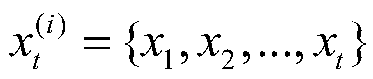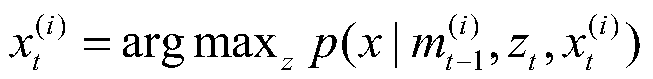Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
336results about How to "Reliable estimate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and system for model-based clustering and signal-bearing medium for storing program of same
InactiveUS6397166B1Reliable estimateDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionData pointCalculated data
A method and system for grouping multiple data points, each data point being a set (e.g., a vector, a tuple, etc.) including a measured dependent value and at least one related independent variable value, include fitting the data into a model relating the independent and dependent variables of the data, and calculating similarity and distance between the data points and groups of the data points, thereby to group the multiple data points.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for adaptively compensating channel or system variations in precoded communications system
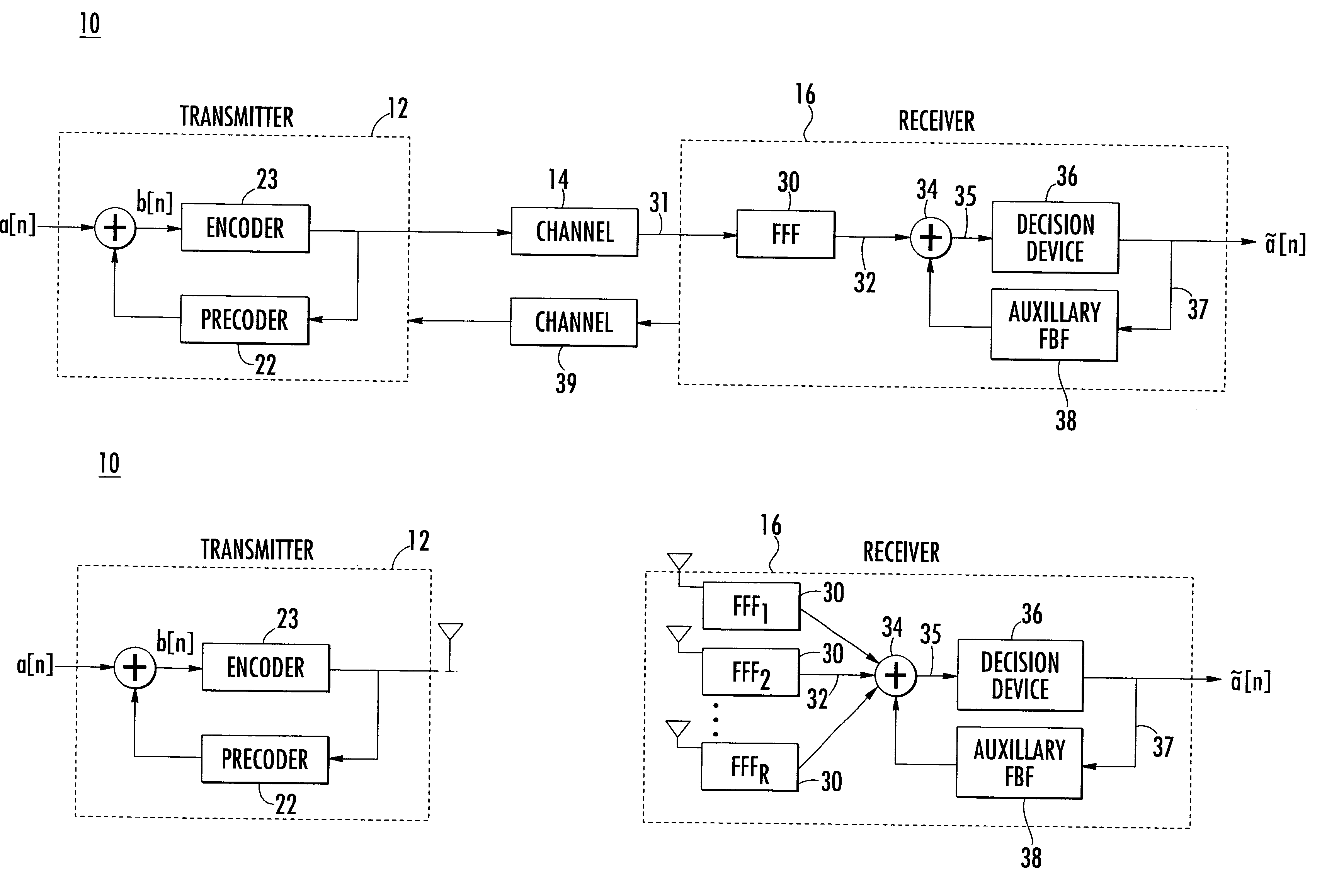
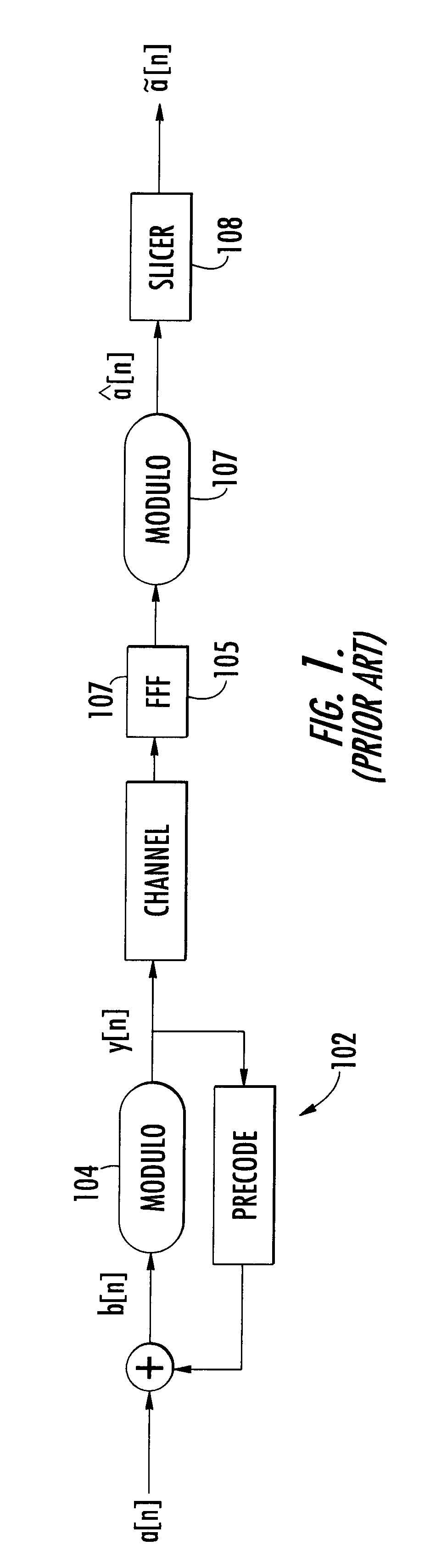
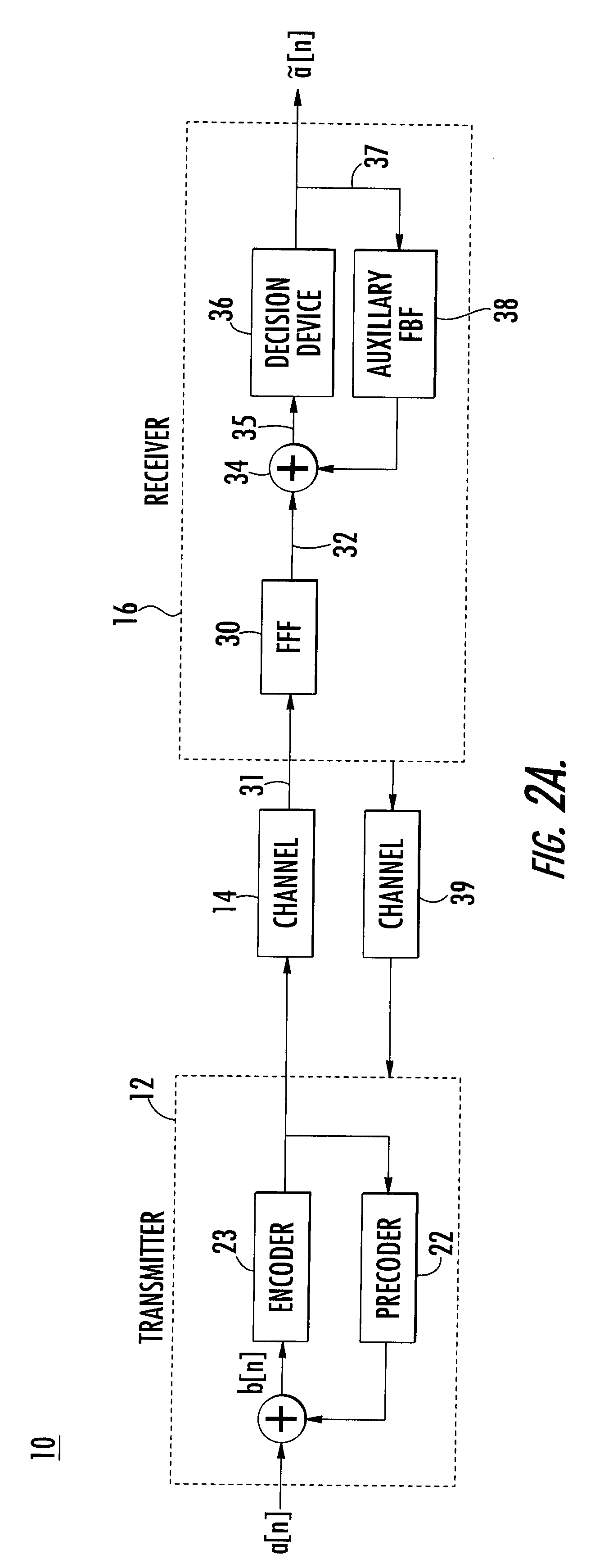
InactiveUS6400761B1Reduce distractionsImprove performanceMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsPrecodingCommunications system
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for adaptively compensating for channel or system variations in which adaptive compensation is used in the receiver of a digital communication system. The transmitter of the digital communication system includes precoding. The adaptive receiver compensation mitigates the interferences not removed by the transmitter precoder. In an embodiment of the invention, the adaptive compensation can be performed using an adaptive feedforward filter (FFF) and a feedback filter (FBF) in the receiver. The FBF output is generated based on previous values of estimates of the transmitted precoded sequence. The determined value of the FBF coefficients can be periodically relayed to the transmitter to update the precoder coefficients of the transmitter. Alternatively, the value of the FBF coefficients can be relayed to the transmitter after the value of the coefficients exceeds a predetermined threshold. Accordingly, the receiver adaptively and automatically compensates for misadjustments of the fixed transmitter precoder with respect to the actual channel at a given point in time.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Integrated Semiconductor Bioarray
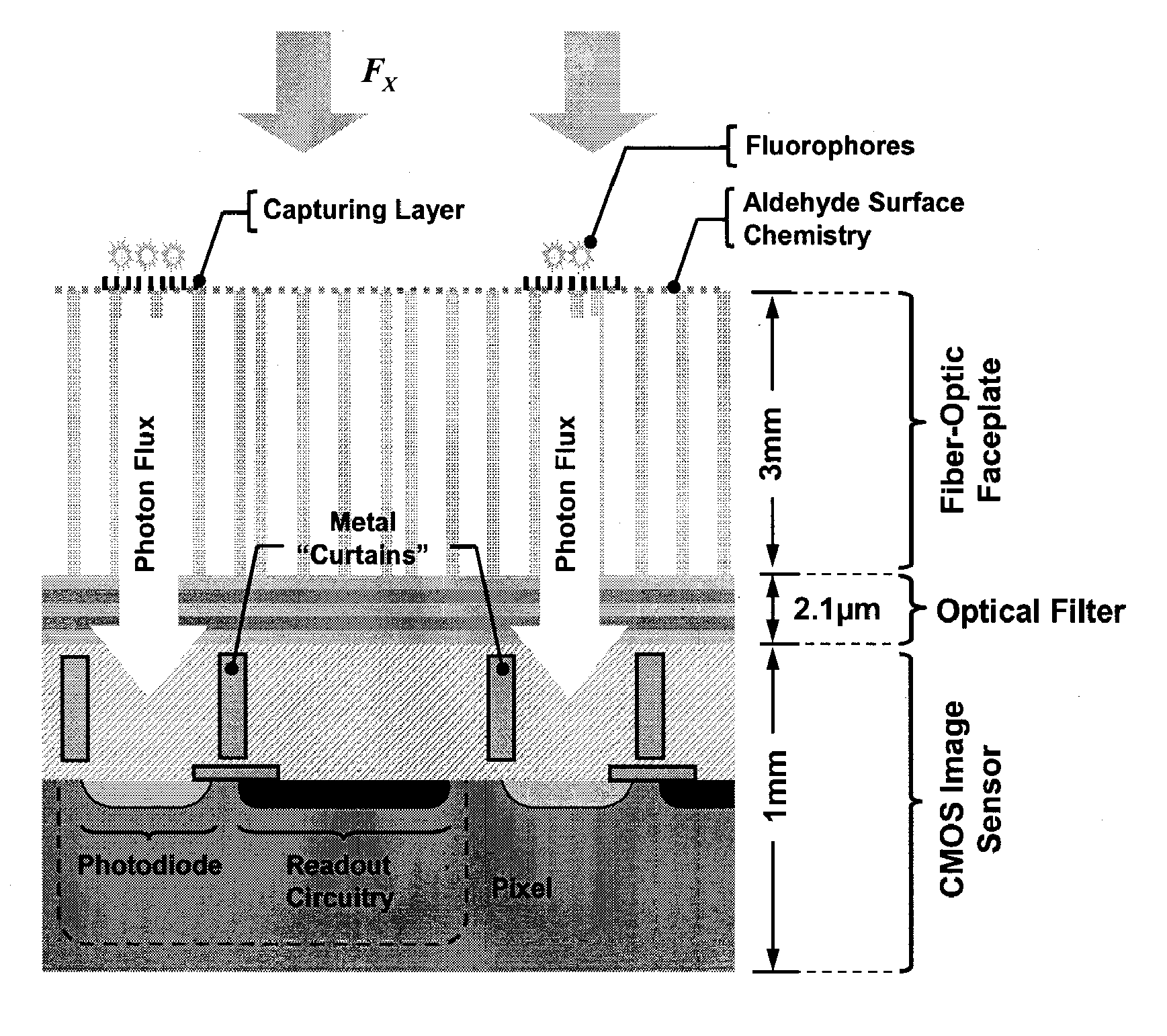
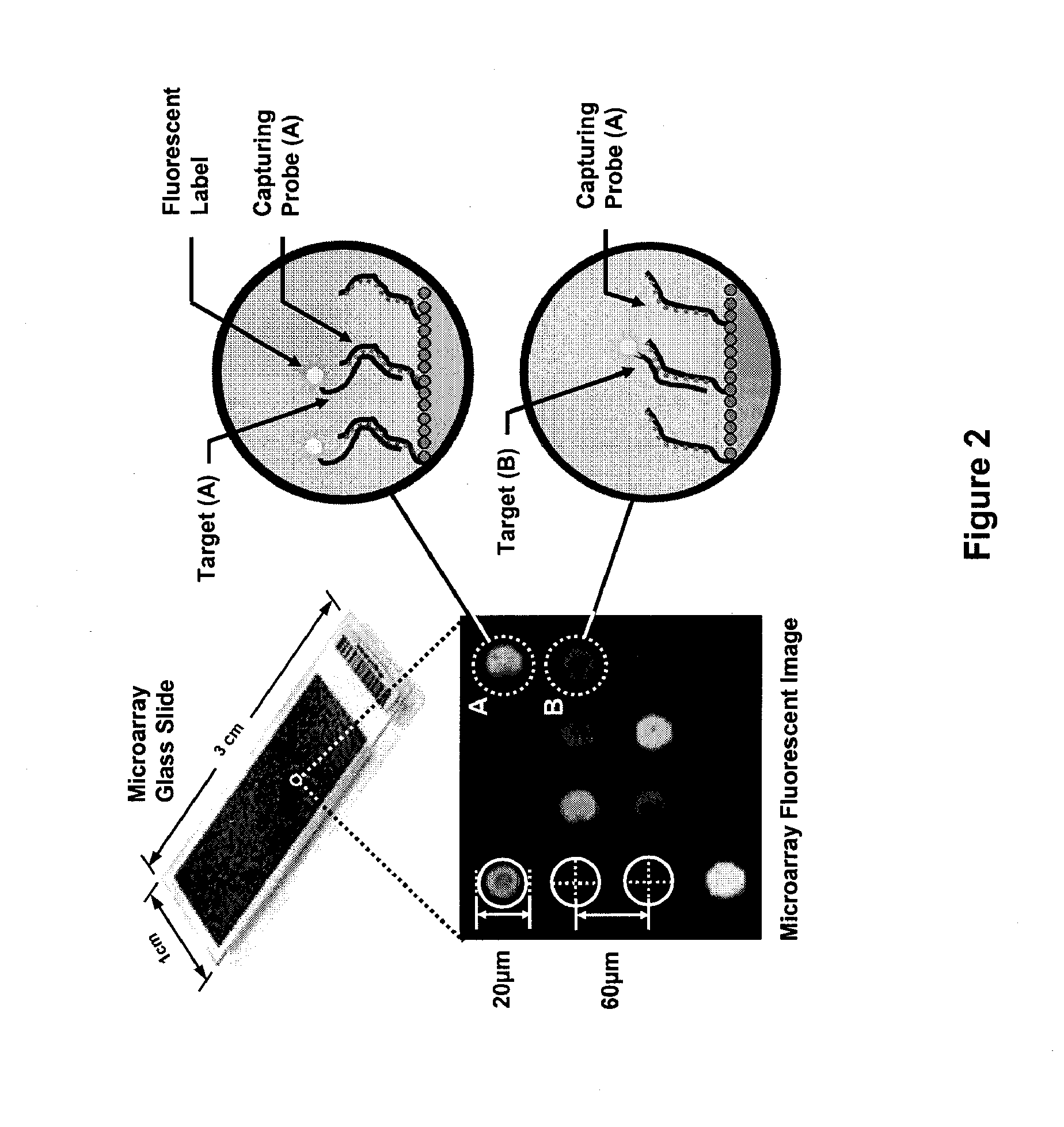
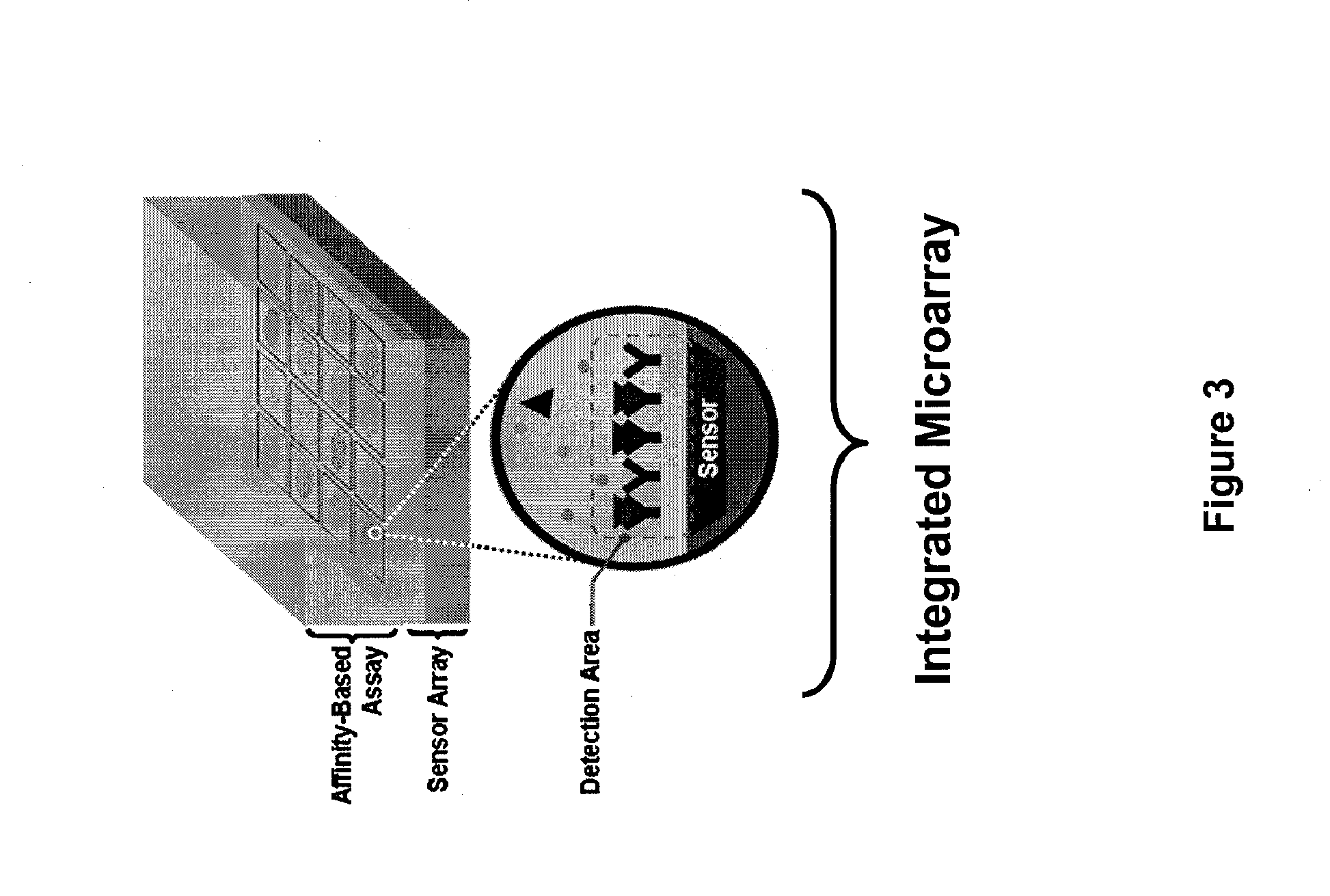
ActiveUS20080081769A1TimeSlow reaction rateMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningAnalyteBiosensor array
A biosensor array, system and method for affinity based assays that are able to simultaneously obtain high quality measurements of the binding characteristics of multiple analytes, and that are able to determine the amounts of those analytes in solution. The invention also provides a fully integrated bioarray for detecting real-time characteristics of affinity based assays.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
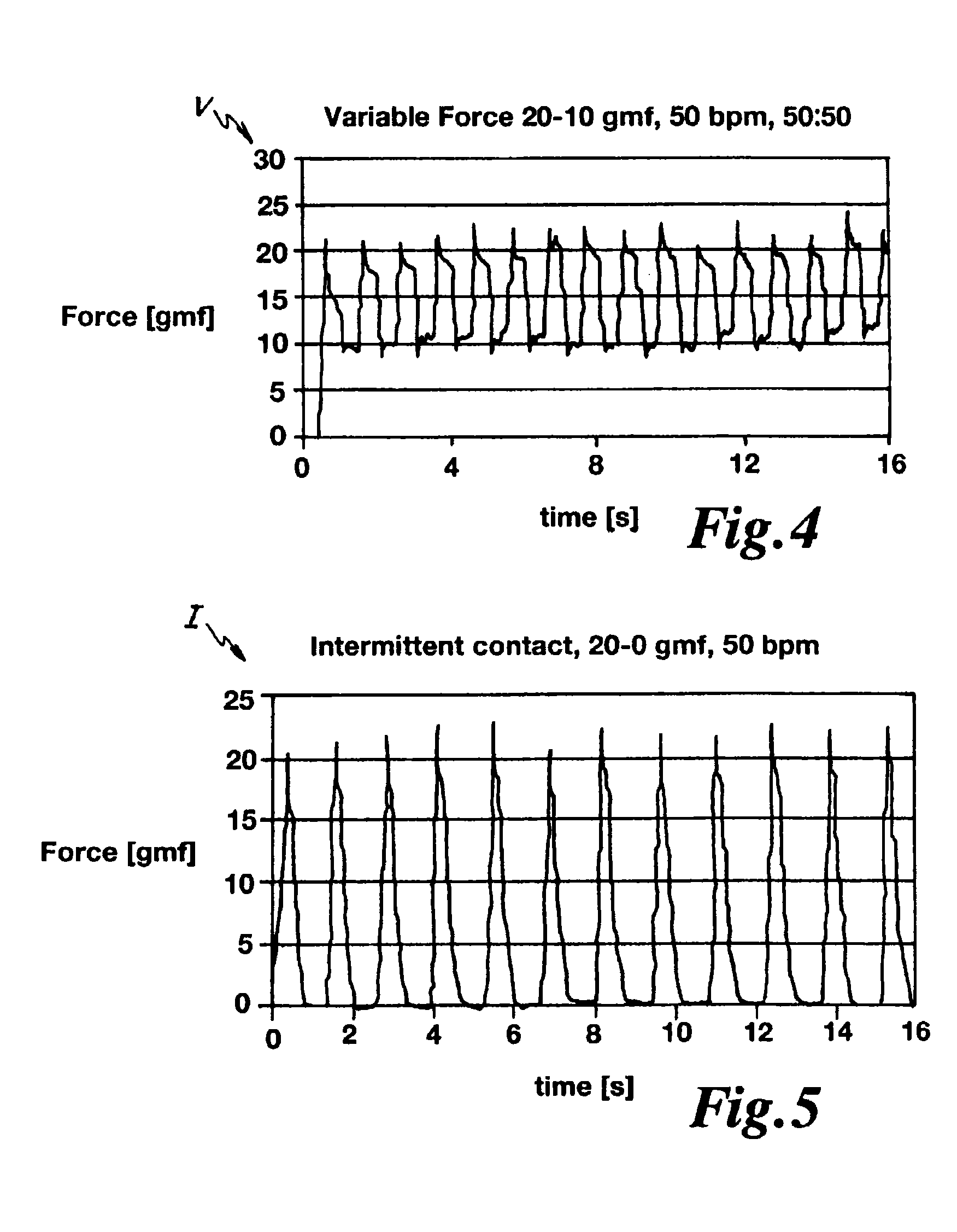
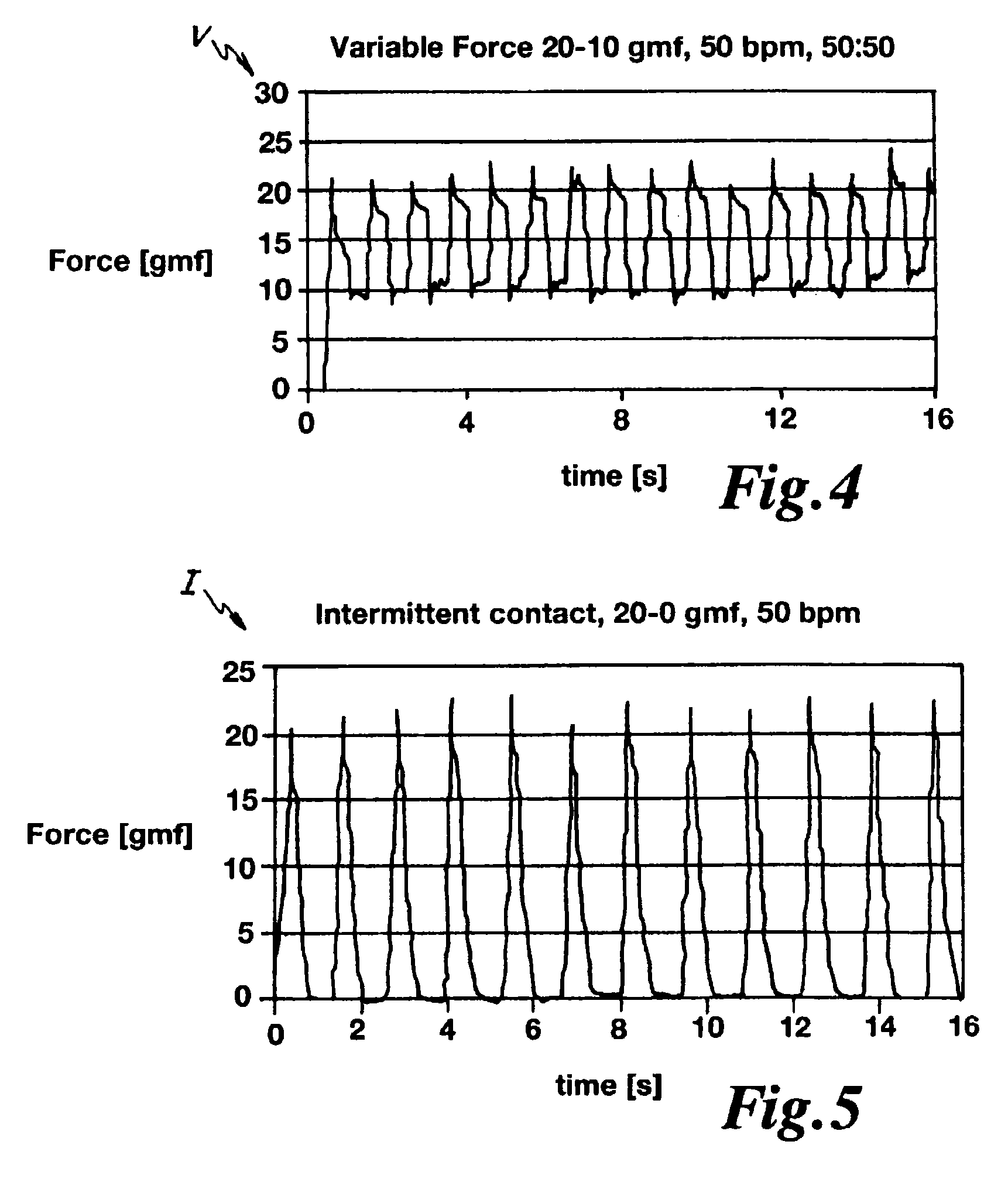
Method and apparatus for controlling lesion size in catheter-based ablation treatment
ActiveUS20100298826A1Prevent steam poppingReliable predictionStrain gaugeDiagnostic recording/measuringTime integralTarget tissue
A method and apparatus that utilizes a force-time integral for real time estimation of lesion size in catheter-based ablation systems. The apparatus measures the force exerted by a contact ablation probe on a target tissue and integrates the force over an energization time of the ablation probe. The force-time integral can be calculated and utilized to provide an estimated lesion size (depth, volume and / or area) in real time. The force-time integral may also account for variations in the power delivered to the target tissue in real time to provide an improved estimation of the lesion size. In one embodiment, the force metric can be used as feedback to establish a desired power level delivered to the probe to prevent steam popping.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
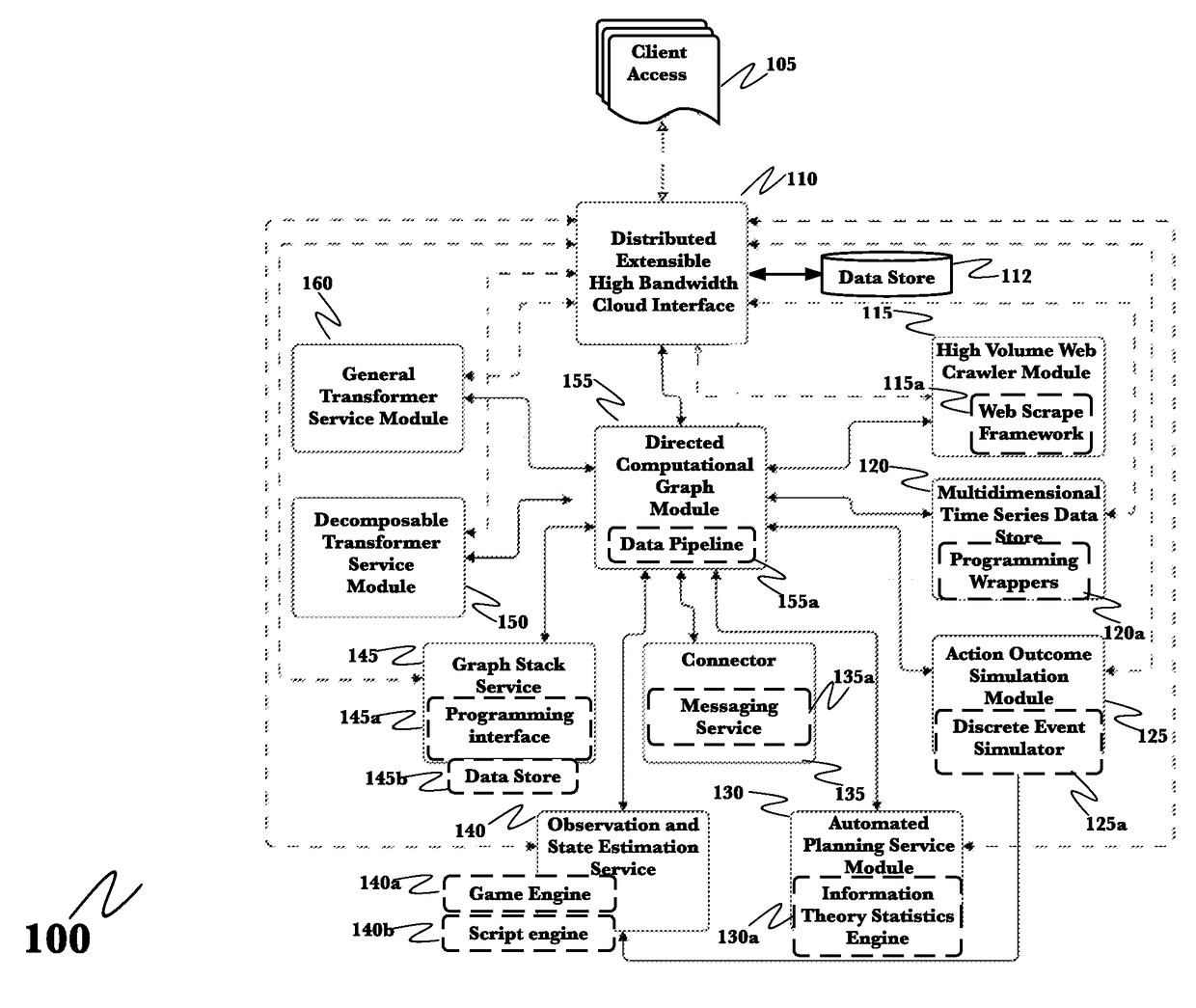
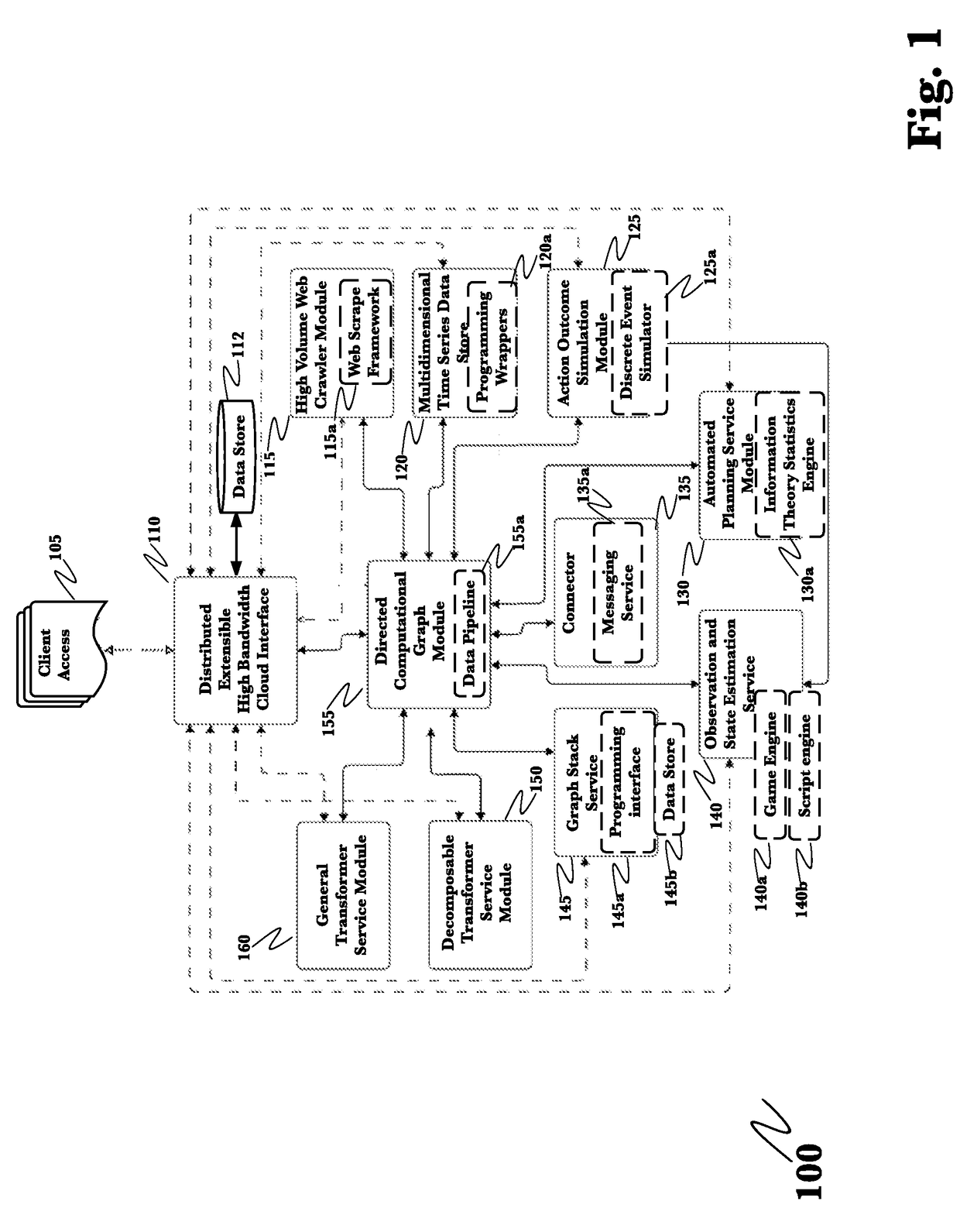
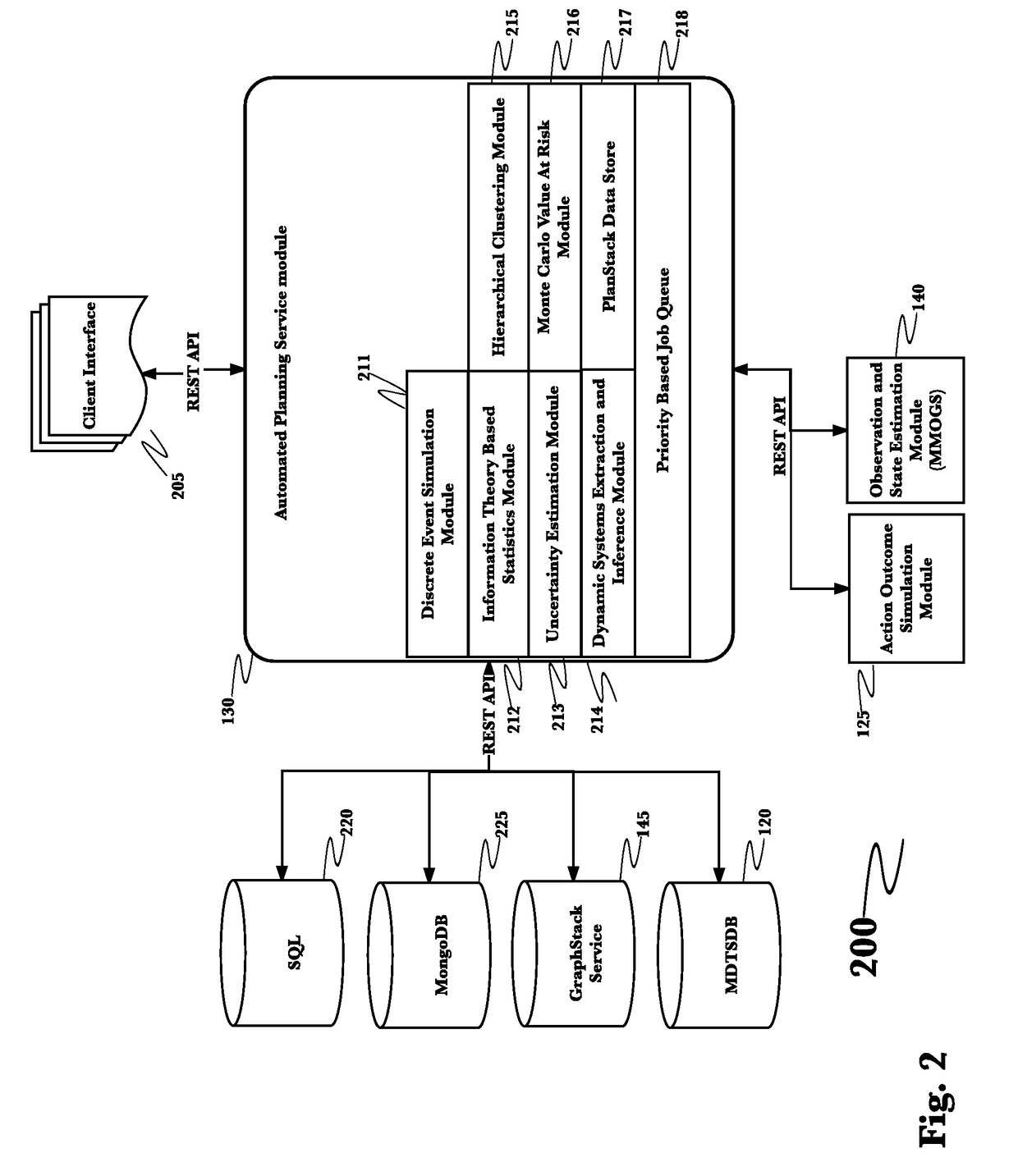
System for automated capture and analysis of business information for reliable business venture outcome prediction
InactiveUS20170124497A1Efficient storageEfficiently manipulateComputing modelsResourcesOperational systemBusiness data
A system for fully integrated collection of business impacting data, analysis of that data and generation of both analysis-driven business decisions and analysis driven simulations of alternate candidate business actions has been devised and reduced to practice. This business operating system may be used predict the outcome of enacting candidate business decisions based upon past and current business data retrieved from both within the corporation and from a plurality of external sources pre-programmed into the system. Both single parameter set and multiple parameter set analyses are supported. Risk to value estimates of candidate decisions are also calculated.
Owner:QOMPLX LLC
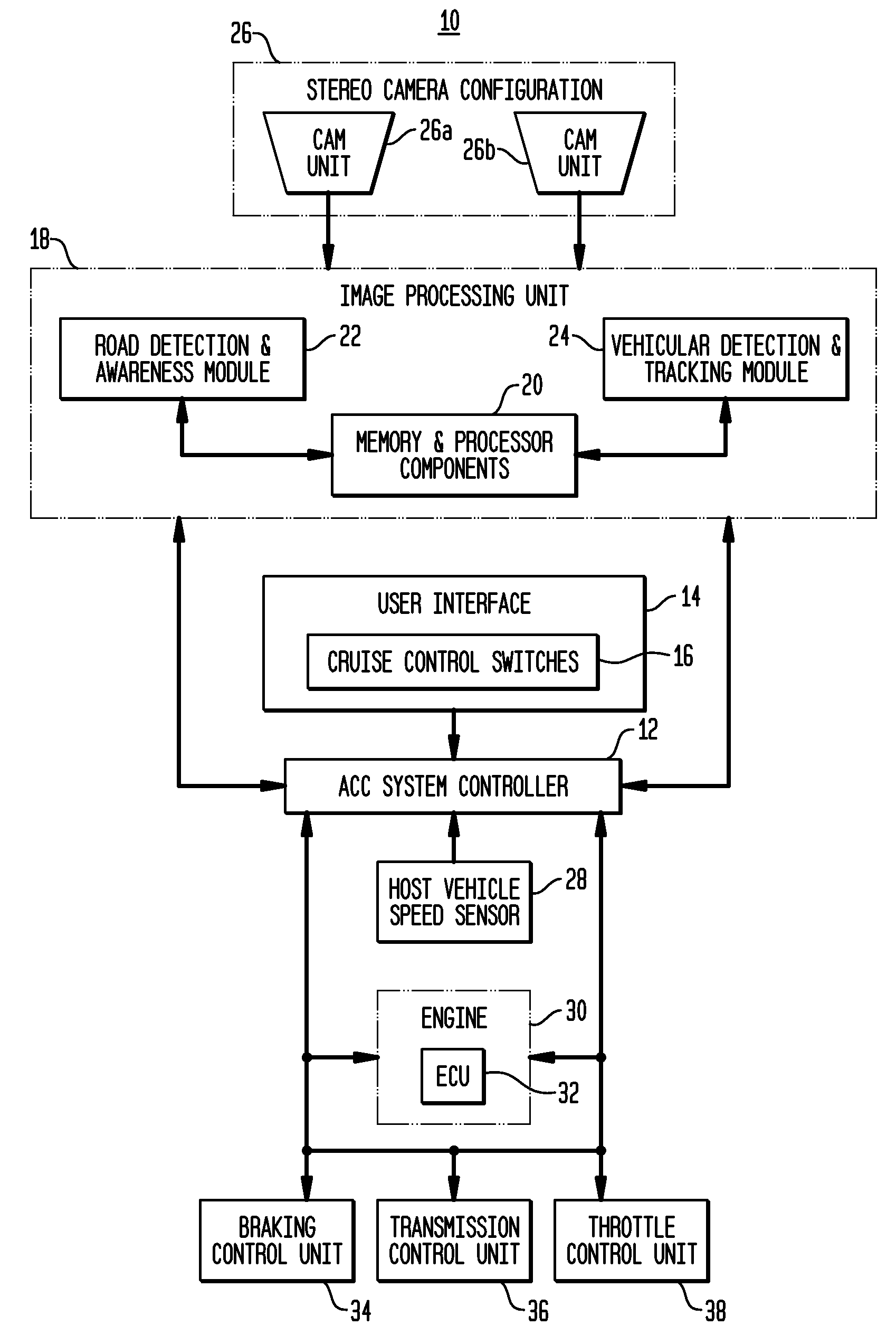
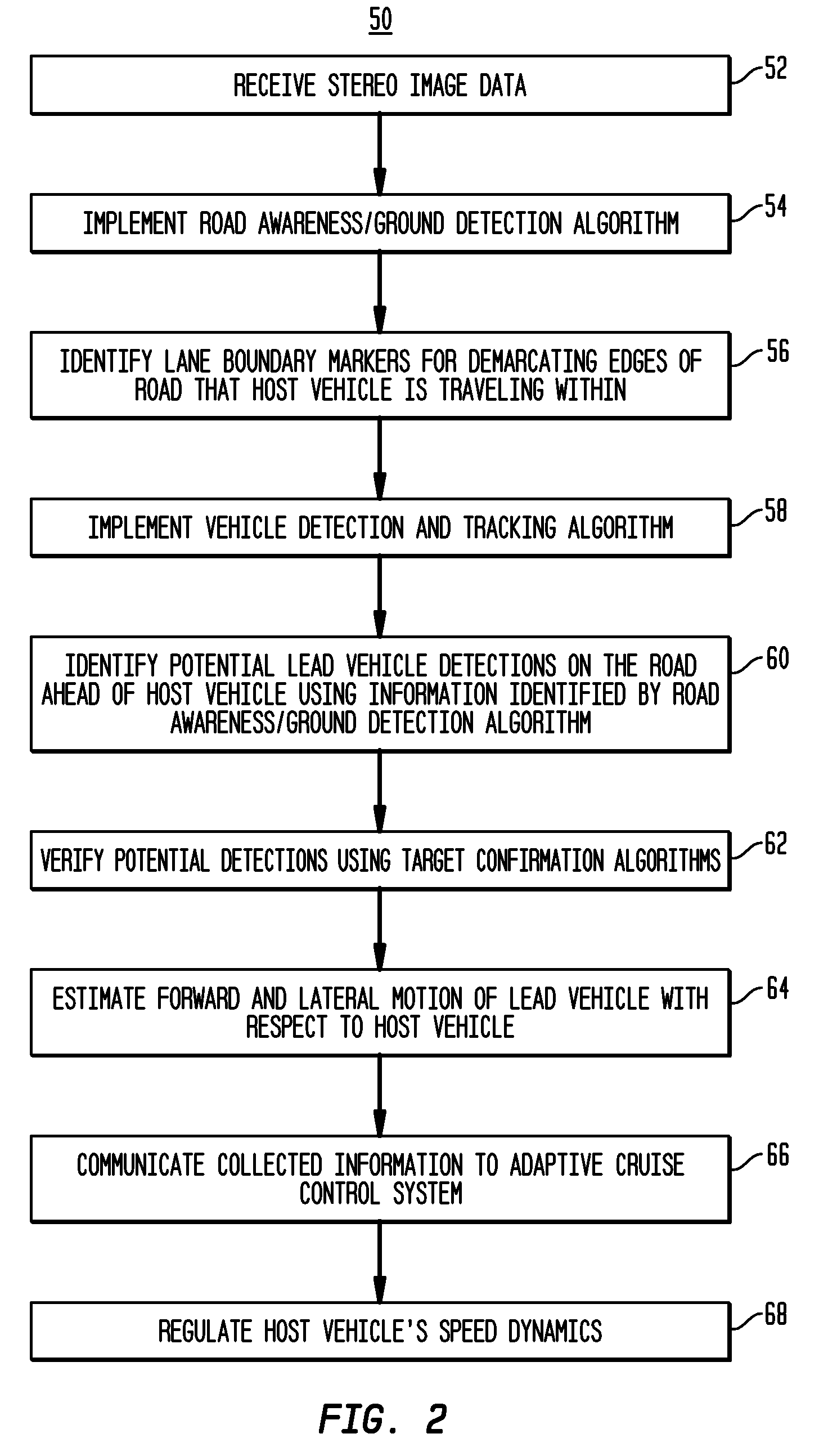
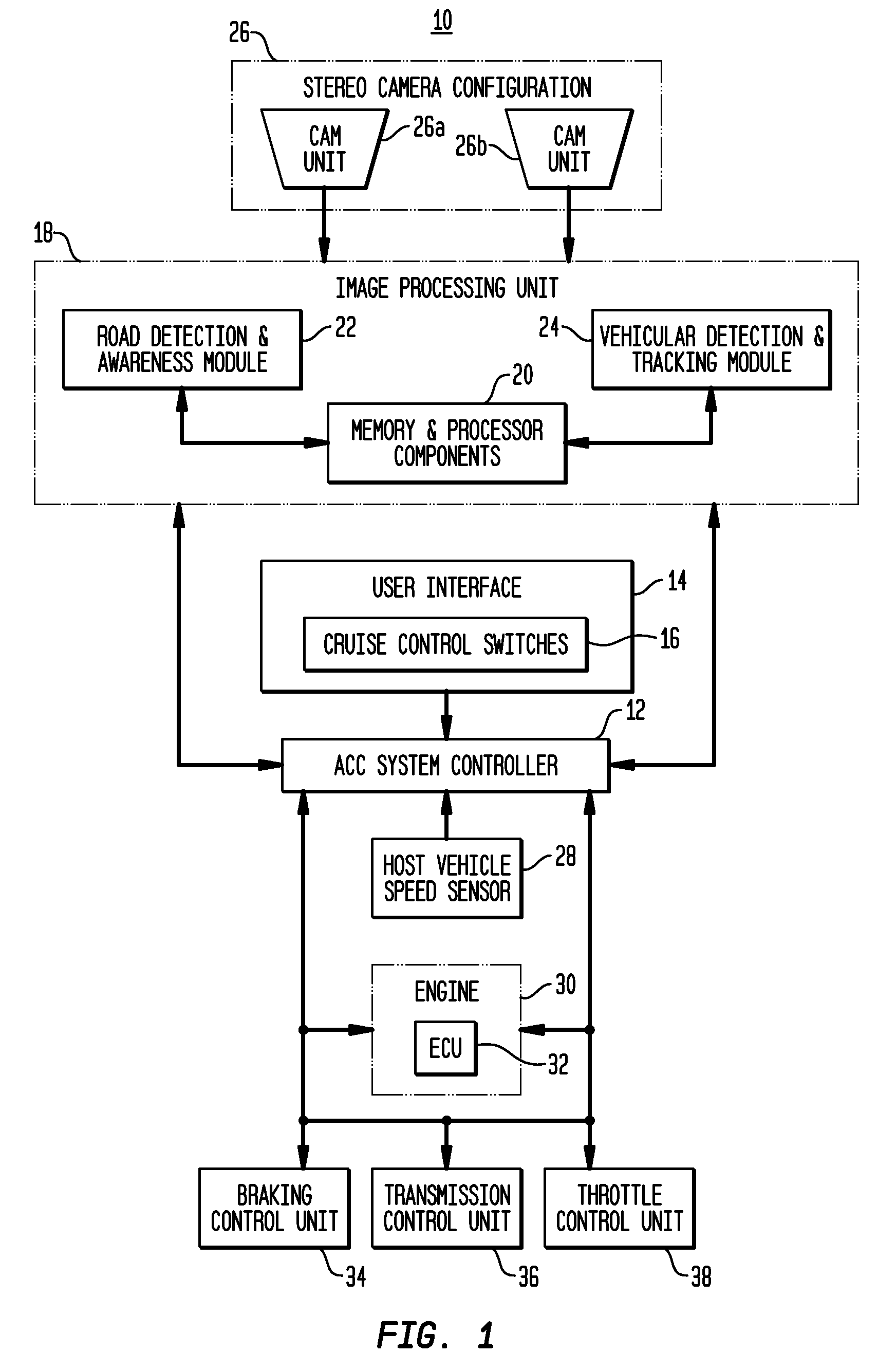
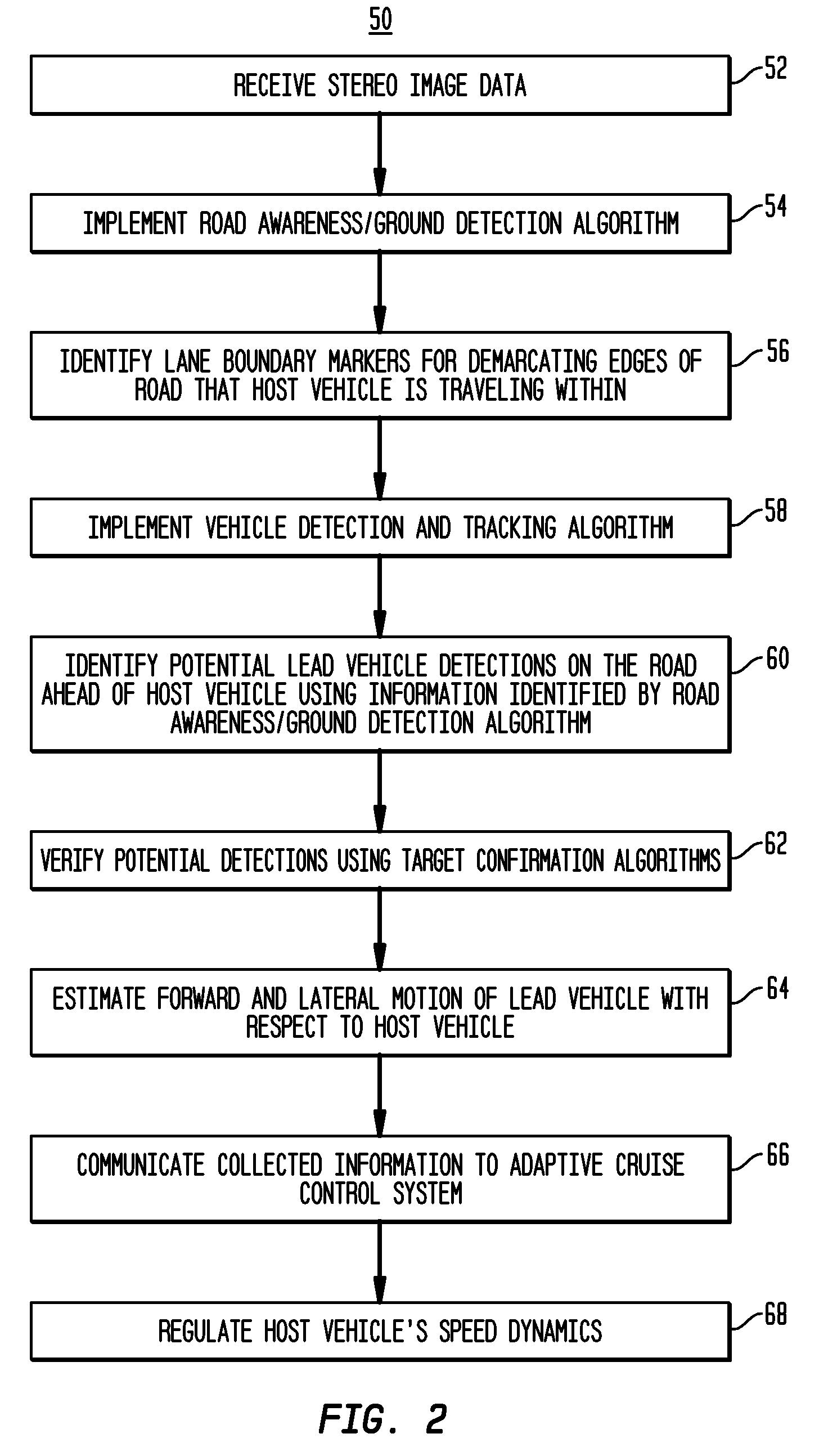
Apparatus and method for object detection and tracking and roadway awareness using stereo cameras
ActiveUS20070255480A1Performance-enhanced approachComponent is expensiveImage analysisDigital data processing detailsControl systemStereo cameras
The present invention provides a collision avoidance apparatus and method employing stereo vision applications for adaptive vehicular control. The stereo vision applications are comprised of a road detection function and a vehicle detection and tracking function. The road detection function makes use of three-dimensional point data, computed from stereo image data, to locate the road surface ahead of a host vehicle. Information gathered by the road detection function is used to guide the vehicle detection and tracking function, which provides lead motion data to a vehicular control system of the collision avoidance apparatus. Similar to the road detection function, stereo image data is used by the vehicle detection and tracking function to determine the depth of image scene features, thereby providing a robust means for identifying potential lead vehicles in a headway direction of the host vehicle.
Owner:ZAMA INNOVATIONS LLC
Method and apparatus for controlling lesion size in catheter-based ablation treatment
ActiveUS8641705B2Prevent steam poppingReliable predictionStrain gaugeDiagnostic recording/measuringTime integralTarget tissue
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
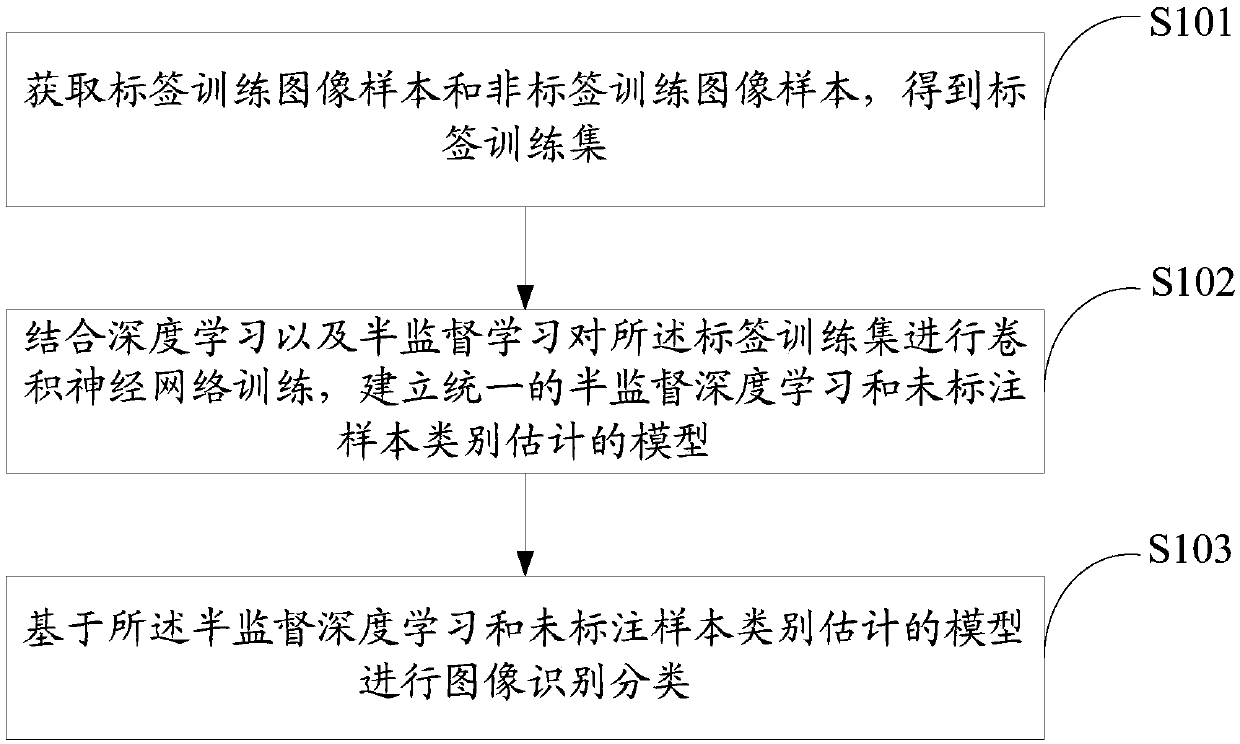
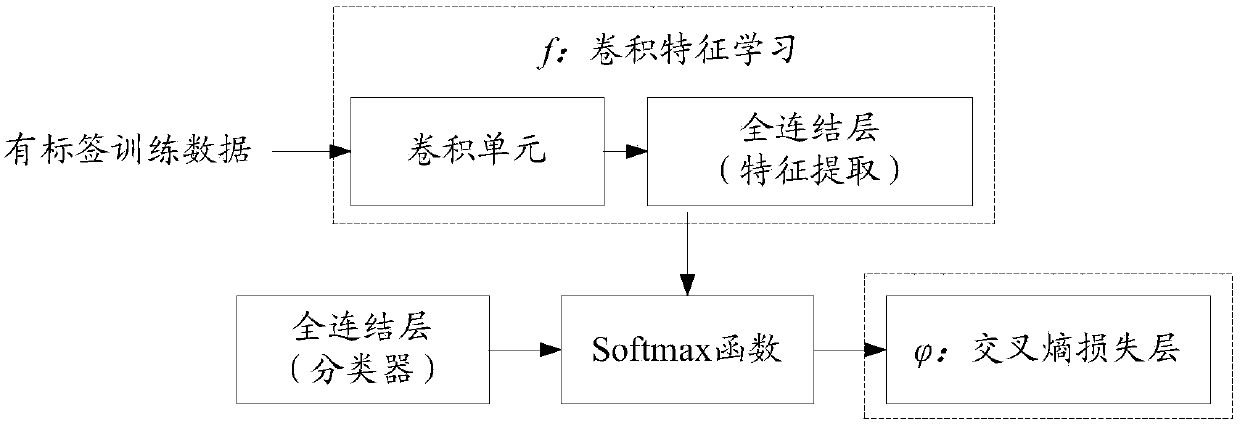
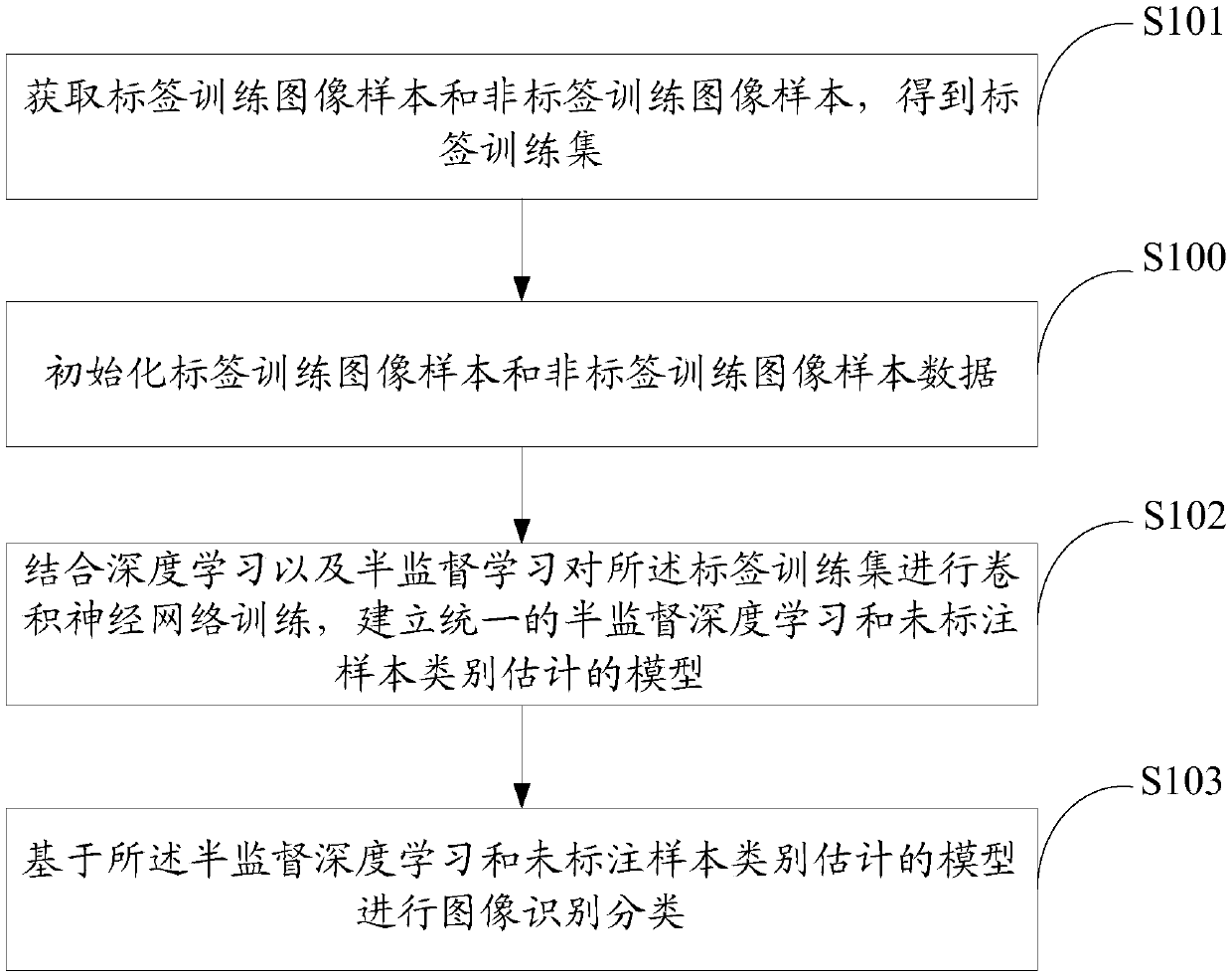
Image classification method and device based on semi-supervised deep learning and storage medium
ActiveCN108416370AReliable estimateAvoid the situation where the final recognition accuracy is not highCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesClassification methodsSupervised learning
The invention discloses an image classification method and device based on semi-supervised deep learning and a storage medium. The method includes: acquiring label training image samples and non-labeltraining image samples, and obtaining a label training set; combining deep learning and semi-supervised learning to carry out training of a convolutional neural network (CNN) on the label training set, and establishing a unified model of semi-supervised deep learning and unlabeled-sample class estimation; and carrying out image recognition / classification on the basis of the model of semi-supervised deep learning and unlabeled sample class estimation. According to the method, distinguishing information hidden in non-label training data can be utilized, high separability of current deep features can also be utilized at the same time, the unlabeled samples can be more efficiently and accurately utilized, and thus better image recognition performance can be obtained.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Method for determining demand and pricing of advertising time in the media industry
The present invention utilizes customer / user generated data and market available data to provide a framework and guidance for a seller to price advertising time and space for programs offered by a media outlet, and to project future demand for advertising time and space. The invention determines the number available advertising spots (avails) that exist in a market, the projected rating of the avail, the historical advertising avail sales price, and a reasonable target price for each avail. It utilizes avail request information from individual advertising agency clients, sellout data from broadcast media, together with ratings and projections from published rating services (such as Neilsen and CMR) to produce a series of reports that provide needed information to create projections of future inventory, demand and pricing ranges. The reports include avail demand and analysis reports, market blueprint reports, market CPP tolerance reports, pricing grids, and market share trend reports.
Owner:WIDEORBIT LLC
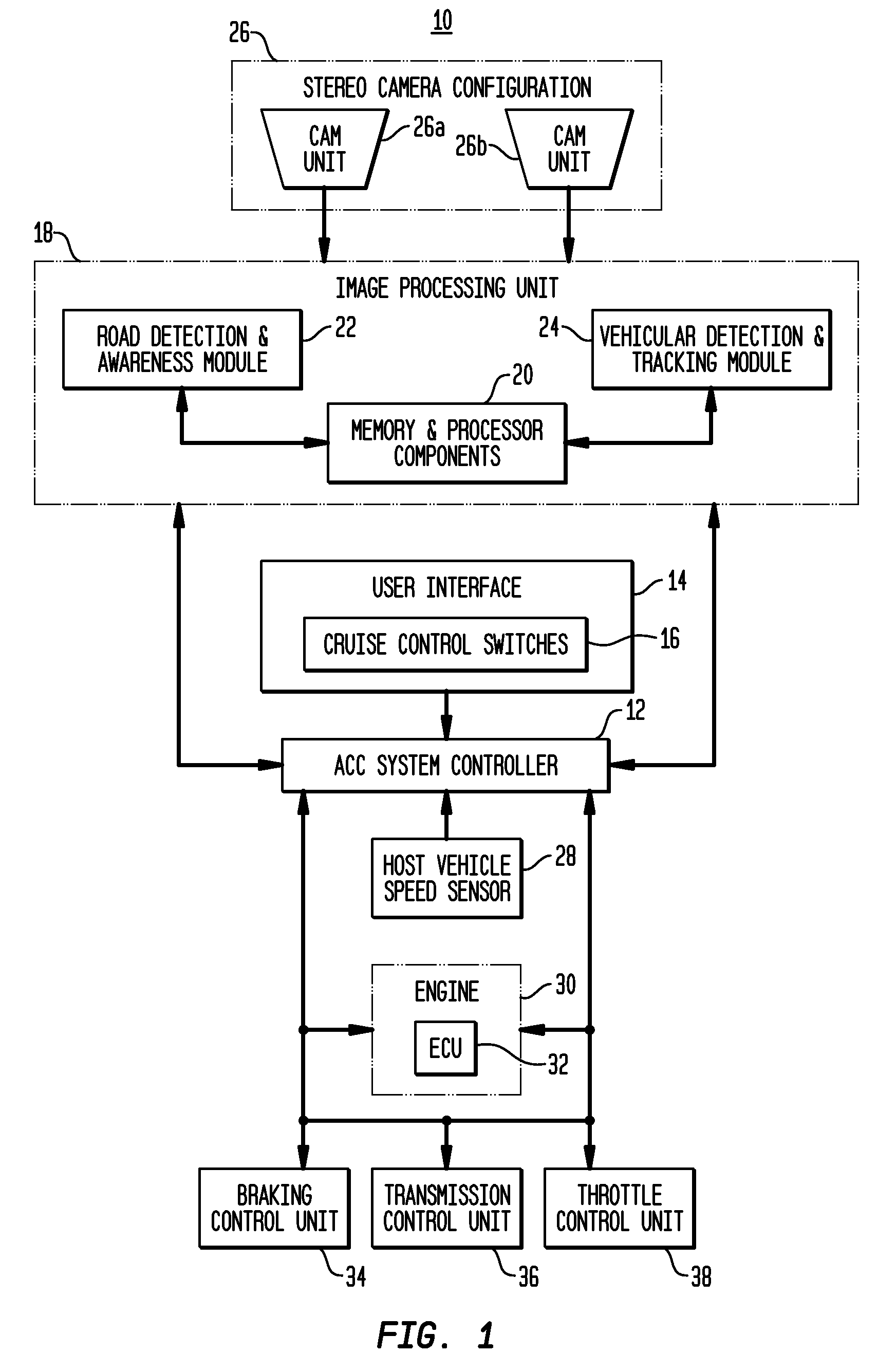
Apparatus and method for object detection and tracking and roadway awareness using stereo cameras
ActiveUS8108119B2Performance-enhanced approachComponent is expensiveImage analysisDigital data processing detailsControl systemStereo cameras
The present invention provides a collision avoidance apparatus and method employing stereo vision applications for adaptive vehicular control. The stereo vision applications are comprised of a road detection function and a vehicle detection and tracking function. The road detection function makes use of three-dimensional point data, computed from stereo image data, to locate the road surface ahead of a host vehicle. Information gathered by the road detection function is used to guide the vehicle detection and tracking function, which provides lead motion data to a vehicular control system of the collision avoidance apparatus. Similar to the road detection function, stereo image data is used by the vehicle detection and tracking function to determine the depth of image scene features, thereby providing a robust means for identifying potential lead vehicles in a headway direction of the host vehicle.
Owner:ZAMA INNOVATIONS LLC
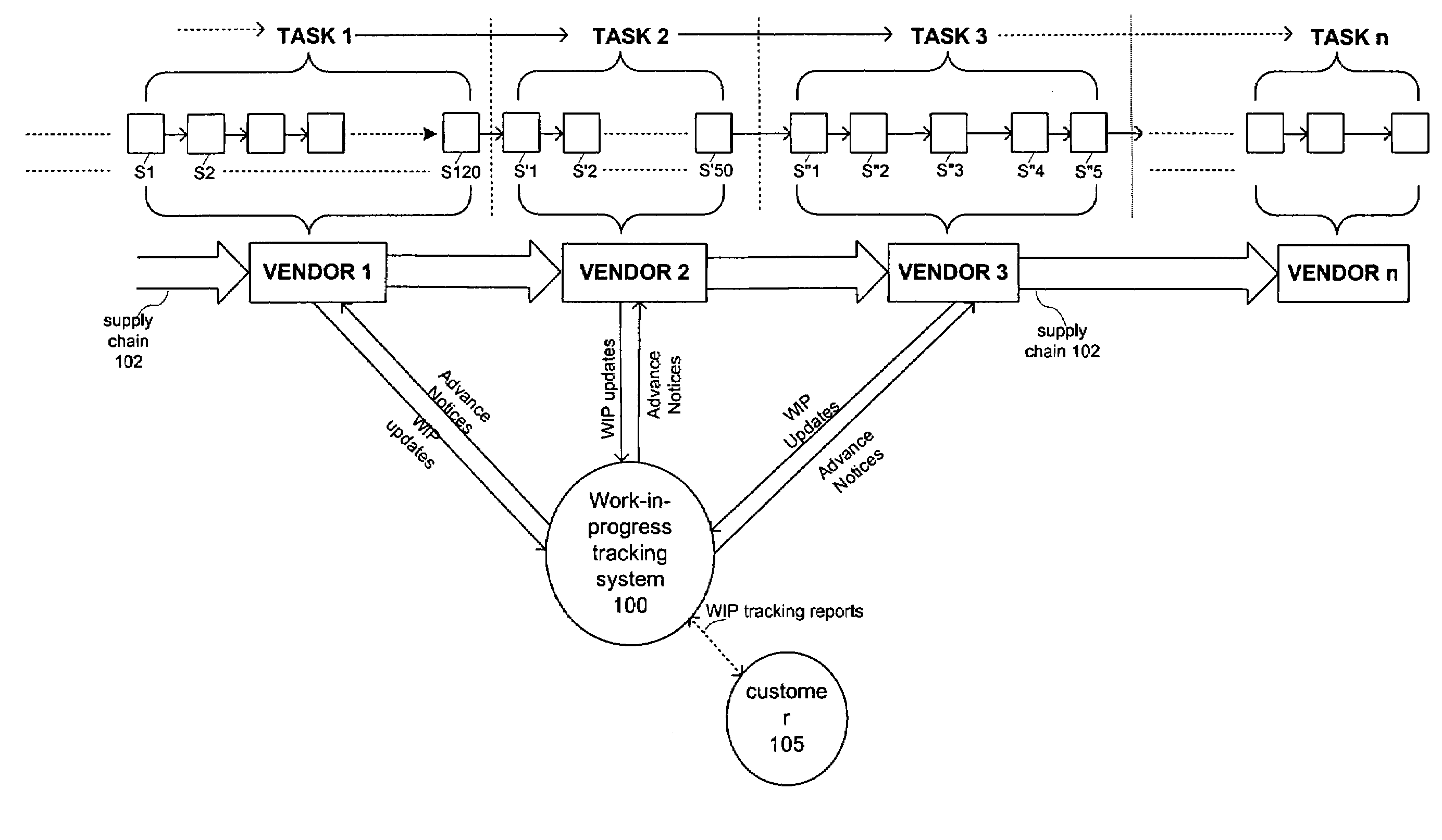
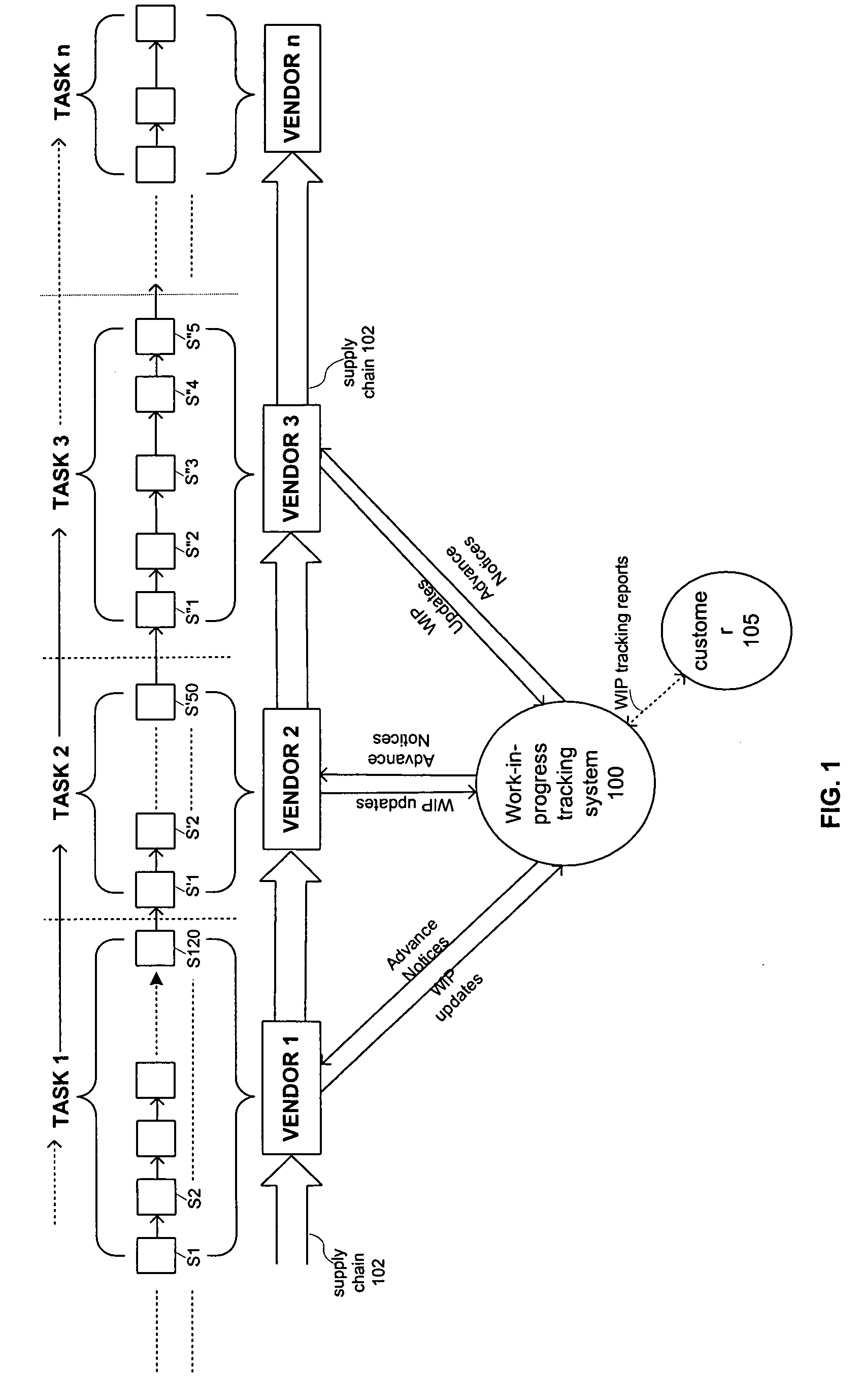
Prediction based optimization of a semiconductor supply chain using an adaptive real time work-in-progress tracking system
InactiveUS7218980B1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsSemiconductorTracking system
A work-in-progress (WIP) tracking system is used to coordinate a semiconductor supply chain operation. The WIP tracking system receives WIP updates from semiconductor supply chain vendors and generates a WIP tracking report in which the volume of WIP is measured in expected good parts. In one variation, rather than reporting the WIP currently located at each step of a vendor's process, the WIP tracking report reflects the WIP located at various stages of the semiconductor manufacturing process, where the vendor's steps are mapped to a fewer number of stages.
Owner:INPHI
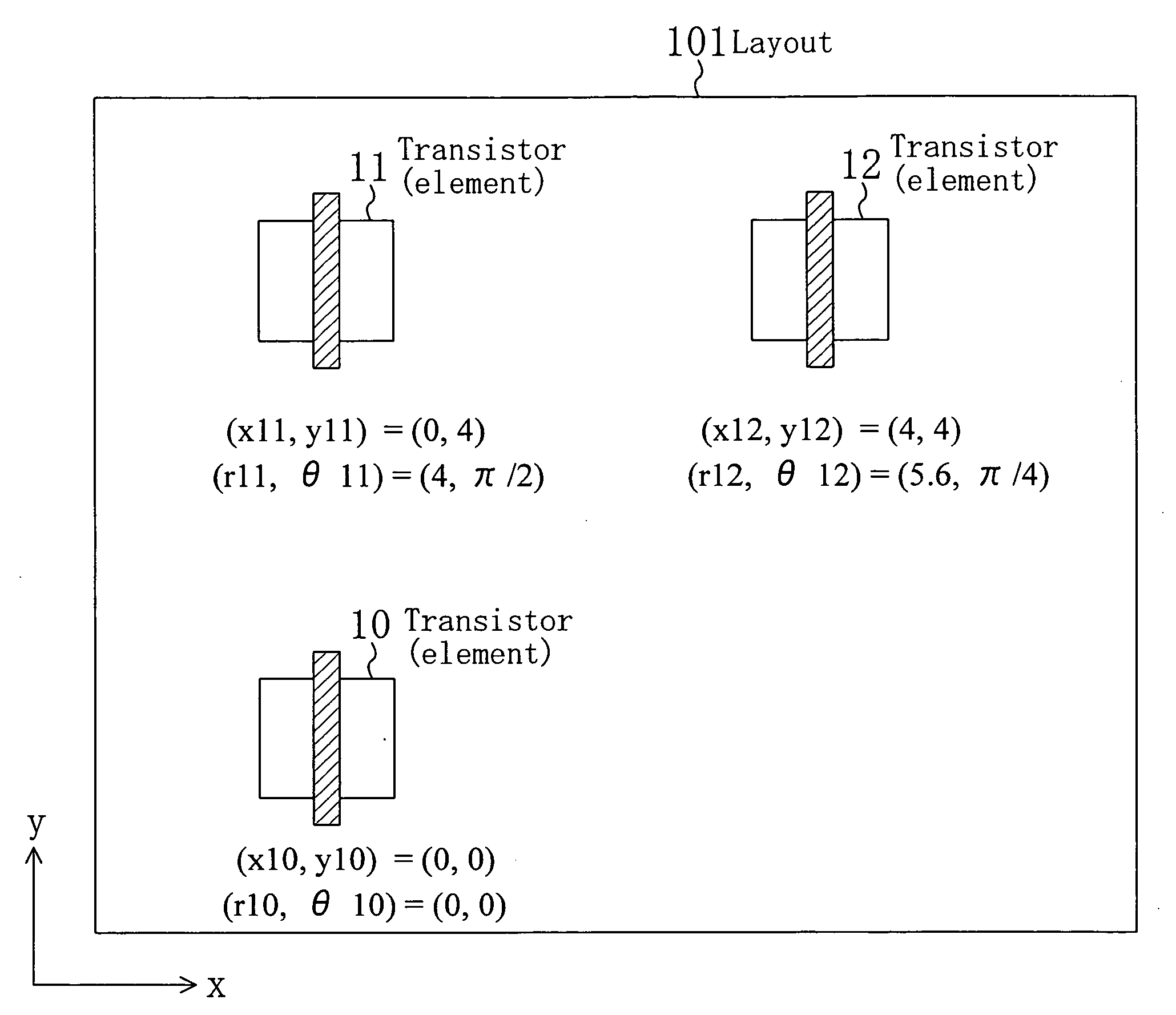
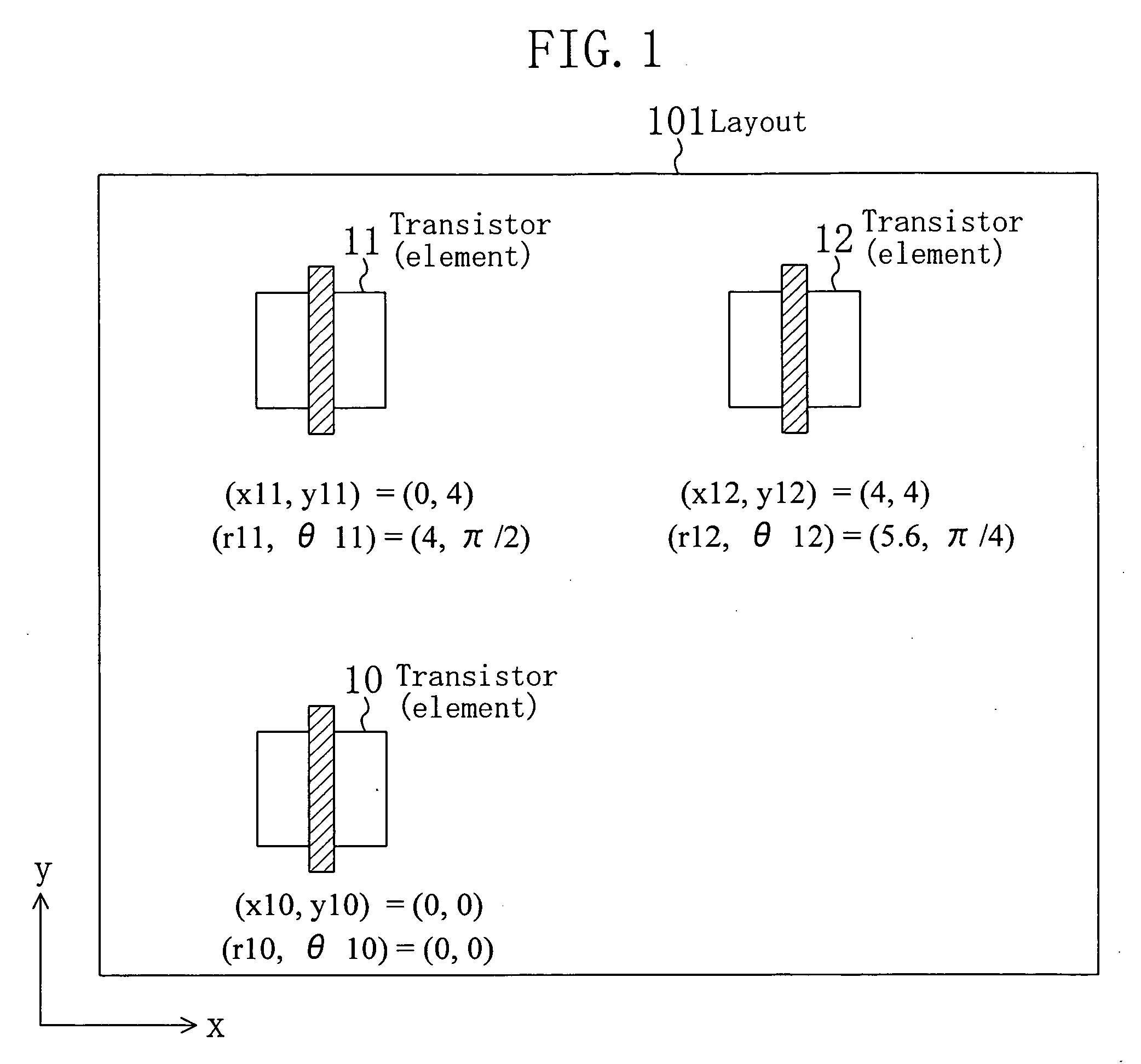
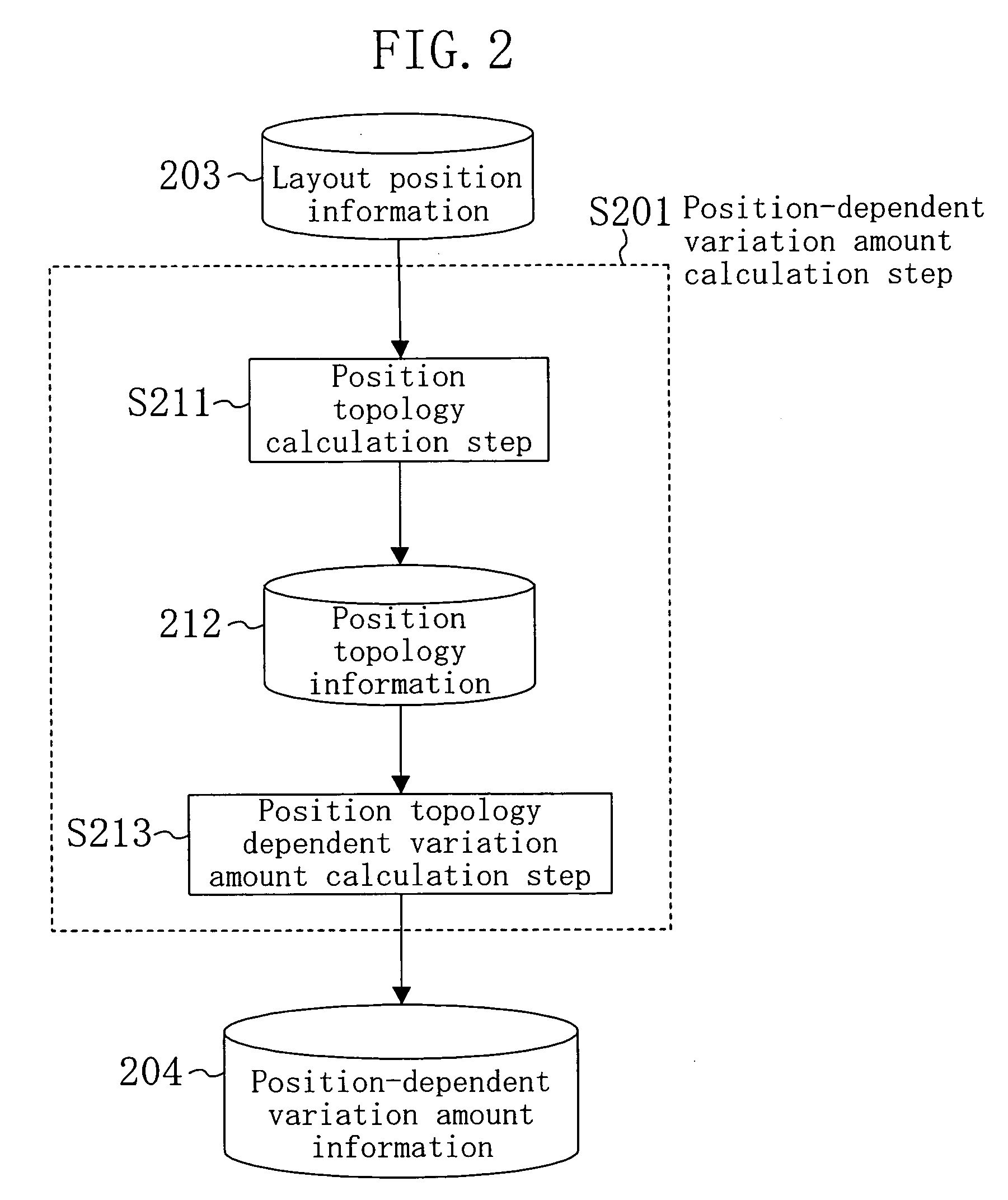
Position-dependent variation amount computation method and circuit analysis method
InactiveUS20070186196A1Extended processing timeEfficient executionDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputer aided designPosition dependentEngineering
Using layout position information as input, in a position-dependent variation amount calculation step, position-dependent variation amount information which is a variation amount of a characteristic parameter or a shape parameter variable depending on an arrangement position of each element constituting a design target semiconductor integrated circuit is calculated. Thereafter, a simulation is performed using circuit information. In the simulation, a value for the circuit information is corrected according to a position-dependent variation amount of the position-dependent variation amount information, and a result of the simulation is calculated. Accordingly, a simulation for a circuit characteristic using a variation amount depending on an arrangement position of a device and the like can be performed with layout position information for a semiconductor integrated circuit.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Apparatus and method for determining battery/cell's performance, age, and health
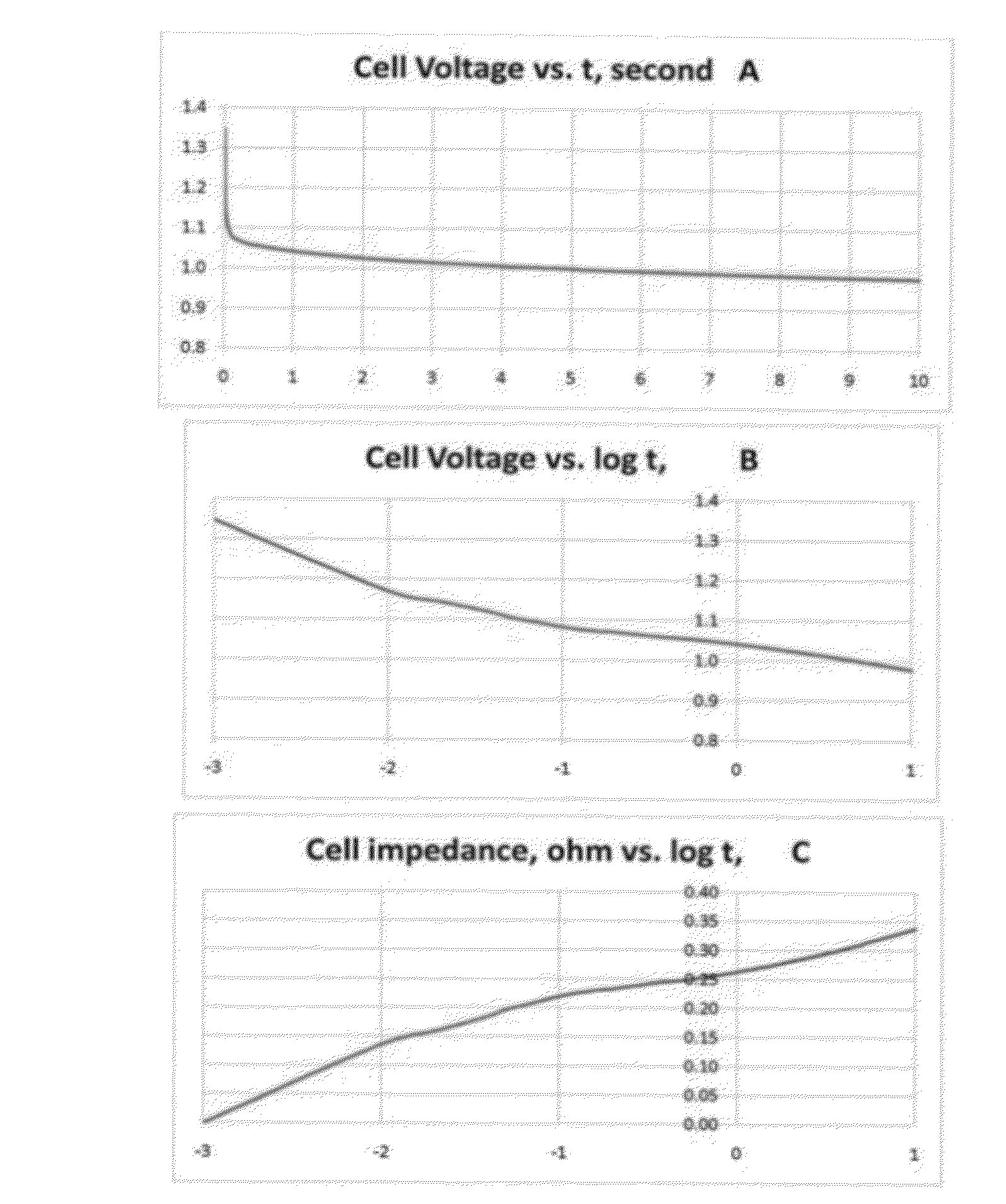
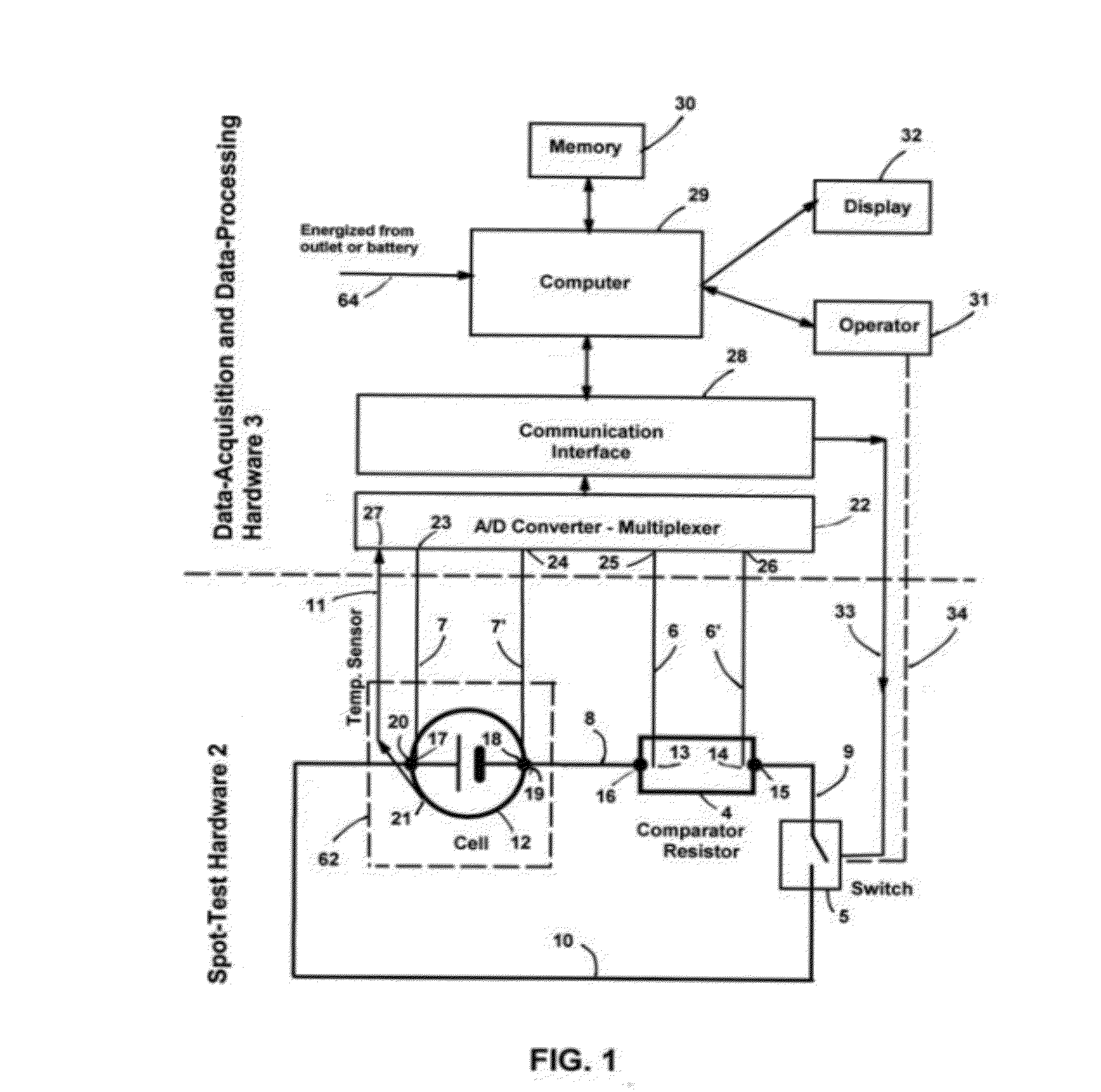
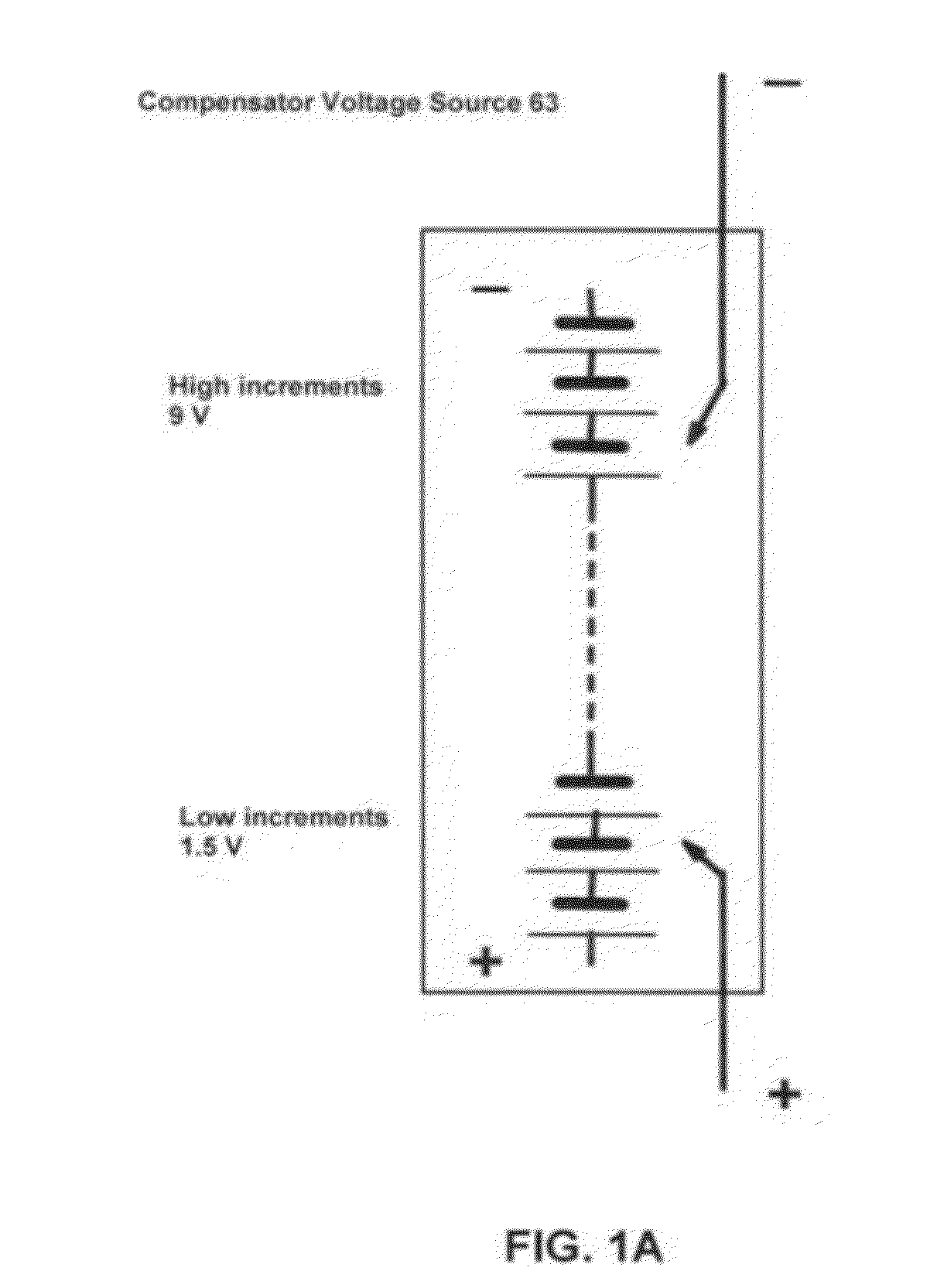
InactiveUS20120310565A1Quick and concise evaluationReliable estimateMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrical testingTime domainVoltage response
A self-energized measuring system for determining primary and secondary battery / cell's performance, age, and health by measuring and recording battery / cell's voltage response to a specified load-changing perturbation spot-test event. The cell's voltage response is compared to a synchronously measured voltage signal of a comparator resistor. The relationship between the two voltage signals is analyzed on logarithmic time scale to determine performance parameters such as cell impedance and power and their variation in the time domain. The cell temperature is also measured for impedance and power normalization for 20 centigrade. Results are compared to a previously generated master data tabulation characteristic of a similar, new cell of perfect health condition. The time-domain performance parameters are related to the performance, age and health of the cell at any particular instant. The evaluation method can be easily adjusted to various battery chemistries, types.
Owner:REDEY LASZLO
Monitoring of the cerebral state of a subject
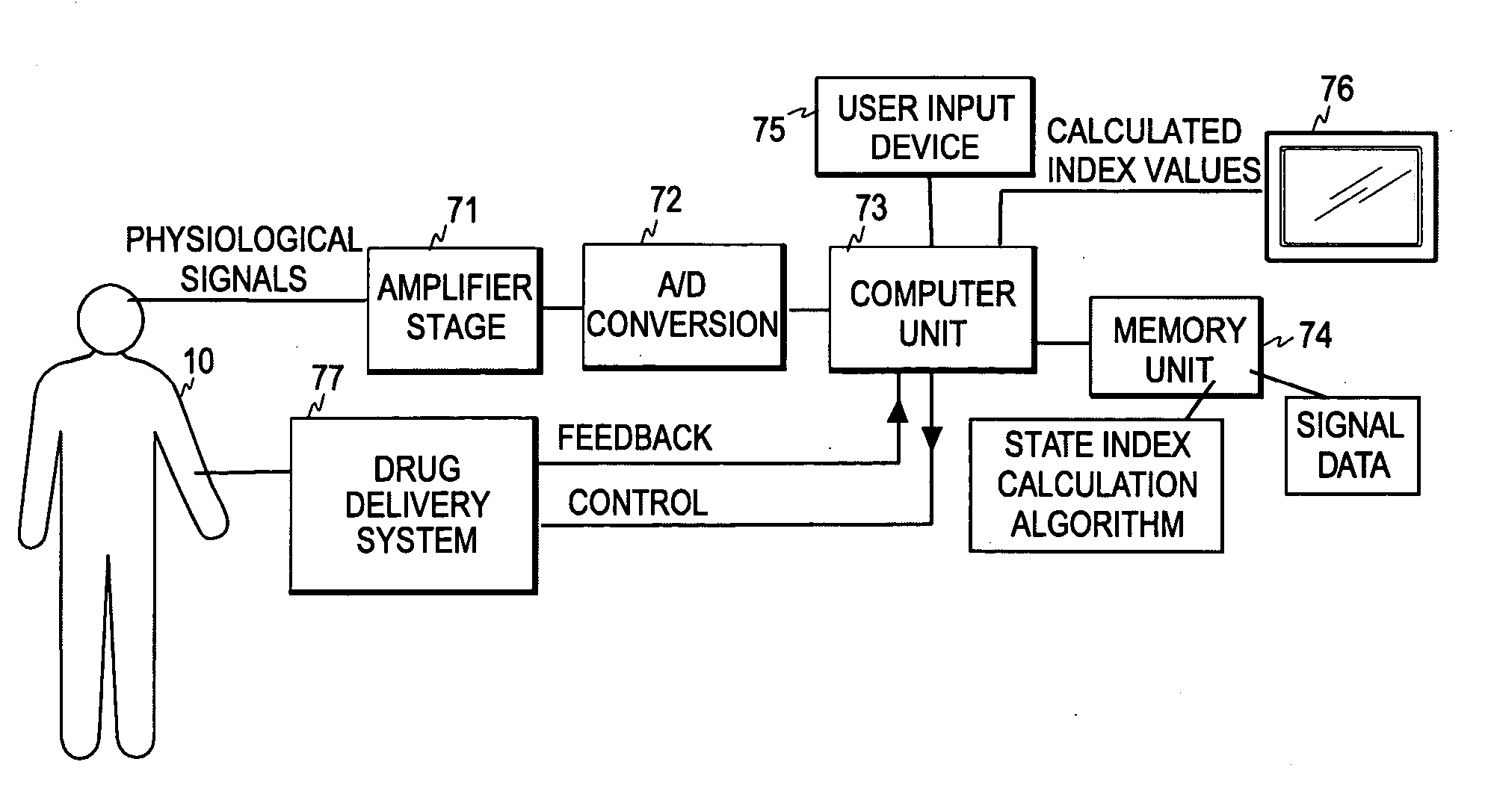
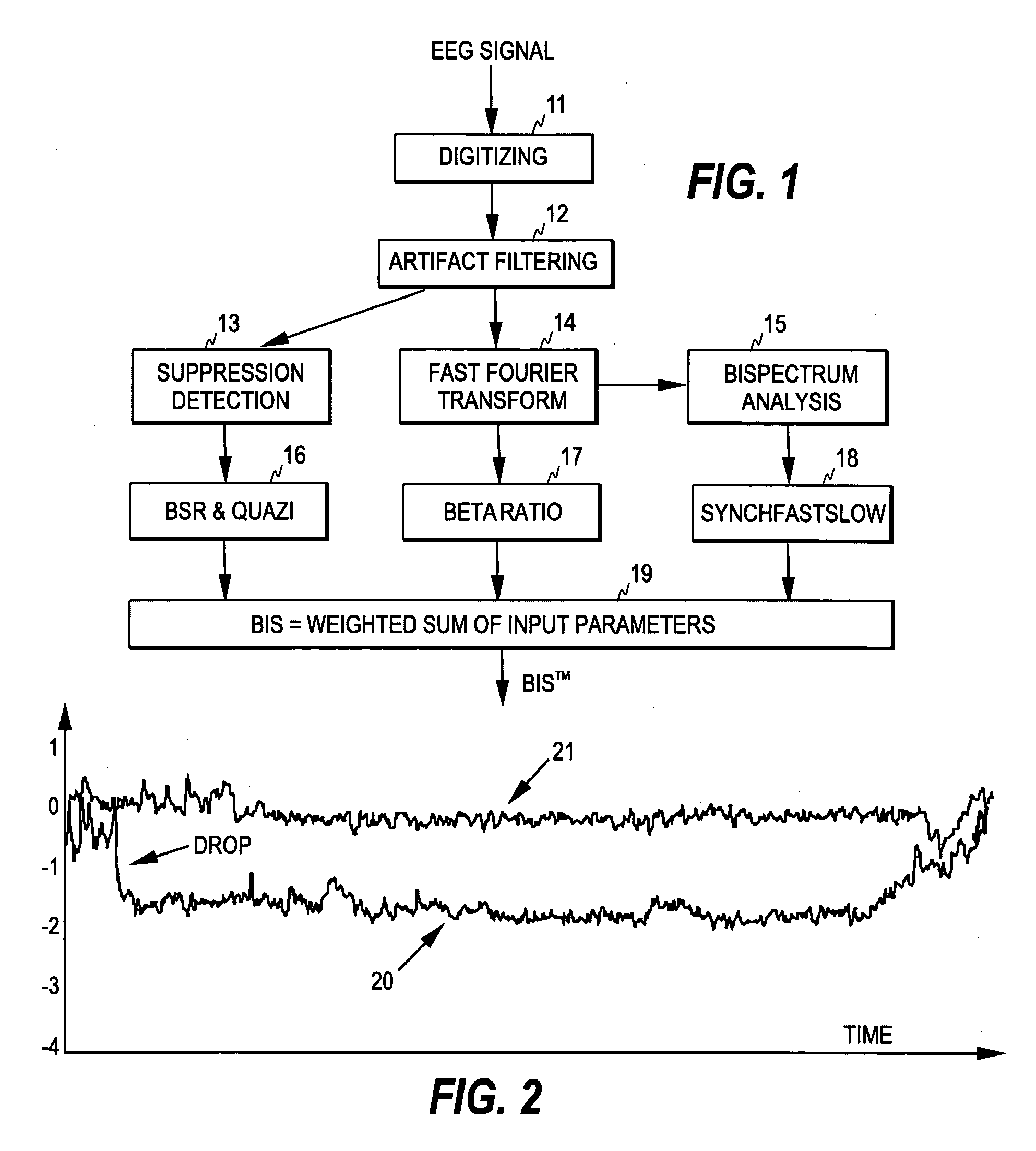
ActiveUS20070010755A1Improve reliabilityImprove applicabilityElectroencephalographySensorsRelative magnitudeBispectral Index Monitor
The invention relates to a method and apparatus for monitoring the cerebral state of a subject. At least one of a first and second parameters is derived from the physiological signal data obtained from the subject, wherein the first parameter is indicative of the sum of spectral values of the physiological signal data in a first frequency band lying above high frequency EEG activity and the second parameter is indicative of the relative magnitudes of a first sum of k-th order spectral values and a second sum of n-th order spectral values. The second sum is calculated over a frequency band lying above high frequency EEG activity (k>2 and n>1). A state index is then formed, which is dependent on the at least one parameter and indicative of the cerebral state of the subject. The first and second parameters may be used in the Bispectral Index (BIS™) algorithm.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
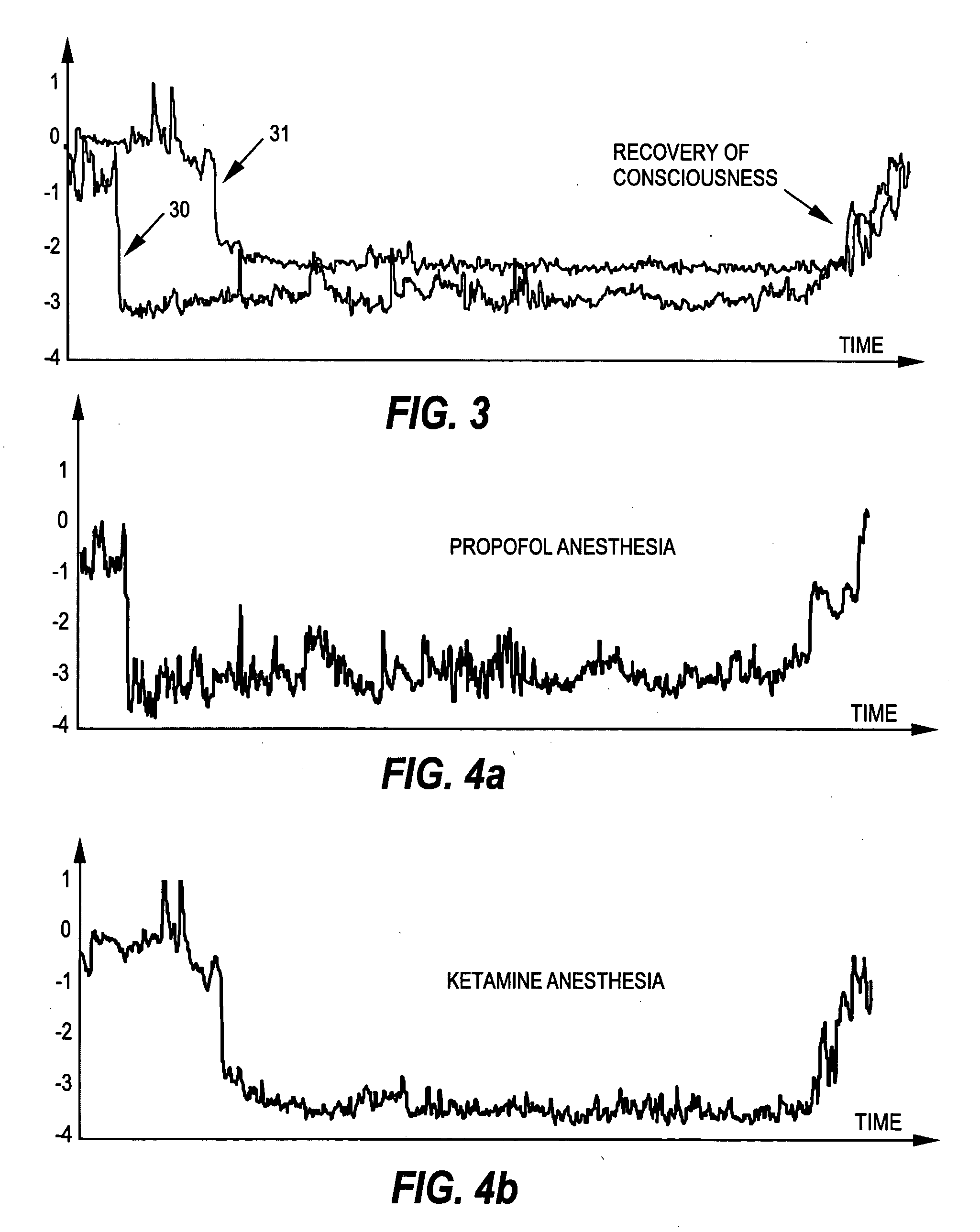
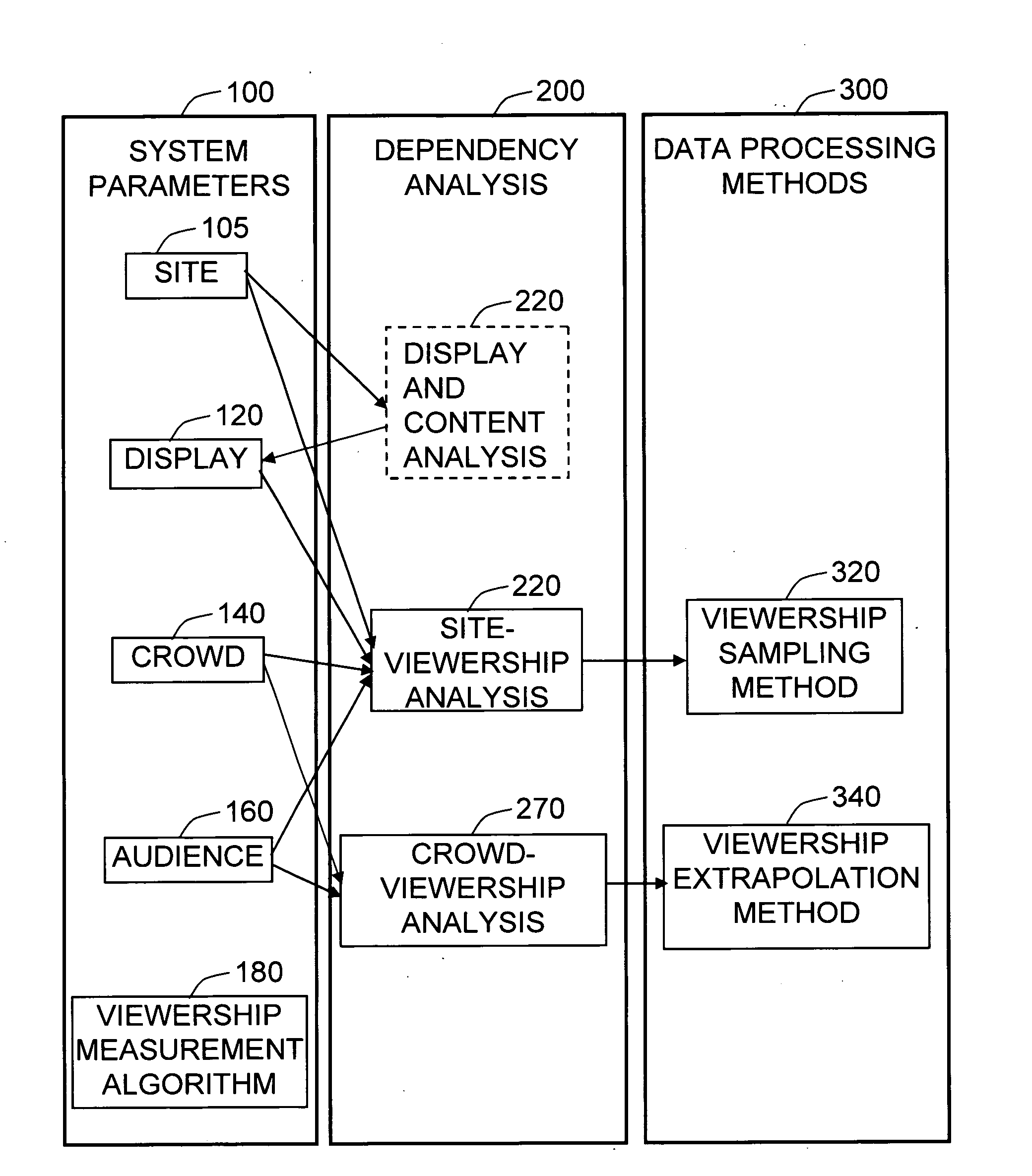
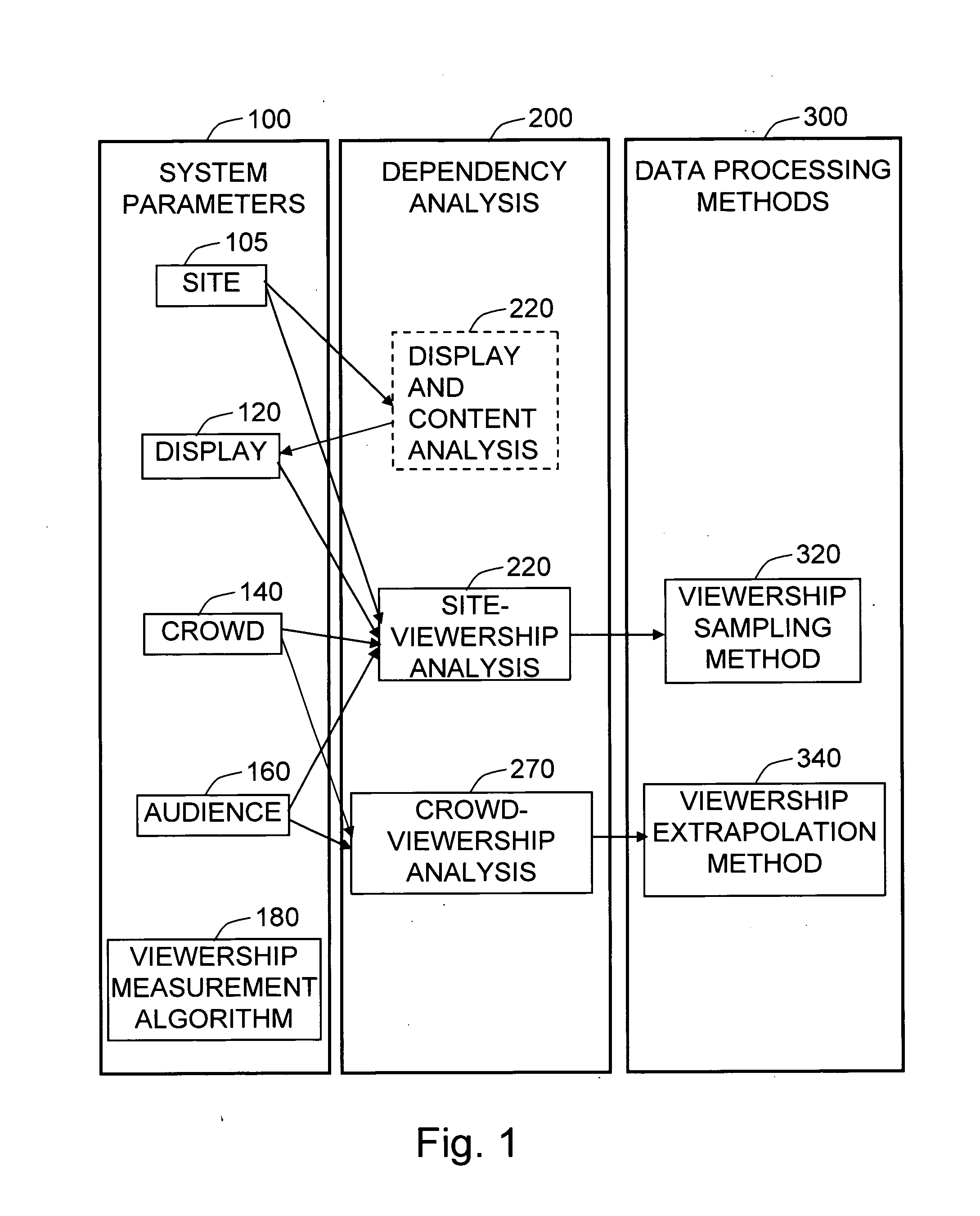
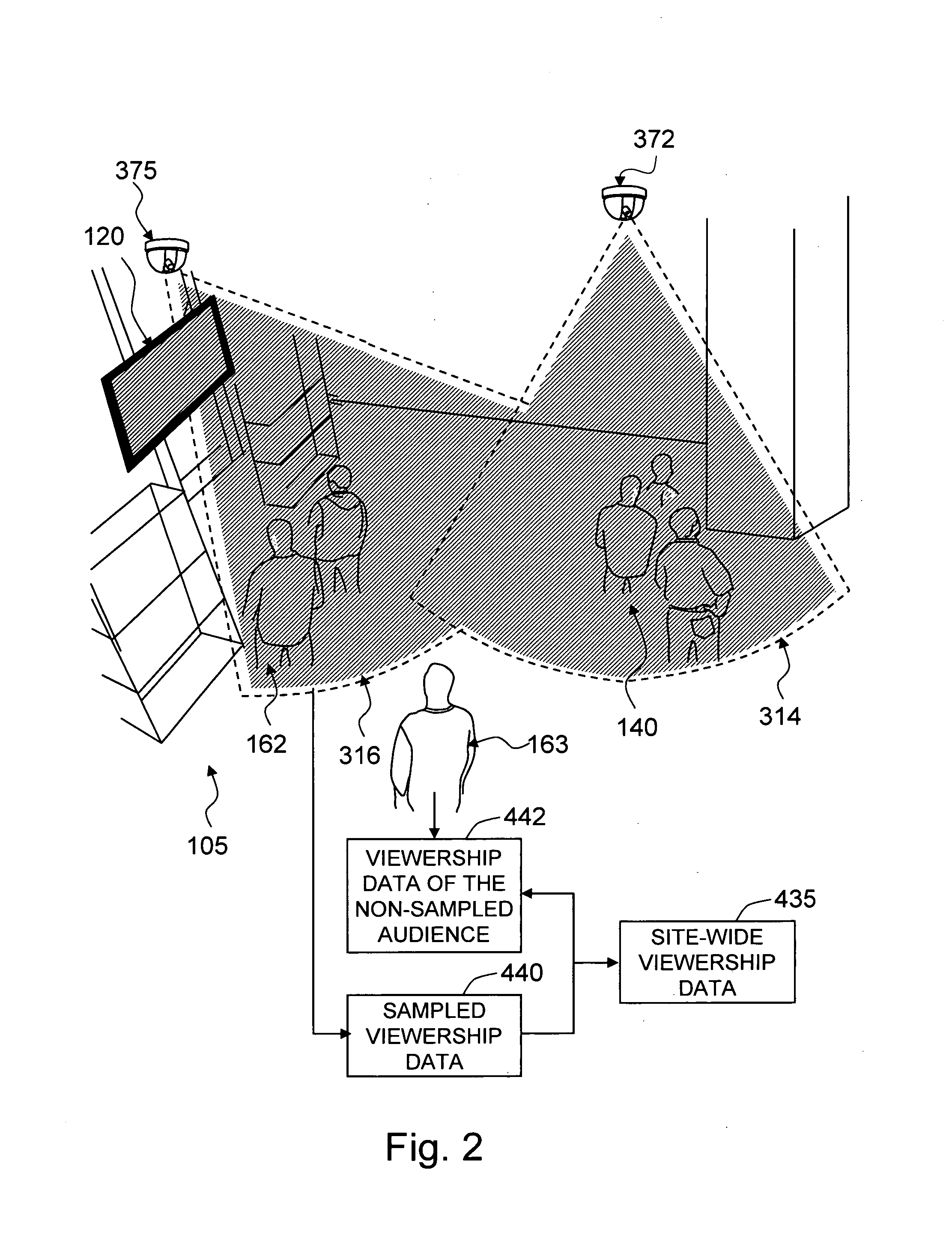
Method and system for media audience measurement and spatial extrapolation based on site, display, crowd, and viewership characterization
InactiveUS20090158309A1Reliable estimateLarge coverageAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionTemporal changeCrowd dynamics
The present invention provides a comprehensive method to design an automatic media viewership measurement system, from the problem of sensor placement for an effective sampling of the viewership to the method of extrapolating spatially sampled viewership data. The system elements that affect the viewership—site, display, crowd, and audience—are identified first. The site-viewership analysis derives some of the crucial elements in determining an effective data sampling plan: visibility, occupancy, and viewership relevancy. The viewership sampling map is computed based on the visibility map, the occupancy map, and the viewership relevancy map; the viewership measurement sensors are placed so that the sensor coverage maximizes the viewership sampling map. The crowd-viewership analysis derives a model of the viewership in relation to the system parameters so that the viewership extrapolation can effectively adapt to the time-changing spatial distribution of the viewership; the step identifies crowd dynamics, and its invariant features as the crucial elements that extract the influence of the site, display, and the crowd to the temporal changes of viewership. The extrapolation map is formulated around these quantities, so that the site-wide viewership can be effectively estimated from the sampled viewership measurement.
Owner:VIDEOMINING CORP
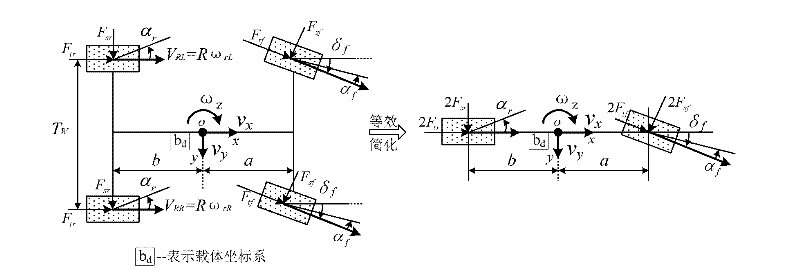
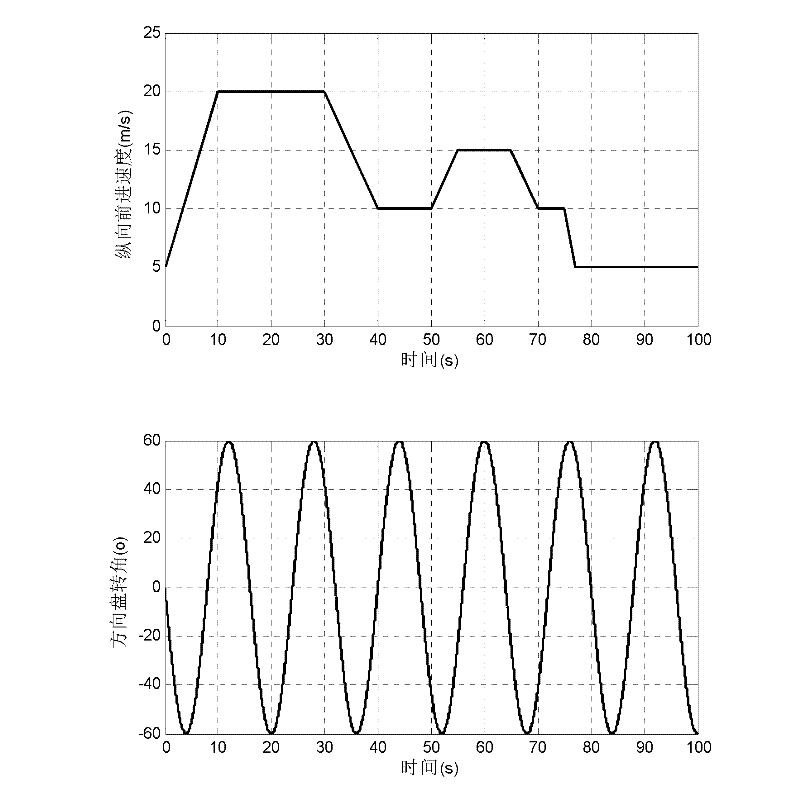
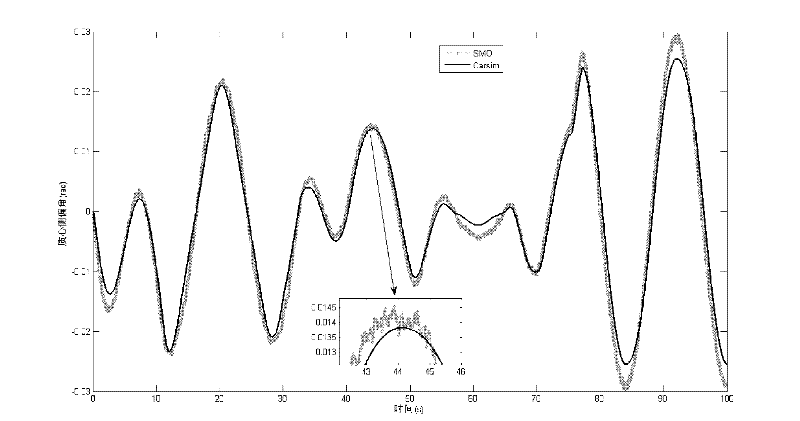
Vehicle running state nonlinear robust estimation method based on sliding mode observer
The invention provides a vehicle running state nonlinear robust estimation method based on a sliding mode observer. The method comprises the following steps of: determining an automotive nonlinear kinetic model closer to the actual situation aiming at high mobility running conditions and complex variable road environments, designing the corresponding sliding mode observer, establishing external input quantity and measurement information of the sliding mode observer system by using low-cost vehicle-mounted wheel speed and steering wheel turning angle sensors, and thus implementing estimation of multiple running states of an automobile by a sliding mode observer estimation recursion algorithm. The method has the characteristics of strong anti-interference capacity, high precision, low cost and the like, and is easy to implement.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
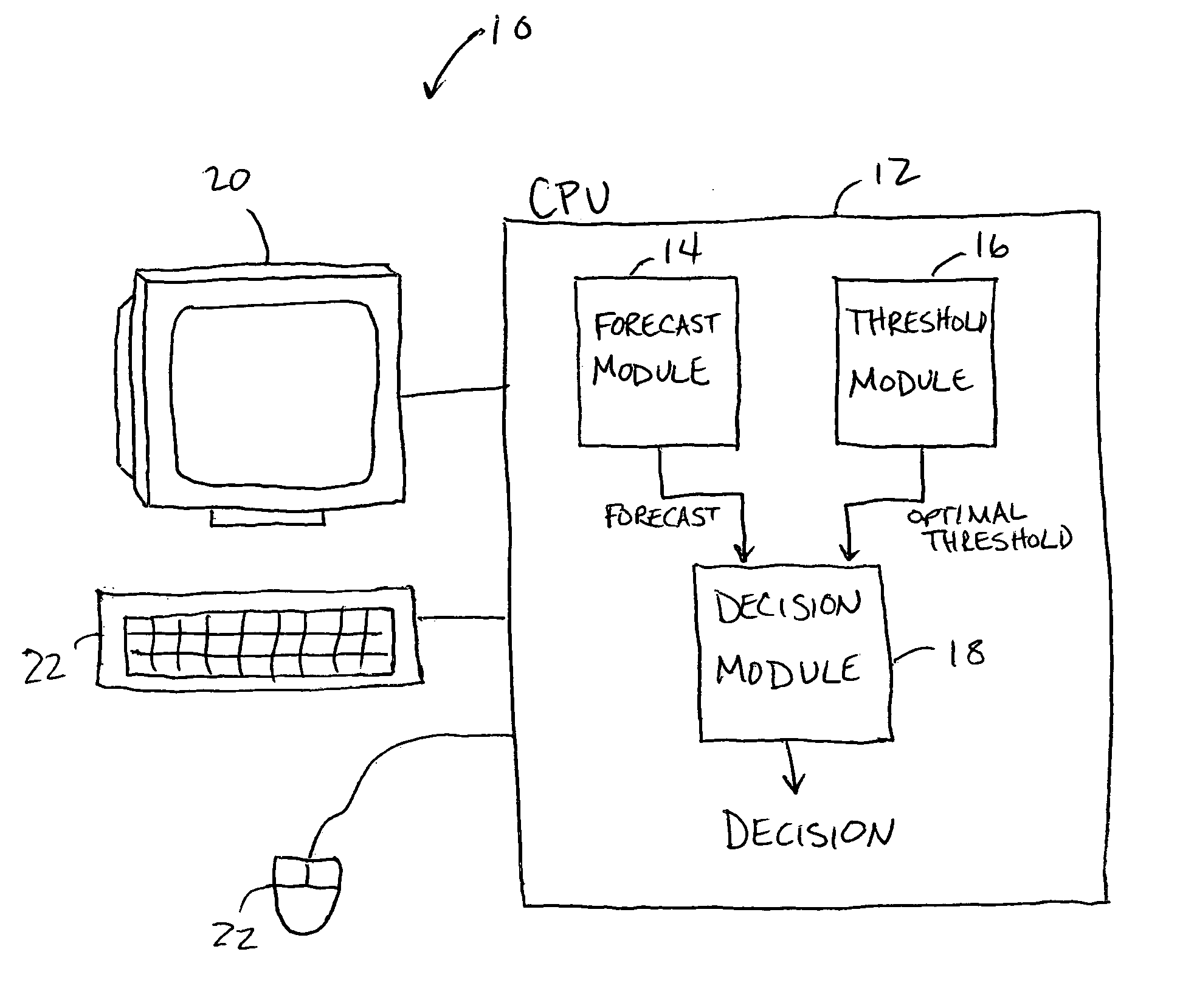
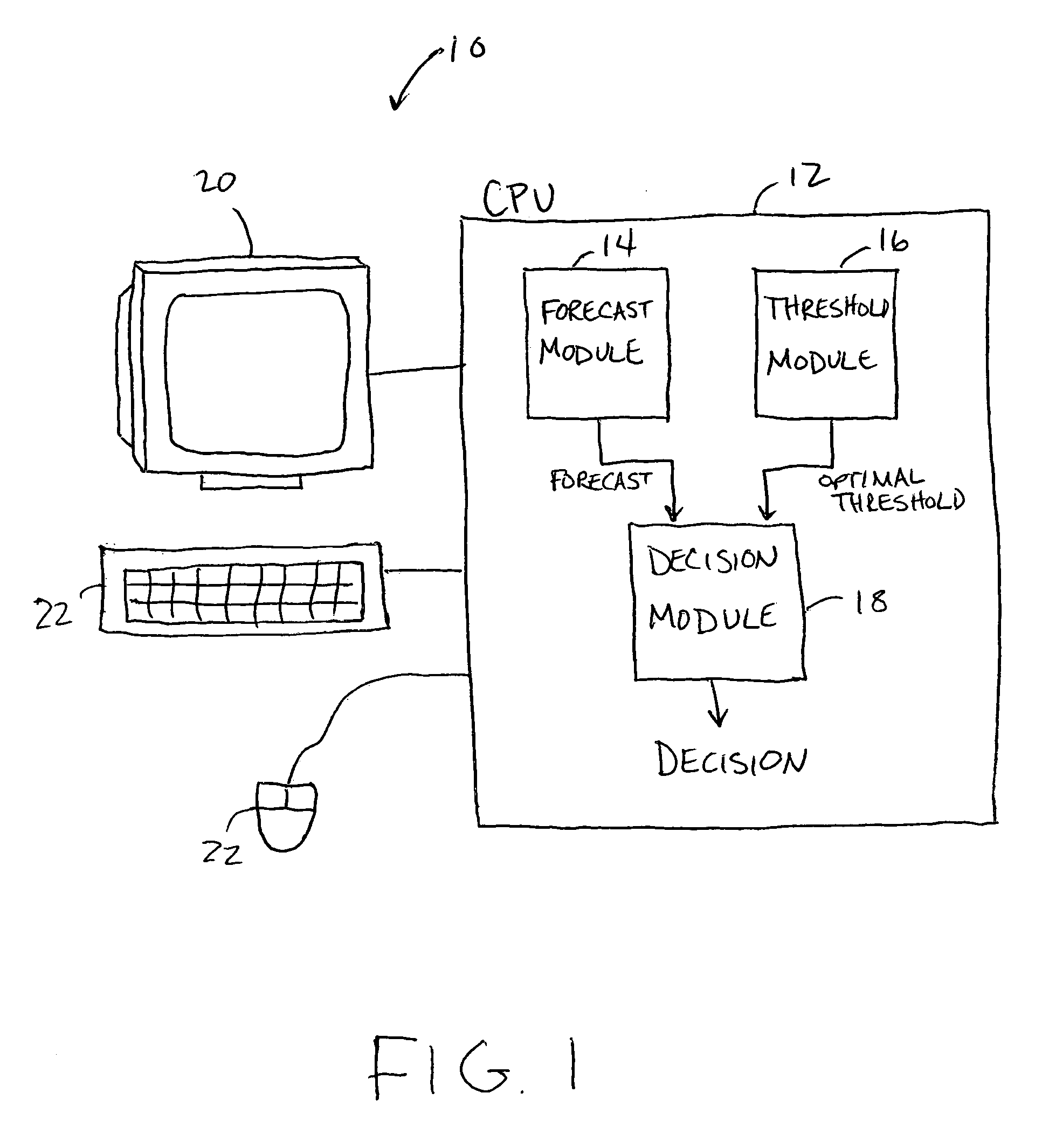
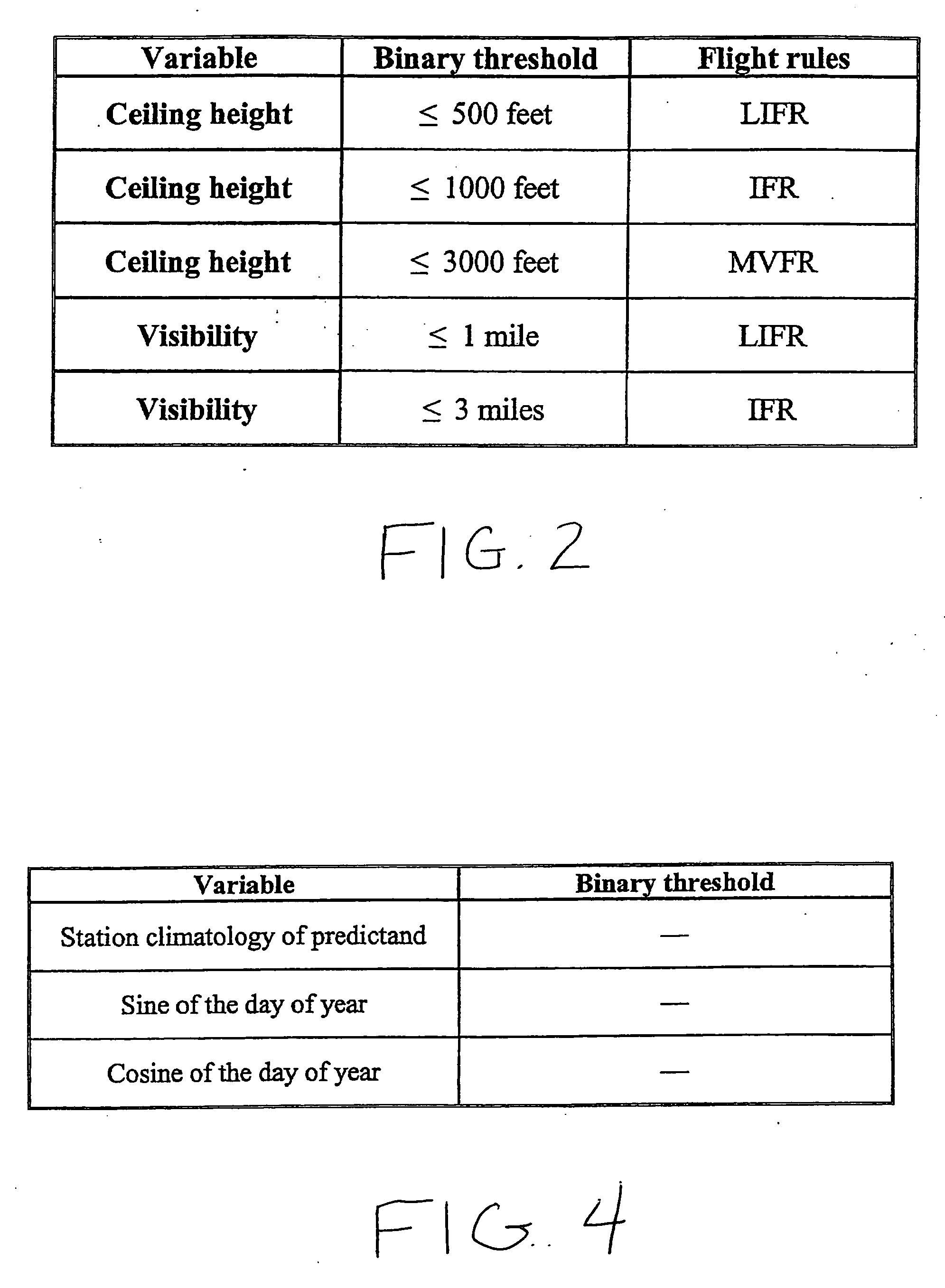
Forecast decision system and method
InactiveUS20060085164A1Increase valueGreat forecast valueAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficVisibilityDecision system
A system and method for making a decision of whether to carry additional fuel on an aircraft for a particular flight based on a forecast, such as for low visibility and ceiling. Preferably, observations-based probabilistic forecasts are utilized. The forecast probability of the weather at the planned aerodrome being below a prescribed minimum level is calculated using statistical regression analysis of past data. An optimal probability is estimated using cost parameters on an individual flight bases. If this forecast probability is greater than the optimal probability for a particular flight, then extra fuel is carried by that flight. This is in contrast to current practice whereby the same categorical forecast is applied to all flights. The combination of improved short-term forecasts and identification of optimal forecast probabilities minimizes the financial impact of errors and weather forecasts on airline operations thereby providing a superior financial outcome.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA THE BOARD THE
Method and apparatus for determining the state of health and state of charge of lithium sulfur batteries
ActiveUS20180095141A1Capacity loseReliable estimationInstruments for road network navigationElectrical testingState dependentModel parameters
Systems and methods for accurately determining the state of health (including state of charge and relative age) of a Lithium Sulfur battery, module or cell. The invention uses an operational model of a Lithium Sulfur cell or battery to predict model parameters under a range of conditions related to state of charge and state of health. Operational models include the memory effect due to the unique chemistry of a Lithium Sulfur cell that precludes the user of other methodologies for State of health determination for Lithium Sulfur batteries. Model parameters are identified in real life applications and parameters are compared to those of the operational Lithium Sulfur model employing Kalman filtering. The output includes an estimate of state of health and other key performance indicators. Key performance indicators are compared with measured values of for example resistance to provide feedback to the estimate process in order to improve accuracy. The system can be implemented as software or firmware in an application.
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
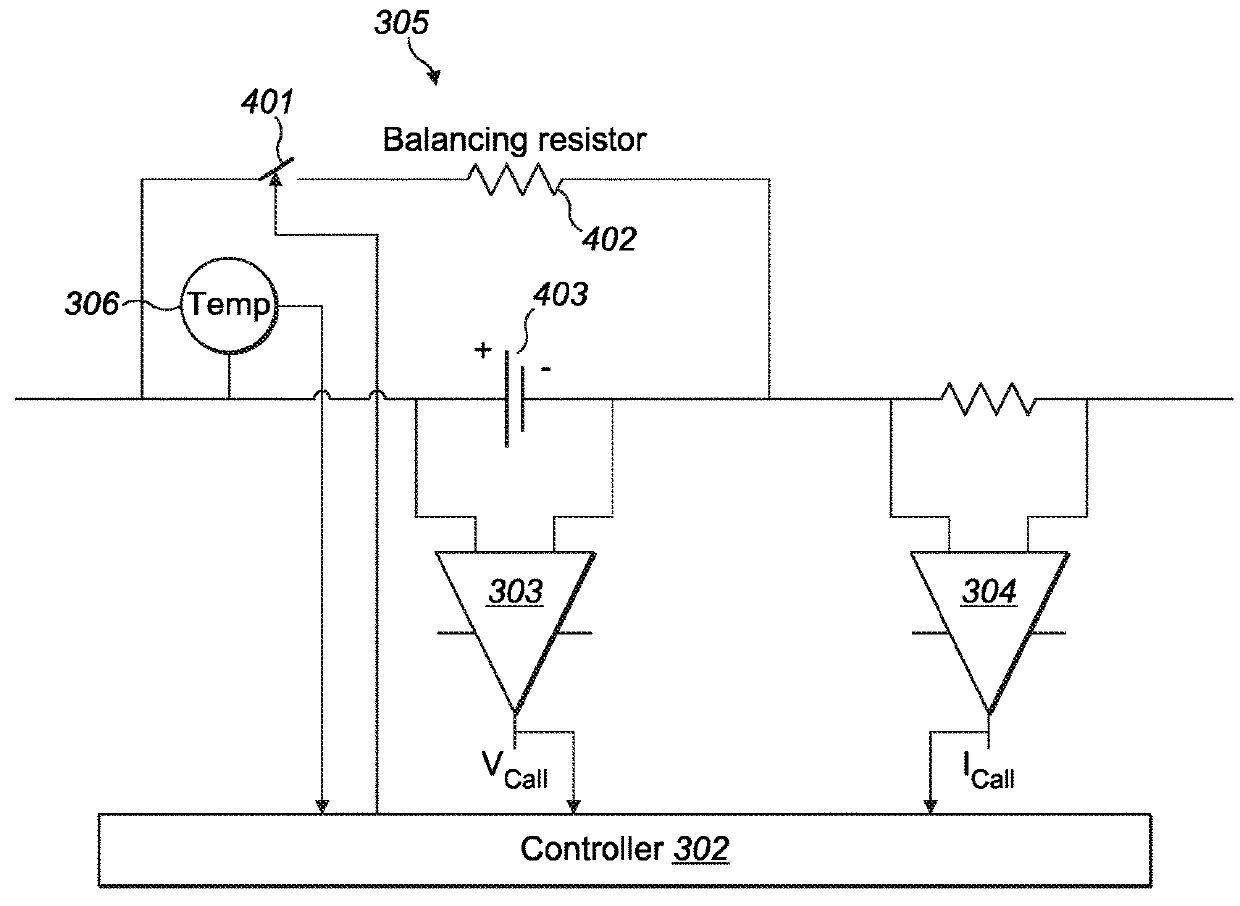
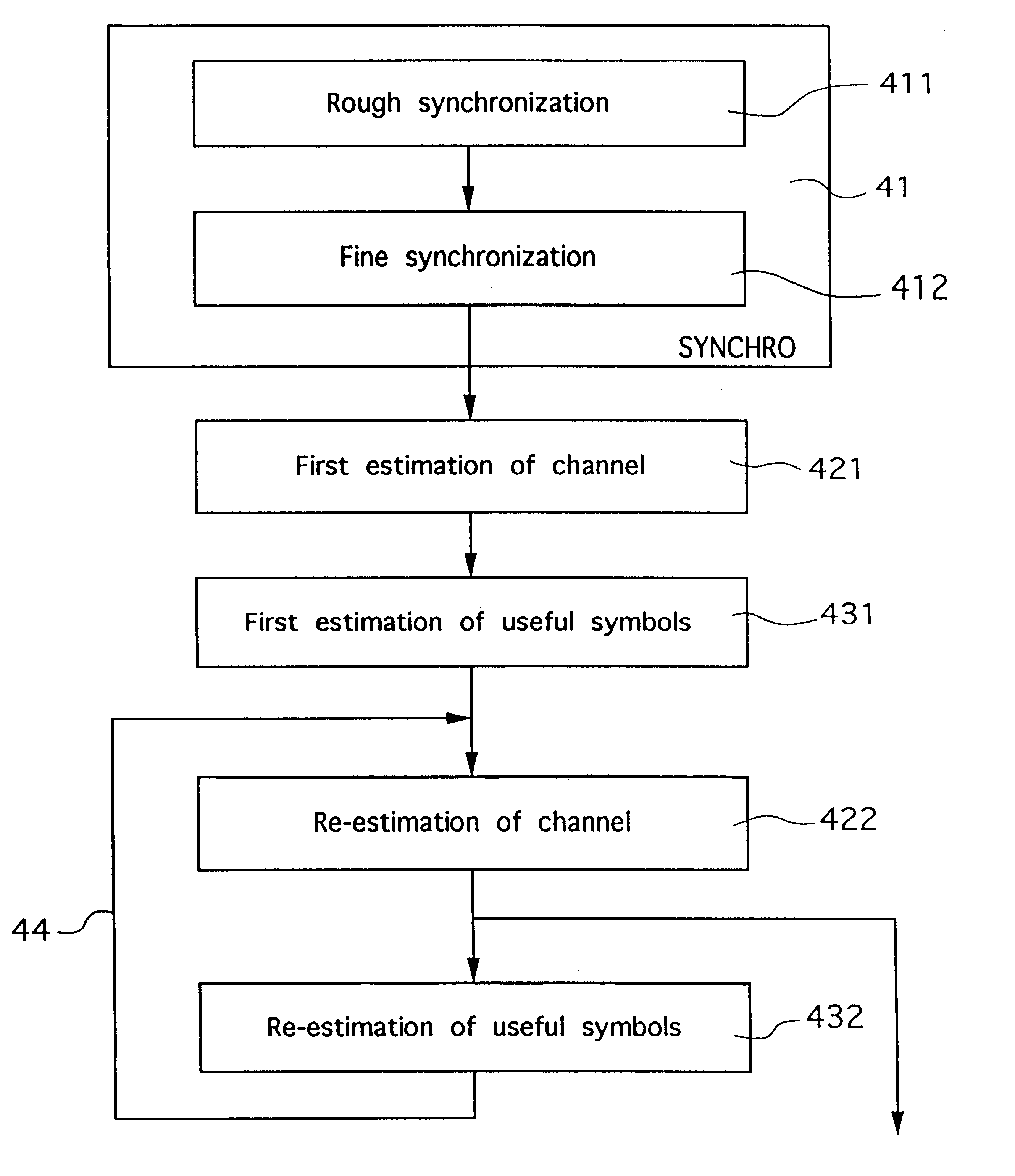
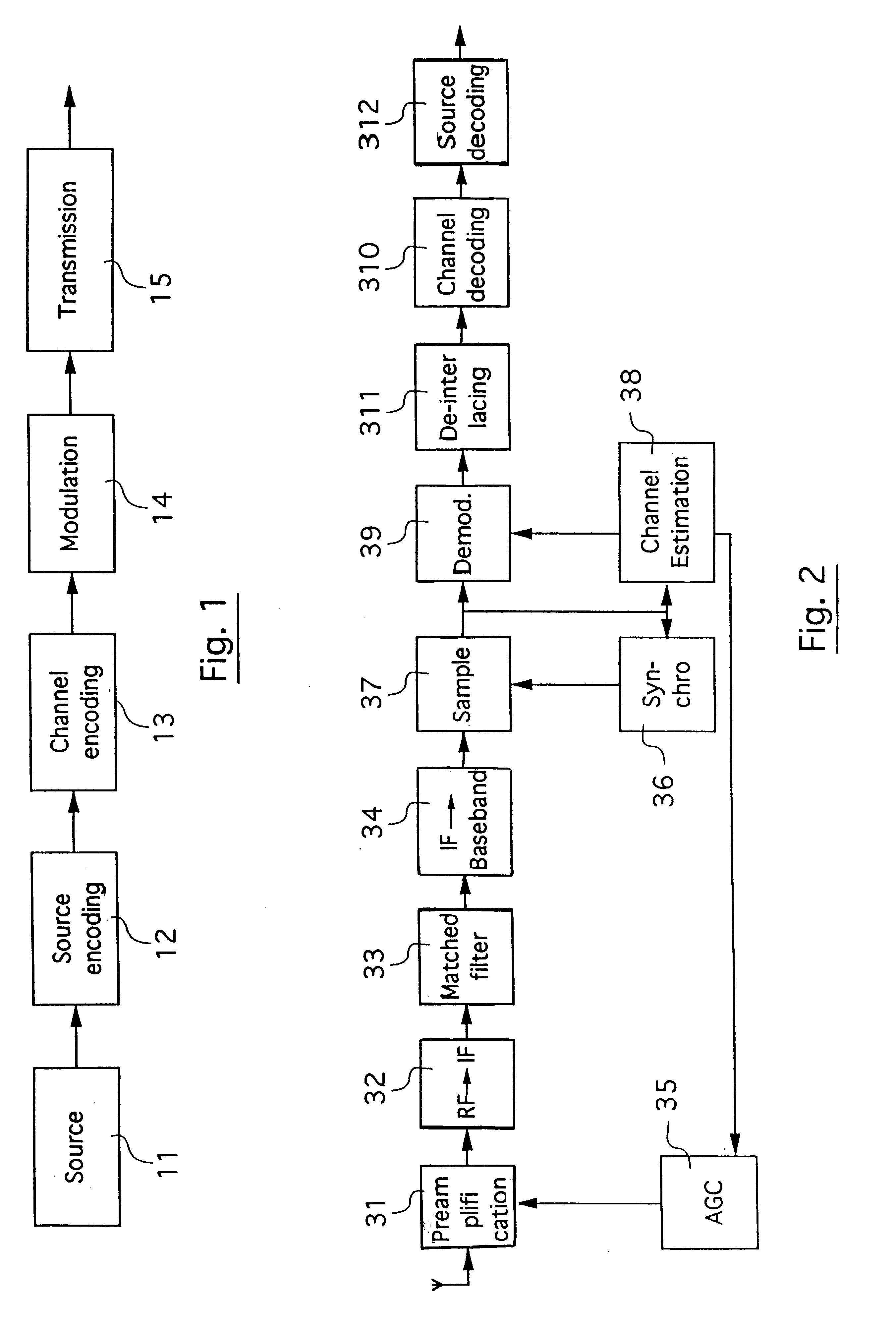
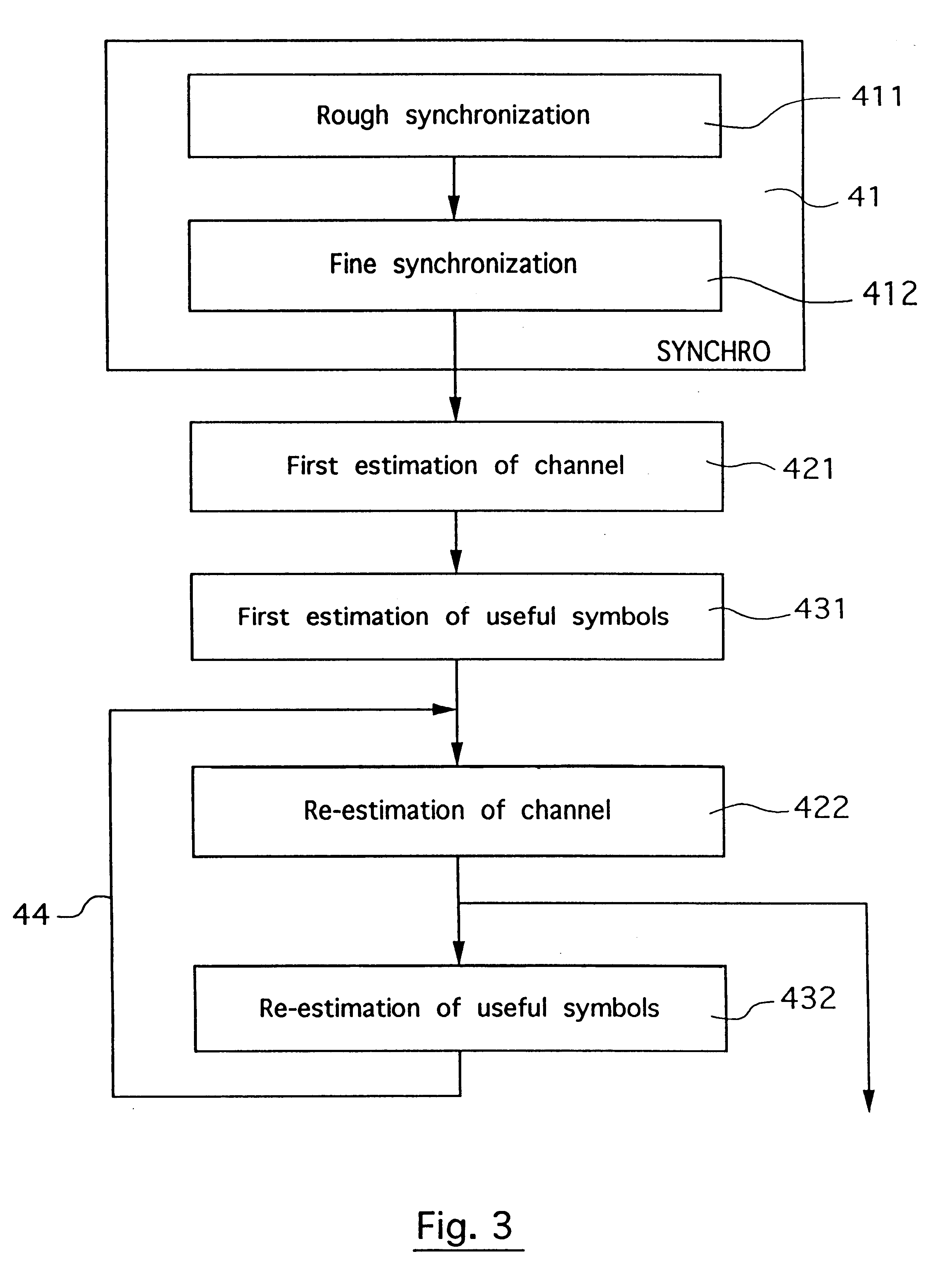
Digital signal with multiple reference blocks for channel estimation, channel estimation methods and corresponding receivers
InactiveUS6263029B1Reliable estimateEffective synchronizationBaseband system detailsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsEstimation methodsComputer science
A digital signal is organized in consecutive data trains each comprising a predetermined number of successive symbols, each of said data trains comprising at least two distinct reference blocks for the estimation of said channel, distributed among the useful symbols representing the source signal to be transmitted, each of said reference blocks being formed by at least one reference symbol known to the receiver and / or identifiable by said receiver. The reference symbols present in the reference blocks may be explicit reference symbols that are fixed and known a priori by said receiver and / or implicit reference symbols produced by the links generated between the useful symbols by an encoding operation. Also disclosed are channel estimation methods implementing an estimation-maximization algorithm and / or using a combination of predetermined basic functions, with a bandwidth greater than or equal to the Doppler power spectrum of said signal.
Owner:WAVECOM SA
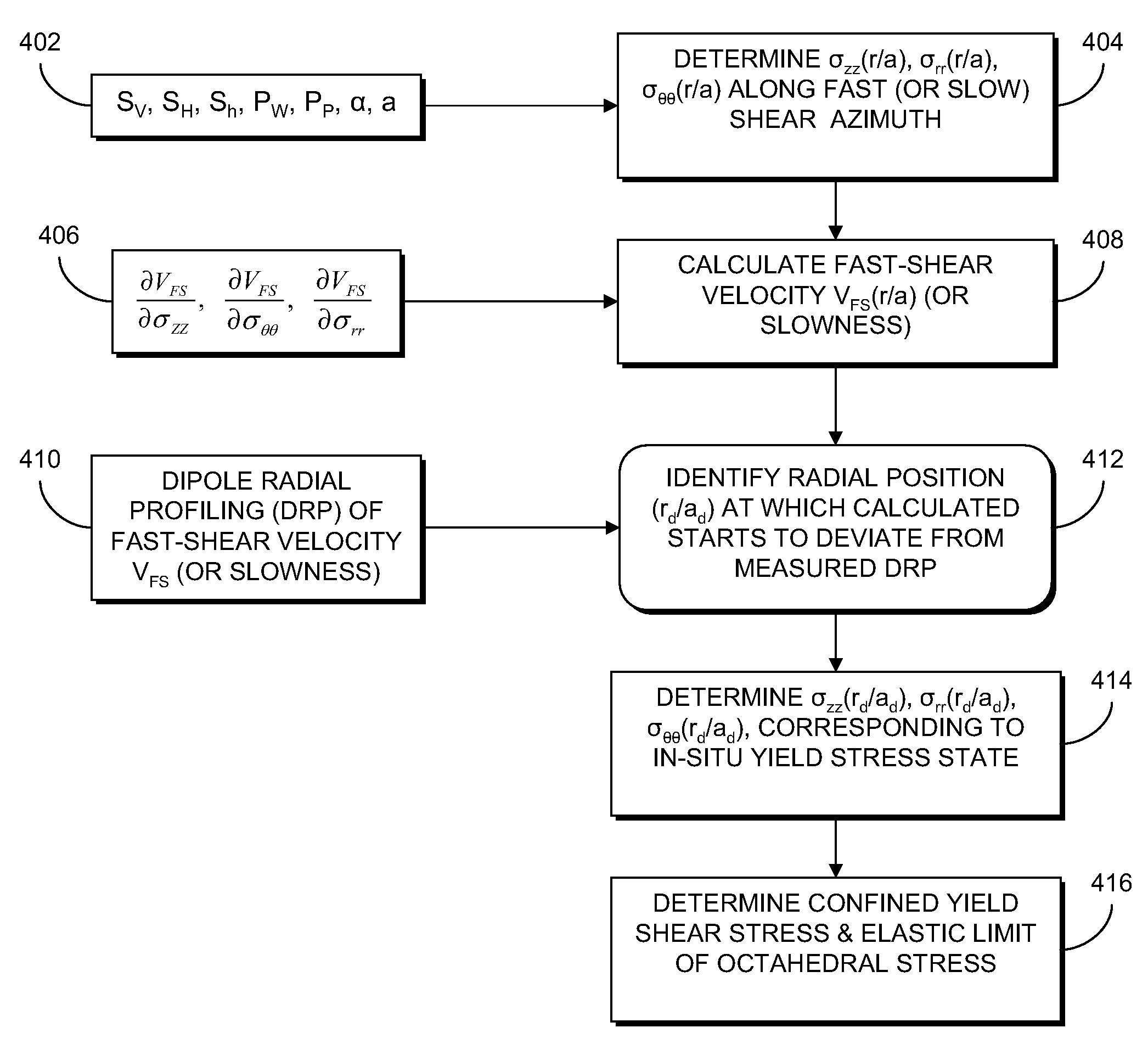
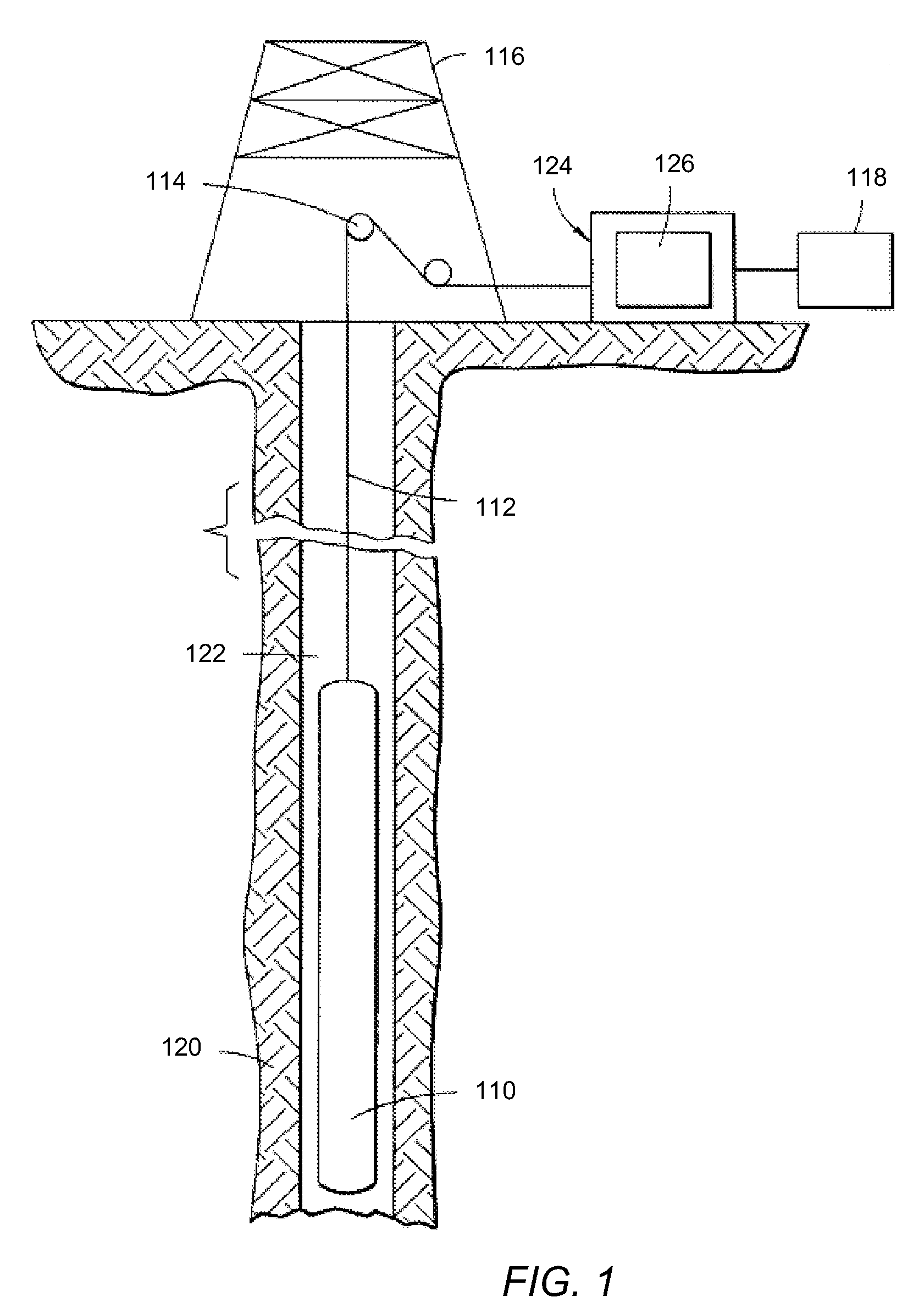
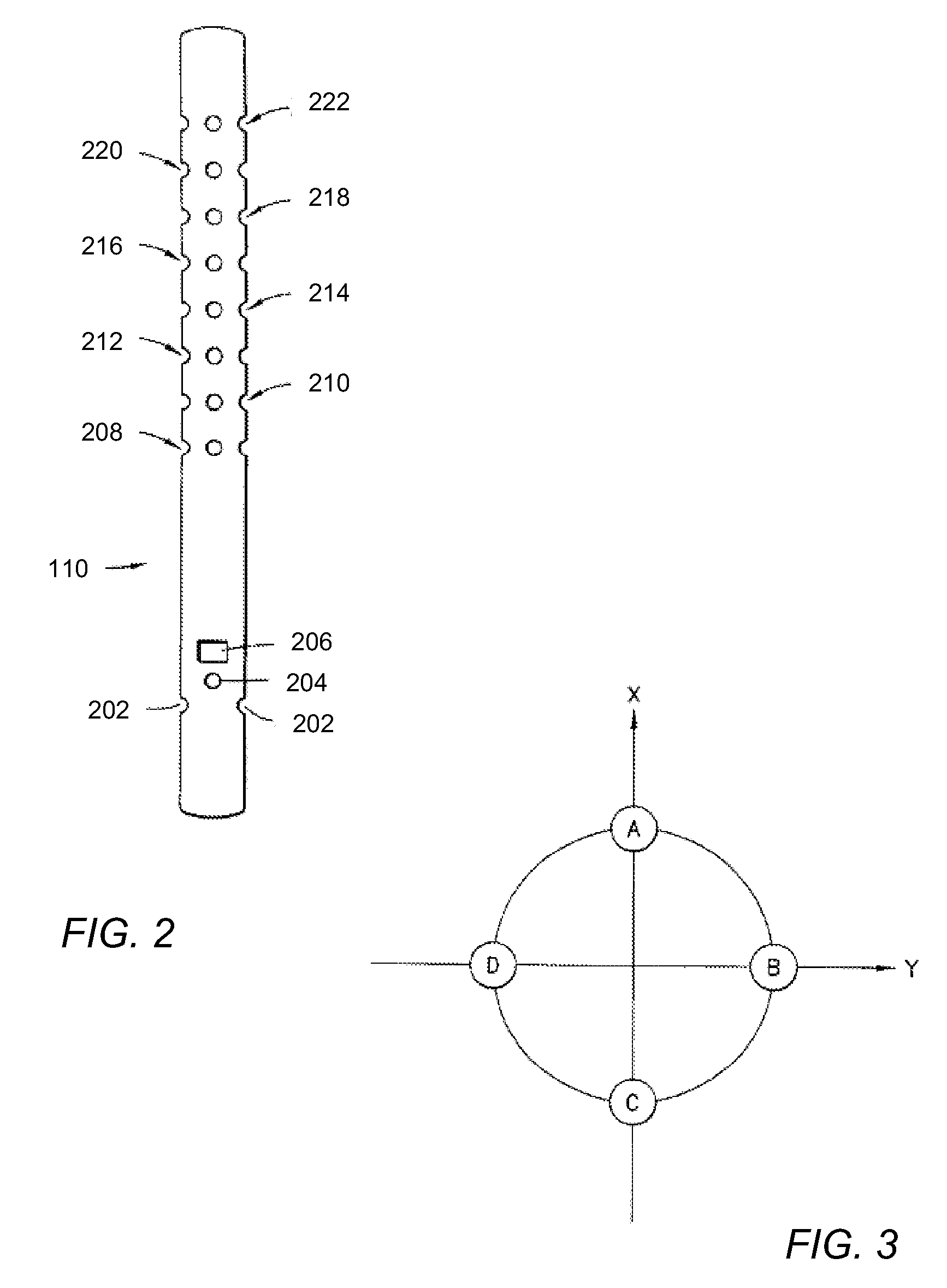
In-situ determination of yield stress state of earth formations
ActiveUS20090109794A1Reliable estimateAccurate representationSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingStressed stateEffective stress
Determination of in-situ rock yield stress state of a geological formation surrounding a borehole includes determining a profile for each of an axial effective, a radial effective, and a hoop effective stress within at least one axial plane containing a borehole axis. A predicted radial shear response radial profile is calculated from the effective stresses within the at least one axial plane. A measurement-based estimate of a shear response radial profile within the at least one axial plane is determined from measured data. A maximum radial distance at which a difference between the predicted and measurement-based shear response radial profiles is identified within the at least one axial plane as being greater than a difference threshold. The respective axial, radial, and hoop stresses, are determined at the identified maximum radial distance. The identified stresses are indicative of an in-situ yield stress state of the rock.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
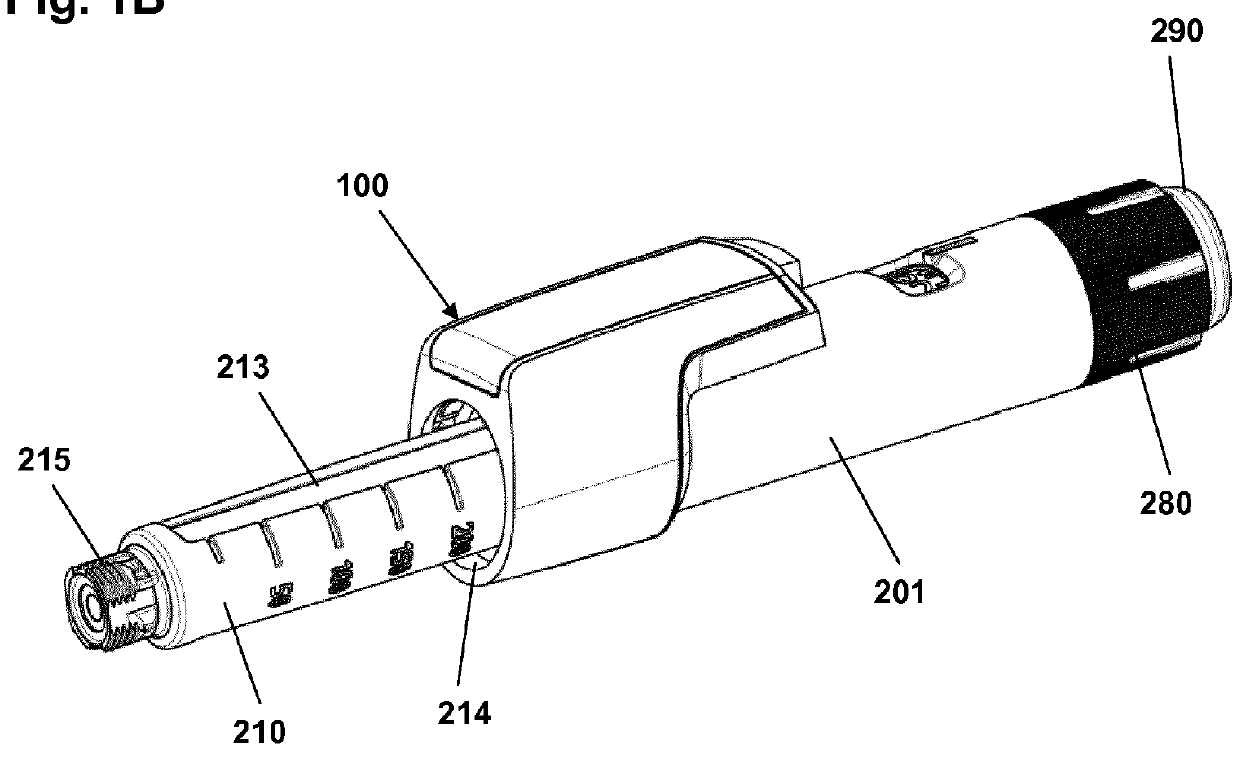
Dose Logging Device for a Drug Delivery Device
ActiveUS20160051760A1Reliable estimateReduce power consumptionAmpoule syringesAutomatic syringesBiomedical engineeringMagnet
A system comprising a sensor assembly adapted to measure a magnetic field, and a mechanical assembly comprising an indicator element with a magnet moving together therewith, the magnet being configured to generate a spatial magnetic field which relative to the sensor assembly varies corresponding to the spatial position and orientation of the magnet, wherein the indicator element is adapted to both rotate and move axially during operation of the assembly. Processor means is configured to determine on the basis of measured values both a rotational position and an axial position of the indicator element.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
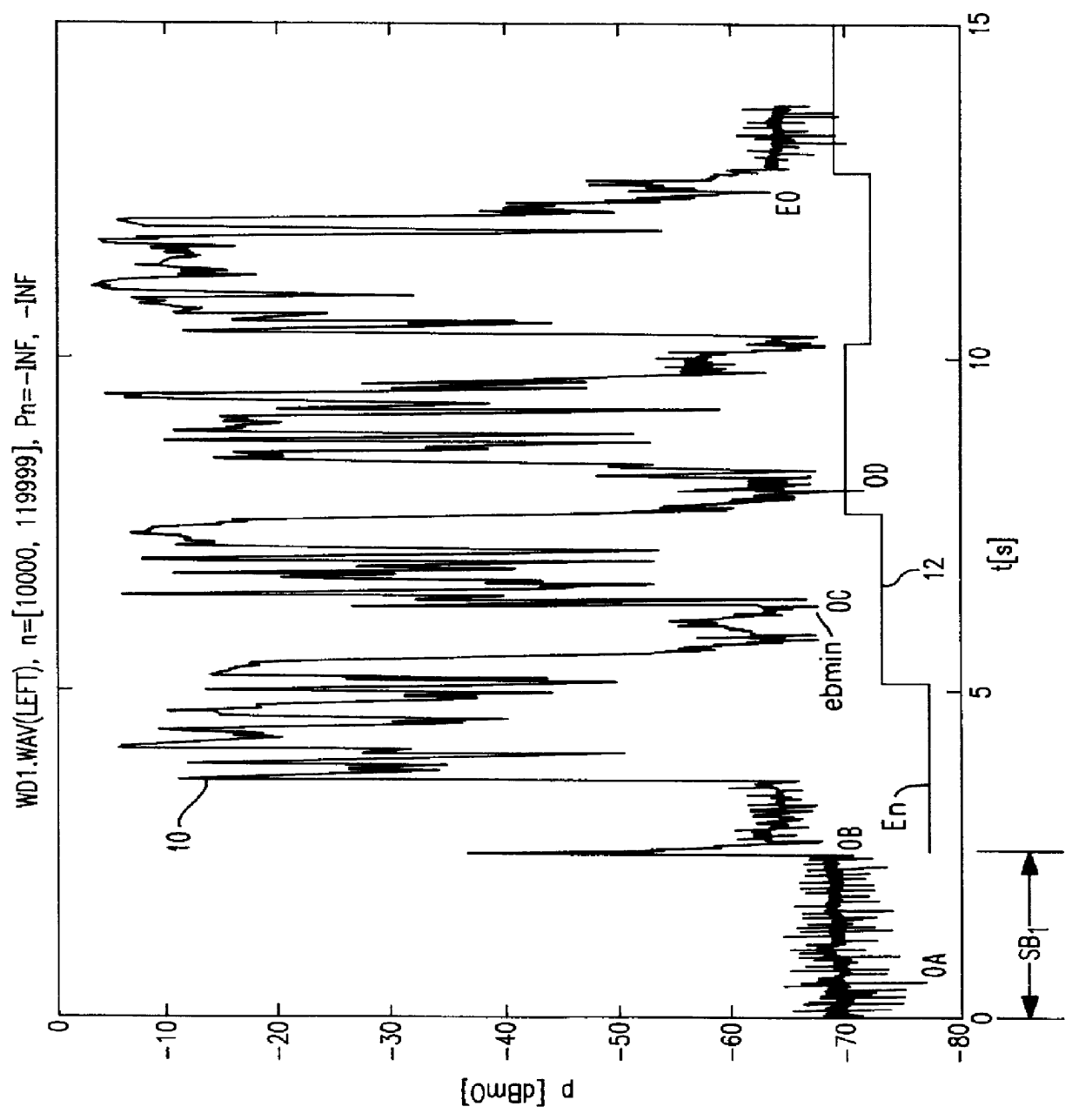
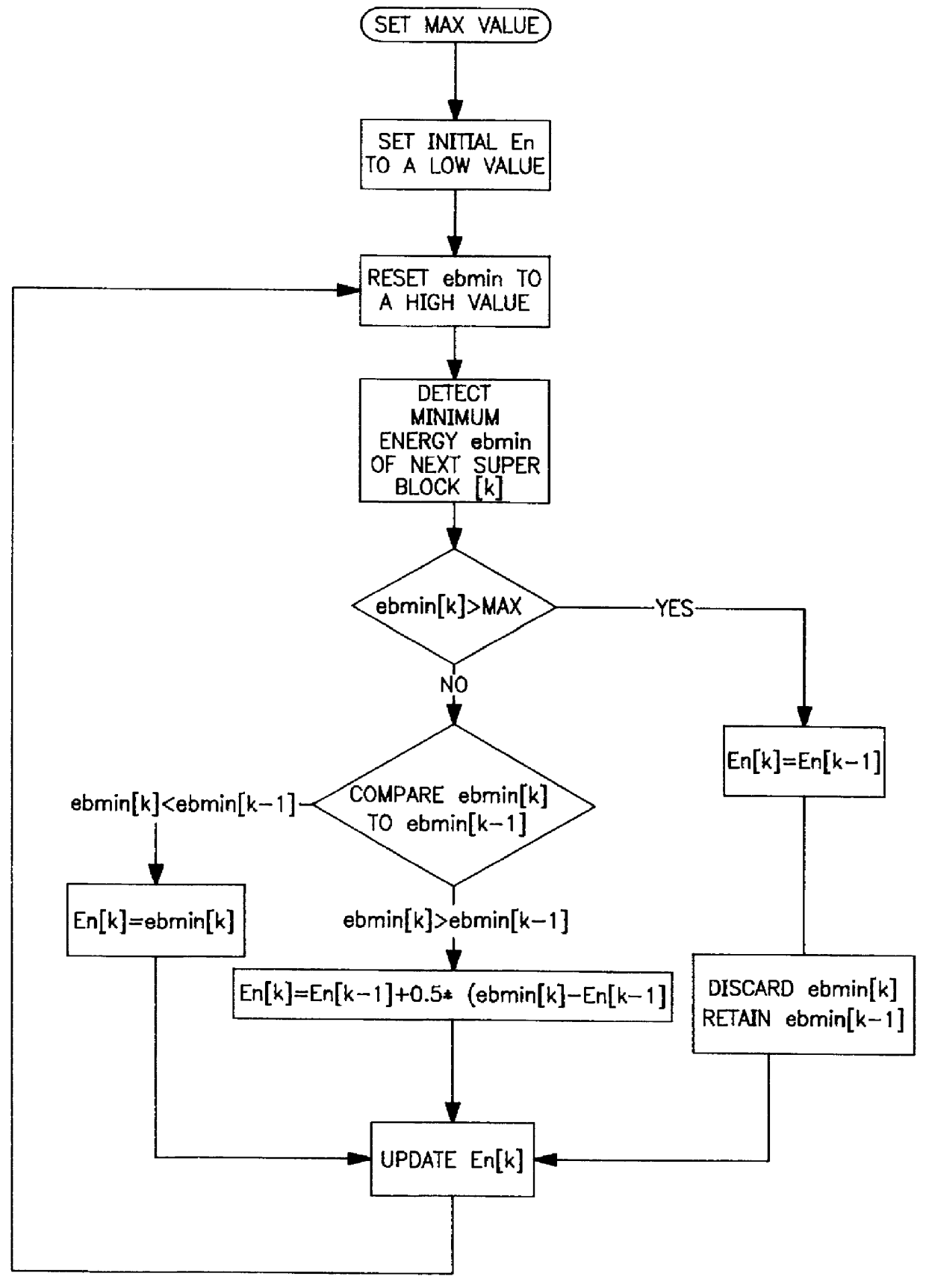
Background energy estimation
InactiveUS6157670AEstimate the background energy level accurately and reliablyEliminate energyReceivers monitoringError preventionEngineeringEnergy estimation
A method of estimating background noise in a signal. The signal is divided into blocks of equal predetermined length. The minimum energy of the signal during the length of each block is determined. The minimum energy determined for the current block is compared to a previous determination of minimum energy. If the current minimum energy exceeds a predetermined maximum energy level, the current block minimum energy is discarded and the previous determination remains unchanged. If the current block minimum energy is below the previous determination, the previous estimate is reduced by the difference between the previous determination and current minimum energy. If the current energy is above the previous determination but below the maximum, the previous estimate is increased by half of the difference between the current energy and the previous estimate. The increase factor may also be adjusted to increase the current estimated energy level by a factor of any amount between and including 0 and 1. The estimation of minimum energy, or background energy, therefore decreases in direct proportion to a drop in minimum energy determination but increases only as a partial factor of new determinations.
Owner:TELOGY NETWORKS
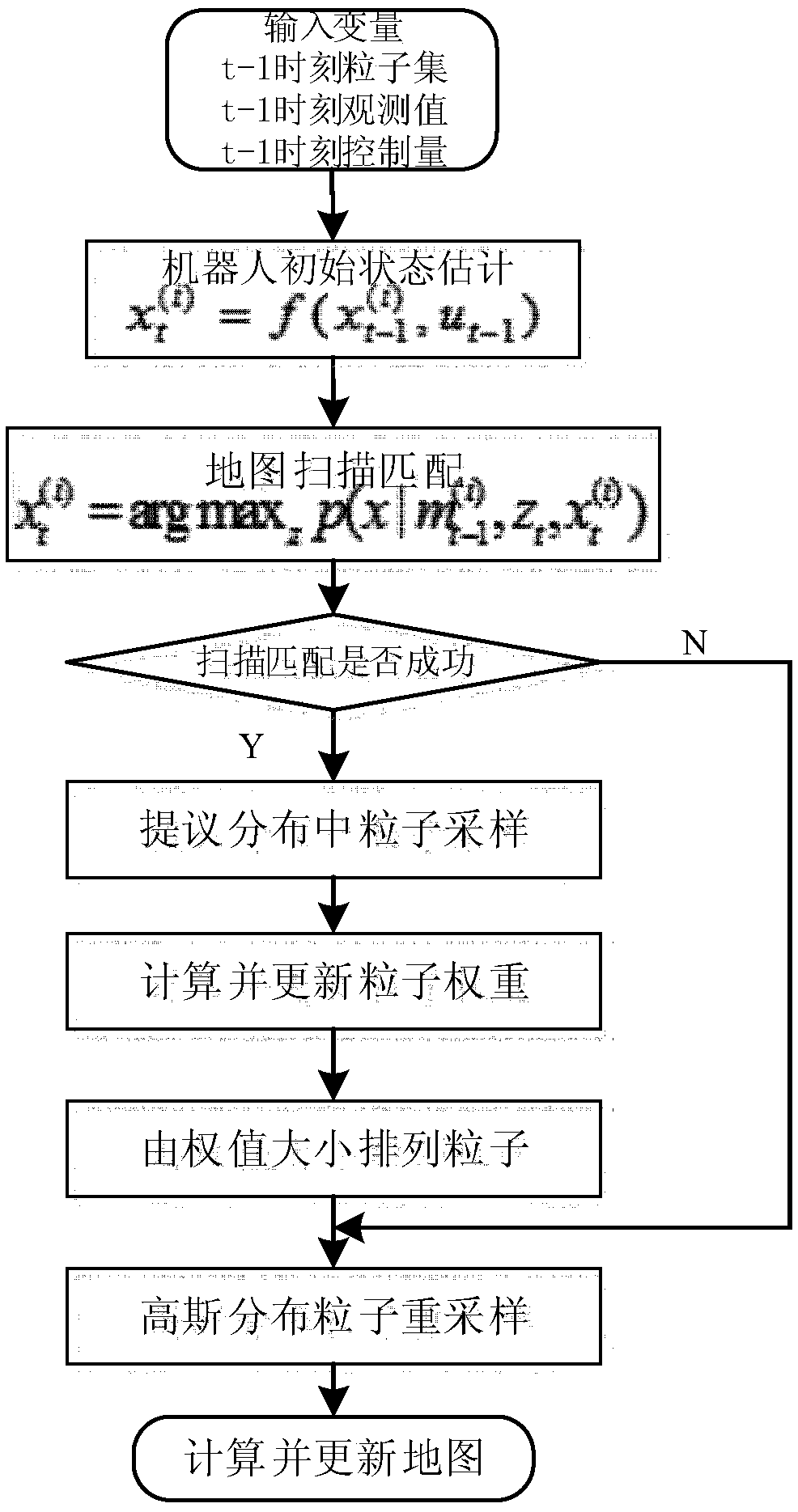
Gaussian distribution based mobile robot simultaneous localization and mapping method
ActiveCN105509755ADiversity guaranteedReliable estimateInstruments for road network navigationSimultaneous localization and mappingComputer graphics (images)
The invention relates to a Gaussian distribution resampling Rao-Blackwellized particle filter based mobile robot simultaneous localization and mapping method. The method comprises the following steps: S1, robot initial pose is estimated according to robot pose and mileometer control information; S2, a scan matching method is executed according to a map; S3, particle sampling is carried out in proposal distribution of trajectory; S4, weight of each particle is calculated and weight of each particle is updated; S5, particle resampling is carried out on the basis of Gaussian distribution: specifically, by sorting particle weight, high-weight particles are dispersed to obtain resampled new particles; and S6, the map is calculated according to robot pose and observation information, and map revision is carried out. By the method, reliable grid map precision can be obtained.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
System for controlling a vehicle with determination of the speed thereof relative to the ground
InactiveUS20100256887A1Reliable estimateSpeed controllerElectric devicesClassical mechanicsElectric machinery
A system for controlling the behaviour of a vehicle relative to the ground is described wherein the linear ground speed of a vehicle that has at least two wheels (1) each equipped with a sensor suitable for supplying a measurement that is a function of the rotation of said wheel is determined at each instant. The system comprises a circumferential speed indicator (101, 102) for each wheel (1) based on the measurement from the corresponding sensor (11) and a system for diagnosing characteristic parameters of the instantaneous condition of said wheels to validate the use of the circumferential speed Vr measured for each of these wheels to produce an estimation of the instantaneous speed Vv of the vehicle relative to the ground. The diagnostic system notably comprises a means (109) of diagnosing loss of road grip of a wheel as a function of its instantaneous acceleration, a means (107) of diagnosing the validity of the wheel speed indication based on a measurement of the road grip coefficient of the wheel and a means (113) of diagnosing the maintaining or restoration of road grip of the wheel as a function of a determination of its slip. A vehicle speed indicator (119) produces an estimation of the vehicle speed relative to the ground as a function of indications that are not rejected on completion of the diagnoses carried out. The invention also targets the application of this speed estimation system to the determination of the instantaneous slip when rolling of the wheels of a vehicle, each coupled to an individual electric machine and to the control of the torque applied to each of these wheels as a function of this slip to improve the behaviour of the vehicle.
Owner:MICHELIN RECH & TECH SA +1
System and method for automatically learning flexible sprites in video layers
ActiveUS7113185B2Simple geometrySimple and efficient to and analyzeImage enhancementImage analysisVideo sequenceVisual perception
A simplified general model and an associated estimation algorithm is provided for modeling visual data such as a video sequence. Specifically, images or frames in a video sequence are represented as collections of flat moving objects that change their appearance and shape over time, and can occlude each other over time. A statistical generative model is defined for generating such visual data where parameters such as appearance bit maps and noise, shape bit-maps and variability in shape, etc., are known. Further, when unknown, these parameters are estimated from visual data without prior pre-processing by using a maximization algorithm. By parameter estimation and inference in the model, visual data is segmented into components which facilitates sophisticated applications in video or image editing, such as, for example, object removal or insertion, tracking and visual surveillance, video browsing, photo organization, video compositing, etc.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Test system for determining a frequency response of a virtual power plant
InactiveUS20140100810A1Faster and simple and more profitable setupReliable estimateCurrent/voltage measurementTesting/monitoring control systemsPower stationComputer module
Disclosed is a test system for determining a frequency response of a virtual power plant connected to a utility grid and including a plurality of distinct power plants. The test system includes a test sequence module for providing a frequency test sequence. The frequency test sequence includes a set of frequency test values; and an injection unit for injecting values of the frequency test sequence simultaneously to nodes of the virtual power plant. A node of the virtual power plant includes any of: a power production unit of a power plant, a power storage unit of a power plant, a plant controller of a power plant. Further described are a virtual power plant and a method of testing a frequency response of a virtual power plant.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method based on slide window for estimating and equalizing channels of block signals containing pilot
InactiveCN1398118AAccurate demodulationReliable receptionEqualisersHigh-definition television systemsMain channelCarrier signal
Channel estimation of block signals containing pilot frequency and balanced method characterizes in containing side channels of force and after of a main channel component in a movable window to determine to get a correct channel estimation interval again to get channel impulse response estimation with the length of N, M or M+2XN, then to take position of home and end of the said window as the positioning information needed by circular convolution of the signal and channel inputs response structure and process the data block via channel transmission as the one after channel distortion via frequency domain balance offset or make time-domain over-sampling channel estimation in the sliding window interval to inerase time-domain resolution of channel estimation. The data block can be IDFT of OFDM or modulated by single carrier.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Integrated semiconductor bioarray
ActiveUS20130225441A1TimeSlow reaction rateMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningAnalyteBiosensor array
A biosensor array, system and method for affinity based assays that are able to simultaneously obtain high quality measurements of the binding characteristics of multiple analytes, and that are able to determine the amounts of those analytes in solution. The invention also provides a fully integrated bioarray for detecting real-time characteristics of affinity based assays.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for determining oscillation values and other vehicle-specific quantities of a vehicle
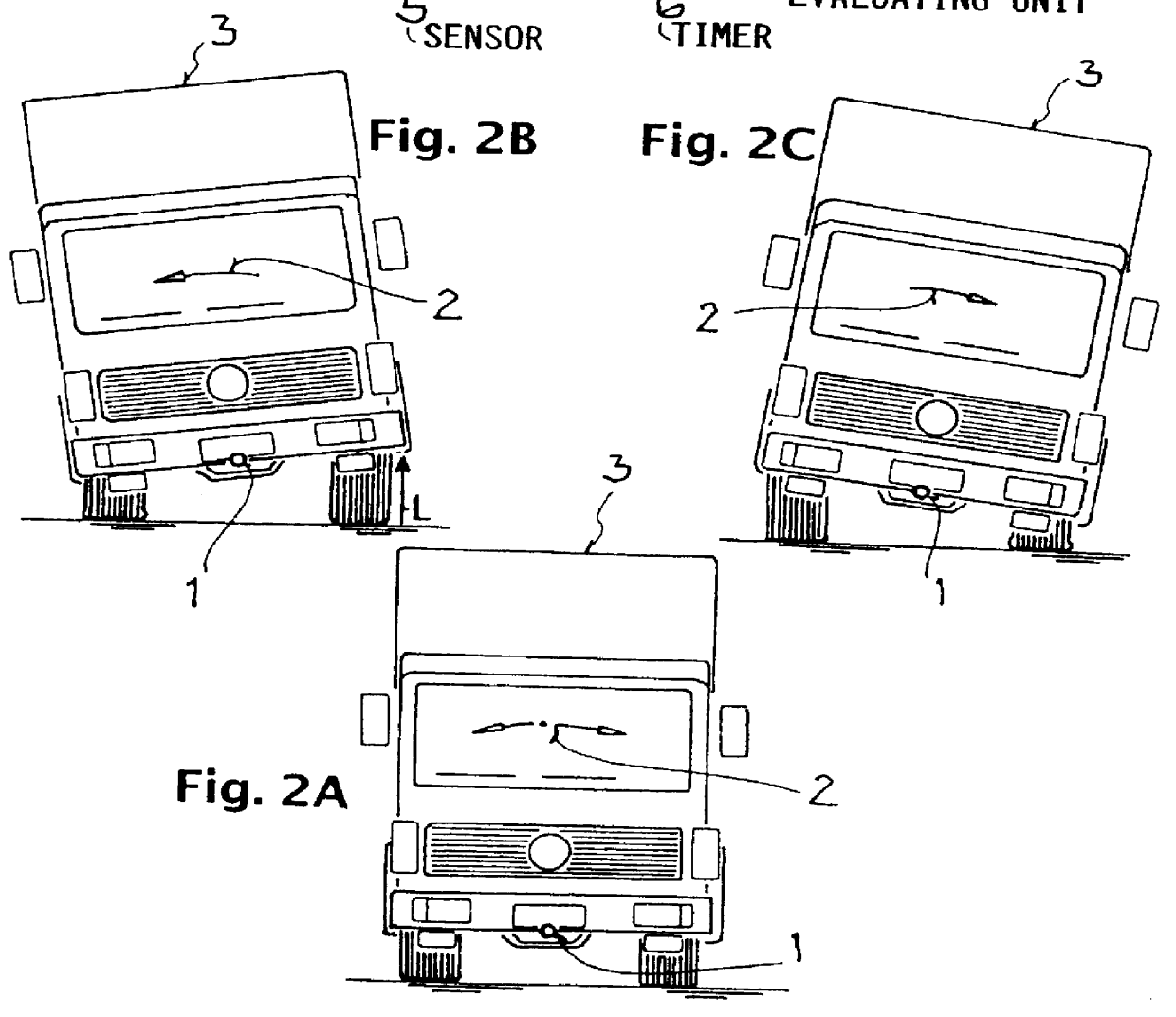
InactiveUS6157295AAccurately and unambiguously calculateReliable estimateVehicle testingPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementRolloverDriver/operator
A method and an apparatus determine the frequency or the period of the natural characteristic oscillation of a vehicle, and therefrom determine the mass of the vehicle and provide a warning if a dangerous oscillation condition exists which could lead to a tipping or rollover of the vehicle. The evaluation is carried out while the vehicle is driving. The apparatus includes a sensor such as a rotation rate sensor, a timer, an evaluating unit, and a warning unit. The method involves measuring the time interval between two characteristic features of the oscillation measured by the sensor, such as zero crossings, minimum points or maximum points of the angular velocity of the oscillation, and then calculating the period and / or the frequency of the oscillation from the measured time interval. Then the moment of inertia and / or the mass of the vehicle can be determined from the period or frequency. Also, if the period or frequency is out of a safe range, a warning is triggered to indicate to the driver of the vehicle that a rollover danger exists.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Method for qulitative evaluation of a digital audio signal
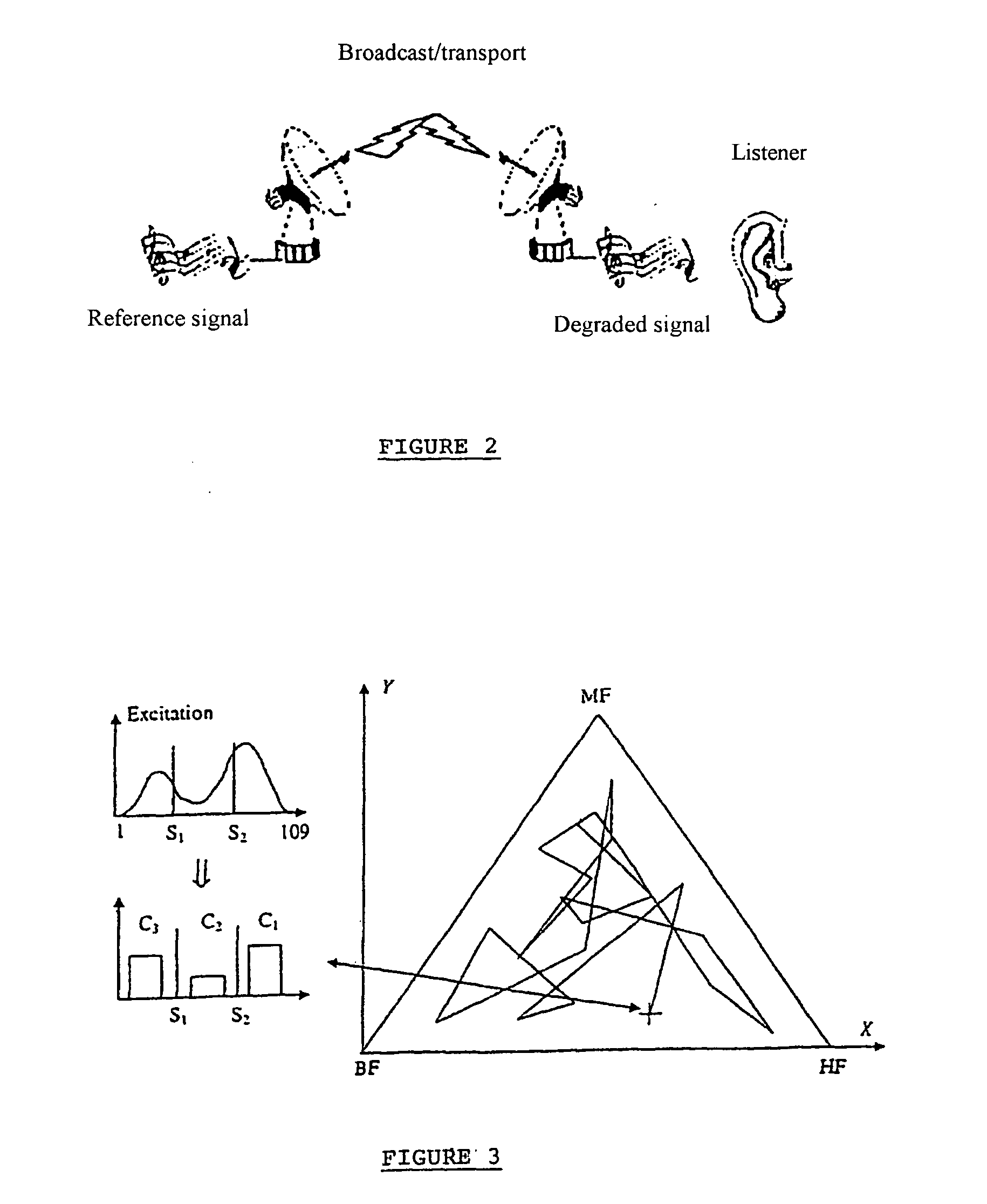
InactiveUS20050143974A1Reduce bitrateReliable estimateSpeech analysisSpecial data processing applicationsFrequency spectrumIndicator vector
The invention relates to a method of qualitatively evaluating a digital audio signal. It calculates a quality indicator consisting of a vector associated with each time window in real time, in continuous time, and in successive time windows. For example, the generation of a quality indicator vector calculates, for a reference audio signal and for an audio signal to be evaluated, the spectral power density of the audio signal, the coefficients of a prediction filter, using an autoregressive method, a temporal activity of the signal or the minimum value of the spectrum in successive blocks of the signal. To evaluate the deterioration of the audio signal, the method may calculate a distance between the vectors of the reference audio signal and the audio signal to be evaluated associated with each time window.
Owner:TELEDIFFUSION DE FRANCE SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com