Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
112 results about "ANILINE BLUE" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dye and chemical solution stains for medical purposes are mixtures of synthetic or natural dyes or nondye chemicals in solutions used in staining cells and tissues for diagnostic histopathology, cytopathology, or hematology.
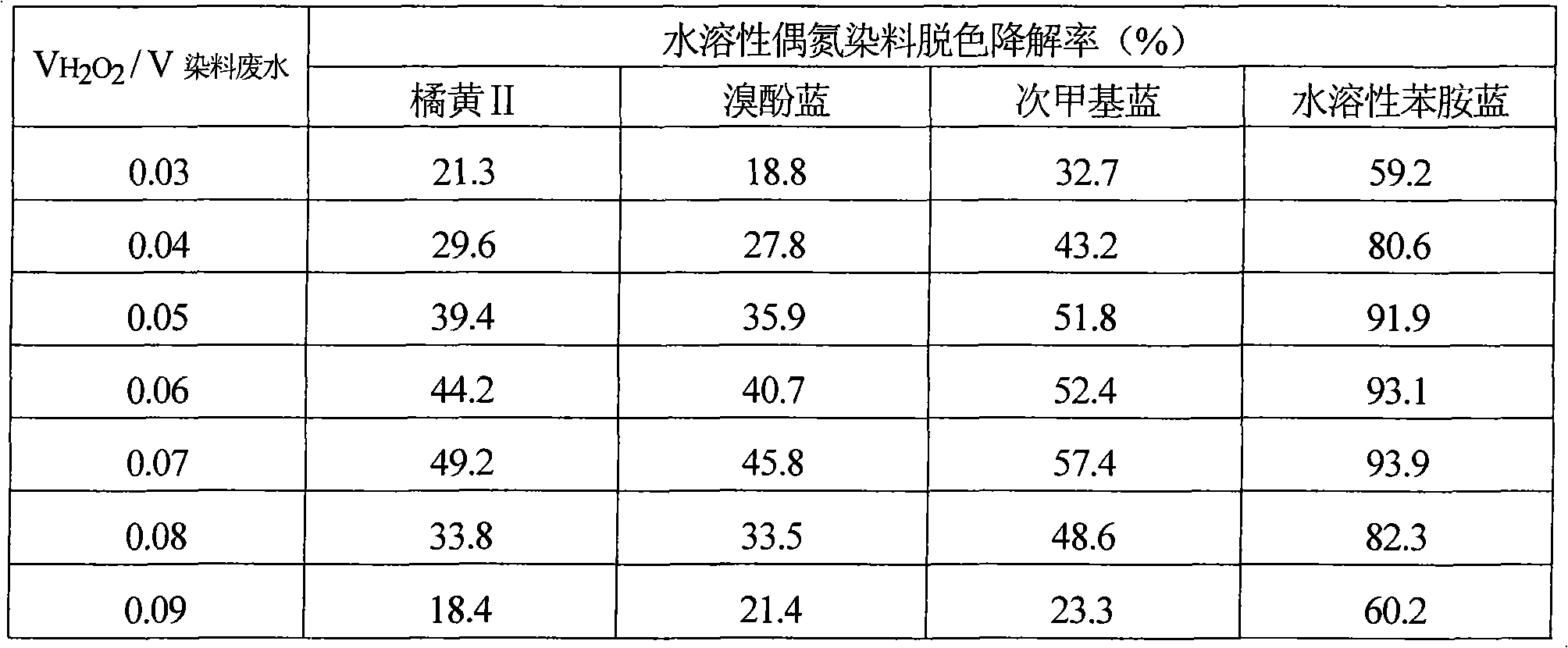
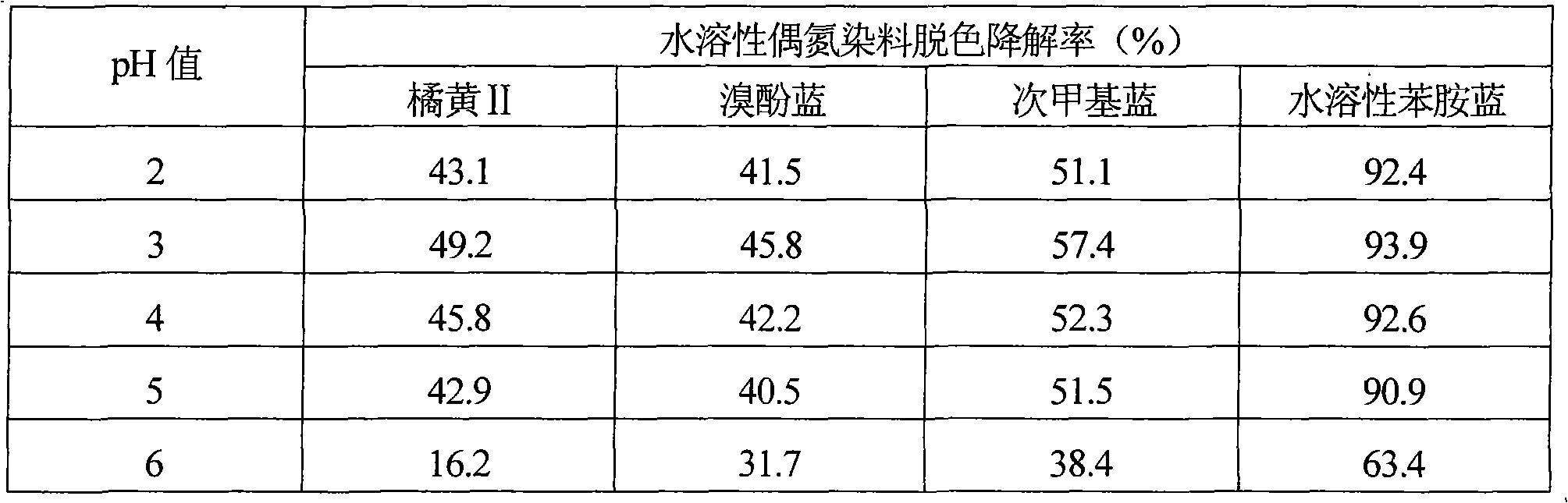
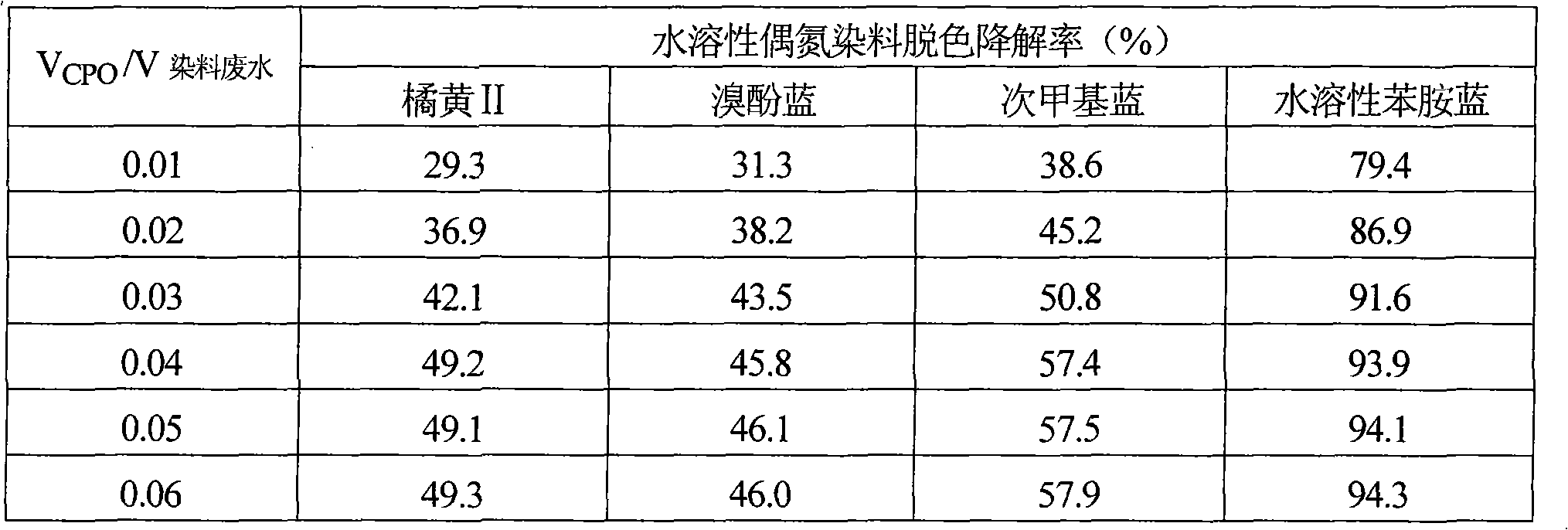
Method for decoloring and degrading soluble azo dyes through catalysis of chloroperoxidase and oxidation of H2O2
InactiveCN101781012AAchieve irreversible decolorization and degradationImprove biodegradabilityWater/sewage treatment by oxidationANILINE BLUETetrabromophenol Blue
The invention discloses a method for decoloring and degrading soluble azo dyes through catalysis of chloroperoxidase and oxidation of H2O2, which comprises the following steps: preparing solution; decoloring and degrading; and computing the decoloring and degrading rate of the azo dyes. In the established method for decoloring and degrading soluble azo dyes orange II, bromophenol blue, methylene blue and soluble aniline blue wastewater through the catalysis of the chloroperoxidase and the oxidation of the H2O2, the H2O2 is used as an oxidant based on a bio-enzyme catalysis degradation system, a large conjugate system and azo structures and other chormophoric groups in the dyes are quickly damaged, irreversible decoloration and degradation of the dyes are realized, and the biochemical quality is improved. The method has the advantages of high speed of decoloring and degrading, high efficiency, simple operating steps, low consumption of the chloroperoxidase and the H2O2, and the like, and can be applied to treatment of industrial wastewater with soluble azo dyes.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Method for observing microscopic structures inside plant roots
InactiveCN102768209ASimple methodEasy to operatePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansPlant rootsFluorescence microscope
The invention relates to a method for observing microscopic structures inside plant roots, which is capable of effectively solving the problem of utilizing a microscope to clearly observe the structures inside the plant roots. The method comprises the steps of digging out the plant roots, washing, shearing the plant roots into small sections, fixing the plant roots by methanol, and then embedding by a sepharose solution, cooling, condensing, trimming into small blocks, after freehand section, placing the small blocks into distilled water in a container, performing lactic acid clearing, covering, dyeing via berberine or fluorescein, bleaching by the water, performing poststaining via toluidine blue O or sarranine O, bleaching by the water, performing water seal, observing and photographing via an inverted fluorescence microscope, and obtaining a clear image. The method can be used for observing the microscopic structures inside the plant roots, thereby being effectively used for the research on classification, auxanology, ecology and physiology of medical plants. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple method, easiness in operation, low cost, low working capacity, high success rate, and good effect, thereby being capable of being used for the research on morphological anatomy of the roots. The method is simpler and more effective for the thinner root sections of the plants.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
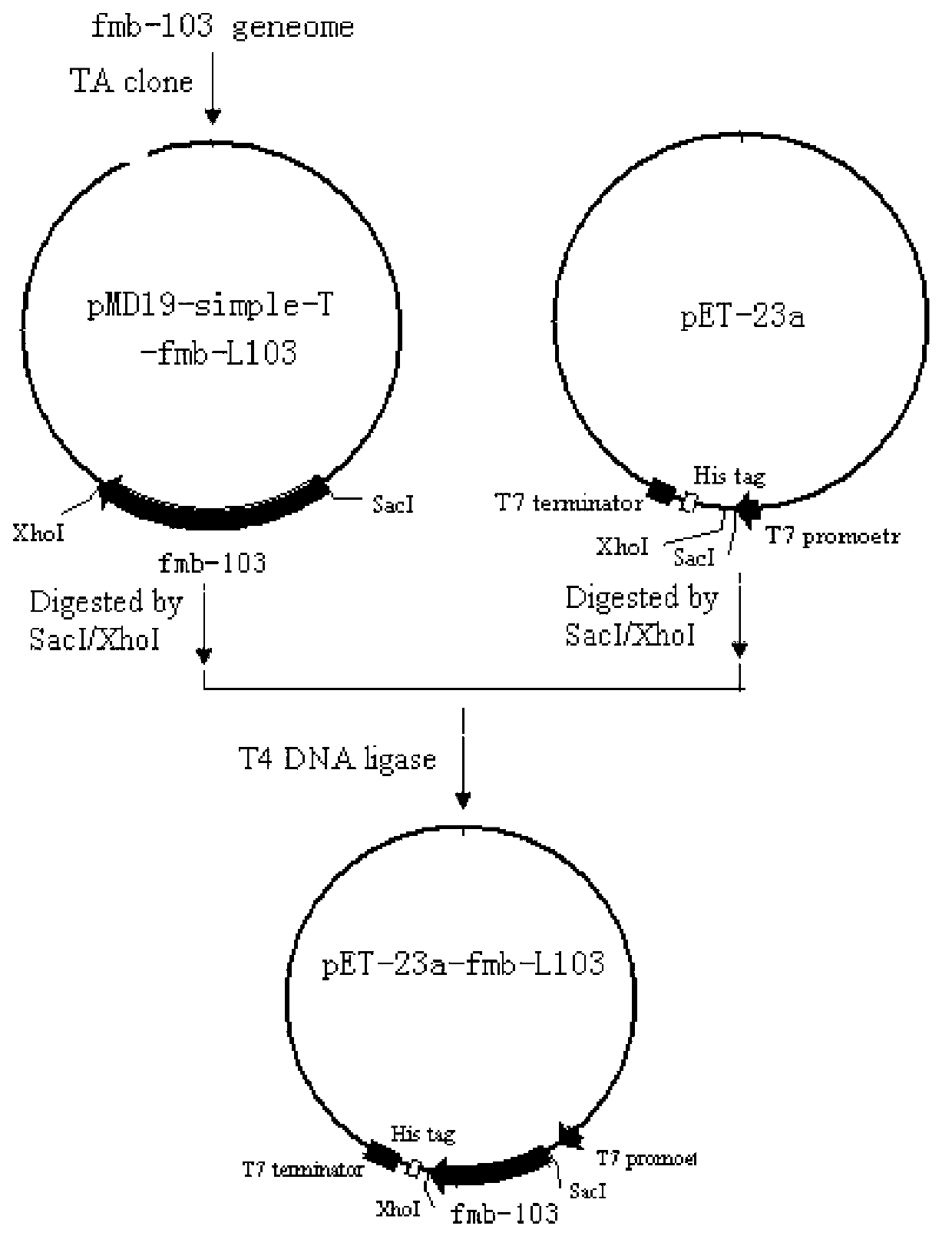
Laccase gene as well as encoded protein and application thereof
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and discloses a laccase gene as well as an encoded protein and an application thereof. The open reading frame sequence of the laccase gene fmb-L103 is shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. The amino acid sequence of the protein encoded by the laccase gene fmb-L103 disclosed by the invention is shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. The laccase gene fmb-L103 disclosed by the invention is applied to decoloration for triphenlmethane dyes. The inventor clones from the selected dead bacillus vallismortis fmb-L103 with a spore laccase activity to obtain a novel prokaryotic laccase gene fmb-L103, and realizes the heterologous efficient expression of escherichia colli expression host bacteria. The recombinase fmb-L103 can be used for efficiently catalyzing the degradation of the triphenlmethane dyes of malachite green, brilliant green and aniline blue.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for quickly identifying cross-compatibility of rose hybrida
The invention provides a method for quickly identifying cross-compatibility of rose hybrida. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: collecting and storing pollen, performing castration, performing artificial pollination, cutting a sample to be identified, fixing the cut sample in FAA stationary liquid, transferring the cut sample to a 70 percent ethanol solution after 24 hours, taking out for washing, placing in an 8mol / L NaOH solution, performing water bath at the temperature of 55 to 60 DEGC for 15 to 20 minutes, and then standing at the temperature of 20 to 28 DEGC for 3 to 3.5 hours, soaking into water for at least 1 hour, transferring to a 0.1 percent dye solution of aniline blue, dyeing for 2 to 3 hours, observing stigma callose deposition, pollen germination and growth of pollen tubes by using a fluorescence microscope to identify the cross-compatibility of rose hybrida. By the method, the cross-compatibility of rose hybrida can be identified within 30 to 48 hours; and moreover, the method is simple and easy to operate and can effectively reduce the waste of breeding resources and improve breeding efficiency.
Owner:FLOWER RES INST OF YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Screening method of high-performance hydrolytic bacterial strain of waste Baijiu distiller grains
InactiveCN108913604AImprove hydrolysis effectOptimize hydrolysis efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism separationCelluloseScreening method
The invention discloses a screening method of a high-performance hydrolytic bacterial strain of waste Baijiu distiller grains. The screening method is characterized by comprising the following steps:step I, directly separating and culturing fungus from effective fungus that possibly hydrolyzes waste Baijiu distiller grains of relevant waste hydrolytic Baijiu distiller grains in a bacterial strainlibrary in a waste Baijiu distiller grains stacking environment; step II, performing the primary screening for the screened fungus successively by virtue of a sodium carboxymethylcellulose-Congo redculture medium, PDA-aniline blue culture medium, and a xylan-Congo red culture medium by adopting the single polymer which is difficult to hydrolyze in the waste Baijiu distiller grains as an exclusive carbon source; step III, culturing the bacterial strain in a waste distiller grain solution adopting the waste Baijiu distiller grain as an exclusive nutritional substance, and determining the capability of the bacterial strain for the waste distiller grains; step IV, performing the enzyme activity test for the composite bacterial strain in the waste Baijiu distiller grain solution, and screening the bacterial group with synergistic effect and high enzyme activity, thus obtaining the high-performance composite hydrolytic bacterial group; and step V, comparing enzyme activity and biomass hydrolytic capability of the high-performance composite bacterial strain with that of the disclosed mutant bacterial strain having the high-performance hydrolytic cellulose.
Owner:GUIZHOU MEDICAL UNIV +1
Method for determining ion content of cationic polyacrylamide by utilizing spectrophotometry
ActiveCN101655461AReduce mistakesImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSpectrophotometryChemistry
The invention discloses a method for determining the ion content of cationic polyacrylamide by utilizing spectrophotometry, which is characterized in that polyvinyl alcohol lemery is prepared into a standard solution, a colloidal titration method of titrating a cationic polyacrylamide dilute solution is adopted, and visible light spectrophotometry is adopted to judge the end point of the titration. The method comprises the concrete steps: 1. preparing the standard solution; 2. preparing the cationic polyacrylamide solution and diluting; 3. regulating the pH value to 1-3 with 1 percent of hydrochloric acid, and adding 100 microlitres of 0.5 percent of toluidine blue indicator; 4. titrating with the standard solution; 5. drawing a photometric titration curve S; 6. and doing a group of blankexperiments by referencing the steps of 1-5. The invention uses the photometric titration to determine the ion content of cationic polyacrylamide and observes the color change of the solution insteadof naked eyes, thereby reducing end point judgment errors and avoiding the determining failure caused by color reversion, and therefore, the goals of increasing the end point judgment precision and the determining result accuracy are achieved.
Owner:BEIJING DRAINAGE GRP CO LTD
Beta-dextran detection method based on fluorescence enhancement principle
InactiveCN105842208AStrong fluorescence enhancement abilityHigh sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescencePhotonicsDextran
The invention discloses a method for detecting β-glucan based on the principle of fluorescence enhancement. The treated silicon wafer is used as the substrate, and titanium dioxide and graphene oxide hydrogel are deposited on the silicon wafer in combination with spin-coating technology to prepare titanium dioxide / Graphene oxide hydrogel one-dimensional photonic crystal, and gold-plated on the photonic crystal by vacuum evaporation method, prepared gold-plated titanium dioxide / graphene oxide hydrogel one-dimensional photonic crystal, and used this photonic crystal as a fluorescence-enhanced Substrate, a method for detecting β-glucan by detecting the fluorescence intensity of the fluorescent complex product specifically combined with aniline blue. The present invention uses gold-plated titanium dioxide / graphene oxide hydrogel one-dimensional photonic crystals as the base, and combines the fluorescence enhancement effects of gold nanoparticles and photonic crystals to cause greater fluorescence enhancement, thereby improving the sensitivity of fluorescence detection. The method is simple and effective, the operation is convenient and the required time is short.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Thermophilic aerophilic thiamine-decomposing bacillus, microbial inoculum and application of microbial inoculum
The invention relates to thermophilic aerophilic thiamine-decomposing bacillus, a microbial inoculum and application of the microbial inoculum. The bacillus can well grow at the temperature of 30-60 DEG C. In an aniline blue decoloration test, a decoloration ring with the diameter of 5cm can be generated within 24h. The microbial inoculum has the advantages of high lignin degradation rate, high temperature resistance, short growth period and the like when being applied to lignin degradation, and particularly can be used for strain resources of high-temperature straw compost.
Owner:江苏进化树生物科技有限公司
Polarized light imaging devices and methods
InactiveUS7627363B2Improve spatial resolutionLimited field of viewDiagnostics using lightLuminescence/biological staining preparationRapid imagingPolarizer
The present invention is directed to a novel multi-spectral contrast agent-enhanced polarized light imaging technique that enables rapid imaging of large tissue fields. The imaging device includes a tunable monochromatic light source and a CCD camera. Linear polarizers are placed into both the incident and collected light pathways in order to limit the measurement volume to the superficial tissue layers. To enhance the tumor contrast in the image, aqueous solutions of toluidine blue or methylene blue are topically applied.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method for simultaneously dyeing mycelial masses and starch in mycorhiza of arethusa
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously dyeing mycelial masses and starch in mycorhiza of arethusa, which comprises the following steps: taking a mycorhiza slice, placing on a glass slide, dripping chloral hydrate iodine solution dye, dyeing, then sucking away the redundant dye, further dripping aniline blue lactoglycerin solution dye, dyeing, then sucking away the redundant dye, and placing under an optical microscope for micro-observation, so that the starch in the mycorhiza is in dark brown and the fungal mycelial masses are in blue. By adopting the method, the mycelial masses and the starch in the mycorhiza can be simultaneously dyed, and the colonization characteristics of fungi of the mycorhiza in a root of the arethusa and the starch distribution characteristics can be simultaneously observed, thereby having important significance for revealing the relationship between digestion and formation of the fungi of the mycorhiza and accumulation and the digestion of a hostcarbohydrate.
Owner:GUIZHOU FRUIT INST
Method for observing deposition of callose of Agrostis stolonifera blade tissues based on paraffin slice and aniline blue fluorescence staining technology
InactiveCN106198465AShorten the experiment timeComplete efficientlyPreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceANILINE BLUECallose
The invention discloses a method for observing the deposition of callose of Agrostis stolonifera blade tissues based on a paraffin slice and an aniline blue fluorescence staining technology. The method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing a medicine; 2, making the paraffin slice sequentially through the steps of material drawing, fixation, dehydration, transparentizing, paraffin impregnation, embedding, slicing, slice flatting, slice drying, staining and slice sealing, staining the obtained slice by using a fluorescence staining agent, and observing and shooting the stained slice under a fluorescence microscope. The method for observing the deposition of callose of Agrostis stolonifera blade tissues based on the paraffin slice and the aniline blue fluorescence staining technology greatly shortens the experiment time of Agrostis stolonifera paraffin slice production, overcomes the difficulty in the production of the small and fine slice of an Agrostis stolonifera blade, breaks restriction brought by the material and environment factors, rapidly and highly-efficiently completes the paraffin slice production process, and finally obtains an excellent callose fluorescence microscopic observation result.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Catalytic reduction hemoglobin electrochemical sensor
InactiveCN105866221AQuick checkSensitive detectionMaterial electrochemical variablesSodium acetateMaterials science
The invention discloses a catalytic reduction hemoglobin electrochemical sensor which can achieve fast and sensitive detection of hemoglobin in a relatively large concentration range; the electrochemical sensor is a three-electrode system composed of a working electrode, a reference electrode and a counter electrode; the working electrode is prepared by the method according to the following steps: putting a three-electrode system with a glassy carbon electrode as the working electrode into a sodium acetate-acetic acid buffer solution having the pH of 5.0 and containing graphene and toluidine blue, and in a potential range of -0.8 to 1.3 V, carrying out cyclic voltammetry scanning for 25 laps at the scanning speed of 100 mV / s, to prepare a graphene / polytoluidine blue modified electrode; and putting a three-electrode system with the prepared graphene / polytoluidine blue modified electrode as the working electrode into an aqueous solution containing chloroplatinic acid and sodium chloride, and applying a -0.7 to -0.8 V constant potential between the working electrode and the reference electrode with the application time of 60-240 s.
Owner:LIAONING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for degrading triphenylmethane dye by utilizing recombinational lipoxygenase
InactiveCN104591407AEfficient productionCatalytic degradationWater contaminantsMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHeterologous
The invention discloses a method for degrading a triphenylmethane dye by utilizing recombinational lipoxygenase and application of the recombinational lipoxygenase rLOX-27853 in degrading the triphenylmethane dye. The amino acid sequence of the recombinational lipoxygenase rLOX-27853 is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The method for degrading the triphenylmethane dye by utilizing the recombinational lipoxygenase comprises the following steps: adding the recombinational lipoxygenase rLOX-27853 to a medium which contains sodium linoleate and the triphenylmethane dye to degrade the medium. The method disclosed by the invention obtains a novel prokaryotic lipoxygenase gene LOX-27853 by cloning from a pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC27853 strain genome and realizes the heterogenetic high-efficiency expression of host bacteria in escherichia coli by utilizing a fermentation culture method, thereby efficiently catalyzing the degradation of the triphenylmethane dyes, namely aniline blue, malachite green and brilliant green.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Sarranine and methyl violet mixed staining method for resin slices and staining solution thereof
InactiveCN104390834ADyeing effect is goodReduce storage requirementsPreparing sample for investigationMethyl violetANILINE BLUE
The invention provides a sarranine and methyl violet mixed staining method for resin slices and a staining solution thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a staining solution, namely preparing 0.5 mass percent of sarranine solution and 1 mass percent of methyl violet solution; and (2) respectively mixing the 0.5 mass percent of sarranine solution and the 1 mass percent of methyl violet solution according to multiple volume ratios, staining resin semithin sections, and observing the microscopic structure under a light microscope. According to the method disclosed by the invention, different histological stain requirements can be met aiming at the toluidine blue-O staining defect, and the method has the advantages of low cost and simplicity in preservation.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Method for treating paddy rice tissues by using prokaryotic expression product and inducing generation of callose
The invention relates to a method for treating paddy rice tissues by using a prokaryotic expression product of a magnaporthe grisea effect protein gene and inducing generation of callose, belonging to the technical field of plant protection and biology. The method is an improvement on the prior art, comprises a prokaryotic expression technology which is the same as that of the conventional method, a protein purifying technology, the wavelength ranges of exciting light and emitted light of a used fluorescence microscope and an aniline blue dyeing method, and is characterized by comprising the following steps of: treating the root tissues of Nipponbare serving as a disease-resistant paddy rice variety with the prokaryotic expression product which is 1.0-10.0 mg / ml in concentration of the magnaporthe grisea effect protein gene is used for treating the root tissues for 12 hours; performing aniline blue dyeing; and directly observing the formation of callose under the fluorescence microscope. The method is easy, convenience, accurate and rapid; and a large amount of spontaneous fluorescence interference can be avoided effectively, and the situation of basic defense reaction of paddy rice can be obtained directly and qualitatively.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Composite reagent for screening early-stage oral intima cell disease and application method thereof
InactiveCN102221526ARaise Response BackgroundReduce false positivesDiagnostic recording/measuringColor/spectral properties measurementsToluidineChemistry
The invention discloses a composite reagent for screening early-stage oral intima cell diseases, which comprises: toluidine blue used as a biochemical reagent of the detection reagent, and acetic acid used as an auxiliary reagent of the detection reagent, wherein the concentration of the toluidine blue solution is 0.2-2%, and the concentration of the acetic acid solution is 0.01-5%. The invention also discloses an application method of the composite reagent for screening early-stage oral intima cell diseases, which is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: firstly gargling with acetic acid for 1-2 min, then gargling with a mixed solution of toluidine blue and acetic acid for 1-2 min, and finally gargling with acetic acid for 1-2 min, wherein the ratio of toluidine blue and acetic acid in the mixed solution is 1:0.5-1.
Owner:叶欣
Collagenous fiber Masson trichrome stain kit, preparation method thereof and staining method
InactiveCN107907397AQuick stainBreaking down the dyeing barriers of dyeing vatsPreparing sample for investigationFiberPhosphomolybdic acid
The invention relates to a collagenous fiber Masson trichrome stain kit, a preparation method thereof and a staining method. The stain kit comprises a kit body, wherein 6 dropping bottles are contained in the kit body; different reagents are respectively contained in the 6 dropping bottles; the volumes of the dropping bottles are 5ml or 10ml; the reagents in the 6 dropping bottles are hematoxylinstaining solution, hydrochloric acid differentiation solution, back-to-blue solution, ponceau acid fuchsin solution, phosphomolybdic acid solution and aniline blue solution separately. The kit performs optimization in terms of the packaging of the kit, formulas of reagents and a staining process, further a collagenous fiber Masson trichrome stain kit based on instillation is assembled, and the kitcan be directly applied to rapid staining of small-scale tissue slices, and has the characteristics of economical efficiency, practicability, special effect and speediness.
Owner:苏州泽科生物科技有限公司
Optimized manufacturing method of paraffin sections of different flower tissues of phalaenopsis amabilis
ActiveCN111257089AShort production methodShorten the timePreparing sample for investigationANILINE BLUEMicroscopic exam
The invention provides an optimized manufacturing method of paraffin sections of different flower tissues of phalaenopsis amabilis. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: (1) fixing;(2) dehydrating; (3) waxing; (4) embedding; (5) slicing and unfolding; (6) dewaxing and rehydrating; (7) toluidine blue dyeing and microscopic examination, and carrying out proper differentiation anddrying according to tissue coloring depth; and (8) performing transparent sealing. Components and operation time of reagents in fixing, softening and dewatering links are optimized for different flower tissues of the phalaenopsis amabilis, the completeness of cells in slices is better kept, and unlignified soft tissues and lignified hard tissues can be clearly distinguished.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL HORTICULTURE RES INST OF GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Oral cancer markers and their detection
Methods of detecting progression from precancer to cancer are provided utilizing toluidine blue staining as well as detecting allelic variation at microsatellite loci. An allelic variation in one or more locus is indicative of a progression from precancer to cancer.
Owner:ZILA INC
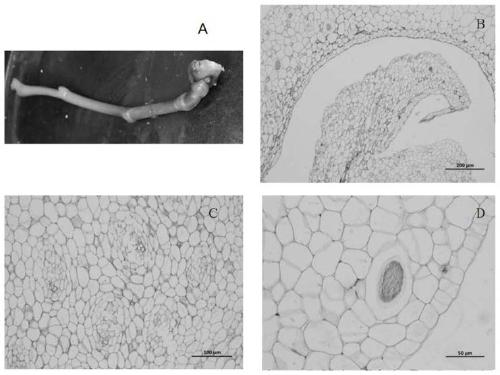
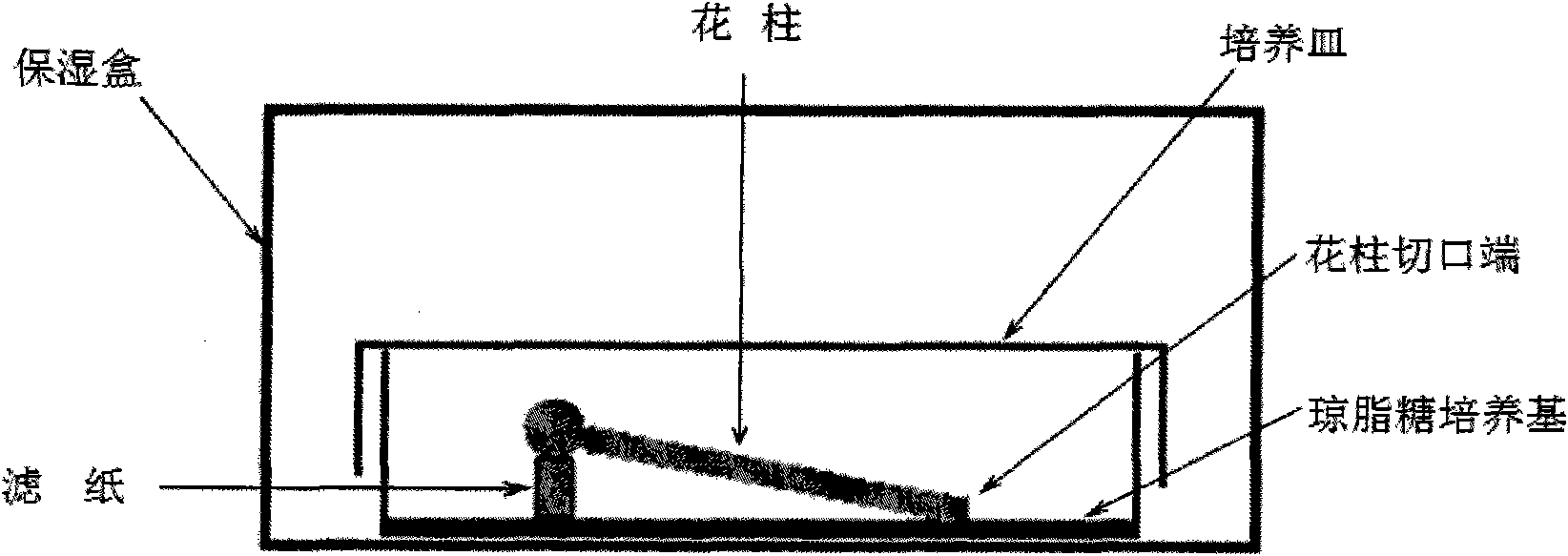
Method for identifying self-fruitful pear varieties by using pollination in vitro
InactiveCN101889543AThe identification method is simpleSimple and fast operationPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAniline blue stainSelf-pollination
The invention discloses a method for identifying self-fruitful pear varieties by using pollination in vitro indoor, belonging to the field of plant breeding. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out self-pollination by using large flower buds; immediately cutting styluses from the base parts of the styluses and the ovaries by using blades after carrying out the self-pollination; placing the styluses on a solid medium, culturing the styluses for 48 hours under the dark environment of 25DEG C, and taking out the styluses; dripping several drips of 0.1 percent aniline blue staining fluid on the base parts of the styluses; and observing the grow of pollen tubes from the base parts of the styluses under a microscope. If the pollen tubes grow from the base parts of the styluses, the variety can be fruitful by using the self-pollination; and if the pollen tubes do not grow from the base parts of the styluses, the variety cannot be fruitful by using the self-pollination. The method solves the problem of identifying the self-fruitful property in large quantity within one year, not only can identify all pear variety resources, but also can reference the identification of the self-fruitful property of other fruit trees and has wide application prospect.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for processing aniline-blue-containing pollution wastewater by using cultivation material of harvested pleurotus eryngii
InactiveCN104495971AAchieve reuseLow selection costWater contaminantsWaste water treatment from textile industryANILINE BLUEOrganic dye
The invention concretely relates to a method for processing aniline-blue-containing pollution wastewater by using a cultivation material of harvested pleurotus eryngii. The method comprises: crushing the cultivation material of harvested pleurotus eryngii by using a crusher, pouring into aniline-blue-containing pollution wastewater, oscillating in a shaking table at a constant temperature, wherein the decoloring conditions for 100 mg / L of the aniline-blue-containing pollution wastewater comprises that the temperature is 20-40 DEG C, the molecular mediator is ABTS with the concentration of 400 mu mol / L, the Mn<2+> concentration is 1-3 mol / L, and the rotation speed is 50-150 rpm. By utilizing pleurotus eryngii cultivation waste material to process dye wastewater, environment is purified and also waste reutilization is realized, so that the method has good development prospect. The cultivation material of harvested pleurotus eryngii is taken as an experiment material for processing dye wastewater, is capable of adsorbing a part of a dye, and also is capable of secreting lignin digestive enzyme for degrading a toxic organic dye with a complex structure, and has important practical meaning on current dye wastewater processing.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Non-toxic coloring agent used for detecting grass endophytic fungi
InactiveCN106353162AEasy to distinguishImprove dyeing effectPreparing sample for investigationColor effectSolvent
The invention provides a non-toxic coloring agent used for detecting grass endophytic fungi. The non-toxic coloring agent comprises aniline blue, lactic acid and solvent. The non-toxic coloring agent is free from phenol harmful to human beings and environment, coloring effect is improved by simply heating slides on alcohol lamp flame during coloring, and distinguish between endogenous fungal hyphae and cell walls is facilitated.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Composite dyeing agent and application thereof
InactiveCN110755642AMake up for the shortcomings that are not easy to observeAccurate guidanceLuminescence/biological staining preparationDiseaseANILINE BLUE
The invention discloses a composite dyeing agent and an application thereof. The composite dyeing agent is mixed liquid consisting of an acetic acid solution, a toluidine blue solution and normal saline, wherein in the mixed liquid, the mass concentration of acetic acid is 1.5%-2%, and the mass concentration of toluidine blue is 0.2%-0.4%. The composite dyeing agent cooperates with a gastroenterological endoscope, so that the focus of a disease, which is difficult to distinguish can be convenient to find, and the composite dyeing agent is particularly used for esophagitis of dogs, and can improve the diagnosis rate and the sensibility of the esophagitis of the dogs.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for evaluating development situation of cuticles of mature apple fruits
InactiveCN103471949AReduce mistakesThe judgment result is objective and accurateTesting foodMaterial weighingANILINE BLUECutin
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Establishment of method for screening and identifying new species of different types of edible fungi
InactiveCN101760505AQuick monitoringEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyManganese peroxidase
The invention provides a new method for screening and identifying genetic breeding new species of edible fungi, which solves the problems of obvious screening mark shortage, a waste of time and heavy work load during identifying whether the edible fungi or the new species contains manganese peroxidase or lignin peroxidase or not and slow qualitative identification and monitoring in the prior art. The new method comprises the following steps of: using aniline blue as one of materials for preparing a solid culture medium; inoculating a strain of the edible fungi to the solid culture medium; viewing the color change condition of the aniline blue solid culture medium after culturing; and identifying whether the edible fungi contains the manganese peroxidase or the lignin peroxidase or the manganese peroxidase and the lignin peroxidase or not. The new method can directly, conveniently and flexibly qualitatively judge whether the edible fungi contains the manganese peroxidase or the lignin peroxidase or not, is especially suitable for qualitatively detect two different types of wood-rotting fungi or new fused strains of other fungi and has low detection cost.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Method for staining and identifying arterial wall components
InactiveCN109187147APreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsFiberParaffin wax
The invention discloses a method for staining and identifying arterial wall components. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: sequentially performing heating, dewaxing, hydrating, hematoxylin iron staining, acid aniline blue staining and acid red staining on arterial sections of paraffin, dehydrating, clarifying and sealing, and enabling different components in the arterial walls to present different colors. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the cell nucleus is stained into dark blue or black to form dots or small strips; elastic fibers are stained into black and are rope-shaped; collagen fibers are stained into blue and are rope-shaped; endothelial cell cytoplasm is stained to be rosy to form strips; and smooth muscle cell cytoplasm is stained tobe rosy to form long shuttles. According to the stained colors and morphological features, the arterial wall components are identified. Different components of the arterial walls present different colors by virtue of staining, the arterial wall components are identified by distinguishing the colors and combining morphological changes, and arterial diagnosis and treatment can be assisted.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV (GUANGZHOU RESPIRATORY CENT)
Separation method of aspergillus tubingensis and application of aspergillus tubingensis
PendingCN114262669AThe separation method is simpleEfficient degradationFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySporeling
The invention relates to a method for separating Aspergillus tubingensis and application of Aspergillus tubingensis, straws are taken as a carrier to extract microorganisms capable of degrading straws, strains can be massively propagated through culture, red brown to brown black conidia are obtained through separation, the conidia are spherical or radial, most of molecular sporophores are generated from a matrix, and most of the molecular sporophores grow from the matrix. Most spore production structures are double layers, and bacterial colonies of top sacs are densely generated; the method comprises the following steps: selecting bacterial colonies, activating the selected bacterial colonies, culturing the bacterial colonies by using an ABTS chromogenic solid culture medium and an aniline blue chromogenic solid culture medium, seeing that decolorized rings are generated after the bacterial strains are dyed, proving that the bacterial strains can secrete laccase and lignin peroxidase, amplifying ITS sequences of the screened bacterial strains, and comparing the sequences in NCBI (National Center of Biotechnology Information) to obtain similar sequence information. A phylogenetic tree is established by utilizing MEGA-X, the strain is determined to be Aspergillus tubingensis, and the Aspergillus tubingensis can be applied to lignin degradation and dye decoloration.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
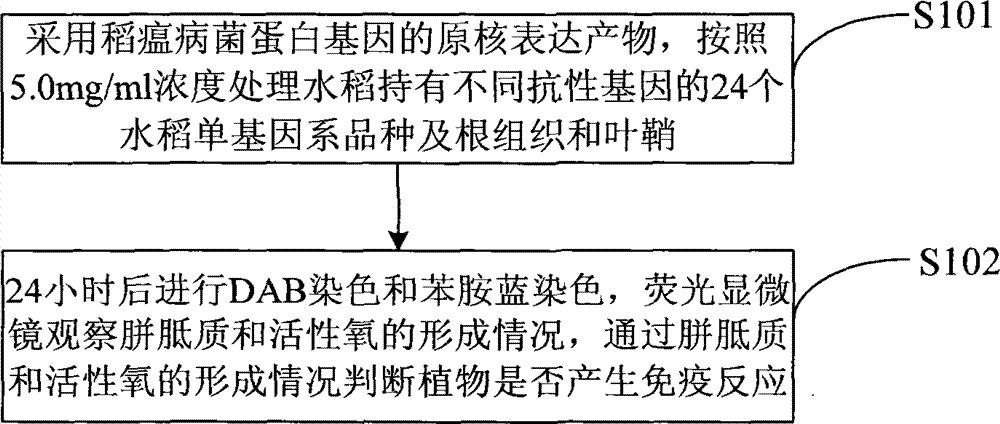
Method for detecting generation of plant immunoreaction
The invention discloses a method for detecting generation of plant immunoreaction. The existing purification expression through prokaryotic expression products and the callose and reactive oxygen observation method are remained the same; the prokaryotic expression products of rice blast mycoprotein genes are adopted; 24 rice single-gene varieties containing different resistance genes, root organizations and sheaths of rice are processed according to the concentration of 5.0 mg / ml; the DAB dyeing and the aniline blue dyeing are implemented after 24 hours; the forming conditions of callose and reactive oxygen are directly observed through a fluorescence microscope; and the generation of the plant immunoreaction is judged through the forming conditions of the callose and the reactive oxygen. The method uses the prokaryotic expression products of purified effect protein genes to process the rice root organizations, and observes the generation of the callose and the reactive oxygen of the root organizations through the fluorescence microscope, so that the generation condition of the rice immunoreaction can be directly obtained, and the rice blast mycoprotein capable of leading a plurality of rice single-gene varieties containing different resistance genes and susceptible varieties to generate the immunoreaction is synchronously obtained.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
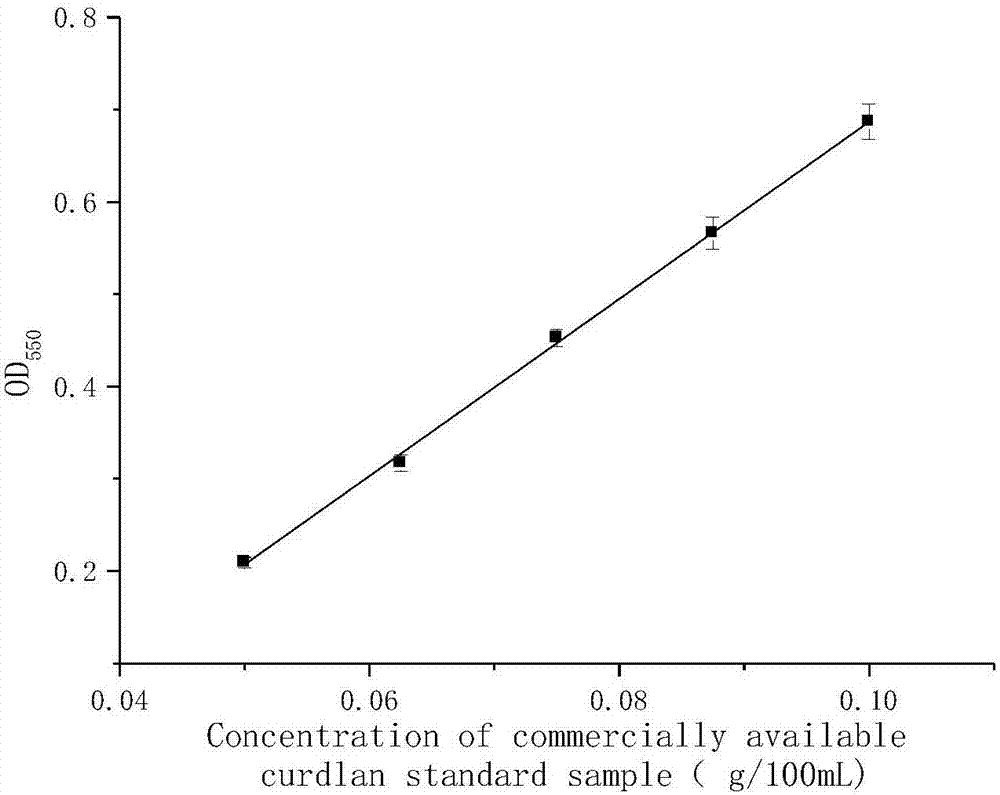
Method for rapidly and specifically detecting curdlan content
InactiveCN107132149AAddressing the disadvantage of non-specificityQuickly Compare Production CapabilitiesWeighing by removing componentColor/spectral properties measurementsANILINE BLUEFermentation broth
The invention belongs to the technical field of food and fermented product detection, and particularly relates to a method for rapidly and specifically detecting curdlan content, and an application of the method. The method for rapidly and specifically detecting the curdlan content includes the steps: preparing aniline blue solution; preparing curdlan standard alkali solution; making a curdlan standard curve; measuring the content of a curdlan sample. According to the method, the content of curdlan in various solution such as fermented solution can be rapidly detected, change of the yield of the curdlan in the fermentation process can be rapidly tracked, fermentation production strategies are correspondingly adjusted, and the production capacity of different strains in the liquid fermentation process is rapidly compared, so that curdlan strain breeding and fermentation control level is promoted.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Acidic lipoxygenase and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses acidic lipoxygenase and a preparation method and application thereof. A novel lipoxygenase gene MxLOX is obtained by cloning from an Myxococcus xanthus DK1622 strain genome, and the amino acid sequence of the novel lipoxygenase gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The lipoxygenase has the highest activity under the conditions that the pH is 3.0 and the temperature is 30 DEG C, and has stable activity under the conditions that the pH is 2.5-5.0 and the temperature is 30 DEG C. Recombinant lipoxygenase rMxLOX can efficiently catalyze degradation of triphenylmethane dyes such as aniline blue and methyl blue, and has an potential application value in treatment of acidic industrial wastewater.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com