Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
452results about How to "Reduce partial pressure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Process for producing a hydrocarbon component of biological origin
ActiveUS20040230085A1Improve performanceLow densityLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionHydrocarbonsIsomerizationHydrocarbon
The invention relates to a process for producing a hydrocarbon component of biological origin. The process comprises at least two steps, the first one of which is a HDO step and the second one is an isomerization step operated using the counter-current flow principle. A biological raw material containing fatty acids and / or fatty acid esters serves as the feed stock.
Owner:OYJ NESTE OIL +1
Method for depositing metal-containing film using particle-reduction step
InactiveUS20160168699A1Reduce surface roughnessSolve the lack of resistanceChemical vapor deposition coatingPlasma techniqueAMINO BASENitride
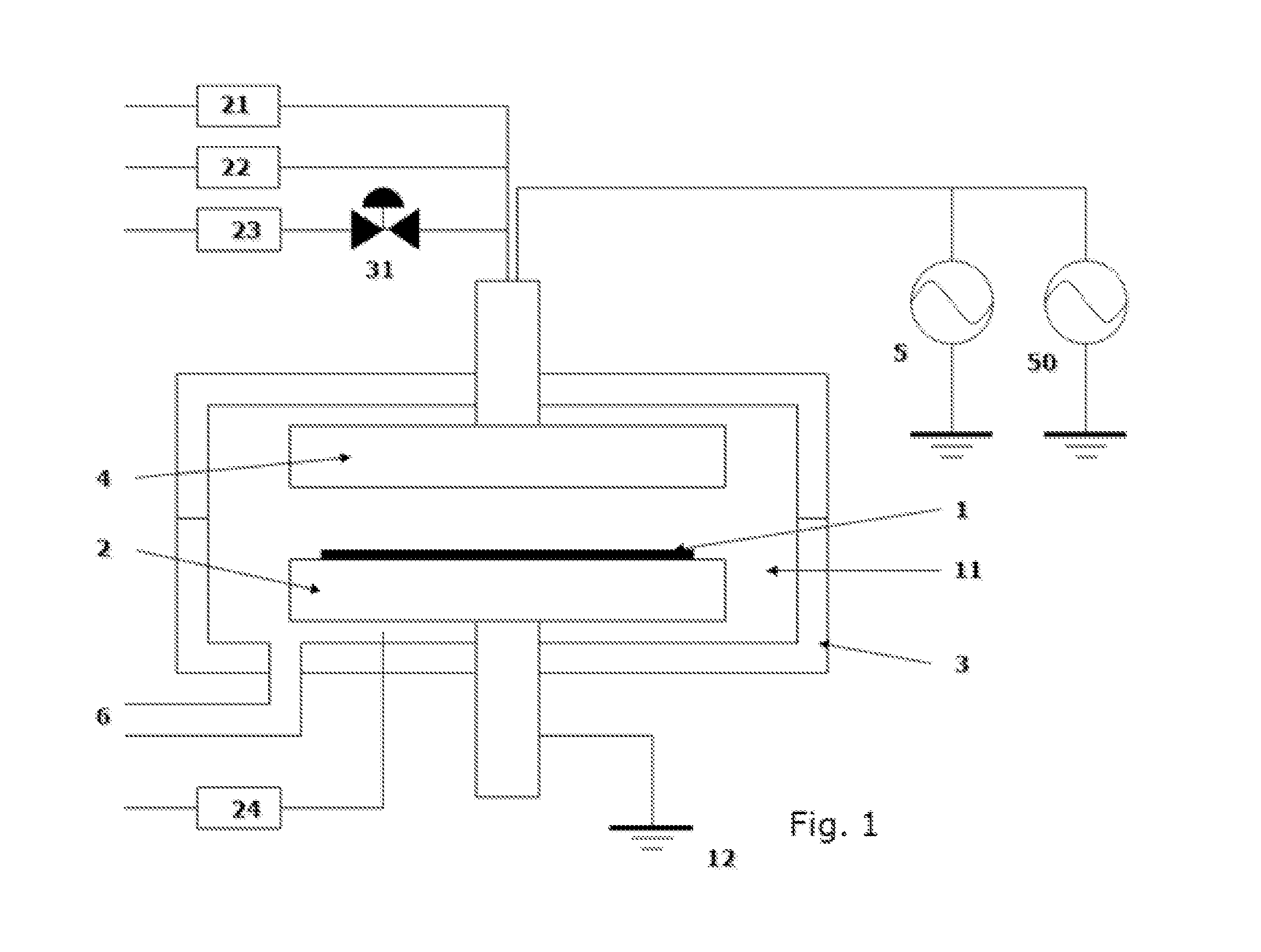
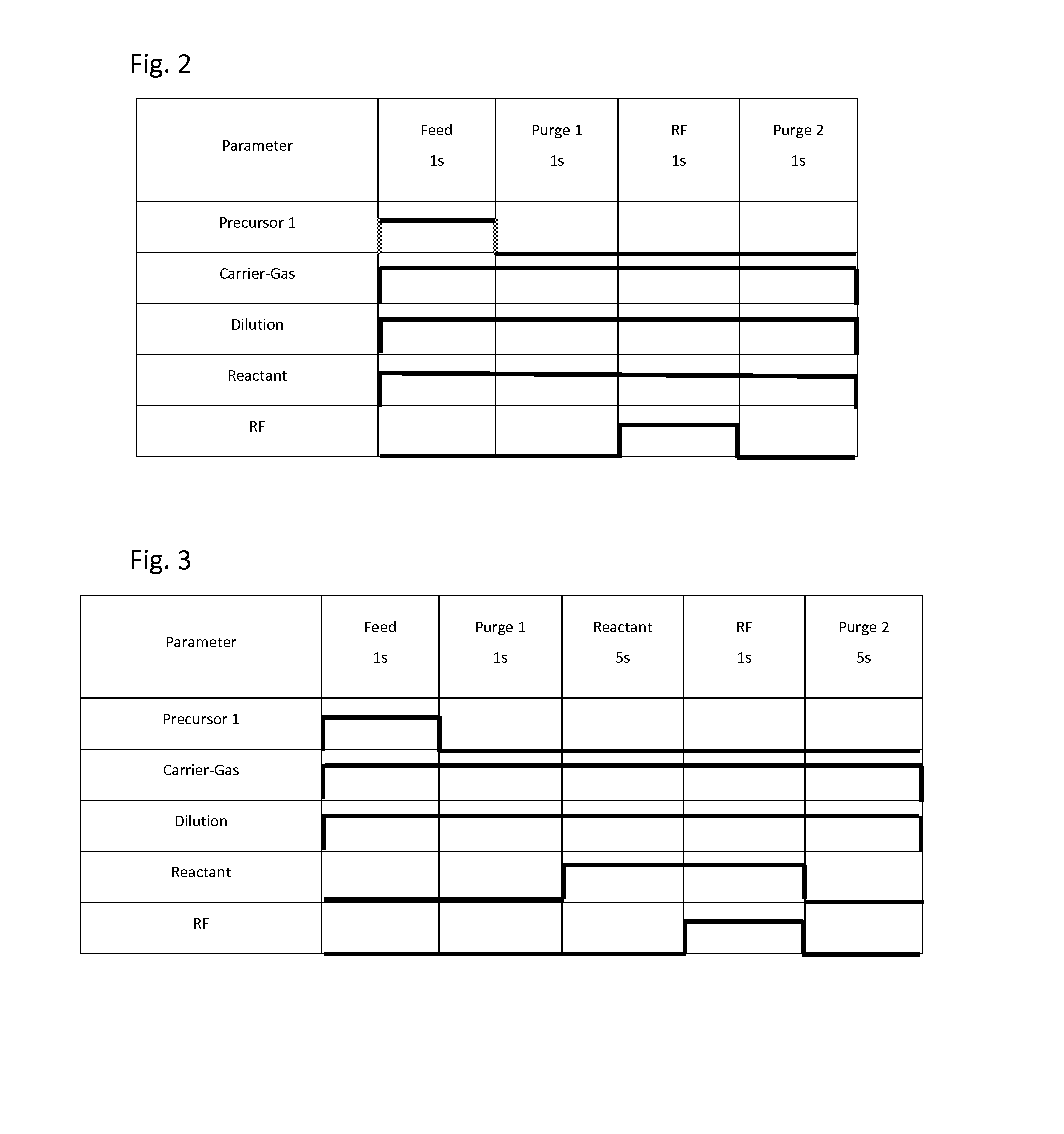
A method for forming a metal oxide or nitride film on a substrate by plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD), includes: introducing an amino-based metal precursor in a pulse to a reaction space where a substrate is placed, using a carrier gas; and continuously introducing a reactant gas to the reaction space; applying RF power in a pulse to the reaction space wherein the pulse of the precursor and the pulse of RF power do not overlap, wherein conducted is at least either step (a) comprising passing the carrier gas through a purifier for reducing impurities before mixing the carrier gas with the precursor, or step (b) introducing the reactant gas at a flow rate such that a partial pressure of the reactant gas relative to the total gas flow provided in the reaction space is 15% or less.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Microcapsules and processes for making the same using various polymers and chitosans
InactiveUS6733790B1Improve stabilityReduce partial pressurePowder deliveryBiocideAnionic polymersAlginic acid
A microcapsule having a mean diameter of from about 0.1 to about 5 mm, a membrane and a matrix containing at least one active principle wherein the microcapsule is the product of the process comprising the steps of (a) forming an aqueous matrix by heating an aqueous solution comprised of a gel former, an anionic polymer selected from the group consisting of a salt of alginic acid and an anionic chitosan derivative and active principle; (b) adding the aqueous matrix to an aqueous solution of chitosan.
Owner:COGNIS IP MANAGEMENT GMBH
Method of forming a glass melt
ActiveUS7454925B2Promote vigorous boilingReduce partial pressureCharging furnaceGlass furnace apparatusMolten glassExcessive Cooling
A method of forming a glass melt including heating a glass feed material in a first melting furnace to form a glass melt, flowing the glass melt into a second melting furnace through a refractory metal connecting tube, and further heating the glass melt in the second melting furnace. The refractory metal connecting tube is heated to prevent the molten glass from excessive cooling, and to ensure that the glass melt entering the second melting furnace is equal to or greater than the temperature of the glass melt in the second melting furnace. An apparatus for performing the method is also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
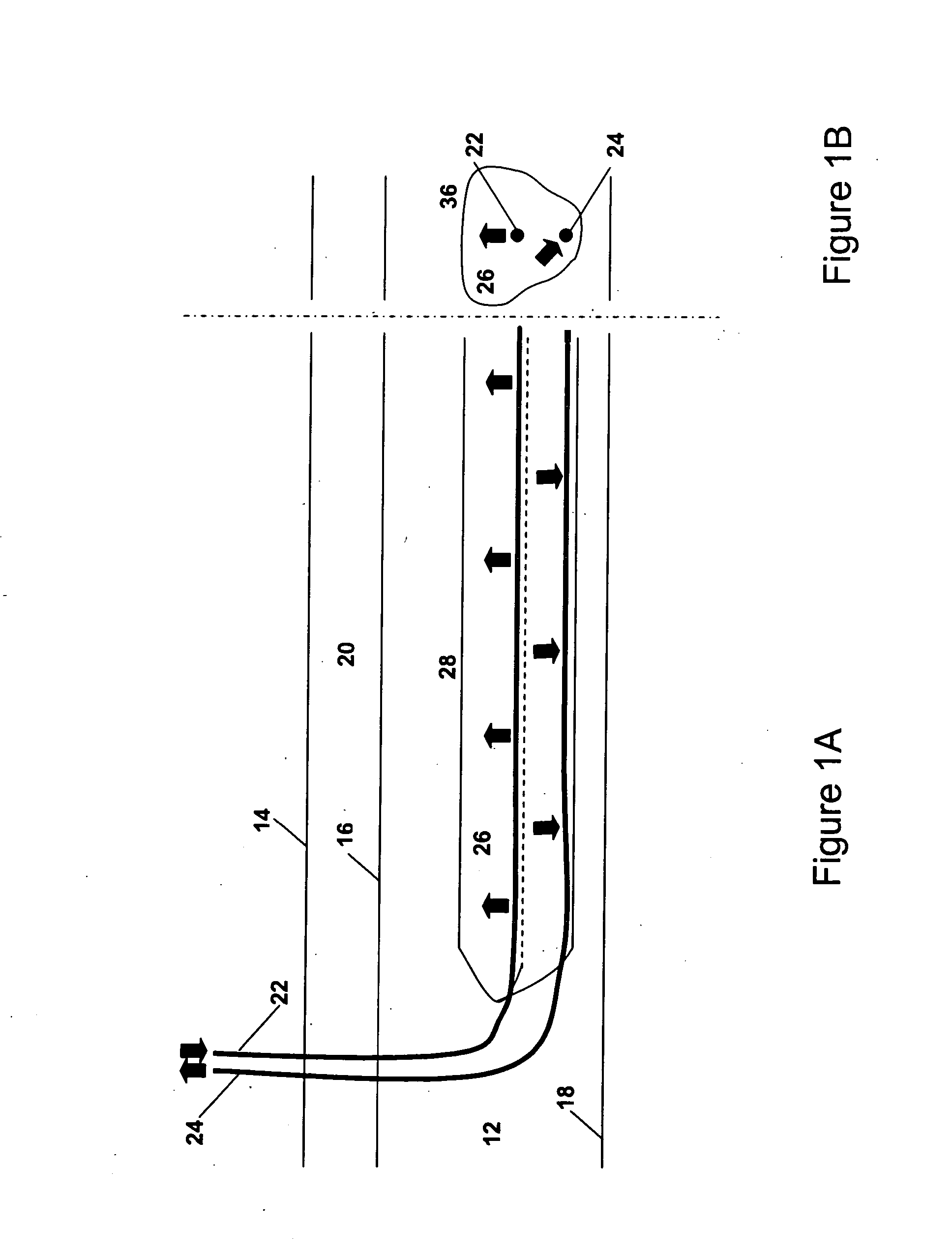
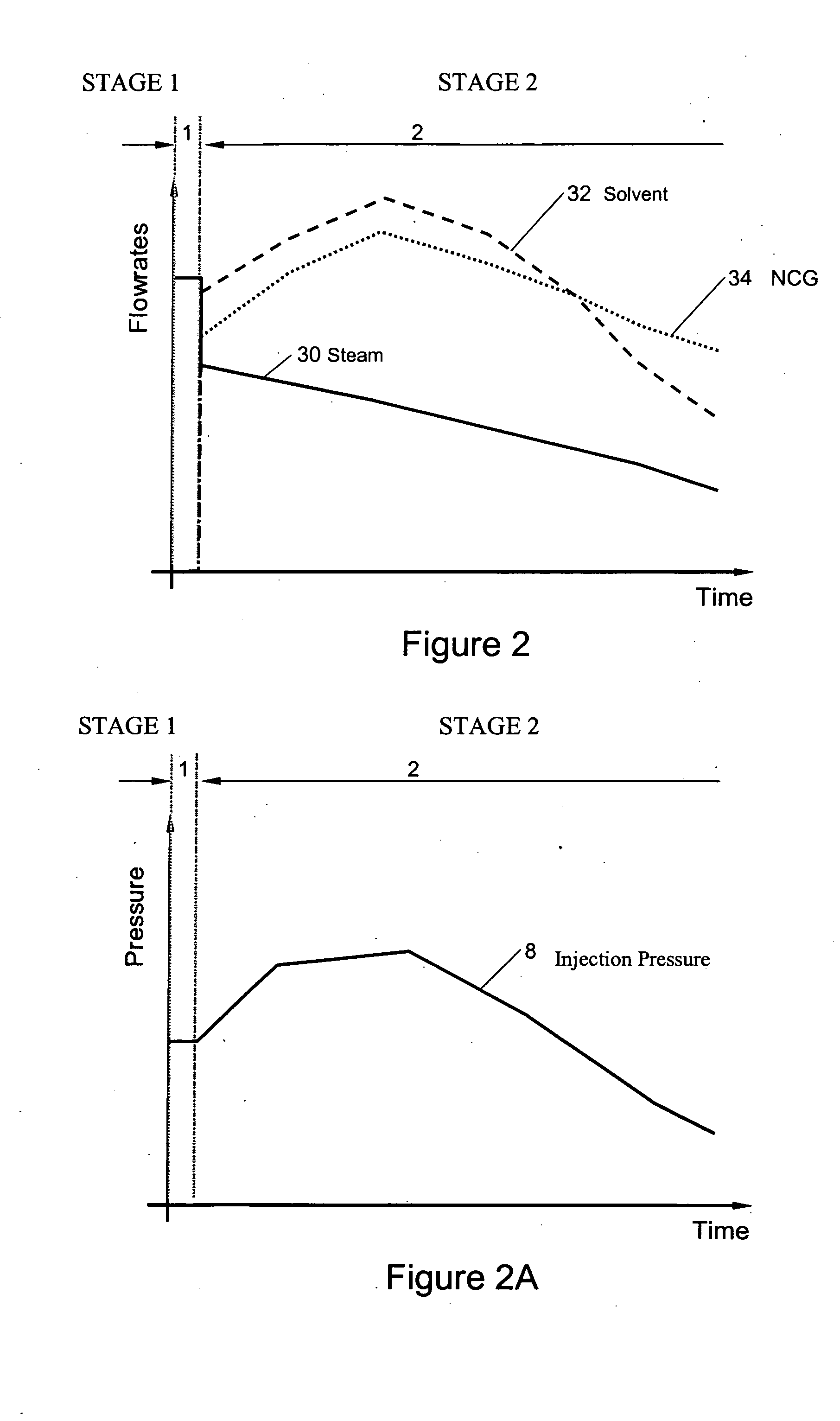
In situ process to recover heavy oil and bitumen
InactiveUS20080017372A1Maximize actionLow viscositySurveyFluid removalHydrocarbon solventsFluid viscosity
An in situ reservoir recovery process consisting of a horizontal injection well and a horizontal production well to extract bitumen or heavy oil from a reservoir. The process consists of a first phase operated at high-pressure in which steam, hydrocarbon solvent and non-condensable gases are injected into the reservoir and a second phase in which the injected fluids are transitioned to a high content of solvent and non-condensable gas and a reduced amount of steam to maintain a warm zone in the neighbourhood of the injection and production wells. The steam injection is sufficient to promote vapor transport of the solvent into the vapor depletion chamber and maintain the process at elevated temperatures in order to maintain low fluid viscosities in the production wellbore and to achieve preferred phase behaviour of the solvent hydrocarbon and the heavy oil or bitumen. The operating pressure of the process is controlled to prevent losses of the solvent hydrocarbon to the formation and to aid in solvent production to the production well in order for future re-cycling.
Owner:PARAMOUNT RESOURCES LTD
Methods of hyperdoping semiconductor materials and hyperdoped semiconductor materials and devices
InactiveUS20030121468A1Avoiding and mitigating formationEasy to operateTransistorPolycrystalline material growthSide effectSemiconductor materials
Methods are disclosed for producing highly doped semiconductor materials. Using the invention, one can achieve doping densities that exceed traditional, established carrier saturation limits without deleterious side effects. Additionally, highly doped semiconductor materials are disclosed, as well as improved electronic and optoelectronic devices / components using said materials. The innovative materials and processes enabled by the invention yield significant performance improvements and / or cost reductions for a wide variety of semiconductor-based microelectronic and optoelectronic devices / systems. Materials are grown in an anion-rich environment, which, in the preferred embodiment, are produced by moderate substrate temperatures during growth in an oxygen-poor environment. The materials exhibit fewer non-radiative recombination centers at higher doping concentrations than prior art materials, and the highly doped state of matter can exhibit a minority carrier lifetime dominated by radiative recombination at higher doping levels and higher majority carrier concentrations than achieved in prior art materials. Important applications enabled by these novel materials include high performance electronic or optoelectronic devices, which can be smaller and faster, yet still capture or emit light efficiently, and high performance electronics, such as transistors, which can be smaller and faster, yet cooler.
Owner:YALE UNIV
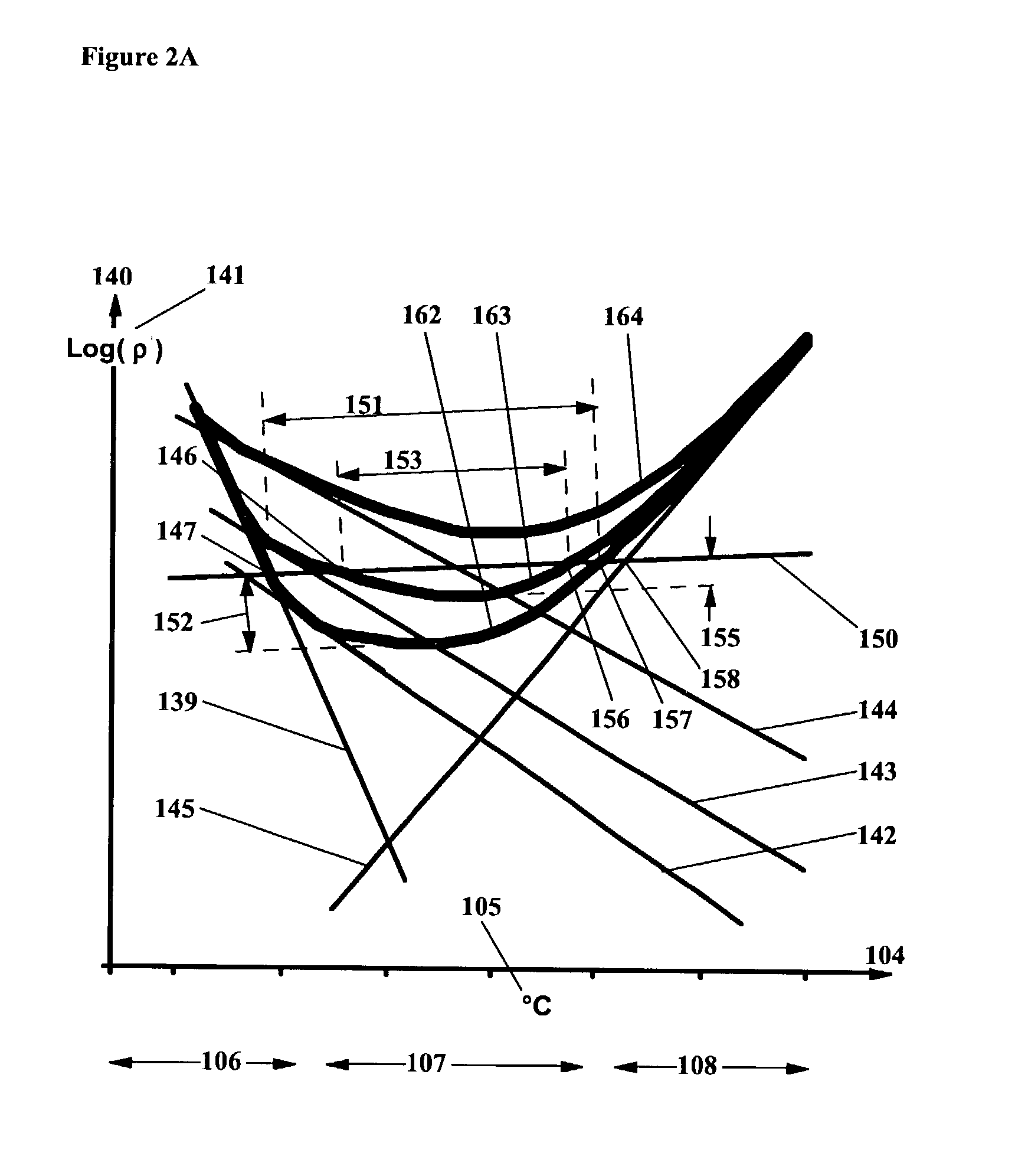
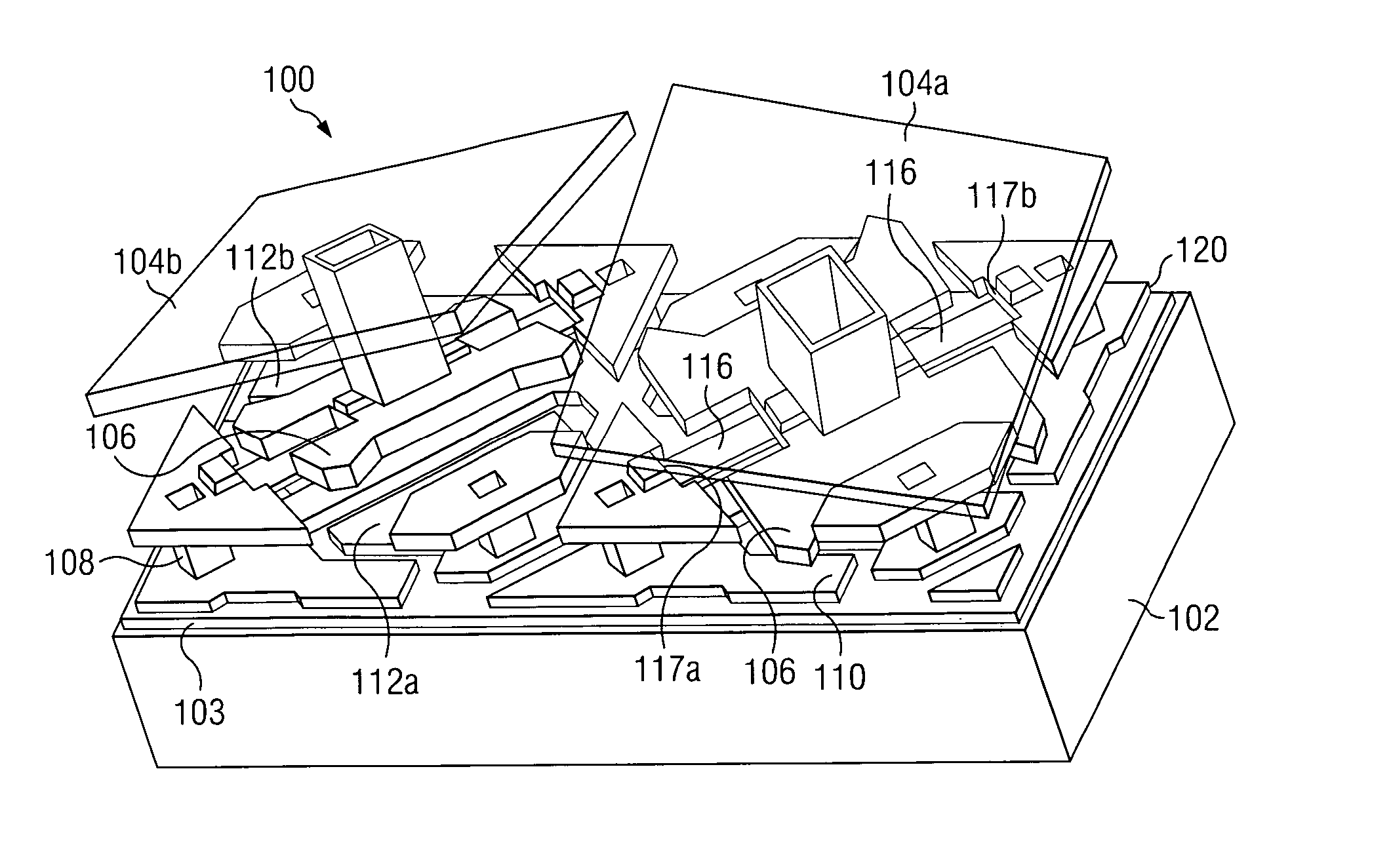
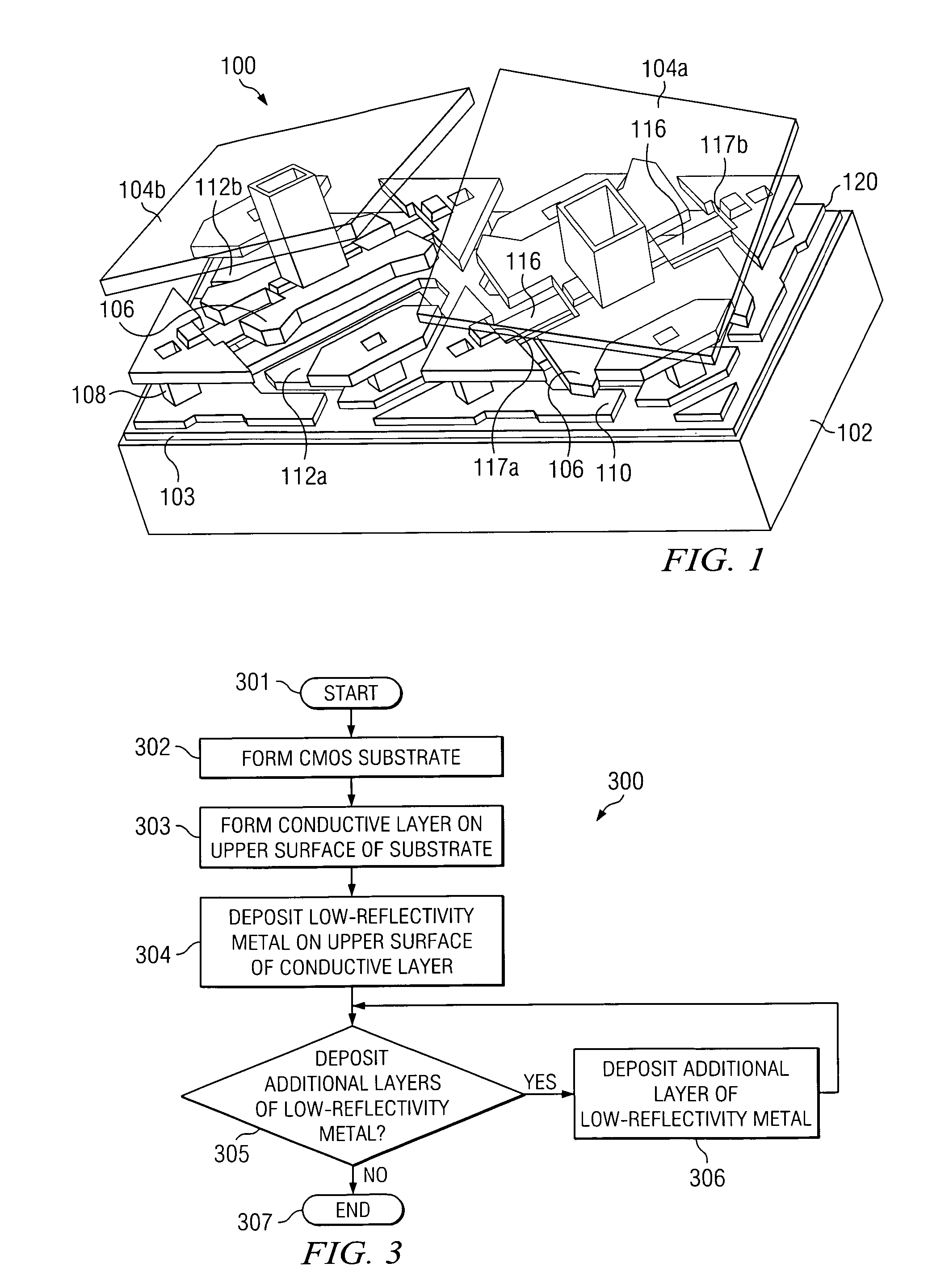
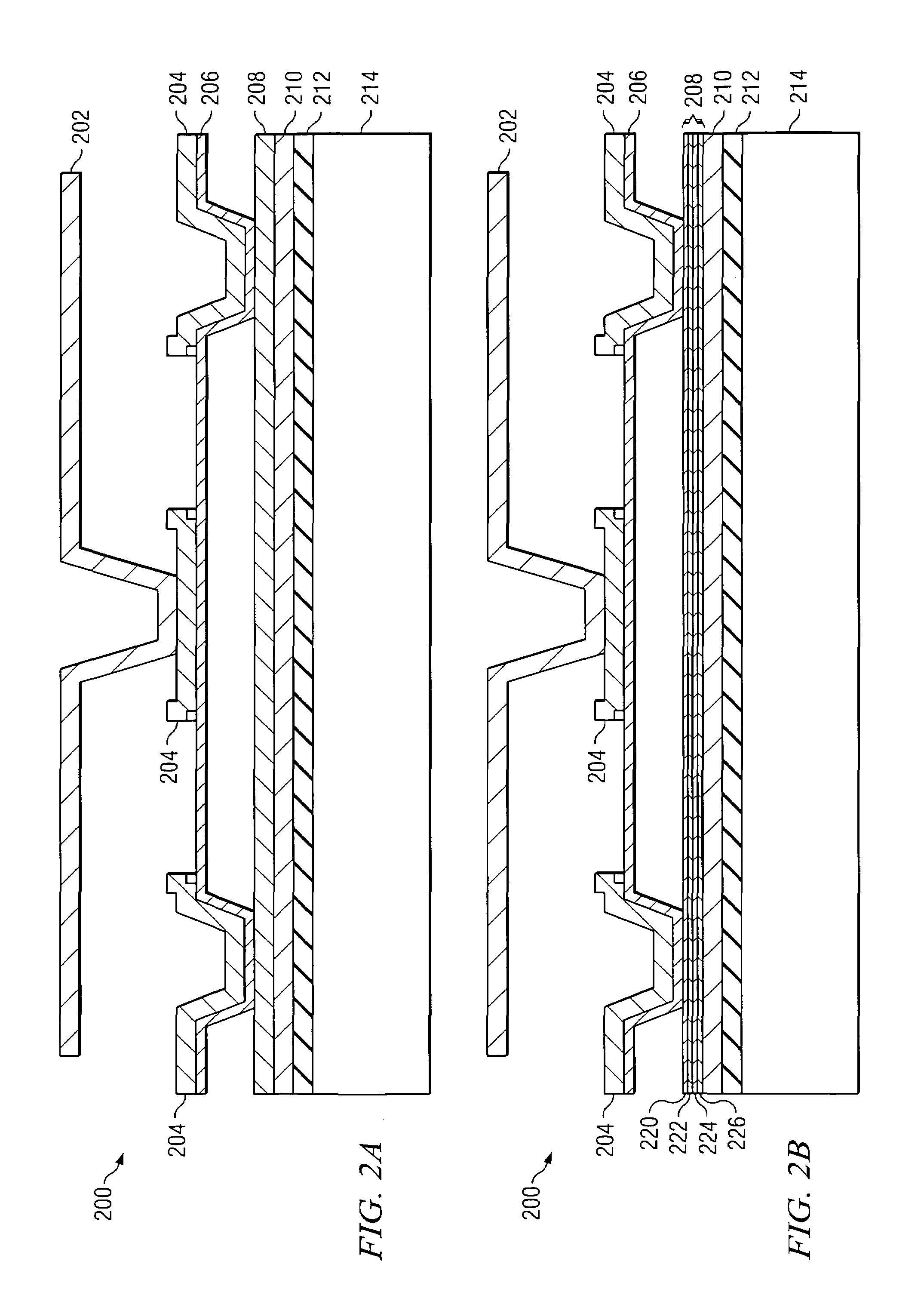
Digital micro-mirror device having improved contrast and method for the same
ActiveUS7184201B2Increase contrastReduce reflectionNon-linear opticsOptical elementsDigital micro mirror deviceElectrical conductor
According to one embodiment of the present invention, a digital micro-mirror device having improved contrast and a method for the same are provided. The digital micro-mirror device includes a plurality of current-carrying conductors on an upper surface of a substrate, each current-carrying conductor having an upper surface; a low-reflectivity metal disposed upon the upper surfaces of the current-carrying conductors; first and second micro-mirrors forming an aperture above the substrate; and wherein the low-reflectivity metal disposed upon on the upper surfaces of the current-carrying conductors reduces reflection of light received through the aperture by the current-carrying conductors.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
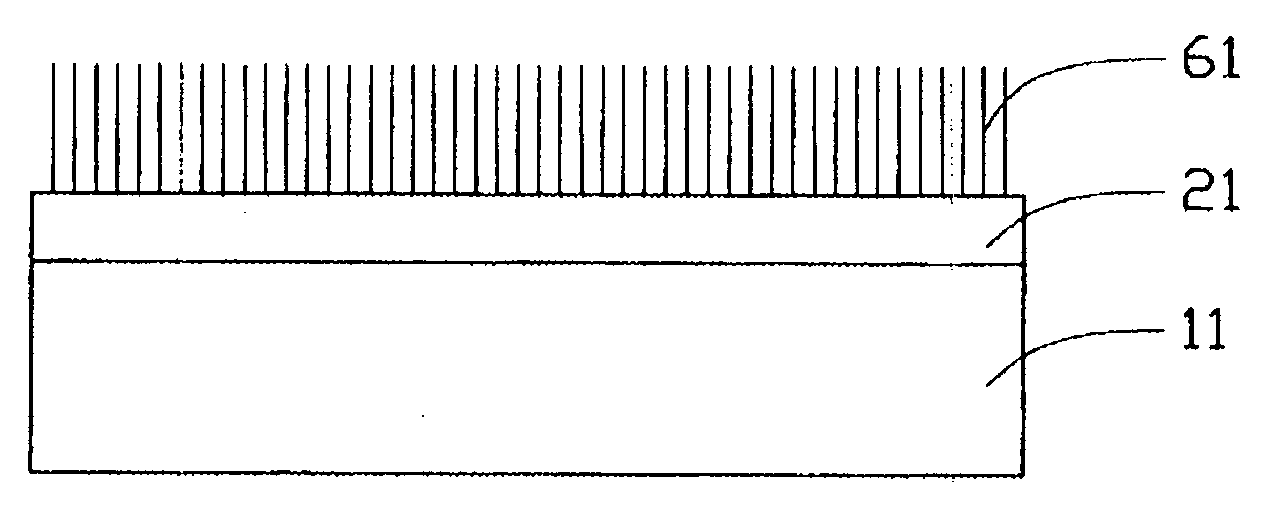
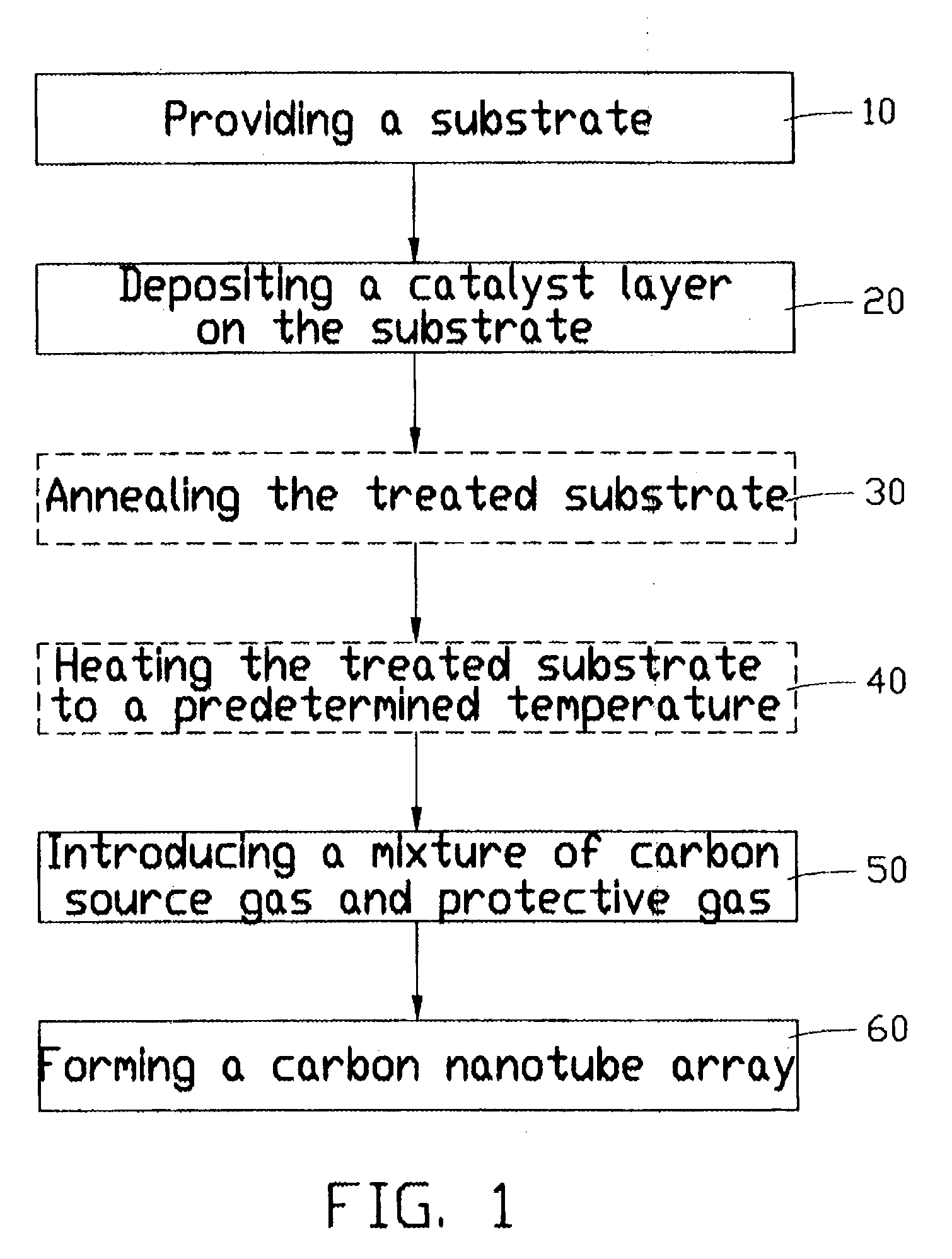
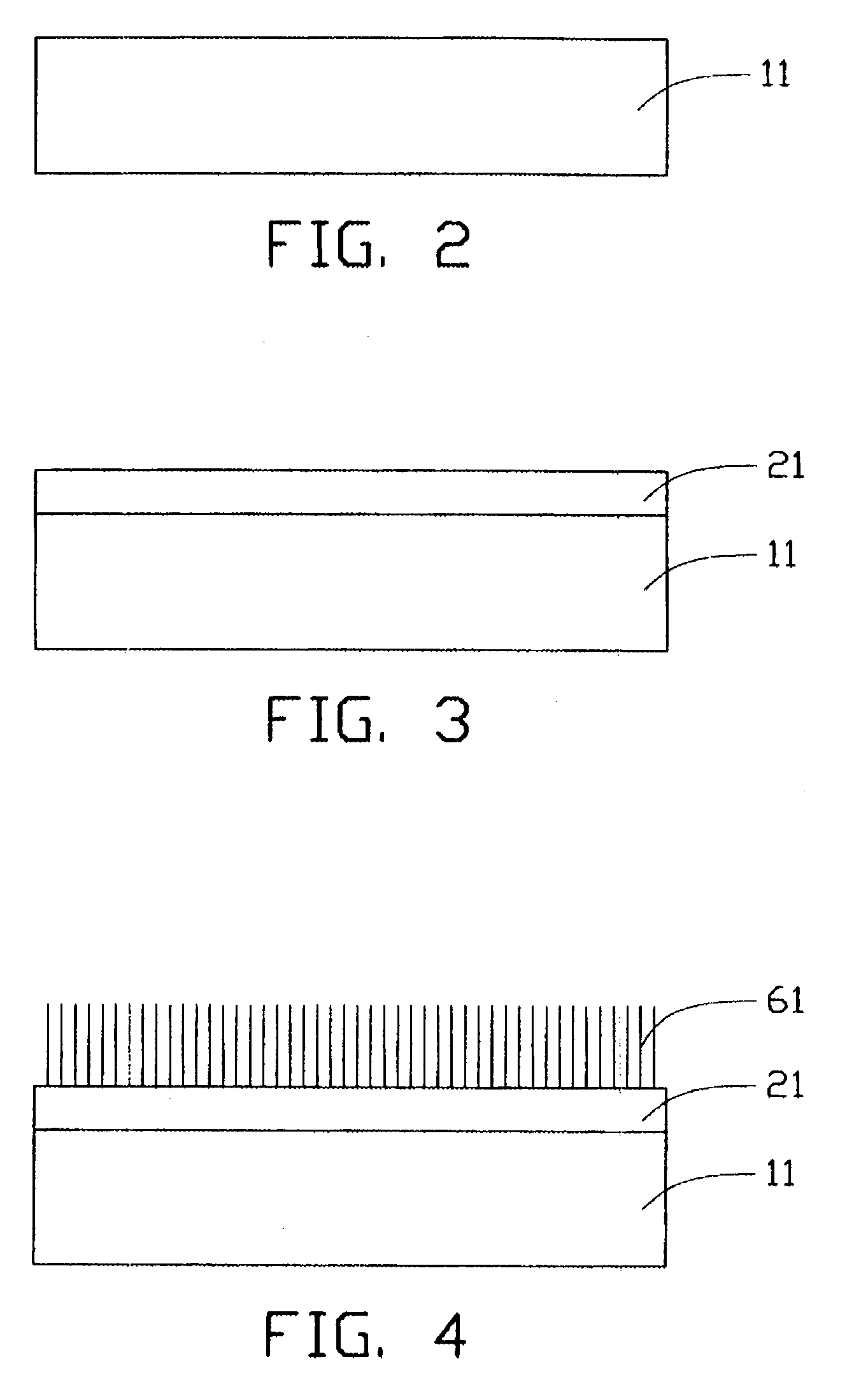
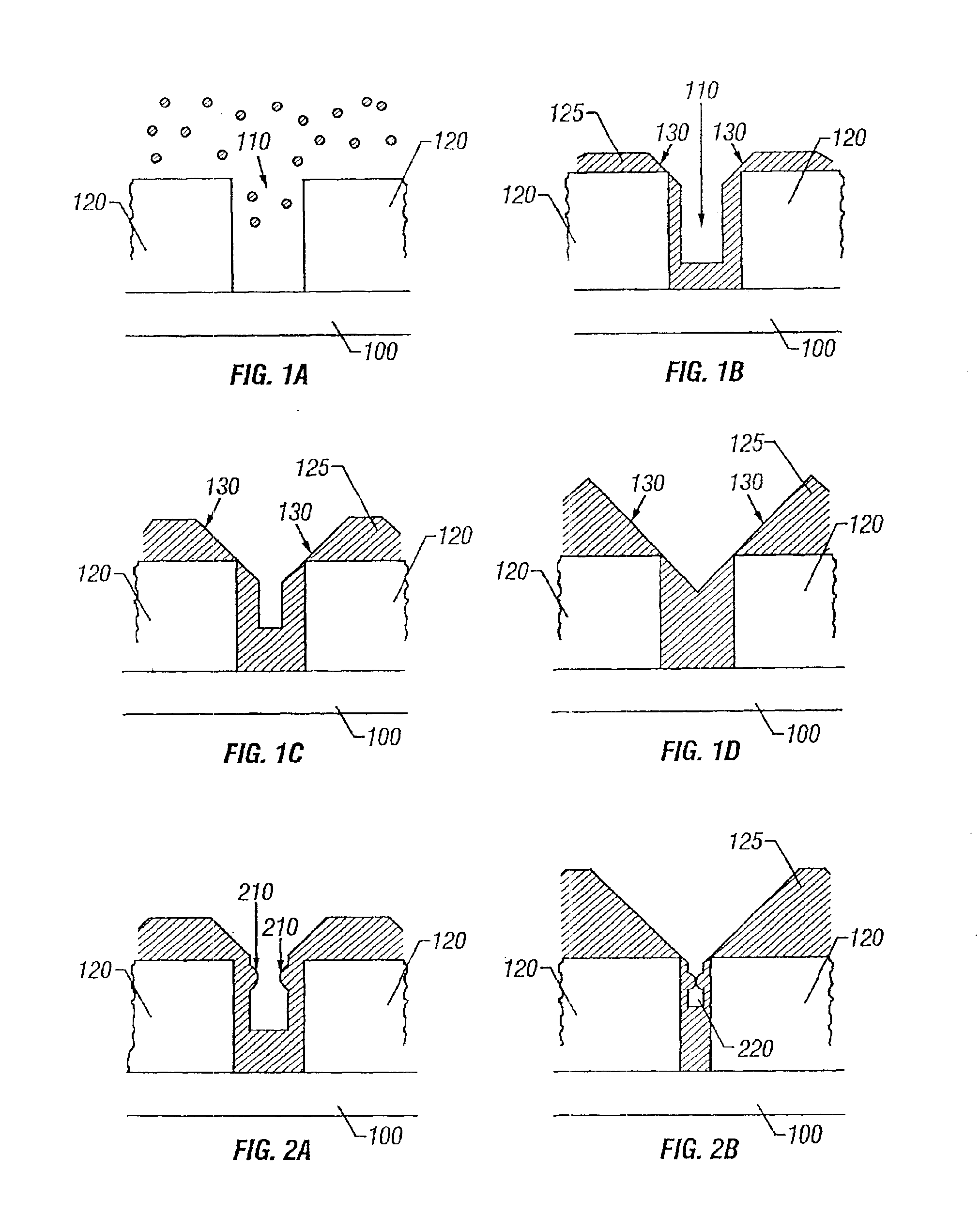
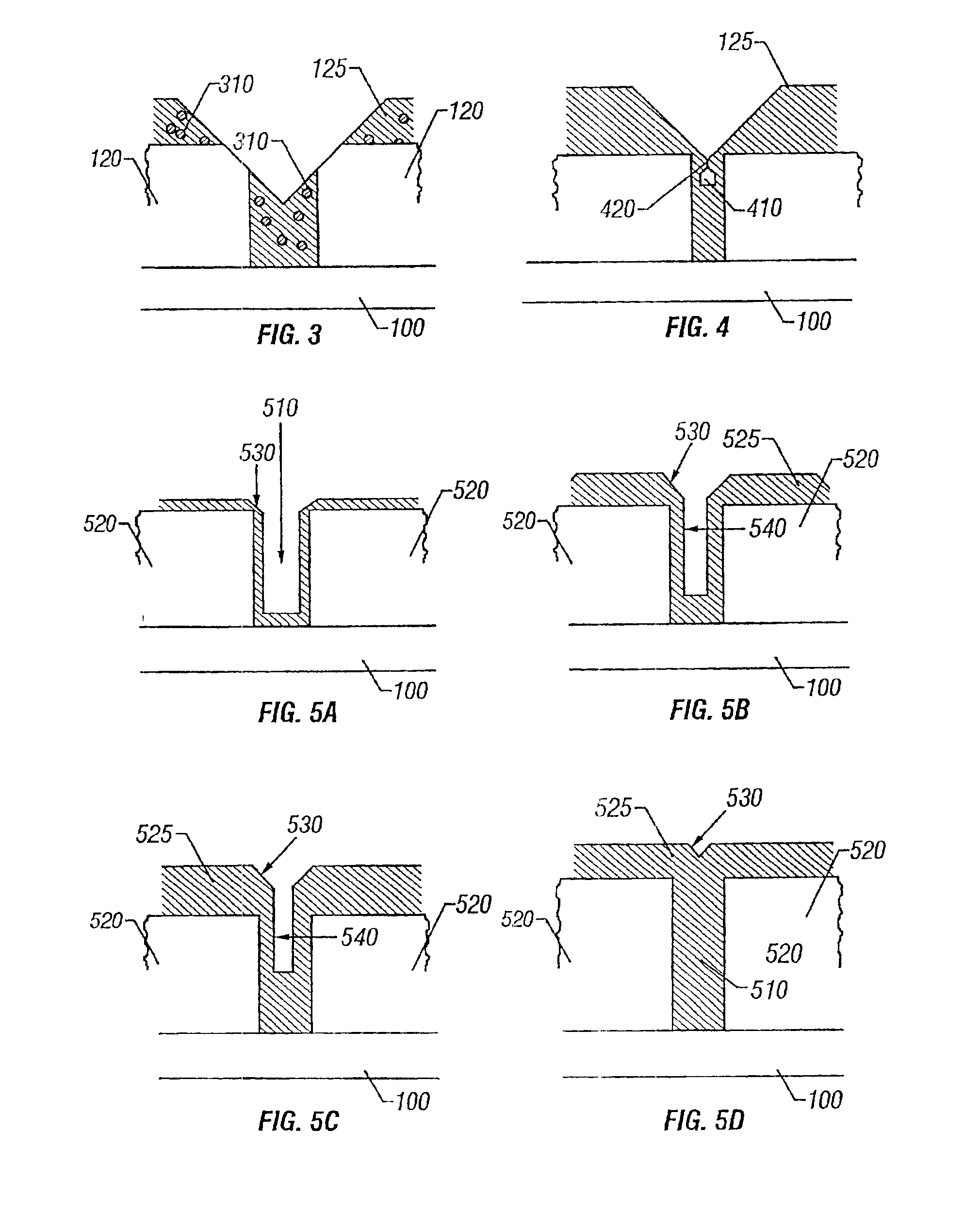
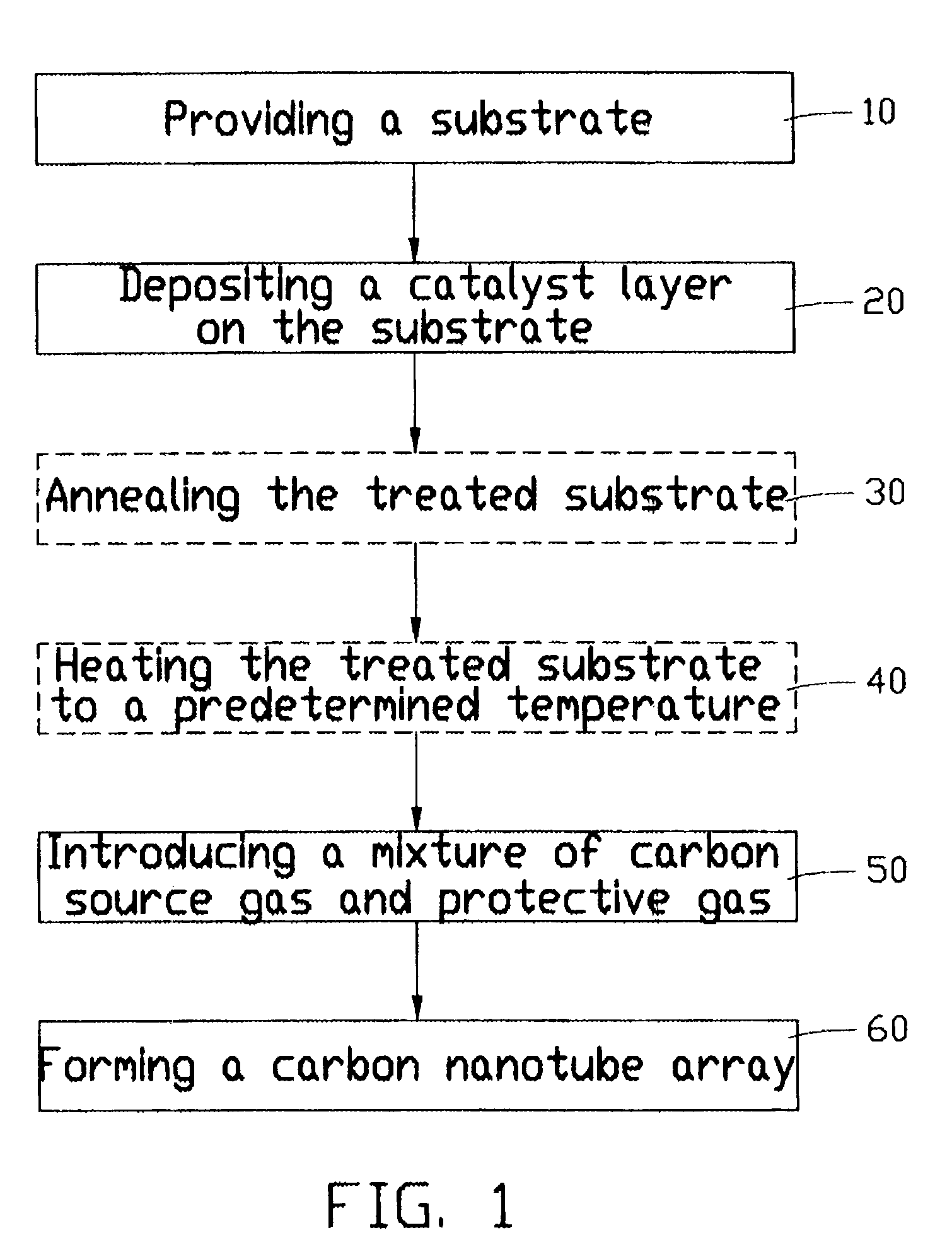
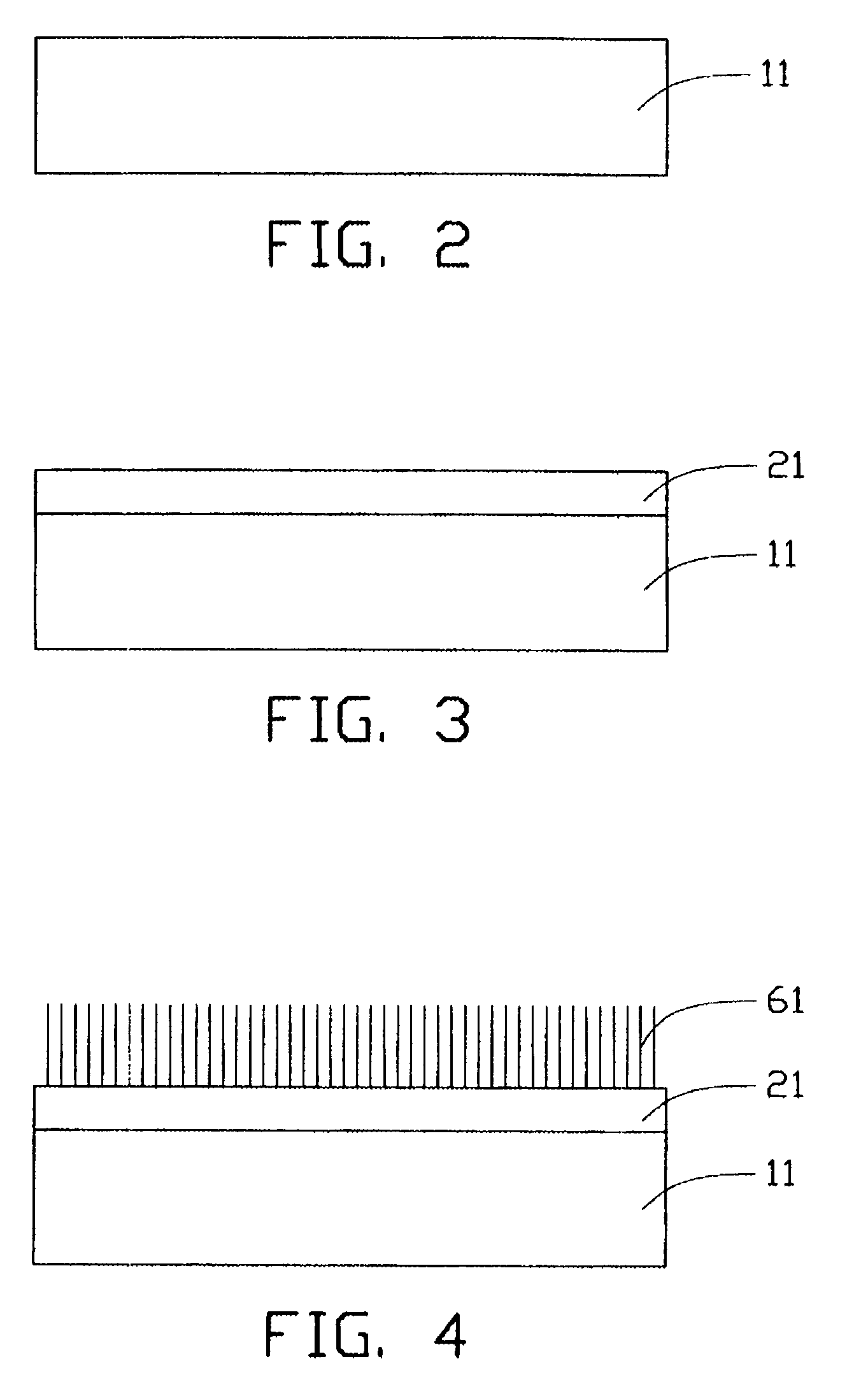
Carbon nanotube array and method for forming same
ActiveUS20040053053A1Reduce partial pressureEasy to bundleMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthMetal catalystCarbon nanotube
A method for forming a carbon nanotube array includes the following steps: providing a smooth substrate (11); depositing a metal catalyst layer (21) on a surface of the substrate; heating the treated substrate to a predetermined temperature in flowing protective gas; and introducing a mixture of carbon source gas and protective gas for 5-30 minutes, thus forming a carbon nanotube array (61) extending from the substrate. When the mixture of carbon source gas and protective gas is introduced, a temperature differential greater than 50° C. between the catalyst and its surrounding environment is created by adjusting a flow rate of the carbon source gas. Further, a partial pressure of the carbon source gas is maintained lower than 20%, by adjusting a ratio of the flow rates of the carbon source gas and the protective gas. The carbon nanotubes formed in the carbon nanotube array are well bundled.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD +1
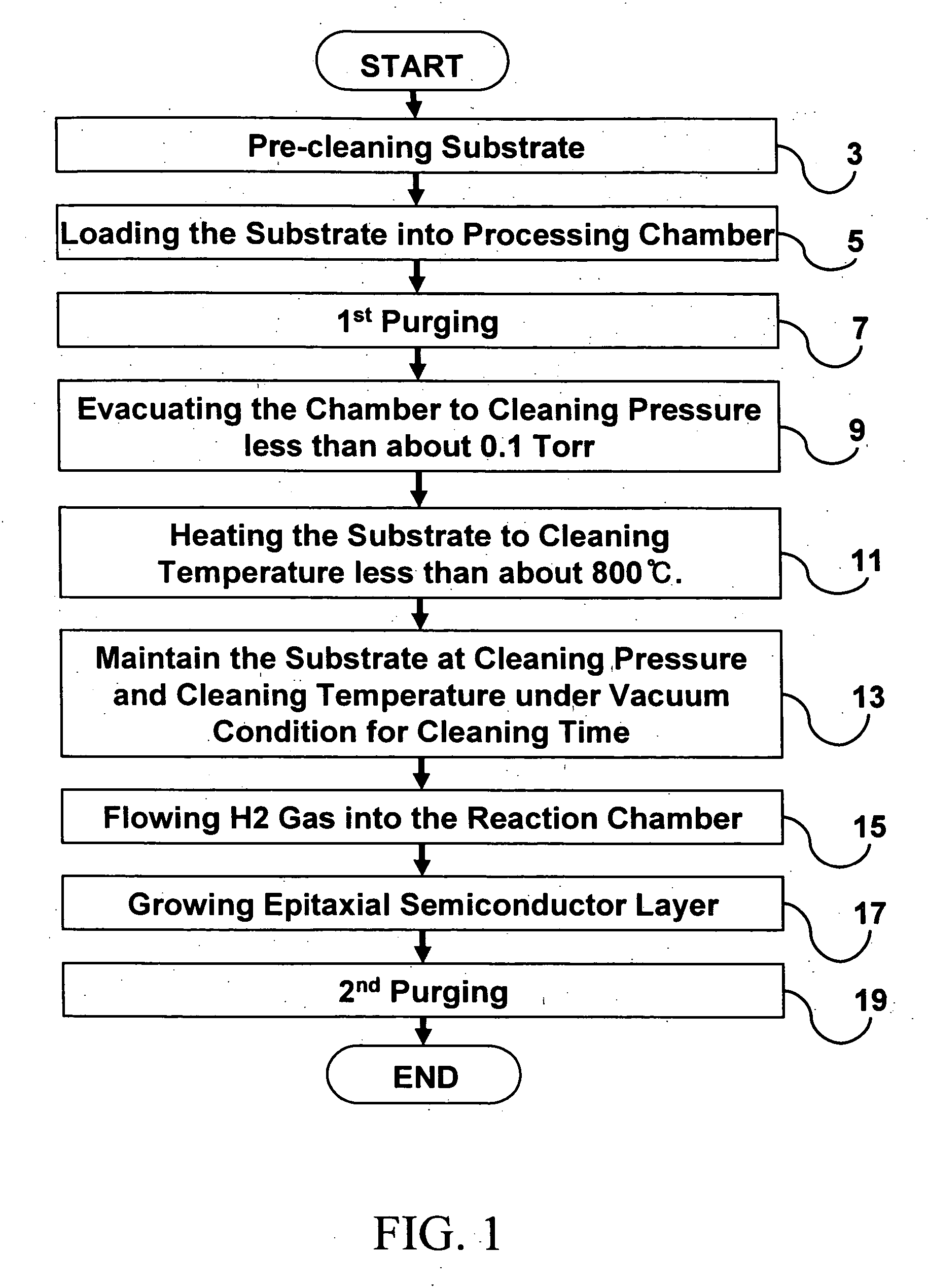
Lid opening/closing system for closed container and substrate processing method using same
ActiveUS7789609B2Improve closureReduce the amount requiredSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingArticle unpackingEngineeringPartial pressure
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Process and equipment for negative pressure benzene removal
ActiveCN101544913ALow boiling pointReduce partial pressureCombustible gas purificationBenzeneThermodynamics
The invention discloses a process and equipment for negative pressure benzene removal , belonging to technology and equipment for recovering resultant in the coking industry, in particular to technology and equipment for removing and recovering benzene contained in coke gas. To solve the problems existing in the prior art, the invention develops the process for non-steam and non-distillation debenzolization under the negative pressure operation condition is developed and designs a novel debenzolization tower thus the disadvantages of equipment and process for benzene removal by adopting tubefurnace for heating rich oil under normal pressure can be overcome. The invention mainly has the advantages that firstly, as benzene is removed by the negative pressure process, the boiling point of the benzene and the partial pressure of the benzene in gaseous phase are lowered, and the benzene can be removed without using direct steam for steaming and blowing, thus waste water generated by the steam is reduced and the environment can not be polluted; secondly, the productive rate of dry coal due to benzene removal is increased to be more than 1.35 percent from the original 1 percent, and the recovery ratio of the benzene is increased to be more than 35 percent; and thirdly, compared with the existing benzene removal process, the process reduces the energy consumption by more than 20 percent.
Owner:JINAN METALLURGICAL CHEM EQUIP CO LTD
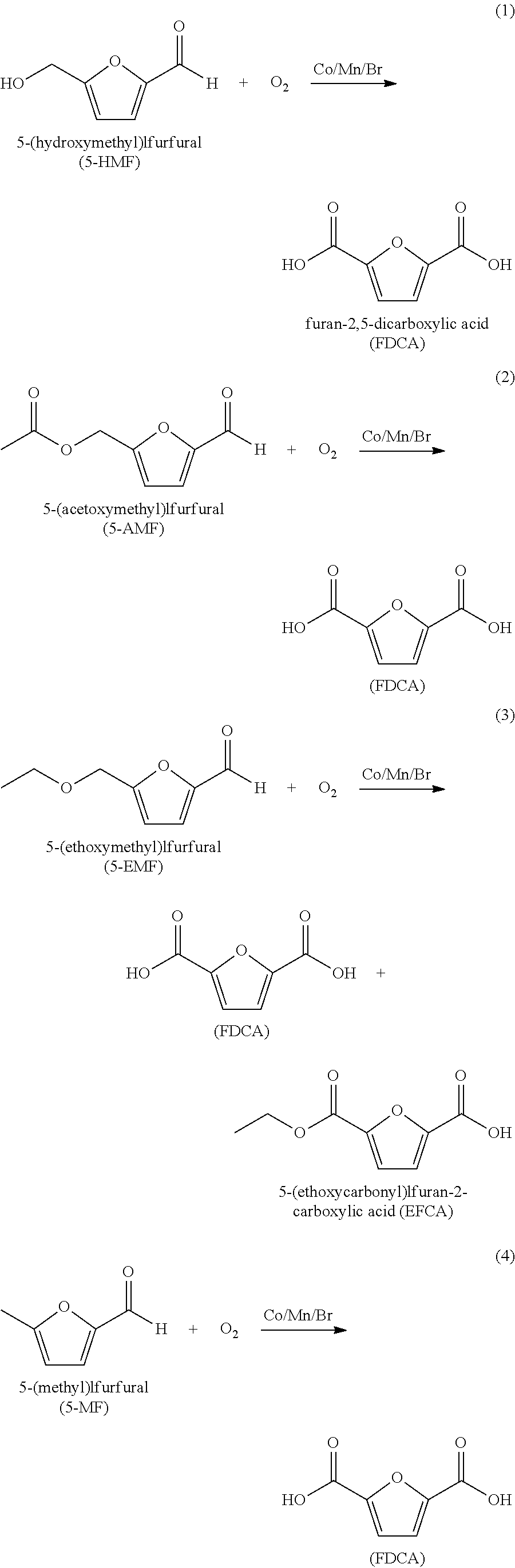
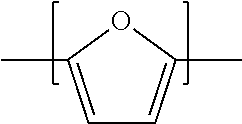
Purifying crude furan 2,5-dicarboxylic acid by hydrogenation
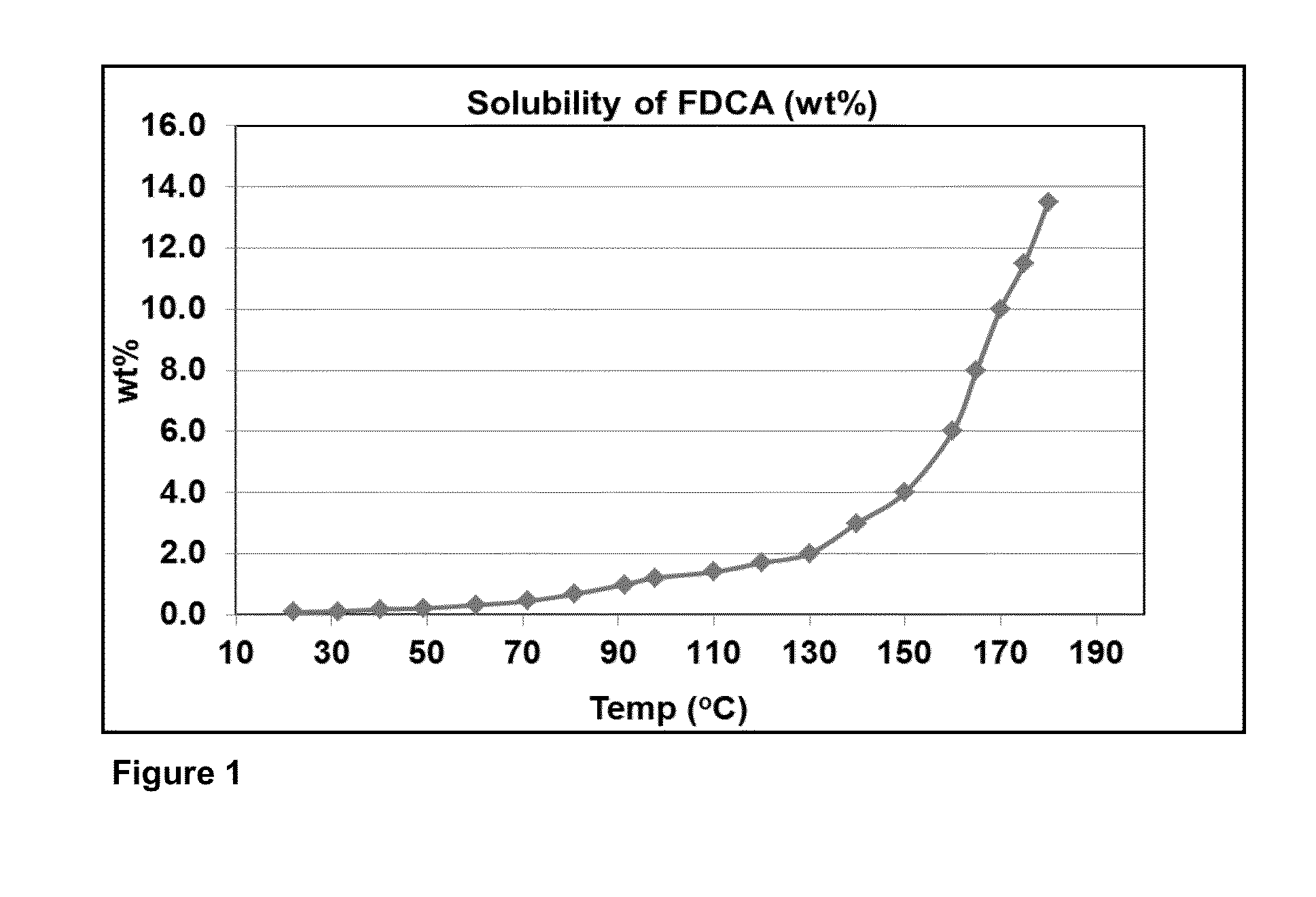
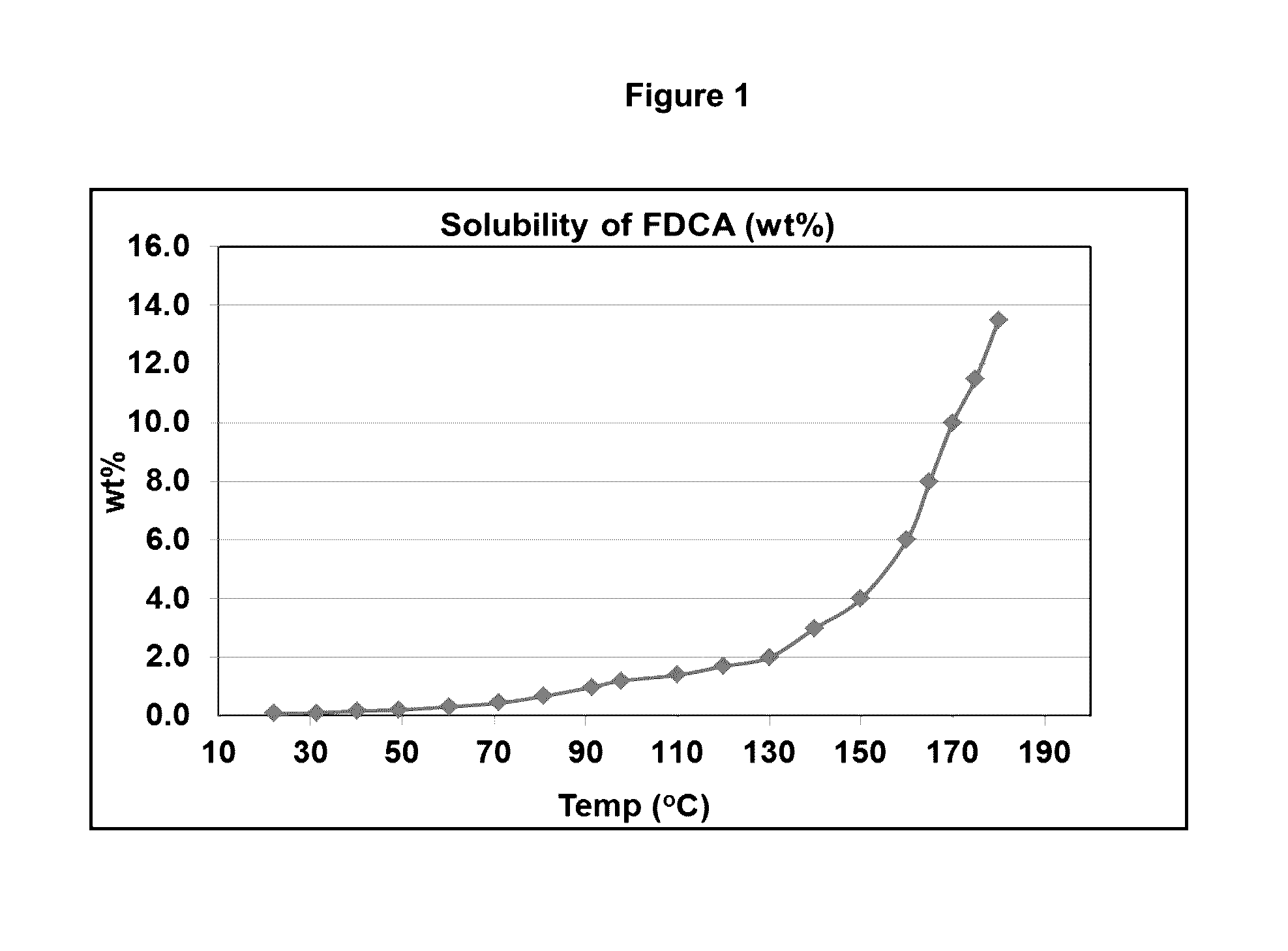
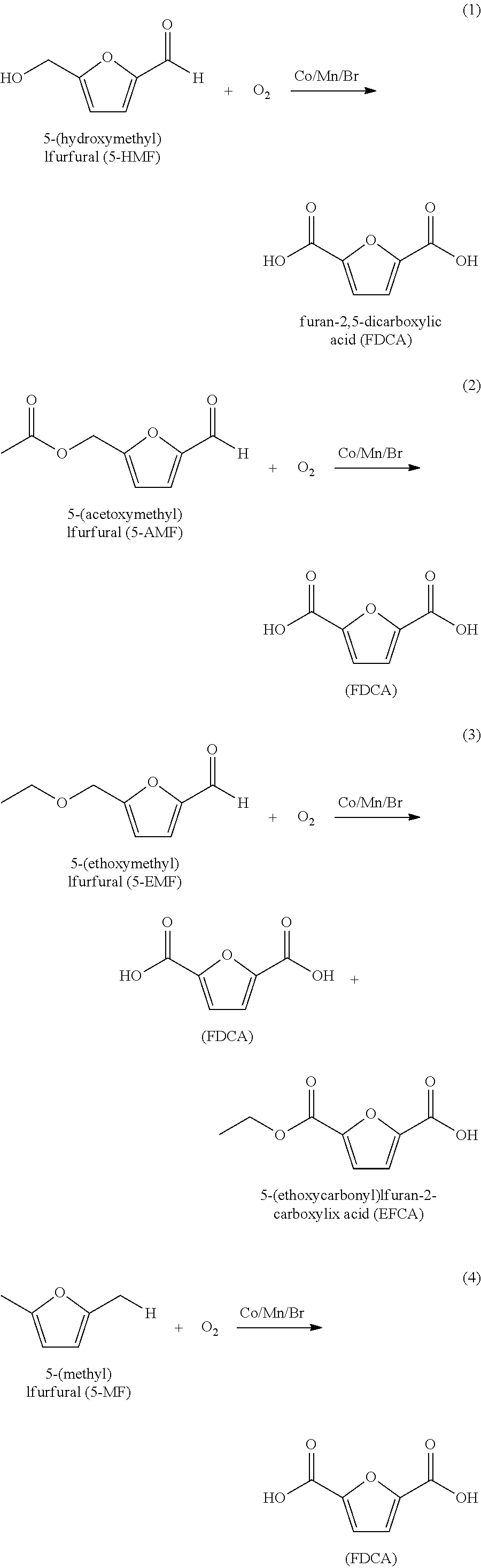
ActiveUS20130345452A1Lower energy requirementsImprove solubilityOrganic chemistryFuranDicarboxylic acid
A process for purifying a crude furan 2,5-dicarboxylic acid composition (cFDCA) by hydrogenation of a FDCA composition dissolved in a hydrogenation solvent such as water, and hydrogenating under mild conditions, such as at a temperature within a range of 130° C. to 225° C. by contacting the solvated FDCA composition with hydrogen in the presence of a hydrogenation catalyst under a hydrogen partial pressure within a range of 10 psi to 900 psi. A product FDCA composition is produced having a low amount of tetrahydrofuran dicarboxylic acid, a low b*, and a low amount of 5-formyl furan-2-carboxylic acid (FFCA).
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
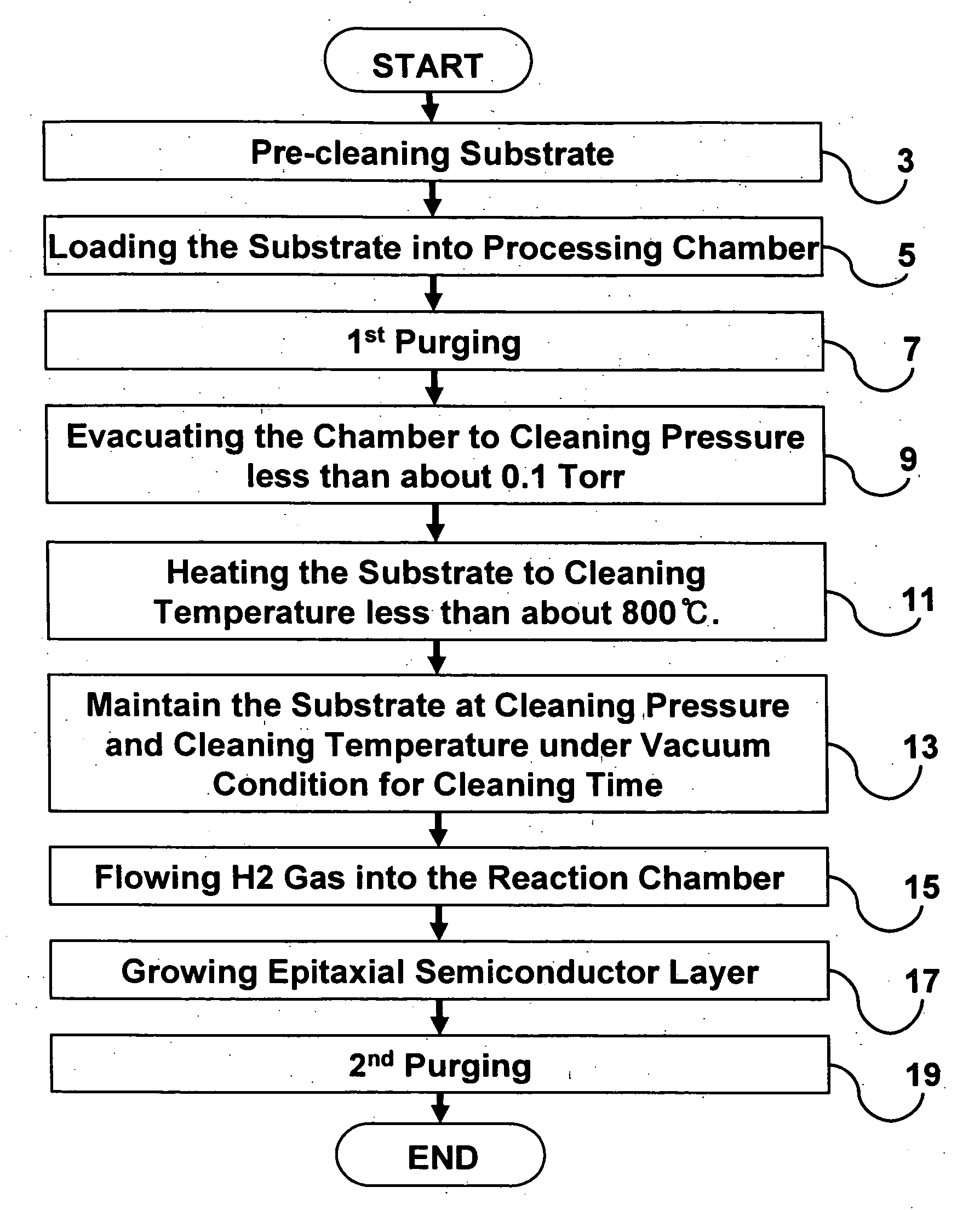
Methods for in-situ cleaning of semiconductor substrates and methods of semiconductor device fabrication employing the same
InactiveUS20060156970A1Reduce the possibilityReduce processing timePolycrystalline material growthMixing/kneading with horizontally-mounted toolsDecompositionGas composition
Provided is an in-situ precleaning method for use in conjunction with epitaxial processes that utilizes temperatures at or below those typically utilized during the subsequent epitaxial deposition under pressure and ambient conditions suitable for inducing decomposition of semiconductor oxides, such as native oxides, from exposed semiconductor surfaces. The reduced temperature and the resulting quality of the cleaned semiconductor surfaces will tend to reduce the likelihood of temperature related issues such as unwanted diffusion, autodoping, slip, and other crystalline stress problems while simultaneously reducing the overall process time. The combination of pressure, ambient gas composition and temperature maintained within the reaction chamber are sufficient to decompose semiconductor oxides present on the substrate surface. For example, the reaction chamber may be operated so that the concentration of evolved oxygen within the reaction chamber is less than about 50%, or even less than 10%, of the equilibrium vapor pressure under the cleaning conditions.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Lid opening/closing system for closed container and substrate processing method using same
ActiveUS20090035099A1Improve closureReduce the amount requiredSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingArticle unpackingEngineeringPartial pressure
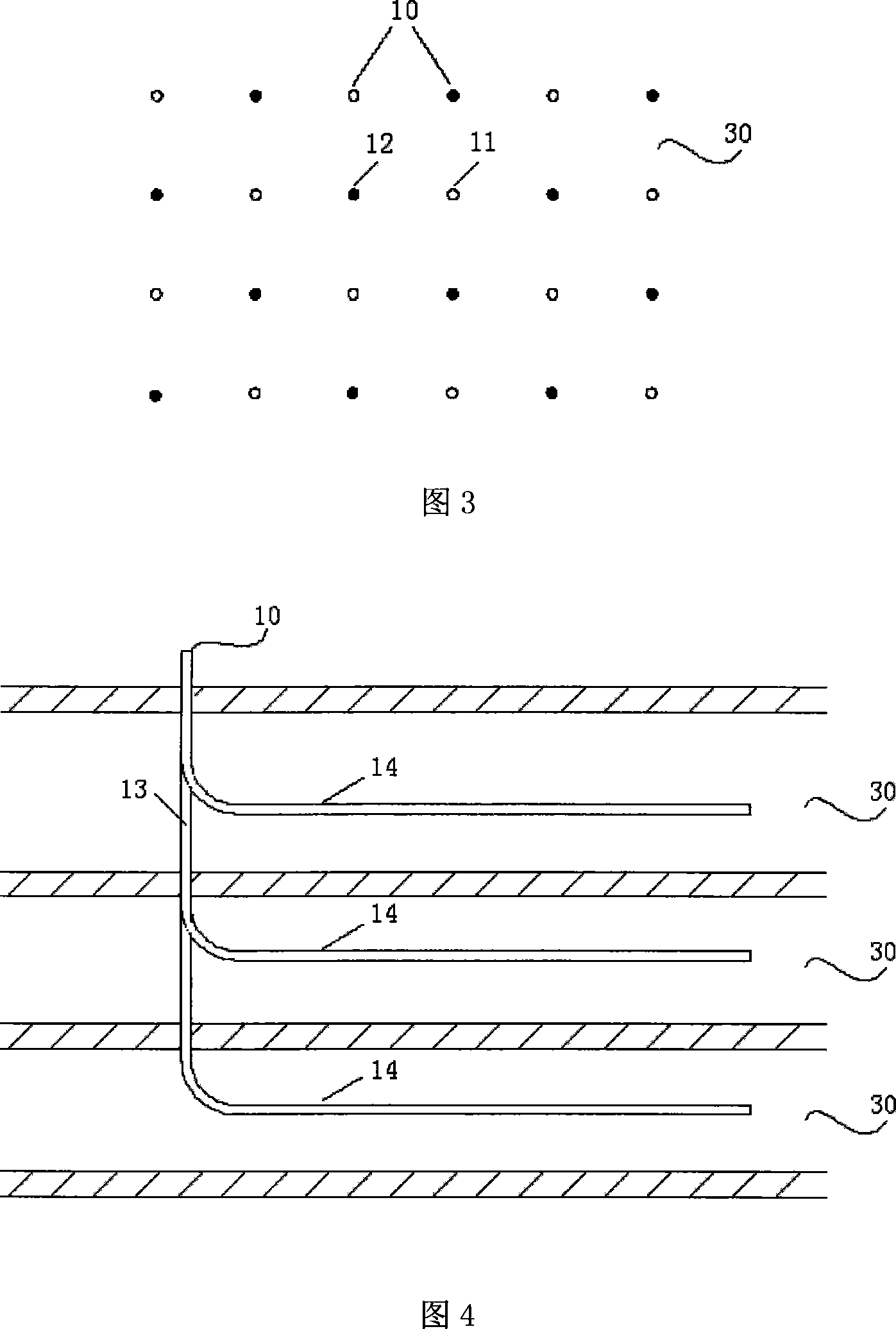
Adjacent to an opening portion 10 in an FISM system is provided an enclosure that encloses the operation space of a door and has a second opening portion 31 opposed to the opening portion 10. A curtain nozzle is provided above the upper edge of the opening portion 10 in the upper portion in the enclosure. A purge gas is supplied from the curtain nozzle along a direction from the upper edge to the lower edge of the opening portion. In addition, a gas outlet through which the purge gas flows from the interior of the enclosure out into the exterior is provided on the wall of the enclosure to which the purge gas flowing in the above described direction is directed, whereby an increase in the partial pressure of oxidizing gases in the interior of the FOUP is prevented.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Purifying crude furan 2,5-dicarboxylic acid by hydrogenation and a purge zone
ActiveUS20160311790A1Lower energy requirementsImprove solubilityOrganic chemistrySolvent extractionFuranCarboxylic acid
A process for purifying a crude furan 2,5-dicarboxylic acid composition (cFDCA) by hydrogenation of a FDCA composition dissolved in a hydrogenation solvent such as water, and hydrogenating under mild conditions, such as at a temperature within a range of 130° C. to 225° C. by contacting the solvated FDCA composition with hydrogen in the presence of a hydrogenation catalyst under a hydrogen partial pressure within a range of 10 psi to 900 psi. A product FDCA composition is produced having a low amount of tetrahydrofuran dicarboxylic acid, a low b*, and a low amount of 5-formyl furan-2-carboxylic acid (FFCA).
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Methods of hyperdoping semiconductor materials and hyperdoped semiconductor materials and devices
InactiveUS7179329B2Easy to operateIncrease computing speedTransistorPolycrystalline material growthSide effectSemiconductor materials
Methods are disclosed for producing highly doped semiconductor materials. Using the invention, one can achieve doping densities that exceed traditional, established carrier saturation limits without deleterious side effects. Additionally, highly doped semiconductor materials are disclosed, as well as improved electronic and optoelectronic devices / components using said materials. The innovative materials and processes enabled by the invention yield significant performance improvements and / or cost reductions for a wide variety of semiconductor-based microelectronic and optoelectronic devices / systems.Materials are grown in an anion-rich environment, which, in the preferred embodiment, are produced by moderate substrate temperatures during growth in an oxygen-poor environment. The materials exhibit fewer non-radiative recombination centers at higher doping concentrations than prior art materials, and the highly doped state of matter can exhibit a minority carrier lifetime dominated by radiative recombination at higher doping levels and higher majority carrier concentrations than achieved in prior art materials. Important applications enabled by these novel materials include high performance electronic or optoelectronic devices, which can be smaller and faster, yet still capture or emit light efficiently, and high performance electronics, such as transistors, which can be smaller and faster, yet cooler.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Fire extinguishing composition generating fire extinguishing substance through high-temperature decomposition
InactiveUS20130181158A1Environment friendly and efficientPrevent wrong additionFire rescueFire extinguisherDecompositionEngineering
The present invention relates to a fire extinguishing composition generating fire extinguishing substance through high-temperature decomposition; the fire extinguishing composition includes a fire extinguishing material which can be decomposed to release substance with fire extinguishing properties during the heating process; the content of the fire extinguishing material is at least 80 wt %; a pyrotechnic agent is adopted as a heat source and a power source in a process of fire extinguishing; and the purpose of fire extinguishing is achieved by: igniting the pyrotechnic agent, generating a large quantity of fire substance from the fire extinguishing composition in the use of high temperature produced by burning pyrotechnic agent, and the fire substance sprays out together with the pyrotechnic agent. Compared with the traditional aerosol fire extinguishing systems, the gas fire extinguishing systems and the water type extinguishing systems, the present invention provides a more efficient and safer fire extinguishing composition.
Owner:XIAN J&R FIRE FIGHTING EQUIP
Light-emitting element and organic electroluminescent display device
InactiveUS20110121346A1Ensure reliabilityAvoid possibilityElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesOrganic layerOptoelectronics
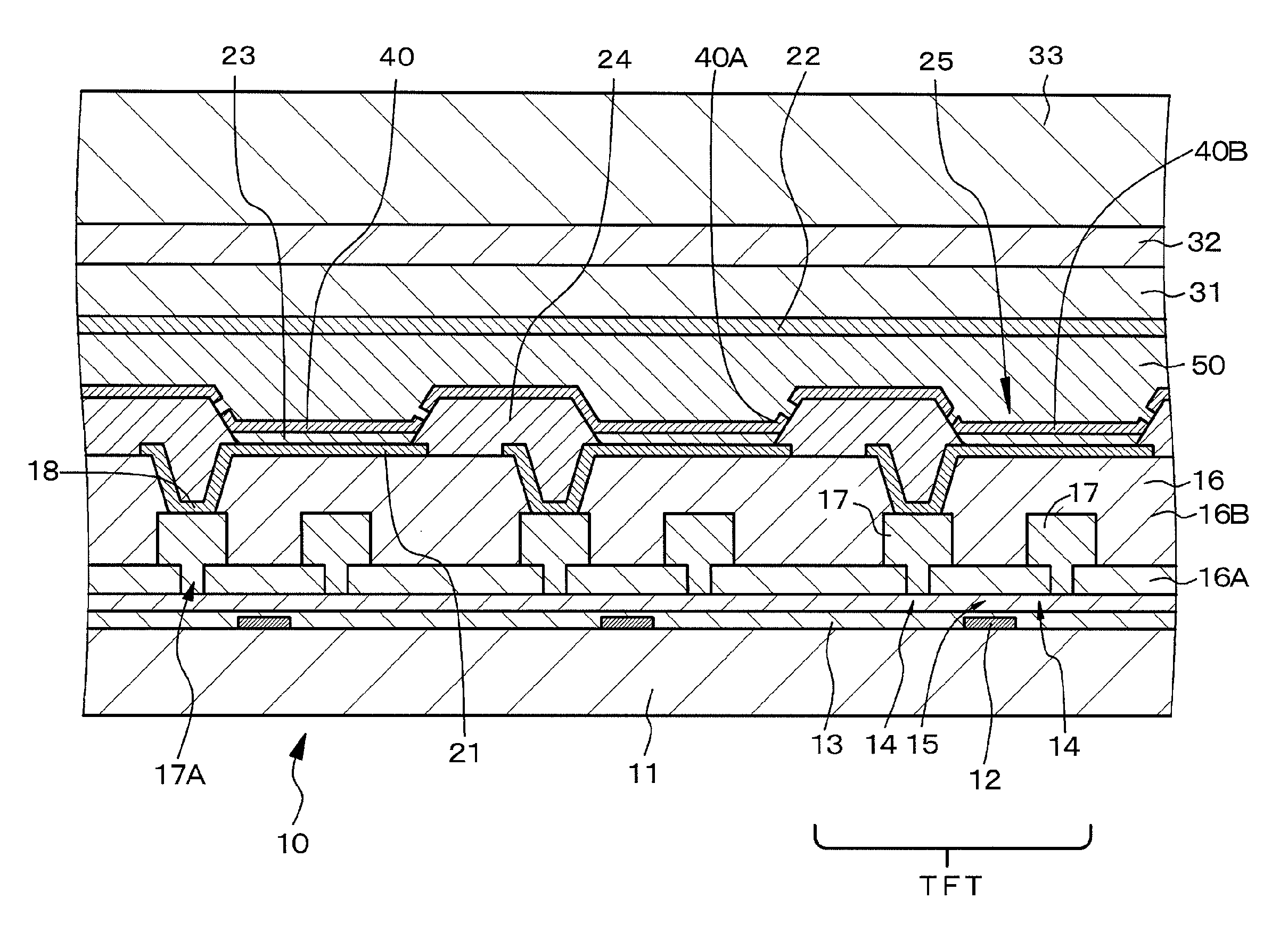
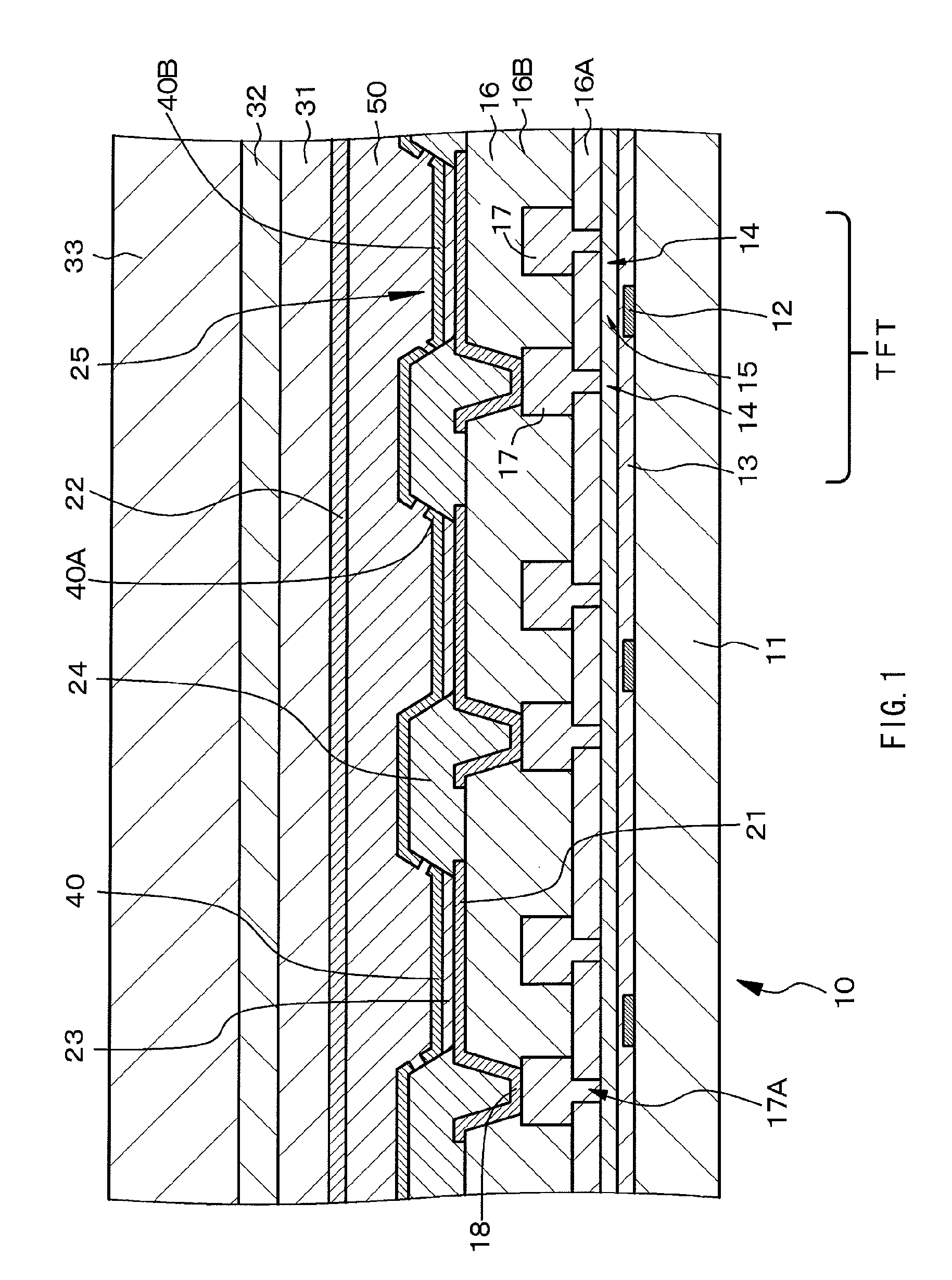
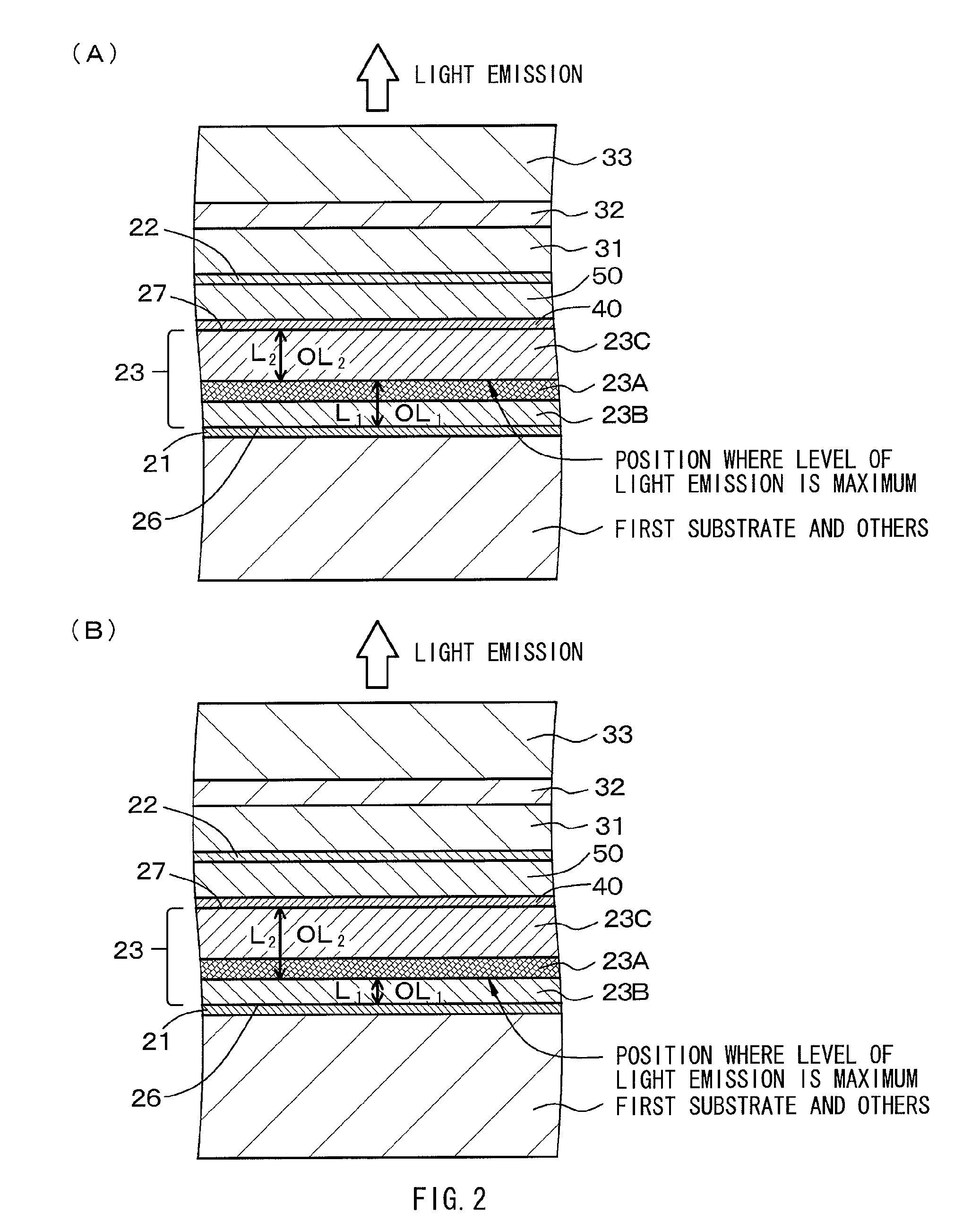
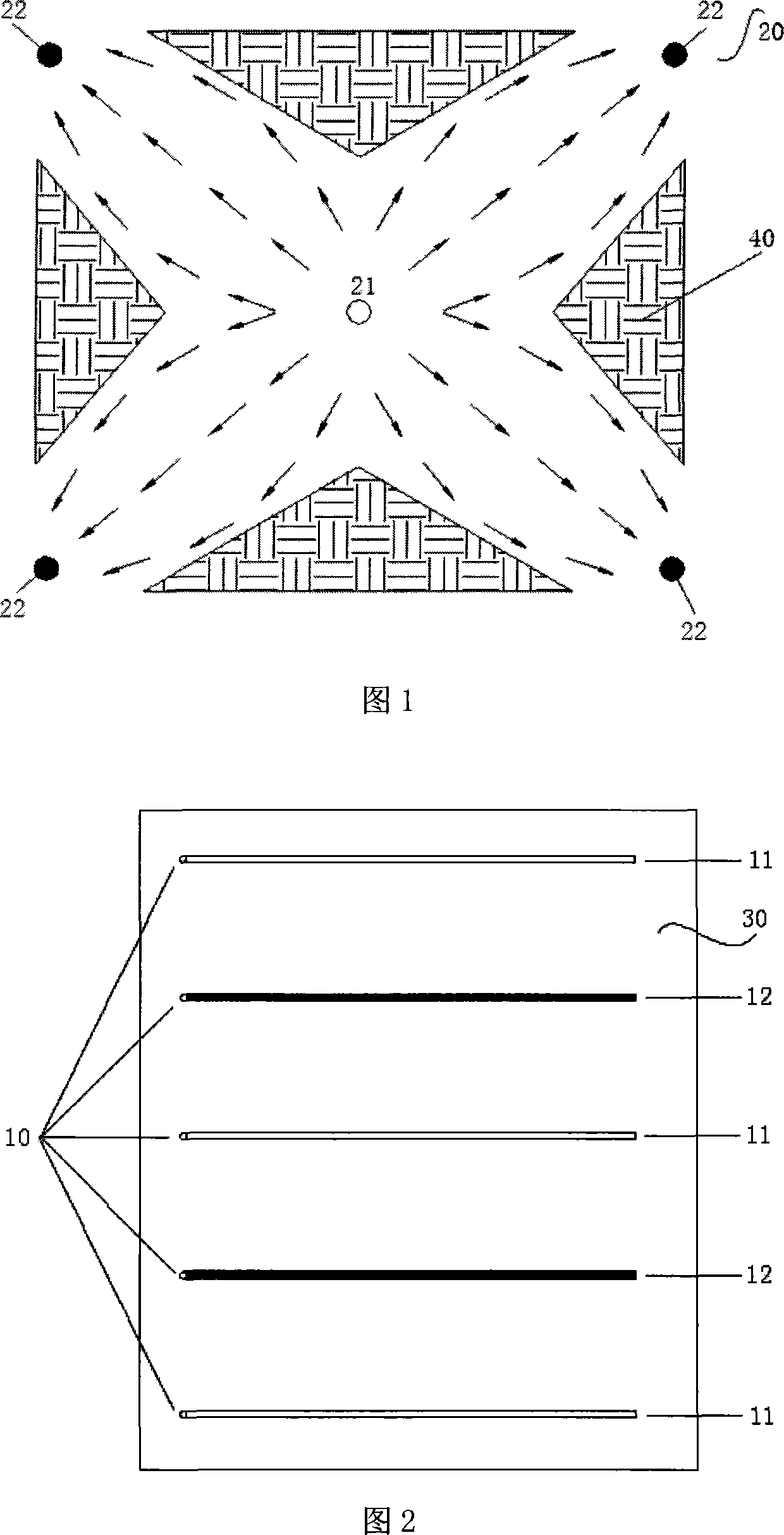
Provided is a light-emitting element in the structure and configuration of causing no possibility of a short circuit between first and second electrodes even if there is any foreign substance or a protrusion on the first electrode. Such a light-emitting element is configured to include, in order, a first electrode 21, an organic layer 23 including a light-emitting layer made of an organic light-emitting material, a semi-transmissive / reflective film 40, a resistance layer 50, and a second electrode 22. The first electrode 21 reflects a light coming from the light-emitting layer, and the second electrode 22 passes through a light coming from the semi-transmissive / reflective film 40 after passing therethrough. The semi-transmissive / reflective film on the organic layer 23 has an average film thickness of 1 nm to 6 nm both inclusive.
Owner:SONY CORP
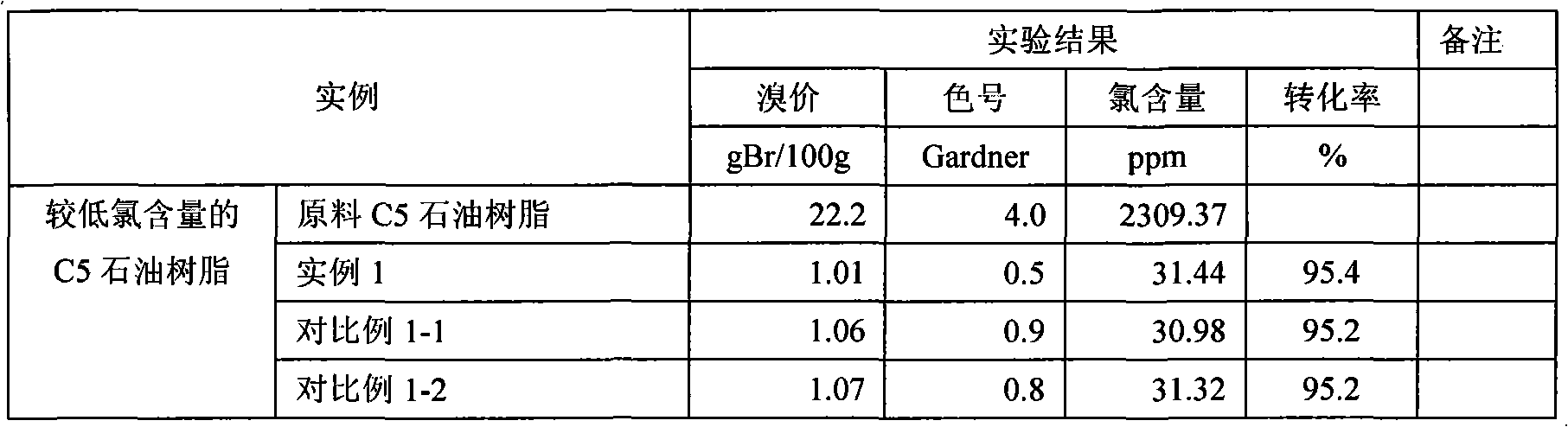
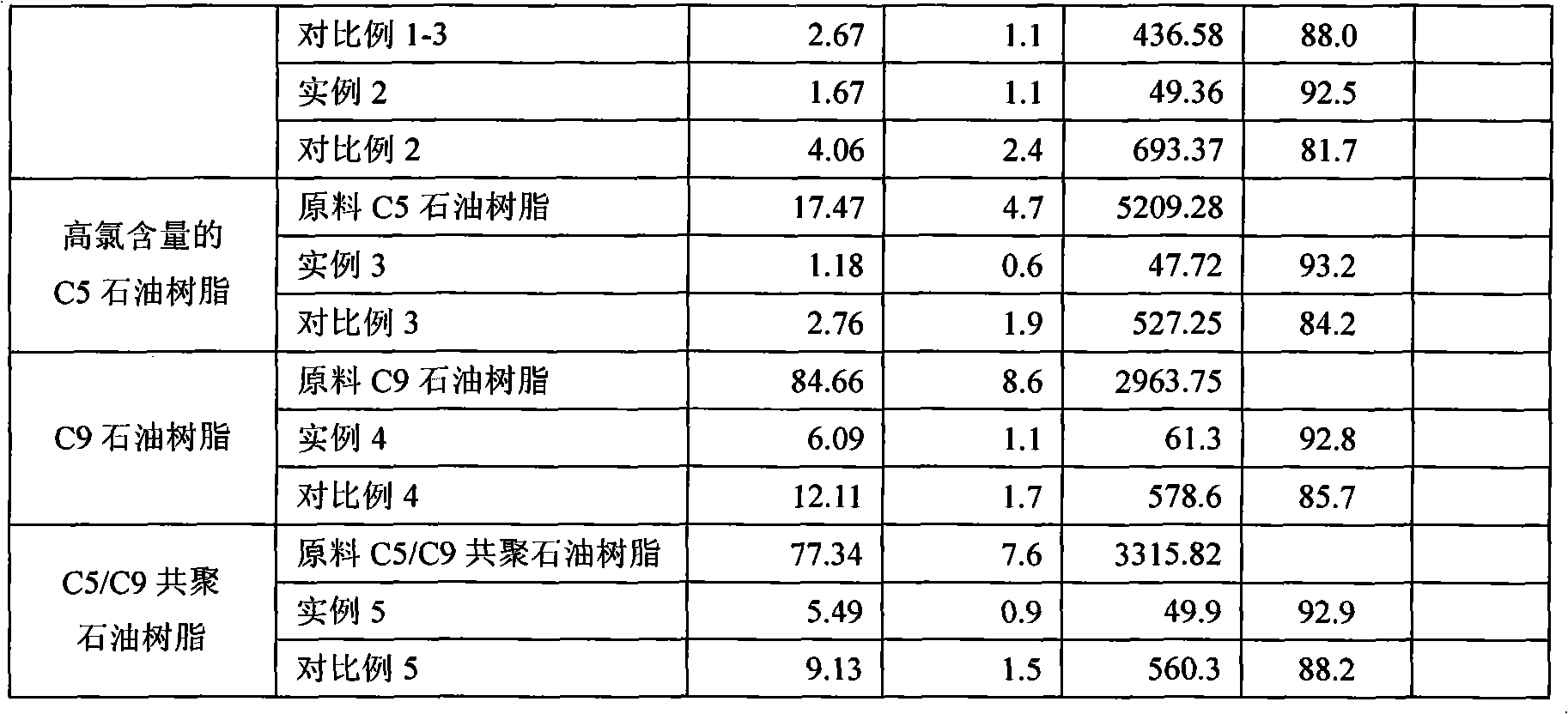
Industrial manufacture method for hydrogenated petroleum resin
ActiveCN102382259ASimplify the caustic cleaning processReduce corrosionPetroleum resinHydrogenation reaction
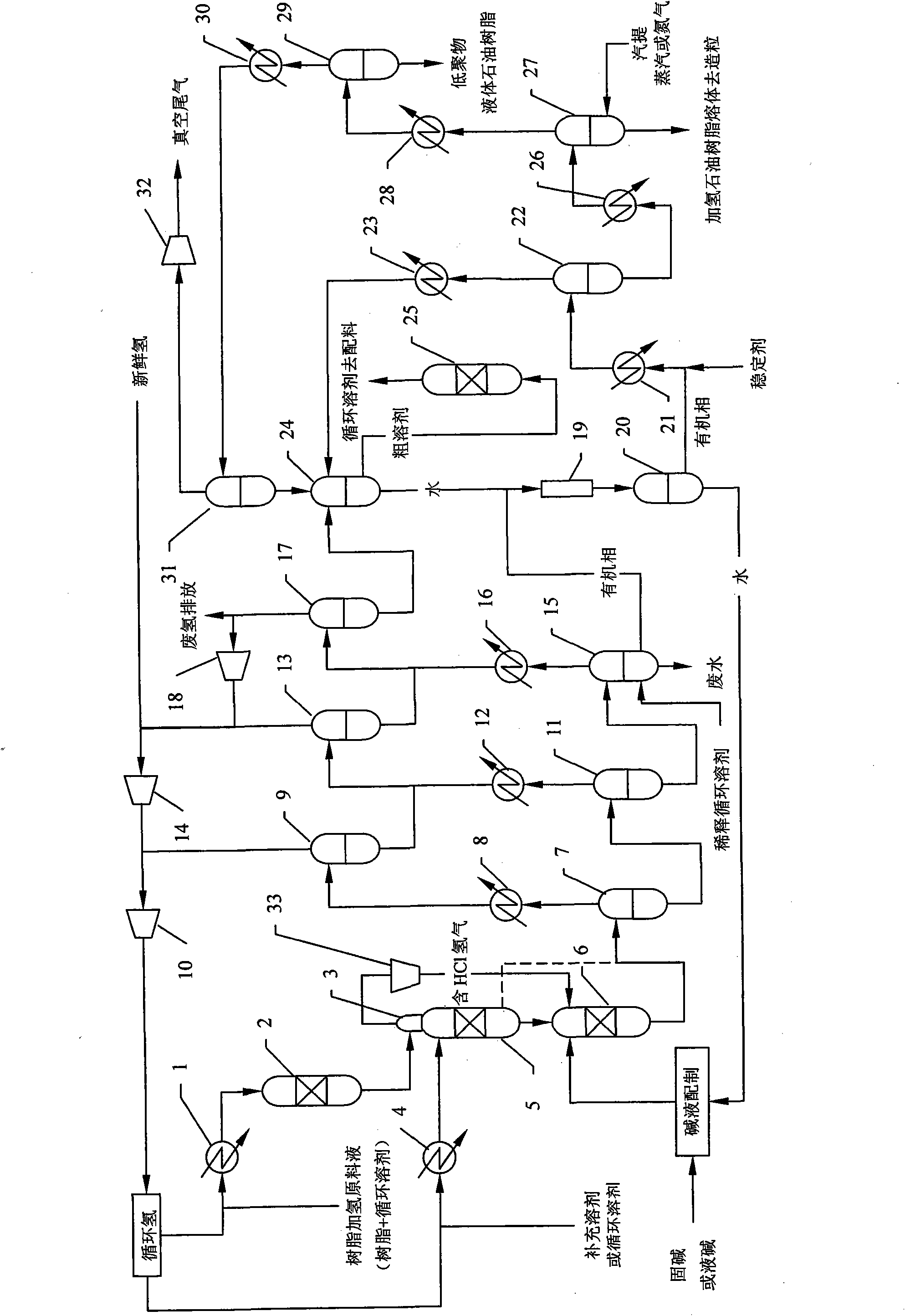
The invention relates to an industrial manufacture method for hydrogenated petroleum resin, which comprises the following steps of: generating hydrogenation reaction on petroleum resin which is obtained by polymerizing cracking C5 and C9 fractions under the proper condition of the existence of hydrogenation catalyst and solvents by adopting the processes of two-section hydrogenation and combination alkaline cleaning neutralization; hydrogenating the unsaturated component in the petroleum resin to reduce double-bond content; hydrogenating a non-ferrous perssad to fade; hydrogenating to remove chlorine retained in the polymerization process; and carrying out alkaline cleaning, water cleaning, stabilizer injection and solvent removal to obtain light or colourless hydrogenated petroleum resin. The method further simplifies the process through the organic combination of unit operation, and the industrial manufacture method for the hydrogenated petroleum resin, which has the advantages of wide adaptability on hydrogenated raw materials, less corrosion on system equipment, high product quality and high production capability is formed.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
Process for producing precooked bacon slices
InactiveUS20090181138A1Small footprintEliminates orBaking ovenCooking vesselsProcess engineeringPercentage reduction
Owner:UNITHERM FOOD SYST LLC
Pretreatment process to remove oxygen from coal en route to a coal pyolysis process as a means of improving the quality of the hydrocarbon liquid product
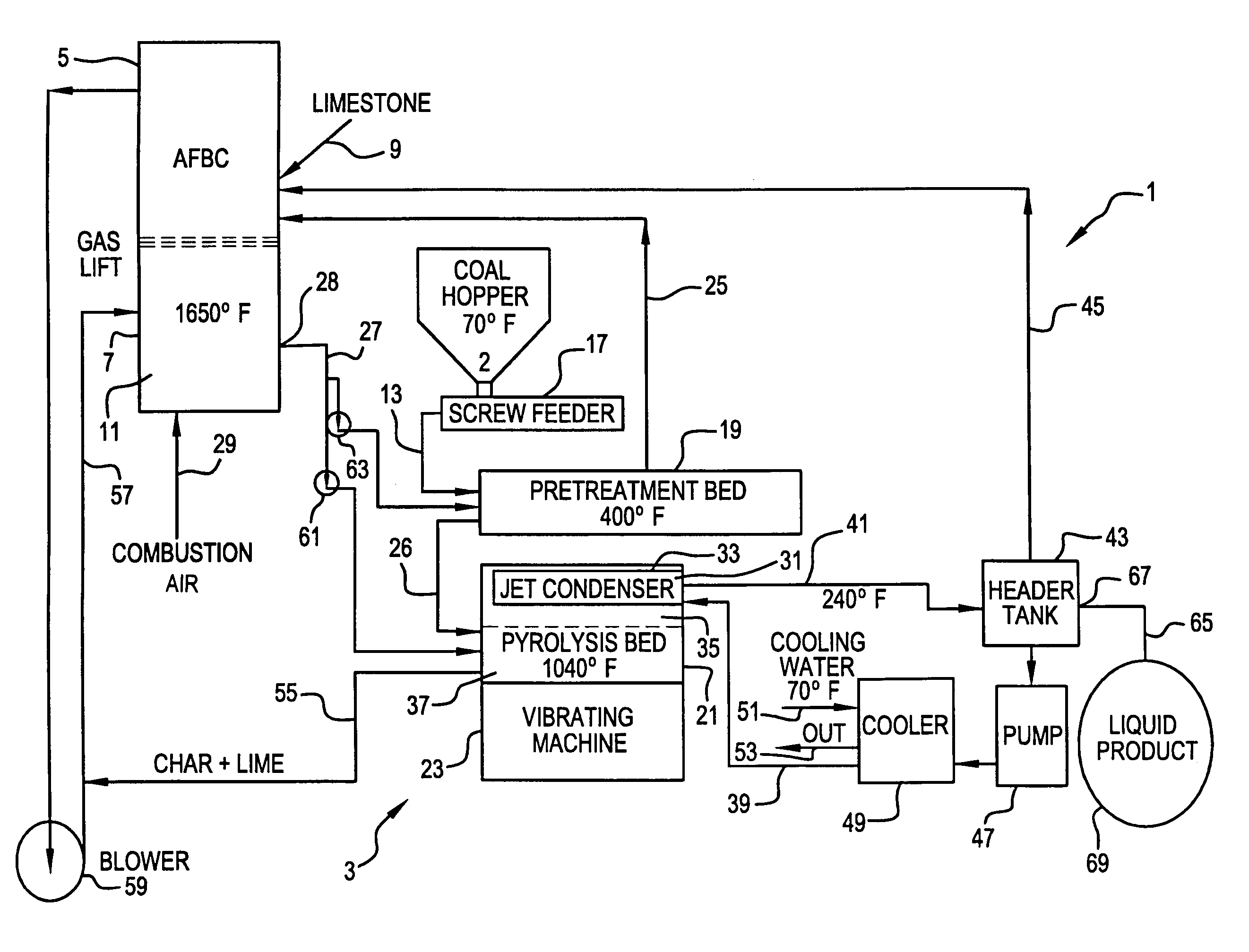
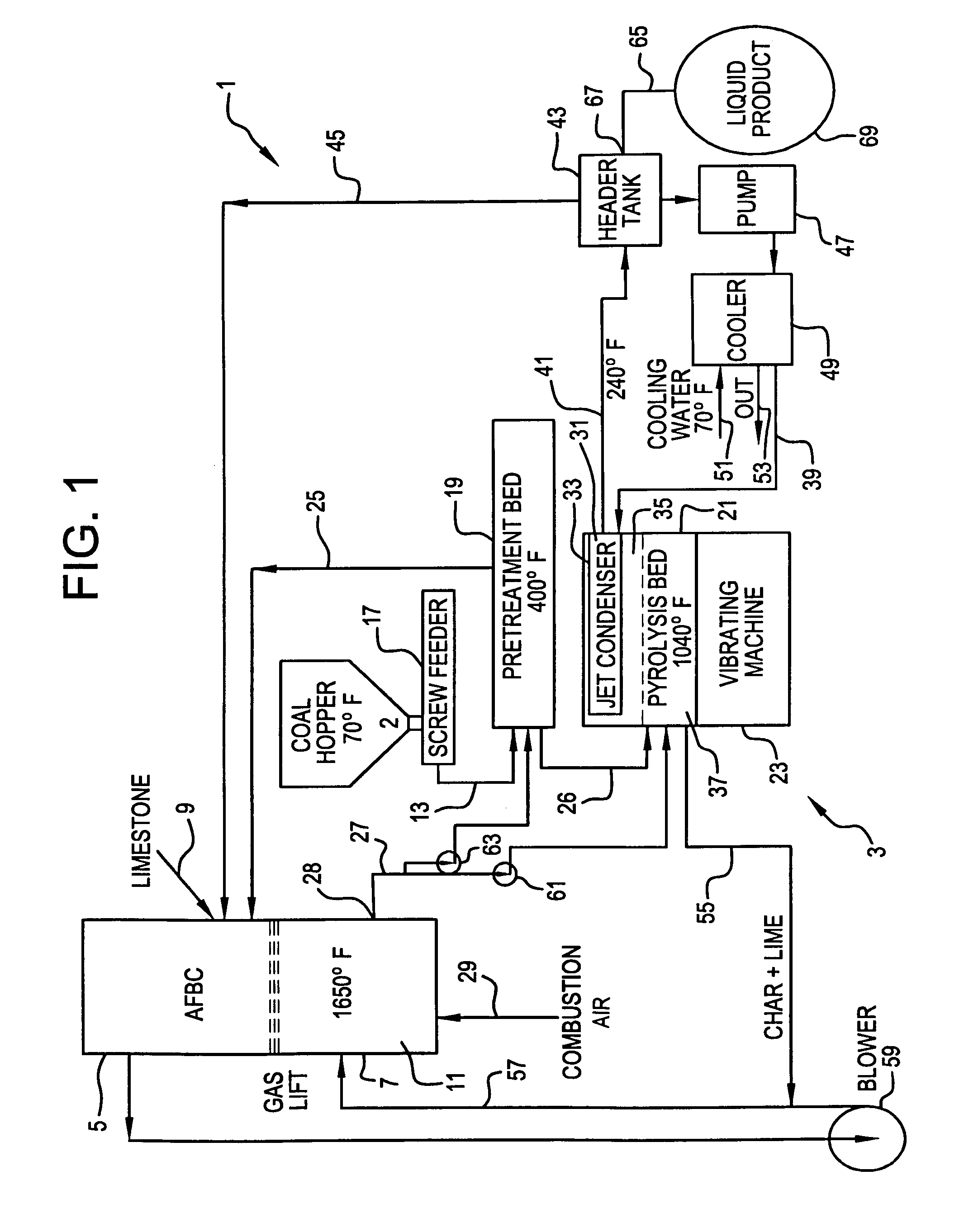
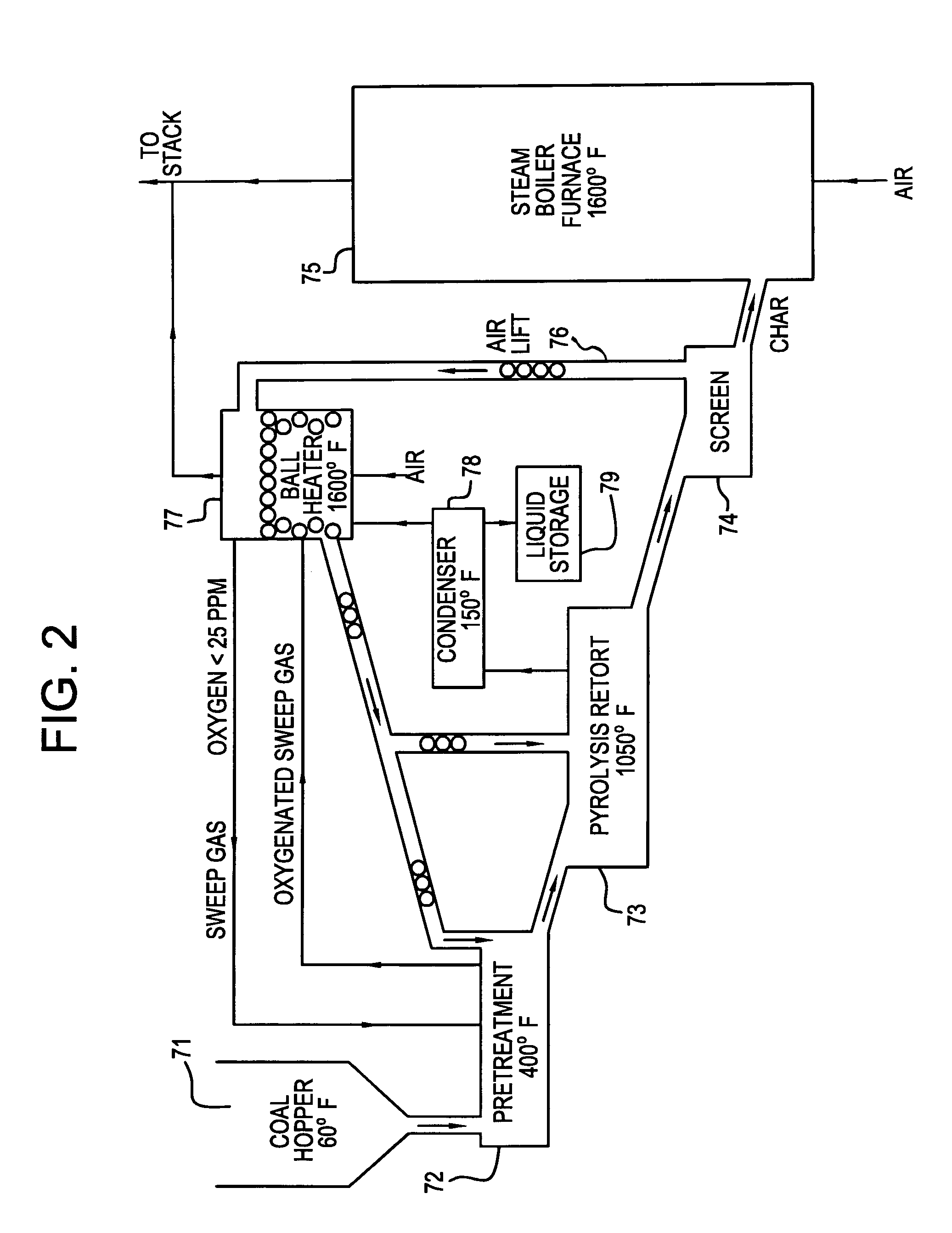
InactiveUS7008459B1Heat loss minimizationOxygen in-leakage can be kept extremely lowMechanical conveying coke ovensDirect heating destructive distillationLiquid productFlue gas
A process and apparatus for coal pyrolysis pretreatment. The apparatus is made up of a pretreatment vessel for holding a bed of coal particles, a preheater for heating the bed of coal particles to a temperature below the coal pyrolysis temperature range and an oxygen remover for removing oxygen released from the heated coal particles. The apparatus can also have a flue gas source as an oxygen removal sweep gas to the bed of coal, a collector for collecting non-condensable combustible gases, and the preheater having a furnace holding ceramic balls which are circulated from the furnace to the bed of coal particles. The process involves heating the bed of coal particles to a temperature below the coal pyrolysis temperature range and preventing air from contacting the bed of coal particles in addition to collecting non-condensable combustible gases or the preheating step accomplished by having a furnace holding ceramic balls which are circulated from the furnace to the bed of coal particles.
Owner:MACLEAN JOHN DR
Process for depositing F-doped silica glass in high aspect ratio structures
InactiveUS6846391B1Reduce effect of sputteringHigh aspect ratio gapDecorative surface effectsVacuum evaporation coatingHigh densityHydrogen
A process for filling high aspect ratio gaps on substrates uses conventional high density plasma deposition processes to deposit fluorine-doped films, with an efficient sputtering inert gas, such as Ar, replaced or reduced with an inefficient sputtering inert gas such as He and / or hydrogen. By reducing the sputtering component, sidewall deposition from the sputtered material is reduced. Consequently, gaps with aspect ratios greater than 3.0:1 and spacings between lines less than 0.13 microns can be filled with low dielectric constant films without the formation of voids and without damaging circuit elements.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method to start a process for producing hydrocarbons from synthesis gas
InactiveUS7855235B2Reduce partial pressureImprove the level ofOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionHydrogenStart up
A method to start a steady state process for producing normally gaseous, liquid and solid hydrocarbons comprises providing a synthesis gas and catalytically converting the synthesis gas into normally gaseous, liquid or solid hydrocarbons. The process involves using at least a portion of the gaseous hydrocarbons produced as a recycle stream to which hydrogen is added prior to its reintroduction into the reactors and as the activity of the catalyst converting the synthesis gas proceeds from start-up towards a steady state, the amount of recycle stream is reduced.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Fire extinguishing composition generating fire extinguishing substance through high-temperature decomposition
ActiveUS9199108B2More environmentally friendly and efficientPrevent wrong additionFire rescueFire extinguisherDecompositionEngineering
The present disclosure relates to a fire extinguishing composition generating fire extinguishing substance through high-temperature decomposition; the fire extinguishing composition includes a fire extinguishing material which can be decomposed to release substance with fire extinguishing properties during the heating process; the content of the fire extinguishing material is at least 80 wt %; a pyrotechnic agent is adopted as a heat source and a power source in a process of fire extinguishing; and the purpose of fire extinguishing is achieved by: igniting the pyrotechnic agent, generating a large quantity of fire substance from the fire extinguishing composition in the use of high temperature produced by burning pyrotechnic agent, and the fire substance sprays out together with the pyrotechnic agent. Compared with the traditional aerosol fire extinguishing systems, the gas fire extinguishing systems and the water type extinguishing systems, the present disclosure provides a more efficient and safer fire extinguishing composition.
Owner:NANO FIRE LLC
Carbon nanotube array and method for forming same
ActiveUS7754182B2Clean evenlyFlat surfaceMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthMetal catalystCarbon nanotube
A method for forming a carbon nanotube array includes the following steps: providing a smooth substrate (11); depositing a metal catalyst layer (21) on a surface of the substrate; heating the treated substrate to a predetermined temperature in flowing protective gas; and introducing a mixture of carbon source gas and protective gas for 5-30 minutes, thus forming a carbon nanotube array (61) extending from the substrate. When the mixture of carbon source gas and protective gas is introduced, a temperature differential greater than 50° C. between the catalyst and its surrounding environment is created by adjusting a flow rate of the carbon source gas. Further, a partial pressure of the carbon source gas is maintained lower than 20%, by adjusting a ratio of the flow rates of the carbon source gas and the protective gas. The carbon nanotubes formed in the carbon nanotube array are well bundled.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD +1
Method of forming a glass melt
ActiveUS20070151297A1Reduce partial pressurePromote vigorous boilingCharging furnaceTank furnacesMolten glassExcessive Cooling
A method of forming a glass melt including heating a glass feed material in a first melting furnace to form a glass melt, flowing the glass melt into a second melting furnace through a refractory metal connecting tube, and further heating the glass melt in the second melting furnace. The refractory metal connecting tube is heated to prevent the molten glass from excessive cooling, and to ensure that the glass melt entering the second melting furnace is equal to or greater than the temperature of the glass melt in the second melting furnace. An apparatus for performing the method is also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method for carburizing workpieces and its application
InactiveUS20110277887A1Excellent surface hardnessReduce wearSolid state diffusion coatingMachines/enginesMetallurgyCarburizing
A method for carburizing workpieces made of steel, particularly workpieces having outer and inner surfaces, the workpiece being held at a temperature in the range of 850 to 1050° C. in an atmosphere containing a gaseous hydrocarbon. At least two different gaseous hydrocarbons are used and / or the workpiece is alternatingly held in the atmosphere containing the gaseous hydrocarbon during a carburizing pulse and in an atmosphere free of hydrocarbon during a diffusion phase. Also described is a use of the method.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Production method of methyl glycolate
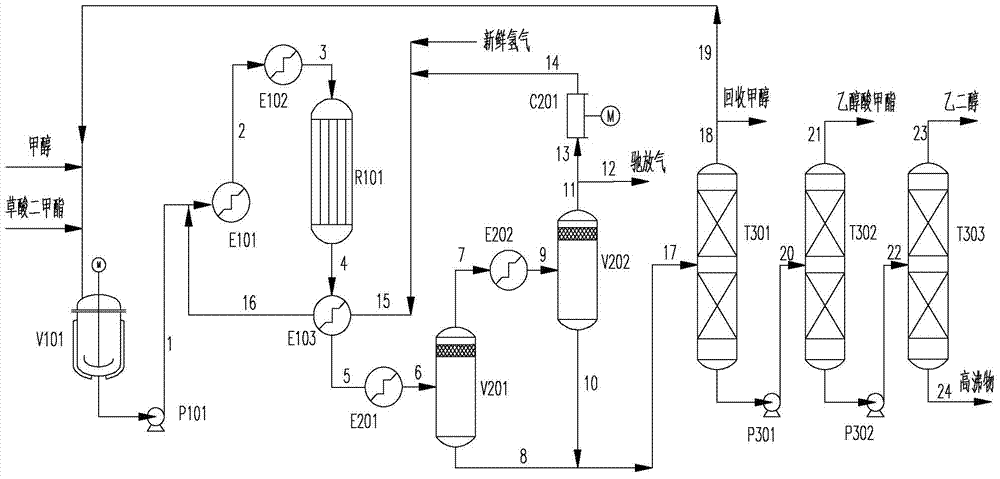
InactiveCN104262152AHigh selectivityReduce partial pressureOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationDistillationMixed materials
The invention relates to a production method of methyl glycolate, aiming to mainly solve the problems of low conversion rate of dimethyl oxalate and low selectivity of methyl glycolate in the prior art. The production method of methyl glycolate comprises the following steps of (1) enabling a mixed material composed of a methanol solution of dimethyl oxalate and feed gas containing hydrogen to be in contact with a silver-containing catalyst in a reactor to react to obtain a mixture flow containing methyl glycolate, carrying out heat exchange, and then, enabling the mixture flow to enter a gas-liquid separation system; (2) sequentially carrying out condensation, primary gas-liquid separation, condensation and secondary low-temperature gas-liquid separation on the mixture flow subjected to heat exchange to obtain crude methyl glycolate; and (3) carrying out reduced-pressure distillation separation on crude methyl glycolate to obtain the methyl glycolate product. According to the technical scheme, the conversion rate of dimethyl oxalate can be higher than 99%, the selectivity of methyl glycolate can be higher than 80%, and the production method can be applied to industrial production of methyl glycolate.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAYI GRP CO
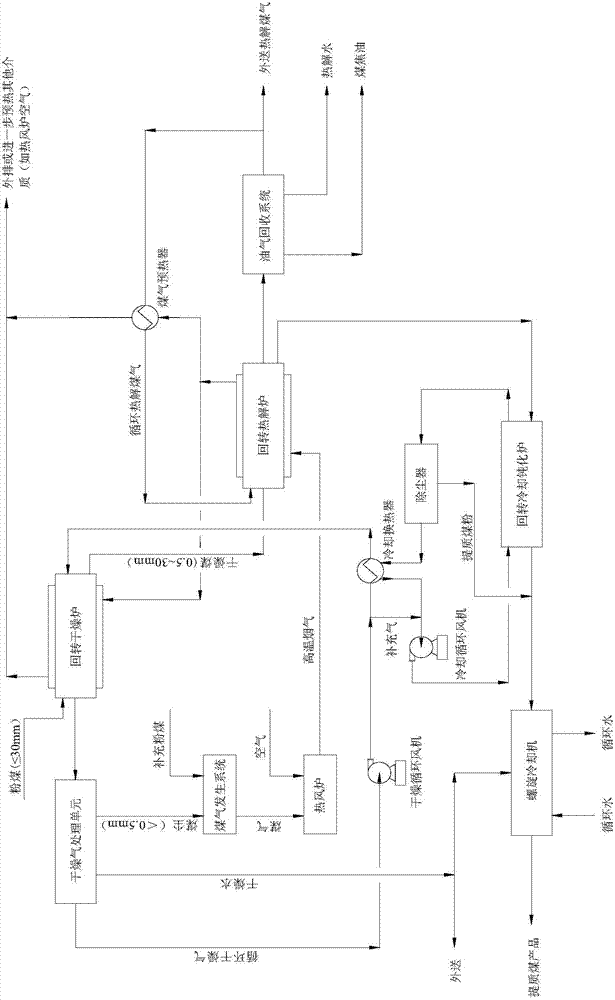
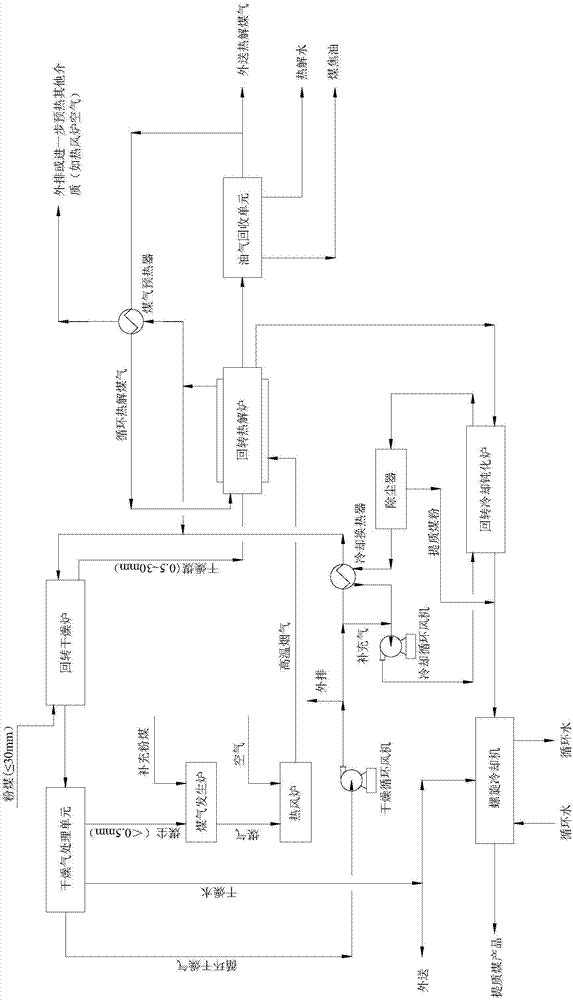
Rotary furnace low-order powdered coal pyrolysis upgrading method with coal gas circulation
ActiveCN104762097AReduce coal dust contentImprove qualitySpecial form destructive distillationGranularityCoal dust
The invention provides a rotary furnace low-order powdered coal pyrolysis upgrading method with coal gas circulation. The rotary furnace low-order powdered coal pyrolysis upgrading method comprises the following steps: heating and drying raw material powdered coal with the granularity less than or equal to 30mm to be 110-280 DEG C in a low-order powdered coal rotary drying system with dust collection, and removing 85% of coal dust with the granularity less than 0.5mm in the powdered coal; feeding the dried coal with the granularity of 0.5-30mm to a downstream rotary pyrolysis system to react at 500-700 DEG C so as to generate upgraded coal and a high-temperature oil gas; feeding the high-temperature upgraded coal to a rotary cooling passivating furnace for primary cooling and medium / low temperature passivation, further cooling by using a spiral cooling machine, spraying water, and discharging out the product; feeding the high-temperature oil gas into an oil gas recycling system, and performing temperature reduction separation, thereby obtaining coal tar, pyrolysis water and pyrolysis coal gas; preheating a part of the pyrolysis coal gas, circulating back to the pyrolysis furnace, and discharging out the rest part of the pyrolysis coal gas.
Owner:SHAANXI COAL & CHEM IND GRP SHENMU TIANYUAN CHEM IND +1
Method for horizontal well mixed gas displacing coal-bed gas
InactiveCN101173604AEnhanced overall recoveryReduce construction cost of displacement miningFluid removalHorizontal wellsProduct gas
The invention discloses a method for displacing coal seam gas via horizontal well mixed gas, relating to the method of coal seam gas coal mining, which comprises the following steps: 1. A plurality of horizontal wells (10) are formed in the coal seam (30) through the horizontal well craft, which comprise injection wells (11) and harvesting wells (12) alternatively arranged at intervals ; 2. A high-pressure injecting equipment is used to inject the mixed gas into the coal seam (30) with coal seam gas via injection wells (11); 3. The mixed gas with coal seam gas is acquired in harvesting wells (12) until the methane concentration is lower than the coal mining concentration and the preservation concentration. The invention has the advantages of considering both the competitive absorption of strong replacement gas and the effect of permeation increase and methane gas partial pressure of feeble replacement gas; improving the recovery factor and the single yield of the coal seam gas, and reducing the coal mining cost of the coal seam gas, simultaneously, mothballing the waste gas geologically, and reducing and sealing waste gas at a maximum.
Owner:INST OF ROCK AND SOIL MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
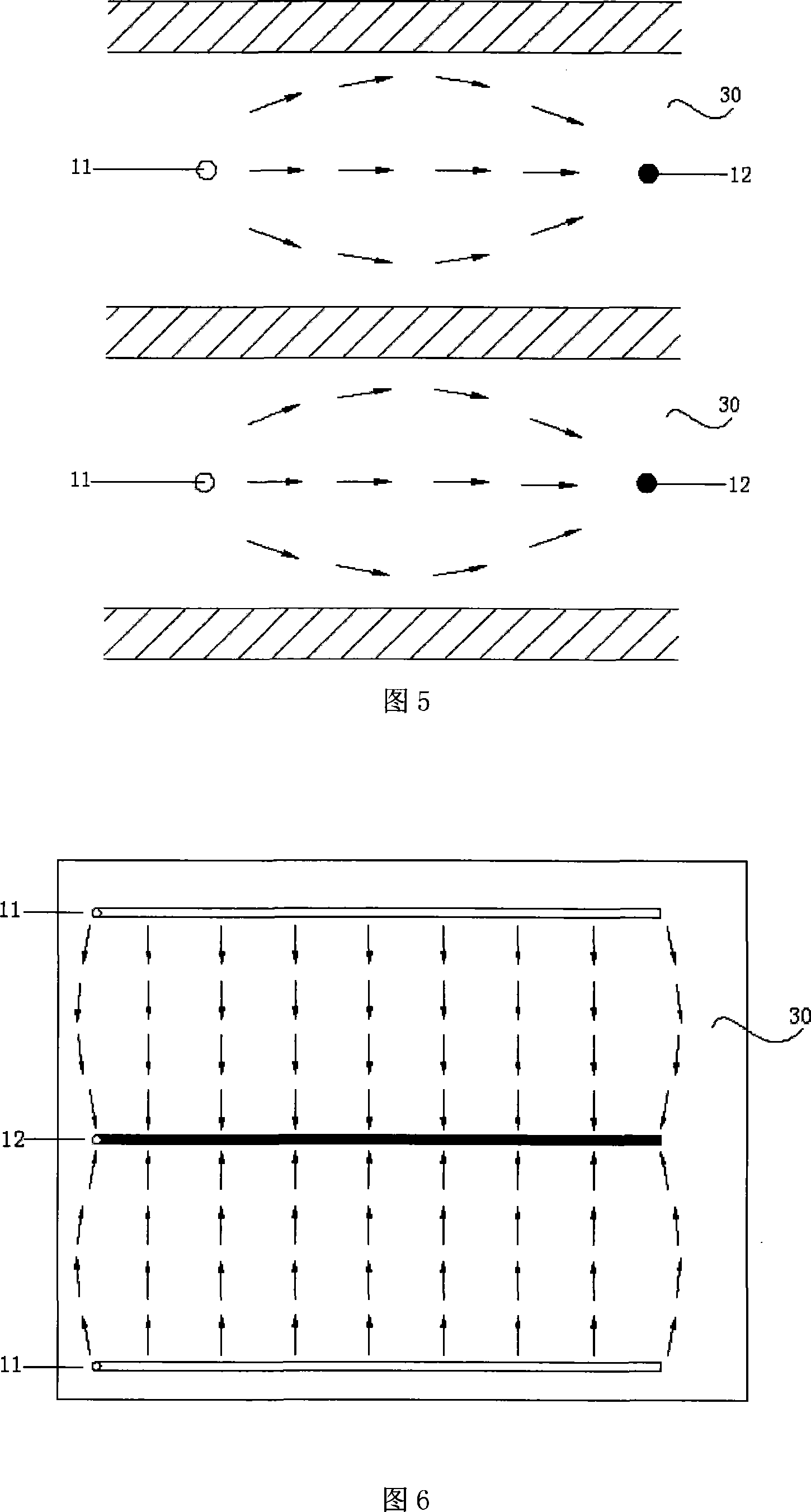
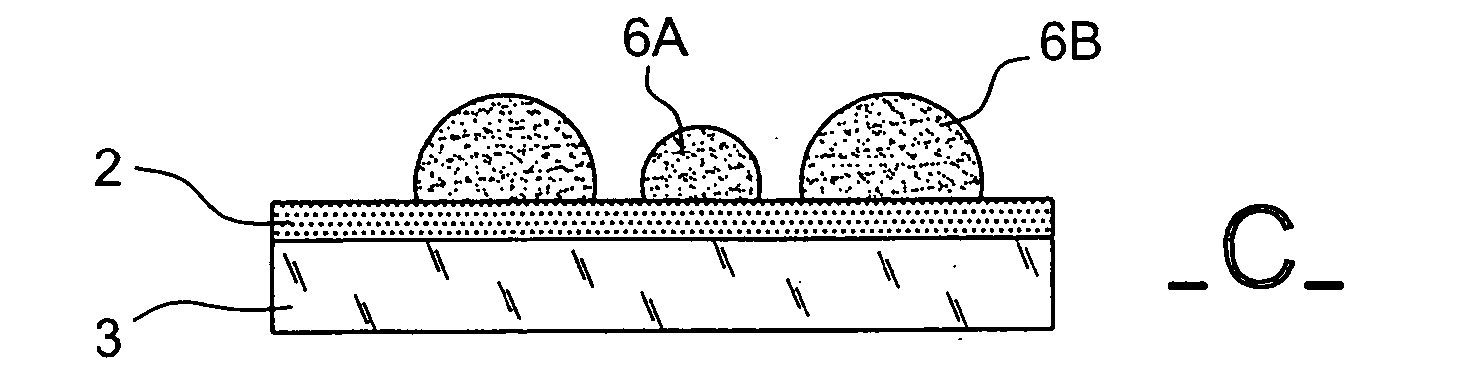
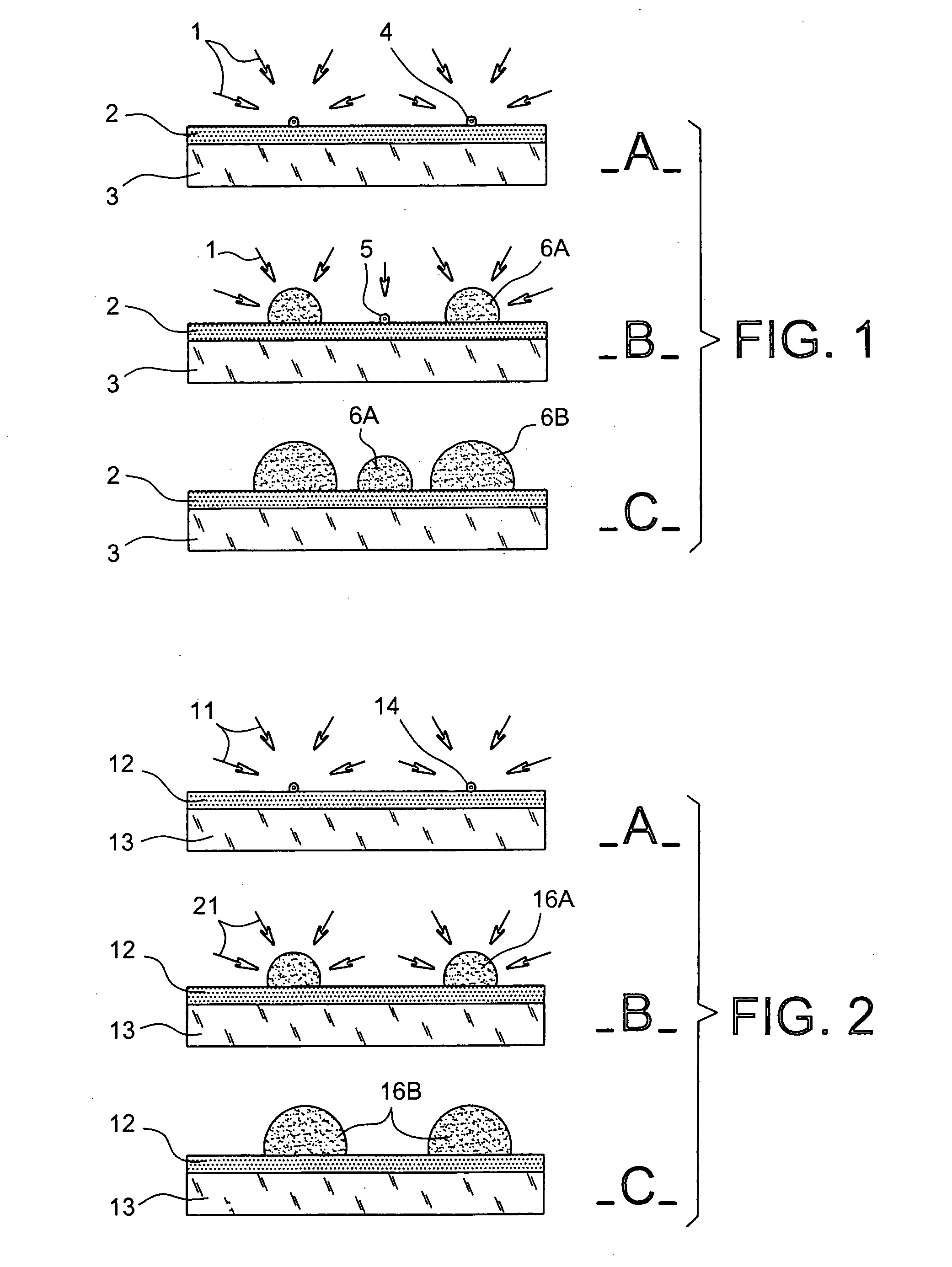
Method for forming, by CVD, nanostructures of semi-conductor material of homogeneous and controlled size on dielectric material
ActiveUS20040147098A1High densityLong exposure timeTransistorPolycrystalline material growthDielectricSemiconductor materials
The invention concerns a method for forming nanostructures of semi-conductor material on a substrate of dielectric material by chemical vapour deposition (CVD). Said method comprises the following steps: a step of forming on the substrate (12) stable nuclei (14) of a first semi-conductor material in the form of islands, by CVD from a precursor (11) of the first semi-conductor material chosen so that the dielectric material (12) accepts the formation of said nuclei (14), a step of forming nanostructures (16A, 16B) of a second semi-conductor material from the stable nuclei (14) of the first semi-conductor material, by CVD from a precursor (21) chosen to generate a selective deposition of the second semi-conductor material only on said nuclei (14). The invention further concerns nanostructures formed according to one of said methods as well as devices comprising said nanostructures.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com