Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
931 results about "Carburizing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
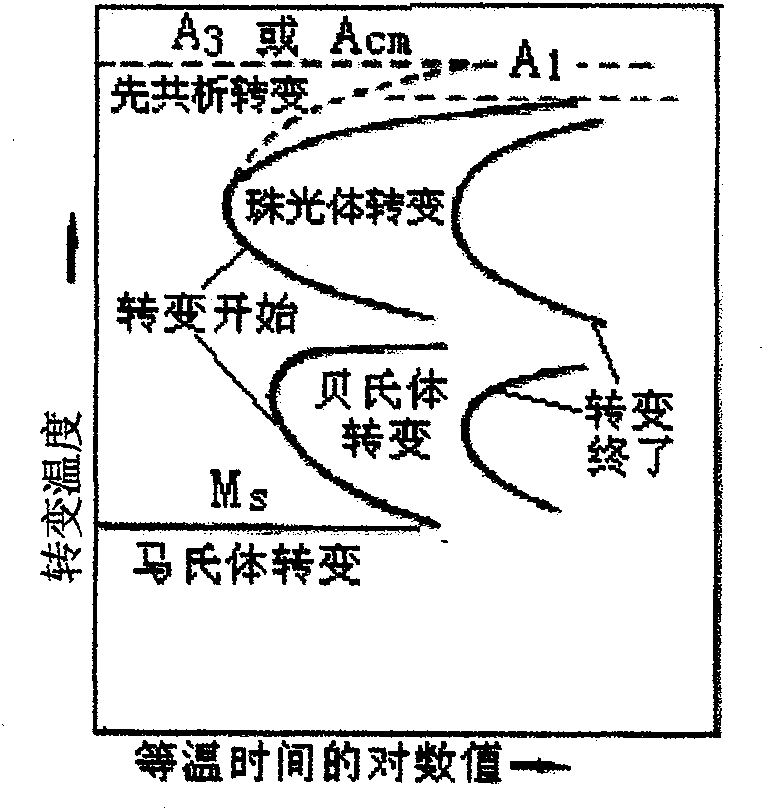
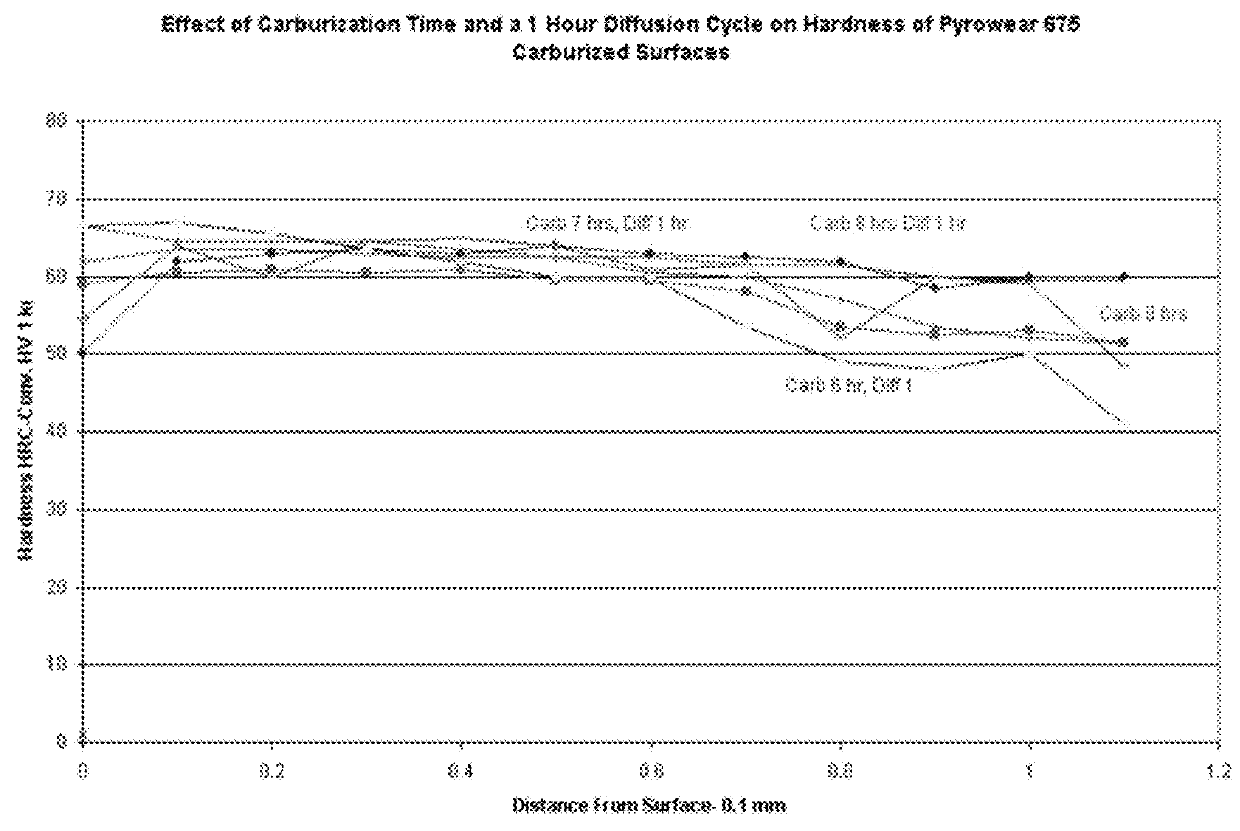
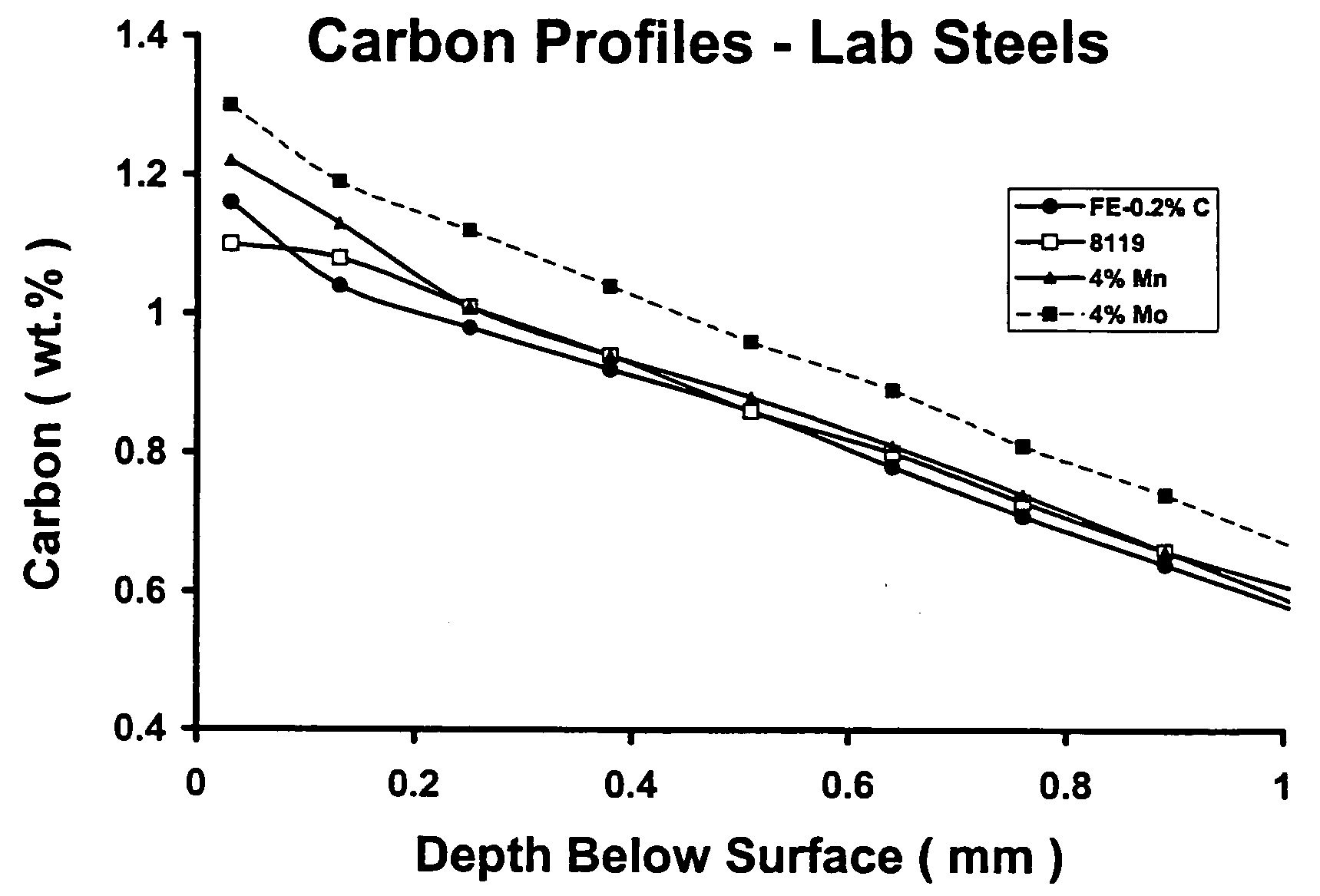
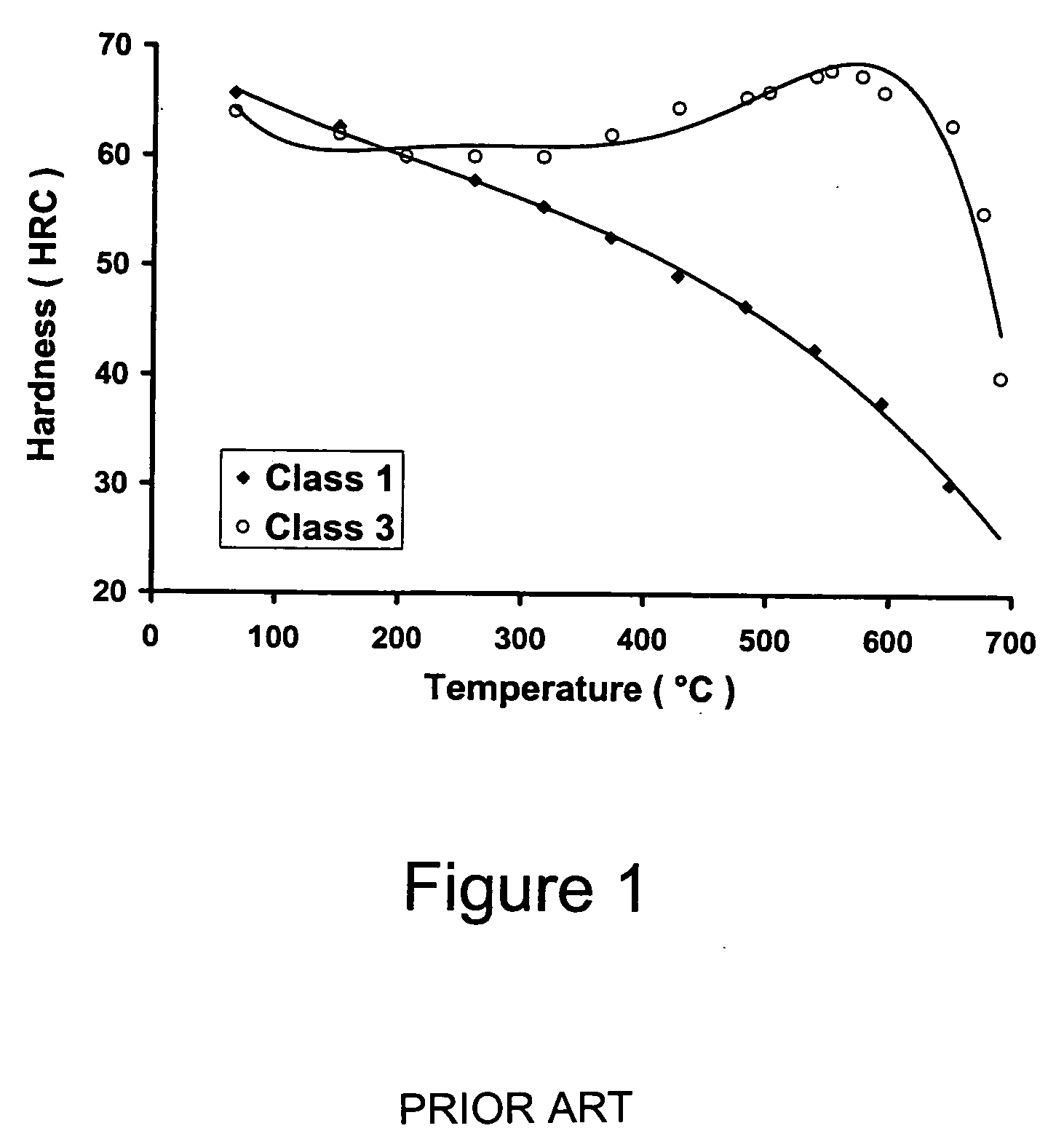
Carburizing, carburising (chiefly British English), or carburization is a heat treatment process in which iron or steel absorbs carbon while the metal is heated in the presence of a carbon-bearing material, such as charcoal or carbon monoxide. The intent is to make the metal harder. Depending on the amount of time and temperature, the affected area can vary in carbon content. Longer carburizing times and higher temperatures typically increase the depth of carbon diffusion. When the iron or steel is cooled rapidly by quenching, the higher carbon content on the outer surface becomes hard due to the transformation from austenite to martensite, while the core remains soft and tough as a ferritic and/or pearlite microstructure.
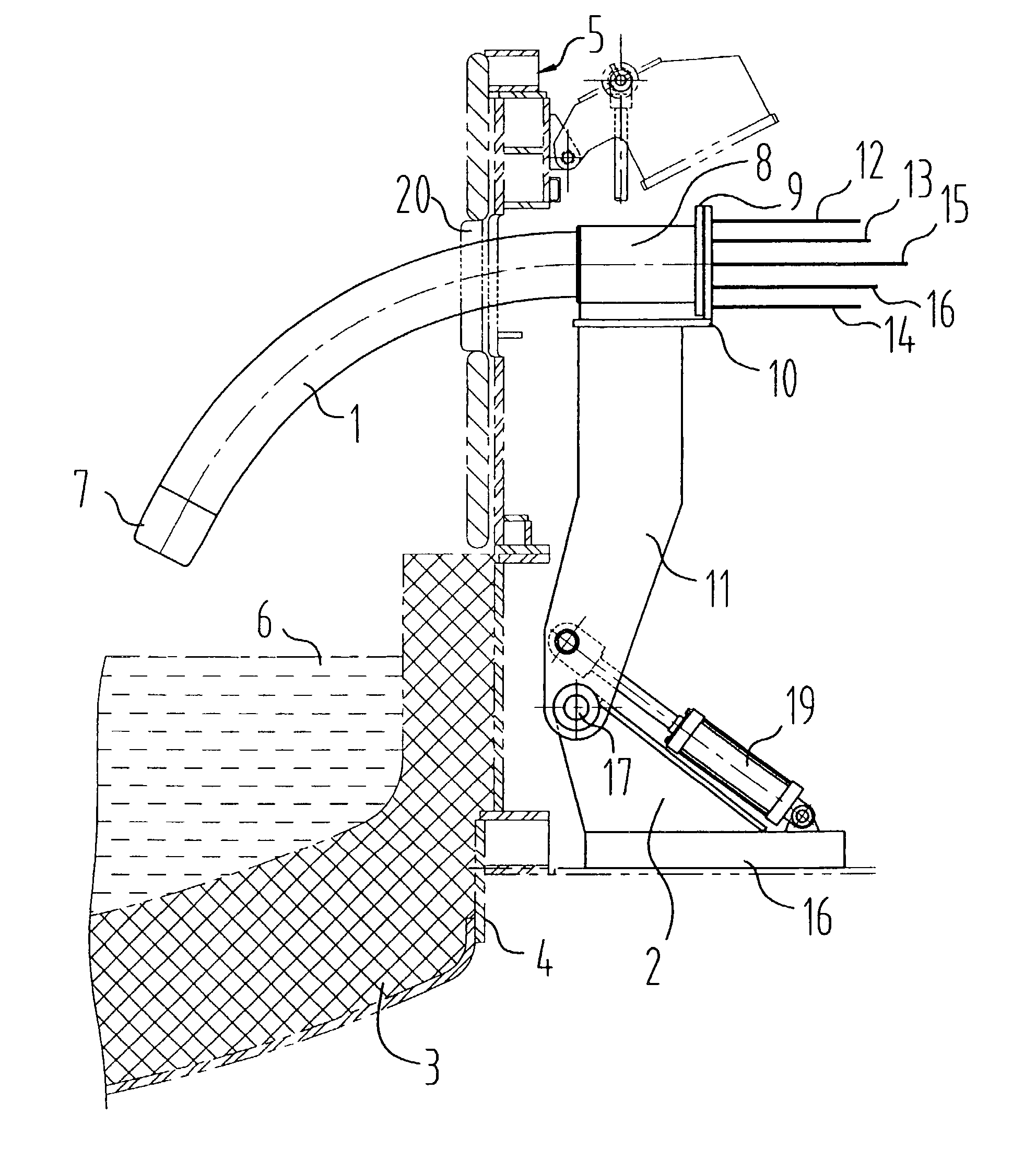
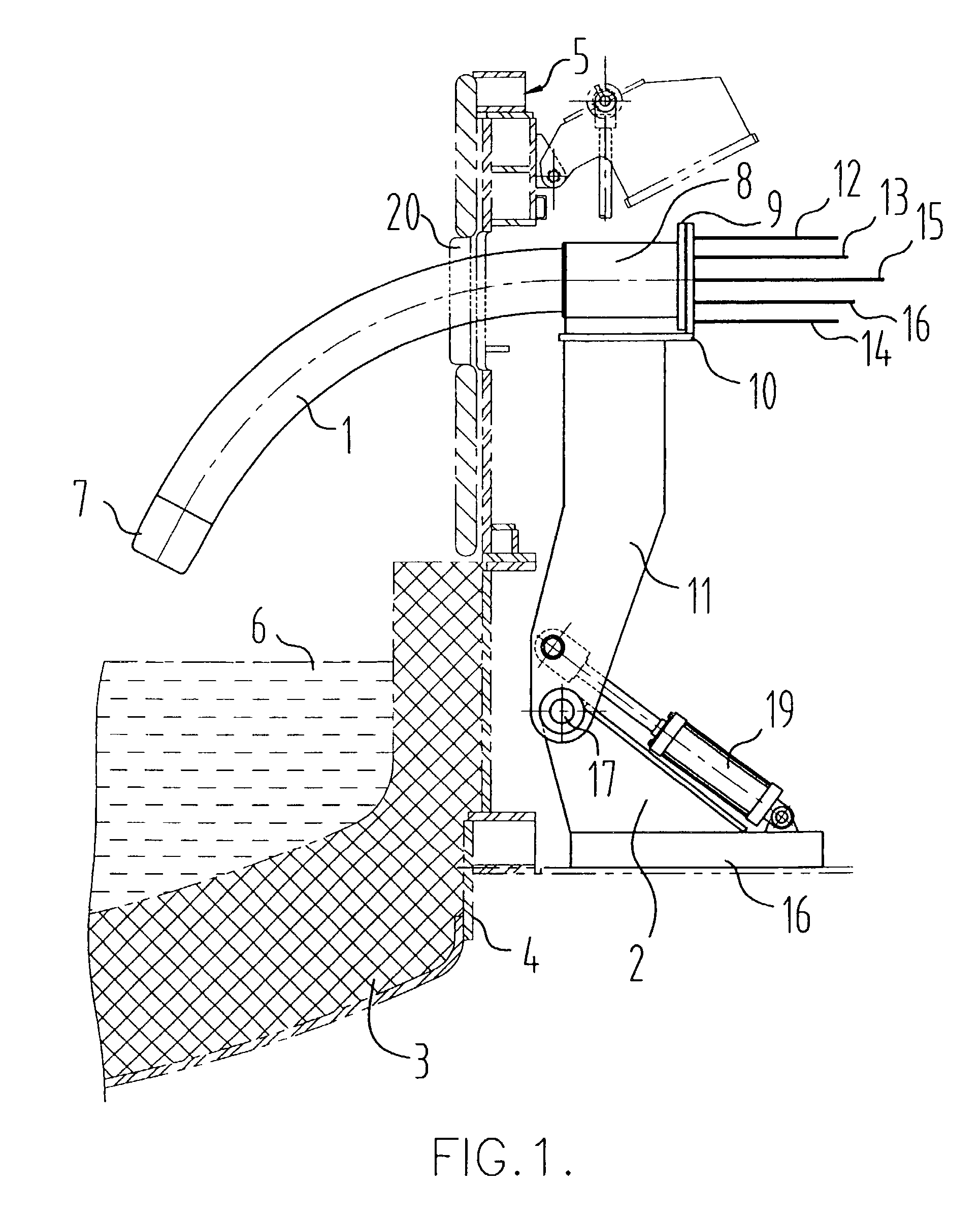
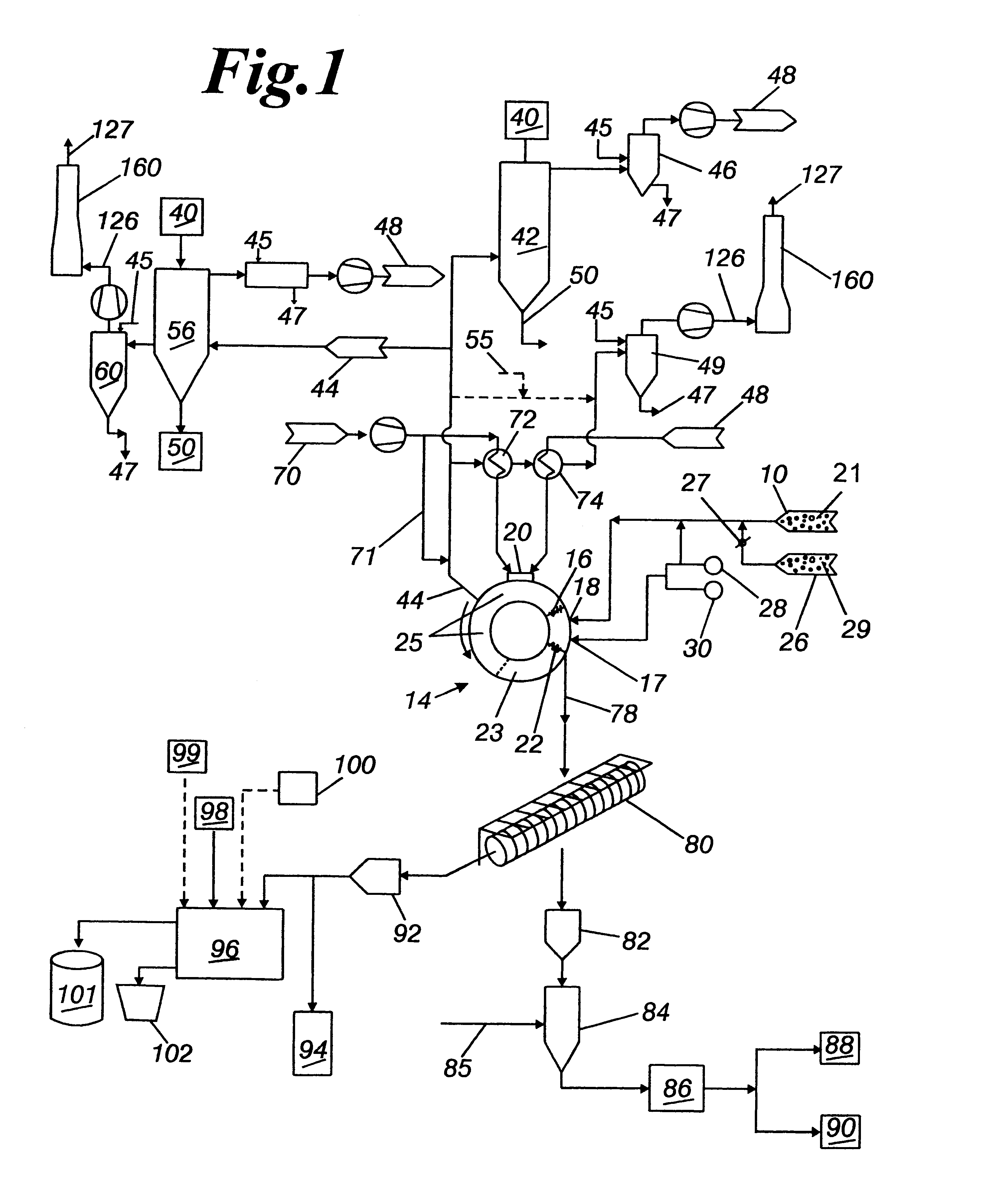
Multi-purpose, multi-oxy-fuel, power burner/injector/oxygen lance device
InactiveUS20030075843A1Reduce the numberSmall sizeTuyeresCharge manipulationSteelmakingLiquid medium
A multi-purpose, multi-oxy-fuel High Temperature Power Burner / Injector / Oxygen Lance, Mechanical System Apparatus Device, for steelmaking from recycled scrap and / or virgin ferrous charge, which can be employed in multi-oxy-fuel (natural gas; pulverized carbonaceous matter; heavy oil), especially by Oxygen Combusted mixture of Natural Gas / Pulverized Carbonaceous Matter in High Temperature Power Burner Mode, for efficient and rapid melting of solid ferrous charge (cold or preheated) in a special steelmaking Metallurgical Furnace or Open Hearth Furnace, Tandem Furnace, BOF, EAF, as its augmenting or only source of thermal energy; more than one Device in Oxygen-Natural Gas / Pulverized Carbonaceous Matter Power Burner Mode, can be employed as the only source of thermal energy in a modified, originally Electric Arc Furnace, as total replacement of Graphite Electrodes and Electric Arc System, the replacement being noticeably more primary energy efficient than the thermal energy provided by Graphite Electrode / Arc System; it also can be employed in an Solid Particles Injector Mode, for injecting of adequately granulated carbonaceous materials or lime into the molten steel for its carburizing or for foamy slag control; further it can be employed in a natural gas shrouded, pulsating oxygen stream, for vertically to the charge oriented soft blow supersonic Oxygen Injection Lance Mode, for decarburization of the molten metal contained in the hearth of the metallurgical furnace and foamy slag control; in one of the embodiments-generally arcuate-pivotally mounted, liquid media cooled composite body, is pivoted into and out of a furnace vessel through a small opening in the shell wall for auto-regulated constant optimal positioning of the Composite Body Tip against solid or molten charge, in each and all multi-purpose modes; furthermore, when inserted into the furnace vessel, the arcuate composite body can be rotated about its longitudinal axis for directing the oxy-fuel high temperature flame towards unmolten charge in the furnace; in an other-generally linear-embodiment, the liquid cooled composite body is attached to the mast type carrier allowing vertical movement of the composite body which enters the furnace vessel through a small opening in the furnace roof; the bimetallic, liquid cooled special tip assembly of both-arcuate and linear embodiments-of the composite body includes easy replaceable, independent, multi-opening nozzles, mounted in a protective, retracted position inside of the liquid cooled special tip assembly.
Owner:EMPCO (CANADA) LTD
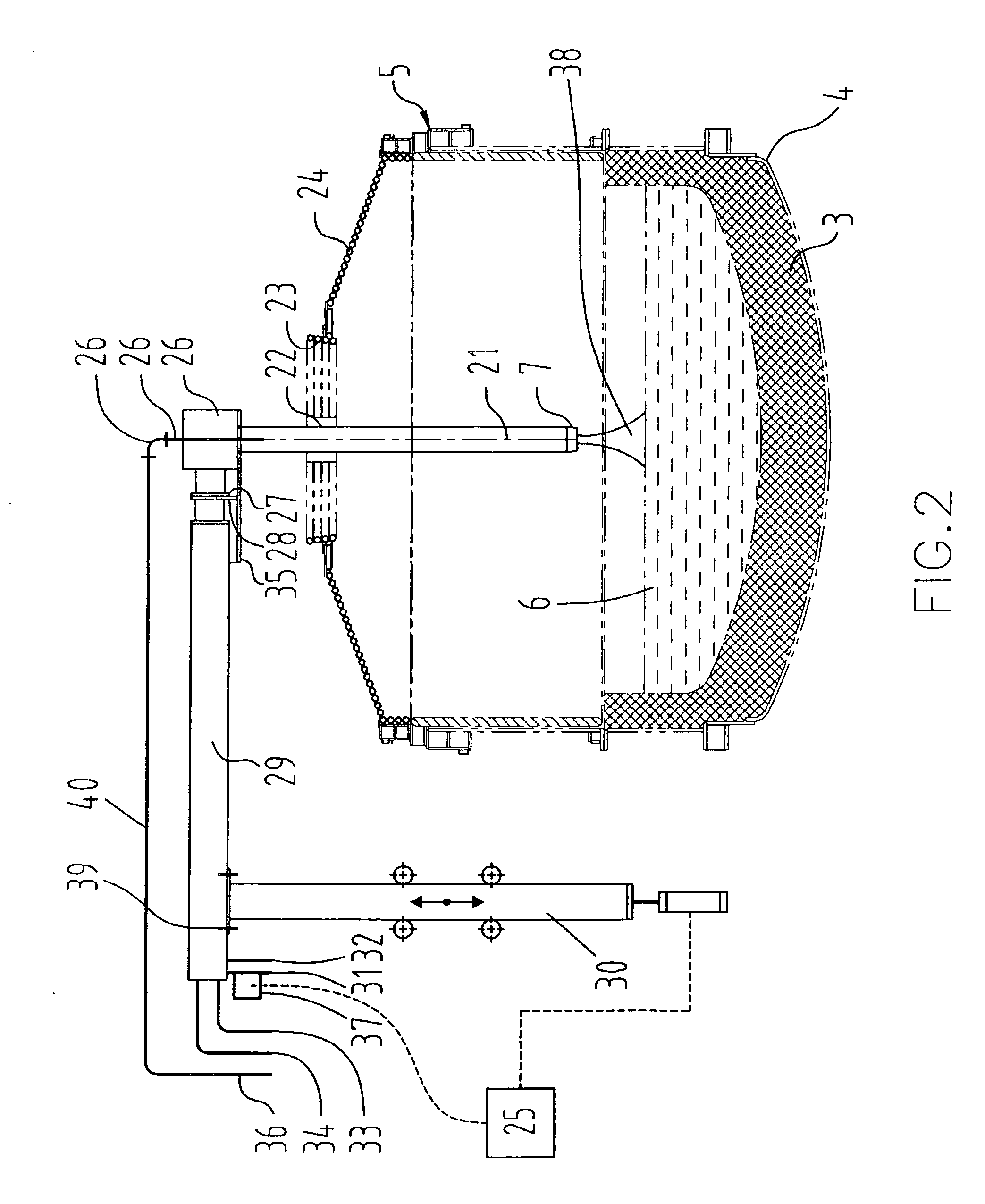
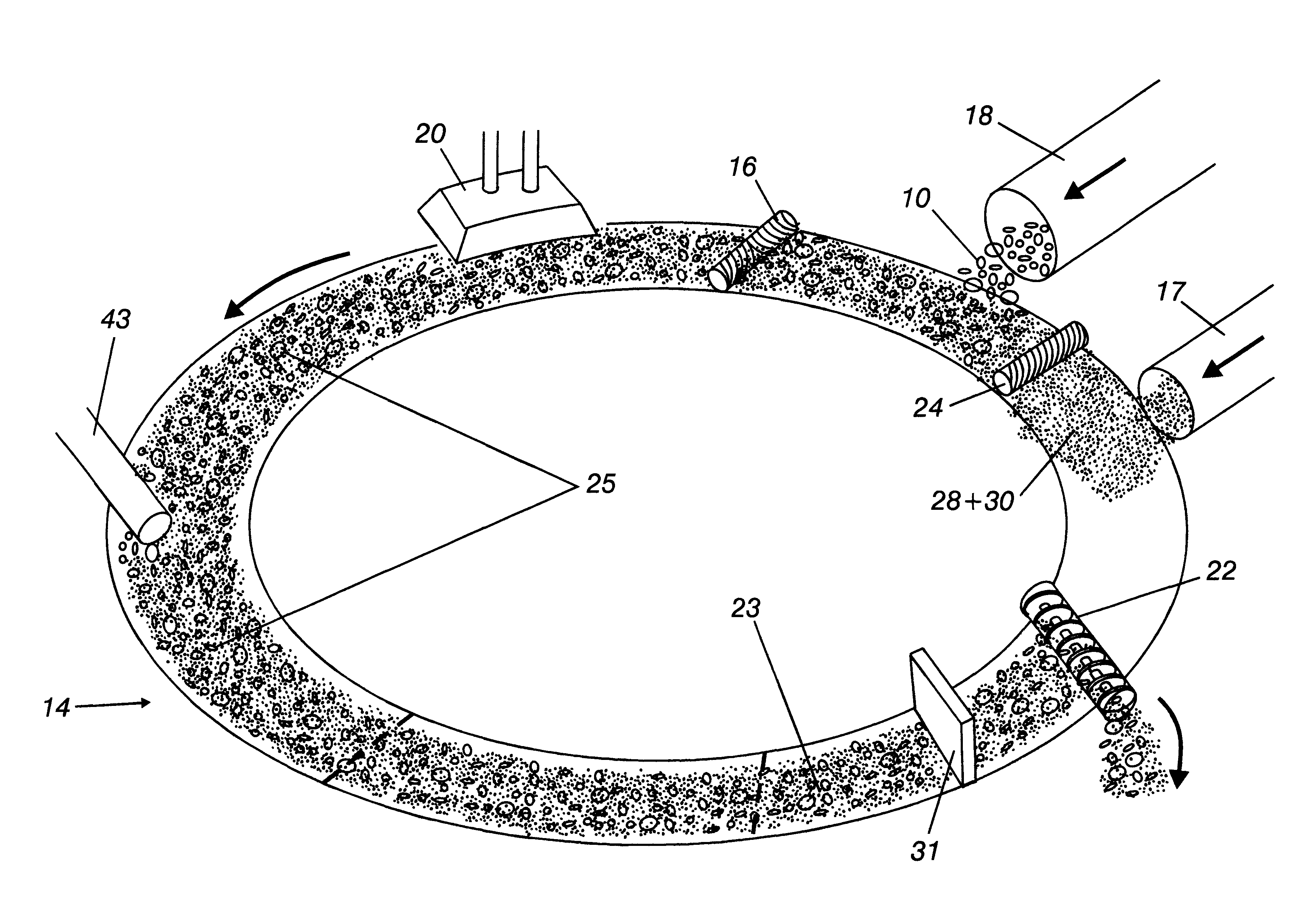
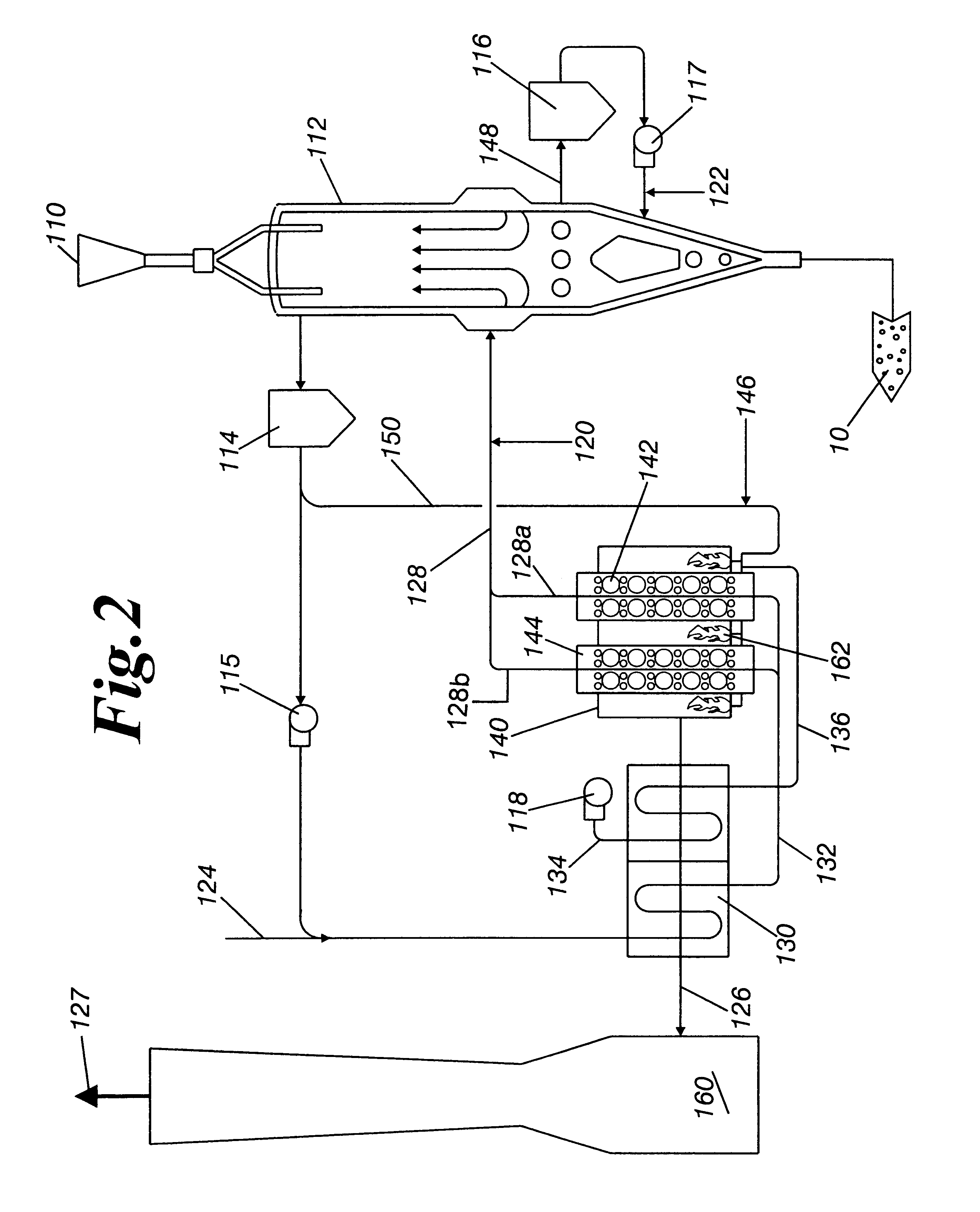
Method of direct iron-making / steel-making via gas or coal-based direct reduction and apparatus
The invention is a method and apparatus for iron-making / steel-making using a modified rotary hearth furnace, that is a finisher-hearth-melter (FHM) furnace. In the method the refractory surface of the hearth is coated with carbonaceous hearth conditioners and refractory compounds, where onto said hearth is charged with pre-reduced metallized iron. The pre-reduced metallized iron is leveled, then heated until molten, and then reacted with the carbon and reducing gas burner gases until any residual iron oxide is converted to iron having a low sulfur content. Nascent slag separates from the molted iron forming carburized iron nuggets. The nuggets are cooled, and then the iron nuggets and the hearth conditioners, including the refractory compounds, are discharged onto a screen, which separate the iron nuggets from the hearth conditioner. The hearth conditioner is recycled, and the iron nuggets are either prepared for sale or for additional treatment, such as alloying, in a final melter, where the final melter is preferably an electric furnace. Exhaust gases from the FHM furnace are recovered for calcining coal into fuel gases and coke.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Manufacturing method of integral herringbone gear shaft
ActiveCN101804548AImprove bending strengthSmall diameterMaterials preparationManufacturing cost reduction
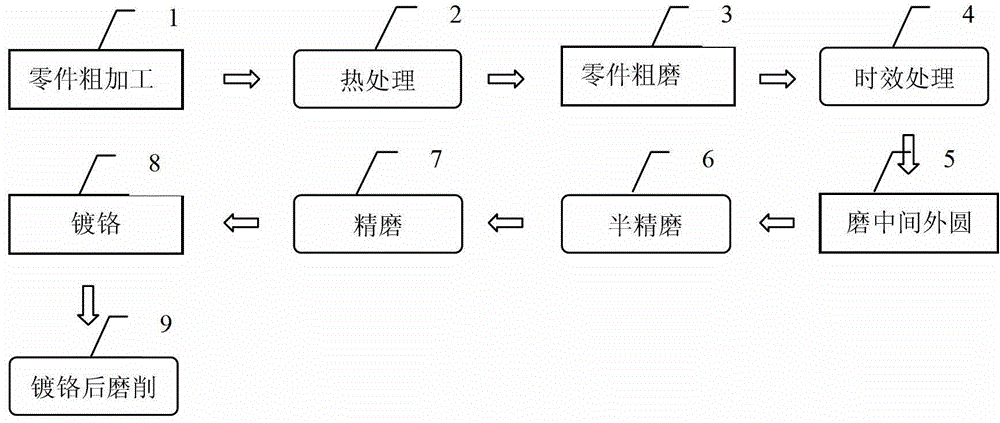
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of an integral herringbone gear shaft, which comprises the following steps that: material preparation: a center hole is drilled on one end of a work piece; primary machining; primary detection; heat treatment; secondary machining; secondary detection; rough milling; chamfering at the gear end; coating anti-carburizing layers on both ends of the herringbone gear shaft so that the depth of a carburized layer is 3.55 to 3.95mm, and quenching so as to enable the hardness of a gear part to reach HRC58 to 62, and to enable the hardness of the heart to reach HRC28 to 33; carrying out shoot peening on a gear surface; tertiary machining; gear shaping; external grinding; fine milling; and inspection. The manufacturing method of the integral herringbone gear shaft has the advantages of improving the bending strength of the gear root, reducing the manufacturing cost and improving the manufacturing precision.
Owner:SHANGHAI ZHENHUA HEAVY IND GRP NANTONG TRANSMISSION MACHINERY
Heat treatment equipment and heat treatment method of metal parts
The invention relates to heat treatment equipment of metal parts, which comprises a heating device and charging barrels, wherein the charging barrels are installed on a rotating disk; the heating device is an electromagnetic induction heating device; the inner diameter of an induction coil is greater than the outer diameter of each charging barrel; when the induction coil is in a working state of energizing and heating, the induction coil is surrounded at the outer side of one of the charging barrels; and the inner cavity of each charging barrel for containing metal parts is a sealed space. The heat treatment method comprises the following steps: after the induction coil is lowered or the charging barrels are lifted and the corresponding charging barrel is sealed, filling inert gases, and heating to the set temperature; adding carbon and / or nitrogen, heating for the set time, and then, stopping heating; lifting the induction coil or lowering the charging barrels, rotating the rotating disk, pouring materials, quenching and cooling to complete the carburization and / or nitridation heat treatment process of the metal parts; simultaneously, rotating the charging barrels containing the metal parts to be treated by heating to the under part of the induction coil; and circularly working. The invention has the advantage of high efficiency and can realize continuous automatic production.
Owner:GUANGZHOU CCM ELECTRICAL APPLIANCE
High-toughness carburized bearing steel with ultra-long contact fatigue life and preparation method thereof
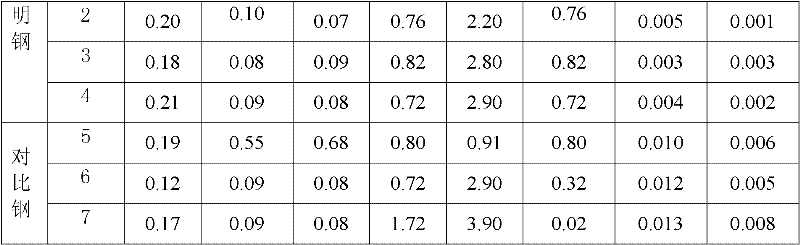
The invention relates to a high-toughness carburized bearing steel with ultra-long contact fatigue life and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of alloy steel. The steel comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.16-0.24% of C, at most 0.10% of Si, at most 0.10% of Mn, 0.30-1.50% of Cr, 1.5-4.5% of Ni, 0.30-1.50% of Mo, 0.02-0.10% of Nb, 0.3-0.9% of V, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities, wherein [N]+[O]+[H]+P+S<=0.0080%, and Ti<=0.0030%. The invention particularly relates to a high-toughness carburized bearing steel which has the advantages of high shock resistance load, stable dimension and ultra-long contact fatigue life in the serve process. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages of high surface hardness, high core toughness, high dimensional stability, high bending fatigue strength limit and ultra-long contact fatigue life.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
Carburization-like overloading tooth component tooth surface laser cladding powder material and repairing method thereof
InactiveCN101100746AImprove repair qualityImprove performanceMetallic material coating processesLaser beam welding apparatusLaser power densityAlloy
A process for laser powder-melting onto the surfaces of the teeth parts that are of heavily loaded cemented steel to be repaired is disclosed herewith. The powder of grains = (-140-+260 mesh) comprises (mass%): C 0.80-1.10, Mn 7.50-9.00, Cr 0.90-1.30, Mo 0.20-0.35, B 2.00-3.50, Si 2.50-3.50, and balanced with Fe with impurities of P not more than 0.06 and S not more than 0.04. Laser power density is equal to 1.0 X 108W-109W / m2 per unit of time. The said powder has good re-melting property, self-enhancing and fatigue-resistance performances, so that it can be used to repair worn gears.
Owner:ACADEMY OF ARMORED FORCES ENG PLA
Protective coating for surface of steel workpiece
The invention relates to a protective coating for the surface of a steel workpiece, which comprises the following components: graphite, sodium silicate and a surface penetrant, wherein the volume ratio of the graphite to the sodium silicate is 1: 3-7; and the surface penetrant accounts for 0.05 to 0.15 percent of the total volume in the components. The coating has the advantages that the coating not only avoids disadvantages caused by usual methods such as adding alloy, performing surface high-frequency quenching, forming carburizing atmosphere and the like, prevents the surface of the steel workpiece from high-temperature oxidation decarbonization, but also improves the hardness of the surface of the steel workpiece (matrix) to realize the improvement of the wear resistance thereof, and solves the existing problems of high production cost, low production efficiency, long production period, large energy consumption and environmental pollution.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA FIRST MACHINERY GRP
High-toughness low-alloy constructional steel and producing method thereof
ActiveCN1920080AMeet the technical requirements of steelGood mechanical propertiesAluminiumHeat processing
The invention relates the low-alloy high-tensile structural steel and preparing method. The components are as follows: C:0.05%-0.60%, Si: 0.05%-0.70%, Mn: 0.5%-2.5%, P: <= 0.04%, S: <=0.04%, Cr: 0-0.70%, Ni: 0-0.70%, molybdenum: 0-0.60%, Cu: 0-0.20%, vanadium: 0.01%-0.30%, Al 0-0.1%, niobium: 0.001%-0.10%, N: 0.004%-0.02%, and the left is Fe. The method comprises the following steps: using revolving furnace to smelt, and using LF furnace to refine. The yield strength as is above 460Mpa, the dynamic ductility Akv is above 27J at low temperature (-40Deg.C), endurance life is above 2 million times, and the finished steel can be used for train brake beam, engineering machinery and hydraulic support without heat treatment. After quenching and high tempering modified heat treatment, the strength for extension of the steel is above 750Mpa, the dynamic ductility Akv is above 150J at low temperature (-40Deg.C). After carbonization, the steel can be used for abrasion-proof driving mechanism elements and parts.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Technology treatment method of machining deformation of long and thin hole shaft type thin-wall part
InactiveCN103331651AImprove rigidityReduce unstable retained austeniteFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesCold treatmentTempering
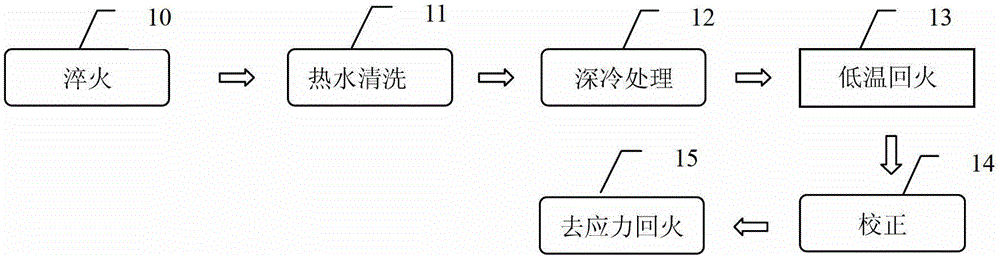
The invention provides a technology treatment method of machining deformation of a long and thin hole shaft type thin-wall part, and aims at providing a technology treatment method of the machining deformation, which is simple in flow, and high in machining precision and yield. The method adopts the following technical scheme that the method comprises the steps that the long and thin hole shaft type thin-wall part after mechanical rough machining and carburizing treatment is subjected to quenching heat treatment, subzero treatment and low temperature tempering treatment. During the quenching heat treatment, the quenching cooling time is 8-11S / mm; when a surface temperature of the part falls to 30-50 DEG C, the part is lifted up from oil; the surface temperature of the part rebounds in air after some time; and when the part is cooled to 30-50 DEG C again, residual oil is rinsed cleanly by hot water greater than or equal to 60 DEG C. During the subzero treatment, the part is transferred to a -70 DEG C to -80 DEG C refrigerator box to be refrigerated for 2-2.5h within 1h after quenching, and then subjected to air cooling for 60-90min till the part reaches a room temperature. During the low temperature tempering treatment, the part is subjected to heat preservation for 3-4h at 160-180 DEG C and the air cooling. The method solves the problem of the machining deformation of the long and thin hole shaft type thin-wall part due to heat treatment stress, grinding stress and the like, and the yield reaches 100%.
Owner:SICHUAN LINGFENG AVIATION HYDRAULIC MACHINERY
High Strength Spring Steel and High Strength Heat Treated Steel Wire for Spring
The present invention provides a high strength heat treated steel wire for spring having a tensile strength of 2000 MPa or more which is coiled in the cold state and can achieve both sufficient atmospheric strength and coilability and spring steel used for that steel wire, that is, a high strength heat treated steel wire for a spring characterized by comprising, by mass %, C: 0.5 to 0.9%, Si: 1.0 to 3.0%, Mn: 0.1 to 1.5%, Cr: 1.0 to 2.5%, V: over 0.15 to 1.0%, and Al: 0.005% or less, controlling N to 0.007% or less, further containing one or two of Nb: 0.001 to less than 0.01% and Ti: 0.001 to less 0.005%, and having a tensile strength of 2000 MPa or more, having cementite-based spheroidal carbides and alloy-based spheroidal carbides in a microscopic visual field satisfying an area percentage of carbides with a circle equivalent diameter of 0.2 μm or more of 7% or less and a density of carbides with a circle equivalent diameter of 1 grain / μm2 or less, having a prior austenite grain size number of #10 or more, and having retained austenite of 15 mass % or less.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL & SUMITOMO METAL CORP
Novel Stainless Steel Carburization Process
InactiveUS20120111454A1Short cycleReaction pressure is loweredSolid state diffusion coatingVacuum furnaceHydrocarbon
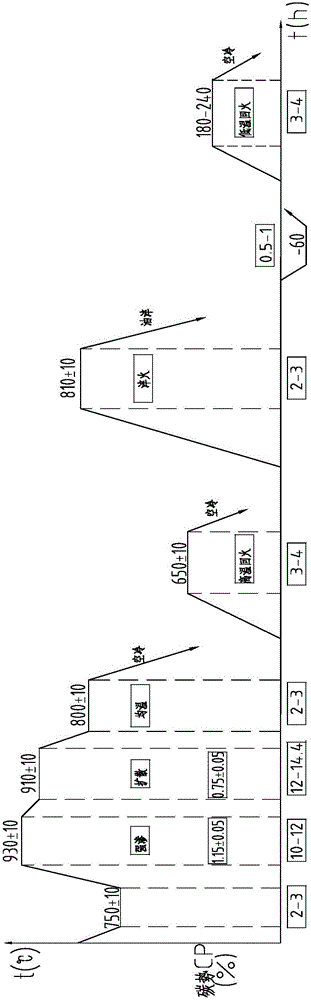
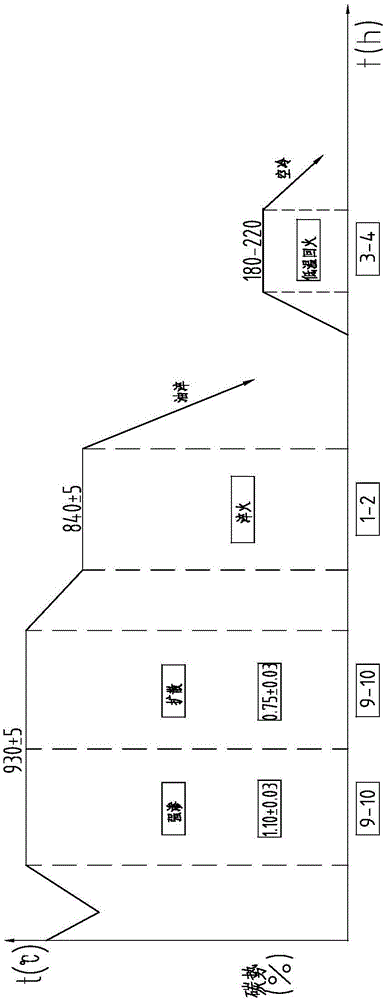
A process for the high temperature carburization of steel comprising heating said steel in a vacuum furnace in the presence of a hydrocarbon carburizing gas in combination with hydrogen wherein said carburizing gas / hydrogen combination is administered to the vacuum furnace by cyclically reducing the pressure in the furnace followed by the pulsed addition of the hydrocarbon carburizing gas with hydrogen at partial pressure followed by a second diffusion cycle wherein the steel is further annealed for a time sufficient to allow for the additional deposition of from about 0.8% to about 3.0% m / o of said carbon onto the surface of said steel to permit the further migration of the carbon from the steel surface to the interior thereof.
Owner:MOYER KENNETH H
Stainless steel and stainless steel pipe having resistance to carburization and coking
ActiveUS20050045251A1Avoid carburizationRecord information storageMagnetic recordingSS - Stainless steelPetrochemical
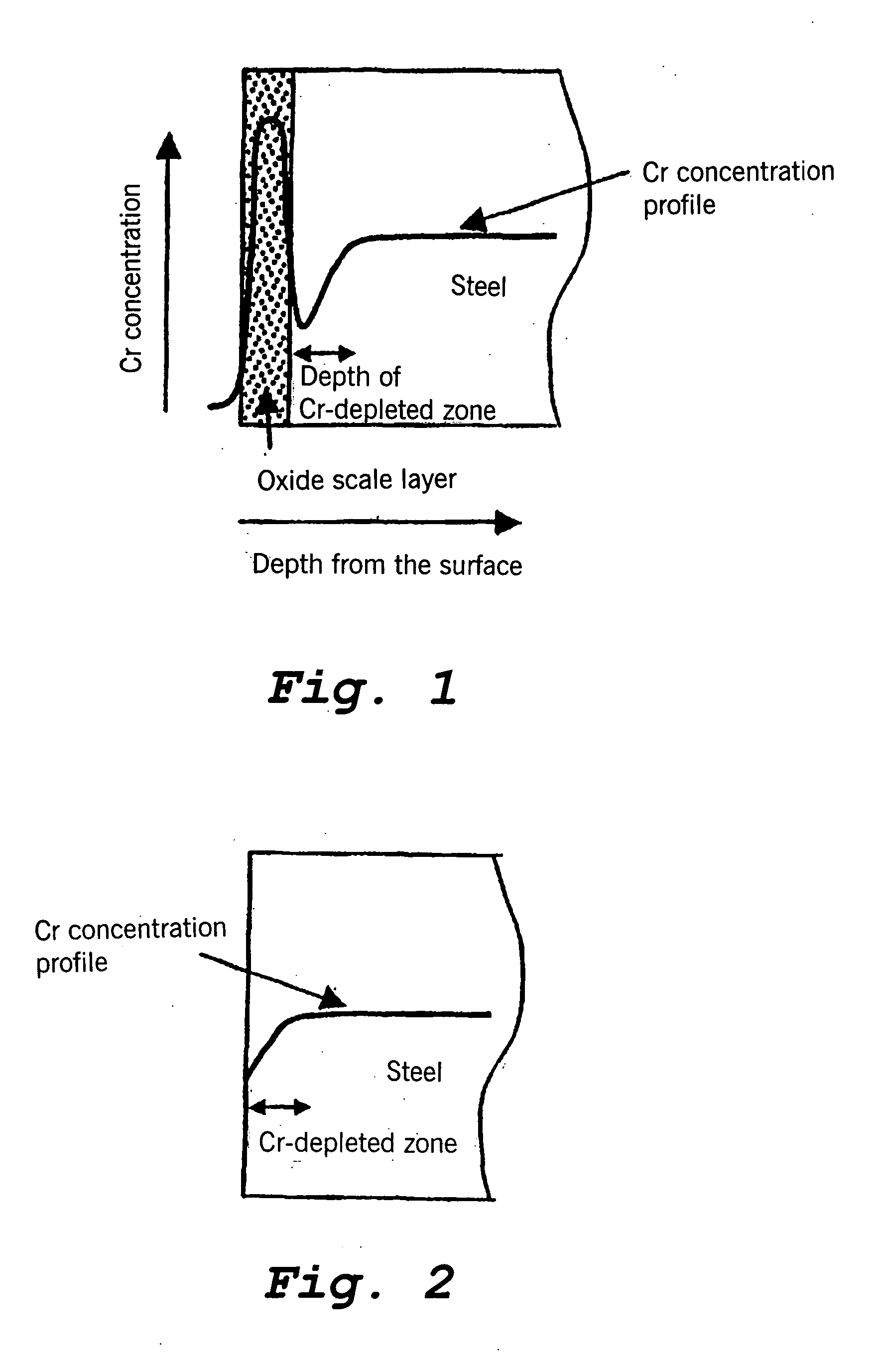
A stainless steel pipe includes a base metal containing 20-35 mass % of Cr, and a Cr-depleted zone is formed in the surface region of the pipe. The Cr concentration in the Cr-depleted zone is at least 10%, and the thickness of the Cr-depleted zone is at most 20 micrometers. A Cr-based oxide scale layer having a Cr content of at least 50% and a thickness of 0.1-15 micrometers may be provided on the outer side of the Cr-depleted zone. An Si-based oxide scale layer with an Si content of at least 50% may be provided between the Cr-based oxide scale layer and the Cr-depleted zone. The pipe is particularly suitable for use in petroleum refineries or petrochemical plants, such as for use as a pipe of a cracking furnace of an ethylene plant.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
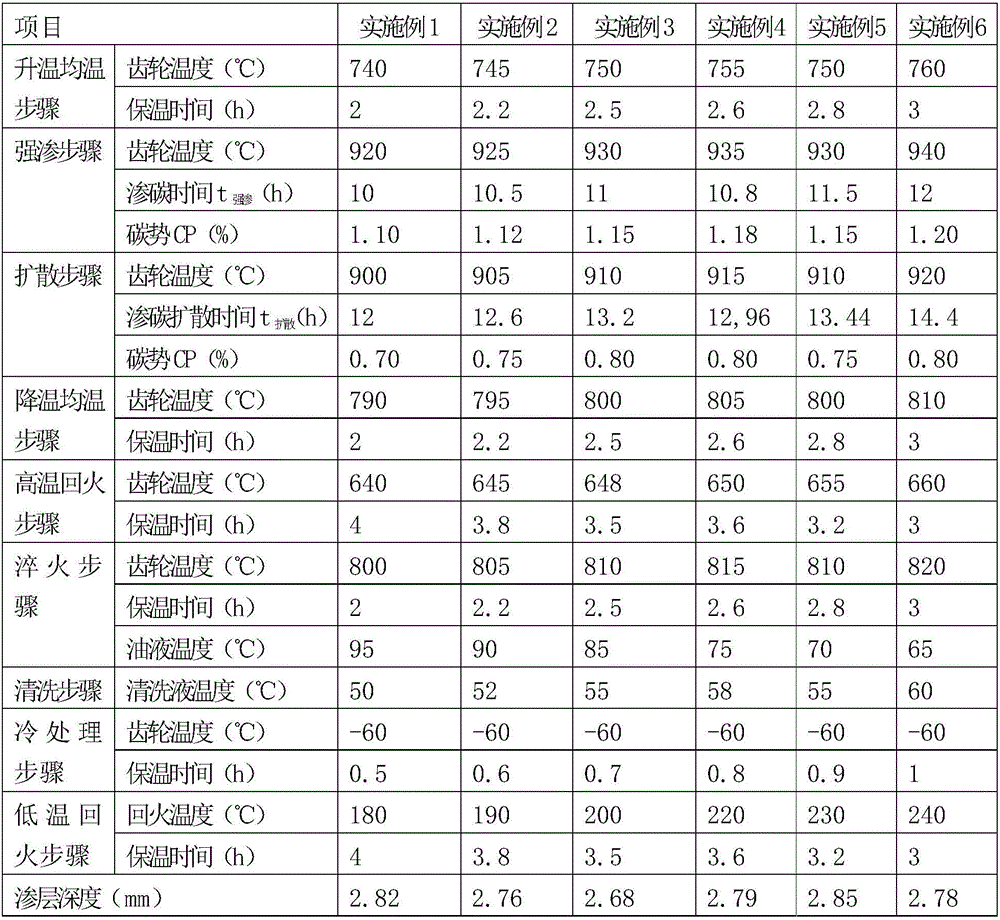
Carburizing and quenching method of low-speed heavy-duty gear
ActiveCN106756753AReduce carbon contentReduce carburizing potentialSolid state diffusion coatingFurnace typesCold treatmentLow speed
The invention relates to a carburizing and quenching method of a low-speed heavy-duty gear. The carburizing and quenching method comprises the steps of (1) temperature increase and temperature uniformization; (2) strong carburizing; (3) diffusion; (4) temperature decrease; (5) high-temperature tempering; (6) quenching; (7) cold treatment; and (8) low temperature tempering. According to the carburizing and quenching method of the low-speed heavy-duty gear, harmful carbide of a gear carburized layer can be effectively removed, dispersively distributed fine granular carbide can be obtained, the content of retained austenite on the surface is greatly decreased, a metallographic structure of the gear surface is improved, the surface hardness and abrasion resistance of the gear are improved, and the heat treatment property of a product is improved.
Owner:CRRC QISHUYAN INSTITUTE CO LTD
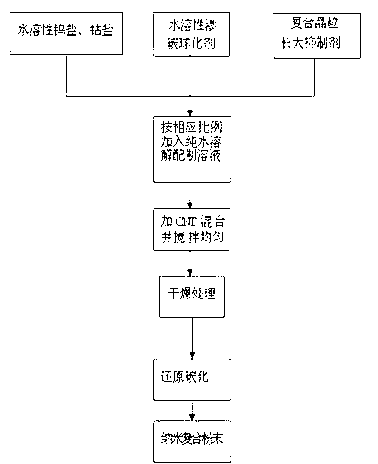
Method for manufacturing nanometer tungsten/cobalt carbide composite powder
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing nanometer tungsten / cobalt carbide composite powder. The method is characterized by comprising technological steps of firstly, dissolving, by mass, 55-92% of water-soluble tungsten salt, 3-40% of water-soluble cobalt salt, 3-6% of water-soluble carburizing and nodulizing agents and 0.1-2% of water-soluble composite grain growth inhibitors into water with the mass 3-5 times that of a mixture of the water-soluble tungsten salt, the water-soluble cobalt salt, the water-soluble carburizing and nodulizing agents and the water-soluble composite grain growth inhibitors to prepare mixed aqueous solution; secondly, adding carbon nano-tubes (CNT) accounting for 1-10% of the total mass of the aqueous solution into the mixed aqueous solution obtained in the first step and enabling the carbon nano-tubes to be uniformly mixed in the mixed aqueous solution; thirdly, performing quick low-temperature spray drying for mixed aqueous solution obtained in the second step to obtain precursor powder of ultrafine tungsten and cobalt composite salt; and fourthly, performing reduction synthesis and carbon conditioning at the temperature ranging from 900 DEG C to 1000 DEG C for the precursor powder obtained in the third step to prepare tungsten / cobalt carbide composite powder materials with nanostructures.
Owner:ADVANCED FOR MATERIALS & EQUIP
Low temperature gas carburizing method for realizing reinforcement and corrosion resistance of austenitic stainless steel
InactiveCN102828145ANo damage to corrosion resistanceImprove corrosion resistanceSolid state diffusion coatingChromium carbideNitrogen
The invention provides a low temperature gas carburizing method for realizing reinforcement and corrosion resistance of austenitic stainless steel, which belongs to the field of chemical heat treatment. The method comprises the following steps: disposing a clean and dry austenitic stainless steel part in a carburizing furnace which is filled with a PTFE activator with an amount in proportion to the mass of the austenitic stainless steel part and tightly covering the cover of the carburizing furnace; blowing in protective nitrogen, powering on and heating the carburizing furnace to a temperature of 550 DEG C so as to allow PTFE to undergo pyrolysis, and activating a passivation film on the surface of austenitic stainless steel in the furnace by using pyrolysis products of PTFE so as to form a conduction channel which is beneficial for diffusion of carbon atoms on the surface of the austenitic stainless steel; and then, pumping out gas in the furnace, blowing in mixed gas of CO, H2 and N2 into the carburizing furnace, carrying out carburizing at a temperature of 460 to 480 DEG C which is lower than the formation temperature of a chromium carbide and carrying out insulation for 48 to 72 hours to complete carburizing. According to the invention, the purpose of realizing reinforcement of the austenitic stainless steel through low temperature carburizing and maintaining excellent corrosion resistance of the austenitic stainless steel are achieved, and the method is simple to implement and has high production efficiency.
Owner:WUHAN RES INST OF MATERIALS PROTECTION
Steel for Nb-Ti composite microalloyed high-temperature vacuum carburizing heavy-duty gear
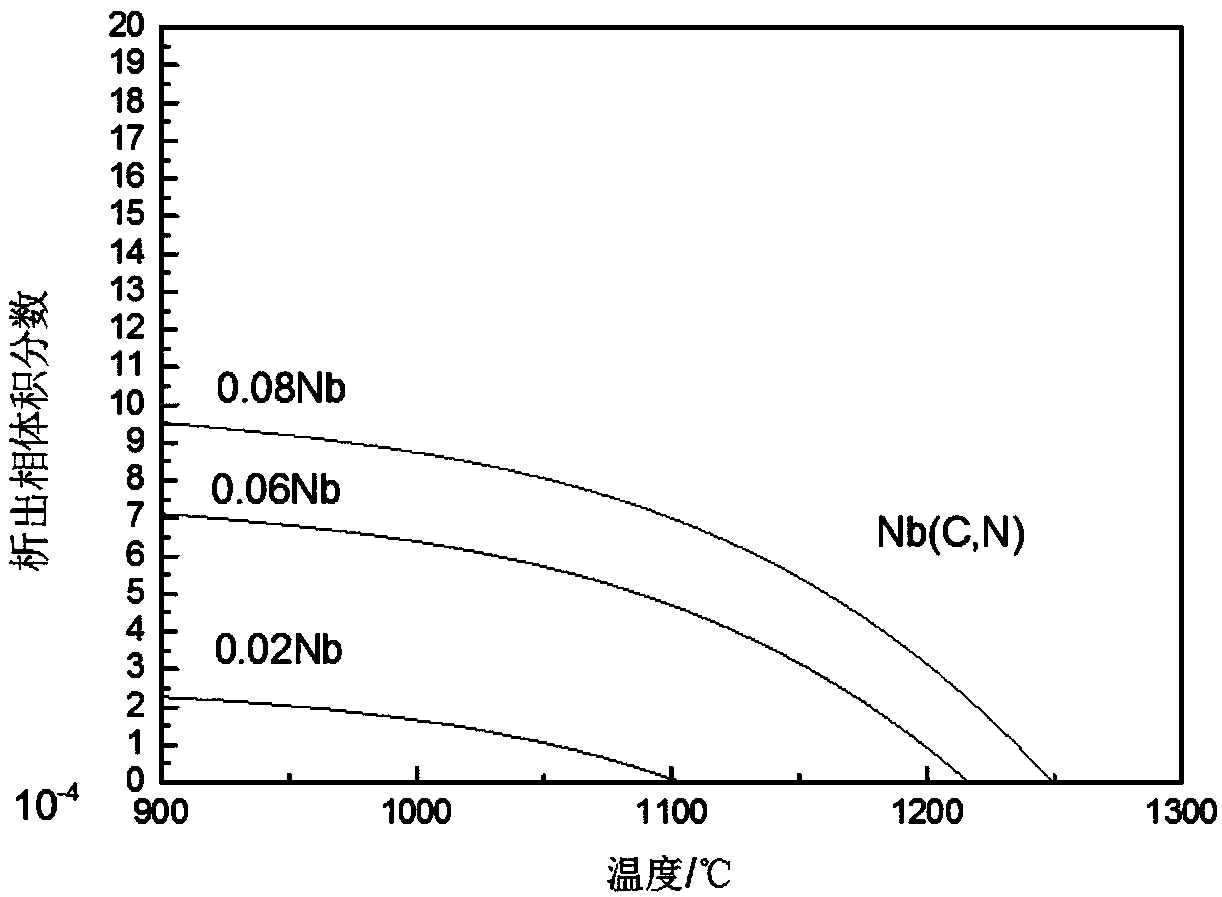
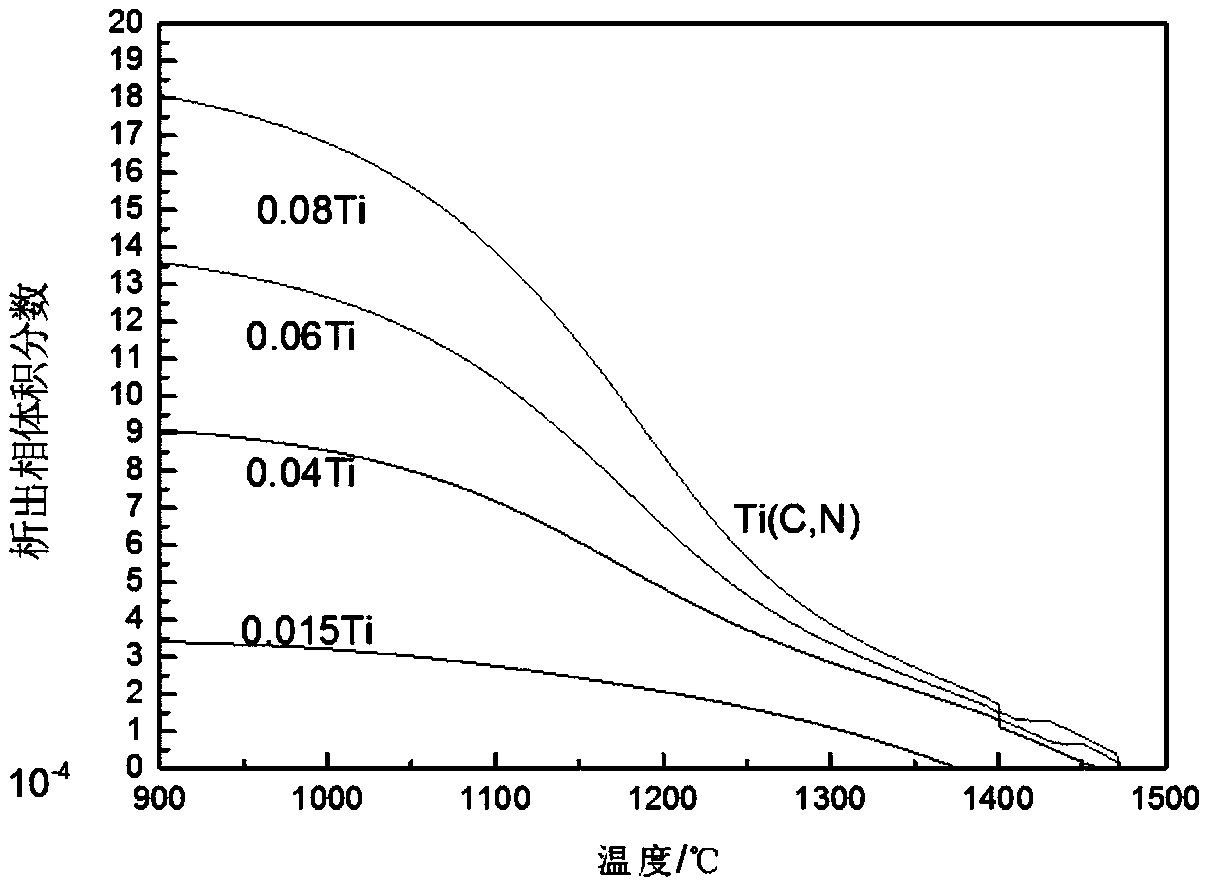
ActiveCN108866439AIncrease carburizing temperatureIncrease productivitySolid state diffusion coatingAustenite grainMetallurgy
The invention relates to steel for an Nb-Ti composite microalloyed high-temperature vacuum carburizing heavy-duty gear. The steel is prepared from the following components in percentage by mass: 0.15-0.23 percent of C, 0.10-0.40 percent of Si, 0.45-0.90 percent of Mn, 1.50-1.80 percent of Cr, 1.40-1.70 percent of Ni, 0.15-0.55 percent of Mo, 0.02-0.08 percent of Nb, 0.015-0.08 percent of Ti, smaller than or equal to 0.020 percent of P, smaller than or equal to 0.020 percent of S and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. For the steel provided by the invention, by adopting a composite microalloying manner, adding Nb and Ti microalloy elements and controlling the contents of the Nb and Ti microalloy elements, a precipitated phase is utilized to pin a crystal boundary to inhibit coarsening and growth of austenite grains in the high-temperature vacuum carburizing process, increase of the steel carburizing temperature of the heavy-duty gear is realized, the gear carburizing heat treatment process time is effectively shortened, the energy consumption is greatly lowered, and the production cost of the gear is saved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Technology for controlling hardness distribution of material for 23CrNi3Mo drill tool
InactiveCN103132087AExtended service lifeBest match statusDrill bitsSolid state diffusion coatingTemperingThermal insulation
The invention relates to a technology for controlling hardness distribution of a material for a 23CrNi3Mo drill tool. After carburization, mild hardness gradient distribution of the drill tool from surface to center is realized, namely, micro hardness from the surface to the center tissue of the drill tool drops mildly, so that after carburization, the drill tool forms a complex phase tissue which has high surface hardness, high center toughness and a transition layer with certain width, the drill tool is good in toughness and is prolonged in service life. The technology comprises the following steps of quenching the carburized drill tool at 880DEG C+ / -10 DEG C; preserving heat for 45 minutes; after thermal insulation, cooling by two sections, wherein the cooling rate is more than or equal to 5 DEG C per second in temperature range of 880-450; cooling to room temperature along with a furnace below 450 DEG C; tempering at 220 DEG C and preserving heat for 120 minutes; and carrying out air cooling to reach room temperature after thermal insulation.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Secondary carburizing technological method of 16Cr3NiWMoVNbE material
The invention relates to a secondary carburizing technological method of a 16Cr3NiWMoVNbE material. The method comprises the steps as follows: protecting a non-carburizing part; carburizing a carburizing part with requirement on a deep layer; continuously processing a part after carburizing until reaching the carburizing layer with requirements on carburizing degree and shallow carburizing layer; not processing the position of the deep carburizing layer; protecting other positions except for the carburizing position; and carburizing for the second time. By adopting the method, the depth of the carburizing layer in the carburizing part at the deep layer is 1.1 to 1.3mm; the depth of the carburizing layer in the carburizing part at the shallow layer is 0.2 to 0.5mm; the surface hardness is more than HRC600 after the carburizing in the deep layer; the surface hardness is more than HRC52 after the carburizing in the shallow layer; the hardness of the core is HRC35 to 45; and the microscopic structure on the surface and the microscopic structure on the core meet corresponding requirements of Aviation Standard 5492.
Owner:HARBIN DONGAN ENGINE GRP
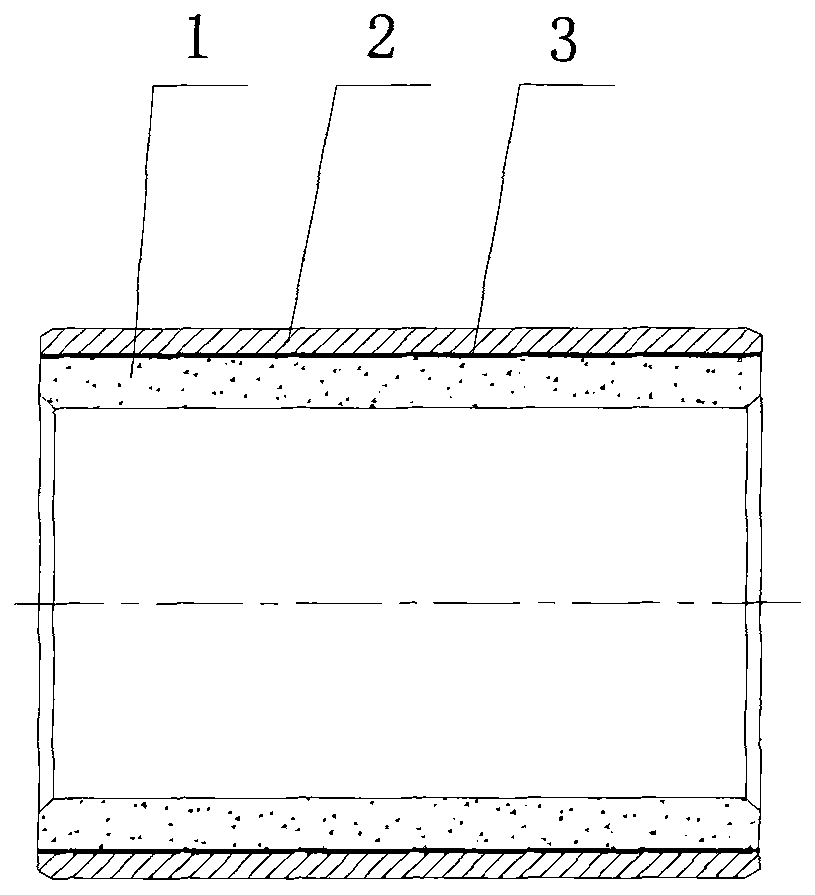
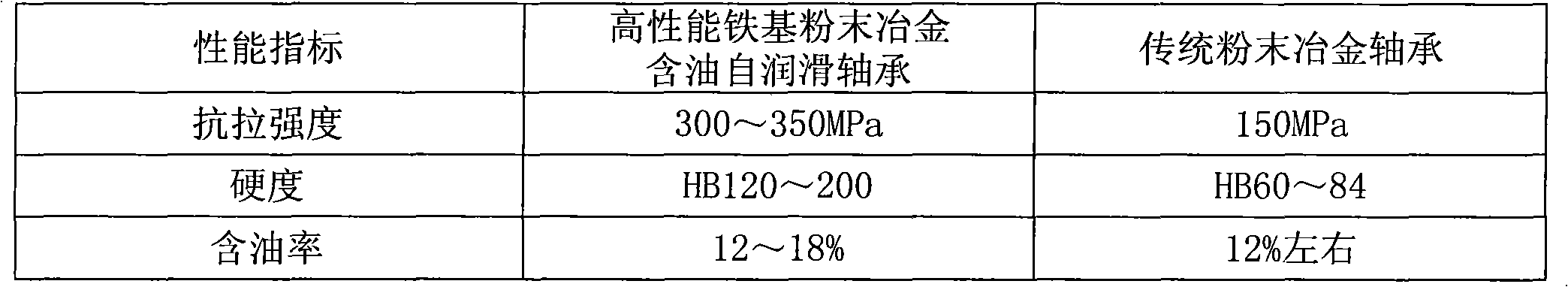
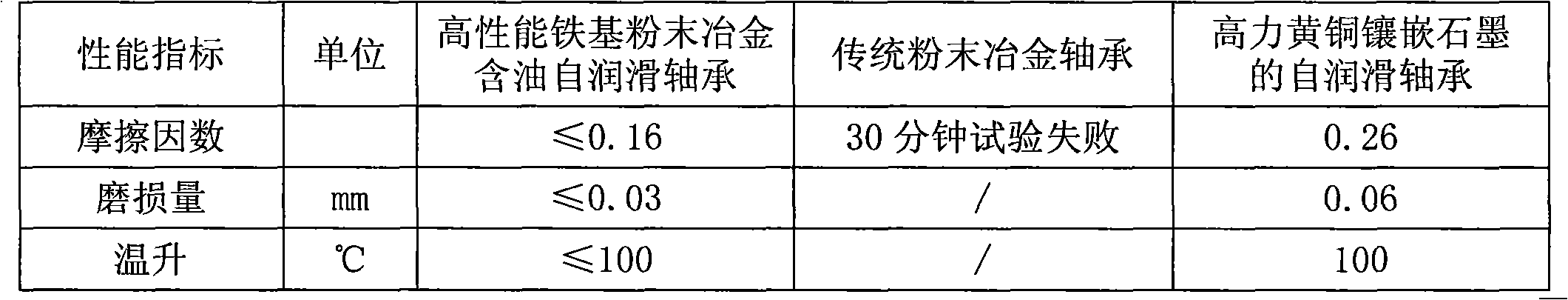
High-performance iron-based powder metallurgy oil-containing self-lubricating bearing and production process thereof
The invention discloses a high-performance iron-based powder metallurgy oil-containing self-lubricating bearing and a production process thereof, aiming to provide a bearing which is suitable for rotating, swinging and linear reciprocating motion under the conditions of high bearing and low speed and is also suitable for places which can not be reached through traditional lubrication or are forbidden to use. The high-performance iron-based powder metallurgy oil-containing self-lubricating bearing is in a shaft sleeve shape and is characterized by comprising the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 18-22 percent of copper powder, 1-4.8 percent of aluminum powder, 0.6-1 percent of graphite, 1-5 percent of hard particle, 1-5 percent of zinc stearate and the balance of iron powder. The high-performance iron-based powder metallurgy oil-containing self-lubricating bearing sequentially comprises the following making process routes according to the raw material composition: mixing the raw materials, pressing into shaft sleeve-shaped blank, vacuum sintering, carburizing, quenching, turning to be in a required geometric size, and carrying out vacuum oil immersion to make a finished product. The high-performance iron-based powder metallurgy oil-containing self-lubricating bearing is superior to a traditional powder metallurgy bearing and a self-lubricating bearing with high force brass embedding graphite in aspects of both the mechanical property and the friction and wear property and also has obvious advantages on the manufacture cost of the product.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHANGSHENG SLIDING BEARINGS
Austenitic heat-resistant stainless steel and processing method thereof
InactiveCN102230137AGood high temperature oxidation resistanceImprove carburization resistanceRare-earth elementManganese
The invention relates to austenitic stainless steel, and in particular relates to austenitic heat-resistant stainless steel and a processing method thereof. The austenitic heat-resistant stainless steel is characterized by comprising the following elements by mass percentage: 0.25-0.45% of carbon, 0.5-2% of silicon, 0.5-2% of manganese, 23-27% of chromium, 6-10% of nickel, 0.15-0.3% of nitrogen, 0.1-0.5% of rare-earth (RE) elements and the balance of iron. The austenitic heat-resistant stainless steel obtained by the processing method has the advantages of good high-temperature oxidation resistance, good carburizing resistance, good sulfurization corrosion resistance and lowered production cost.
Owner:XUANDA IND GRP
Method for carburizing workpieces and its application
InactiveUS20110277887A1Excellent surface hardnessReduce wearSolid state diffusion coatingMachines/enginesMetallurgyCarburizing
A method for carburizing workpieces made of steel, particularly workpieces having outer and inner surfaces, the workpiece being held at a temperature in the range of 850 to 1050° C. in an atmosphere containing a gaseous hydrocarbon. At least two different gaseous hydrocarbons are used and / or the workpiece is alternatingly held in the atmosphere containing the gaseous hydrocarbon during a carburizing pulse and in an atmosphere free of hydrocarbon during a diffusion phase. Also described is a use of the method.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Full-steel-scrap electric arc furnace cleanness rapid smelting method
ActiveCN107502702AImprove cleanlinessShorten the smelting cycleProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceSteelmakingElectric arc furnace
The invention belongs to the technical field of electric arc furnace steelmaking and particularly relates to a full-steel-scrap electric arc furnace cleanness rapid smelting method which is applicable to the 30-300t full-steel-scrap electric arc furnace smelting process. According to the full-steel-scrap electric arc furnace smelting process, spray guns buried in refractory materials on the side faces of the furnace bottom of an electric arc furnace are used for blowing different types of media at different smelting stages; at the stage of recarburization and melting acceleration, melting-down of a molten pool is accelerated through carburization, and the carbon content of the molten pool is increased. At the stage of high-efficiency dephosphorization and deep denitrification, molten pool reaction is intensified to conduct high-efficiency dephosphorization and deep denitrification. Accordingly, the smelting rhythm of the full-steel-scrap electric arc furnace is accelerated, the dephosphorization and denitrification effects are improved, the cleanness of molten steel is improved, and full-steel-scrap electric arc furnace cleanness rapid smelting is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Manufacturing method for cross axle of universal coupling
InactiveCN101131183AImprove toughnessHigh strengthYielding couplingSolid state diffusion coatingCouplingHigh wear resistance
The centerpiece for universal coupling is made with high quality low carbon alloy structural steel 20CrMnTi, and through blanking, precise die forging, normalizing, machining, surface carburizing, surface hardening, low temperature tempering and finish grinding. It his excellent mechanical performance, including high toughness, high strength and high wear resistance, and can ensure smooth running, high safety, high reliability and long service life of the coupling.
Owner:邹树林
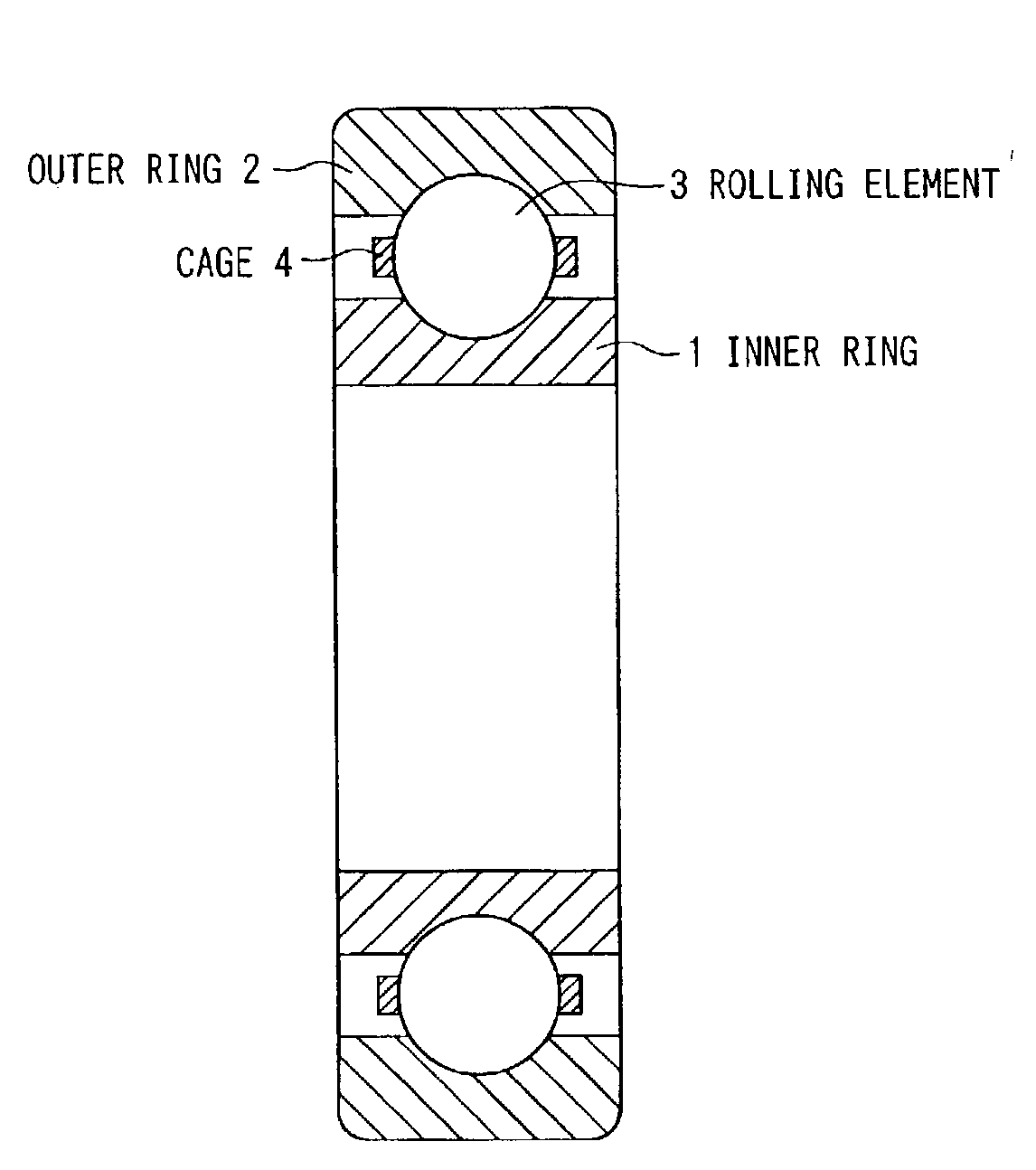
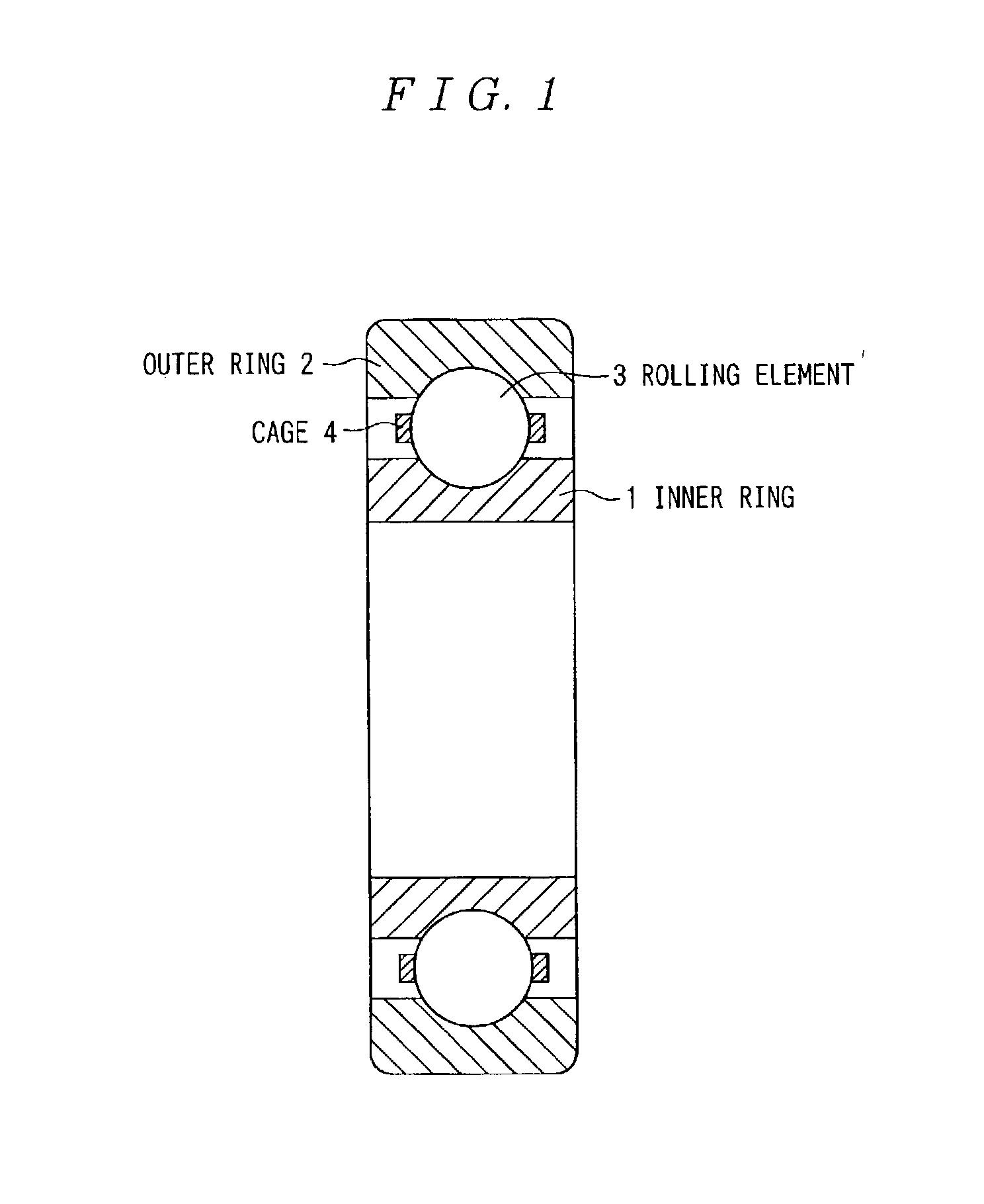
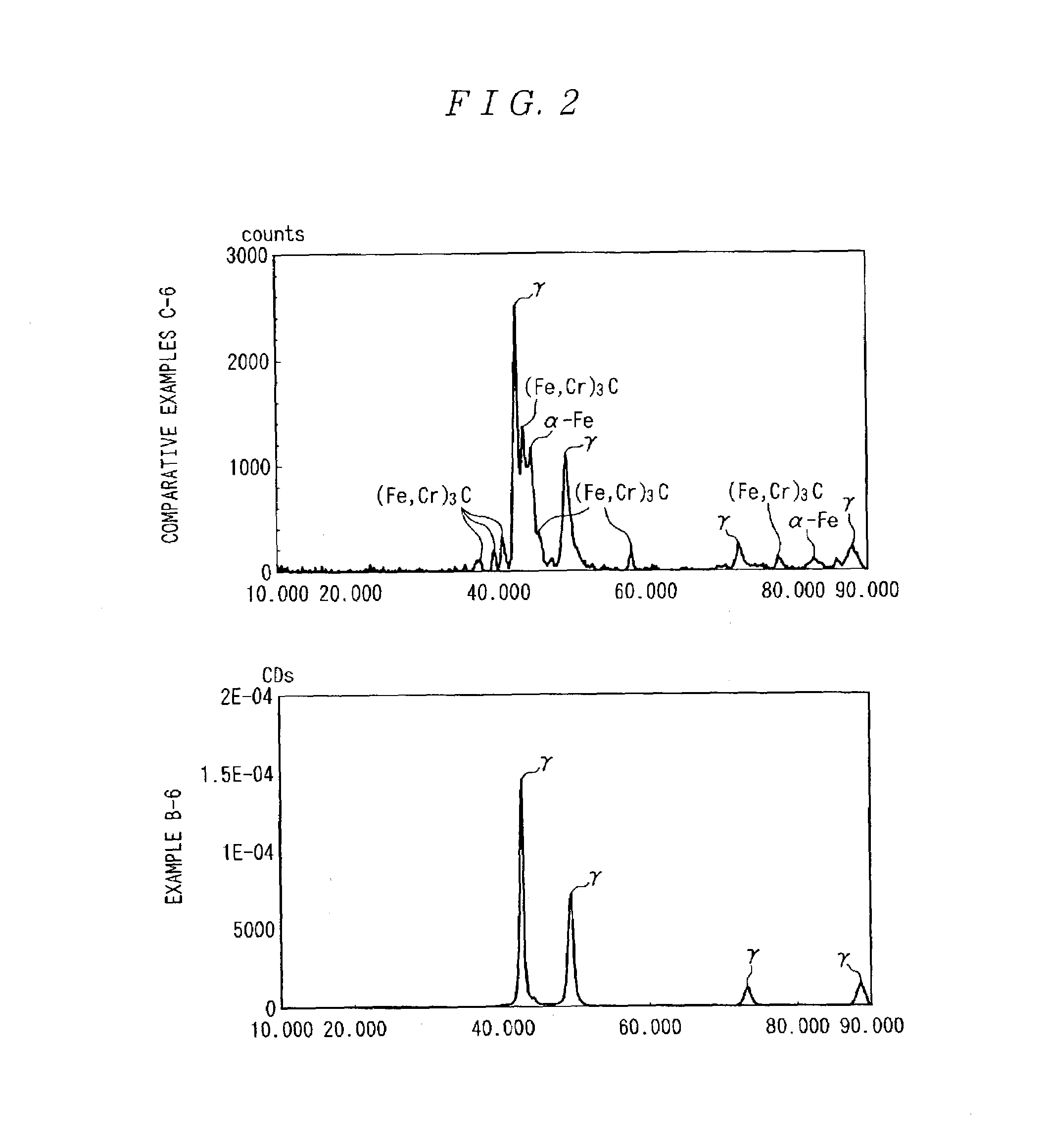
Rolling support device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7122086B2Increased durabilityIncrease resistanceBearing componentsSolid state diffusion coatingCarbideHardness
A rolling support device excellent in both of the characteristics of durability and corrosion resistance is provided. The inner ring (1) and the outer ring (2) comprises an austenitic stainless steel and has, on a raceway surface, a carburizing hardened layer containing no substantial carbides at a Vickers hardness (Hv) of 650 or more. The carburizing hardened layer is formed by applying fluoriding and then applying carburizing at a temperature of 540° C. or lower. The rolling element (3) is made of Si3N4.
Owner:NSK LTD
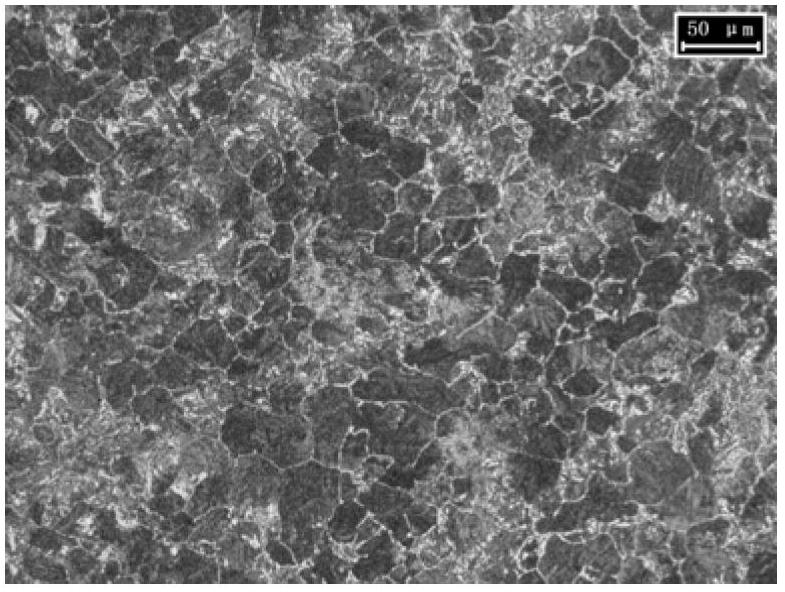
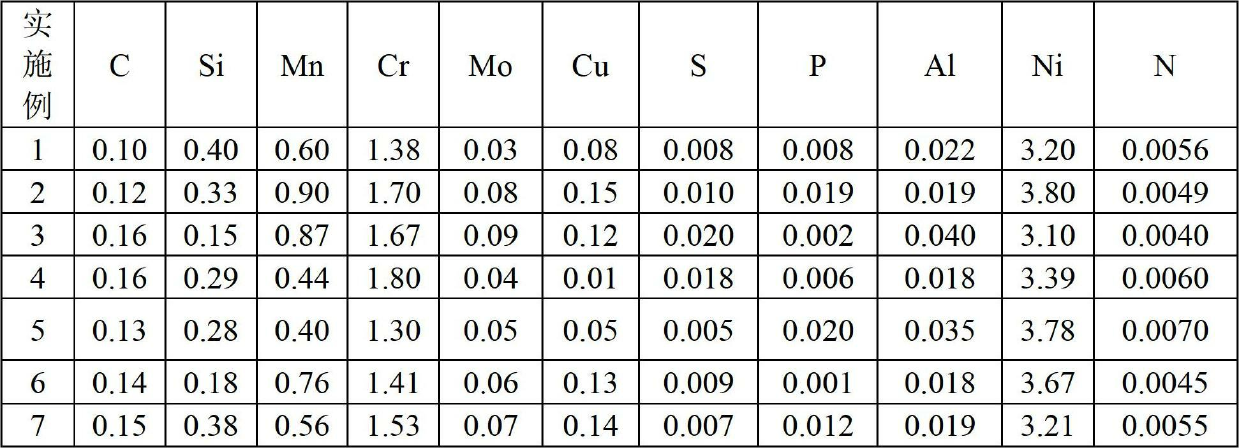
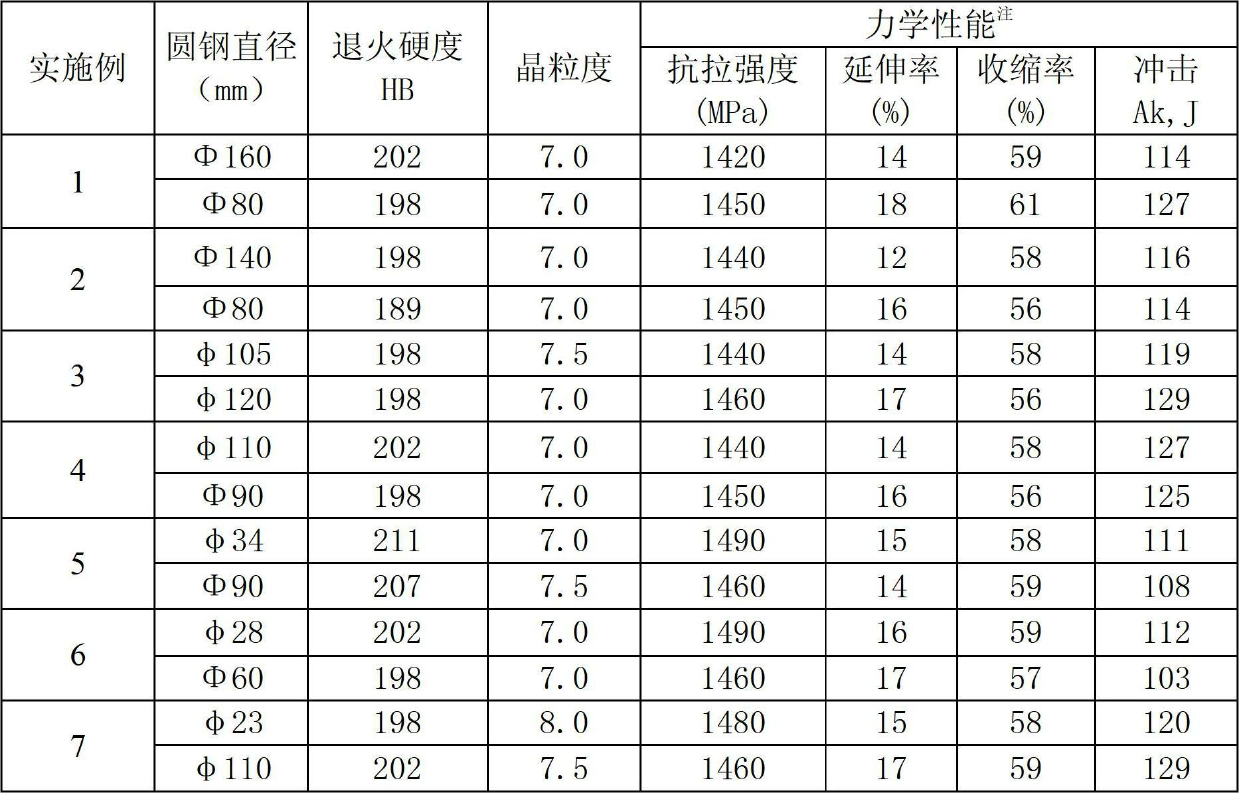
Carburizing bearing steel
The invention discloses a carburizing bearing steel, which comprises the following chemical elements in percentage by mass: 0.10-0.16% of carbon, 0.40-0.90% of manganese, 0.15-0.40% of silicon, 1.30-1.80% of chromium, 3.10-3.80% of nickel, 0.02-0.09% of molybdenum, 0.015-0.040% of aluminum and 0.0040-0.0070% of nitrogen, less than or equal to 0.0010% of oxygen, less than or equal to 0.020% of phosphorus, 0.005-0.020% of sulfur, less than or equal to 0.0020% of titanium, less than or equal to 0.15% of copper, less than or equal to 0.025% of tin, less than or equal to 0.015% of antimony, less than or equal to 0.030% of arsenic, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities, wherein the ratio of aluminum / nitrogen is more than or equal to 3. The carburizing bearing steel disclosed by the invention is easy for carburizing surface treatment, and has excellent strength and toughness.
Owner:宝钢特钢有限公司
Method for manufacturing nanometer tungsten/cobalt carbide composite powder
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing nanometer tungsten / cobalt carbide composite powder. The method includes steps of firstly, dissolving, by mass, 55-92% of water-soluble tungsten salt, 3-40% of water-soluble cobalt salt, 3-6% of water-soluble carburizing and nodulizing agents and 0.1-2% of water-soluble composite grain growth inhibitors into water with the mass 3-5 times that of a mixture of the water-soluble tungsten salt, the water-soluble cobalt salt, the water-soluble carburizing and nodulizing agents and the water-soluble composite grain growth inhibitors to prepare mixed aqueous solution; secondly, adding nanometer carbon black accounting for 1-10% of the total mass of the aqueous solution into the mixed aqueous solution obtained in the first step, stirring the nanometer carbon black in the mixed aqueous solution at the rate of 10-30 revolutions per minute for 30-60 minutes so that the nanometer carbon black can be uniformly mixed in the mixed aqueous solution; thirdly, performing quick low-temperature spray drying for mixed aqueous solution obtained in the second step to obtain precursor powder of ultrafine tungsten and cobalt composite salt; and fourthly, performing reduction synthesis and carbon conditioning at the temperature ranging from 900 DEG C to 1000 DEG C for the precursor powder obtained in the third step to manufacture tungsten / cobalt carbide composite powder materials with nanostructures.
Owner:ANHUI RONGDA COMPOSITE POWDERS TECH
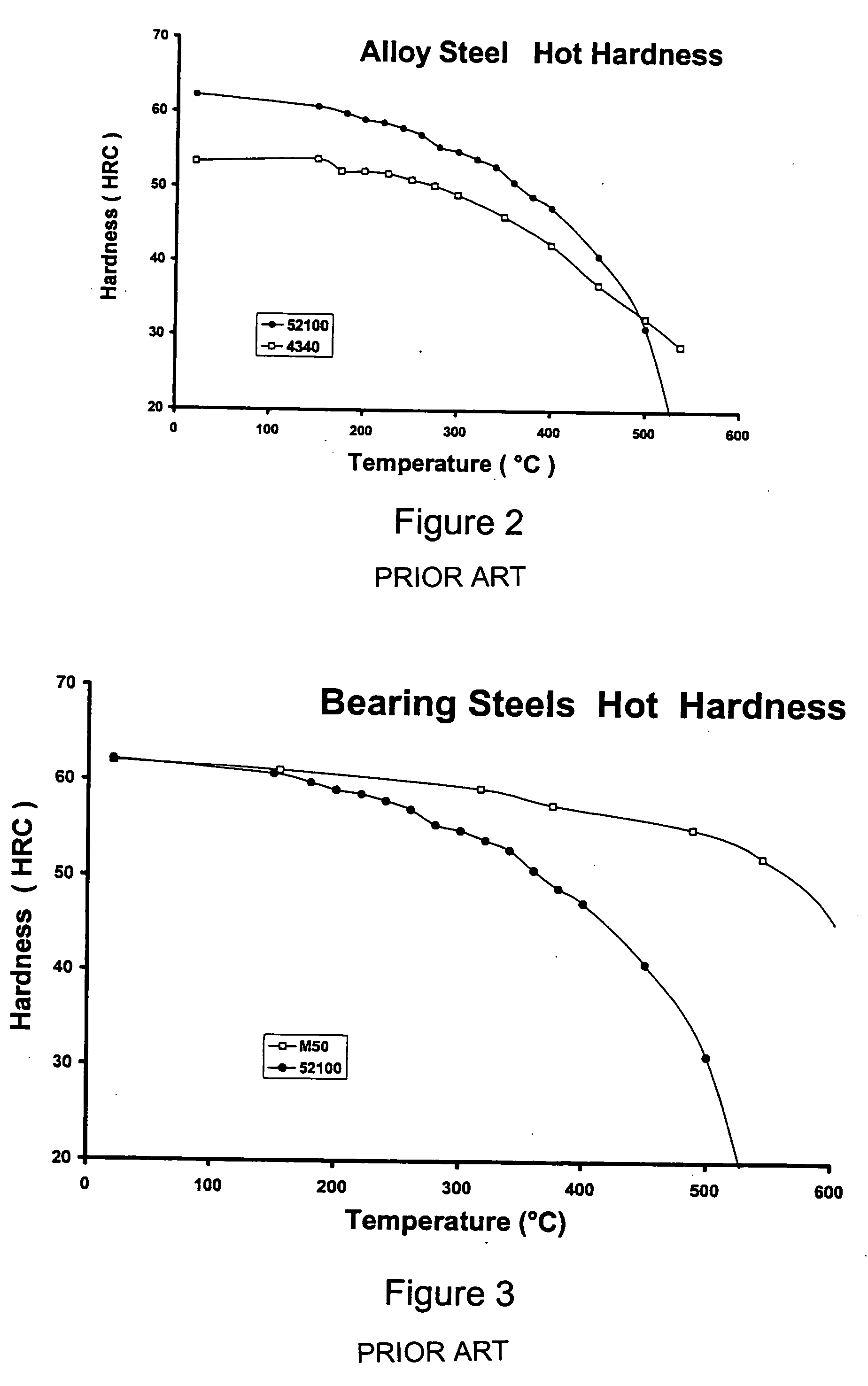
Mo-V-Ni high temperature steels, articles made therefrom and method of making
InactiveUS20080145264A1Good hot hardnessEnhance carbon diffusionSolid state diffusion coatingHigh carbonHardness
Low carbon carburizing (surface hardening) and higher carbon through hardening steels primarily containing molybdenum, vanadium and nickel and, to a lesser amount, chromium used for rolling contact bearings, gears and other similar applications where high hardness at elevated temperatures is required. The alloy steel includes, in % by weight: 0.05% to 1.25% C; up to 1.25% Cr; 0.40% to 4% Mn; up to 4.0% Mo; up to 2.0% V; 1.0% to 3.0% Ni; 4% to 8% (Mo+V+Ni+Cr); less than 0.20% Si; and balance Fe plus incidental additions and impurities. The method for providing a steel having improved hardness at elevated temperatures includes the steps of: (a) providing an alloy including, in % by weight: less than 1.25% Cr, 0.4% to 4% Mn, up to 4% Mo, up to 2% V, 1 to 3% Ni, 4% to 8% (Mo+V+Ni+Cr), less than 0.2% Si, a C content selected from one of 0.05% to 0.40% C defining a carburizing steel or greater than 0.40% to 1.25% C defining a through hardening steel, and the balance Fe plus incidental additions and impurities; (b) performing a step selected from the group consisting of (i) subjecting the carburizing steel to carburizing and quenching to provide a quenched carburized steel, or (ii) subjecting the high carbon steel to hot working to provide a wrought high carbon steel; (c) preheating the quenched carburized steel or wrought high carbon steel and then austenitizing said steel to provide an austenitized steel; (d)quenching the austenitized steel to provide quenched austenitized steel; and (e) tempering the quenched austenitized steel followed by air cooling.
Owner:THE TIMKEN CO
Method for processing rectangular-tooth spline sleeve using 42CrMoE high-quality alloy steel as material
InactiveCN102534374AImprove wear resistanceImprove bending abilityCouplings for rigid shaftsPhosphorylationThermal treatment
The invention discloses a method for processing a rectangular-tooth spline sleeve using 42CrMoE high-quality alloy steel as a material, belonging to the technical field of thermal treatment. The method comprises the steps of: free forging of a blank, normalizing treatment, rough turning, hardening and tempering thermal treatment, finish turning, spline drawing, drilling, burr gripping, carburization treatment, surface deposition treatment, phosphorylation treatment, electroplating, drying and detection. In the invention, due to the new material and new technology, the wear resistance of the produced rectangular-tooth spline sleeve is greatly enhanced, the phenomenon of crack of the rectangular-tooth spline sleeve is avoided, the surface is smooth, the friction is low, the heat dissipation is good, and the service life is prolonged, thus the processing technology is widely applied.
Owner:无锡市万邦机械制造厂
Steel and steel wire for high strength spring
Disclosed is a spring steel for spring steel wires which exhibits both high strength and good workability in cold coiling. This spring steel comprises, in mass %, 0.45 % to 0.70 % of C, 1.0 % to 3.0 % of Si, 0.05 % to 2.0 % of Mn, 0.015 % or less of P, 0.015 % or less of S, 0.0015 % to 0.0200 % of N, and 0.000 2% to 0.01 % of t-O, and limits Al <= 0.01 % and Ti <= 0.003 %. Also disclosed is a spring steel wire using such a spring steel. The spring steel is further characterized in that, with respect to cementite spherical carbides on a microscopic observation plane, the percentage of the area occupied by carbides having a circle-equivalent diameter of 0.2 mu m or more is 7 % or less, the density of carbides having a circle-equivalent diameter of 0.2 mu m to 3 mu m is 1 piece / m<2> or less, the density of carbides having a circle-equivalent diameter of more than 3 mu m is 0.001 piece / m<2> or less, the grain size number of prior austenite is 10 or higher, the amount of residual austenite is 15 mass % or less, and the area percentage of a thin region, where the density of cementite carbides having a circle-equivalent diameter of 2 mu m or more is low, is 3 % or less.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Surface metallurgy technique for cobalt-containing super-hard high-speed steel
The invention relates to a surface metallurgy process of cobalt containing super-hard high-speed steel, which pertains to the surface metallurgical field. The invention is characterized in that: first, a double-layer glow discharging ion metallic cementation technique is used for filtering an alloying element on the surface of Fe-based material with lower cost so as to form a surface alloying layer; then, a carburizing treatment is carried out to form a surface high-speed steel alloying layer; thereafter, a thermal treatment is carried out to lead the surface high-speed steel alloying layer to have the excellent properties of the super-hard high-speed steel. The hardening characteristics of the super-hard high-speed steel is that fine and dispersed alloy carbide and intermetallic compound are precipitated to generate hardening, the surface hardness of the filtered workpiece reaches at 1000-1150HV after quenching and tempering treatment. The invention has the advantages that: since coarse primary carbide is not formed during the crystallizing process, formidable inhomogeneous carbide in the traditional production of smelting, forging-rolling high-speed steel is solved. Fine and dispersed carbide on the surface metallurgical high-speed greatly improves the hardening effect, saves a great deal of alloying elements, reduces the cost and is capable of being widely used for manufacturing cutting tools of various machine tools.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com