Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
11447 results about "Semiconductor components" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
High-density three-dimensional memory cell
InactiveUS6952030B2High densityReduce the overall heightTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical conductorHigh density
A three dimensional monolithic memory comprising a memory cell allowing for increased density is disclosed. In the memory cell of the present invention, a bottom conductor preferably comprising tungsten is formed. Above the bottom conductor a semiconductor element preferably comprises two diode portions and an antifuse. Above the semiconductor element are additional conductors and semiconductor elements in multiple stones of memories. The arrangement of processing steps and the choice of materials decreases aspect ratio of each memory cell, improving the reliability of gap fill and preventing etch undercut.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Multi-dice chip scale semiconductor components and wafer level methods of fabrication
InactiveUS6841883B1Promote formationAdditive manufacturing apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSealantPolymer
A semiconductor component includes a base die and a secondary die stacked on and bonded to the base die. The base die includes conductive vias which form an internal signal transmission system for the component, and allow the circuit side of the secondary die to be bonded to the back side of the base die. The component also includes an array of terminal contacts on the circuit side of the base die in electrical communication with the conductive vias. The component can also include an encapsulant on the back side of the base die, which substantially encapsulates the secondary die, and a polymer layer on the circuit side of the base die which functions as a protective layer, a rigidifying member and a stencil for forming the terminal contacts. A method for fabricating the component includes the step of bonding singulated secondary dice to base dice on a base wafer, or bonding a secondary wafer to the base wafer, or bonding singulated secondary dice to singulated base dice.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
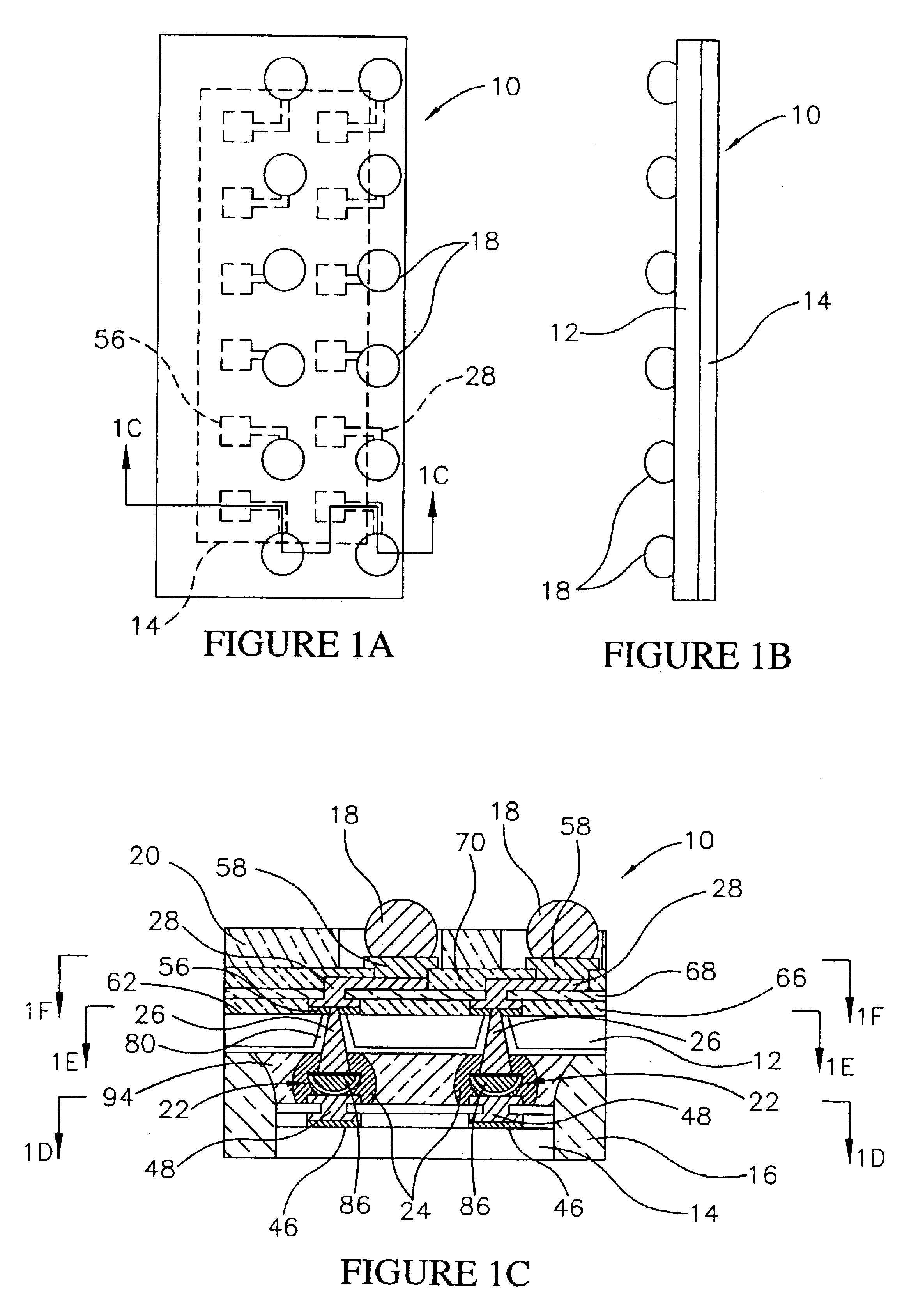
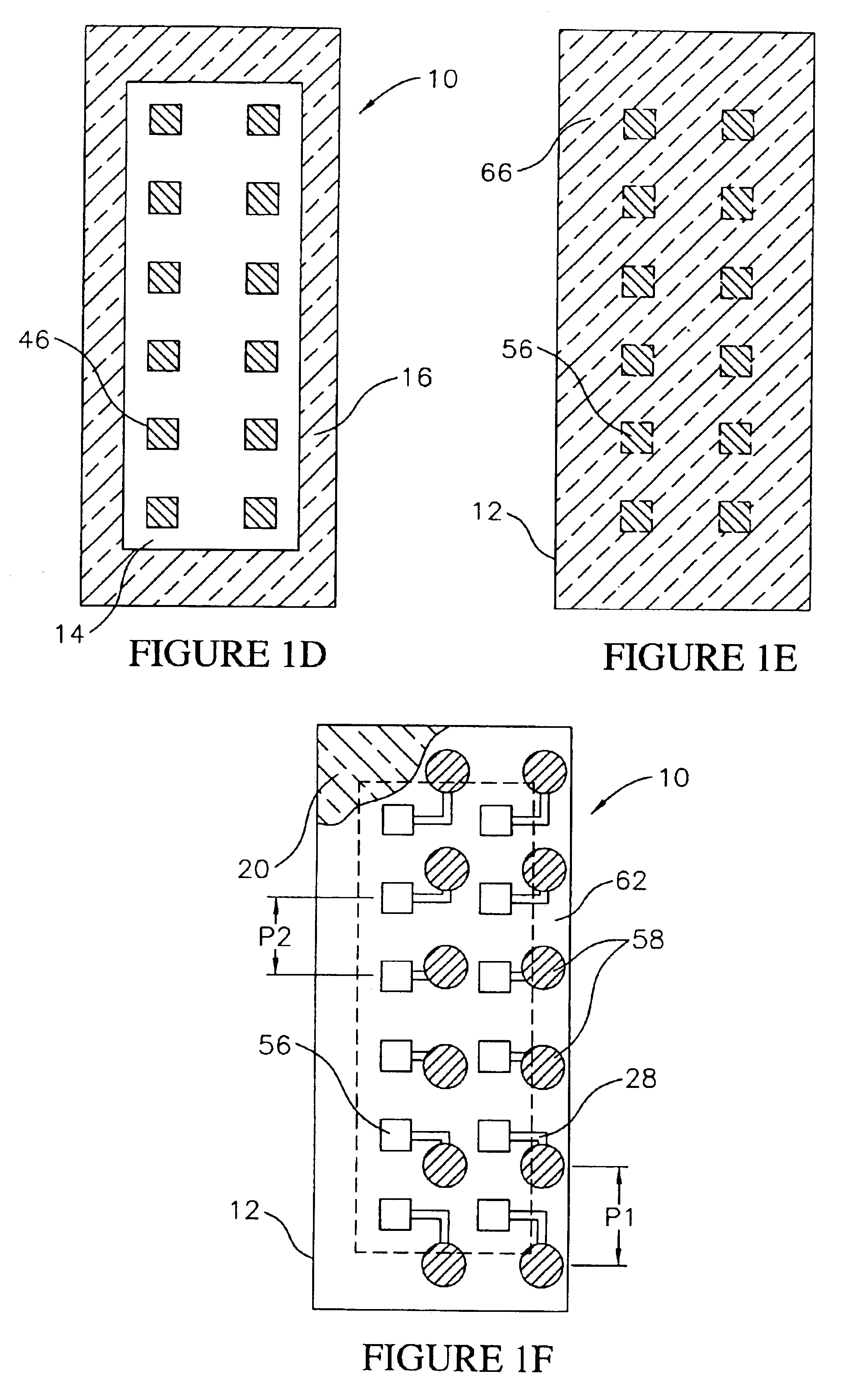
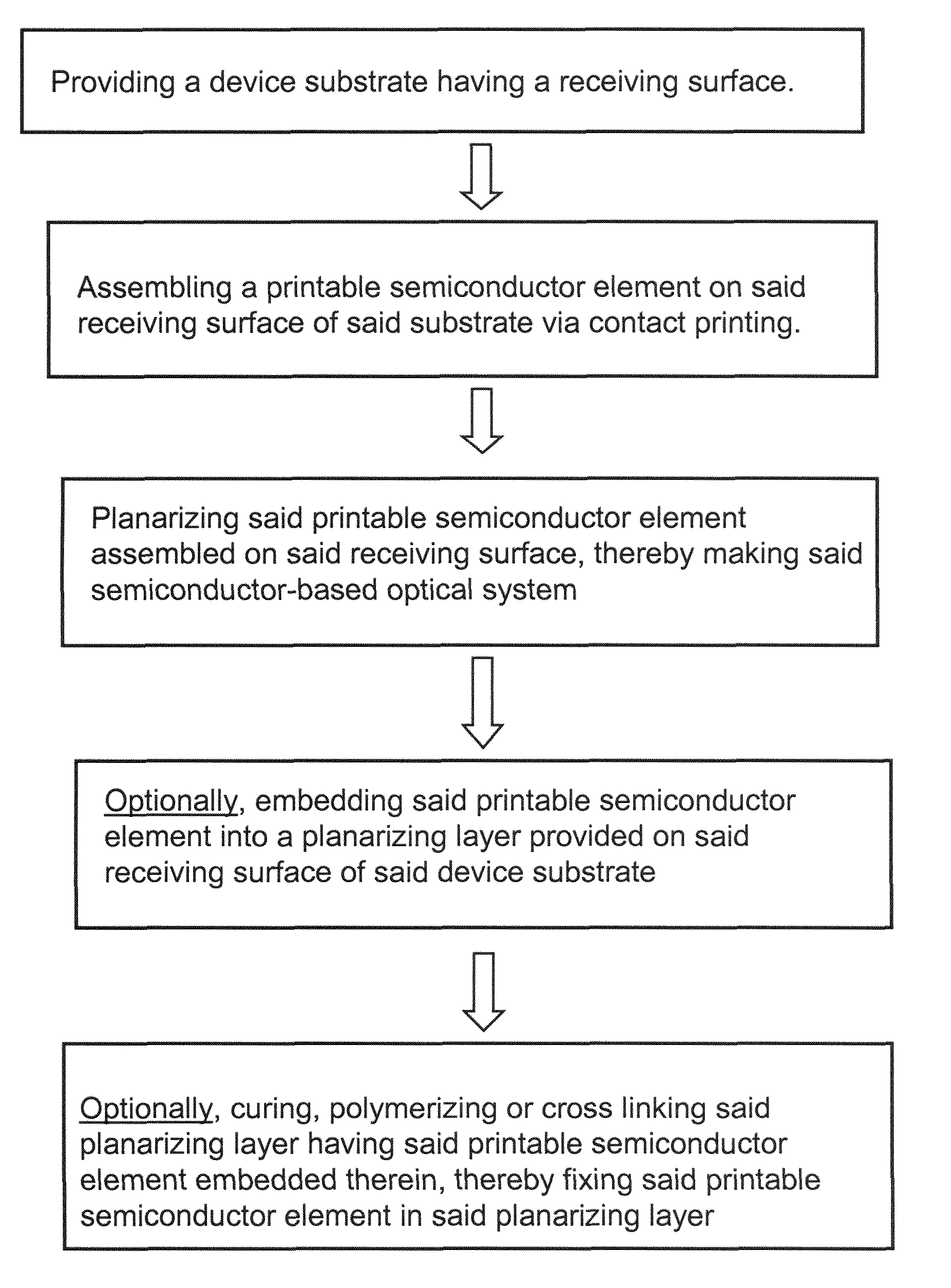
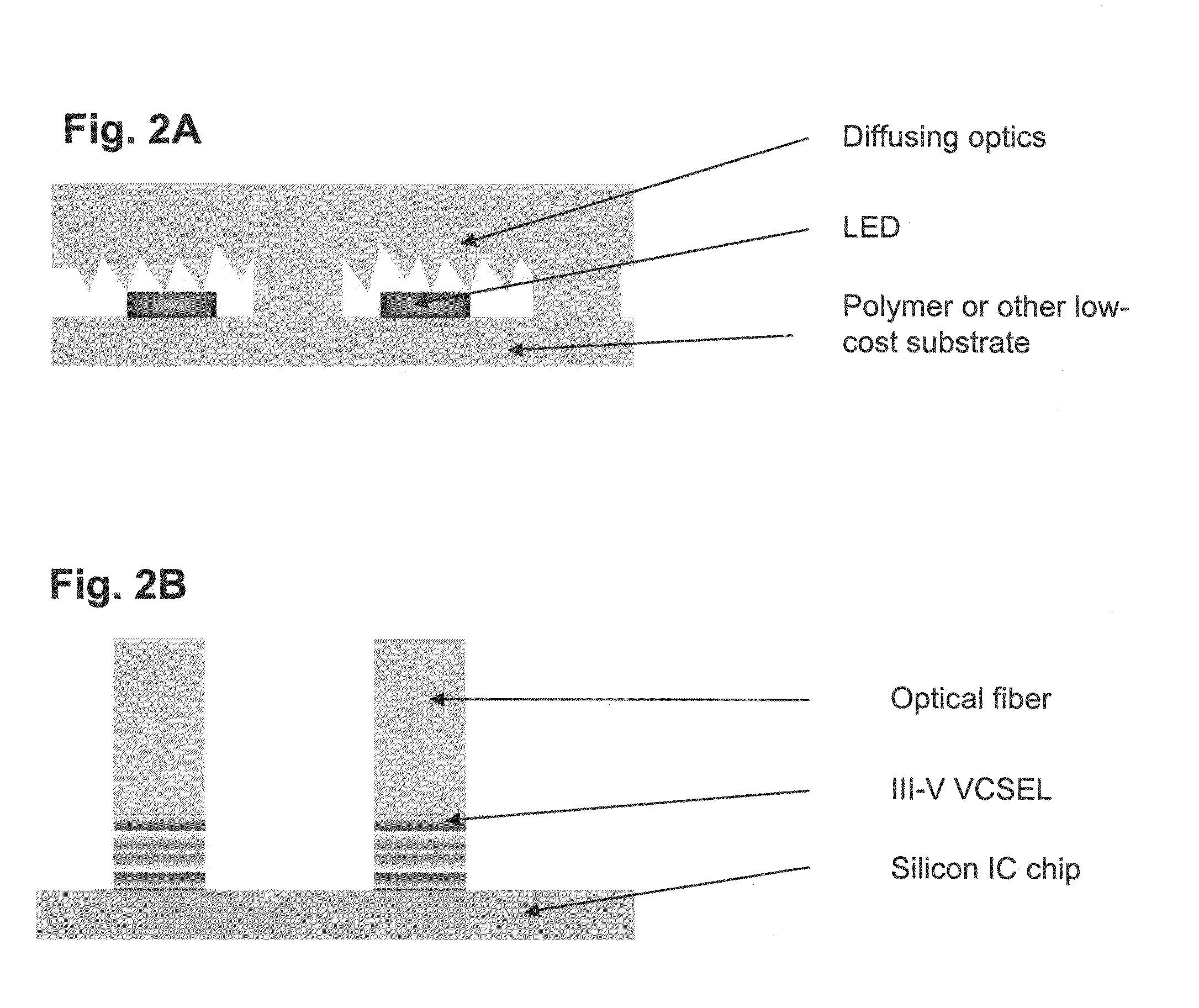
Optical systems fabricated by printing-based assembly
ActiveUS7972875B2Low costImprove performanceFinal product manufactureNanoinformaticsLight sensingSingle crystal
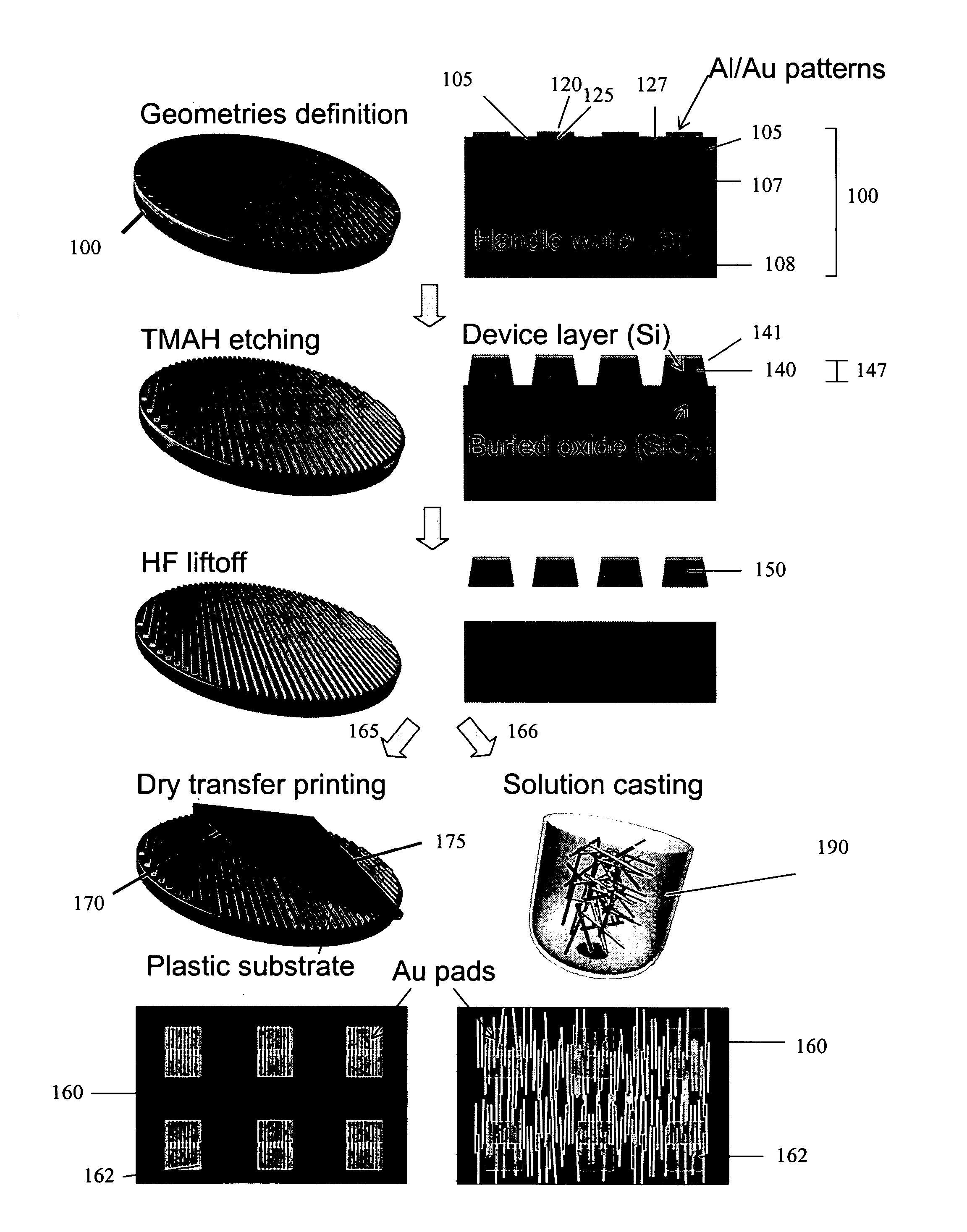
Provided are optical devices and systems fabricated, at least in part, via printing-based assembly and integration of device components. In specific embodiments the present invention provides light emitting systems, light collecting systems, light sensing systems and photovoltaic systems comprising printable semiconductor elements, including large area, high performance macroelectronic devices. Optical systems of the present invention comprise semiconductor elements assembled, organized and / or integrated with other device components via printing techniques that exhibit performance characteristics and functionality comparable to single crystalline semiconductor based devices fabricated using conventional high temperature processing methods. Optical systems of the present invention have device geometries and configurations, such as form factors, component densities, and component positions, accessed by printing that provide a range of useful device functionalities. Optical systems of the present invention include devices and device arrays exhibiting a range of useful physical and mechanical properties including flexibility, shapeability, conformability and stretchablity.
Owner:X DISPLAY CO TECH LTD +1
Stretchable semiconductor elements and stretchable electrical circuits
ActiveUS20060038182A1Complete release is preventedLow costTransistorDecorative surface effectsStretchable electronicsSemiconductor structure
The invention provides methods and devices for fabricating printable semiconductor elements and assembling printable semiconductor elements onto substrate surfaces. Methods, devices and device components of the present invention are capable of generating a wide range of flexible electronic and optoelectronic devices and arrays of devices on substrates comprising polymeric materials. The present invention also provides stretchable semiconductor structures and stretchable electronic devices capable of good performance in stretched configurations.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Interconnect structure for stacked semiconductor device
InactiveUS6465892B1Shorten the line lengthEasy to produceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialInterconnection
In a multi-layer interconnection structure, the wiring length is to be reduced, and the interconnection is to be straightened, at the same time as measures need to be taken against radiation noise. To this end, there is disclosed a semiconductor device in which plural semiconductor substrates, each carrying semiconductor elements, are bonded together. On each semiconductor substrate is deposited an insulating layer through which is formed a connection wiring passed through the insulating layer so as to be connected to the interconnection layer of the semiconductor element. On a junction surface of at least one of the semiconductor substrates is formed an electrically conductive layer of an electrically conductive material in which an opening is bored in association with the connection wiring. The semiconductor substrates are bonded together by the solid state bonding technique to interconnect the connection wirings formed on each semiconductor substrate.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD +9
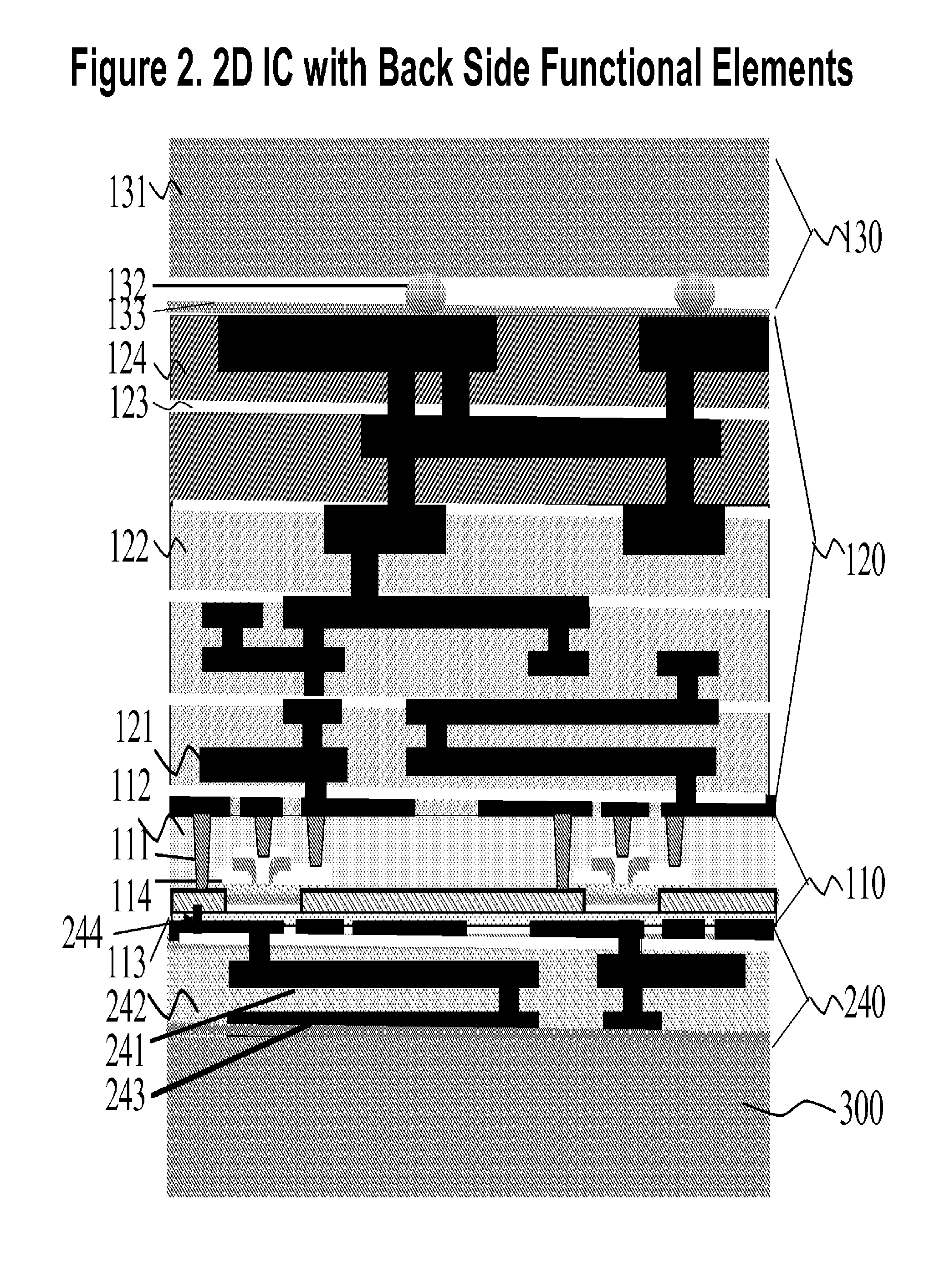
Layer transfer process and functionally enhanced integrated circuits produced thereby
InactiveUS20100081232A1Low costFunction increaseSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringIntegrated circuit
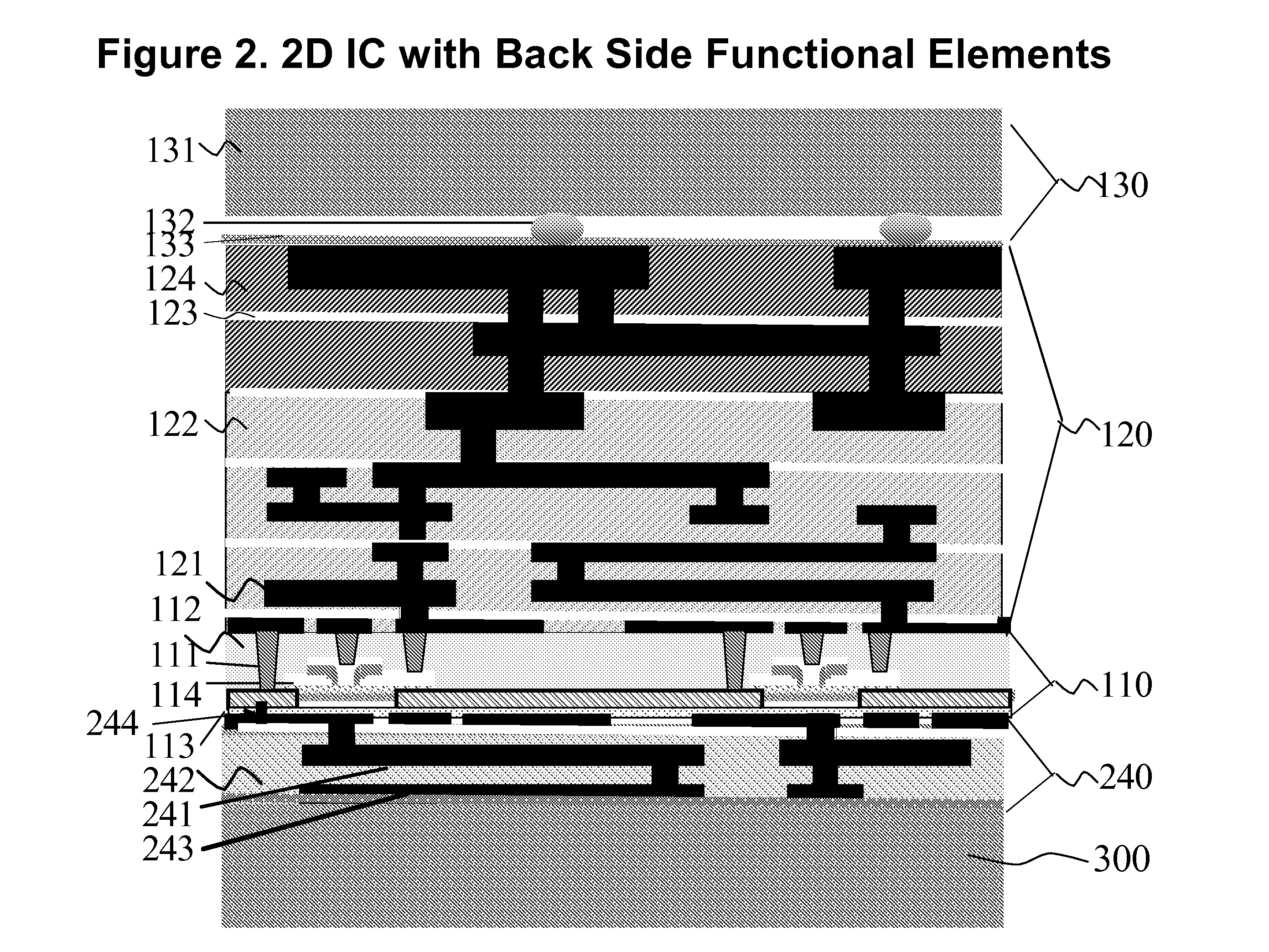
A structure for a semiconductor components is provided having a device layer sandwiched on both sides by other active, passive, and interconnecting components. A wafer-level layer transfer process is used to create this planar (2D) IC structure with added functional enhancements.
Owner:LINKEDIN
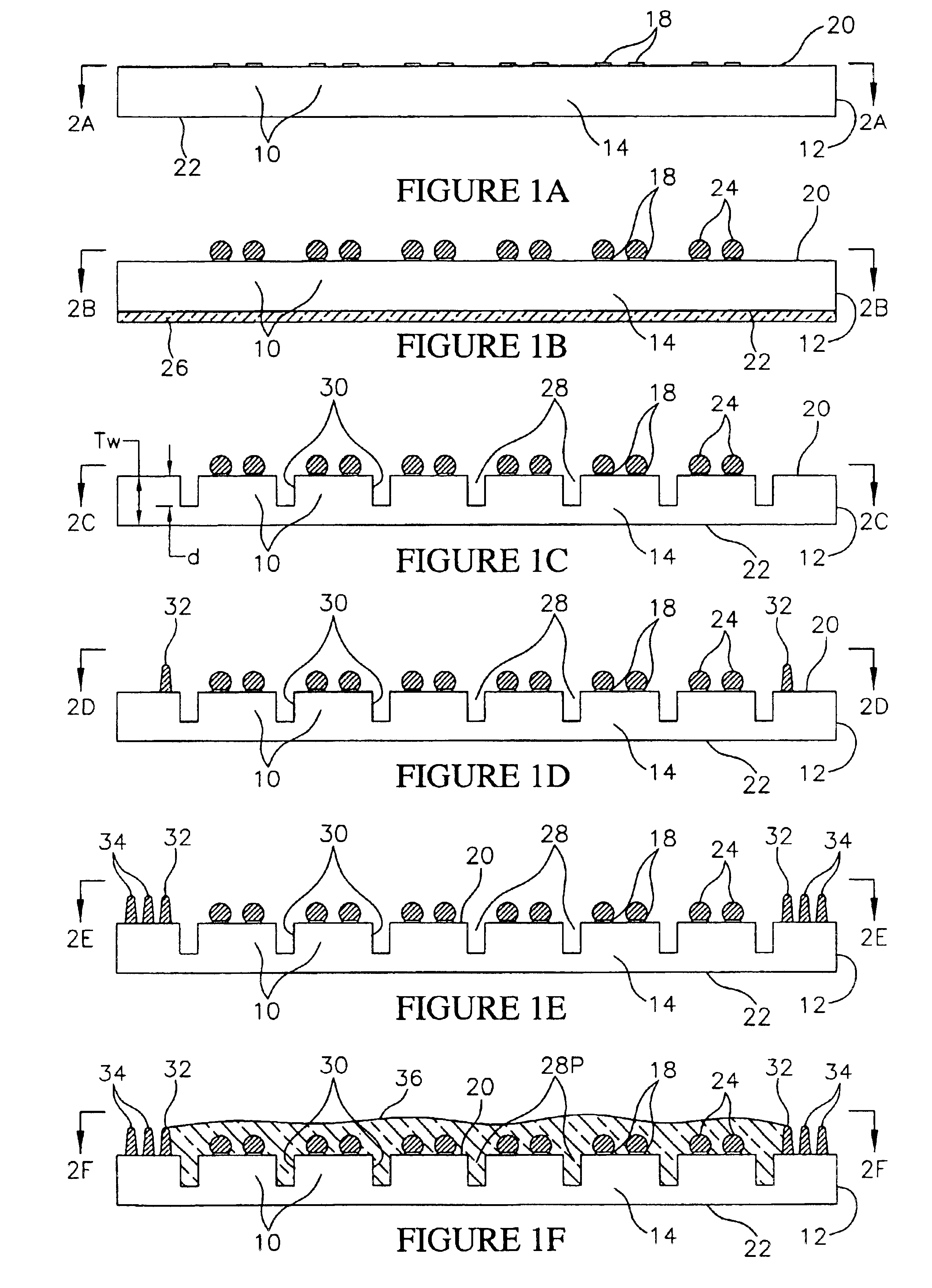
Method for fabricating encapsulated semiconductor components
InactiveUS6908784B1Easy to testAdditive manufacturing apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringPolymer
A semiconductor component includes a thinned semiconductor die having protective polymer layers on up to six surfaces. The component also includes contact bumps on the die embedded in a circuit side polymer layer, and terminal contacts on the contact bumps in a dense area array. A method for fabricating the component includes the steps of providing a substrate containing multiple dice, forming trenches on the substrate proximate to peripheral edges of the dice, and depositing a polymer material into the trenches. In addition, the method includes the steps of planarizing the back side of the substrate to contact the polymer filled trenches, and cutting through the polymer trenches to singulate the components from the substrate. Prior to the singulating step the components can be tested and burned-in while they remain on the substrate.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
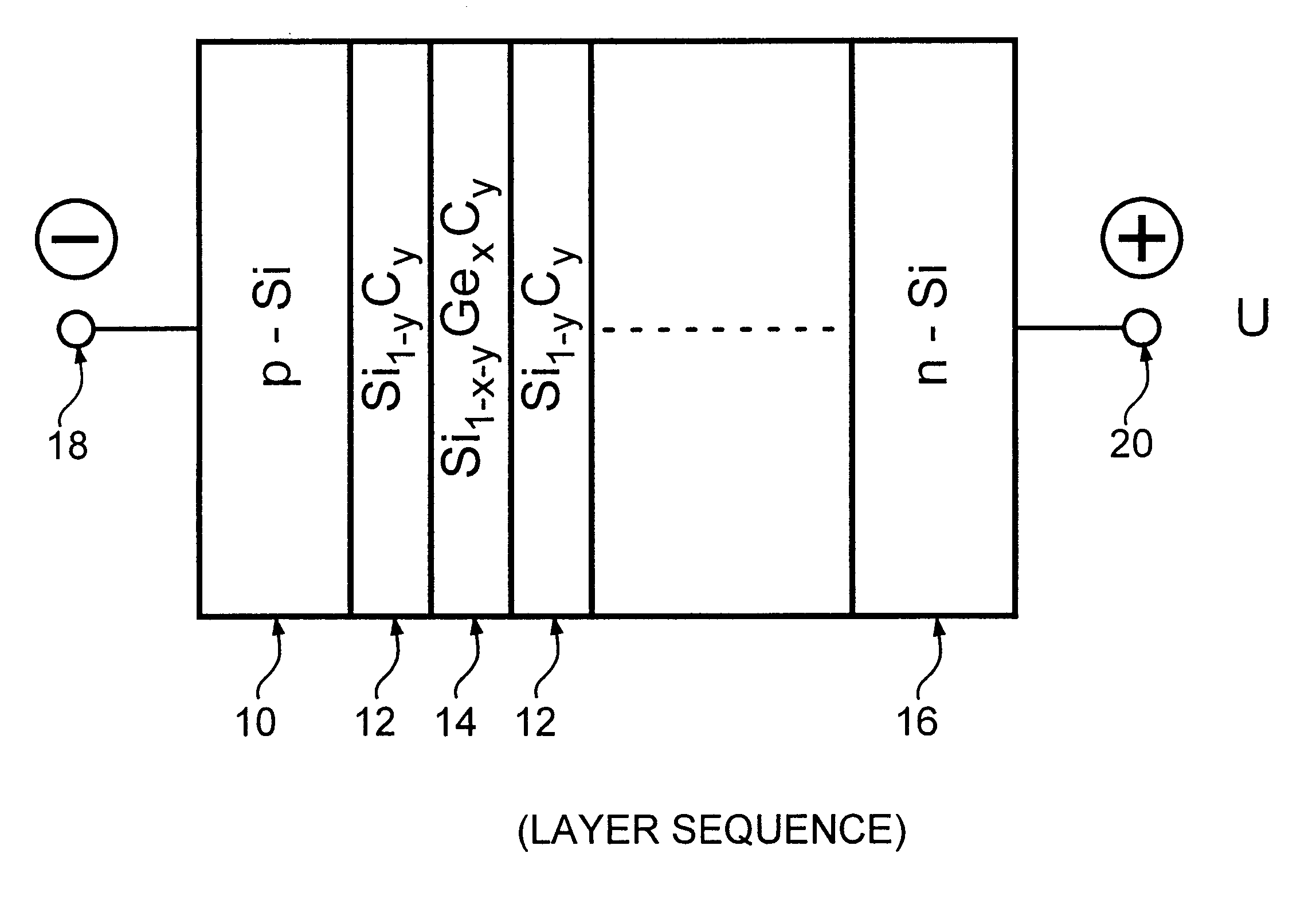
Semiconductor components, in particular photodetectors, light emitting diodes, optical modulators and waveguides with multilayer structures grown on silicon substrates
InactiveUS6403975B1Cost advantagePromote absorptionNanoopticsNon-linear opticsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
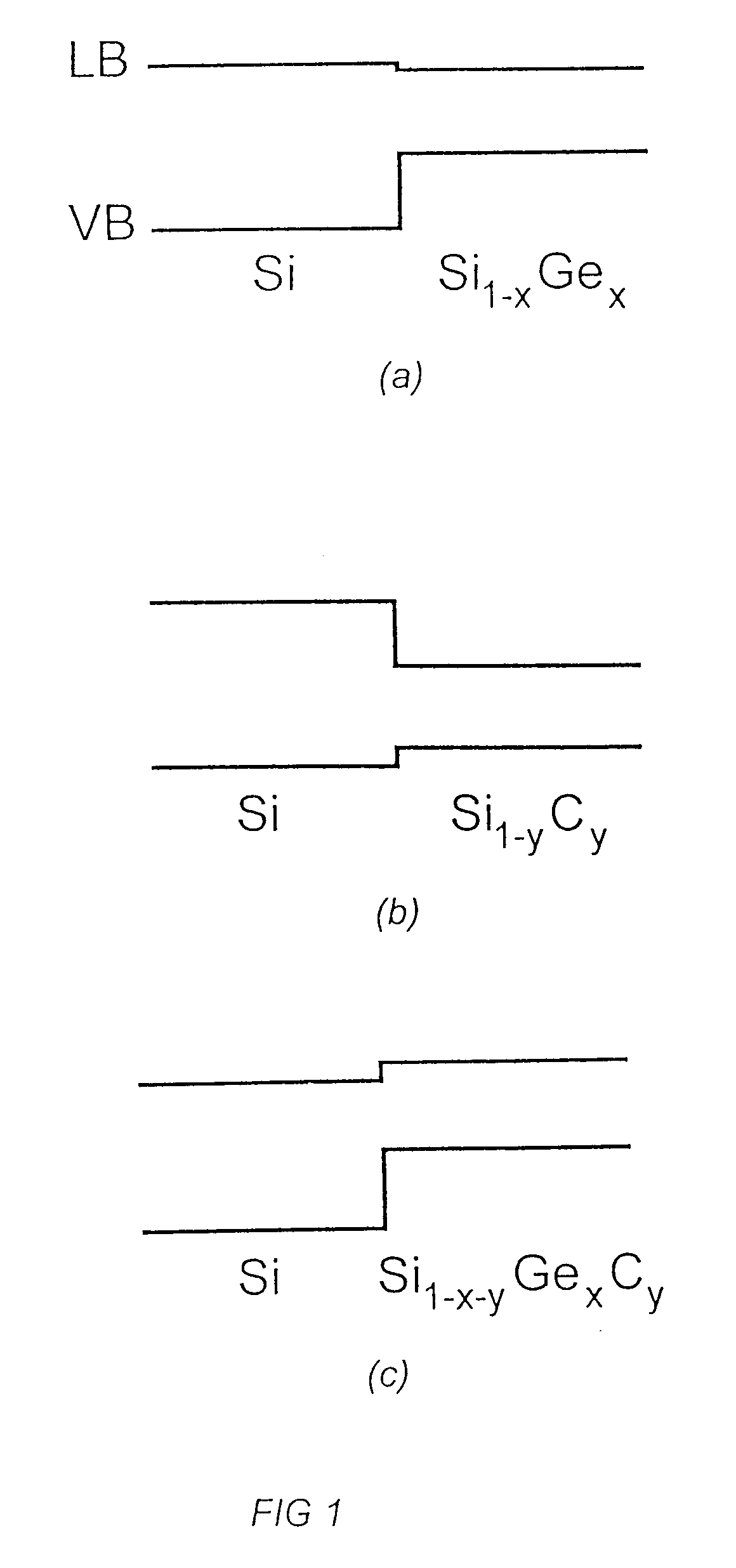
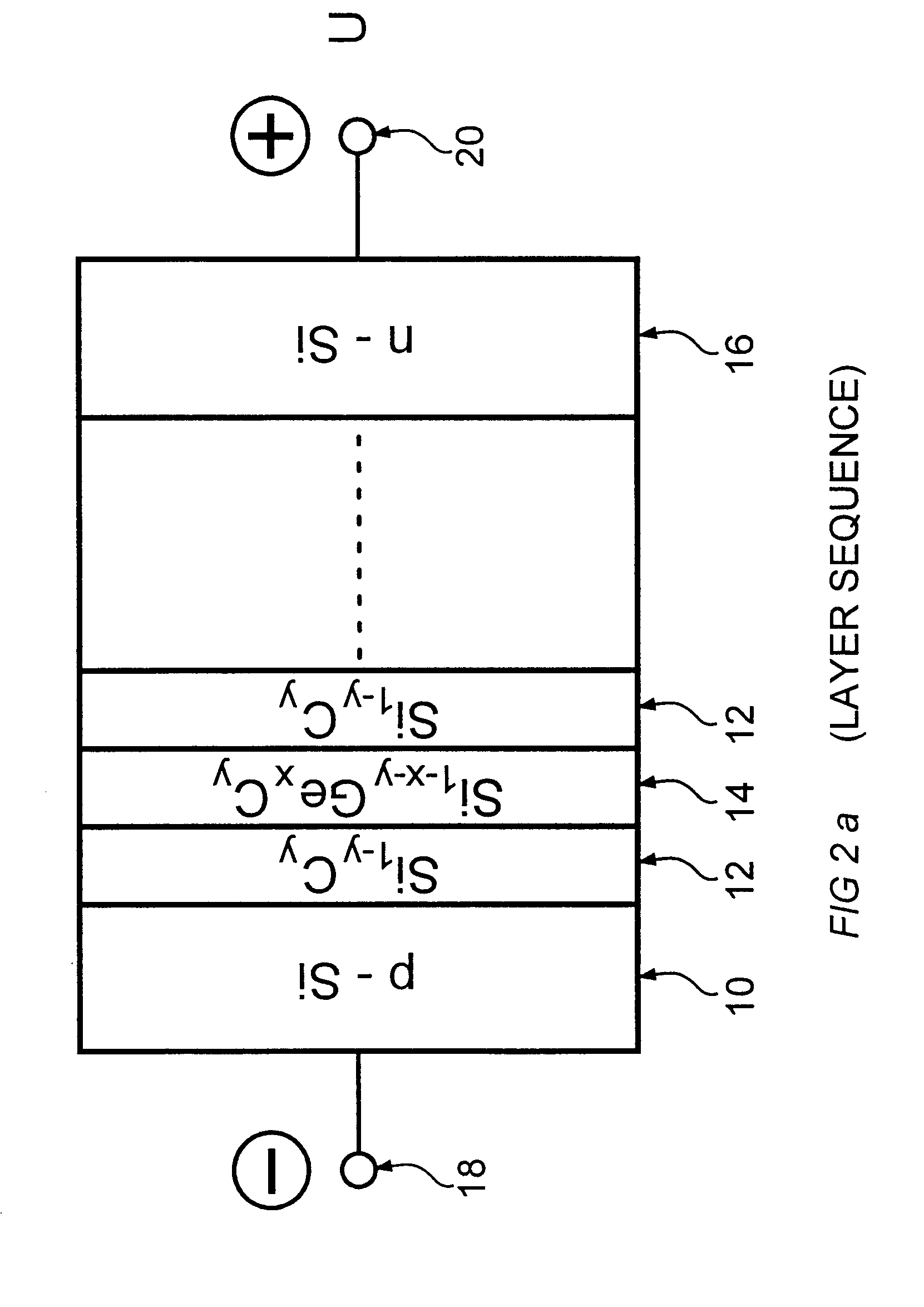
A semiconductor component, selected from the group comprising a photodetector, a light emitting diode, an optical modulator and a waveguide. The semiconductor component comprises an Si substrate, an active region formed on said substrate, and an Si capping layer on said active region. In one embodiment the active region is a superlattice comprising alternating layers of Si1-yCy and Si1-x-yGexCy, with the atomic fraction y of the Si1-x-yGexCy layers being equal to or different from the atomic fraction y of the Si1-yCy layers. In another embodiment it is a superlattice comprising a plurality of periods of a three-layer structure comprising Si, Si1-yCy and Si1-xGex layers. In a third embodiment it is a superlattice comprising a plurality of periods of a three-layer structure comprising Si, Si1-yCy and Si1-x-yGexCy layers, with the atomic fraction y of the Si1-x-yGexCy layers being equal to or different from the atomic fraction y of the Si1-yCy layers. The components have faborable optical and electrical properties and are suitable for integration on a Si substrate.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Light emitting diode, optical semiconductor element and epoxy resin composition suitable for optical semiconductor element and production methods therefor
InactiveUS20030080341A1Light emission characteristicSuppress the variation in the chromaticity of the light emittedDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsEpoxyLight-emitting diode
A light emitting diode comprising an LED chip having a light emitting layer made of a nitride compound semiconductor and a light transmitting resin that includes a fluorescent material which absorbs at least a part of light emitted by the LED chip and emits light of a different wavelength, wherein the fluorescent material includes a fluorescent particles of small particle size and a fluorescent particles of large particle size, the fluorescent particles of large particle size being distributed in the vicinity of the LED chip in the light transmitting resin to form a wavelength converting layer, the fluorescent particles of small particle size being distributed on the outside of the wavelength converting layer in the light transmitting resin.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
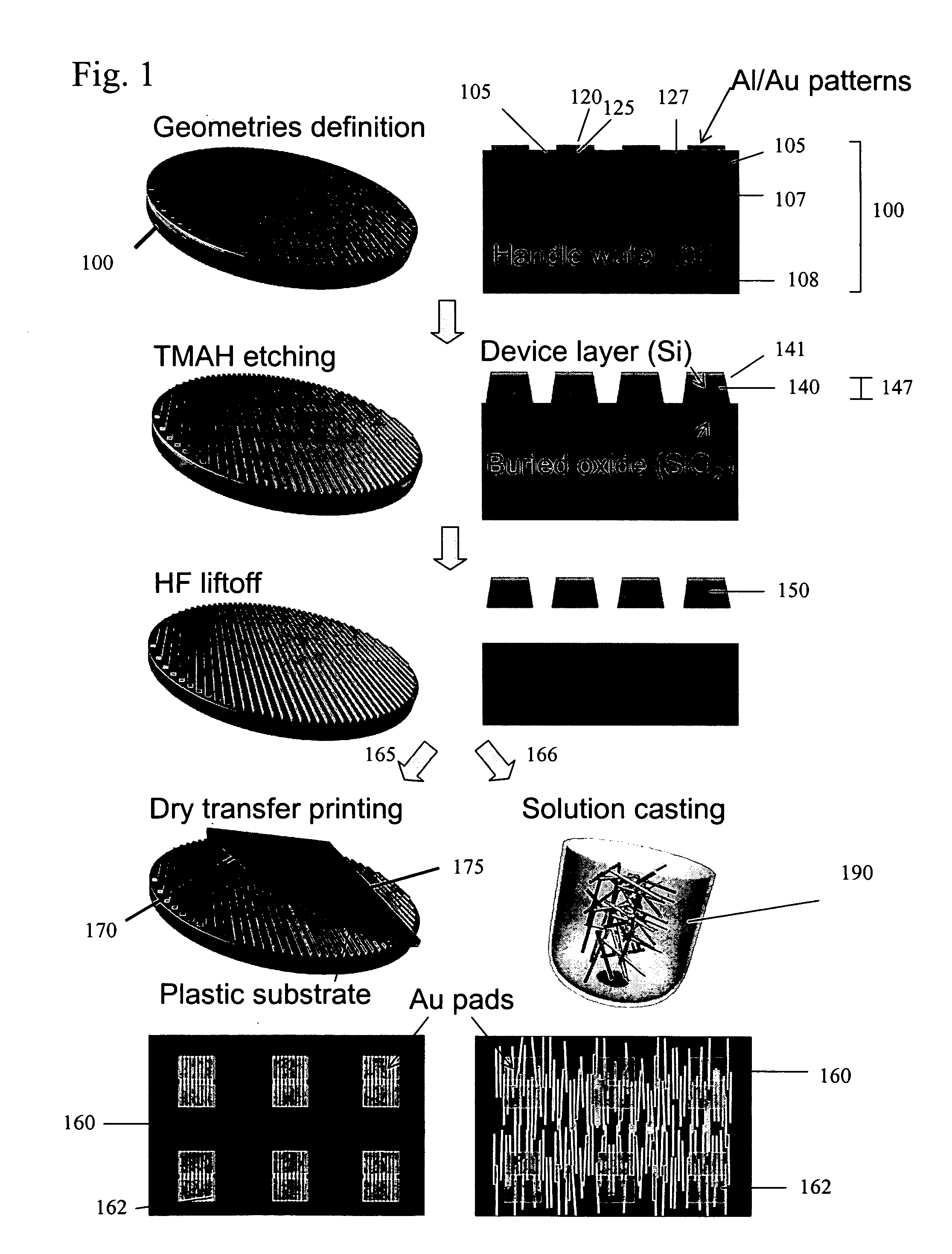
Printing semiconductor elements by shear-assisted elastomeric stamp transfer
ActiveUS8506867B2Sacrificing printing yield and accuracyIncrease chanceConfectionerySolid-state devicesEngineeringVertical displacement
Provided are methods and devices for transfer printing of semiconductor elements to a receiving surface. In an aspect, the printing is by conformal contact between an elastomeric stamp inked with the semiconductor elements and a receiving surface, and during stamp removal, a shear offset is applied between the stamp and the receiving surface. The shear-offset printing process achieves high printing transfer yields with good placement accuracy. Process parameter selection during transfer printing, including time varying stamp-backing pressure application and vertical displacement, yields substantially constant delamination rates with attendant transfer printing improvement.
Owner:X DISPLAY CO TECH LTD
High density chip carrier with integrated passive devices
InactiveUS6962872B2Reduce inductanceEasy accessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsHigh densityEngineering
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Chips having rear contacts connected by through vias to front contacts
InactiveUS20080246136A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSemiconductor device
A microelectronic unit is provided in which front and rear surfaces of a semiconductor element may define a thin region which has a first thickness and a thicker region having a thickness at least about twice the first thickness. A semiconductor device may be present at the front surface, with a plurality of first conductive contacts at the front surface connected to the device. A plurality of conductive vias may extend from the rear surface through the thin region of the semiconductor element to the first conductive contacts. A plurality of second conductive contacts can be exposed at an exterior of the semiconductor element. A plurality of conductive traces may connect the second conductive contacts to the conductive vias.
Owner:INVENSAS CORP
Pattern Transfer Printing by Kinetic Control of Adhesion to an Elastomeric Stamp
ActiveUS20090199960A1Keep the distanceEasy transferFinal product manufactureDecorative surface effectsSpatial OrientationsElastomer
The present invention provides methods, systems and system components for transferring, assembling and integrating features and arrays of features having selected nanosized and / or microsized physical dimensions, shapes and spatial orientations. Methods of the present invention utilize principles of ‘soft adhesion’ to guide the transfer, assembly and / or integration of features, such as printable semiconductor elements or other components of electronic devices. Methods of the present invention are useful for transferring features from a donor substrate to the transfer surface of an elastomeric transfer device and, optionally, from the transfer surface of an elastomeric transfer device to the receiving surface of a receiving substrate. The present methods and systems provide highly efficient, registered transfer of features and arrays of features, such as printable semiconductor element, in a concerted manner that maintains the relative spatial orientations of transferred features.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
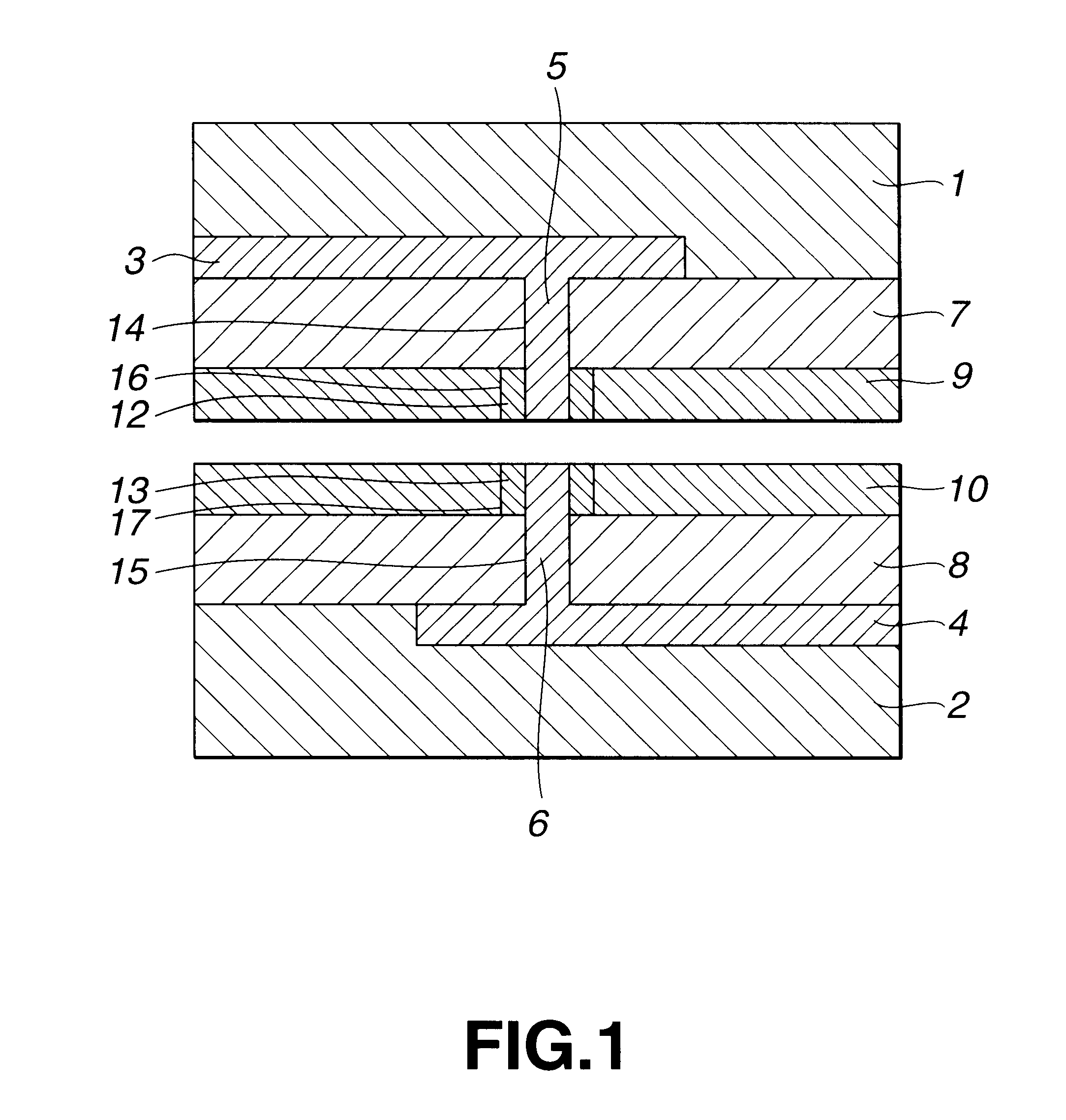
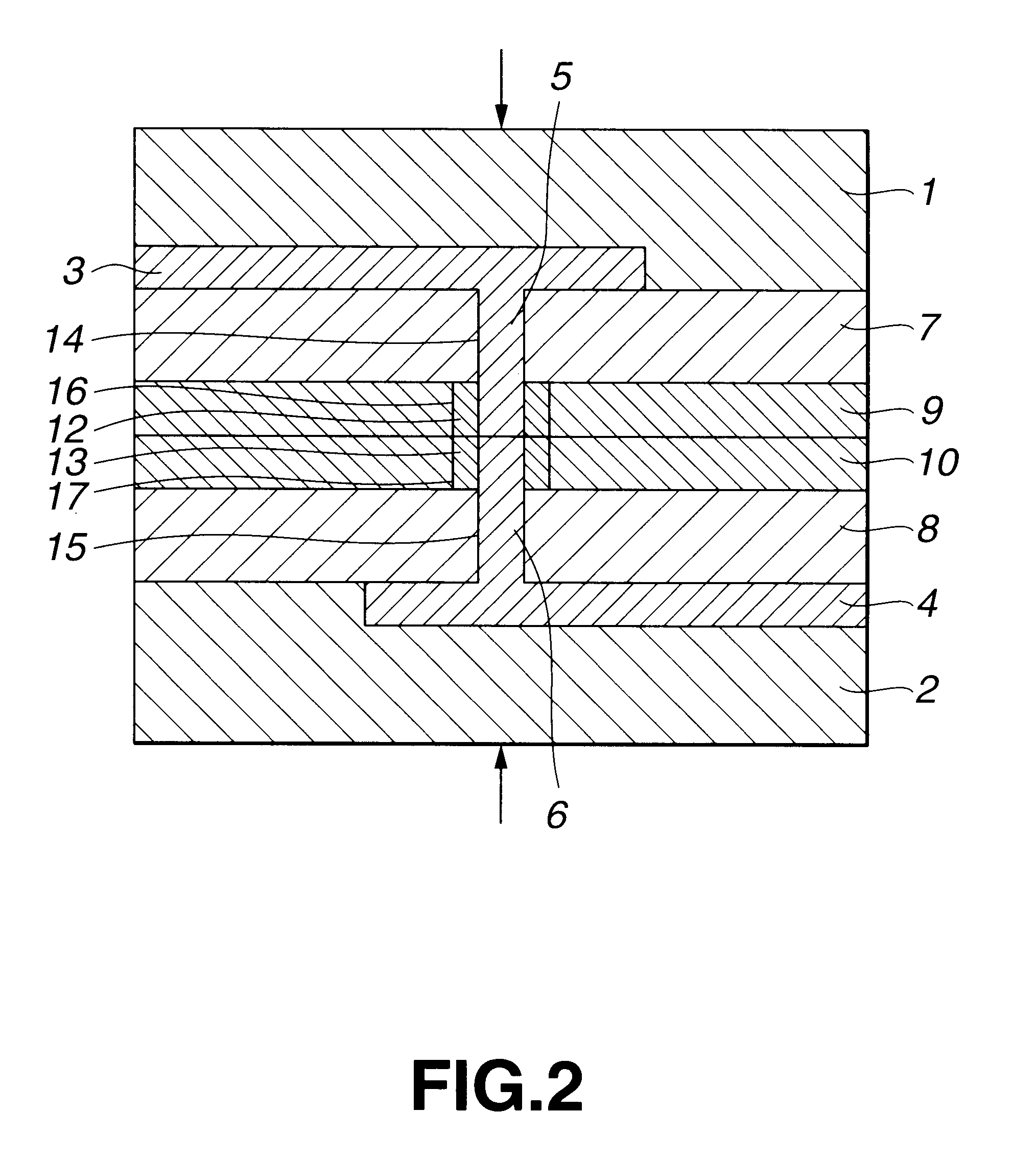
Structure and method of a strained channel transistor and a second semiconductor component in an integrated circuit
A semiconductor chip includes a semiconductor substrate 126, in which first and second active regions are disposed. A resistor 124 is formed in the first active region and the resistor 124 includes a doped region 128 formed between two terminals 136. A strained channel transistor 132 is formed in the second active region. The transistor includes a first and second stressor 141, formed in the substrate oppositely adjacent a strained channel region 143.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
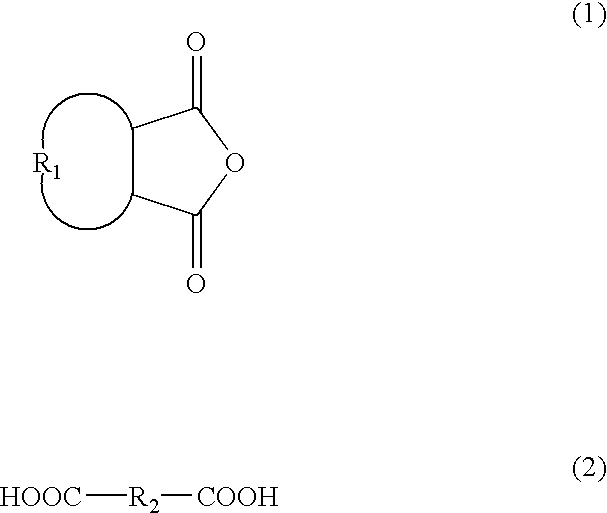
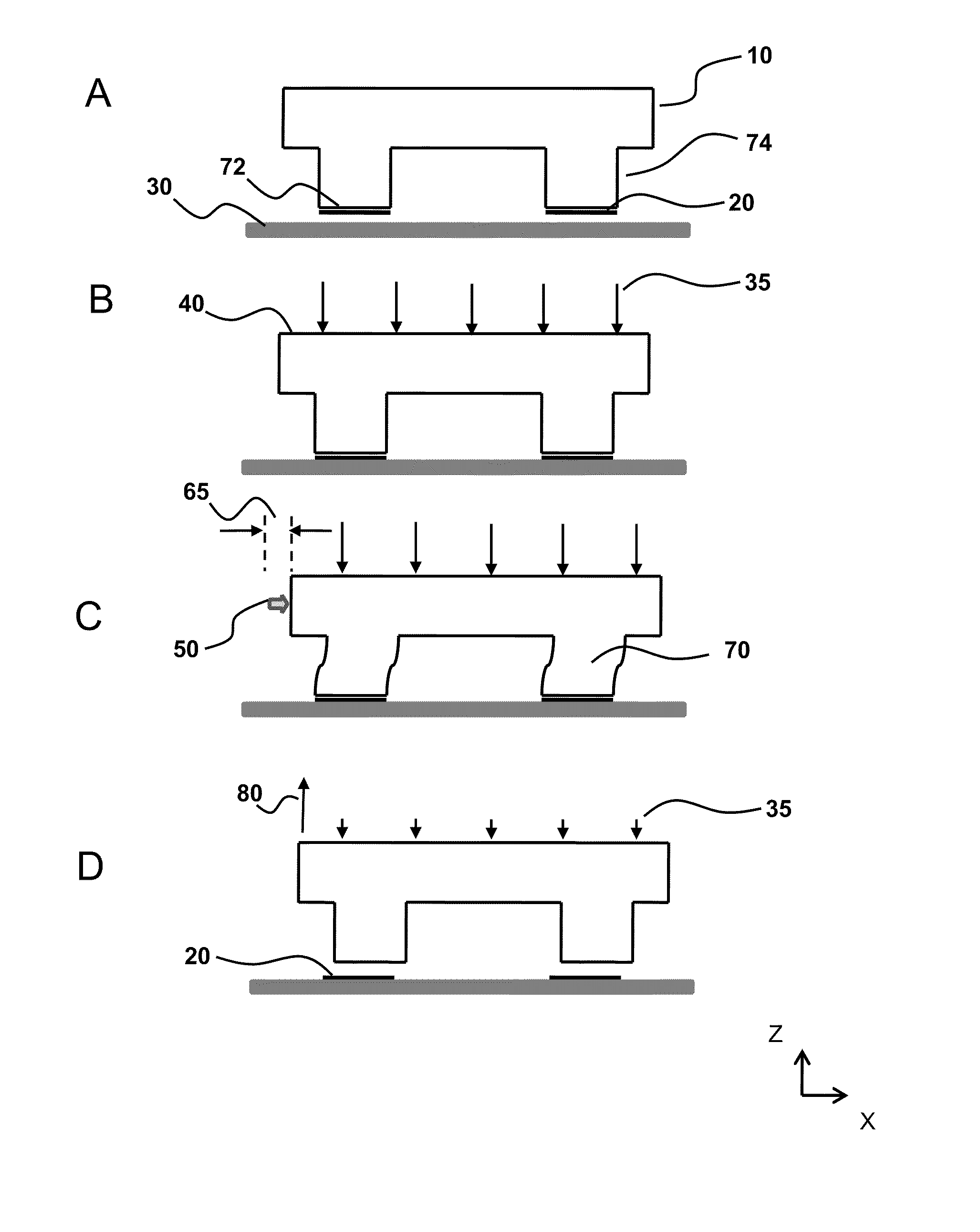
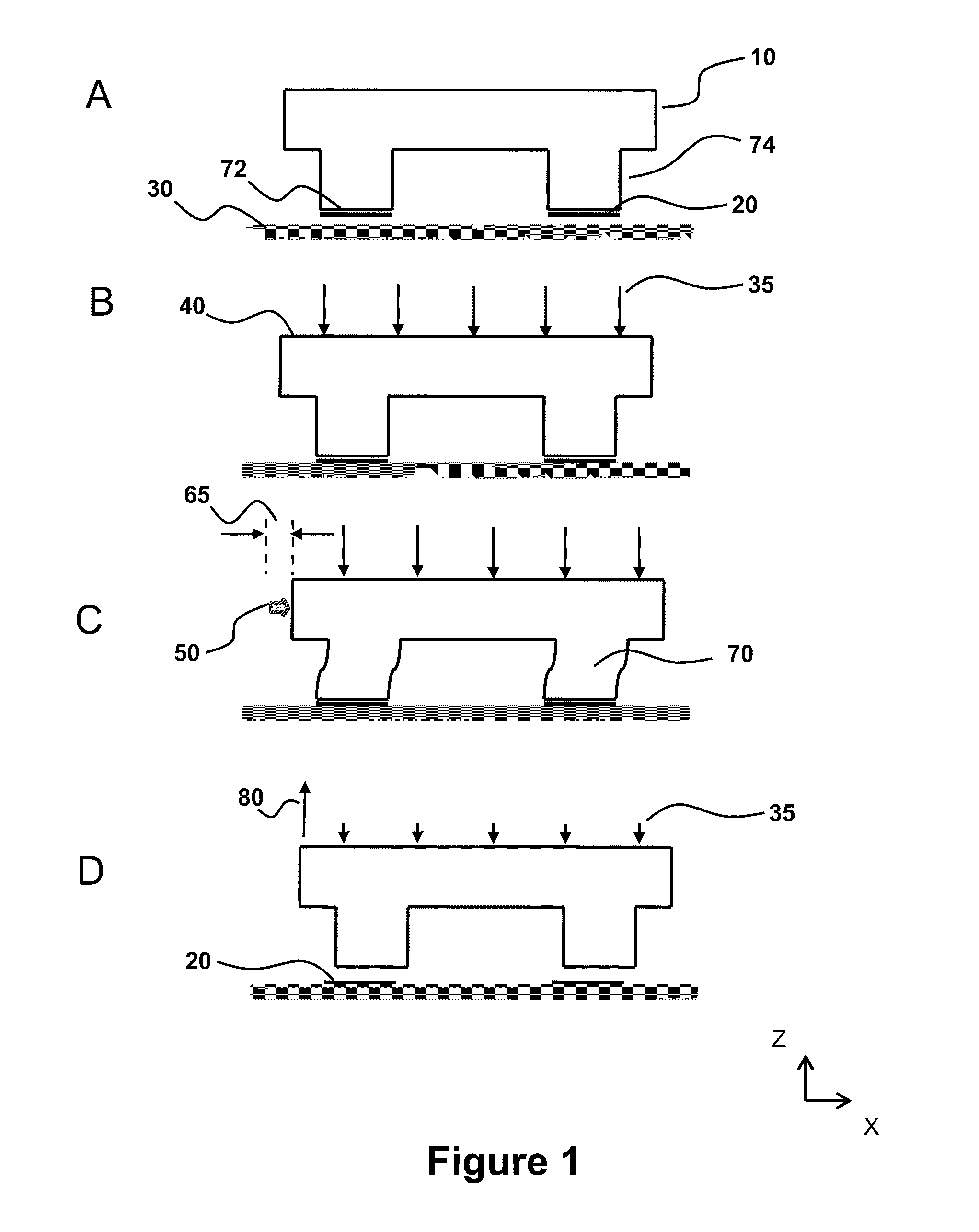
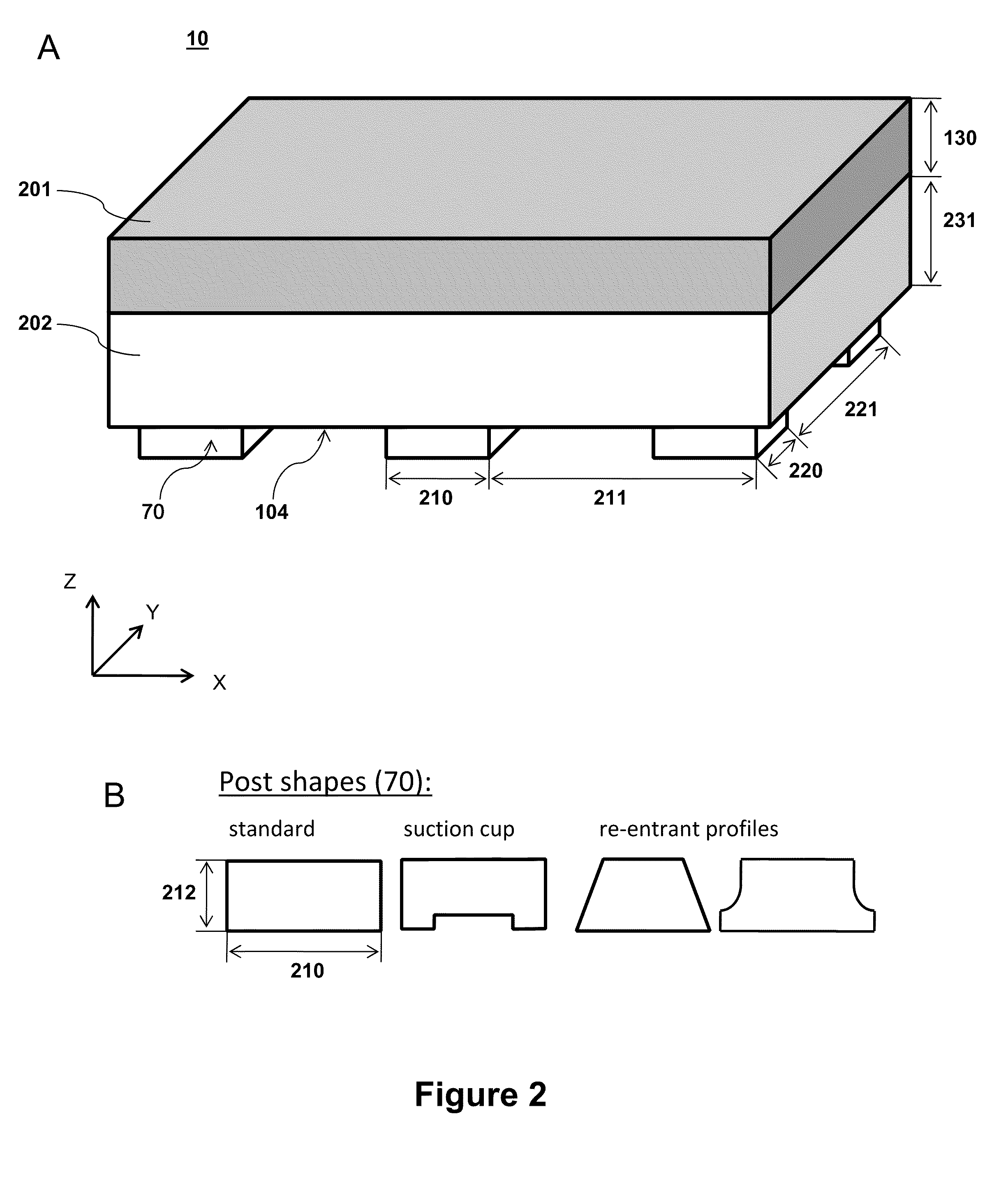
Methods for filling a gap feature on a substrate surface and related semiconductor device structures
PendingUS20190067014A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDeposition processSubstrate surface
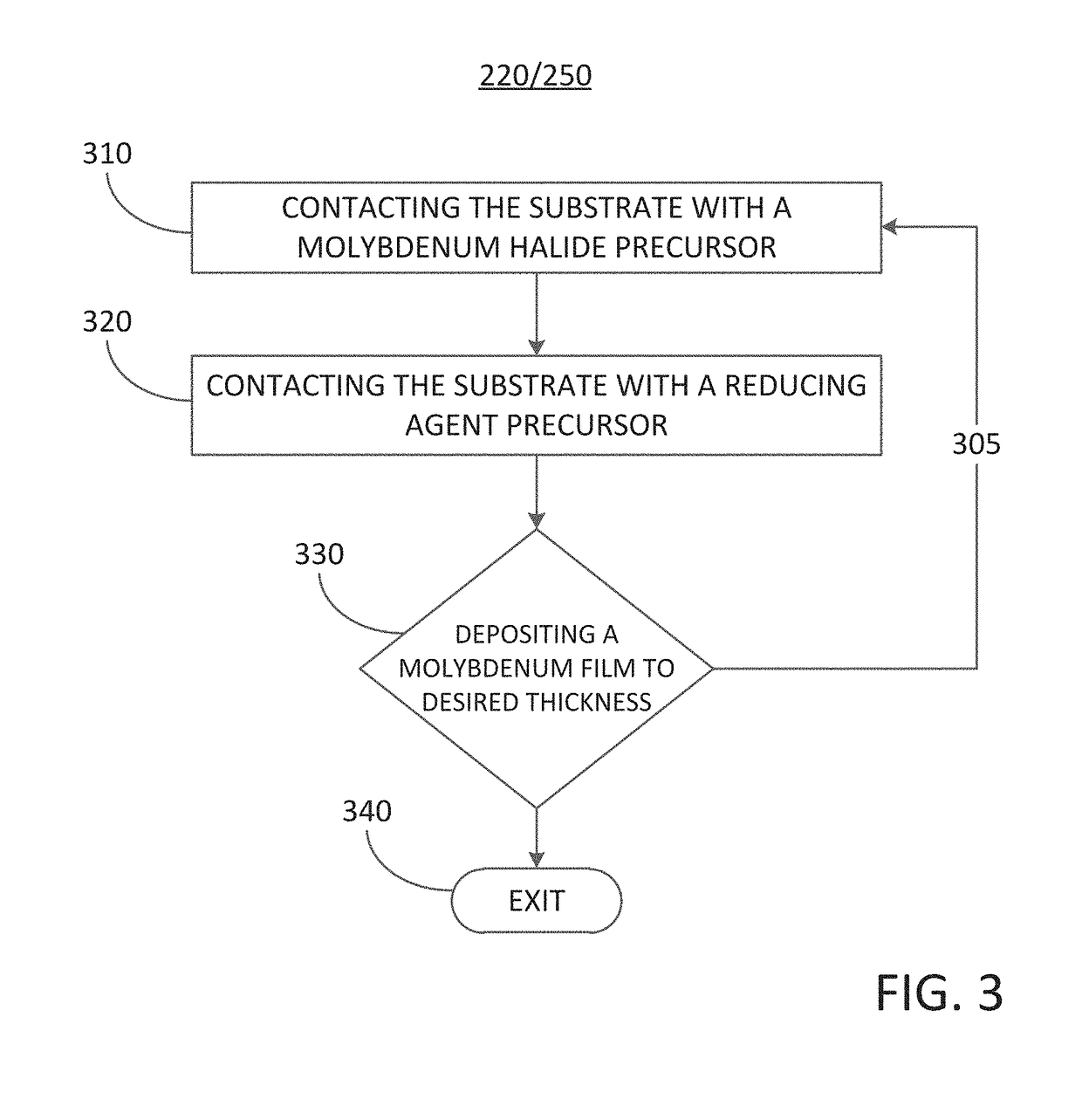
Methods for filling a gap feature on a substrate surface are disclosure. The methods may include: providing a substrate comprising one or more gap features into a reaction chamber; and partially filling the one or more gap features with a molybdenum metal film by a cyclical deposition-etch process, wherein a unit cycle of the cyclical deposition-etch process comprises: partially filling the one or more gap features with a molybdenum metal film by a performing at least one unit cycle of a first cyclical deposition process; and partially etching the molybdenum metal film. The methods may also include: filling the one or more gap features with molybdenum metal film by performing at least one unit cycle of a second cyclical deposition process. Semiconductor device structures including a gap fill molybdenum metal film disposed in one or more gap features in or on a surface of a substrate formed by the methods of the disclosure are also disclosed.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Layer Transfer Process and Functionally Enhanced Integrated Circuits Products Thereby
InactiveUS20080277778A1Low costFunction increaseSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTransfer procedureEngineering
A structure for a semiconductor components is provided having a device layer sandwiched on both sides by other active, passive, and interconnecting components. A wafer-level layer transfer process is used to create this planar (2D) IC structure with added functional enhancements.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Rectifier circuit, power supply circuit, and semiconductor device
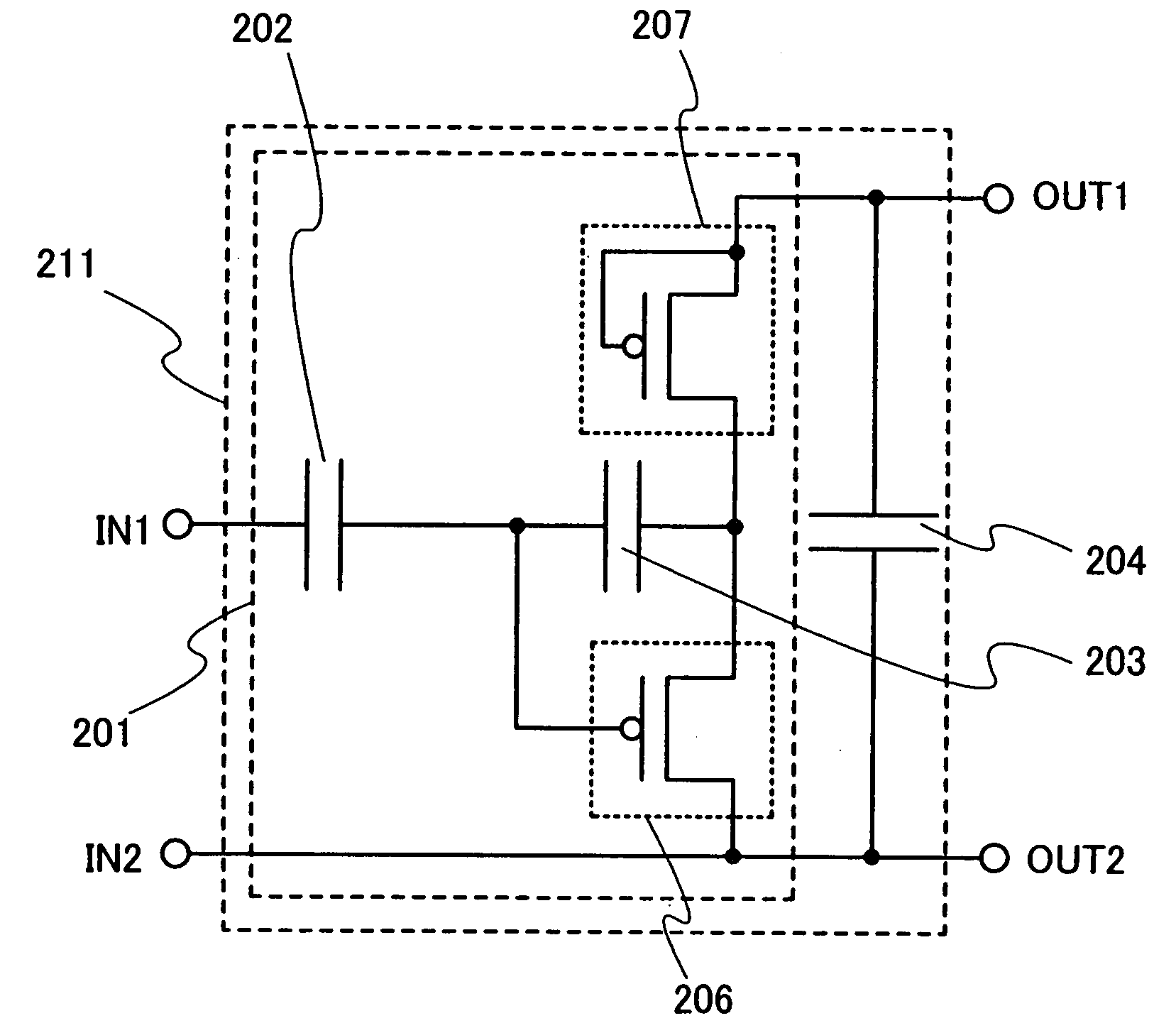
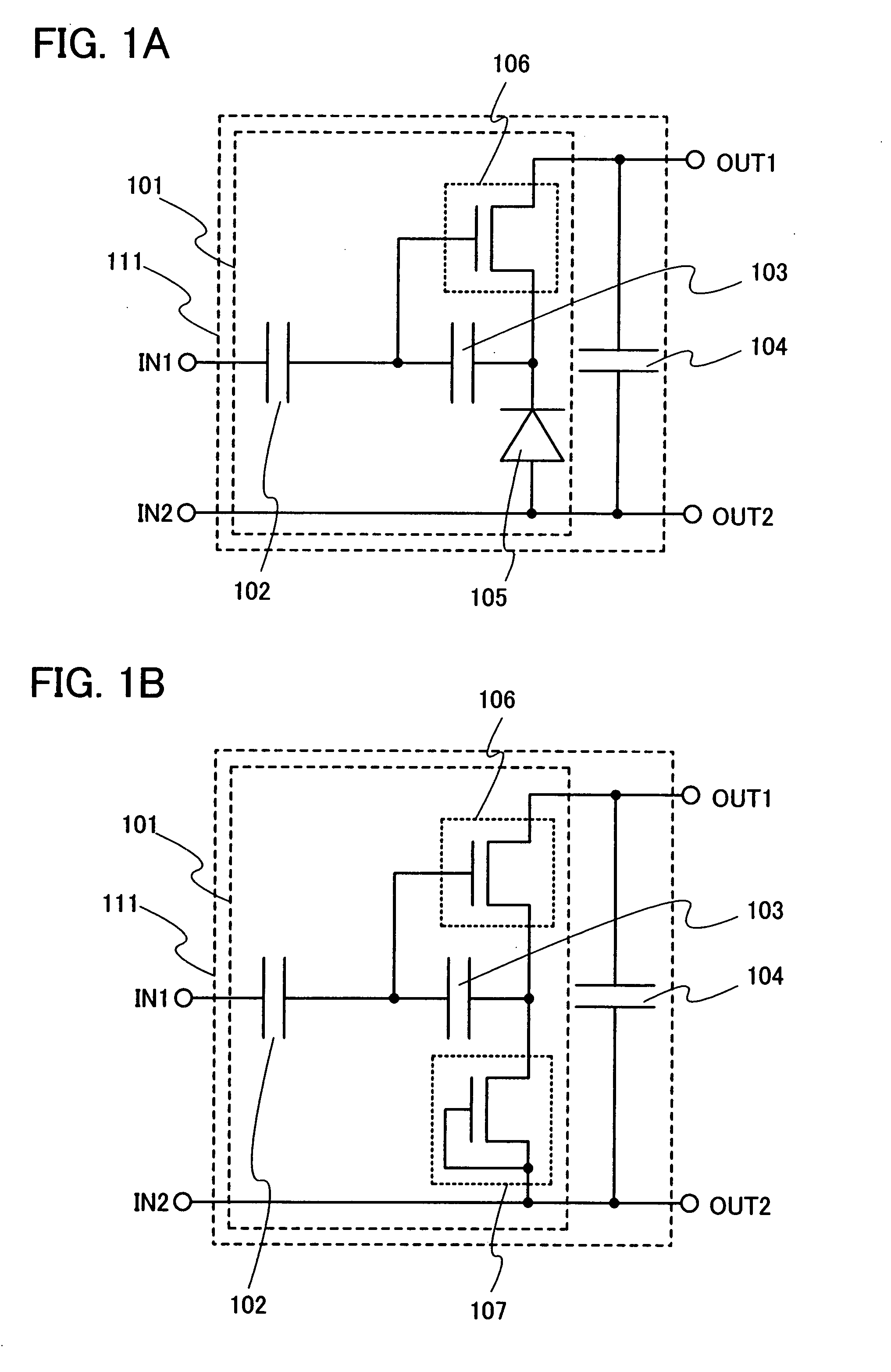
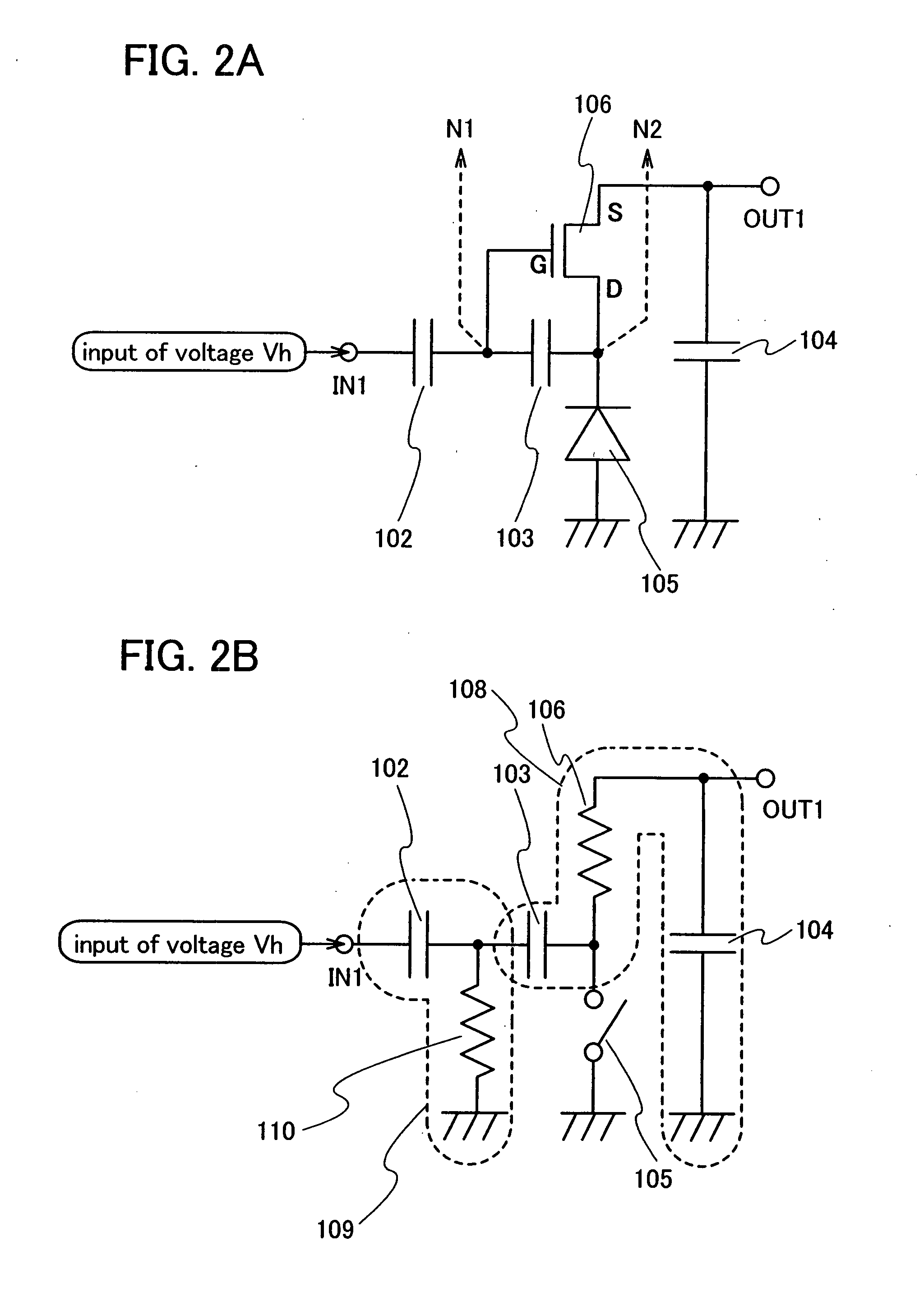
It is an object of the present invention to provide a rectifier circuit that can suppress deterioration or dielectric breakdown of a semiconductor element due to excessive current. A rectifier circuit of the present invention includes at least a first capacitor, a second capacitor, and a diode which are sequentially connected in series in a path which connects an input terminal and one of two output terminals, and a transistor. The second capacitor is connected between one of a source region and a drain region and a gate electrode of the transistor. Further, the other one of the source region and the drain region and the other one of two output terminals are connected each other.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device
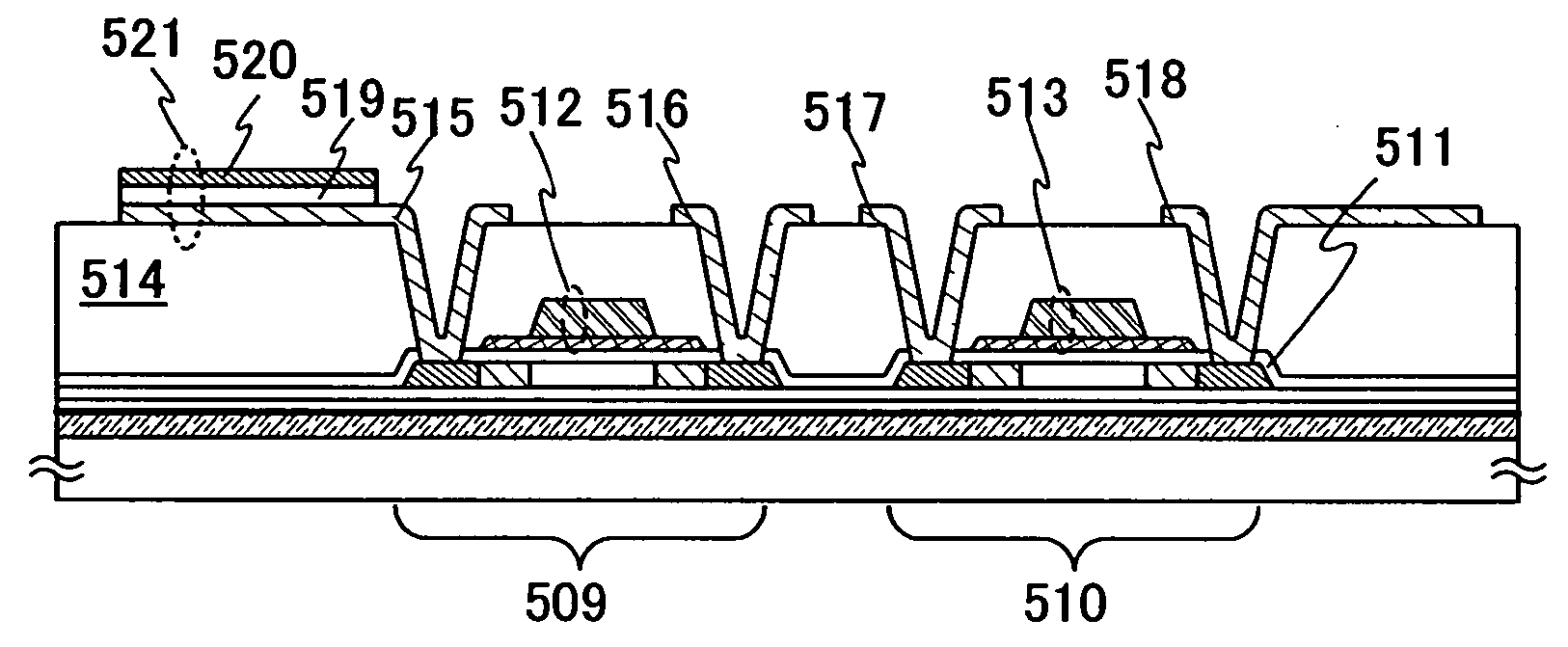
InactiveUS20040195572A1Improve rigidityStable separationTransistorSolid-state devicesData rateElectric signal
A semiconductor device which has a high performance integrated circuit formed of an inexpensive glass substrate and capable of processing a large amount of information and operating at higher data rates. The semiconductor device includes semiconductor elements stacked by transferring a semiconductor element formed on a different substrate. A resin film is formed between the stacked semiconductor elements and a metal oxide film is partially formed between the stacked semiconductor elements as well. A first electric signal is converted to an optical signal in a light emitting element electrically connected to one of the stacked semiconductor elements. Meanwhile, the optical signal is converted to a second electric signal in a light receiving element electrically connected to another one of the stacked semiconductor elements.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
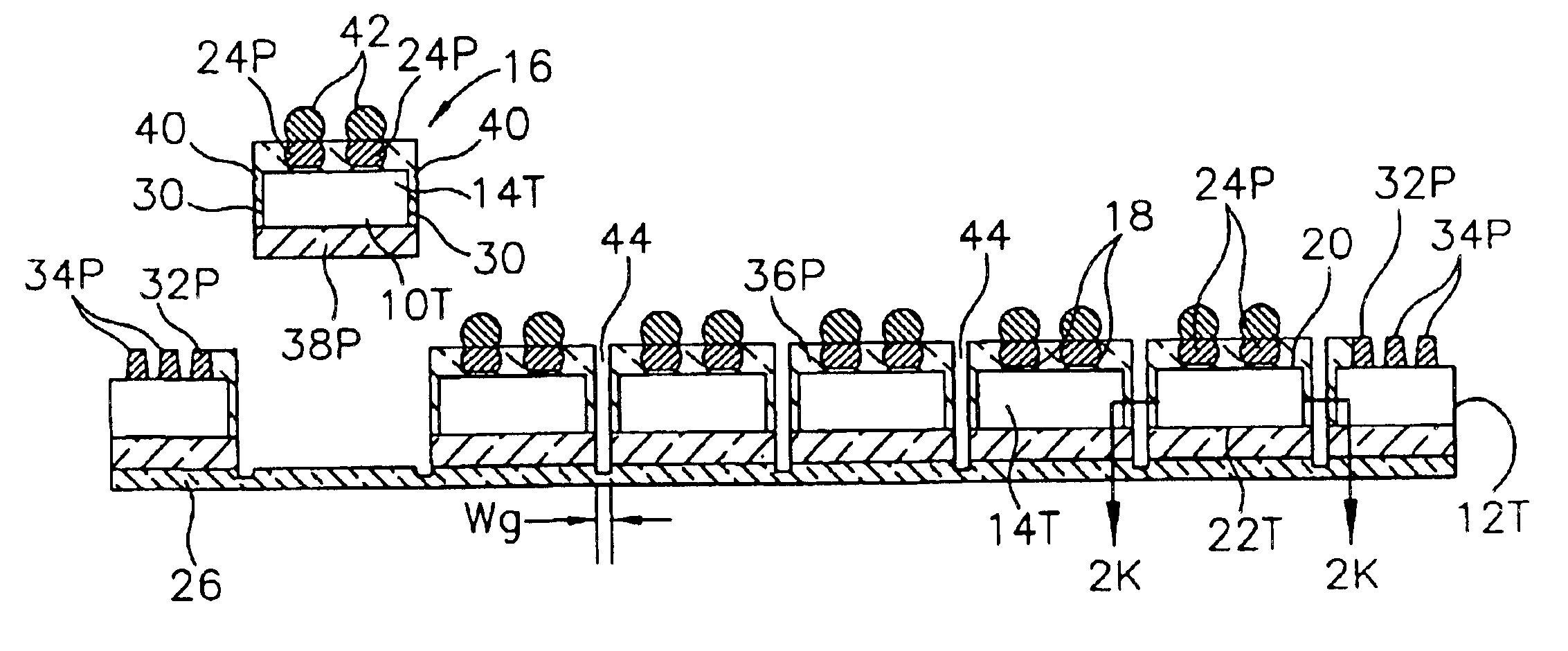
Semiconductor component and interconnect having conductive members and contacts on opposing sides
InactiveUS6903443B2Easy to manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsSemiconductor packageElectronic assemblies
A method for fabricating semiconductor components and interconnects includes the steps of providing a substrate, such as a semiconductor die, forming external contacts on opposing sides of the substrate by laser drilling vias through the substrate, and forming conductive members in the vias. The conductive members include enlarged terminal portions that are covered with a non-oxidizing metal. The method can be used to fabricate stackable semiconductor packages having integrated circuits in electrical communication with the external contacts. The method can also be used to fabricate interconnects for electrically engaging packages, dice and wafers for testing or for constructing electronic assemblies.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20090079000A1Difference in mobilityReduce power consumptionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialPlane orientation
An object is to realize high performance and low power consumption in a semiconductor device having an SOI structure. In addition, another object is to provide a semiconductor device having a high performance semiconductor element which is more highly integrated. A semiconductor device is such that a plurality of n-channel field-effect transistors and p-channel field-effect transistors are stacked with an interlayer insulating layer interposed therebetween over a substrate having an insulating surface. By controlling a distortion caused to a semiconductor layer due to an insulating film having a stress, a plane orientation of the semiconductor layer, and a crystal axis in a channel length direction, difference in mobility between the n-channel field-effect transistor and the p-channel field-effect transistor can be reduced, whereby current driving capabilities and response speeds of the n-channel field-effect transistor and the p-channel field-effect can be comparable.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Methods for forming a semiconductor device structure and related semiconductor device structures
Methods for forming a semiconductor device structure are provided. The methods may include forming a molybdenum nitride film on a substrate by atomic layer deposition by contacting the substrate with a first vapor phase reactant comprising a molybdenum halide precursor, contacting the substrate with a second vapor phase reactant comprise a nitrogen precursor, and contacting the substrate with a third vapor phase reactant comprising a reducing precursor. The methods provided may also include forming a gate electrode structure comprising the molybdenum nitride film, the gate electrode structure having an effective work function greater than approximately 5.0 eV. Semiconductor device structures including molybdenum nitride films are also provided.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method for Transferring Semiconductor Element, Method for Manufacturing Semiconductor Device, and Semiconductor Device
ActiveUS20090001504A1Improve bonding strengthLow pour pointSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransistor channelMonocrystalline silicon
A transistor formed on a monocrystalline Si wafer is temporarily transferred onto a first temporary supporting substrate. The first temporarily supporting substrate is heat-treated at high heat so as to repair crystal defects generated in a transistor channel of the monocrystalline Si wafer when transferring the transistor. The transistor is then made into a chip and transferred onto a TFT substrate. In order to transfer the transistor which has been once separated from the monocrystalline Si wafer, a different method from a stripping method utilizing ion doping is employed.
Owner:SHARP KK
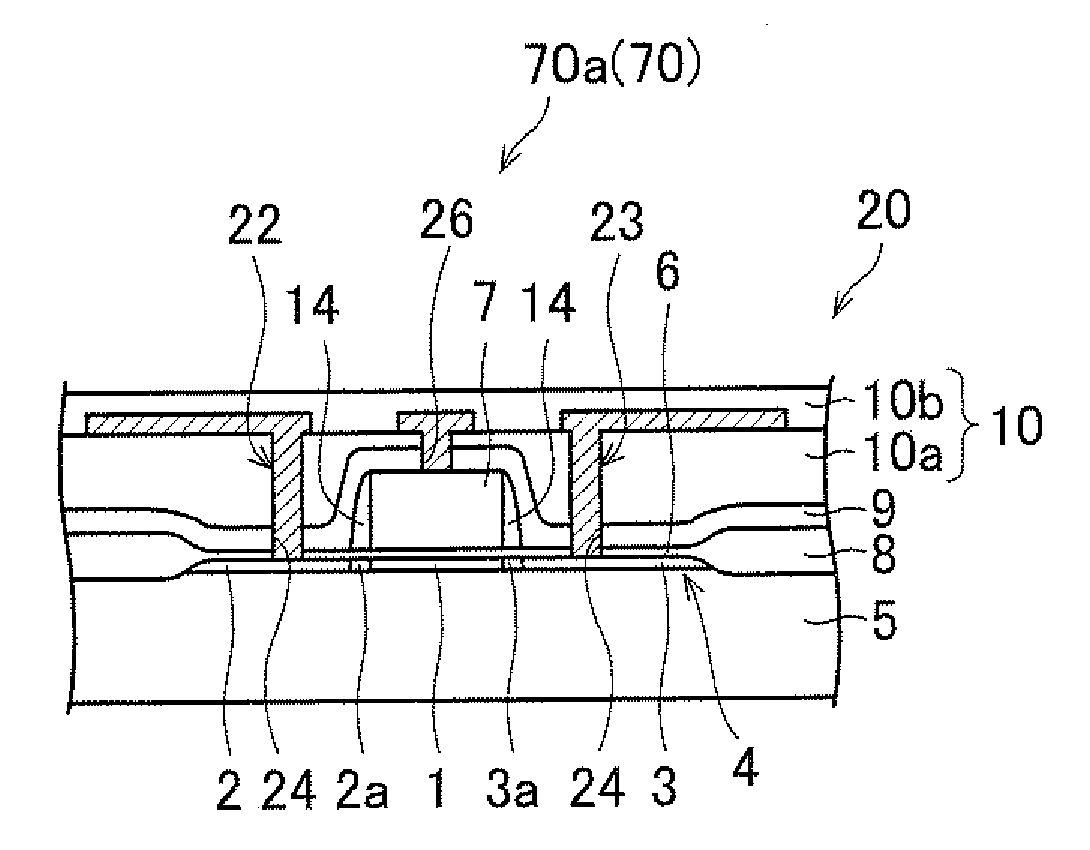
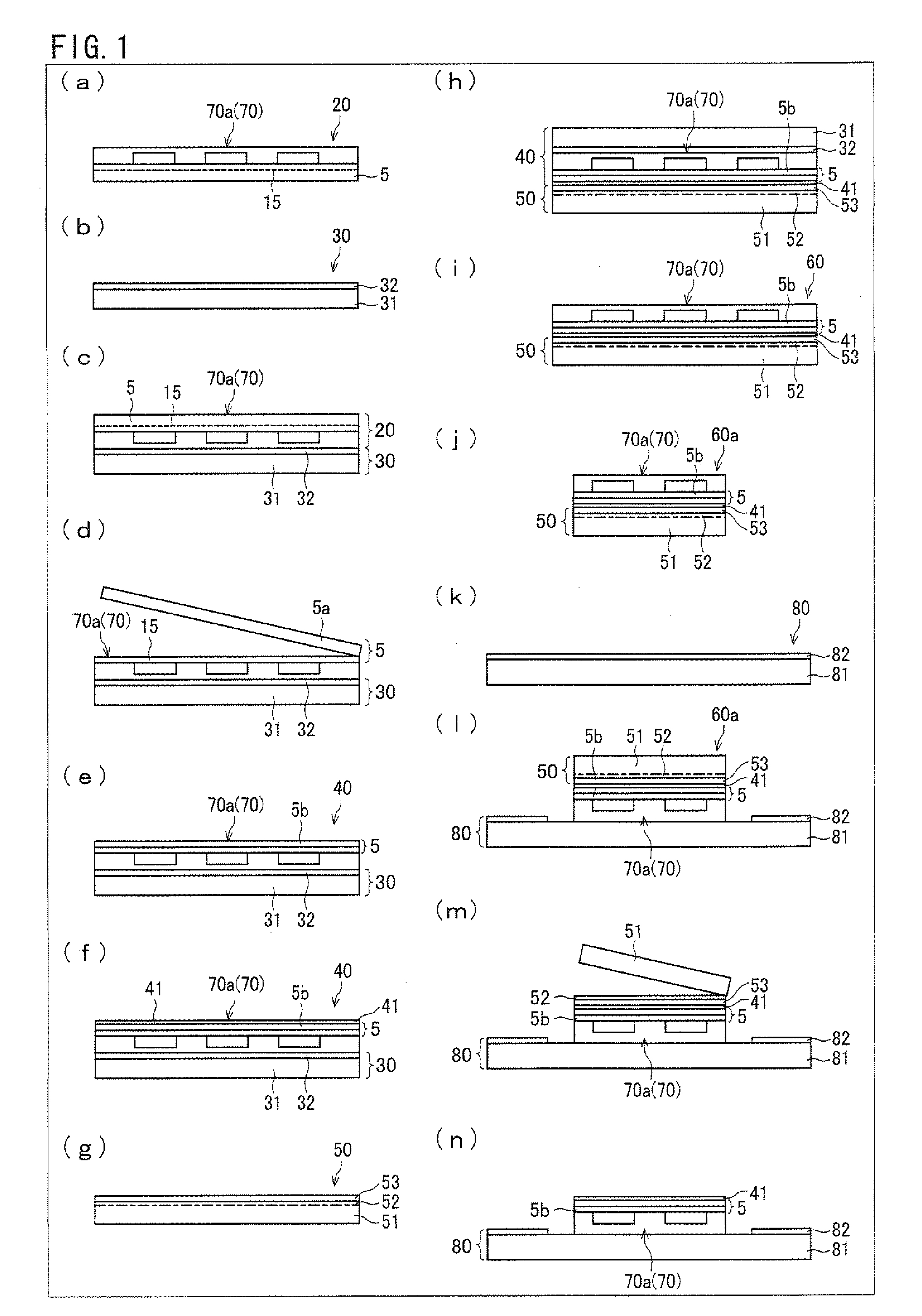
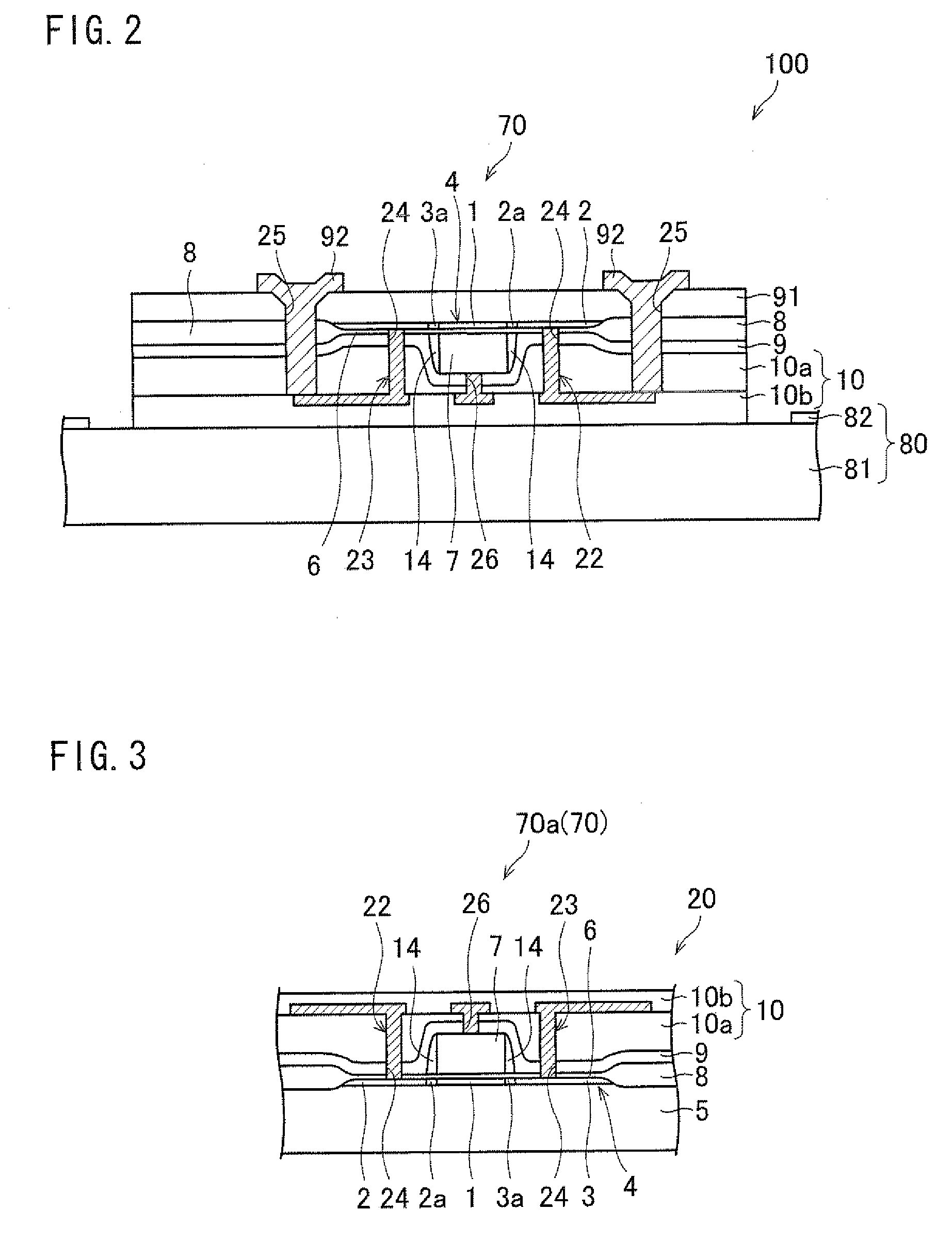
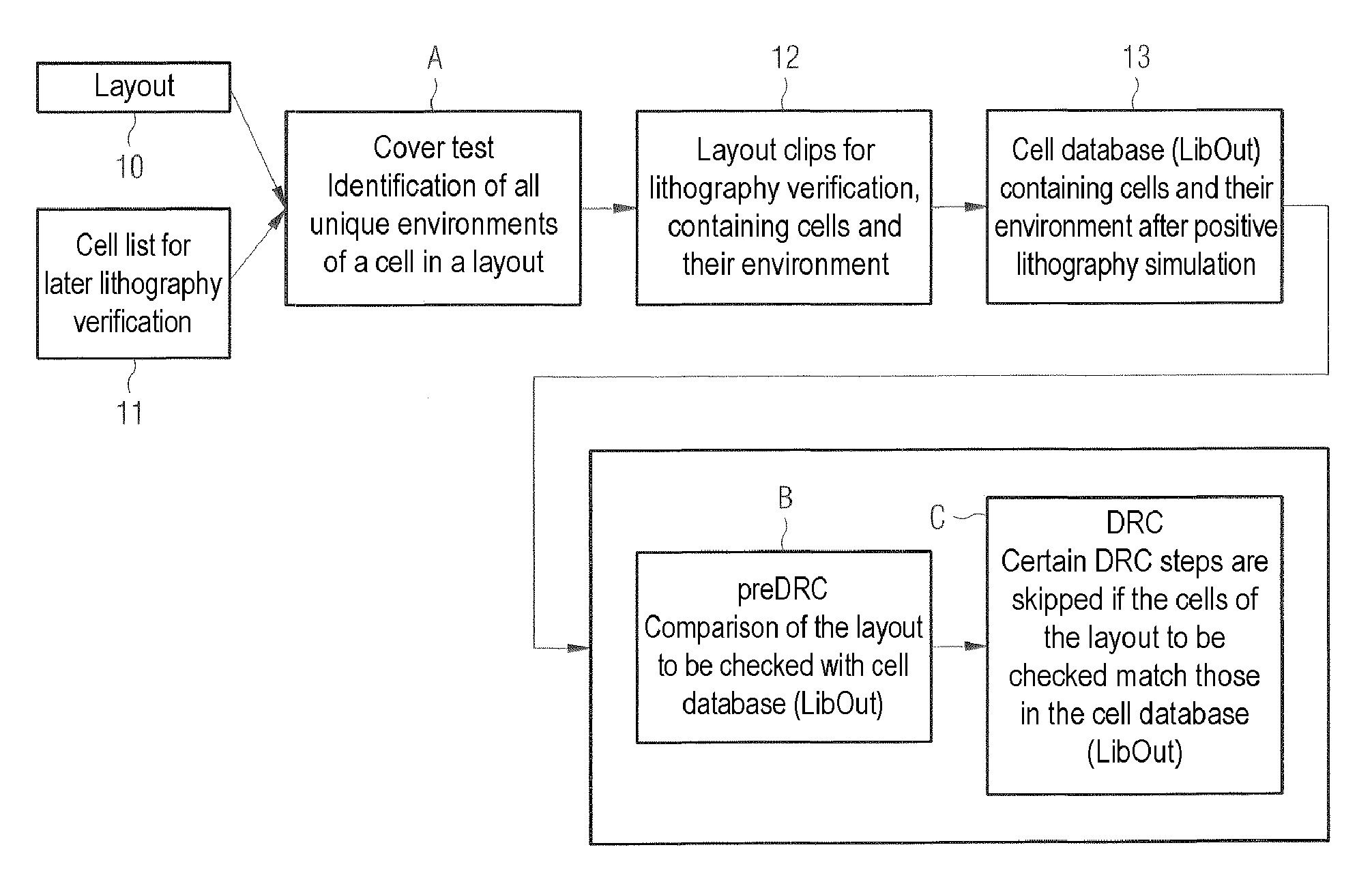
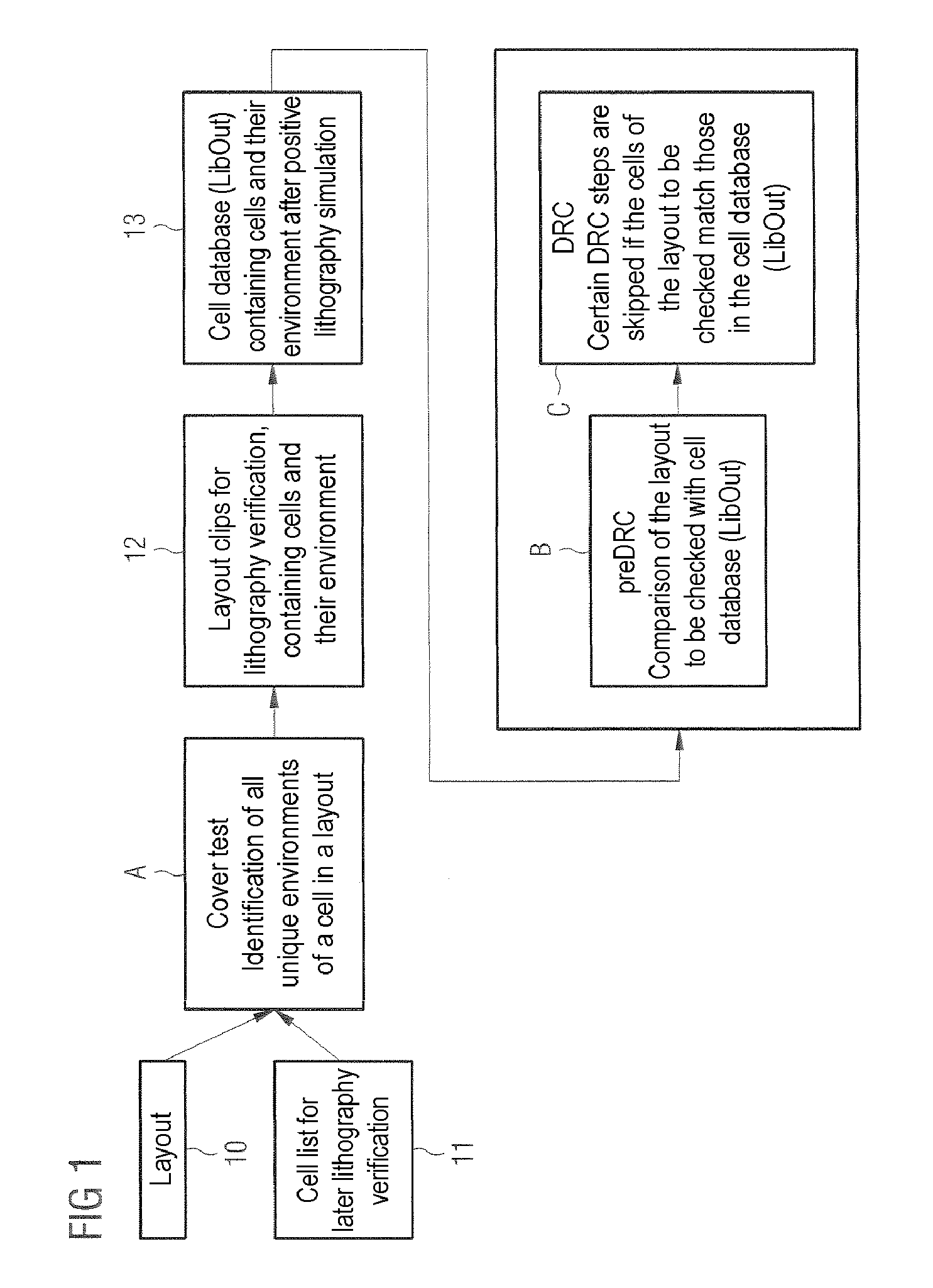
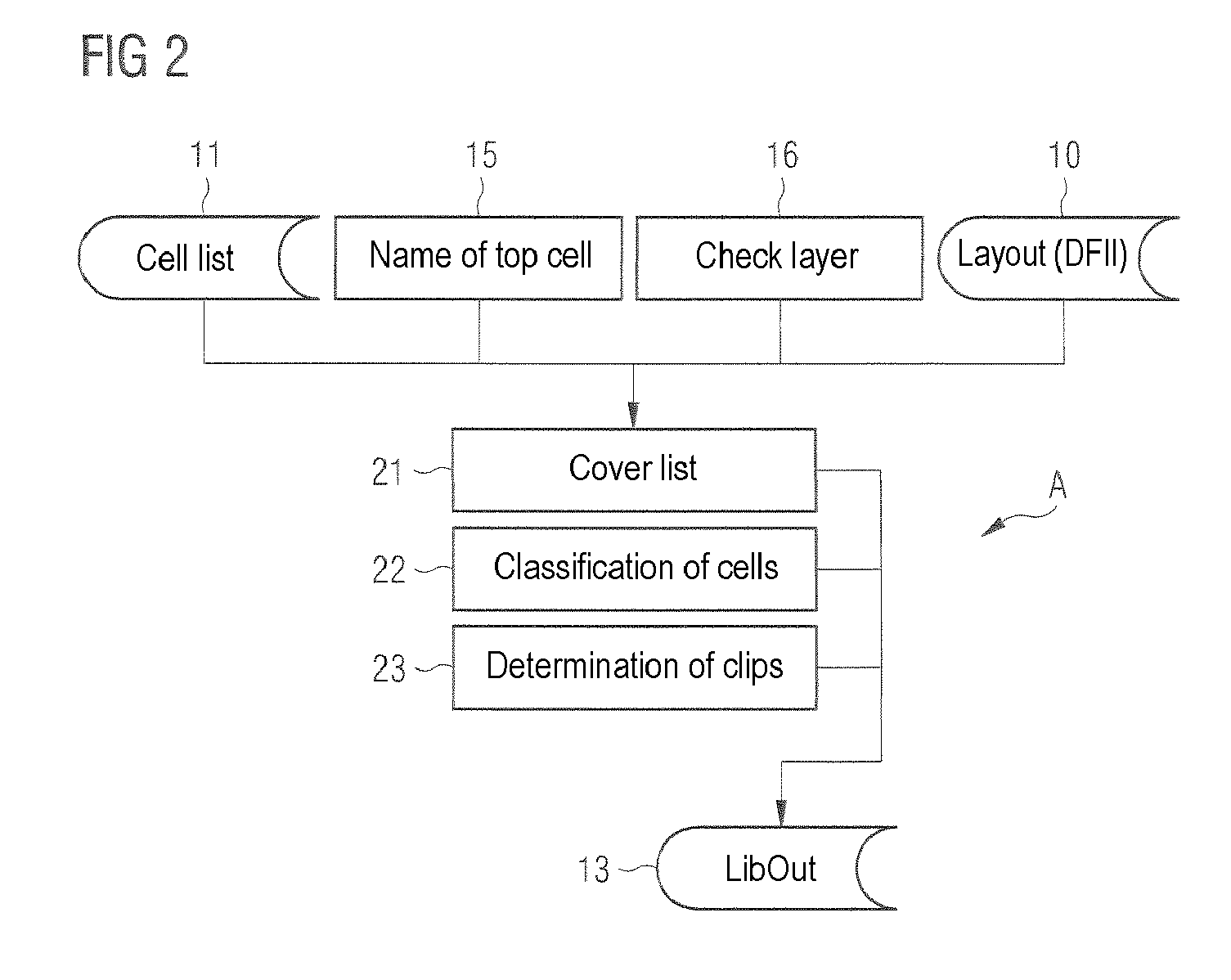
Method and device for classifying cells in a layout into a same environment and their use for checking the layout of an electronic circuit
InactiveUS7665051B2Originals for photomechanical treatmentComputer aided designComputer scienceSemiconductor components
A method and a device can be used for checking the layout of an electronic circuit of a semiconductor component. For example, the method includes an automatic classification of cells in at least one layout into a cell database, and an automatic layout checker comparing the cell database to a layout to be checked.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
Substrate processing system, transfer module, substrate processing method, and method for manufacturing semiconductor element
ActiveUS20130202387A1Reduced footprintImprove throughputSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConveyor partsComputer moduleEngineering
A substrate processing system is provided with: a first transfer unit, which extends from a loader module to a first processing chamber for processing substrates, to transfer the substrates; and a second transfer unit, which is provided below or above the first transfer unit and extends from the loader module to a second processing chamber for processing substrates, to transfer the substrates. The first processing chamber and the second processing chamber do not overlap in the vertical direction, and are disposed at positions separated from each other in a plan view. At the same time, at least a part of the first transfer unit and at least a part of the second transfer unit overlap each other in the vertical direction.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS8044464B2Guaranteed high speed operationReduce power consumptionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor packagePlane orientation
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
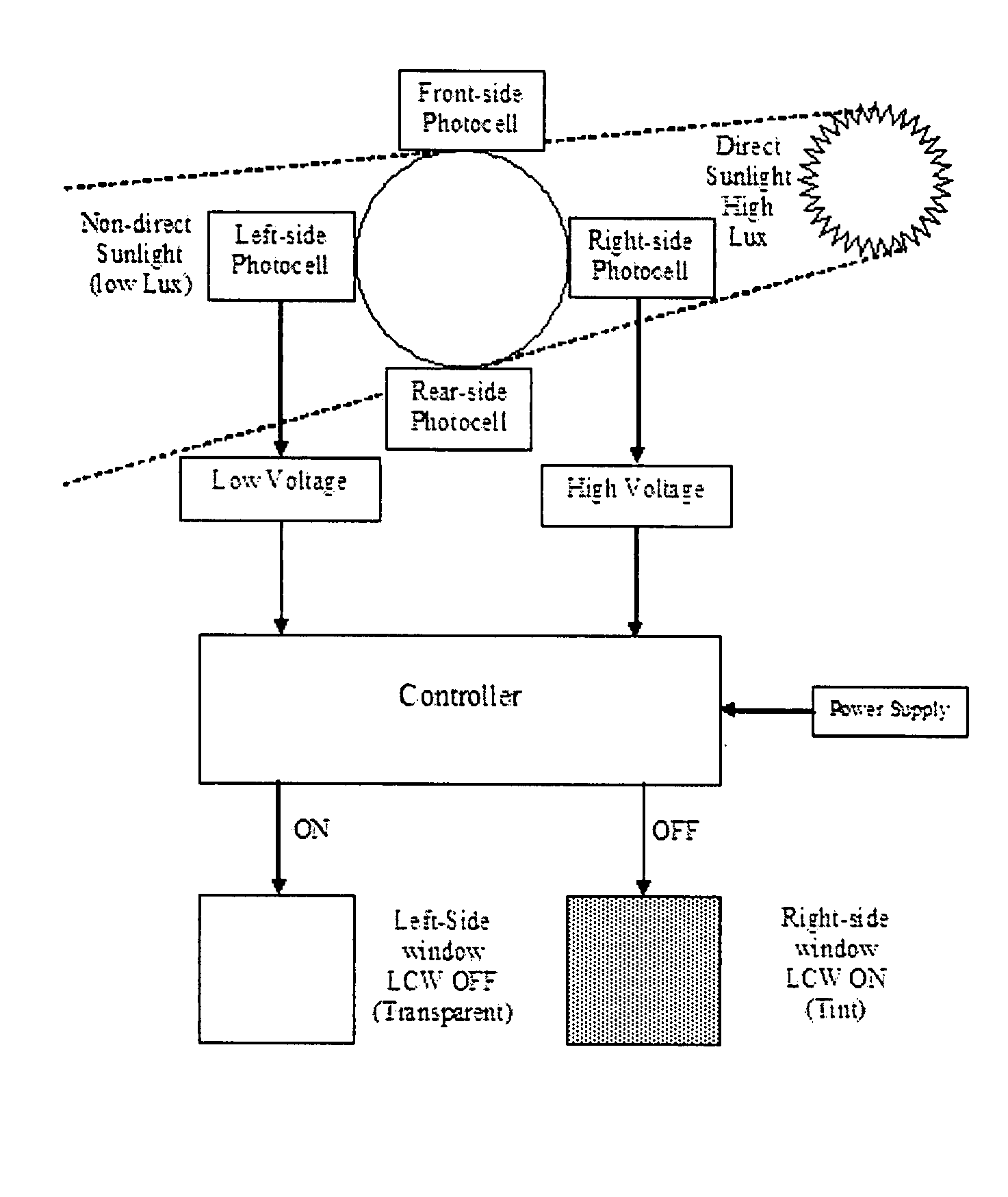
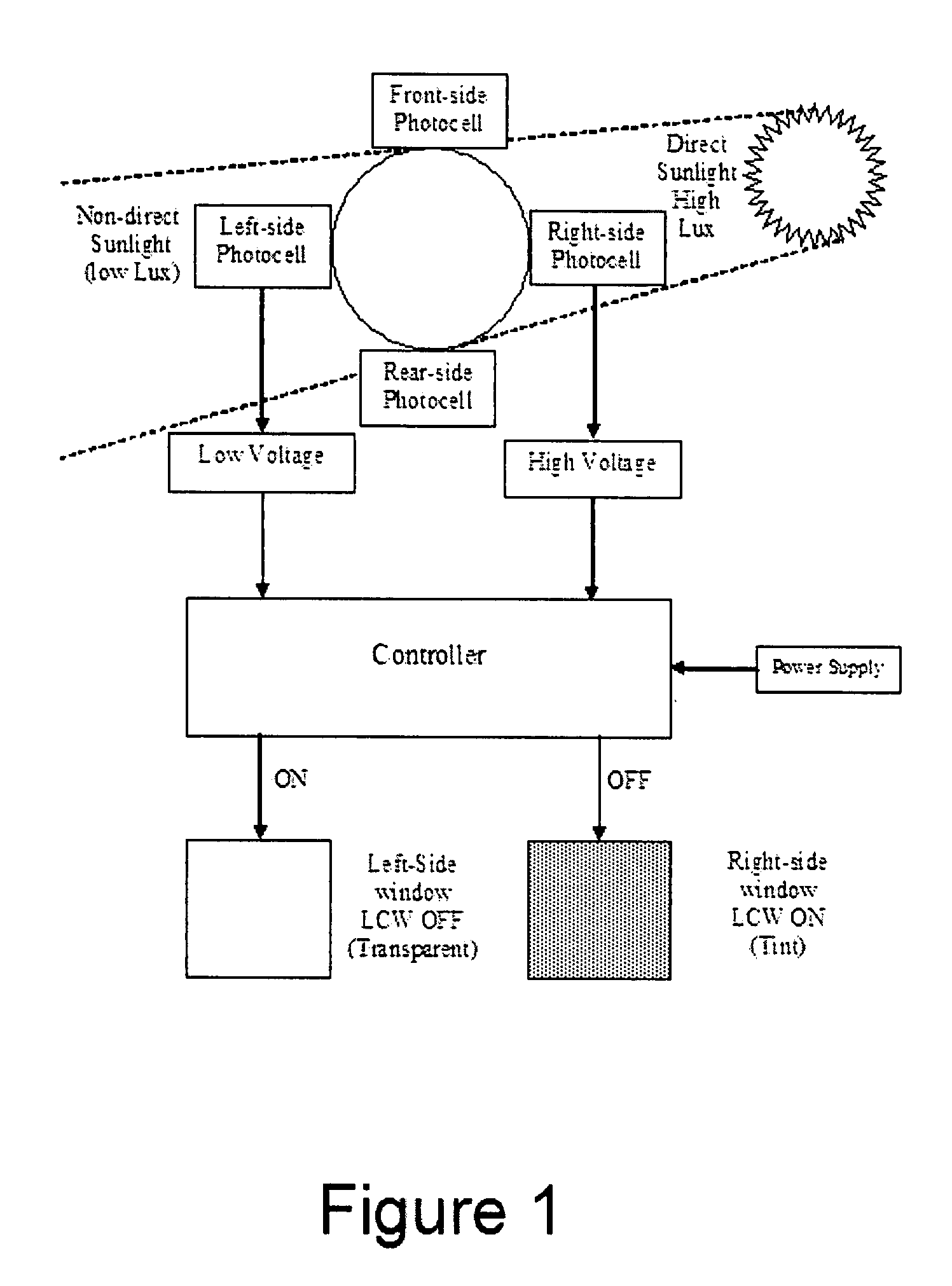
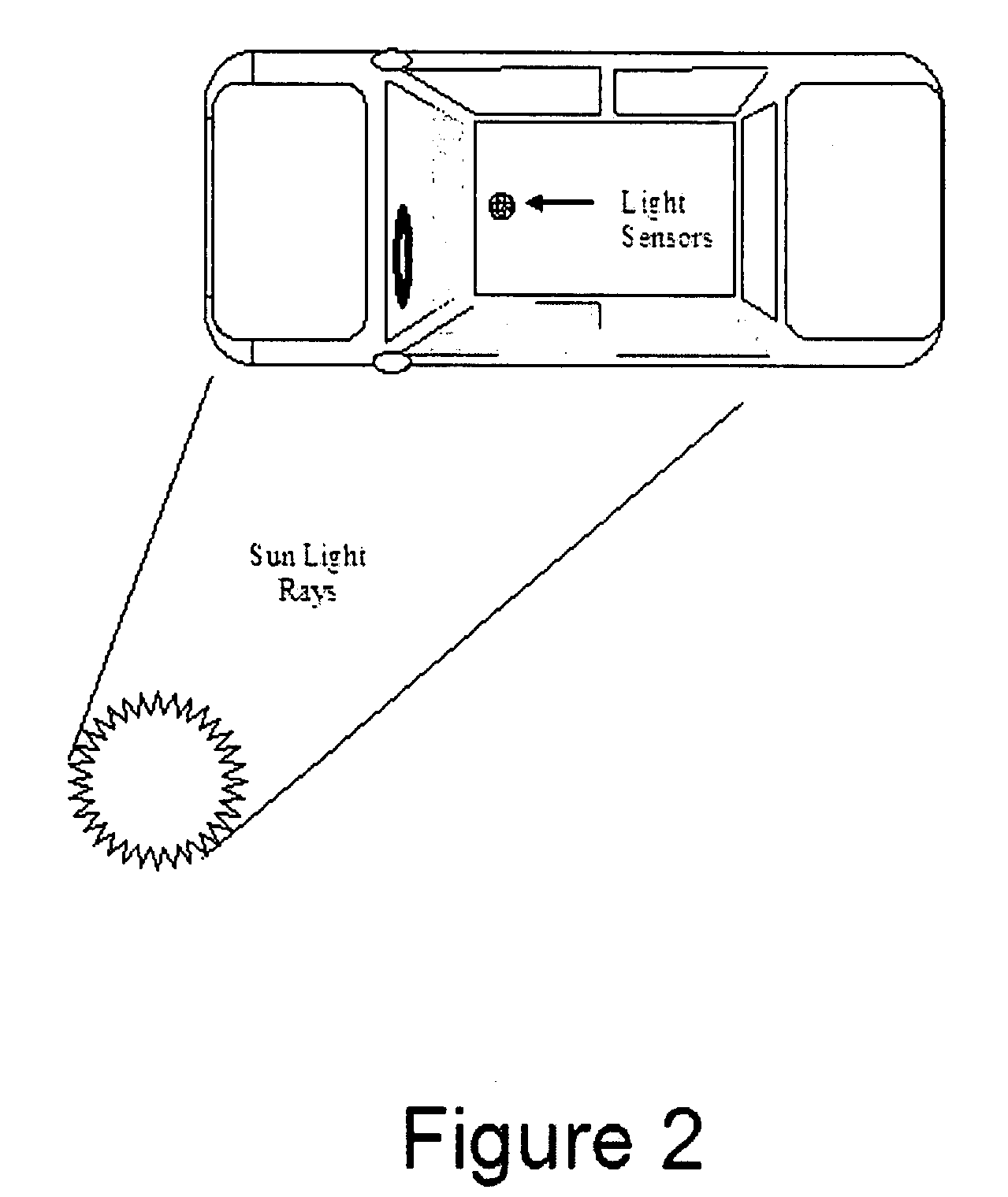
Electronic Window Shading System for Houses, Transport Vehicles and the Like
InactiveUS20090027759A1Reduce condensationConvenient lightingLight dependant control systemsAntiglare equipmentSuspended particlesTelecommunications
There is disclosed an automatic electronic window shading (tinting) system for houses and transport vehicles such as automobiles, RV's, trains, boats and the like, to provide shading for people to protect them from exposure to harmful direct sunlight, by providing the windows of said houses and transport vehicles with display elements and light (photocell / photovoltaic) sensors. The system comprises liquid crystal, electrochromic, suspended particle device (SPD), or NanoChromics display (NCD) element attached to a part of a transparent body (such as the windows) and a liquid crystal, electrochromic, suspended particle device (SPD), or NanoChromics display (NCD) controlling semiconductor element controlling the operation of the display element.
Owner:KUWAIT UNIV
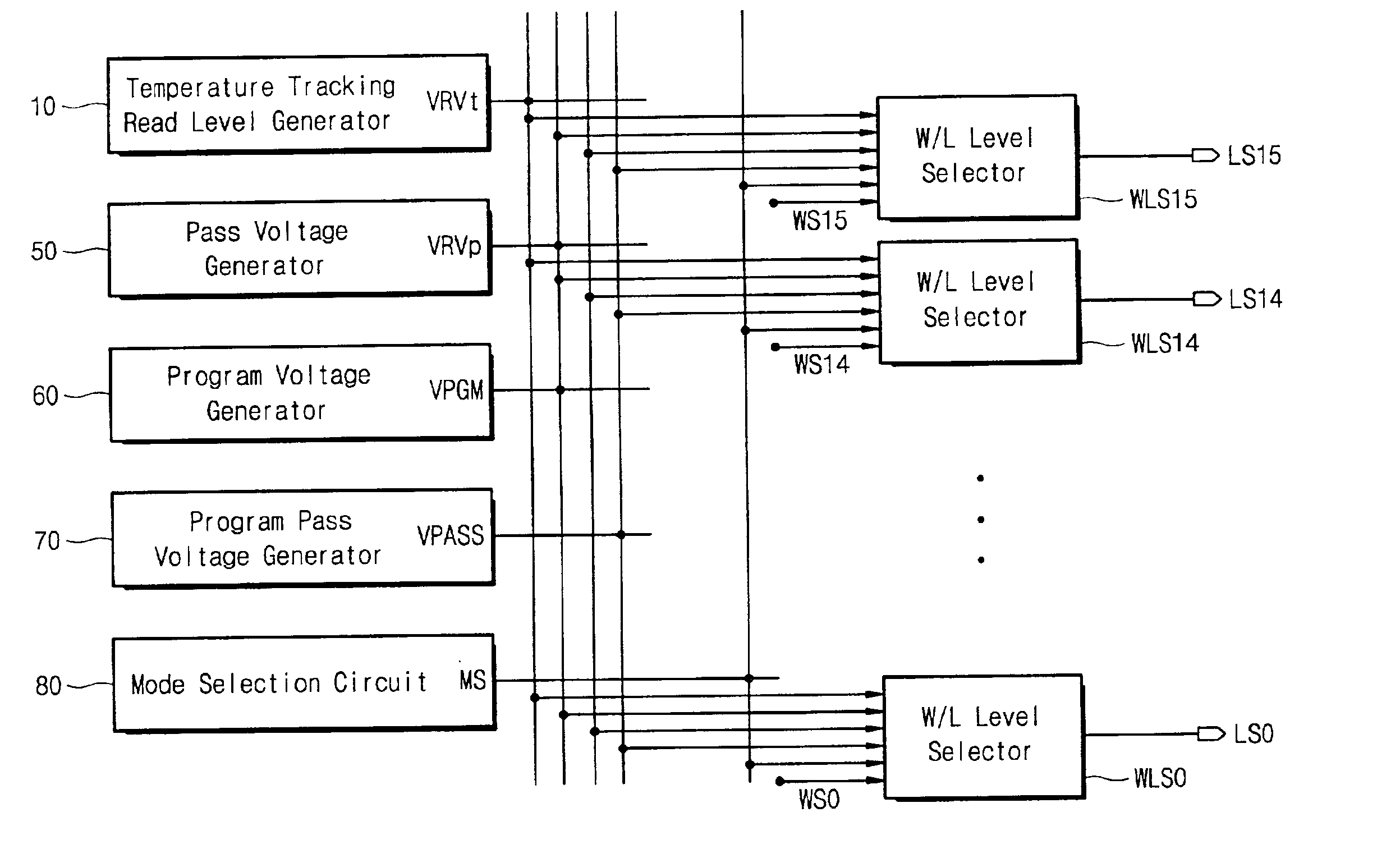
Multi-level flash memory with temperature compensation
InactiveUS6870766B2Reliable functionOperational reliability is increasedRead-only memoriesDigital storageHemt circuitsEngineering
A multi-level semiconductor memory device preferably includes a plurality of wordlines connected to memory cells configured to store multi-level data. A first circuit supplies a temperature-responsive voltage to a selected wordline in order to read a state of a selected memory cell. A second circuit supplies a predetermined voltage to non-selected wordlines. The first circuit preferably includes a semiconductor element that varies its resistance in accordance with temperature. Reliable program-verifying and reading functions are preferably provided despite migration of threshold voltage distribution profiles due to temperature variations.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
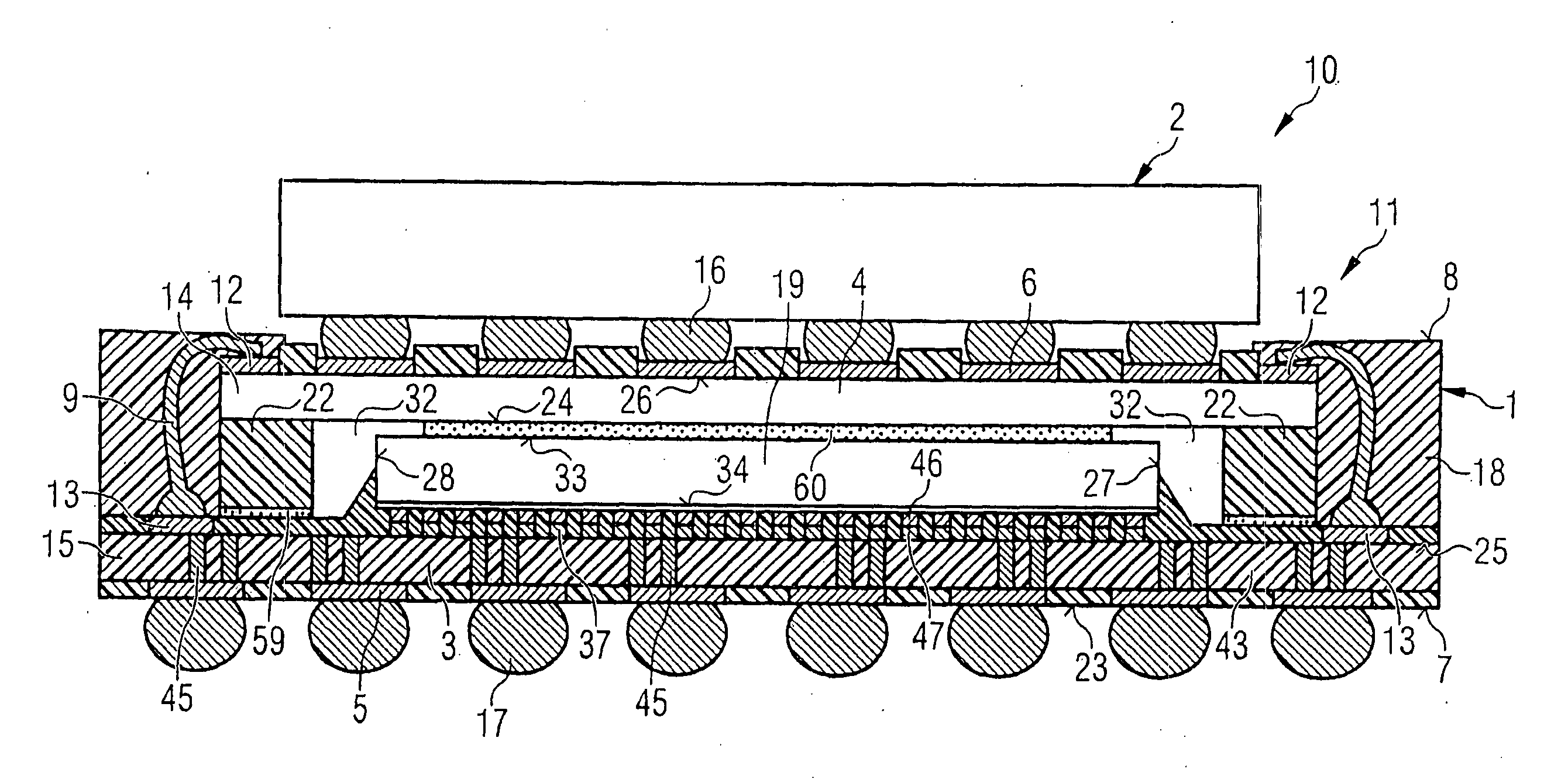
Wiring board embedded with spherical semiconductor element
InactiveUS20070069393A1Provide flexibilityThin thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHigh densityElectronic equipment
A double-sided or multilayer wiring board having high-density wiring is obtained by embedding a spherical semiconductor element in an electrically insulating substrate which composes the wiring board, and a thin electronic device can be provided using such a wiring board. Furthermore, a flexible double-sided or multilayer wiring board which is capable of being housed in a limited space while keeping a desired form can be provided by embedding the spherical semiconductor element, and a thin electronic device can be provided using a variety of such wiring boards by imparting different types of flexibility to desired parts of such a wiring board as required.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
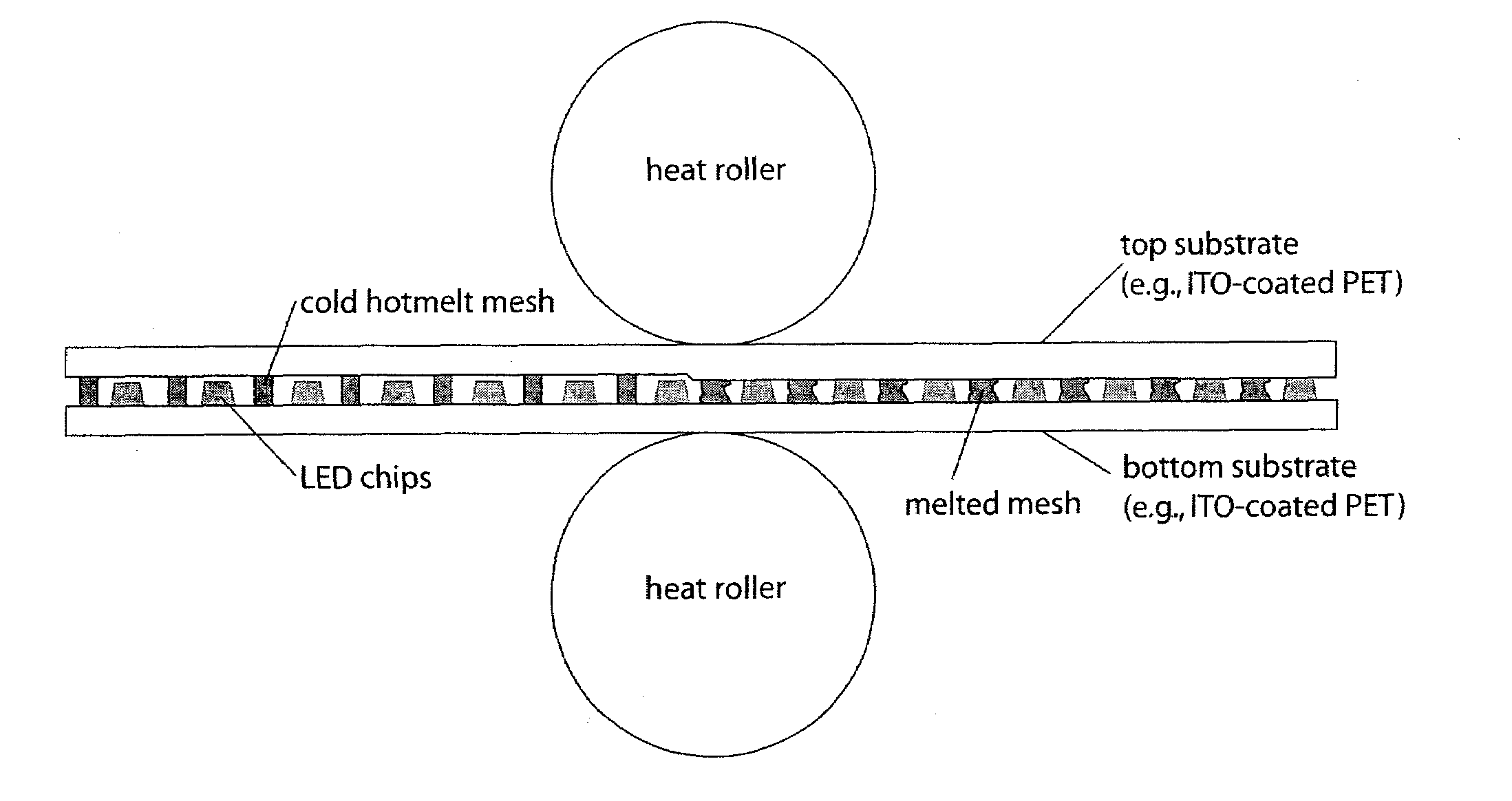
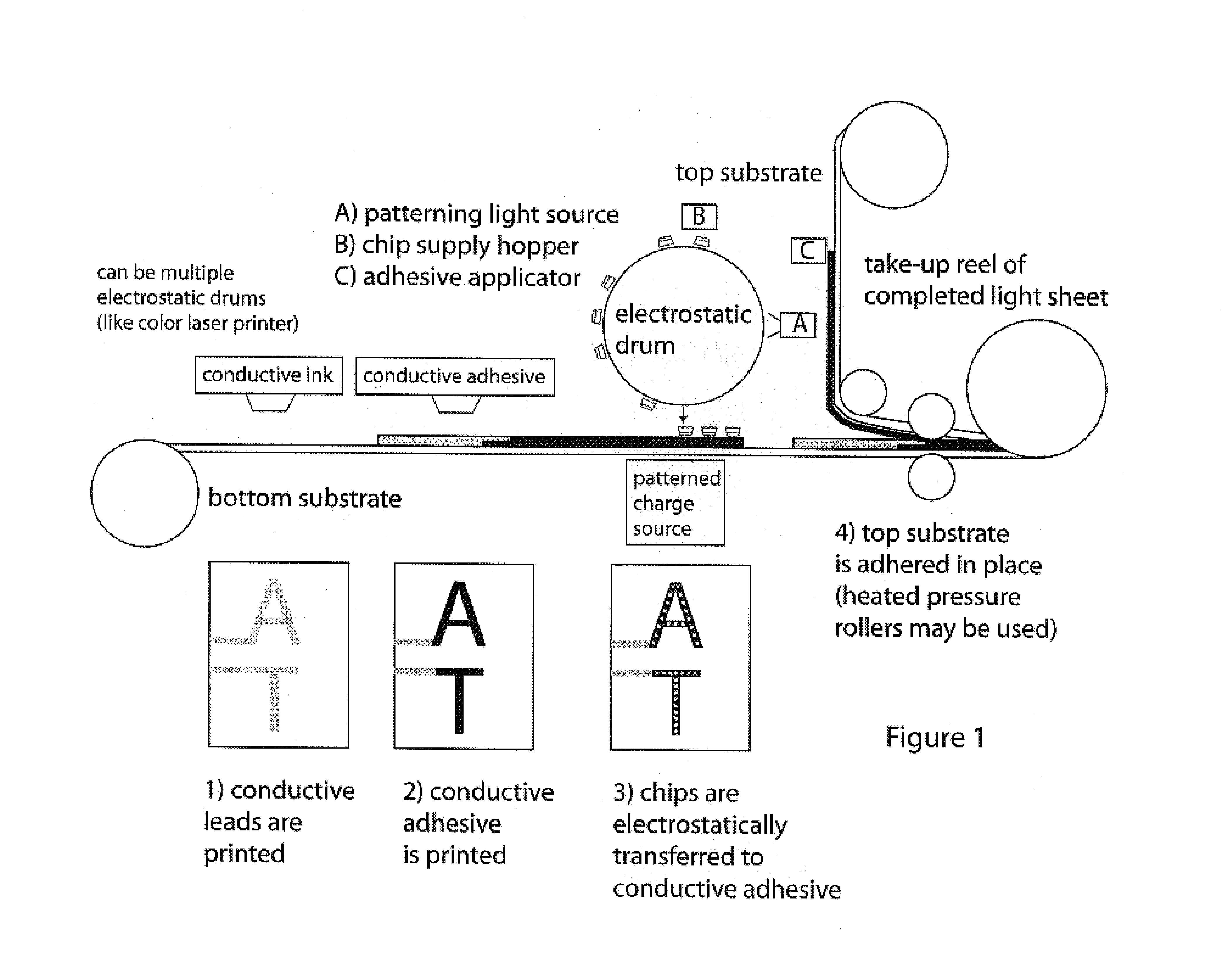
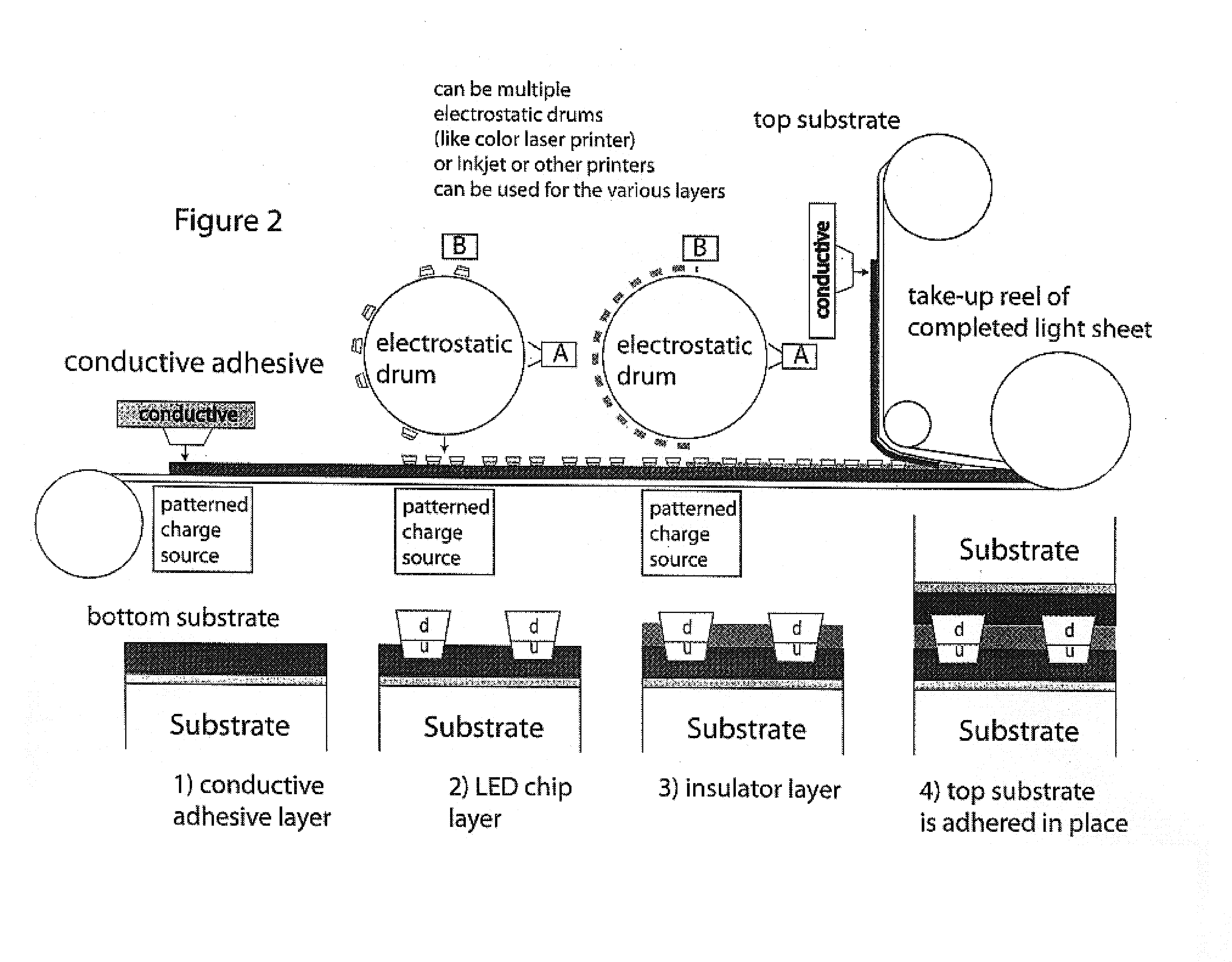
Roll-to-roll fabricated light sheet and encapsulated semiconductor circuit devices
InactiveUS7259030B2Easy to adaptHigh yieldFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesAdhesiveEngineering
Owner:ARTICULATED TECH LLC
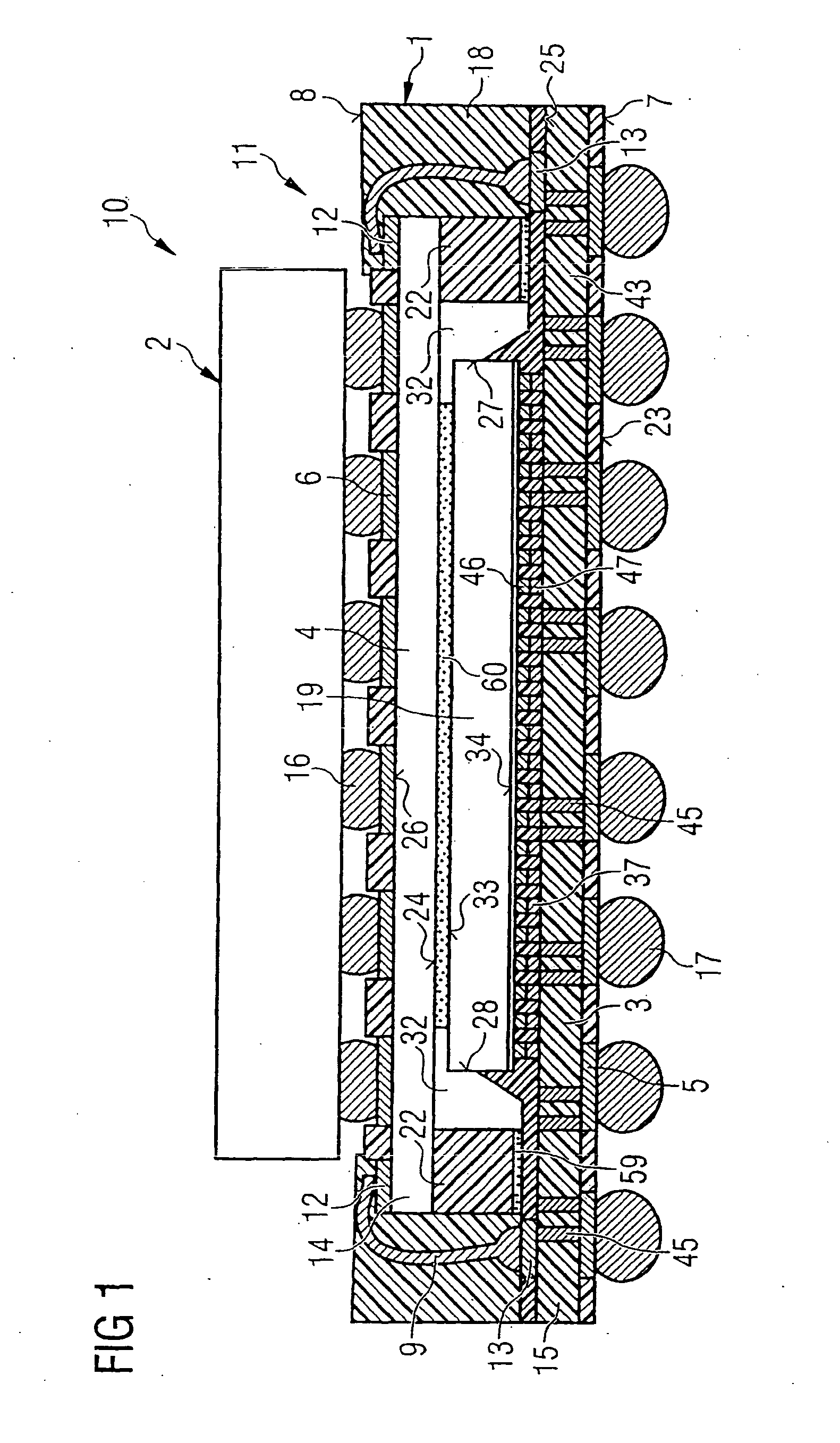
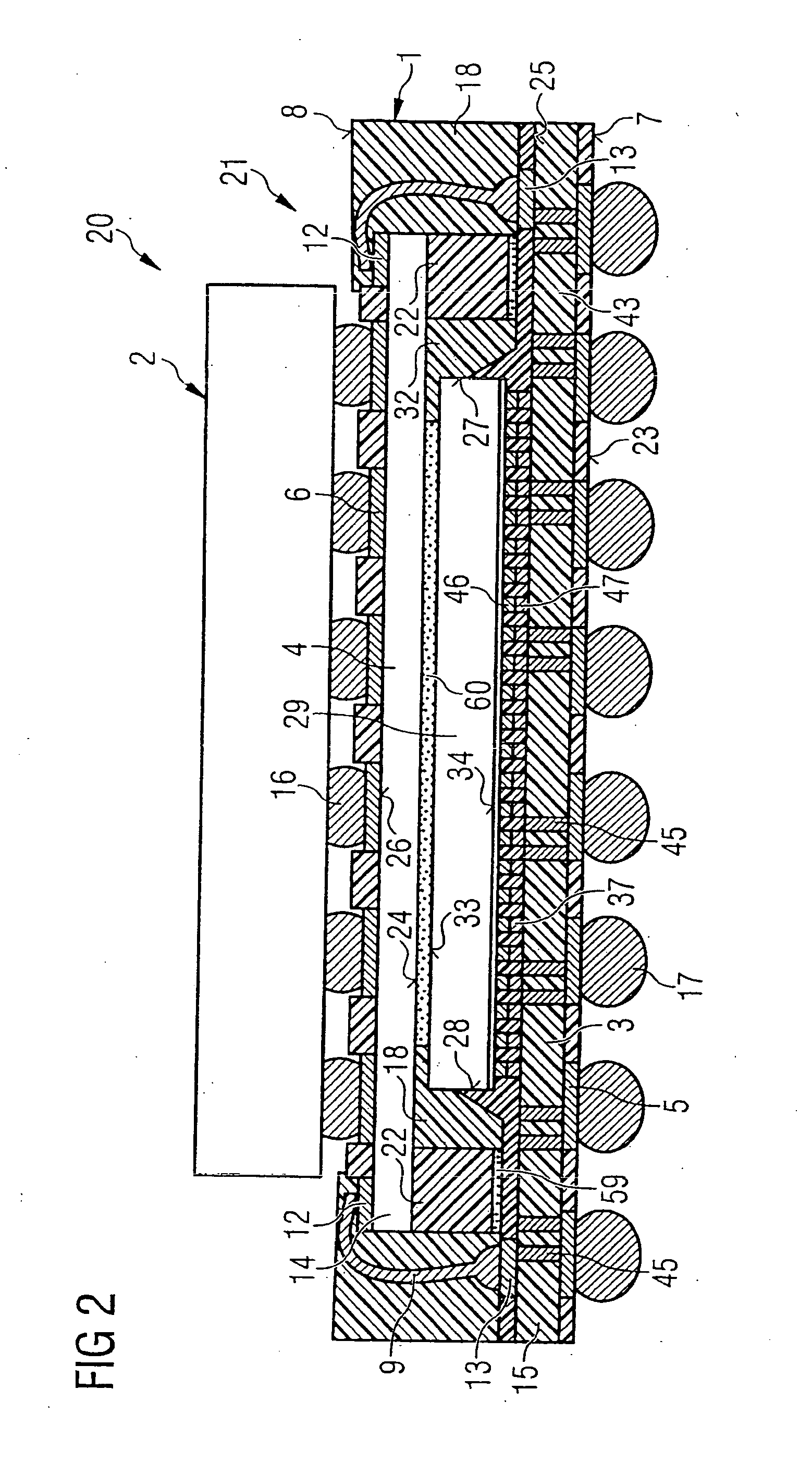
Semiconductor module with a semiconductor stack, and methods for its production
InactiveUS20050133932A1Reduce complexityImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesContact padEngineering
An electronic semiconductor module component with a semiconductor stack includes semiconductor components arranged in a vertically stacked relationship. A basic semiconductor component includes a lower interposing unit, on which lower external contact pads are arranged. The basic semiconductor component further includes an upper interposing unit, on which upper external contact pads are arranged. The two interposing units are electrically connected to one another via bonding connections disposed at their edge areas. The basic semiconductor component is a compact component on which different, customer-specific semiconductor components can be stacked.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com