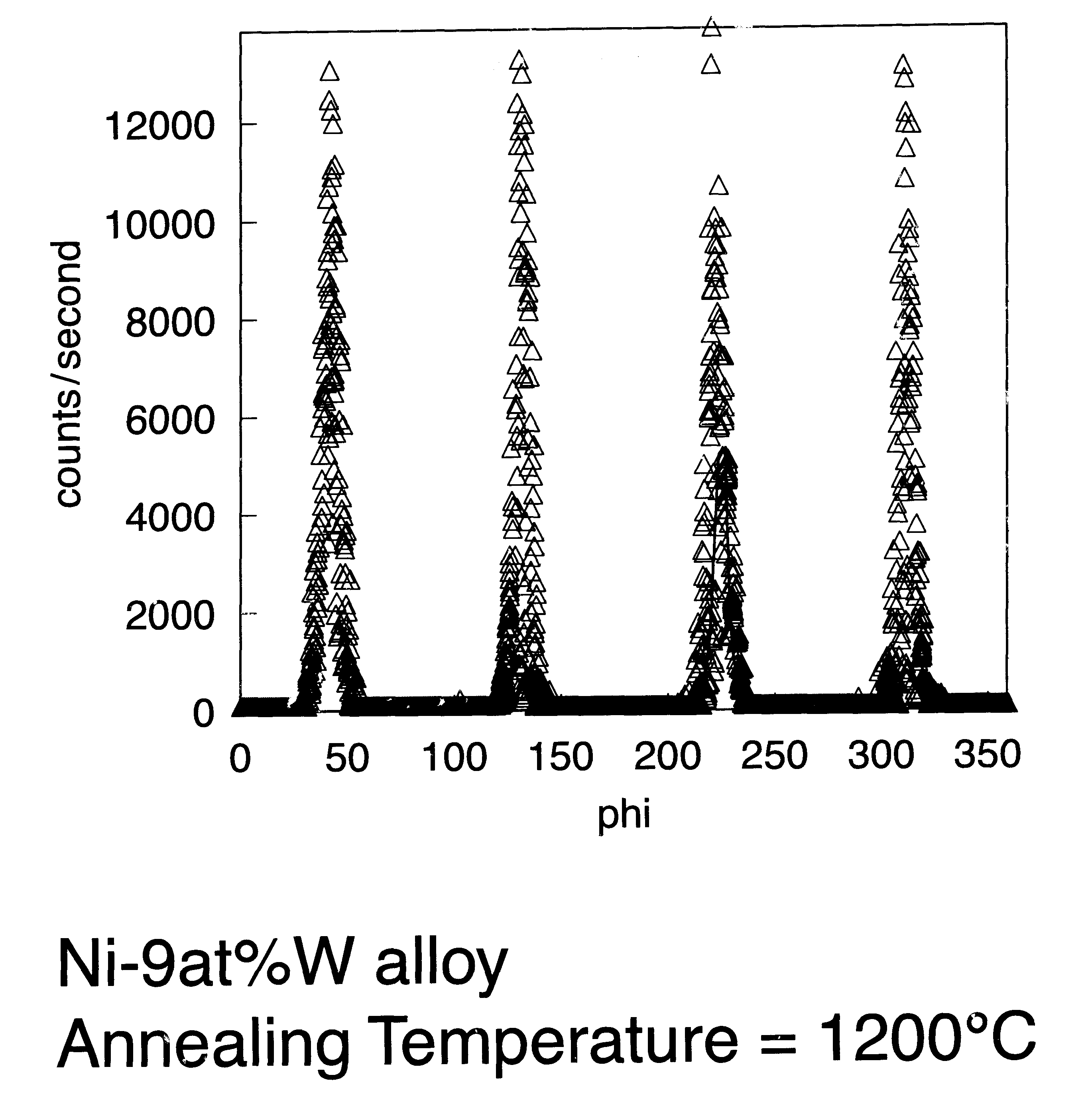
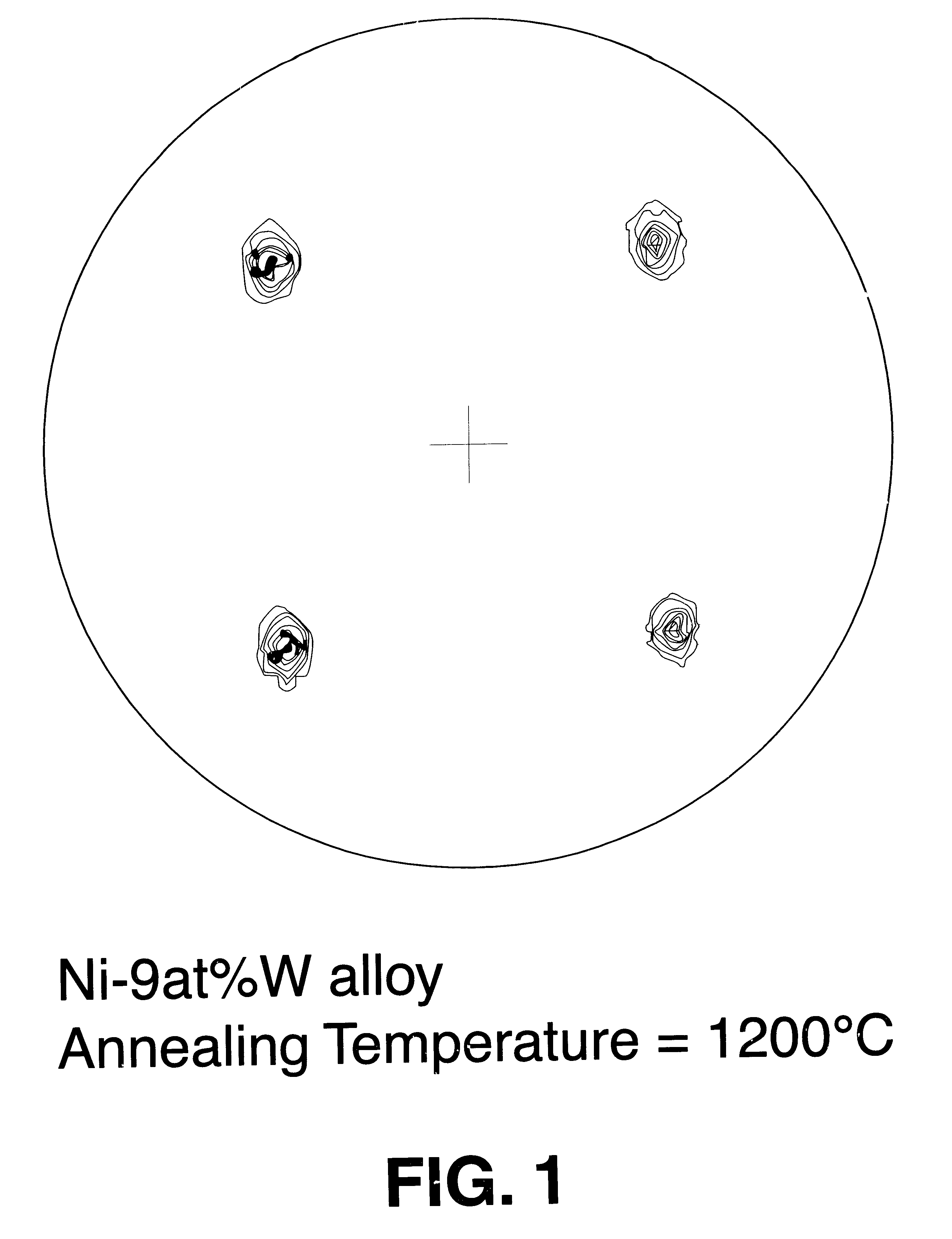
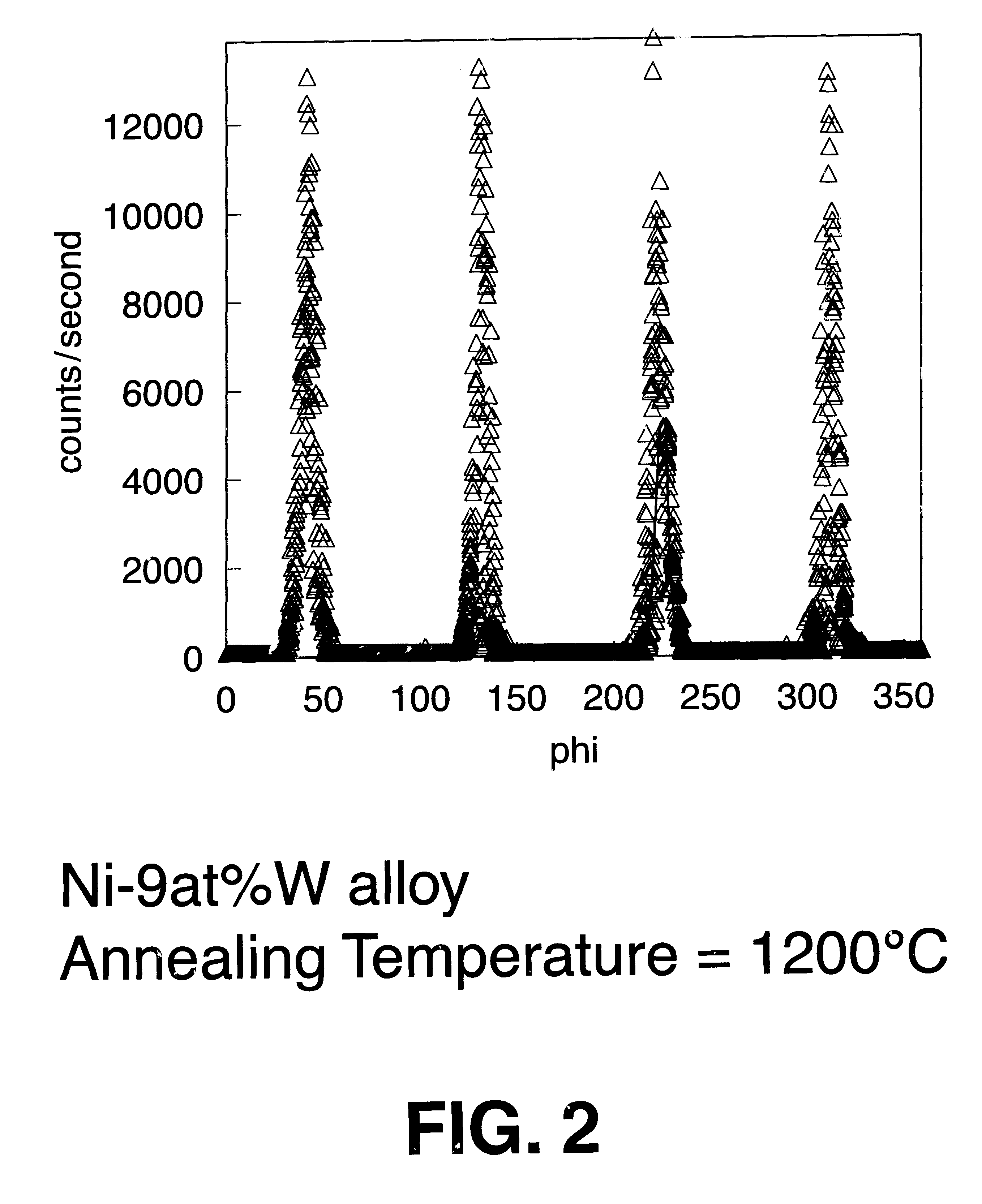
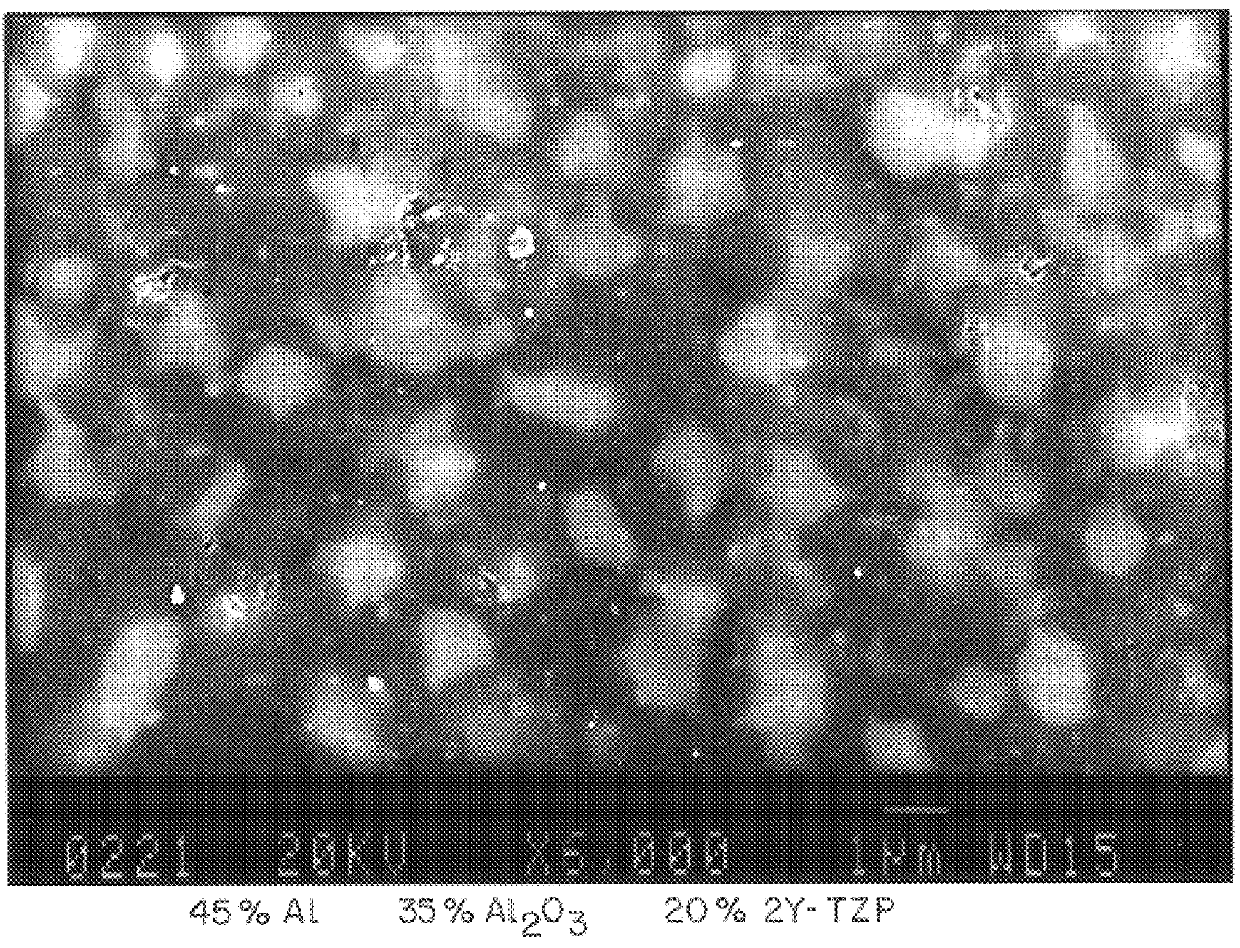
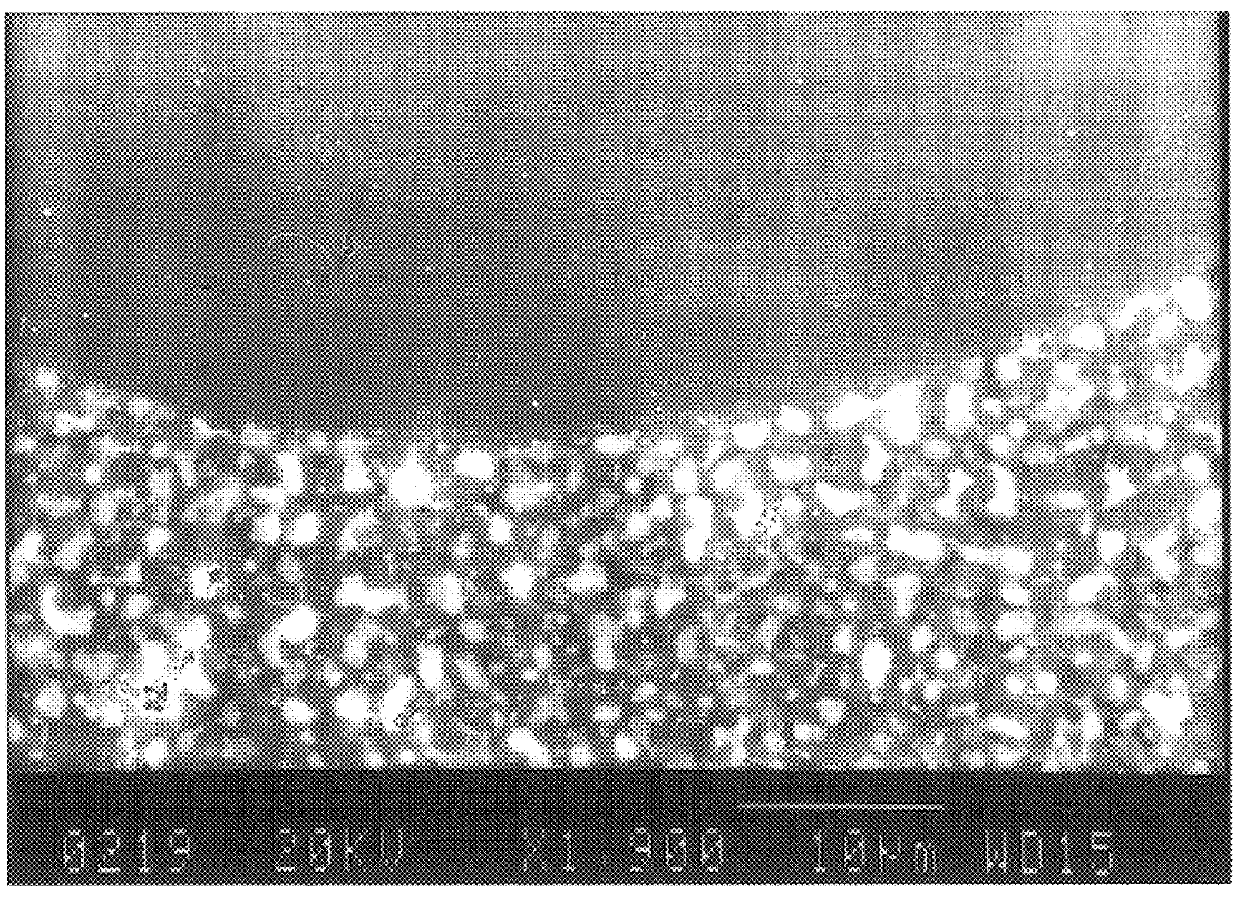
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7386 results about "Powder metallurgy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Powder metallurgy (PM) is a term covering a wide range of ways in which materials or components are made from metal powders. PM processes can avoid, or greatly reduce, the need to use metal removal processes, thereby drastically reducing yield losses in manufacture and often resulting in lower costs.
Titanium group powder metallurgy
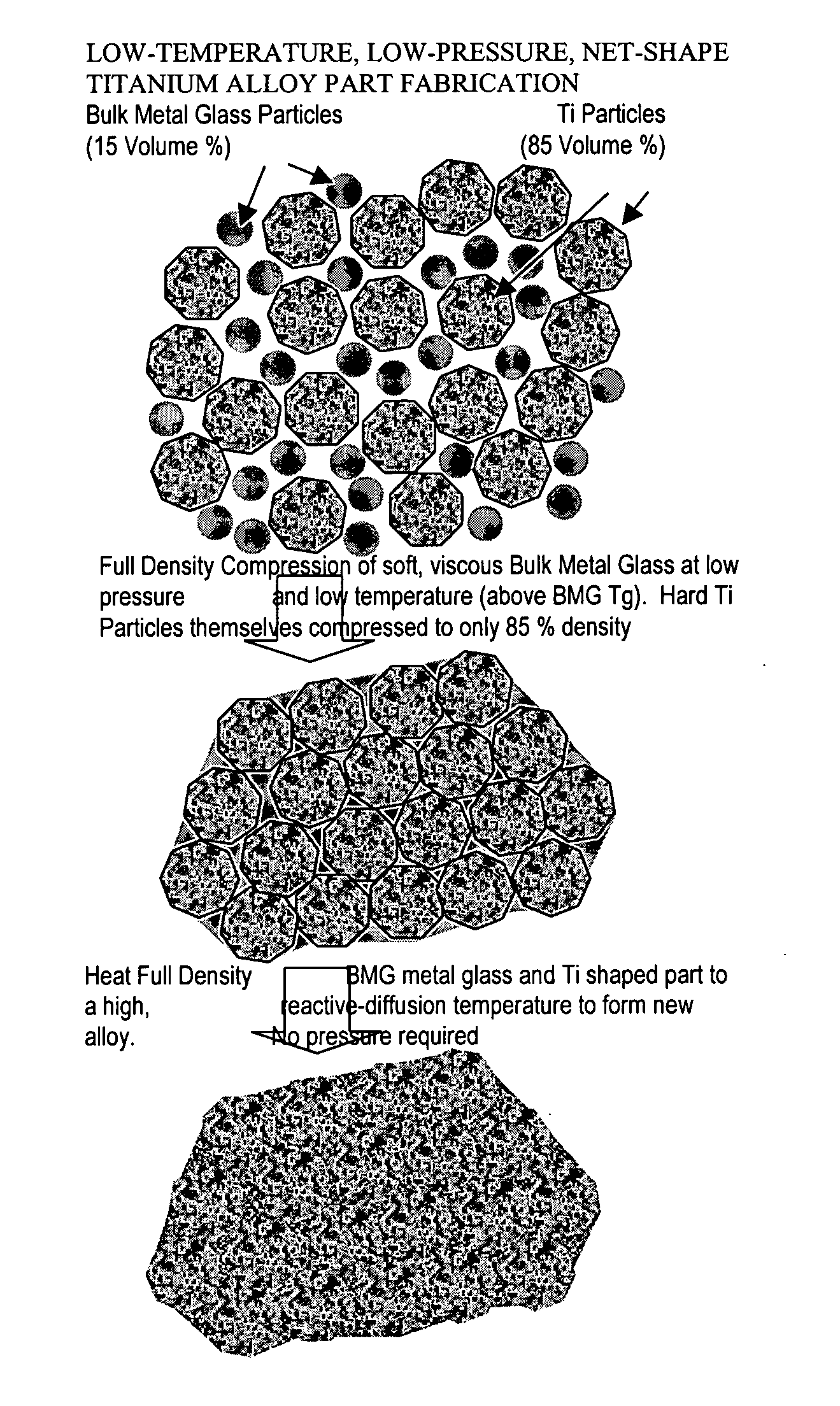
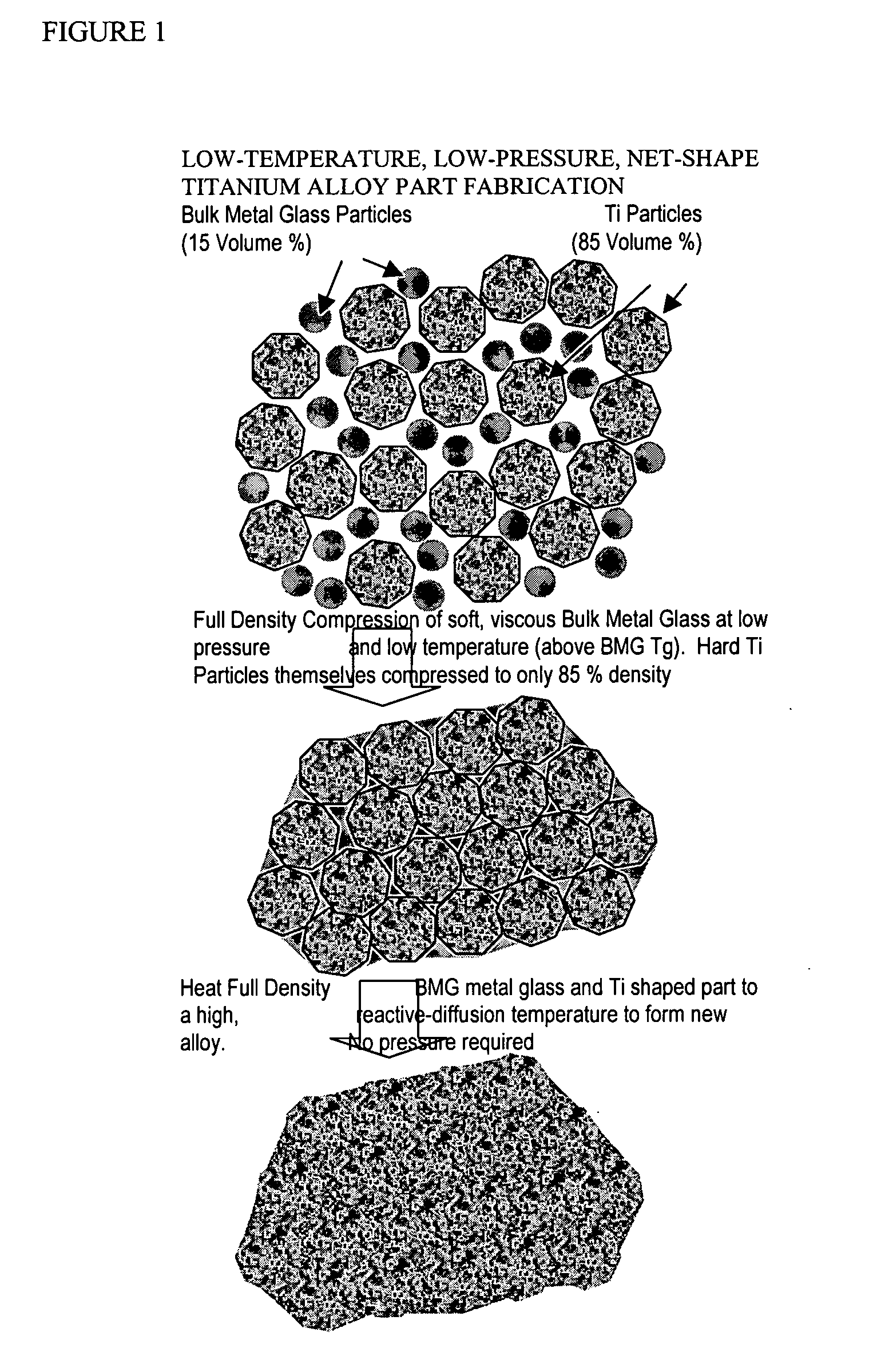
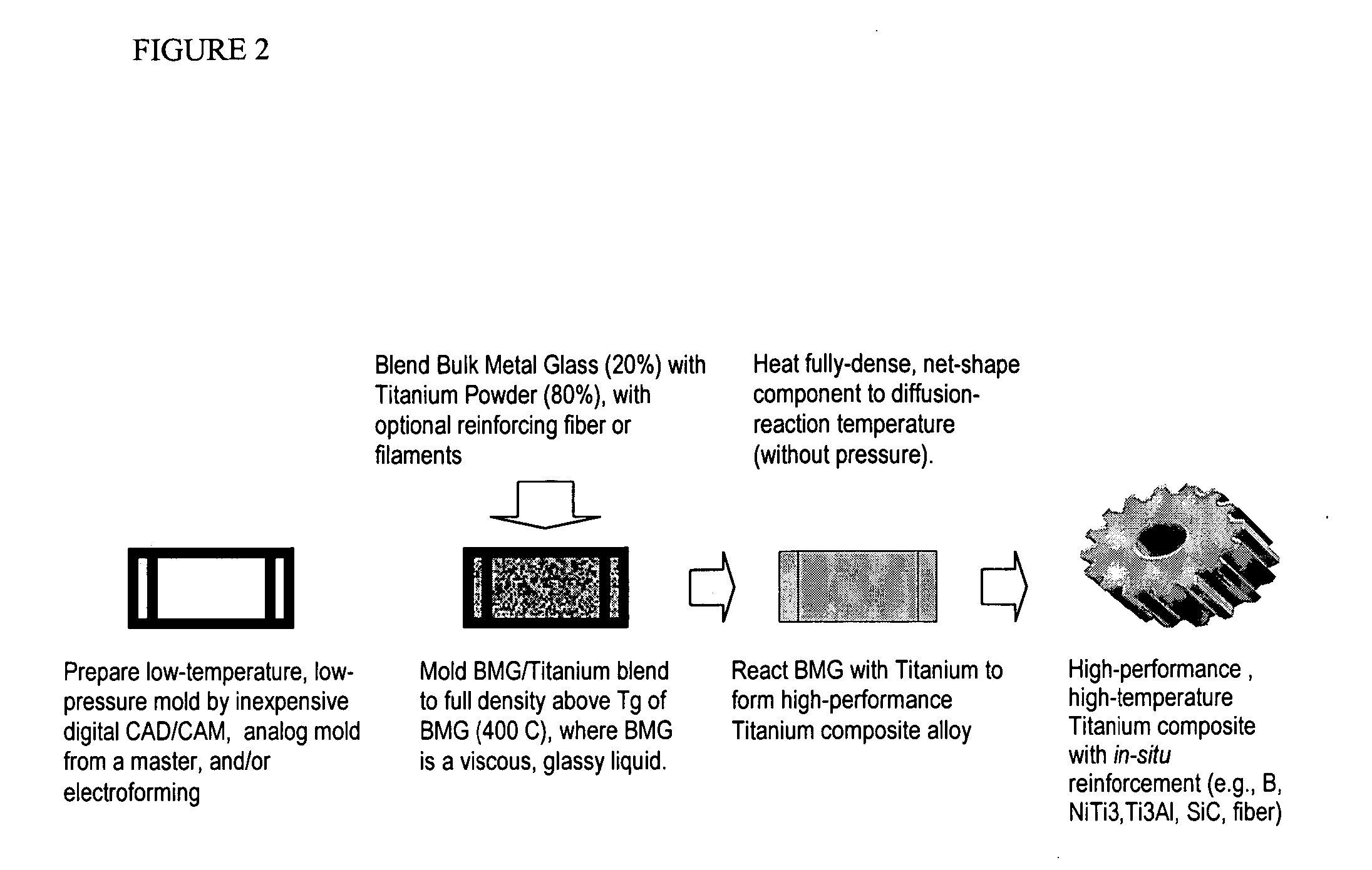
InactiveUS20050084407A1Excellent cold formabilityImprove hardenabilityVitrificationVolumetric Mass Density
Methods and compositions relating to powder metallurgy in which an amorphous-titanium-based metal glass alloy is compressed above its glass transition temperature Tg with a titanium alloy powder which is a solid at the compression temperature, to produce a compact with a relative density of at least 98%.
Owner:MYRICK JAMES J
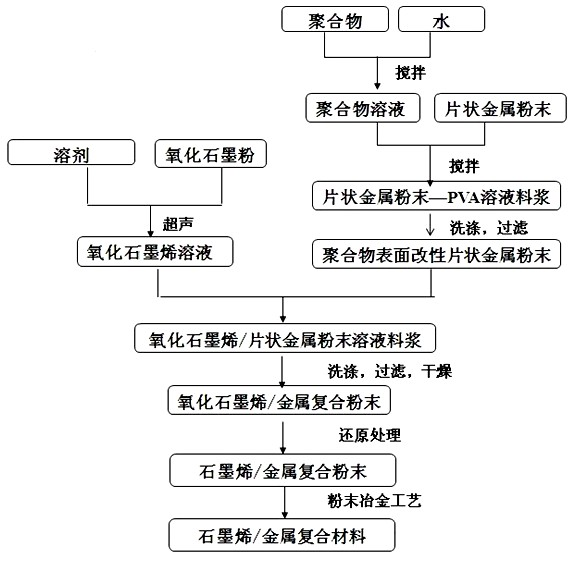
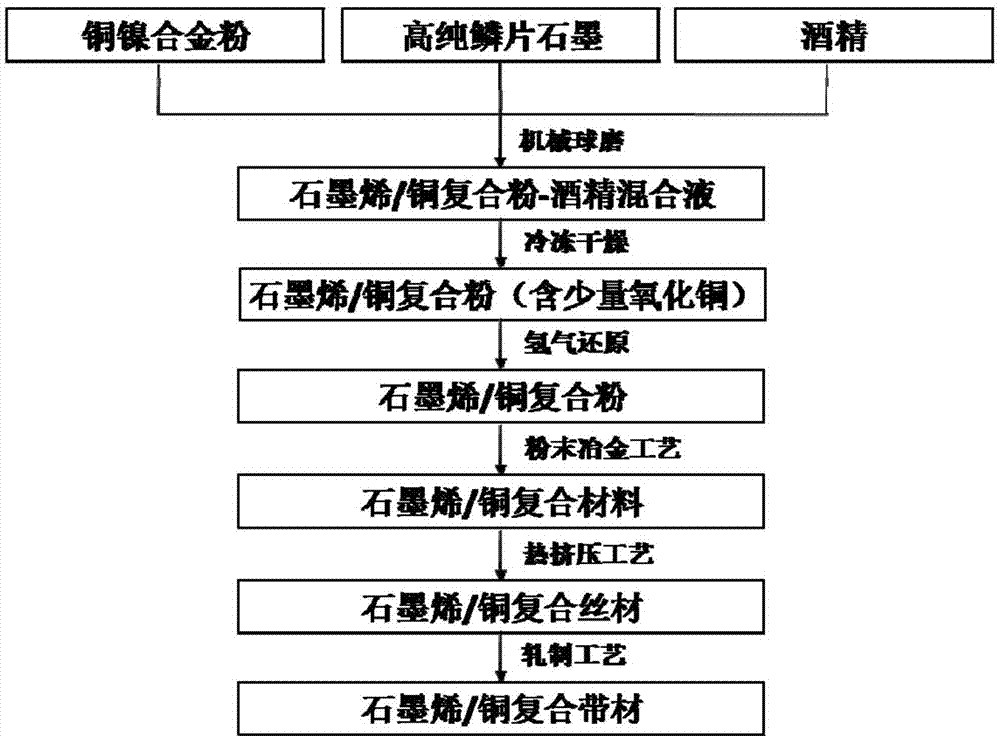
Preparation method of graphene reinforced metal-matrix composite
ActiveCN102329976AFacilitate induced orientation distributionPotential for large-scale applicationMetal matrix compositeCvd graphene
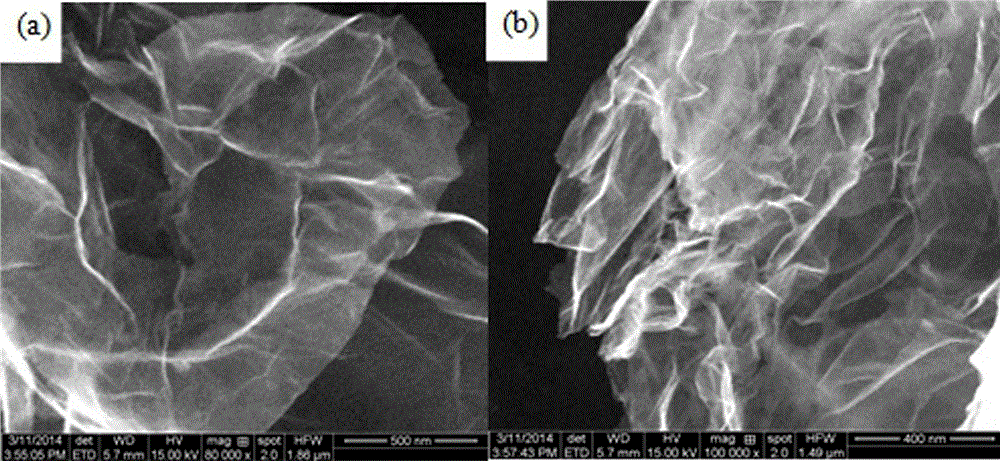
The invention discloses a preparation method of a graphene reinforced metal-matrix composite, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, dispersing the graphene oxide on the surface of the flaky metal powder; and then obtaining the graphene / metal composite powder through the reducing treatment; and at last, carrying out densification treatment by adopting a powder metallurgic technology to obtain the compact graphene reinforced metal-matrix composite. The flaky metal powder has the plane two-dimensional form, is inclined to the directional piling to form a laminated structure, and is helpful for inducing the graphene orientation distribution and giving play to the reinforcing effect. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple and feasible, is capable of regulating the graphene content and is suitable for preparing the massive composite.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Surface modified particulate and sintered or injection molded products
ActiveUS20150080495A1Simple technologyWeaken energyConductive materialCeramic shaping apparatusParticulatesPolymer science
Disclosed are interfacially modified particulate and polymer composite material for use in injection molding processes, such as metal injection molding and additive process such as 3D printing. The composite material is uniquely adapted for powder metallurgy processes. Improved products are provided under process conditions through surface modified powders that are produced by extrusion, injection molding, additive processes such as 3D printing, Press and Sinter, or rapid prototyping.
Owner:TUNDRA COMPOSITES LLC
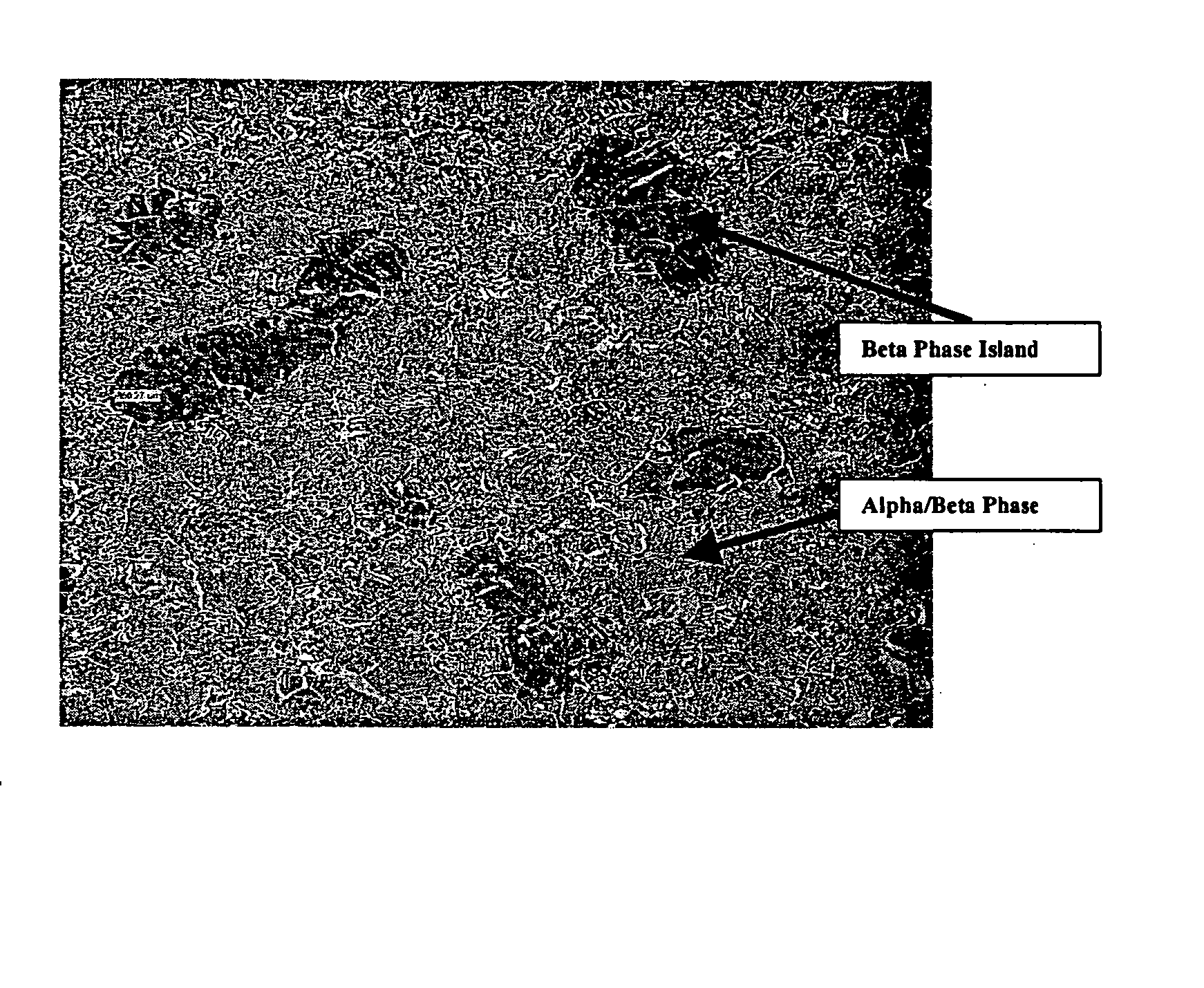
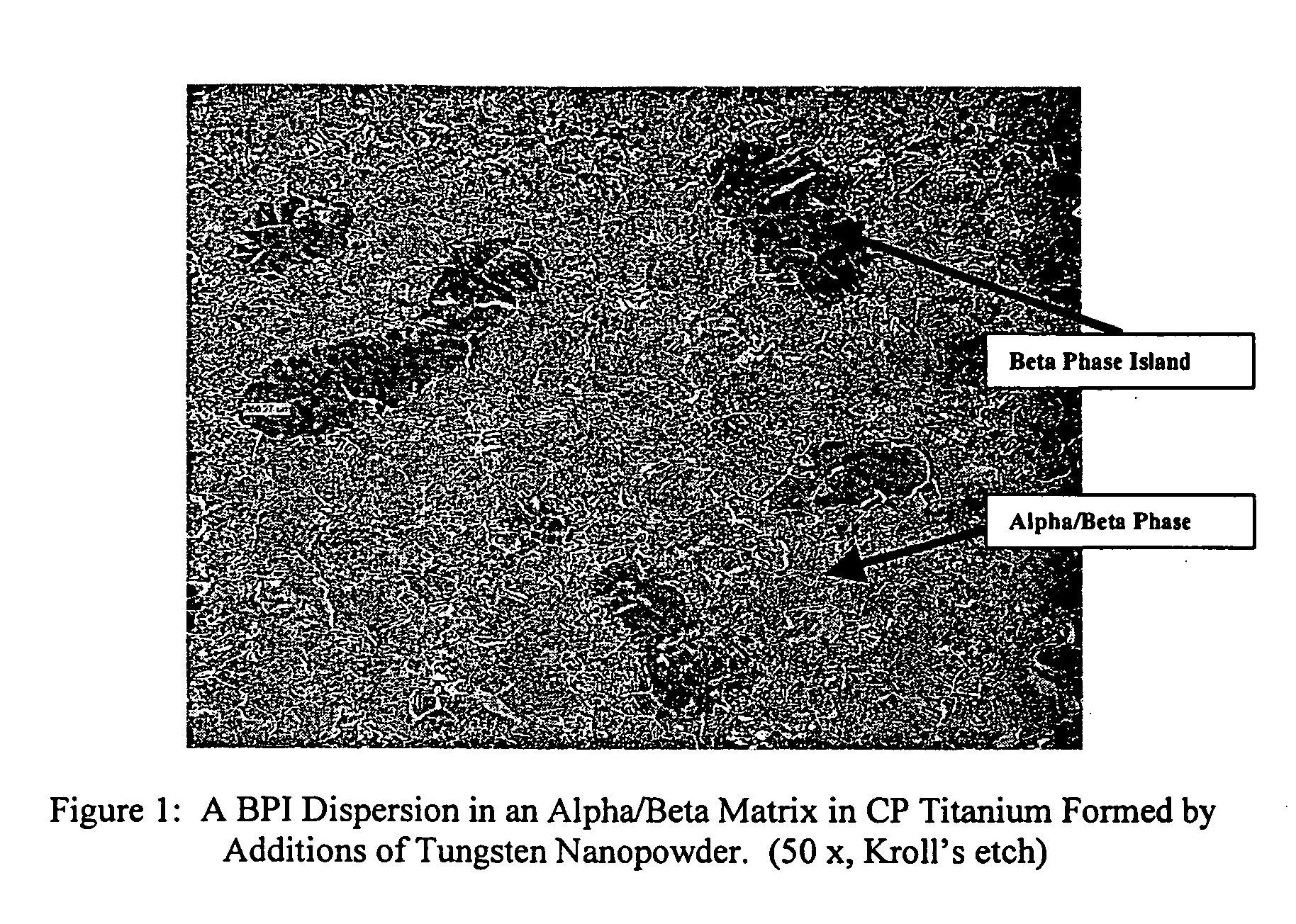
Titanium tungsten alloys produced by additions of tungsten nanopowder
Disclosed herein are titanium-tungsten alloys and composites wherein the tungsten comprises 0.5% to 40% by weight of the alloy. Also disclosed is a method of making such alloys and composites using powders of tungsten less then 3 μm in size, such as 1 μm or less. Also disclosed is a method of making the titanium alloy by powder metallurgy, and products made from such alloys or billets that may be cast, forged, or extruded. These methods of production can be used to make titanium alloys comprising other slow-diffusing beta stabilizers, such as but not limited to V, Nb, Mo, and Ta.
Owner:DYNAMET TECH
Short fiber-particle synergetically-reinforced copper-based composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a copper-based composite material, and particularly relates to a short fiber-particle synergetically-reinforced copper-based composite material which is prepared through powder metallurgy. Short fibers and particles are used as reinforced phases, the content of the short fiber is 0.1-0.1 wt%, and the content of reinforcement particles is 0.1-10 wt%. The short fibers can be carbon nanotubes, carbon nanofibers, ceramic short fibers, and the like, and the particles used as reinforced phases can be aluminum oxide, zirconium oxide, magnesium oxide, titanium dioxide, silicon carbide, titanium carbide, tungsten carbide, silicon nitride, aluminum nitride, titanium nitride, titanium diboride, Ti3SiC2, and the like. The composite material is prepared through the steps of mixing, forming, sintering and processing, and the room temperature and the high temperature strength of the composite material can be increased by more than 3 times in comparison with those of pure copper; the electrical conductivity of the composite material can reach more than 80% of that of pure copper; the thermal conductivity of the composite material can reach more than 70% of that of pure copper; the coefficient of friction of the composite material can be reduced to be below 70% of that of pure copper; and the wear rate of the composite material can be reduced to be below 50% of that of pure copper.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Low oxygen refractory metal powder for powder metallurgy
InactiveUS6261337B1Electrolytic capacitorsTransportation and packagingMetallic hydrogenOxygen content
One step process for producing formed Ta / Nb powder metallurgy products using Ta and / or Nb hydride powders with an oxygen content greater than a target level, e.g., 300 ppm, heating the metal hydride in the presence of another metal having a higher affinity for oxygen, removing the other metal and any reaction byproducts, to form a metal powder with an oxygen content less than the target level and forming a metallurgical product from said oxygen reduced Ta / Nb powder with an oxygen content less than the target level.
Owner:H C STARCK INC
Preparation method of copper-plated graphene reinforced metal-based composite
InactiveCN104451227AInterface is well integratedHigh densityLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingMetallurgyMetal matrix composite
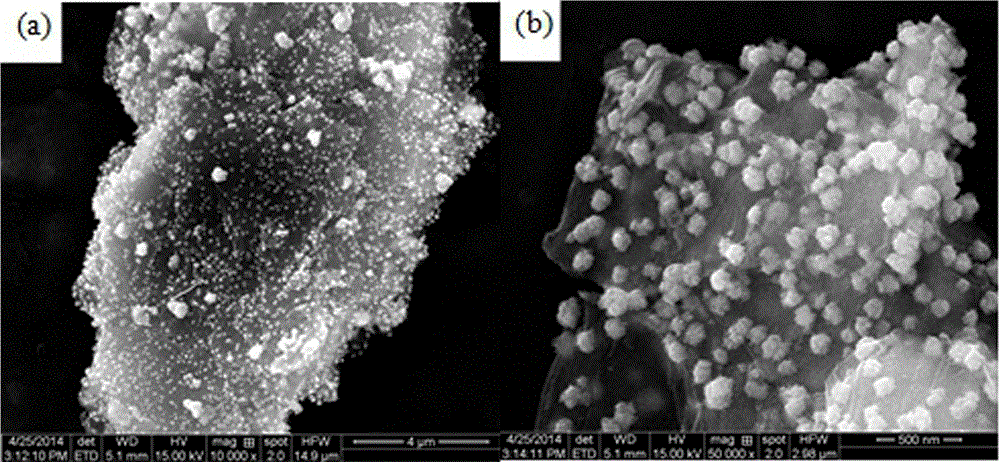
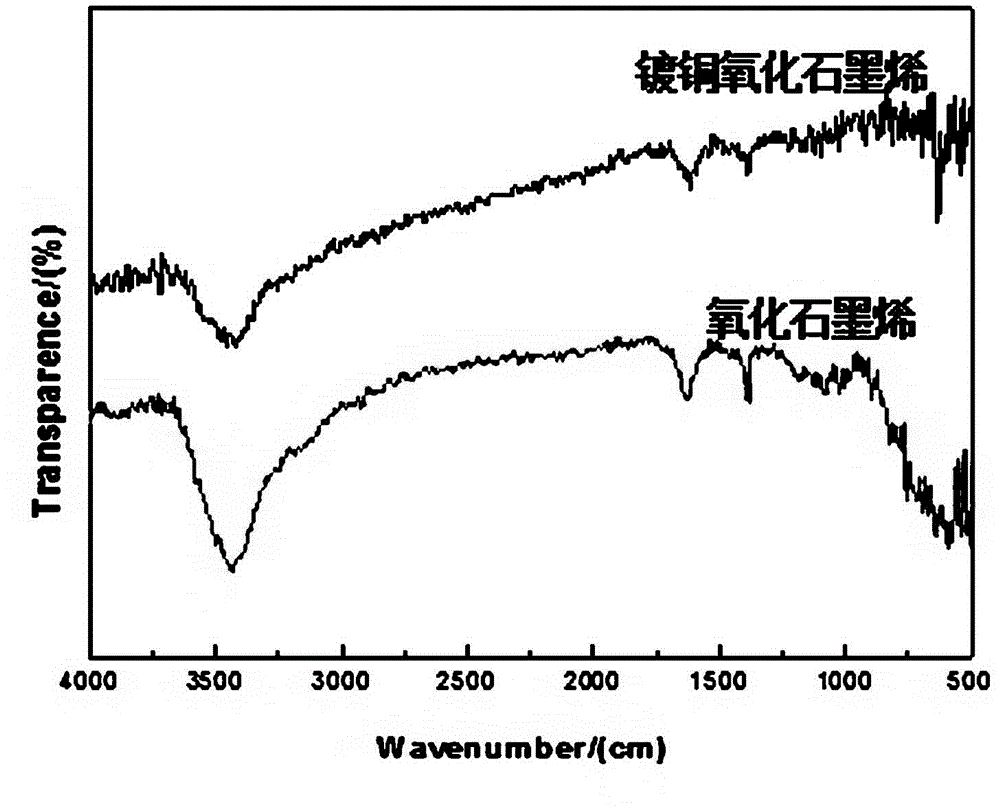
The invention discloses a preparation method of a copper-plated graphene reinforced metal-based composite. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, chemically plating the surfaces of oxidized graphene powder with copper to obtain copper-plated graphene powder; ball-grinding and mixing the copper-plated graphene powder and metal powder to obtain copper-plated graphene / metal mixed powder; and performing warm-pressing forming to the copper-plated graphene / metal mixed powder by adopting powder metallurgy warm-pressing technology, sintering, and performing composite processing and forming by adopting extrusion, forging, rolling and other technologies. The copper-plated graphene powder is adopted as a reinforcing body, the preparation method is simple, the cost is low, the designability is strong, and the copper-plated graphene reinforced metal-based composite which is good in interface binding, high in compactness and good in mechanical performance and thermophysical performance can be obtained.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
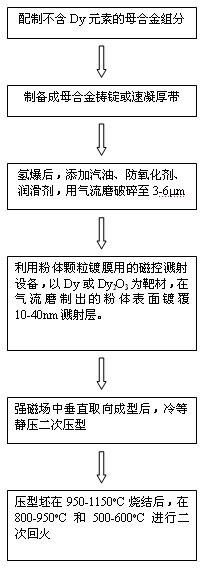
A preparation method of high-performance sintered NdFeB with low dysprosium content
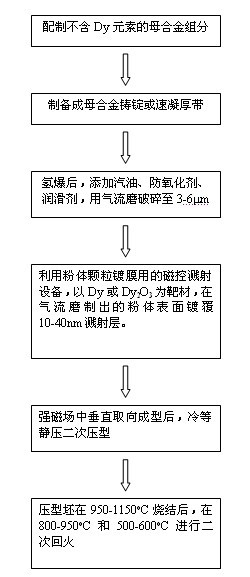
The invention discloses a method for preparing sintered NdFeB with low dysprosium (Dy) content and high performance; the method comprises the following steps of: sputtering and plating the Dy element on the surface of jet mill powder by using the powder plate technology based on magnetron sputtering on the basis of preparing NdFeB powder, and then sufficiently dispersing the Dy element to micron-sized NdFeB crystal particles by dispersing the Dy element at high temperature in the sintering and tempering process, thereby achieving the effect of improving magnetic performance of the sintered NdFeB. Compared with the introduction of the Dy element in the proportioning process of the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages: the low dysprosium content and high performance is limited in the nano-size by adopting the physical gas-phase deposition, the consumption quantity of the Dy element during the production process is controlled effectively and the preparationof sintered NdFeB with low dysprosium content and high performance is realized. Compared with the sintered NdFeB of the same components prepared by the traditional casting and powder metallurgy process, both the intrinsic coercivity and the maximum magnetic energy product of the sintered NdFeB rare-earth permanent magnetic material obtained according to the invention are improved obviously; compared with the sintered NdFeB with the same performance prepared by the traditional casting and powder metallurgy process, the dosage of the dysprosium element is reduced remarkably. The method can be widely applicable to producing and manufacturing sintered NdFeB with high performance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
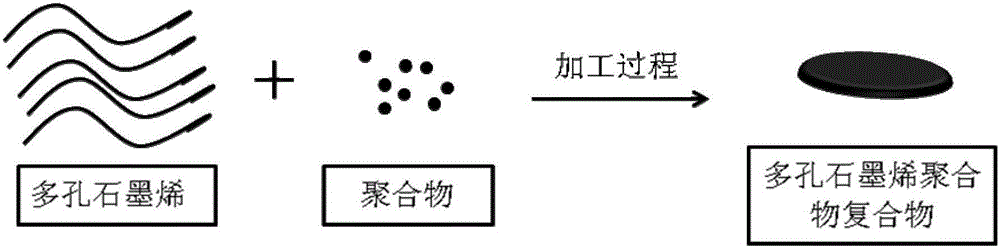
Porous graphene/polymer composite structure and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a porous graphene / polymer composite structure, and a preparation method and application thereof. The composite structure mainly comprises a compound formed by porous graphene and more than one polymer and / or polymer monomer. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: compounding polymers and / or polymer monomers with porous graphene to form a target product, wherein the compounding manner comprises single-screw / double-screw fusing processing, injection molding, blow molding, melt spinning, solution spinning, electrostatic spinning, electrostatic spraying, powder metallurgy, liquid mixing or high speed mechanical stirring dispersion. The invention is simple in process, wide in source of raw materials, easy to implement in large scale, low in cost, safe, environment-friendly and free from toxic and harmful wastes, and the product obtained is excellent in thermal and electric properties, and has wide application prospect in the fields of heat conduction, radiation, electric conduction, anti-static electricity, electromagnetic shielding and the like.
Owner:苏州格瑞丰纳米科技有限公司
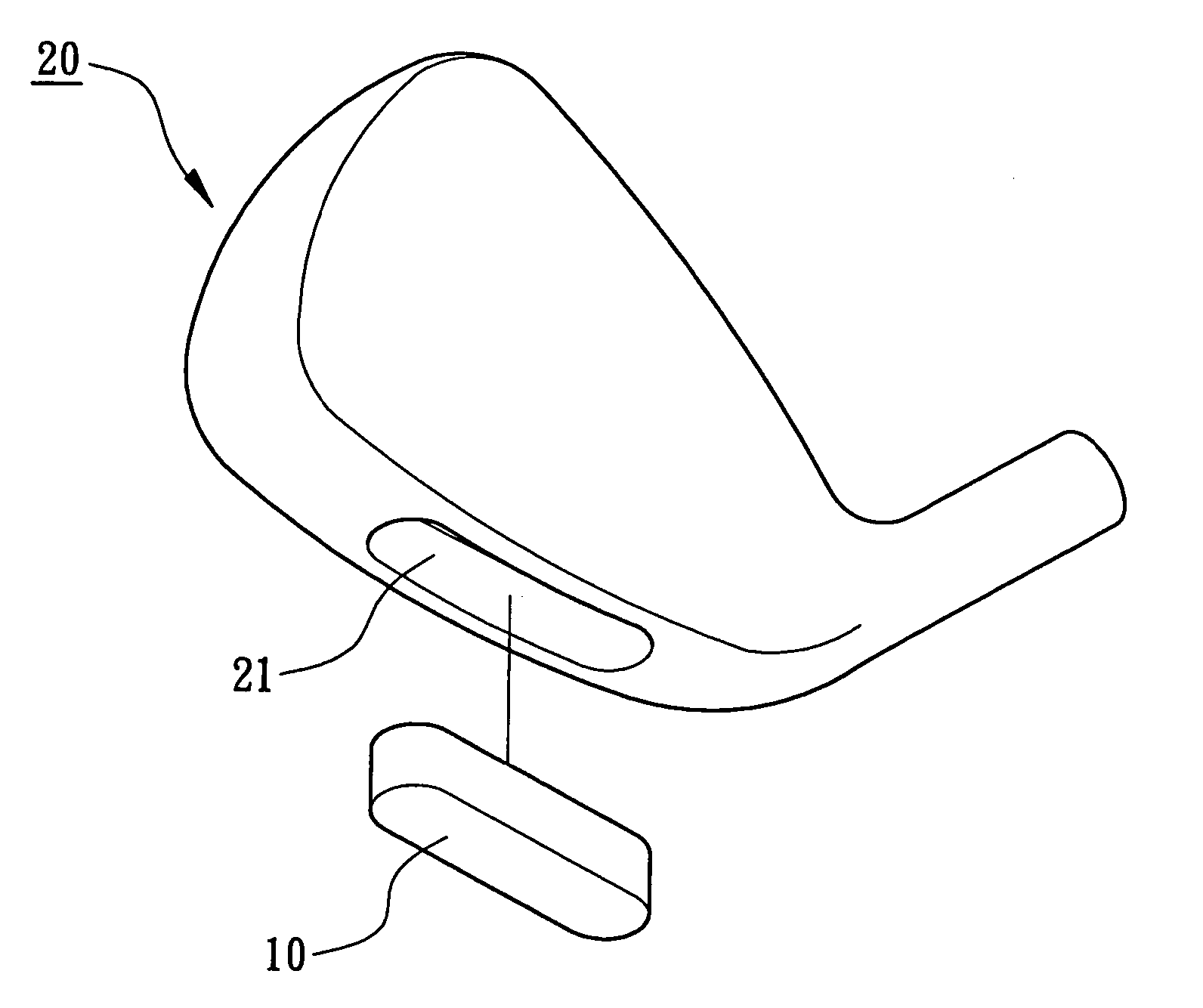
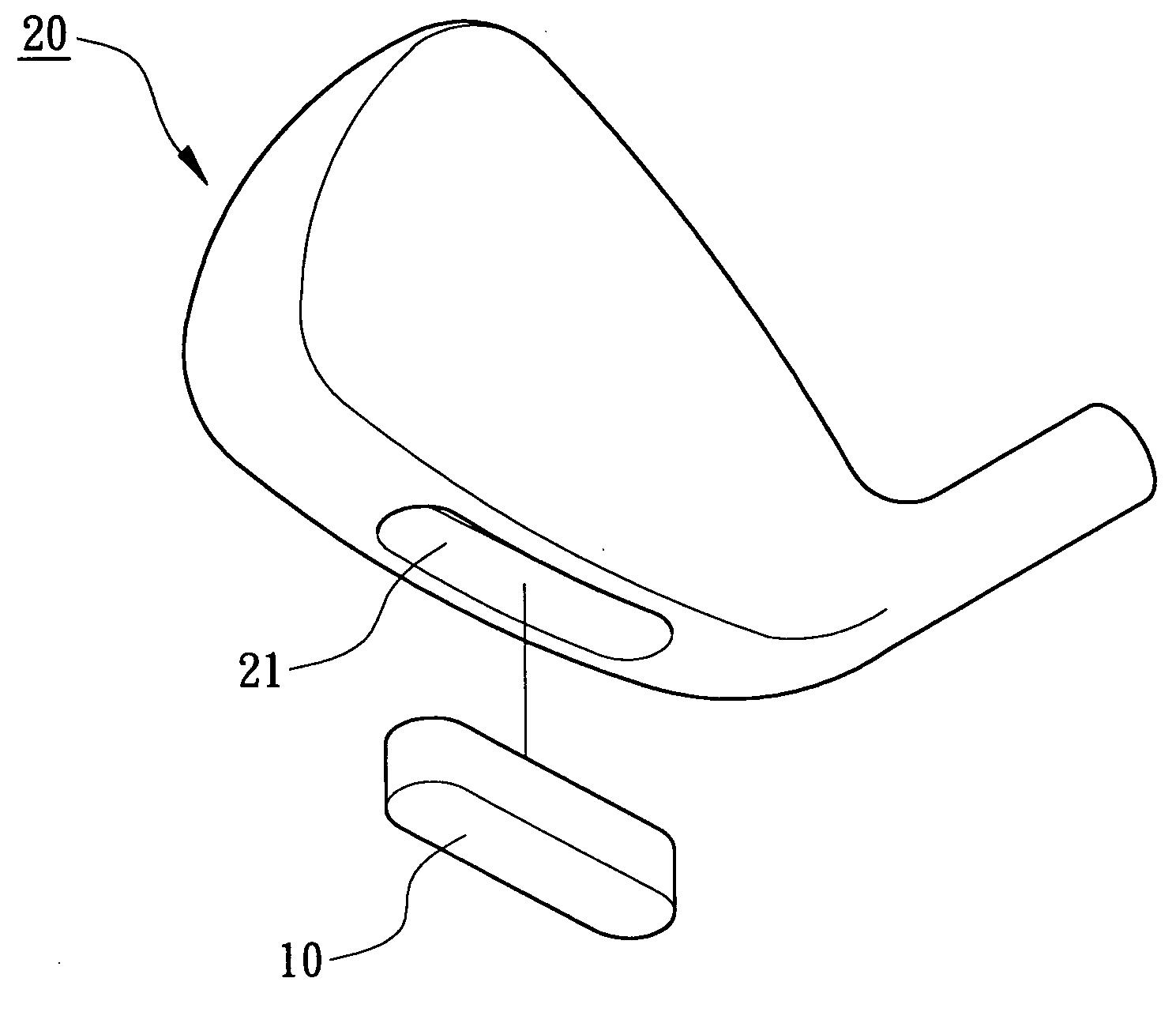
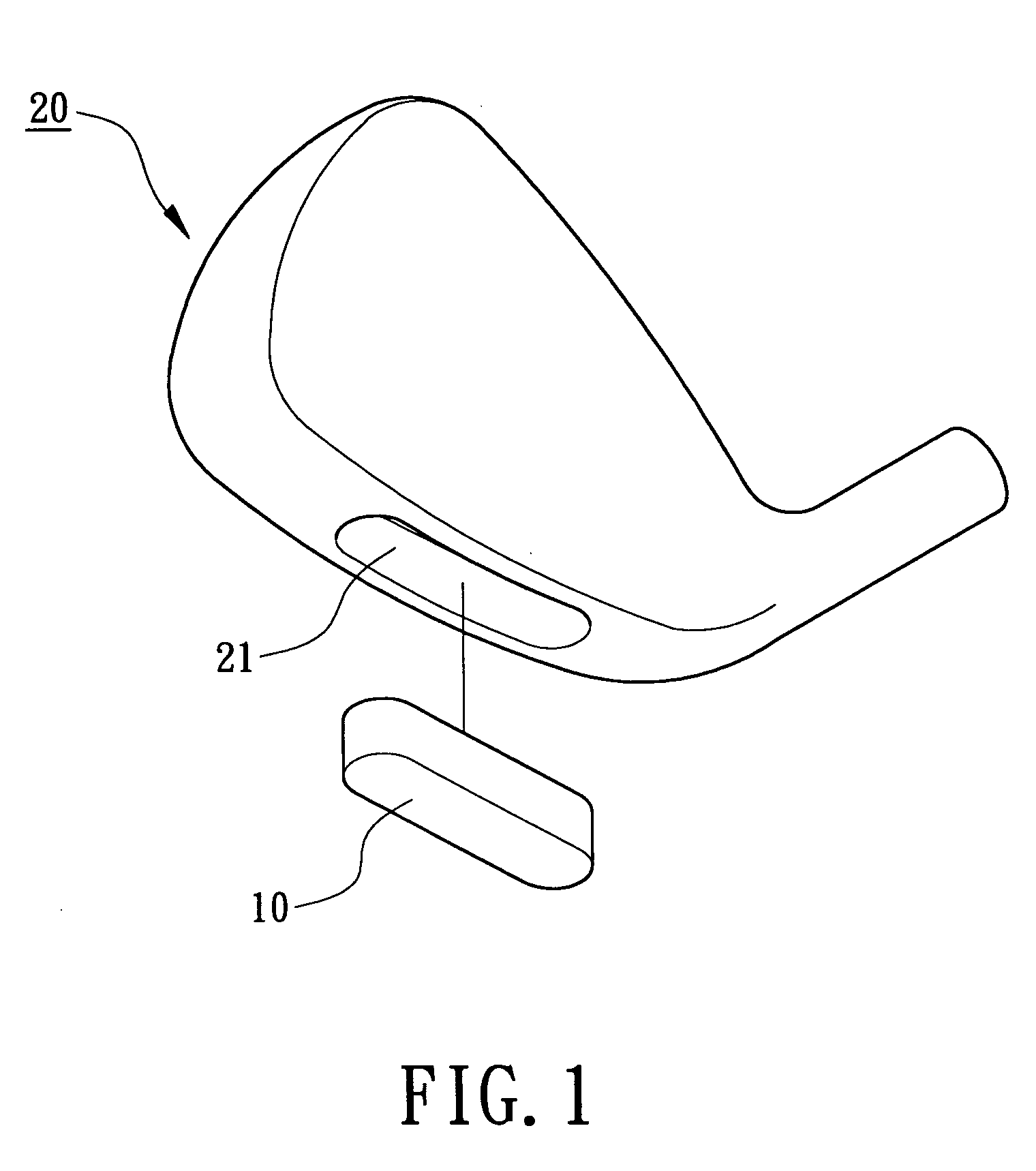
Weight member for a golf club head
InactiveUS20050227781A1High densityImprove rust resistanceGolf clubsRacket sportsSpecific gravityPowder metallurgy
A weight member for a golf club head is made of a WMoNi alloy by powder metallurgy or a precision casting process. The WMoNi alloy includes tungsten 1-35 wt %, molybdenum 4-55 wt %, and nickel 25-95 wt %, and has a specific gravity ranging between 8.6 and 13.3. Molybdenum increases the density of the weight member and improves the rust-resisting property of the weight member. The tungsten, molybdenum, and nickel provide a uniform metallographic phase. Uniformity of polishing of the weight member is thus improved.
Owner:FUSHENG IND CO LTD
Graphene/copper composite and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a graphene / copper composite and a preparation method of the graphene / copper composite. Copper-nickel alloy powder and crystalline flake graphite are ball-milled mechanically jointly, alcohol is added as a wet milling medium during mechanical ball milling, and copper powder oxidation can be avoided. Graphene is stripped from the graphite by virtue of a mechanical force; at the same time, due to the presence of copper-nickel micro powder, a stripping process of the graphite is promoted; the spherical copper-nickel alloy powder is changed into sheeted powder by the action of the ball milling to obtain graphene / copper composite powder preliminarily; and a graphene / copper composite block, a composite wire and a composite tape are obtained by powder metallurgy, hot extrusion and rolling technologies. According to the composite, the graphene is dispersed uniformly; interface bonding between a matrix and a reinforcement; and the graphene / copper composite has excellent physical properties. According to the composite and the method, a technology is simple, a process is easy to control, and a scale production application is easy to achieve.
Owner:SHANGHAI HIWAVE COMPOSITE MATERIALS CO LTD
High intensity focused ultrasound transducer with acoustic lens
A focused ultrasound transducer includes a first ultrasonic emitter and at least one metallic ultrasonic lens acoustically coupled thereto. The emitter generates ultrasonic energy that propagates along a beam path projecting therefrom. The at least one metallic ultrasonic lens is positioned at least partially in the beam path so that it can direct (e.g., focus, defocus, and / or collimate) in at least one direction (or along at least one plane) at least some of the ultrasonic energy propagating from the emitter. The metallic lens may be formed by extrusion, by molding (e.g., diecast molding or thermoforming), or by sintering (e.g., powder metallurgy). The metallic lens also advantageously functions as a heat sink, improving thermal performance of the ultrasound transducer.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Method for manufacturing tungsten-based materials and articles by mechanical alloying
A method of producing a high-density article is presented comprising selecting one or more primary tungsten-containing constituents with densities greater than 10.0 g / cc and one or more secondary constituents with densities less than 10.0 g / cc, co-milling the mixture of constituents in a high-energy mill to obtain mechanical alloying effects, then processing the resulting powder product by conventional powder metallurgy to produce an article with bulk density greater than 9.0 g / cc.
Owner:AMICK DARRYL DEAN
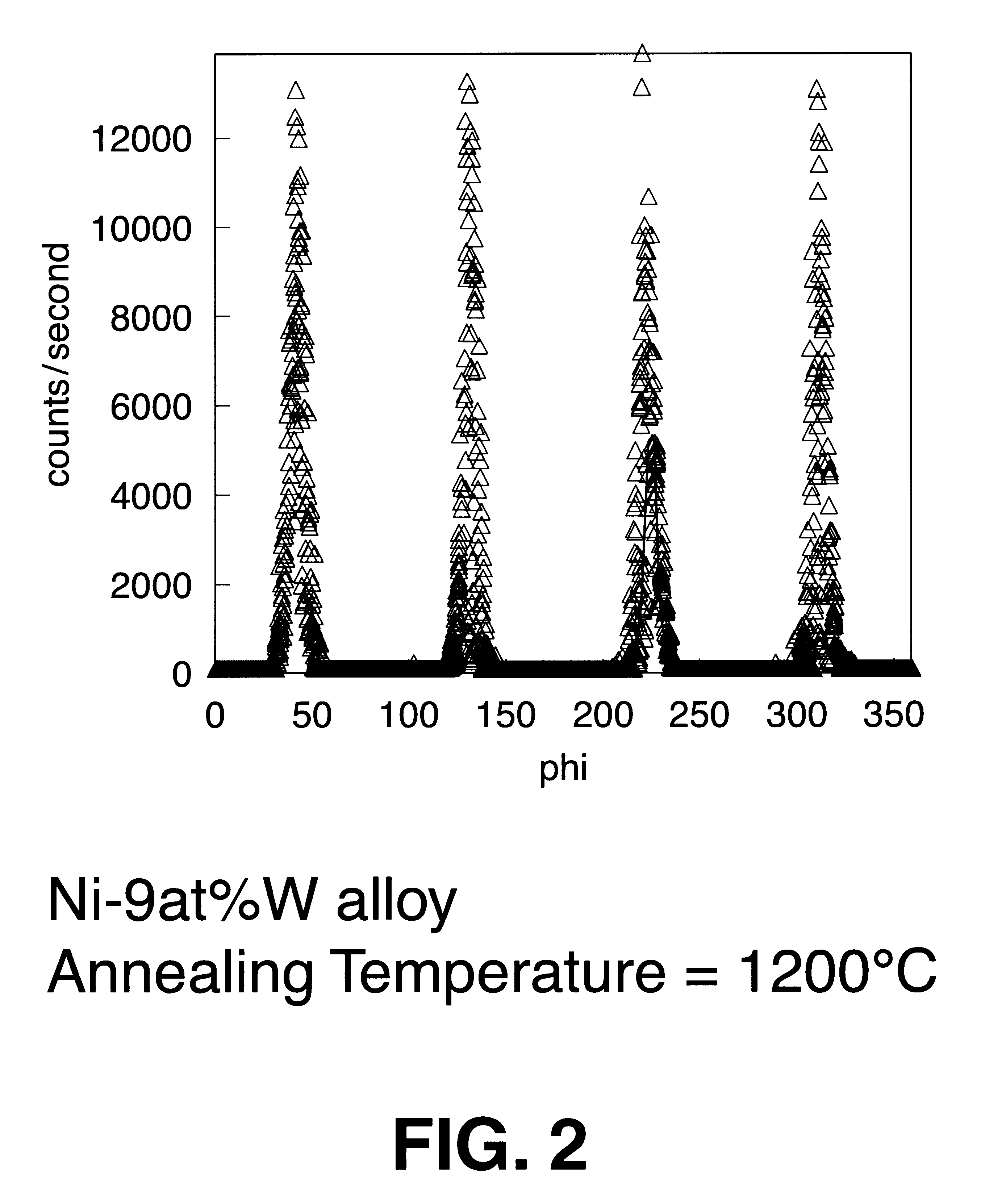
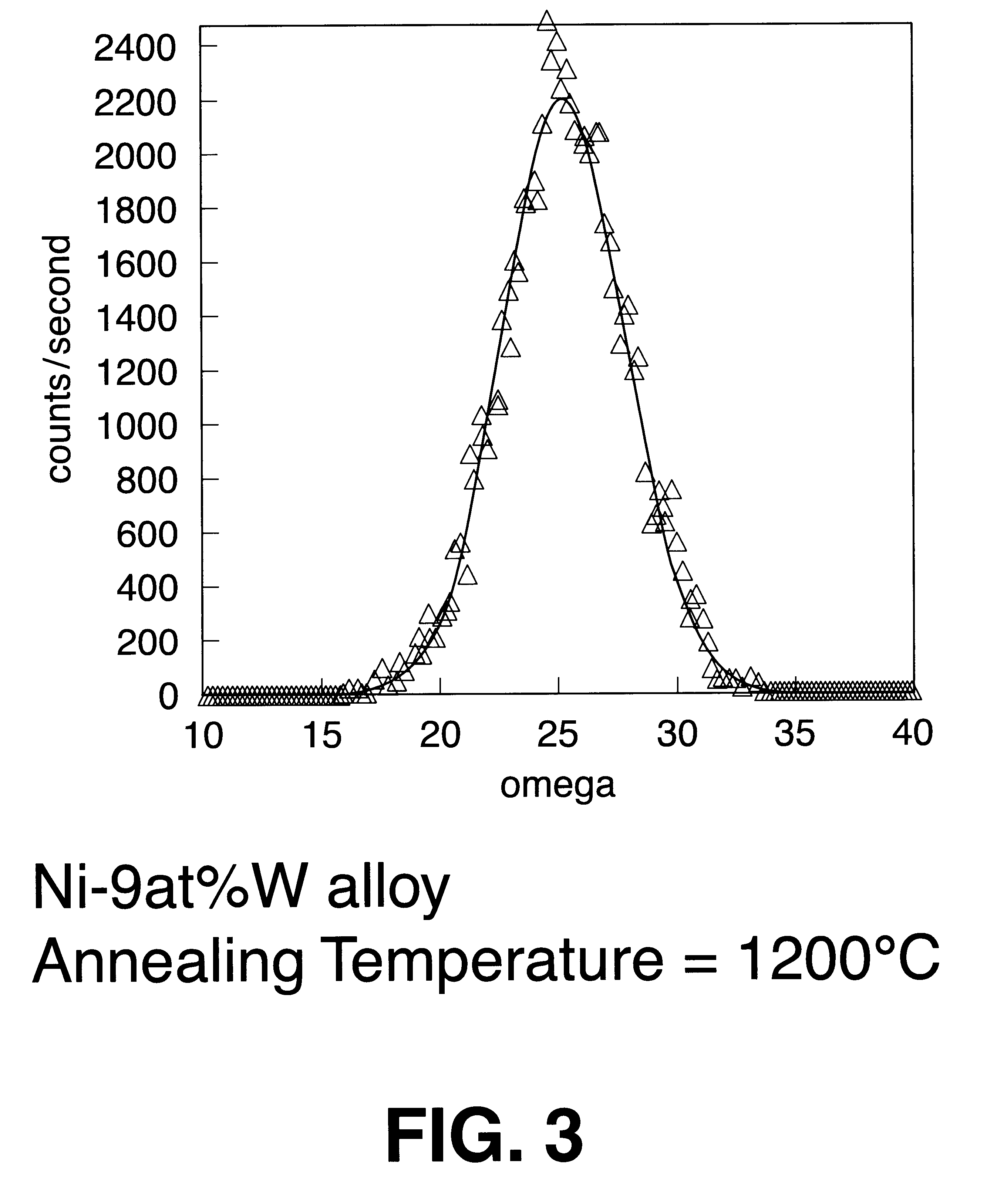
Method for forming biaxially textured articles by powder metallurgy
InactiveUS6447714B1Improve superconductivityPolycrystalline material growthFrom solid stateRare earthAlloy
A method of preparing a biaxially textured alloy article comprises the steps of preparing a mixture comprising Ni powder and at least one powder selected from the group consisting of Cr, W, V, Mo, Cu, Al, Ce, YSZ, Y, Rare Earths, (RE), MgO, CeO2, and Y2O3; compacting the mixture, followed by heat treating and rapidly recrystallizing to produce a biaxial texture on the article. In some embodiments the alloy article further comprises electromagnetic or electro-optical devices and possesses superconducting properties.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Weight member for a golf club head
A weight member for a golf club head is made of a WMoNi alloy by powder metallurgy or a precision casting process. The WMoNi alloy includes tungsten 1-70 wt %, molybdenum 4-55 wt %, and nickel 25-95 wt %. Molybdenum increases the density of the weight member and improves the rust-resisting property of the weight member. The tungsten, molybdenum, and nickel provide a uniform metallographic phase. Uniformity of shining finishing of the weight member is thus improved.
Owner:FUSHENG IND CO LTD
Device and method for preparing spherical titanium powder and titanium alloy powder through gas atomization
ActiveCN104475744AAvoid pollutionHigh sphericityGranulation by liquid drop formationHigh frequency powerTitanium alloy
The invention relates to a device and method for preparing spherical titanium powder and titanium alloy powder through gas atomization, which belongs to the field of powder metallurgy industry. The device comprises a vacuum chamber, a continuous feeder for titanium or titanium alloy wires / rods is arranged outside the vacuum chamber, a dynamic sealing device is arranged at the top of the vacuum chamber, a metal straightening device is arranged inside the vacuum chamber, an atomizing chamber is arranged below the vacuum chamber, a gas atomization nozzle is installed between the atomizing chamber and the vacuum chamber, the center hole of the nozzle is internally provided with a wire / rod guiding device, a high-frequency smelting coil is installed below the nozzle, wherein the dynamic sealing device, the straightening device, the guiding device and the high-frequency smelting coil are installed on the same axis; a heat dissipation cover is installed inside the atomizing chamber, a protective cover is arranged at the top of the heat dissipation cover, and the centers of the heat dissipation cover and protective cover and the center of the high-frequency smelting coil are on the same axis; a powder collecting pot is arranged below the atomizing chamber. By means of controlling the diameters of the wires, the atomizing gas pressure and the power of a high-frequency power supply, titanium and titanium alloy powder with different particle sizes and particle size distributions can be obtained.
Owner:有研增材技术有限公司
Textured-grain-powder metallurgy tantalum sputter target
InactiveUS7081148B2Improve sputtering uniformityImprove uniformityCellsVacuum evaporation coatingElectronTantalum
The sputter target includes a tantalum body having tantalum grains formed from consolidating tantalum powder and a sputter face. The sputter face has an atom transport direction for transporting tantalum atoms away from the sputter face for coating a substrate. The tantalum grains have at least a 40 percent (222) direction orientation ratio and less than a 15 percent (110) direction orientation ratio in an atom transport direction away from the sputter face for increasing sputtering uniformity, the tantalum body being free of (200)–(222) direction banding detectable by Electron Back-Scattering Diffraction and wherein the sputter target has a purity of at least 99.99 (%) percent.
Owner:PRAXAIR ST TECH INC
Production of an aluminide containing ceramic moulding
InactiveUS6025065AFast heatingLow heating rateSynthetic resin layered productsCeramic layered productsOxide ceramicMetal powder
PCT No. PCT / EP95 / 03347 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 19, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 19, 1997 PCT Filed Aug. 23, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 20902 PCT Pub. Date Jul. 11, 1996A ceramic formed body containing a) 5 to 70 vol % of at least on intermetallic aluminide phase which additionally may contain aluminum or / and aluminum alloy, and b) 30 to 95 vol % of one or more ceramic phases which form a solid interconnecting skeleton and wherein the intermetallic phase or phases consist of predominantly interconnected areas with average sizes of 0.1 to 10 mu m, is obtained by sintering, in a non-oxidizing atmosphere, of a powder metallurgically green body which consists of a mixture of finely dispersed powder of aluminum, one or more ceramic substances and maybe further metals such that the mixture contains at least one oxide ceramic or / and metallic powder which, during sintering, reacts with aluminum thereby forming an aluminide and maybe Al2O3.
Owner:CLAUSSEN NILS
Powder metallurgy sputtering targets and methods of producing same
A method of forming a sputtering target and other metal articles having controlled oxygen and nitrogen content levels and the articles so formed are described. The method includes surface-nitriding a deoxidized metal powder and further includes consolidating the powder by a powder metallurgy technique. Preferred metal powders include, but are not limited to, valve metals, including tantalum, niobium, and alloys thereof.
Owner:GLOBAL ADVANCED METALS USA
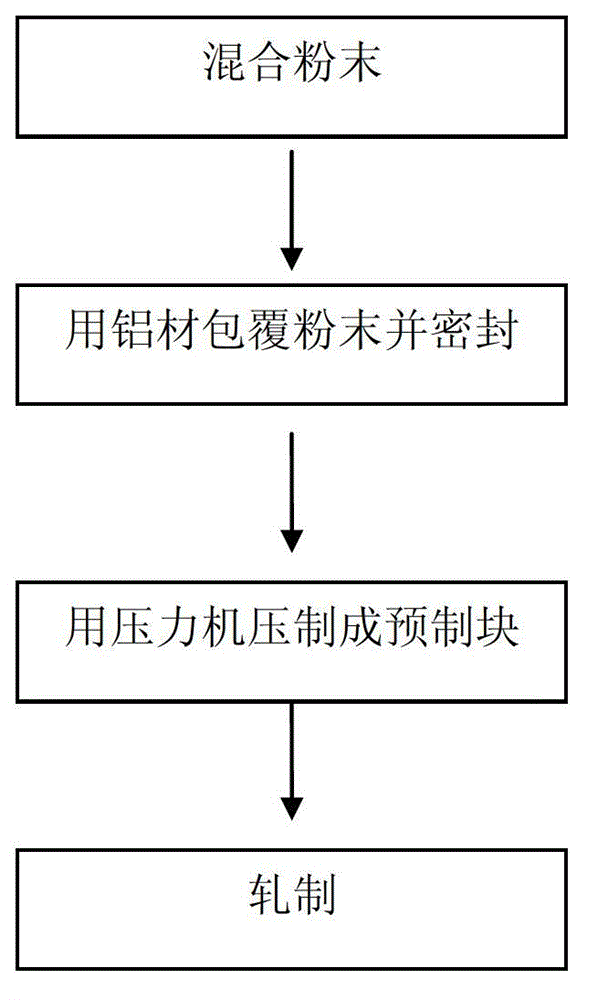
Preparation method for carbon nanomaterial enhanced aluminum base composite material
The invention discloses a preparation method for a carbon nanomaterial enhanced aluminum base composite material, which is similar to a powder metallurgy method, i.e. an aluminum material cladding powder processing and forming method. The preparation method is mainly used for solving the problem of precise mould requirement in the powder metallurgy process. The method is realized by the following steps of: 1) carrying out annealing treatment to pure aluminum or aluminum alloy material, carrying out alkali liquor cleaning and clean water cleaning to the surface of the pure aluminum or aluminum alloy material, and airing or drying after cleaning; 2) fully mixing and evenly stirring the pure aluminum or aluminum alloy powder with carbon nanomaterial at a certain ratio, i.e. at the mass fraction of the carbon nanomaterial of 0.1-8%; 3) cladding mixed powder by the pure aluminum or aluminum alloy material processed in step 1, compacting, sealing, and pressing into a precast block by a press; and 4) rolling the precast block obtained in step 3 into a final finished product. The preparation method for the carbon nanomaterial enhanced aluminum base composite material, which is disclosed by the invention, has the advantages of low cost, short flow, simpleness in operation and easiness in realizing industrialization.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
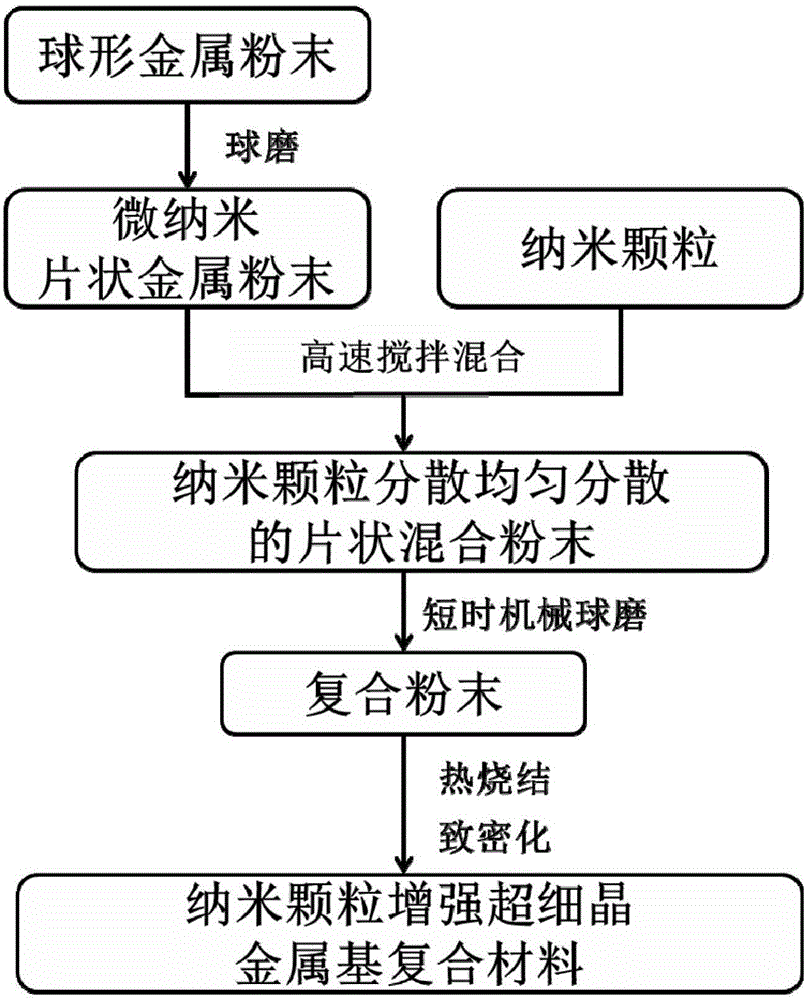
Powder metallurgy preparation method for nano-particle reinforced ultra-fine grain metal-matrix composite
The invention provides a powder metallurgy preparation method for a nano-particle reinforced ultra-fine grain metal-matrix composite. According to the method, a metal-matrix grain refining process and a nano-particle dispersing process are carried out in steps. The method comprises the steps that firstly, micro-nano flaky metal-matrix powder is prepared in advance; nano-particles and the flaky metal-matrix powder are stirred and mixed in a stirrer at the high speed under protective atmosphere, and by means of high shear force and pressure generated between stirring blades and a tank body, the nano-particles are uniformly dispersed to the surface of the micro-nano flaky metal-matrix powder; through short-time mechanical ball-milling treatment, the nano metal particles are embedded into the micro-nano flaky metal-matrix powder, so that composite powder of nano-particle reinforced metal is obtained; and compression moulding, sintering and compacting treatment are conducted, so that the ultra-fine grain metal-matrix composite with the nano-particles uniformly dispersed is obtained. By means of the powder metallurgy preparation method, time and energy are saved; cost is low; the application range is wide; and the prepared material is high in comprehensive mechanical performance and has large-scale application potential.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Nitrogen-containing nickel-free stainless steel and metallurgy forming process for powder thereof
The invention provides a nitrogenous nickel-free stainless steel and a powder-metallurgical molding technology, relating to the field of stainless steel production. Nitrogenous stainless steel powder and a prepared cementing agent are mixed evenly in a mixing machine and then crashed to injection molding feedstock; injection molding blanks with smooth surfaces and without macro defects are obtained by an injection molder under appropriate injection temperature and injection pressure; after degreasing by chlorylene solvent, thermal degreasing and presintering are carried out to the injection molding blanks, thermal degreasing blanks with certain strength and without defects are obtained; the thermal degreasing blanks are sintered and densified in nitrogen based atmosphere, therefore, products with higher density and more excellent performance can be obtained. The nitrogenous nickel-free stainless steel of the invention can solve the problems that resource price of the nickel-contained stainless steel is expensive and the contained nickel thereof is harmful to human health and the like, extends the application scope of nitrogenous austenitic stainless steel. The materials prepared by using the nitrogenous nickel-free stainless steel of the invention are better than traditionally smelted austenitic stainless steel in terms of performance and the nitrogenous nickel-free stainless steel of the invention is resource saving and environmentally friendly.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
High-silicon aluminum alloy cylinder sleeve material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101457318AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove tribological propertiesRefining (metallurgy)Manufacturing technology
The invention discloses a high silicon aluminum alloy cylinder sleeve material and a manufacturing method thereof., Ingredients of the material by weight percent are as follows: Si: 18.0%-25.0%; Fe: 3.5%-6.0%; Ni: 1%-2%; Cu: 1.5%-3.0%; Mg: 0.5%-1.0%; Mn: 0.5%-1.5%; V: 0.1%-0.5%; Sr: 0.05%-0.15%; and the balance of Al. The manufacturing method thereof comprises the following steps: 1, composition design and accurate mixture which uses an intermediate alloy for quantitative mixture; 2, smelting, covering and refining; 3, injection deposition; 4, extrusion processing; 5, heat treatment; 6, mechanical processing and honing processing. The material and the manufacturing method lead the high silicon aluminum alloy products to have high comprehensive mechanical property characteristics which are superior to mechanical property characteristics of cast iron cylinder sleeve material, have frictional property which are superior to frictional property of steel and cast iron cylinder sleeve material, and have great compatibility with thermophysical property of aluminum piston alloy material, thereby obviously narrowing the gap for cylinder matching. The manufacturing method is characterized in that: the manufacturing process of injection deposition is employed, which serves as a primary means in manufacturing the high silicon aluminum alloy, is superior to the powder metallurgy process and the die-casting process, and can use conventional processing equipment and process conditions.
Owner:NO 52 INST OF CHINA NORTH IND GRP CORP
Steel-based copper alloy dual-metal sliding bearing and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101649858ALow costImprove carrying capacityBearing componentsReflex reflectorsStearic acidLubrication
The invention discloses a dual-metal sliding bearing and a preparation method thereof. Carbon steel or stainless steel is taken as an outer layer material, and a powder metallurgy material taking a copper alloy as a basal body is taken as an inner layer material; the inner surface of the outer layer material is electroplated to form an electroplated copper layer with the thickness of 4-8 micrometres; the inner layer material comprises the following components by weight percent: 1%-20% of aluminum, 1%-8% of titanium, 1%-15% of stannum, 0.1%-5% of ferrum, 0.1%-2% of phosphorus, 0.1%-5% of nickel, at least one of 0.1%-2% of graphite and 0.1%-2% of molybdenum disulfide or 0.1%-2% of zinc stearate, and the balance of copper; and the bearing is impregnated with lubricating oil. The dual-metal sliding bearing has the advantages of low cost, high carrying capability, self-lubrication, excellent abrasion resisting capability, and the like, and can be widely applied to reciprocating swing positions of a swing arm, a bucket rod, a bucket, and the like of a large-tonnage and high-power excavator.
Owner:COB PRECISION PARTS
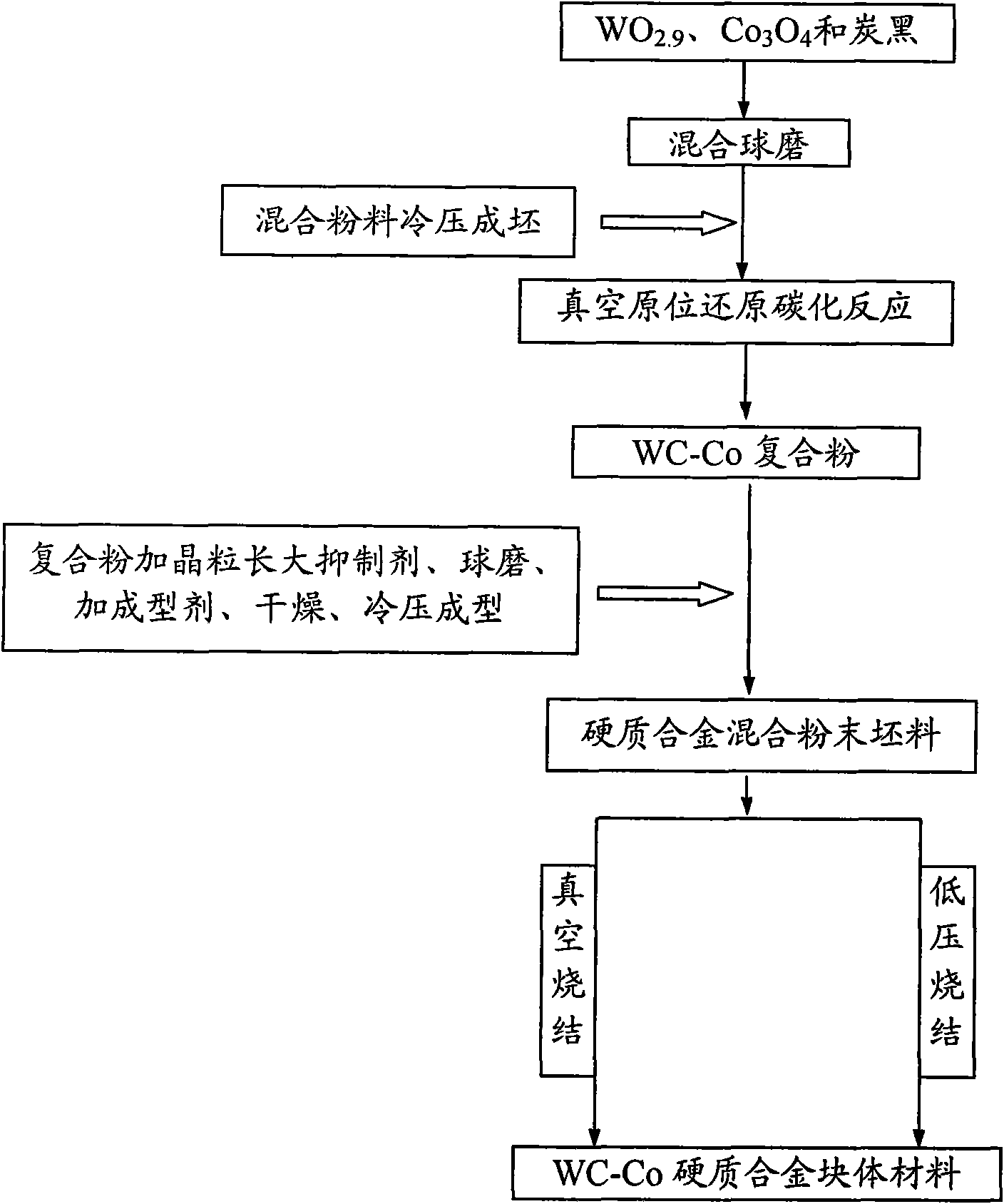
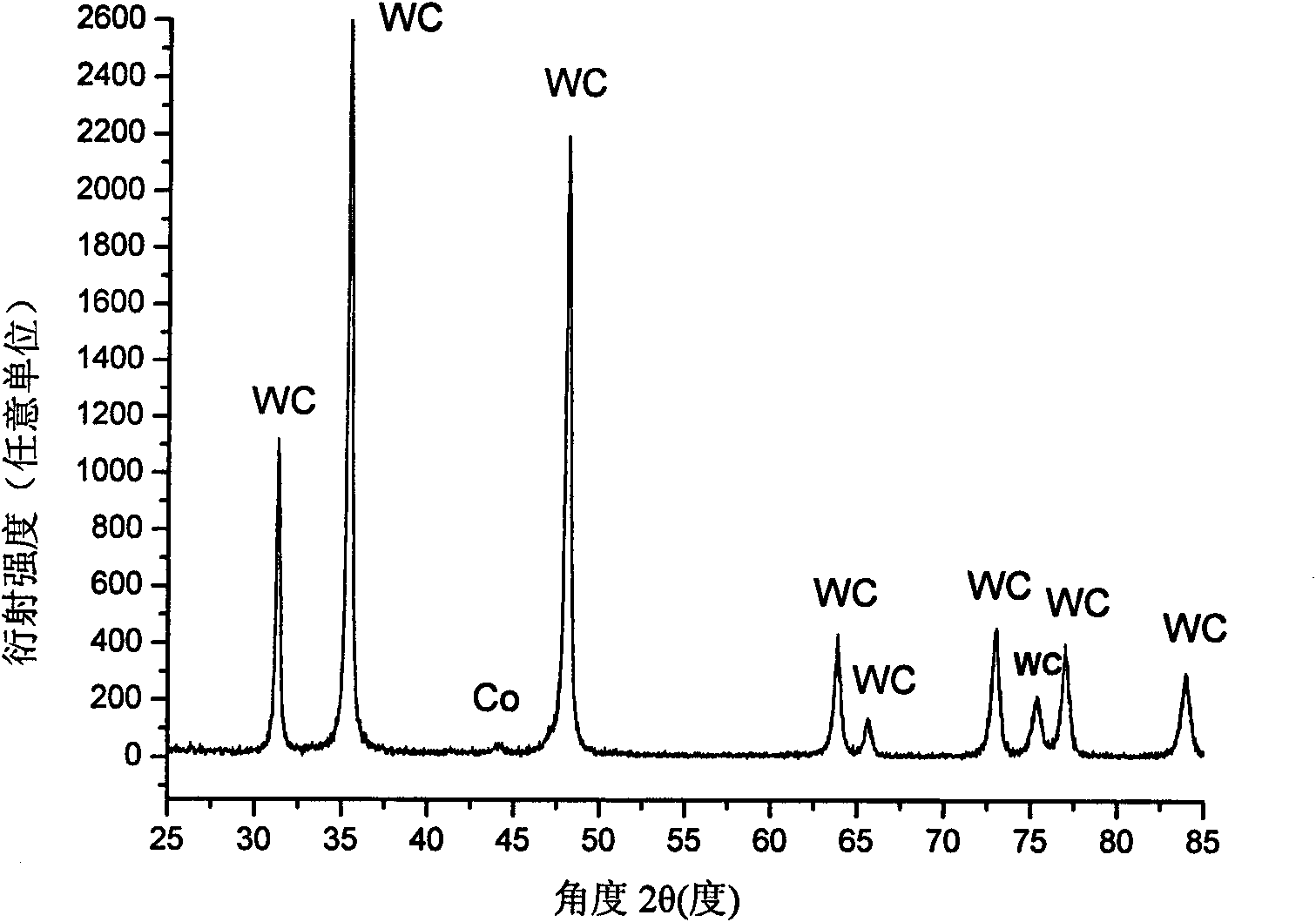
Industrialized preparation method of WC-Co hard alloy with low cost and high performance
ActiveCN101624673ASolve the problem that it is difficult to mix evenlyReduce energy consumptionPolyethylene glycolPrice ratio
The invention relates to an industrialized preparation method of a WC-Co hard alloy with low cost and high performance, which belongs to the technical field of hard alloys and powder metallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: taking WO2.9, Co3O4 and carbon soot as raw materials, and computing the usage ratio of the three materials according to the requirement of the Co content in a final hard alloy block material; adding 0-1.0 percent by weight of grain growth inhibitor into the prepared WC-Co composite powder, and adding polyethylene glycol as a forming agent into a ball milling tank 4-8 hours before ball milling is finished, wherein 30-80ml of polyethylene glycol is added into the powder material per kilogram; acquiring WC-Co mixed powder with a nanocrystal structure after ball milling, and putting the mixed powder into a mould for press forming after vacuum drying; and sintering the mixed powder stock after press forming in a mode of vacuum sintering or low-pressure sintering. The industrialized preparation method markedly shortens a production period, the provided integrated preparation course markedly reduces the production cost while ensuring the high performance of the hard alloy and has a high performance-price ratio, and the preparation method is suitable for industrialized scale production.
Owner:北硬科技香河有限公司
Biaxially textured articles formed by powder metallurgy
InactiveUS6331199B1Improve superconductivitySynthetic resin layered productsInorganic material magnetismRare earthAlloy
A biaxially textured alloy article comprises Ni powder and at least one powder selected from the group consisting of Cr, W, V, Mo, Cu, Al, Ce, YSZ, Y, Rare Earths, (RE), MgO, CeO2, and Y2O3; compacted and heat treated, then rapidly recrystallized to produce a biaxial texture on the article. In some embodiments the alloy article further comprises electromagnetic or electro-optical devices and possesses superconducting properties.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
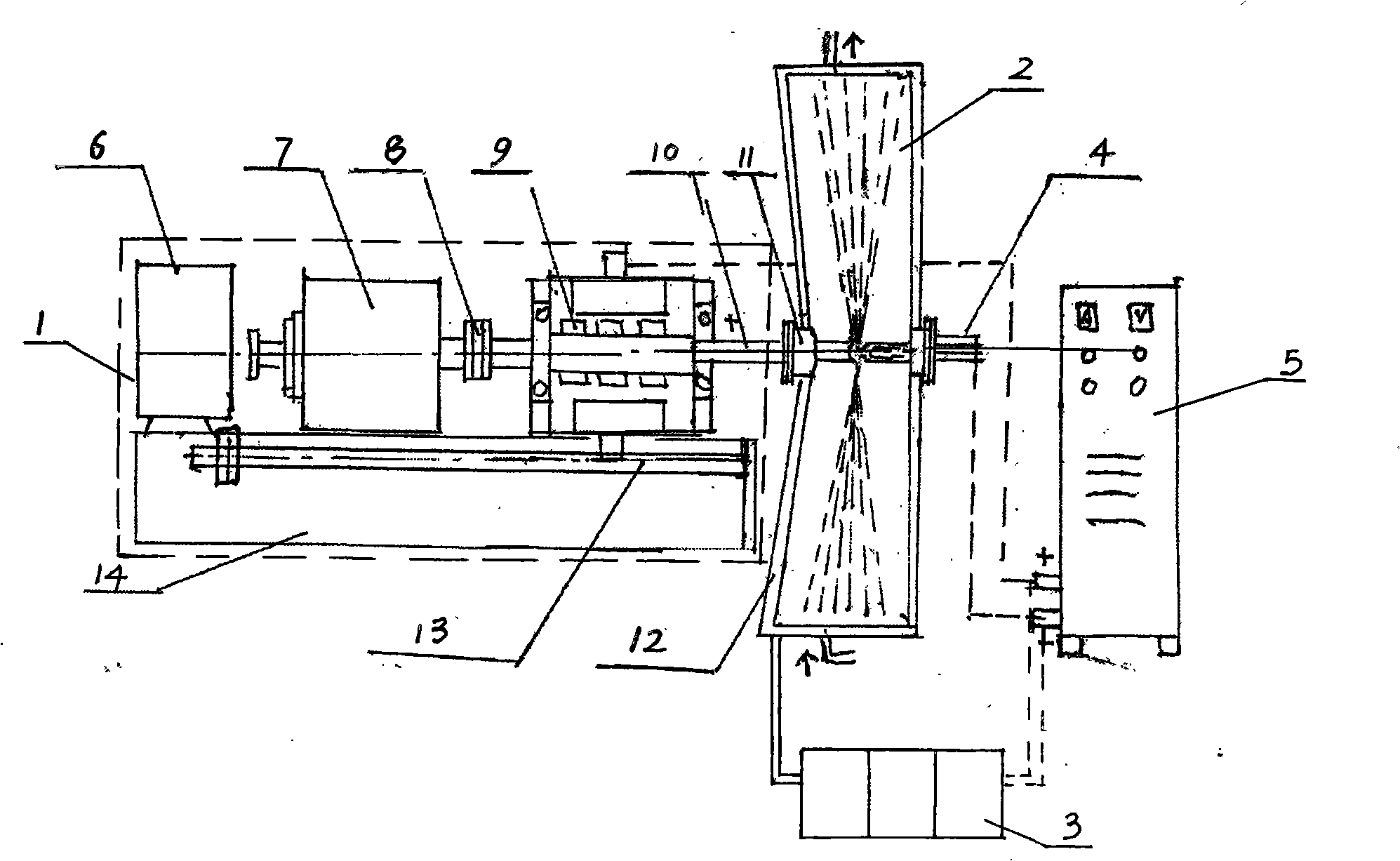
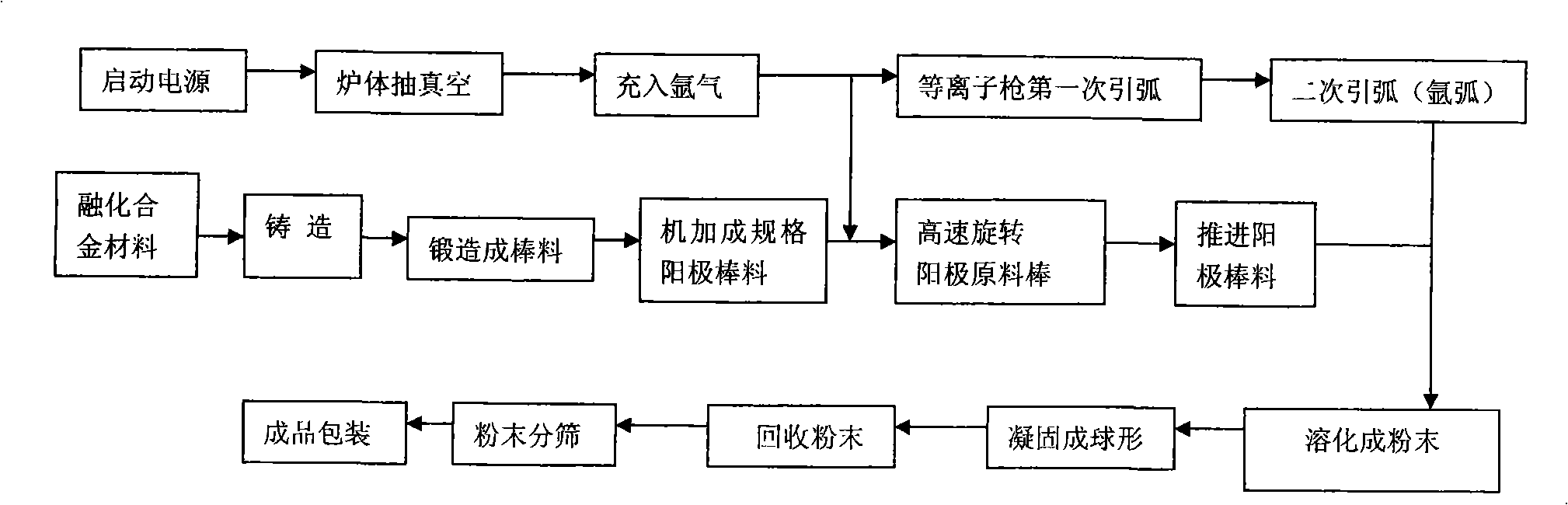
Plasma rotating electrode milling machine group and technique
The invention relates to a plasma rotary electrode powder milling set and a process thereof, relating to the technical field of powder metallurgy. The milling set comprises a rotating feeding mechanism, a vacuum furnace, a vacuum unit, a plasma gun device and an electrical source. The rotating feeding mechanism is arranged at the exterior of one side of the vacuum furnace; the plasma gun device is arranged at the interior of the other side of the vacuum furnace; the vacuum unit is communicated with the vacuum furnace through a ventilation pipe, wherein, the vacuum furnace body has a double-decker sandwich structure, and cooling circulating water is injected into the sandwich structure; a receiving mechanism is arranged at the bottom part of the vacuum furnace, wherein, the receiving mechanism comprises two cut-off valves connected in series. The process includes the following steps: metal is processed into electrode bars; low-voltage heavy current is applied to the electrode bars to melt the electrode bars in a highly vacuumized melting chamber through the high temperature produced by the cathode arc of the plasma gun, and to eject the molten metal instantly by the strong centrifugal force produced through the high-speed rotation of the electrode bars to produce fine metal powders. The invention is characterized in that the yield of perfect spherical metal powders is up to 97 percent, and the powders are free from the contamination of any microelement.
Owner:张建利
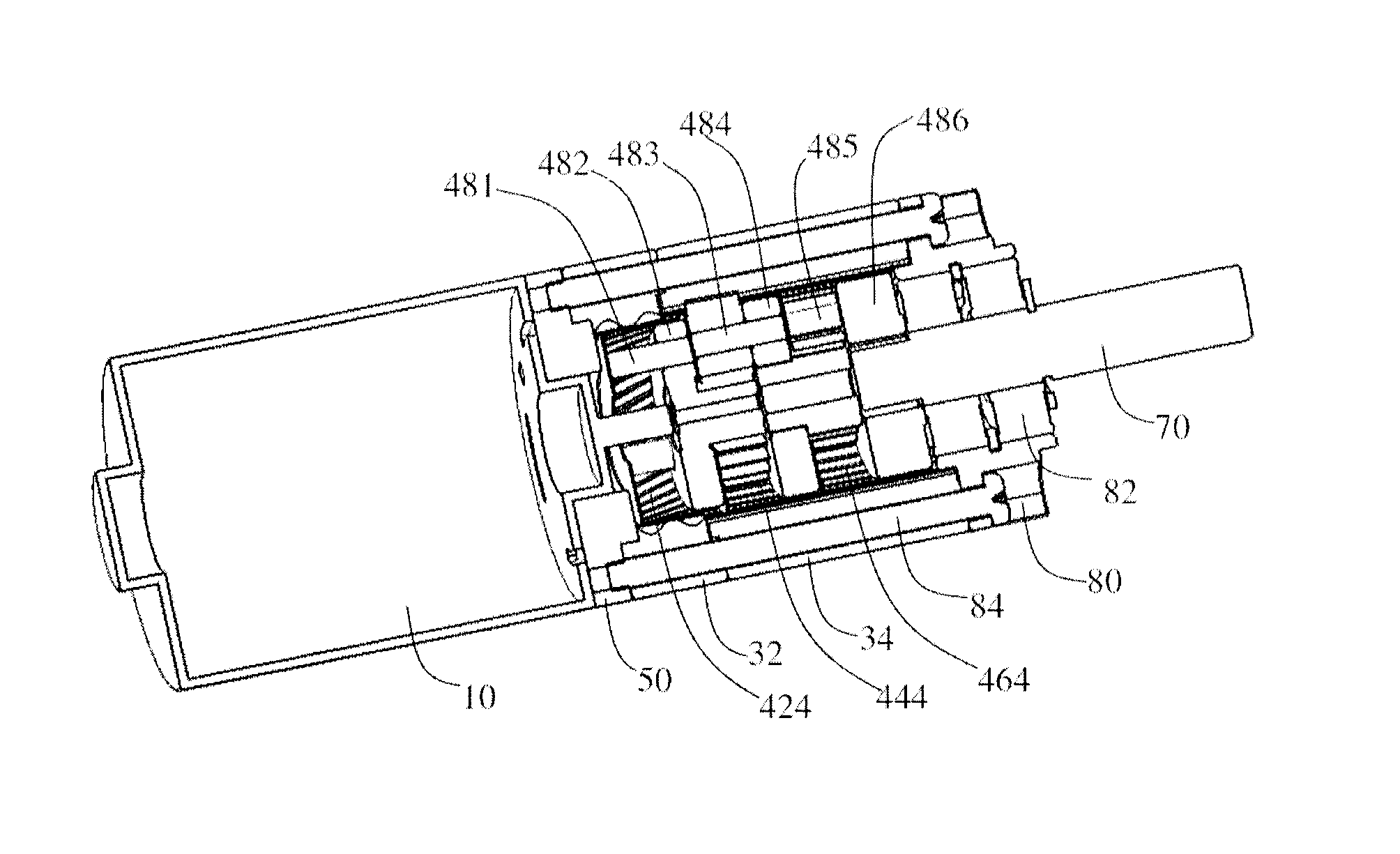
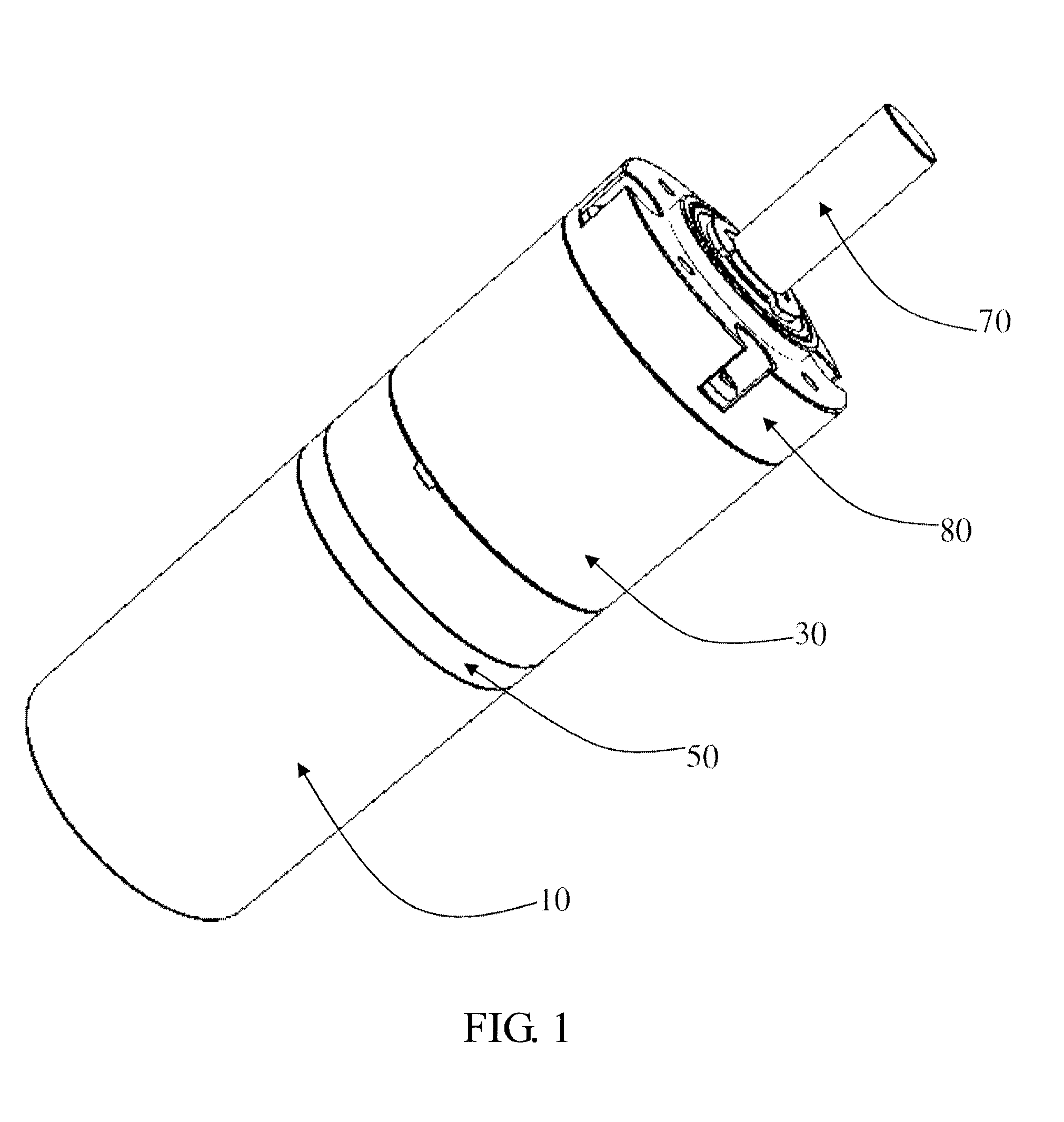
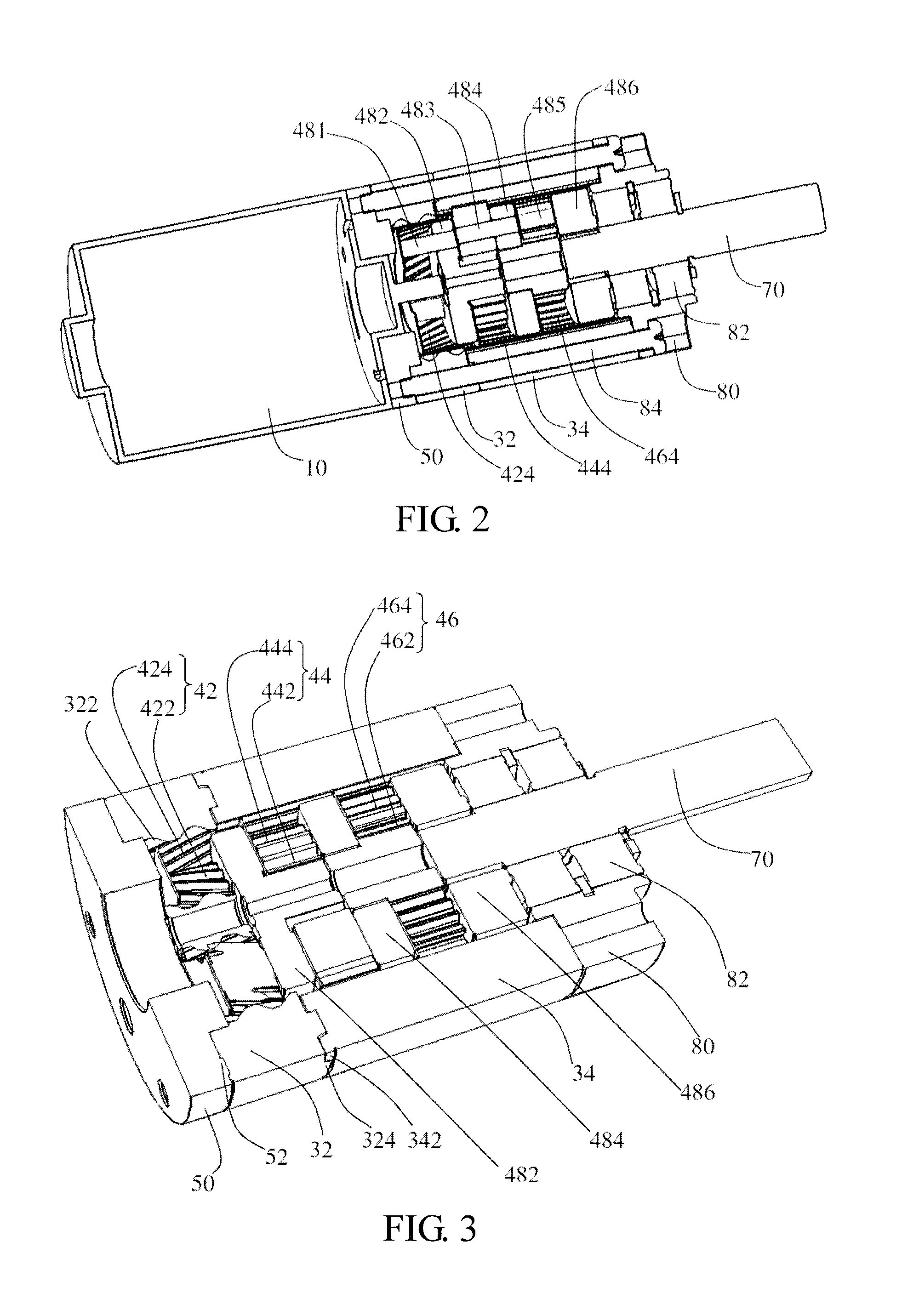
Drive unit
The planetary gear train includes a first sun gear driven by the motor, a first ring gear, a first carrier, and a plurality of first planetary gears arranged at one side of the first carrier and meshing with the first sun gear and the first ring gear. The first sun gear, first planetary gears and first ring gear are helical gears so that meshing surface is increased. Helical teeth formed on an inner surface of the first ring gear mesh with the helical teeth of the first planetary gears. Therefore, the operation is stable and the noise is low. The planetary gears are made of plastic to further decrease the noise. The first ring gear is made by sintered powder metallurgy.
Owner:JOHNSON ELECTRIC SA
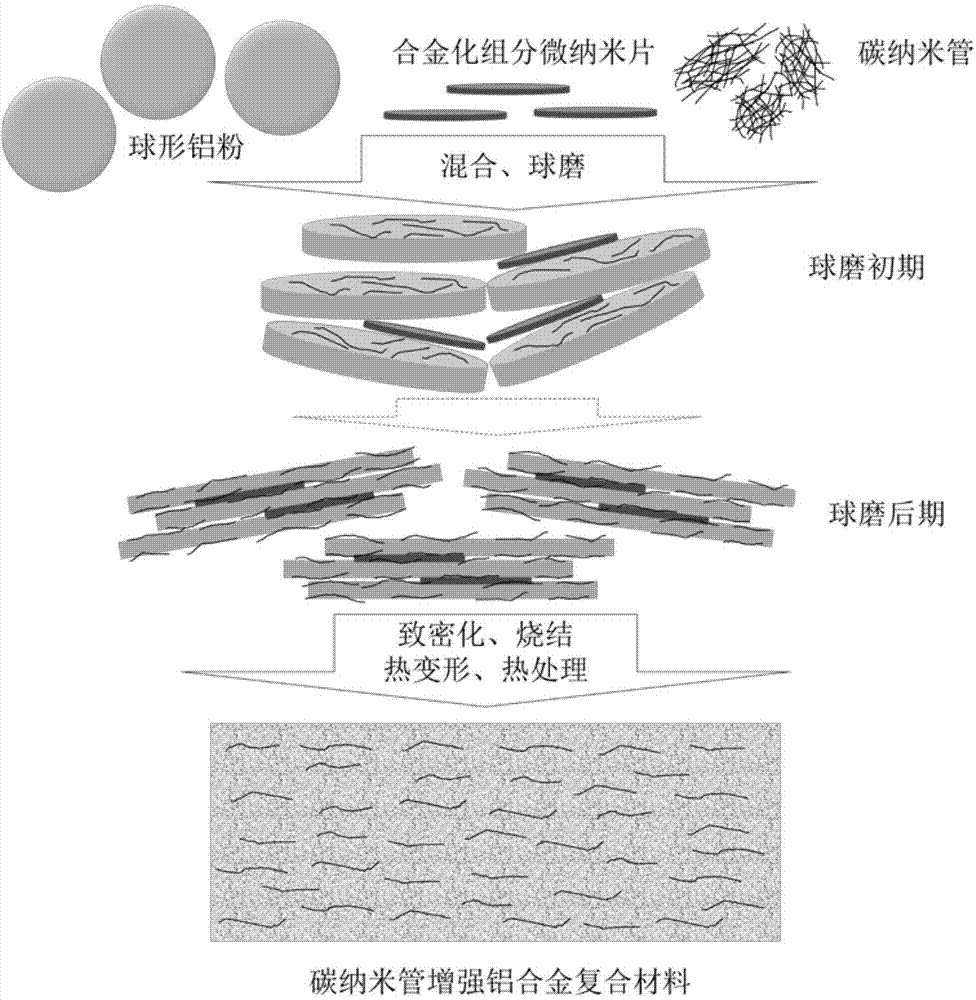
Powder metallurgy preparation method of carbon nanotube reinforced aluminum alloy composite material
ActiveCN103789564ARapid precipitation strengtheningReliable and efficient processMicro nanoThermal deformation
The invention provides a powder metallurgy preparation method of a carbon nanotube reinforced aluminum alloy composite material. The method comprises the following steps: pre-preparing micro-nano flake powder of an alloying component, subsequently ball-milling the powder with a carbon nanotube and spherical pure aluminum powder to prepare flake composite powder, and further performing densifying, sintering, thermal deformation processing and thermal treatment to achieve alloying so as to finally obtain the carbon nanotube reinforced aluminum alloy composite material. Uniform compounding of the matrix aluminum powder, the carbon nanotube and the alloying component can be achieved through limited ball-milling, and meanwhile dangerous elements or uneasy grinding elements such as magnesium and silicon which are high in activity and likely to combust and explode are avoided by adopting the stable and easily ground pre-alloying aluminum powder, so that the security and the reliability are improved; in addition, because of large interlayer boundary and small layer thickness distance, the flake structure is beneficial for uniformly dispersing the alloying component and forming refined dispersed separated phase. The method is beneficial for bringing the effects of composite reinforcement of carbon nanotubes and alloy reinforcement into play to the maximum extent, is energy-saving and time-saving, and is safe and feasible.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Ceramic material with amorphous/nanocrystalline structure and method of producing the same
The invention aims at disclosing a ceramics material with an amorphous / nanocrystalline structure and a preparation method thereof. The method solves the problems that in the existing preparation process of ceramics composite material, the sintering temperature is high, the sintering time is long and the performance of the product is weak. The ceramics material of the invention is manufactured by subjecting a main phase ceramics powder and an additive phase ceramics powder to powder metallurgy technique. The method has the following steps: 1. the raw material of ceramics powder is granulated into ceramics composite powder; 2. heat treatment is carried out on the ceramics composite powder; 3. after the heat treatment, shaping and heat insulation sintering are carried out on the obtained composite powder, thus finally obtaining the ceramics material. In the invention, the sintering temperature in the preparation process of ceramics materials is lowered, the sintering time is shortened, and in particular, the internal arrangement of the amorphous / nanocrystalline structure in the ceramics materials improves strength, toughness, hardness of the ceramics materials of the ceramics materials, enhances high temperature resistance, wear resistance, corrosion resistance and chemical stability thereof.
Owner:哈尔滨霈泽材料科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com