Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
213 results about "Cell organisation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cellular organization refers to the components of a cell and how these individual parts are arranged within the cell. Cells are the smallest organizational levels of living organisms. All animal cells contain four basic components.
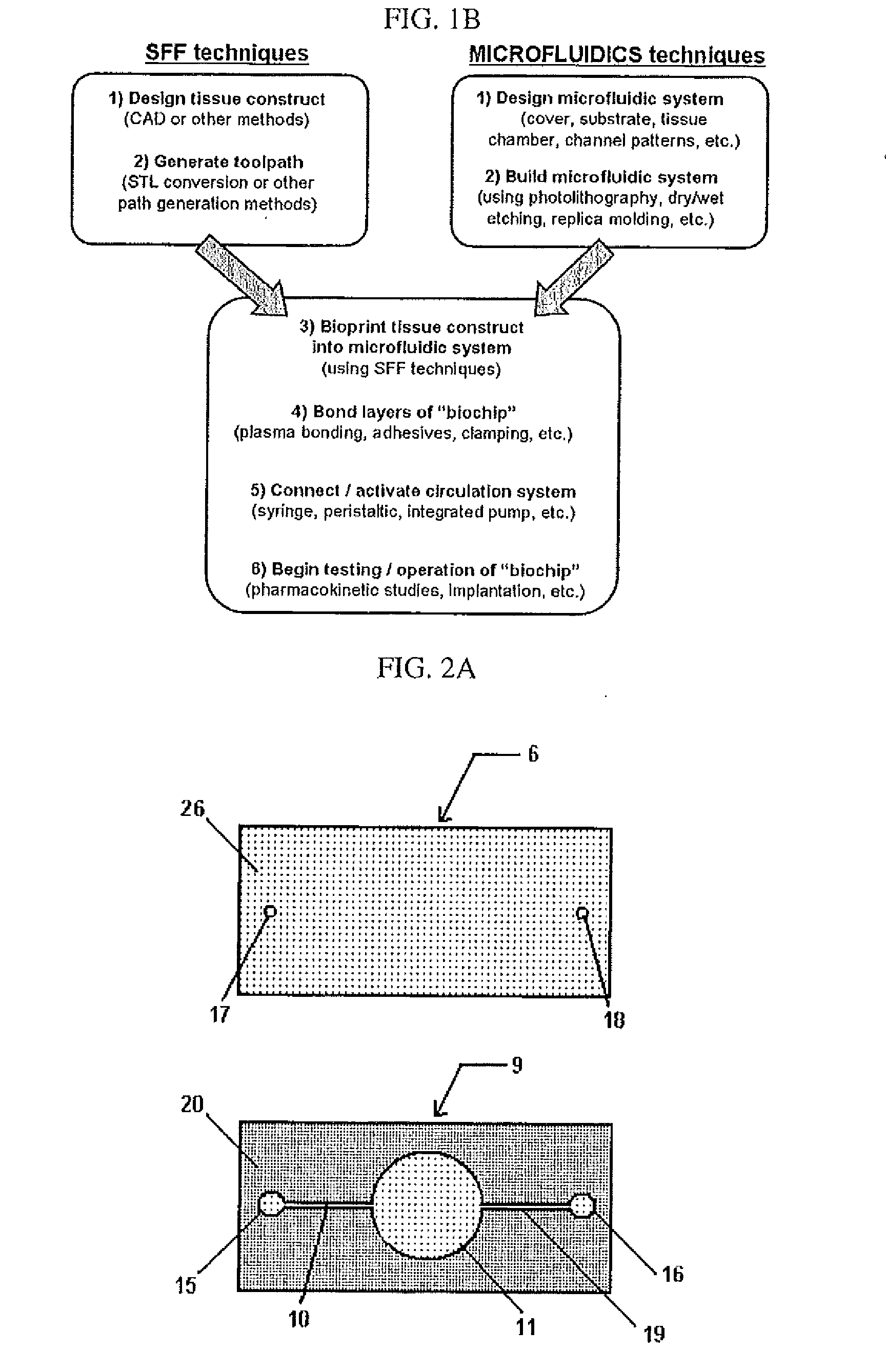
Perfused three-dimensional cell/tissue disease models
ActiveUS20050260745A1Easy to primeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLymphatic SpreadPathology diagnosis
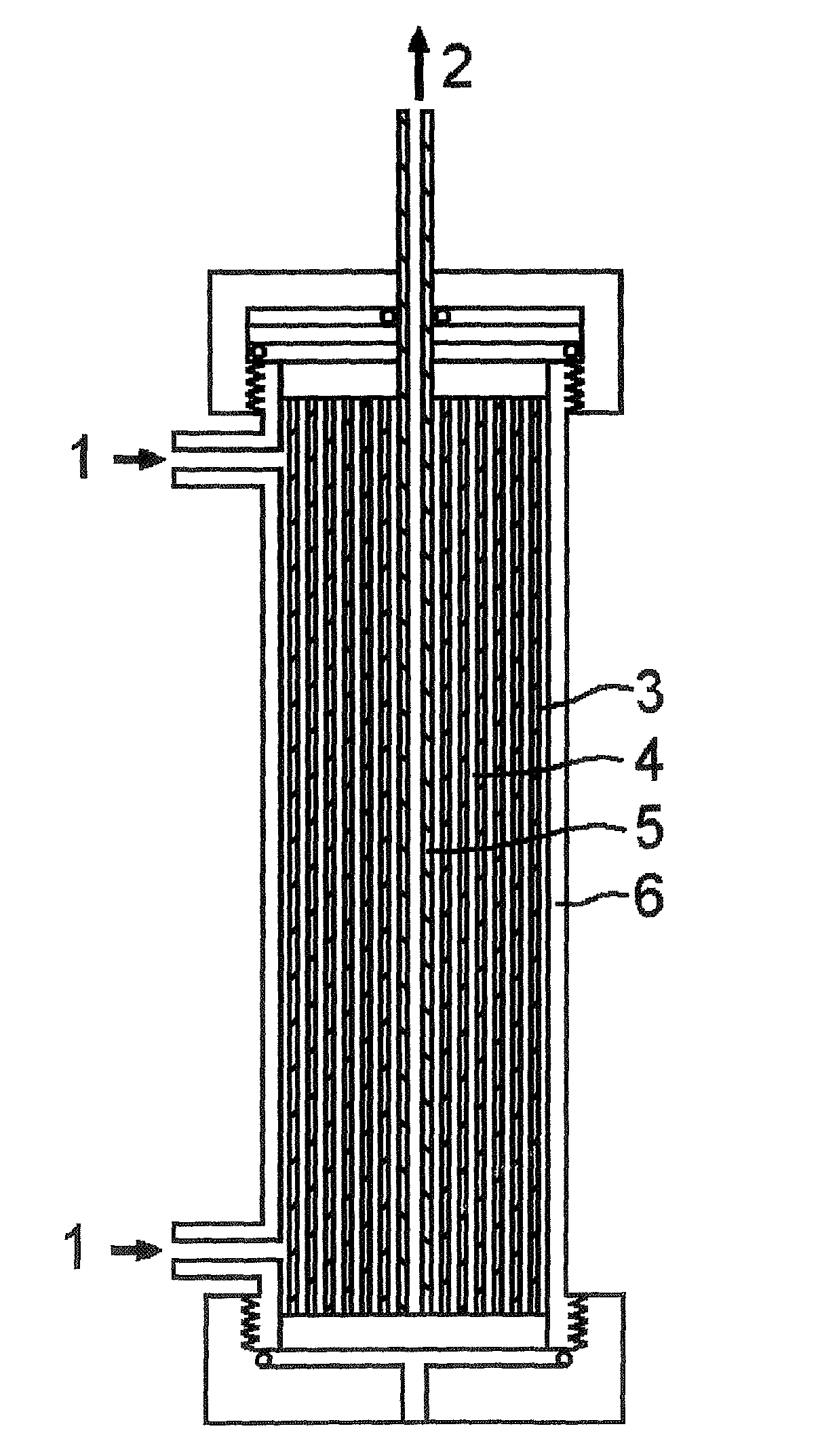
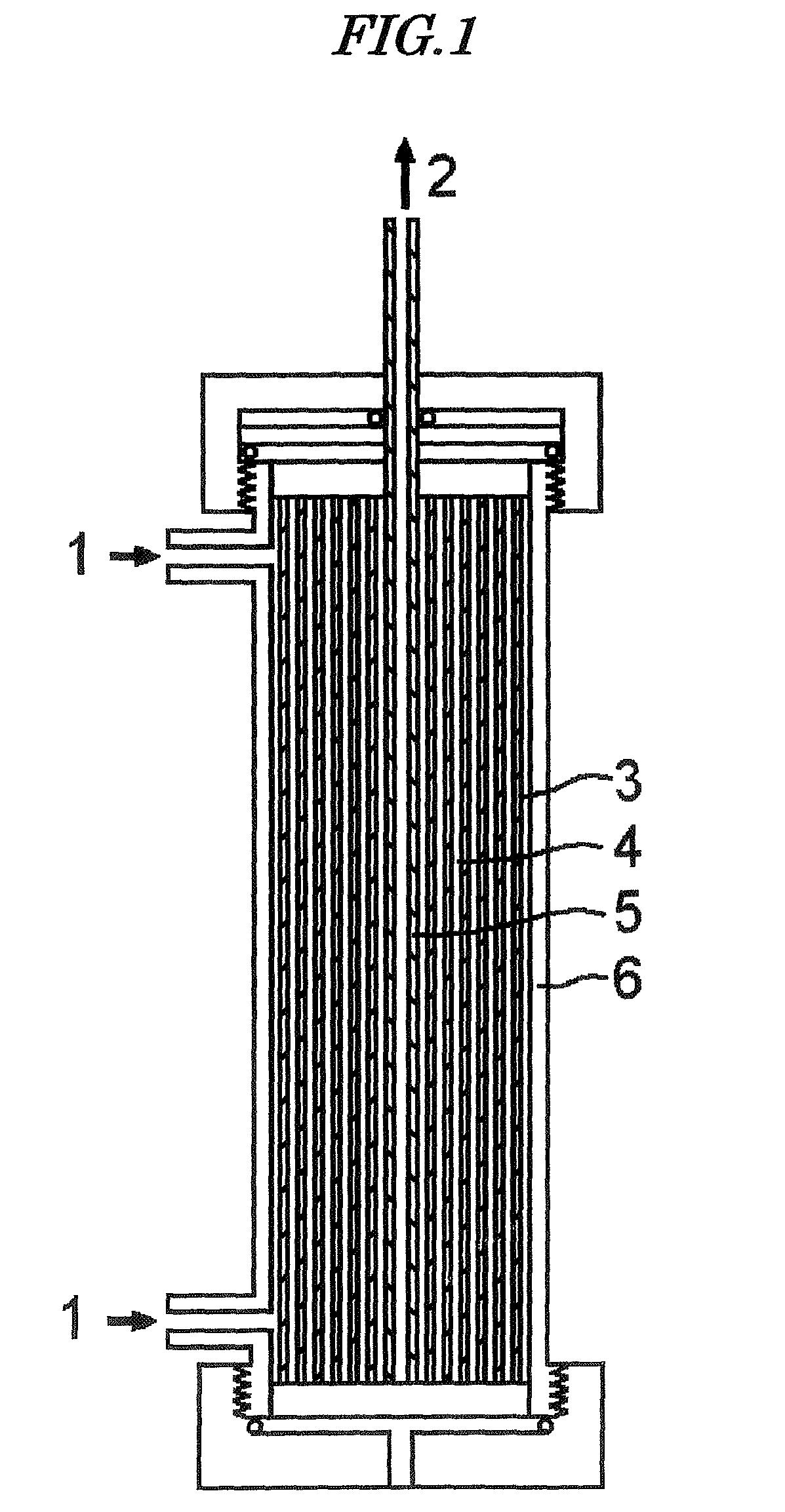
A system has been constructed that recapitulate the features of a capillary bed through normal human tissue. The system facilitates perfusion of three-dimensional (3D) cell monocultures and heterotypic cell co-cultures at the length scale of the capillary bed. A major feature is that the system can be utilized within a “multiwell plate” format amenable to high-throughput assays compatible with the type of robotics commonly used in pharmaceutical development. The system provides a means to conduct assays for toxicology and metabolism and as a model for human diseases such as hepatic diseases, including hepatitis, exposure-related pathologies, and cancer. Cancer applications include primary liver cancer as well as metastases. The system can also be used as a means of testing gene therapy approaches for treating disease and inborn genetic defects.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Compositions comprising nanostructures for cell, tissue and artificial organ growth, and methods for making and using same
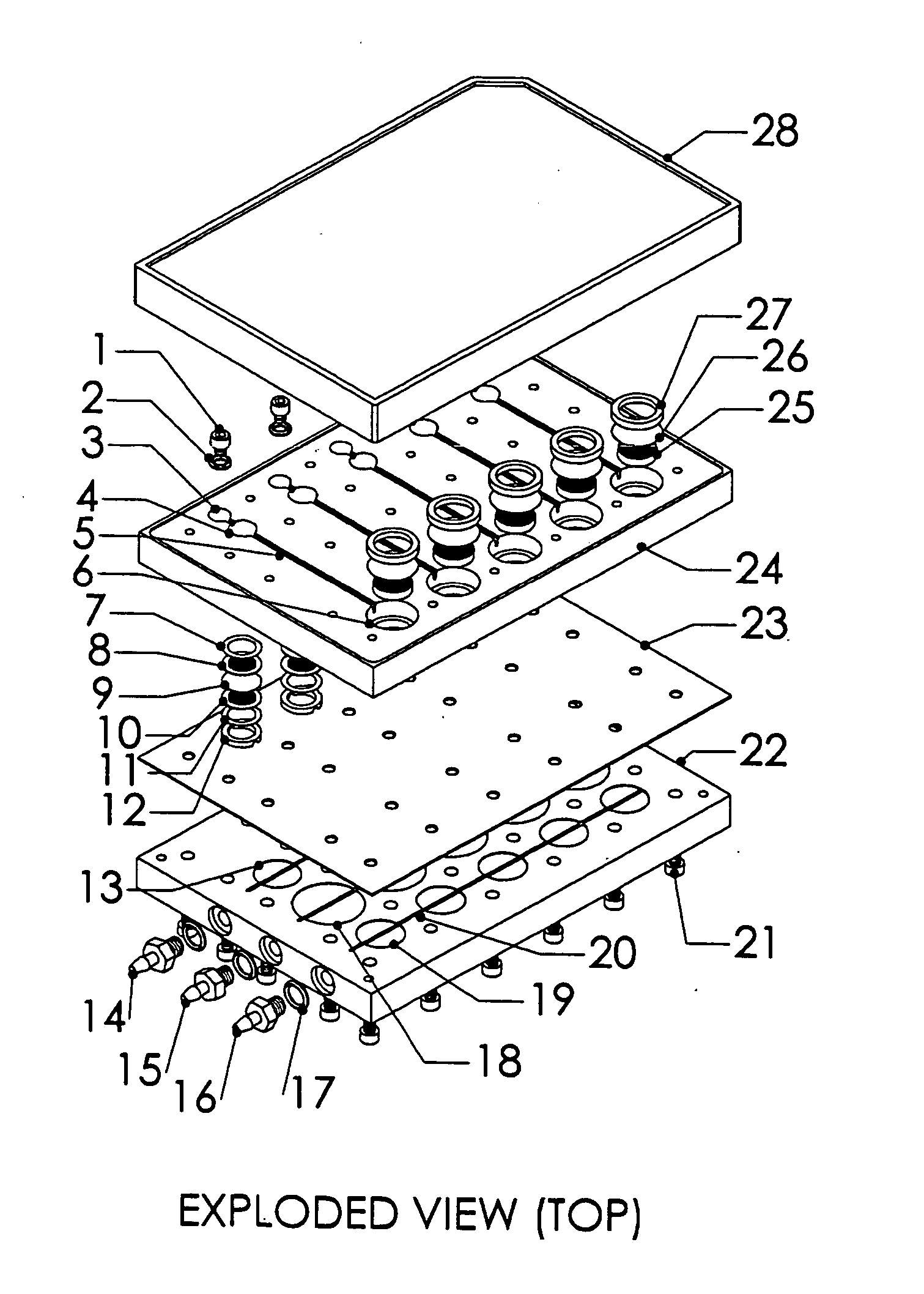
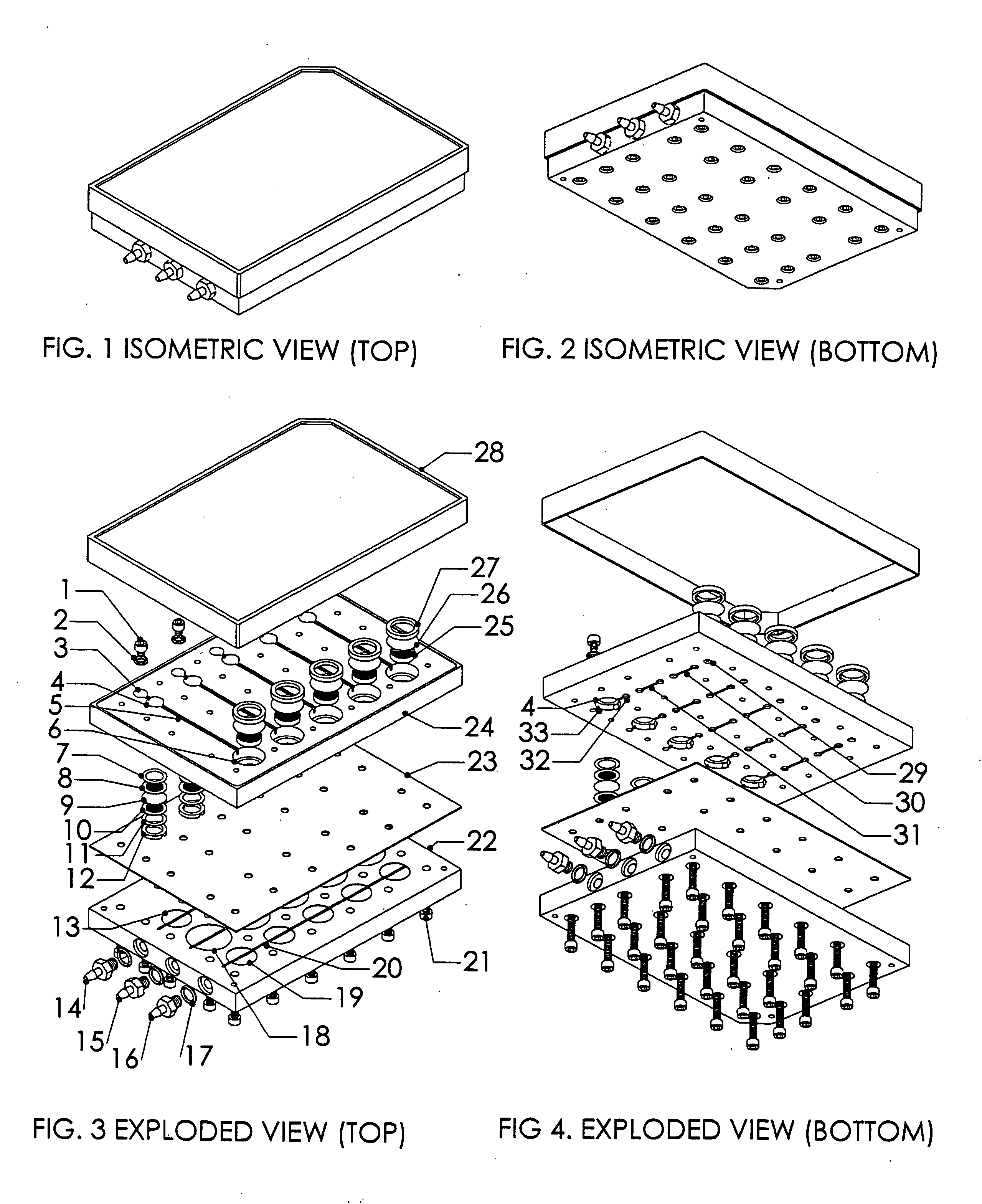
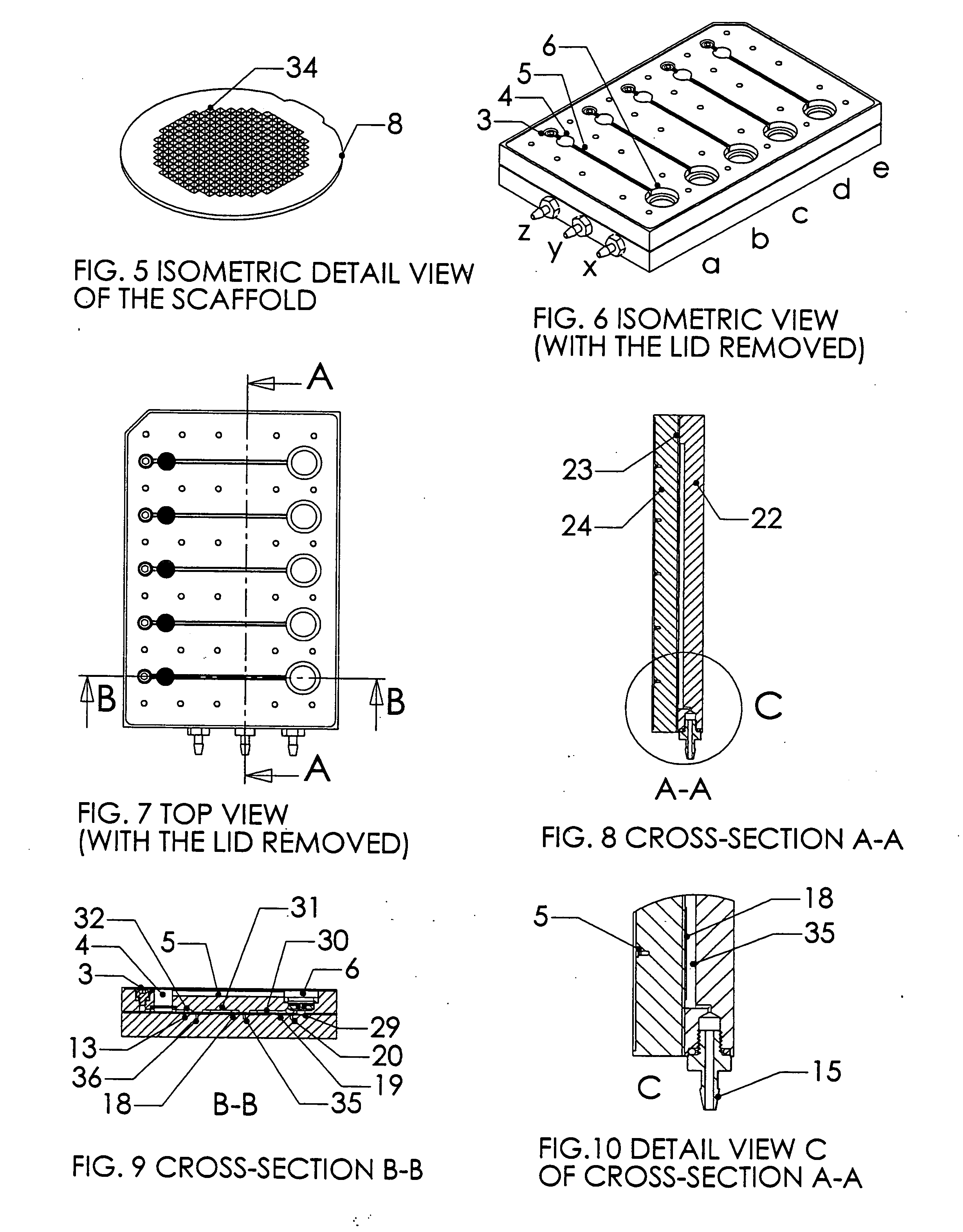
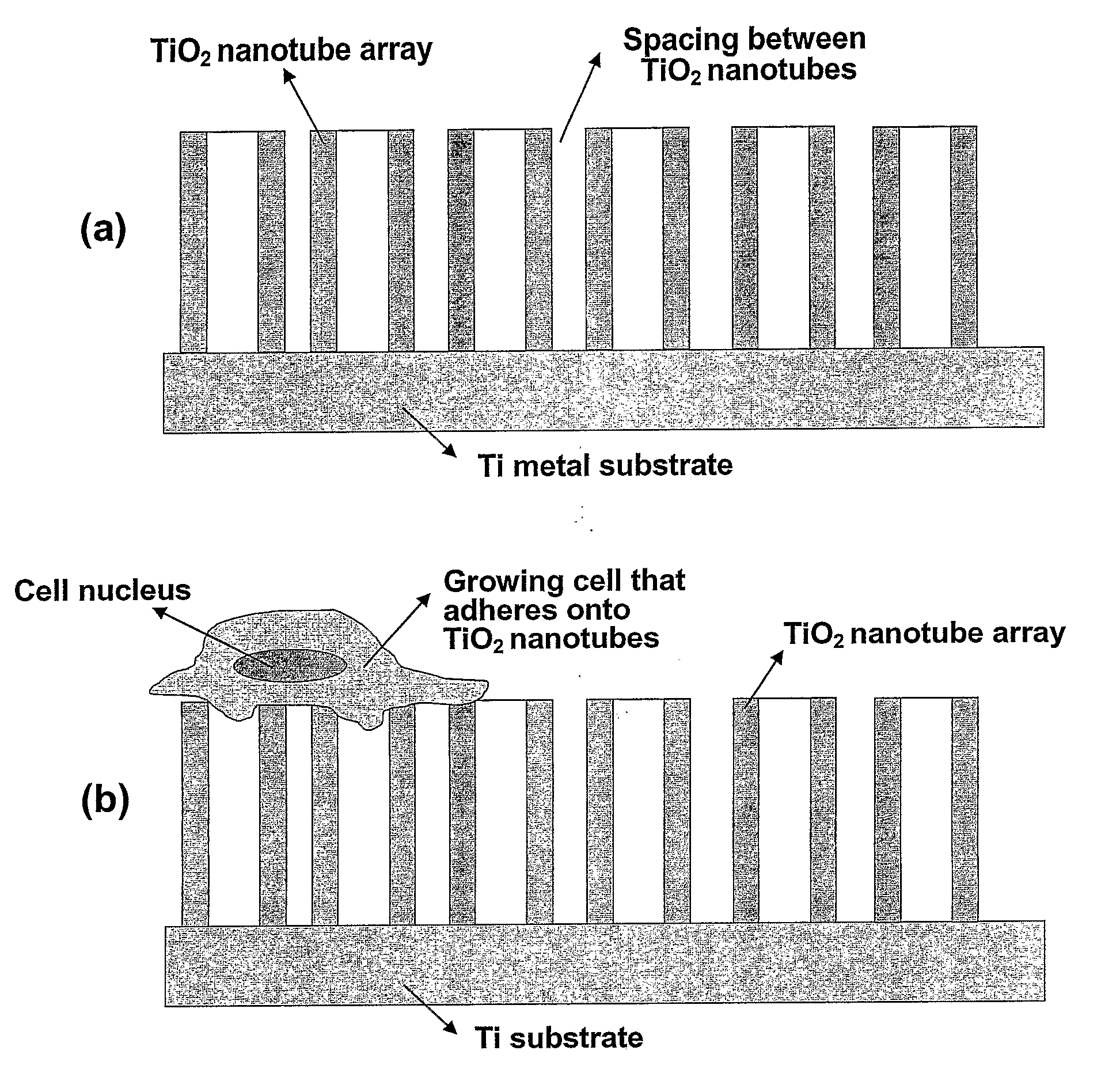
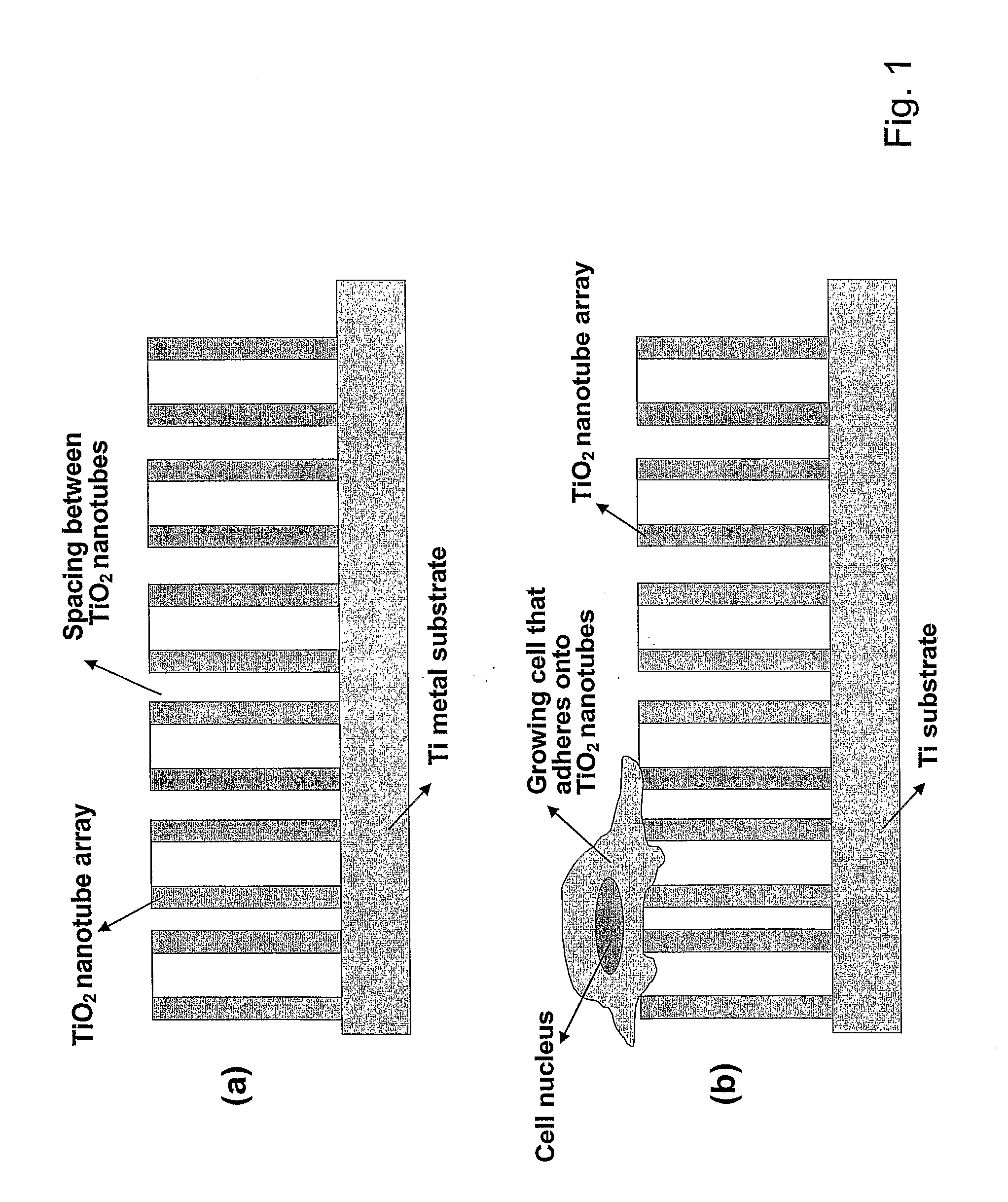
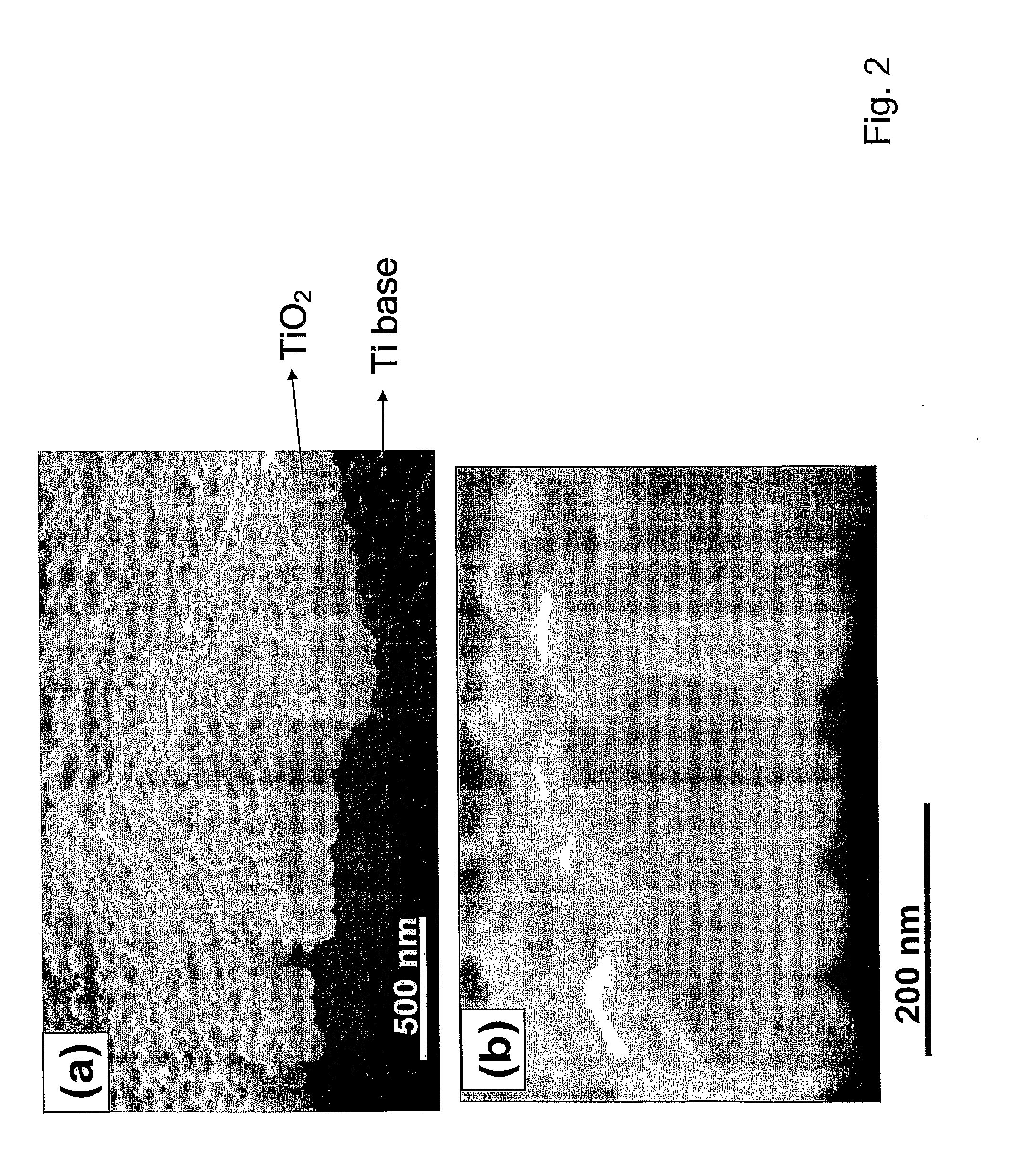
ActiveUS20090220561A1Improve bone formationIncreased durabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysis componentsIn vivoNanostructure
The invention provides articles of manufacture comprising biocompatible nanostructures comprising nanotubes and nanopores for, e.g., organ, tissue and / or cell growth, e.g., for bone, kidney or liver growth, and uses thereof, e.g., for in vitro testing, in vivo implants, including their use in making and using artificial organs, and related therapeutics. The invention provides lock-in nanostructures comprising a plurality of nanopores or nanotubes, wherein the nanopore or nanotube entrance has a smaller diameter or size than the rest (the interior) of the nanopore or nanotube. The invention also provides dual structured biomaterial comprising micro- or macro-pores and nanopores. The invention provides biomaterials having a surface comprising a plurality of enlarged diameter nanopores and / or nanotubes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Control of gene expression
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Method of inhibiting gene expression
InactiveUS20050004064A1Improve stabilityGenetic material ingredientsFermentationNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
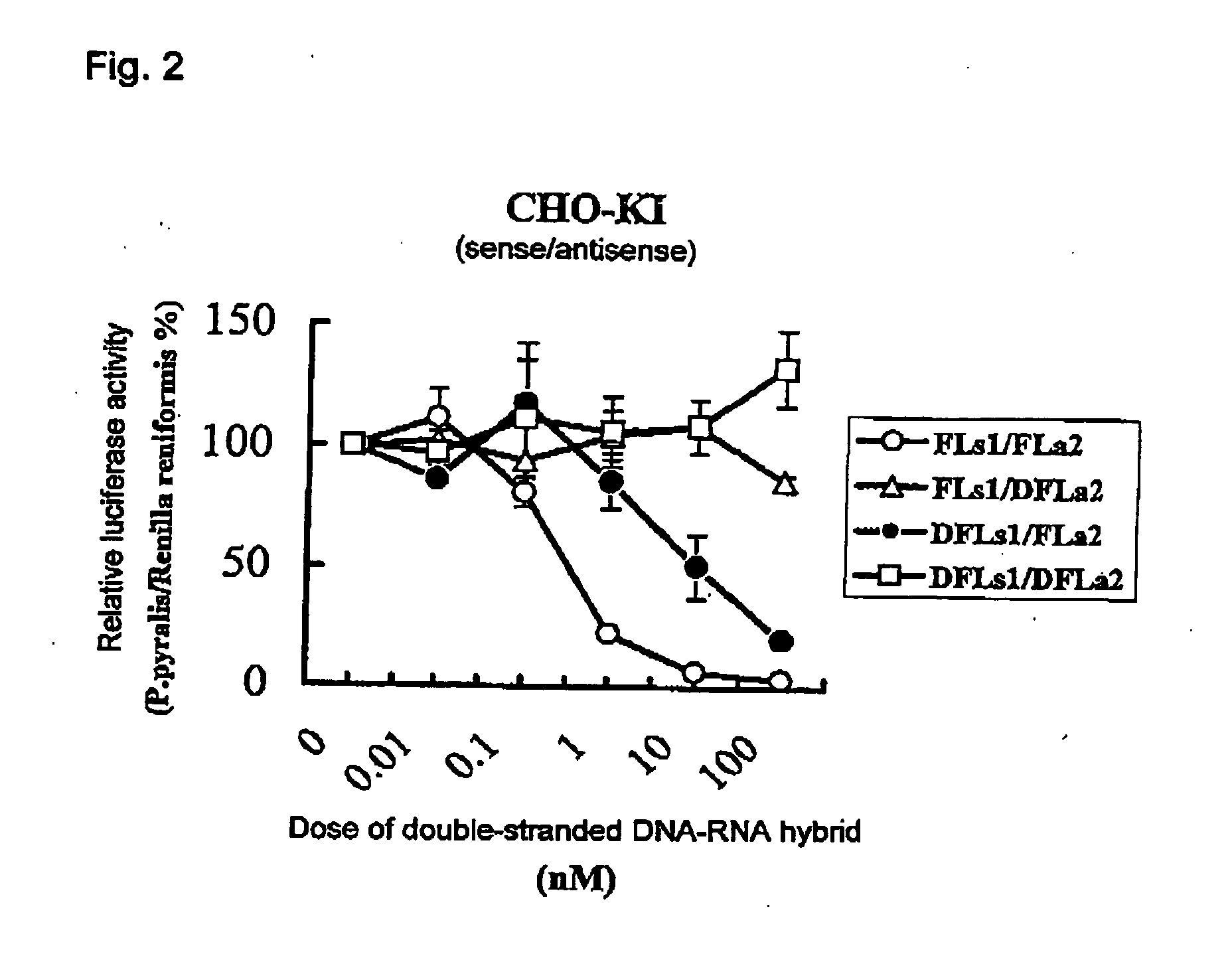
The present invention relates to a method for inhibiting expression of a target gene, which comprises transfecting a cell, tissue, or individual organism with a double-stranded polynucleotide comprising DNA and RNA having a substantially identical nucleotide sequence with at least a partial nucleotide sequence of the target gene.
Owner:ALPHAGEN +1
Peptide linkers for polypeptide compositions and methods for using same
ActiveUS20120232021A1Facilitate targeted deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLysosomal storage disordersPeptide
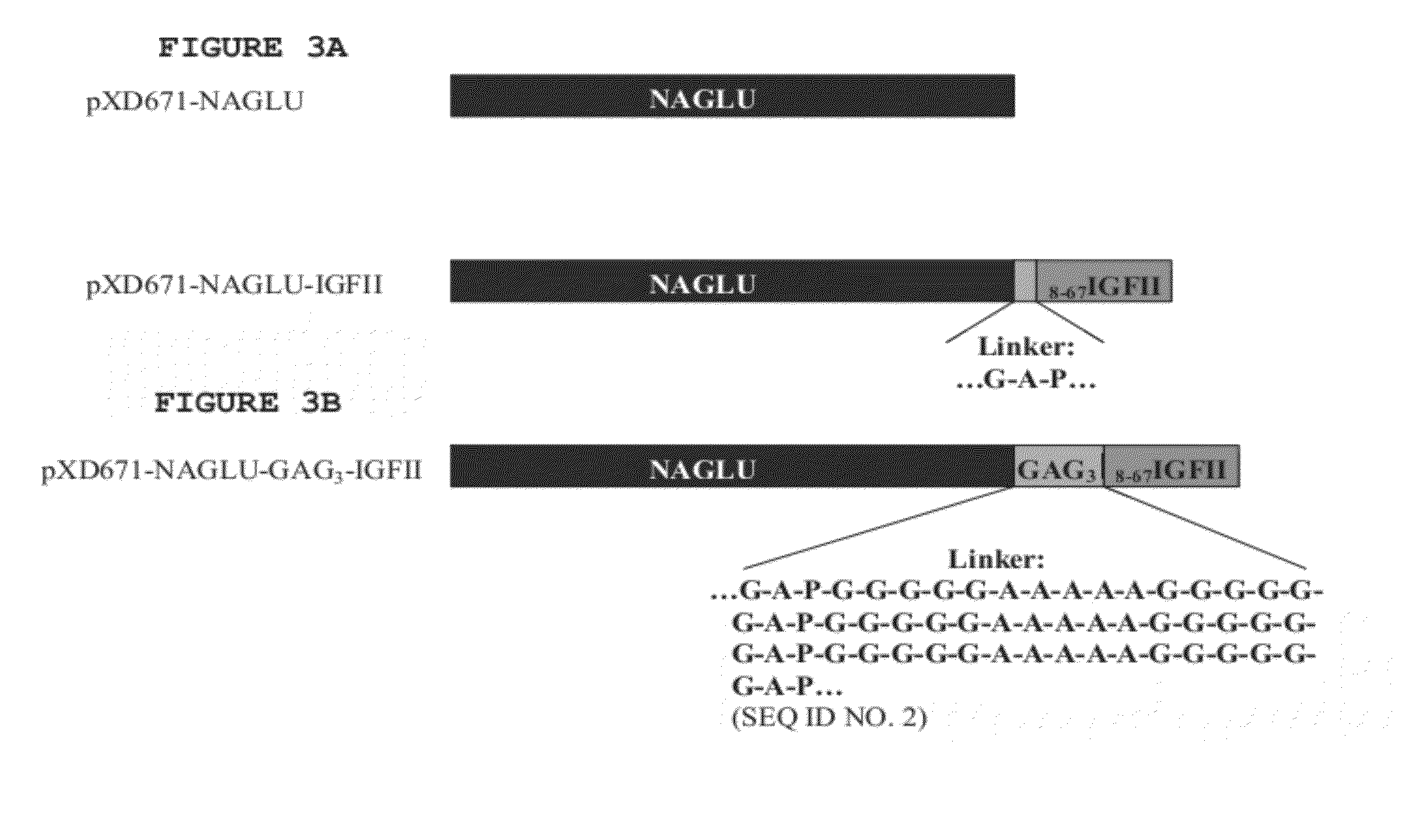
Disclosed herein are novel peptide linkers and polypeptide compositions comprising the linkers (e.g., chimeric polypeptides) and methods of using the polypeptide compositions. The compositions and methods are particularly useful for targeting / delivering a polypeptide or protein of interest (e.g., a therapeutic polypeptide) to a cell, tissue or organ of interest in order to treat various diseases or disorders (e.g., lysosomal storage disorders).
Owner:SHIRE HUMAN GENETIC THERAPIES INC
Nanotopographic Compositions and Methods for Cellular Organization in Tissue Engineered Structures
ActiveUS20080026464A1Additive manufacturing apparatusPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCell typeNanotopography
The present invention relates to tissue engineered compositions and methods comprising nanotopographic surface topography (“nanotopography”) for use in modulating the organization and / or function of multiple cell types.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Structurally modified acellular tissue engineering scaffolds and methods of production
ActiveUS20070248638A1Seed efficiency be facilitateImprove seeding efficiencyCell culture supports/coatingUnknown materialsBiomedical implantFreeze dry
Methods are provided for producing a bioscaffold from natural tissues by oxidizing a decellularized tissue to produce a bioscaffold having pores therein. The pore size and porosity is increased to better accommodate intact cells so that live cells can better infiltrate and inhabit the bioscaffold. The bioscaffold may be freeze-dried or lyophilized, sterilized and (optionally) aseptically packaged for subsequent use. A further aspect of the present invention is a bioscaffold produced by the processes described herein. Methods of treatment using the bioscaffold as a graft or as a biomedical implant for implantation are also provided. Also provided are methods of seeding a bioscaffold with mammalian cells, wherein the seeding carried out either in vitro or in vivo, and wherein a bioscaffold produced as described herein is utilized for said seeding.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIVERSITY
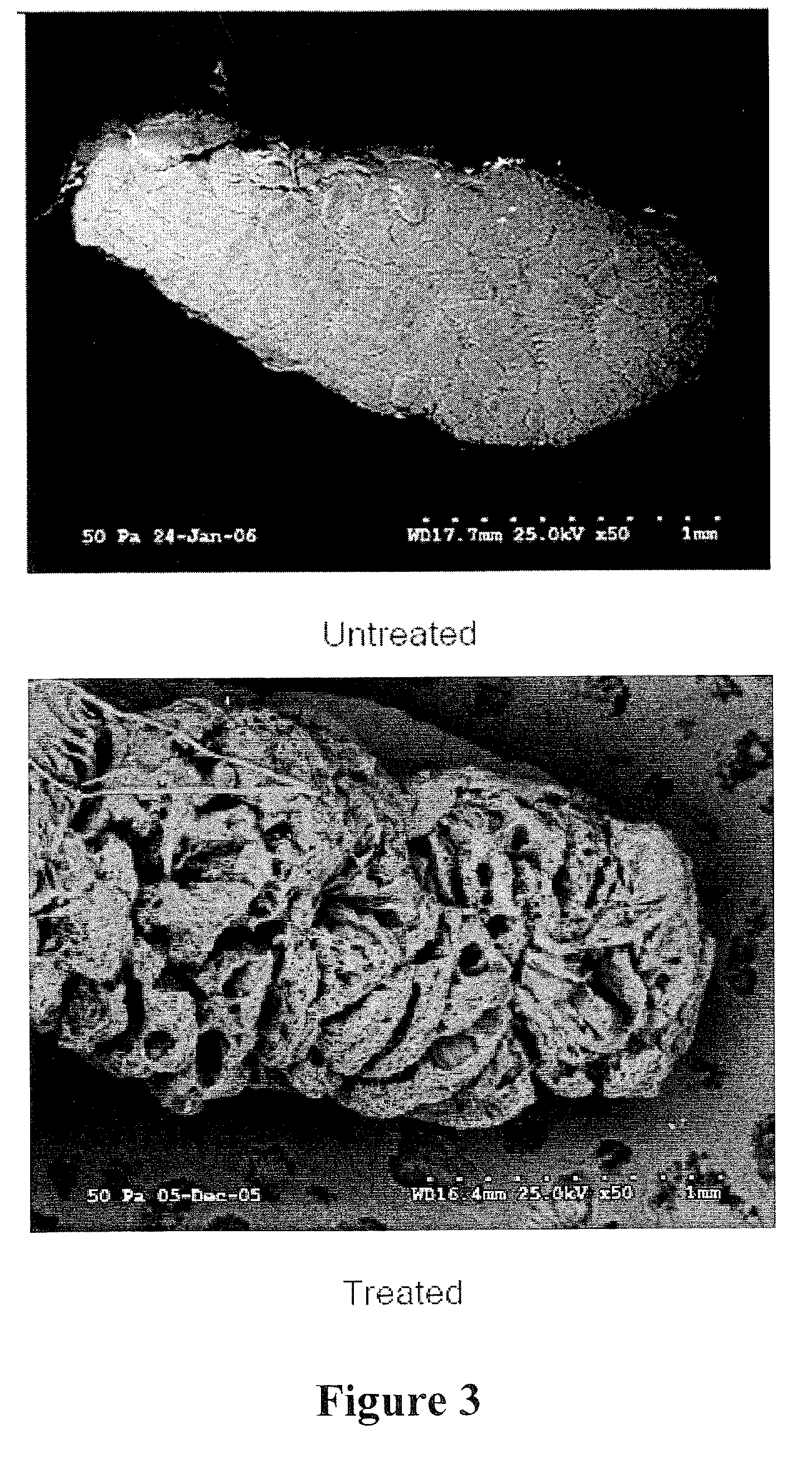
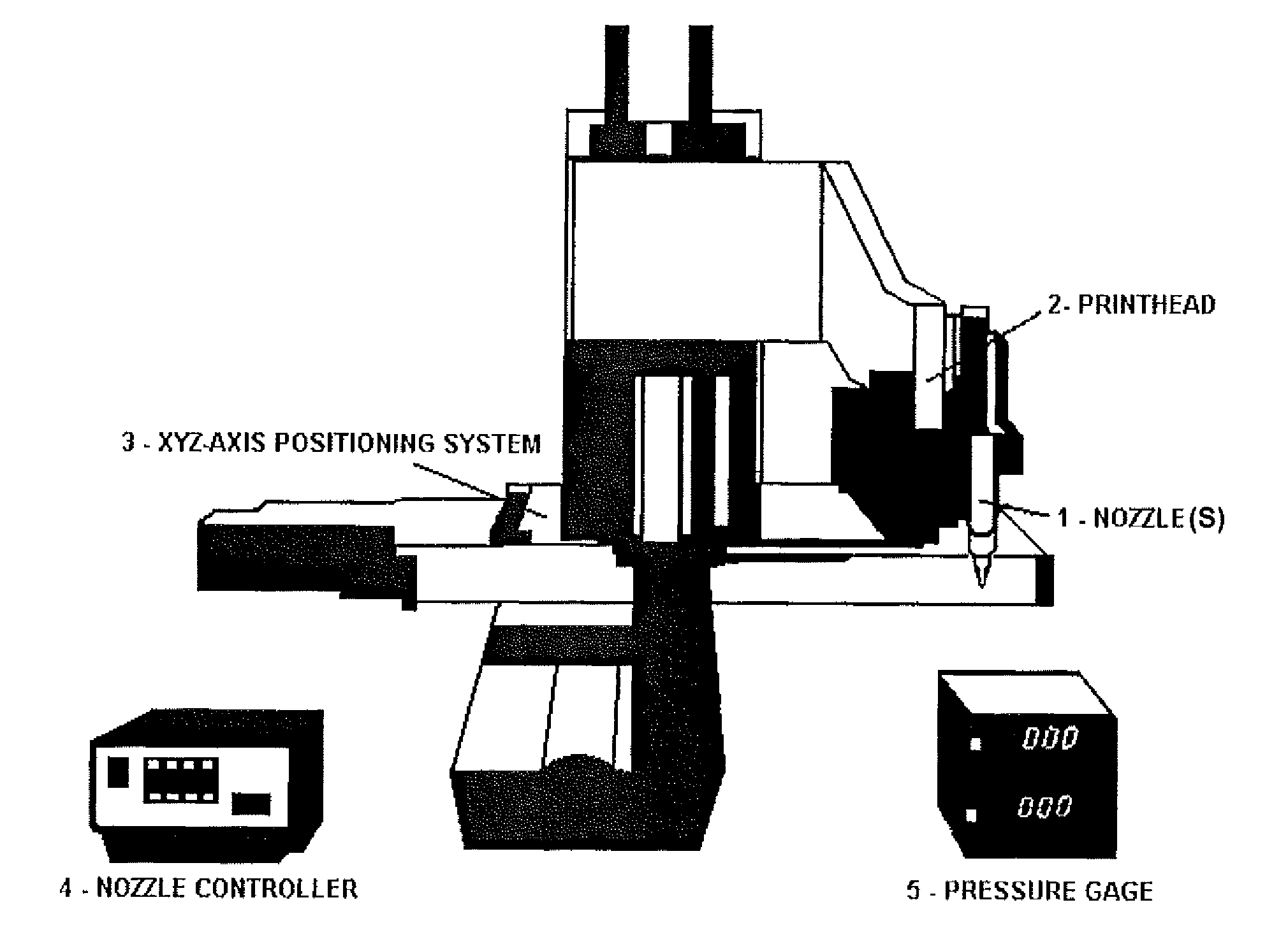
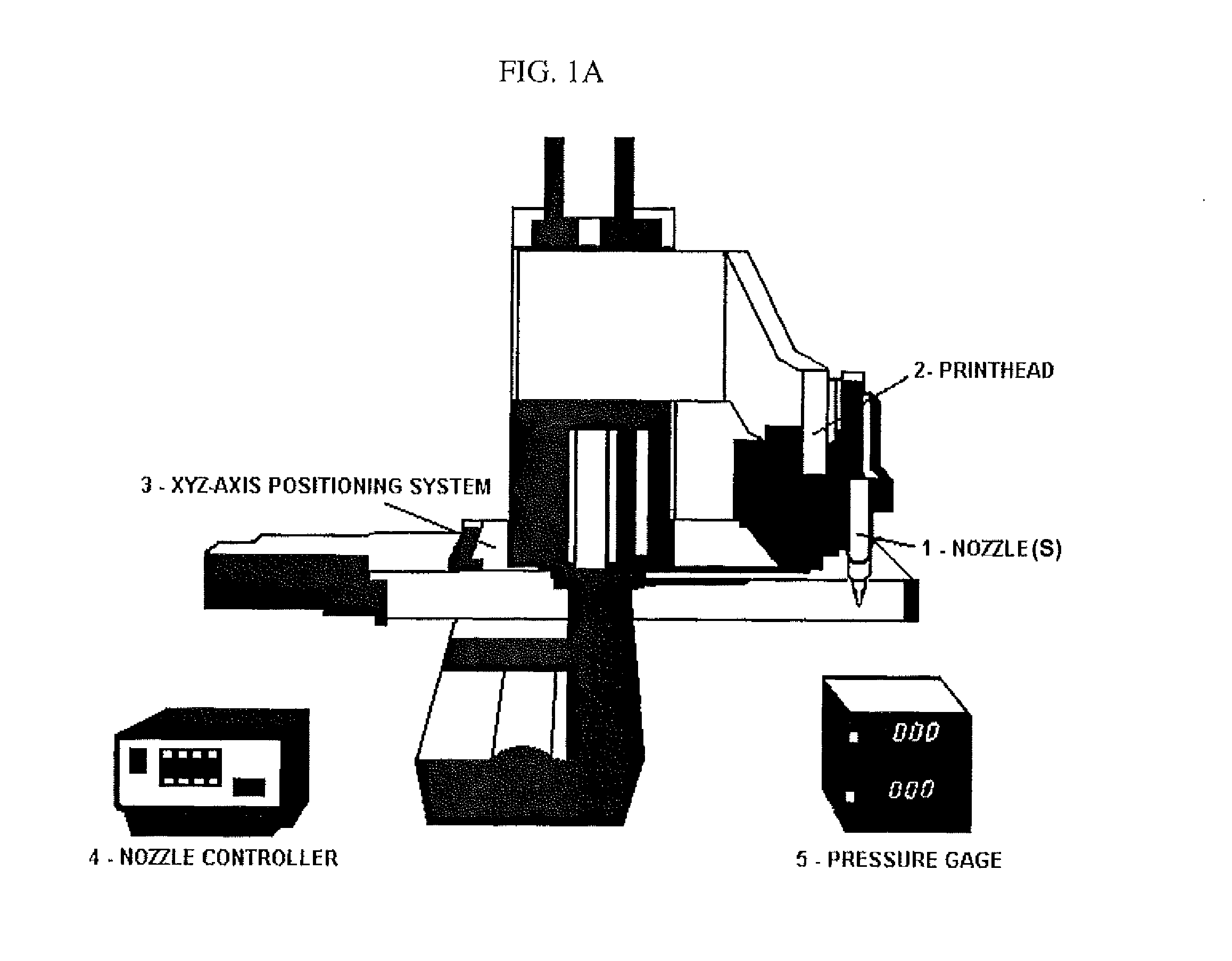
Compositions and Methods for Functionalized Patterning of Tissue Engineering Substrates Including Bioprinting Cell-Laden Constructs for Multicompartment Tissue Chambers
InactiveUS20110136162A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical treatmentDrug metabolism
The present invention relates to microfluidic systems and methods for monitoring or detecting a change in a characteristic of an input substance. Specifically, the invention relates to a model for in vitro pharmacokinetic study and other pharmaceutical applications, as well as other uses including computing, sensing, filtration, detoxification, production of chemicals and biomolecules, testing cell / tissue behavior, toxicology, drug metabolism, drug screening, drug discovery, and implantation into a subject. The present invention also relates to systems and methods of a microplasm functionalized surface patterning of a substrate. The present invention represents an improvement over existing plasma systems used to modify the surface of a substrate, as the present invention creates surface patterning without the use of a mask, stamp or a chemical treatment.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Universal stem cells
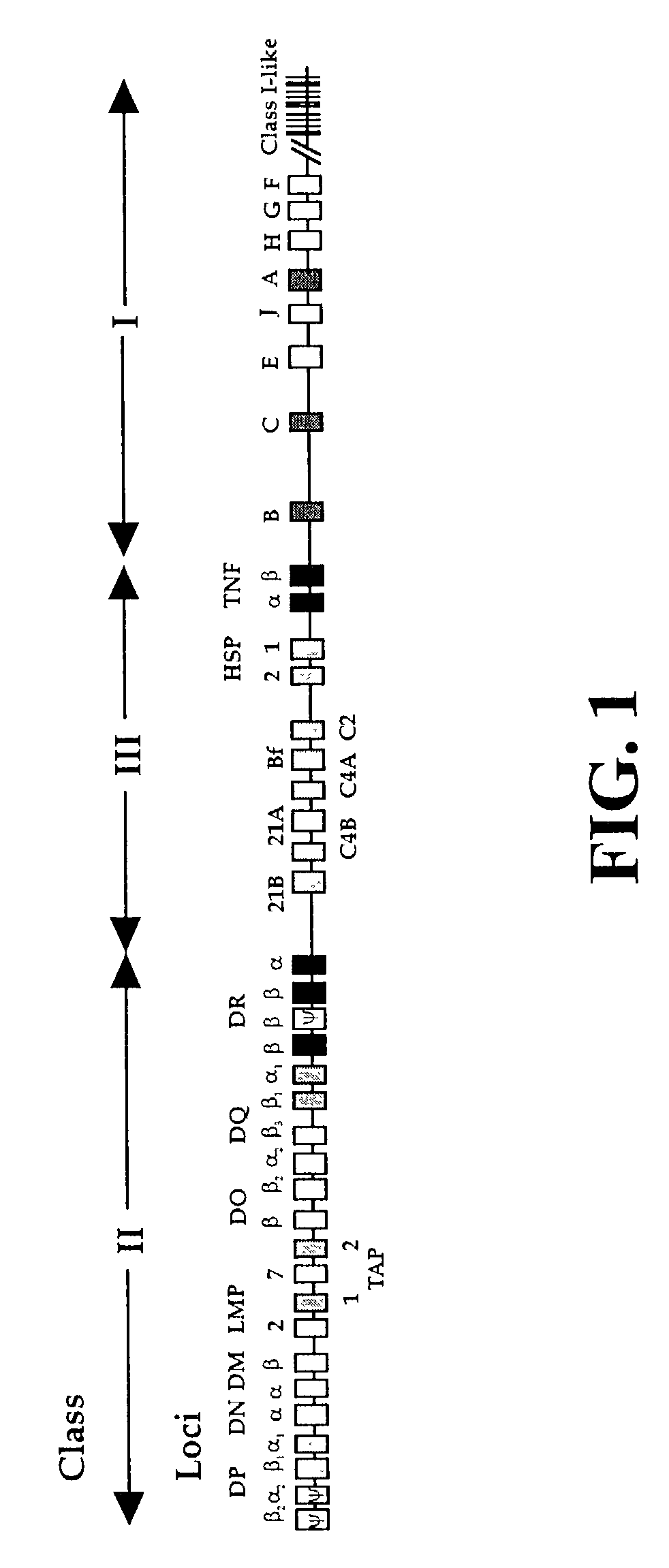
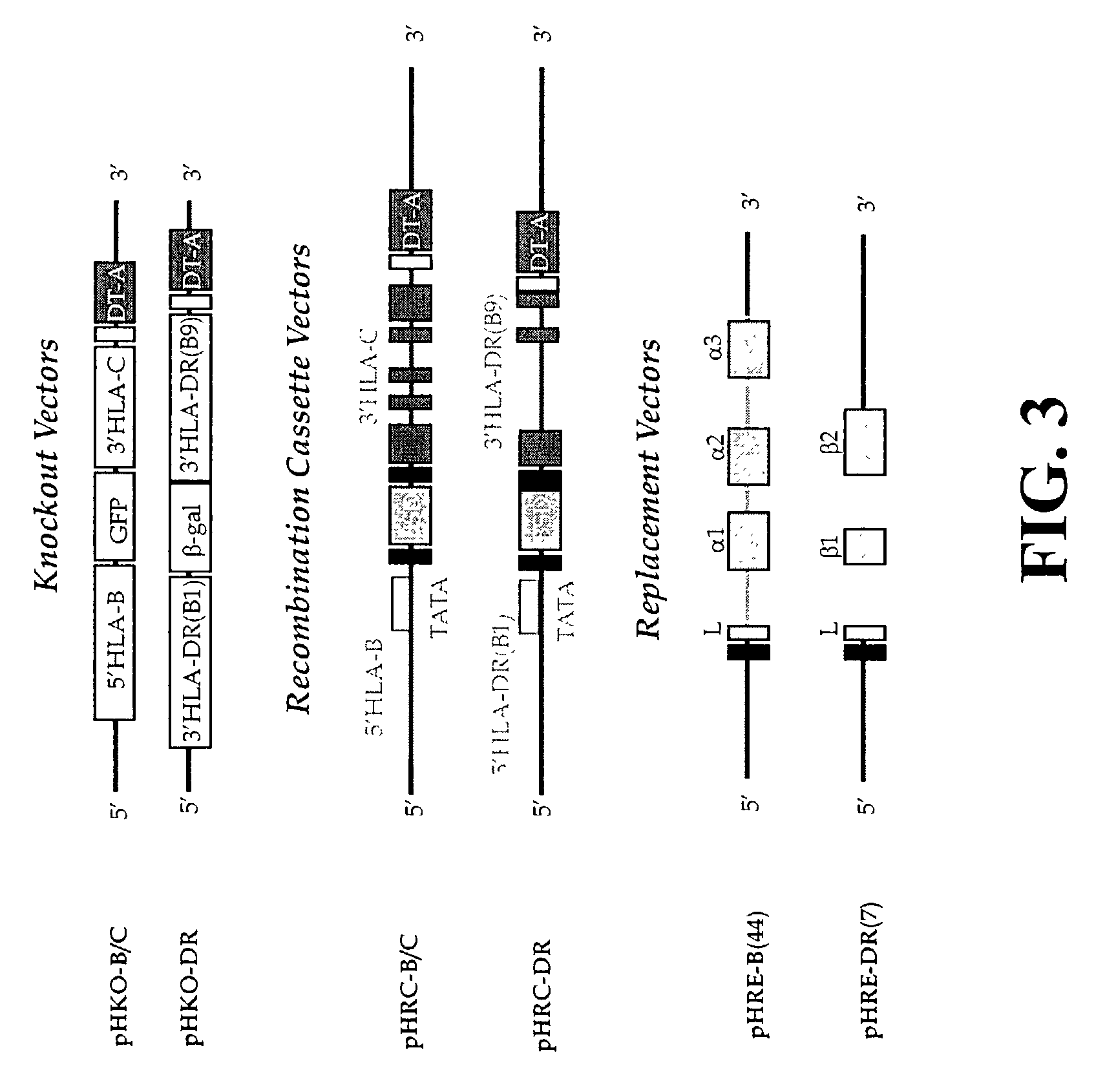
The subject invention pertains to materials and methods for preparing multi-potential stem cells having a pre-selected expression of MHC antigens. Stem cells of the subject invention can be used to generate histocompatible tissues / organs for transplantation. The process of the subject invention comprises the use of targeting vectors capable of gene knockout, insertion of site-specific recombination cassettes, and the replacement of histocompatibility alleles in the stem cell. Novel knockout vectors are used to delete designated regions of one chromosome. Recombination cassette vectors are then used to delete the same region on the second chromosome and deposit a site-specific recombination cassette which can be utilized by replacement vectors for inserting the new MHC genes on the chromosome of the engineered cell. The subject invention also pertains to cells, tissues, and transgenic mammal prepared using the methods and materials of the invention.
Owner:MORPHOGENESIS
Inorganic Nanoparticles of High Density to Destroy Cells In-Vivo
ActiveUS20110213192A1Safely employedEfficient emissionsBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsHigh energy photonIsotope
The present application relates to novel excitable particles which can be used in the health sector. It more particularly relates to particles which can generate electrons and / or high energy photon when excited by ionizing radiations such as X- Rays, γ-Rays, radioactive isotope and / or electron beams, and to the uses thereof in health, in particular in human health. The inventive particles are made of an inorganic material comprising oxygen, in particular an oxide, said material having an adequate density, and can be activated in vitro, ex vivo, or in vivo, by controllable external excitation, in order to disturb, alter or destroy target cells, tissues or organs. The invention also relates to methods for the production of said particles, and to pharmaceutical or medical device compositions containing same.
Owner:NANOBIOTIX SA
Gynogenetic or androgenetic production of pluripotent cells and cell lines, and use thereof to produce differentiated cells and tissues
InactiveUS20030129745A1Rejection is prevented and reducedEliminate, orMammal material medical ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPrimateEmbryo
Methods for obtaining pluripotent (embryonic stem) cells from parthenogenetic embryos, especially primates, are provided. These cells are useful for producing differentiated cells, tissues and organs, especially human and non-human primate cells, tissues and organs.
Owner:ROBL JAMES M +2
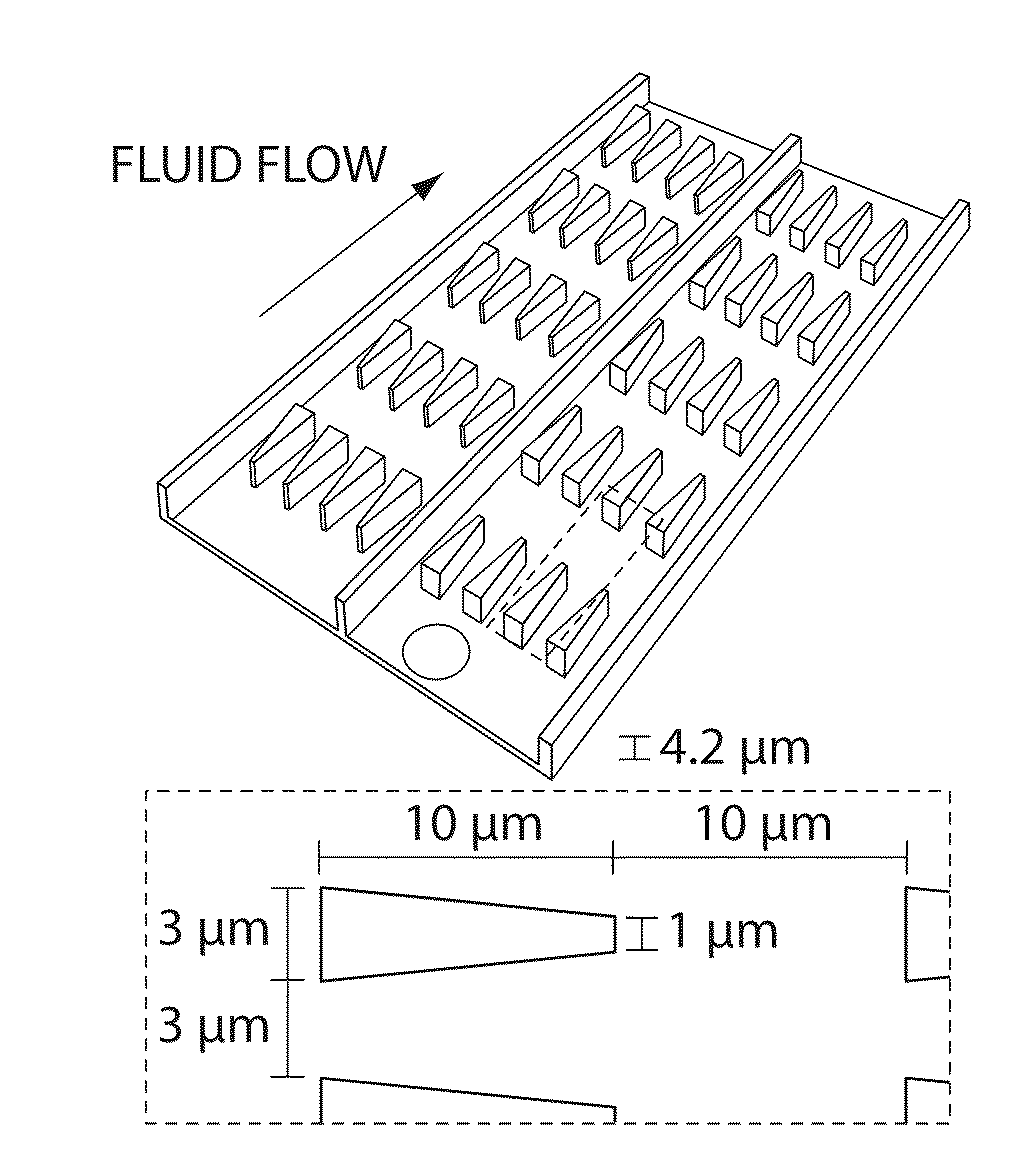
Three dimensional cell cultures in a microscale fluid handling system
InactiveUS20040259177A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTest agentCell layer
The present invention provides a novel microscale fluid handling system for initiating, culturing, manipulating and assaying three-dimensional multicellular assembly. The system including a microfluidic device and three-dimensional multicellular tissue surrogate assembly. The device of the invention includes at least one microfluidic channel; and at least one chamber, wherein the walls of the chamber are lined with a cell layer; and wherein fluid medium flows through each of the channels and chambers. Also, disclosed are methods for using the device to introducing test agents to the multicellular assemblies to observe biological responses thereof.
Owner:BELLBROOK LABS
Three dimensional cell culture construct and apparatus for its making
InactiveCN101245313AWell-defined structureEasy to useTissue/virus culture apparatusBiological material testing proceduresFiberNormal cell
The present invention relates to a three dimensional construct formed from non-biodegradable and non-cytotoxic polymers that provide an internal and external space for living cells to attach, proliferate and differentiate. The construct is composed of polymer struts and / or fibers which are joined together in a designed 3 dimensional pattern. The 3 dimensional cell culture construct (cell culture insert) is intended to be used together with cell / tissue culture plate, tissue culture flask, bioreactor and the like under normal cell culture conditions. The invention further provides methods of making the 3 dimensional cell culture construct. Finally, the invention provides kits comprising one or more 3 dimensional porous cell culture construct in a package together with other cell culture supplies, such as tissue culture plate and flasks.
Owner:刘青
Tissue engineering scaffold
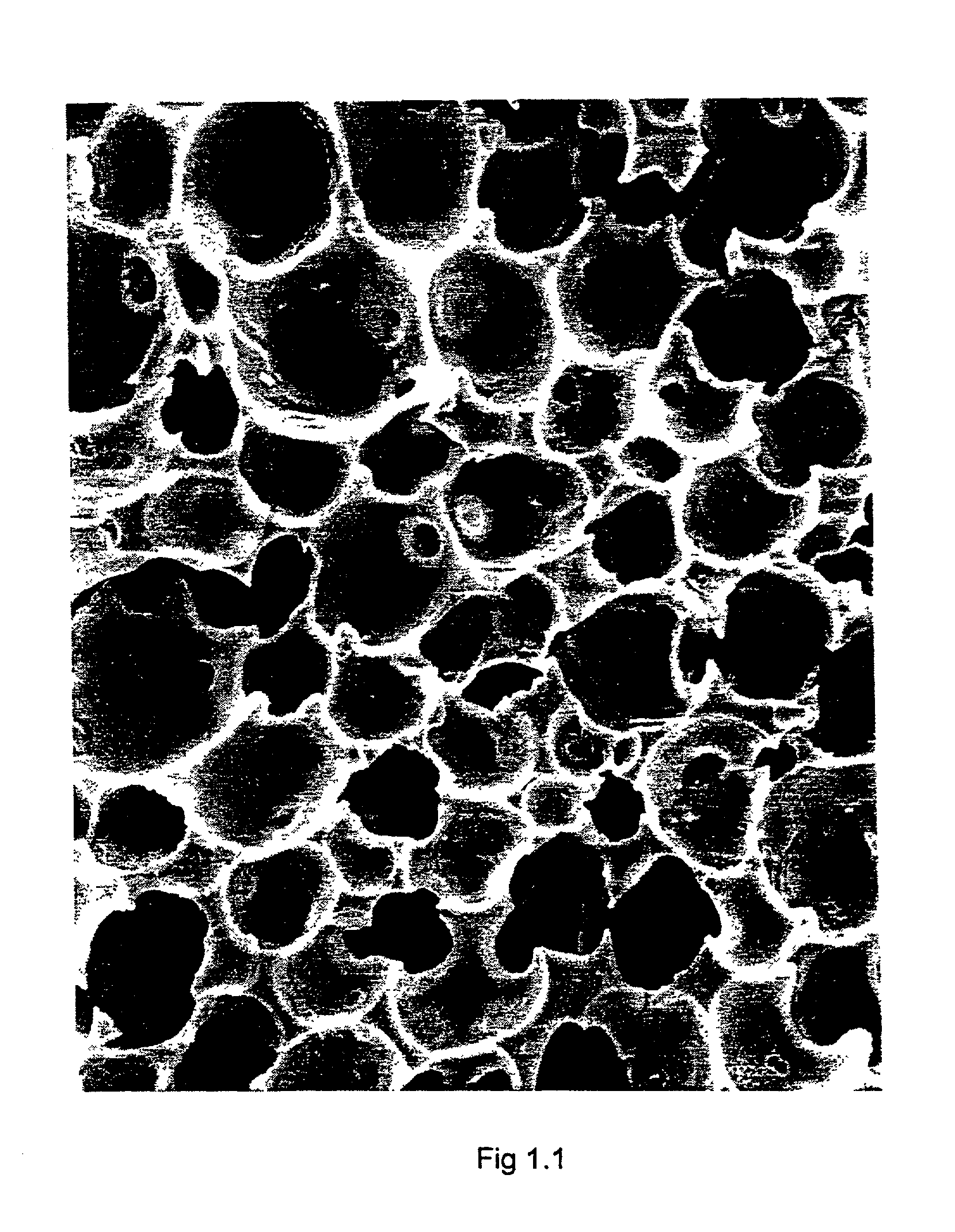
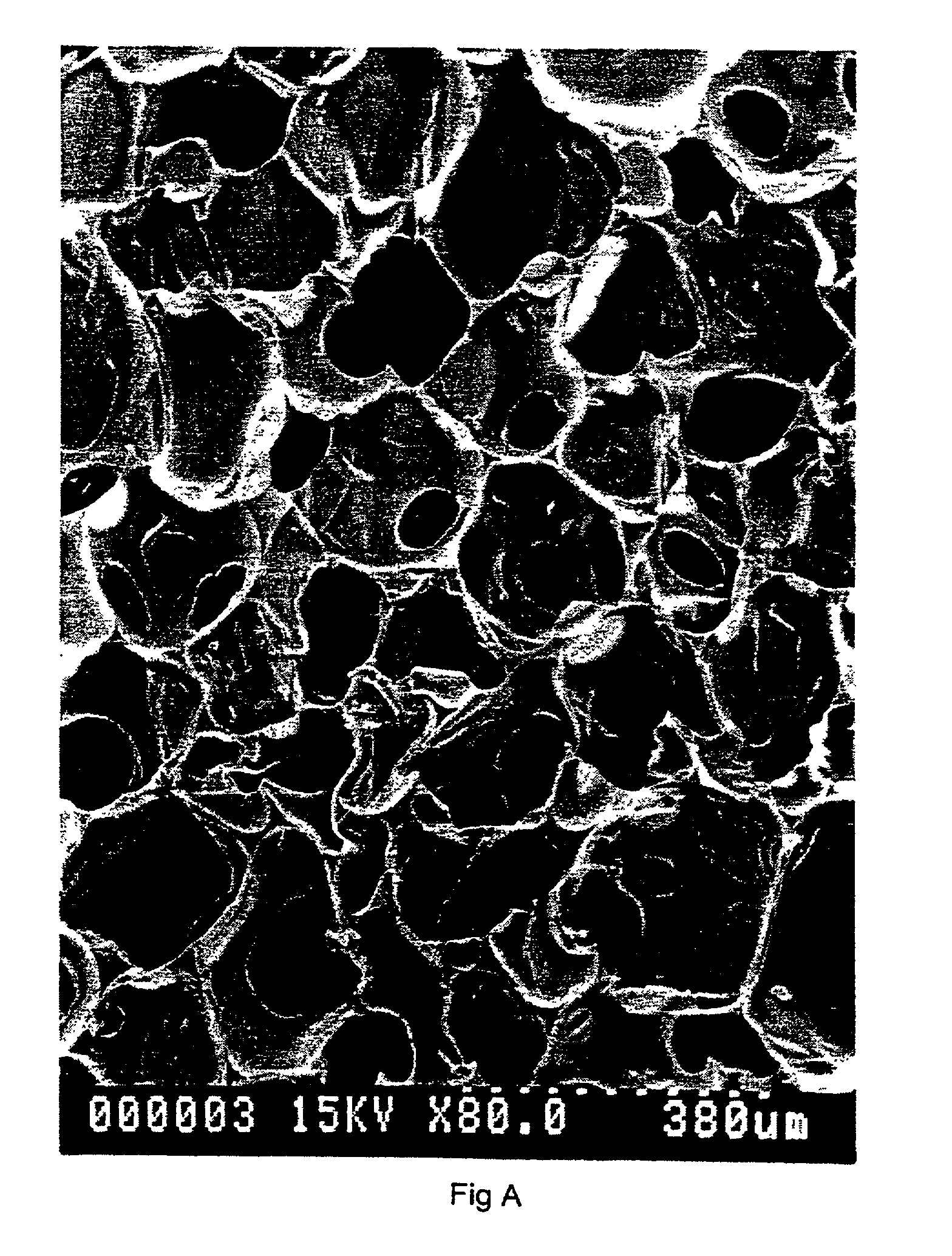
A tissue engineering scaffold for cell, tissue or organ growth comprises a biocompatible porous polyurethane cellular material comprising a plurality of substantially spherical voids of diameter from 20 to 300 microns, preferably 80 to 200 microns, interconnected by generally elliptically shaped pores. The cellular material has a void content of from 85% to 98% and a surface area to volume of from 5 to 400 mm2 / mm3, ideally from 20 to 80 mm2 / mm3.
Owner:SALVIAC
SYSTEMS, APPARATUS, AND/OR METHODS UTILIZING LASER GENERATING PULSES OF LIGHT, PULSED SOUND FREQUENCIES AND/OR PULSED ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS (EMFs) FOR IMPROVING PROPER SYSTEMS, APPARATUS, AND/OR METHODS UTILIZING LASER GENERATING PULSES OF LIGHT, PULSED SOUND FREQUENCIES AND/OR PULSED ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS (EMFs) FOR IMPROVING PROPERTIES OR FUNCTIONS OF CELLS, TISSUES, PROTEINS, FATS, OR ORGANS IN VITRO, IN VIVO, OR IN SITU
InactiveUS20200094066A1Improve propertiesUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyCell organisationEngineering
Owner:HEATH STEPHAN
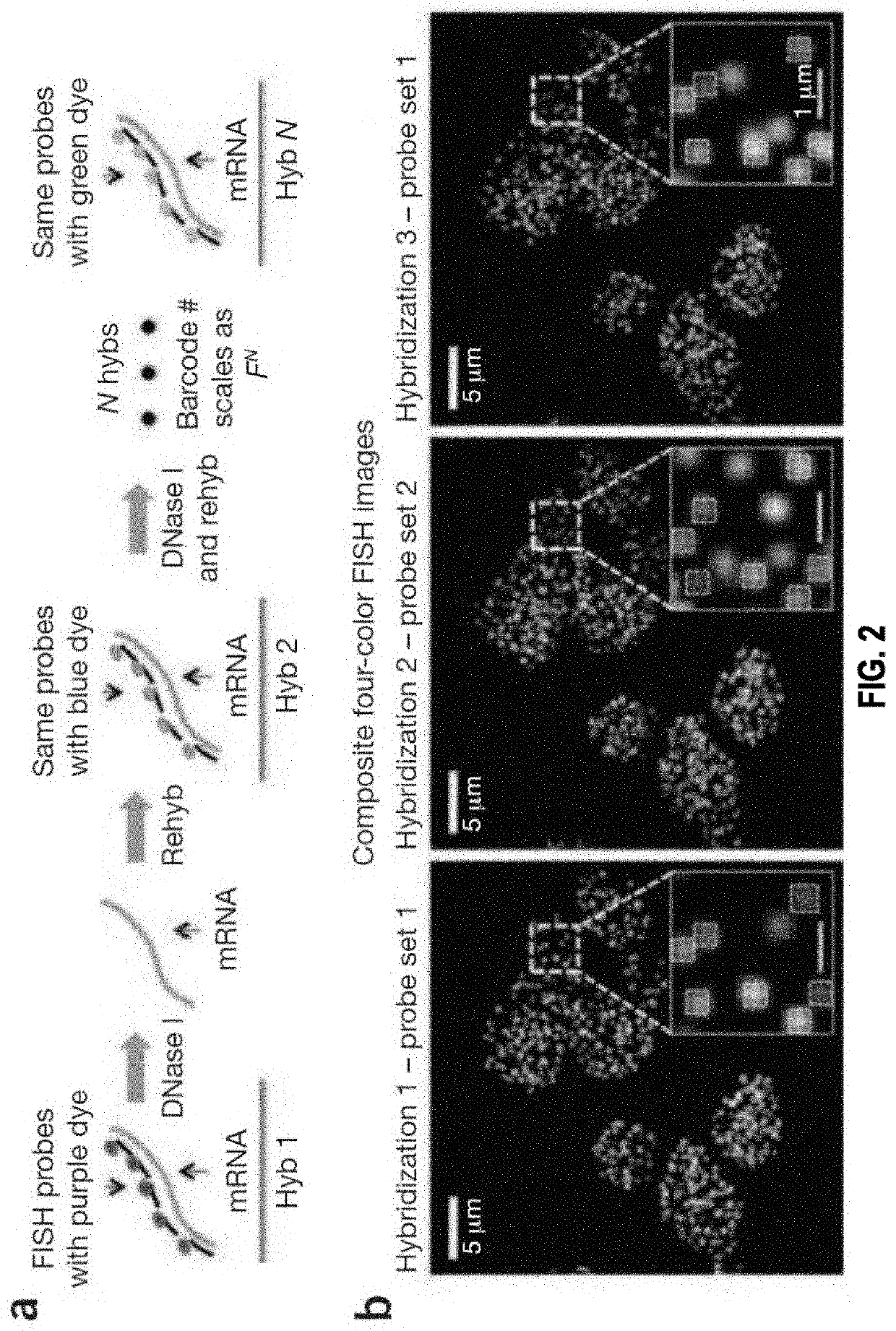
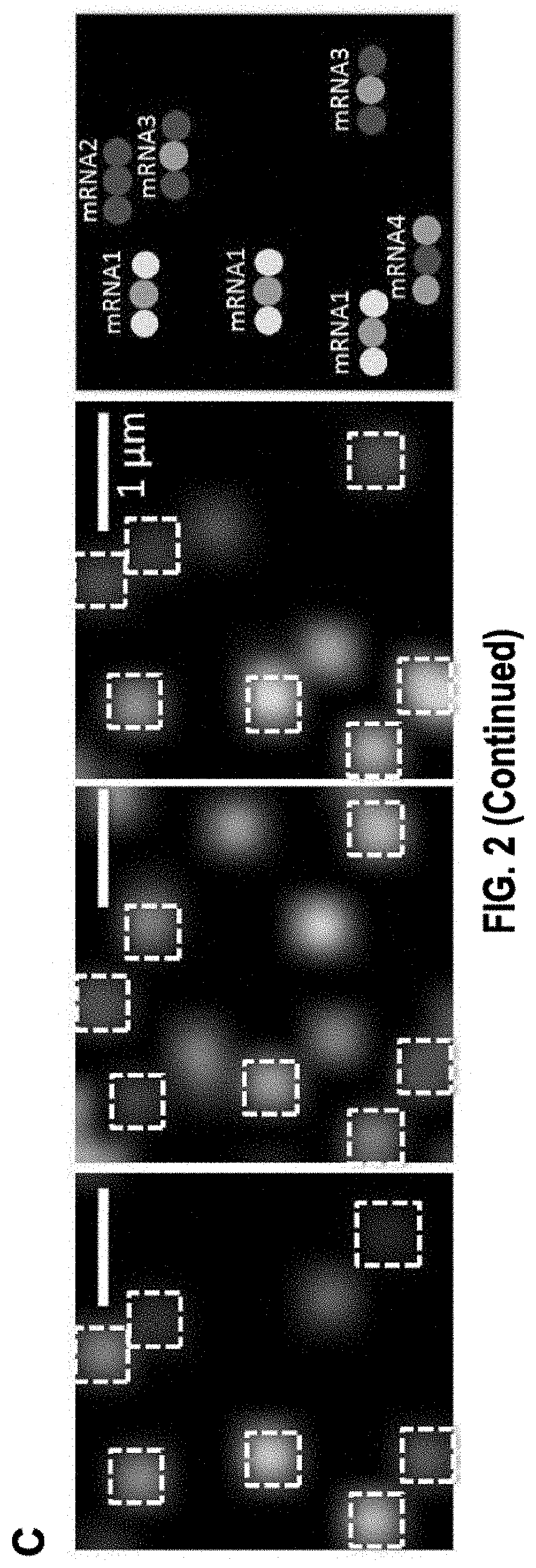
Sequential probing of molecular targets based on pseudo-color barcodes with embedded error correction mechanism
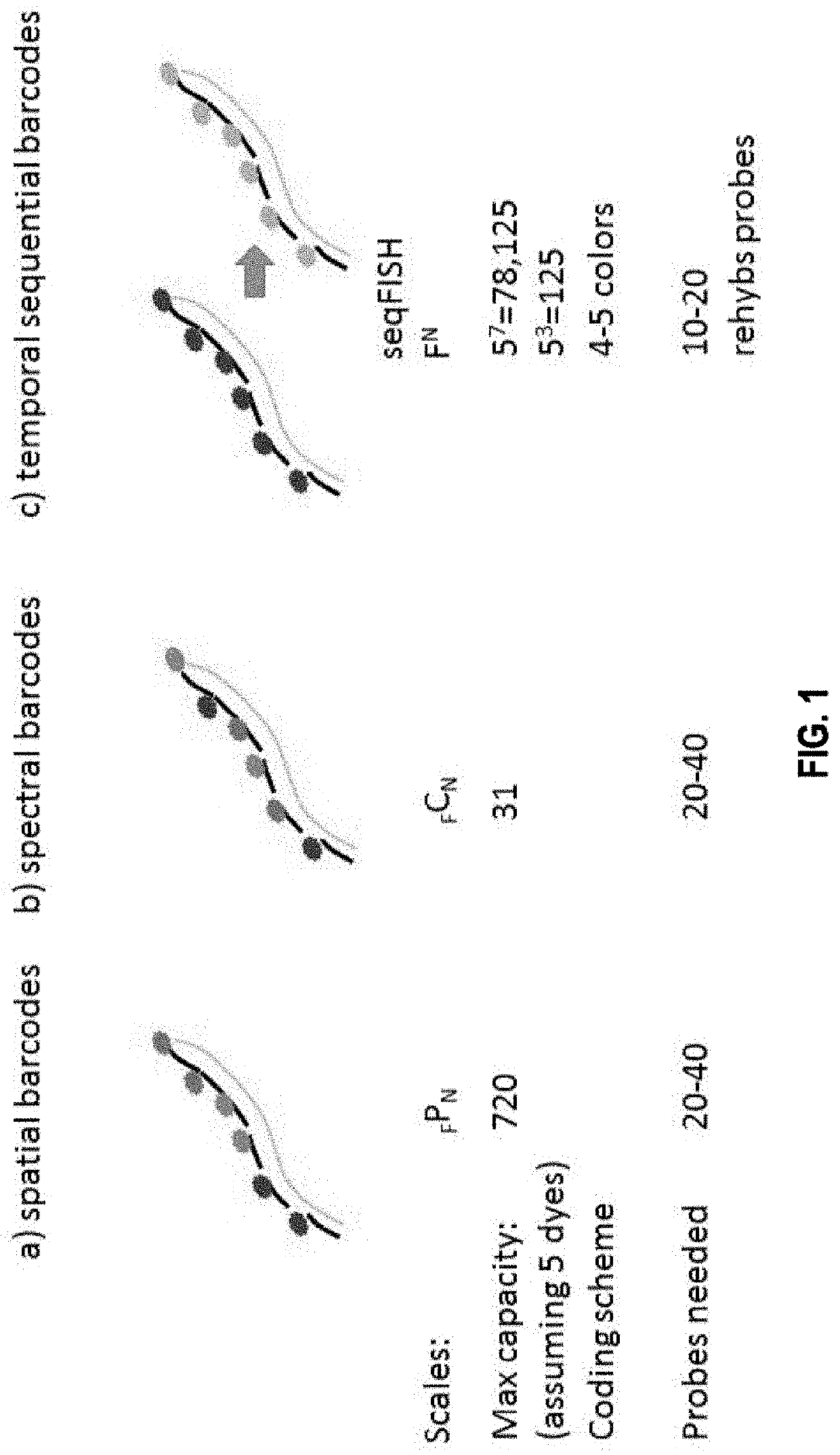
PendingUS20210017587A1Reduce development riskSlow onsetMicrobiological testing/measurementColor signalVisual perception
The present invention, among other things, provides technologies for detecting and / or quantifying nucleic acids in cells, tissues, organs or organisms. Pre-designed barcodes are associated specific molecular targets through sequential hybridization experiments. A pseudo-color based barcoding scheme is developed to overcome limitations in the previous generation of the technology such as lack of visual signals that can be associated with the probes or small internal within cell when carrying out in situ experiments. The current method can be applied to both in vitro and in situ analysis. According to the method, each barcoding round comprises multiple serial hybridizations where a small number of colored signals (that are associated with probes) are used in each hybridization experiment within a serial hybridization round. Images from each serial hybridization experiment within the same serial hybridization round are combined to form a composite image for each barcoding round. In each barcoding round, the same set of molecular targets are analyzed. After all barcoding rounds are completed, associated of the barcode with these molecular targets is completed.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
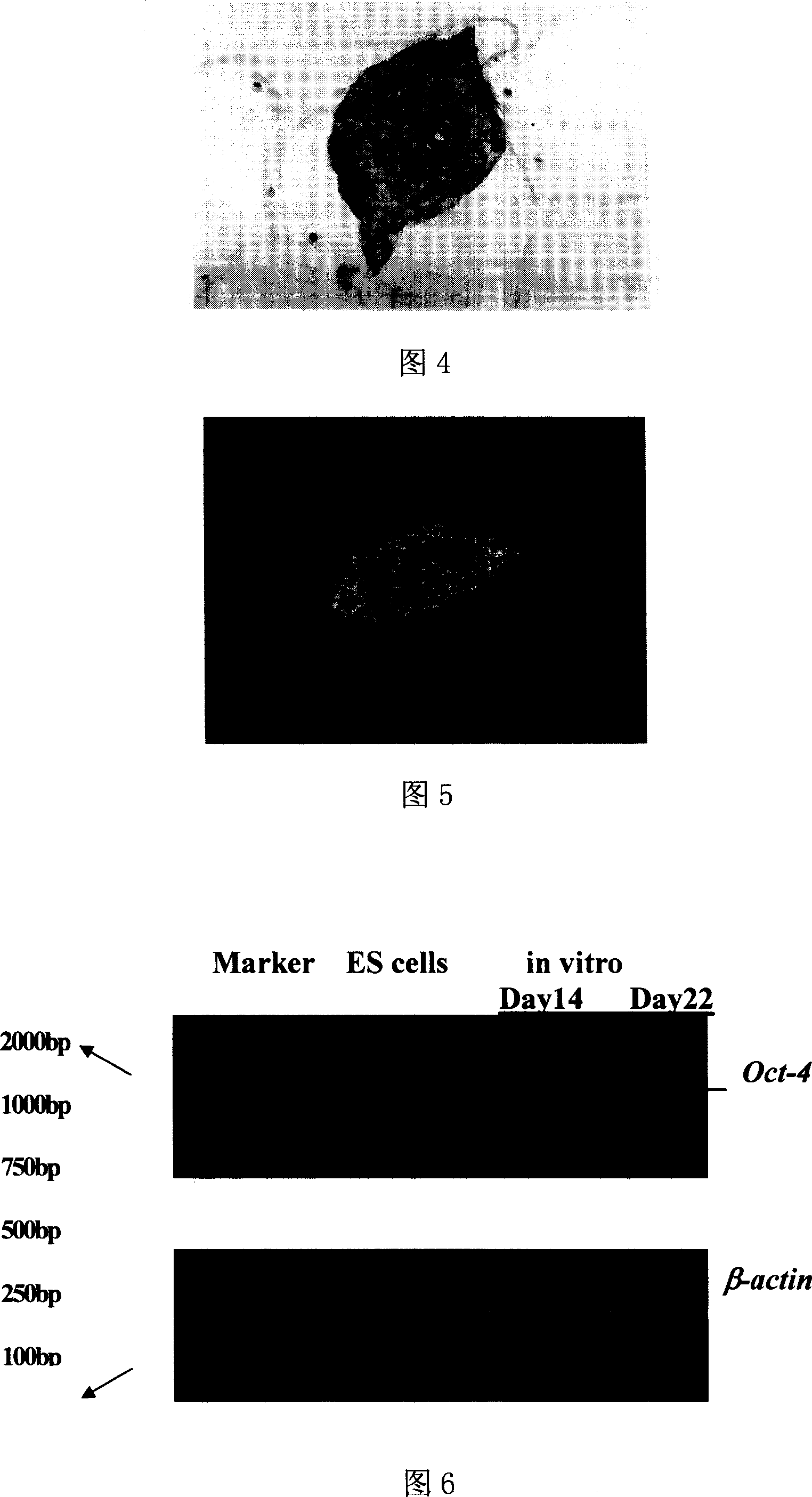
Method for construction of stem cell in-vitro multiplication and differentiation microenvironment
InactiveCN1962855APromote proliferationMaintain biological activityNervous system cellsArtificial cell constructsHigh densityCell organisation
The invention discloses a constructing method of stem cell breeding and differentiation microenvironment in vitro in the stem cell tissue engineering domain, which comprises the following steps: adopting sodium alginate and polylysine as material to prepare APA microencapsulation ES cell; adding microencapsulation ES cell in the ES growing culture medium; stewing at 37 Deg C in the culture box with 5% CO2; changing culture medium every 2-3d to obtain the product. The invention simplifies the operation to generate high-density and large scale augmentation, which can inhibit or delay the oriental differentiation for ES cell.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Micro-flow control chip for cell tissue culture and real-time monitoring and use method thereof
ActiveCN108485972AEasy to controlEasy to detectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrofluidic channelCell tissue culture
The invention discloses a micro-flow control chip for cell tissue culture and real-time monitoring and a use method thereof. The chip comprises a glass substrate layer and a PDMS micro-flow channel layer positioned on the glass substrate layer; the glass substrate layer comprises a glass substrate and a plurality of pairs of microelectrodes arranged on the glass substrate layer; the PDMS micro-flow channel layer comprises a plurality of independent micro-fluidic channels; the microelectrodes on the glass substrate are corresponding to the micro-flow channels on the PDMS micro-flow channel layer one by one; the microelectrodes are electrically connected with an external circuit. The use method comprises the steps of cell capture, cell tissue culture, electrical impedance spectroscopy detection and tissue release. The chip disclosed by the invention is processed by a transparent substrate, microscopic imaging can be taken as a supplementary means of the electrical impedance spectroscopydetection, and the dynamic growth and the physiological behavior of cell tissues and other biological processes are subjected to observation and in-situ analysis. The micro-flow control chip can be used in the fields of biological research, drug screening and the like of cells or tissues.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Polycation-functionalized nanoporous silicon carrier for systemic delivery of gene silencing agents
InactiveUS20160369269A1Reduce the amount requiredLess toxicityOrganic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryNanoporous siliconCell organisation
Disclosed are methods and compositions containing functionalized nanoporous silicon particles, useful in a variety of diagnostic and / or therapeutic regimens for delivery of genetic constructs to one or more cells, tissues, and / or organs of interest. Also provided are methods for introducing into selected host cells one or more selected nucleic acid molecules. The present disclosure is also directed to a method of treating a tumor, comprising the step of administering to an individual one or more of the compositions and formulations thereof as described herein.
Owner:THE METHODIST HOSPITAL
Nonlinear optical detection of fast cellular electrical activity
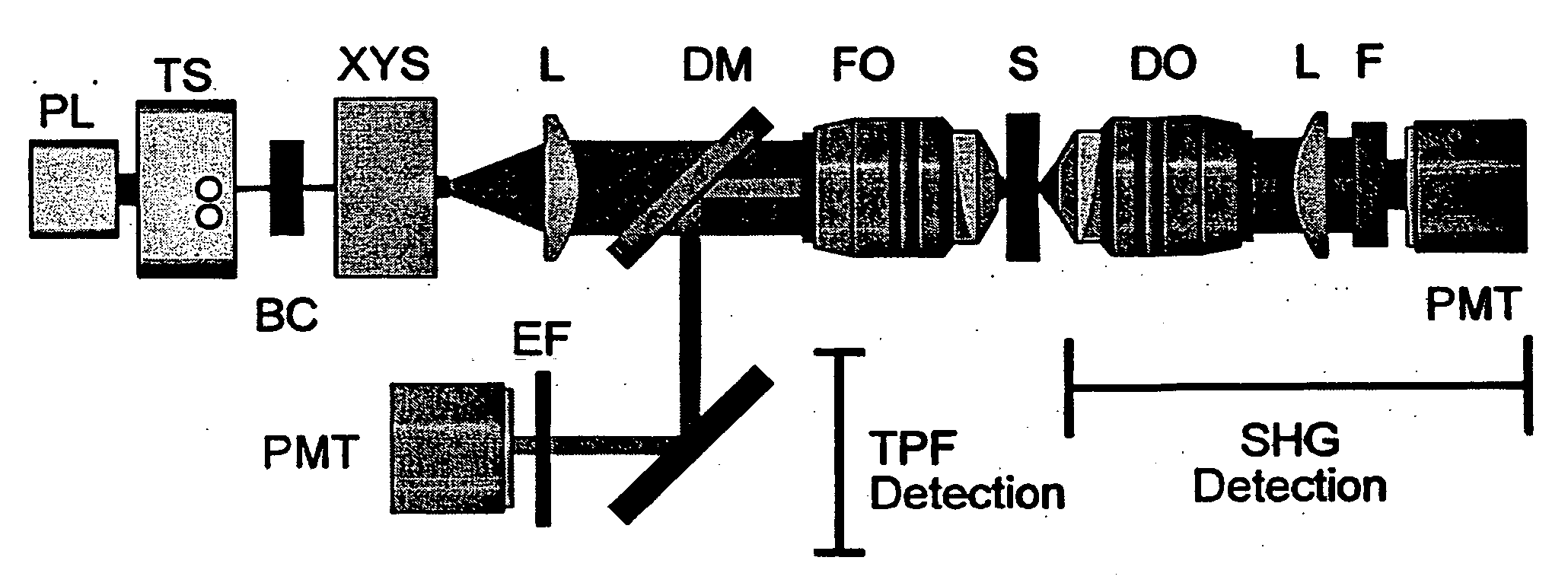
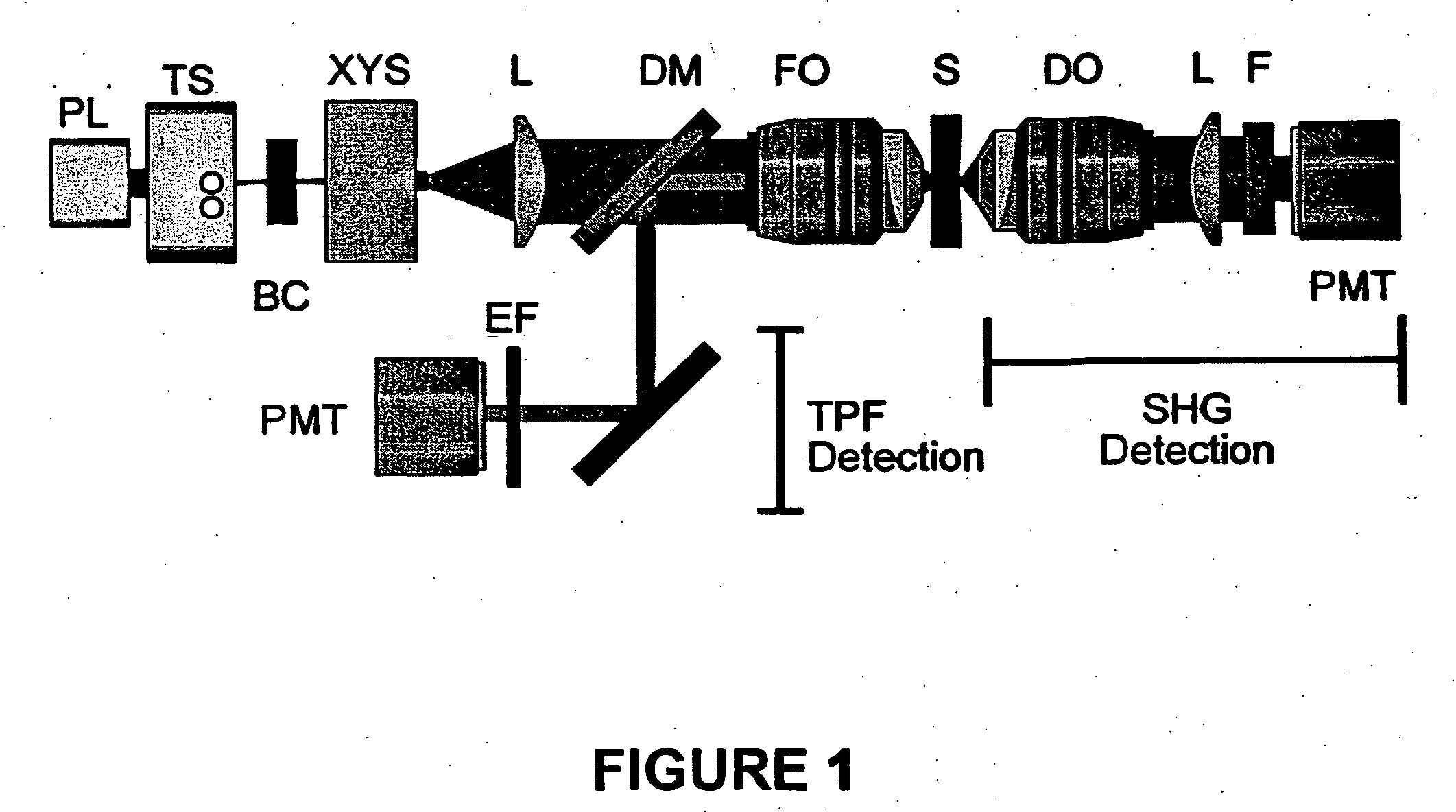
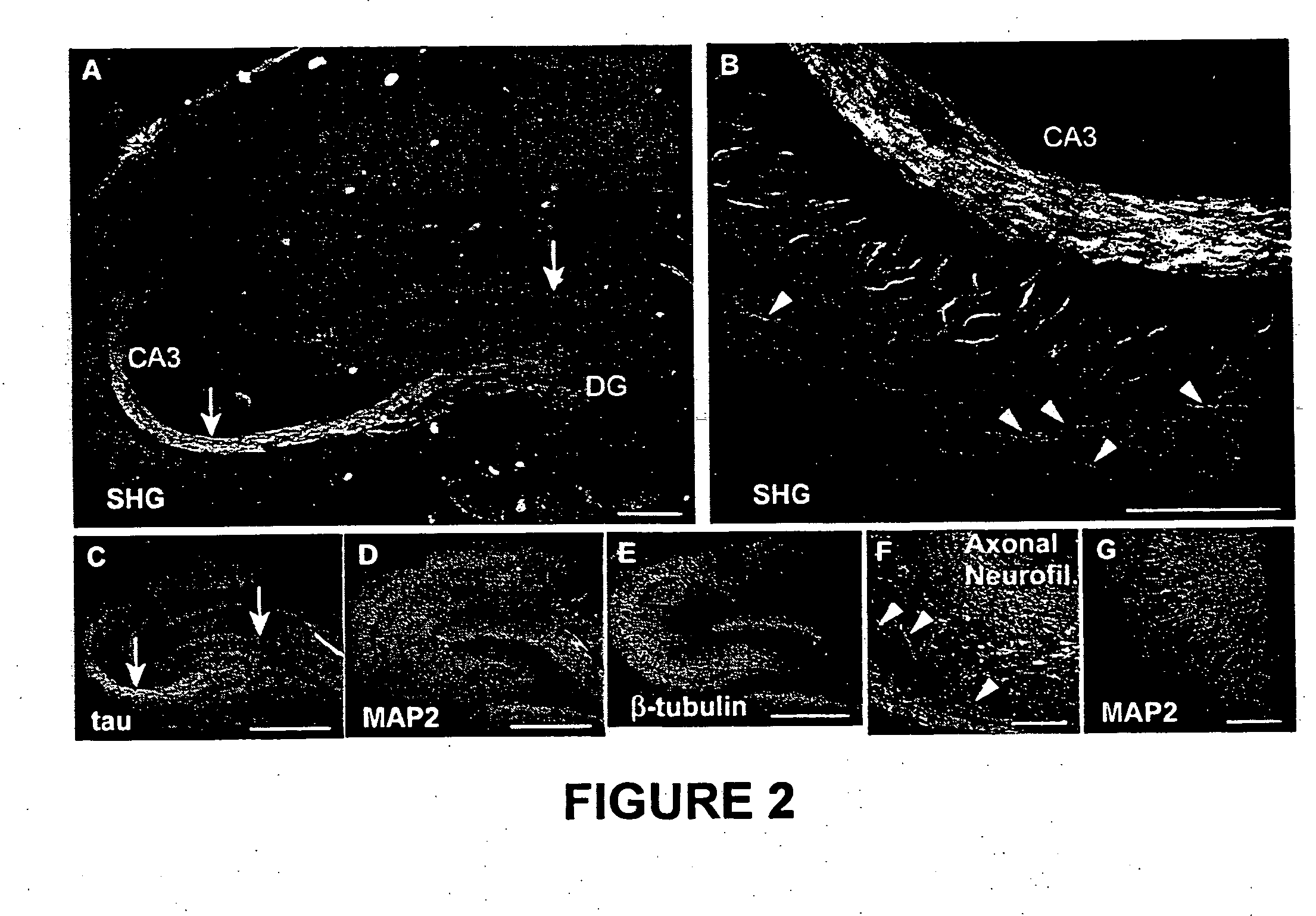
InactiveUS20050259249A1Maximum sensitivityReduce photodamageRadiation pyrometryPreparing sample for investigationCell membraneOrganism
The present invention is directed to various methods involving nonlinear microscopy and dyes that are sensitive to fast cellular membrane potential signals and capable of generating nonlinear optical signals. The present invention includes methods of producing high spatiotemporal resolution images of electrical activity in cellular tissue, as well as methods of detecting and investigating disease within a particular cellular tissue of a living organism. The present invention further relates to methods of detecting membrane potential signal changes in a neuron or a part of a neuron, as well as in a population of cells.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC +1
Computational methods and compositions
The invention in some aspects relates to methods, devices and compositions for evaluating material properties, such as mechanical and rheological properties of substances, particularly biological substances, such as cells, tissues, and biological fluids. In some aspects, the invention relates to methods, devices and compositions for evaluating material properties of deformable objects, such as cells. In further aspects, the invention relates to methods, devices and compositions for diagnosing and / or characterizing disease based on material properties of biological cells.
Owner:BROWN UNIV RES FOUND INC +1
Porous sheet-form material for cell culture, and bioreactor and culturing method utilizing same
InactiveUS8435781B2Stable recoveryNot easy to growBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh cellCell adhesion
The present invention provides a bioreactor having a system that can grow cells, tissue, etc. while maintaining or improving their function, and finally recover the cells as they are with good efficiency. The bioreactor has a porous sheet-form material disposed in its main body, the porous sheet-form material being formed from a nonwoven fabric, etc. having high cell affinity in order to retain cells. This porous sheet-form material has a thermosensitive polymer and a cell-adhesive substance incorporated thereinto, and the porous sheet-form material is not only cell-adhesive but also allows cells and tissue to be detached from the porous sheet-form material as they are by, for example, cooling from 37° C. to 25° C. Furthermore, in order to efficiently ensure the bioactivity or the survival of the cells, it is arranged so that circulation of a culture medium in a culturing space of the bioreactor is of a radial flow type.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP KYUSHU INST OF TECH (JP)
Activatable particles, preparations and uses.
The invention relates to activatable novel particles which can be used in the health sector. The invention more particularly relates to composite particles which can generate free radicals or heat when excited by X-rays. The invention also relates to the uses thereof in human health. The inventive particles comprise an inorganic-based, and optionally organic-based, nucleus and can be activated in vivo in order to mark or affect cells, tissue or organs. The invention further relates to methods for the production of said particles, and pharmaceutical or diagnostic compositions containing them.
Owner:NANOBIOTIX SA
Inorganic nanoparticles of high density to destroy cells in-vivo
ActiveUS8845507B2Safely employedEfficient emissionsBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsRadio isotopesHigh energy photon
The present application relates to novel excitable particles which can be used in the health sector. It more particularly relates to particles which can generate electrons and / or high energy photon when excited by ionizing radiations such as X-Rays, γ-Rays, radioactive isotope and / or electron beams, and to the uses thereof in health, in particular in human health. The inventive particles are made of an inorganic material comprising oxygen, in particular an oxide, said material having an adequate density, and can be activated in vitro, ex vivo, or in vivo, by controllable external excitation, in order to disturb, alter or destroy target cells, tissues or organs. The invention also relates to methods for the production of said particles, and to pharmaceutical or medical device compositions containing same.
Owner:NANOBIOTIX SA
Method for Modulating MicroRNA Content in Living Beings and the Use Thereof
The present invention relates to a method for modulating miRNA content in living beings and the use thereof, whereof the miRNAs are delivered initiatively and selectively by microparticles / MVs / exosomes to the circulatory system and target cells / tissues to perform various functions. The invention provides a novel combination of molecules that mediates the inter-cellular communication: the miRNAs secreted by cells through cellular MVs. Meanwhile, the present invention also provides a method for preparing cellular MVs entrapping certain miRNAs, and, according to the regulation and modification of gene expression in cells and tissues with the miRNA-entrapping cellular MVs, provides a novel method for modulating miRNA content in living beings, which is effective and adoptable to all cell types.
Owner:JIANGSU MINGMA BIOTECH
Low-temperature storage liquid for cells, sodium alginate gel, cell gel, preparation method, use method and application thereof
PendingCN109221088AKeep aliveFor subsequent applicationCell dissociation methodsDead animal preservationWound dressingAdenosine
The invention belongs to the technical field of storage, regeneration and repair of cells and discloses low-temperature storage liquid for cells. The low-temperature storage liquid is mainly preparedfrom the following components in percent by mass: 0.8%-1.5% of mannitol, 2%-3% of human serum albumin, 3%-7% of low-molecular dextran, 0.1-0.3% of glutathione, 0.5%-2% of epigallocatechin gallate, 3%-5% of adenosine, 0.5%-1% of glucose, 0.8% of NaCl, 0.2% of KCl, 0.1% of CaCl2 and the balance of water. The invention also provides sodium alginate gel, which contains sodium alginate, calcium chloride, hyaluronic acid and the low-temperature storage liquid for the cells and the like, and also provides cell gel and a preparation method thereof as well as application of the low-temperature storageliquid for the cells, the sodium alginate gel and the cell gel. The invention has the advantages that the low-temperature storage liquid for the cells can maintain cell activity for longer time at temperature of 2-8 DEG C, the sodium alginate gel can be used as temporary short-term storage materials of cells from various sources and brackets of cell tissue engineering, and the cell gel can be usedas a medical wet wound dressing and can be used for repairing soft tissues, refractory-healing wound skins and mucosal wound injuries.
Owner:CHENGDU YUANSHAN BIOTECH CO LTD
Integrated system for biological tissue treatment and cell collection
ActiveCN103343086ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell organisationCell aggregation
The invention relates to an integrated system for biological tissue treatment and cell collection. The integrated system comprises three parts, namely a collection container for optionally pre-filling protecting liquid or solid for collecting and storing treated cells or cell aggregates, a sieve chamber for carrying samples and separating cells or cell aggregates from cell tissues or organs, and a roller, wherein a rolling disc of the roller is embedded with a rolling disc elbow board and is connected with a hand spike for exerting power and rotating the rolling disc. The three parts are connected with one another and assembled together through threads and threaded sealing covers. After the cells and the cell aggregates are collected, the collection container is sealed by a full closed cover for storage, and the used sieve chamber and roller can be discarded.
Owner:CRYSTALGEN NINGBO BIOTECH
Technology for regulating and controlling Jak-Stat pathway to differentiate, dedifferentiate and rejuvenate cells, and application of technology
PendingCN110423719AAccelerated agingPromote apoptosisCosmetic preparationsVirusesProtein targetCytokine
The present invention belongs to the technical field of cell biology and particularly relates to a technology for regulating and controlling a Jak-Stat pathway to differentiate, dedifferentiate and rejuvenate cells, and an application of the technology. Rejuvenated cell products and / or cell products of different lineage types are obtained by small molecule compound combination, cytokine combination or recombinant protein combination, a gene editing technology and a transgenic technology to quantitatively and / or regularly regulate and control gene or protein targets of the Jak-Stat signaling pathways in cells. The provided technology for regulating and controlling the Jak-Stat signal pathway, and the product / derivatives of the cell product can be used for re-programming cells, tissues, organs and organisms, construct tissue engineering materials, repair damages of tissues and organs of mammals and the aged and degenerated tissues and organs, delay or reverse aging processes of the cells, tissues, organs and organisms, and can be used for immunoregulation of the cells, tissues, organs and organisms.
Owner:YUNNAN JICI INSITUTE FOR REGENERATIVE MEDICINE CO LTD
Methods and compositions for molecular imaging
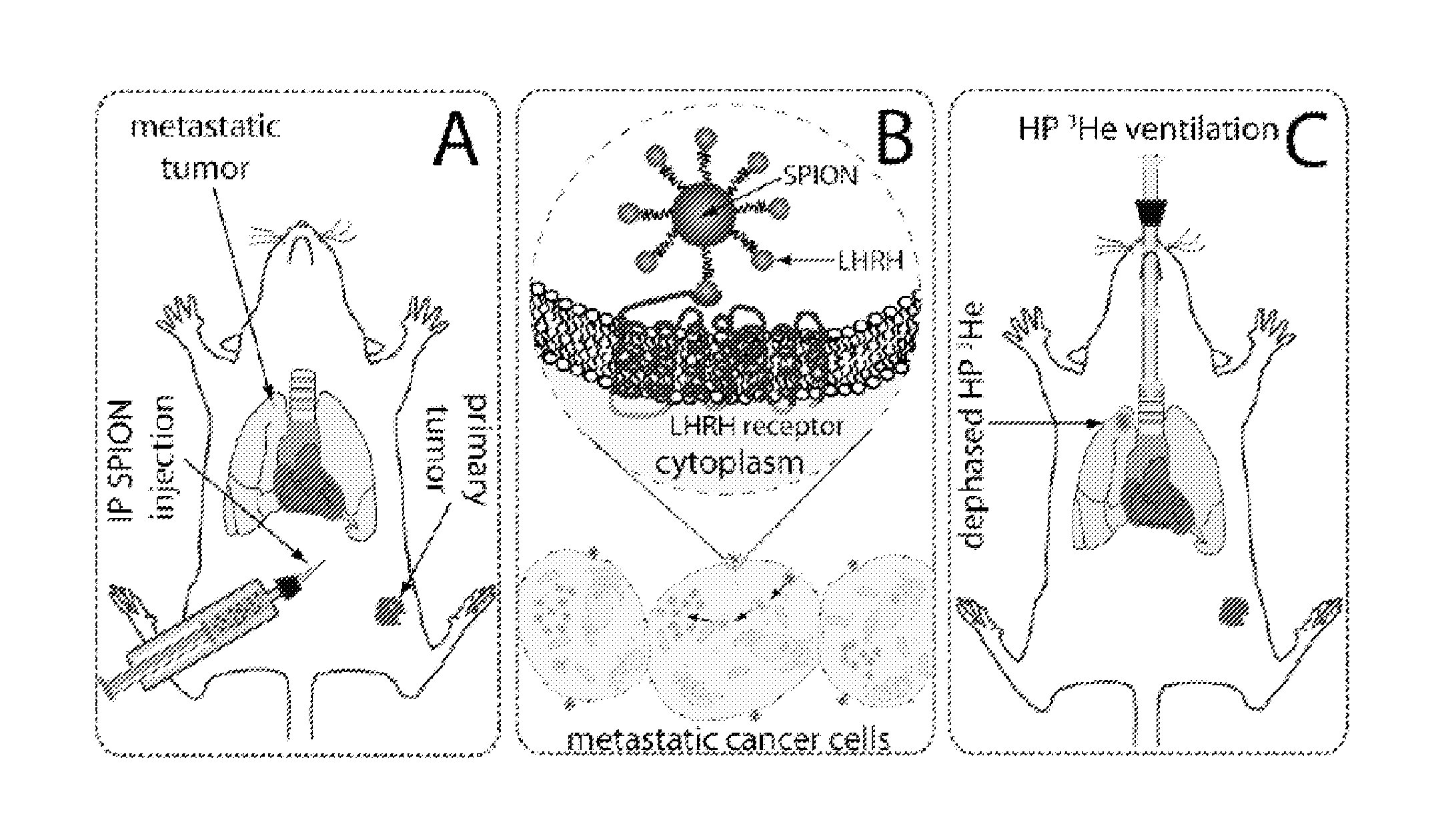
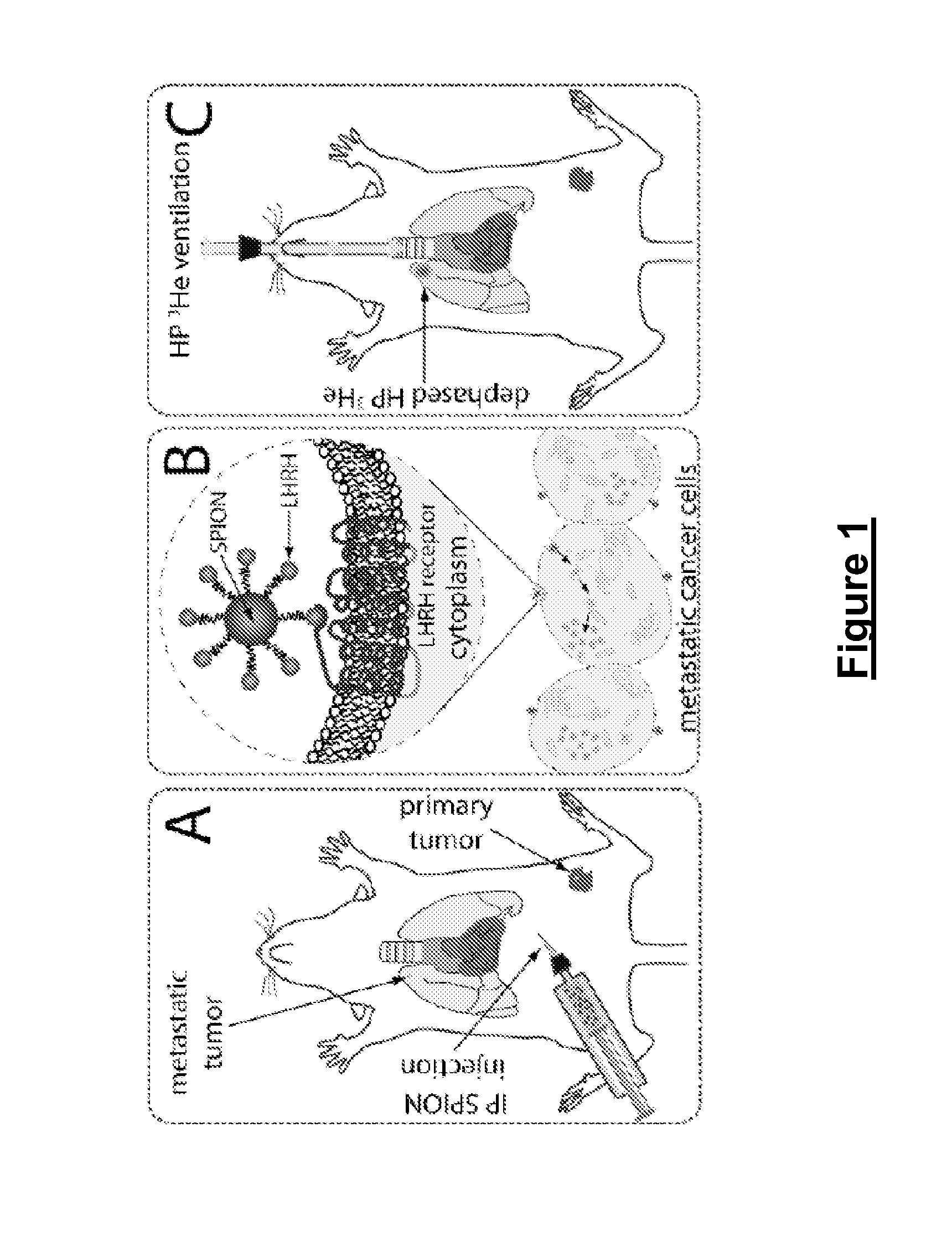
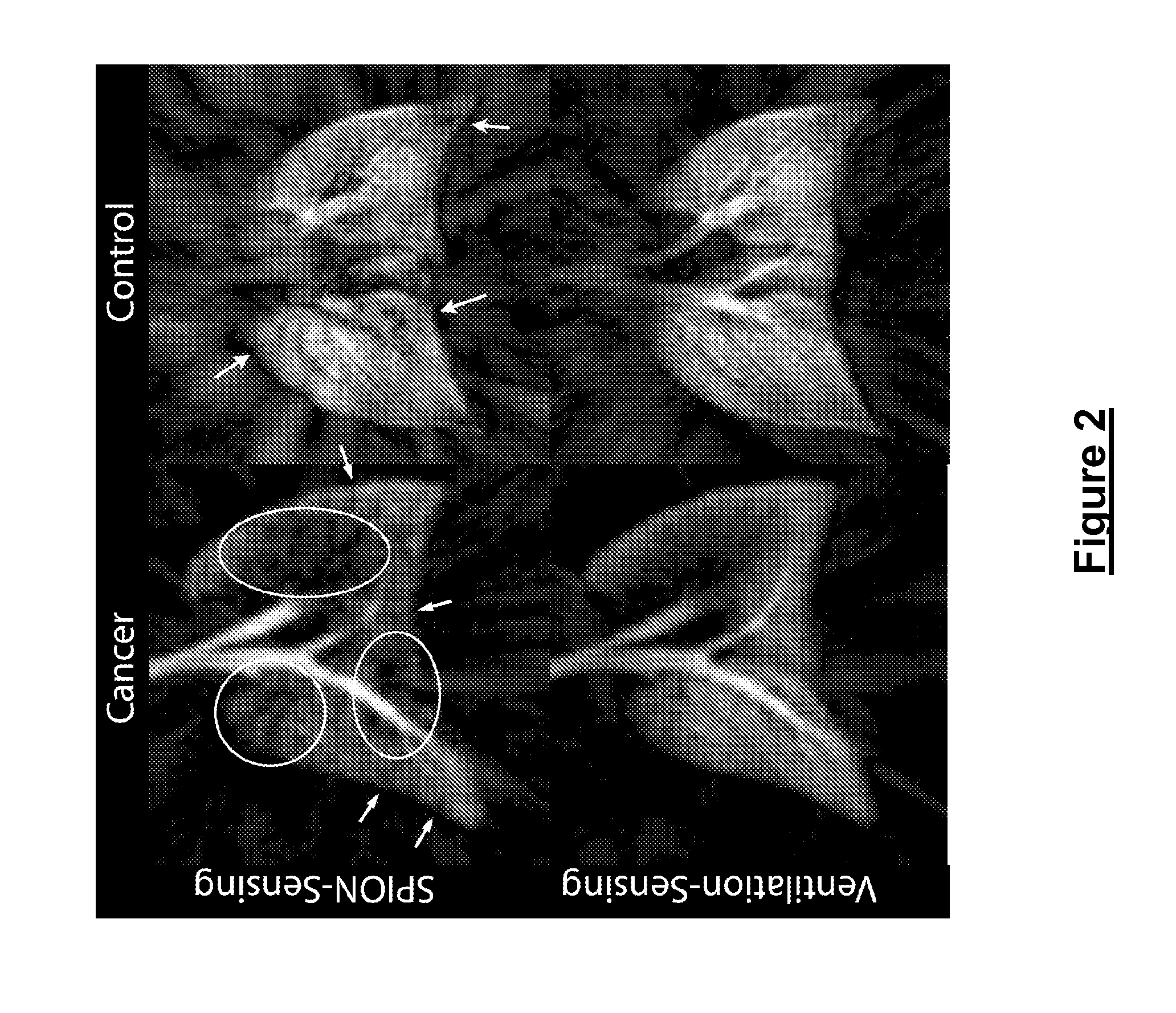
Methods for imaging a target cell, tissue, or organ in a subject. In some embodiments, the methods include the steps of (a) administering to the subject a contrast agent that includes a paramagnetic or superparagmanetic material and a targeting moiety that targets the contrast agent to the cell, tissue, or organ; (b) introducing into the target cell, tissue, or organ, or into the vicinity thereof, a hyperpolarized gas; and (c) imaging the target cell, tissue, or organ by detecting the presence of the contrast agent in, on, or near the target cell, tissue, or organ. Also provided are methods for screening for metastasis of a tumor and / or a cancer to the lung of a subject, methods for imaging a cavity in a subject, methods for imaging a target cell, tissue, or organ in a cavity, compositions for performing the disclosed methods, and systems and kits that include the disclosed compositions and / or reagents for performing the disclosed methods.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
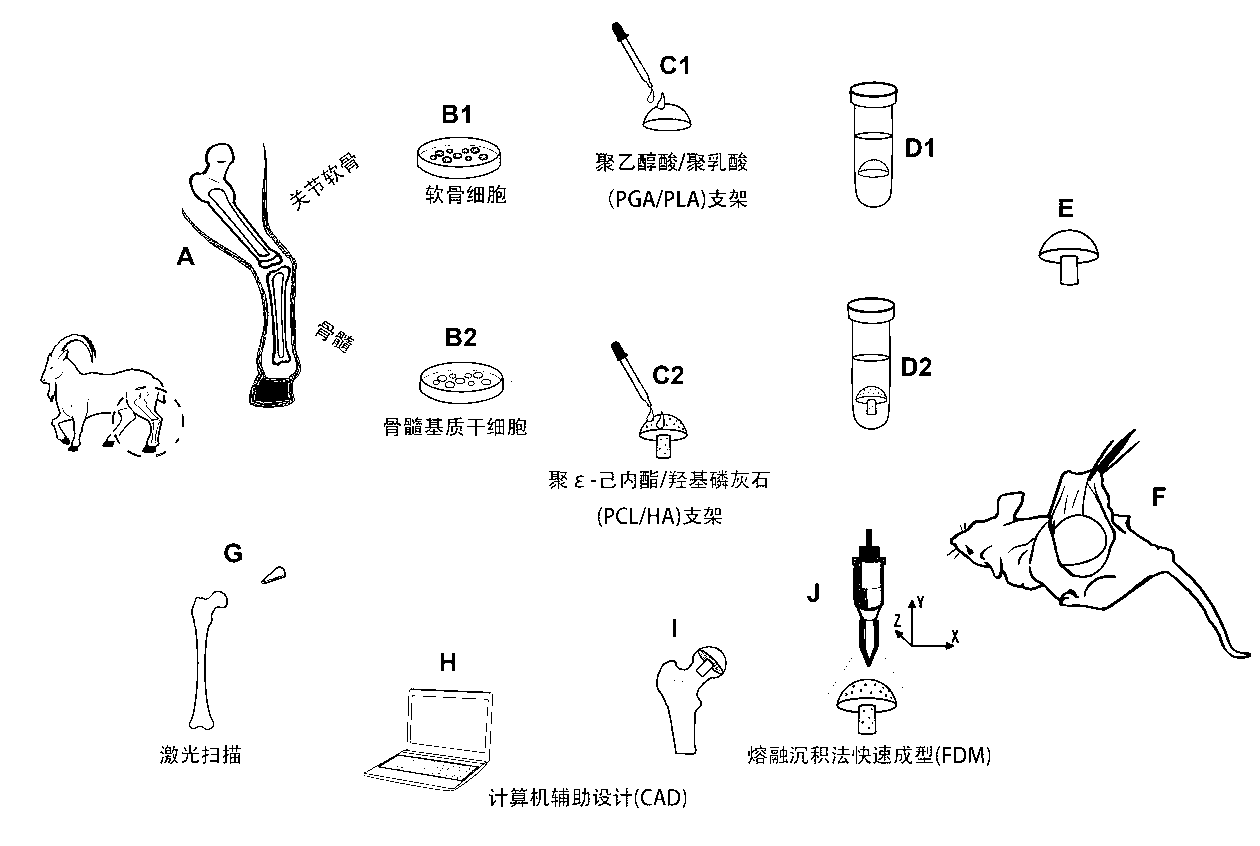
Biphysic tissue engineering joint scaffold as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103285429APrecisely Controllable Morphological StructurePrecisely controllable internal structureProsthesisBiomechanicsRegeneration tissue
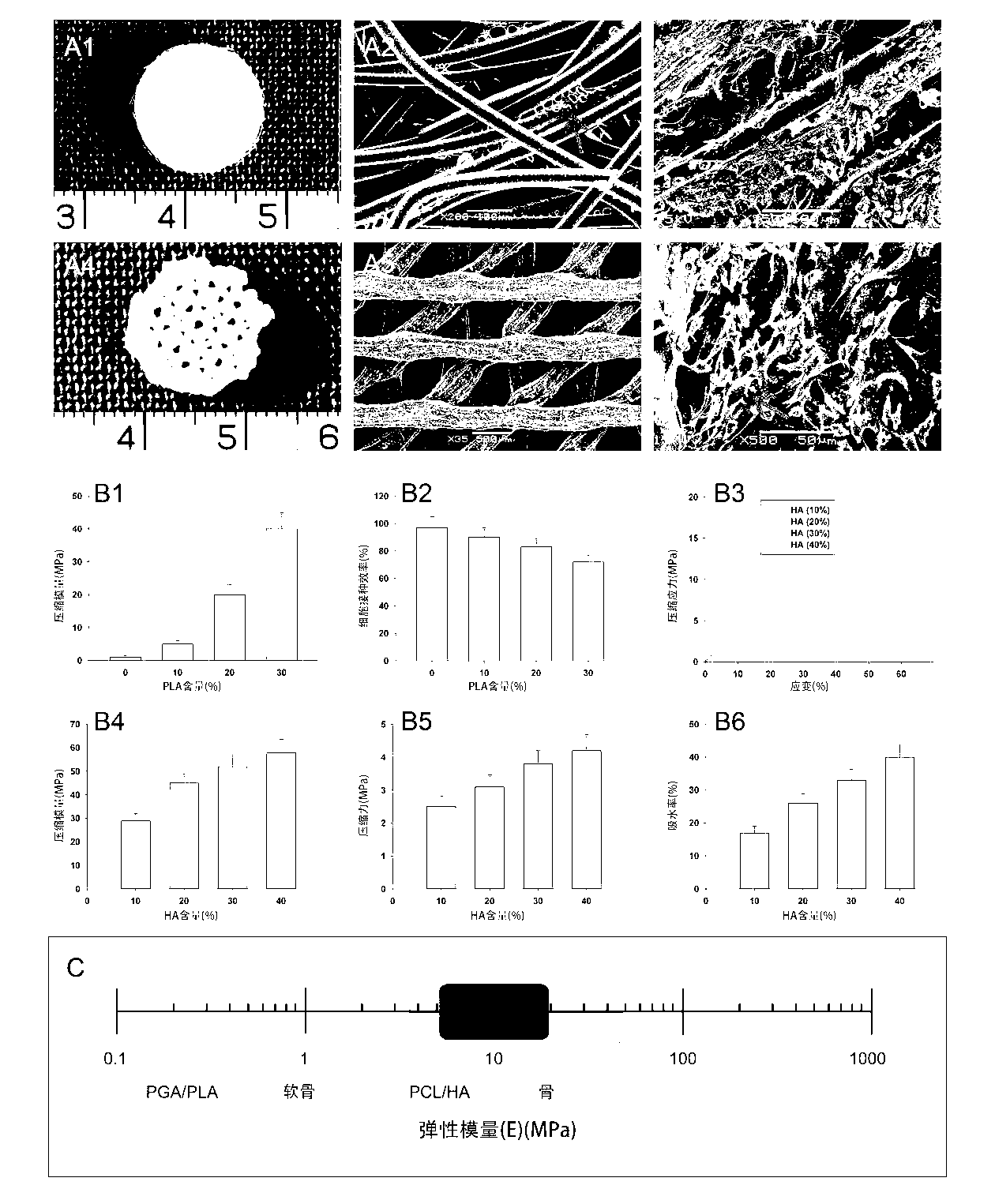
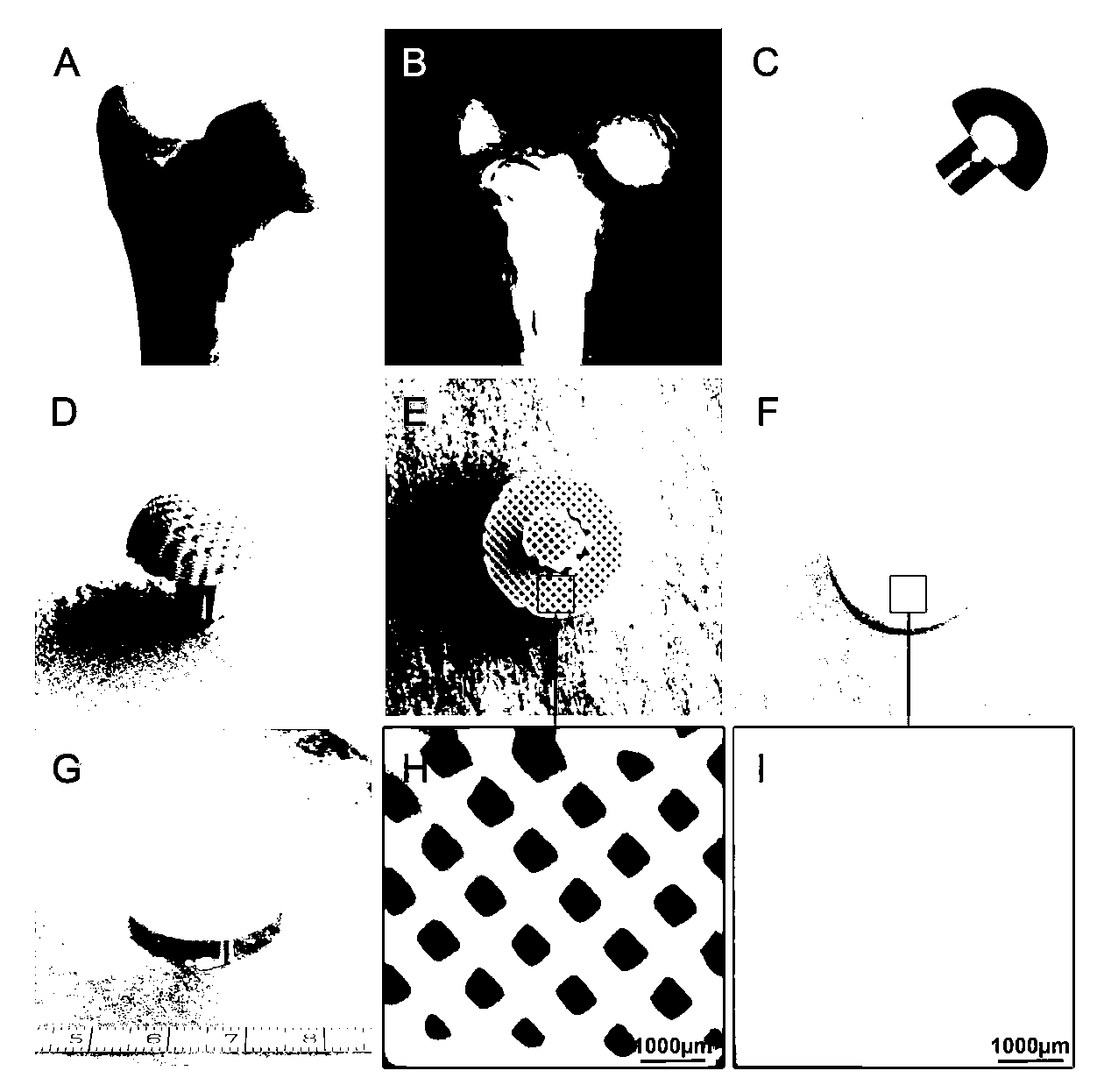
The invention relates to a biphysic tissue engineering joint scaffold as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The biphysic tissue engineering joint scaffold consists of a phrenology scaffold and a cartilage scaffold, wherein the cartilage scaffold is a PGA / PLA scaffold; the phrenology scaffold is a PCL / HA scaffold. The invention also provides a biphysic cell-tissue engineering joint scaffold constructor as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The biphysic tissue engineering joint scaffold as well as the preparation method and the application thereof have the advantages that the biphysic tissue engineering joint scaffold is manufactured by utilizing a CAD / CAM technology, the external form and interior structure are accurate and controllable, the phrenology and the cartilage are matched with each other, the biphysic cell-tissue engineering joint scaffold constructor is formed by compositing seed cells by utilizing a tissue engineering technology, the tissue engineering joint can be regenerated in vivo and has the biological and mechanical biomechanical characteristics of the normal joint, an interface of a regenerated bones and the cartilage is well integrated, and the possibility is provided for performing biological reconstruction through the tissue engineering joint instead of the existing artificial joint.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com