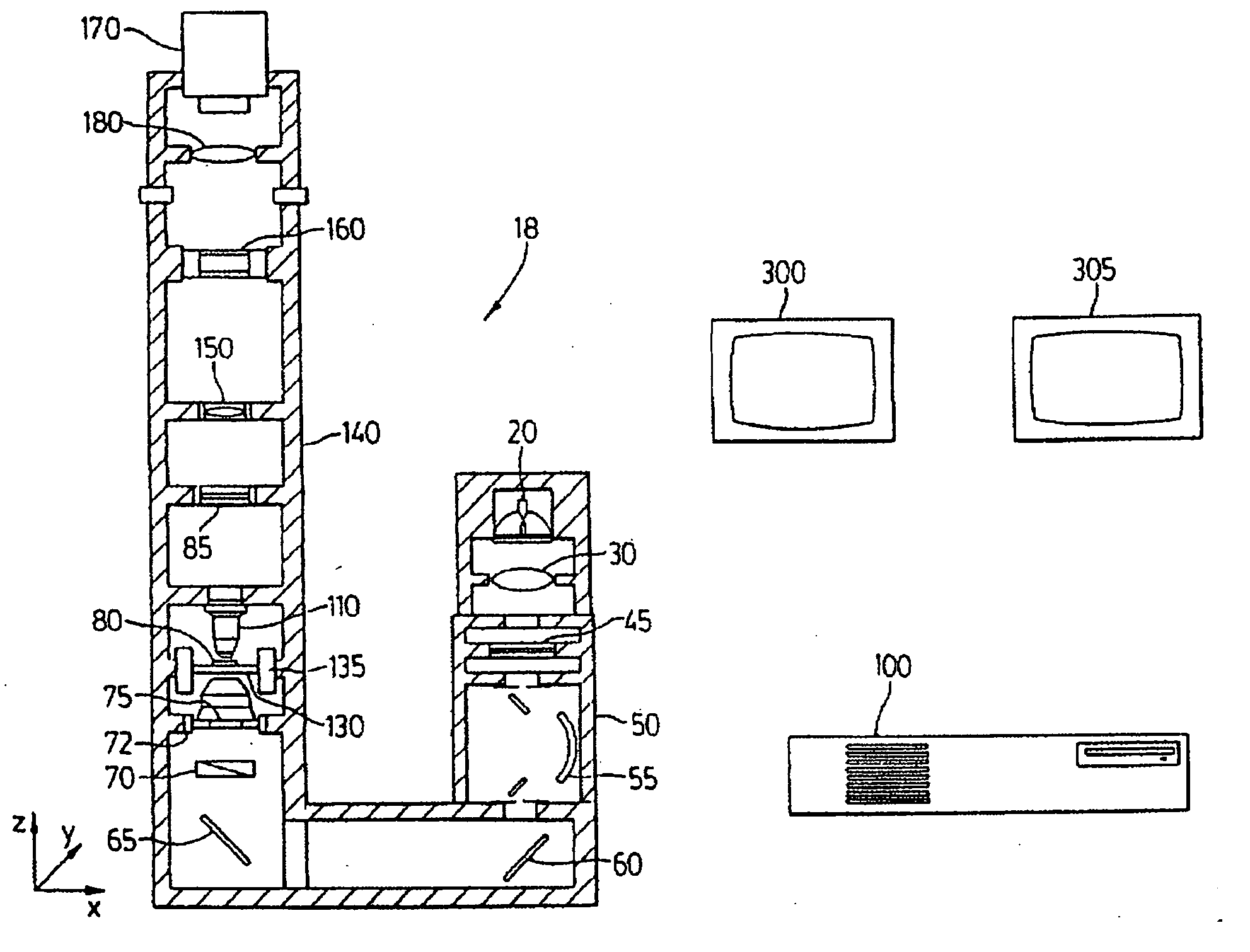
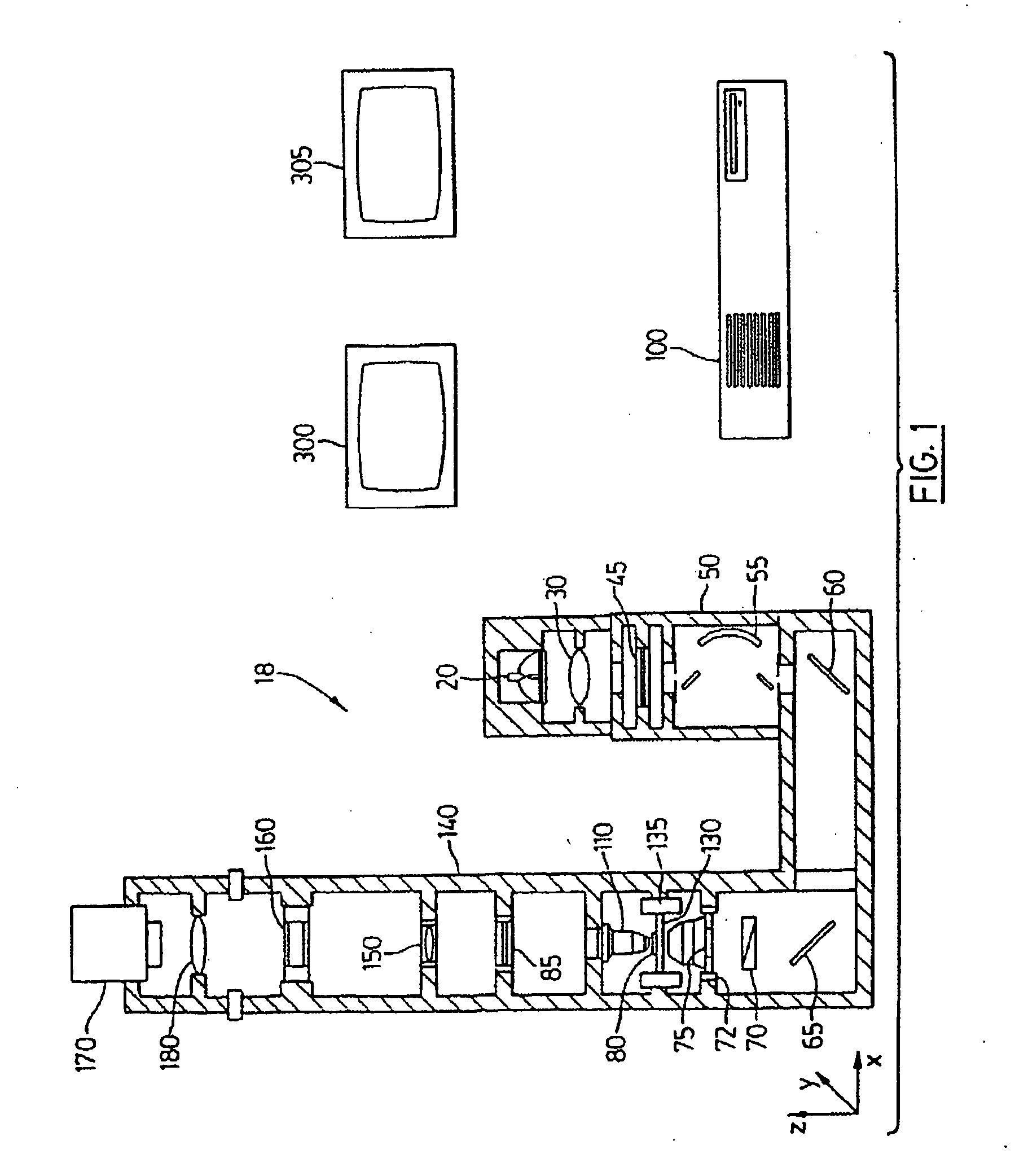
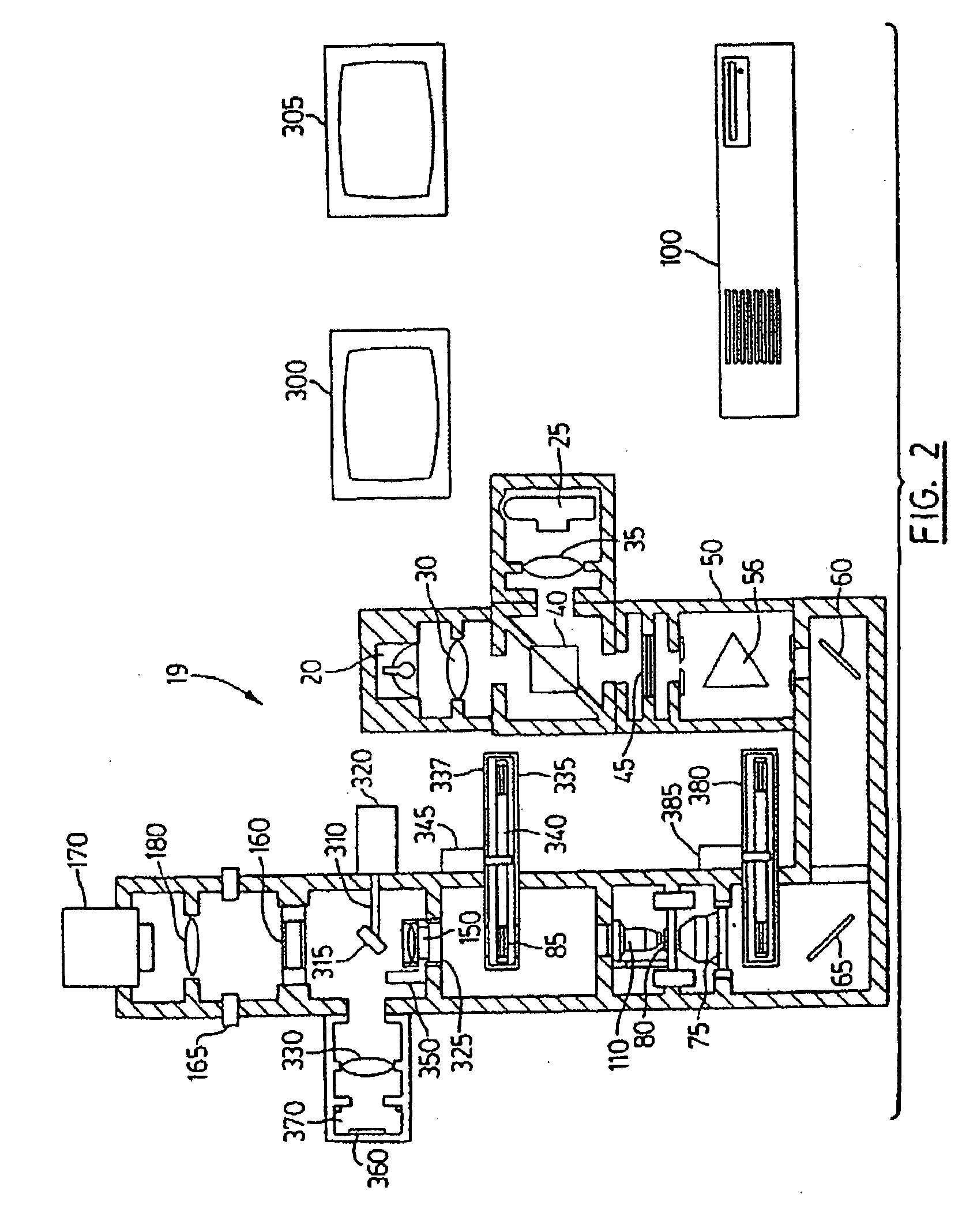
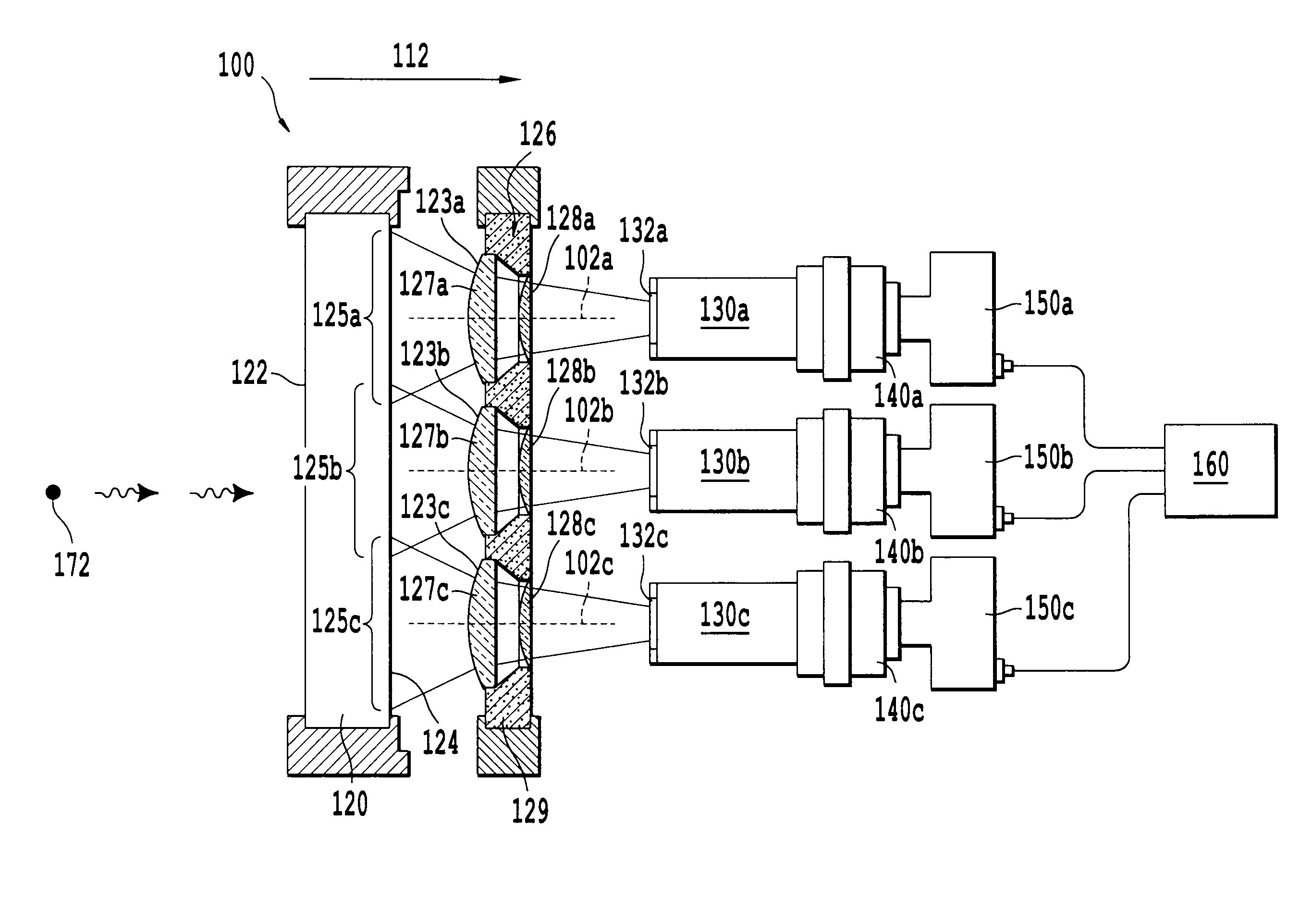
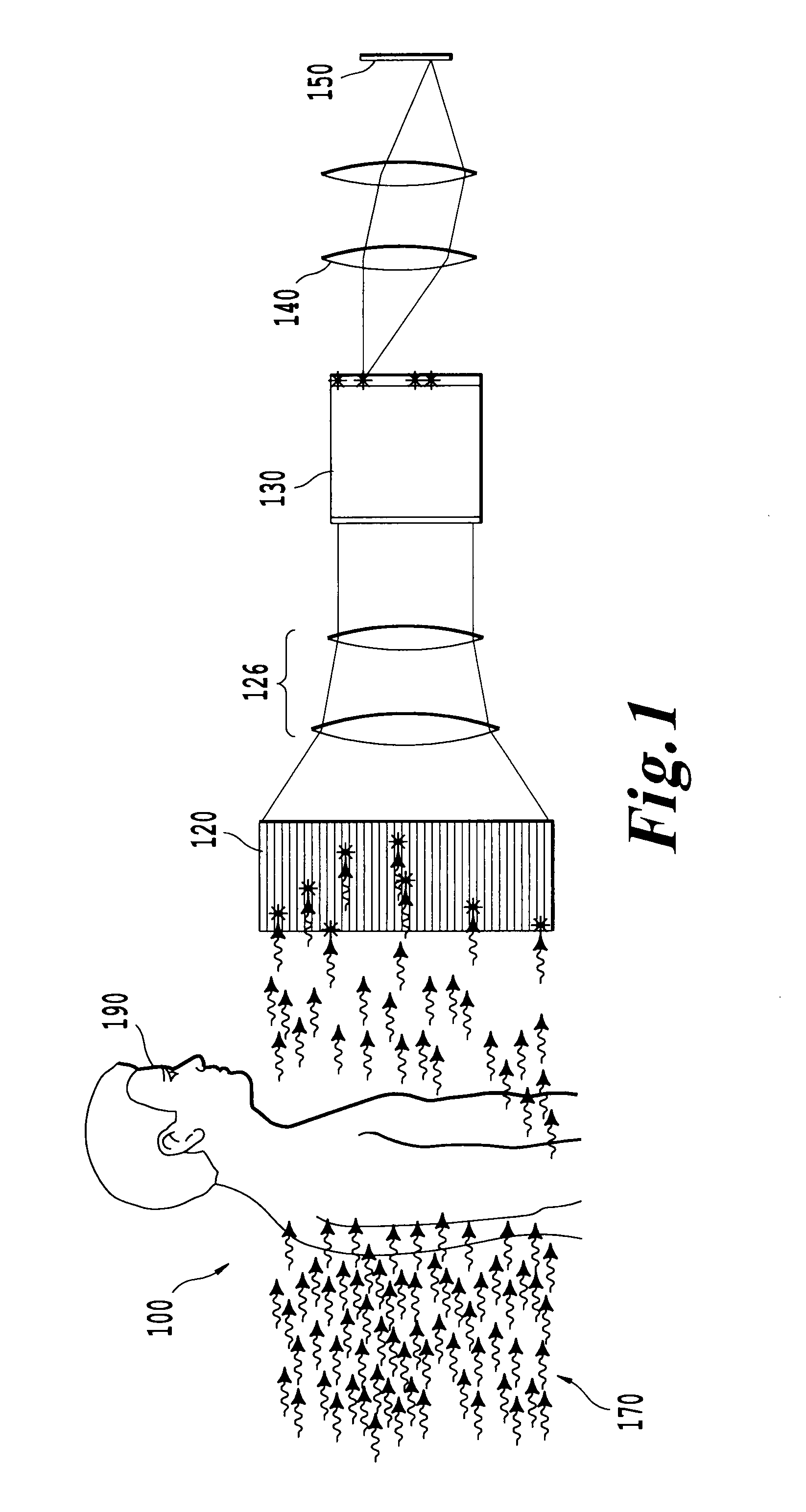
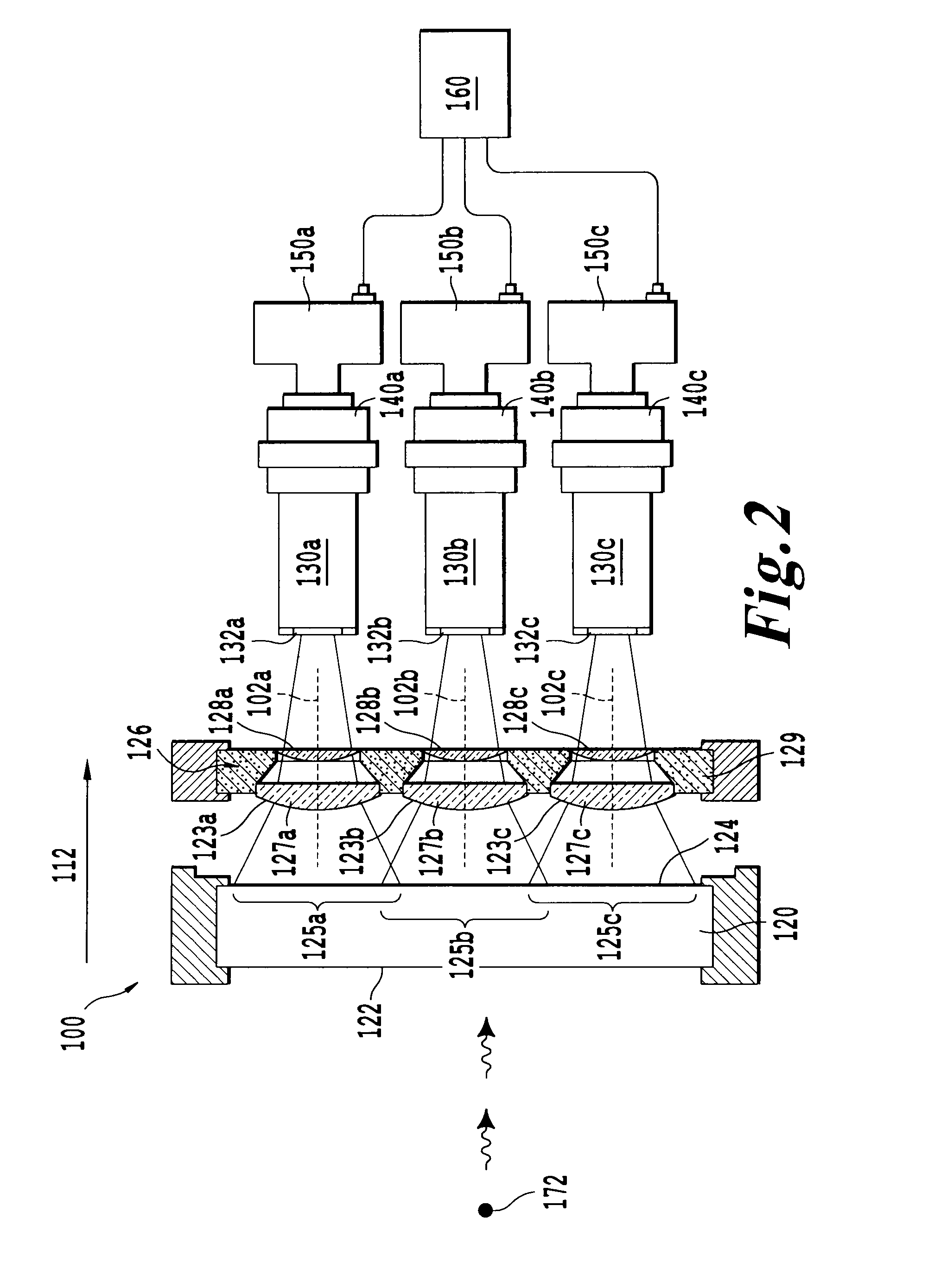
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
577 results about "Image intensifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An image intensifier or image intensifier tube is a vacuum tube device for increasing the intensity of available light in an optical system to allow use under low-light conditions, such as at night, to facilitate visual imaging of low-light processes, such as fluorescence of materials in X-rays or gamma rays (X-ray image intensifier), or for conversion of non-visible light sources, such as near-infrared or short wave infrared to visible. They operate by converting photons of light into electrons, amplifying the electrons (usually with a microchannel plate), and then converting the amplified electrons back into photons for viewing. They are used in devices such as night vision goggles.
Color translating UV microscope
A color translating UV microscope for research and clinical applications involving imaging of living or dynamic samples in real time and providing several novel techniques for image creation, optical sectioning, dynamic motion tracking and contrast enhancement comprises a light source emitting UV light, and visible and IR light if desired. This light is directed to the condenser via a means of selecting monochromatic, bandpass, shortpass, longpass or notch limited light. The condenser can be a brightfield, darkfield, phase contrast or DIC. The slide is mounted in a stage capable of high speed movements in the X, Y and Z dimensions. The microscope uses broadband, narrowband or monochromat optimized objectives to direct the image of the sample to an image intensifier or UV sensitive video system. When an image intensifier is used it is either followed by a video camera, or in the simple version, by a synchronized set of filters which translate the image to a color image and deliver it to an eyepiece for viewing by the microscopist. Between the objective and the image intensifier there can be a selection of static or dynamic switchable filters. The video camera, if used, produces an image which is digitized by an image capture board in a computer. The image is then reassembled by an overlay process called color translation and the computer uses a combination of feedback from the information in the image and operator control to perform various tasks such as optical sectioning and three dimensional reconstruction, coordination of the monochromater while collecting multiple images sets called image planes, tracking dynamic sample elements in three space, control of the environment of the slide including electric, magnetic, acoustic, temperature, pressure and light levels, color filters and optics, control for microscope mode switching between transmitted, reflected, fluorescent, Raman, scanning, confocal, area limited, autofluorescent, acousto-optical and other modes.
Owner:RICHARDSON TECH
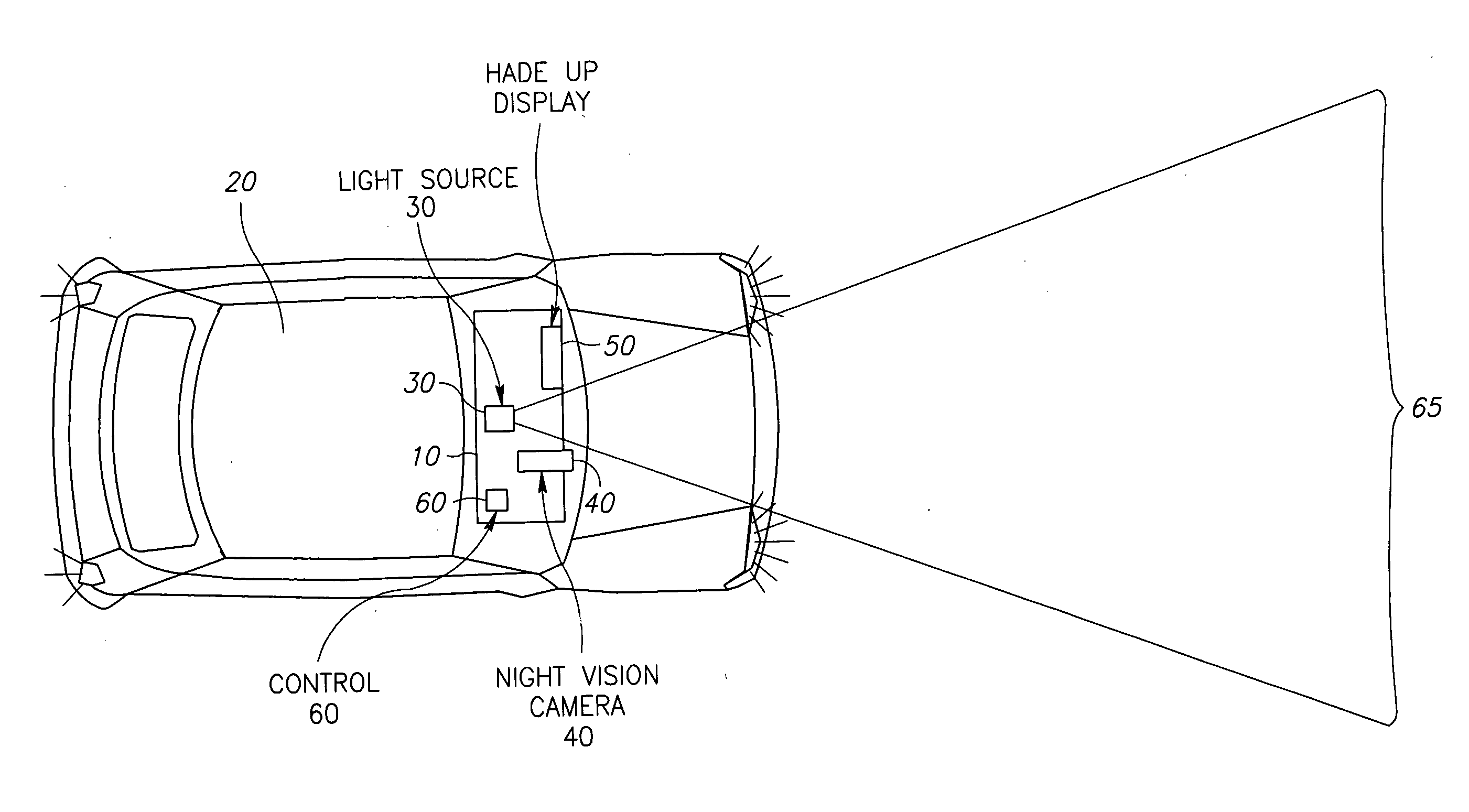
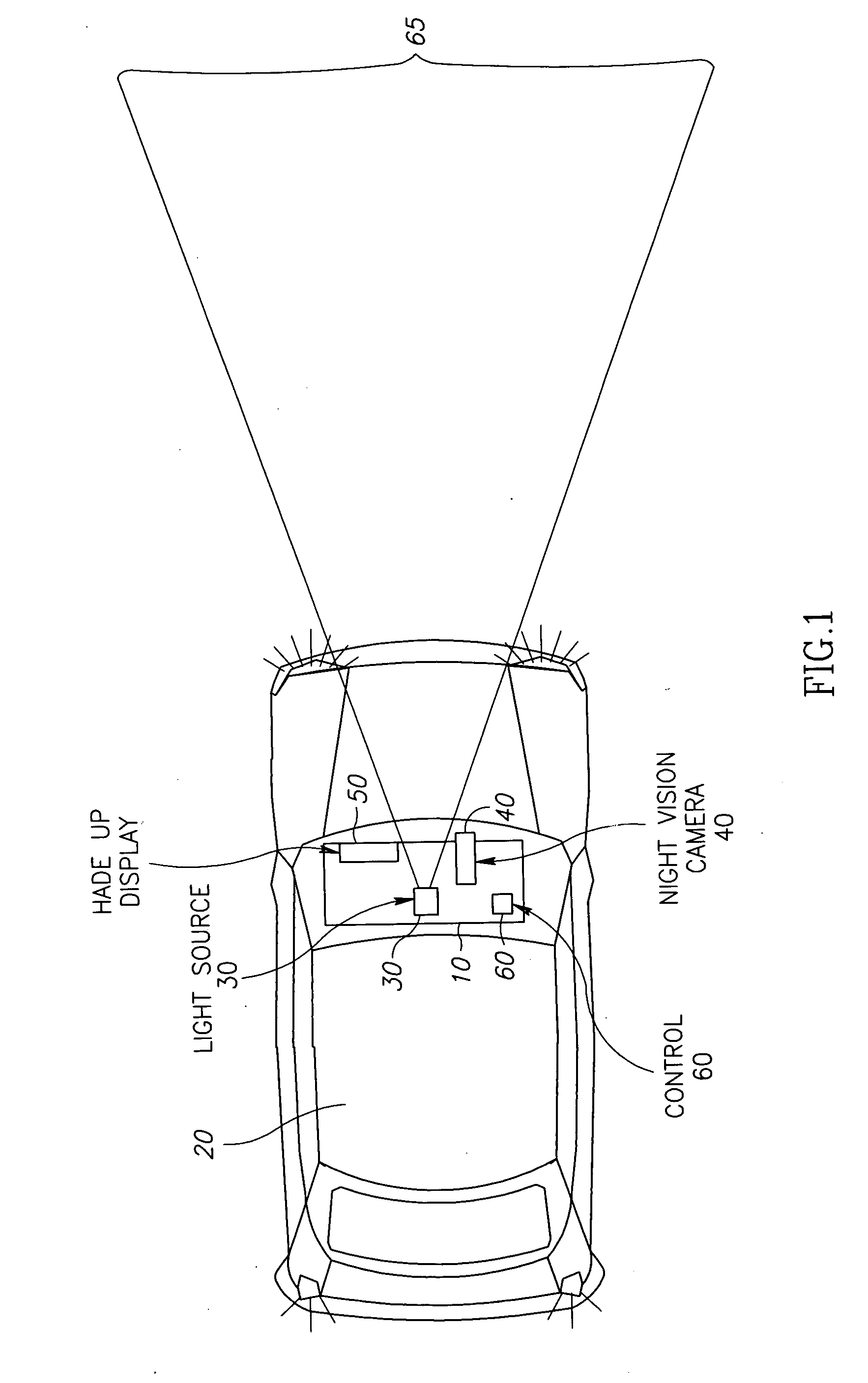
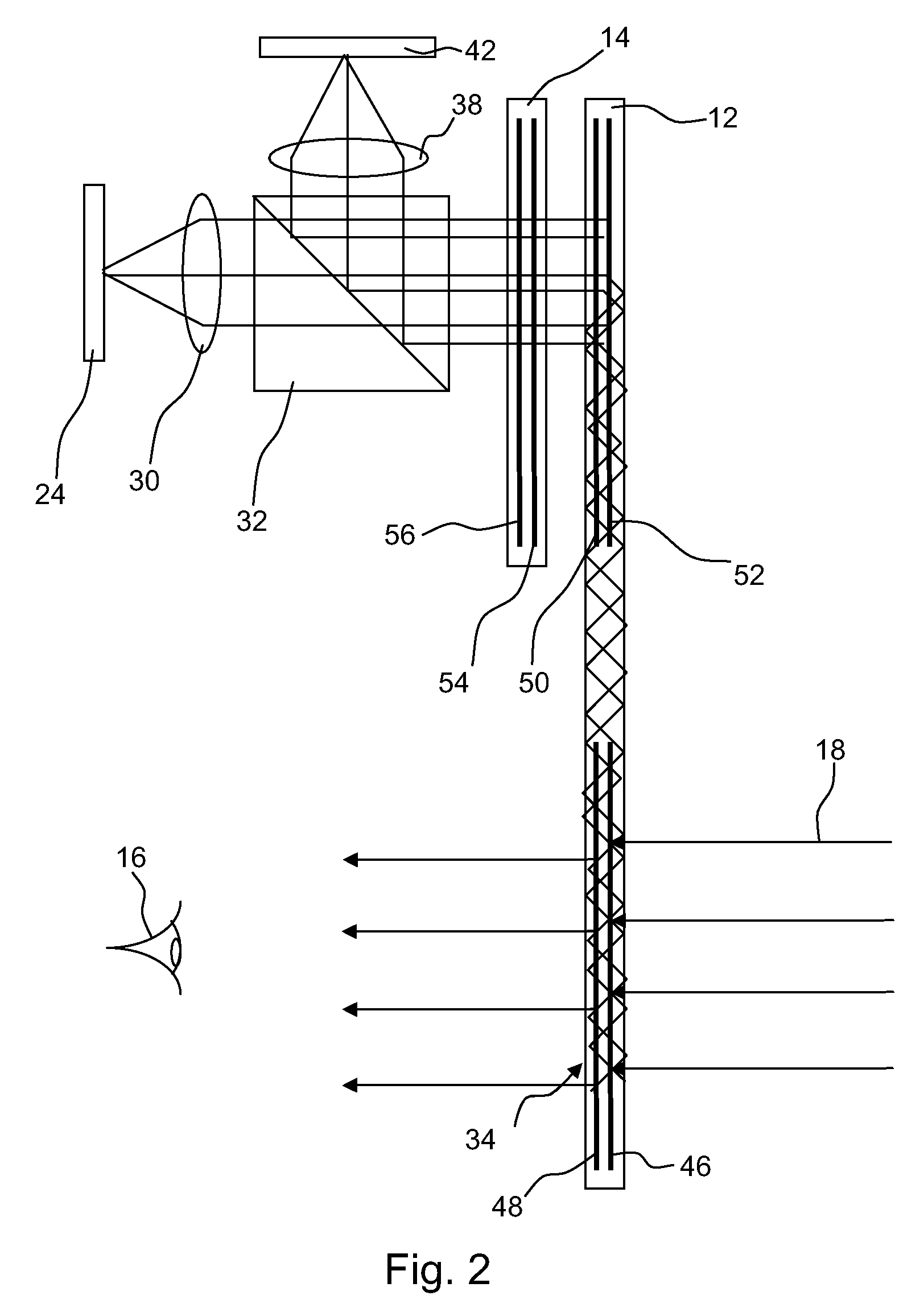
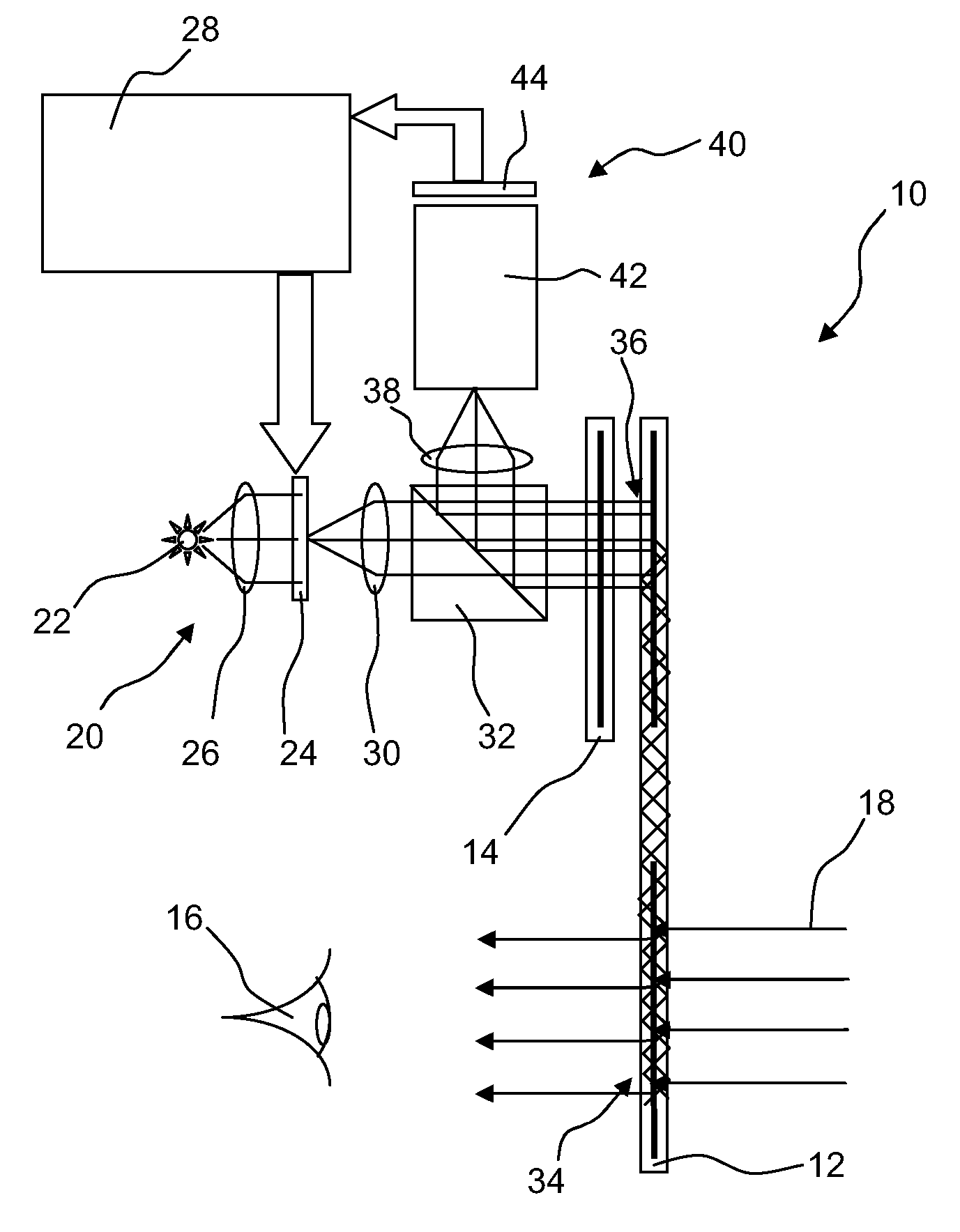
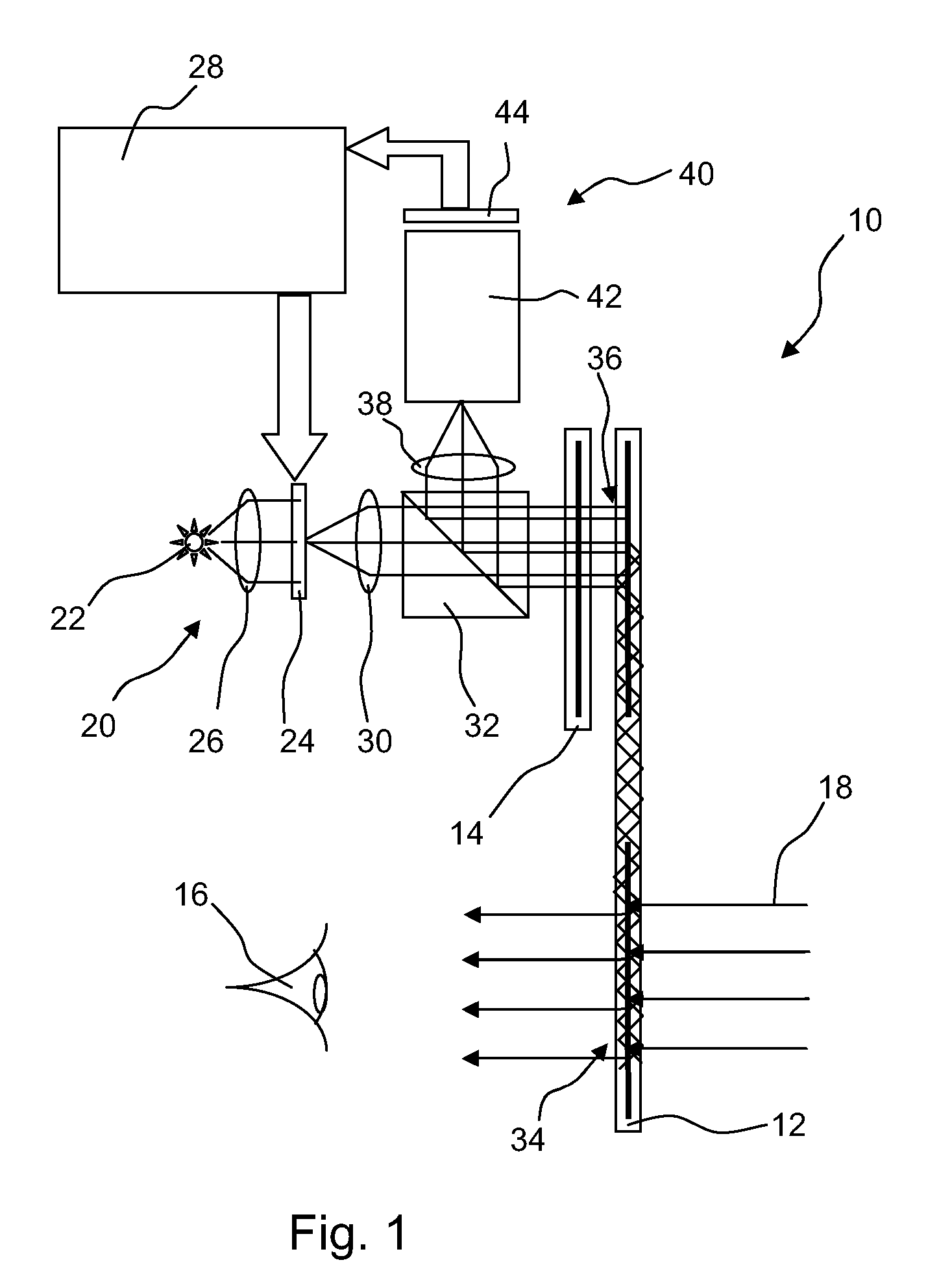
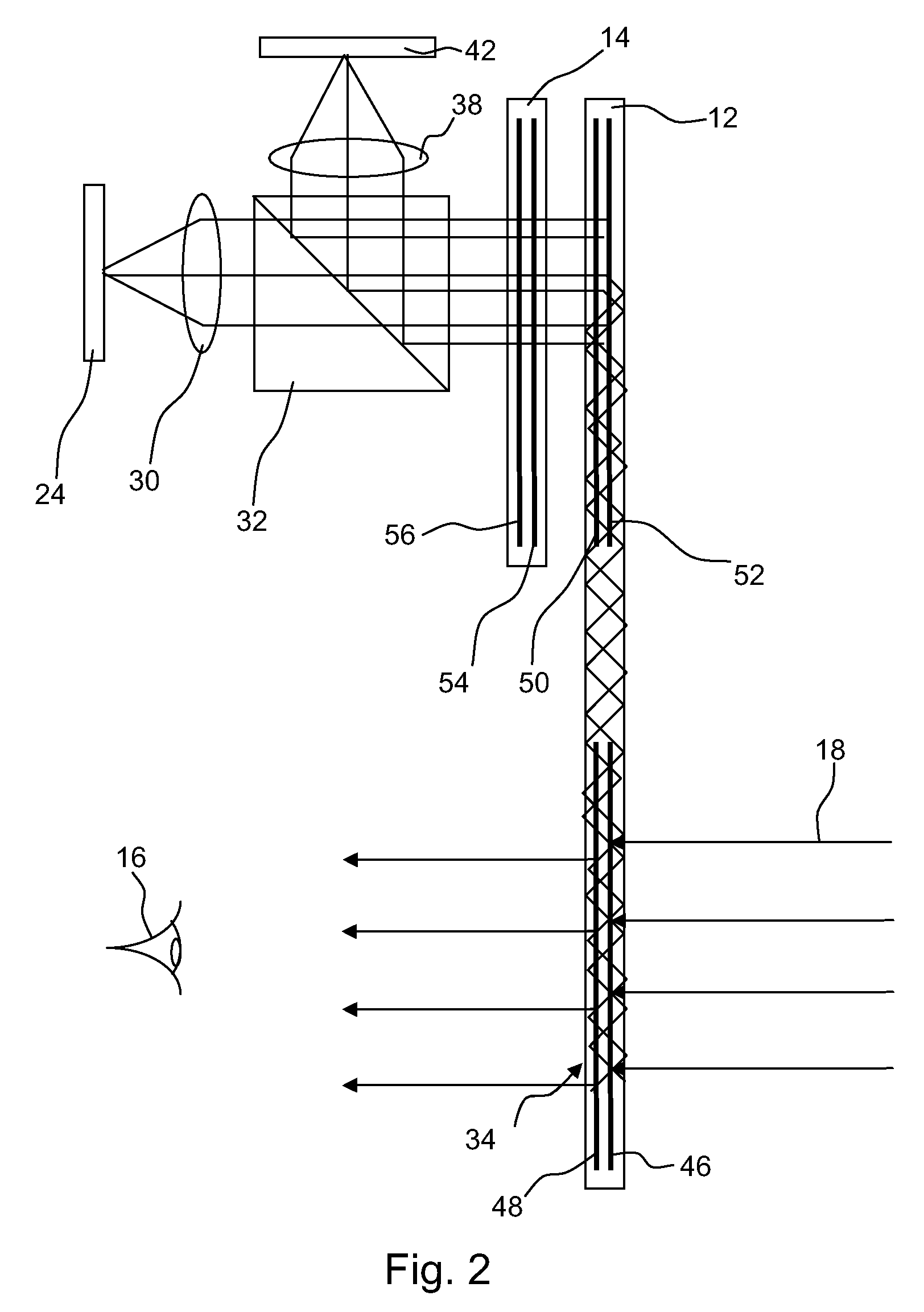
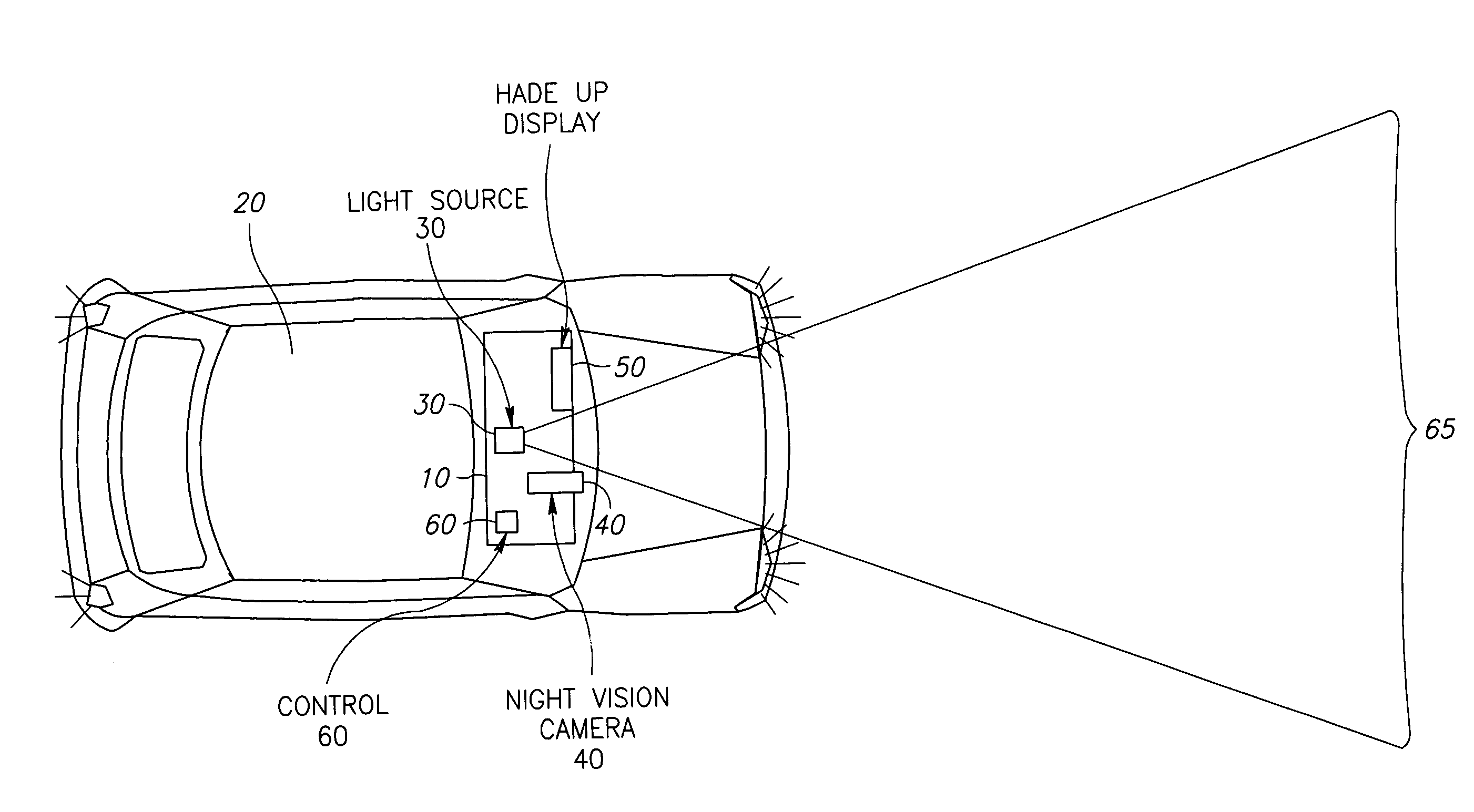
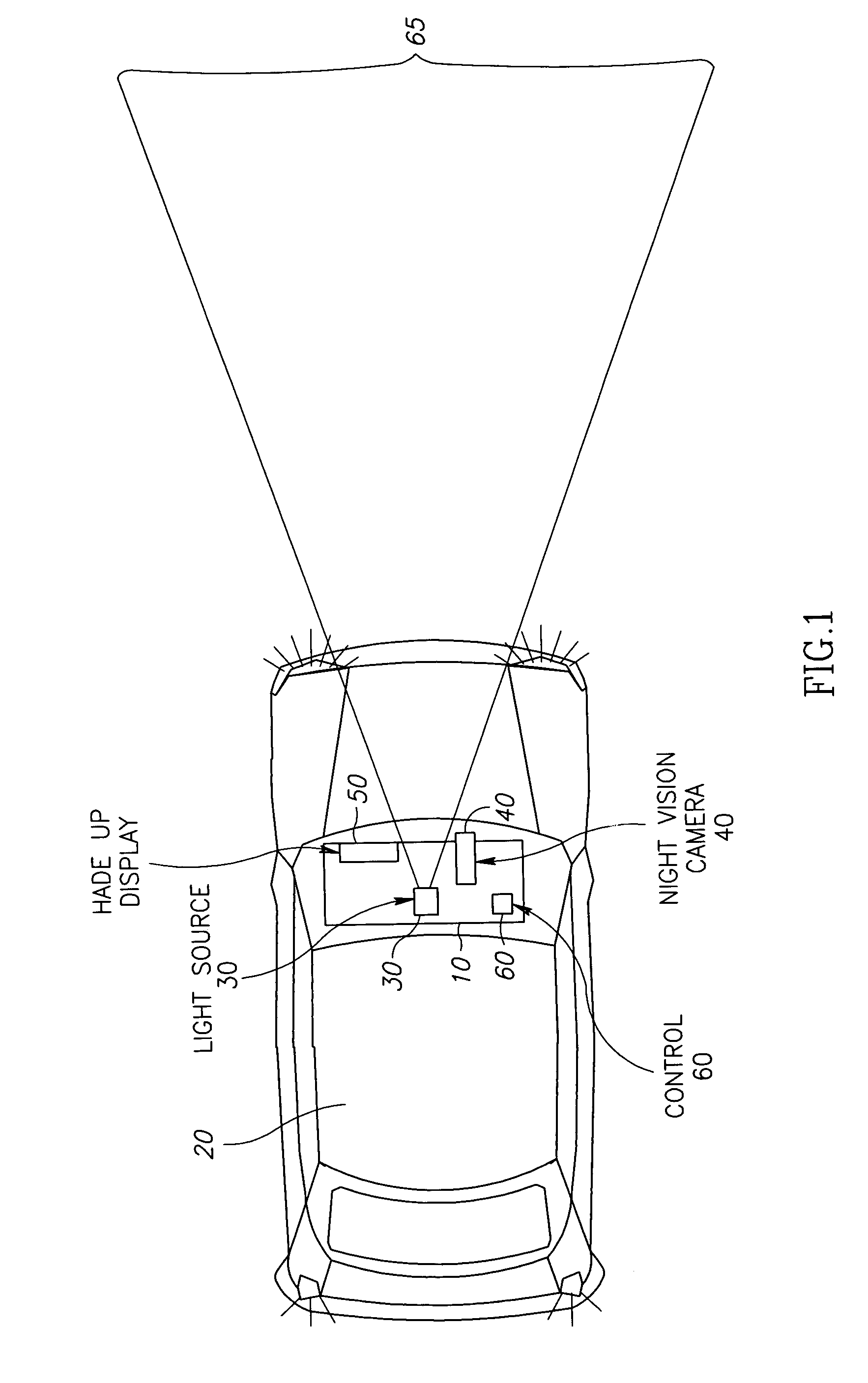
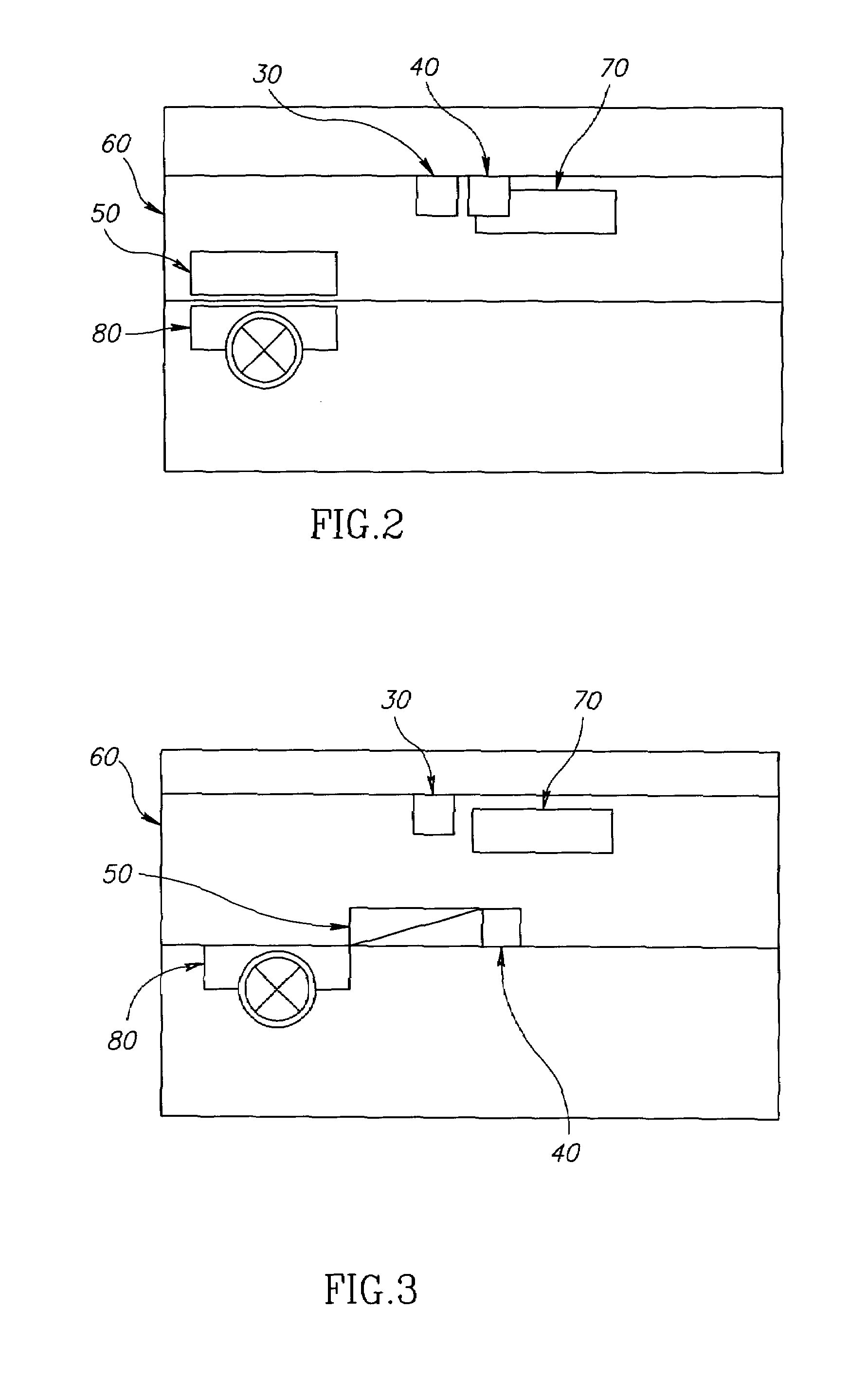
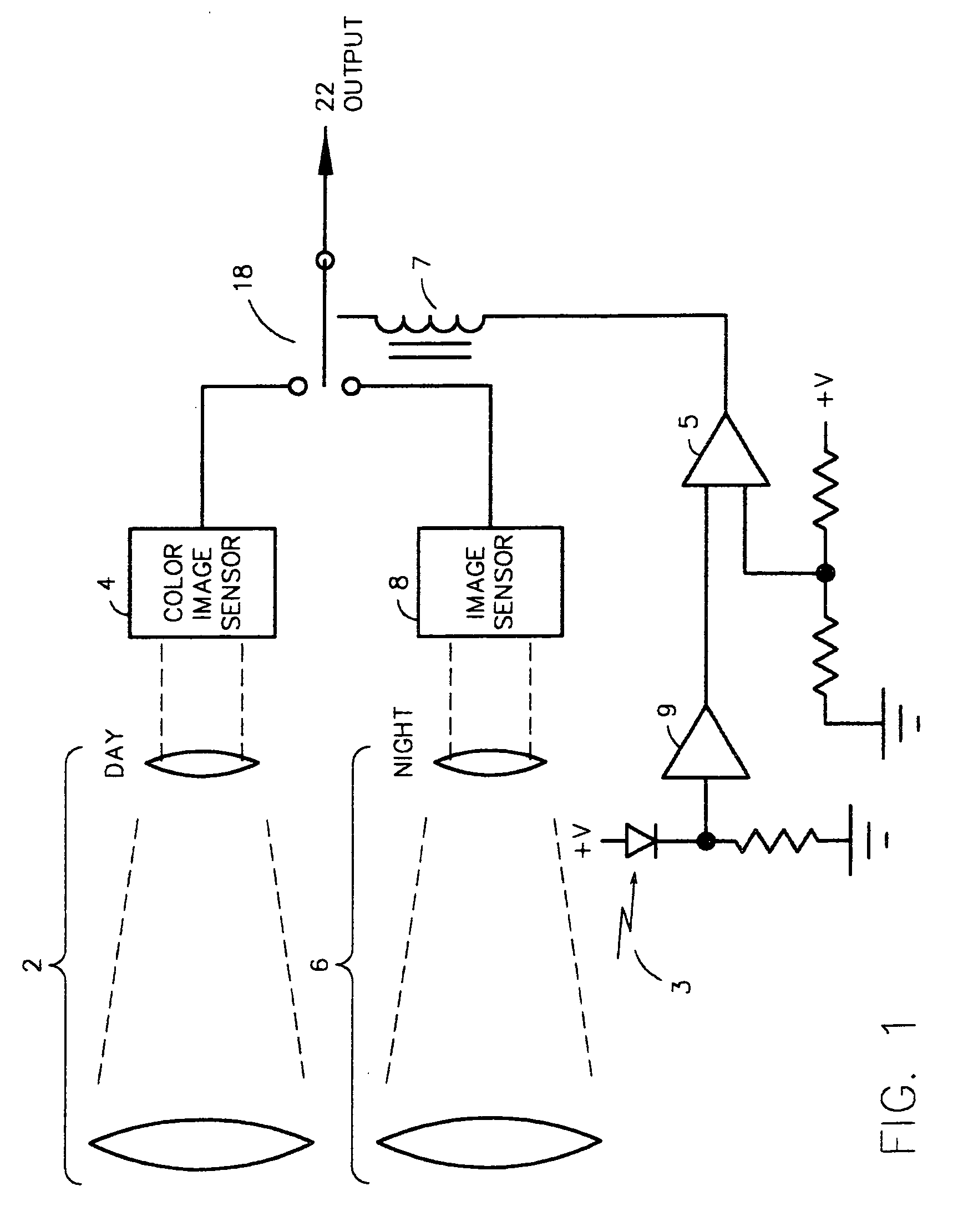
Vehicle mounted night vision imaging system and method
ActiveUS20050269481A1Increase rangeMaximizing abilitySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansNight visionVisibility
A vehicle mounted imaging system and method, enabling selective imaging of objects in a low-visibility environment. The system includes a light source providing non-visible light pulses and a camera having an image intensifier enabled to gate selected received images. The light source may be a laser generator, which may be enabled to generate a pulse width related to the depth of a field to be imaged. The gated image intensifier may determine gating time spans according to the depth of a field to be imaged.
Owner:ELBIT SYST LTD
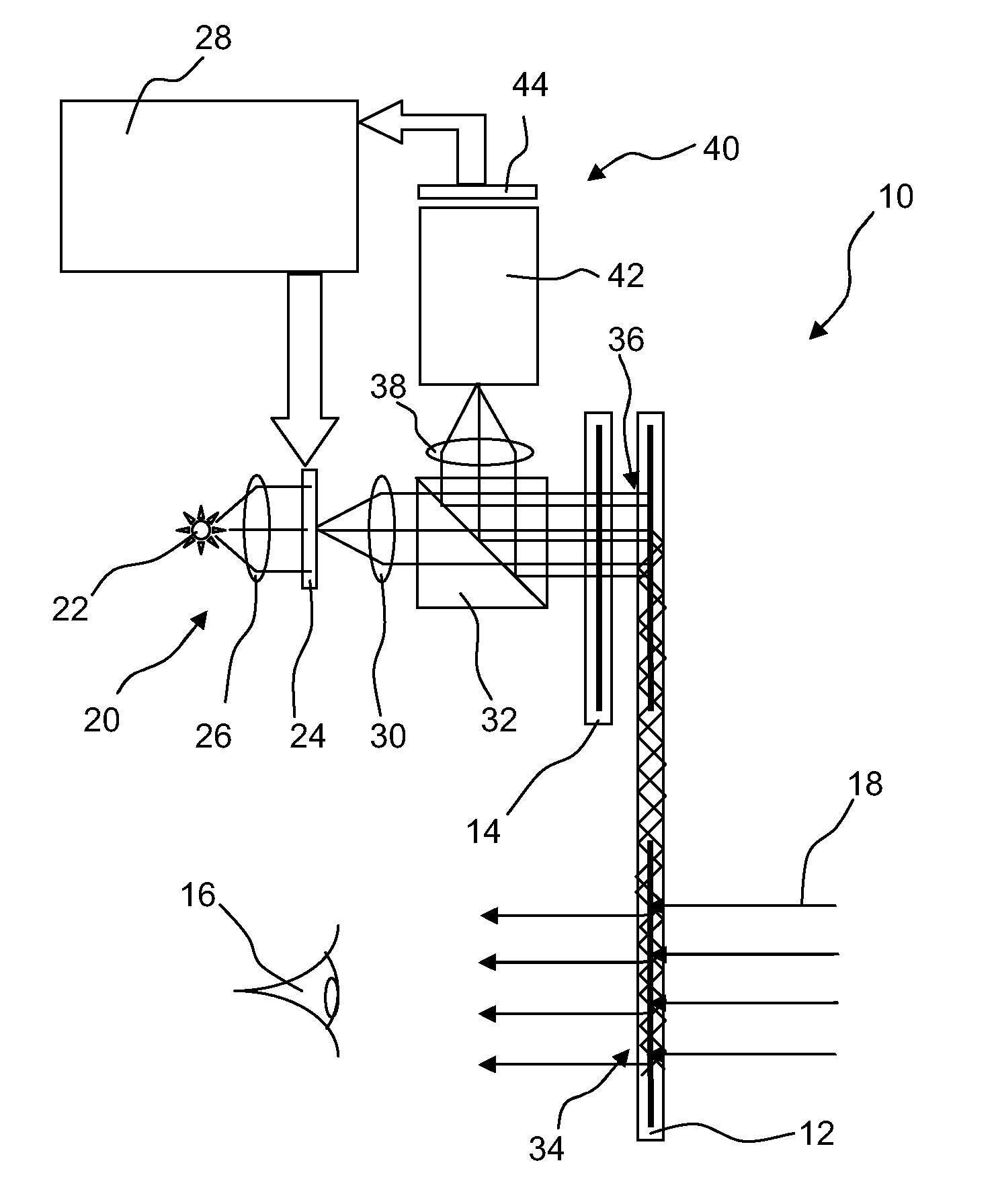
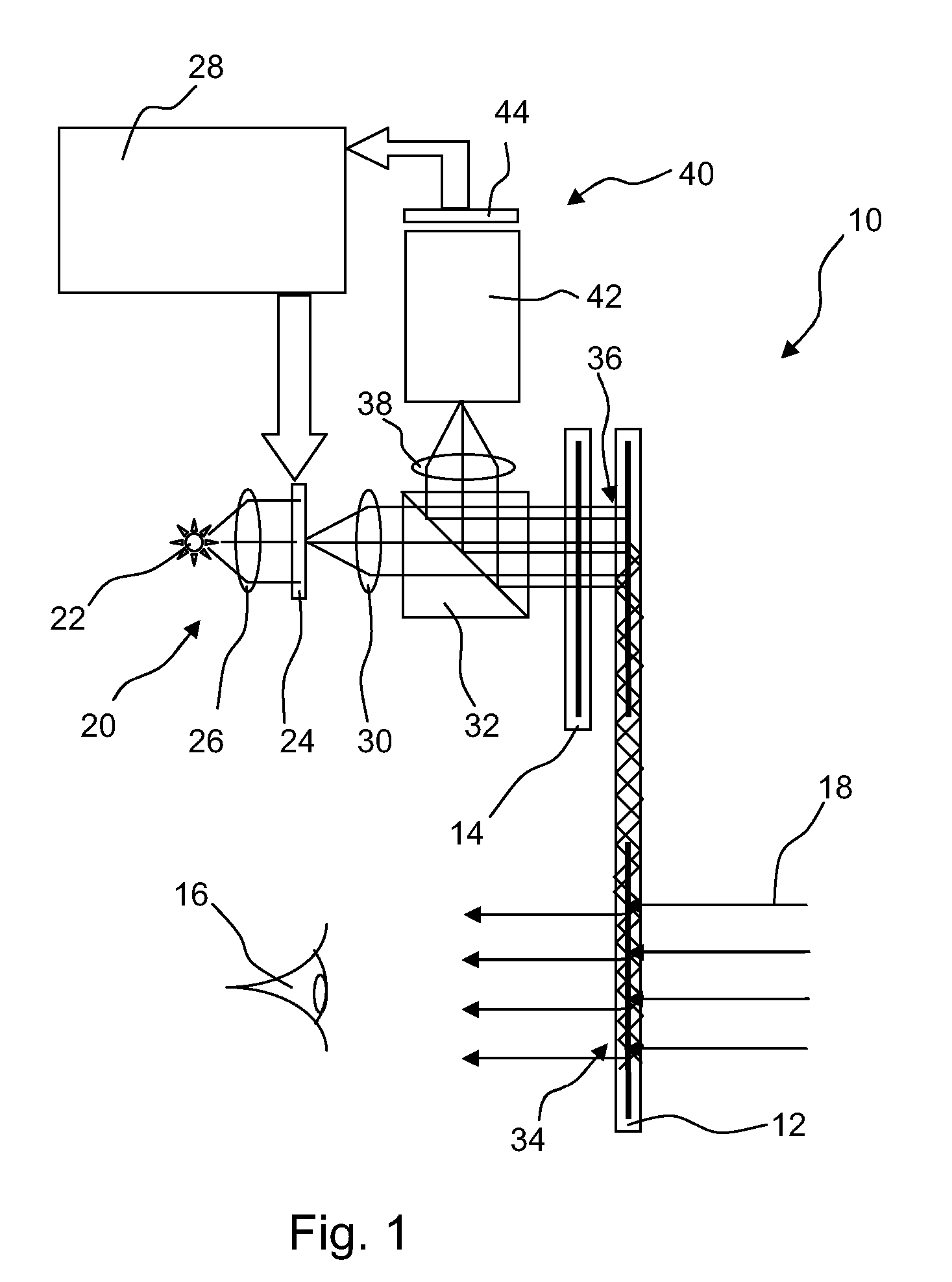
Display systems
ActiveUS8355610B2Reduce impactCathode-ray tube indicatorsCoupling light guidesCouplingForward looking
A primary waveguide and a coupling waveguide are arranged so a user can view light from a forward scene through the primary waveguide. An image source generates an image which is diffractively coupled into the primary waveguide and internally reflected to an exit area for diffraction towards the user. Light from the forward looking scene is diffracted into the primary waveguide to be internally reflected and coupled to a image intensifier tube assembly. The image intensifier tube assembly enhances light from the forward looking scene and drives the image source such that an image of the enhanced light is overlaid on light from a forward scene at exit area.
Owner:SNAP INC
Improvements in or relating to display systems
A primary waveguide and a coupling waveguide are arranged so a user can view light from a forward scene through the primary waveguide. An image source generates an image which is diffractively coupled into the primary waveguide and internally reflected to an exit area for diffraction towards the user. Light from the forward looking scene is diffracted into the primary waveguide to be internally reflected and coupled to a image intensifier tube assembly. The image intensifier tube assembly enhances light from the forward looking scene and drives the image source such that an image of the enhanced light is overlaid on light from a forward scene at exit area.
Owner:SNAP INC
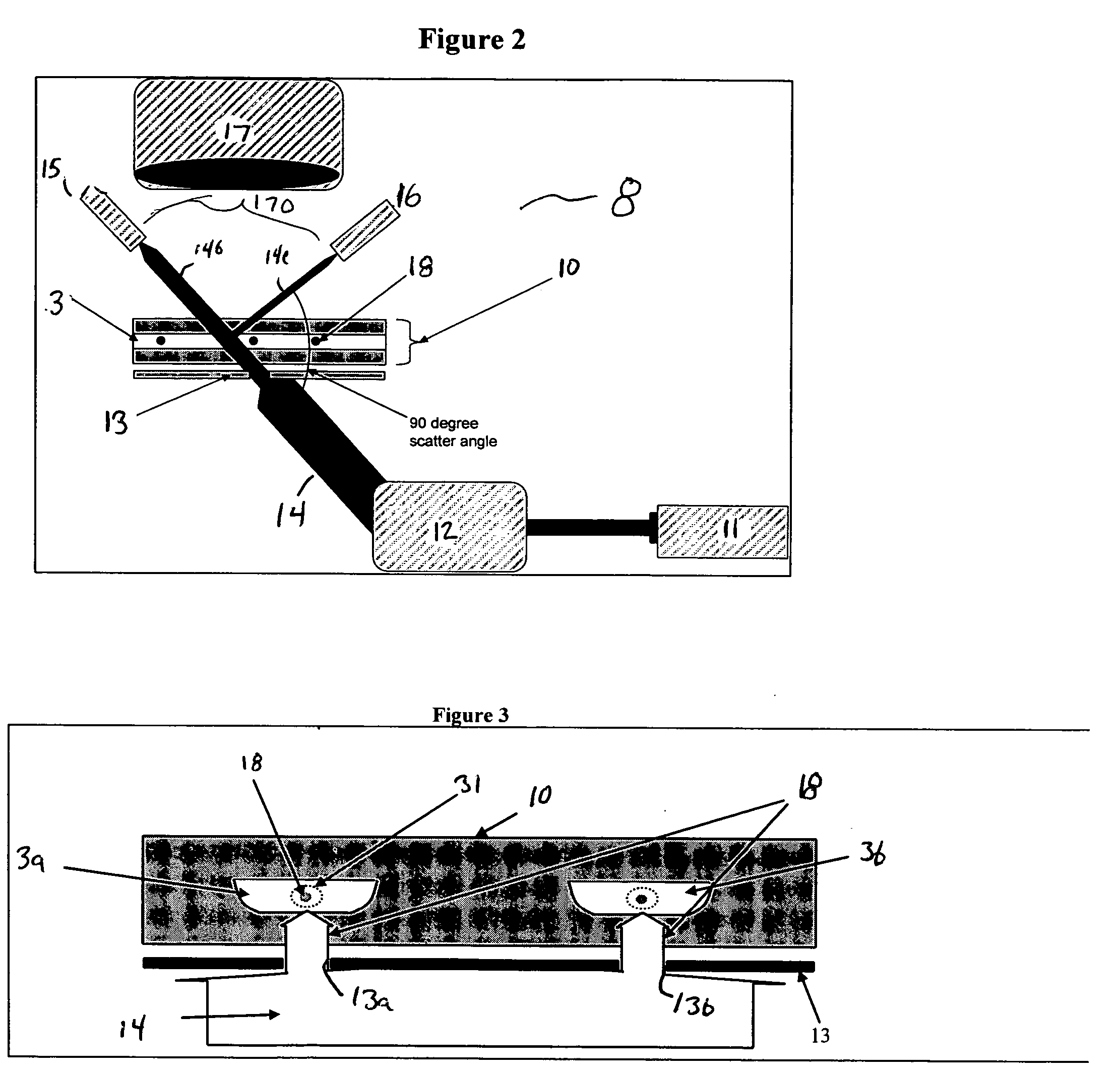
Optical detector for a particle sorting system
ActiveUS7298478B2Accurate and Efficient MonitoringCost effectivelyRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationData acquisitionMicrofluidic channel
An optical system for acquiring fast spectra from spatially channel arrays includes a light source for producing a light beam that passes through the microfluidic chip or the channel to be monitored, one or more lenses or optical fibers for capturing the light from the light source after interaction with the particles or chemicals in the microfluidic channels, and one or more detectors. The detectors, which may include light amplifying elements, detect each light signal and transducer the light signal into an electronic signal. The electronic signals, each representing the intensity of an optical signal, pass from each detector to an electronic data acquisition system for analysis. The light amplifying element or elements may comprise an array of phototubes, a multianode phototube, or a multichannel plate based image intensifier coupled to an array of photodiode detectors.
Owner:CYTONOMEST
Dynamic radiation therapy simulation system
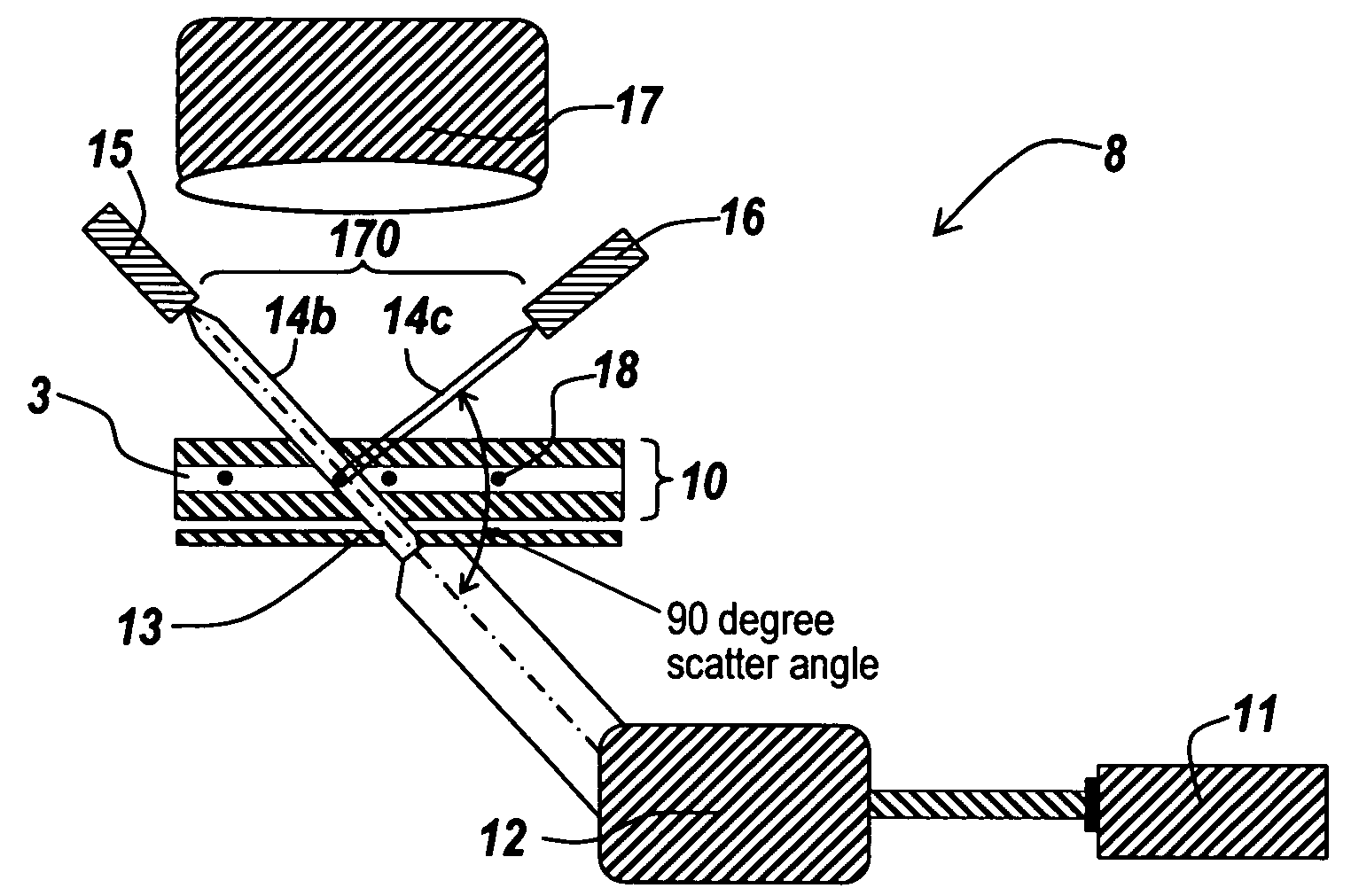
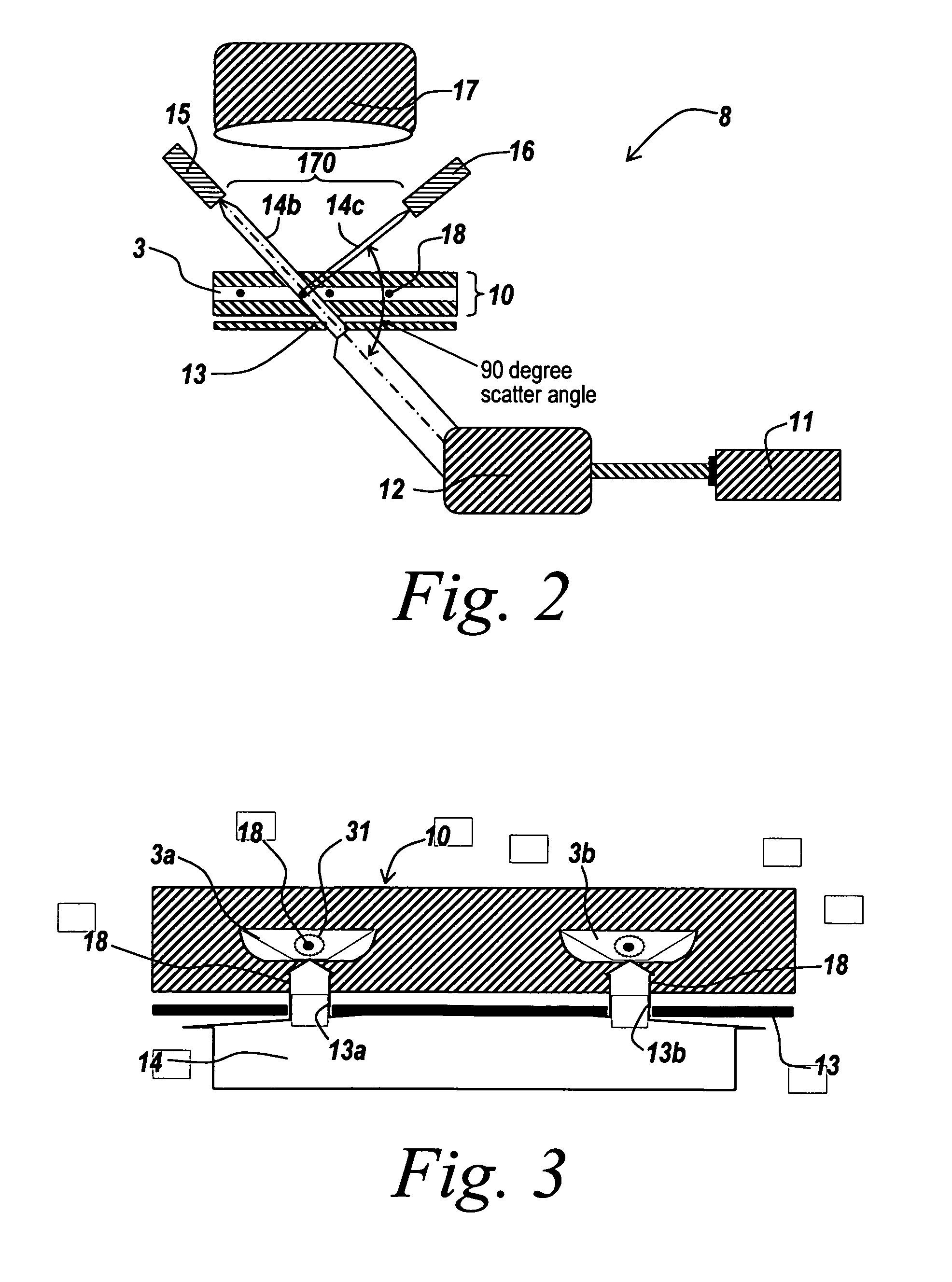
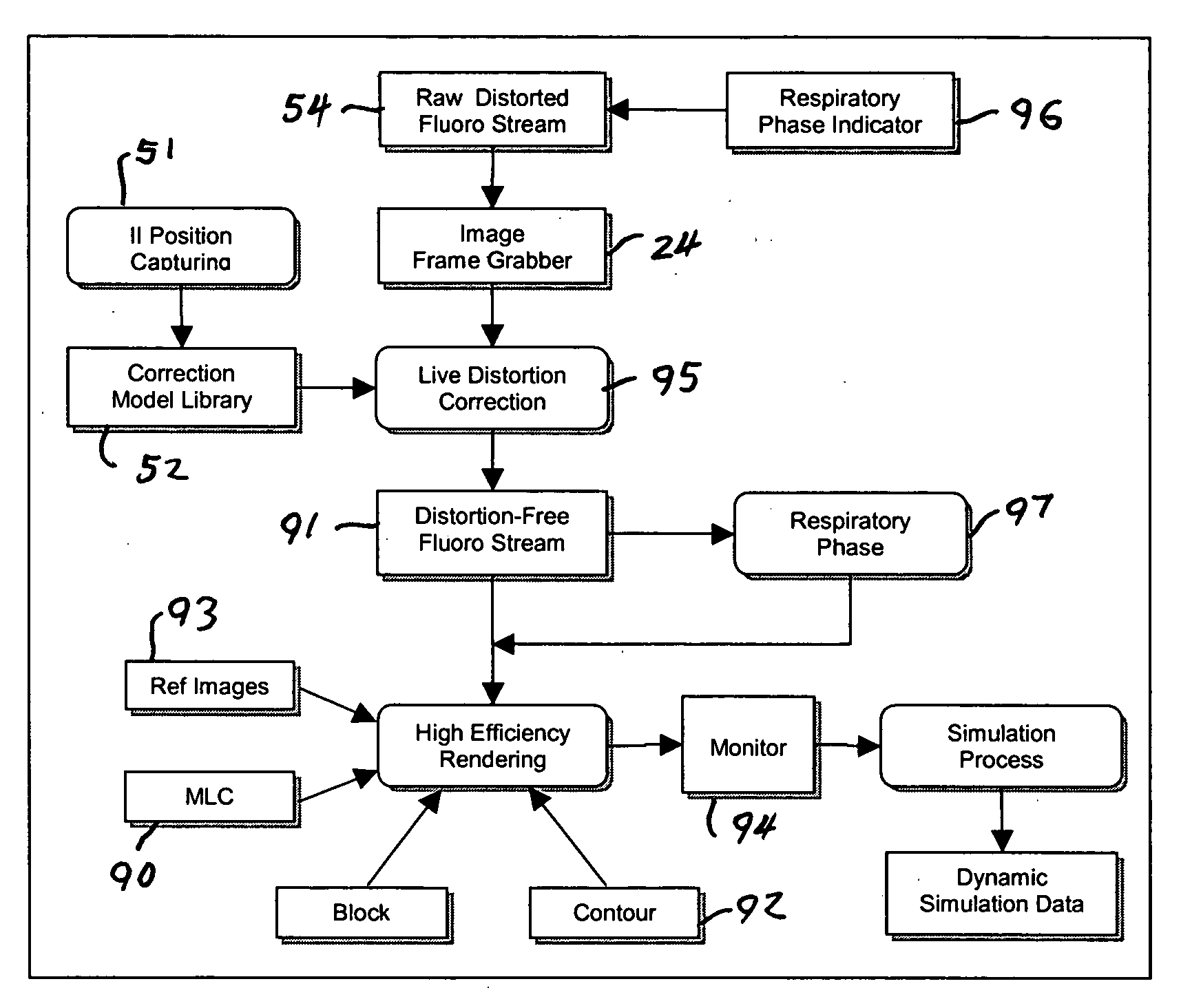
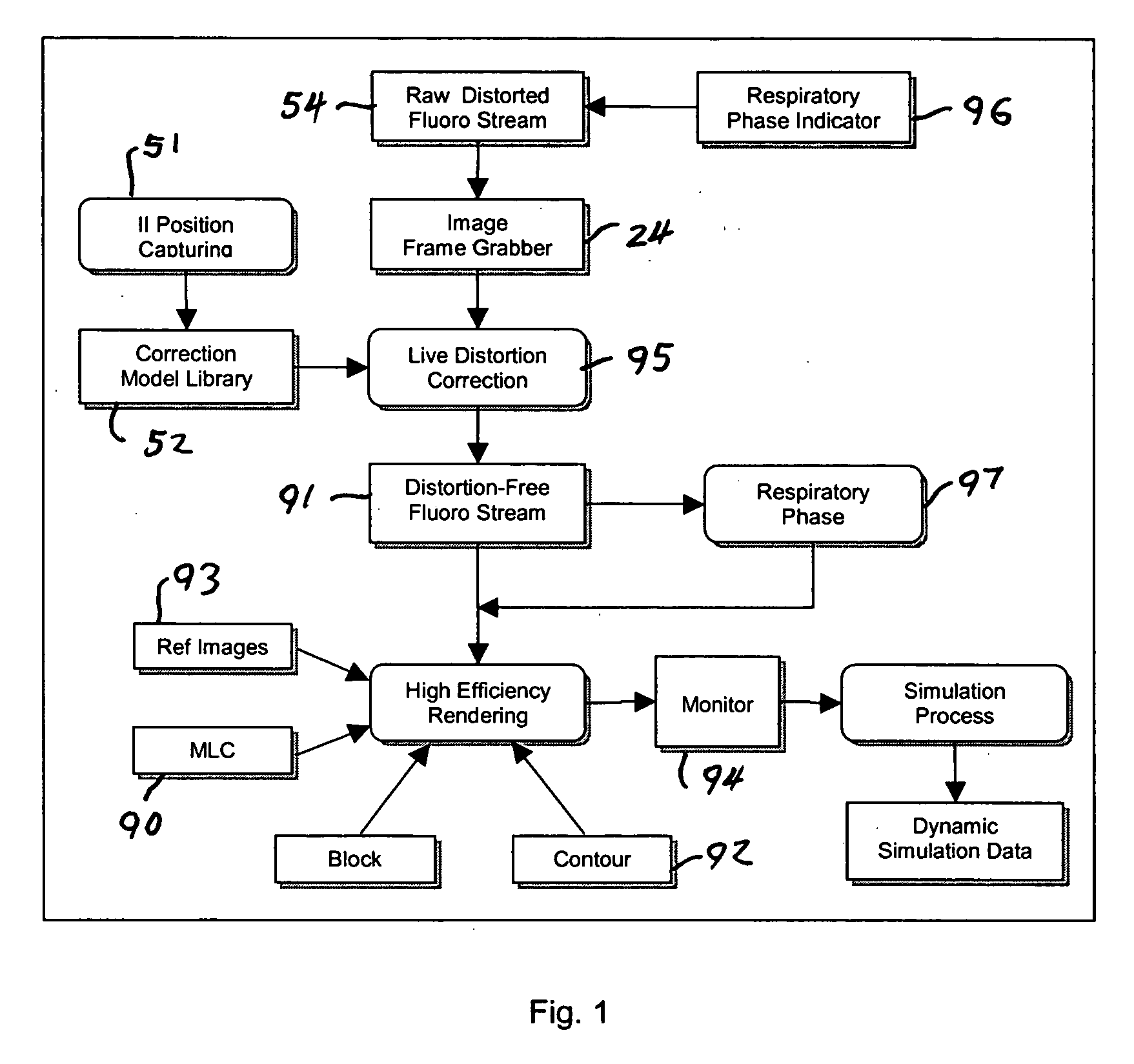
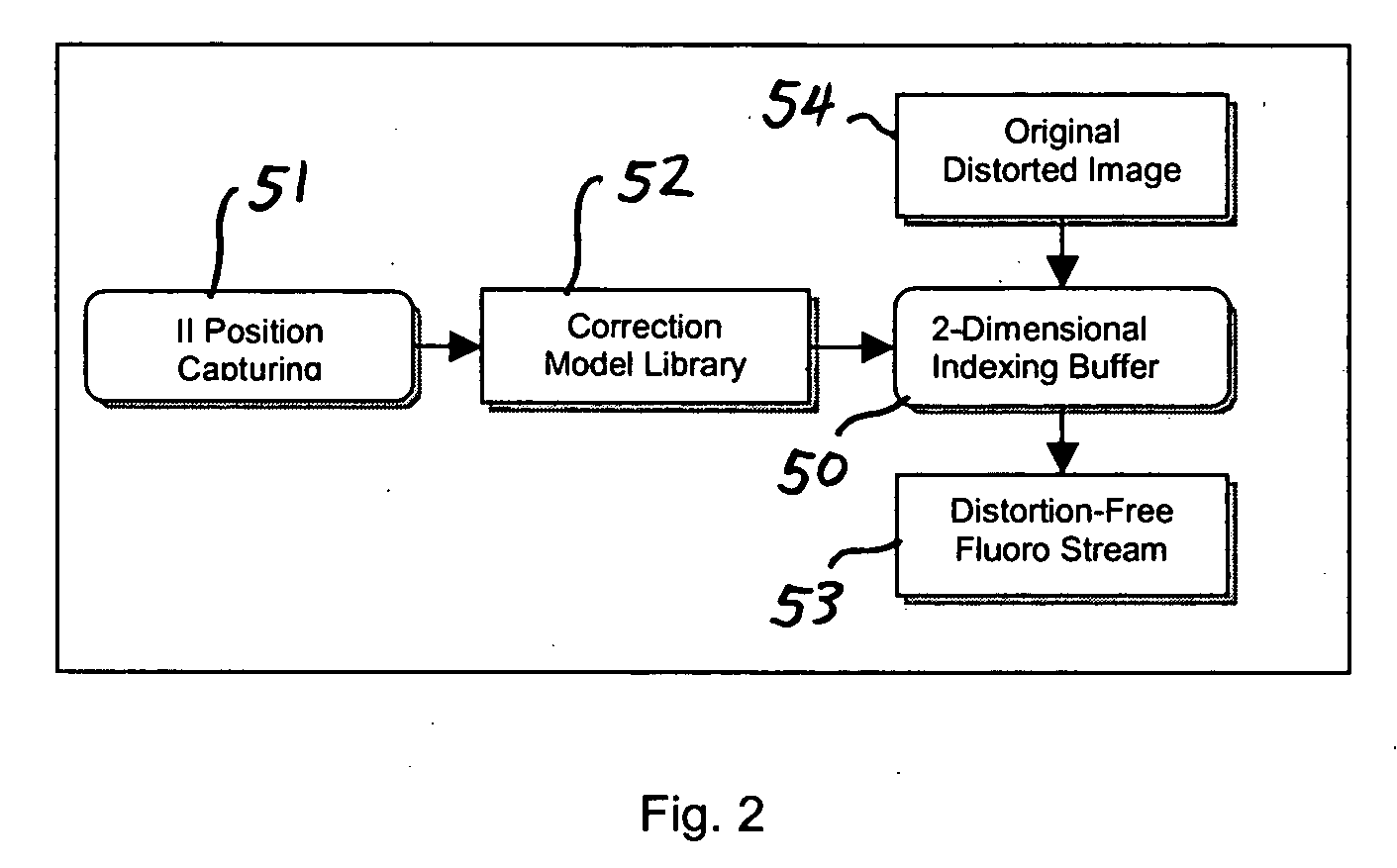
InactiveUS20060291621A1Accurate treatment of tumorAccurate imagingMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingFluoroscopic imageRadiology
A system for dynamic treatment simulation for radiotherapy. Software is implemented on a computer system to perform dynamic simulation by displaying every segment of dynamic treatment beams on top of real-time fluoroscopic image sequences. Automated distortion correction of the fluoroscopic image due to the image intensifier is performed in real-time. A respiration phase indicator measures changes in circumference of the patient's chest through the movement of a radio-opaque marker that appears directly in the fluoroscopic images of the patient.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Optical detector for a particle sorting system
ActiveUS20050128479A1Accurate and Efficient MonitoringLow costRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationData acquisitionPhotodiode
An optical system for acquiring fast spectra from spatially channel arrays includes a light source for producing a light beam that passes through the microfluidic chip or the channel to be monitored, one or more lenses or optical fibers for capturing the light from the light source after interaction with the particles or chemicals in the microfluidic channels, and one or more detectors. The detectors, which may include light amplifying elements, detect each light signal and transducer the light signal into an electronic signal. The electronic signals, each representing the intensity of an optical signal, pass from each detector to an electronic data acquisition system for analysis. The light amplifying element or elements may comprise an array of phototubes, a multianode phototube, or a multichannel plate based image intensifier coupled to an array of photodiode detectors.
Owner:CYTONOMEST
Vehicle mounted night vision imaging system and method
ActiveUS7733464B2Increase rangeMaximizing abilityOptical rangefindersSolid-state devicesVisibilityNight vision
A vehicle mounted imaging system and method, enabling selective imaging of objects in a low-visibility environment. The system includes a light source providing non-visible light pulses and a camera having an image intensifier enabled to gate selected received images. The light source may be a laser generator, which may be enabled to generate a pulse width related to the depth of a field to be imaged. The gated image intensifier may determine gating time spans according to the depth of a field to be imaged.
Owner:ELBIT SYST LTD
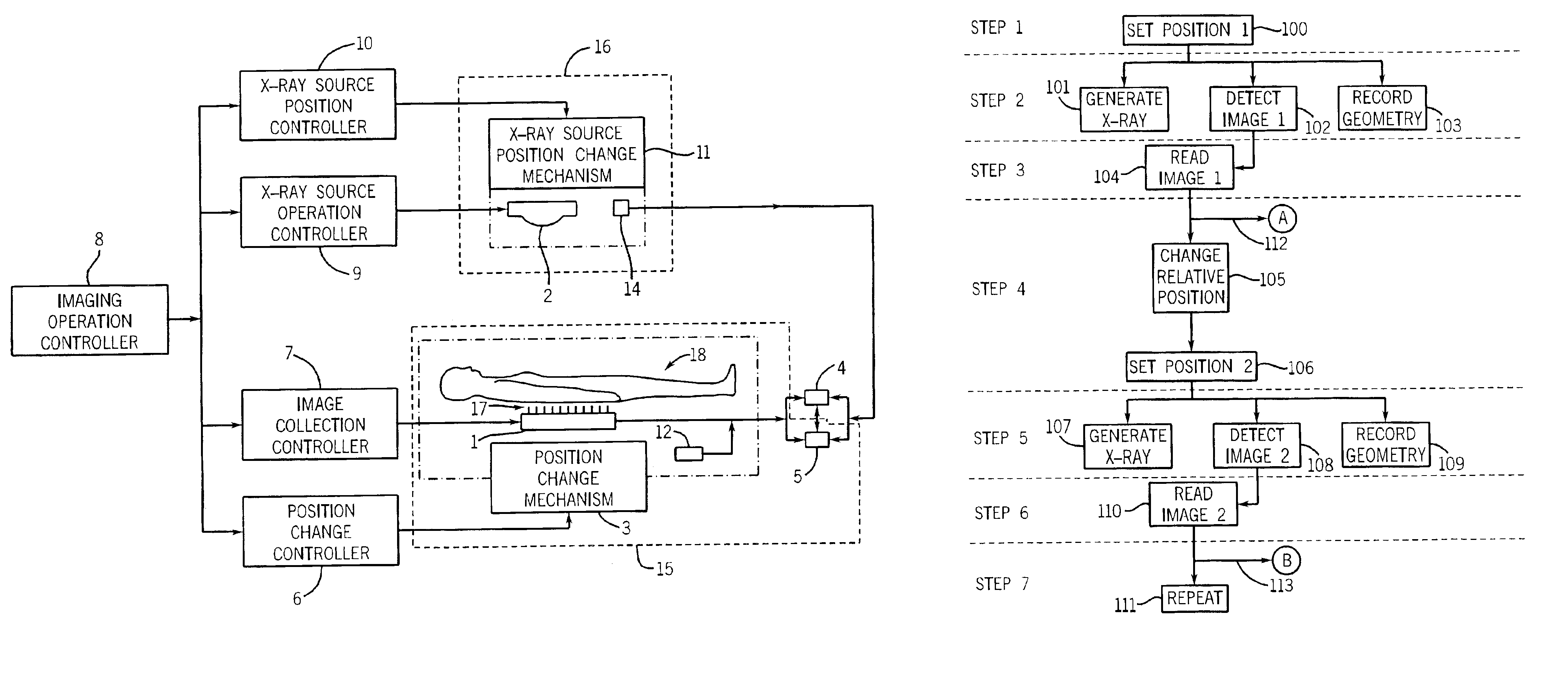
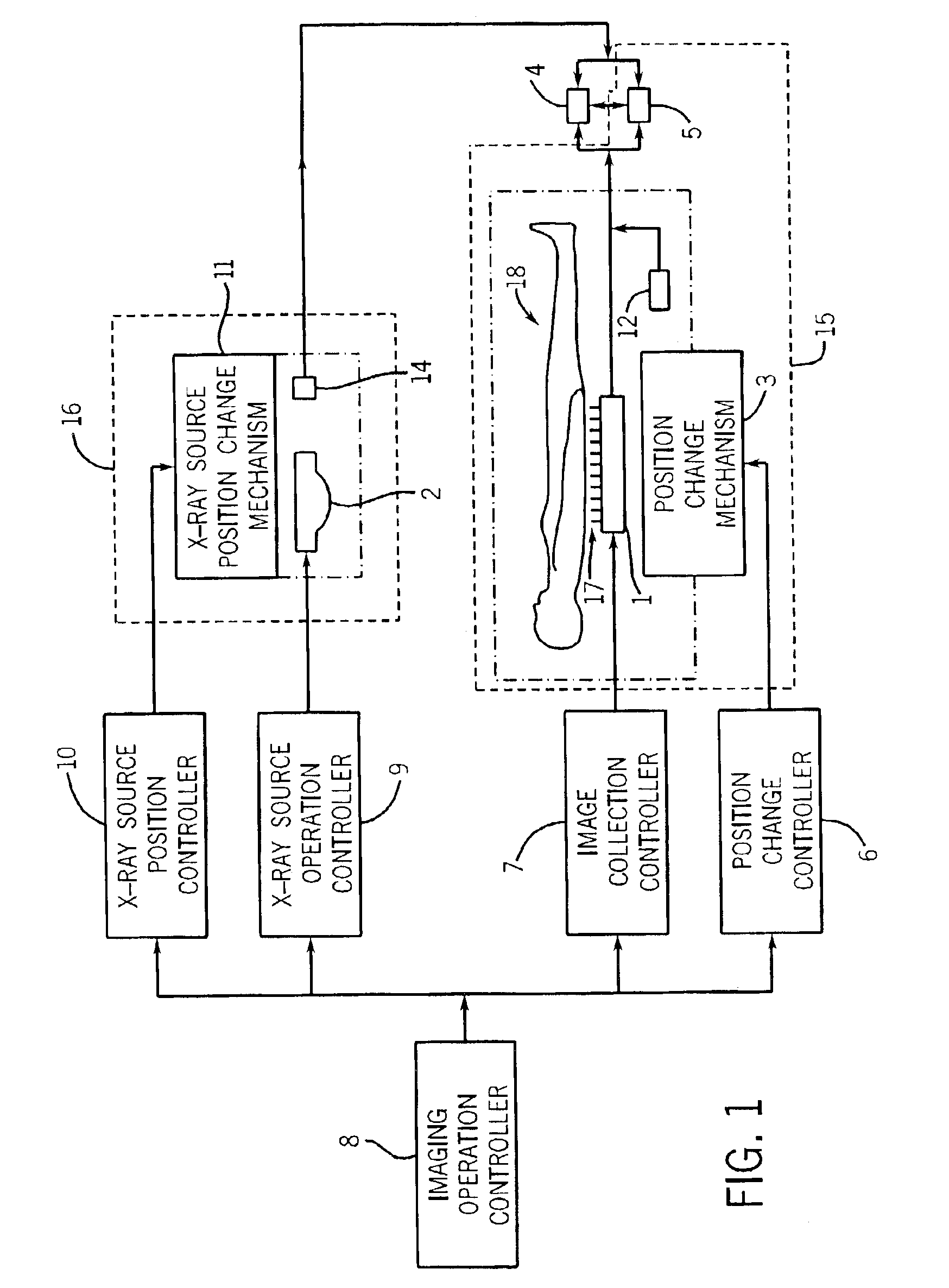
Image pasting using geometry measurement and a flat-panel detector
InactiveUS6944265B2Promote sportsX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationFlat panel detectorMeasurement device
A device for use in image pasting is described. The device includes a digital x-ray detector capable of automatic digital imaging without the use of an image intensifier; the detector preferably being a flat-panel detector. Additionally, an image pasting system using a solid-state detector is described. The system can connect the detected images to a display via a network (such as a WAN, a LAN, or the internet). Further, an image geometry measurement device for use in pasting x-ray images is disclosed. The geometry measurement device helps determine the relative position of two images to be used in image pasting. This information can be used alone, or in connection with an image pasting algorithm. Still further, methods of forming composite images are disclosed using a flat-panel detector and using the geometry of the images. The disclosed devices and systems can be integrated with other digital image pasting technology.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Time resolution fluorescence spectral measuring and image forming method and its device
InactiveCN1912587ADifferent temporal resolutionsAchieving high-sensitivity detectionFluorescence/phosphorescencePhotocathodePicosecond
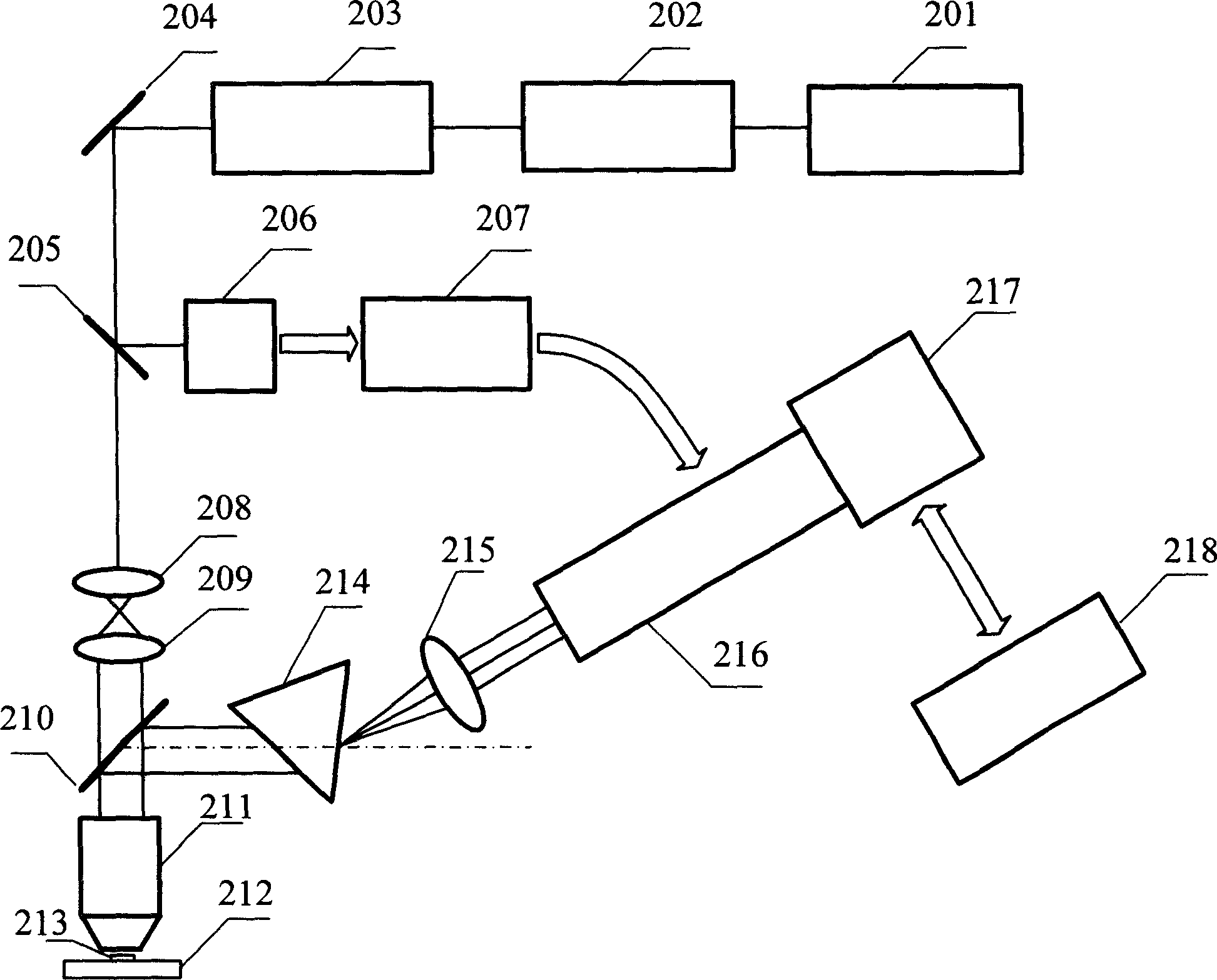
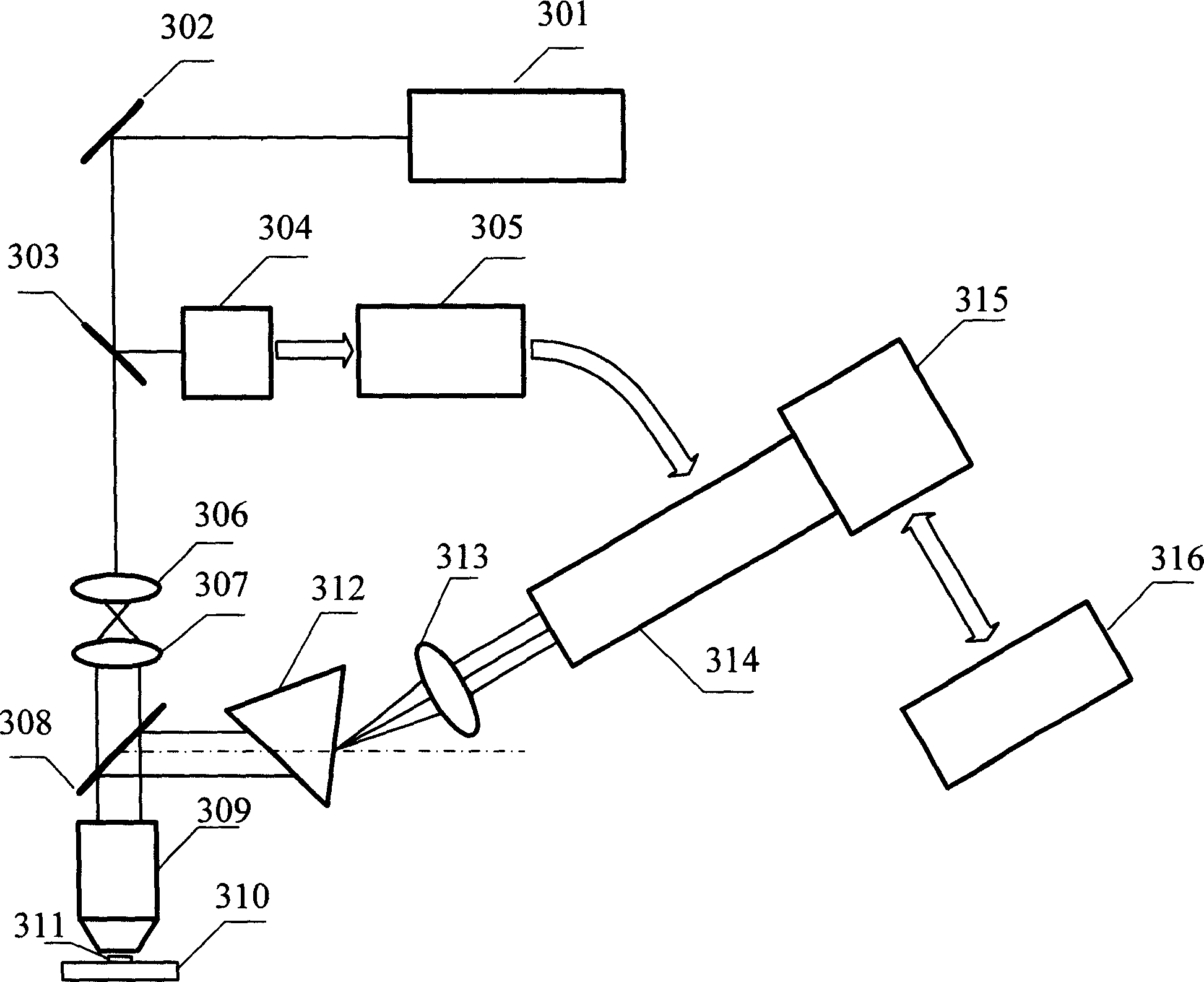
A method of using picosecond scan camera to simultaneously obtain fluorescent light spectrum and fluorescent lifetime of sample includes focusing blue violet light emitted by laser on sample by objective to excite sample single photon, collecting fluorescent from sample then splitting it and focusing it to be image on photoelectric cathode of picosecond scan camera, setting dispersion direction of fluorescent to be the same as slit direction of said camera but to be vertical to scan direction in order to measure out fluorescent lifetime of different light spectrum simultaneously under coaction of scan circuit and image intensifier deflection system.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Low-photon flux image-intensified electronic camera
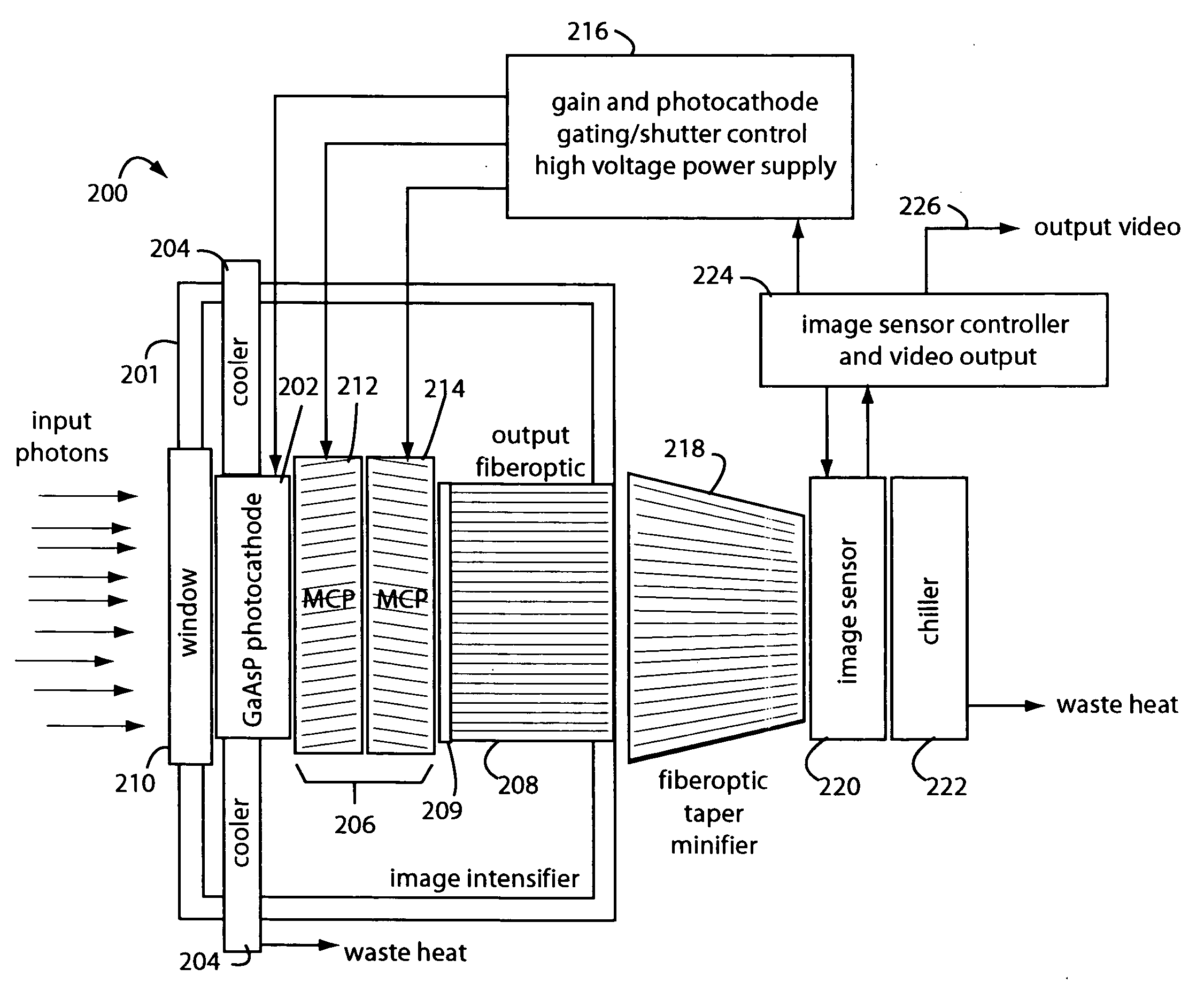
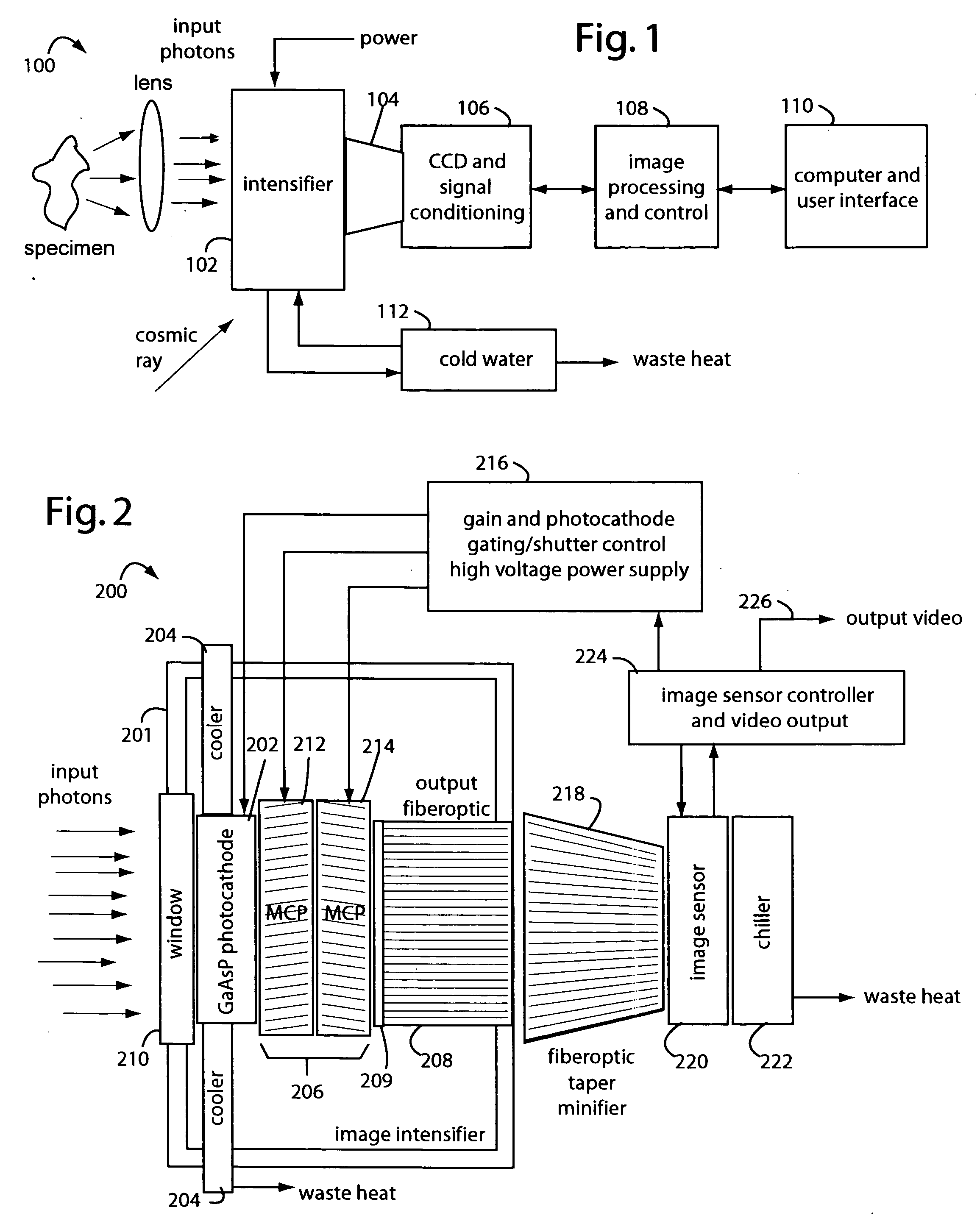
ActiveUS20060081770A1Low backgroundZero effective read noiseSolid-state devicesMultiplier circuit arrangementsGallium arsenide phosphidePhotocathode
A low-photon flux image-intensified electronic camera comprises a gallium arsenide phosphide (GaAsP) photocathode in a high vacuum tube assembly behind a hermetic front seal to receive image photons. Such is cooled by a Peltier device to −20° C. to 0° C., and followed by a dual microchannel plate. The microchannels in each plate are oppositely longitudinally tilted away from the concentric to restrict positive ions that would otherwise contribute to the generation high brightness “scintillation” noise events at the output of the image. A phosphor-coated output fiberoptic conducts intensified light to an image sensor device. This too is chilled and produces a camera signal output. A high voltage power supply connected to the dual microchannel plate provides for gain control and photocathode gating and shuttering. A fiberoptic taper is used at the output of the image intensifier vacuum tube as a minifier between the internal output fiberoptic and the image sensor.
Owner:STANFORD PHOTONICS
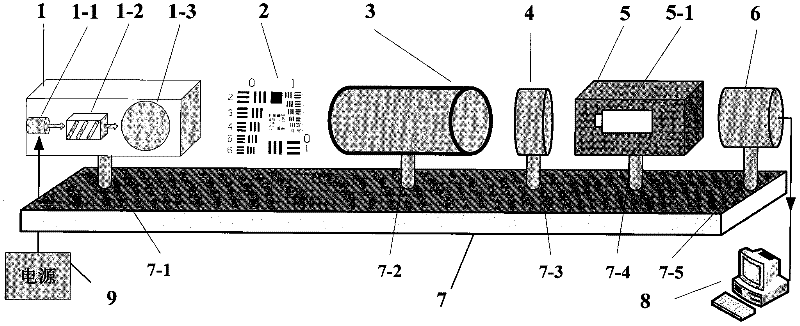
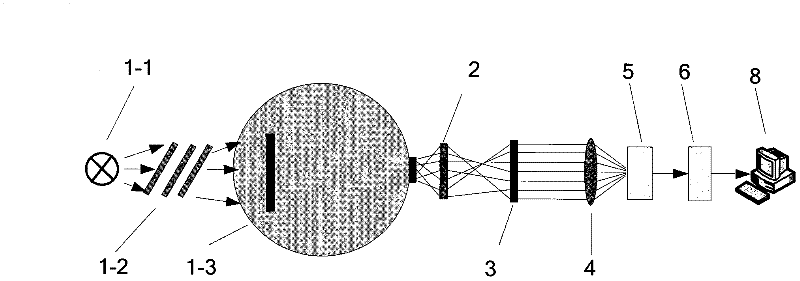
Resolving power measuring device and resolving power evaluation method for three-generation dim light image intensifier
ActiveCN102353519AImprove uniformityCancel noiseTesting optical propertiesMeasurement deviceOptical measurements
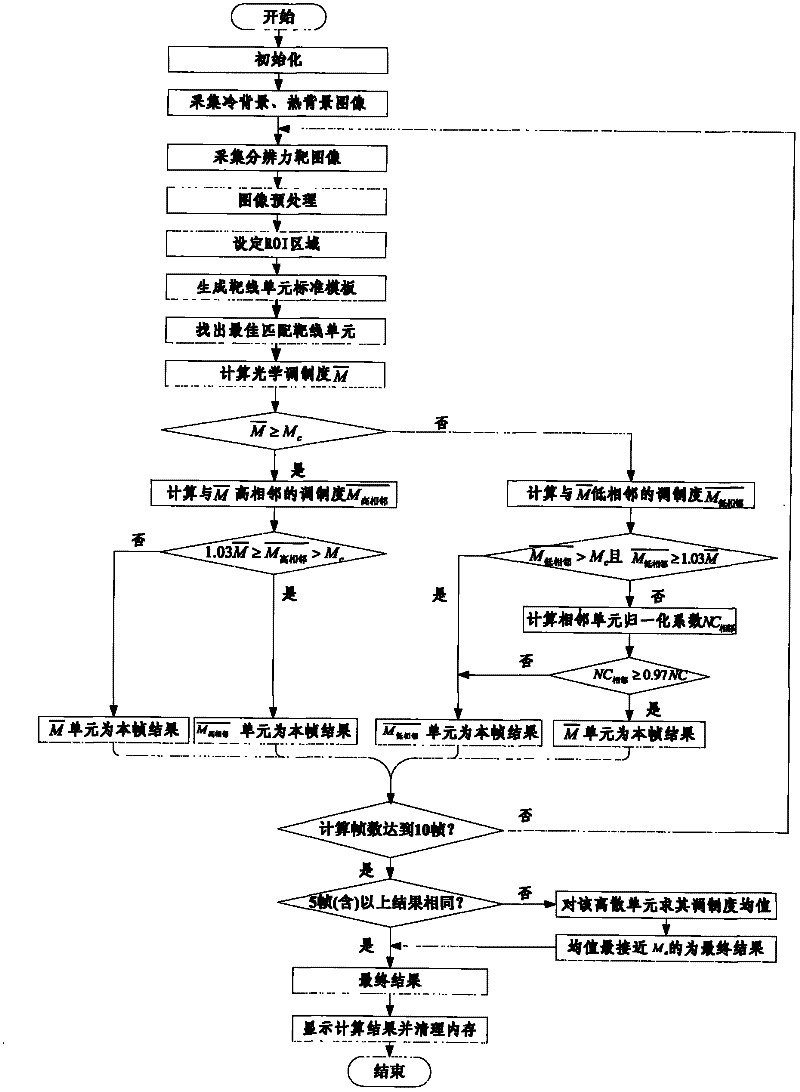
The invention discloses a resolving power measuring device and a resolving power evaluation method for a three-generation dim light image intensifier, and belongs to the field of optical measurement and metering. The resolving power measuring device is characterized by consisting of a light source component, a resolving power target, a collimator tube, an imaging objective lens, a test camera obscura, a charge coupled device (CCD) camera and a computer. The resolving power evaluation method comprises the following steps of: imaging the resolving power target irradiated by a standard light source to a fluorescent screen by using a measured image intensifier; converting into a frame image of a target line by using the CCD camera, and transmitting into the computer; successively processing asingle frame image of the target line by using a normalized cross correlation model and an optical modulation degree model through internal image processing software of the computer to acquire a single frame processing result; and analyzing multi-frame processing results and performing corresponding supplement operation to acquire a final resolving power evaluation result. By the device and the method, the problem of objective evaluation during resolving power measurement of the three-generation dim light image intensifier is solved; and the device and the method can be popularized to other measurement fields such as an intensified charge coupled device (ICCD) measurement field and the like where resolving power is required to be objectively evaluated, and have wide application prospects.
Owner:CHINA NORTH IND NO 205 RES INST
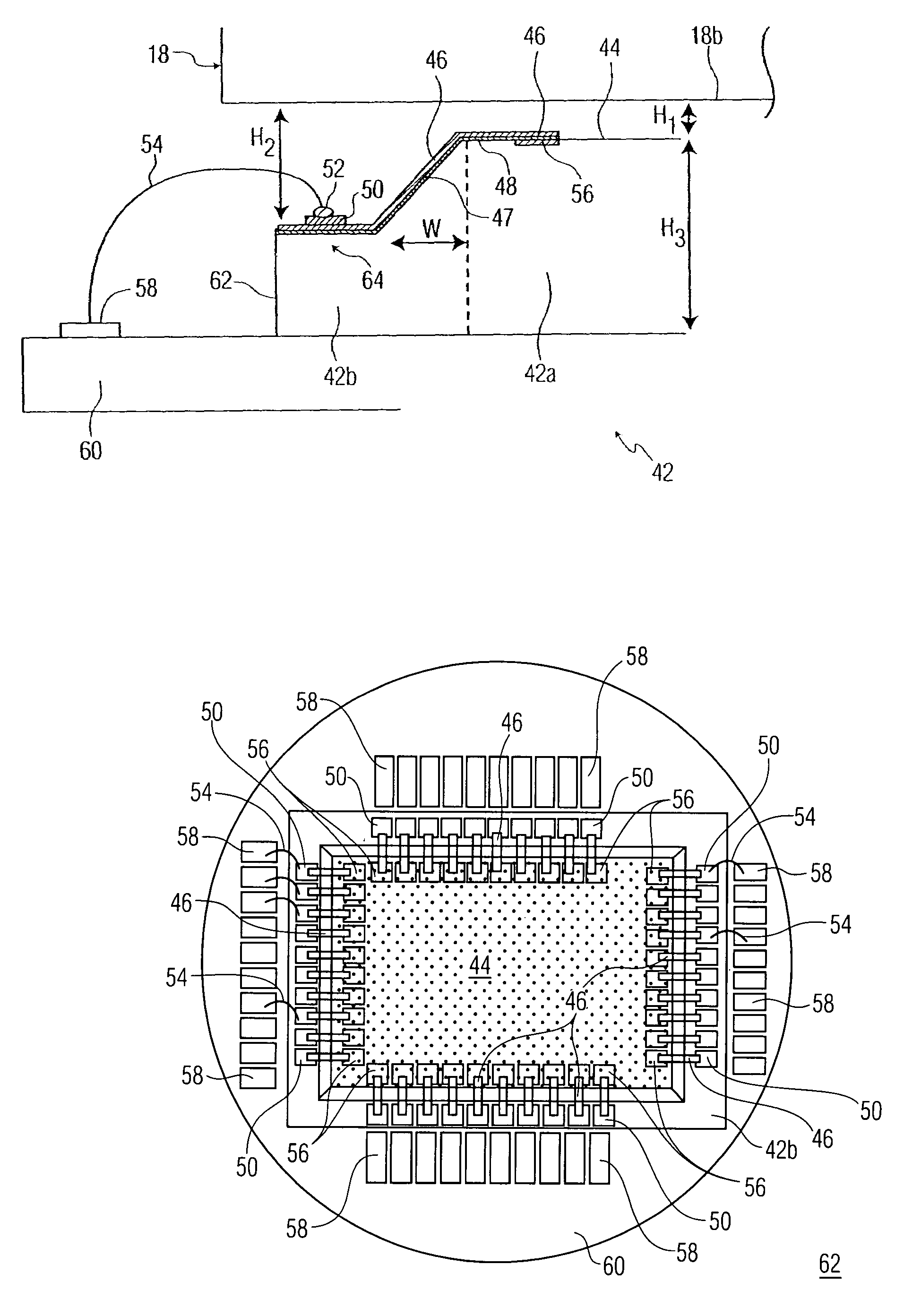
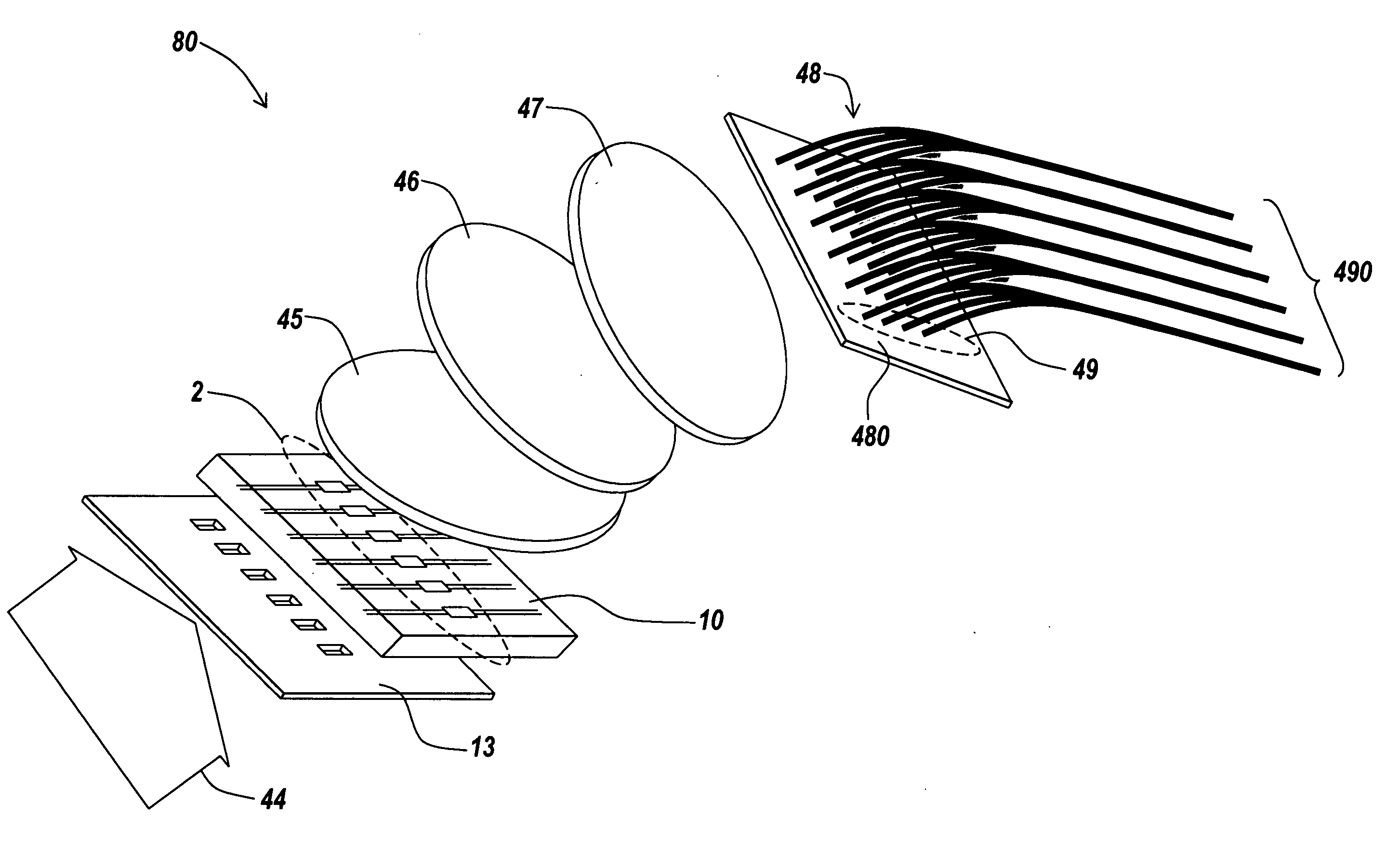
Low profile wire bond for an electron sensing device in an image intensifier tube
An electron sensing device for receiving electrons from an output surface of an electron gain device has a silicon die including an active surface area for positioning below the output surface of an electron gain device. The silicon die also includes a silicon step formed below and surrounding the active surface area, and a first array of bond pads formed on the silicon step for providing output signals from the silicon die. When the electron sensing device is positioned below the electron gain device, a tight vertical clearance is formed between the output surface of the electron gain device and the active surface area of the electron sensing device.
Owner:EXCELIS INC
Wavelength conversion device with avalanche multiplier
InactiveUS20050083567A1Improve device performanceEfficient detectionTelevision system detailsLaser detailsPhotodetectorLength wave
A wavelength conversion device includes a photodetector for generating a photocurrent in response to the detection of radiation at a first wavelength. An avalanche multiplier amplifies the signal photocurrent and feeds this to a light emitting element that produces radiation at a second wavelength shorter than the first wavelength and corresponding to the detected radiation at the first wavelength. The components are assembled together in an integrated stacked arrangement either by epitaxial growth or wafer fusion of the individual components. The device is useful as an image intensifier or thermal imaging device.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Fluoroscopy operator protection device
ActiveUS20090232282A1Patient positioning for diagnosticsX-ray tube vessels/containerX-rayRadiation shield
A radiation protection device attaches to the C-arm of a fluoroscope and shields and collimates the X-ray beam between the X-ray source and the patient and between the patient and the image intensifier. One embodiment has a radiation shield of X-ray opaque material that surrounds the C-arm of the fluoroscopy system, the X-ray source and the image intensifier. A padded slot fits around the patient's body. Another embodiment has conical or cylindrical radiation shields that extend between the X-ray source and the patient and between the patient and the image intensifier. The radiation shields have length adjustments and padded ends to fit the device to the patient. The radiation protection device may be motorized to advance and withdraw the radiation shields. A blanket-like radiation shield covers the patient in the area surrounding where the X-ray beam enters the body.
Owner:RADIACTION
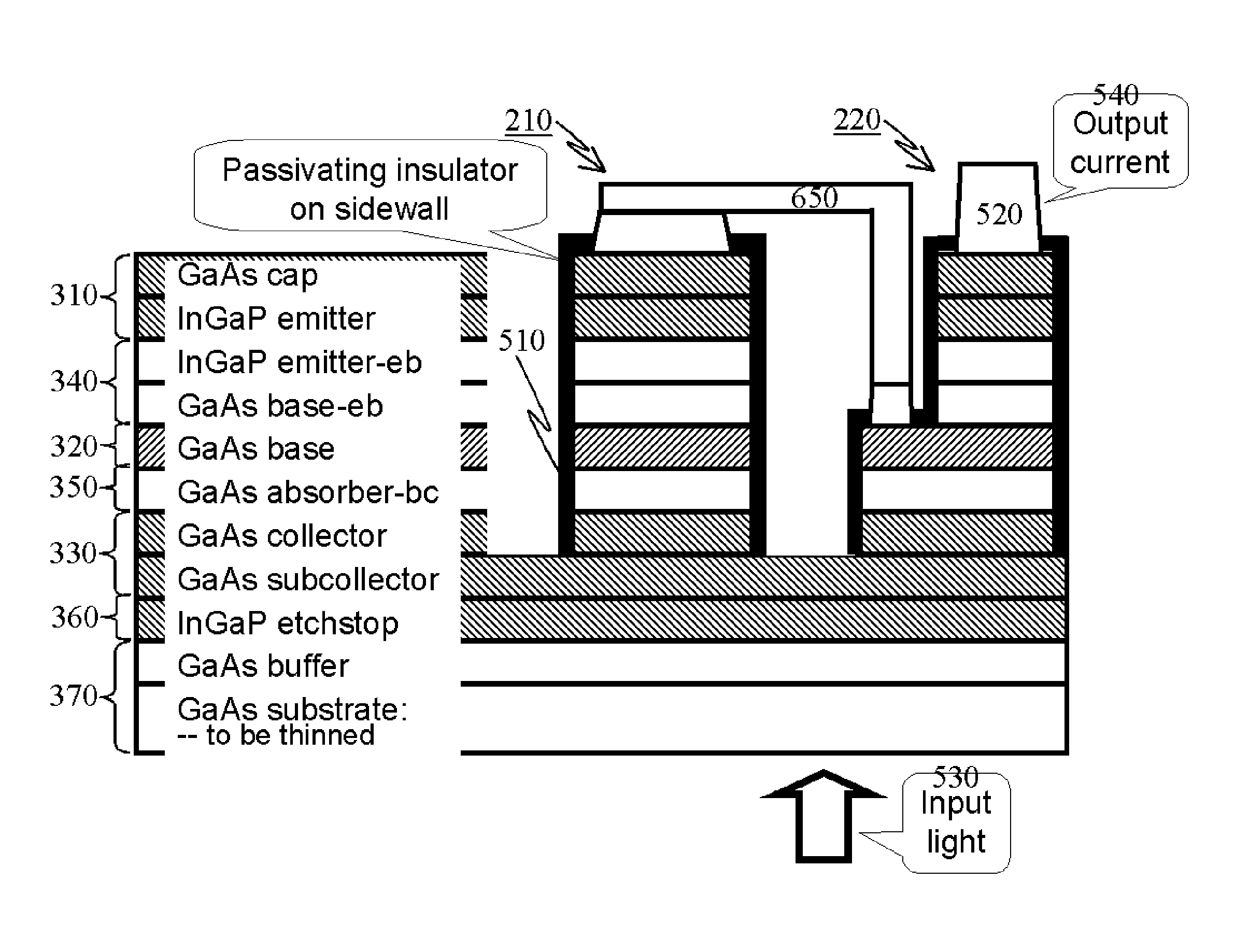
Image intensifier using high-sensitivity high-resolution photodetector array
This invention discloses the design of a semiconductor-based image intensifier chip and its constituent photodetector array device based on sidewall-passivated mesa heterojunction phototransistors (HPTs).
Owner:WAVEFRONT HLDG
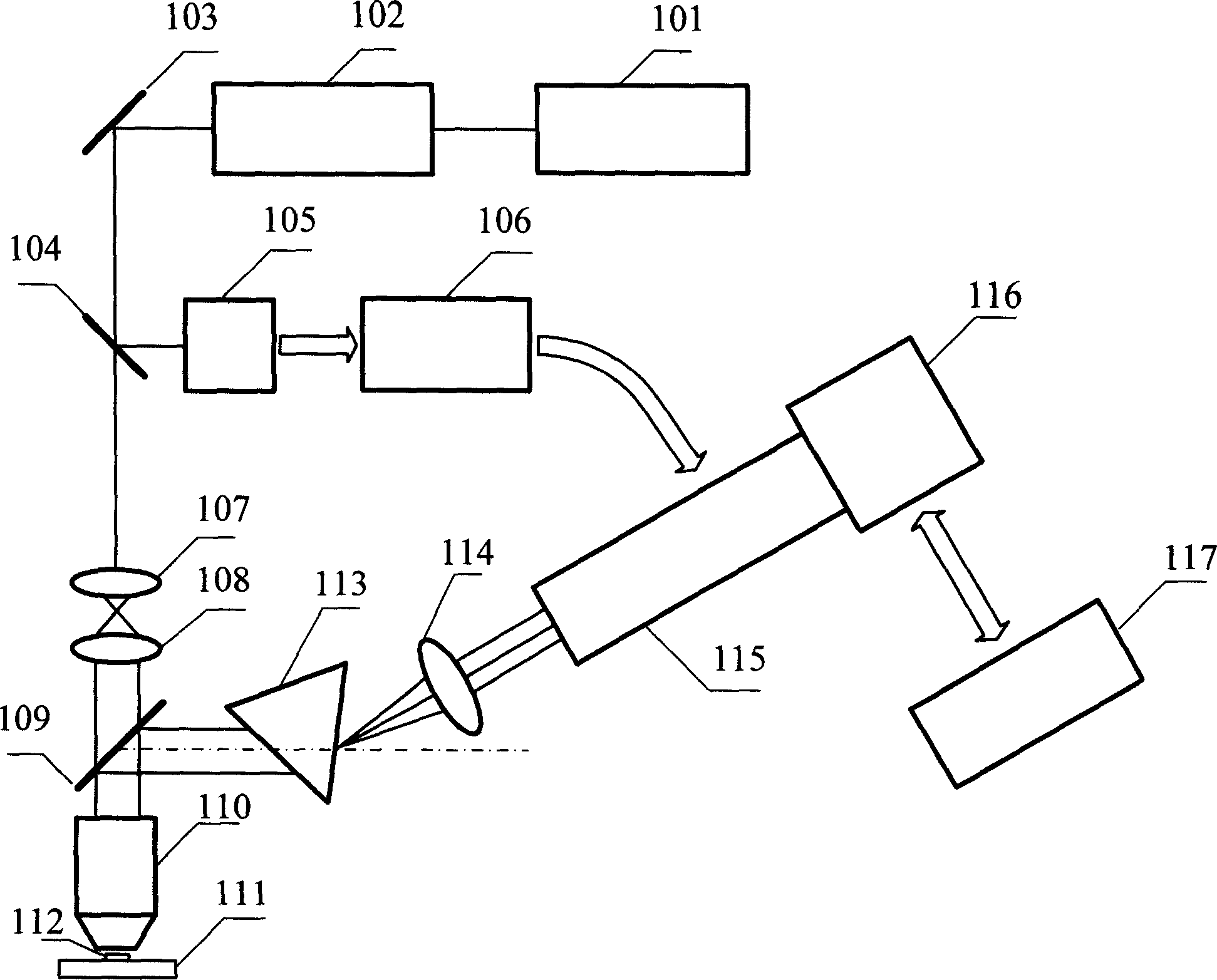
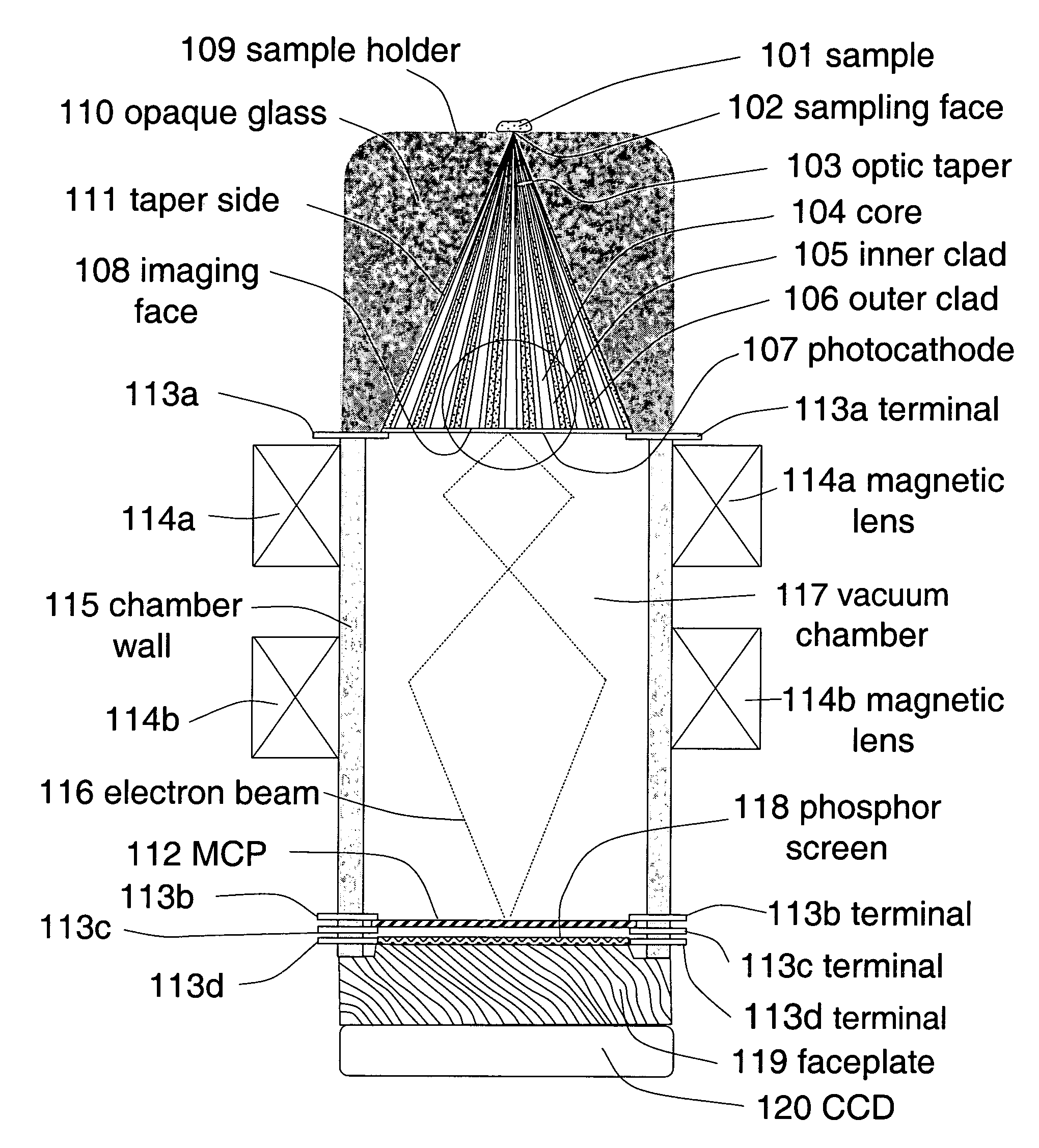
Contact-field optical microscope
InactiveUS7006741B1Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingBundled fibre light guidePhotocathodeOpto electronic
A broad-spectrum, high spatial and time resolution contact-field optical microscope comprises a fiber optical taper, a vacuum chamber, a photocathode, a magnetic lens photoelectron image enlarger, a micro-channel plate image intensifier, a phosphor screen and a CCD. Sample is placed directly in contact with a smaller sampling face of the optical taper. Light which is emitted, reflected or transmitted by the sample is launched into each of the fiber core ends on the sampling face and conveyed by the optical fibers to a larger imaging face of the optical taper, thereby presenting an enlarged image at the imaging face. The image is converted into a photoelectron image by photocathode which is deposited on the surface of the imaging face. The photoelectron image is further enlarged by magnetic lenses and intensified by micro-channel plate. The enlarged and enhanced electron image is displayed on phosphor screen and coupled through faceplate to CCD.
Owner:YU BI
Optical detector for a particle sorting system
ActiveUS20060274313A1Accurate and Efficient MonitoringCost effectivelyRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationData acquisitionPhotodiode
Owner:CYTONOMEST
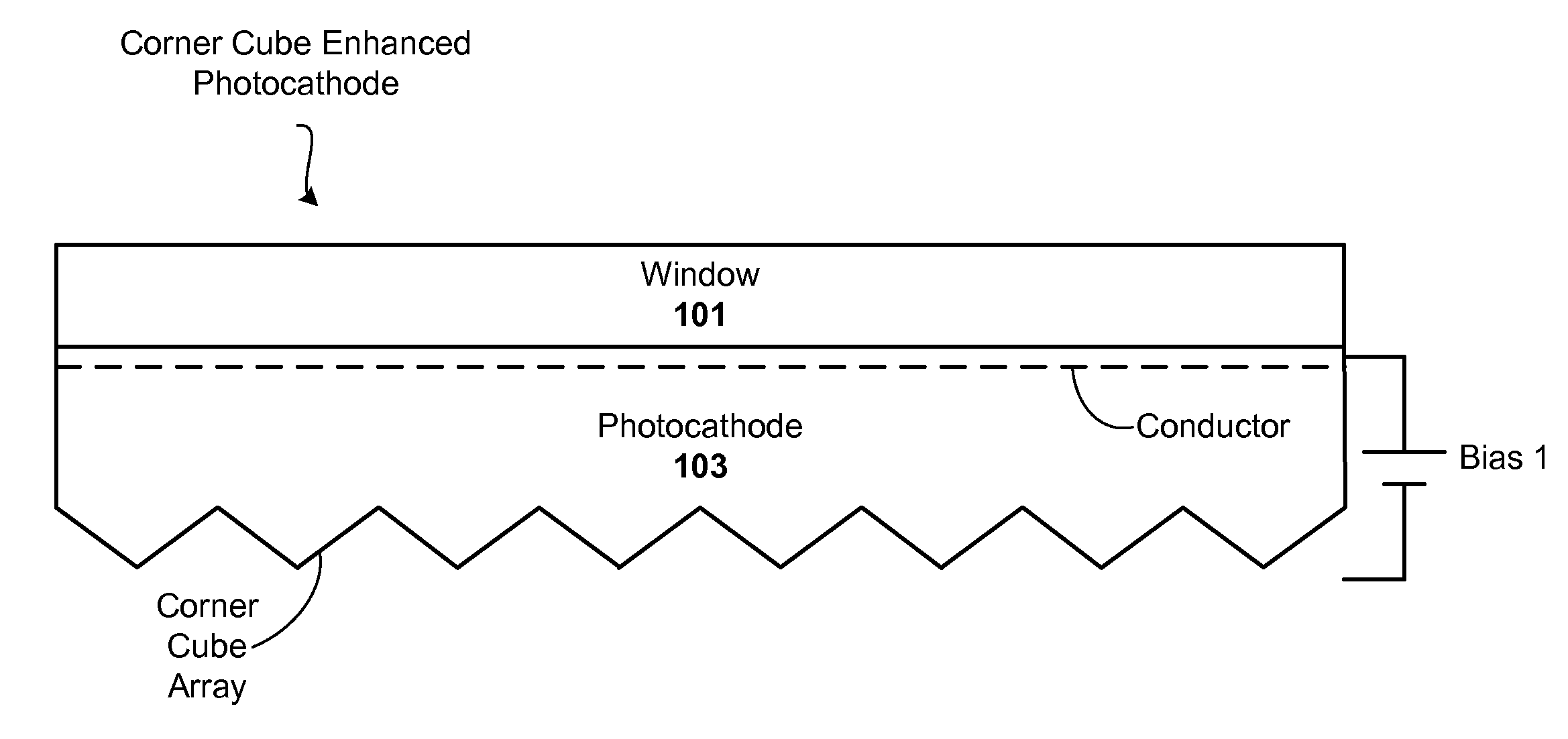
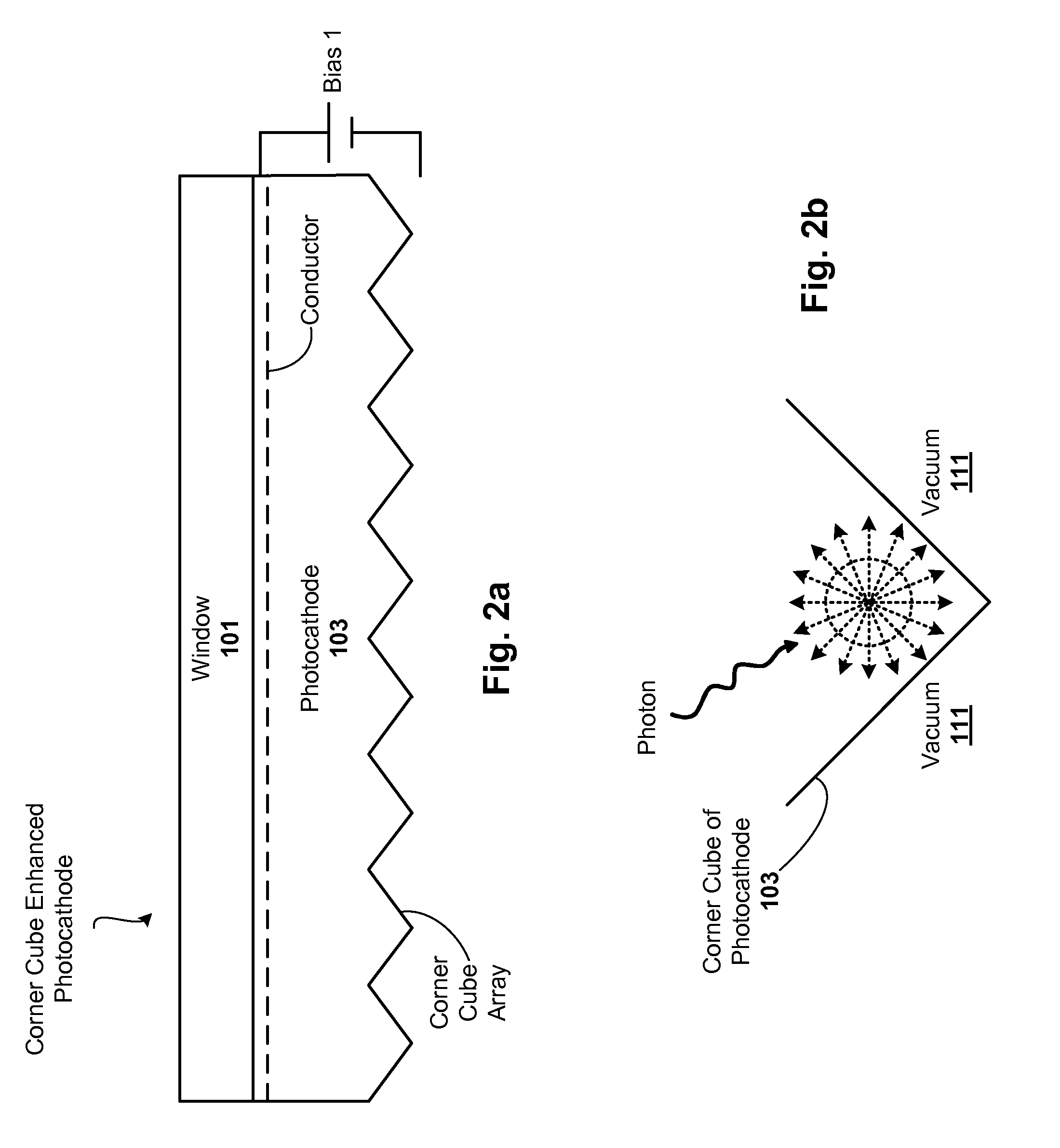
Corner cube enhanced photocathode
ActiveUS20120012811A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhoto-emissive cathodes manufactureQuantum efficiencyPhotocathode
Techniques are disclosed for improving the quantum efficiency of photocathode devices. The techniques allow for an increase in the optical thickness of the photocathode device, while simultaneously allowing for an increase in the probability of electron escape into the vacuum of the device. The techniques are particularly useful in detector and imaging. In one embodiment, a photocathode device is provided that has an array of corner cubes fabricated in a surface of the photocathode. The corner cube array is made of the same material as the photocathode layer. The device may be, for example, a detector or image intensifier that operates in the UV, visible, and IR light spectrums, and may further include a gain medium, anode, and readout device. Techniques for forming the device are also provided.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Optical detection device for corona discharge
InactiveCN101706548AEasy for quantitative analysisLow visible light transmittance requirementTesting dielectric strengthFault locationCamera lensSignal processing circuits
The invention discloses an optical detection device for corona discharge. An atmospheric ultraviolet window band imaging detection optical path thereof comprises a stray light shield, an atmospheric ultraviolet window band ultraviolet lens, an atmospheric ultraviolet window band band-pass ultraviolet filter, an ultraviolet image intensifier, a light cone, a CCD or CMOS area array image sensor, an image processing circuit and a first liquid crystal display which are arranged in sequence. A solar blind ultraviolet band non-imaging detection optical path thereof comprises a total emission mirror, a spectroscope, a solar blind ultraviolet band-pass filter, a solar blind ultraviolet lens, a multiplier phototube, a signal processing circuit module and a second liquid crystal display. The device has the main advantages that the corona detection data is more complete and reliable, and the failure level of corona discharge and discharge degree are convenient to be analyzed.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Advanced Image Intensifier Assembly
InactiveUS20090108180A1Function increaseImprove abilitiesMultiplier cathode arrangementsMultiplier circuit arrangementsPhotocathodeElectromagnetic interference
An advanced image intensifier assembly provides enhanced functionality. A grounded photocathode provides shielding from electromagnetic interference, improving the ability to work in multiple light conditions. Bi-directional wireless communication and non-volatile storage allow critical information to be permanently stored and read wirelessly at a scanning station, easing in identification of units. Because bi-directional communication components can be embedded within an image intensifier assembly, existing end-user night vision devices can be upgraded by simply replacing the image intensifier assembly. For enhanced safety, a programmable shutdown capability is provided. This renders the device inoperative in the absence of continuous input, either wireless or manual, from an authorized operator, thus rendering the device useless if captured by enemy combatants. Finally, direct 1-volt operation enables the device to be powered by, for example, a single AA battery.
Owner:SALDANA MICHAEL R
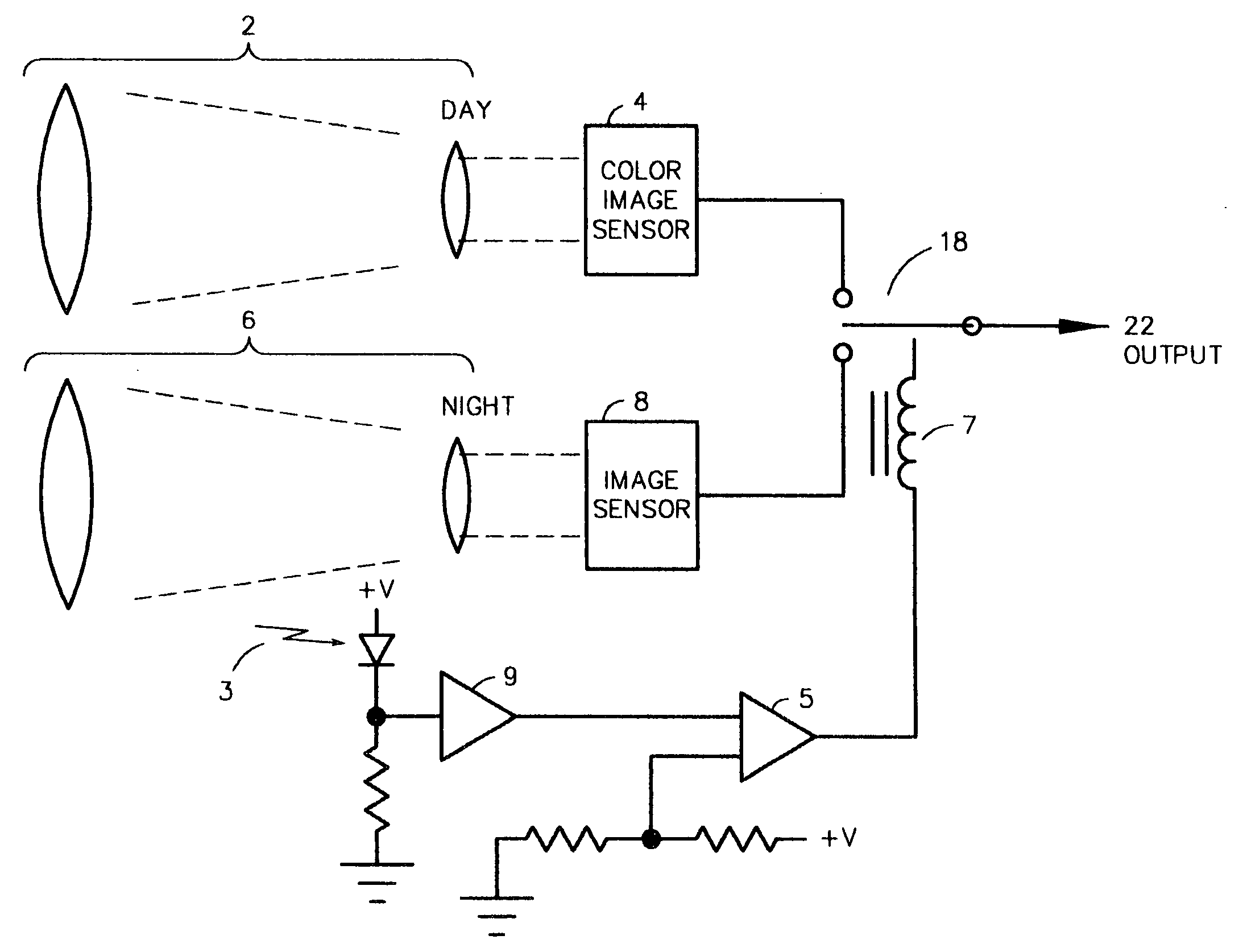
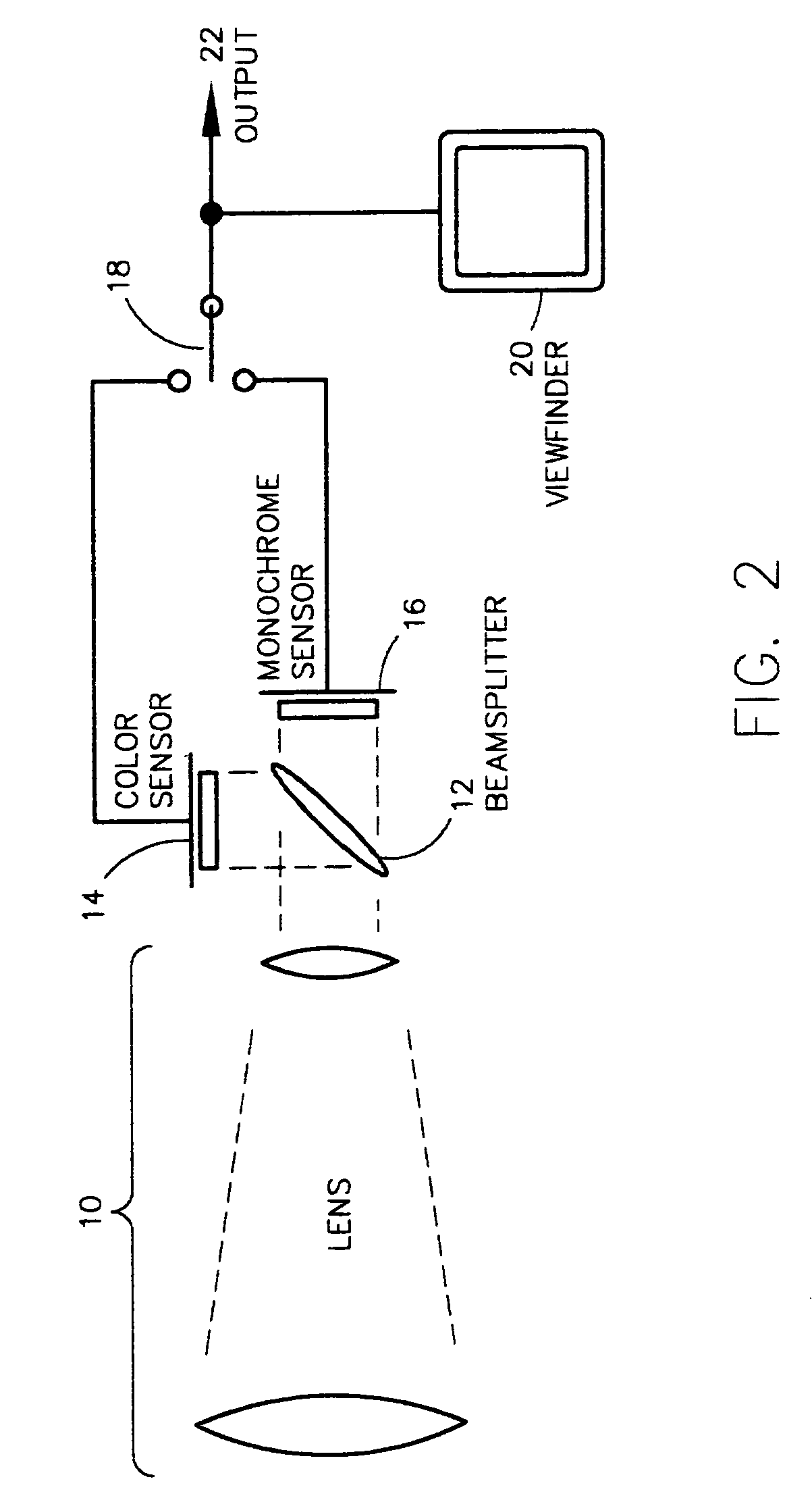
Dual-mode camera
InactiveUS20070052810A1Effectively overcomes sizeEffectively overcomes weightTelevision system detailsCamera body detailsCamera lensColor image
Owner:PR NEWSWIRE
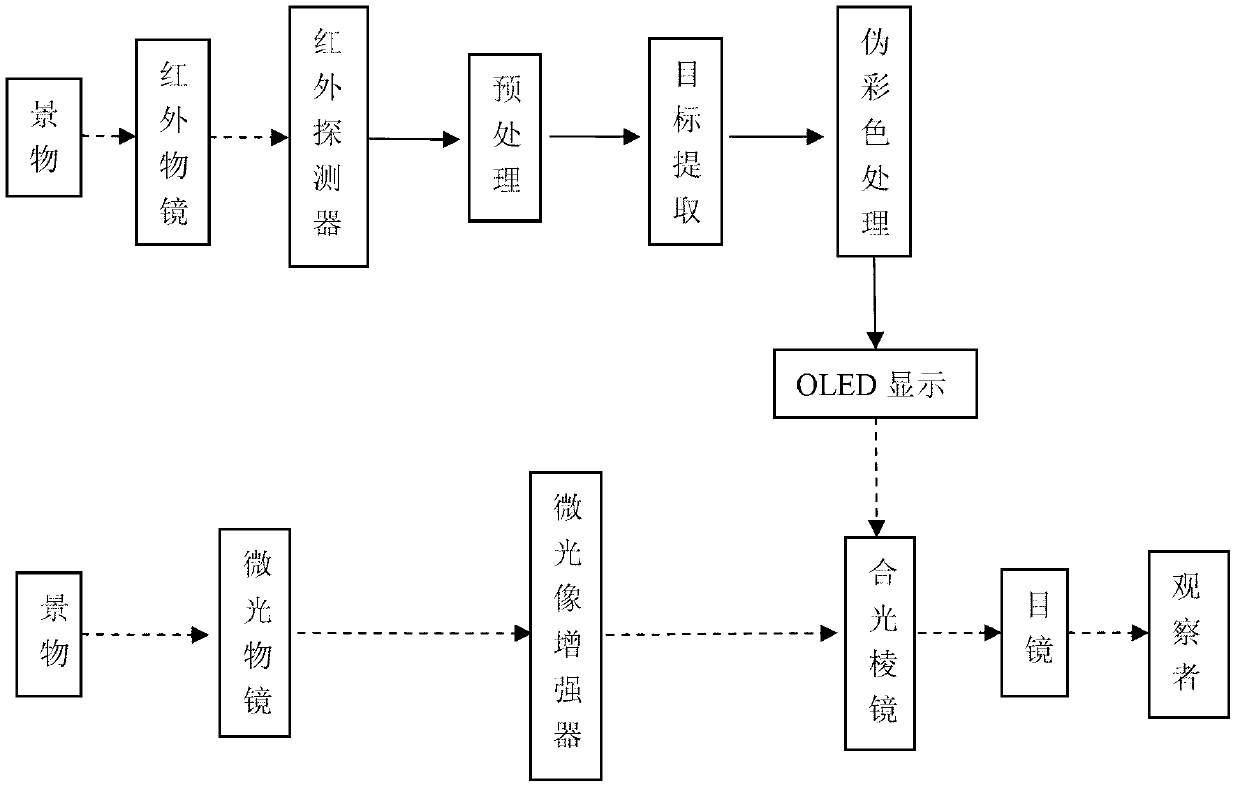
Infrared/ glimmer image fusion night vision system
The invention discloses an infrared / glimmer image fusion night vision system, which consists of a glimmer object glass group, a glimmer image intensifier, an infrared object glass group, an uncooling long-wave infrared detector, an image processing circuit module, an electric signal transmission line, an OLED (organic light emitting diode) minitype display, an integrated optical prism and an eye lense system. The night vision system takes a glimmer image as the background, and the image fusion of a glimmer channel and an infrared channel is realized in a mode that a pseudo-color infrared target is optically projected. In order to obtain the good image fusion effect, the glimmer object glass group and the infrared object glass group both satisfy one time of magnifying power; an infrared image is subjected to denoising and enhancing pretreatments, target extraction and the electronic registration of the image; and then, a gray level image is subjected to pseudo-color treatment and is then output to the OLED minitype display for color display. The fused image has a clear glimmer background and an outstanding infrared target. The night vision system has the advantages of small size and light weight, can work for a long time and is especially suitable for night vehicle driving and for a single person to carry, observe and use.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PHYSICS
Movement compensation method of surgical robot for positioning and guiding for bone surgery
InactiveCN104799933AQuick positioning guideAccurate positioning guideOsteosynthesis devicesSurgical operationX-ray
The invention provides a movement compensation method of a surgical robot for positioning and guiding for bone surgery, and belongs to the technical field of CAD minimally invasive bone surgery treatment. The method is characterized in that a target cover fixed on an image intensifier of a C-shaped arm X-ray machine replaces the traditional three-dimensional calibration frame, so that the operation time and radiation quantity can be reduced; meanwhile, a tracer fixed on the target cover is used for acquiring the image exterior perspective parameters of the C-shaped arm X-ray machine through an optical positioning subsystem; the DLT method is adopted to solve the interior perspective parameters; the route is planned and reconstructed according to the pole line geometric principle and binocular vision algorithm; the tracers are also fixed on a patient and a double-plane surgical robot and used for tracking the location; therefore, a spatial coordinate transmission relationship among the image, the target cover, the patient and the double-plane surgical operator is built; the spatial transformation matrix is utilized to solve the problem of dynamic coordinate error caused by opposite movement of the double-plane surgical robot and the patient while reducing the surgical operation time and the radiation quantity on the basis of automatic accurate positioning of the traditional double-plane surgical robot.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and system thereof for measuring time of exposure of door-control type image intensifier
InactiveCN101644887AThe test data is accurateOptical apparatus testingPhotographyUltra high speedLaser array
The invention provides a method and a system thereof for measuring the time of exposure of a door-control type image intensifier, which are suitable for measuring the time of exposure of various ultra-high speed photoelectric cameras adopting the door-control type image intensifier as a shutter. The method adopts picosecond (ps) pulsed laser for illumination, n times n pieces of optical fibers thelength of which is distributed in an equidifferent way form a laser array with n times n points in the way of delay, the laser array is regarded as a shoot target and is imaged on the door-control type image intensifier by an objective lens, the door-control type image intensifier outputs an image, the image is coupled with a CCD camera, the CCD camera records the quantity of the shot laser arraypoints, the space number of the laser points is calculated and then times time interval so as to obtain the time of exposure of the door-control type image intensifier. The invention can be directlyused for marking the time of exposure of ultra-high speed photoelectric framing cameras, and has broad application prospect in the field of researching the door-control type image intensifier as wellas in the measurement of time of exposure of the ultra-high speed photoelectric framing cameras.
Owner:INST OF FLUID PHYSICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Modular panoramic night vision goggles
InactiveUS7072107B2Lower performance requirementsPrecise alignmentTelevision system detailsColor television detailsNight visionOptical Module
A modular binocular-like vision assembly (300) has individual interconnecting inner (320, 330) and outer (310, 340) optical modules. Each module is separately sealed and self-contained and includes image intensifier means for converting incoming light to an intensified visible image for presentation to the eyes of the observer in low light conditions. Electrical connectors are provided between the modules for permitting free flow of electrical power and information between the modules. Attaching system is provided for removably attaching the outer modules to the inner modules to deliver a panoramic field of vision and removal of any single module from the assembly will not break any pressure seals or degrade the optical performance of the removed module or the remaining modules.
Owner:NIGHT VISION CORP +1
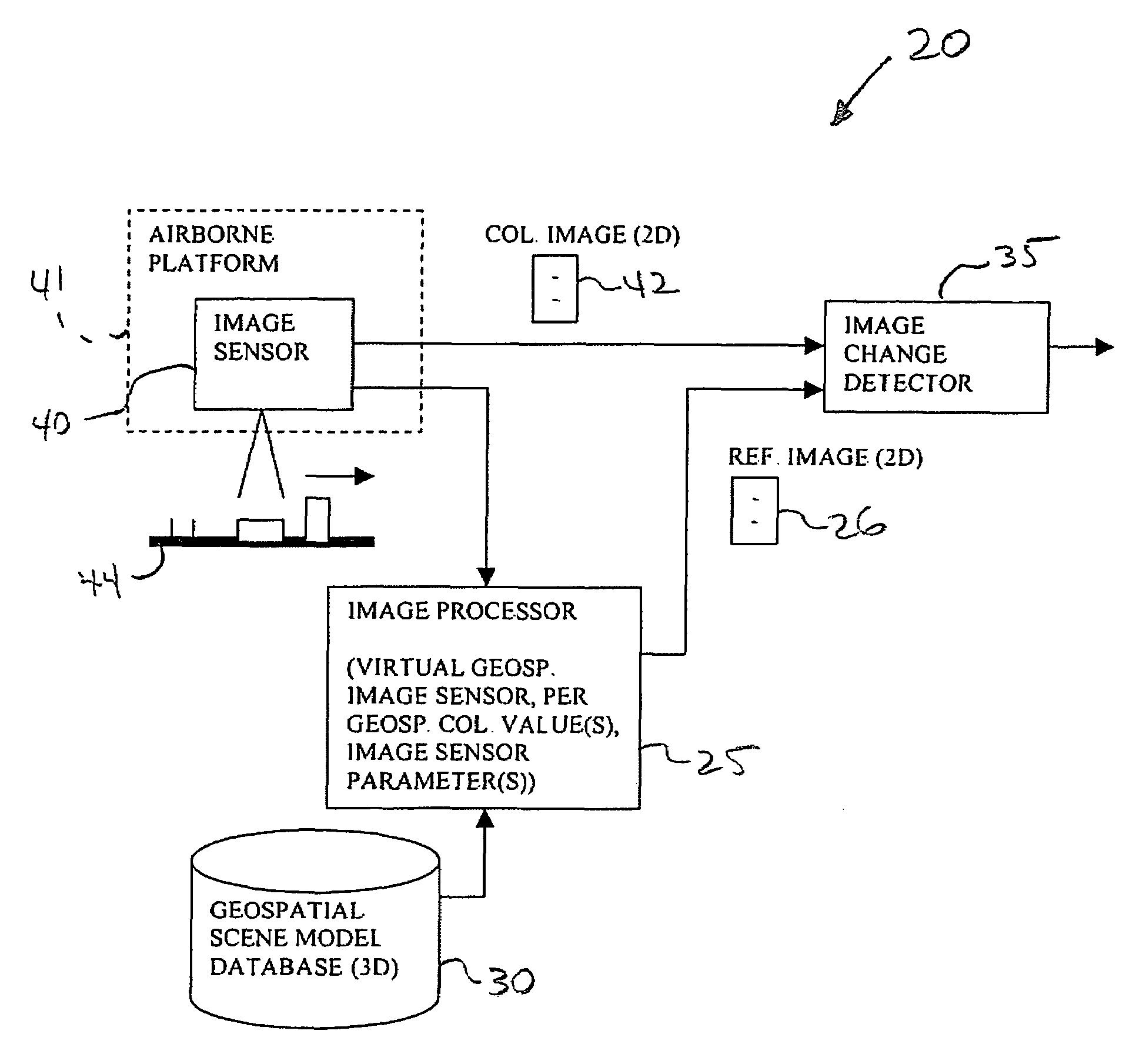
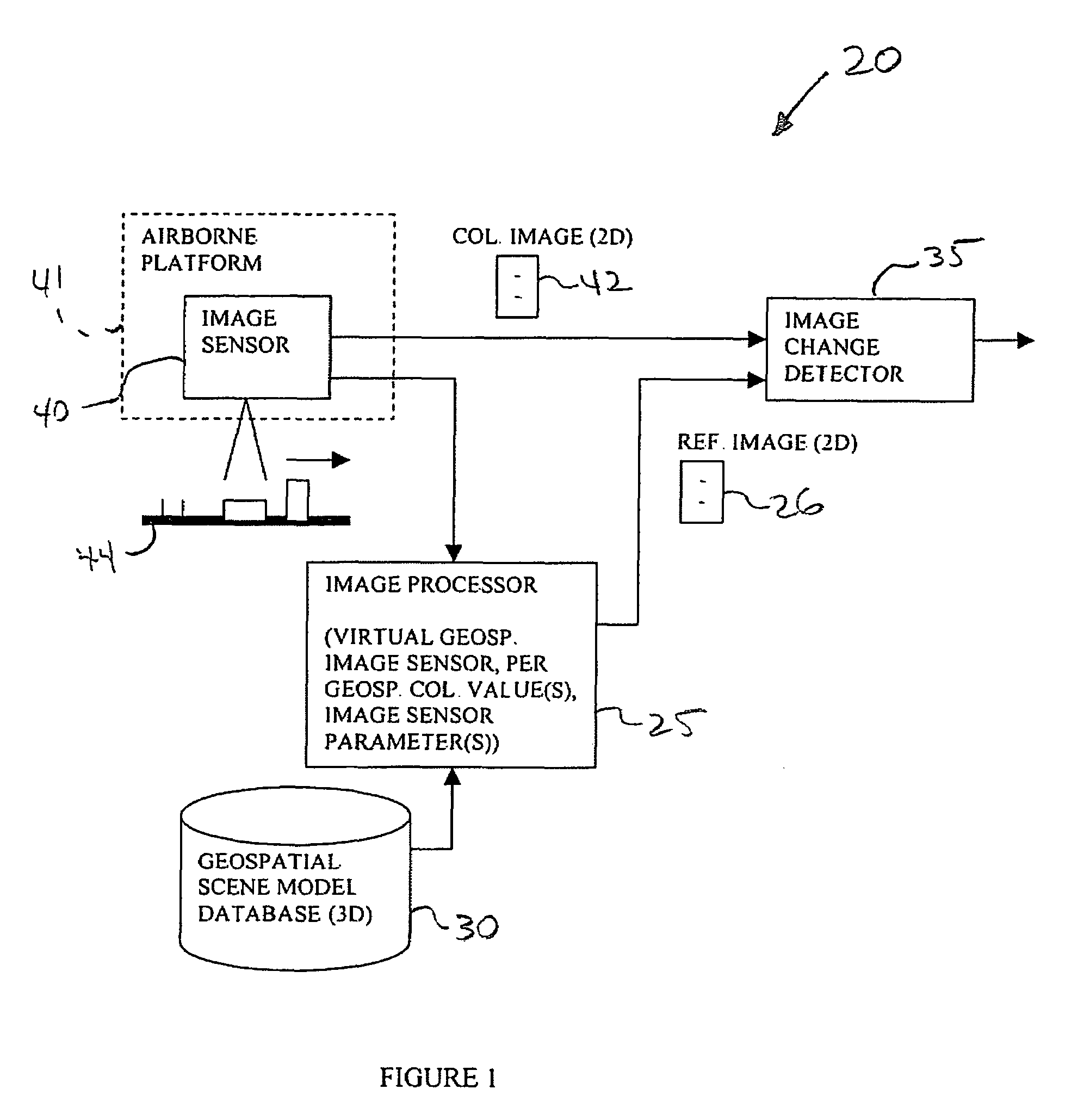
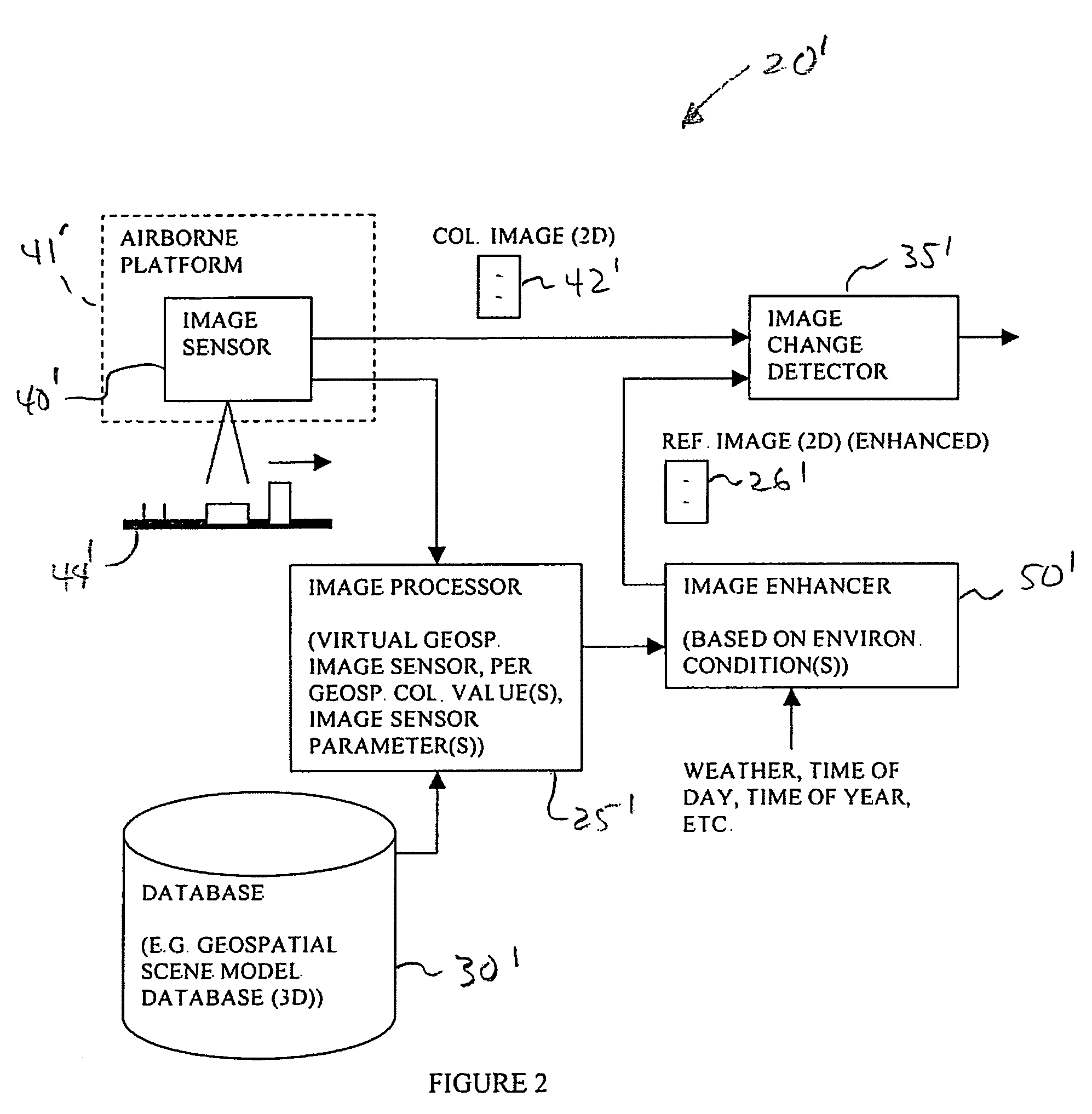
Geospatial image change detecting system with environmental enhancement and associated methods
InactiveUS7603208B2Improve accuracyEasy to operateImage enhancementImage analysisTime of dayImage processor
An image change detecting system may include an image processor cooperating with the database for generating a reference geospatial image corresponding to the collected geospatial image, an image enhancer for enhancing at least one of the reference geospatial image and the collected geospatial image based upon at least one environmental condition, and a change detector cooperating with the image processor and the image enhancer. The change detector may detect a change between the collected geospatial image and the reference geospatial image with at least one thereof enhanced by the image enhancer based upon the at least one environmental condition. The environmental condition may include a weather condition, a time of day, or a time of year. The environmental condition may be typically associated with the collected geospatial image.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
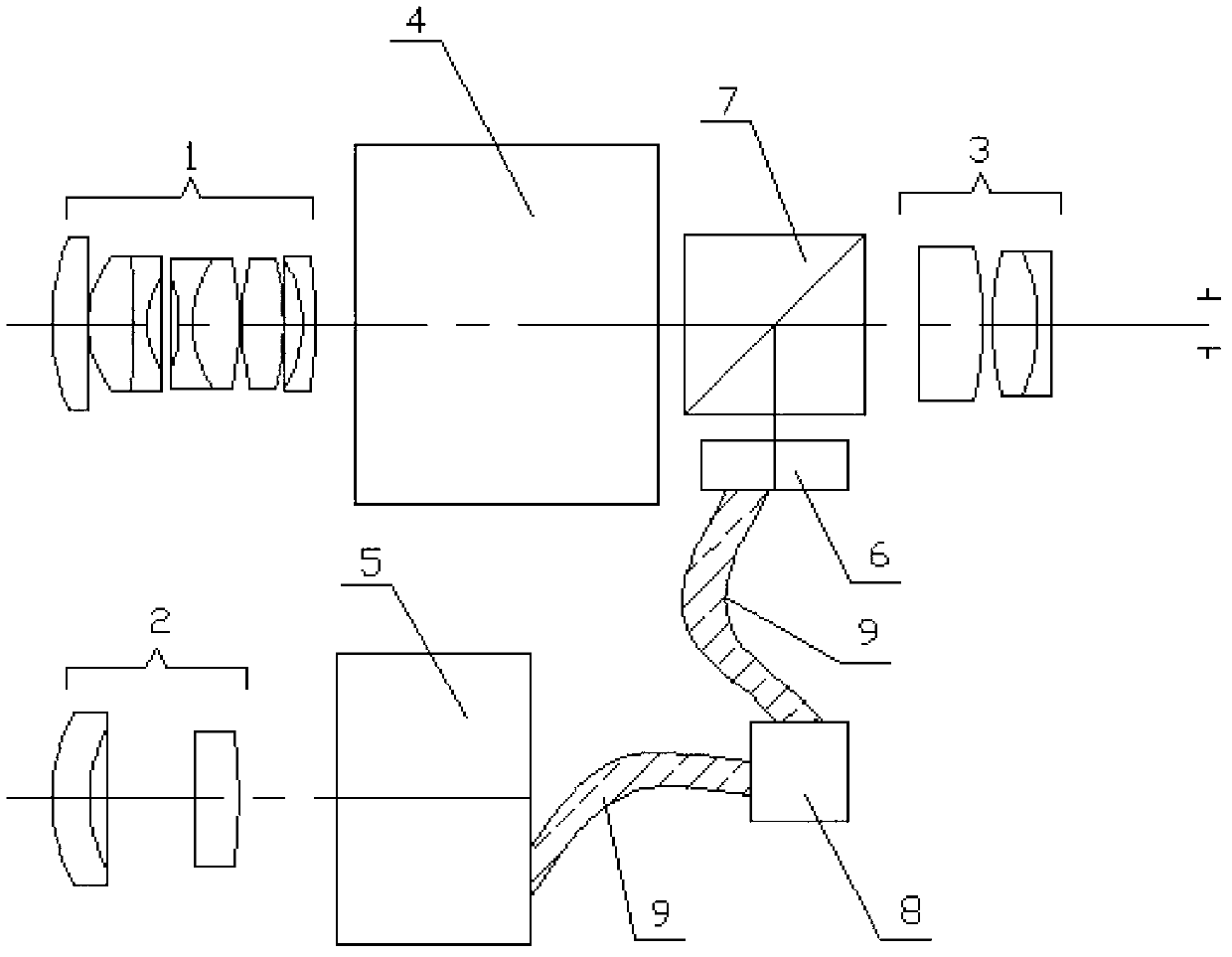
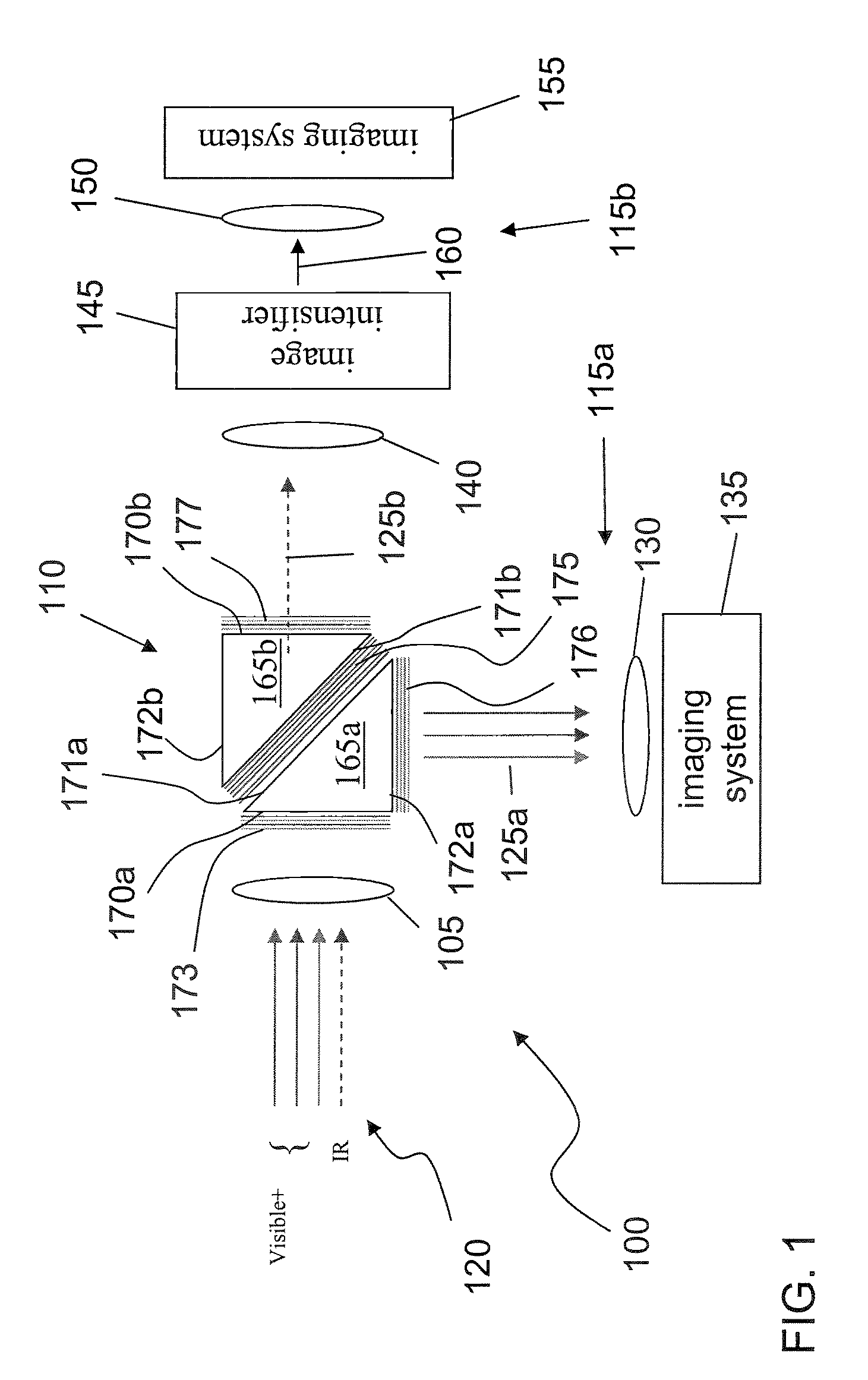
Imaging system
InactiveUS20080237771A1Extended service lifeAvoid lostTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesSpectral bandsPhotocathode
A viewing system configured to combine multiple spectral images of a scene, the system includes a spectral beam separator configured to split an incoming beam of radiation into a first and a second beam of radiation, the first beam of radiation including radiations substantially in a first spectral band and the second beam of radiation including radiations substantially in a second spectral band; an image intensifier configured to intensify the second beam of radiation, the image intensifier including a photocathode configured to produce a flux of photoelectrons with substantially increased efficiency when exposed to the second beam of radiation, the photocathode constructed and arranged to substantially absorb all the radiations in the second beam of radiation; a current amplifier configured to amplify the flux of photoelectrons; and a display system configured to display an image of the scene in the second spectral band based on the amplified flux of electrons simultaneously with an image of the scene in the first spectral band.
Owner:SUBRAHMANYAM PILLA
X-ray detector including scintillator, a lens array, and an image intensifier
ActiveUS20100140487A1Material analysis by optical meansTomographyOptical radiationSolid state detector
An X-ray detection device including a scintillator configured to convert gamma rays or X-rays into optical radiation, an optical image intensifier configured to intensify the optical radiation to generate intensified optical radiation, an optical coupling system configured to guide the intensified optical radiation, and a solid state detector configured to detect the intensified optical radiation to generate an interaction image representing an X-ray energy emission and to perform photon counting based on data of the interaction image.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Color translating UV microscope
A color translating UV microscope for research and clinical applications involving imaging of living or dynamic samples in real time and providing several novel techniques for image creation, optical sectioning, dynamic motion tracking and contrast enhancement comprises a light source emitting UV light, and visible and IR light if desired. This light is directed to the condenser via a means of selecting monochromatic, bandpass, shortpass, longpass or notch limited light. The condenser can be a brightfield, darkfield, phase contrast or DIC. The slide is mounted in a stage capable of high speed movements in the X, Y and Z dimensions. The microscope uses broadband, narrowband or monochromat optimized objectives to direct the image of the sample to an image intensifier or UV sensitive video system. When an image intensifier is used it is either followed by a video camera, or in the simple version, by a synchronized set of filters which translate the image to a color image and deliver it to an eyepiece for viewing by the microscopist. Between the objective and the image intensifier there can be a selection of static or dynamic switchable filters. The video camera, if used, produces an image which is digitized by an image capture board in a computer. The image is then reassembled by an overlay process called color translation and the computer uses a combination of feedback from the information in the image and operator control to perform various tasks such as optical sectioning and three dimensional reconstruction, coordination of the monochromater while collecting multiple images sets called image planes, tracking dynamic sample elements in three space, control of the environment of the slide including electric, magnetic, acoustic, temperature, pressure and light levels, color filters and optics, control for microscope mode switching between transmitted, reflected, fluorescent, Raman, scanning, confocal, area limited, autofluorescent, acousto-optical and other modes.
Owner:1192062 ALBERTA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com