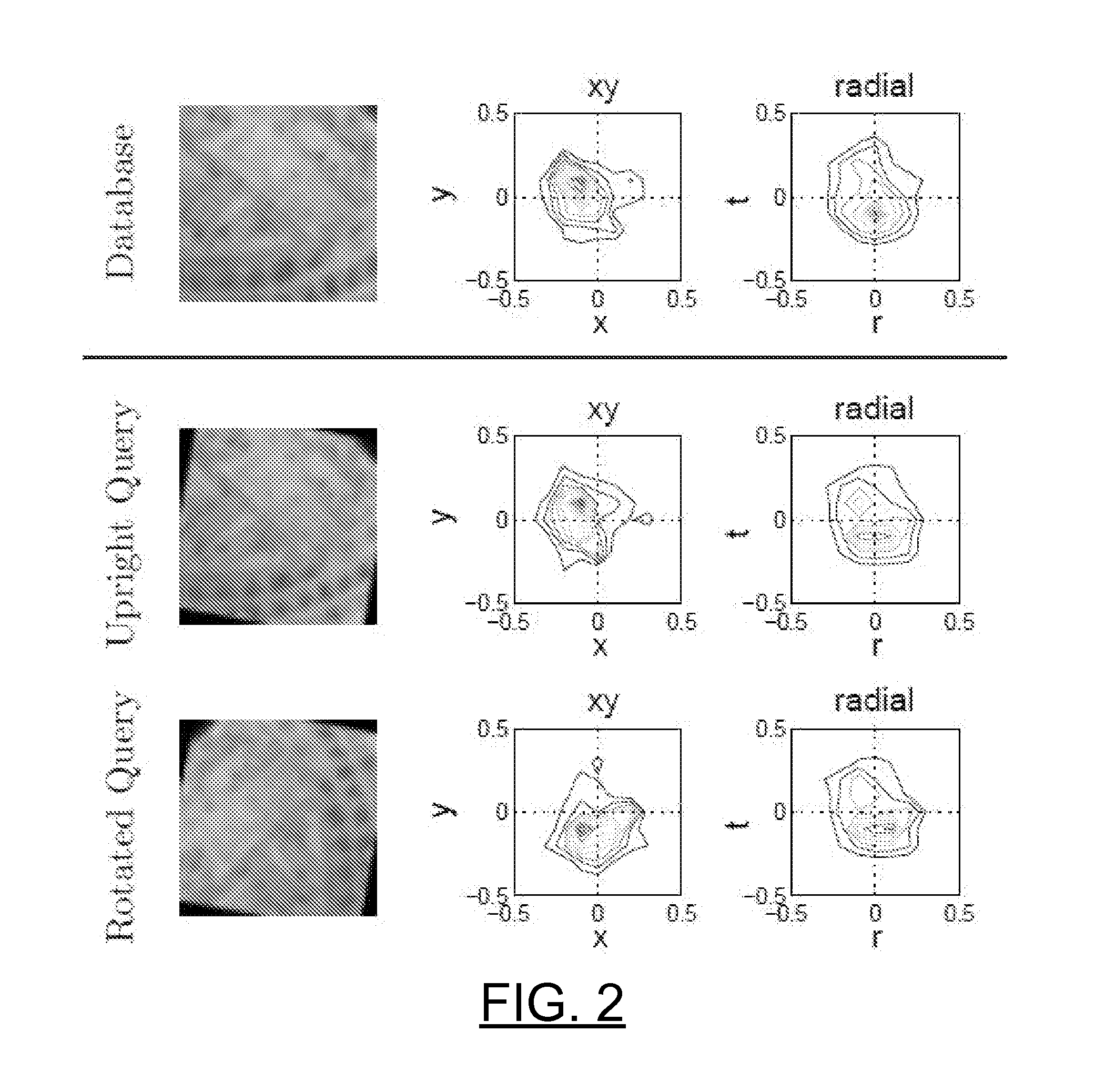
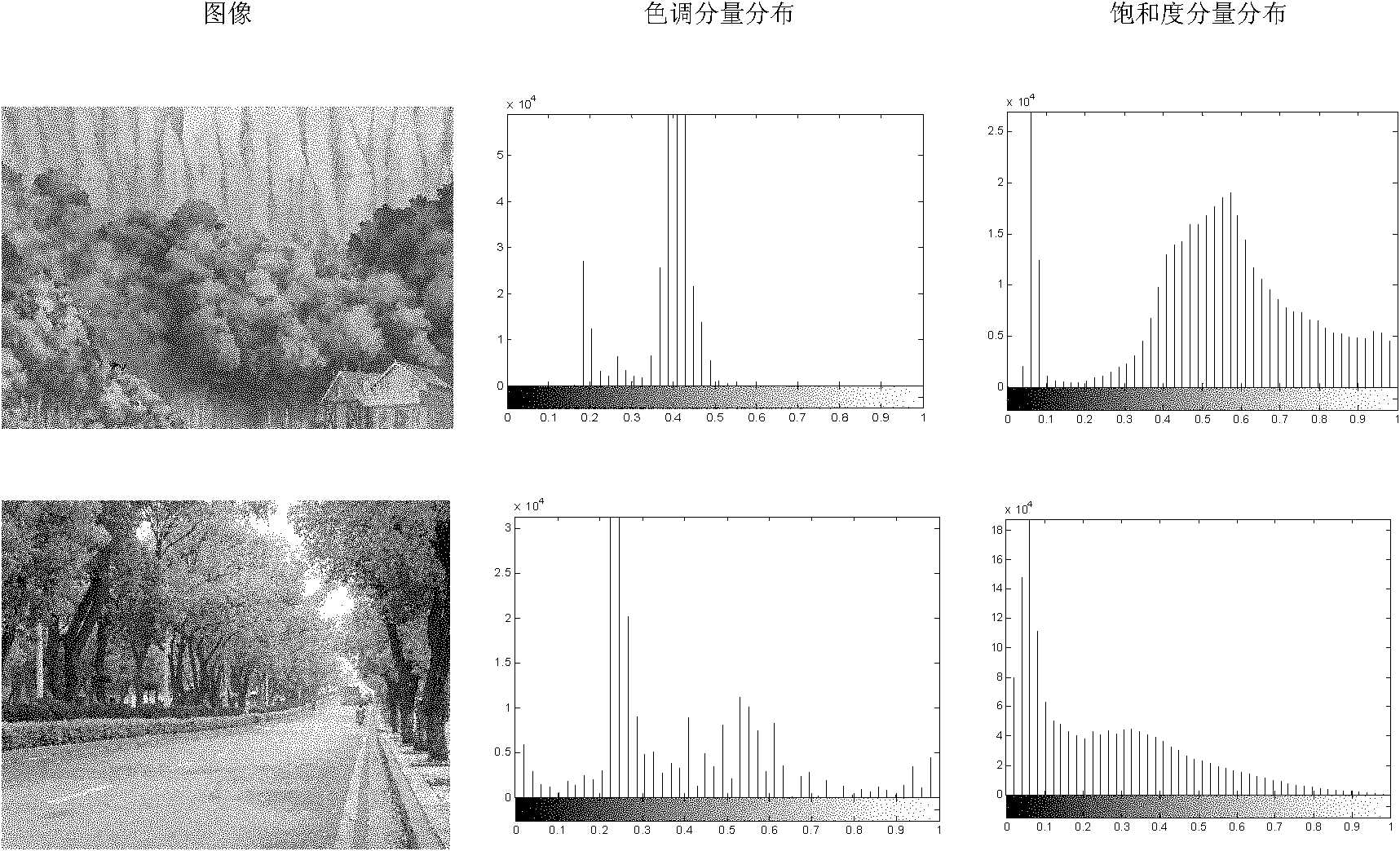
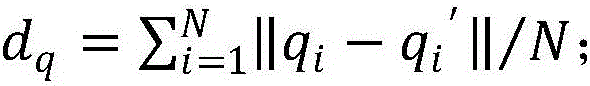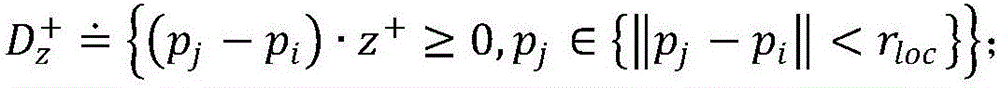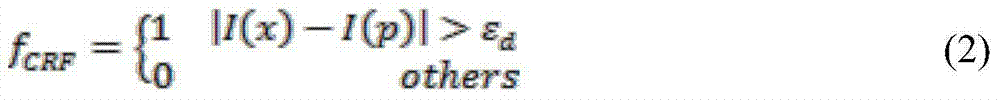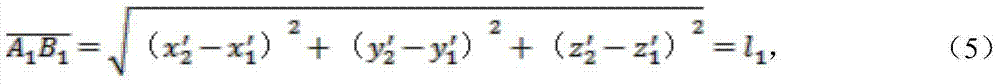Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
497 results about "Invariant feature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An object that does not change or its characteristic when the object is viewed under different circumstances. Features that are invariant and are unaffected by manipulations of the observer or object. INVARIANT FEATURE: "Invariant Feature is object recognition by humans or machines ". APPARENT DISTANCE.
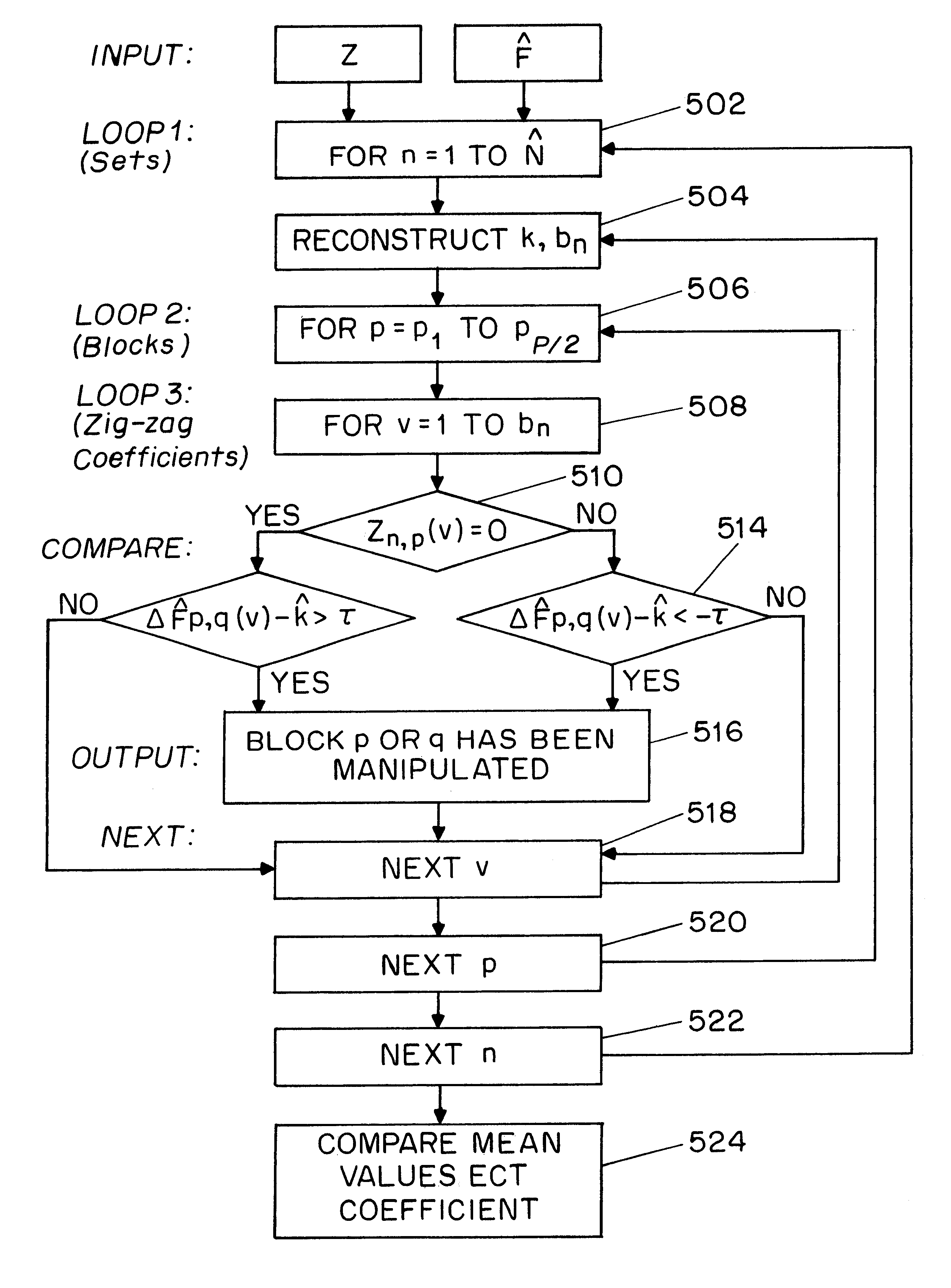
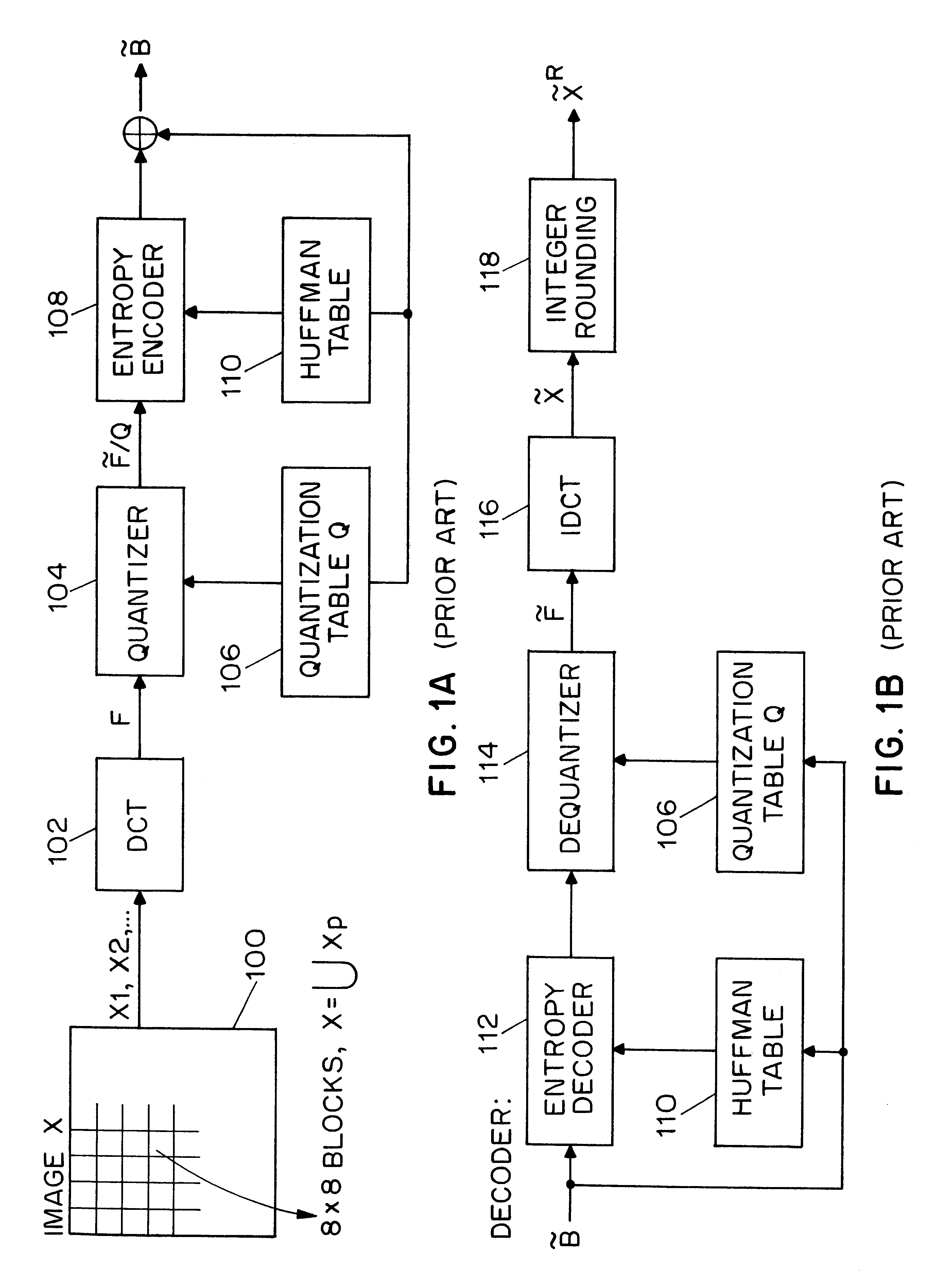
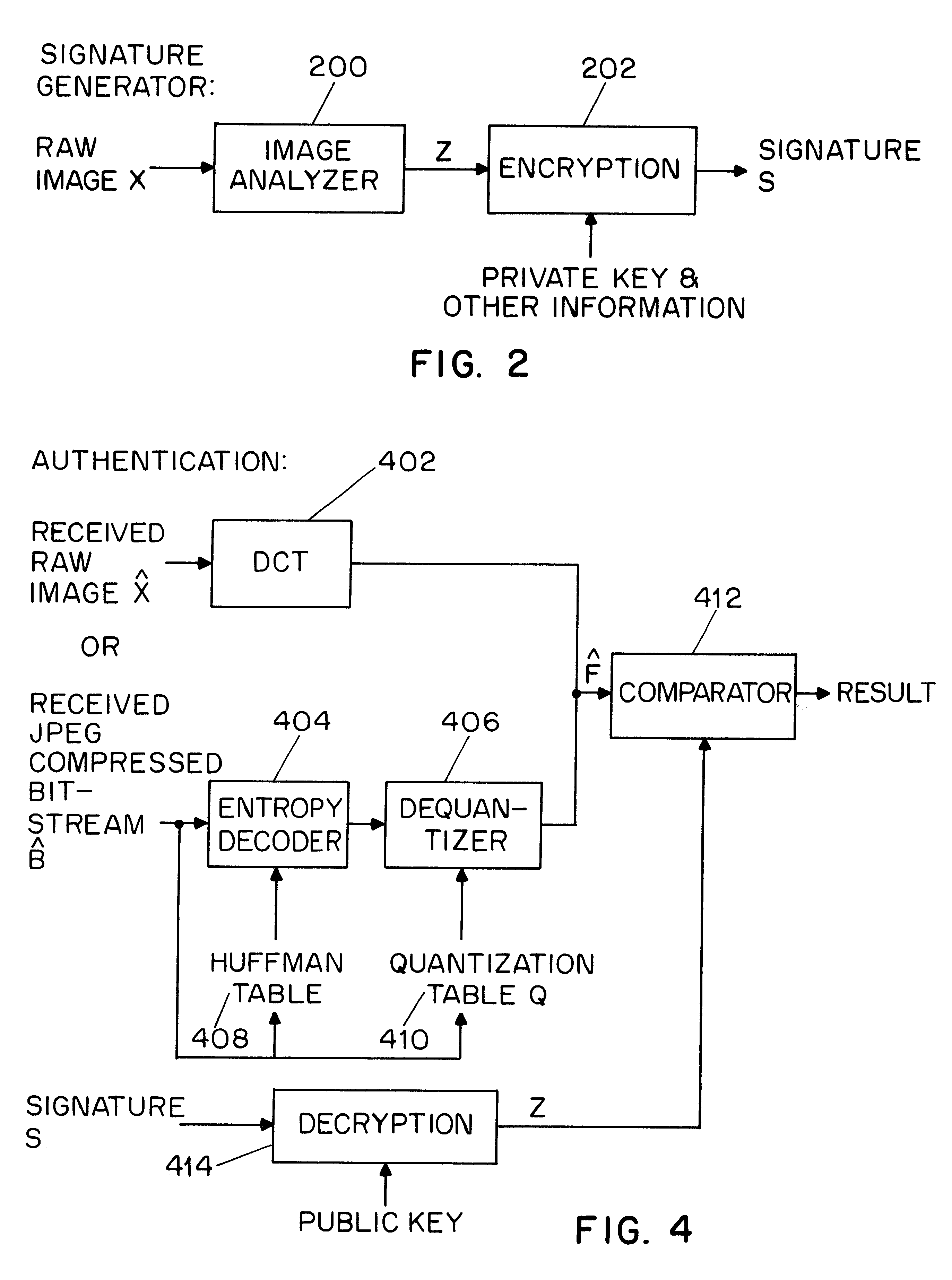
Method and apparatus for image authentication
InactiveUS6532541B1User identity/authority verificationImage watermarkingDigital signatureDiscrete cosine transform
A system for authentication of a digital image includes a signature generator for creating a robust digital signature for an original image based on instrument features of the image. An authentication processor extracts a set of invariant features for the original image from the digital signature, generates a corresponding set of invariant features for the present image to be authenticated and compares the two sets of invariant features to determine whether the image has been subjected to malicious manipulation. The invariant features include the polarity and magnitude of the difference between discrete cosine transform coefficients at corresponding coefficient locations in selected image block pairs. The intensity of the original image is also authenticated by comparing a mean value of coefficient of the original image to the mean value of the coefficient of the present image.
Owner:NAT SCI FOUND NSF
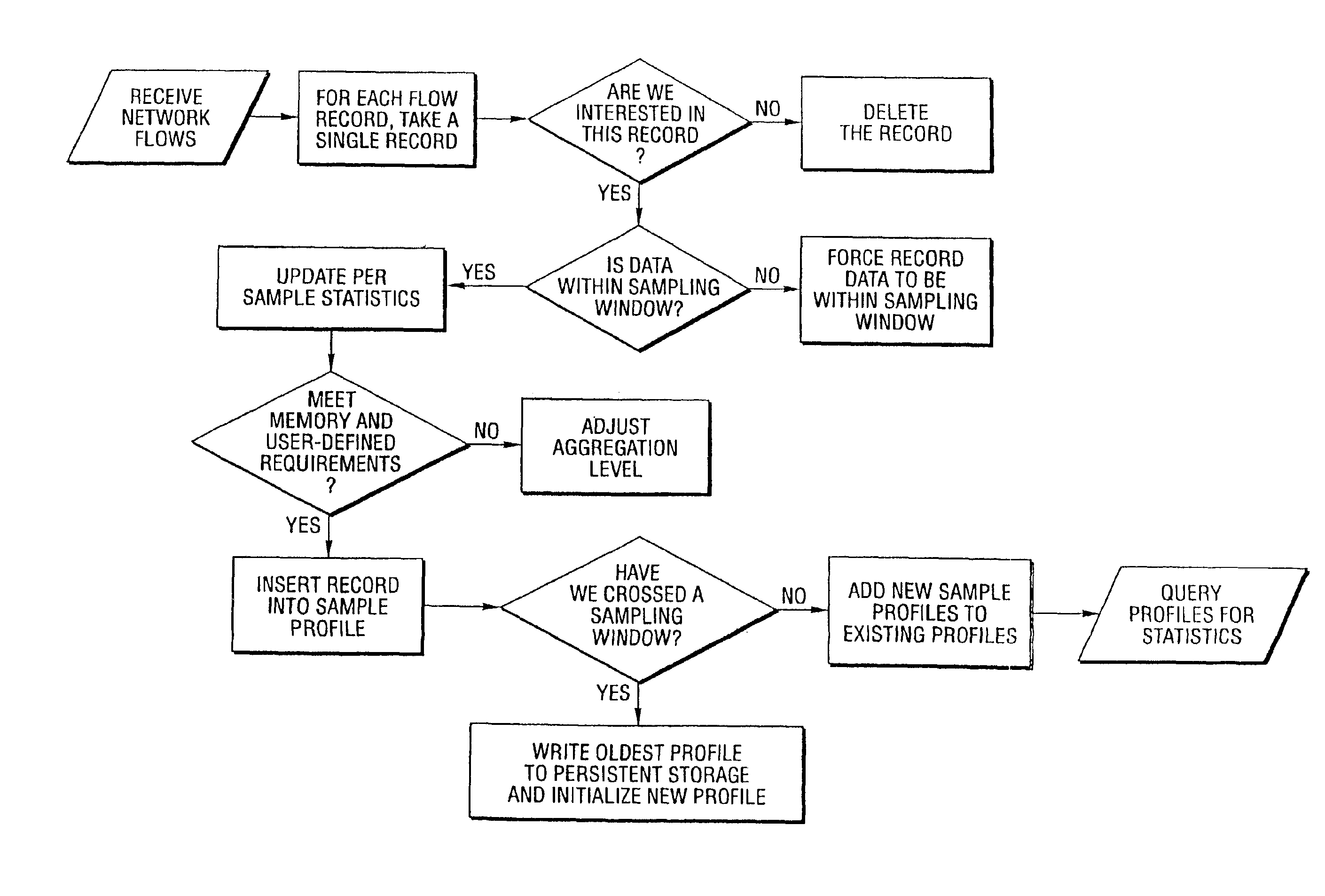
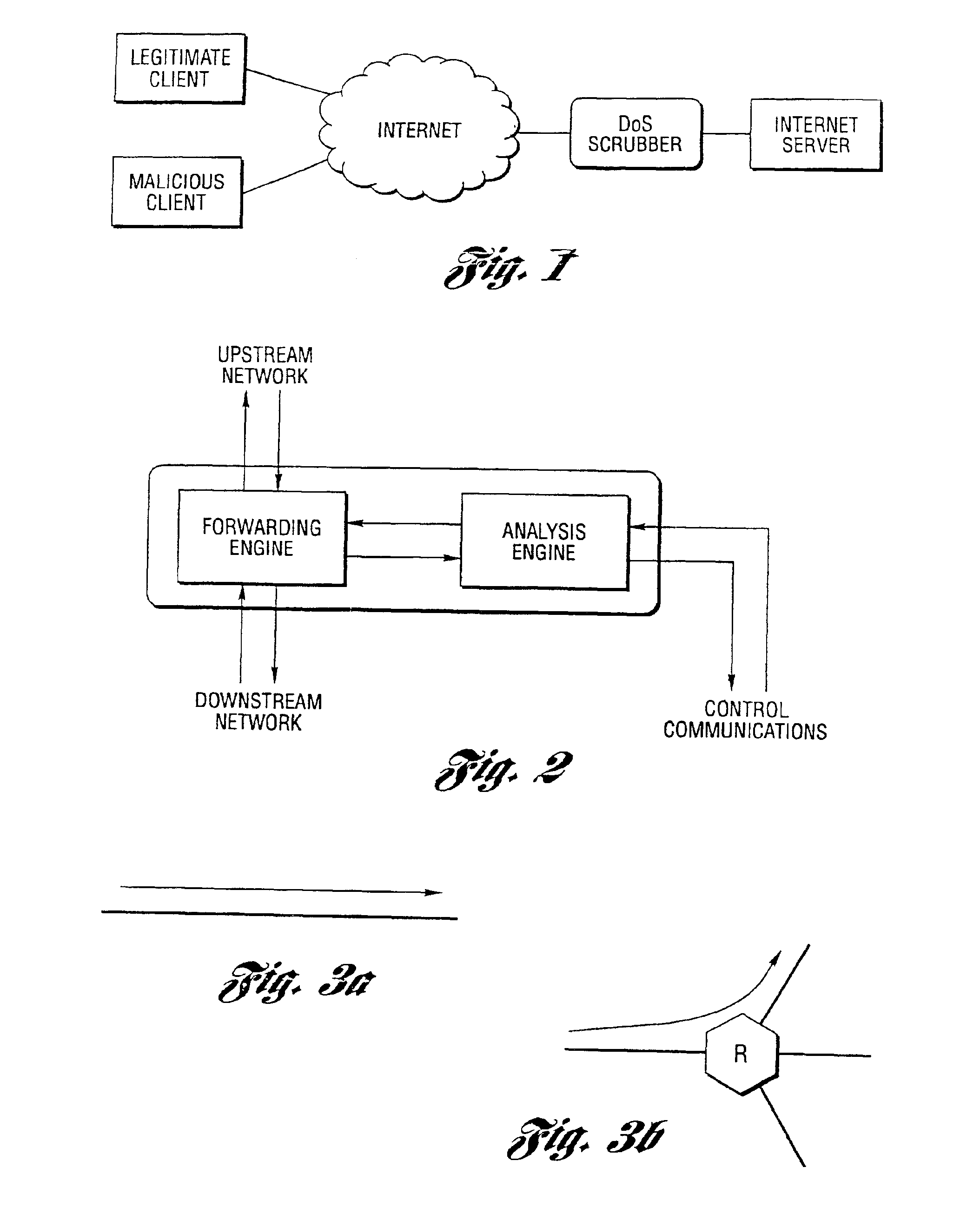
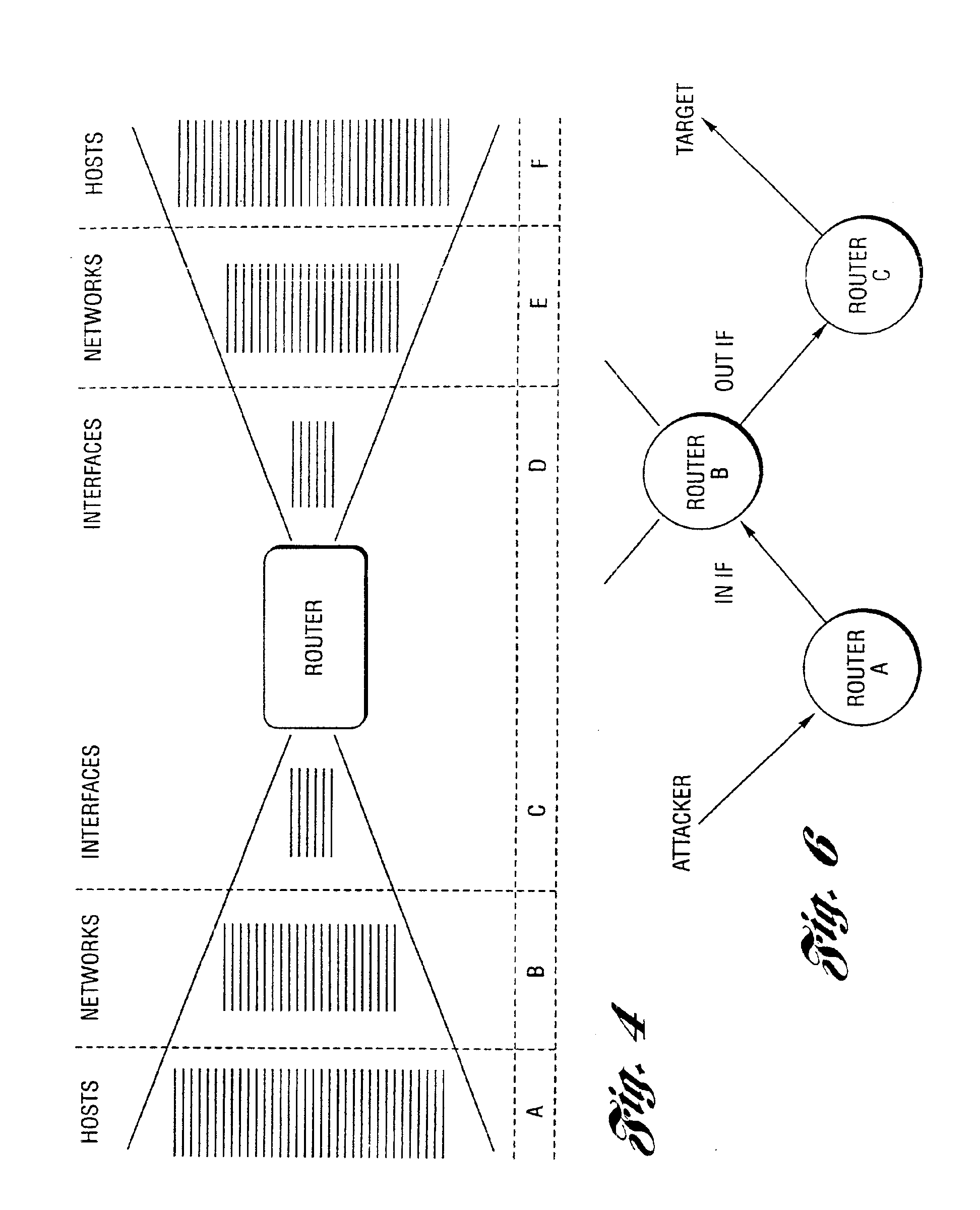
Method and system for profiling network flows at a measurement point within a computer network
InactiveUS6944673B2Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksTraffic characteristicMeasurement point
A method and system for profiling network flows at a measurement point within a computer network is provided. The method includes measuring network flows having invariant features at a measurement point located within routing infrastructure of the computer network to obtain flow statistics. The method also includes aggregating the flow statistics to obtain a traffic profile of the network flows at the measurement point. The method and system utilize the natural hierarchy in the Internet addressing scheme to provide a means for making tractable measurements of network traffic in high-speed networks. Moreover, the method and system adapt dynamically to the changing underlying traffic characteristics to maintain a maximum memory footprint for the profiles. The method and system adapt by adjusting the level of aggregation of the traffic endpoints along a scale from Interface to fully specified network address.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
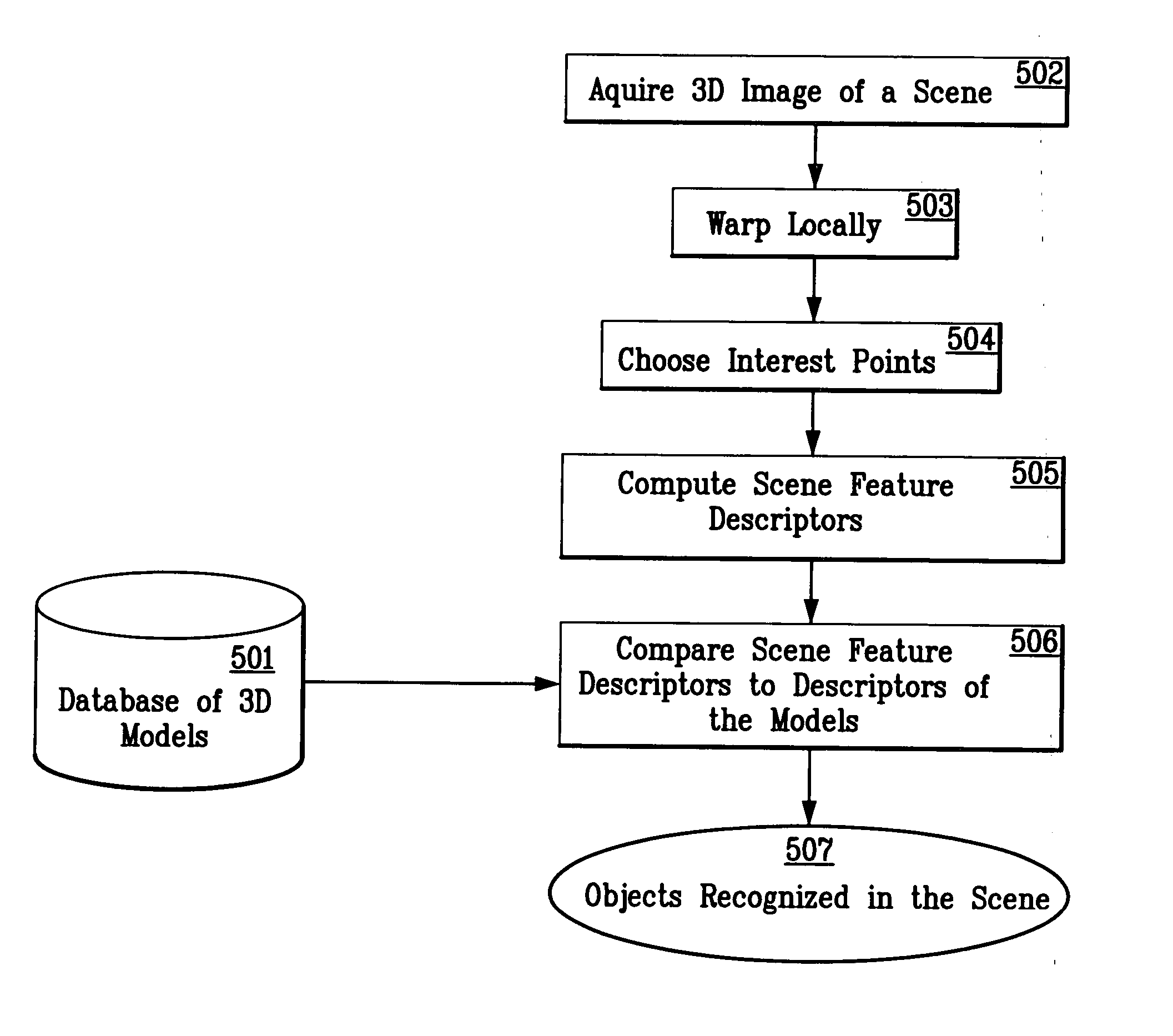
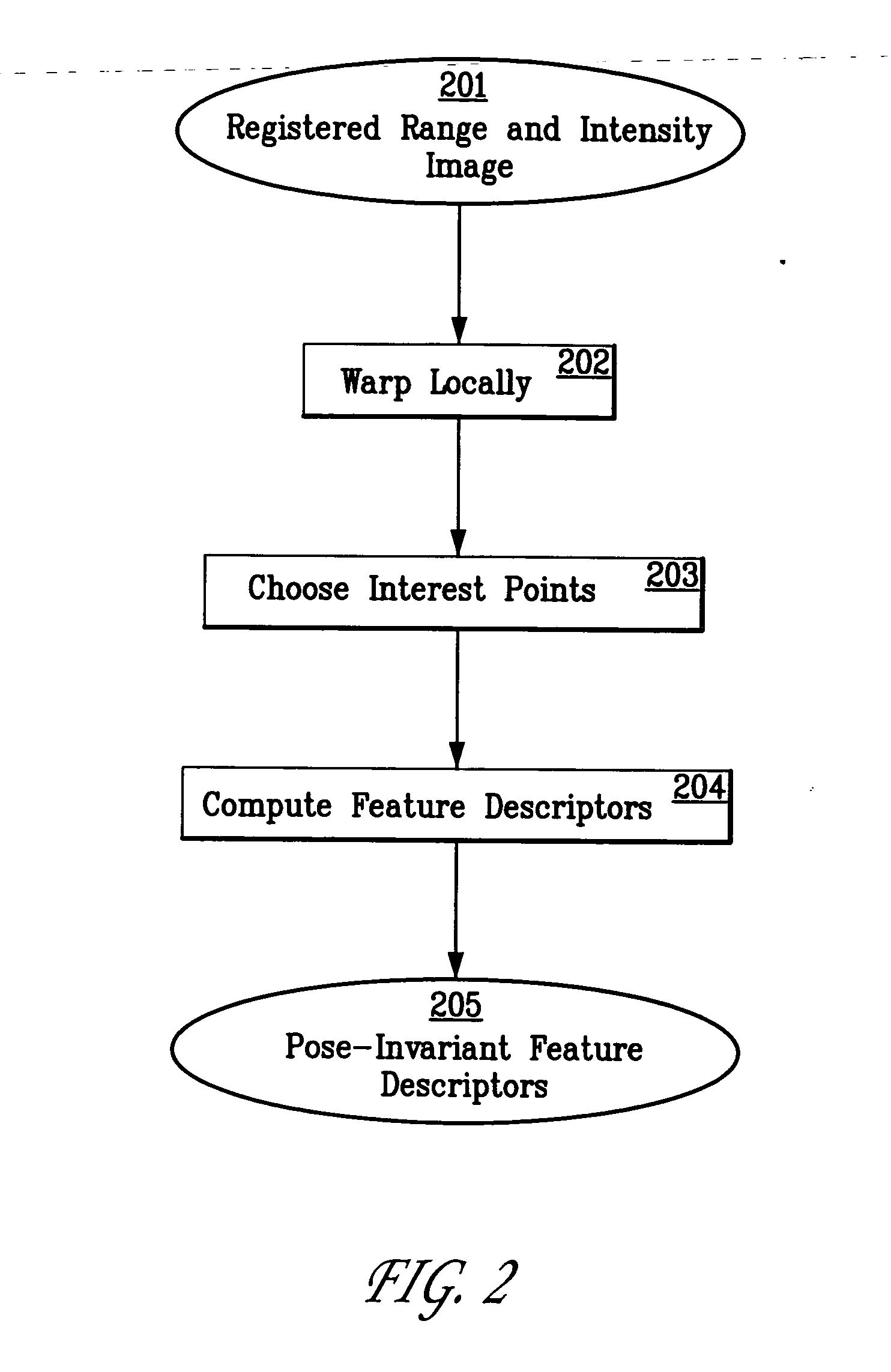
System and method for 3D object recognition using range and intensity
A system and method for performing object and class recognition that allows for wide changes of viewpoint and distance of objects is disclosed. The invention provides for choosing pose-invariant interest points of a three-dimensional (3D) image, and for computing pose-invariant feature descriptors of the image. The system and method also allows for the construction of three-dimensional (3D) object and class models from the pose-invariant interest points and feature descriptors of previously obtained scenes. Interest points and feature descriptors of a newly acquired scene may be compared to the object and / or class models to identify the presence of an object or member of the class in the new scene.
Owner:STRIDER LABS
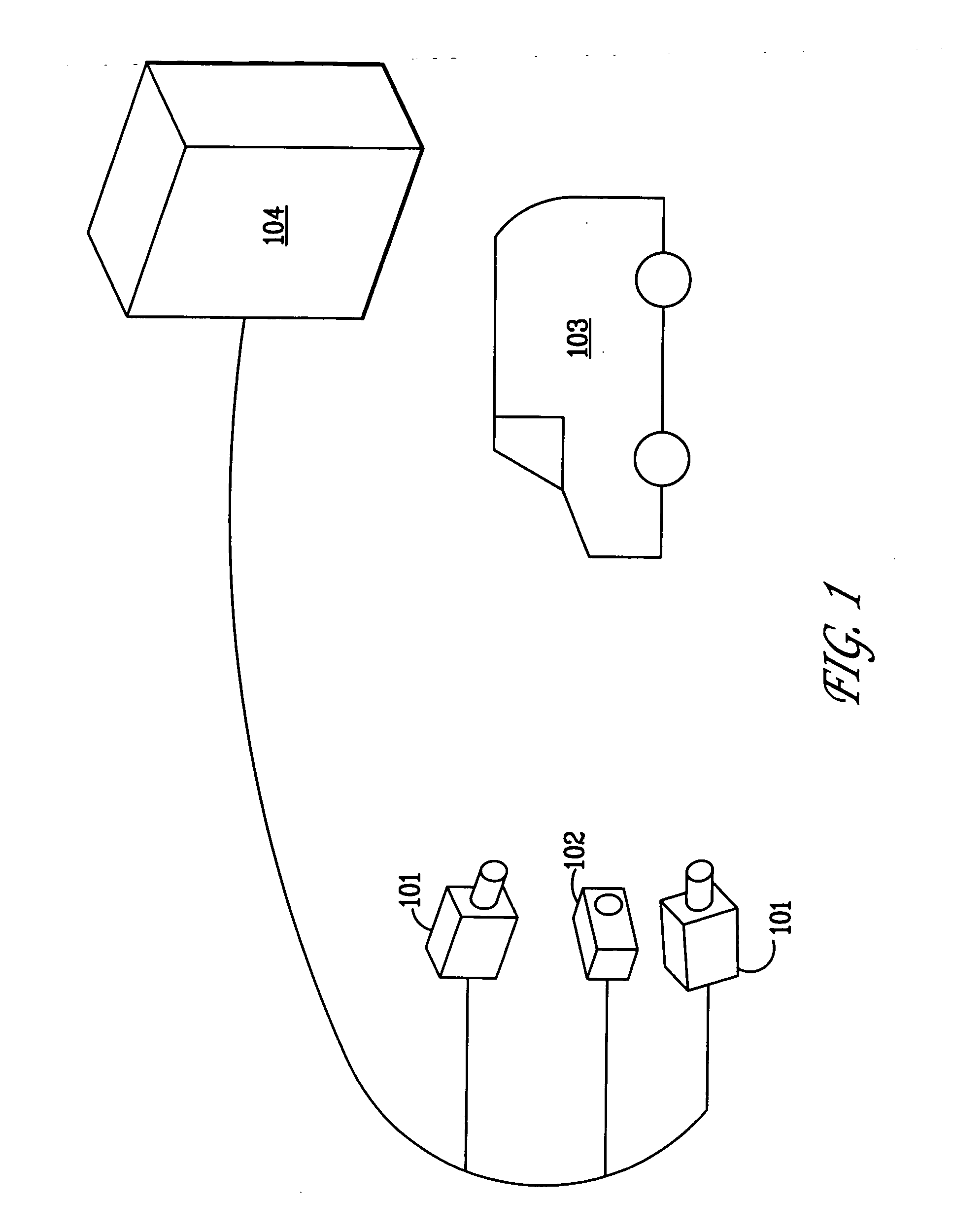
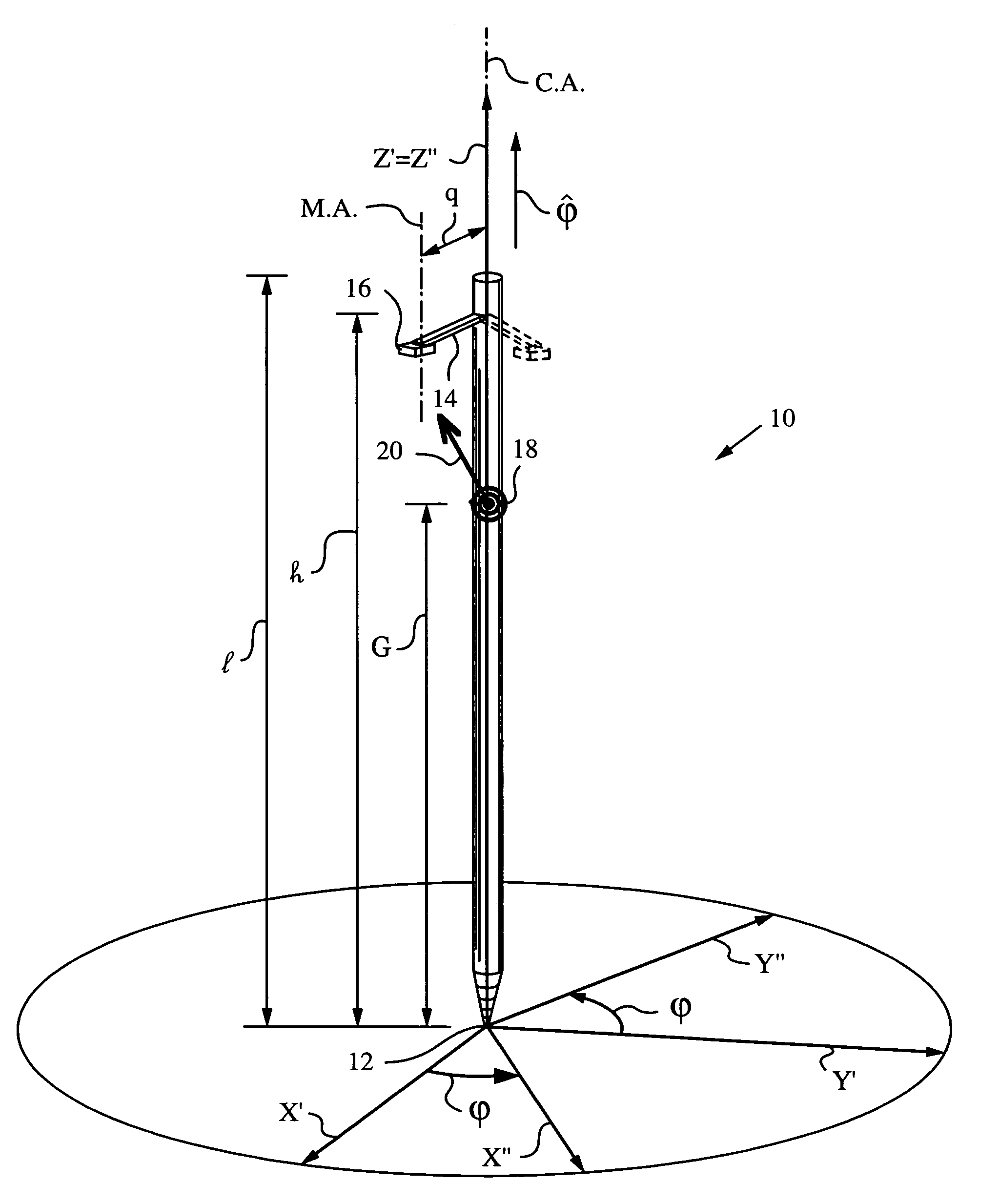
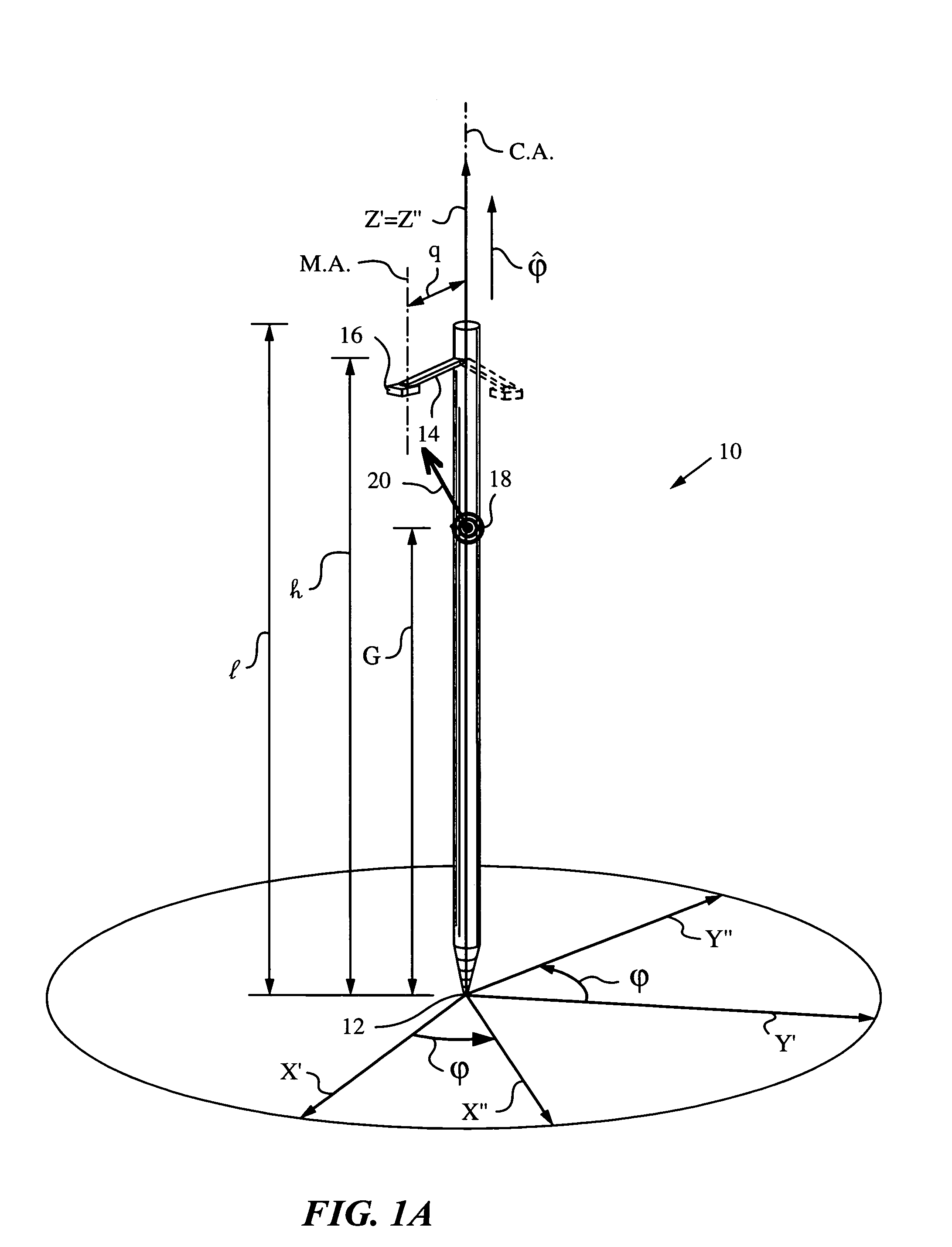
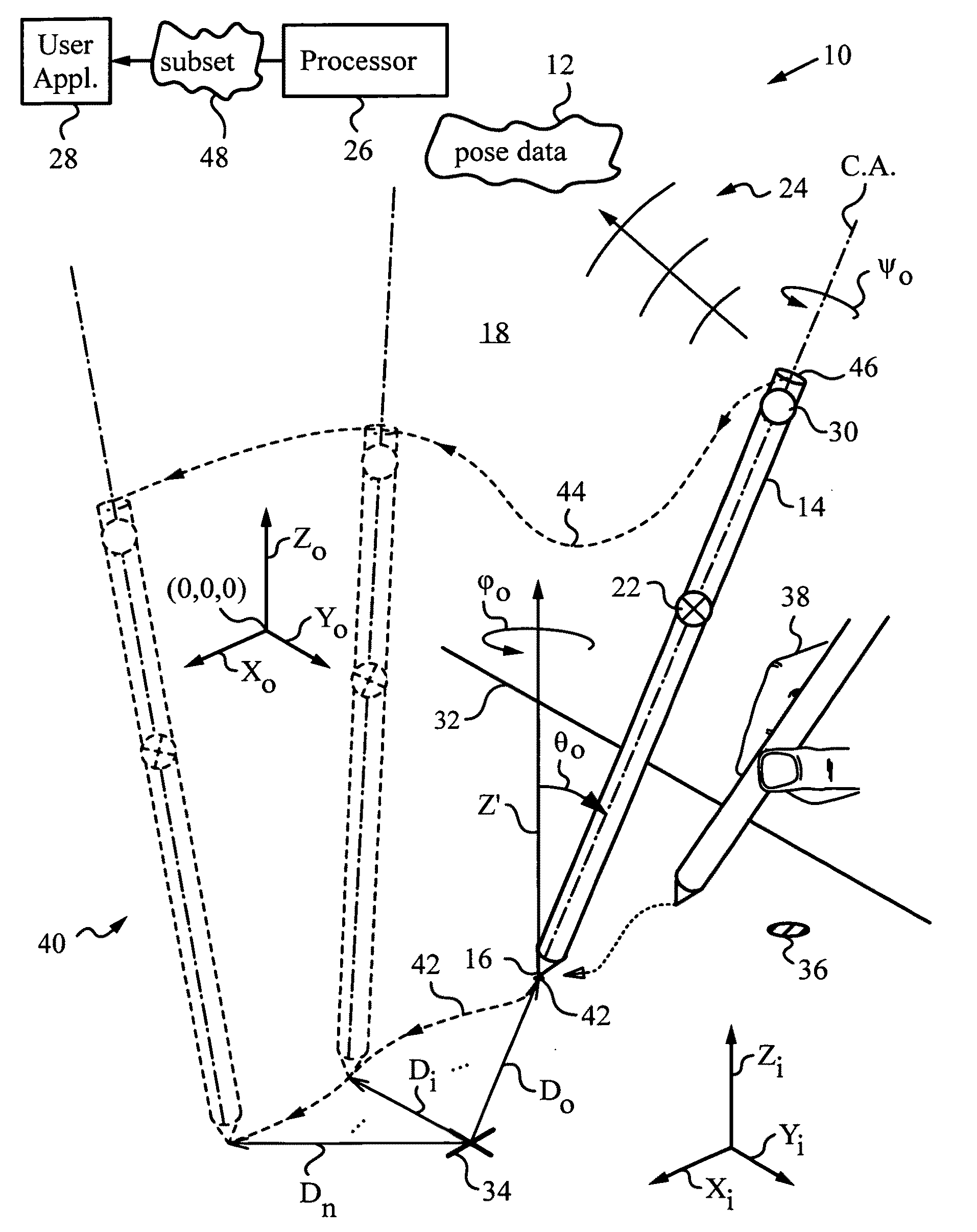
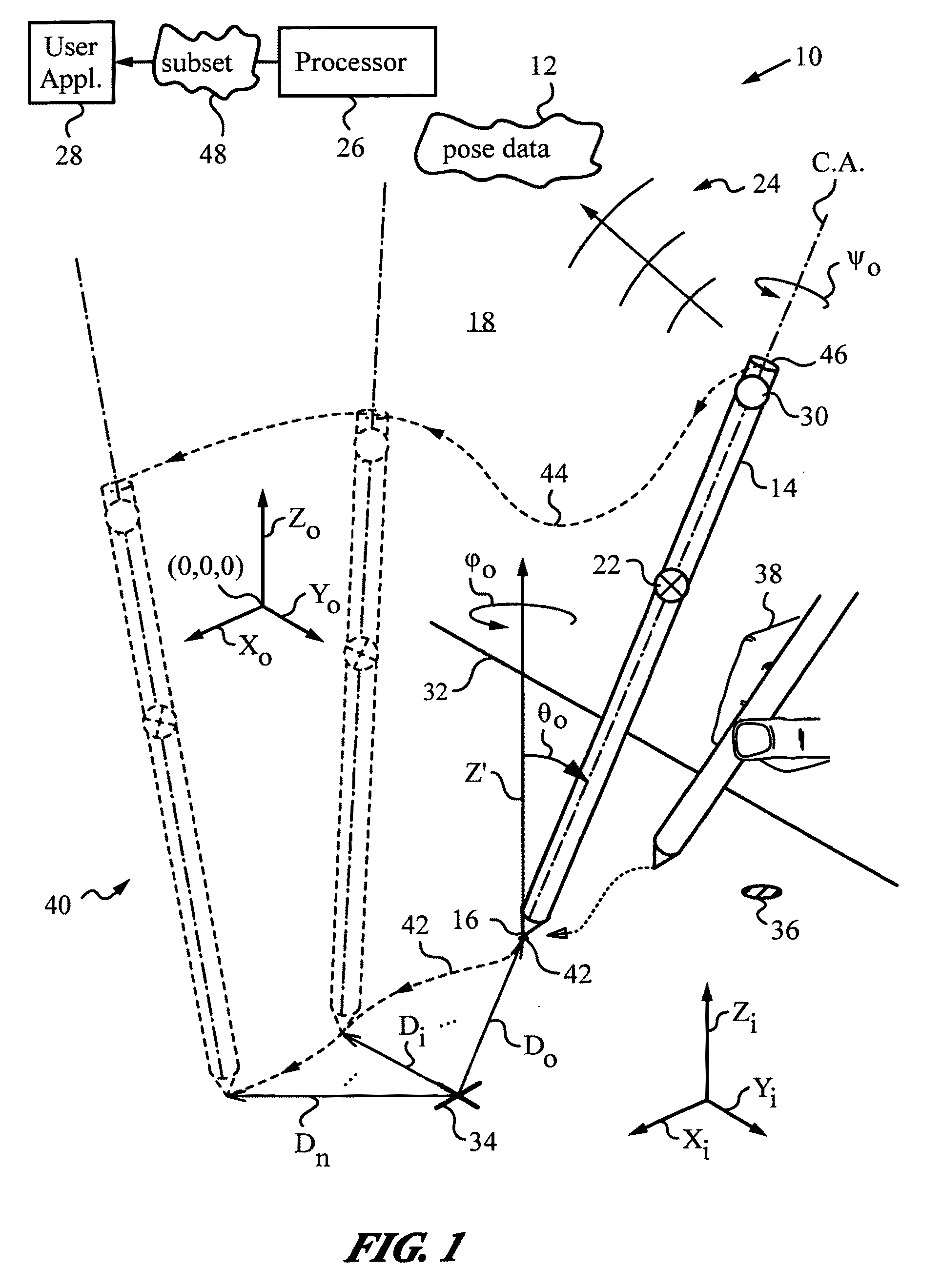
Method and apparatus for determining absolute position of a tip of an elongate object on a plane surface with invariant features
ActiveUS7088440B2Input/output for user-computer interactionAngle measurementMicro structureRobotic arm
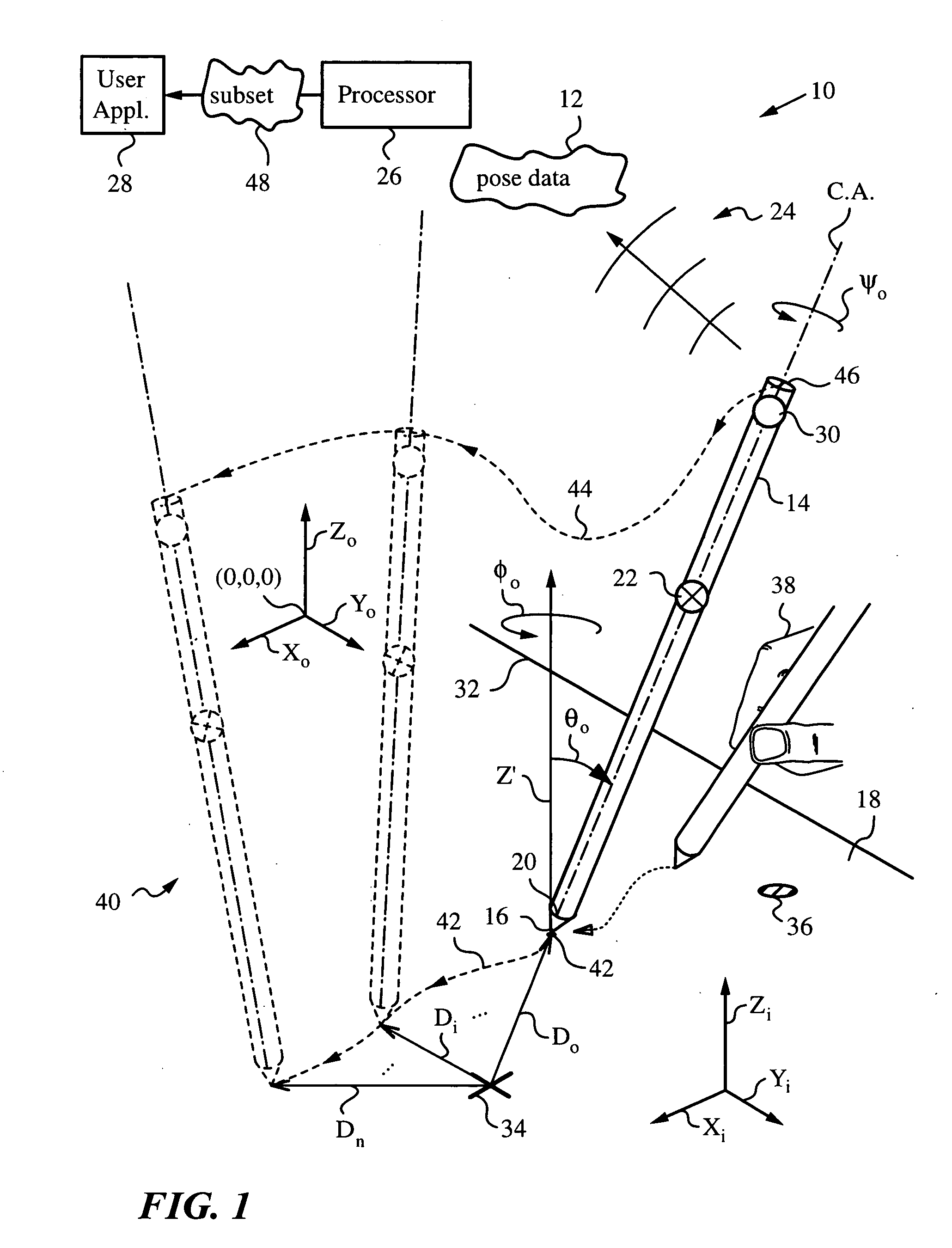
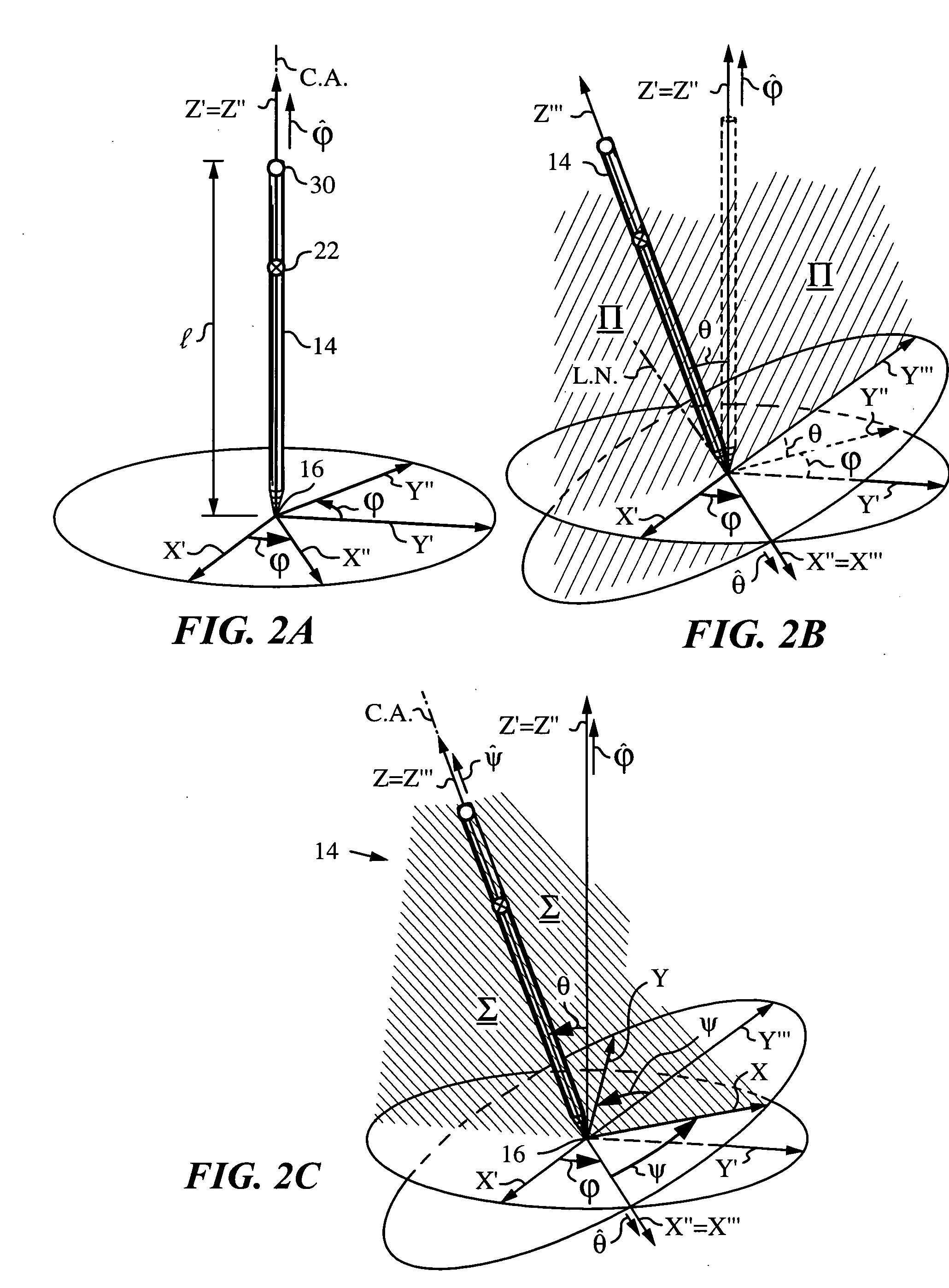
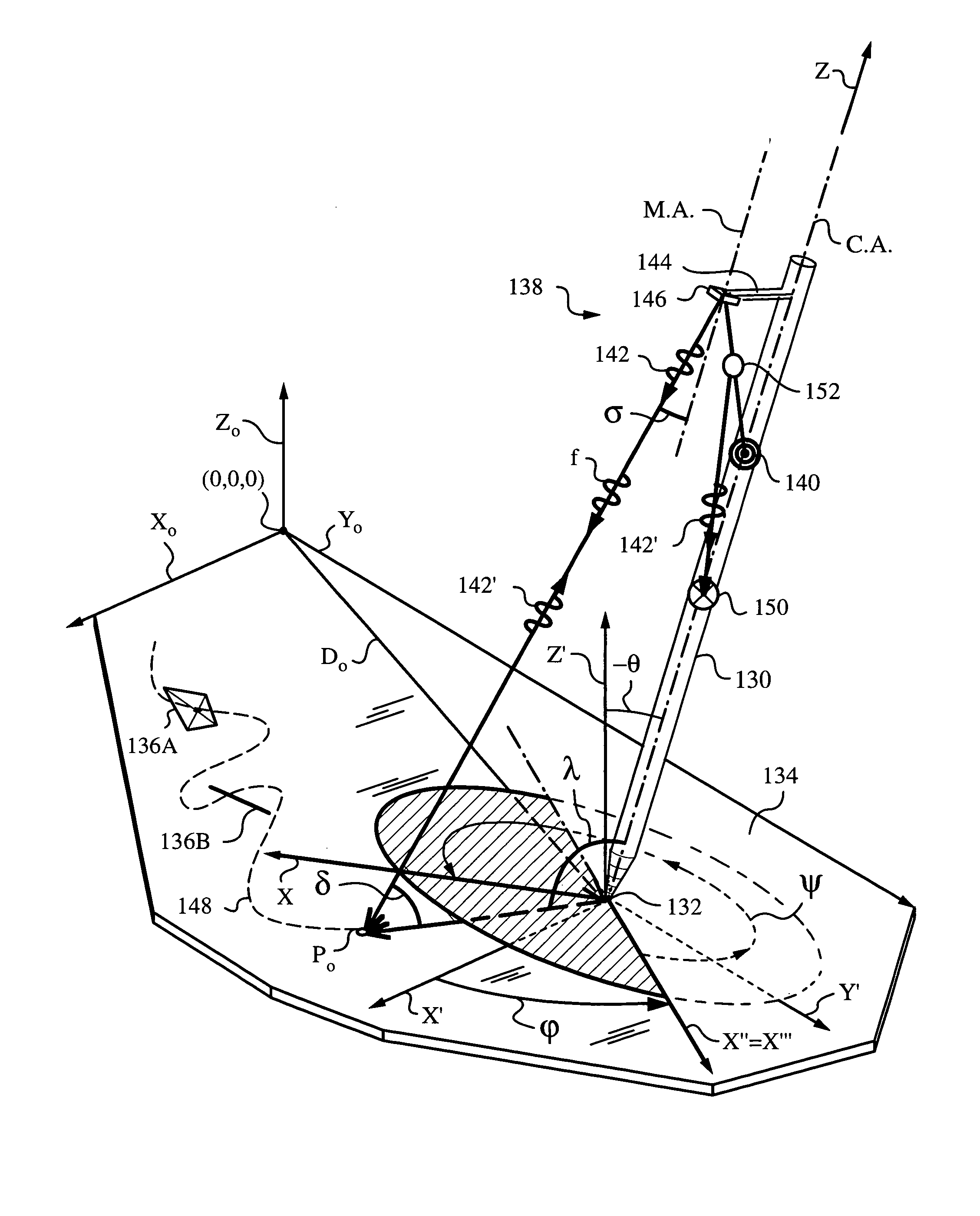
A method and apparatus for determining a pose of an elongate object and an absolute position of its tip while the tip is in contact with a plane surface having invariant features. The surface and features are illuminated with a probe radiation and a scattered portion, e.g., the back-scattered portion, of the probe radiation returning from the plane surface and the feature to the elongate object at an angle τ with respect to an axis of the object is detected. The pose is derived from a response of the scattered portion to the surface and the features and the absolute position of the tip on the surface is obtained from the pose and knowledge about the feature. The probe radiation can be directed from the object to the surface at an angle σ to the axis of the object in the form of a scan beam. The scan beam can be made to follow a scan pattern with the aid of a scanning arrangement with one or more arms and one or more uniaxial or biaxial scanners. Angle τ can also be varied, e.g., with the aid of a separate or the same scanning arrangement as used to direct probe radiation to the surface. The object can be a pointer, a robotic arm, a cane or a jotting implement such as a pen, and the features can be edges, micro-structure or macro-structure belonging to, deposited on or attached to the surface which the tip of the object is contacting.
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
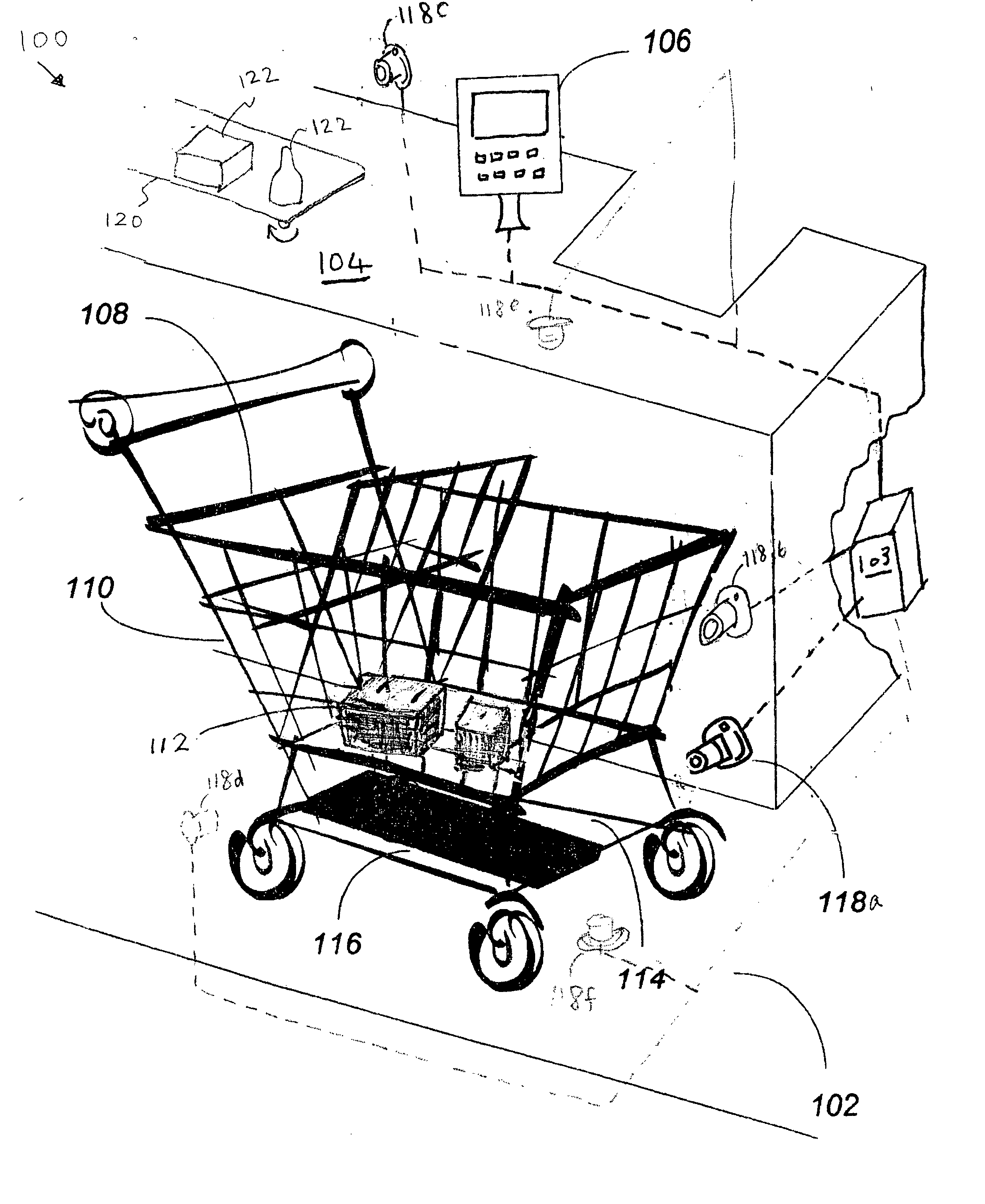
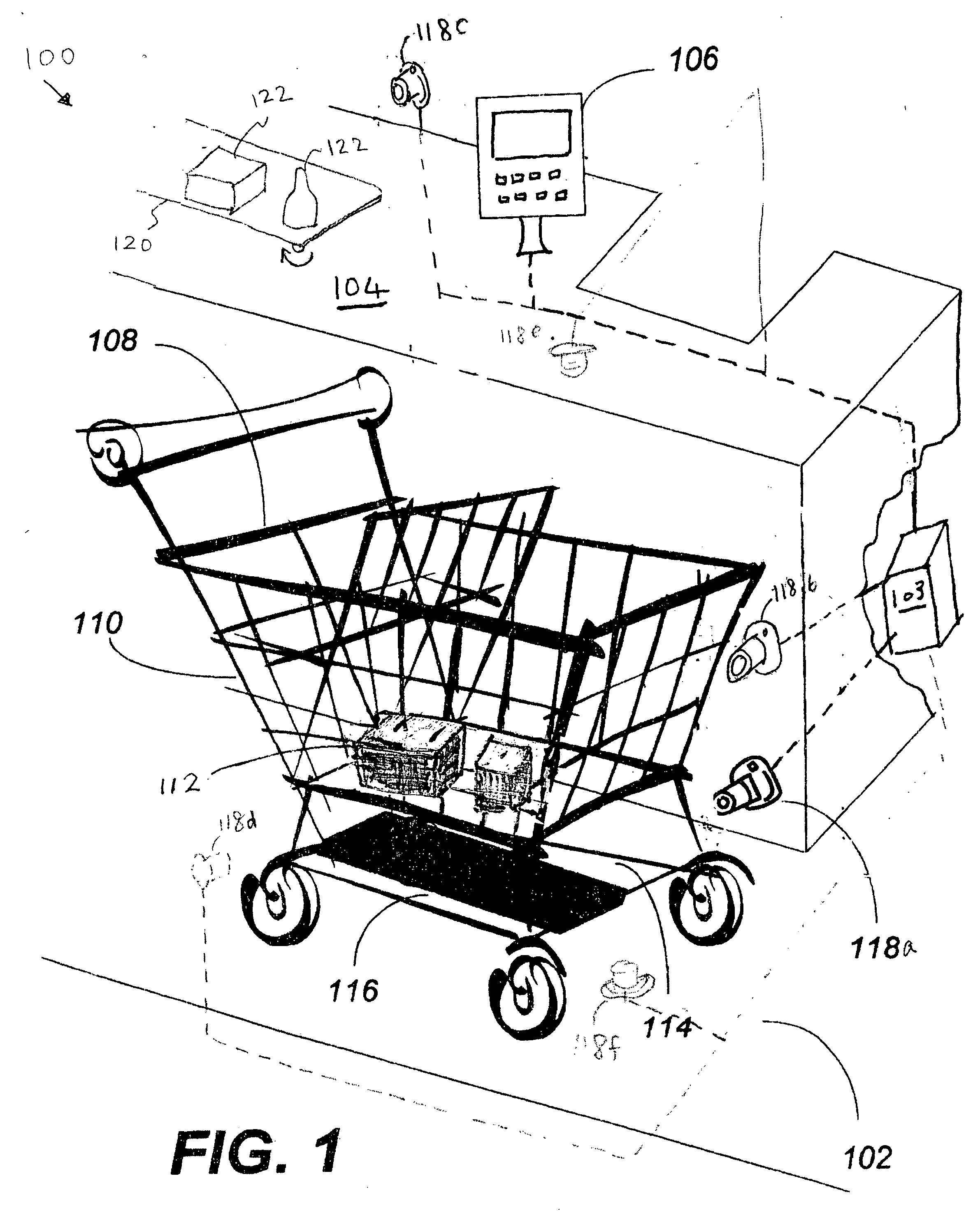
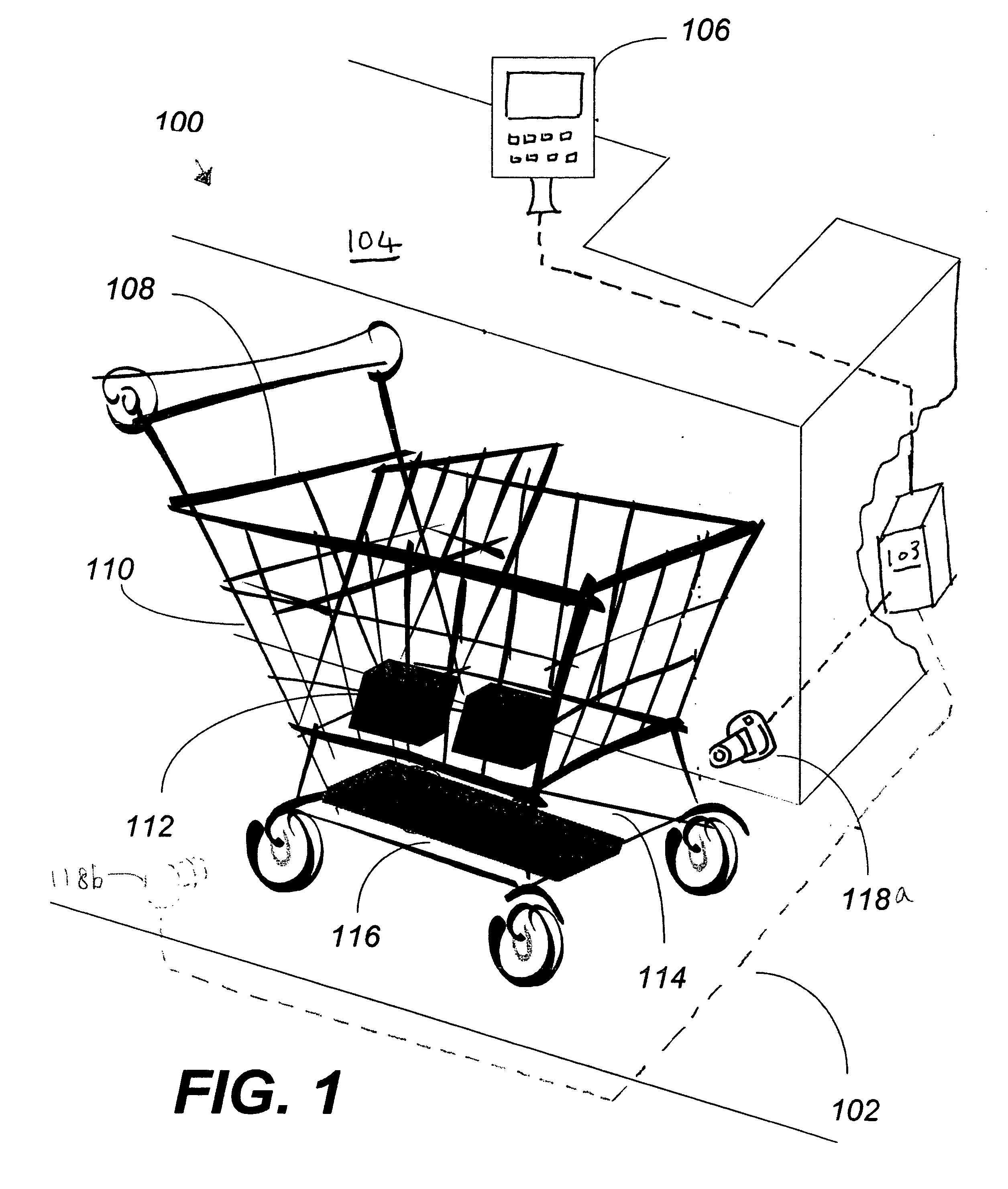
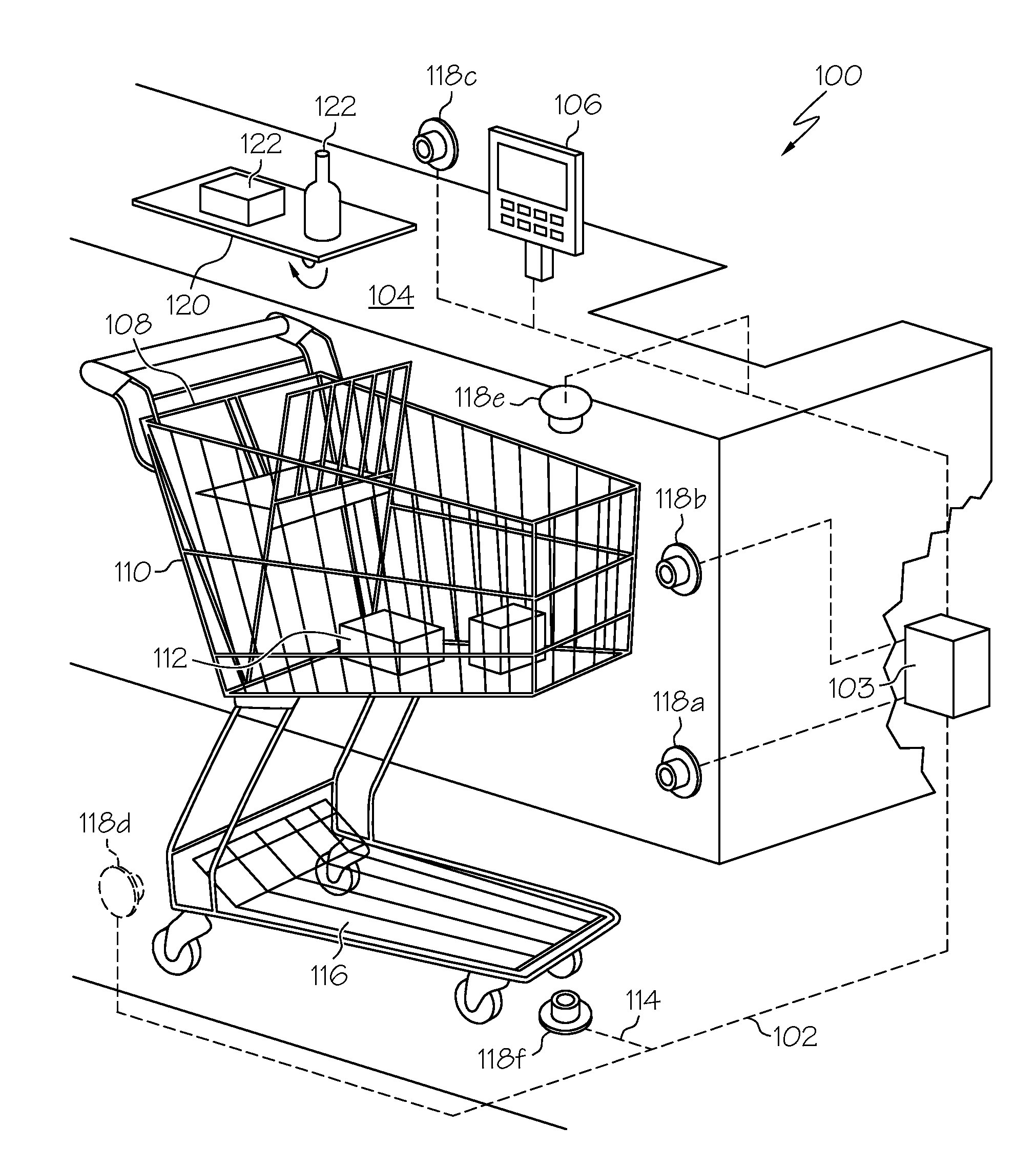
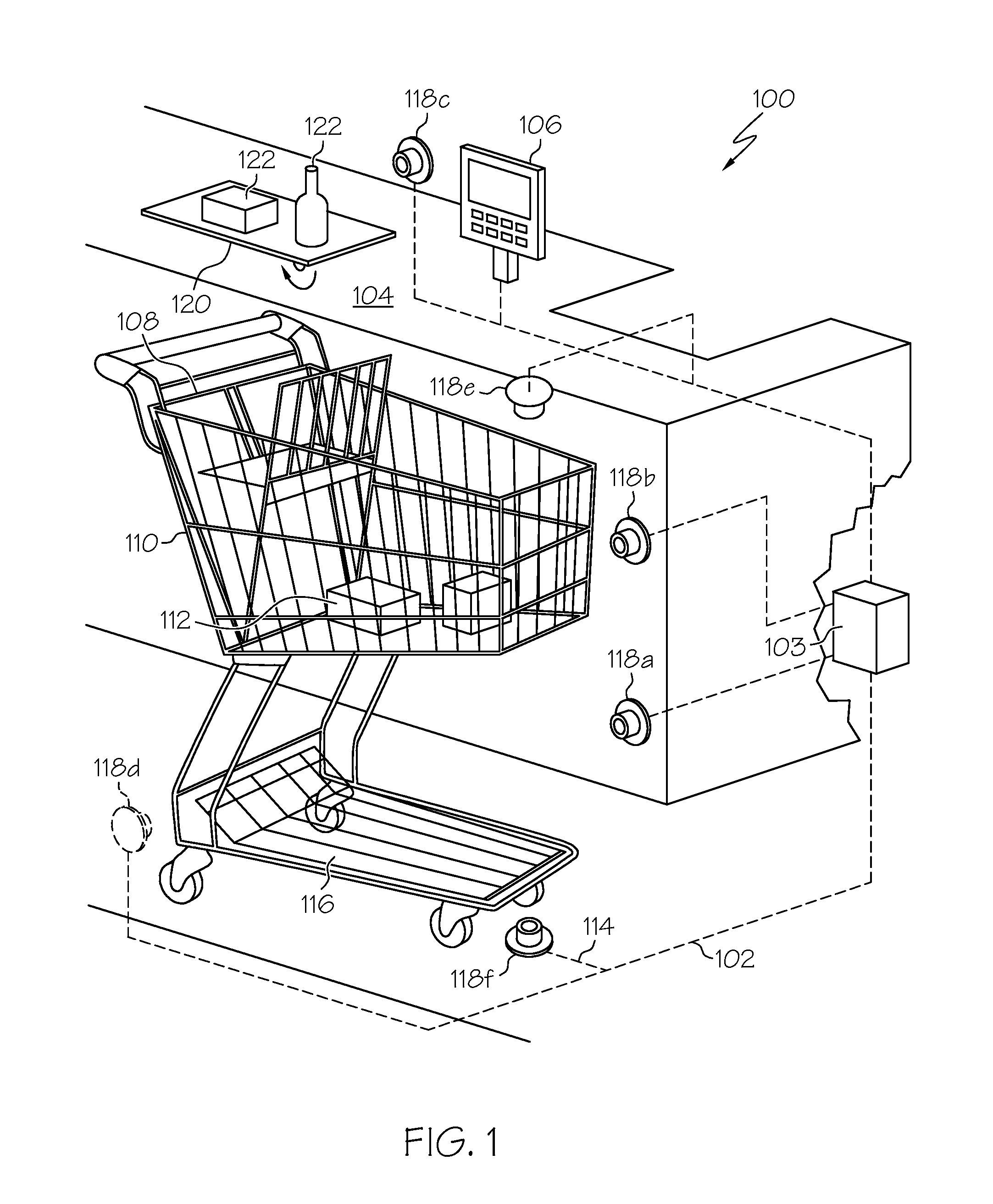
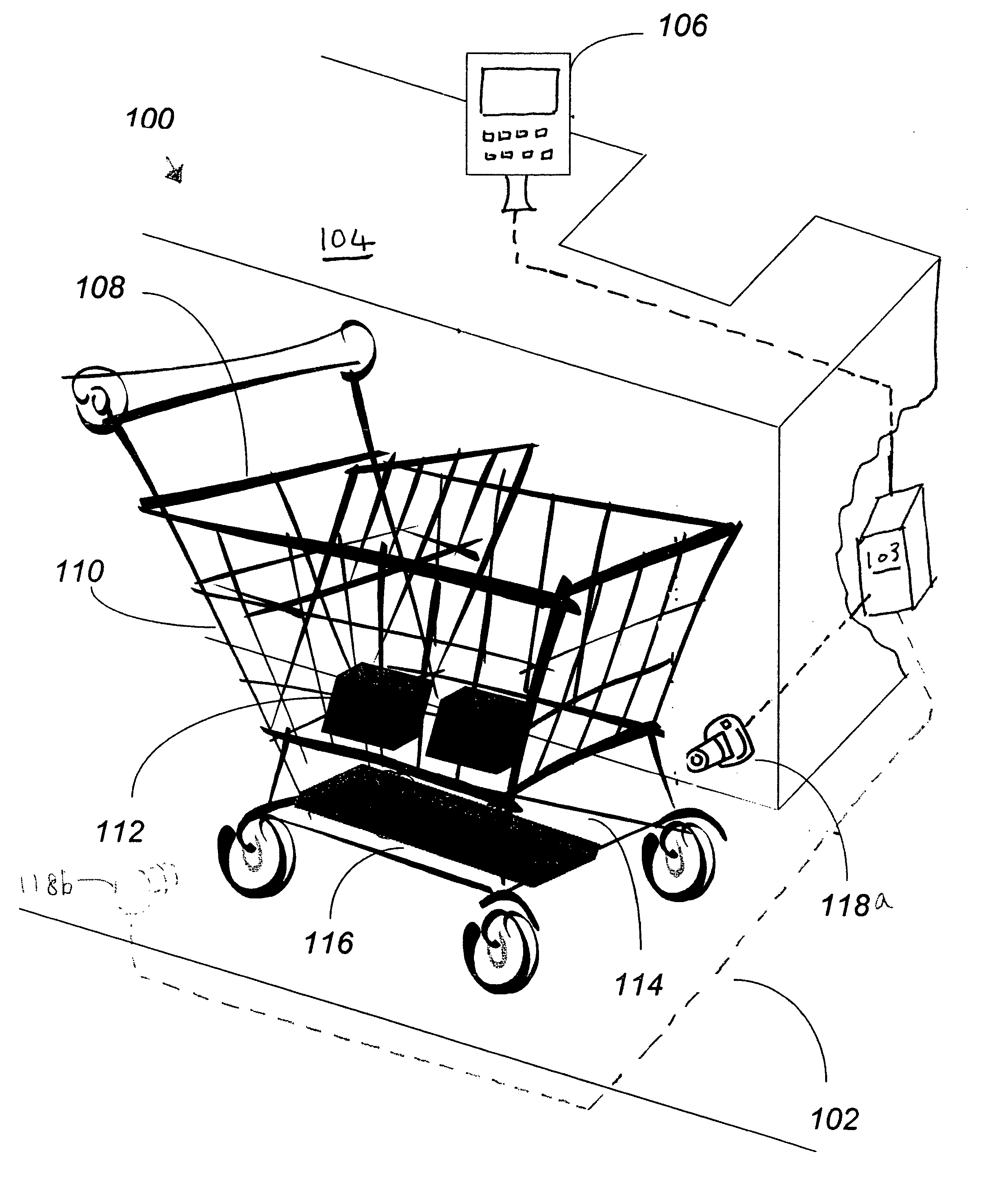
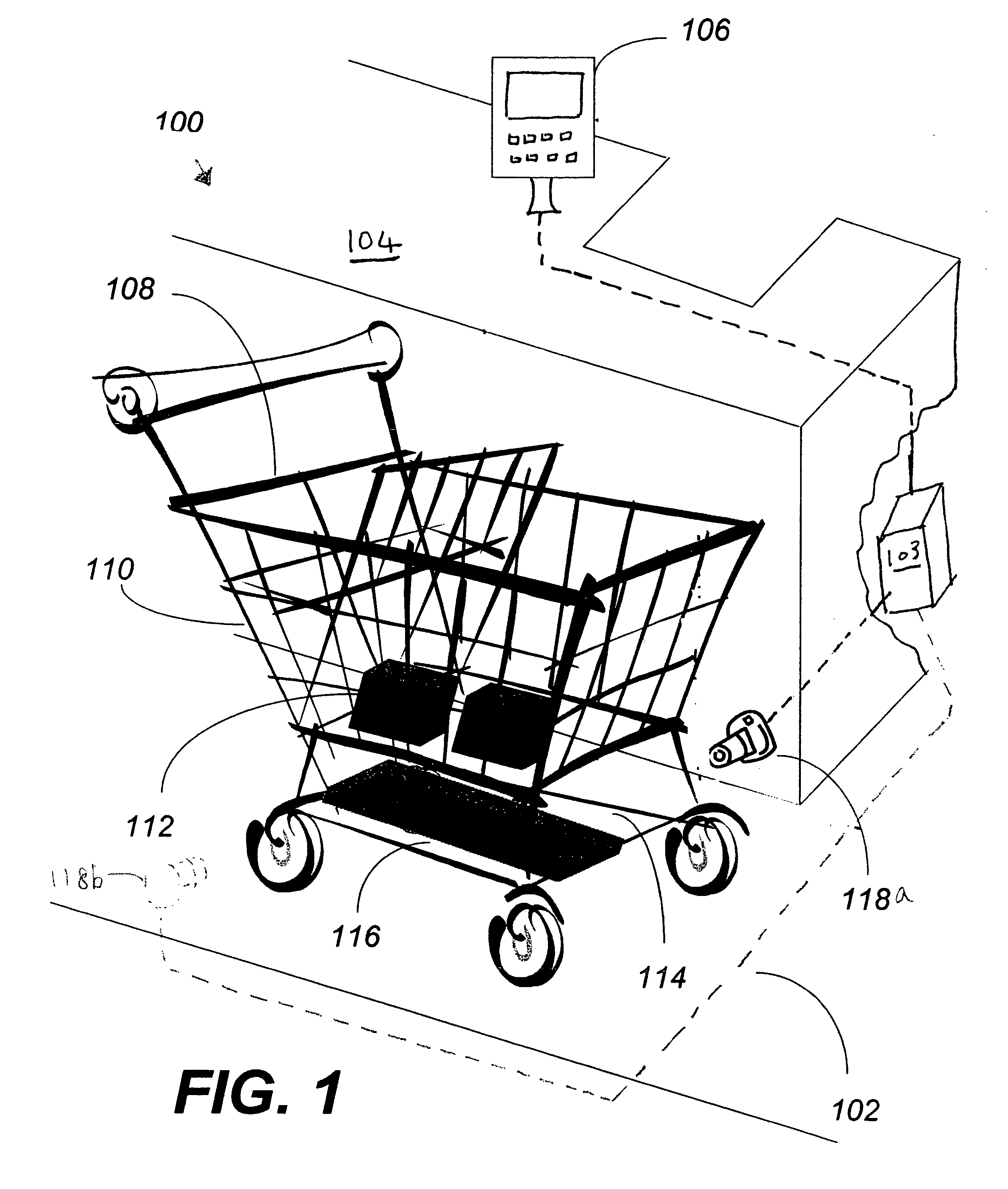
Method of merchandising for checkout lanes
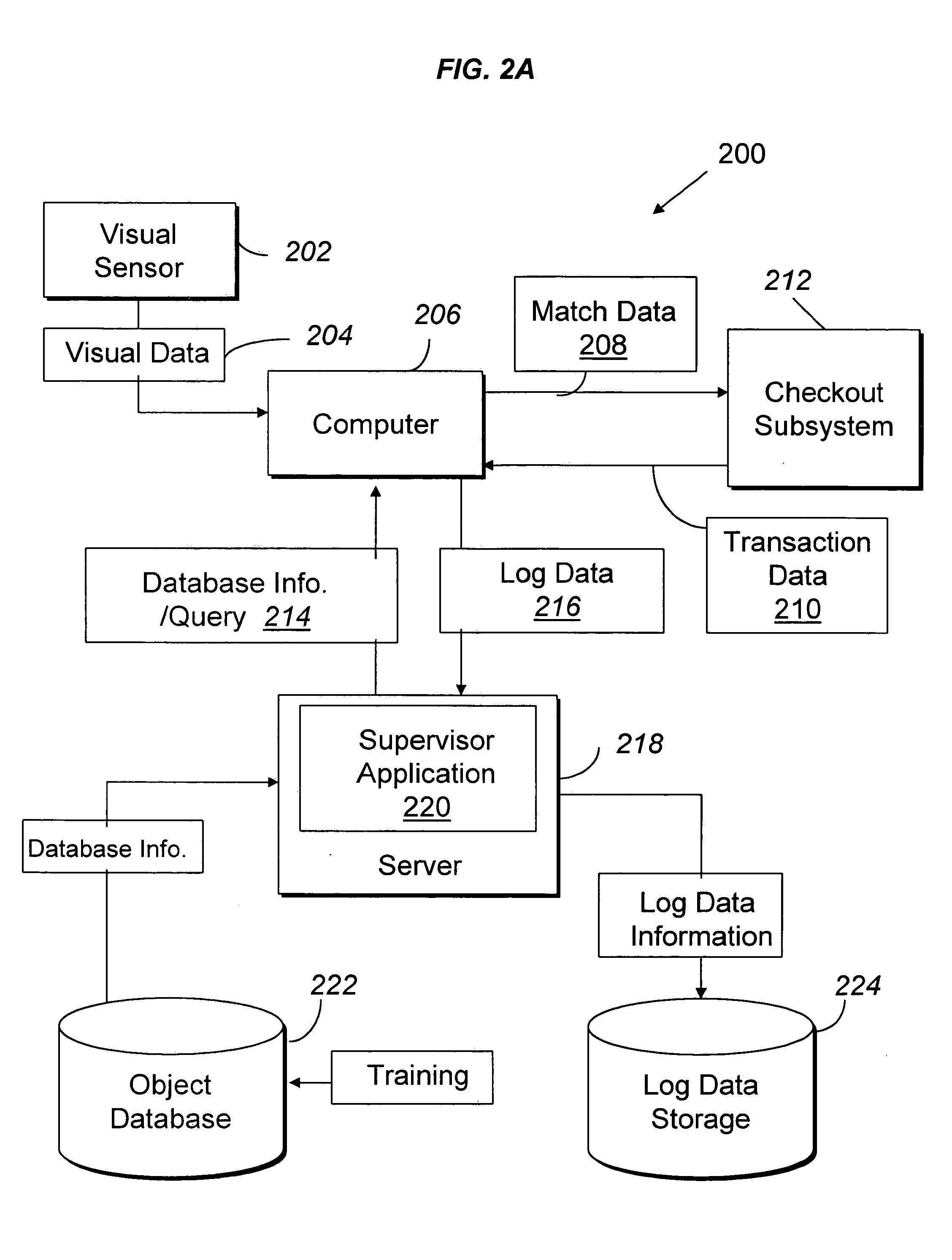
ActiveUS20050189412A1Reduces and prevents bottom-of-the-basket lossImprove checkout speedCredit registering devices actuationCash registersComing outArtificial intelligence
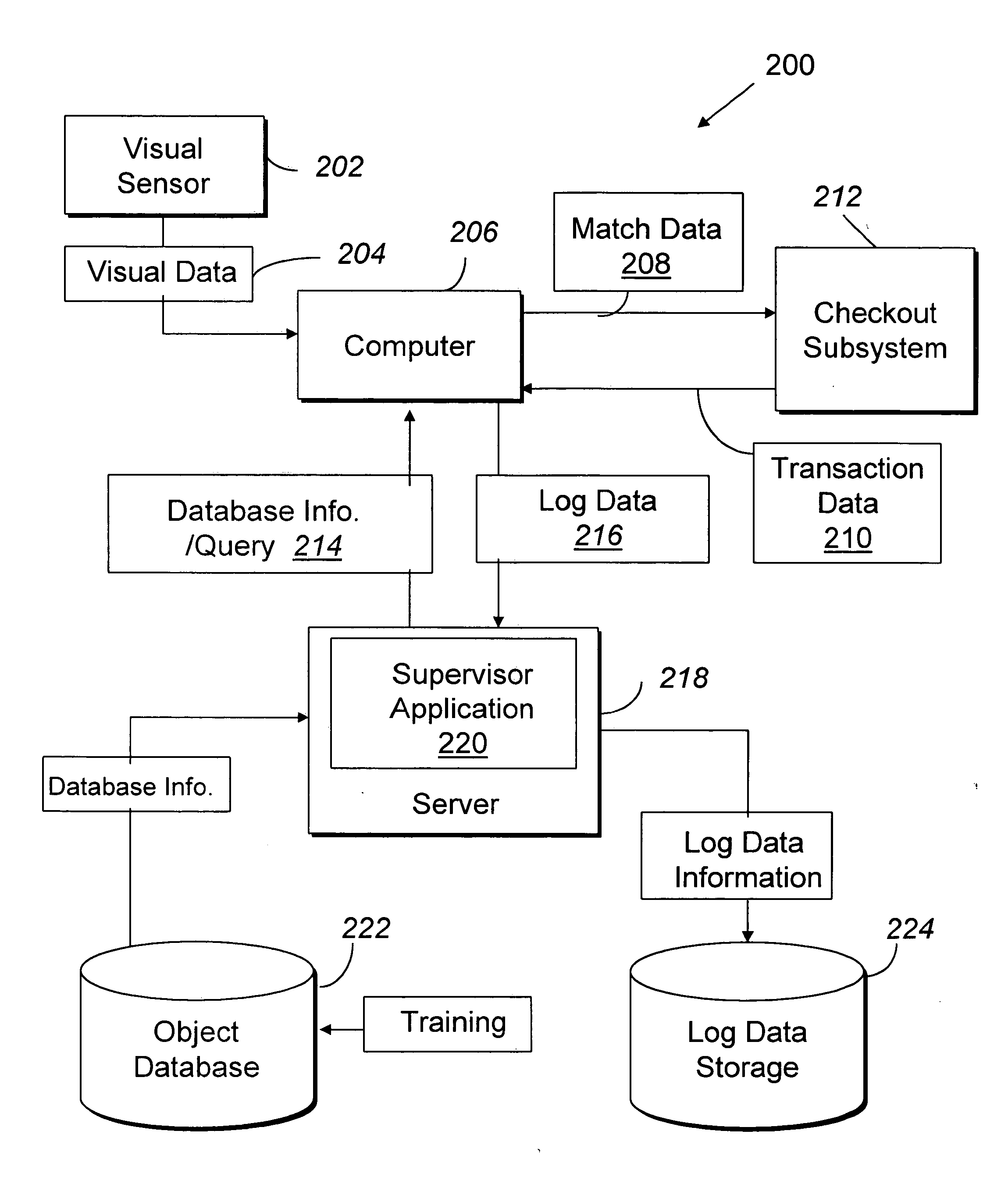
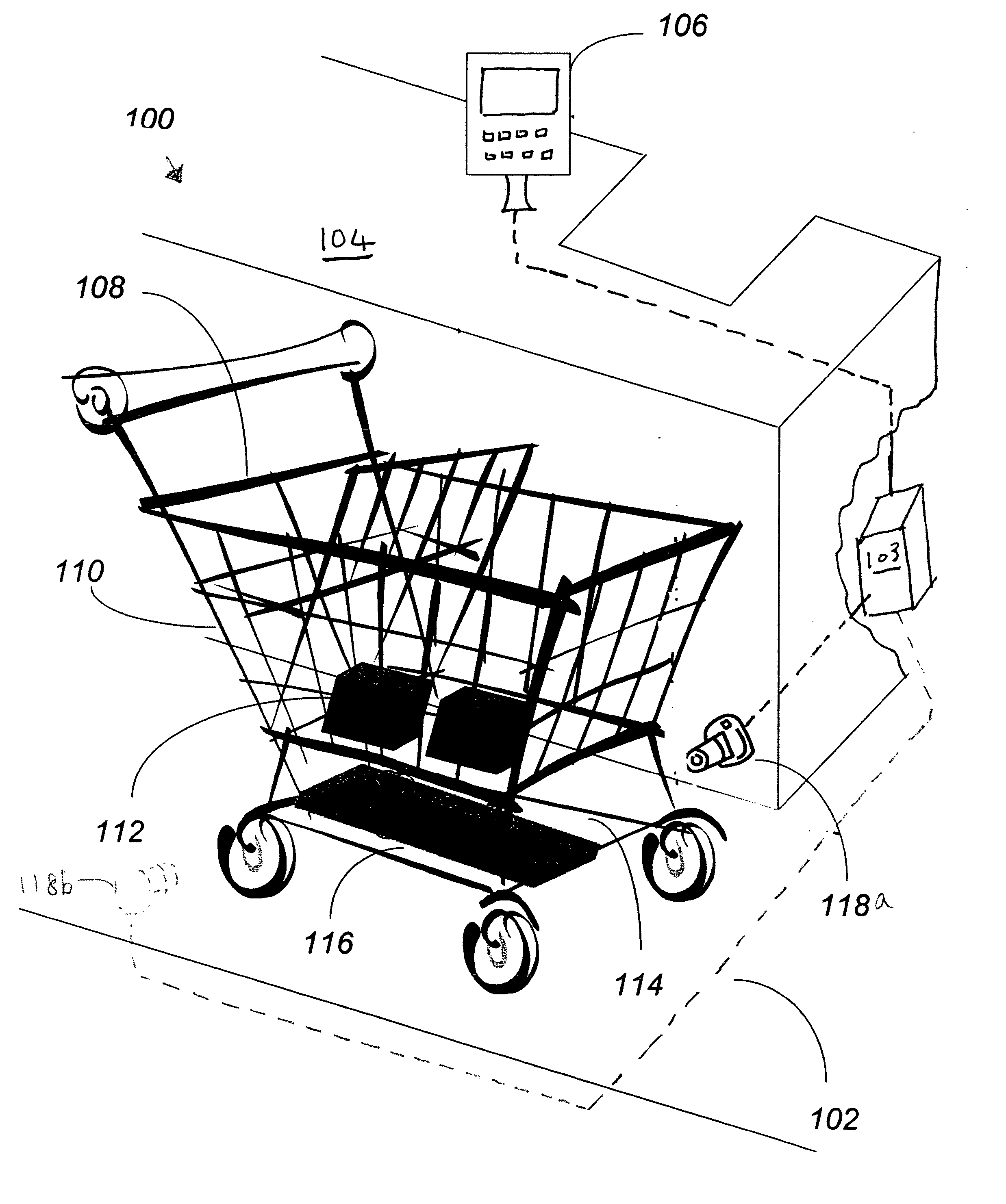
Methods and computer readable media for recognizing and identifying items located on the belt of a counter and / or in a shopping cart of a store environment for the purpose of reducing / preventing bottom-of-the-basket loss, checking out the items automatically, reducing the checkout time, preventing consumer fraud, increasing revenue and replacing a conventional UPC scanning system to enhance the checking out speed. The images of the items taken by visual sensors may be analyzed to extract features using the scale-invariant feature-transformation (SIFT) method. Then, the extracted features are compared to those of trained images stored in a database to find a set of matches. Based on the set of matches, the items are recognized and associated with one or more instructions, commands or actions without the need for personnel to visually see the items, such as by having to come out from behind a check out counter or peering over a check out counter.
Owner:DATALOGIC ADC
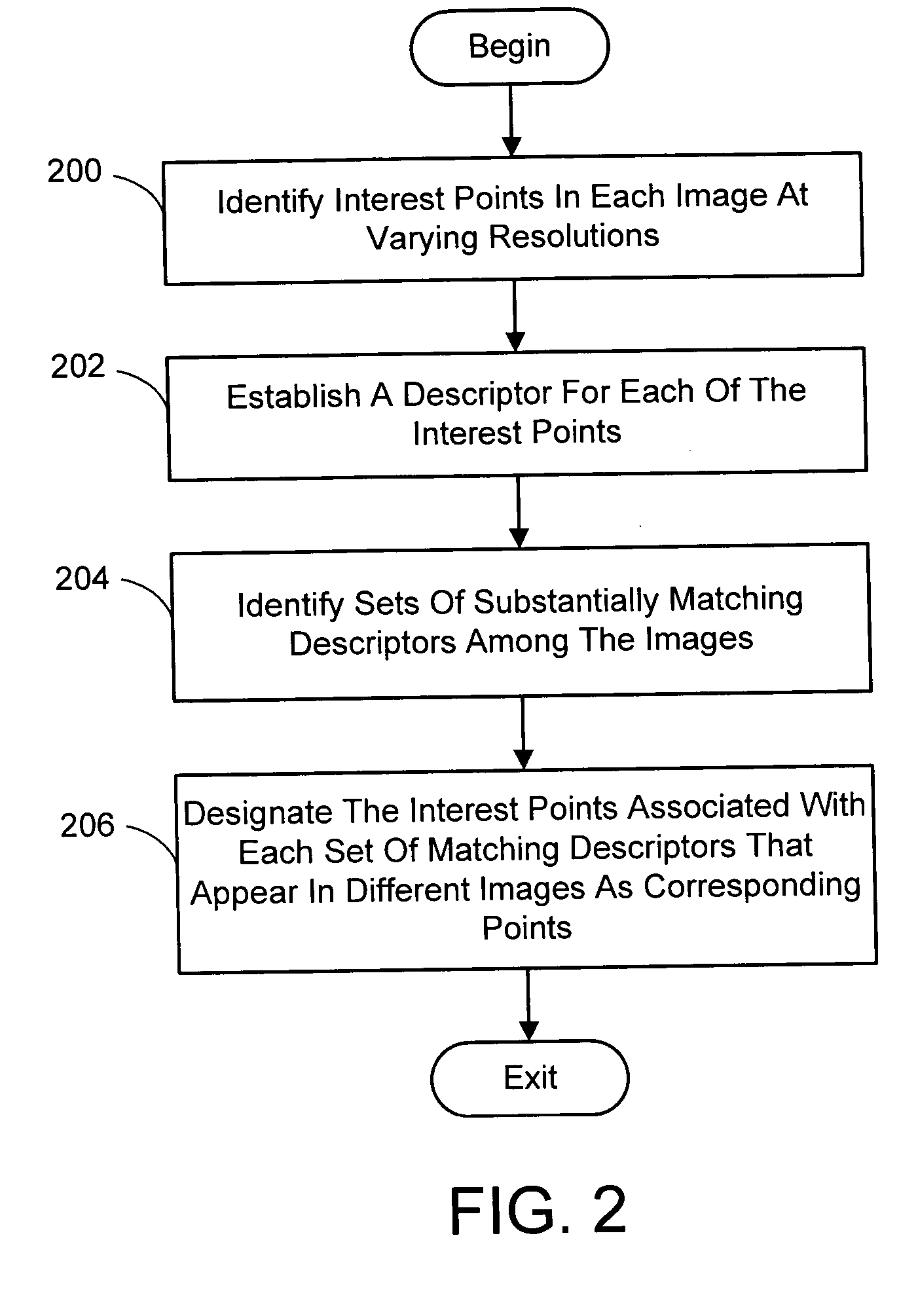
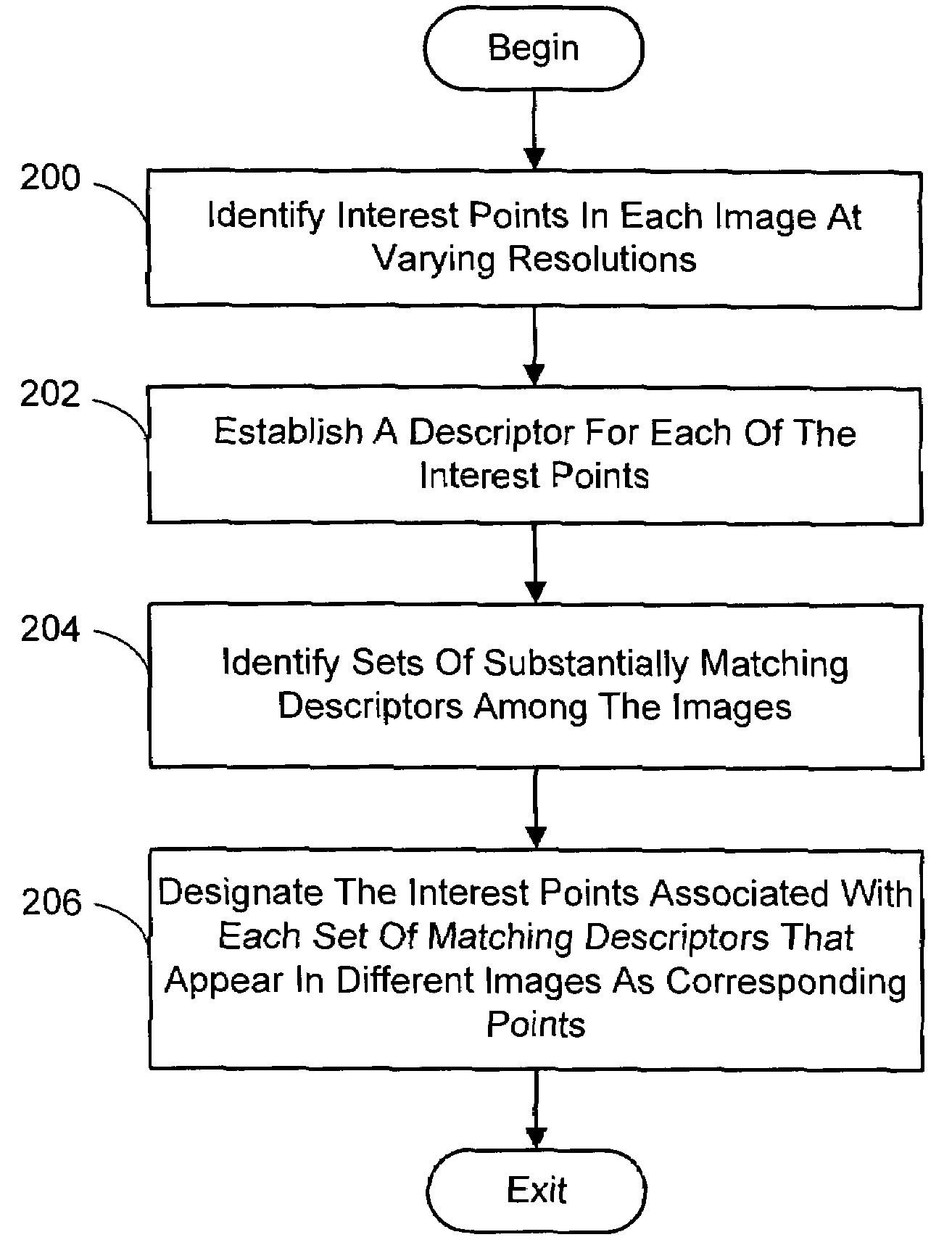
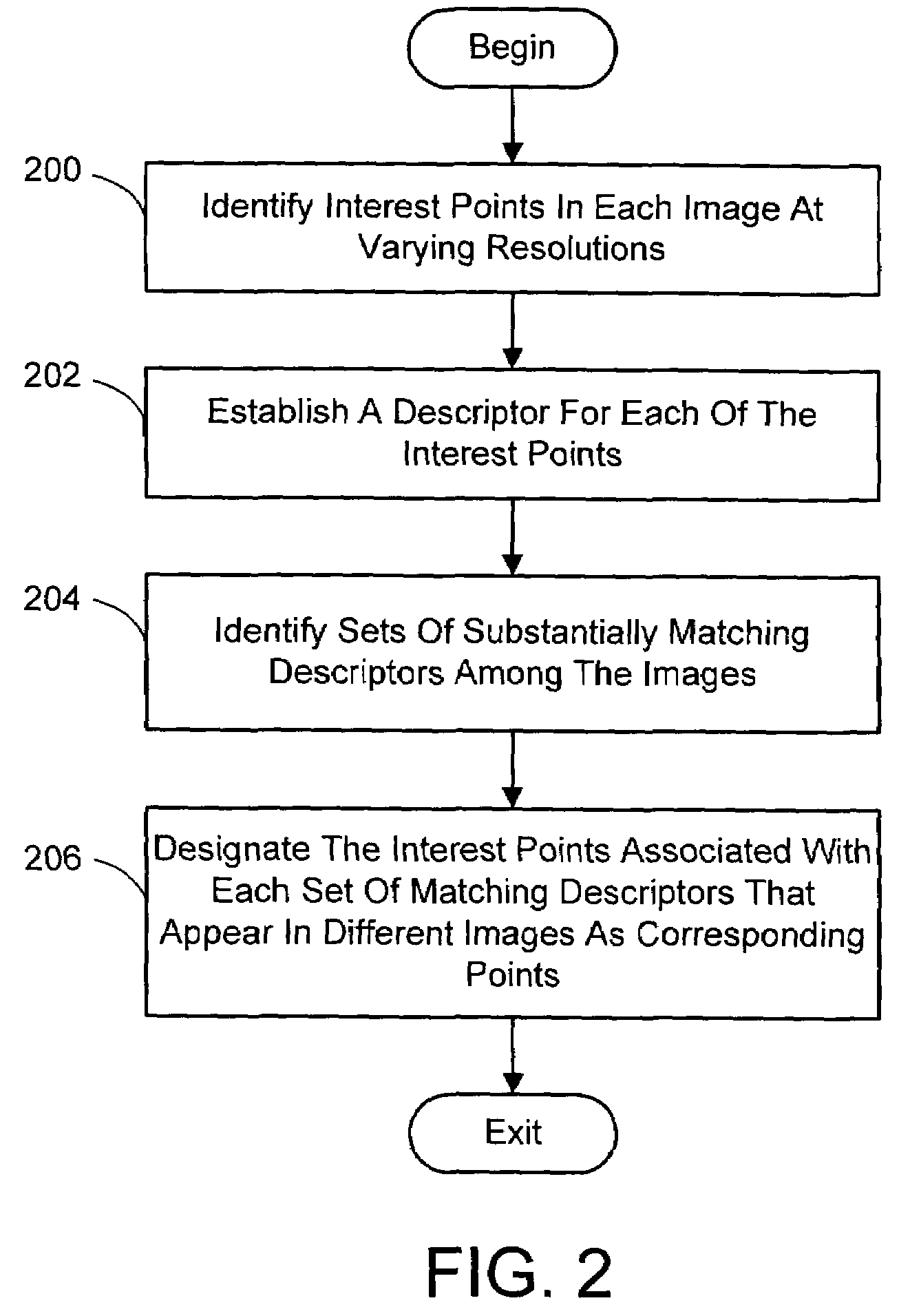
Multi-image feature matching using multi-scale oriented patches
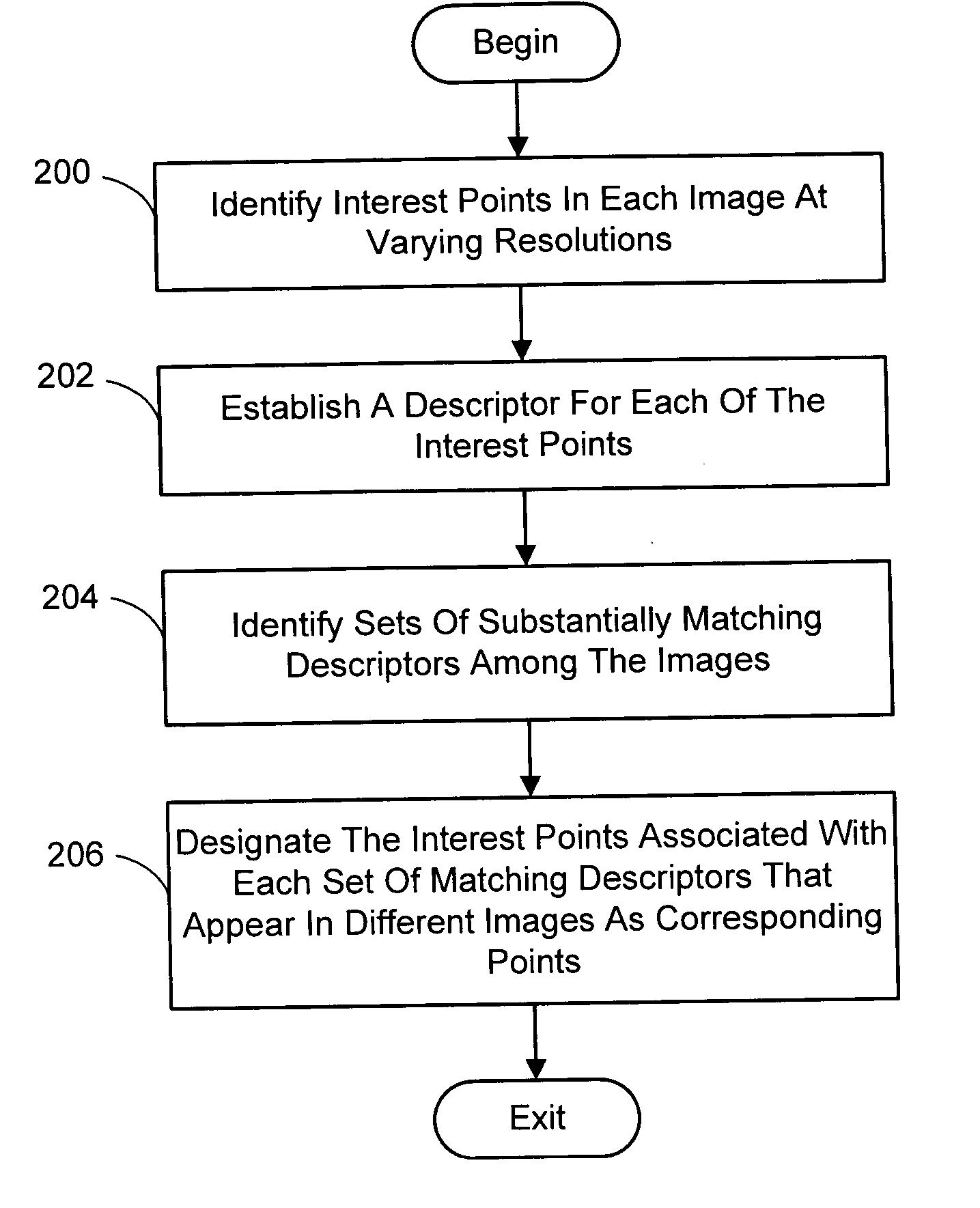
InactiveUS20050238198A1Quick extractionEasy to liftConveyorsImage analysisPattern recognitionNear neighbor
A system and process for identifying corresponding points among multiple images of a scene is presented. This involves a multi-view matching framework based on a new class of invariant features. Features are located at Harris corners in scale-space and oriented using a blurred local gradient. This defines a similarity invariant frame in which to sample a feature descriptor. The descriptor actually formed is a bias / gain normalized patch of intensity values. Matching is achieved using a fast nearest neighbor procedure that uses indexing on low frequency Haar wavelet coefficients. A simple 6 parameter model for patch matching is employed, and the noise statistics are analyzed for correct and incorrect matches. This leads to a simple match verification procedure based on a per feature outlier distance.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
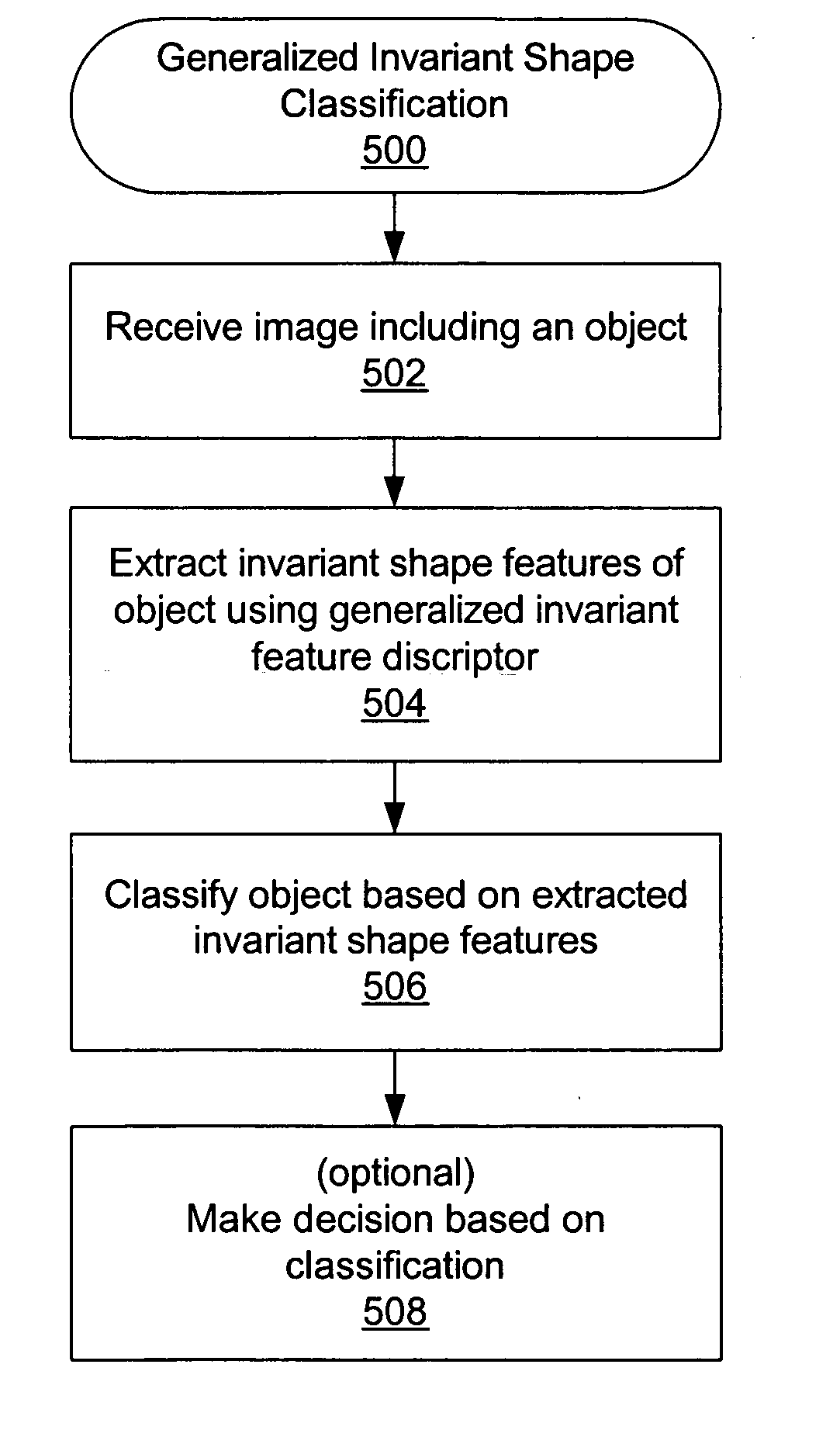
Shape feature extraction and classification
ActiveUS20060008151A1Facilitates characterizationFacilitates discriminationCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorComputer science
System and method for analyzing an image. A received image, comprising an object or objects, is optionally preprocessed. Invariant shape features of the object(s) are extracted using a generalized invariant feature descriptor. The generalized invariant feature descriptor may comprise a generalized invariant feature vector comprising components corresponding to attributes of each object, e.g., related to circularity, elongation, perimeter-ratio-based convexity, area-ratio-based convexity, hole-perimeter-ratio, hole-area-ratio, and / or functions of Hu Moment 1 and / or Hu Moment 2. Non-invariant features, e.g., scale and reflection, may be extracted to form corresponding feature vectors. The object is classified by computing differences between the generalized invariant feature vector (and optionally, non-invariant feature vectors) and respective generalized invariant feature vectors corresponding to reference objects, determining a minimum difference corresponding to a closest reference object or class of reference objects of the plurality of reference objects, and outputting an indication of the closest reference object or class as the classification.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Processing pose data derived from the pose of an elongate object
ActiveUS20050168437A1Apparent advantageInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsTemporal resolutionImage resolution
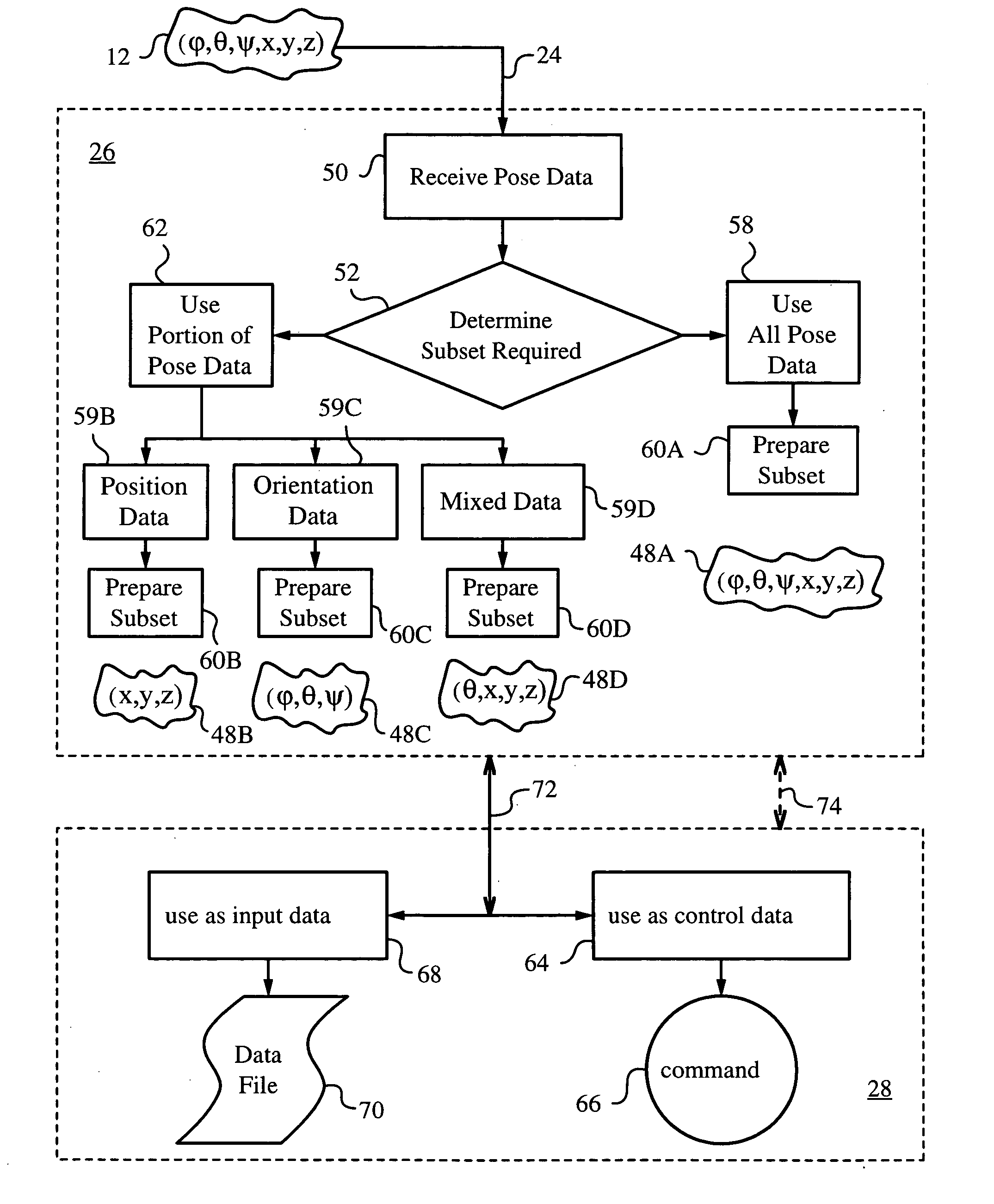
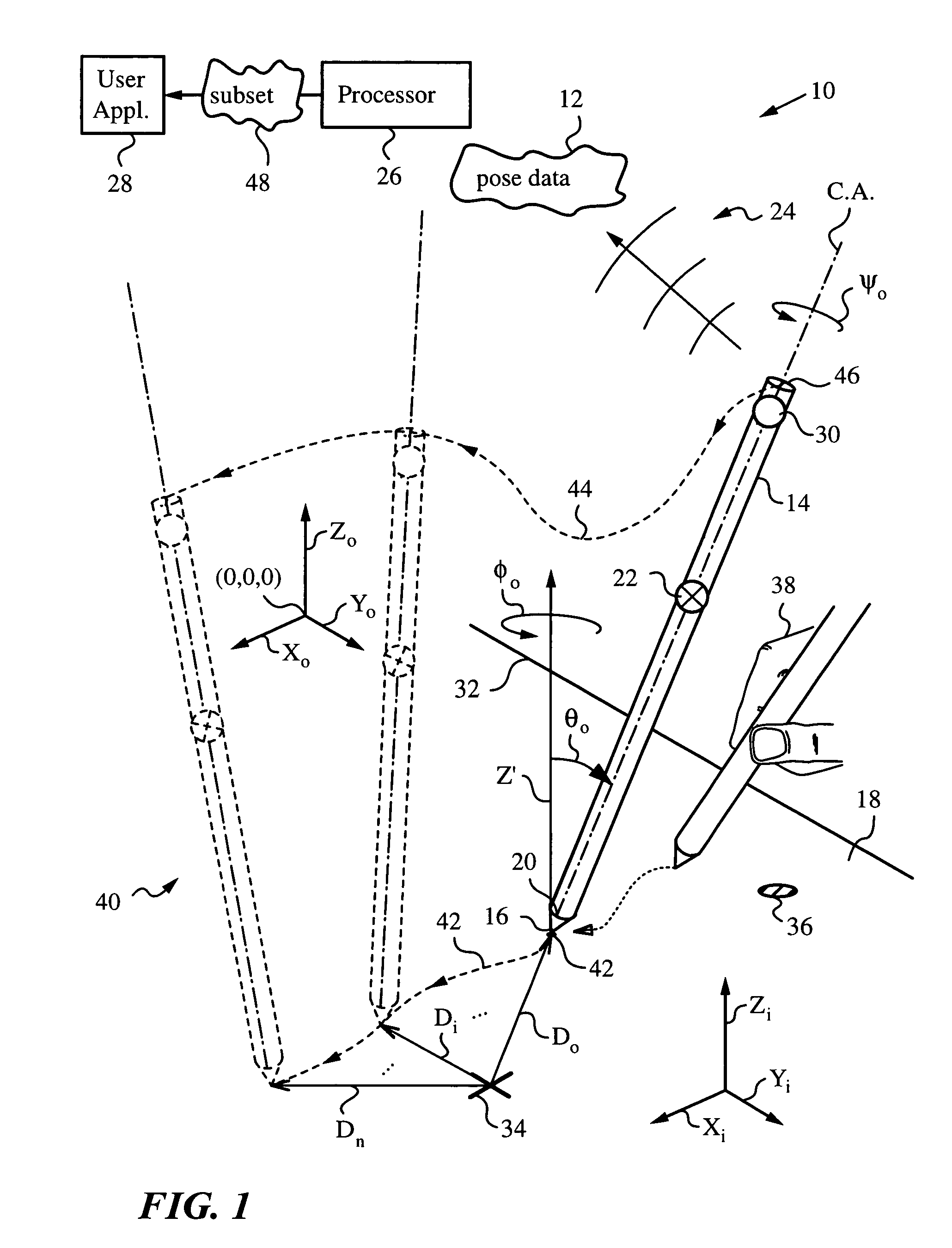
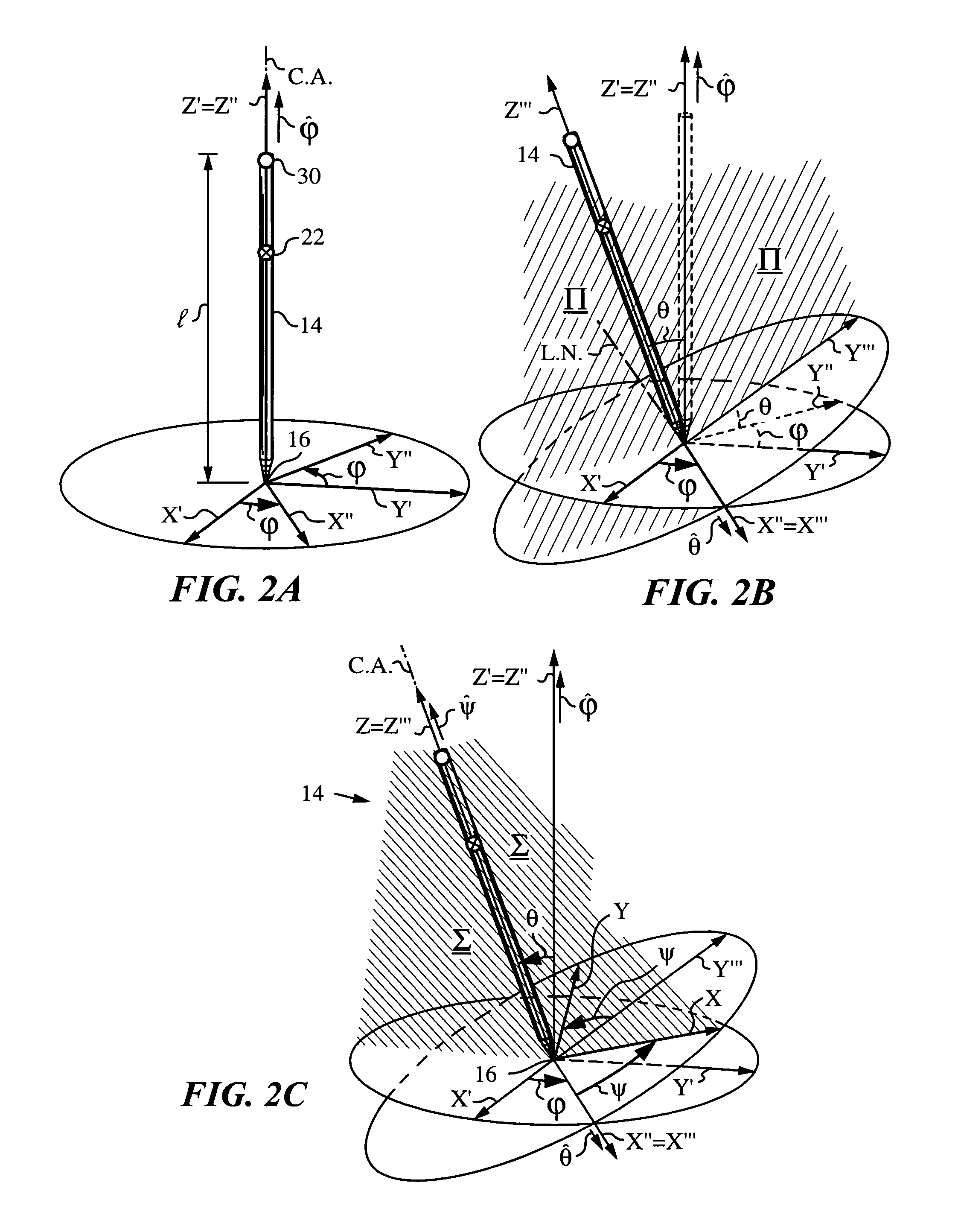
An apparatus and method for processing pose data derived from a pose of an elongate object such as, for example, a jotting implement, a pointer, a robotic arm or a cane. The elongate object has a tip contacting a plane surface with one or more invariant features. The pose of the elongate object is measured optically from on-board by an optical measuring system with the aid of the invariant feature. The pose is used for preparing a corresponding pose data and a subset of the pose data is identified and transmitted to an application such as a user application, where the subset can serve as command data or input data. Since the elongate object moves while its tip is contacting the surface the pose is measured periodically at sufficiently frequent measurement times ti to describe the motion at a desired temporal resolution. The subset can include all or a portion of the orientation data that describe the orientation of the elongate object in space and / or position data of the tip on the surface. The position can be a relative position of the tip with respect to any feature or its previous position, or an absolute position in world coordinates. The subset can also contain a mix of orientation and position data.
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
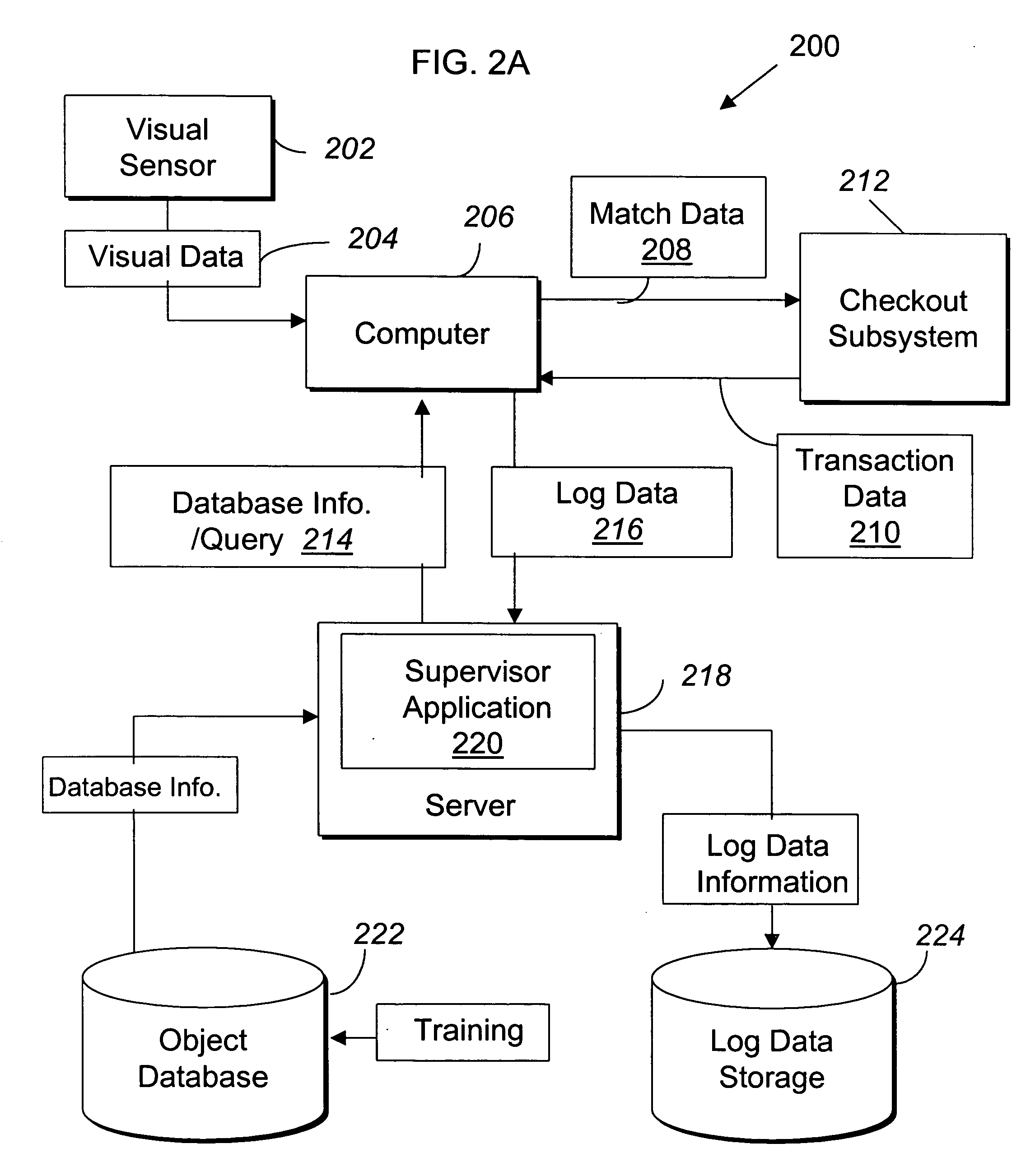
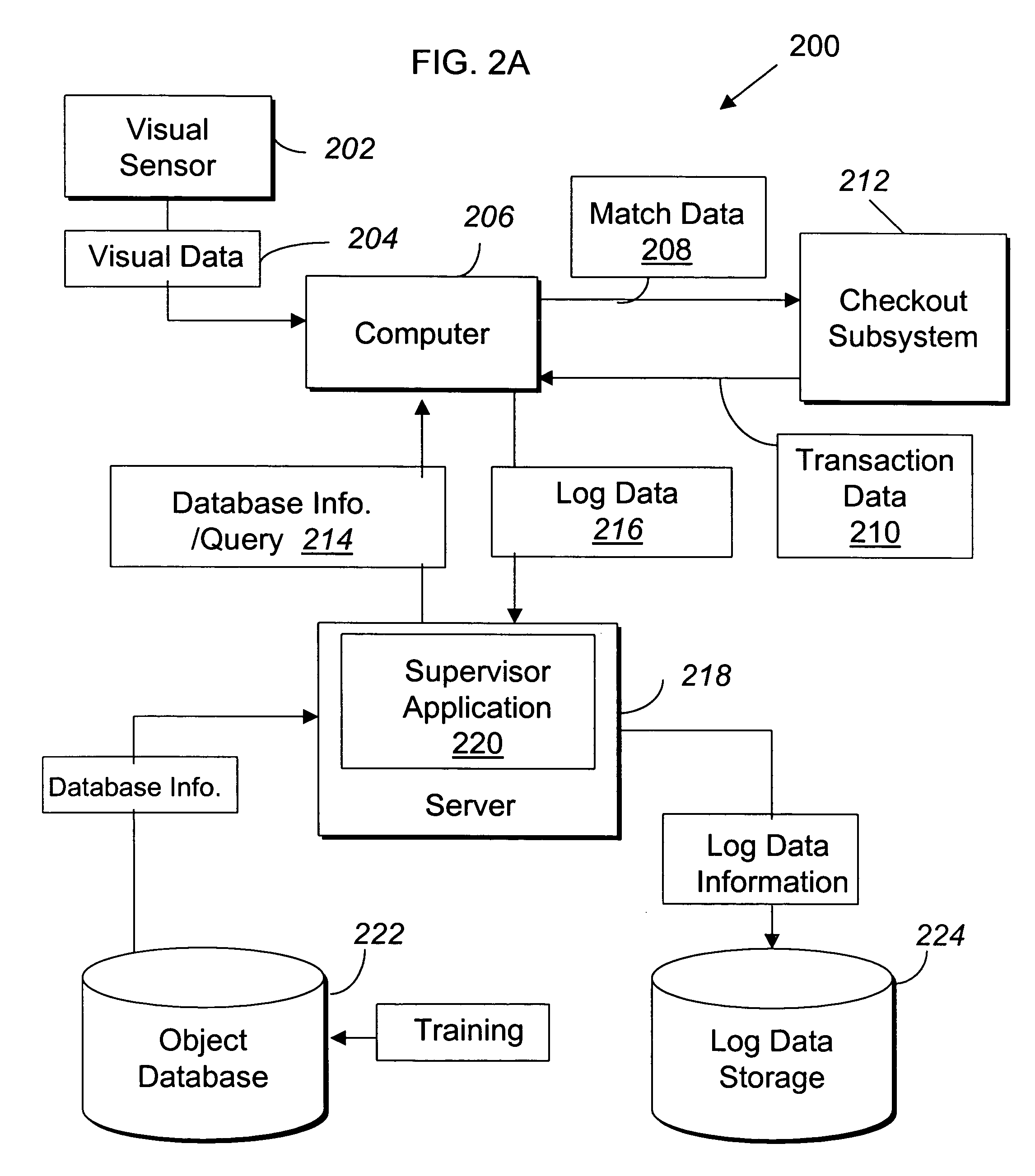
Systems and methods for merchandise checkout
ActiveUS20050189411A1Reduce and prevent lossReduce and prevent and fraudCredit registering devices actuationCash registersPattern recognitionVision sensor
Systems and methods for recognizing and identifying items located on the lower shelf of a shopping cart in a checkout lane of a retail store environment for the purpose of reducing or preventing loss or fraud and increasing the efficiency of a checkout process. The system includes one or more visual sensors that can take images of items and a computer system that receives the images from the one or more visual sensors and automatically identifies the items. The system can be trained to recognize the items using images taken of the items. The system relies on matching visual features from training images to match against features extracted from images taken at the checkout lane. Using the scale-invariant feature transformation (SIFT) method, for example, the system can compare the visual features of the images to the features stored in a database to find one or more matches, where the found one or more matches are used to identify the items.
Owner:DATALOGIC ADC
Method of merchandising for checkout lanes
ActiveUS7246745B2Reduces or prevents bottom-of-the-basket lossIncrease speedCredit registering devices actuationCash registersComing outArtificial intelligence
Owner:DATALOGIC ADC
Improved multi-instrument reading identification method of transformer station inspection robot
InactiveCN103927507AImprove robustnessMeet the requirements of automatic detection and identification of readingsCharacter and pattern recognitionHough transformScale-invariant feature transform
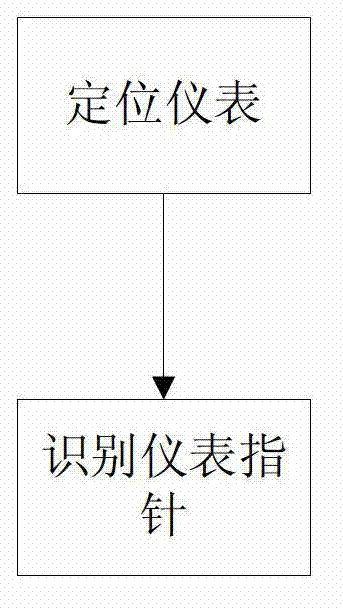
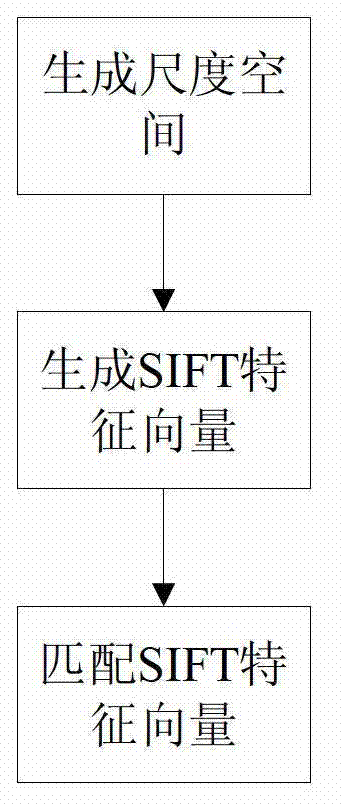
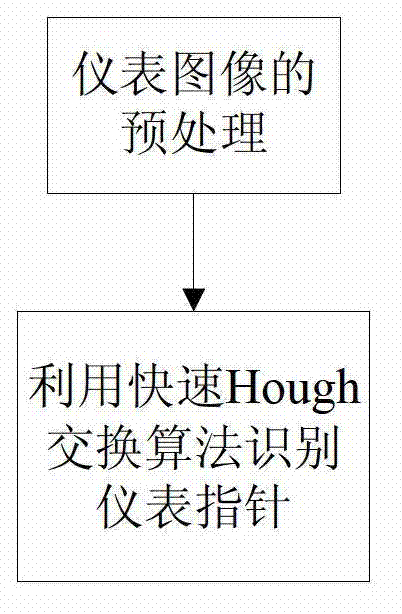
The invention discloses an improved multi-instrument reading identification method of a transformer station inspection robot. In the method, first of all, for instrument equipment images of different types, equipment template processing is carried out, and position information of min scales and max scales of each instrument in a template database. For the instrument equipment images acquired in real time by the robot, a template graph of a corresponding piece of equipment is scheduled from a background service, by use of a scale invariant feature transform (SIFT) algorithm, an instrument dial plate area sub-image is extracted in an input image in a matching mode, afterwards, binary and instrument point backbone processing is performed on the dial plate sub-image, by use of rapid Hough transform, pointer lines are detected, noise interference is eliminated, accurate position and directional angel of a pointer are accurately positioned, and pointer reading is finished. Such an algorithm is subjected to an on-site test of some domestic 500 kv intelligent transformer station inspection robot, the integration recognition rate of various instruments exceeds 99%, the precision and robustness for instrument reading are high, and the requirement for on-site application of a transformer station is completely satisfied.
Owner:STATE GRID INTELLIGENCE TECH CO LTD
Remote sensing image registration method of multi-source sensor
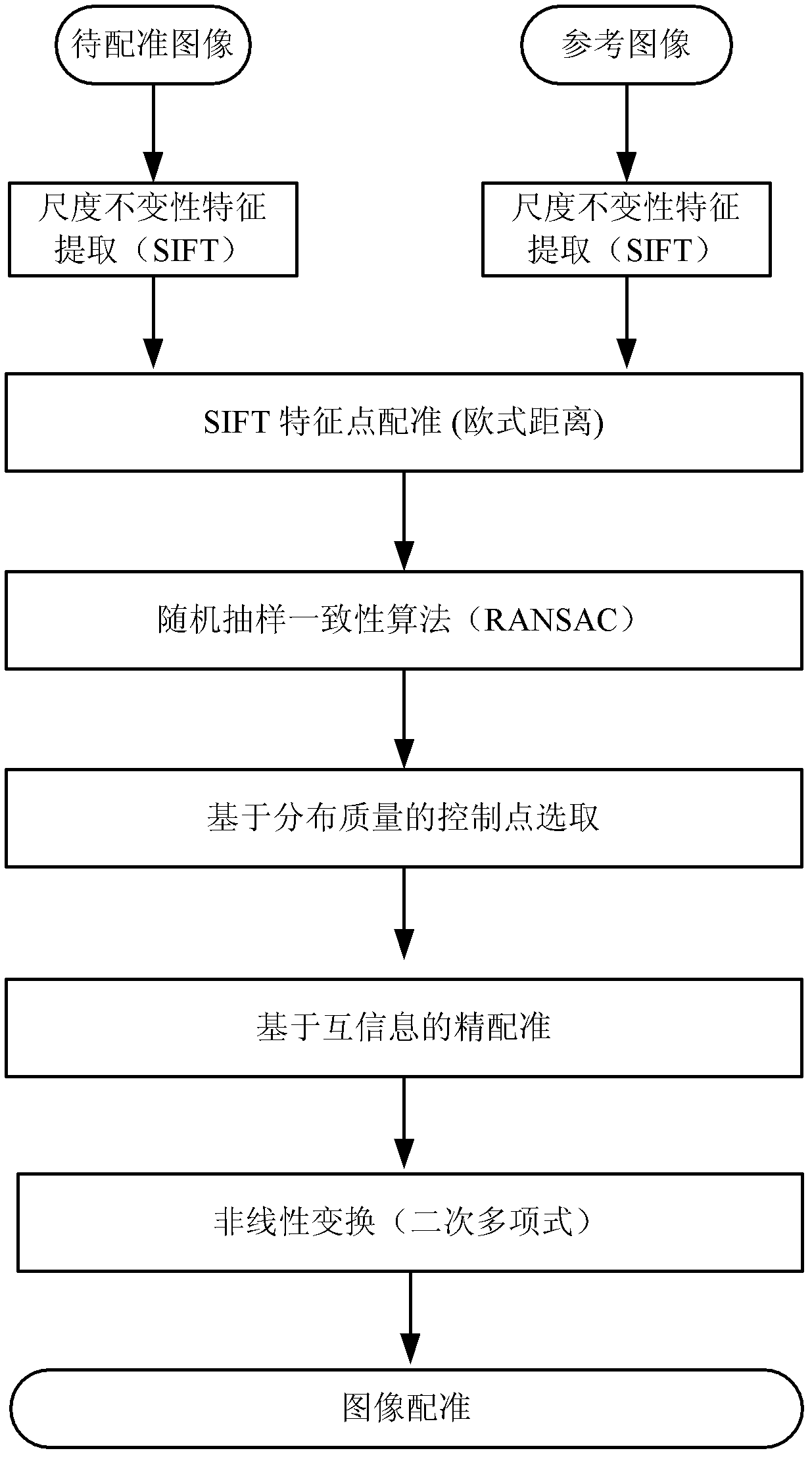
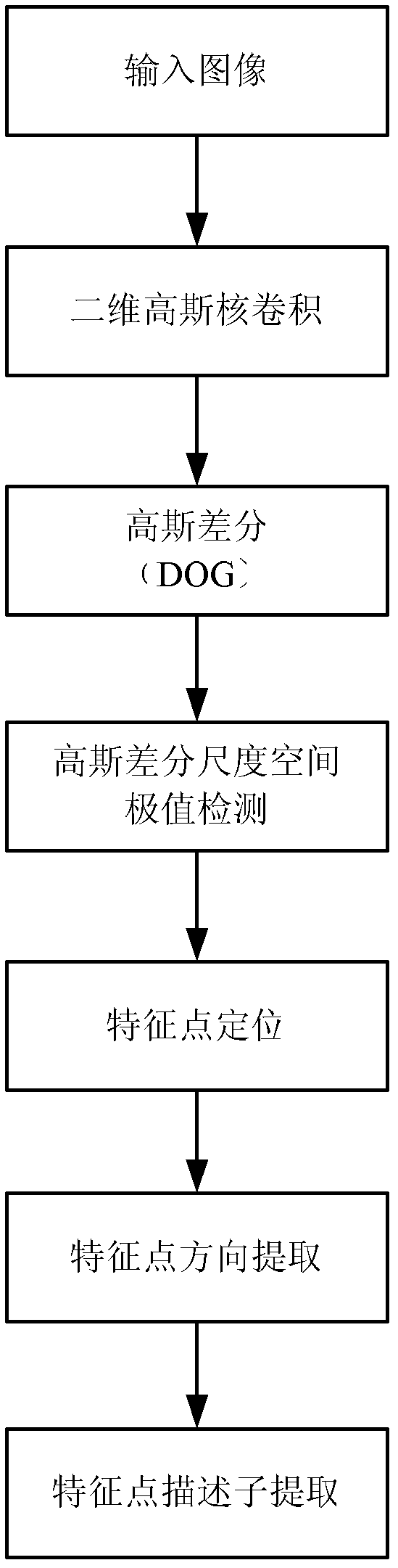
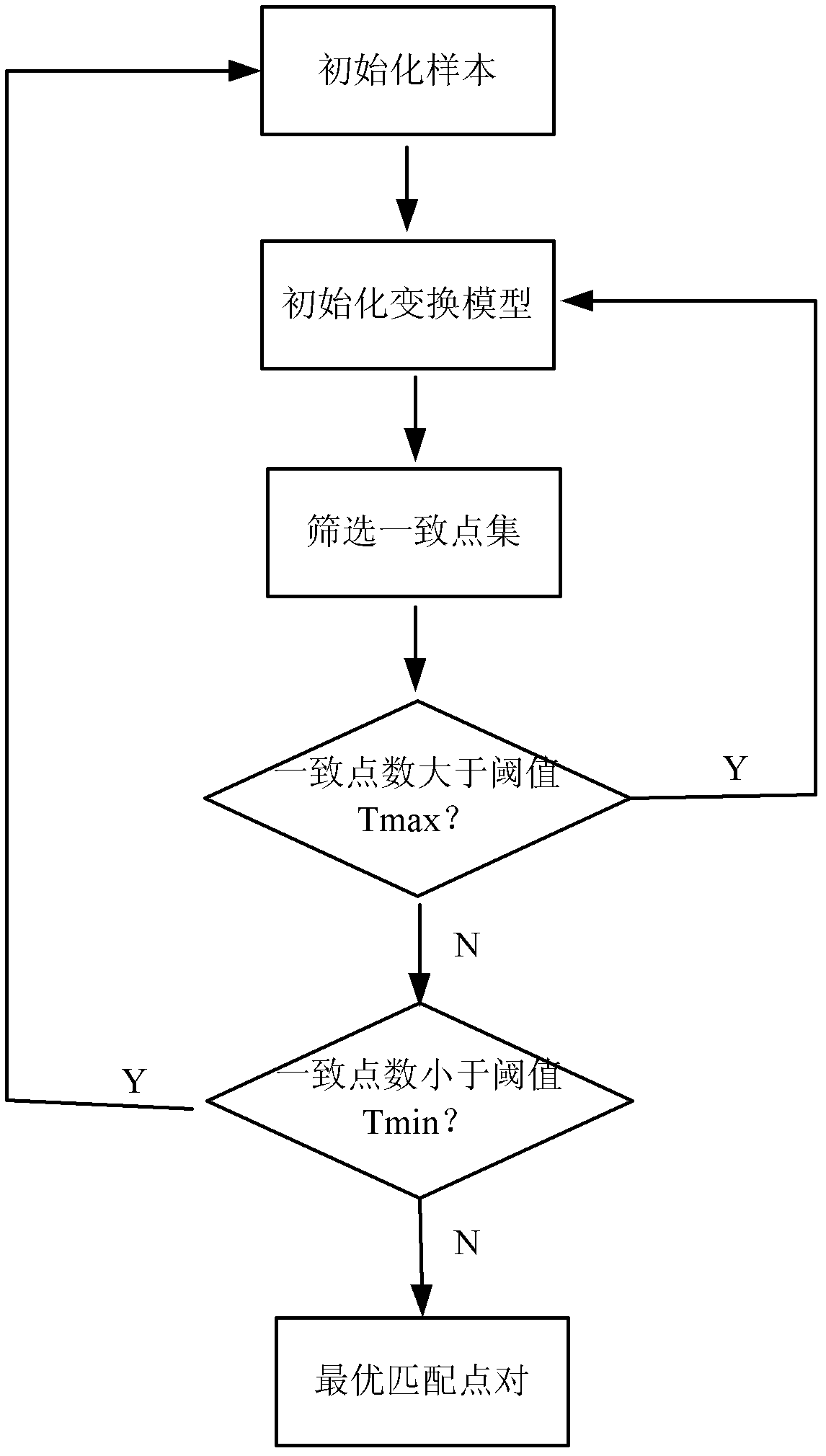
ActiveCN103020945AQuick registrationPrecise registrationImage analysisWeight coefficientMutual information
The invention provides a remote sensing image registration method of a multi-source sensor, relating to an image processing technology. The remote sensing image registration method comprises the following steps of: respectively carrying out scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT) on a reference image and a registration image, extracting feature points, calculating the nearest Euclidean distances and the nearer Euclidean distances of the feature points in the image to be registered and the reference image, and screening an optimal matching point pair according to a ratio; rejecting error registration points through a random consistency sampling algorithm, and screening an original registration point pair; calculating distribution quality parameters of feature point pairs and selecting effective control point parts with uniform distribution according to a feature point weight coefficient; searching an optimal registration point in control points of the image to be registered according to a mutual information assimilation judging criteria, thus obtaining an optimal registration point pair of the control points; and acquiring a geometric deformation parameter of the image to be registered by polynomial parameter transformation, thus realizing the accurate registration of the image to be registered and the reference image. The remote sensing image registration method provided by the invention has the advantages of high calculation speed and high registration precision, and can meet the registration requirements of a multi-sensor, multi-temporal and multi-view remote sensing image.
Owner:济钢防务技术有限公司
System and methods for merchandise checkout
ActiveUS7100824B2Increase incomeReduce or prevent loss or fraudCredit registering devices actuationCash registersPattern recognitionComputerized system
Systems and methods for recognizing and identifying items located on the lower shelf of a shopping cart in a checkout lane of a retail store environment for the purpose of reducing or preventing loss or fraud and increasing the efficiency of a checkout process. The system includes one or more visual sensors that can take images of items and a computer system that receives the images from the one or more visual sensors and automatically identifies the items. The system can be trained to recognize the items using images taken of the items. The system relies on matching visual features from training images to match against features extracted from images taken at the checkout lane. Using the scale-invariant feature transformation (SIFT) method, for example, the system can compare the visual features of the images to the features stored in a database to find one or more matches, where the found one or more matches are used to identify the items.
Owner:DATALOGIC ADC
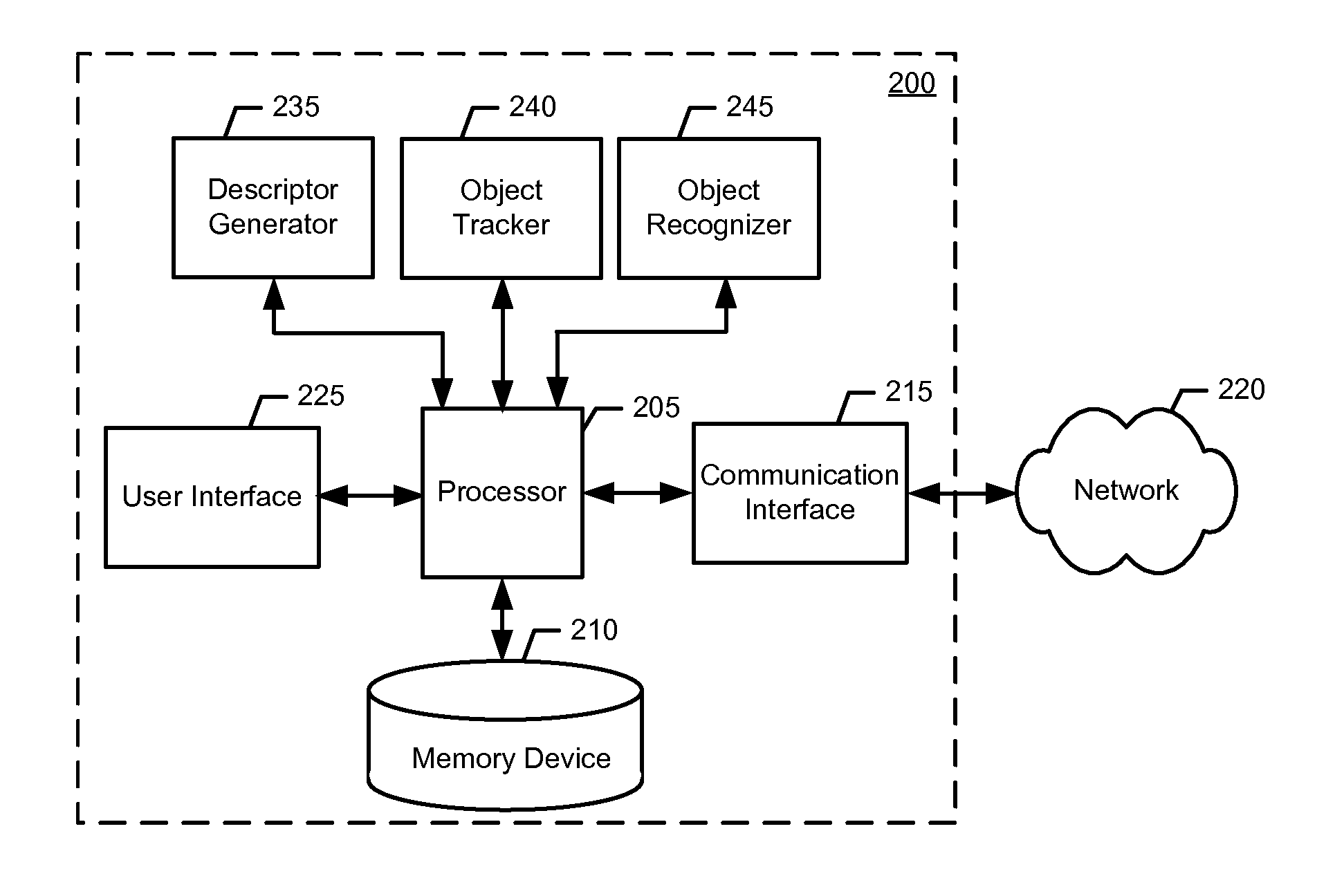
Method and apparatus for tracking and recognition with rotation invariant feature descriptors
ActiveUS20110286627A1Sufficiently robustCheap computerImage enhancementImage analysisPyramidInvariant feature
Various methods for tracking and recognition with rotation invariant feature descriptors are provided. One example method includes generating an image pyramid of an image frame, detecting a plurality of interest points within the image pyramid, and extracting feature descriptors for each respective interest point. According to some example embodiments, the feature descriptors are rotation invariant. Further, the example method may also include tracking movement by matching the feature descriptors to feature descriptors of a previous frame and performing recognition of an object within the image frame based on the feature descriptors. Related example methods and example apparatuses are also provided.
Owner:NOKIA CORP +1
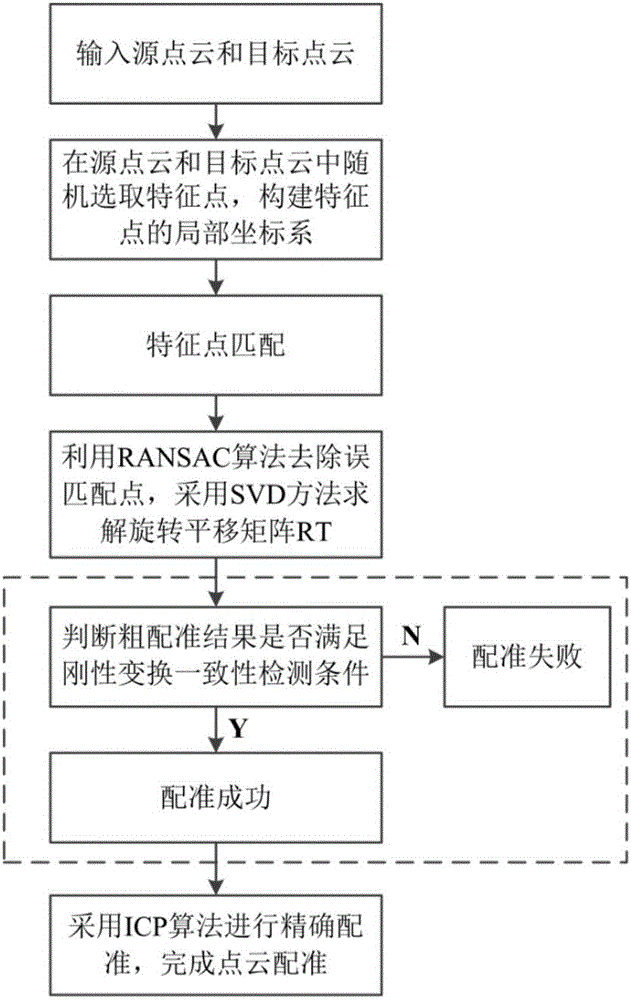
Automatic registration method for three-dimensional point cloud data
InactiveCN106780459AReduce manual pasteEliminate workloadImage enhancementImage analysisPoint cloudSystem transformation
The invention discloses an automatic registration method for three-dimensional point cloud data. The method comprises the steps that two point clouds to be registered are sampled to obtain feature points, rotation invariant feature factors of the feature points are calculated, and the rotation invariant feature factors of the feature points in the two point clouds are subjected to matching search to obtain an initial corresponding relation between the feature points; then, a random sample consensus algorithm is adopted to judge and remove mismatching points existing in an initial matching point set to obtain an optimized feature point corresponding relation, and a rough rigid transformation relation between the two point clouds is obtained through calculation to realize rough registration; a rigid transformation consistency detection algorithm is provided, a local coordinate system transformation relation between the matching feature points is utilized to perform binding detection on the rough registration result, and verification of the correctness of the rough registration result is completed; and an ICP algorithm is adopted to optimize the rigid transformation relation between the point cloud data to realize automatic precise registration of the point clouds finally.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
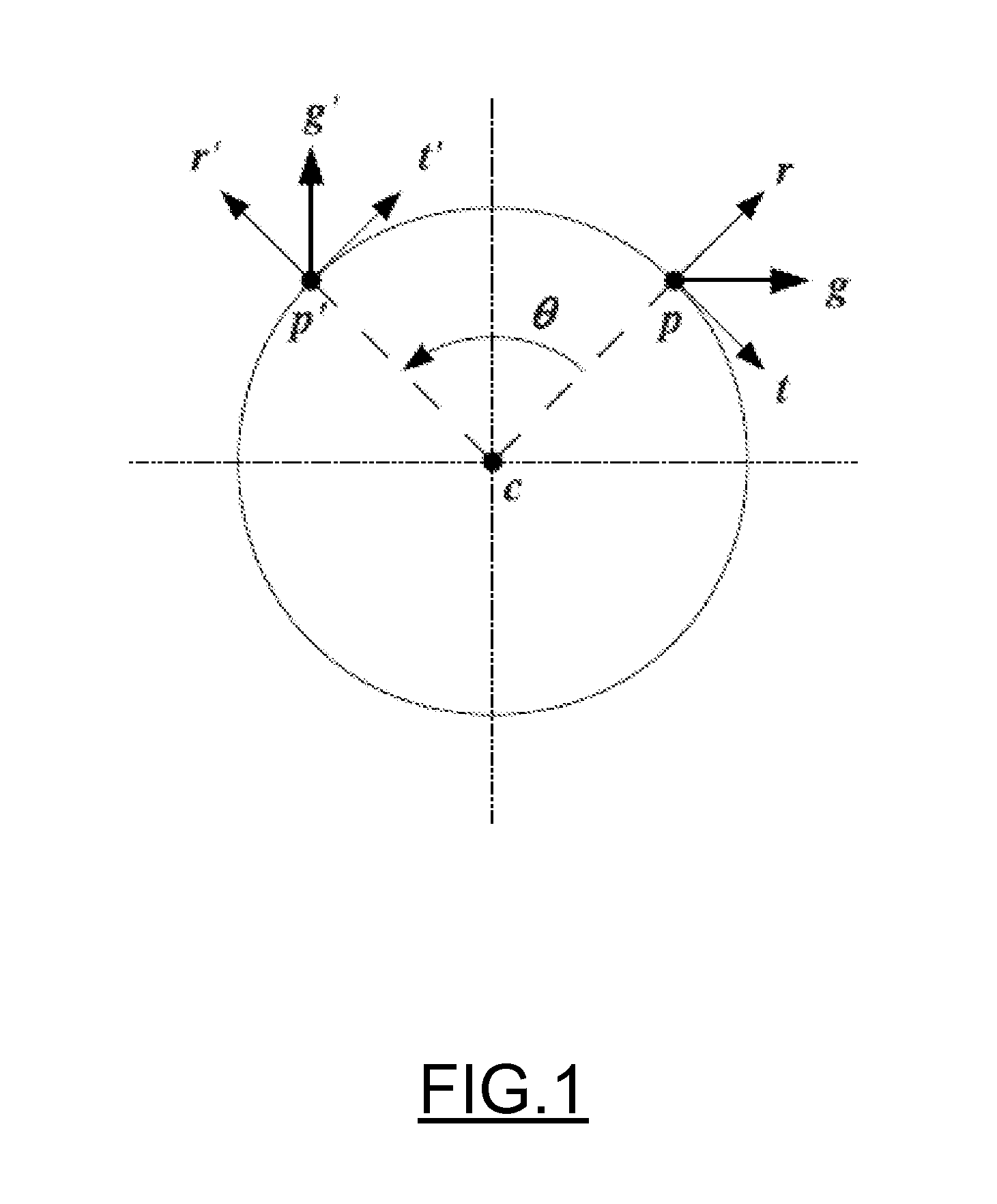
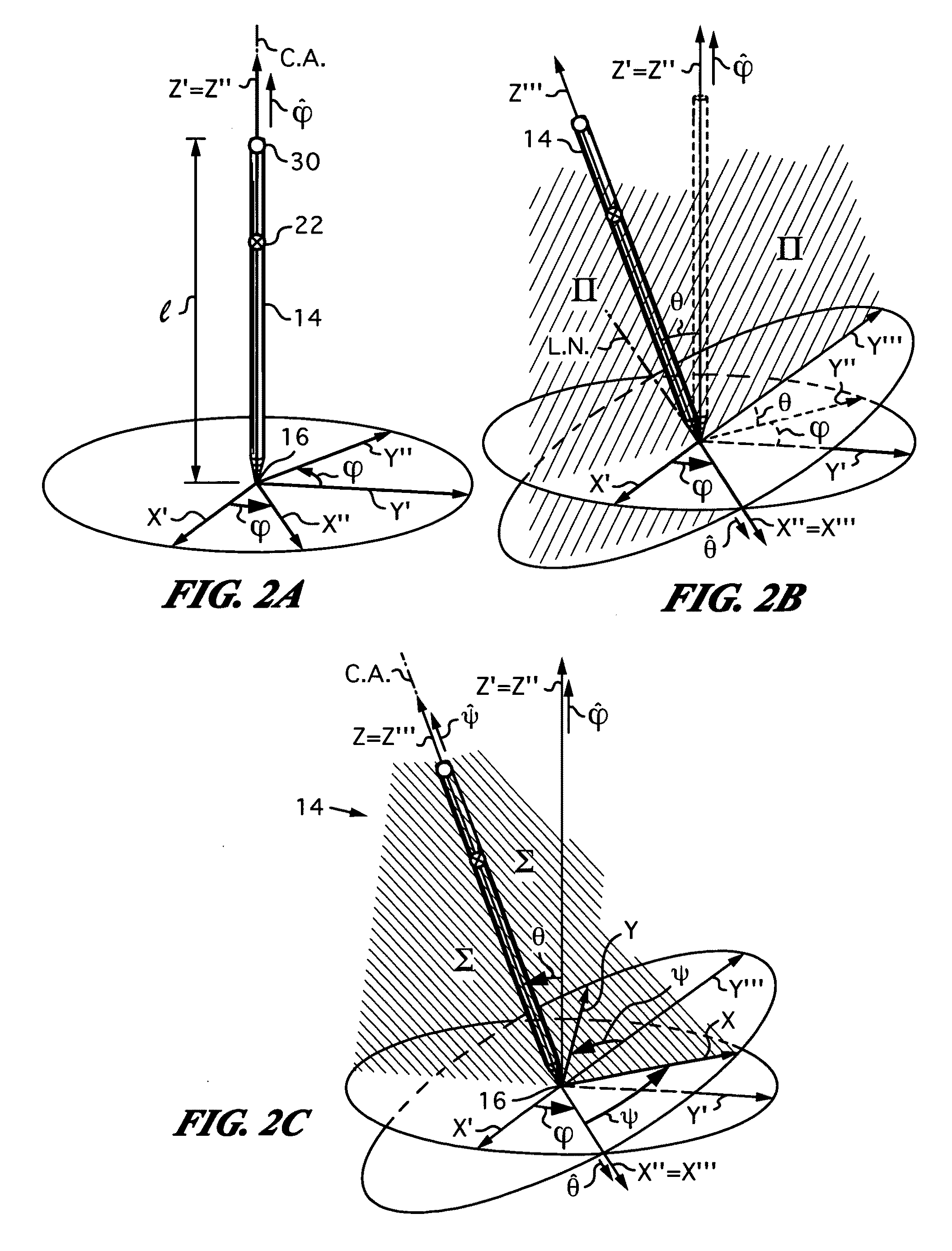
Apparatus and method for determining an absolute pose of a manipulated object in a real three-dimensional environment with invariant features
InactiveUS20100001998A1High optical contrastImproved signal-to-noise ratio performanceImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurement deviceTelecommunications link
An apparatus and method for optically inferring an absolute pose of a manipulated object in a real three-dimensional environment from on-board the object with the aid of an on-board optical measuring arrangement. At least one invariant feature located in the environment is used by the arrangement for inferring the absolute pose. The inferred absolute pose is expressed with absolute pose data (φ,θ,ψ,x,y,z) that represents Euler rotated object coordinates expressed in world coordinates (Xo,Yo,Zo) with respect to a reference location, such as, for example, the world origin. Other conventions for expressing absolute pose data in three-dimensional space and representing all six degrees of freedom (three translational degrees of freedom and three rotational degrees of freedom) are also supported. Irrespective of format, a processor prepares the absolute pose data and identifies a subset that may contain all or fewer than all absolute pose parameters. This subset is transmitted to an application via a communication link, where it is treated as input that allows a user of the manipulated object to interact with the application and its output.
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
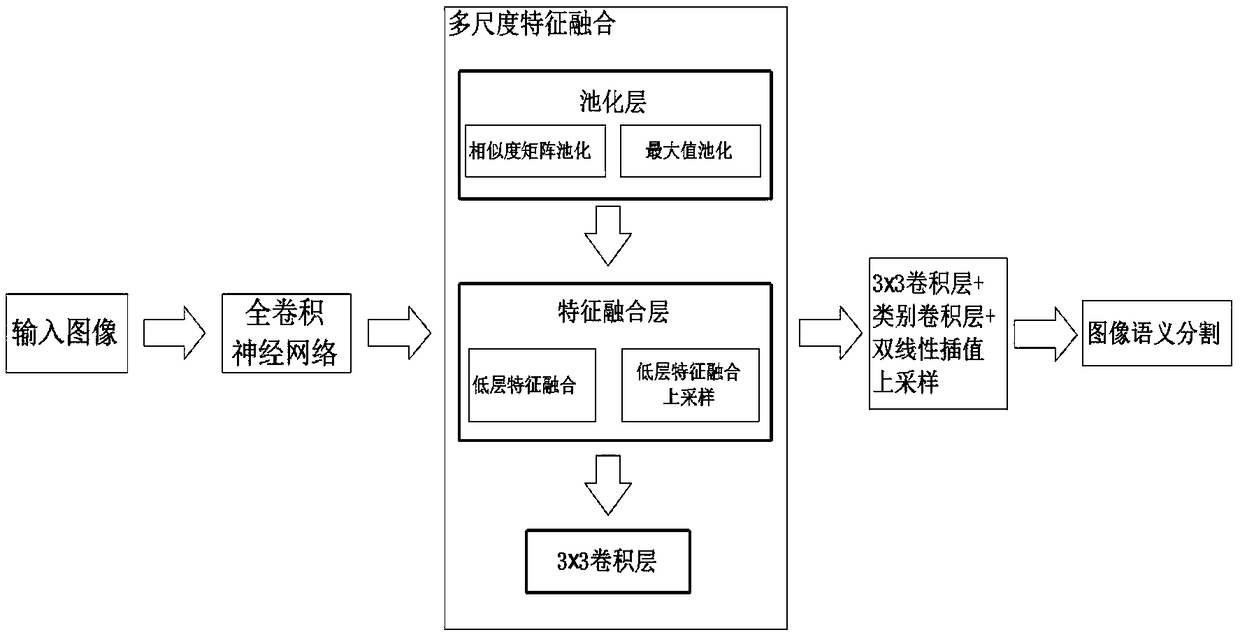
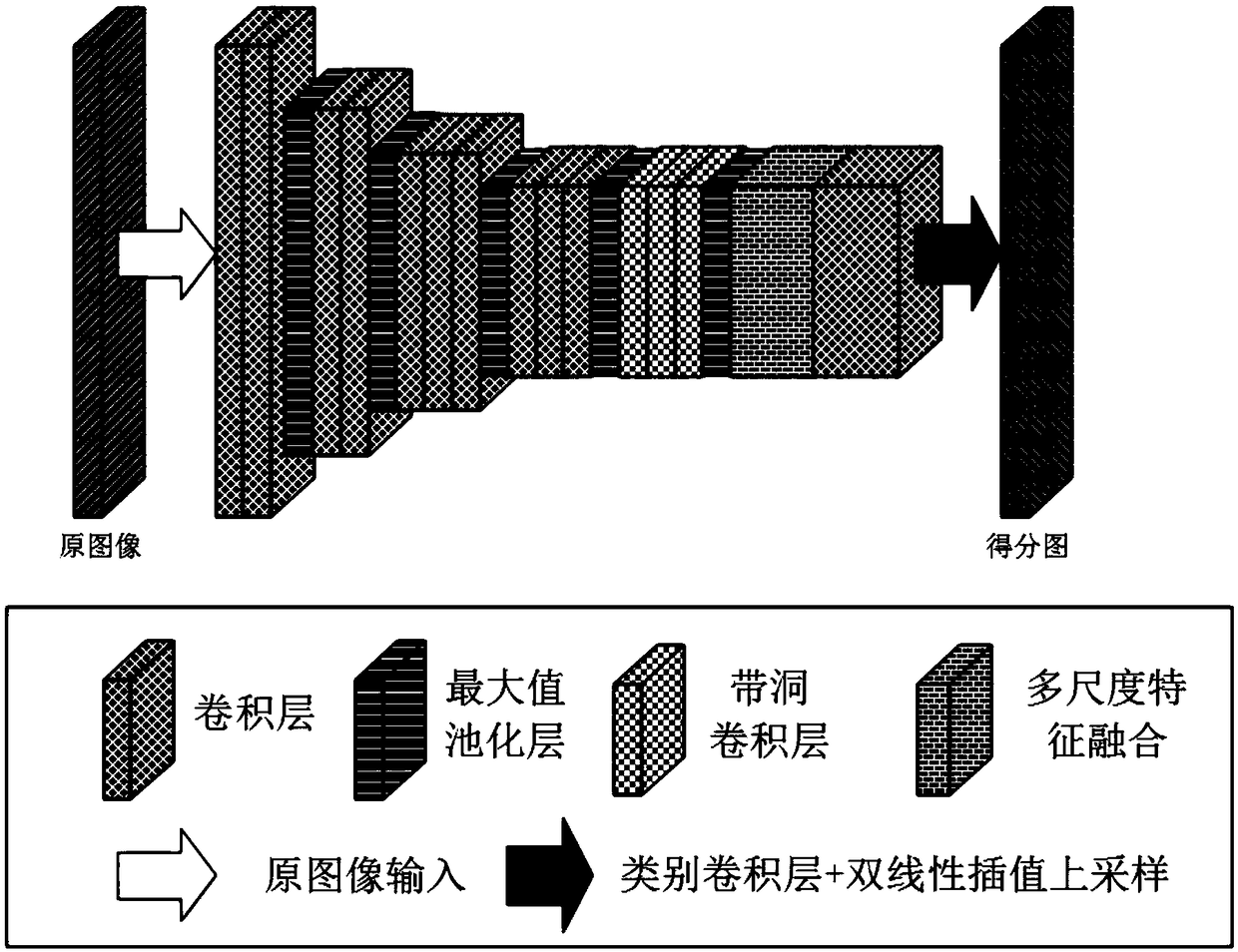
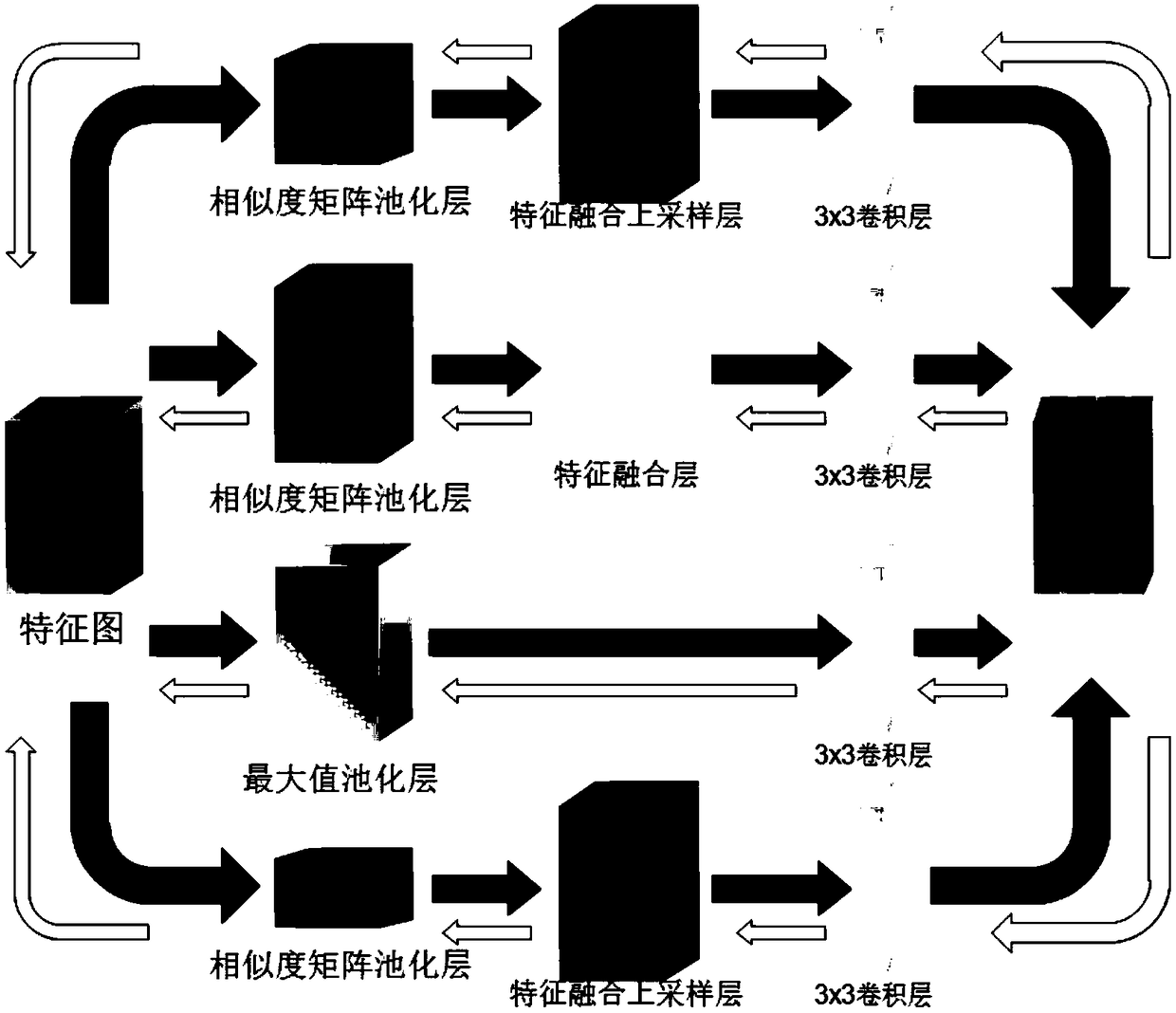
Full convolutional network semantic segmentation method based on multi-scale low-level feature fusion
ActiveCN108830855AEasy to identifyMulti-global feature informationImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionScale downDeep level
The invention discloses a full convolutional network (FCN) semantic segmentation method based on multi-scale low-level feature fusion. The method comprises firstly extracting the dense feature of an input image by using the FCN; and then subjecting the extracted feature images to multi-scale feature fusion, including steps of subjecting the input feature images to multi-scale pooling to form a plurality of processing branches; then performing low-level feature fusion on the pooled scale-invariant feature maps in respective branches and performing low-level feature fusion upsampling on the pooled scale-down feature maps in respective branches; inputting the feature maps into a 3*3 convolutional layer to learn deeper features and reduce the number of channels of output feature maps; then combining the output feature maps of respective branches in a channel number splicing manner, and obtaining a score map having a size the same as that of an original image by a class convolutional layerand bilinear interpolation upsampling. In combination with local low-level feature information and global multi-scale image information, the effect of image semantic segmentation is significant.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Multi-image feature matching using multi-scale oriented patches
InactiveUS7382897B2Quick extractionEasy to liftConveyorsImage analysisPattern recognitionNear neighbor
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
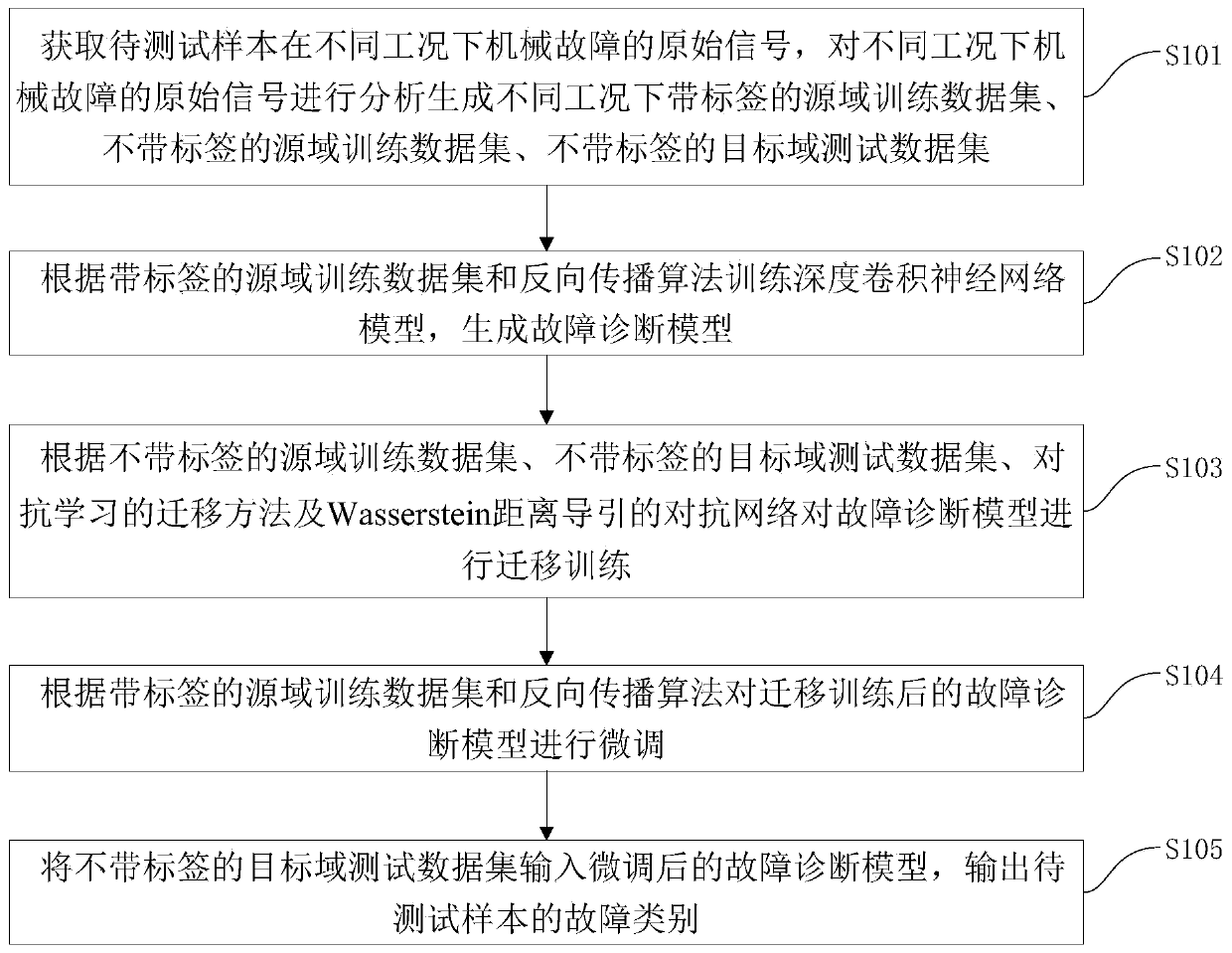
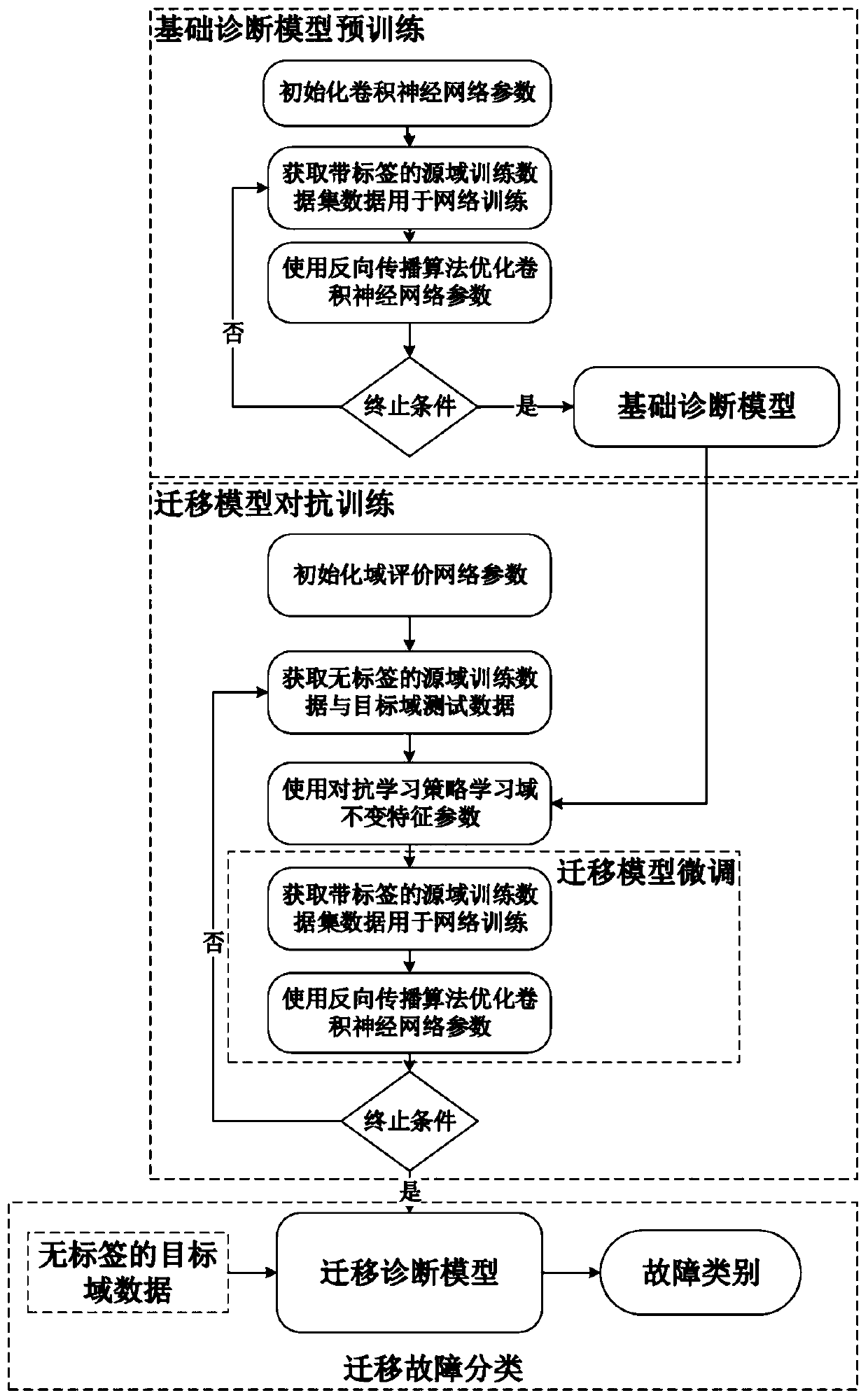
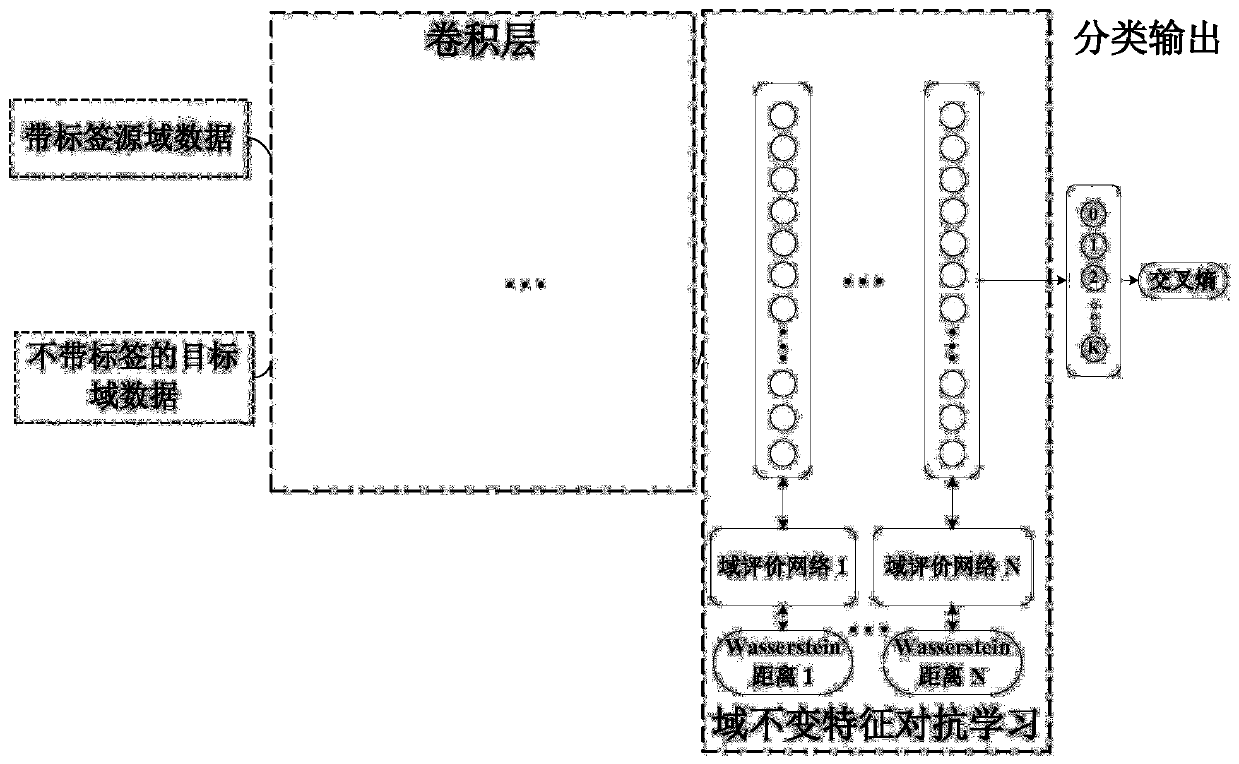
Mechanical failure migration diagnosis method and system based on adversarial learning
ActiveCN109947086AAchieve migrationAvoid Migration ProblemsElectric testing/monitoringNerve networkData set
The invention discloses a mechanical failure migration diagnosis method and system based on adversarial learning. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring and analyzing original signals ofmechanical failure under different working conditions to generate a labeled source domain training dataset, an unlabelled source domain training dataset and a target domain test dataset under different working conditions; training a deep convolutional neutral network model according to the labeled source domain training dataset and a back propagation algorithm to generate a failure diagnosis model; training the failure diagnosis model according to the unlabelled source domain training dataset and the target domain test dataset; fine adjusting the trained failure diagnosis model according to the labeled source domain training dataset and the back propagation algorithm; inputting the unlabelled target domain test dataset into the fine adjusted failure diagnosis model, and outputting the failure category of a to-be-tested sample. By means of the method, the domain invariant feature is obtained with the adversarial learning method, migration among different domains is realized, and intelligent diagnosis of mechanical failure under variable working conditions is realized.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
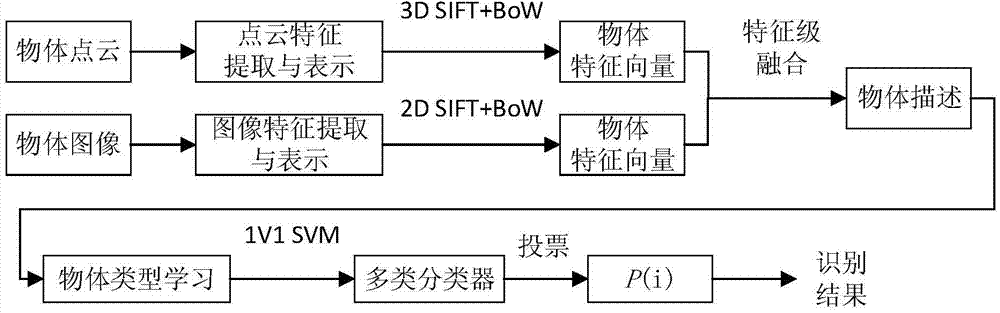
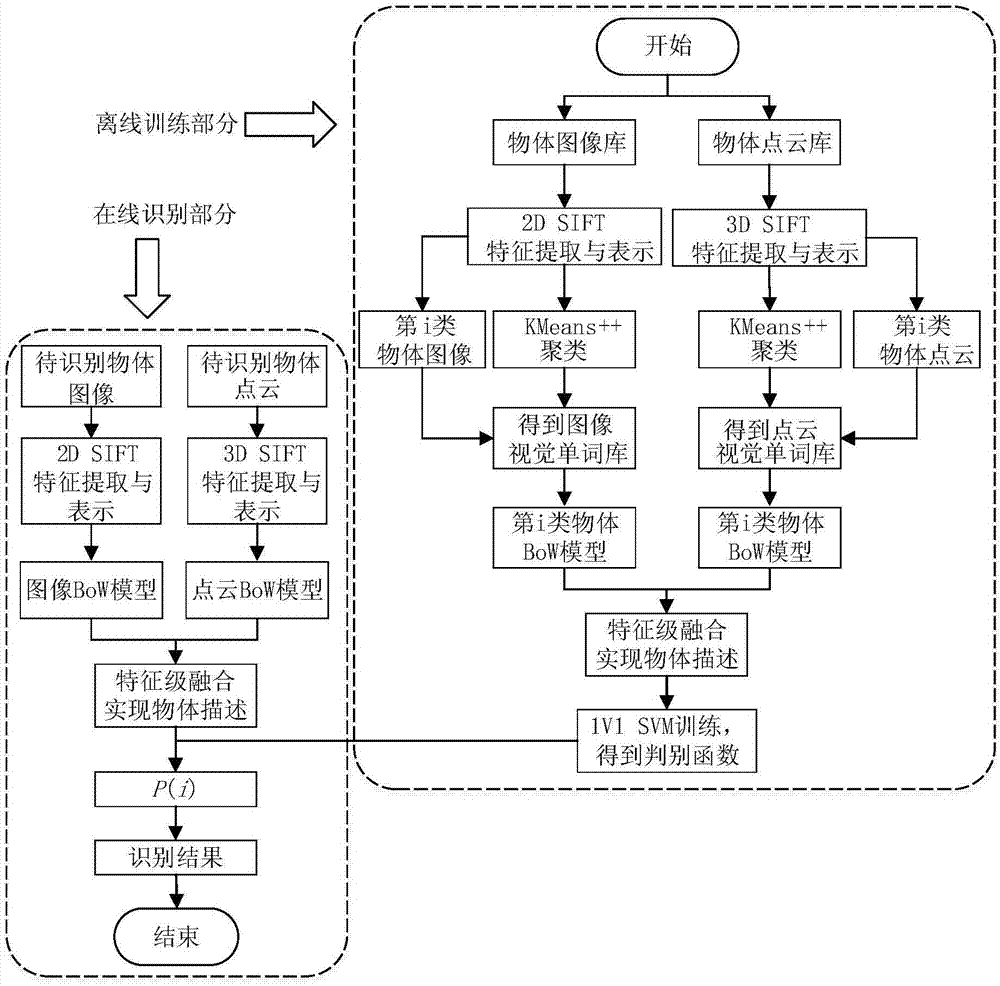
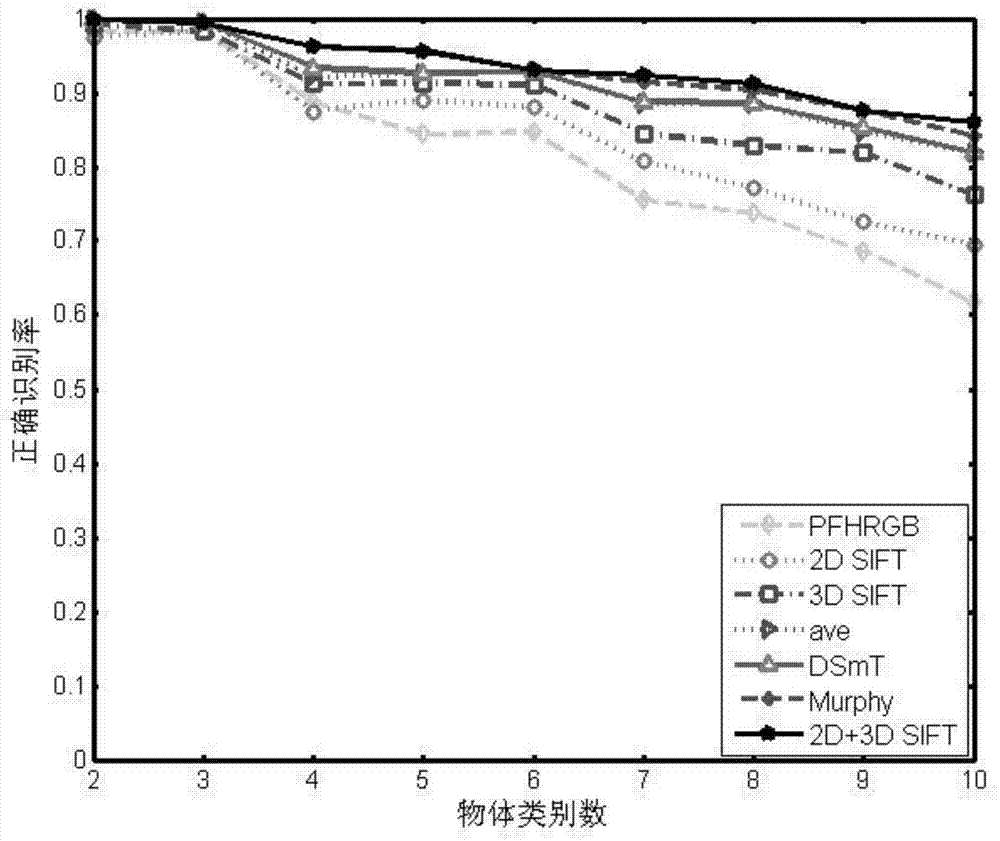
Ordinary object recognizing method based on 2D and 3D SIFT feature fusion
ActiveCN104715254ASolve the problem of low single feature recognition rateCharacter and pattern recognitionSupport vector machineFeature vector
The invention discloses an ordinary object recognizing method based on 2D and 3D SIFT feature fusion. The ordinary object recognizing method based on 2D and 3D SIFT feature fusion aims to increase the ordinary object recognizing accuracy. A 3D SIFT feather descriptor based on a point cloud model is provided based on Scale Invariant Feature Transform, SIFT (2D SIFT), and then the ordinary object recognizing method based on 2D and 3D SIFT feature fusion is provided. The ordinary object recognizing method based on 2D and 3D SIFT feature fusion comprises the following steps that 1, a two-dimension image and 2D and 3D feather descriptors of three-dimension point cloud of an object are extracted; 2, feather vectors of the object are obtained by means of a BoW (Bag of Words) model; 3, the two feature vectors are fused according to feature level fusion, so that description of the object is achieved; 4, classified recognition is achieved through a support vector machine (SVN) of a supervised classifier, and a final recognition result is given.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Shape feature extraction and classification
ActiveUS7668376B2Subsequent processing of the image more effective or easierCancel noiseColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionFeature vectorComputer science
System and method for analyzing an image. A received image, comprising an object or objects, is optionally preprocessed. Invariant shape features of the object(s) are extracted using a generalized invariant feature descriptor. The generalized invariant feature descriptor may comprise a generalized invariant feature vector comprising components corresponding to attributes of each object, e.g., related to circularity, elongation, perimeter-ratio-based convexity, area-ratio-based convexity, hole-perimeter-ratio, hole-area-ratio, and / or functions of Hu Moment 1 and / or Hu Moment 2. Non-invariant features, e.g., scale and reflection, may be extracted to form corresponding feature vectors. The object is classified by computing differences between the generalized invariant feature vector (and optionally, non-invariant feature vectors) and respective generalized invariant feature vectors corresponding to reference objects, determining a minimum difference corresponding to a closest reference object or class of reference objects of the plurality of reference objects, and outputting an indication of the closest reference object or class as the classification.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
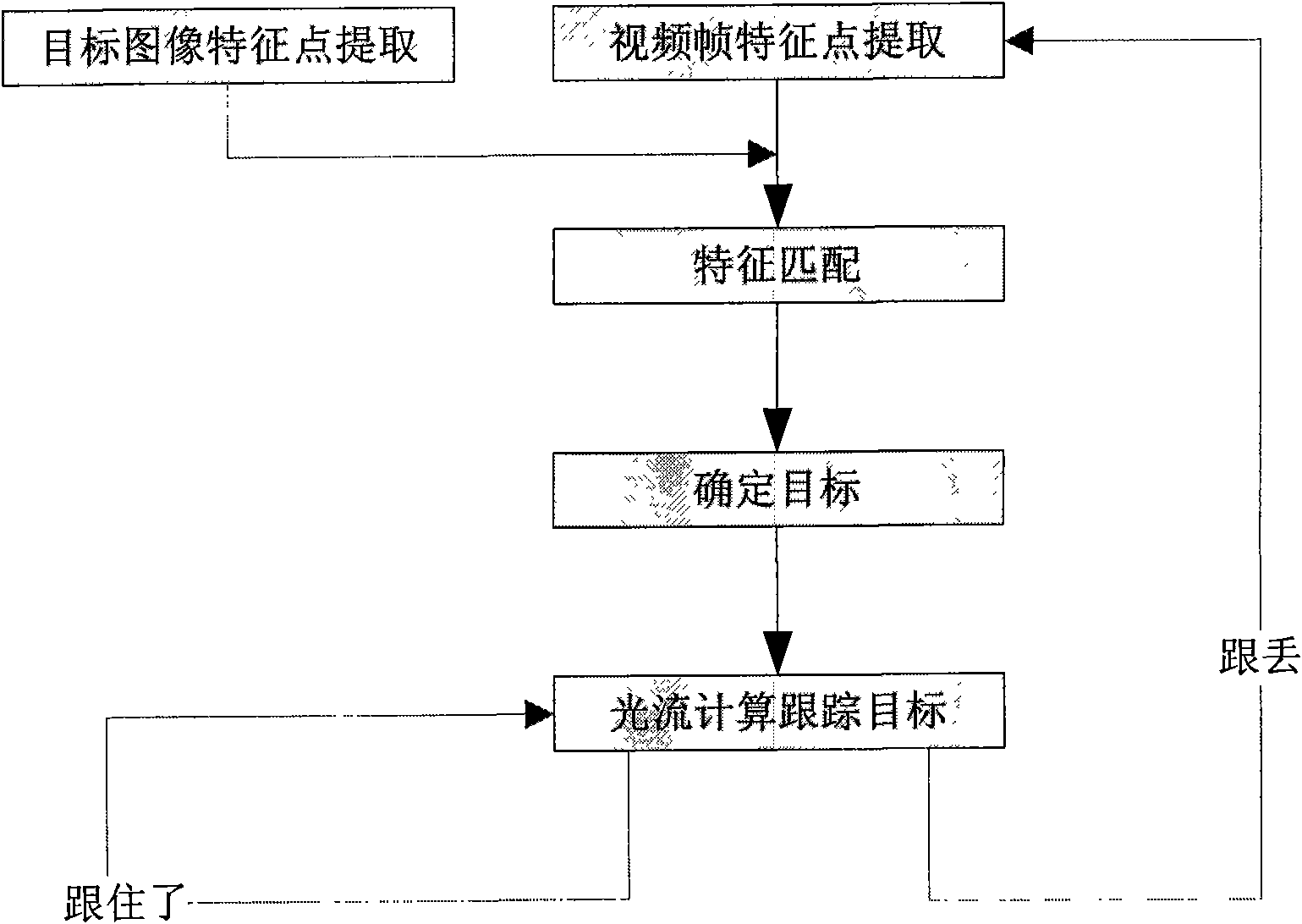
Target automatically recognizing and tracking method based on affine invariant point and optical flow calculation
InactiveCN101770568AImprove matching accuracyExact matchImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionVideo monitoringGoal recognition
The invention discloses a target automatically recognizing and tracking method based on affine invariant points and optical flow calculation, which comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out image pretreatment on a target image and video frames and extracting affine invariant feature points; then, carrying out feature point matching, eliminating mismatching points; determining the target recognition success when the feature point matching pairs reach certain number and affine conversion matrixes can be generated; then, utilizing the affine invariant points collected in the former step for feature optical flow calculation to realize the real-time target tracking; and immediately returning to the first step for carrying out the target recognition again if the tracking of middle targets fails. The feature point operator used by the invention belongs to an image local feature description operator which is based on the metric space and maintains the unchanged image zooming and rotation or even affine conversion. In addition, the adopted optical flow calculation method has the advantages of small calculation amount and high accuracy, and can realize the real-time tracking. The invention is widely applied to the fields of video monitoring, image searching, computer aided driving systems, robots and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
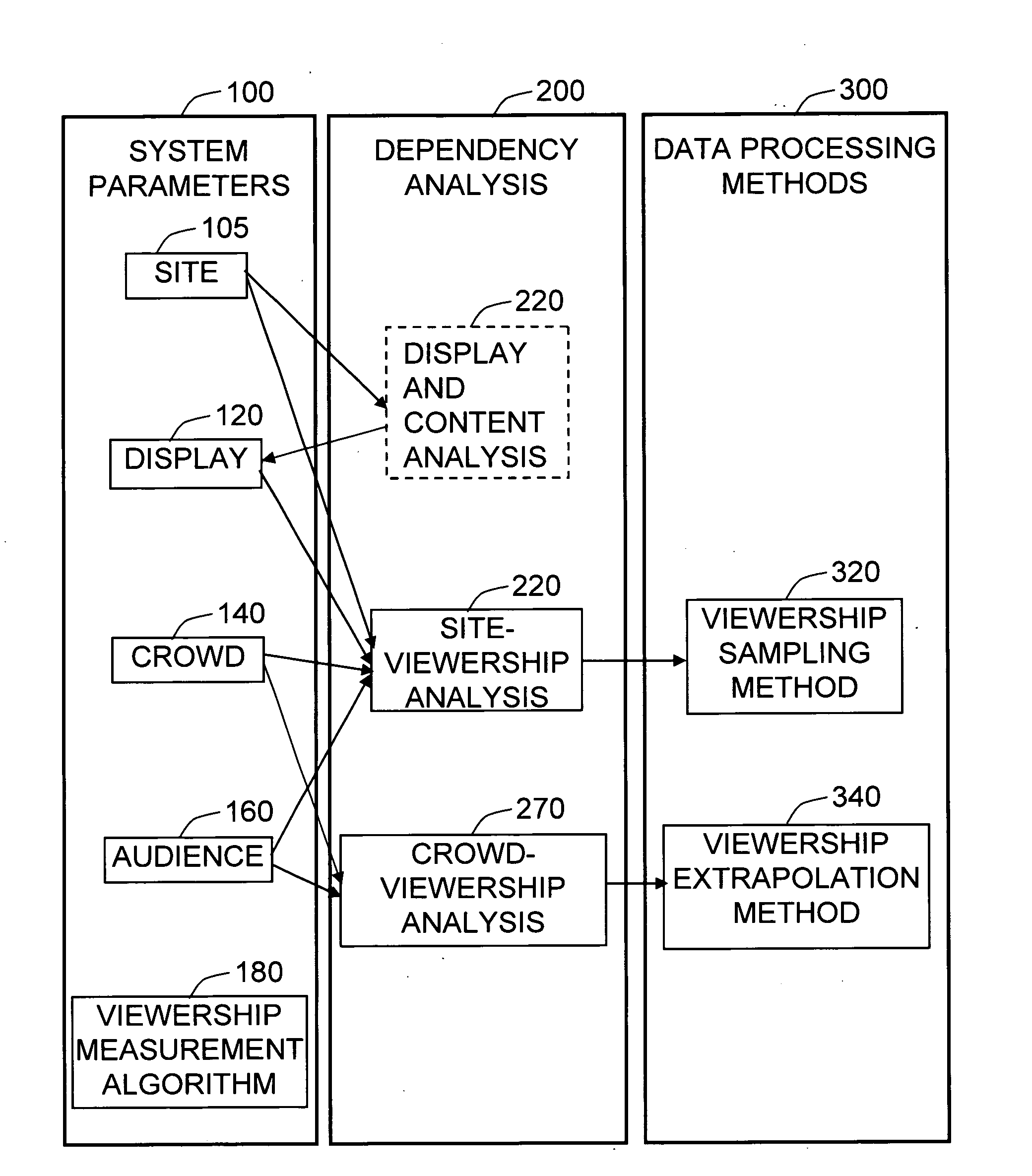
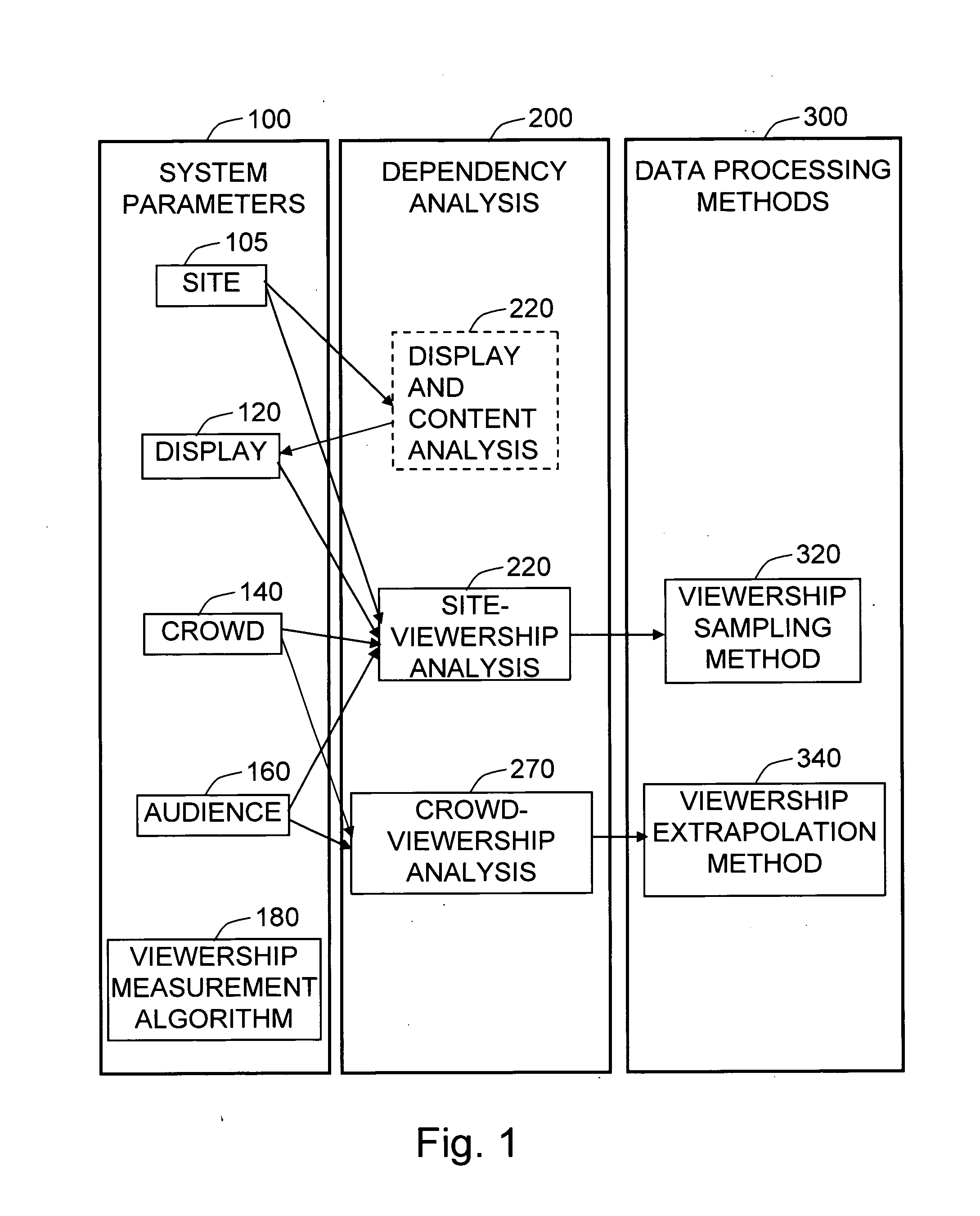
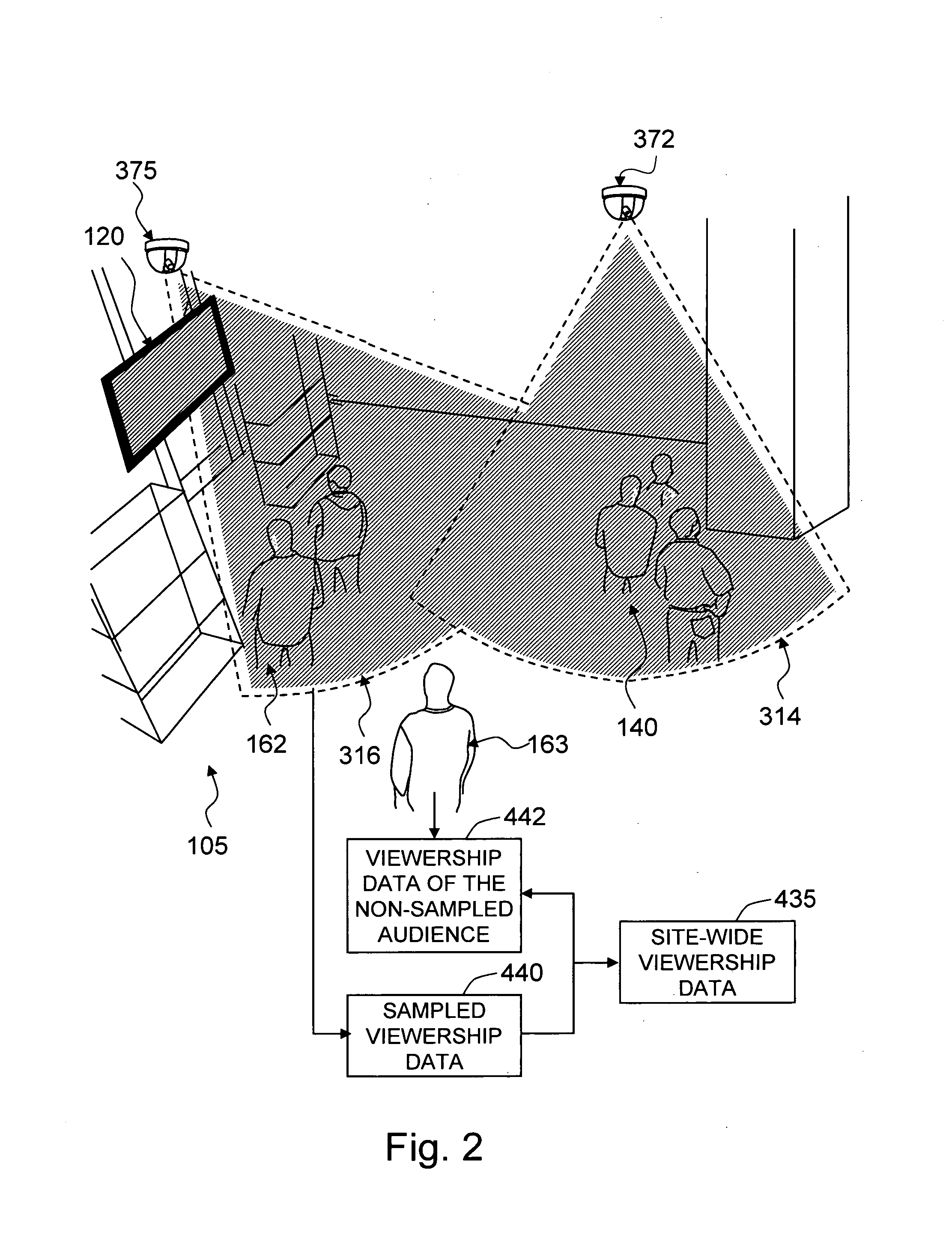
Method and system for media audience measurement and spatial extrapolation based on site, display, crowd, and viewership characterization
InactiveUS20090158309A1Reliable estimateLarge coverageAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionTemporal changeCrowd dynamics
The present invention provides a comprehensive method to design an automatic media viewership measurement system, from the problem of sensor placement for an effective sampling of the viewership to the method of extrapolating spatially sampled viewership data. The system elements that affect the viewership—site, display, crowd, and audience—are identified first. The site-viewership analysis derives some of the crucial elements in determining an effective data sampling plan: visibility, occupancy, and viewership relevancy. The viewership sampling map is computed based on the visibility map, the occupancy map, and the viewership relevancy map; the viewership measurement sensors are placed so that the sensor coverage maximizes the viewership sampling map. The crowd-viewership analysis derives a model of the viewership in relation to the system parameters so that the viewership extrapolation can effectively adapt to the time-changing spatial distribution of the viewership; the step identifies crowd dynamics, and its invariant features as the crucial elements that extract the influence of the site, display, and the crowd to the temporal changes of viewership. The extrapolation map is formulated around these quantities, so that the site-wide viewership can be effectively estimated from the sampled viewership measurement.
Owner:VIDEOMINING CORP
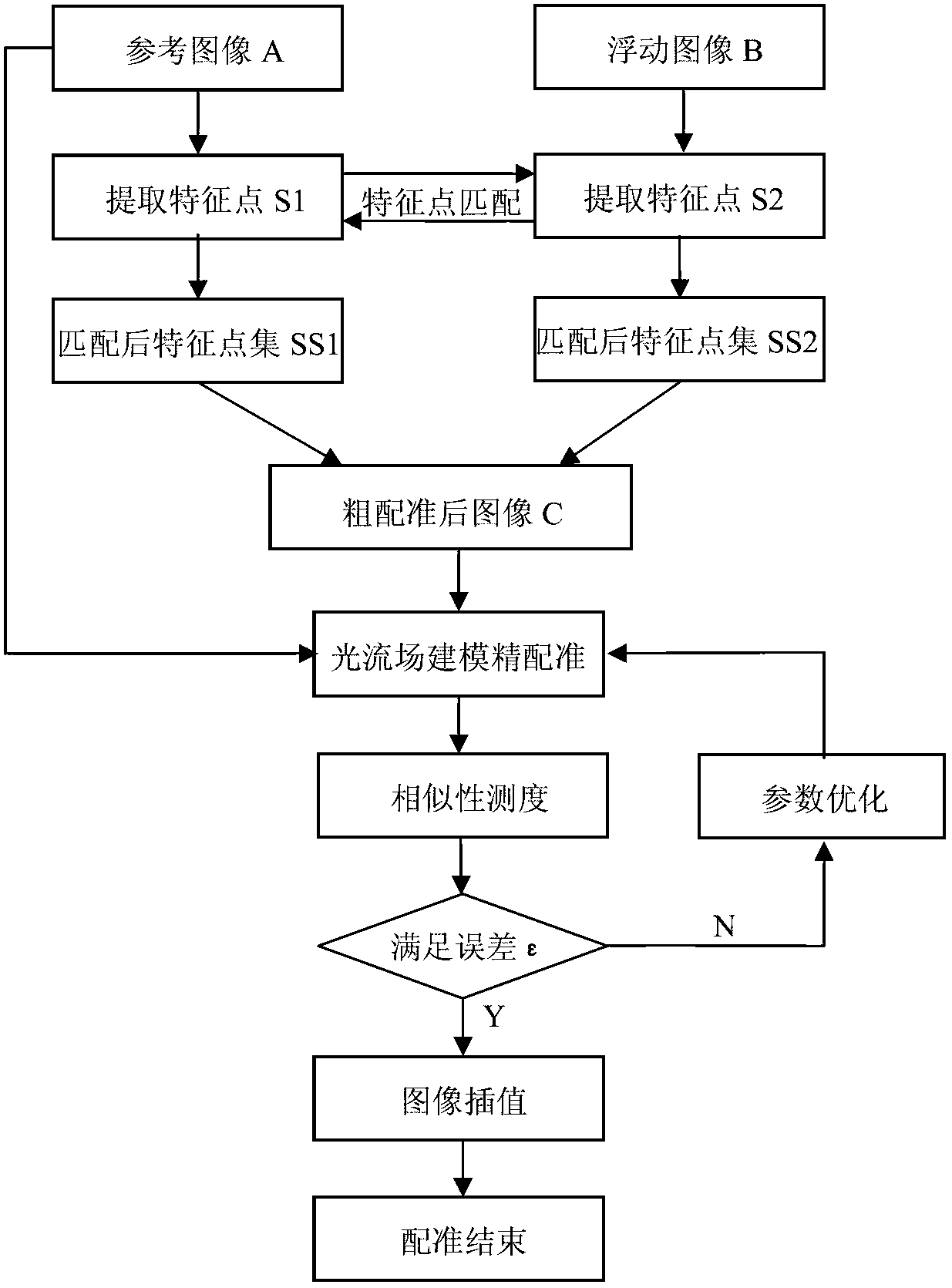
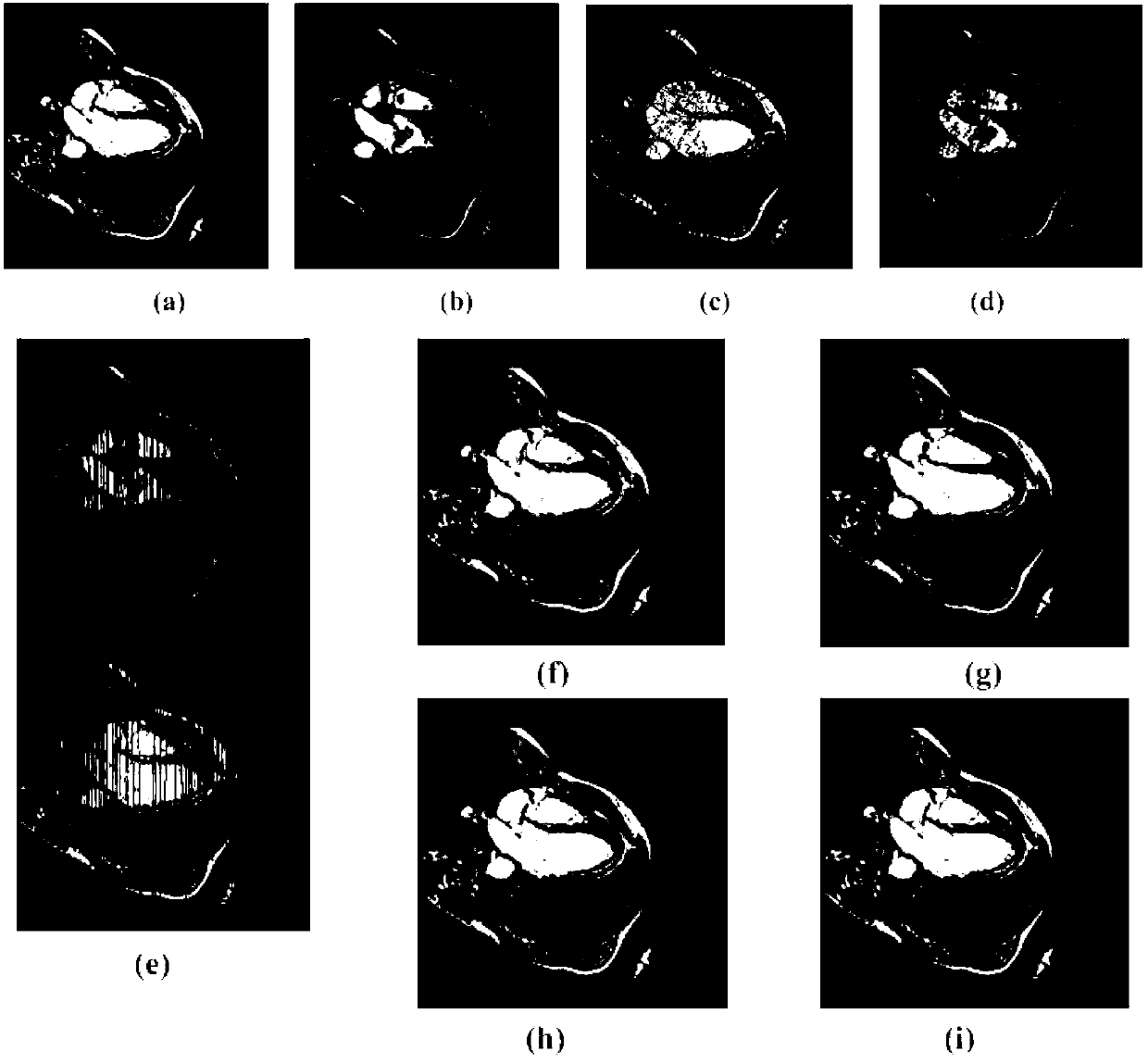
Non-rigid heart image grading and registering method based on optical flow field model
ActiveCN102722890AStrong anti-noise abilityImprove robustnessImage analysisGeometric image transformationImaging processingScale-invariant feature transform
The invention discloses a non-rigid heart image grading and registering method based on an optical flow field model, which belongs to the technical field of image processing. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining an affine transformation coefficient through the scale invariant characteristic vectors of two images, and obtained a rough registration image through affine transformation; and obtaining bias transformation of the rough registration image by using an optical flow field method, and interpolating to obtain a fine registration image. In the non-rigid heart image grading and registering method, an SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature Transform) characteristic method and an optical flow field method are complementary to each other, the SIFT characteristic is used for making preparations for increasing the converging speed of the optical flow field method, and the registration result is more accurate through the optical flow field method; and the characteristic details of a heart image are better kept, higher anti-noising capability and robustness are achieved, and an accurate registration result is obtained. Due to the adopted difference value method, a linear difference value and a central difference are combined, and final registration is realized by adopting a multi-resolution strategy in the method simultaneously.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
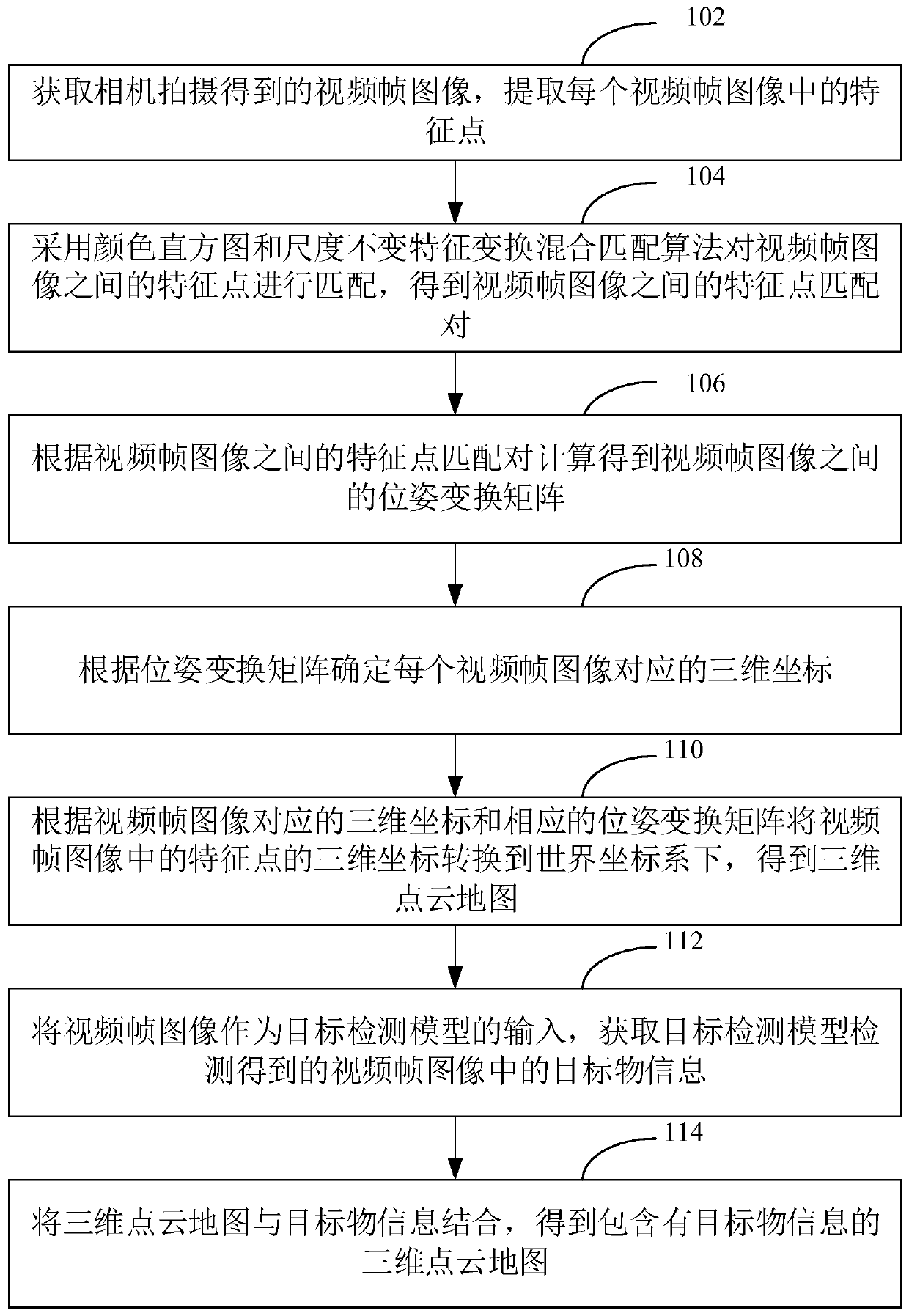
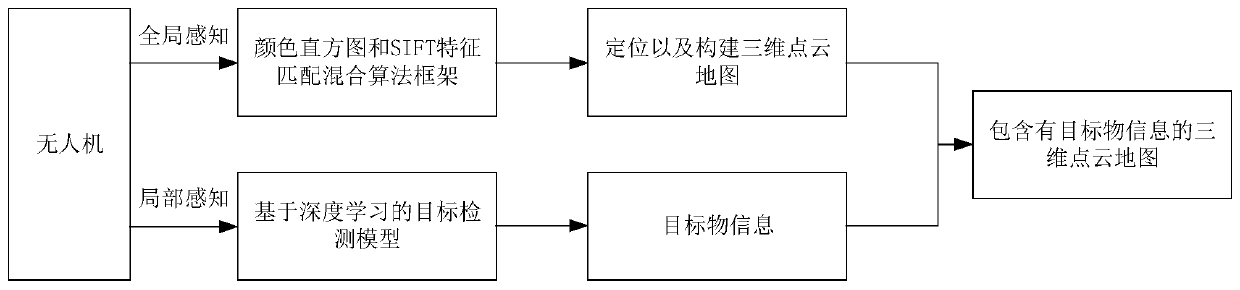
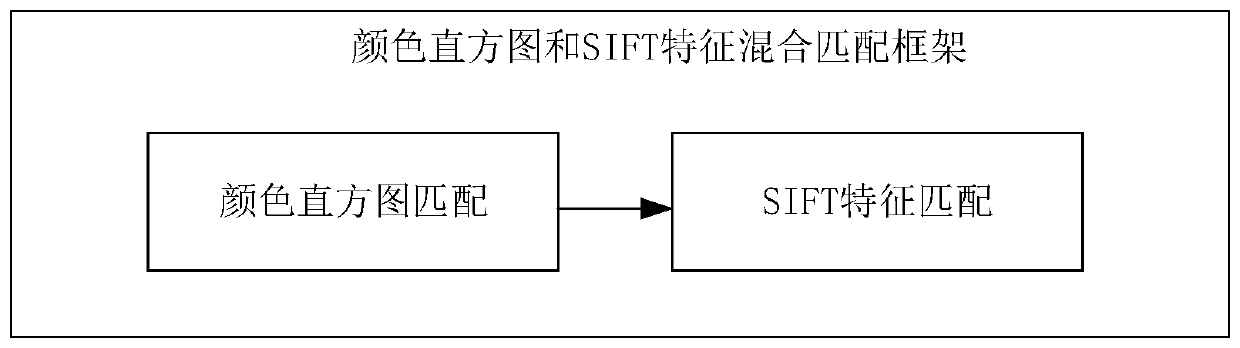
Unmanned aerial vehicle three-dimensional map construction method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
The invention relates to an unmanned aerial vehicle three-dimensional map construction method. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining a video frame image shot by a camera, extracting feature points in each video frame image; matching the feature points by adopting a color histogram and scale invariant feature transformation hybrid matching algorithm to obtain feature point matchingpairs; calculating according to the feature point matching pairs to obtain a pose transformation matrix; determining a three-dimensional coordinate corresponding to each video frame image according tothe pose transformation matrix, and converting the three-dimensional coordinates of the feature points in the video frame image into a world coordinate system to obtain a three-dimensional point cloud map, taking the video frame image as the input of a target detection model to obtain target object information, and combining the three-dimensional point cloud map with the target object informationto obtain the three-dimensional point cloud map containing the target object information. According to the method, the real-time performance and accuracy of three-dimensional point cloud map construction are improved, and rich information is contained. In addition, the invention further provides an unmanned aerial vehicle three-dimensional map construction device, computer equipment and a storagemedium.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Image registration system and method thereof
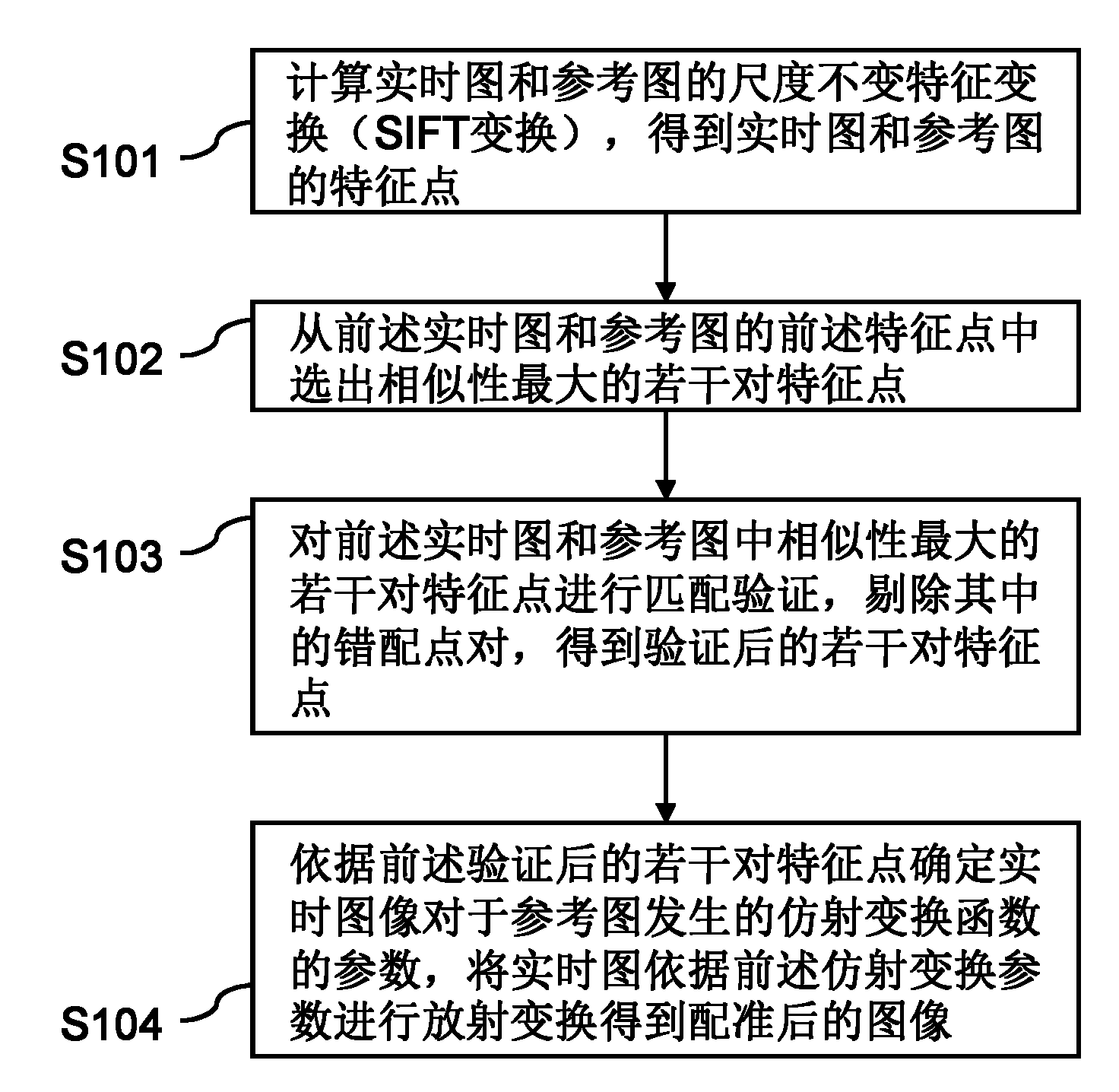
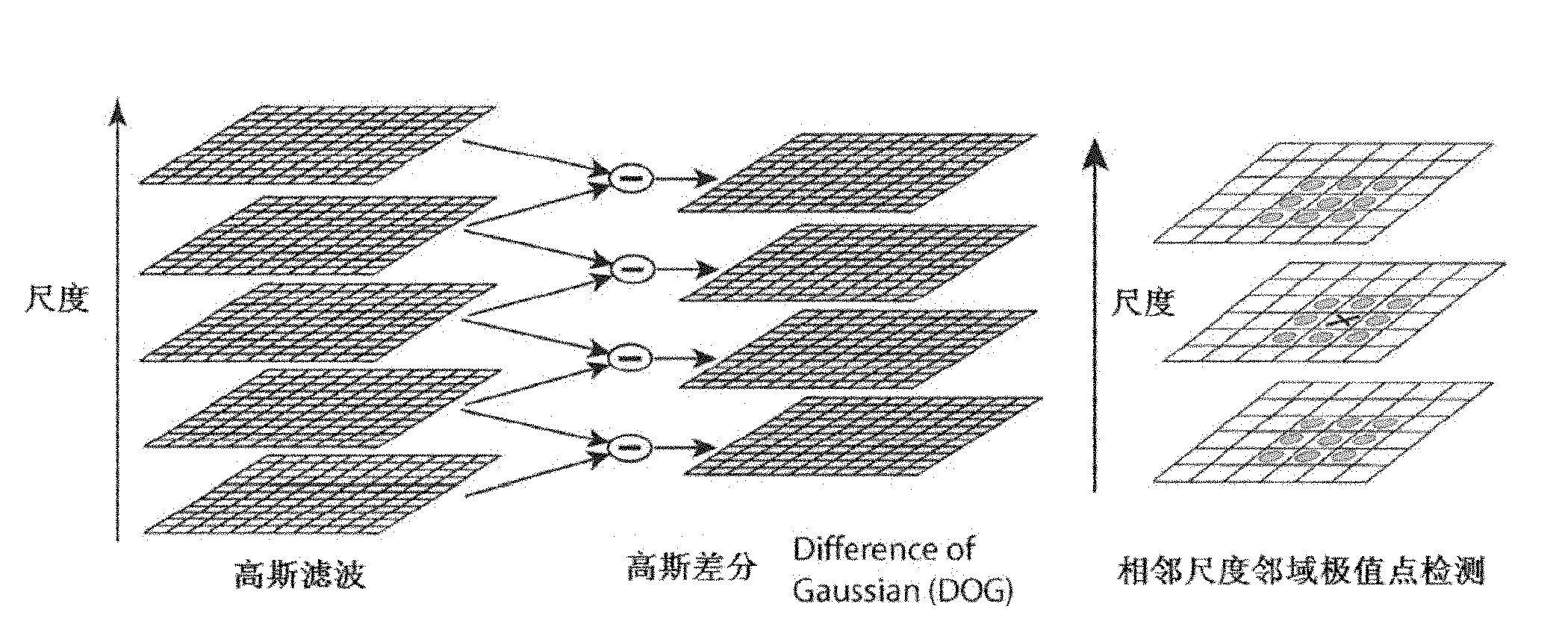
InactiveCN102005047AImprove accuracyImprove registration accuracyImage analysisScale-invariant feature transformReference image
The invention provides an image registration system and a method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly calculating scale invariant feature transform (SIFT transform) of a real-time image and a reference image to obtain feature points of the real-time image and the reference image; selecting a plurality of pairs of feature points with maximum similarity from the feature points of the real-time image and the reference image; carrying out matching verification of the plurality of pairs of feature points with maximum similarity selected from the feature points of the real-time image and the reference image and rejecting a mismatching point pair therein to obtain a plurality of pairs of feature points which are verified; according to the plurality of pairs of feature points which are verified, determining the parameter of an affine transformation function of the real-time image relative to the reference image; and carrying out radioactive transform of the real-time image according to the affine transformation parameter to obtain the registered image. The system and the method are difficult to influence and high in registration accuracy.
Owner:江苏博悦物联网技术有限公司
Processing pose data derived from the pose of an elongate object
ActiveUS8542219B2Input/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsTemporal resolutionOn board
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
Rapid volume measurement method based on spatial invariant feature
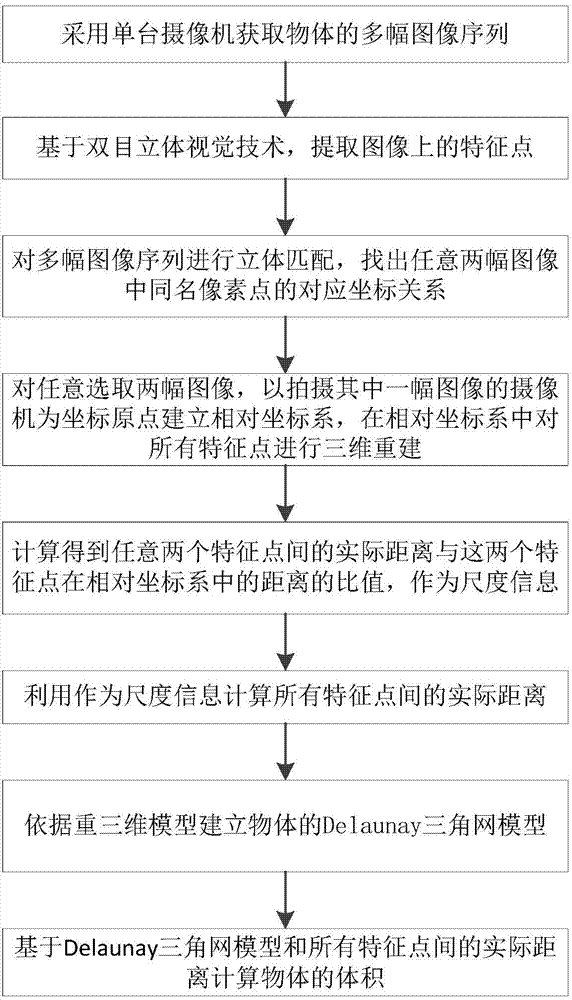
ActiveCN104778720AQuick measurementTo achieve the purpose of photogrammetryImage analysisPoint cloudVolume computation
The invention provides a rapid volume measurement method based on a spatial invariant feature. The method comprises the steps that feature point extracting and matching and three-dimensional reconstruction are performed on acquired images; the distance proportion of the actual distances among feature points to the real world in a relative coordinate system is added in three-dimensional point cloud to serve as scale information; a Delaunay triangular mesh is built by utilizing a three-dimensional coordinate of the feature points, boundary edge detection elements are added, and an optimal datum plane is fit; the triangular mesh is projected to the datum plane according to the discrete integral thought to determine the volume of an irregular object surrounded by the triangular mesh. The measurement of the actual distances among all the feature points of an object can be completed by utilizing a camera and a ruler, and the trouble of field measurement can be omitted; meanwhile, a data structure used for detecting the boundary edge is added when the Delaunay triangular mesh is built, the peripheral datum plane constituting a boundary curve surface can be effectively obtained, and the method can be further used in volume calculation.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for automatically tagging animation scenes for matching through comprehensively utilizing overall color feature and local invariant features
InactiveCN102012939AHigh speedGood auxiliary effectImage analysisSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionScale-invariant feature transform
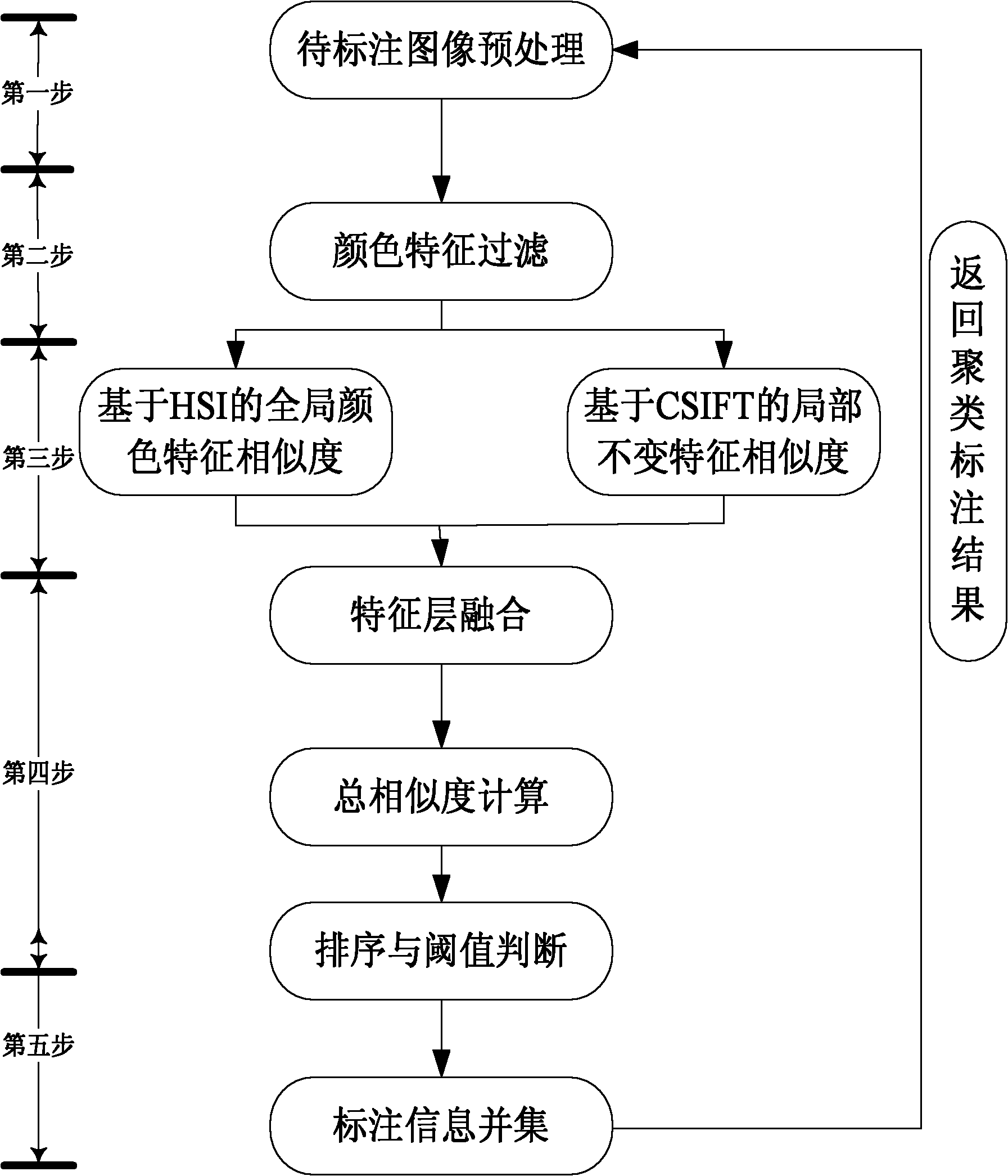
The invention discloses a method for automatically tagging animation scenes for matching through comprehensively utilizing an overall color feature and local invariant features, which aims to improve the tagging accuracy and tagging speed of animation scenes through comprehensively utilizing overall color features and color-invariant-based local invariant features. The technical scheme is as follows: preprocessing a target image (namely, an image to be tagged), calculating an overall color similarity between the target image and images in an animation scene image library, and carrying out color feature filtering on the obtained result; after color feature filtering, extracting a matching image result and the colored scale invariant feature transform (CSIFT) feature of the target image, and calculating an overall color similarity and local color similarities between the matching image result and the CSIFT feature; fusing the overall color similarity and the local color similarities so as to obtain a final total similarity; and carrying out text processing and combination on the tagging information of the images in the matching result so as to obtain the final tagging information of the target image. By using the method provided by the invention, the matching accuracy and matching speed of an animation scene can be improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
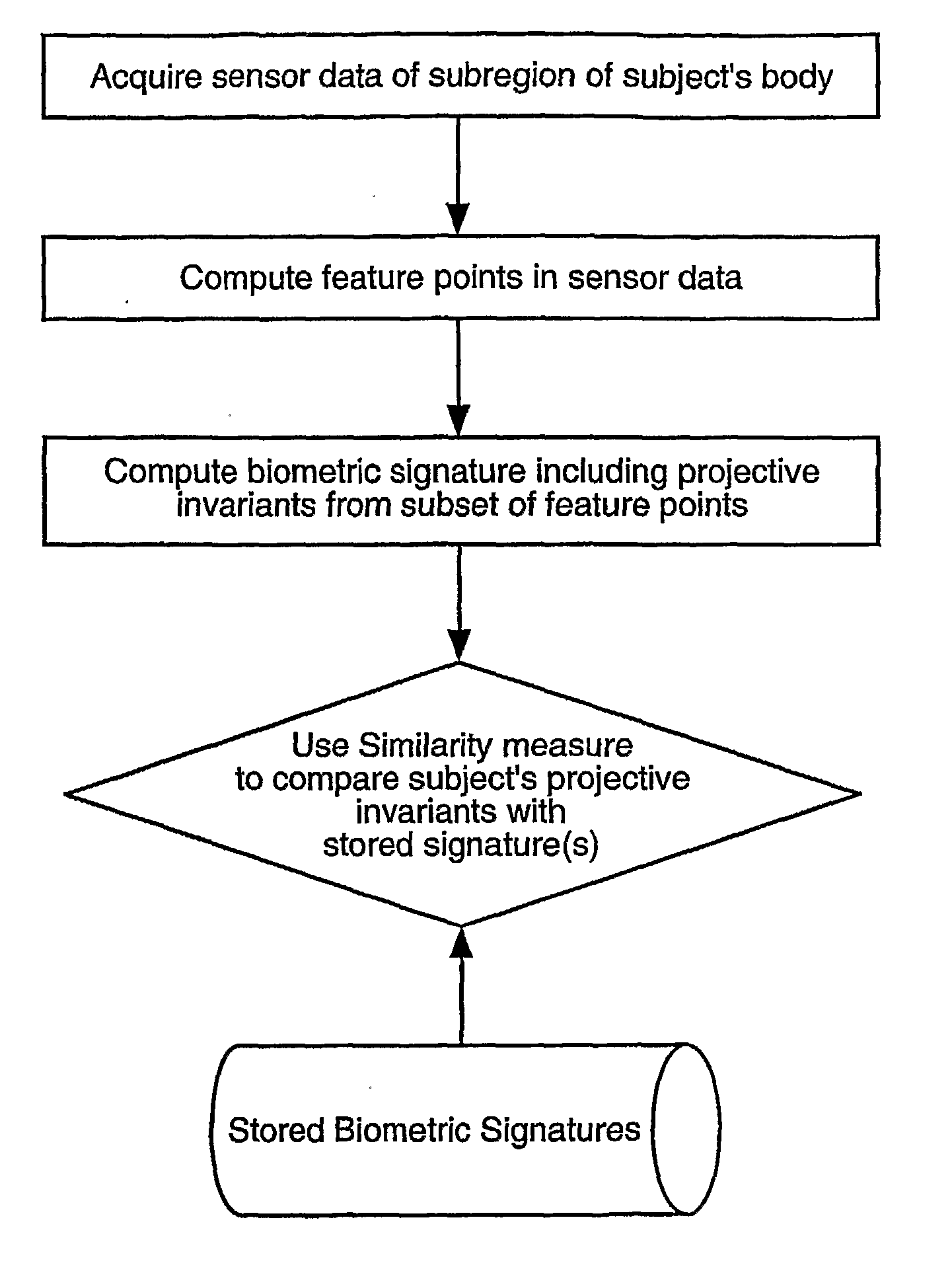
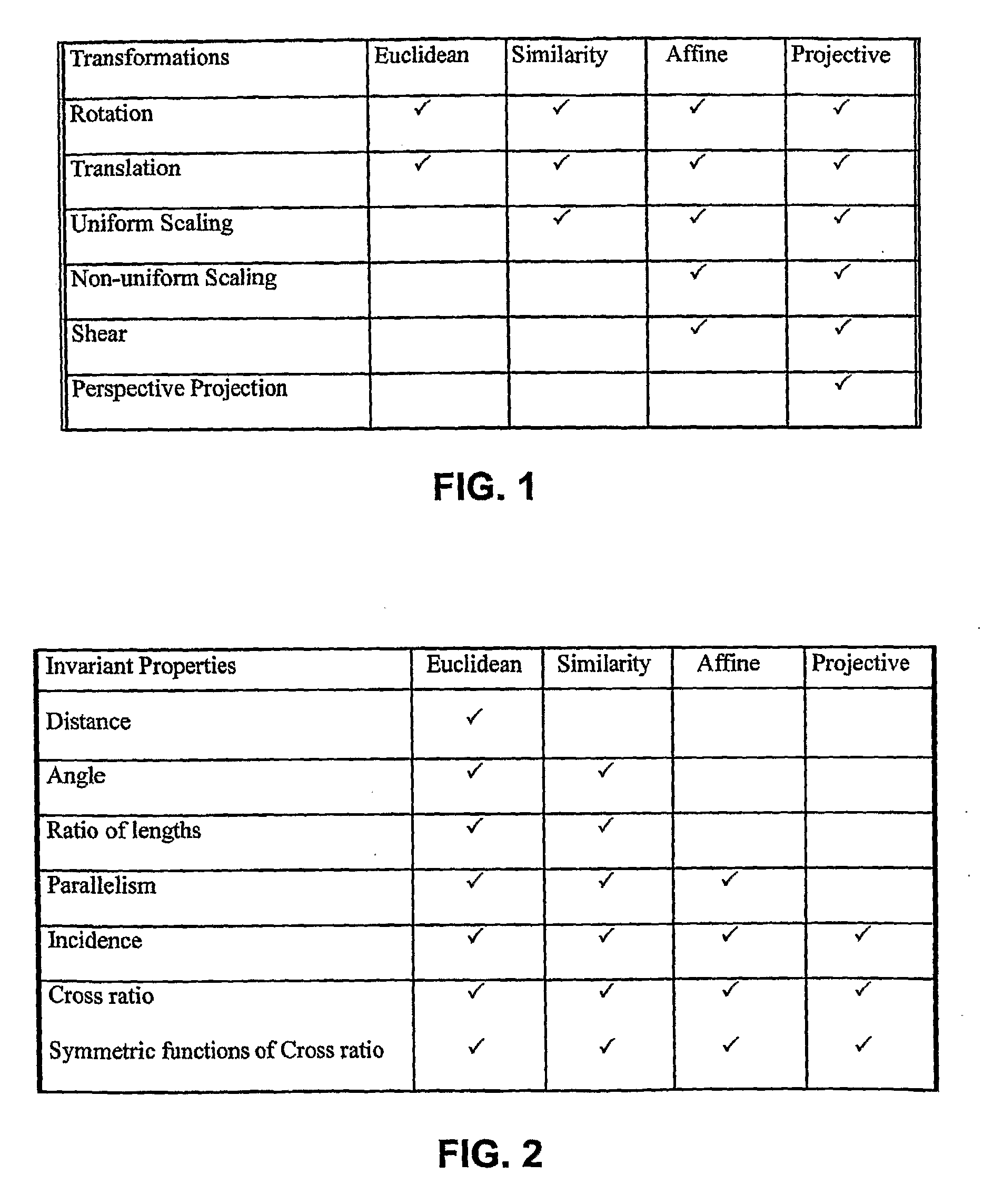
Biometric signatures and identification through the use of projective invariants
InactiveUS20070274574A1Character and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionHuman body
Techniques, systems and methods for obtaining biometric signatures and identification are described. Broadly stated, embodiments of the present invention utilize specified geometric principles t provide means for accurate biometric identification using projective invariant features of a subregion of the human body. The present invention provides a means for computing biometric signatures and identification that are projective invariant and hence are not impacted by the viewing angle of the subregion of the human body containing the biometric data. This novel invention removes the restriction, often implicit in the previous work, of the imaging or sensing system being in a fixed repeatable (and generally orthogonal) viewing position. This invention can be applied across a wide range of biometrics, although it is most easily applicable to features that are approximately co-planar. A plurality of such projective invariant features can be used to define a biometric signature to either verify an individual's identity, or recognize an individual from a database of already known persons.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com