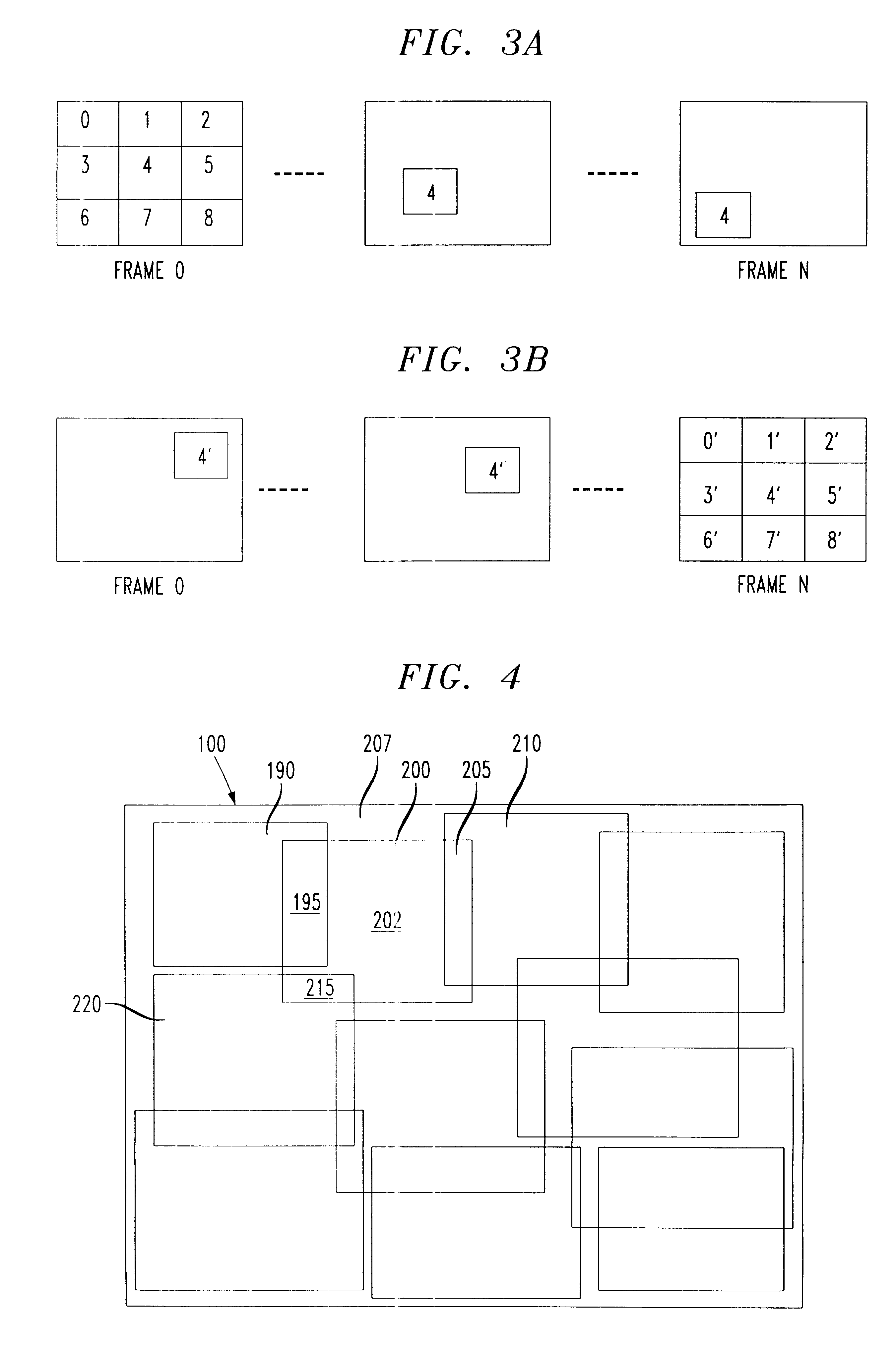
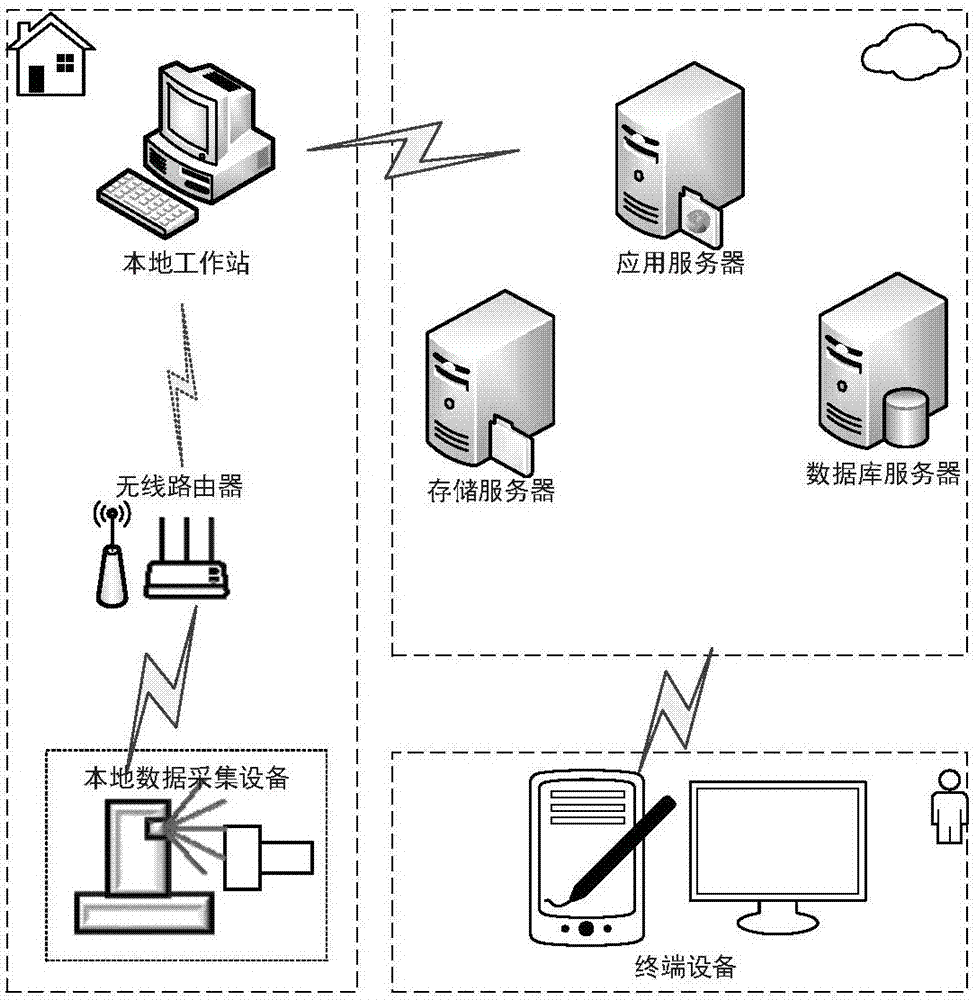
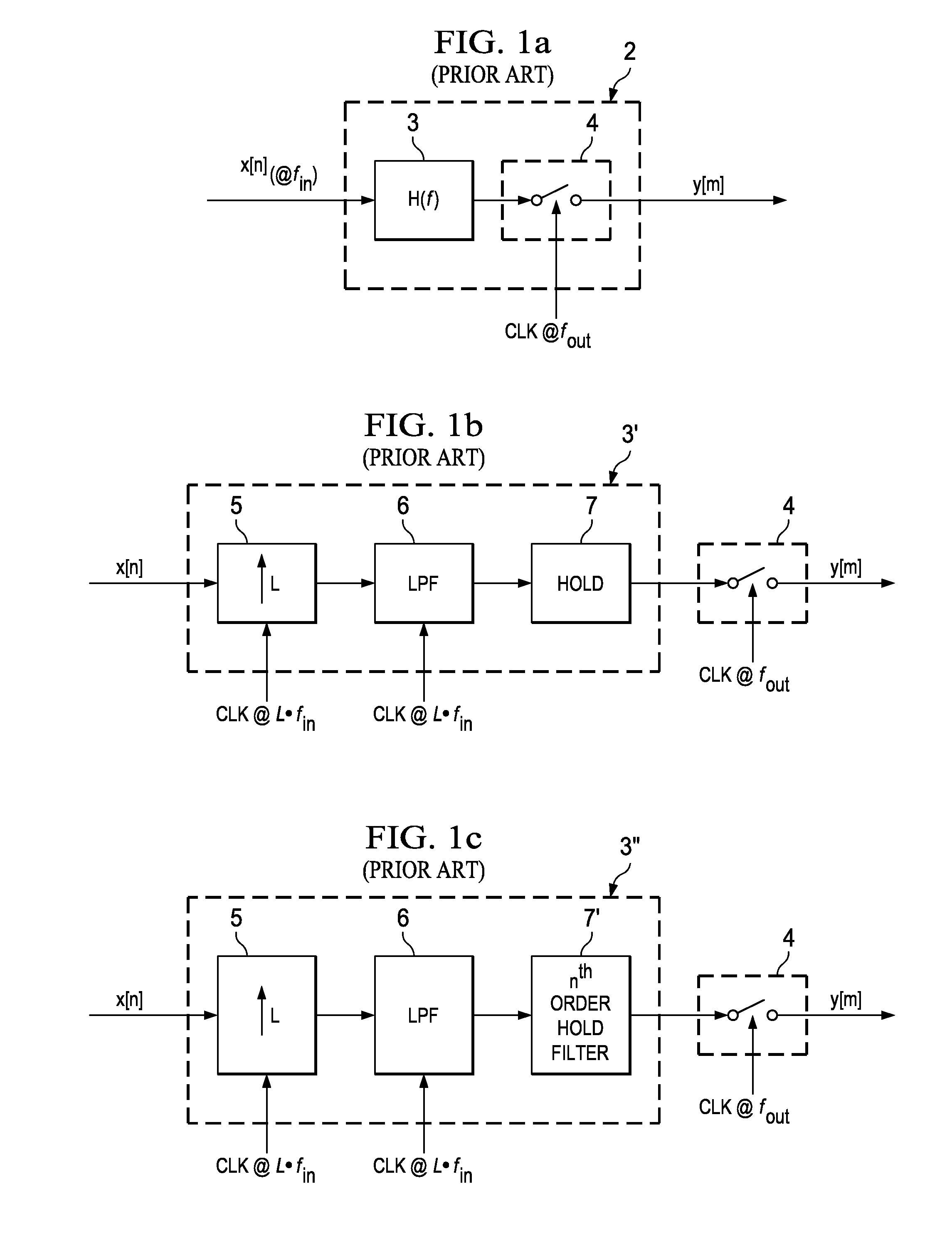
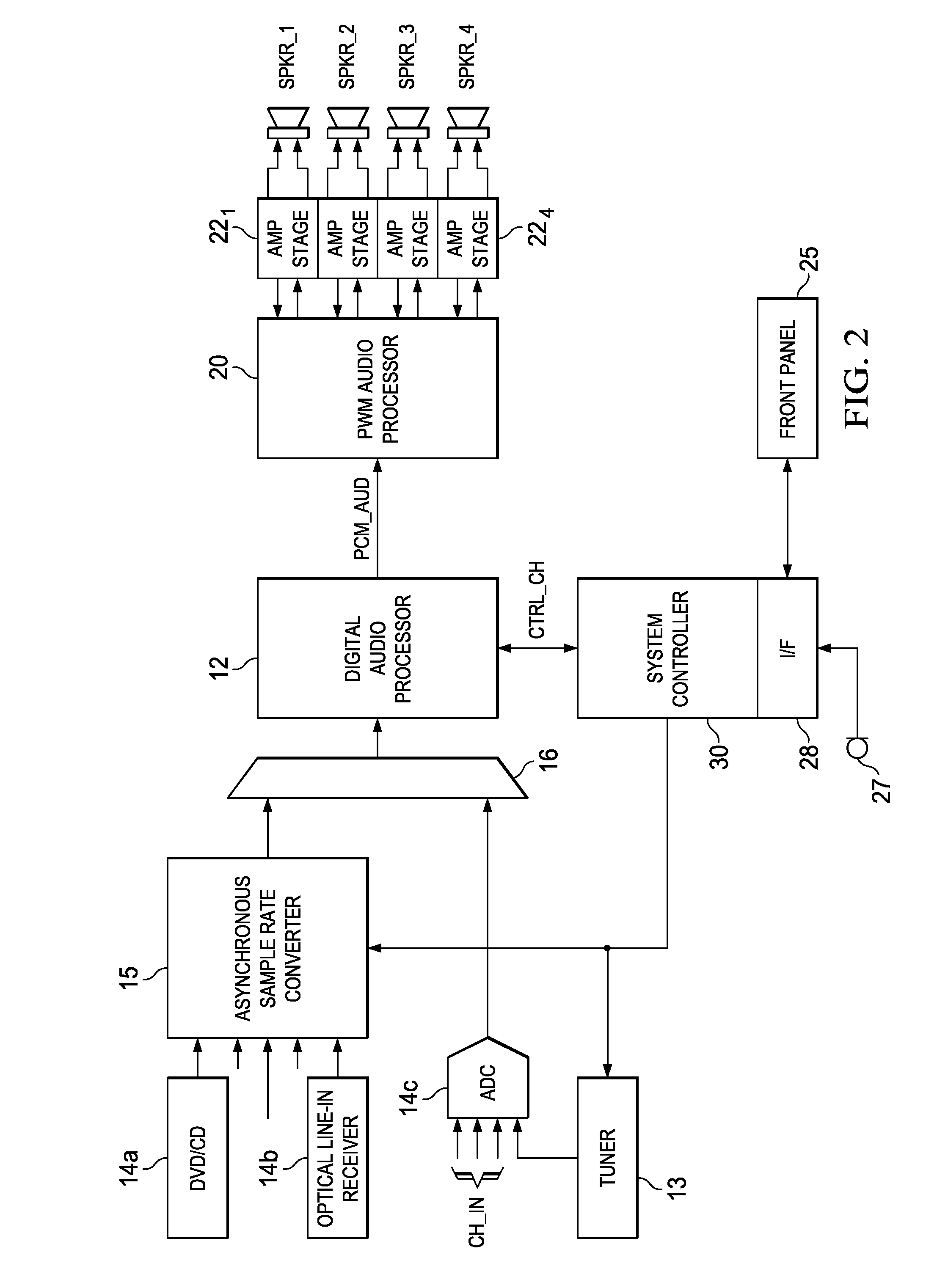
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
543 results about "Upsampling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
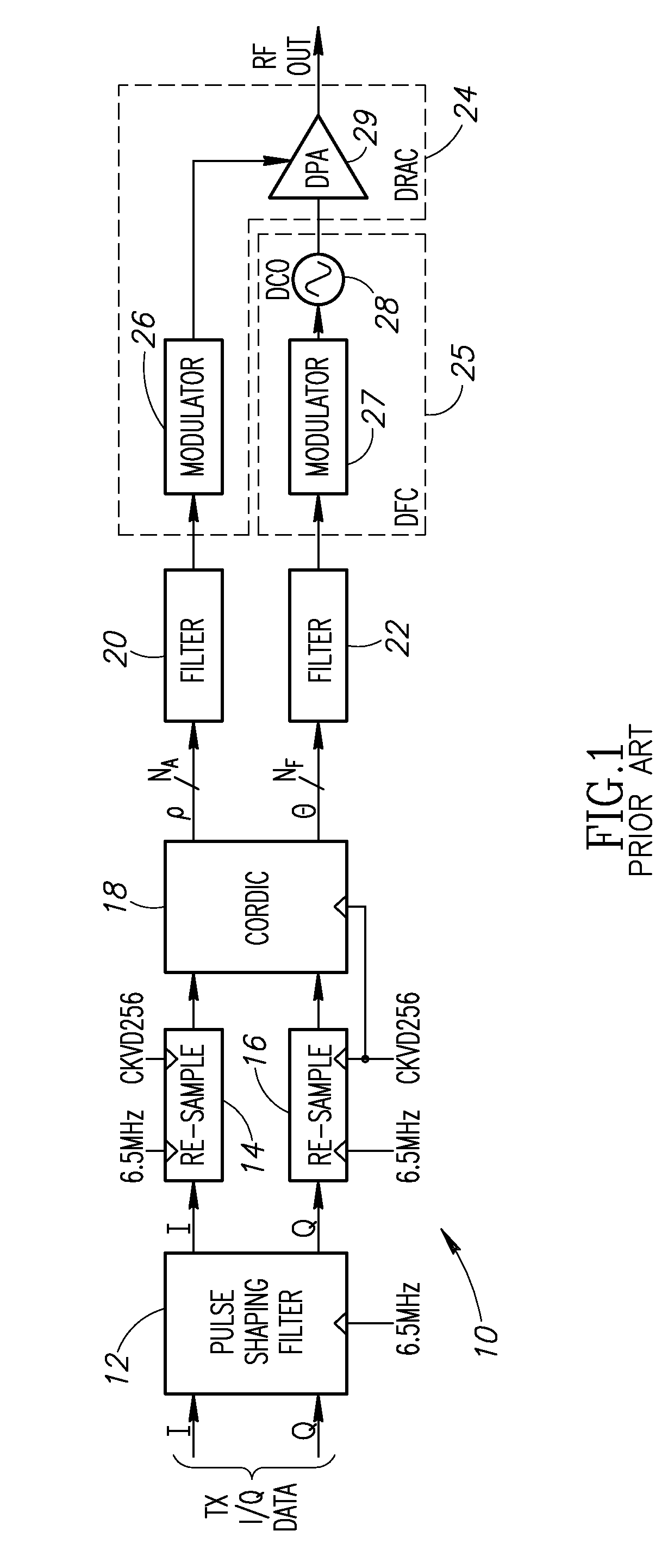
In digital signal processing, upsampling, expansion, and interpolation are terms associated with the process of resampling in a multi-rate digital signal processing system. Upsampling can be synonymous with expansion, or it can describe an entire process of expansion and filtering (interpolation). When upsampling is performed on a sequence of samples of a signal or other continuous function, it produces an approximation of the sequence that would have been obtained by sampling the signal at a higher rate (or density, as in the case of a photograph). For example, if compact disc audio at 44,100 samples/second is upsampled by a factor of 5/4, the resulting sample-rate is 55,125.
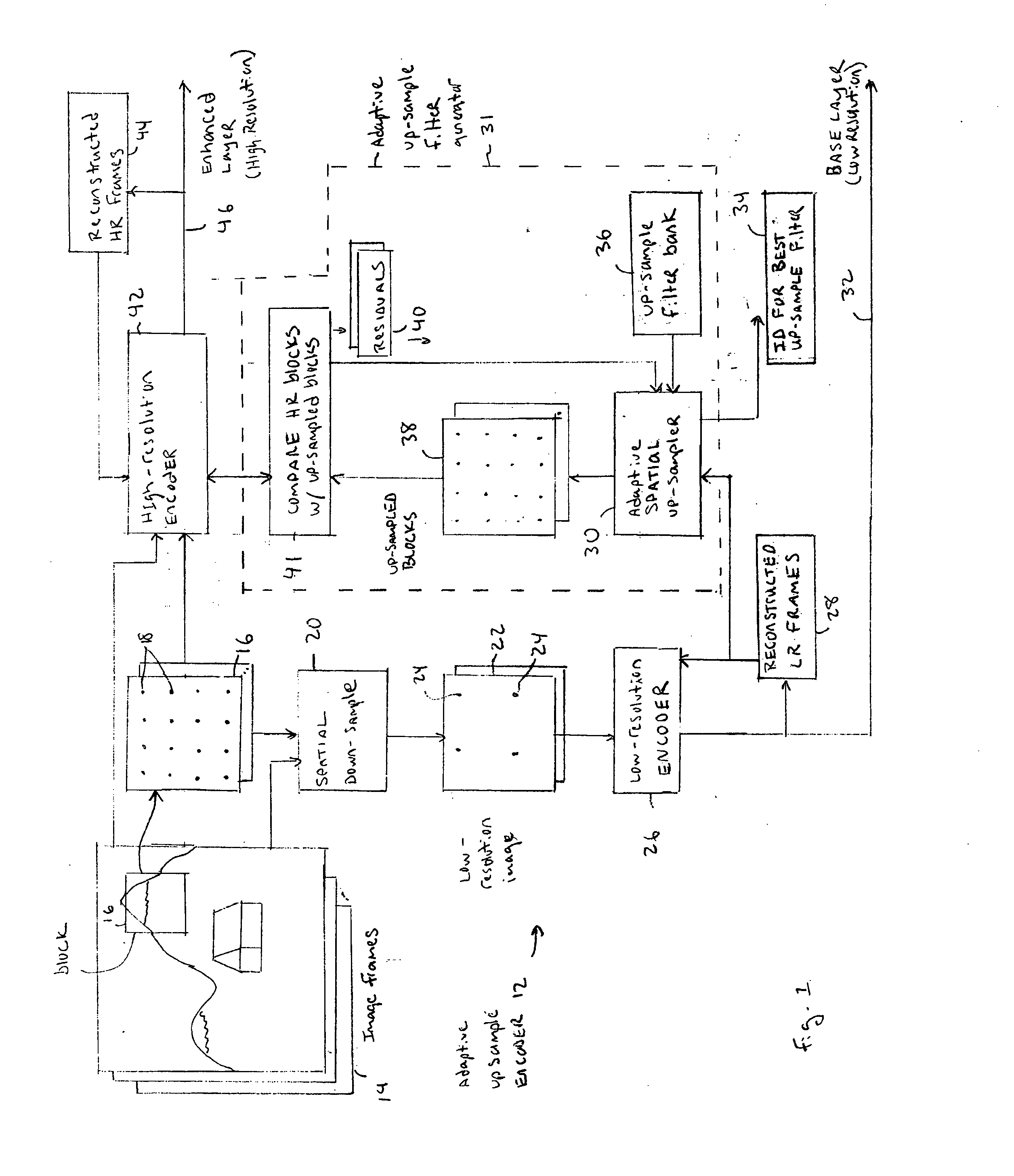
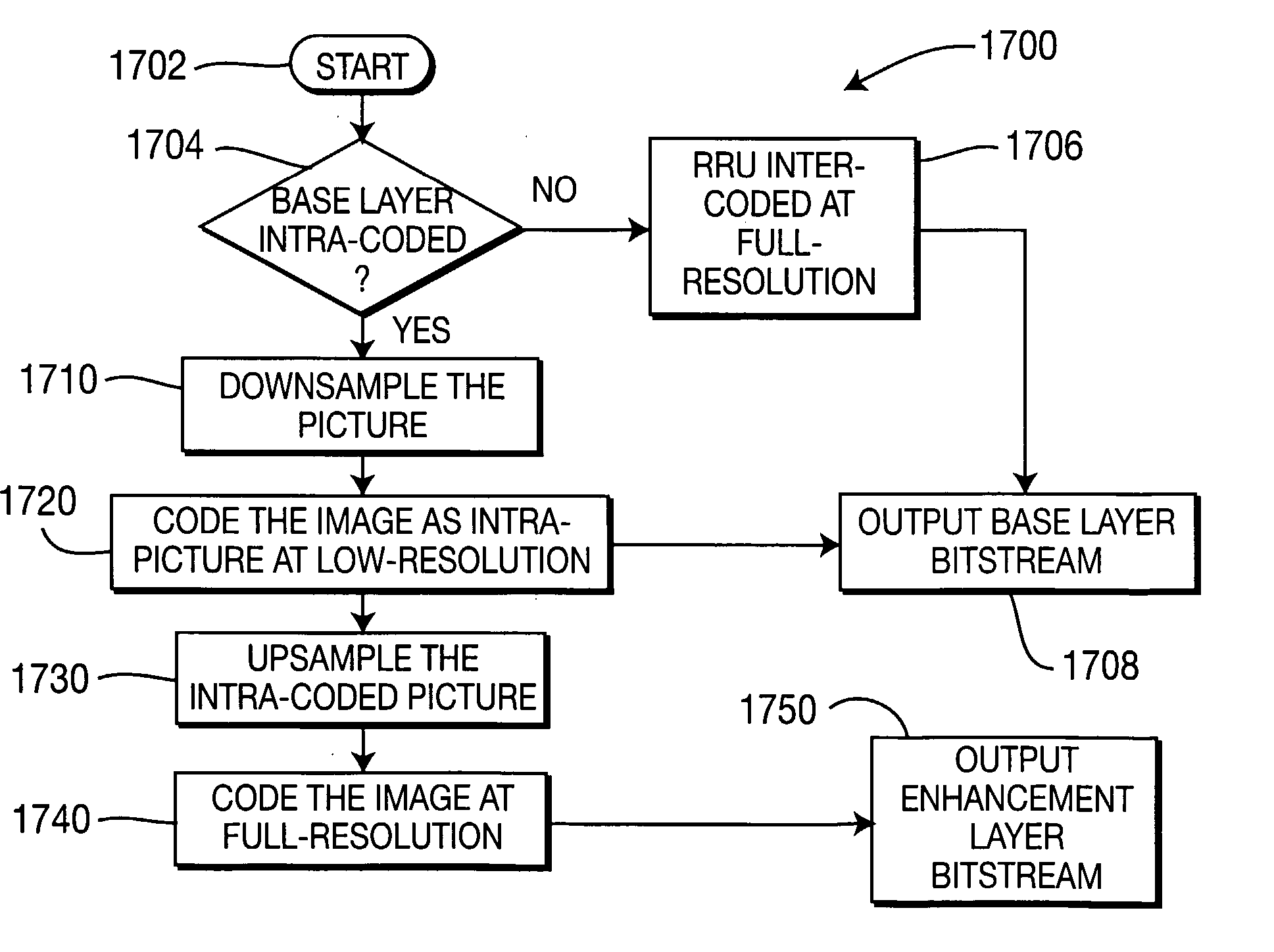
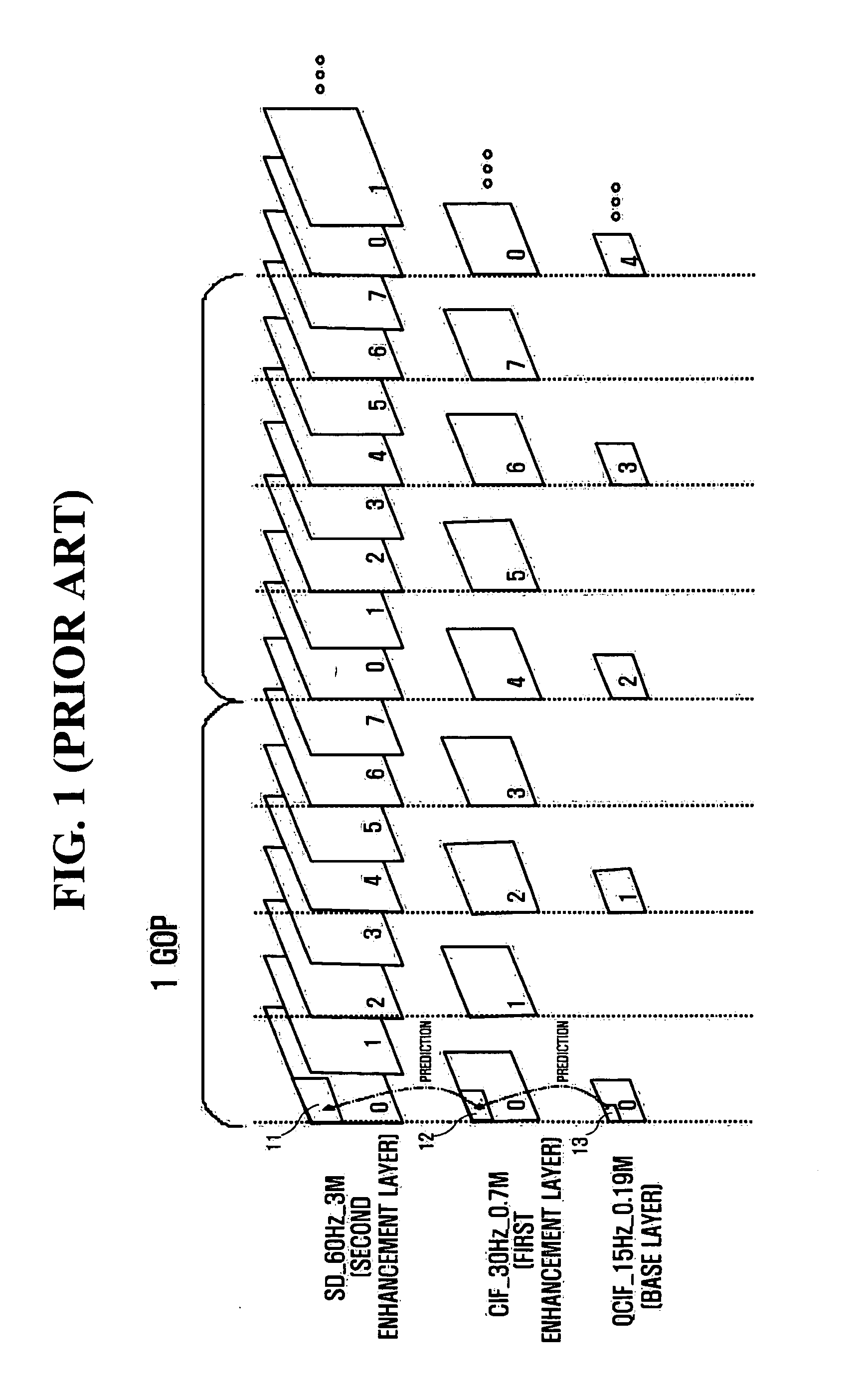
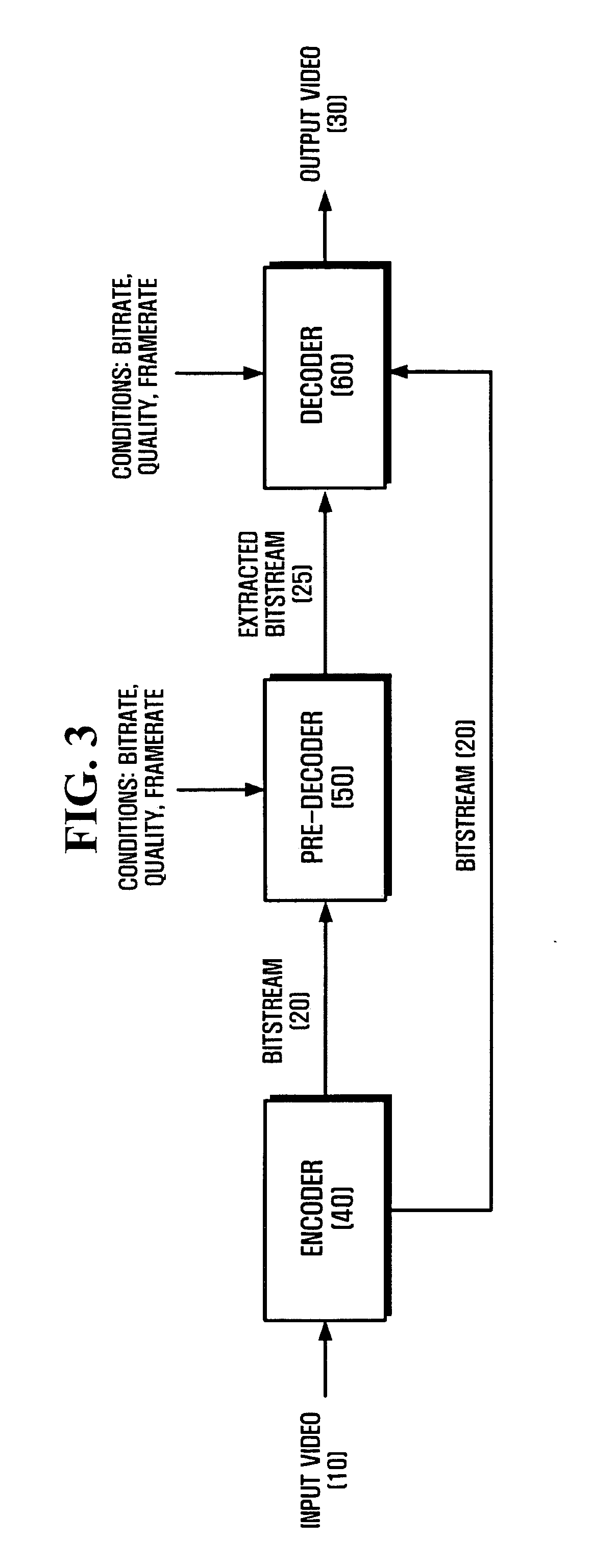
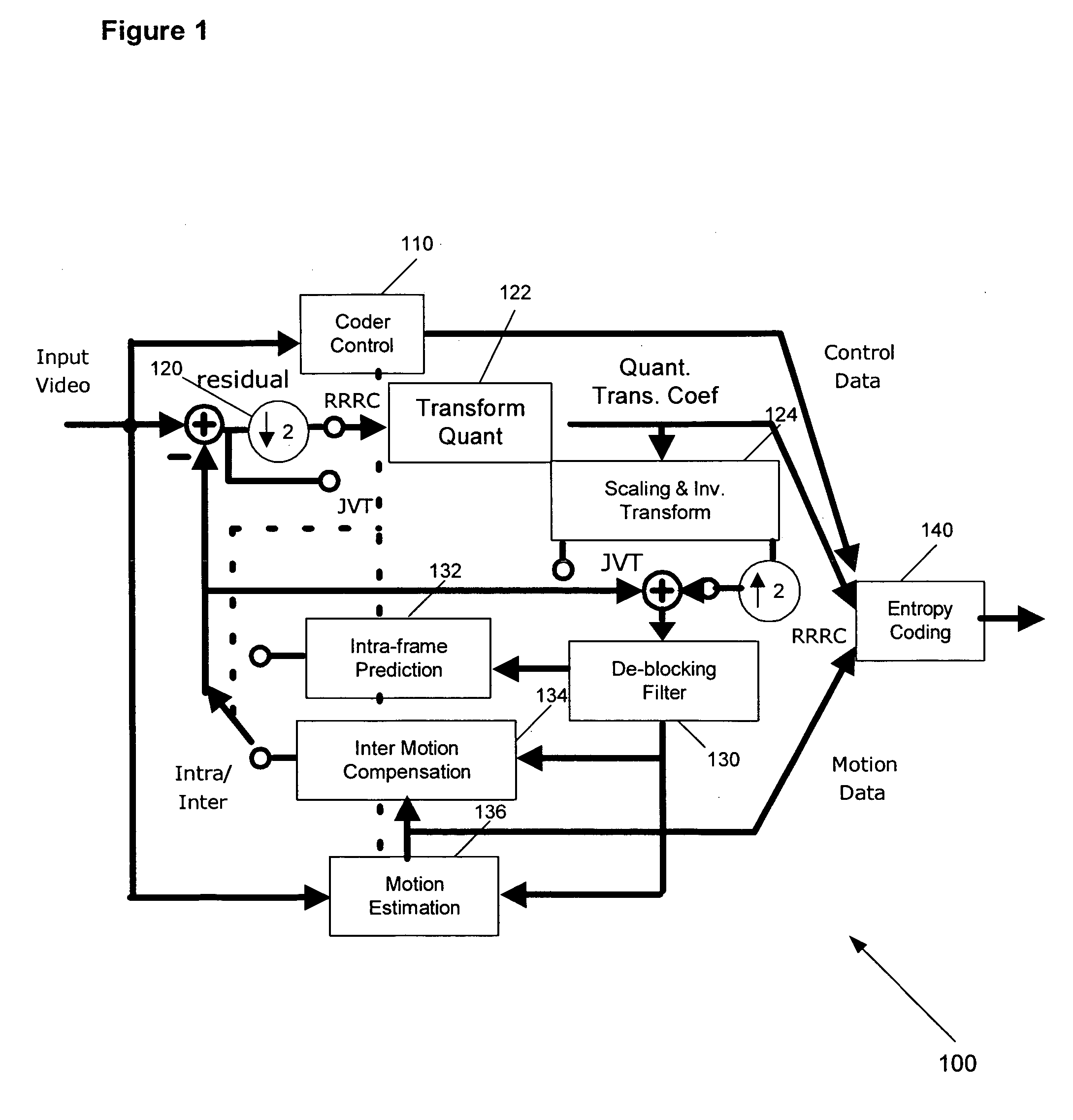
Method and apparatus for adaptive up-scaling for spatially scalable coding
InactiveUS20060268991A1Improve compression efficiencyImageColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImage resolutionSelf adaptive
Adaptive up-sample filtering is used to improve compression efficiency of spatially scalable coding systems by more effectively predicting the high-resolution (enhanced-layer) video (or image) from the low-resolution lower-layer video (or image). Different up-sample filters adaptive to local image properties are selectively used for different portions of a low resolution frame to generate a better up-sampled image. Selection between different up-sample filters is determined by a variety of different information available to both the encoder and decoder. In one embodiment, the up-sample filters are selected by the encoder and then explicitly identified to the decoder. Other techniques are then used to minimize the cost of transmitting the up-sample filter identifiers. In alternative embodiments, the encoder and decoder independently make up-sample filters selections.
Owner:SHARP KK
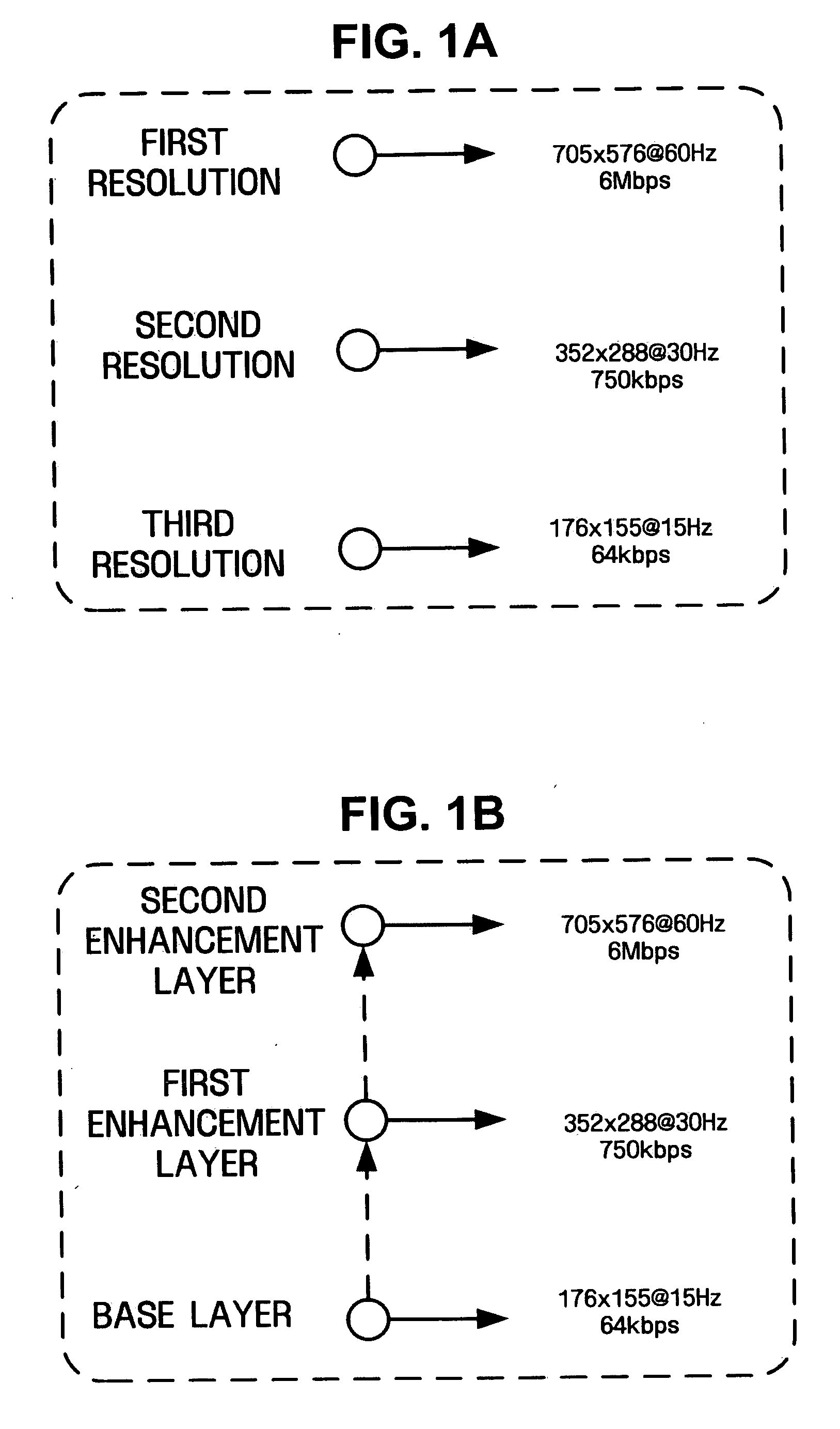
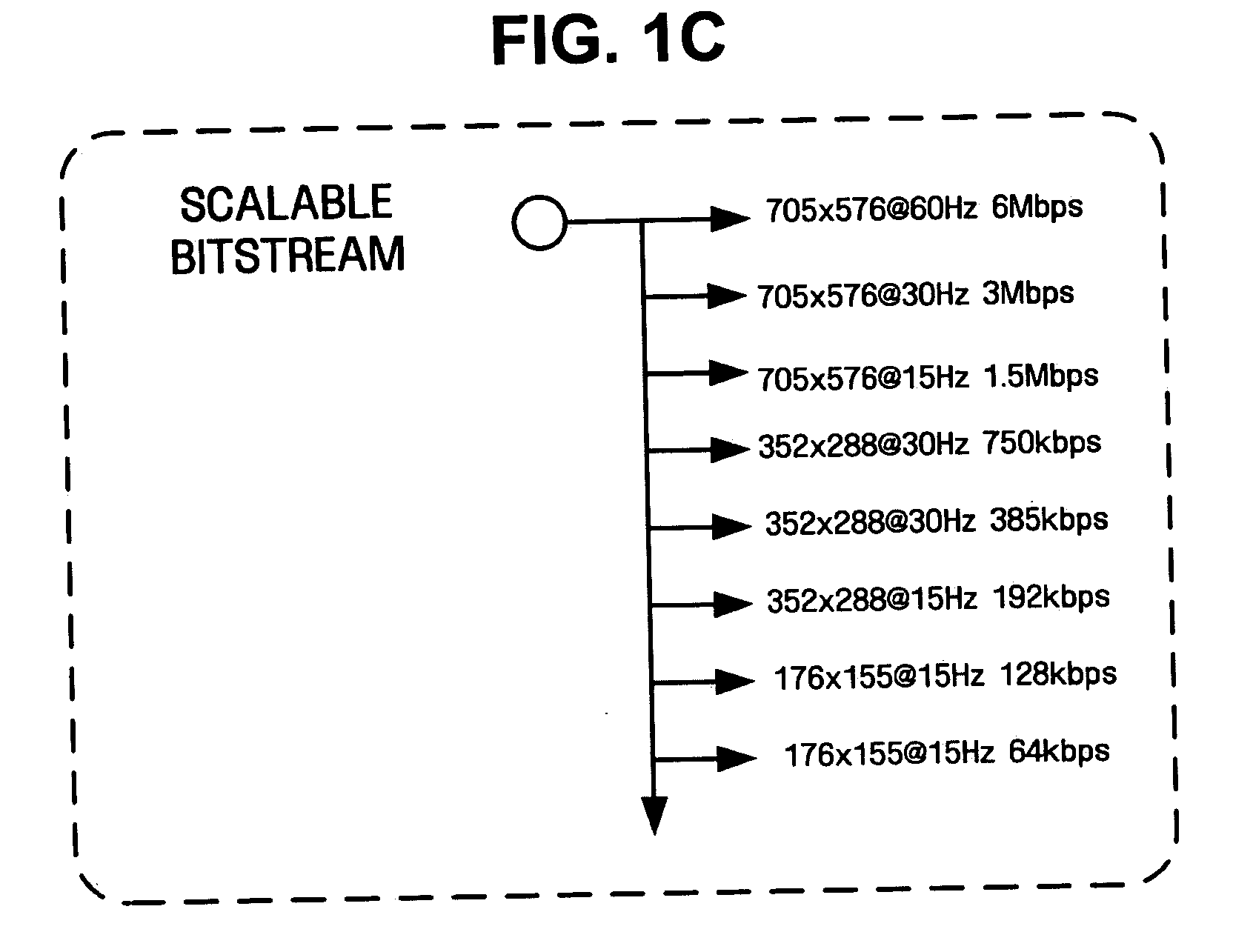
Video encoding and decoding methods and systems for video streaming service
InactiveUS20050195900A1Improve coding efficiencyImprove efficiencyPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputer graphics (images)Video encoding
Video encoding and decoding methods and systems for video streaming are provided. The video encoding method includes encoding first resolution frames using scalable video coding, upsampling the first resolution frames to a second resolution, and encoding second resolution frames using scalable video coding with reference to upsampled versions of the first resolution frames.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
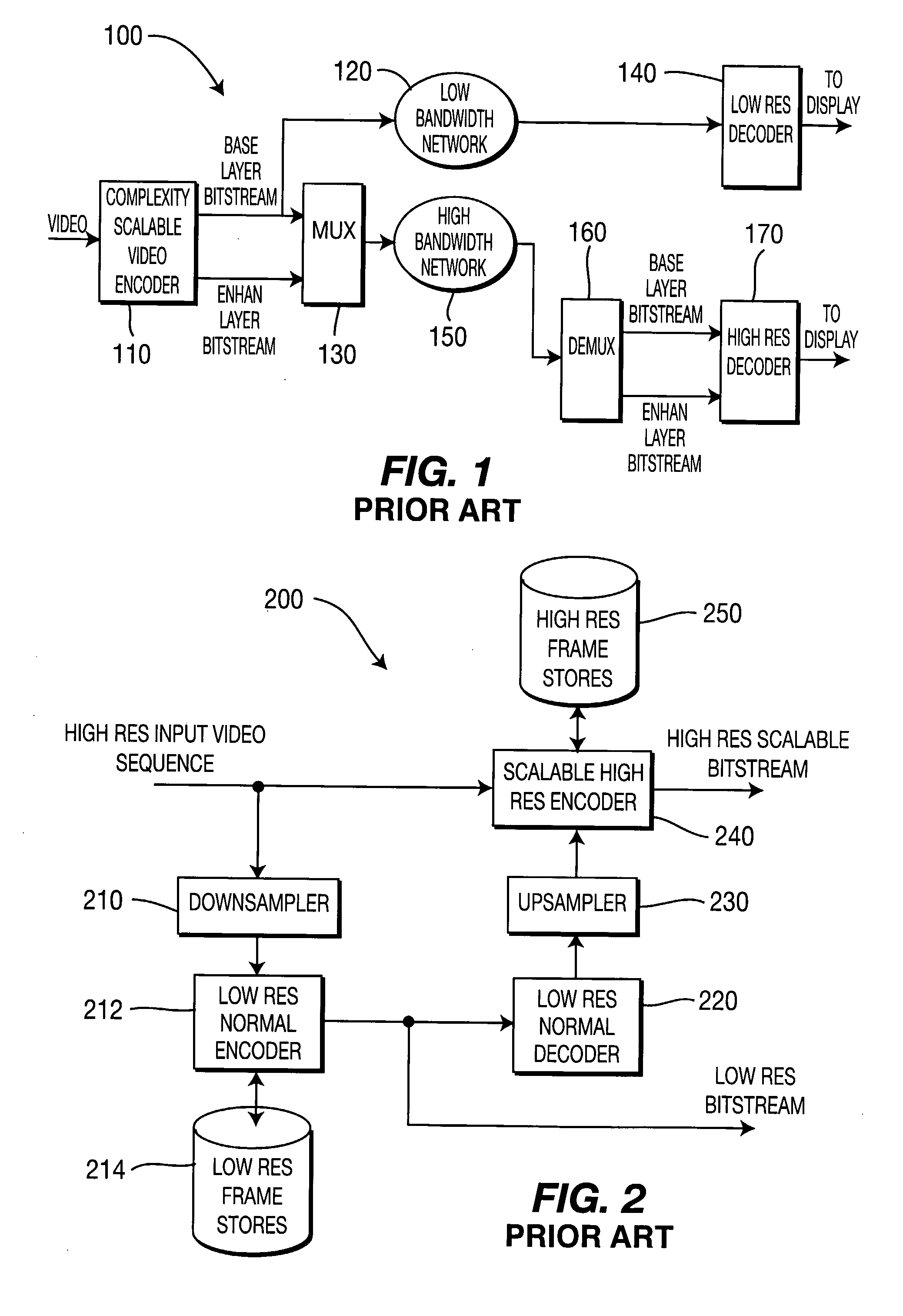
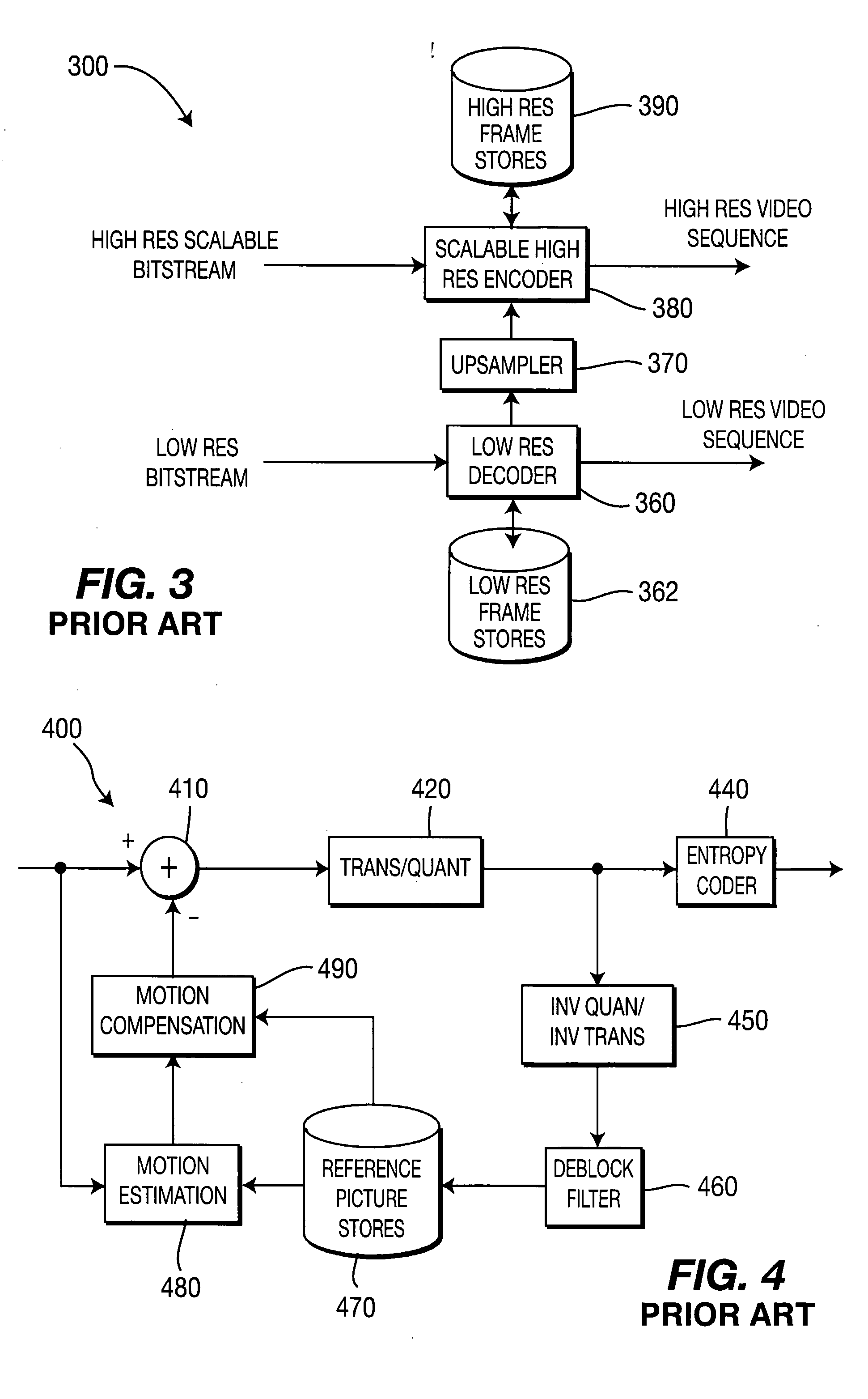
Method And Apparatus For Complexity Scalable Video Encoding And Decoding
InactiveUS20070286283A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionVideo bitstream
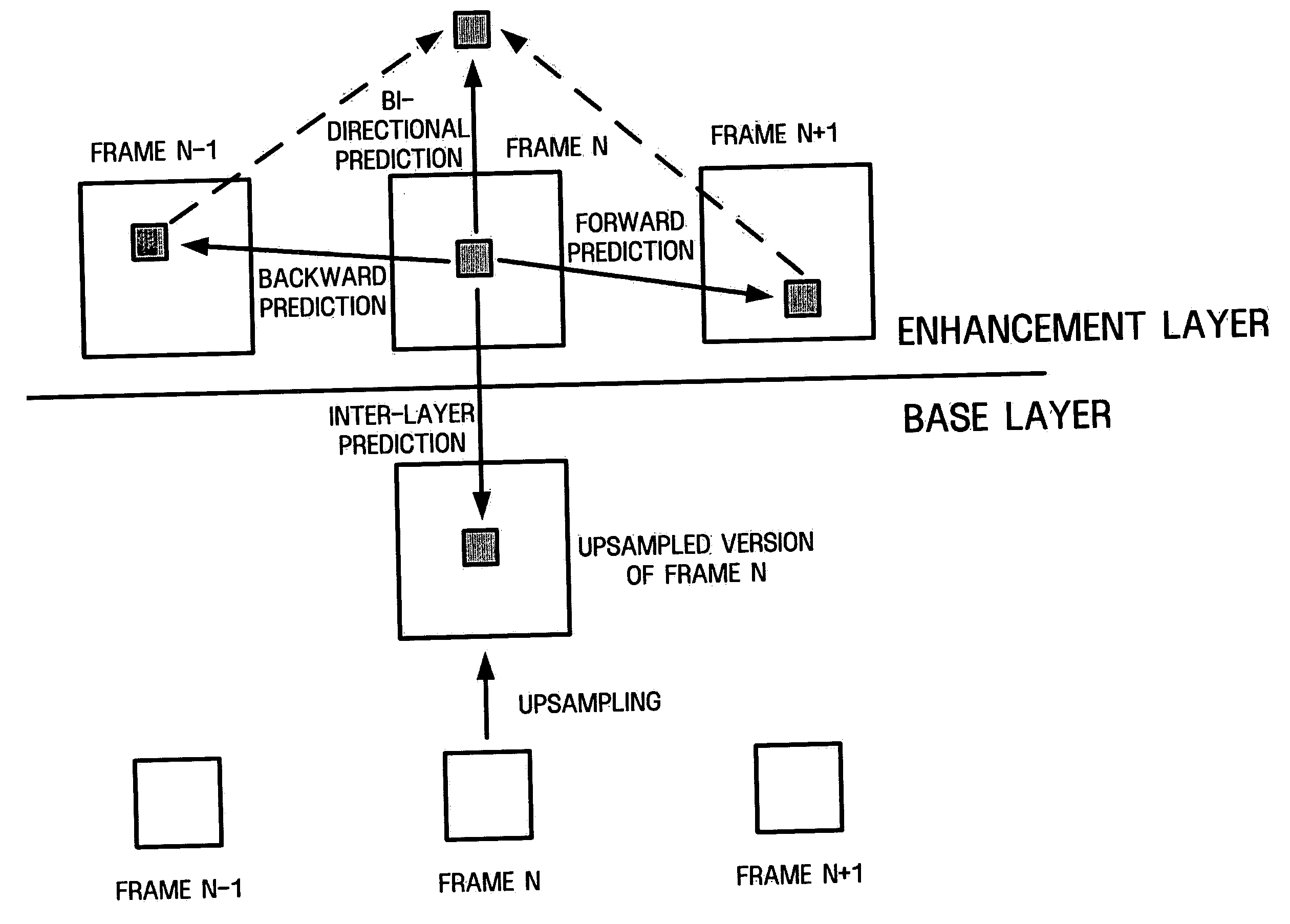
There are provided scalable complexity video decoder and encoders for respectively decoding and encoding a video bitstream. A scalable complexity video decoder includes a first combiner, a second combiner, and a deblocking filter. The first combiner is for combining full resolution motion compensated predictions and decoded upsampled base layer residuals to form reconstructed upsampled base layer pictures for display without any deblocking operations applied thereto. The second combiner, in signal communication with the first combiner, is for combining the reconstructed upsampled base layer pictures with decoded enhancement layer residuals to form reconstructed full resolution enhancement layer pictures. The deblocking filter, in signal communication with the second combiner, is for performing deblocking operations on only the reconstructed full resolution enhancement layer pictures to output filtered reconstructed full resolution enhancement layer pictures for display.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
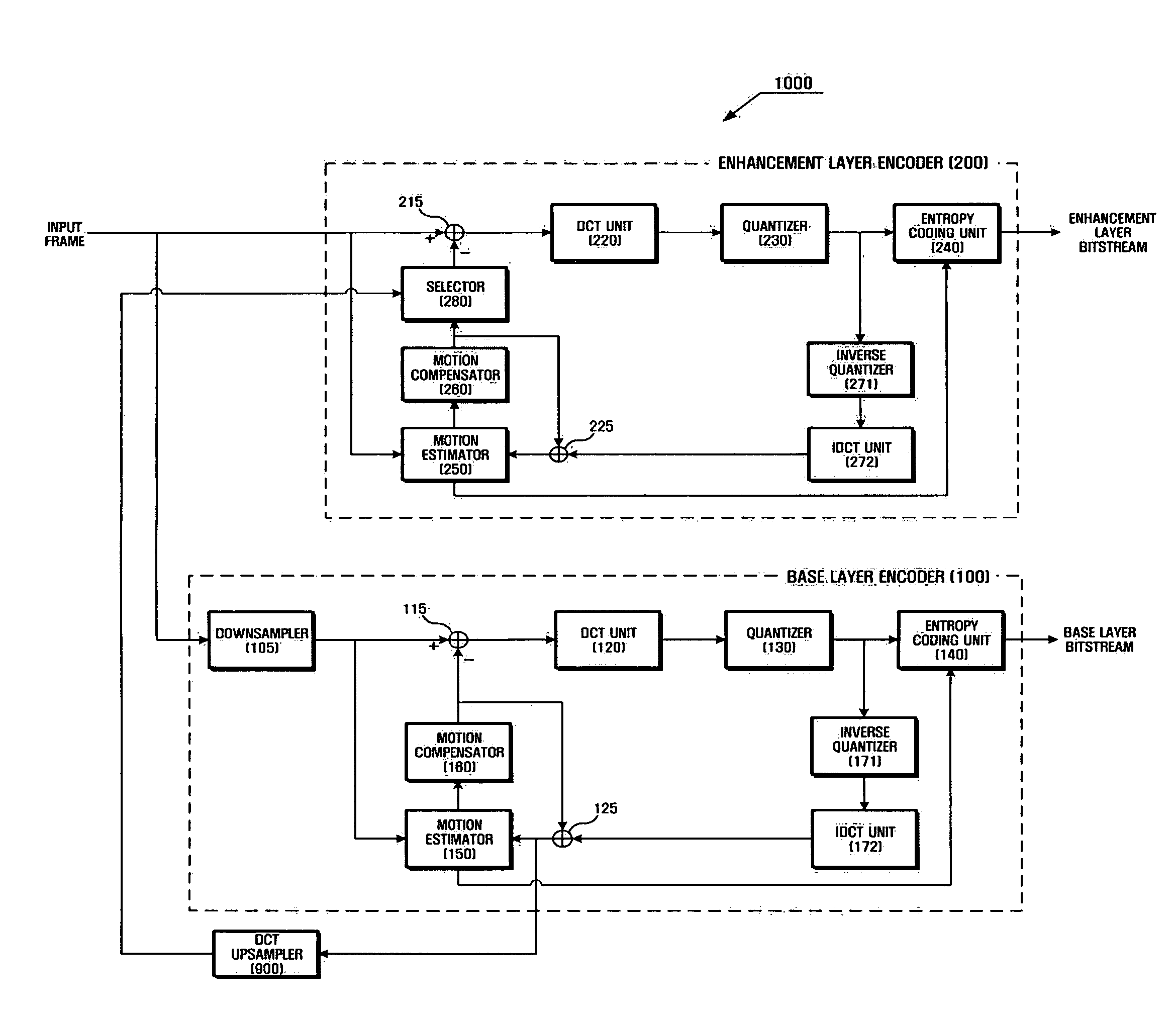
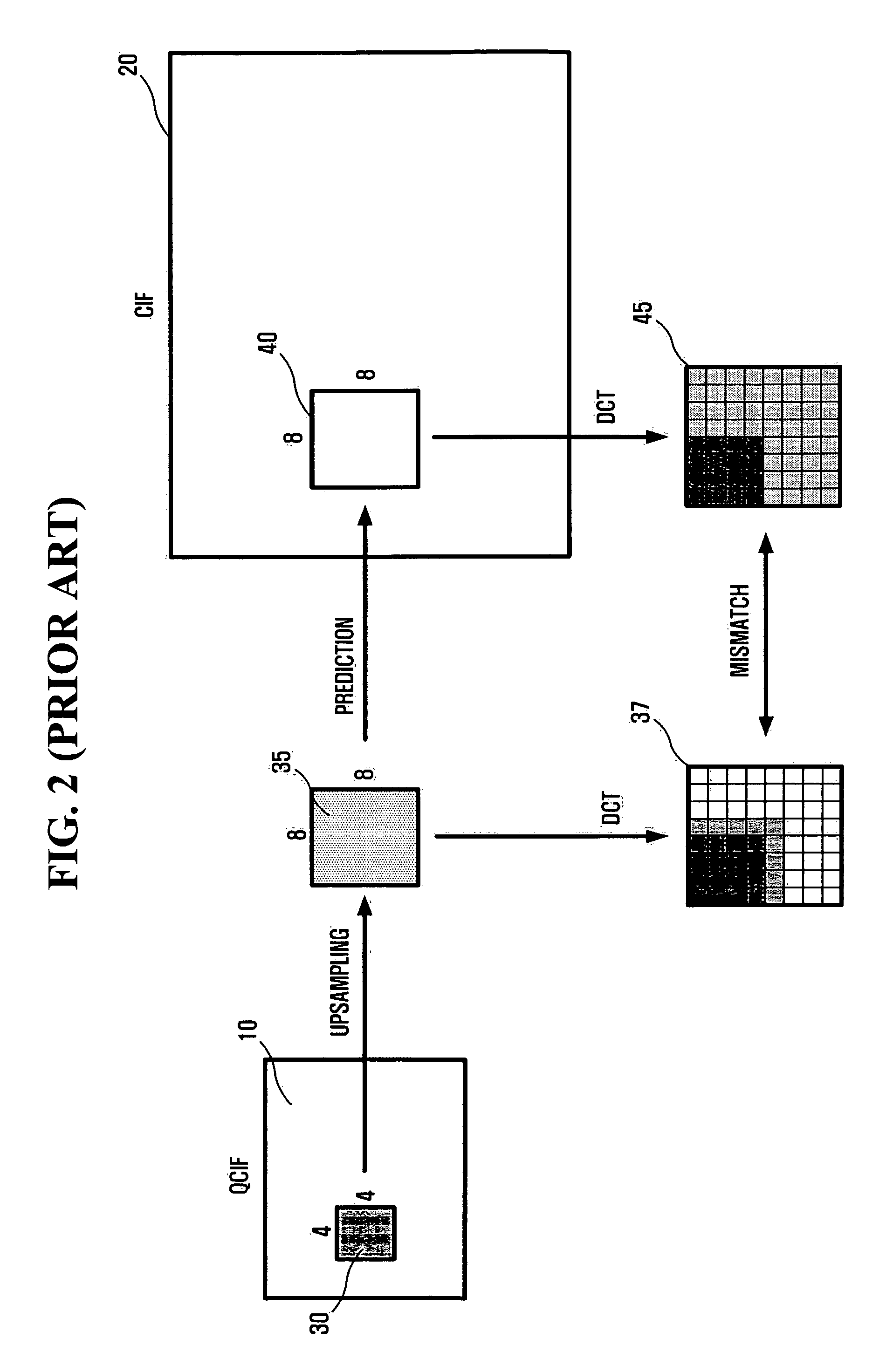
Method and apparatus for encoding/decoding multi-layer video using DCT upsampling
InactiveUS20060120448A1Reduce mismatchRotating vibration suppressionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCoding decodingDiscrete cosine transform
A method and apparatus for more efficiently upsampling a base layer to perform interlayer prediction during multi-layer video coding are provided. The method includes encoding and reconstructing a base layer frame, performing discrete cosine transform (DCT) upsampling on a second block of a predetermined size in the reconstructed frame corresponding to a first block in an enhancement layer frame, calculating a difference between the first block and a third block generated by the DCT upsampling, and encoding the difference.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
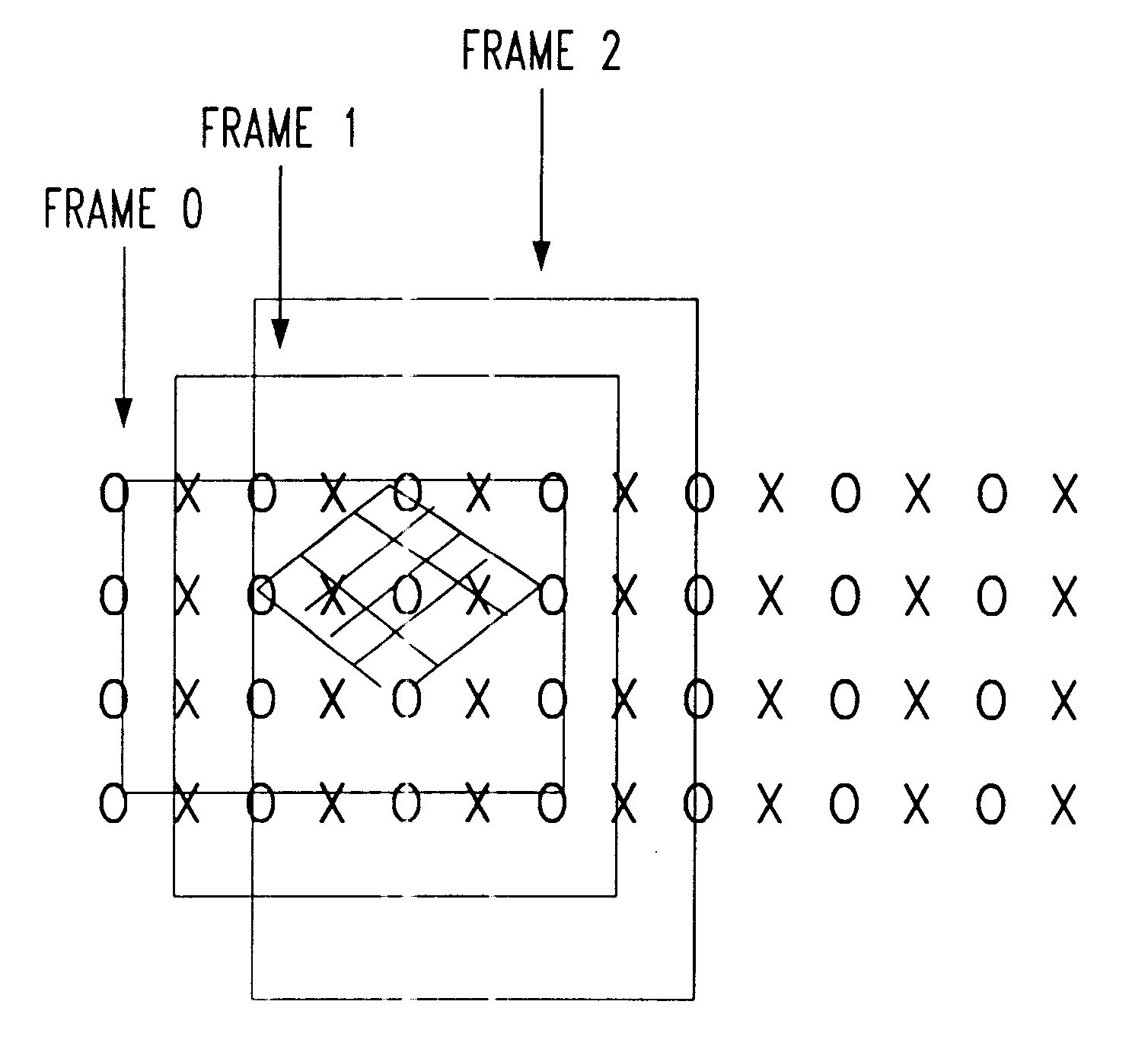
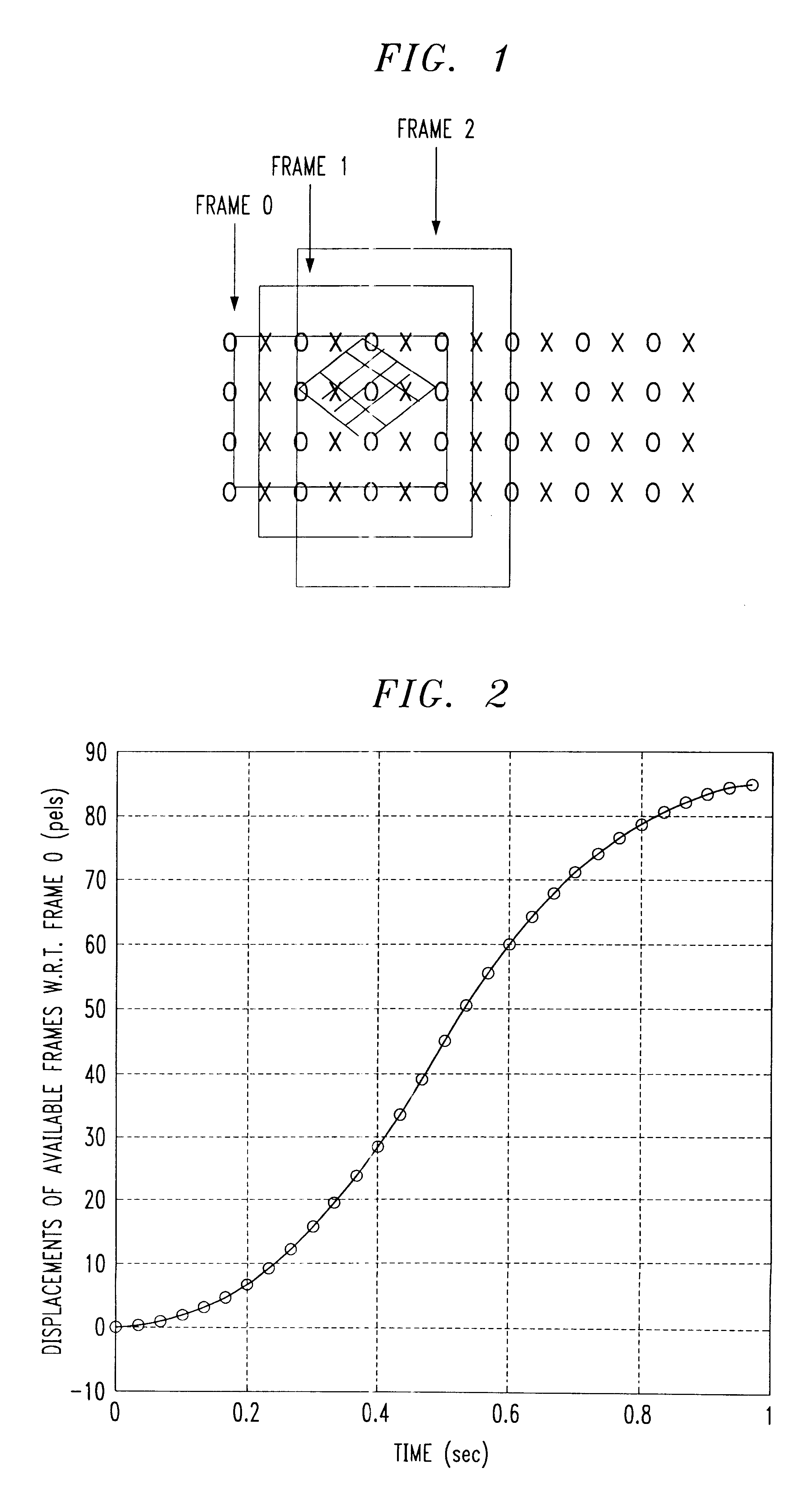
Motion compensation image interpolation-frame rate conversion for HDTV
InactiveUS6229570B1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesHigh-definition televisionComputer graphics (images)
A process for up-converting an existing video source signal having a low frequency (frames / second) to a high frequency signal for use with High Definition Television (HDTV). The process samples the existing frames in the existing video signal and calculates integer displacements of pels within the existing frames. A polynomial curve fit is then performed on the displacements to obtain estimates of horizontal and vertical displacements of each block in each existing frame. Based on the alignment of the blocks within a sampling grid on each frame, the blocks are segregated into groups. The block groups are then used to interpolate missing or required frames of the high frequency signal in a piecemeal manner by utilizing blocks of a particular block group to estimate a corresponding block in a frame of the high frequency signal.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
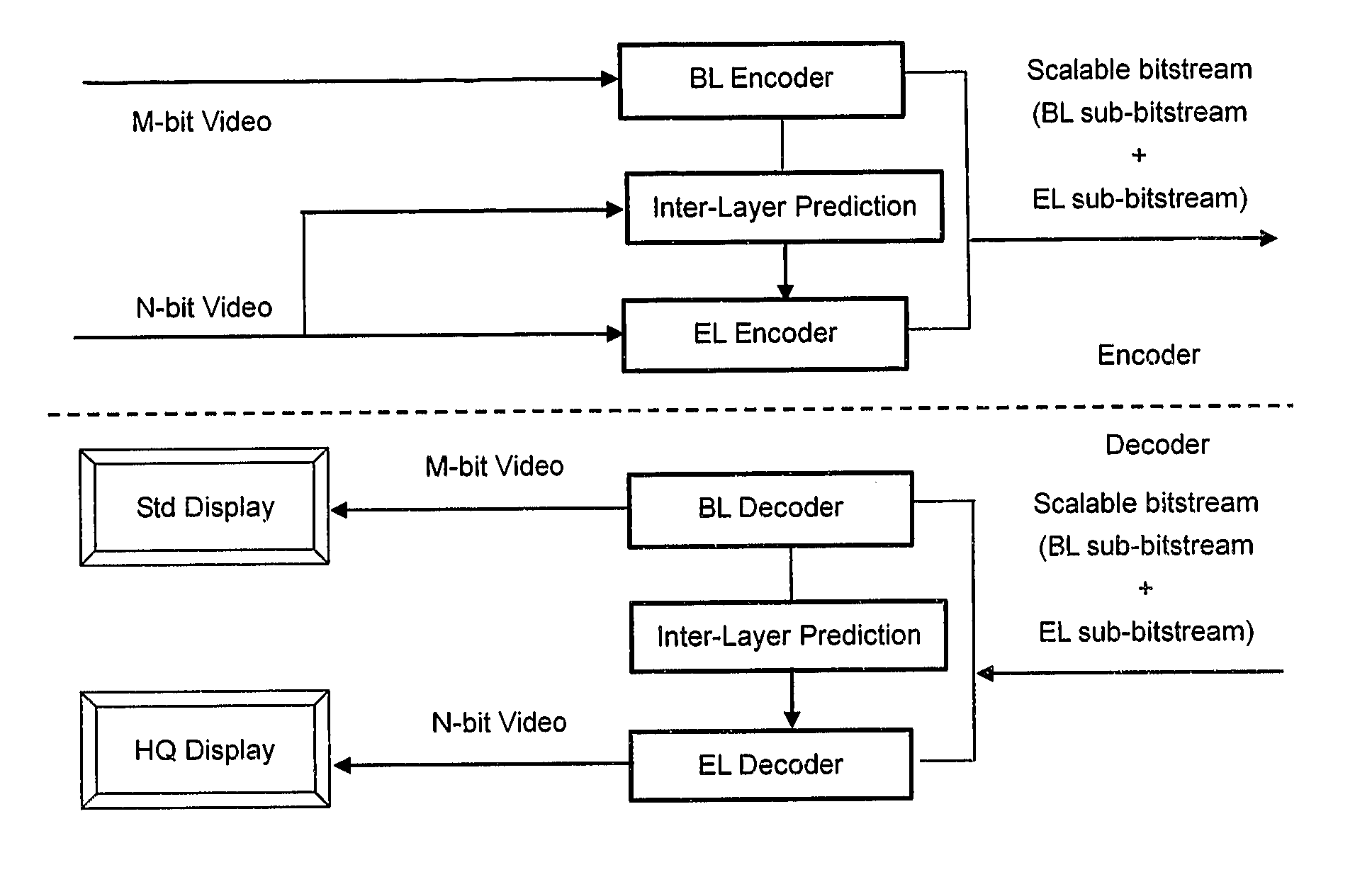
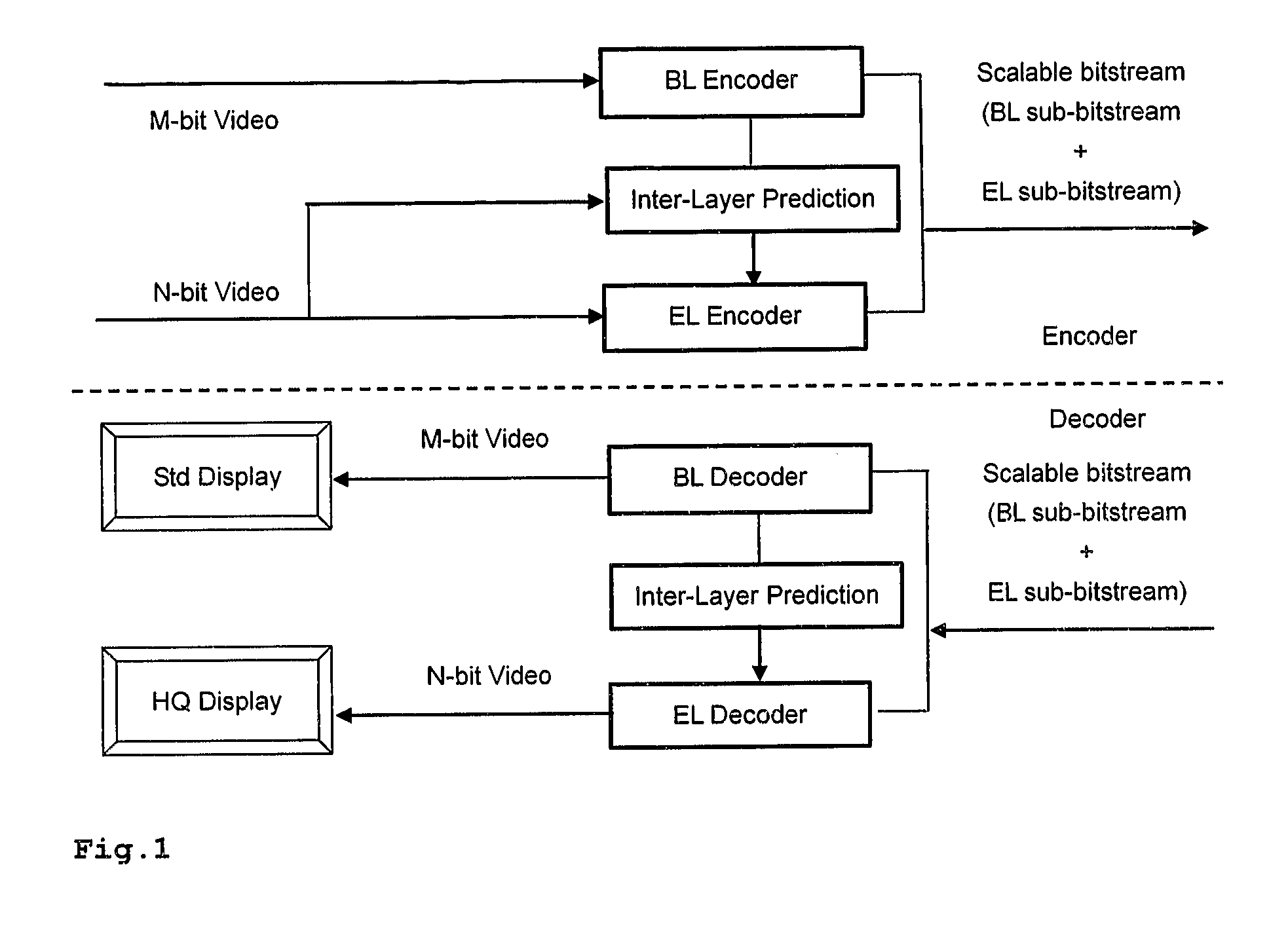
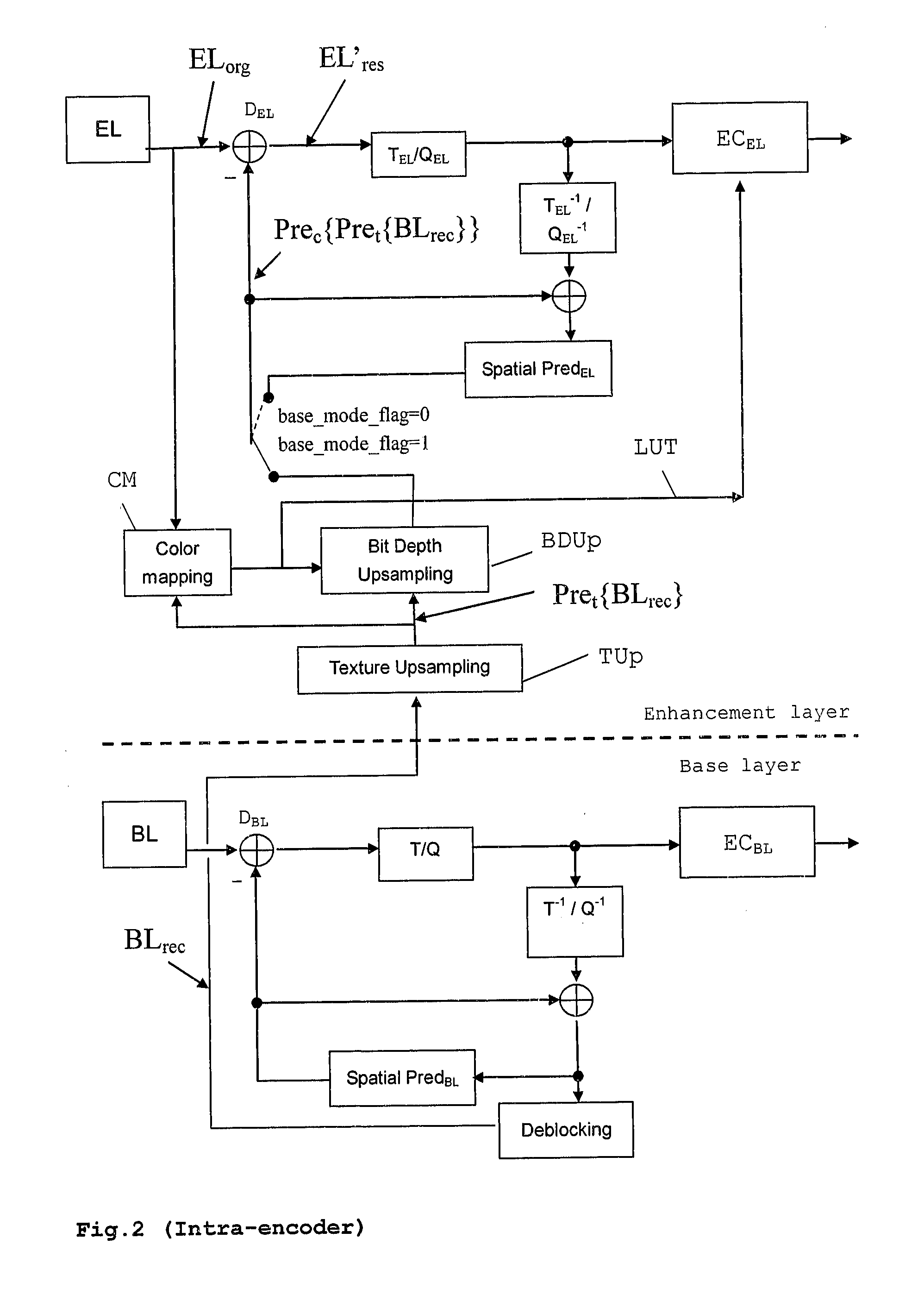
Method and apparatus for encoding and/or decoding video data using enhancement layer residual prediction for bit depth scalability
InactiveUS20100135393A1Improve coding efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionVideo bitstream
A scalable video bitstream may have an H.264 / AVC compatible base layer and a scalable enhancement layer, where scalability refers to color bit depth. The H.264 / AVC scalability extension SVC provides also other types of scalability, e.g. spatial scalability where the number of pixels in BL and EL are different. According to the invention, BL information is upsampled in two logical steps, one being texture upsampling and the other being bit depth upsampling. Texture upsampling is a process that increases the number of pixels, and bit depth upsampling is a process that increases the number of values that each pixel can have, corresponding to the pixels color intensity. The upsampled BL data are used to predict the collocated EL. The BL information is upsampled at the encoder side and in the same manner at the decoder side, wherein the upsampling refers to spatial and bit depth characteristics.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Low noise encoding and decoding method
InactiveUS6873368B1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionLow noiseDecoding methods
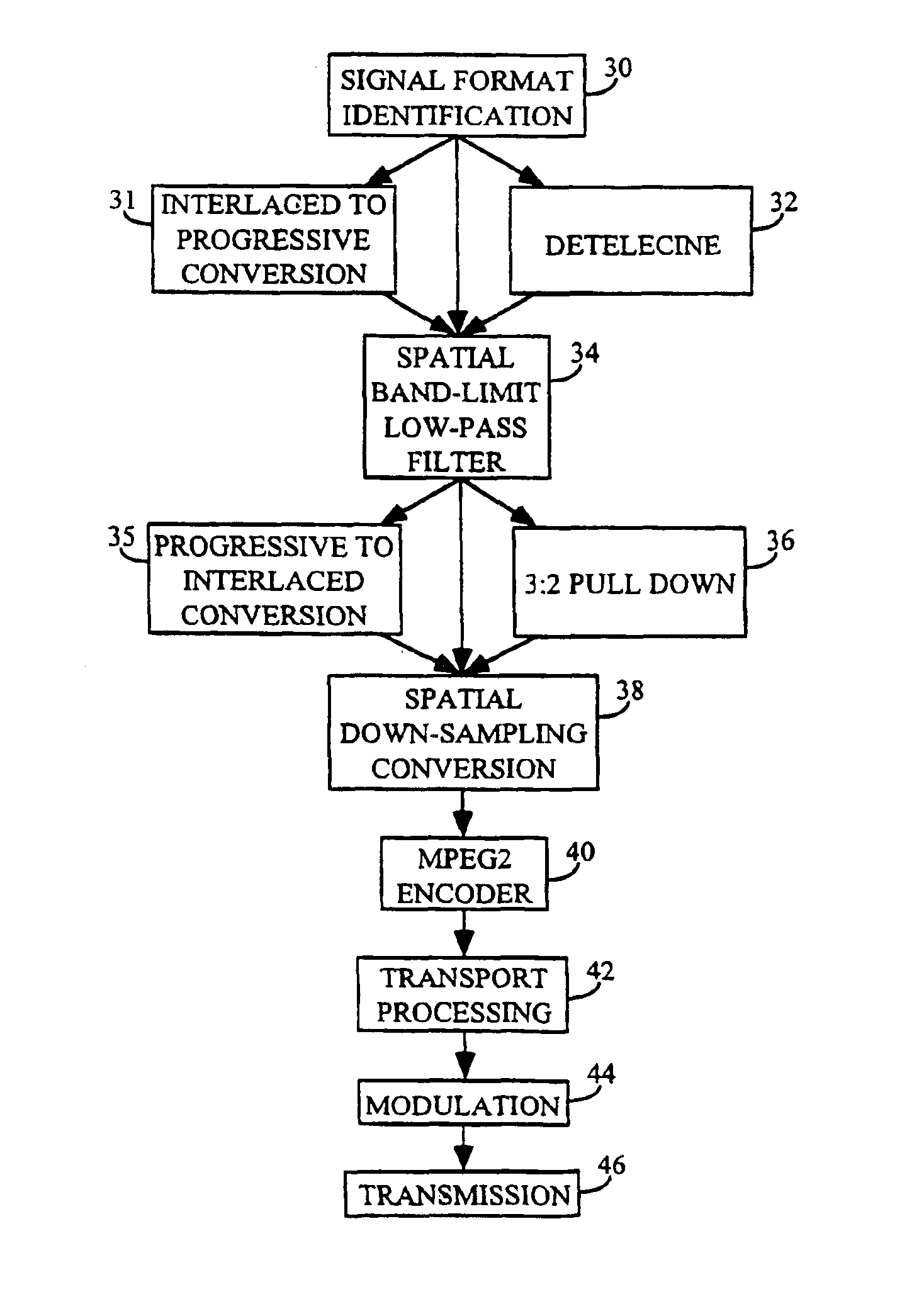
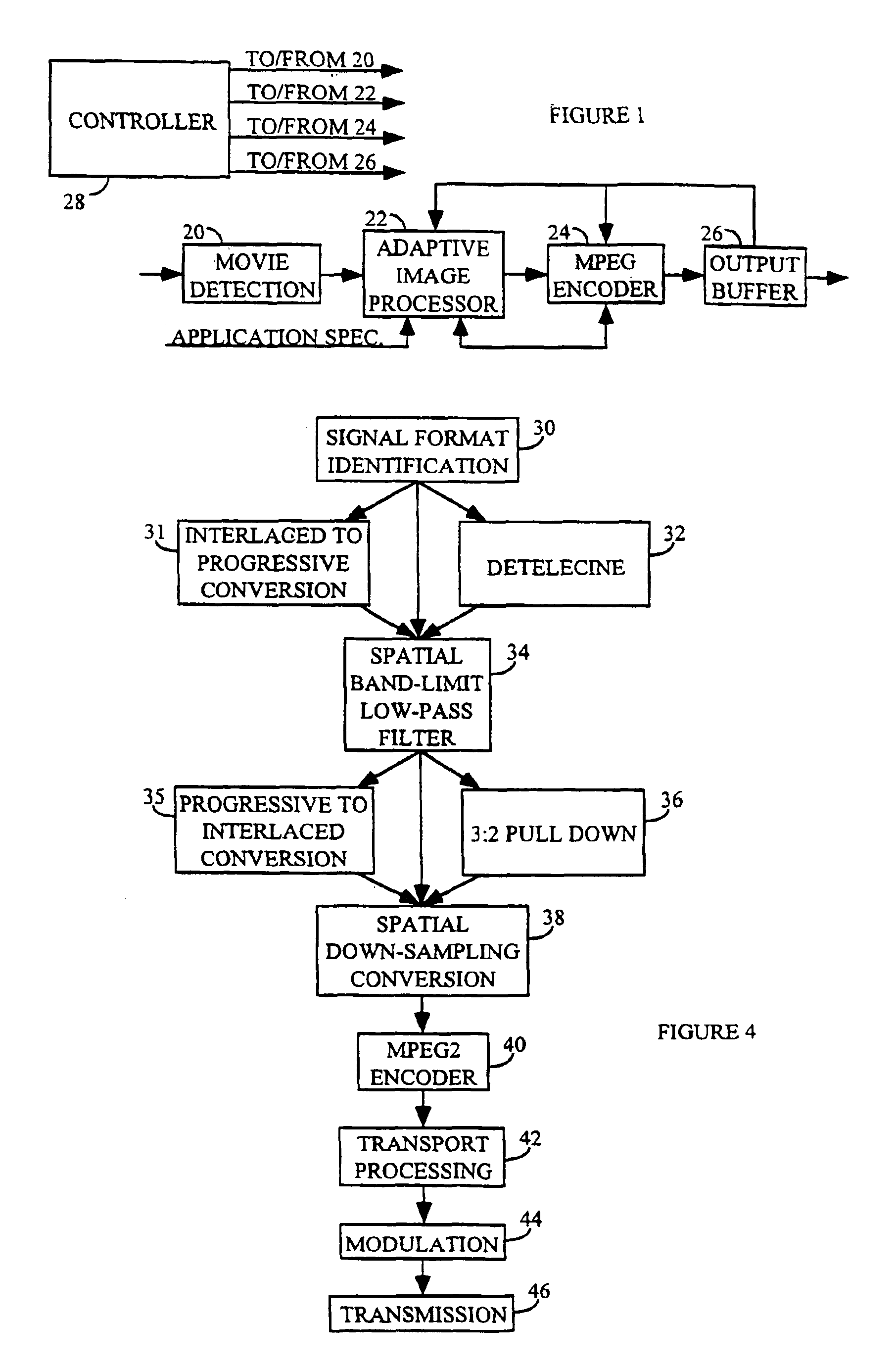
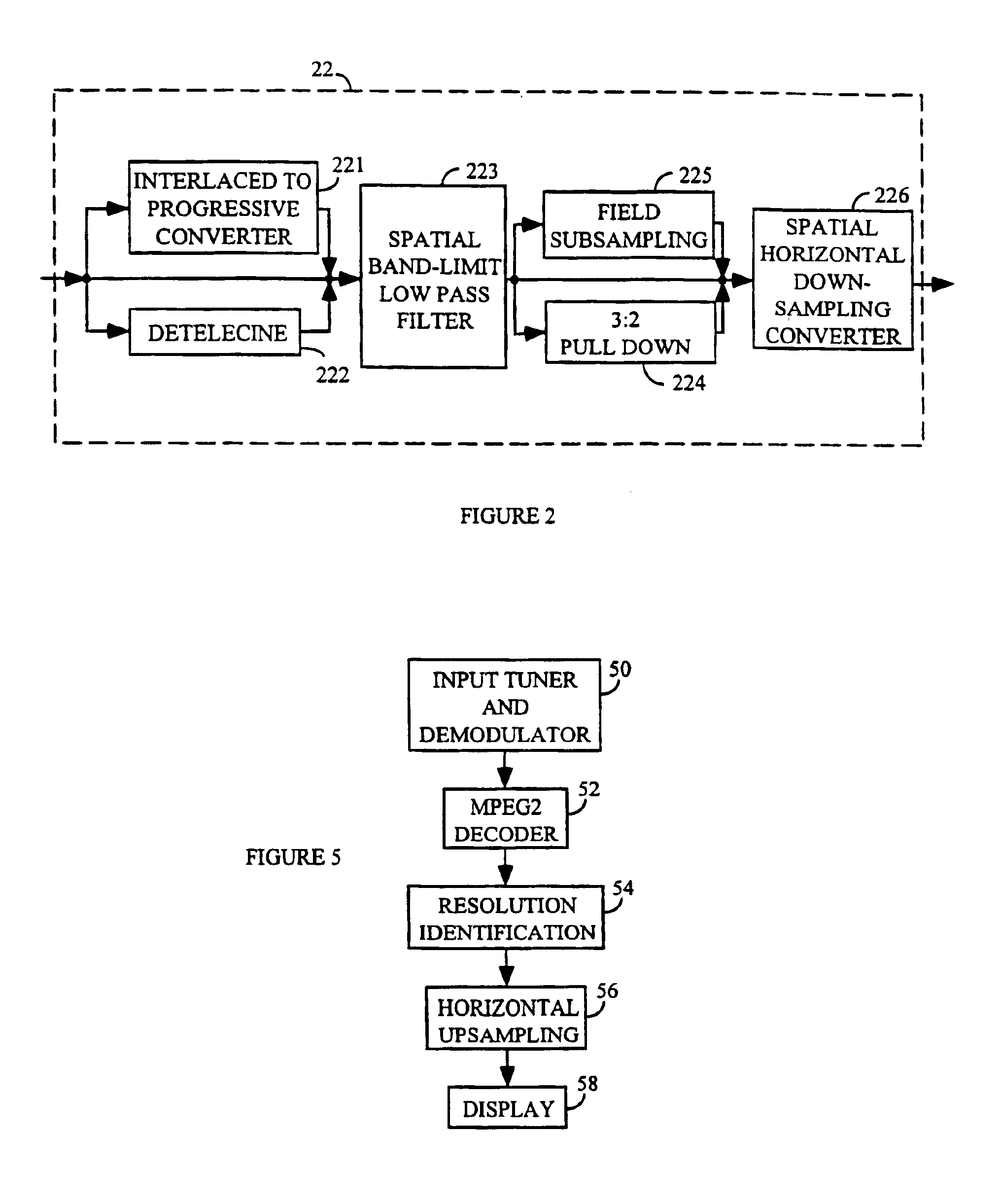
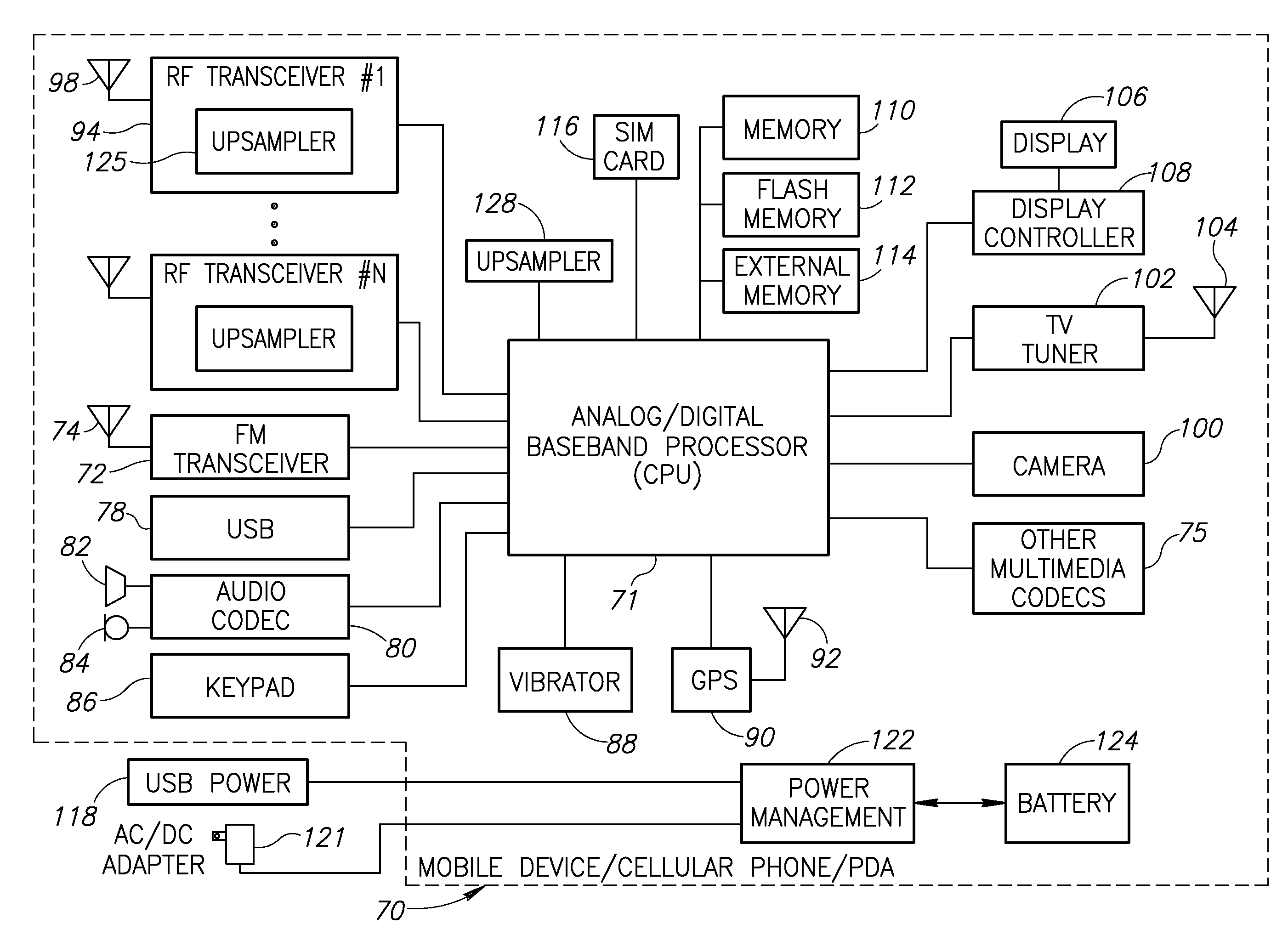
An adaptive digital image processor precedes an MPEG2 encoder. The processor receives a high definition video signal intended for broadcast or storage, and adaptively low-pass filters the signal. The signal is subjected to low-pass two-dimensional filtering to eliminate encoding artifacts and related noise. The video signal is then horizontally down-sampled to create a lower resolution hybrid signal. A receiver decodes and decompresses the hybrid signal. The hybrid signal is upsampled to its original resolution using existing hardware and software with a software modification.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Automated cardiac volume segmentation
ActiveUS20180259608A1Verify accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresMissing data
Systems and methods for automated segmentation of anatomical structures, such as the human heart. The systems and methods employ convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to autonomously segment various parts of an anatomical structure represented by image data, such as 3D MRI data. The convolutional neural network utilizes two paths, a contracting path which includes convolution / pooling layers, and an expanding path which includes upsampling / convolution layers. The loss function used to validate the CNN model may specifically account for missing data, which allows for use of a larger training set. The CNN model may utilize multi-dimensional kernels (e.g., 2D, 3D, 4D, 6D), and may include various channels which encode spatial data, time data, flow data, etc. The systems and methods of the present disclosure also utilize CNNs to provide automated detection and display of landmarks in images of anatomical structures.
Owner:ARTERYS INC
Efficient scalable coding concept
ActiveUS20150304667A1Alleviate decoder 's burdenReduce the numberColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionOverlayData stream
Scalable coding concepts are described. One aspect improves parallel decoding of inter-dependent layers of a multi-layer video data stream by introducing a long-term syntax element structure for guaranteeing that during a predetermined time period the pictures of the dependent layer are subdivided so that borders of the spatial segments of the pictures of the second layer and the spatial segments of the first layer overlay. Another aspect concerns upsampling from base layer to enhancement layer. Another aspect introduces a long-term syntax element structure allowing the decoder to determine the inter-layer offset for a predetermined time period. Another aspect introduces a type indicator field changing a way a layer indicator field within the NAL unit headers is to be interpreted. Another aspect allows different codecs / standards to be used for the different layers. Another aspect concerns a syntax element structure which indicates the inter-layer offset in units of the base layer blocks.
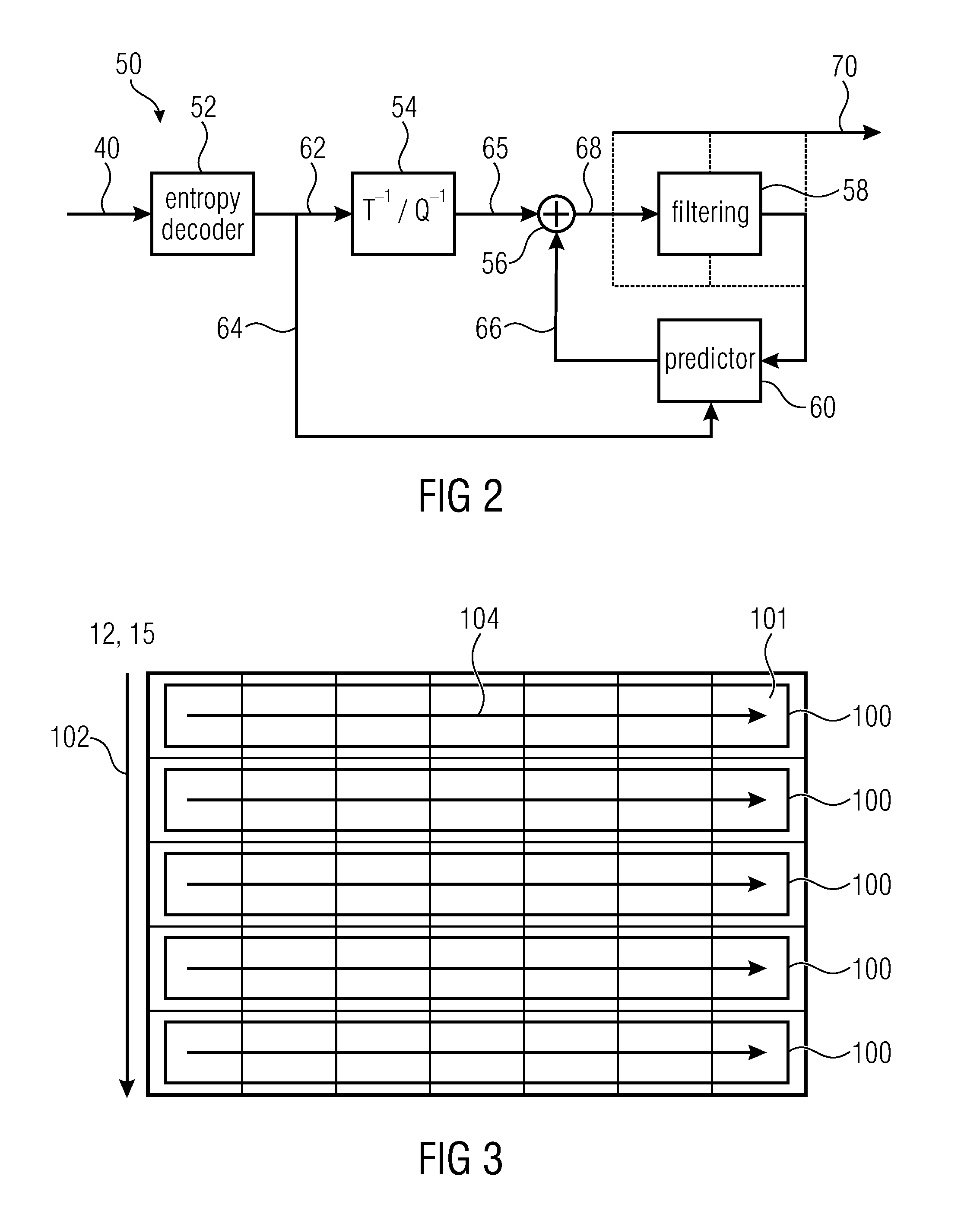
Owner:GE VIDEO COMPRESSION LLC
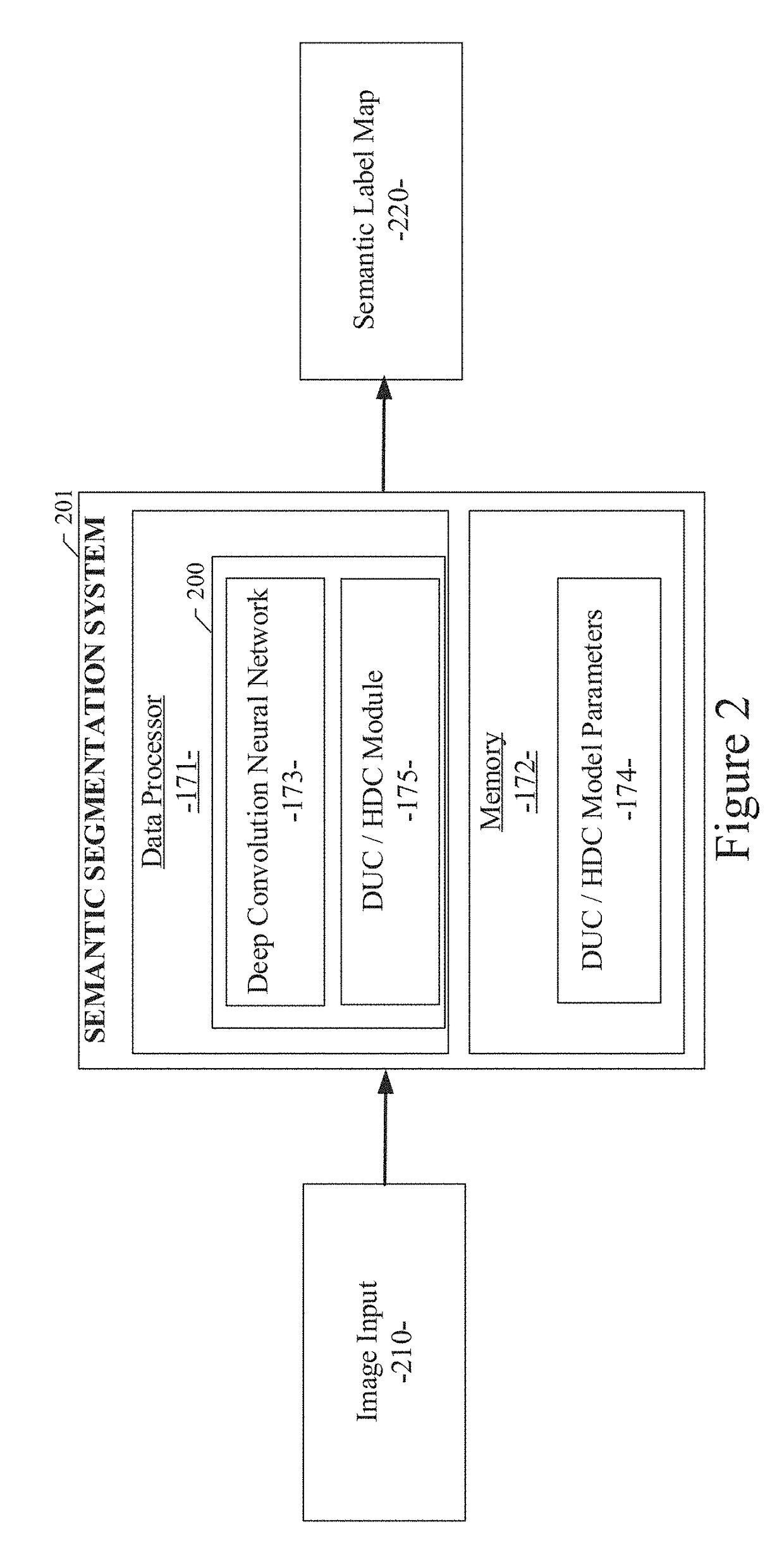
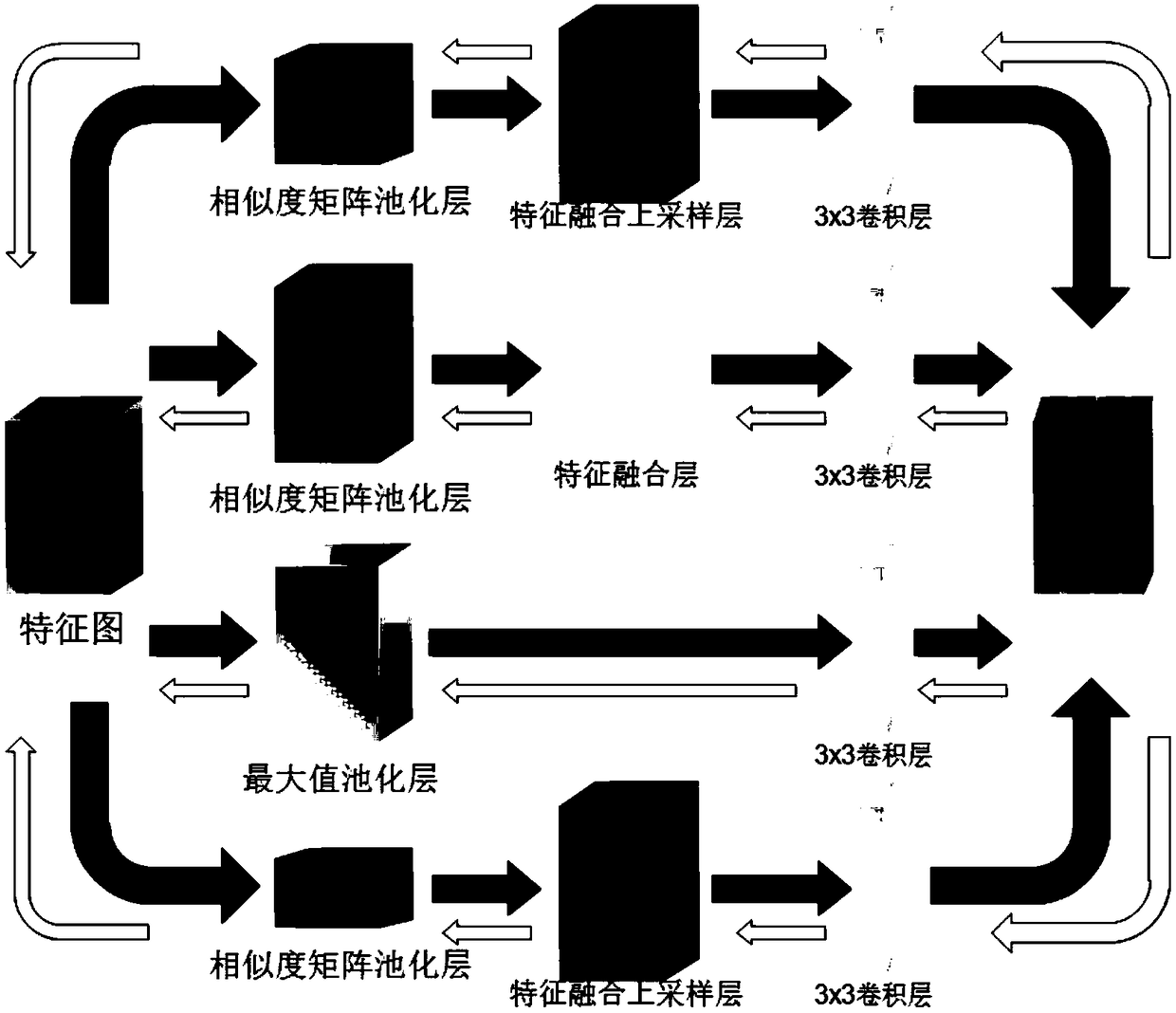
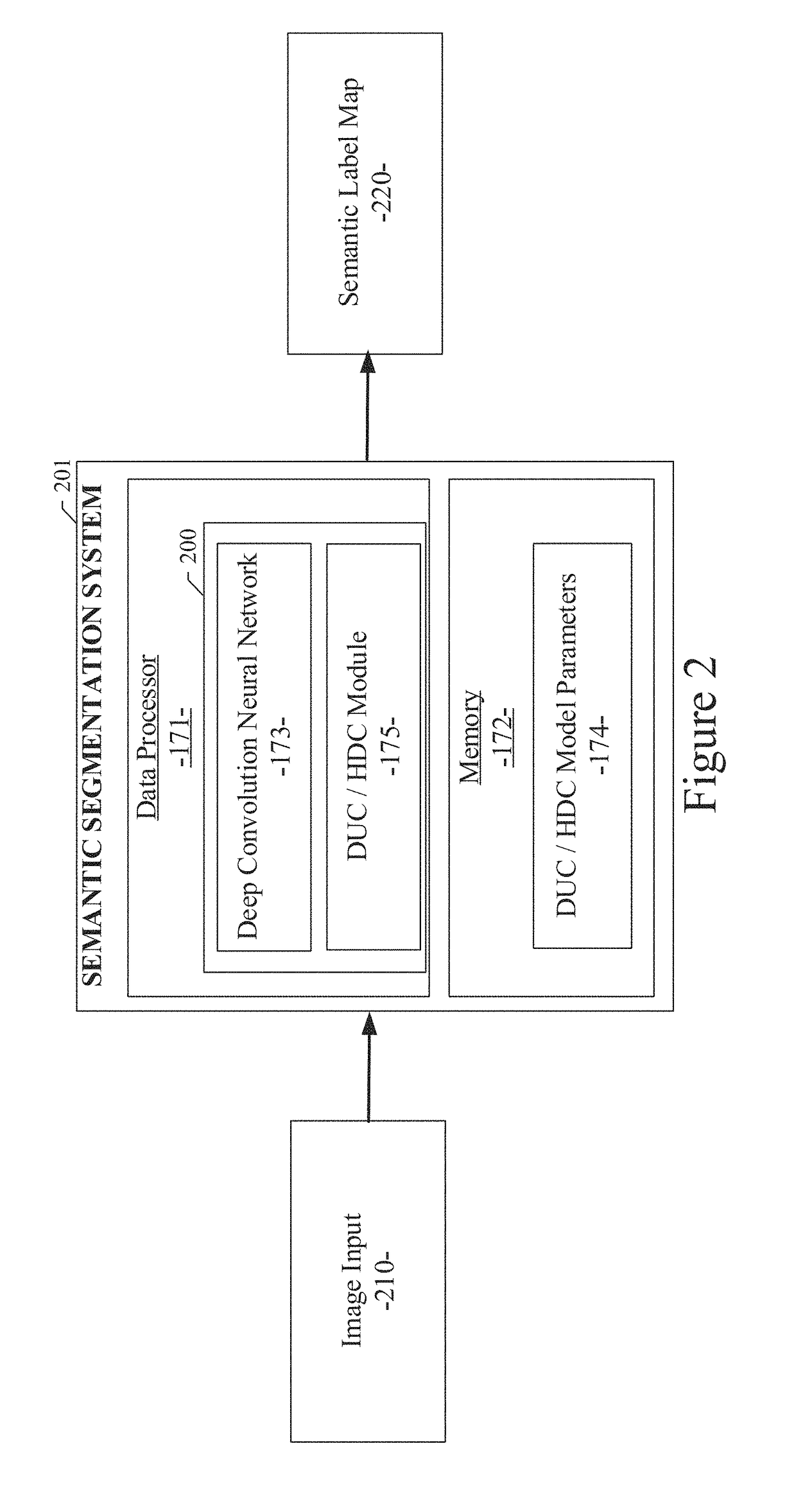
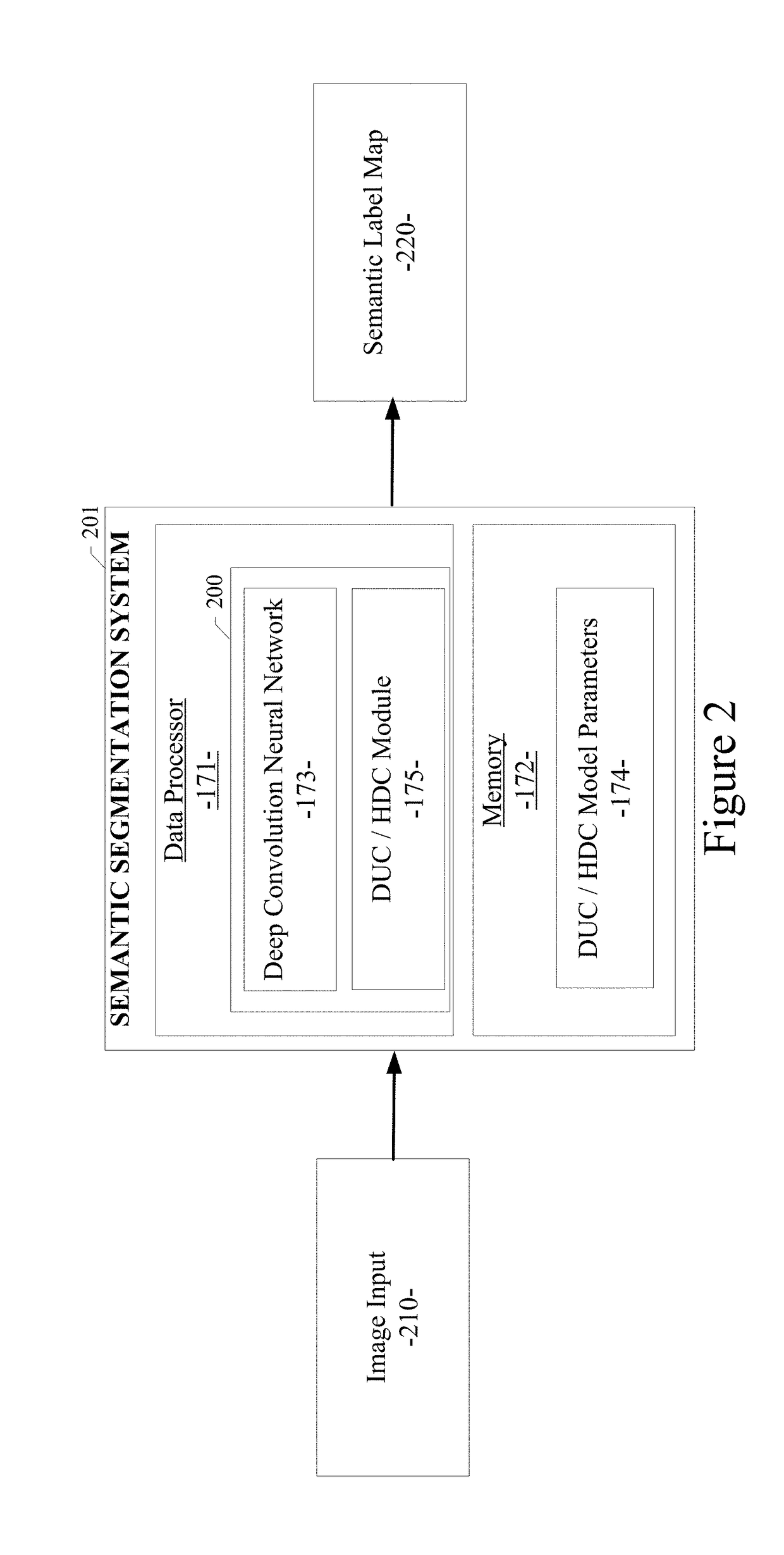
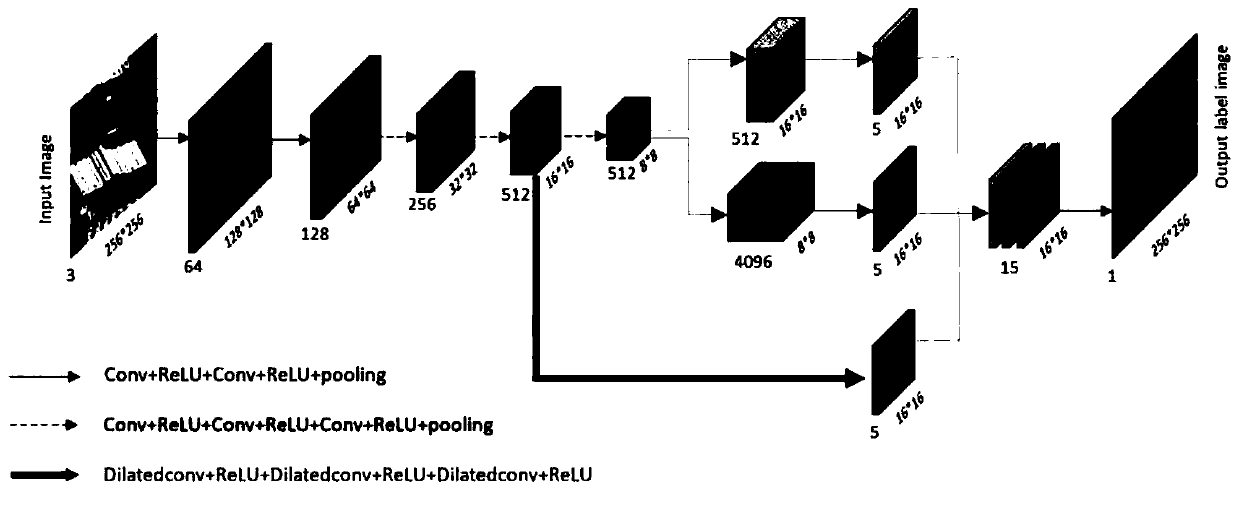
System and method for semantic segmentation using dense upsampling convolution (DUC)
ActiveUS9953236B1Efficient amplificationImprove segmentationAutonomous decision making processCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionConvolution
A system and method for semantic segmentation using dense upsampling convolution (DUC) are disclosed. A particular embodiment includes: receiving an input image; producing a feature map from the input image; performing a convolution operation on the feature map and reshape the feature map to produce a label map; dividing the label map into equal subparts, which have the same height and width as the feature map; stacking the subparts of the label map to produce a whole label map; and applying a convolution operation directly between the feature map and the whole label map without inserting extra values in deconvolutional layers to produce a semantic label map.
Owner:TUSIMPLE INC
Scalable video coding method and apparatus using base-layer
InactiveUS20060013313A1Low rateIncrease bitrateColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer graphics (images)Video encoding
A method of more efficiently conducting temporal filtering in a scalable video codec by use of a base-layer is provided. The method of efficiently compressing frames at higher layers by use of a base-layer in a multilayer-based video coding method includes (a) generating a base-layer frame from an input original video sequence, having the same temporal position as a first higher layer frame, (b) upsampling the base-layer frame to have the resolution of a higher layer frame, and (c) removing redundancy of the first higher layer frame on a block basis by referencing a second higher layer frame having a different temporal position from the first higher layer frame and the upsampled base-layer frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
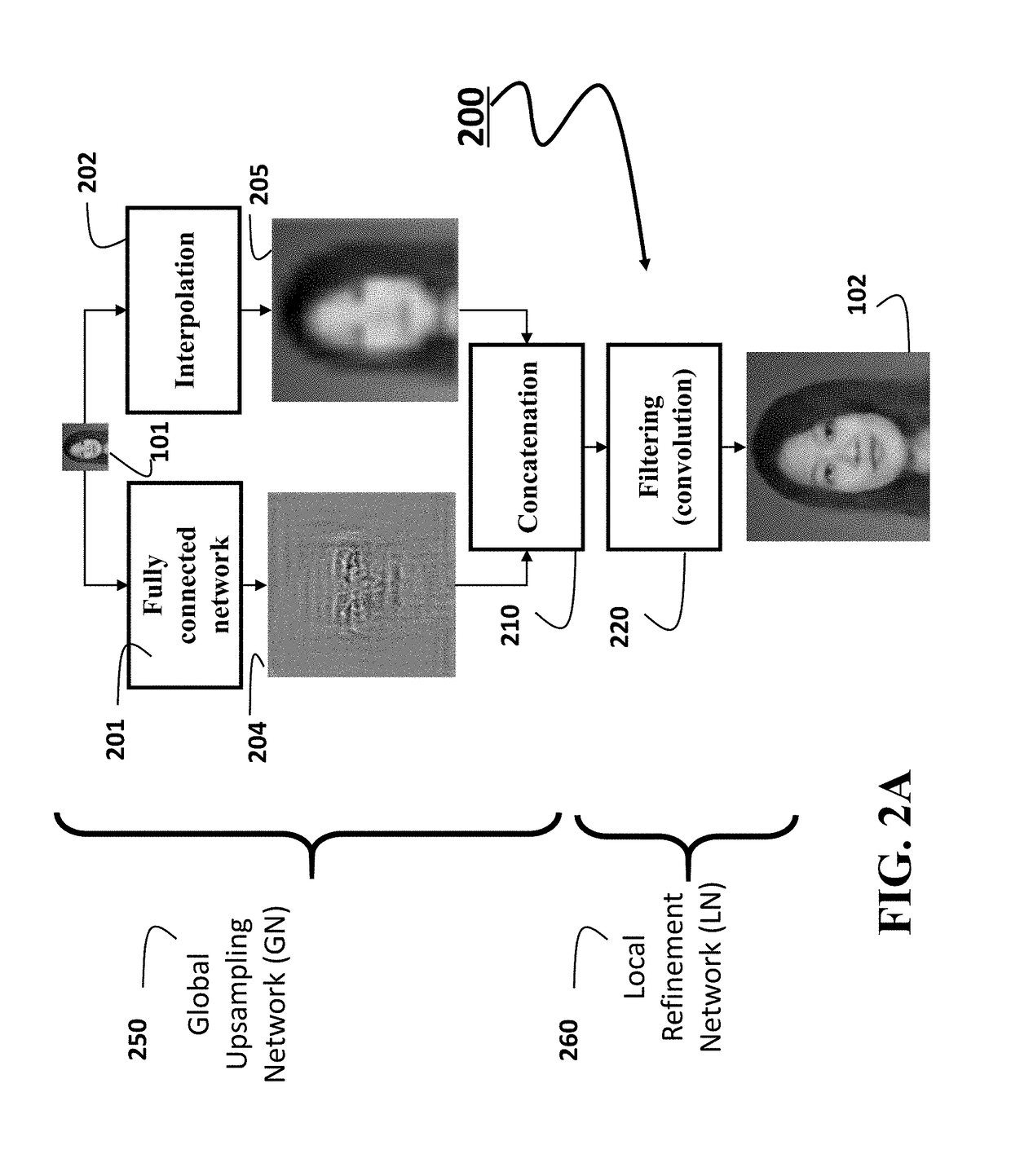
Image Upsampling using Global and Local Constraints
ActiveUS20170256033A1Accurate recoveryHigh-resolution imageImage enhancementImage analysisTensorConvolution
A method upsamples an image using a non-linear fully connected neural network to produce only global details of an upsampled image and interpolates the image to produce a smooth upsampled image. The method concatenates the global details and the smooth upsampled image into a tensor and applies a sequence of nonlinear convolutions to the tensor using a convolutional neural network to produce the upsampled image.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
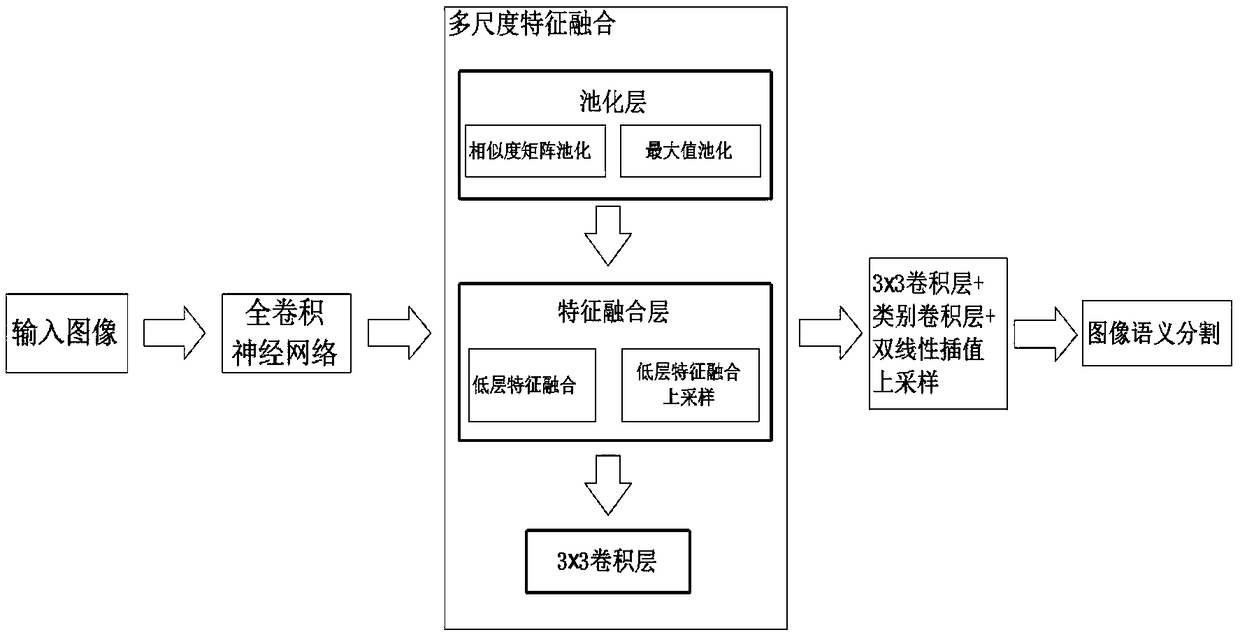
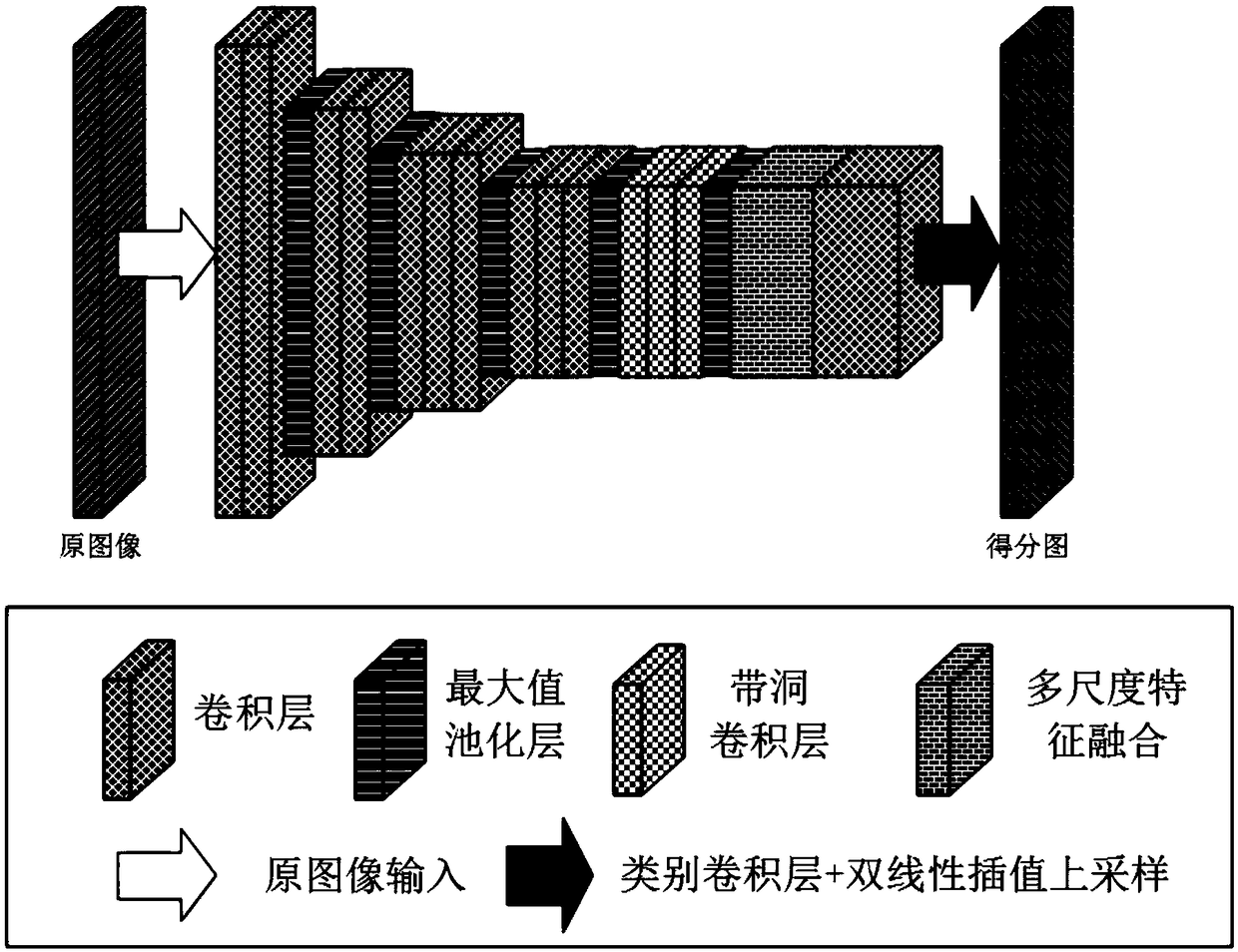
Full convolutional network semantic segmentation method based on multi-scale low-level feature fusion
ActiveCN108830855AEasy to identifyMulti-global feature informationImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionScale downDeep level
The invention discloses a full convolutional network (FCN) semantic segmentation method based on multi-scale low-level feature fusion. The method comprises firstly extracting the dense feature of an input image by using the FCN; and then subjecting the extracted feature images to multi-scale feature fusion, including steps of subjecting the input feature images to multi-scale pooling to form a plurality of processing branches; then performing low-level feature fusion on the pooled scale-invariant feature maps in respective branches and performing low-level feature fusion upsampling on the pooled scale-down feature maps in respective branches; inputting the feature maps into a 3*3 convolutional layer to learn deeper features and reduce the number of channels of output feature maps; then combining the output feature maps of respective branches in a channel number splicing manner, and obtaining a score map having a size the same as that of an original image by a class convolutional layerand bilinear interpolation upsampling. In combination with local low-level feature information and global multi-scale image information, the effect of image semantic segmentation is significant.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Upsampling/interpolation and time alignment mechanism utilizing injection of high frequency noise
InactiveUS20100135368A1Increase sampling rateReduce areaDigital technique networkSecret communicationIntegratorFrequency spectrum
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of upsampling / interpolating a discrete-time input sample stream with time alignment utilizing the addition of randomized high frequency noise. The upsampling mechanism is an effective implementation of a second order interpolator that eliminates the need for a conventional filter as the filtering action is effectively built into the mechanism. The upsampling mechanism takes the derivative of the discrete-time input sample stream, thereby effectively providing another order of interpolation over a conventional interpolator. Before outputting the interpolated signal, an integrator takes the integral of the interpolated samples. Any processing performed between the derivative and integrator blocks effectively provides an additional order of interpolation. High frequency noise (i.e. dithering) is added to the differentiated samples in order to eliminate the spectral regrowth spurs that would otherwise appear in the output after rounding. Delay alignment is performed on the differentiated samples in order to time align both phase / frequency and amplitude samples that are processed on different paths.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Single-image super-resolution reconstruction method based on deep residual network
InactiveCN107358575AImprove rebuild speedAchieving continuous scalingGeometric image transformationReconstruction methodImage compression
The invention discloses a single-image super-resolution reconstruction method based on a deep residual network. The method of the invention mainly comprises a first step of performing block extraction and pixel averaging processing on an image in a sample image database to obtain a corresponding high resolution and low resolution training image sets; a second step of constructing a deep convolutional neutral network with a residual structure for iterative training, and then inputting the training set obtained in the first step to the neural network constructed in the second step for iterative training; and a third step of according to a data model obtained by training, realizing the continuous up-scaling of the input low resolution image through the combination of iterative operation and an interpolation algorithm. By introducing a deep residual network and introducing an upsampling layer at the end of the network, the method of the invention accelerates the processing speed of the image up-scaling, enhances the display effect of the image details, obtains a better image super-resolution reconstruction effect, and has a wide range of applications in the image high definition display, image compression, security checks and other fields.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
System and method for image upsampling using natural image statistics of first and second derivatives
ActiveUS8369653B1Simple and efficient to implementEfficient to implementGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsProgram instruction
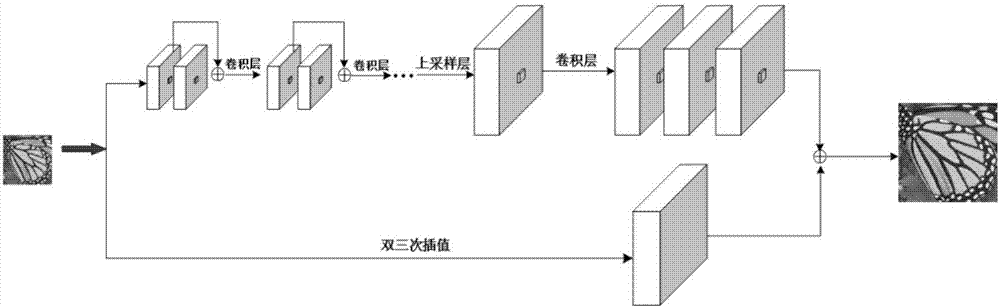
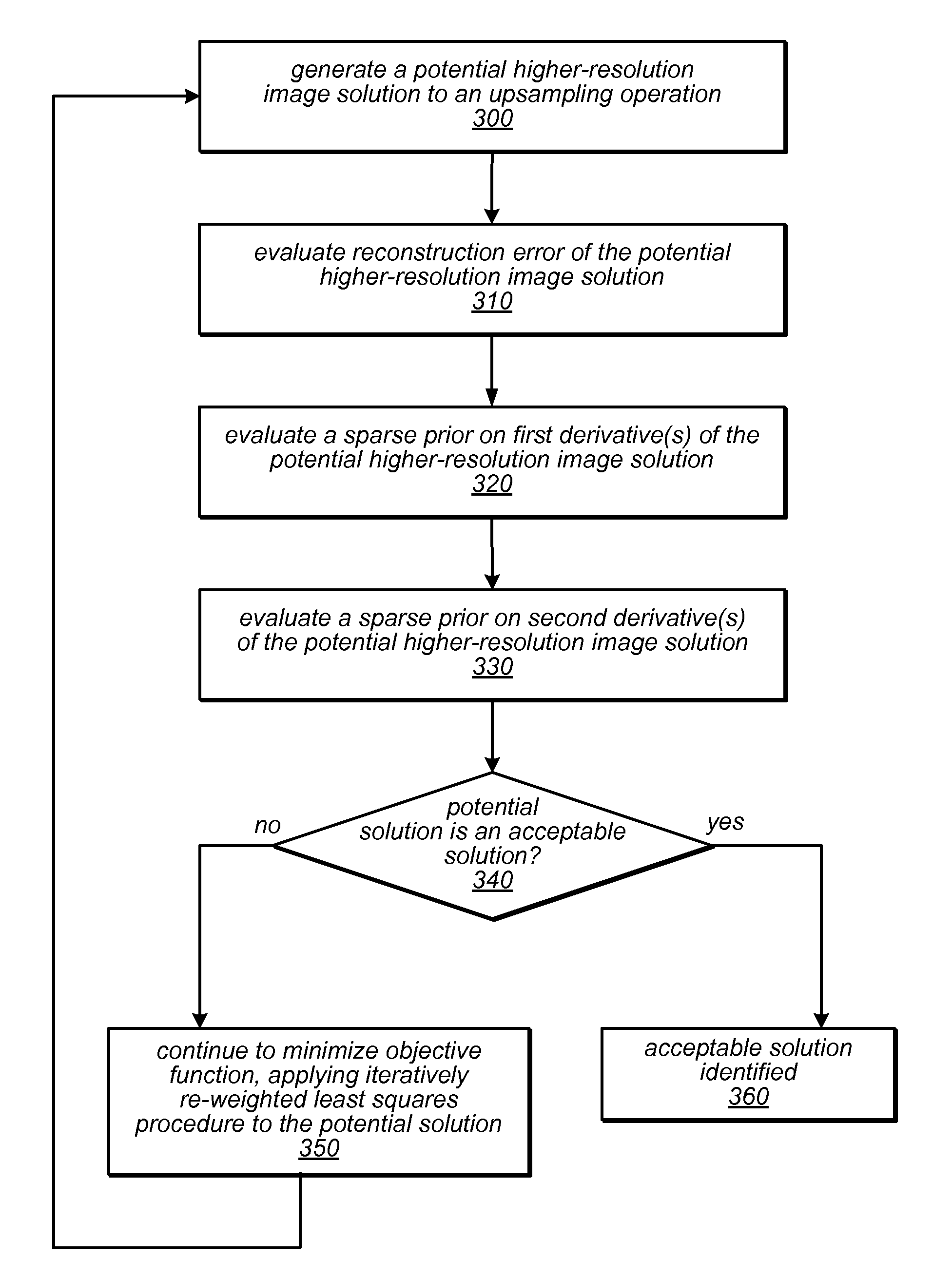
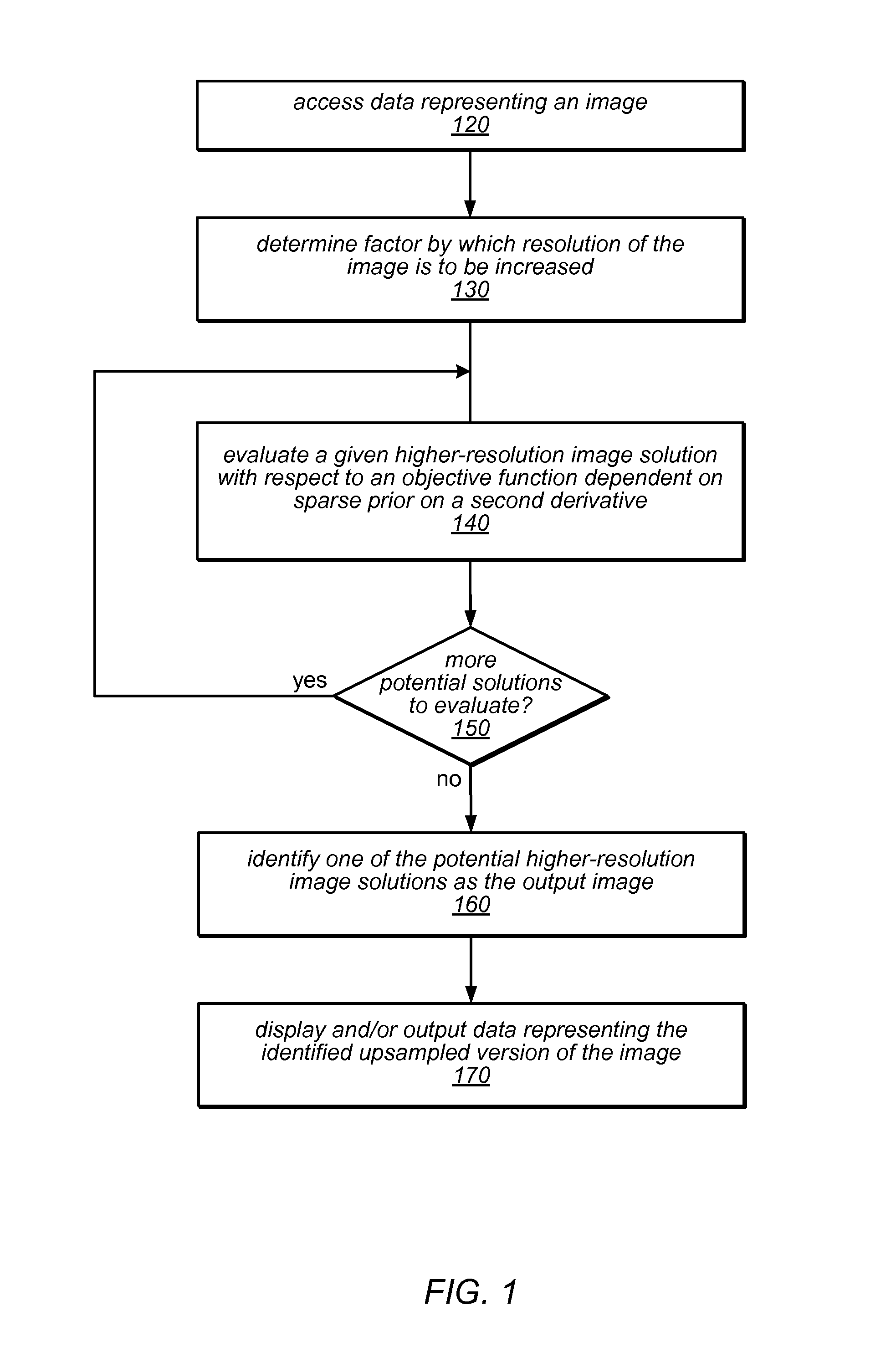
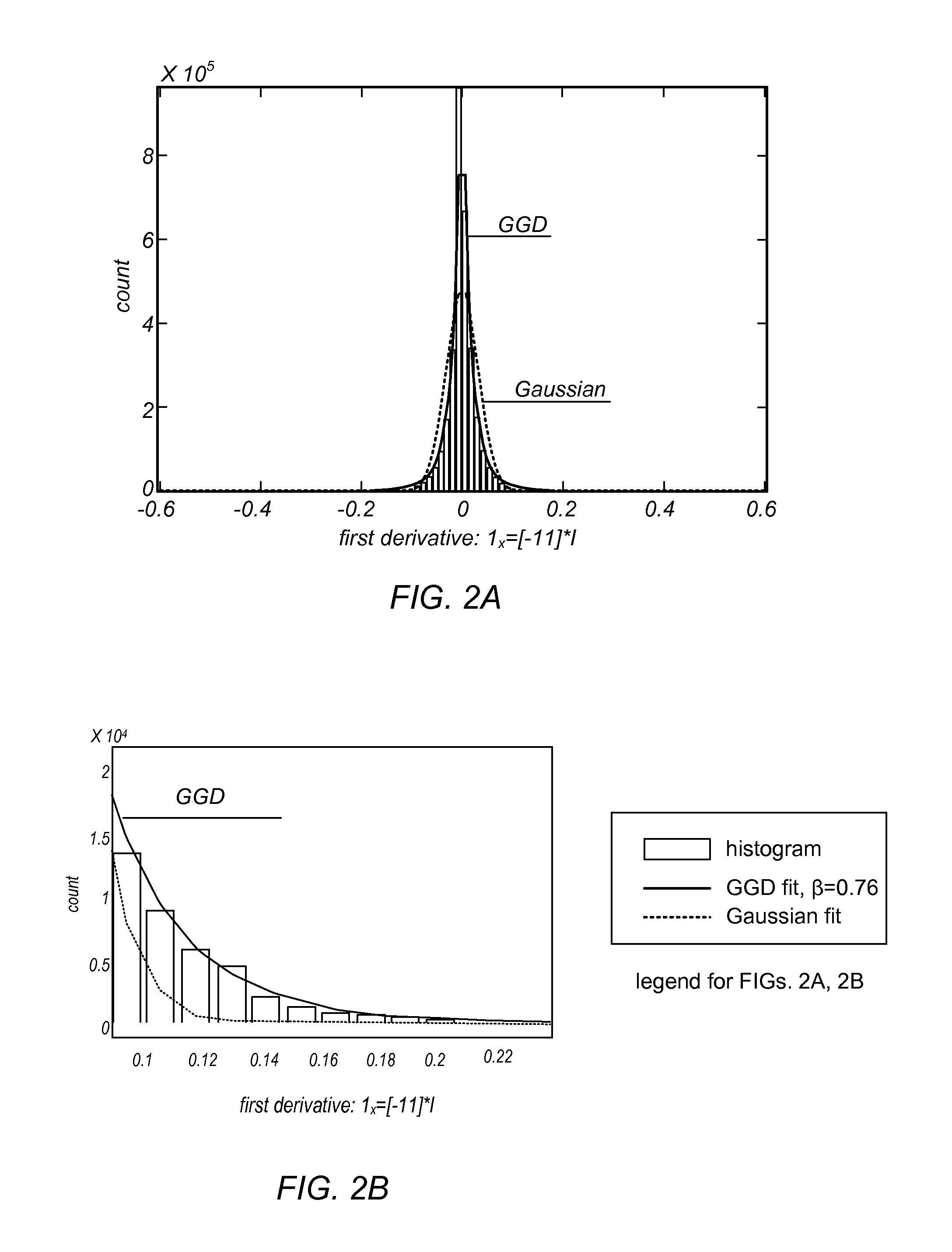
Systems and methods for upsampling input images may evaluate potential upsampling solutions with respect to an objective function that is dependent on a sparse derivative prior on second derivative(s) of the potential upsampling solutions to identify an acceptable higher-resolution output image. The objective function may also be dependent on fidelity term(s) and / or sparse derivative prior(s) on first derivative(s) of potential upsampling solutions. The methods may include applying the iteratively re-weighted least squares procedure in minimizing the objective function and generating improved candidate solutions from an initial solution. The identified solution may be stored as a higher-resolution version of the input image in memory, and made available to subsequent operations in an image editing application or other graphics application. The methods may produce sharp results that are also smooth along edges. The methods may be implemented as program instructions stored on computer-readable storage media, executable by a CPU and / or GPU.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
Joint bilateral upsampling
InactiveUS7889949B2Solve excessive overheadGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmImage resolution
A “Joint Bilateral Upsampler” uses a high-resolution input signal to guide the interpolation of a low-resolution solution set (derived from a downsampled version of the input signal) from low-to high-resolution. The resulting high-resolution solution set is then saved or applied to the original input signal to produce a high-resolution output signal. The high-resolution solution set is close to what would be produced directly from the input signal without downsampling. However, since the high-resolution solution set is constructed in part from a downsampled version of the input signal, it is computed using significantly less computational overhead and memory than a solution set computed directly from a high-resolution signal. Consequently, the Joint Bilateral Upsampler is advantageous for use in near real-time operations, in applications where user wait times are important, and in systems where computational costs and available memory are limited.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
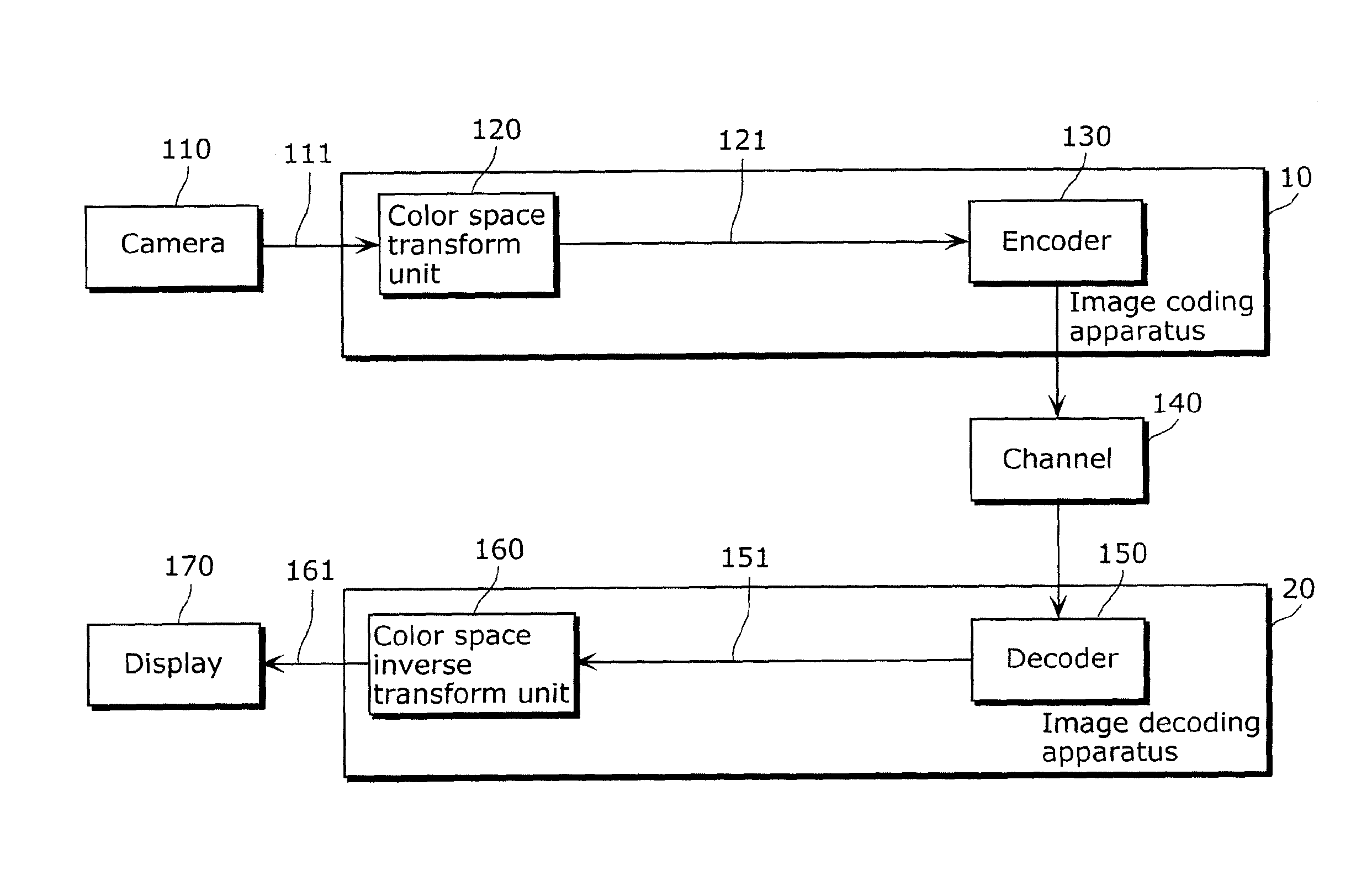
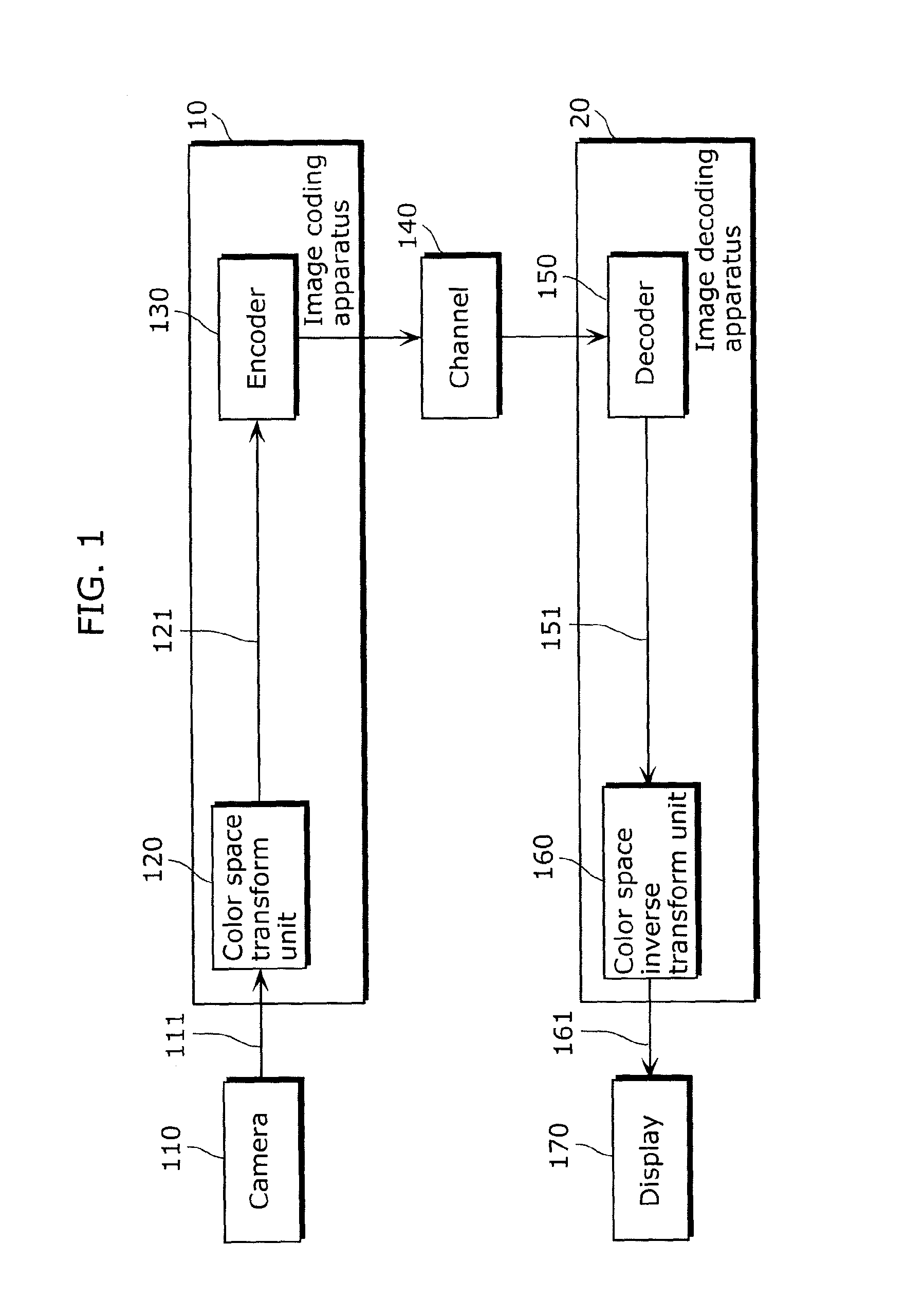
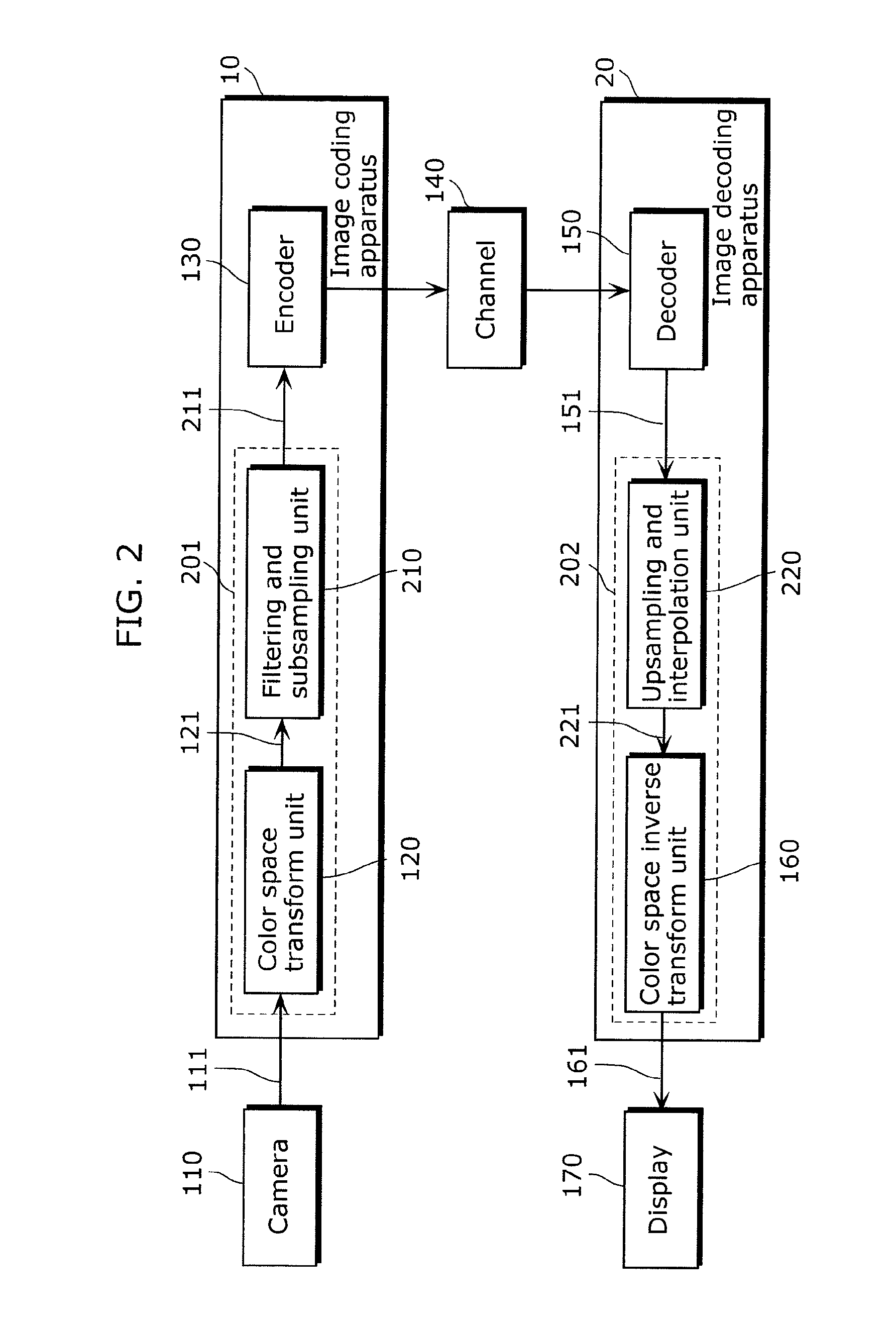
Image coding method, image decoding method, image coding apparatus, image decoding apparatus, program and integrated circuit
InactiveUS20100208989A1Quality improvementKeeping the decoding apparatus less complexCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationDecoding methodsColor image
An image coding method includes transforming a color space of a color image from a first color space to a second color space to generate a color space transformed color image (S12), removing part of samples included in the color space transformed color image to generate a subsampled color image (S13), coding the subsampled color image to generate a coded color image (S14), determining an upsampling coefficient used for upsampling (S16), determining a color space inverse transform coefficient for inversely transforming the color space from the second color space to the first color space (S17), and outputting the coded color image, the upsampling coefficient, and the color space inverse transform coefficient (S19).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
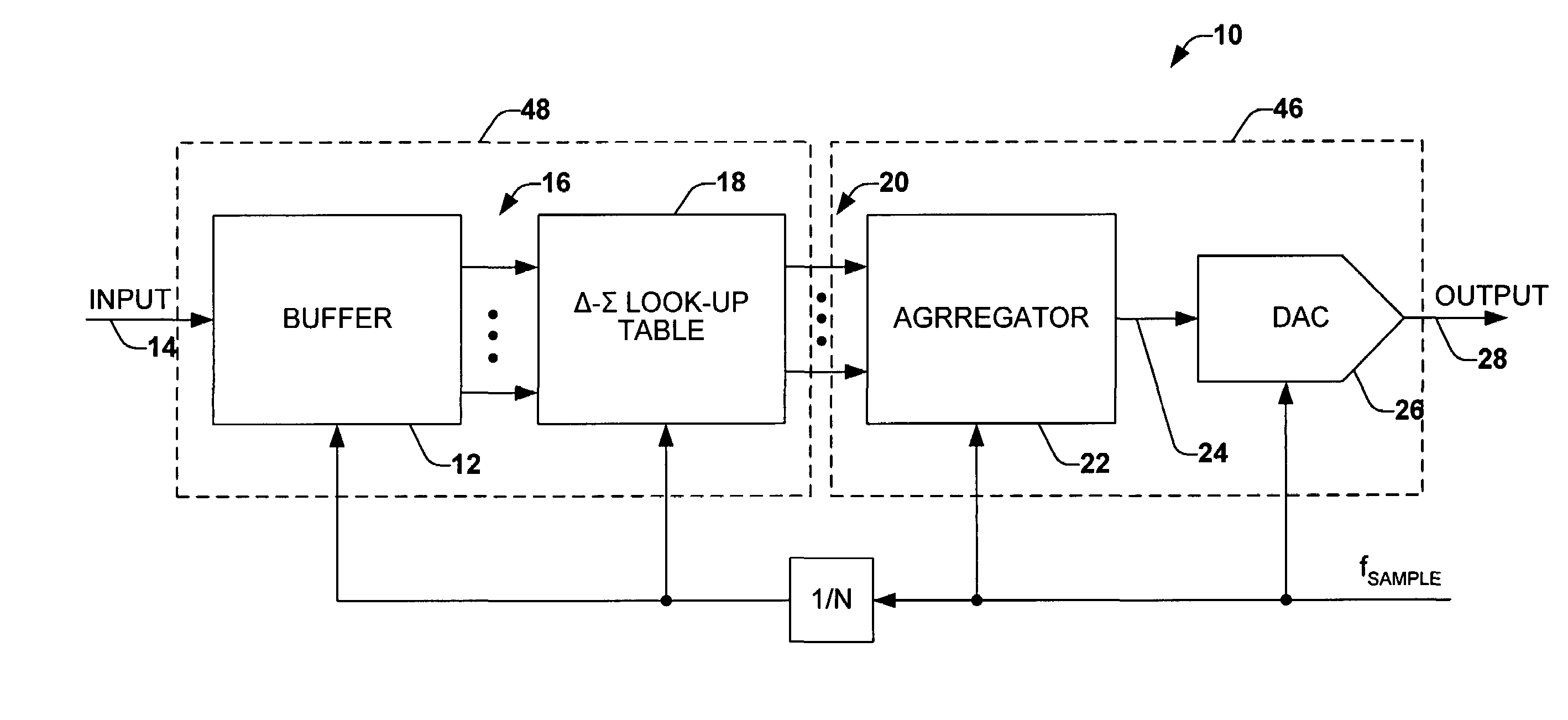
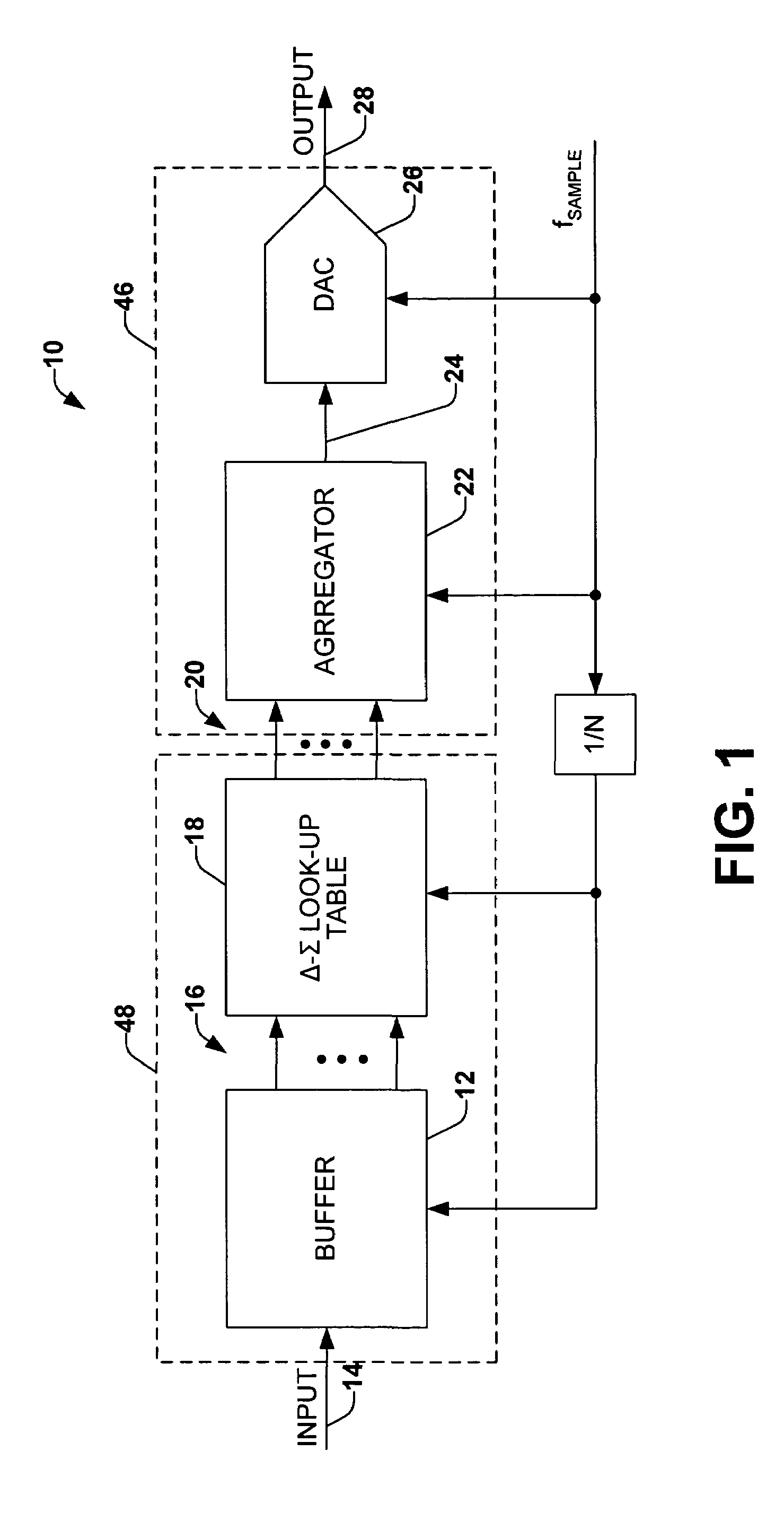
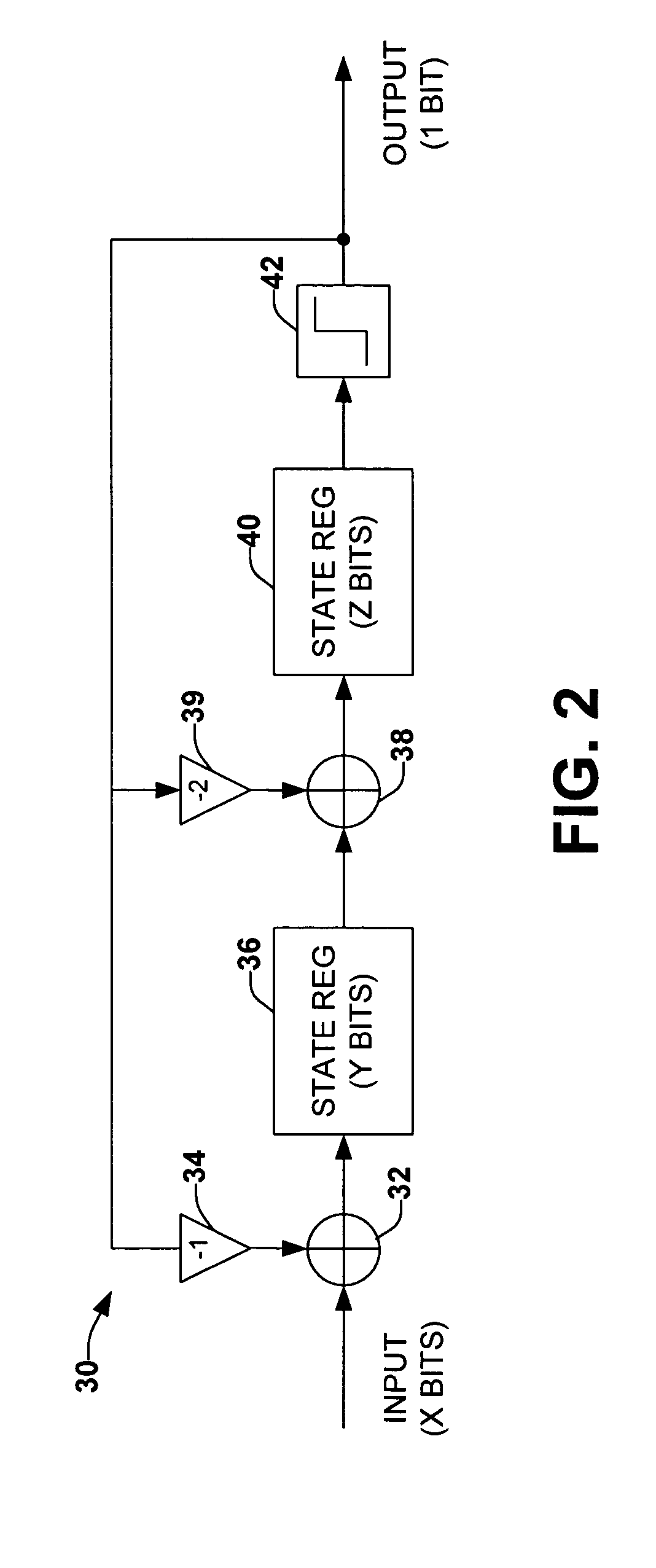
Look-up table delta-sigma conversion
Signal conversion is implemented employing a memory system operating as a look-up table that stores a plurality of sets of output samples associated with each of a plurality of respective input samples. The look-up table thus can generate a corresponding set of output samples in response to a given input sample, thereby emulating desired digital upsampling and delta-sigma modulation. The output samples can be aggregated, such as by multiplexing, to provide an output data stream at a desired sample rate.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
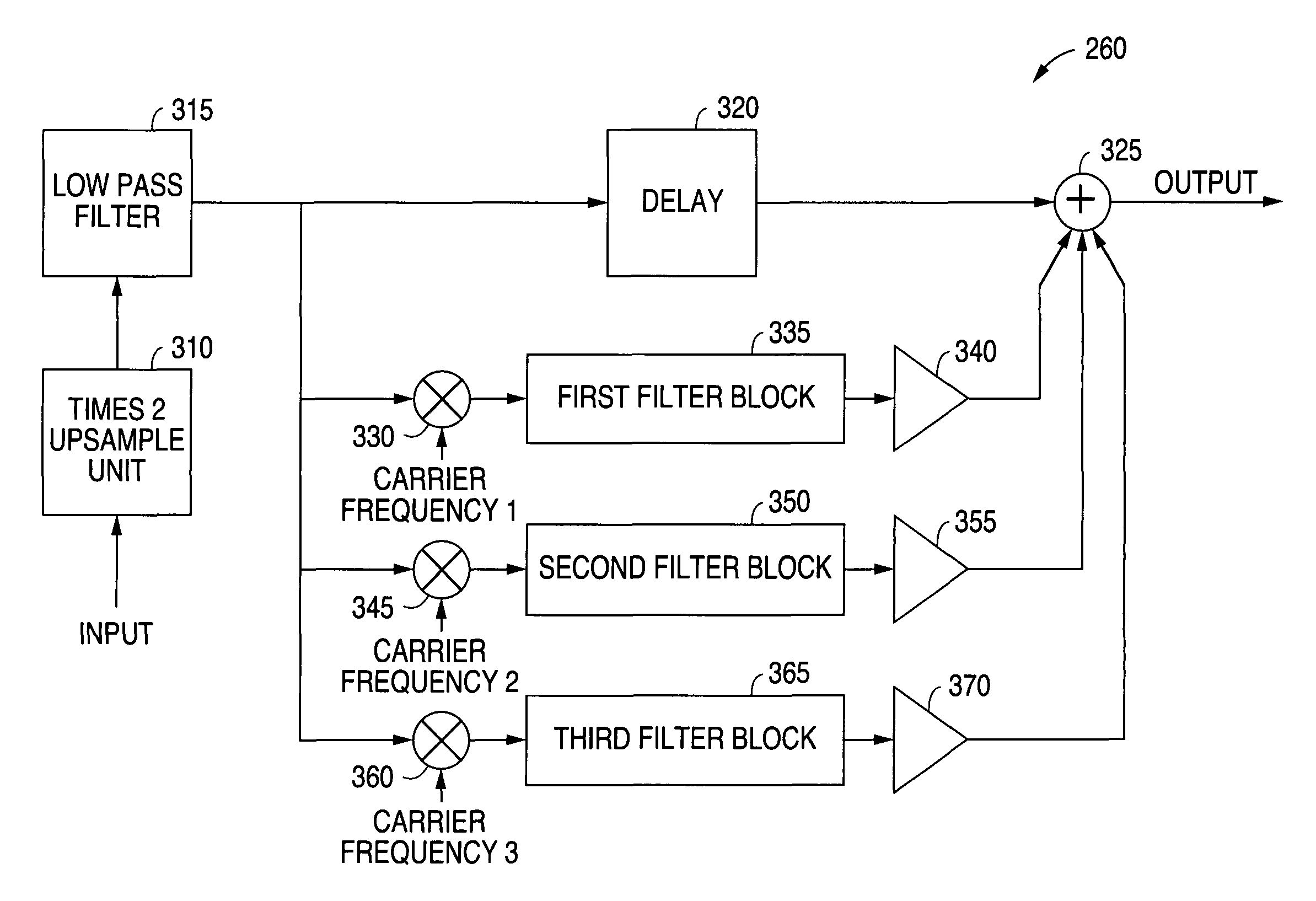
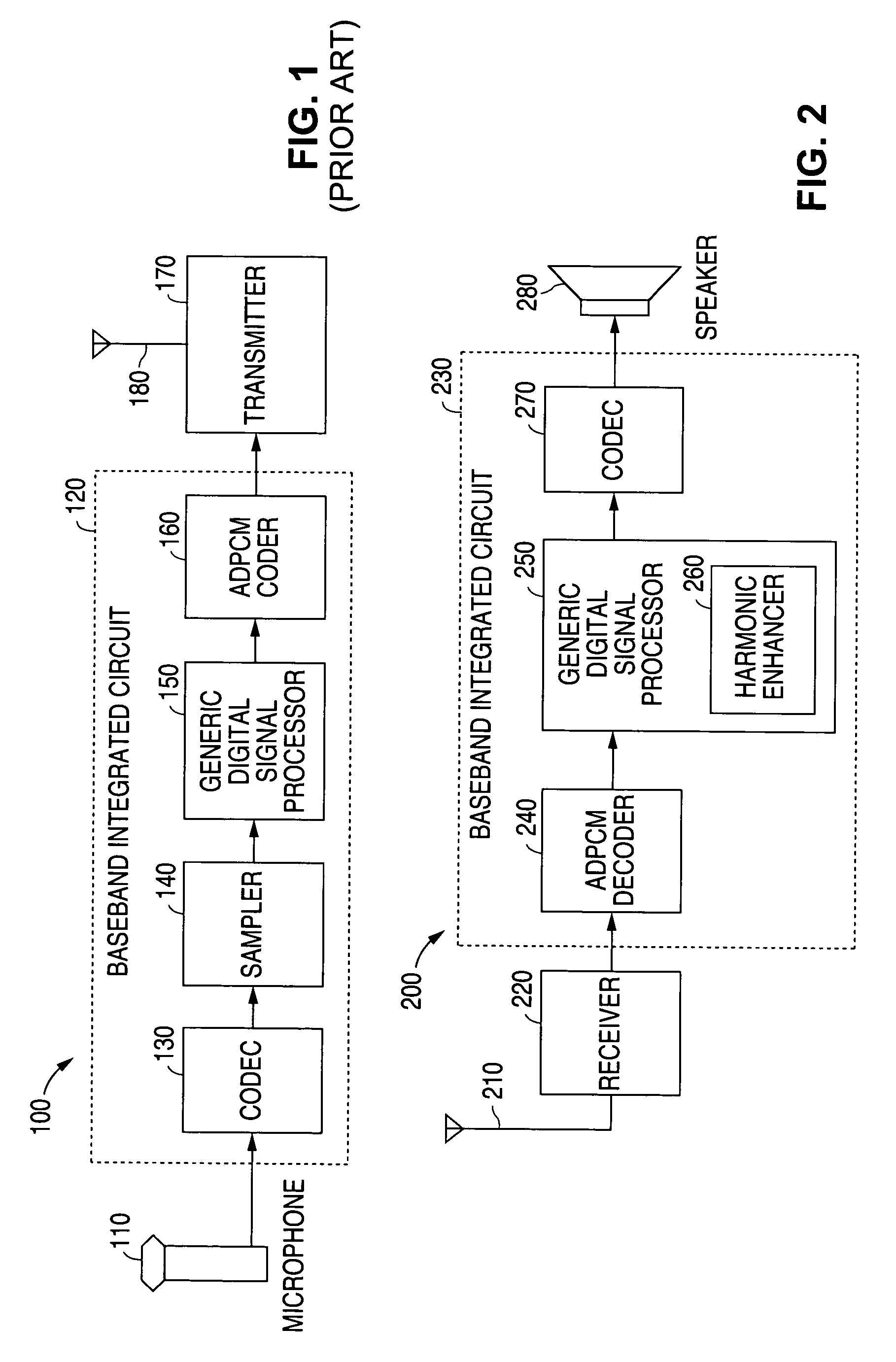
System and method for reconstructing high frequency components in upsampled audio signals using modulation and aliasing techniques
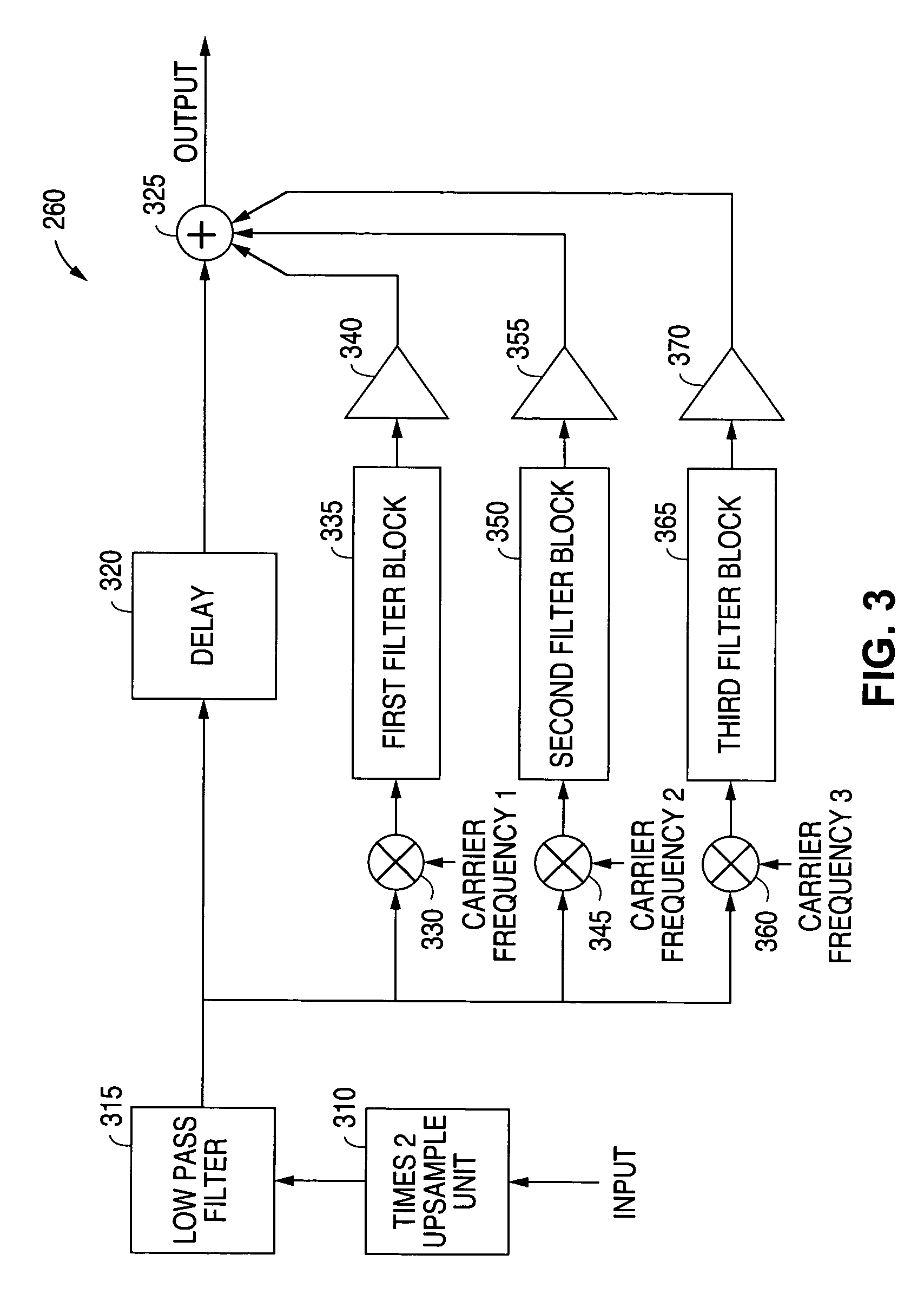
ActiveUS7916876B1Improve voice qualityHigh bandwidthElectrophonic musical instrumentsGain controlFrequency spectrumCarrier signal
A system and method is disclosed for reconstructing high frequency components of a digital audio signal using a harmonic enhancer in a baseband integrated circuit of a receiver handset. The original spectrum of the digital audio signal is upsampled in a times two (2) upsample unit to double the size of the bandwidth. A low pass filter then removes a high frequency alias of the original spectrum. The spectrum is then modulated with a first carrier frequency and sent to a first filter bank where a low pass filter and a high pass filter shape the modulated harmonic spectrum. After gain adjustment, the modulated harmonic spectrum is added to a delayed version of the original spectrum. Additional harmonic spectra are similarly created at other carrier frequencies and added to the audio output spectra to reconstruct high frequency components of the audio signal.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR BV
Chroma upsampling method and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20050030422A1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsDigital videoComputer graphics (images)
A unique method for chroma vertical upsampling used, for example, for conversion of the “4:2:0” format chroma information used in many applications of digital video, to the “4:2:2” or “4:4:4” format, is presented. This conversion is required so that video encoders can effect the display of this chroma information with a minimum of visible artifacts. The present invention carries out chroma vertical upsampling on a pixel by pixel basis. This chroma vertical upsampling is performed as a function of the amount of motion associated with each pixel as detected between 2 or more fields, and the field, frame and progressive sequence characteristics of the incoming video signal data.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
System and method for occluding contour detection
ActiveUS10067509B1Efficient amplificationImprove segmentationMathematical modelsImage analysisSystems approachesConvolution
A system method for occluding contour detection using a fully convolutional neural network is disclosed. A particular embodiment includes: receiving an input image; producing a feature map from the input image by semantic segmentation; applying a Dense Upsampling Convolution (DUC) operation on the feature map to produce contour information of objects and object instances detected in the input image; and applying the contour information onto the input image.
Owner:TUSIMPLE INC
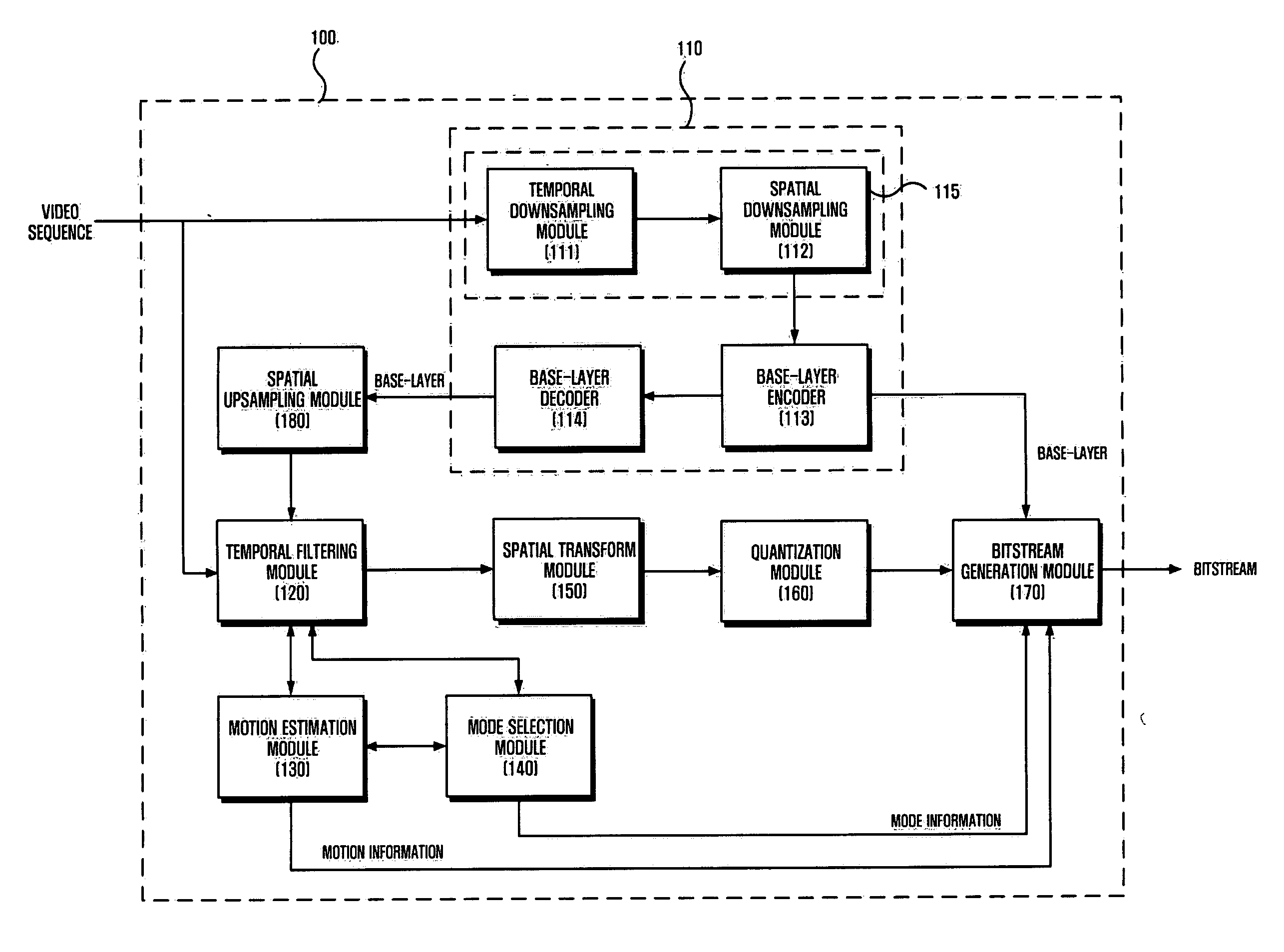
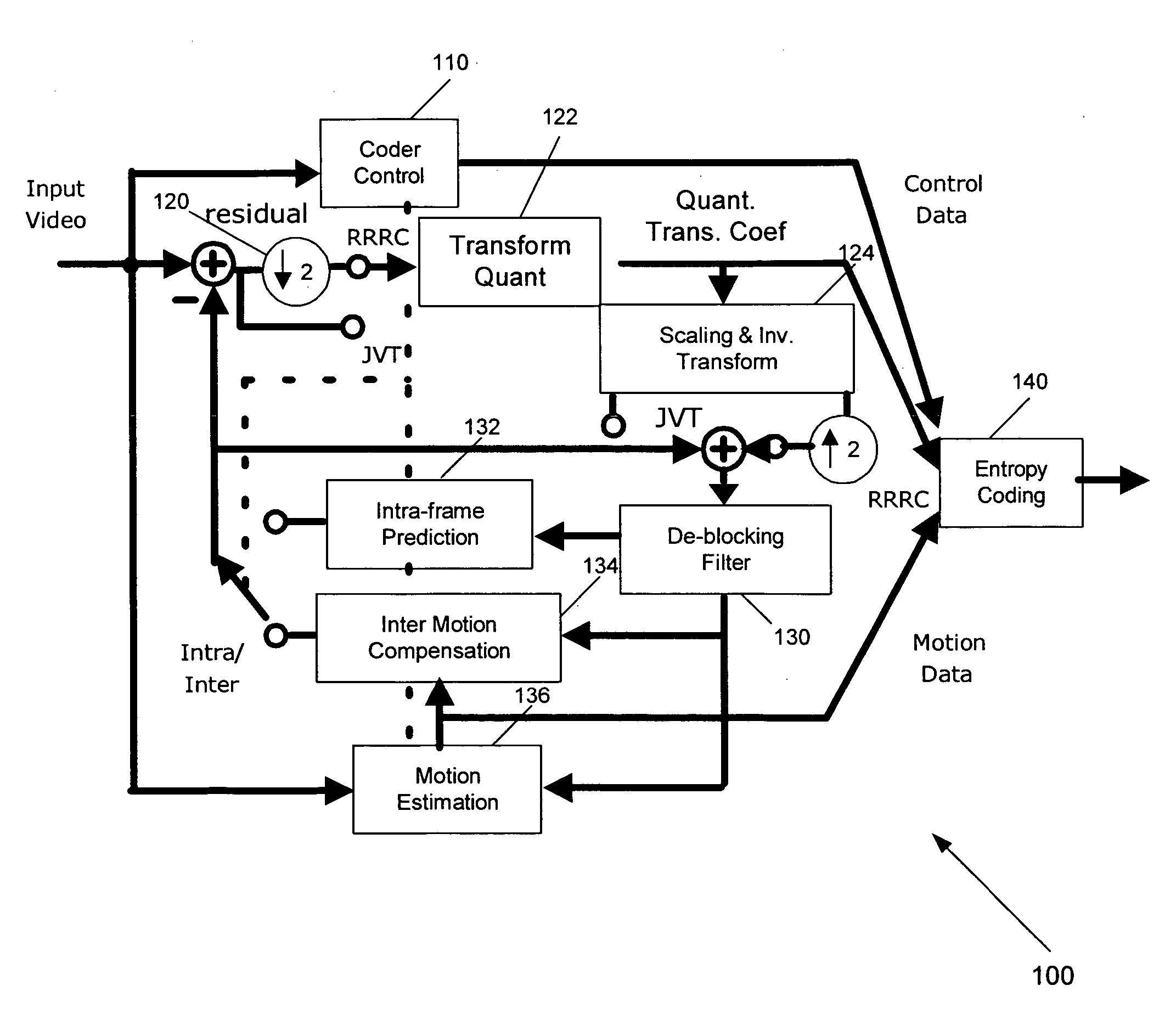
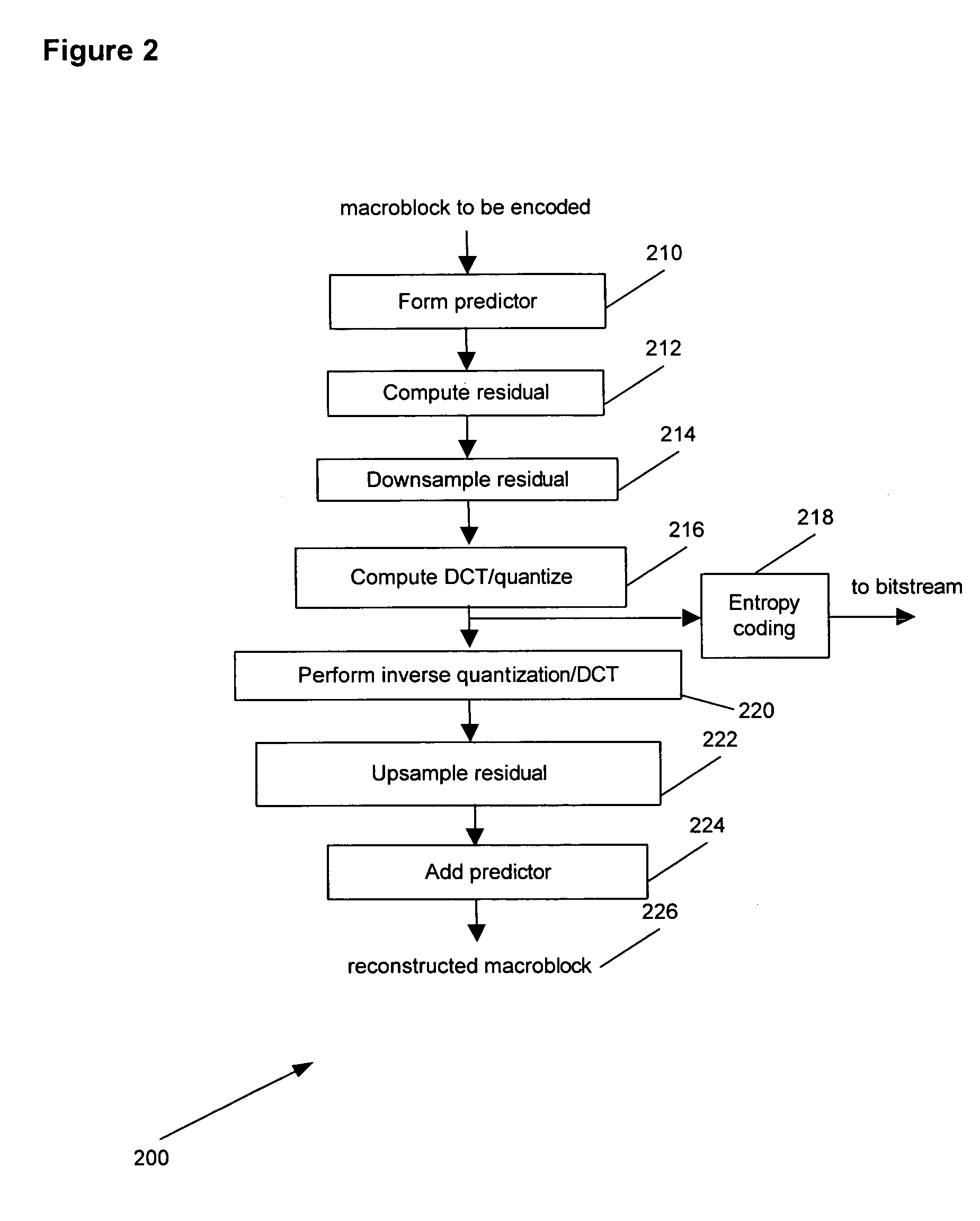
Macro-block based mixed resolution video compression system
InactiveUS20060245502A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionSignal on
A system and method of compressing a video signal can include the steps of: receiving a video signal, the video signal including frames; analyzing, for each frame, the video signal on a macroblock-by-macroblock level; determining whether to downsample a macroblock residual for each of the macroblocks; selectively downsampling a macroblock residual for some of the macroblocks; and coding the macroblocks. A system and method of decompressing a video signal can include the steps of receiving a compressed video signal, the video signal including frames; analyzing, for each frame, the video signal on a macroblock-by-macroblock level; determining whether to upsample a macroblock residual for each of the macroblocks; selectively upsampling a macroblock residual for some of the macroblocks; and decoding the macroblocks.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
System and method for occluding contour detection
ActiveUS20180259970A1Efficient amplificationImprove segmentationMathematical modelsAutonomous decision making processSystems approachesComputer science
A system method for occluding contour detection using a fully convolutional neural network is disclosed. A particular embodiment includes: receiving an input image; producing a feature map from the input image by semantic segmentation; applying a Dense Upsampling Convolution (DUC) operation on the feature map to produce contour information of objects and object instances detected in the input image; and applying the contour information onto the input image.
Owner:TUSIMPLE INC
Remote sensing image semantic segmentation method based on migration VGG network
ActiveCN110059772AGood segmentation effectShort training timeCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesPattern recognitionNerve network
The invention discloses a remote sensing image semantic segmentation technology based on a VGG network. The method comprises the following steps: 1, randomly cutting the high-resolution remote sensingimage for training and the corresponding label image into small images; dividing the network structure into an encoding part and a decoding part; adopting the depooling path and the deconvolution path to double the resolution of the coded information; carrying out channel connection on a characteristic image and a result of cavity convolution, recovering the characteristic image to an original size through deconvolution upsampling, inputting an output label image into a PPB module for multi-scale aggregation processing, and finally, updating network parameters in a random gradient descent mode by taking cross entropy as a loss function; inputting the small images formed by sequentially cutting the test images into a neural network to predict corresponding label images, and splicing the label images into an original size. According to the technical scheme, the segmentation precision of the model is improved, the complexity of the network is reduced, and the training time is saved.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
Single image super-resolution reconstruction method combining depth learning and gradient transformation
ActiveCN106204489AAdvantages of subjective visual effectsHigh objective evaluation parameter valueImage enhancementImage analysisFine structureReconstruction method
The invention discloses a single image super-resolution reconstruction method combining depth learning and gradient transformation. The method comprises the steps that a super-resolution method based on depth learning is used to carry out upsampling on an input low-resolution image to acquire an upsampling image; a gradient operator is used to carry out gradient-extracting on the upsampling image; a depth convolutional neural network is used to convert extracted gradient; a cost function is reconstructed by using the input low-resolution image and the converted gradient as constraints; a gradient descent method is used to optimize the reconstructed cost function to acquire a final output high-resolution image. According to the single image super-resolution reconstruction method provided by the invention, the reconstructed image has a fine structure in the subjective visual effect, is free of artificial effect, and has a high objective evaluation parameter value. The invention provides the effective single image super-resolution reconstruction method.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
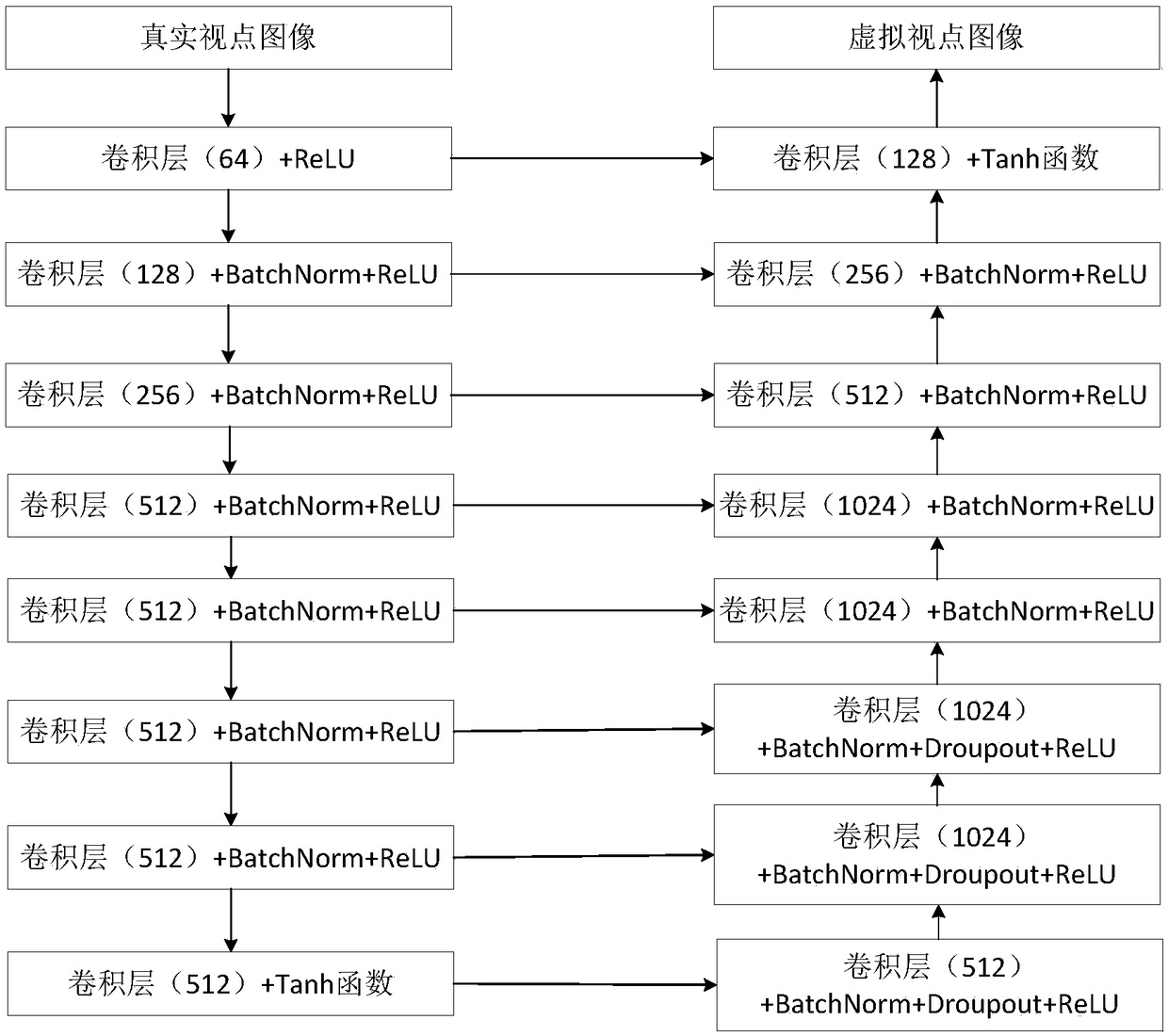
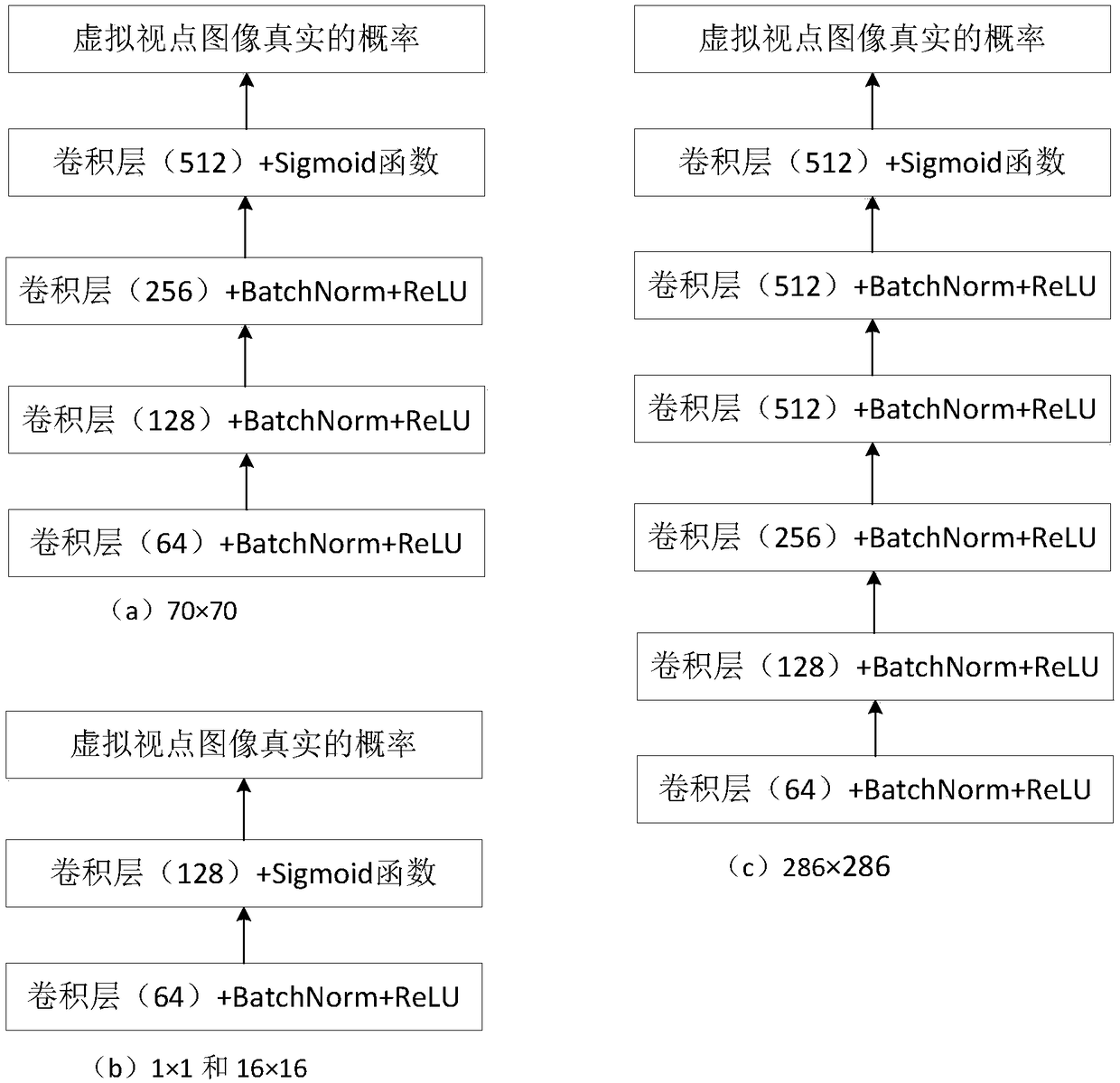
Virtual viewpoint image generation method based on generation type confrontation network
The invention relates to a virtual viewpoint image generation method based on a generation type confrontation network. The method comprises the following steps: first step, making a data set: obtaining an image pair necessary for training the generation type confrontation network; constructing a model: the structures used by a generator and a discriminator are that batch normalization layers BatchNorm and nonlinear operation unit ReLU activation functions are connected behind convolutional layers, all convolutional layers use a 4*4 convolution kernel size, the step size is set as 2, the lengthand width are both reduced to a half of the original length and width when downsampling is performed on a feature image, the length and width are both amplified to twice of the original length and width during upsampling, and a Dropout layer sets a Dropout rate as 50%; the RelU activation function is LeakyReLu; defining the loss; and training and testing the model.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Instance segmentation method and device based on feature attention and sub-upsampling
ActiveCN110532955AImprove effectivenessImprove accuracyBiometric pattern recognitionNeural architecturesFeature vectorFeature based
The invention discloses an instance segmentation method based on feature attention and sub-upsampling. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a to-be-segmented original image; extracting a feature map from the original image through a feature global network, and determining a region of interest in the feature map, the feature global network comprising an attention module; aligning and extracting a region of interest from the feature map; and classifying the extracted regions of interest, and generating segmentation masks for the extracted regions of interest by utilizing sub-pixel up-sampling so as to realize instance segmentation of the original image. The method has the advantages that the attention module is added when the feature map is extracted; according to the embodiment of the invention, redundant information and fusion information can be deleted by applying channel transformation after maximum pooling and average pooling operations, the effectiveness of an image featurevector is improved. Meanwhile, the accuracy of segmentation and detection in instance segmentation is improved under the condition of not reducing the speed in combination with a sub-pixel up-samplingmode, and the occupied memory is not increased.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
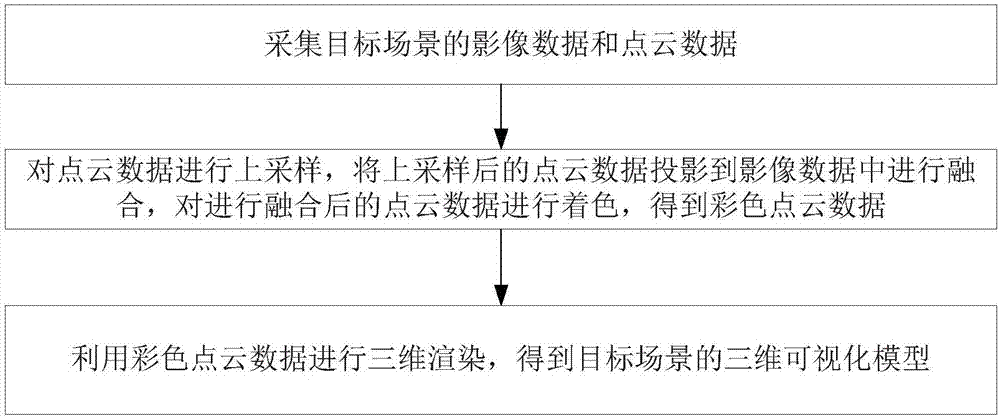
Three-dimensional visualization method based on point cloud and image data and system thereof
ActiveCN107194983AHigh resolutionIncrease profitImage enhancementImage analysisPoint cloudData acquisition
The invention discloses a three-dimensional visualization method based on point cloud and image data and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps of collecting image data and point cloud data of a target scene; carrying out upsampling on the point cloud data, projecting the point cloud data after the upsampling to the image data so as to carry out fusion, coloring the fused point cloud data and acquiring the colorful point cloud data; and using the colorful point cloud data to carry out three-dimensional rendering and acquiring a three-dimensional visualization model of the target scene. In the invention, point-cloud three-dimensional visualization from data acquisition and fusion to final rendering display is realized, which is good for development of a laser point cloud technology; and accessibility and usability of the point cloud data to a common user are increased.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Efficient asynchronous sample rate conversion
ActiveUS8369973B2Improve efficiencyRecalculation of filter coefficients is minimizedDigital technique networkCode conversionSample rate conversionComputer science
Asynchronous sample rate conversion for use in a digital audio receiver is disclosed. Different algorithms are applied for the upsampling and downsampling cases. In the upsampling case, the input signal is upsampled and filtered, before the application of a finite impulse response (FIR) filter. In the downsampling case, the input signal is filtered by an FIR filter, and then filtered and downsampled. The FIR coefficients of the fractional delay FIR filter are calculated by evaluation of polynomial expressions over intervals of the filter impulse response, at times corresponding to the input sample points.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com