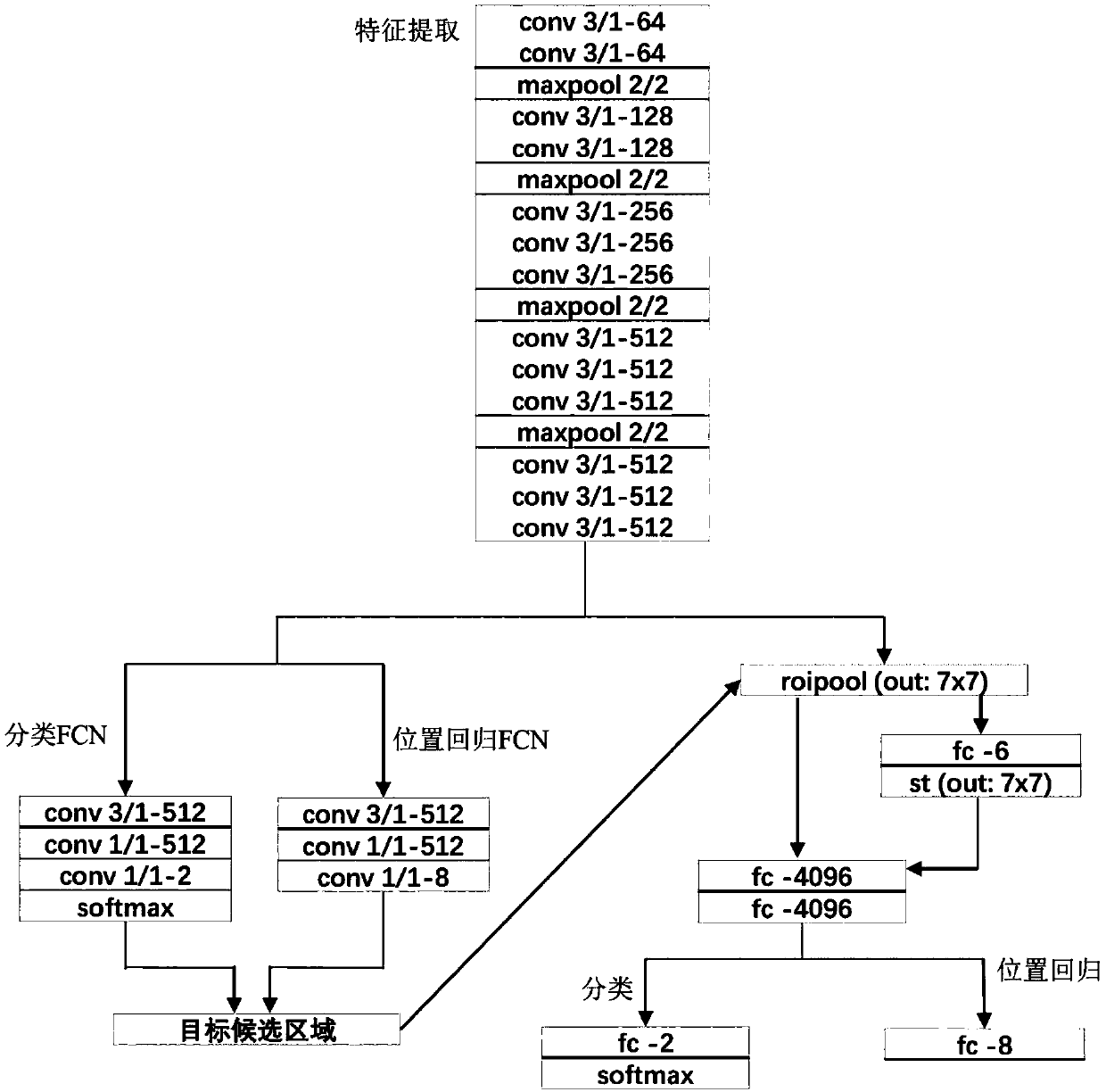
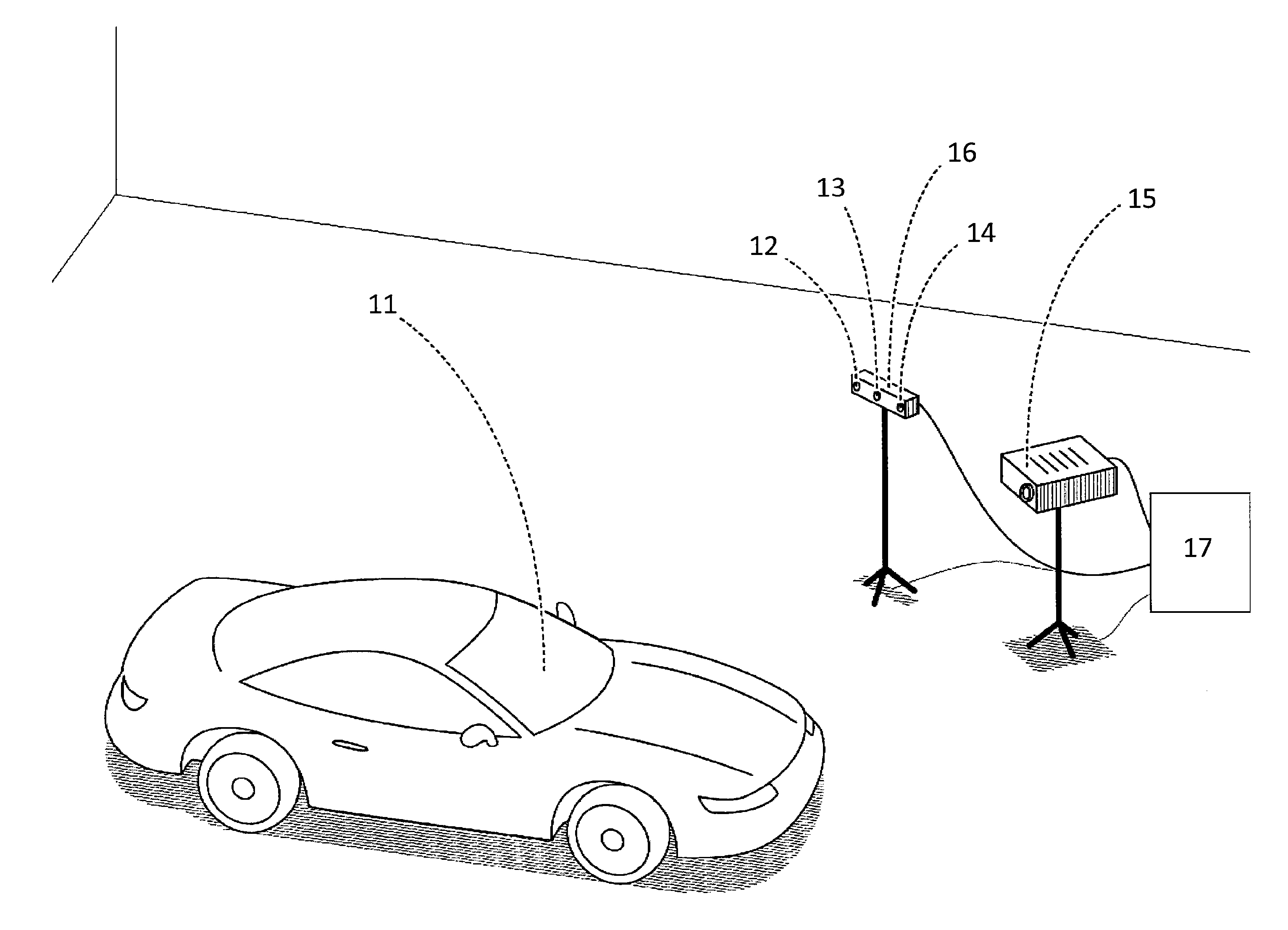
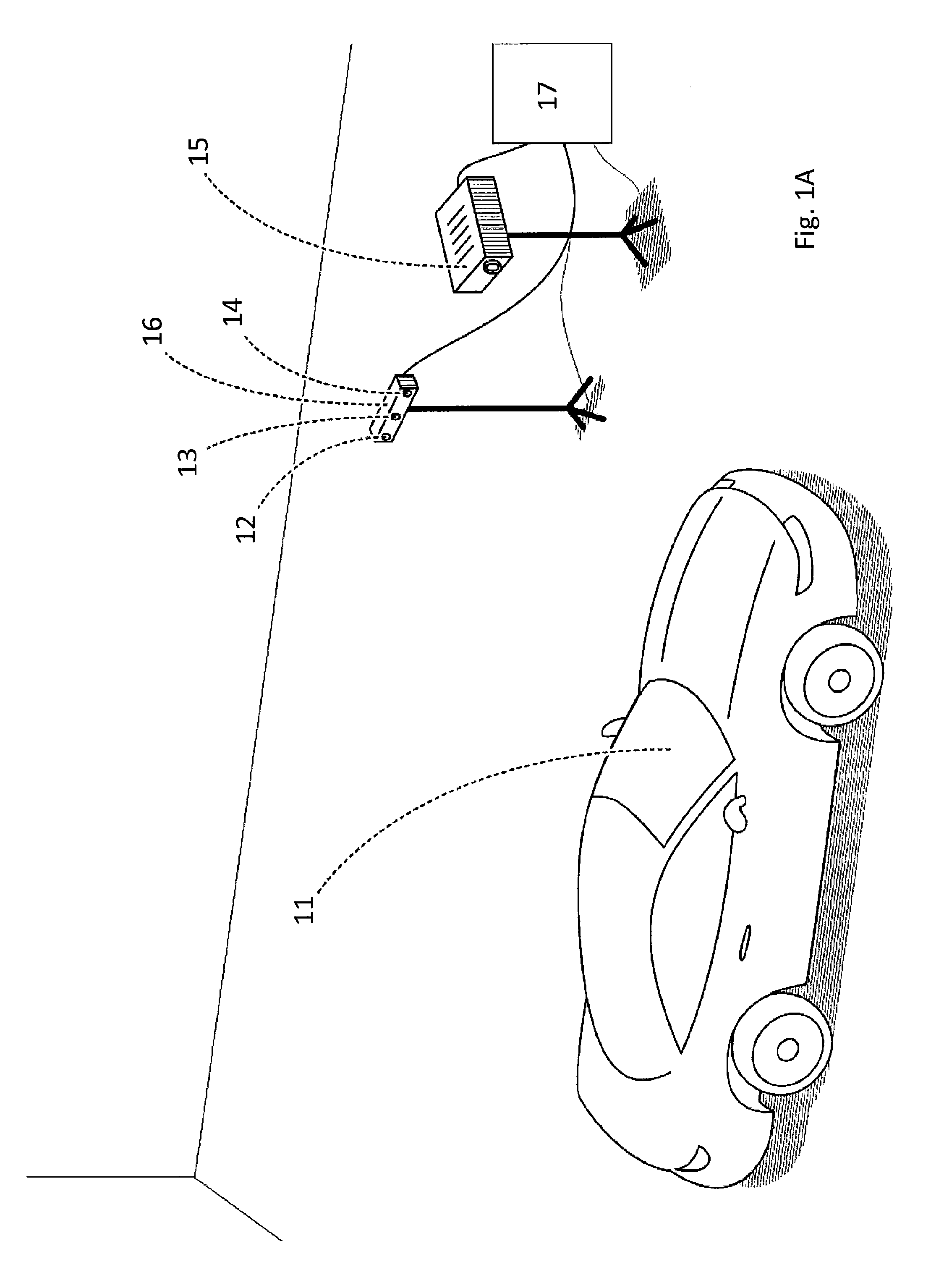
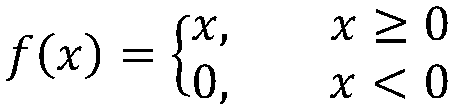Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
652 results about "Spatial transformation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
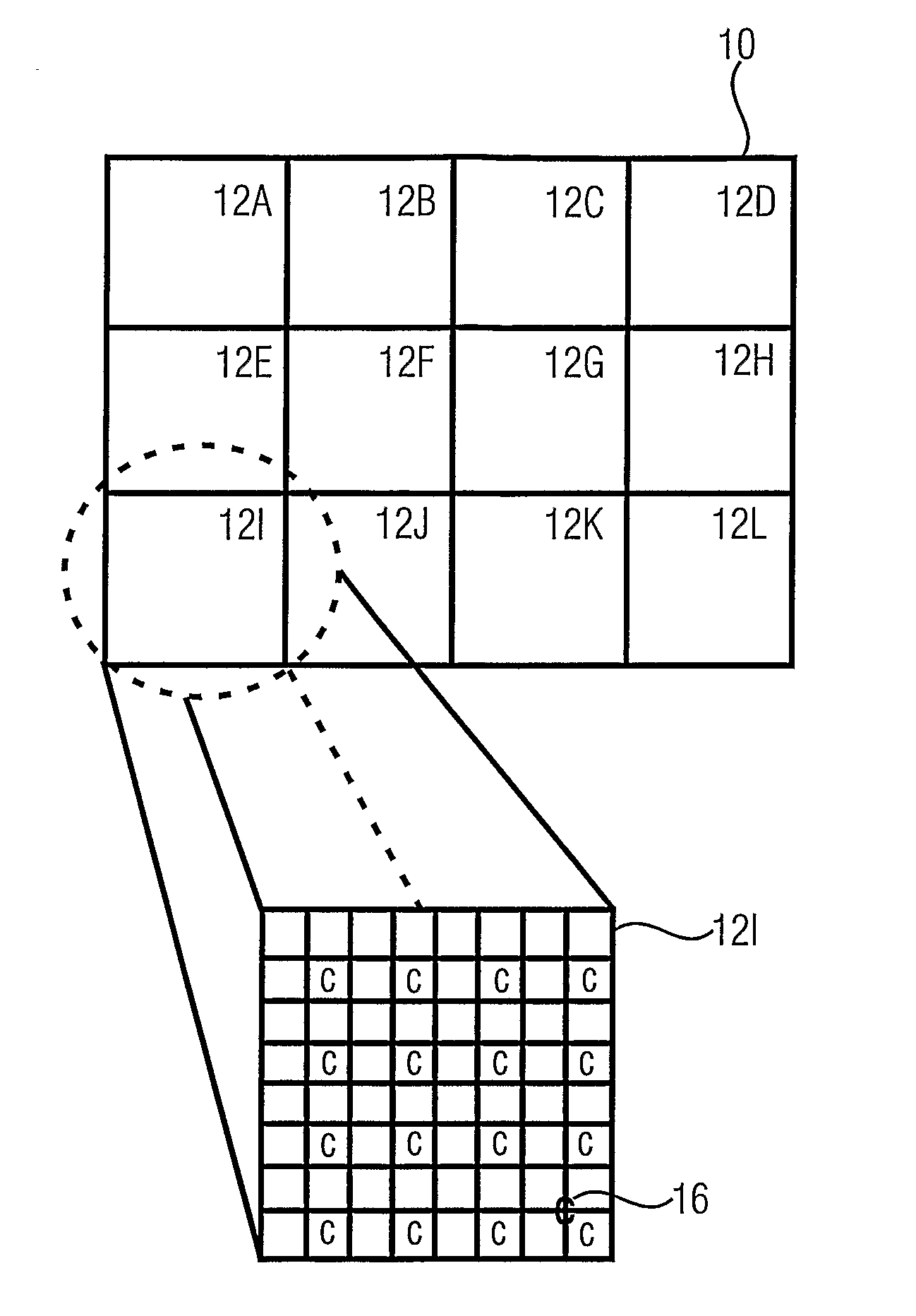
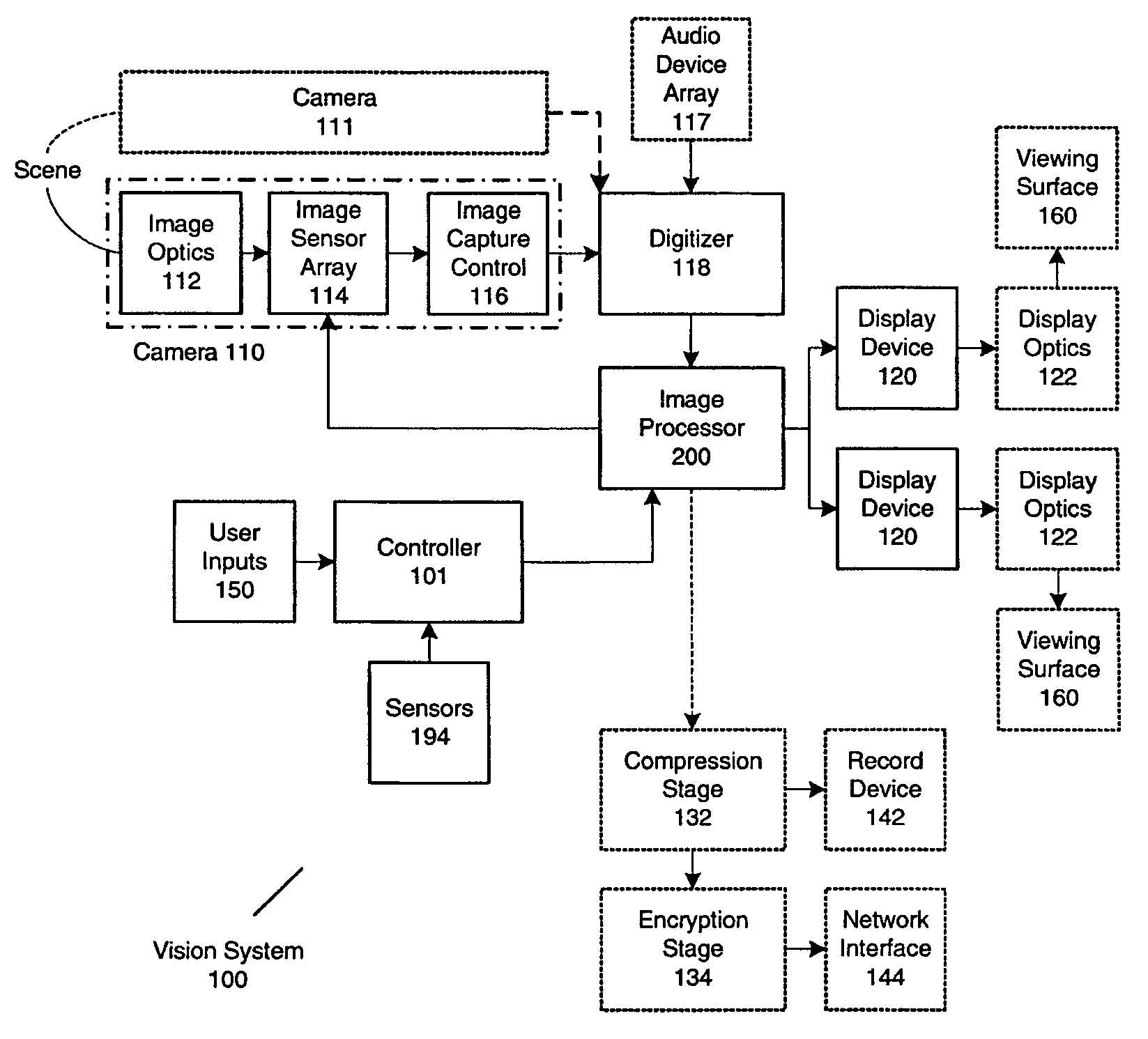
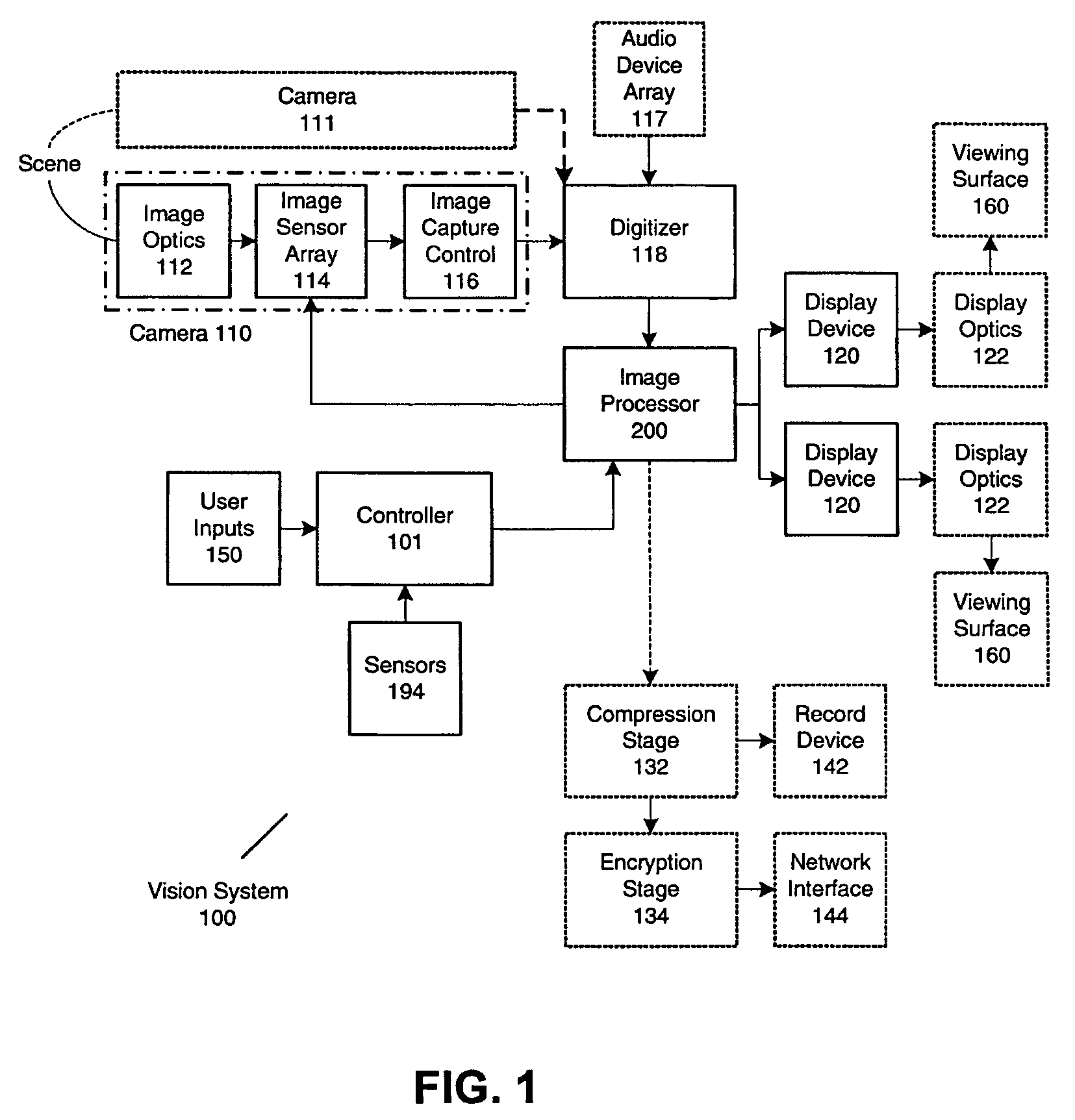
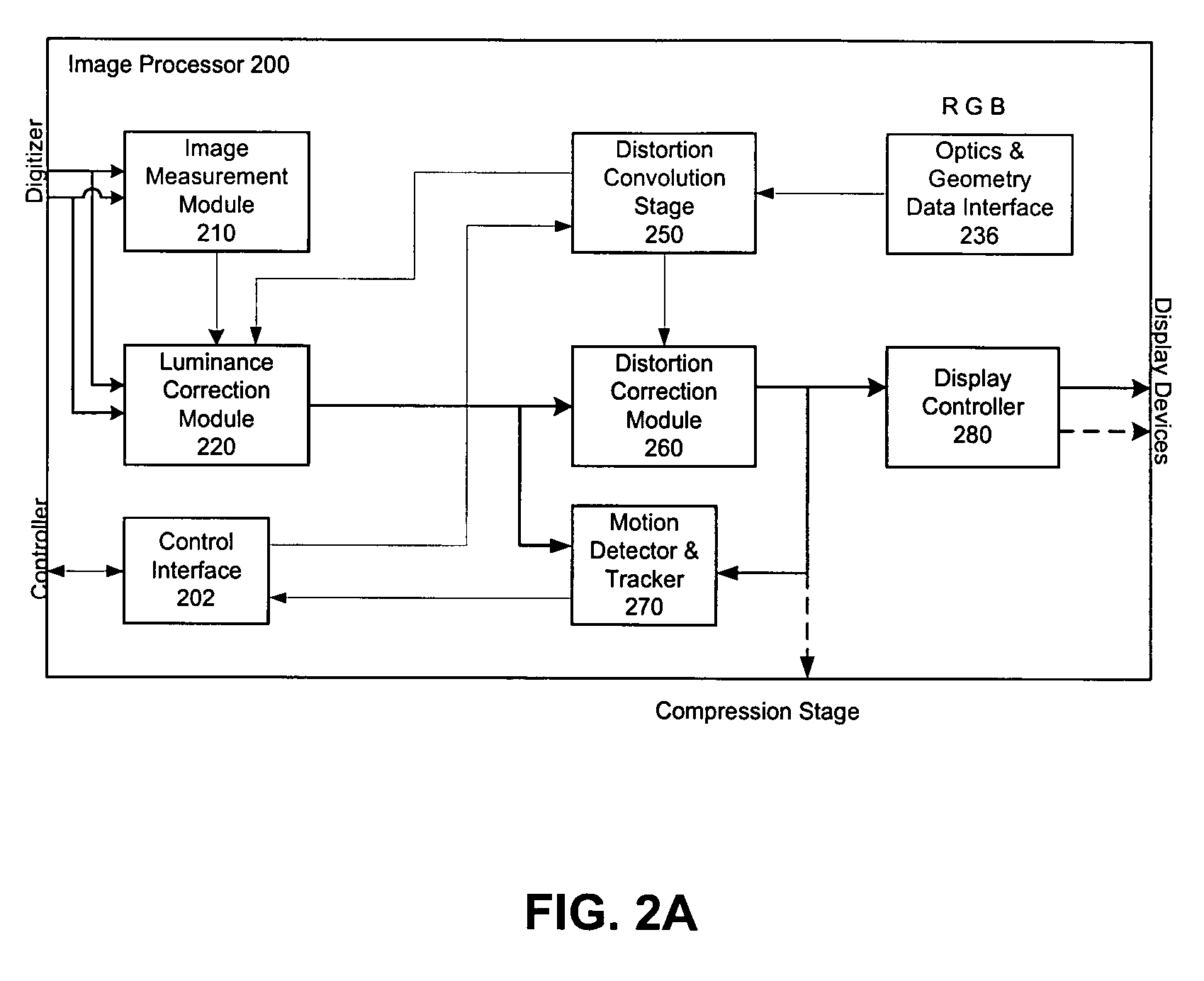
Spatial Transformation. Abstract. A spatial transformation of an image is an alteration that changes the image’s orientation or ‘layout’ in the spatial domain. Spatial transformations change the position of intensity information but, at least ideally, do not change the actual information content.
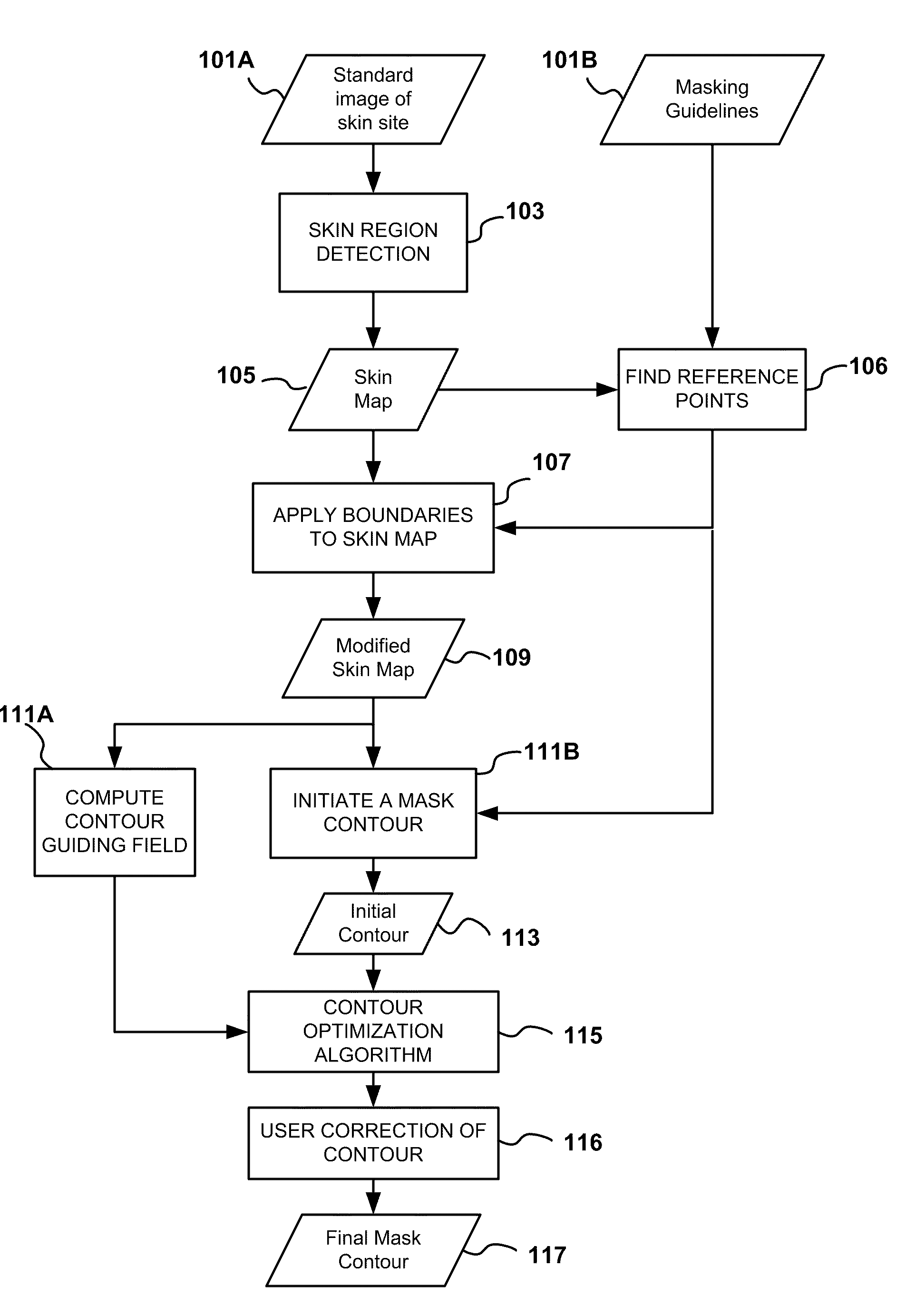
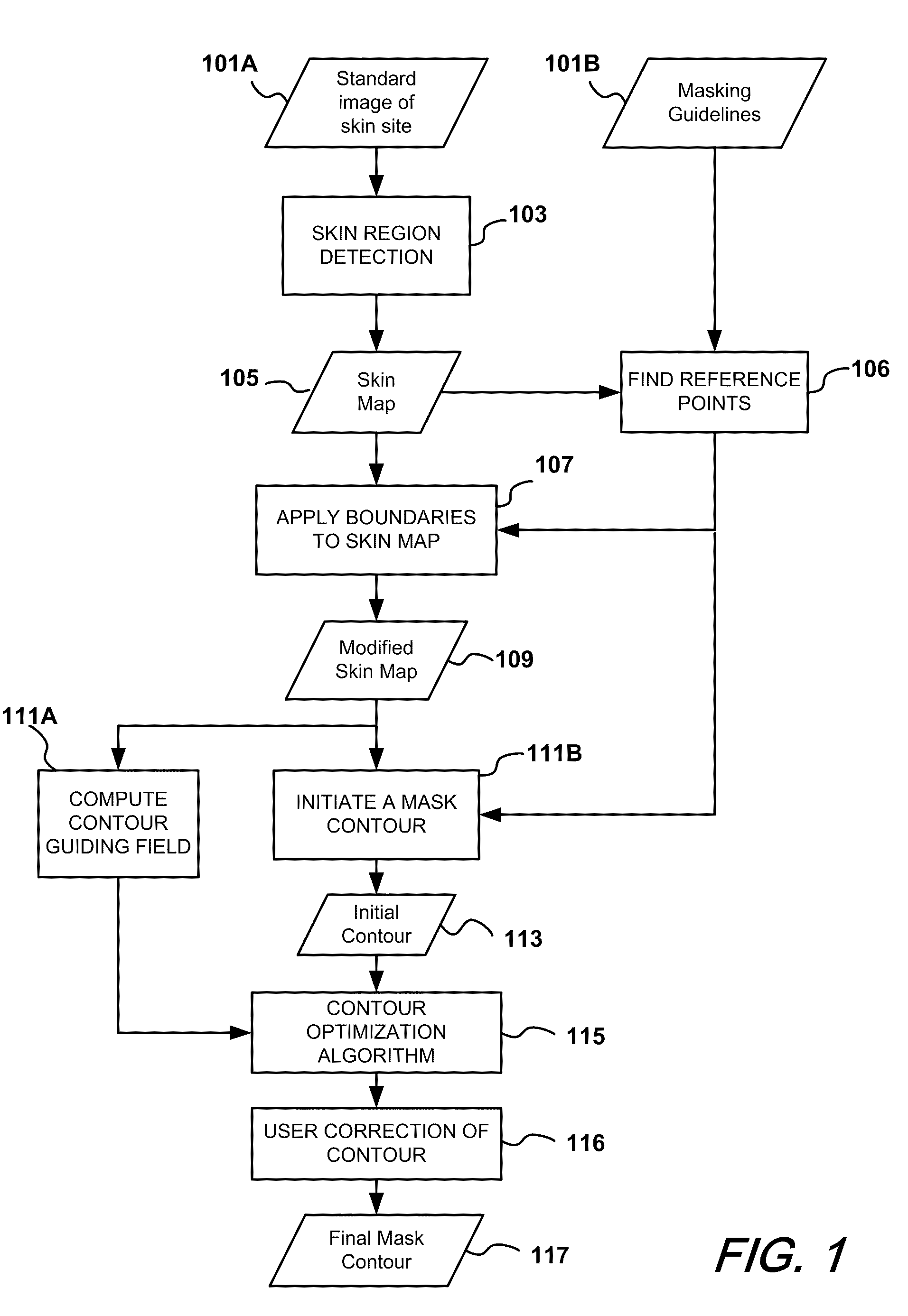
Automatic mask design and registration and feature detection for computer-aided skin analysis
ActiveUS20090196475A1Avoiding skin regions not useful or amenableCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringDiagnostic Radiology ModalityNose
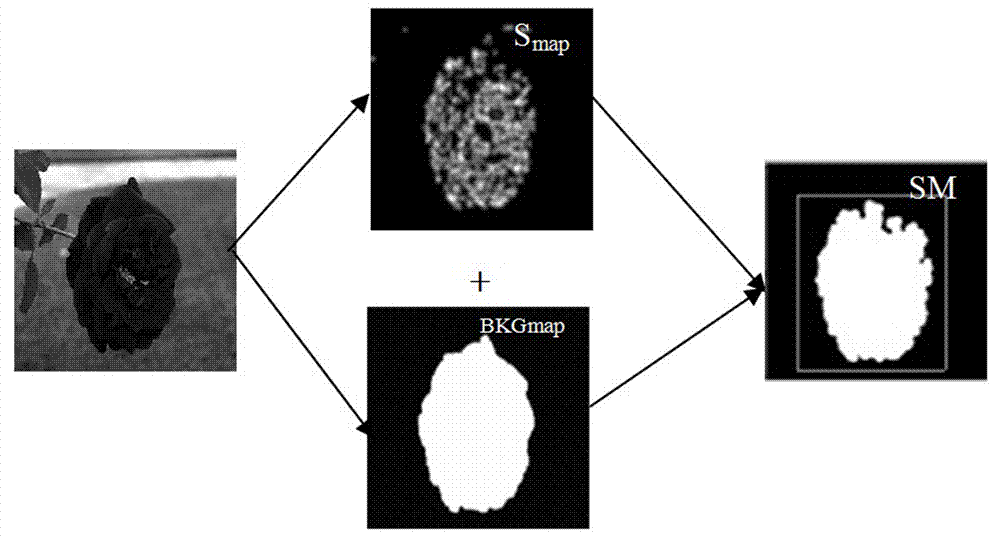
Methods and systems for automatically generating a mask delineating a region of interest (ROI) within an image containing skin are disclosed. The image may be of an anatomical area containing skin, such as the face, neck, chest, shoulders, arms or hands, among others, or may be of portions of such areas, such as the cheek, forehead, or nose, among others. The mask that is generated is based on the locations of anatomical features or landmarks in the image, such as the eyes, nose, eyebrows and lips, which can vary from subject to subject and image to image. As such, masks can be adapted to individual subjects and to different images of the same subjects, while delineating anatomically standardized ROIs, thereby facilitating standardized, reproducible skin analysis over multiple subjects and / or over multiple images of each subject. Moreover, the masks can be limited to skin regions that include uniformly illuminated portions of skin while excluding skin regions in shadow or hot-spot areas that would otherwise provide erroneous feature analysis results. Methods and systems are also disclosed for automatically registering a skin mask delineating a skin ROI in a first image captured in one imaging modality (e.g., standard white light, UV light, polarized light, multi-spectral absorption or fluorescence imaging, etc.) onto a second image of the ROI captured in the same or another imaging modality. Such registration can be done using linear as well as non-linear spatial transformation techniques.
Owner:CANFIELD SCI
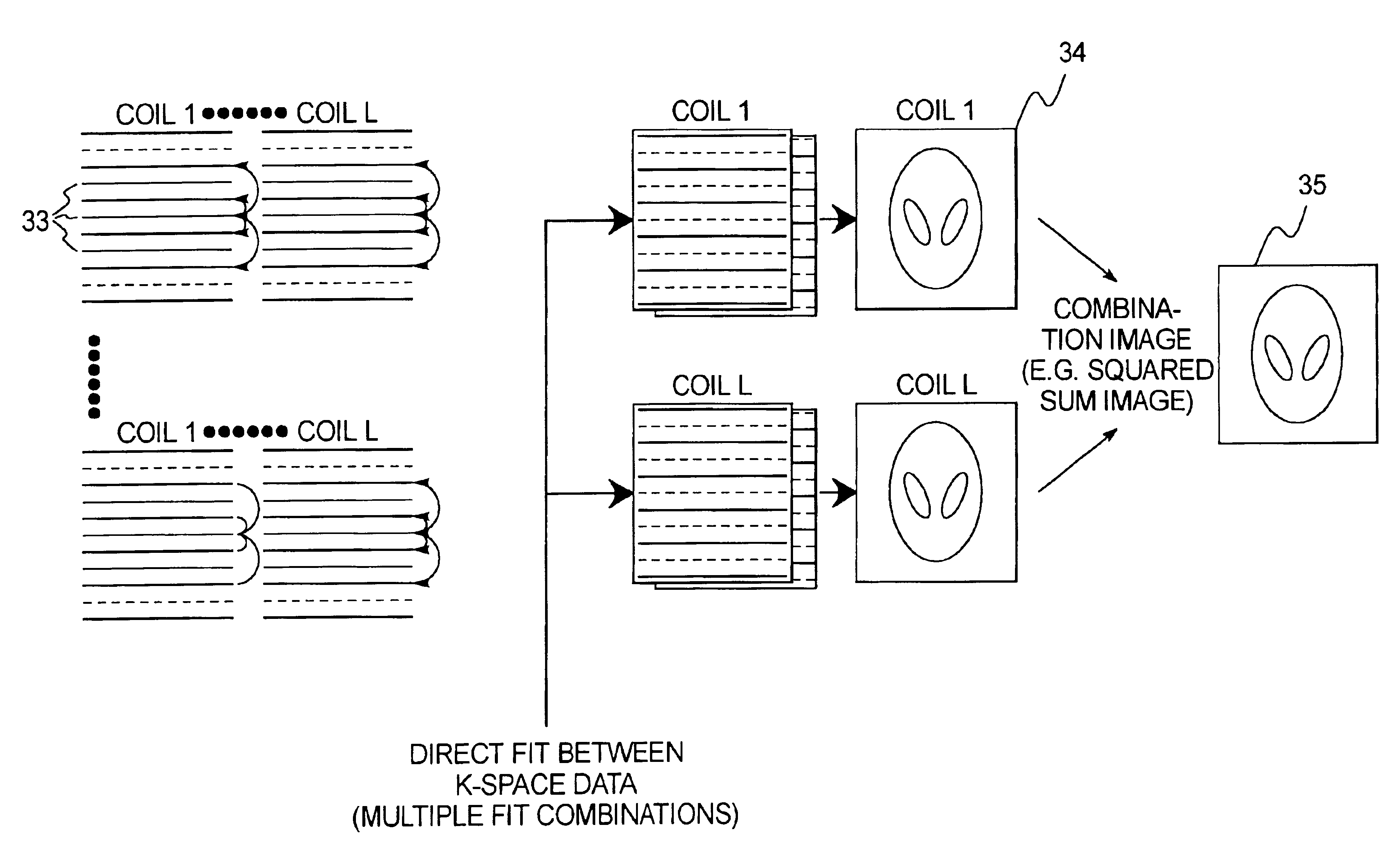
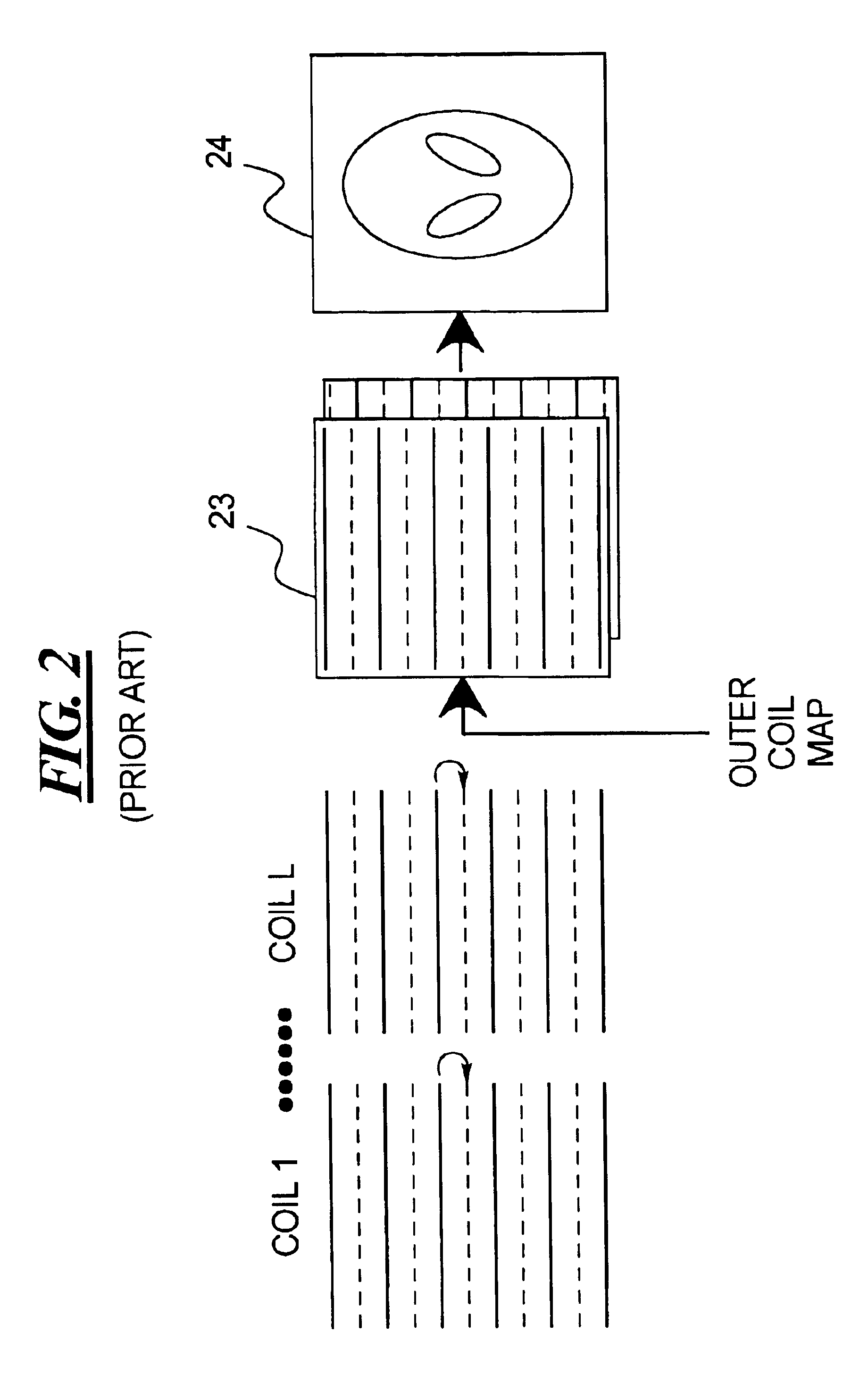
Magnetic resonance imaging method and apparatus employing partial parallel acquisition, wherein each coil produces a complete k-space datasheet
InactiveUS6841998B1Quality improvementMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionDatasheetData set
In a method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging of an interconnected region of a human body on the basis of a partially parallel acquisition (PPA) by excitation of nuclear spins and measurement of the radio-frequency signals produced by the excited nuclear spins, a number of spin excitations and measurements of an RF response signal are implemented simultaneously in every component coil of a number of RF reception coils. As a result a number of response signals are acquired that form a reduced dataset of received RF signals for each component coil. Additional calibration data points are acquired for each reduced dataset. A complete image dataset is formed for each component coil on the basis of the reduced dataset for that component coil and at least one further, reduced dataset of a different component coil. A spatial transformation of the image dataset of each component coil is implemented in order to form a complete image of each component coil.
Owner:GRISWOLD MARK
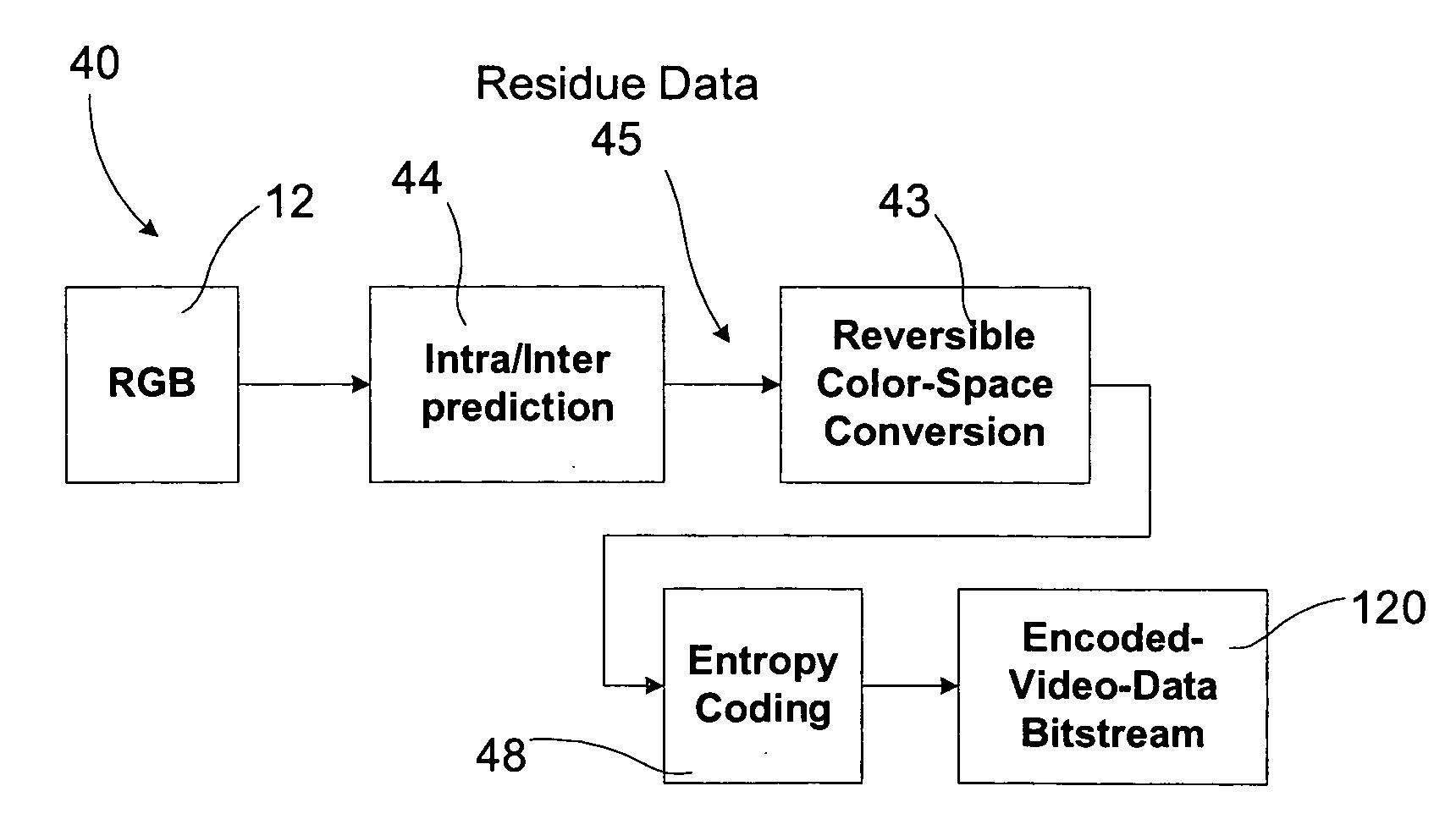
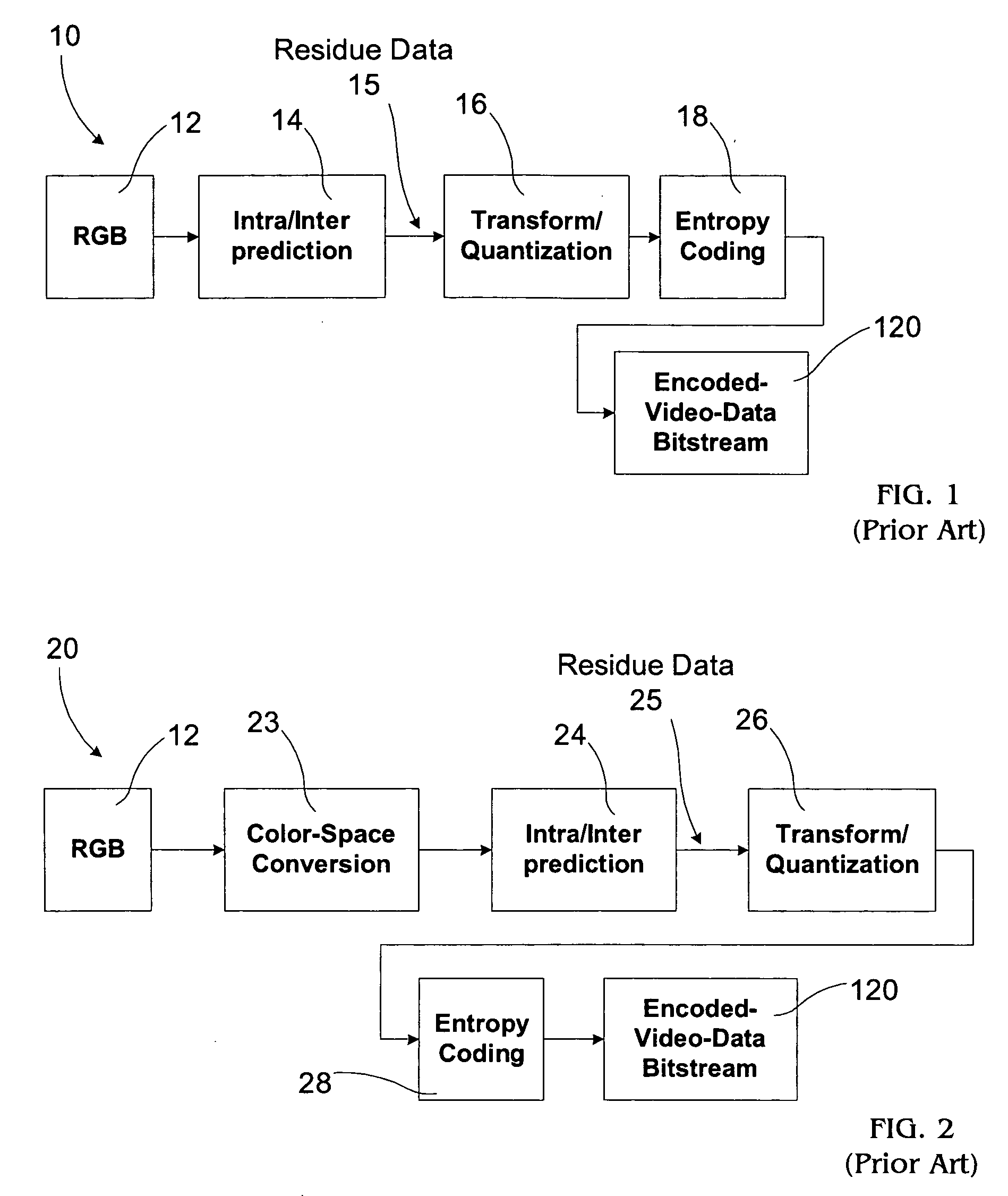
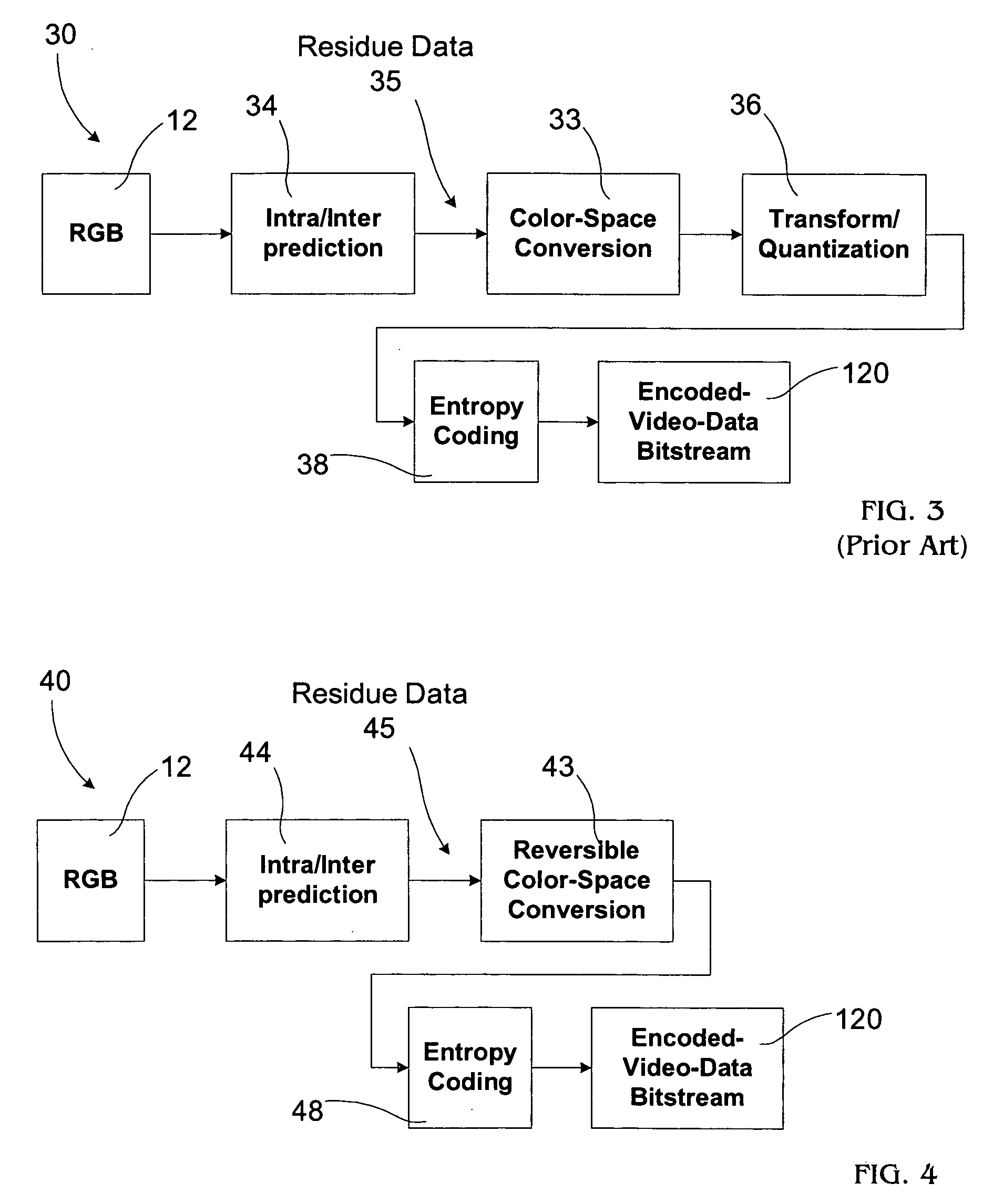
Video coding with residual color conversion using reversible YCoCg
InactiveUS20050259730A1Improve coding efficiencyHigh color fidelityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionLossless codingFrame based
A video coding algorithm supports both lossy and lossless coding of video while maintaining high color fidelity and coding efficiency using an in-loop, reversible color transform. Accordingly, a method is provided to encode video data and decode the generated bitstream. The method includes generating a prediction-error signal by performing intra / inter-frame prediction on a plurality of video frames; generating a color-transformed, prediction-error signal by performing a reversible color-space transform on the prediction-error signal; and forming a bitstream based on the color-transformed prediction-error signal. The method may further include generating a color-space transformed error residual based on a bitstream; generating an error residual by performing a reversible color-space transform on the color-space transformed error residual; and generating a video frame based on the error residual.
Owner:SHARP LAB OF AMERICA INC
Methods for visualizing transformations among related series of graphs
A method for displaying in a coherent manner the changes over time of a web site's structure, usage, and content is disclosed. Time tubes are generated by a method of displaying a related series of graphs. Time tubes illustrate changes in a graph that undergoes one or more transformations from one state to another. The transformations are displayed using the length of the cylindrical tube, filling the length of the time tube with planar slices which represent the data at various stages of the transformations. Time tubes may encode several dimensions of the transformations simultaneously by altering the representation of size, color, and layout among the planar slices. Temporal transformations occur when web pages are added or deleted over time. Value-based transformations include node colors, which may be used to encode a specific page's usage parameter. Spatial transformations include the scaling of physical dimension as graphs expand or contract in size. The states of a graph at various times are represented as a series of related graphs. In a preferred embodiment, an inventory of all existing nodes is performed so as to generate a list of all nodes that have existed at any time. This inventory is used to produce a layout template in which each unique node is assigned a unique layout position. To produce each planar slice, the specific nodes which exist in the slice are placed at their respective positions assigned in the layout template. In another aspect, corresponding nodes in planar slices are linked, such as with translucent streamlines, in response to a user selecting a node in a planar slice by placing his cursor over the selected node, or to show clustering of two or more nodes in one planar slice into a single node in an adjacent planar slice.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
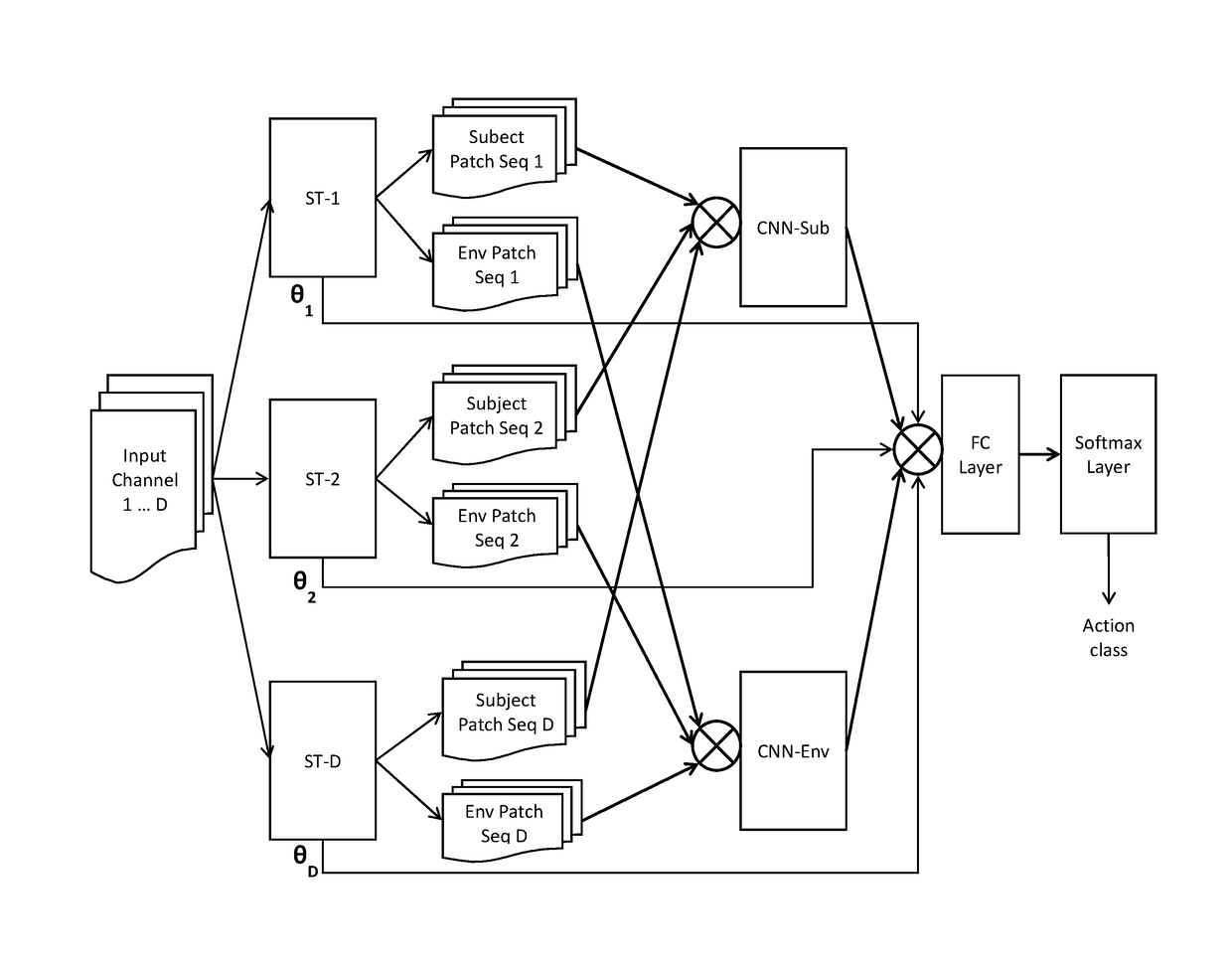
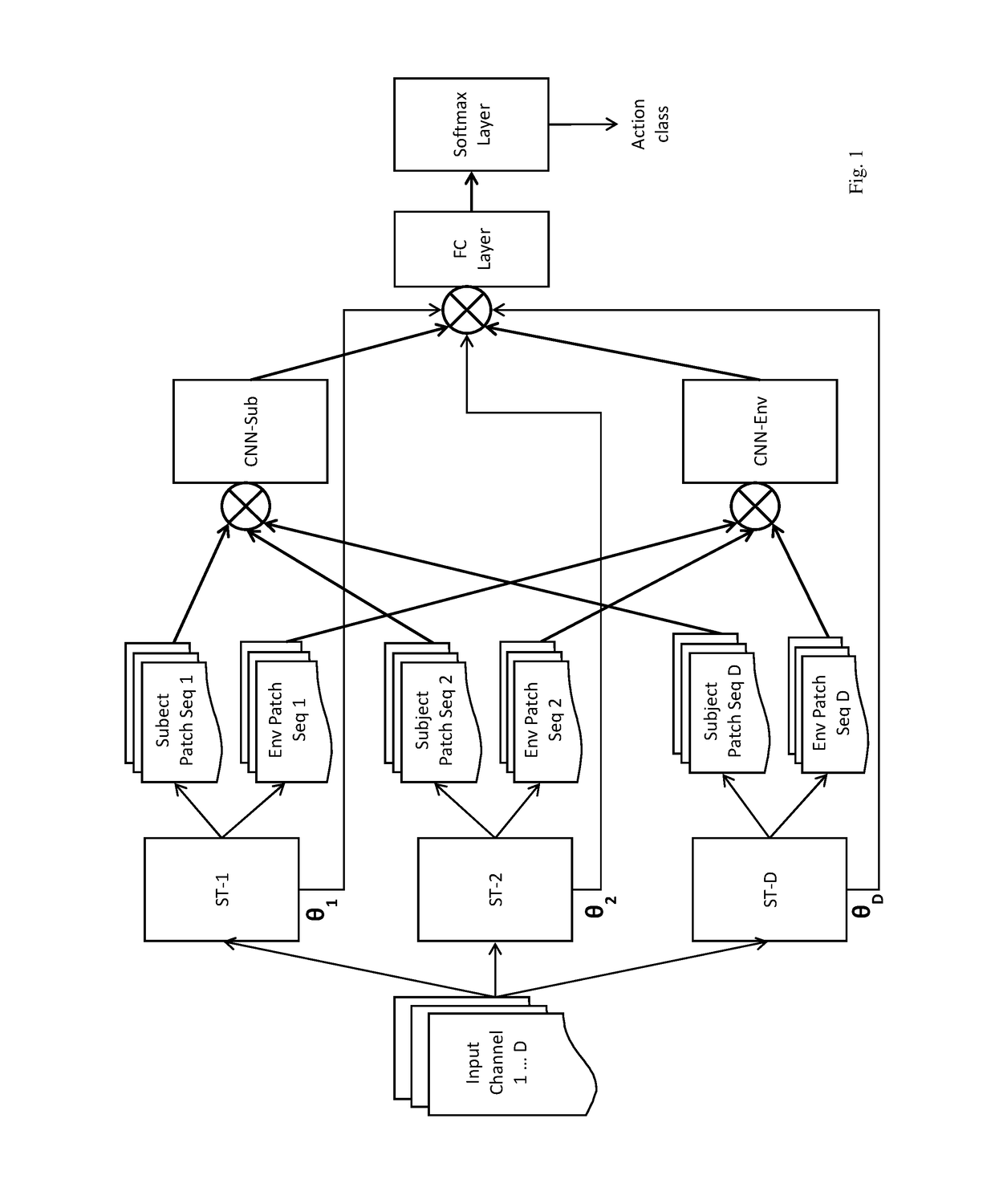
Self-attention deep neural network for action recognition in surveillance videos
An artificial neural network for analyzing input data, the input data being a 3D tensor having D channels, such as D frames of a video snippet, to recognize an action therein, including: D spatial transformer modules, each generating first and second spatial transformations and corresponding first and second attention windows using only one of the D channels, and transforming first and second regions of each of the D channels corresponding to the first and second attention windows to generate first and second patch sequences; first and second CNNs, respectively processing a concatenation of the D first patch sequences and a concatenation of the D second patch sequences; and a classification network receiving a concatenation of the outputs of the first and second CNNs and the D sets of transformation parameters of the first transformation outputted by the D spatial transformer modules, to generate a predicted action class.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA LAB U S A INC
Image processing apparatus and method, and computer-readable storage medium
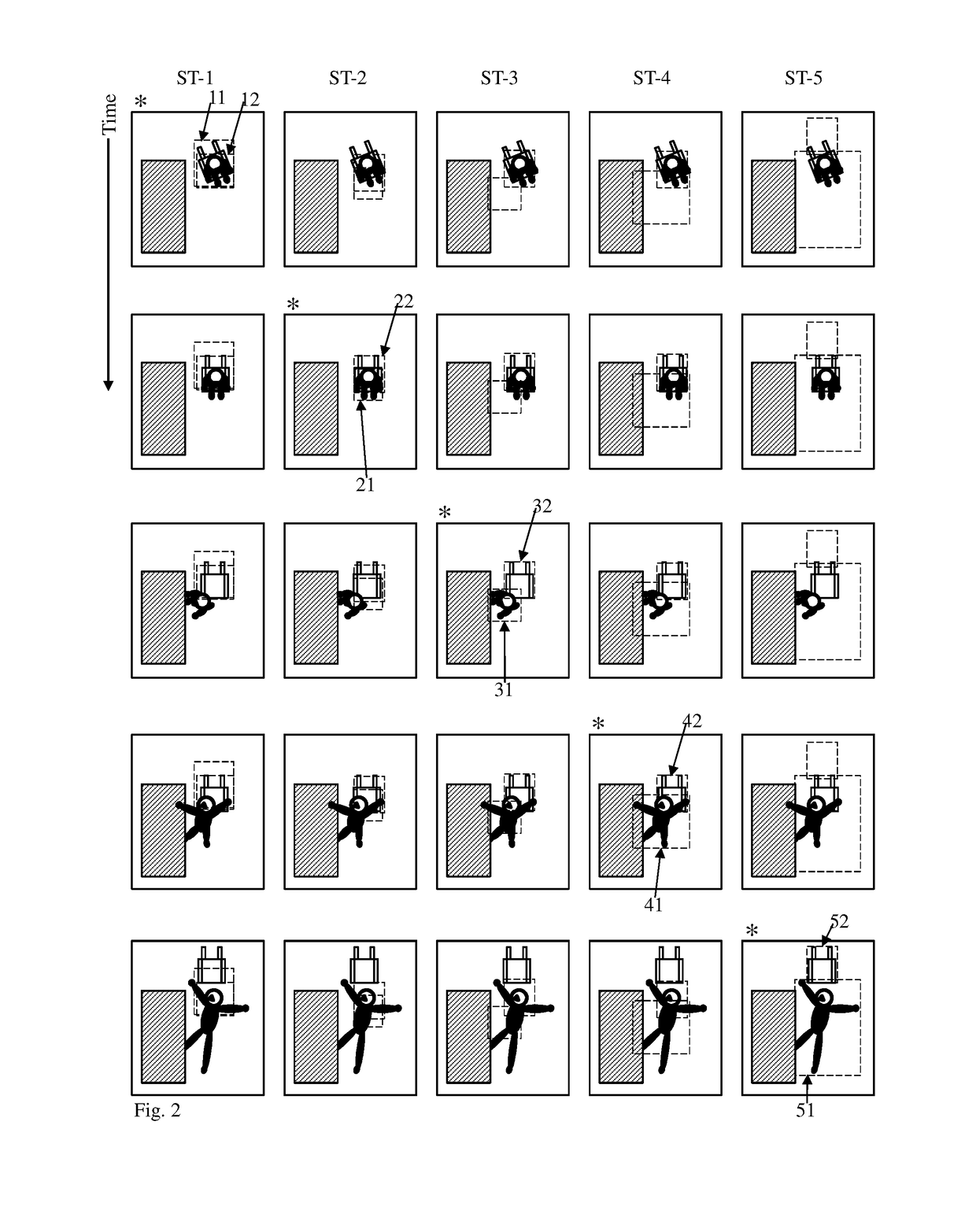
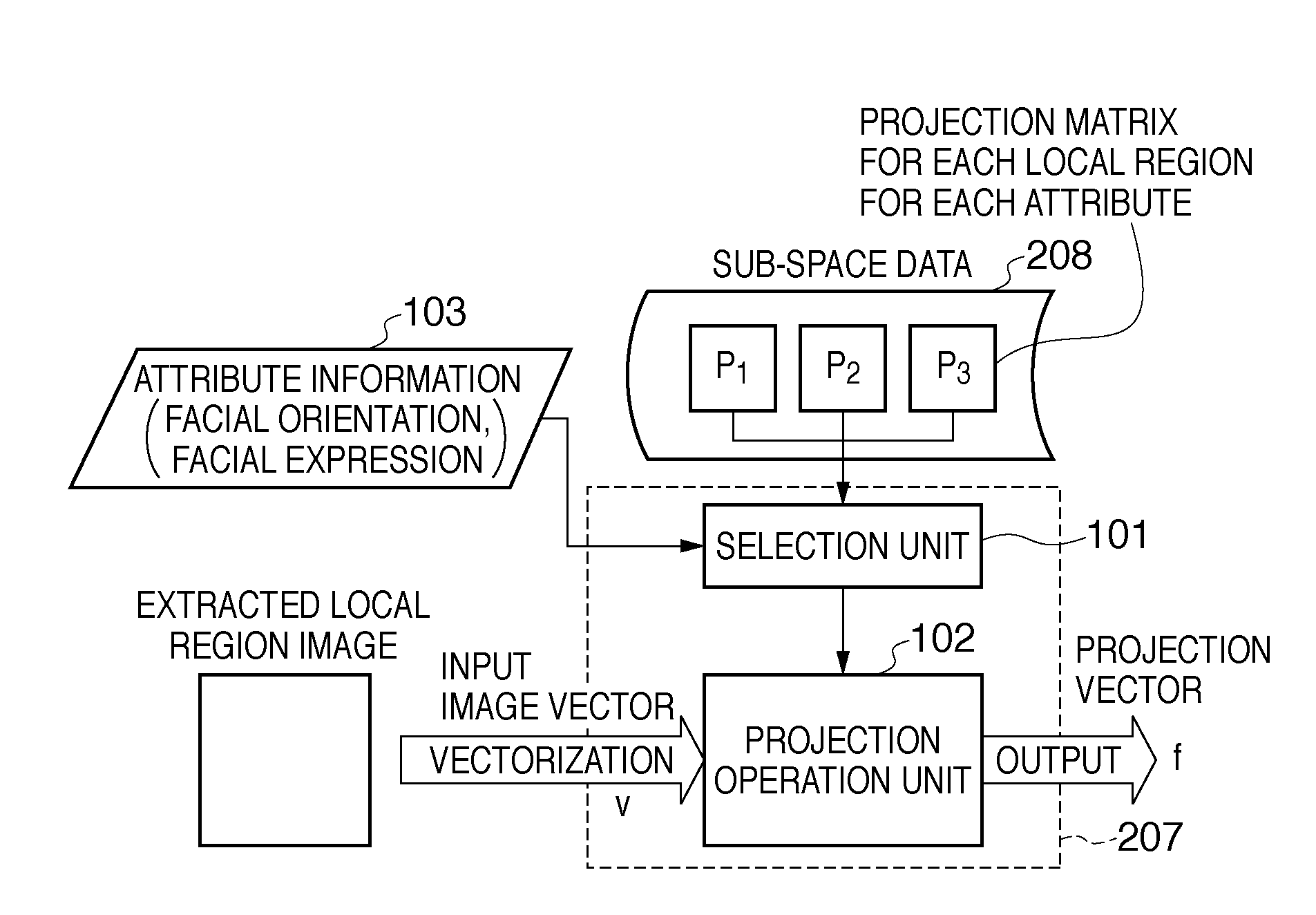
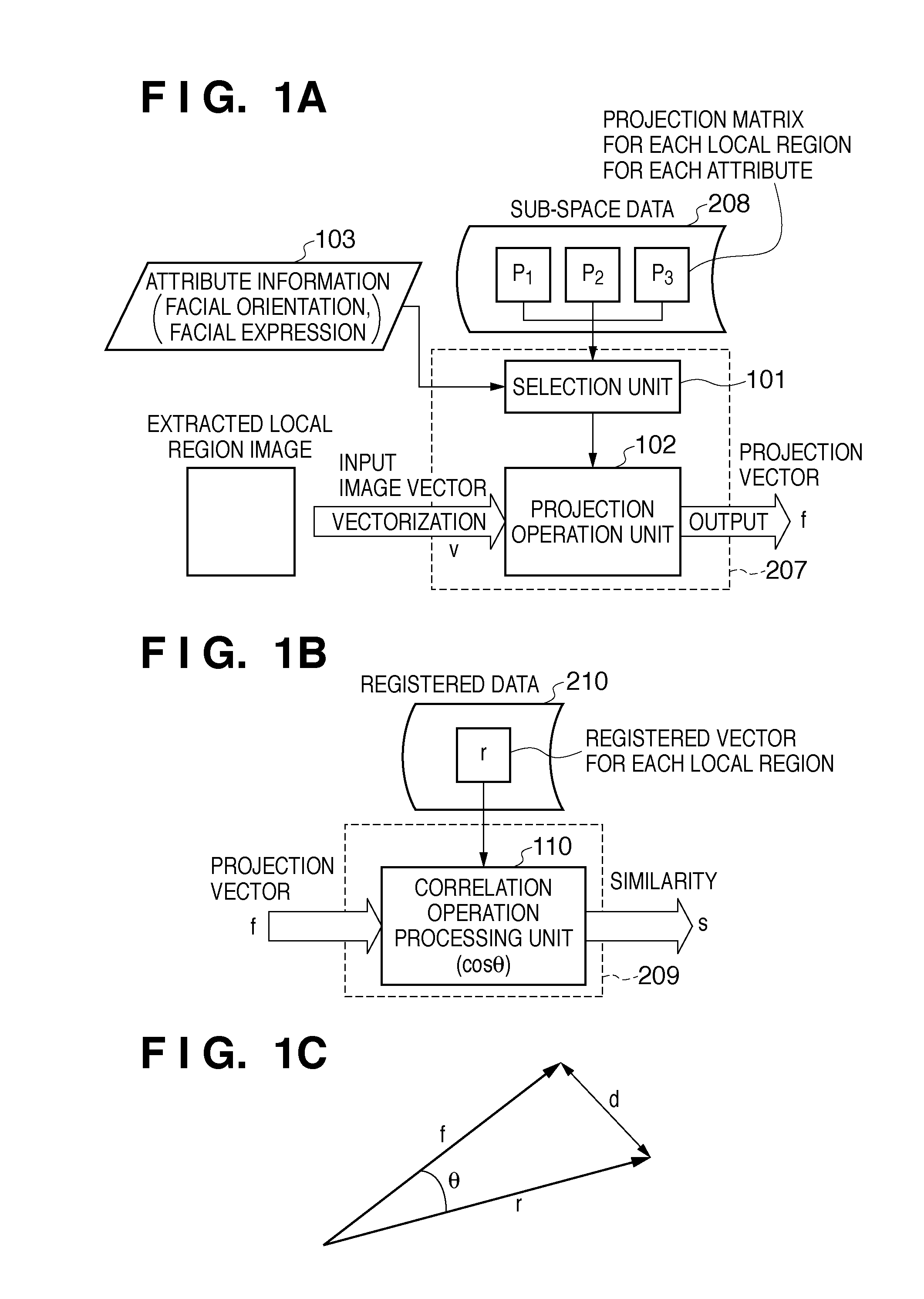
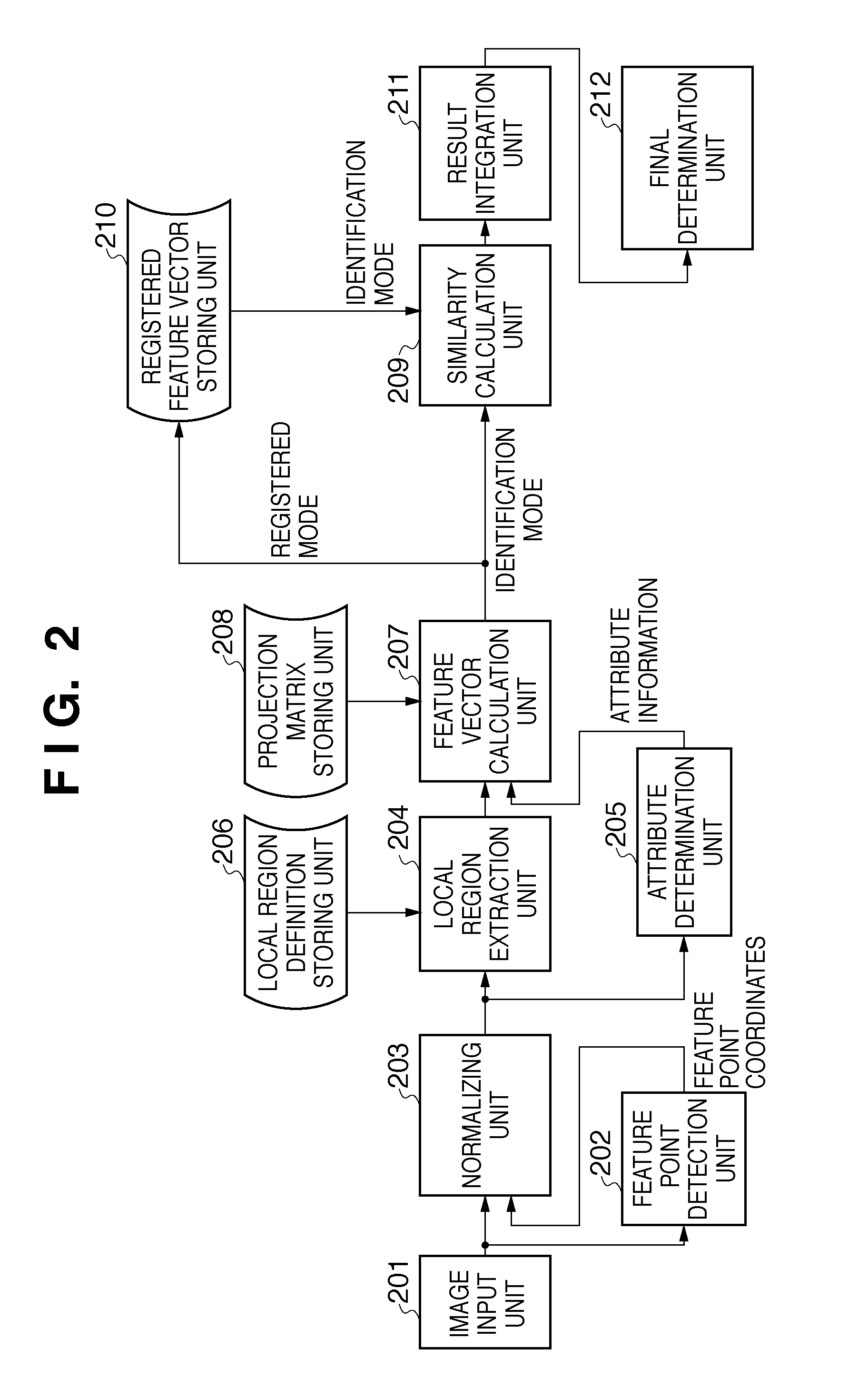
ActiveUS20110091113A1Increasing parameterIncreasing processing loadGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingSpatial transformation
An image processing apparatus classifies a variation of a target object included in an image from a specific state as one of a plurality of types of attributes, and holds, for each variation attribute, a correction parameter for spatial transformation that corrects the target object to the specific state. The image processing apparatus generates an input image vector by vectorizing at least a partial region of the input image, and determines a variation attribute by detecting a variation of the target object from the specific state in the input image. Then, the image processing apparatus generates a transformed image vector by performing the spatial transformation on the input image vector, using a correction parameter selected based on the determined variation attribute from among the correction parameters held for respective variation attributes.
Owner:CANON KK
Holographic spectral filter
Method and apparatus are contemplated for receiving from an input, an optical signal in a volume hologram comprising a transfer function that may comprise temporal or spectral information, and spatial transformation information; diffracting the optical signal; and transmitting the diffracted optical signal to an output. A plurality of inputs and outputs may be coupled to the volume hologram. The transformation may be a linear superposition of transforms, with each transform acting on an input signal or on a component of an input signal. Each transform may act to focus one or more input signals to one or more output ports. A volume hologram may be made by various techniques, and from various materials. A transform function may be calculated by simulating the collision of a design input signal with a design output signal.
Owner:STEYPHI SERVICES DE
Virtual reality modelling
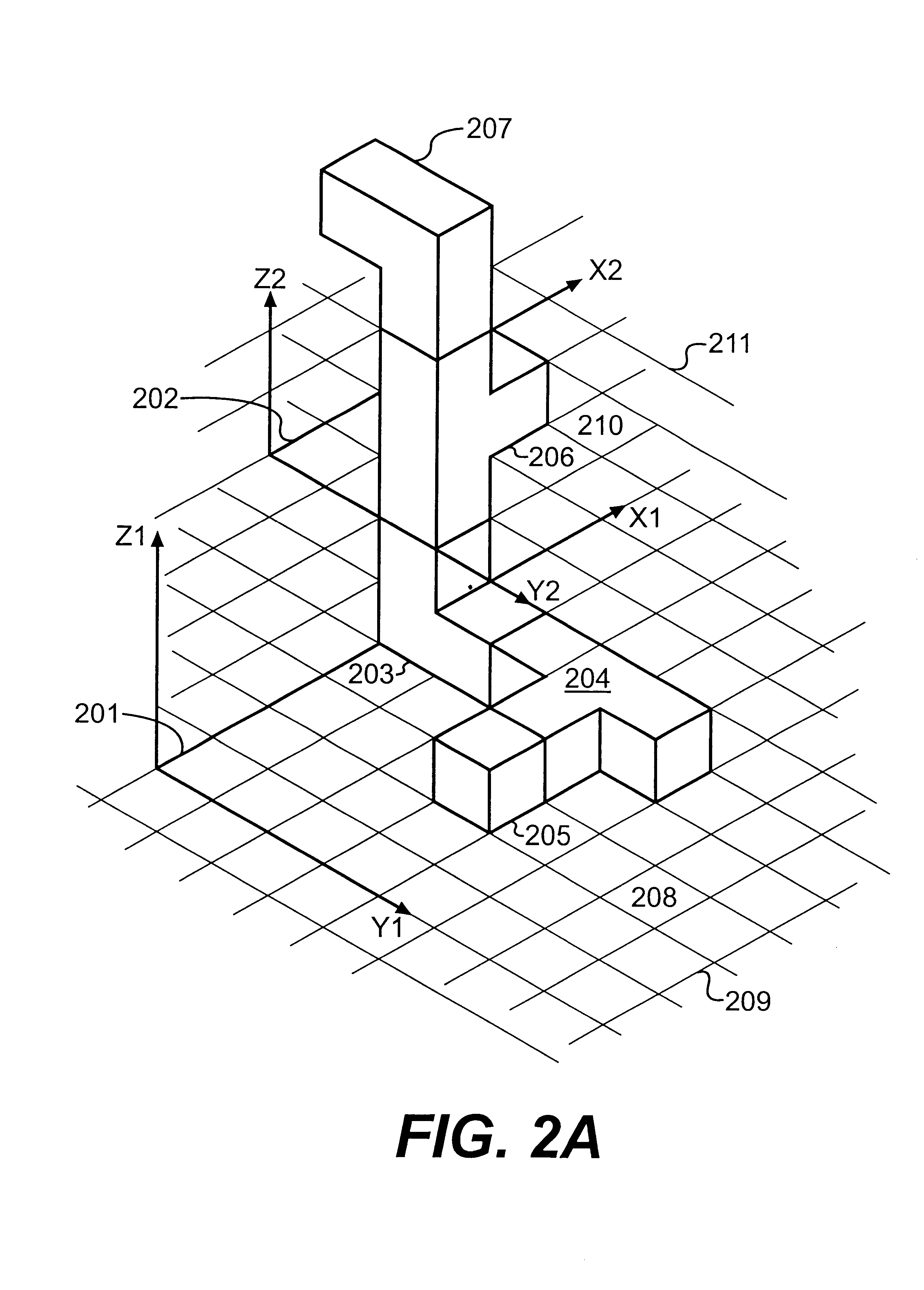
InactiveUS6389375B1Compact representationGenerate fastData processing applicationsComputation using non-denominational number representationCo ordinateSpatial transformation
A model of a geometrical object comprising: bits in a first data structure encoded to identify a first set of elements from a collection of representations of geometrical shapes for a collection of elements and to represent positions of the elements by means of integer co-ordinates in a first system of co-ordinates; bits in a second data structure encoded to identify a second set of elements from said collection and to represent positions of the elements by means of integer co-ordinates in a second system of co-ordinates; bits in a third data structure encoded to represent a spatial transformation of the second system of co-ordinates relatively to the first system of co-ordinates. Thereby it is possible to create a very compact representation of a model of a geometrical object. The model-prima facia-seems to be constrained very hard, but is in fact a very flexible and easy to access model.
Owner:LEGO AS
Method of texture-based color document segmentation
InactiveUS6993185B2Noise generatedCharacter and pattern recognitionNoise reductionAlternative methods
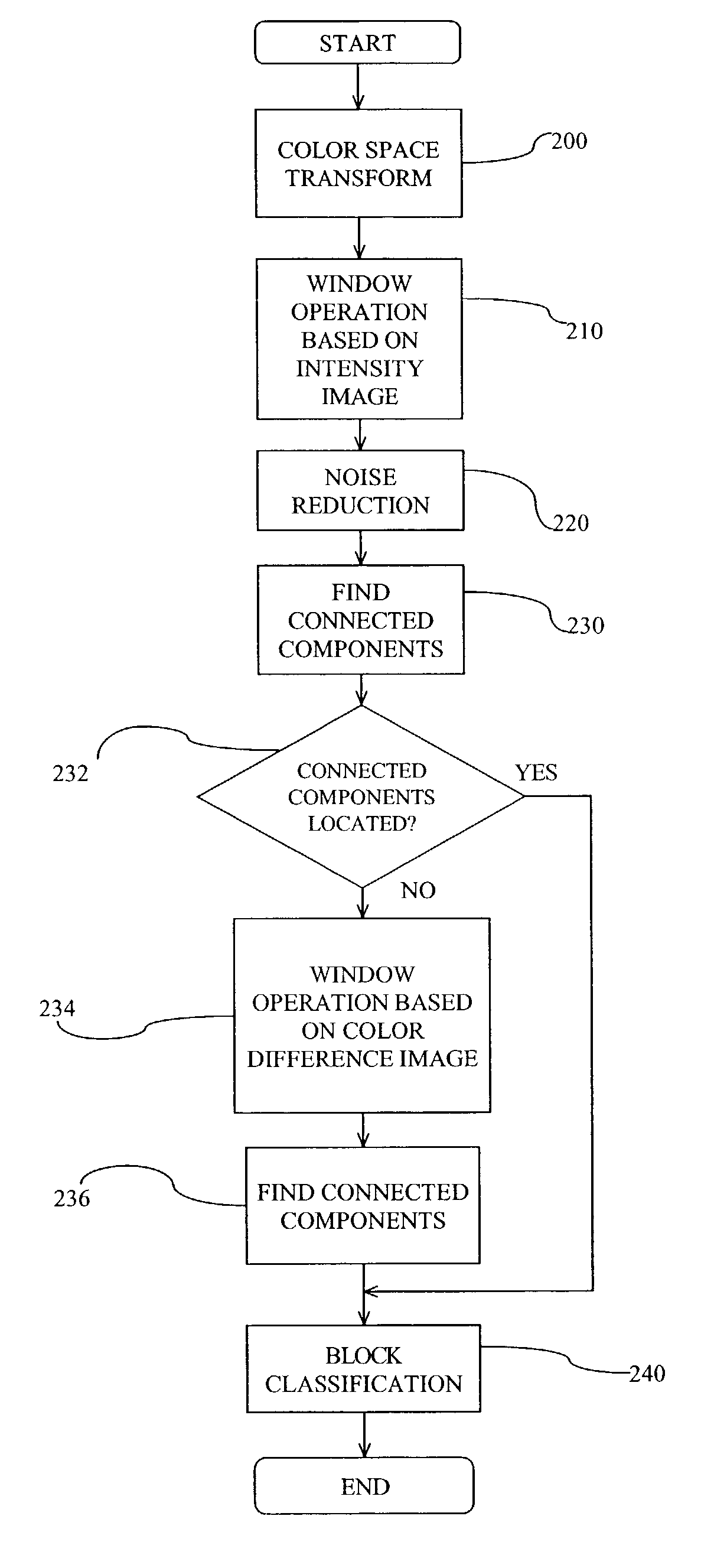
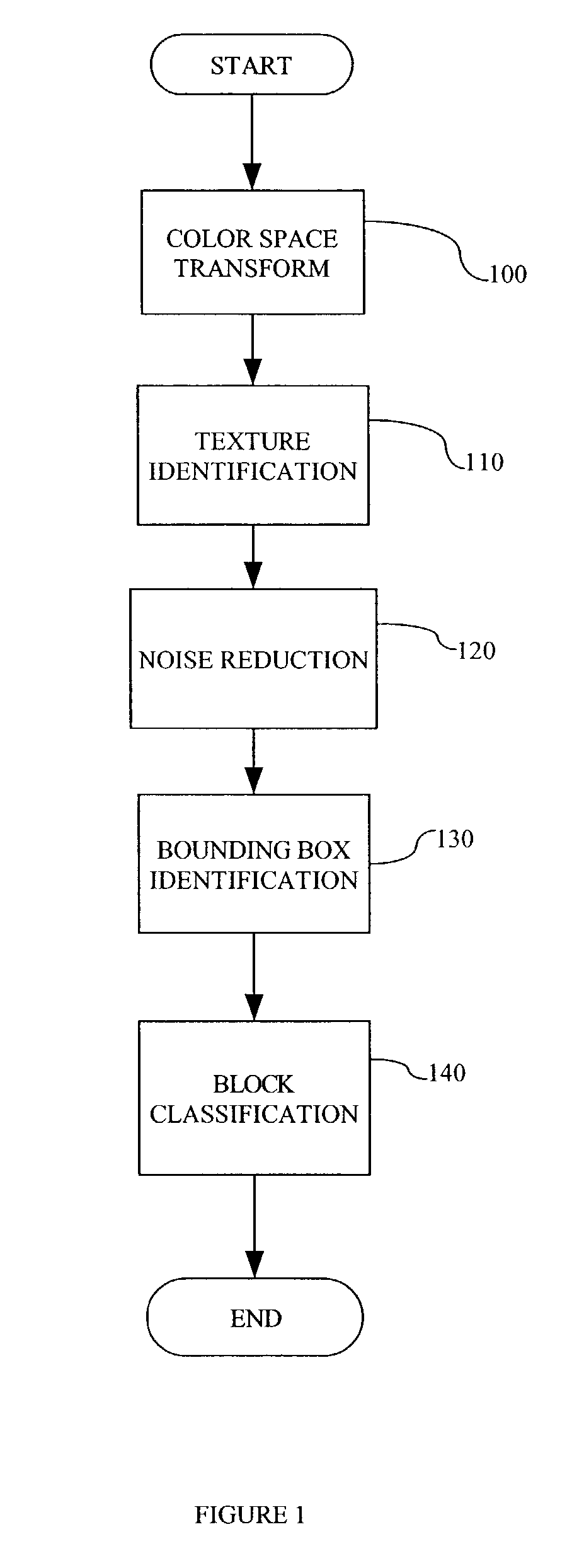
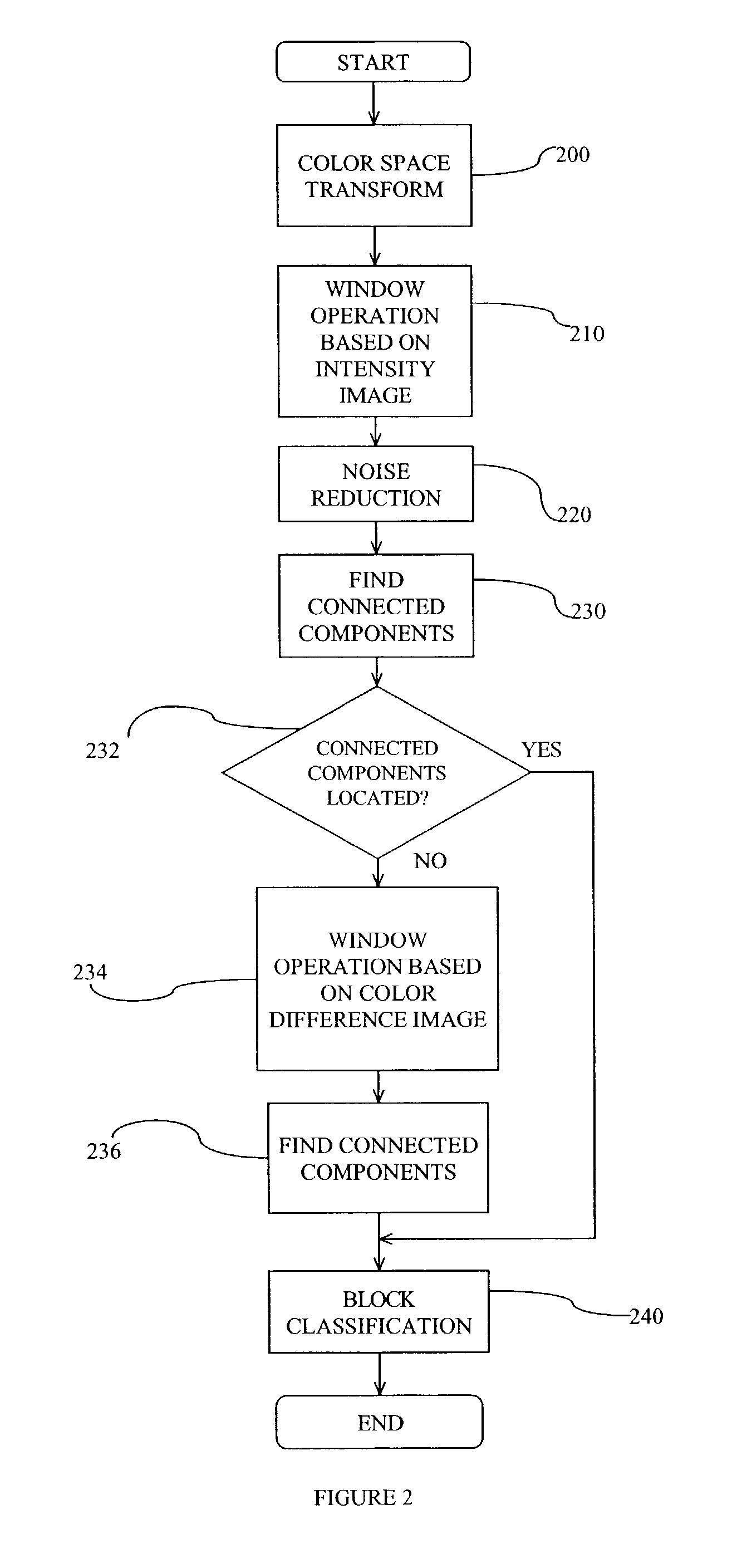
A method for segmenting a color document into regions of text and halftone discriminates between text and halftone by examining the texture of the document. A color document is digitized, and a color space transform is preferably applied to the digitized document. The texture of the document is identified and a noise reduction step is preferably applied. Bounding boxes (blocks) within the document are identified and then the areas within the bounding boxes are classified as either text or halftone. Two alternative methods are described for examining the document texture. In the first method, a windowing operation is applied to either an intensity image or a color difference image. In the second method, a wavelet transform step combined with Fuzzy K-Mean clustering is applied. Bounding boxes are classified as either text or halftone based upon the relative periodicity of a horizontal or vertical (or both) histogram of each bounding box.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
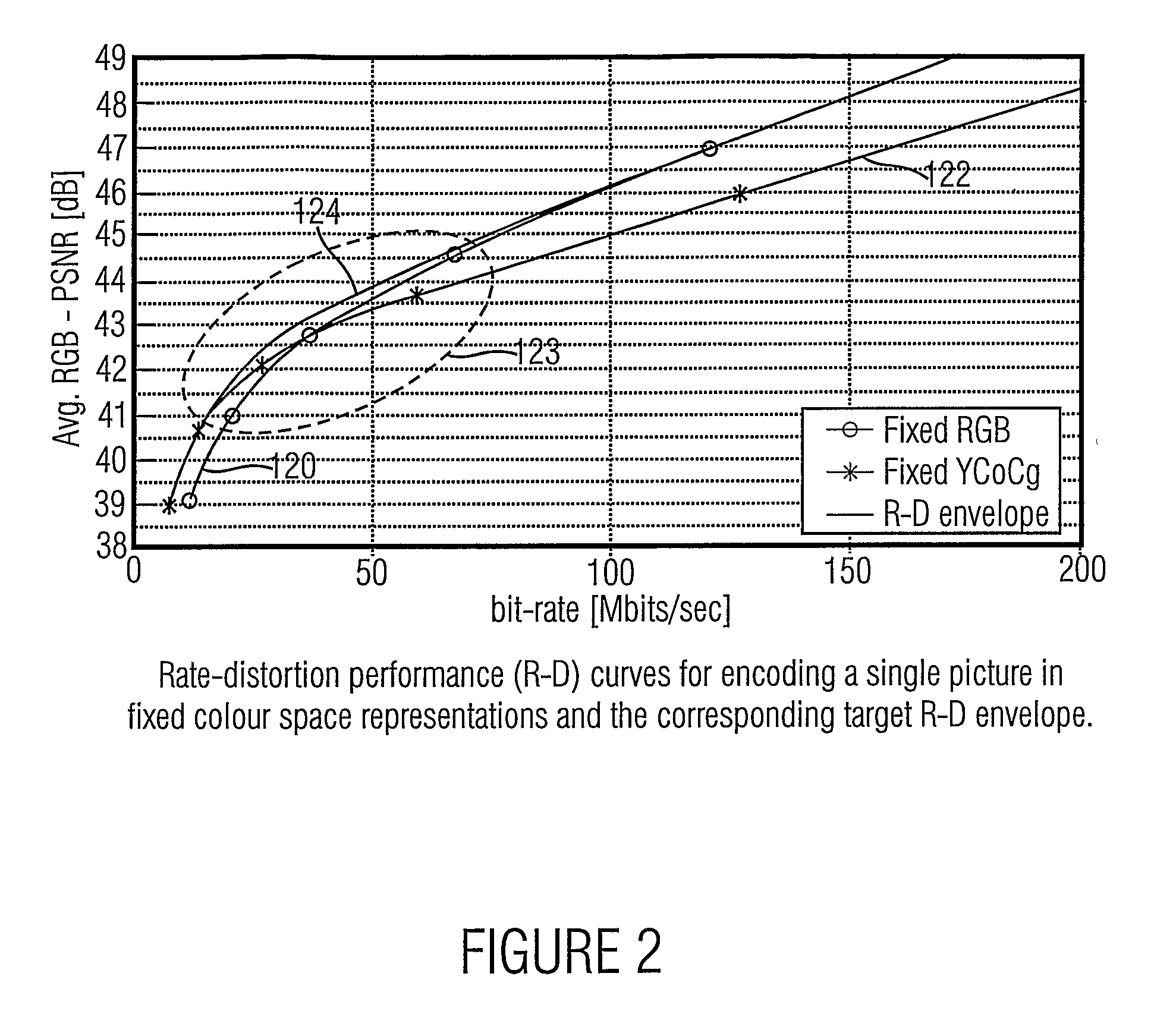
Picture coding using adaptive color space transformation
ActiveUS20090168894A1Quality improvementEncoded highly efficientColor television with pulse code modulationColor signal processing circuitsComputer graphics (images)Spatial transformation
The present invention is based on the finding that pictures or a picture stream can be encoded highly efficient when a representation of pictures is chosen that is having different picture blocks, wherein each picture block is carrying picture information for picture areas smaller than the full area of the picture and when the different picture blocks are carrying the picture information either in a first color-space representation or in a second color-space-representation. Since different color-space-representations have individual inherent properties with respect to their describing parameters, choosing an appropriate color-space-representation individually for the picture blocks results in an encoded representation of pictures that is having a better quality at a given size or bit rate.
Owner:GE VIDEO COMPRESSION LLC
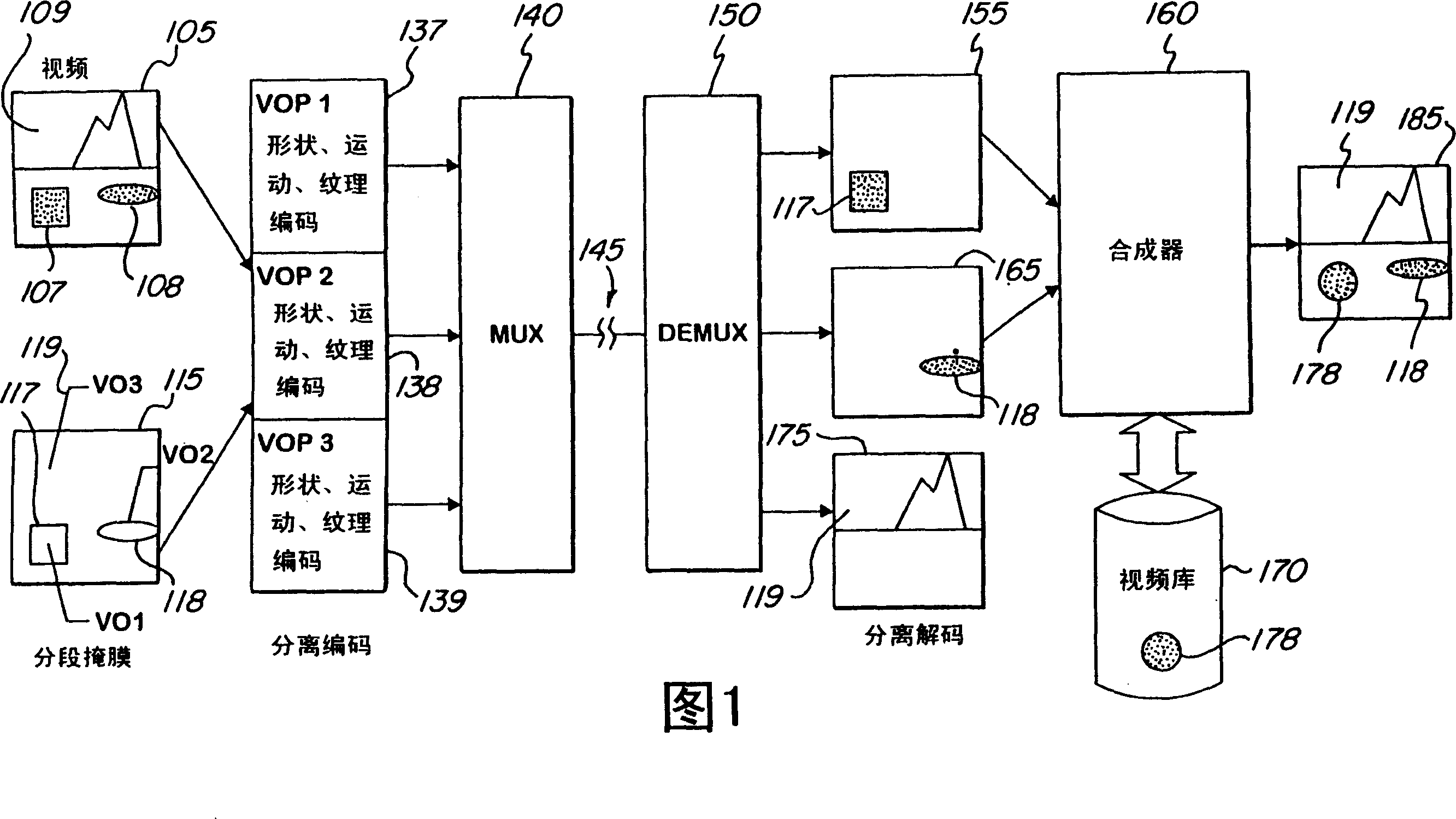
Method for coding two-directional predictive video object planes and decoding device
InactiveCN1551636APulse modulation television signal transmissionImage analysisStereoscopic videoDigital video
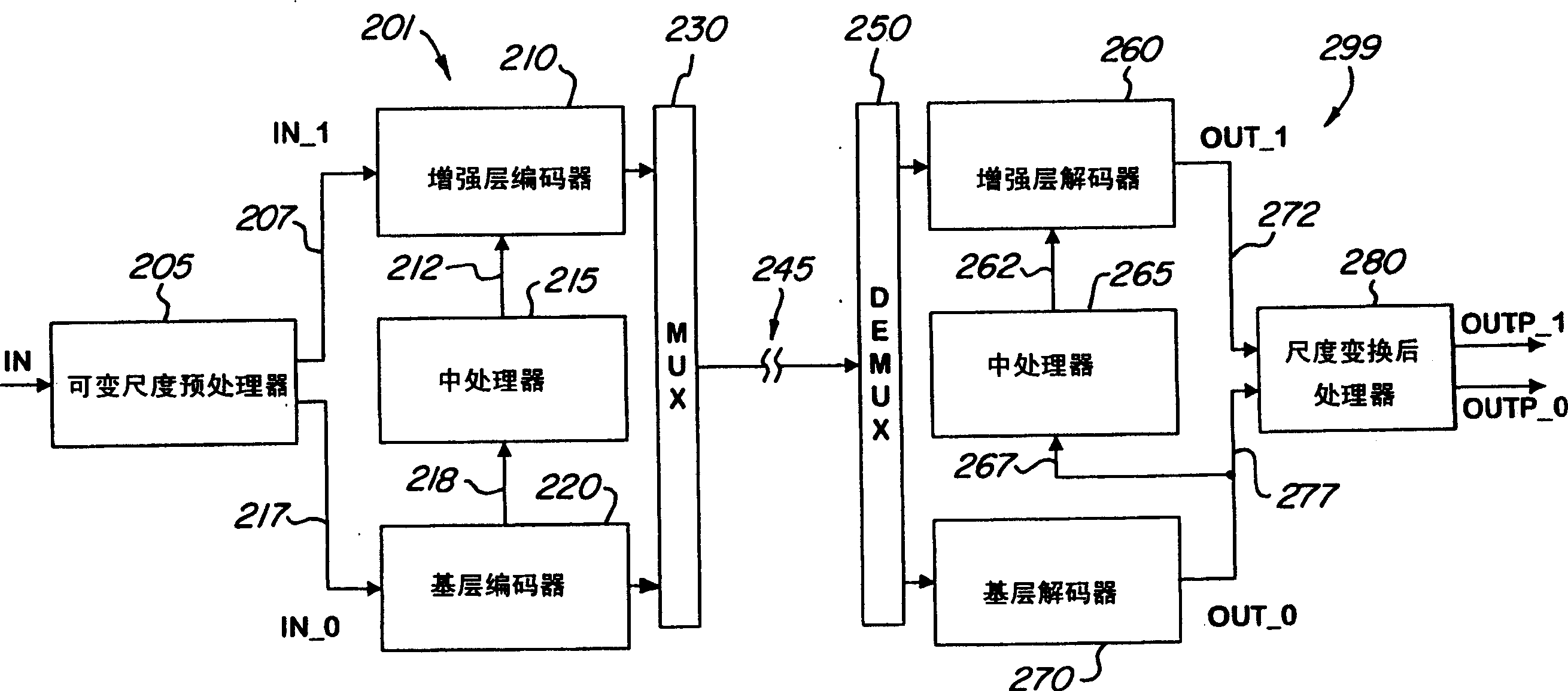
Temporal and spatial scaling of video images including video object planes (VOPs) (117, 118, 119, 405, 415, 420, 430, 520, 522, 524, 526, 532, 542, 705, 730, 750, 760, 780, 790, 805, 815, 820, 830, 850, 860, 880, 890) in an input digital video sequence is provided. Coding efficiency is improved by adaptively compressing scaled field mode video. Upsampled VOPs (450, 490, 522, 542, 750, 790) in the enhancement layer are reordered to provide a greater correlation with the input video sequence based on a linear criteria. The resulting residue is coded using a spatial transformation such as the DCT. A motion compensation scheme is used for coding enhancement layer VOPs (450, 460, 480, 490, 522, 524, 526, 542, 750, 760, 780, 790, 850, 860, 880, 890) by scaling motion vectors which have already been determined for the base layer VOPs (405, 415, 420, 430, 520, 532, 705, 730, 805, 815, 820, 830). A reduced search area whose center is defined by the scaled motion vectors is provided. The motion compensation scheme is suitable for use with scaled frame mode or field mode video. Various processor configurations achieve particular scaleable coding results. Applications of scaleable coding include stereoscopic video, picture-in-picture, preview access channels, and ATM communications.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
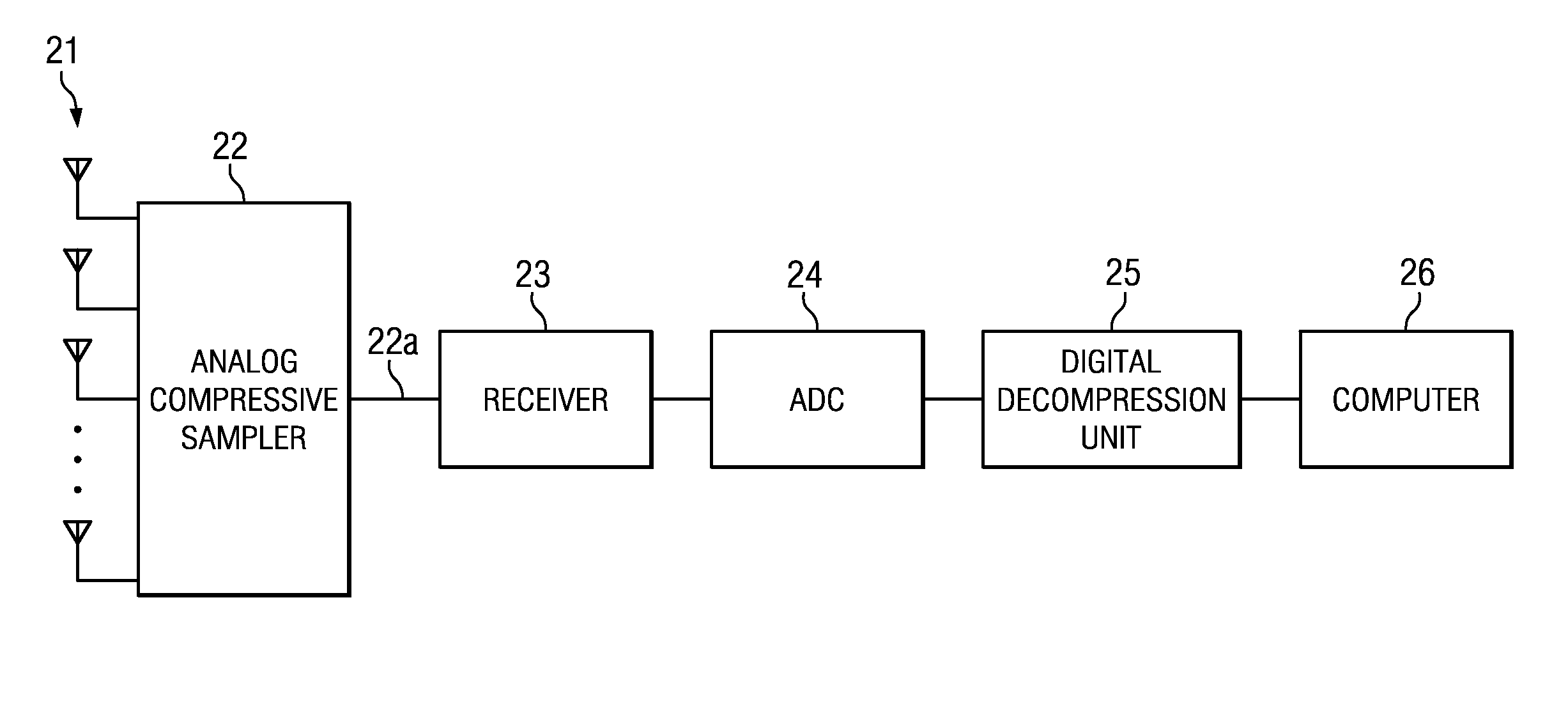
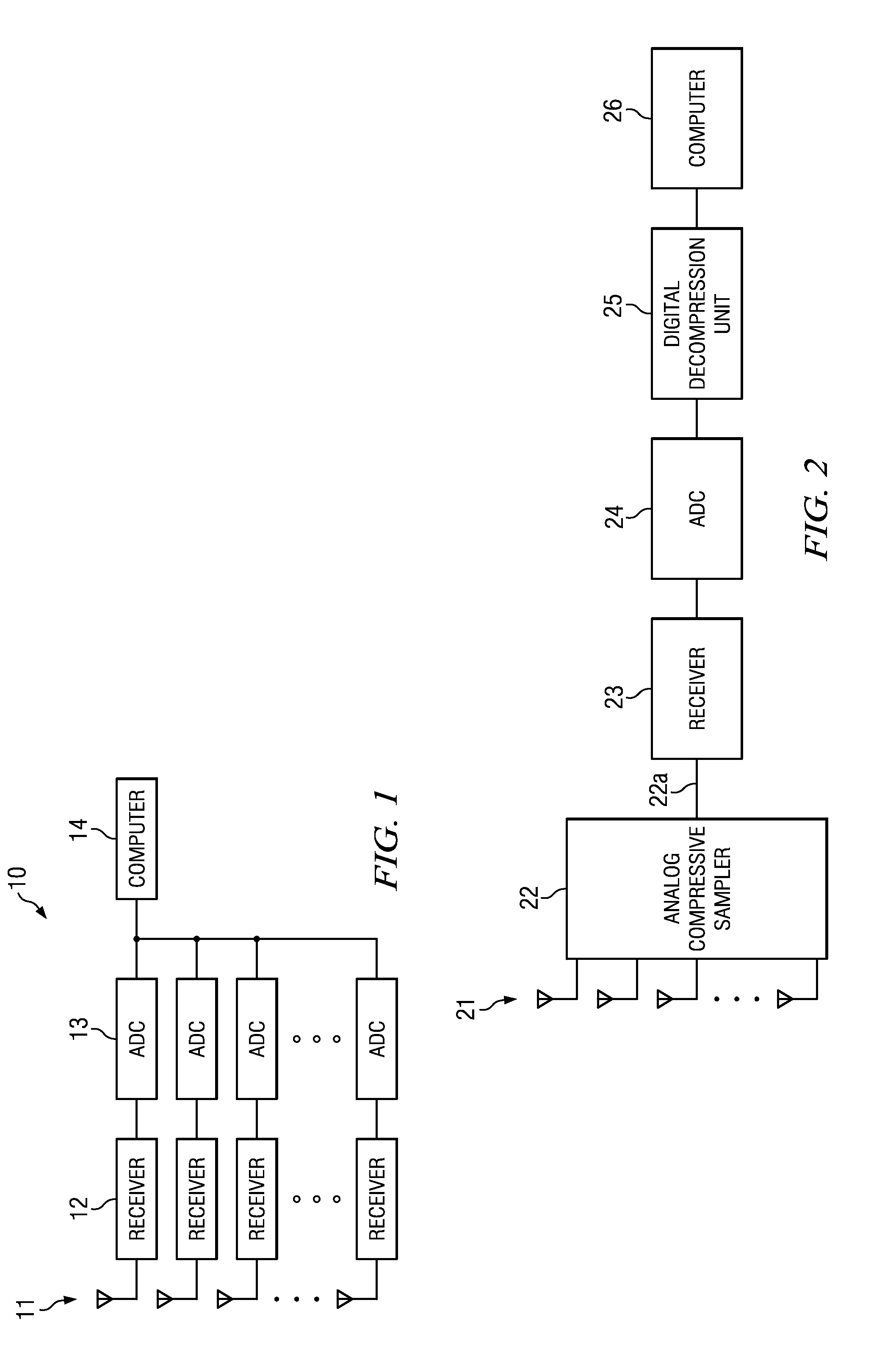
Sensor Array Processor with Multichannel Reconstruction from Random Array Sampling
A method and system for reconstructing random samples taken across multiple sensors of a sensor array, so that each sensor's output is reconstructed. The samples are processed using a compressive sensing process. The compressive sensing process uses a time-space transform basis that represents the multi-channel data in terms of both a frequency component and an azimuthal component.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
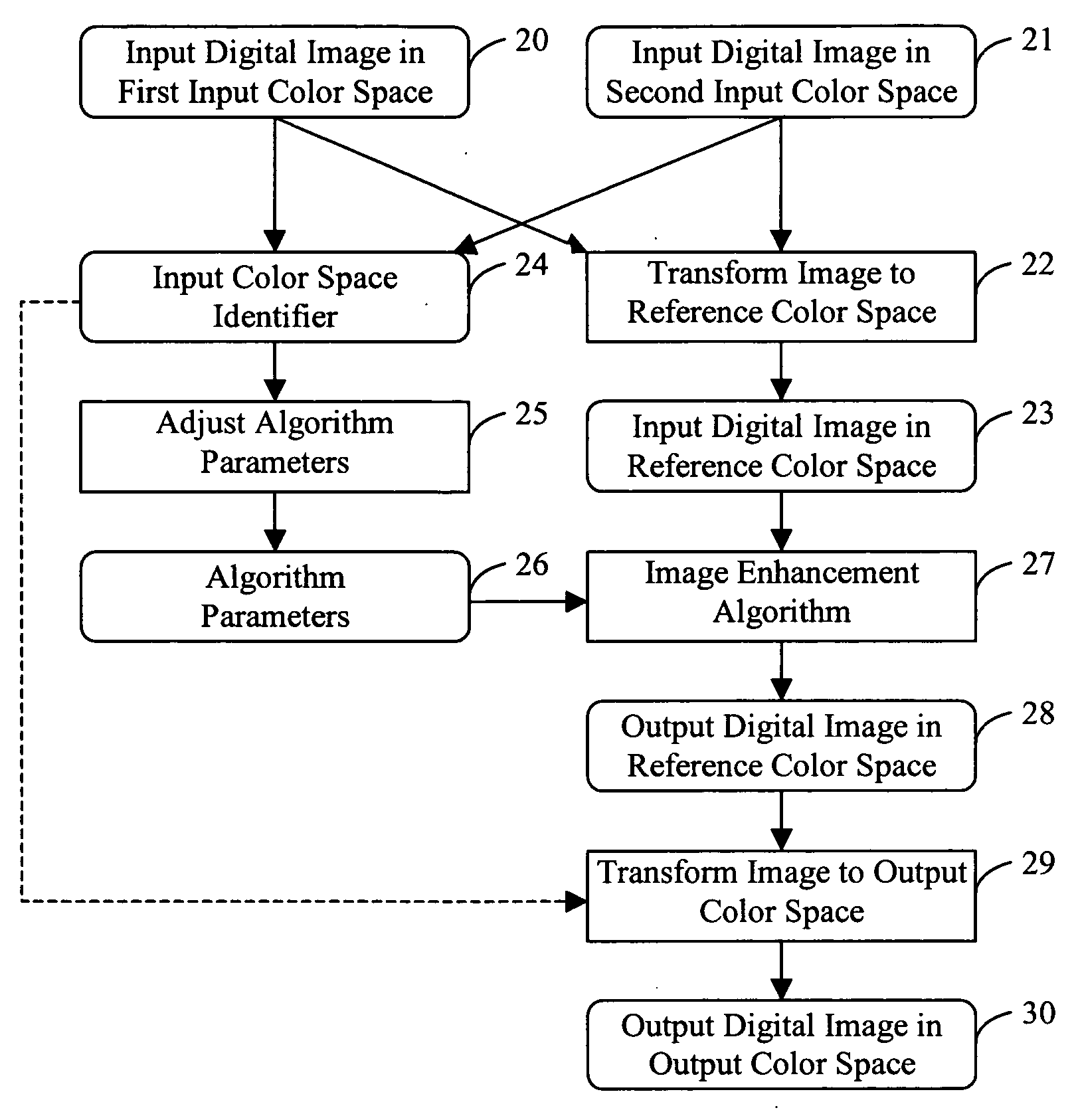
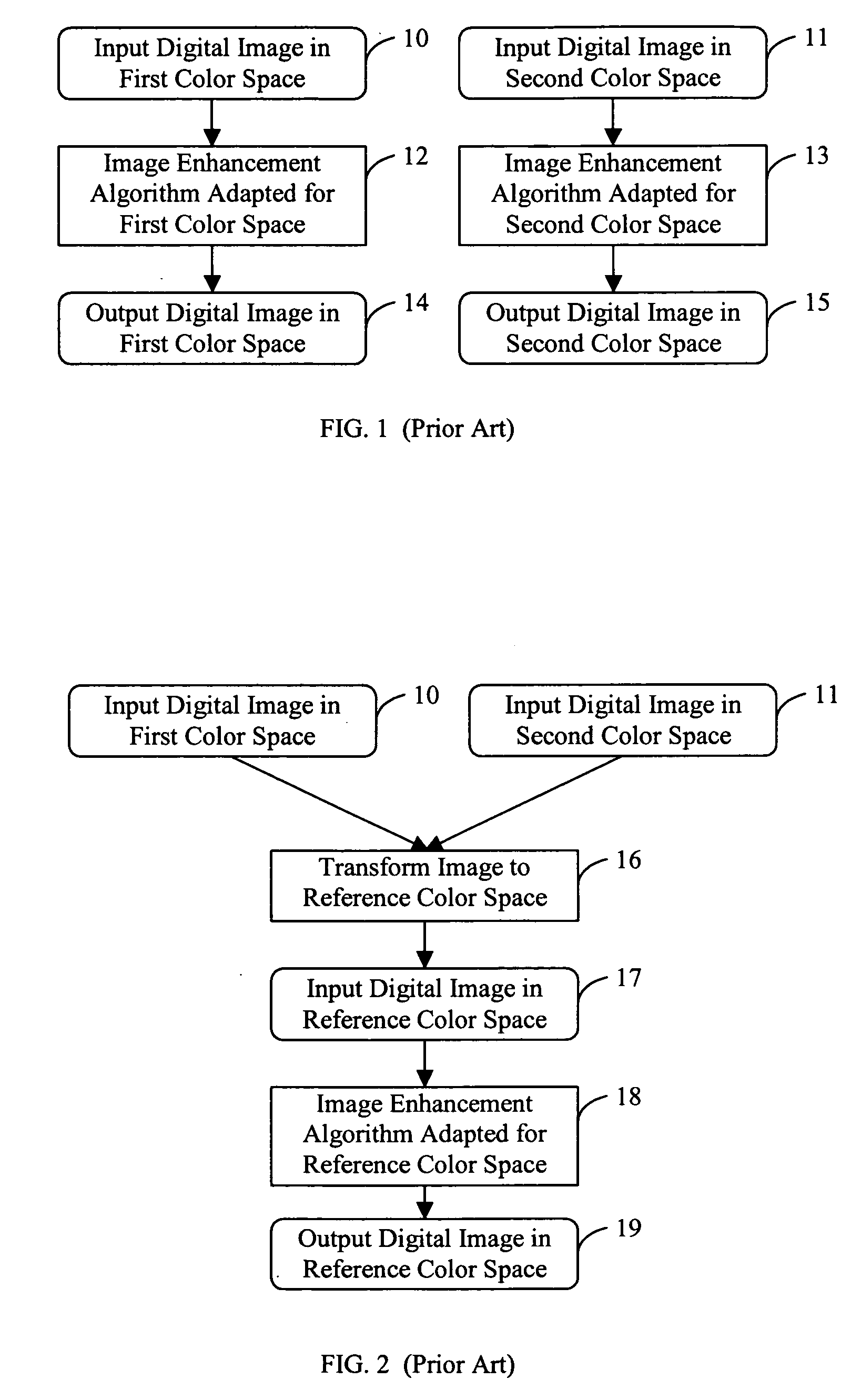
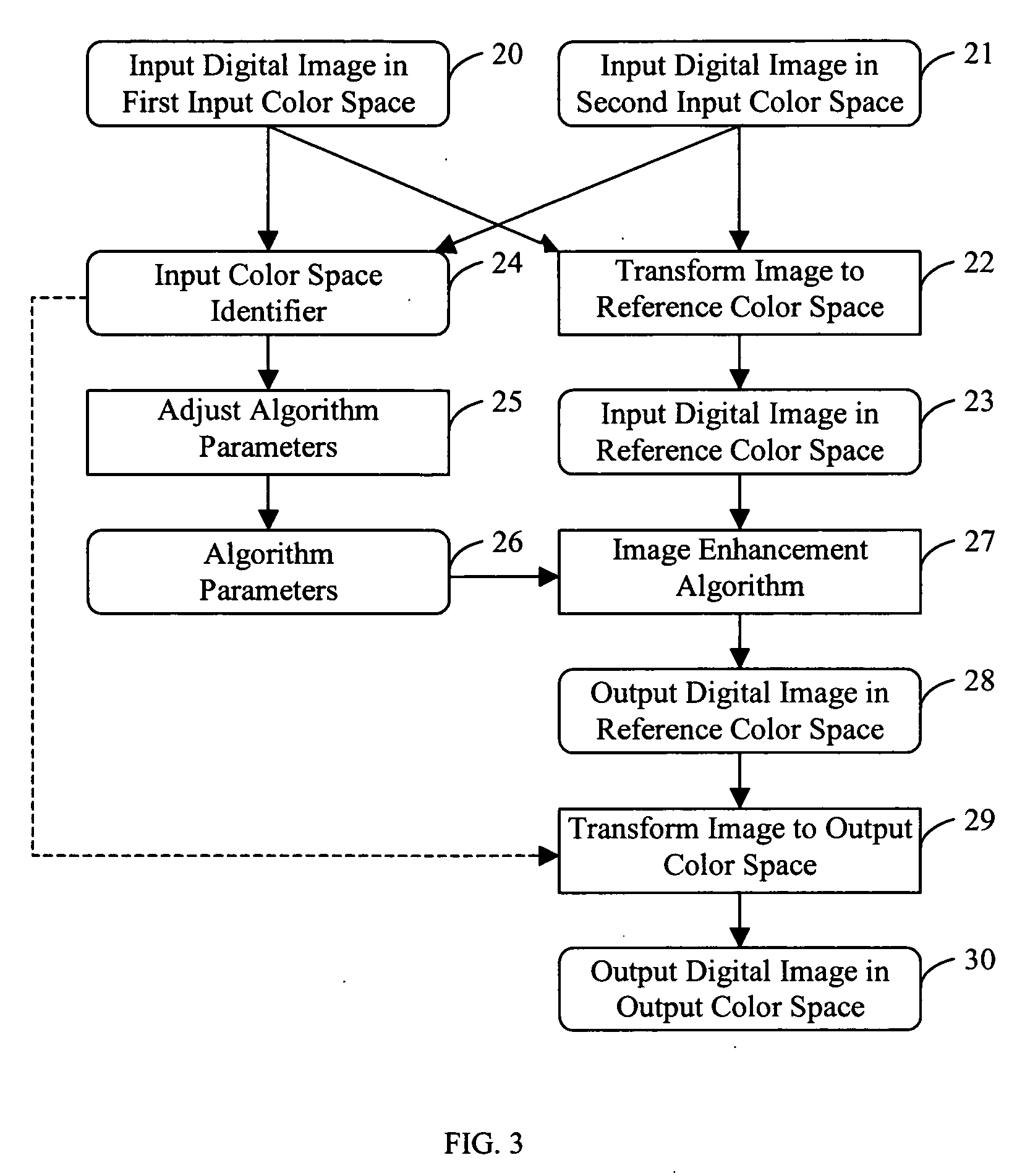
Applying an adjusted image enhancement algorithm to a digital image
InactiveUS20050152612A1Enhance the imagePromote resultsImage enhancementImage analysisDigital imageSpatial transformation
A method is described for applying an image enhancement algorithm to input digital images represented in different input color spaces including identifying the input color space of an input digital image, and applying a color space transformation to the input digital image represented in the input color space to form a corresponding input digital image in a reference color space. The method also includes adjusting one or more algorithm parameters of the image enhancement algorithm in response to the identified input color space, and applying the image enhancement algorithm with the one or more adjusted algorithm parameters to the corresponding input digital image in the reference color space to produce an enhanced digital image in the reference color space.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
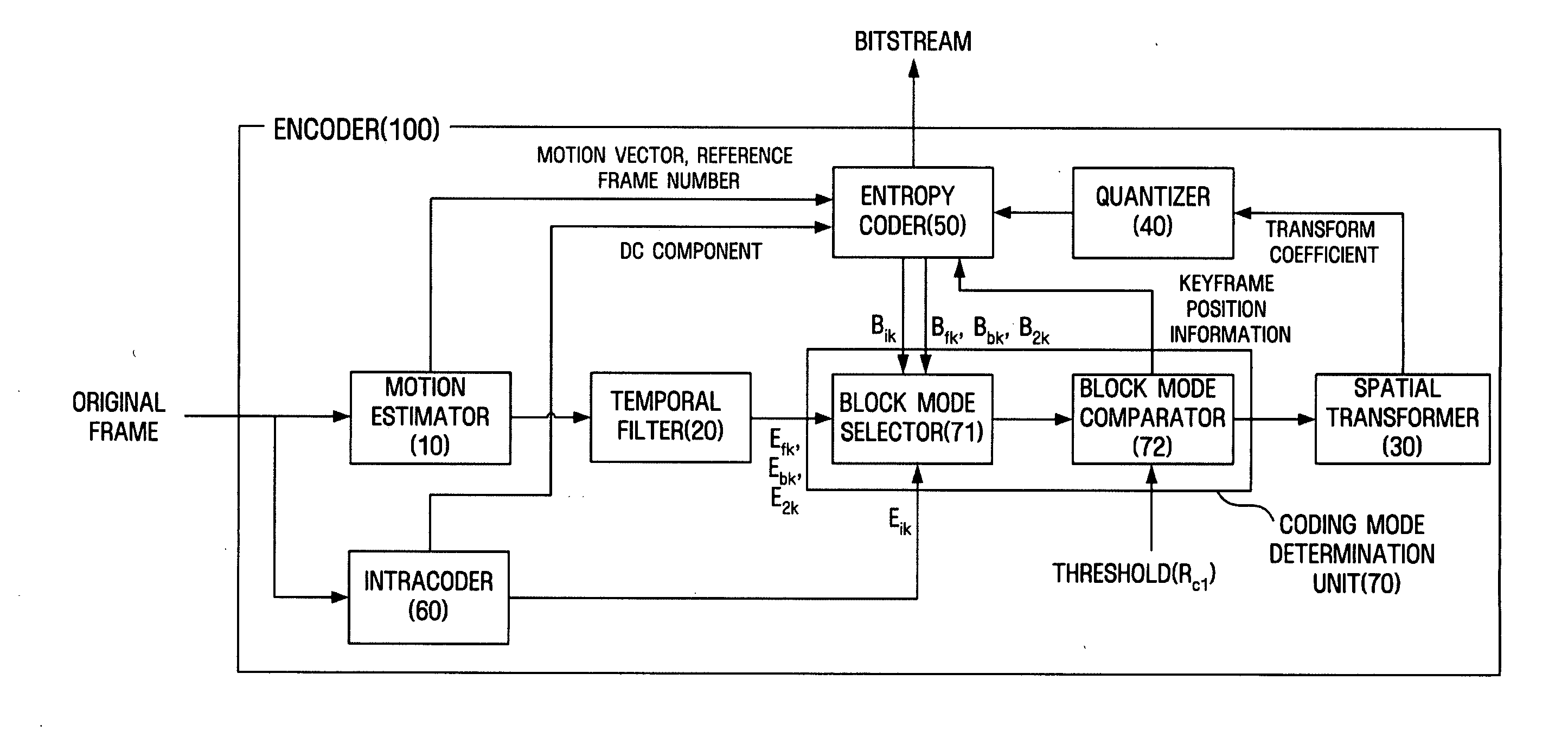
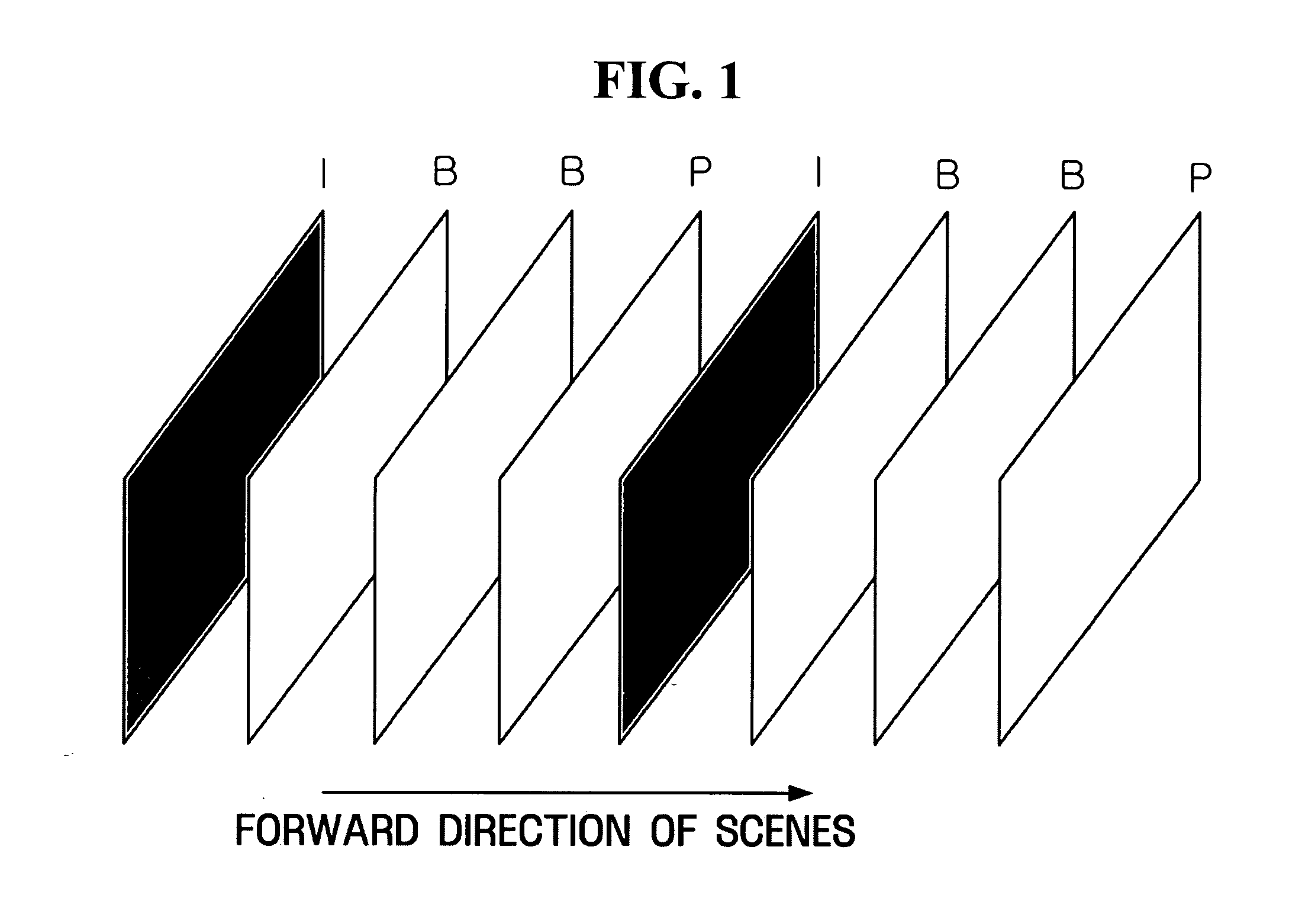
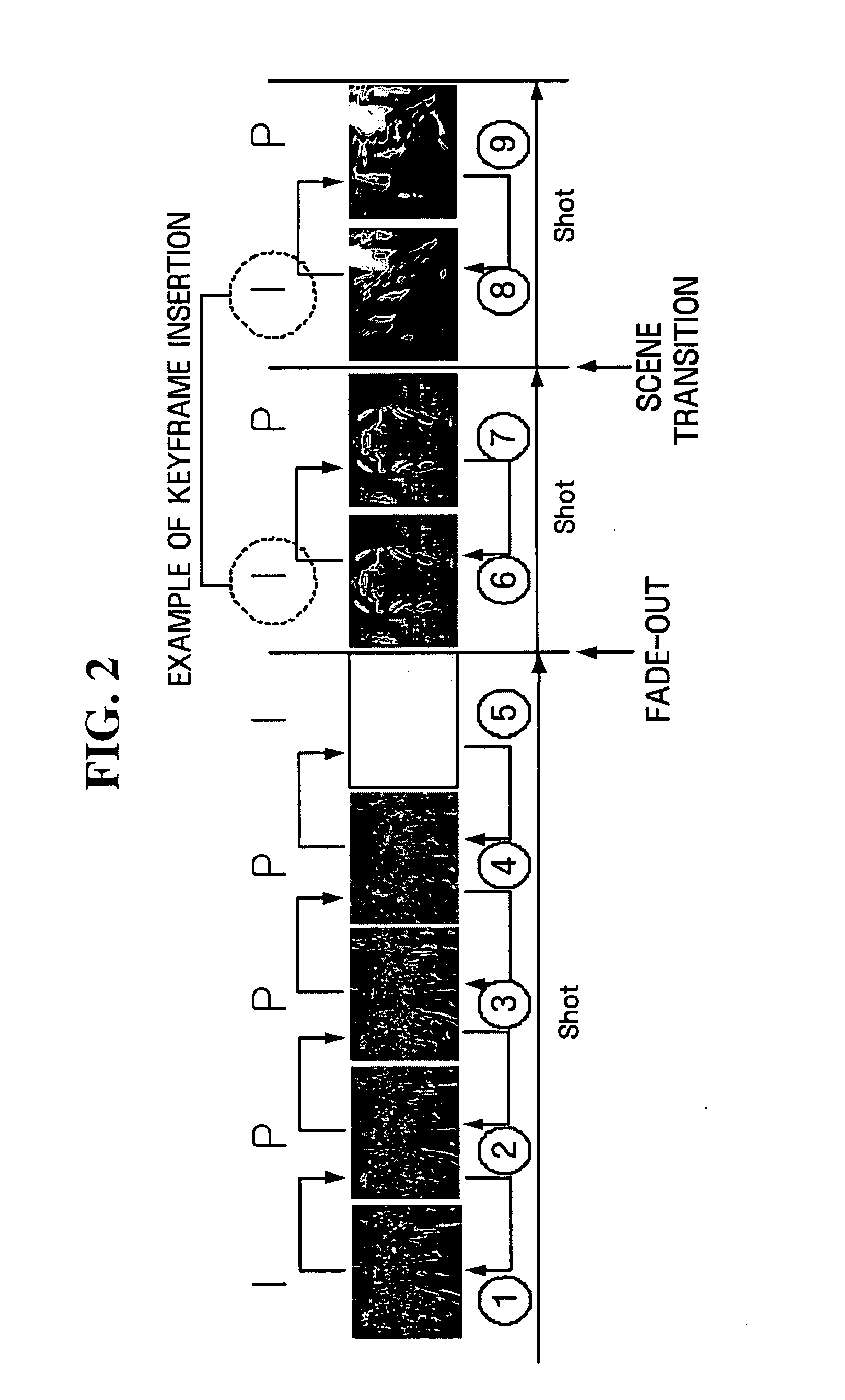
Video coding apparatus and method for inserting key frame adaptively
InactiveUS20050169371A1Minimal costTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionTransformerVideo encoding
A method of adaptively inserting a key frame according to video content to allow a user to easily access a desired scene. A video encoder includes a coding mode determination unit receiving a temporal residual frame with respect to an original frame, determining whether the original frame has a scene change by comparing the temporal residual frame with a predetermined reference, determining to encode the temporal residual frame when it is determined that the original frame does not have the scene change, and determining to encode the original frame when it is determined that the original frame has the scene change, and a spatial transformer performing spatial transform on either of the temporal residual frame and the original frame according to the determination of the coding mode determination unit and obtaining a transform coefficient. A keyframe is inserted according to access to a scene based on the content of an image, so that usability of a function allowing access to a random image frame is increased.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
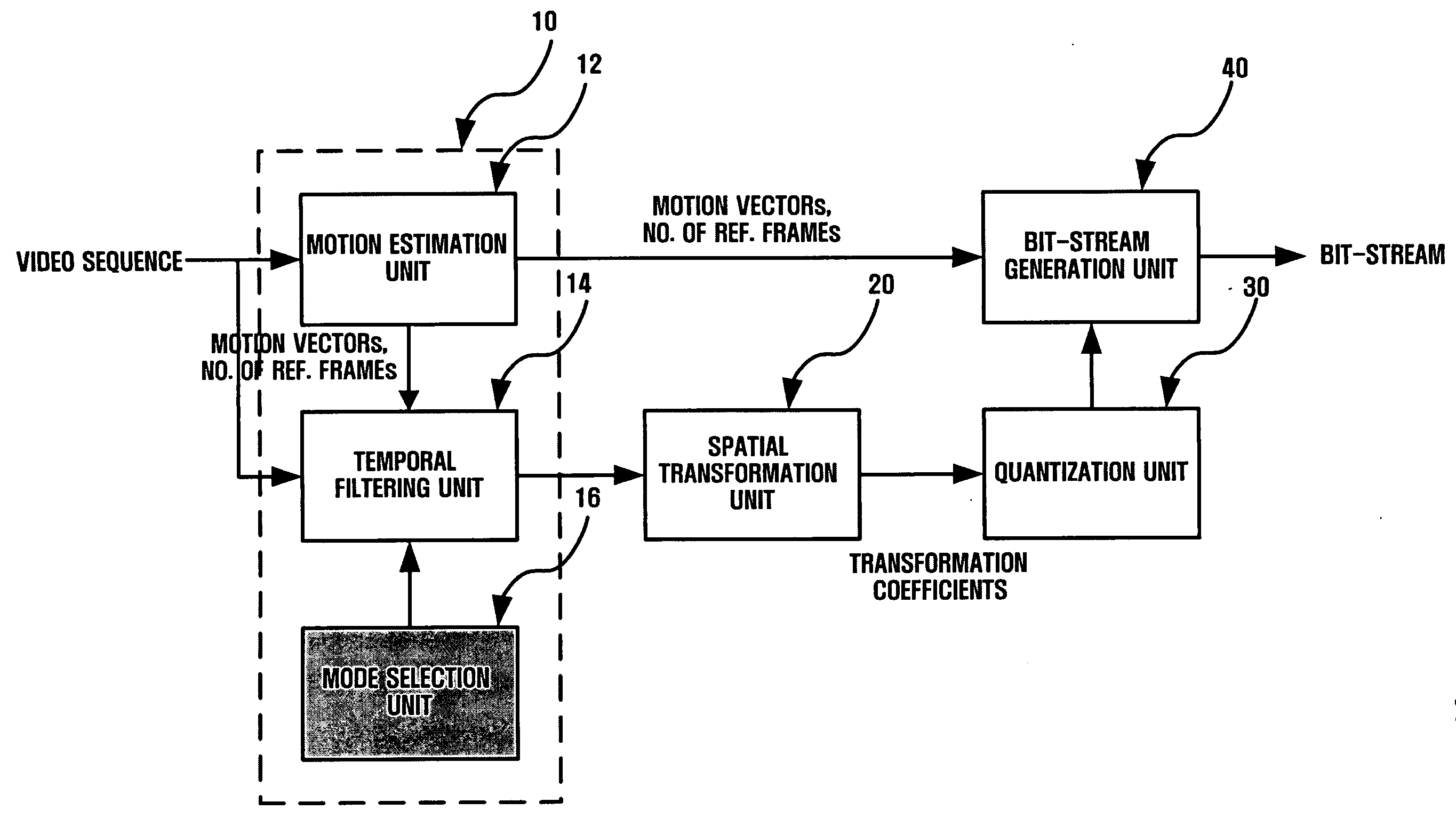
Method and apparatus for scalable video encoding and decoding
InactiveUS20050117647A1Eliminate spaceColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer graphics (images)Video encoding
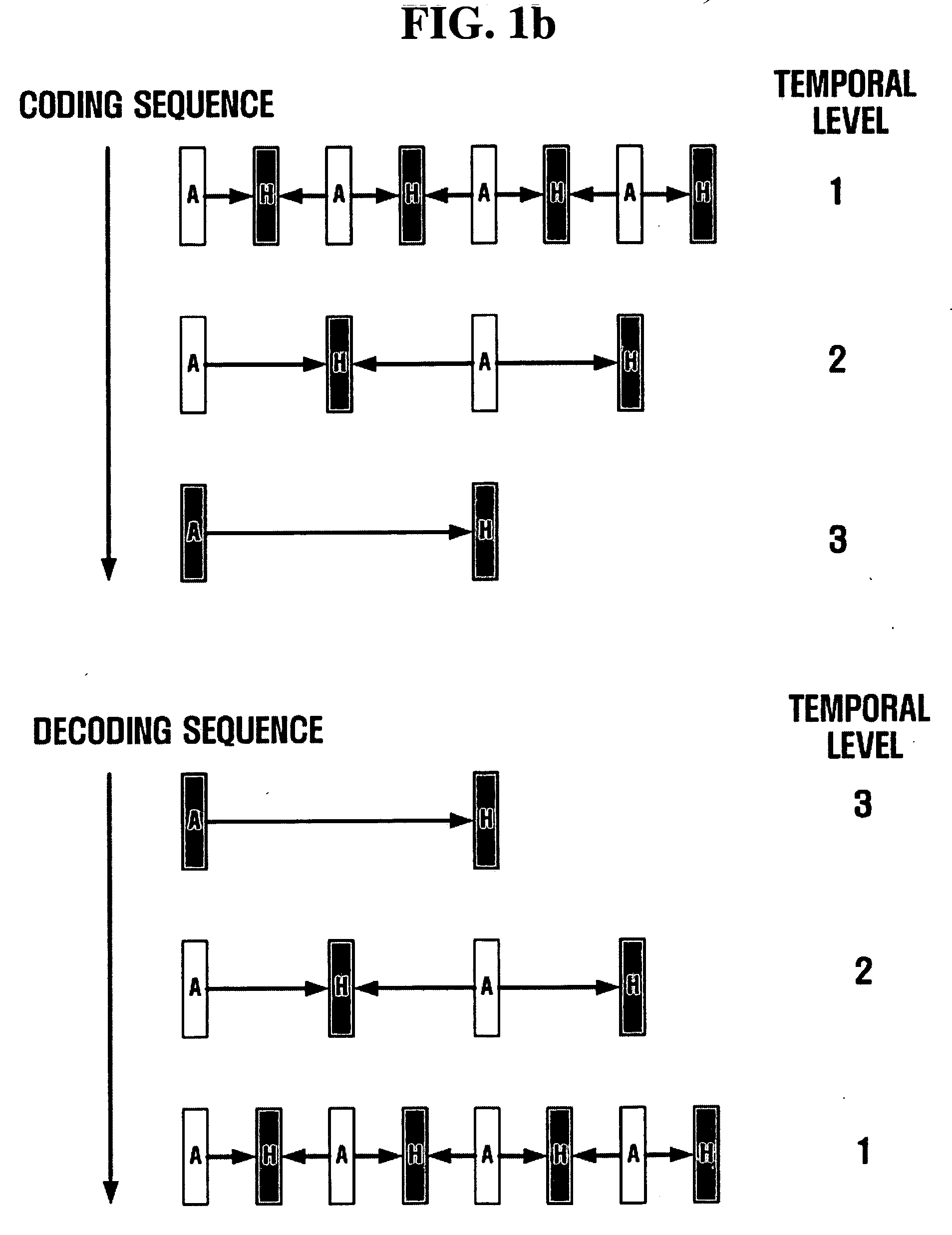
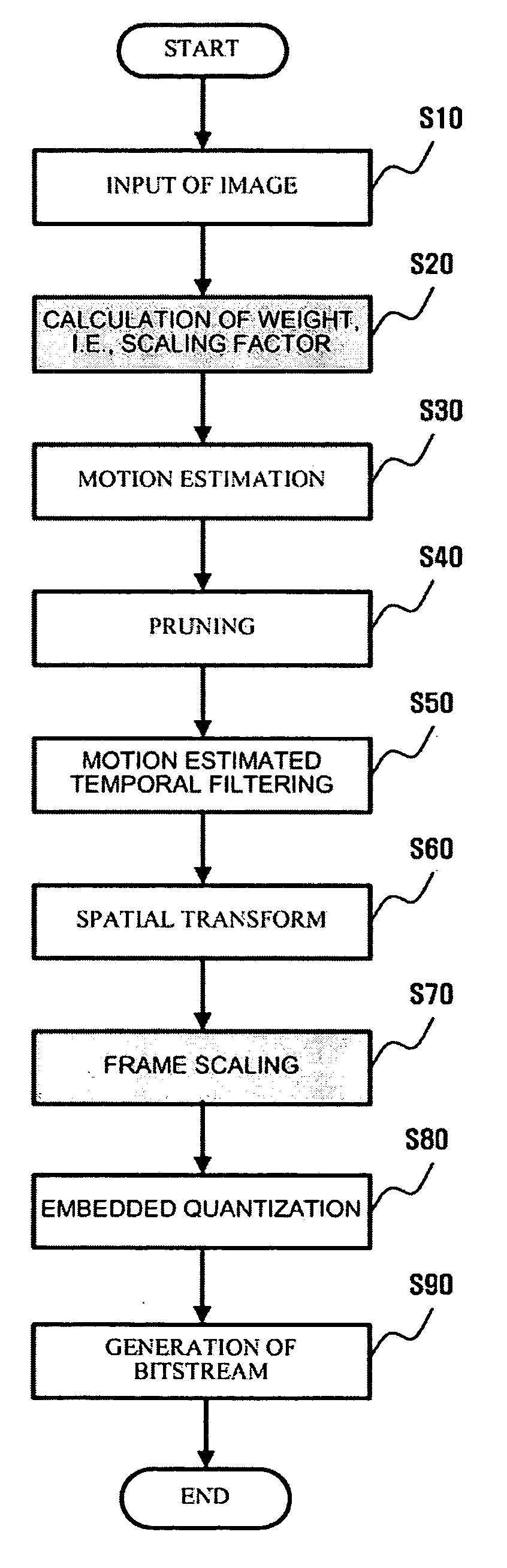
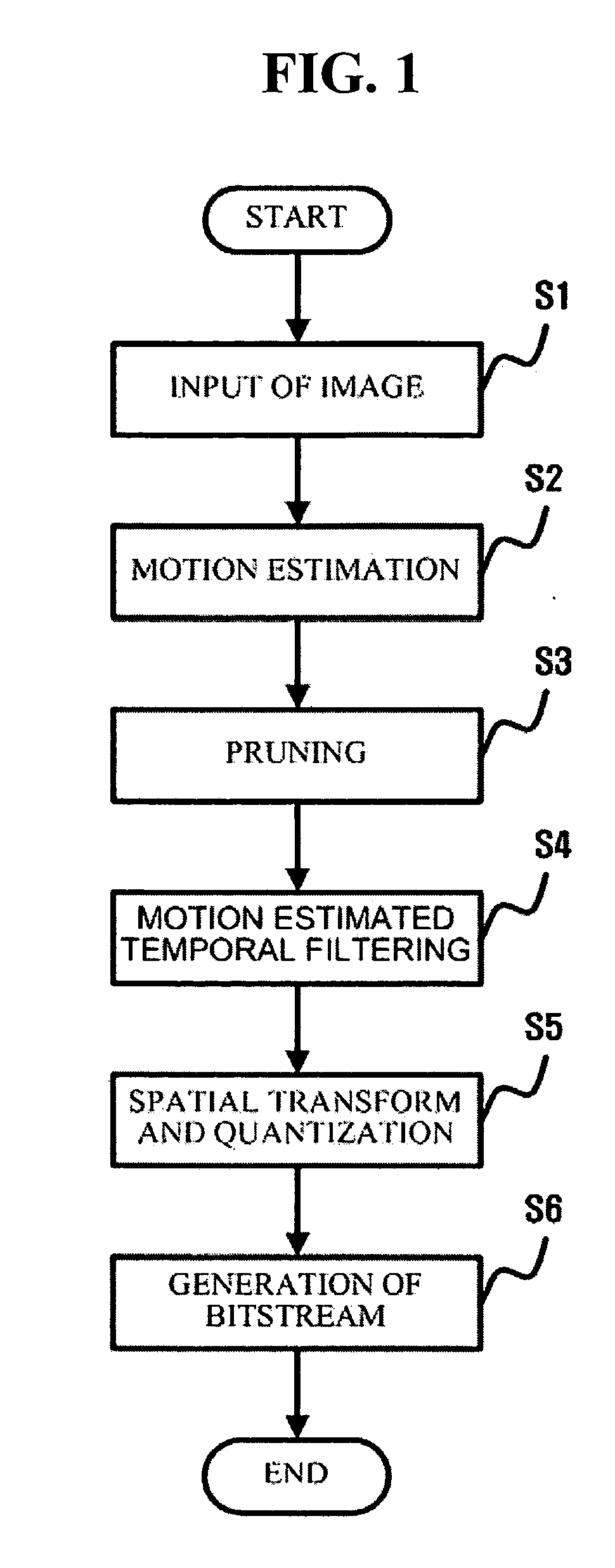
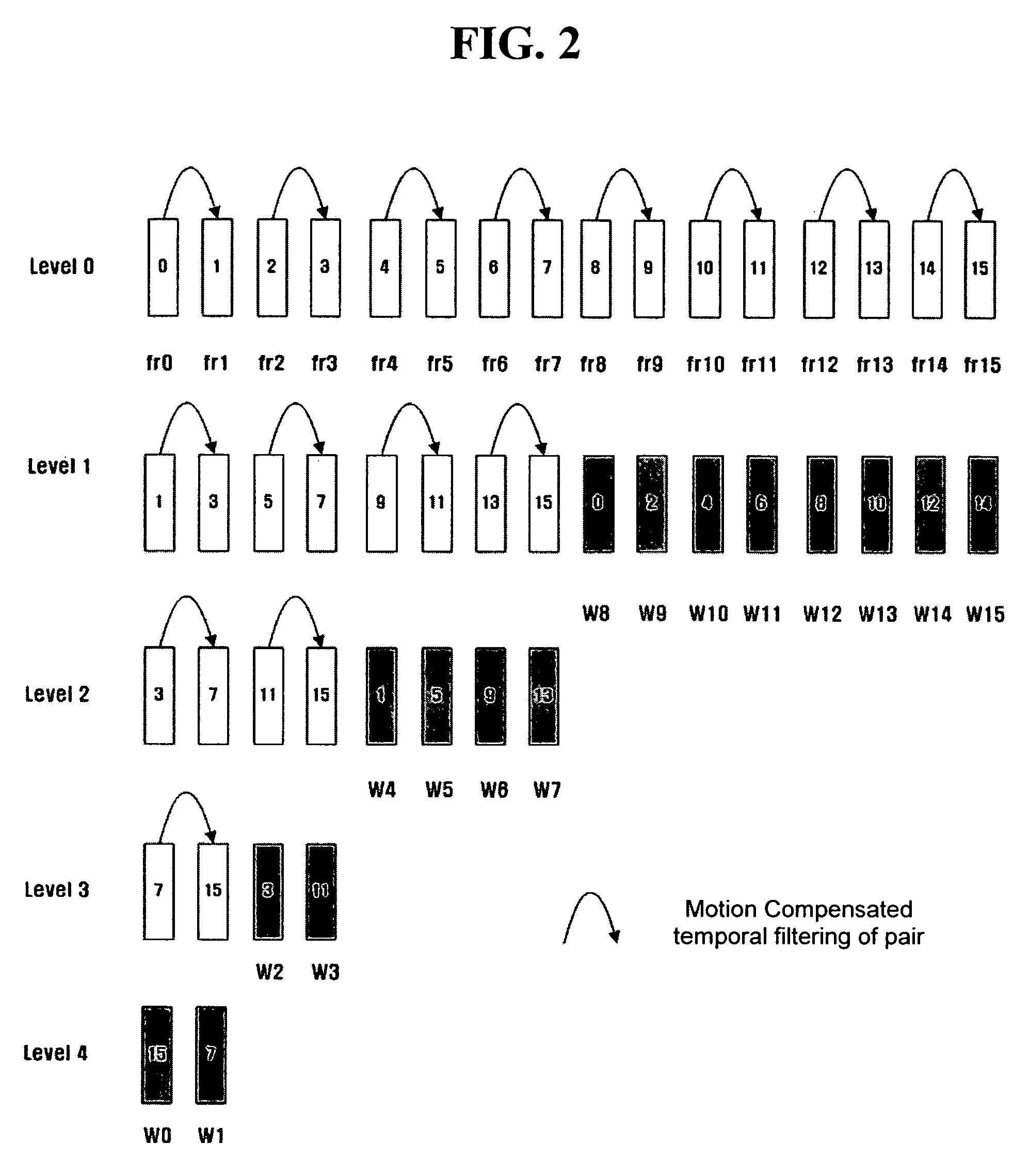
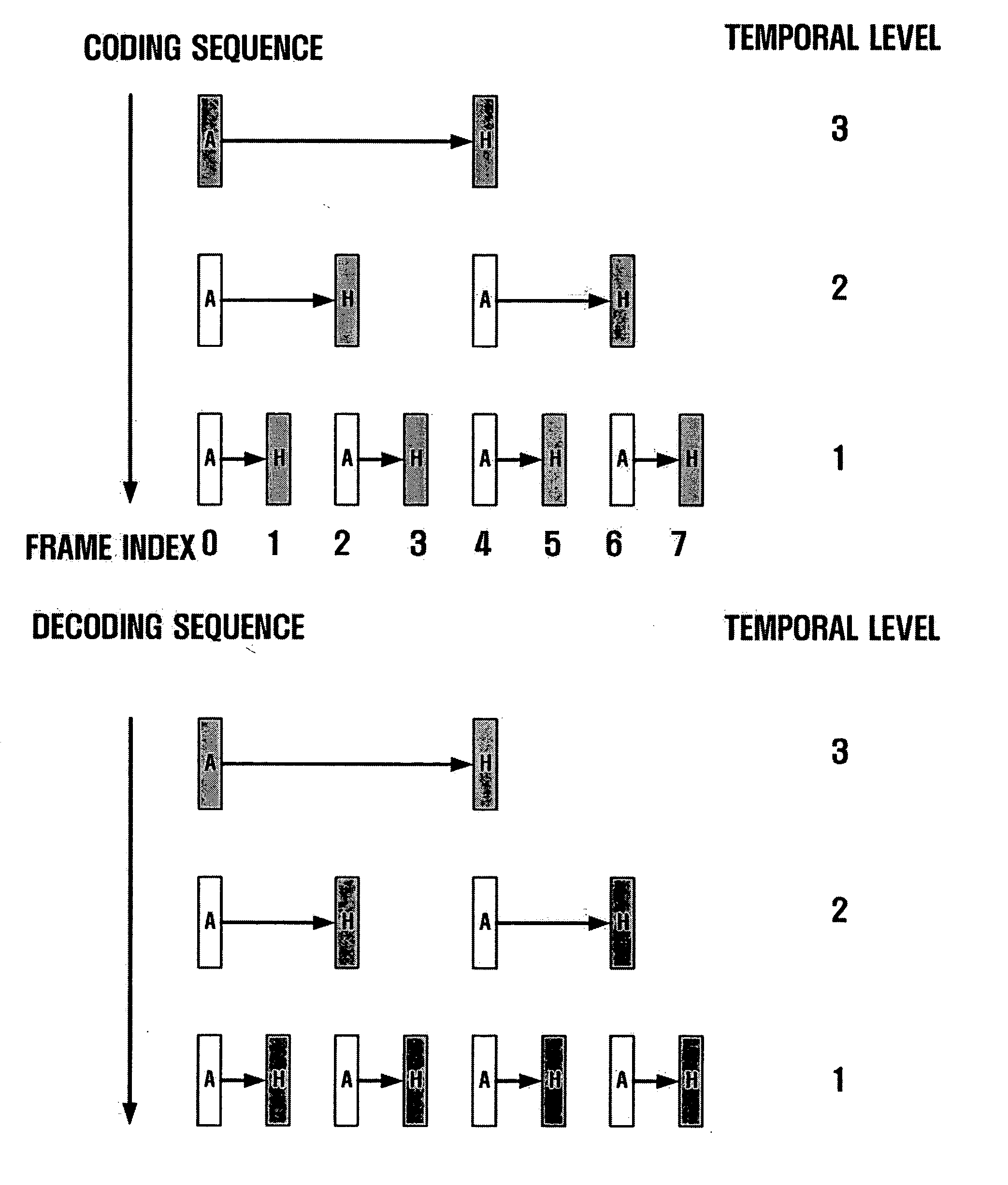
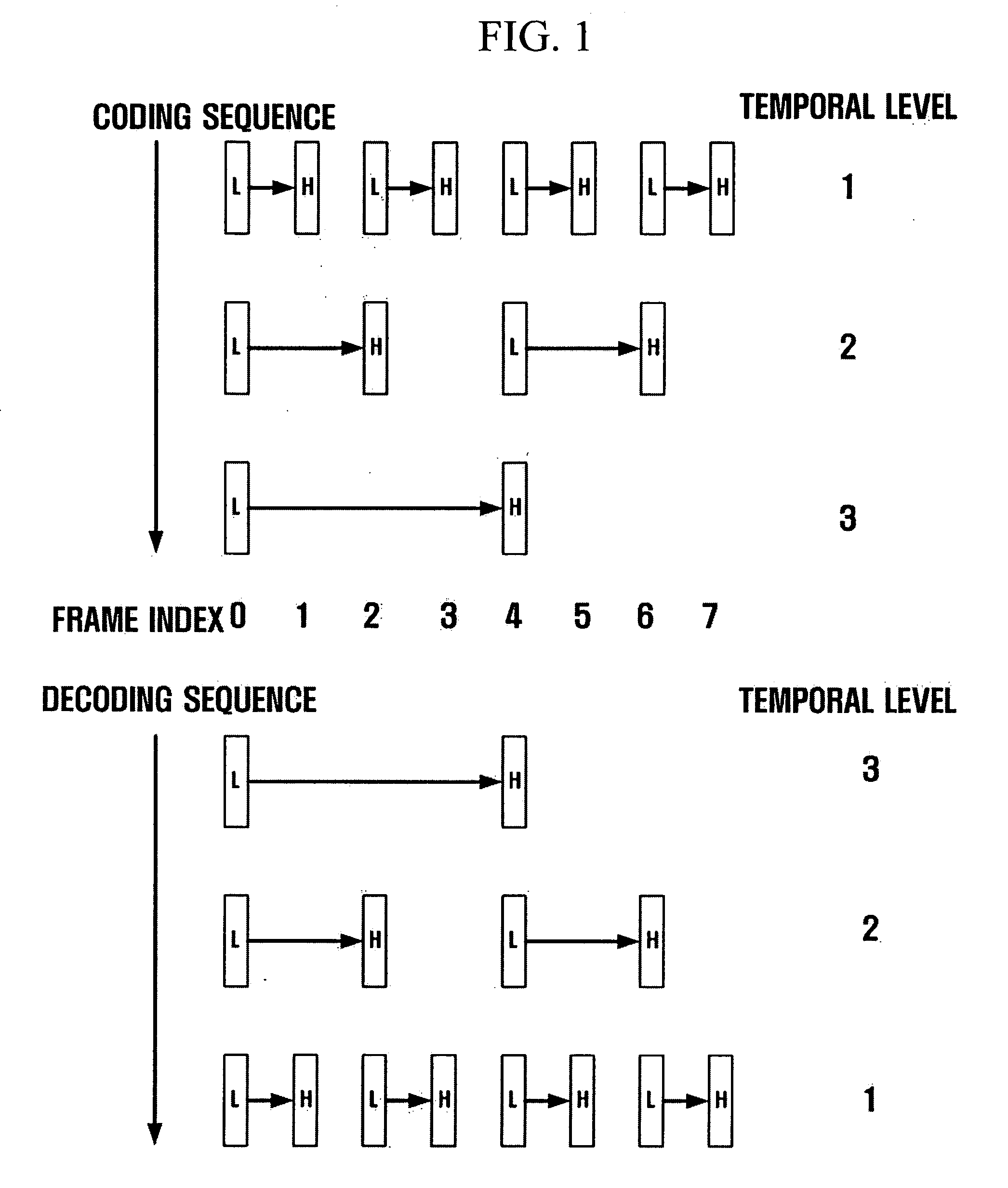
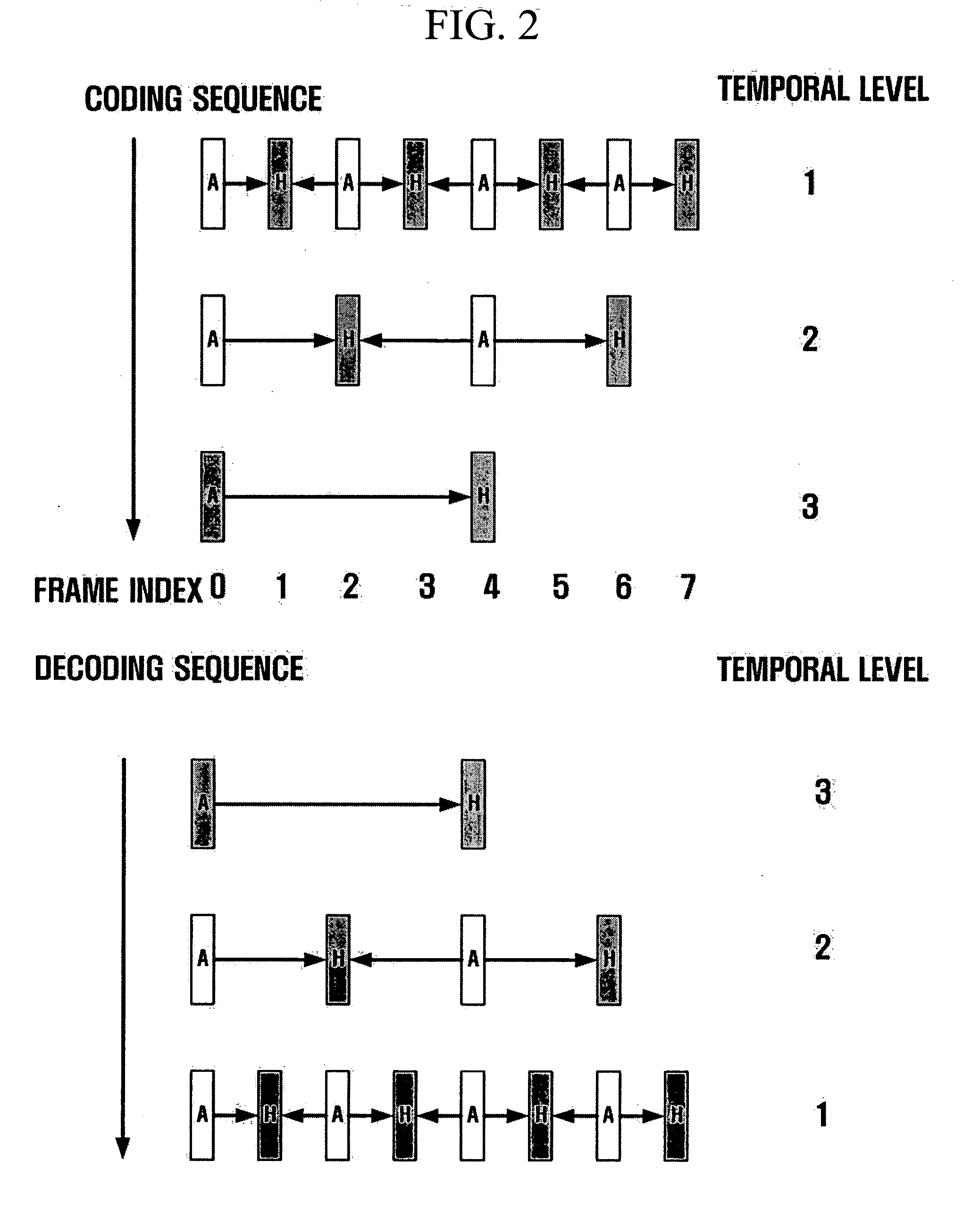
A method and apparatus for scalable video and decoding are provided. A method for video coding includes eliminating temporal redundancy in constrained temporal level sequence from a plurality of frames constituting a video sequence input, and generating a bit-stream by quantizing transformation coefficients obtained from the frames whose temporal redundancy has been eliminated. A video encoder for performing the encoding method includes a temporal transformation unit, a spatial transformation unit, a quantization unit, and a bit-stream generation unit. A video decoding method is in principle performed inversely to the video coding sequence, wherein decoding is performed by extracting information on encoded frames by receiving bit-streams input and interpreting them.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
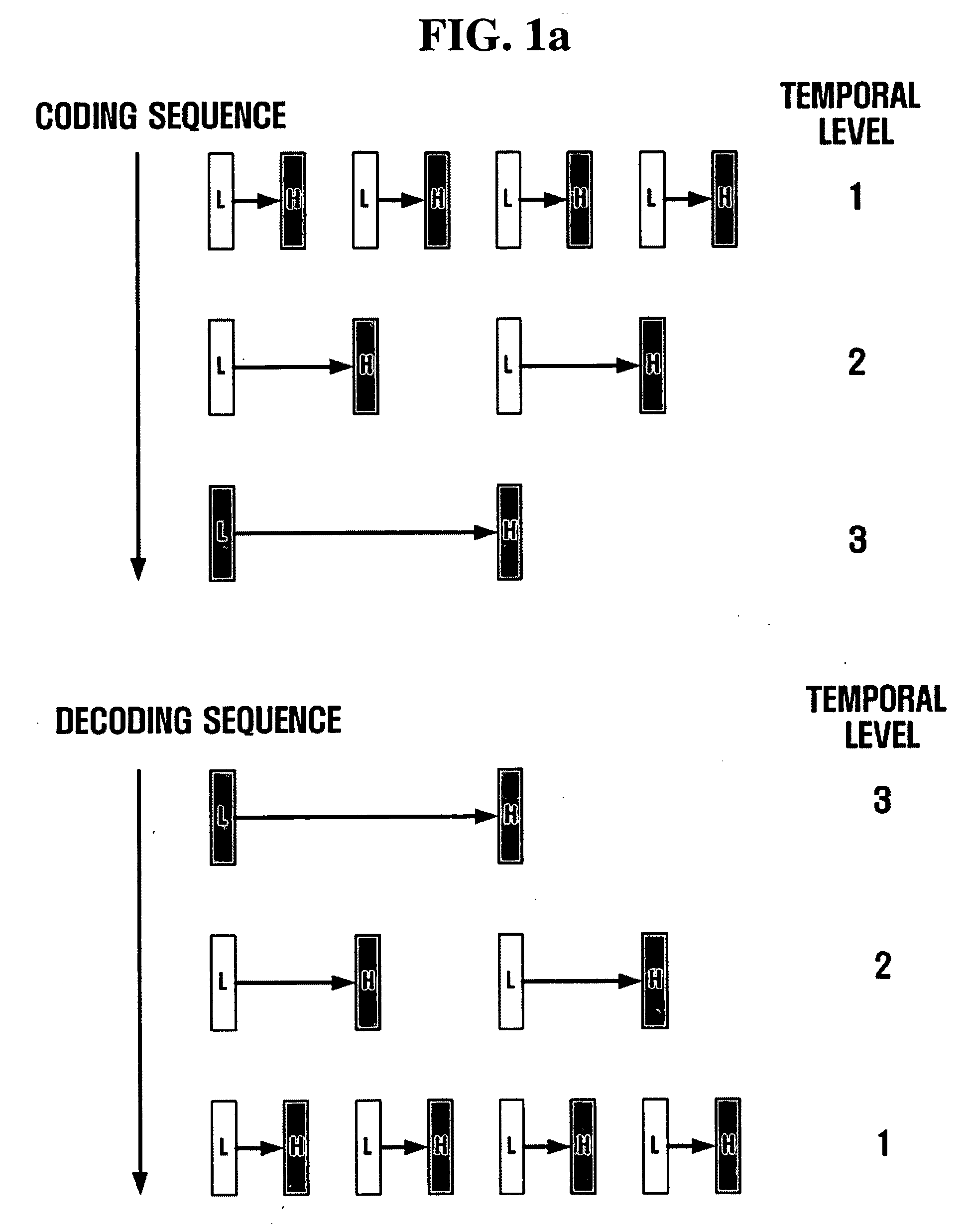
Scalable video coding and decoding methods, and scalable video encoder and decoder
InactiveUS20050047509A1Slow changeEliminate spaceColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureGroup of pictures
Scalable video coding and decoding methods, a scalable video encoder, and a scalable video decoder. The scalable video coding method includes receiving a GOP, performing temporal filtering and spatial transformation thereon, quantizing and generating a bitstream. The scalable video encoder for performing the scalable video coding method includes a weight determination block which determines a weight for scaling. The scalable video decoding method includes dequantizing the coded image information obtained from a received bitstream, performing descaling, inverse spatial transformation, and inverse temporal filtering on the scaled transform coefficients, thereby recovering video frames. The scalable video decoder for performing the scalable video decoding method includes an inverse weighting block. The standard deviation of Peak Signal to Noise Ratios (PSNRs) of frames included in a group of pictures (GOP) is reduced so that video coding performance can be increased.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
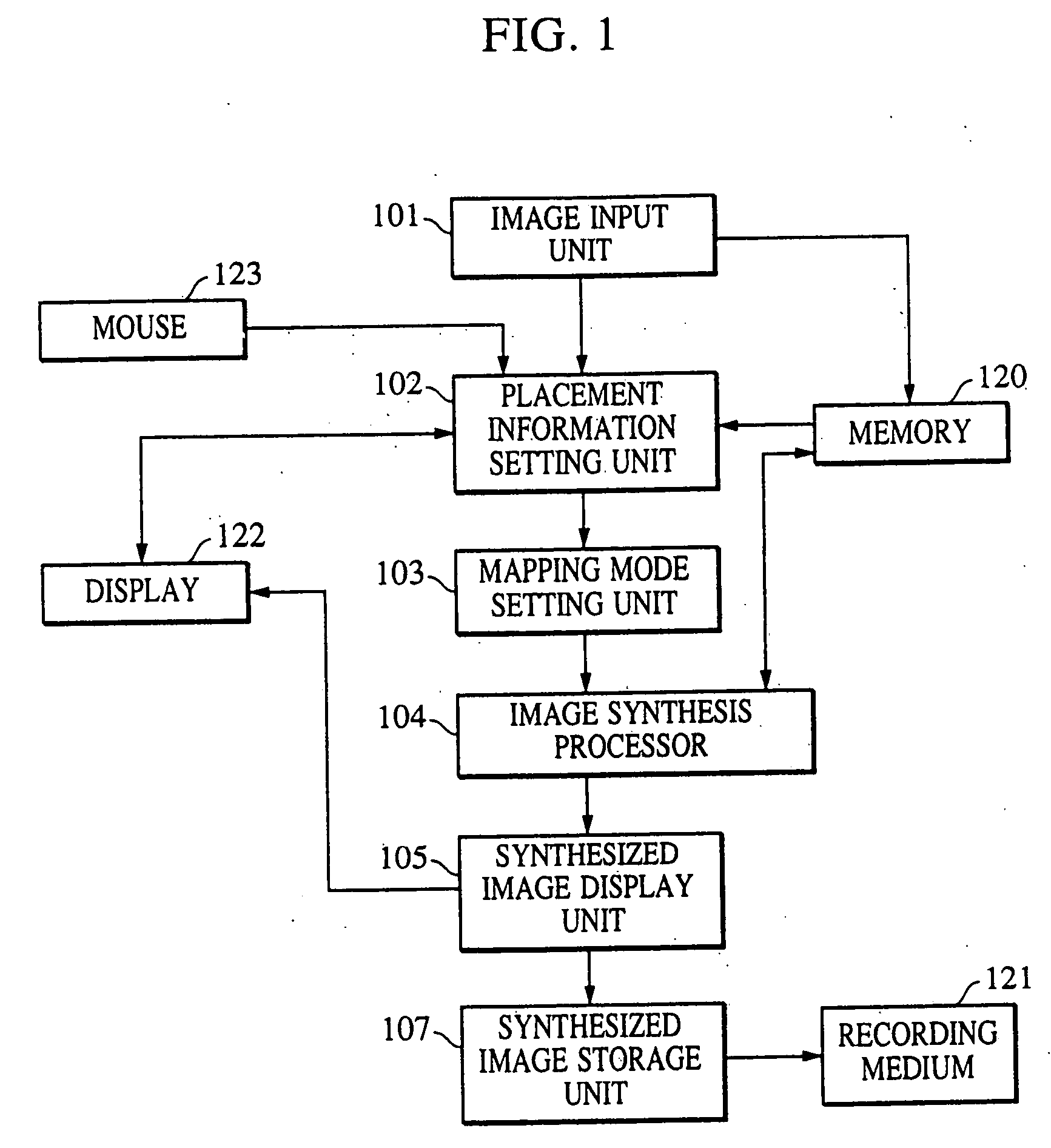
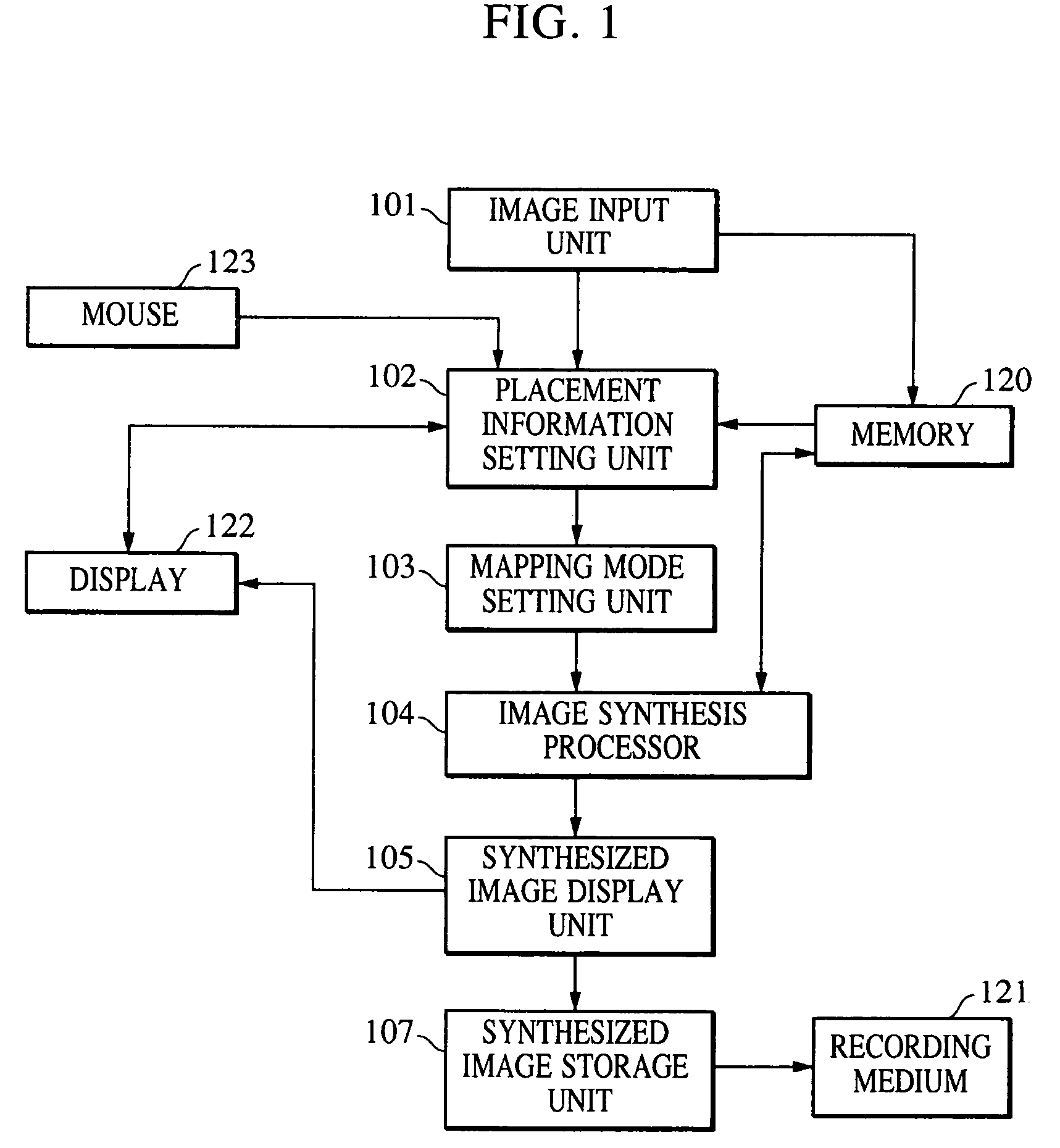
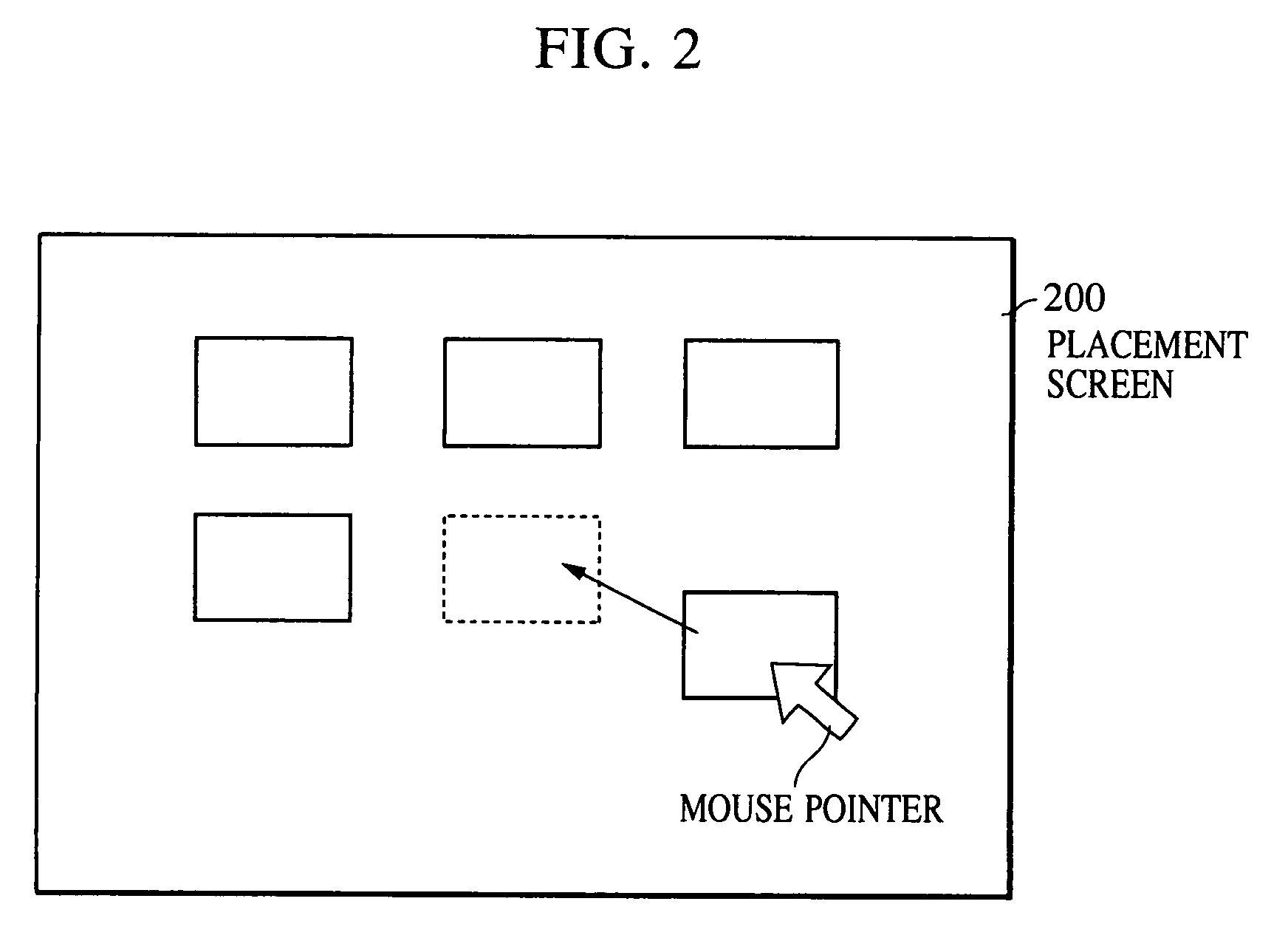
Image synthesis method, image synthesis apparatus, and storage medium
InactiveUS20060238536A1Easy to set upQuality improvementGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Spatial transformation
An image synthesis method includes a placement information obtaining step of obtaining placement information about a plurality of images in which adjacent images have a common subject region, and a synthesis step of combining the images using a mapping mode in accordance with the placement information. Prior to performing mapping transformation of the input images, coordinate-space transformation parameters for transforming the coordinate space of one image among the images into the coordinate space of another image are generated. The images are combined based on a given mapping mode and the coordinate-space transformation parameters.
Owner:CANON KK
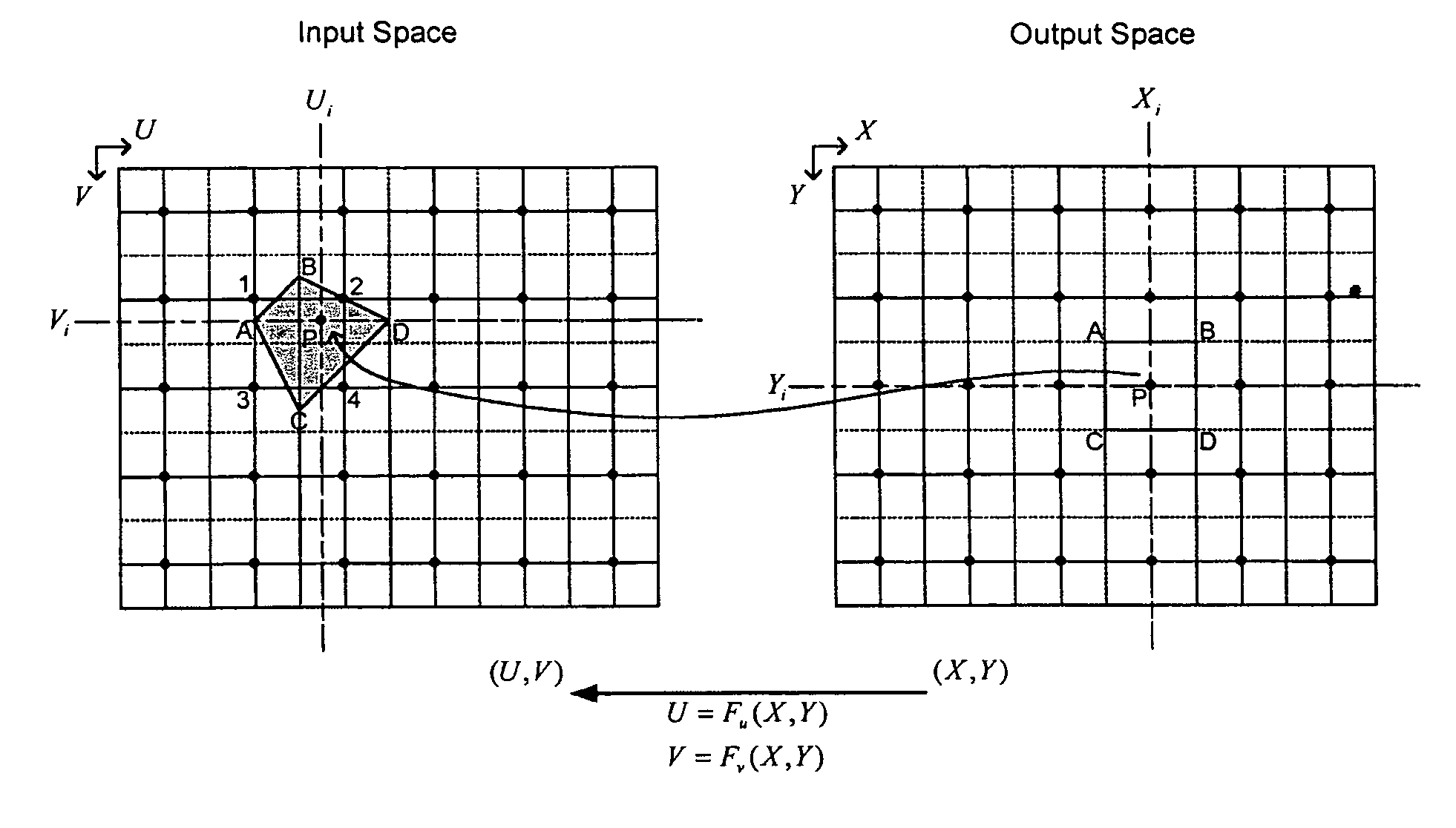
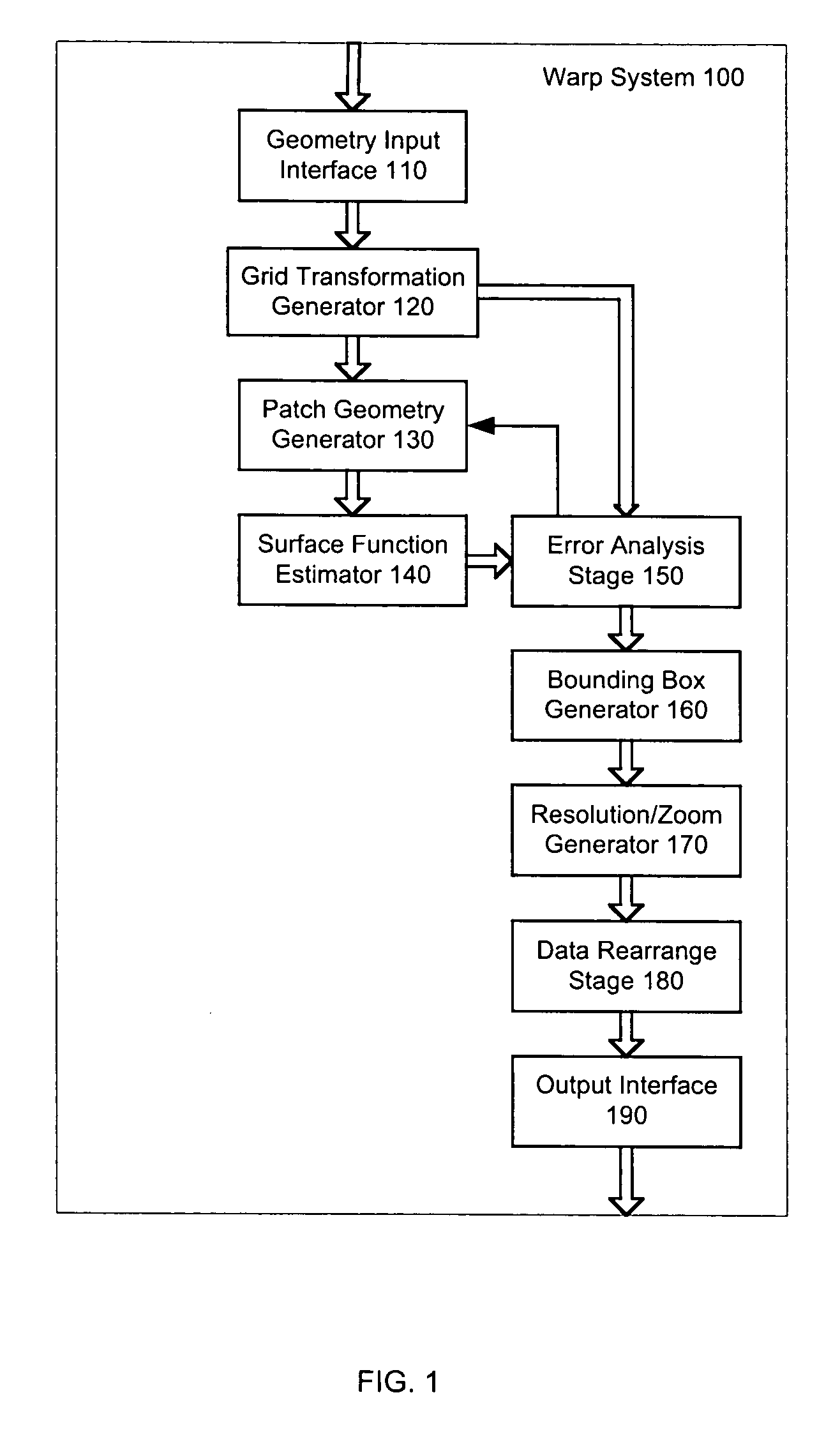
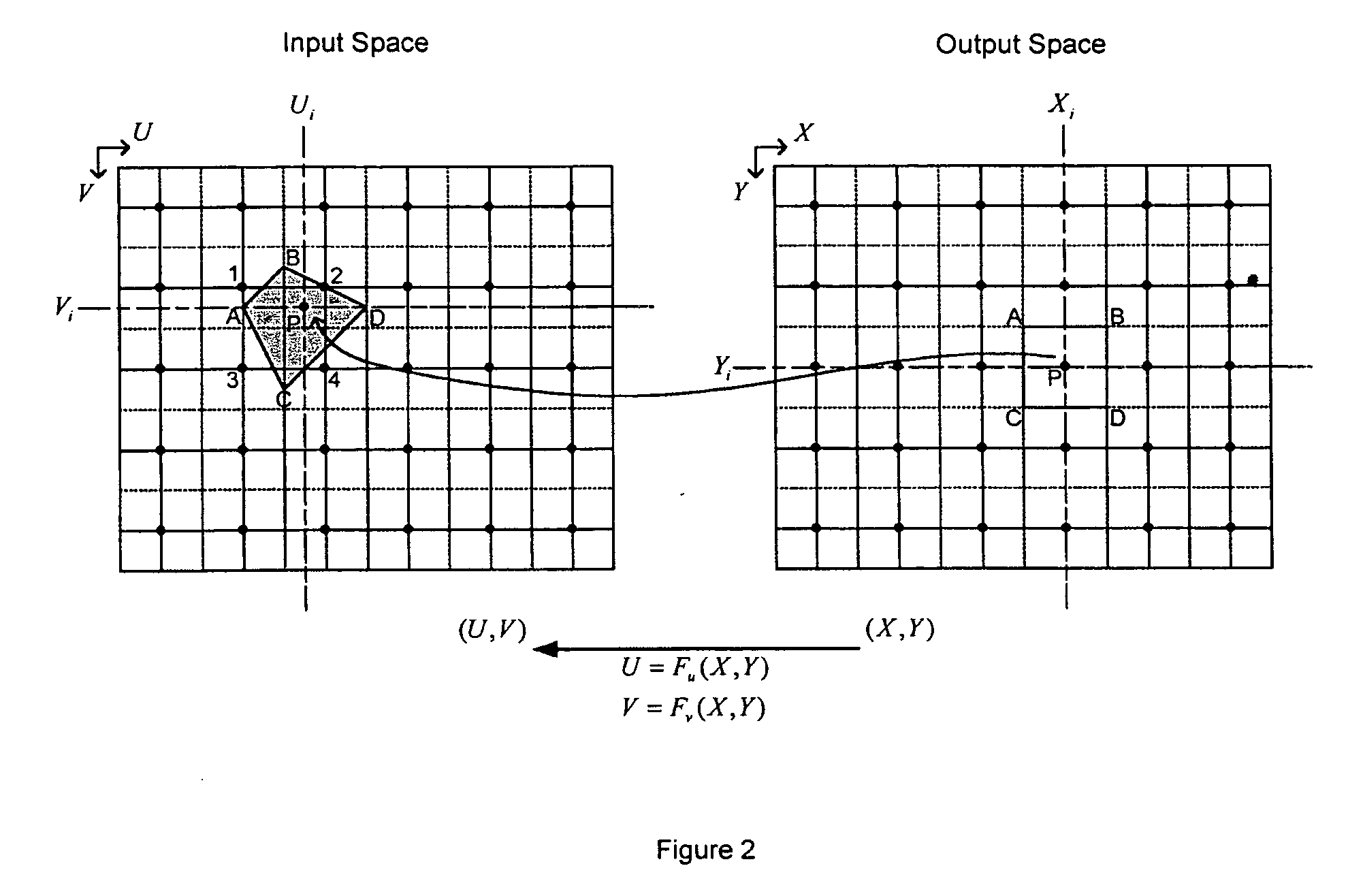
System and method for representing a general two dimensional spatial transformation
ActiveUS20060050074A1Geometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionData setImage resolution
A system and method for representing a two-dimensional spatial transformation that describes the transformation by an inverse mapped grid data set. The grid data for each coordinate is surface fitted on an array of rectangular patches defined in the output space using numerical techniques. Error analysis determines whether a finer mesh resolution is required for surface fitting. The spatial transformation is then defined by the array of rectangular surface patches and the set of surface coefficients such that the spatial transformation can be executed through evaluation of the surface polynomials. The two-dimensional surface polynomial representation allows the transformation to be easily adjusted for scale changes and zooming and panning effects.
Owner:GEO SEMICONDUCTOR INC
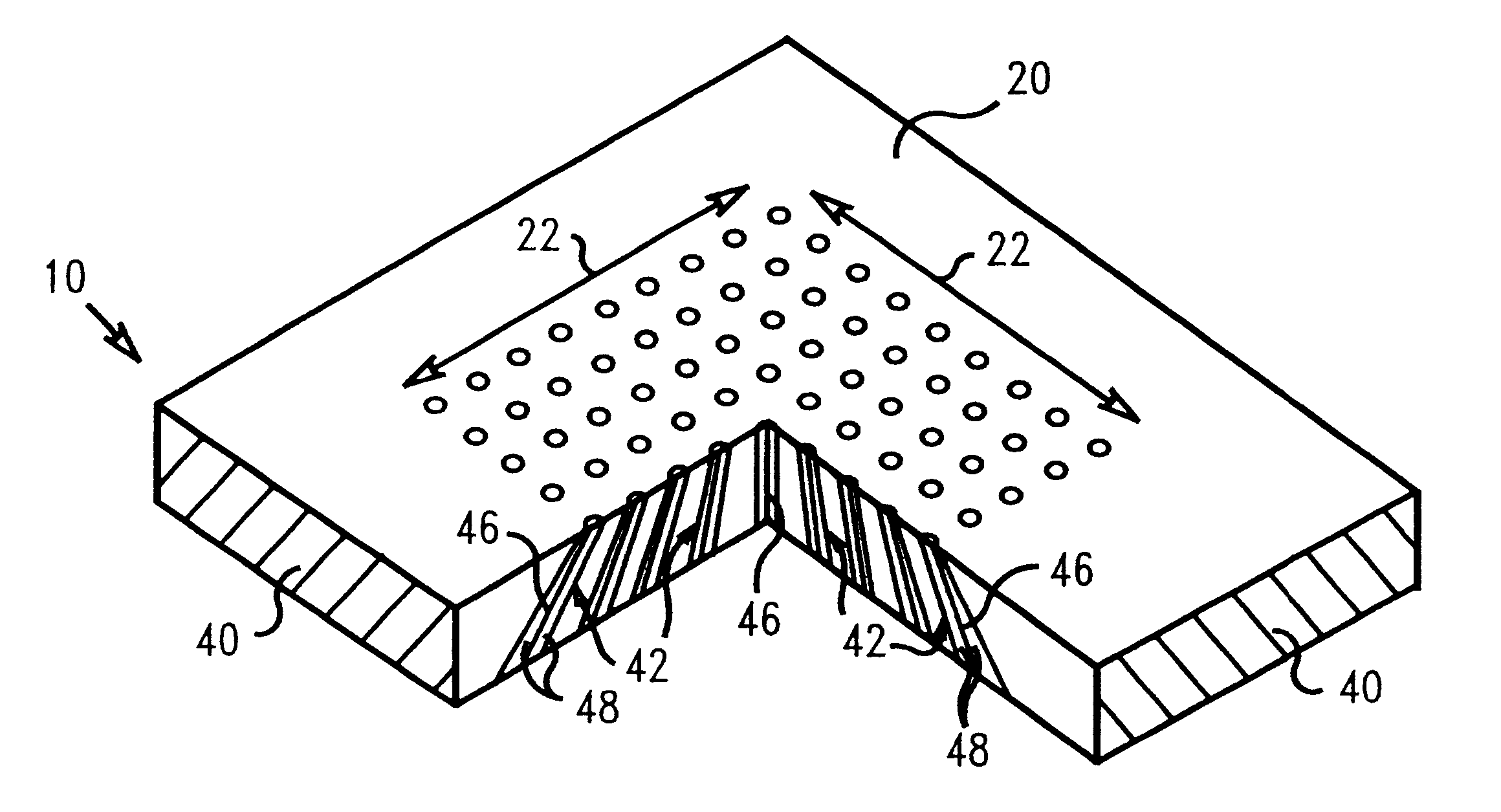
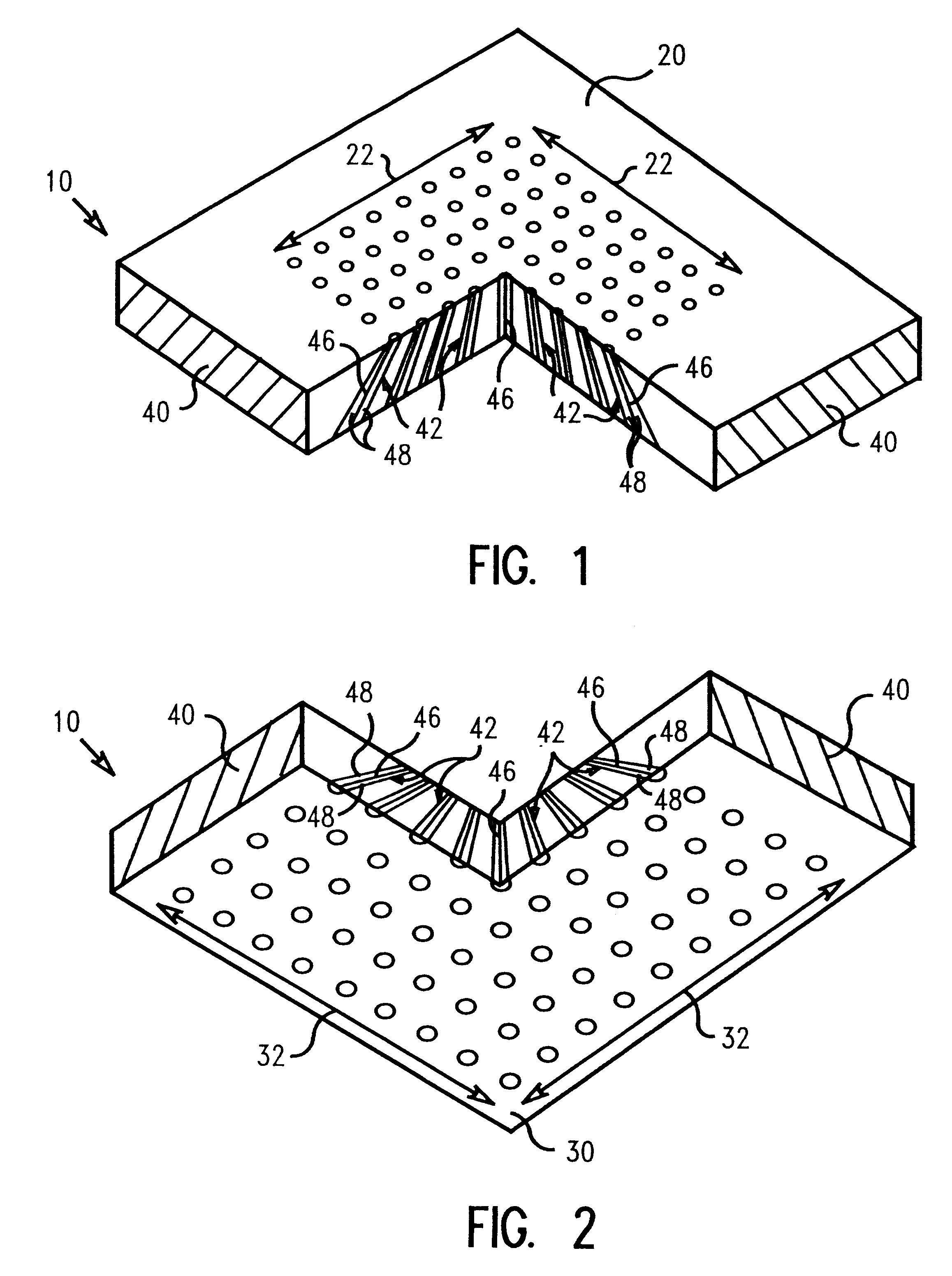
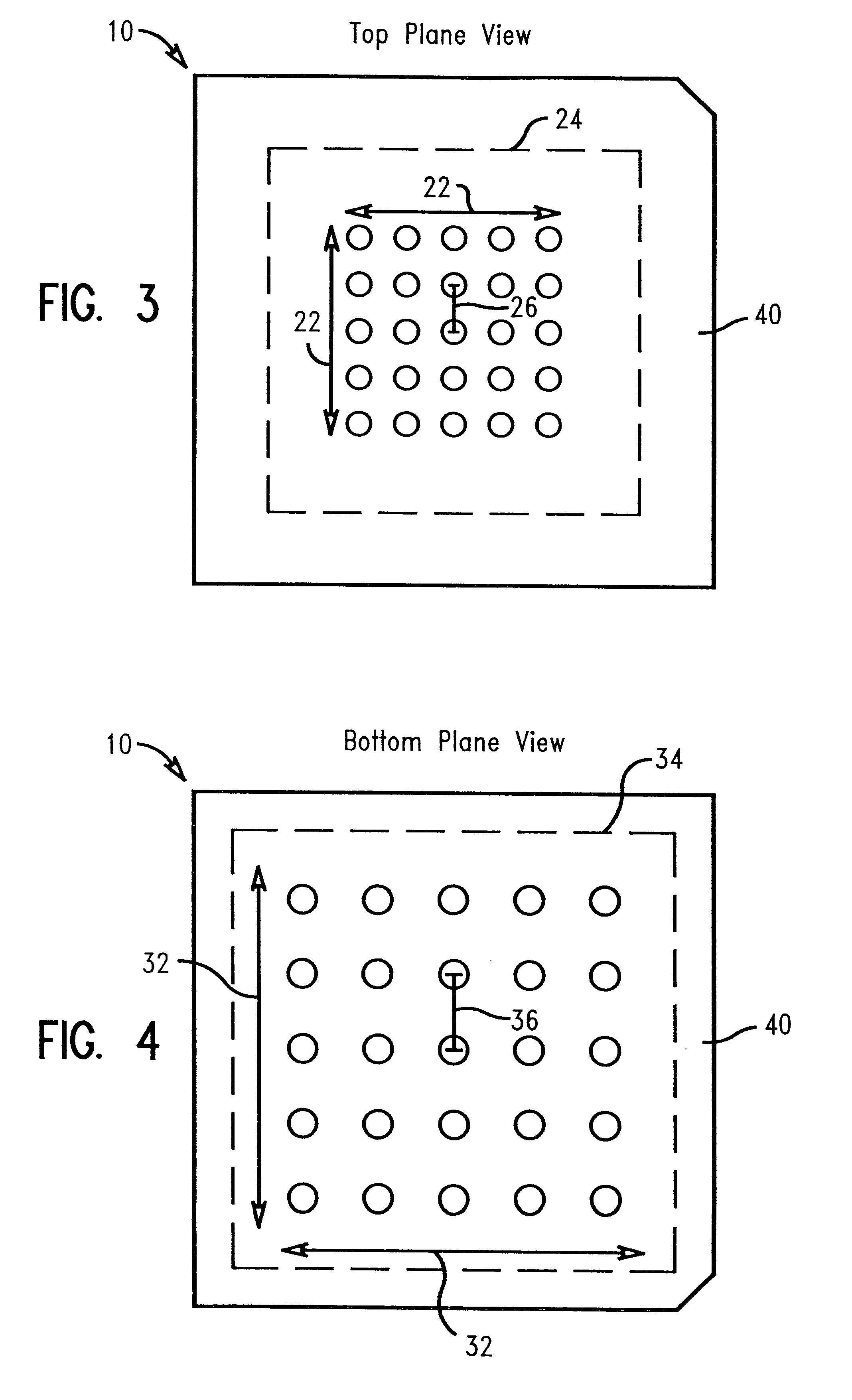
Spatial transformation interposer for electronic packaging
InactiveUS6332782B1Firmly connectedSmall sizePrinted circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInterposerInterconnection
An interconnect substrate structure for electrical interconnection between two electronic modules having differing conductive array parameters. The interconnect structure comprises an interposer having a top surface and a bottom surface; a first set of conductive arrays having a first conductive array parameter on the top surface, and a second set of conductive arrays having a second conductive array parameter on the bottom surface, the second conductive array and the first conductive array having differing parameters. A plurality of conductors traverses a thickness of the interposer, with the conductors comprising a conductive material optionally coated with a dielectric material, the conductors having a first end at the first conductive arrays and a second end at the second conductive arrays, whereby the conductors connecting the first and second conductive arrays therein are adapted to spatially transform the differing parameters to provide an electrical interconnection. A conductive matrix surrounds the conductors. The first set of conductive arrays comprise the same conductive array parameters as a first electronic module and the second set of conductive arrays comprise the same conductive array parameters as a second electronic module.
Owner:IBM CORP
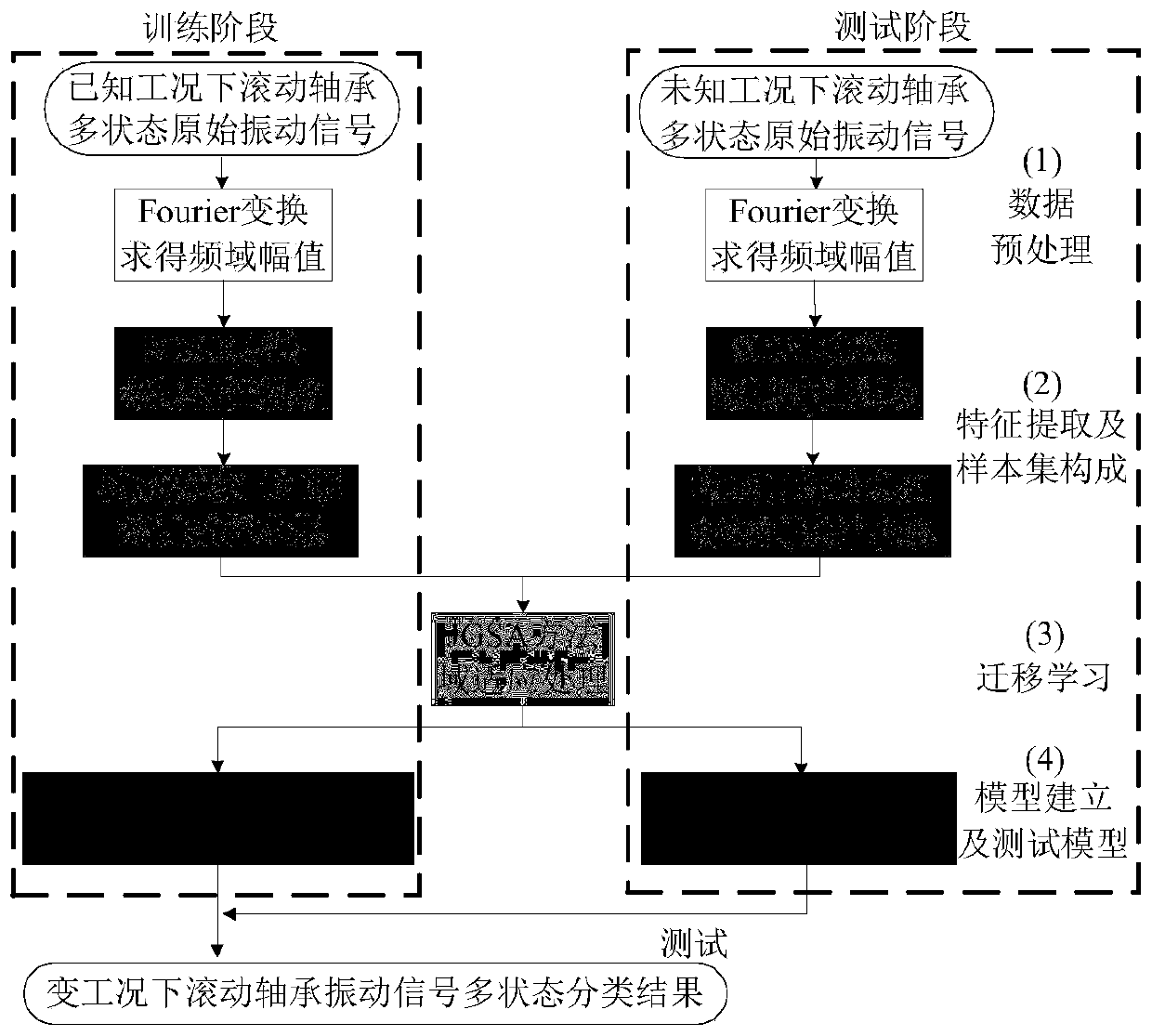
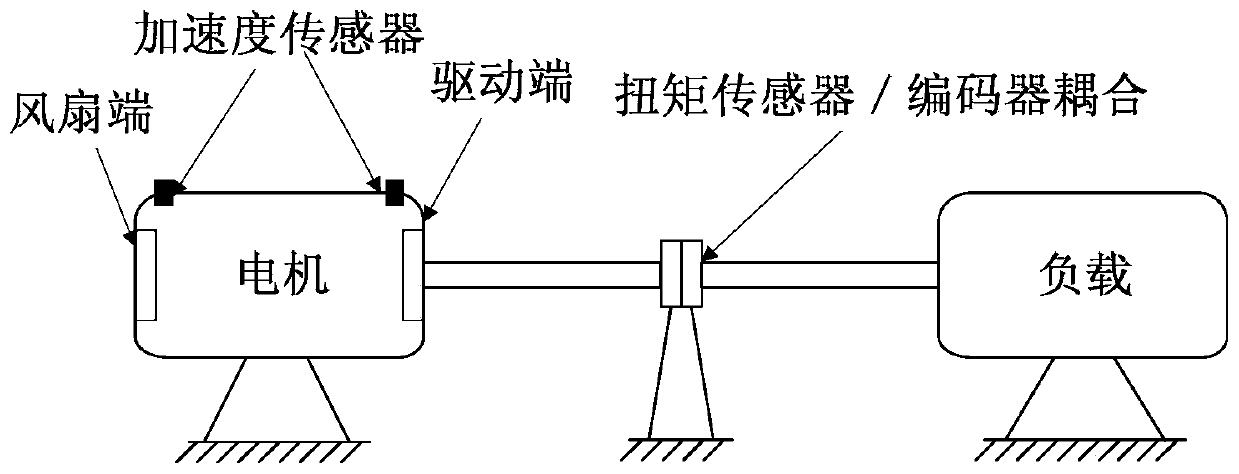
A rolling bearing fault diagnosis method under variable working conditions based on deep features and transfer learning
ActiveCN109902393AMitigate the effects of differences in the distribution of different vibration characteristicsSolve the problem of difficult multi-state deep feature extractionMachine bearings testingSpecial data processing applicationsLearning basedFeature extraction
The invention discloses a deep feature and transfer learning-based rolling bearing fault diagnosis method under variable working conditions, relates to the technical field of fault diagnosis, and aimsto solve the problem of low state identification accuracy of different fault positions and different performance degradation degrees of a rolling bearing under the variable working conditions. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out feature extraction on the vibration signal frequency domain amplitude of the rolling bearing by adopting SDAE to obtain vibration signal deepfeatures, and forming a source domain feature sample set and a target domain feature sample set; then, adopting the JGSA to carry out domain adaptation processing on the source domain feature sample and the target domain feature sample, the purpose of reducing distribution offset and subspace transformation difference of feature samples between domains is achieved, and domain offset between different types of feature samples is reduced. And finally, completing rolling bearing multi-state classification under variable working conditions through a K nearest neighbor algorithm. Compared with other methods, the method disclosed by the invention shows better feature extraction capability under the variable working condition of the rolling bearing, the sample feature visualization effect of therolling bearing is optimal, and the fault diagnosis accuracy of the rolling bearing under the variable working condition is high.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
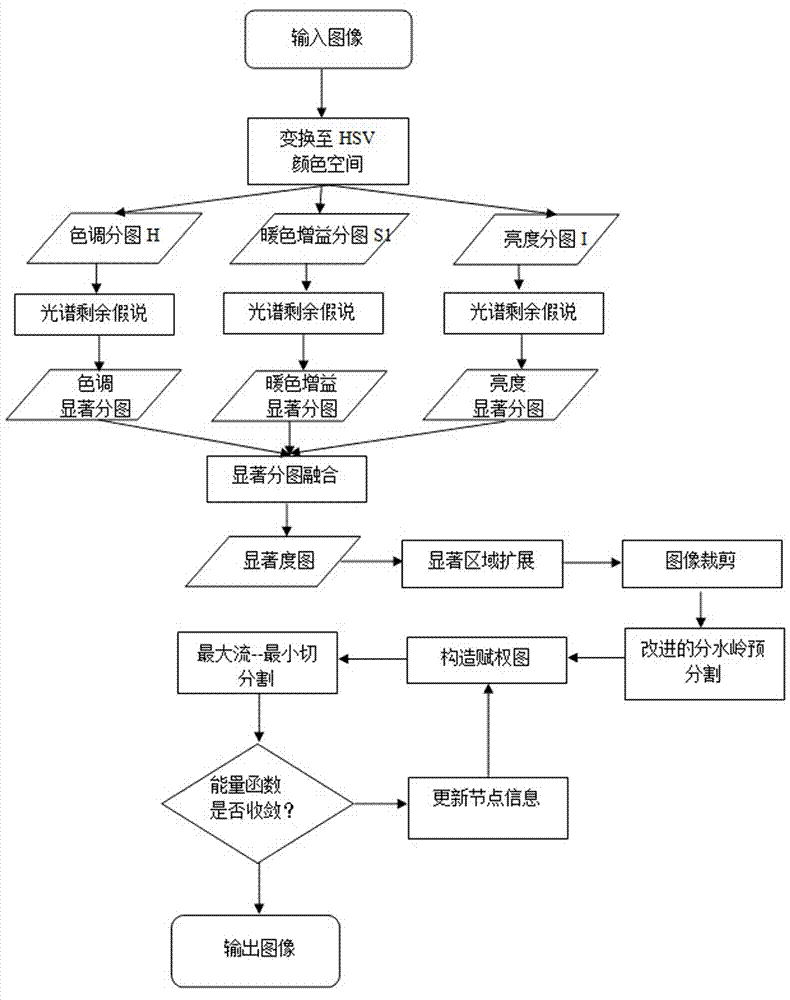
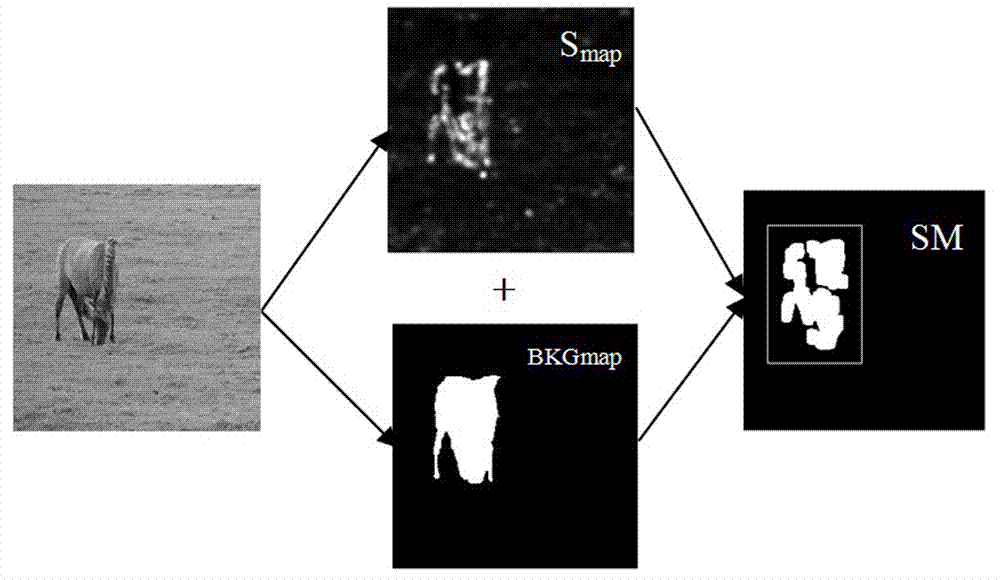
Automatic digging method for remarkable objects of color images
ActiveCN102968782AOvercoming the Problem of Human InteractionFast and effective extractionImage analysisColor imageEnergy functional
The invention discloses an automatic digging method for remarkable objects of color images. The automatic digging method for the remarkable objects of the color images is characterized by comprising the steps of changing a red green blue (RGB) color space of the images into a hue saturation value (HSV) color space and calculating significance of targets in the aspects of hue, saturation and warm color gain; obtaining a rectangular frame surrounding a significance region according to a significance level image and performing rectangular frame expansion, wherein images surrounded by the expanded rectangular frame serve as follow-up processing images; using an improved watershed algorithm to pre-divide input image contents, using pre-divided super pixel subregions to replace weighted graphs formed by dividing pixel point structural graph, and adopting a maximum flow-minimum dividing strategy to perform division till energy functions are converged to obtain divided images. By means of an automatic image digging technology, the remarkable objects in scene can be quickly and effectively dug, and digging efficiency, the quality and the like are improved remarkably.
Owner:SERCOMM ELECTRONICS SUZHOU CO LTD
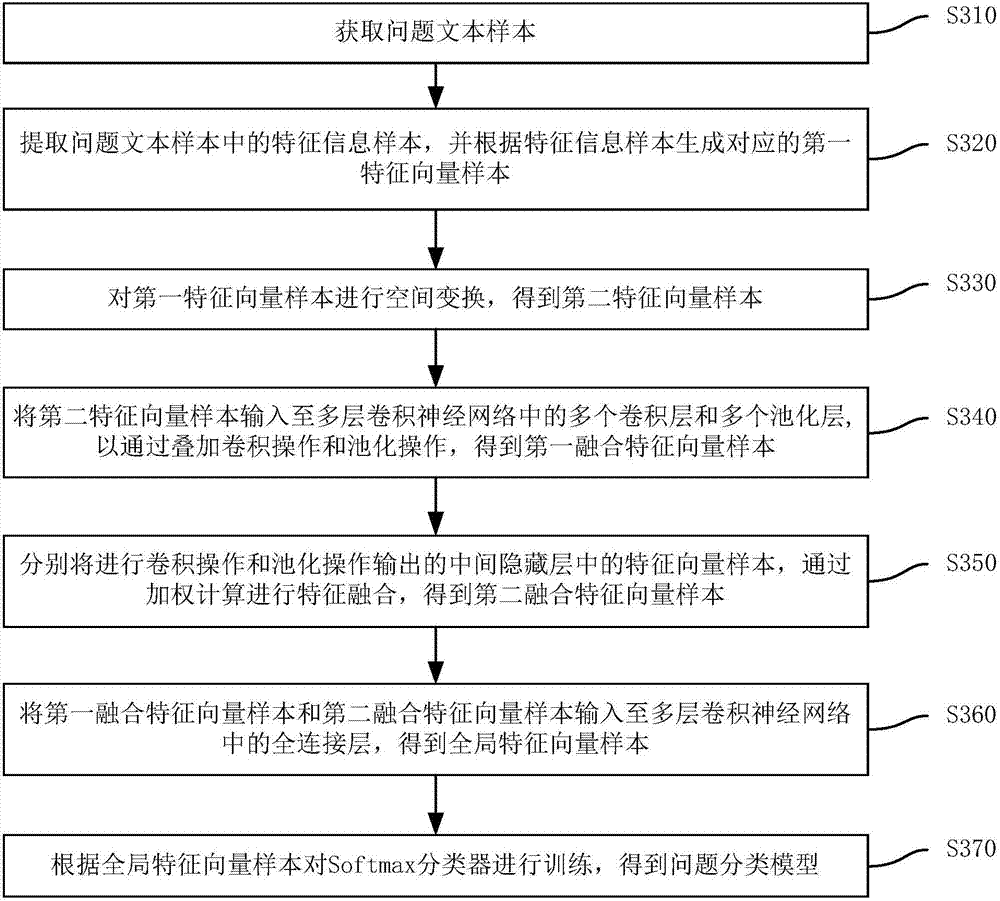
Deep learning-based question classification model training method and apparatus, and question classification method and apparatus
ActiveCN107291822AImprove experienceRapid positioningMachine learningSpecial data processing applicationsFeature vectorClassification methods
The invention discloses a deep learning-based question classification model training method and apparatus, and a question classification method and apparatus. The question classification model training method comprises the steps of extracting feature information samples in question text samples, and generating corresponding first eigenvector samples; performing spatial transformation on the first eigenvector samples to obtain second eigenvector samples; inputting the second eigenvector samples to a plurality of convolutional layers and a plurality of pooling layers in a multilayer convolutional neural network, and by superposing convolution operation and pooling operation, obtaining first fusion eigenvector samples; inputting the first fusion eigenvector samples to a full connection layer in the multilayer convolutional neural network to obtain global eigenvector samples; and training a Softmax classifier according to the global eigenvector samples to obtain a question classification model. The method can avoid a large amount of overheads of manual design of features; and through the question classification model, a more accurate classification result can be obtained, so that locating of standard question and answer is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
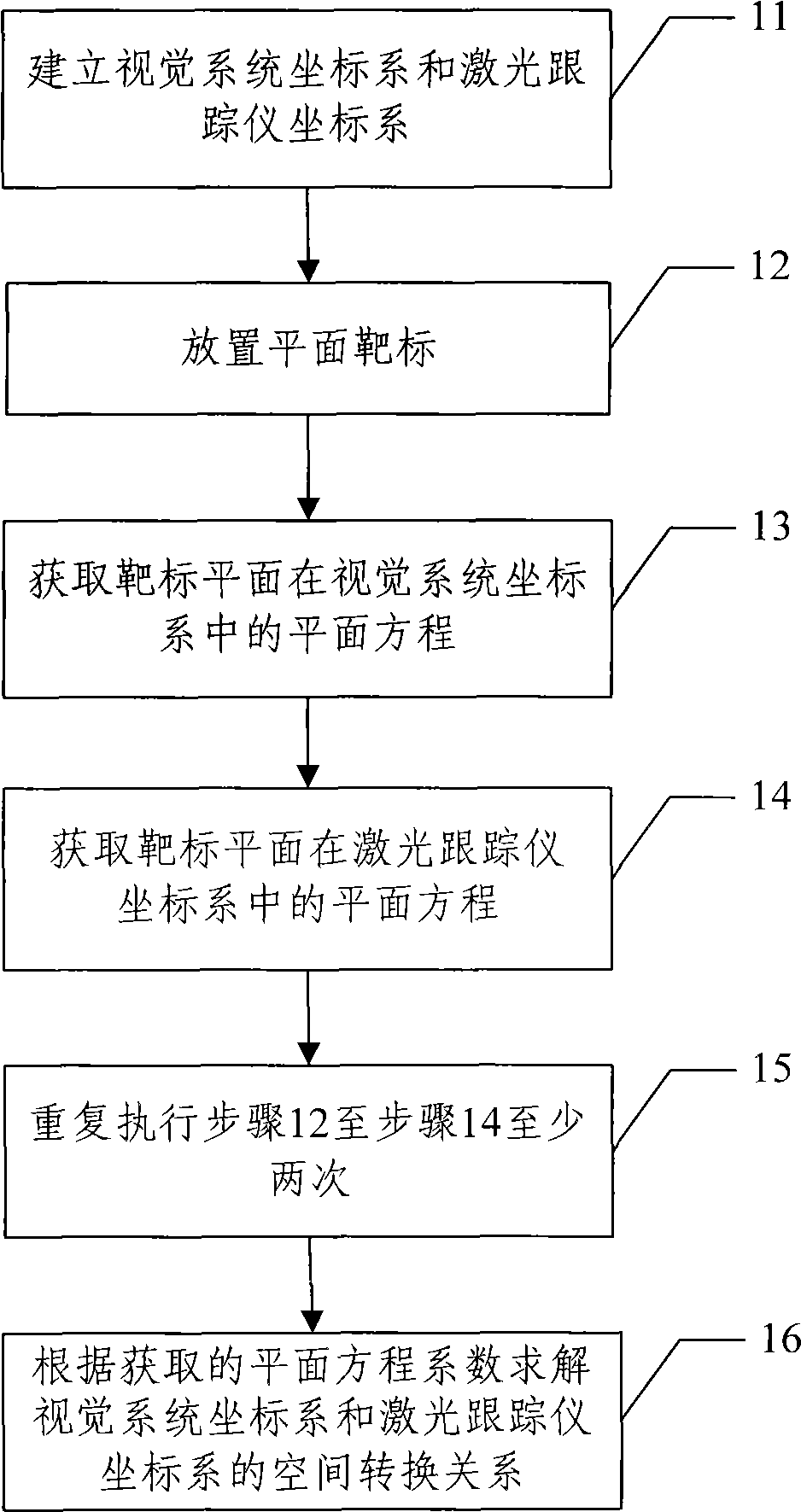
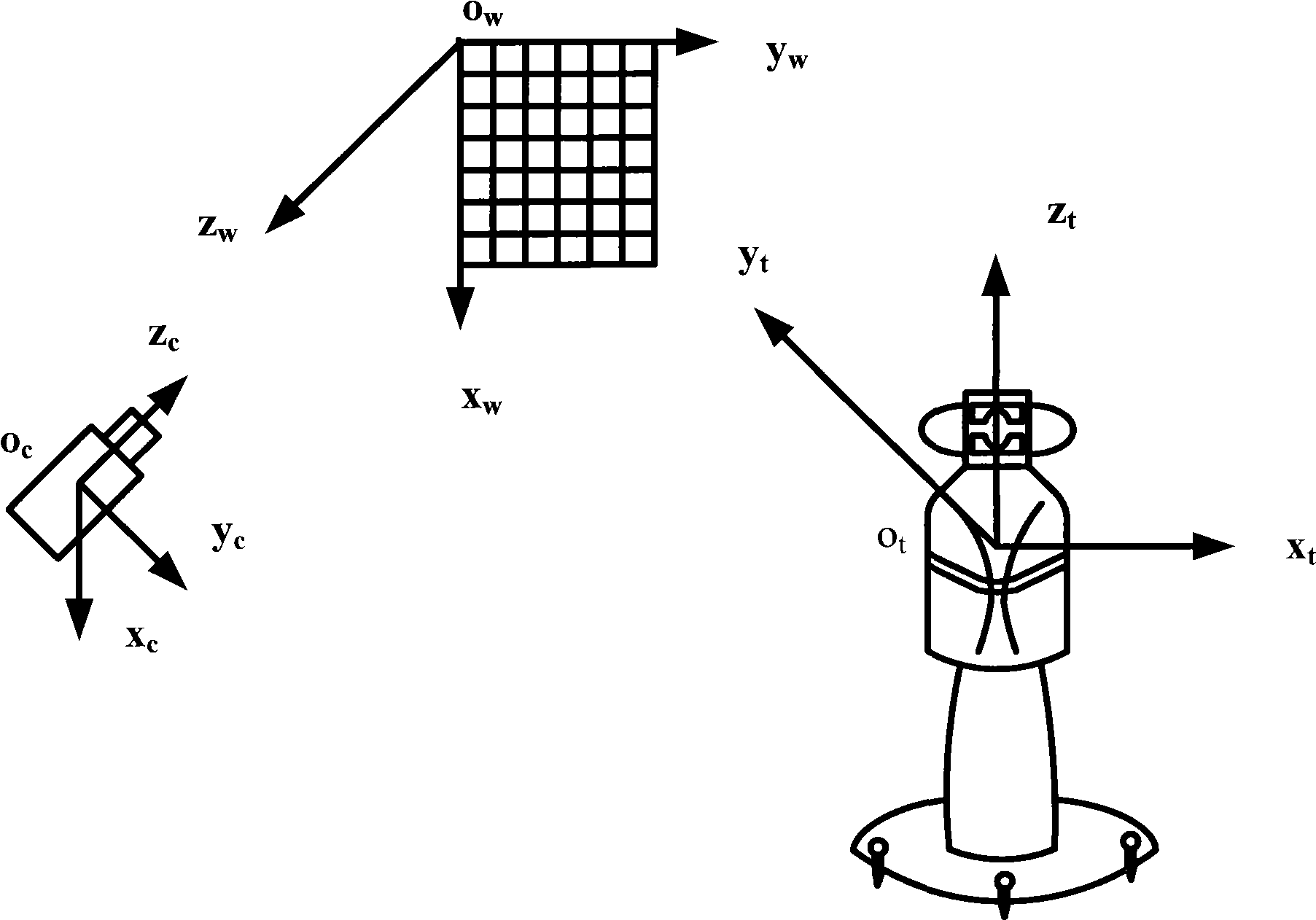
Global calibration method of laser tracking visual guidance measurement system
InactiveCN101532821AGlobal Calibration ImplementationImplement automatic assemblyUsing optical meansButt jointPlane equation
A global calibration method of a laser tracking visual guidance measurement system comprises the steps of determining a visual system coordinate system and a laser tracker coordinate system; putting a plane target for at least three times and obtaining plane equations of the target plane, where the plane target is located in the visual system coordinate system and the laser tracker coordinate system at each putting position; and calculating a spatial transformation relation of the visual system coordinate system and the laser tracker coordinate system according to the coefficients of the obtained plane equations. The global calibration method of a laser tracking visual guidance measurement system in the invention realizes the global calibration of the laser tracking visual guidance measurement system by obtaining the plane equations of the target plane in the visual system coordinate system and the laser tracker coordinate system at the at least three positions of the plane target, so as to realize automatic assembly and butt joint of large-sized components, to improve assembly efficiency, and to save assembly cost.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Deep learning method for ship detection in high-resolution visible remote sensing images
ActiveCN108960143AEasy to identifyImprove robustnessScene recognitionPattern recognitionSpatial transformation
The invention provides a deep learning method for ship detection in high-resolution visible remote sensing images, which comprises the following steps: firstly, reading and preprocessing image data; secondly, extracting the features of the whole image; thirdly, screening out target candidate regions after extracting the abstract features of the image in the convolution layer; fourthly, cutting outthe feature blocks of each target candidate region on the feature map corresponding to the whole image, and using the pooling layer in the region of interest to normalize the sizes of the feature blocks; fifthly, sending the features to the full connection layer to get spatial transformation parameters, and sending the spatial transformation parameters and the features to the spatial transformation layer to get the features after deformation correction; and sixthly, carrying out classification and position correction again on the target candidate regions according to the corrected features. The robustness of the detection method to target rotation and other deformation is enhanced, and the detection effect of ship targets in high-resolution visible remote sensing images is improved. The method can be applied to the detection of ship targets in high-resolution visible remote sensing images, and has broad application prospects and values.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Method of and system for projecting digital information on a real object in a real environment
ActiveUS20150350618A1Expand field of viewReduce field of viewTelevision system detailsImage analysisObject basedSpatial transformation
A method of projecting digital information on a real object in a real environment includes the steps of projecting digital information on a real object or part of a real object with a visible light projector, capturing at least one image of the real object with the projected digital information using a camera, providing a depth sensor registered with the camera, the depth sensor capturing depth data of the real object or part of the real object, and calculating a spatial transformation between the visible light projector and the real object based on the at least one image and the depth data. The invention is also concerned with a corresponding system.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and apparatus for scalable video encoding and decoding
InactiveUS20050117640A1Color television with pulse code modulationPulse modulation television signal transmissionComputer graphics (images)Video encoding
Disclosed is a scalable video coding algorithm. A method for video coding includes temporally filtering frames in the same sequence to a decoding sequence thereof to remove temporal redundancy, obtaining and quantizing transformation coefficients from frames whose temporal redundancy is removed, and generating bitstreams. A video encoder comprises a temporal transformation unit, a spatial transformation unit, a quantization unit and a bitstream generation unit to perform the method. A method for video decoding is basically reverse in sequence to the video coding. A video decoder extracts information necessary for video decoding by interpreting the received bitstream and decoding it. Thus, video streams may be generated by allowing a decoder to decode the generated bitstreams, while maintaining the temporal scalability on an encoder-side.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Image synthesis method, image synthesis apparatus, and storage medium
InactiveUS7098914B1Quality improvementImprove efficiencyGeometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Spatial transformation
An image synthesis method includes a placement information obtaining step of obtaining placement information about a plurality of images in which adjacent images have a common subject region, and a synthesis step of combining the images using a mapping mode in accordance with the placement information. Prior to performing mapping transformation of the input images, coordinate-space transformation parameters for transforming the coordinate space of one image among the images into the coordinate space of another image are generated. The images are combined based on a given mapping mode and the coordinate-space transformation parameters.
Owner:CANON KK
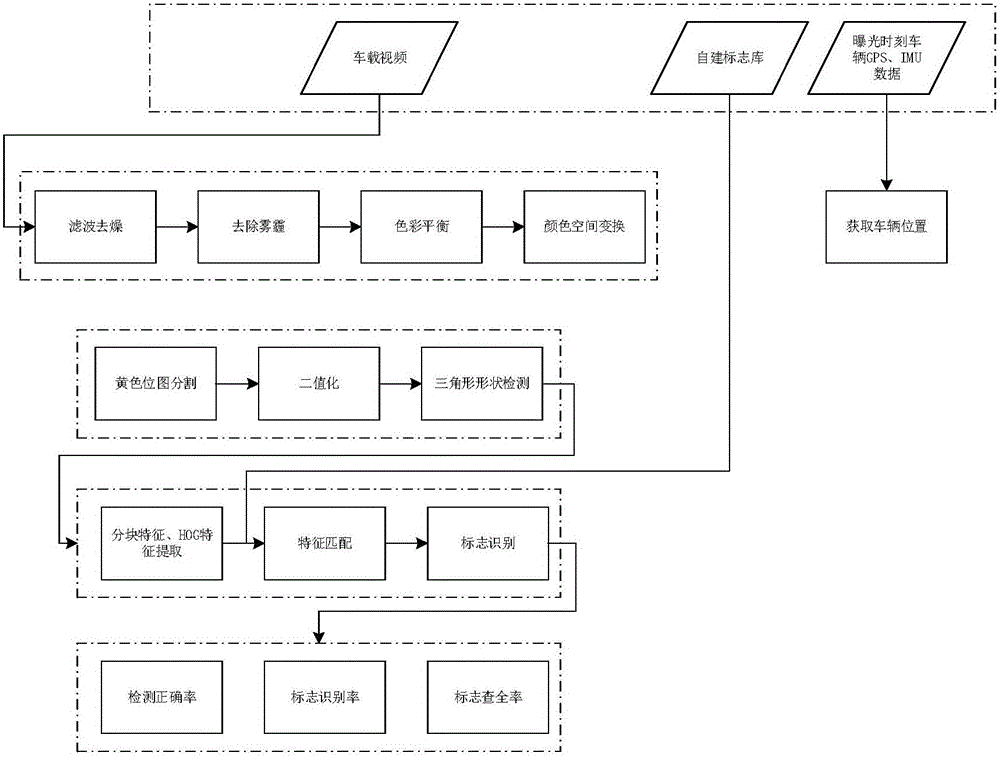
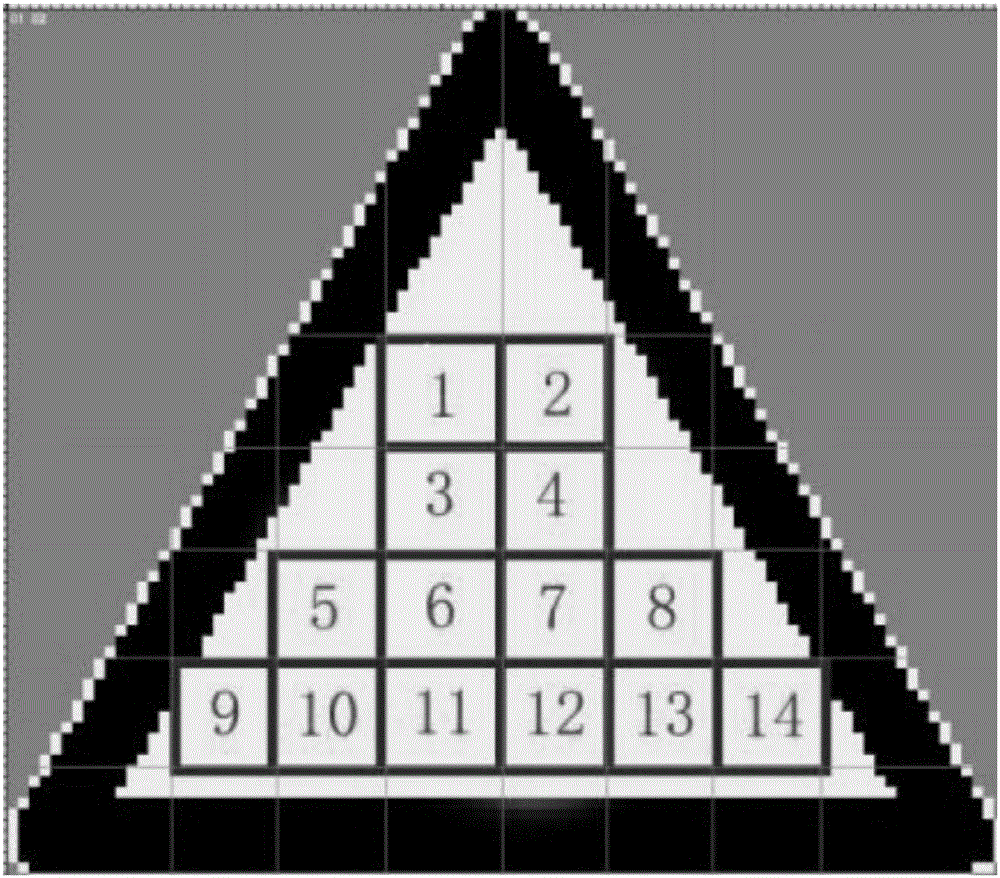
Road warning mark detection and recognition method based on block recognition
ActiveCN105809138AHigh saturationEasy to detectCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionSign detection
The invention discloses a road warning mark detection and recognition method based on block recognition. The method comprises the following steps of performing HSV (Hue, Saturation and Value) color spatial alternation on vehicle-mounted video data and performing binarization processing; extracting profile information of a binarization image, and judging the shape of the binarization image according to the geometrical characteristics of the binarization image so as to detect a warning mark region; extracting block features and HOG (Histogram of Oriented Gradient) features of the warning mark region; matching out the type of a mark to be recognized by using a mark base as the standard; and obtaining the mark detection result. The method has the advantages that the high mark recognition correct rate can be ensured; and the missing detection is effectively reduced, so that the better mark detection result is obtained. A good application value is realized in the field of intelligent traffic.
Owner:北京图迅丰达信息技术有限公司
Panoramic vision system and method
ActiveUS7576767B2Eliminating exposureExpand coverageTelevision system detailsTelevision conference systemsProjection opticsDistortion free
Owner:GEO SEMICONDUCTOR INC
Correction method for fisheye image distortion
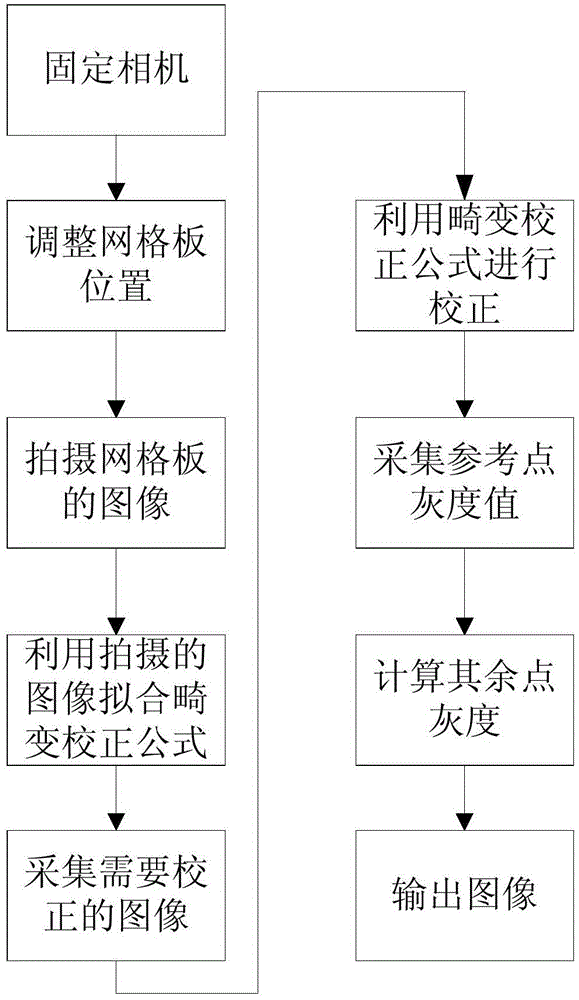
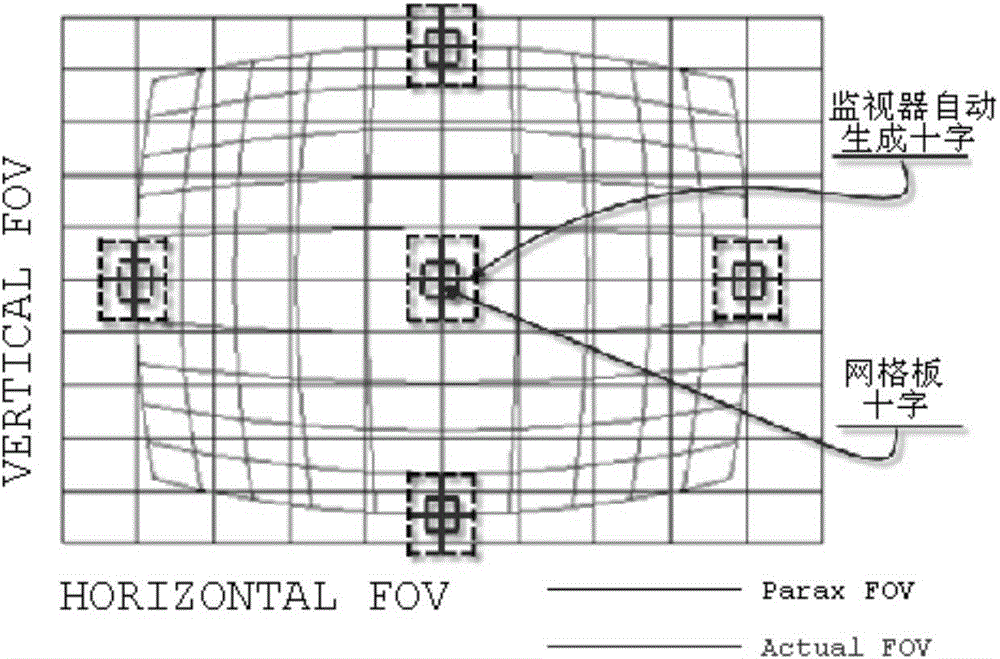
InactiveCN104537616AEasy to measureEasy to operateImage enhancementGeometric image transformationSpatial transformationCorrection method
The invention discloses a correction method for fisheye image distortion. The method includes the following steps that firstly, a fisheye image of a standardized test grid plate and an actual image of the fisheye image are obtained; secondly, distortion measurement is conducted on the obtained fisheye image, and distortion coefficients are calibrated according to a polar coordinate model; thirdly, correction is conducted according to a correction model, and in order to guarantee correction precision, sectioned correction is conducted according to a central view field, a middle view field and an edge view field during correction; fourthly, pixels obtained after spatial alternation are endowed with corresponding gray values through a bilinear interpolation method so that the gray value of an original position can be restored. Reverse operation is simple, measurement precision is high, and the correction method is easily achieved in hardware systems such as an EPGA and a DSP. The correction method has high practical value.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com