Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1861 results about "Nitriding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nitriding is a heat treating process that diffuses nitrogen into the surface of a metal to create a case-hardened surface. These processes are most commonly used on low-carbon, low-alloy steels. They are also used on medium and high-carbon steels, titanium, aluminium and molybdenum. In 2015, nitriding was used to generate unique duplex microstructure (Martensite-Austenite, Austenite-ferrite), known to be associated with strongly enhanced mechanical properties...
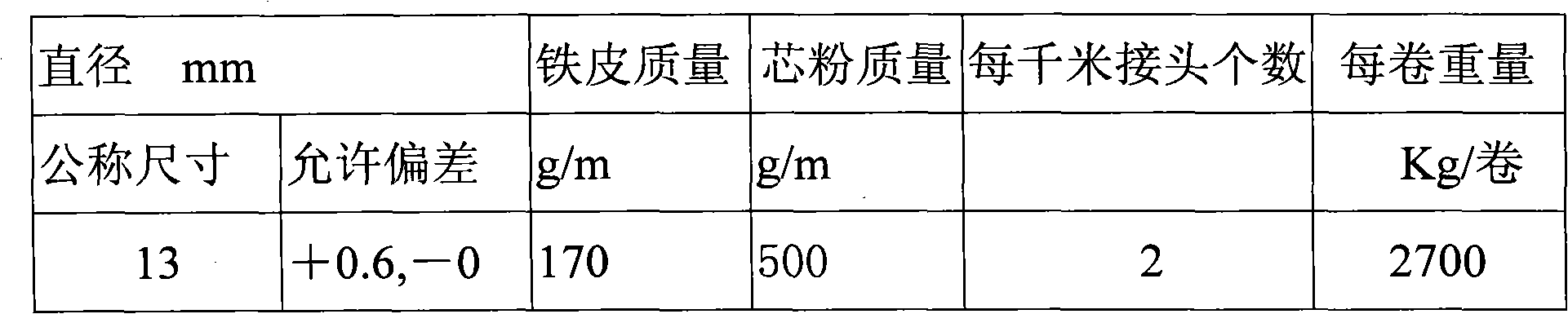
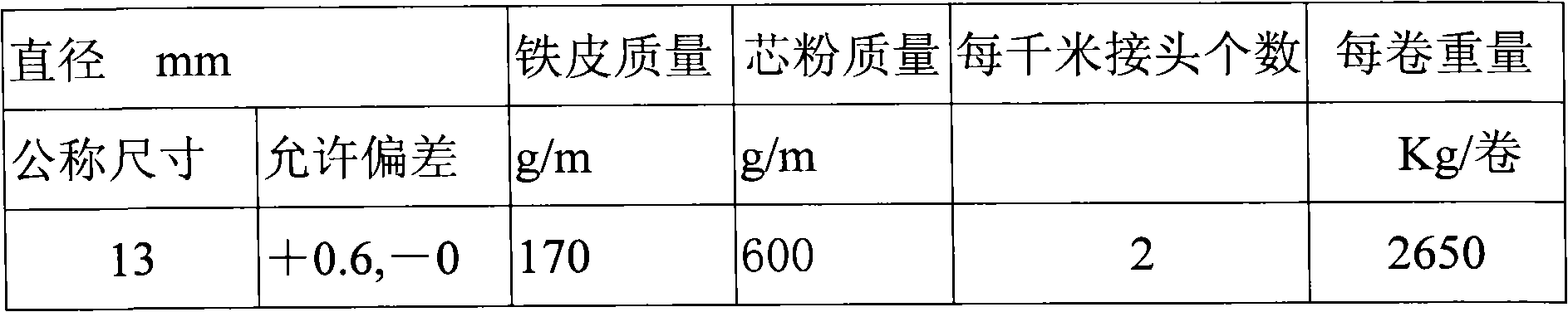
Metallurgical V-N microalloying and compound deoxidation cored wire
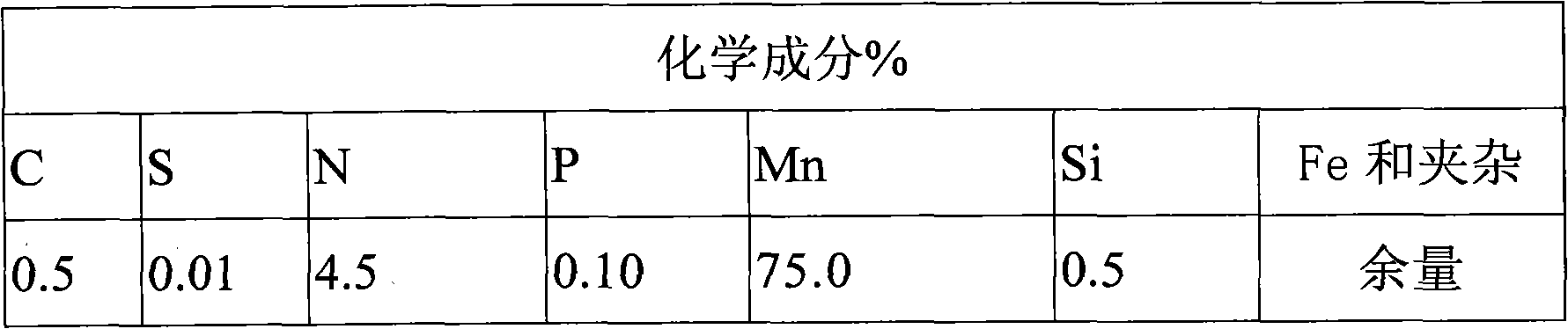
A metallurgical V-N microalloying and compound deoxidation cored wire contains a core wire and a cladding steel belt. The technical key point of the cored wire is as follows: the core wire of the cored wire consists of a vanadium-increasing agent, a nitrogen-increasing agent and a deoxidizing nitrogen-fixing agent of which particle sizes are less than 6mm, wherein the vanadium-increasing agent is ferrovanadium, nitrided ferrovanadium or vanadium pentoxide; the nitrogen-increasing agent is ferrosilicon nitride, silicomanganese nitride, ferromanganese nitride, ferrochromium nitride, silicon nitride, aluminum nitride or calcium cyanamide; and the deoxidizing nitrogen-fixing agent contains one or more of aluminum, calcium, magnesium and barium, and can also contain one or more of titanium, zirconium, niobium, manganese, chromium, silicon, carbon and iron. By adopting the cored wire, the V / N ratio of steel can get closer to the optimal proportion, the enhancing function of vanadium can be utilized furthest, vanadium resources can be saved, the recovery rate of nitrogen is high, the nitrogen content is stable, the compound deoxidation function can also be realized, the V-N microalloying cost can be reduced and the quality of steel can be increased.
Owner:侯巍 +2
Short fiber-particle synergetically-reinforced copper-based composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a copper-based composite material, and particularly relates to a short fiber-particle synergetically-reinforced copper-based composite material which is prepared through powder metallurgy. Short fibers and particles are used as reinforced phases, the content of the short fiber is 0.1-0.1 wt%, and the content of reinforcement particles is 0.1-10 wt%. The short fibers can be carbon nanotubes, carbon nanofibers, ceramic short fibers, and the like, and the particles used as reinforced phases can be aluminum oxide, zirconium oxide, magnesium oxide, titanium dioxide, silicon carbide, titanium carbide, tungsten carbide, silicon nitride, aluminum nitride, titanium nitride, titanium diboride, Ti3SiC2, and the like. The composite material is prepared through the steps of mixing, forming, sintering and processing, and the room temperature and the high temperature strength of the composite material can be increased by more than 3 times in comparison with those of pure copper; the electrical conductivity of the composite material can reach more than 80% of that of pure copper; the thermal conductivity of the composite material can reach more than 70% of that of pure copper; the coefficient of friction of the composite material can be reduced to be below 70% of that of pure copper; and the wear rate of the composite material can be reduced to be below 50% of that of pure copper.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Increasing reliability of copper-based metallization structures in a microstructure device by using aluminum nitride
ActiveUS20080179741A1Improve adhesionSuperior performance characteristicSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSelf limitingCopper
By forming an aluminum nitride layer by a self-limiting process sequence, the interface characteristics of a copper-based metallization layer may be significantly enhanced while nevertheless maintaining the overall permittivity of the layer stack at a lower level.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
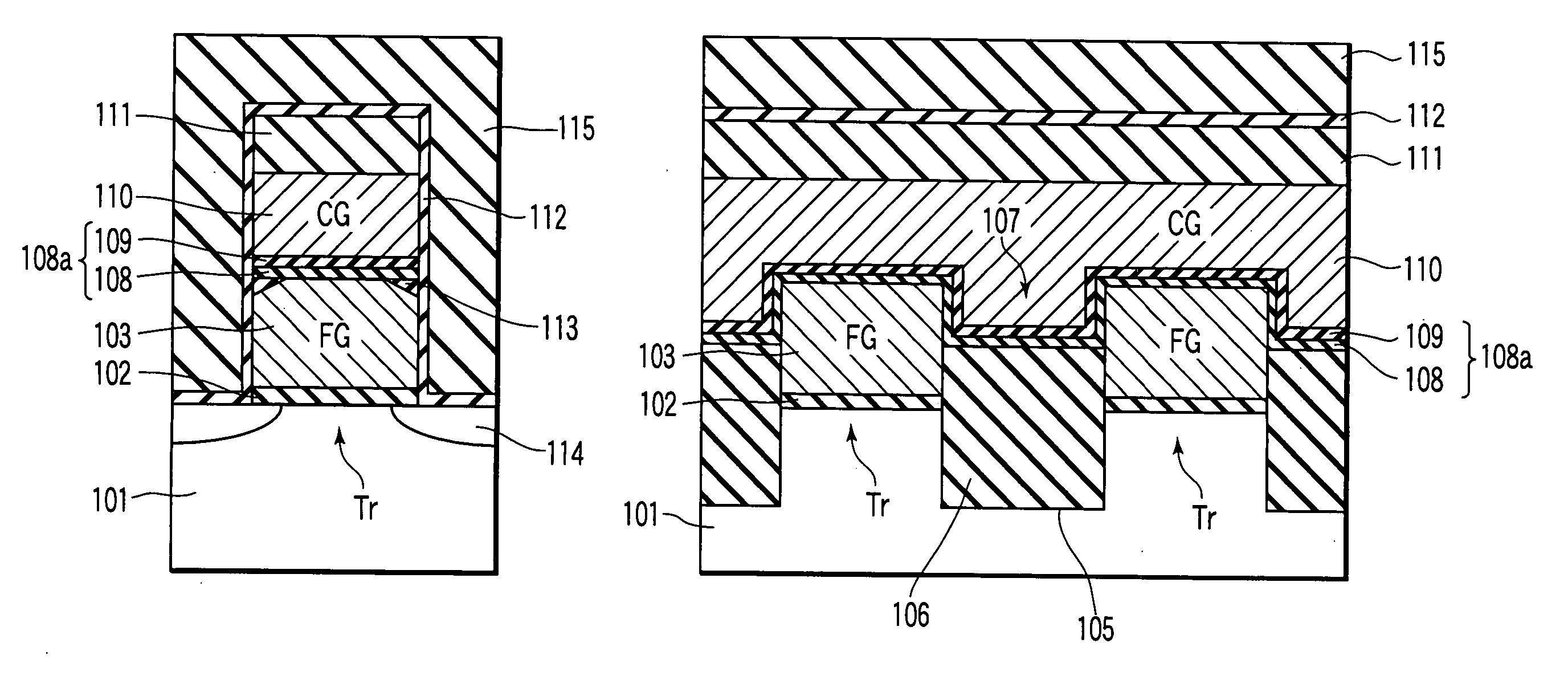
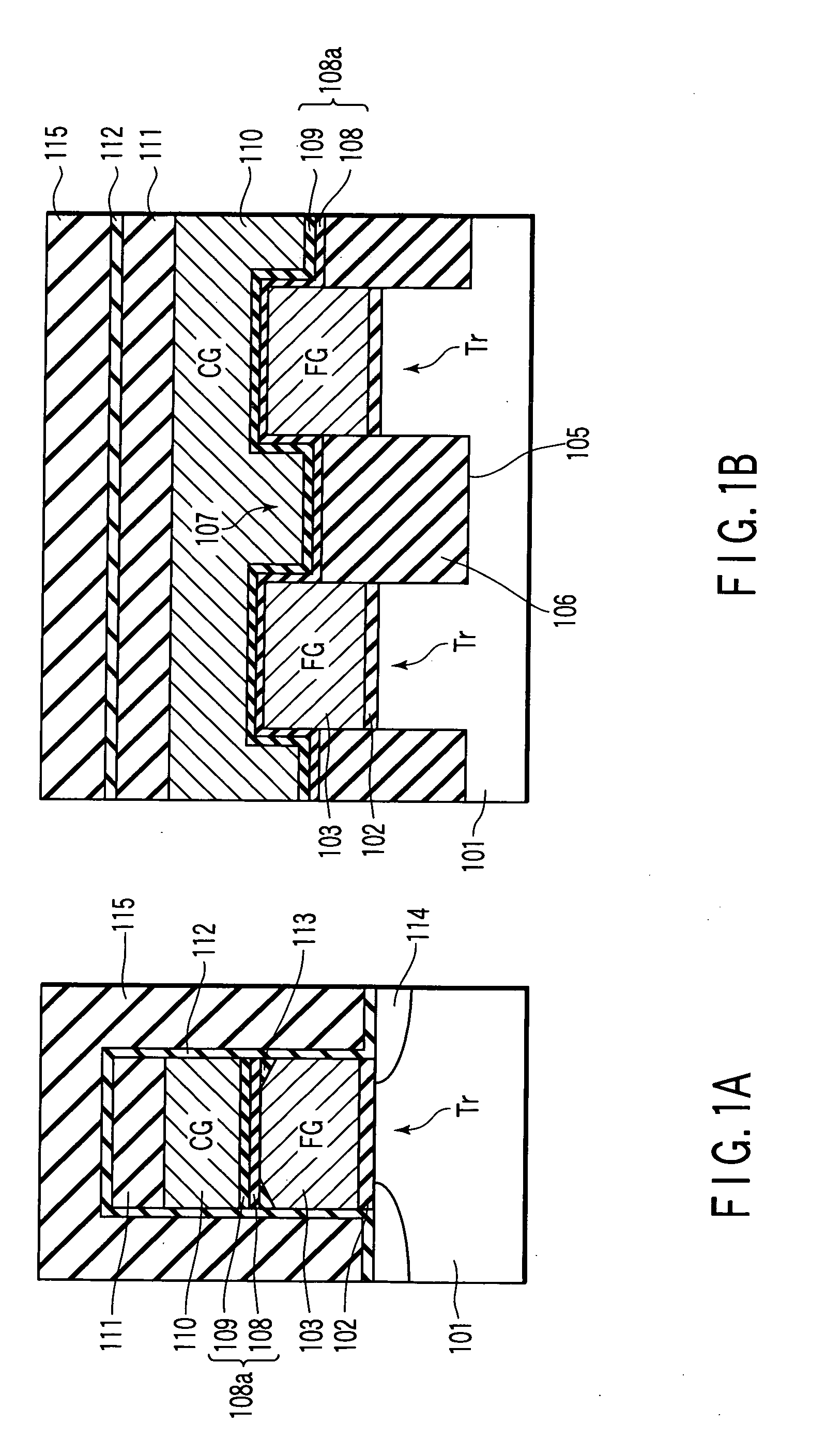
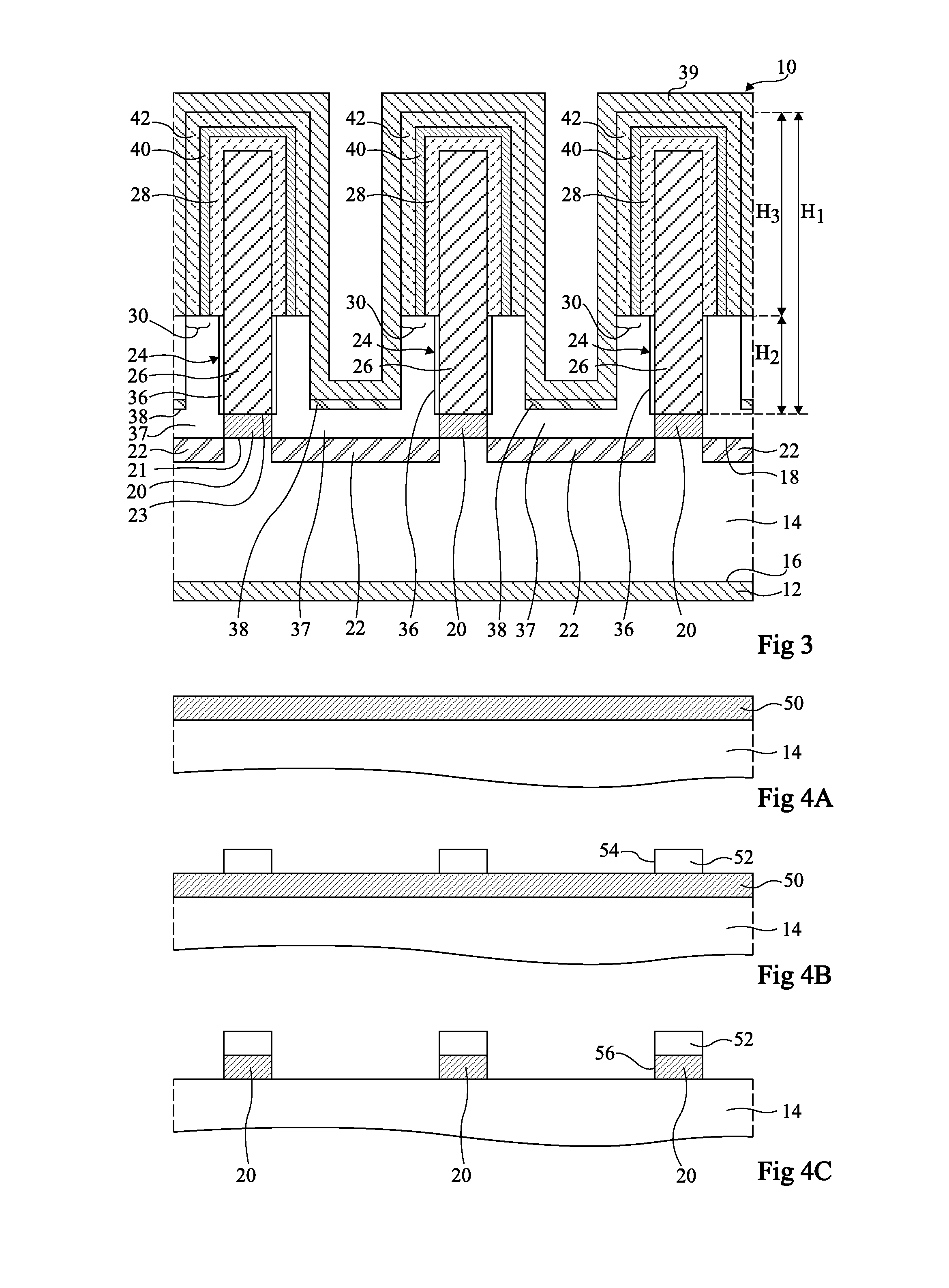
Semiconductor memory device and method of manufacturing the same
A semiconductor memory device manufacturing method includes forming a floating gate electrode above a semiconductor substrate, forming an interelectrode insulating film above the floating gate electrode, forming a first radical nitride film on a surface of the interelectrode insulating film by first radical nitriding, and forming a control gate electrode on the first radical nitride film.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Heat Sink Having a Cooling Structure with Decreasing Structure Density
InactiveUS20160069622A1Increase distanceReduce material densityLighting support devicesDigital data processing detailsSelective laser meltingCarbon nanotube
A heat sink for cooling a heat generating device comprises a body part with a first surface for contacting the heat generating device, and a second surface contacting a cooling part, and the cooling part including a cooling structure. The structure density of the cooling structure decreases with increasing distance to body part. The cooling structure may be a three dimensional structure e.g. a grid or a lattice, but the cooling structure may also be fins projecting or extending from the second surface of the body part. The heat sink can be manufactured using additive manufacturing e.g. selective laser melting process (SLM). The heat sink can be made of metals e.g. aluminum, copper, ceramics e.g. aluminium nitride (AlN), silicon carbide or a composite containing graphite, graphene or carbon nanotubes.
Owner:ALEXIOU & TRYDE HLDG APS
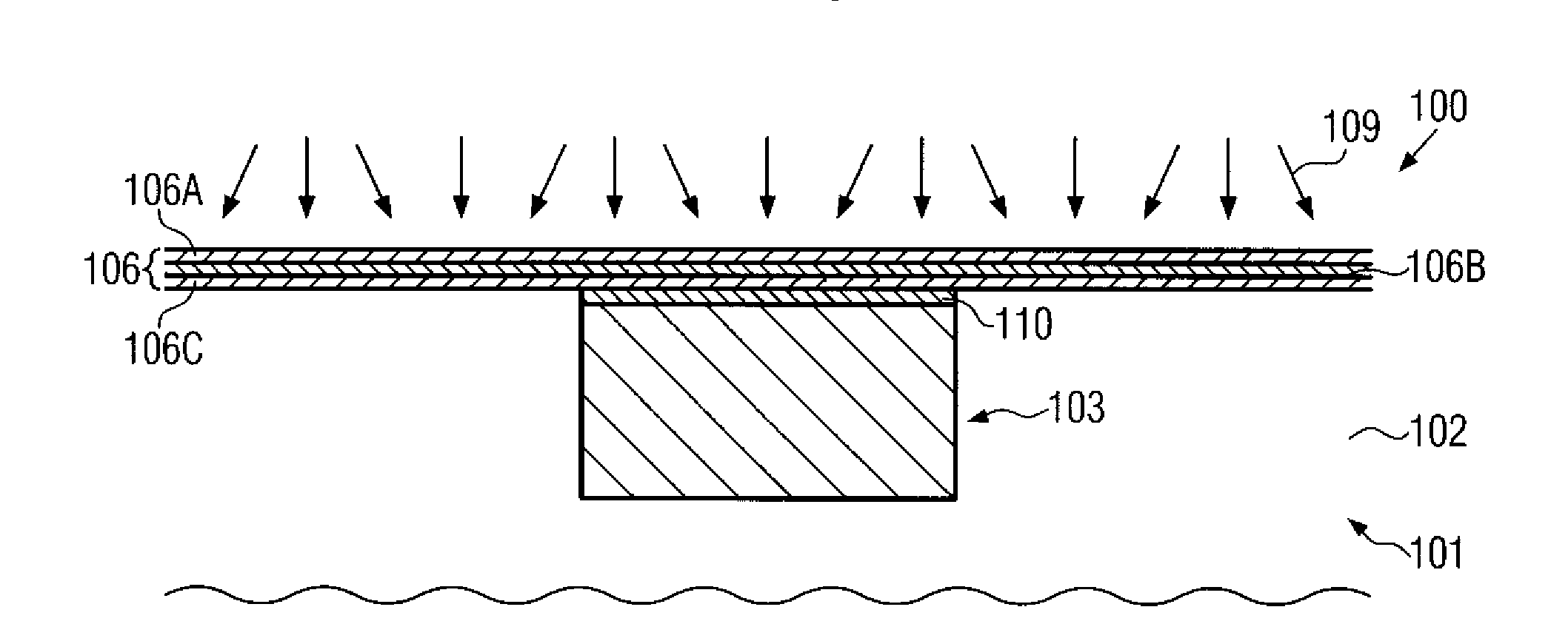
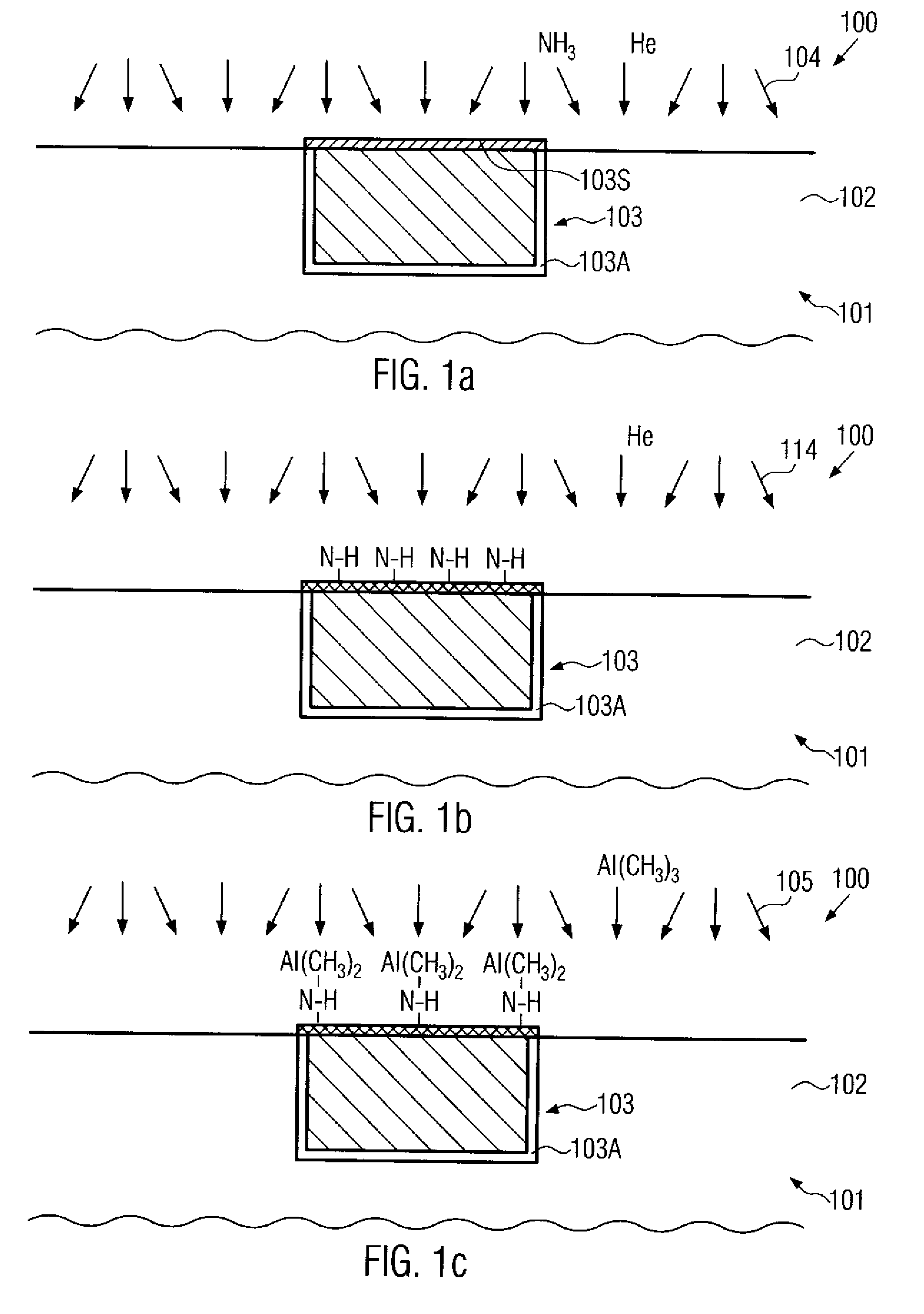
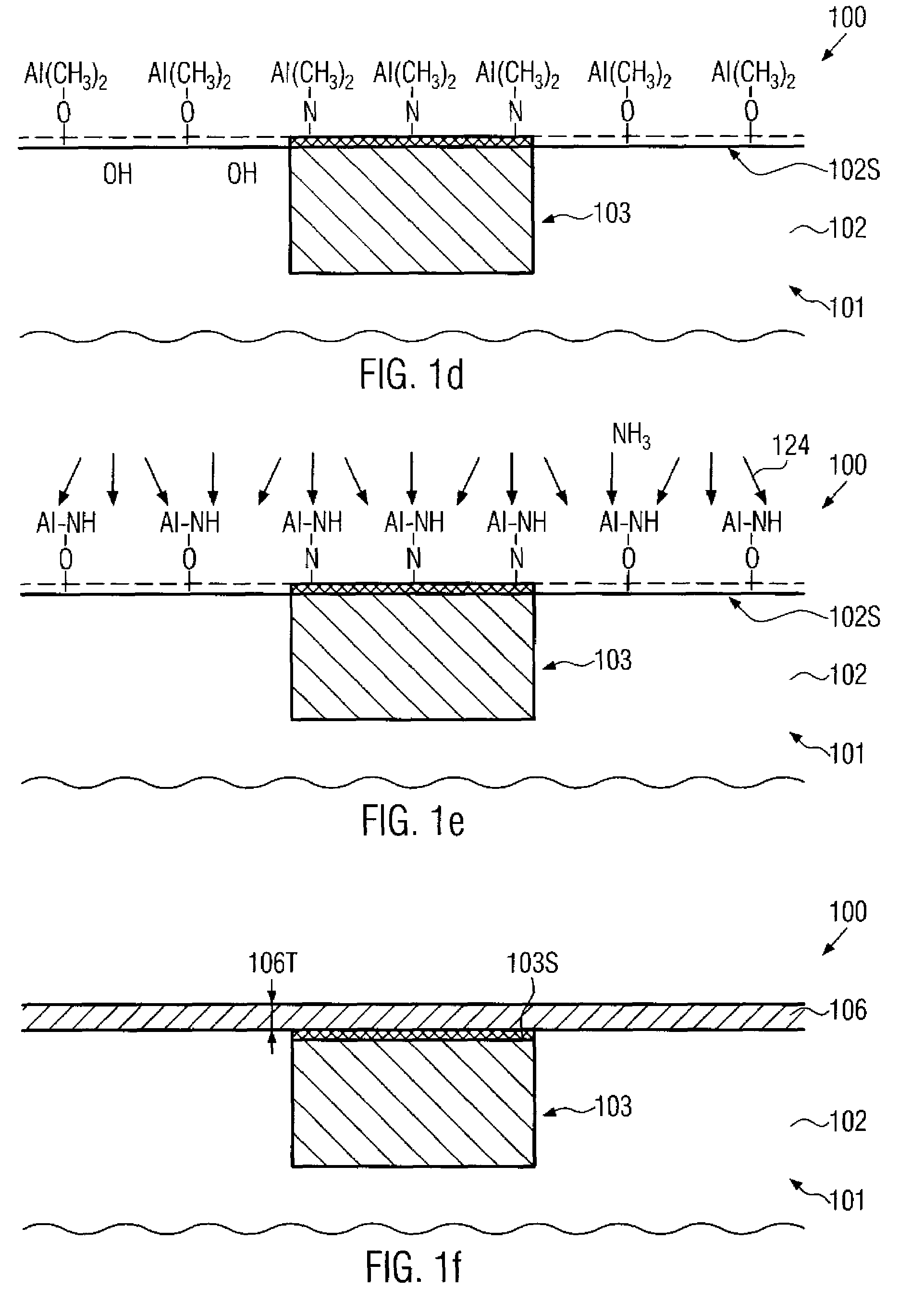
Method for depositing nanolaminate thin films on sensitive surfaces
InactiveUS20060079090A1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen halideCorrosive chemical
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Orientating silicon steel, manufacturing process and equipment
ActiveCN1796587AReduce energy consumptionReduce manufacturing costSolid state diffusion coatingFurnace typesSiliconHot rolled
This invention relates to an oriented silicon steel and its processing method and equipment. It comprises of 0.035~0.060% of C, 2.5~3.5% of Si, 0.08~1.8% of Mn, 0.005~0.010% of S, 0.015~0.035% of Al, 0.0050~0.0090% of N, 0.01~0.15% of Sn, 0.010~0.030% of P and 0.05~0.12% of Cu, with the rest iron. The processing method includes: a) smelting; b) hot rolling. Billets are heated to 1100~1200 deg.C and rolling temperature is lower than 1200 deg.C with a finishing temperature of above 850 deg.C and a coiling temperature of below 650 deg.C; c) normalizing. Hot-rolled boards are normalizing annealed at 1050~1180 deg.C for 1~20 seconds and 850~950 deg.C for 30~200 seconds and then cooled quickly; d) cold rolling. Boards are rolled to product thickness by one-off cold rolling or repetitious cold rolling with intermediate annealing; e) nitriding, decarbonization and high-temperature and hot-leveling annealing with boards coated with high-temperature annealing isolation agents mainly made of MgO.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
High-entropy alloy binder phase-based nitrogen-containing hard alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high-entropy alloy binder phase-based nitrogen-containing hard alloy, wherein the binder phase of the nitrogen-containing hard alloy is high-entropy alloy, and the hard phase of the nitrogen-containing hard alloy is uniformly distributed WC (Wolfram Carbide) and carbon nitride solid solution; the high-entropy alloy binder phase is at least four of iron, cobalt, nickel, chromium, aluminum, vanadium, titanium, copper, zirconium, molybdenum and manganese; the molar ratio of content of each element is 5-35 percent; the carbon nitride solid solution is at least one of Ti(Cx, N1-x) and (Ti, M1, ......)(Cx, N1-x); and M1 component in the (Ti, M1, ......)(Cx, N1-x) is at least one of W, Mo, Ta, Nb, V, Cr, Zr, Hf, Y and lanthanides. According to a preparation method of the high-entropy alloy binder phase-based nitrogen-containing hard alloy, the alloy comprises the raw material components in percentage by weight: 3-25 percent of high-entropy alloy binder phase, 45-96.9 percent of WC powder and 0.1-30 percent of carbon nitride solid solution powder, wherein the nitrogen element in the nitrogen-containing hard alloy is introduced through the carbon nitride solid solution. The preparation method of the multi-element composite carbon nitride solid solution-based nitrogen-containing hard alloy comprises the following steps of: (1) mixing through ball milling; (2) shaping; and (3) performing low-pressure sintering.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method of Forming a Self Aligned Copper Capping Layer
InactiveUS20080311739A1Prevent further spreadPreventing inter-metal line leakageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCopper interconnectChemical exposure
A method of forming a capping layer on a copper interconnect line (14). The method comprises providing a layer (20) of Aluminium over the interconnect line (14) and the dielectric layer (10) in which it is embedded. This may be achieved by deposition or chemical exposure. The structure is then subjected to a process, such as annealing or further chemical exposure, in an environment containing, for example, Nitrogen atoms, so as to cause indiffusion of Al into the copper line (14) and nitridation to form a diffusion barrier 26 of the intermetallic compound CuAlN.
Owner:NXP BV
Lightweight dry refractory
A dry refractory composition having superior insulating value. The dry refractory composition also may have excellent resistance to molten metals and slags. The composition includes filler lightweight material, which may be selected from perlite, vermiculite, expanded shale, expanded fireclay, expanded alumina silica hollow spheres, bubble alumina, sintered porous alumina, alumina spinel insulating aggregate, calcium alumina insulating aggregate, expanded mulllite, cordierite, and anorthite, and matrix material, which may be selected from calcined alumina, fused alumina, sintered magnesia, fused magnesia, silica fume, fused silica, silicon carbide, boron carbide, titanium diboride, zirconium boride, boron nitride, aluminum nitride, silicon nitride, Sialon, titanium oxide, barium sulfate, zircon, a sillimanite group mineral, pyrophyllite, fireclay, carbon, and calcium fluoride. The composition also may include dense refractory aggregate, which may be selected from calcined fireclay, calcined Chamotte, a sillimanite group mineral, calcined bauxite, pyrophyllite, silica, zircon, baddeleyite, cordierite, silicon carbide, sintered alumina, fused alumina, fused silica, sintered mullite, fused mullite, fused zirconia, sintered zirconia mullite, fused zirconia mullite, sintered magnesia, fused magnesia, sintered spinel, and fused spinel refractory grog, a heat activated bonding agent, and a dust suppressant.
Owner:ALLIED MINERAL PROD
Nitrogen-containing alloy and method for producing phosphor using the same
InactiveUS20090140205A1Suppress rapid progressHigh performanceLuminescent compositionsFluorescenceNitrogen gas
There is provided a method for industrially producing a phosphor with high performance, in particular, high brightness. There is also provided a nitrogen-containing alloy and an alloy powder that can be used for the production method. A method for producing a phosphor includes a step of heating a raw material for the phosphor under a nitrogen-containing atmosphere, in which an alloy containing two or more different metal elements constituting the phosphor is used as the whole or part of the raw material for the phosphor, and in the heating step, the heating is performed under conditions such that the temperature change per minute is 50° C. or lower.It is possible to suppress the rapid progress of a nitridation reaction in heat treatment in producing the phosphor using an alloy for a phosphor precursor as the whole or part of the raw material, thereby industrially producing the phosphor with high performance, in particular, high brightness.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Chromium nitride aluminum-titanium composite coating, cutter deposited with same, and preparation method
InactiveCN102166849AHigh hardnessStrong adhesionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingOxidation resistantHigh surface
The invention discloses a chromium nitride aluminum-titanium composite coating, a cutter deposited with the same, and a preparation method. A Cr bonding layer, a CrN supporting layer and a main wear-resistant layer are sequentially deposited on a cutter substrate, wherein the main wear-resistant layer is a multi-layer composite coating composed of a TiAlN layer in a nanocrystalline structure and a CrTiAlN layer in a superlattice structure in an alternate mode, thereby obtaining the cutter with the chromium nitride aluminum-titanium composite coating. The chromium nitride aluminum-titanium composite coating provided by the invention combines the advantages of high hardness, low friction coefficient, strong adhesive force and high oxidation resistance temperature of the superlattice structure and nanocrystalline structure. The obtained cutter has high surface hardness, relatively strong film-base adhesive force, good wear resistance and good high temperature resistance.
Owner:YICHANG HOUHUANG VACUUM TECH
Preparation method of wear-resistant high-chromium cast iron
The invention discloses a preparation method of wear-resistant high-chromium cast iron and belongs to the technical field of metal materials. According to the preparation method, common scrap steel, carburant, ferrochromium, ferromolybdenum, copper plates, ferrochromium nitride, ferrosilicon, ferromanganese, ferroboron and aluminum are smelted in an electric furnace so as to form the wear-resistant high-chromium cast iron. The molten wear-resistant high-chromium cast iron comprises the following chemical components in percentage by mass: 3.0-3.5% of C, 18-25% of Cr, 0.3-0.5% of Mn, 0.3-0.5% of Si, 0.18-0.25% of N, 0.5-0.8% of Mo, 0.2-0.4% of B, 0.08-0.12% of Al, 0.5-1.0% of Cu, less than 0.05% of S, less than 0.05% P and the balance of Fe. Molten iron is treated with an inoculator when taken out from the electric furnace, and is treated with a suspending agent when poured, so as to obtain fine solidification structures. Therefore, the wear-resistant high-chromium cast iron has excellent properties.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
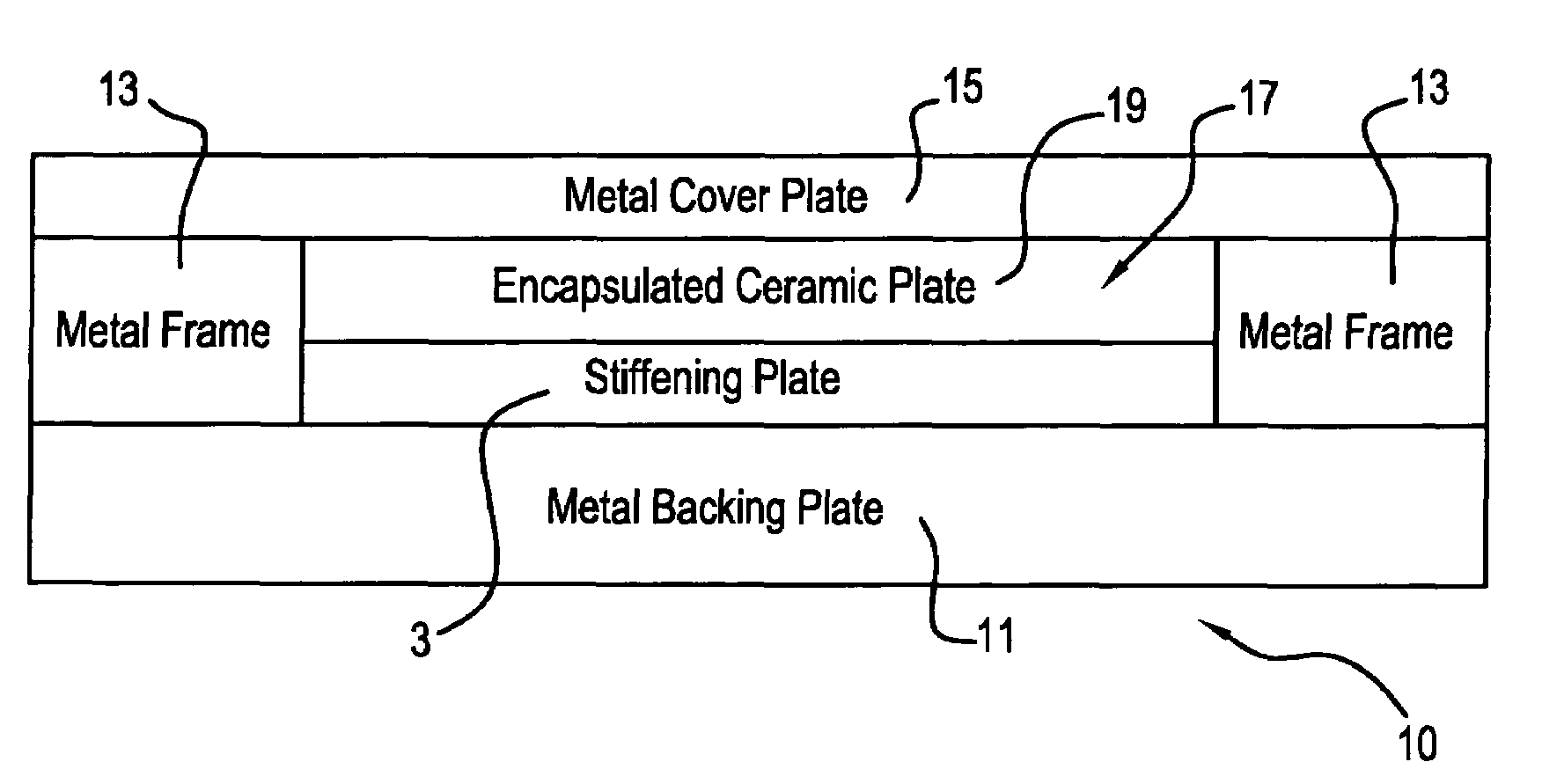
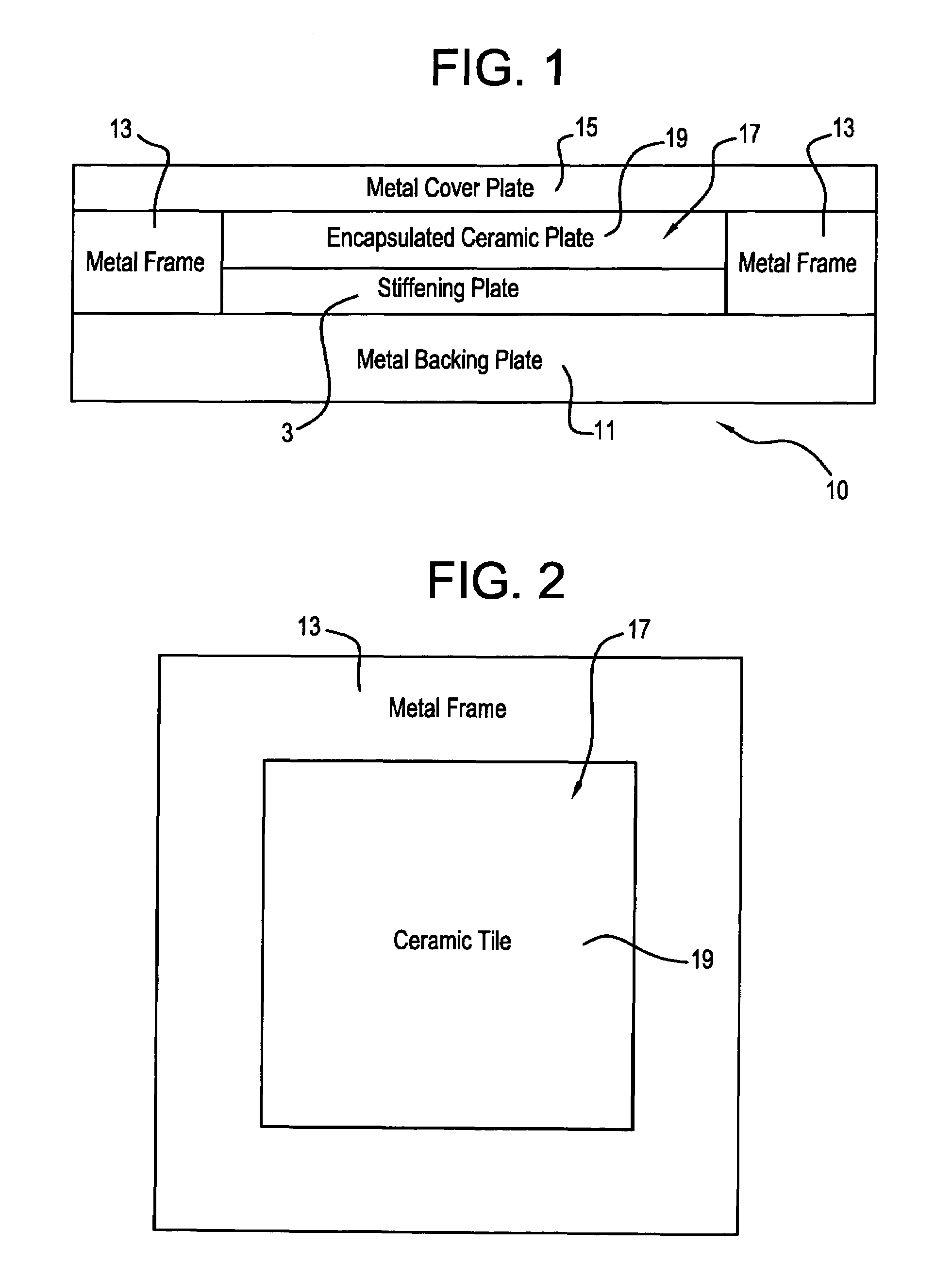
Ceramic armor and method of making by encapsulation including use of a stiffening plate
InactiveUS7069836B1Improve simplicityDoor/window protective devicesArmoured vehiclesCeramic compositeBoron carbide
A ceramic armor is disclosed in several embodiments. In a first embodiment, a metal base plate has a metal frame assembled on it having a central opening into which the ceramic material and stiffening plate are placed. A cover plate is placed over the frame to enclose the ceramic material on all sides. In a second embodiment, the frame has an open central area that has two crossing walls that define four sub-chambers. Four sets of ceramic material and stiffening plate are placed in the respective sub-chambers and a covering plate is placed over them. In a further embodiment, the frame has a plurality of cavities mechanically formed in it. A stiffening plate and a ceramic tile or plate are placed in each cavity and a cover plate is placed over the frame. The metal used to encapsulate the ceramic material may, if desired, comprise a Titanium alloy such as Ti-6Al-4V, and the ceramic material may comprise Silicon Carbide, Boron Carbide, Tungsten Carbide, Titanium Diboride, Aluminum Oxide or Aluminum Nitride. The stiffening plate is preferably made of a Ti—TiB cermet composite but may also be comprised of an armor ceramic such as WC, TiB2, Al2O3 or B4C. A hot pressing procedure is carried out on the armor to cause the metal to plastically deform about the encapsulated ceramic material.
Owner:BAE SYST ADVANCED CERAMICS
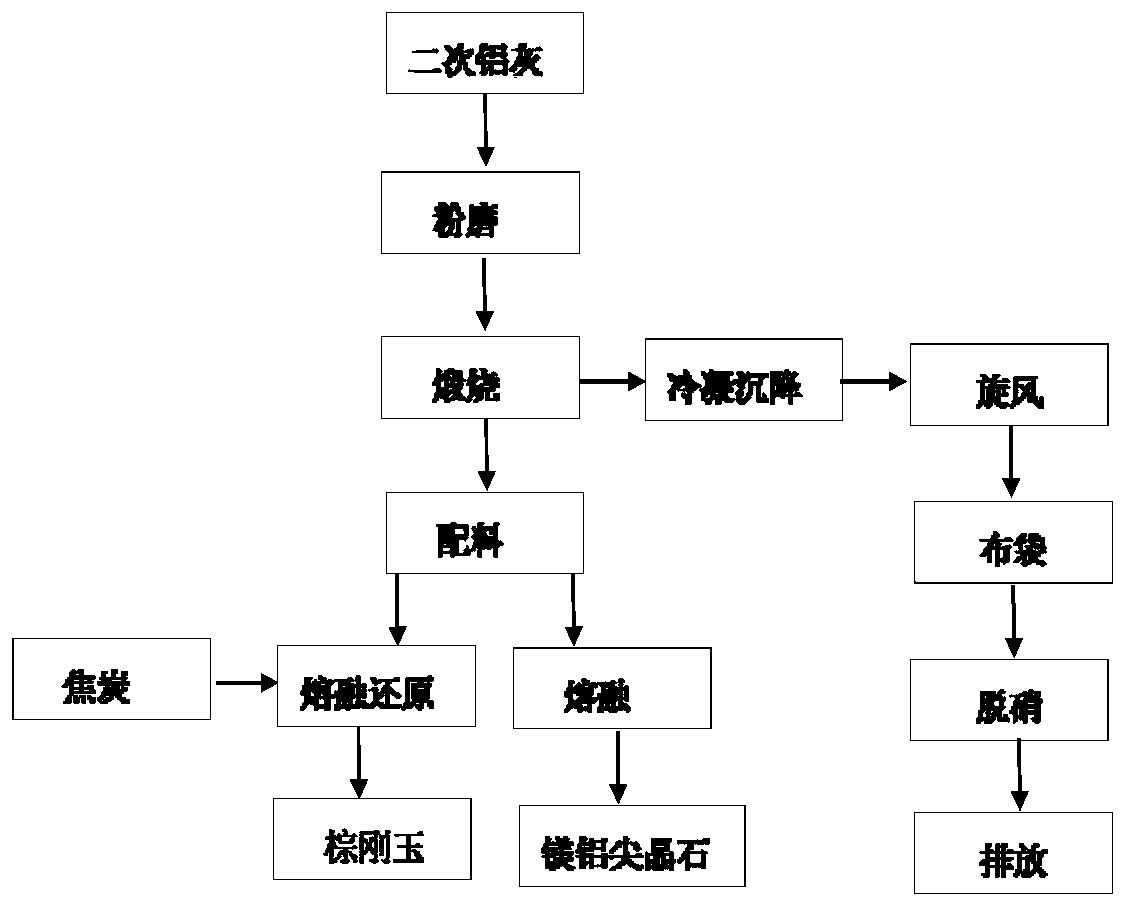
Method of manufacturing refractory material by innocent treatment of secondary aluminum ash
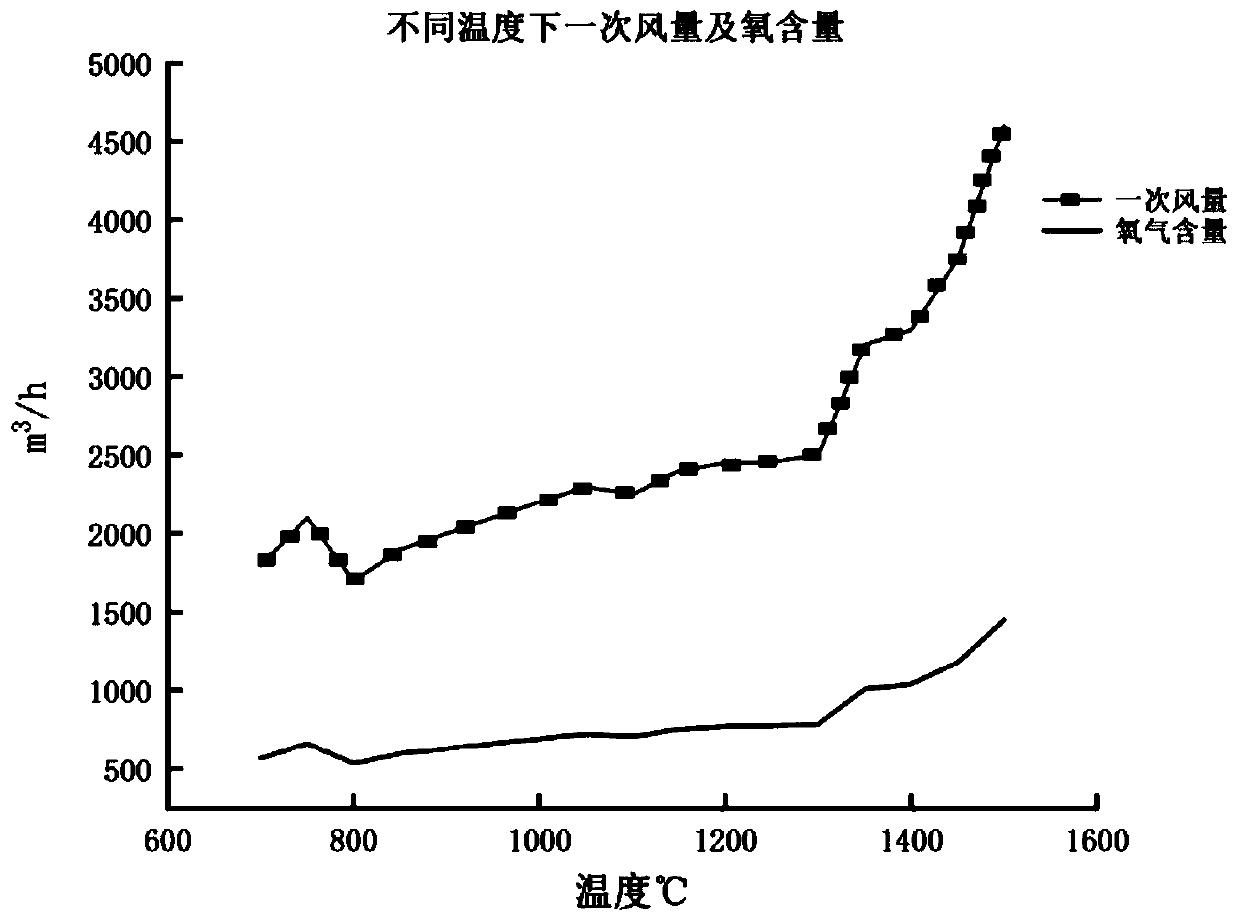
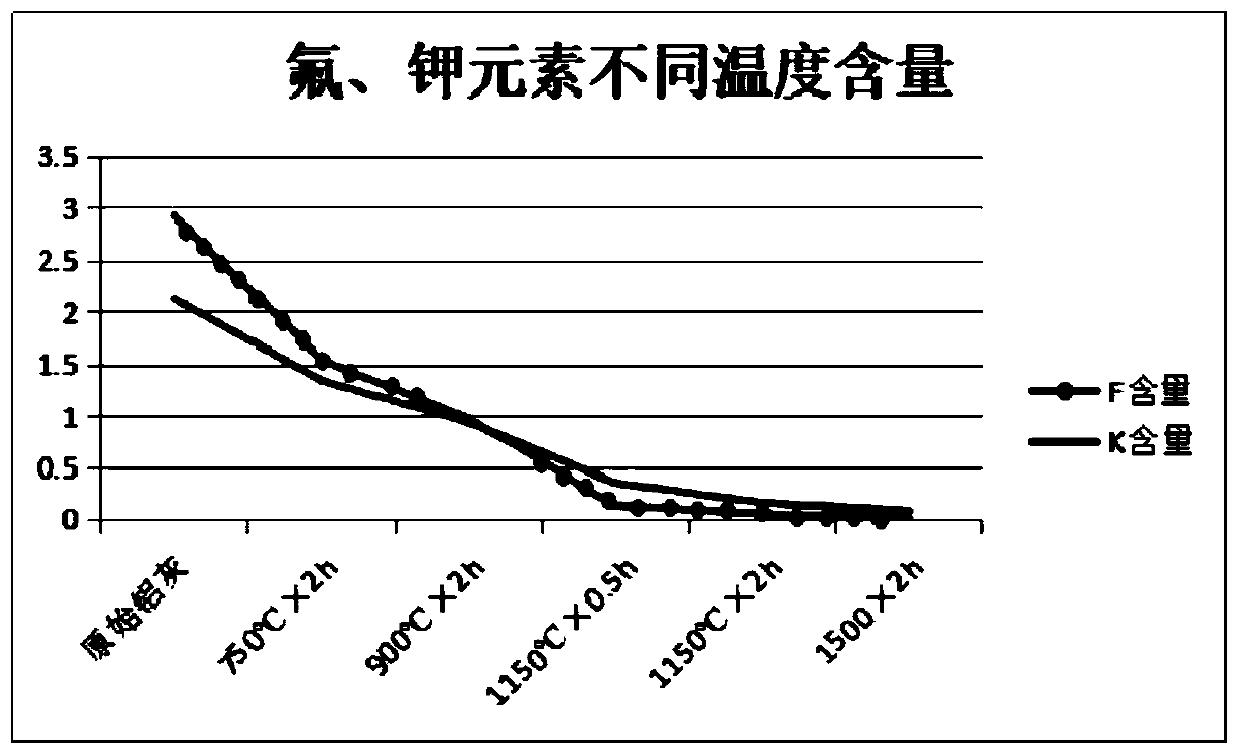
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a refractory material by innocent treatment of secondary aluminum ash, and belongs to the field of aluminum industry. The method comprises the following steps: further grinding the secondary aluminum ash until 80% of the secondary aluminum ash passes through a screen with the pore diameter of 74 microns; and calcining the secondary aluminum ash for 0.5-4 hours at the temperature of 1150-1550 DEG C in an oxidizing atmosphere with the oxygen content of 12%-18% to convert metal aluminum, aluminum nitride and aluminum carbide in the secondary aluminum ash into aluminum oxide and volatilize the fluoride salt and chloride salt in the secondary aluminum ash, thereby producing a calcined oxide; cooling the waste flue gas containing fluoride salt and chlorate produced in the calcining process for recovery, and denitrifying and discharging the flue gas. The calcined oxide is independently prepared or mixed with an additive, and the aluminum-magnesium refractory material is prepared after electric arc melting. The preparation method can be used for preparing the refractory material with high purity.
Owner:BEIJING MINING & METALLURGICAL TECH GRP CO LTD
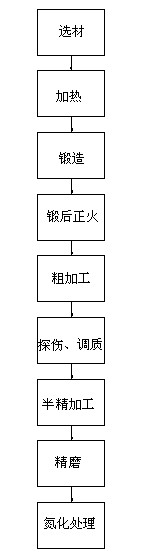
Method for manufacturing bevel gear of axle gear box for diesel locomotives
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a bevel gear of an axle gear box for diesel locomotives, which comprises the steps of blank forging, blank heat-treatment, gear-blank processing, gear-shape processing, gear-end processing, gear-surface heat-treatment, precise reference modification and gear-shape finish-machining, wherein the step of blank heat-treatment comprises the sub-steps of normalizing and thermal refining; the step of gear-blank processing comprises the sub-steps of rough turning and finish turning; the step of gear-shape processing comprises the sub-steps of gear milling, gear hobbing or gear shaping; the step of gear-surface heat-treatment comprises the sub-steps of nitriding, surface quenching and tempering; the step of precise reference modification comprises the sub-steps of end face modification and centre hole modification; and the step of gear-shape finish-machining comprises the sub-steps of gear grinding and polishing. By using the method disclosed by the invention, the production efficiency of the bevel gear can be improved, and the consumption amount and production cost of raw materials can be reduced; and meanwhile, the method is simple in process, and the manufactured bevel gear is long in service life.
Owner:常州市万航工矿设备有限公司
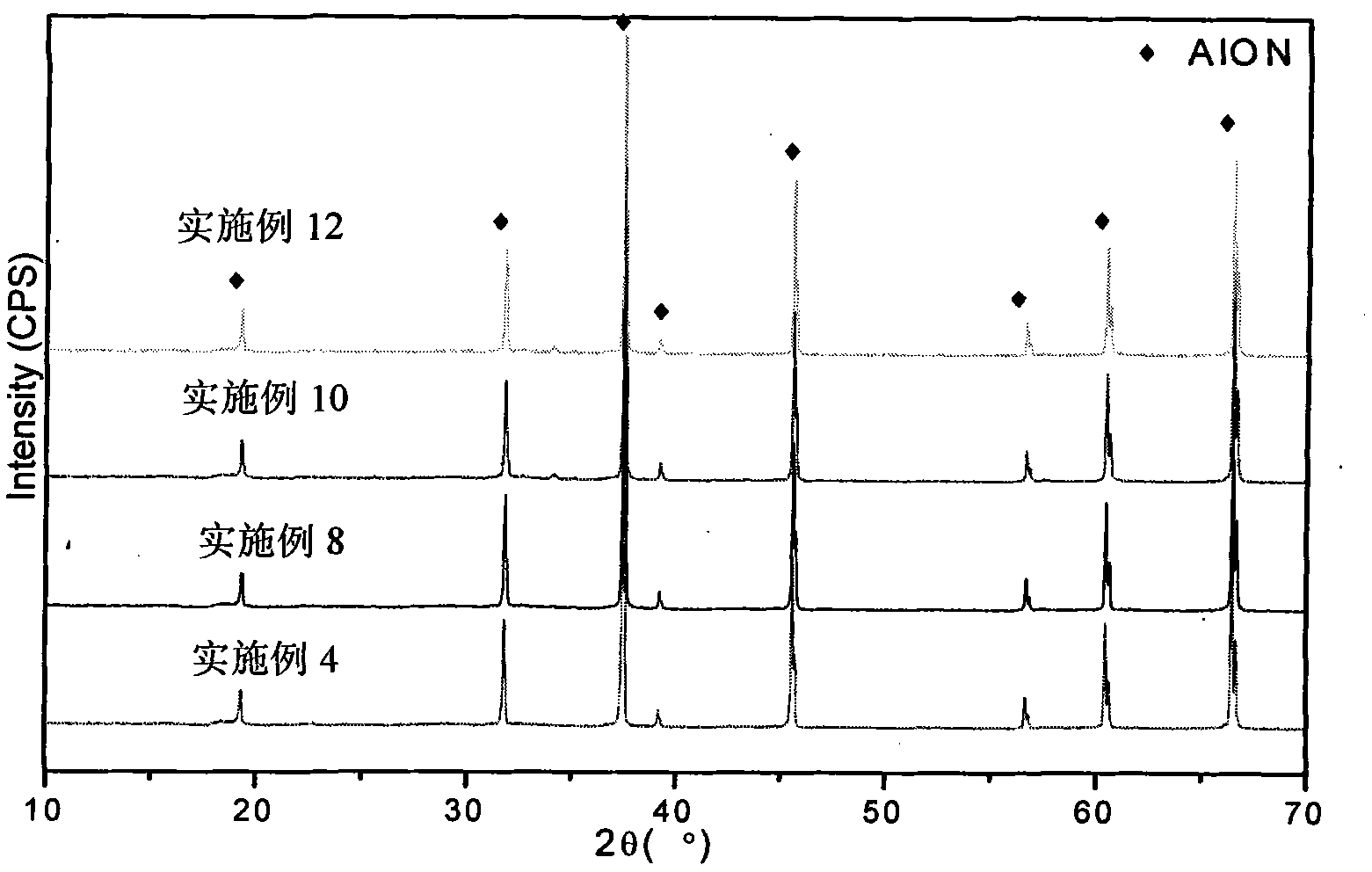
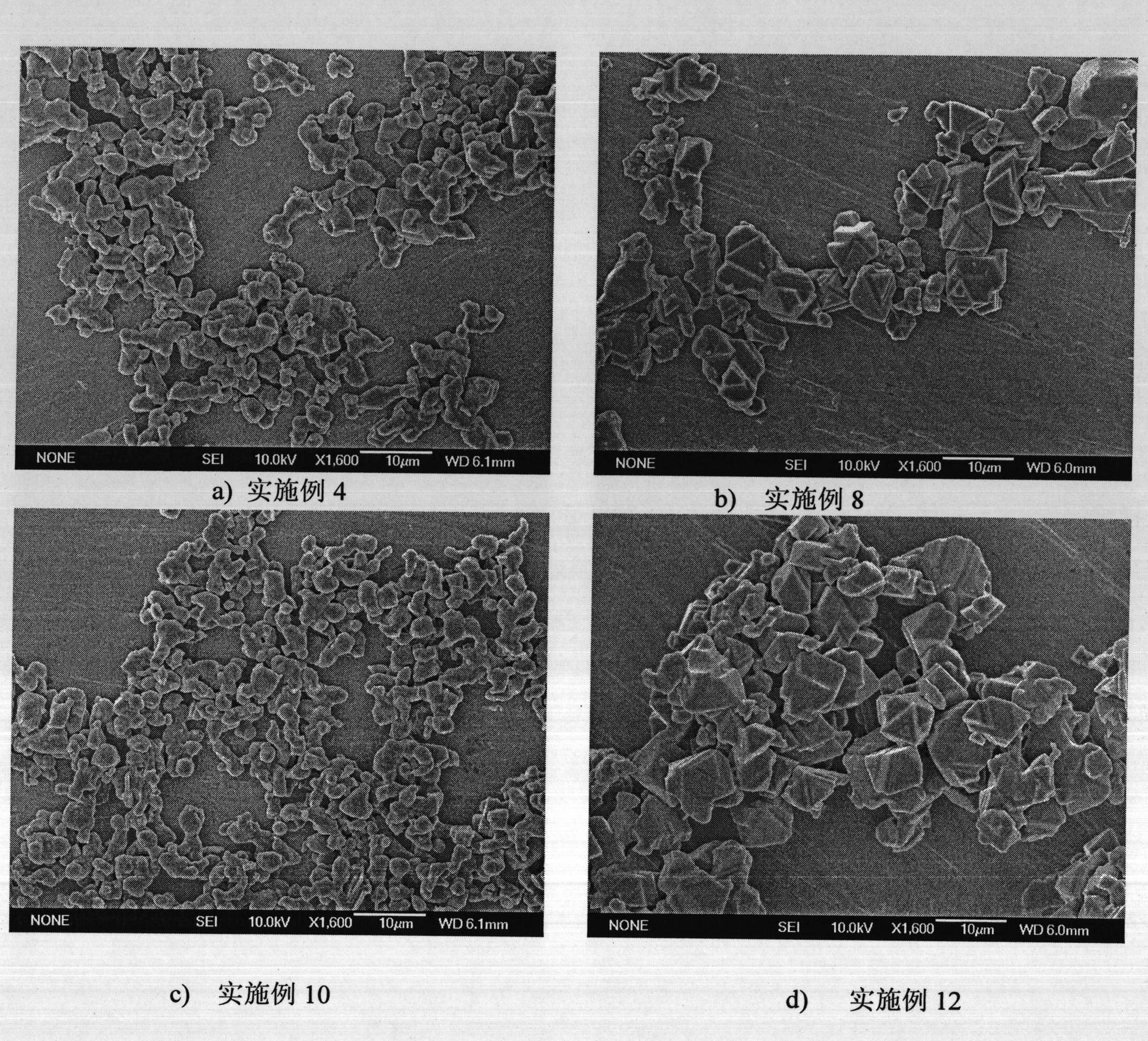
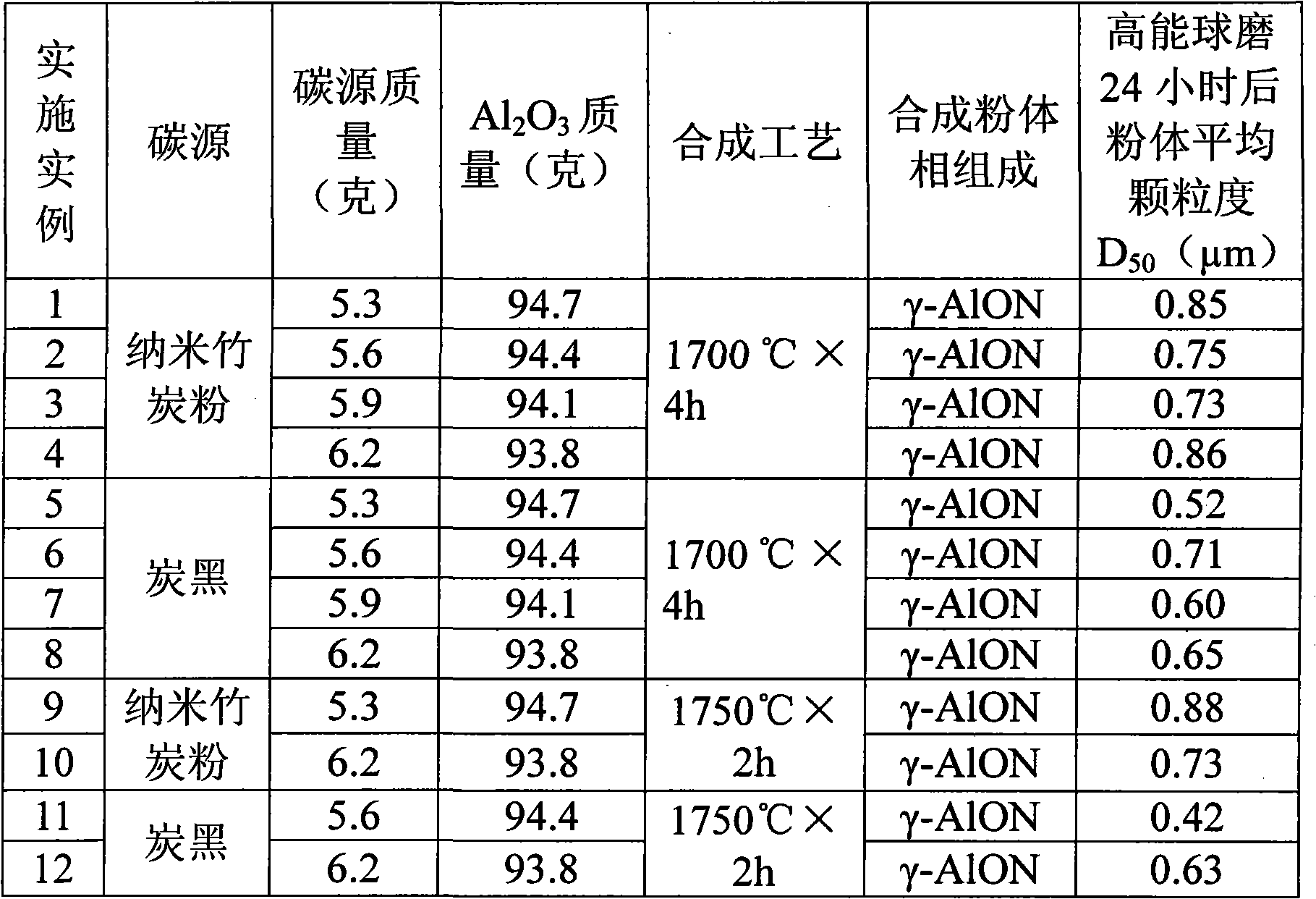
Preparation method of superfine and high-purity gamma-ALON transparent ceramics powder
The invention relates to a preparation method of superfine and high-purity gamma-ALON transparent ceramics powder, belonging to the filed of transparent ceramics material preparation. In the invention, the gamma-ALON transparent ceramics powder is prepared by combining a high energy ball mill with a carbothermic reduction nitriding method. The method of the invention is characterized by comprising the following steps: taking the gamma-Al2O3 powder with high specific surface area and carbon source, i.e. carbon black or nanometer powdered carbon as raw materials, mixing evenly by a wet process high energy ball mill and then drying; placing into a combined crucible of alumina and graphite to carry out the carbothermic reduction nitriding reaction; decarburizing by low-temperature process; and finally obtaining superfine and high-purity gamma-ALON transparent ceramics powder after being crushed by the high energy ball mill. The invention can synthesize pure phase alumina powder under the lower resultant temperature, has simple and feasible process, saves cost, and is suitable for industry production.
Owner:SHANGHAI FRP RES INST
Ultra supercritical heat-resistant steel welding rod and production method thereof
InactiveCN103737199AGood workmanshipGood mechanicalWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaFerrosiliconManganese
The invention discloses an ultra supercritical heat-resistant steel welding rod which is composed of an H08A core wire and coating wrapping the surface of the core wire, wherein contents of sulfur, phosphorus, arsenic, aluminum and the like in the H08A core wire are low, and the coating comprises components of 30%-39% of marbles, 22%-30% of fluorites, 6%-9% of rutiles, 7.5%-8.6% of ferromolybdenum, 29%-31% of chromium metal, 5%-9% of silica powder, 2%-5% of ferrosilicon, 1%-1.8% of ferrovanadium, 0.4%-0.8% of ferroniobium, 1.8%-2.8% of nickel powder, 0.4%-0.8% of sodium carbonate, 0.4%-0.8% of carboxyl methyl cellulose (CMC), 0.2%-0.6% of amorphous graphite, 0.6%-1.5% of nitrogen-bearing ferrochromium, 1.6%-3% of electrolytic manganese, 3%-3.8% of cobalt powder and 4%-5% of ferroboron.
Owner:ATLANTIC CHINA WELDING CONSUMABLES
Dispersion hardening alloy and method for the production of the alloy
InactiveUS6231807B1High temperature strengthImprove creep strengthSolid state diffusion coatingTitaniumAlloy
A dispersion hardened FeCrAl-alloy and method of its production which includes in one step, forming a nitride dispersion in a FeCr-alloy, whereby this nitride dispersion includes one or more of the basic elements hafnium, titanium and zirconium, and, in a later step aluminum is added to the nitrided FeCr-alloy. The unfavorable formation of aluminum nitrides has thereby been avoided by adding aluminum after the nitriding. A FeCrAl-alloy with high high temperature strength and high creep strength has thereby been achieved.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
Method for enhancing fretting fatigue resistance of alloys
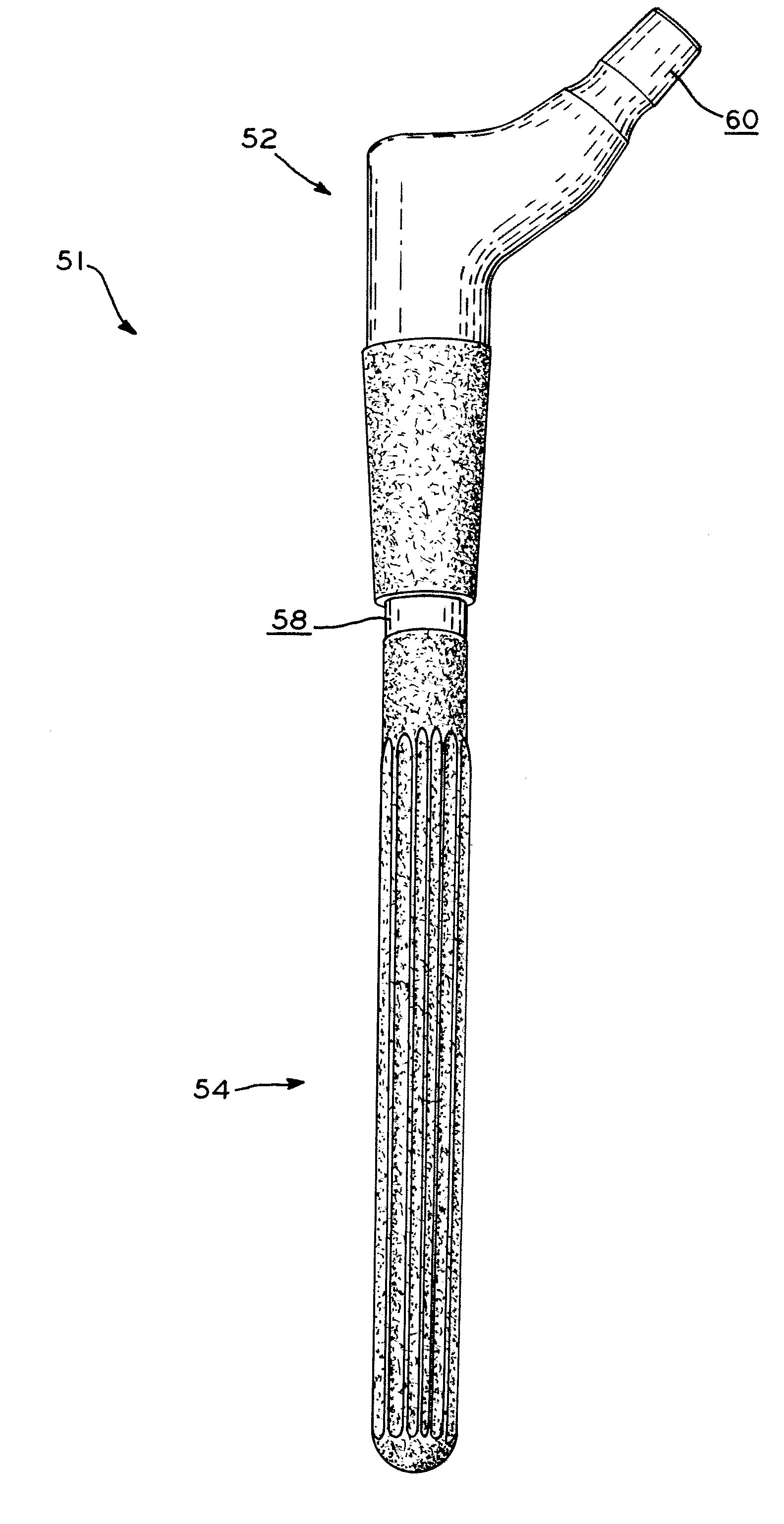
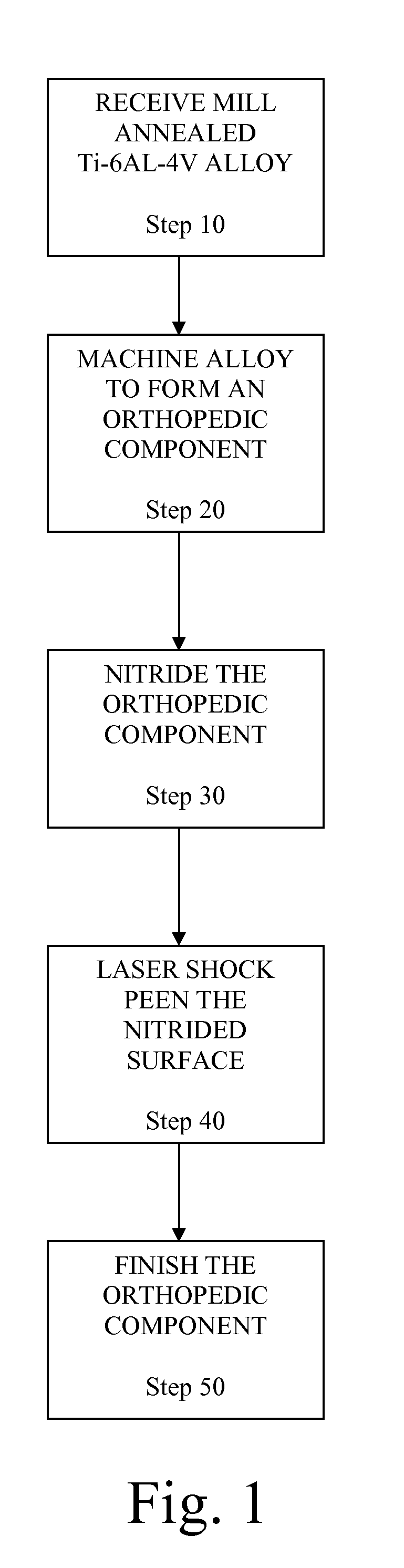
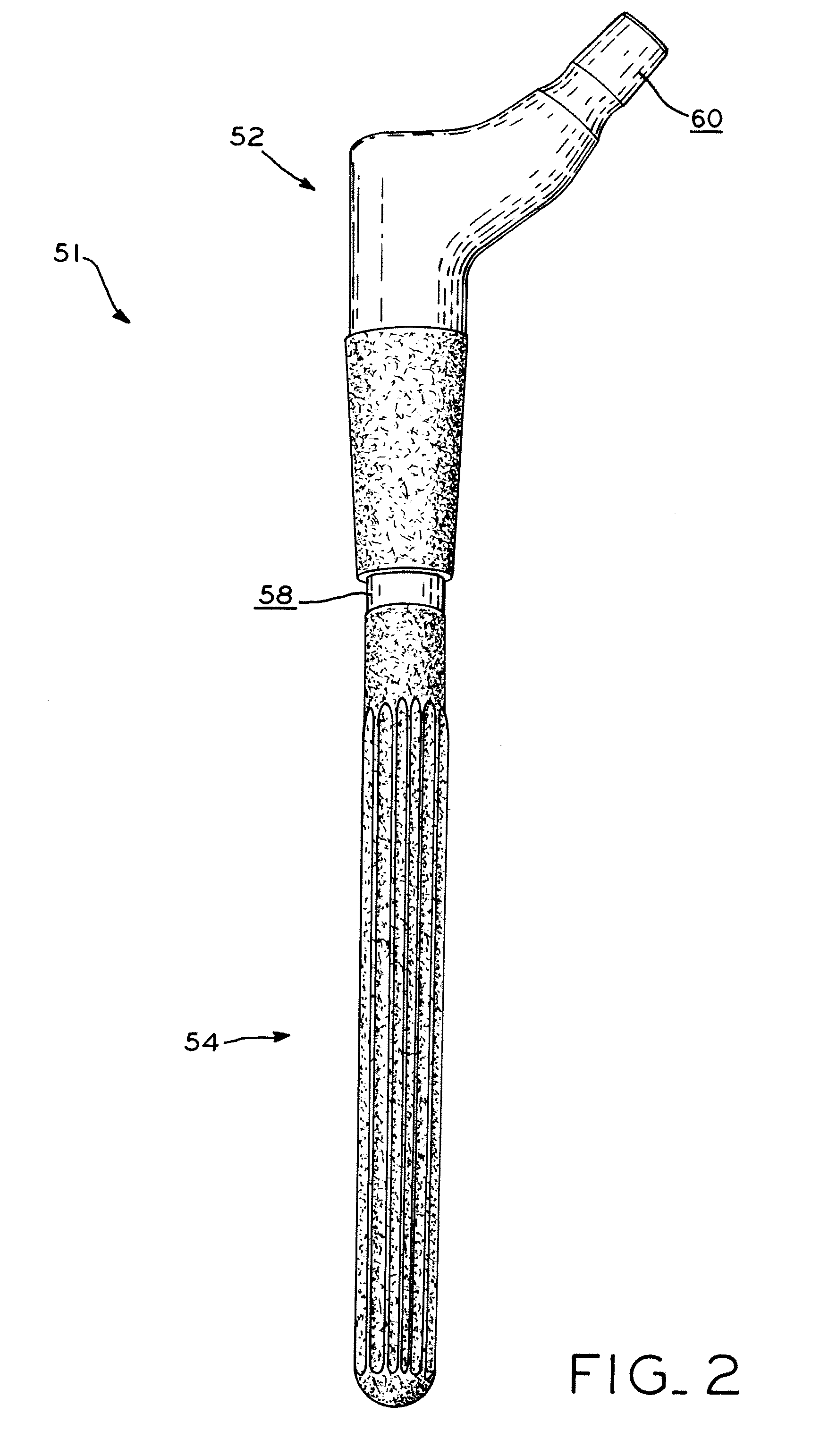
A method for increasing the fretting fatigue resistance of an alloy by prehardened a surface of the alloy followed by laser shock peening the prehardened surface. In one exemplary embodiment, an orthopedic prosthesis is formed from a titanium alloy and subjected to surface nitriding followed by laser shock peening. By nitriding the titanium alloy, the hardness of the alloy's surface is increased. Then, by subjecting the nitrided surface of the alloy to laser shock peening, the fretting fatigue of the nitrided surface may be increased by more than 100%.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
A method for sintering silicon carbide by nitriding reaction of crystalline silicon cutting waste
The invention belongs to the field of secondary resource integrated utilization, and specially relates to a method for sintering silicon carbide through a crystalline silicon cutting waste material nitridation reaction. The method comprises the following steps of mixing a crystalline silicon cutting waste material and ultrafine silicon carbide micro-powder produced in production of silicon carbide cutting powder, wherein the weight of free silicon is 5 to 25% of the total weight of the mixed material, adding a binder into the mixed material, preparing into a green compact, feeding high purity nitrogen with purity above 99 wt% into a nitriding furnace, and heating the green compact for nitridation treatment to obtain silicon carbide products sintered through a silicon nitride reaction. The method has the advantages that main raw materials adopted by the method are waste materials from industrial production and has a wide source and a low price and thus the waste materials are changed into things of value; the time spent on production processes is short; a production temperature is low; and a production cost is reduced greatly.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
Gear thermal precision forging machining process adopting carburizing steel 20CrMnTi as material
InactiveCN102764838AOvercome concentrated stressOvercome the defect of easily broken teethMetal-working apparatusWheelsSand blastingMachining process
The invention discloses a gear thermal precision forging machining process adopting carburizing steel 20CrMnTi as a material. The process especially comprises the following steps of: upsetting prolonging, blank manufacturing, die forging, burring, forging aftert-reatment (including quenching, tempering thermal treatment; accomplishing the gear thermal treatment through nitriding, surface quenching and normalizing; and finally carrying out sand blasting to remove a scale cinder and the surface acid treatment), and tooth profile cold-finish. By utilizing the process, the fogging process is simplified, the procedures are reduced; the processed product is good in quality; the production in scale can be realized so as to achieve the purposes of good quality, material conservation, energy conservation and time saving; and meanwhile the service life of a mold can be improved greatly, so that the wear resistance of the manufactured gear is enhanced greatly; the gear point-corrosion spalling is overcome; the strength is improved greatly; the service life is prolonged; and the cost is reduced.
Owner:无锡市钻通工程机械有限公司
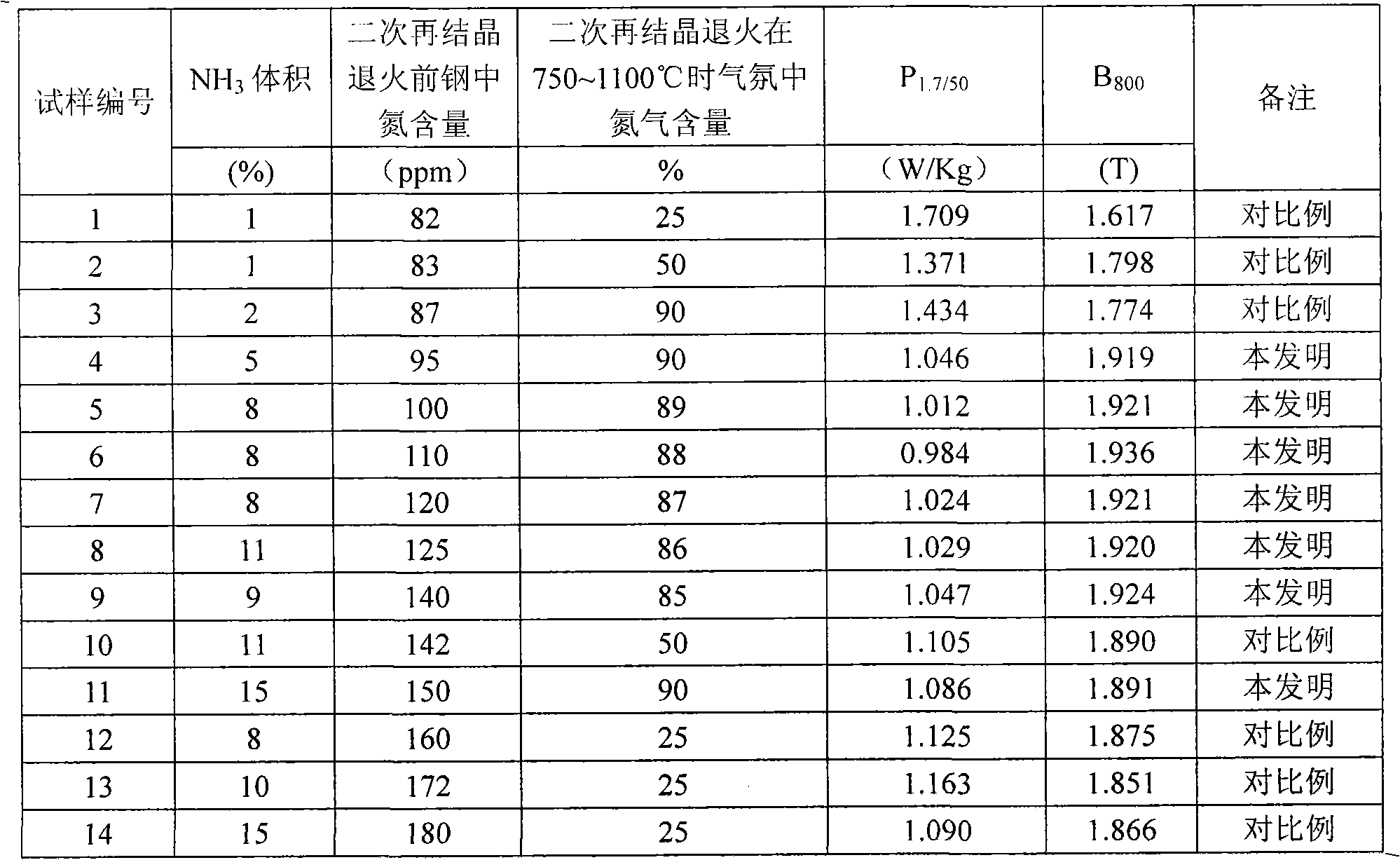
Method for producing high magnetic induction grain-oriented silicon steel
The invention relates to a method for producing high magnetic induction grain-oriented silicon steel, and belongs to the technical field of silicon steel production. The process comprises the following steps of: smelting, refining, and performing continuous casting to obtain a casting blank; performing hot rolling; normalizing, namely performing normalizing annealing and cooling; performing cold rolling at one time, wherein the cold rolling reduction ratio is 85 to 90 percent; nitriding by using a nitriding medium, namely dry NH3 at the temperature of between 600 and 740 DEG C for 5 to 40 seconds; decarburizing at the temperature of between 750 and 850 DEG C for 60 to 360 seconds, wherein the dew-point temperature is 25 DEG C; and annealing at a high temperature, and coating a stress coating. The method has the advantages that: a plate blank low-temperature heating process of nitriding at the temperature of between 600 and 740 DEG C and decarburizing annealing is adopted, the nitriding of a steel plate is not influenced by an oxidation film, the steel plate is uniformly nitrided, and efficiency is high; by controlling the nitriding and decarburizing processes, an appropriate amount of effective (Al, Si) N inhibitor is formed, and high magnetic property is achieved; and nitriding is performed at a low temperature, so energy consumption is low, and production cost is reduced.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Method for manufacturing hammer lever of electrohydraulic hammer
ActiveCN101890622AExtended service lifeSolid state diffusion coatingFurnace typesEngineeringProlongation
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a hammer lever of an electrohydraulic hammer, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of material section, heating, forging, normalizing treatment after forging, rough machining, flaw detection, corresponding tempering treatment, semifinishing, fine grinding, nitridation treatment, polishing, and the like, especially adopting a two-stage gas nitriding process which plays a key role in the prolongation of the service life of the hammer rod. The invention can greatly prolong the service life of the hammer level of the electrohydraulic hammer, and average hammering frequency is improved by 18 times or so from original 65,000 to 1,200,000 under the situation that other conditions are not changed.
Owner:CHONGQING CHANGZHENG HEAVY IND
Method for producing low nitriding amount and high magnetic induction oriented silicon steel strip
InactiveCN101775548AReduce contentUnlimited scaleSolid state diffusion coatingMetal rolling arrangementsChemical compositionTransformer
The invention discloses a method for producing a low nitriding amount and high magnetic induction oriented silicon steel strip, which comprises the procedures of controlling chemical components in a continuous casting blank, heating to 1,100-1,200 DEG C, hot rolling to form a hot-rolling steel strip with the thickness of 2.0-2.5mm, carrying out two-section normalizing annealing, coldly rolling to form a cold-rolling steel strip with the thickness of 0.23-0.30mm once, and carrying out continuous decarburization processing, continuous nitridation processing and secondary recrystallization annealing processing, conventionally cooling, and the like. In the procedure of the continuous nitridation processing, the N in the cold-rolling steel strip is controlled to be 0.0095-0.0150 in percentage by weight; in the procedure of the secondary recrystallization annealing processing, when the steel strip is heated to 750-1,100 DEG C, the volume rate of N2 is controlled to be 75-90 percent relative to the total volume rate of the N2-H2 atmosphere; and finally, the low nitriding amount and high magnetic induction oriented silicon steel strip is prepared. The invention has proper heat treatment temperature on a plate blank, low manufacture cost and high product quality and can meet the requirements of the high-quality oriented silicon steel for an iron core of a transformer.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司
Optoelectric device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20150280053A1Accurately and uniformly controllingLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsNitridingSemiconductor components
A method for manufacturing an optoelectric device comprising a semiconductor substrate, pads on a surface of the substrate; semiconductor elements, each element being in contact with a pad; and a dielectric region extending in the substrate from the surface and connecting, for each pair of pads, one of the pads in the pair to the other pad in the pair, the method successively comprising the forming of the pads and the forming of the region, wherein the region is formed by nitriding of the substrate, the method comprising the successive steps of: depositing a layer on the substrate; forming portions on the layer; etching the parts of the layer which are not covered with the portions to form the pads; removing the portions; and nitriding the pads and the parts of the substrate which are not covered with the pads, wherein the nitriding step successively comprises: a first step of nitriding of the pads at a first temperature; and a second step of nitriding of the parts of the substrate which are not covered with the pads at a second temperature different from the first temperature.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Salt bath nitrogenization heat treatment method for metal surface
InactiveCN101144148ASolve heat treatment problemsReduce distortionSolid state diffusion coatingPotassiumHeat treating
The present invention relates to a metal surface salt bath nitride nitriding heat treatment method which belongs to the metal part surface heat treatment technology field. The method is performed in the following technical process: first, loading and clamping: the metal part is hung and arranged in a charging basket; second, nitriding: the metal part hung and arranged in the charging basket is positioned in a nitriding furnace, heated and charged with nitriding salt for salt bath and nitriding, and heat is preserved for 30-80 minutes in the condition that the temperature is 540-570 DEG C; third, cleaning: the nitrided metal part is cleaned, and the water temperature is controlled at 60-80 DEG C; the nitriding salt in the nitriding working process comprises carbamide, potassium chloride or barium chloride, sodium carbonate, and K 2 S, etc., according to the weight percentage, the composition of each component is respectively: 30-40 percent of carbamide, 20-28 percent of potassium chloride or barium chloride, 38-44 percent of sodium carbonate, and 0.0001-0.1 percent of K 2 S, and the sum of the weight percentage of each component is 100 percent. The present invention has the advantages of smaller deformability, short time, high efficiency, and wide application range; and also can achieve the effect of reducing the cost obviously.
Owner:孙国飞
Method for preparing superfine titanium carbonitride
The invention belongs to the field of metal ceramic material preparation, and provides a method for preparing superfine titanium carbonitride. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, ball-milling and mixing nano TiO2 with an organic carbon source, and preparing into a piece material in a cold pressing mode; feeding the piece material into a vacuum sensing furnace, vacuumizing till the pressure inside the furnace is less than or equal to 50Pa, increasing the temperature to 300-800 DEG C and preserving the temperature for 0.5-2h; subsequently increasing the temperature to be 1000-1900 DEG C and preserving the temperature for 0.5-2h, wherein vacuumizing is constantly performed in the temperature preservation process; stopping vacuumizing after the temperature preservation is accomplished, introducing nitrogen so as to make the pressure in the furnace be of 1.1-1.2 atmosphere pressures; preserving the temperature for 1-4h to sufficiently nitridize the raw material; and subsequently decreasing the temperature, taking out the piece material, crushing, ball-milling and grading so as to obtain the superfine titanium carbonitride of which the Fisher particle size is less than 1mm. A TiCN powder material prepared by using the method is high in purity, few in impurities, small in particle size, uniform in particle size distribution and spherical in morphology, and can be used as a raw material of a cutting tool, a metal ceramic, a spraying material and the like.
Owner:长沙伟徽高科技新材料有限公司
48MnV nitrogenous steel and nitrogen adding process thereof
The invention belongs to the field of metallurgy and relates to 48MnV nitrogenous steel and a nitrogen adding process thereof. The 48MnV nitrogenous steel comprises the following components: 0.45-0.51% of C, 0.17-0.37% of Si, 1.00-1.20% of Mn, 0.06-0.11% of V, 0.000-0.025% of Ti, 0.05-0.25% of Cr, 0.00-0.06% of Mo, 0.00-0.06% of Ni, 0.00-0.20% of Cu, 0.0080-0.0150% of N, at most 0.035% of P, at most 0.035% of S, at most 0.020% of O, 0.087-0.097% of Ceq and the balance of Fe and impurities; and the nitrogen adding process is carried out while the N content is controlled to be 0.0080-0.0150%, preferably 0.0090-0.0120%, wherein the target value is 0.0110%, and a manganese nitride iron wire is fed into the steel according to the calculated quantity in one step after a vacuum process is completed. By changing the pre-vacuum nitrogen adding and alloying into the post-vacuum nitrogen adding and alloying, the invention changes the technological process of pre-vacuum nitrogen alloying and post-vacuum slight nitrogen regulation in the metallurgy field, thereby enabling the 48MnV nitrogenous steel to obtain good comprehensive mechanical properties, and improving the strength and toughness.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com