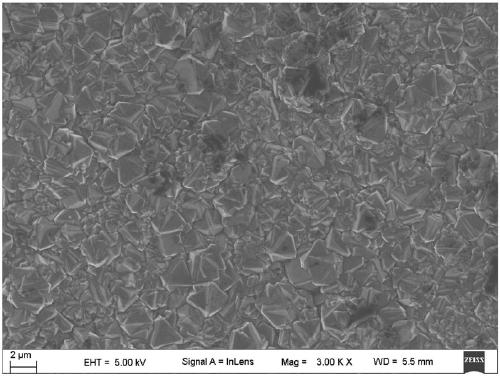
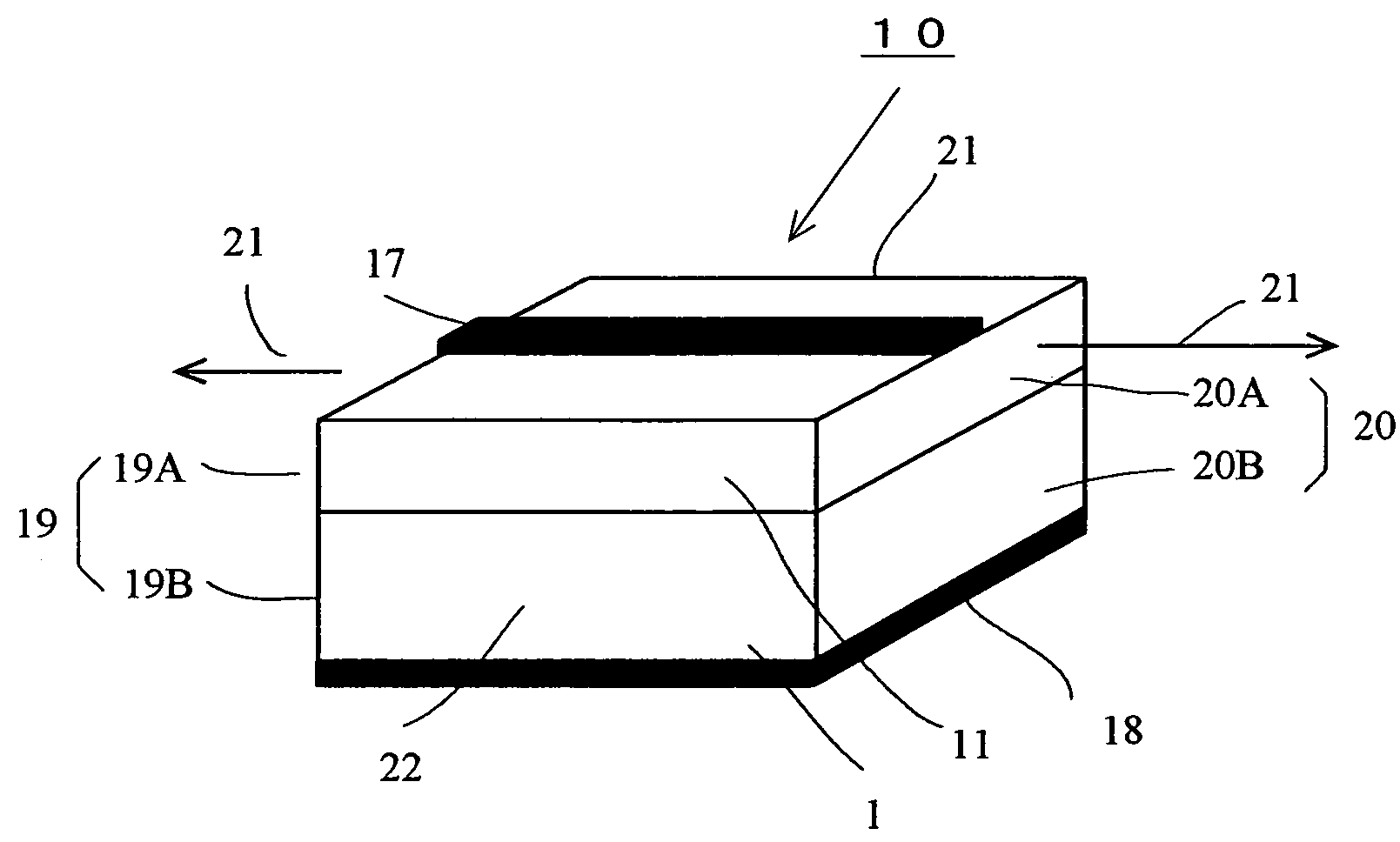
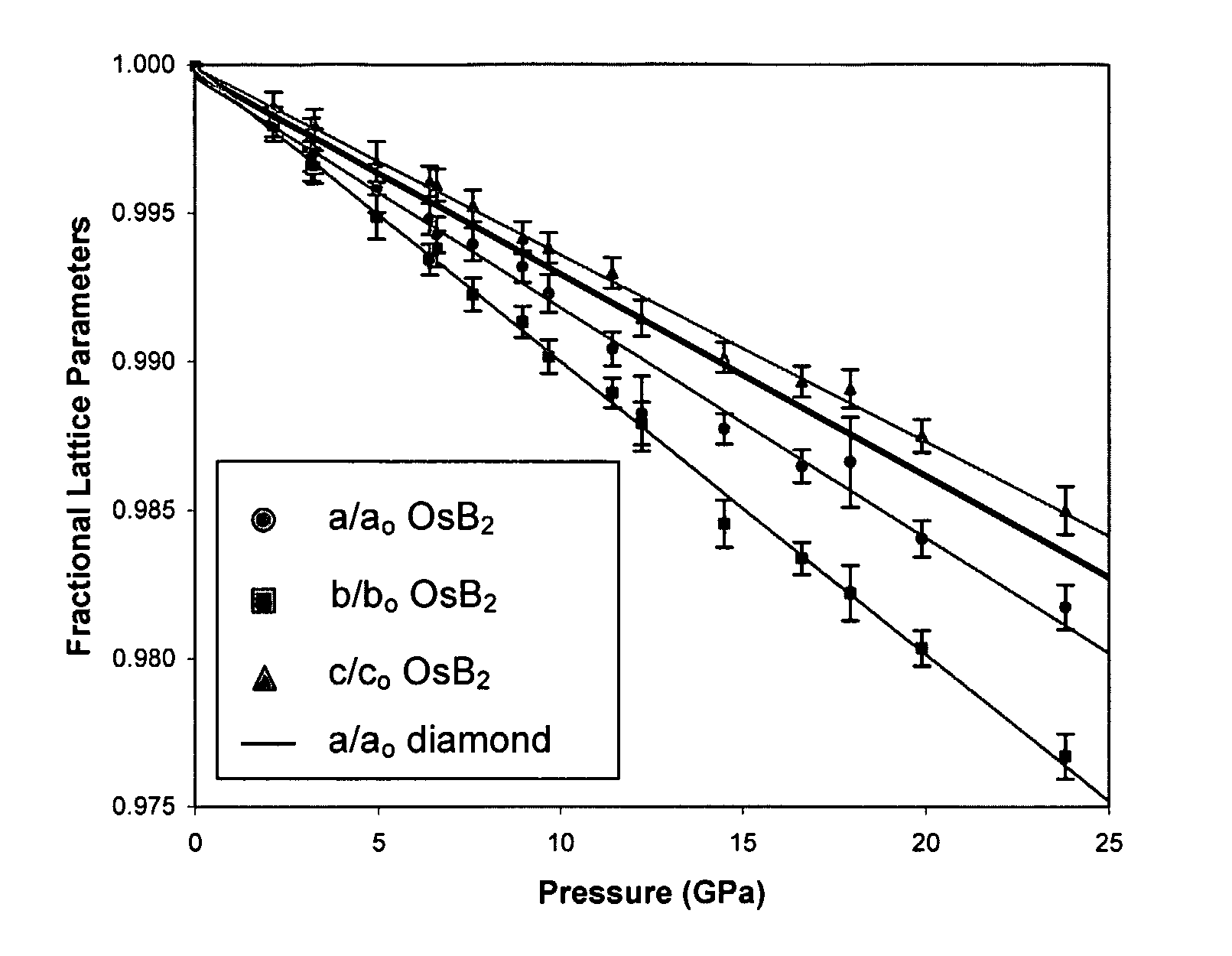
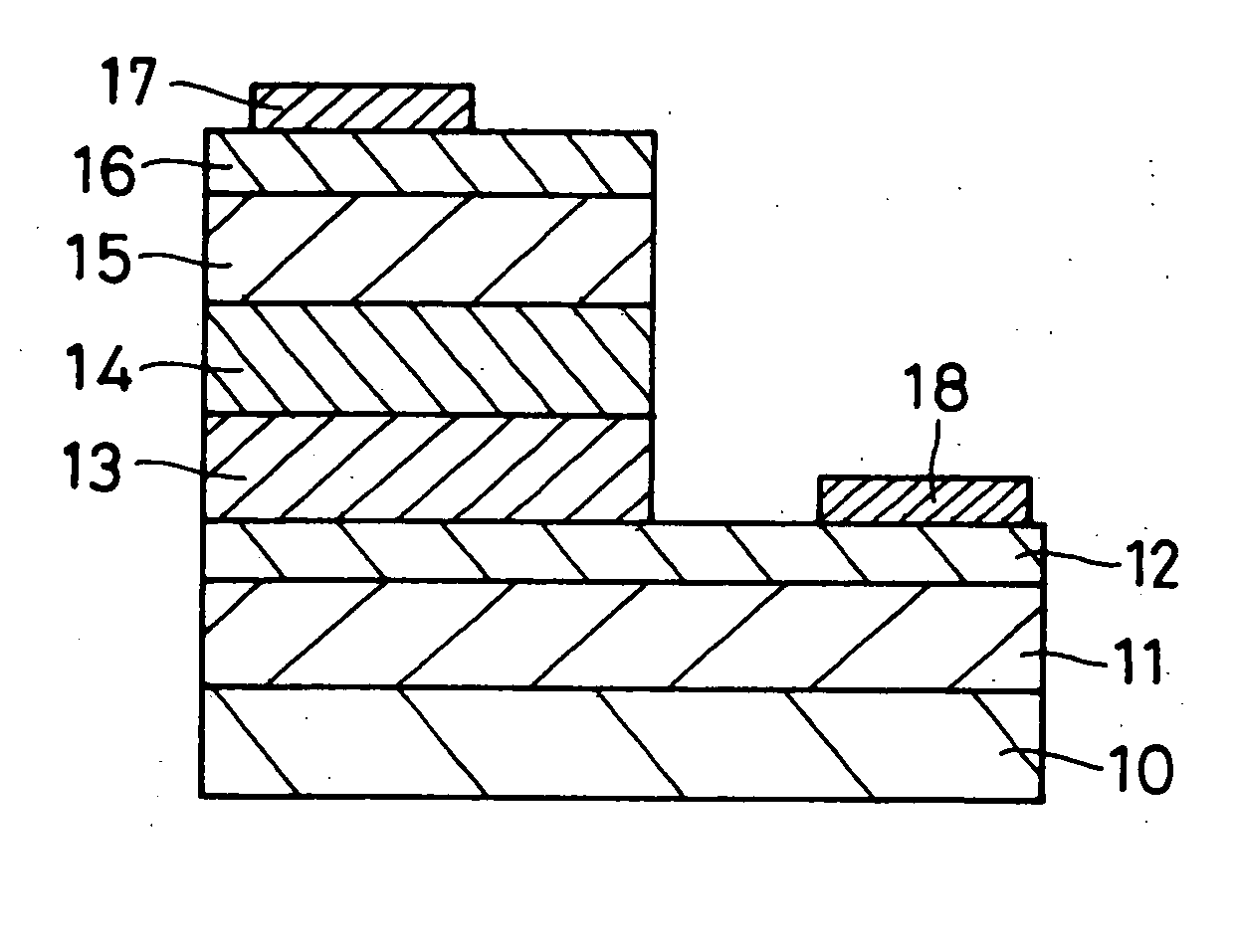
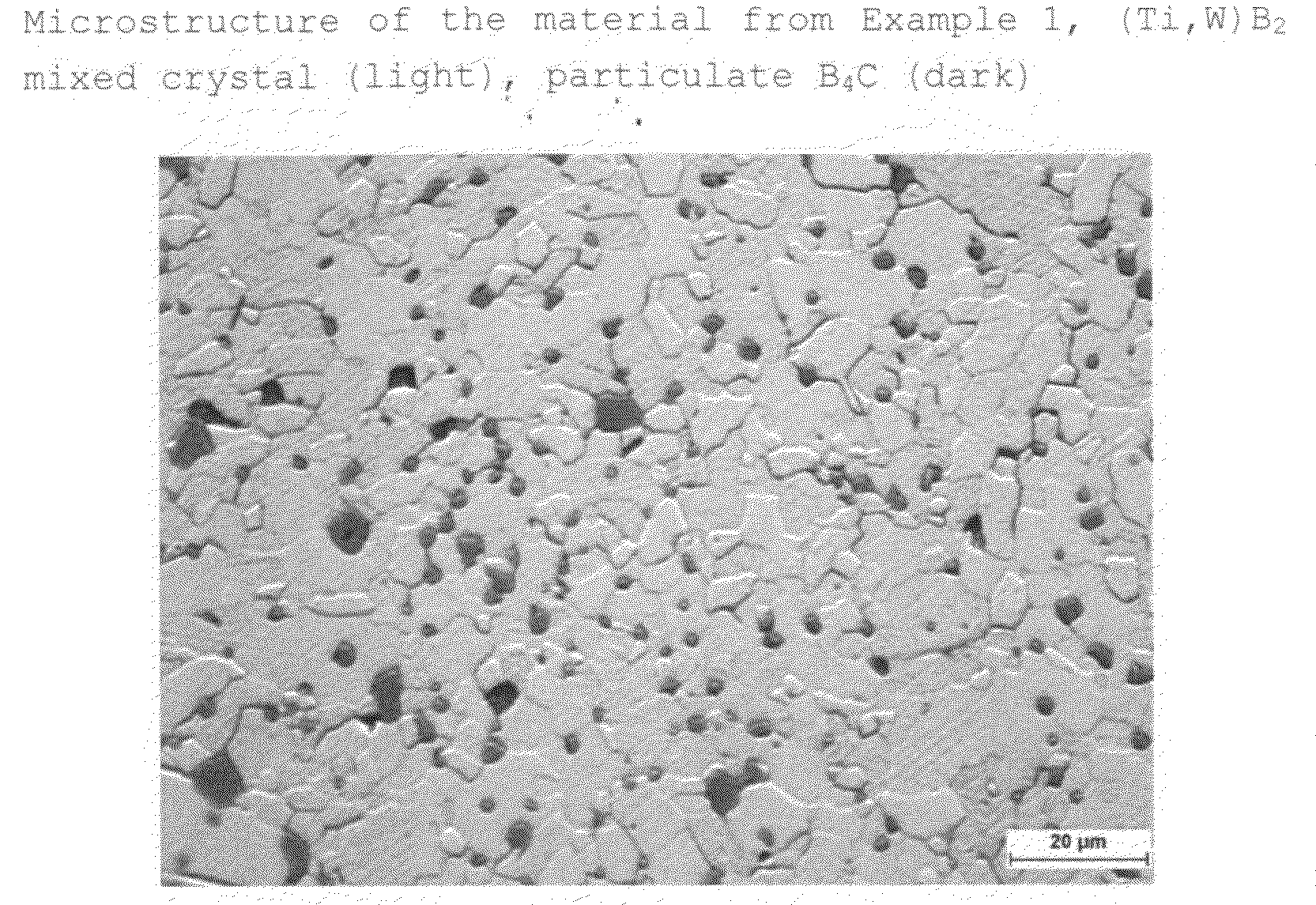Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
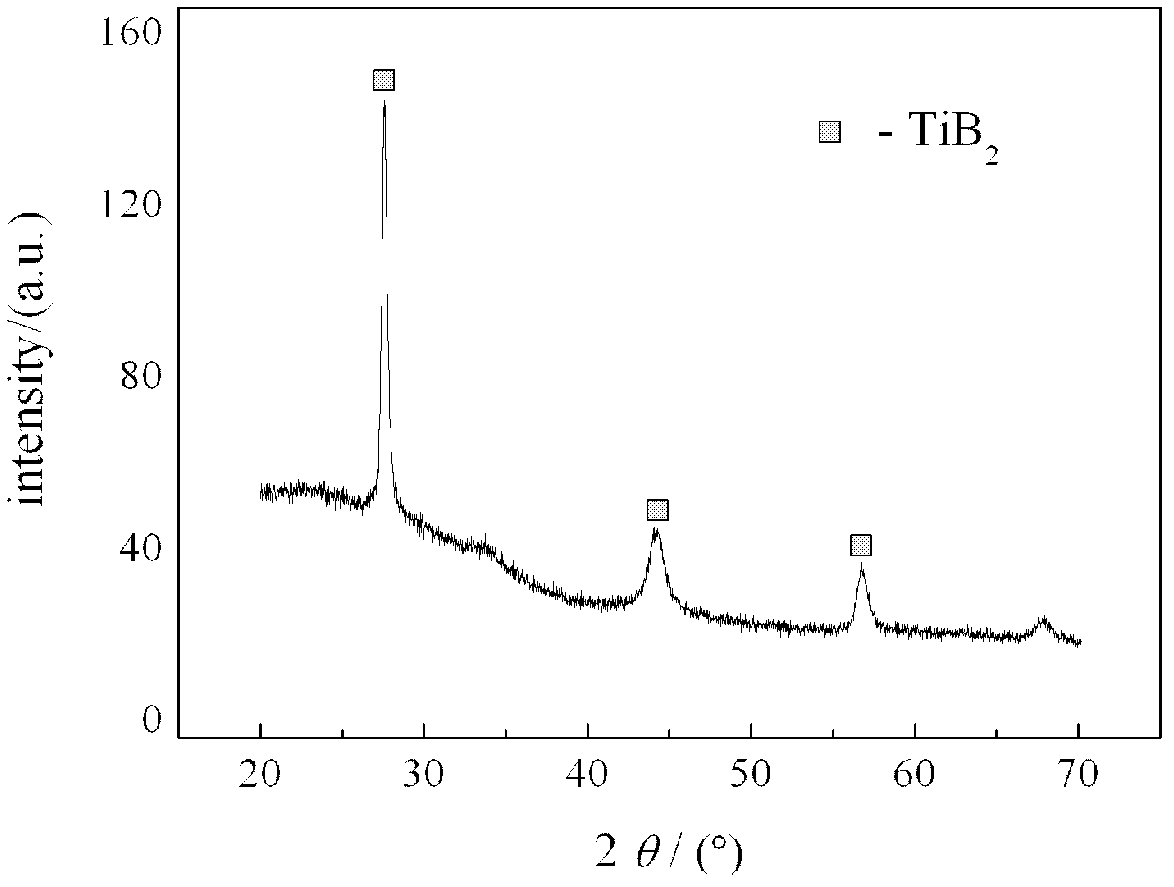
186 results about "Diboride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Diboride may refer to: Aluminium diboride, compound of aluminium and boron Hafnium diboride, ultra-high temperature ceramic composed of hafnium and boron Magnesium diboride, inexpensive and simple superconductor Rhenium diboride, synthetic superhard material Titanium diboride, extremely hard ceramic compound composed of titanium and boron Zirconium diboride, highly covalent refractory ceramic material with a hexagonal crystal structure
Coated pressing surfaces for abrasion resistant laminate and making laminates therefrom
A press plate for producing decorative laminate from resin impregnated paper, with alumina particles on its pressing surface, is coated with diborides selected from the group consisting of hafnium diboride, molybdenum diboride, tantalum diboride, titanium diboride, tungsten diboride, vanadium diboride, or zirconium diboride or mixtures thereof for making the press plate resistant to scratching. The preferred diborides are titanium and zirconium. The most preferred diboride is titanium. The color, gloss and surface appearance of laminate pressed with a titanium diboride coated press plate is substantially the same as laminate pressed with the press plate before coating.
Owner:WILSONART
Zirconium and Hafnium Boride Alloy Templates on Silicon for Nitride Integration Applications
InactiveUS20080164570A1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBorideSemiconductor structure
Semiconductor structures are provided comprising a substrate and a epitaxial layer formed over the substrate, wherein the epitaxial layer comprises B; and one or more element selected from the group consisting of Zr, Hf and Al and has a thickness greater than 50 nm. Further, methods for integrating Group III nitrides onto a substrate comprising, forming an epitaxial buffer layer of a diboride of Zr, Hf, Al, or mixtures thereof, over a substrate; and forming a Group III nitride layer over the buffer layer, are provided which serve to thermally decouple the buffer layer from the underlying substrate, thereby greatly reducing the strain induced in the semiconductor structures upon fabrication and / or operation.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Ceramic material suitable for repair of a space vehicle component in a microgravity and vacuum environment, method of making same, and method of repairing a space vehicle component
A precursor of a ceramic adhesive suitable for use in a vacuum, thermal, and microgravity environment. The precursor of the ceramic adhesive includes a silicon-based, preceramic polymer and at least one ceramic powder selected from the group consisting of aluminum oxide, aluminum nitride, boron carbide, boron oxide, boron nitride, hafnium boride, hafnium carbide, hafnium oxide, lithium aluminate, molybdenum silicide, niobium carbide, niobium nitride, silicon boride, silicon carbide, silicon oxide, silicon nitride, tin oxide, tantalum boride, tantalum carbide, tantalum oxide, tantalum nitride, titanium boride, titanium carbide, titanium oxide, titanium nitride, yttrium oxide, zirconium, diboride, zirconium carbide, zirconium oxide, and zirconium silicate. Methods of forming the ceramic adhesive and of repairing a substrate in a vacuum and microgravity environment are also disclosed, as is a substrate repaired with the ceramic adhesive.
Owner:COI CERAMICS
Cubic boron nitride compact
The present invention relates to CBN briquetting which contains CBN and matrix phase, the matrix phase combines with a second horniness phase and maximum titanium diboride, thereinto, the second horniness phase is selected from TiCN, TiC, TiN or its mixture and solid solution, the XRD peak height of thetitanium diboride peak (101)(after back ground emendation) is below 12 percent of the CBN peak (111) height.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX ABRASIVES
Sintered Material, Sinterable Powder Mixture, Method for Producing Said Material and Use Thereof
InactiveUS20090121197A1Improve mechanical propertiesSimple and inexpensiveThermometer detailsConductive materialParticulatesBoride
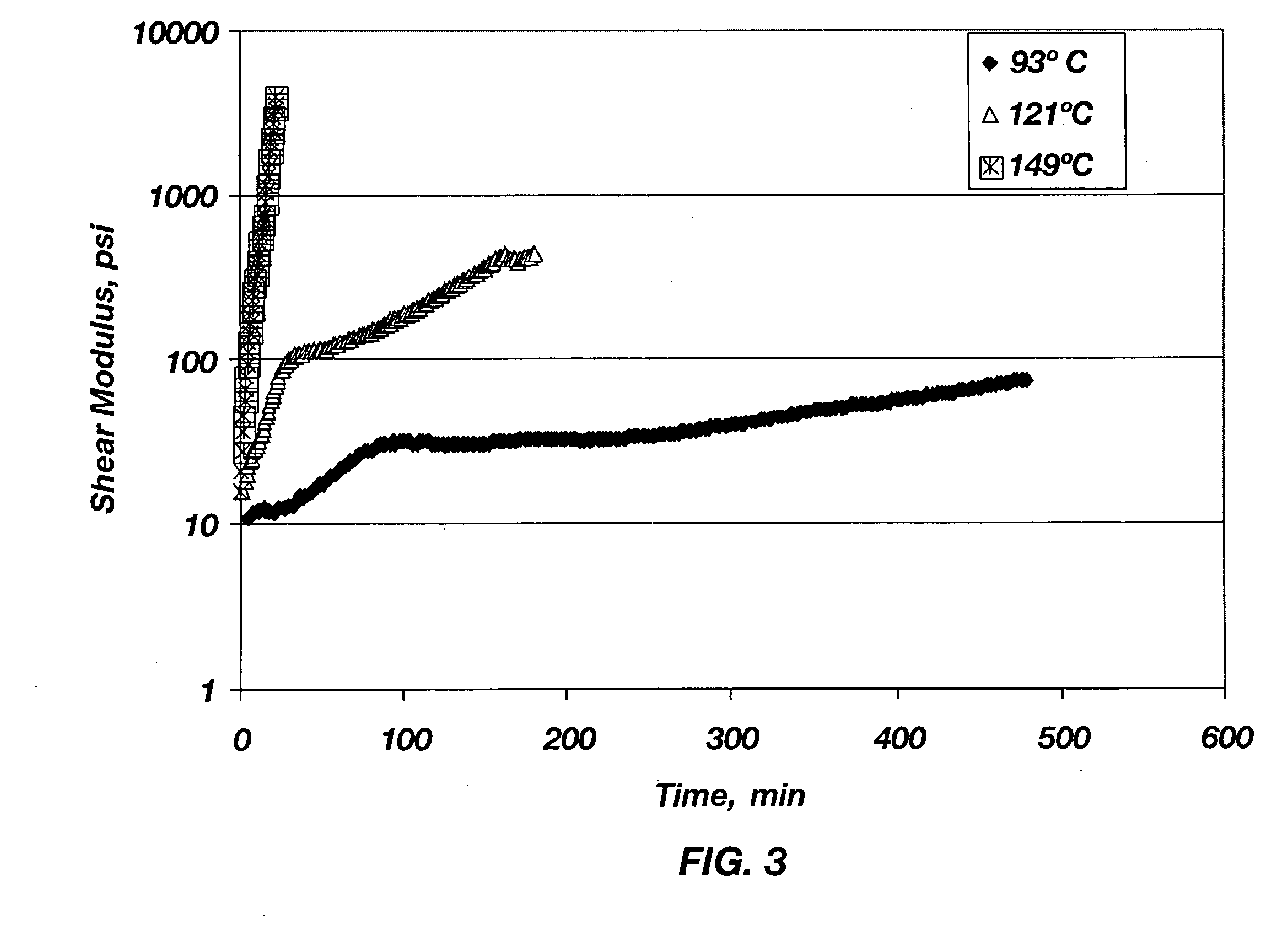
The invention relates to a sintered material which is based on transition metal diborides and comprisesa) as main phase, 90-99% by weight of a fine-grained transition metal diboride or transition metal diboride mixed crystal comprising at least two transition metal diborides or mixtures of such diboride mixed crystals or mixtures of such diboride mixed crystals with one or more transition metal diborides, where the transition metals are selected from sub-groups IV to VI of the Periodic Table,b) as second phase, 1-5% by weight of particulate boron carbide and / or silicon carbide andc) optionally as third phase, up to 5% by weight of a non-continuous, oxygen-containing grain boundary phase.The invention further relates to a pulverulent sinterable mixture for producing such a sintered material, processes for producing the sintered material, preferably by pressureless sintering, and also to the use of the sintered material as corrosion protection material for salt and metal melts, in particular cryolite-containing melts.
Owner:ESK CERAMICS GMBH & CO KG
Ceramic product containing nano attapulgite for daily use
The invention relates to a ceramic product for daily use, and particularly relates to a ceramic product containing nano attapulgite for daily use and a fabrication technology thereof. The ceramic product is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 50-55 parts of natural clay, 20-23 parts of kaolin clinker, 12-14 parts of potash feldspar, 5-6 parts of dolomite, 2-3 parts of ammonium alum, 40-45 parts of kaolin, 1-2 parts of zirconium dioxide, 10-15 parts of nano attapulgite, 3-5 parts of nanometer titania, 1-2 parts of tantalum diboride, 1-2 parts of vanadium boride and 5-6 parts of assistant. The unique properties of the nano materials such as the nano attapulgite, nanometer titania and the like are utilized, so that the sintering temperature is reduced, and the production energy consumption is reduced; by combining with other raw materials, the finally prepared product has good whiteness and glossiness, and is tight in glaze adhesion, uniform in color and luster, non-toxic and harmless, beautiful and durable, and wide in application range, and the shock resistance is improved.
Owner:安徽省含山瓷业股份有限公司
Boron doped diamond electrode and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a boron doped diamond electrode. The boron doped diamond electrode comprises an electrode substrate, transition layers and boron doped diamond film layers; the transition layersare arranged on one side or the two sides of the electrode substrate; the boron doped diamond film layers are arranged on the transition layers; the transition layers are made of one or more of titanium diboride, niobium diboride, tantalum diboride and wolfram diboride; and the electrode substrate is made of titanium, niobium, tantalum or wolfram. According to the boron doped diamond electrode, materials such as the titanium diboride are used to form the transition layers between the electrode substrate and boron doped diamond films, so that a loose carbide layer is effectively prevented frombeing formed on the surface of a metal substrate, binding force between the boron doped diamond films and the substrate is increased, and the boron doped diamond films are high in quality, are denseand have no holes; the boron doped diamond electrode is used for treating an anode of high concentrated organic wastewater by an electrochemical advanced oxidation method; the corrosion resistance ishigh; the working life of the electrode is long; and the treatment efficiency is high. The invention further provides a preparation method of the boron doped diamond electrode.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Diboride single crystal substrate, semiconductor device using this and its manufacturing method
Disclosed are a diboride single crystal substrate which has a cleavage plane as same as that of a nitride compound semiconductor and is electrically conductive; a semiconductor laser diode and a semiconductor device using such a substrate and methods of their manufacture wherein the substrate is a single crystal substrate 1 of diboride XB2 (where X is either Zr or Ti) which is facially oriented in a (0001) plane 2 and has a thickness of 0.1 mm or less. The substrate 1 is permitted cleaving and splitting along a (10-10) plane 4 with ease. Using this substrate to form a semiconductor laser diode of a nitride compound, a vertical structure device can be realized. Resonant planes of a semiconductor laser diode with a minimum of loss can be fabricated by splitting the device in a direction parallel to the (10-10) plane. A method of manufacture that eliminates a margin of cutting is also realized.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI +1
Preparation method of high-strength silicon carbide porous ceramic
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-strength silicon carbide porous ceramic. Raw materials are composed of 98%-99% of mixture of alpha-silicon carbide powder and beta-silicon carbide powder, 0.1%-1.0% of aluminum diboride and 0.5%-1% of polycarbosilane, by weight percent. The method comprises the following steps: 1) adding the raw materials into an organic dispersing solvent, ball-milling, mixing and drying; 2) dry-pressing and forming the obtained silicon carbide compound powder under the 45-55 MPa; and 3) placing a silicon carbide blank into a vacuum pressure-less sintering furnace, for sintering at two steps, thereby obtaining the high-strength silicon carbide porous ceramic. The preparation method is simple and the prepared silicon carbide porous ceramic is characterized by high mechanical strength, suitable porosity, and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing titanium-diboride-based ceramic composite material
The invention provides a method for preparing a titanium-diboride-based ceramic composite material in order to solve problems existing in an existing method for preparing the titanium-diboride-based ceramic composite material, and belongs to the technical field of materials. The method includes the following steps that (1) TiB2 powder is evenly mixed with a carbon source and screened, and particles with the particle size ranging from 24 meshes to 60 meshes are selected as mould pressing materials; (2) the mould pressing materials are subjected to mould pressing and dried to obtain a TiB2-based biscuit; (3) the TiB2-based biscuit serves as a framework, Si is adopted as an infiltration agent for vacuum infiltration. The method is simple in step and low in temperature requirement, the titanium-diboride-based ceramic composite material high in compactness can be obtained under the condition that preparing cost is low, and the size change of a sample in the preparing process is smaller than 0.1%, so that the method belongs to net-size sintering. Besides, the method can be used for producing products in various complex shapes.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Cubic boron nitride compact
ActiveCN101084170AImprove overall lifespanImprove wear resistanceTurning toolsShaping cuttersDiborideCarbide
The present invention relates to CBN briquetting which contains CBN and matrix phase, the matrix phase combines with a second horniness phase and maximum titanium diboride, thereinto, the second horniness phase is selected from TiCN, TiC, TiN or its mixture and solid solution, the XRD peak height of thetitanium diboride peak (101)(after back ground emendation) is below 12 percent of the CBN peak (111) height.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX ABRASIVES
Osmium Diboride Compounds and Their Uses
ActiveUS20070224100A1High hardnessIncrease electron densityPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesRheniumDiboride
Osmium, when combined with boron alone, or in combination with rhenium, ruthenium or iron, produces compounds that are ultra-hard and incompressible. These osmium diboride compounds are useful as a substitute to for other super or ultra-hard materials that are used in cutting tools and as abrasives. The osmium diboride compounds have the formula OsxM1-xB2 where M is rhenium, ruthenium or iron and x is from 0.01 to 1, except when x is not 1 and M is rhenium, x is from 0.01 to 0.3.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Wear-resistant LED heat dispersion coating and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a wear-resistant LED heat dispersion coating which is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 40-45 parts of acrylic resin, 7-10 parts of polyoxamide resin, 12-17 parts of methyl methacrylate, 10-14 parts of 4-cyclohexanedimethanol, 4-6 parts of fatty amine, 1-3 parts of allyl glycidyl ether, 5-8 parts of teflon powder, 1-2 parts of cross-linking agent TAIC, 2-3 parts of tributyl tin chloride, 15-18 parts of ethylene glycol, 4-6 parts of tungsten carbide powder, 3-5 parts of molybdenum diboride, 10-14 parts of silicon dioxide powder and 4-5 parts of film-forming aid. As teflon powder is added into the coating, the coating surface has good lubricating property, the wear resistance is improved, the surface tension is low and the coating has antifouling and dustproof effects; as tungsten carbide powder, molybdenum diboride and silicon dioxide powder are added into the coating, the wear resistance of the coating is improved, the heat dispersion effect is enhanced and the coating is ageing-resistant; due to the film-forming aid, the coating has good film-forming property and is easy to coat.
Owner:程实
Technique for preparing titanium diboride (TiB2) coating on metal surface
The present invention relates to a technique for preparing a titanium diboride (TiB2) coating on a metal surface. In the technique, advantages of a plasma spraying technique and a laser remelting technique are combined, defects such as poor thermal shock resistance and bad compactness of the TiB2 coating obtained by the plasma spraying technique are overcome, and problems that fusion covering of a boride is difficult by a laser fusion covering technique and the coating is large in stress and poor in uniformity are solved. A layer of TiB2 coating is prefabricated on a metal matrix through the laser spraying technique, a porosity factor of the coating is controlled through technological parameters, and then laser remelting treatment is performed on the coating, thus to obtain a dense TiB2 coating in metallurgical bonding with the matrix on the metal surface. With adoption of the obtained TiB2 coating, the surface strength of the metal matrix and the service time of the metal matrix in a corrosive environment can be notably raised.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Semiconductor apparatus, method for growing nitride semiconductor and method for producing semiconductor apparatus
InactiveUS20050006635A1Reduce dislocation densityAvoid leaningPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBorideDiboride
A semiconductor apparatus includes a substrate made of a diboride single crystal expressed by a chemical formula XB2, in which X includes at least one of Tl, Zr, Nb and Hf, a semiconductor buffer layer formed on a principal surface of the substrate and made of AlyGa1-yN (0<y≦1), and a nitride semiconductor layer which is formed on the semiconductor buffer layer and which includes at least one kind or plural kinds selected from among 13 group elements and As.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Titanium diboride-nickel coating or film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103160776AHigh hardnessImprove conductivityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingDiborideGas phase
The invention relates to a preparation method of a titanium diboride-nickel coating or film. By using the method, a metal Ni toughened TiB2 coating or film is prepared through in-situ synthesis; and the coating has hardness up to higher than 25GPa, good conductive properties, good toughness, corrosion resistance and erosion resistance, and excellent friction and wear performance, and can be widely applied to the fields of cutting tool, mold, electric contact and protection. The preparation process has advantages of simpleness, short production cycle and low cost, and is convenient for industrialized mass production.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Titanium-diboride-zirconium-diboride coating of periodic multilayer structure and preparation method and application of titanium-diboride-zirconium-diboride coating
ActiveCN106987800AReduce coefficient of frictionLow friction resistanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingDiborideSteel ball
The invention belongs to the field of surface protection technologies and related coating technologies and discloses a titanium-diboride-zirconium-diboride coating of a periodic multilayer structure and a preparation method and application of the titanium-diboride-zirconium-diboride coating. With titanium diboride ceramic targets and zirconium diboride ceramic targets as raw materials, the coating is formed by periodically superposing titanium diboride nanometer ceramic layers and zirconium diboride nanometer ceramic layers on a base body in an alternative sputtering deposition manner by means of multi-target magnetic control sputtering. According to the coating, due to the fact that the nanometer multilayer structure is introduced, the frictional coefficient of a multilayer film is lower than the frictional coefficient of two single layers, and the coefficient of friction between the multilayer film and a GCr15 steel ball is lower than 0.30, so that the excellent wear resistance is presented, and the titanium-diboride-zirconium-diboride coating can be used as a protection coating for engineering application occasions needing the high hardness and high wear resistance, such as protection of surfaces of products of mechanical parts, knife dies and the like. The titanium-diboride-zirconium-diboride coating is convenient to operate, simple in process, short in manufacturing period, low in cost and capable of facilitating large-scale industrial production.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of binary tungsten boride superhard material
ActiveCN107473237ASolve the problem that the target product cannot be generatedEasy to manufactureMetal boridesSuperhard materialHigh energy
The invention discloses a preparation method of a binary tungsten boride superhard material, which comprises: by adopting a mechanical alloy method and utilizing high-energy ball milling, in the argon shield atmosphere, using high purity tungsten powder and boron powder as raw materials to directly synthesize tungsten diboride powder in a powder state under room temperature, and then carrying out thermal processing on the synthetic powder to prepare a tungsten tetraboride material. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple and convenient in preparation process and high in controllability, adopts atmosphere sintering in the sintering stage, has no other special requirements for equipment, and is high in universality.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Osmium diboride compounds and their uses
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Boron carbide based sintered compact and method for preparation thereof
A boron carbide based sintered body having a four-point flexural strength of at least 400 MPa and a fracture toughness of at least 2.8 MPa·m1 / 2, which has the following two preferred embodiments. (1) A boron carbide-titanium diboride sintered body obtained by sintering a mixed powder of a B4C powder, a TiO2 powder and a C powder while reacting them under a pressurized condition and comprising from 95 to 70 mol % of boron carbide and from 5 to 30 mol % of titanium diboride, wherein the boron carbide has a maximum particle diameter of at most 5 μm. (2) A boron carbide-chromium diboride sintered body containing from 10 to 25 mol % of CrB2 in B4C, wherein the sintered body has a relative density of at least 90%, boron carbide particles in the sintered body have a maximum particle diameter of at most 100 μm, and the abundance ratio (area ratio) of boron carbide particles of from 10 to 100 μm to boron carbide particles having a particle diameter of at most 5 μm, is from 0.02 to 0.6.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Cubic boron nitride compact
The present invention relates to CBN briquetting which contains CBN and matrix phase, the matrix phase combines with a second horniness phase and maximum titanium diboride, thereinto, the second horniness phase is selected from TiCN, TiC, TiN or its mixture and solid solution, the XRD peak height of thetitanium diboride peak (101)(after back ground emendation) is below 12 percent of the CBN peak (111) height.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX ABRASIVES
High-flame-retardant, low-smoke and halogen-free cable material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103351508AHigh Material Oxygen IndexImprove flame retardant performanceInsulated cablesInsulated conductorsLow-density polyethyleneBenzoic acid
The invention provides a high-flame-retardant, low-smoke and halogen-free cable material and a preparation method thereof. The material is prepared from the following raw material by weight parts: 60-67 parts of low-density polyethylene, 3-4 parts of magnesium hydroxide, 25-28 parts of montmorillonite, 2-3 parts of zinc borate, 3-4 parts of a silane coupling agent KH 550, 1-2 parts of ferriferrous oxide, 3-4 parts of tantalum boride, 1-2 parts of tantalum diboride, 1-2 parts of tert-butyl benzoic acid, 2-3 parts of triphenyl phosphate, 2-3 parts of ferrocene, 2-3 parts of gamma-methacryloxy propyl trimethoxy silane, 4-6 parts of polyvinyl acetate, 2-3 parts of dibutyltin dilaurate, 1-2 parts of cyanuric acid zinc, 1-2 parts of zinc oxide, 3-4 parts of soybean oil, 16-18 parts of aluminium hydroxide, 25-29 parts of attapulgite, 1-2 parts of a promoter DTDM, 1-2 parts of a antioxidant MB, 1-2 parts of an anti-scorching agent CTP, 12-14 parts of carbon black N220, 8-10 parts of carbon black N 660 and 6-8 parts of modified diatomite. According to the invention, the zinc borate and the aluminium hydroxide are combined as the flame retardant, thereby improving performances of flame retardation. The method is simple in technology and convenient to produce; the produced cable materials are high in oxygen index, that is, being higher than 40, and excellent in fire resistance. A vertical flame class experiment of the material reaches a supreme grade, that is, FV-0 grade, and a smoke density of the material is lower than that of other similar products.
Owner:ANHUI CABLE
Method for low temperature preparation of diboride-carbide solid solution multiphase ceramic by reaction hot press sintering method
The invention relates to a method for low temperature preparation of a diboride-carbide solid solution multiphase ceramic by a reaction hot press sintering method, and belongs to the technical field of multiphase ceramic materials. The problem of high sintering temperature of an existing diboride-carbide multiphase ceramic is solved. According to the method for the low temperature preparation of the diboride-carbide solid solution multiphase ceramic by the reaction hot press sintering method, transition metal diboride and carbide which can produce solid phase exchange are selected, a compositepowder body is prepared by a high energy ball milling process, under the protection of vacuum or inert atmosphere, and the reaction hot press sintering is carried out to prepare the dense diboride-carbide solid solution multiphase ceramic. The solid-phase reaction and solid solution coupled synergistic process in the sintering process is fully used, compared with traditional hotpress sintering process for the preparation of multiphase ceramic materials directly using target diboronized and carbide powder bodies, the sintering temperature of the materials can be reduced by 250 DEG C to 400 DEGC, it is ensured that the material grain size is uniform and small by low temperature sintering, and the strength and toughness of the multiphase ceramic obtained are significantly improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
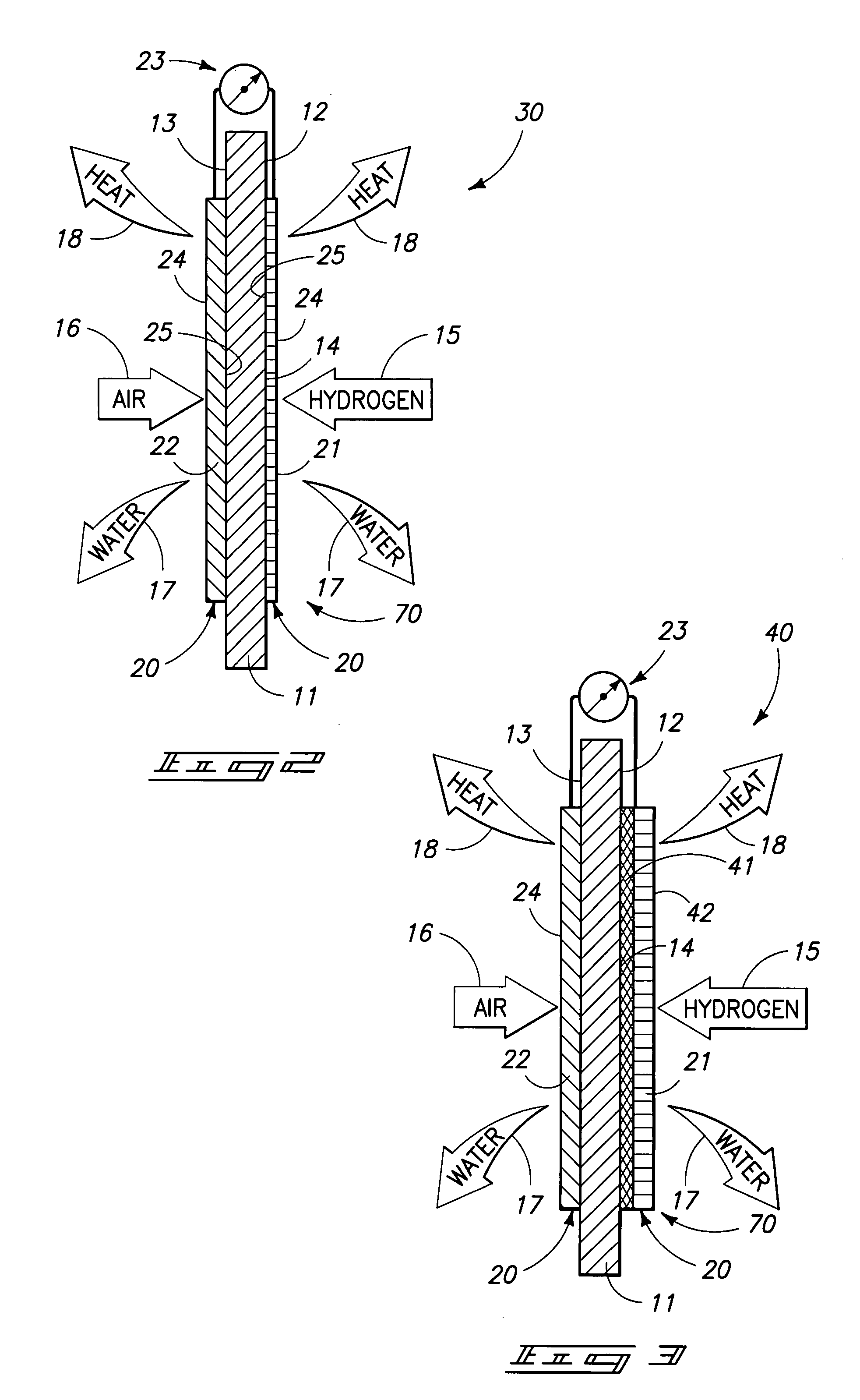
Proton exchange membrane fuel cell
A proton exchange membrane fuel cell is described and which includes a proton exchange membrane having at least one gas diffusion layer which is juxtaposed relative thereto, and which is fabricated, at least in part, of a porous, electrically conductive, inorganic material which is selected from the group comprising metal diborides, metal disilicides, metal nitrides, metal carbides, and composites, laminates and solid solutions thereof.
Owner:EMERGENT POWER
Silicon carbide ceramic and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108455988ASolve the technical problem of anti-oxidation performance reductionImprove antioxidant capacityDiborideOxidation resistant
The invention relates to the field of ceramic materials, in particular to a silicon carbide ceramic and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the silicon carbide ceramic provided bythe invention comprises the following steps: step one, mixing silicon carbide powder, aluminum oxide powder and Re2O3 powder to obtain silicon carbide-aluminum oxide-Re2O3 mixed powder; step two, mixing the silicon carbide-aluminum oxide-Re2O3 mixed powder with tantalum diboride powder to obtain silicon carbide-aluminum oxide-Re2O3-tantalum diboride mixed powder; and step three, pelleting and sintering the silicon carbide-aluminum oxide-Re2O3-tantalum diboride mixed powder to obtain the silicon carbide ceramic. The silicon carbide ceramic solves the technical problem that the oxidation resistance is reduced due to the fact that a silicon dioxide protective film generated after a liquid-phase sintered silicon carbide ceramic is oxidized in the prior art is broken. The silicon carbide ceramic obtained by the method is high in compactness and high in oxidation resistance, and can be widely applied to the fields of mechanical engineering, chemical engineering, micro-electronics, automobiles, petroleum, processing and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
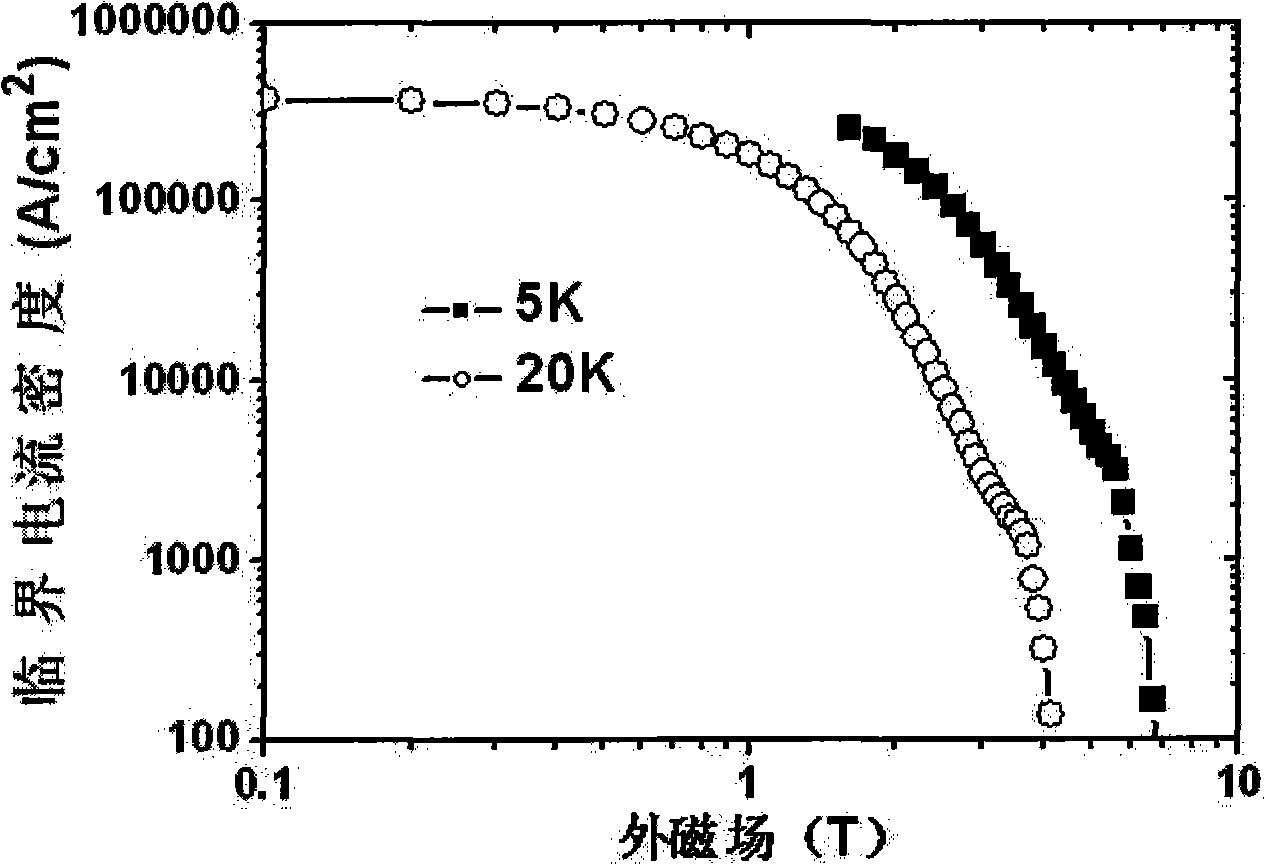
Method for preparing magnesium diboride superconductive wire and strip
InactiveCN101279740AImprove compactnessFirmly connectedSuperconductors/hyperconductorsMetal boridesHigh magnesiumDiboride
The invention relates to a method for preparing a magnesium boride superconducting line and belt material. The preparation method is that a. preparation of precursor powder: high magnesium diboride MgBx powder is taken as the precursor powder, wherein, x is more than or equal to 4 and less than or equal to 12; or magnesium powder and amorphism boron powder are mixed according to 1:3-20 of stoichiometric ratio between magnesium and boron to form the precursor powder; b. putting into a magnesium pipe: the precursor powder is put into a magnesium pipe, compacted and sealed; c. putting into a canning pipe: the magnesium pipe is put into a metal canning pipe and is sealed after the metal canning pipe is fully filled with metal powder as a barrier layer; or the magnesium pipe is first put into a barrier layer metal pipe and then is put into the metal canning pipe and the metal canning pipe is sealed; d. moulding treatment: the metal canning pipe is produced into line and belt material; e. heat treatment: the metal canning pipe is put into a pipe typed furnace and under the protection of argon, the temperature is raised to 700-1200 DEG C by the speed of 1-10 DEG C / minute, preserved for 1-30 hours and then cooled to room temperature. The MgB2 superconducting line and belt material prepared by the method has high compactability, good grain connectivity and even cross section.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Vehicle plastic
The present invention discloses a vehicle plastic, which comprises the following raw materials: a nylon 6 material, graphene, titanium dioxide, zirconium silicate, a terpene resin, polytetrafluoroethylene, dibutyl phthalate, poly aluminium chloride, acrylamide, aluminum nitrate, a petroleum resin, polyethylene wax, chlorosulfonated polyethylene, calcium stearate, ultra low density polyethylene and an auxiliary agent, wherein the auxiliary agent is prepared from the following raw materials: clay, sepiolite powder, vermiculite powder, 1,6 hexanediol diacrylate, montmorillonite powder, sodium carbonate, sodium fluorosilicate, silver nitrate, vanadium diboride, clove oil, regular fused alumina powder, and a silane coupling agent. According to the present invention, the lightweight polyolefin is used to modify the nylon material, such that the performance of the traditional nylon material is improved, the obtained can be adapted to the specific use environment, has good processability and good mechanical property, and further has characteristics of high hardness, oxidation aging resistance, heat aging resistance, water resistance, oil resistance, static electricity resistance, and safe use.
Owner:TIANJIN SHENGJINTE AUTO PARTS
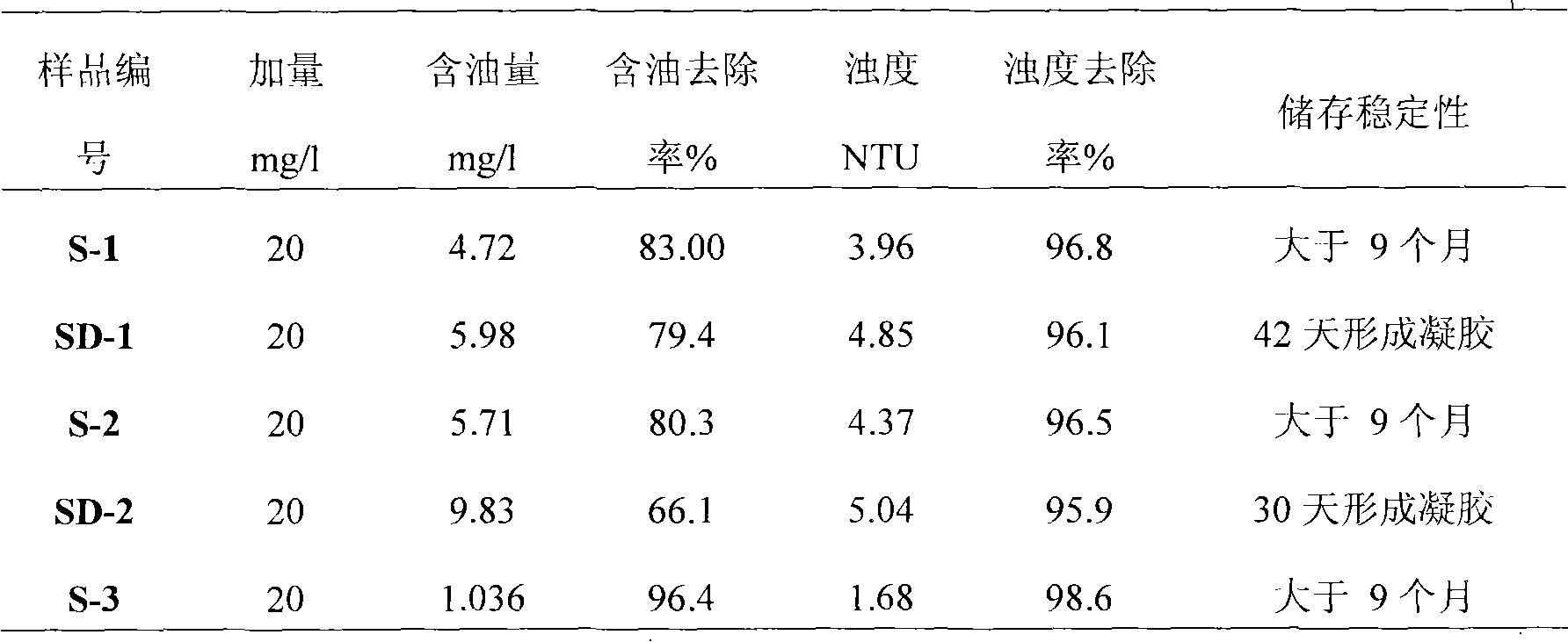
Preparation method of polysilicate diboride flocculant
ActiveCN101823783AImprove stabilityGood storage stabilityWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationDiborideTurbidity
The invention provides a preparation method of a polysilicate diboride flocculant, in the technical scheme, the following substances are adopted as the raw materials by the 100 mass parts of the polysilicate diboride flocculant: 1 to 20 parts of alkali metal silicate, 1 to 8 parts of zinc salt, 1 to 6 parts of aluminum salt and 1 to 4 parts of organic boric acid ester; the preparation method comprises the following preparation steps that: (1) water respectively prepares the alkali metal silicate, the aluminum salt and the zinc salt into 1 to 40 weight percent of solution; (2) acid is used for regulating the pH value of the alkali metal silicate solution which is prepared in step (1) to be less than 6 or more than 10, the reaction temperature is regulated to be 0 to 60DEG C, polymerization is carried out for 1 to 10h, and aging is carried out for 1 to 24h; and (3) the organic boric acid ester and the zinc salt and the aluminum salt solution which are prepared in step (1) are added into an aged sample in step (2), the reaction temperature is regulated to be 0 to 60DEG C, and the materials react for 1 to 10h and stay still for 2 to 24h. The polysilicate diboride flocculant has excellent turbidity flocculation effect and oil removing effect, and can simultaneously improve the stable storage performance.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Titanium diboride reinforced CuW alloy in-situ synthesis method
ActiveCN109207764AAvoid surface contaminationEasy to manufactureContactsCompression moldingSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a titanium diboride reinforced CuW alloy in-situ synthesis method. The method comprises the steps of evenly mixing W powder, B powder and induced copper powder and conducting compression molding on the mixture to obtain a tungsten compact; putting the tungsten compact into an atmosphere sintering furnace for sintering to obtain a tungsten skeleton; putting a CuTi alloy on the tungsten compact and then putting the CuTi alloy and the tungsten compact into a graphite crucible paved with graphite paper, conducting infiltration in the sintering furnace to obtain the in-situsynthesis titanium diboride reinforced CuW alloy. According to the method, a ceramic phase TiB2 is generated in a CuW material in situ through the sintering-filtration method. In the presence of the low-work-function ceramic phase, electric arcs are effectively dispersed, so that the electric arc ablation resistance of a CuW contact material is improved.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
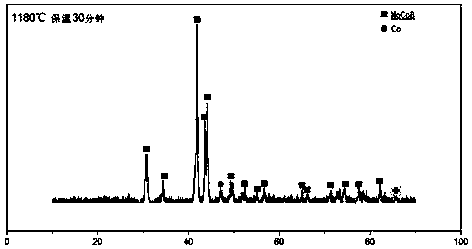
Molybdenum-cobalt-boron ternary boride base metal ceramic material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a molybdenum-cobalt-boron ternary boride base metal ceramic material and a preparation method thereof. The process comprises the following steps: simple-substance molybdenum powder, cobalt powder and boron powder are used raw materials for ball-mill mixing, drying, formation and sintering to prepare ternary boride base metal ceramic; a main phase is a MoCoB type diboride with an orthorhombic structure; contained hard phases are two similarly stable MoCoB phases; and bonded phases are Co or CoB compounds or solid solution of the two. The boron content (the atomic ratio B / Mo is more than 1.1) is increased in the ratio; the liquid phase appearance temperature of a ternary system is reduced; the sintering temperature is reduced; the preparation process is simplified; the cost is reduced; more excellent phase structures can be obtained through low-temperature sintering; and the oriented growth of grains is prevented. The Rockwell hardness is not lower than 83.5 HRA.The material can serve as cutting tool and mold structures and structural part or wear resisting part materials, improves the toughness, the hardness and the wear resistance of metal, and is high in oxidation resistance and stable in chemical property.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com