Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
308 results about "Hematocrit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The hematocrit (/hɪˈmætəkrɪt/) (Ht or HCT), also known by several other names, is a blood test that measures the volume percentage (vol%) of red blood cells (RBC) in blood. The measurement depends on the number and size of red bloods cells. It is normally 40.7% to 50.3% for men and 36.1% to 44.3% for women. It is a part of a person's complete blood count results, along with hemoglobin concentration, white blood cell count, and platelet count. Because the purpose of red blood cells is to transfer oxygen from the lungs to body tissues, a blood sample's hematocrit—the red blood cell volume percentage—can become a point of reference of its capability of delivering oxygen. Hematocrit levels that are too high or too low can indicate a blood disorder, dehydration, or other medical conditions. An abnormally low hematocrit may suggest anemia, a decrease in the total amount of red blood cells, while an abnormally high hematocrit is called polycythemia. Both are potentially life-threatening disorders.
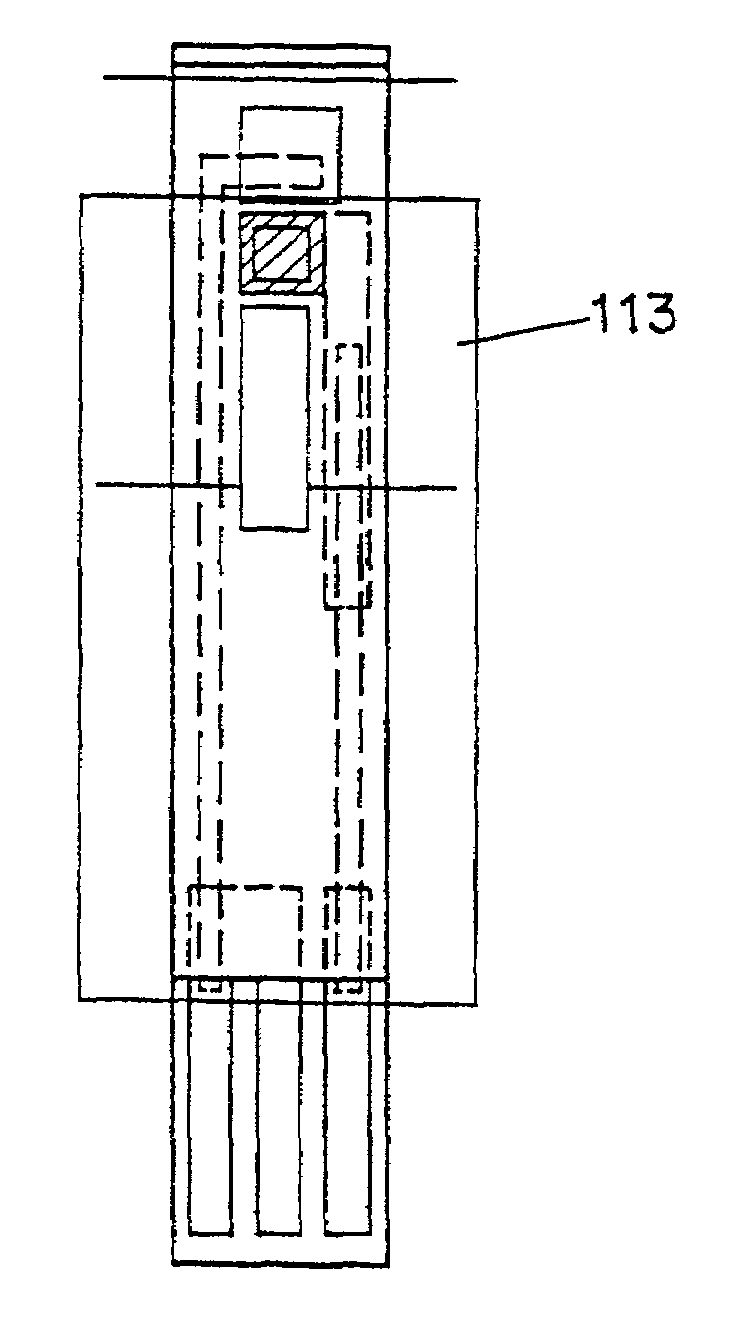
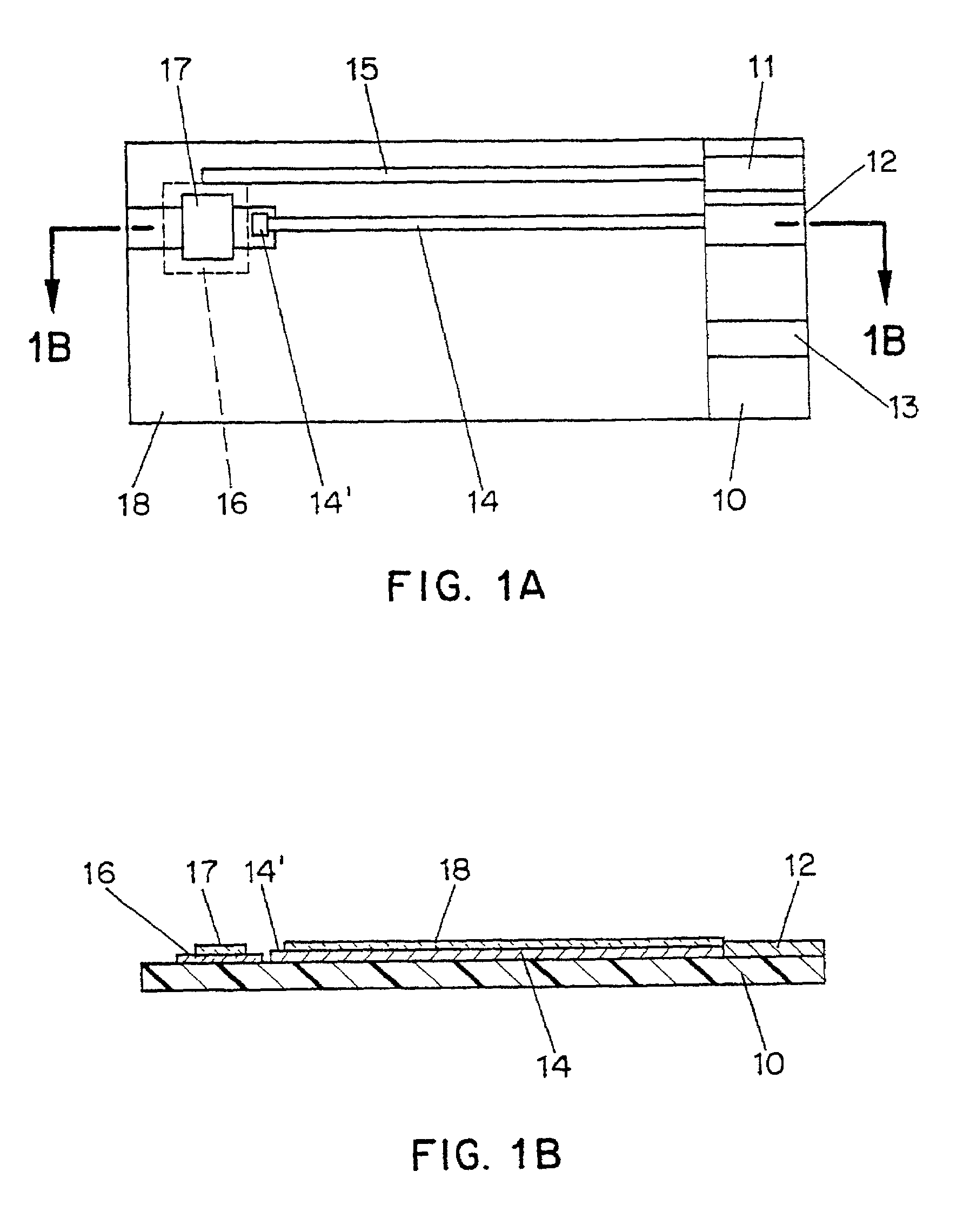
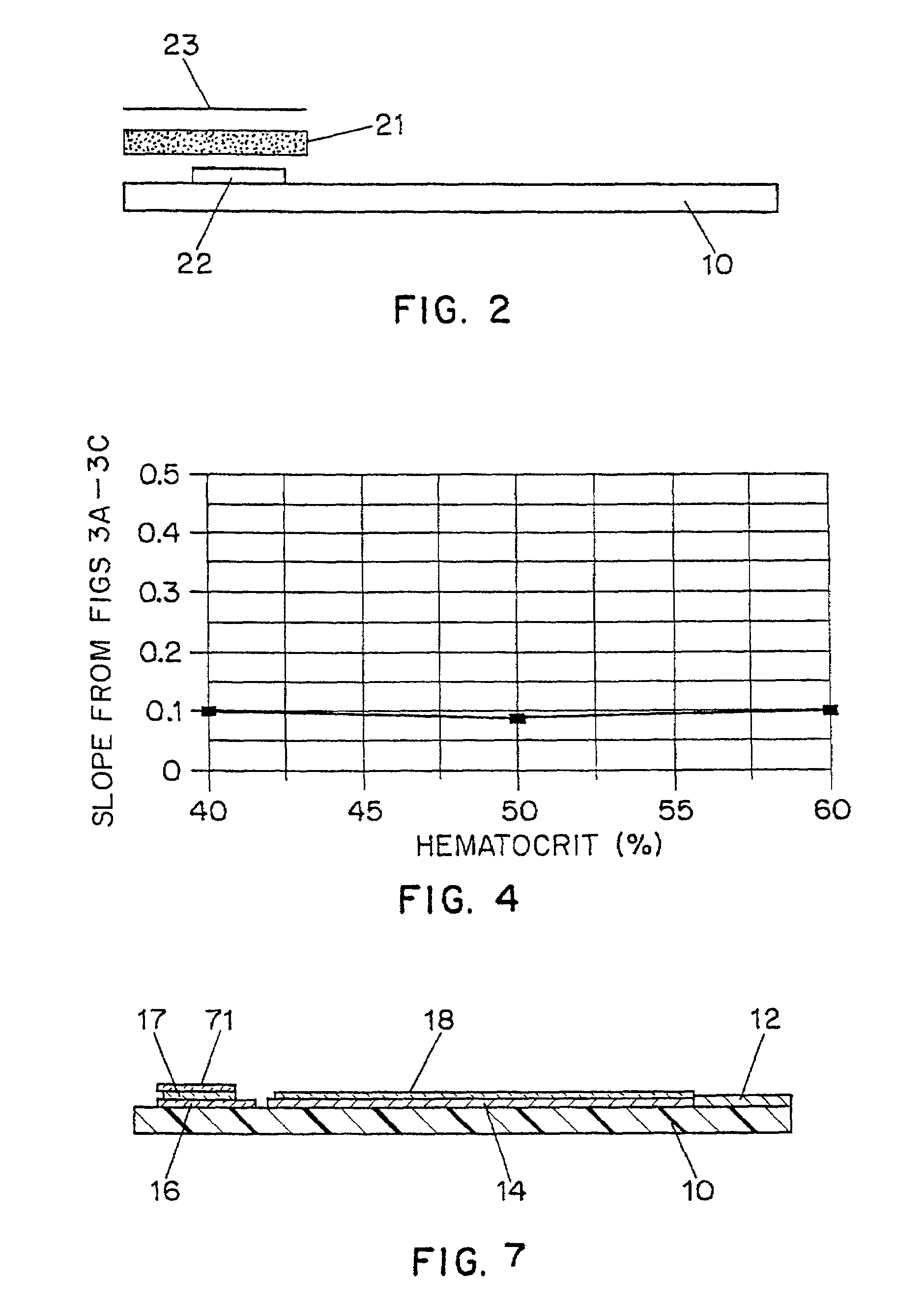
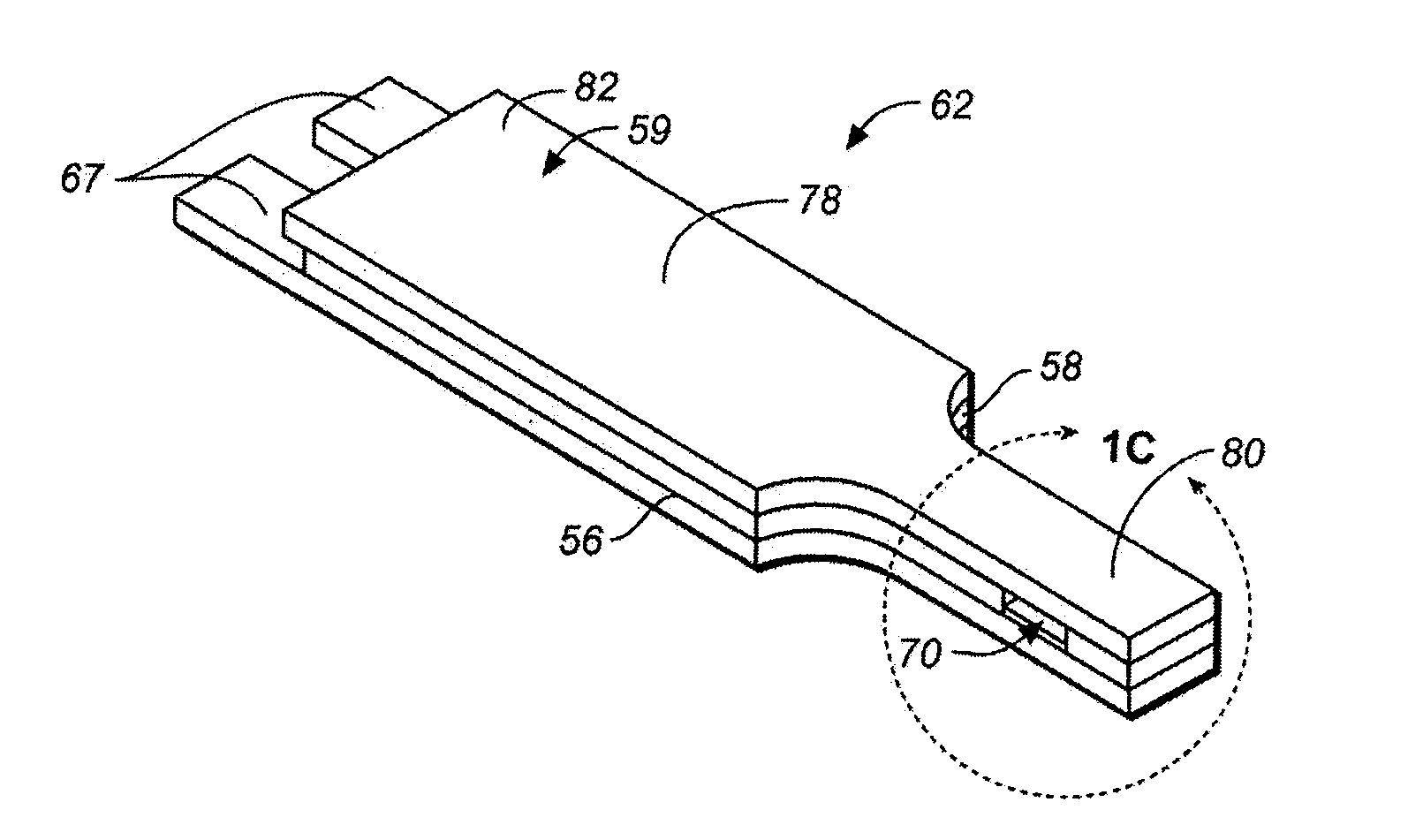
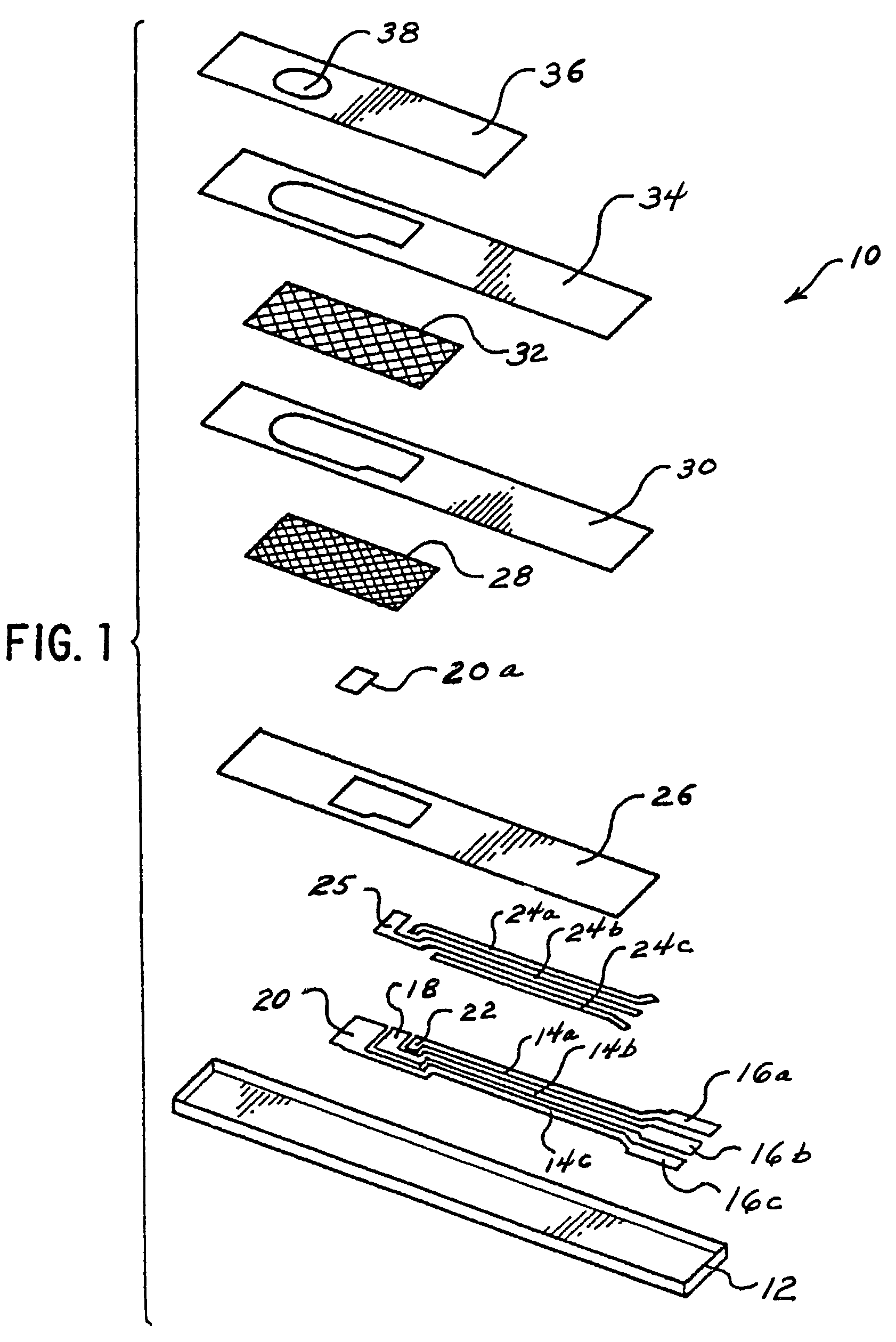
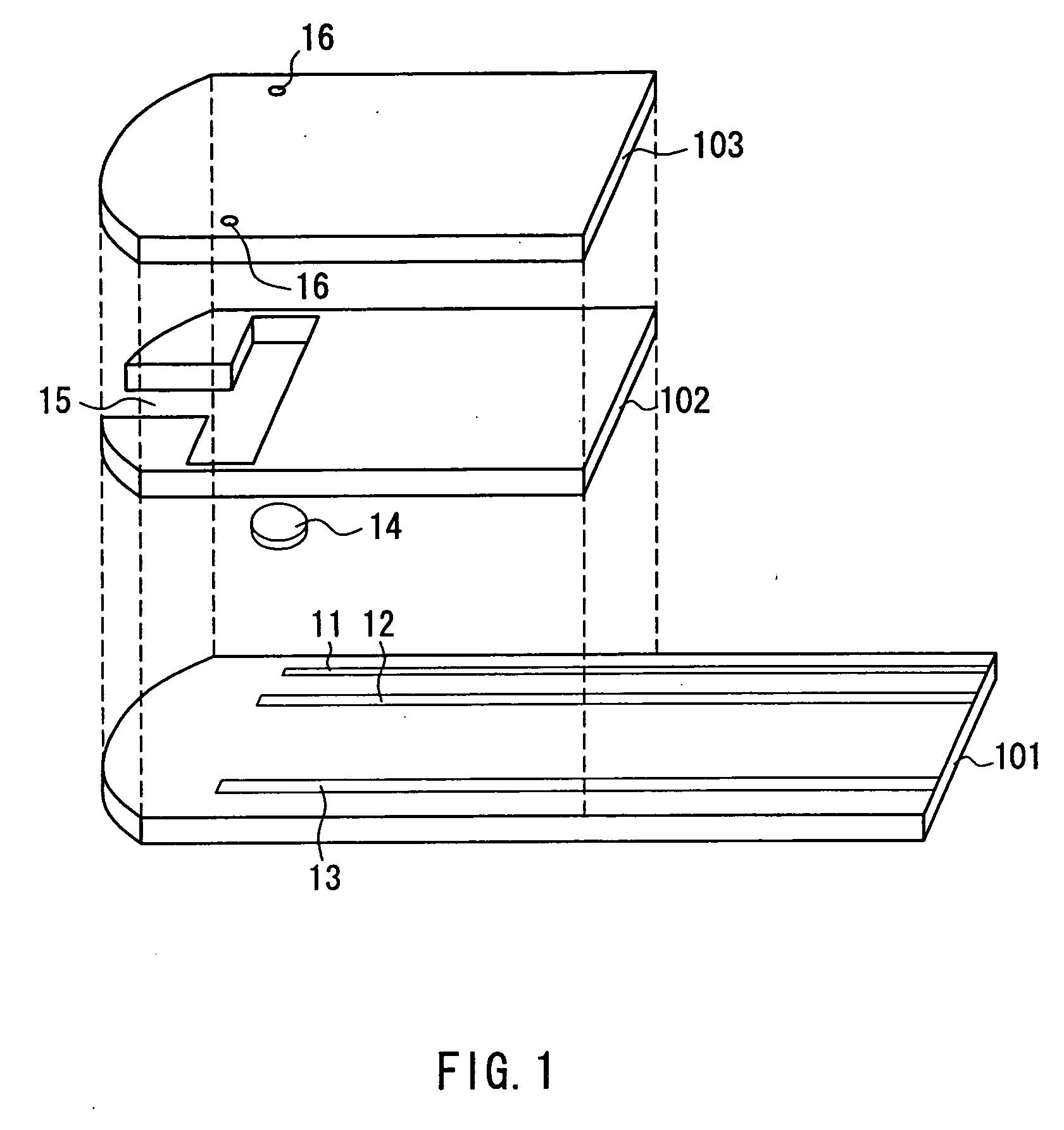
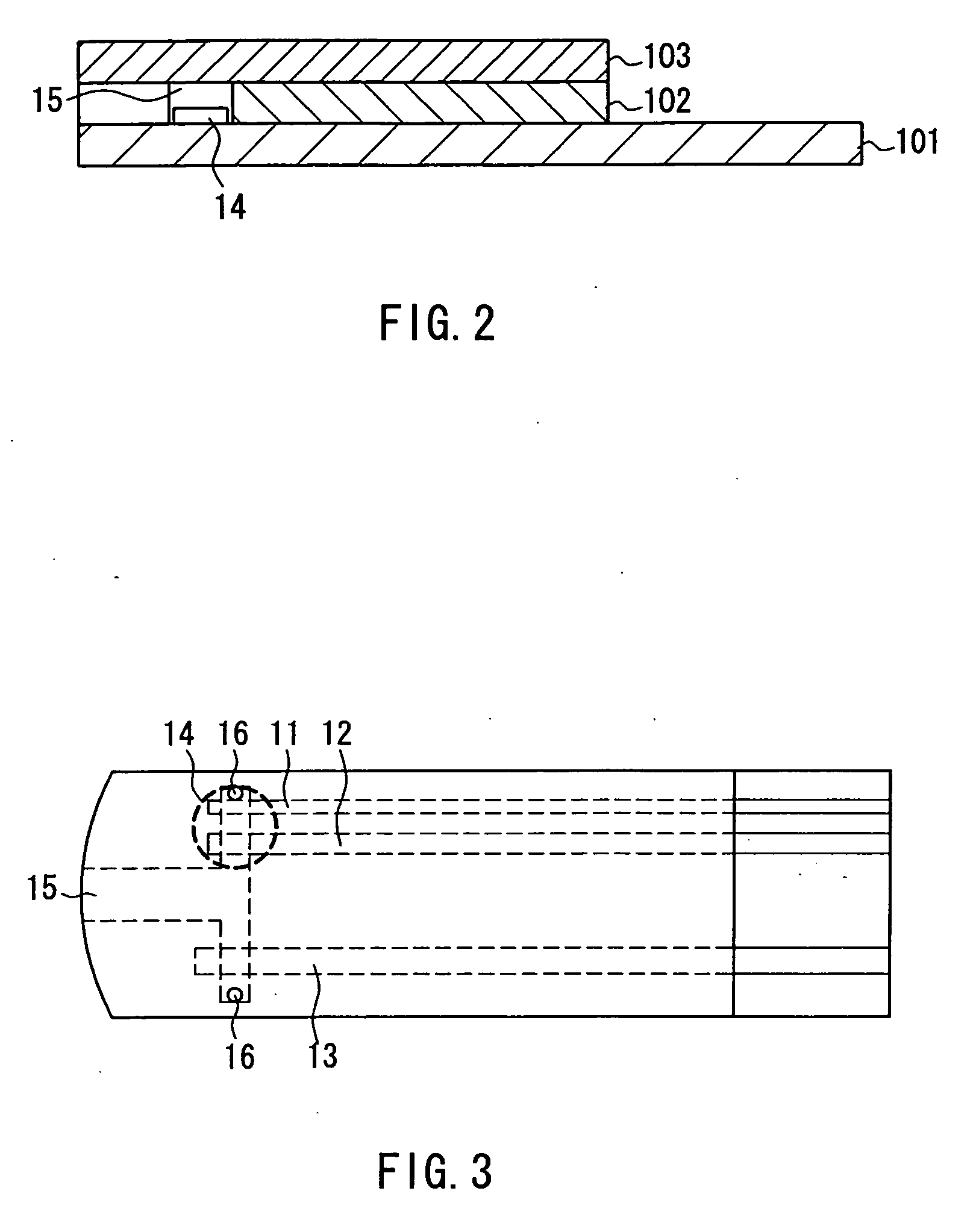
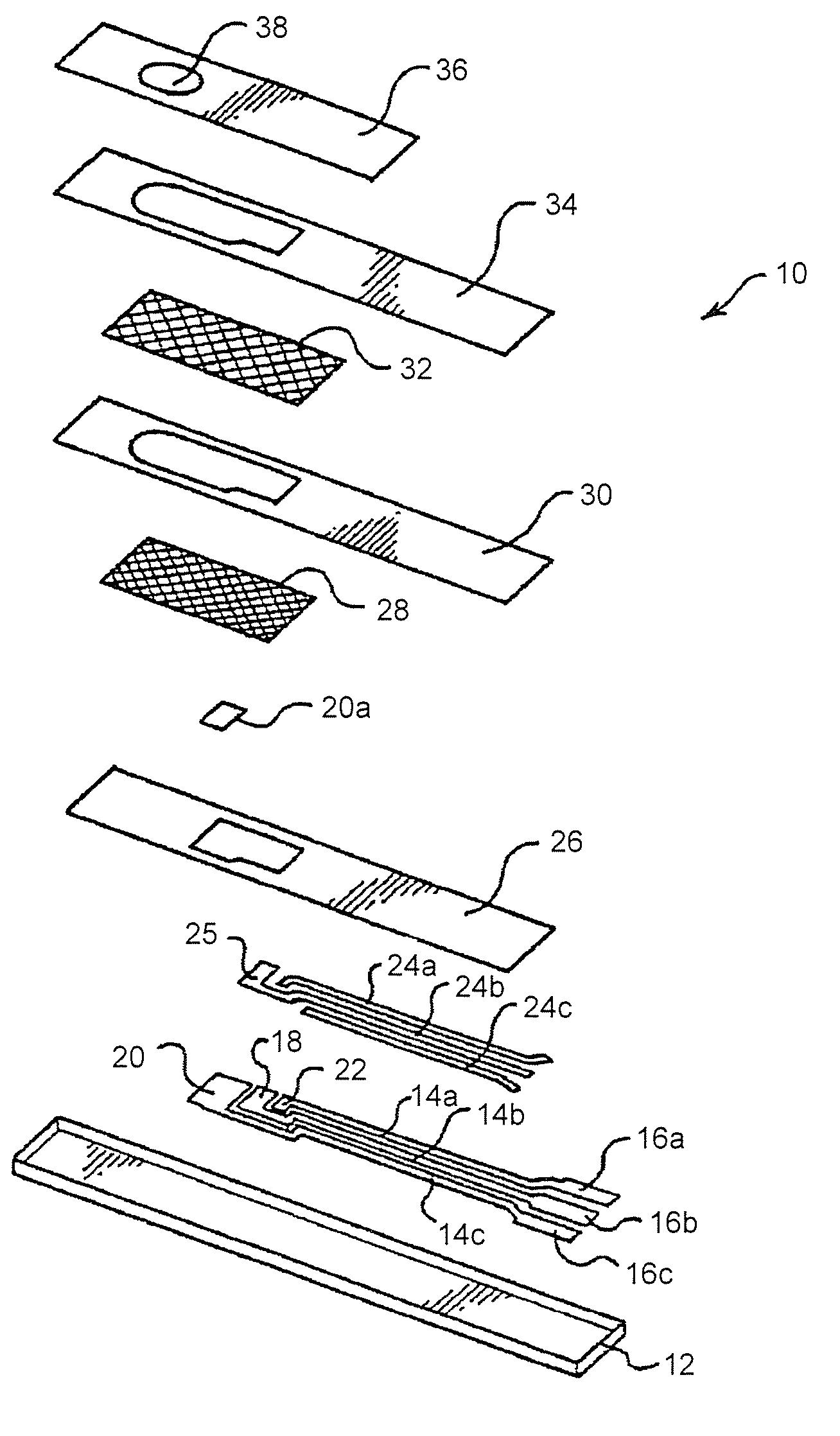
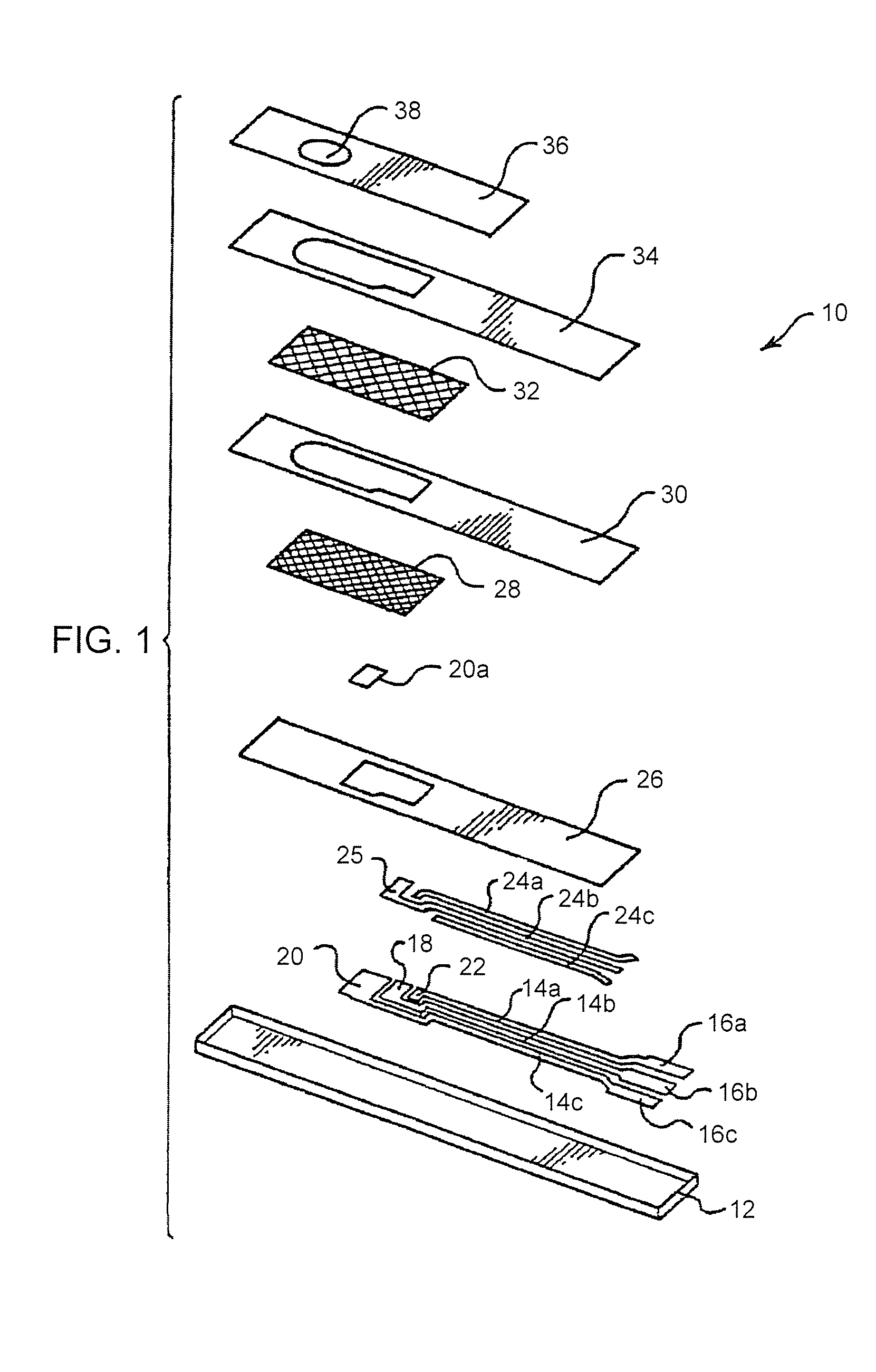
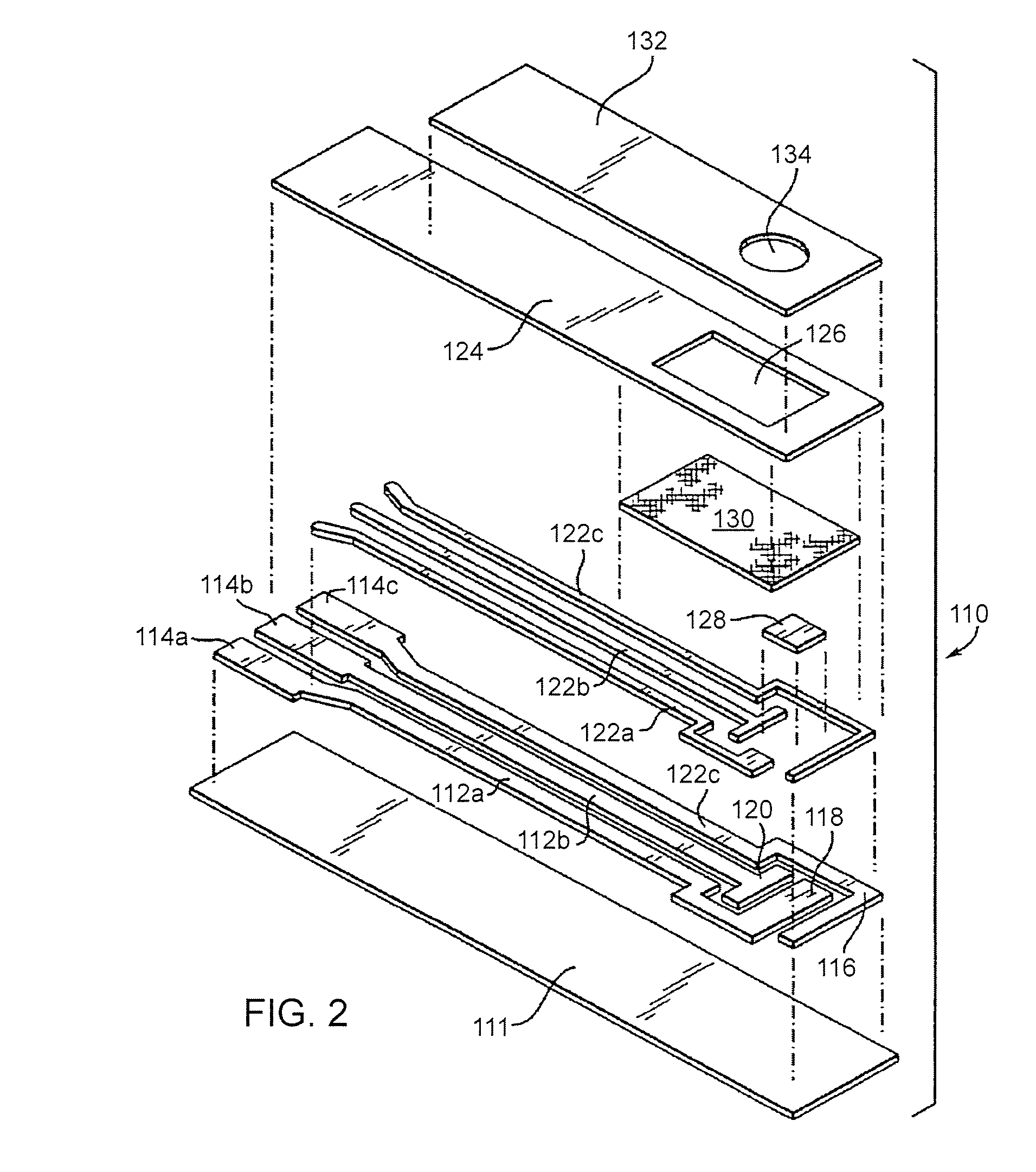
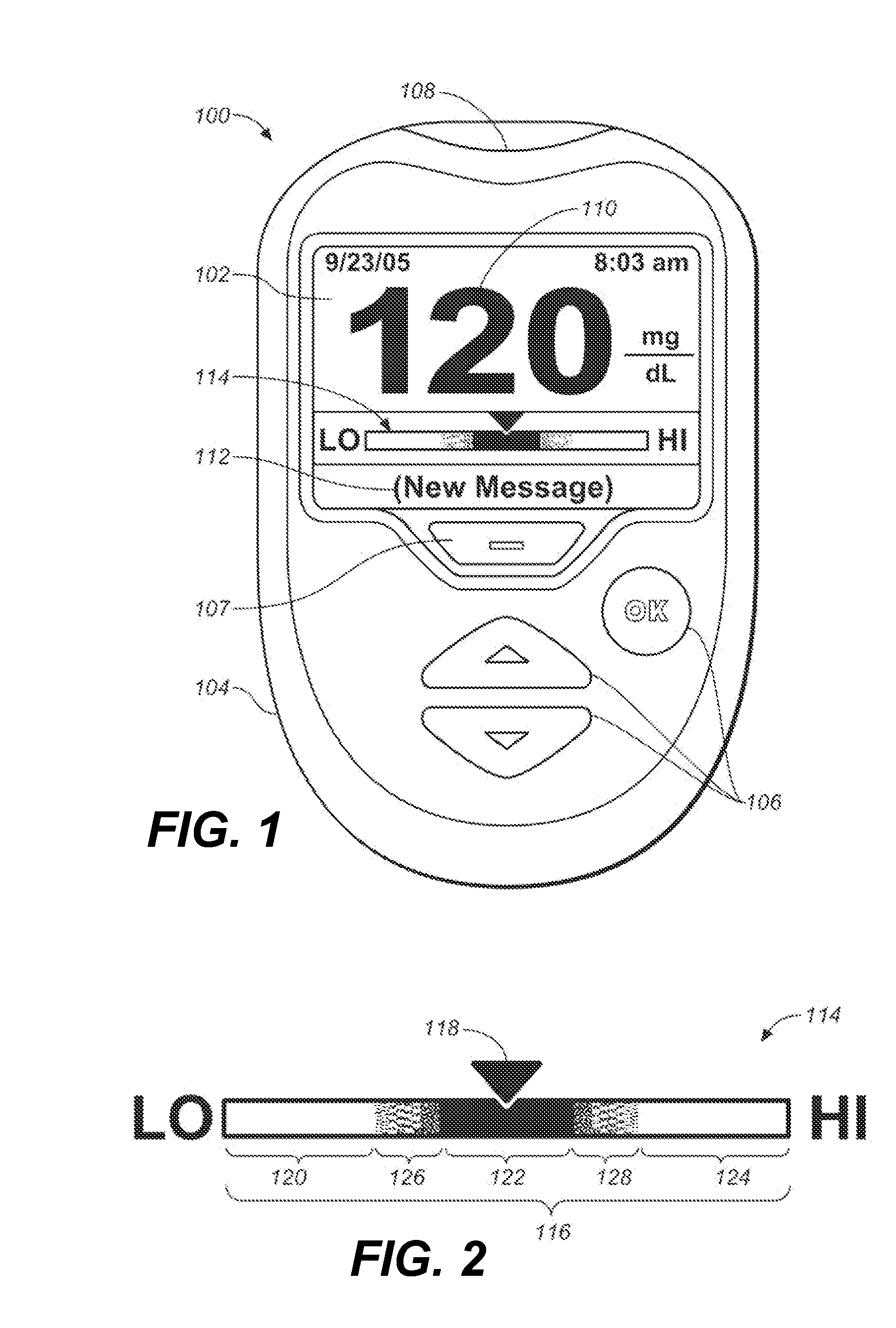
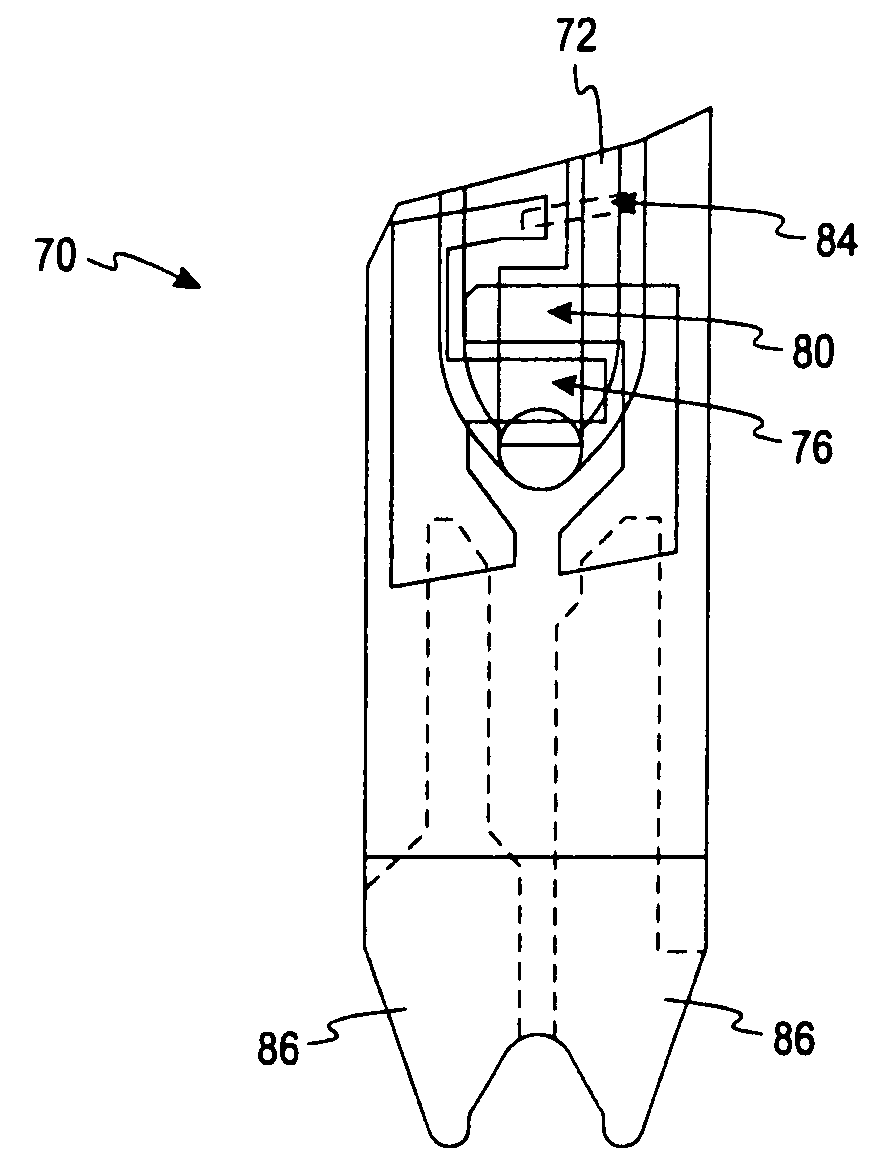
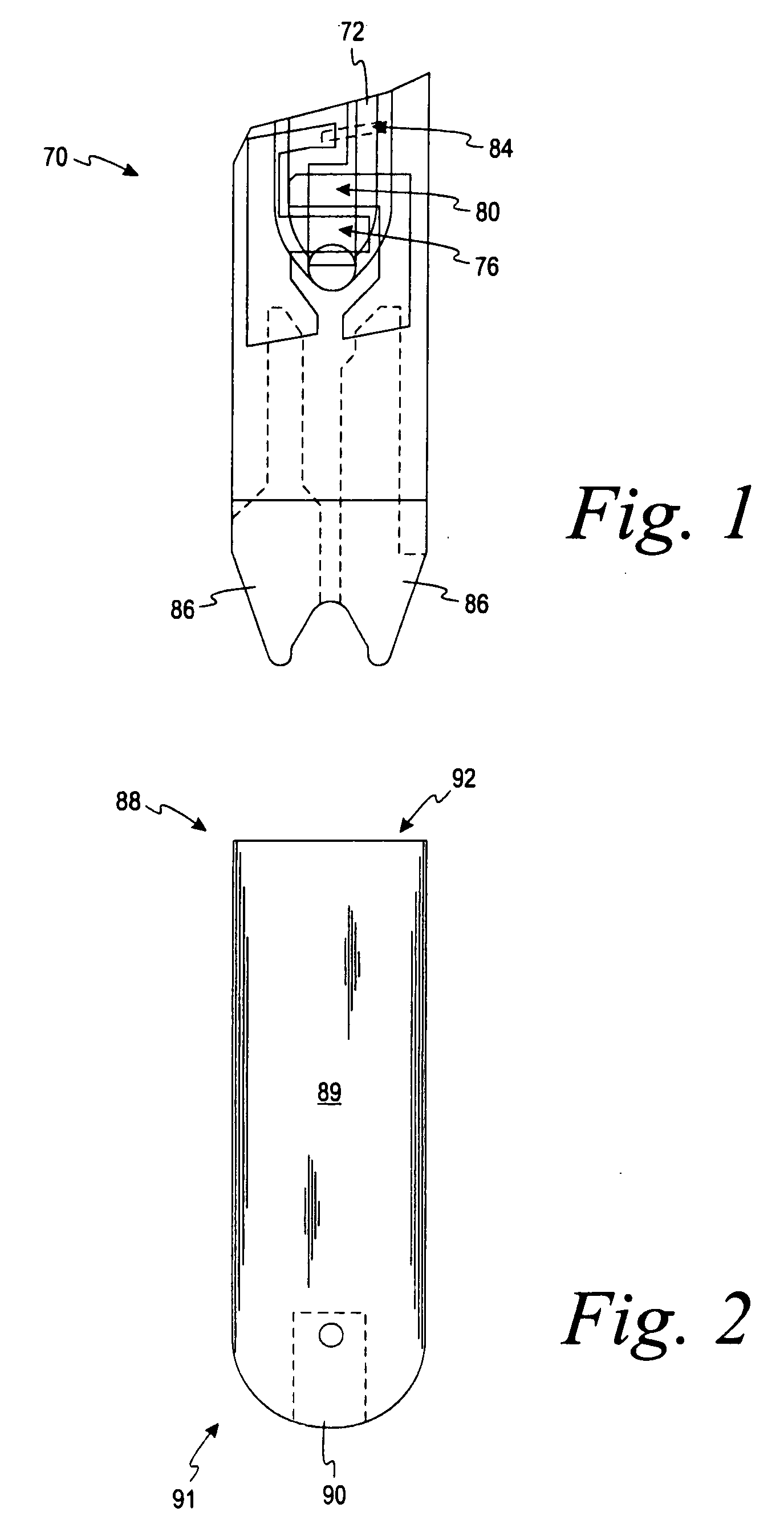
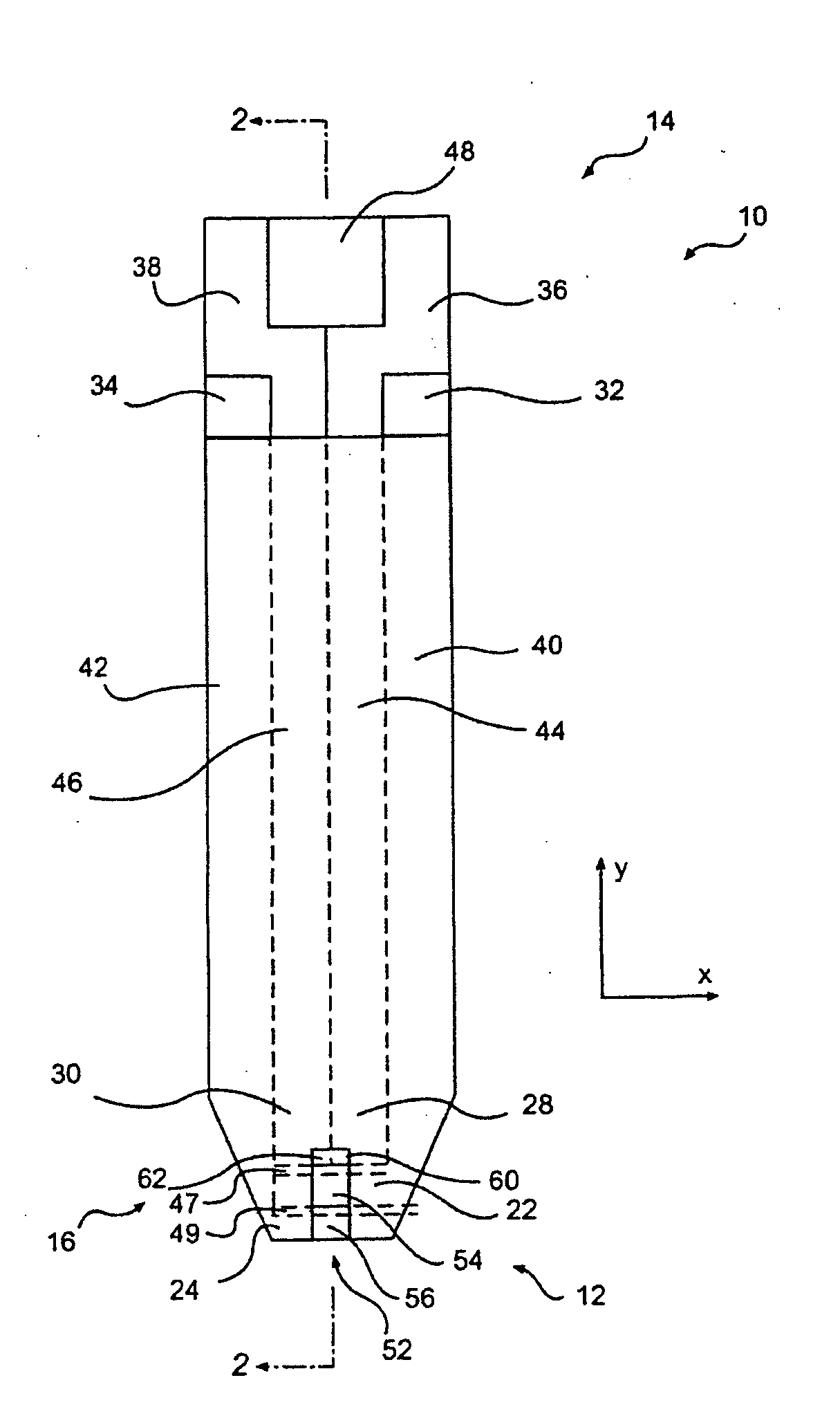
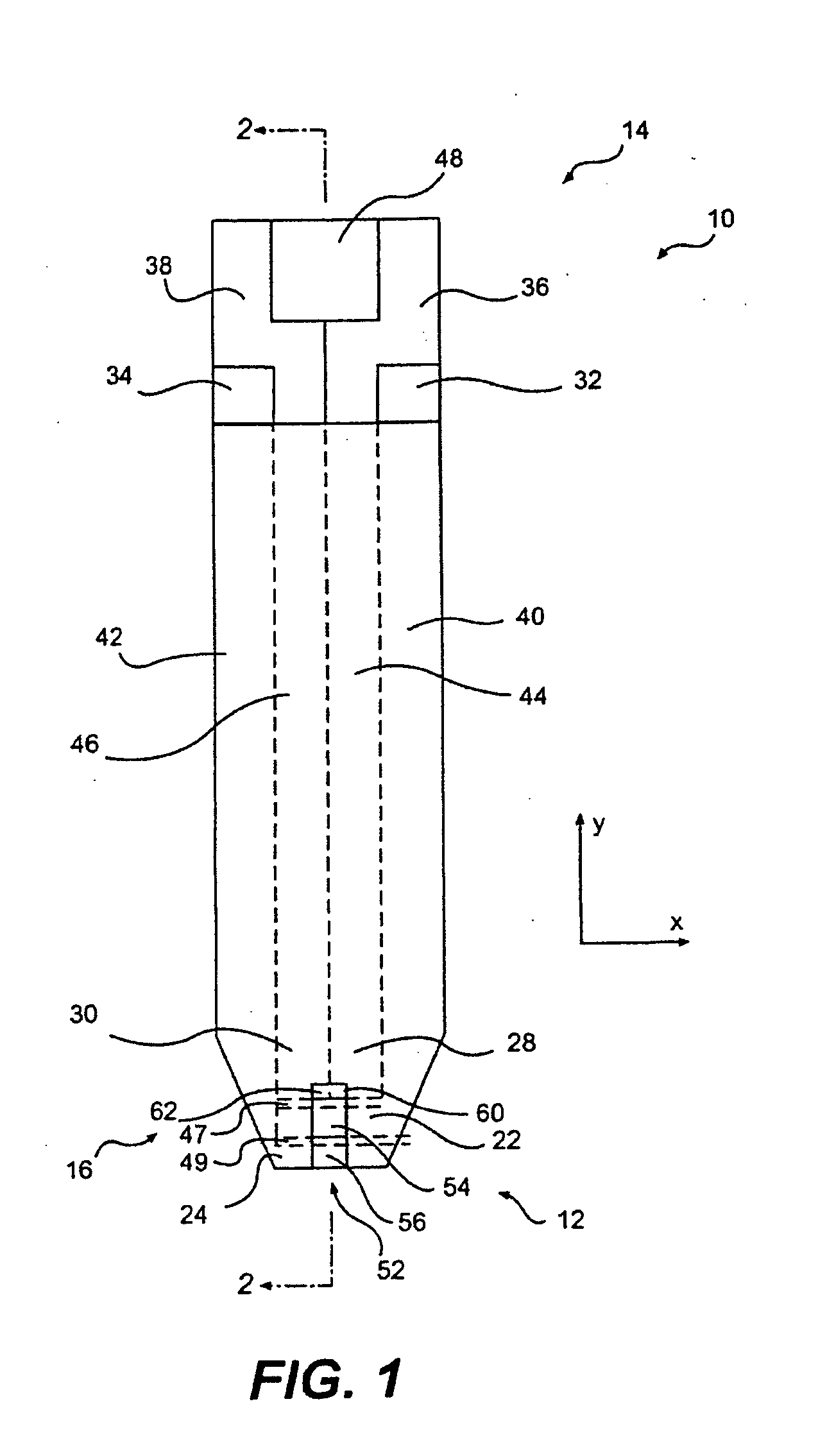
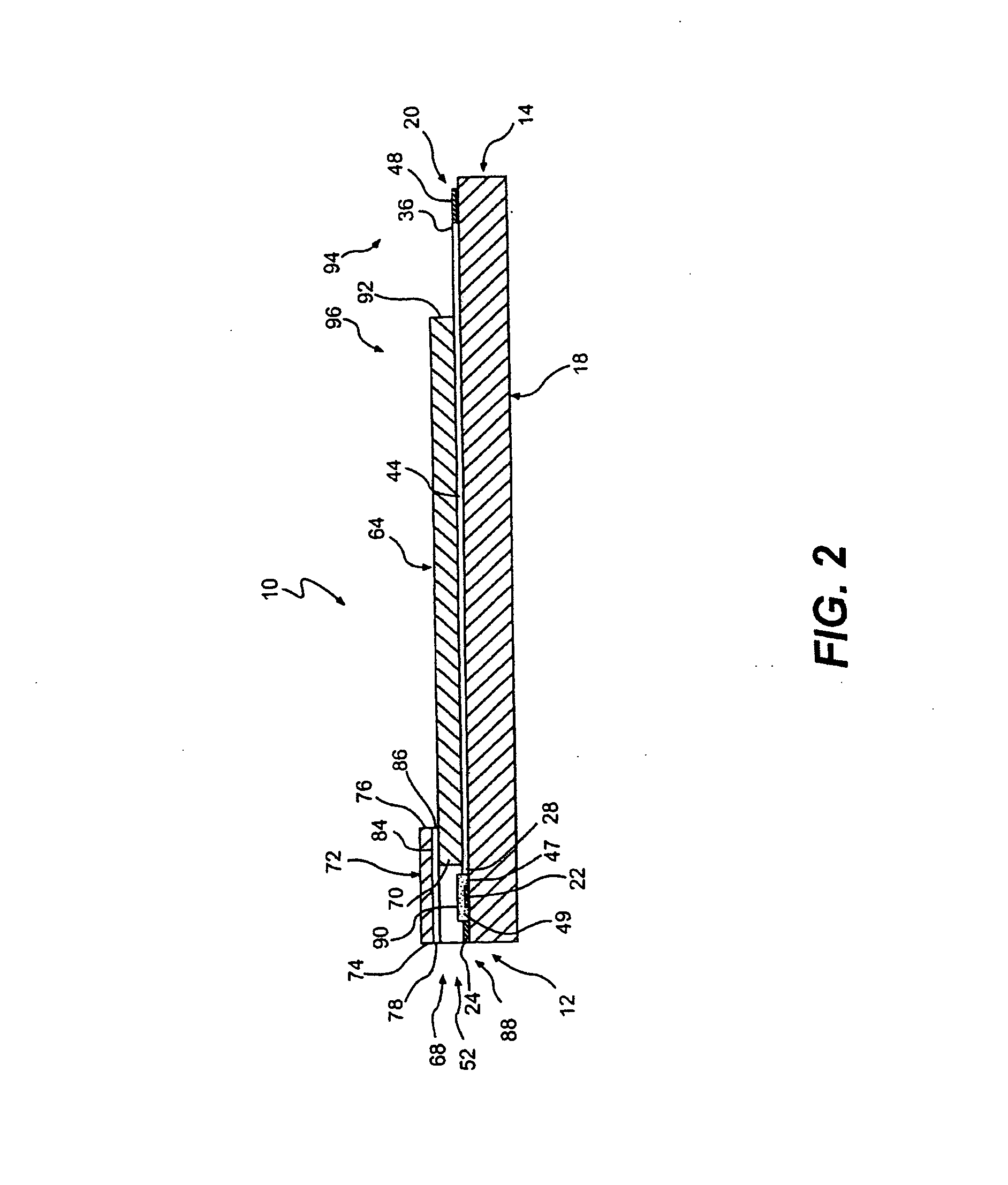
Disposable test strips with integrated reagent/blood separation layer
An improved disposable glucose test strip for use in a test meter of the type which receives a disposable test strip and a sample of blood from a patient and performs an electrochemical analysis using a non-conductive integrated reagent / blood separation layer (17) containing a filler, an enzyme effective to oxidize glucose, e.g., glucose oxidase, and a mediator effective to transfer electrons from the enzyme. The integrated layer formulation is printed over a conductive carbon element (16) to form a working electrode. The filler, for example a silica filler, is selected to have a balance of hydrophobicity such that on drying it forms a two-dimensional network on the surface of the conductive element. The response of this test strip is essentially temperature independent over relevant temperature ranges and is substantially insensitive to the hematocrit of the patient.
Owner:SELFCARE +1
System and method for measuring an analyte in a sample
ActiveUS20090184004A1Interference minimizationLess of concentration profileImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteConcentrations glucose
Methods of determining a corrected analyte concentration in view of some error source are provided herein. The methods can be utilized for the determination of various analytes and / or various sources of error. In one example, the method can be configured to determine a corrected glucose concentration in view of an extreme level of hematocrit found within the sample. In other embodiments, methods are provided for identifying various system errors and / or defects. For example, such errors can include partial-fill or double-fill situations, high track resistance, and / or sample leakage. Systems are also provided for determining a corrected analyte concentration and / or detecting some system error.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Electrochemical methods and devices for use in the determination of hematocrit corrected analyte concentrations
InactiveUS6890421B2Weather/light/corrosion resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteBlood cell
Methods and devices for determining the concentration of an analyte in a physiological sample are provided which correct for errors in the analyte concentration measurement which are due to the hematocrit of the sample.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
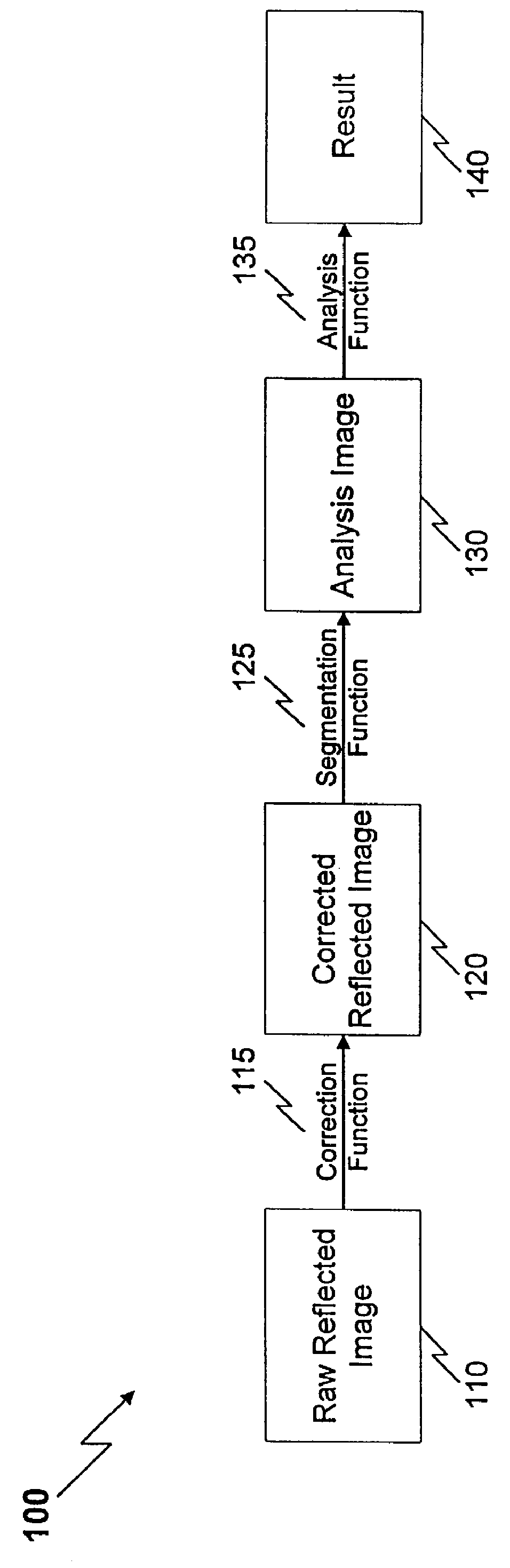
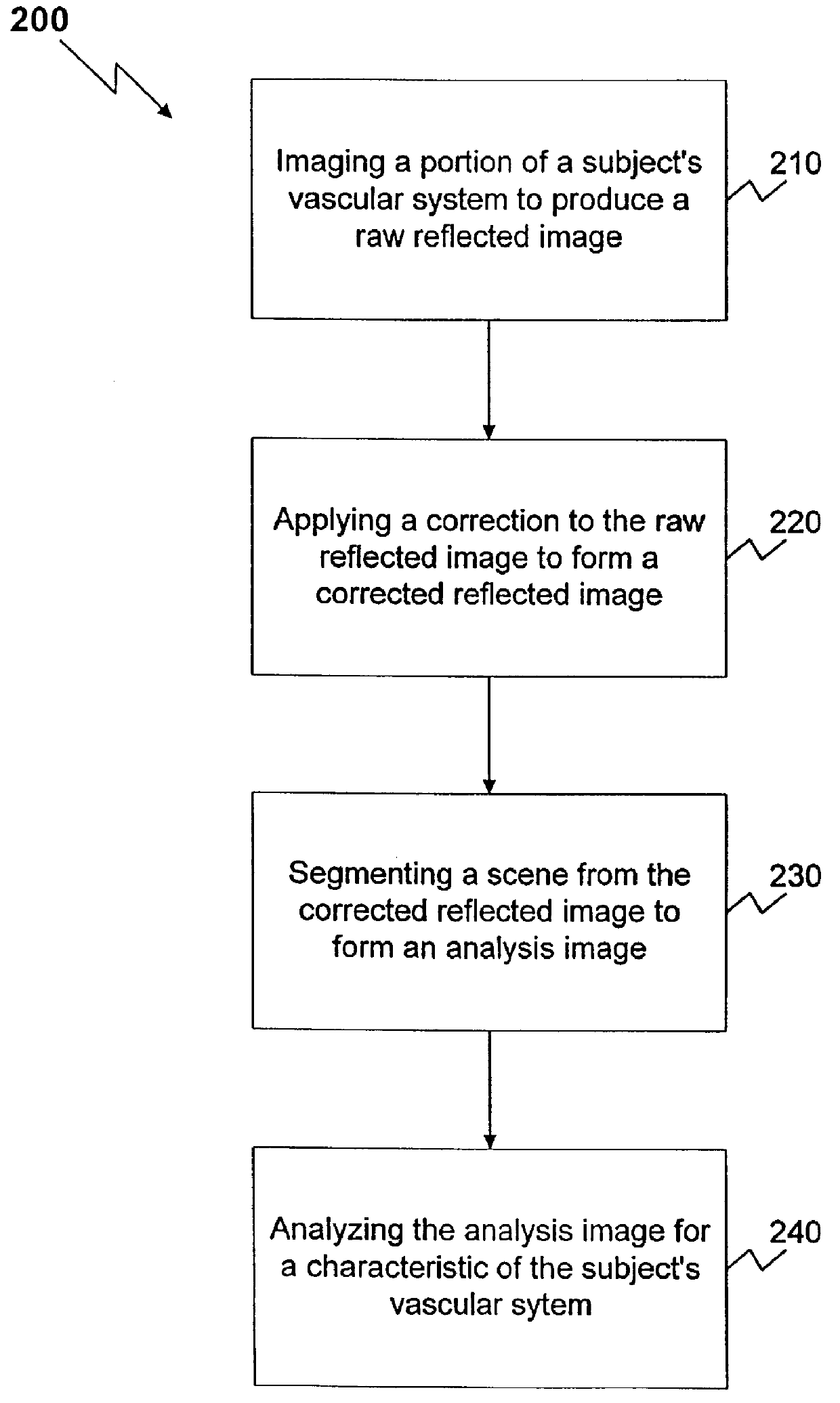
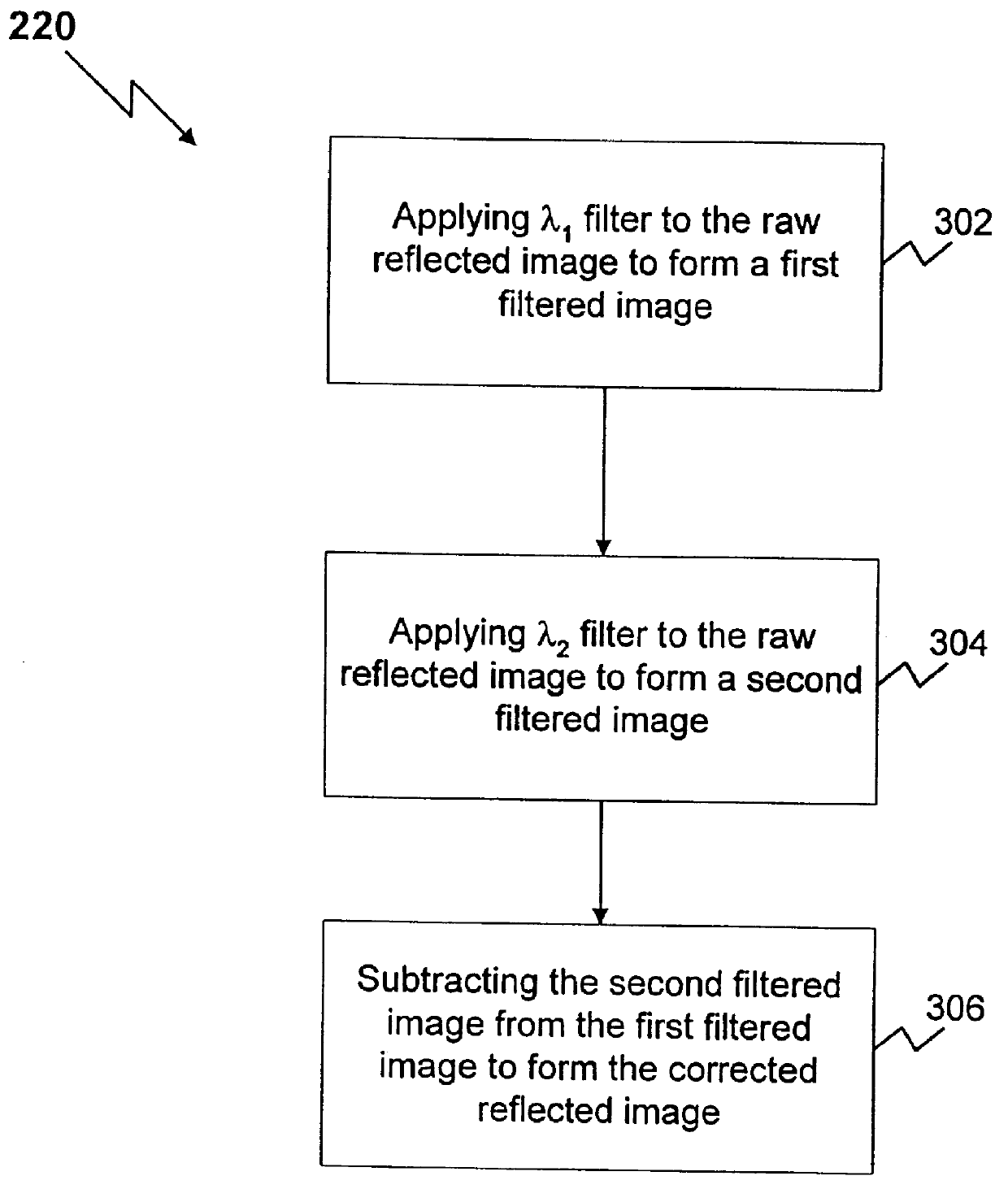
Method and apparatus for reflected imaging analysis
InactiveUS6104939AQuick measurementPolarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsWhite blood cellPolarizer
Method and apparatus for reflected imaging analysis. Reflected imaging is used to perform non-invasive, in vivo analysis of a subject's vascular system. A raw reflected image (110) is normalized with respect to the background to form a corrected reflected image (120). An analysis image (130) is segmented from the corrected reflected image to include a scene of interest for analysis. The method and apparatus can be used to determine such characteristics as the hemoglobin concentration per unit volume of blood, the number of white blood cells per unit volume of blood, a mean cell volume, the number of platelets per unit volume of blood, and the hematocrit. Cross-polarizers can be used to improve visualization of the reflected image.
Owner:INTPROP MVM
Biosensor having improved hematocrit and oxygen biases
ActiveUS7501053B2Accurate responseDesensitizationImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsQuinoneManganese
A biosensor that utilizes a mediator, i.e., an isomer of phenanthroline quinone, 1,10-phenanthroline-5,6-dione, and a metal ion, such as manganese, with an enzyme dependent upon NAD(P)+, such as, for example, glucose dehydrogenase, for improving the hematocrit bias and oxygen bias of biosensors. The electrodes of the biosensors employing this mediator and a metal ion provide an accurate clinical response over a hematocrit range that ranges from about 20% to about 70% and over an oxygen tension range that ranges from about 1 kPa to about 20 kPa.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
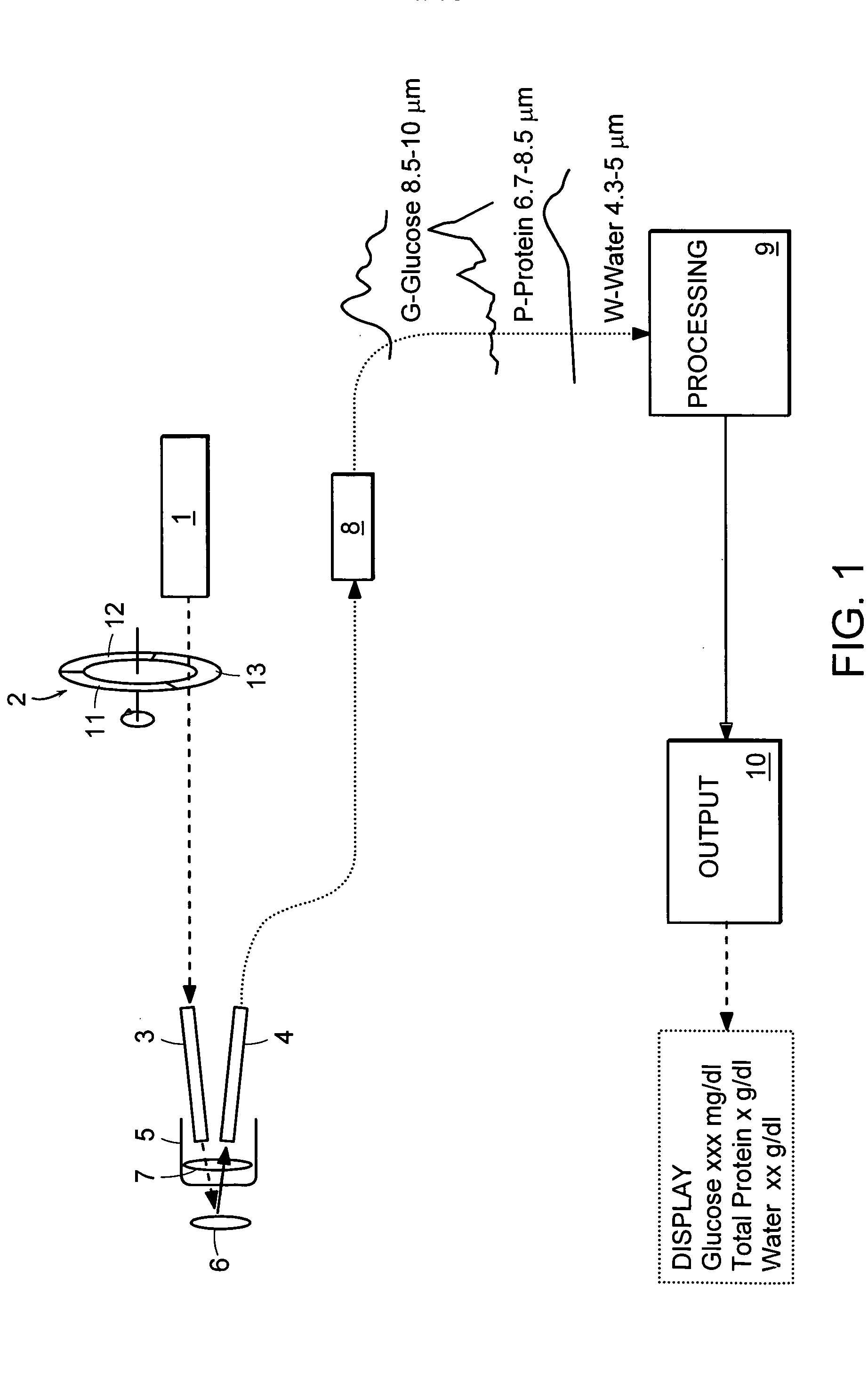
Non-invasive blood component measurement system
Non-invasive, optical apparatus and methods for the direct measurement of hemoglobin derivatives and other analyte concentration levels in blood using diffuse reflection and transmission spectroscopy in the wavelength region 400-1350 nm which includes the transparent tissue window from approximately 610 to 1311 nanometers and, using diffuse reflection spectroscopy, the mid-infrared region from 4.3-12 microns in wavelength. Large area light collection techniques are utilized to provide a much larger pulsate signal than can be obtain with current sensor technology. Sensors used in separate or simultaneous precision measurements of both diffuse reflection and transmission, either separately or simultaneously, from pulsate, blood-perfused tissue for the subsequent determination of the blood analytes concentrations such as arterial blood oxygen saturation (SaO2), carboxyhemoglobin (COHb), oxyhemoglobin (OHb), deoxyhemoglobin (dOHb), methemoglobin (metHb), water (H2O), hematocrit (HCT), glucose, cholesterol and proteins such as albumin and other analytes components.
Owner:3WAVE OPTICS
Electrochemical methods and devices for use in the determination of hematocrit corrected analyte concentrations
InactiveUS20050176153A1Electrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementElectrical batteryBlood cell
Methods and devices for determining the concentration of an analyte in a physiological sample are provided. In the subject methods, the physiological sample is introduced into an electrochemical cell having a working and reference electrode. A first electric potential is applied to the cell and the resultant cell current over a period of time is measured to determine a first time-current transient. A second electric potential of opposite polarity is then applied and a second a time-current transient is determined. The preliminary concentration of the analyte is then calculated from the first and / or second time-current transient. This preliminary analyte concentration less a background value is then multiplied by a hematocrit correction factor to obtain the analyte concentration in the sample, where the hematocrit correction factor is a function of the preliminary analyte concentration and the variable γ of the electrochemical cell. The subject methods and devices are suited for use in the determination of a wide variety of analytes in a wide variety of samples, and are particularly suited for the determination of analytes in whole blood or derivatives thereof, where an analyte of particular interest is glucose.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
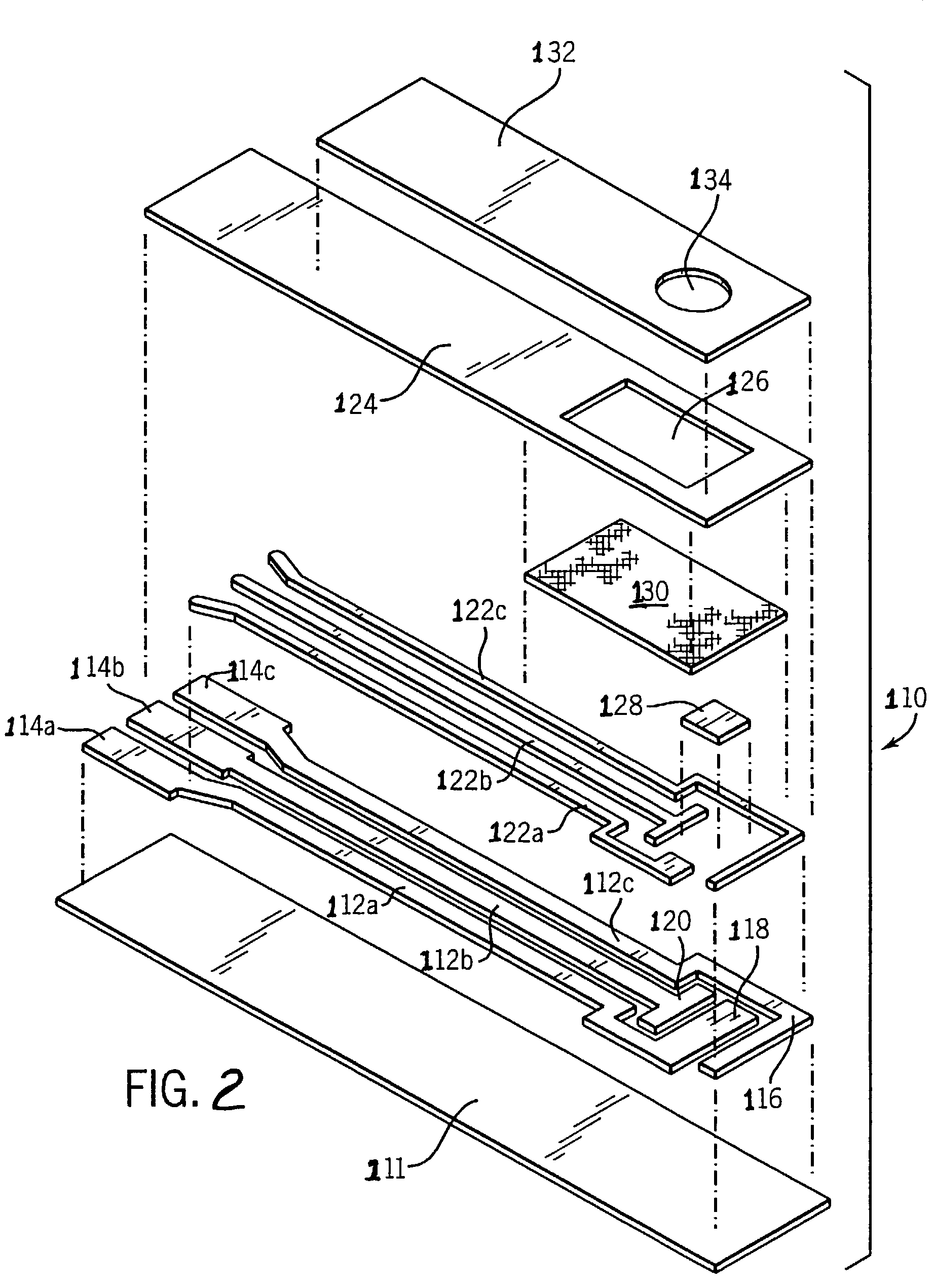
Method of measuring blood component, sensor used in the method, and measuring device
ActiveUS20070131565A1Easy to measureImprove accuracyImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOxidoreductasePhysics
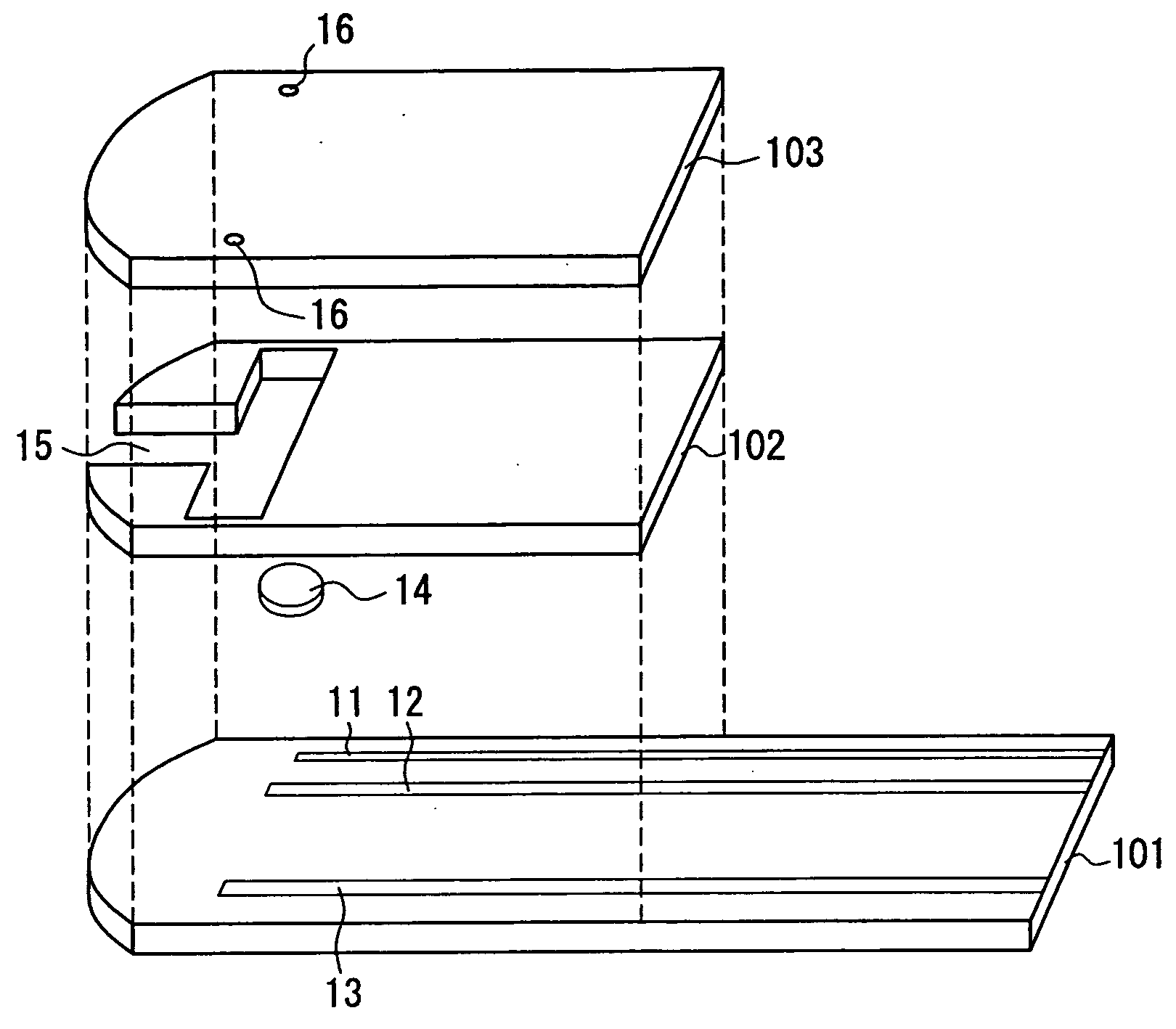
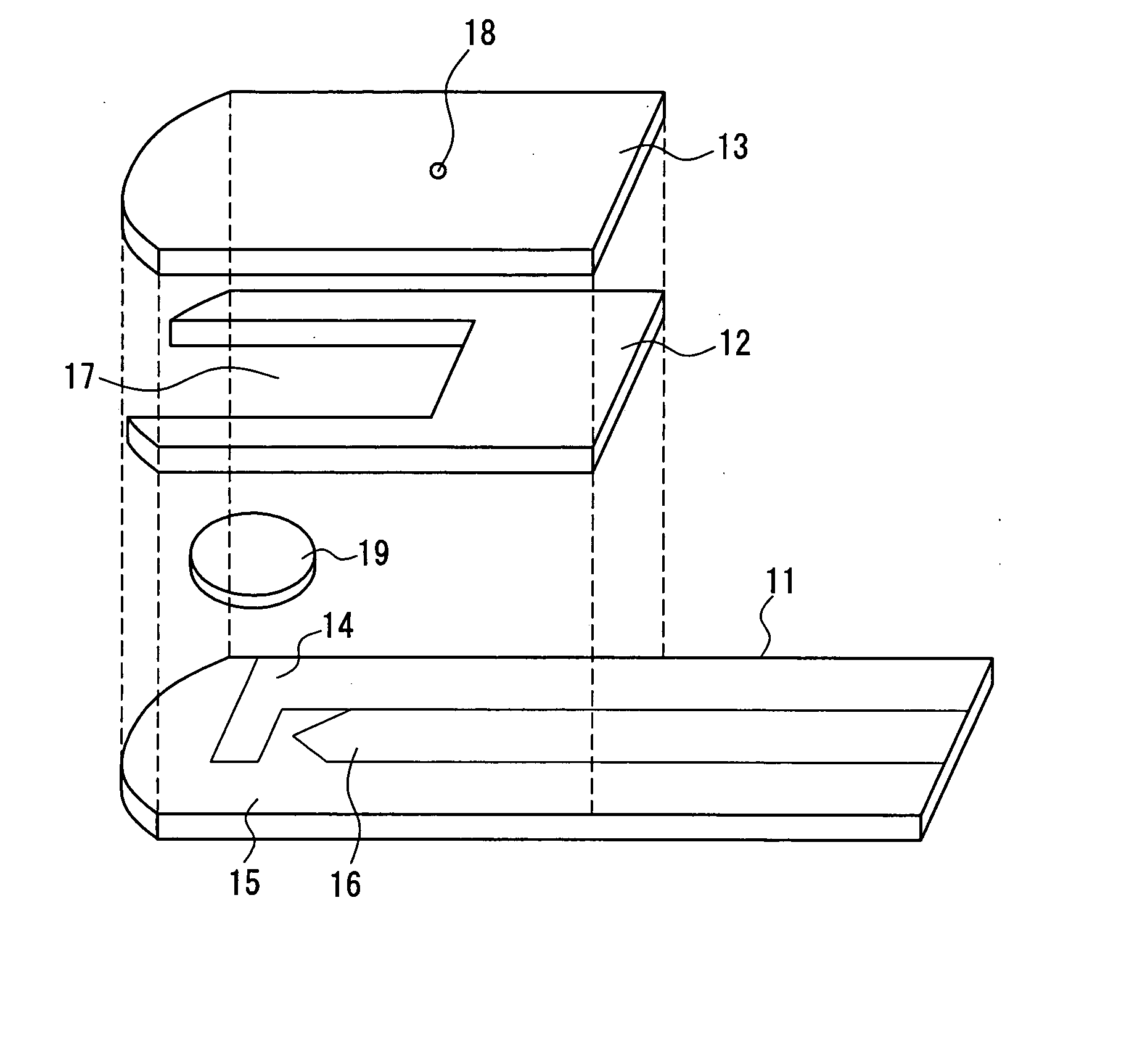
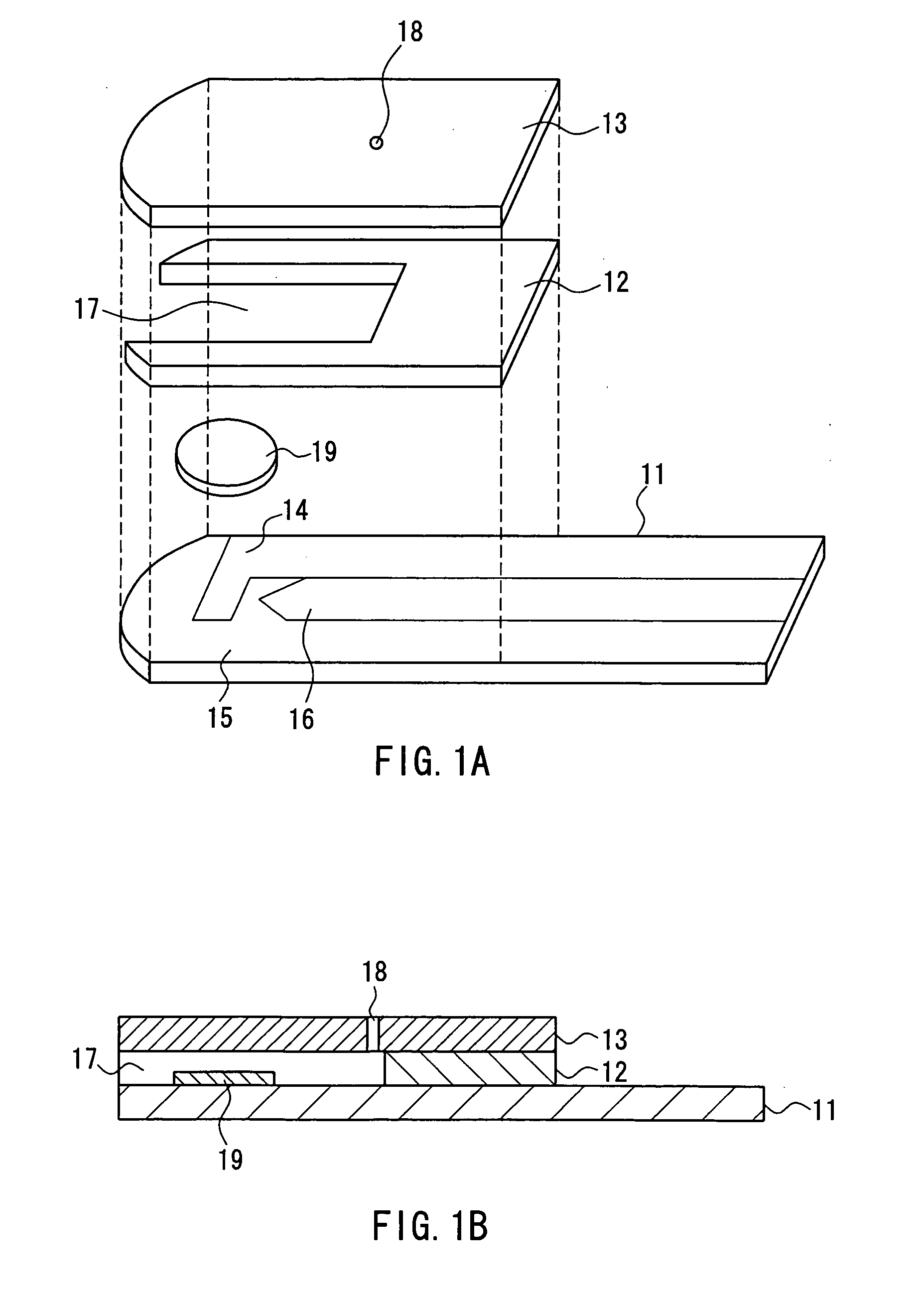
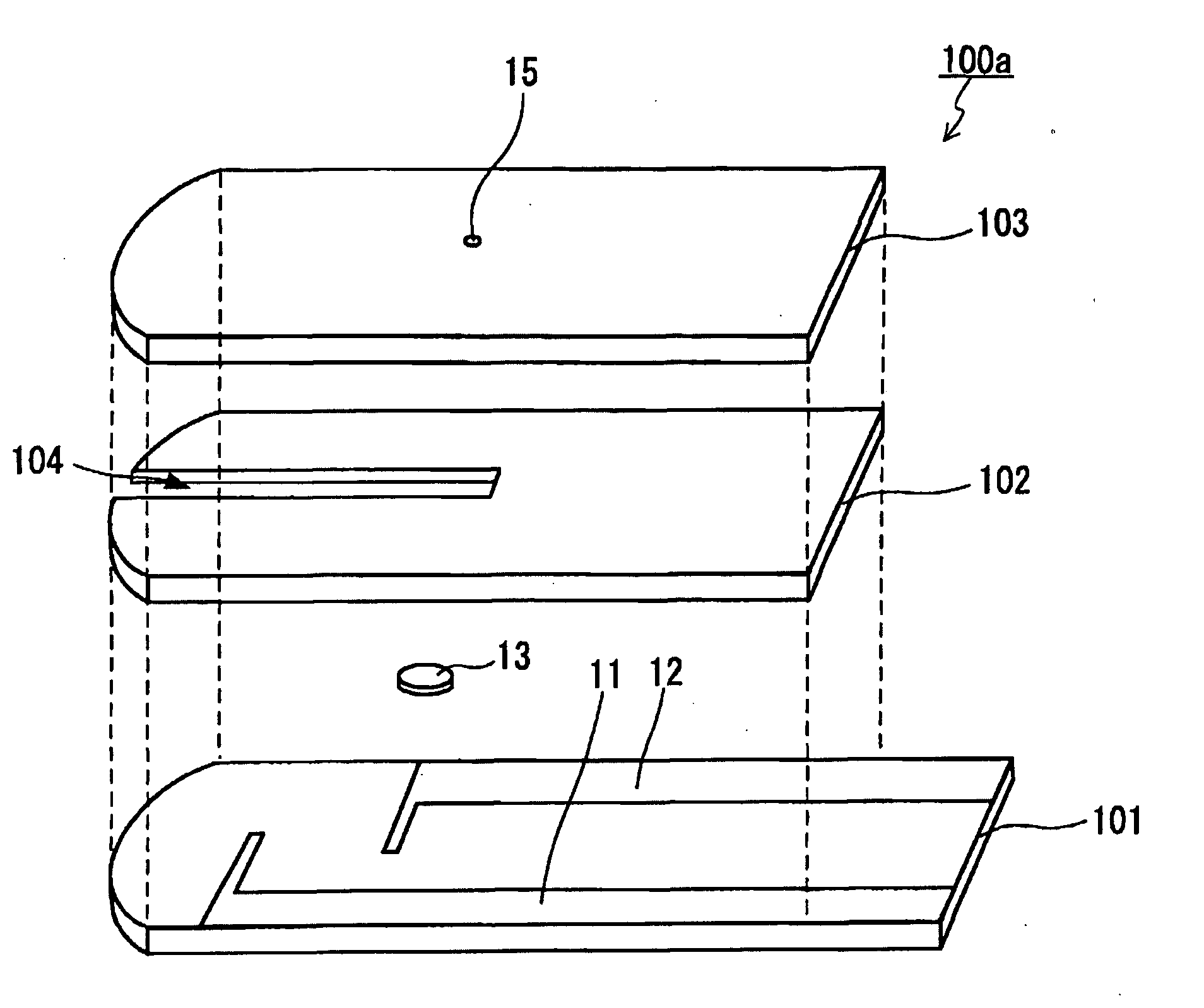
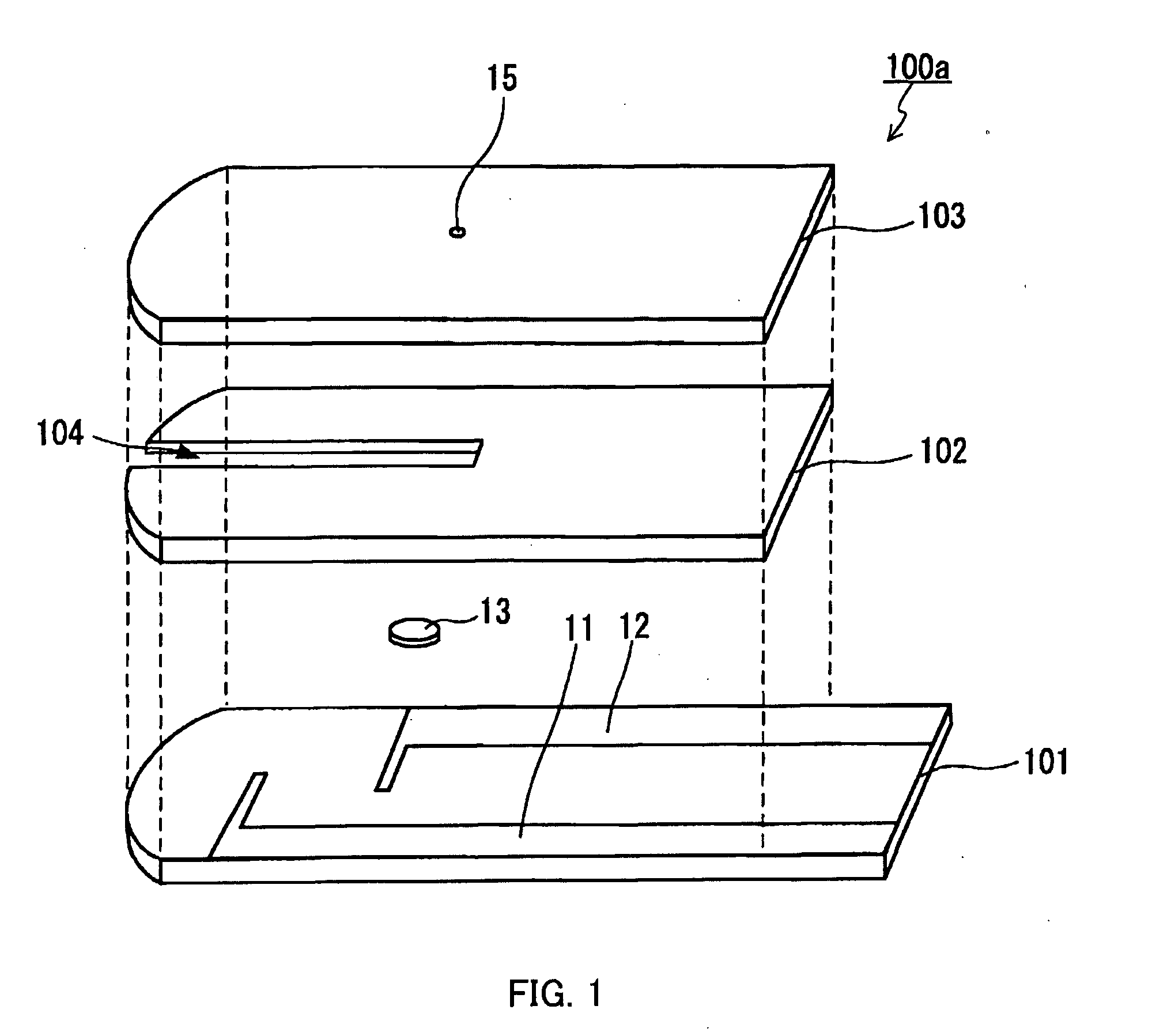
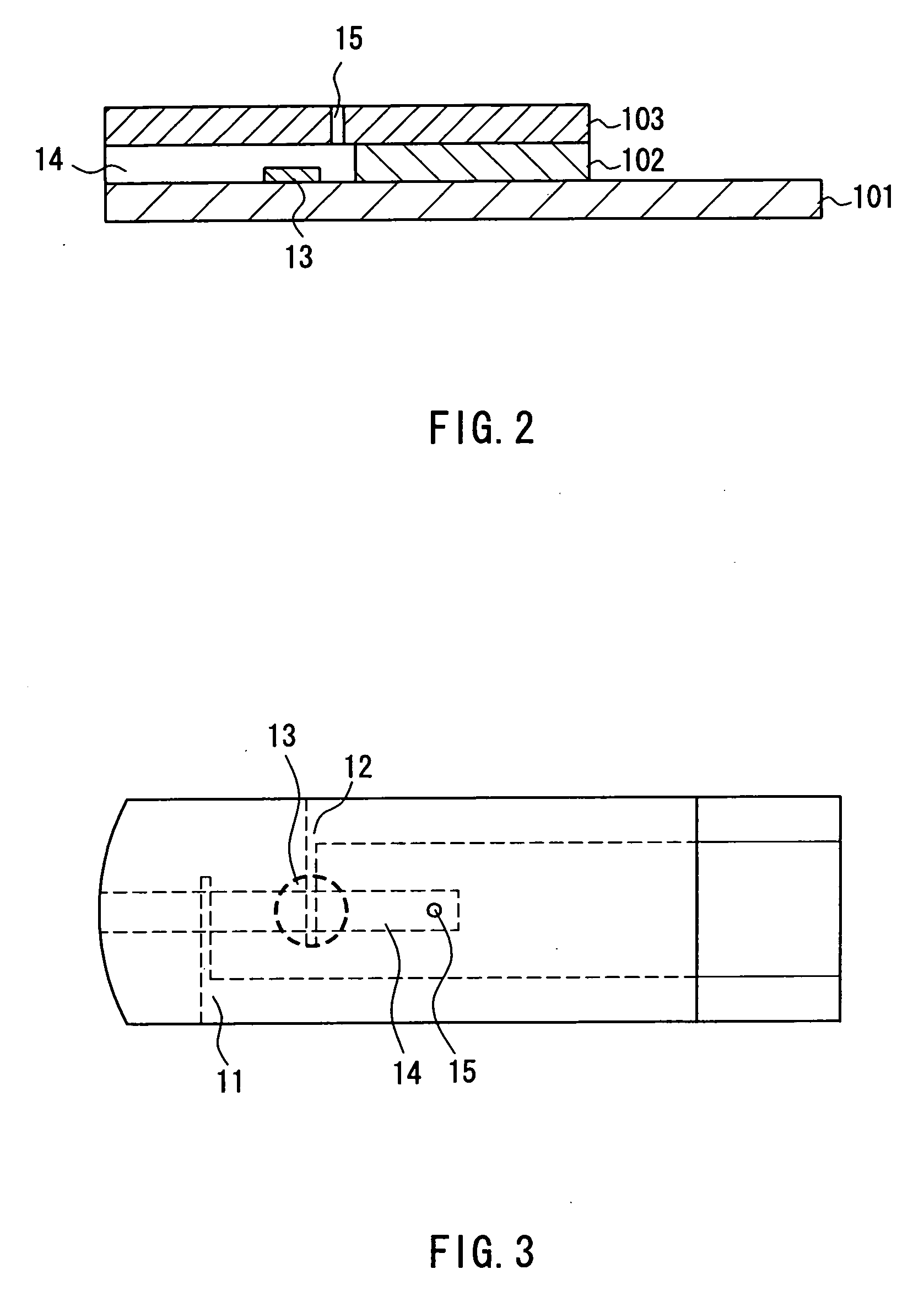
The present invention provides a method of measuring a component in blood, by which an amount of the component can be corrected accurately by measuring a hematocrit (Hct) value of the blood with high accuracy and high reliability and also provides a sensor used in the method. The sensor for measuring a component in blood has a first analysis portion and a second analysis portion. The first analysis portion has a first electrode system (11,12) and a reagent layer (14), and the reagent layer (14) has an oxidoreductase that acts on the component and a mediator. In the first analysis portion, the component in the blood is measured by causing a redox reaction of the component with the oxidoreductase in the presence of the mediator and detecting a redox current caused when a voltage is applied by the first electrode (11,12). The second analysis portion has a working electrode and a counter electrode, and a mediator is provided on the counter electrode but not on the working electrode. In the second analysis portion, a Hct value of the blood is measured by supplying the blood to the electrode system, applying a voltage to cause a current to flow, and detecting a value of the current. Using this Hct value, the amount of the component is corrected.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Analyte determination method and analyte meter
The presence of oxygen or red blood cells in a sample applied to an electrochemical test strip that makes use of a reduced mediator is corrected for by an additive correction factor that is determined as a function of the temperature of the sample and a measurement that reflects the oxygen carrying capacity of the sample. The measured oxygen carrying capacity can also be used to determine hematocrit and to distinguish between blood samples and control solutions applied to a test strip.
Owner:AGAMATRIX INC
Method of measuring blood component and sensor used in the method
ActiveUS20050145490A1Great HctConvenient amountImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRed blood cellOxidoreductase
A sensor for blood component analysis that can correct the effect of a hematocrit easily is provided. The sensor includes an analysis portion including a working electrode, a counter electrode, and a reagent portion. The reagent portion includes an oxidoreductase that reacts with the blood component and a mediator, and the blood component is measured by causing a redox reaction between the blood component and the oxidoreductase in the presence of the mediator and detecting a redox current generated by the redox reaction by the working electrode and the counter electrode. In this sensor, the reagent portion further includes a hemolyzing agent (e.g., sodium cholate) for hemolyzing an erythrocyte, and when detecting the redox current, the erythrocyte is hemolyzed with the hemolyzing agent so as to cause hemoglobin released to an outside of the erythrocyte to react with the mediator and a current generated by this reaction also is detected to correct an effect of a hematocrit.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
System and Methods for Determining an Analyte Concentration Incorporating a Hematocrit Correction
Methods and devices for determining the concentration of a constituent in a physiological sample are provided. The blood sample is introduced into a test strip with portions of the blood sample being directed to both a first capillary and a second capillary. The first capillary configured to electrochemically determine a concentration of a first analyte in a blood sample by measuring a signal across a set of electrodes. The second capillary is configured to determine a hematocrit value of the blood sample by measuring a signal across a second set of electrodes.
Owner:NIPRO DIAGNOSTICS INC
System and methods for providing corrected analyte concentration measurements
InactiveUS20070235346A1Eliminate the effects ofOffsetting effectImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteGlucose polymers
Methods and devices for determining the concentration of a constituent in a physiological sample are provided. The physiological sample is introduced into an electrochemical cell having a working and counter electrode. At least one electrochemical signal is measured based on a reaction taking place at the cell. The preliminary concentration of the constituent is then calculated from the electrochemical signal. This preliminary concentration is then multiplied by a hematocrit correction factor to obtain the constituent concentration in the sample, where the hematocrit correction factor is a function of the at least one electrochemical signal. The subject methods and devices are suited for use in the determination of a wide variety of analytes in a wide variety of samples, and are particularly suited for the determination of analytes in whole blood or derivatives thereof, where an analyte of particular interest is glucose.
Owner:NIPRO DIAGNOSTICS INC
Red blood cell processing systems and methods which control red blood cell hematocrit
InactiveUS7011761B2Optimize procedure timeAvoid adjustmentLiquid separation auxillary apparatusWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationMedicineHandling system
Processing systems and methods comprise a separation device that, in use, performs a separation process including separation of red blood cells from blood or a suspension containing red blood cells. The systems and methods include an outlet line coupled to the separation device to remove red blood cells from the separation device, at least in part, while the separation process occurs. A sensor associated with the outlet line senses hematocrit of red blood cells removed from the separation device and generates a sensed hematocrit output. A controller is coupled to the separation device to control removal of red blood cells from the separation device based, at least in part, upon the sensed hematocrit output.
Owner:FENWAL
Methods and apparatuses for conducting assays
ActiveUS20060019319A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsParticulatesAnalyte
Disclosed are methods for conducting assays of samples, such as whole blood, that may contain cells or other particulate matter. Also disclosed are systems, devices, equipment, kits and reagents for use in such methods. One advantage of certain disclosed methods and systems is the ability to rapidly measure the concentration of an analyte of interest in blood plasma from a whole blood sample without blood separation and hematocrit correction.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
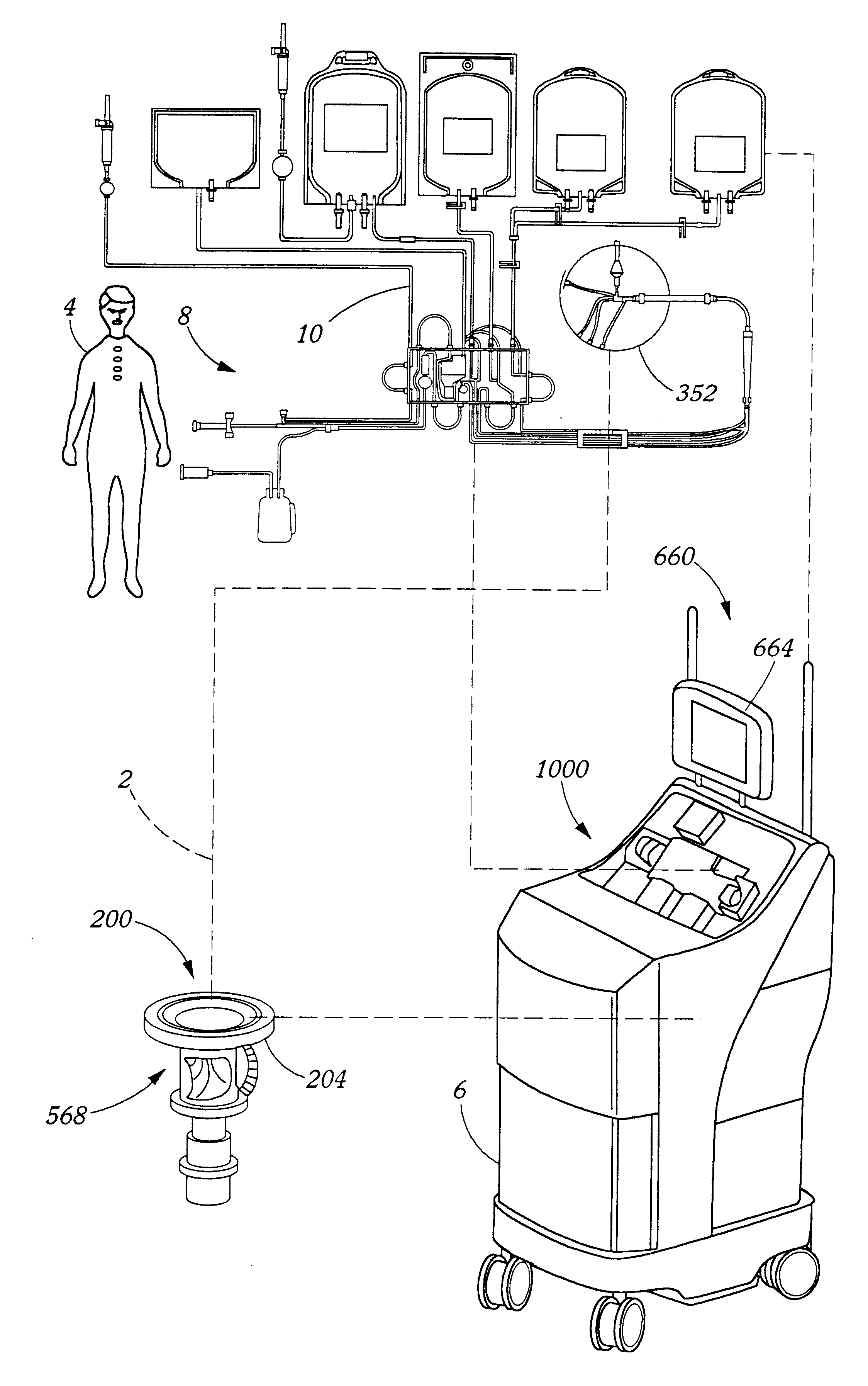
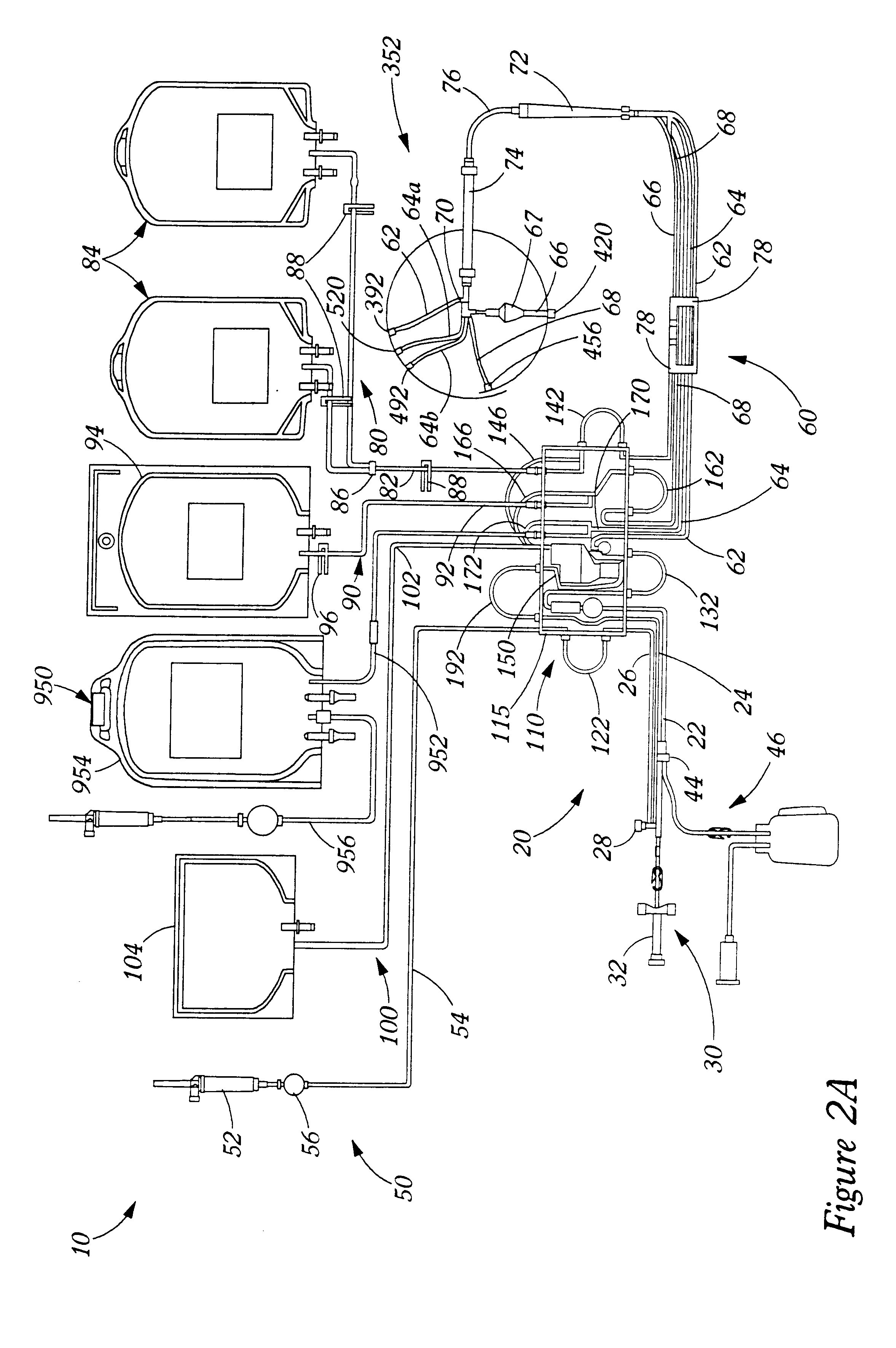
Extracorporeal blood processing methods and apparatus
InactiveUS6899691B2Improving automated responseImprove responseOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationSpecific volumeEngineering
A method and apparatus for controlling a fluid separation system in response to fluid pressure changes in a fluid flow, said method comprising the steps of sensing a fluid pressure; comparing the fluid pressure to a threshold value, and if the fluid pressure is below the threshold value, then pausing fluid flow for a selected period. During the selected period, either the fluid pressure sensed automatically resolves or the method further comprises a step of setting a fall alarm condition. The method and apparatus may further include interpreting a particular quantity of below threshold fluid pressure occurrences where the fluid pressure is below the threshold value occurring within a particular time period, and then, signalling an alarm. Threshold values may be calculated by the method or apparatus according to a formula such as the following:Threshold Value=Config+75−0.3309*Qin / (1−Hin)−0.3026*Qn / (1−Hn);where,Config=a configuration pre-selected pressure value;Qin=fluid flow rate in the inlet tubing line;Hin=Hematocrit in the inlet tubing line;Qn=fluid flow rate in the needle; andHn=Hematocrit in the needle.
Owner:TERUMO BCT
Biosensor having improved hematocrit and oxygen biases
ActiveUS20060201805A1Improved hematocrit bias and oxygen biasAccurate responseImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteOxygen
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
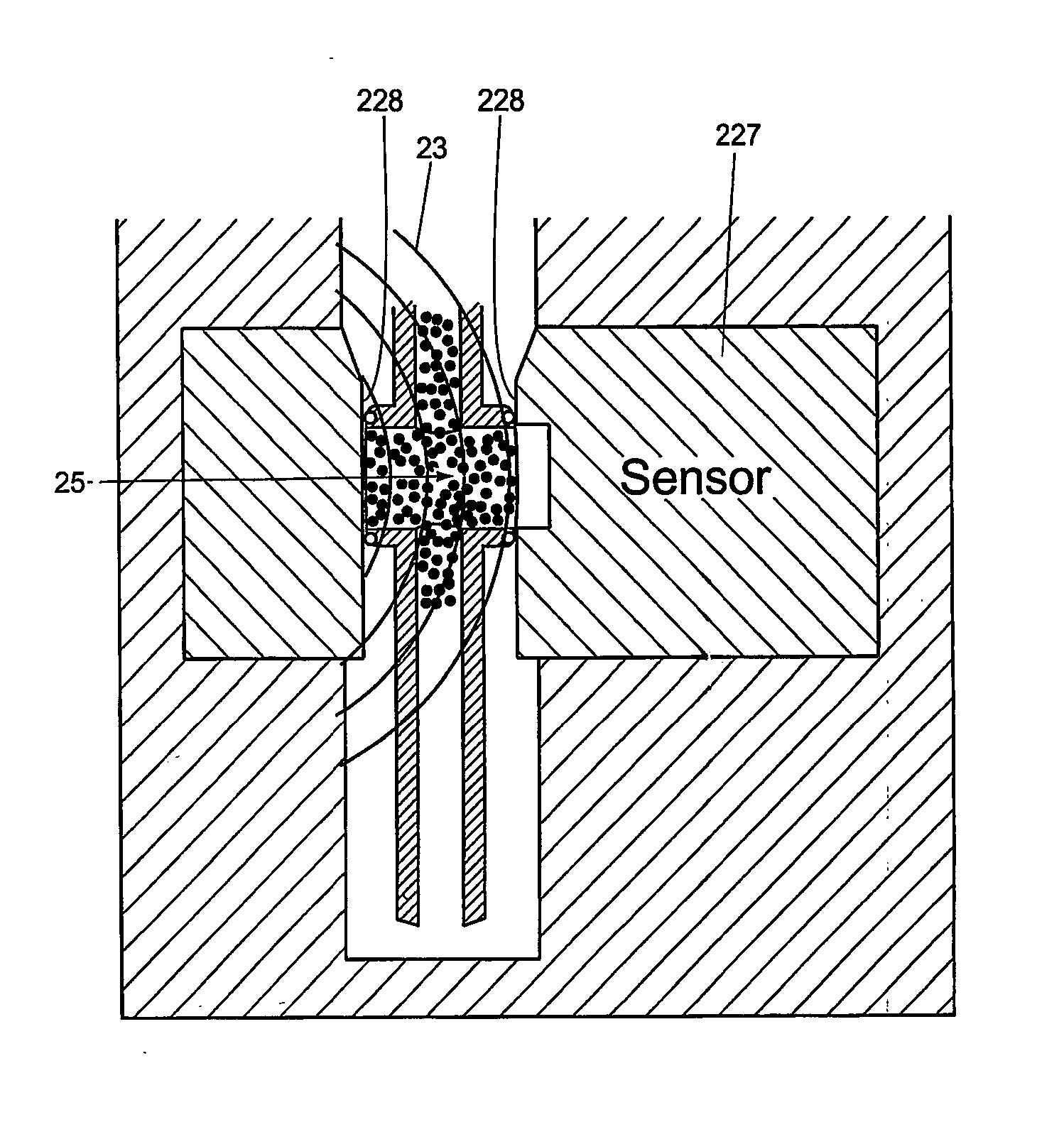
Method for measuring hematocrit value of blood sample, method for measuring concentration of analyte in blood sample, sensor chip and sensor unit
InactiveUS20100276303A1Addressing Insufficient SensitivityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteRedox
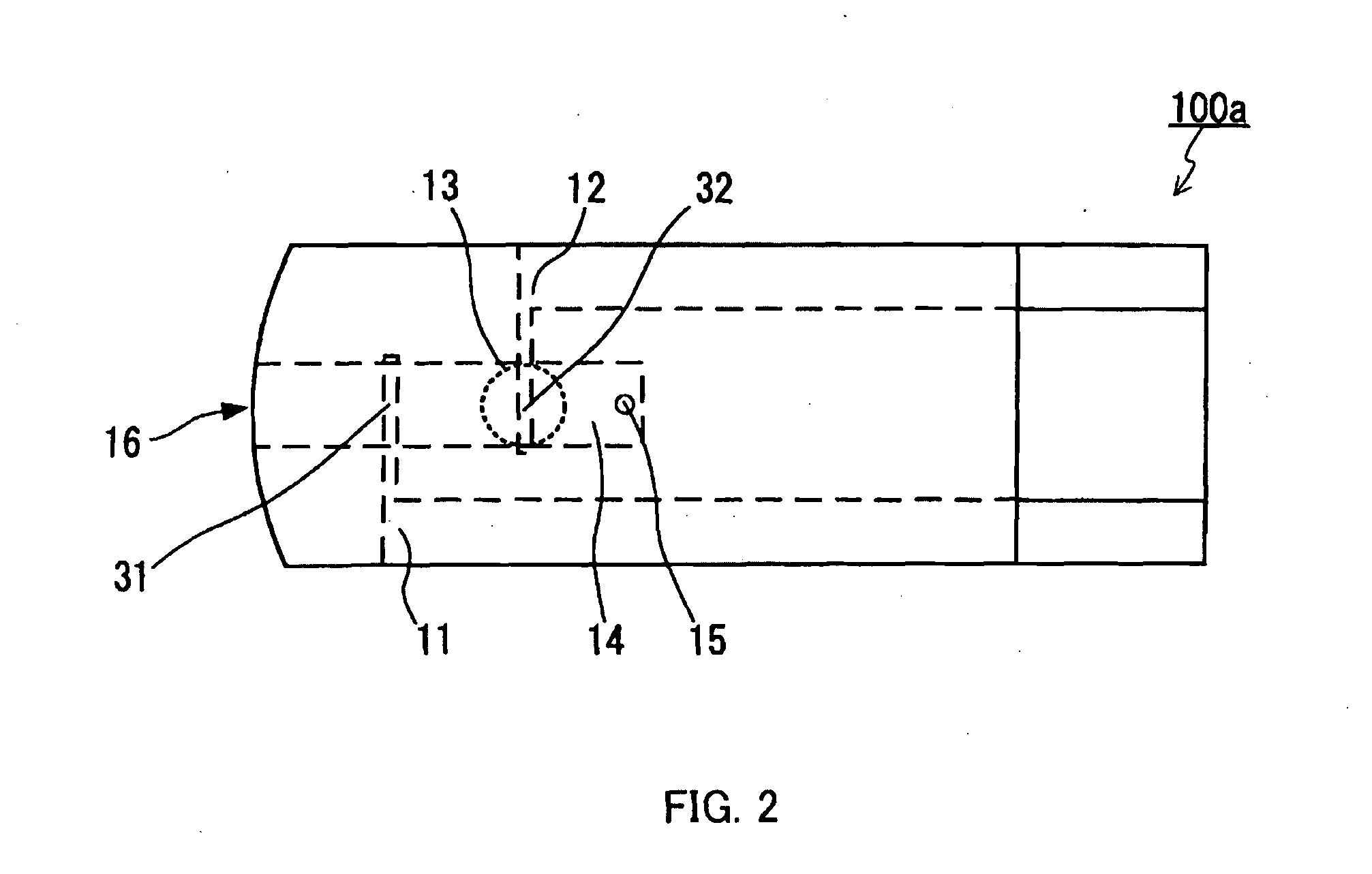
A voltage is applied across a counter electrode and a working electrode while an oxidant of a redox substance is in contact with the counter electrode and is not substantially in contact with the working electrode, and thereby metal that readily undergoes electrolytic oxidation forming at least part of a surface of the working electrode is oxidized while the oxidant in contact with the working electrode is reduced, such that a current produced upon the oxidation and the reduction is measured. According to the above constitution, while lowering the voltage applied across the working electrode and the counter electrode, a hematocrit value of a blood sample can be measured stably with satisfactory detection sensitivity. This measurement can be carried out, for example, with a sensor chip comprising a working electrode 11, a counter electrode 12, and a blood sample holder 14 in communication with a blood sample inlet 16, wherein a portion 31 of the working electrode 11 is disposed closer to the blood sample inlet 16 than a portion 32 of the counter electrode is, a surface of the portion 31 includes the metal that readily undergoes electrolytic oxidation, and a reagent 13 containing the oxidant is disposed in contact with the portion 32.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Systems and methods for determining a substantially hematocrit independent analyte concentration
InactiveUS20110162978A1Reduce probabilityLess producedImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteTester device
A method and system is provided to allow for determination of substantially Hematocrit independent analyte concentration. In one example, an analyte measurement system is provided that includes a test strip and a test meter. The test strip includes a reference electrode and a working electrode, in which the working electrode is coated with a reagent layer. The test meter includes an electronic circuit and a signal processor. The electronic circuit applies a plurality of voltages to the reference electrode and the working electrode over respective durations. The signal processor is configured to determine a substantially hematocrit-independent concentration of the analyte from a plurality of current values as measured by the processor upon application of a plurality of test voltages to the reference and working electrodes over a plurality of durations interspersed with rest voltages lower than the test voltages being applied to the electrodes.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
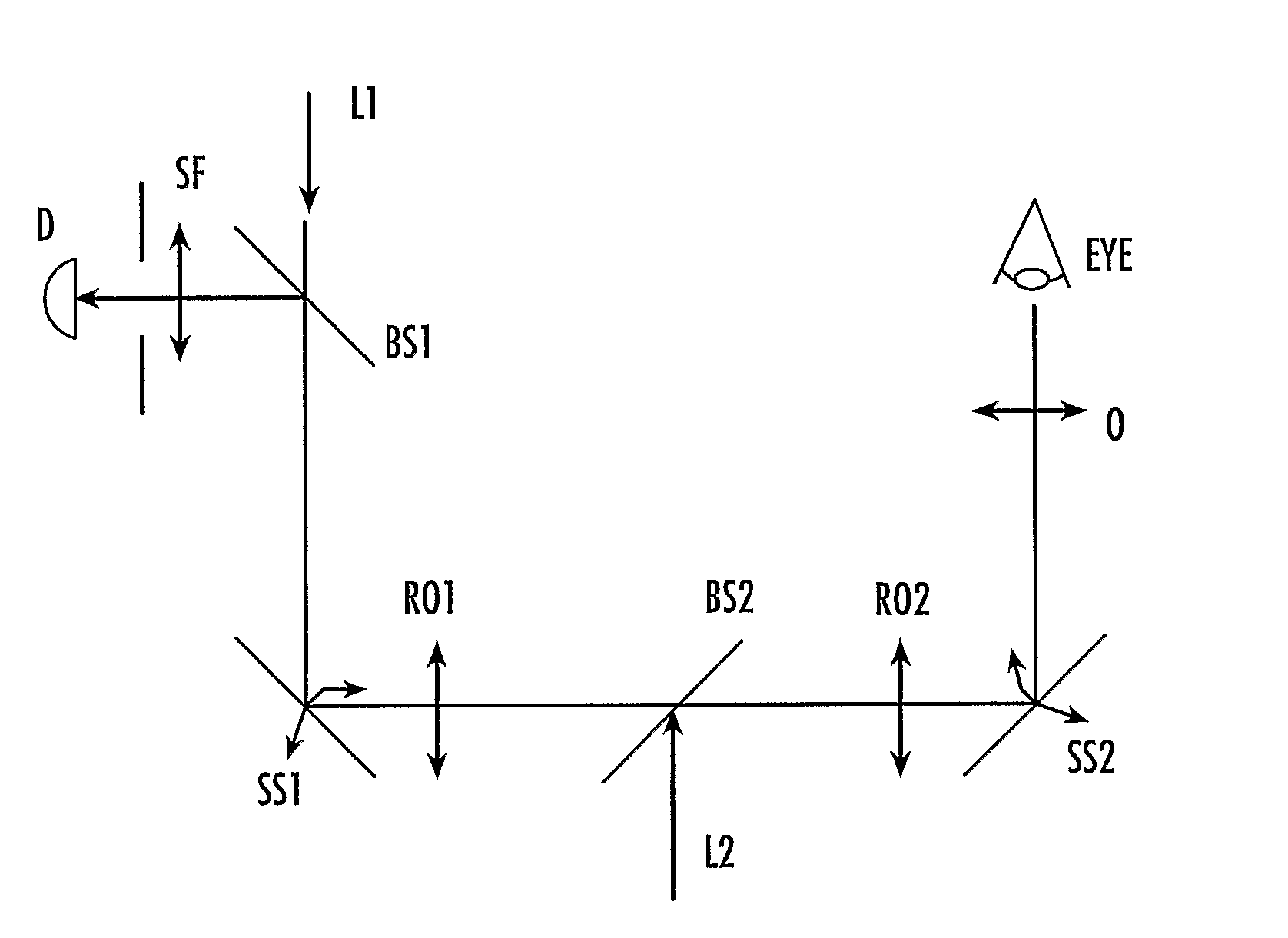
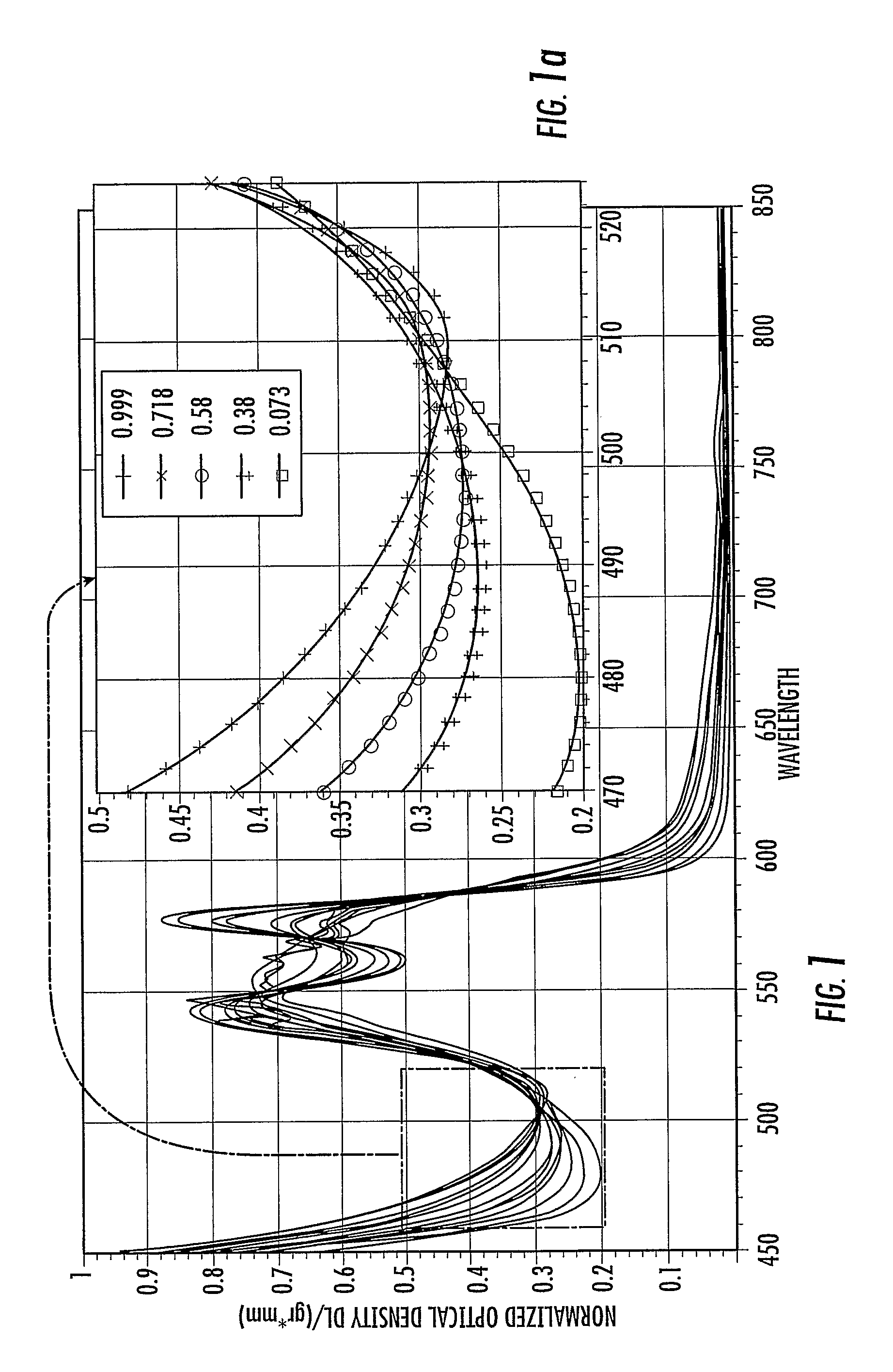
Method and device for determining oxygen saturation of hemoglobin, for determining hematocrit of blood, and/or for detecting macular degeneration
InactiveUS20100030042A1Accurately determineImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostic recording/measuringFiberOptical density measurement
A method and device for accurately determining oxygen saturation of hemoglobin by the measurement of the optical density of a sample, such as a blood vessel, in response to illumination by light having at least three wavelengths (λi, λ2, λ3, . . . ) within a range of about 460 nm to about 523 nm. The hematocrit of a sample may be determined from optical density measurements at the three or more wavelengths in conjunction with a known path length. The device may be an intravenous or intra-arterial fiber optic catheter used to deliver the interrogating light signal to the blood and to detect the reflected signal. A method and device of determining the thickness of the retinal well using spectroscopic information are also disclosed.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND +1
Implantable multi-wavelength venous oxygen saturation and hematocrit sensor and method
An intravenous implantable optical sensor assesses the relative absorbance of multiple wavelengths of light in order to determine oxygen saturation. The calculation of oxygen saturation is enhanced by use of a function of hematocrit which is derived from the relative absorbance of light of an isobestic wavelength along two different length paths through the blood. The use of the hematocrit-dependent term and multiple wavelengths of light to calculate oxygen saturation provides results that are less susceptible to noise and variation in hematocrit and thus provides a more accurate measure of oxygen saturation over a wider range of conditions than previously possible. The optical sensor may form part of an implantable system which performs the calculation of oxygen saturation and uses the results for a diagnostic or therapeutic purpose.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
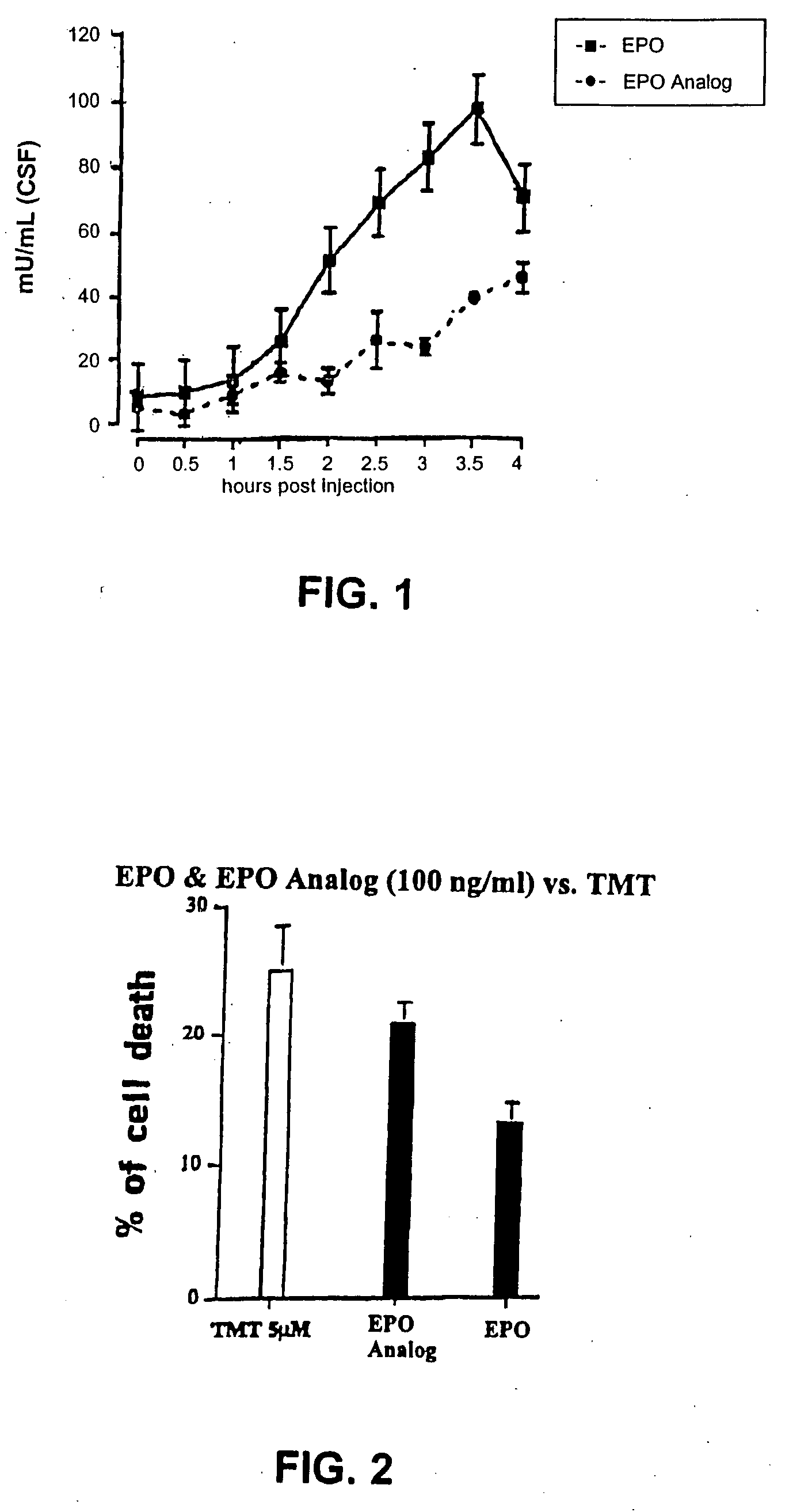
Long acting erythropoietins that maintain tissue protective activity of endogenous erythropoietin
Methods for increasing the hematocrit of an individual while maintaining the tissue protective activities of endogenous erythropoietin through the administration of a pharmaceutical compound containing chemically modified long acting erythropoietin. Also disclosed are the new chemically modified long acting erythropoietins, methods of producing the chemically modified long acting erythropoietins, and compositions comprising the chemically modified long acting erythropoietins.
Owner:THE KENNETH S WARREN INST +1
Method and Apparatus for Ultrasonic Determination of Hematocrit and Hemoglobin Concentrations
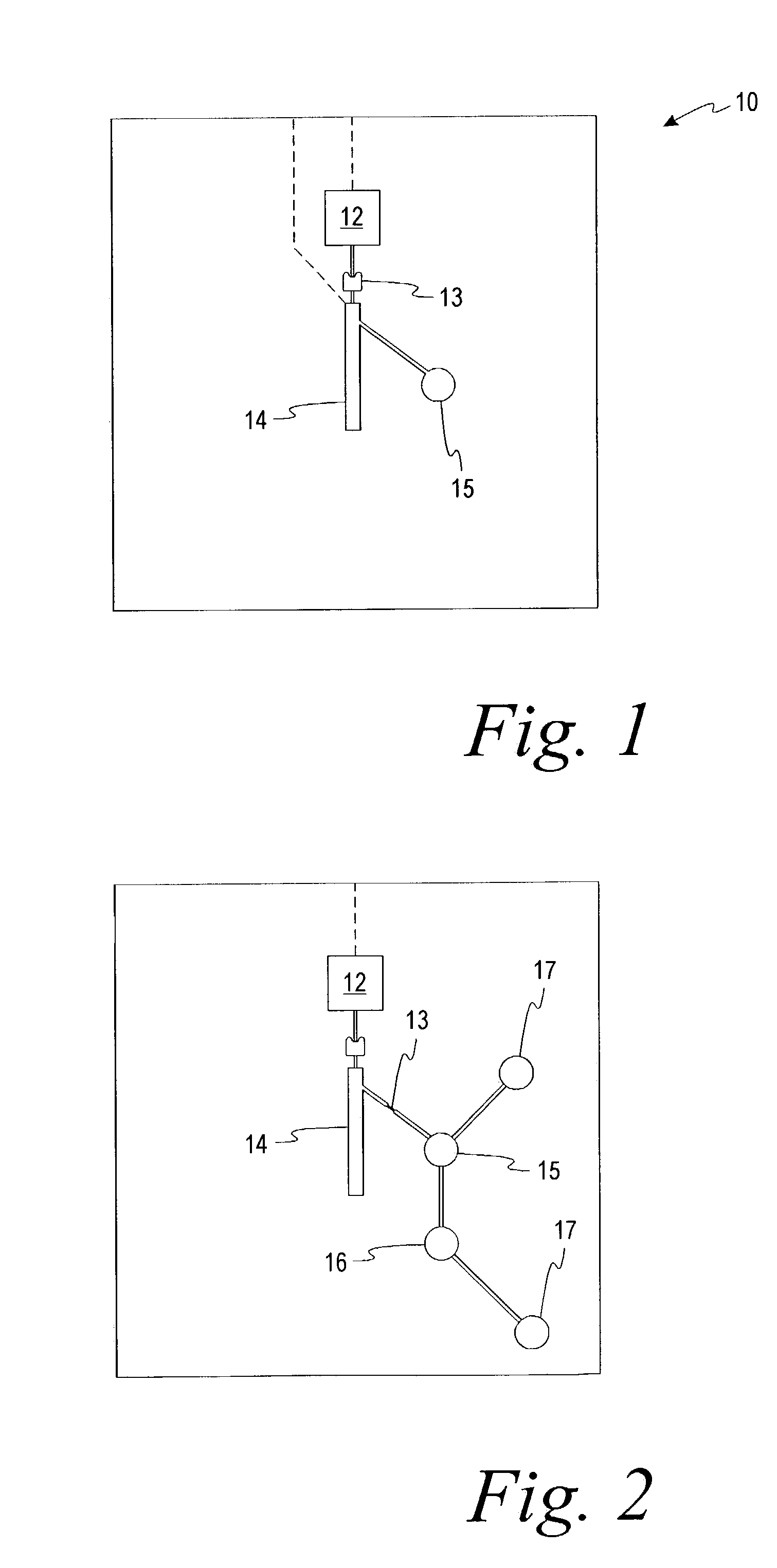
ActiveUS20070266778A1Simple accurate quick measurementVibration measurement in solidsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedicinePoint of care device
An ultrasonic field-portable system for accurately measuring hematocrit (HCT) and hemoglobin concentration (HGB) in small food samples. The system includes an analyzer (10) that allows extremely accurate measurements of blood hematocrit from only one or two drops of +>>d collected in a disposable sampling device (12) that is then inserted into the analyzer (10). The system is compact enough to package into a point of care device, making it a point of care device with accuracy comparable to larger CBC lab equipment.
Owner:SEPARATIONS TECH
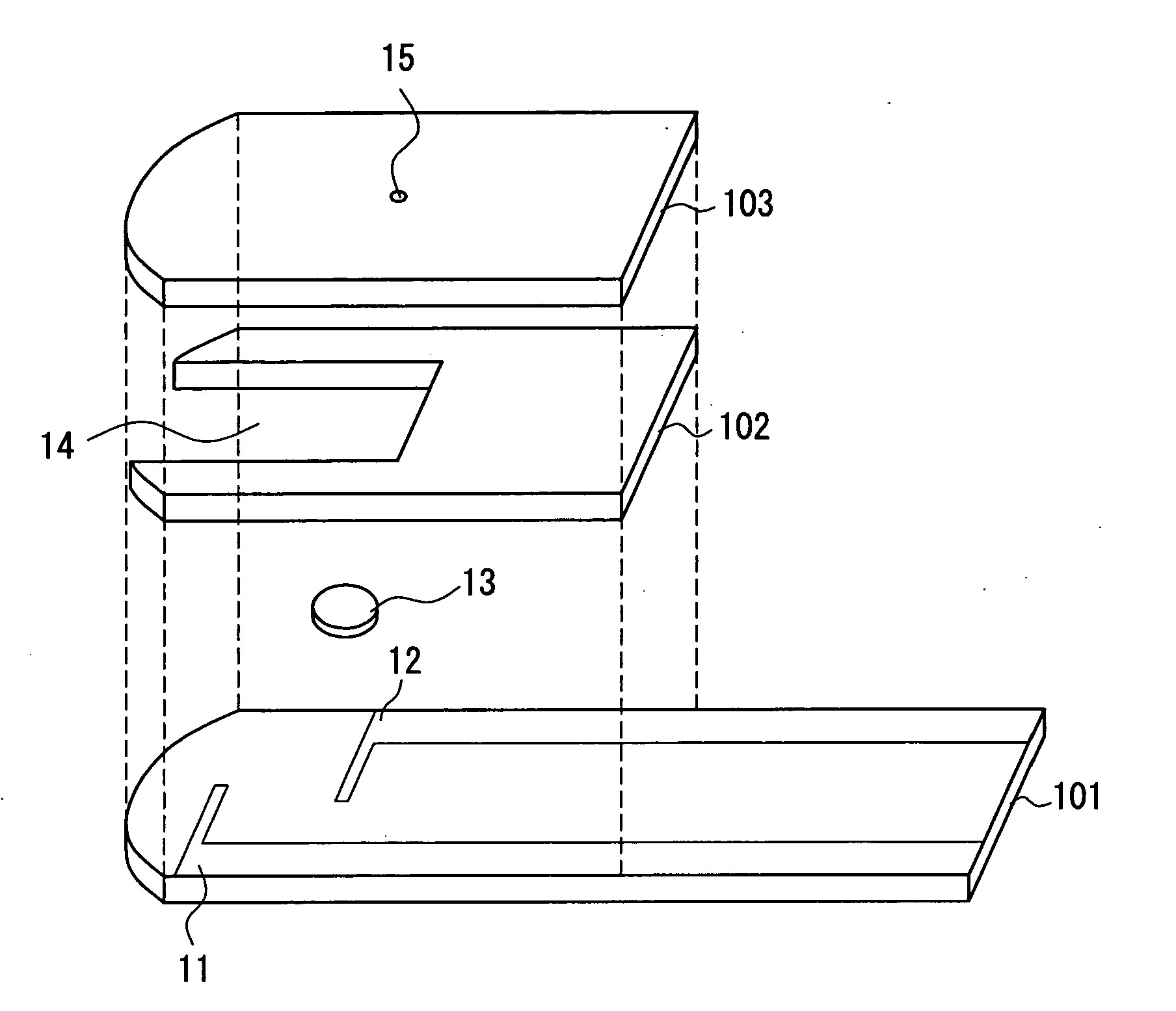
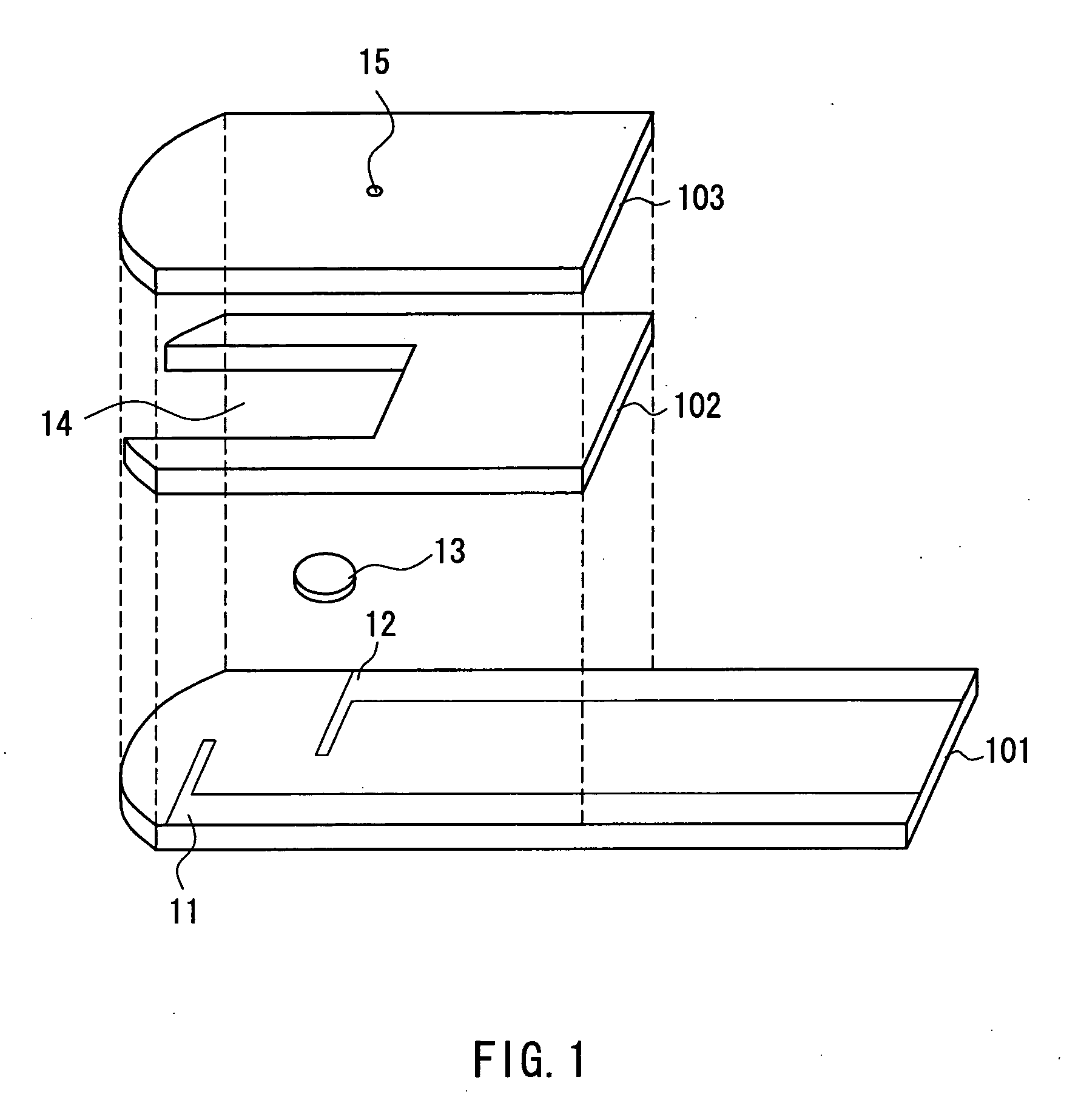
Method of measuring hematocrit (hct), sensor used in the method, and measuring device
ActiveUS20070062822A1High sensitivityHigh measurement accuracyImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMeasurement deviceRedox
The present invention provides a method of electrochemically measuring a hematocrit (Hct) value using a sensor, capable of achieving excellent measurement accuracy and reliability and also provides a sensor used in the method. The method of electrochemically measuring a hematocrit (Hct) value of blood include: providing an electrode system having a working electrode (11) and a counter electrode (12), in which a redox substance is provided on the counter electrode (12) but not on the working electrode (11); supplying blood to the electrode system; applying a voltage to the electrode system in this state to cause an oxidation current or a reduction current to flow between the working electrode (11) and the counter electrode (12); detecting the oxidation current or the reduction current; and determining a Hct value based on a value of the detected current.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Dual Frequency Impedance Measurement of Hematocrit in Strips
This invention is a method for determining a hematocrit value. The steps include applying a first pulse of potential excitation at a first frequency to a test strip containing a fluid sample. The method also includes applying a second pulse at a second frequency that is higher than the first frequency. Based on first and second impedance measurements associated with each pulse, a hematocrit value may be determined. Also, a concentration of an analyte contained within the fluid sample may be determined based on the hematocrit value.
Owner:NIPRO DIAGNOSTICS INC
Method of enhancing the efficacy of anti-tumor agents
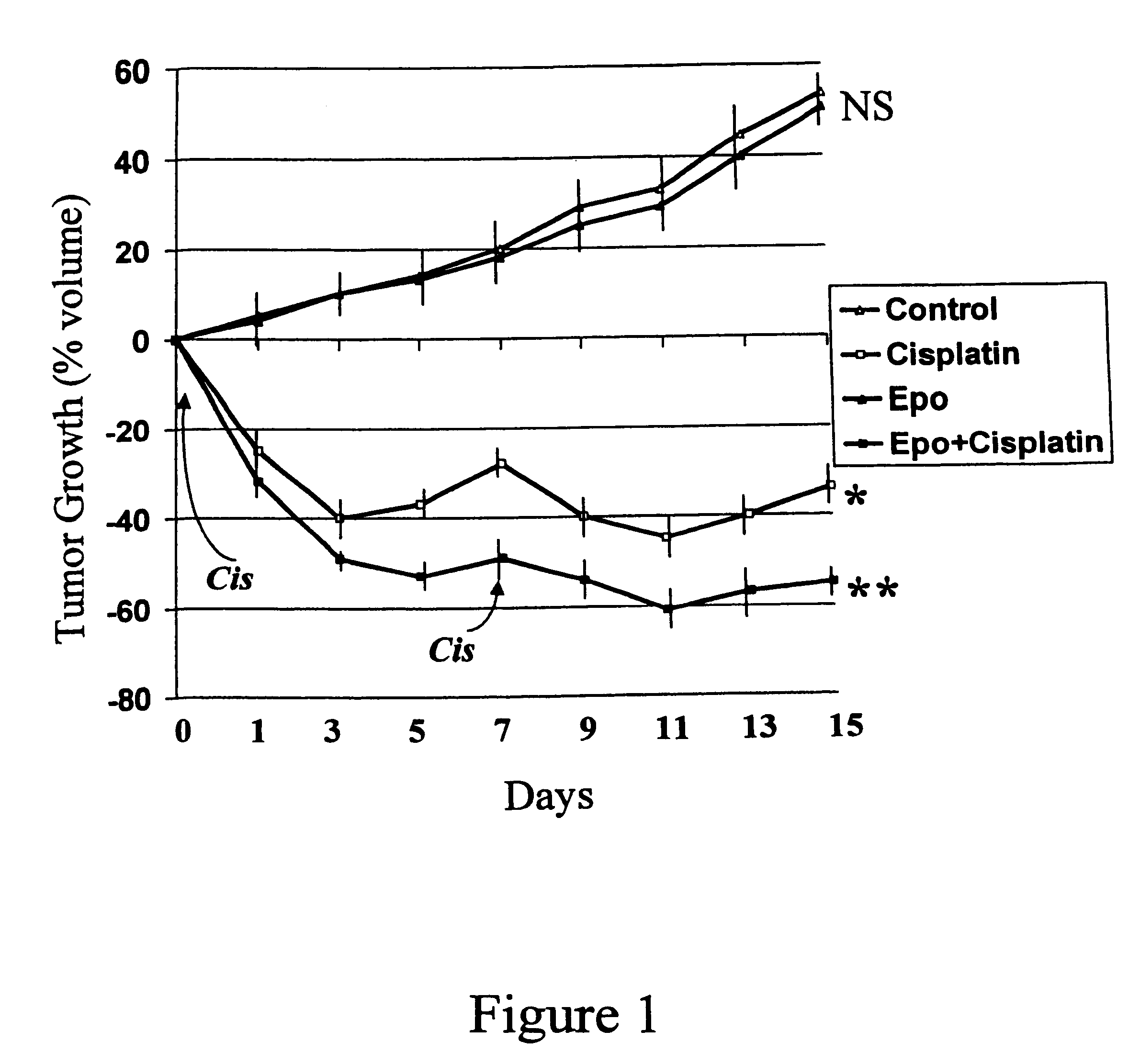
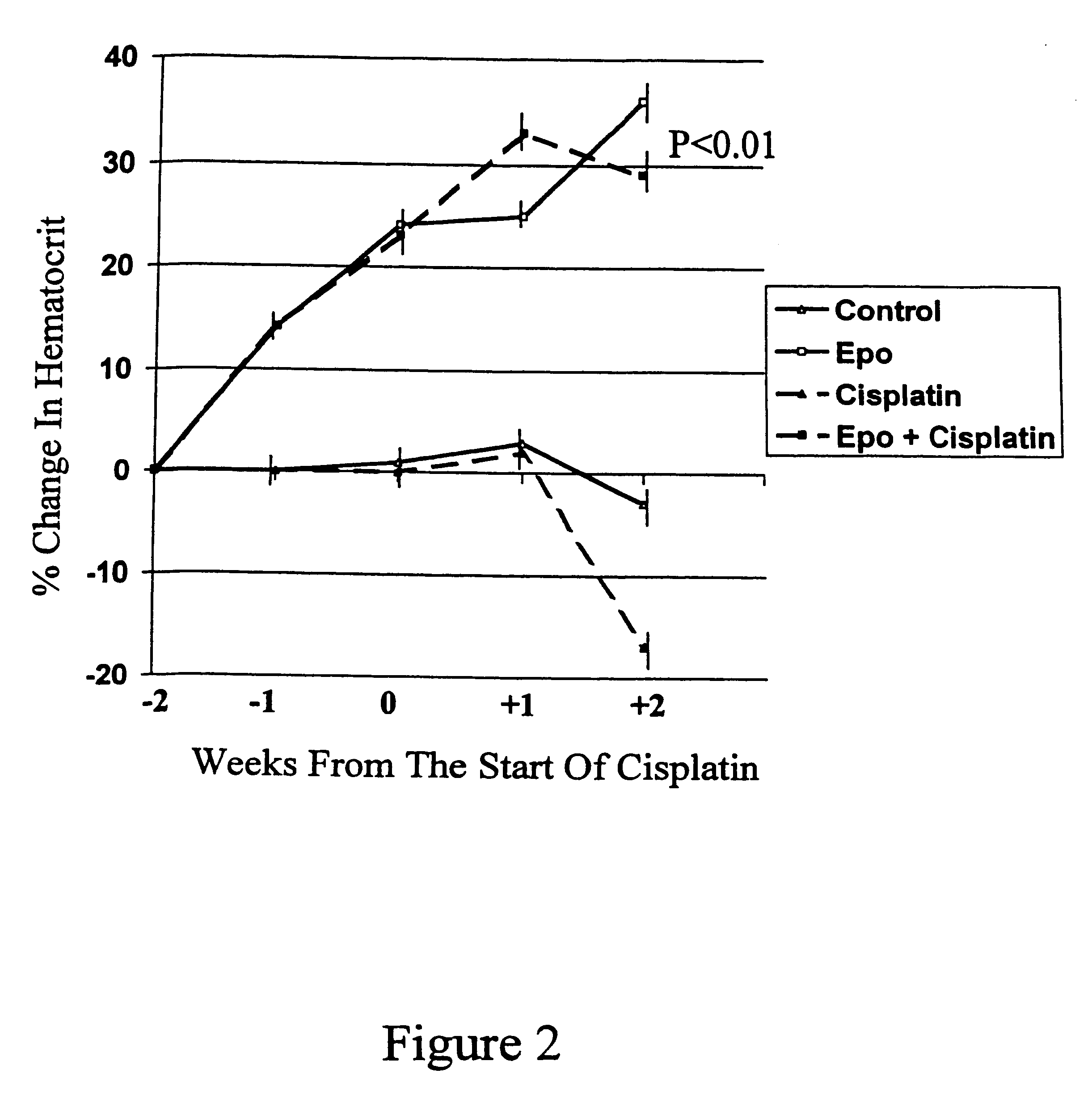
InactiveUS6426094B2Good curative effectHeavy metal active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsSolid tumorCancer research
A method for enhancing the effect of anti-tumor agents on solid tumors is provided. The method comprises administering to an individual an anti-tumor agent and a hematocrit elevator. The hematocrit elevator may be administered before or concurrently with the anti-tumor agent.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
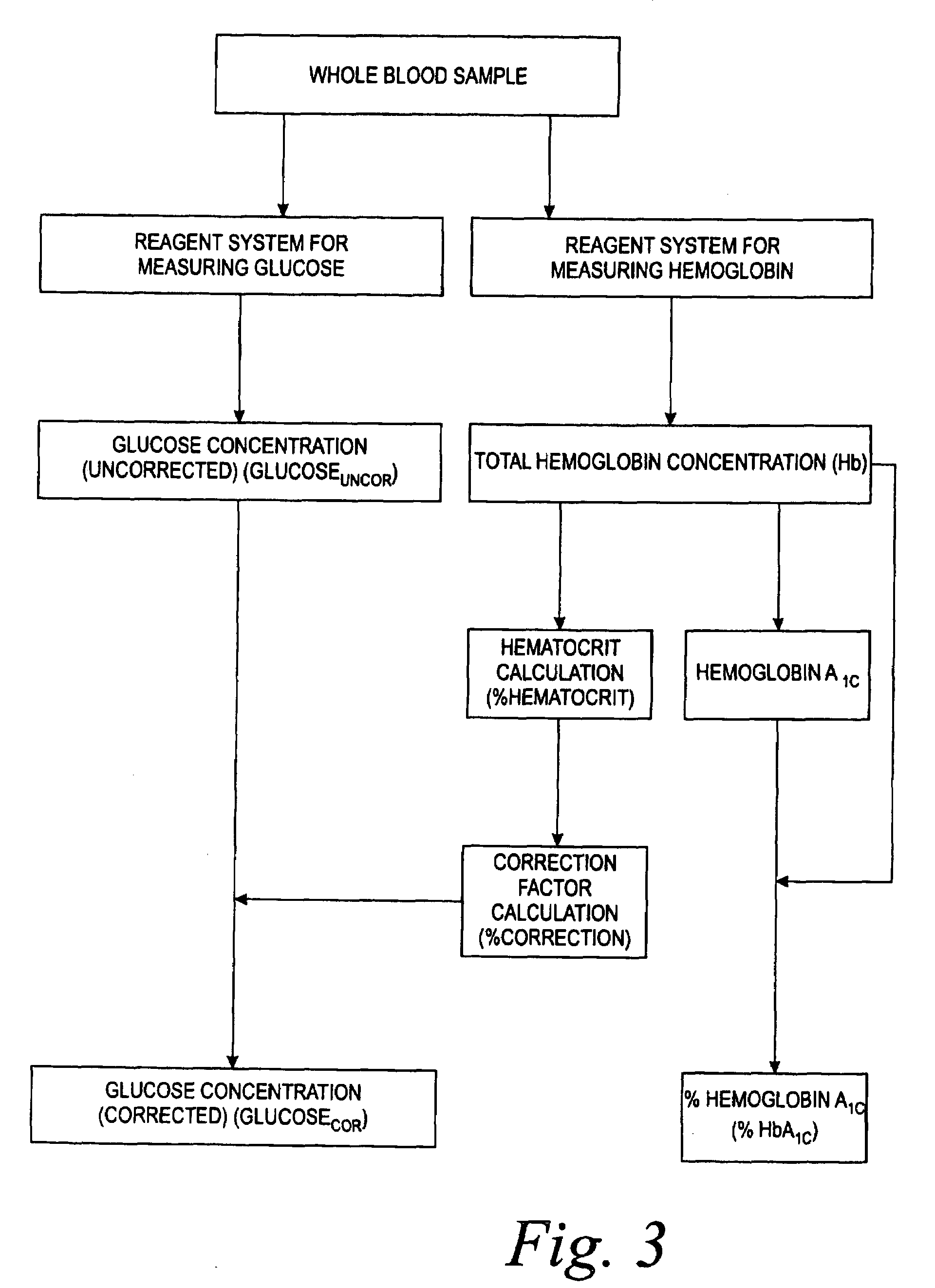
Method for performing correction of blood glucose assay bias using blood hemoglobin concentration
A device and method for determining a correction factor for correcting the blood glucose assay bias based on sample hematocrit interference in a testing device using the blood hemoglobin concentration. The hemoglobin assay and the glucose assay may be performed using a single combination monitoring device.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Method and apparatus for separation of particles in a microfluidic device
InactiveUS7094354B2Easy to separateIncrease the areaBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRed blood cellSpecific volume
A microfluidic device provides separation of particles in a liquid sample, particularly, separation of a sample of whole blood into its components for further analysis. Separation into red blood cells and plasma occurs within a few seconds after the blood sample has been transferred into a separation chamber with the application of centrifugal force of less than about five times gravity. With the application of greater force measurement of hematocrit is possible.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Gel formation to reduce hematocrit sensitivity in electrochemical test
InactiveUS20080149480A1Reduce inaccuracyReduce sensitivityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSpecific volumeElectrochemistry
Devices for determining the concentration of a constituent in a physiological sample that comprise gel matrices to filter red blood cells are provided. Examples of such devices include a biosensor comprising, on a support substrate, a sample reception region for receiving a blood sample; at least one electrode; and a reaction reagent system that is located in a gel matrix. The gel matrix disclosed herein is sufficient to prevent at least some of the red cells in the blood sample from contacting the electrode, and thus reduce the hematocrit sensitivity in the measurement.
Owner:NIPRO DIAGNOSTICS INC
Method and apparatus for ultrasonic determination of hematocrit and hemoglobin concentrations
ActiveUS7523649B2Simple accurate quick measurementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsVibration measurement in solidsPoint of care deviceBiomedical engineering
An ultrasonic field-portable system for accurately measuring hematocrit (HCT) and hemoglobin concentration (HGB) in small food samples. The system includes an analyzer (10) that allows extremely accurate measurements of blood hematocrit from only one or two drops of +>>d collected in a disposable sampling device (12) that is then inserted into the analyzer (10). The system is compact enough to package into a point of care device, making it a point of care device with accuracy comparable to larger CBC lab equipment.
Owner:SEPARATIONS TECH
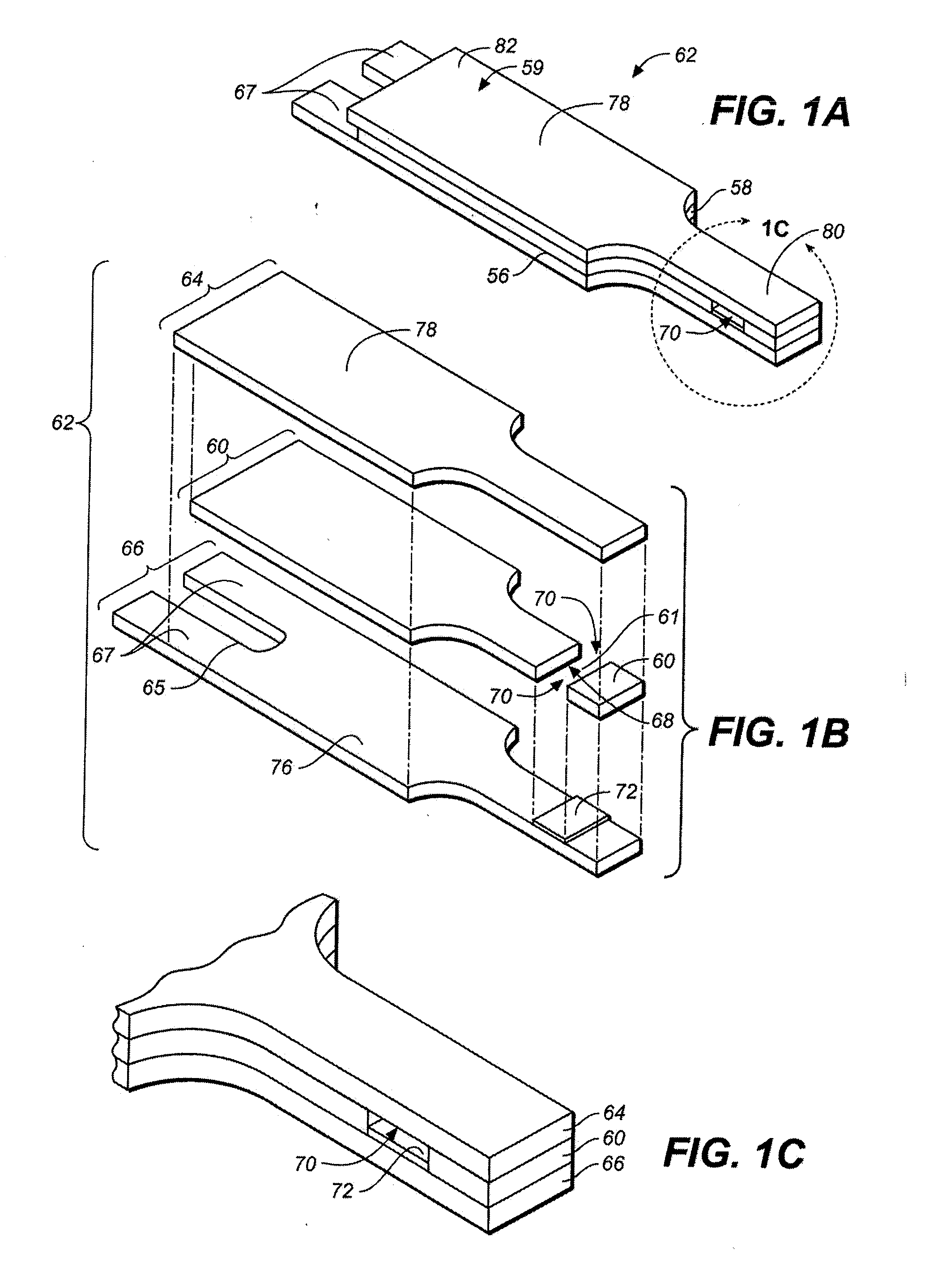
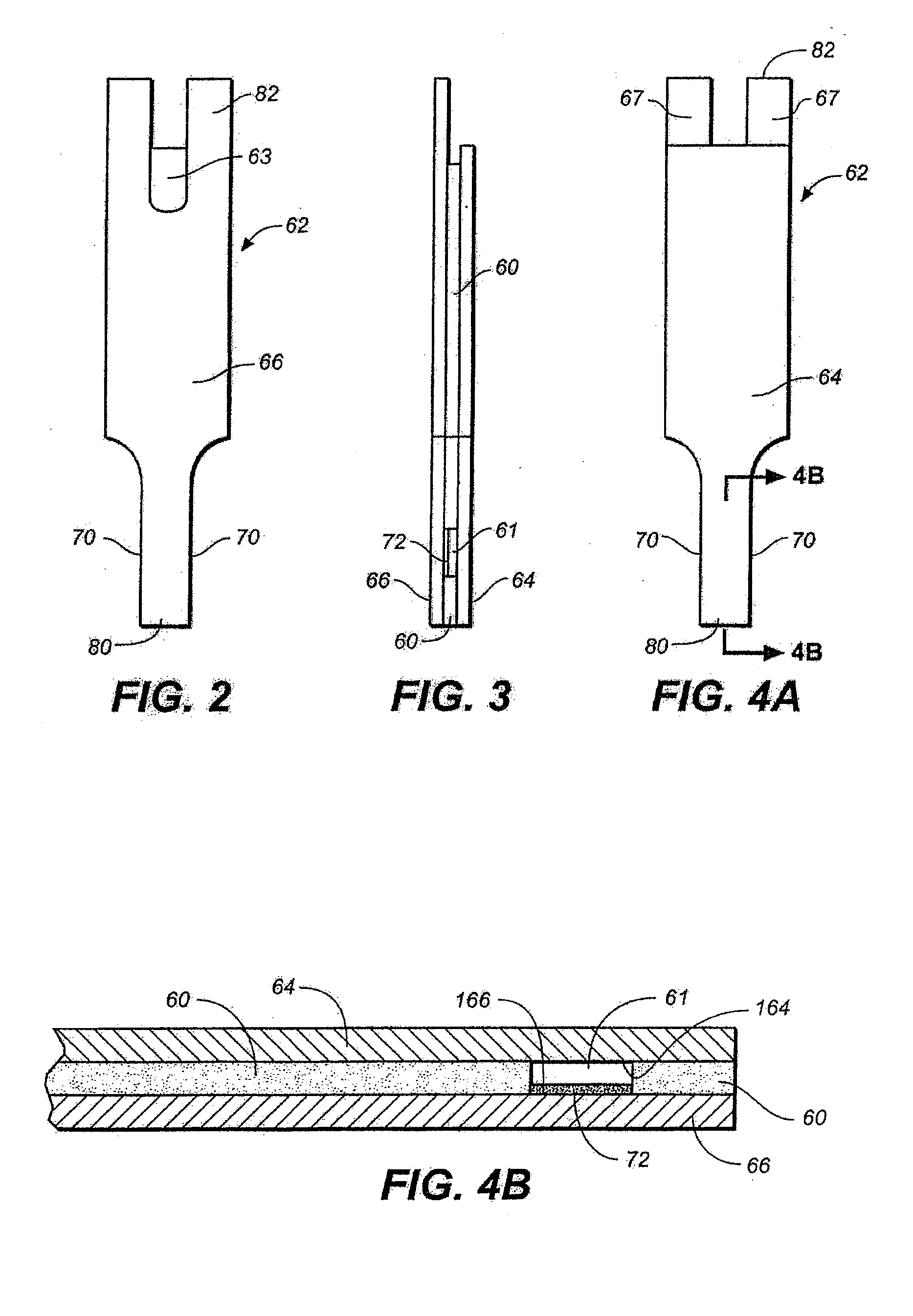
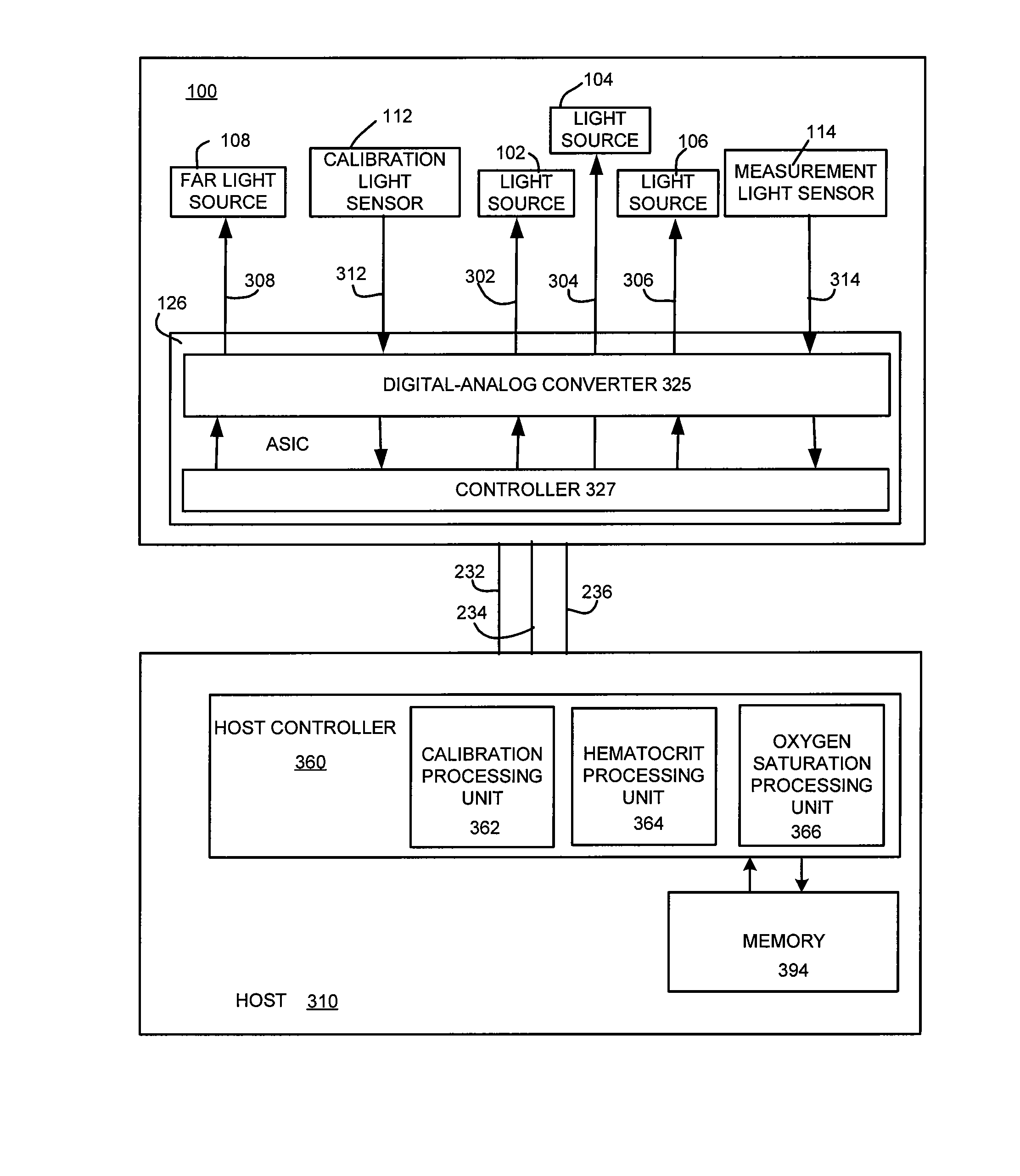
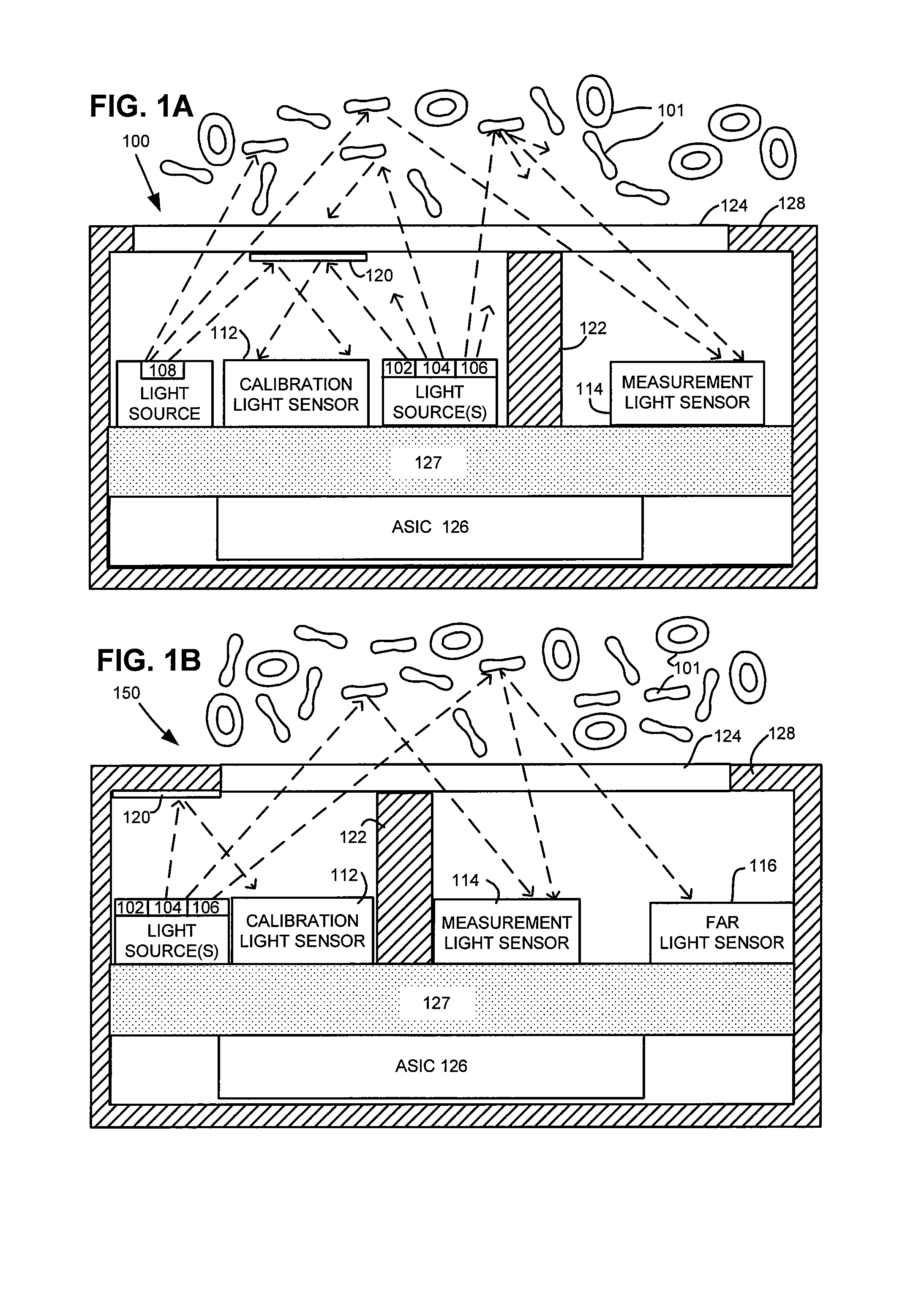
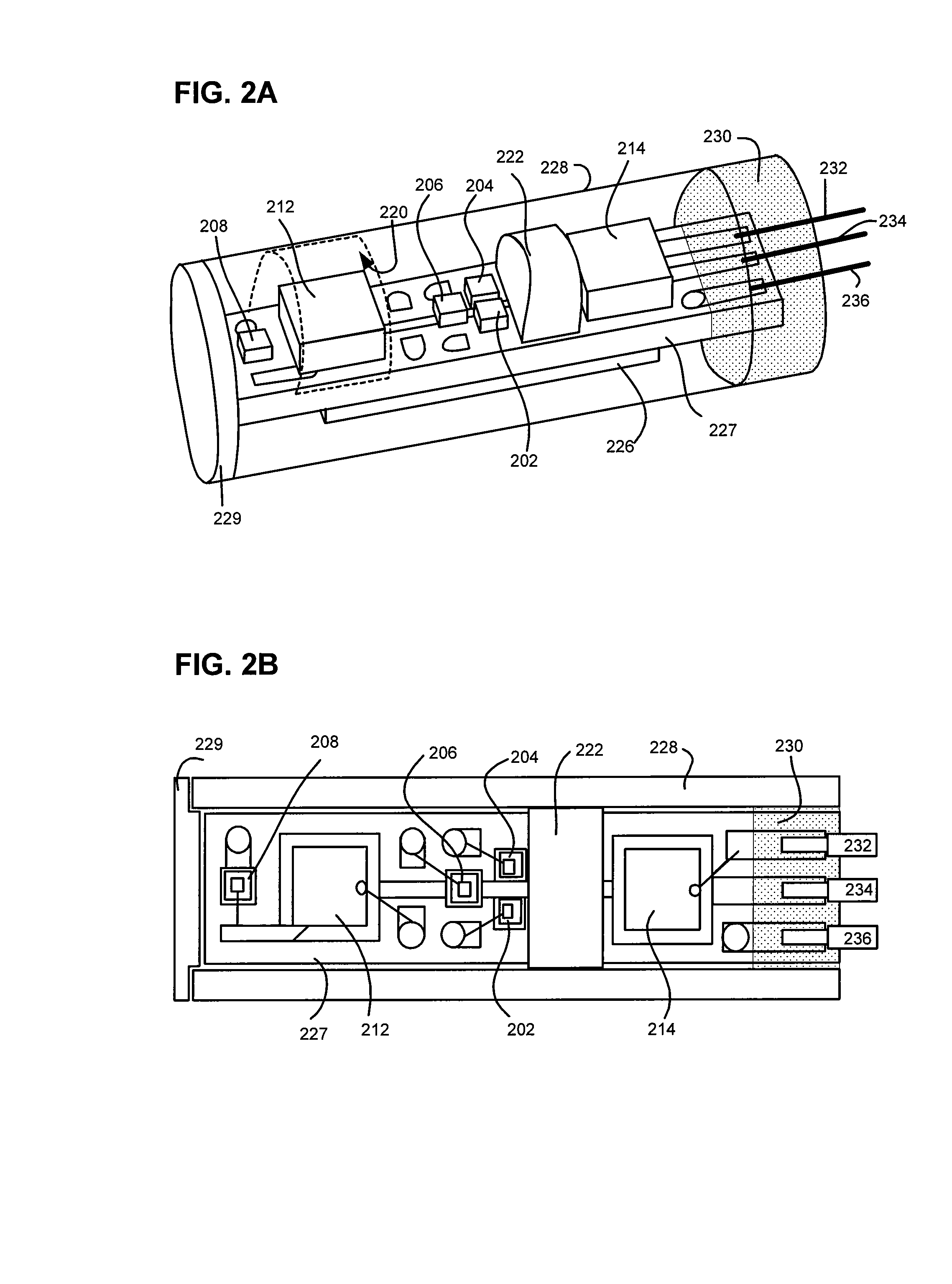
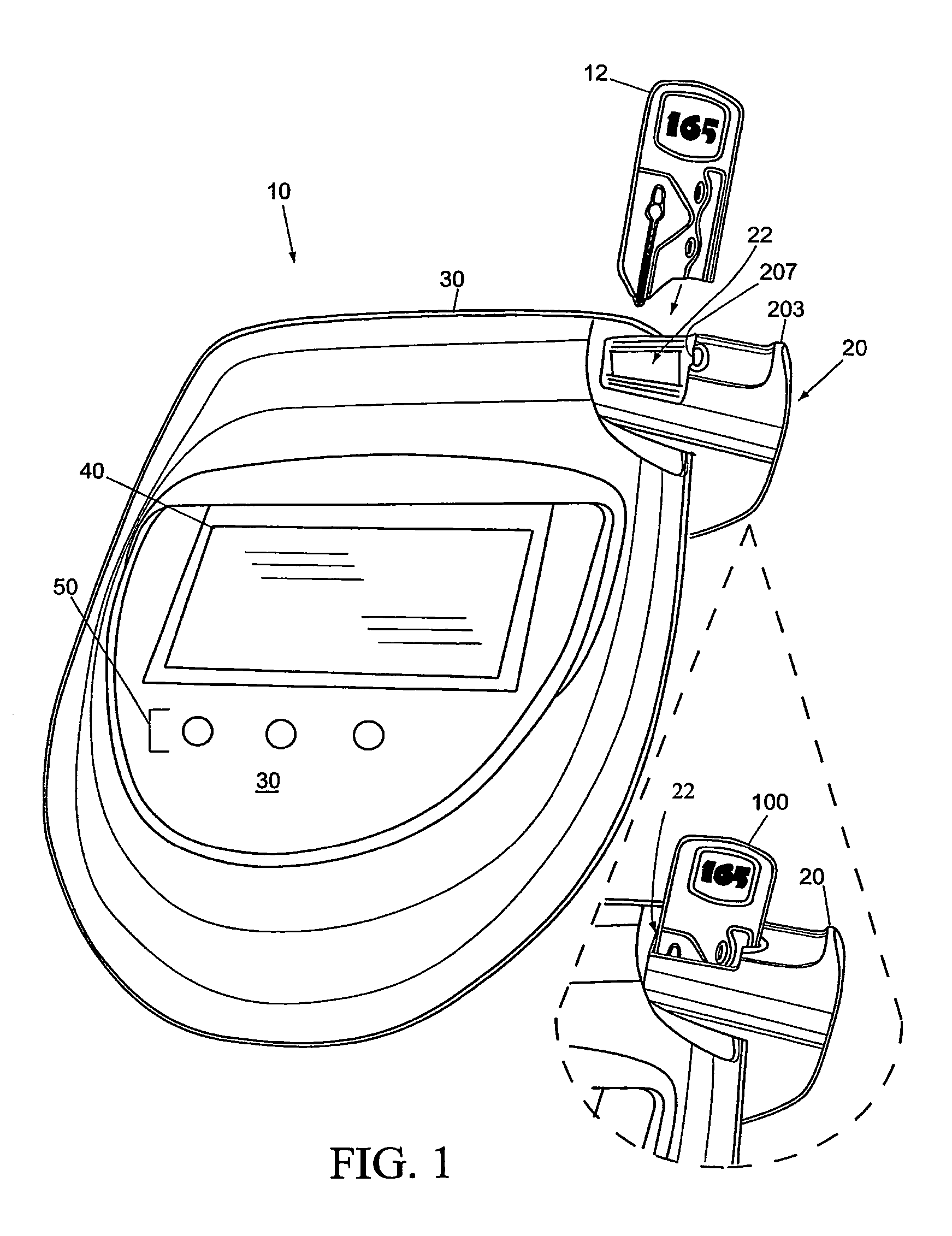
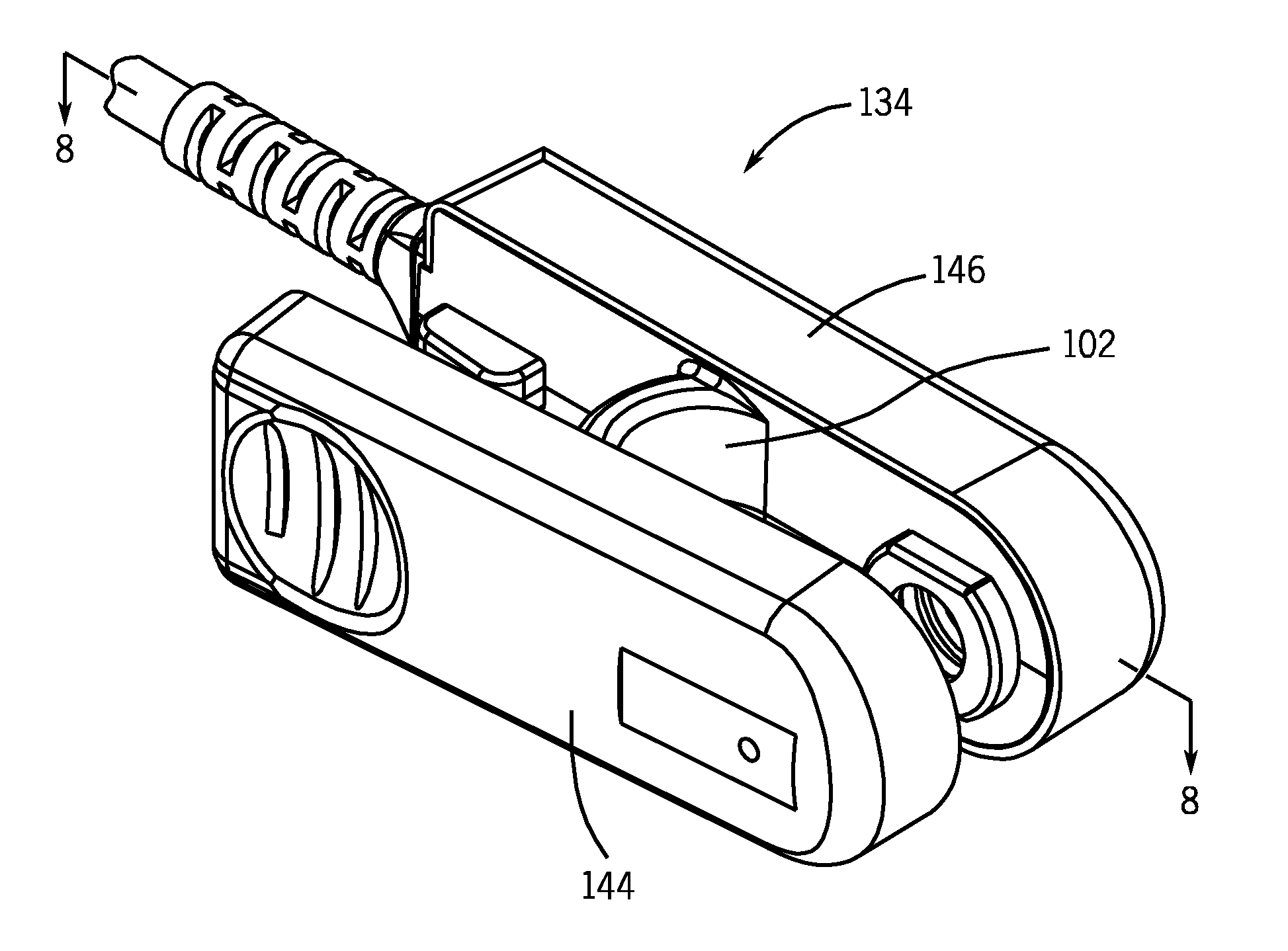
Sensor Clip Assembly for an Optical Monitoring System
ActiveUS20120120384A1Easily integrated into other electronicLow heat generationOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesMonitoring systemOxygen saturation
A sensor clip assembly for an optical blood monitoring system includes a circuit board with a microprocessor that is programmed with a ratiometric model to calculate hematocrit and / or oxygen saturation levels of a patient.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com