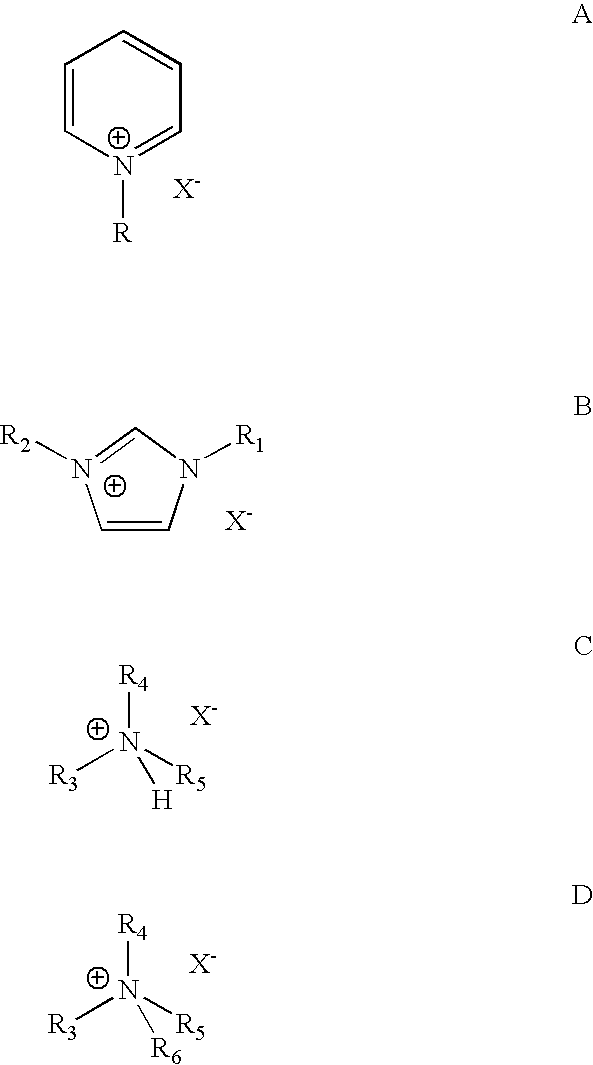
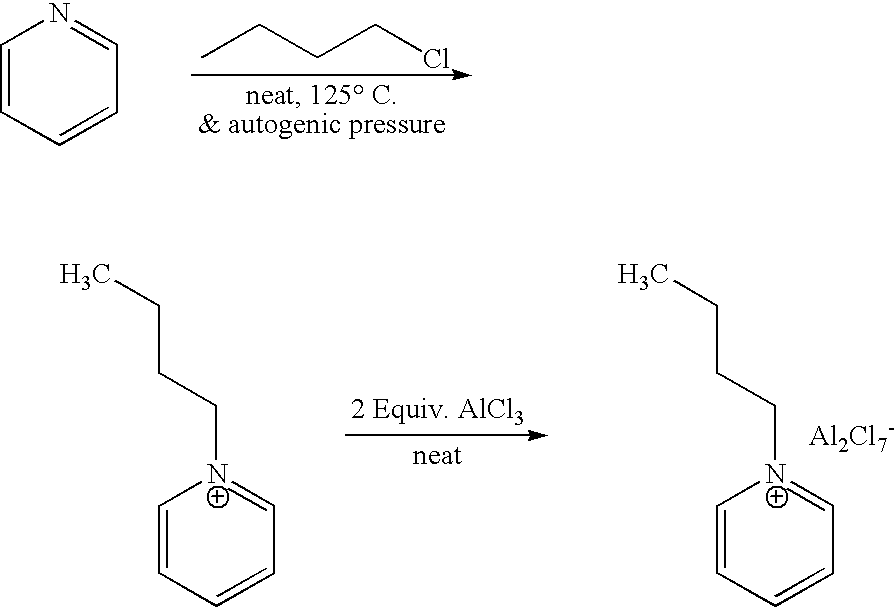
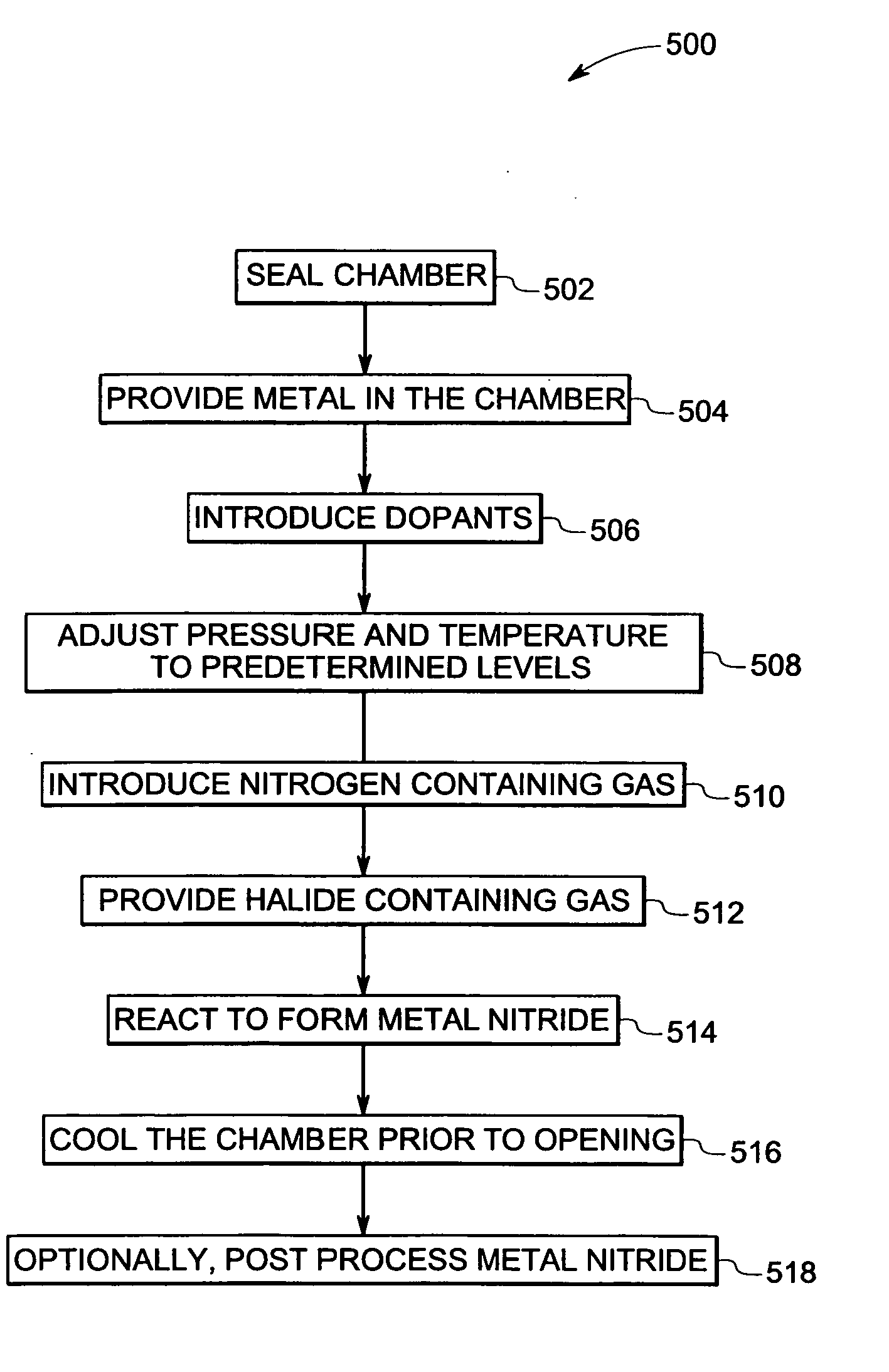
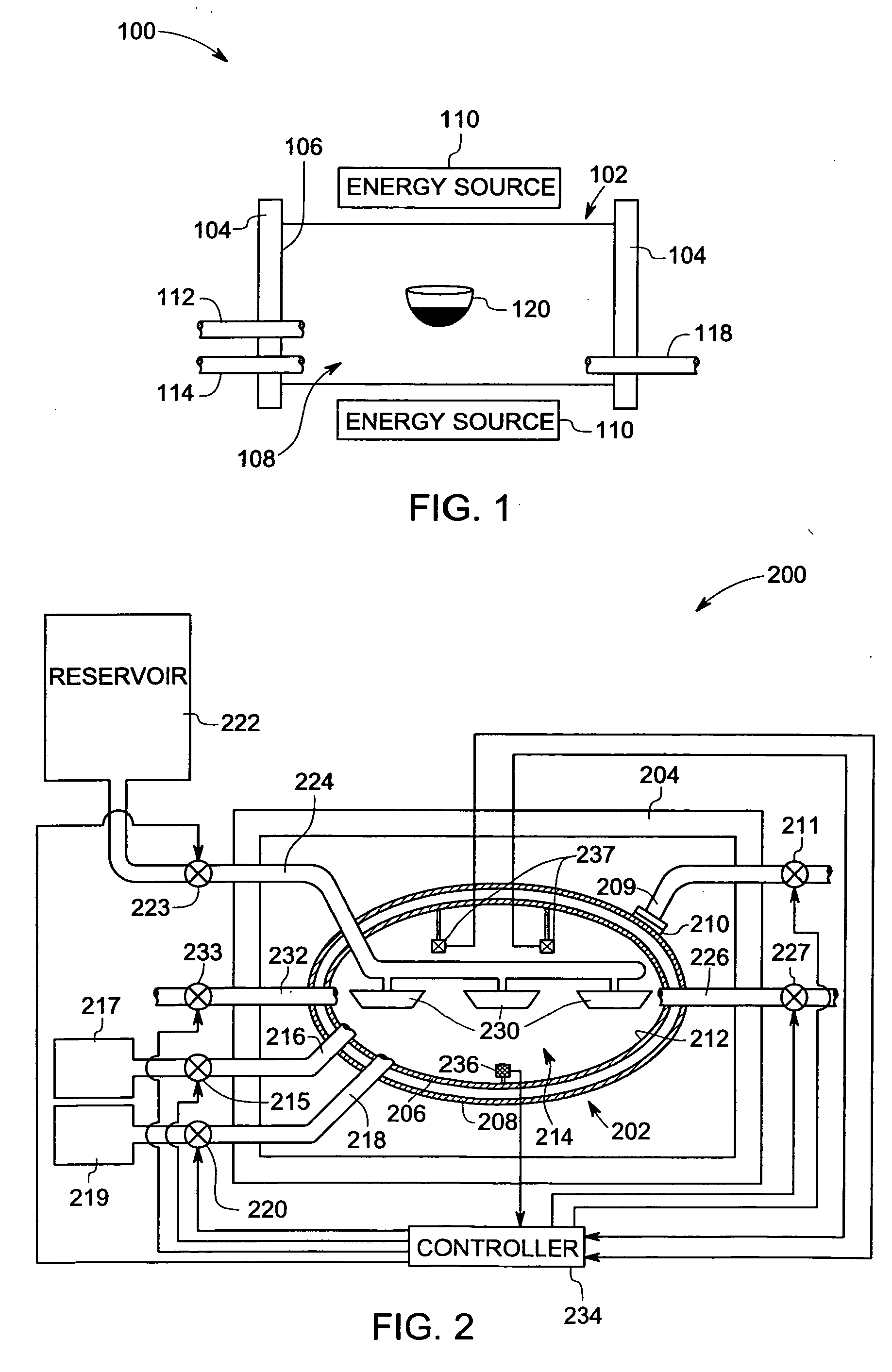
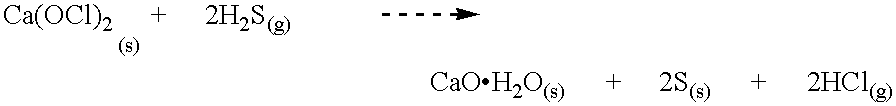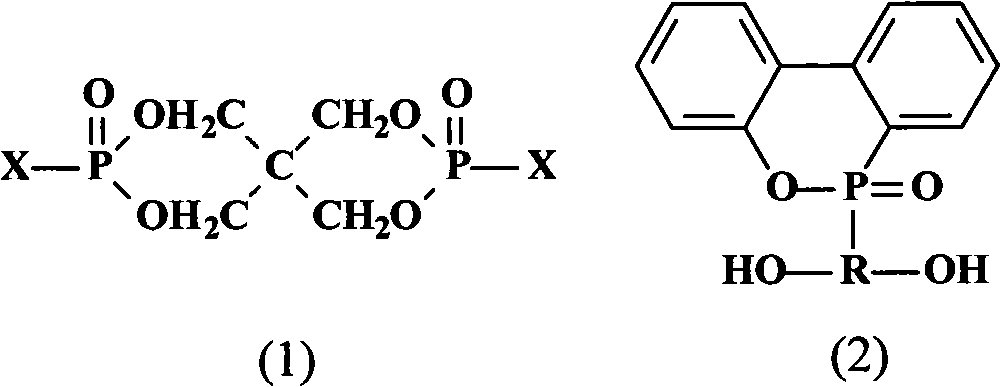Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
514 results about "Hydrogen halide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hydrogen halides are diatomic inorganic compounds with the formula HX where X is one of the halogens: fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, or astatine. Hydrogen halides are gases that dissolve in water to give acids which are commonly known as hydrohalic acids.
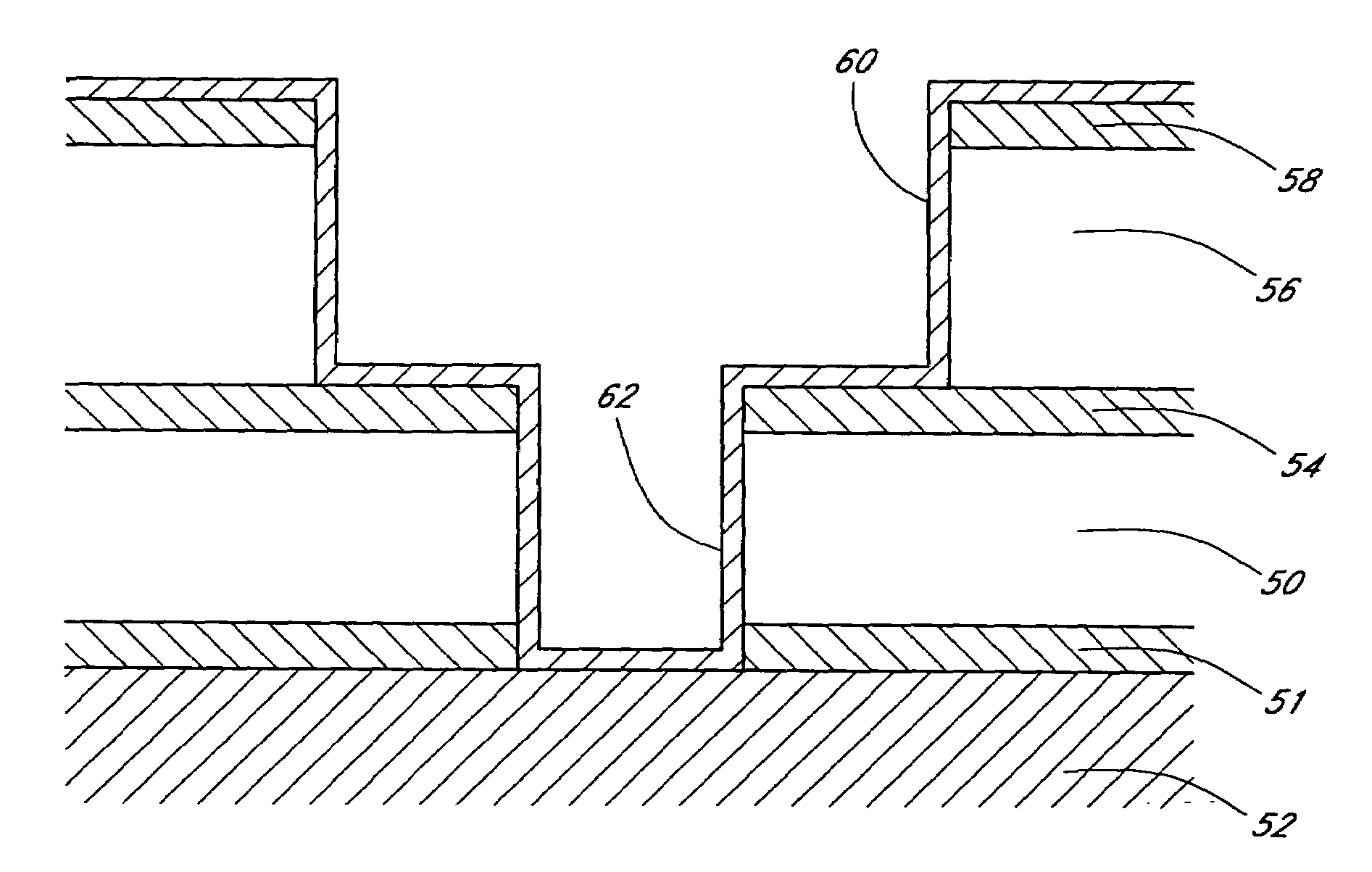
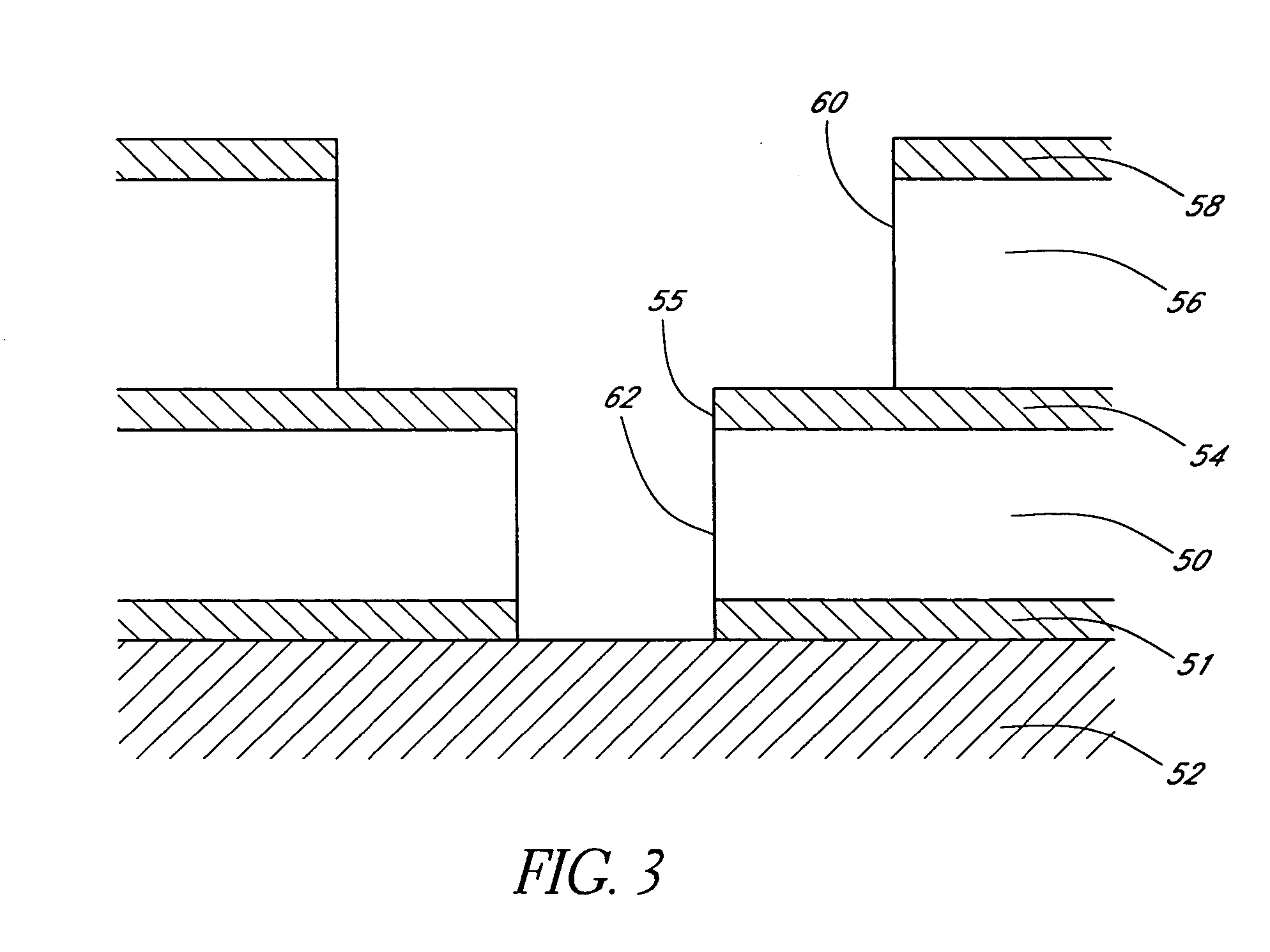
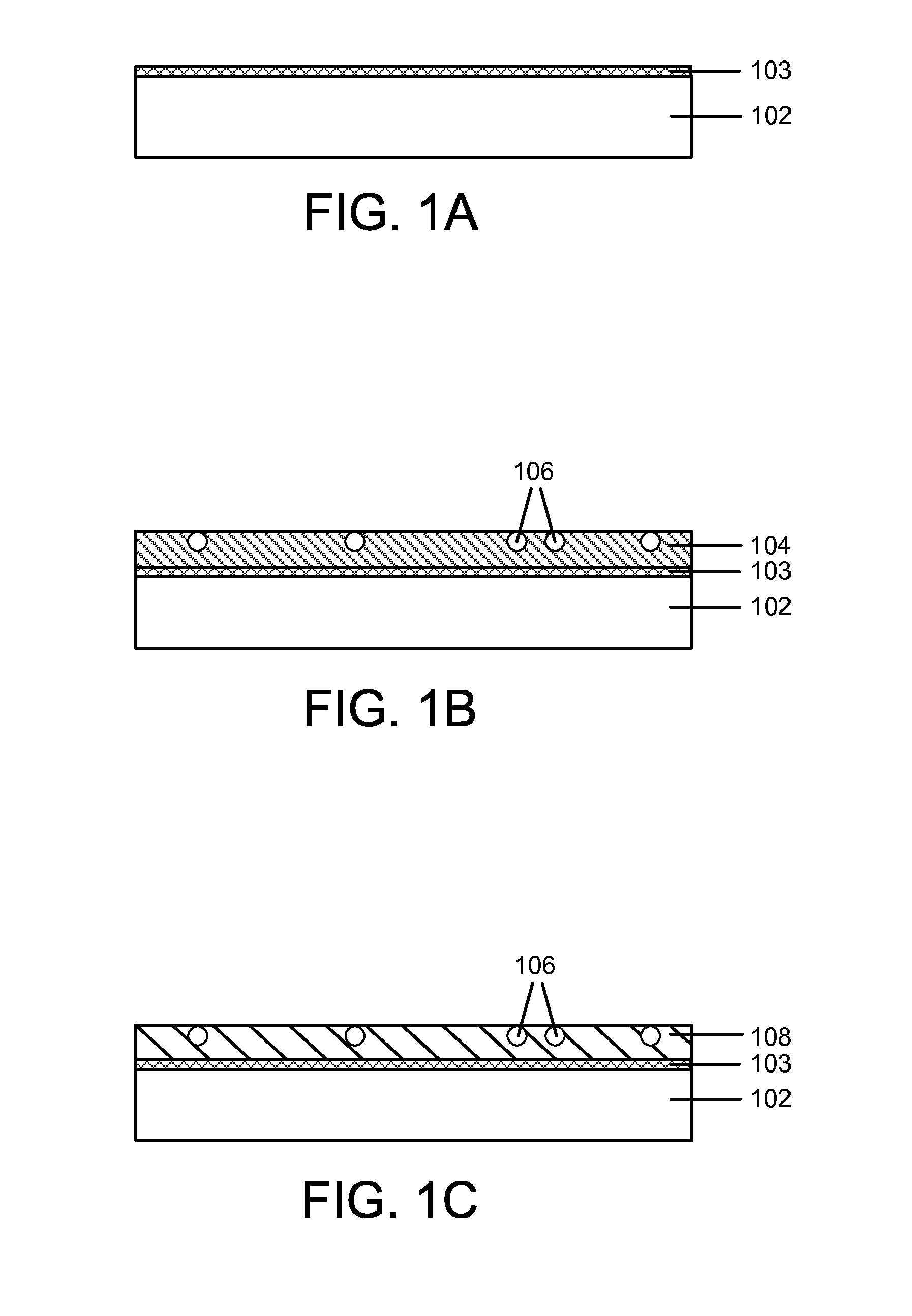
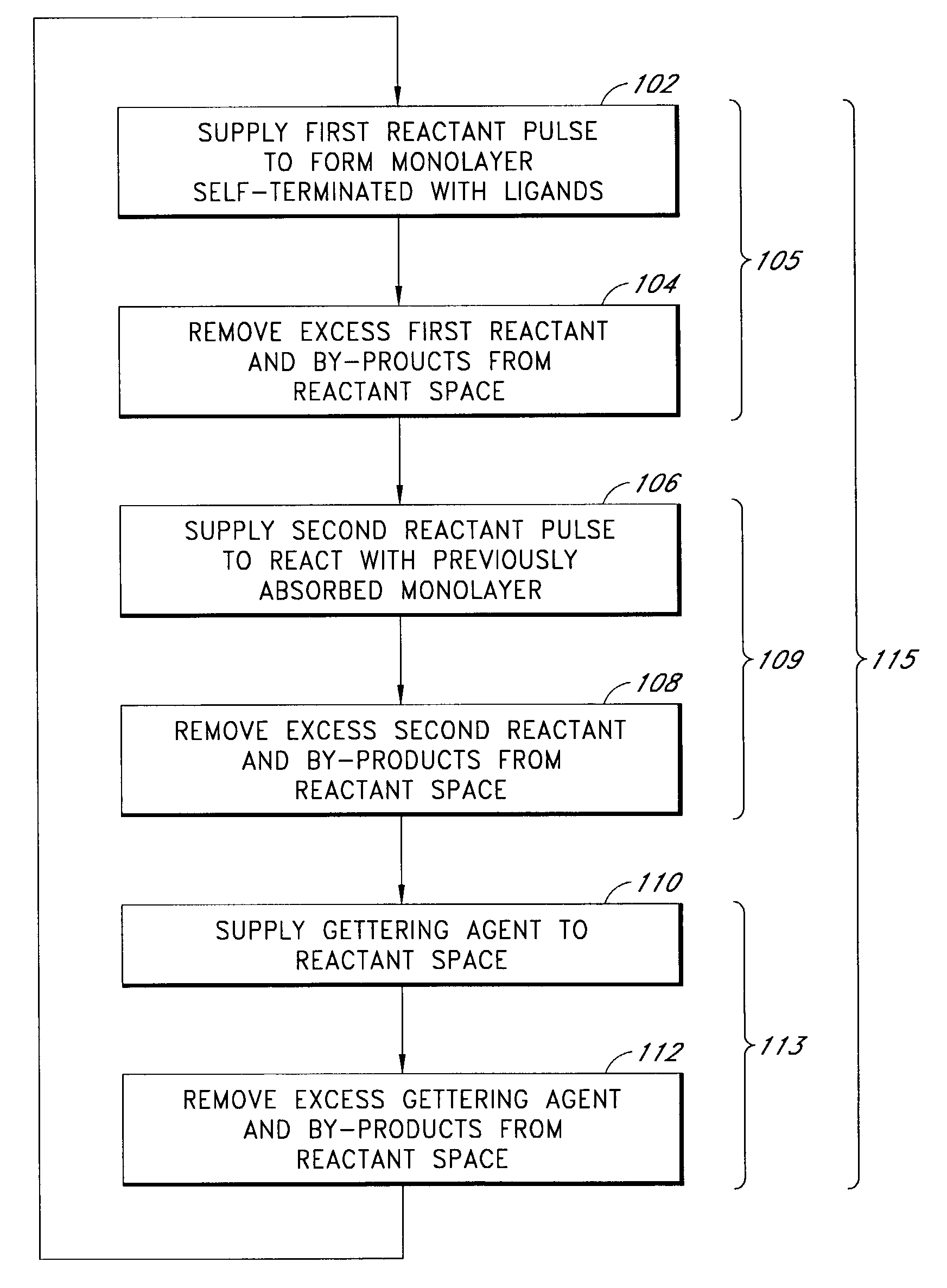
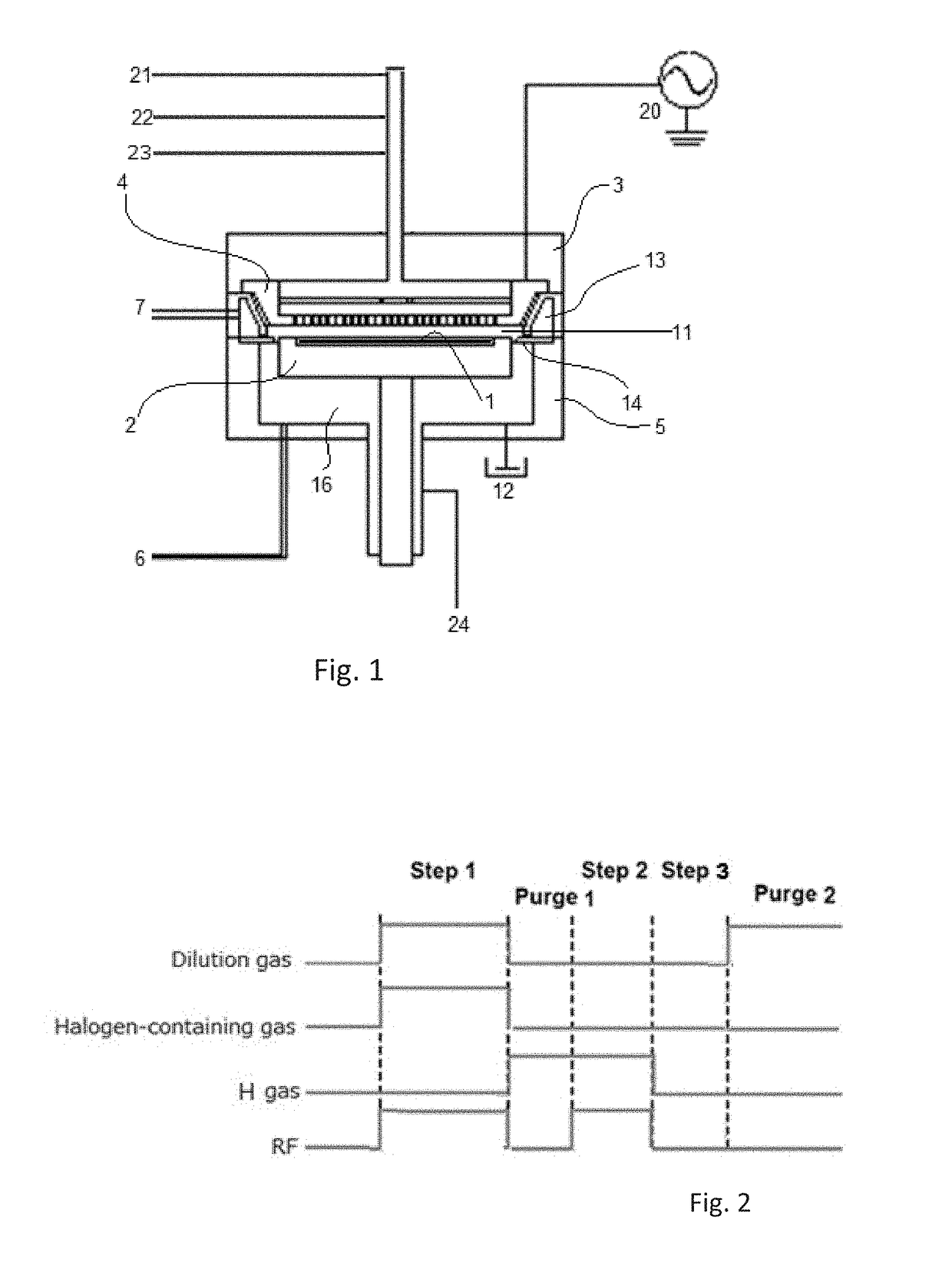
Metal nitride carbide deposition by ALD
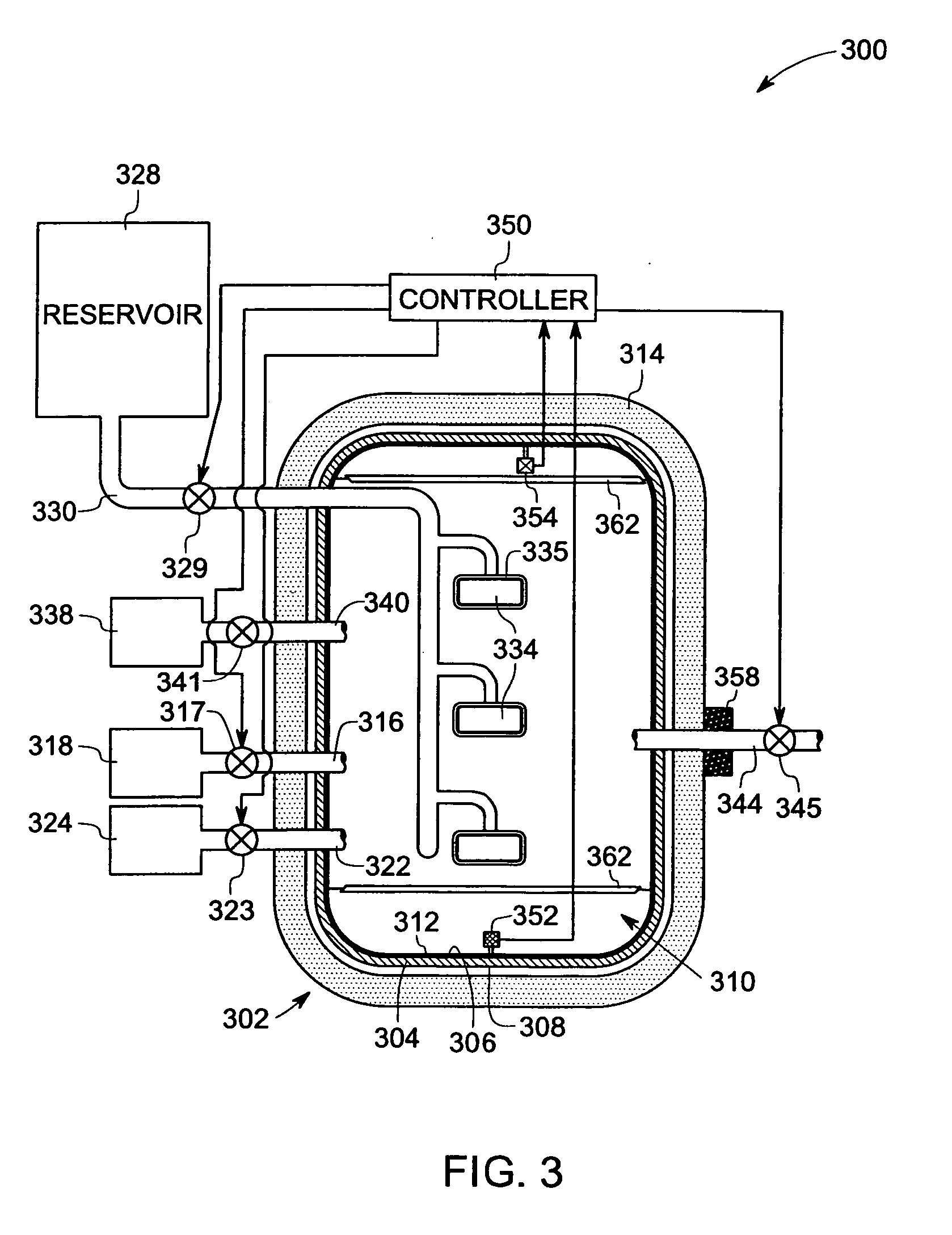
InactiveUS7410666B2Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHydrogen halideCorrosive chemical
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Method for depositing dielectric films
ActiveUS20130344248A1Reduces and substantially eliminates amountGood control over concentrationChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogen halideDecomposition
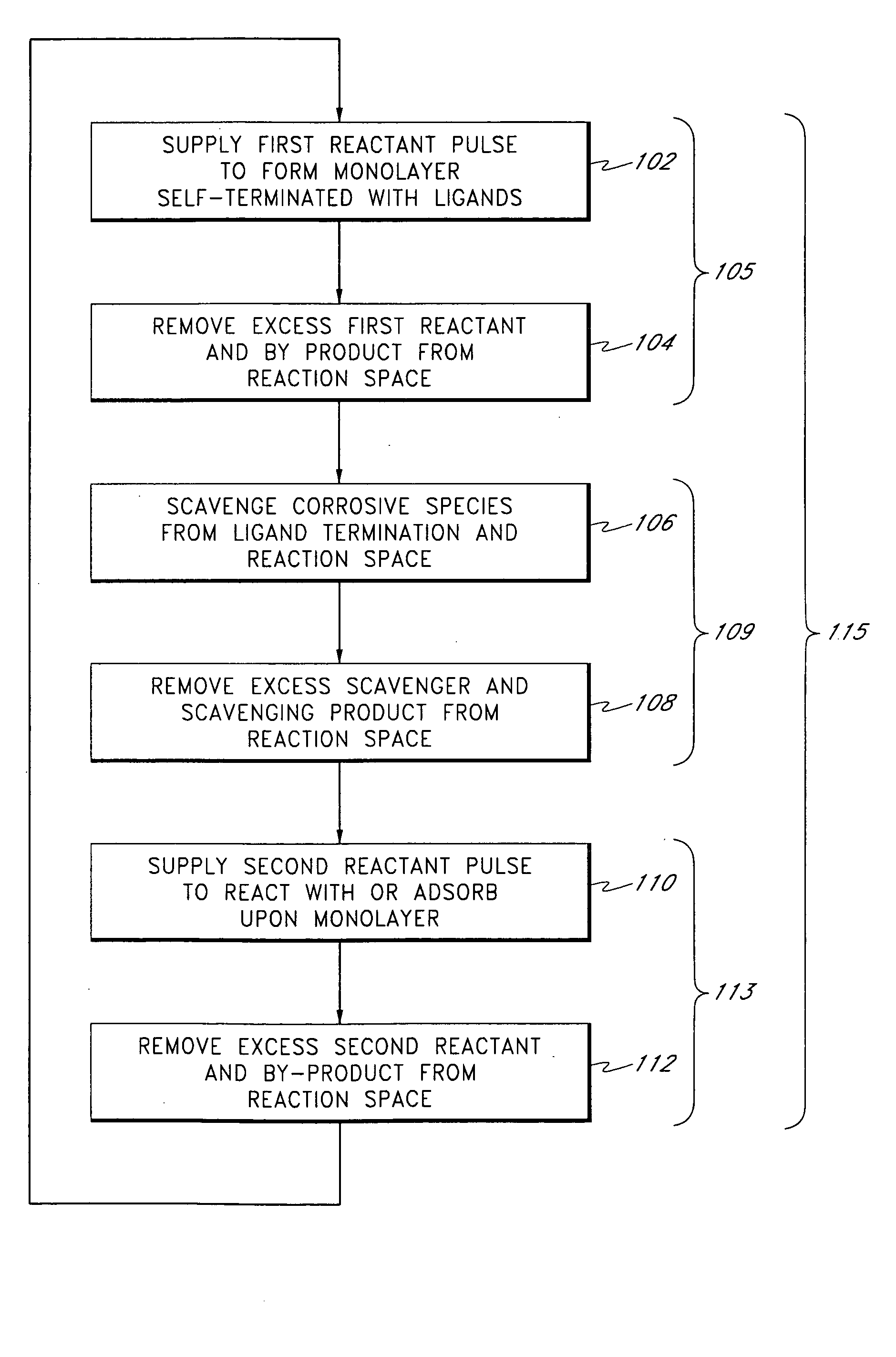
A method is provided for depositing a dielectric film on a substrate. According to one embodiment, the method includes providing the substrate in a process chamber, exposing the substrate to a gaseous precursor to form an adsorbed layer on the substrate, exposing the adsorbed layer to an oxygen-containing gas, a nitrogen-containing gas, or an oxygen- and nitrogen-containing gas, or a combination thereof, to form the dielectric film on the substrate, generating a hydrogen halide gas in the process chamber by a decomposition reaction of a hydrogen halide precursor gas, and exposing the dielectric film to the hydrogen halide gas to remove contaminants from the dielectric film.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Metal nitride deposition by ALD with reduction pulse
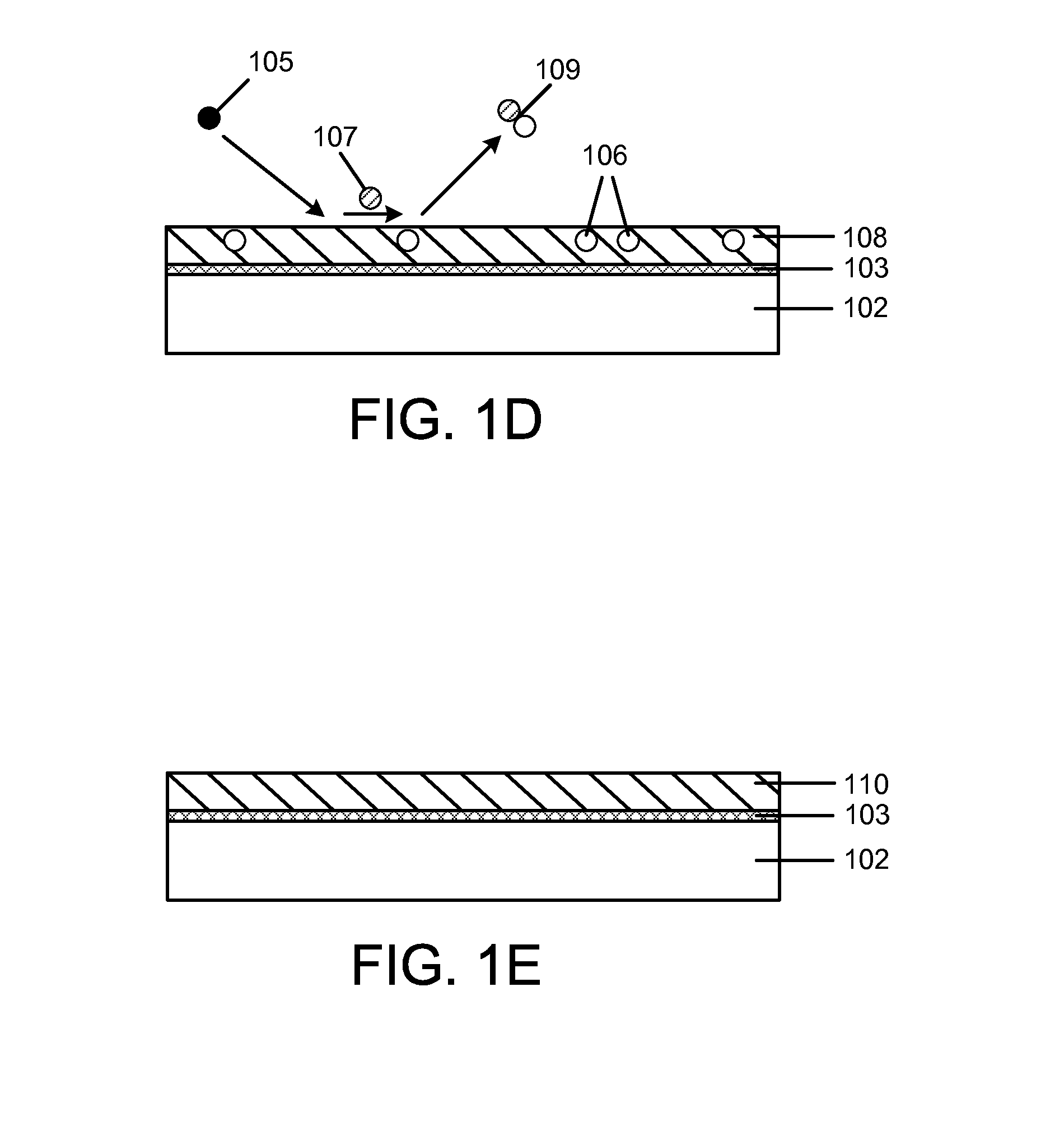
The present methods provide tools for growing conformal metal thin films, including metal nitride, metal carbide and metal nitride carbide thin films. In particular, methods are provided for growing such films from aggressive chemicals. The amount of corrosive chemical compounds, such as hydrogen halides, is reduced during the deposition of transition metal, transition metal carbide, transition metal nitride and transition metal nitride carbide thin films on various surfaces, such as metals and oxides. Getter compounds protect surfaces sensitive to hydrogen halides and ammonium halides, such as aluminum, copper, silicon oxide and the layers being deposited, against corrosion. Nanolaminate structures incorporating metallic thin films, and methods for forming the same, are also disclosed.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
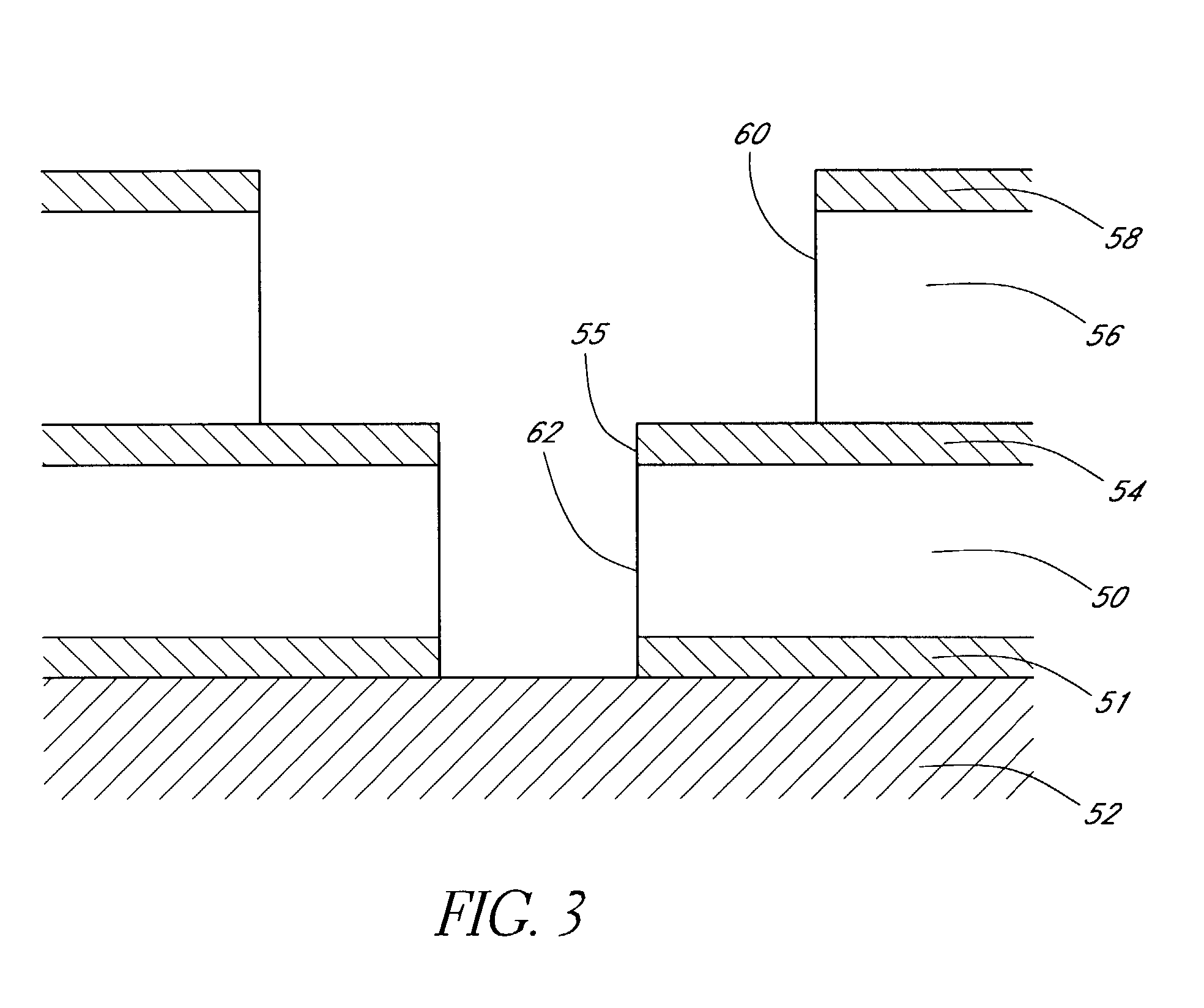
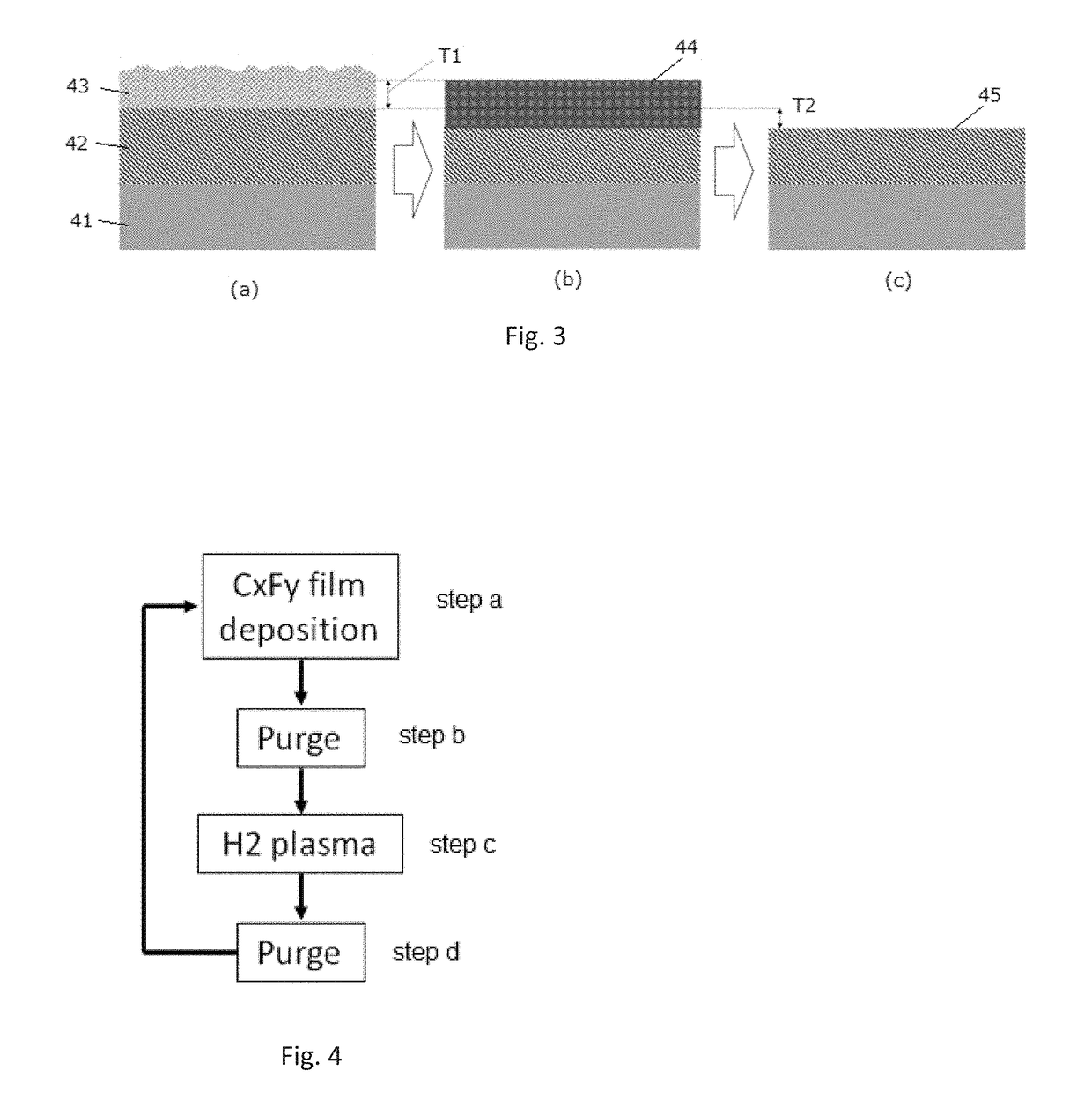
Method of atomic layer etching using hydrogen plasma
ActiveUS20180350620A1High selectivityImprove controllabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen halideHydrogen
A method for etching a target layer on a substrate by a dry etching process includes at least one etching cycle, wherein an etching cycle includes: depositing a carbon halide film using reactive species on the target layer on the substrate; and etching the carbon halide film using a plasma of a non-halogen hydrogen-containing etching gas, which plasma alone does not substantially etch the target layer, thereby generating a hydrogen halide as etchant species at a boundary region of the carbon halide film and the target layer, thereby etching a portion of the target layer in the boundary region.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Alkylation process using an alkyl halide promoted ionic liquid catalyst
ActiveUS7531707B2Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrocarbonsHydrogen halideAlkane
A process for the production of a high quality gasoline blending components from refinery process streams by the alkylation of light isoparaffins with olefins using an ionic liquid catalyst is disclosed. The alkylation process comprises contacting a hydrocarbon mixture comprising at least one olefin having from 2 to 6 carbon atoms and at least one isoparaffin having from 3 to 6 carbon atoms under alkylation conditions, said catalyst comprising a mixture of at least one acidic ionic liquid and at least one alkyl halide. The alkylhalide by reacting to at least a portion of the olefin with a hydrogen halide.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Method for making crystalline composition
InactiveUS20070141819A1Polycrystalline material growthNitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compoundsHydrogen halideNitrogen
A method of making a metal nitride is provided. The method may include introducing a metal in a chamber. A nitrogen-containing material may be flowed into the chamber. Further, a hydrogen halide may be introduced. The nitrogen-containing material may react with the metal in the chamber to form the metal nitride.
Owner:SLT TECH
Preparation of fluorinated olefins via catalytic dehydrohalogenation of halogenated hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20090043136A1Physical/chemical process catalystsPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offHalohydrocarbonHydrogen atom
A process for making a fluorinated olefin having the step of dehydrochlorinating a hydrochlorofluorocarbon having at least one hydrogen atom and at least one chlorine atom on adjacent carbon atoms, preferably carried out in the presence of a catalyst selected from the group consisting of (i) one or more metal halides, (ii) one or more halogenated metal oxides, (iii) one or more zero-valent metals / metal alloys, (iv) a combination of two or more of the foregoing.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method for depositing nanolaminate thin films on sensitive surfaces
InactiveUS20050106877A1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen halideCorrosive chemical
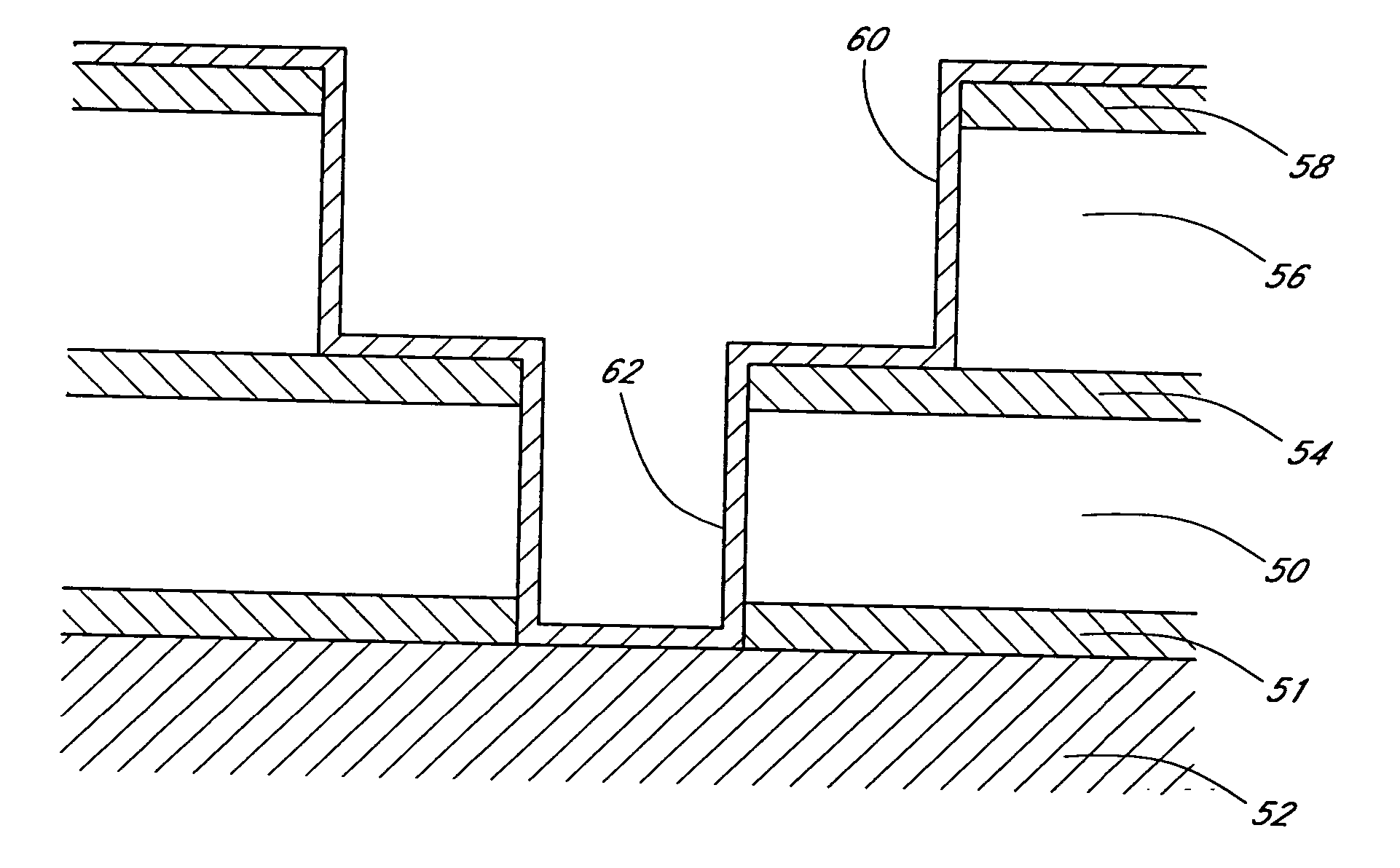
The present method provides tools for growing conformal metal nitride, metal carbide and metal thin films, and nanolaminate structures incorporating these films, from aggressive chemicals. The amount of corrosive chemical compounds, such as hydrogen halides, is reduced during the deposition of transition metal, transition metal carbide and transition metal nitride thin films on various surfaces, such as metals and oxides. Getter compounds protect surfaces sensitive to hydrogen halides and ammonium halides, such as aluminum, copper, silicon oxide and the layers being deposited, against corrosion. Nanolaminate structures (20) incorporating metal nitrides, such as titanium nitride (30) and tungsten nitride (40), and metal carbides, and methods for forming the same, are also disclosed.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
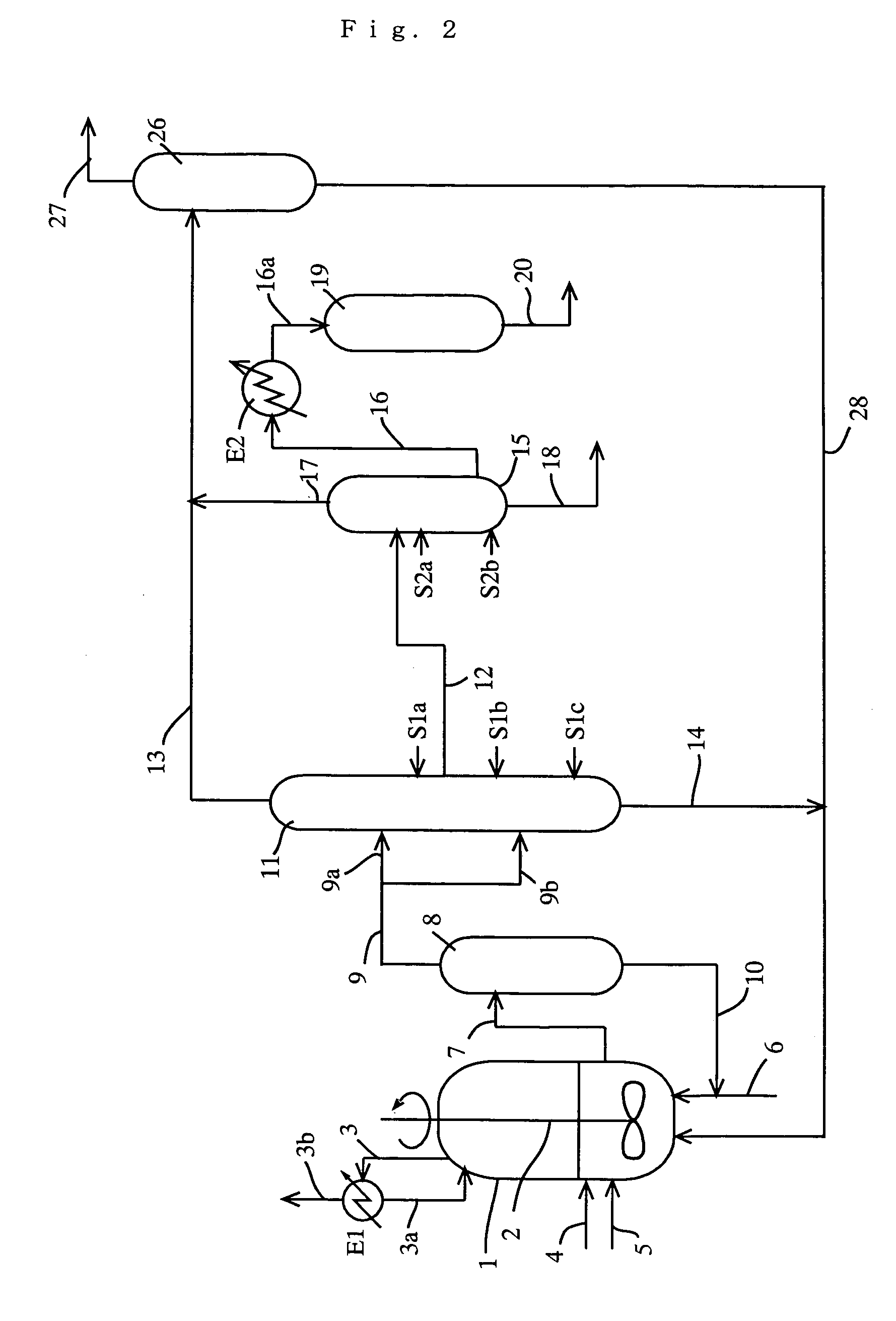
Hydrocarbon synthesis
InactiveUS20050171393A1Valid conversionMolecular sieve catalystLiquid hydrocarbon mixtures productionHydrogen halideOxygen
A method of synthesizing hydrocarbons from smaller hydrocarbons includes the steps of hydrocarbon halogenation, simultaneous oligomerization and hydrogen halide neutralization, and product recovery, with a metal-oxygen cataloreactant used to facilitate carbon-carbon coupling. Treatment with air or oxygen liberates halogen and regenerates the cataloreactant.
Owner:REACTION 35 LLC
Implants with textured surface and methods for producing the same
ActiveUS7901462B2High retention rateConvenient coatingDental implantsBone implantHydrogen halideChloride
Compositions and methods are provided for preparing a metal substrate having a uniform textured surface with a plurality of indentations with a diameter in the nanometer and micrometer range. The textured surface is produced by exposing the substrate to an etching fluid comprising a hydrogen halide acid and / or an oxyacid, a chloride containing compound, and an oxidizing agent. The etching solution can be used at ambient temperature without damaging the metal elements on the substrate surface. This textured surface enhances adherence of coatings or cells onto the textured surface, improves the retention of proteins on the surface, and encourages bone in-growth.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Metal nitride carbide deposition by ALD
InactiveUS20060078679A1Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHydrogen halideCorrosive chemical
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Process for producing carboxylic acid
InactiveUS7678940B2Efficient separationHigh purityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound separation/purificationHydrogen halideAlcohol
A process for producing a purified carboxylic acid having “n+1” carbon atoms comprises feeding a carboxylic acid stream containing a carboxylic acid having “n+1” carbon atoms, a hydrogen halide, a lower boiling point (bp) component, a higher bp component, and others to a first distillation column; separating a lower bp fraction containing part of the lower bp component and a higher bp fraction containing part of the higher bp component in the first column; withdrawing a side stream containing at least the carboxylic acid by side cut from the first column; feeding the side stream to a second distillation column; separating a lower bp fraction containing part of the lower bp component and a higher bp fraction containing part of the higher bp component in the second column; and withdrawing a side stream containing the carboxylic acid by side cut from the second column to recover a purified carboxylic acid; and the process further comprises feeding at least one first component (A) selected from the group consisting of an alcohol, corresponding to the carboxylic acid, having “n” carbon atom(s), and an ester of the alcohol with the carboxylic acid to the first column, and if necessary water. Such a process ensures reduction of the concentration of the hydrogen halide in the purified carboxylic acid.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Method for depositing nanolaminate thin films on sensitive surfaces
InactiveUS20060079090A1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen halideCorrosive chemical
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
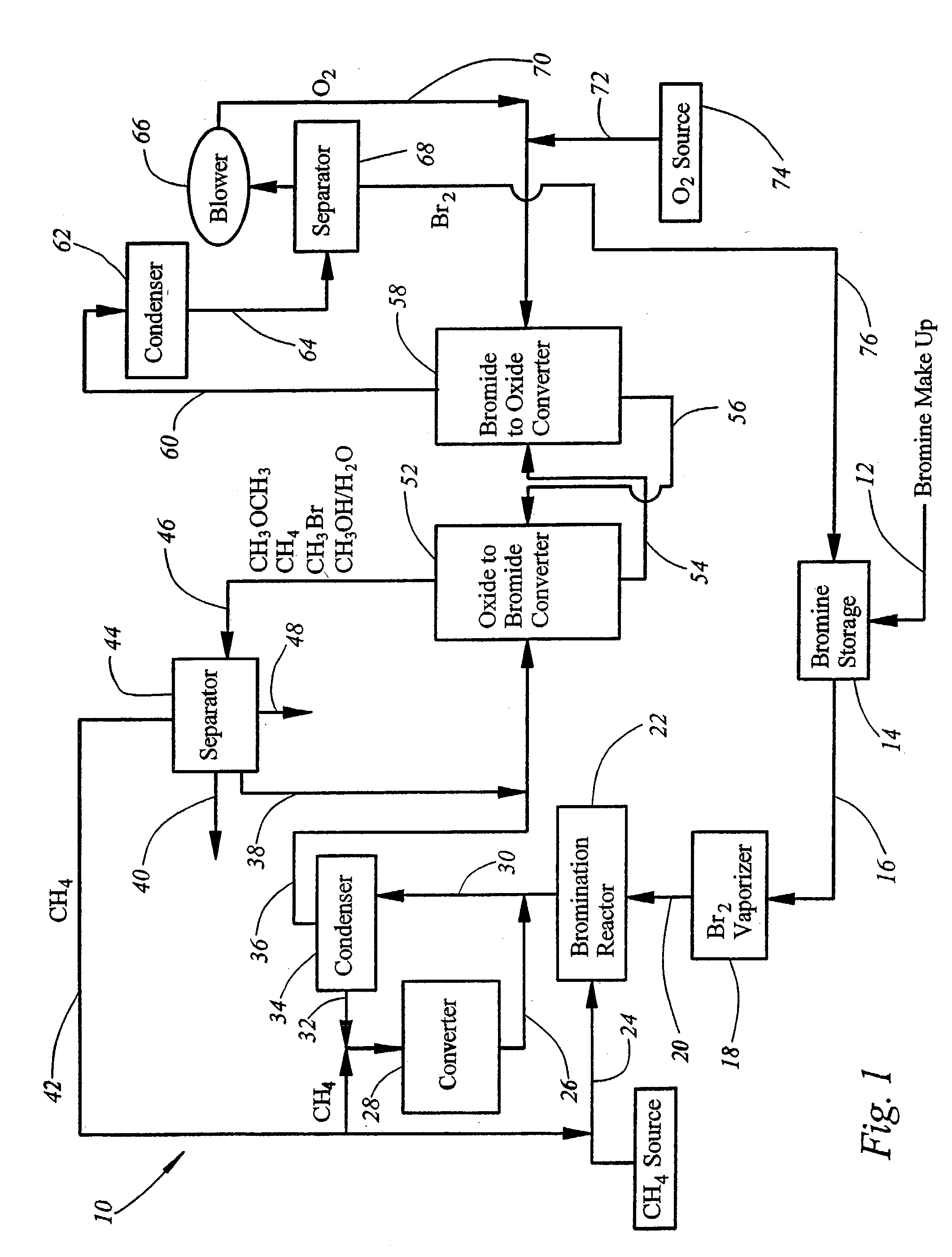
Integrated process for synthesizing alcohols, ethers, aldehydes, and olefins from alkanes
InactiveUS7148390B2Less corrosiveImprove securityOrganic compound preparationChemical industryHydrogen halideAlkane
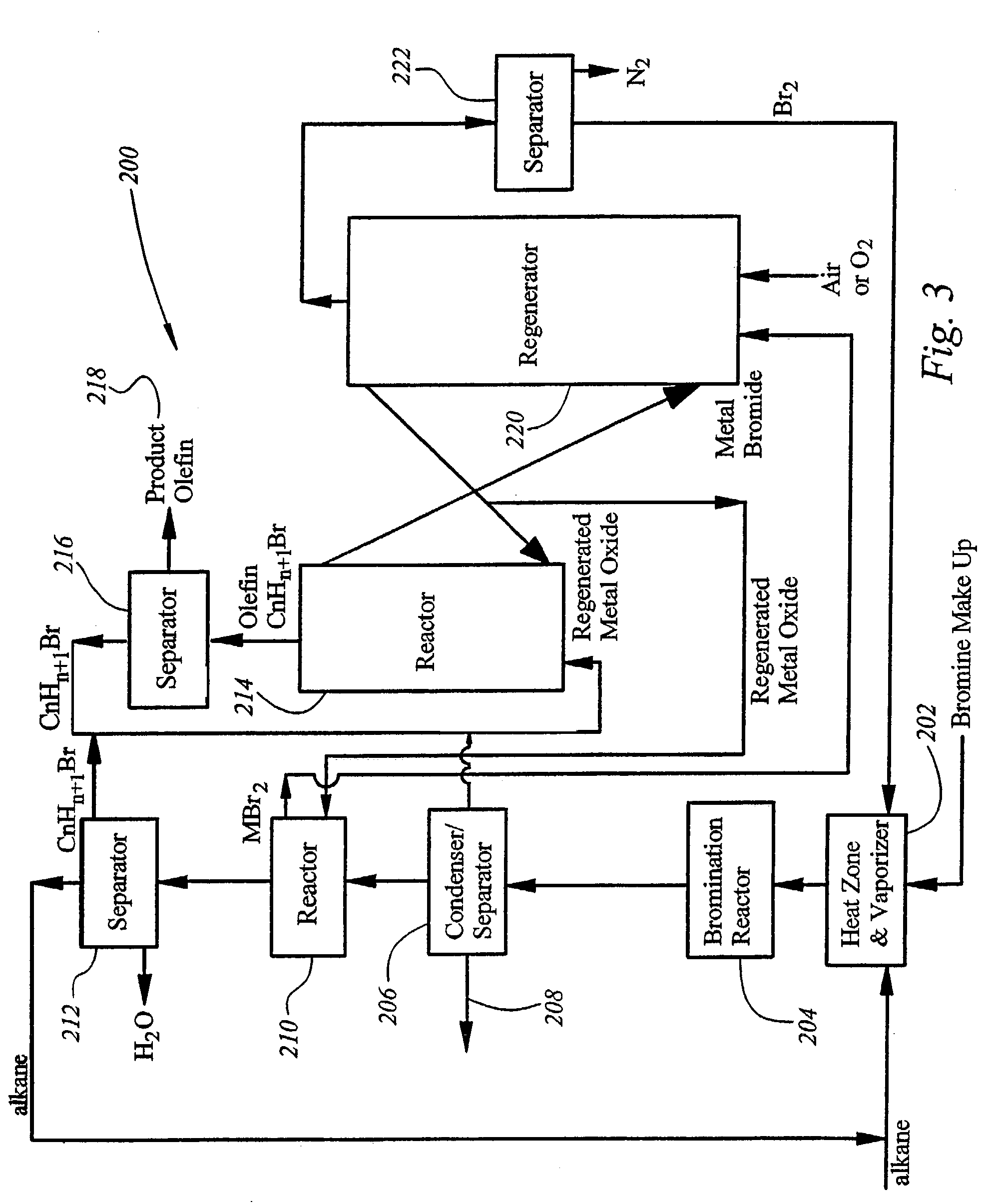
Alcohols, ethers, aldehydes, and olefins are manufactured from alkanes by mixing an alkane and a halogen selected from the group including chlorine, bromine, and iodine in a reactor to form alkyl halide and hydrogen halide. The alkyl halide only or the alkyl halide and the hydrogen halide are directed into contact with metal oxide to form an alcohol and / or an ether, or an olefin and metal halide. The metal halide is oxidized to form original metal oxide and halogen, both of which are recycled.
Owner:REACTION 35 LLC
High-temperature hydrogenation and purification process for liquefied gas materials
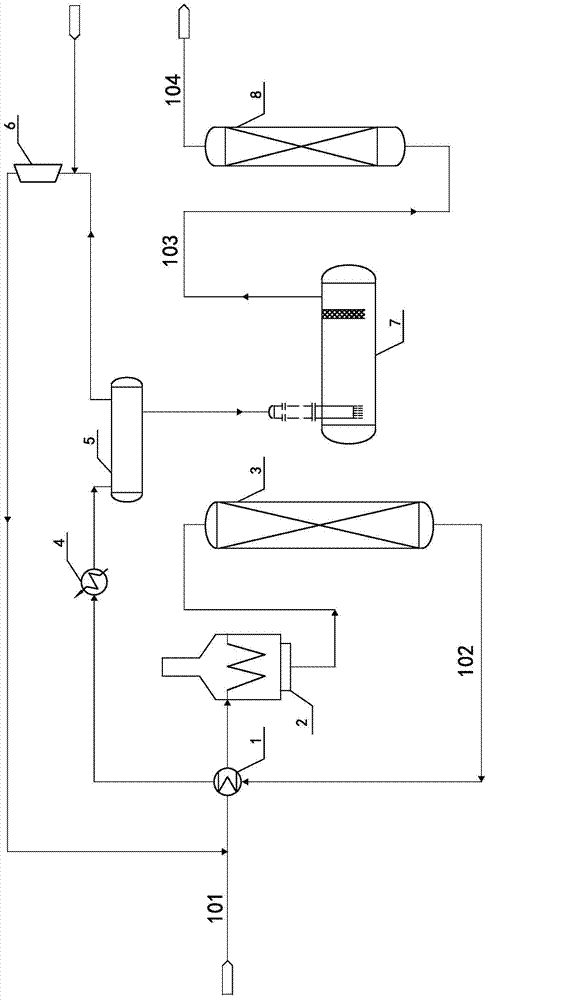
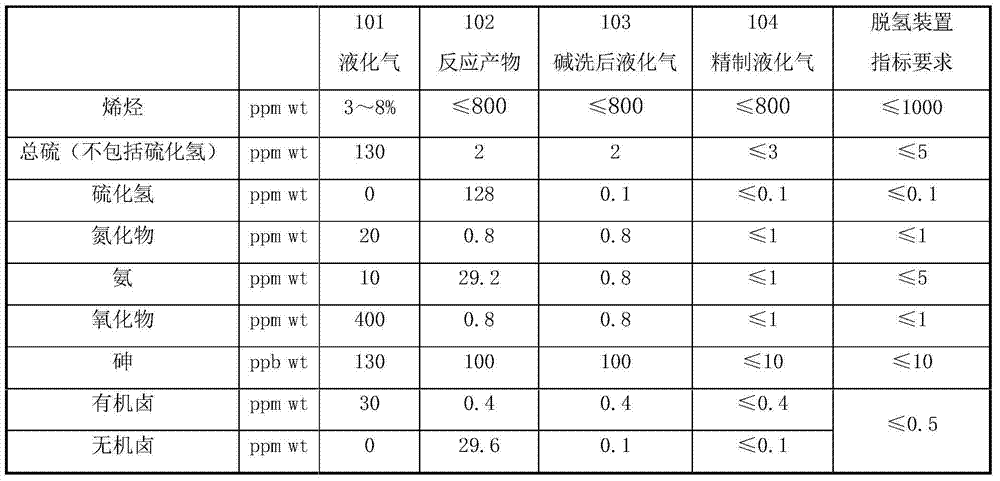
The invention relates to a purification process of liquefied gas and particularly provides a high-temperature hydrogenation and purification process for liquefied gas materials. The high-temperature hydrogenation and purification process is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) carrying out heat exchange on raw material liquefied gas and a reactor outlet product in a heat exchanger, heating by a heating furnace to a reaction temperature, then feeding the material into a reactor from the top, carrying out saturation hydrogenation on olefin in the material to obtain alkane, and respectively hydrogenating and converting sulfide, oxide, nitride and halide into hydrogen sulfide, water, ammonia and hydrogen halide; (2) carrying out sufficient heat exchange on the reactor outlet product and the raw material by an efficient heat exchanger, carrying out water cooling by a water cooler and enabling the material to enter a gas-liquid separation tank, compressing a flashing gas phase and fresh hydrogen by a compressor and circulating to the raw material liquefied gas; (3) enabling the flashing liquid phase to enter an alkali washing deposition tank and carrying out fiber membrane alkali washing to remove hydrogen sulfide, ammonia and hydrogen halide; (4) enabling the material which is subjected to the alkali washing to enter a dearsenicator, and removing arsenic and metal to obtain refined liquefied gas. The high-temperature hydrogenation and purification process mainly aims at a project which is very strict in requirement on the impurity content of a catalyst, and is short in flow, small in investment, low in cost and less in solid wastes.
Owner:山东海成石化工程设计有限公司
Improved synthesis method for glufosinate and analogue thereof
InactiveCN102399240AReduce generationReduce processing costsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsDiethyl phosphateHydrogen halide
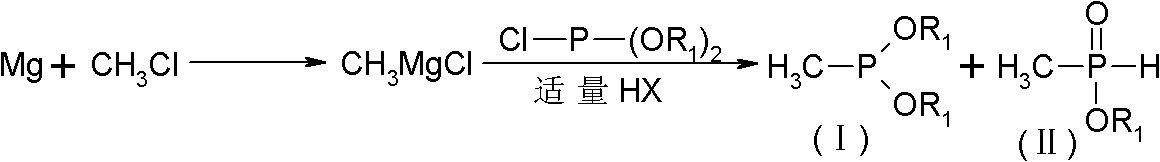
The invention discloses a comprehensive method for synthesizing glufosinate and analogue thereof by using phosphorus trichloride, triethyl phosphate and chloromethane as initiative raw materials. The method comprises the following steps of: performing Grignard, disproportionation and coupling; introducing a proper amount of hydrogen halide; and synthesizing to obtain two intermediates, namely methyl diethyl phosphate (intermediate I) and methyl phosphinate (intermediate II), wherein the two intermediates can synthesize the glufosinate and the analogue thereof. By the method, the glufosinate and the analogue thereof are synthesized by completely utilizing the methyl diethyl phosphate and the methyl phosphinate synthesized by a Grignard route; yield is increased; production cost is reduced; and three wastes are reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU YOUTH CHEM +1
Method for producing highly purified, granular silicium
InactiveUS7001579B2Minimum formation of dustMinimizing reactionSiliconChemical/physical processesHydrogen halideHydrogen
The invention relates to a method for producing granular silicon by thermal decomposition of a gas containing silicon in a fluidized bed, said decomposition occurring in the presence of free-flowing mobile elements. Preferably, said free-flowing mobile elements become devoid of silicon in a separate procedural step, said silicon being deposited during decomposition of gas containing silicon, by reacting with hydrogen halides, halogens, alkyl halogenides, aryl halogenides or combinations of halogen and / or hydrogen halide and / or oxidized mineral acids and / or by thermal treatment of said elements.
Owner:SOLARWORLD
Halogen-free flame-retardant rigid polyurethane foamed plastic and preparation method for same
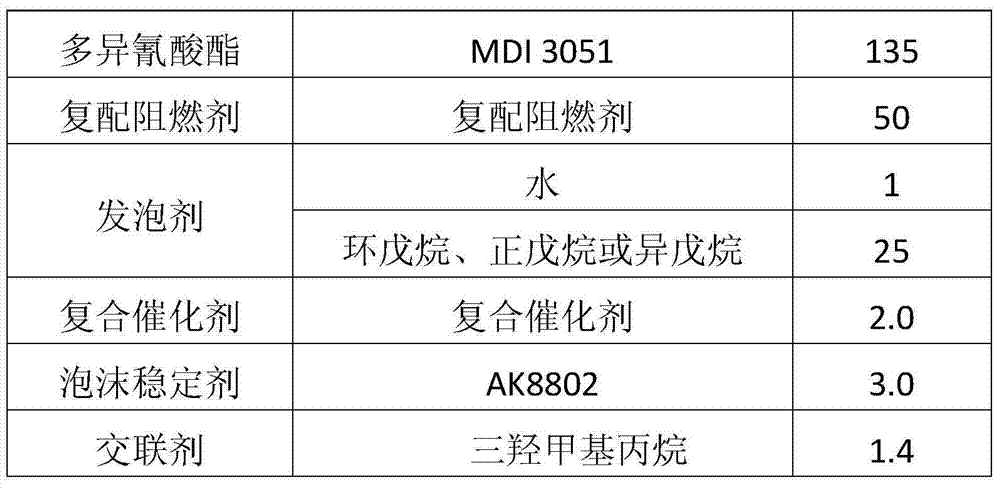
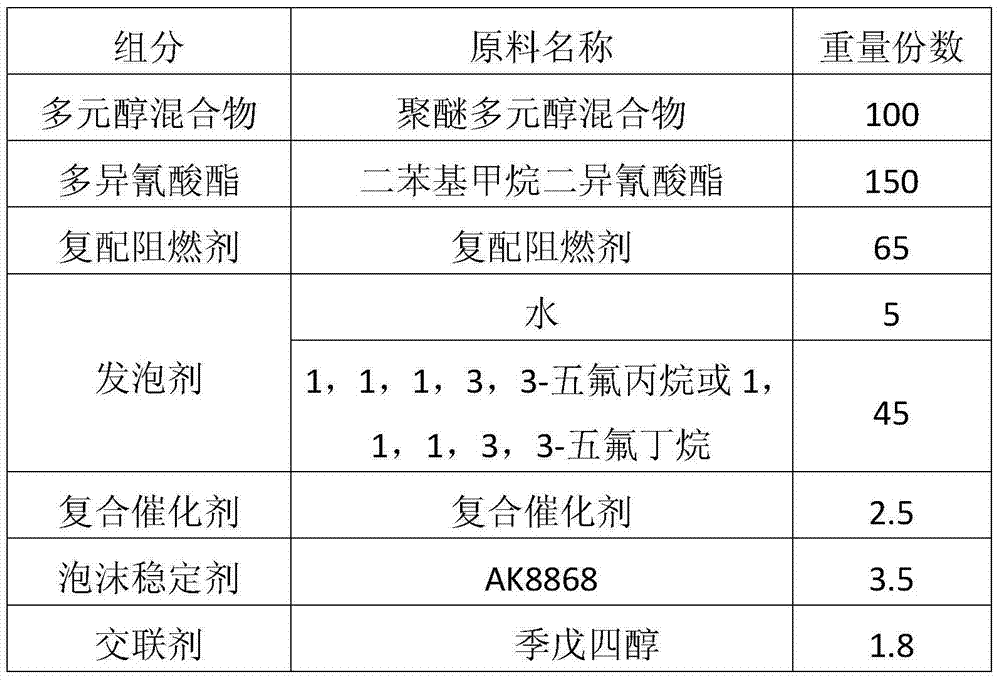
ActiveCN103694438ALittle impact on physical propertiesGood physical propertiesHydrogen halideToxic gas
The invention discloses halogen-free flame-retardant rigid polyurethane foamed plastic and a preparation method for the same. The polyurethane foamed plastic consists of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 100 parts of polyalcohol mixture, 105 to 180 parts of polyisocyanate, 20 to 80 parts of compound halogen-free flame retardant, 1 to 50 parts of foaming agent, 1 to 3 parts of composite catalyst, 2 to 4 parts of foam stabilizer and 1 to 2 parts of cross-linking agent. An obtained product is high in flame retardance and environment-friendly, the raw materials are free of halogen, and the production of toxic gas such as hydrogen halide during combustion is avoided; the raw materials are readily available and low in cost, so that the preparation cost of the polyurethane foamed plastic is greatly lowered; the polyurethane foamed plastic also has the characteristic of wide application range, and is applied to cold storage and heat-preservation industries of external wall heat-preservation of buildings, heat-preservation of pipelines, refrigerators, freezers and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
Carbonylation process
ActiveUS20070293695A1Organic compound preparationPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionHydrogen halideCarboxylic acid
Disclosed is a carbonylation process for the production of carboxylic acids, carboxylic acid esters and / or carboxylic acid anhydrides wherein a carbonylation feedstock compound selected from one or more organic oxygenates such as alcohols, ethers, and esters is contacted with carbon monoxide in the presence of a carbonylation catalyst and one or more onium compounds. The carbonylation process differs from known carbonylation processes in that a halide compound such as a hydrogen halide, typically hydrogen iodide, and / or alkyl halide, typically methyl iodide, extraneous or exogenous to the carbonylation process is not fed or supplied separately to the process.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
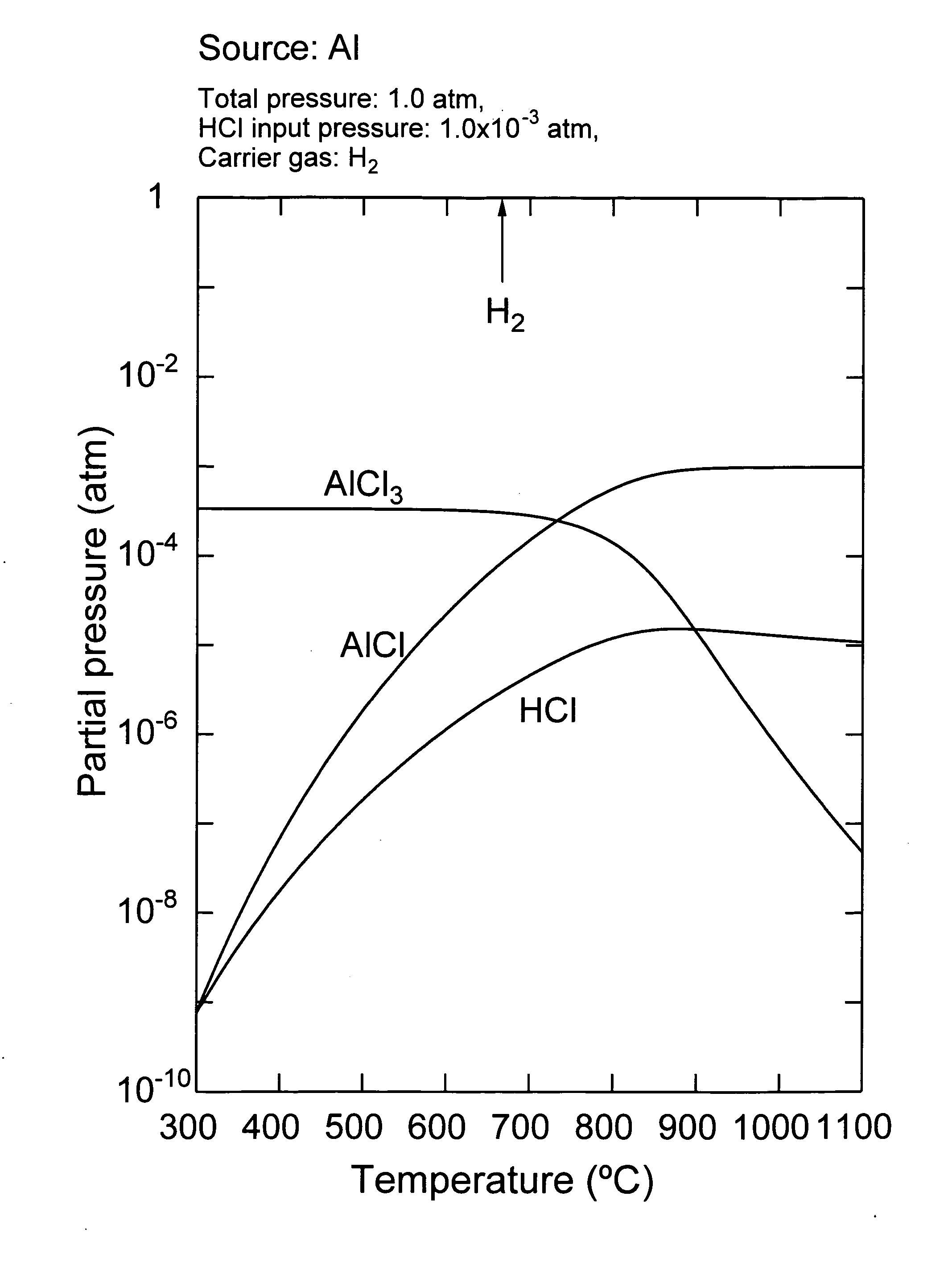
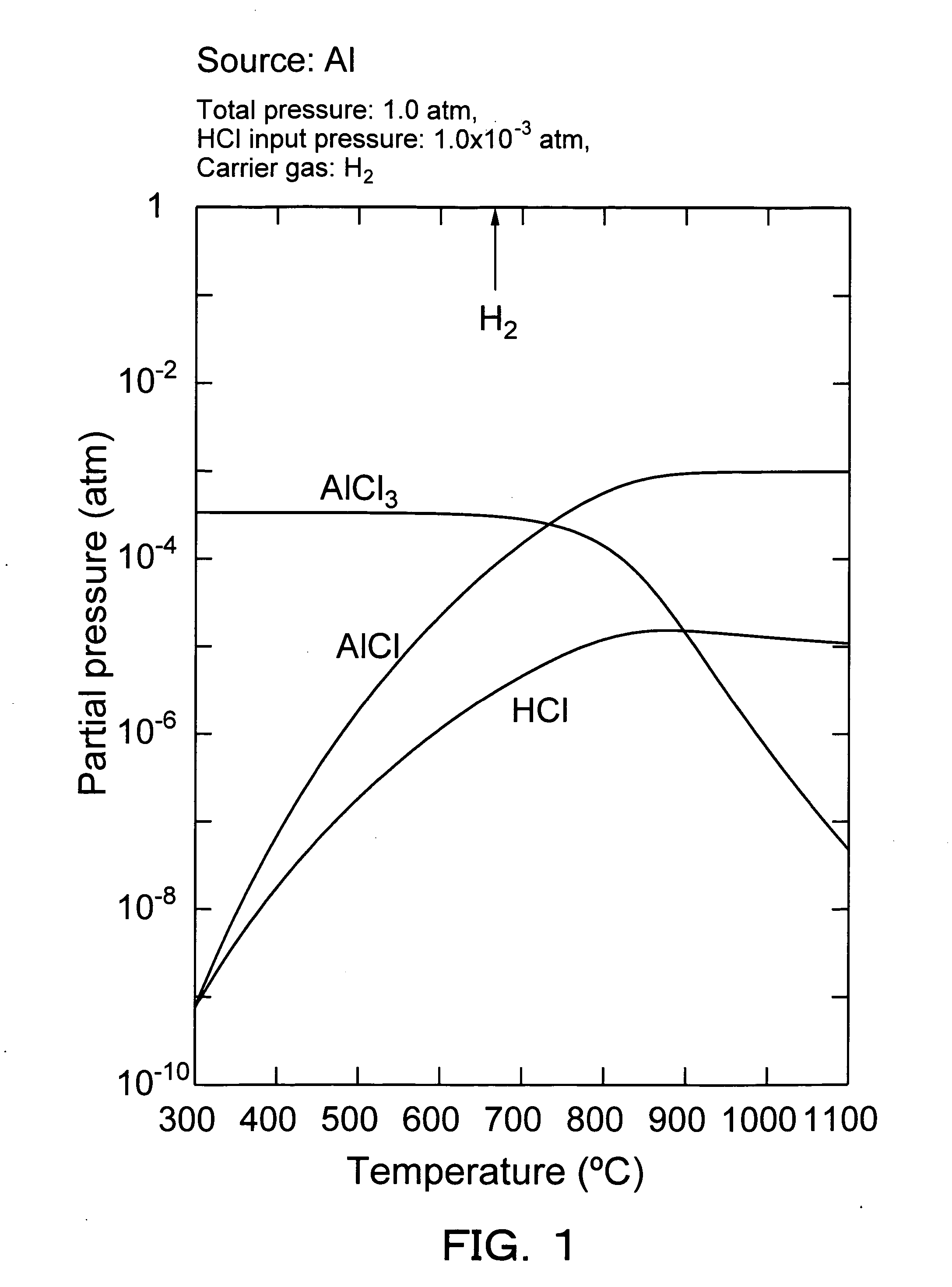
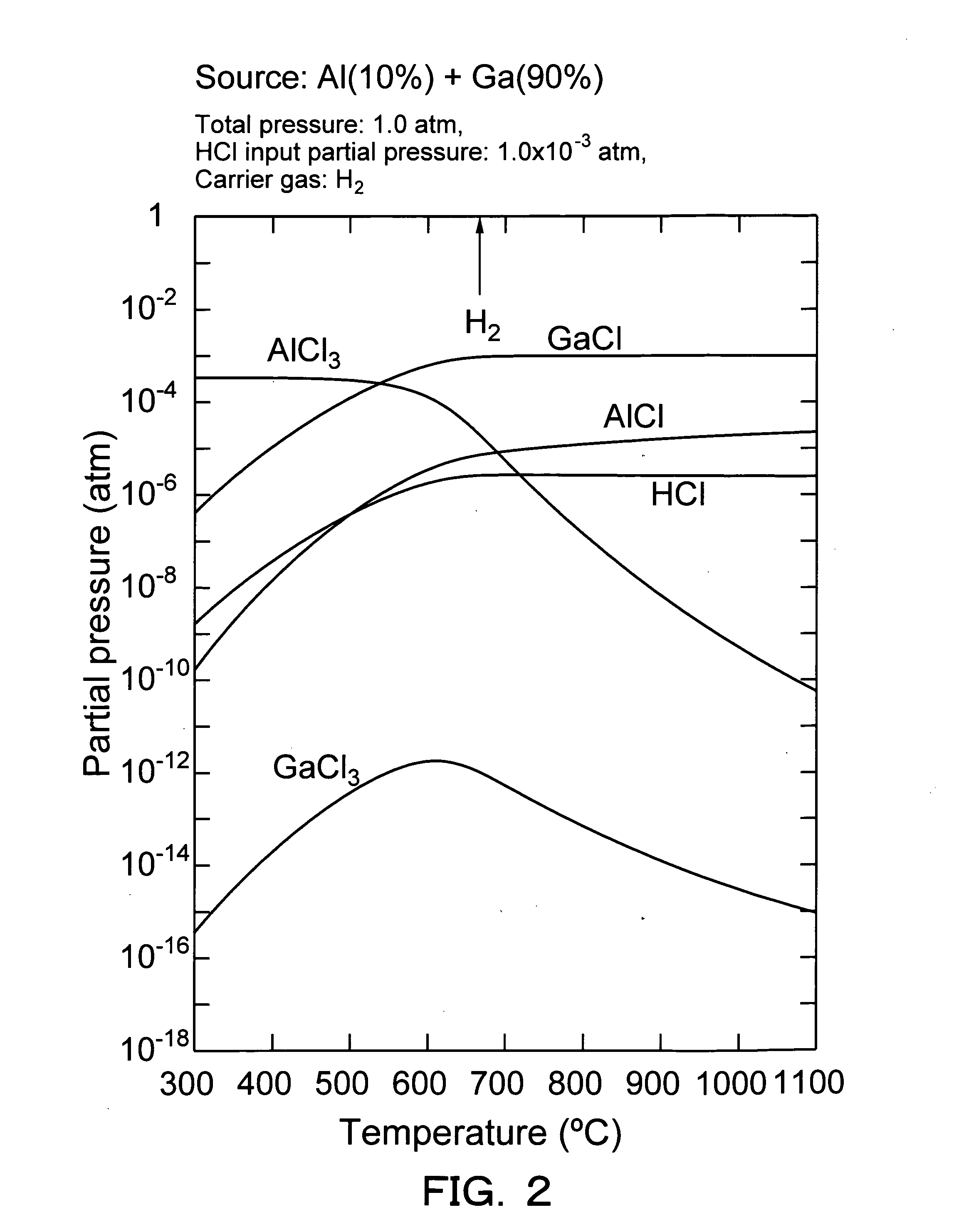
Vapor phase growth method for al-containing III-V group compound semiconductor, and method and device for producing al-containing IIl-V group compound semiconductor
InactiveUS20050166835A1Inhibits the formation of cracksAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthHydrogen halideGas phase
Owner:NOKODAI TLO KK
Hydrolysis method for material containing hydrolysable halogen atom
ActiveCN102234117AAvoids problems with clogging gaseous product channelsRelieve stressSilicaPreparation from chloridesHalogenGaseous hydrogen
The invention discloses a short-procedure, less-investment and simple-operation hydrolysis method for a material containing hydrolysable halogen atom. The method is characterized in that: a material containing hydrolysable halogen atom and a material containing water are subjected to mixing and reacting in a mixing and reaction unit; at least one reactant reacts as completely as possible through controlling reaction conditions, in particular, a key point is that the resulting reaction products are dried solid oxide and gaseous hydrogen halide, then the solid oxide is removed from a gas-solid separation and purification unit, and the gaseous hydrogen halide is processed through a gas product cleaning unit. The solid oxide and the gaseous hydrogen halide prepared through the method are valuable commodities, and the gaseous hydrogen halide further can be applicable for a synthesis process of halide. In addition, the method can be applicable for processing industrial waste containing the hydrolysable halogen atom, and producing solid oxides and hydrogen halide through adopting compounds containing the hydrolysable halogen atom.
Owner:刘基扬
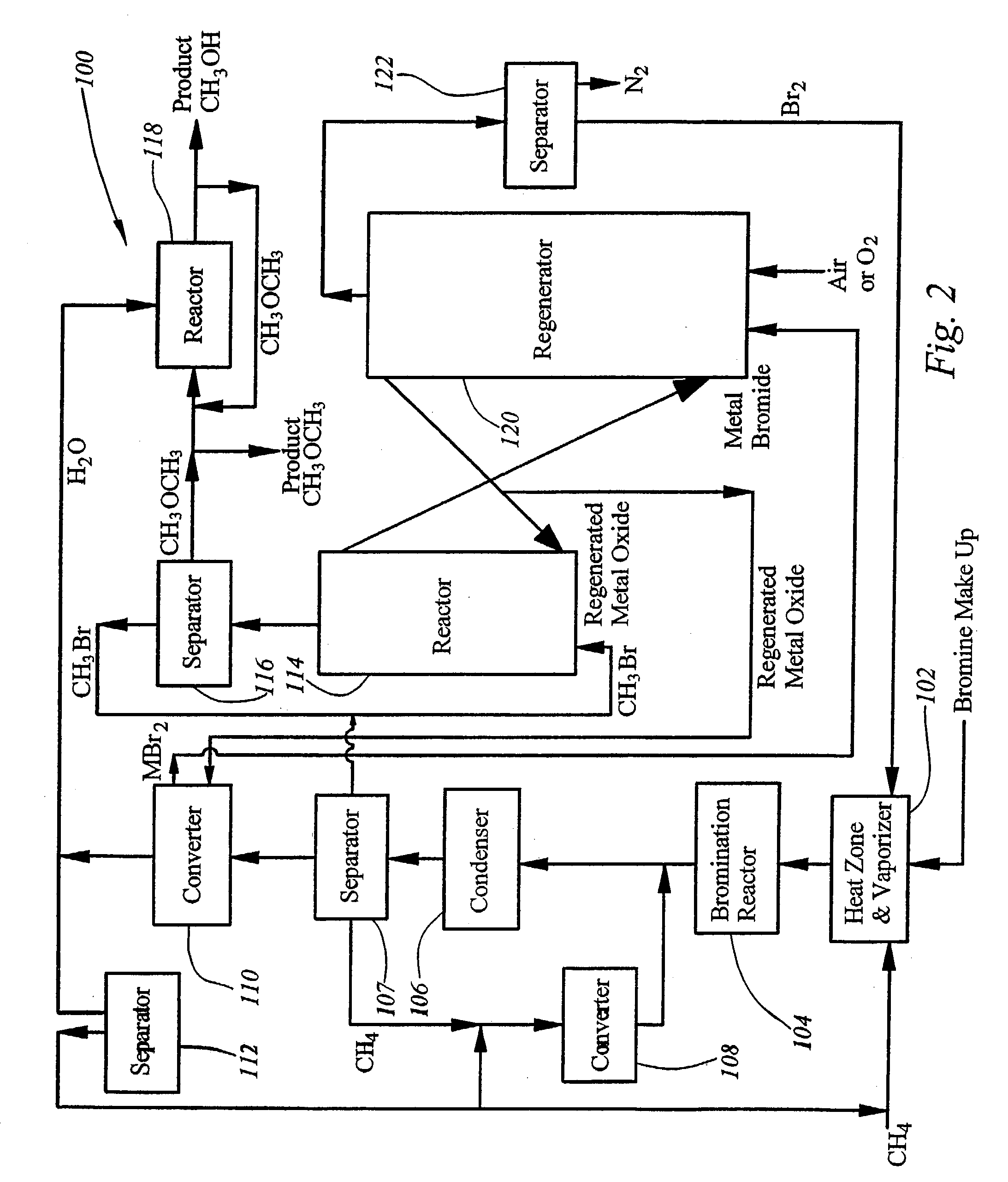
Continuous Process for Converting Natural Gas to Liquid Hydrocarbons
A method comprising: providing an alkyl halide stream; contacting at least some of the alkyl halides with a coupling catalyst to form a product stream comprising higher hydrocarbons and hydrogen halide; contacting the product stream with a solid reactant to remove at least a portion of the hydrogen halide from the product stream; and reacting the solid reactant with a source of oxygen to generate a corresponding halogen.
Owner:REACTION 35 LLC
Stability of polyurethane polyol blends containing halogenated olefin blowing agent
ActiveUS20150197614A1Uniform cell structureEasy to prepareOther chemical processesHydrogen halidePolymer science
A polyol pre-mix composition includes a blowing agent having a halogenated hydroolefin, a polyol, a catalyst composition, and an antioxidant. The antioxidant may be, for example, a benzene diol or a benzene triol or other polyhydroxy-substituted aromatic compound, which is optionally substituted with one or more substituents such as alkyl groups. A two-part system for producing a thermosetting foam blend includes (a) a polyisocyanate and, optionally, one or more isocyanate compatible raw materials; and (b) the polyol pre-mix composition. A method for producing a thermosetting foam blend includes combining: (a) a polyisocyanate; and (b) the polyol pre-mix composition.
Owner:ARKEMA INC
Hydrogen sulfide abatement with scale control and/or well acidizing
InactiveUS6375907B1Avoid disadvantagesLow costHydrogen bromideLiquid degasificationHydrogen halidePower station
The emissions of hydrogen sulfide during the production of natural gas, oil or geothermal fluids from subterranean formations and the subsequent processing of these fluids is reduced by converting the hydrogen sulfide into a hydrogen halide or a halogen acid and then using the hydrogen halide or halogen acid for scale control and / or well acidizing. In a preferred embodiment, hydrogen sulfide produced with geothermal fluids is converted into hydrochloric acid, which is then used to reduce pH and control scale formation during the extraction of energy from geothermal fluids in a geothermal power plant.
Owner:UNION OIL OF CALIFORNIA
Hydrocarbon synthesis
InactiveUS20080188697A1Molecular sieve catalystLiquid hydrocarbon mixtures productionHydrogen halideOxygen
A method of synthesizing hydrocarbons from smaller hydrocarbons includes the steps of hydrocarbon halogenation, simultaneous oligomerization and hydrogen halide neutralization, and product recovery, with a metal-oxygen cataloreactant used to facilitate carbon-carbon coupling. Treatment with air or oxygen liberates halogen and regenerates the cataloreactant.
Owner:REACTION 35 LLC
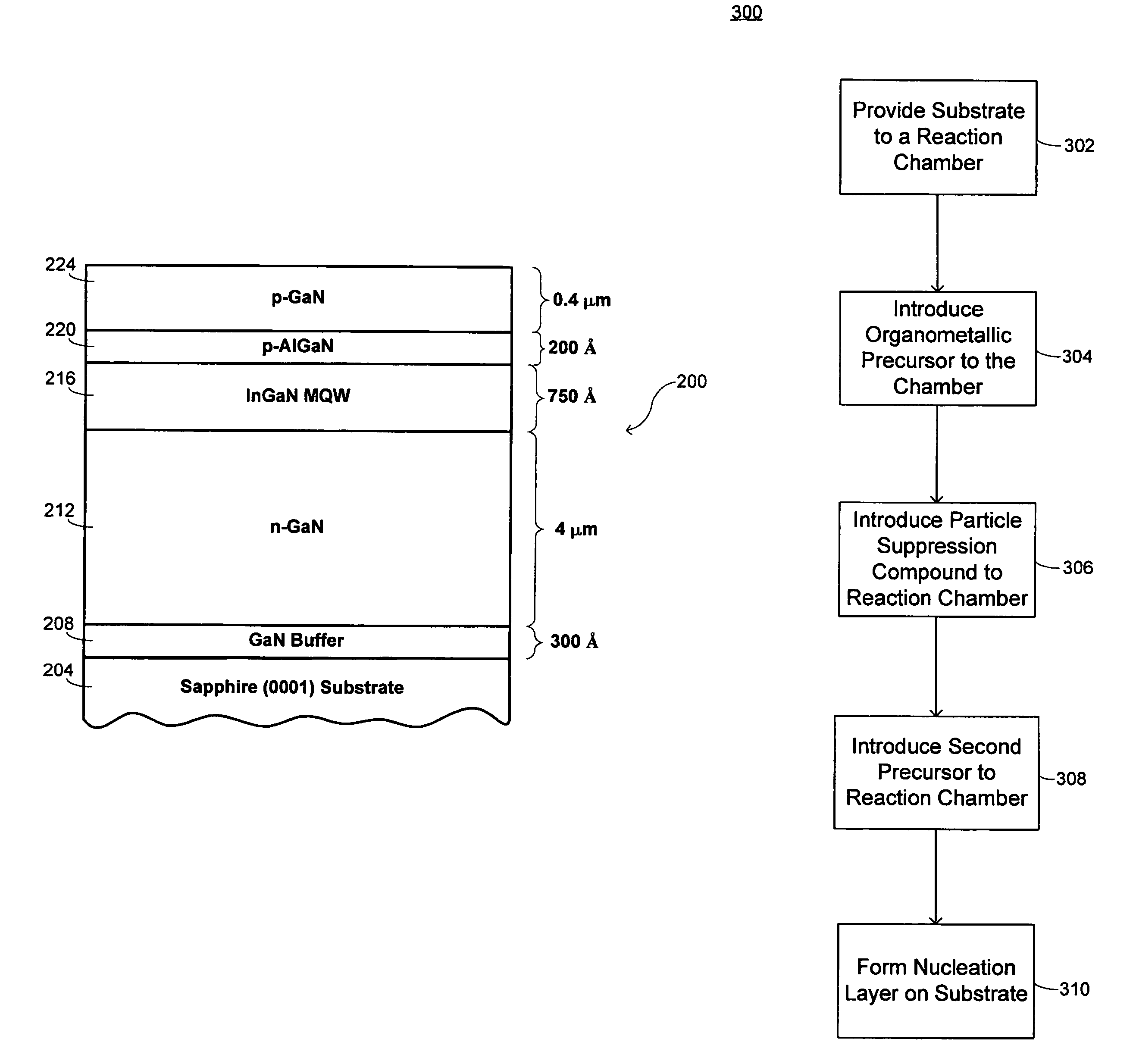
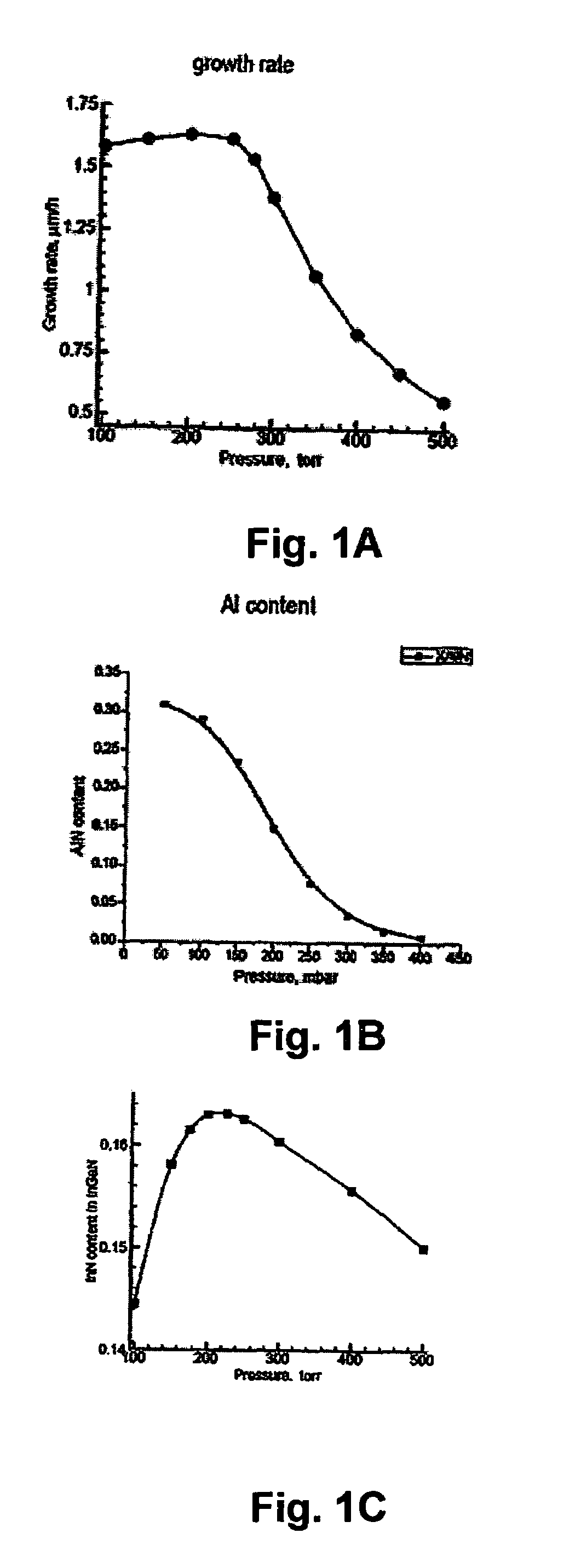
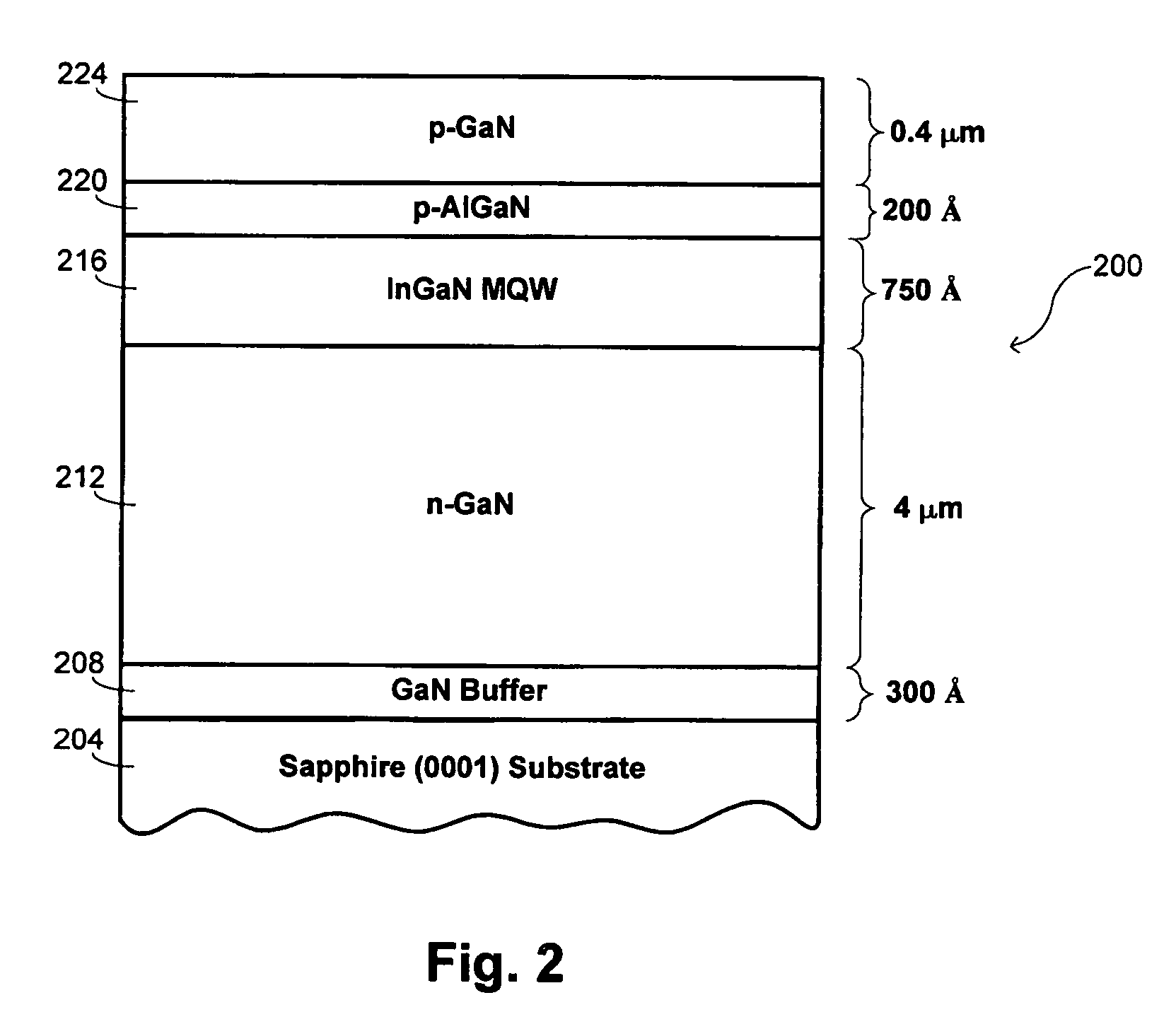
Parasitic particle suppression in growth of III-V nitride films using MOCVD and HVPE
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Preparation method of catalyst for preparing propylene by virtue of propane dehydrogenation
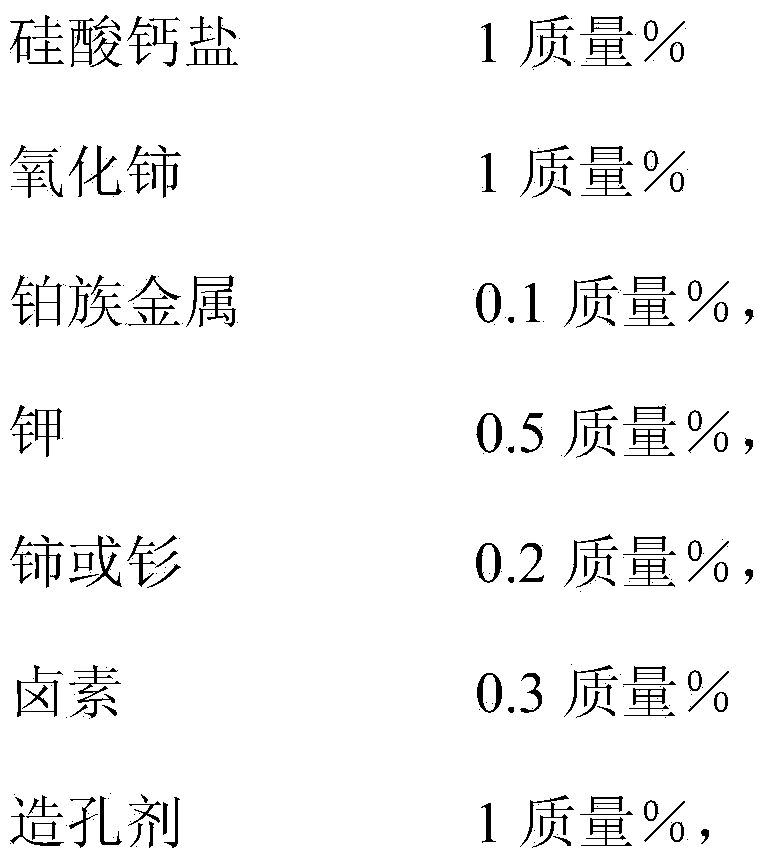
InactiveCN104368364AAvoid it happening againAvoid Contaminated SituationsPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrocarbonsCalcium silicateHydrogen halide
The invention discloses a preparation method of a catalyst for preparing propylene by virtue of propane dehydrogenation. The catalyst comprises an aluminum oxide carrier and active components with the following contents in percentage by mass calculated based on the carrier: 1-3% of calcium silicate salt, 1-3% of cerium oxide, 0.1-2.0% of a platinum group metal, 0.5-5.0% of potassium, 0.2-5.0% of cerium or samarium, 0.3-10% of halogen, 1-5% of a pore forming agent and the balance of impurities, wherein the molar ratio of cerium or samarium to the platinum group metal is 7:8; the platinum group metal is platinum; and halogen is chlorine. The preparation method comprises the following steps: soaking, drying and roasting the aluminum oxide carrier by using a soluble compound solution of cerium or samarium and a calcium silicate salt solution, then soaking, drying and roasting by using a solution containing compounds of the platinum group metal and hydrogen halide, and then soaking, drying and roasting by using a potassium salt solution; and then mixing cerium oxide and the pore forming agent with corresponding amounts, and roasting for 3 hours at 600 DEG C to obtain the catalyst for preparing propylene by virtue of propane dehydrogenation.
Owner:华玉叶
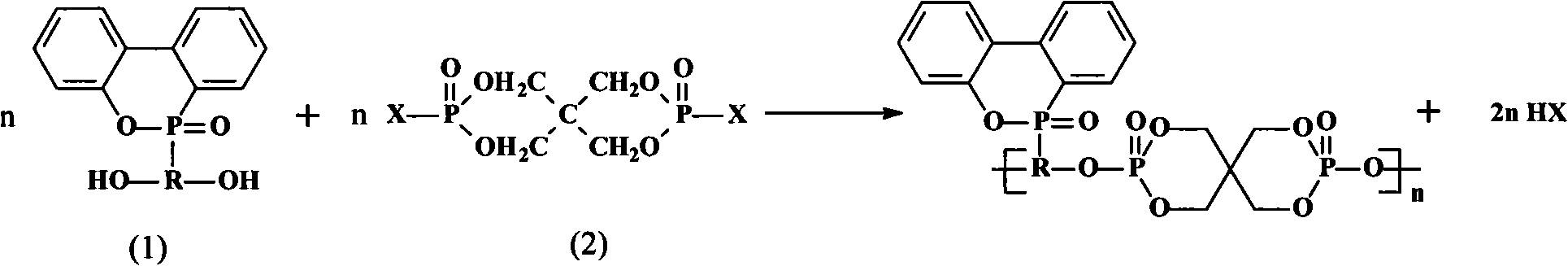
Polymeric phosphorus-containing flame retardant with DOPO as lateral group and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101613374AEasy to prepareEasy post-processingGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsBromineRetardation effect
The invention discloses a polymeric phosphorus-containing flame retardant with 9,10-dihydro-9-oxa-10-phosphaphenanthrene-10-oxide as a lateral group and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps: placing aromatic dihydric phenol and pentaerythritol diphosphate diphosphoryl chloride (or bromine) which are modified by the 9,10-dihydro-9-oxa-10-phosphaphenanthrene-10-oxide in an anhydrous acetonitrile solvent based on reaction mol ratio, heating the obtained mixture to 80 DEG C in an inert atmosphere, agitating and reacting until no halogen hydride is released, cooling the obtained mixture to the room temperature, and depressurizing the mixture to remove the solvent. The obtained product has high phosphorus content, very good expansibility and char formation, and good flame retardation effect. When flame retardation is performed on epoxy resin, the limiting oxygen index of the obtained product is greatly improved and the vertical burning scale reaches V-0 level; and the polymeric phosphorus-containing flame retardant has the advantage of overcoming the disadvantages of low thermal decomposition temperature, poor compatibility with polymer matrix and easy migration in the existing micromolecular phosphorus flame retardants. The preparation method has the advantages of being simple and feasible, using no catalyst and simple post-treatment process.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
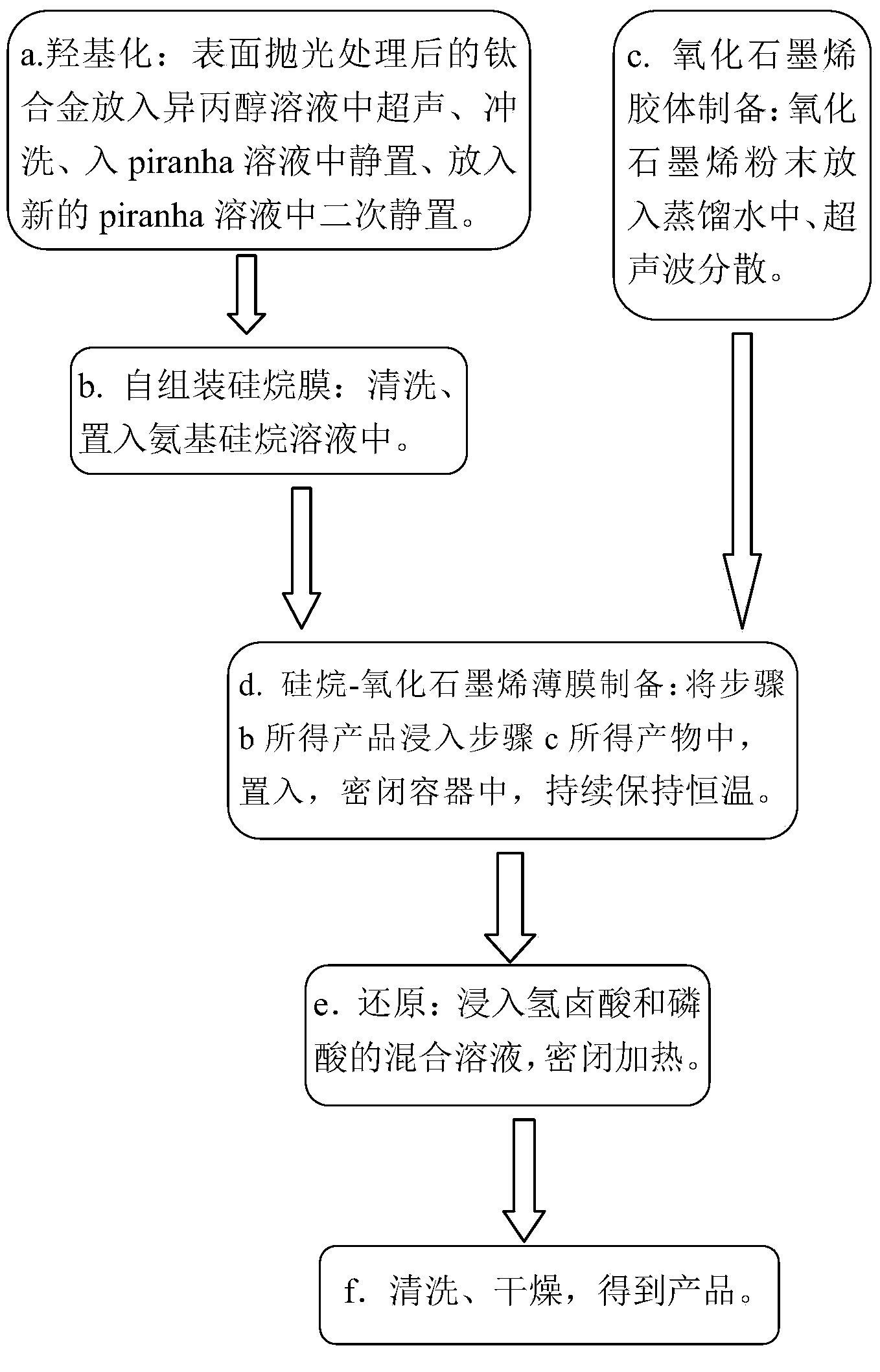
Method for preparing graphene film on surface of titanium alloy
InactiveCN104018145AReduce coefficient of frictionHigh strengthSolid/suspension decomposition chemical coatingHydrogen halideSilanes
The invention discloses a method for preparing a graphene film on the surface of titanium alloy. The method specifically comprises the following steps of putting a medical titanium alloy into a piranha solution and carrying out hydroxylation treatment, and then putting into an amino silane solution, and self-assembling a silane film; carrying out ultrasonic treatment on graphene oxide powder to obtain a stable graphene oxide colloid; immersing the titanium alloy of which the surface is attached with the silane film in the graphene oxide colloid to prepare a silane-graphene oxide film; and finally, reducing the graphene oxide film with hydrogen halide acid, and drying to obtain the reduced graphene oxide composite film. The method disclosed by the invention is simple and causes no harm to experiment operators, and the obtained film has the advantages of good integrity, high strength, low coefficient of friction and excellent wear resistance and is expected to become a medical joint material.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Methods for pretreatment of group iii-nitride depositions
InactiveUS20120295428A1Reduce threading dislocation densityLower regulation pressureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHydrogen halidePre treatment
Embodiments of the present disclosure relate to methods for pretreatment of substrates and group III-nitride layers for manufacturing devices such as light emitting diodes (LEDs), laser diodes (LDs) or power electronic devices. One embodiment of the present disclosure provides a method including providing one or more substrates having an aluminum containing surface in a processing chamber and exposing a surface of each of the one or more substrates having an aluminum containing surface to a pretreatment gas mixture to form a pretreated surface. The pretreatment gas mixture includes ammonia (NH3), an aluminum halide gas (e.g., AlCl3, AlCl) and an etchant containing gas that includes a halogen gas (e.g., Cl2) or hydrogen halide gas (e.g., HCl).
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com