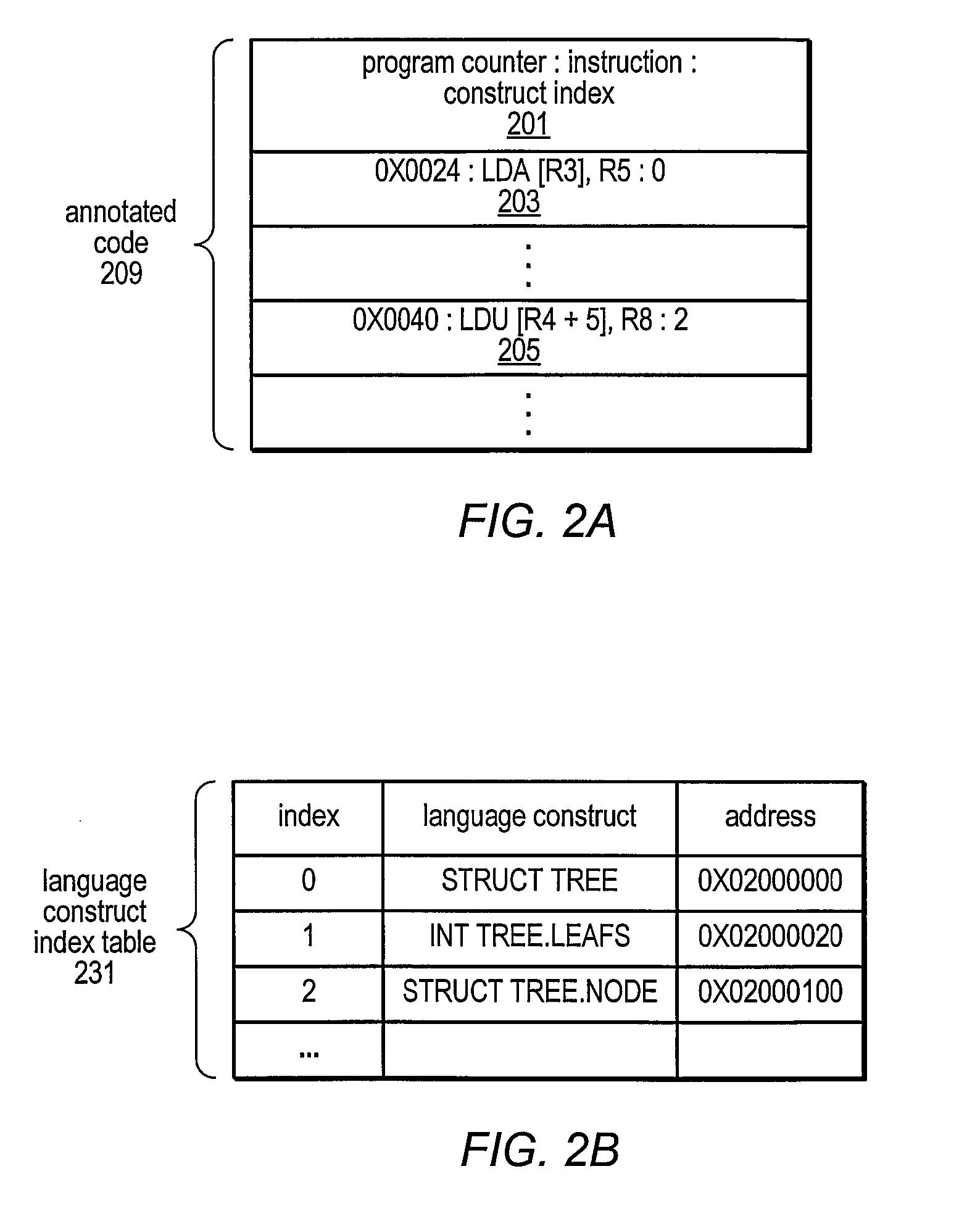
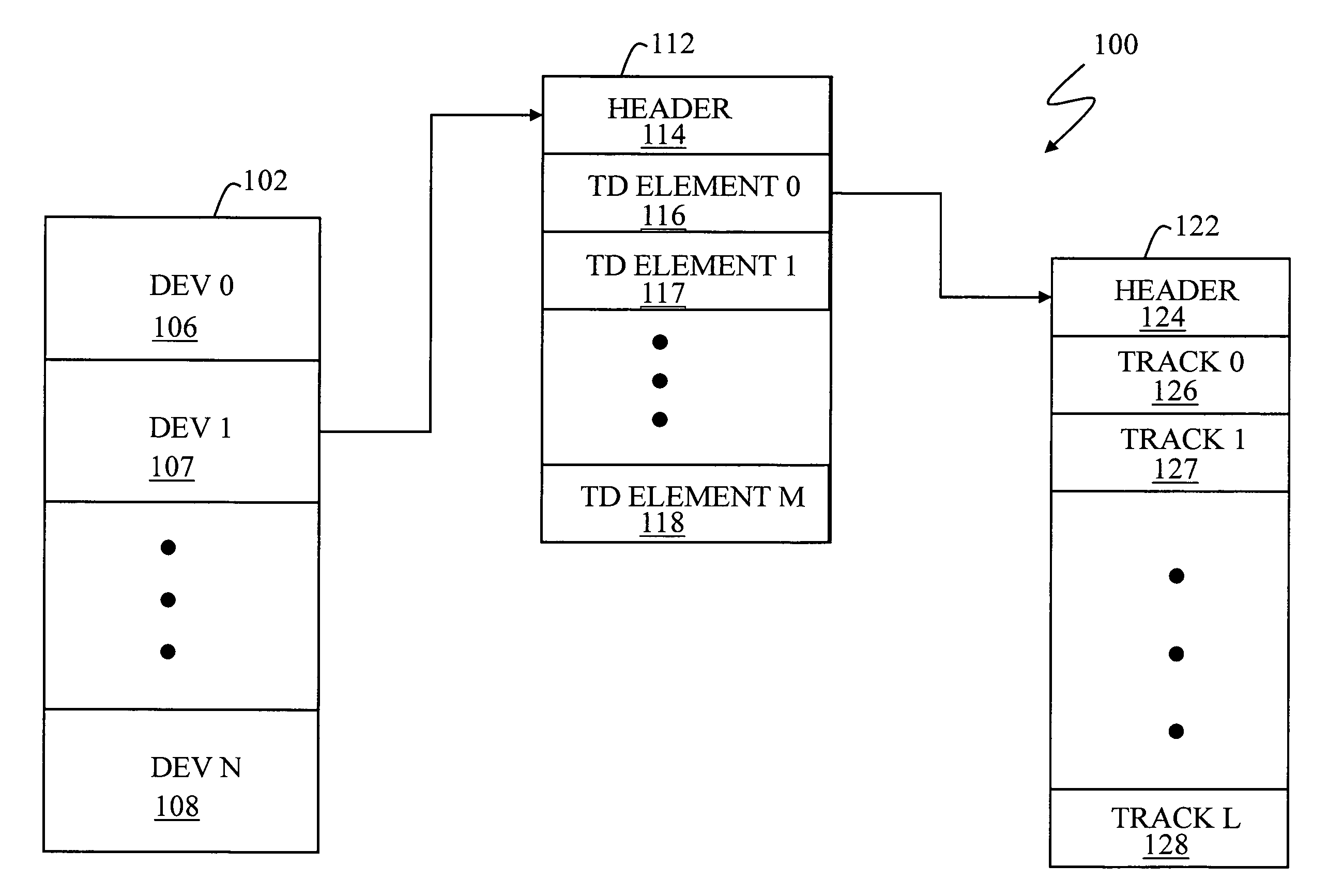
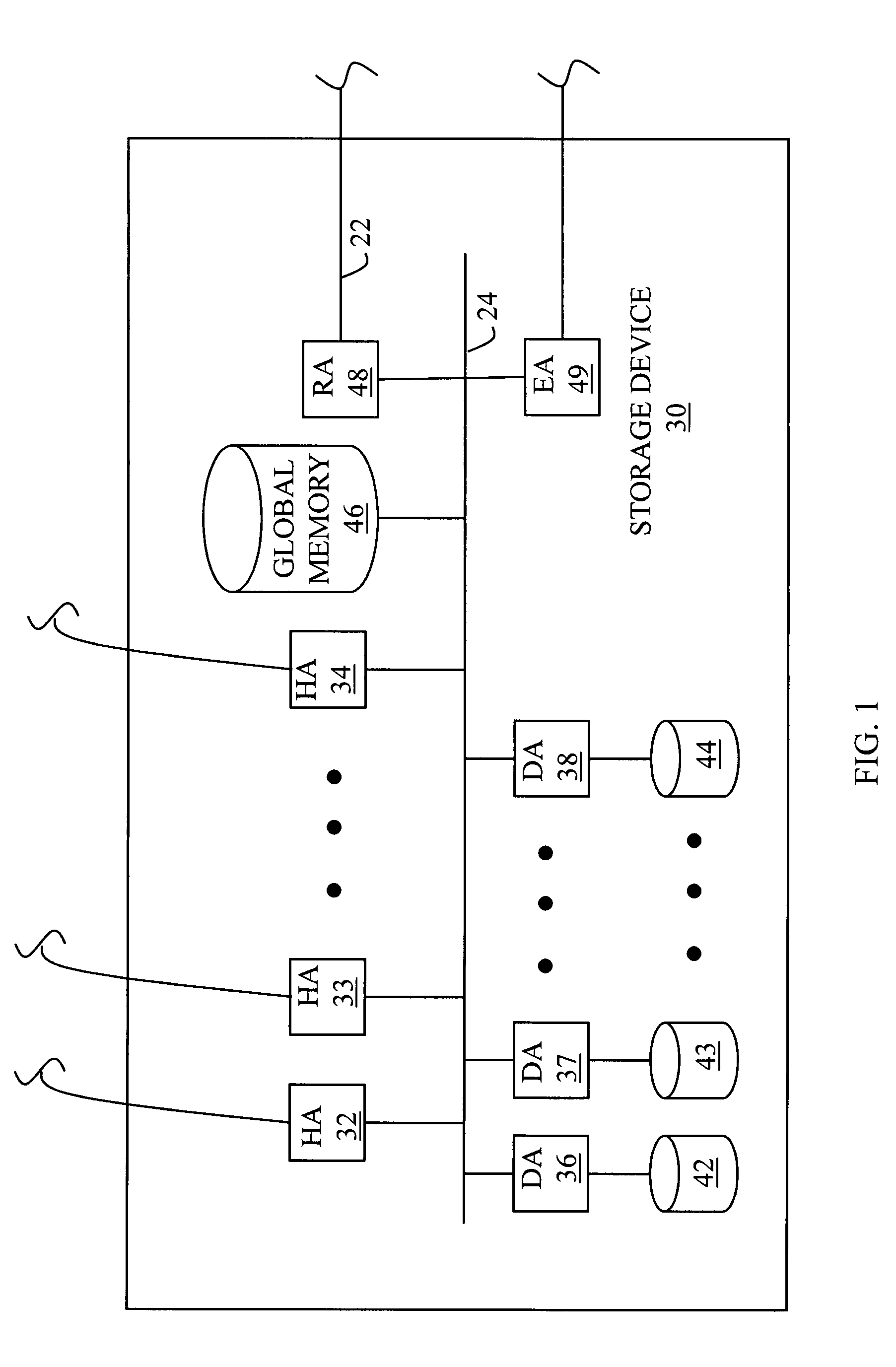
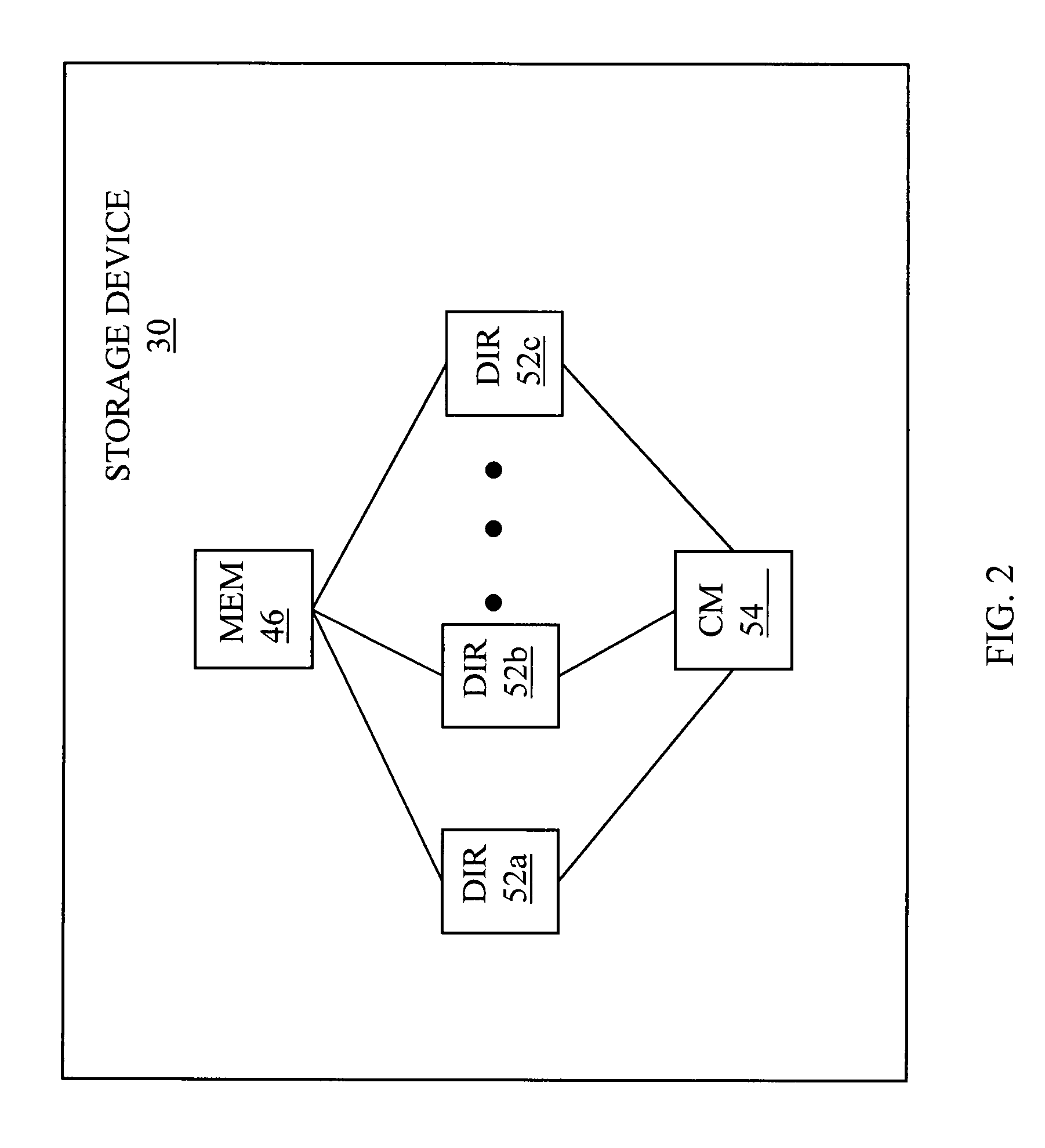
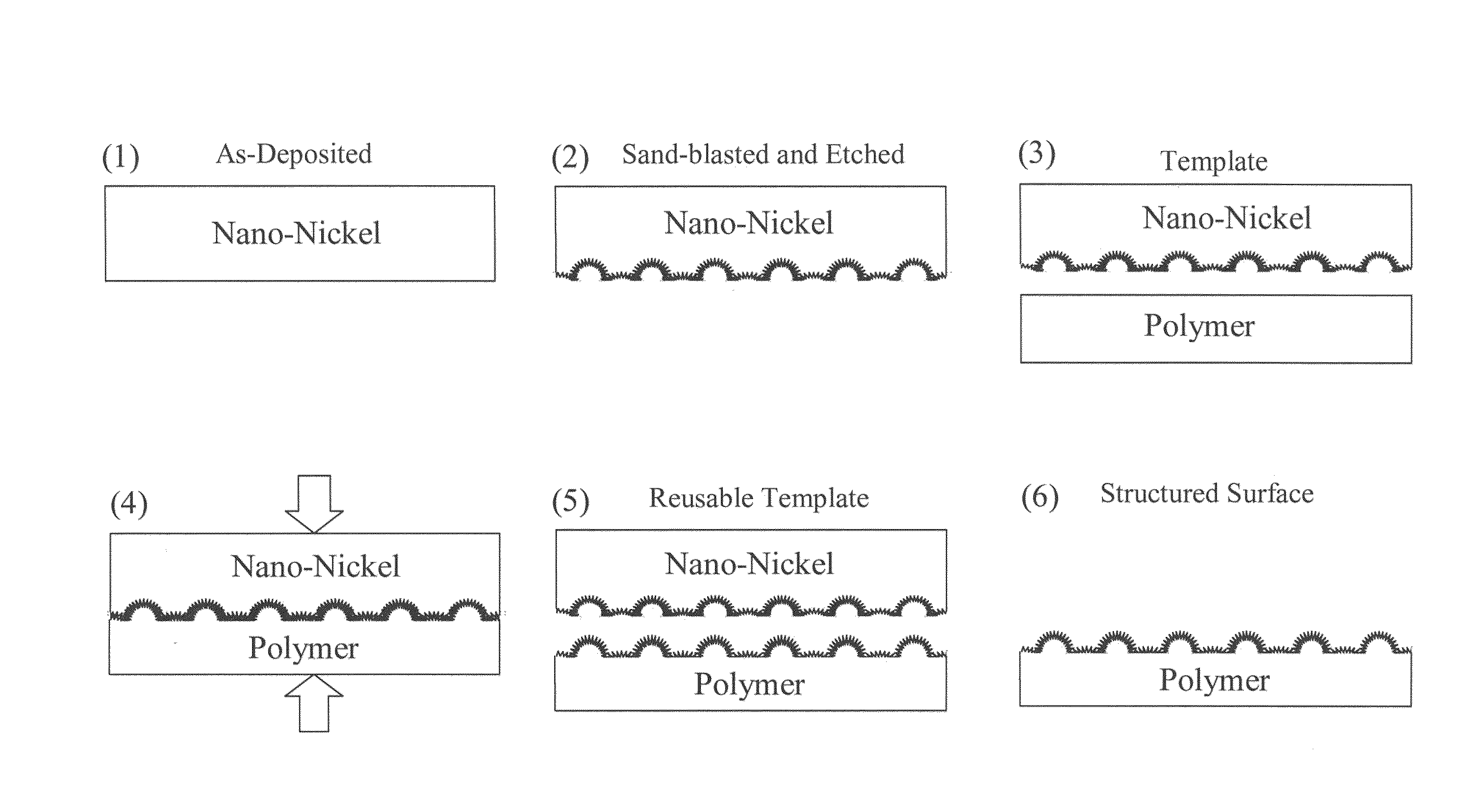
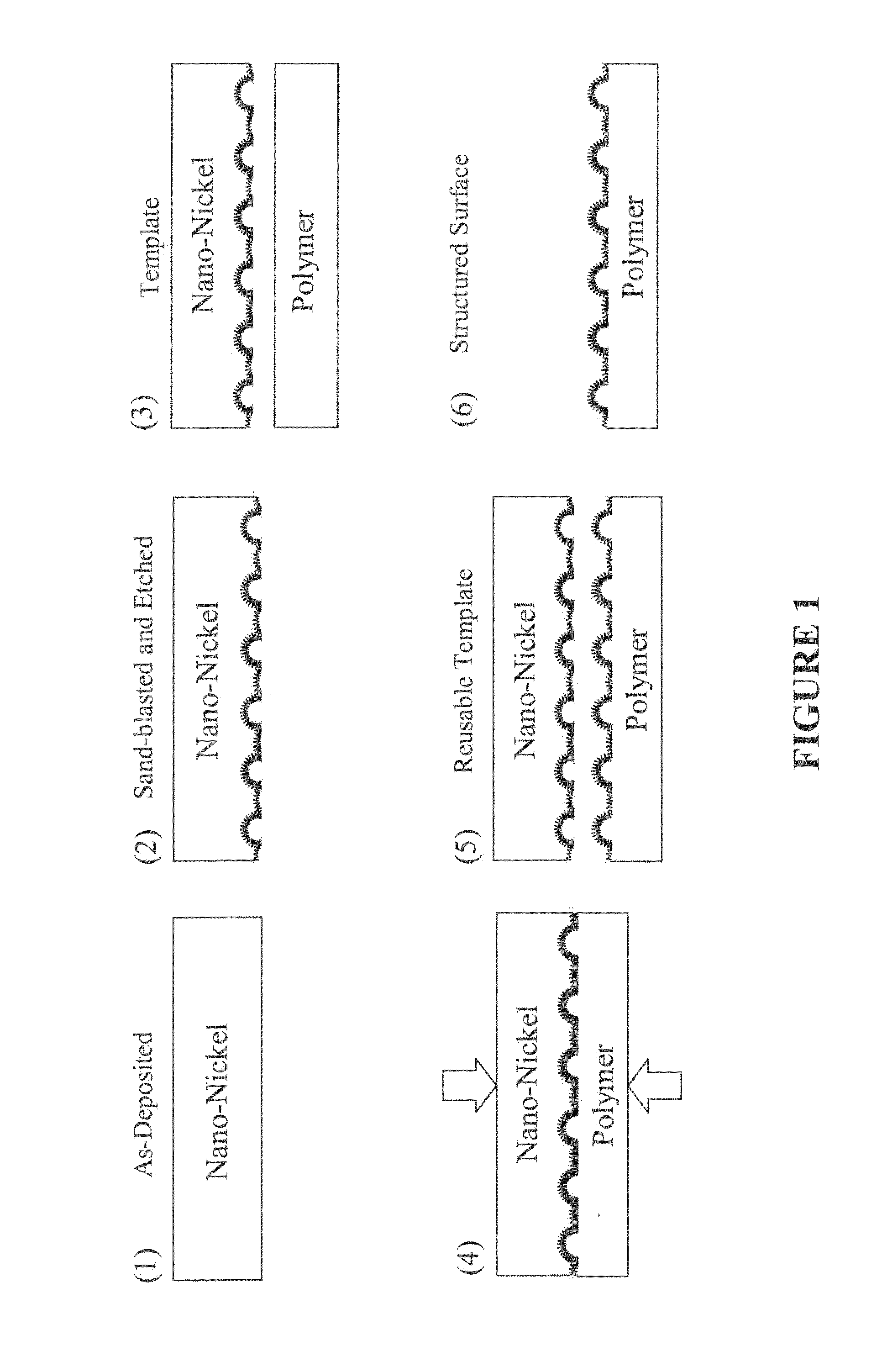
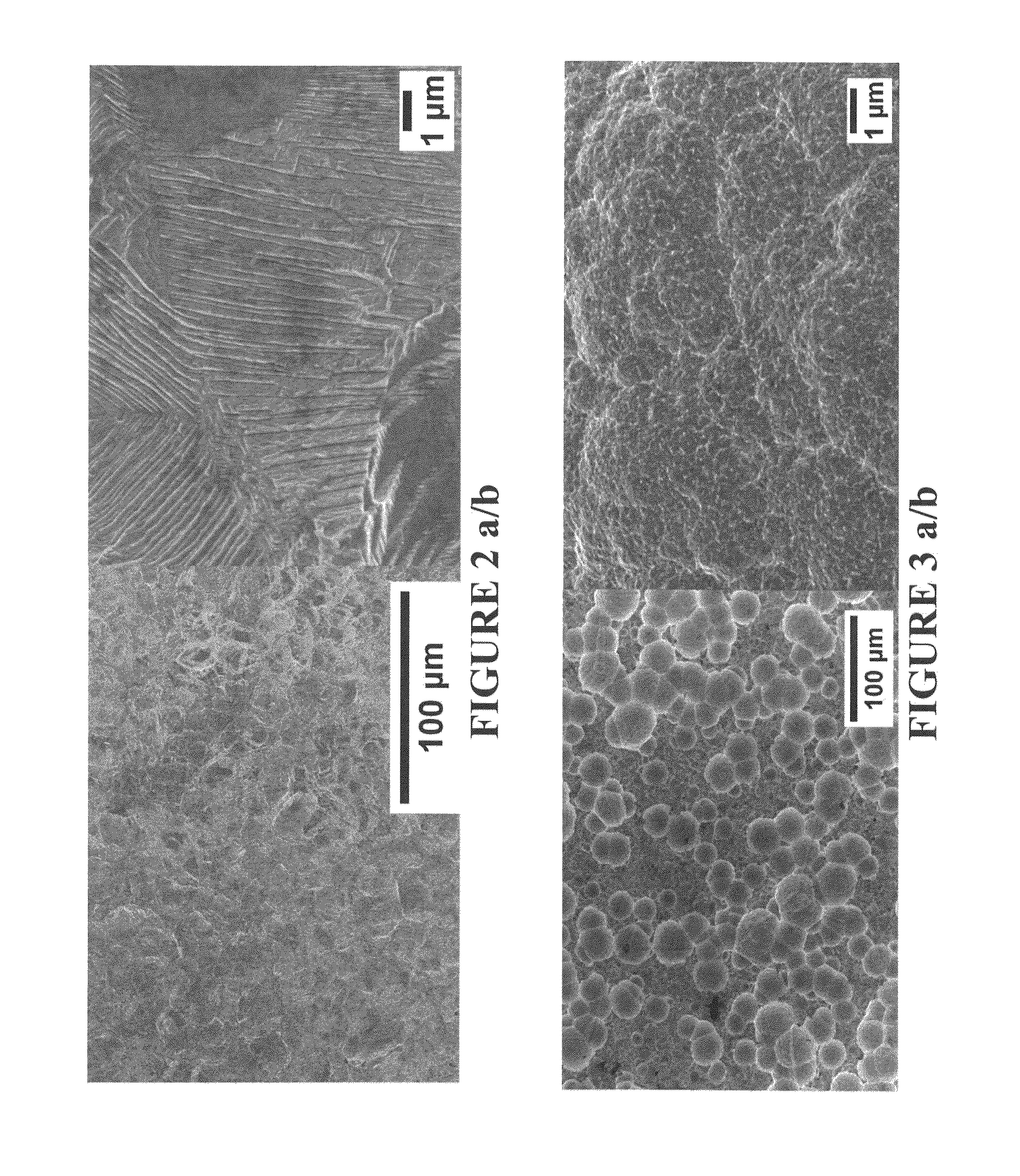
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4803 results about "Fine grain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fine grain refers to the types of wood that have very small, tight lines in the wood. It may also be referred to as a smooth grain. Fine grain woods have natural lines in the wood that are small and very close together.
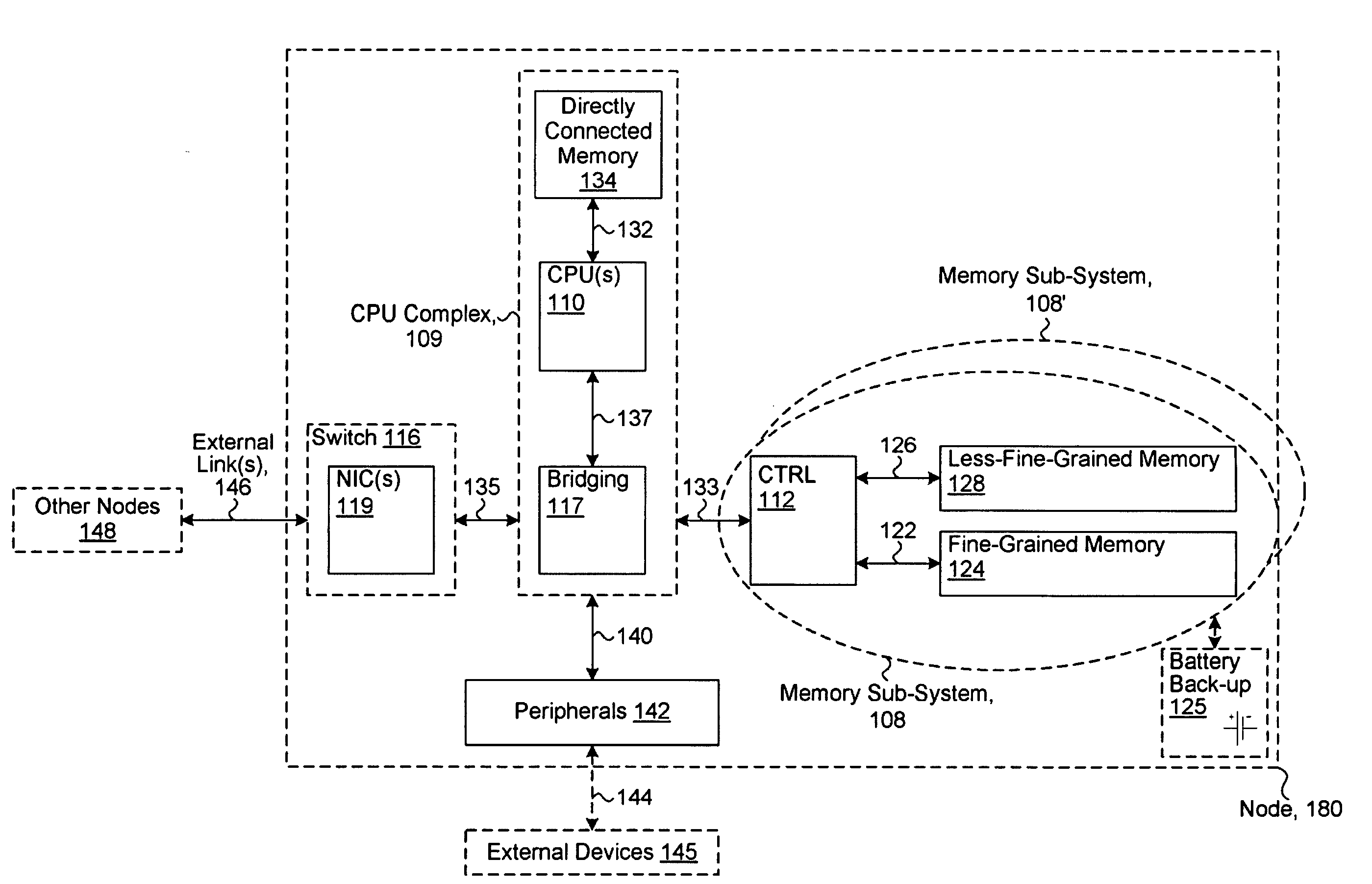
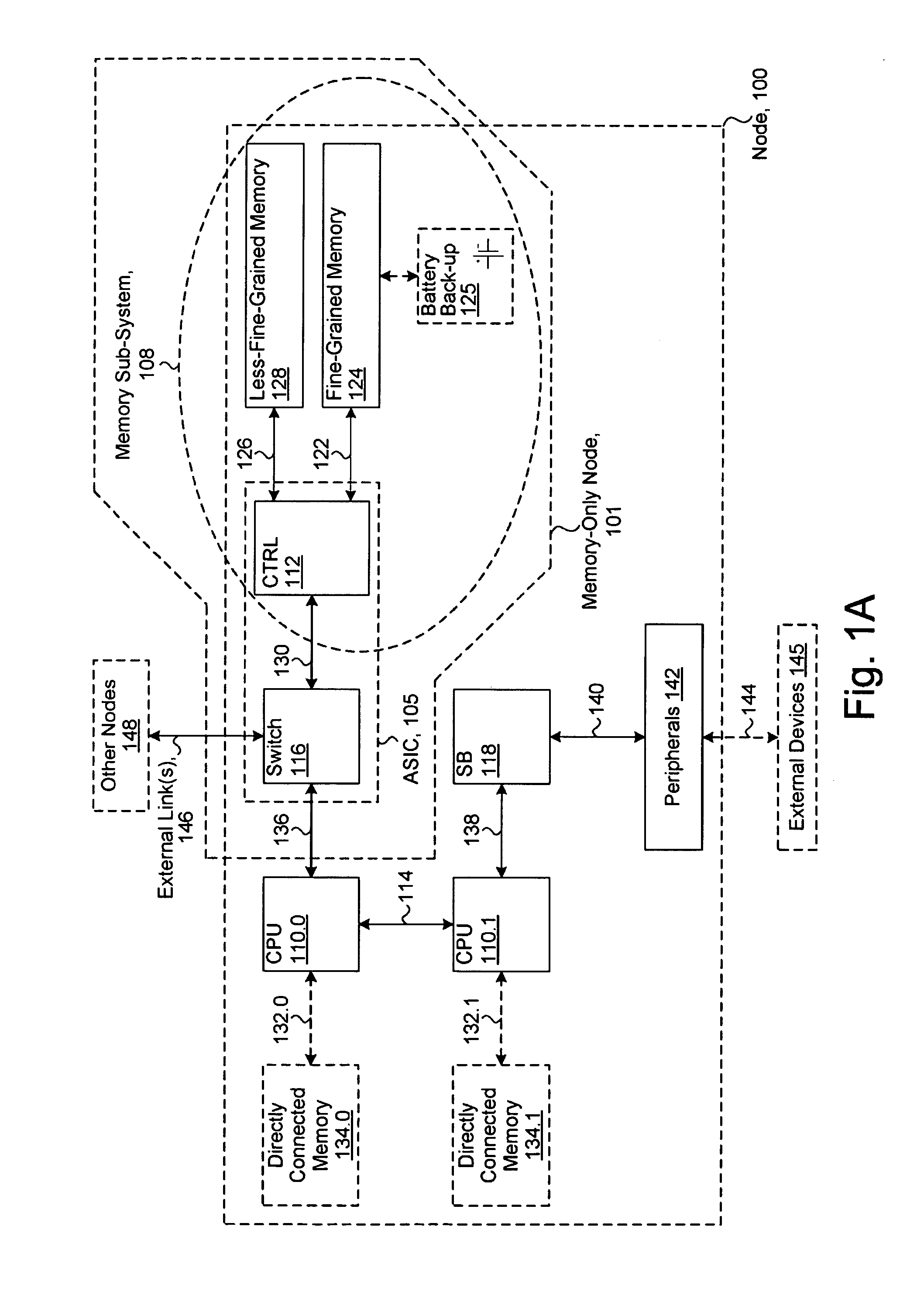
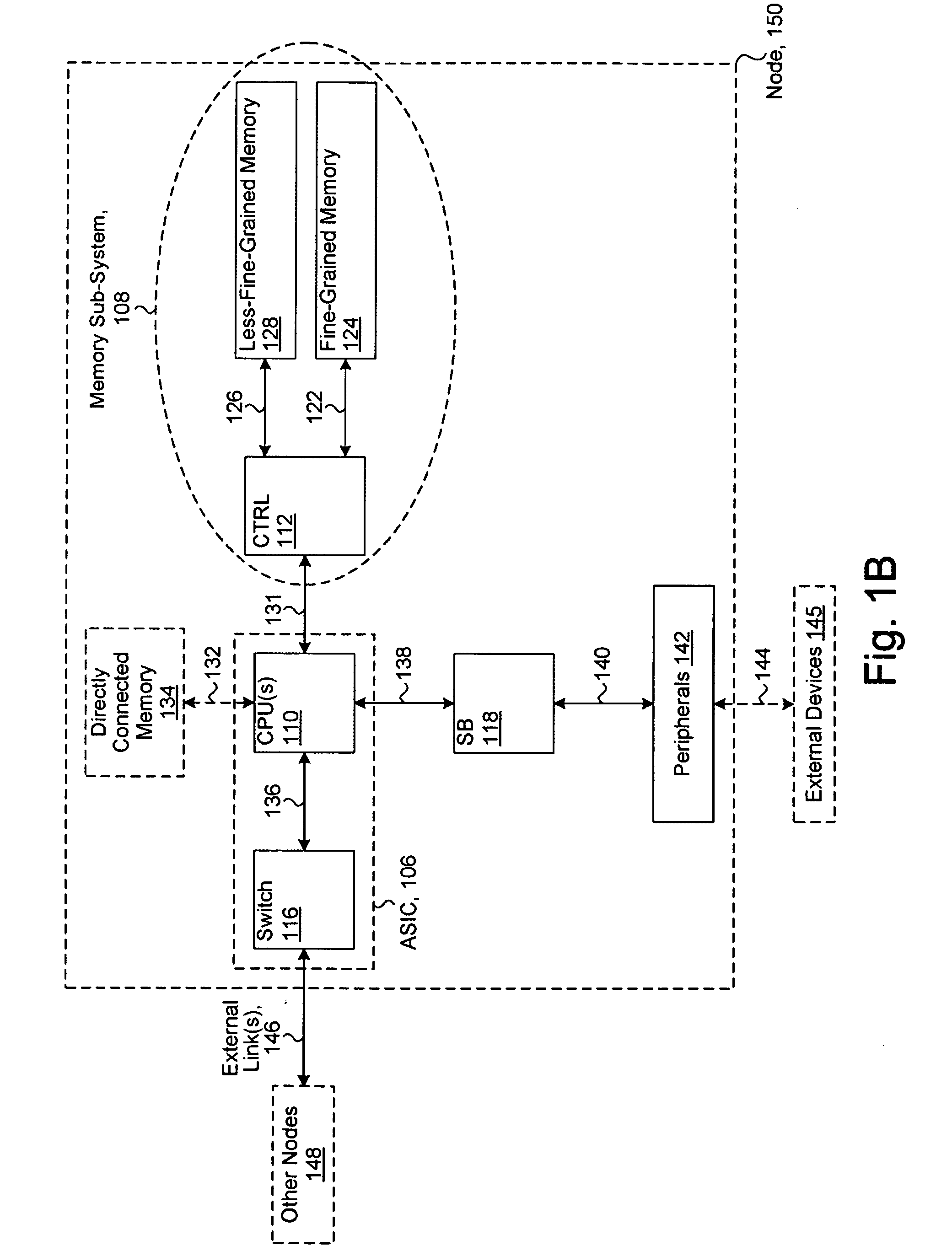
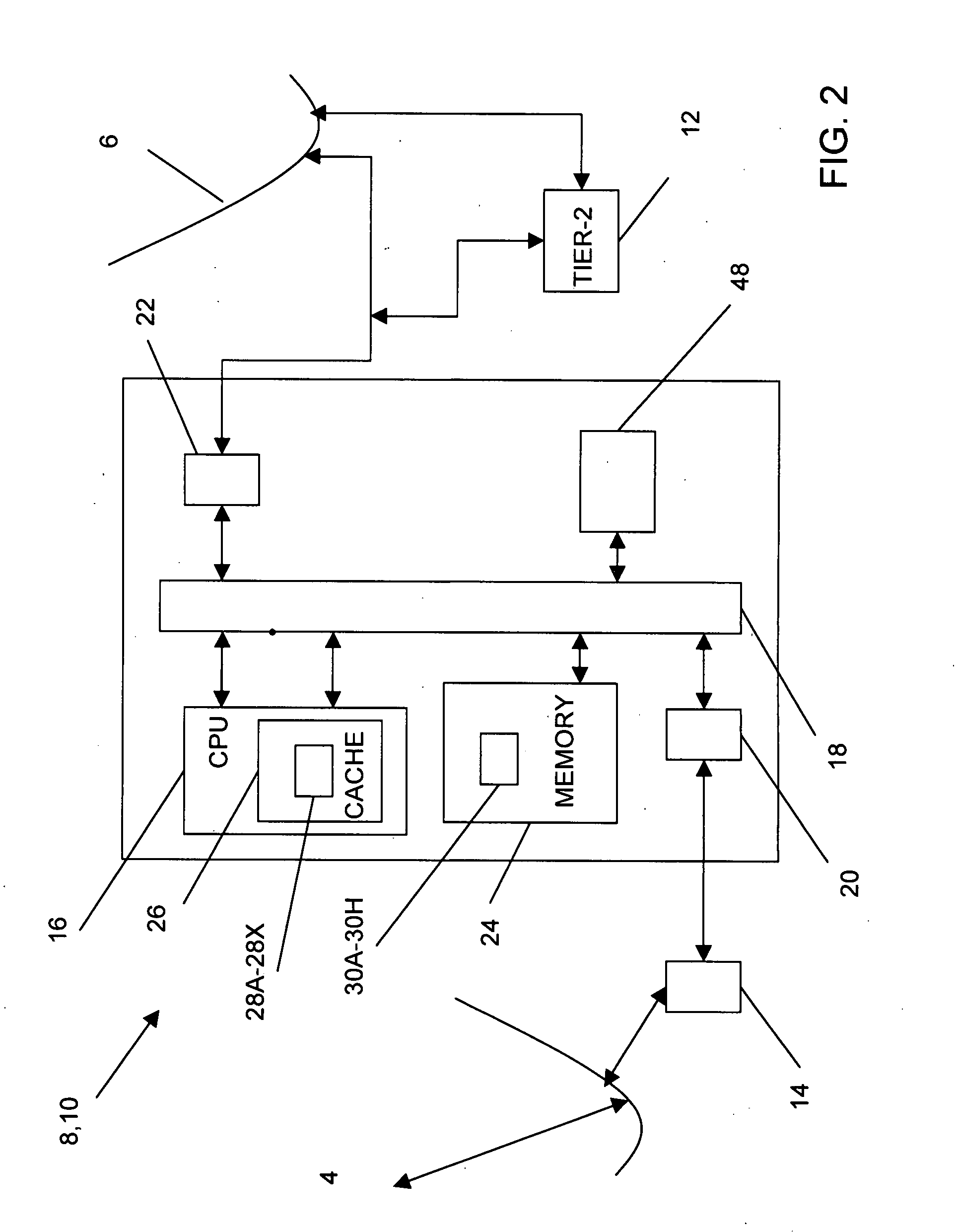
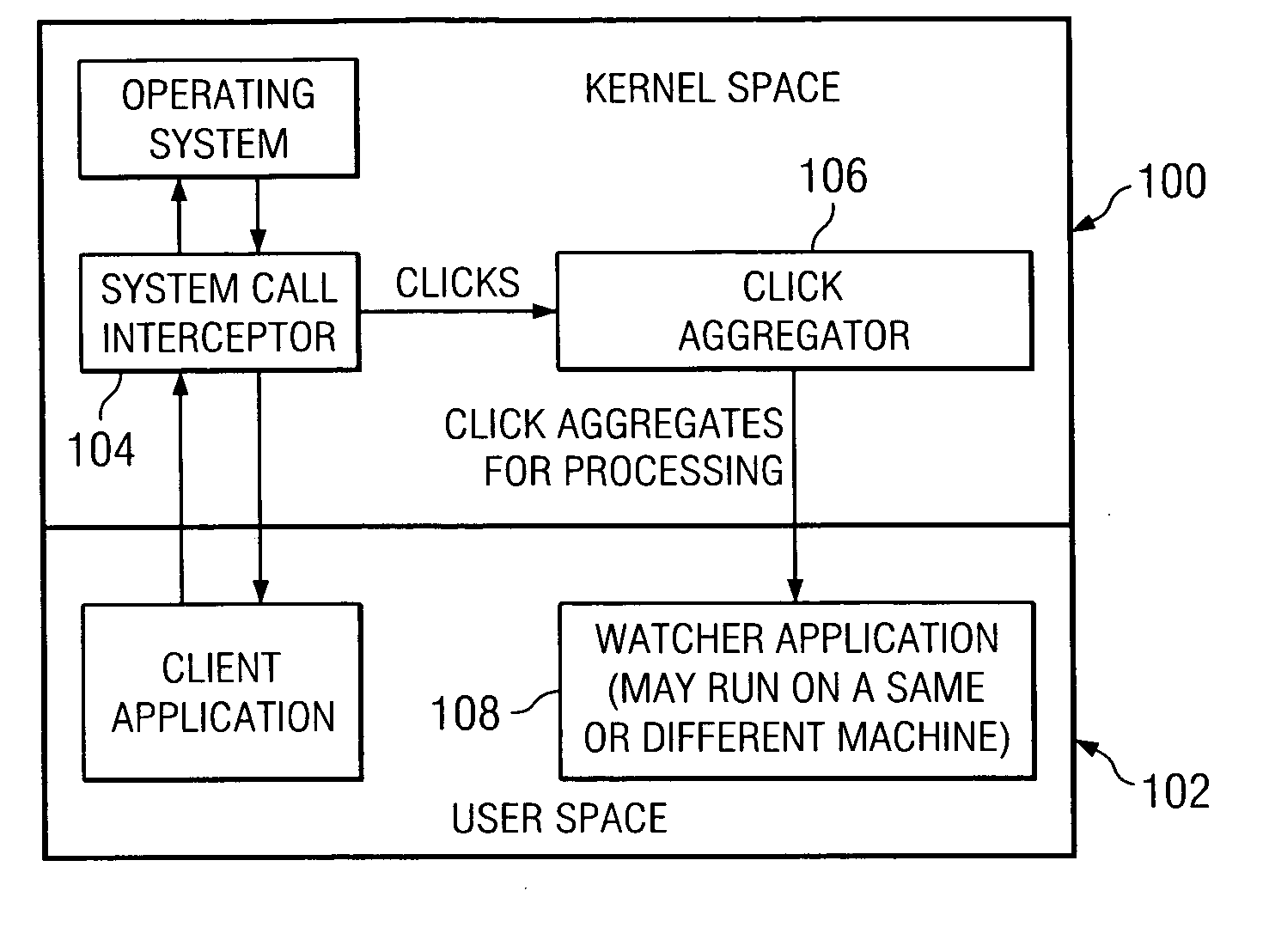
System including a fine-grained memory and a less-fine-grained memory
ActiveUS20080301256A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTData processing systemWrite buffer
A data processing system includes one or more nodes, each node including a memory sub-system. The sub-system includes a fine-grained, memory, and a less-fine-grained (e.g., page-based) memory. The fine-grained memory optionally serves as a cache and / or as a write buffer for the page-based memory. Software executing on the system uses n node address space which enables access to the page-based memories of all nodes. Each node optionally provides ACID memory properties for at least a portion of the space. In at least a portion of the space, memory elements are mapped to locations in the page-based memory. In various embodiments, some of the elements are compressed, the compressed elements are packed into pages, the pages are written into available locations in the page-based memory, and a map maintains an association between the some of the elements and the locations.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
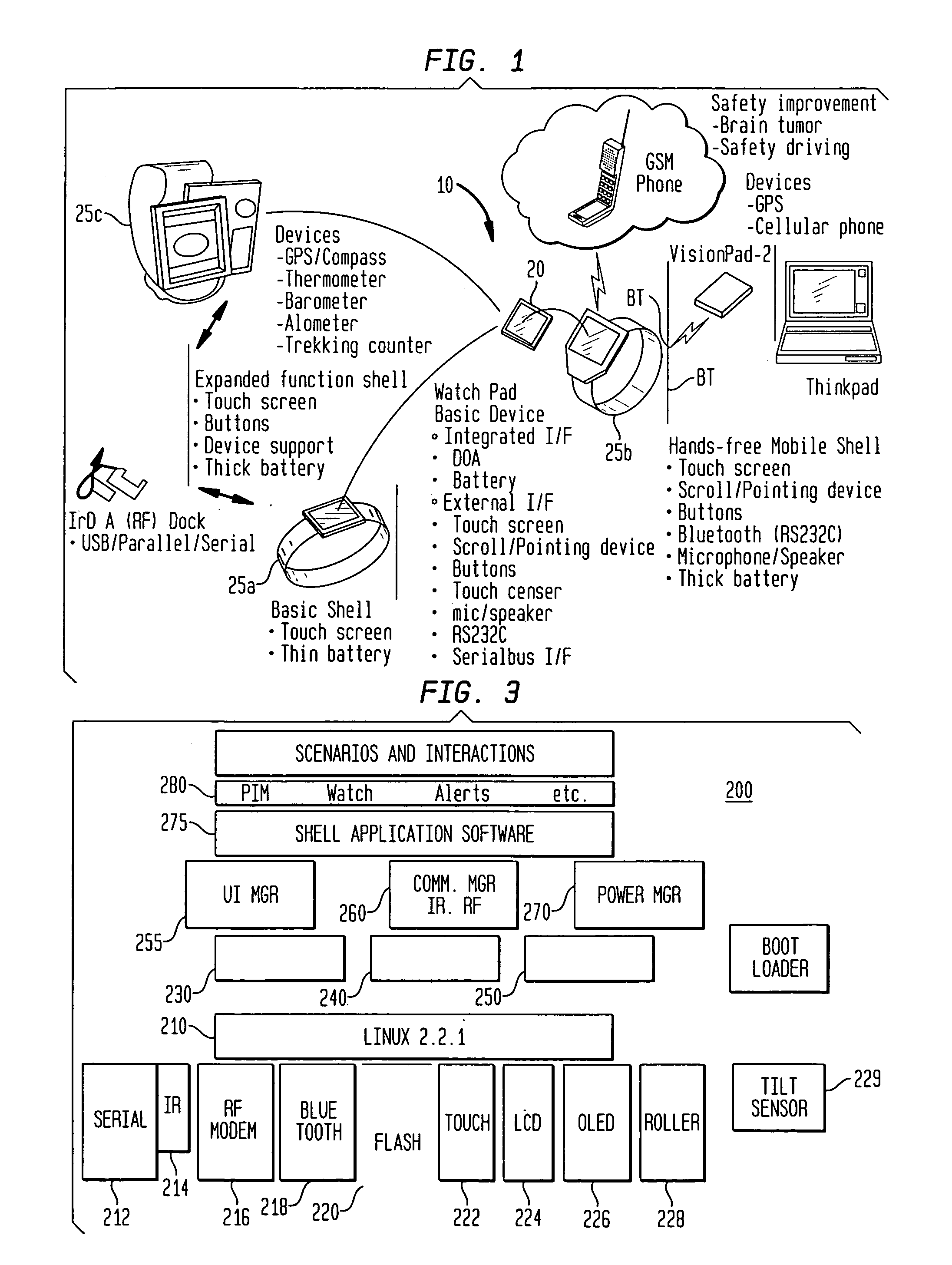
Method and apparatus for dynamically controlling scroller speed employed for a user interface of a wearable appliance
InactiveUS7081905B1Amount of user manipulation of the scroller to get to a particular positionElectric indicationFrequency stabilisation mechanismDisplay deviceHuman–computer interaction
A wearable mobile computing device / appliance (e.g., a wrist watch) with a high resolution display that is capable of wirelessly accessing information from the network and a variety of other devices. The Wrist Watch device / appliance includes a user interface that is used to efficiently interact with alarms, time keeping functions and notifications on the watch via use of a scroll device implementing dynamic scroll speed controller capability which enables seamless fine-grain and coarse-grain scroll and / or cursor movement through displayed content without notice to the user of the scroll device.
Owner:IBM CORP
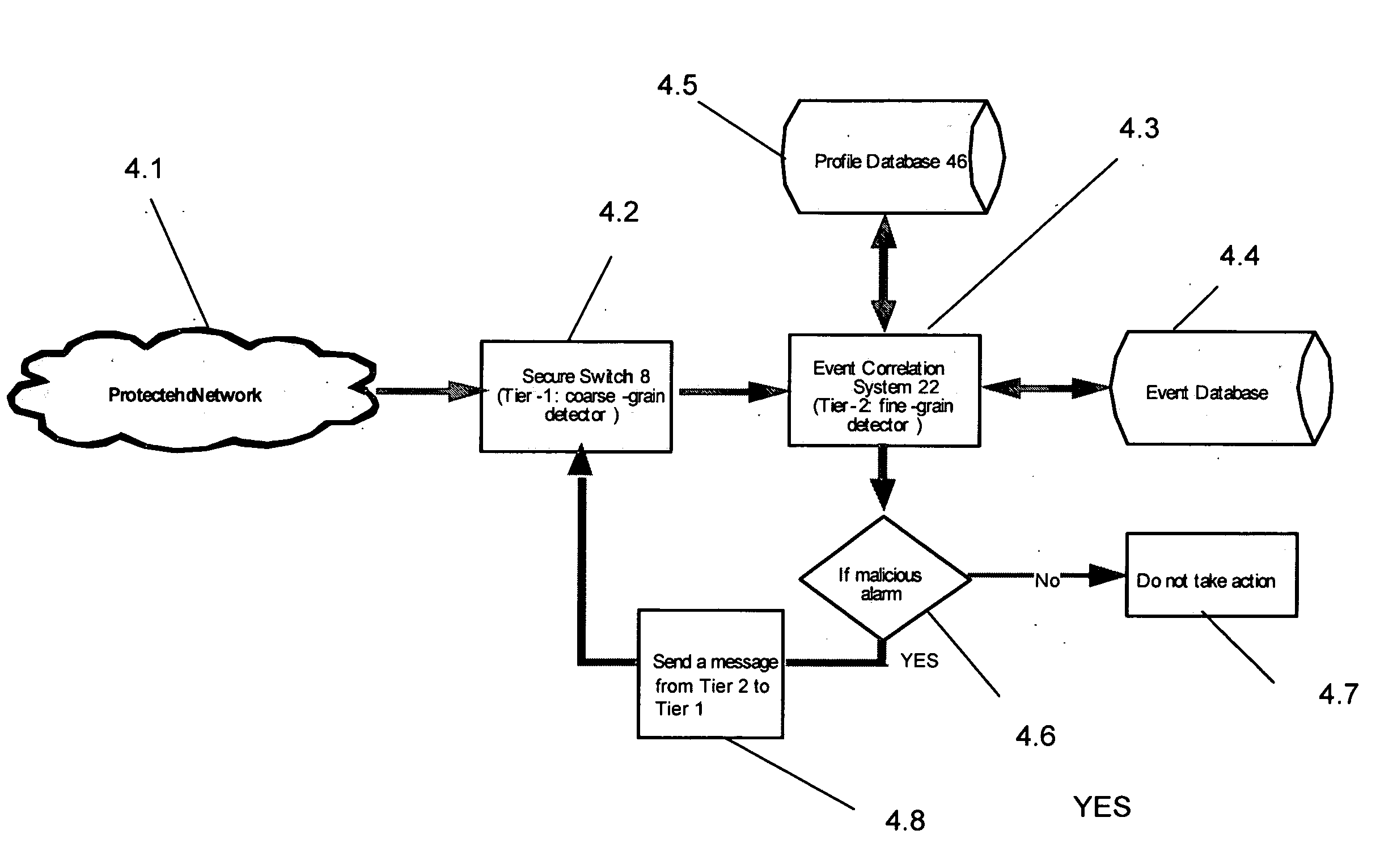
Method, system and computer-readable media for reducing undesired intrusion alarms in electronic communications systems and networks
InactiveUS20080295172A1Reduce probabilityHigh speed detectionMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionCommunications systemElectronic communication
A method, system and computer-readable media that enable the employment of an intrusion detection process are provided. This present invention is able to differentiate between certain malicious and benign incidents by means of a two-stage anomaly-based intrusion detection and prevention system. The invented system works at high-speed and with low-memory resources requirements. In particular, the invented method is implemented in a two-stage detector that performs coarse grain detection using sub-profiles 30A-30H (key features extracted from a profile) at one stage and fine grain (detailed behavioral profile) detection at another stage to eliminate unwanted attacks and false positives. Furthermore, in order to suppress specific alarms, the invented system allows the administrator to specify detailed profiles 32A-32H. By using a sub-profile extractor, a sub-profile is extracted, which is then downloaded into the coarse grain detector.
Owner:NEVIS NETWORLS INC
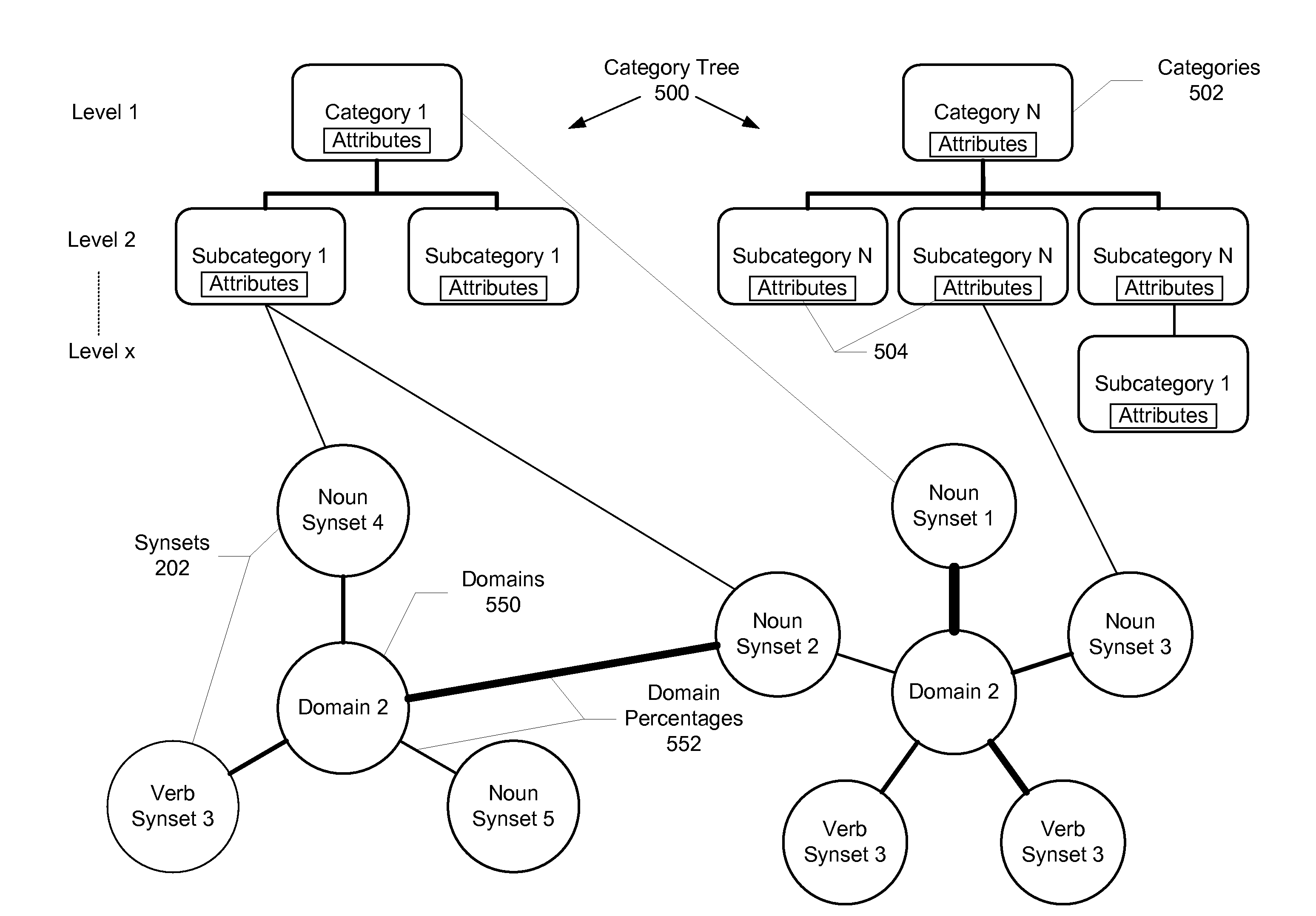
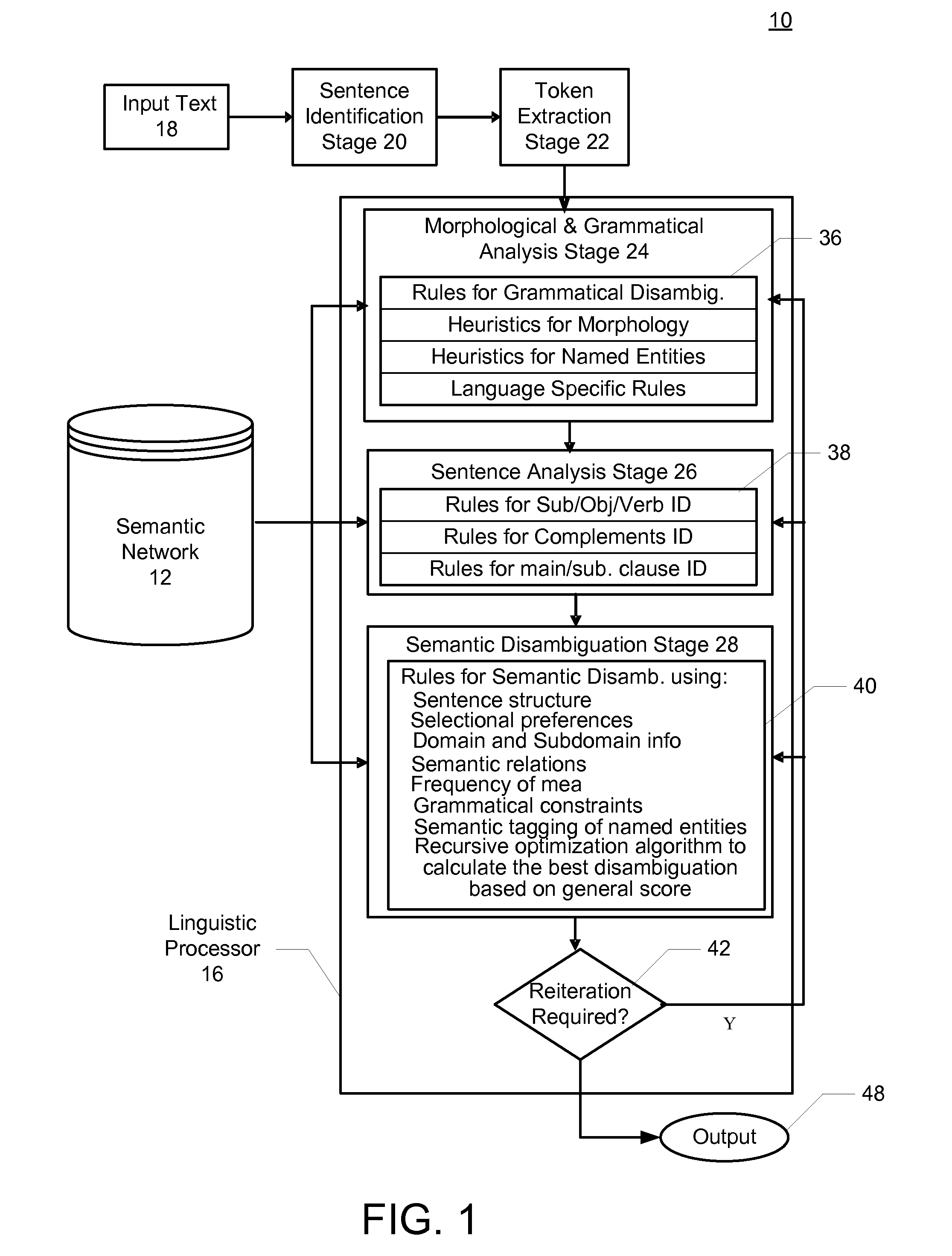
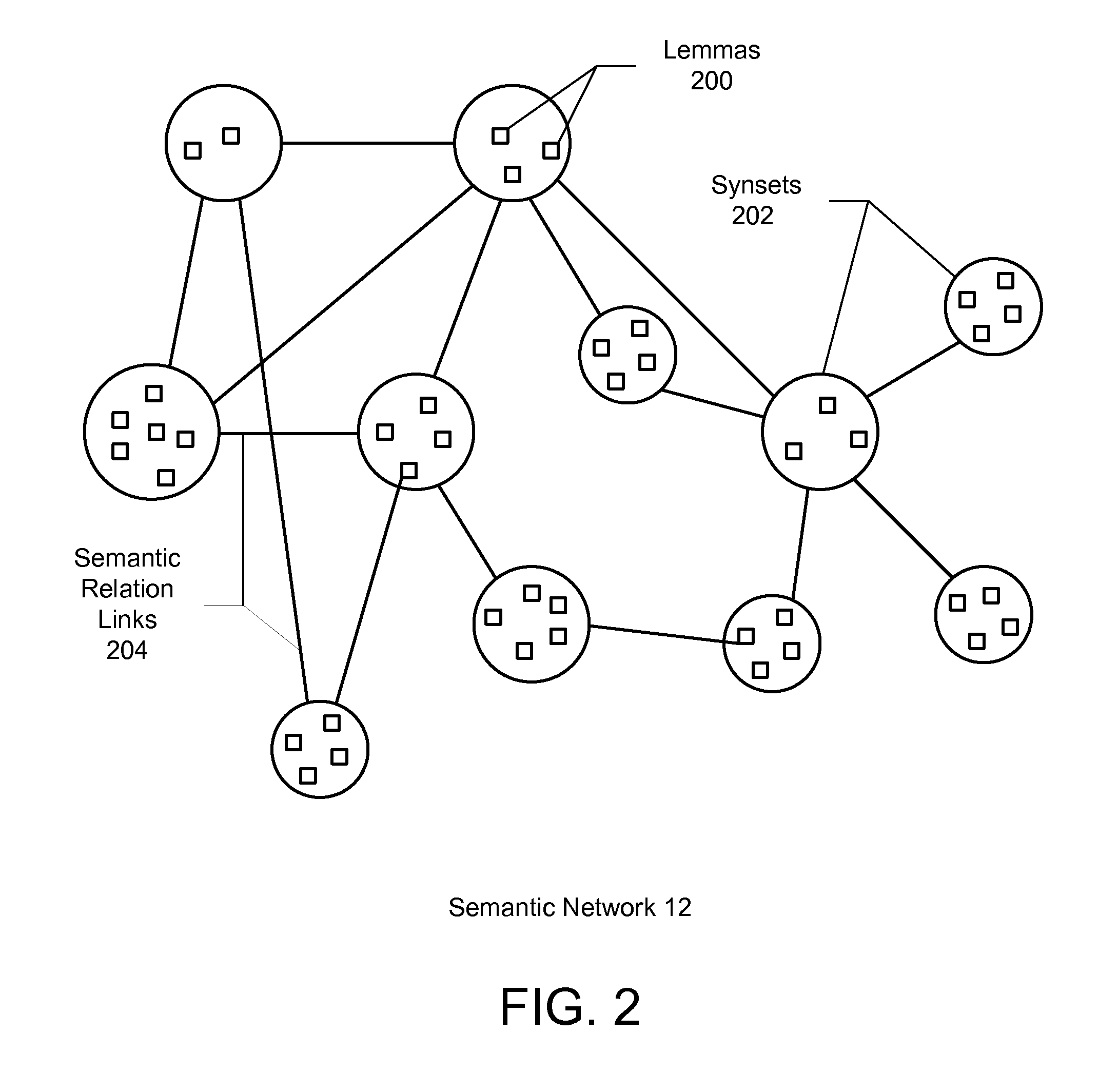
Method and system for automatically extracting relations between concepts included in text
ActiveUS7899666B2Complete understandingSemantic analysisSpecial data processing applicationsSemantic networkHuman language
A method and system for automatically extracting relations between concepts included in electronic text is described. Aspects the exemplary embodiment include a semantic network comprising a plurality of lemmas that are grouped into synsets representing concepts, each of the synsets having a corresponding sense, and a plurality of links connected between the synsets that represent semantic relations between the synsets. The semantic network further includes semantic information comprising at least one of: 1) an expanded set of semantic relation links representing: hierarchical semantic relations, synset / corpus semantic relations verb / subject semantic relations, verb / direct object semantic relations, and fine grain / coarse grain semantic relationship; 2) a hierarchical category tree having a plurality of categories, wherein each of the categories contains a group of one or more synsets and a set of attributes, wherein the set of attributes of each of the categories are associated with each of the synsets in the respective category; and 3) a plurality of domains, wherein one or more of the domains is associated with at least a portion of the synsets, wherein each domain adds information regarding a linguistic context in which the corresponding synset is used in a language. A linguistic engine uses the semantic network to performing semantic disambiguation on the electronic text using one or more of the expanded set of semantic relation links, the hierarchical category tree, and the plurality of domains to assign a respective one of the senses to elements in the electronic text independently from contextual reference.
Owner:EXPERT AI SPA
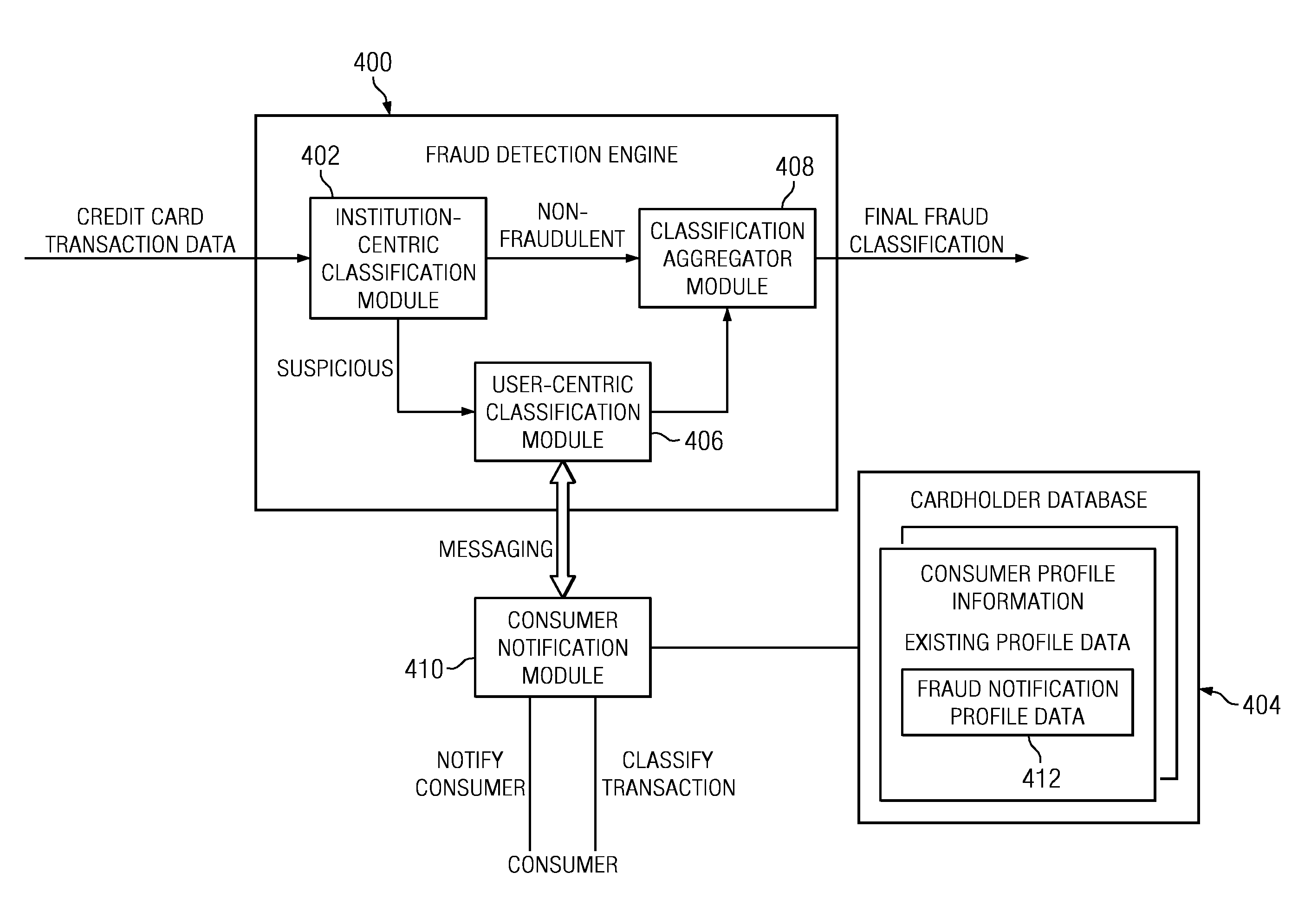
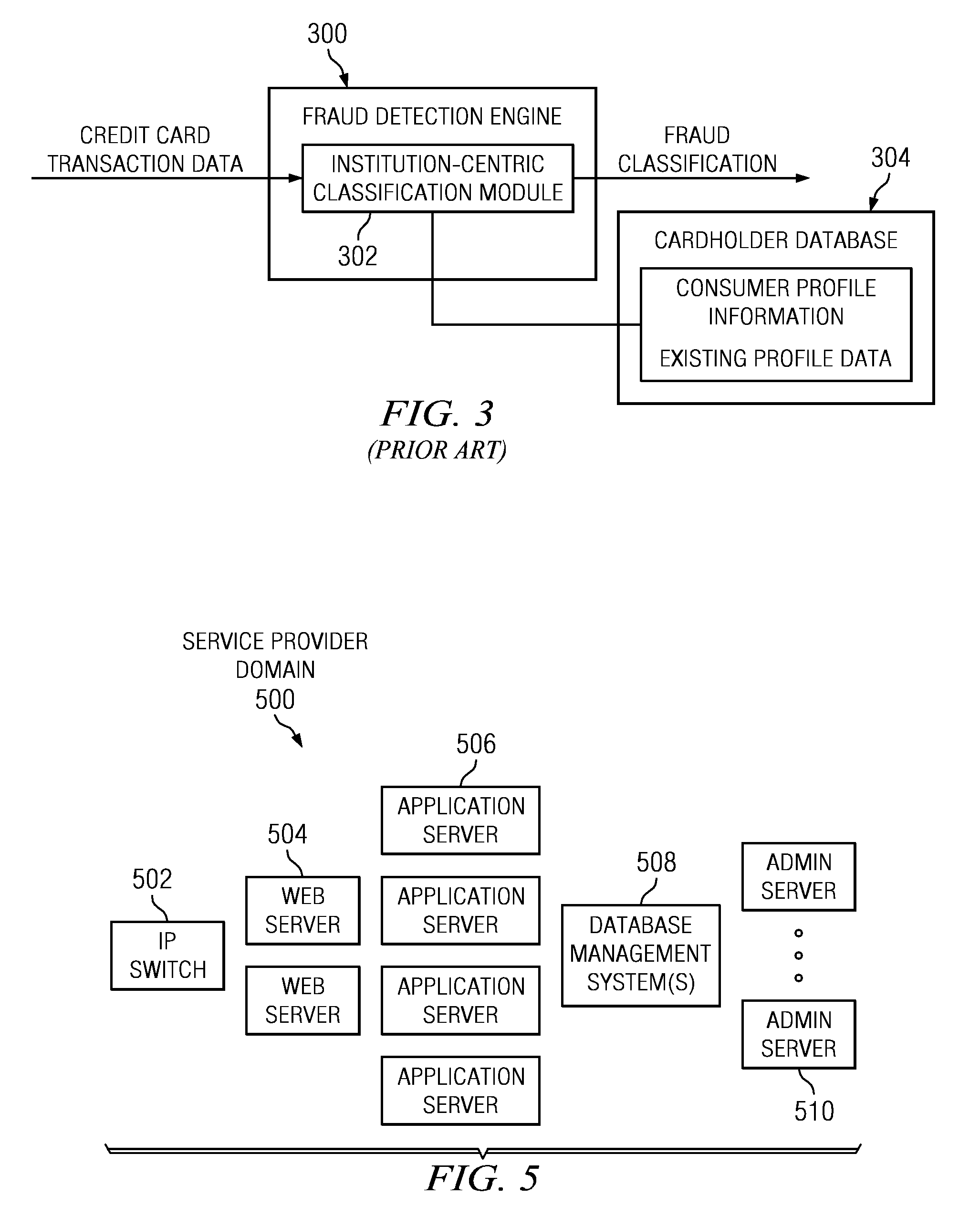
Method and System for Identification By A Cardholder of Credit Card Fraud
A method for fraud detection leverages an existing financial institution's fraud classification functionality, which produces a first level detection, with a “user-centric” classification functionality, which produces a “second” or more fine-grained detection regarding a potentially fraudulent transaction. After passing through an existing (“institution-centric”) fraud detection technique, a transaction that has been identified as potentially fraudulent is then subject to further analysis and classification at the “user” level, as it is the user is presumed to be the best source of knowledge of the legitimate credit card use. Information about the transaction is shared with the consumer, preferably via one or more near real-time mechanisms, such as SMS, email, or the like. Based on the user's response (or lack thereof, as the case may be), one or more business rules in the institution's fraud detection system can then take an appropriate action (e.g., no action, reverse the transaction if complete, deny the transaction if in-progress, or the like).
Owner:IBM CORP
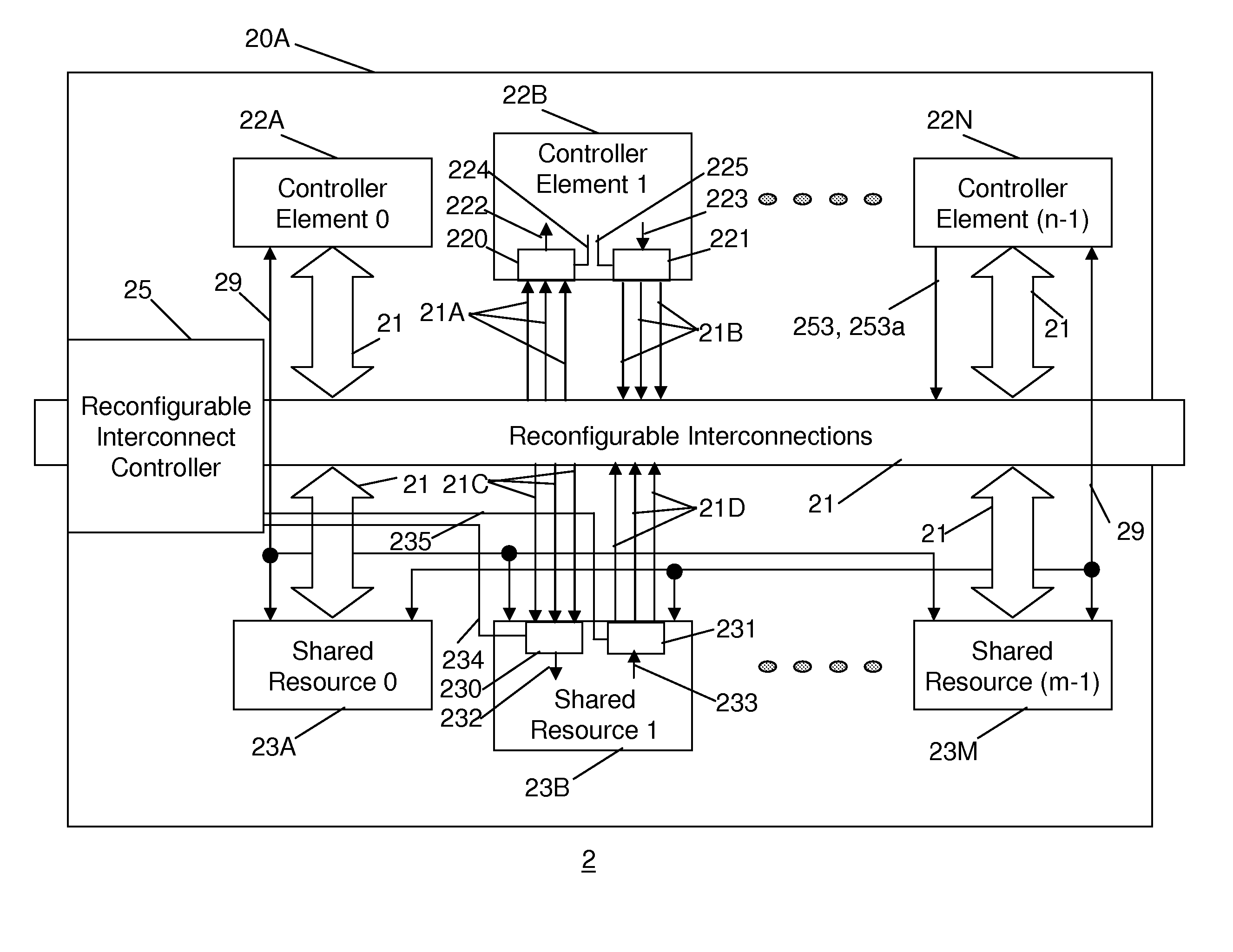
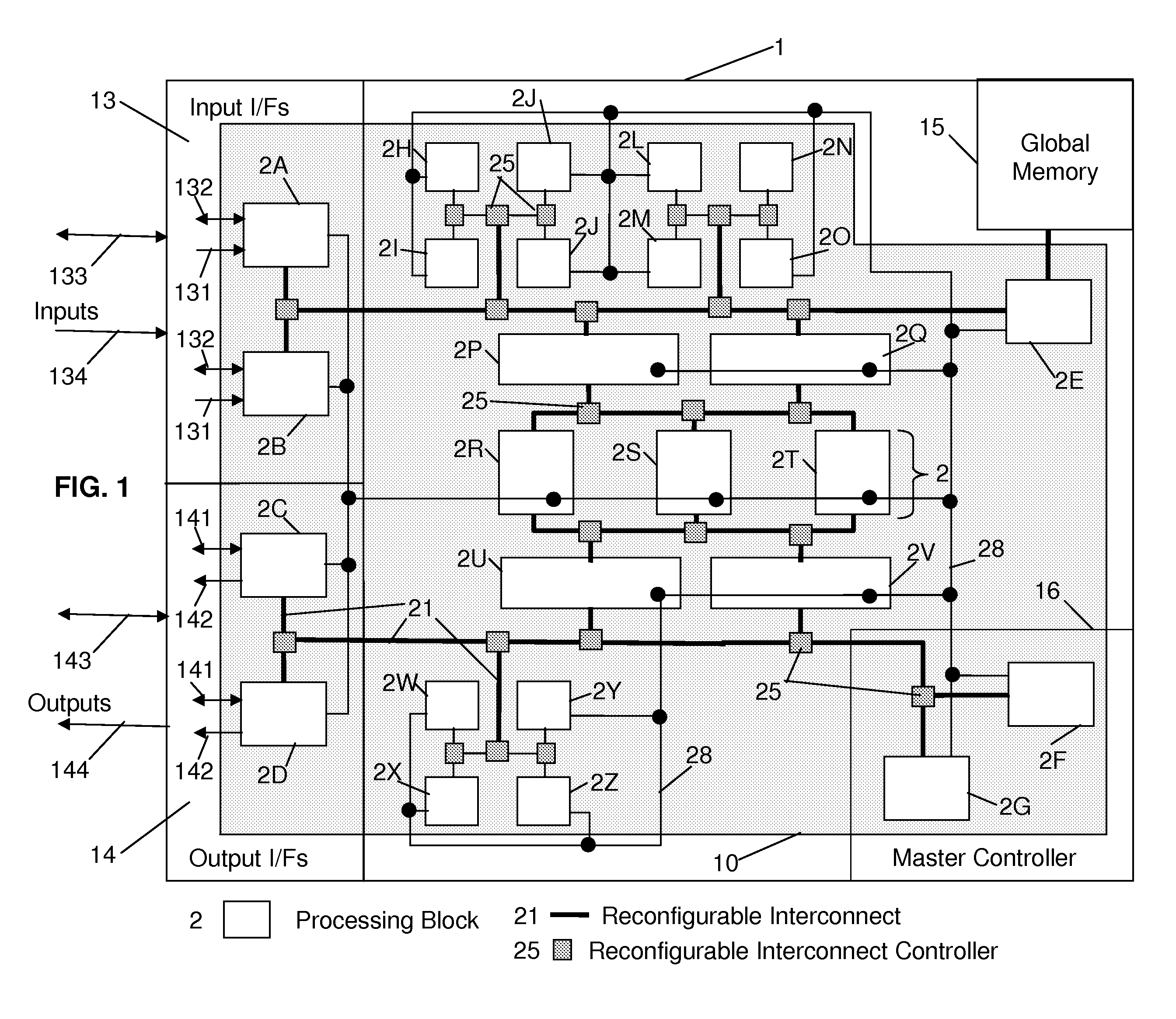
Reconfigurable integrated circuit
InactiveUS20070143577A1Energy efficient ICTArchitecture with single central processing unitNon real timeResource block
A reconfigurable integrated circuit is provided wherein the available hardware resources can be optimised for a particular application. Dynamically reconfiguring (in both real-time and non real-time) the available resources and sharing a plurality of processing elements with a plurality of controller elements achieve this. In a preferred embodiment the integrated circuit includes a plurality of processing blocks, which interface to a reconfigurable interconnection means. A processing block has two forms, namely a shared resource block and a dedicated resource block. Each processing block consists of one or a plurality of controller elements and a plurality of processing elements. The controller element and processing element generally comprise diverse rigid coarse and fine grained circuits and are interconnected through dedicated and reconfigurable interconnect. The processing blocks can be configured as a hierarchy of blocks and or fractal architecture.
Owner:AKYA HLDG
Integrated system for network layer security and fine-grained identity-based access control
ActiveUS6986061B1Simple technologyUser identity/authority verificationDigital computer detailsKey exchangeMedia access control
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
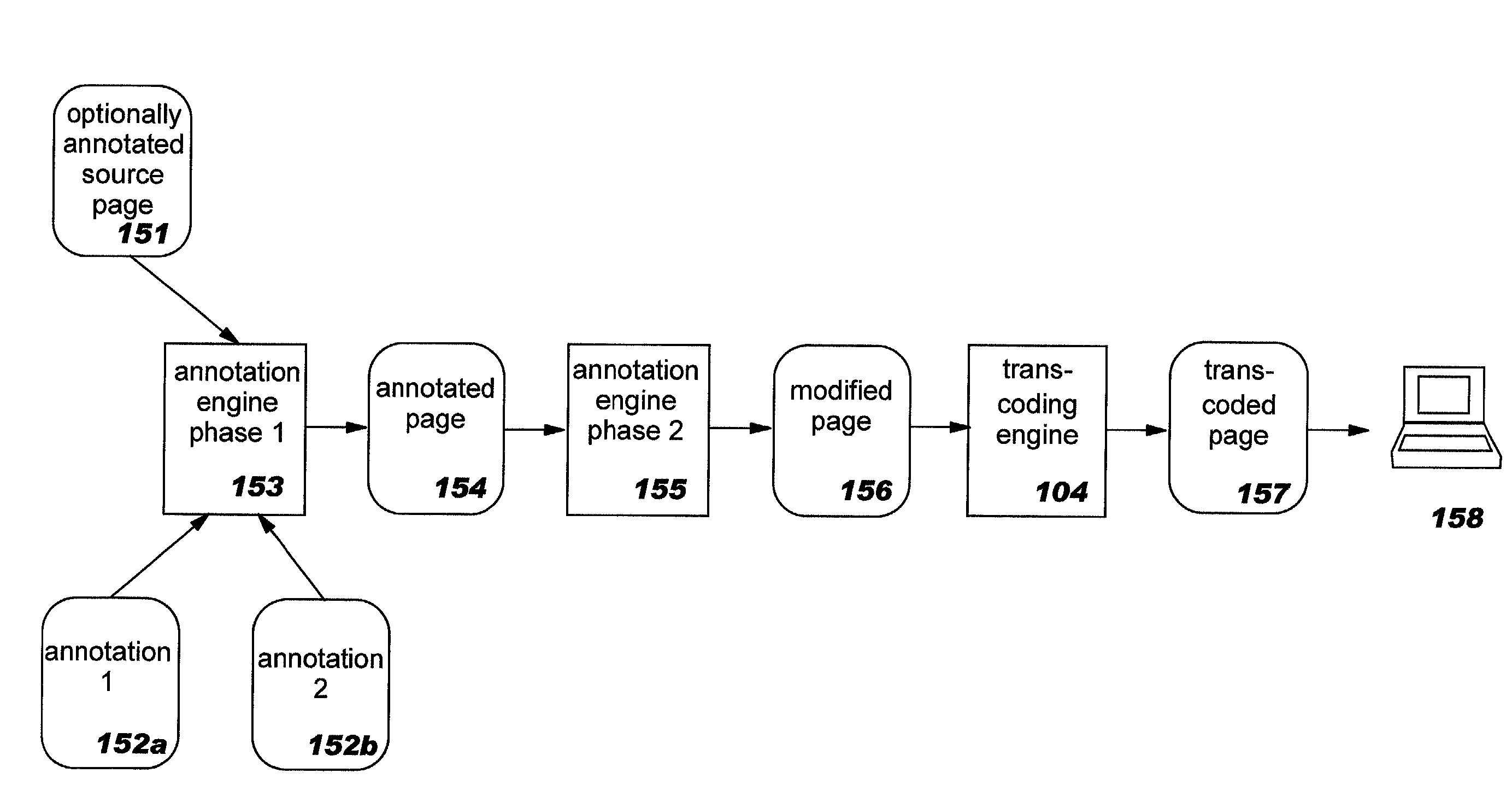
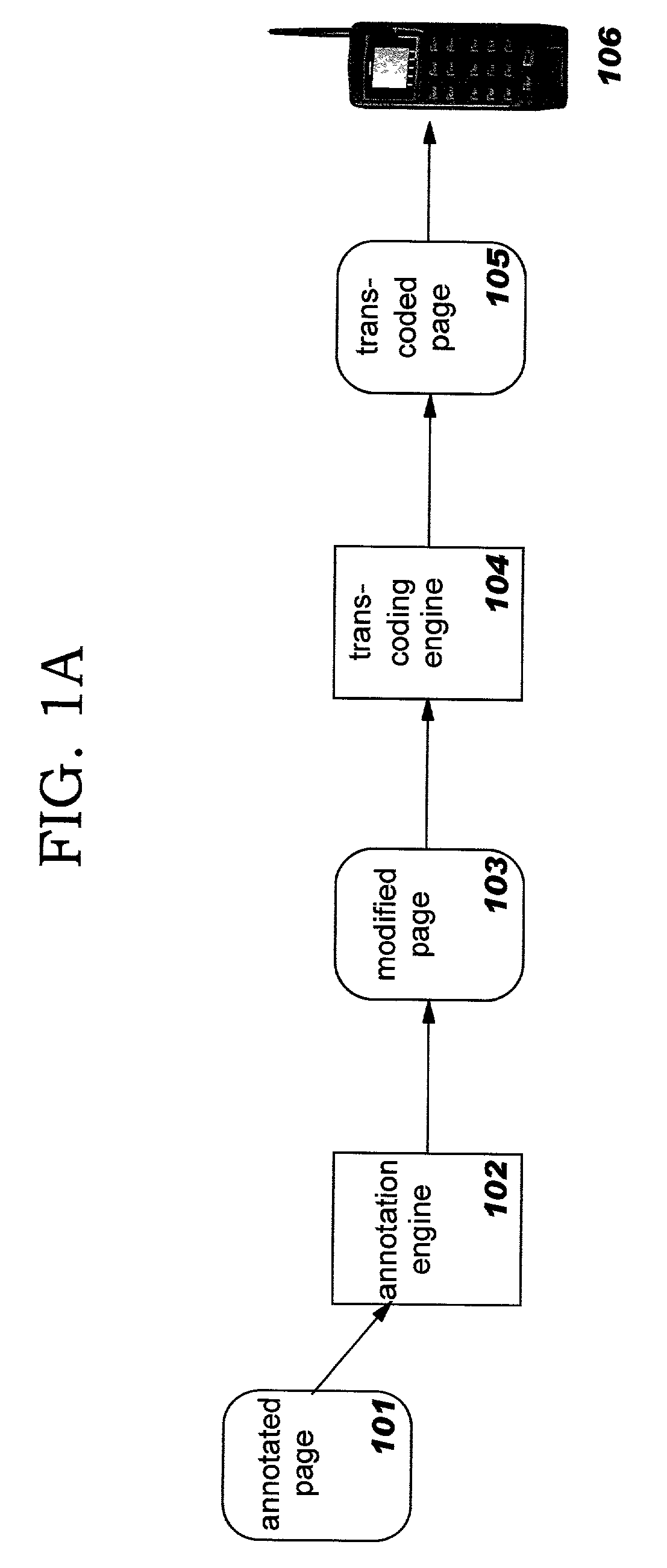
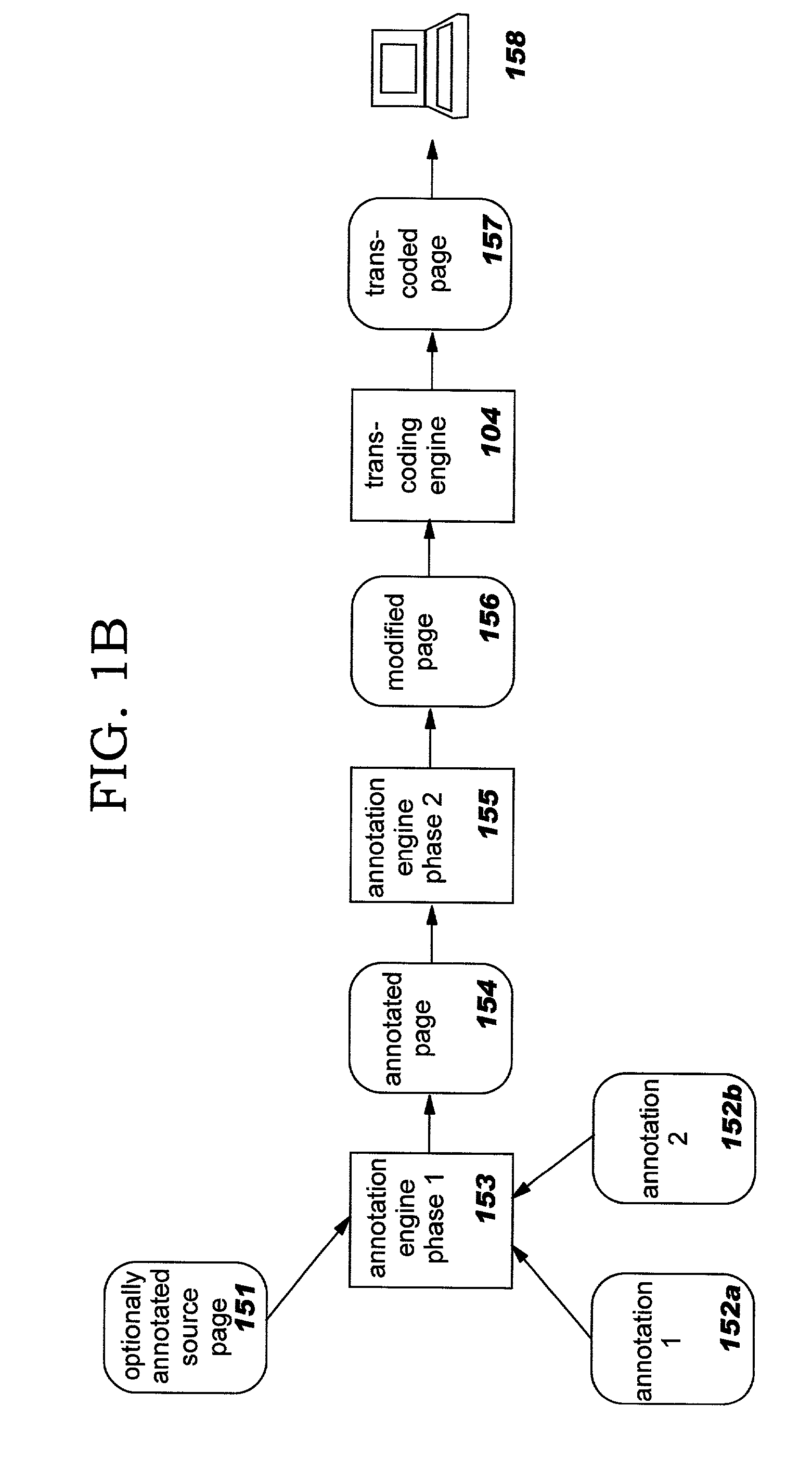
Enhanced transcoding of structured documents through use of annotation techniques
InactiveUS20030018668A1Digital data information retrievalDigital computer detailsDocumentation procedureTranscoding
Methods, systems, and computer program products for improving the transcoding operations which are performed on structured documents (such as those encoded in the Hypertext Markup Language, or "HTML") through use of annotations. Source documents may be annotated according to one or more types of annotations. Representative types of annotations direct an annotation engine to perform selective clipping of document content, provide enhanced HTML form support, request node and / or attribute replacement or the insertion of HTML or other rendered markup syntax, and direct a transcoding engine to provide fine-grained transcoding preference support (such as controlling transcoding of tables on a per-row or per-column basis). The disclosed techniques may be used with statically-generated document content and with dynamically-generated content. Annotation is performed as a separate step preceding transcoding, and a modified document resulting from processing annotations may therefore be re-used for multiple different transcoding operations.
Owner:IBM CORP
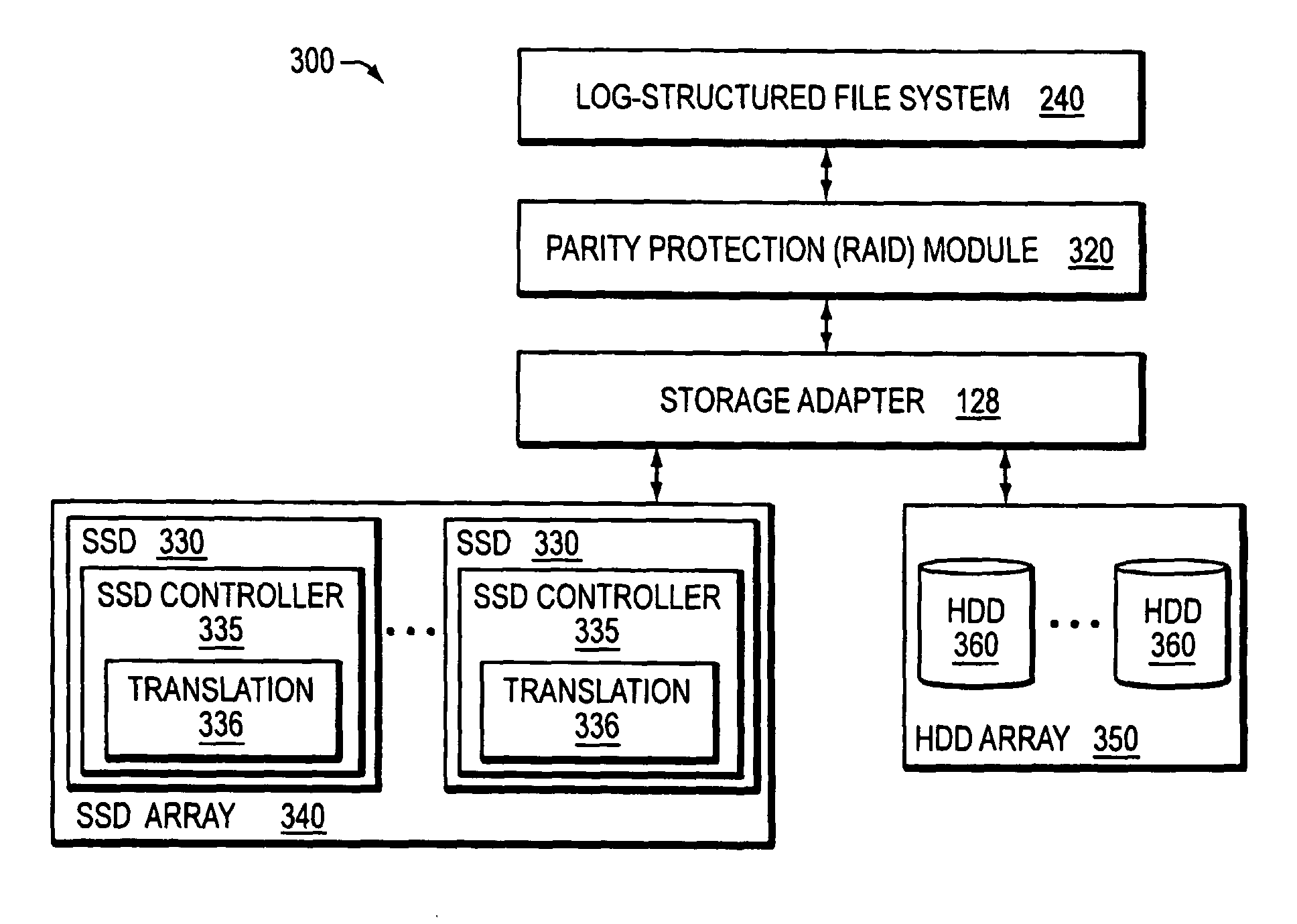
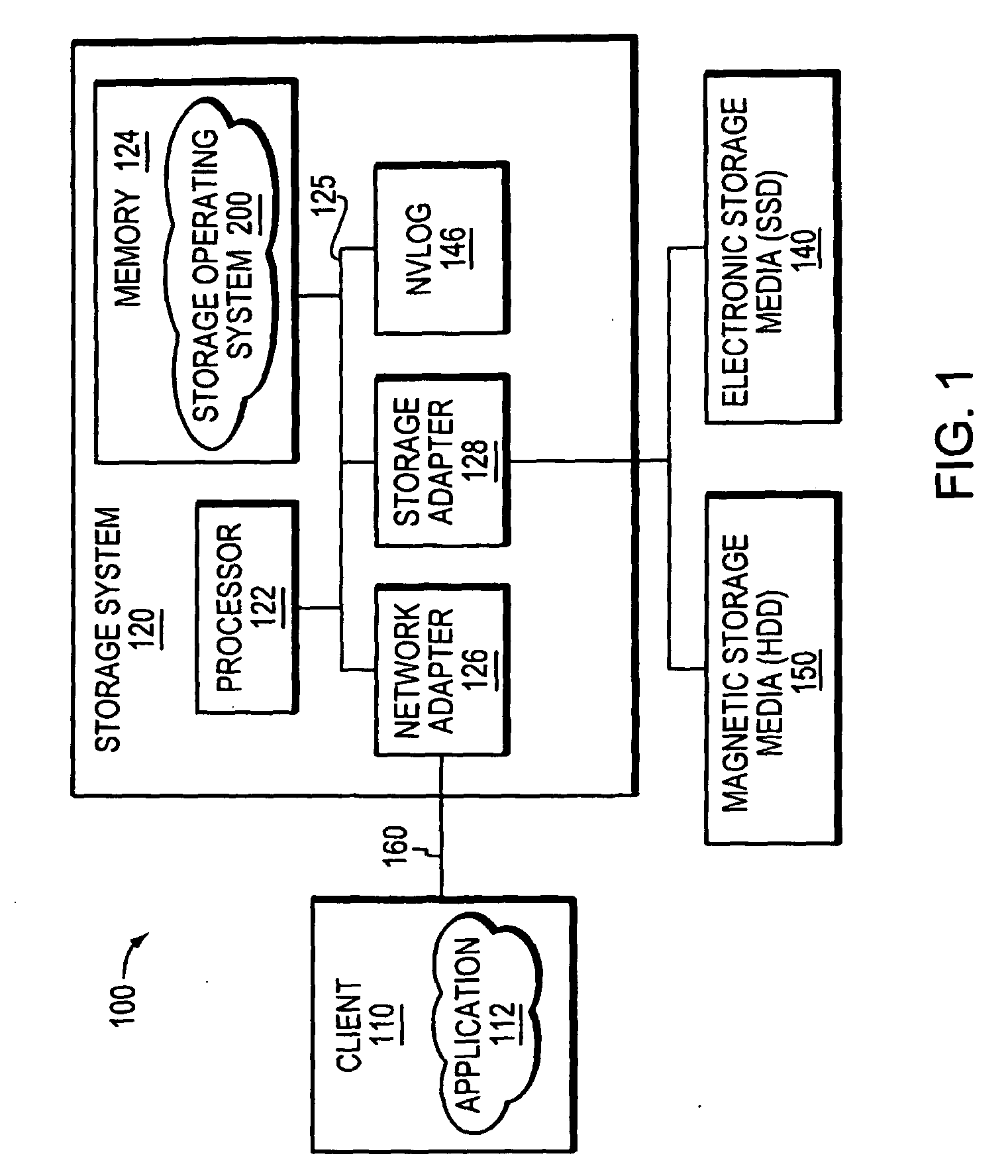
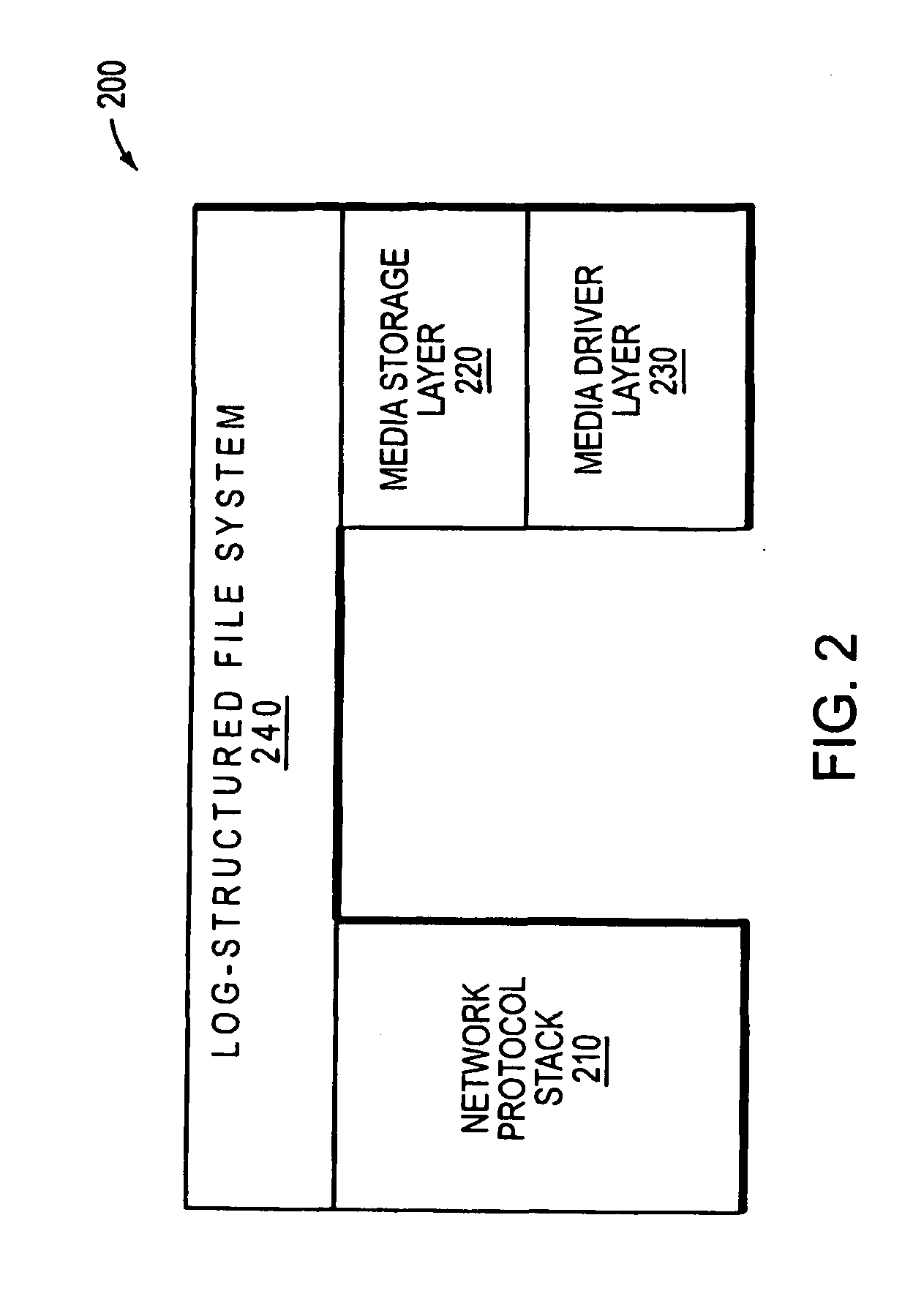
Hybrid media storage system architecture
ActiveUS20110035548A1Improved performance characteristicsOvercome disadvantagesDigital data information retrievalError detection/correctionFile systemGranularity
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
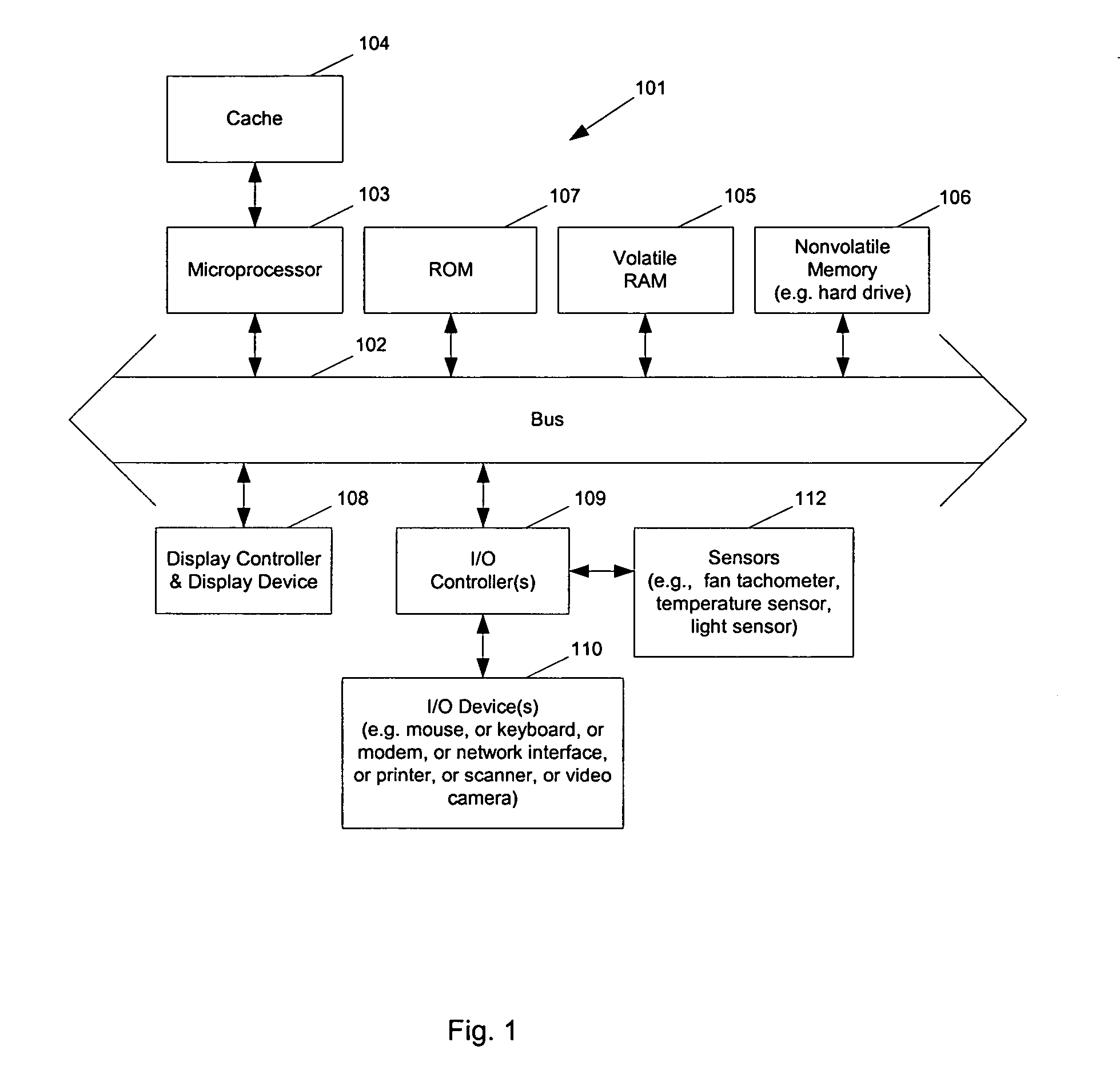
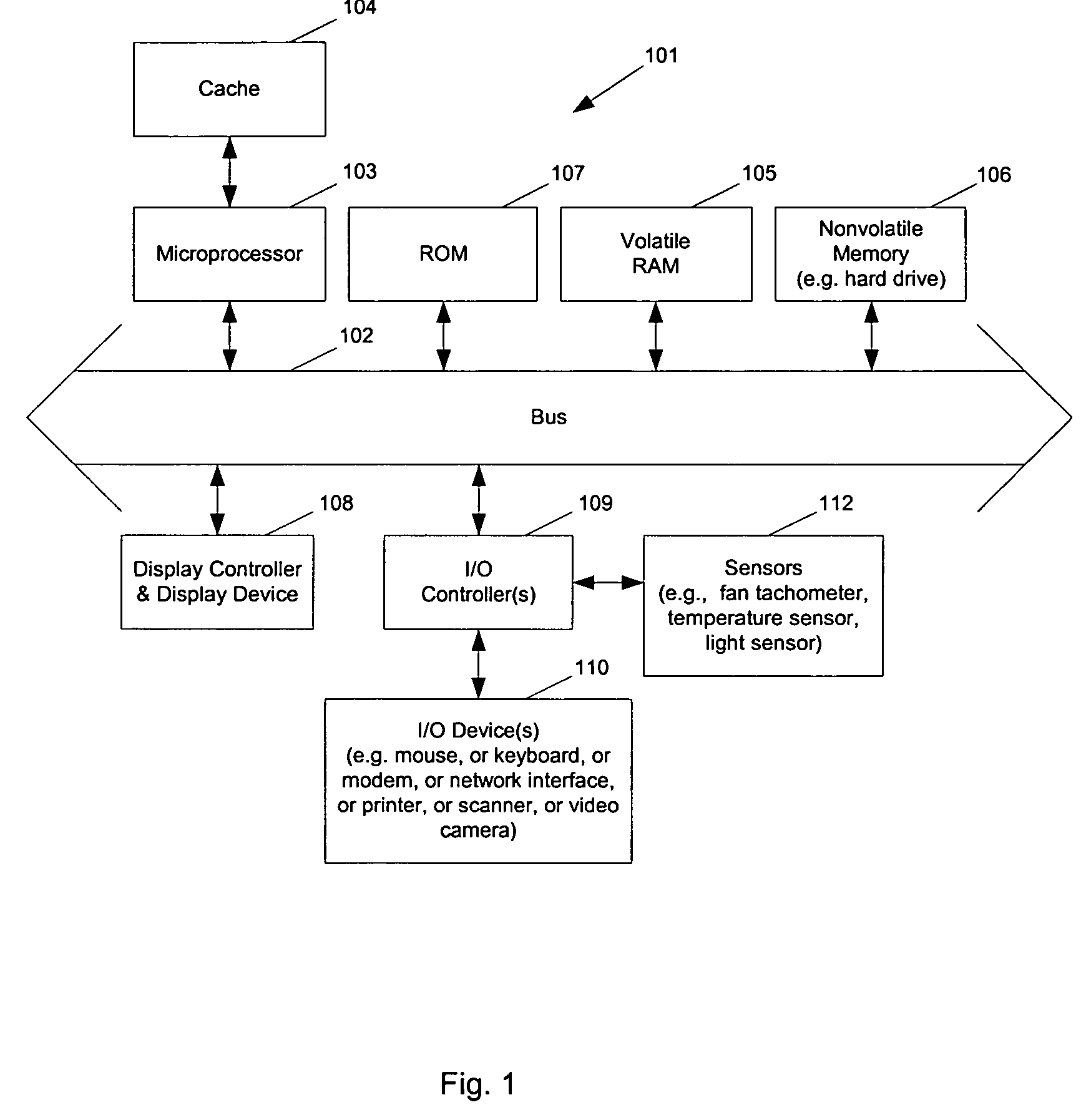
Methods and apparatuses for operating a data processing system
ActiveUS20050049729A1Balance performanceShorten speedMultiplex communicationVolume/mass flow measurementHeat sensitiveThermistor
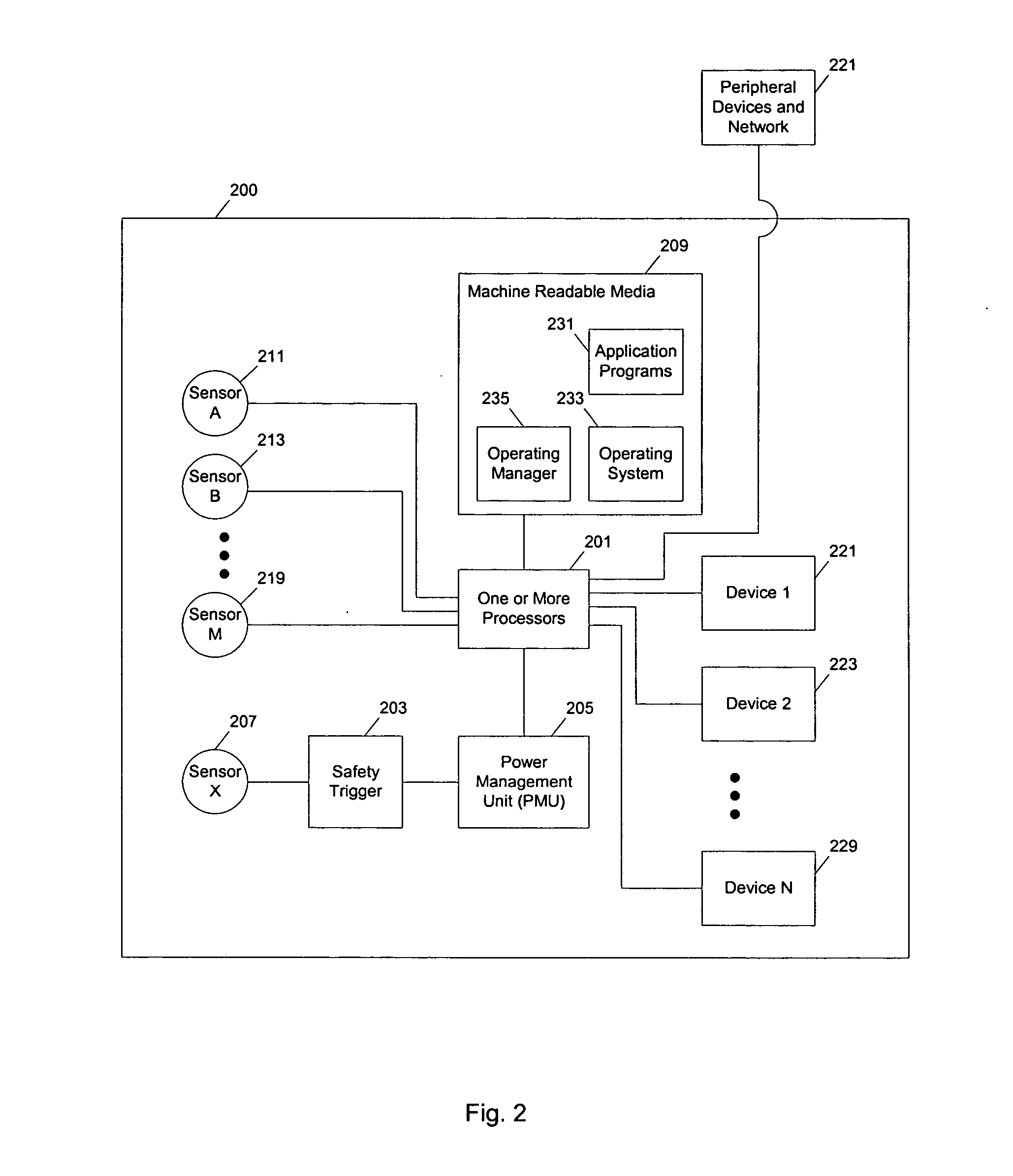
Methods and apparatuses to manage working states of a data processing system. At least one embodiment of the present invention includes a data processing system with one or more sensors (e.g., physical sensors such as tachometer and thermistors, and logical sensors such as CPU load) for fine grain control of one or more components (e.g., processor, fan, hard drive, optical drive) of the system for working conditions that balance various goals (e.g., user preferences, performance, power consumption, thermal constraints, acoustic noise). In one example, the clock frequency and core voltage for a processor are actively managed to balance performance and power consumption (heat generation) without a significant latency. In one example, the speed of a cooling fan is actively managed to balance cooling effort and noise (and / or power consumption).
Owner:APPLE INC
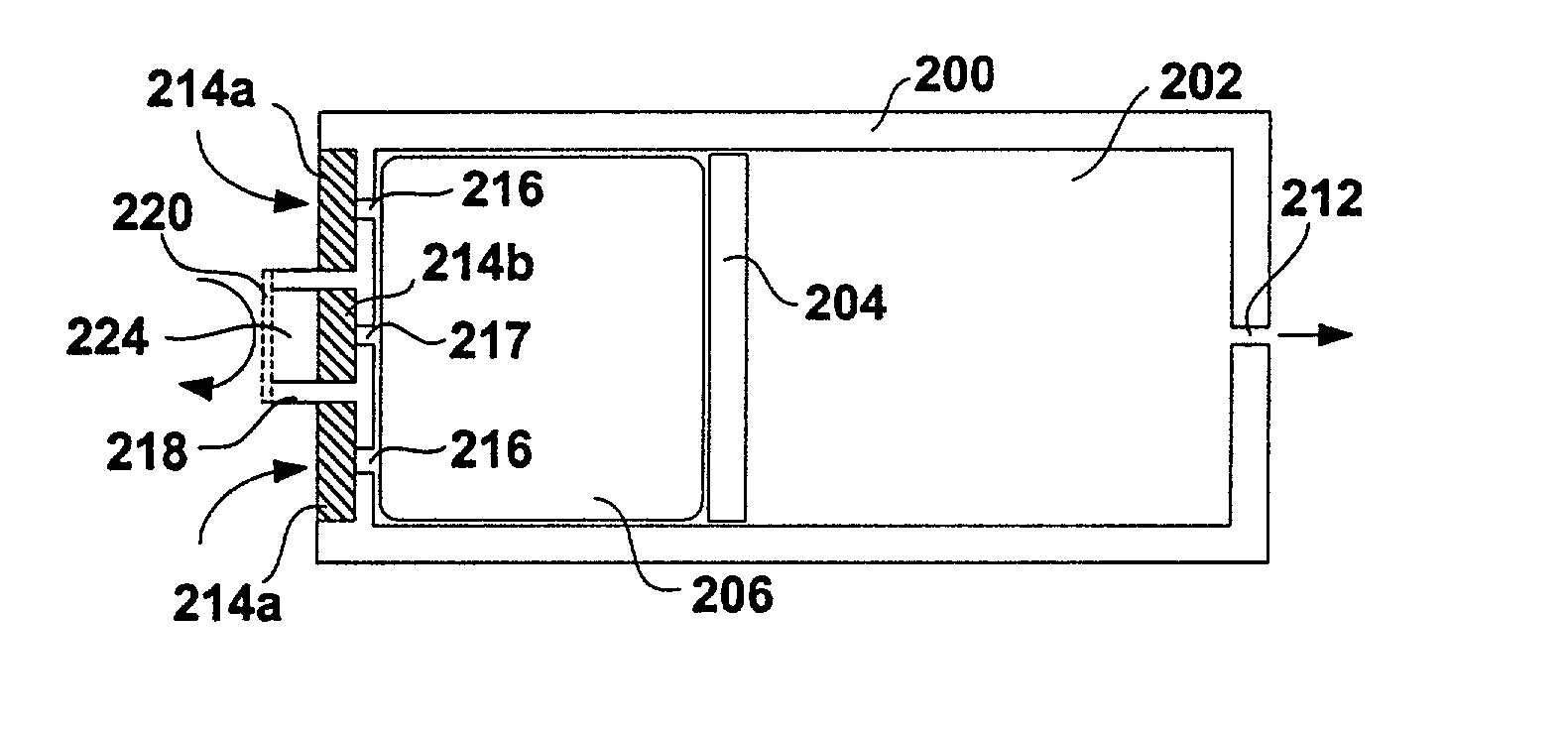
Methods and implantable devices and systems for long term delivery of a pharmaceutical agent
InactiveUS6436091B1Improve delivery rateMedical devicesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismSemipermeable membraneImplanted device
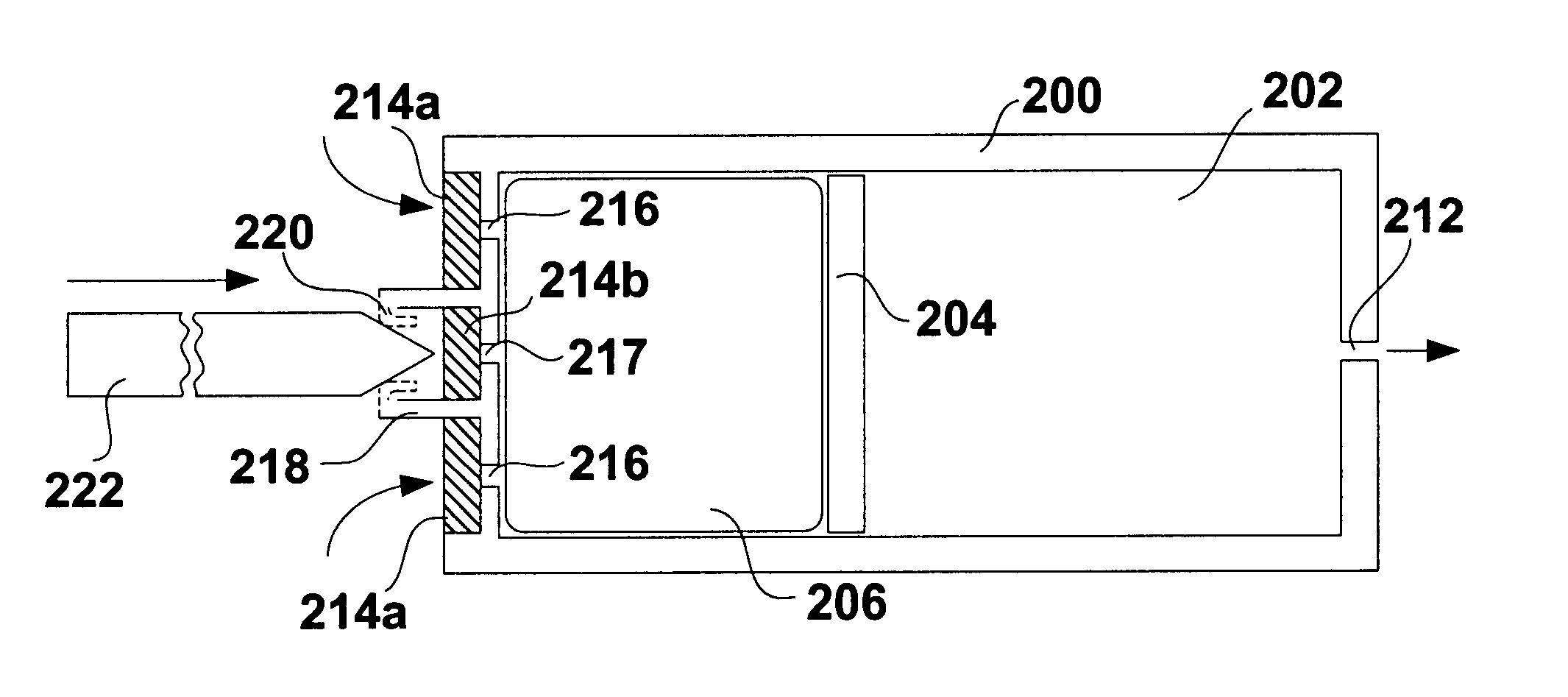
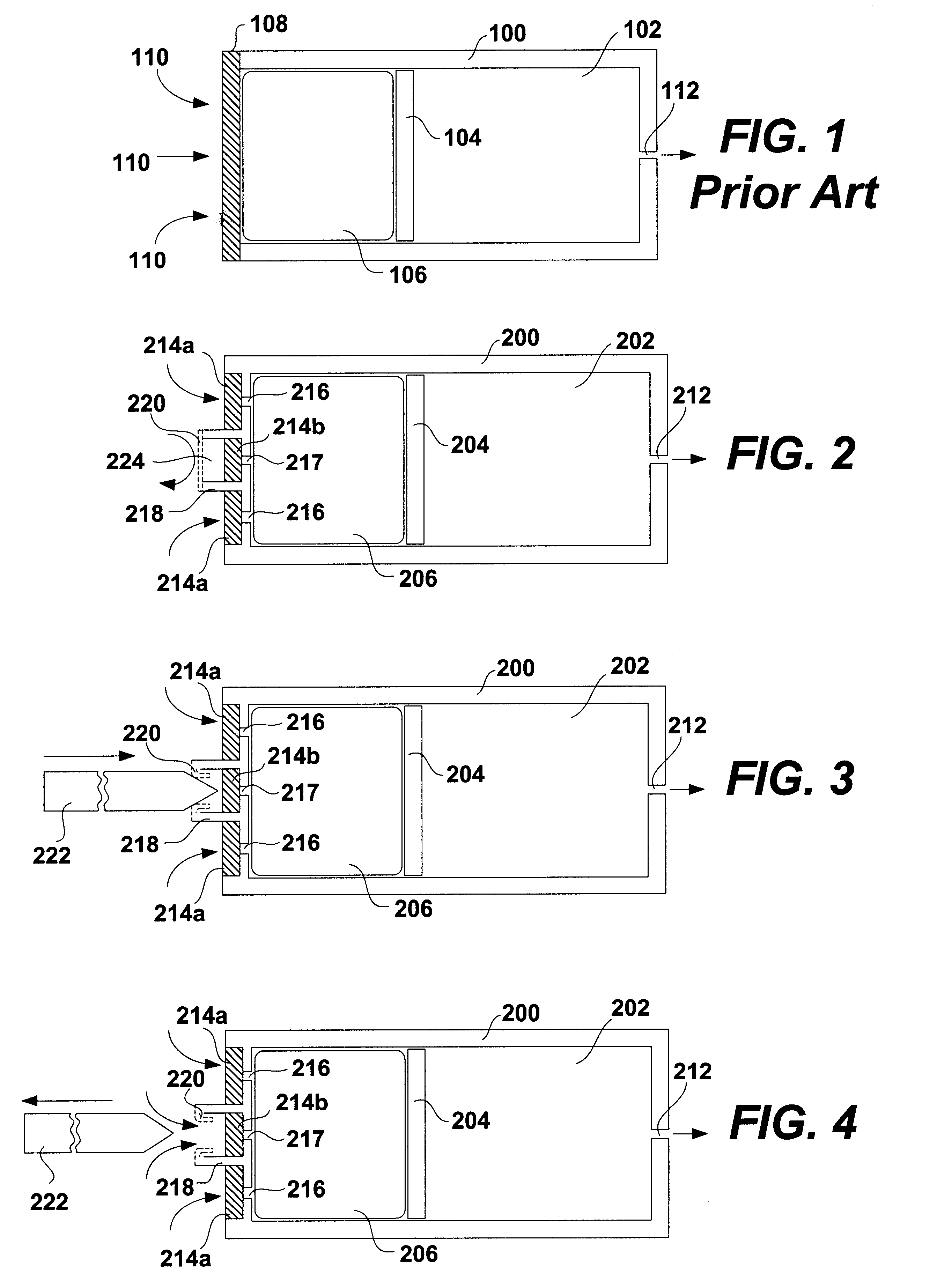
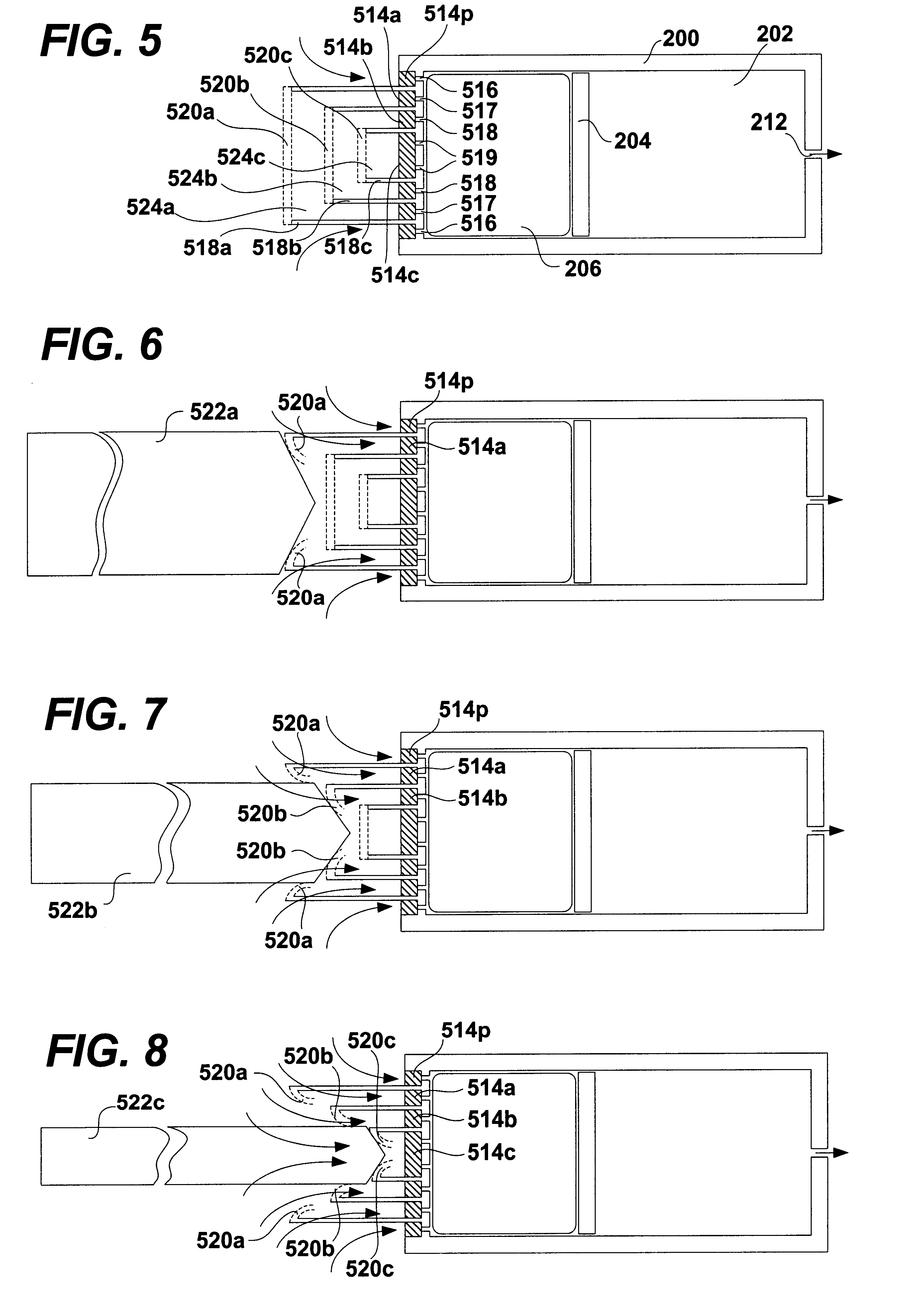
Implantable devices and osmotic pump and catheter systems for delivering a pharmaceutical agent to a patient at selectable rates include an impermeable pump housing and a moveable partition disposed within the housing, the partition dividing the housing into an osmotic driving compartment having an open end and a pharmaceutical agent compartment having a delivery orifice. A plurality of semi permeable membranes may be disposed in the open end of the osmotic driving compartment and a number of impermeable barriers may seal selected ones of the plurality of semi permeable membranes from the patient until breached. Breaching one or more of the impermeable barriers increases the surface area of semi permeable membrane exposed to the patient and controllably increases the delivery rate of the pharmaceutical agent through the delivery orifice and catheter. Each of the plurality of semi permeable membranes may have a selected surface area, composition and / or thickness, to allow a fine-grained control over the infusion rate while the pump is implanted in the patient.
Owner:MICROSOLUTIONS
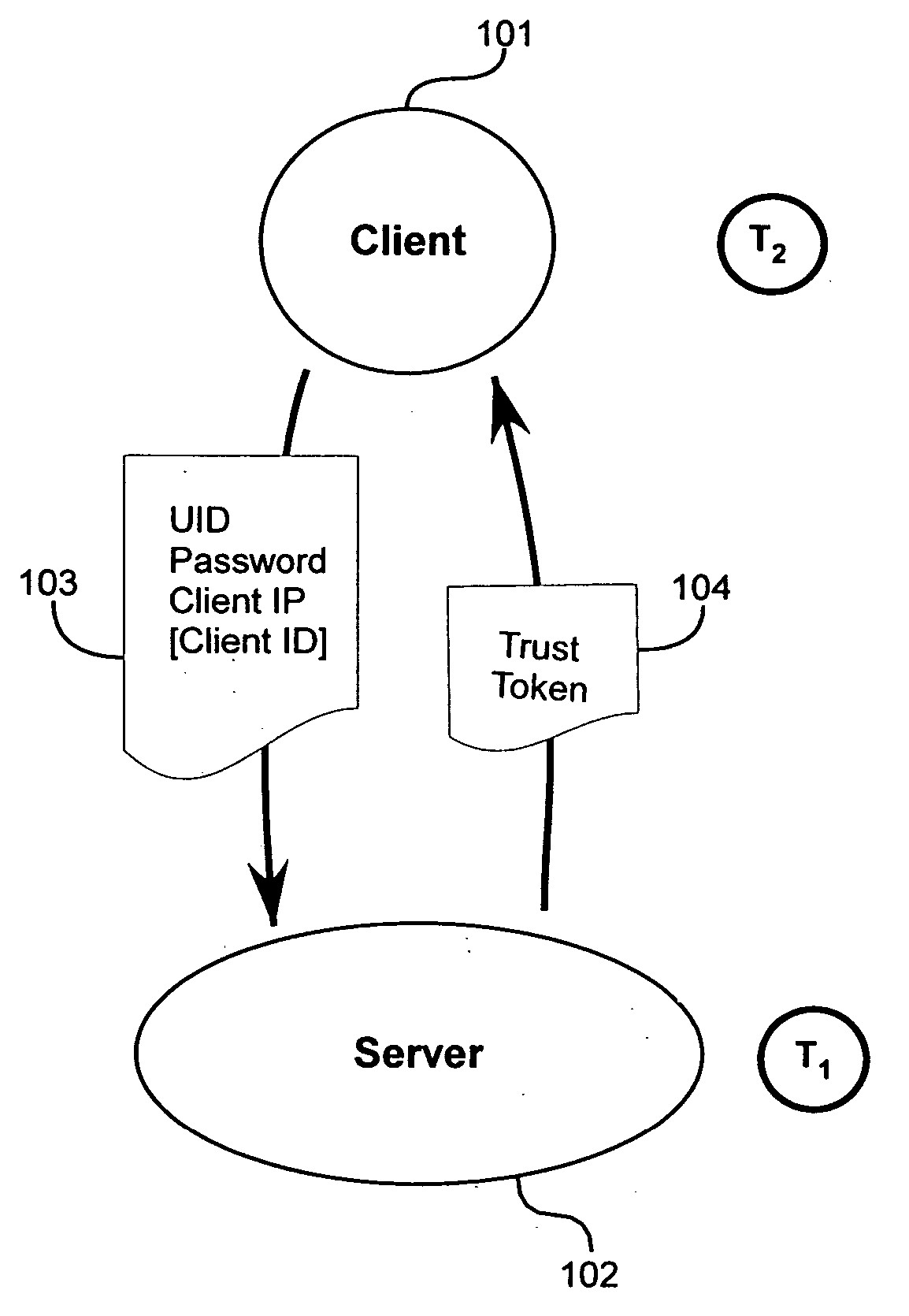
Method and apparatus for trust-based, fine-grained rate limiting of network requests
ActiveUS20050108551A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationRate limitingInternet traffic
A method and apparatus for fine-grained, trust-based rate limiting of network requests distinguishes trusted network traffic from untrusted network traffic at the granularity of an individual user / machine combination, so that network traffic policing measures are readily implemented against untrusted and potentially hostile traffic without compromising service to trusted users. A server establishes a user / client pair as trusted by issuing a trust token to the client when successfully authenticating to the server for the first time. Subsequently, the client provides the trust token at login. At the server, rate policies apportion bandwidth according to type of traffic: network requests that include a valid trust token are granted highest priority. Rate policies further specify bandwidth restrictions imposed for untrusted network traffic. This scheme enables the server to throttle untrusted password-guessing requests from crackers without penalizing most friendly logins and only slightly penalizing the relatively few untrusted friendly logins.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
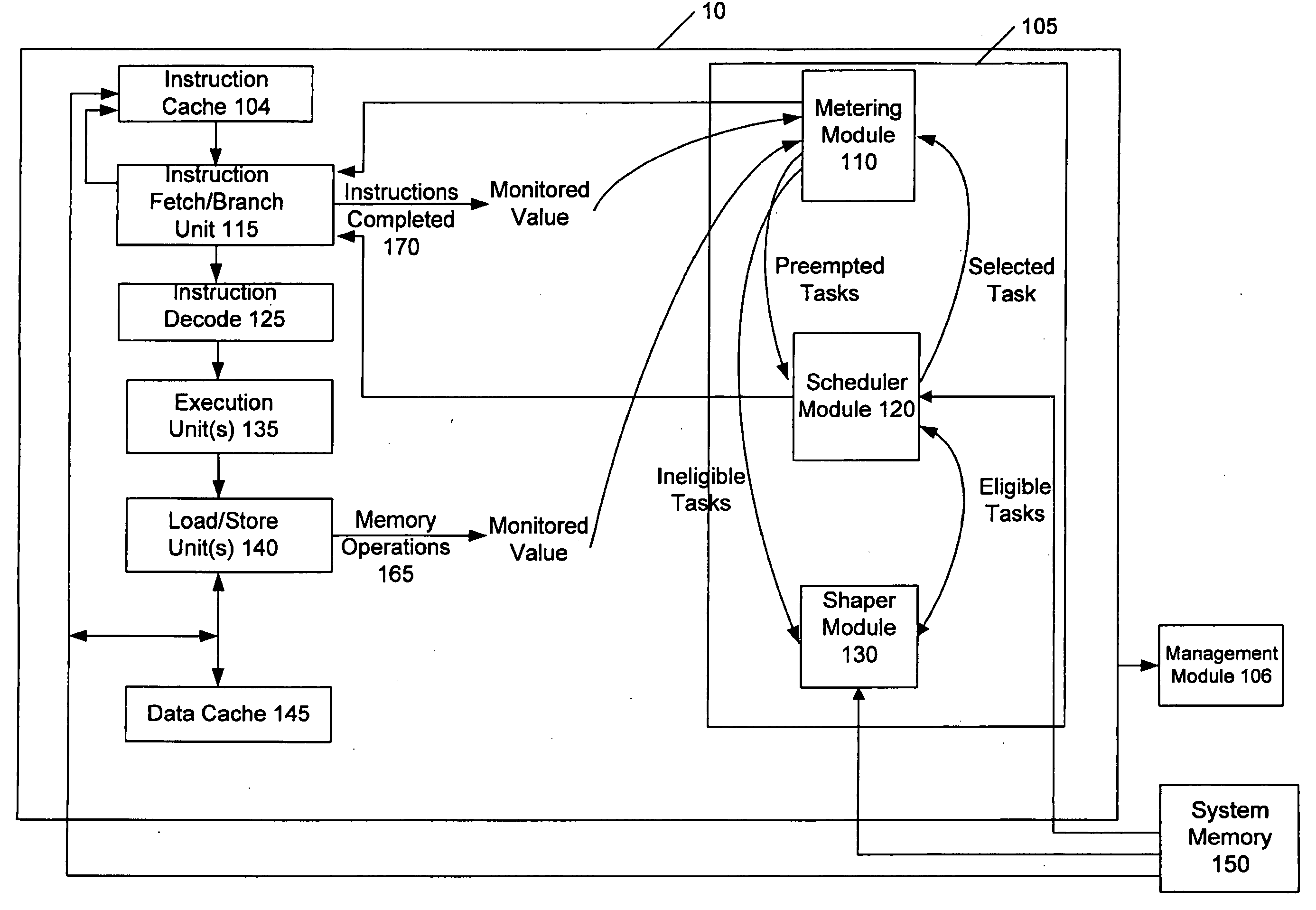
Apparatus and method for profiling system events in a fine grain multi-threaded multi-core processor
A system and method for profiling runtime system events of a computer system may include associating a data source type with detected system events. The system events may be detected dependent on information included in a reply message received by a processor in response to a data request or other transaction request message. The reply message may include information characterizing a source type of a source of data included in the reply message. The source type information may indicate that the source is remote or local; that it is a shared or a private storage location; that the data is supplied via a cache-to-cache transfer; or that the data is sourced from a coherency domain other than that of the requesting process. Instructions, events, messages, and replies may be sampled, and extended address information corresponding to the samples may be stored in an event set database for performance analysis.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Storage management for fine grained tiered storage with thin provisioning
ActiveUS7949637B1Digital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsStorage managementThin provisioning
A system for managing data includes providing at least one logical device having a table of information that maps sections of the logical device to sections of at least two storage areas. Characteristics of data associated with a one section of the logical device may be evaluated. The section of the data may moved between the at least two storage areas from a first location to a second location according to a policy and based on the characteristics of the data. A copy of the data may be retained in the first location and a list maintained that indentifies the copy of the data in the first location. The system provides for garbage collection processing for memory management.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
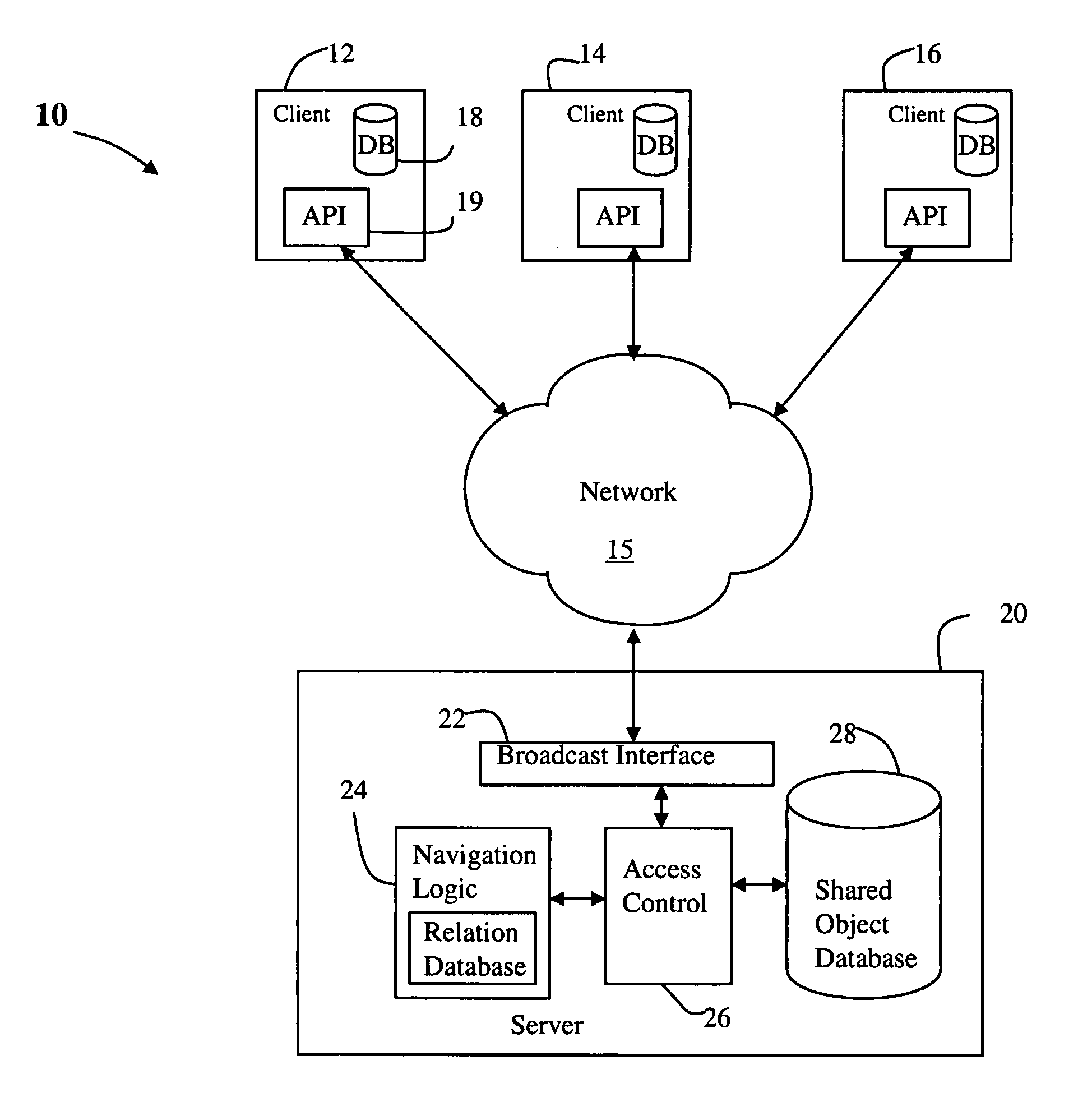
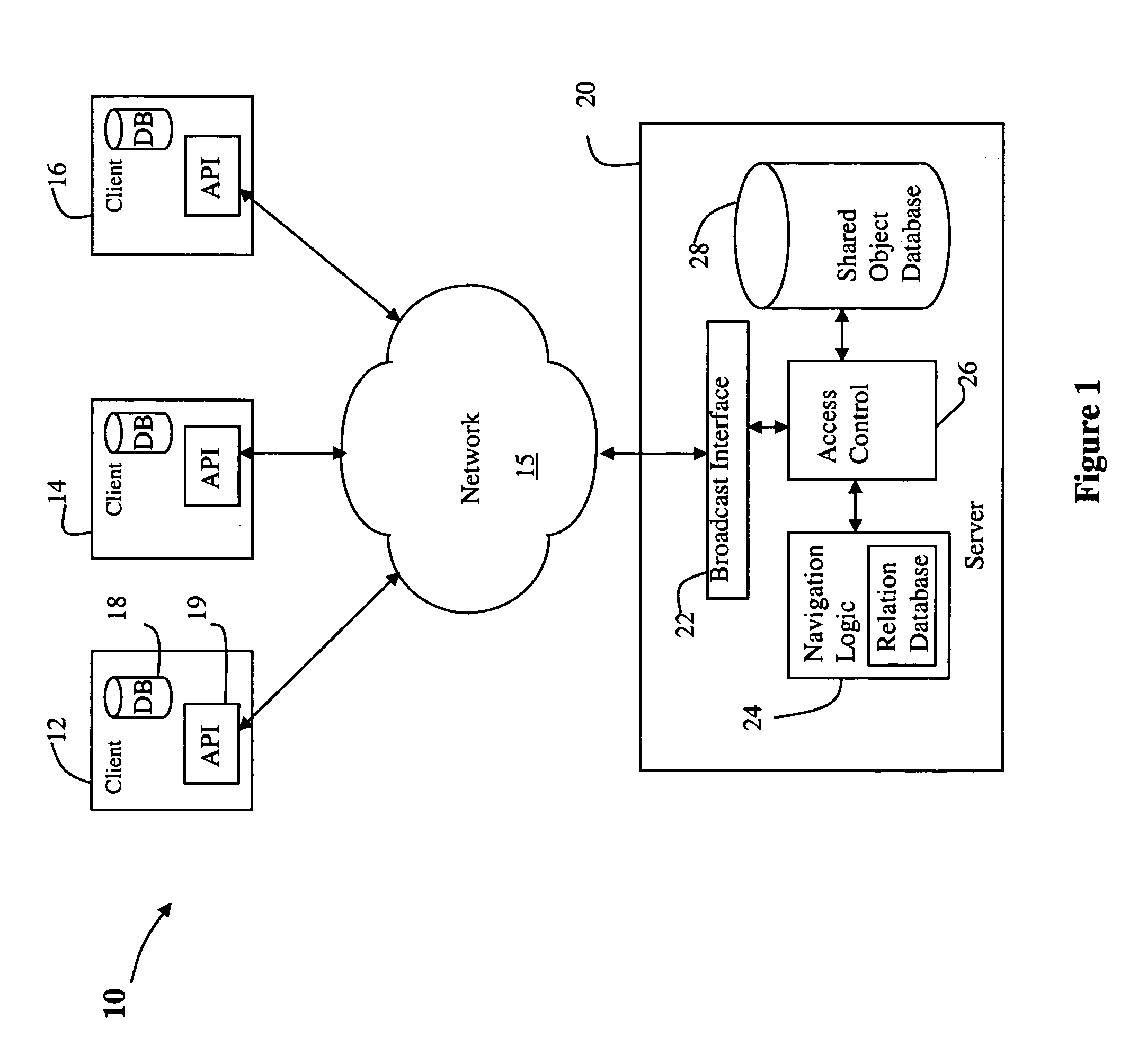
Method and apparatus for persistent real-time collaboration
InactiveUS20050165859A1More complex collaborationEffective controlOffice automationMemory systemsApplication softwareClient-side
A collaboration server is described that enables both real-time conferencing and content management. Thus, client applications can connect to the server to share data and collaborate in real-time. The server allows fine grained sharing of any type of content using generic shared objects (GSO). Each GSO holds one or more pieces of persistent information and defines a list of people who are allowed to access the information. Each GSO also represents a persistent conferencing session., i.e., if clients modify GSOs, modifications are broadcast to all the other clients on the list of the shared object if they are connected. The server also manages relationships between shared objects; i.e., shared objects could be contained in other shared objects or reference other shared objects.
Owner:IBM CORP
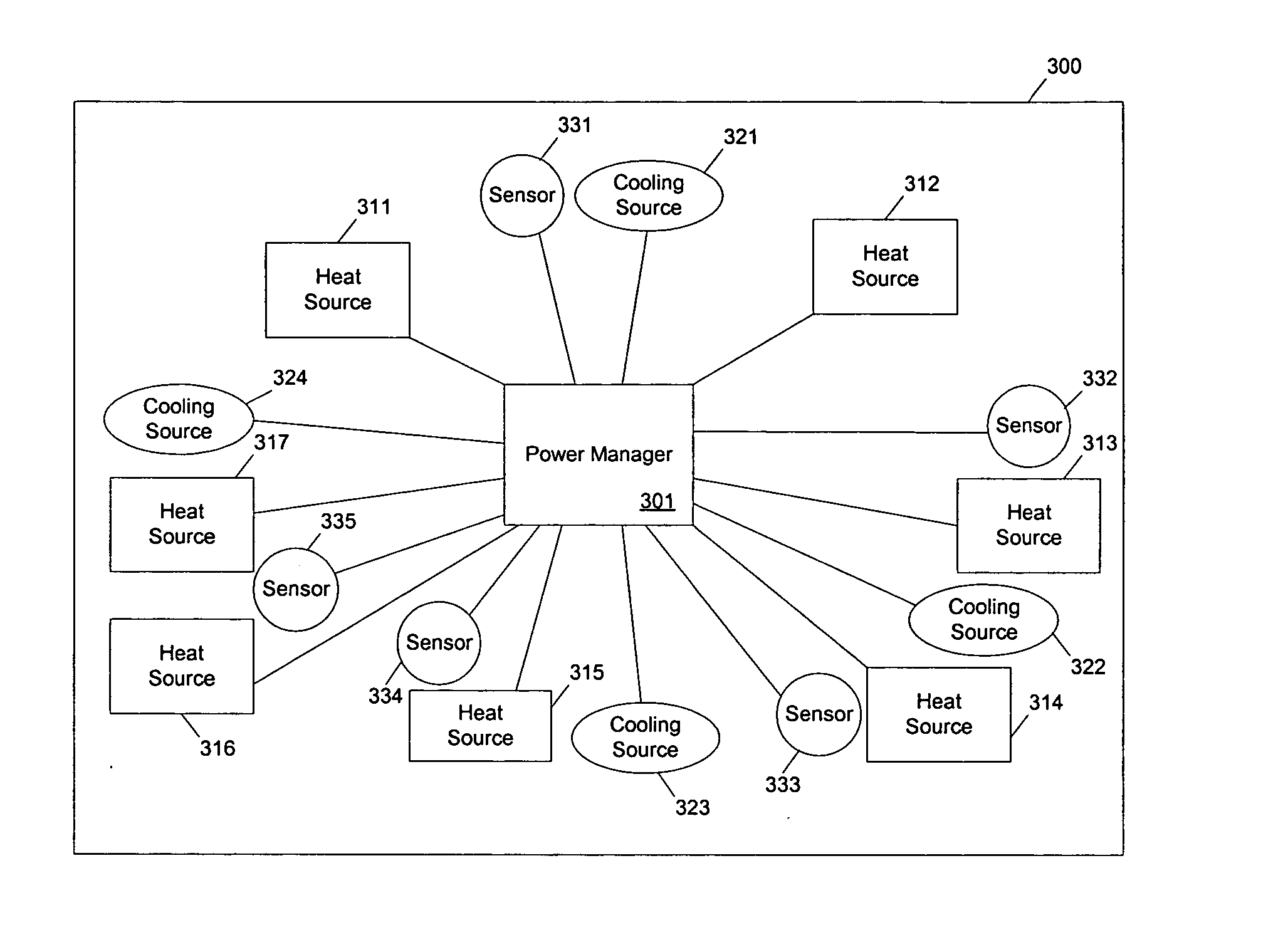
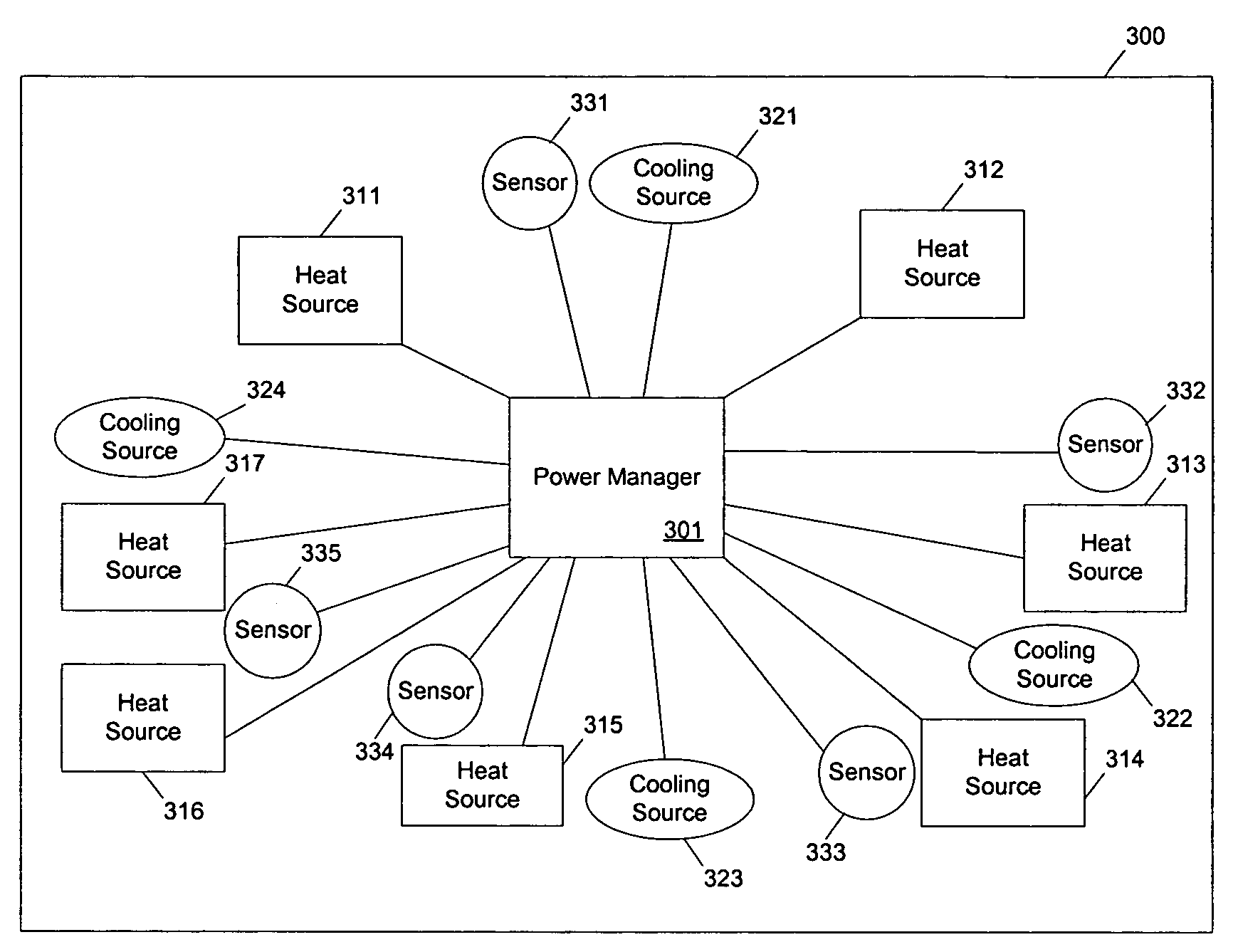
Methods and apparatuses for controlling the temperature of a data processing system
ActiveUS7451332B2Low heat generationImprove performanceEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementHard disc driveHeat sensitive
Methods and apparatuses to manage working states of a data processing system. At least one embodiment of the present invention includes a data processing system with one or more sensors (e.g., physical sensors such as tachometer and thermistors, and logical sensors such as CPU load) for fine grain control of one or more components (e.g., processor, fan, hard drive, optical drive) of the system for working conditions that balance various goals (e.g., user preferences, performance, power consumption, thermal constraints, acoustic noise). In one example, the clock frequency and core voltage for a processor are actively managed to balance performance and power consumption (heat generation) without a significant latency. In one example, the speed of a cooling fan is actively managed to balance cooling effort and noise (and / or power consumption).
Owner:APPLE INC
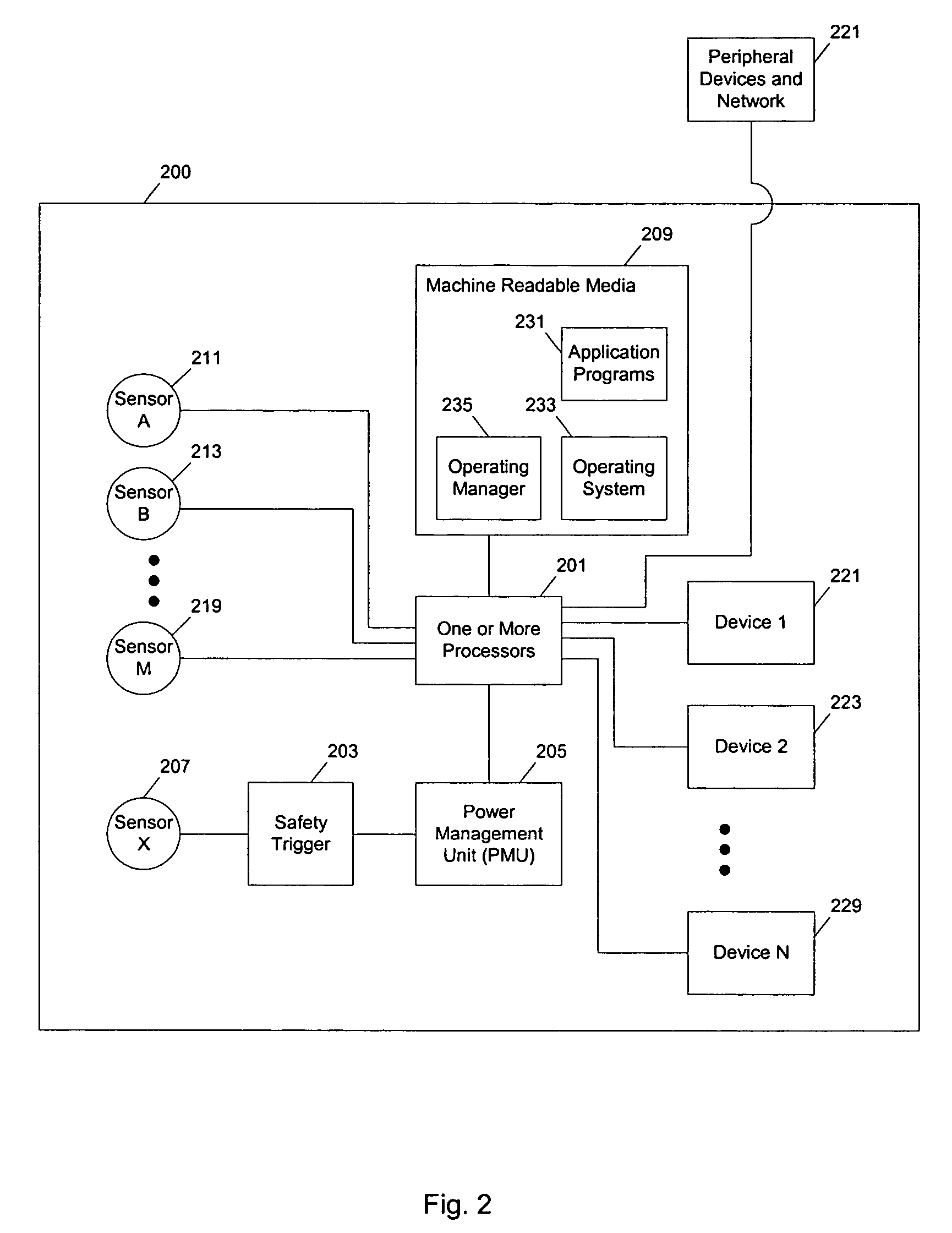
Method and apparatus for fine grain performance management of computer systems
InactiveUS20090055829A1Readily apparentMultiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsSufficient timeComputerized system
A system and method to control the allocation of processor (or state machine) execution resources to individual tasks executing in computer systems is described. By controlling the allocation of execution resources, to all tasks, each task may be provided with throughput and response time guarantees. This control is accomplished through workload metering shaping which delays the execution of tasks that have used their workload allocation until sufficient time has passed to accumulate credit for execution (accumulate credit over time to perform their allocated work) and workload prioritization which gives preference to tasks based on configured priorities.
Owner:VIRTUALMETRIX
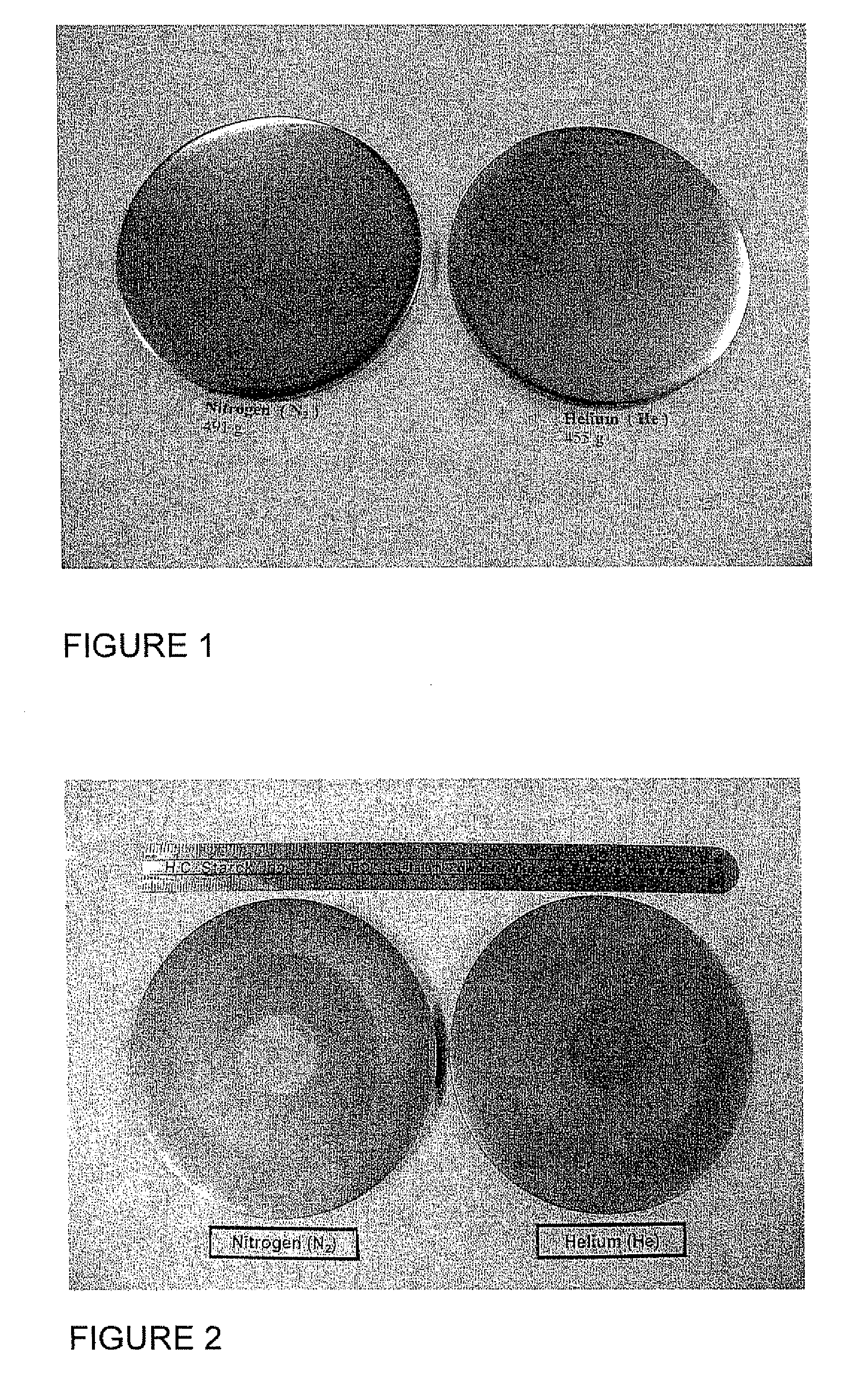
Fine Grained, Non Banded, Refractory Metal Sputtering Targets with a Uniformly Random Crystallographic Orientation, Method for Making Such Film, and Thin Film Based Devices and Products Made Therefrom
ActiveUS20080271779A1Cost-effectively createCost effectiveLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingFilm baseThermal expansion
The invention relates to a sputtering target which has a fine uniform equiaxed grain structure of less than 44 microns, no preferred texture orientation as measured by electron back scattered diffraction (“EBSD”) and that displays no grain size banding or texture banding throughout the body of the target. The invention relates a sputtering target with a lenticular or flattened grain structure, no preferred texture orientation as measured by EBSD and that displays no grain size or texture banding throughout the body of the target and where the target has a layered structure incorporating a layer of the sputtering material and at least one additional layer at the backing plate interface, said layer has a coefficient of thermal expansion (“CTE”) value between the CTE of the backing plate and the CTE of the layer of sputtering material. The invention also relates to thin films and their use of using the sputtering target and other applications, such as coatings, solar devices, semiconductor devices etc. The invention further relates to a process to repair or rejuvenate a sputtering target.
Owner:H C STARCK GMBH +1
Methods and implantable devices and systems for long term delivery of a pharmaceutical agent
InactiveUS20040111080A1Improve delivery ratePharmaceutical delivery mechanismMedical devicesSemipermeable membraneImplanted device
Implantable devices and osmotic pump and catheter systems for delivering a pharmaceutical agent to a patient at selectable rates include an impermeable pump housing and a moveable partition disposed within the housing, the partition dividing the housing into an osmotic driving compartment having an open end and a pharmaceutical agent compartment having a delivery orifice. A plurality of semi permeable membranes may be disposed in the open end of the osmotic driving compartment and a number of impermeable barriers may seal selected ones of the plurality of semi permeable membranes from the patient until breached. Breaching one or more of the impermeable barriers increases the surface area of semi permeable membrane exposed to the patient and controllably increases the delivery rate of the pharmaceutical agent through the delivery orifice and catheter. Each of the plurality of semi permeable membranes may have a selected surface area, composition and / or thickness, to allow a fine-grained control over the infusion rate while the pump is implanted in the patient.
Owner:MICROSOLUTIONS
Coated powder particles for producing three-dimensional bodies by means of a layer constituting method
InactiveUS20060251535A1Good storage stabilityHigh distinctnessAdditive manufacturing apparatusTransportation and packagingOrganic solventLaser light
The invention relates a powder material consisting of coated particles for a powder-based rapid generative prototyping methods, in particular by compressing a 3D binder. Said powder material consists of individual plastic, metal and / or ceramic particles and / or granules. A coating essentially consists of an adhesive agent which can be activated by a liquid binder, light or laser light, and of sinterable or glass-forming fine-grained material. Said invention also relates to a method for compressing 3D binder with the aid of an organic solvent having a water content less than 45% and to sintered bodies, in particular for moulding or precision mechanical engineering, which are fixed to each other by sintering or glass formation from a fine grained material.
Owner:PFEIFER ROLF +2
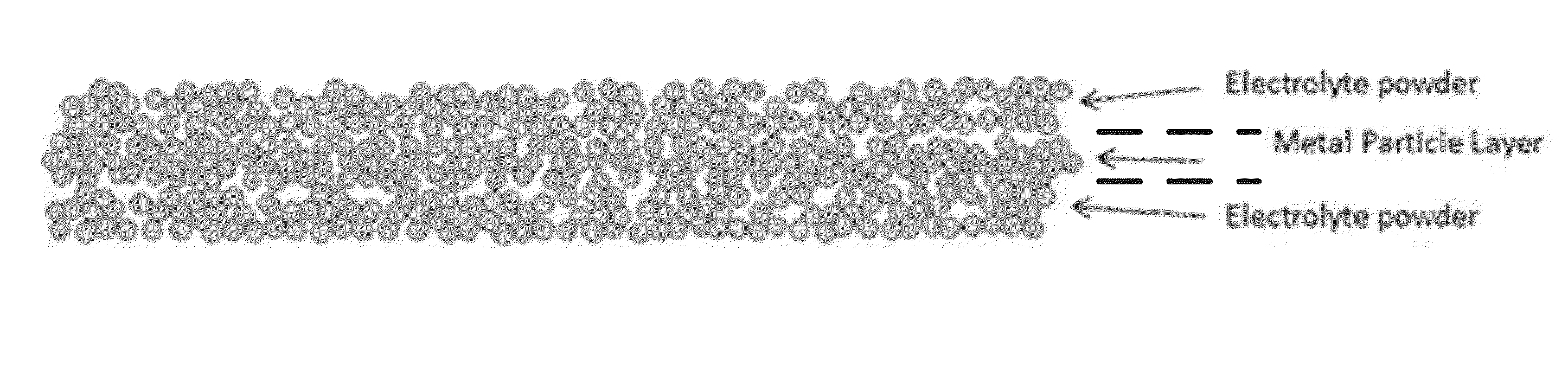
Garnet materials for li secondary batteries and methods of making and using garnet materials
Set forth herein are garnet material compositions, e.g., lithium-stuffed garnets and lithium-stuffed garnets doped with alumina, which are suitable for use as electrolytes and catholytes in solid state battery applications. Also set forth herein are lithium-stuffed garnet thin films having fine grains therein. Disclosed herein are novel and inventive methods of making and using lithium-stuffed garnets as catholytes, electrolytes and / or anolytes for all solid state lithium rechargeable batteries. Also disclosed herein are novel electrochemical devices which incorporate these garnet catholytes, electrolytes and / or anolytes. Also set forth herein are methods for preparing novel structures, including dense thin (<50 um) free standing membranes of an ionically conducting material for use as a catholyte, electrolyte, and, or, anolyte, in an electrochemical device, a battery component (positive or negative electrode materials), or a complete solid state electrochemical energy storage device. Also, the methods set forth herein disclose novel sintering techniques, e.g., for heating and / or field assisted (FAST) sintering, for solid state energy storage devices and the components thereof.
Owner:QUANTUMSCAPE BATTERY INC
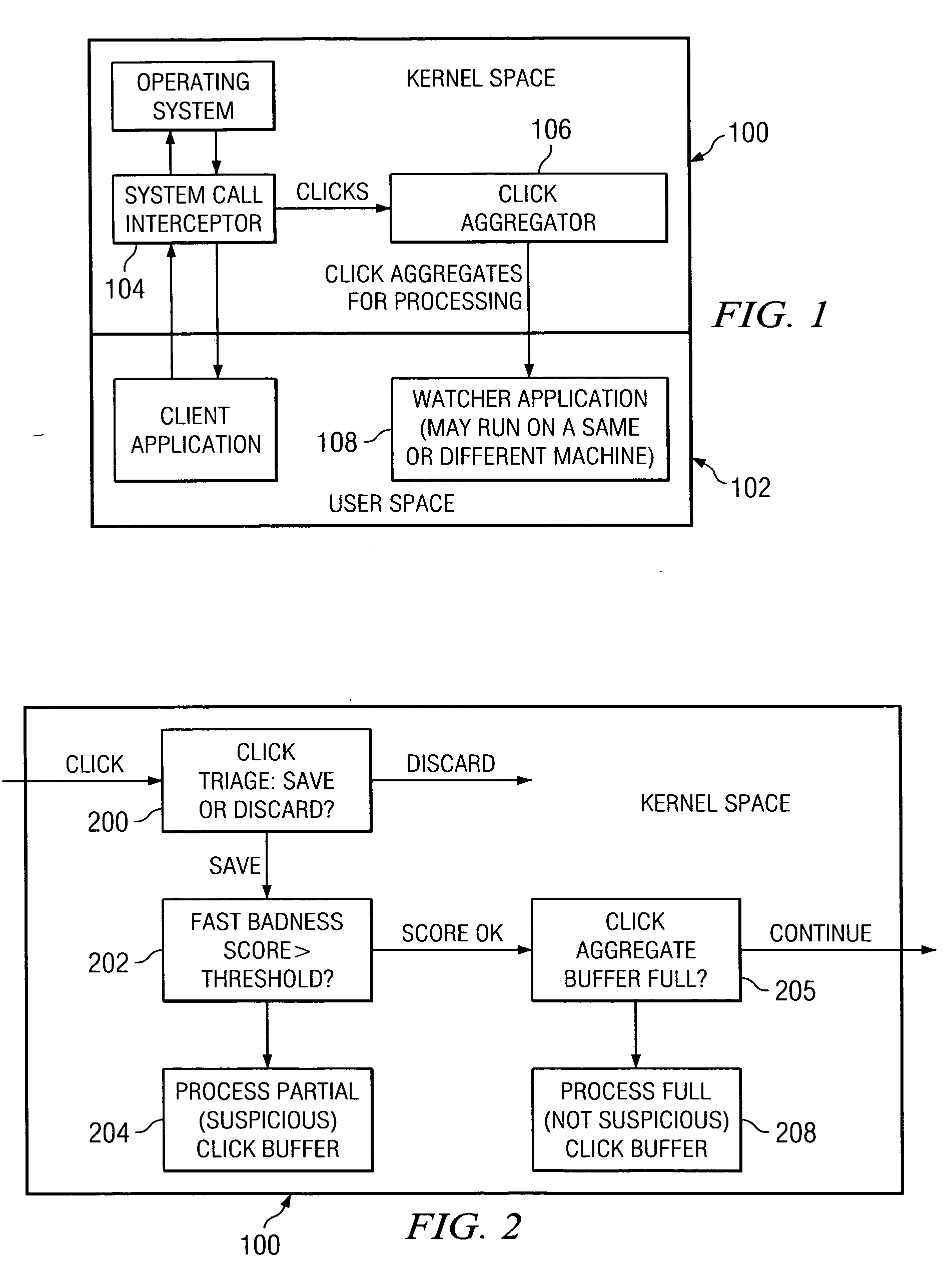
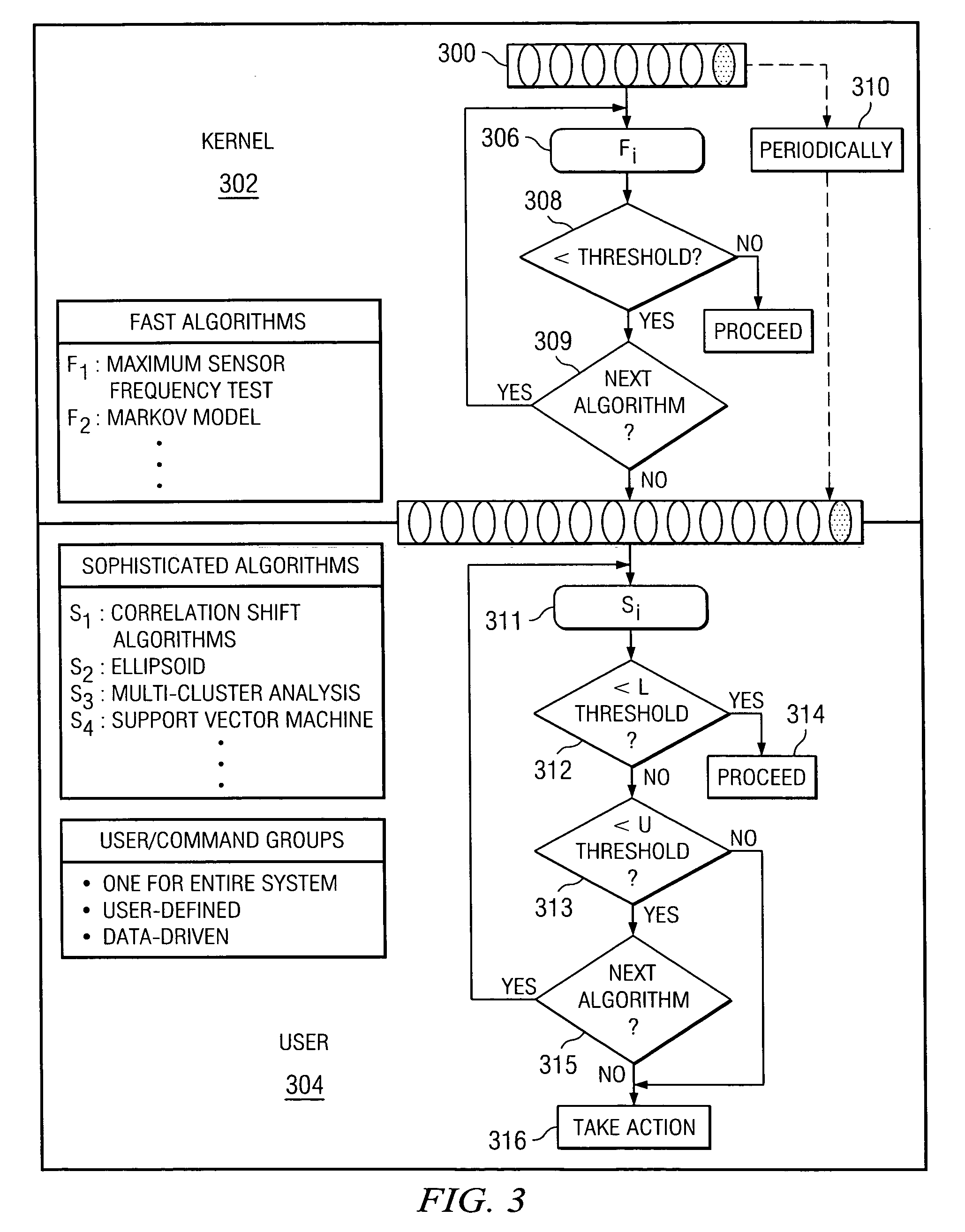
Method and system for detecting intrusive anomalous use of a software system using multiple detection algorithms
InactiveUS20060085854A1Improve detection accuracyAccurate detectionMemory loss protectionDetecting faulty computer hardwareCountermeasureSoftware system
A method of detecting an intrusion into (or an anomaly in a behavior of) a target software system begins by instrumenting the target software system to generate behavior data representing a current observation or observation aggregate. The method then determines whether the current observation or observation aggregate warrants a second level examination; preferably, this determination is made by processing the current observation or observation aggregate through a first level detection algorithm that provides a first, provisional indication of a possible intrusion. If a result of executing the first level detection algorithm indicates that the current observation or observation aggregate warrants a second level examination, the method continues by processing the current observation or observation aggregate through at least one or more second level detection algorithms to provide a second, more definite, fine grain indication of a possible intrusion. The observation aggregates used by the first and second level detection algorithms may be the same or different. The first and second level detection algorithms may be executed in the same or different systems, machines or processors. The target software system operation may be suspended as the current observation or observation aggregate is processed through the one or more second level detection algorithms. A given action (e.g., sending an alert, logging the event, activating a countermeasure, or the like) may be taken if the result of the second level examination indicates a possible intrusion. Multiple algorithms may be executed together within a single examination level, with the individual results then analyzed to obtain a composite result or output indicative of intrusive or anomalous behavior.
Owner:STRATACLOUD
Trusted services broker for web page fine-grained security labeling
InactiveUS6311269B2Limit installationNeed to installWeb data retrievalDigital data processing detailsPasswordRandom assignment
Arbitrarily fine-grained limitation of access to information stored in a resource of a data processor network is provided in a manner compatible with existing network browsers by mapping user identity and credentials with randomly assigned security cookie information which thus serves as a surrogate credential accompanying each user request during a session. Labels are imbedded within HTML files / text which may embody any desired security policy, including mandatory access control (MAC) arrangements which are not available through native browser functions. Data is retrieved in response to a user request which includes a security cookie from a location in the resource which is not directly accessible through use of a URL; the location being stored in a configuration file which is hidden from users. The retrieved data is then filtered in accordance with labels provided for each page and / or embedded in the text and used to build a response which may include hypertext links or other user interfaces for transmission to the user. Provision is made for viewing or changing of labels, credentials and passwords.
Owner:LEIDOS INNOVATIONS TECH INC
Systems and Methods for Fine Grain Policy Driven Cookie Proxying
ActiveUS20090193129A1Sacrificing securitySacrificing integrityMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionInternet privacyClient-side
The present solution enables a client that is not configured to use cookies to access resources of the server that uses cookies for communications with the clients. An intermediary deployed between a client and a server intercepts and modifies transmissions between the client and the server to compensate for the mismatch in configuration of the cookies between the client and the server. The present disclosure relates to a method for managing cookies by an intermediary for a client. An intermediary receives a response from a server to a request of a client. The response may comprise a uniform resource locator (URL) and a cookie. The intermediary may modify the response by removing the cookie from the response and inserting a unique client identifier into the URL. The intermediary may store the removed cookie in association with the unique client identifier and forward the modified response to the client.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
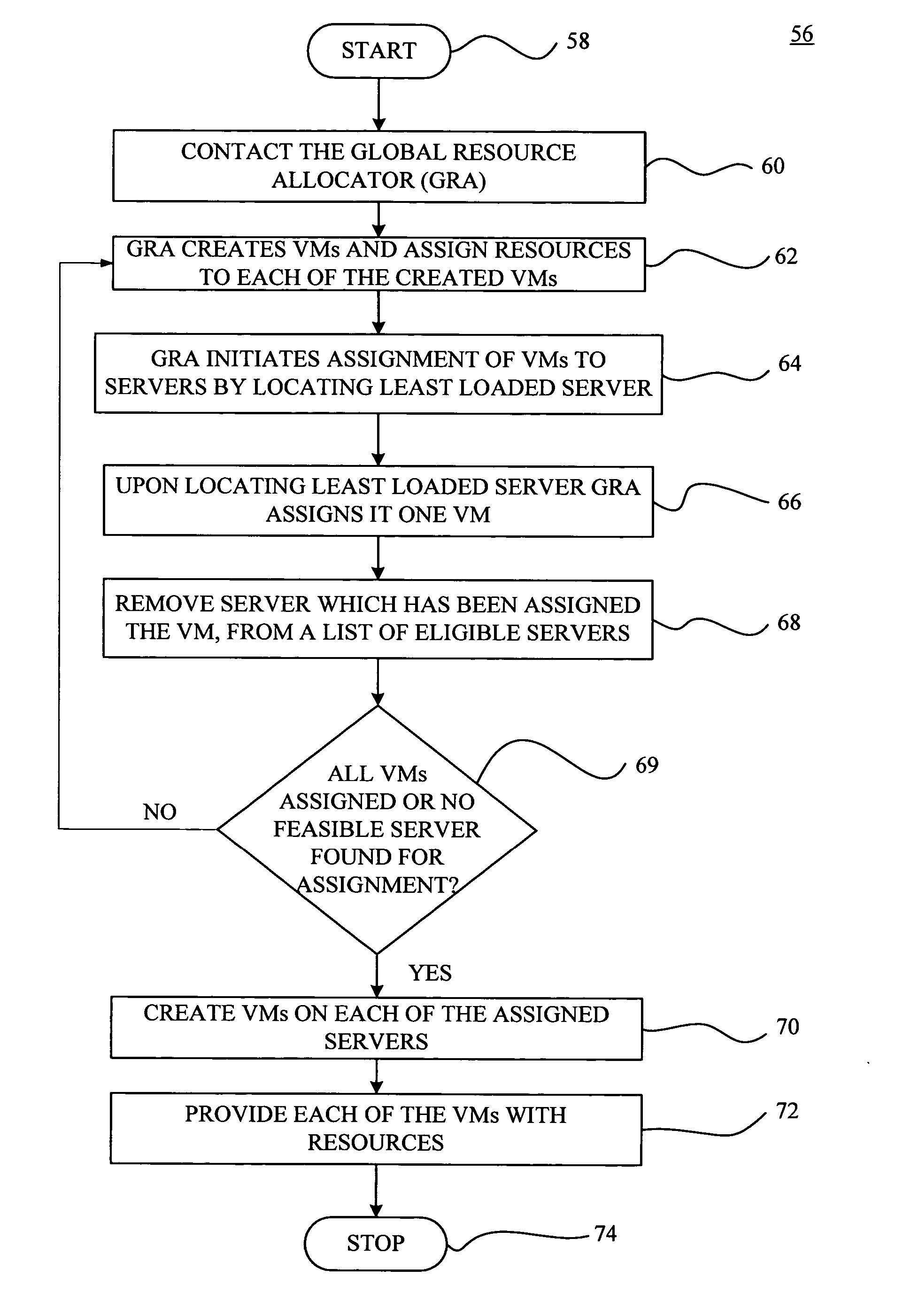
System and method for providing a scalable on demand hosting system
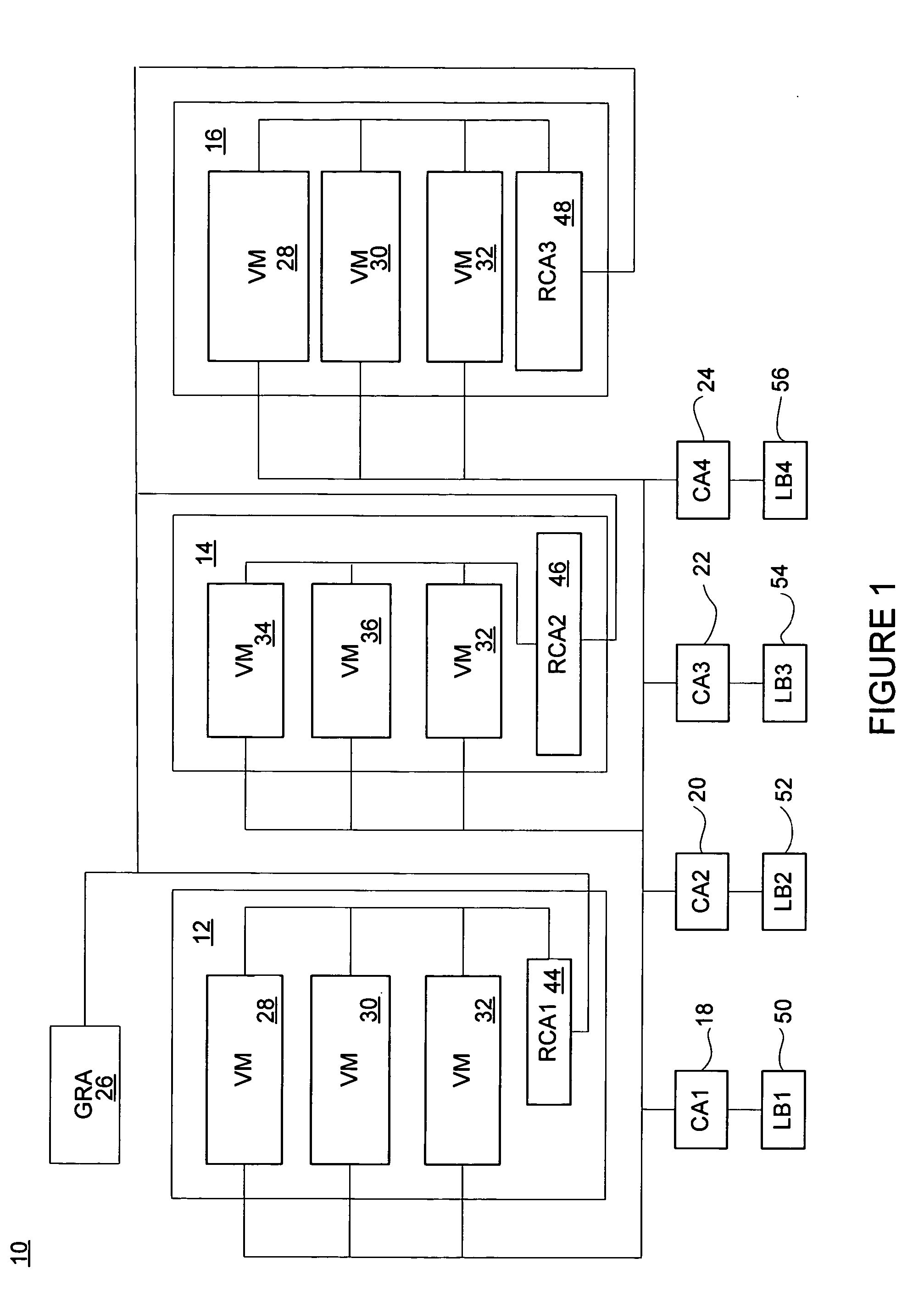
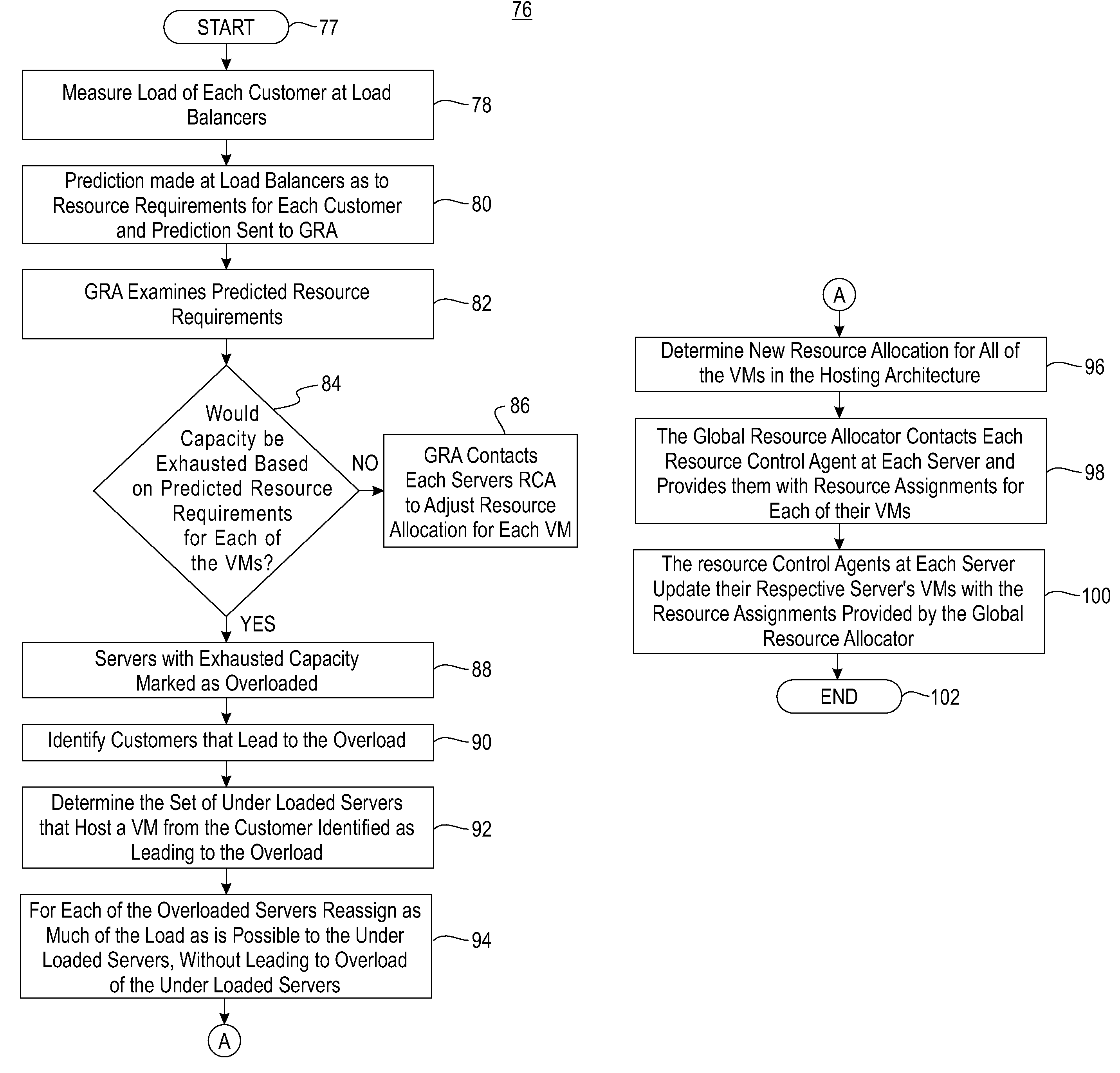
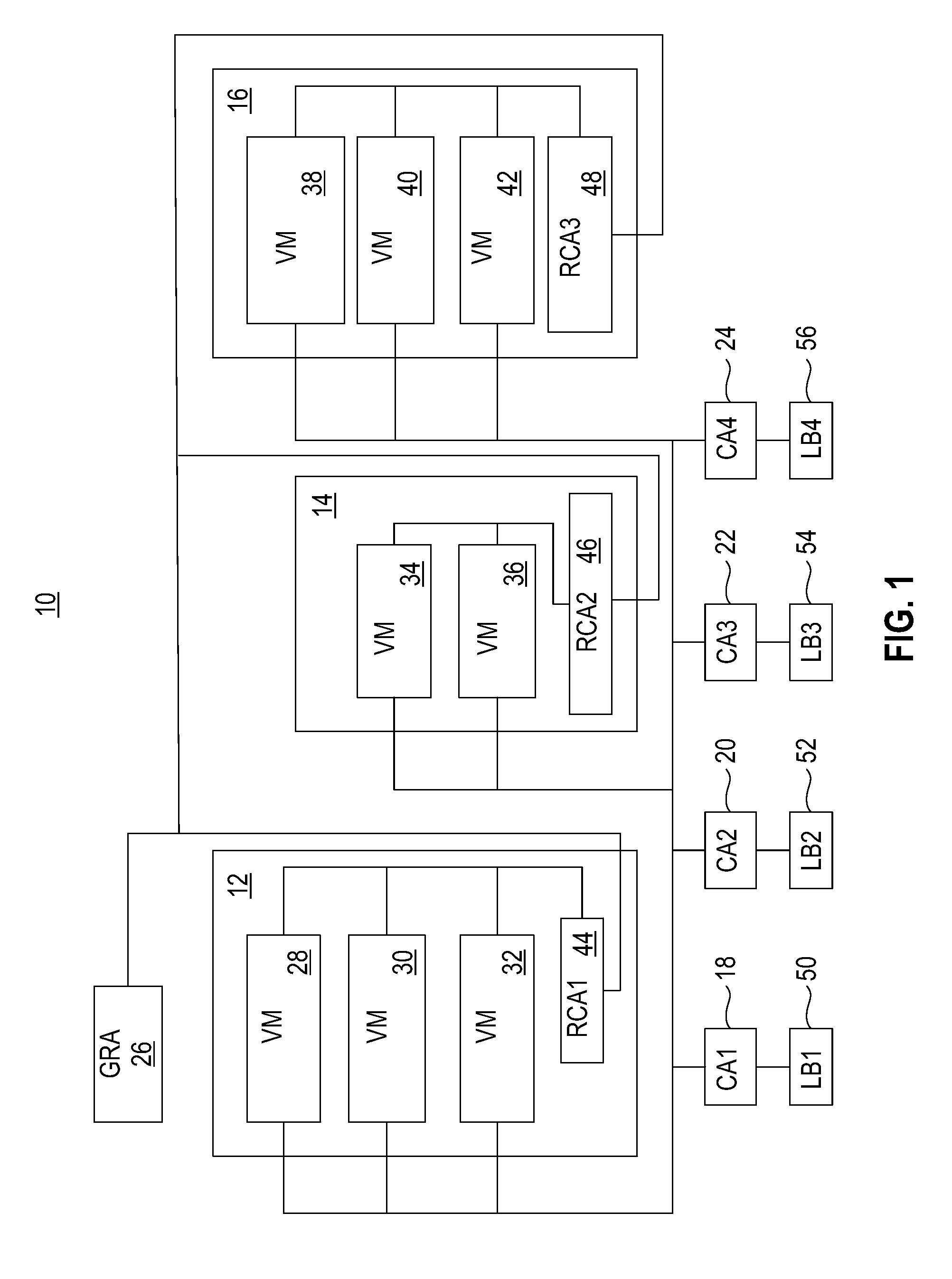
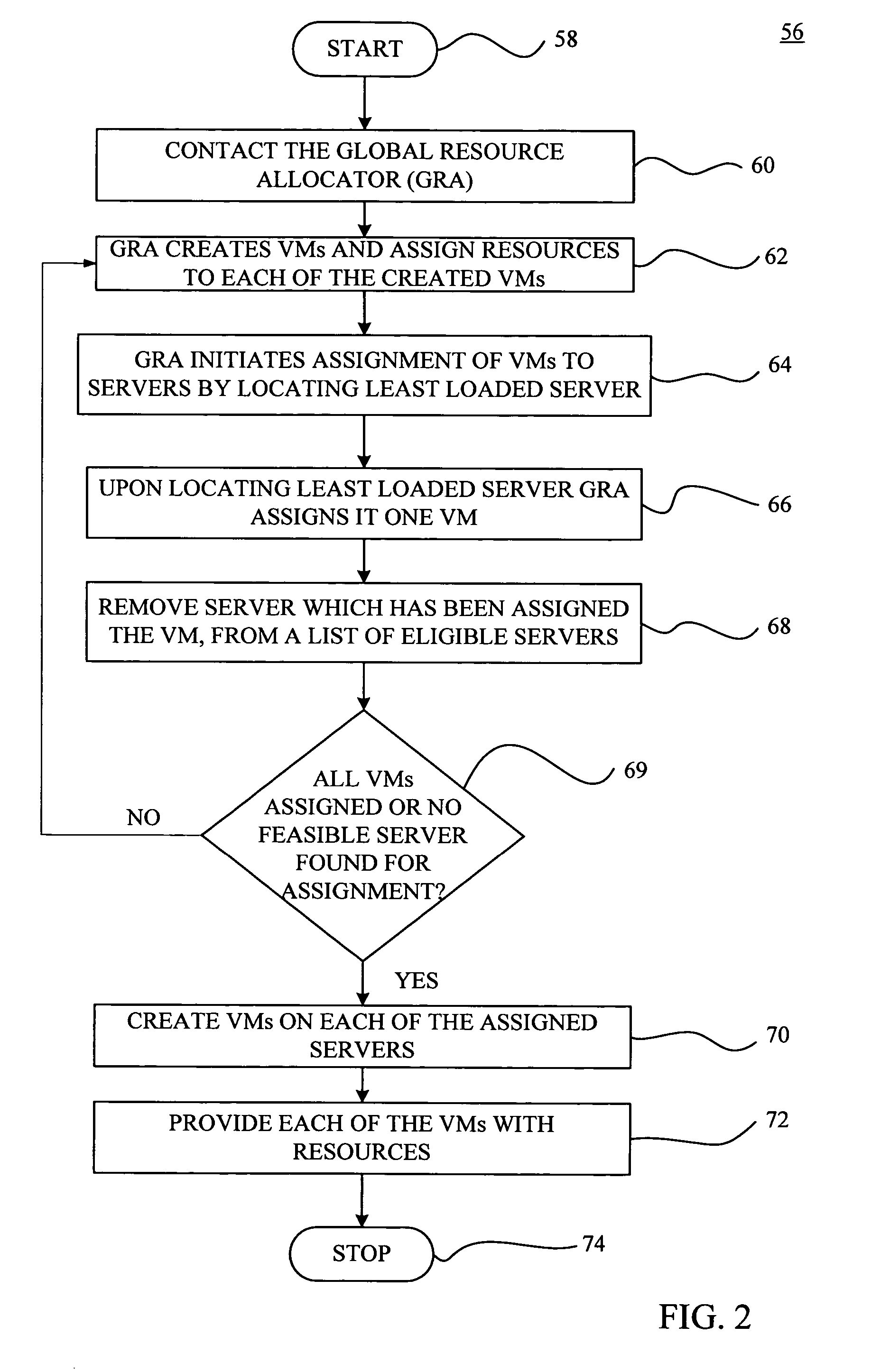
ActiveUS20050108712A1Fine grained controlDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsResource managementWorkload
A VM based hosting architecture system in which finder grain control in optimizing multiple workloads across multiple servers is provided. The system includes a plurality of servers to be utilized by multiple workloads. In addition, the system includes a plurality of virtual machines (VMs) at each of the plurality of servers, wherein the plurality of VMs at each of the plurality of servers each serve a different one of the multiple workloads. Moreover, the system includes resource management logic to distribute server resources to each of the plurality of VMs according to predicted resource needs of each of the multiple workloads. Each of the multiple workloads are distributed across the plurality of servers, wherein fractions of each of the multiple workloads are handles by the plurality of VMs. The distribution of multiple workloads over multiple servers has the effect of achieving a finer grain control in optimizing workloads across the plurality of servers.
Owner:DAEDALUS BLUE LLC
Method and apparatus for dynamic lock granularity escalation and de-escalation in a computer system
A method and apparatus for dynamic lock granularity escalation and de-escalation in a computer system is provided. Upon receiving a request for a resource, a scope of a previously granted lock is modified. According to one embodiment, hash lock de-escalation is employed. In hash lock de-escalation, the scope of the previously granted lock held on a set of resources is reduced by de-escalating the previously granted lock from a coarser-grain lock to one or more finer-grain locks on members of the set. According to another embodiment, hash lock escalation is employed. In hash lock escalation, the scope of previously granted locks held on one or more members of the set of resources are released and promoted into a coarser-grain lock that covers the set of resources as well as the requested resource.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System and method for providing a scalable on demand hosting system
ActiveUS7437730B2Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsResource managementDistributed servers
A VM based hosting architecture system in which finer grain control in optimizing multiple workloads across multiple servers is provided. The system includes a plurality of servers to be utilized by multiple workloads. In addition, the system includes a plurality of virtual machines (VMs) at each of the plurality of servers, wherein the plurality of VMs at each of the plurality of servers each serve a different one of the multiple workloads. Moreover, the system includes resource management logic to distribute server resources to each of the plurality of VMs according to predicted resource needs of each of the multiple workloads. Each of the multiple workloads are distributed across the plurality of servers, wherein fractions of each of the multiple workloads are handled by the plurality of VMs. The distribution of multiple workloads over multiple servers has the effect of achieving a finer grain control in optimizing workloads across the plurality of servers.
Owner:DAEDALUS BLUE LLC
Web based data collaboration tool
A web based data collaboration tool includes a dynamic international collaborative environment in which system partners, including customers, technology partners and suppliers, can exchange information between one another in a truly collaborative environment. The web based data collaboration tool includes unique “fine grain” security at both the document and sub-document level. This allows one source document to be shared between the system partners, including partners from different companies and those located in different countries, based upon an individual document / sub-document security profile. Further, the web based data collaboration tool includes a secure “Sandbox” for peer-to-peer sharing of sensitive documents and electronically incorporates a business area export representative (BAER) approval process that includes the required retention of International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) documents making the web based data collaboration tool fully ITAR compliant.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Articles with super-hydrophobic and/or self-cleaning surfaces and method of making same
ActiveUS20110287203A1Lower contact angleLarge scaleDischarging arrangementMouldsFine grainSelf-cleaning surfaces
Super-hydrophobic and self-cleaning articles produced by imprinting exposed surfaces with suitable fine-grained and / or amorphous metallic embossing dies to transfer a dual surface structure, including ultra-fine features less than or equal to 100 nm embedded in and overlaying a surface topography with macro-surface structures greater than or equal to 1 micron are disclosed.
Owner:INTEGRAN TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com