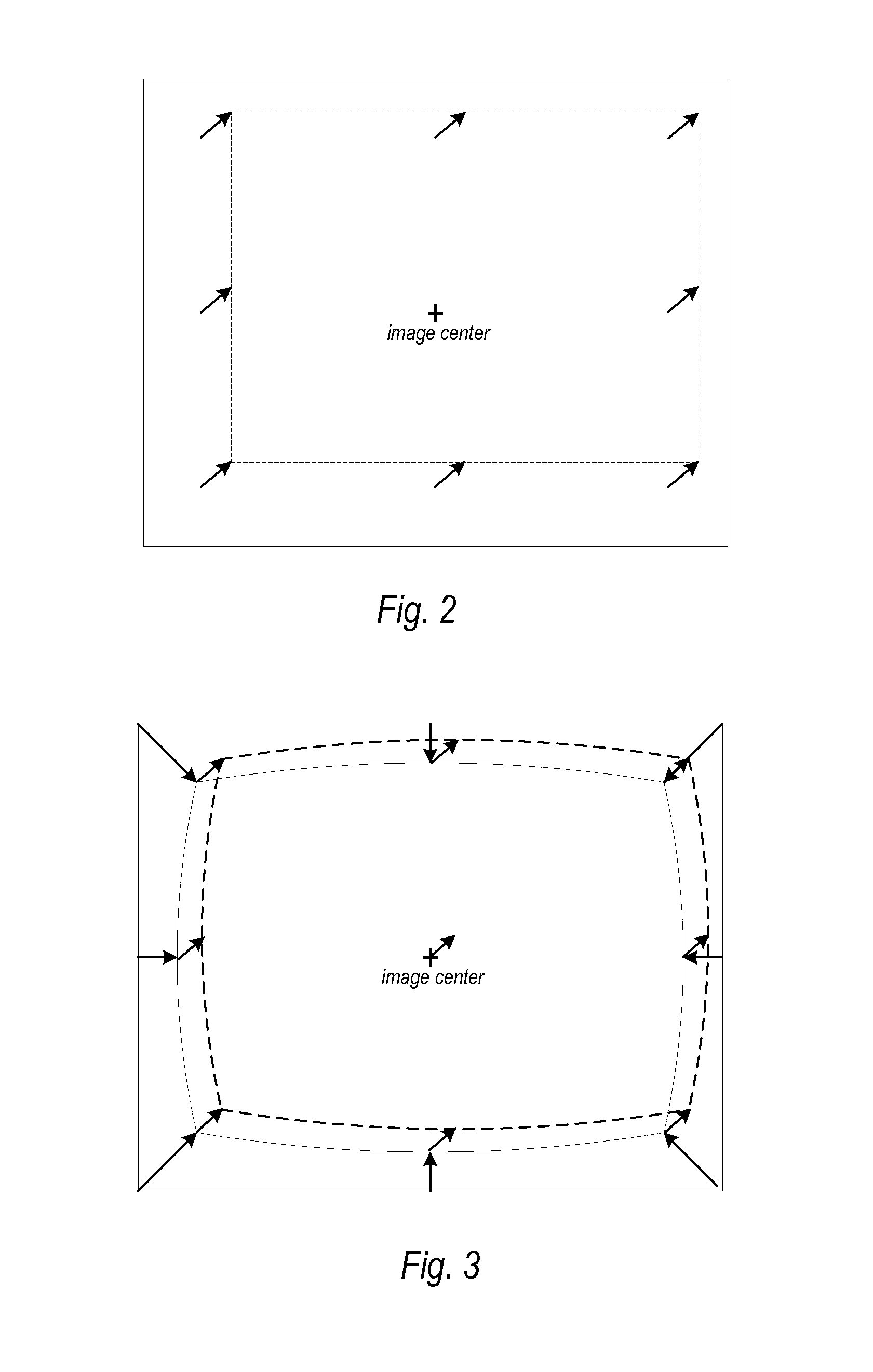
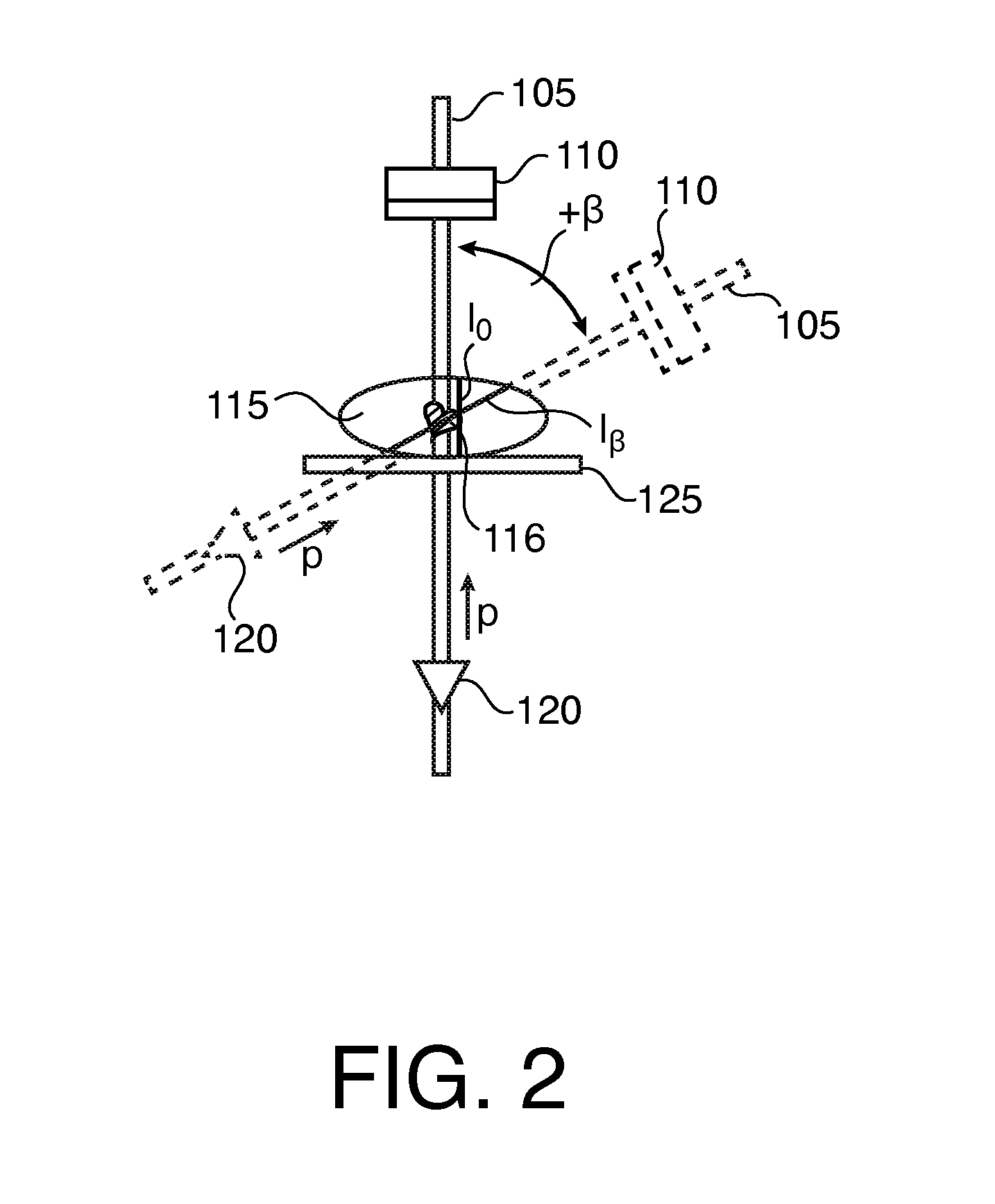
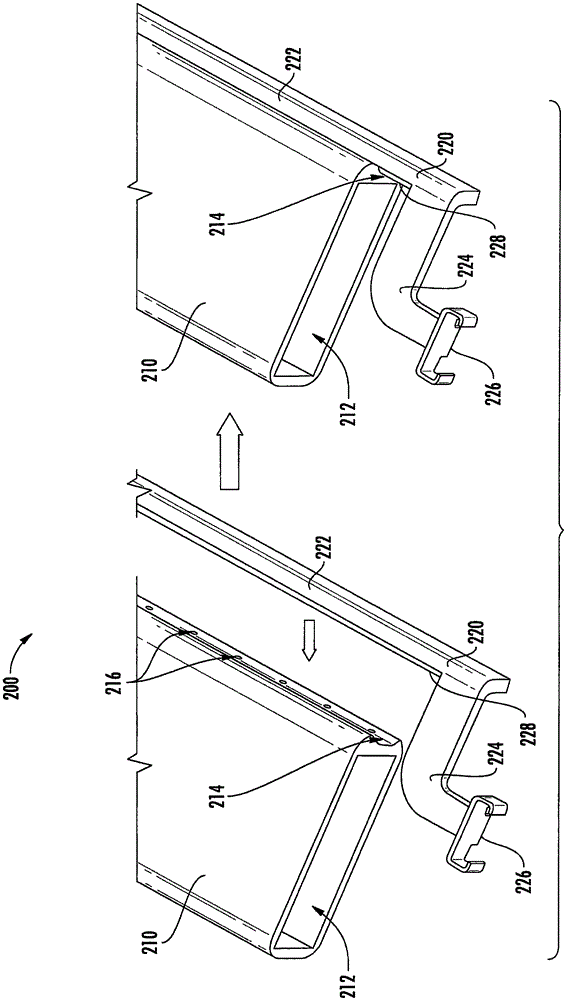
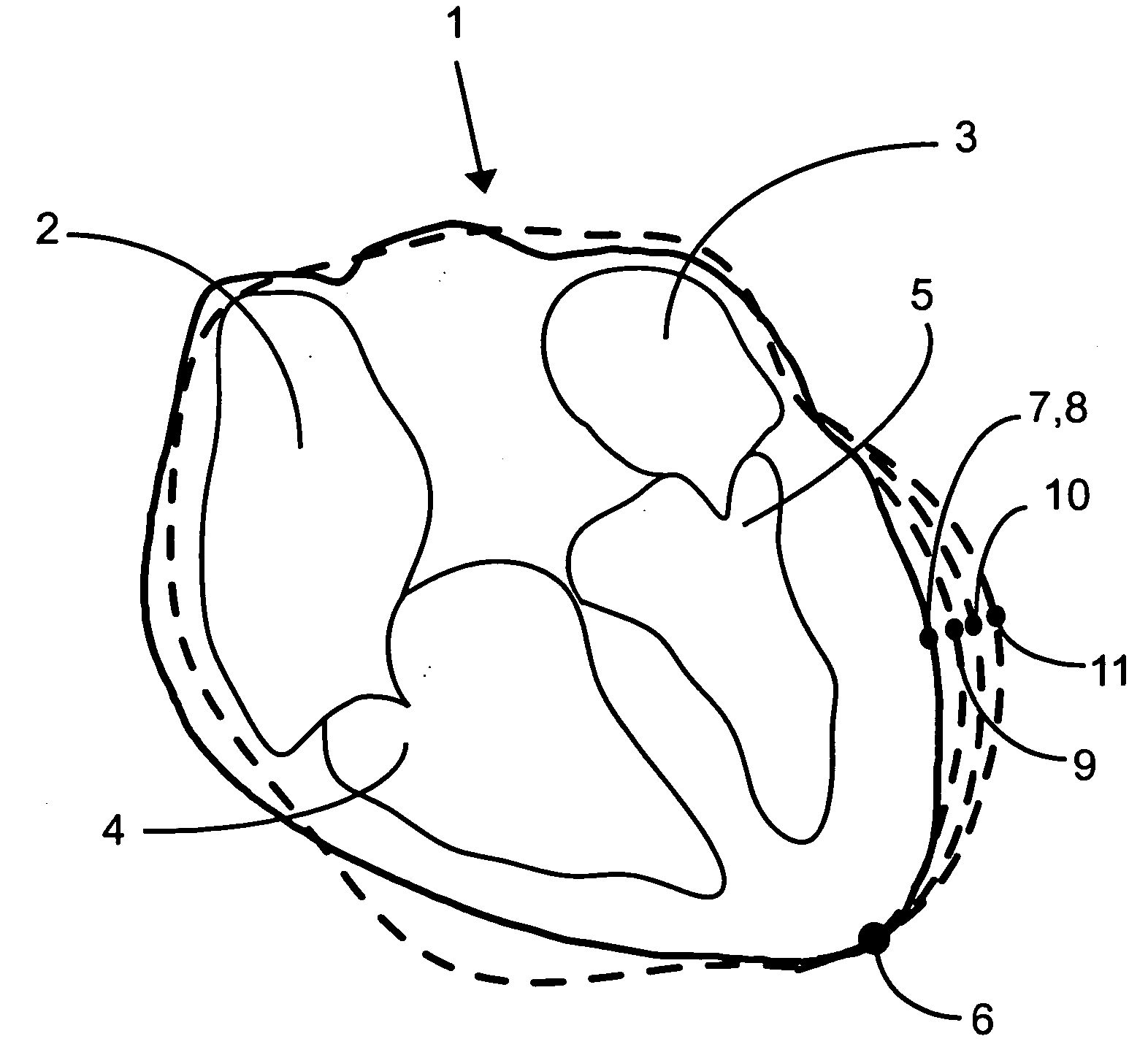
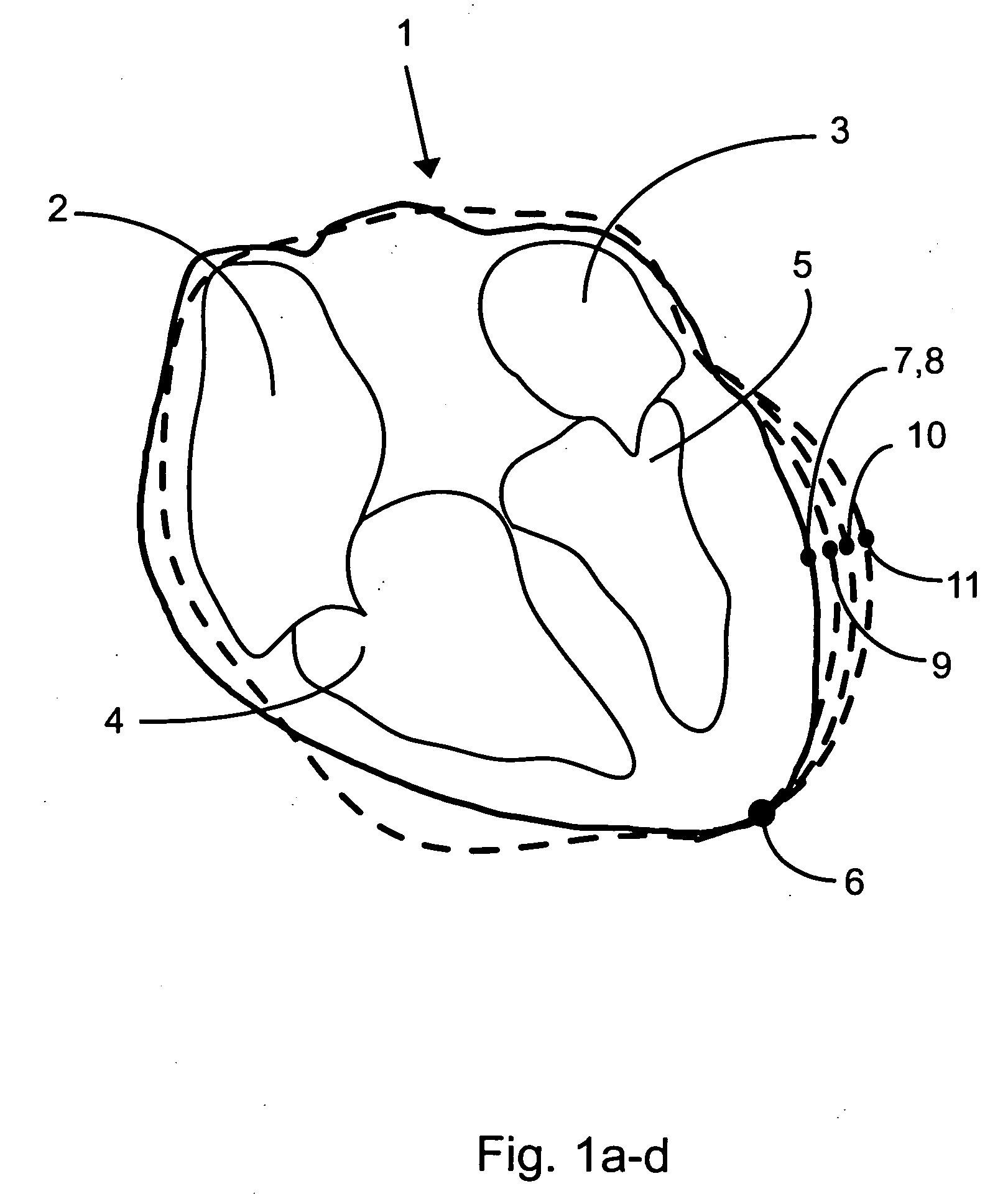
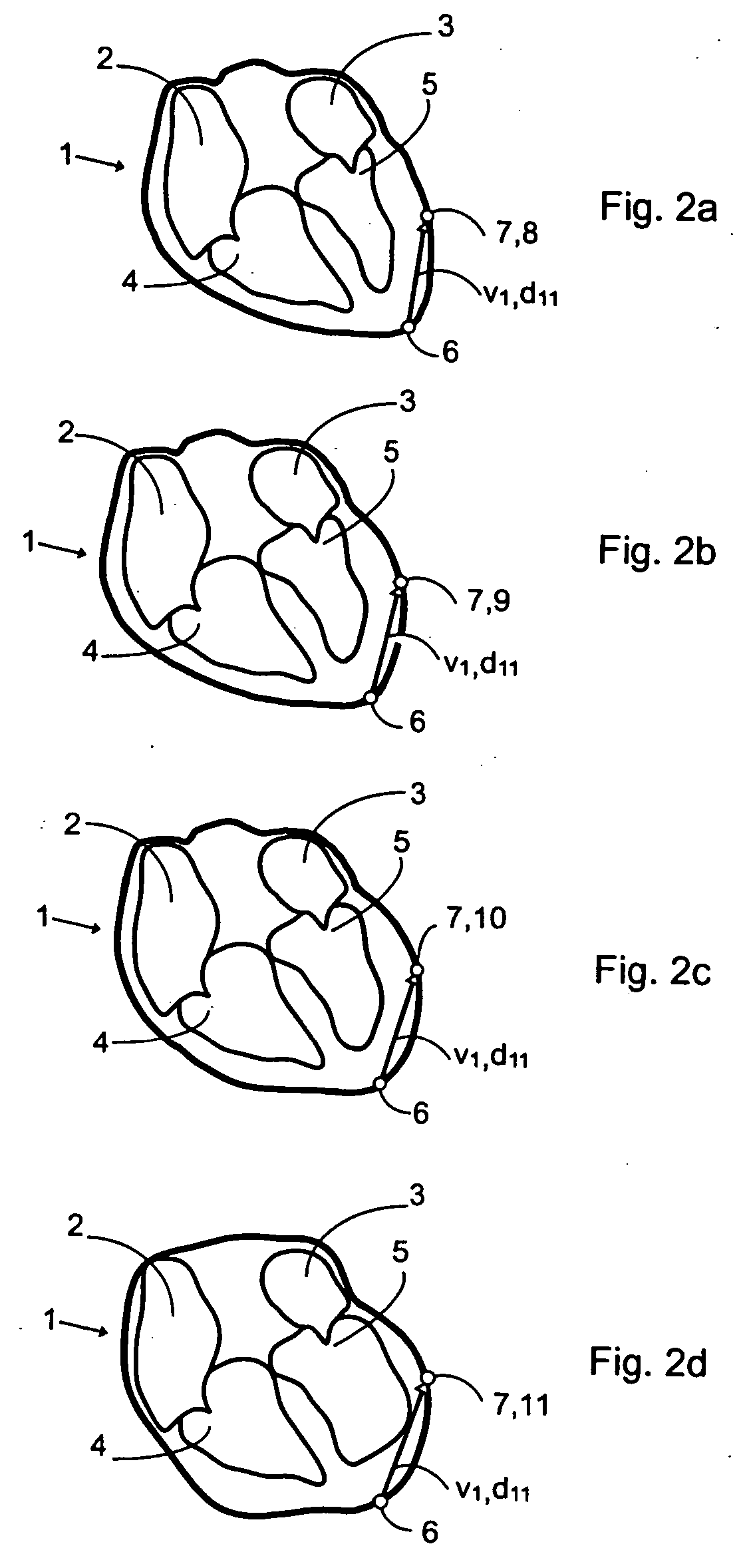
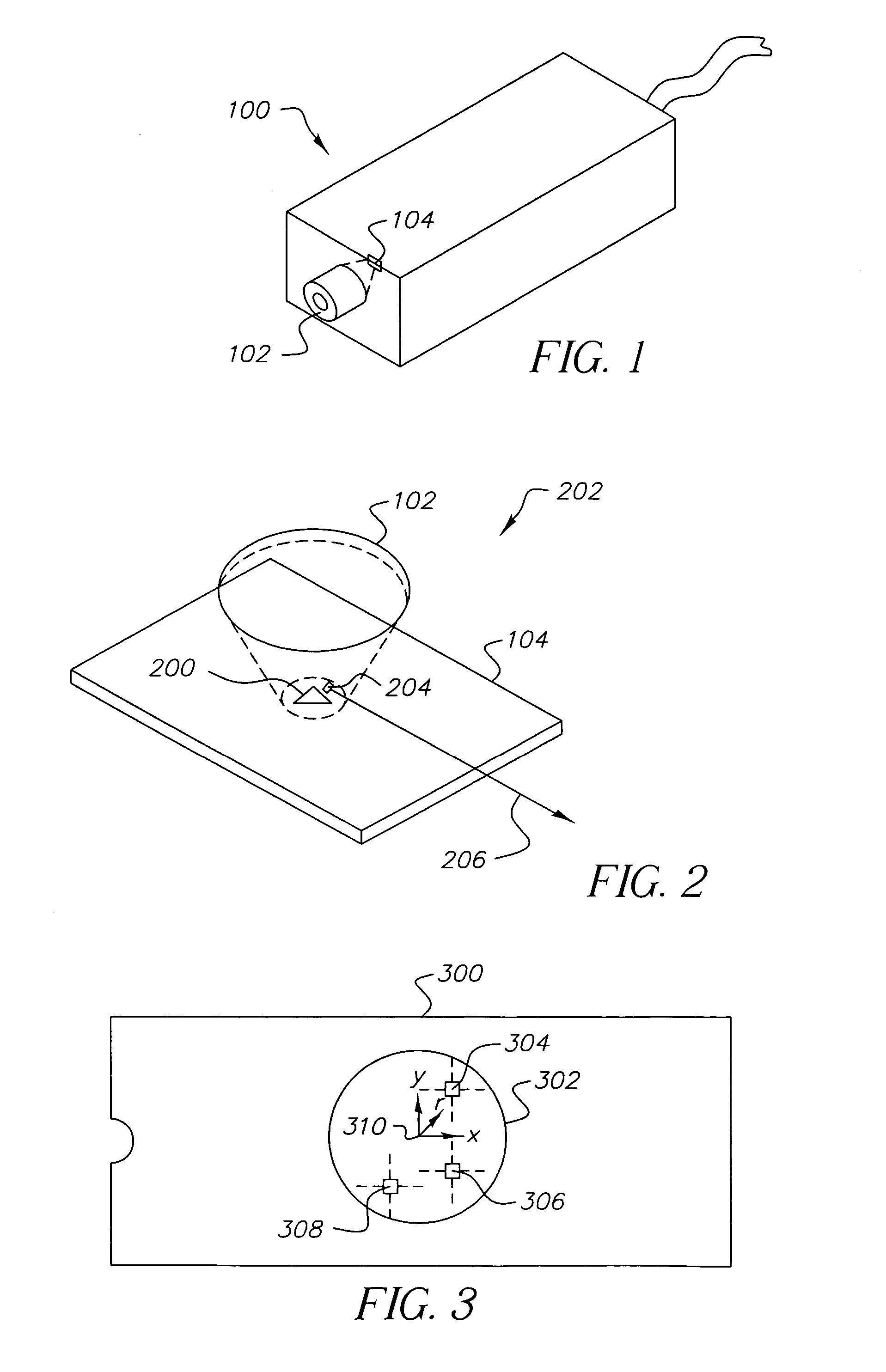
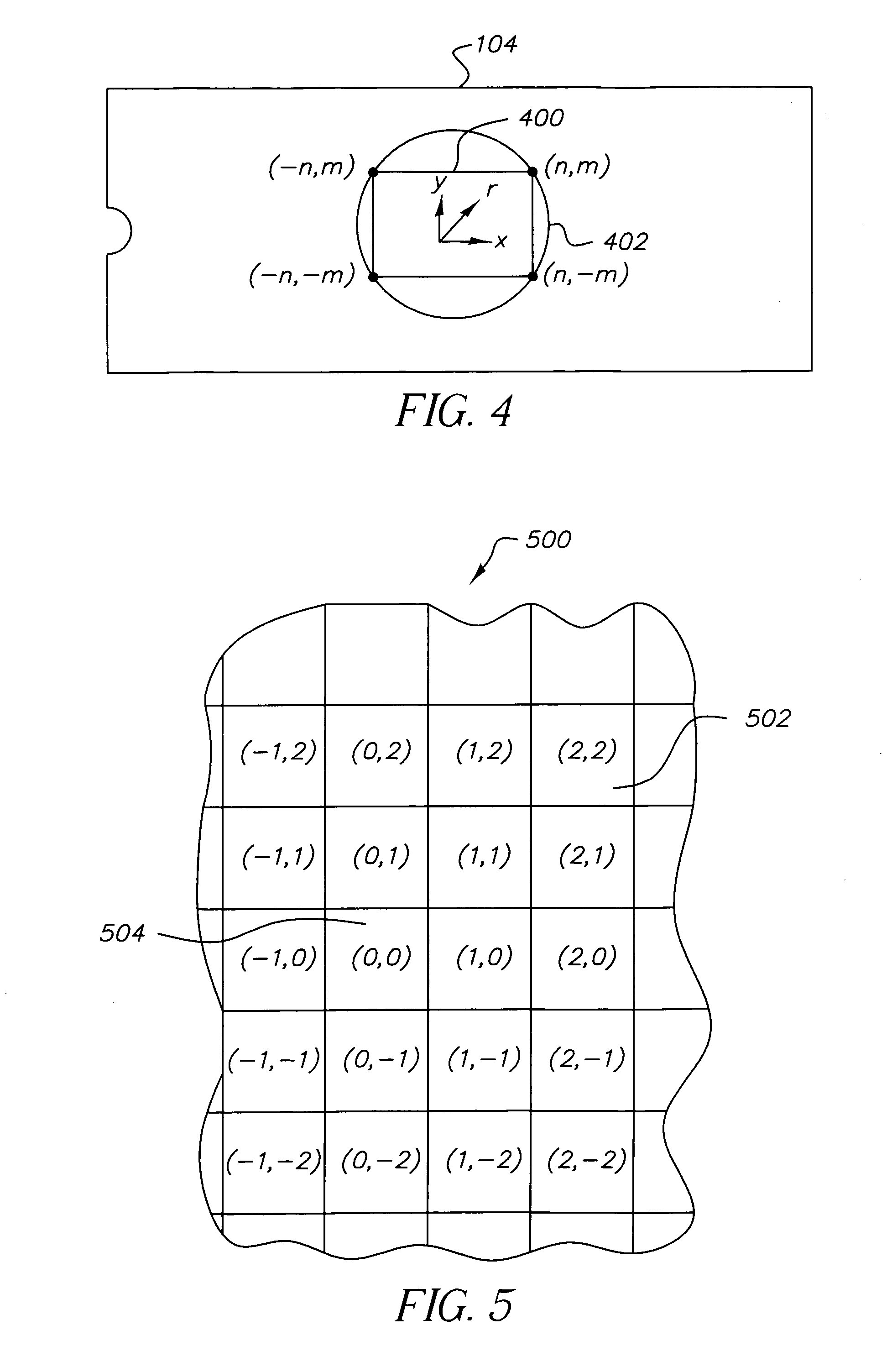
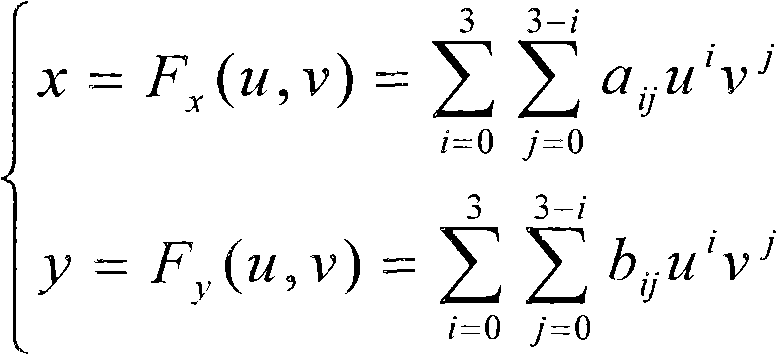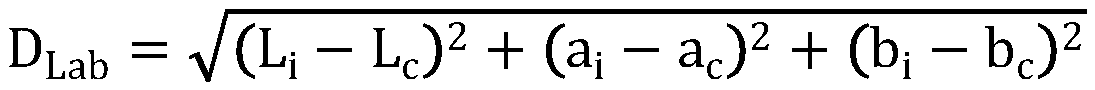Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
233 results about "Image geometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
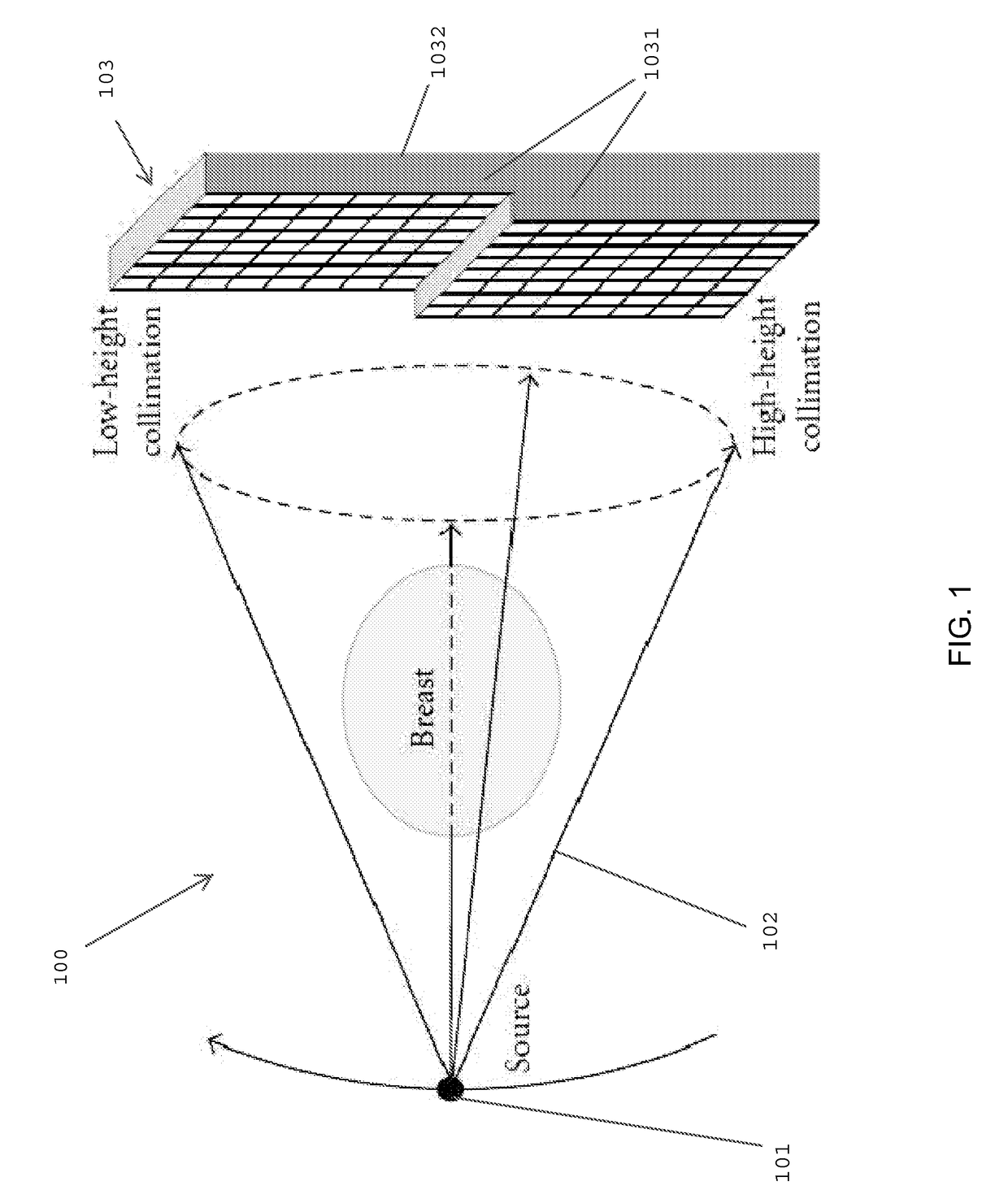
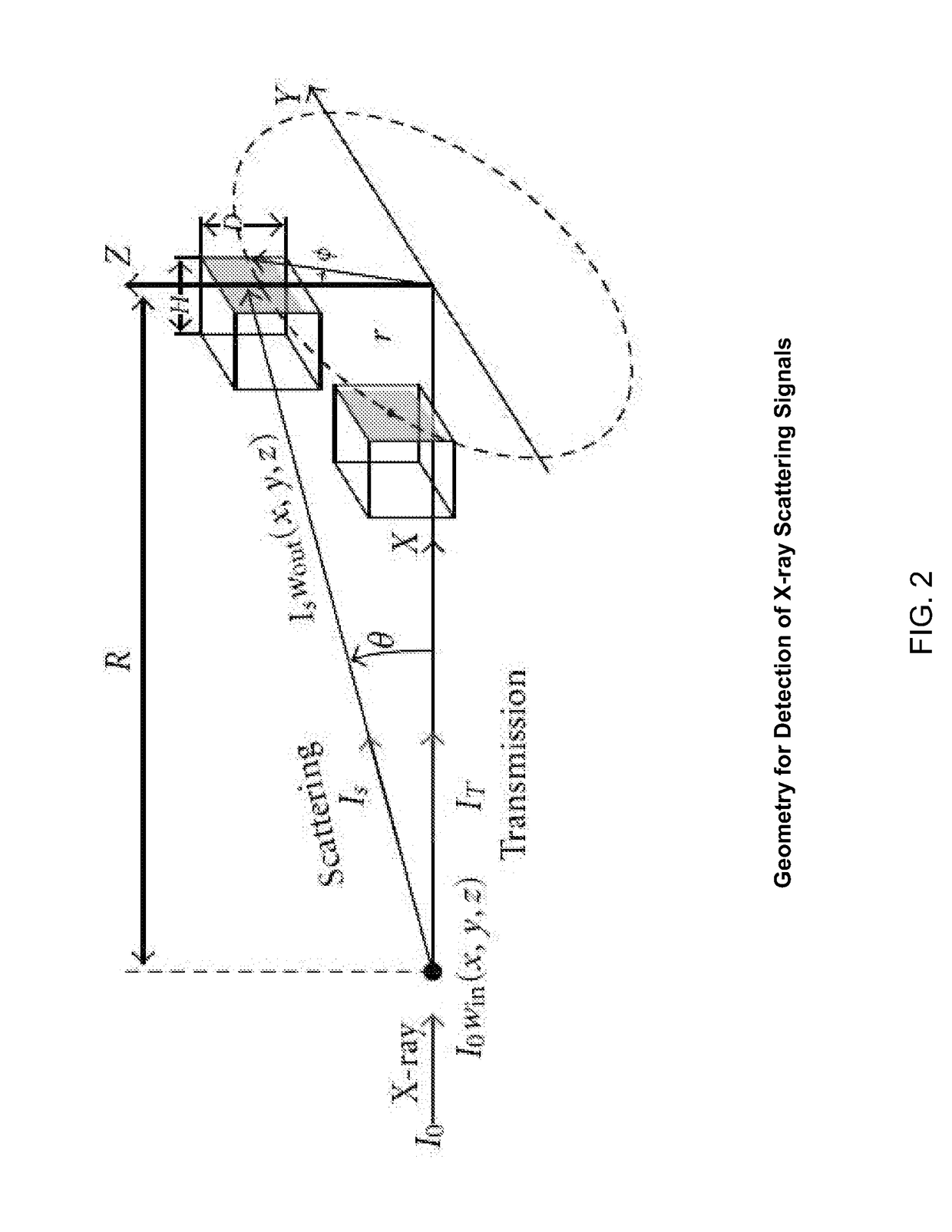
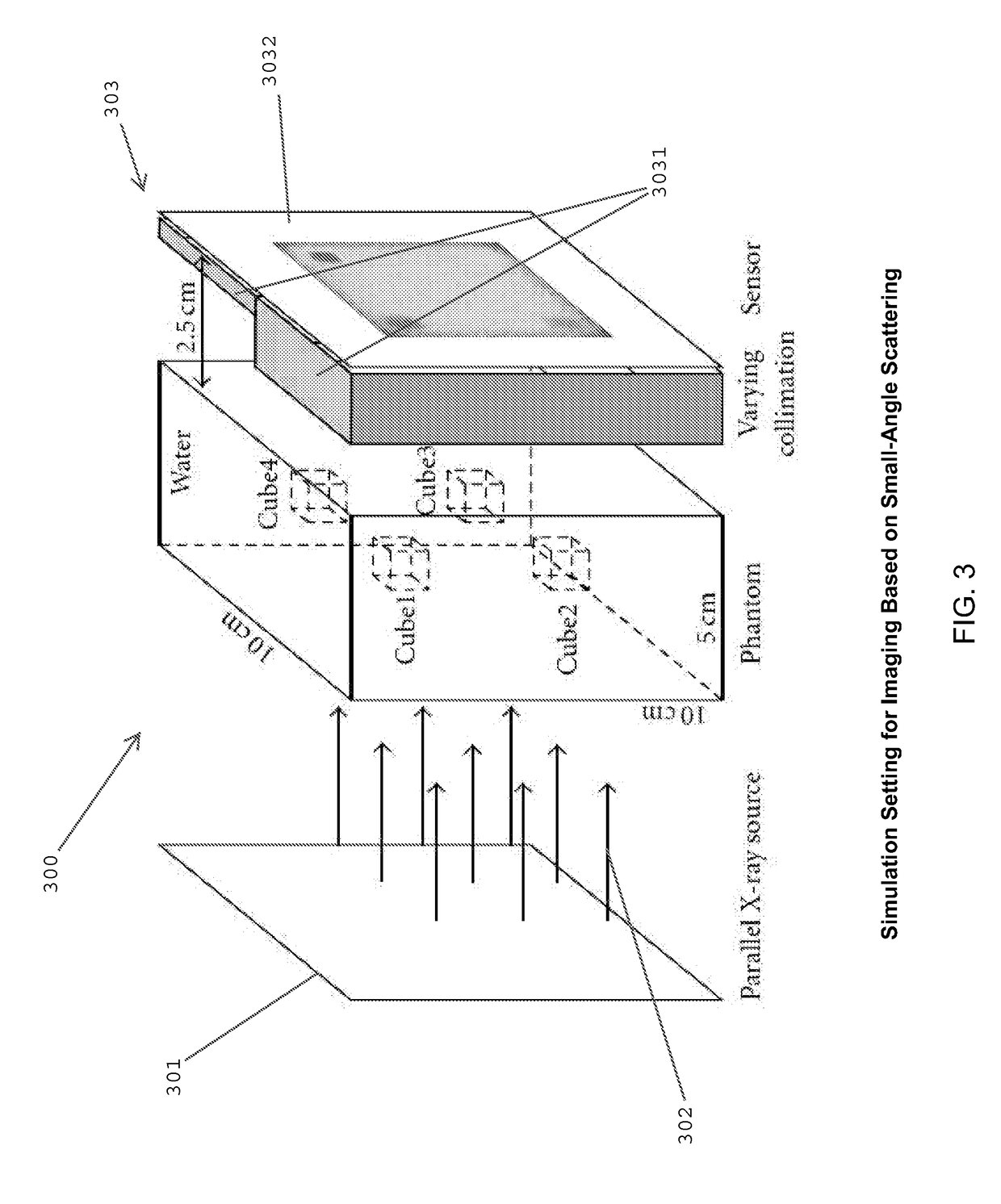
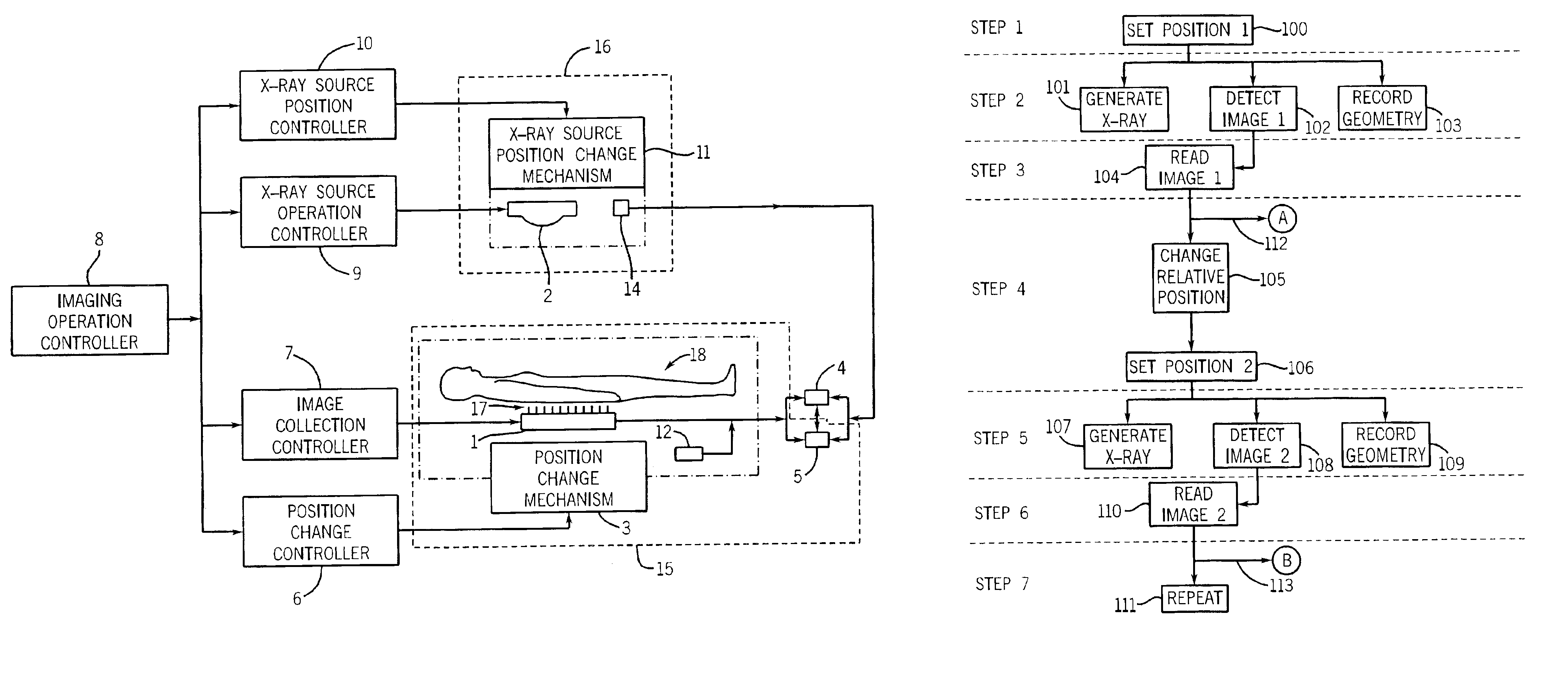
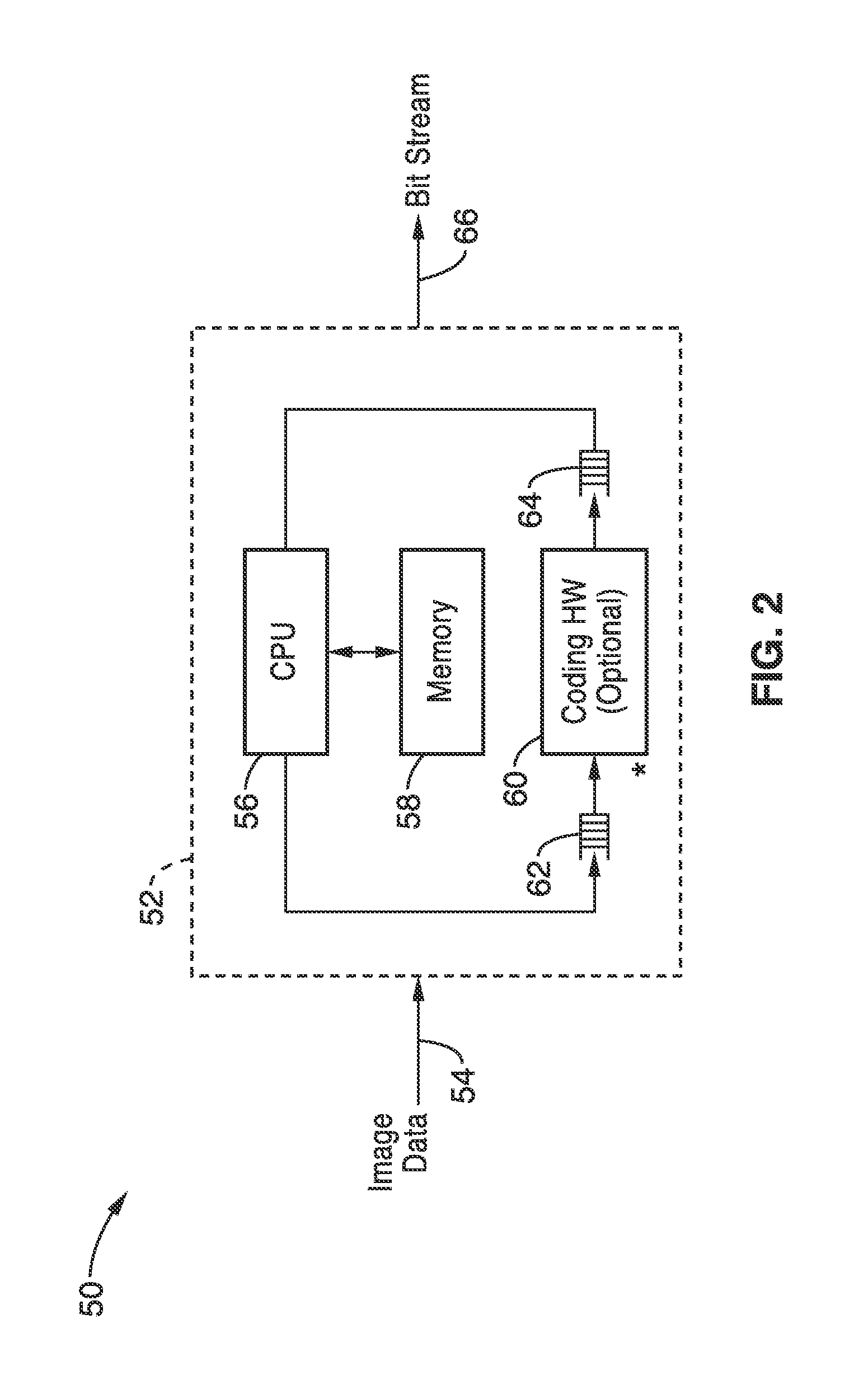
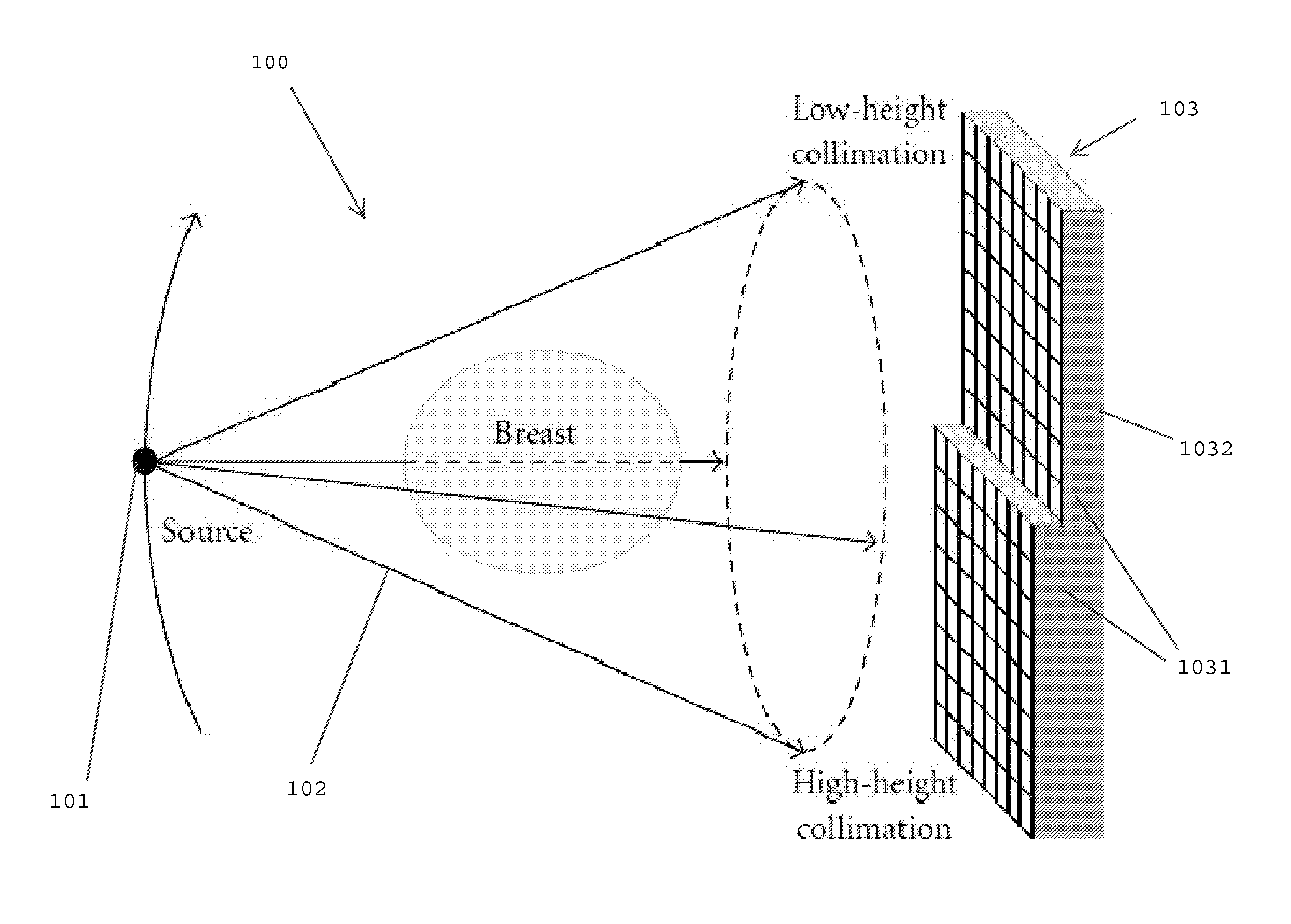
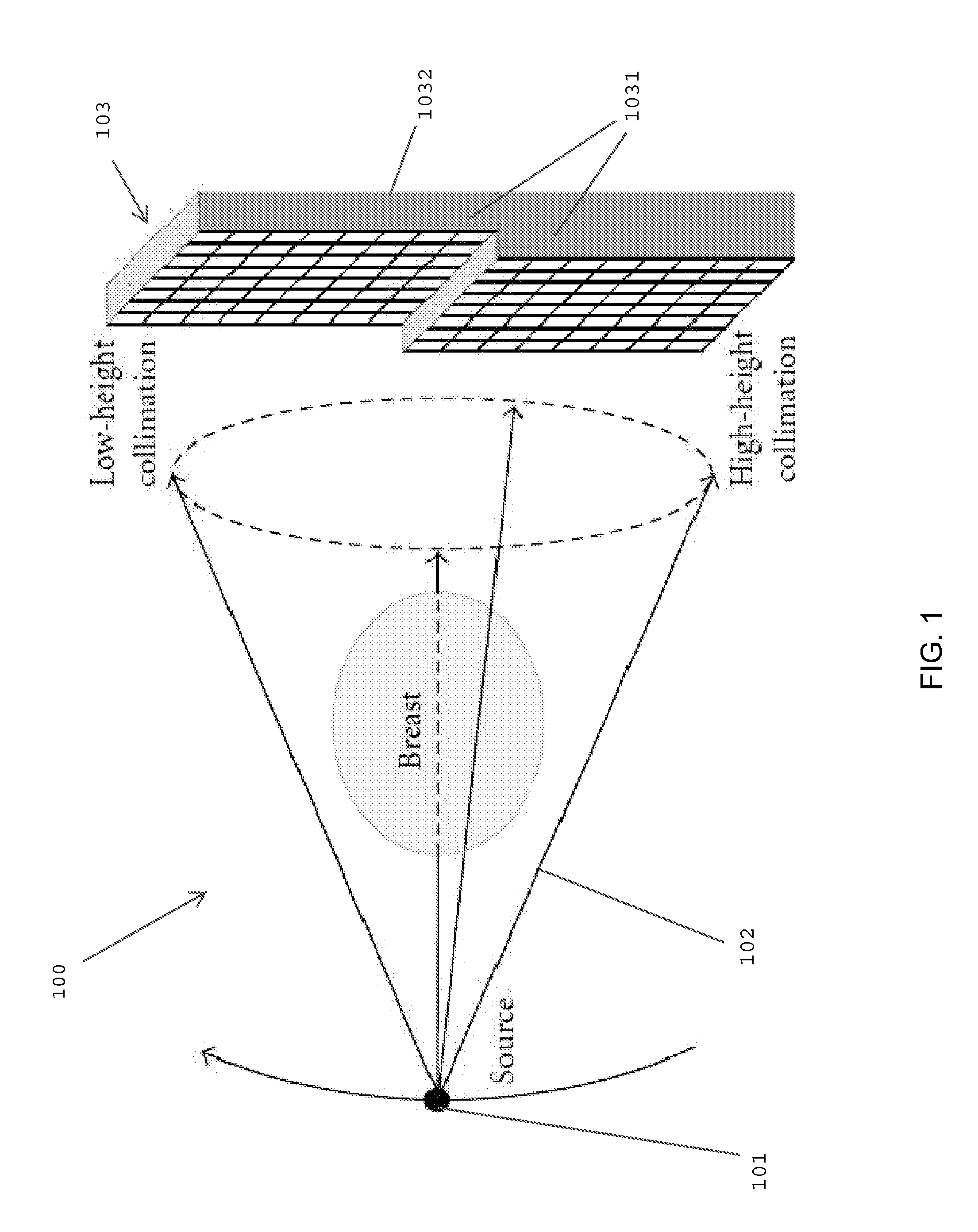
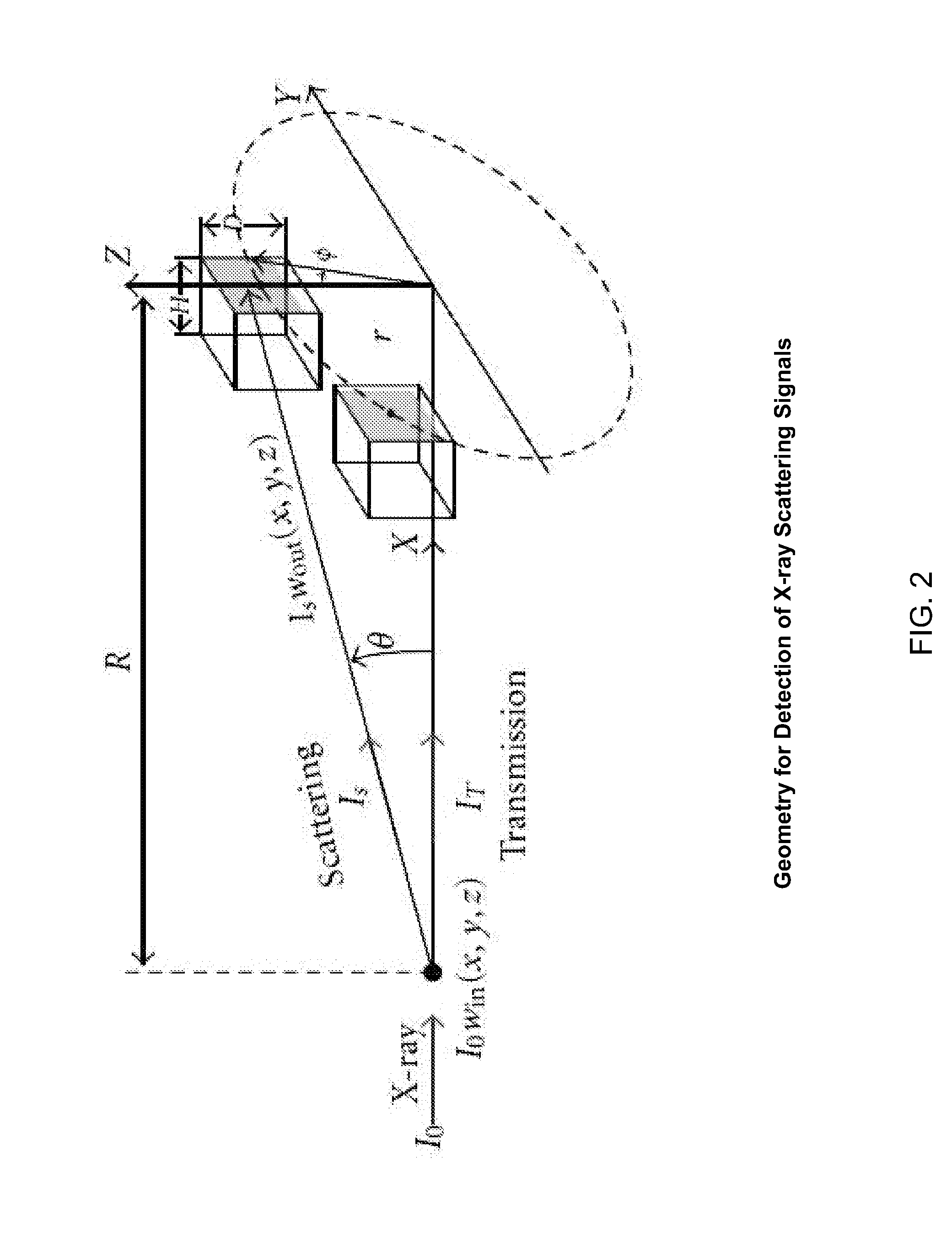
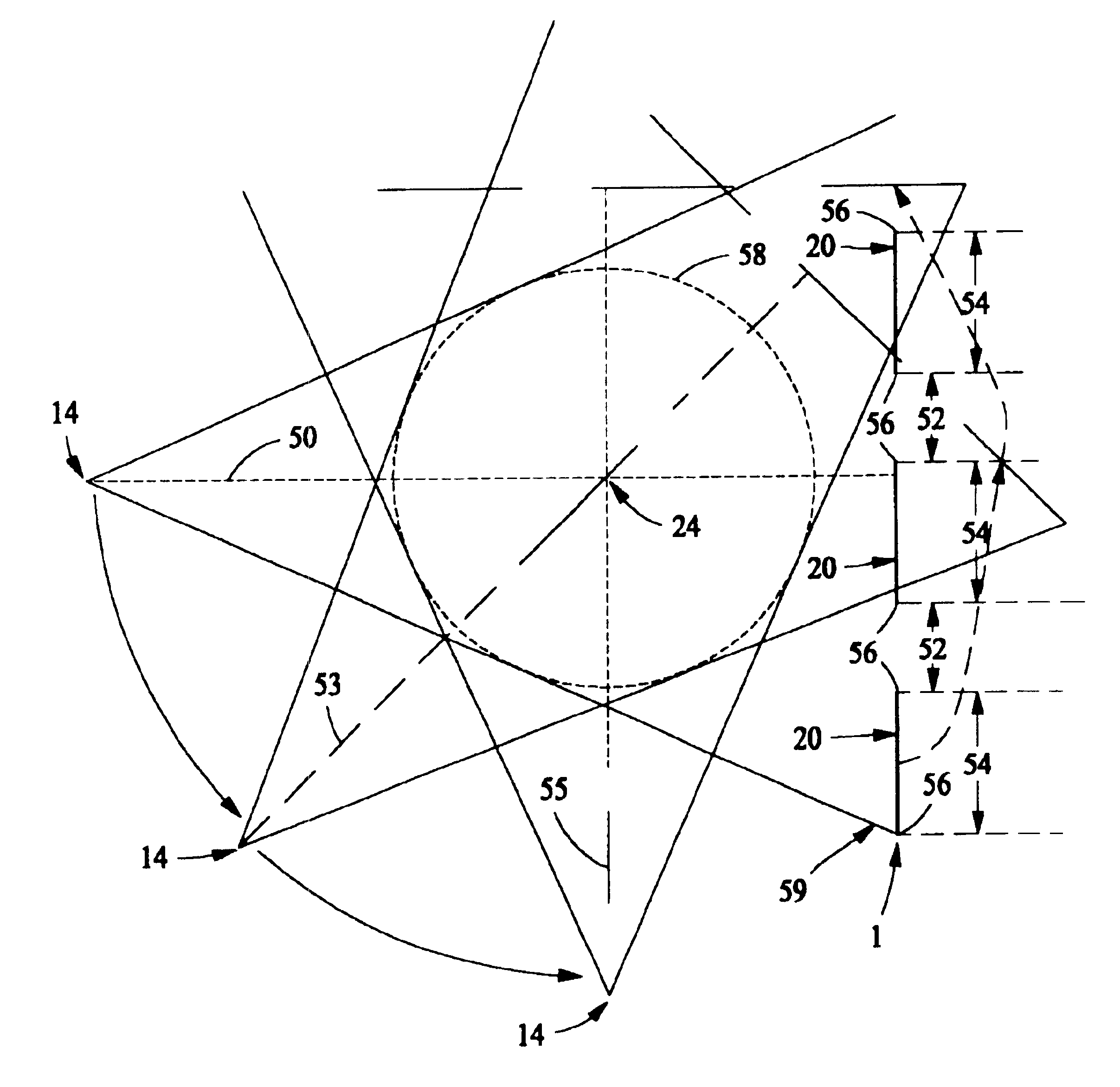
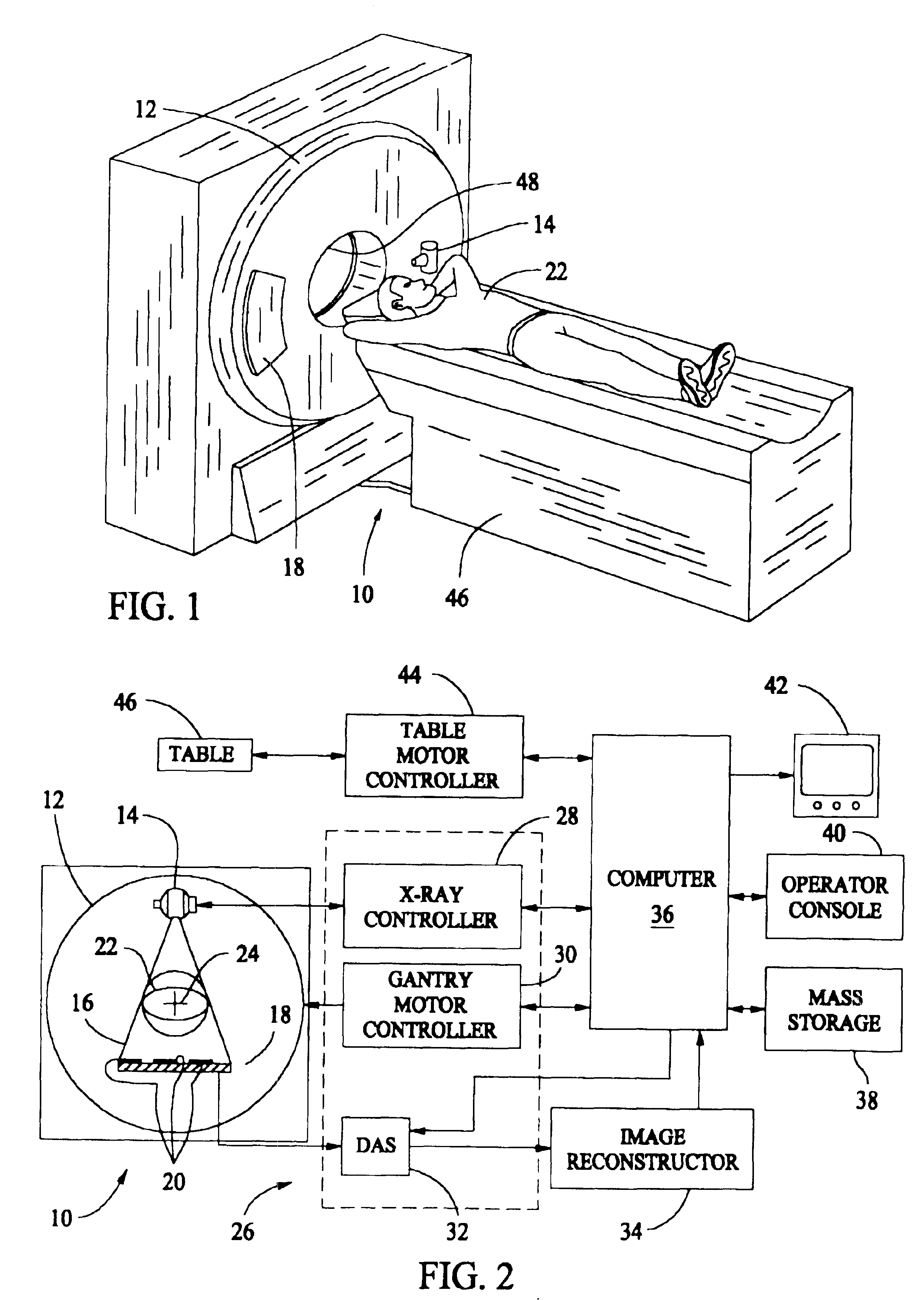
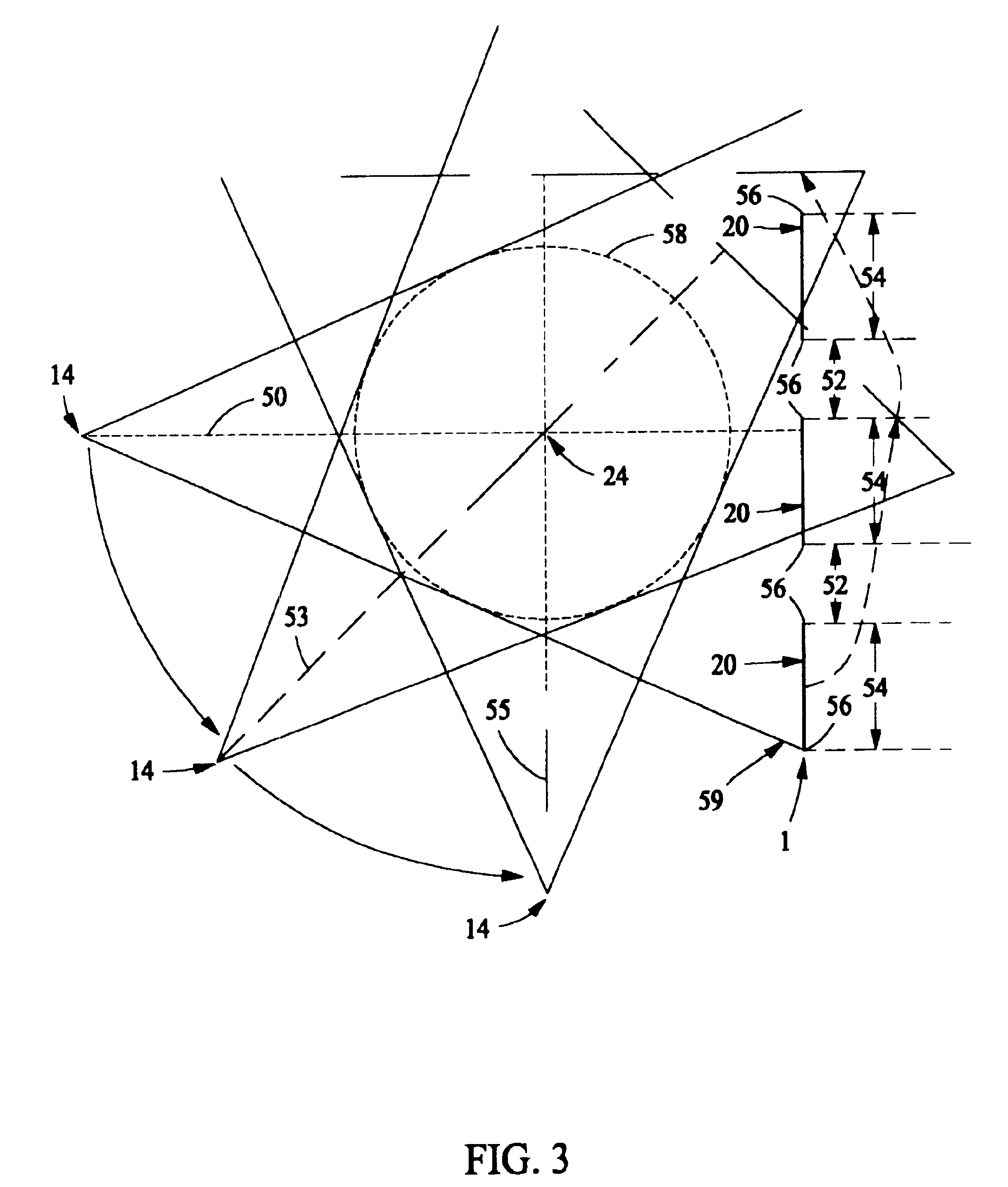
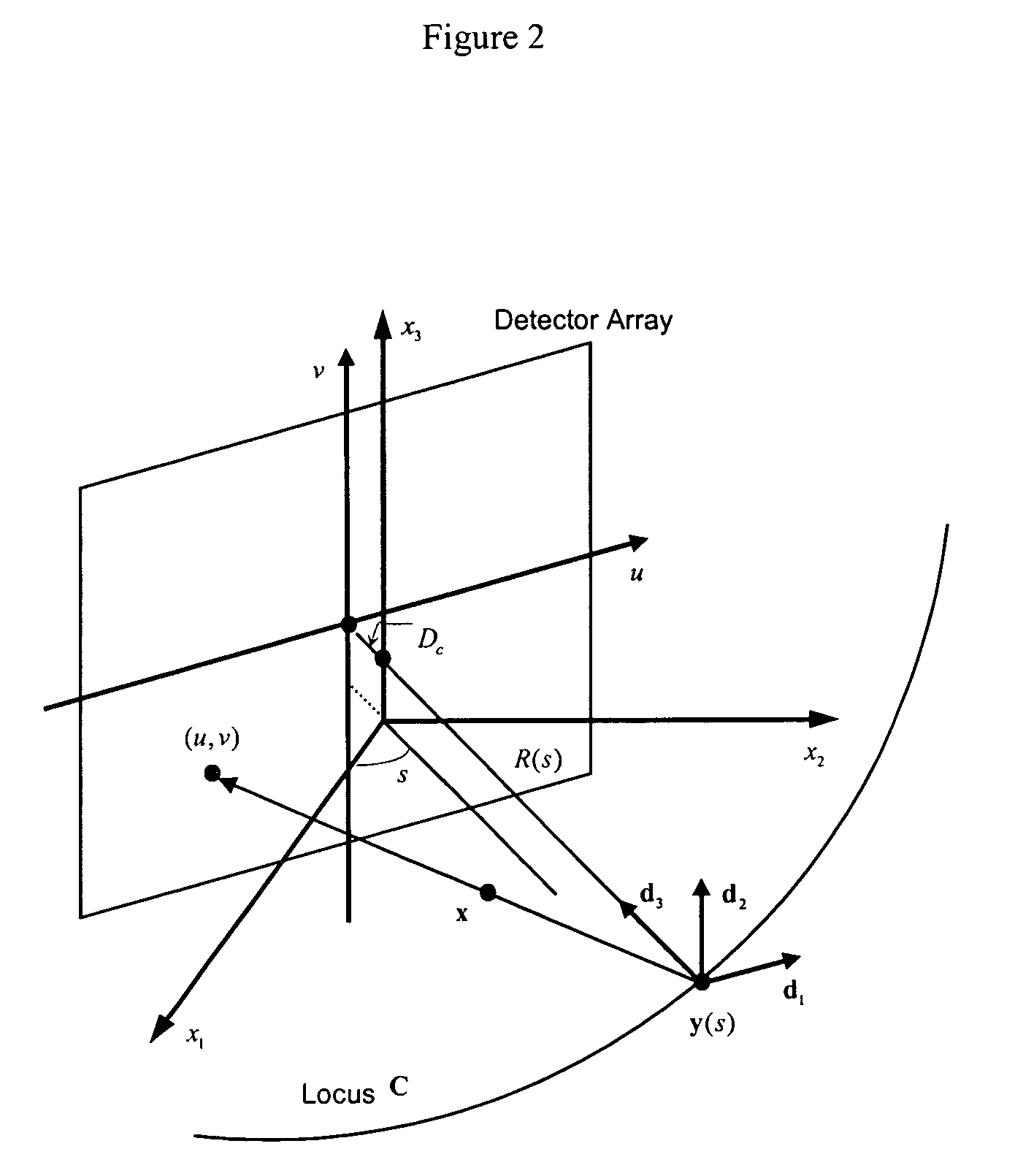
Multi-parameter X-ray computed tomography
ActiveUS8121249B2Eliminate crosstalkIncrease sampling rateRadiation/particle handlingTomographyData setX-ray
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
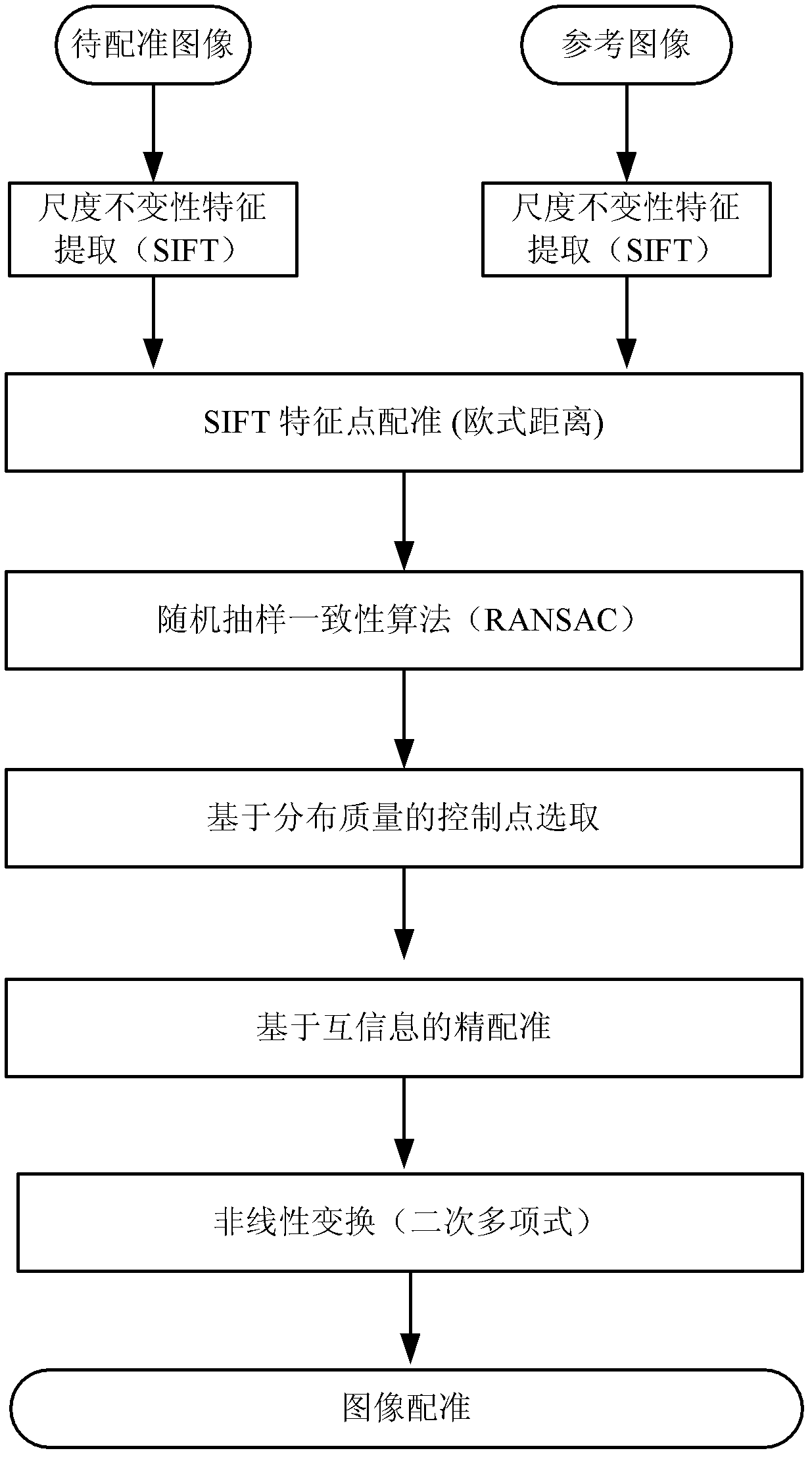
Remote sensing image registration method of multi-source sensor
ActiveCN103020945AQuick registrationPrecise registrationImage analysisWeight coefficientMutual information
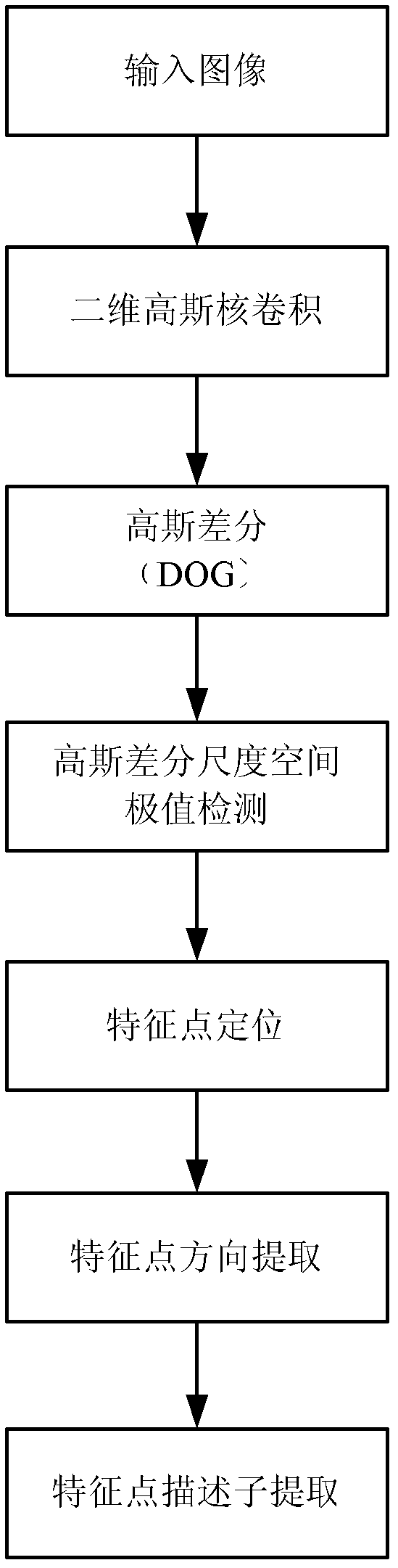
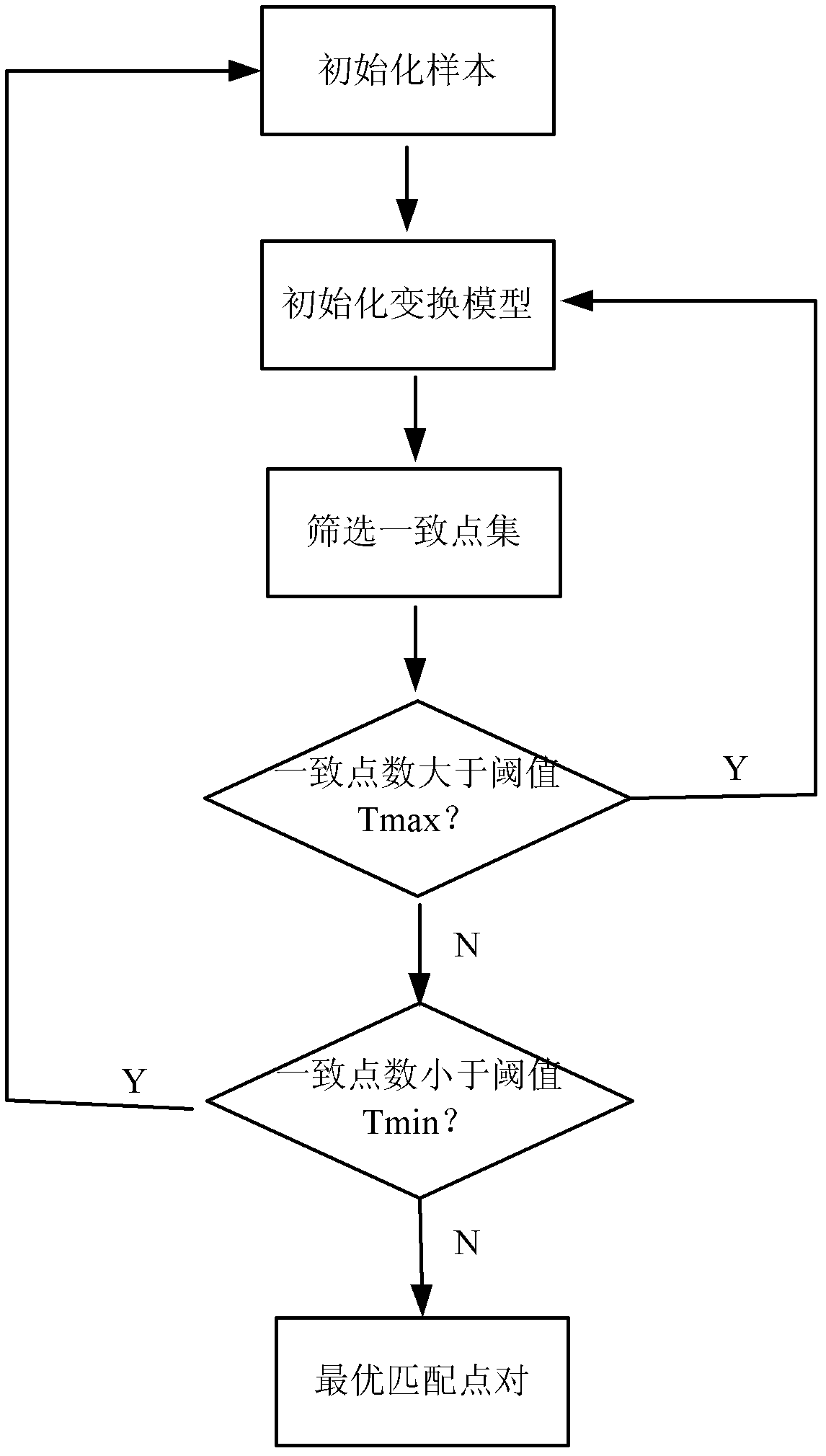
The invention provides a remote sensing image registration method of a multi-source sensor, relating to an image processing technology. The remote sensing image registration method comprises the following steps of: respectively carrying out scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT) on a reference image and a registration image, extracting feature points, calculating the nearest Euclidean distances and the nearer Euclidean distances of the feature points in the image to be registered and the reference image, and screening an optimal matching point pair according to a ratio; rejecting error registration points through a random consistency sampling algorithm, and screening an original registration point pair; calculating distribution quality parameters of feature point pairs and selecting effective control point parts with uniform distribution according to a feature point weight coefficient; searching an optimal registration point in control points of the image to be registered according to a mutual information assimilation judging criteria, thus obtaining an optimal registration point pair of the control points; and acquiring a geometric deformation parameter of the image to be registered by polynomial parameter transformation, thus realizing the accurate registration of the image to be registered and the reference image. The remote sensing image registration method provided by the invention has the advantages of high calculation speed and high registration precision, and can meet the registration requirements of a multi-sensor, multi-temporal and multi-view remote sensing image.
Owner:济钢防务技术有限公司
System and method for identifying qr code
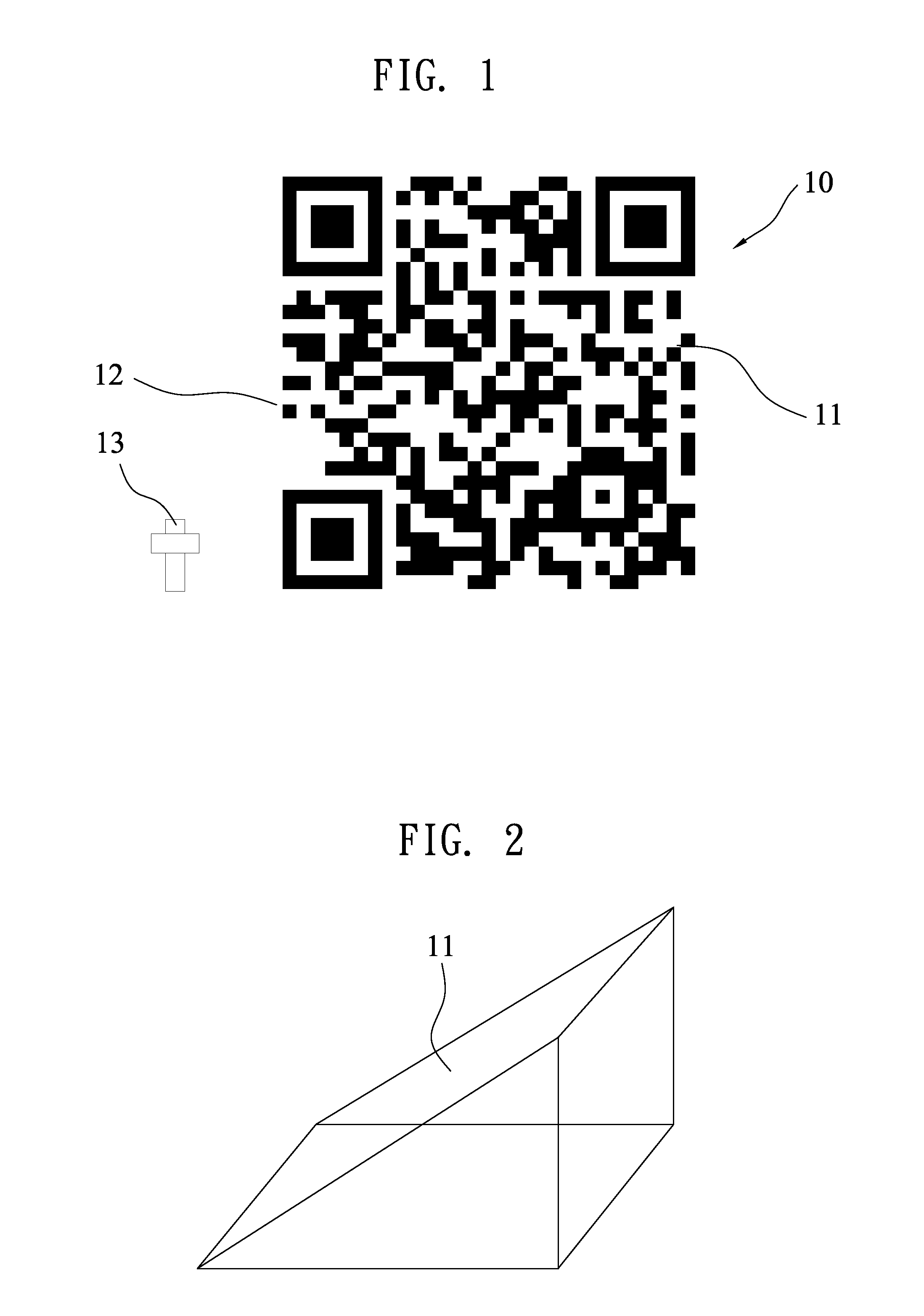
InactiveUS20120024952A1Efficiently and stably identifiedStable and efficient methodSensing by electromagnetic radiationImage geometry
Disclosed is a system and method for identifying a QR (Quick Response) code. The method includes steps of simultaneously obtaining a first image and a second image respectively representing the QR code, geometrically transforming the second image into a third image, subtracting each pixel value and the average pixel value of the first image and the third image to respectively form a fourth image and a fifth image, comparing each of corresponding pixels of the fourth image and the fifth image to form a sixth image, and setting each pixel of the sixth image into 1 if each pixel is over a threshold and setting each pixel into 0 if each pixel is below the threshold.
Owner:CHENG UEI PRECISION IND CO LTD
System, computer program and method for 3D object measurement, modeling and mapping from single imagery
InactiveUS20080089610A1Create efficientlyImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionThree dimensional measurementComputerized system
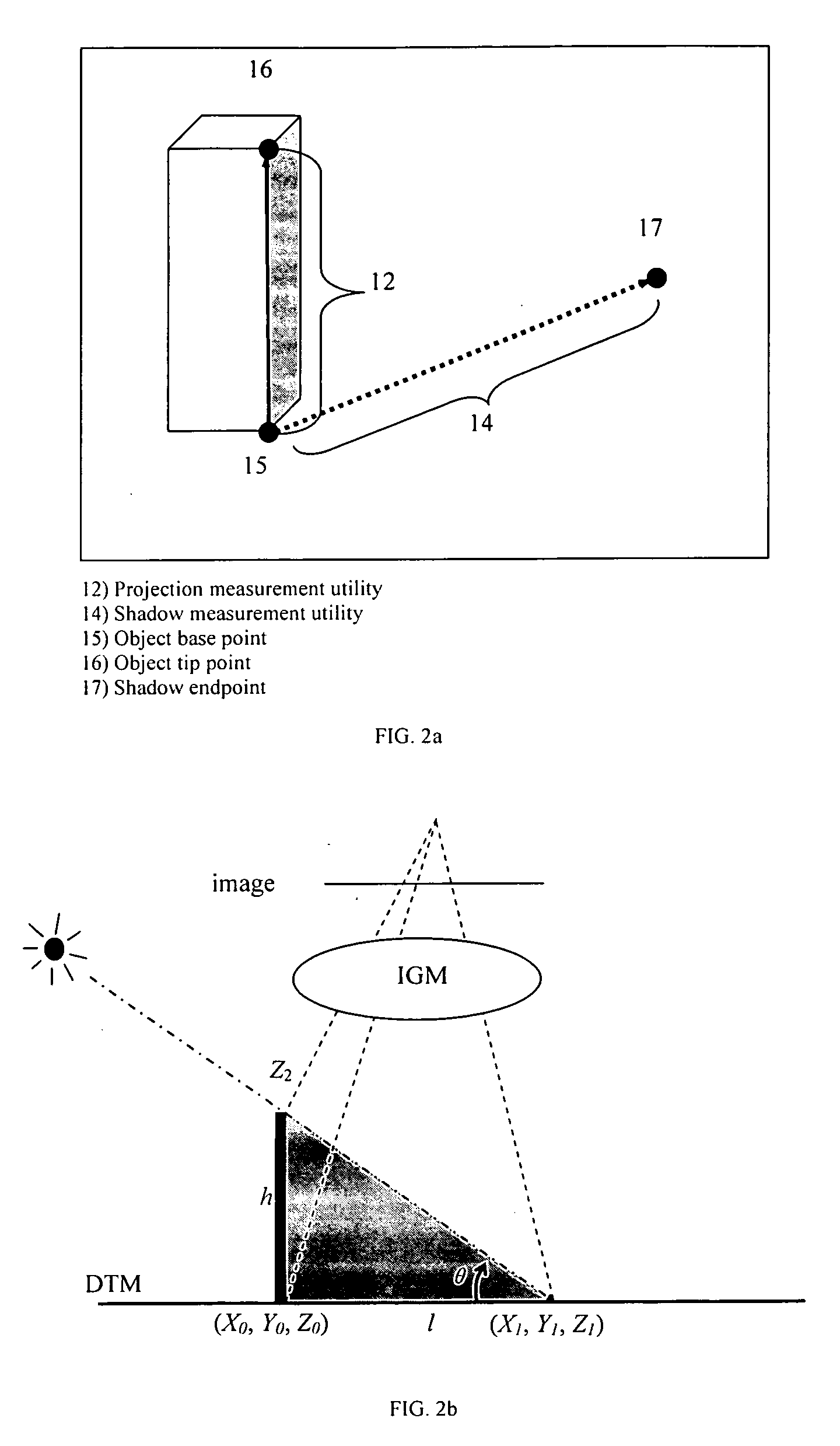
A method for deriving three-dimensional measurement information and / or creating three-dimensional models and maps, from single images of at least one three-dimensional object is provided. The method includes the steps of: (a) obtaining at least one two-dimensional single image of the object, the image consisting of image data and being associated with an image geometry model (IGM); (b) deriving three-dimensional coordinate information associated with the image, based on the IGM, and associating the three-dimensional coordinate information with the image data; (c) analyzing the image data so as to: (i) measure the projection of the object using the IGM to derive measurement data including the height and / or point-to-point distances pertaining to the object; and / or (ii) measure the shadow of the object to derive measurement data including the height and / or point-to-point distance pertaining to the object; and (d) obtaining three-dimensional measurements based on the projection and / or shadow measurements of the object. In another aspect of the method, the method includes the further step of creating three-dimensional models or maps based on the projection and / or shadow measurements. A series of algorithms are also provided for processing the method of the invention. A computer system and related computer program for deriving three-dimensional measurement information and / or creating three-dimensional models and maps, from single images of at least one three-dimensional object is provided based on the disclosed method is also provided.
Owner:MICROSOFT CORP
Methods and apparatus for camera calibration based on multiview image geometry
ActiveUS8368762B1Relaxes camera calibration setupSimple working processTelevision systemsMathematical modelIntrinsics
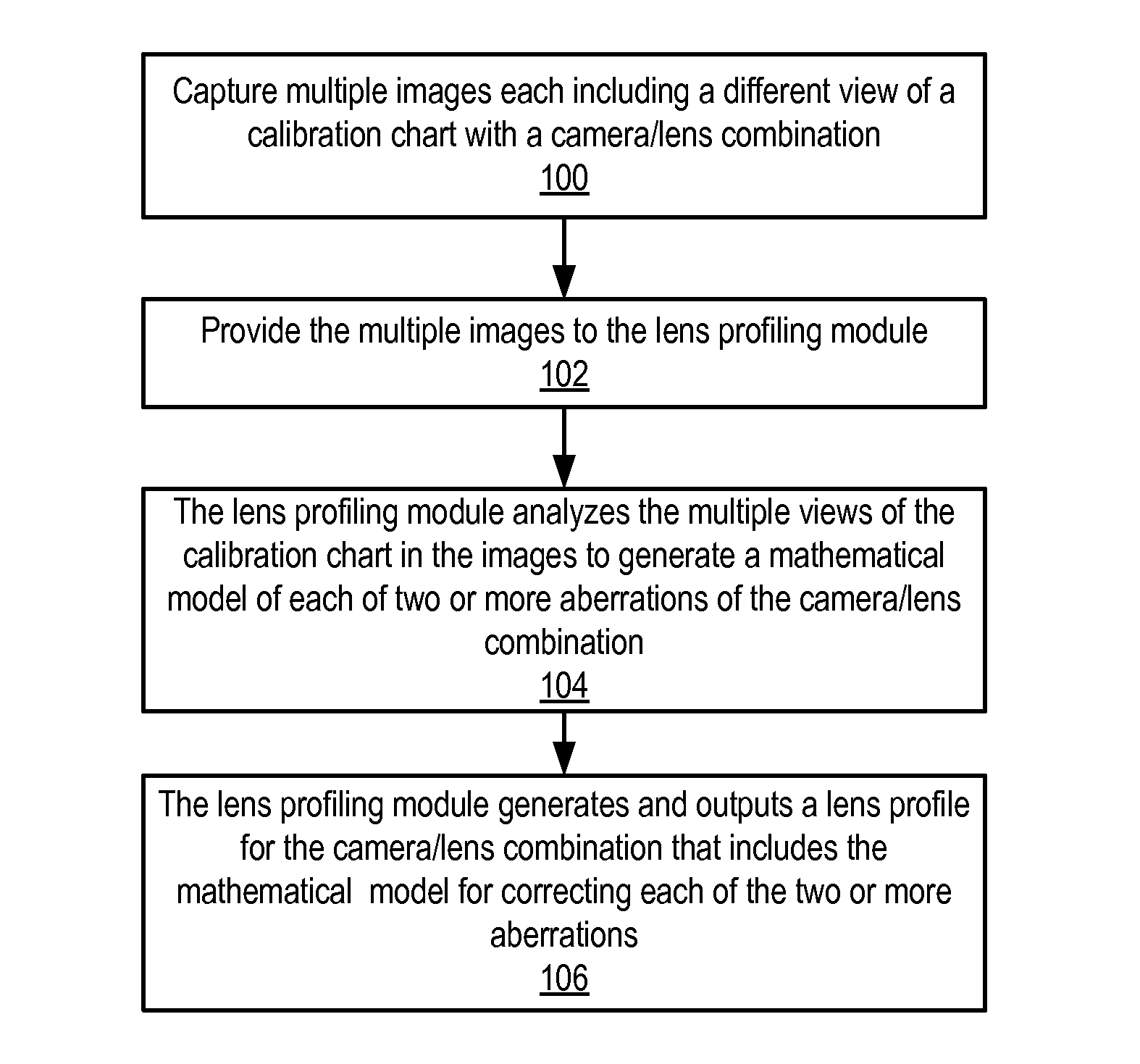
Methods and apparatus for camera calibration based on multiview image geometry. A lens profiling module may estimate two or more mathematical models for correcting aberrations in images in a single pass from a set of calibration images captured with a camera / lens combination. For example, the module may estimate the lens aberrations of geometric distortion, lateral chromatic aberration, and vignette models in a single pass. The module may determine point correspondences, 3D transformations, and camera intrinsics for views of calibration charts captured in the images. The module estimates the mathematical models for the two or more types of aberrations from the information determined from the views of the calibration charts. The module may automatically determine an optimal model complexity when estimating the mathematical models. The estimated models may be written or appended to a lens profile for the camera / lens combination used to captured the calibration images.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Real-time feedback for preventing high dose c-arch geometry positions
ActiveUS20140307855A1Reduce total usageSmall impactLocal control/monitoringRadiation safety meansSoft x rayImaging quality
The present invention relates to an apparatus for aiding operation of an interventional x-ray imager during image acquisition, to a method of aiding operation of an x-ray imager, to an interventional x-ray imager, to a computer program element and to a computer readable medium. The X-ray imager is capable of varying X-ray dosages depending on differences in X-ray attenuation levels across an object of interest to be imaged and is capable of assuming any one of a plurality of imaging geometry positions when acquiring an image. An indication, visual, acoustic or haptic, to the operator of an X-ray imager is provided on the incurred change in X-ray dosage when changing from a current projection view to an updated projection view, provided that a given constant image quality is to be maintained throughout the different views.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
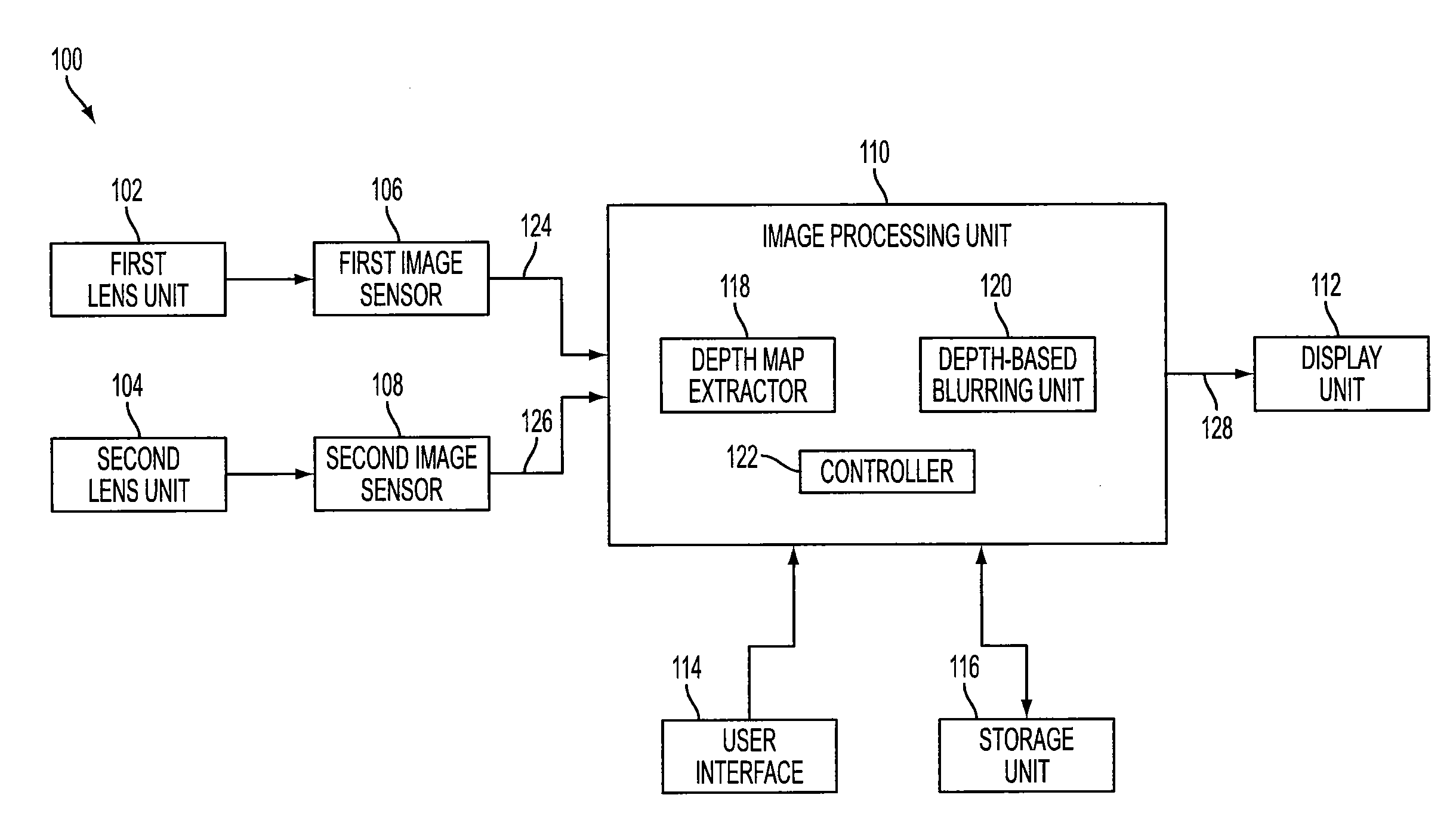
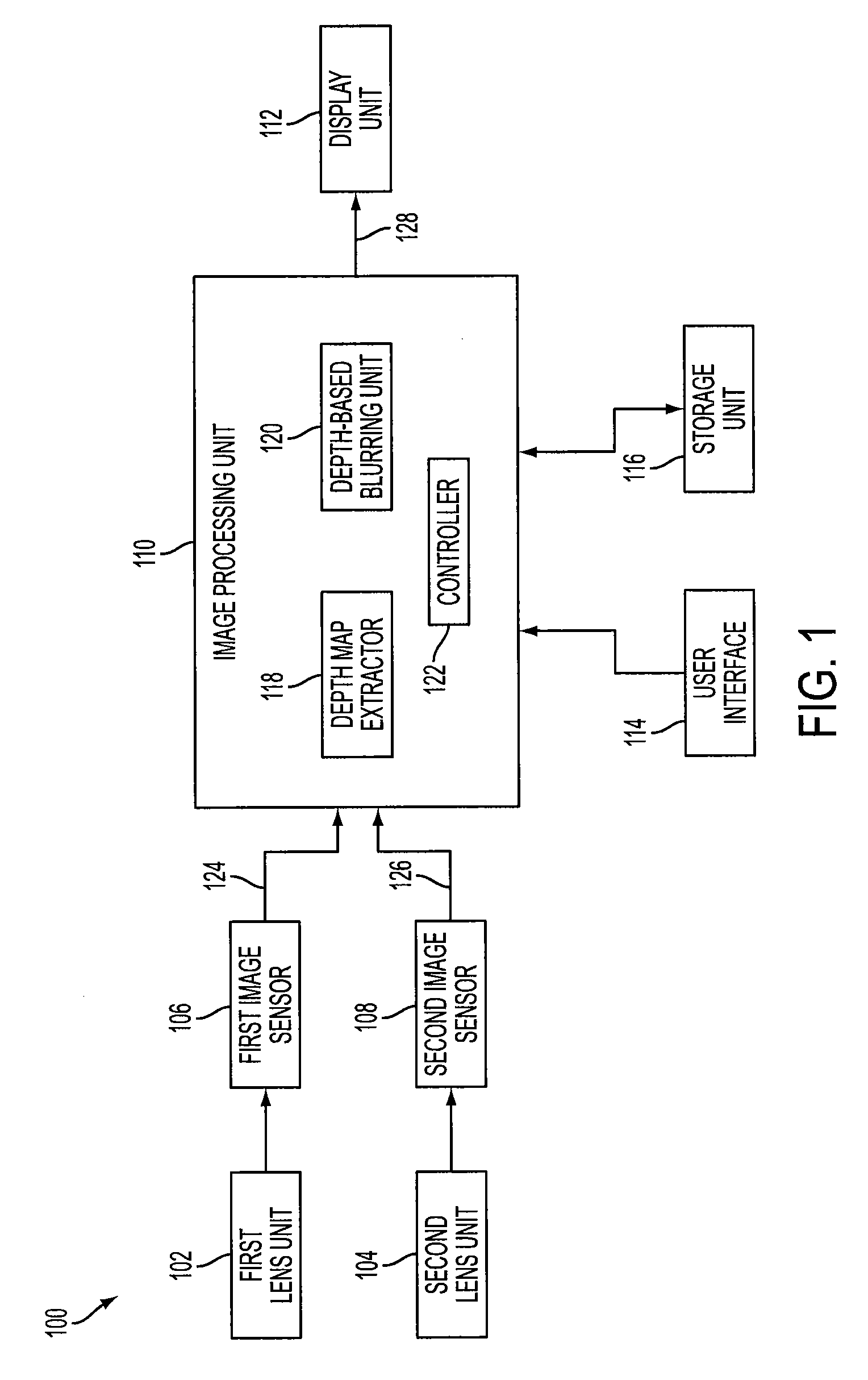
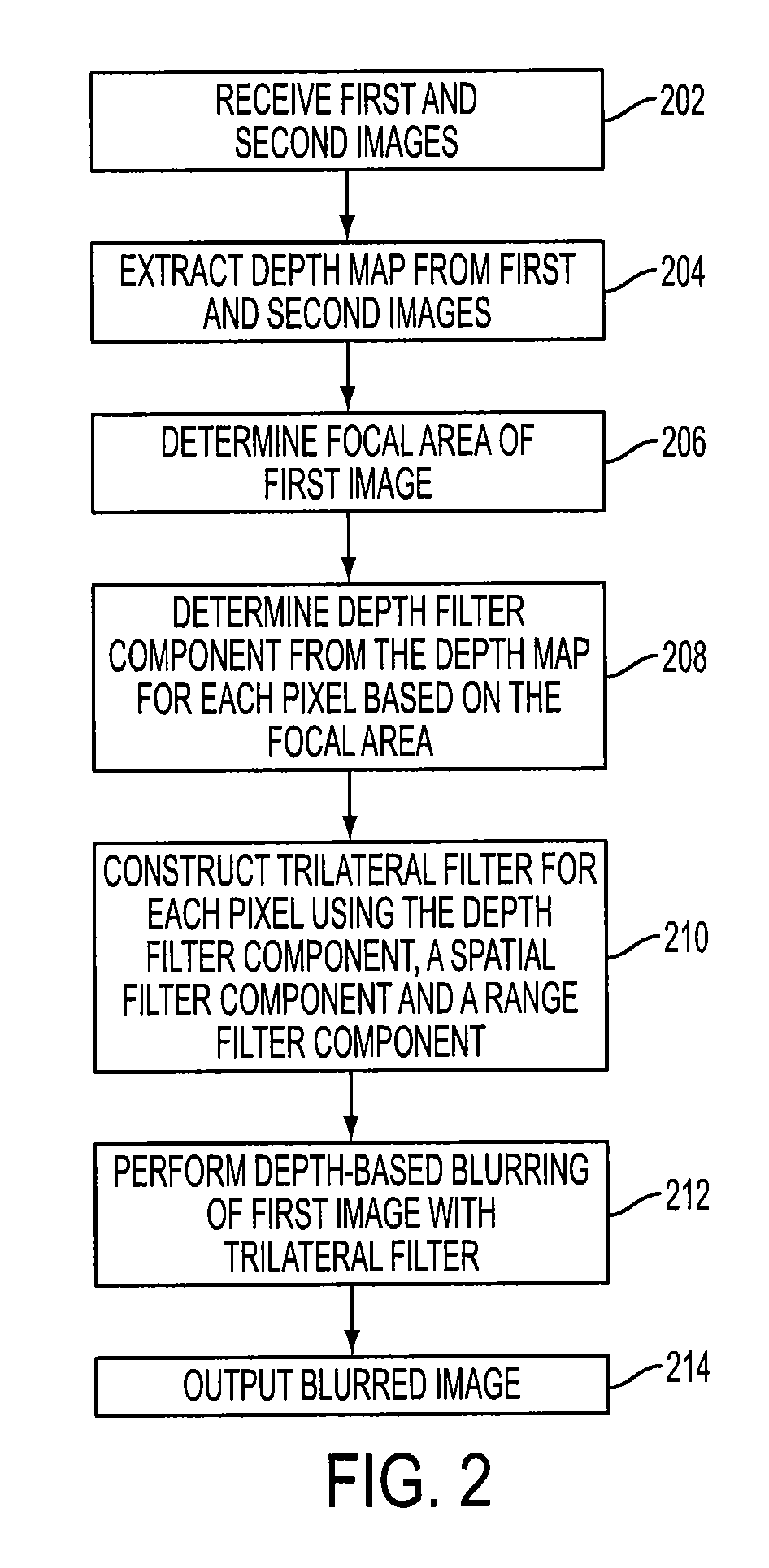
Method of depth-based imaging using an automatic trilateral filter for 3D stereo imagers
A system of stereo imagers, including image processing units and methods of blurring an image, is presented. The image is received from an image sensor. For each pixel of the image, a depth filter component is determined based on a focal area of the image and a depth map associated with the image. For each pixel of the image, a trilateral filter is generated that includes a spatial filter component, a range filter component and the depth filter component. The respective trilateral filter is applied to corresponding pixels of the image to blur the image outside of the focal area. A refocus area or position may be determined by imaging geometry or may be selected manually via a user interface.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Laparoscopic camera navigation trainer
A system for training users of laparoscopic cameras includes geometric targets disposed in spaced relation upon a base such that acquiring a laparoscopic view of each geometric target requires a change in the orientation of a laparoscopic camera. Each geometric target has disposed thereon an image of the same geometric shape, and each geometric target has an orientation line disposed thereon. The system accommodates both straight and angled laparoscopes. A method for training a person includes providing a system described above and allowing the person to use the laparoscopic camera to acquire images geometric targets. A preferred method includes the steps of having the user repeatedly acquire geometric targets with a 0 degree laparoscope until the measured time is less than a first time threshold and then having the user repeatedly acquire geometric targets with an angled laparoscope until the measured time is less than a second time threshold.
Owner:THE ADMINISTRATORS OF THE TULANE EDUCATIONAL FUND
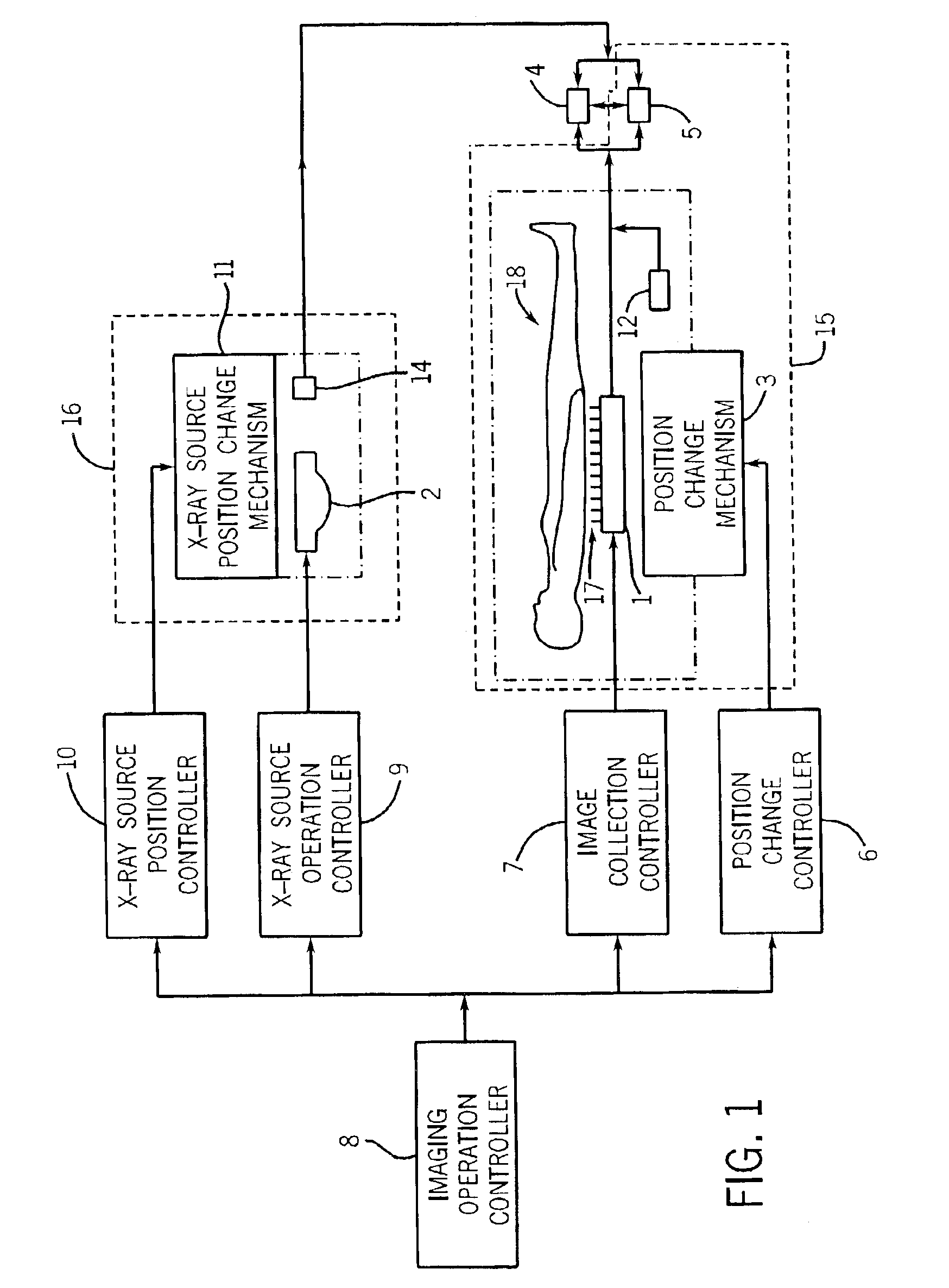
Image pasting using geometry measurement and a flat-panel detector
InactiveUS6944265B2Promote sportsX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationFlat panel detectorMeasurement device
A device for use in image pasting is described. The device includes a digital x-ray detector capable of automatic digital imaging without the use of an image intensifier; the detector preferably being a flat-panel detector. Additionally, an image pasting system using a solid-state detector is described. The system can connect the detected images to a display via a network (such as a WAN, a LAN, or the internet). Further, an image geometry measurement device for use in pasting x-ray images is disclosed. The geometry measurement device helps determine the relative position of two images to be used in image pasting. This information can be used alone, or in connection with an image pasting algorithm. Still further, methods of forming composite images are disclosed using a flat-panel detector and using the geometry of the images. The disclosed devices and systems can be integrated with other digital image pasting technology.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Systems and methods of non-standard spiral cone-beam computed tomography (CT)
InactiveUS20060050842A1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSpiral Cone-Beam Computed TomographyFiltration
Provided herein are methods of reconstructing an image from projection data provided by a tomography scanner that is based on geometric optics comprising scanning an object in a cone-beam imaging geometry following a non-standard spiral path or a general piecewise smooth scanning path wherein projection data is generated and reconstructing an image according to a closed-form formula that is either in the filtered backprojection (FBP) or backprojection filtration (or backprojected filtration, BPF) formats. Also provided herein are associated systems and apparatuses for tomographic imaging.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
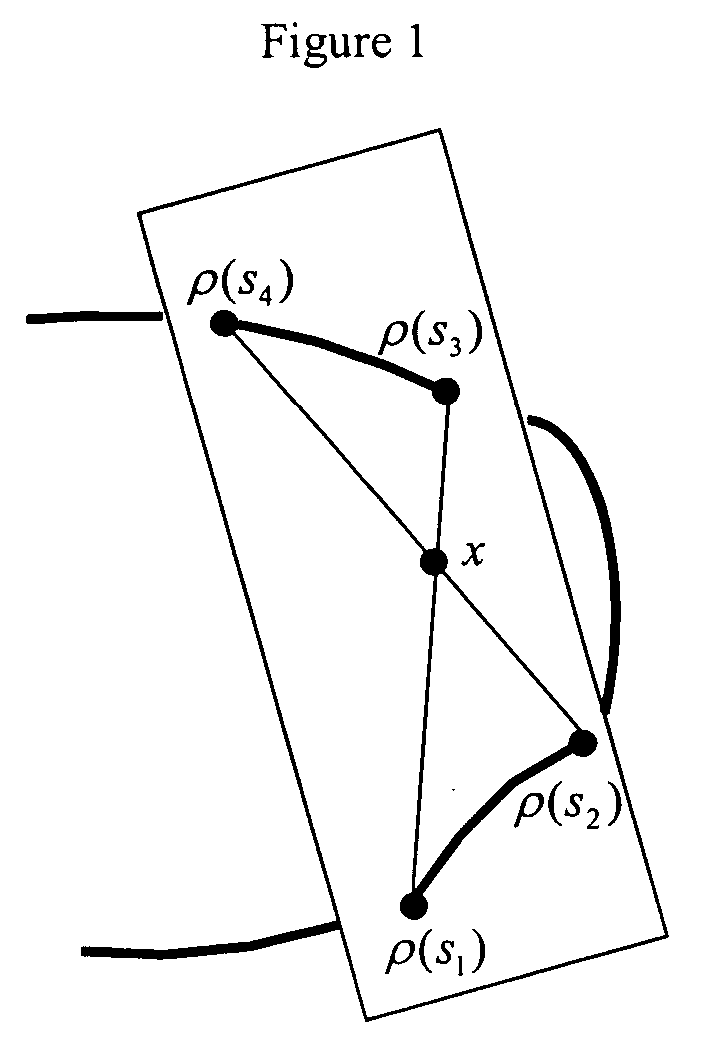
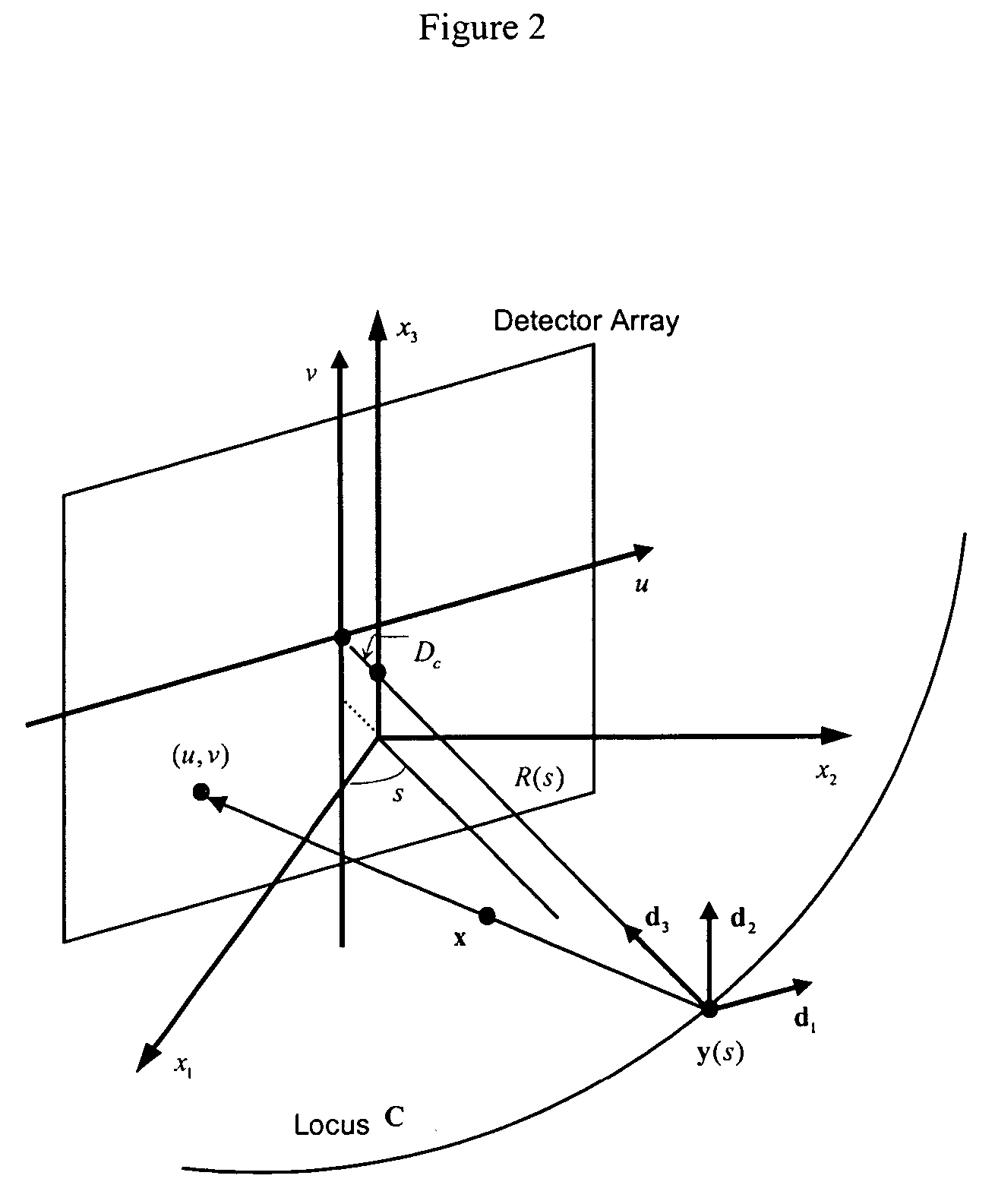
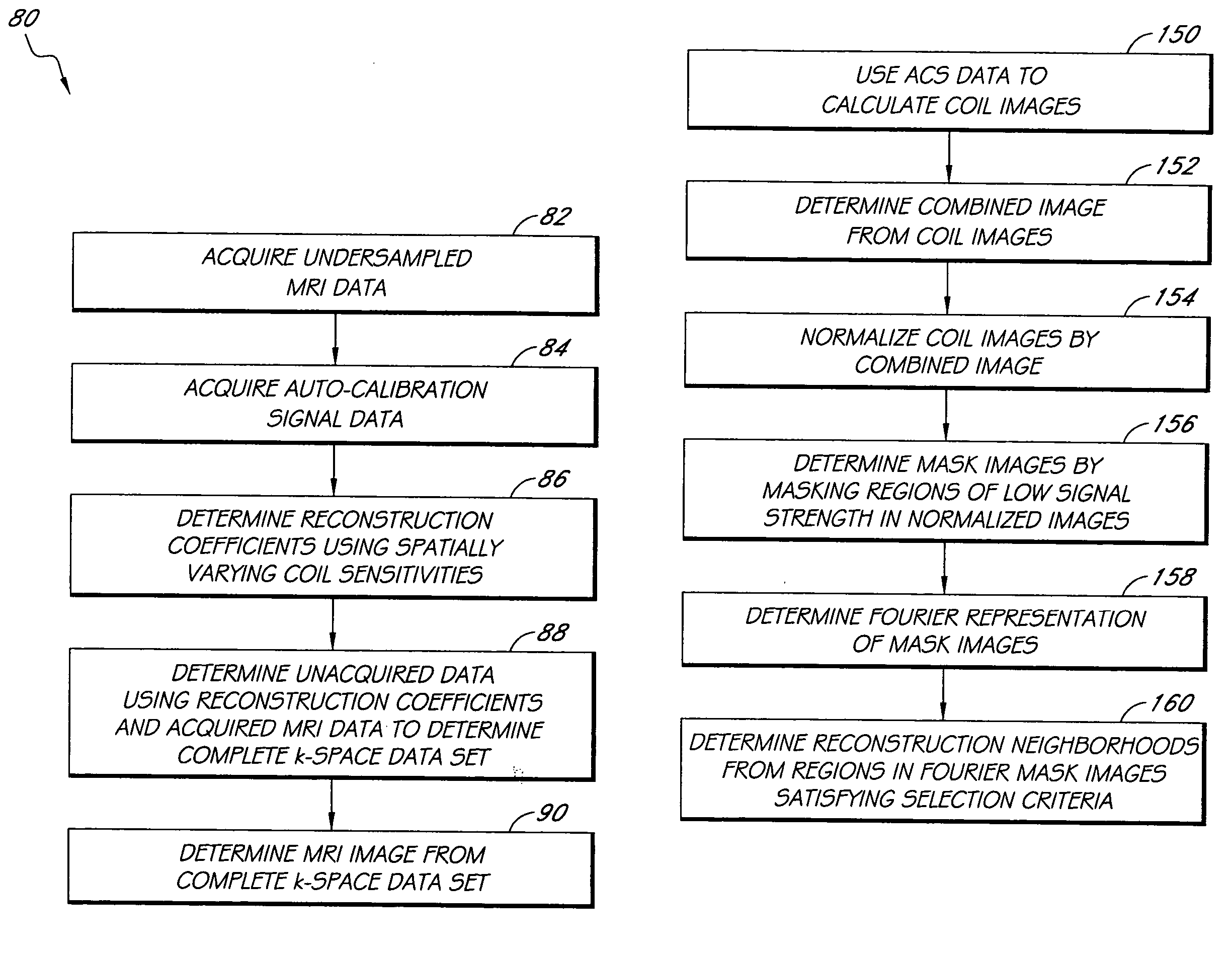
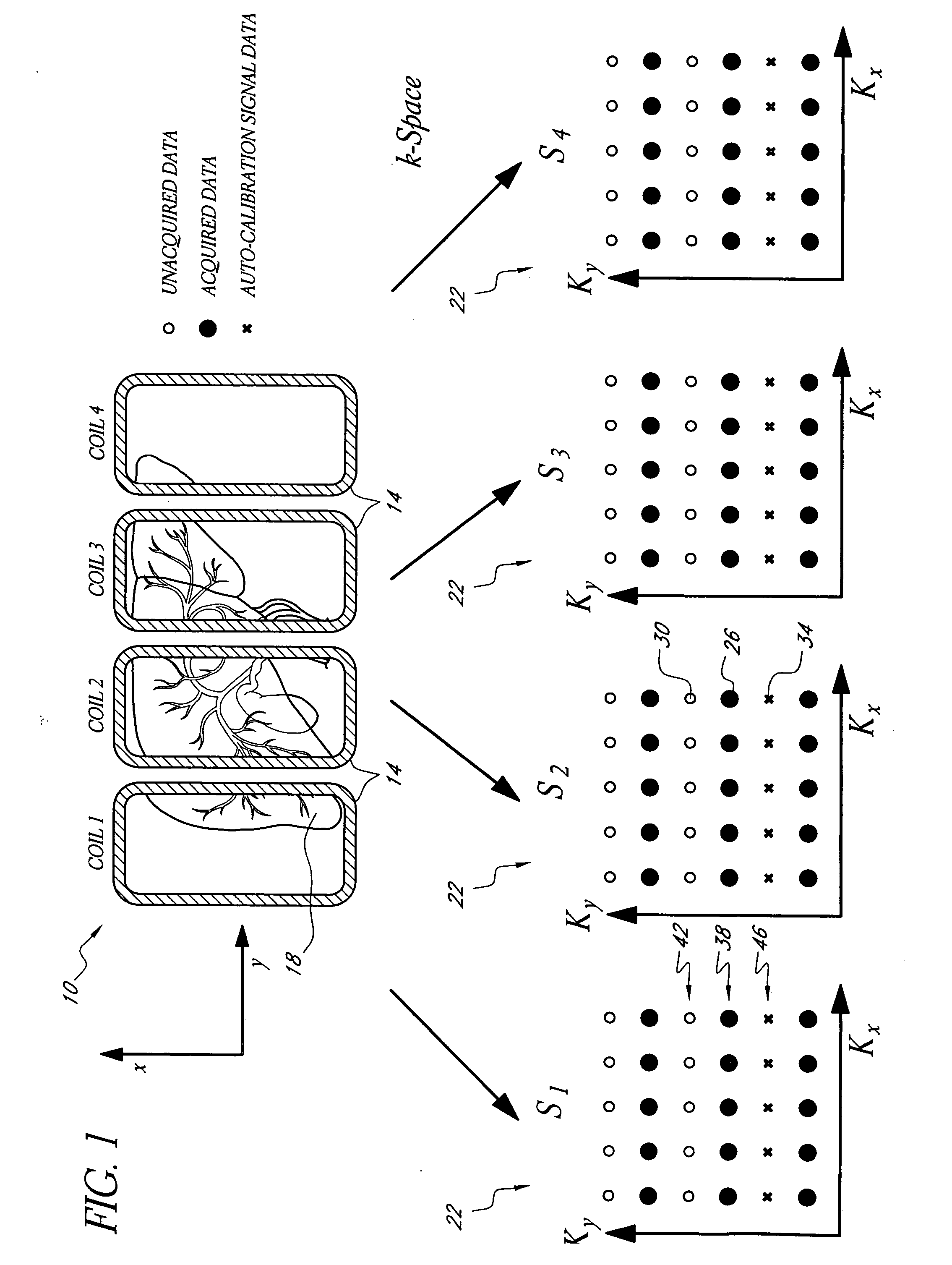
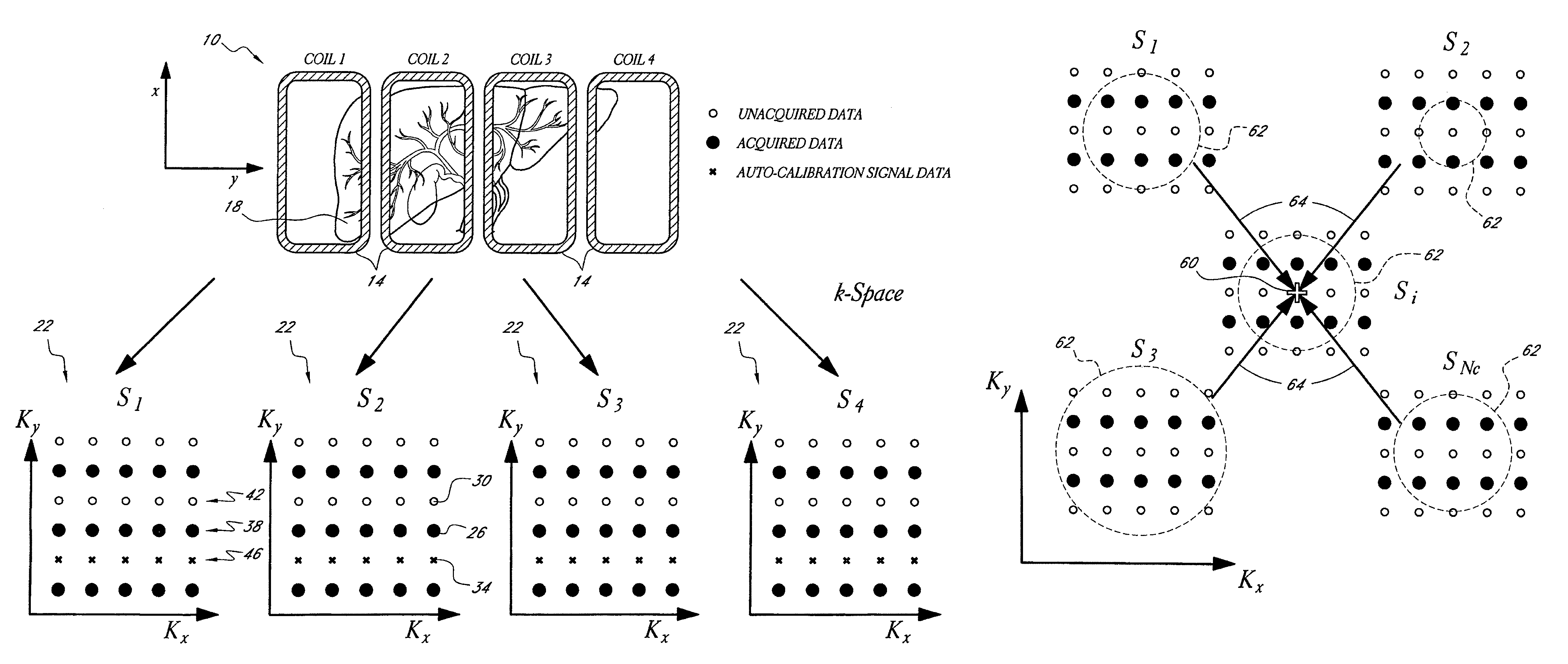
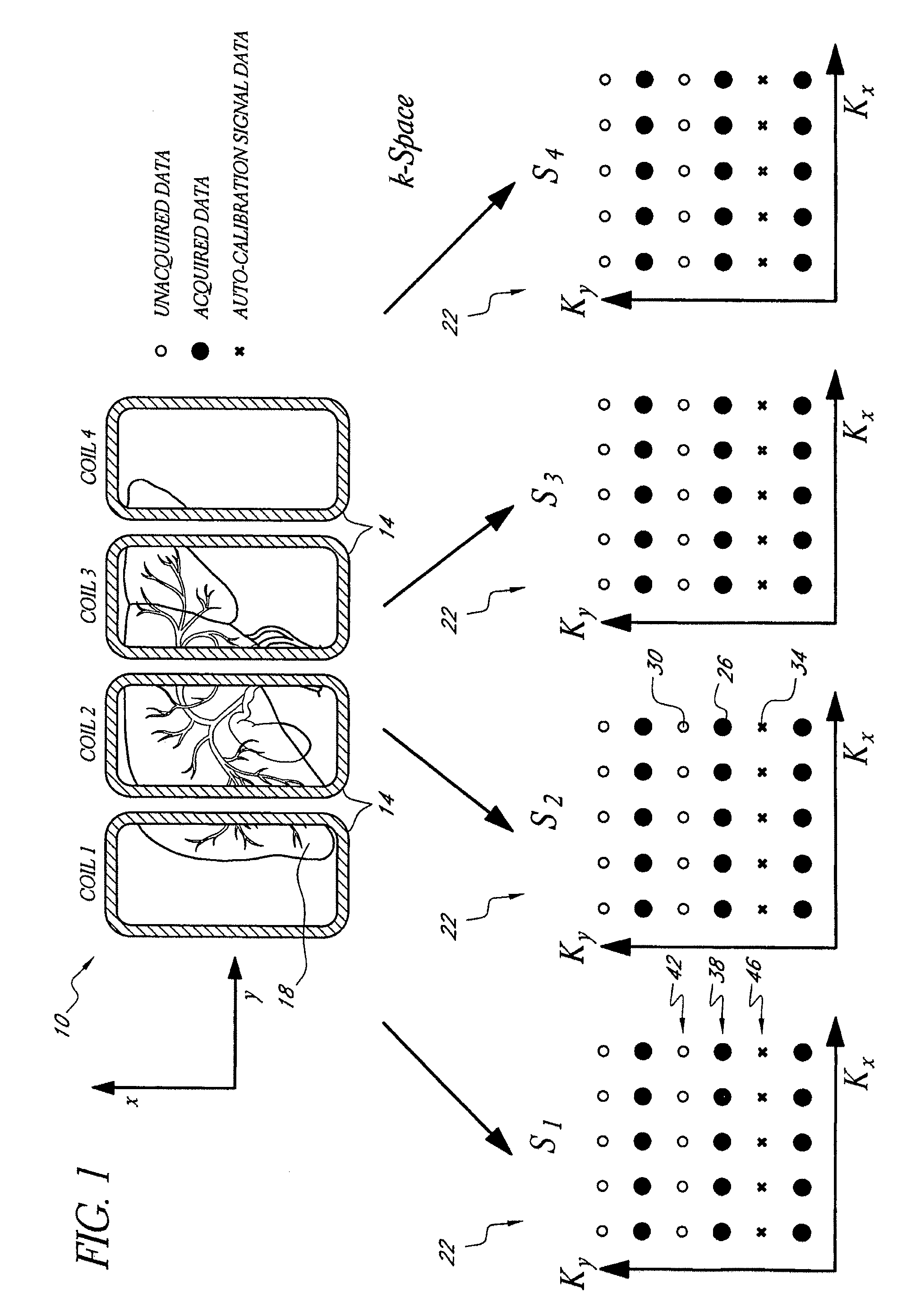
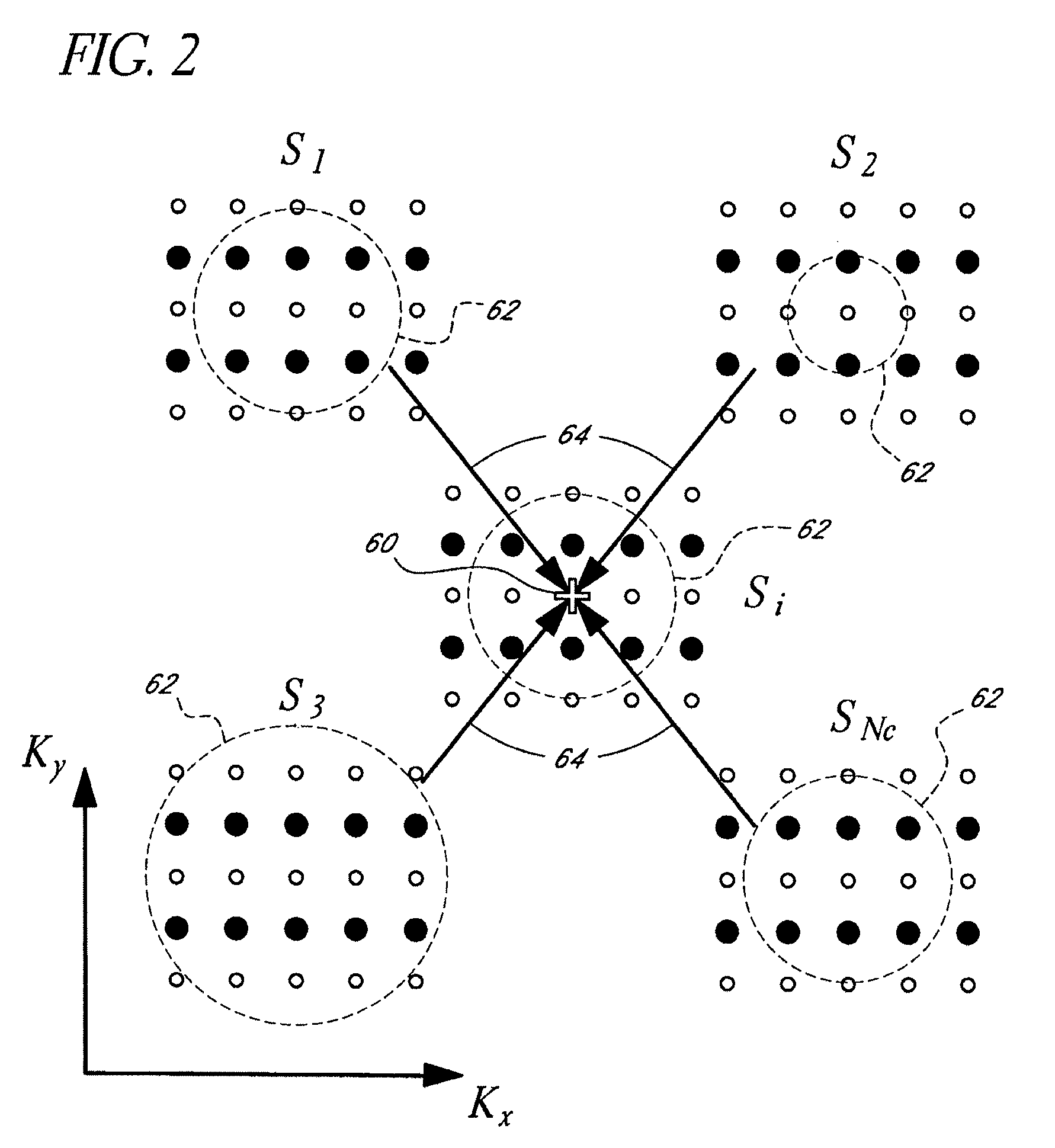
Systems and methods for image reconstruction of sensitivity encoded MRI data
Methods and systems in a parallel magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system utilize sensitivity-encoded MRI data acquired from multiple receiver coils together with spatially dependent receiver coil sensitivities to generate MRI images. The acquired MRI data forms a reduced MRI data set that is undersampled in at least a phase-encoding direction in a frequency domain. The acquired MRI data and auto-calibration signal data are used to determine reconstruction coefficients for each receiver coil using a weighted or a robust least squares method. The reconstruction coefficients vary spatially with respect to at least the spatial coordinate that is orthogonal to the undersampled, phase-encoding direction(s) (e.g., a frequency encoding direction). Values for unacquired MRI data are determined by linearly combining the reconstruction coefficients with the acquired MRI data within neighborhoods in the frequency domain that depend on imaging geometry, coil sensitivity characteristics, and the undersampling factor of the acquired MRI data. An MRI image is determined from the reconstructed unacquired data and the acquired MRI data.
Owner:THE UNIV OF UTAH
Signal Processors and Methods for Estimating Geometric Transformations of Images for Digital Data Extraction
ActiveUS20170193628A1Accurate measurementAccurate locationGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital dataConfidence metric
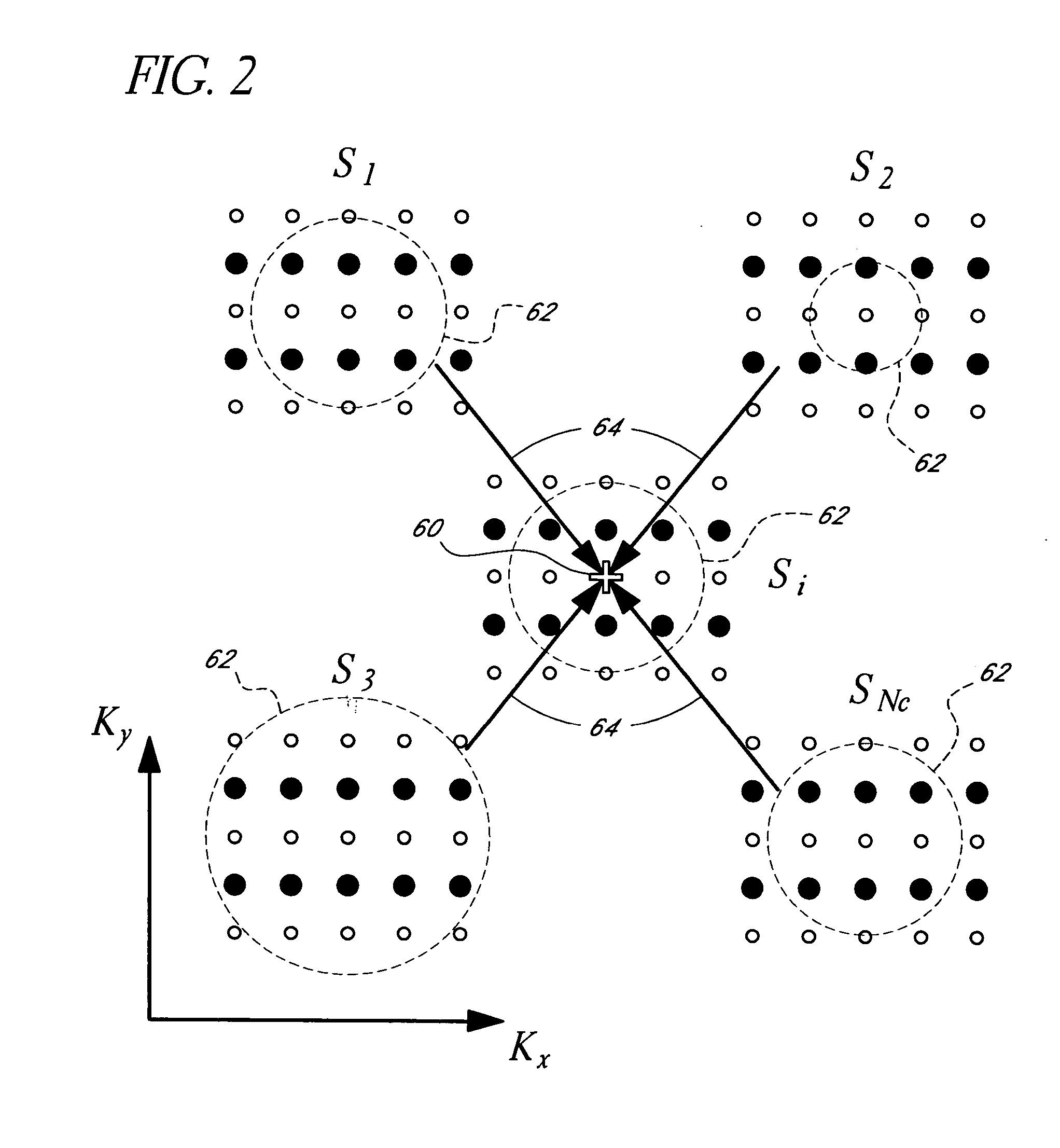
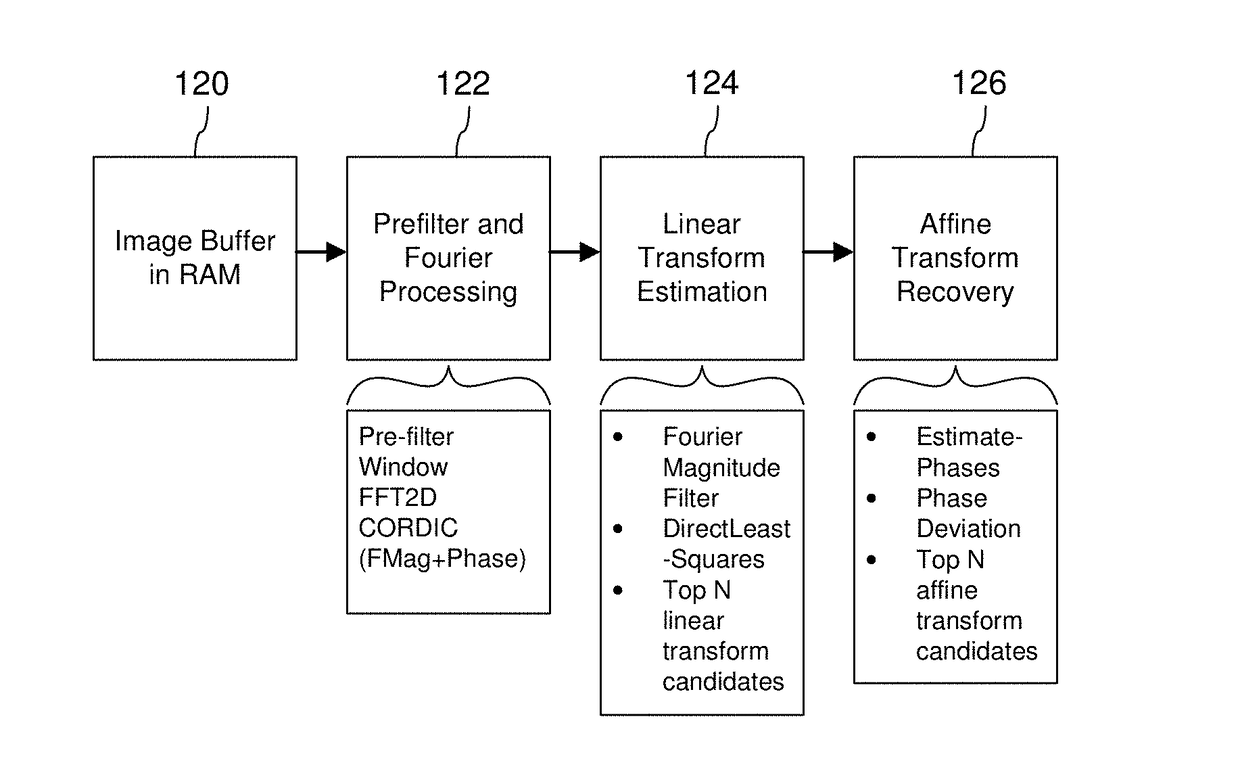
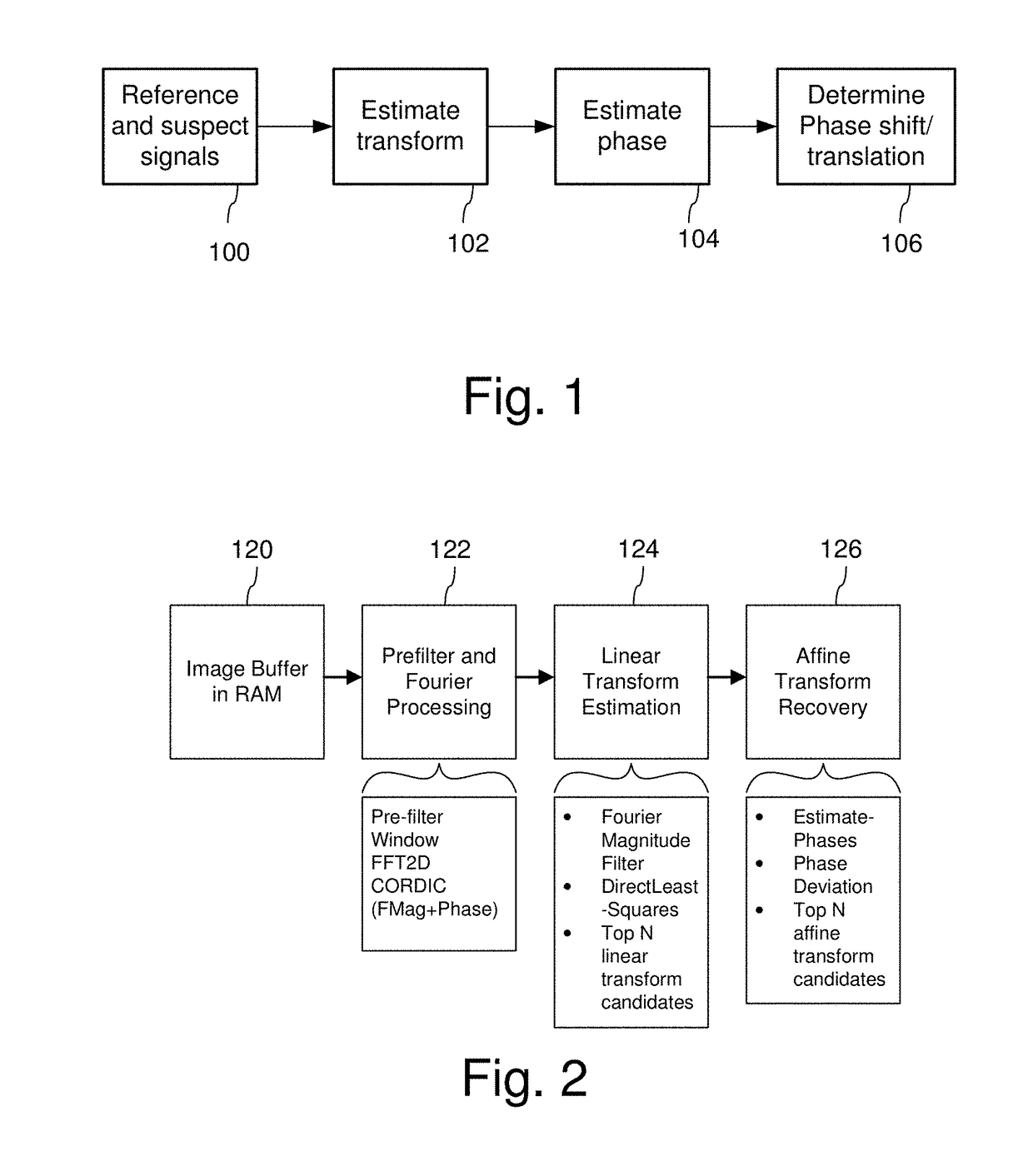
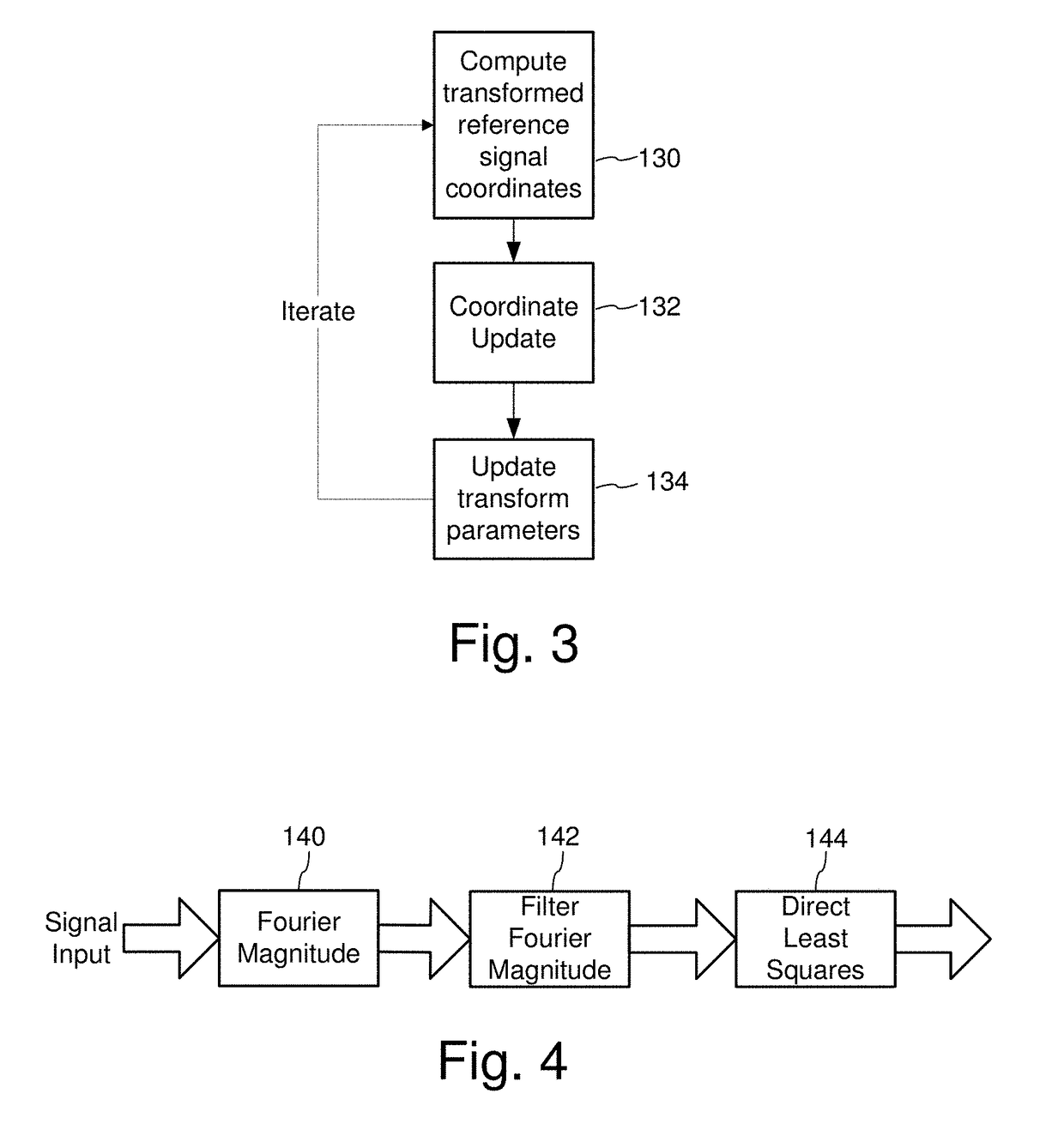
Signal processing devices and methods estimate a geometric transform of an image signal. From a seed set of transform candidates, a direct least squares method applies a seed transform candidate to a reference signal and then measures correlation between the transformed reference signal and an image signal in which the reference signal is encoded. Geometric transform candidates encompass differential scale and shear, which are useful in approximating a perspective transform. For each candidate, update coordinates of reference signal features are identified in the image signal and provided as input to a least squares method to compute an update to the transform candidate. The method iterates so long as the update of the transform provides a better correlation. At the end of the process, the method identifies a geometric transform or set of top transforms based on a further analysis of correlation, as well as other results. Phase characteristics are exploited in the process of updating coordinates and measuring correlation. The geometric transform is used as an approximation of the geometric distortion of an image after digital data is encoded in it, and is used to compensate for this distortion to facilitate extracting embedded digital messages from the image. Due to the errors in the approximation, a signal confidence metric is determined and used to weight message symbol estimates extracted from the image.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
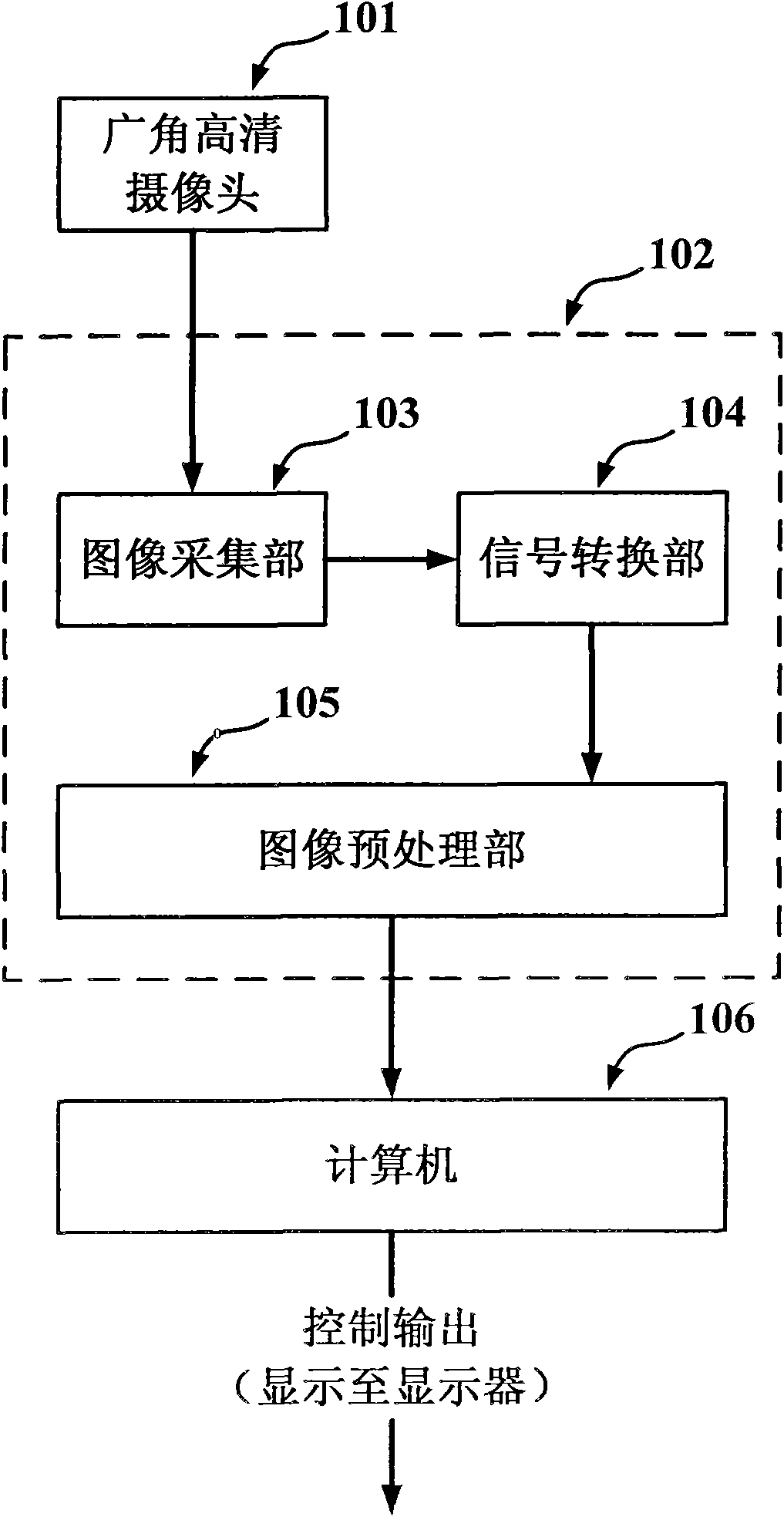
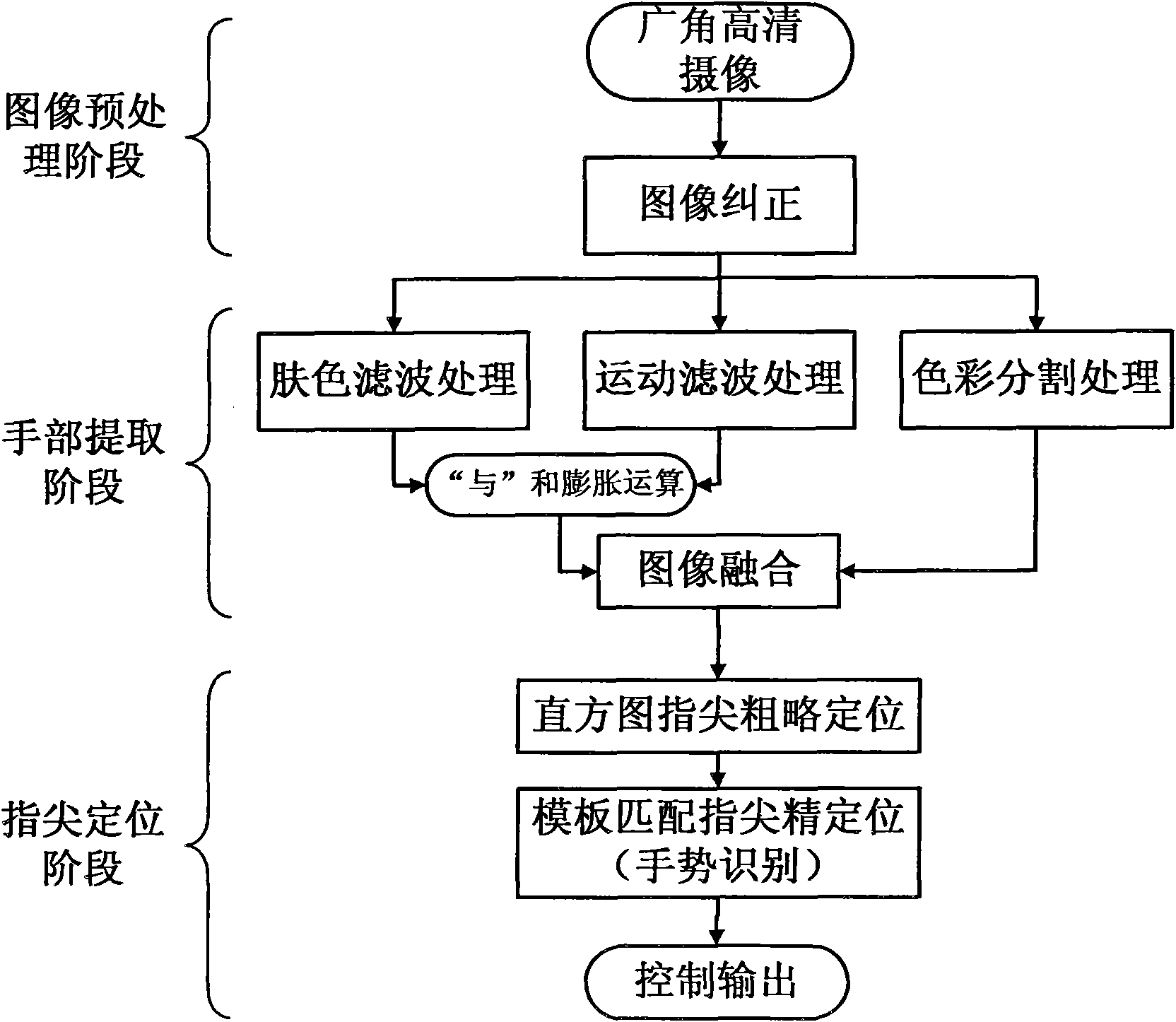
Method for quick-speed human-computer interaction based on finger tip tracking
InactiveCN101593022AImprove perceived efficiencyEasy to detectInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionTip positionFinger tracking
The invention discloses a method for quick human-computer interaction based on finger tip tracking, which comprises the following steps: firstly, preprocessing an image, adopting a wide-angle high-definition camera to perform high-resolution image pick-up on an indoor area, and performing image geometric distortion correction on the obtained images; secondly, extracting hand images, processing the obtained corrected images by a skin color filter, a motion filter and a color splitter, merging the results, and splitting the hand images out of the obtained corrected images; and finally, performing finger tip positioning: applying a histogram to perform rough finger tip positioning, using the rough position of a finger tip as a center to construct a searching window, and performing precise finger tip positioning through template matching. The method effectively improves the perceiving efficiency of scene images, achieves finger detection and positioning in a large range, judges the image distance between two eyes as a basis to perform the finger tip positioning without prior knowledge of the environment, and has outstanding distance robustness.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
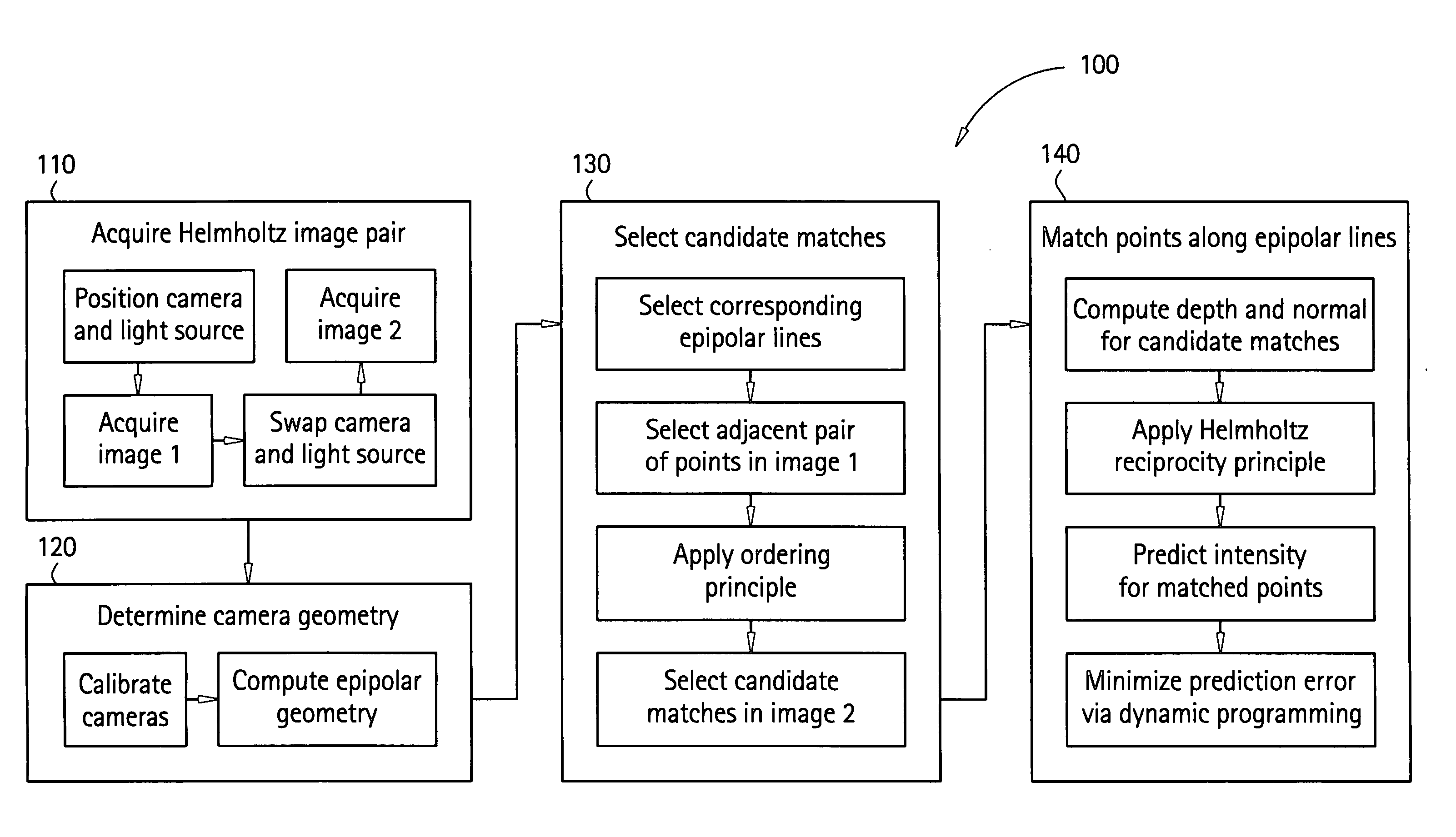
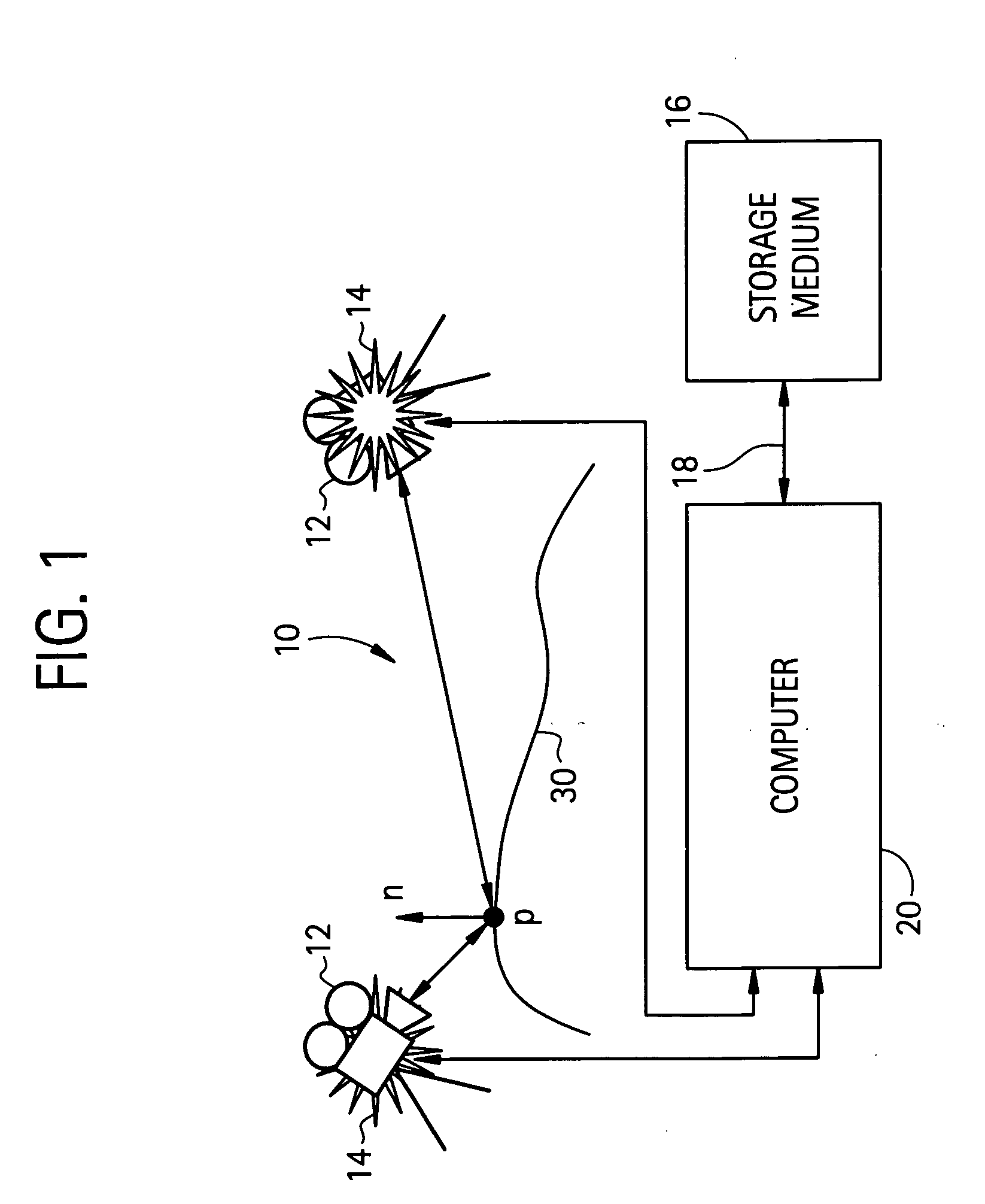
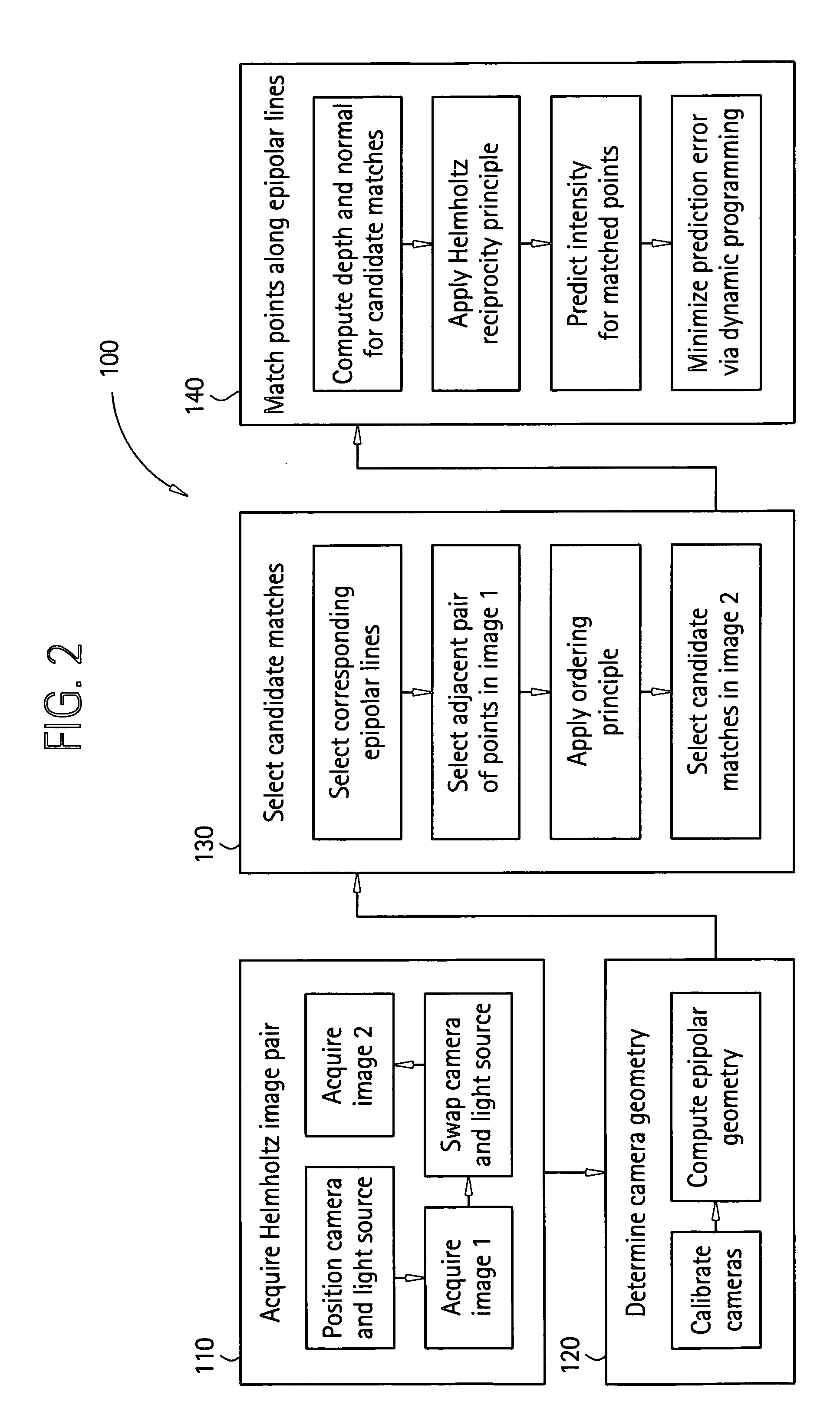
Surface reconstruction and registration with a Helmholtz reciprocal image pair
InactiveUS20050074162A1Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionImage estimationMethod of images
A method of image reconstruction comprising: obtaining a Helmholtz reciprocal pair of images of an object, the images comprising a first image and a corresponding reciprocal image; determining an imaging geometry associated with the obtaining; selecting a plurality of points in the first image and identifying corresponding candidate points in the corresponding reciprocal image; matching a selected point of the plurality of points and a candidate point of the corresponding candidate points. A method of image registration with an object comprising: obtaining a Helmholtz reciprocal pair of images of an object, the Helmholtz reciprocal pair of images comprising a first image and a corresponding reciprocal image; estimating a pose for the object; predicting an estimated image corresponding to the pose and one image of the reciprocal pair of images; comparing the estimated image with a corresponding actual image from the pair of images; and refining the estimating a pose based on the comparing.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
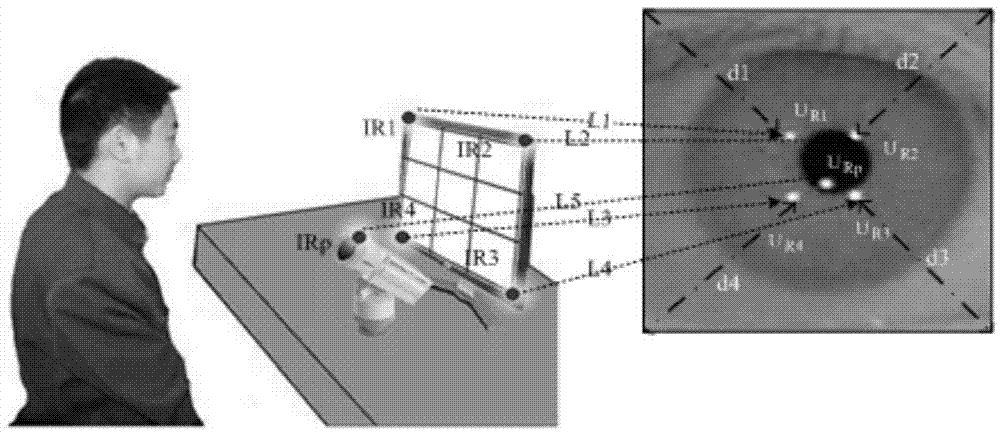
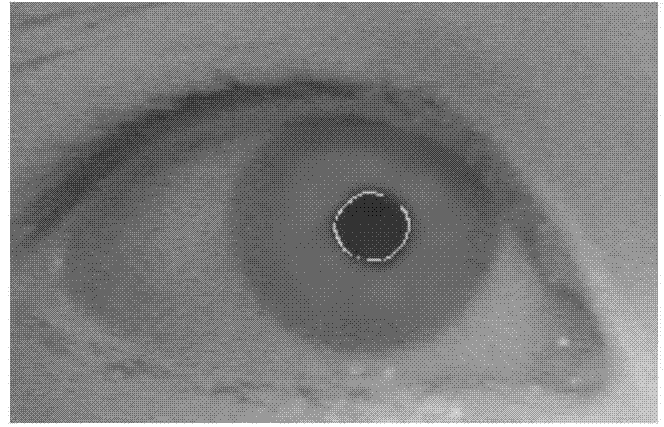
Non-contact sight-line tracking method based on self-adaptive calibration
The invention provides a non-contact sight-line tracking method based on self-adaptive calibration. A light spot characteristic extracting method combining the BFS algorithm, image geometric features and gray features is used for accurately matching light spots with corresponding light sources; by means of a fitting method comprising the steps that circular fitting is conducted through a one-dimension edge detection operator and least square ellipse fitting, and noisy points are removed until the center of an ellipse is fixed, the accurate centers of pupils are obtained finally. Besides, a dynamically self-adaptive calibration is provided, and existing space mapping model precision is improved effectively.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Image capture apparatus and control method therefor
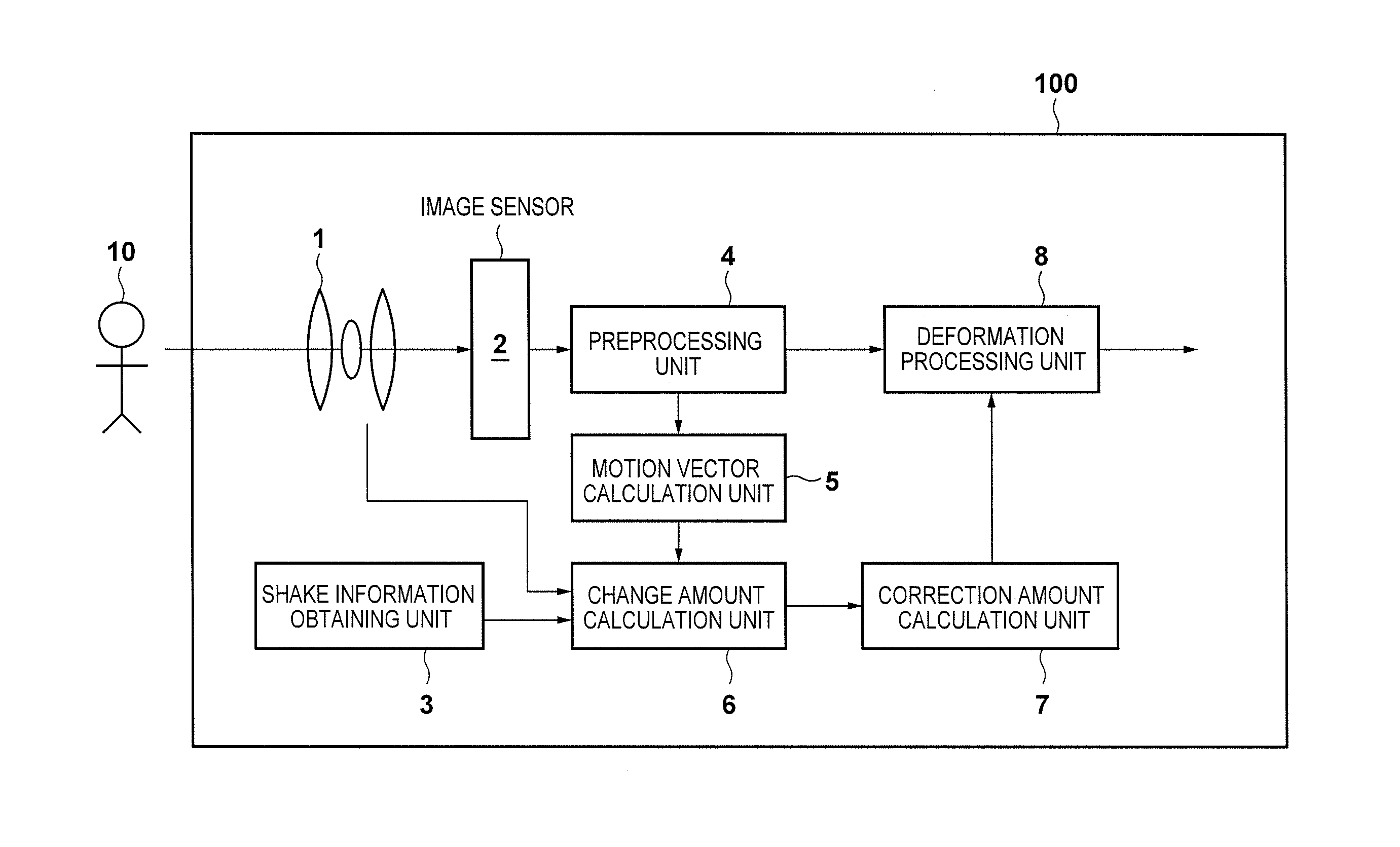
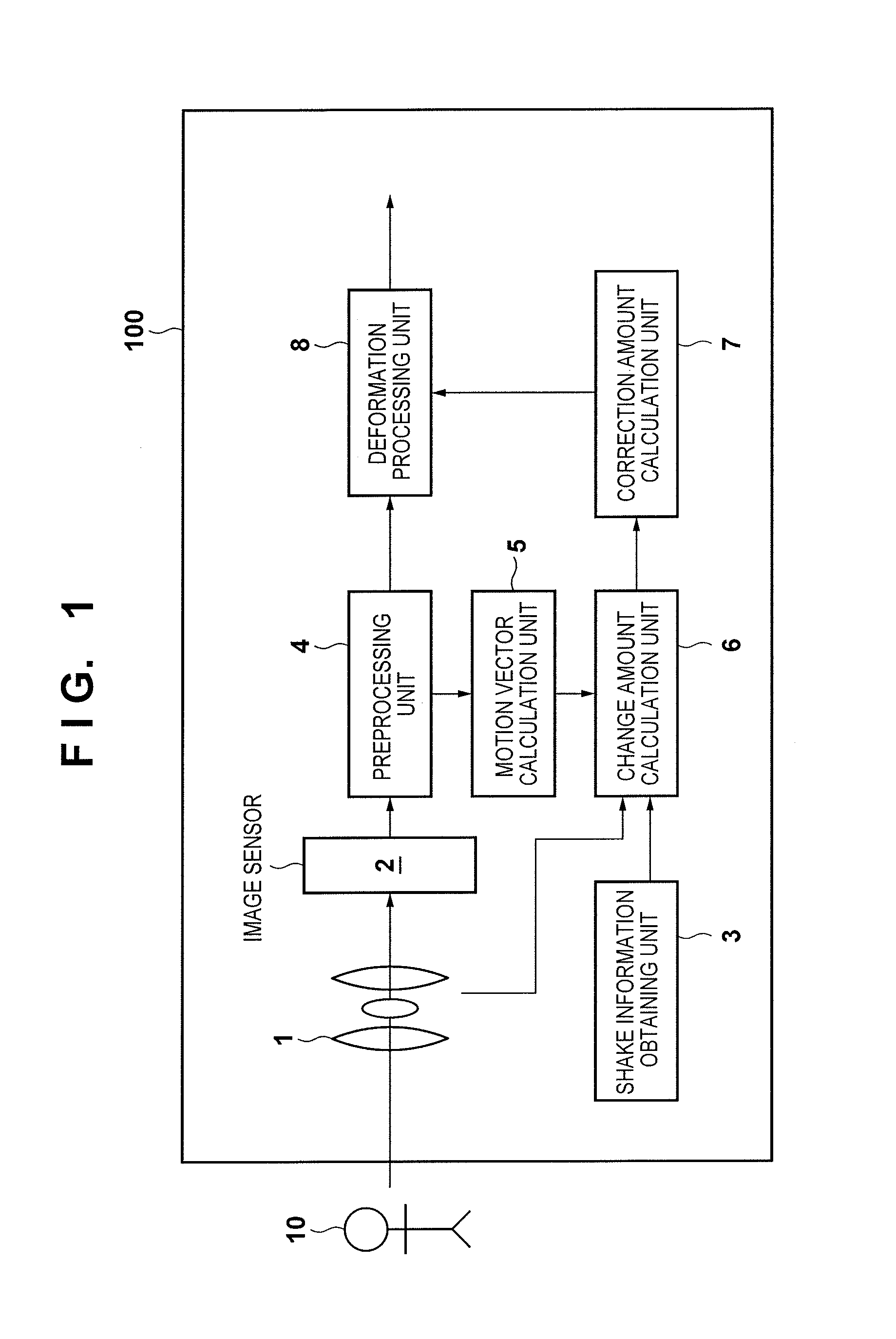
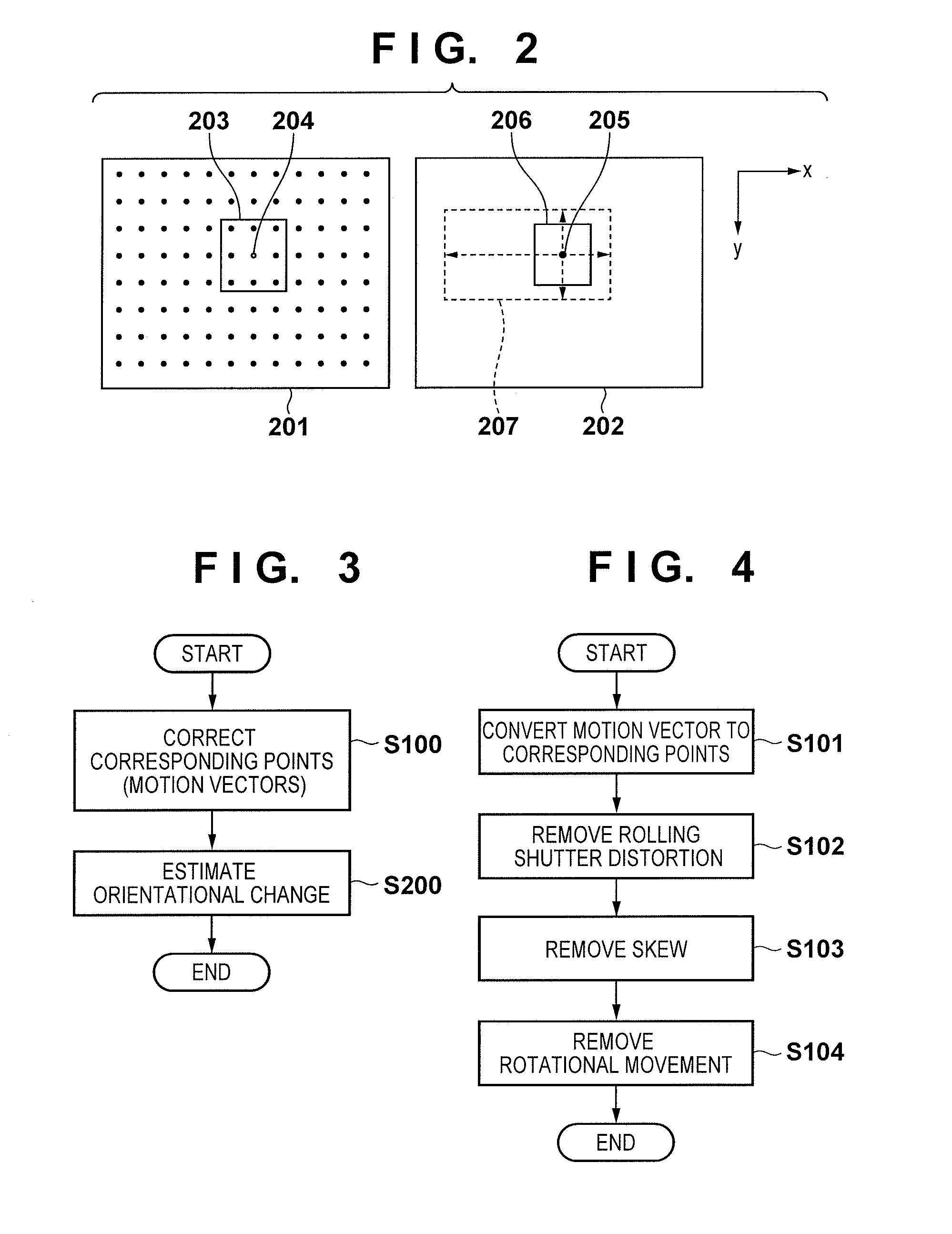
ActiveUS20150085149A1Accurate correctionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical axisExposure
An amount of change between images is calculated based on a motion vector between images obtained by an image sensor and on shake information related to a shake in a rotational direction around at least an axis perpendicular to an optical axis of an imaging optical system. Then, based on a shake correction amount determined based on the shake information and the amount of change, an image obtained by the image sensor is geometrically deformed. The amount of change is a shake component of the image capture apparatus in a direction perpendicular to the optical axis, and is calculated after cancelling at least one of a change between images caused by the shake in the rotational direction included in the shake information and a change between images caused by an influence of a difference between exposure periods of the image sensor.
Owner:CANON KK
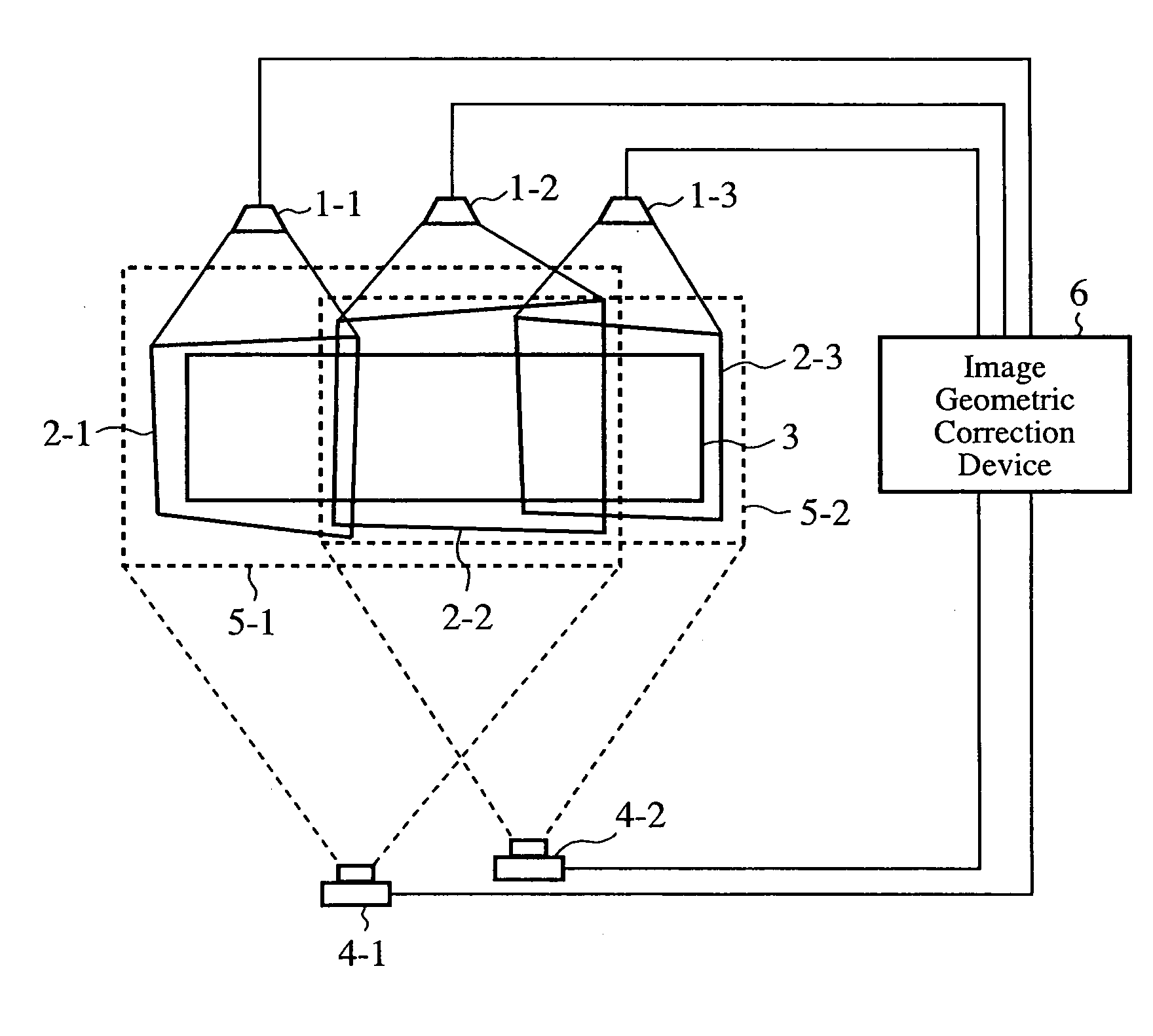
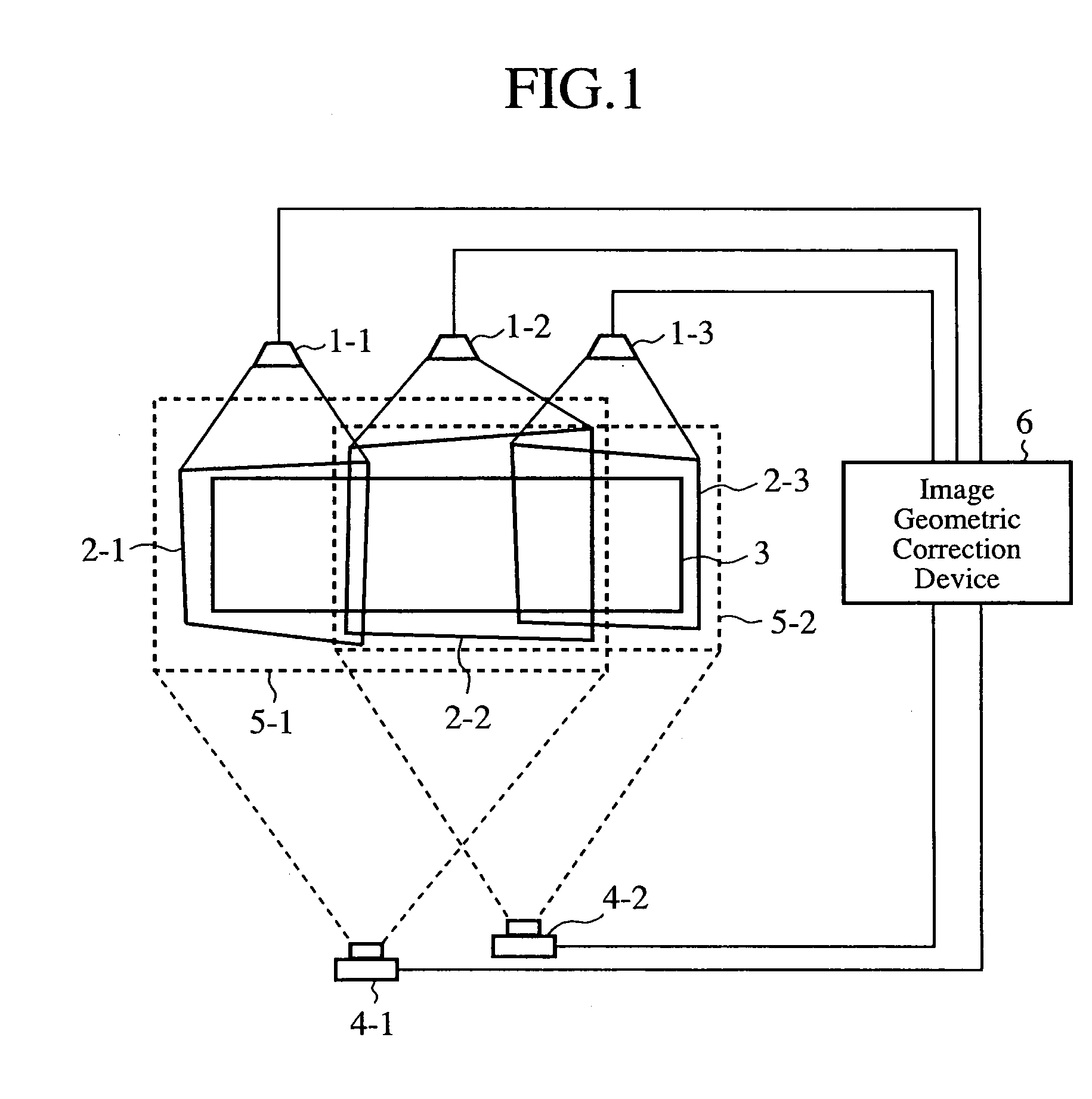
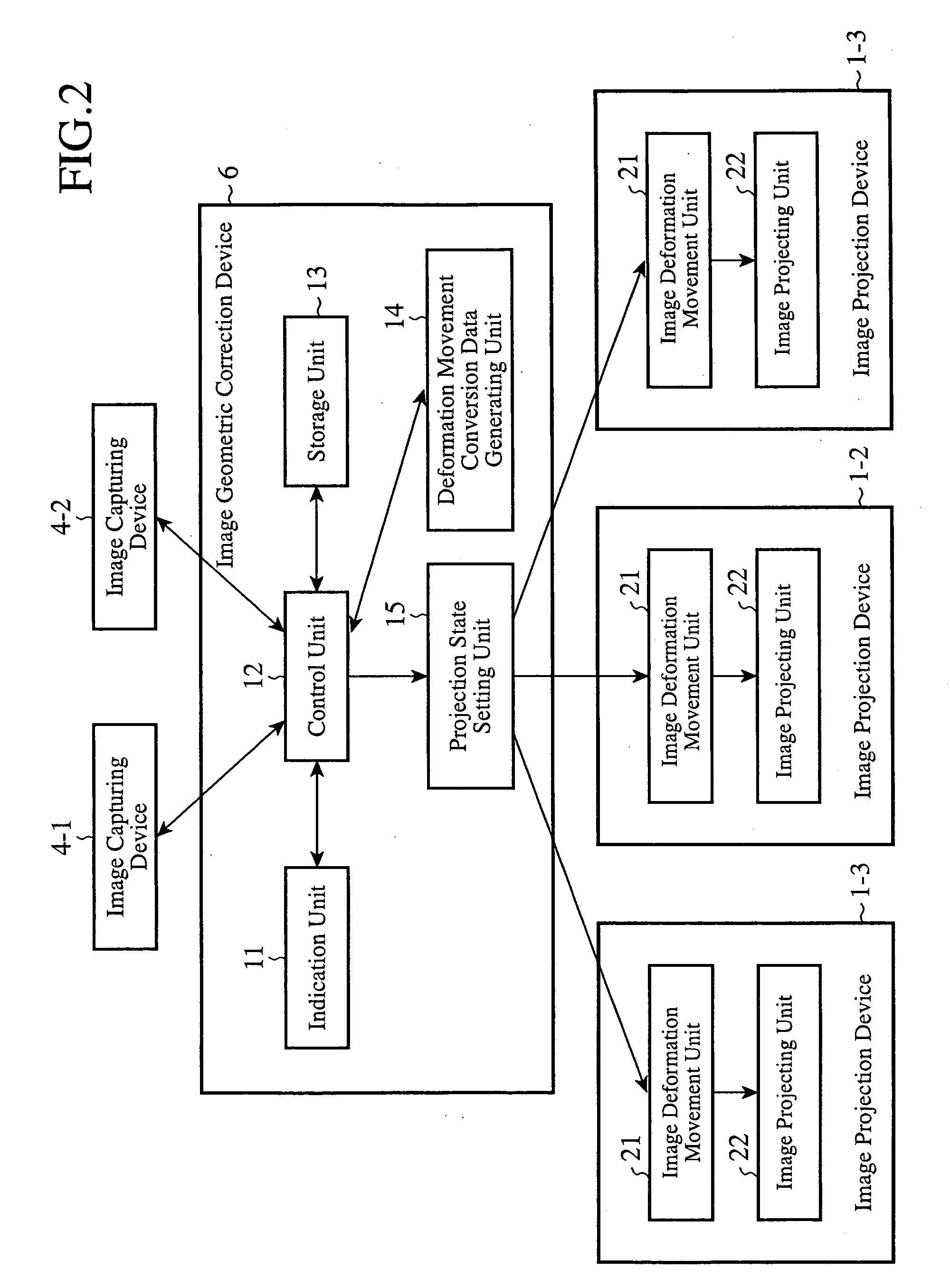
Image Projection System and Image Geometric Correction Device
An image geometric correction device 6 unifies the coordinate systems of images captured by image capturing devices 4-1 and 4-2 into a coordinate system, and makes a geometric correction to the images projected by image projection devices 1-1, 1-2, and 1-3 on the basis of an image projection region E in the coordinate system into which the coordinate systems of the captured images are unified. As a result, the image geometric correction device can make a geometric correction to the projected images without strictly placing the image capturing devices 4-1 and 4-2 at predetermined positions.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method for fine correcting satellite remote sensing image geometry based on topographic line
InactiveCN101050961AGeometric error reductionRealize geometric fine correctionImage enhancementPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryDescent directionSatellite image
A geometric precise-correcting method of satellite remote sensing image based on form line includes calling on digital DRM, confirming maximum dropping direction, storing drop amount as C, confirming threshold a by man-machine interaction, storing comparison result of C and a as D, vectoring D to obtain valley linear file E, obtaining array F by calculation on highest mass point Max of A, repeating above said step to obtain peak linear file E2, superposing called on satellite image with vector E1 and E2, storing surface feature coordinate as G and carrying out fitting-correction.
Owner:SOUTHWEST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Systems and methods for image reconstruction of sensitivity encoded MRI data
ActiveUS7511495B2Magnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionParallel magnetic resonance imagingData set
Methods and systems in a parallel magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system utilize sensitivity-encoded MRI data acquired from multiple receiver coils together with spatially dependent receiver coil sensitivities to generate MRI images. The acquired MRI data forms a reduced MRI data set that is undersampled in at least a phase-encoding direction in a frequency domain. The acquired MRI data and auto-calibration signal data are used to determine reconstruction coefficients for each receiver coil using a weighted or a robust least squares method. The reconstruction coefficients vary spatially with respect to at least the spatial coordinate that is orthogonal to the undersampled, phase-encoding direction(s) (e.g., a frequency encoding direction). Values for unacquired MRI data are determined by linearly combining the reconstruction coefficients with the acquired MRI data within neighborhoods in the frequency domain that depend on imaging geometry, coil sensitivity characteristics, and the undersampling factor of the acquired MRI data. An MRI image is determined from the reconstructed unacquired data and the acquired MRI data.
Owner:THE UNIV OF UTAH
Intraoral tomosynthesis systems, methods and computer readable media for dental imaging
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL +1
Method and system for measuring in a dynamic sequence of medical images
The present invention relates to a method and a system for measuring in a dynamic sequence of medical images of a moving body part. A reference point being fixed relative to an image geometry and at least one measurement point are defined in the moving body part in one image in the sequence of images. The reference point is then automatically indicated and the at least one measurement point is then automatically tracked in all of the images of the sequence. A length and a direction of at least one vector extending from the reference point to one of the at least one measurement points for each pair of reference point and one measurement point is automatically determined in all of the images of the sequence and at least one of a rate of change of the length and the direction of the at least one vector is automatically determined between selected images in the sequence of images.
Owner:SECTRA IMTEC
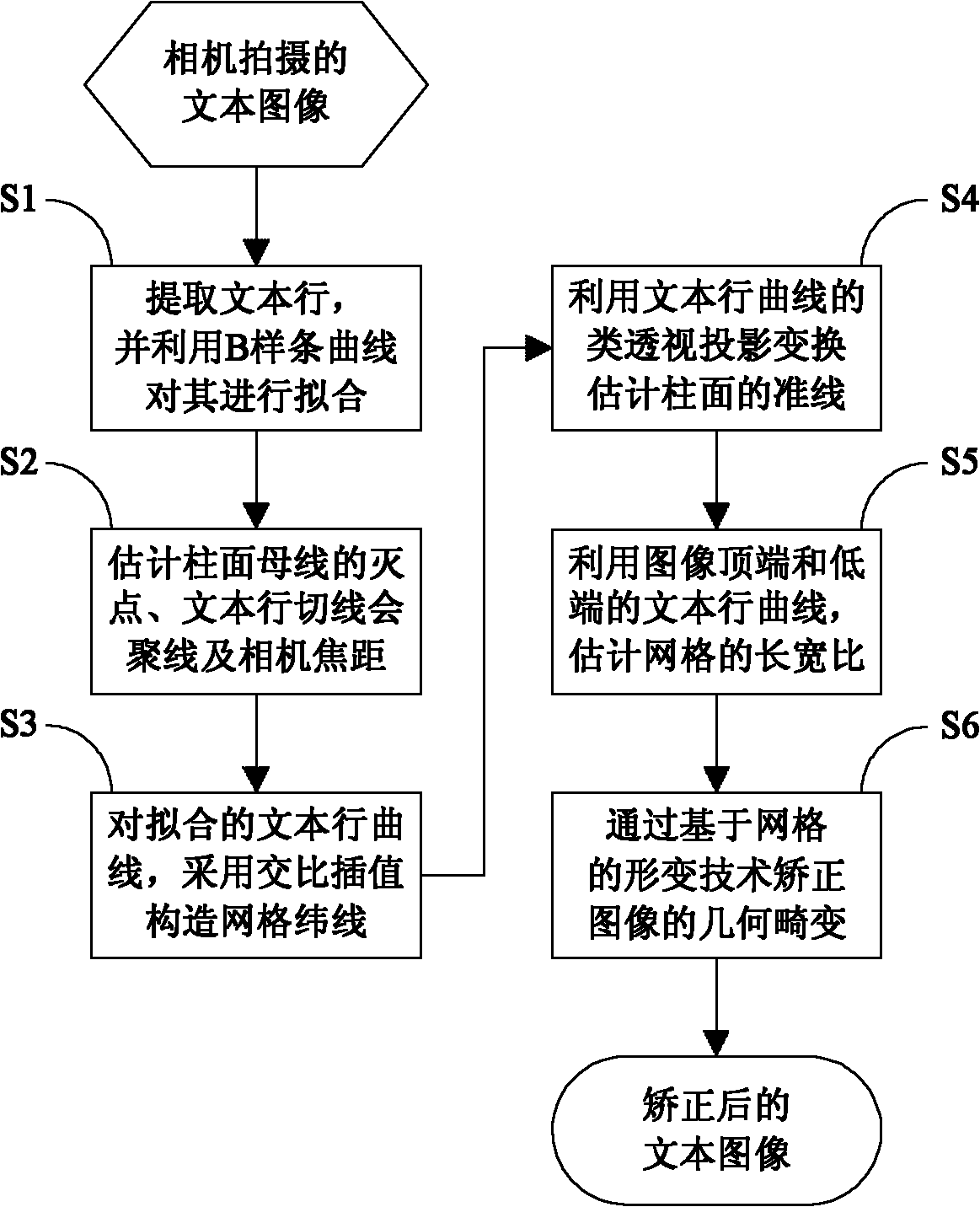
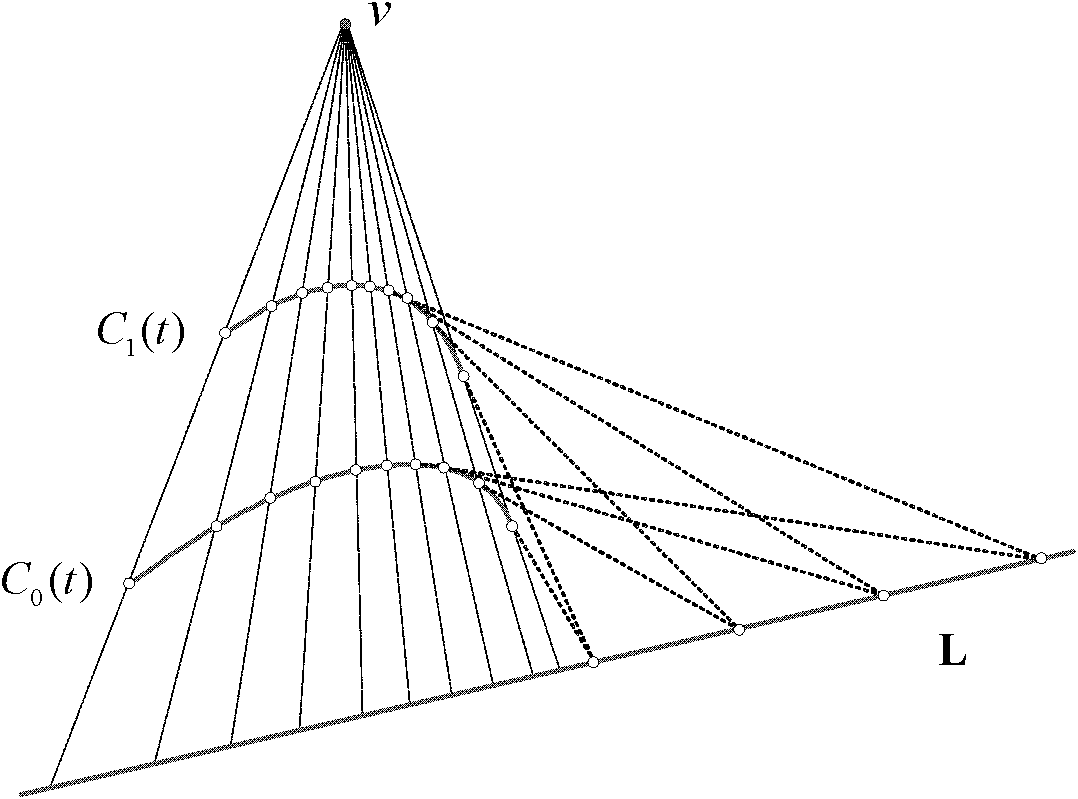
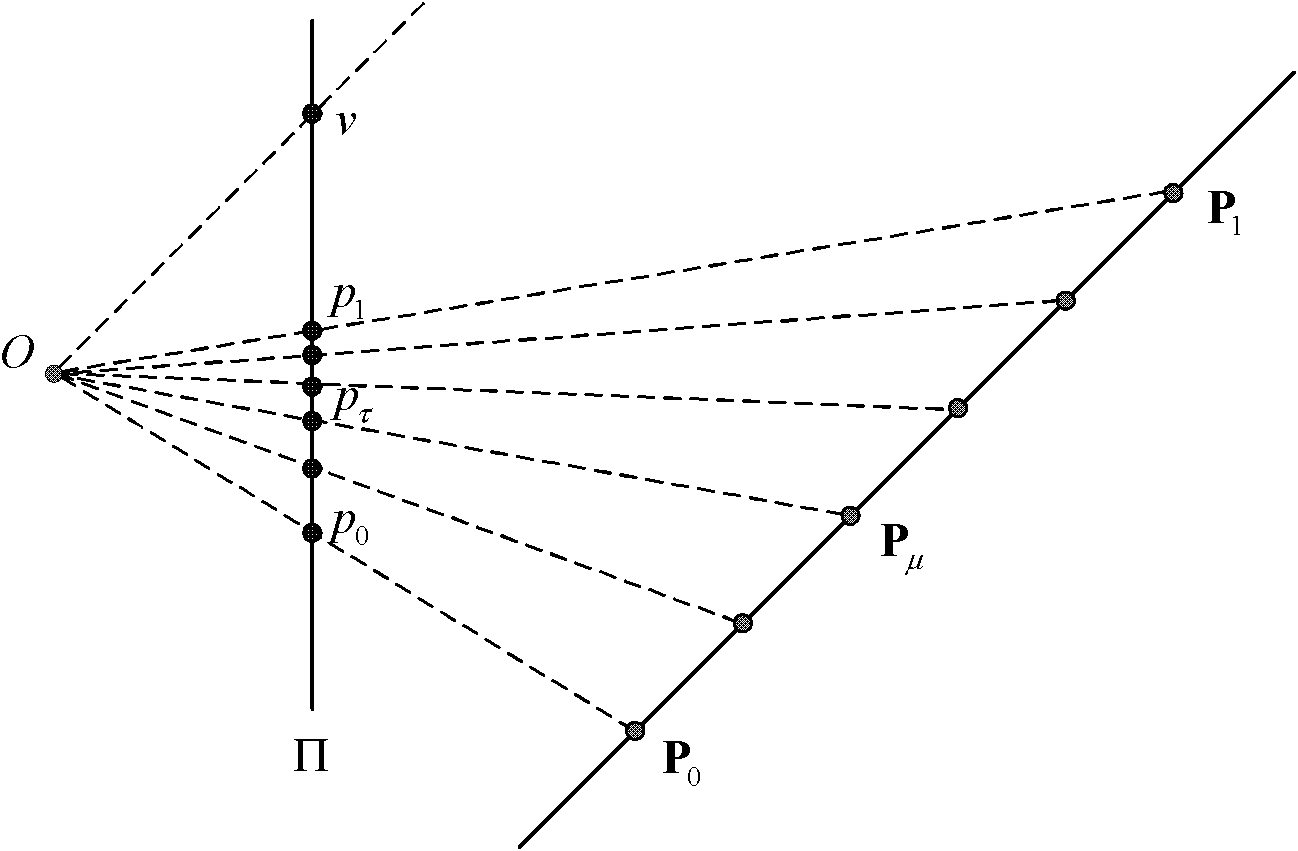
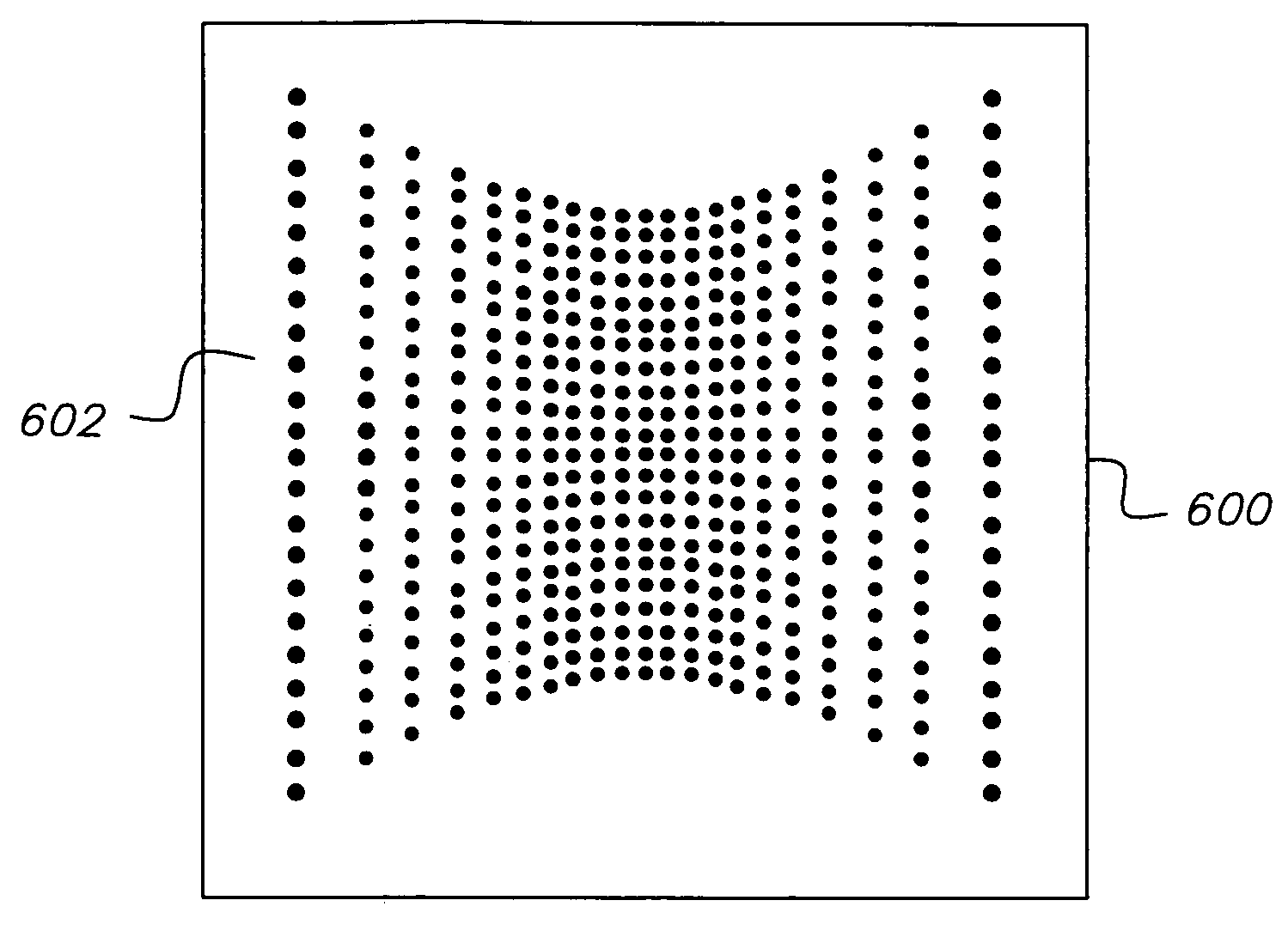
Method for correcting geometric distortion of text image
ActiveCN102208025AAchieve correctionSimple thinkingCharacter and pattern recognitionNonlinear deformationAlgorithm
The invention provides a method for correcting geometric distortion of a text image. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting a text row, in a horizontal direction, of the text image, fitting the text row by using a B-spline curve to obtain a text row curve; estimating a vanishing point of a cylindrical surface straight bus, a text row tangent convergence line and a focal length parameter of a camera by using the tangent convergence symmetry of the text row curve; constructing latitude lines of an isometric grid for the fit text row curve by adopting a crossratio interpolation value; estimating a directrix of the cylindrical surface by using similar perspective projection transformation of the text row curve and constructing longitude lines of the isometric grid; estimatinga length-to-width ratio of the isometric grid by using the text row curves at the top end and the bottom end of the image; and mapping meshes of each isometric grid into a square grid through a deformation technology based on the grid to finish the correction of the geometric distortion of the text image. By the method, the problem that perspective distortion, nonlinear deformation distortion andcompound distortion of the perspective distortion and the nonlinear deformation distortion cannot be corrected at the same time in the prior art can be solved; therefore, total correction of the geometric distortion of the text image shot by the camera can be realized.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Electronic imaging system having a sensor for correcting perspective projection distortion
InactiveUS7224392B2High densityReduce needTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsOptical communicationComputer science
An electronic imaging system for capturing an image of a scene includes an optical system for producing an optical image of the scene, an imaging sensor having a surface in optical communication with the optical system, and a plurality of imaging elements distributed on the surface of the imaging sensor according to a distribution representable by a nonlinear function in which the relative density of the distributed imaging elements is greater toward the center of the sensor. Such a distribution provides physical coordinates for the imaging elements corresponding to a projection of the scene onto a non-planar surface, thereby compensating for perspective distortion of the scene onto the non-planar surface and alleviating the need to perform geometric warping of the images after they have been captured.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
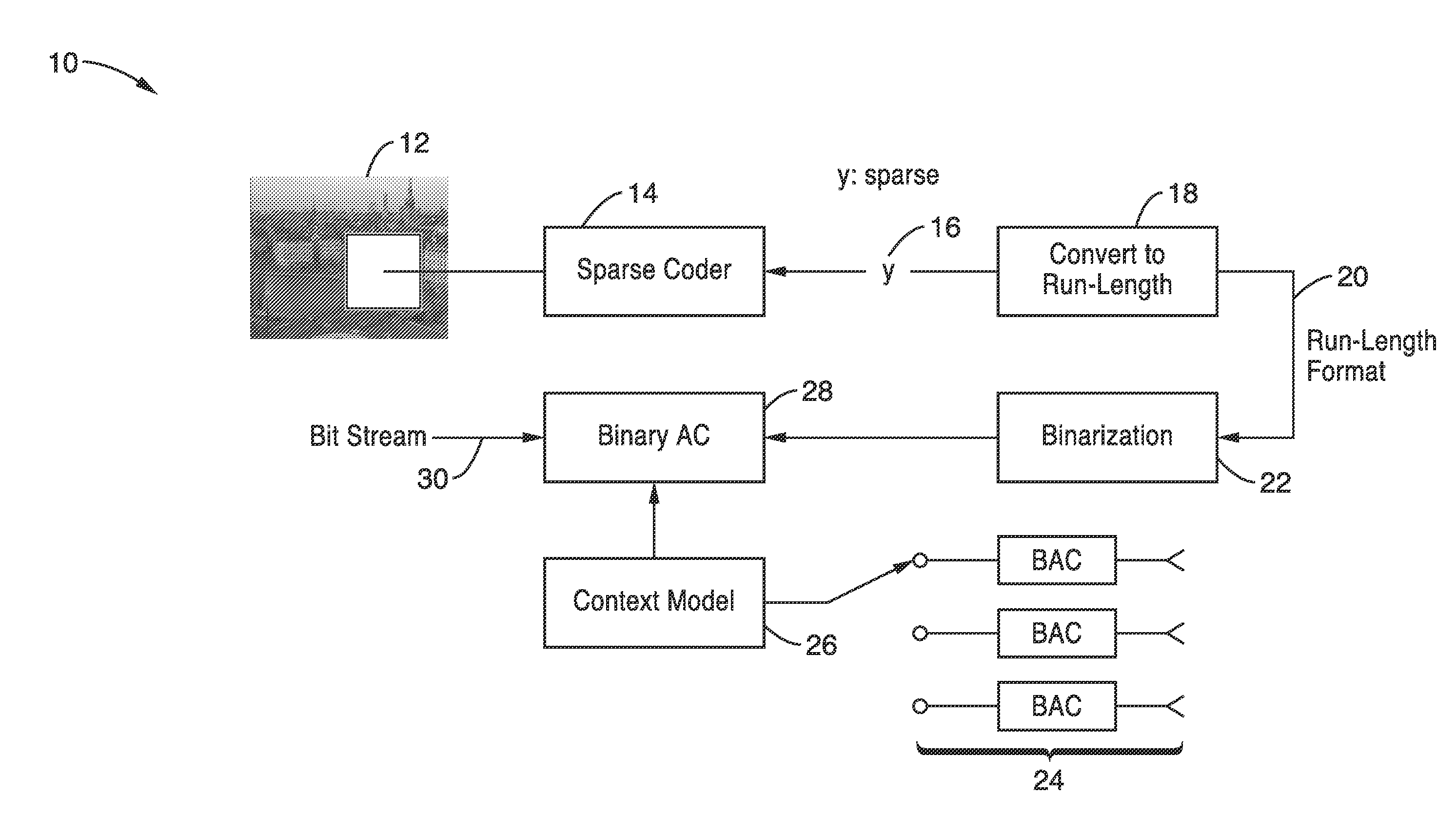
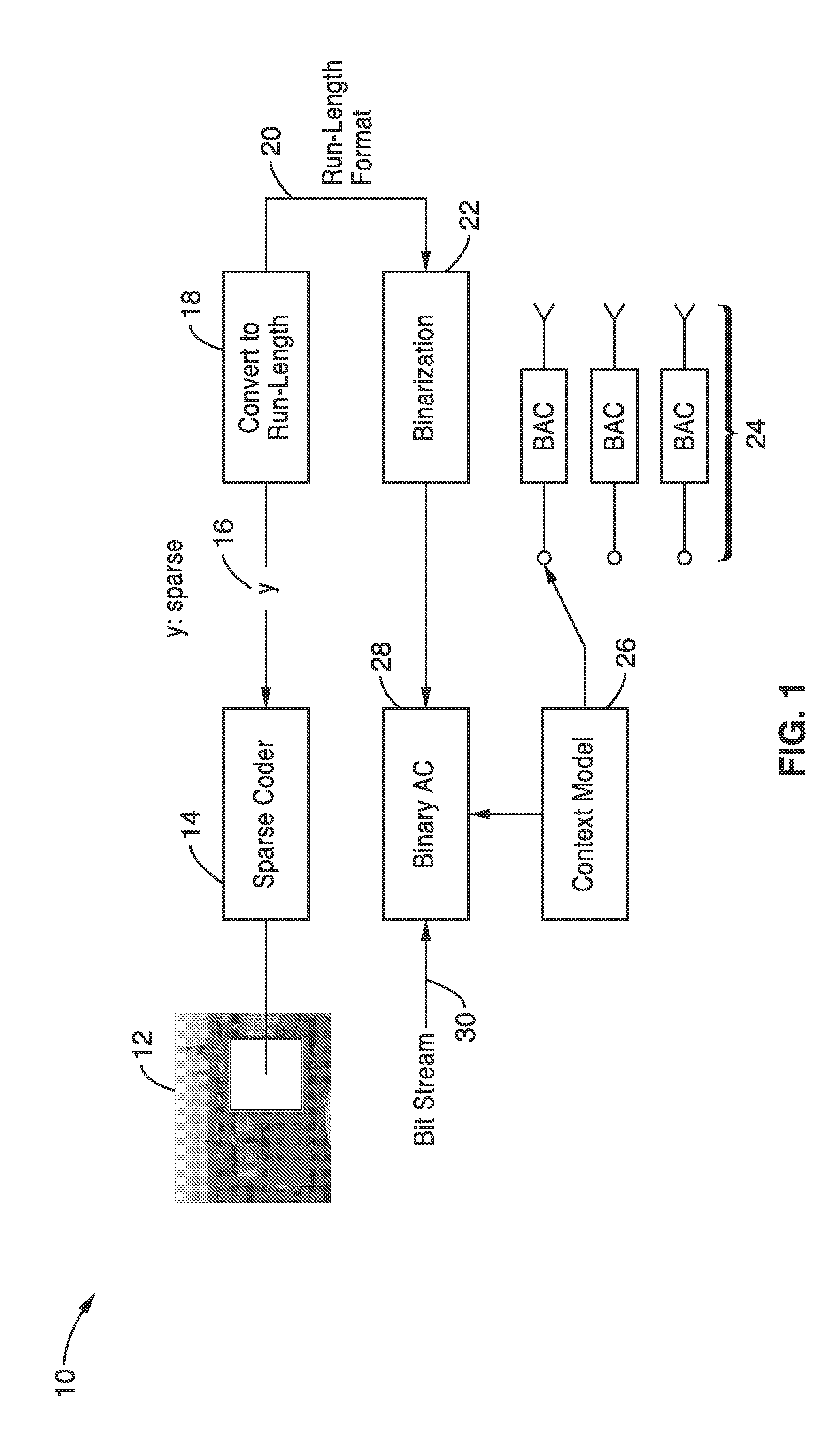
Run length coding with context model for image compression using sparse dictionaries
InactiveUS20120057799A1Reduce impactIncrease productionCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionContext modelAlgorithm
Apparatus and methods for coding images geometric vector quantization (GVQ) having an over-complete dictionary which produces a sparse vector of coefficients as it contains large runs of zeros. The sparse encoding is particularly well suited for use with run-length entropy coding techniques. Image blocks are sparse coded using GVQ, with the vector of coefficients converted to RUN-LENGTH symbols, and binarized into a set of binary symbols. At least a portion of the binary symbols are used as contexts which can be selected when performing binary arithmetic coding of the binary coded RUN and LENGTH data to generate a bit stream containing the encoded image that provides enhanced compression.
Owner:SONY CORP
Multi-Parameter X-Ray Computed Tomography
ActiveUS20100310037A1Improve imaging resolutionReduce X-ray doseRadiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsData setX-ray
The present invention relates to the field of x-ray imaging. More particularly, embodiments of the invention relate to methods, systems, and apparatus for imaging, which can be used in a wide range of applications, including medical imaging, security screening, and industrial non-destructive testing to name a few. Specifically provided as embodiments of the invention are systems for x-ray imaging comprising: a) a first collimator-and-detector assembly having a first operable configuration to provide at least one first dataset comprising primary x-ray signals as a majority component of its data capable of being presented as a first image of an object subjected to x-ray imaging; b) a second collimator-and-detector assembly having a second operable configuration or wherein the first collimator-and-detector assembly is adjustable to a second configuration to provide at least one second dataset comprising primary and dark-field x-ray signals as a majority component of its data capable of being presented as a second image of the object; and c) a computer operably coupled with the collimator-and-detector assemblies comprising a computer readable medium embedded with processing means for combining the first dataset and the second dataset to extract the dark-field x-ray signals and produce a target image having higher contrast quality than the images based on the first or second dataset alone. Such systems can be configured to comprise at least two collimator-and-detector assemblies or configurations differing with respect to collimator height, collimator aperture, imaging geometry, or distance between an object subjected to the imaging and the collimator-and-detector assembly.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Methods and apparatus for computed tomography imaging
InactiveUS6901131B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingRotational axisComputed tomography
A method for arranging detector sections for an imaging system that has a field of view that is defined by a rotational axis and imaging geometry is provided. The method includes providing a plurality of detector sections, and arranging the detector sections in an asymmetric arrangement about a central axis of the field of view.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
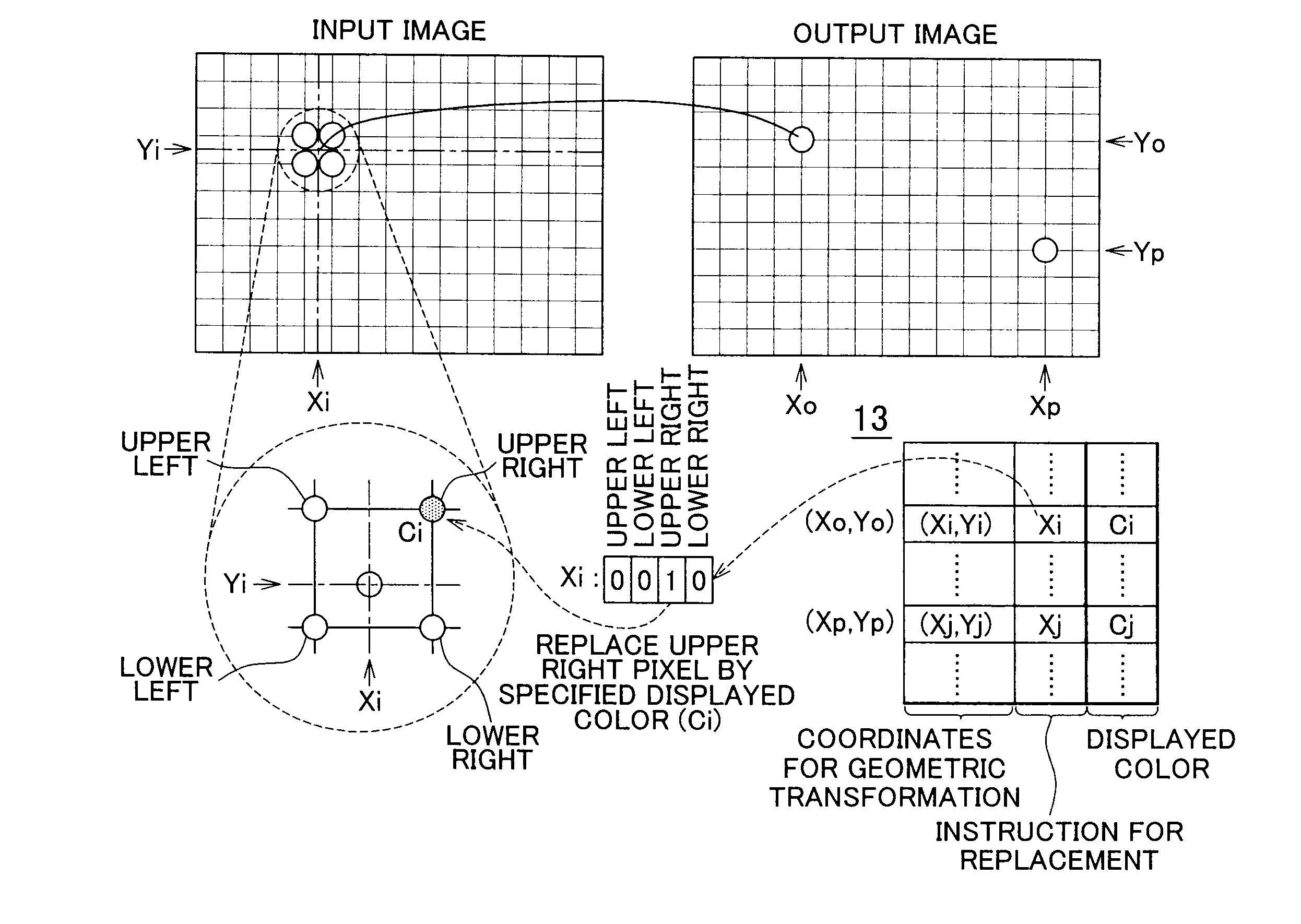
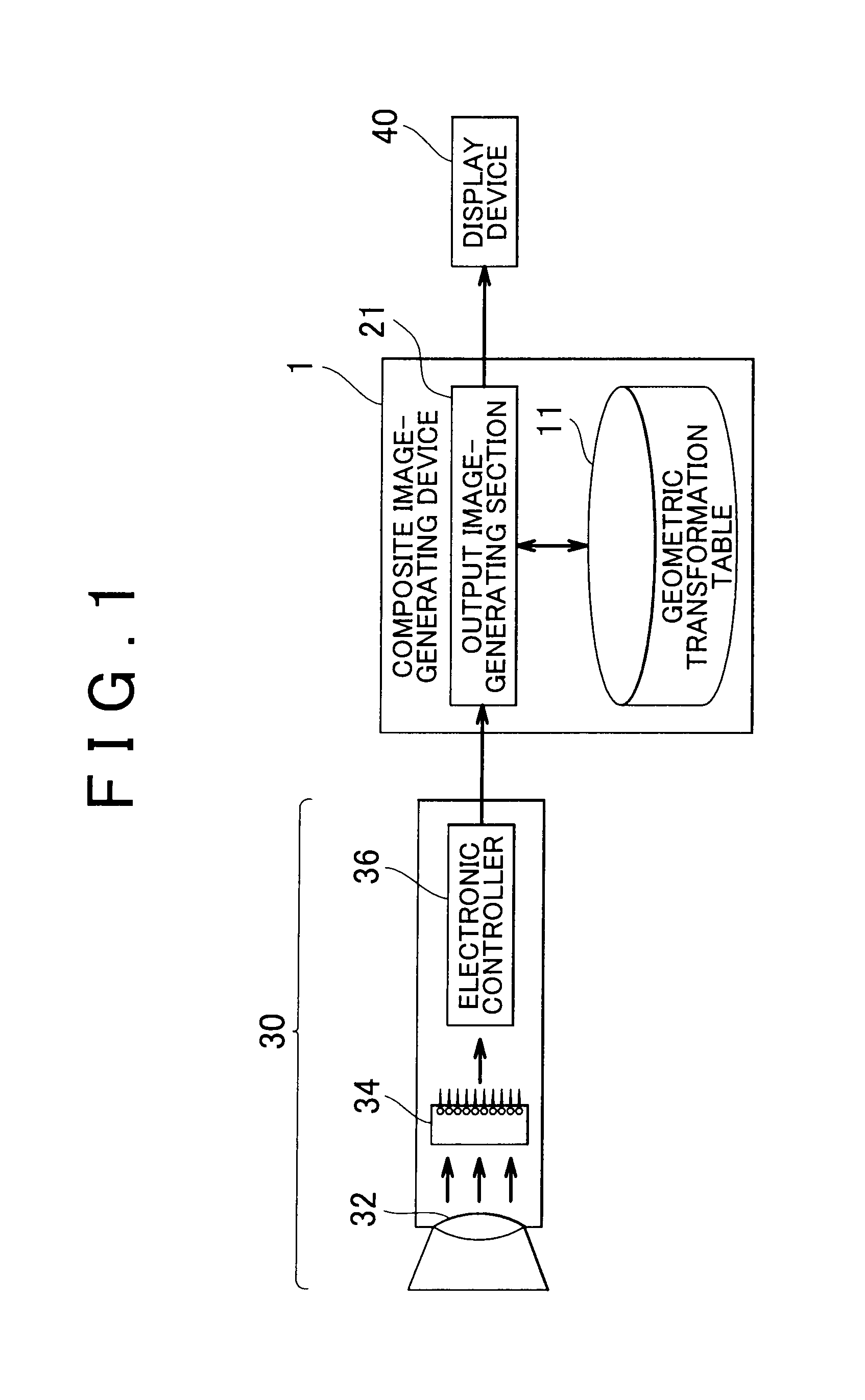
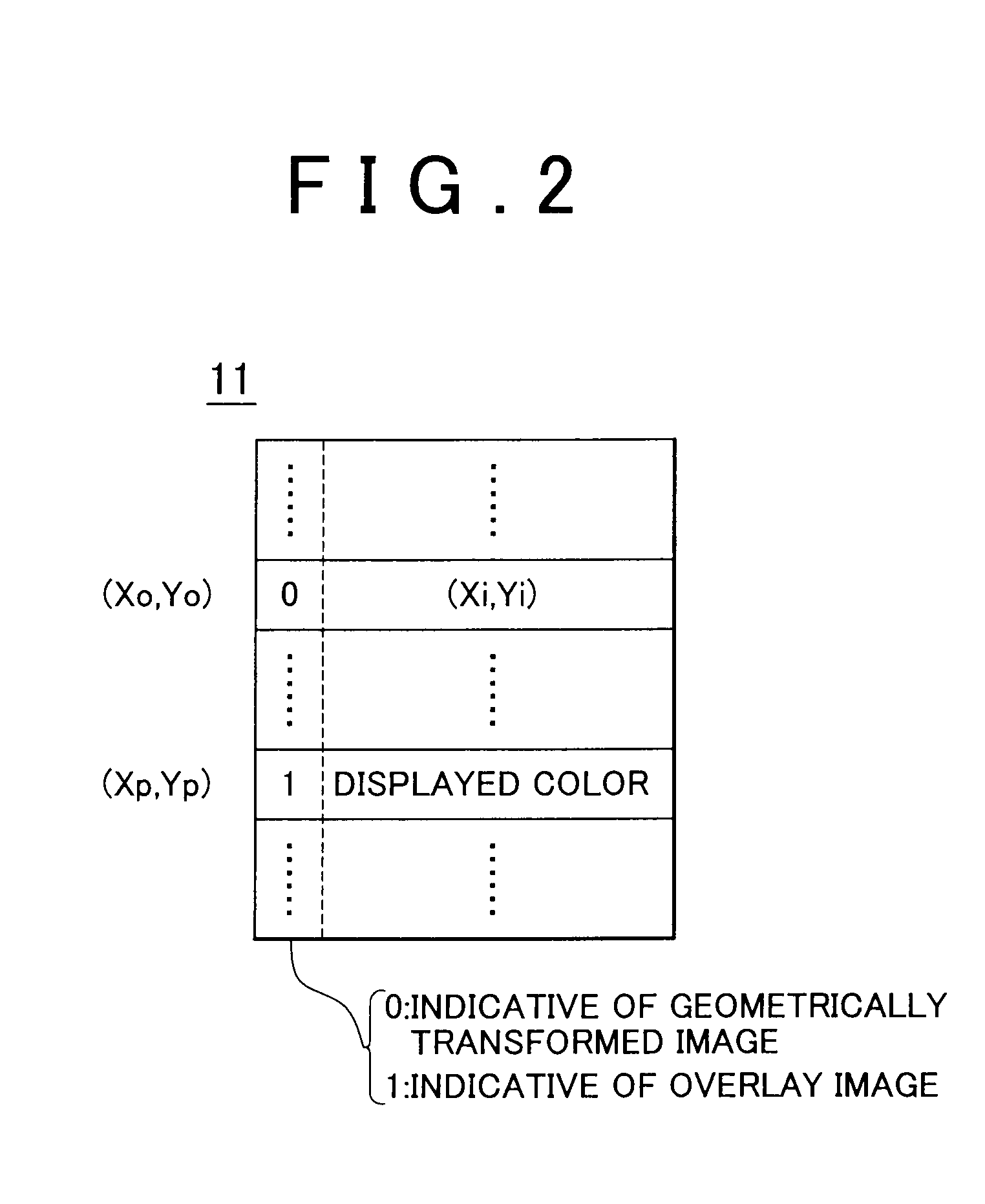
Composite image-generating device and computer-readable medium storing program for causing computer to function as composite image-generating device
InactiveUS20090066726A1Low costOptimize spaceImage enhancementGeometric image transformationPosition dependentImage geometry
A composite image-generating device includes: a geometric transformation table that assigns coordinates corresponding to positions of pixels of an output image on an input image received from a capturing section; and an output image-generating section that generates the output image by superimposing an overlay image based on overlay data associated with the positions of the pixels of the output image in the geometric transformation table on an image obtained by geometrically transforming the input image according to the geometric transformation table.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Systems and methods of non-standard spiral cone-beam computed tomograpy (CT)
InactiveUS7372937B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationFiltrationImage geometry
Provided herein are methods of reconstructing an image from projection data provided by a tomography scanner that is based on geometric optics comprising scanning an object in a cone-beam imaging geometry following a non-standard spiral path or a general piecewise smooth scanning path wherein projection data is generated and reconstructing an image according to a closed-form formula that is either in the filtered backprojection (FBP) or backprojection filtration (or backprojected filtration, BPF) formats. Also provided herein are associated systems and apparatuses for tomographic imaging.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
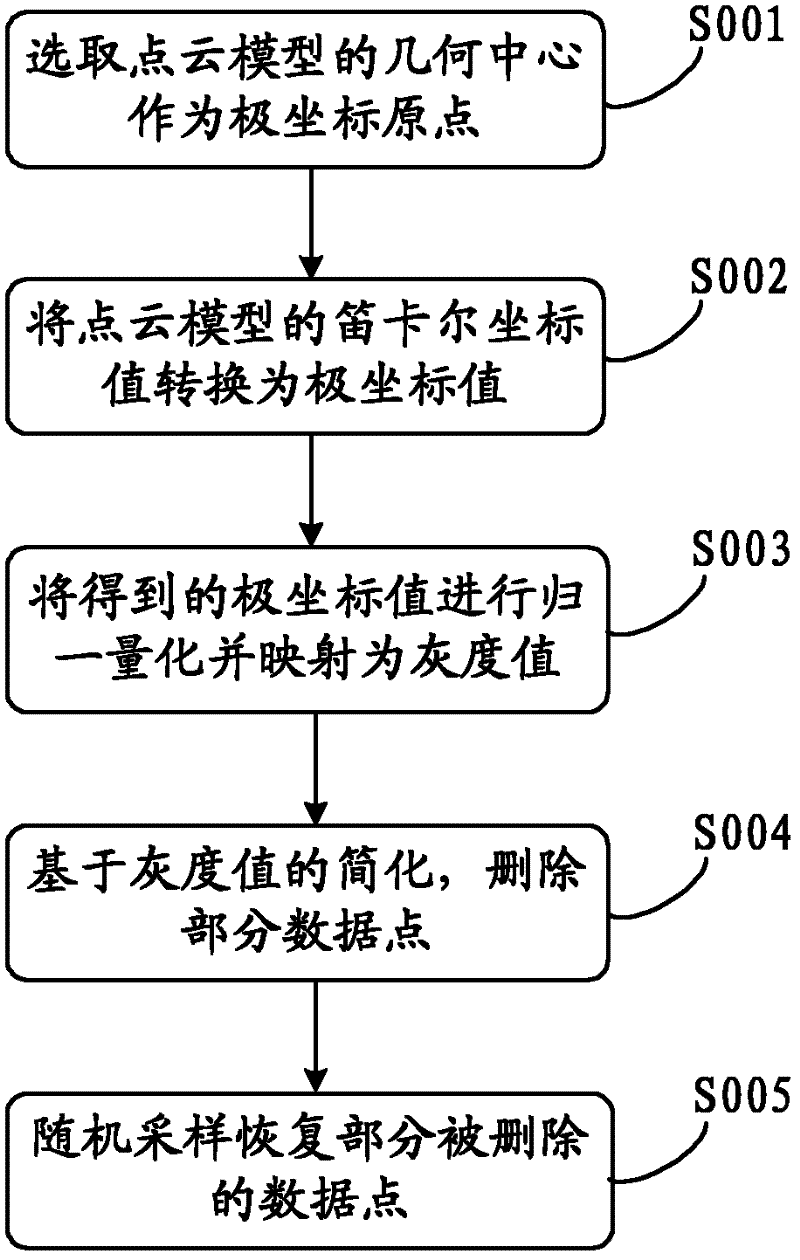
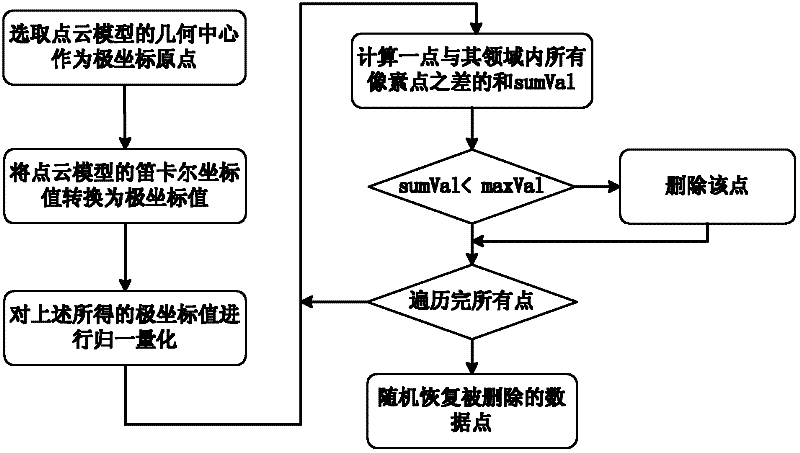
A Simplification Method of Digital Geometric Image Based on Point Cloud Model
The invention discloses a digital geometric image simplification method based on a point cloud model, comprising the following steps: step 1: selecting the geometric center of the point cloud model as the origin of polar coordinates; step 2: converting the Cartesian coordinate value of the point cloud model into polar coordinates Coordinate value; Step 3: Normalize and quantize the obtained polar coordinate value and map it to a gray value; Step 4: Delete some data points based on the simplification of the gray value; Step 5: Randomly sample and restore some deleted data points . It combines the two methods of geometric image and random sampling. First, the geometric image is simplified for the point cloud data. The simplified point cloud model can maintain the main geometric features in the original model. Then, the idea of random sampling is introduced, and the deleted point set Random sampling is carried out, and the sampled points are added to the simplified model, so as to avoid the influence of holes on the subsequent surface reconstruction method, and realize a fast feature-preserving point cloud model simplification.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
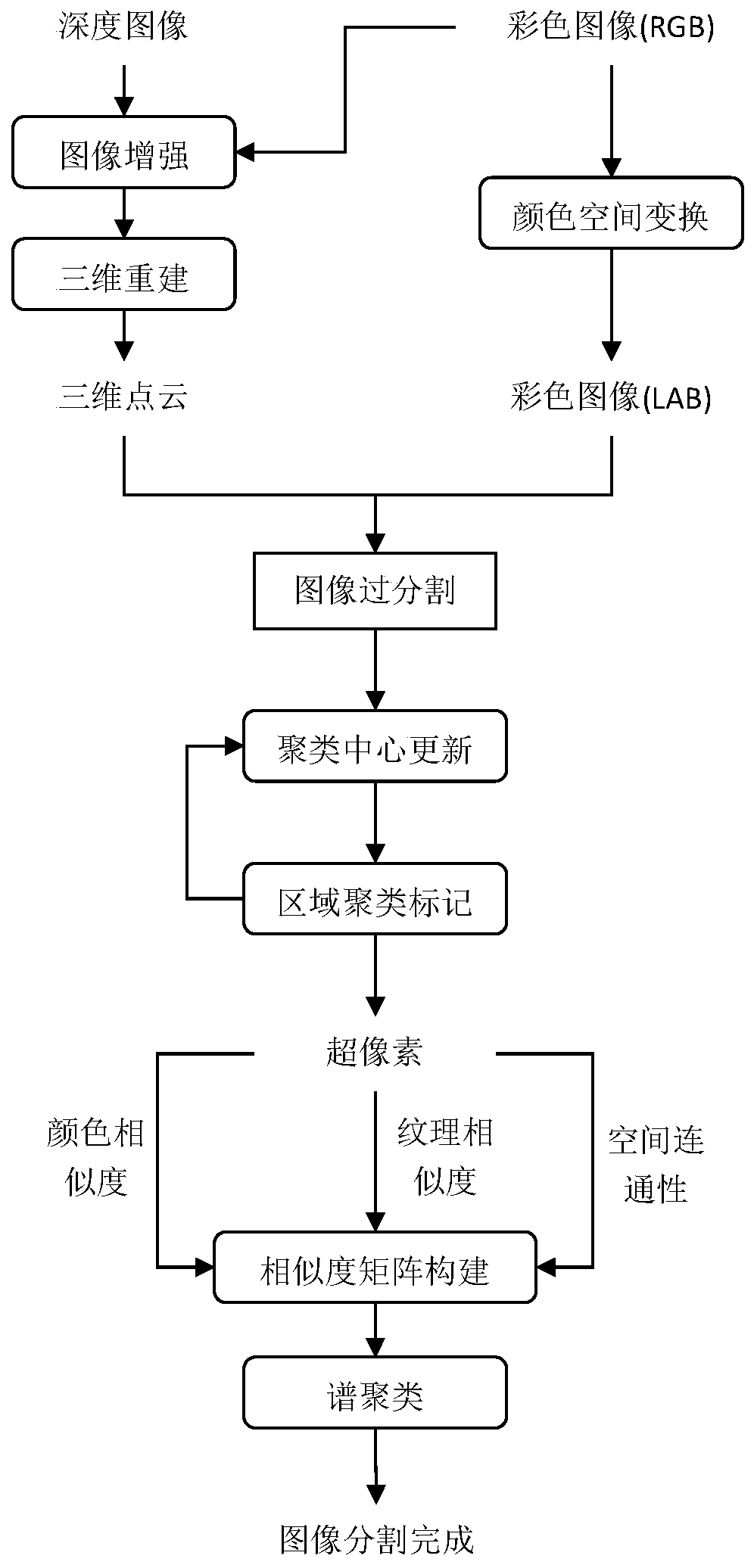
Image segmentation method fusing depth and color information
PendingCN110610505AQuality improvementHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisPoint cloudImage geometry
The invention provides an image segmentation method fusing the depth and color information, and the method mainly comprises the steps of carrying out RGB-D data preprocessing, carrying out the medianfiltering under the guidance of the image edge information, and improving the quality of a depth image; carrying out RGB-D image super-pixel segmentation, fusing the color and depth information, andcarrying out over-segmentation on the image; and merging the super-pixels, merging the similar super-pixels by adopting a spectral clustering method based on a graph theory, converting the clusteringinto a graph division problem, and completing the image segmentation. According to the invention, the depth map is converted into the three-dimensional point cloud according to the imaging geometry principle, and then the image is segmented by integrating the depth information and the color information, so that the image segmentation quality and precision are improved.
Owner:SIASUN CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com