Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
144 results about "Depth filter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
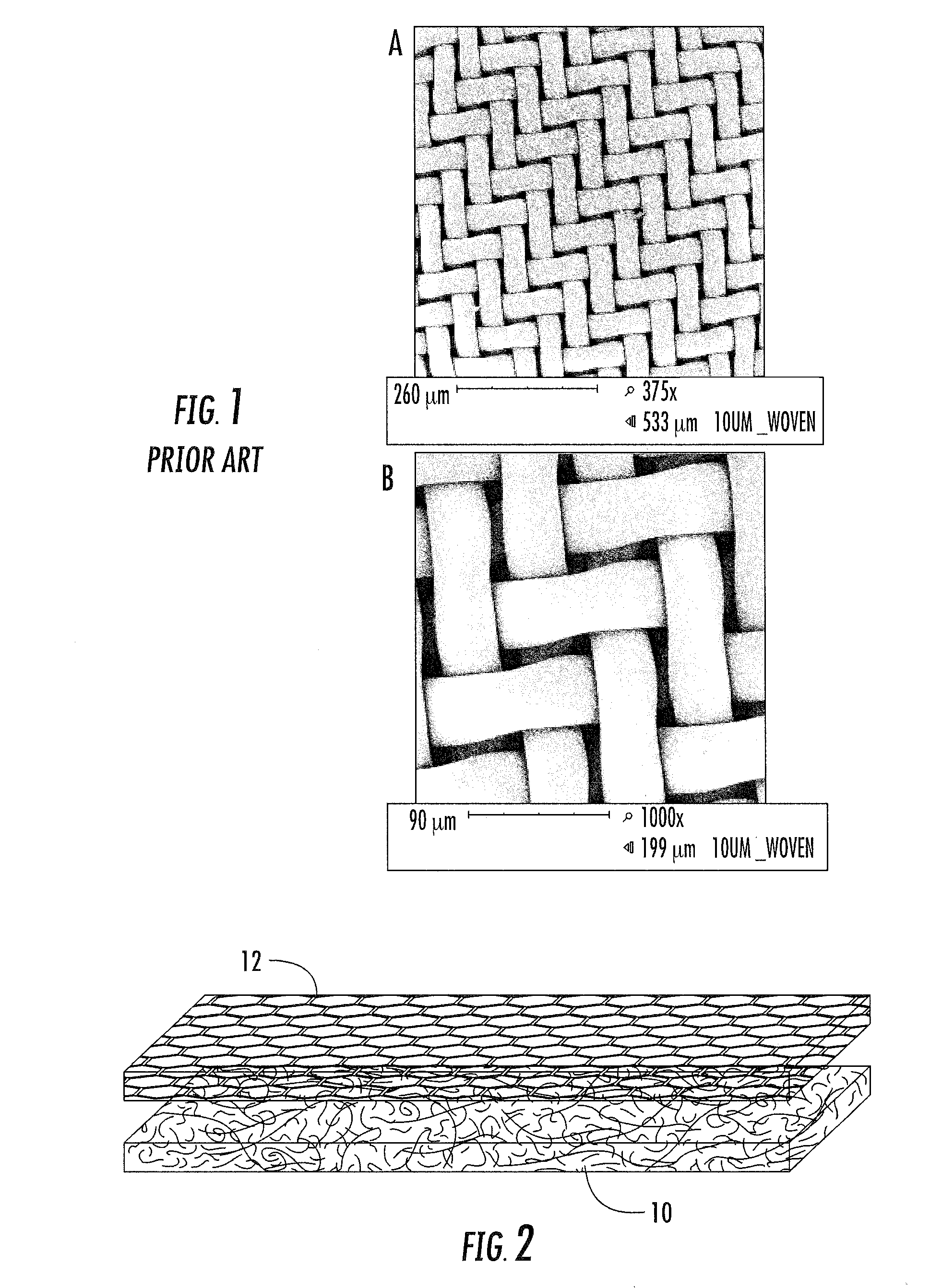
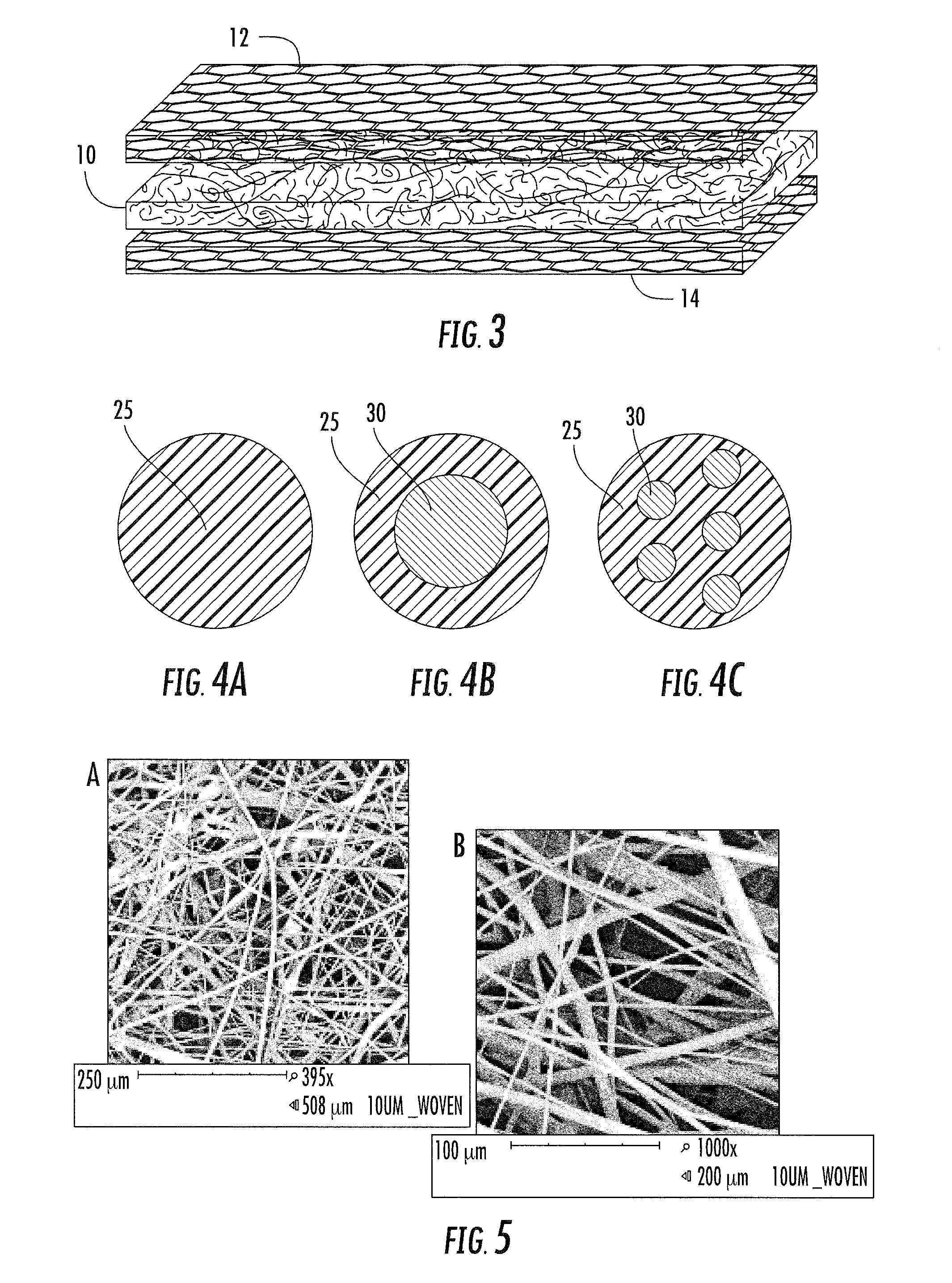
Depth filters are the variety of filters that use a porous filtration medium to retain particles throughout the medium, rather than just on the surface of the medium. These filters are commonly used when the fluid to be filtered contains a high load of particles because, relative to other types of filters, they can retain a large mass of particles before becoming clogged.
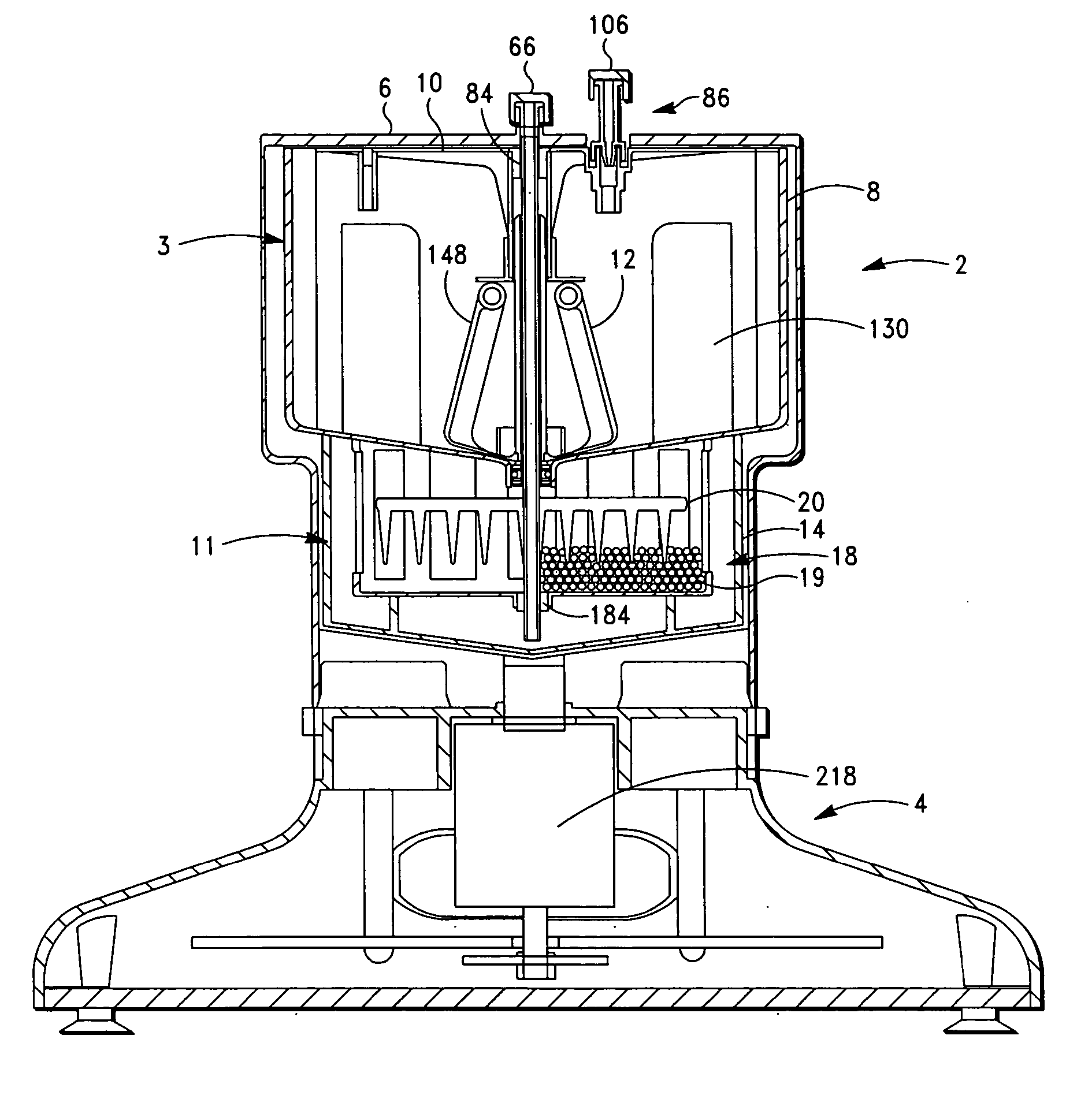
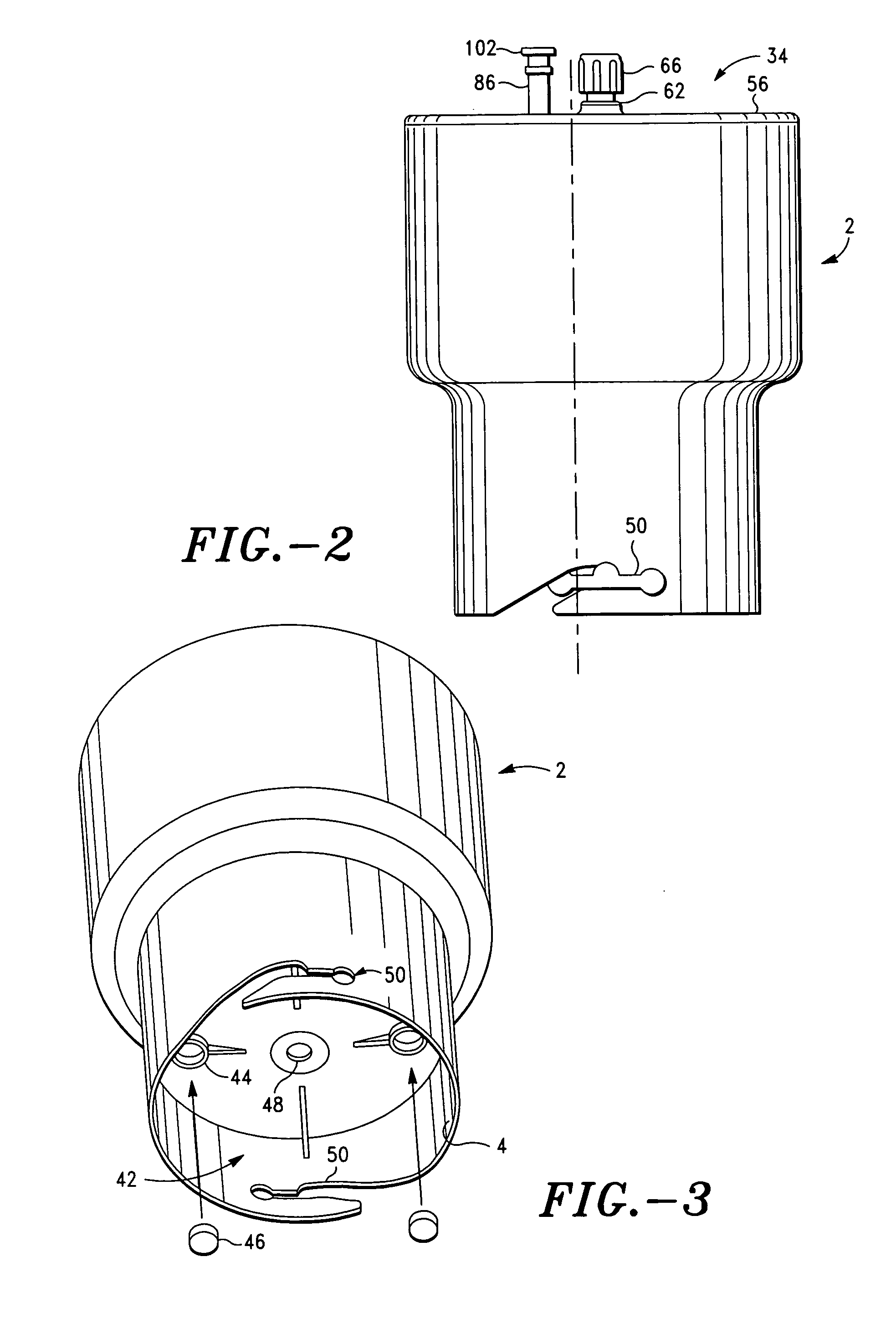
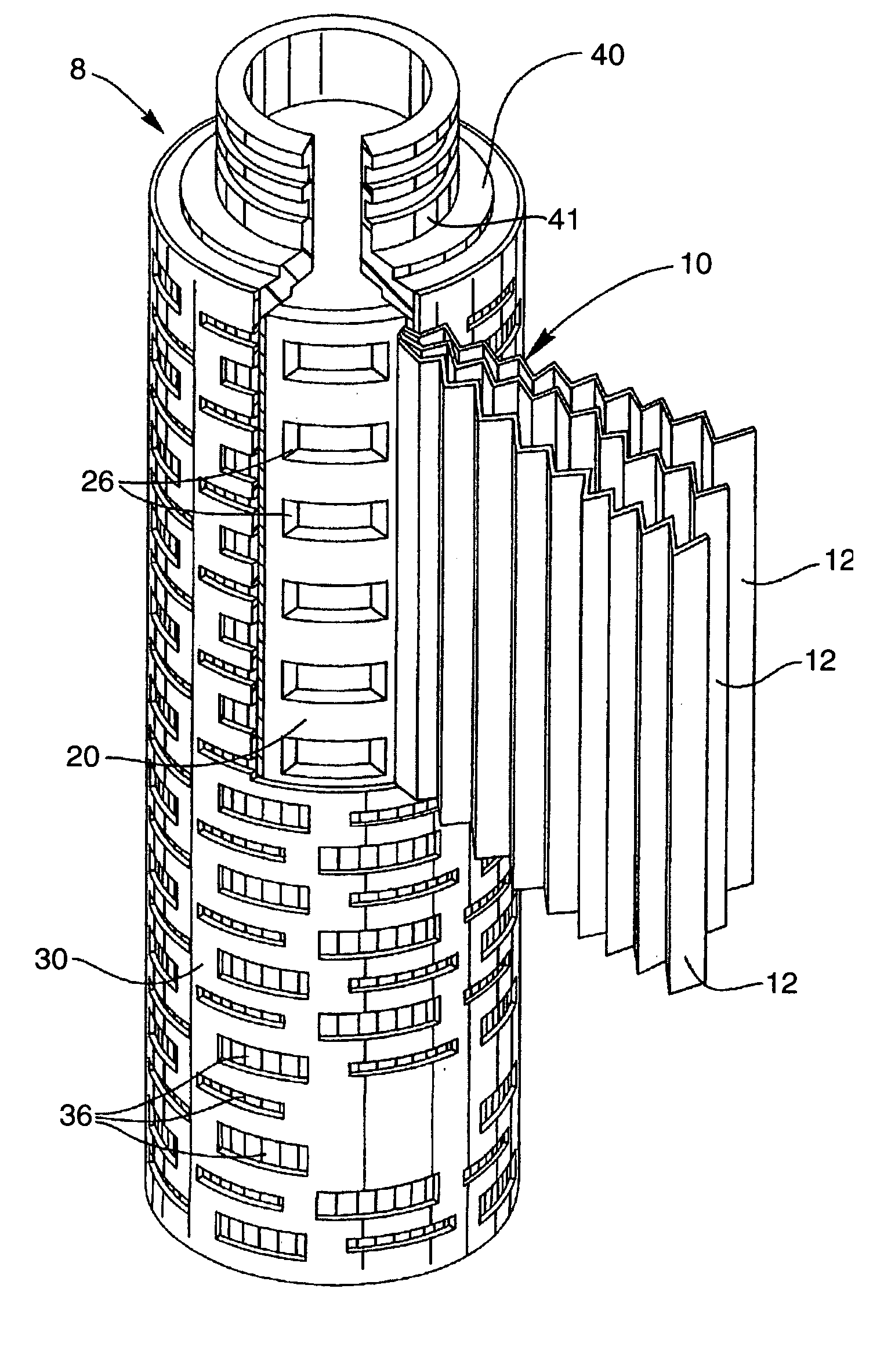
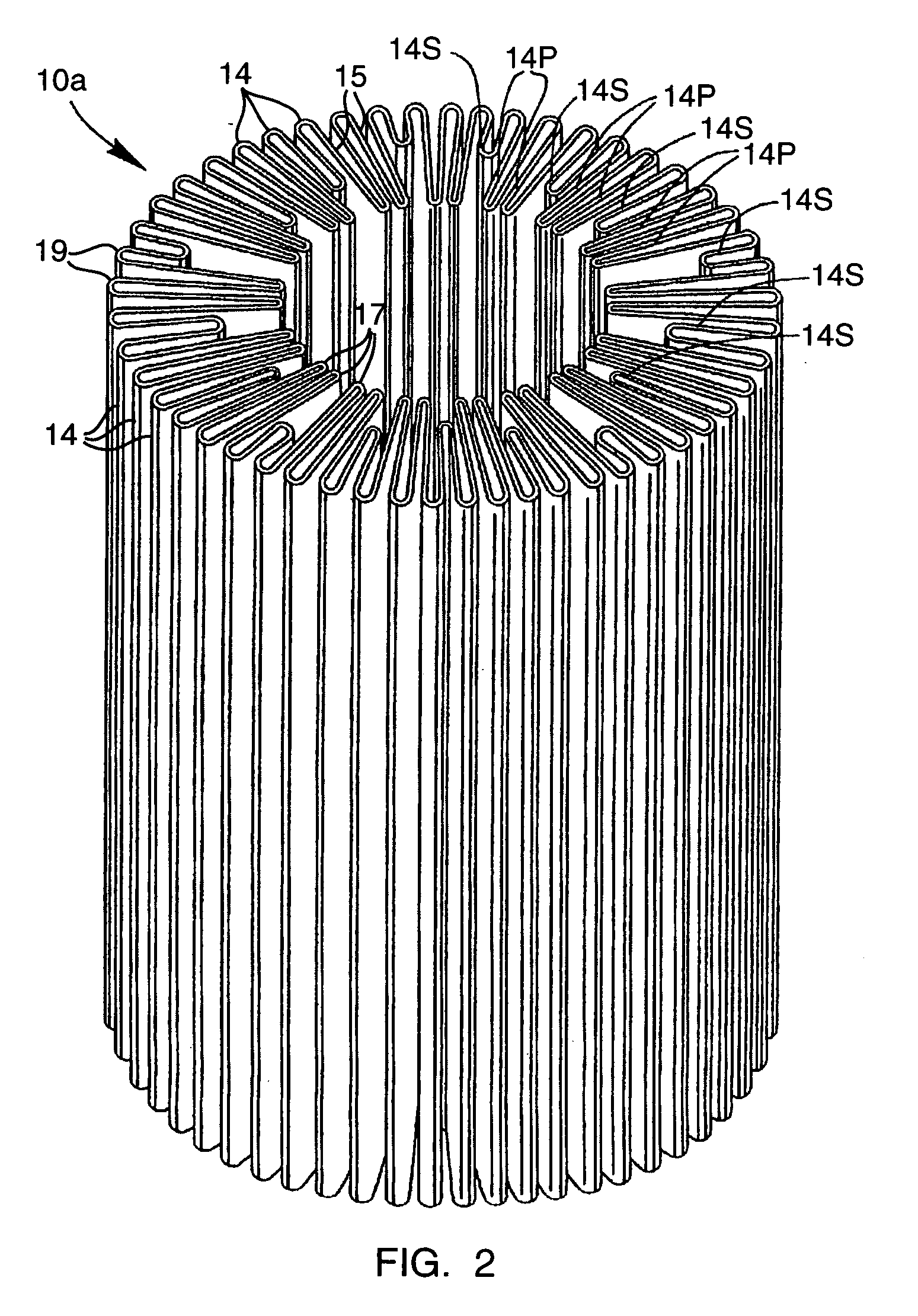
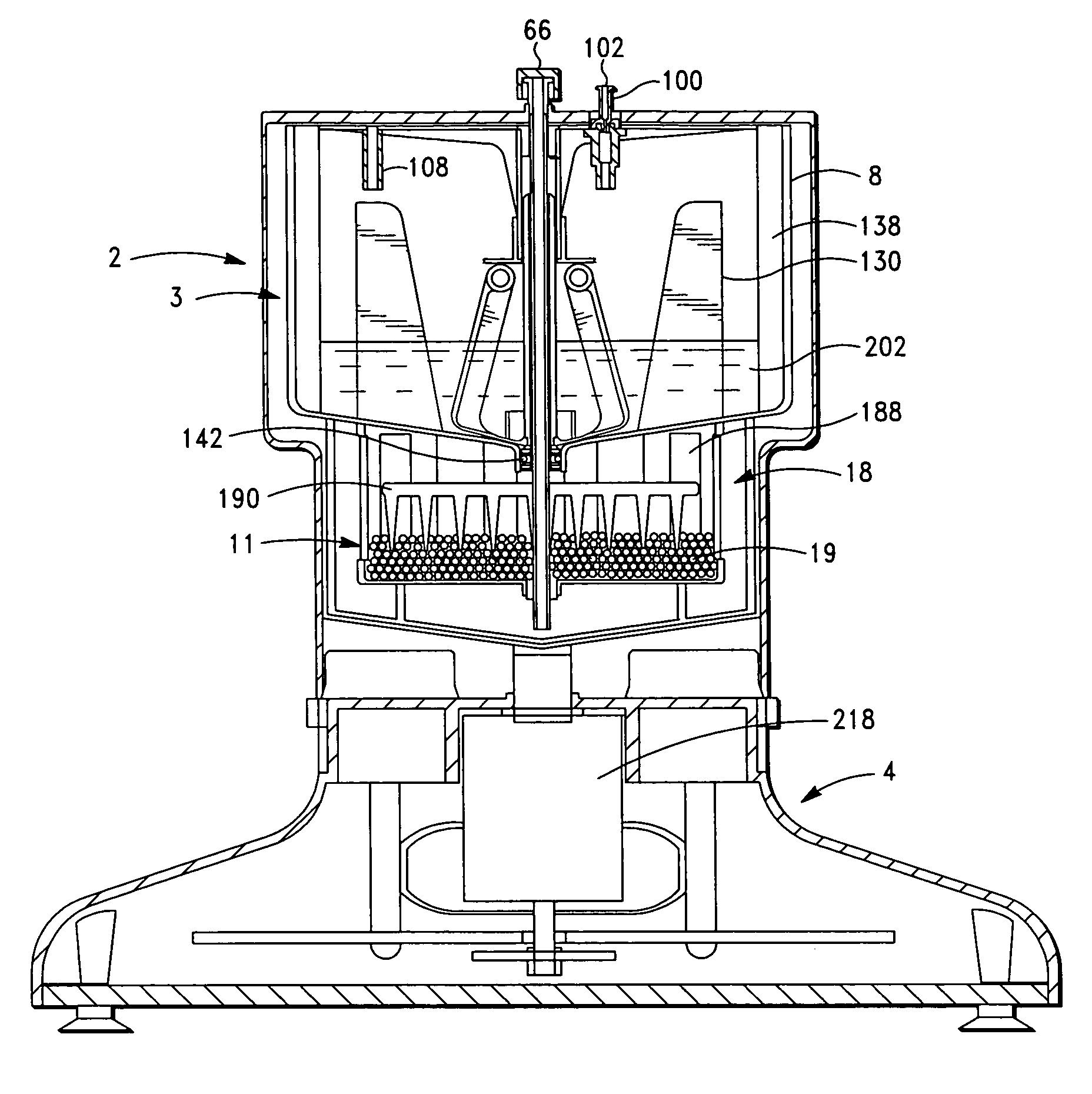
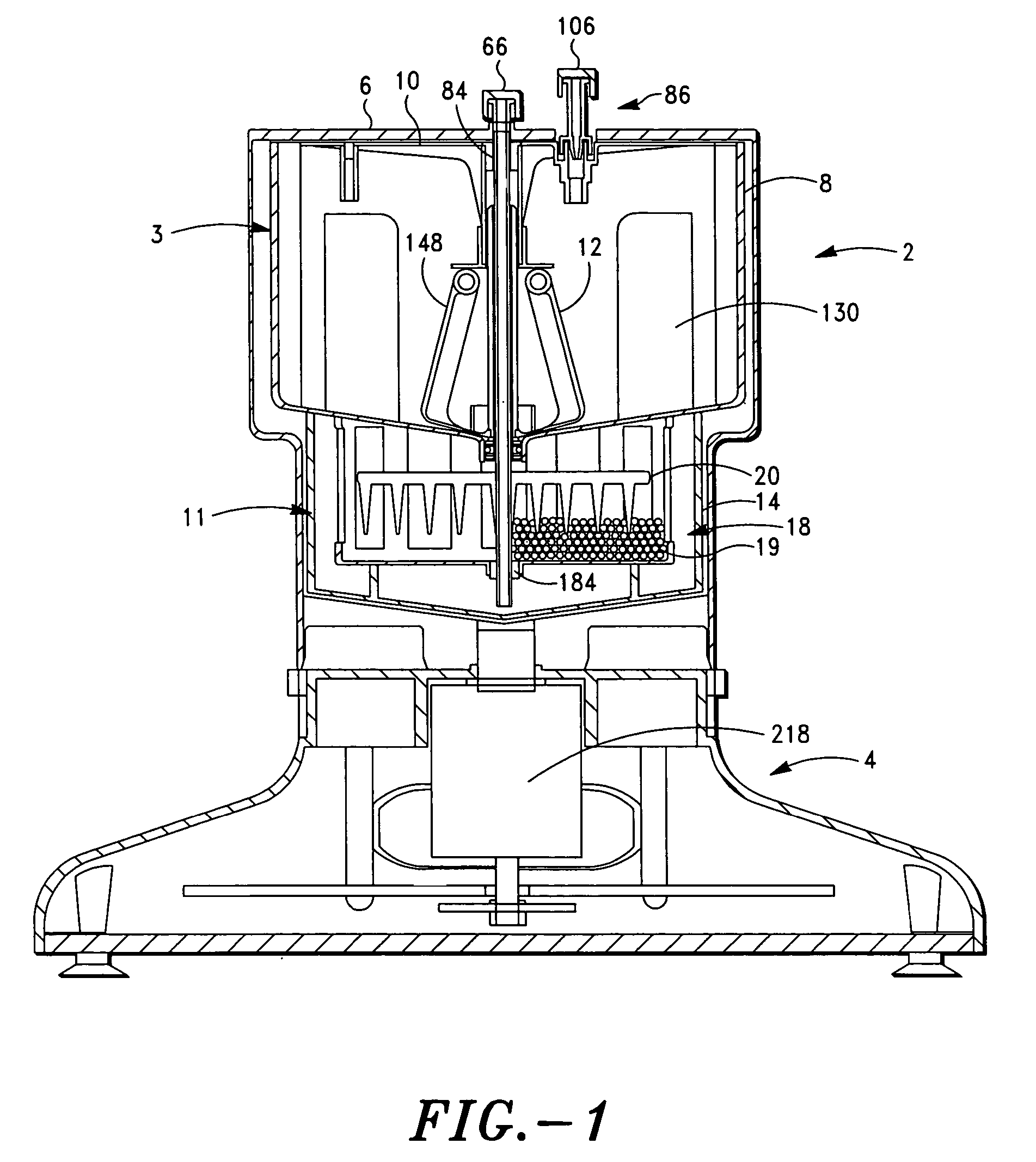
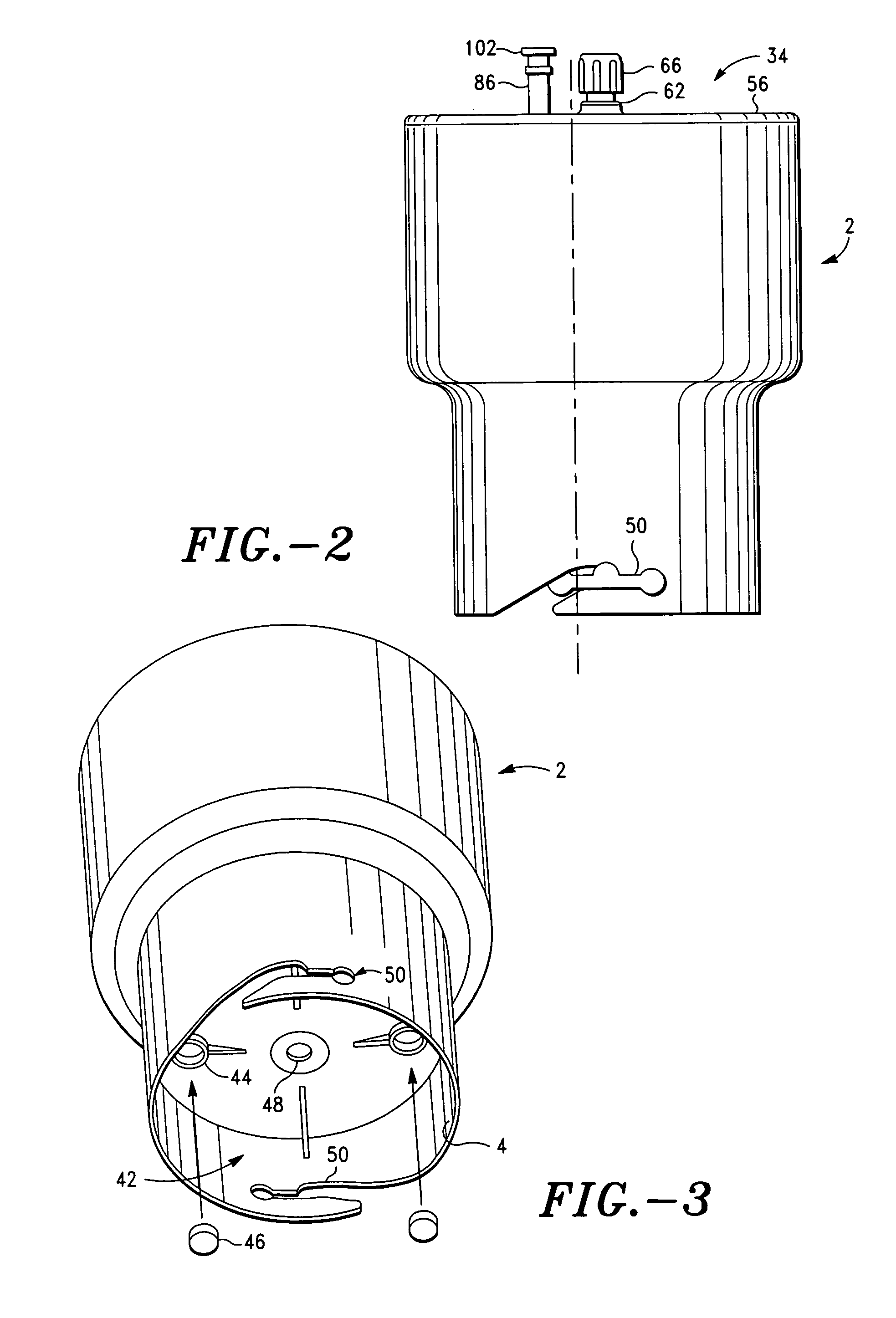
Apparatus and method for preparing platelet rich plasma and concentrates thereof
ActiveUS20060175244A1Increase in platelet levelAvoid assemblyRotary centrifugesMedical devicesRed blood cellEngineering
A PRP separator-concentrator comprising a housing, a separation assembly, and a concentration assembly. The concentration assembly has a concentration sump. An axially concentric rigid stationary outlet tube is secured to the housing and extends through the separation assembly to the sump. The separation assembly is attached to and positioned above the concentration assembly to form a combined separator-concentrator assemblage that is rotatable about the outlet tube. The separation assembly includes a separation chamber lined with a depth filter having pores and passageways that are sized to receive and entrap erythrocytes during centrifuging. The concentration chamber has a floor for supporting desiccated beads and a wall with at least one opening closed with a screen. The concentrator can have a distribution of upright screen supports, the upright screen supports having an inner surface and an outer surface, the cylindrical screen being supported on the outer surface of the upright screen supports. A stationary bead rake can be secured to the stationary tube and extend outward therefrom, the rake having distal ends that are spaced at a distance from the upright screen supports. The rake can comprise a longitudinal body, the center of which is secured to the rigid outlet tube. The separator-concentrator includes a valve assembly connecting the separation chamber and the concentration chamber. PRP concentrate is produced by contacting PRP with desiccated beads while the beads are stirred with a stationary rake, and rotating the concentration chamber at centrifugal speeds to separate PRP concentrate from the beads.
Owner:BIOMET BIOLOGICS +1
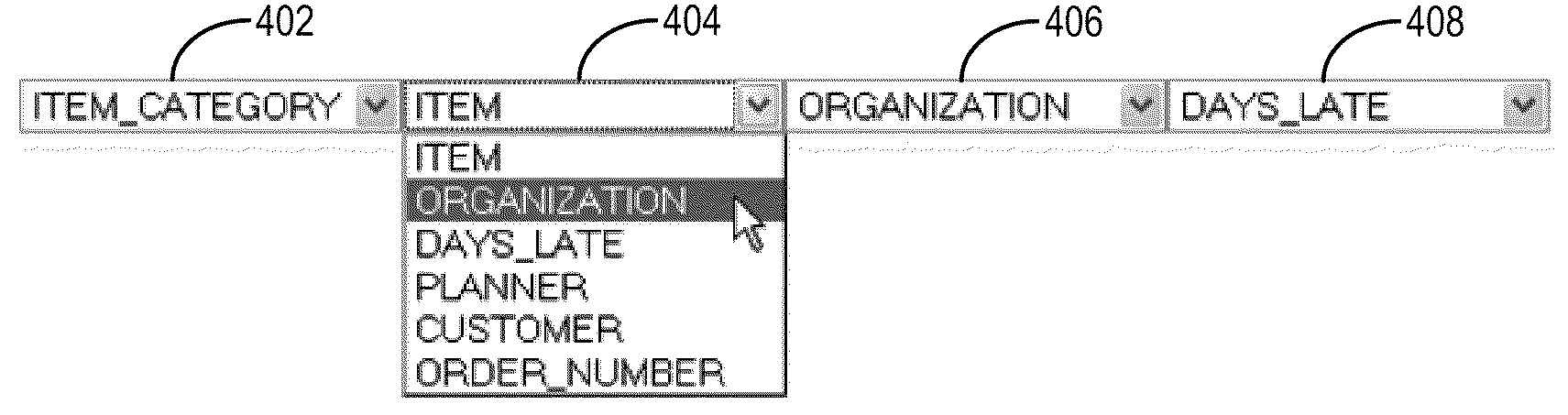
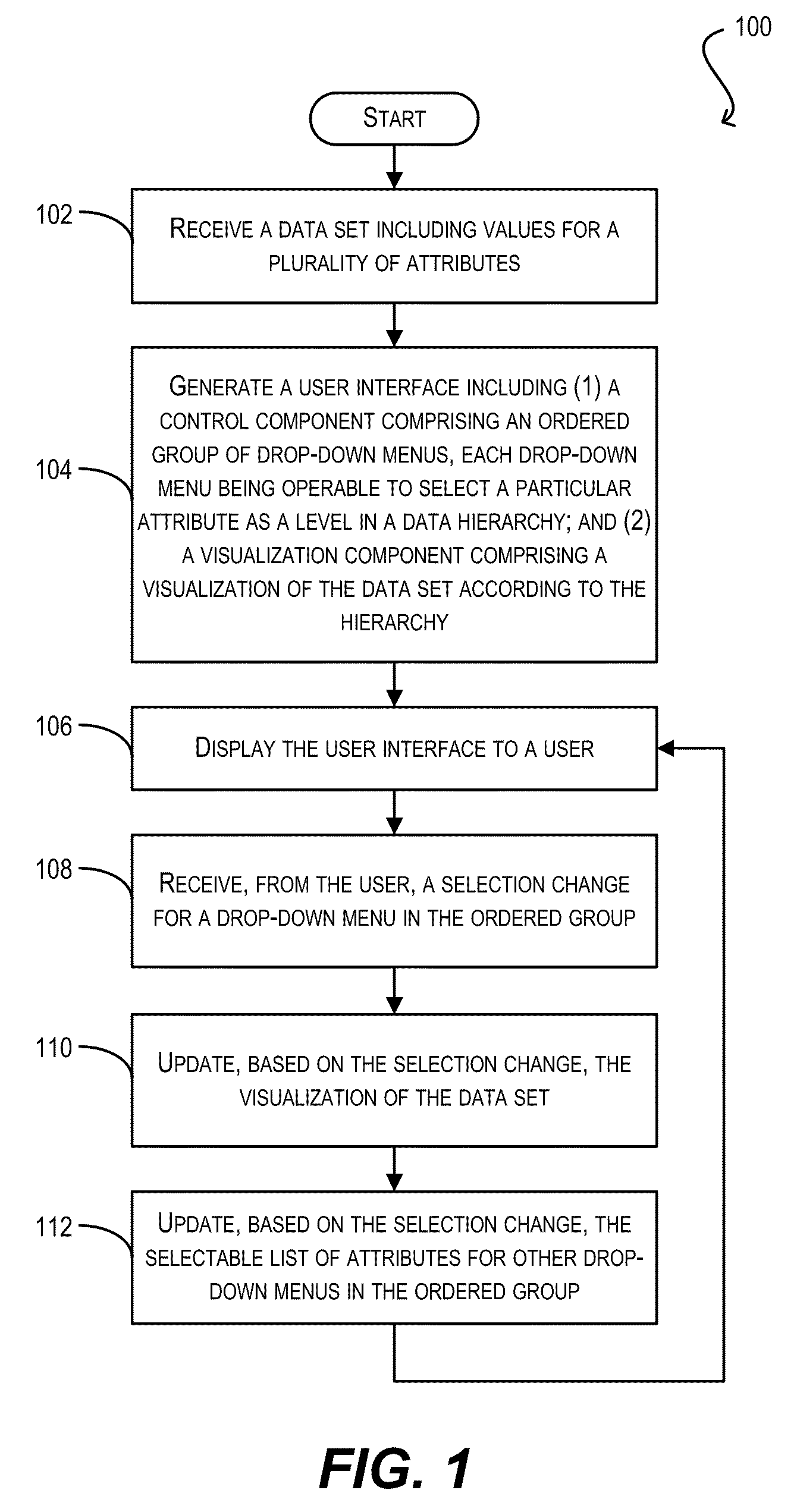
User interface controls for specifying data hierarchies
ActiveUS20110016432A1Good specificationEasy to understandVisual data mining2D-image generationData setControl data
User interface controls that facilitate the specification / modification of data hierarchies. In one set of embodiments, a first UI control component can be provided that comprises an ordered group of drop-down menus. Each drop-down menu in the ordered group can be populated with a selectable list of attributes from a data set and can be associated with a level in a data hierarchy. By selecting values using the various drop-down menus, a user can interactively specify a data hierarchy for the data set. The data set can then be visualized according to the specified hierarchy. In further embodiments, a second UI control component can be provided in addition to the first UI control component. The second UI control component can allow a user to interactively enable or disable certain drop-down menus in the ordered group, thereby acting as a “depth filter” for controlling the depth of the data hierarchy.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Process for removing protein aggregates and virus from a protein solution
InactiveUS7118675B2Less-expensive to purchaseLess-expensive to operateComponent separationSolvent extractionProtein solutionFree protein
A process is provided for selectively removing protein aggregates from a protein solution in a normal flow (NFF) filtration process. Preferably, it relates to a process for selectively removing protein aggregates from a protein solution in a normal flow (NFF) filtration process and virus particles from a protein solution in a two-step filtration process. In a first step, a protein solution is filtered through one or more layers of adsorptive depth filters, charged or surface modified microporous membranes or a small bed of chromatography media in a normal flow filtration mode of operation, to produce a protein aggregate free stream. The aggregate free protein stream can then be filtered through one or more ultrafiltration membranes to retain virus particles at a retention level of at least 3 LRV and to allow passage therethrough of an aggregate free and virus free protein solution.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Cell-cultivating device
ActiveUS7033823B2Reduces cell injury cellReduces cell even cell mortalityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotechnologyAdhesion process
The present invention claims and discloses a novel apparatus and method for efficiently cultivating cells with minimal mortality in order to harvest a maximum amount of cellular products generated by the cultivated cells. More particularly, the present invention teaches a method and a device for plating cells and causing maximum adherence of cells of interest. Furthermore, the present invention also teaches a growth substrate means that is capable of providing the largest surface area for cell adhesion and functions as an oxygenator, a depth filter and a static mixer to maximize the production of cellular products by intermittently and periodically provide sufficient oxygen and nutrients to the cells without causing cell death. The device of the present invention is economical and can be disposable thus eliminating complications caused by sterlization and is capable of periodically and intermittently provide oxygen and nutrients to cells, through controlling the amount of culture medium that comes into contact with the growth substrate means.
Owner:CESCO BIOENGINEERING CO LTD
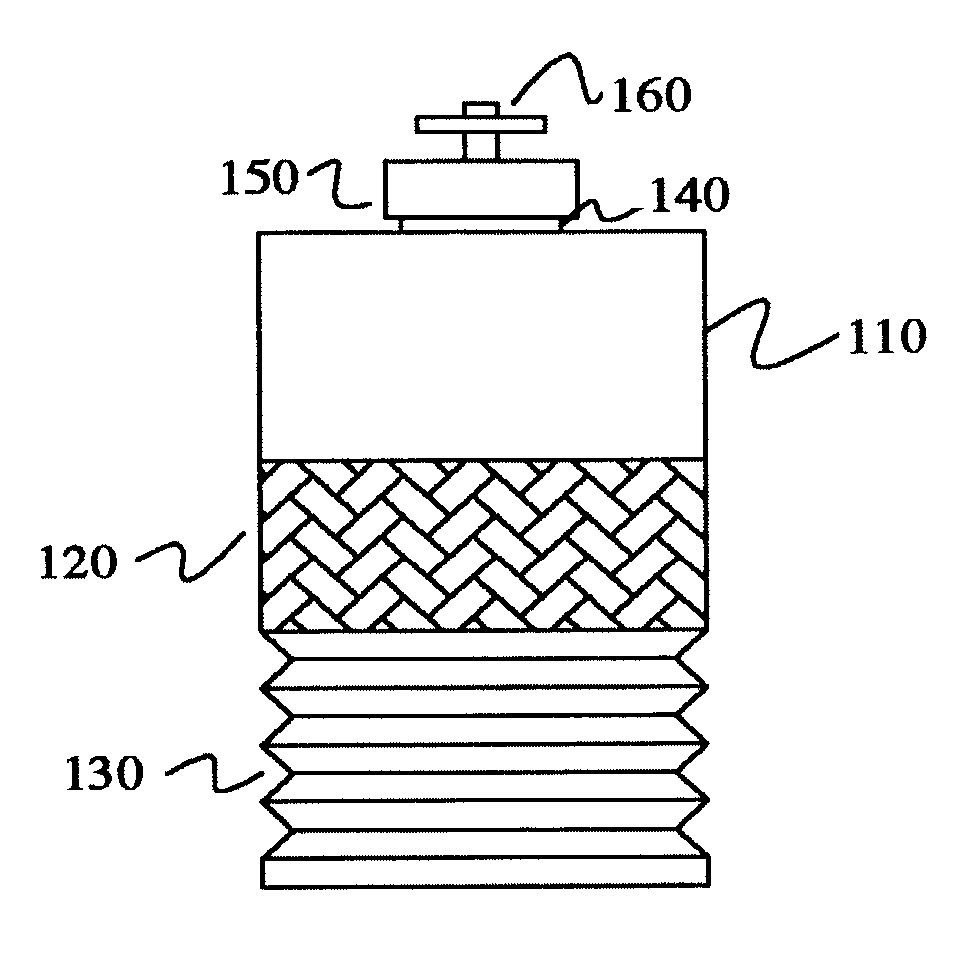
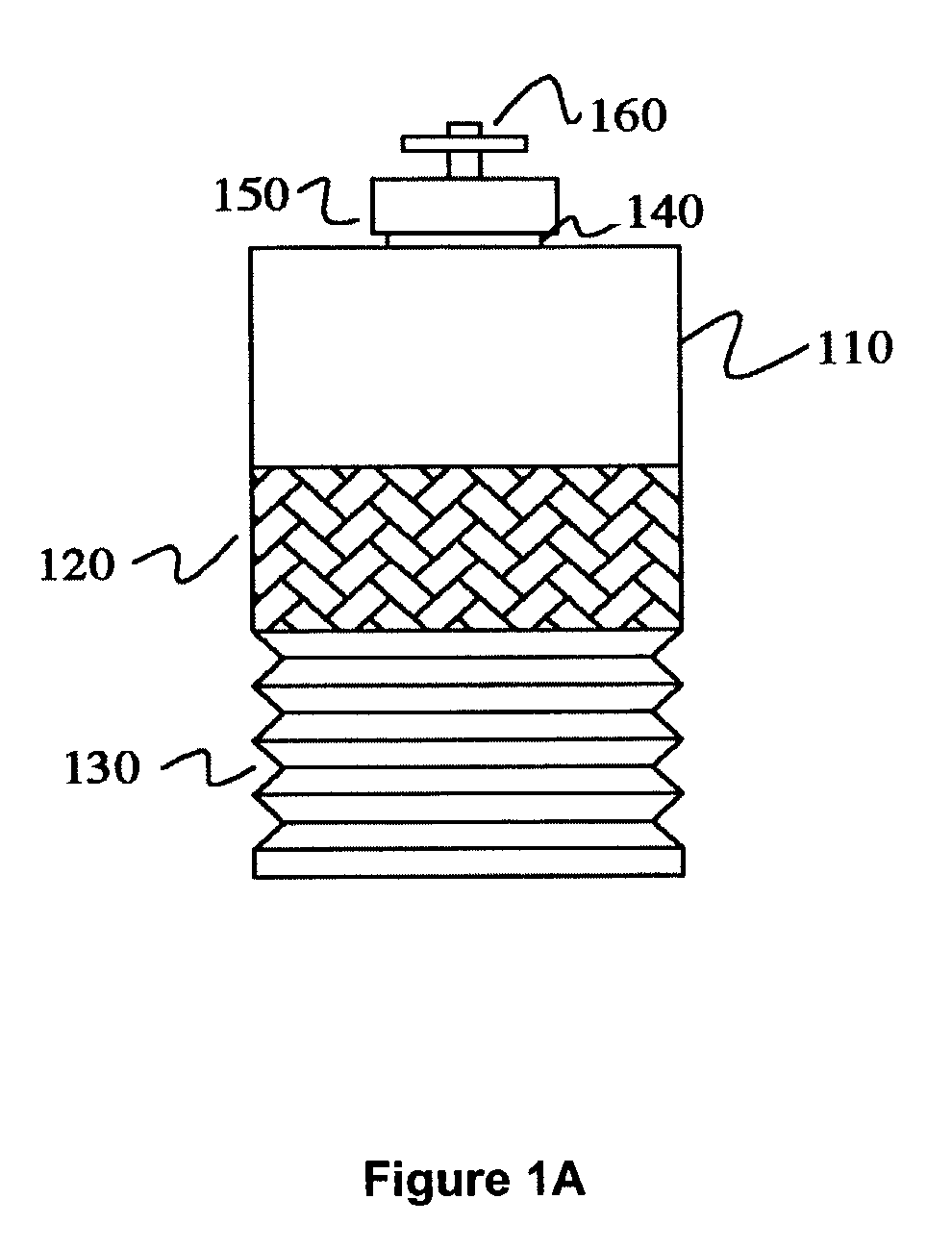
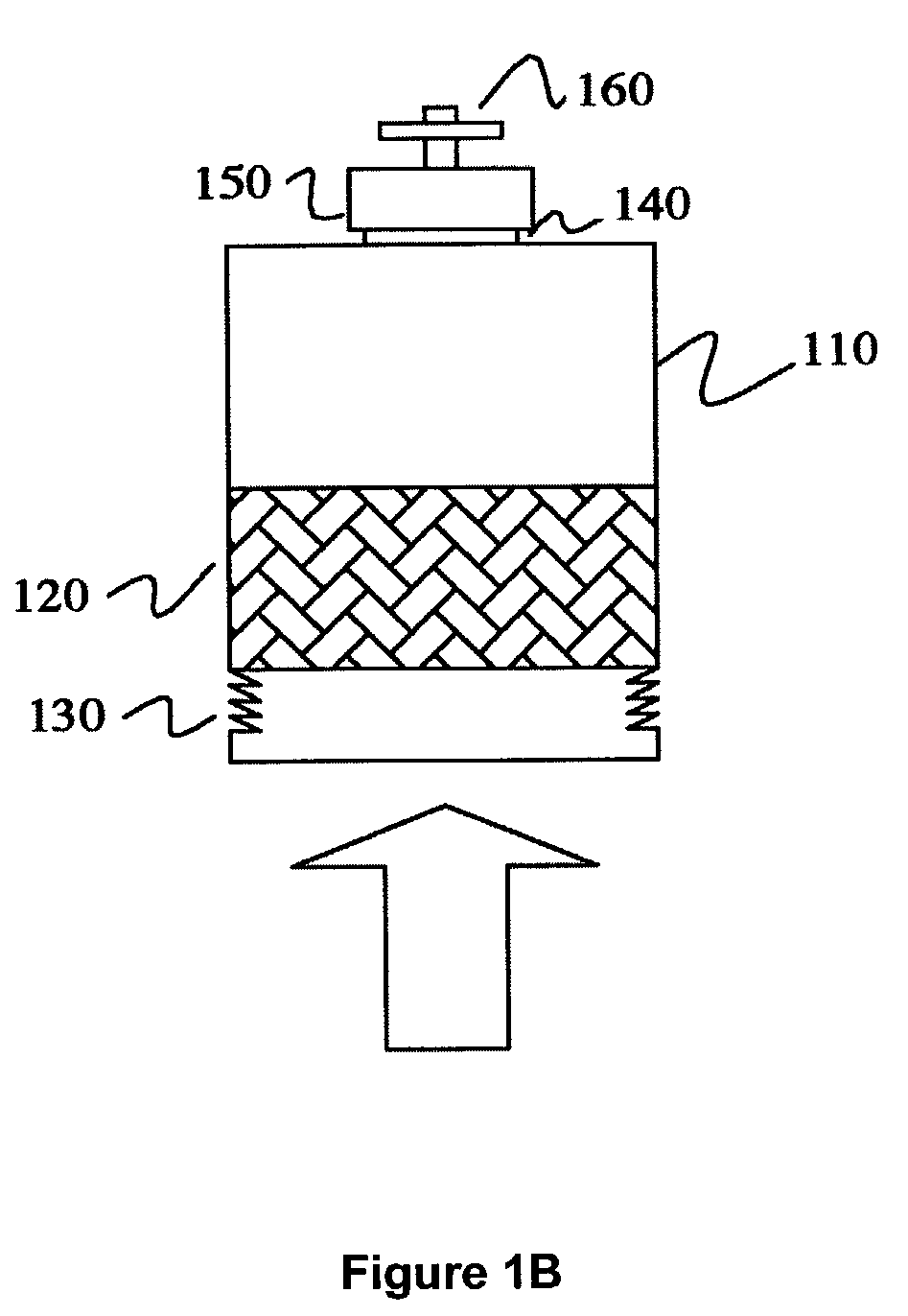
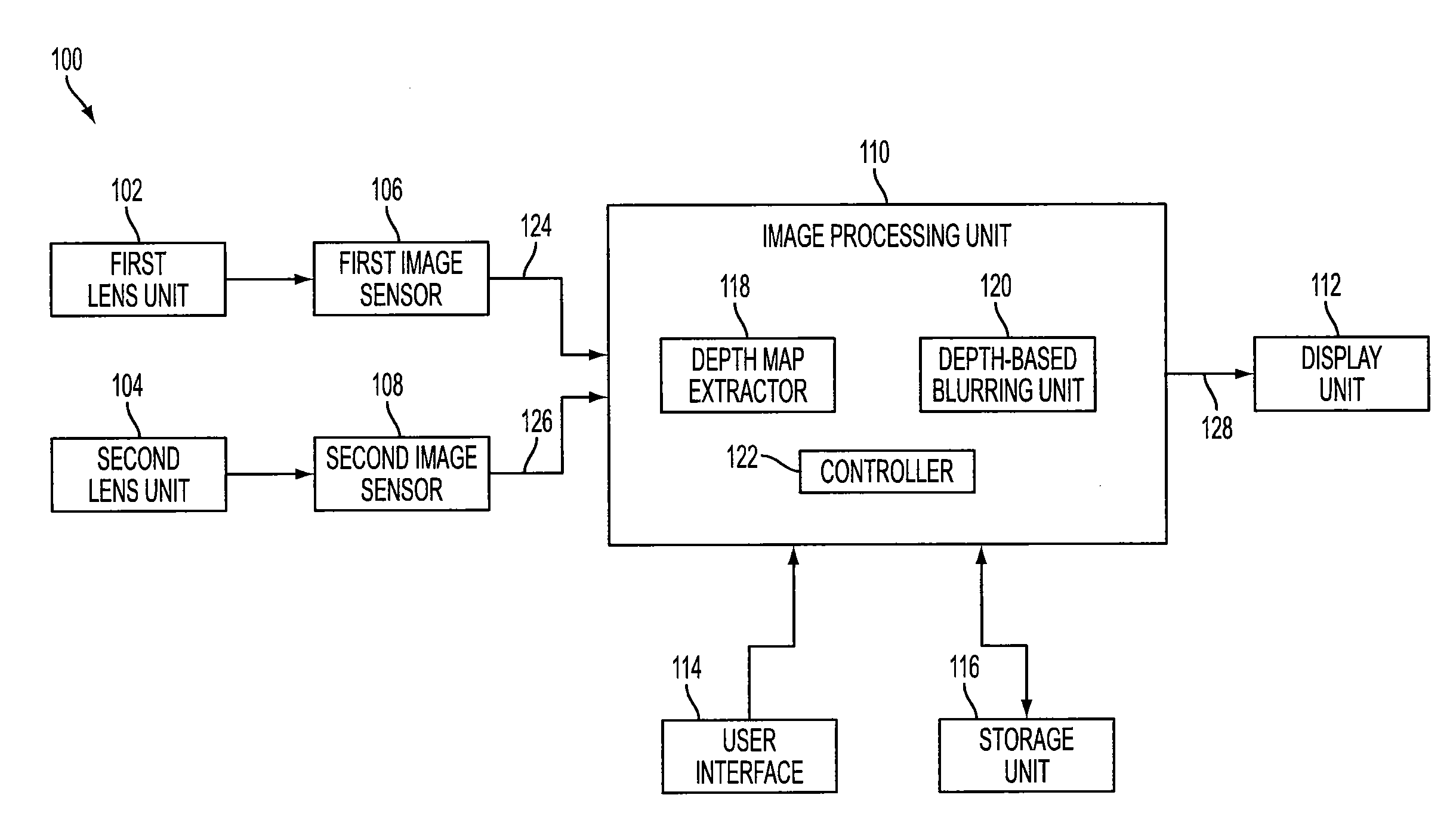
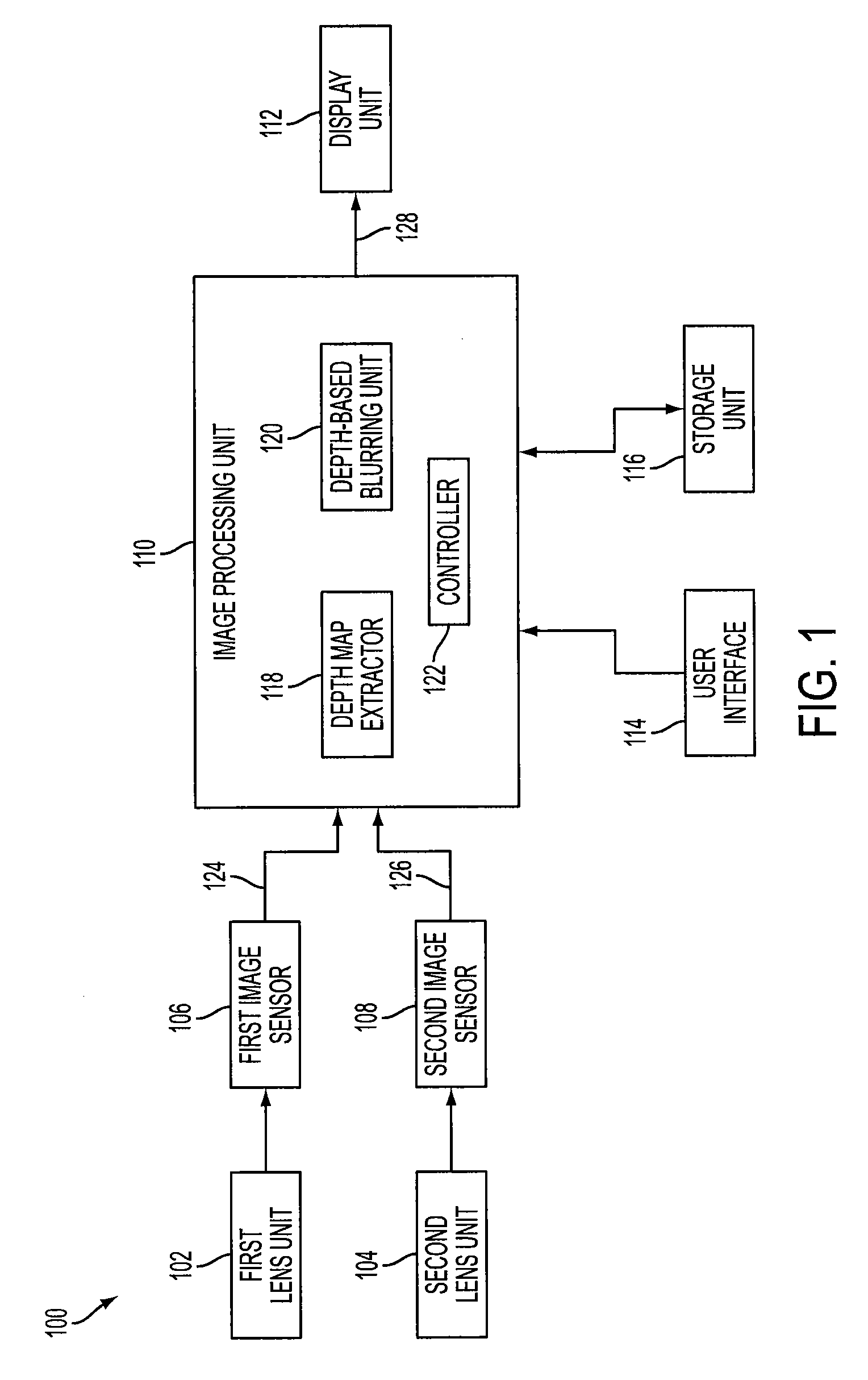
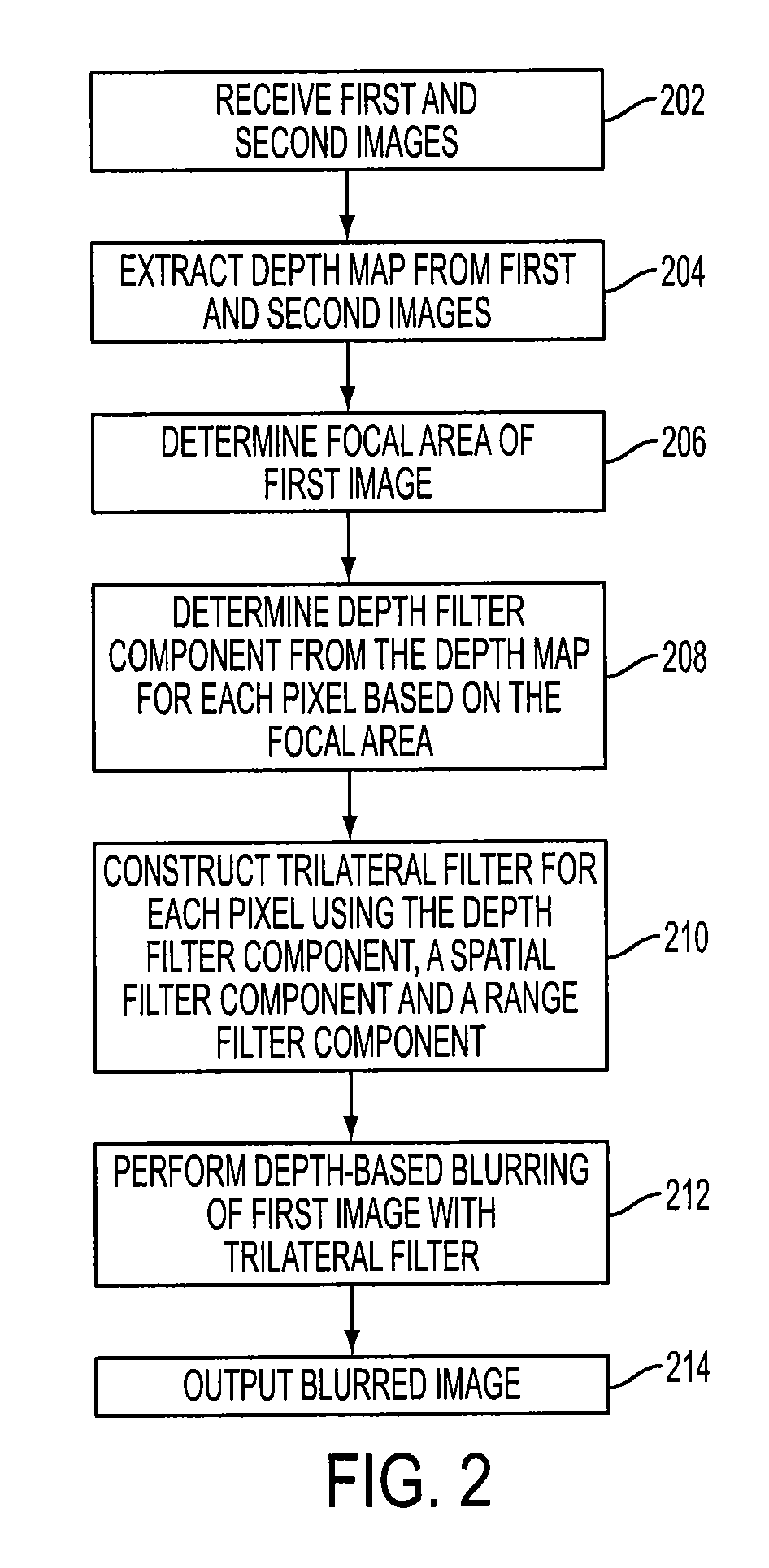
Method of depth-based imaging using an automatic trilateral filter for 3D stereo imagers
A system of stereo imagers, including image processing units and methods of blurring an image, is presented. The image is received from an image sensor. For each pixel of the image, a depth filter component is determined based on a focal area of the image and a depth map associated with the image. For each pixel of the image, a trilateral filter is generated that includes a spatial filter component, a range filter component and the depth filter component. The respective trilateral filter is applied to corresponding pixels of the image to blur the image outside of the focal area. A refocus area or position may be determined by imaging geometry or may be selected manually via a user interface.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Filtration cartridge and process for filtering a slurry
InactiveUS7247245B1Low compressibilitySemi-permeable membranesSettling tanks feed/dischargeFiberSlurry
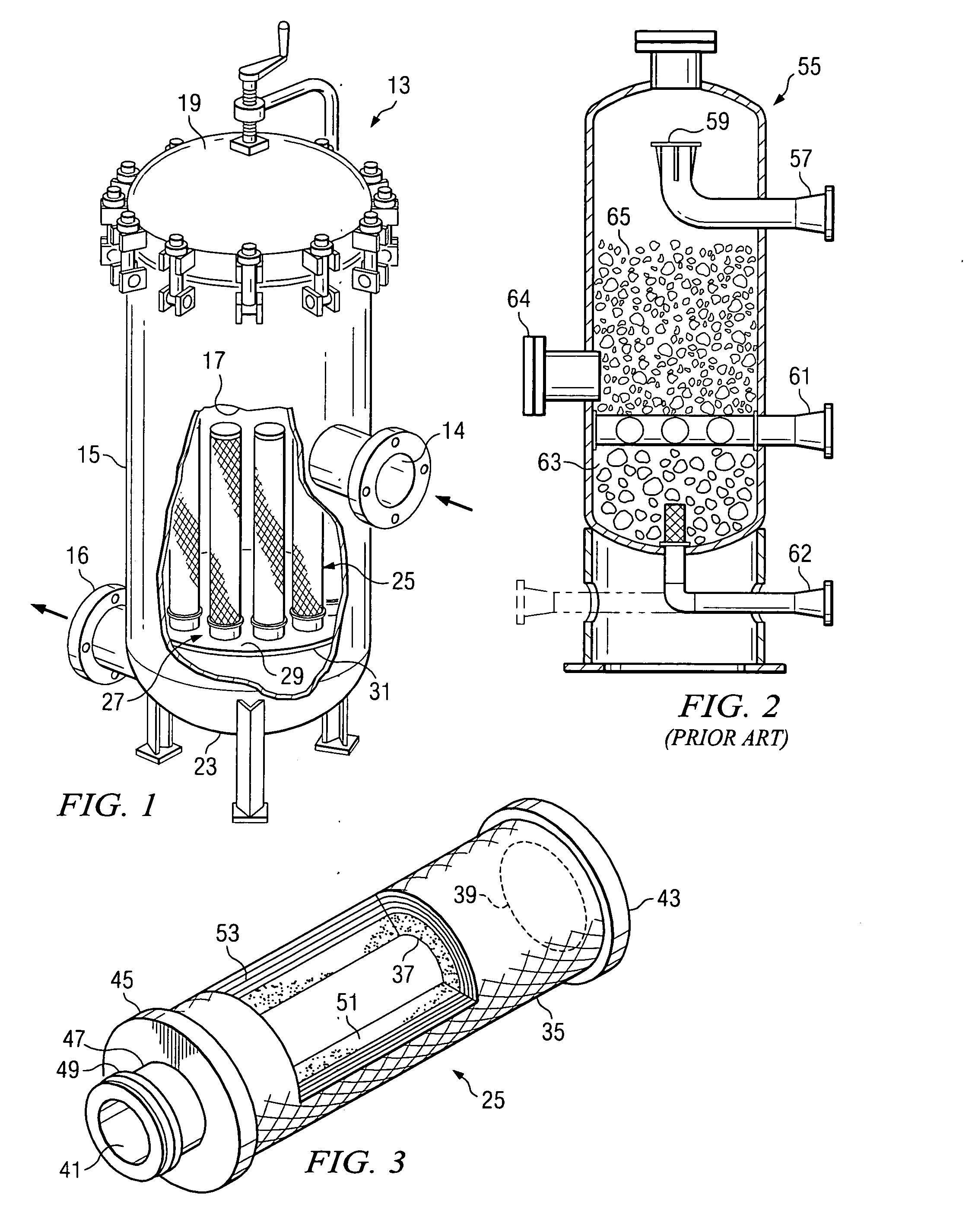
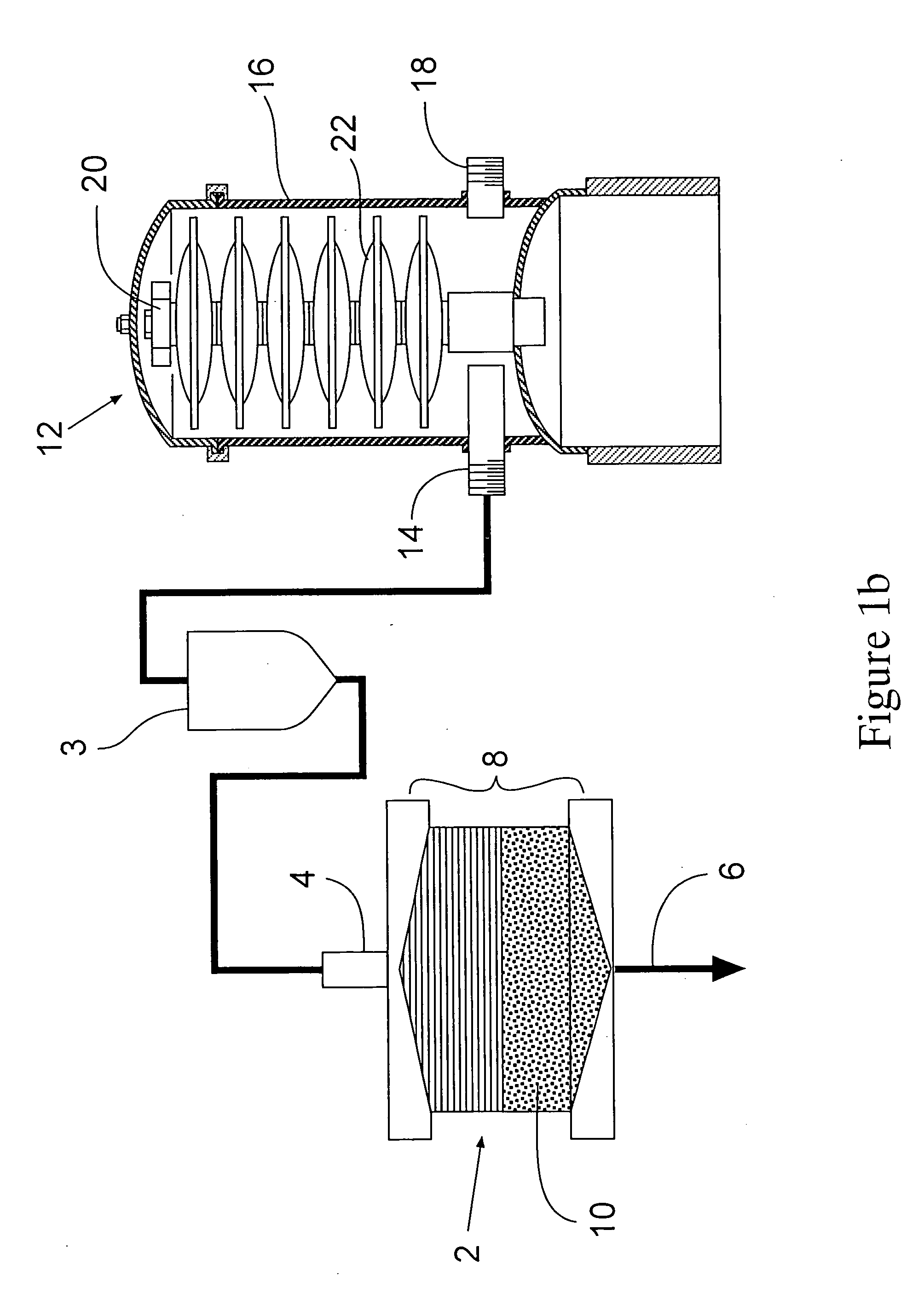
A depth filter design is disclosed which has little if any open void area upstream of the media. Preferably, it also has little if any open void area downstream of the media as well. A preferred embodiment uses layers of stacked, fibrous media with several of the layers being separated from the others by spacers which serve to compress the media and to prevent the bypass of fluid around the media adjacent the inner wall of the housing. Several designs for attaching the end caps which allow for the compression of the media are also disclosed.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
System and method for adaptive tile depth filter
InactiveUS20070273689A1Easy for washing outSave memory bandwidth3D-image renderingComputational scienceThree dimensional graphics
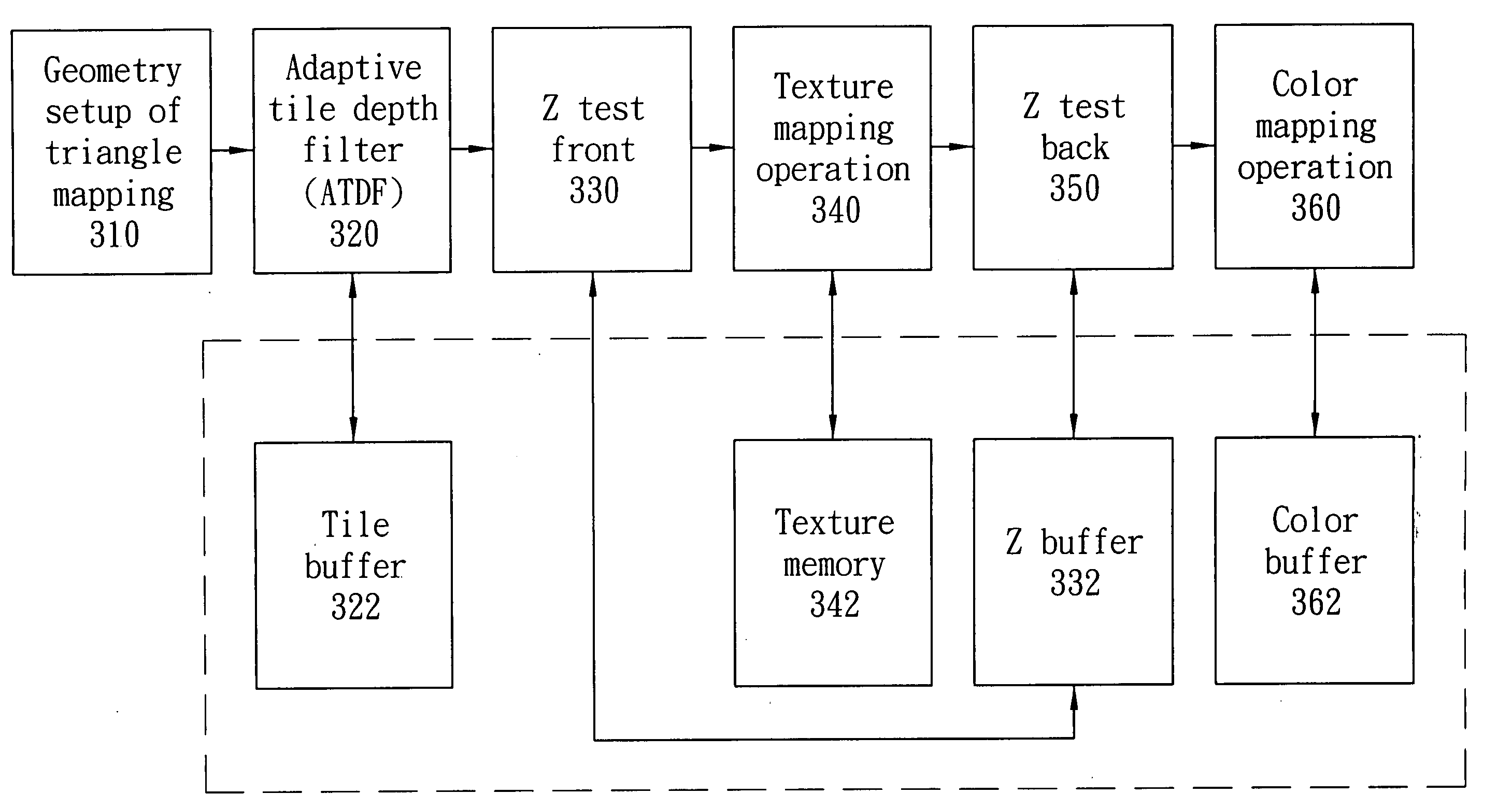
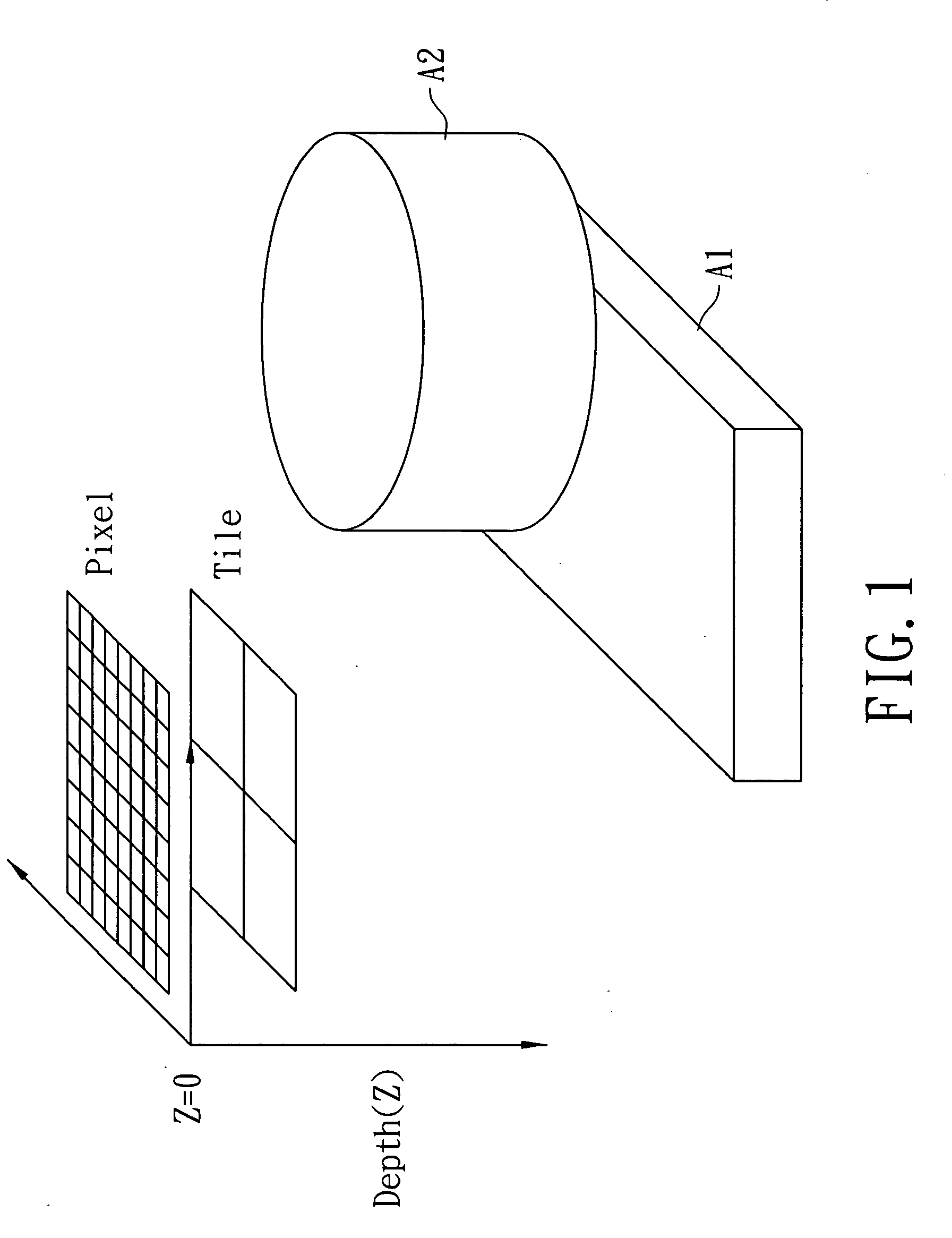
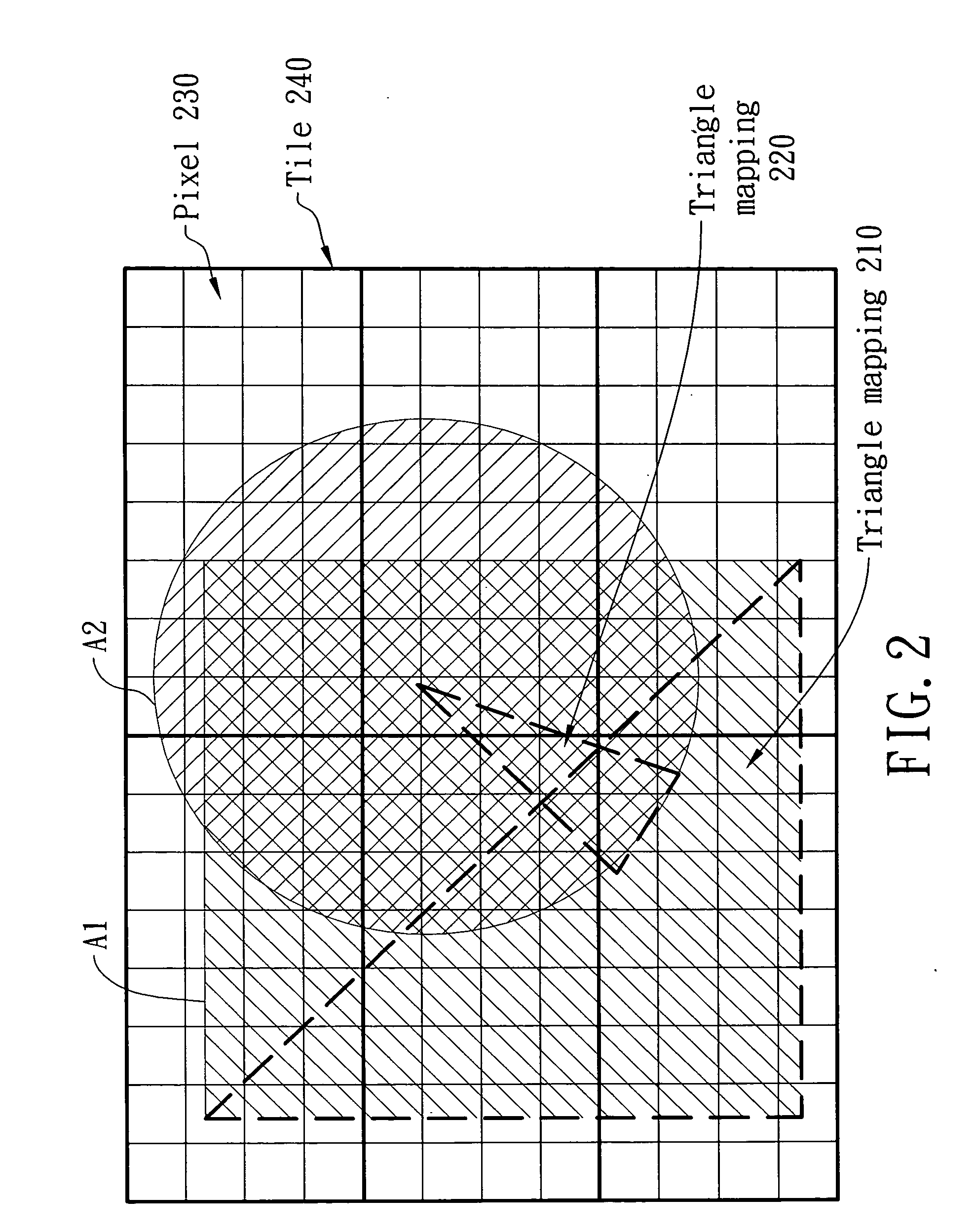
An efficient system and method for adaptive tile depth filter (ATDF) is disclosed. The key concept of this system and method is to consider more occlusion conditions in order to achieve a better performance of filter before the conventional Z test process in three dimensional graphics pipeline. Two occlusion criteria, Zmax and Zmin (depth range in a tile), are introduced first for occlusion and non-occlusion fragments in a tile. The points between Zmax and Zmin are in uncertain fragment which may need to go through the later Z test. Moreover, a new technique, coverage mask, can further filter the points in the uncertain fragment to a final uncertain fragment and non-occlusion fragment. Besides, the coverage mask can be used to efficiently decide which tile needs the further sub-tile depth filter.
Owner:ITE TECH INC
Pleated multi-layer filter media and cartridge
InactiveUS20060107639A1Easy to useSave spaceCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationParticulatesFilter media
A pleated filter element includes a composite depth filter medium formed into a plurality of pleats. The composite depth filter medium includes a plurality of depth filter media layers. Each of the plurality of depth filter media layers includes adsorber particulate matter. Each of the plurality of depth filter media layers may have a thickness less than about 1300 microns. The plurality of depth filter media layers may have at least 50% by weight of adsorber particulate matter.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Apparatus and method for preparing platelet rich plasma and concentrates thereof
ActiveUS7824559B2Increase in platelet levelAvoid assemblyRotary centrifugesMedical devicesEngineeringBlood plasma
A PRP separator-concentrator comprising a housing, a separation assembly, and a concentration assembly. The concentration assembly has a concentration sump. An axially concentric rigid stationary outlet tube is secured to the housing and extends through the separation assembly to the sump. The separation assembly is attached to and positioned above the concentration assembly to form a combined separator-concentrator assemblage that is rotatable about the outlet tube. The separation assembly includes a separation chamber lined with a depth filter having pores and passageways that are sized to receive and entrap erythrocytes during centrifuging. The concentration chamber has a floor for supporting desiccated beads and a wall with at least one opening closed with a screen. The concentrator can have a distribution of upright screen supports, the upright screen supports having an inner surface and an outer surface, the cylindrical screen being supported on the outer surface of the upright screen supports. A stationary bead rake can be secured to the stationary tube and extend outward therefrom, the rake having distal ends that are spaced at a distance from the upright screen supports. The rake can comprise a longitudinal body, the center of which is secured to the rigid outlet tube. The separator-concentrator includes a valve assembly connecting the separation chamber and the concentration chamber. PRP concentrate is produced by contacting PRP with desiccated beads while the beads are stirred with a stationary rake, and rotating the concentration chamber at centrifugal speeds to separate PRP concentrate from the beads.
Owner:BIOMET BIOLOGICS +1
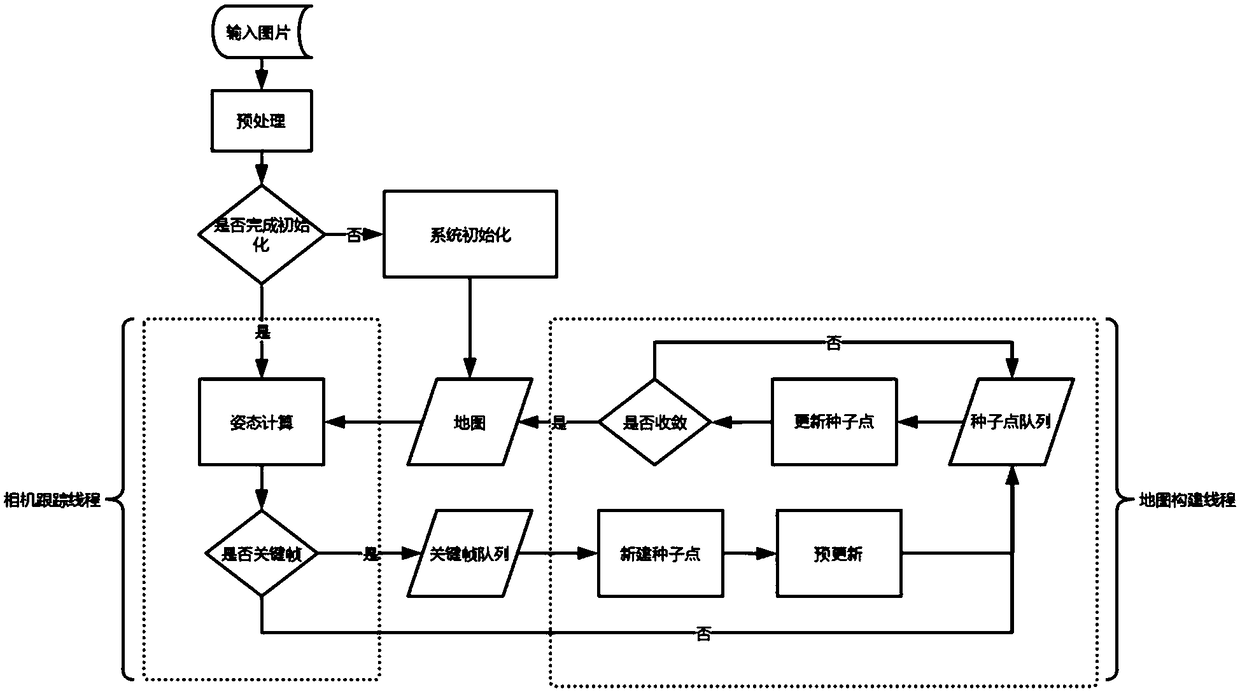
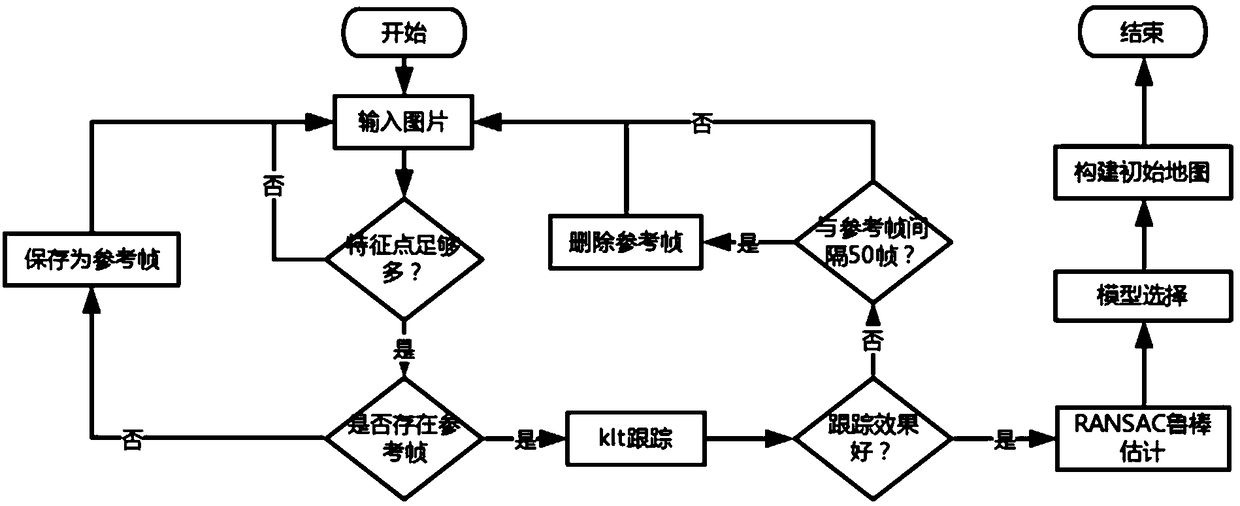
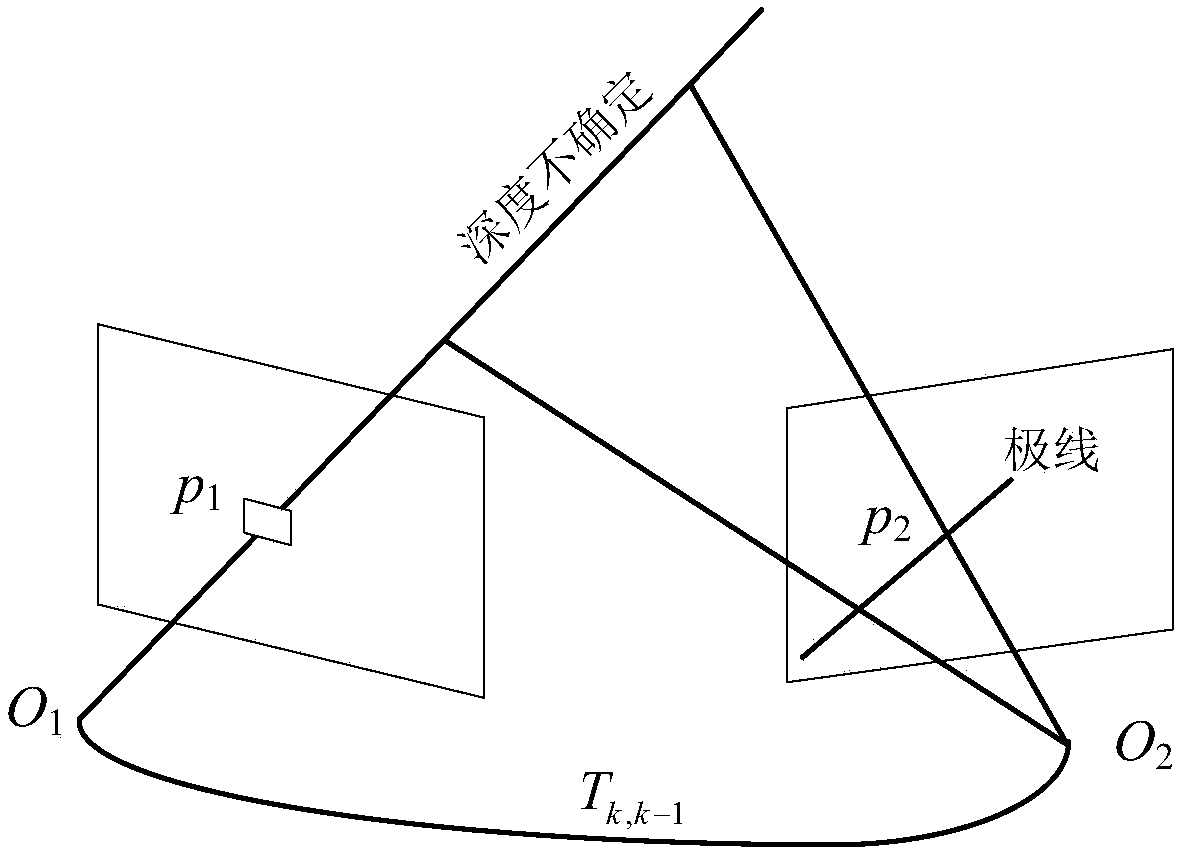
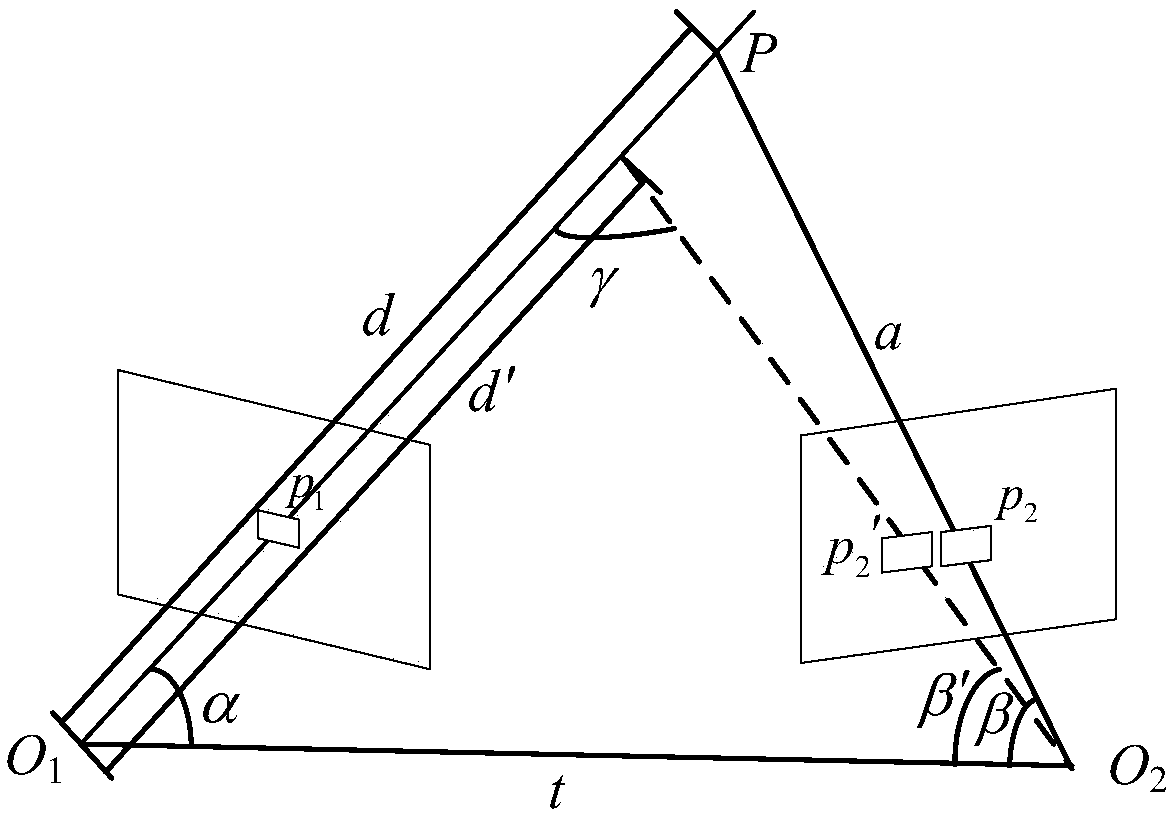
Monocular vision odometer positioning method and positioning system based on semi-direct method
The invention discloses a monocular vision odometer positioning method and a positioning system based on a semi-direct method. The method includes: entering a target scene through a monocular camera and recording scene image data; preprocessing the obtained scene image d and detecting feature points; conducting initialization of the system initializes, tracking the obtained feature points, takingthe tracked feature point pair set as the data set of a robust algorithm, extracting the line features from the scene image, and using the semi-direct method to estimate the pose of the camera; selecting the key frames in the image taken by the camera; performing map construction. The invention realizes a robust and high-quality initialization process. The method selects a key frame to update thedepth information of the three-dimensional feature once when each three-dimensional feature is added to the depth filter for the first time, thereby reducing the uncertainty of the depth information of the new three-dimensional feature and accelerating the convergence of the depth. The reference frame of three-dimensional features is updated to shorten the time interval between the reference frameand the current frame and to reduce the sensitivity to illumination changes.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
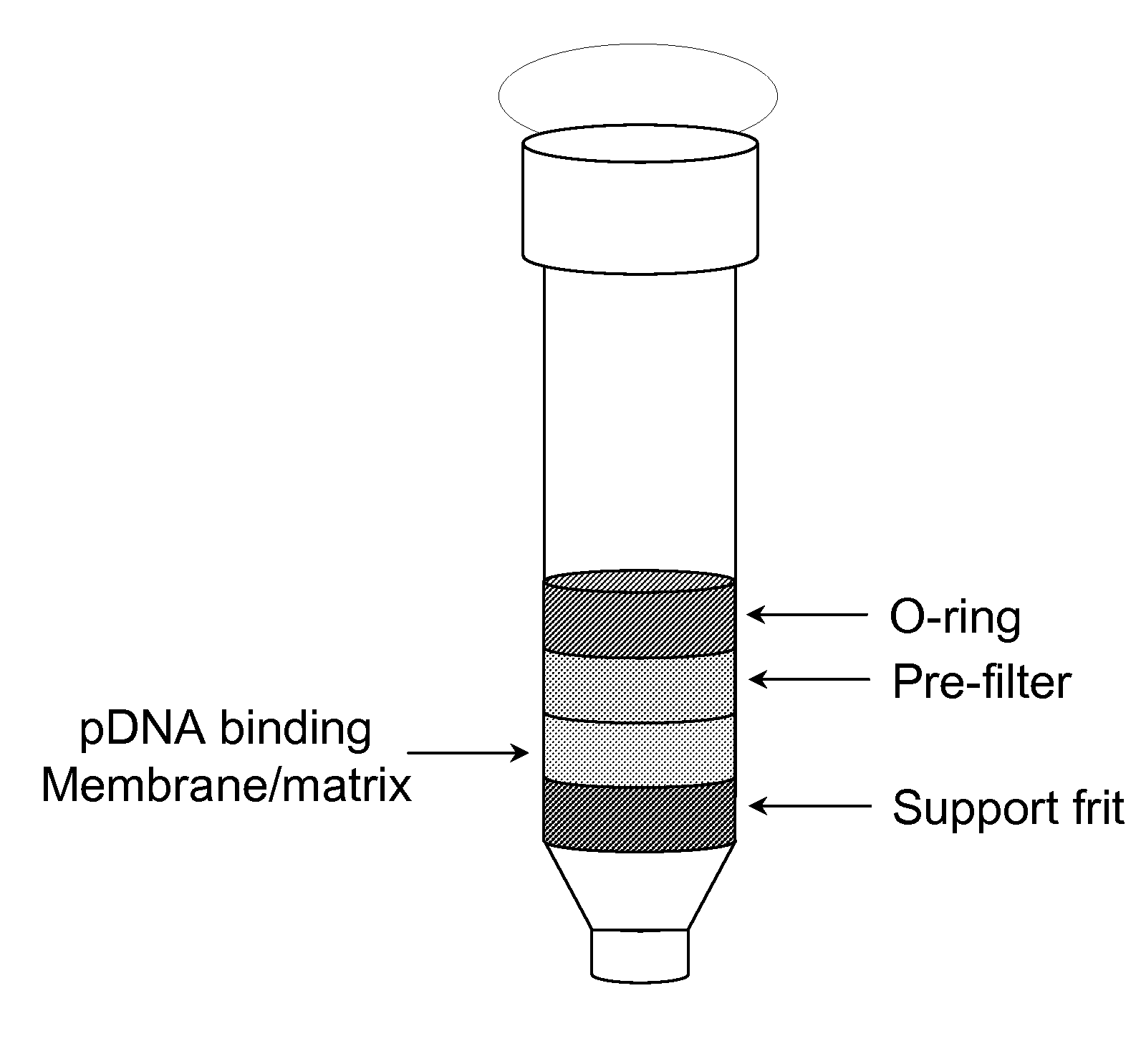
Modified spin column for simple and rapid plasmid DNA extraction
InactiveUS20080300397A1Rapid isolationImprove system performanceSamplingSugar derivativesCellular DebrisSpins
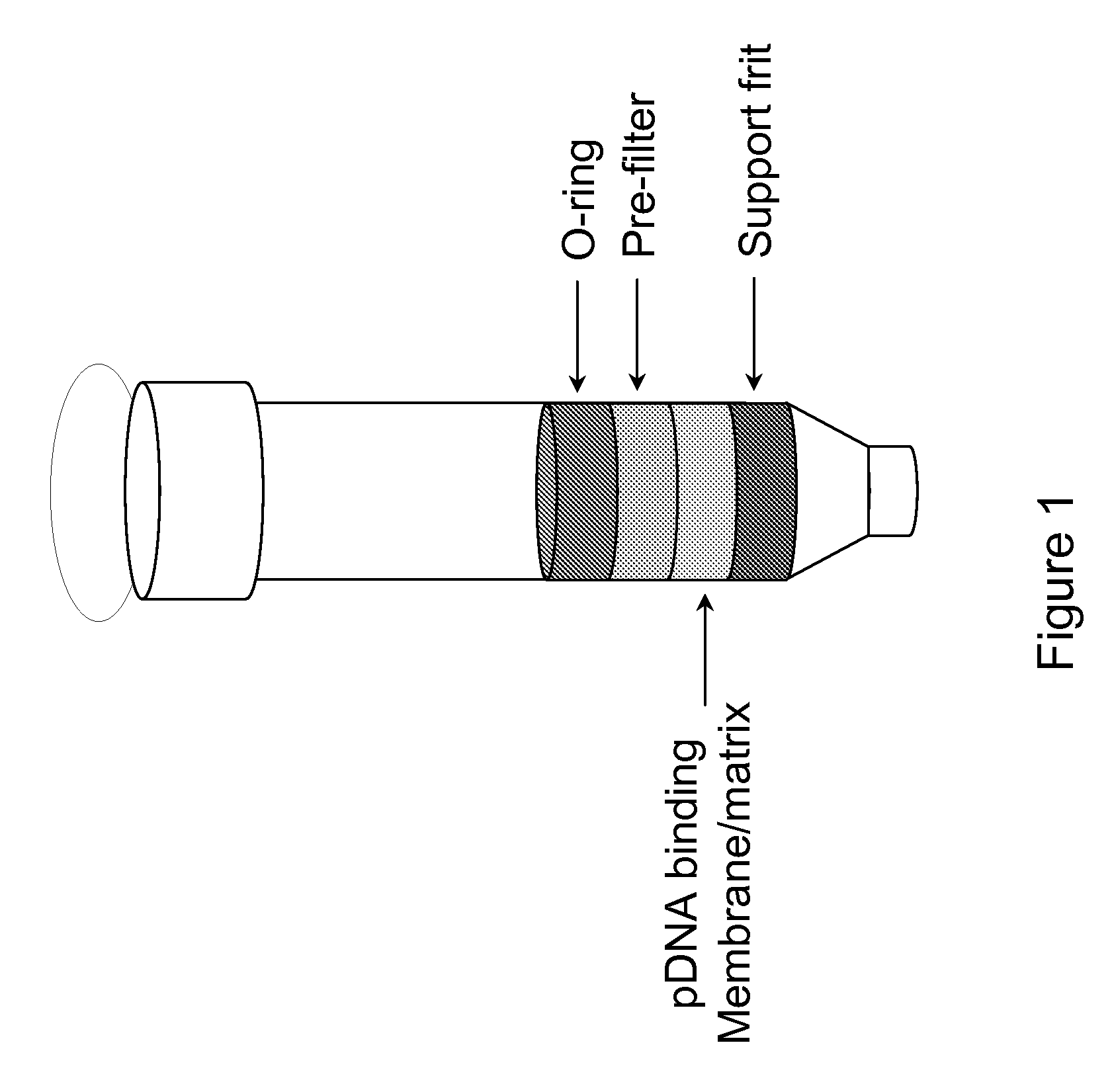
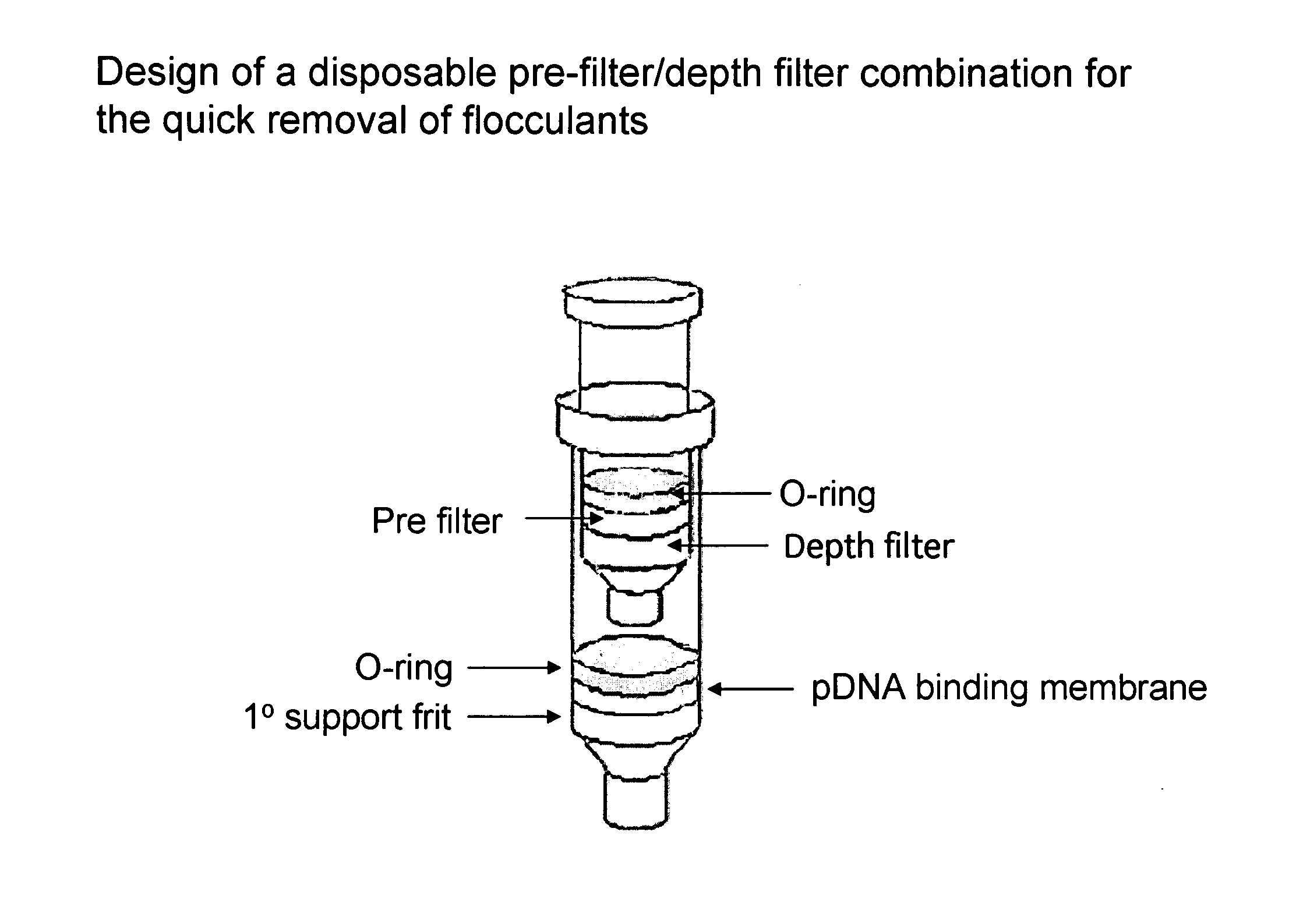
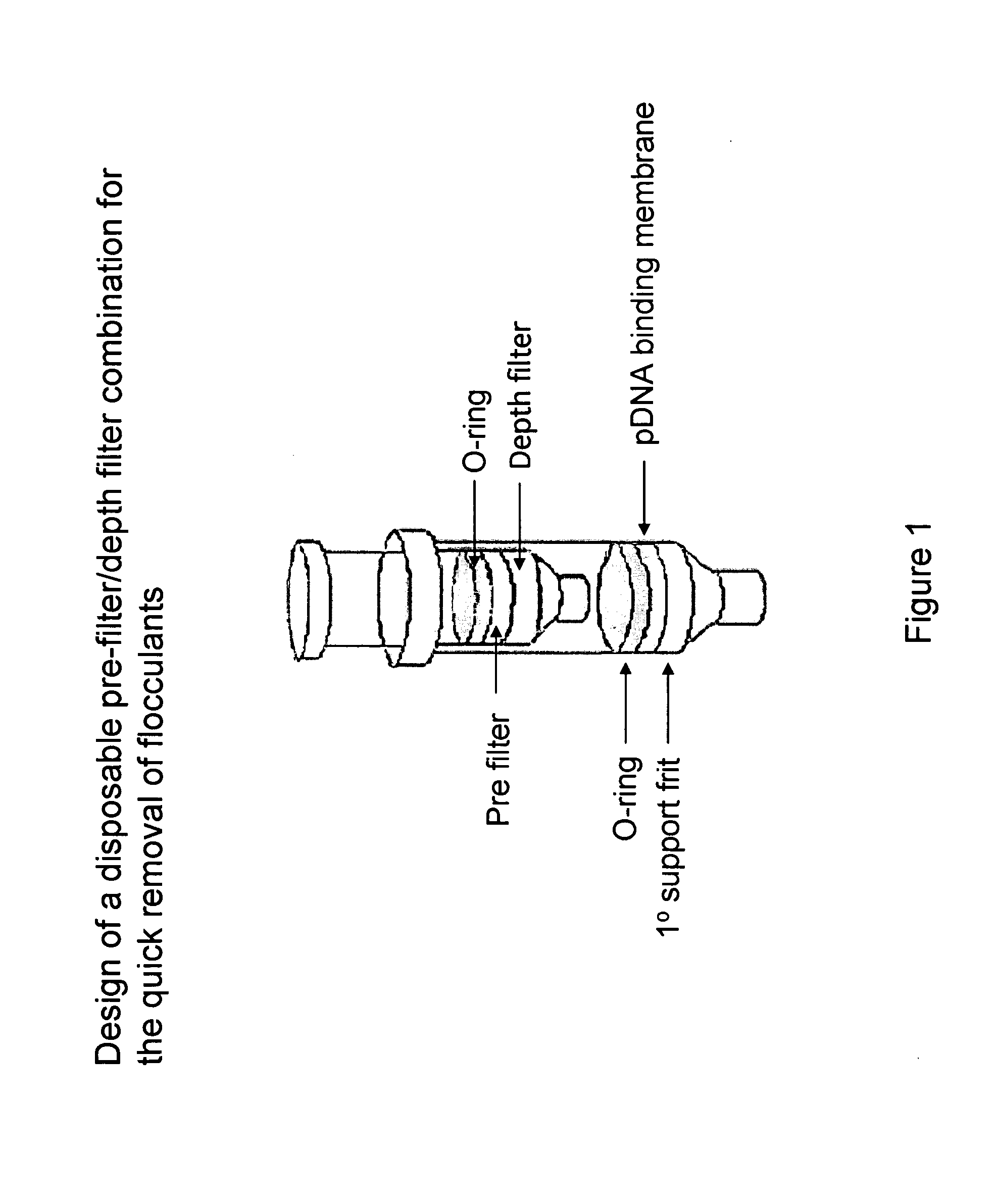
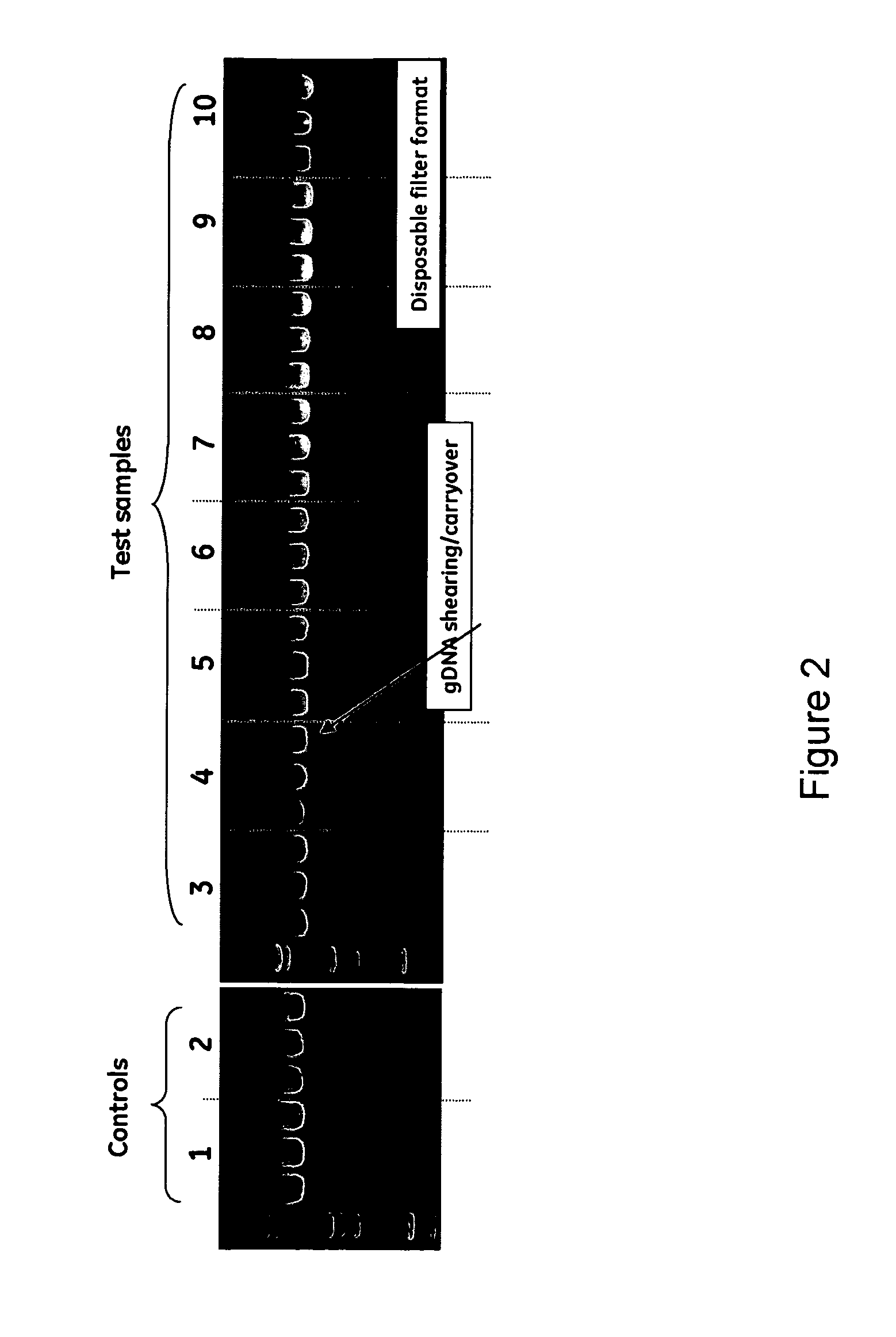
The invention relates to a modified spin column for the isolation and purification of plasmid DNA. A pre-filtration disc is included in a traditional spin column. During plasmid DNA isolation, the lysate can be loaded directly to the modified spin column, eliminates the need to first remove the flocculants containing cellular debris. This results in a much shortened process. Variation of the invention includes a depth filter in between the pre-filtration disc and the main separation matrix. Also provided are kits for isolation of plasmid DNA including the modified spin columns.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
Process for removing protein aggregates and virus from a protein solution
InactiveUS7465397B2Less-expensive to purchaseLess-expensive to operateSolvent extractionUltrafiltrationProtein solutionUltrafiltration
A process is provided for selectively removing protein aggregates from a protein solution in a normal flow (NFF) filtration process. Preferably, it relates to a process for selectively removing protein aggregates from a protein solution in a normal flow (NFF) filtration process and virus particles from a protein solution in a two-step filtration process. In a first step, a protein solution is filtered through one or more layers of adsorptive depth filters, charged or surface modified microporous membranes or a small bed of chromatography media in a normal flow filtration mode of operation, to produce a protein aggregate free stream. The aggregate free protein stream can then be filtered through one or more ultrafiltration membranes to retain virus particles at a retention level of at least 3 LRV and to allow passage therethrough of an aggregate free and virus free protein solution.
Owner:EMD MILLIPORE CORP
Miniprep system for simple and rapid plasmid DNA extraction
InactiveUS20080299621A1Rapid isolationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCellular DebrisSpins
The invention relates to a modified microspin system for the isolation and purification of plasmid DNA. A disposable pre-filter column is used in combination with the traditional microspin column for increase speed and quality of plasmid DNA preparation. The disposable pre-filter column includes a pre-filter and a depth filter for optimal result. During plasmid DNA isolation, the lysate can be loaded directly to the assembly including the disposable pre-filter column and the microspin column. A quick spin causes the plasmid DNA to bind to the microspin column while the flocculents remain on top of the disposable pre-filter column, eliminates the need to first remove the flocculants containing cellular debris. This results in a much shortened process. Also provided are kits for isolation of plasmid DNA including the pre-filter column and the microspin columns.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
Pleated multi-layer filter media and cartridge
InactiveUS7645312B2Easy to useSave spaceCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationParticulatesFilter media
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Bodily fluid analysis system
InactiveUS20060062688A1Avoiding pressure injuriesAvoid filteringAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorRed blood cellEngineering
A bodily fluid analyzer including a test strip holder comprising a base and a snap-on cover which completely enclose the test strip except for a sample port in the cover and a sensor port in the base. The test strip is compressed between the base and cover in a sample container having a well-defined sample volume. The test strip comprises a woven dispersement layer, a depth filter containing a reagent, an asymmetrical membrane containing additional reagent, and a colorimetric detection membrane in a vertical stack. The red blood cells are removed from the colorimetric detection area by slowing their vertical movement and stopping flow when the detection membrane is saturated. A minimum value of the reflectance in a color range is used to determine a characteristic of the bodily fluid.
Owner:POLYMER TECH SYST
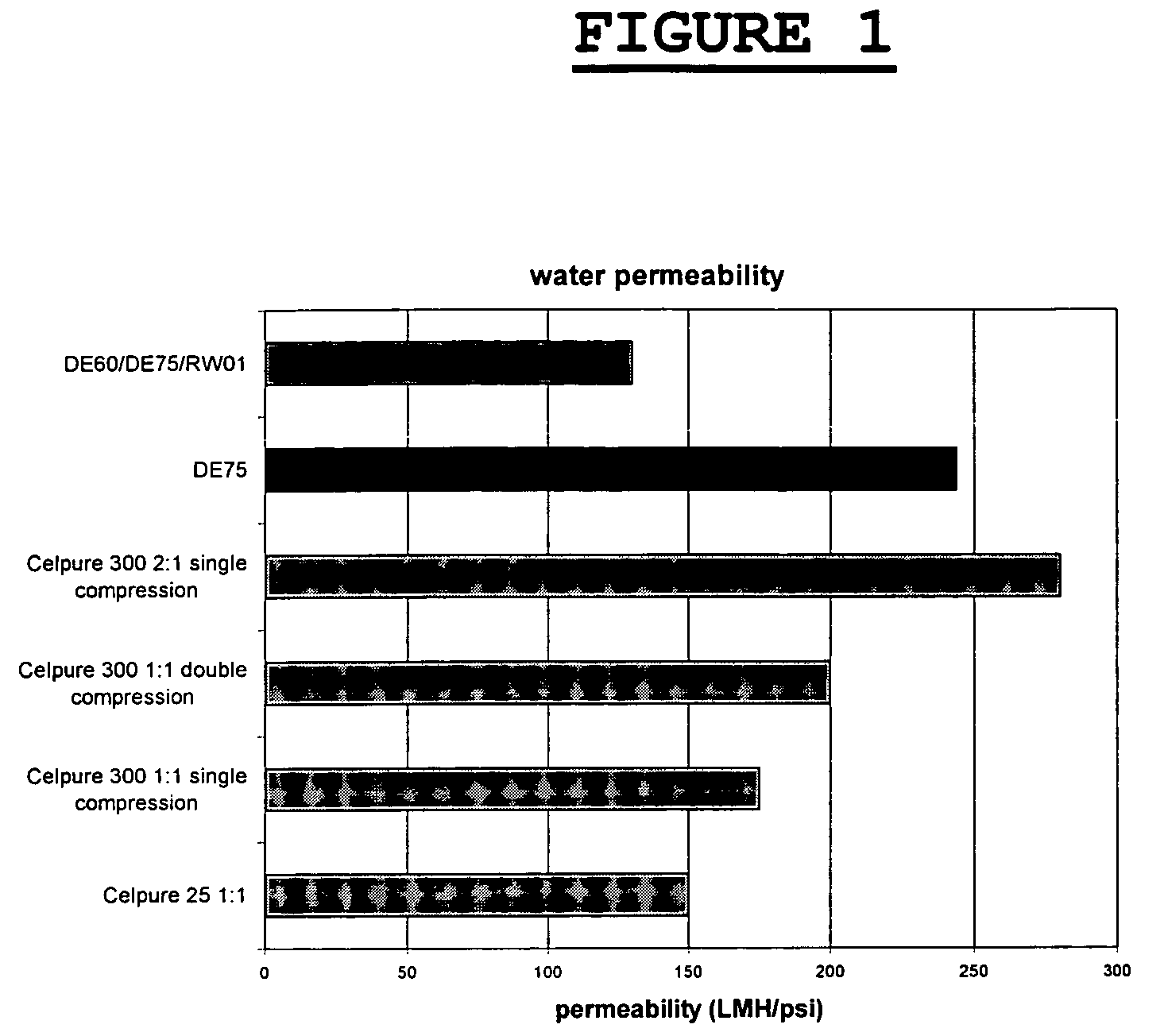
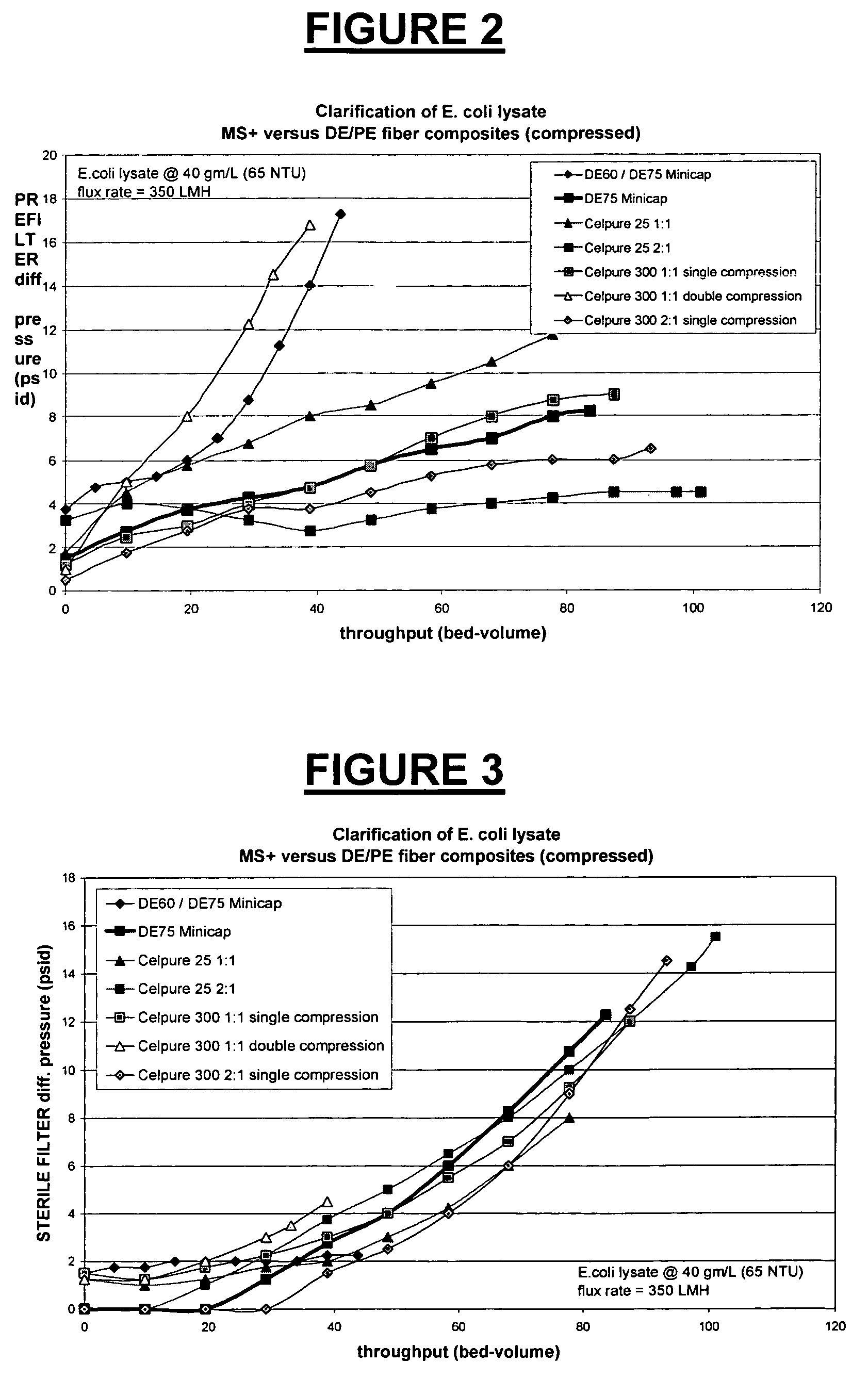
Depth Filters For Disposable Biotechnological Processes
InactiveUS20130012689A1Avoid concentrationEfficient separationIon-exchanger regenerationUltrafiltrationChemical treatmentColloidal particle
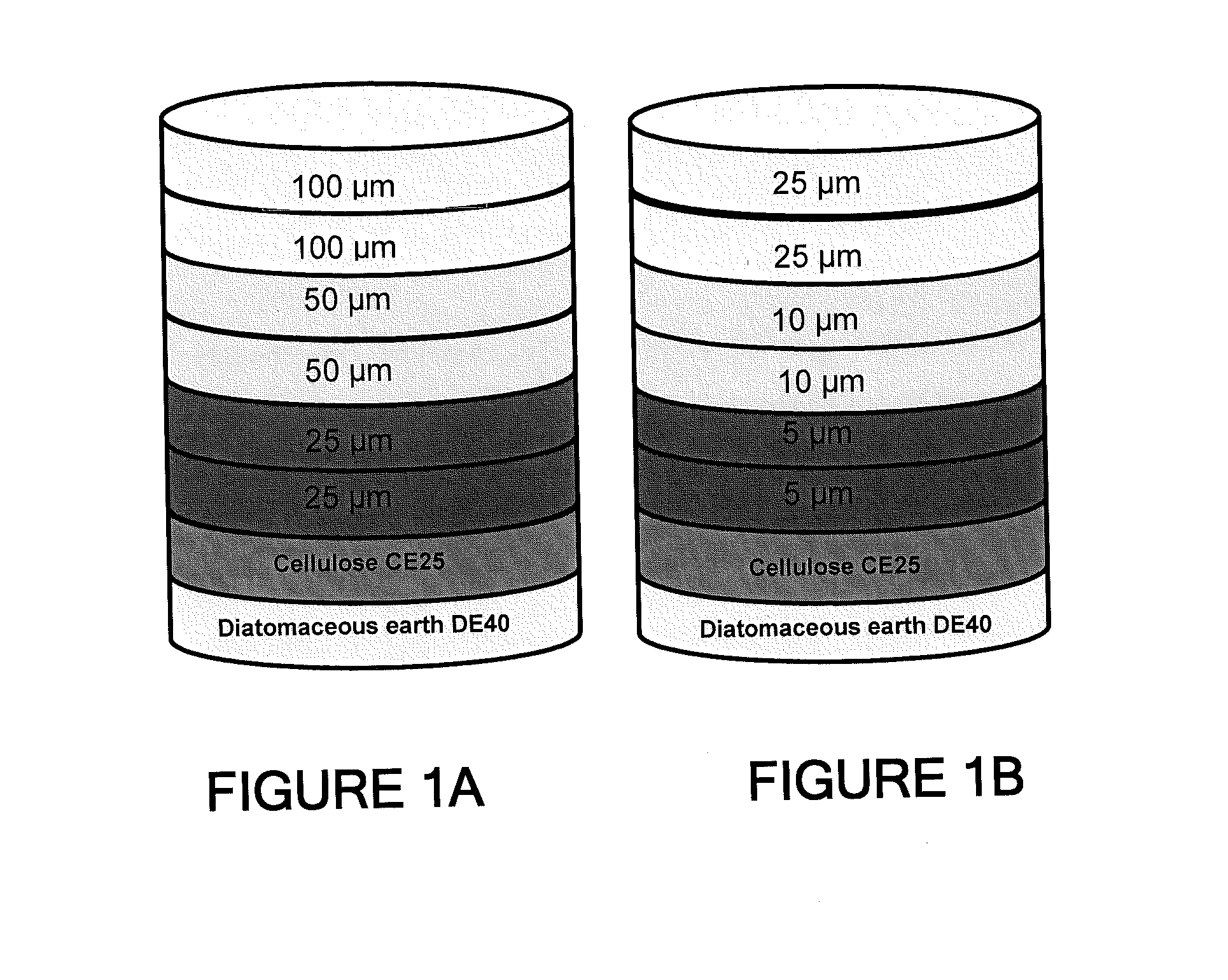
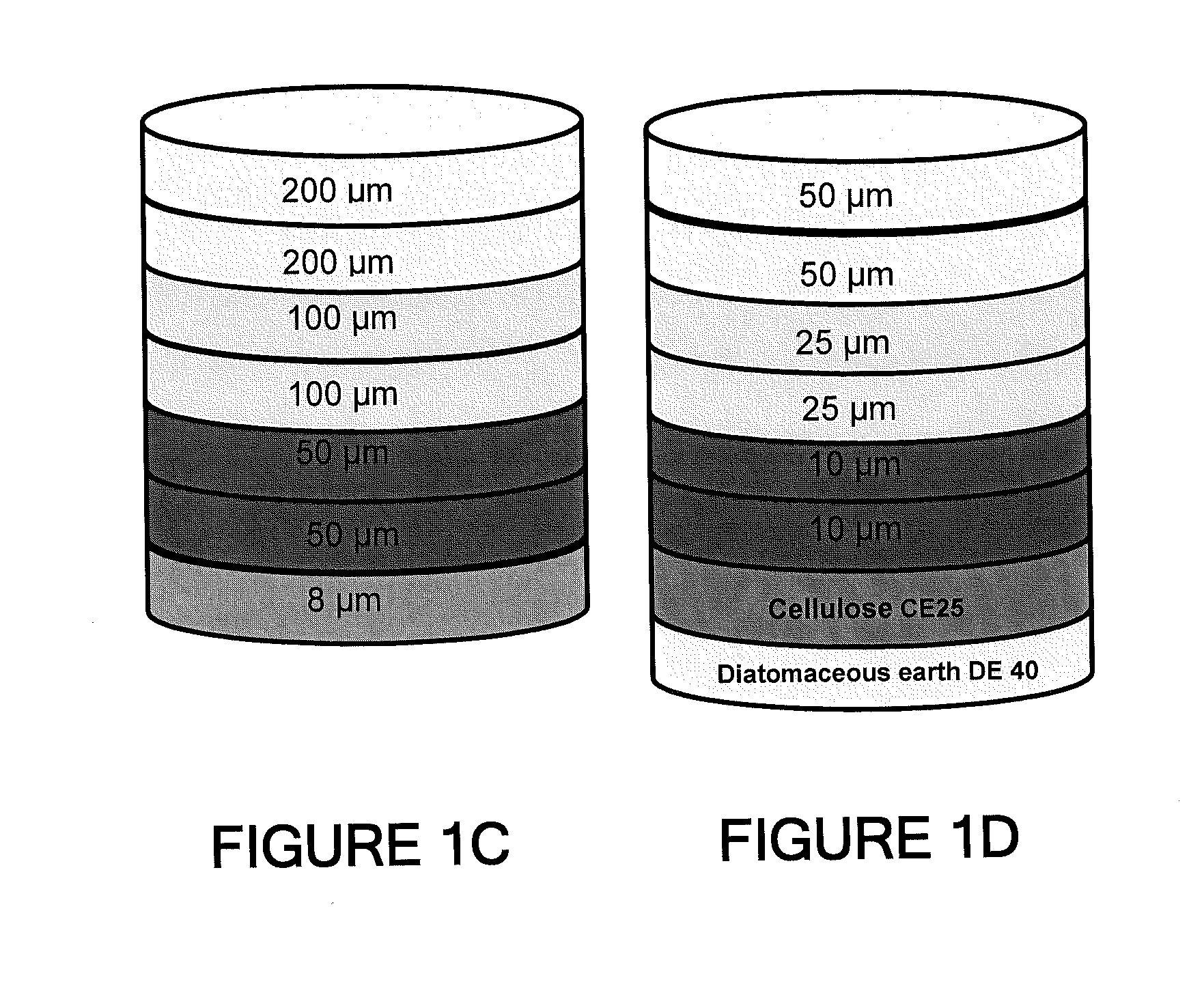
A process for the primary clarification of feeds, including chemically treated flocculated feeds, containing the target biomolecules of interest such as mAbs, mammalian cell cultures, or bacterial cell cultures, using a primary clarification depth filtration device without the use of a primary clarification centrifugation step or a primary clarification tangential flow microfiltration step. The primary clarification depth filtration device contains a porous depth filter having graded porous layers of varying pore ratings. The primary clarification depth filtration device filters fluid feeds, including chemically treated flocculated feeds containing flocculated cellular debris and colloidal particulates having a particle size distribution of approximately about 0.5 μm to 200 μm, at a flow rate of about 10 litres / m2 / hr to about 100 litres / m2 / hr. Kits and methods of using and making the same are also provided.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Prefilter system for biological systems
ActiveUS7390403B2Reduce presenceHigh yieldIon-exchanger regenerationUltrafiltrationFiberUltrafiltration
The present invention is to a prefilter for purification systems such as affinity chromatography columns and ultrafiltration systems. The prefilter, positioned upstream of the system inlet, reduces the presence of non-specific binding (NSB) species that enter the system, thereby extending the yield, capacity and lifetime of the system. Suitable agents include but are not limited to hydrophobic entities; lipophilic entities; activated carbon; charged cation or anion entities; ligands; particles such as fumed silica, glass, controlled pore glass or derivitized version of each; silica or silicates; and combinations thereof. The material(s) can be incorporated into a variety of media such as fibers, beads, membranes and the like and then incorporated into a variety of device designs including lenticular pads, depth filters, bead containing columns, spiral wound devices, TFF devices and the like.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Hybrid filter element and method
InactiveUS20070251876A1Eliminate needImprove fermentation effectMembrane filtersLoose filtering material filtersHybrid filterFilter media
The present invention relates to an apparatus for filtering a gas or liquid stream of impurities and to filter elements used in such an apparatus. The apparatus includes a closed vessel having a longitudinally extending length, an initially open interior, an input port at one extent and an output port at an opposite extent thereof. A partition located within the vessel interior divides the vessel interior into a first stage and a second stage. At least one opening is provided in the partition. A filter element is disposed within the vessel to extend from within the first stage. The filter element is made up of a carbon block filter media surrounded by a protective porous depth filter media.
Owner:PERRY EQUIPMENT
Adsorbent filter media for removal of biological contaminants in process liquids
ActiveUS7673757B2Reduce the amount of solutionReduce pollutionOther chemical processesMembrane filtersSorbentFixed bed
Adsorbent filter media particularly suited for removal of biological contaminants in process liquids. A porous fixed bed of adsorbent material is formed, using only a granular adsorbent and a water-insoluble thermoplastic binder. The resulting composite filter allows for a higher amount of adsorbent with smaller adsorbent particles than conventional depth filters. Elimination of cellulose fiber, as well as the elimination of the thermoset binder, results in reduced contamination of the process liquid.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Cartridge filter combining a depth filter and a sub-micron filter, and ro pre-treatment method
A cartridge filter assembly includes a depth filter element and a downstream second filter element. The depth filter element has a mass of melt-blown polymer filaments. The depth filter removes 0.5 to 10 micron sized contaminants at an efficiency of 90% or more. The depth filter preferably comprises multiple zones occupying different depths, with one or more melt-blown polymer filaments traversing two or more of the zones. The second filter element comprises nano-fibers having a diameter of 1 micron or less, and removes a material percentage of contaminants that are less than 1 micron in size, preferably less than 0.5 microns in size. The depth filter element may be in the form of a tube and the second filter element may be in the form of a pleated sheet located inside of the depth filter. The cartridge filter assembly may be used to pre-treat a feed water upstream of an RO membrane. The SDI of the feed water may be reduced to 3 or less or 2 or less.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Prefilter system for biological systems
ActiveUS20050205489A1Reduce presenceHigh yieldIon-exchanger regenerationUltrafiltrationFiberUltrafiltration
The present invention is to a prefilter for purification systems such as affinity chromatography columns and ultrafiltration systems. The prefilter, positioned upstream of the system inlet, reduces the presence of non-specific binding (NSB) species that enter the system, thereby extending the yield, capacity and lifetime of the system. Suitable agents include but are not limited to hydrophobic entities; lipophilic entities; activated carbon; charged cation or anion entities; ligands; particles such as fumed silica, glass, controlled pore glass or derivitized version of each; silica or silicates; and combinations thereof. The material(s) can be incorporated into a variety of media such as fibers, beads, membranes and the like and then incorporated into a variety of device designs including lenticular pads, depth filters, bead containing columns, spiral wound devices, TFF devices and the like.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Three-dimensional non-woven filter
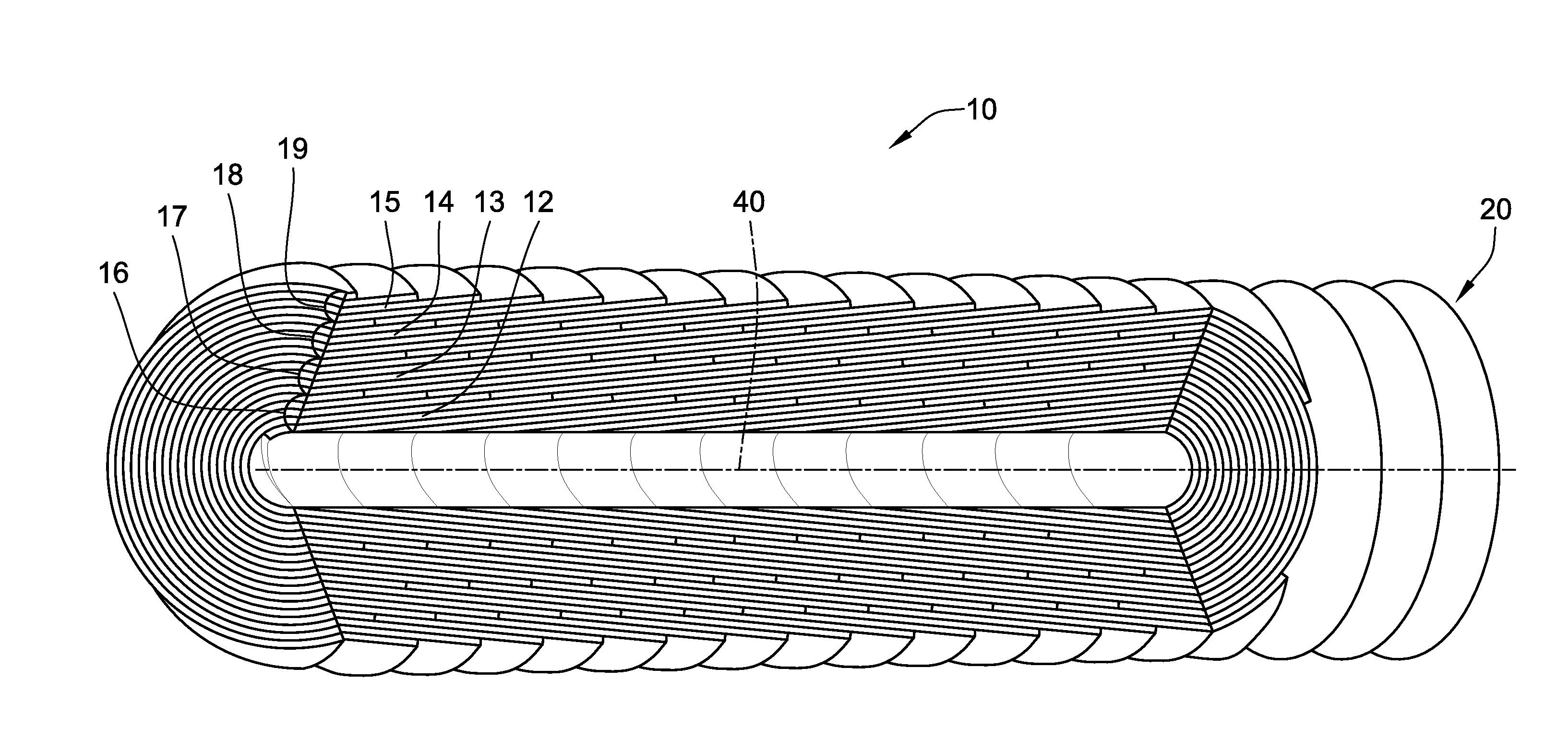
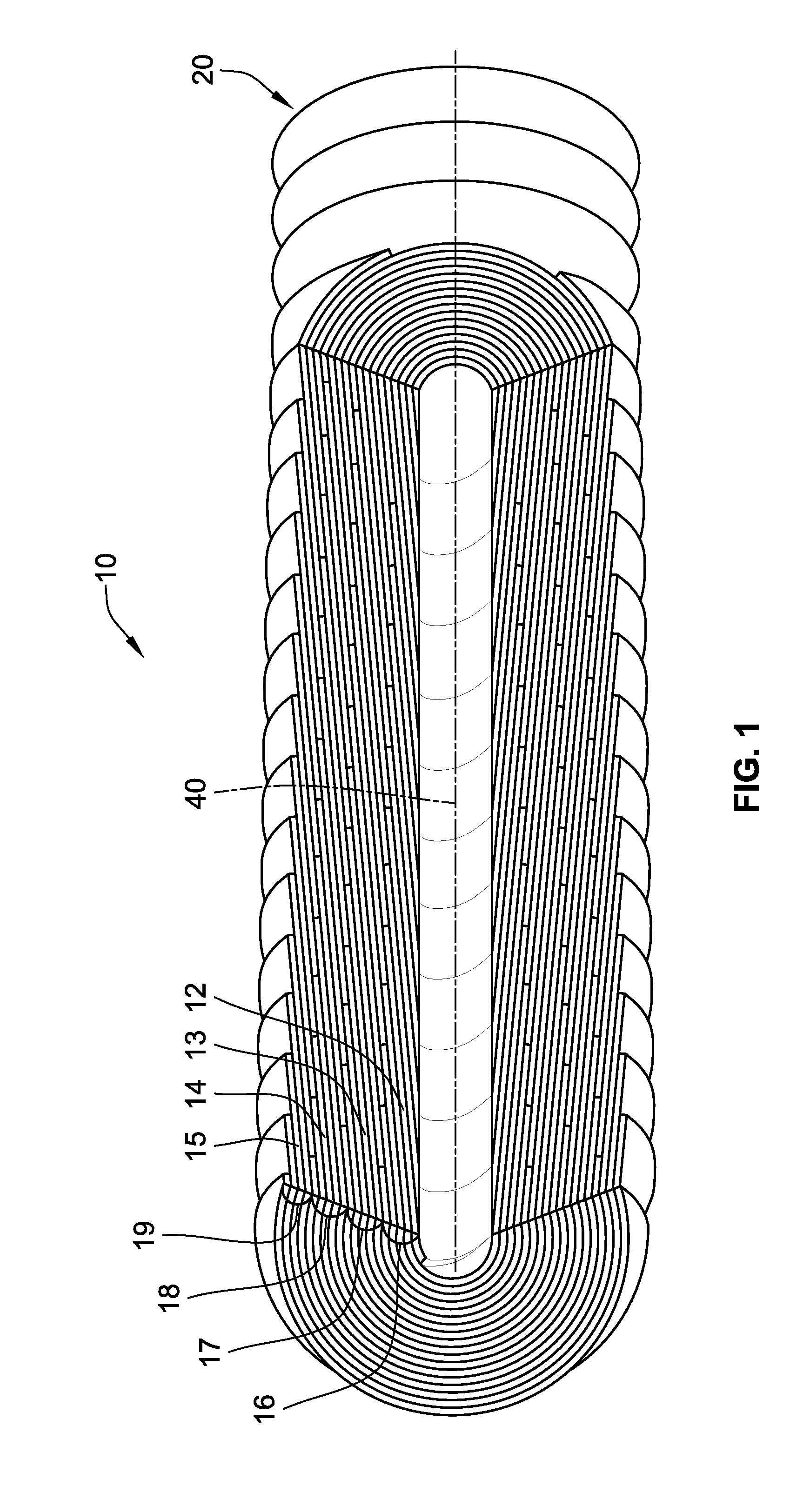
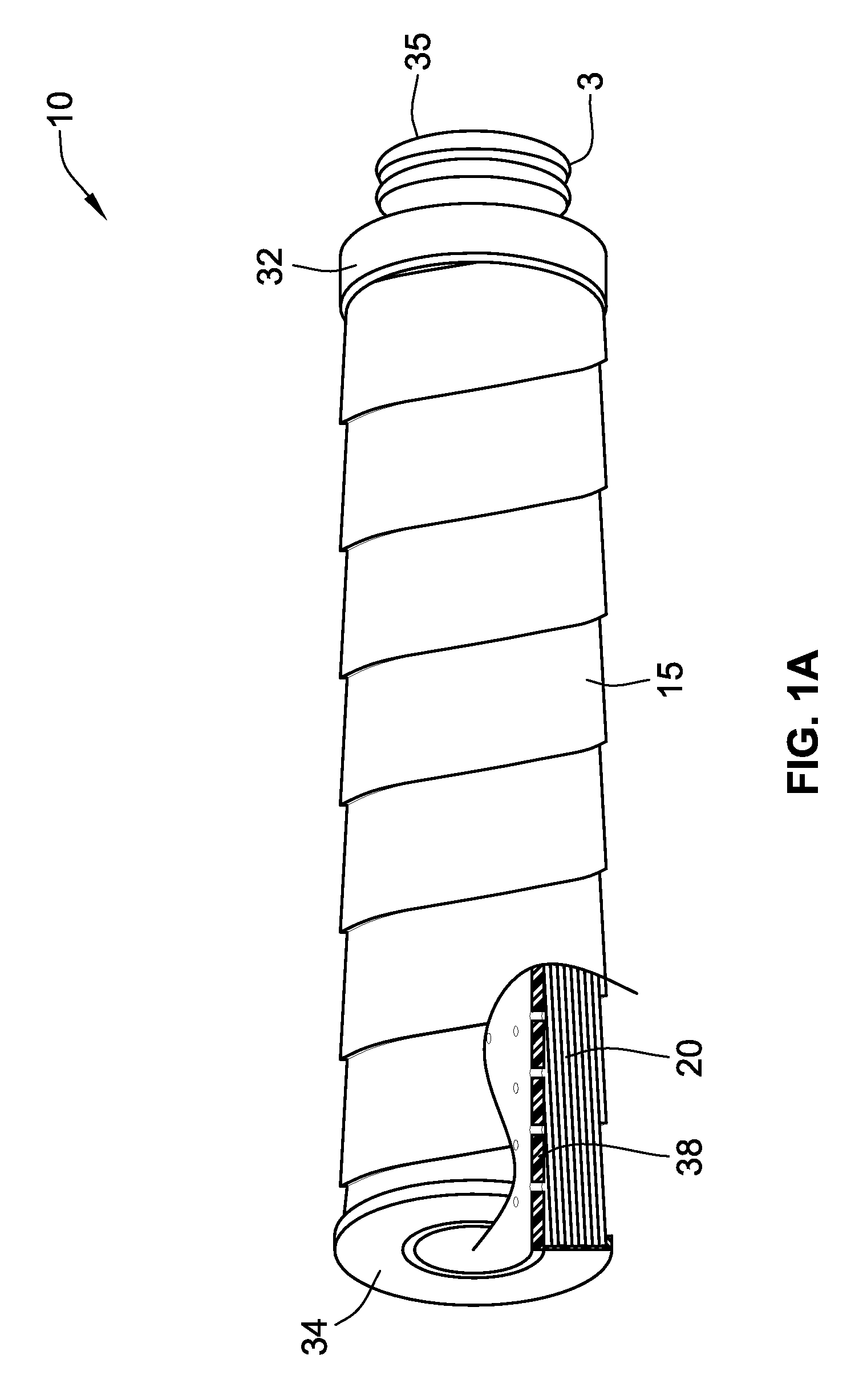
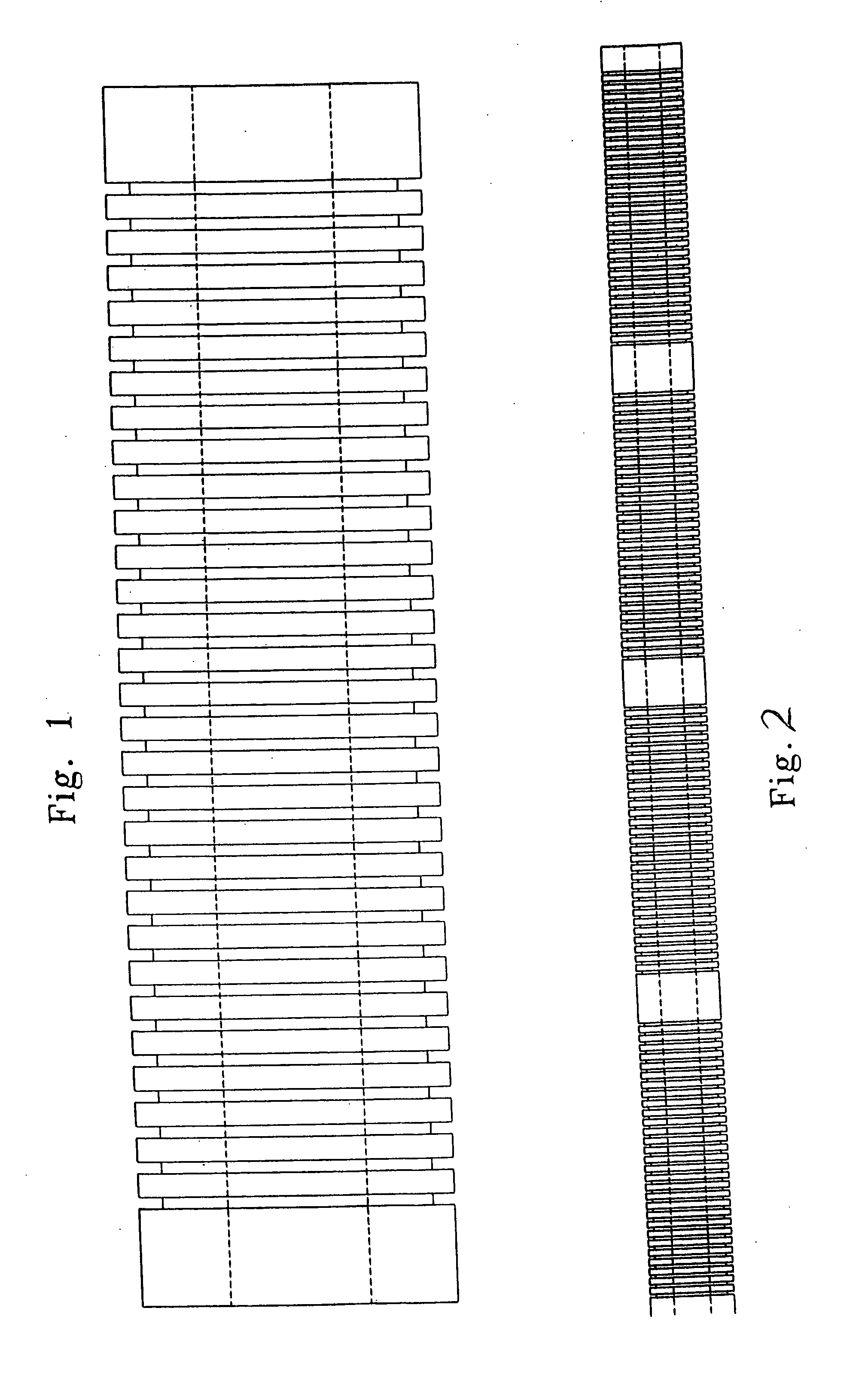
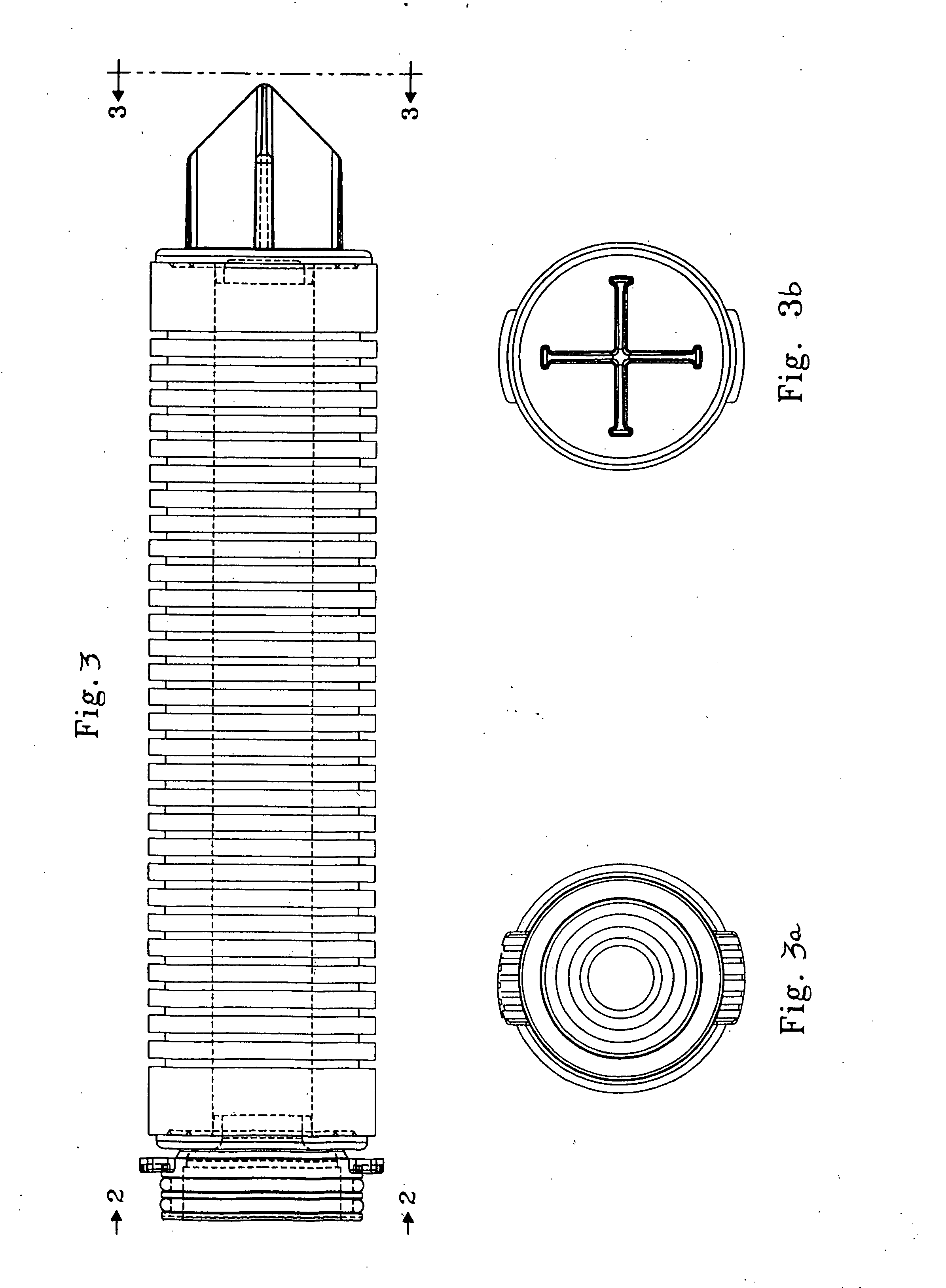
A non-woven depth filter cartridge includes a cylindrical mass of essentially continuous melt-blown polymer filaments and an essentially continuous traversing melt-blown polymer filament extending through the mass. The mass has a depth dimension, a longitudinal dimension, and a circumferential dimension. The mass includes a plurality of layers, each of the plurality of layers being generally oriented in the longitudinal and circumferential dimensions. The traversing filament is generally oriented in the depth dimension and extends through one or more layers of the mass. In one embodiment, the layers of the mass comprise concentric zones. The traversing filament is intentionally deposited and positioned to improve the physical properties of the filter cartridge.
Owner:GE OSMONICS INC
Non-pleated tubular depth filter having fine fiber filtration media
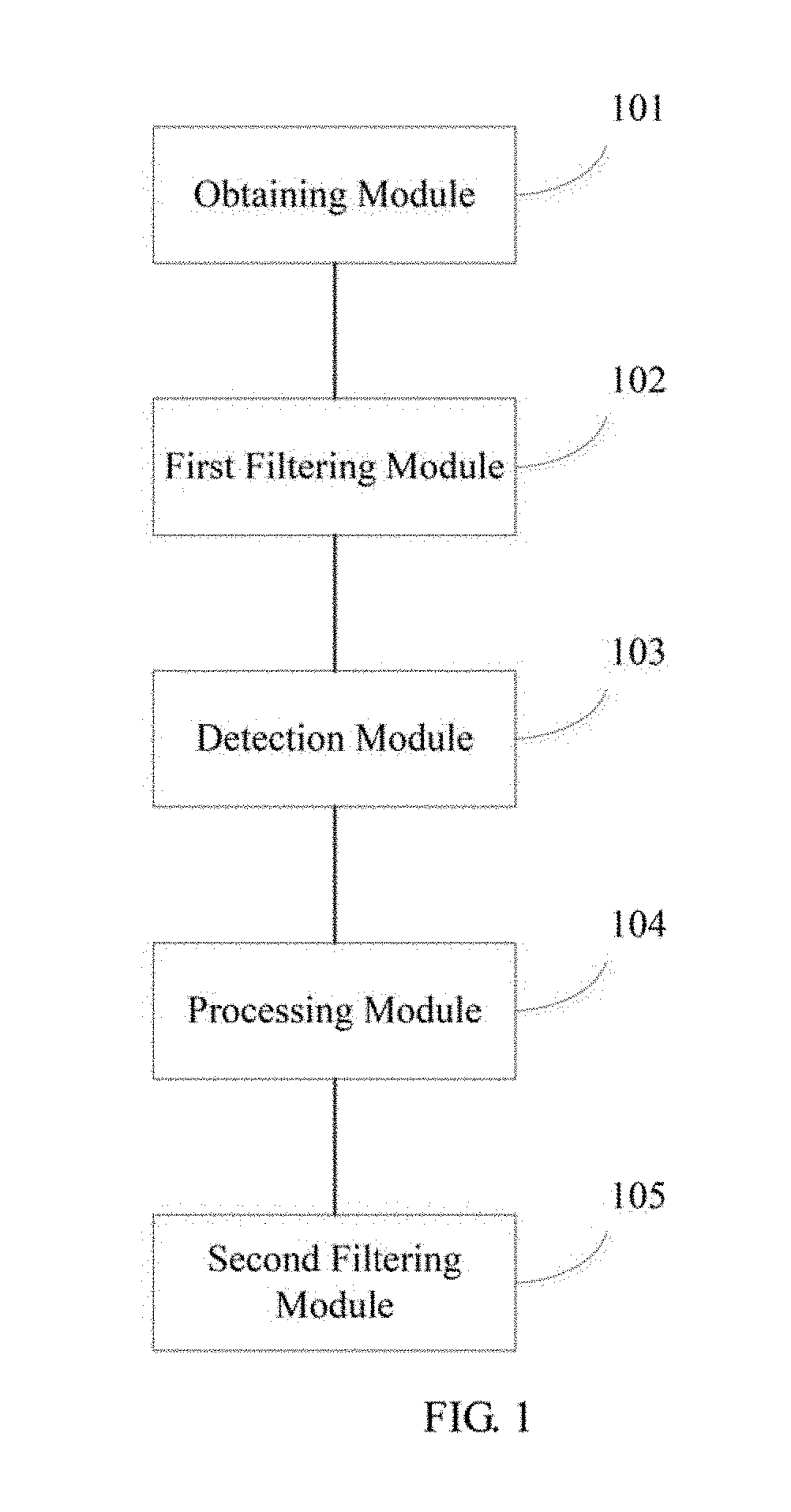
ActiveUS20110210059A1Improve efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologySemi-permeable membranesFiberEngineering
A non-pleated depth filter element in the form of a tubular ring of depth filter media is provided. Multiple wraps of sheets, some including fine fibers, are employed. The depth filter element has particular applications to liquid filtration applications.
Owner:CLARCOR INC
Method and apparatus for image processing, and robot using the same
InactiveUS20190197735A1Quality improvementImprove practicalityImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingColor map
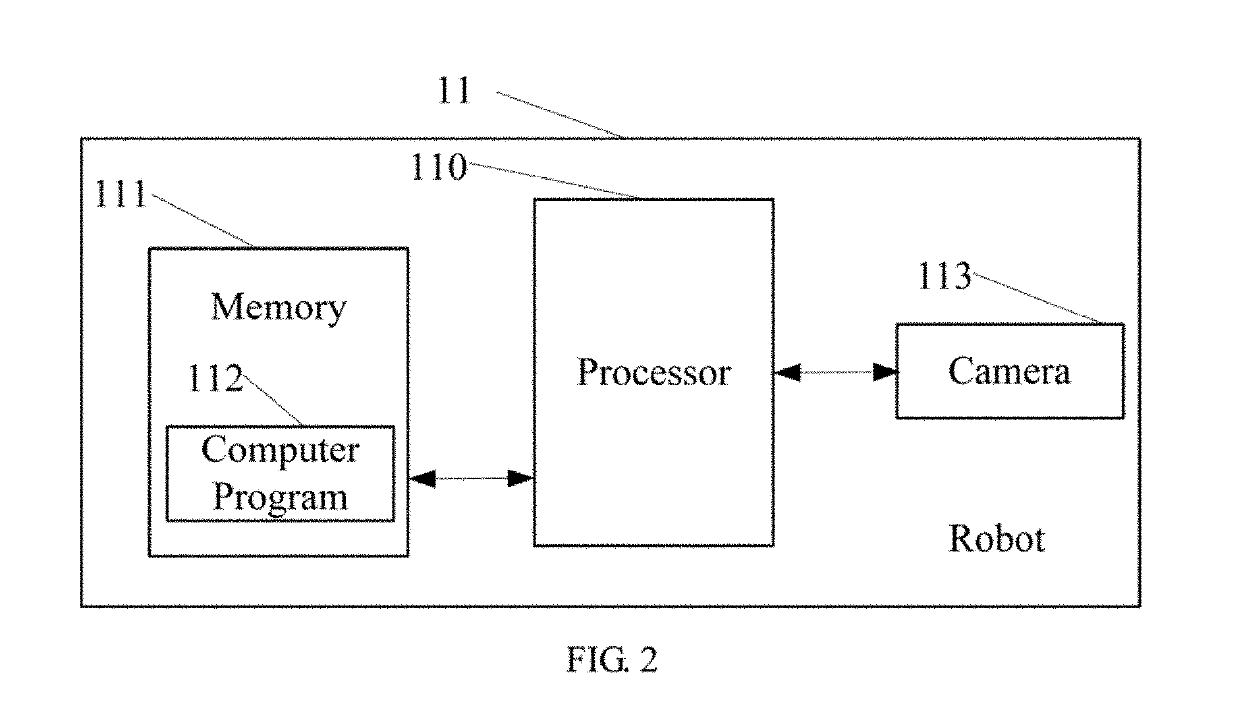
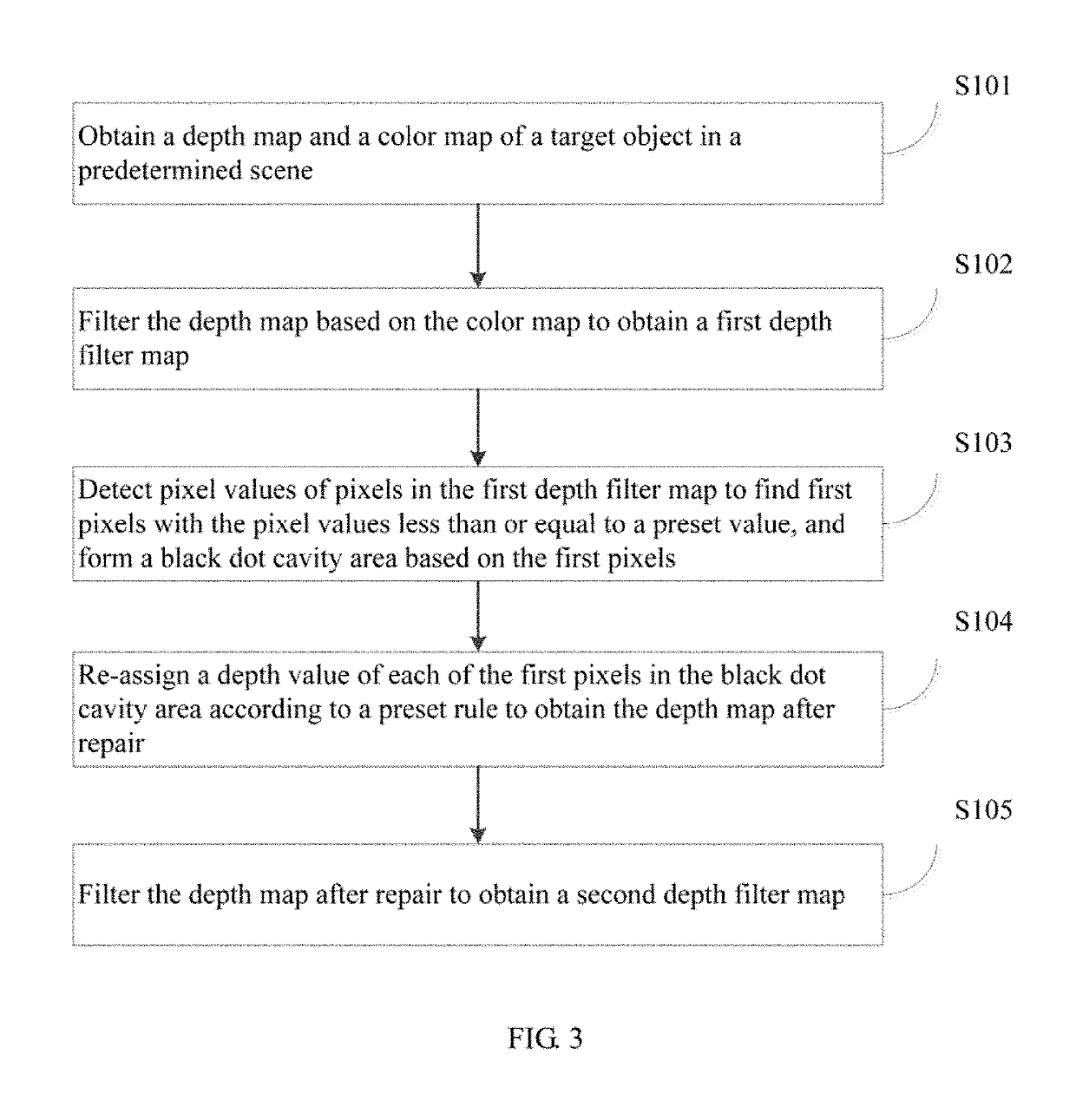
The present disclosure provides a method and an apparatus for image processing, and a robot using the same. The method includes: obtaining a depth map and a color map of a target object in a predetermined scene; filtering the depth map based on the color map to obtain a first depth filter map; detecting pixel values of pixels in the first depth filter map to obtain one or more first pixels, and forming a black dot cavity area based on the one or more first pixels; re-assigning a depth value of each of the one or more first pixels in the black dot cavity area according to a preset rule to obtain the depth map after repair; and filtering the depth map after repair to obtain a second depth filter map. The present disclosure is capable of improving the quality of the depth map.
Owner:UBTECH ROBOTICS CORP LTD
Fabrication of filter elements using polyolefins having certain rheological properties
InactiveUS20040245171A1Economic advantageLoose filtering material filtersGravity filtersPolymer sciencePolyolefin
The present disclosure relates to filter elements and more particularly to filter elements prepared from improved polyolefin polymers, presently preferably polypropylene, characterized by a specific rheology. Most particularly, the present disclosure relates to polypropylene that has a specific molecular weight and molecular weight distribution, among other properties and / or characteristics, and / or polypropylene that has been adjusted in viscosity, molecular weight and molecular weight distribution, among other properties and / or characteristics, and its use in making depth filter elements. The present disclosure further relates to processes and / or systems for producing improved polyolefin polymers, e.g., polypropylenes and their use in fabricating advantageous filter elements.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
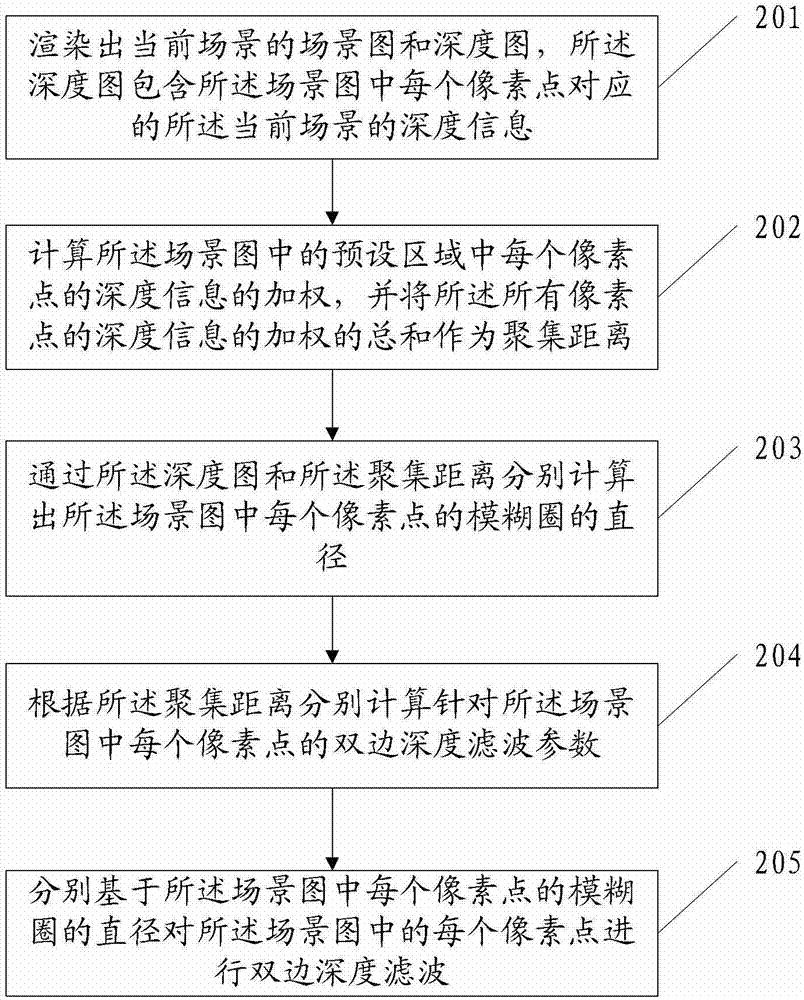
Image rendering method and equipment
InactiveCN102968814AImprove efficiencyAchieve depth of field effect3D-image renderingConfusionComputer vision
The embodiment of the invention discloses an image rendering method. The method comprises the following steps of: rendering a scene graph and a depth graph of a current scene, wherein the depth graph comprises depth information (of the current scene) corresponding to each pixel point in the scene graph; calculating the weight of the depth information of each pixel point in a preset area in the scene graph, wherein the total sum of the weights of the depth information of all the pixel points is taken as a gathering distance; respectively calculating the diameters of confusion circles of the pixel points in the scene graph by virtue of the depth graph and the gathering distance; and respectively carrying out bilateral depth filtering on each pixel point in the scene graph based on the diameter of the confusion circle of each pixel point in the scene graph. Correspondingly, the embodiment of the invention further provides image rendering equipment. The image rendering method and equipment provided by the embodiment of the invention can improve the efficiency of image rendering.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
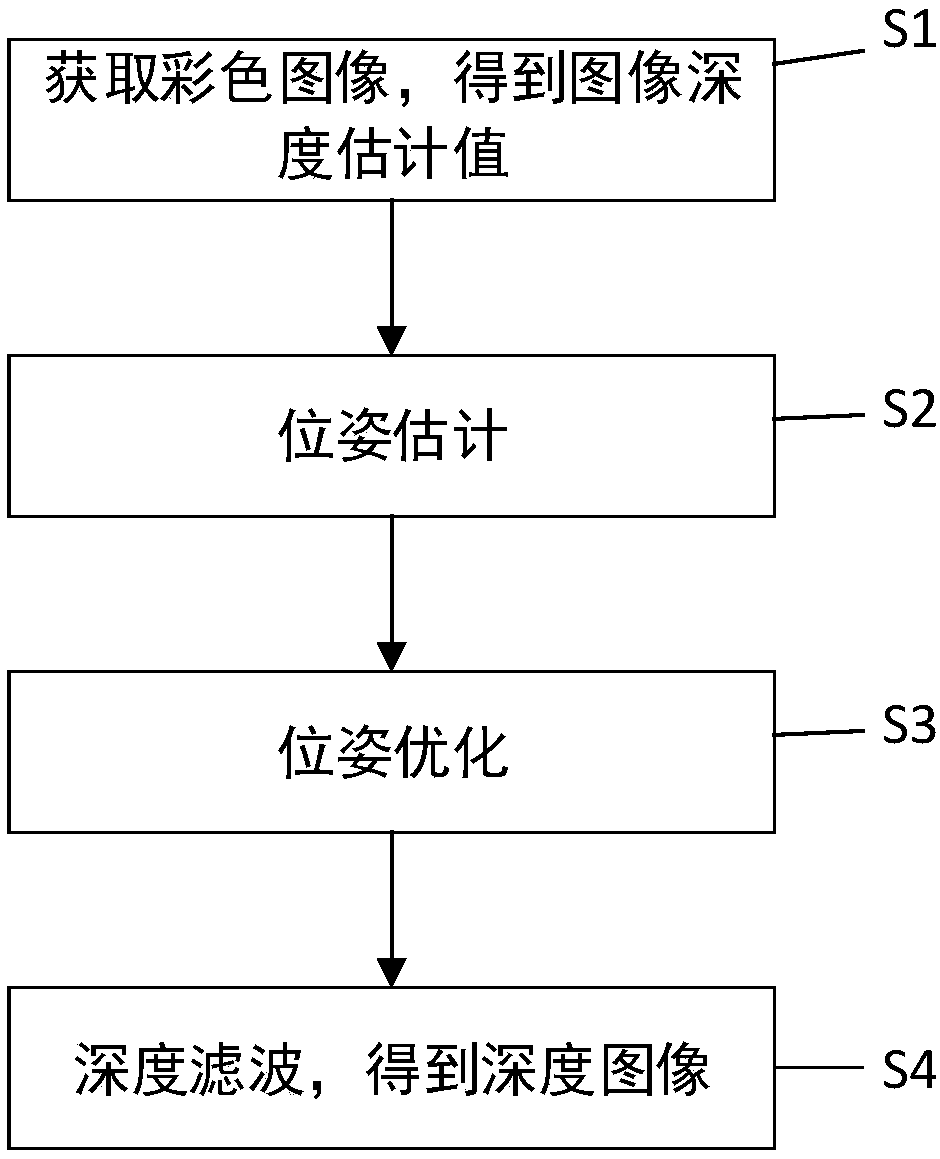
Image depth estimation method and system based on CNN (Convolutional Neural Network) and depth filter
InactiveCN108615244AOptimizing Camera PoseOvercomes unsuitability for outdoor environmentsImage enhancementImage analysisEstimation methodsLine search
The invention discloses an image depth estimation method and system based on a CNN (Convolutional Neural Network) and a depth filter. The image depth estimation method comprises the steps of obtainingimage depth estimation values based on the CNN, extracting local features points from the image, and establishing a minimum photometric error equation to solve the relative pose of a camera; optimizing the camera pose based on the feature points matched by polar line searching, selecting an image block by taking the feature points as a center, performing polar line searching on the image block toobtain the optimum matching, constructing a bundle adjustment equation according to the optimum matching to optimize the relative pose; and performing depth value filtering based on the camera pose,namely, filtering depth values by adopting Gaussian integration until the depth values converge. The image depth estimation method overcomes a problem of inaccurate image depth and a problem of absolute scale loss of monocular vision, and can be applied to many fields such as three-dimensional scene reconstruction, indoor positioning and augmented reality.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Elastomeric depth filter
ActiveUS20140332476A1Sufficient flexibilityLoose filtering material filtersGravity filtersElastomerParticulates
The present disclosure provides a depth filter medium comprising at least one elastomeric nonwoven web strengthened by combination with one or more structural support layers. The resulting material is particularly useful in the field of filtration, wherein particulates captured within the elastomeric nonwoven web can be readily released, such as by applying pressure to the web through backwashing. The elastomeric nonwoven web advantageously can stretch under such pressure and return substantially to its original structure and shape upon the removal of the pressure, rendering the filter available for reuse.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Filtering unit and ballast water production equipment provided with same
InactiveCN102316952AAvoid shockCurb processing costsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationSelf-bailing equipments/scuppersWater productionFilter system
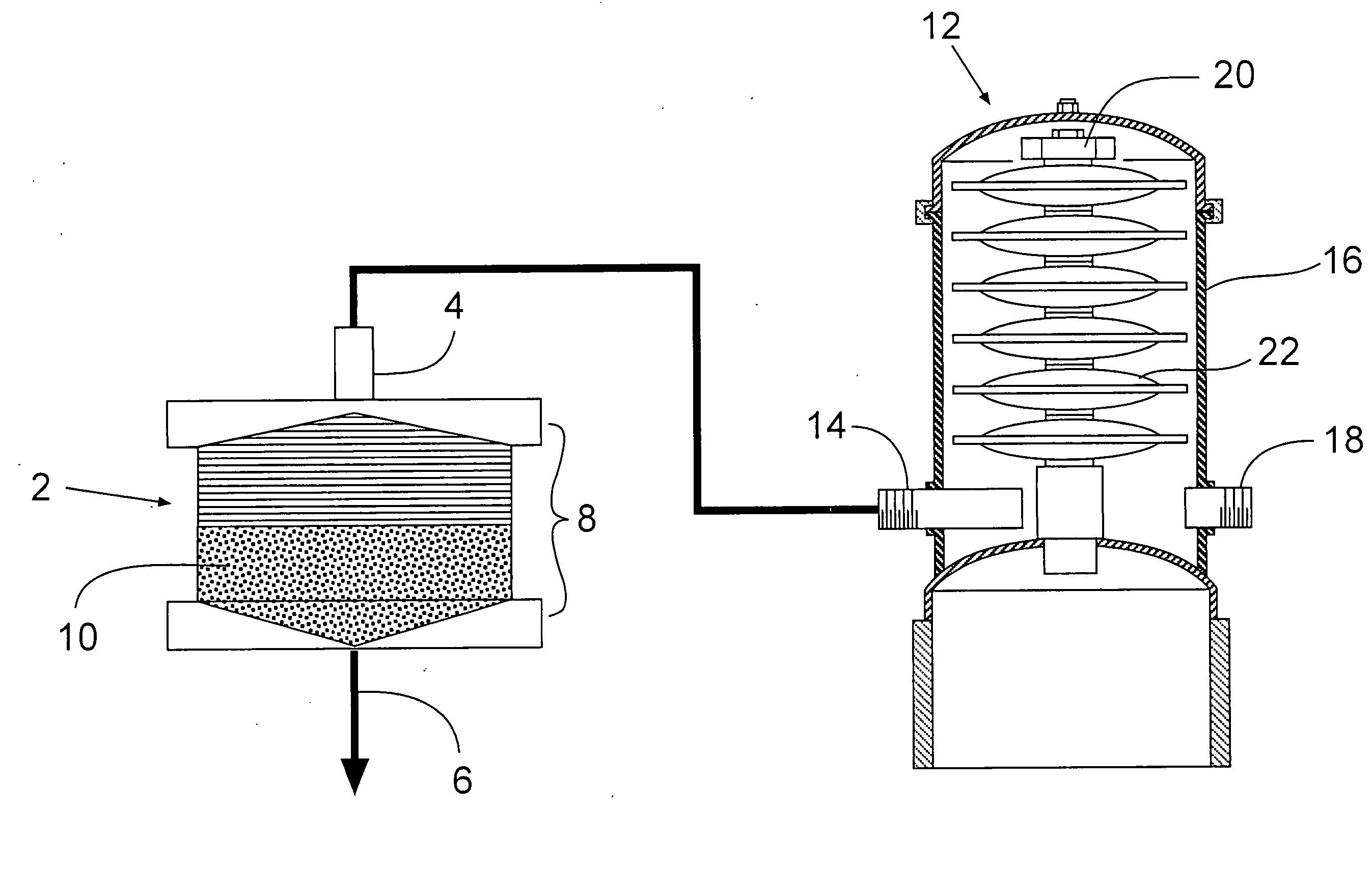
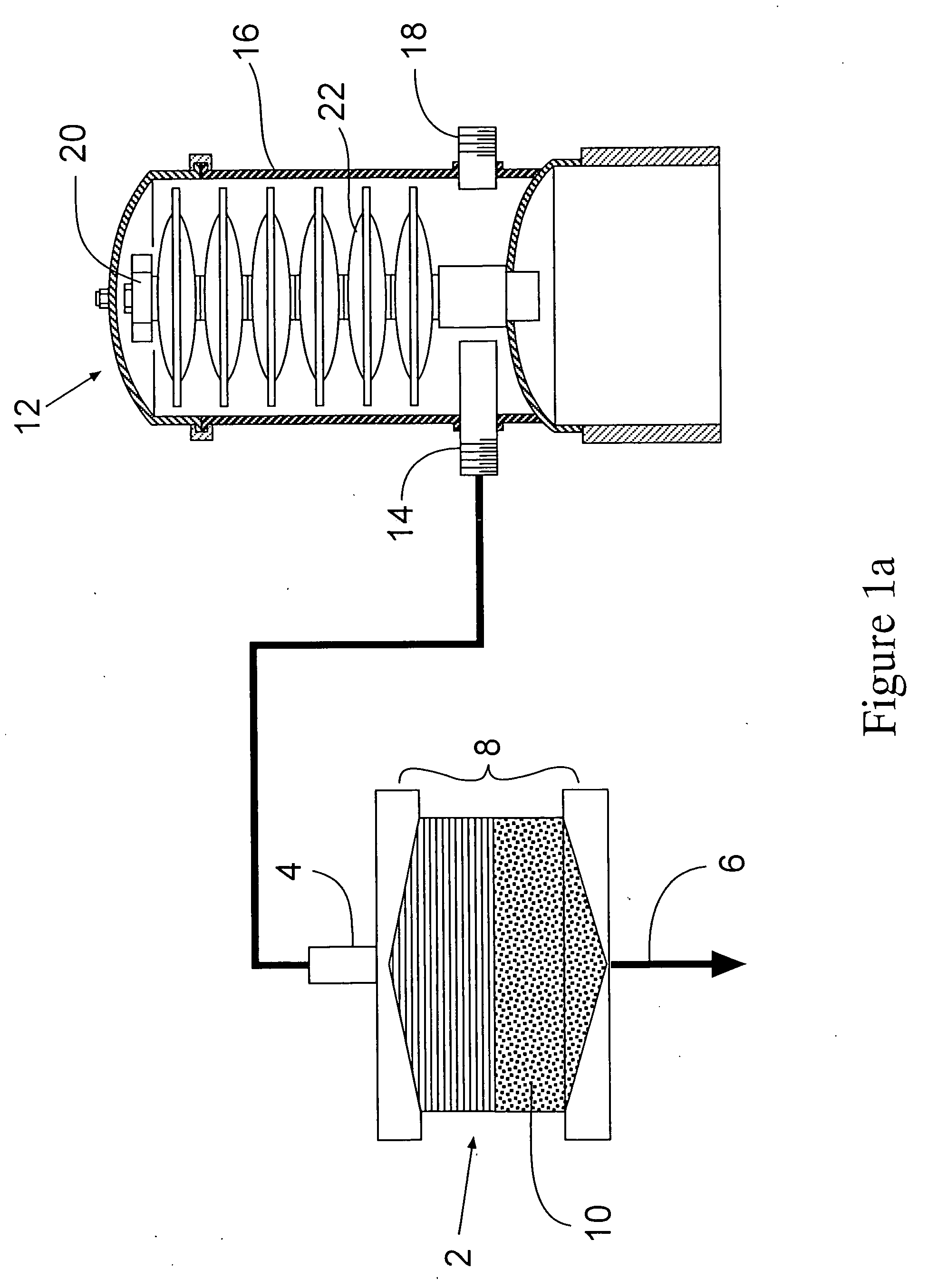
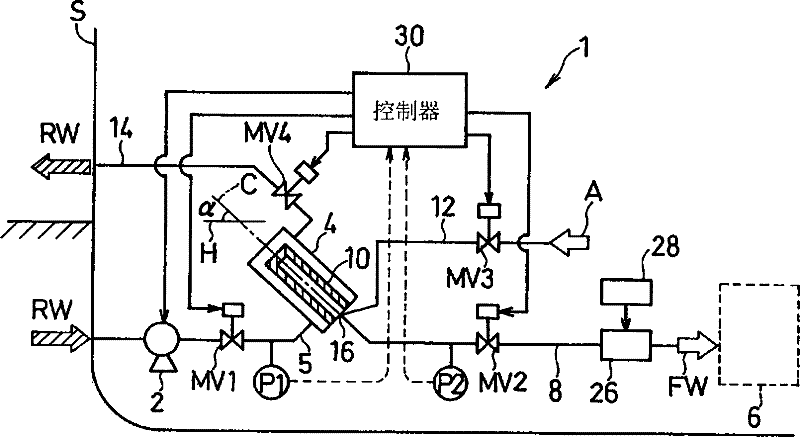
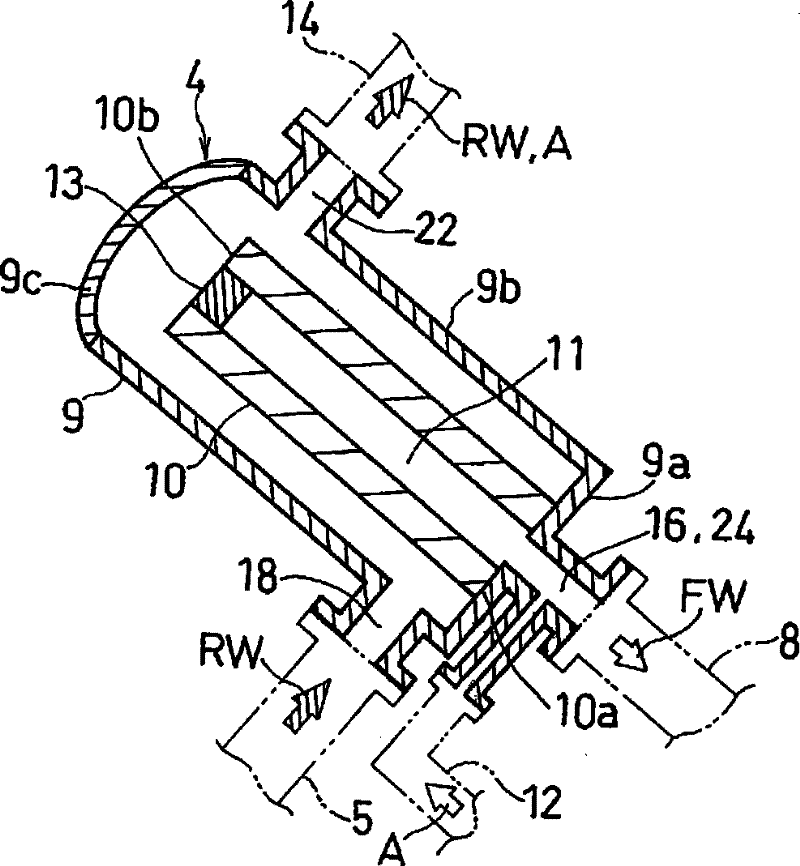
The invention refers to a filtering unit and ballast water production equipment provided with same. The filtering system (1) in ballast water production equipment in a ship (S) is provided with a filtering unit (4) for filtering raw water (RW) taken into the ship (S) and supplying the filtered raw water to a ballast tank (6), a gas supply path (12) for supplying compressed air (A) to a depth filter (10) that forms a filtering membrane in the filtering unit (4) to thereby clean the depth filter, and a discharge path (14) for discharging the compressed air (A) that has cleaned the depth filter (10), together with the raw water (RW) in the depth filter (10), to the outside of the ship (S), the discharge path being connected to the filtering unit (4), wherein the pore diameter of the filtering membrane that forms the depth filter (10) falls within the range of 1-25 [mu]m.
Owner:KURARAY CO LTD
System and Method of Fluid Filtration Utilizing Cross-Flow Currents
InactiveUS20070163941A1Easy maintenanceOperating periodMembranesSettling tanks feed/dischargeParticulatesDual stage
A filter system and method of filtering a feed liquid utilizing a combined plurality of filter assemblies. Each filter assembly includes a filter housing, a filter cartridge and a spiral passageway for imparting secondary flow currents, particularly Dean-Flow currents, to fluid flowing within the spiral passageways to prevent particulate build-up on filter surfaces so as to extend filter life and duration between replacement. The filter system can be operated within positive or negative pressure filtration processes. A dual-stage filtration process utilizing a cap filter and a cylindrical depth filter is also disclosed.
Owner:DUAL VORTEX MICROFILTRATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com