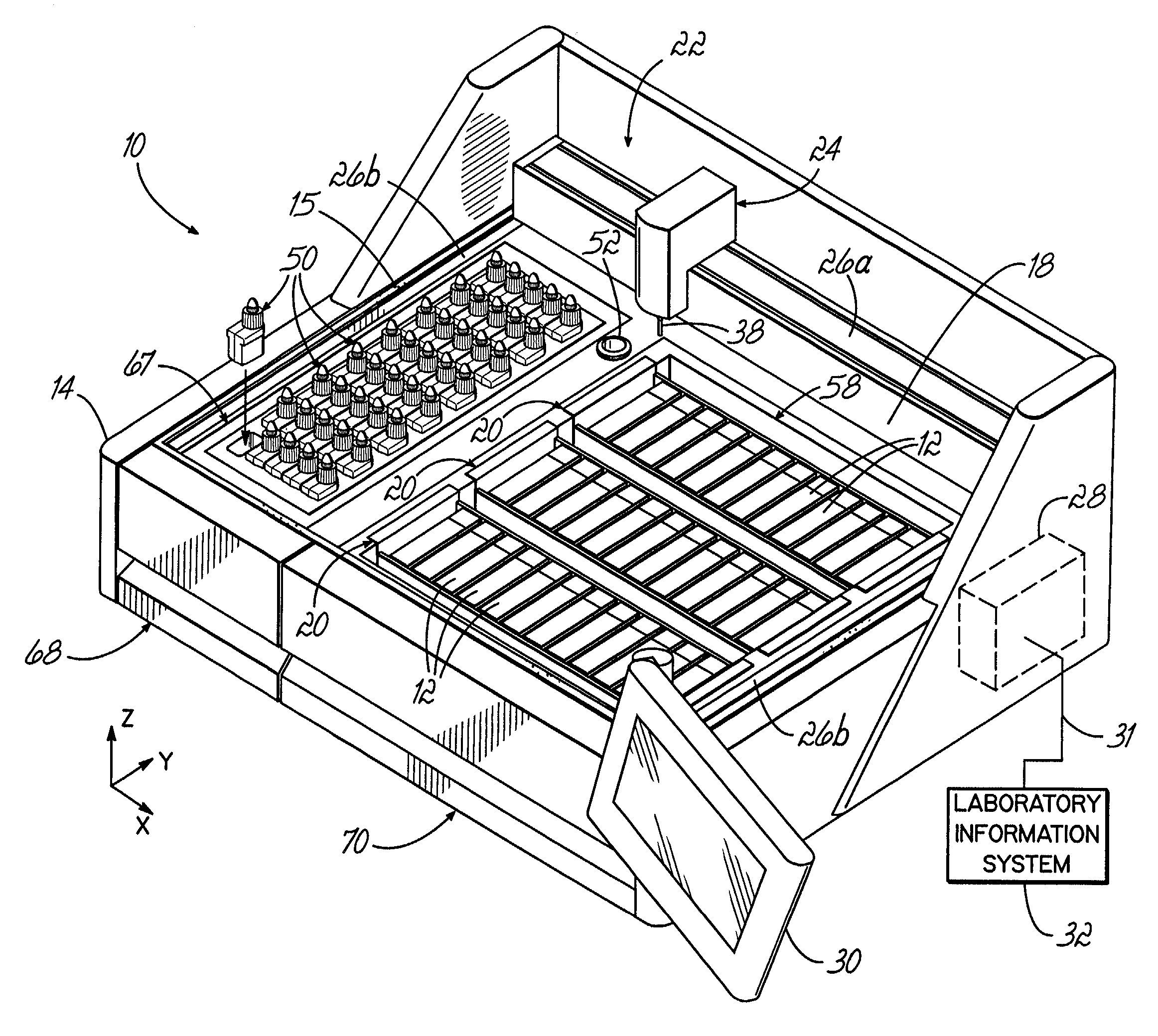
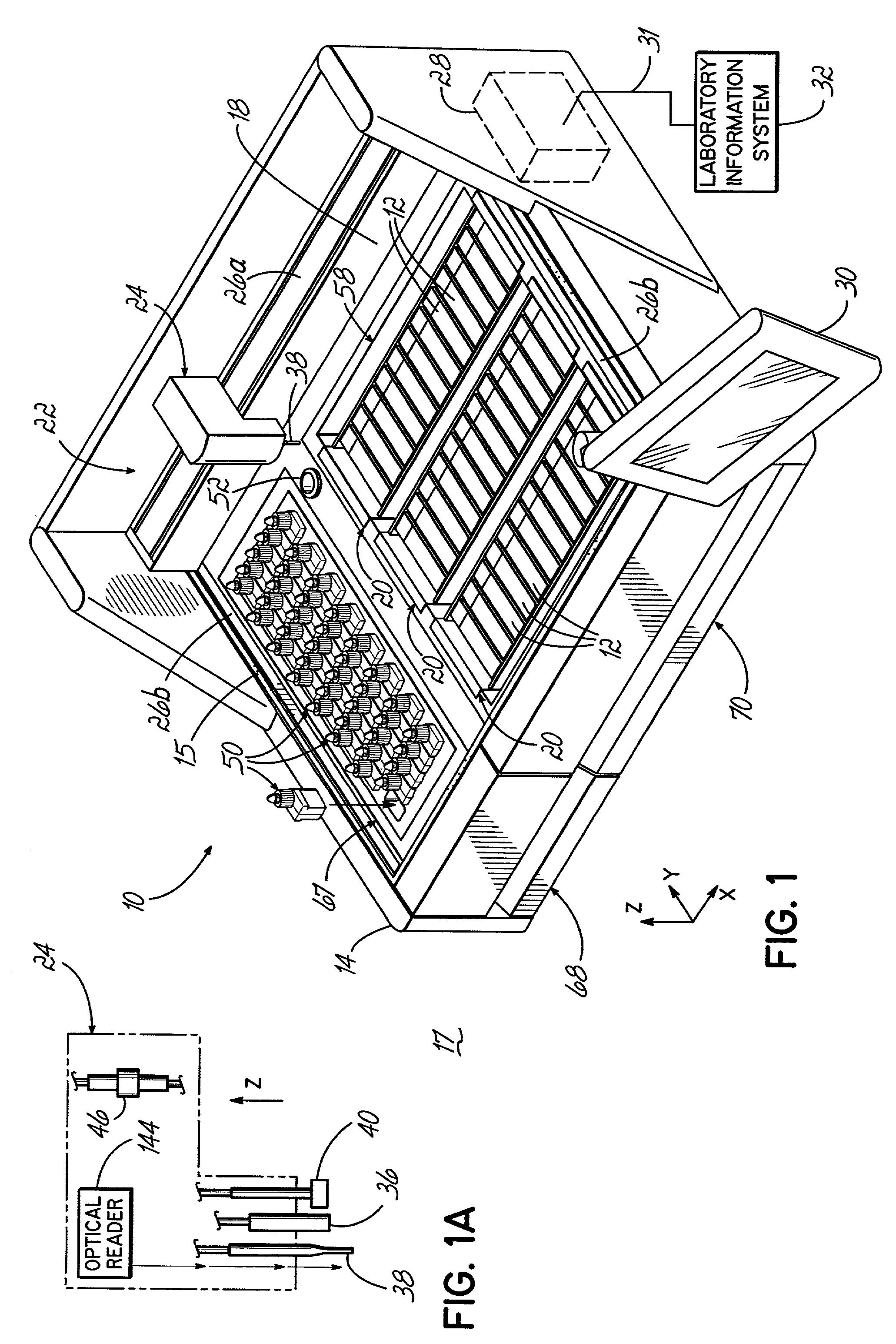
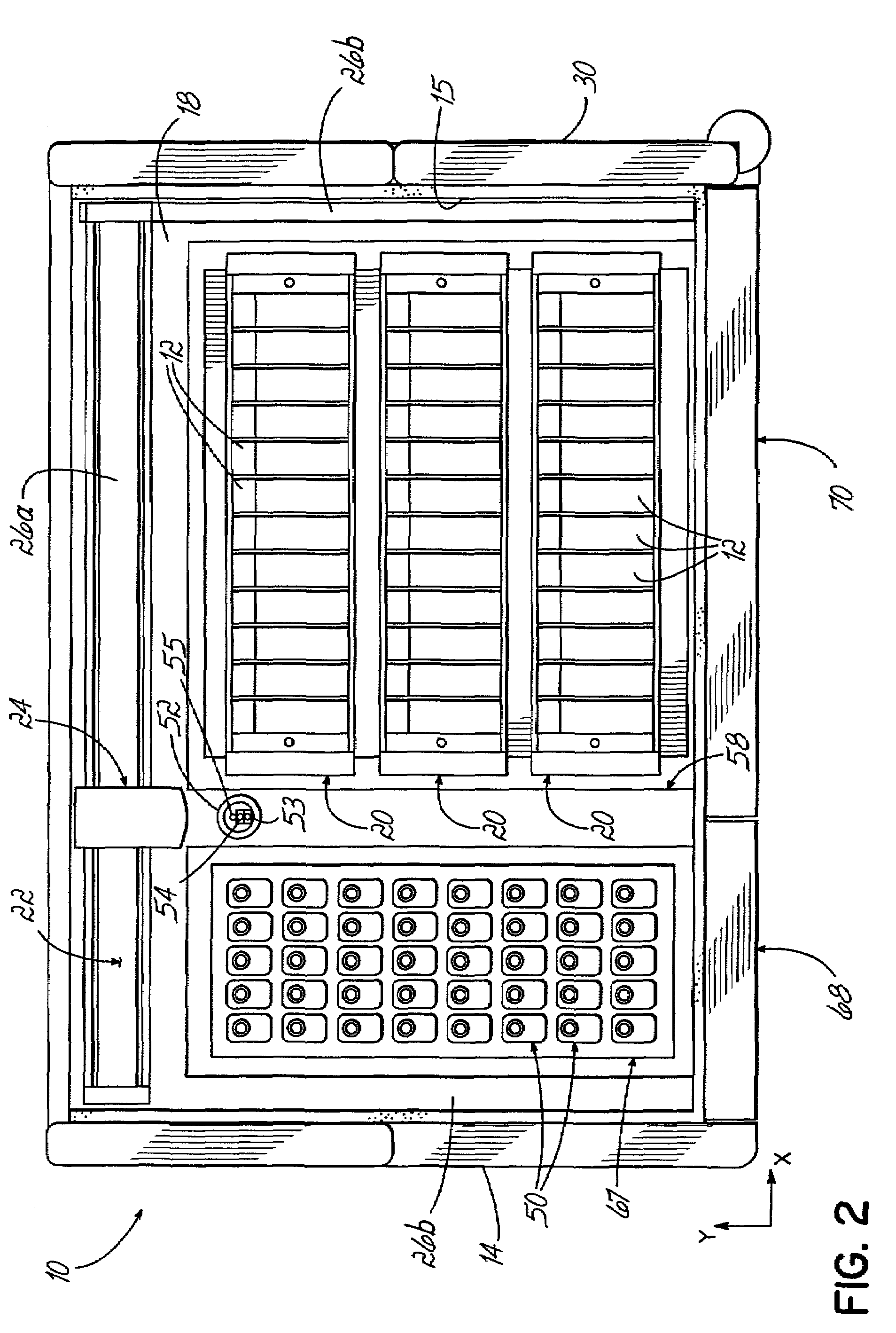
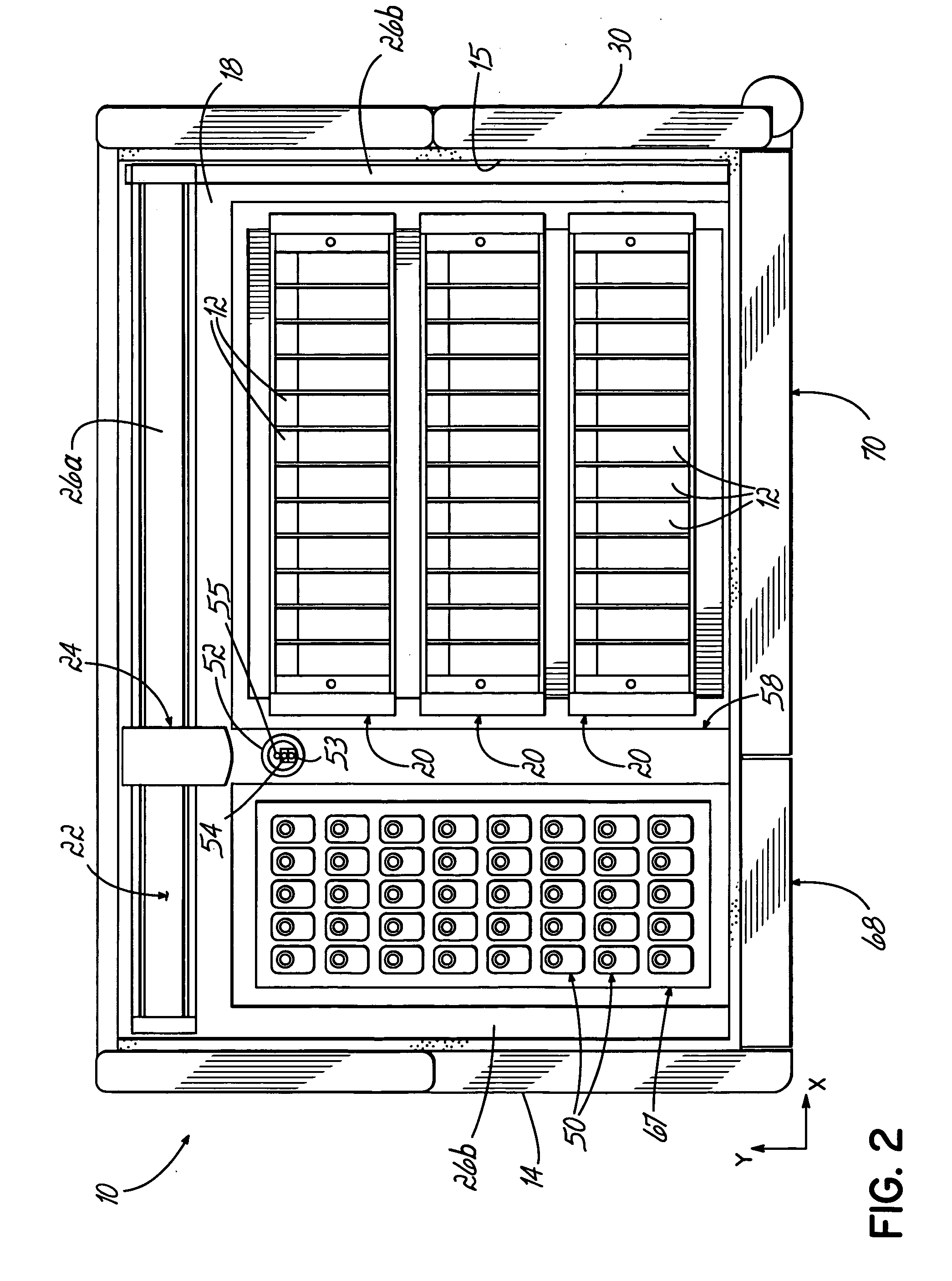
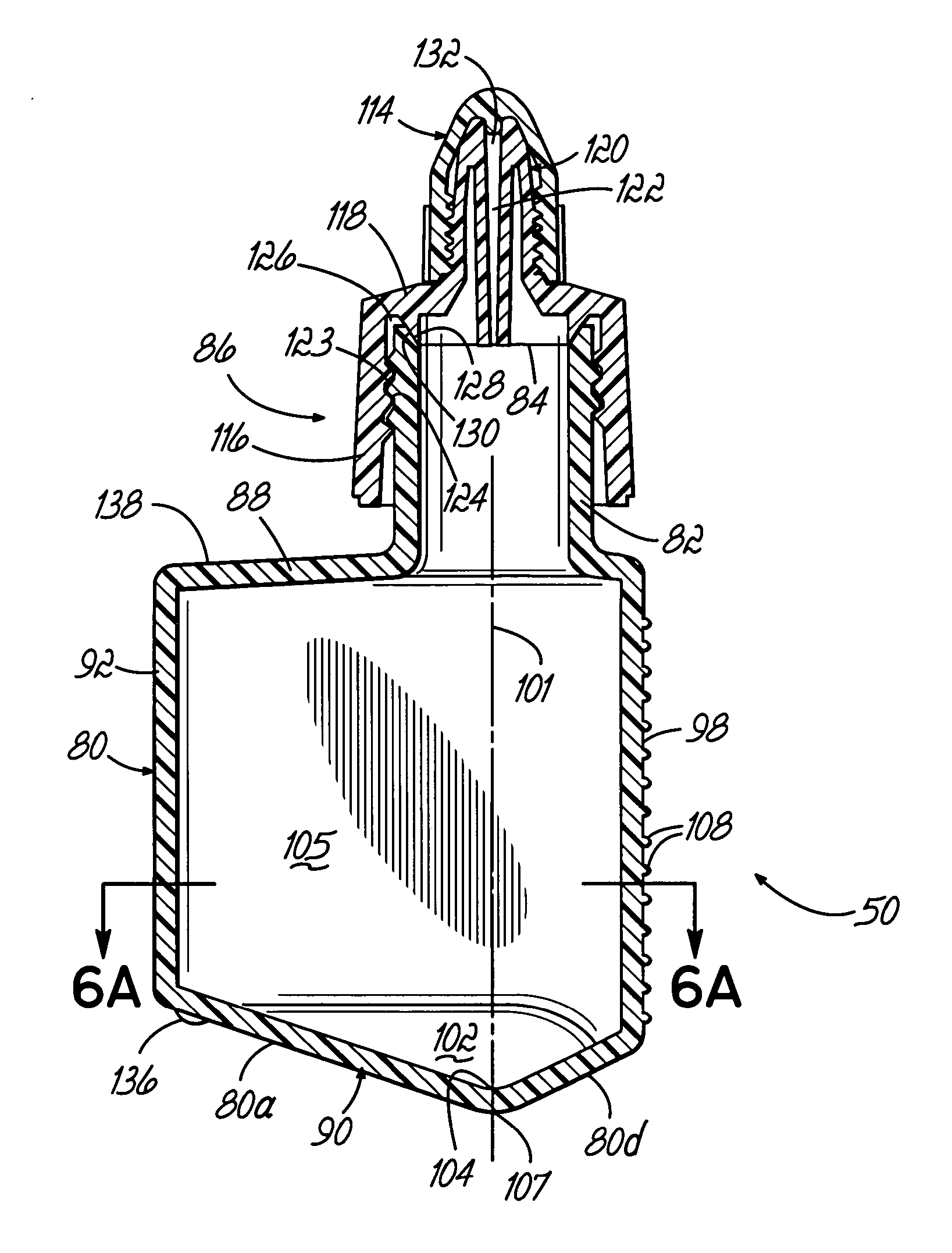
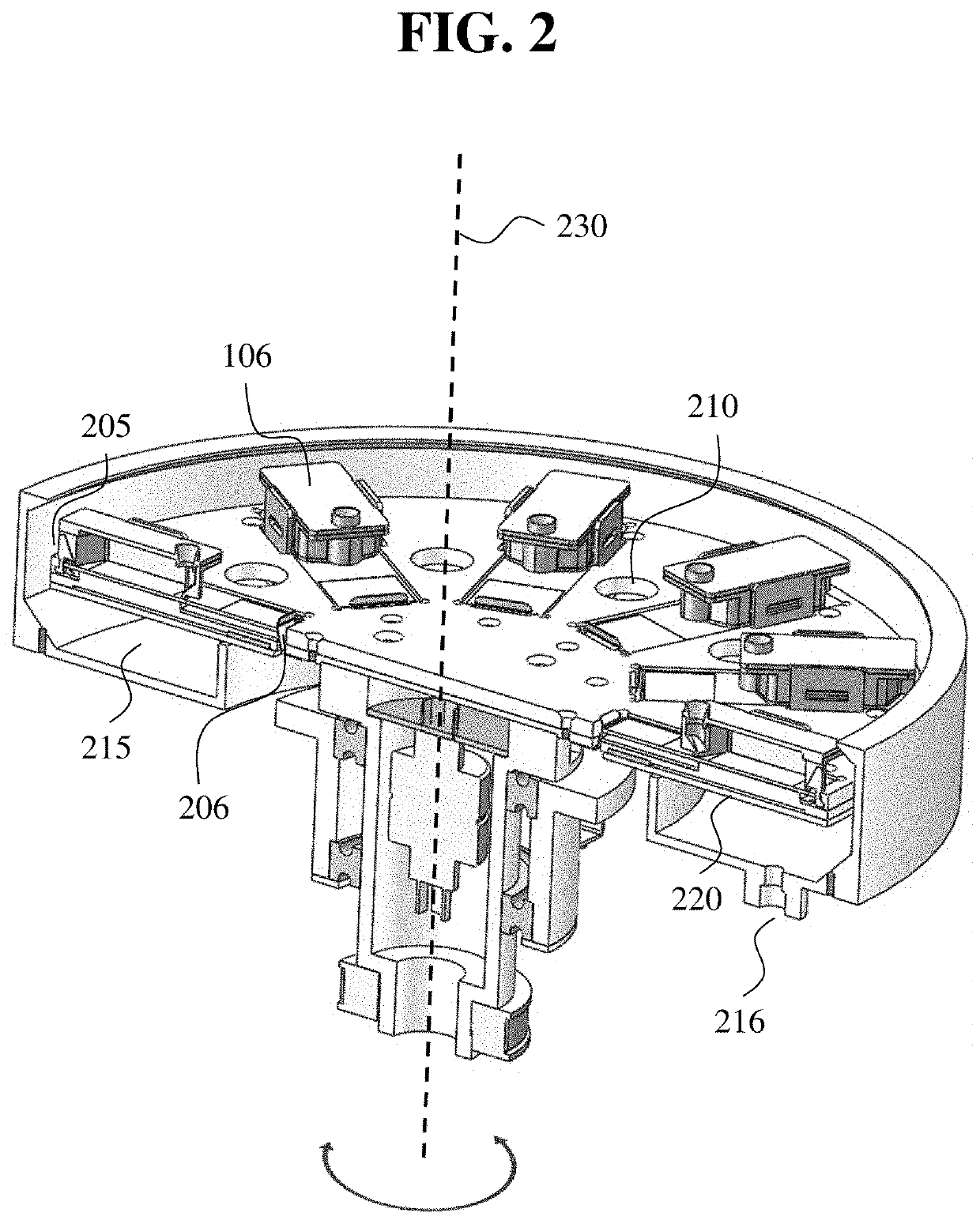
An automated staining system and a reagent container designed for use with the automated staining apparatus. The reagent container includes a reagent containment section capable of containing a volume of a reagent. The reagent containment section includes an upper wall and a base wall that are spaced apart along an axis. The base wall includes a well having a nadir that is aligned axially with an access opening in the upper wall so that a reagent probe entering the opening parallel to said axis will travel toward the nadir. In another aspect of the invention, the reagent container may include a two-dimensional data element containing reagent information. The staining apparatus may include one removable drawer for holding reagent containers and another removable drawer holding slides.
Owner:LAB VISION CORP
Automated lean methods in anatomical pathology
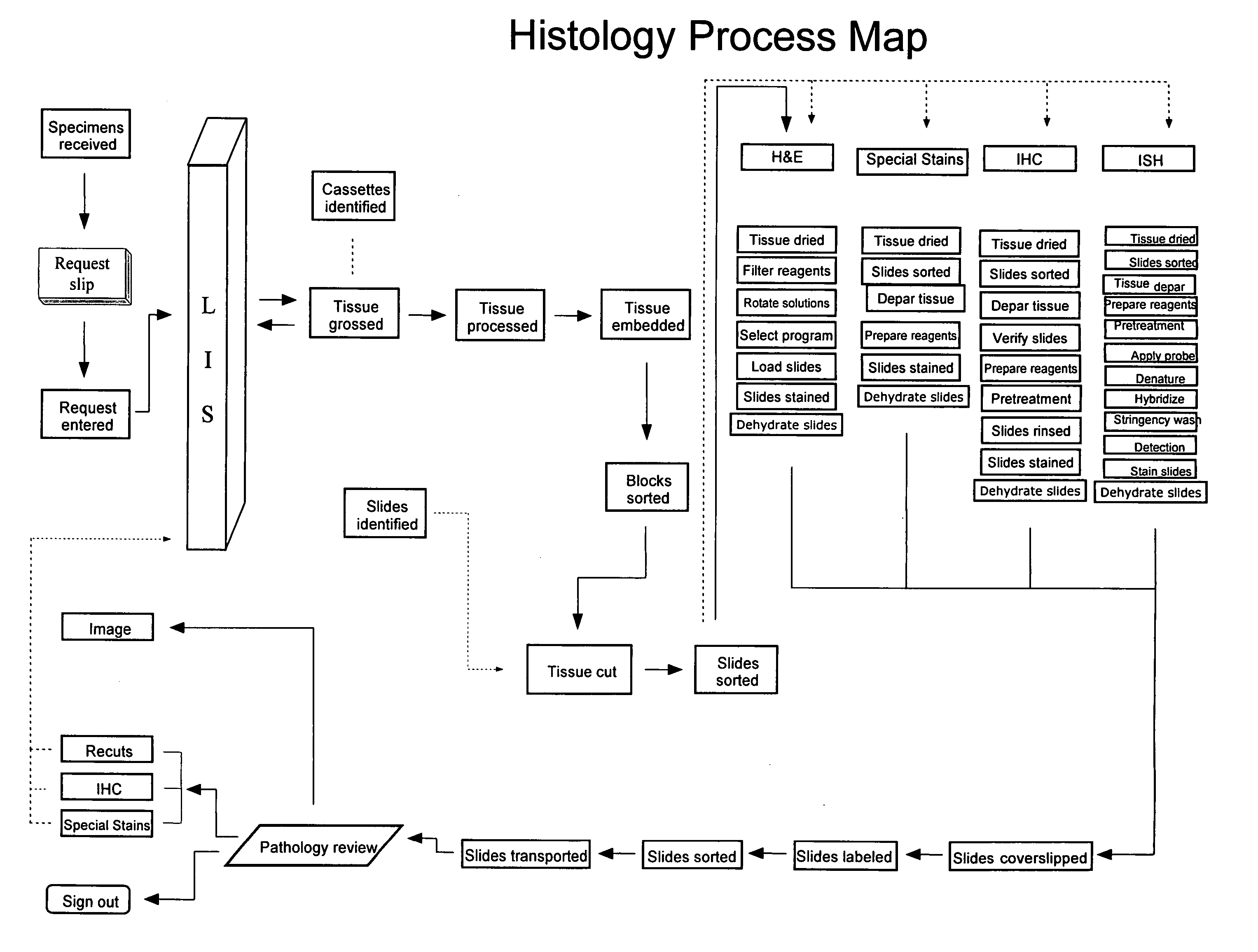
An embodiment of the method of the invention is a method of automating information flow in a laboratory performing tissue staining comprising positioning a networked label printer adjacent to a cutting station, the printer configured to access patient data directly or indirectly from the hospital LIS, the printer being configured with a data element scanner in electronic communication with said printer; inputting data from a tissue cassette-associated data element at said printer, whereby inputting data comprises reading the data from the cassette-associated data element and uploading the cassette data to the LIS; identifying the corresponding test protocol identifier and then downloading the test protocol data to the printer; printing information on labels corresponding to each test specified in the LIS for the patient; attaching a single label to each slide; and cutting a tissue section for each labeled slide and mounting the section on the slide.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Method for Determining Effectiveness of Medicine Containing Antibody as Component
InactiveUS20130230866A1High sensitivityWide rangeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTissue stainingTreatment effect
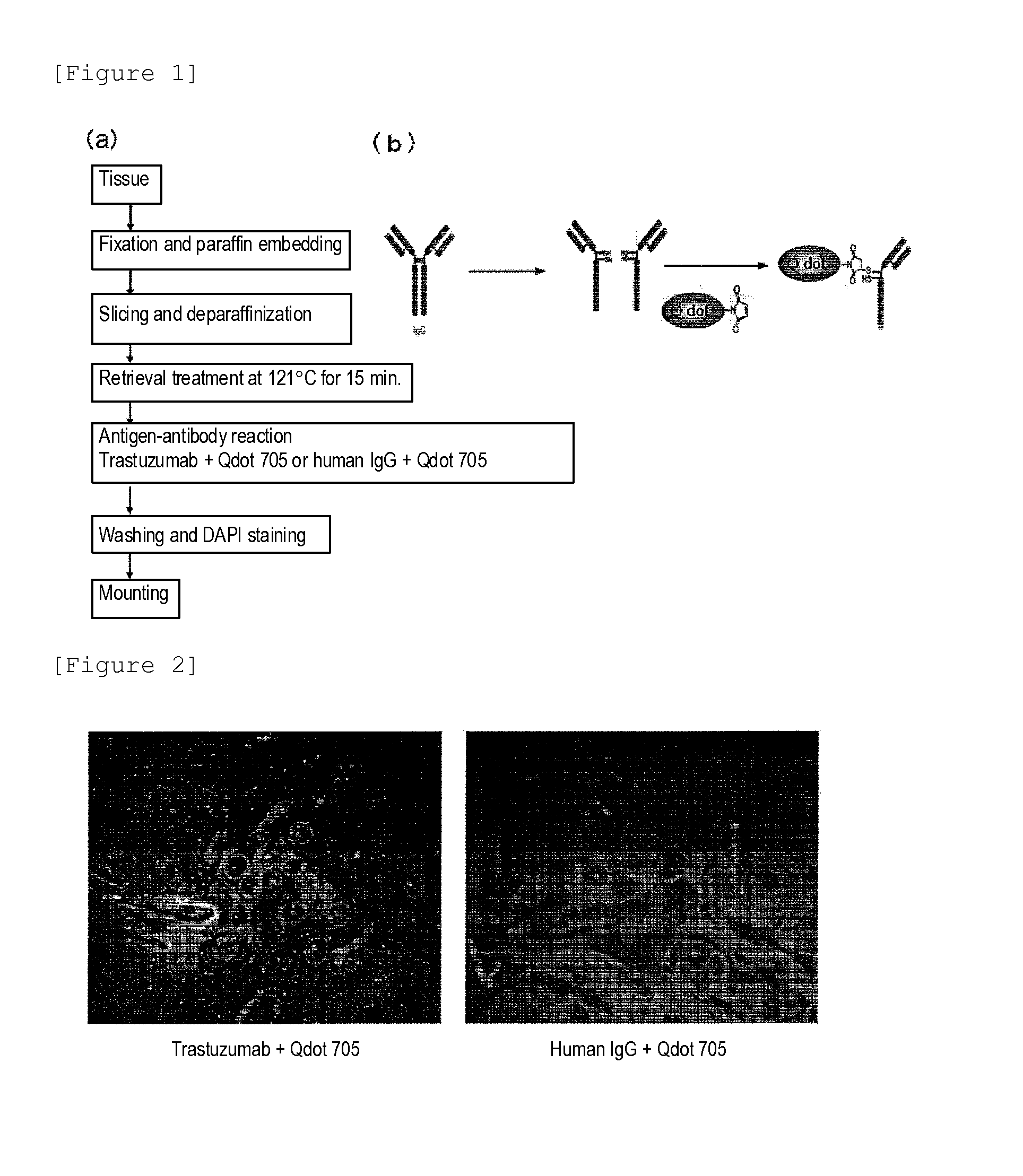
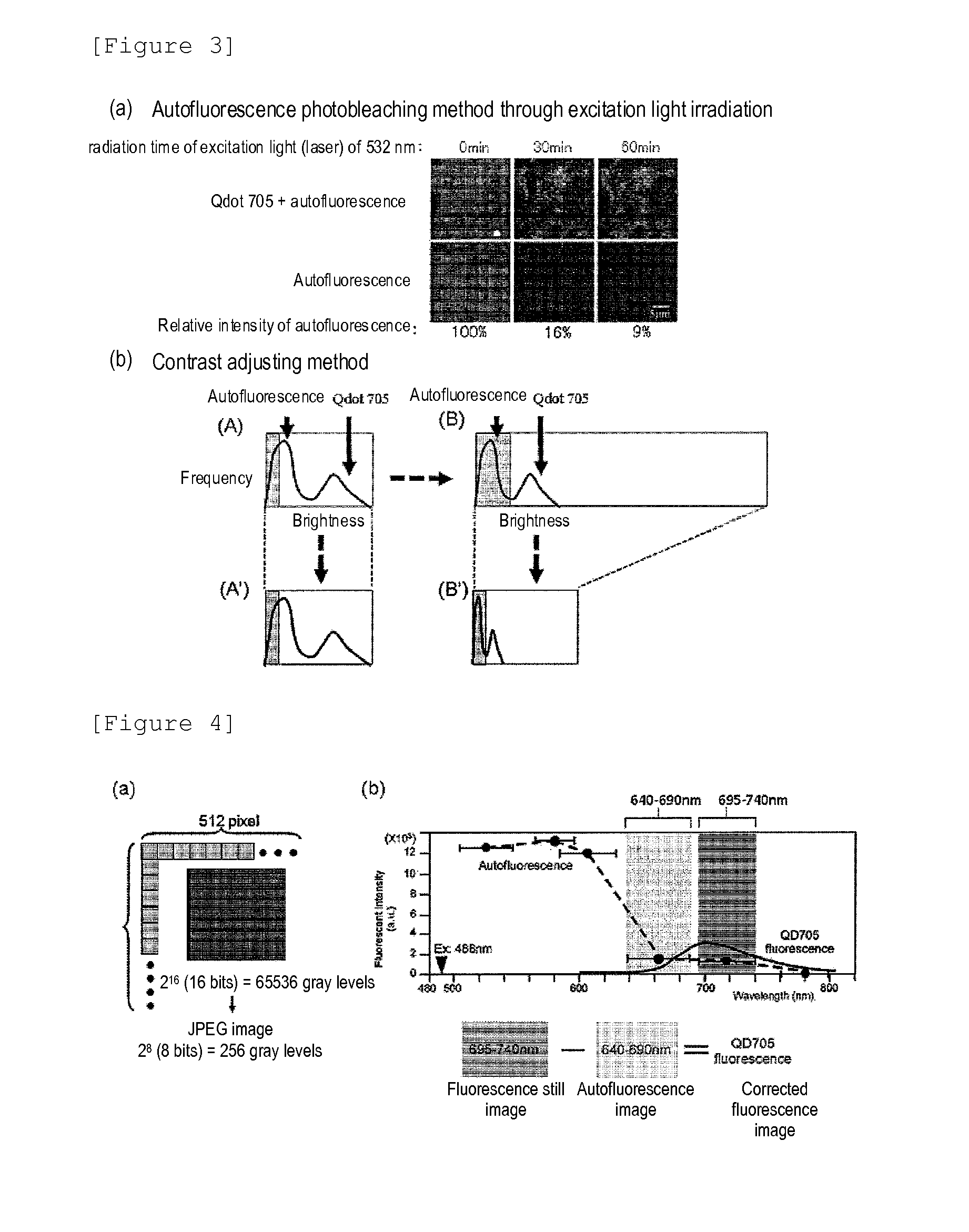
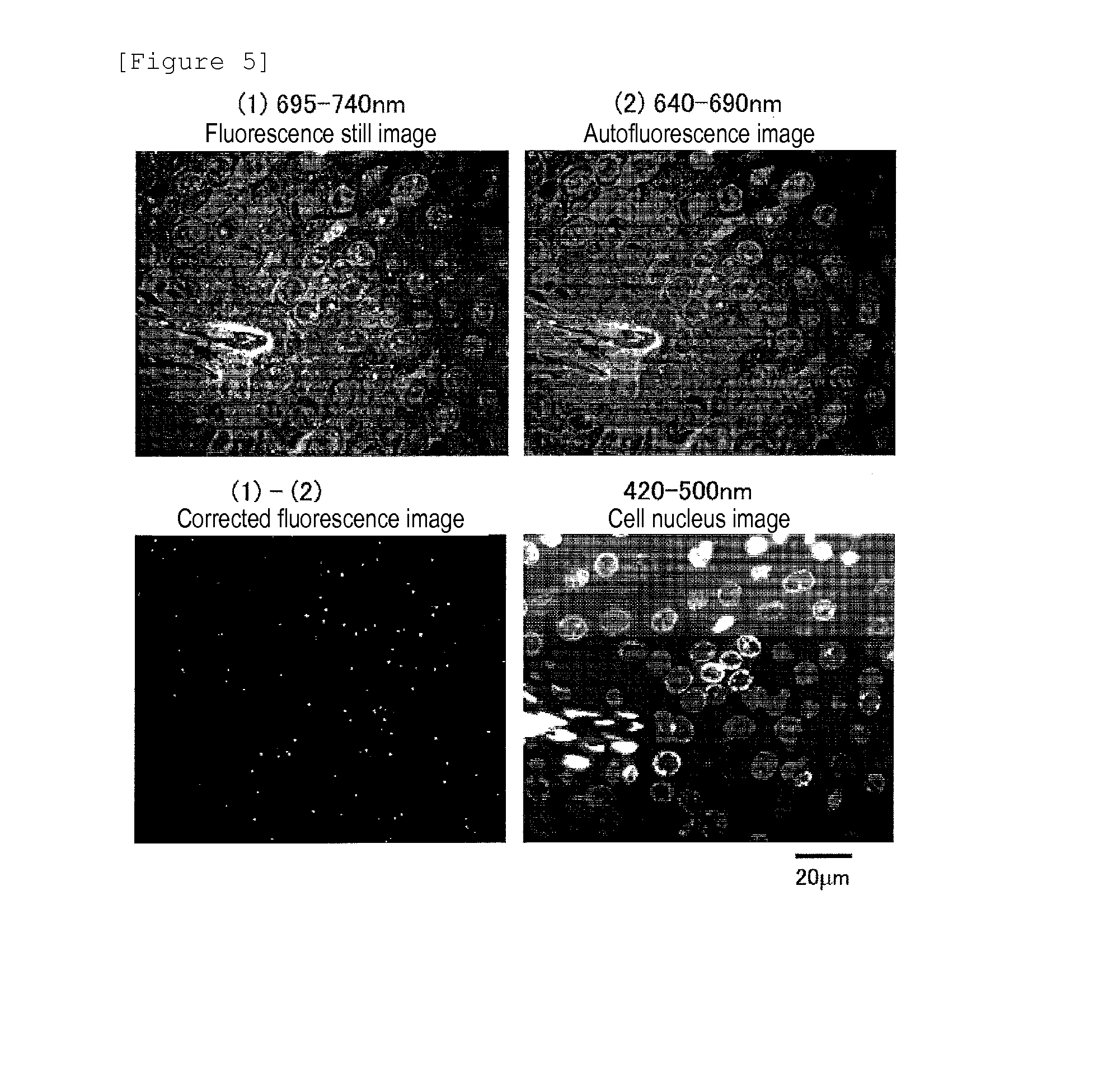
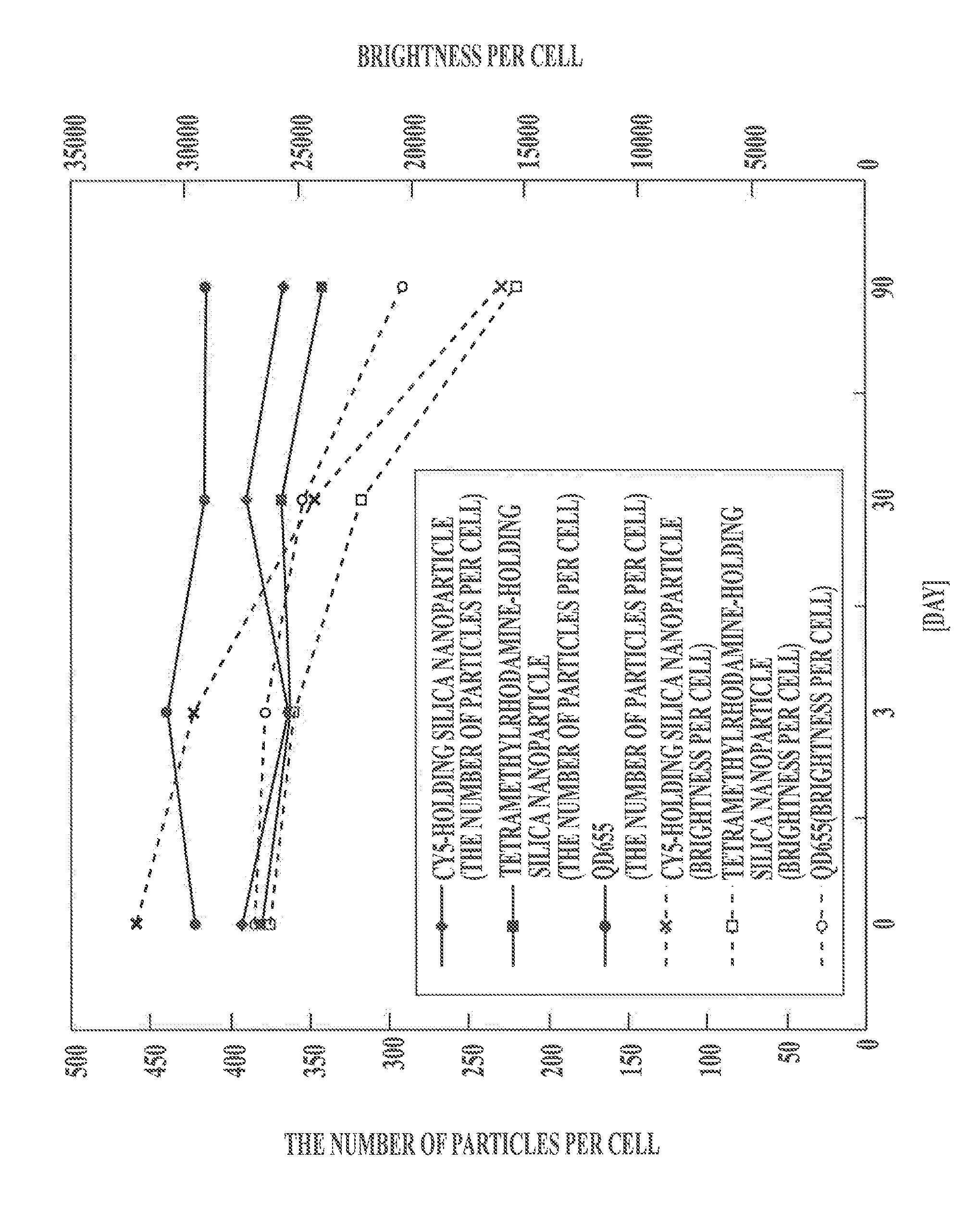
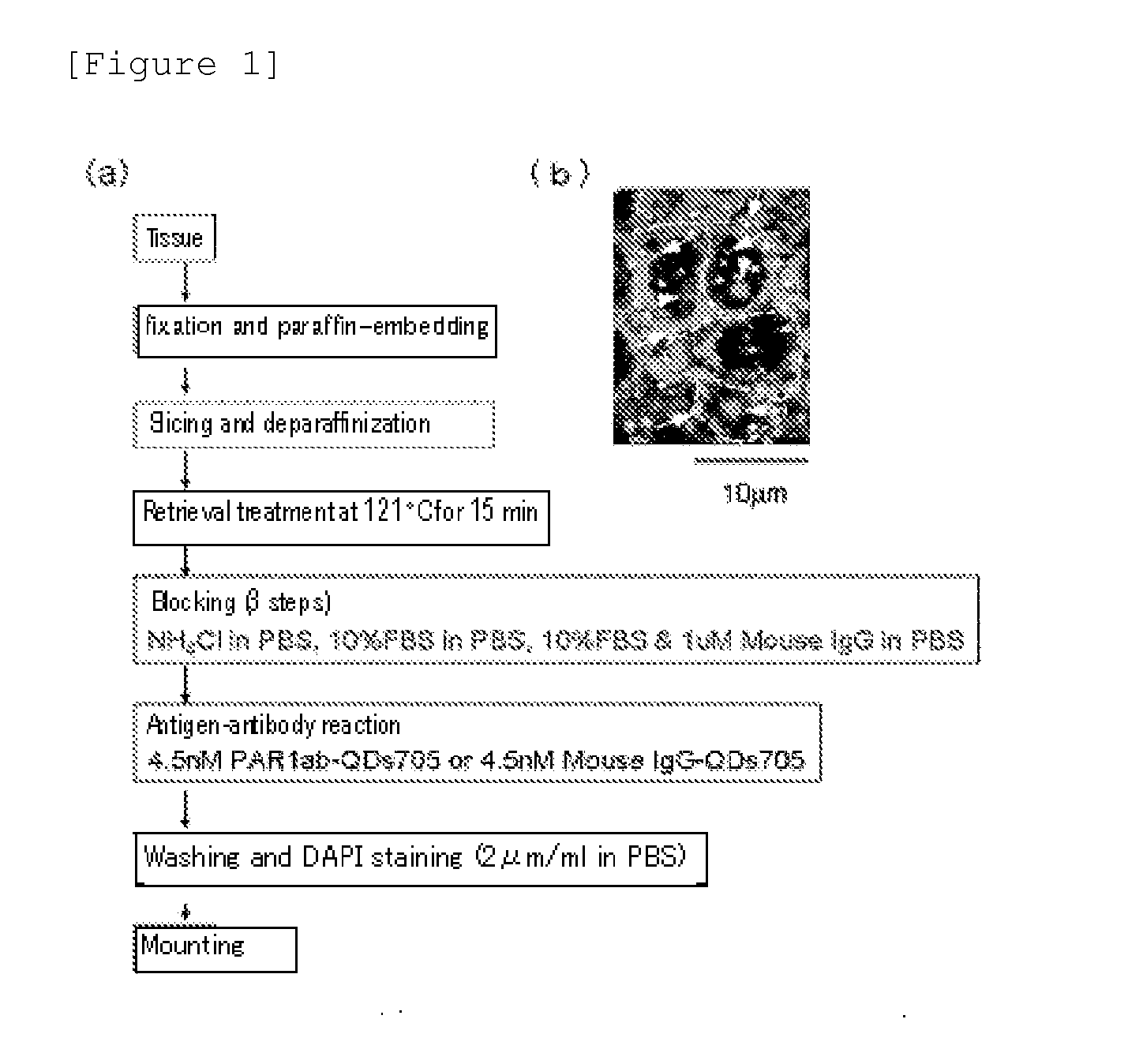
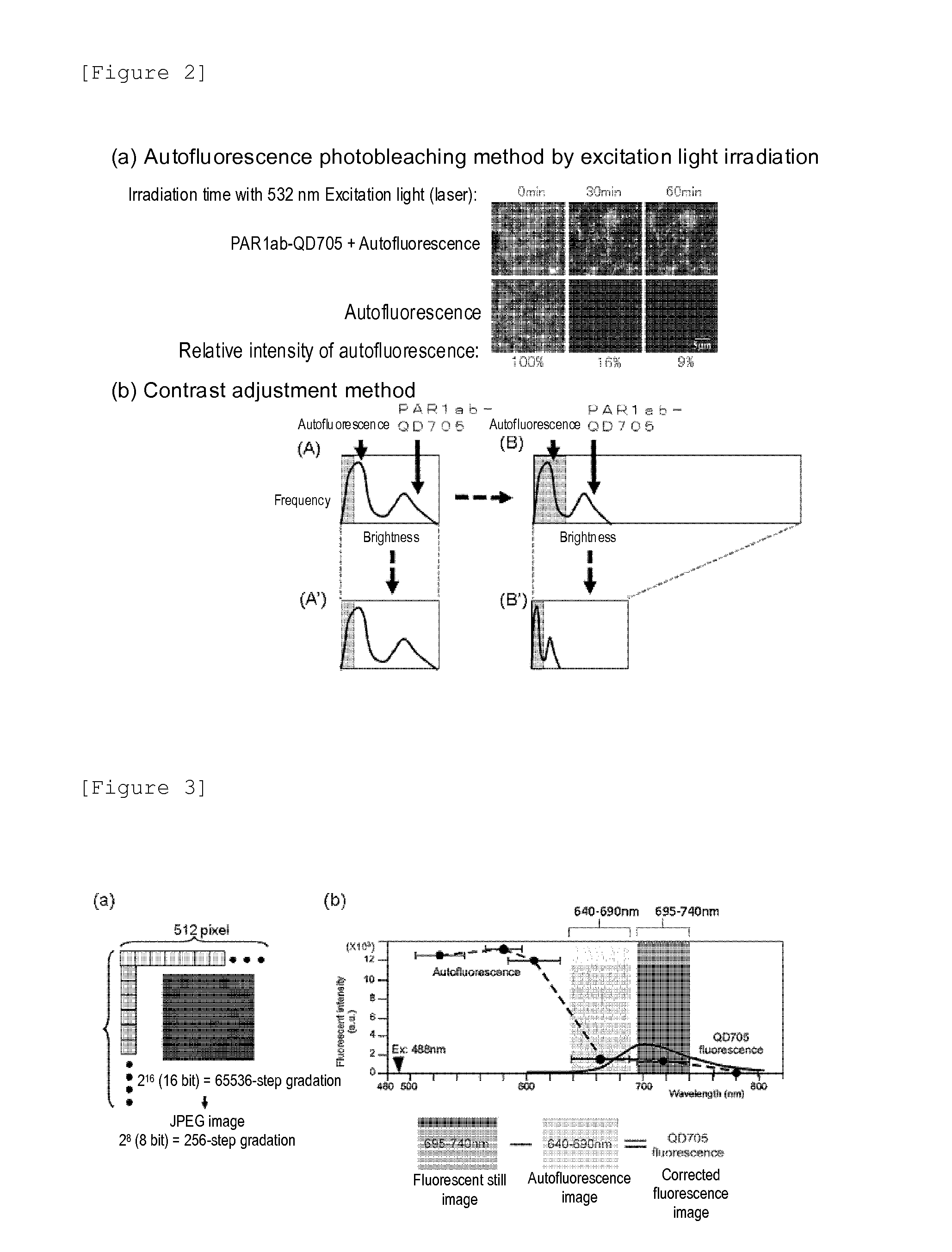
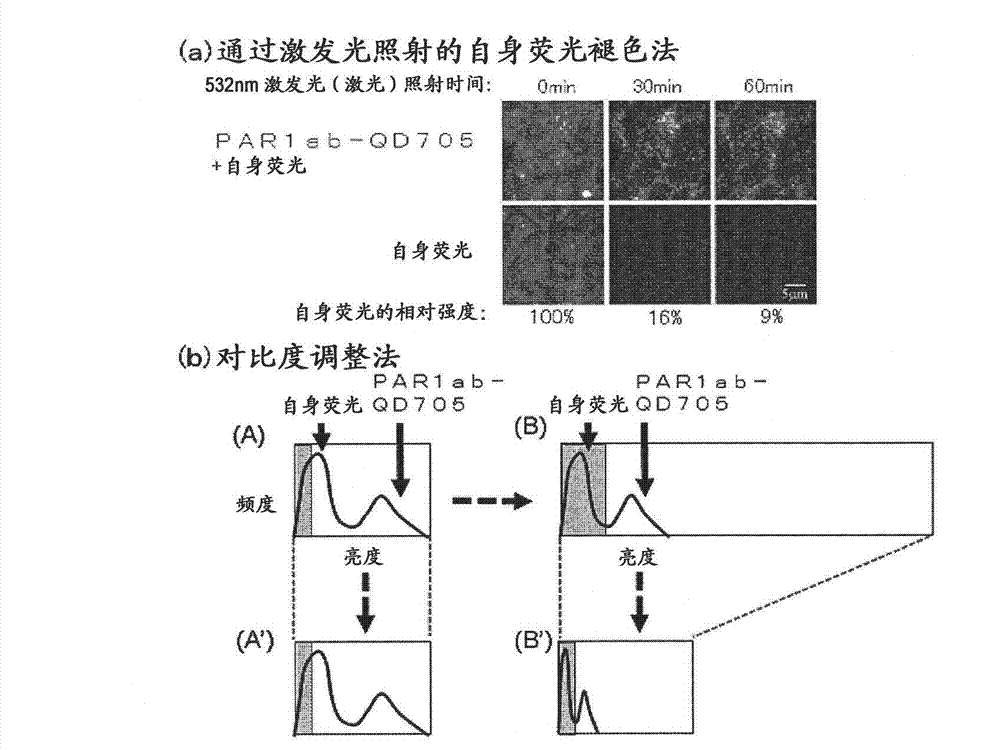
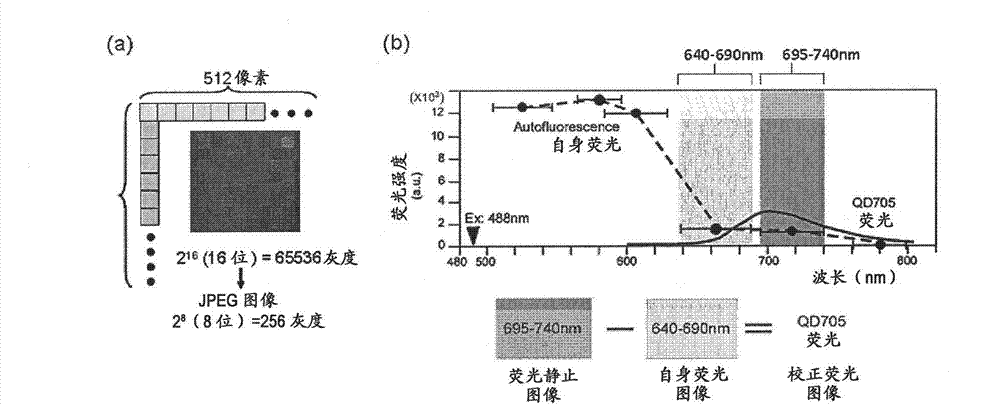
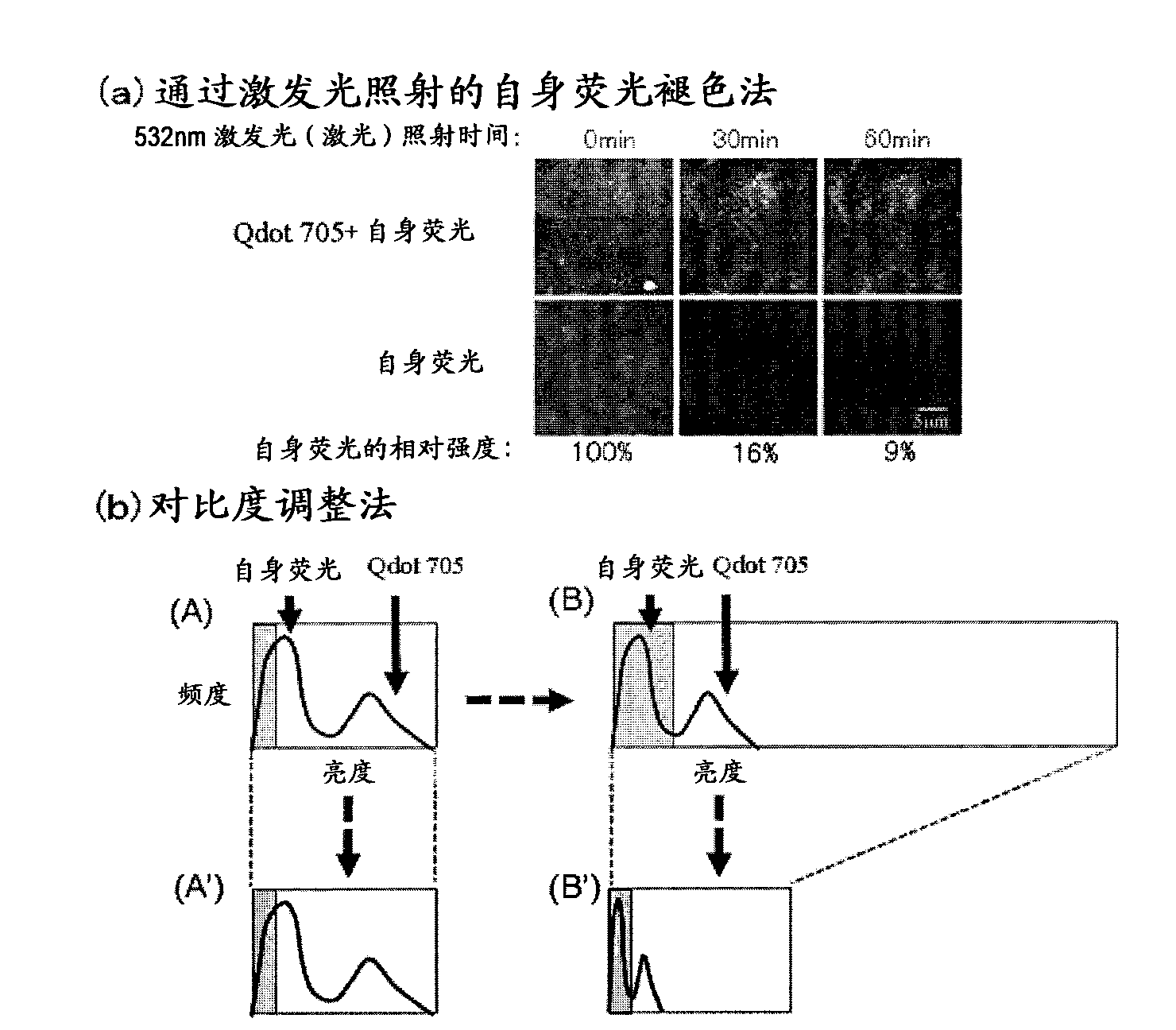
Protein recognized by an antibody used as an active ingredient of an antibody medicine such as trastuzumab or an antibody used for targeting a target site of an active ingredient is highly accurately quantitatively determined by employing a quantitative tissue staining method of biological tissues, thereby providing a method for determining therapeutic effectiveness of a medicine containing such an antibody as a component. The effectiveness of a medicine containing an antibody as a component is determined by employing a tissue staining method comprising the steps of: labeling the antibody in the medicine containing an antibody as a component with a fluorescent material and contacting the thus fluorescence-labeled antibody with a tissue sample; obtaining a fluorescence image by irradiating, with excitation light, a tissue site contacted with the antibody; obtaining an autofluorescence image in the same field of view and at the same focus as in the fluorescence image in a close region on a shorter wavelength side or a longer wavelength side of an acquisition wavelength region of fluorescence emitted by the fluorescent material; obtaining a corrected fluorescence image by performing image processing for removing fluorescence brightness of the autofluorescence image from fluorescence brightness of the fluorescence image; counting the number of cells in the tissue site contacted with the antibody; measuring average fluorescence brightness per fluorescent particle; and calculating the number of fluorescent particles per cell.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Electrophoretic in situ tissue staining
InactiveUS20050074890A1Easy to moveReduce background stainingElectrotherapyAnalysis using chemical indicatorsDiffusionTissue staining
The present invention introduces a radically different way of accelerating biomolecule conjugates into tissue, and hence towards their targets for purposes of tissue staining. The invention provides for an order of magnitude improvement over the prior art diffusion process used to stain tissue. The invention comprises a method of tissue staining by applying an electric field to a tissue sample in the presence of an electrolyte and biomolecular conjugates of interest suspended in the electrolyte. Typical staining times are reduced to seconds as opposed to 30-120 minutes common in the prior art. The invention is also directed to devices for performing the method.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Automated tissue staining system and reagent container
InactiveUS20050191214A1Container decorationsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsTissue stainingEngineering
An automated staining system and a reagent container designed for use with the automated staining apparatus. The reagent container includes a reagent containment section capable of containing a volume of a reagent. The reagent containment section includes an upper wall and a base wall that are spaced apart along an axis. The base wall includes a well having a nadir that is aligned axially with an access opening in the upper wall so that a reagent probe entering the opening parallel to said axis will travel toward the nadir. In another aspect of the invention, the reagent container may include a two-dimensional data element containing reagent information. The staining apparatus may include one removable drawer for holding reagent containers and another removable drawer holding slides.
Owner:LAB VISION CORP
Tissue staining method, tissue evaluation method and biosubstance detection method
ActiveUS20130157895A1Good for observationHigh sensitivityMaterial nanotechnologyPreparing sample for investigationTissue stainingMedicine
A tissue staining method which comprises: staining a tissue with a staining reagent wherein a biosubstance recognition site is bonded to particles carrying multiple fluorescent substances accumulated therein; in the stained tissue, counting fluorescent points or measuring fluorescent brightness; and evaluating the expression level of a biosubstance, which matches the biosubstance recognition site, in the aforesaid tissue on the basis of the number of the fluorescent points or fluorescent brightness that was measured.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Method for determining cancer onset or cancer onset risk
InactiveUS20130203082A1High sensitivityExclude influenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTissue stainingCancer cell
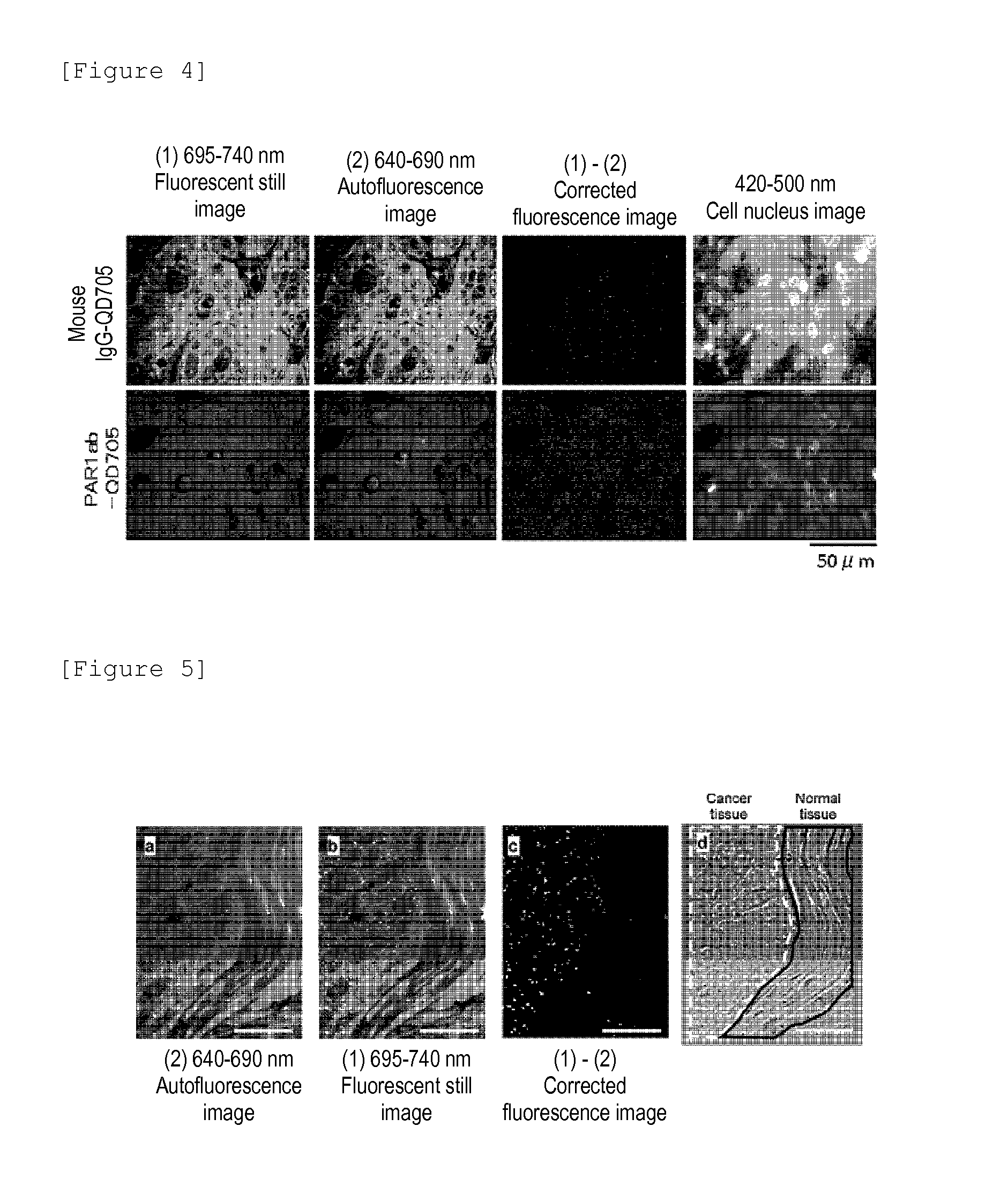
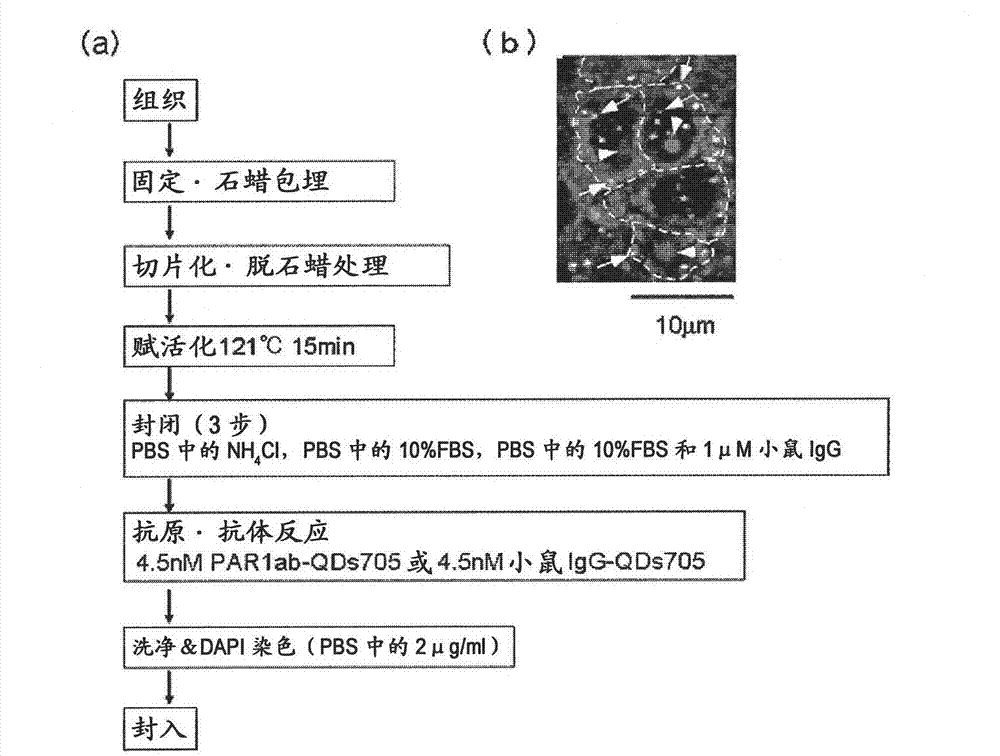
A highly accurate and quantitative method for determining cancer onset or cancer onset risk by a quantitative tissue staining method in biological tissues using an antibody capable of recognizing a cancer growth regulatory factor or cancer metastasis regulatory factor such as PAR1 antibody, which inhibits the cancer cell mobility and infiltration is provided. Cancer onset or cancer onset risk is determined using the tissue staining method comprising the steps of: labeling an antibody which recognizes a cancer growth regulatory factor or cancer metastasis regulatory factor with a fluorescent material, and contacting the fluorescent-labeled antibody with a tissue sample; irradiating a tissue site in contact with the antibody with excitation light to acquire a fluorescence image; acquiring an autofluorescence image in a vicinity region of a short wavelength side or long wavelength side of an acquisition region of fluorescence wavelength emitted by the fluorescent material, in the same field of vision and in the same focal point as those of the fluorescence image; acquiring a corrected fluorescence image by image processing to eliminate a fluorescent brightness of the autofluorescence image from the fluorescent brightness of the fluorescence image; counting the number of cells at the tissue site in contact with the antibody; measuring a mean fluorescent brightness of a single fluorescent particle; and calculating the number of fluorescent particles per cell.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Methods and compositions for a microemulsion-based tissue treatment
The invention is directed to methods and compositions for deparaffinizing paraffin-embedded biological samples for subsequent tissue staining. The compositions are microemulsions that may include water / oil / surfactant microemulsions, and optionally a cosurfactant. The microemulsions enable deparaffinization without the use of xylene or toluene, and also enable solvent exchange without the use of intermediary alcohol dehydration or alcohol rehydration compositions.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Automated tissue staining system and reagent container
InactiveUS20060127283A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTissue stainingEngineering
An automated staining system and a reagent container designed for use with the automated staining apparatus. The reagent container includes a reagent containment section capable of containing a volume of a reagent. The reagent containment section includes an upper wall and a base wall that are spaced apart along an axis. The base wall includes a well having a nadir that is aligned axially with an access opening in the upper wall so that a reagent probe entering the opening parallel to said axis will travel toward the nadir. In another aspect of the invention, the reagent container may include a two-dimensional data element containing reagent information. The staining apparatus may include one removable drawer for holding reagent containers and another removable drawer holding slides.
Owner:LAB VISION CORP
Cell tissue dyeing method and dyeing machine
ActiveCN101464236AReduce dosageLow costPreparing sample for investigationTissue stainingControl system
The invention provides a cell tissue staining method which can keep a slide still and control the flow mode of a staining solution, and a staining machine thereof. The staining machine mainly comprises a liquid storage tank, a solenoid valve, a dye vat, a machine frame, a control system, a transition block and a liquid collection device; the liquid storage tank is positioned at the upper part of the machine frame; the dye vat is positioned at the lower part of the machine frame; the liquid collection device and the solenoid valve are positioned between the liquid storage tank and the dye vat; the liquid storage tank is connected with the liquid collection device through the solenoid valve; and the liquid collection device is connected with the dye vat through the transition block. The method is characterized in that the natural liquid level pressure difference of the staining solution serves as a liquid working power source during the entire process of staining; the staining solution in the liquid storage tank flows into the liquid collection device through the solenoid valve; the staining solution in the liquid collection device is heated to the temperature set for staining, and then flows into the dye vat provided by a slide through the transition valve; and the staining process is completed by the slide in the dye vat. Compared with the traditional staining machine which keeps staining solution still and controls the model of slide movement, the invention is advanced and can achieve the effects of enhancing staining effect, improving staining efficiency, saving energy, reducing pollution and saving staining cost.
Owner:WUHAN LANDING INTELLIGENCE MEDICAL CO LTD
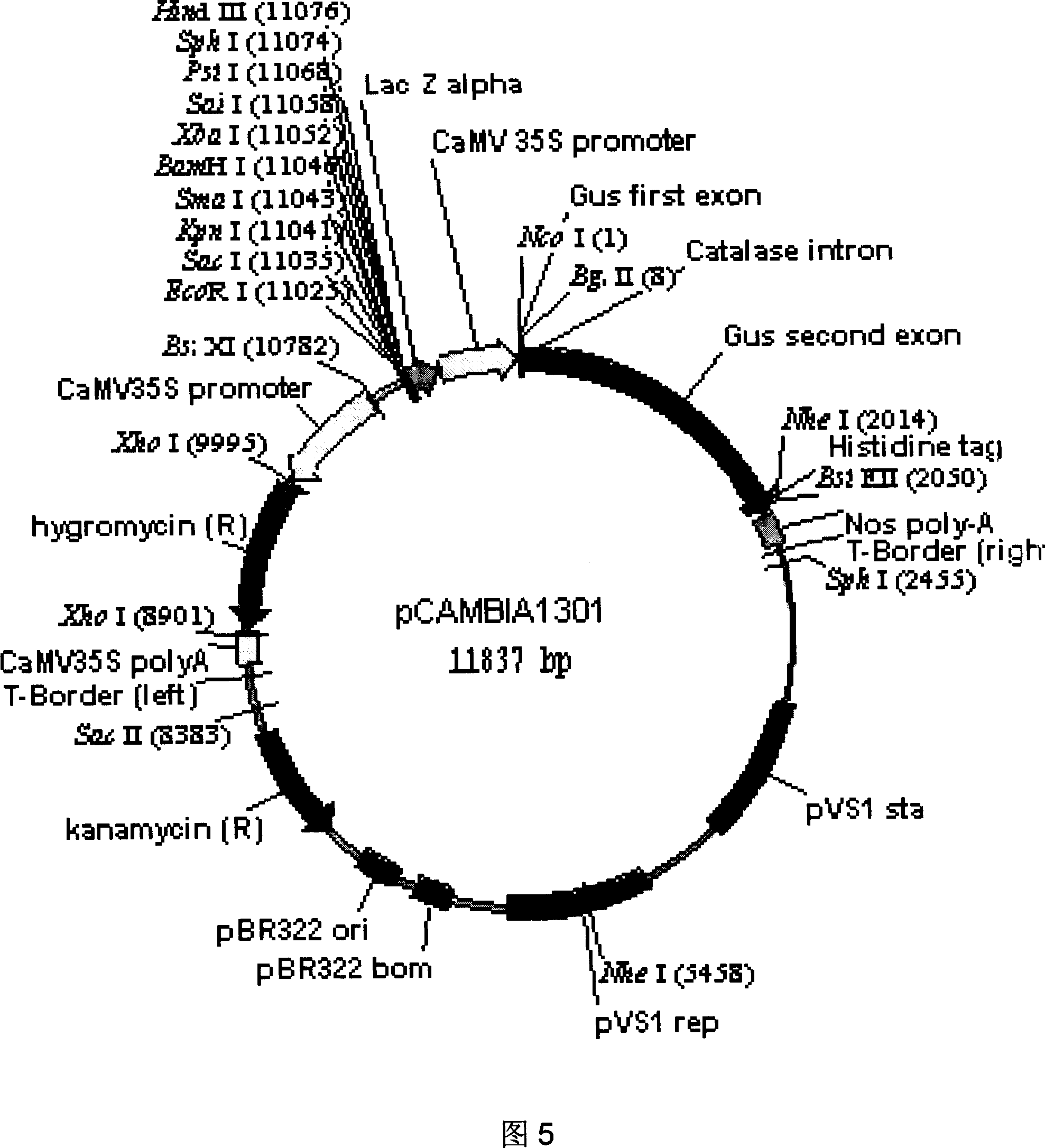
Rice high efficient expression starter and application thereof
InactiveCN100999736AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGenetically modified riceAgricultural science
The present invention relates to one kind of high efficiency expression promoter of rice and its application. The promoter has the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.1. It is shown by means of cloning one Os252 promoter to be predicted to express in stem in high efficiency, constituting GUS fused expression vector transferred to rice and performing PCR detection and chemical GUS tissue staining, that Os252 promoter has expression in the leaf, stem and seed albumen of rice. It is shown by means of GUS enzyme activity measurement that Os252 promoter has enzyme activity in leaf and seed albumen of rice about twice that of 35S promoter and enzyme activity in stem slighter lower than that of 35S promoter, and is one high efficiency expressed promoter. The present invention may be used in the genetic improvement and production research of rice.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Compositions and methods for simultaneous inactivation of alkaline phosphatase and peroxidase enzymes during automated multiplex tissue staining assays
ActiveUS20180120202A1Short amount of timeHydrogen peroxideOrganic chemistryTissue stainingPeroxiredoxin
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Devices and components for automated tissue processing and staining and uses thereof
The present disclosure provides devices for processing, such as staining, a tissue sample on a microscope slide. In some embodiments, the tissue staining device described herein is capable of, e.g., automating, in whole or in part, a tissue staining protocol (including a chemical staining protocol and / or an immuno-based staining protocol) or a tissue dehydration protocol. Also provided in other aspects of the disclosure are components, methods of use, systems, and kits associated with the devices described herein.
Owner:NOVODIAX
Method for quickly preparing hard tissue slice and application of the method
ActiveCN108918215AComplete structureQuality improvementPreparing sample for investigationTissue stainingSlice thickness
The invention relates to a method of quickly preparing a hard tissue slice, which includes the steps of: 1) immobilizing the hard tissue in paraformaldehyde and soaking the hard tissue in a sucrose water solution; 2) embedding the hard tissue with an embedding agent and rapid-freezing the hard tissue to cure the embedding agent; 3) tightly adhering one side of the sample to an adhesion film strip,and slicing the hard tissue at -25 to -30 DEG C in the direction being parallel with the surface of the adhesion film strip, slicing thickness being 6-8 [mu]m; 4) placing the film strip, with the hard tissue slice, on an anti-stripping glass slide, tightly adhering the hard tissue slice on the film strip with the anti-stripping glass slide through ultraviolet curable glue, then initiating the polymerization of the ultraviolet curable glue under ultraviolet light and removing the adhesion film strip on the surface of the hard tissue slice, thus obtaining the hard tissue slice. The invention also claims to protect application of the hard tissue slice, prepared through the method, in tissue staining. The method is easy to master and is low-cost and quick (only need three days).
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Sarranine and methyl violet mixed staining method for resin slices and staining solution thereof
InactiveCN104390834ADyeing effect is goodReduce storage requirementsPreparing sample for investigationMethyl violetANILINE BLUE
The invention provides a sarranine and methyl violet mixed staining method for resin slices and a staining solution thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a staining solution, namely preparing 0.5 mass percent of sarranine solution and 1 mass percent of methyl violet solution; and (2) respectively mixing the 0.5 mass percent of sarranine solution and the 1 mass percent of methyl violet solution according to multiple volume ratios, staining resin semithin sections, and observing the microscopic structure under a light microscope. According to the method disclosed by the invention, different histological stain requirements can be met aiming at the toluidine blue-O staining defect, and the method has the advantages of low cost and simplicity in preservation.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
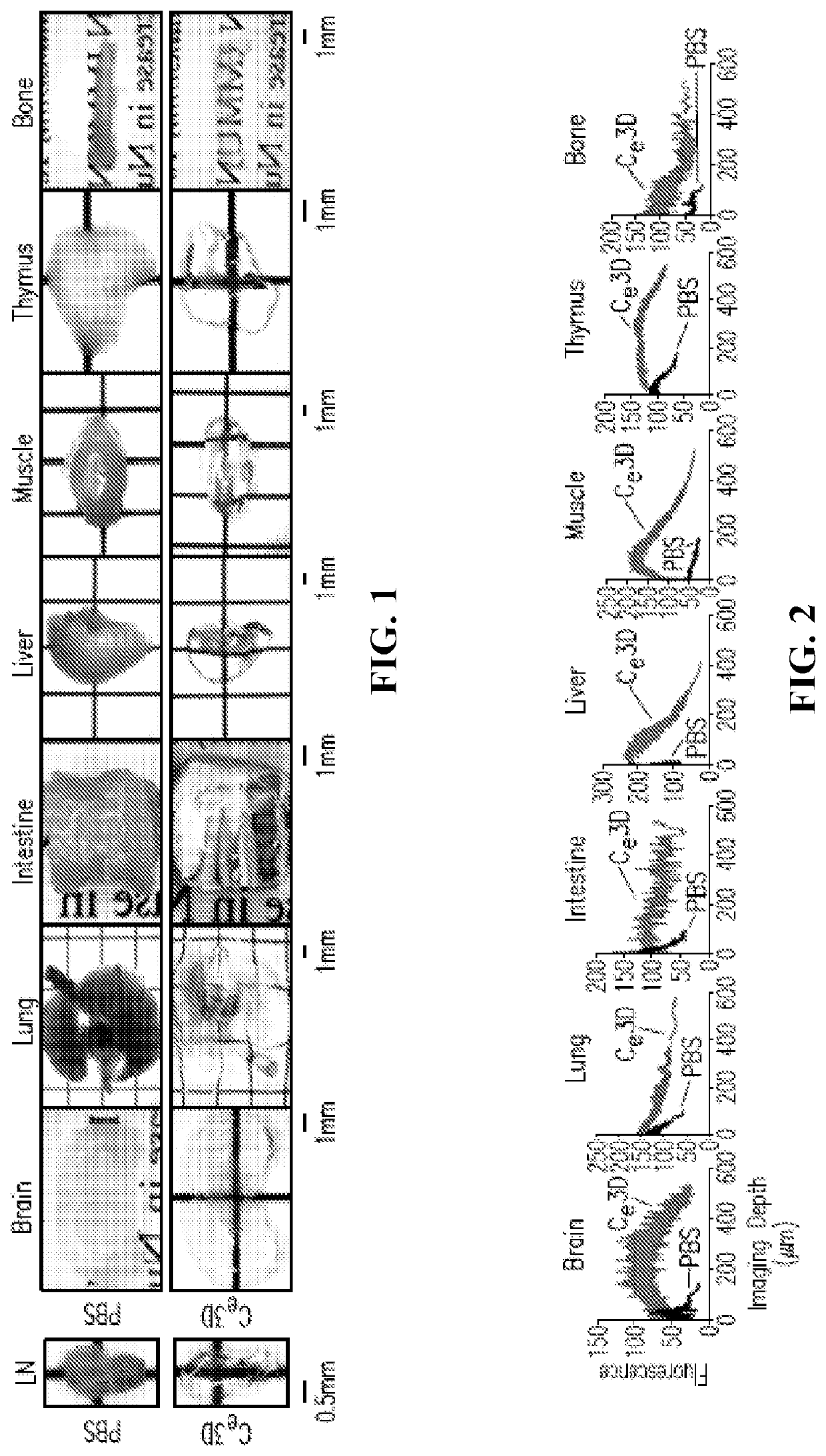
Simultaneous dehydration and staining of tissue for deep imaging
A biopsy-sized tissue sample is stained for quick imaging. A significant amount of permeation enhancer is included in a mixed solution of permeant enhancer, fixative or dehydrant, and one or two fluorescent dyes to simultaneously dehydrate and dye the tissue sample. The permeation enhancer, e.g., 10% to 50% in the mixed solution, achieves an image of dyed tissue in the contacted tissue sample at a depth of at least 200 um within no more than 1.5 hours. One of the fluorescent dyes is a fluorescent nuclear dye such as DAPI, SYTOX green, acridine orange, propidium iodide, or a Hoechst dye. The other fluorescent dye is a fluorescent protein dye such as eosin or rhodamine B. The tissue sample is cleared with a clearing agent having a refractive index of at least 1.4[R2], e.g., using BABB. The mixed solution may further include Chloroform or other morphology preservative.
Owner:APPLIKATE TECH INC
Organism tissue staining method
InactiveCN1441239AOK or notEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationTissue stainingFluorescence
The present invention relates to organism tissue staining method with RE fluorescent complex. The staining reagent used in the present invention is solution of RE fluorescent complex, and the solution is dropped onto the organism tissue or the test sample is soaked in the solution for 0.5-3 min before flushing with distilled water. Under the exciting of ultraviolet light, the configuration and detailed structure of the stainless tissue sample may be observed in fluorescent microscope. The said method has simple operatino and short period, and the sample needs no pre-treatment and unlimited. The reagent has no or only weak toxicity and the staining process has no influence on the structure of tissue or cell. The tissue may be extracorporeal or intracorporeal.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
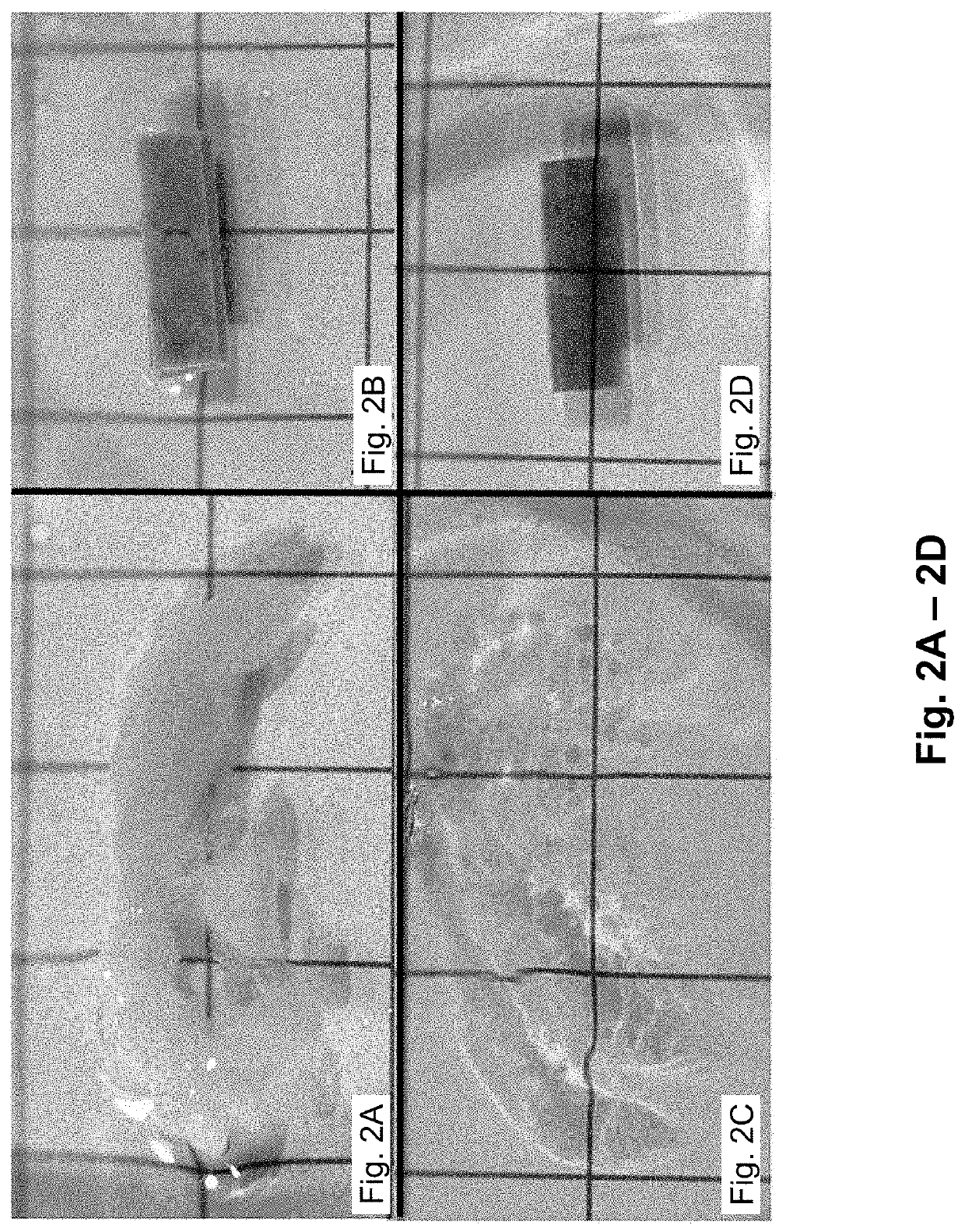
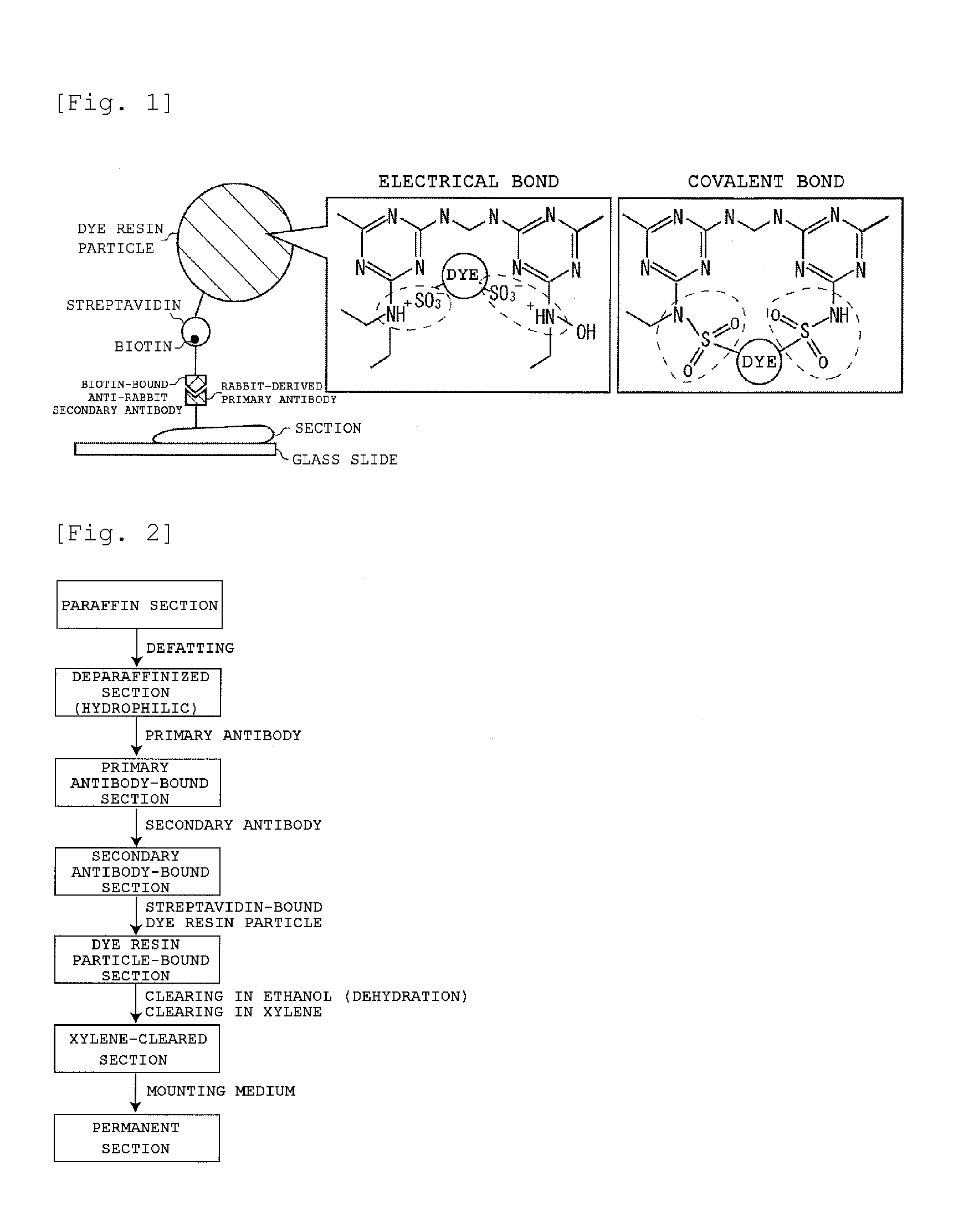
Staining agent for staining tissue, production method for staining agent for staining tissue and tissue staining kit including staining agent for staining tissue
ActiveUS20160018300A1Fluorescent signal enhancementAvoid bleedingPreparing sample for investigationOrganic dyesTissue stainingFluorescence
An object of the present invention is to provide: a staining agent for tissue staining which has an improved fluorescence signal evaluation accuracy; and a tissue staining kit comprising the staining agent. The staining agent for tissue staining contains, as a staining component, dye-resin particles comprising thermosetting resin particles and a fluorescent dye immobilized on the resin particles, wherein the resin particles contains a substituent having an electric charge opposite to that of the fluorescent dye and forms an ionic bond or a covalent bond with the fluorescent dye, and the dye-resin particles have a particle size variation coefficient of 15% or less.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Method for staining tissue
ActiveUS20150064717A1High quantitativityImprove accuracyPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansTissue stainingFluorescence
Provided is a method for staining a tissue enabling highly precise staining, by which the expression amount and / or the location of a biological substance in a tissue sample can be detected with a high quantitativity together with detailed information that can be obtained by bright field observation.The tissue staining method of the present invention is a method for staining a tissue, in which both staining that allows bright field observation and fluorescence staining are carried out for the same specific biological substance.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Efficient high-purity automatic dyeing method and high-purity automatic dyeing machine provided with slide automatic drying device
InactiveCN105158044AGood dyeing effectNo pollutionPreparing sample for investigationEngineeringPollution
The invention relates to a biological tissue dyeing method and a biological tissue dyeing machine. An efficient high-purity automatic dyeing method is characterized by including the following steps that (1) a high-purity automatic dyeing machine provided with a slide automatic drying device is prepared; (2) automatic dyeing is carried out on each bottle according to set time; (3) after dyeing, the drying device starts and blows hot air to a basket containing samples for drying, and washing is carried out according to set time; (4) after washing, the drying device starts and continuously blow hot air to the washed basket containing the samples for drying; (5) the step (2) to step (4) are repeated, dyeing, stoving, washing and drying are carried out according to preset programs, and every time a reagent bottle runs, a washing cylinder dries biological tissue specimens through the drying device. The method and the dyeing machine save time and can dry all cylinders, no liquid is left on the specimens, reagent pollution is not caused, and the dyeing effect of the dyeing machine is very remarkable.
Owner:湖北泰维科技实业股份有限公司
Lactobacillus rhamnosus, microbial agent and food product
ActiveCN111154682AImprove protectionReduce integrity breachesMilk preparationBacteriaBiotechnologyInflammatory factors
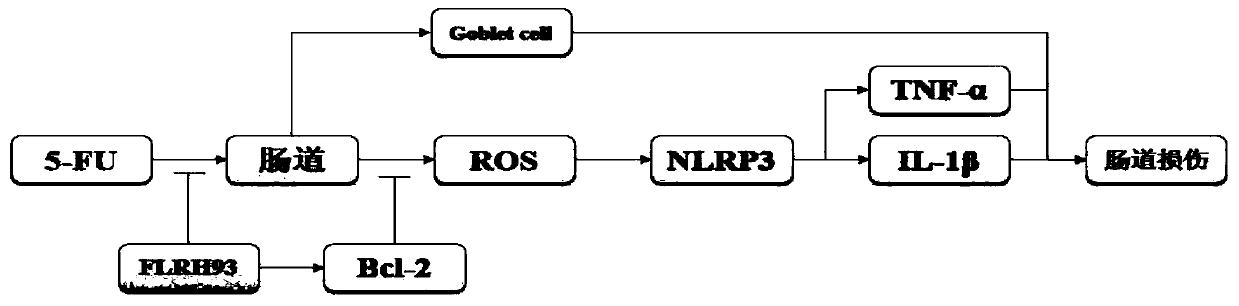
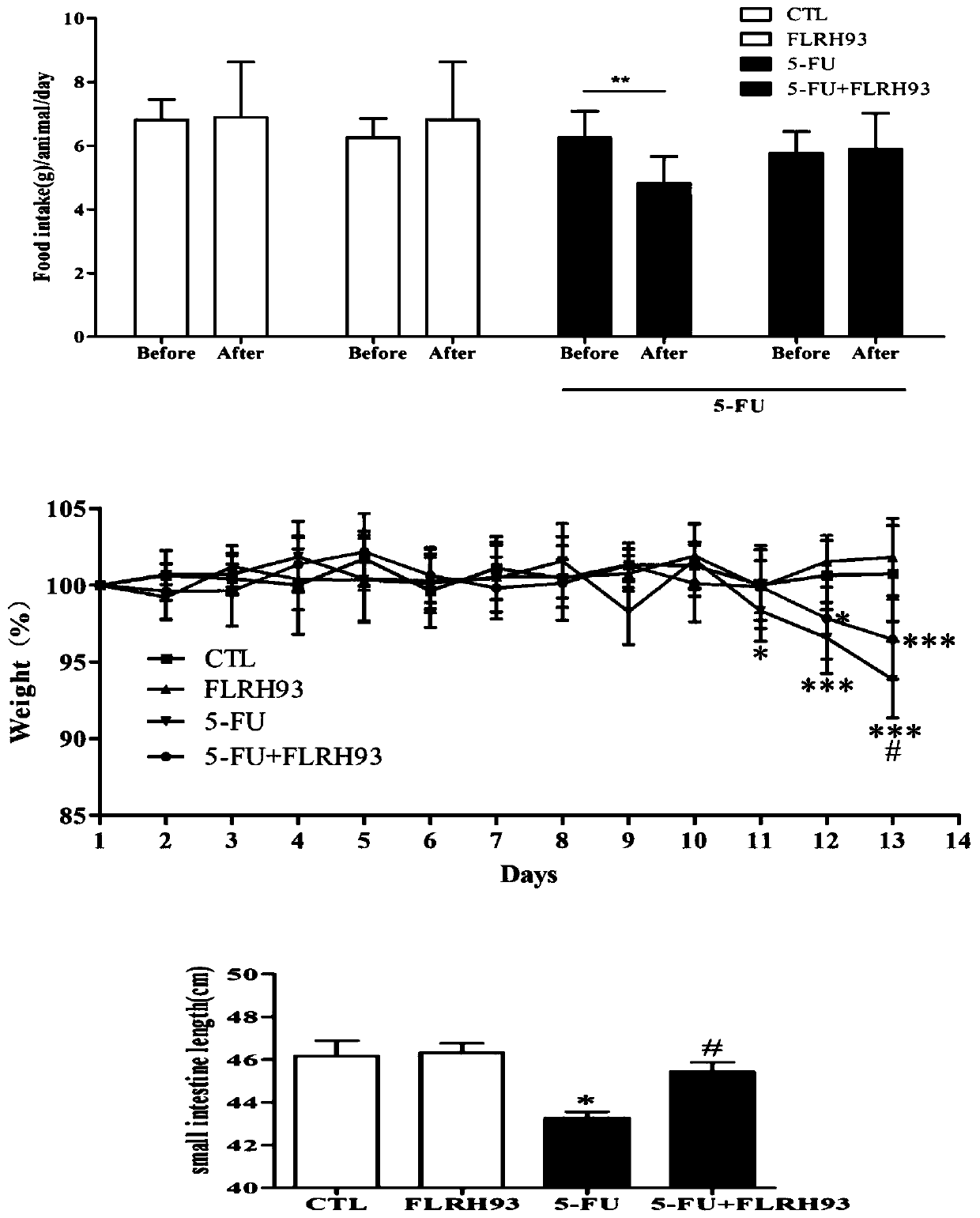
The invention discloses lactobacillus rhamnosus FLRH93. The lactobacillus rhamnosus FLRH93 is preserved in the Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center, and has a preservation number of GDMCC No:60956. Animal damage intervention experiment results show that the lactobacillus rhamnosus FLRH93 can obviously improve the intestinal injury caused by drugs; tissue staining sections show that the strain maintains the integrity of a small intestine structure, reduces the loss of goblet cells after drug treatment, and can regulate and control the secretion of Bcl-2 and NLRP3, thereby reducing generation of inflammatory factors IL1-beta and TNF-alpha. The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The strain provided by the invention can improve the survival rate of mice withdrug injury and can also remarkably promote healing of wound skin.
Owner:深圳市沁帆科技有限公司
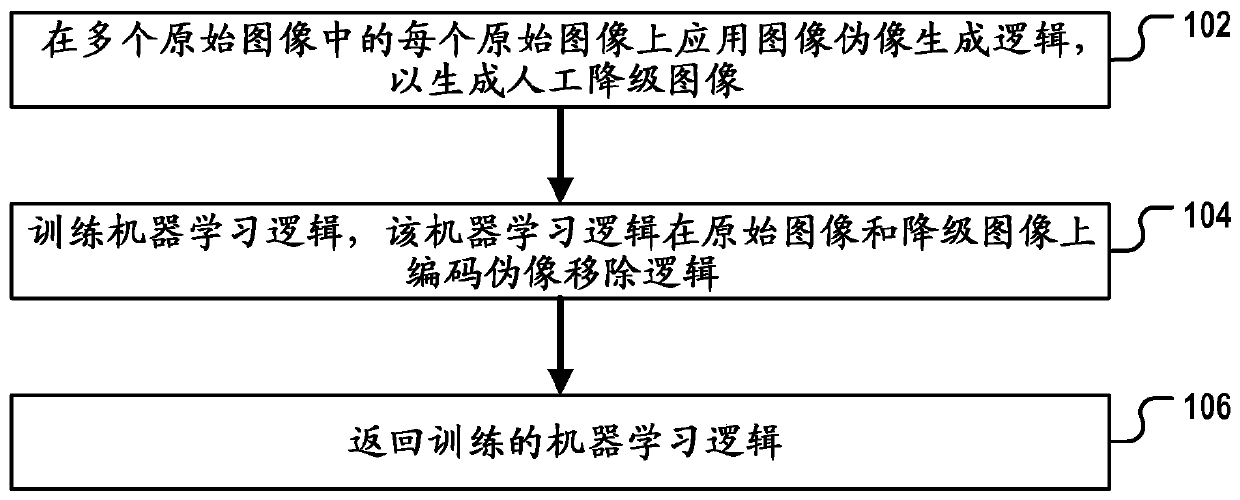
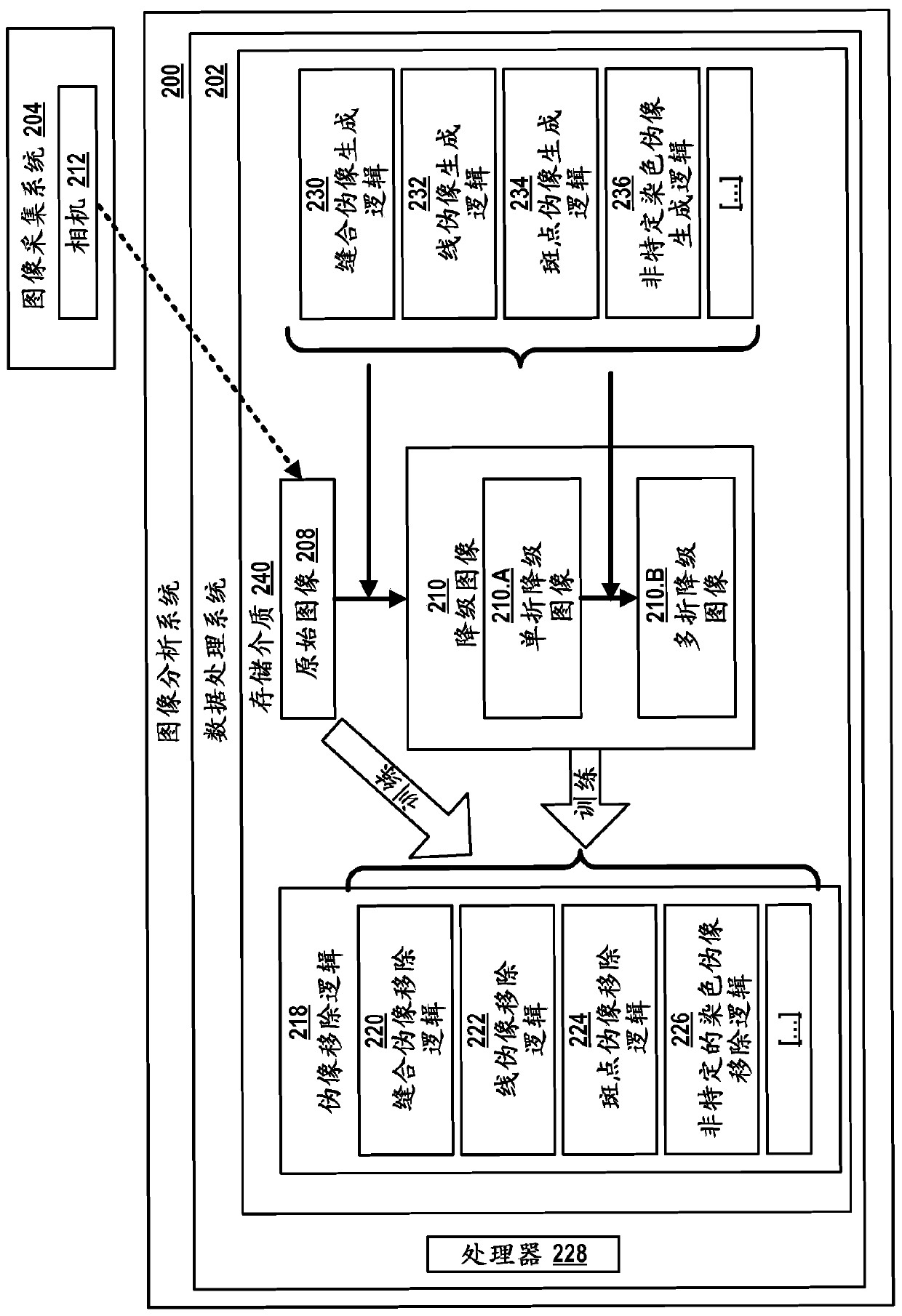
Artifacts removal from tissue images
The invention relates to a digital pathology method of generating program logic configured for removing artifacts from digital tissue images. The method comprises generating, for each of a plurality of original images, a first artificially degraded image by applying a first image-artifact-generation logic on each of the original images; and generating the program logic by training an untrained version of a first machine-learning logic that encodes a first artifacts-removal logic on the original images and their respectively generated first degraded images; and returning the trained first machine-learning logic as the program logic or as a component thereof. The first image-artifact-generation logic is A) an image-acquisition-system-specific image-artifact-generation logic or B) a tissue-staining-artifact-generation logic.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Method for determining cancer onset or cancer onset risk
Provided is a method for highly accurately and quantitatively determining cancer onset or cancer onset risk by quantitative tissue-staining which is conducted in a biotissue with the use of an antibody capable of recognizing a cancer proliferation inhibitor or a cancer metastasis inhibitor, for example, PAR1 antibody inhibiting the mobility and infiltrating properties of cancer cells. Cancer onset or cancer onset risk is determined by a tissue staining method, said method comprising: a step for labeling an antibody, which is capable of recognizing a cancer proliferation inhibitor or a cancer metastasis inhibitor, with a fluorescent substance and then contacting the fluorescent-labeled antibody with a tissue sample; a step for irradiating a tissue site, which has been contacted with said antibody, with an excitation light to give a fluorescence image; a step for acquiring an intrinsic fluorescence image in a neighborhood region on a shorter or longer wavelength side, compared with the region wherein the wavelength of the fluorescence emitted by the fluorescent substance is acquired, in the same visual field at the same focus point as said fluorescence image; a step for conducting an image processing for removing the fluorescent brightness of said intrinsic fluorescence image from the fluorescent brightness of said fluorescence image to give a corrected fluorescence image; a step for counting cells at the tissue site which has been contacted with the antibody; a step for measuring the average fluorescent brightness per fluorescent particle; and a step for calculating the fluorescent particle count per cell.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Same-section multi-target protein immunohistochemical or immunofluorescent labeling method
The invention provides a same-section multi-target protein immunohistochemical or immunofluorescent labeling method. The method comprises the following steps of: unfolding slices in corresponding liquid in the process of slicing a tissue wax block, selecting two continuously connected slices in the process of catching a target slice, placing the back surface of the first slice upwards in the process of catching the slice by employing a glass slide, and placing the front surface upwards in the process of catching the second slice, so that the condition that the surfaces of the two tissue slice for staining belong to the same slicing surface is ensured; and respectively performing immunohistochemical or immunofluorescent staining on different target proteins for two slices from the same slicing surface, performing overlap comparison on the tissue staining result in a same area, so as to realize existential analysis of a same cell or tissue site multi-target protein. The effect of performing multi-target protein labeling on the same cell or tissue site to be detected is achieved.
Owner:FUZHOU MAIXIN BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for determining effectiveness of medicine containing antibody as component
InactiveCN103154741APromote cancer treatmentMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDisease diagnosisTissue stainingTrastuzumab
Provided is a method for determining effectiveness of medicine containing, as components, antibodies that are active components of an antibody preparation such as trastuzumab, or antibodies for a target to a target site of active component, by determining the quantity of the protein recognized by the antibodies with high accuracy, in a quantitative tissue staining method for biological tissue. The effectiveness of the medicine containing antibodies as components is determined by using the tissue staining method including the following steps: a step of labeling the antibodies in a medicine that contains antibodies as components with a fluorescent substance, and bringing the fluorescently labeled antibodies into contact with a tissue sample; a step of irradiating the tissue site contacted with the antibodies with excitation light to obtain a fluorescence image; a step of obtaining an intrinsic fluorescence image in the vicinity of the short-wavelength side or long-wavelength side of the acquisition area of fluorescence wavelength emitted from the fluorescent substance, in the same field of vision and in the same focus as those of the fluorescence image; a step of obtaining a collected fluorescence image by image-processing to eliminate the fluorescent intensity of the intrinsic fluorescence image from the fluorescent intensity of the fluorescence image; a step of counting the number of cells at the tissue site contacted with the antibodies; a step of measuring the average fluorescent intensity of one particle of fluorescent particles; and a step of calculating the number of fluorescent particles per cell.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Automated lean methods in anatomical pathology
ActiveUS20170030810A1Withdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationTissue stainingPatient data
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Indicarmine mucosa staining agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104127888AEarly treatmentNo side effectsIn-vivo testing preparationsChemical reactionTissue staining
The invention relates to an indicarmine mucosa staining agent used for endoscopic staining development, and a preparation method thereof. The indicarmine mucosa staining agent comprises 0.15-0.25wt% of indicarmine and 99.75-99.85wt% of purified water. The display of the microstructure by utilizing the difference of the color obtained after the deposition of the staining agent belongs to a physical effect and has no chemical reactions, the infection focus cannot be observed by using tissue staining, and the staining agent does not react with mucosa tissues. The staining agent is deposited on the mucosal fold, is not absorbed, does not combine with mucus, is discharged from the body through the intestinal tract, has no side effects, has no restricted theoretic use dosage, is easy to flush, and can repeatedly stain until a satisfactory effect is reached.
Owner:贵州高澄医疗器械有限公司
Tissue staining method
ActiveUS10551378B2Diagnostic precision is enhancedImprove conveniencePreparing sample for investigationAntigenTissue staining
It is an object of the present invention to provide a tissue staining method that makes it possible to observe both information on the morphology of a tissue and information on a biological substance such as an antigen molecule to be detected on a single section and in a single view field. The present invention provides a tissue staining method, including carrying out (A) a HE (hematoxylin-eosin) staining, and (B) a histochemical staining, serially on a single tissue section, wherein the histochemical staining is defined as a histochemical technique for detecting a biological substance to be detected in a tissue in a visible manner by use of a binding reaction between the biological substance to be detected and a probe biological substance capable of binding specifically to the biological substance to be detected.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Method for staining tissue
ActiveUS9970847B2High quantitativityImprove accuracyPreparing sample for investigationBiological testingTissue stainingFluorescence
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Method and composition for optical clearing of tissues
ActiveUS20200209117A1Easy to useExcellent tissue transparencyPreparing sample for investigationTissue stainingOptical clearing
Disclosed are compositions, methods, and kits for clearing tissue that preserve cellular morphology, reporter fluorescence, and epitope labeling which allow for quantitative phenotypic analysis of intact organs. The compositions include, for example, a compound of formula R1—C(X)—NR2R3, wherein R1 is alkyl, haloalkyl, hydroxyalkyl, amino, or alkylamino, X is O or S, and R2 and R3 are independently H, alkyl, or hydroxyalkyl, a salt thereof, or a combination thereof, and at least one non-ionic density gradient medium. Also disclosed are methods for clearing tissue comprising positioning a tissue in a tissue clearing composition and allowing a tissue clearing composition to permeate the tissue. Further disclosed are methods for visualizing tissue characteristics which involve fixing a tissue, staining the tissue, positioning the tissue in the tissue clearing composition and allowing the tissue clearing composition to permeate the tissue, and imaging the tissue utilizing a microscope or tissue scanning device.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com