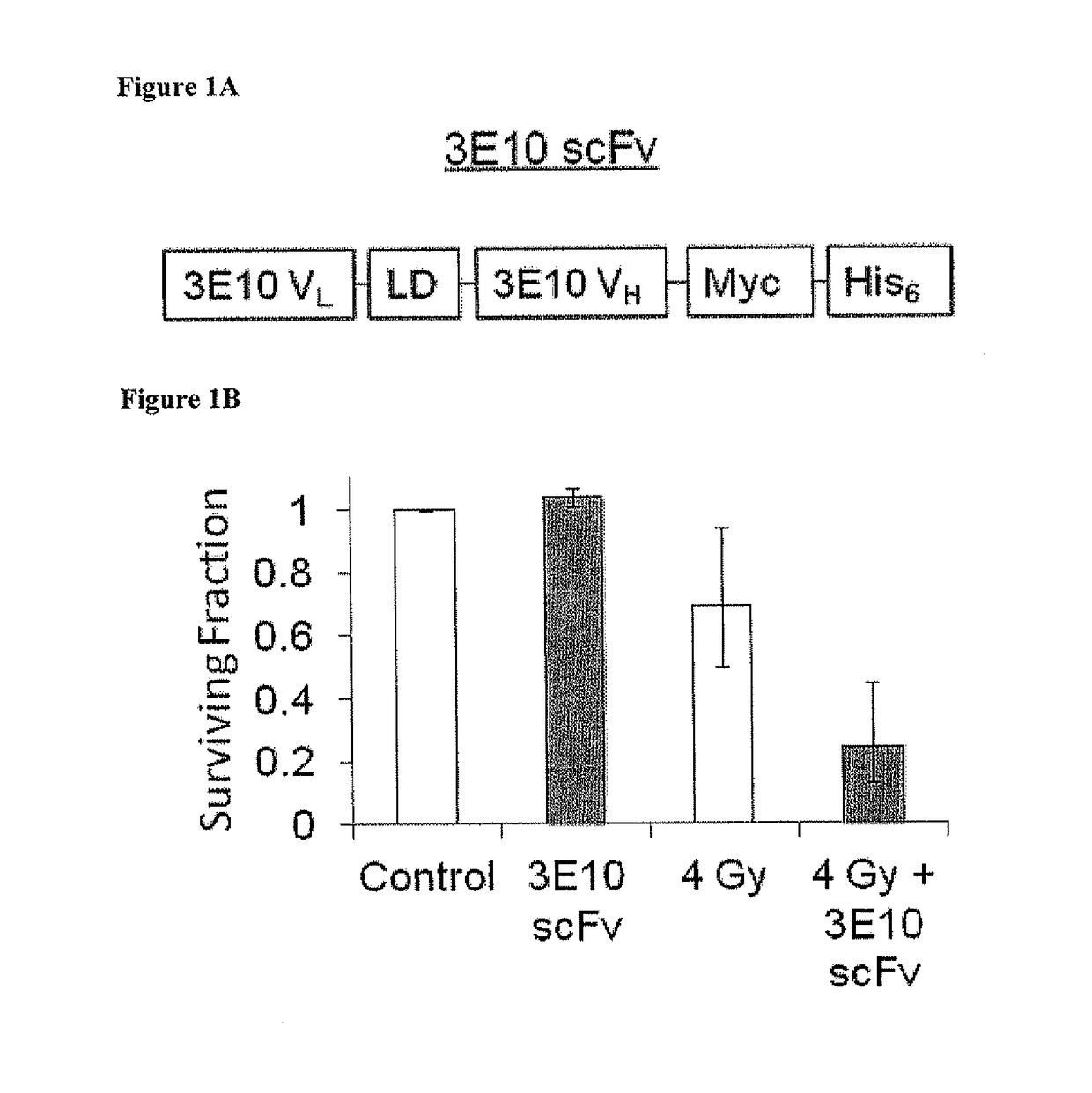
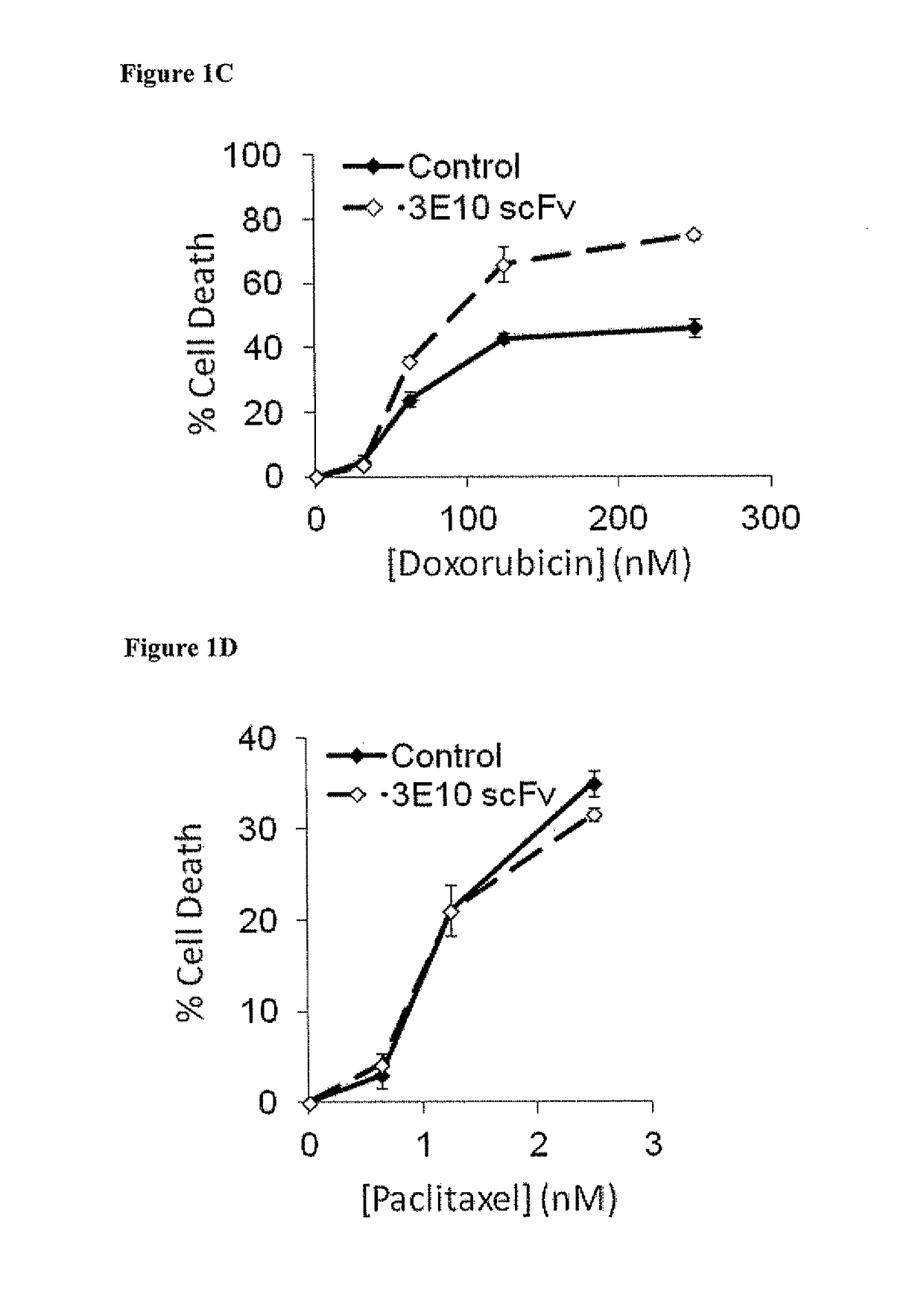
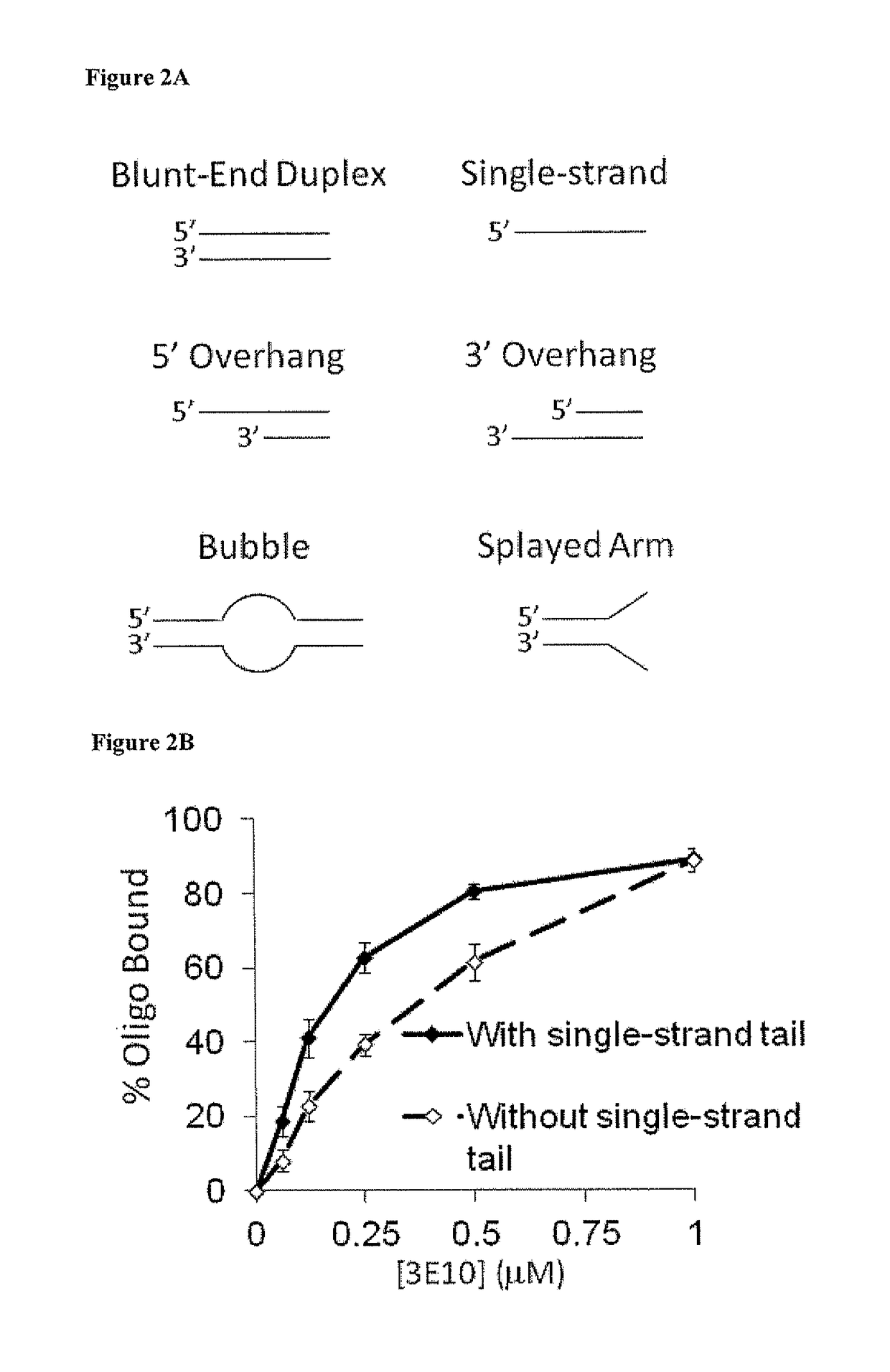
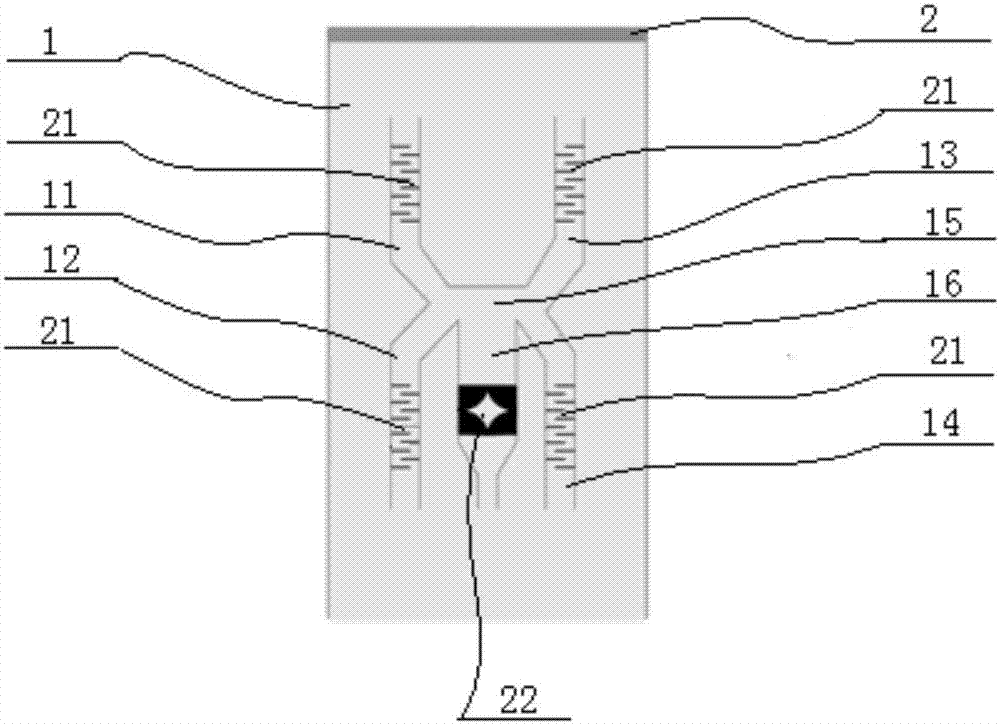
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
185 results about "Treated cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
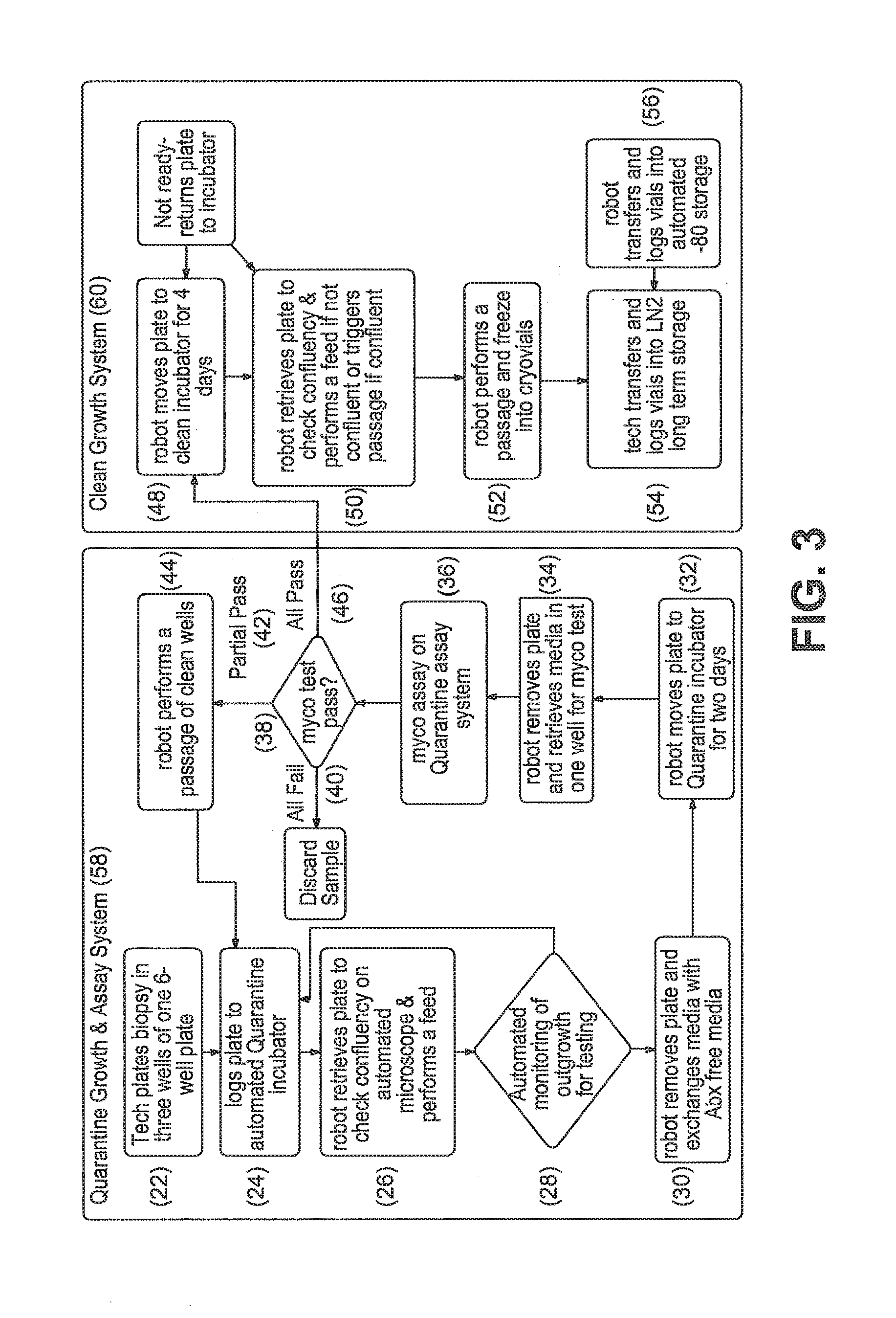
Biological Cell Acoustic Enhancement and Stimulation
InactiveUS20080045882A1Improve efficiencyAccelerate patient recoverySonopheresisUltrasound therapyBiological cellAcoustic energy
A method for enhancing the uptake of a therapeutic biological agent by treated cells. A low-power, unfocused field of acoustic energy is directed at the treated cells after the delivery of the therapeutic agent to the treated cells. A related method for stimulating either neural cells or cells in a cell culture. A portable sized device provides the field, and may include either an array of emitters or a scanable emitter.
Owner:FINSTERWALD P MICHAEL
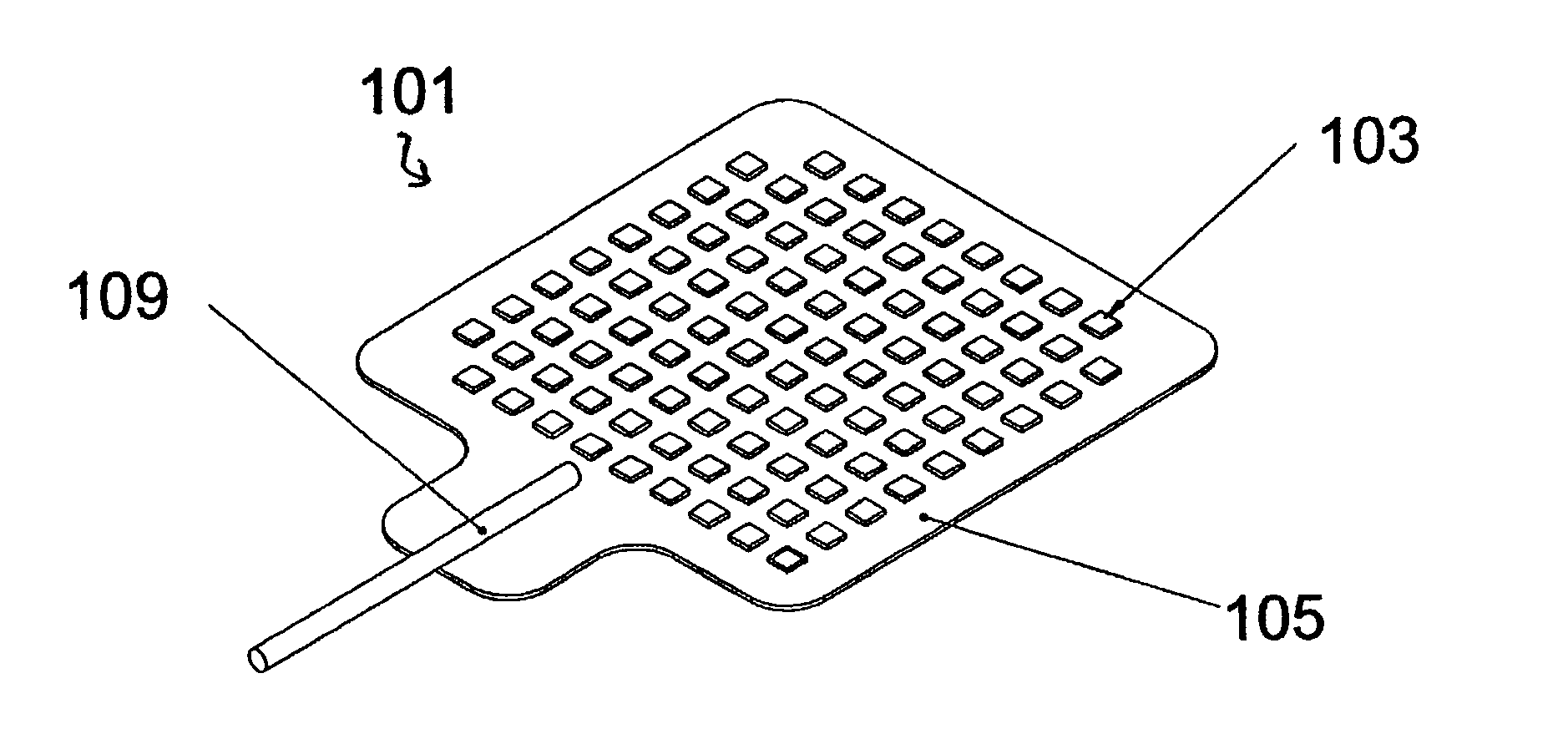
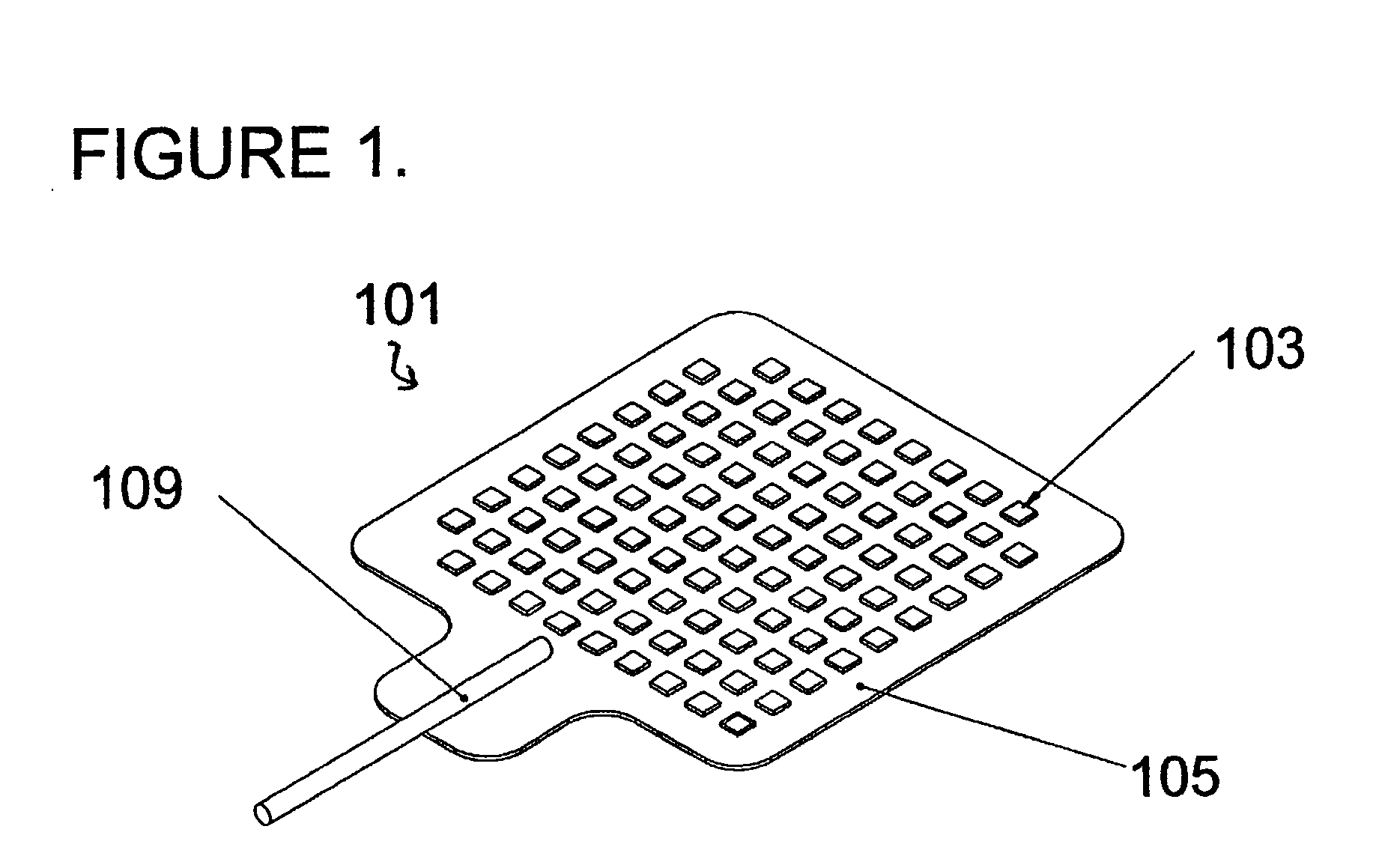
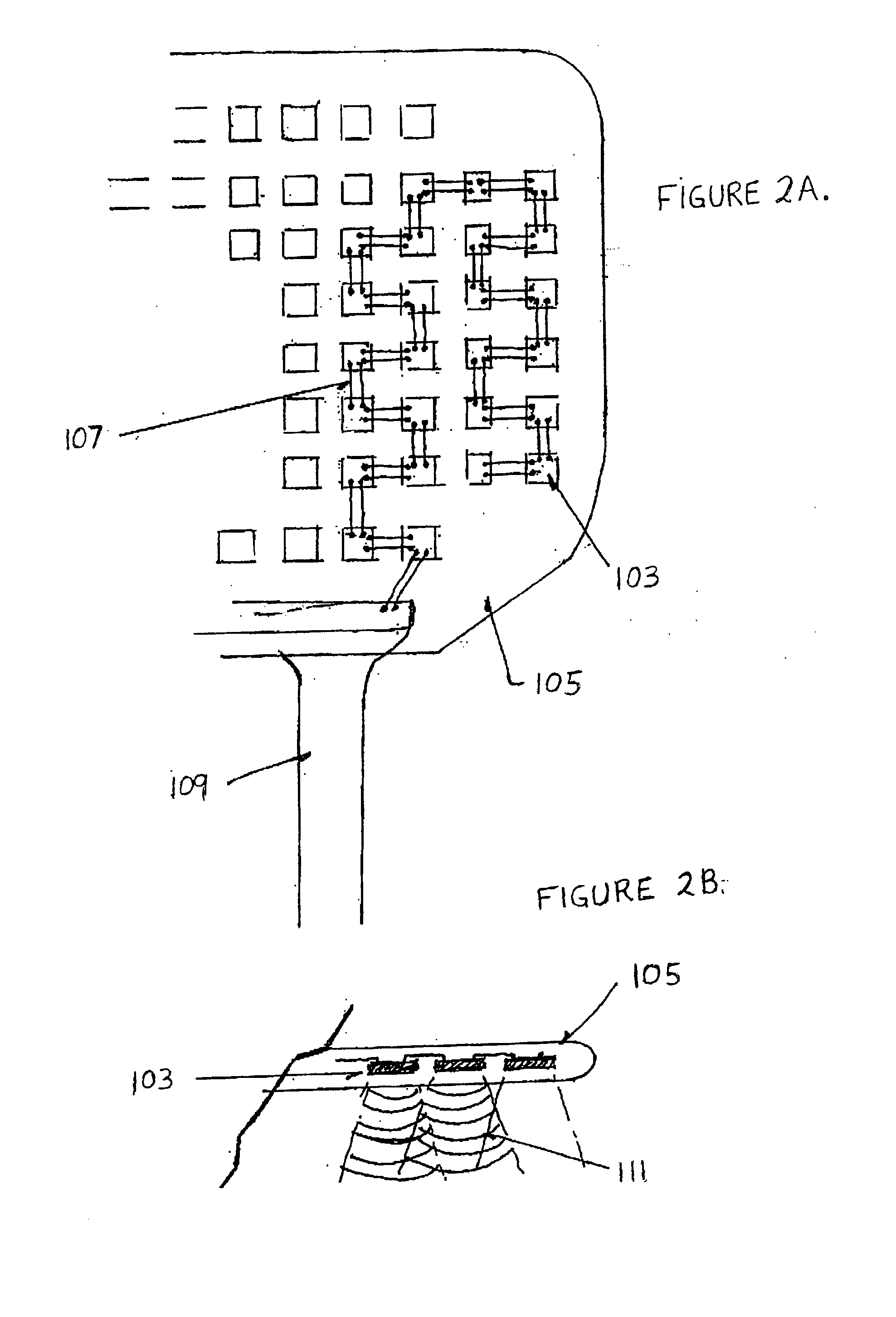
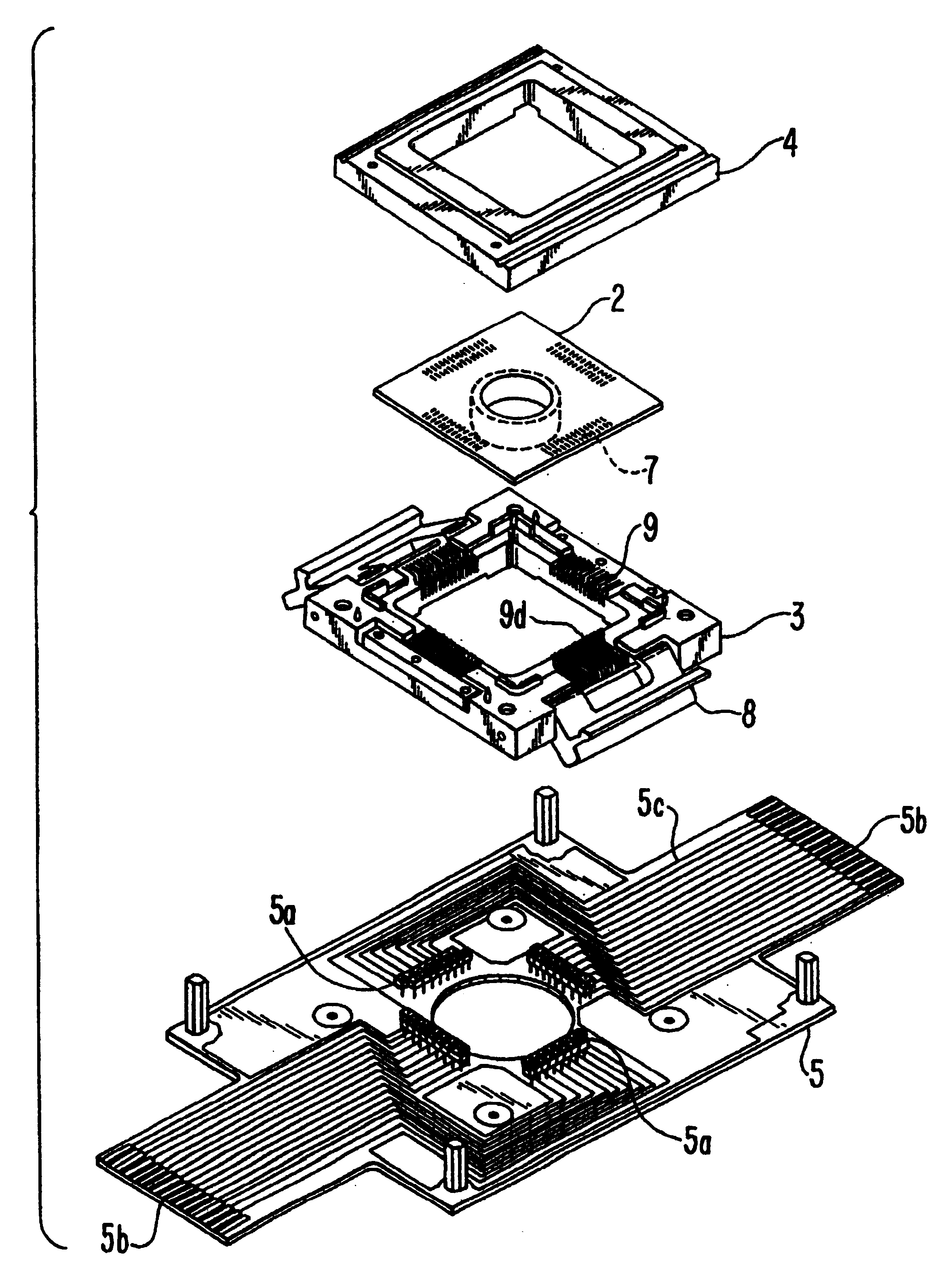
Cell potential measurement apparatus having a plurality of microelectrodes
InactiveUSRE38323E1Precise positioningReduce surface resistanceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMeasurement devicePotential change
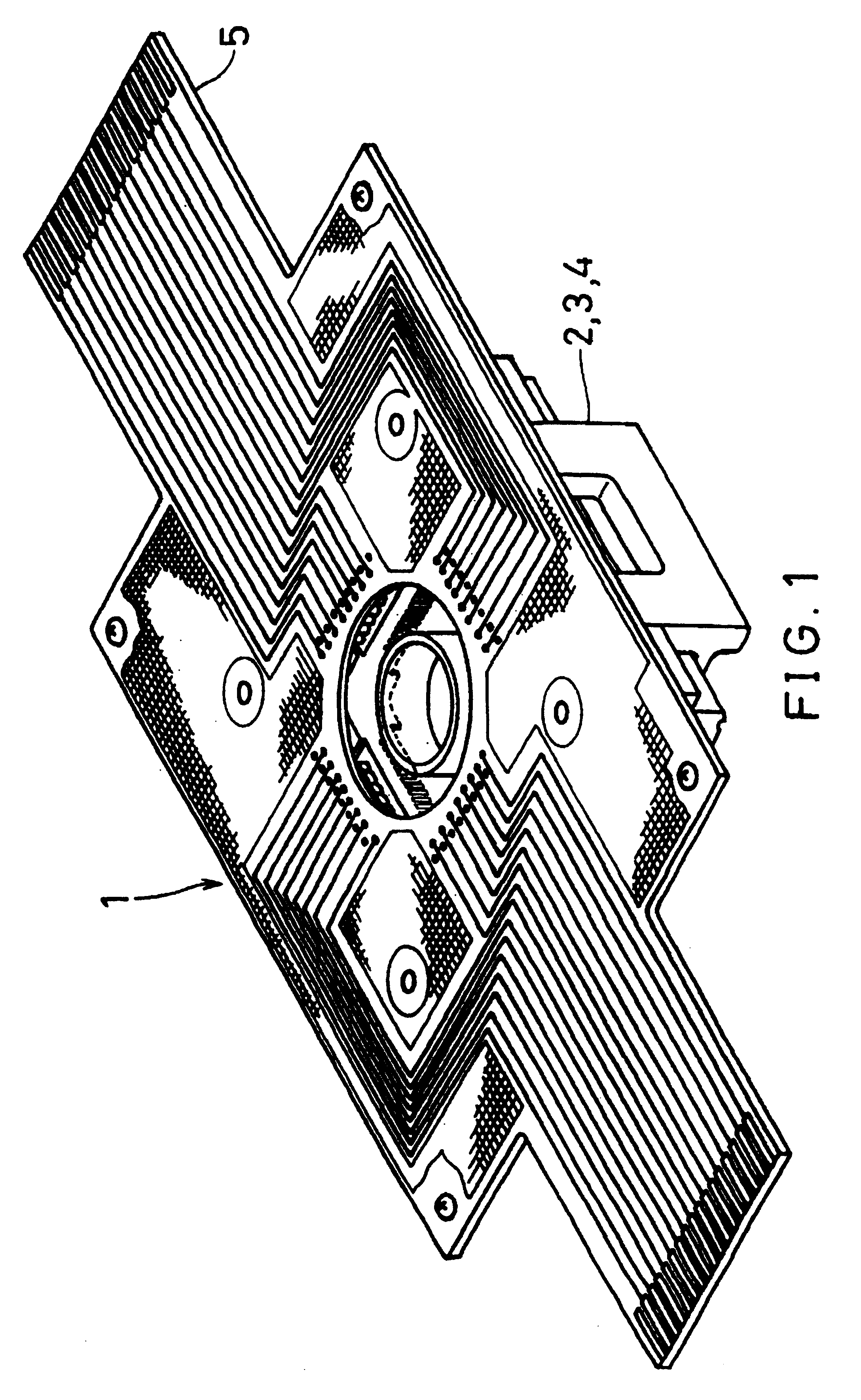
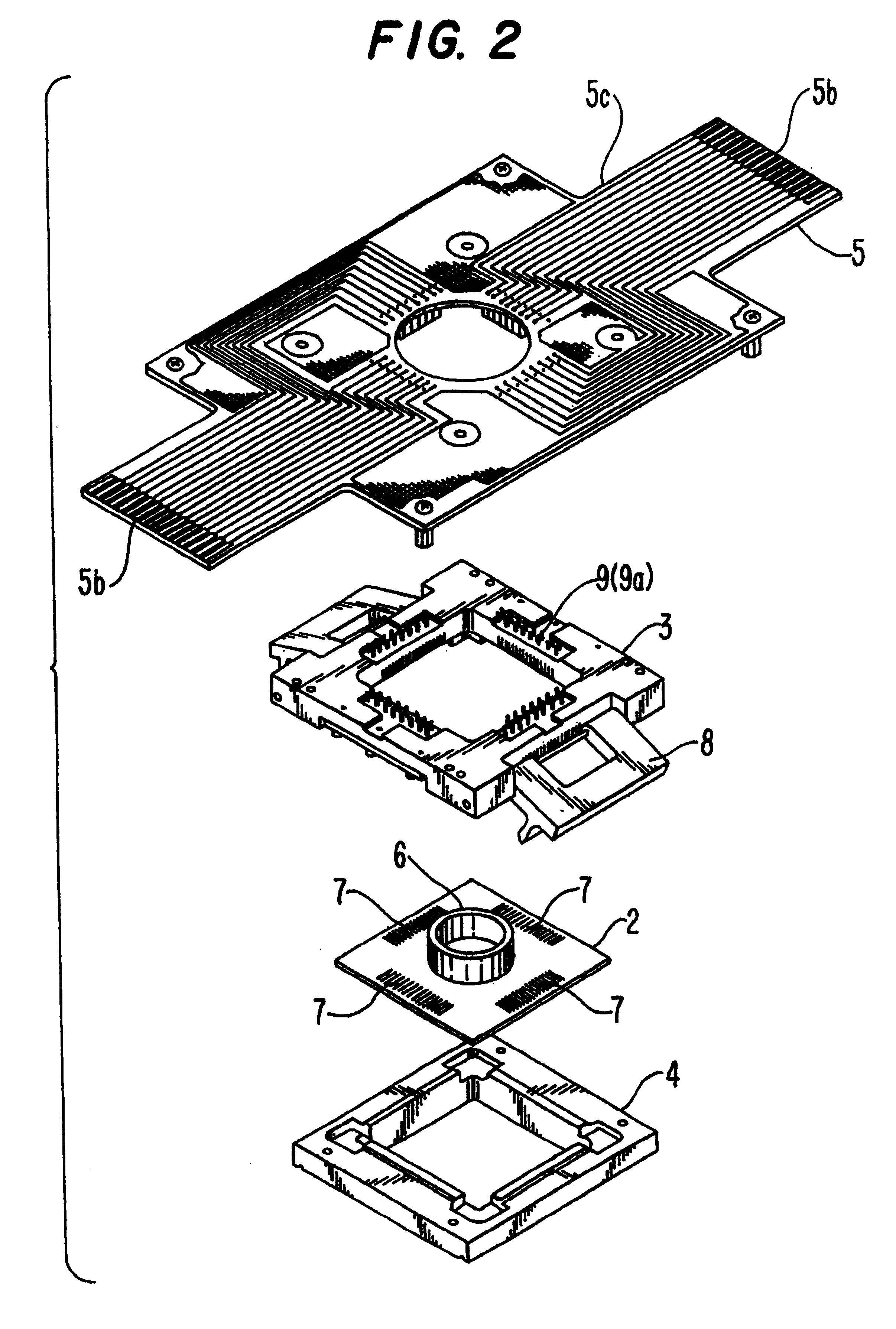
A cell potential measurement apparatus, which uses a planar electrode enabling a multi-point simultaneous measurement of potential change arising from cell activities, is provided which can conduct measurements accurately and efficiently as well as can improve convenience of arranging measurement results. According to the configuration of the cell potential measurement apparatus of this invention, it includes an integrated cell holding instrument 1, which includes a planar electrode provided with a plurality of microelectrodes arranged in a matrix form on the surface of a substrate, a cell holding part for placing cells thereon, drawer patterns from the microelectrodes, and electric contact points for outside connections; an optical observation means 20 for optical observations of cells; a stimulation signal supply means 30 to be connected to the cell holding instrument for providing electric stimulation to the cells; and a signal processing means 30 to be connected to the cell holding instrument for processing an output signal arising from electric physiological activities of the cells. It is preferable that a cell culturing means 40 is also provided for maintaining a culture atmosphere of the cells placed on the integrated cell holding instrument.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Methods and compositions for the preparation and use of fixed-treated cell-lines and tissue in fluorescence in situ hybridization
InactiveUS6995020B2Easy to detectReduced autofluorescenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical treatmentTreated cell
This invention relates to methods for the detection of one or more mRNA transcripts in paraffin-embedded tissue by “mRNA liberation in fixed-treated tissue or ‘MLIFTT’”. This method includes treating the tissue with ammonia-ethanol and sodium borohydride combined with pressure cooking of the tissue. The chemical treatments reduce the tissue autofluorescence and the physical treatments overcome the interference created by the fixation-induced chemical bonds. The methods of the present invention can be utilized to identify a plurality of mRNA transcripts in a microarray format.
Owner:AUREON LAB INC +2
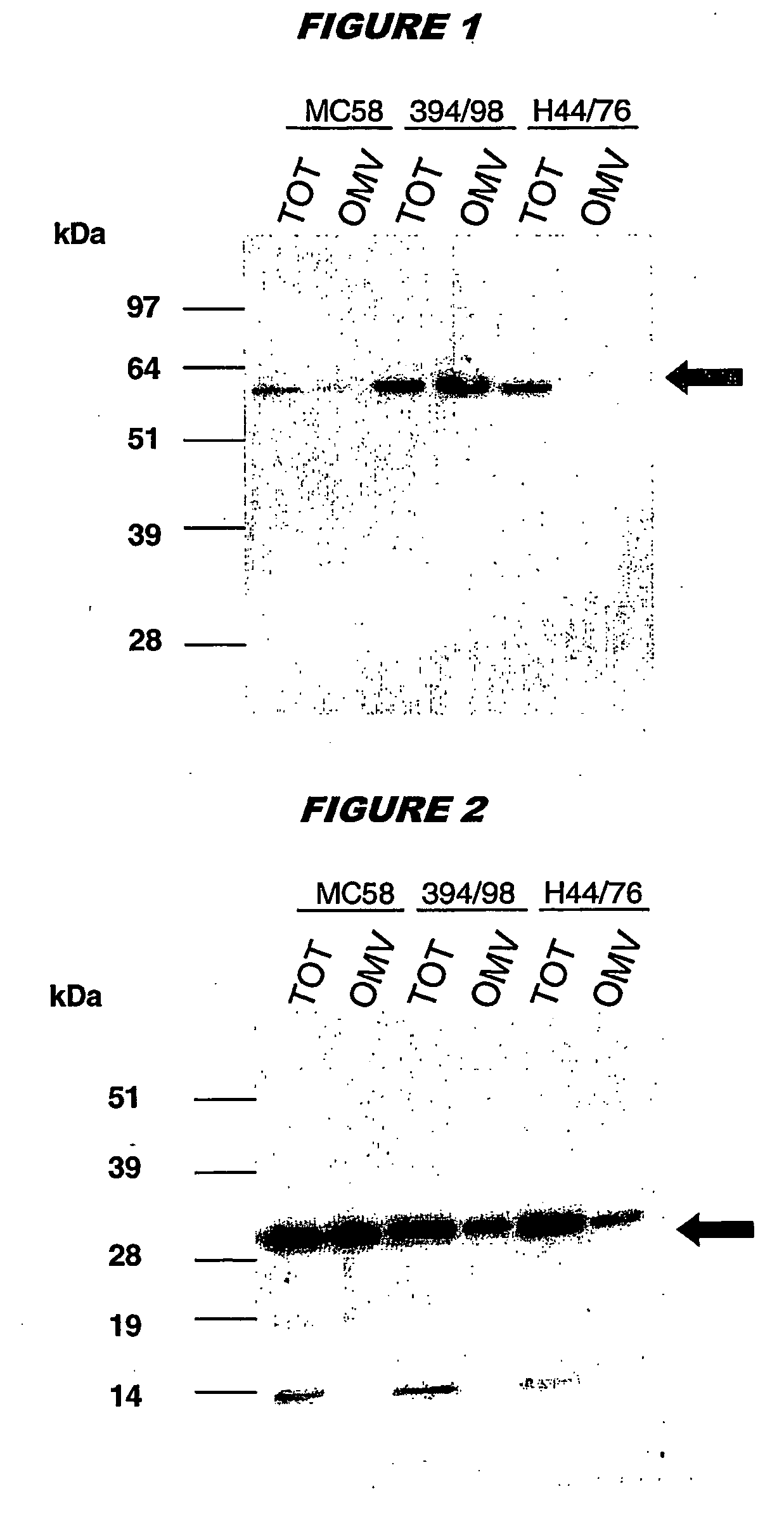
Bacterial outer memberane vesicles
InactiveUS20060166344A1Good curative effectAvoid problemsAntibacterial agentsBacteriaImmunogenicityTreated cell
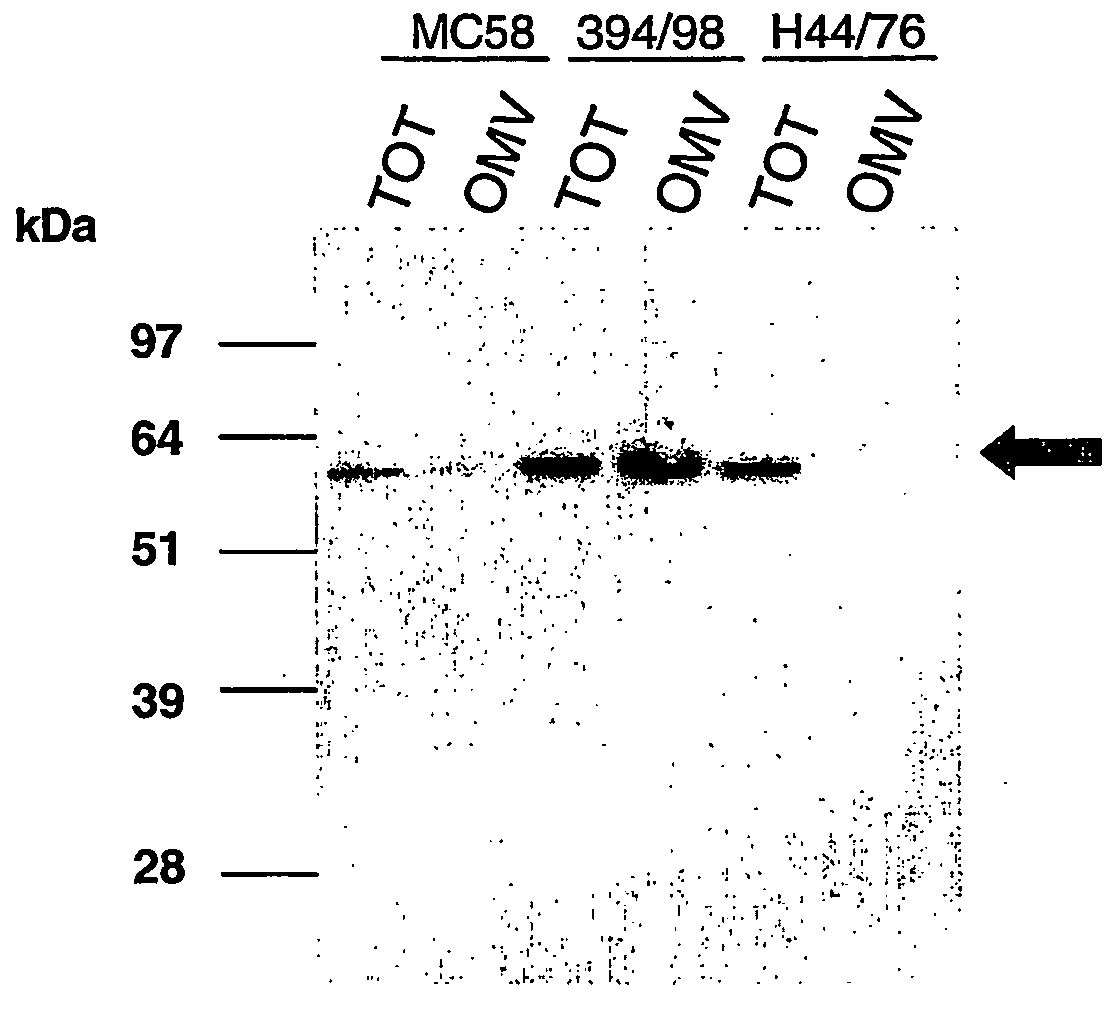
Existing methods of meningococcal OMV preparation involve the use of detergent during disruption of the bacterial membrane. According to the invention, membrane disruption is performed substantially in the absence of detergent. The resulting OMVs which retain important bacterial immunogenic components, particularly (i) the protective NspA surface protein, (ii) protein NMB2132 and (iii) protein NMB 1870. A Typical process involves the following steps: (a) treating bacterial cells in the substantial absence of detergent; (b) centrifuging the composition from step (a) to separate the outer membrane vesicles from treated cells and cell debris, and collecting the supernatant; (c) performing a high speed centrifugation of the supernatant from step (b) and collecting the outer membrane vesicles in a pellet; (d) re-dispersing the pellet from step (c) in a buffer; (e) performing a second high speed centrifugation in accordance with step (c), collecting the outer membrane vesicles in a pellet; (f) re-dispersing the pellet from step (e) in an aqueous medium.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
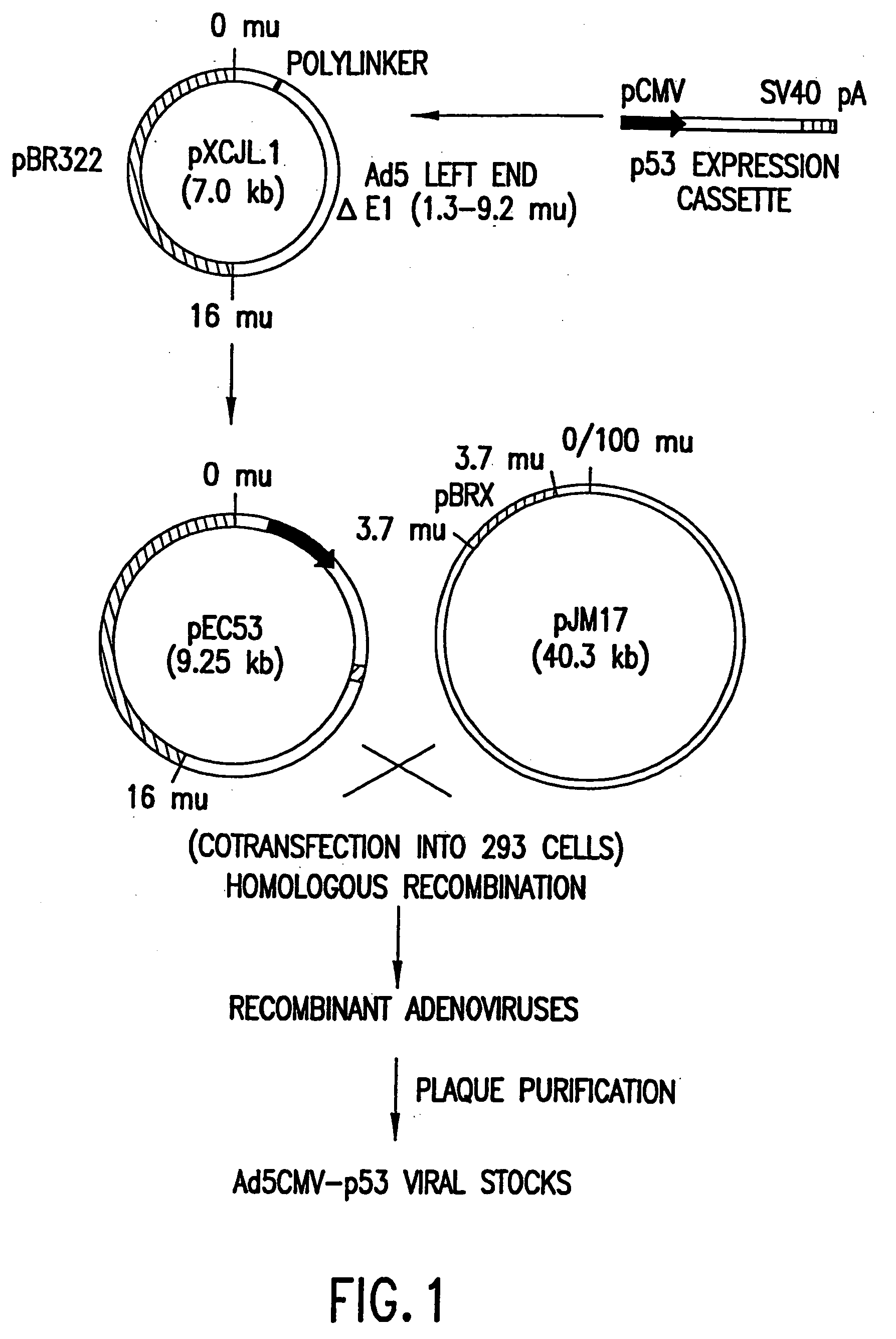
Methods and compositions comprising DNA damaging agents and p53
InactiveUS20050089511A1Improve the level ofLow cellular uptakeOrganic active ingredientsElectrotherapyRegimenCancer cell
The present invention relates to the use of tumor suppressor genes in combination with a DNA damaging agent or factor for use in killing cells, and in particular cancerous cells. A tumor suppressor gene, p53, was delivered via a recombinant adenovirus-mediated gene transfer both in vitro and in vivo, in combination with a chemotherapeutic agent. Treated cells underwent apoptosis with specific DNA fragmentation. Direct injection of the p53-adenovirus construct into tumors subcutaneously, followed by intraperitoneal administration of a DNA damaging agent, cisplatin, induced massive apoptotic destruction of the tumors. The invention also provides for the clinical application of a regimen combining gene replacement using replication-deficient wild-type p53 adenovirus and DNA-damaging drugs for treatment of human cancer.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
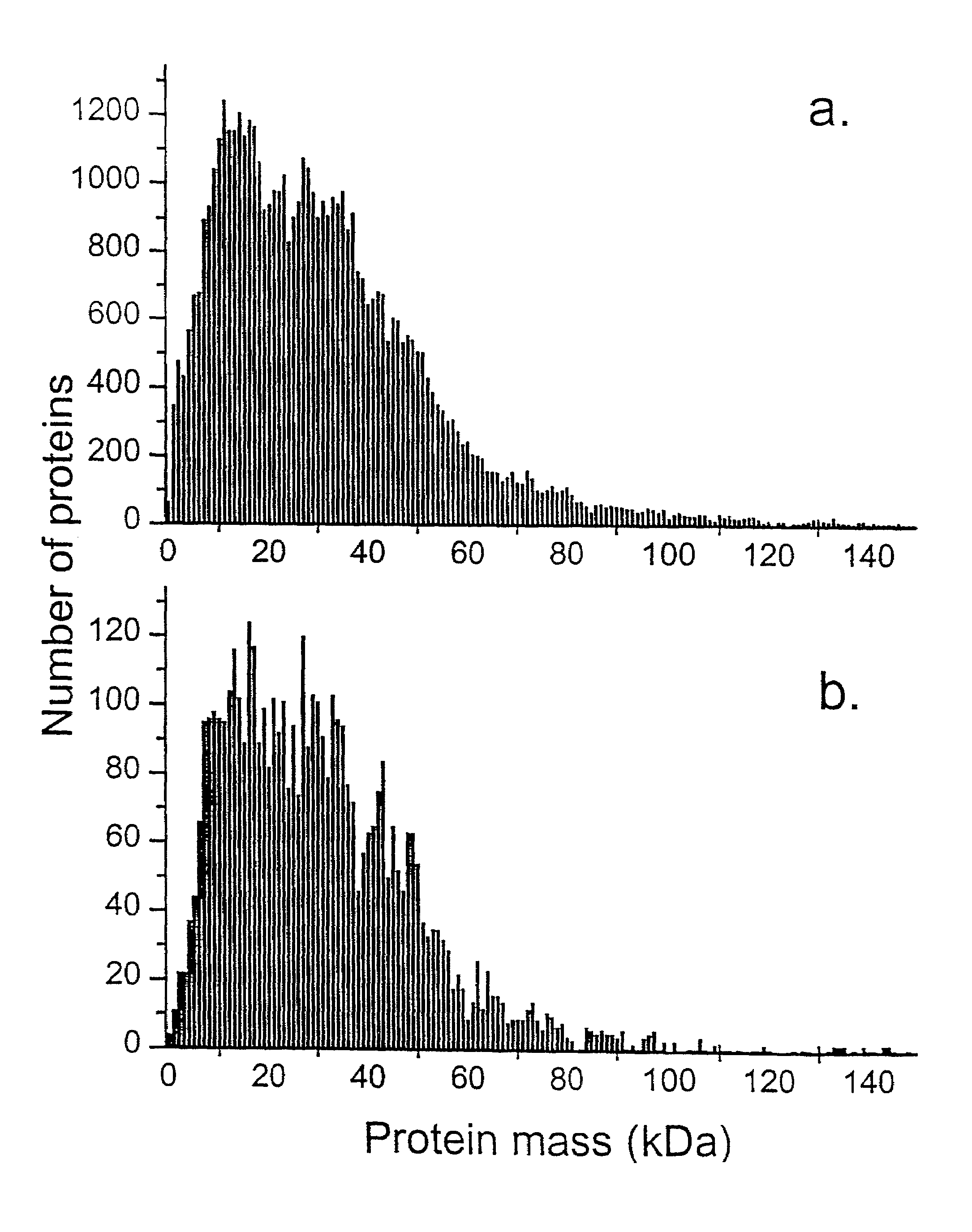
Methods for identifying and classifying organisms by mass spectrometry and database searching
InactiveUS7020559B1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingSequence databaseProtein molecules
A method for rapid identification of biological materials is presented, which exploits the wealth of information contained in genome and protein sequence databases (5). In a preferred embodiment, the method utilizes the masses of a set of ions by MALDI TOF mass spectrometry of intact or treated cells (1). Subsequent correlation (4) of each ion in the set to a protein, along with the organismic source of the protein, is performed by searching a database comprising protein molecular weights (9).
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF +1
Methods for promoting fusion and reprogramming of somatic cells
InactiveUS20110136145A1Microbiological testing/measurementGenetically modified cellsDemethylaseMethyltransferase Gene
The invention features methods for reprogramming somatic cells by treating the cells with one or more agents to induce de-differentiation, in particular by targeting demethylase and methyltransferase genes. The invention also features methods of monitoring somatic cell fusion and reprogramming and methods of identifying agents that alter somatic cell fusion and reprogramming. The invention also features reprogrammed cells and kits.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Compositions and methods for increasing cellular far and bleaching skin
InactiveUS20110150798A1Reduce tissue damageCut skinOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsLipid contentPharmacology
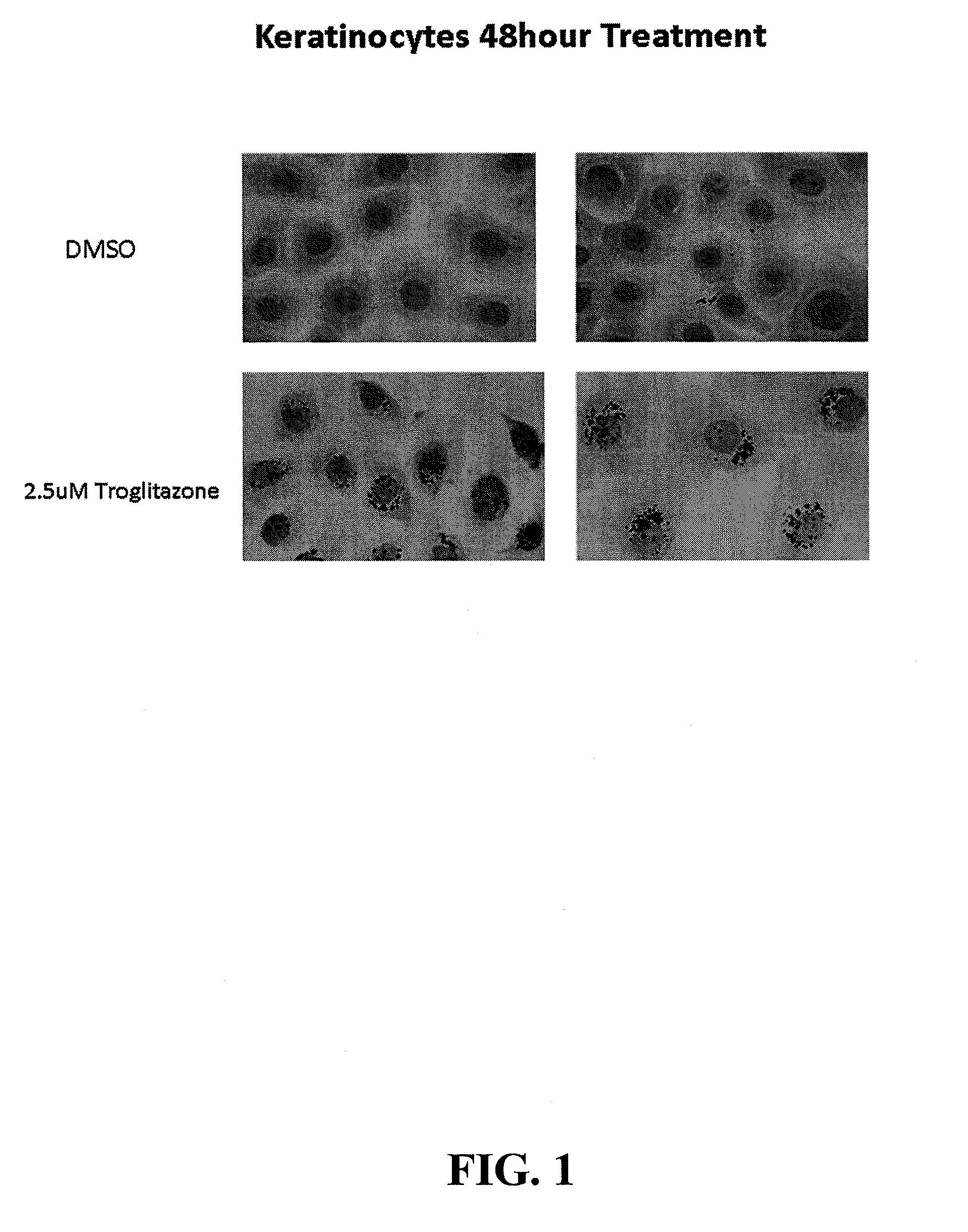
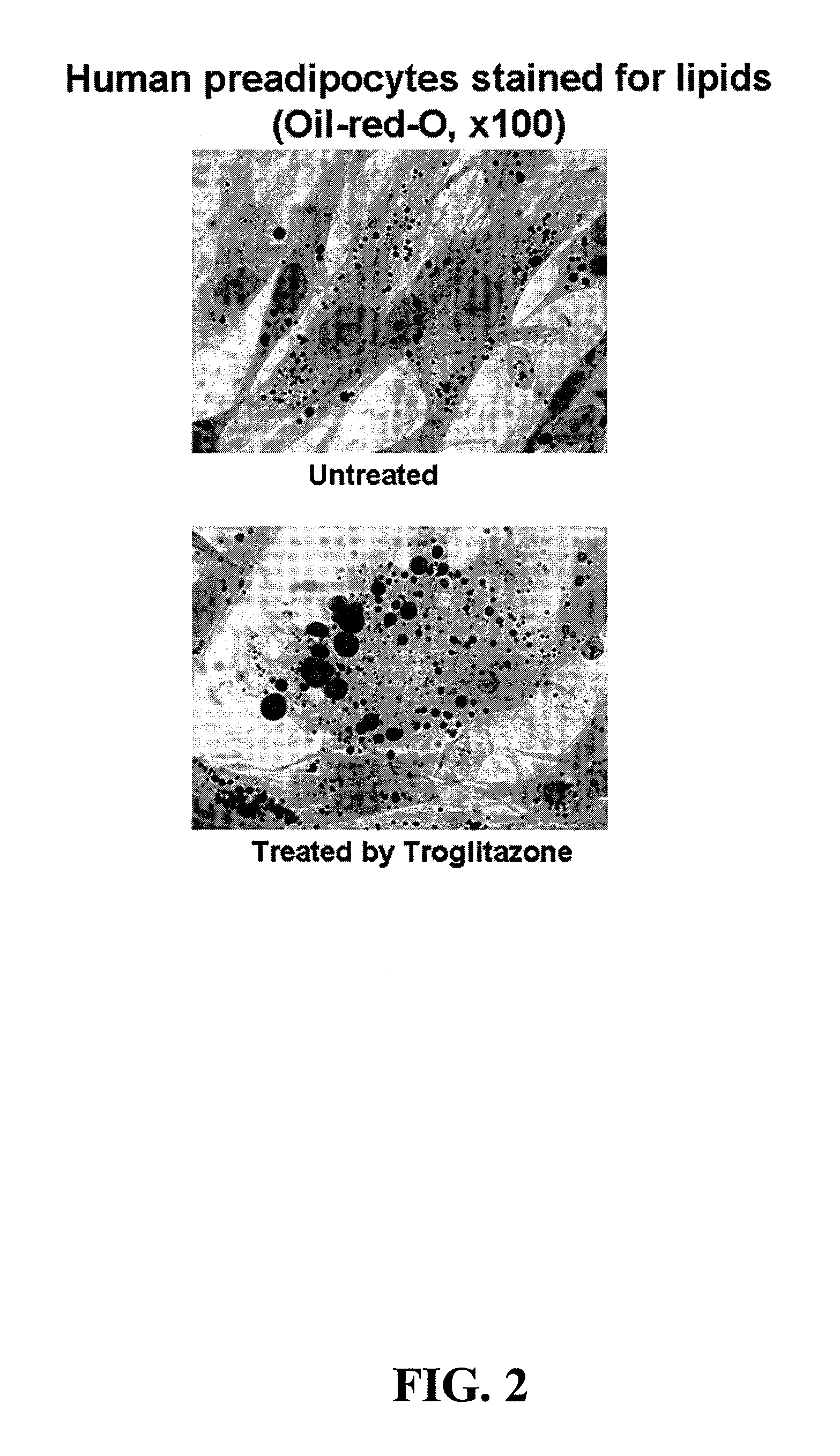
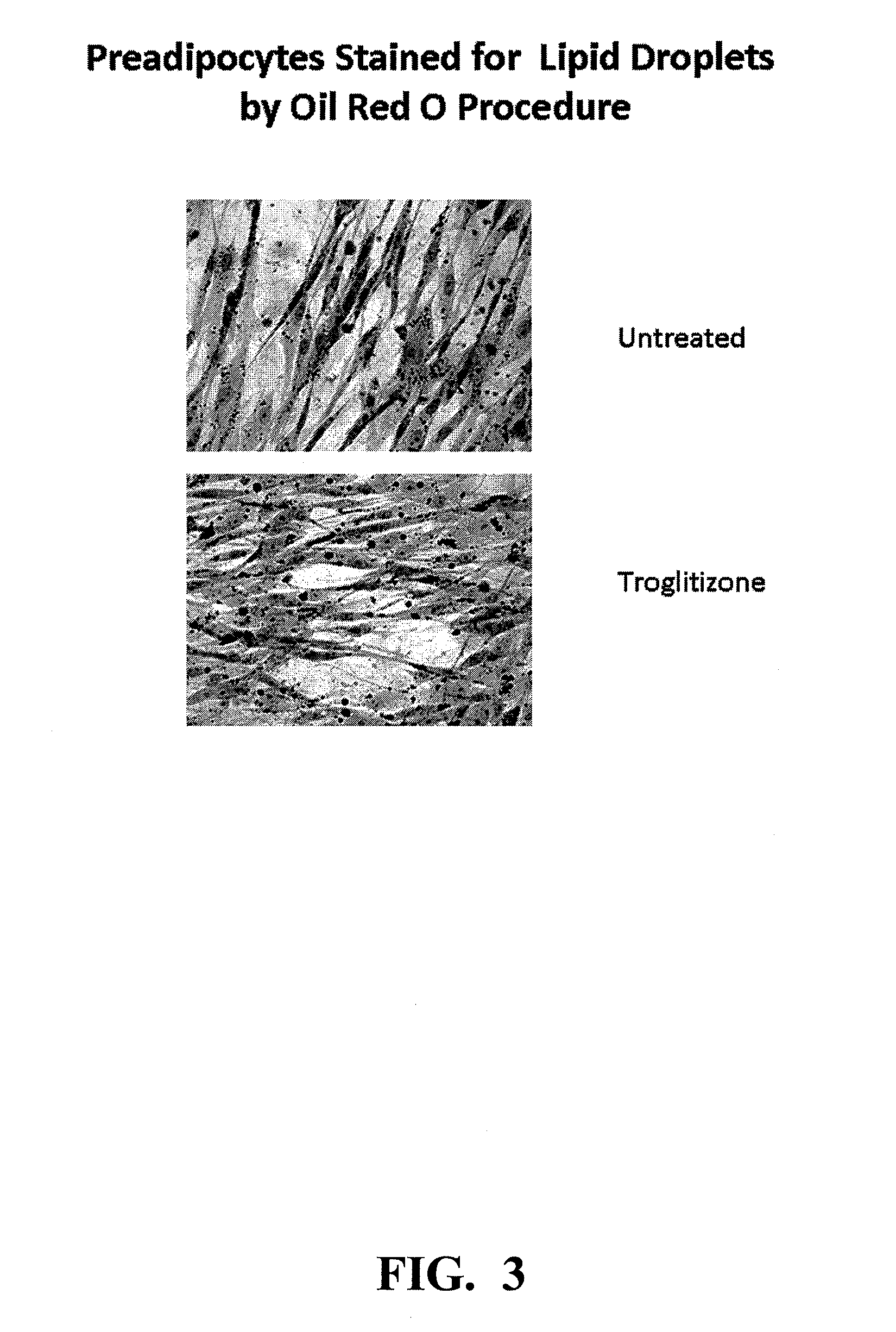
Compositions and methods are disclosed for the treatment of cells, such as keratinocytes and adipocytes, to increase their lipid content and compositions and methods are disclosed for treatment of skin cells to diminish the appearance of blemishes.
Owner:0901911 B C UNLIMITED LIABILITY
Agonists that enhance binding of integrin-expressing cells to integrin receptors
ActiveUS20130236434A1Enhance integrin-mediated bindingHigh retention rateBiocideCarbamic acid derivatives preparationAgonistTreated cell
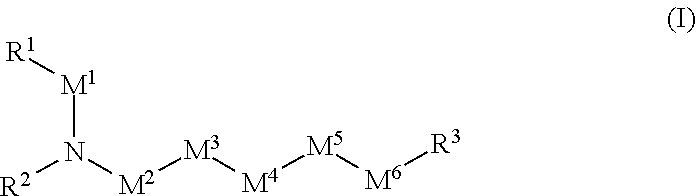
A method of enhancing binding of cells to an integrin-binding ligand comprises treating integrin-expressing cells in vitro with an agonist of integrin, wherein the integrin is selected from the group consisting of α4β1, α5β1, α4β7, αvβ3 and αLβ2, and contacting the treated cells with an integrin-binding ligand; integrin agonist compounds having the general formula I; methods of treating integrin-expressing cells with such agonists to enhance binding; and therapeutic methods comprising administering agonist-treated cells or agonist compounds to a mammal.
Owner:TEXAS HEART INST
Restoration of methylation states in cells
InactiveUS20060188986A1Easy to useHigh magnificationCell differentiationMicrobiological testing/measurementReprogrammingCell type
A method for altering a characteristic or state of a cell, or reprogramming a cell, comprising treating a first cell type with an agent capable of altering a characteristic or state in a cell or reprogramming a cell, and determining the degree of alteration of the treated cell by measuring the methylation signature within the genome of the treated cell, wherein a given methylation signature is indicative of an altered characteristic or state of the treated cell. The preferred substance for treating the first cell is a cellular extract, lysate or component from a second cell type, the second cell type having a desired characteristic, or being the desired cell type the first cell type is to be reprogrammed to. The examples show the methylation state of a fibroblast cell being reprogrammed to that of an immune system T cell.
Owner:HUMAN GENETIC SIGNATURES PTY LTD
Integrated system for biological tissue treatment and cell collection
ActiveCN103343086ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell organisationCell aggregation
The invention relates to an integrated system for biological tissue treatment and cell collection. The integrated system comprises three parts, namely a collection container for optionally pre-filling protecting liquid or solid for collecting and storing treated cells or cell aggregates, a sieve chamber for carrying samples and separating cells or cell aggregates from cell tissues or organs, and a roller, wherein a rolling disc of the roller is embedded with a rolling disc elbow board and is connected with a hand spike for exerting power and rotating the rolling disc. The three parts are connected with one another and assembled together through threads and threaded sealing covers. After the cells and the cell aggregates are collected, the collection container is sealed by a full closed cover for storage, and the used sieve chamber and roller can be discarded.
Owner:CRYSTALGEN NINGBO BIOTECH
Method for analysis of cellular DNA content
ActiveCN102971617AMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationAPOPTOSIS/NECROSISNucleotide
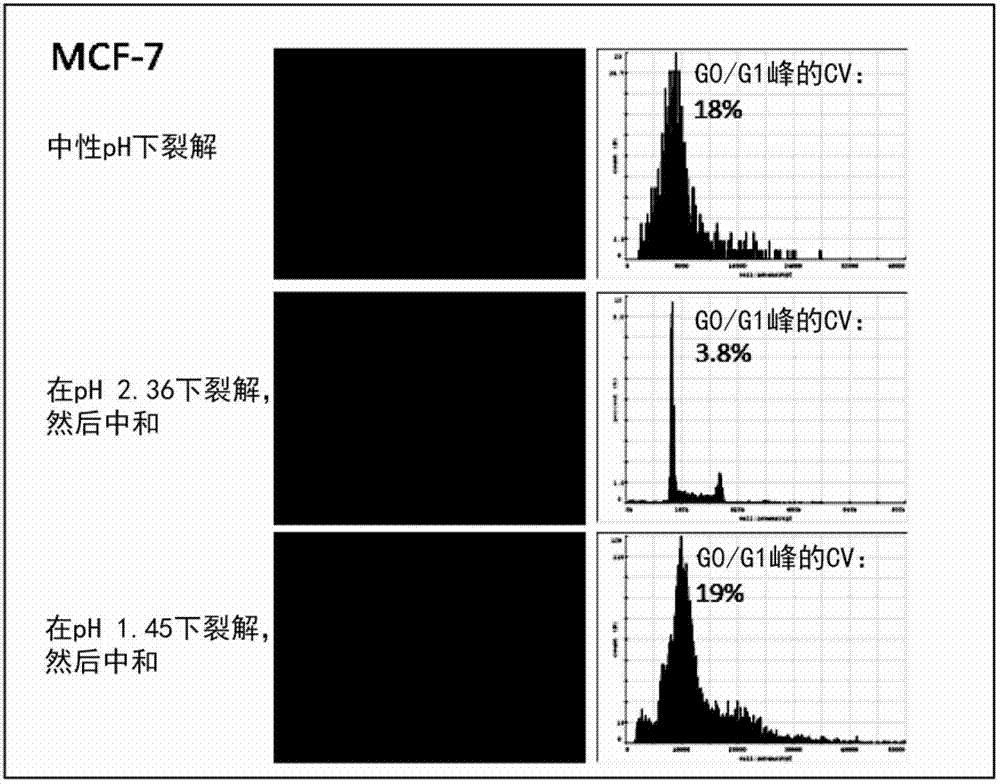
Disclosed is a fast and simple method for quantification of nucleic acid of biological cells as 2 -step protocol. In the first step cells are treated with an acidic solution containing a non- ionic detergent and a fluorescent DNA specific label. In the second step the sample may be neutralised. Determining of the content of nucleic can be performed by fluorescence microscopy. The method may also be used for obtaining information of cell cycle analysis, ploidy determination, measurements of nucleotide incorporation and assays for proliferation, health, stress level, apoptosis, necrosis, or other state of conditions of cells. The invention also relates to a kit of parts comprising an acidic agent, a detergent, a labelling agent and optionally a neutralization agent.
Owner:CHEMOMETEC AS
Compositions and methods for isolation, propagation, and differentiation of human stem cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS7632680B2Maximizes therapeutic benefitBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAutologous transplantationTreated cell
The invention is directed to the field of human stem cells and includes methods and compositions for isolating, propagating, and differentiating human stem cells. The invention provides therapeutic uses of the methods and compositions, including autologous transplantation of treated cells into humans for treatment of Parkinson's and other neuronal disorders.
Owner:LEVESQUE BIOSCI
Nanometer-material-photothermal-effect-based cell detection method and cell detection device
ActiveCN104655594AThe detection method is simpleNo complicated steps requiredAnalysis by material excitationPhosphateTreated cell
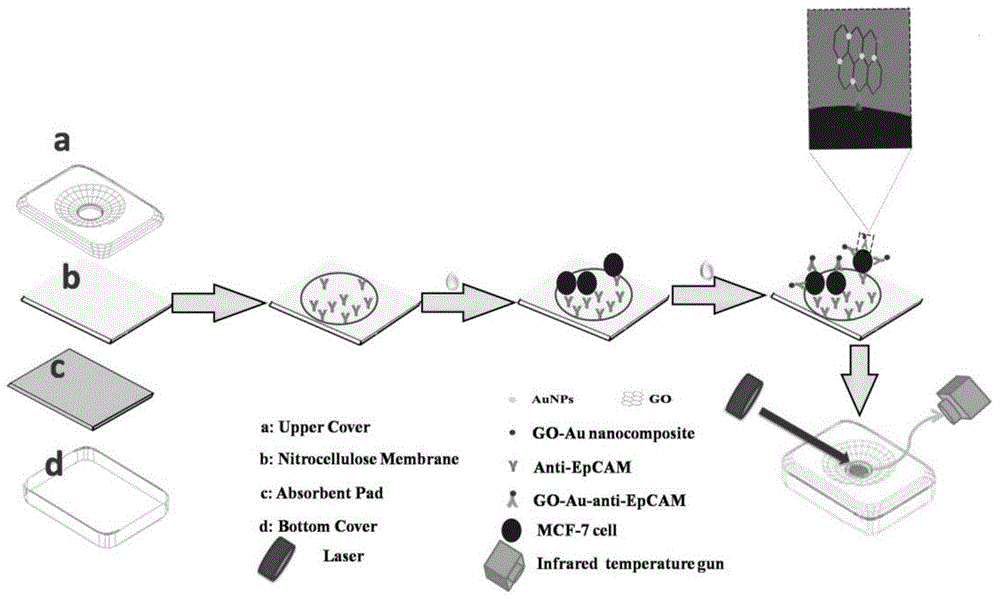
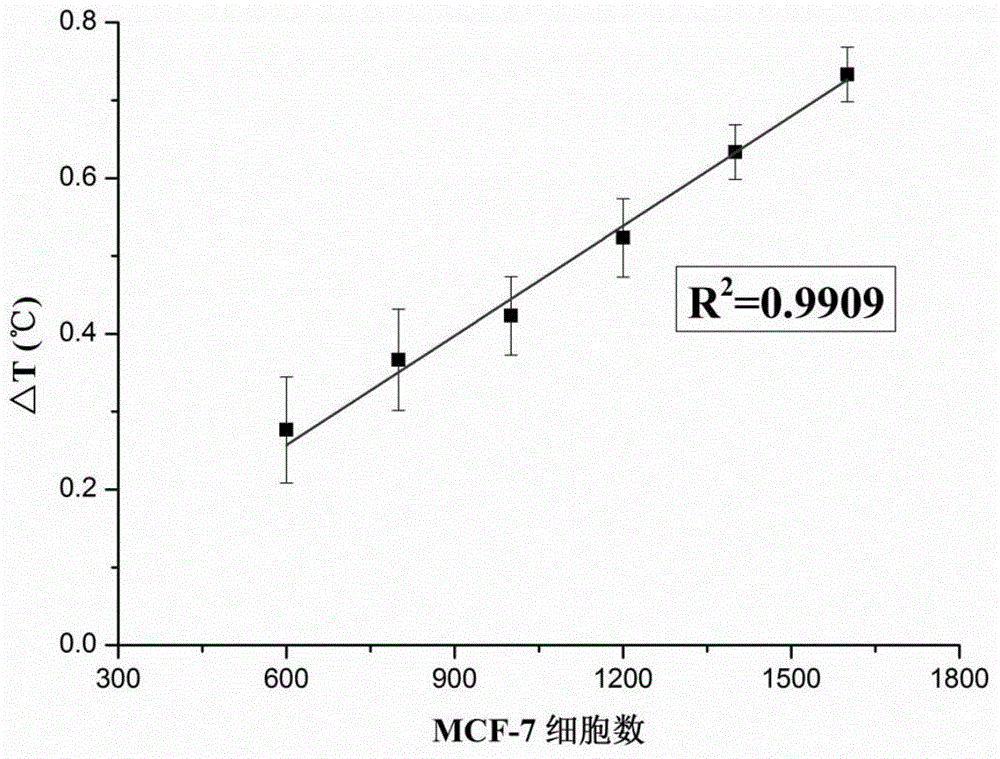
The invention discloses a nanometer-material-photothermal-effect-based cell detection method and a cell detection device. The method comprises the following detecting steps: (1) centrifuging cell solution to be detected, discharging supernatant, redissolving with PBS (Phosphate buffer solution) and centrifuging again, repeating the operations, discharging supernatant, and dissolving centrifuged precipitates with 10mul of PBS buffer solution; (2) dropwise adding the treated cell sample onto a sample adding area of an infiltration test strip, and washing for three times with PBST (Phosphate buffer solution-tween) solution; (3) adding with 5-20muL of grapheme-gold-antibody compound into the sample adding area of the infiltration test strip, washing for three times with PBST solution and airing; and (4) radiating the sample adding area of the detection device with laser with the excitation wavelength of 808nm for 10-90s, recording the temperature before and after radiation, calculating the temperature difference, and drawing a calibration curve by use of the cell number as an x-coordinate and the temperature difference as a y-coordinate, wherien when one sample is detected, the temperature difference of the sample is detected and is substituted into the calibration curve to calculate the cell number. The detection device and the detection method have the advantages that the detection method is simple, the detection time is short, the detection sensitivity is high and the like.
Owner:山东师大瑞柏生物科技有限公司
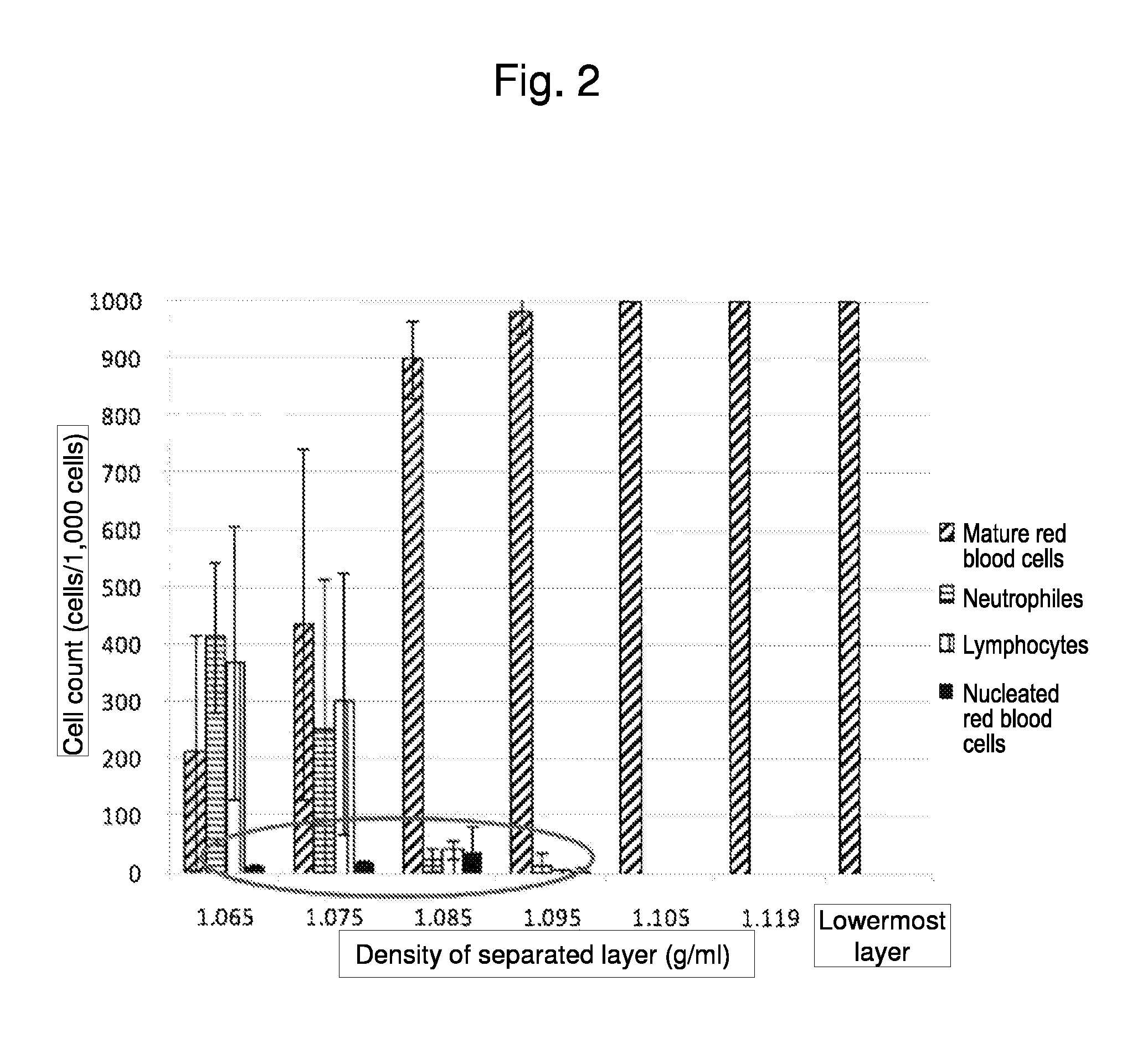
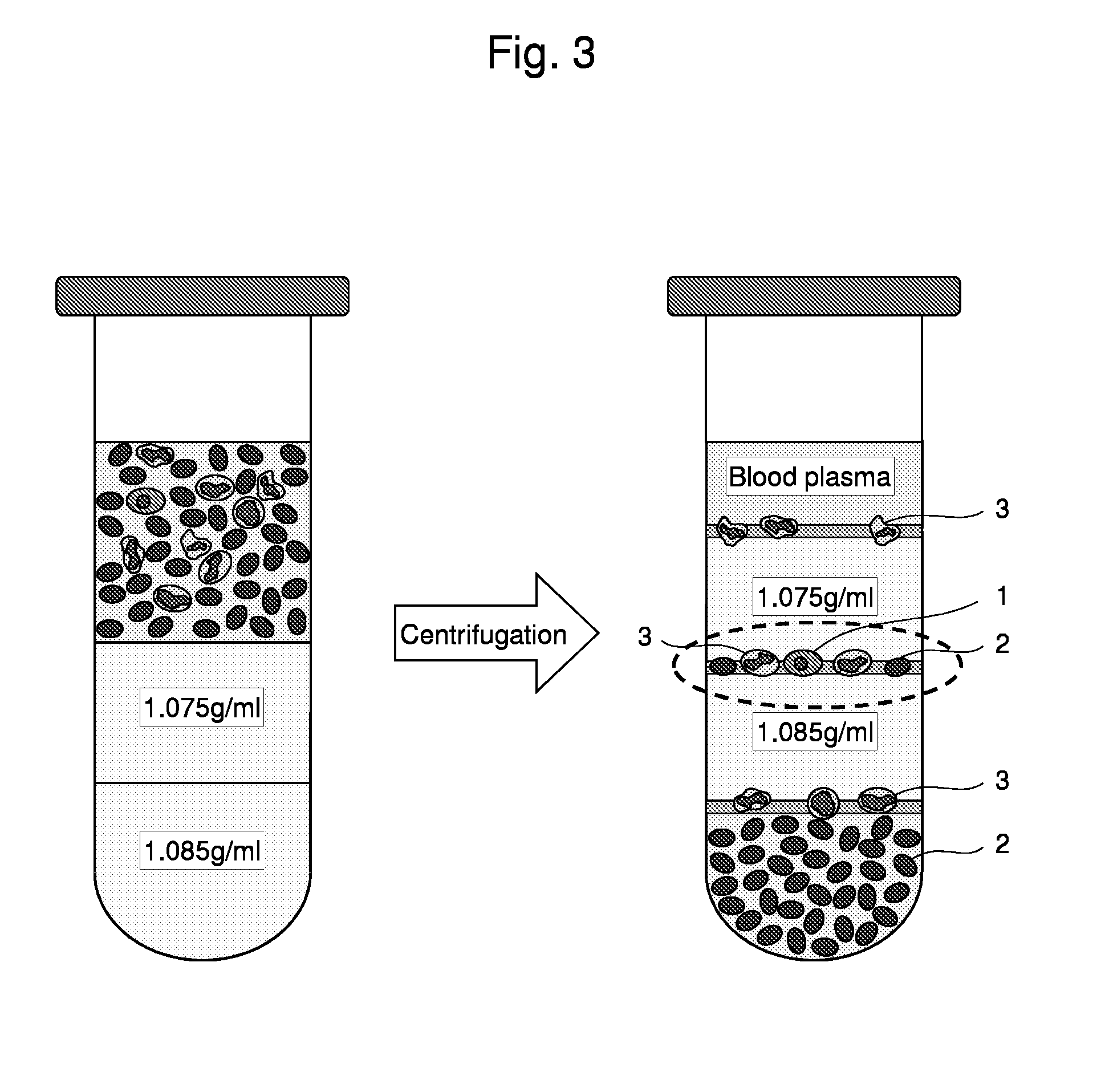
Method for collecting nucleated red blood cells via density-gradient centrifugation utilizing changes in blood cell density
ActiveUS20130072402A1Cell count is reducedIncreased riskMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCell FractionRed blood cell
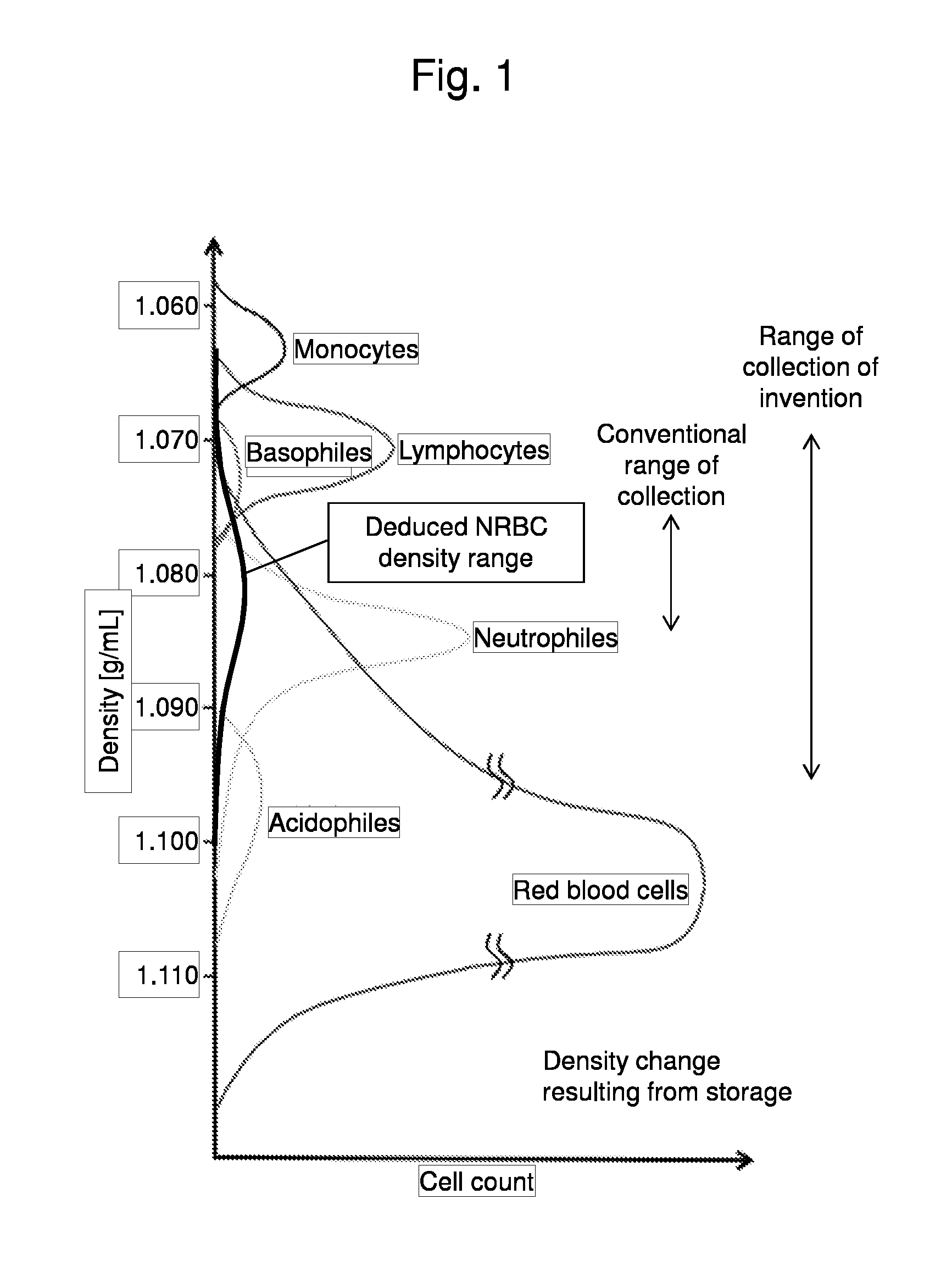
This invention provides a method for concentrating and collecting small quantities of fetal nucleated red blood cells contained in the maternal blood. The method for concentrating and collecting nucleated red blood cells from the maternal blood comprises: (i) subjecting the maternal blood to a first density-gradient centrifugation and collecting a cell fraction containing nucleated red blood cells; (ii) treating the cell fraction containing nucleated red blood cells so as to selectively changes the density of the nucleated red blood cells from that of the white blood cells; and (iii) subjecting the treated cell fraction containing the nucleated red blood cells to a second density-gradient centrifugation so as to collect a fraction containing nucleated red blood cells.
Owner:JAPAN ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH +2
Systems and methods for producing stem cells differentiated cells, and genetically edited cells
PendingUS20160222355A1Low variabilityImprove work performanceSkeletal/connective tissue cellsArtificially induced pluripotent cellsCells panelGenetically engineered
The present invention provides systems and methods for obtaining, generating, culturing, and handling cells, such as stem cells (including induced pluripotent stem cells or iPSCs), differentiated cells, and genetically engineered cells, as well as cells and cell panels produced using such systems and methods, and uses of such cells and cell panels.
Owner:NEW YORK STEM CELL FOUND
Methods and compositions for the preparation and use of fixed-treated cell-lines and tissue in fluorescence in situ hybridization
InactiveUS20050019779A1Easy to useShorten the timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical treatmentFluorescence
This invention relates to methods for the detection of one or more mRNA transcripts in paraffin-embedded tissue by “mRNA liberation in fixed-treated tissue or ‘MLIFTT’”. This method includes treating the tissue with ammonia-ethanol and sodium borohydride combined with pressure cooking of the tissue. The chemical treatments reduce the tissue autofluorescence and the physical treatments overcome the interference created by the fixation-induced chemical bonds. The methods of the present invention can be utilized to identify a plurality of mRNA transcripts in a microarray format.
Owner:AUREON LAB INC +2
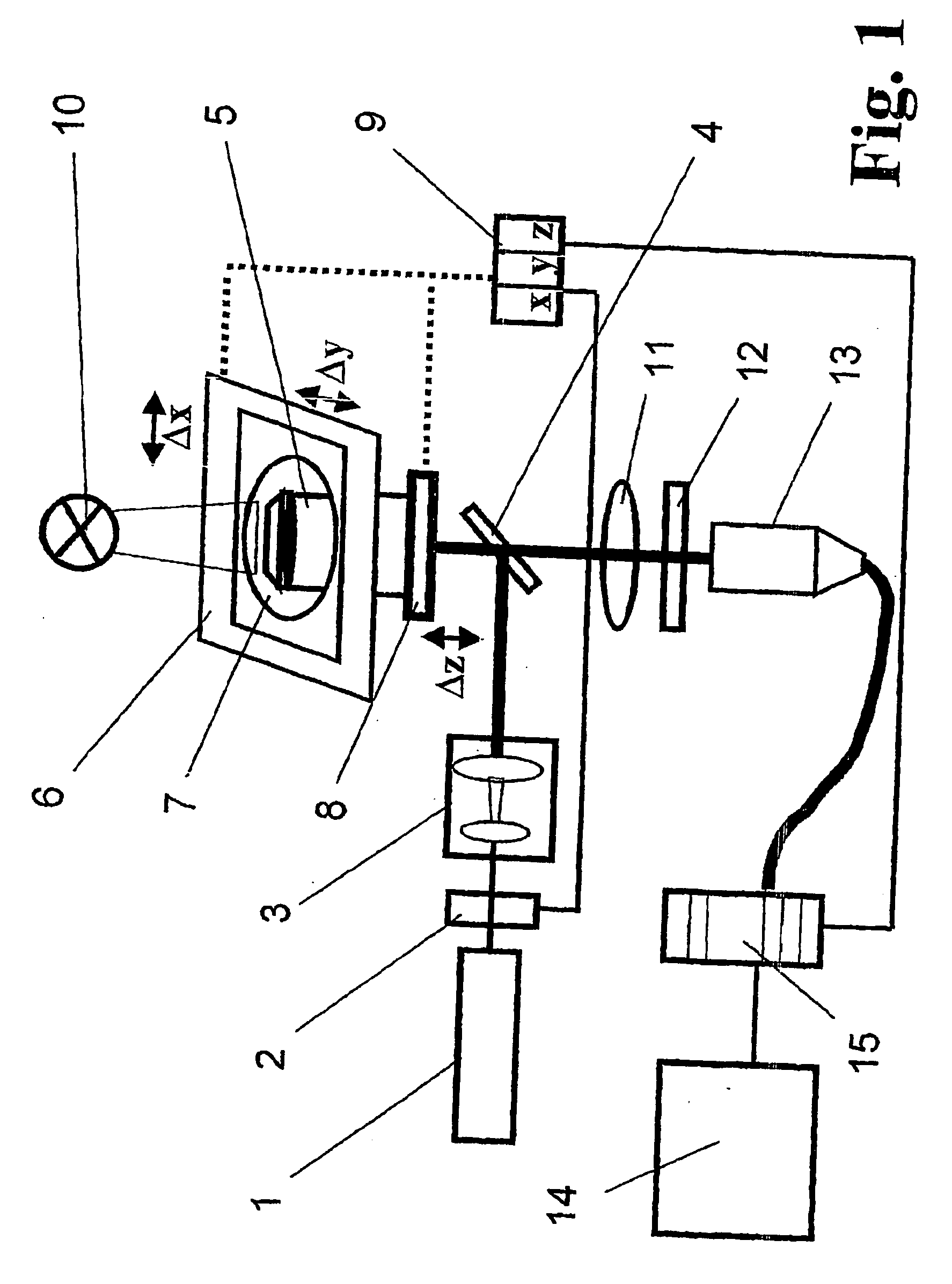
Method for transferring molecules in vital cells by means of laser beams and arrangement for carrying out said method
ActiveUS20060141624A1High transfer efficiencyImprove accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSide effectCell membrane
The invention relates to an optical method for targeted transfer of molecules, preferably of DNA, RNA, peptides, amino acids and proteins, into vital cells by means of laser radiation and to an arrangement for implementing the method. The object of the invention, to find a novel possibility for targeted molecule transfer into the interior of vital cells, particularly the transfer of DNA, RNA, peptides, amino acids and proteins, which achieves a high transfer efficiency while extensively excluding destructive side effects such as a lethal effect on a treated cell, is met according to the invention in that cellular membranes are opened transiently for the molecule transfer by multiple laser pulses in the microjoule range or less and a pulsed, near-infrared laser beam with a pulse width in the femtosecond range is directed in each instance to a submicrometer spot of a membrane of the vital cell for an irradiation period of less than one second.
Owner:KOENIG KARSTEN
Solution for diagnosing or treating tissue pathologies
InactiveUS7348361B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideAmino-Levulinic AcidDelta aminolevulinate
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL) +1
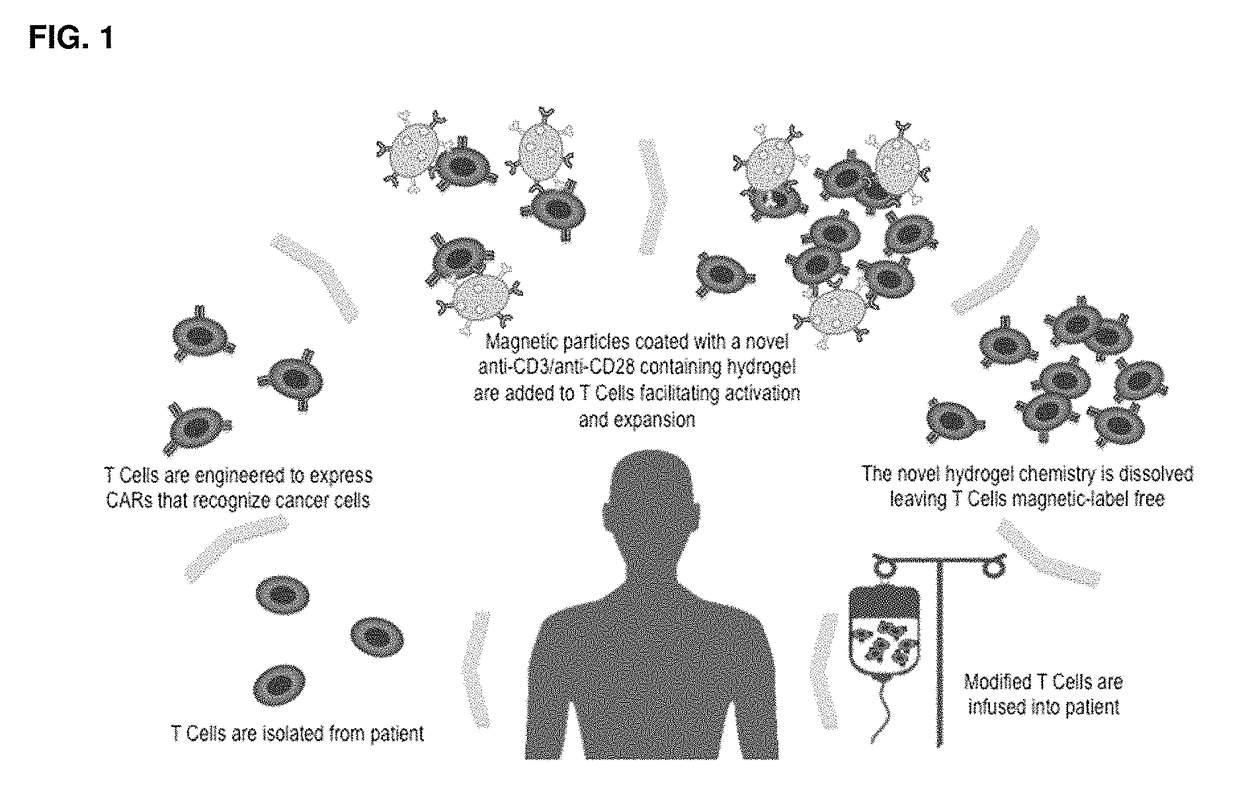
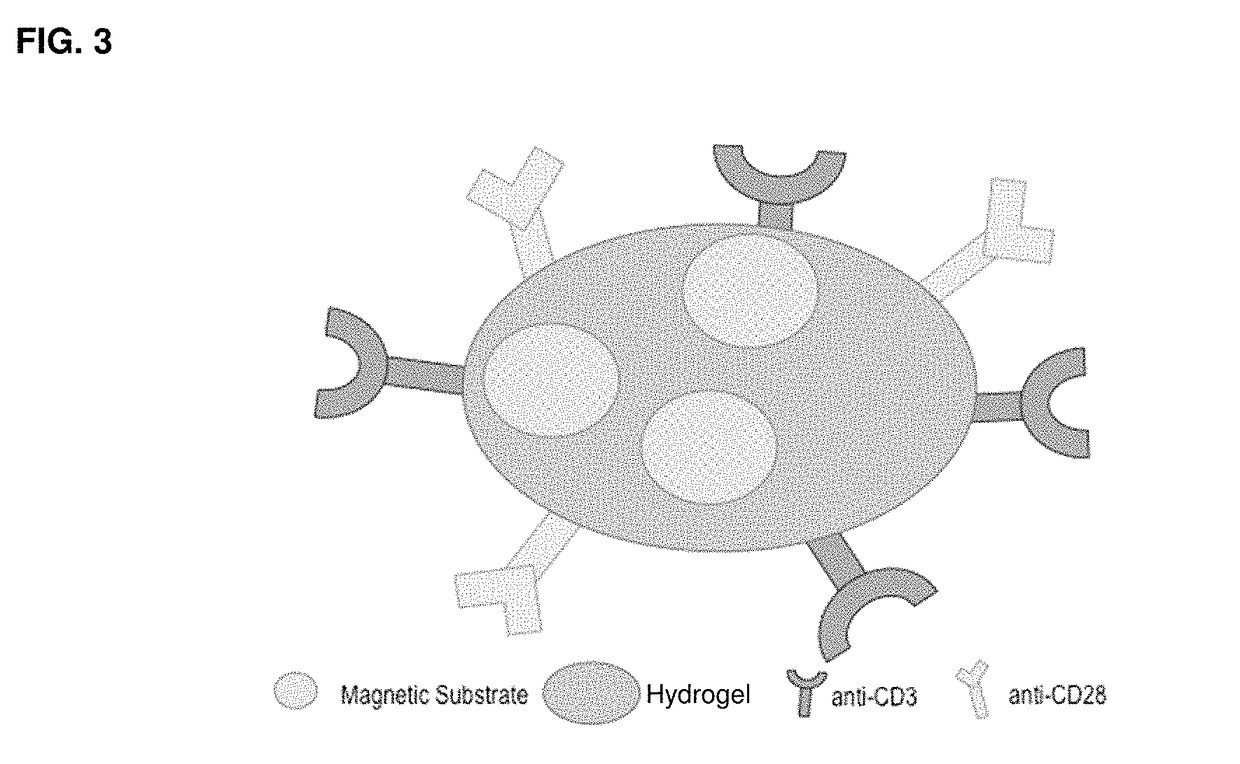
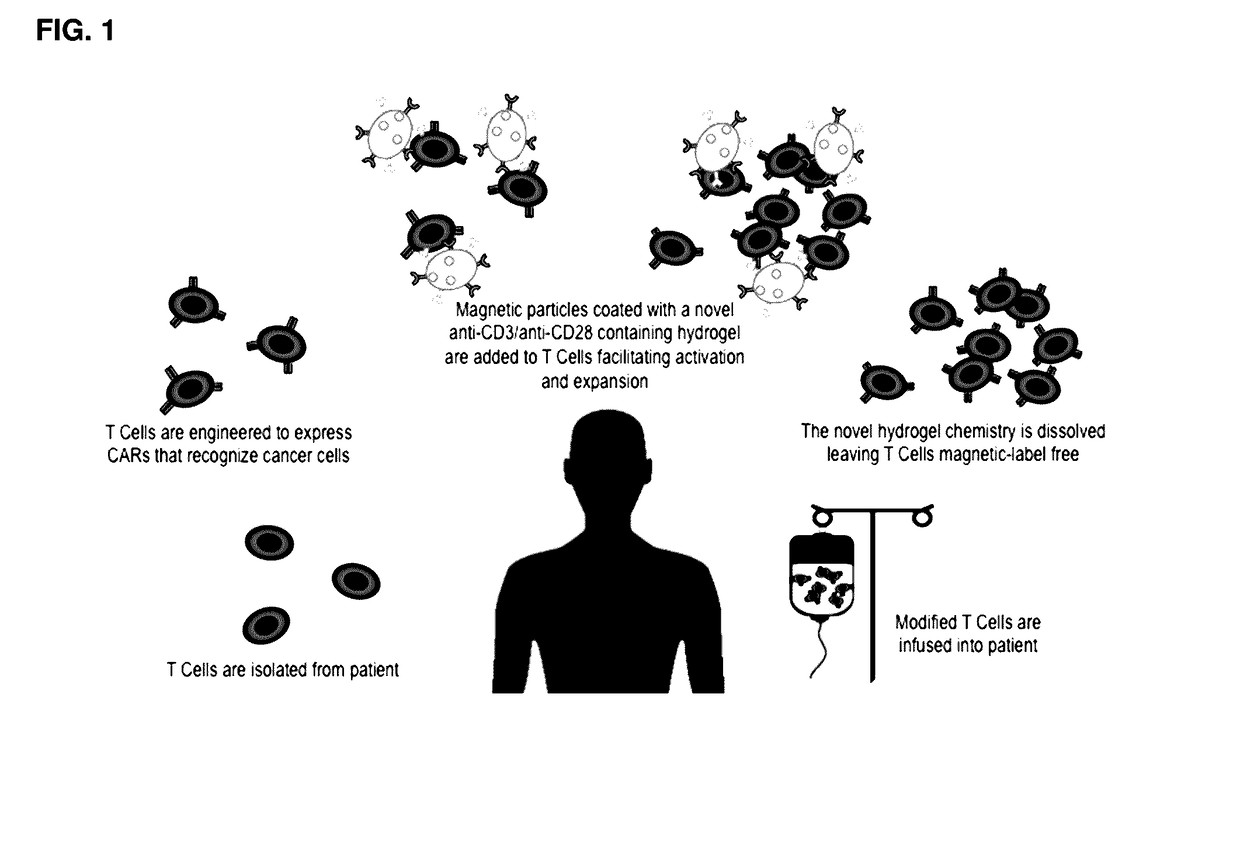
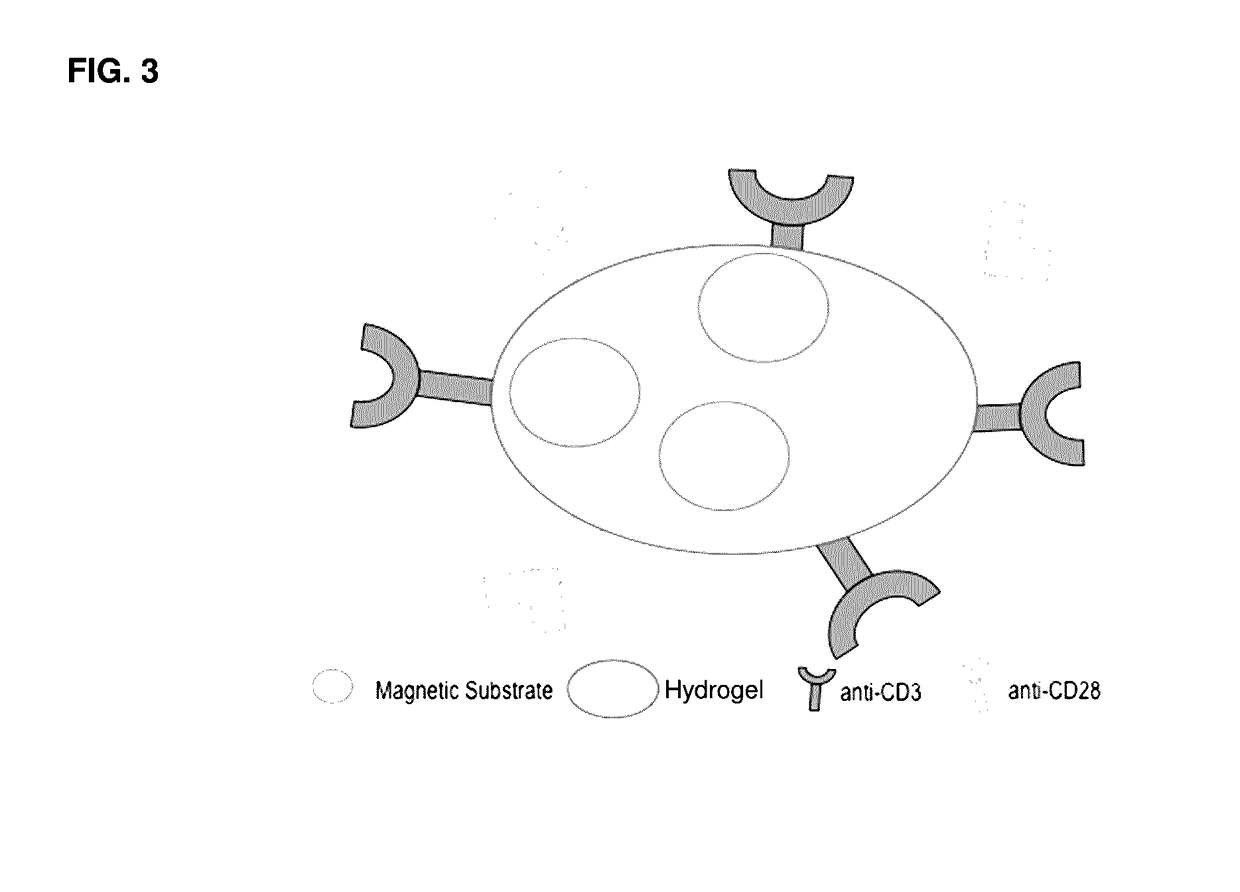
Methods and compositions for activation or expansion of T lymphocytes
ActiveUS9790467B2Dissolve fastGenetically modified cellsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsLymphocyteT lymphocyte
The invention features a complex that binds to, stimulates, and expands a desired T cell population and facilitates separation of the target population from a sample. The complex can be gently dissociated from the binding unit after separating the desired T cell population, representing a safe and efficient approach for processing T cells for clinical use. Invention also provides methods of using such complexes as part of adoptive T cell therapy systems.
Owner:QT HLDG
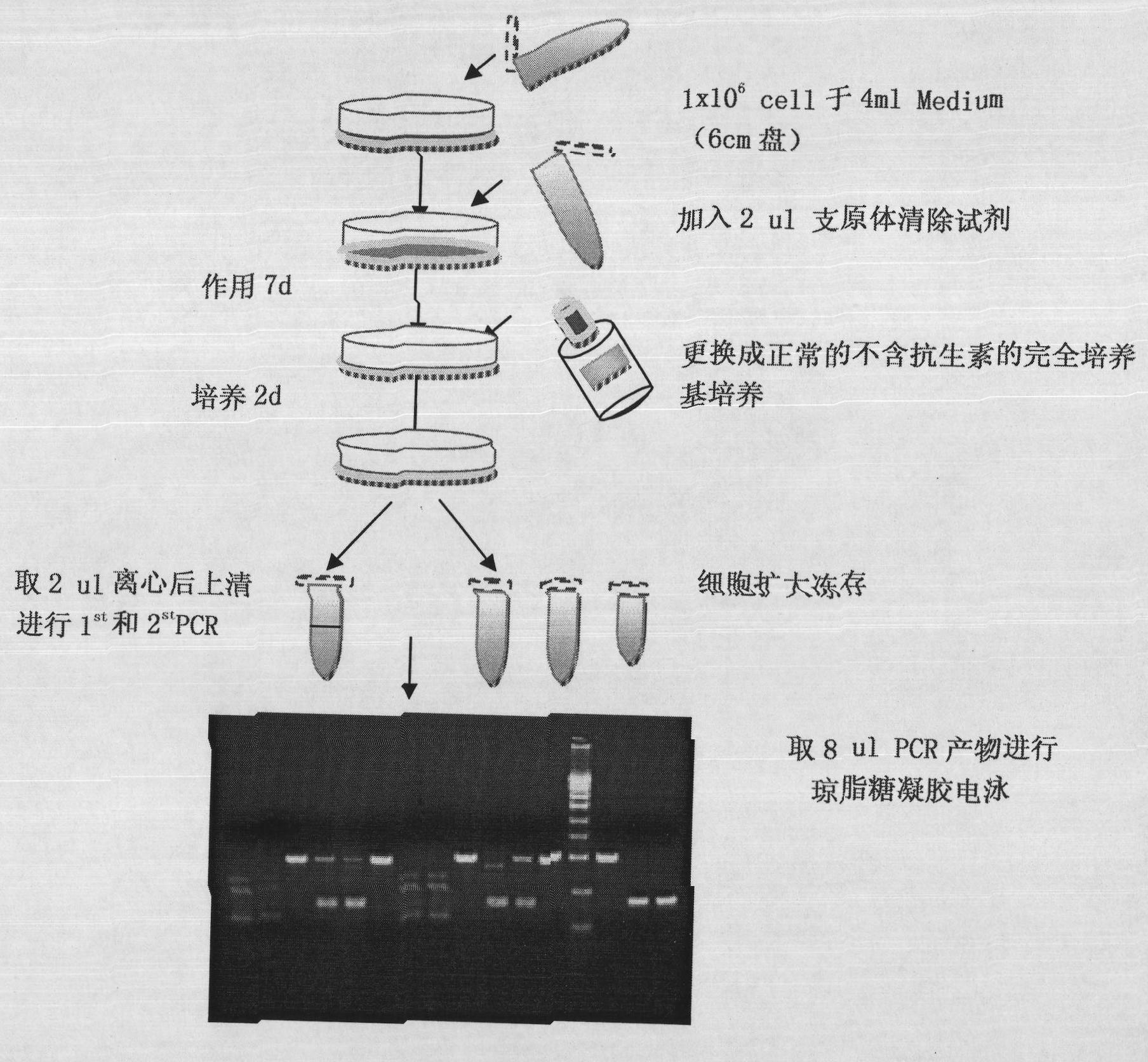
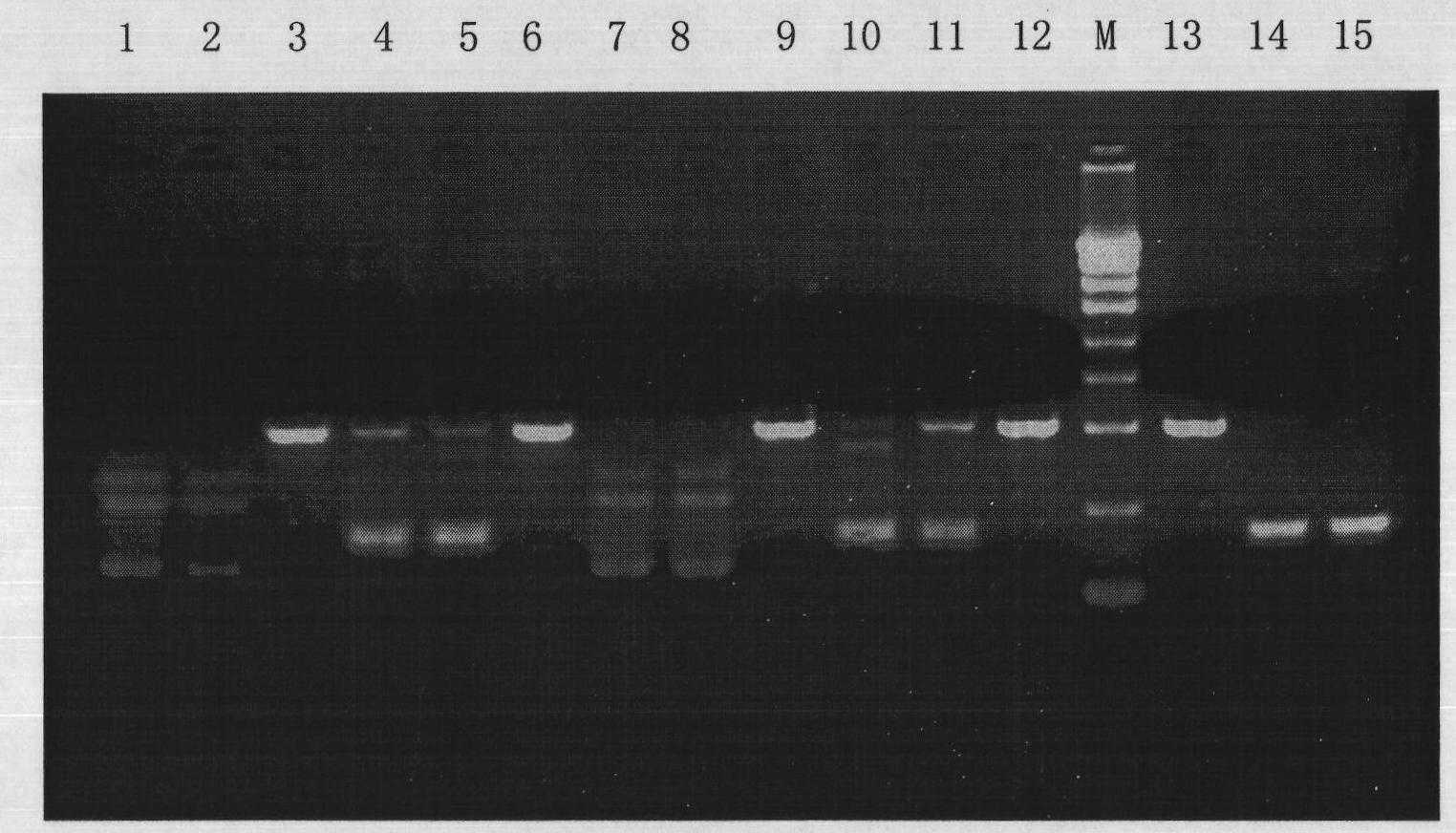
Mycoplasma clearing reagent and application thereof
InactiveCN101851603AEffectively suppress and killEfficient killingAnimal cellsAntibiotic YMacrolide resistance
The invention relates to a mycoplasma clearing reagent and application thereof. The mycoplasma clearing reagent of the invention comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 1.3 to 1.5 percent of fluoroquinolones antibiotics, 0.3 to 0.5 percent of tetracyclines derivatives, 0.1 to 0.3 percent of macrolides antibiotics and 97.7 to 98.3 percent of buffer solution, can most effectively inhibit and kill mycoplasmas, and has a short period, namely, all the mycoplasmas can be killed in only one week without influencing the metabolism of cells per se; and the treated cells have smooth surfaces, substantially have no black particles and are difficult to be re-infected by the mycoplasmas.
Owner:上海龙鼎医药科技有限公司
Methods and compositions for activation or expansion of t lymphocytes
ActiveUS20170081636A1Dissolve fastGenetically modified cellsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsT lymphocyteBiological activation
The invention features a complex that binds to, stimulates, and expands a desired T cell population and facilitates separation of the target population from a sample. The complex can be gently dissociated from the binding unit after separating the desired T cell population, representing a safe and efficient approach for processing T cells for clinical use. Invention also provides methods of using such complexes as part of adoptive T cell therapy systems.
Owner:QT HLDG
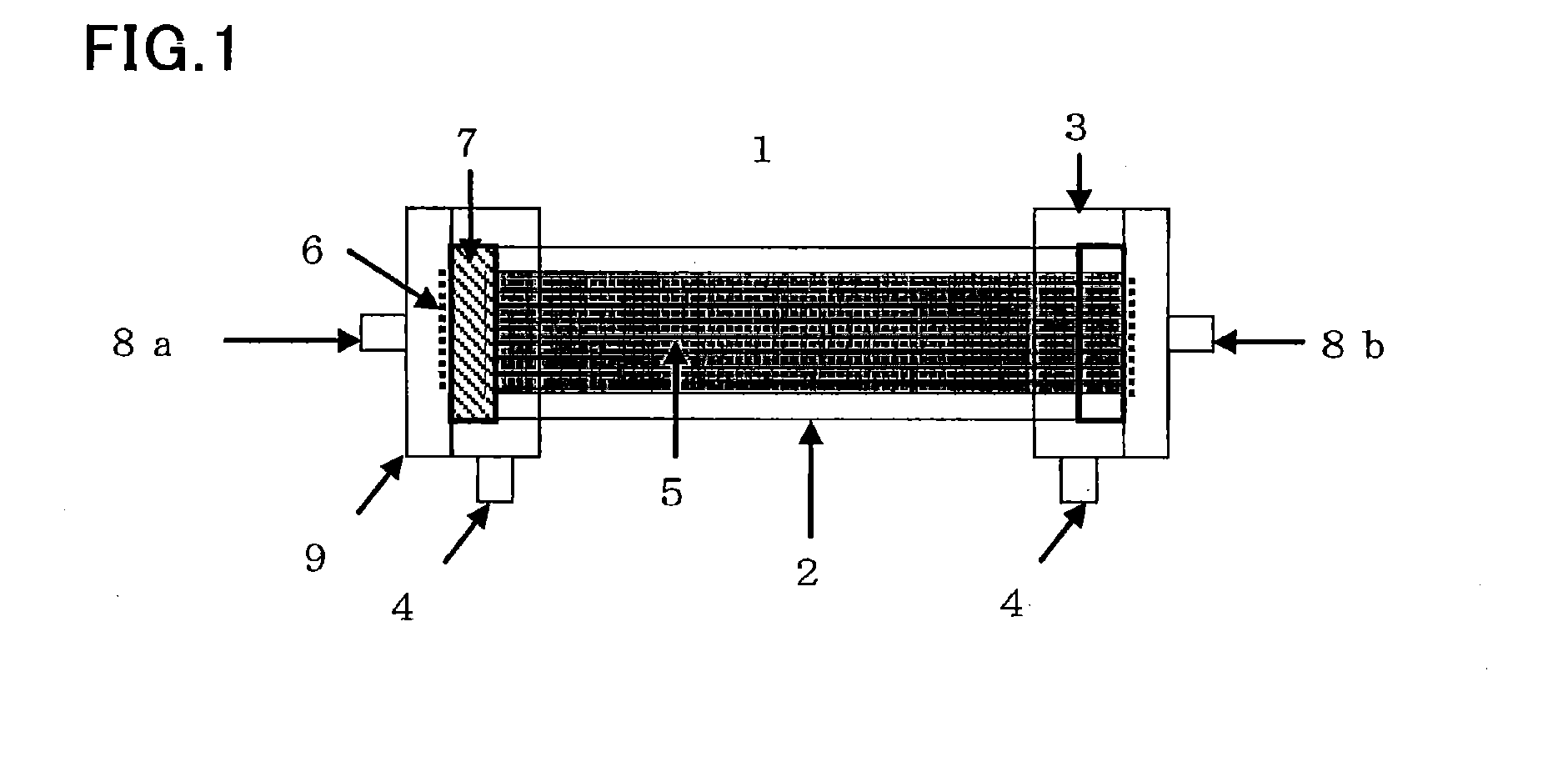
Method for producing cell concentrate
ActiveUS20140287502A1Reduce cloggingImprove survivabilityAnimal cellsMembranesHollow fibreBiochemistry
The present invention provides a method that allows the preparation of a cell concentrate in a short time without loss of cells and great damage on cells by simple operations. The present invention provides a method for producing a cell concentrate using an inside-out filtration system for processing a cell suspension, the system including: a cell suspension inlet port; a filtrate outlet port; a cell suspension outlet port; and a hollow fiber separation membrane interposed between the cell suspension inlet port and the cell suspension outlet port, wherein the hollow fiber separation membrane is provided with inner pores with an average pore size of 0.1 μm to 10 μm, and the quotient of the division of an initial filtrate flow rate by a linear velocity of the cell suspension flowing through the hollow fibers is 2.5 or less.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Cell-penetrating anti-DNA antibodies and uses thereof inhibit DNA repair
ActiveUS9701740B2Good curative effectIncrease cell ' sensitivityHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsCancer cellSynthetic lethality
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +2
Micro-fluidic chip, system and method for sorting and enriching cells in cerebrospinal fluid
ActiveCN107189929AGuaranteed forceConsistent Micropump ForceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnimal cellsMicroscopic observationEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of biochemical separation and analysis, and particularly relates to a micro-fluidic chip, a system and a method for sorting and enriching cells in cerebrospinal fluid. The chip can avoid pretreatment operations such as sample pretreatment and cell labeling and realize fast and efficient sorting and enriching functions for a small quantity of cells in the cerebrospinal fluid and further can realize in-situ counting and fast distinguishing of the small quantity of cells in the cerebrospinal fluid in combination with an in-situ microtechnique. The system integrates fast and efficient separation and enrichment of the small quantity of cells in the cerebrospinal fluid and in-situ microscopic observation, can realize sorting, enrichment, counting, observation and detection for the small quantity of cells in the cerebrospinal fluid, is high in functionality and high in efficiency, and can be used for clinical fast and efficient detection for cerebrospinal fluid cells.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for transferring molecules in vital cells by means of laser beams and arrangement for carrying out said method
ActiveUS7892837B2High transfer efficiencyImprove accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSide effectNear infrared laser
The invention relates to an optical method for targeted transfer of molecules, preferably of DNA, RNA, peptides, amino acids and proteins, into vital cells by means of laser radiation and to an arrangement for implementing the method. The object of the invention, to find a novel possibility for targeted molecule transfer into the interior of vital cells, particularly the transfer of DNA, RNA, peptides, amino acids and proteins, which achieves a high transfer efficiency while extensively excluding destructive side effects such as a lethal effect on a treated cell, is met according to the invention in that cellular membranes are opened transiently for the molecule transfer by multiple laser pulses in the microjoule range or less and a pulsed, near-infrared laser beam with a pulse width in the femtosecond range is directed in each instance to a submicrometer spot of a membrane of the vital cell for an irradiation period of less than one second.
Owner:KOENIG KARSTEN
Constant temperature nucleic acid amplification fast detecting reagent kit for bacillus coli O157 and use method thereof
InactiveCN101343661AStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliPositive control
The invention discloses an escherichia coli O157 mediated isothermal nucleic acid amplification rapid detecting kit and a use method thereof. The kit comprises a primer mixed liquor, which adopts the sequence: an outer primer 1: GCTATACCACGTTACAGCGTG, an outer primer 2: ACTACTC AACCTTCCCCAGTTC, an inner primer 1: GCTCTTGCCACAGACTGCACATTCGTTGACTACTTC TTATCTGG, an inner primer 2: CTGTGACAGCTGAAGCTTTACGCGAAATCCCCTCTGAATTTGCC, a phosphate buffer solution PBS, paraformaldehyde, polylysine, lysozyme, proteinase K, RNase, BstDNA polymerase, a reaction solution, a sample pretreatment solution, a chromogenic agent, positive control and negative control. Highly specific, rapid, efficient and sensitive and simple situ detection for escherichia coli O157 can be realized through the escherichia coli O157 immobilized processing, cell permeability processing, mediated isothermal amplification for genes, and determining the results of the reaction products by using the kit.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
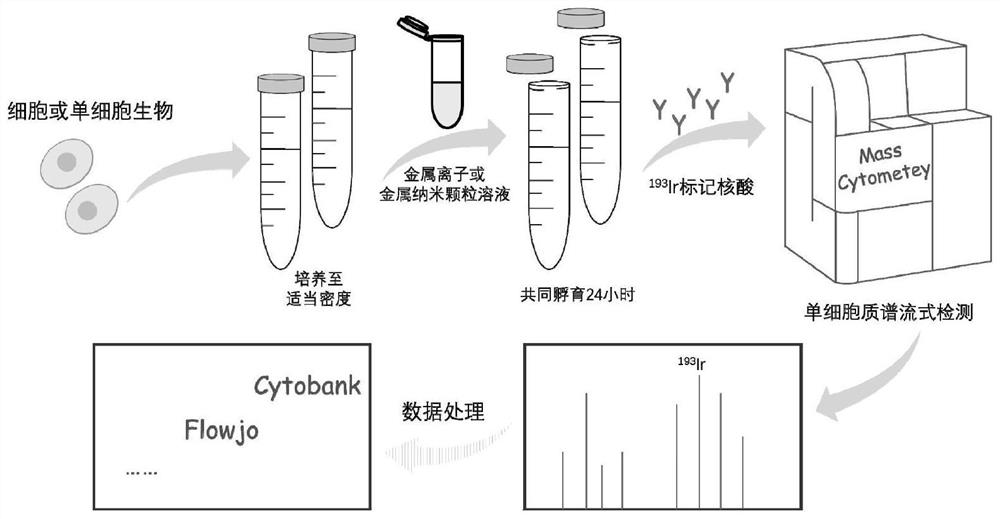
High-throughput detection method for metal ions and metal nanoparticles based on single cell enrichment and single cell mass spectrometry
ActiveCN111982789AAvoid introducingEasy to trainIndividual particle analysisBiological testingDead cellCell mass
The invention discloses a high-throughput detection method for metal ions and metal nanoparticles based on single cell enrichment and single cell mass spectrometry. The invention provides a method fordetecting the metal ions and metal nanoparticles. The method comprises the following steps: absorbing and enriching the metal ions and the metal nanoparticles by utilizing cells or unicellular organisms; marking the treated cells or single-cell organisms by using a metal isotope A, wherein the metal isotope A is other metal isotopes except a to-be-detected metal element and can be used for marking survival and dead cells or single-cell organisms at the same time; and then carrying out single-cell mass spectrometry flow detection to obtain an intracellular signal intensity value of the to-be-detected metal element, and further calculating to obtain the content of the to-be-detected metal element in a to-be-detected sample. The sample pretreatment is simple, and no harmful reagent is introduced; the demand on samples is very small; the flux is high; the sensitivity is high; cell-related metal signals may be differentiated.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polypeptide biological nano surface for serum-free cell culture and preparation method
ActiveCN102533632AImprove grafting efficiencyGood biocompatibilityTissue cultureChemical synthesisUltraviolet lights
The invention discloses a polypeptide biological nano surface for serum-free cell culture and a preparation method thereof. The polypeptide biological nano surface is prepared from the following steps of: pre-treating cell culture surface by plasma, then exposing the cell culture surface in air or oxygen, then spreading a polypeptide solution on the cell culture surface, and irradiating under ultraviolet light to obtain the polypeptide biological nano surface for serum-free cell culture. The obtained polypeptide biological nano surface is stable, can be stored for a long time at normal temperature, is definite in grafting ingredients on the grafted surface, and can substitute for routine various protein-coated surfaces in the market, so that cells realize excellent wall adhesion and proliferation under the serum-free condition; and as compared with various animal-derived protein-coated surface, short peptide has the characteristics of no heterology or weak heterology, therefore, the chemically synthesized polypeptide grafted surface greatly reduces clinical application risk, thereby laying a solid foundation for subsequent clinical application.
Owner:BEAVERNANO TECH
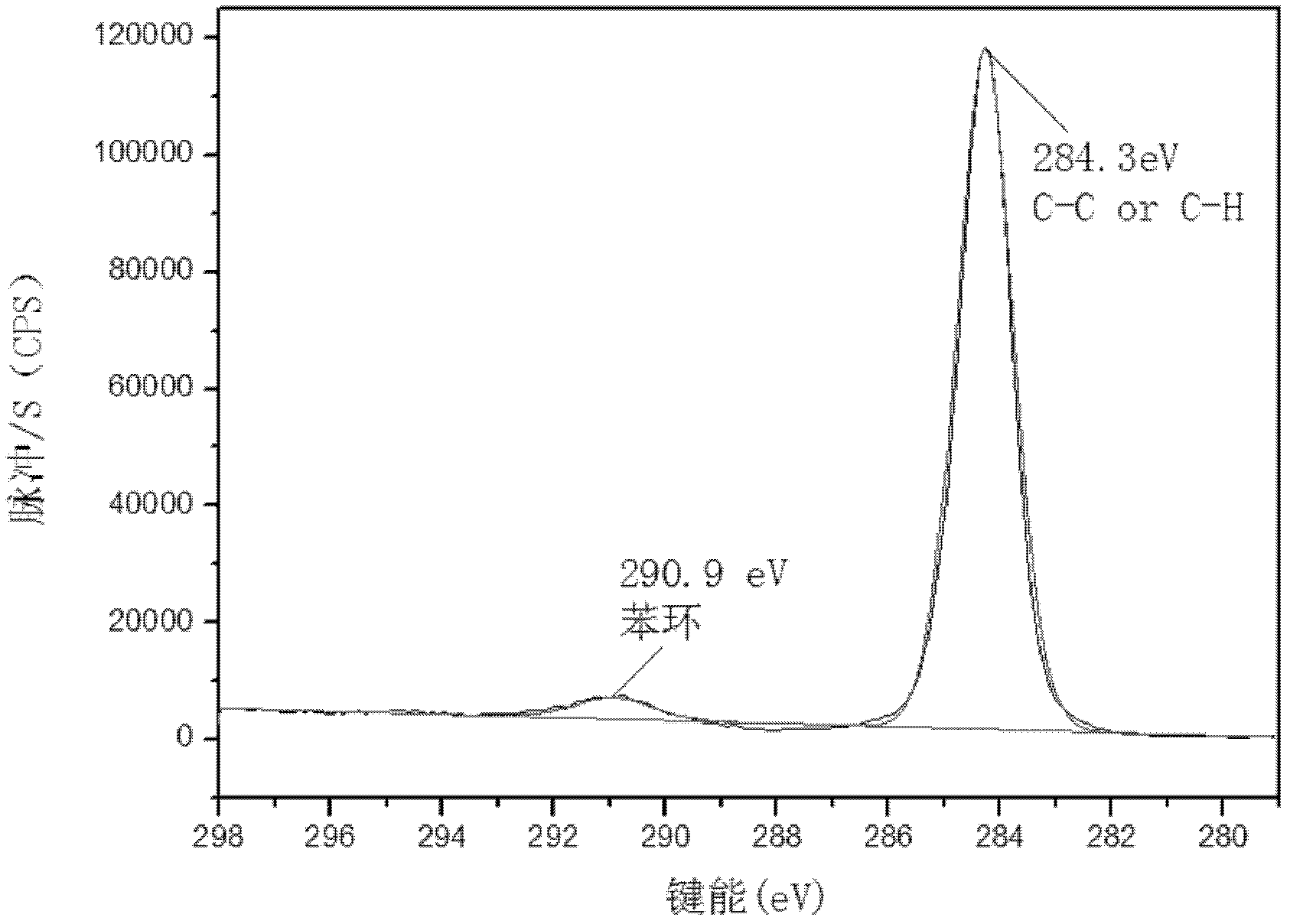
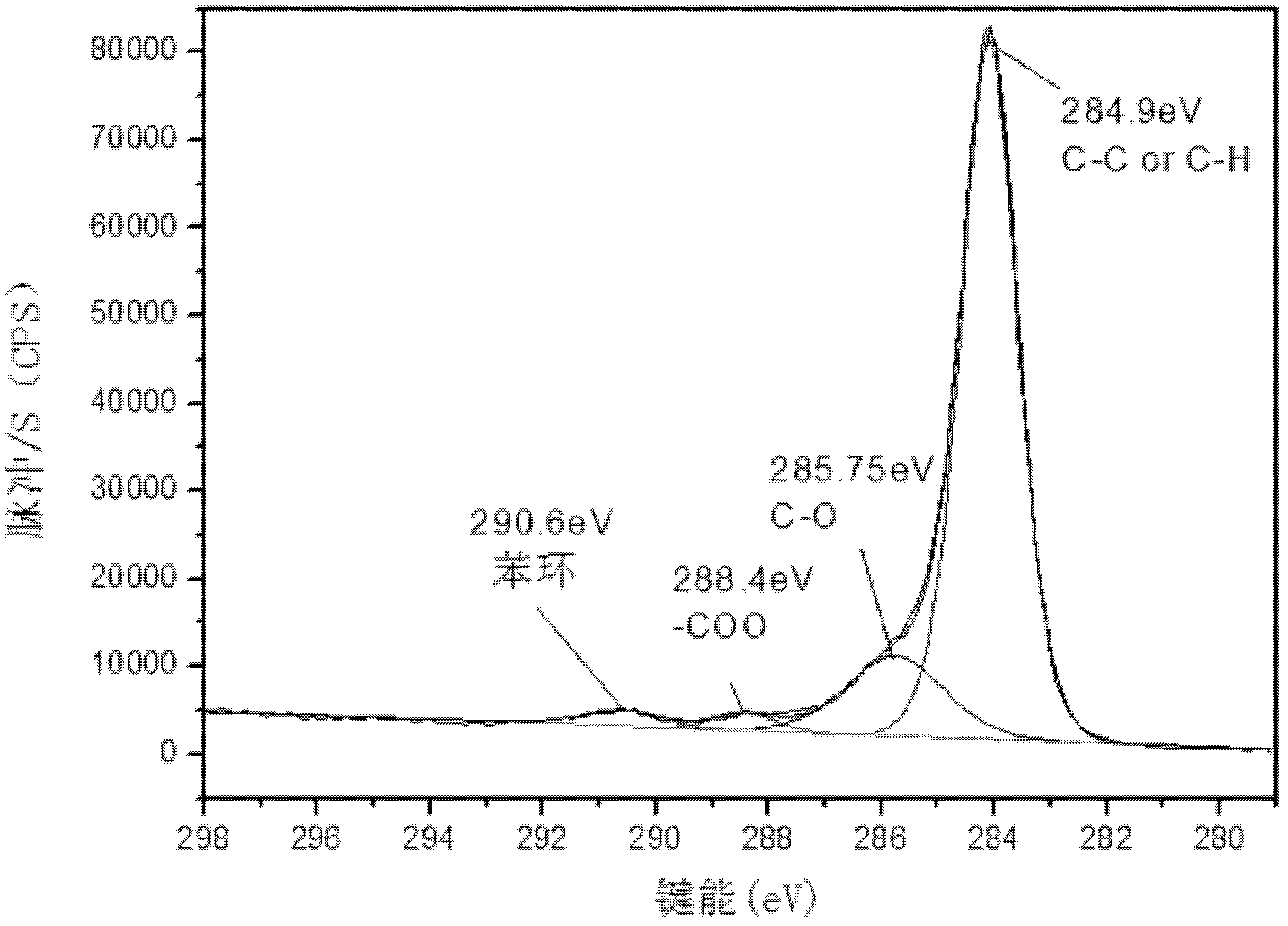
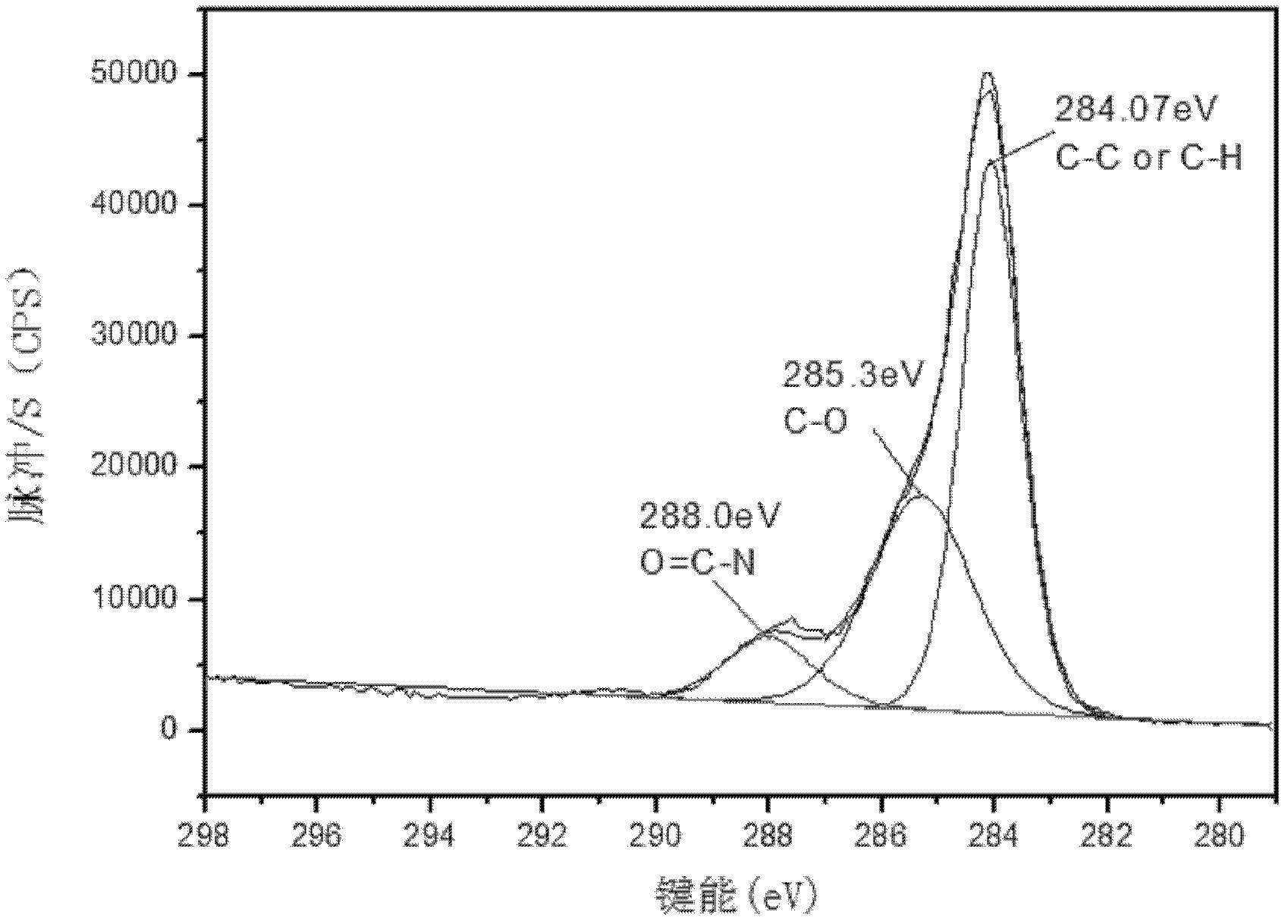
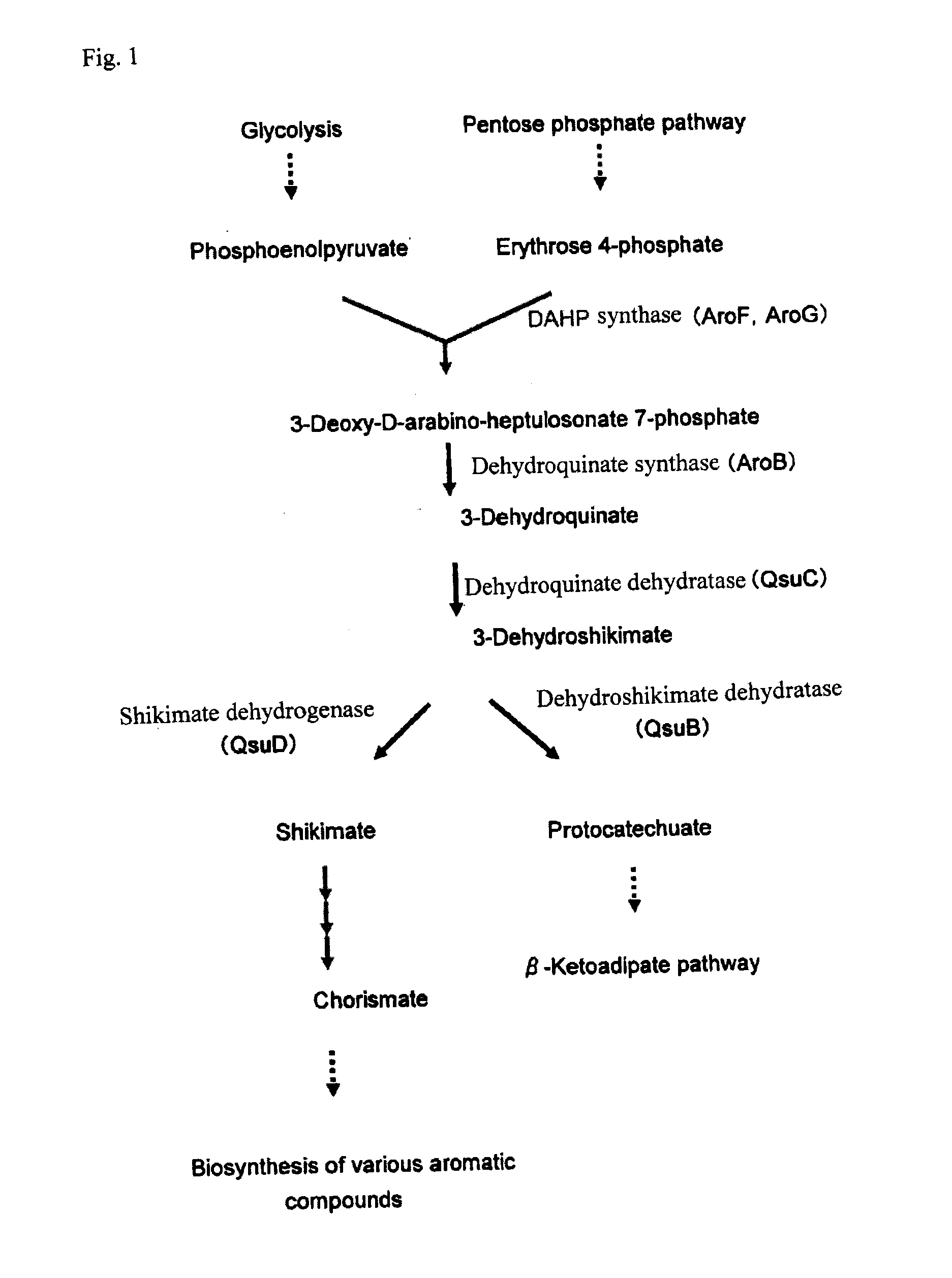
Method for producing polymer, method for producing organic acid, and organic acid-producing microorganism
The present invention provides a method of producing a polymer, which comprises the step of performing a polymerization reaction using, as a starting material, an organic acid obtained by allowing a microorganism or a treated cell thereof to act on an organic raw material, wherein said microorganism has an ability to produce an organic acid and has been modified so as to produce less aromatic carboxylic acid as compared to an unmodified strain.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com