Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
750 results about "Exertion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Exertion is the physical or perceived use of energy. Exertion traditionally connotes a strenuous or costly effort, resulting in generation of force, initiation of motion, or in the performance of work. It often relates to muscular activity and can be quantified, empirically and by measurable metabolic response.
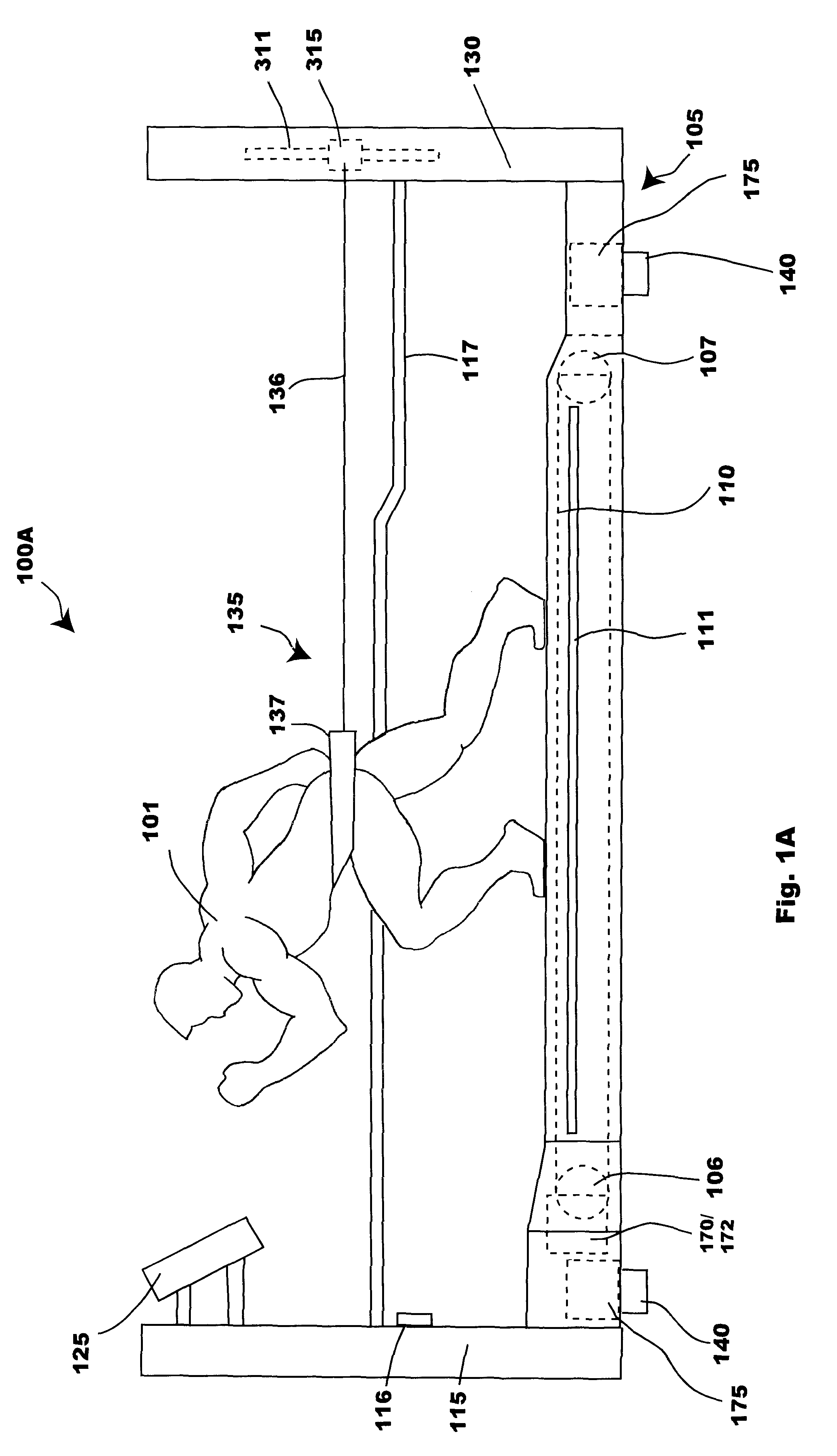
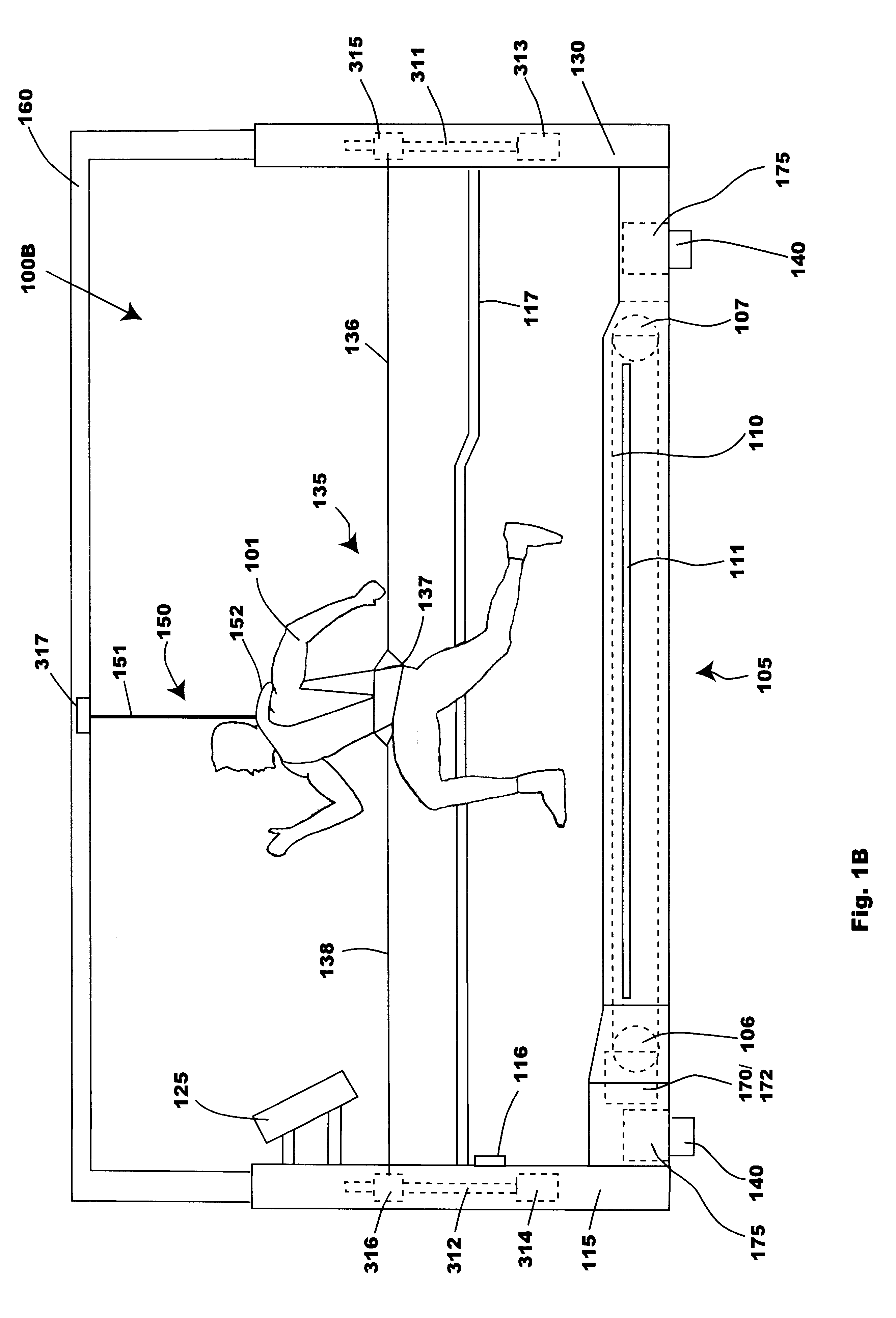
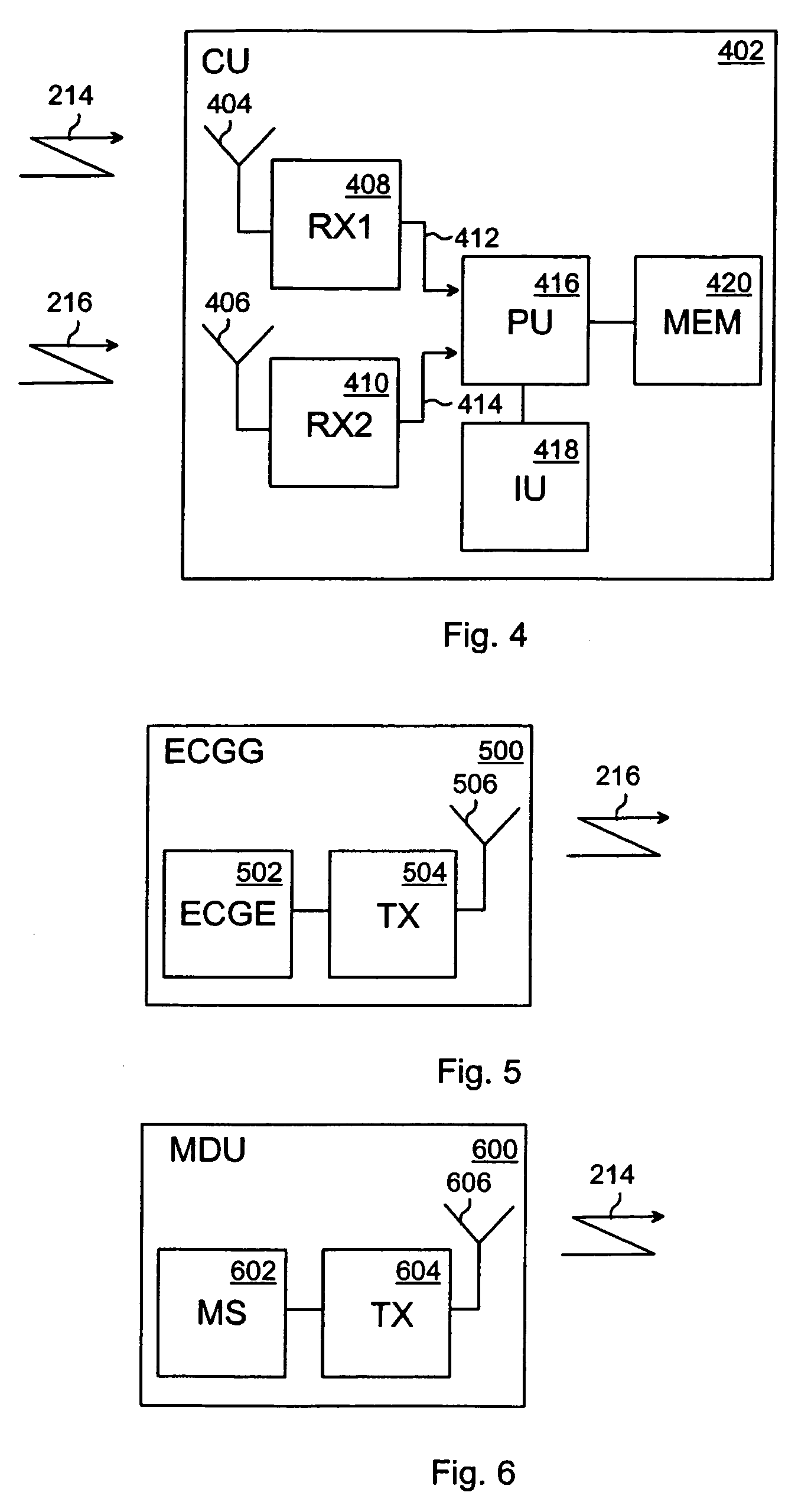
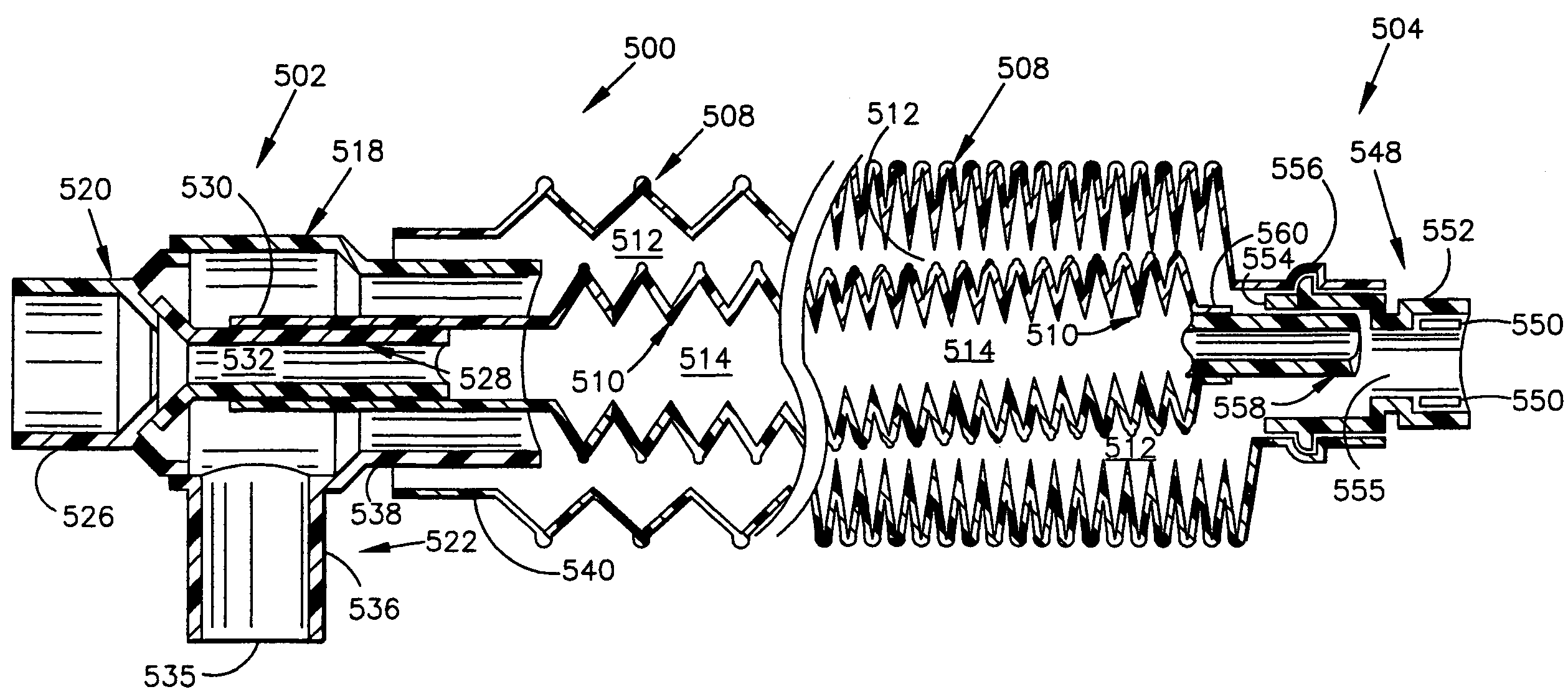
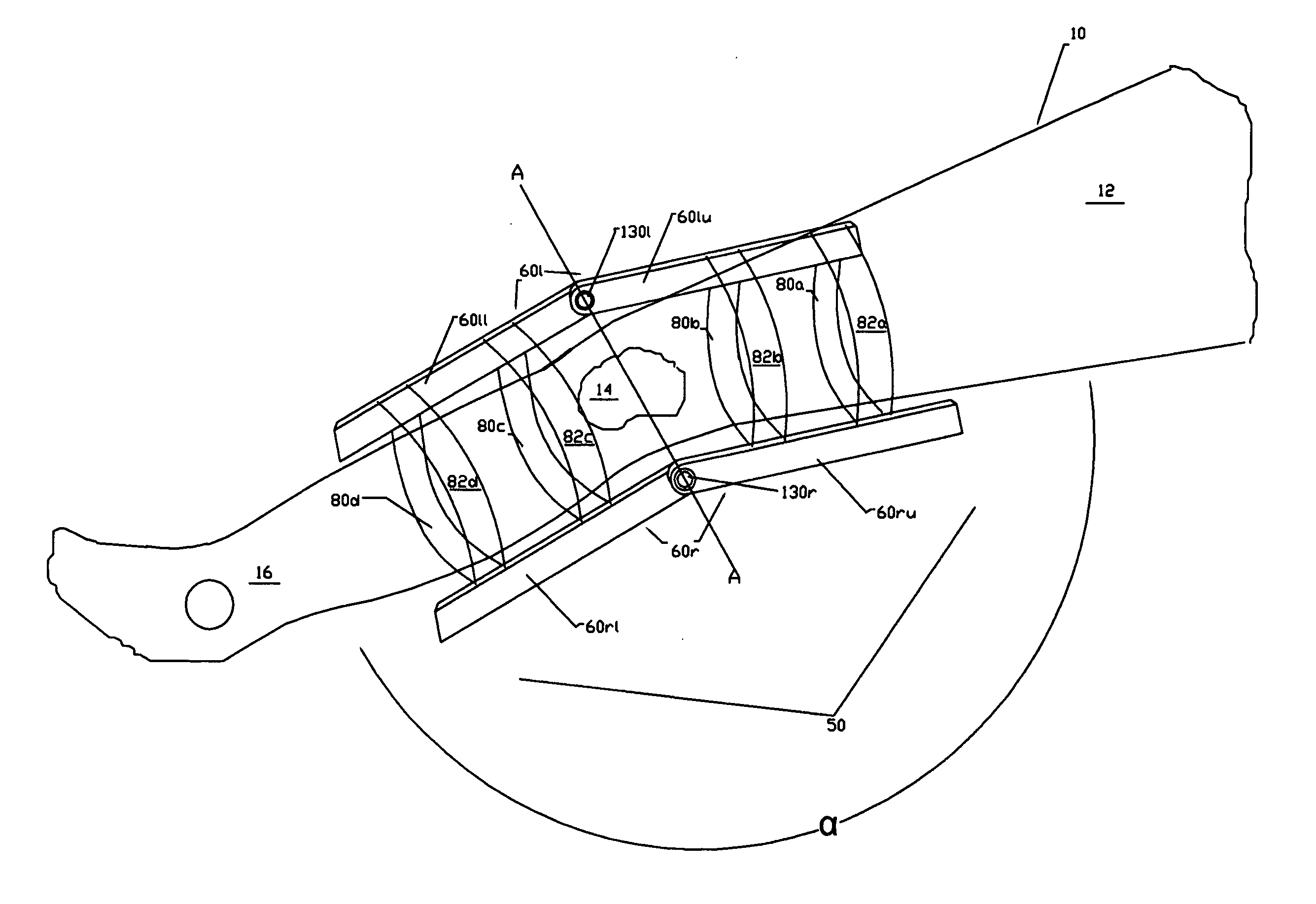
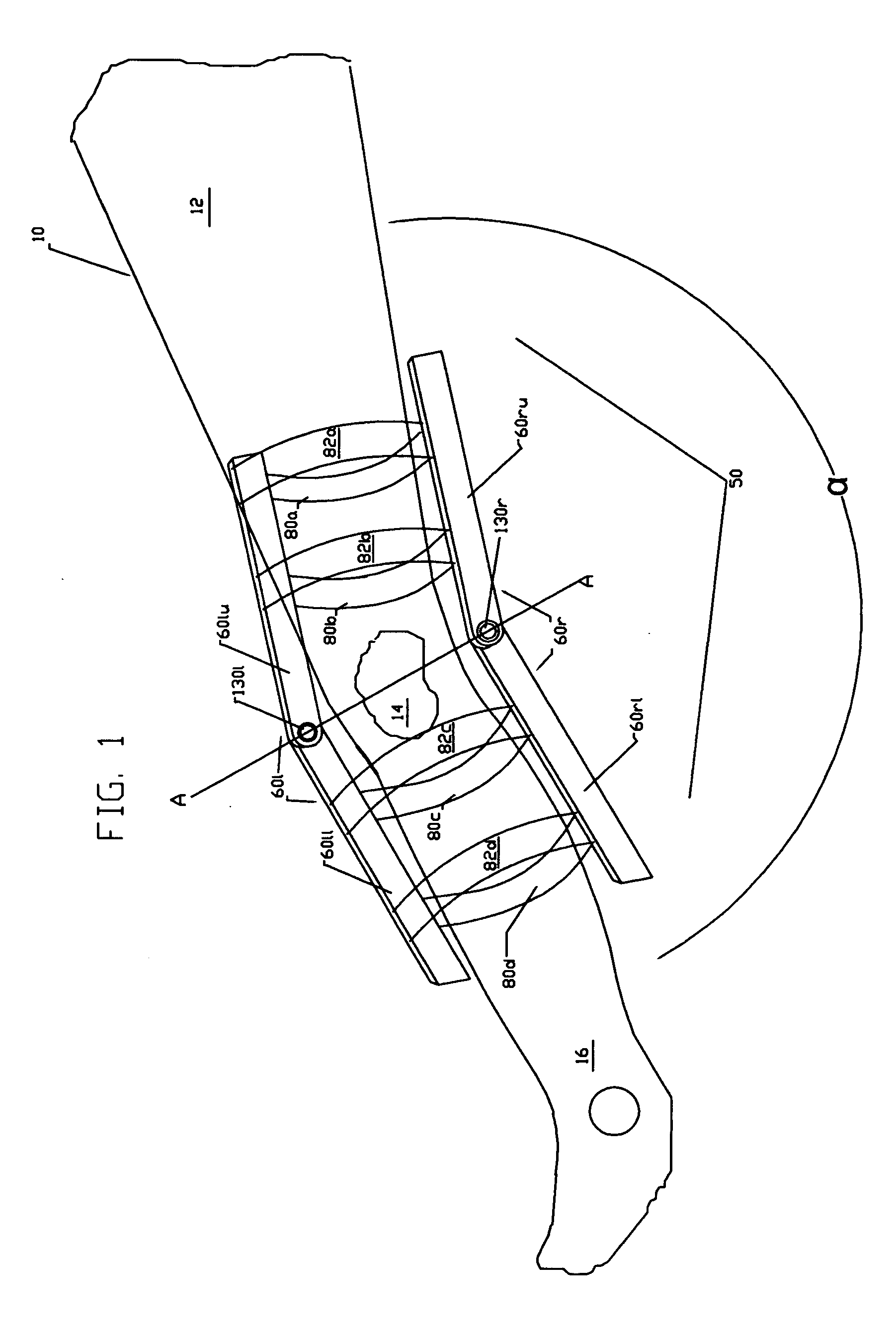
Bipedal locomotion training and performance evaluation device and method
InactiveUS6454679B1Effective mass reductionTherapy exerciseMovement coordination devicesExercise performanceForce velocity
A bipedal locomotion exercise and performance evaluation apparatus including a revolving belt, a harness for securing the position of a subject on the belt, a harness-force measuring means, and a belt volocity monitoring and controlling means. The harness may be secured on various points of a subject and includes push / pull engagement means. An overhead harness may be used to reduce effective body mass. The velocity of the belt may be controlled by a unidirectional or bidirectional motor / brake system. Velocity of the belt may also be controlled by a brake only. A digital processor may be used to control the motor and / or brake as a function of the forces applied allowing multiple operating modes. Recording of velocity and force as functions of time facilitates analysis of exercise performance. The apparatus allows exertions throughout the first quadrant of a force-velocity-duration space, and outside that first quadrant.
Owner:RADOW SCOTT BRIAN
Method, performance monitor and computer program for determining performance
ActiveUS20070082789A1Monitor performanceElectromyographyEvaluation of blood vesselsExertionComputer science
The invention relates to a method, a user-specific performance monitor and a computer program for determining the user's performance. In the method, the performance power of a physical exercise is determined by means of user movement data registered by the user-specific performance monitor. Further, the exertion level corresponding to the performance power of the physical exercise is determined by means of physiological information measured from the user, the physiological information being registered by the user-specific performance monitor; and the user's performance is estimated by means of the performance power of the physical exercise and the exertion level corresponding to the performance power of the physical exercise.
Owner:POLAR ELECTRO
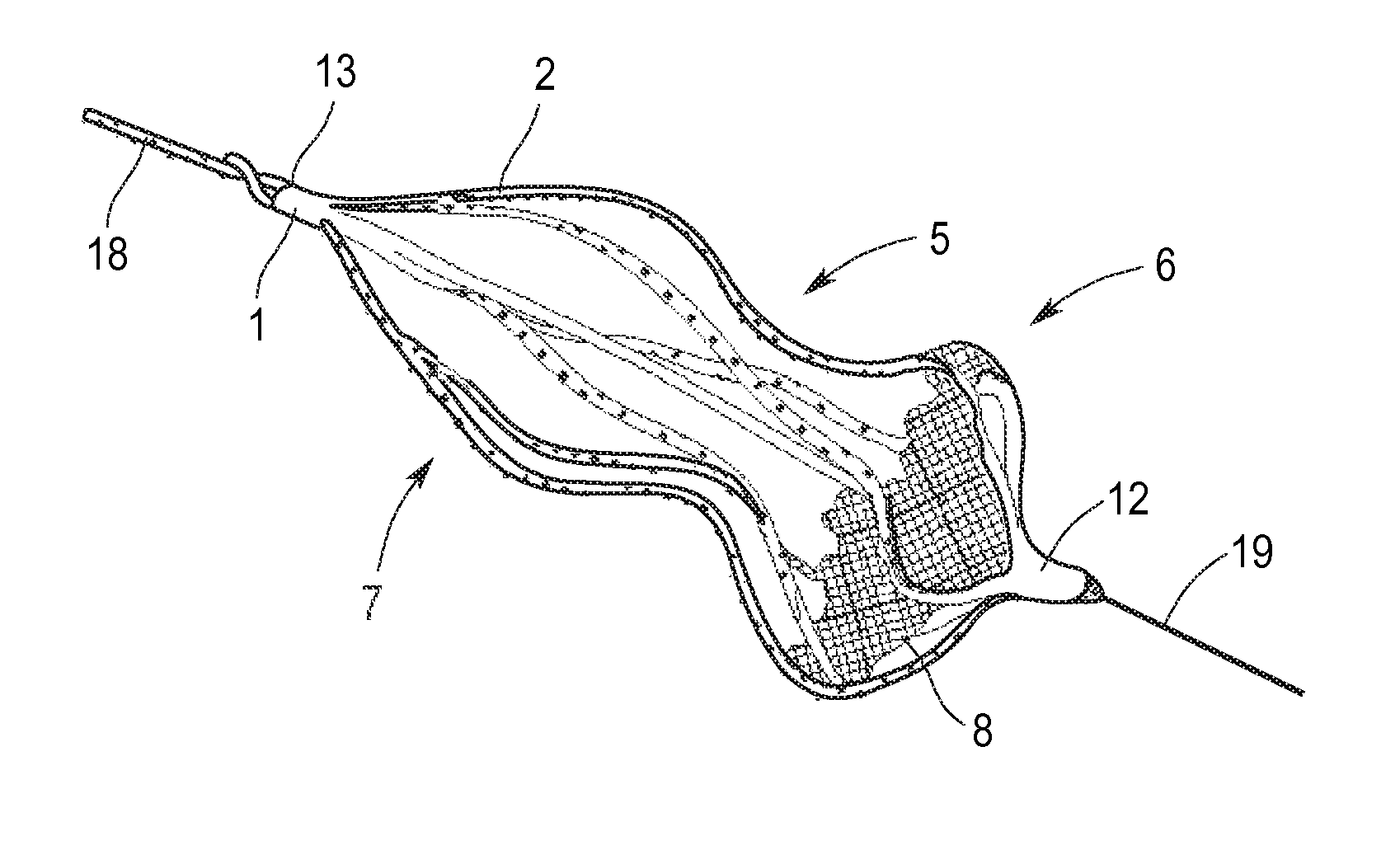
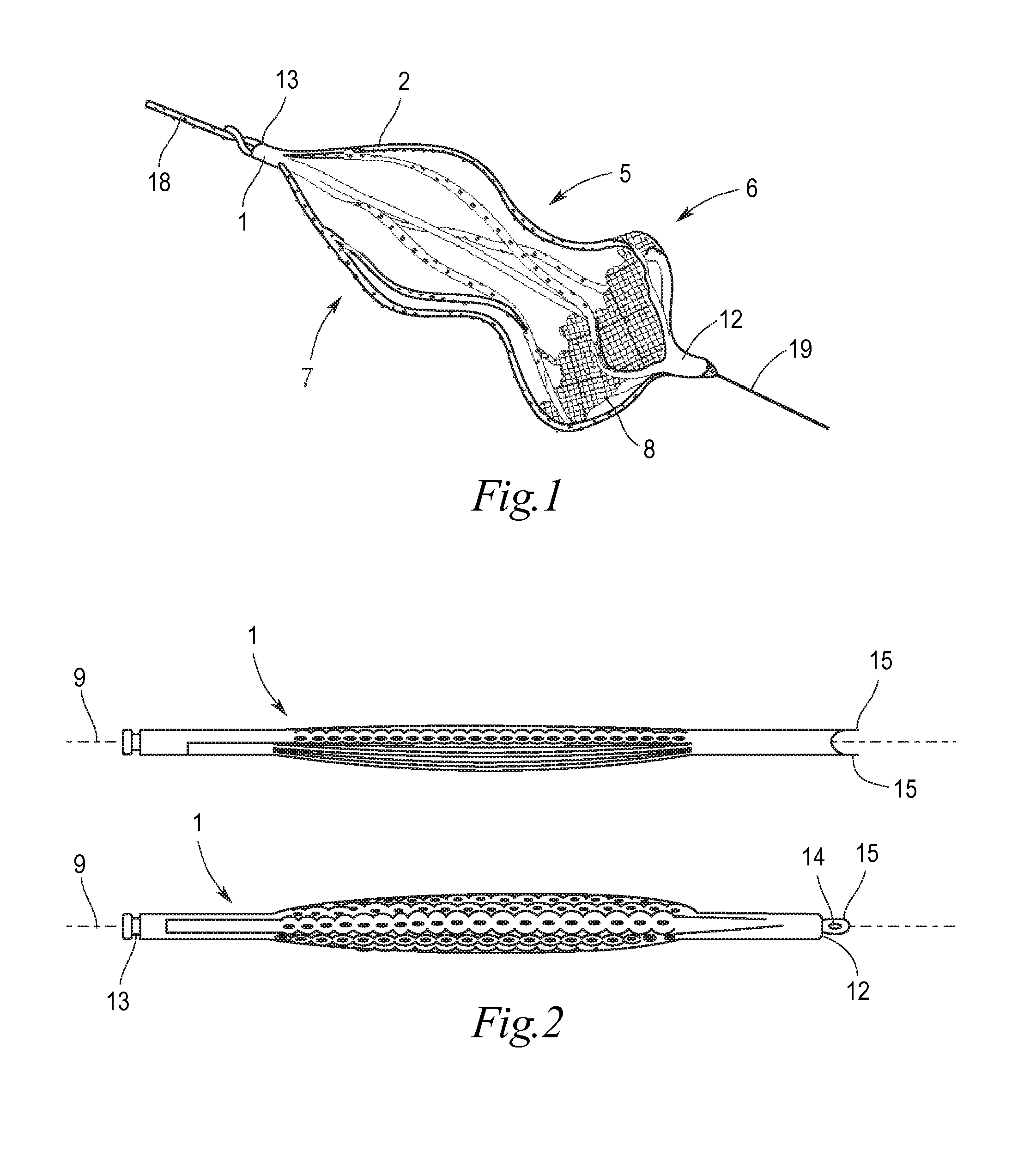
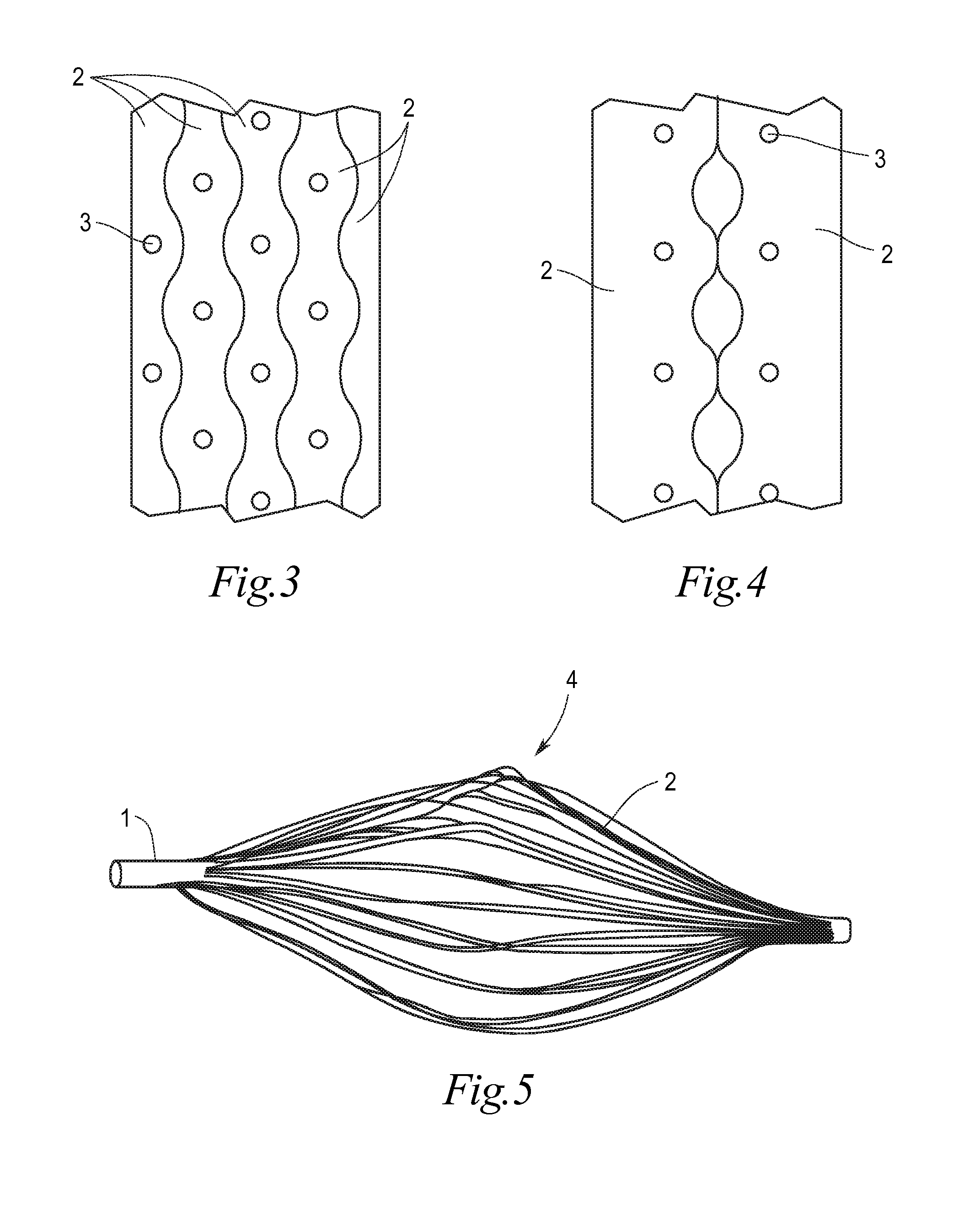
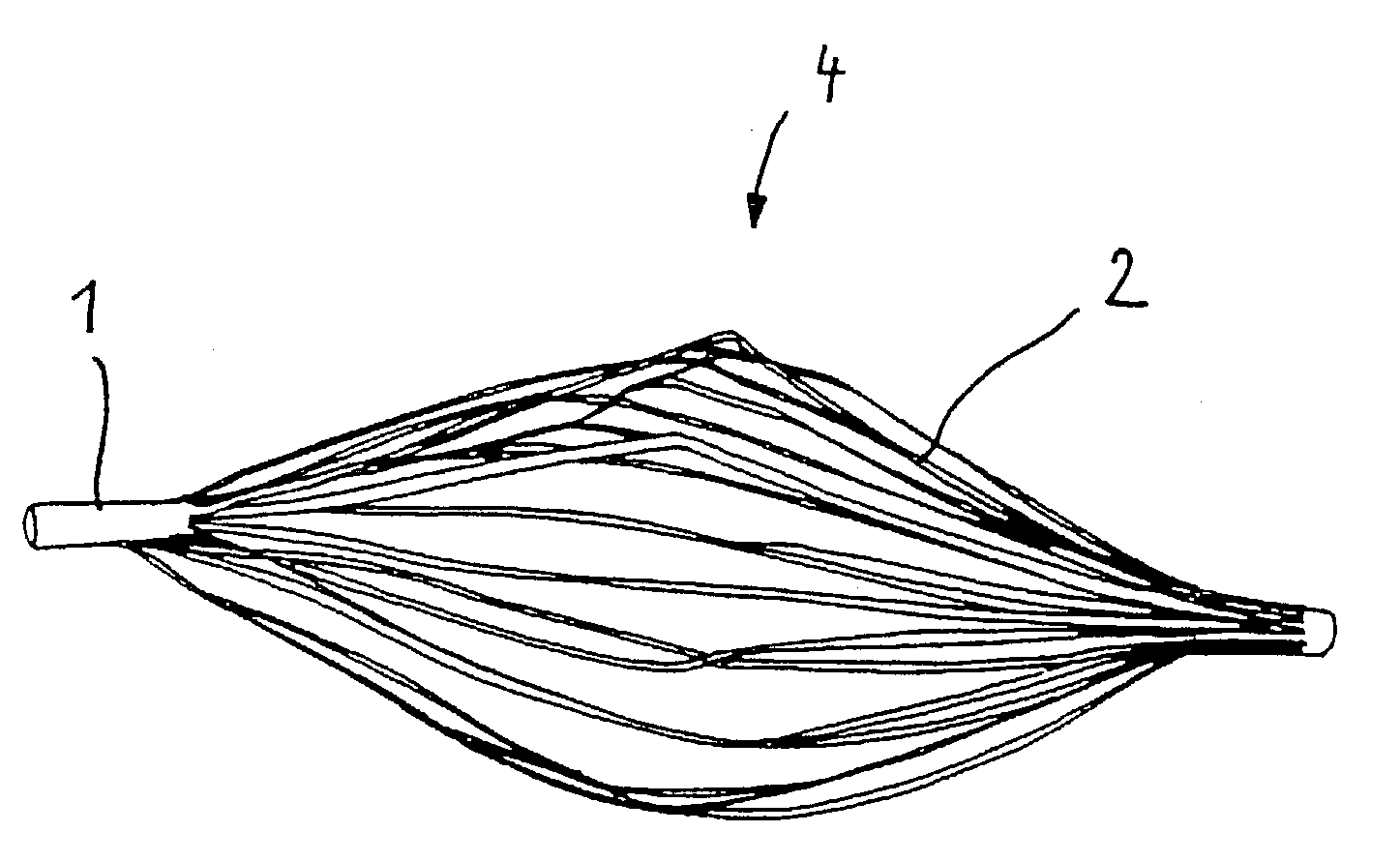
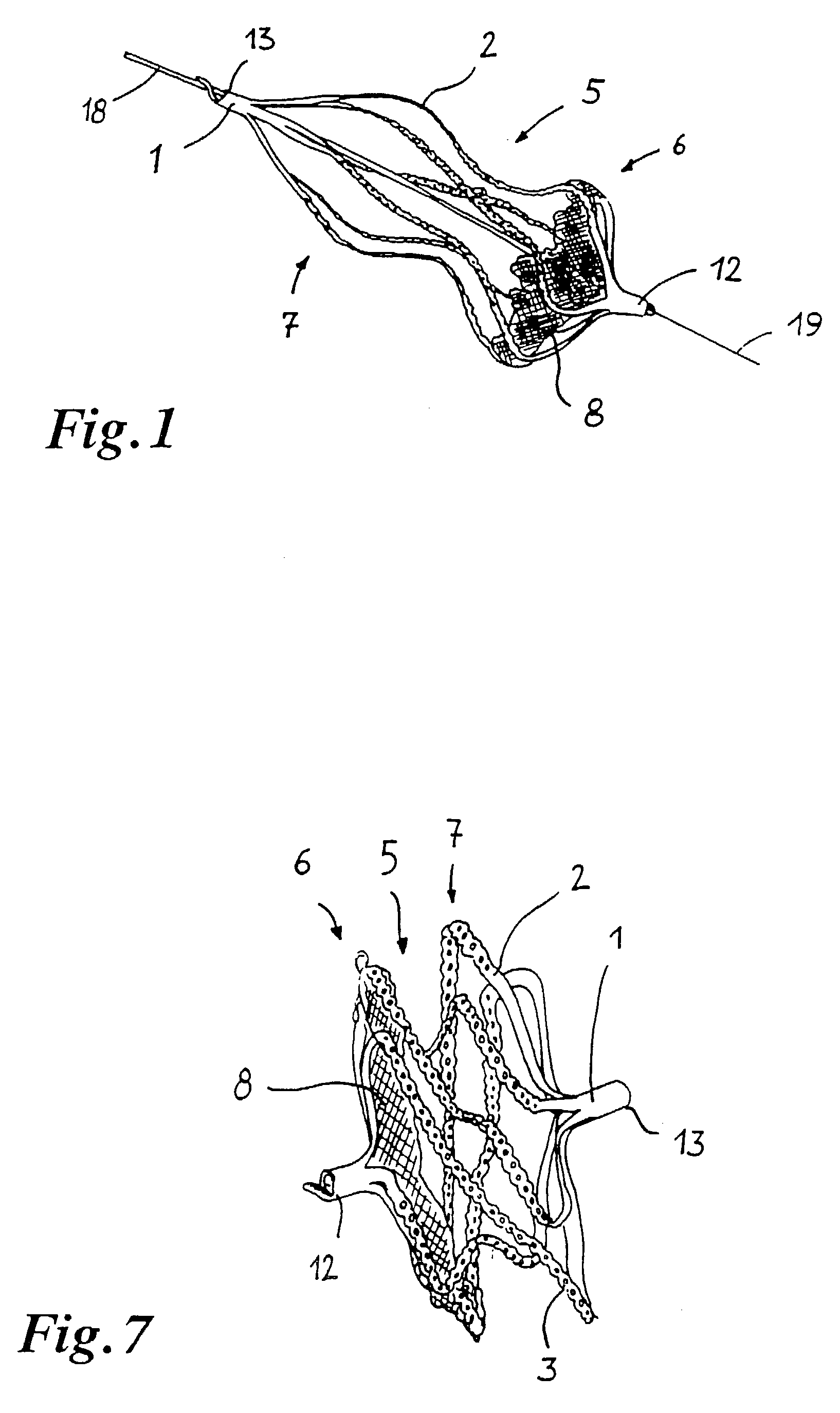
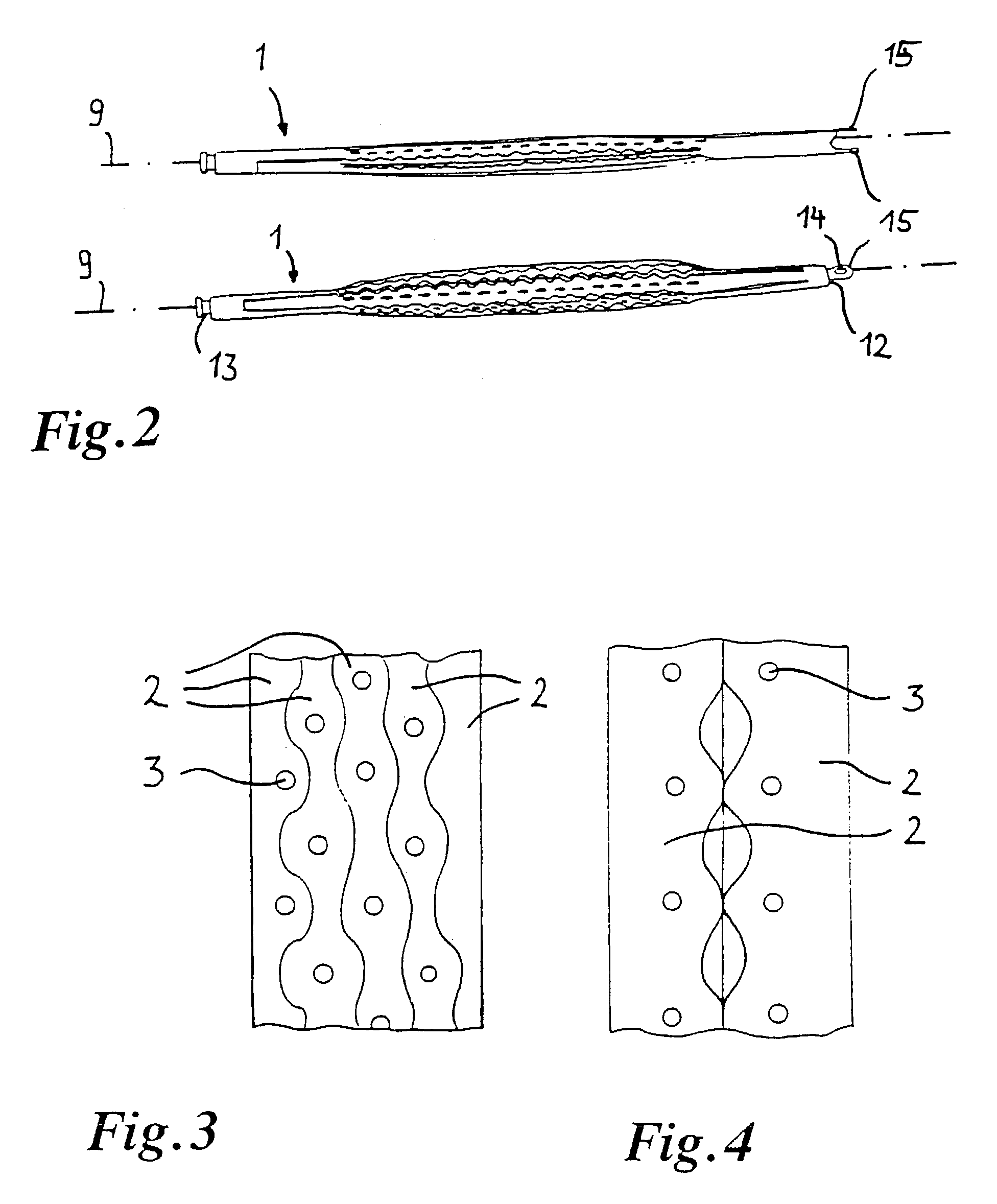
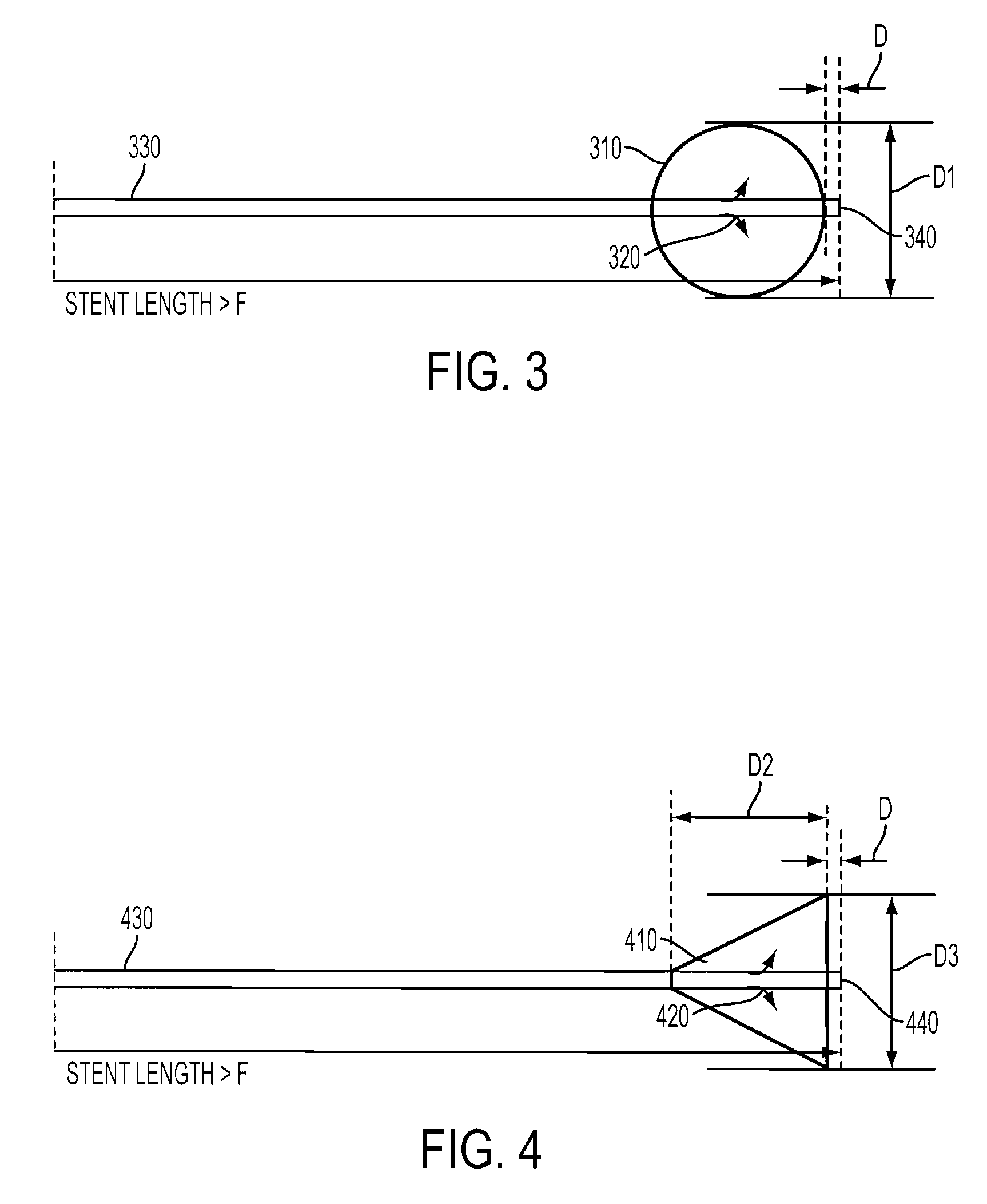
Implant for the closing of defect openings in the body of a human or animal and a system for the placement of such an implant
InactiveUS7097653B2Quick upgradeReduce effortDilatorsSurgical veterinaryExertionBiomedical engineering
An implant for the closing of defect openings in the body of a human or animal is proposed, with a load-bearing structure which, in a first operating state (primary form), has a great ratio of length to transverse extent along an axis (9) and, at least in a further operating state (secondary form), has a much smaller ratio of length to transverse extent along the axis (9), the load-bearing structure (1) being capable of being reversibly transformed from the secondary form into the primary form by exertion of a force against elastic material forces, the secondary form assuming approximately the form of a double disc with a proximal disc element (7) and a distal disc element (6) for receiving the surroundings of the defect opening between the disc elements, and the load-bearing structure (1) being formed essentially in one piece without joining connections, and a placement system.
Owner:PFM MEDICAL
Implant for the closing of defect openings in the body of a human or animal and a system for the placement of such an implant
InactiveUS20030171774A1Quick upgradeReduce effortDilatorsTubular organ implantsCircular discExertion
An implant for the closing of defect openings in the body of a human or animal is proposed, with a load-bearing structure which, in a first operating state (primary form), has a great ratio of length to transverse extent along an axis (9) and, at least in a further operating state (secondary form), has a much smaller ratio of length to transverse extent along the axis (9), the load-bearing structure (1) being capable of being reversibly transformed from the secondary form into the primary form by exertion of a force against elastic material forces, the secondary form assuming approximately the form of a double disc with a proximal disc element (7) and a distal disc element (6) for receiving the surroundings of the defect opening between the disc elements, and the load-bearing structure (1) being formed essentially in one piece without joining connections, and a placement system.
Owner:PFM MEDICAL
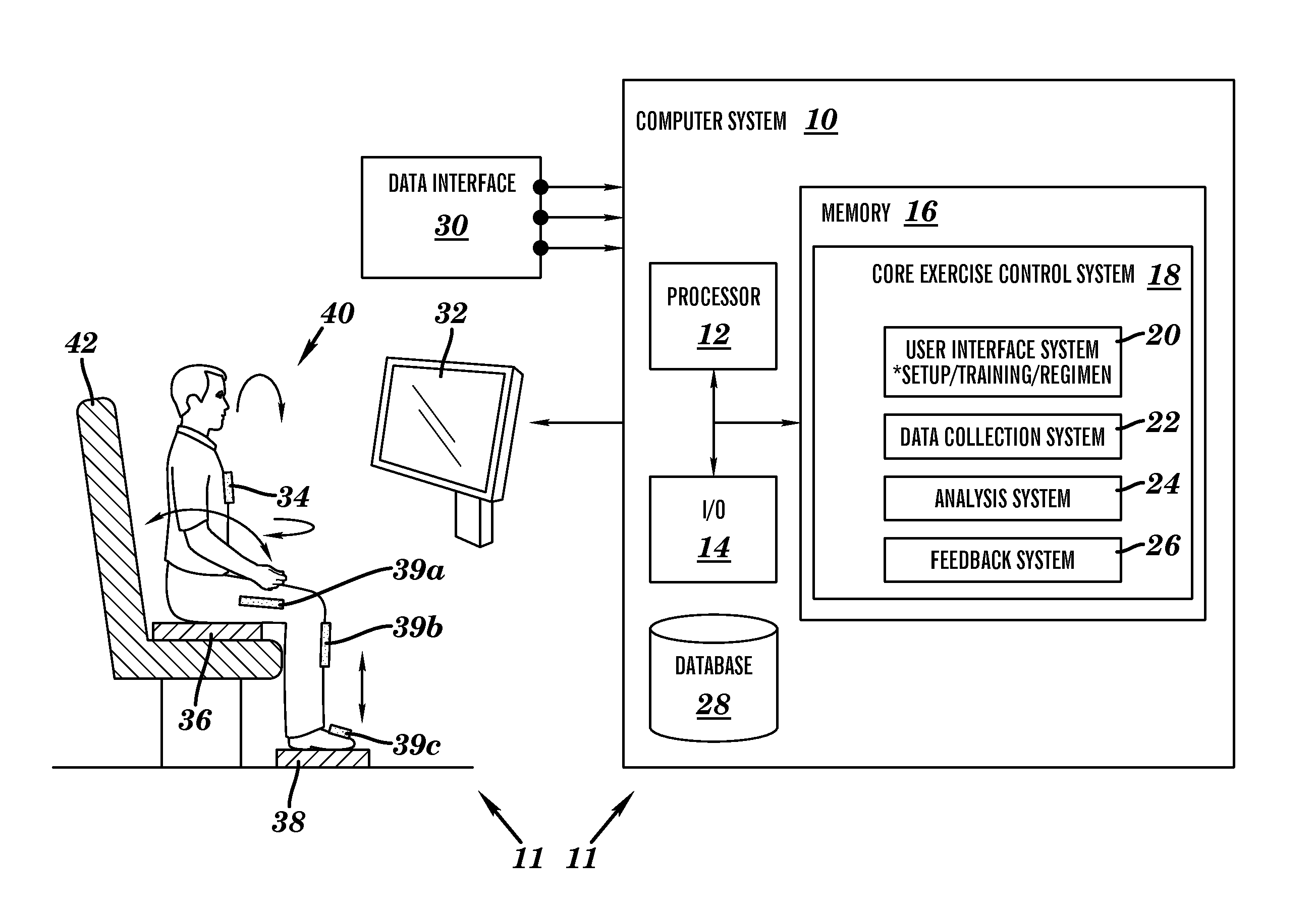
Sensor based exercise control system
InactiveUS20110269601A1Promote sportsStrengthen core musclesGymnastic exercisingPosition fixationControl systemExertion
A system and method for exercising core muscles, particularly the lumbar intrinsic musculature, including the multifidi. A system is disclosed that includes: a first sensor for detecting upper body exertions of a user engaged in an exercise; a second sensor for detecting lower torso exertions for the user engaged in the exercise; a third sensor for detecting lower extremity exertions for the user engaged in the exercise; a control system for processing sensor data from the first, second and third sensor, said control system including: a user interface system for communicating information with the user; a data collection system for collecting sensor data; an analysis system for analyzing the sensor data and determining if the user is performing the exercise in a technically correct manner; and a feedback system for alerting the user when the exercise is not being performed in the technically correct manner.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
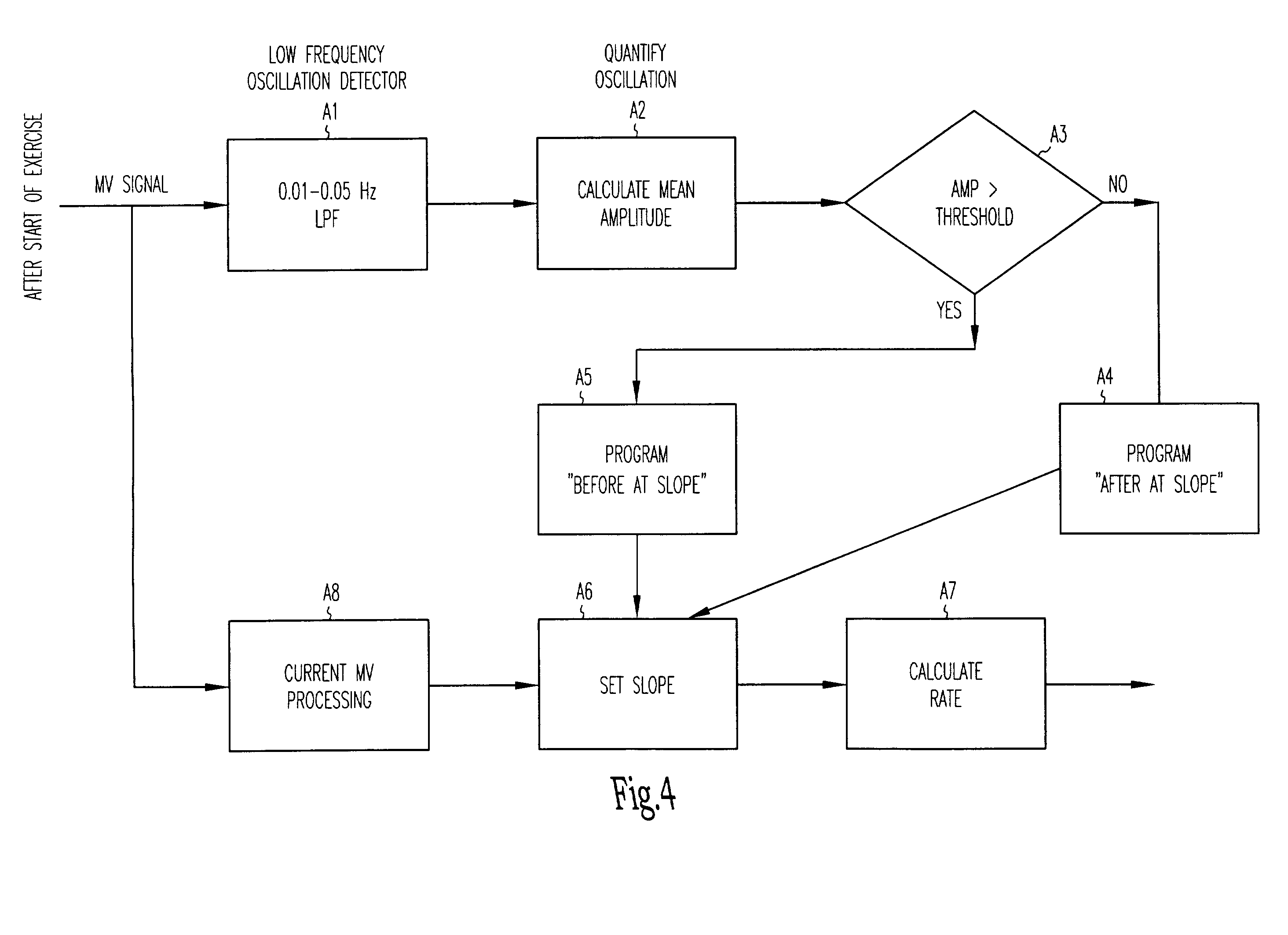
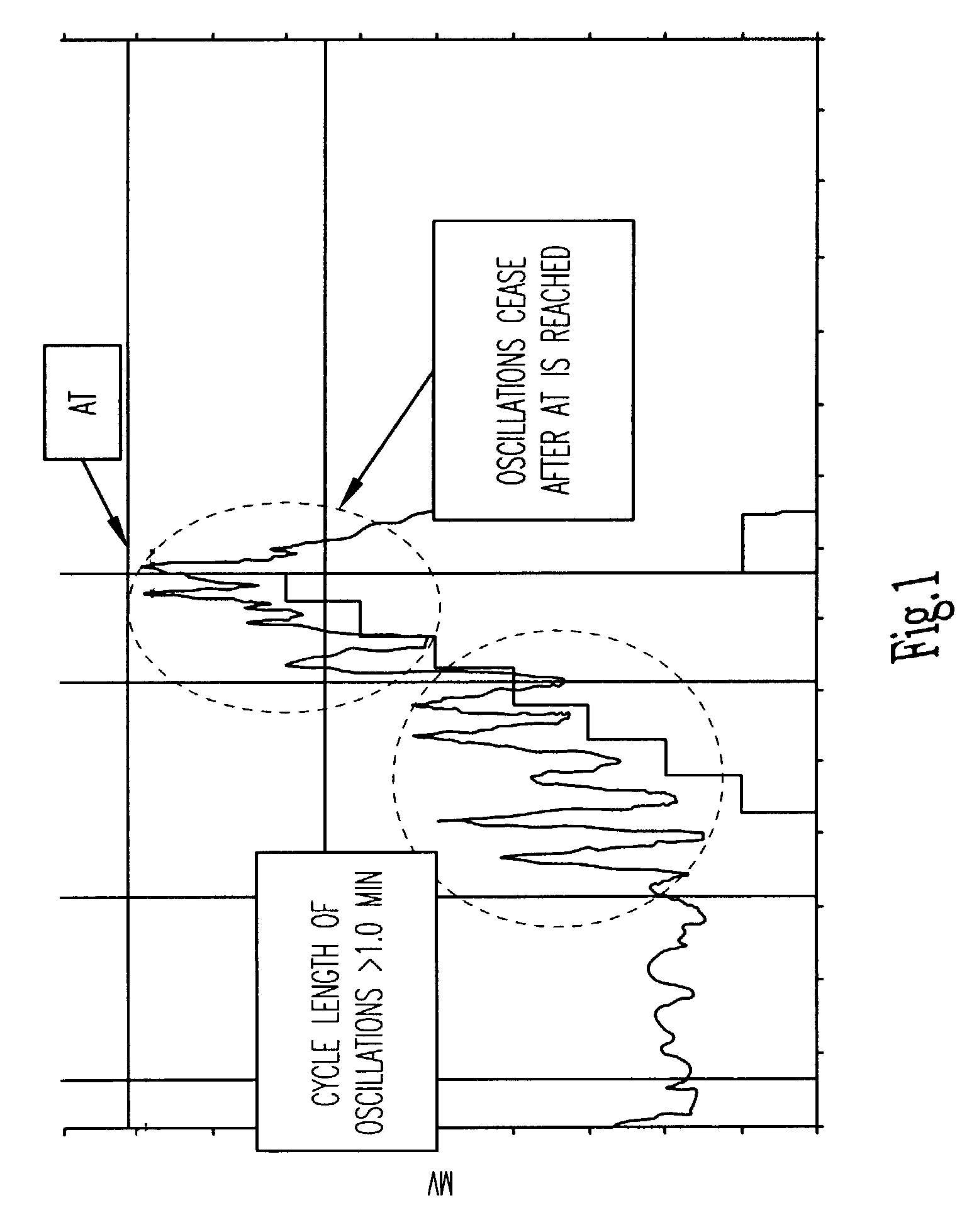
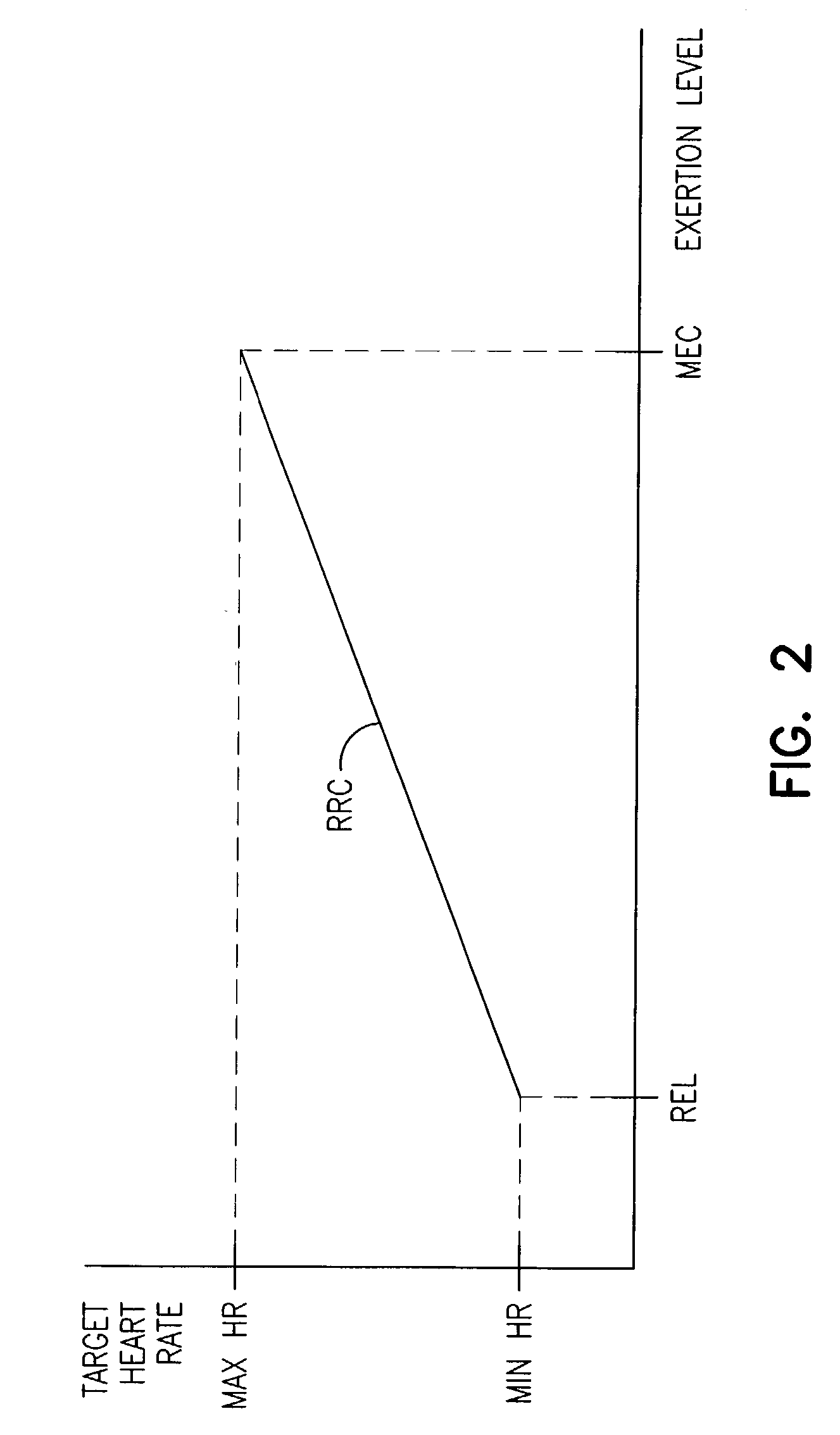
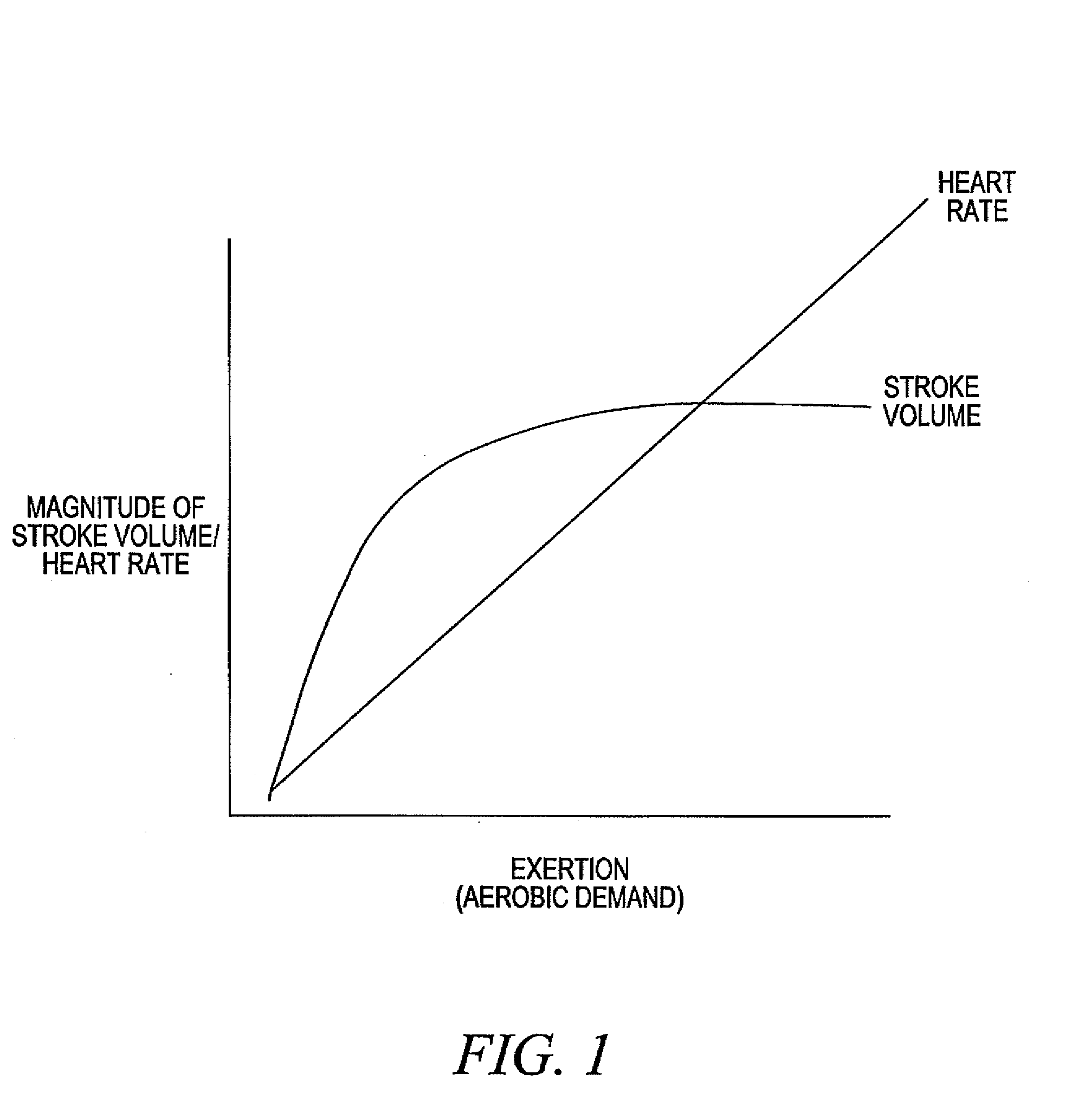
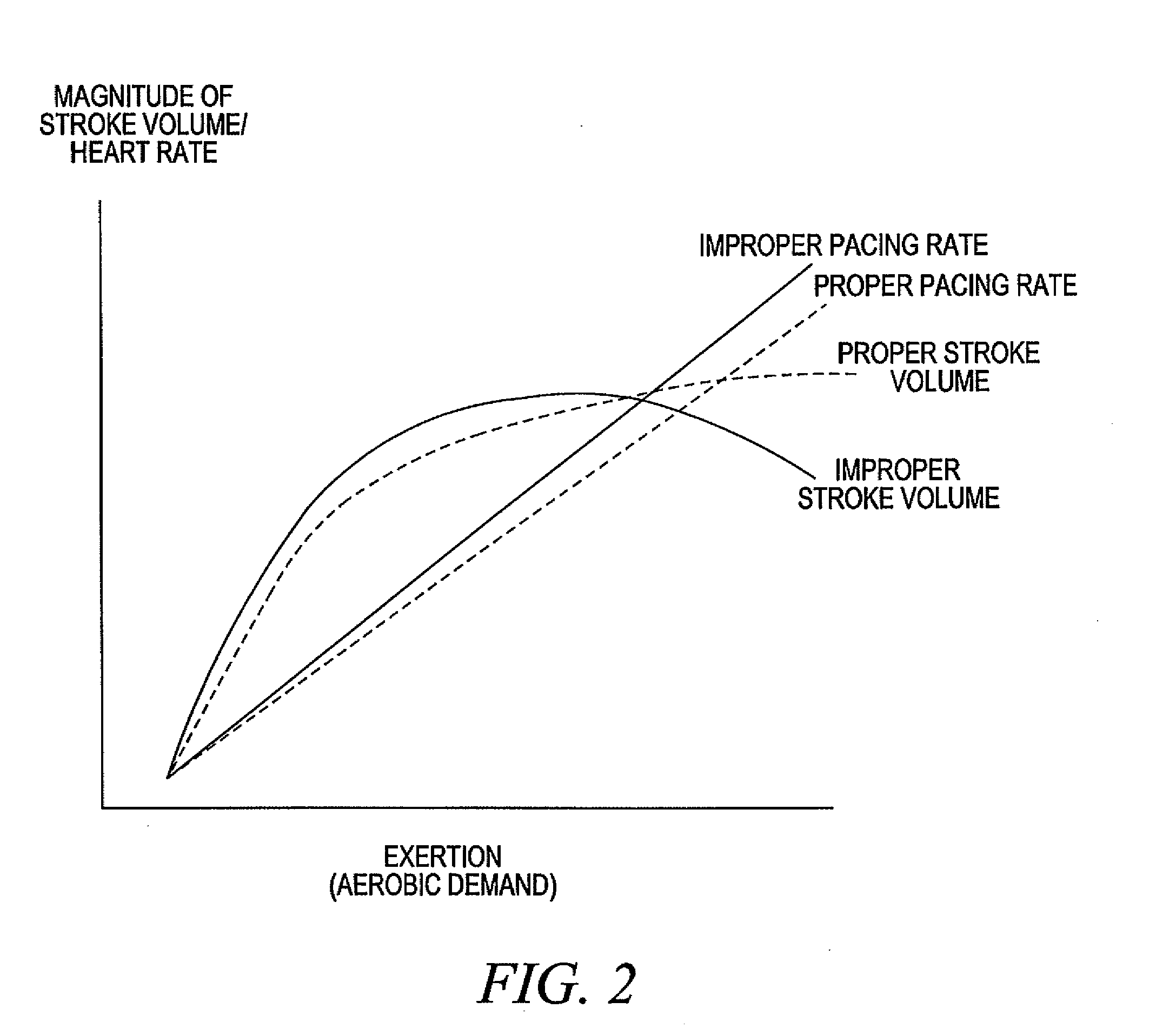
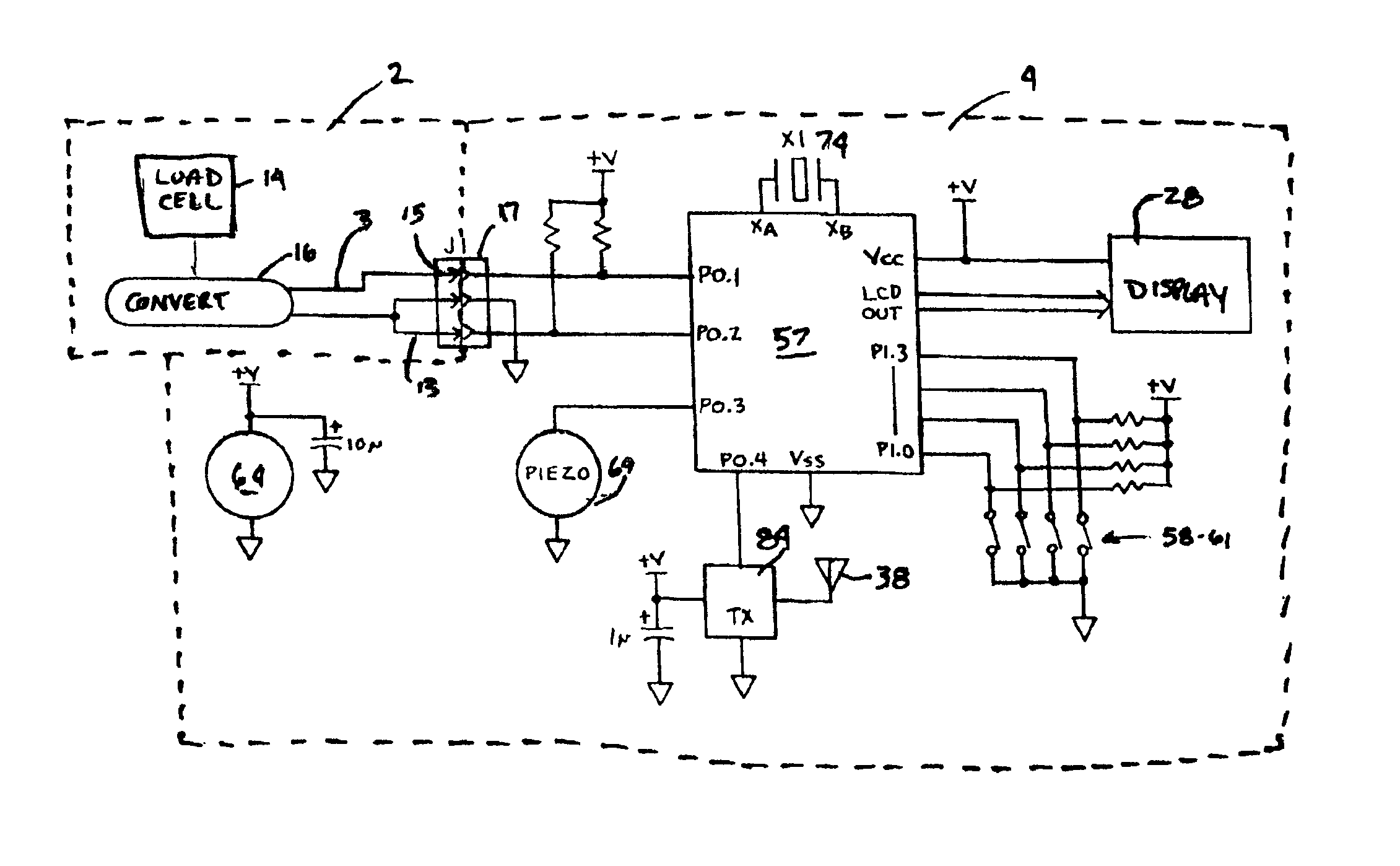
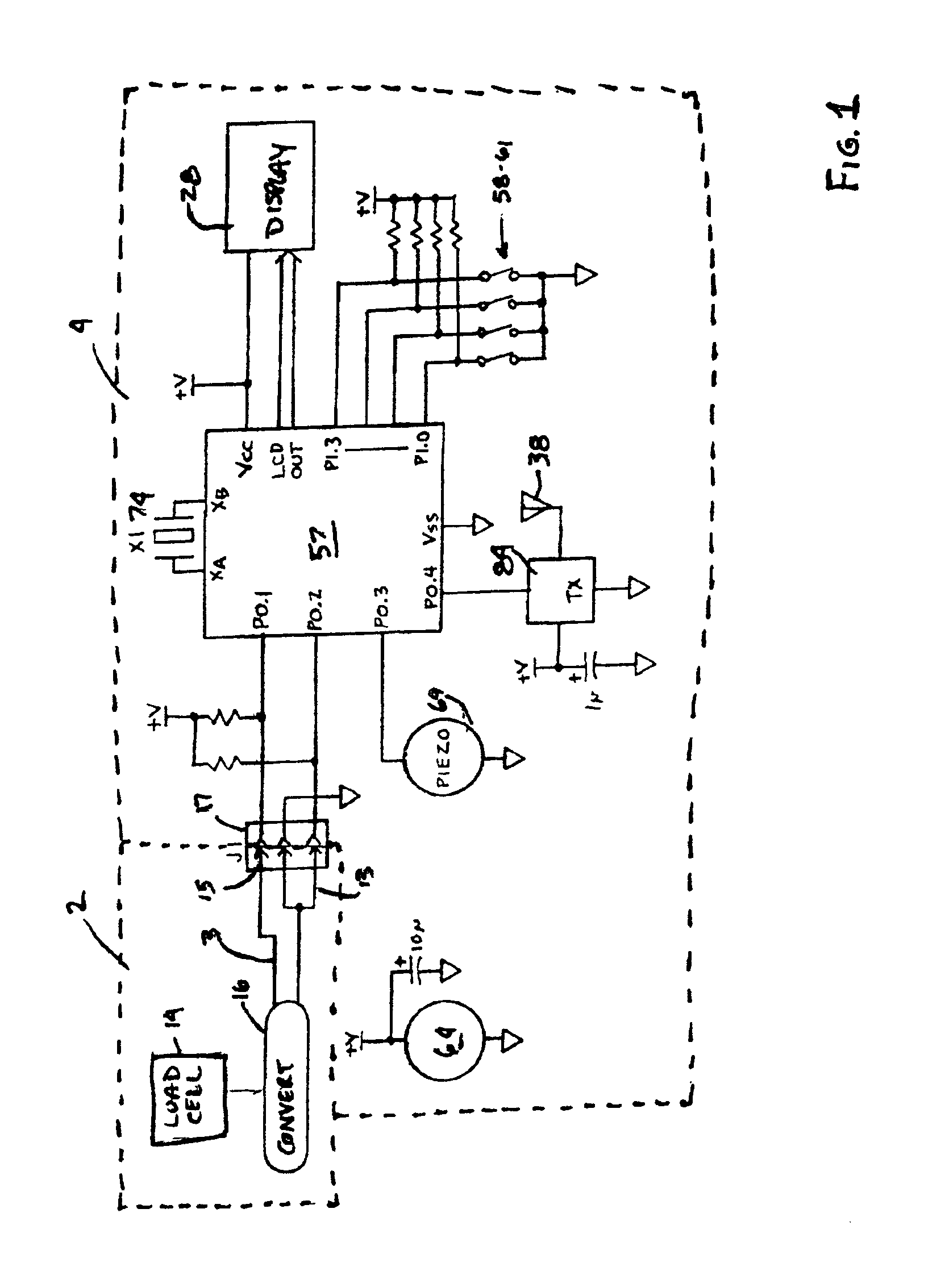
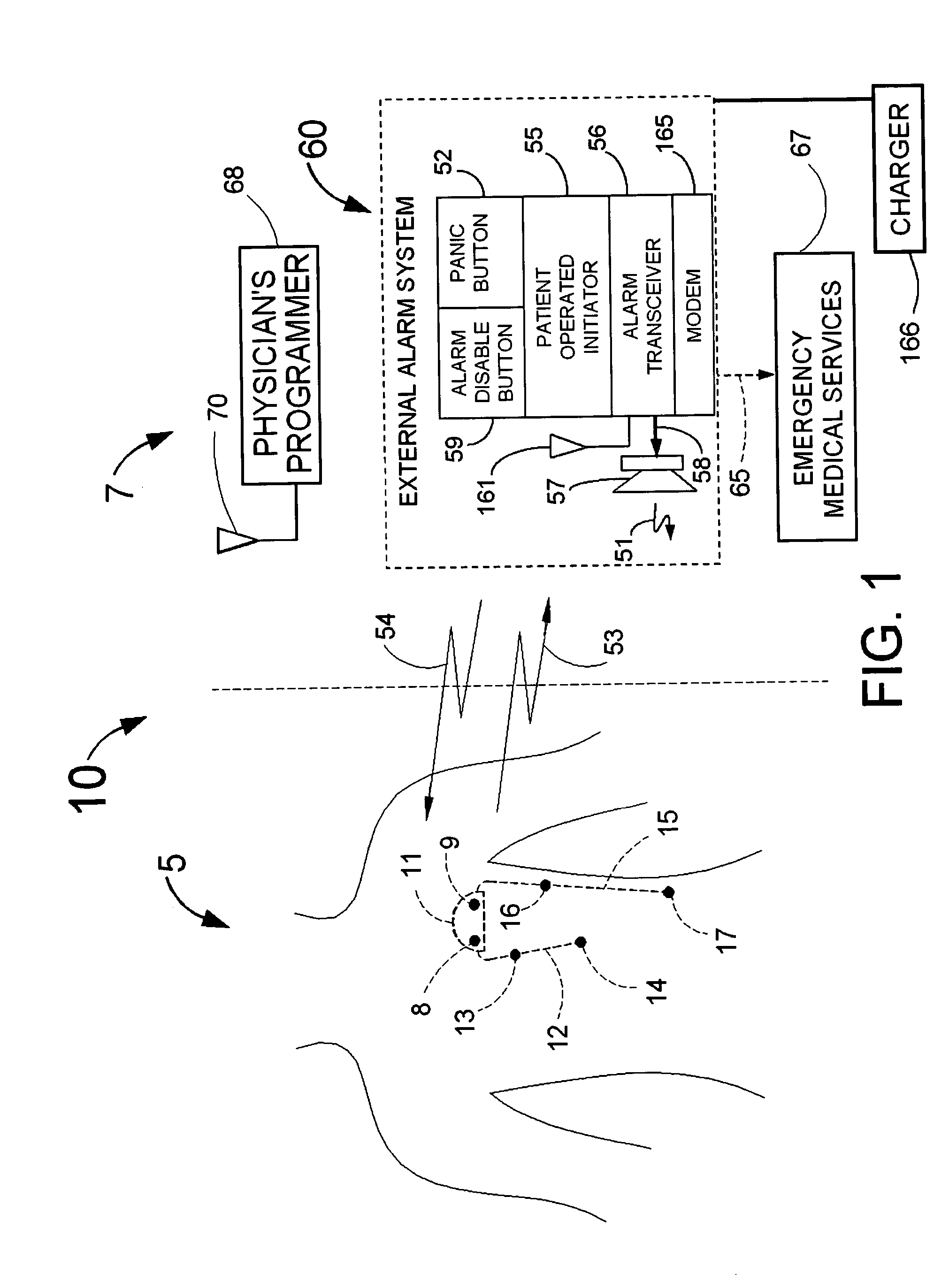
Adjustment of the breakpoint of the rate response curve based on minute ventilation values
A method and system for operating a rate-adaptive pacemaker utilizing minute ventilation to measure exertion level. The method is applicable to heart failure patients who exhibit an oscillatory minute ventilation pattern.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method and apparatus for improved hemostasis and damage control operations
InactiveUS6998510B2Improved hemostatic packing in trauma careGood hemostasisPlastersBaby linensTamponadePERITONEOSCOPE
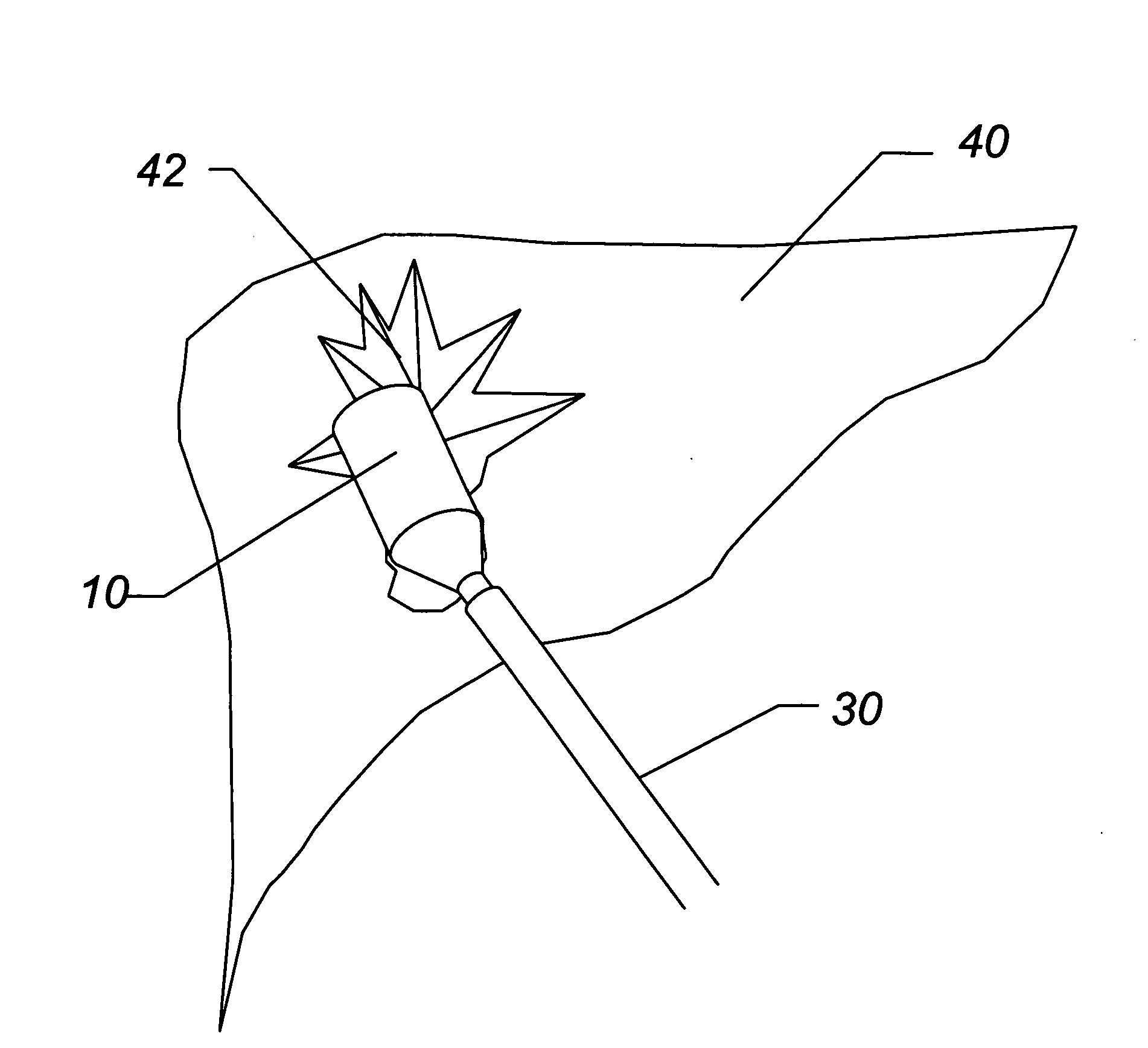
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in traumatized patients. The devices utilize fluid impermeable outer surfaces and distributed pressure to achieve tamponade and hemostasis, primarily by exertion of pressure. The devices are capable of serving as carriers for throabogenic or antipathogenic agents. Peripheral haemostatic packing devices include optional adhesive hemostatic barriers to cover the entire wound area over the hemostatic pack. The hemostatic packing devices may be placed and removed by open surgery or laparoscopic access without generating excessive re-bleeding, and may further comprise antimicrobial or thrombogenic regions.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
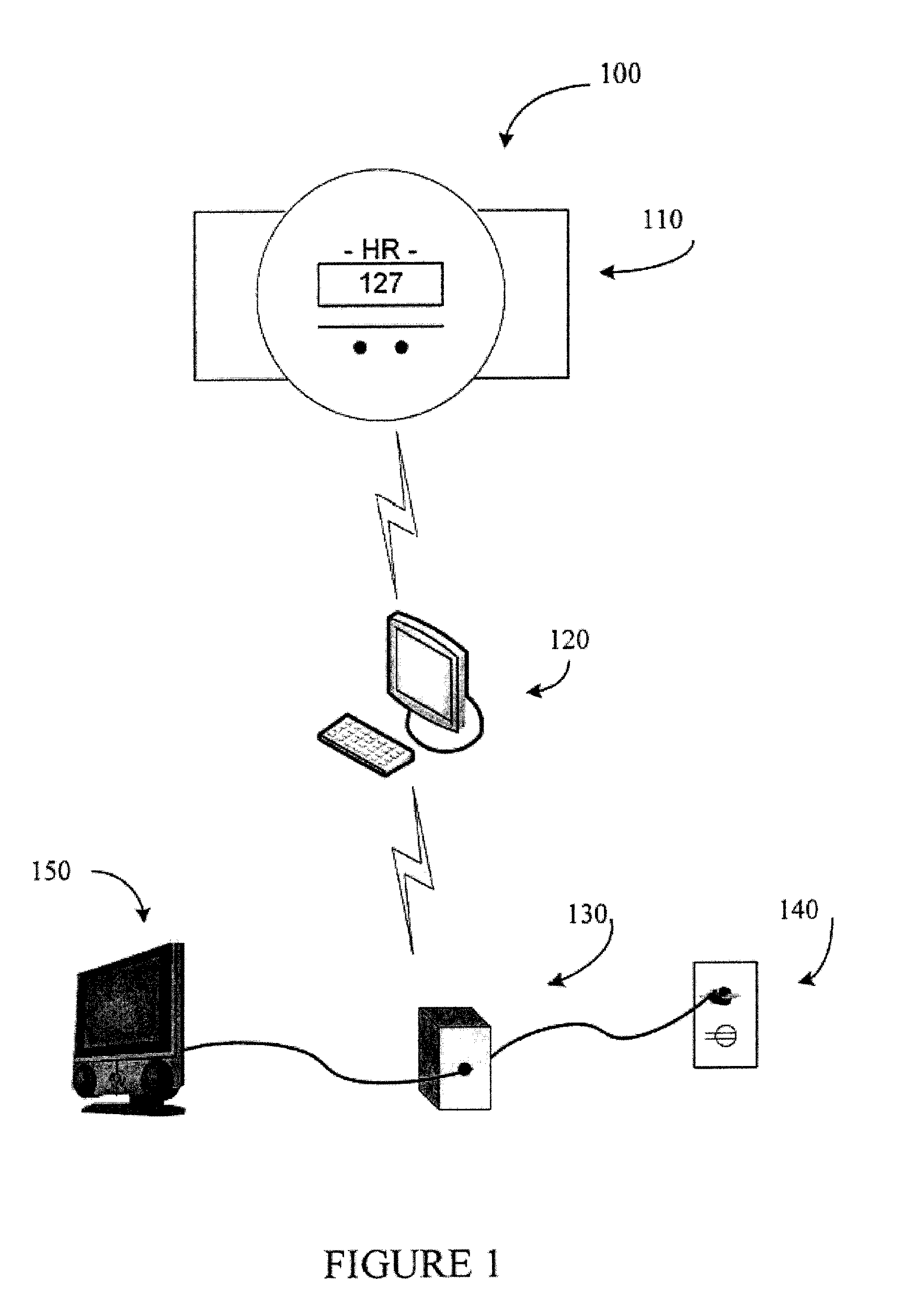
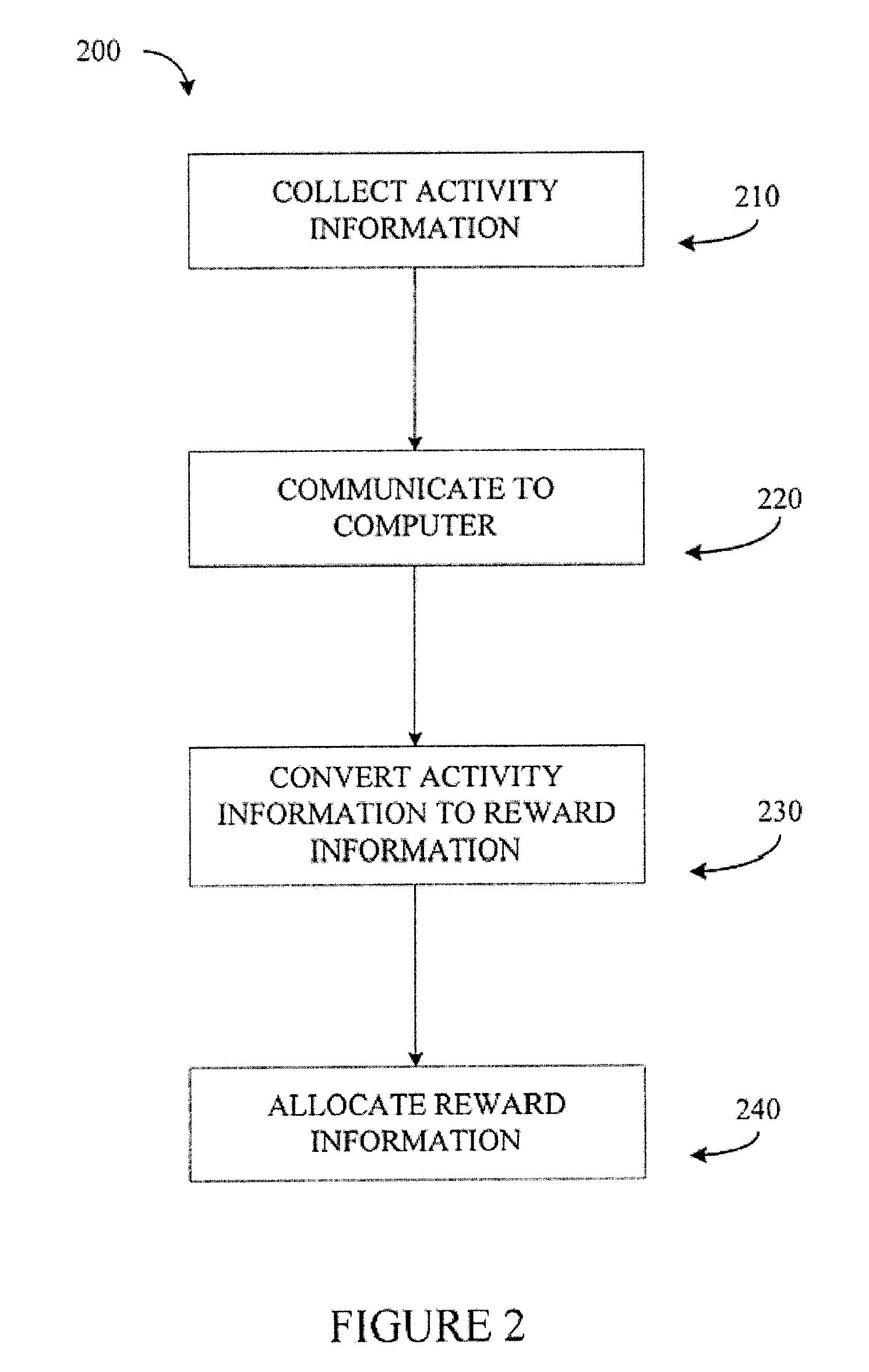
Physical Activity Reward System
A physical activity reward system and method which rewards a person performing physical activity with a reward, such as use of an appliance such a TV viewing time. The system includes a physical activity monitor capable of generating activity information proportionate to the amount of exertion or work done. The system may be used to record and keep track of the reward points or information. The system may further control the supply of electricity to an appliance through an electrical control module. The electrical control module may be interposed between a source of household electrical current and an electrical appliance such as a TV set.
Owner:LIFE4KIDS
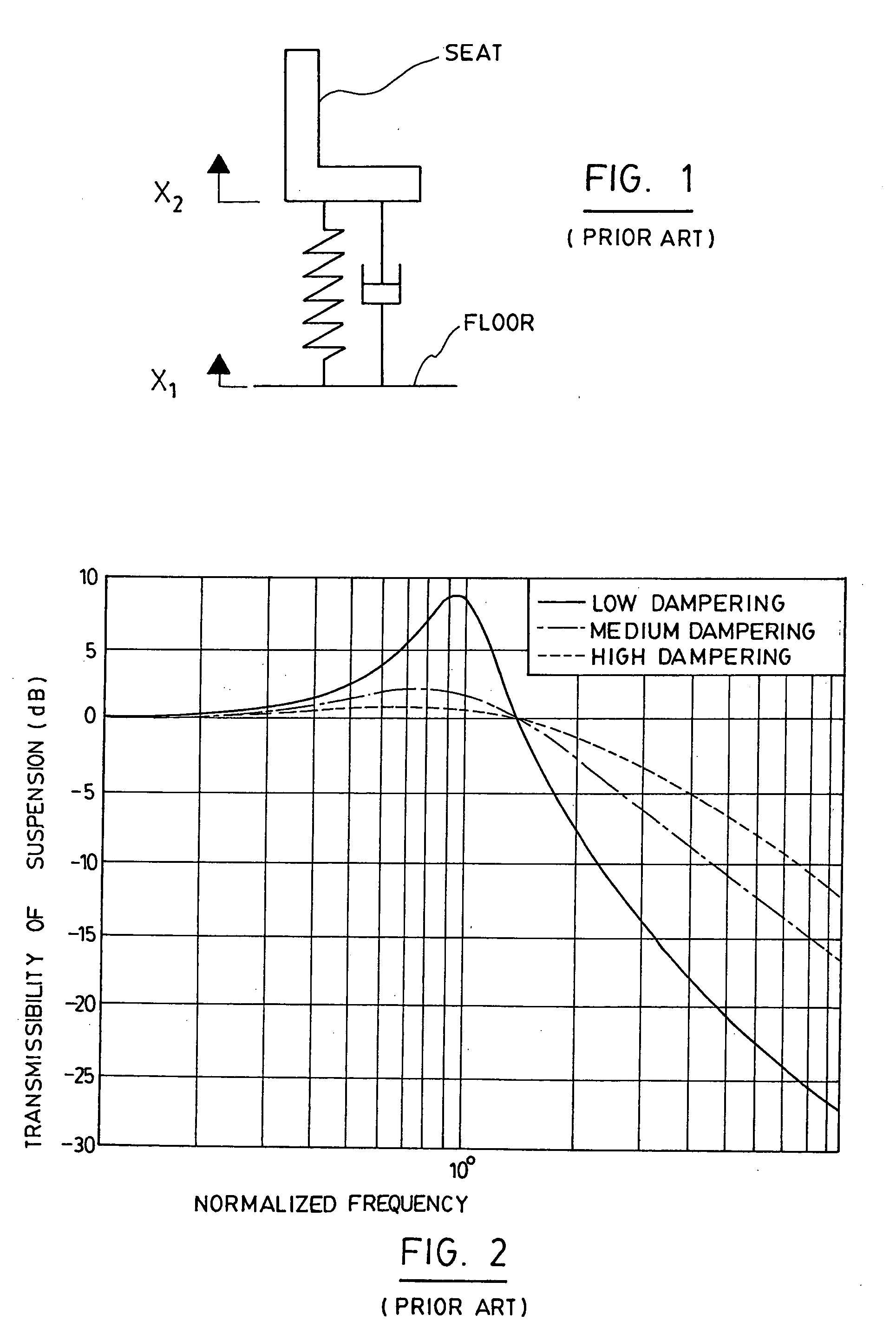
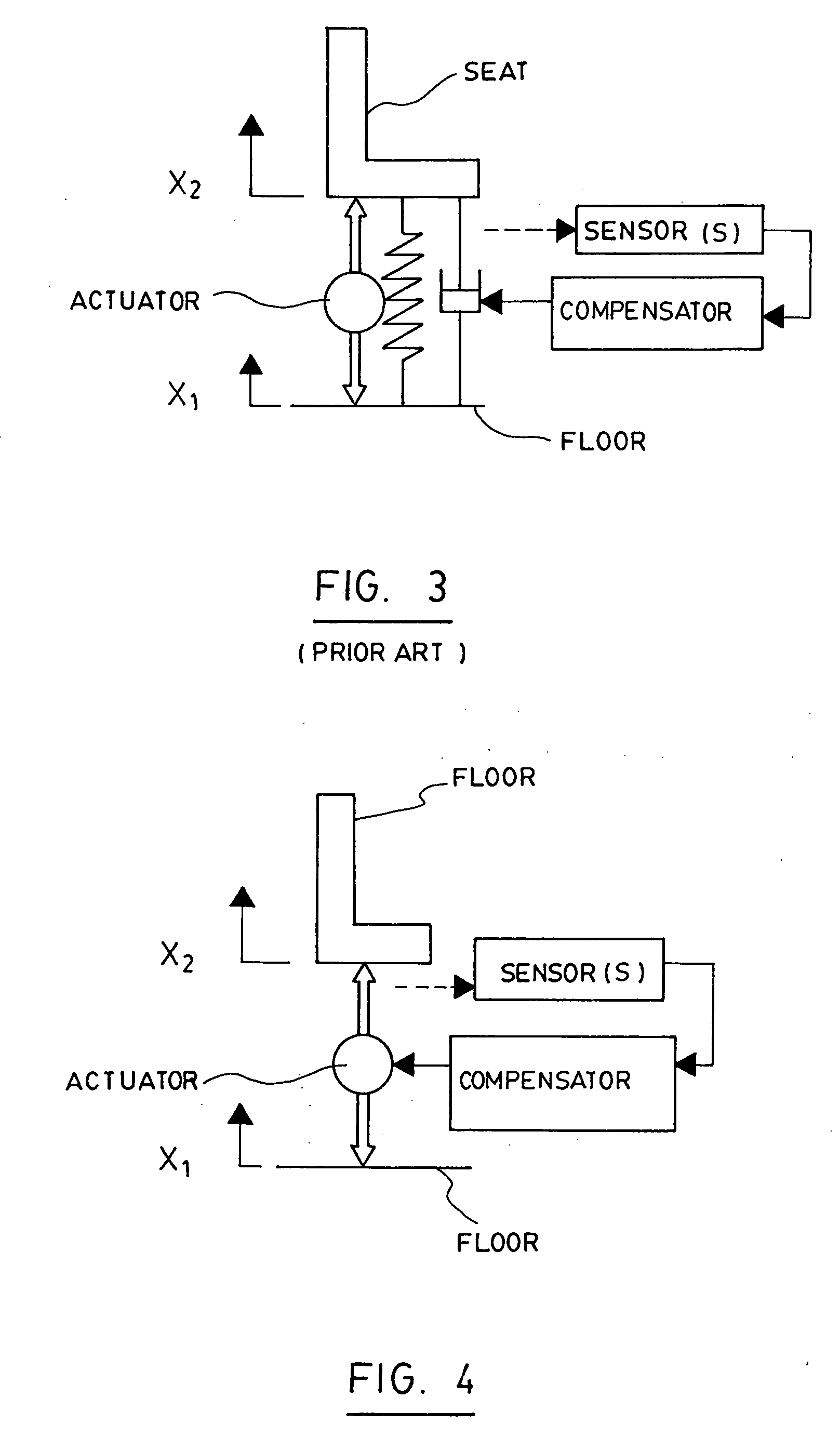
Active seat suspension
InactiveUS20060237885A1Reducing size of actuatorHigh frequencyPortable framesStands/trestlesDriver/operatorExertion
An active suspension for a driver seat of a bus or a heavy vehicle which comprises an electric actuator allowing the exertion of the force between the floor of the vehicle and the bottom of the seat. The adjustment of the height of the seat is accomplished by an electric actuator or by an independent mechanical system. A controller generates a control force calculated from measurements obtained by sensors located at different locations on the suspension. Forces exerted by the electric actuator can be relieved by passive element placed in parallel which cannot assume by themselves the role of a suspension for a given application.
Owner:BAULTAR I D
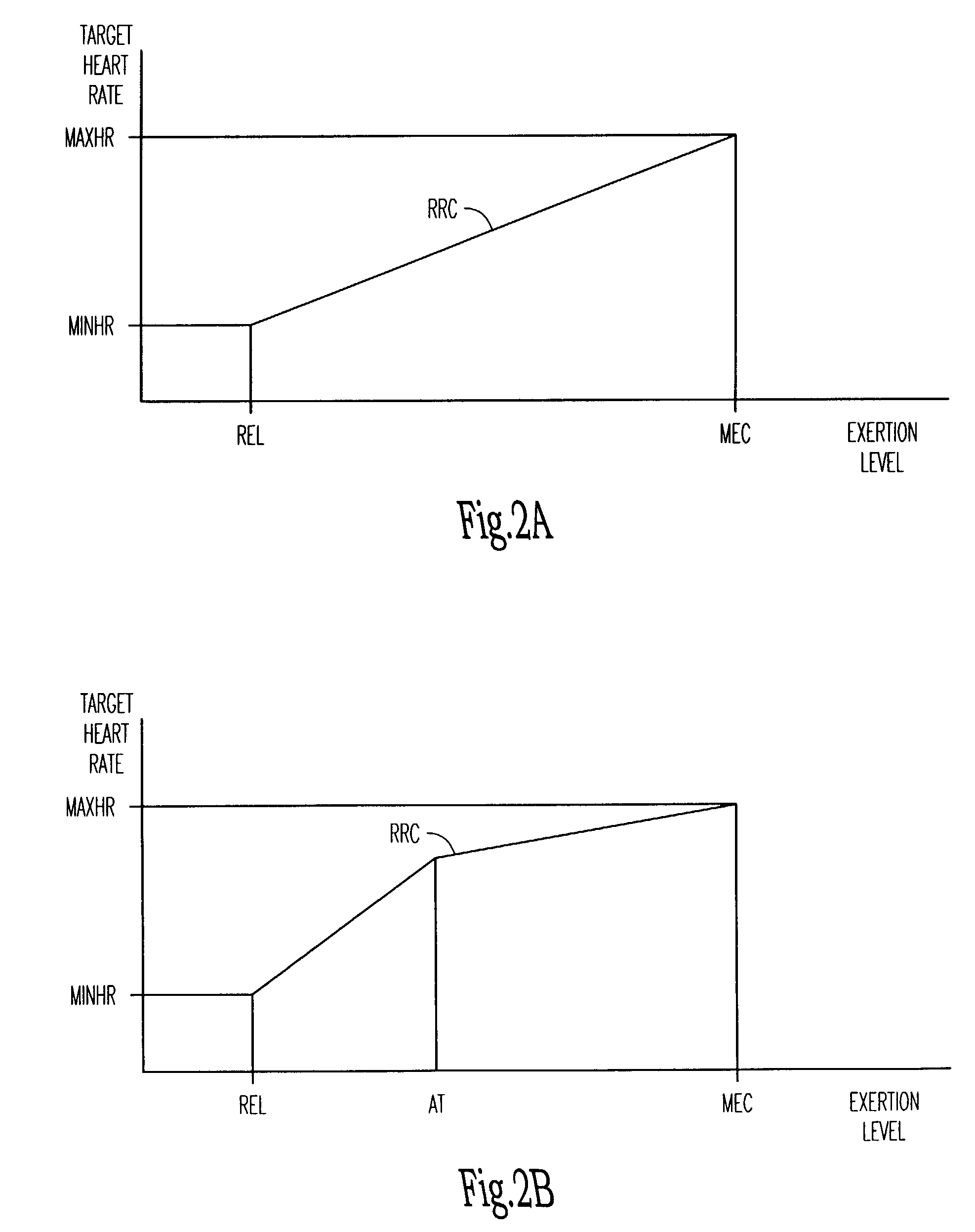
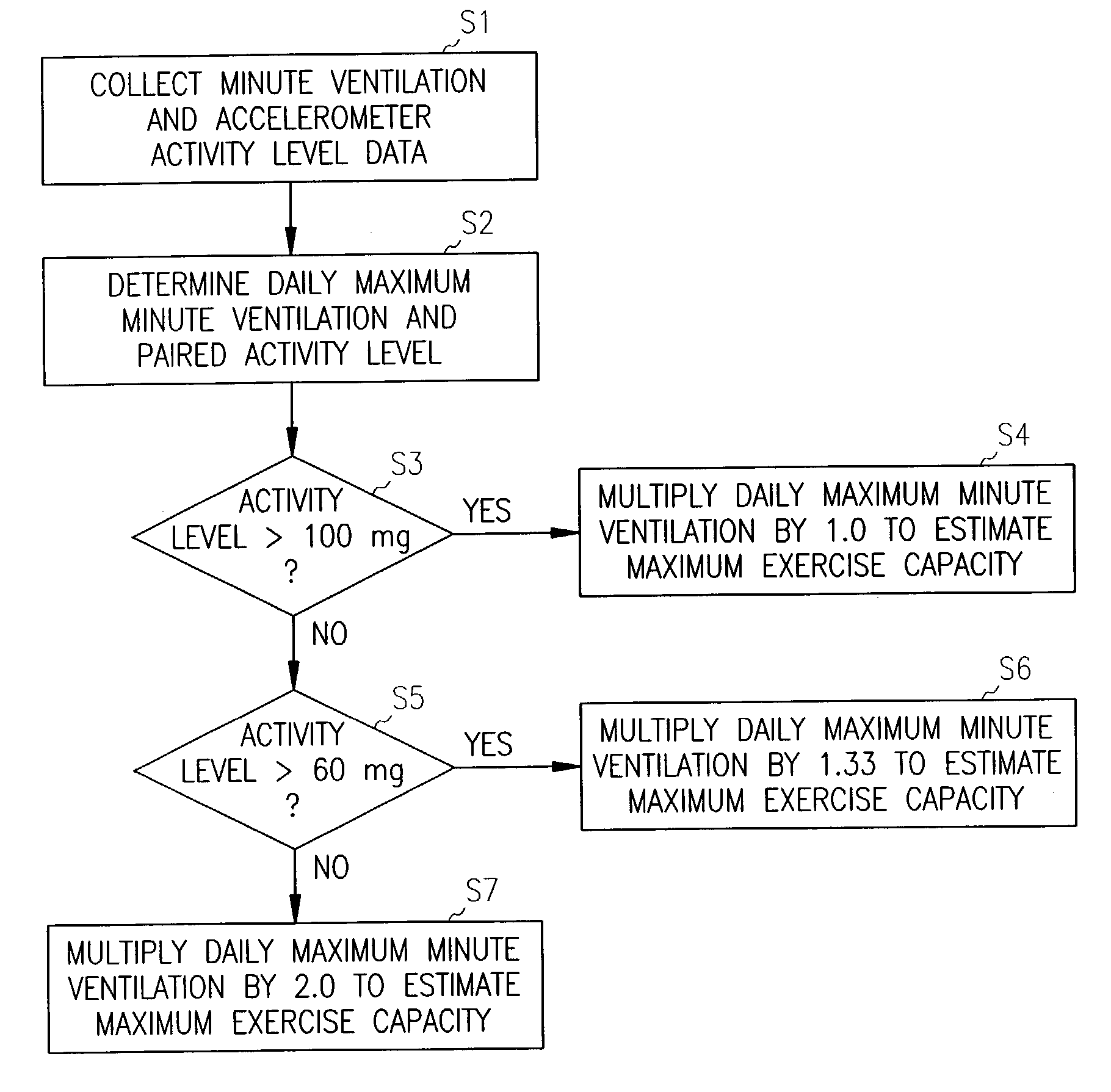
Rate-adaptive therapy with sensor cross-checking
A method and system for automatically adjusting the operating parameters of a rate-adaptive cardiac pacemaker in which maximum exertion levels attained by the patient are measured at periodic intervals and stored in order to compute or update a maximum exercise capacity. The slope of the rate-response curve is then adjusted to map an exertion level corresponding to the updated maximum exercise capacity to a maximum allowable pacing rate. In accordance with the invention, a maximum exercise capacity is determined by cross-checking periodic maximum exertion level sensor values with a motion-level sensor value.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method and apparatus for hemostasis
InactiveUS20080132820A1Different compressibilityDifferent resilienceNon-adhesive dressingsPlastersTrauma surgeryTourniquet time
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in patients who have received skin-penetrating wounds to the periphery, including the head, arms, and legs. Such haemostatic packing devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery, or military setting. The devices utilize fluid impermeable barriers surrounded by exterior dams and pressure to achieve tamponade and hemostasis, primarily by exertion of force to hold the dams against the skin surrounding a wound. The devices are capable of serving as carriers for thrombogenic, antimicrobial or antipathogenic agents. The devices do not require the use of adhesives to work as they are attached to the patient using mechanical locking devices. Peripheral haemostatic packing devices include optional adhesive hemostatic barriers to attach at least a portion of the device to the skin or to assist with initial coupling of a hold-down strap to another strap using a more secure mechanical lock. The peripheral hemostatic packing system does not completely surround the extremity having the wound and therefore do not cause a tourniquet effect. The peripheral hemostatic packing system preferably is held against the skin surrounding a wound by a force that is generally unidirectional and substantially perpendicular to the plane in which the skin of the wound resides.
Owner:BUCKMAN ROBERT F +2
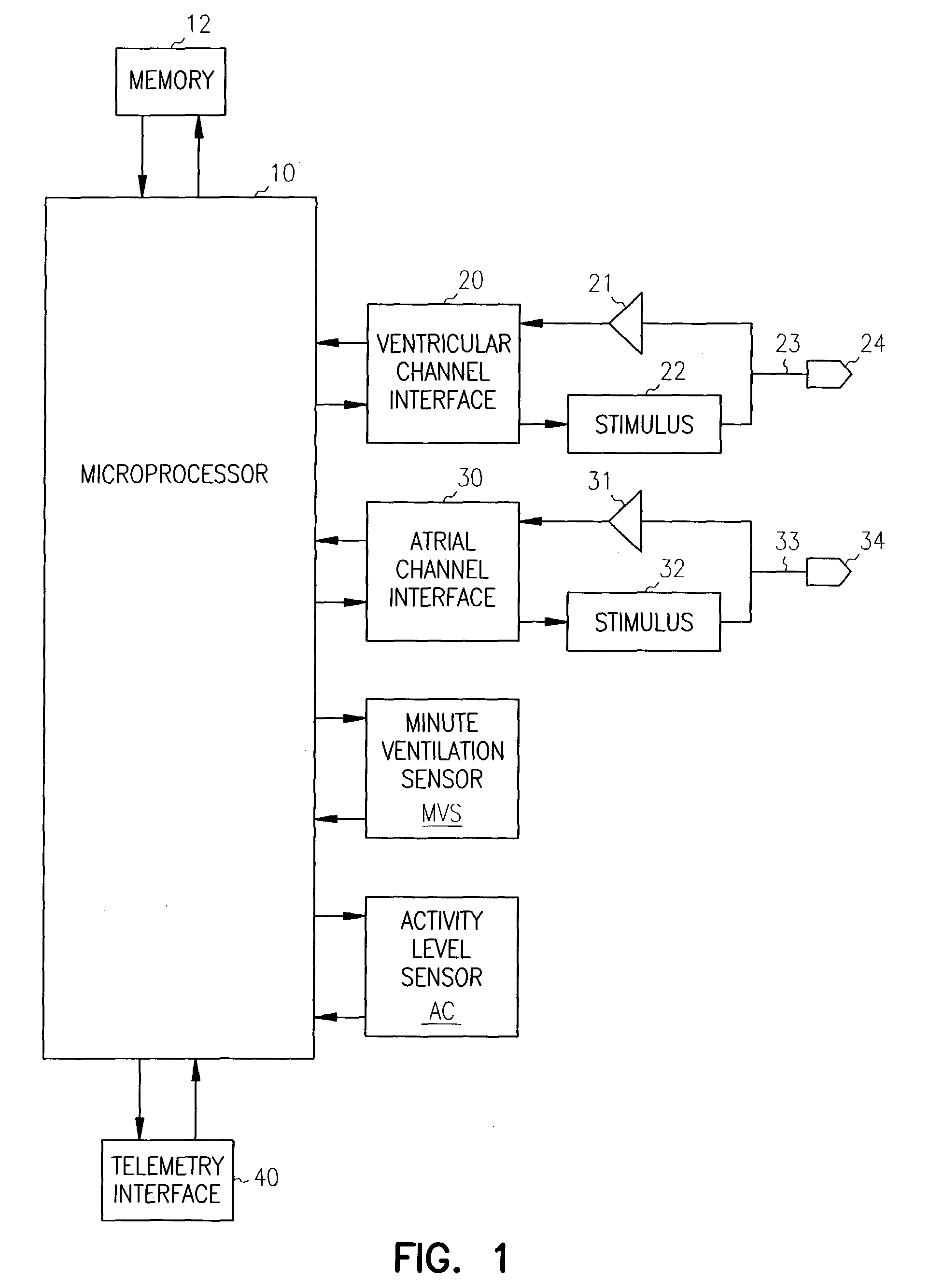
Rate Adaptive Cardiac Pacing Systems and Methods
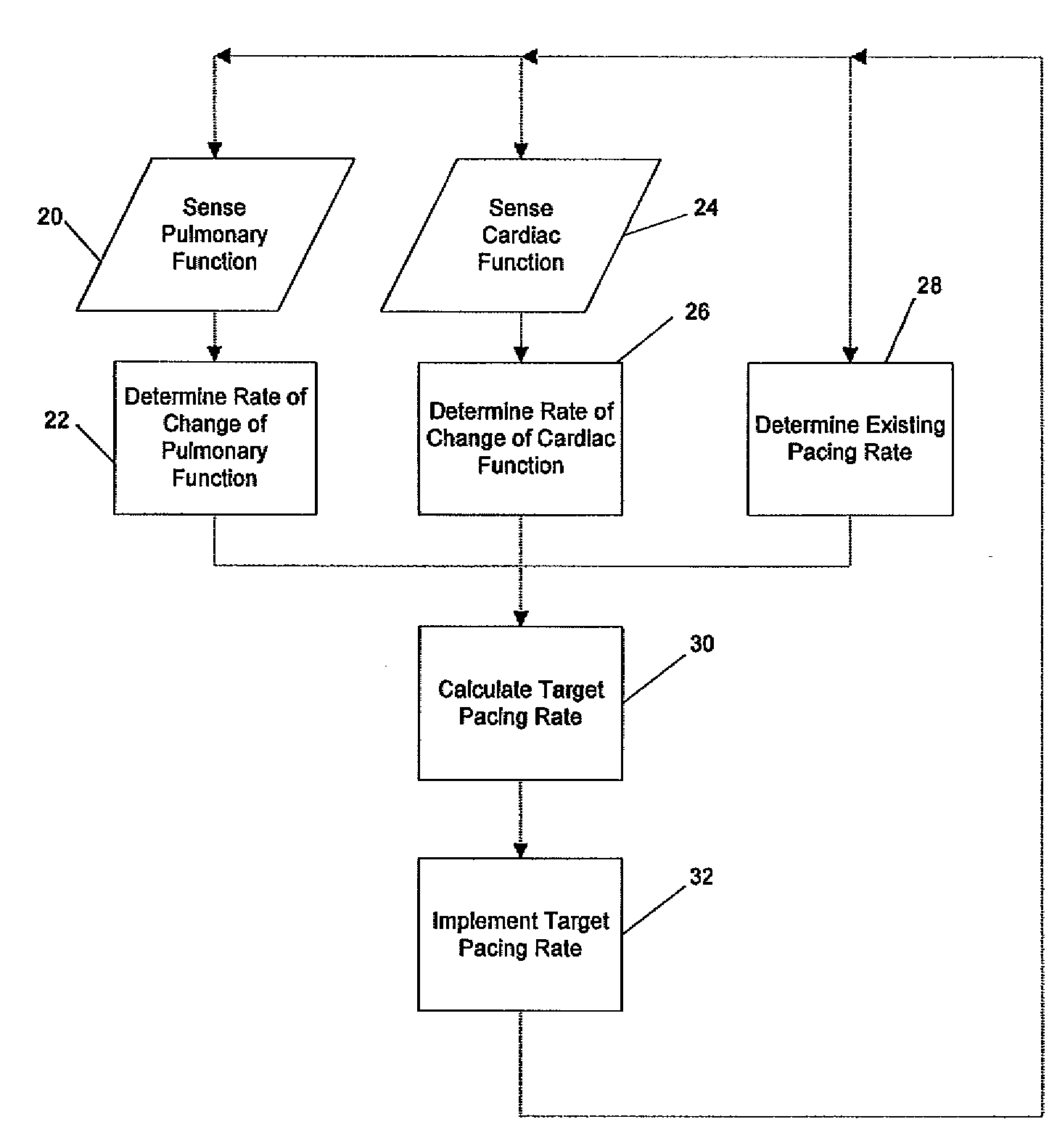
The invention relates to cardiac rhythm management systems, and more particularly, to rate adaptive cardiac pacing systems and methods. In an embodiment, the invention includes a method for providing rate-adaptive cardiac pacing therapy from an implantable medical device, the method including sensing a pulmonary function of a patient; determining a rate of change in the pulmonary function; sensing a cardiac function of the patient; determining a rate of change in the cardiac function; and calculating a target pacing rate based on an existing pacing rate, the rate of change in the pulmonary function, and the rate of change in the cardiac function. In an embodiment, the invention includes a method of controlling a cardiac rhythm management device in response to exertion of a patient, the method including sensing the patient's pulmonary function at a first time t1 and at a second time t2; calculating a rate of change of the pulmonary function between time t1 and time t2; sensing the patient's cardiac function at time t3 and t4; calculating a rate of change of the cardiac function between time t3 and time t4; and setting a desired pacing rate. Embodiments of the invention also include cardiac rhythm management devices.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Apparatus for monitoring and displaying exertion data
An apparatus for monitoring and displaying information related to pressure exerted at a point of interest during an isometric exercise includes a fabric base, adapted to receive a body part. A sensor is attached to the fabric base and disposed at the point of interest during the isometric exercise, and measures a pressure magnitude at the point of interest and provides a pressure signal corresponding to the pressure magnitude. A processing unit is attached to the fabric base and receives the pressure signal, processes the pressure signal to derive information that is meaningful to a user, and generates a display corresponding to the information derived from the pressure signal.
Owner:SMITH CARL M
Variable stride exercise device
Owner:NAUTILUS INC
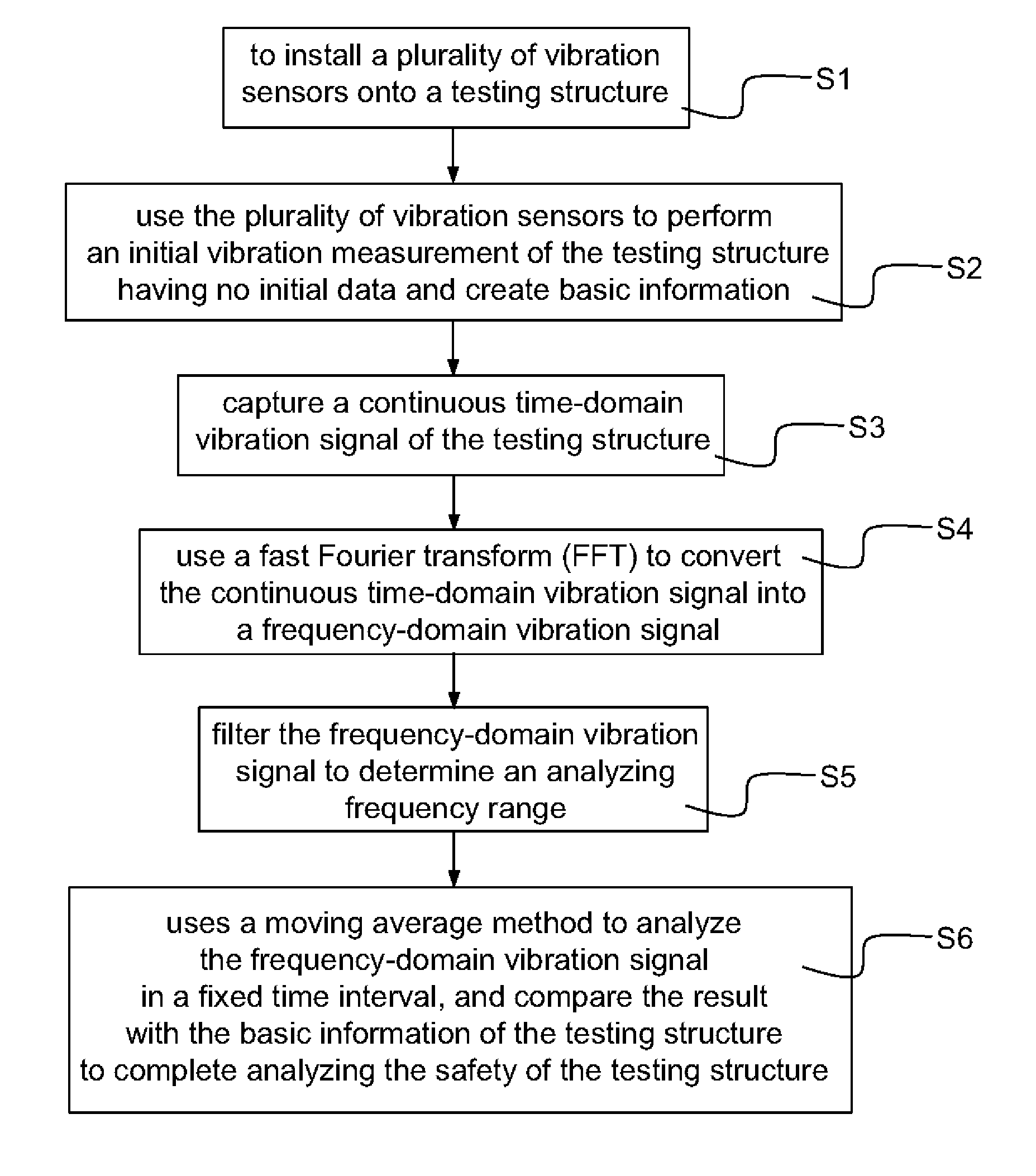
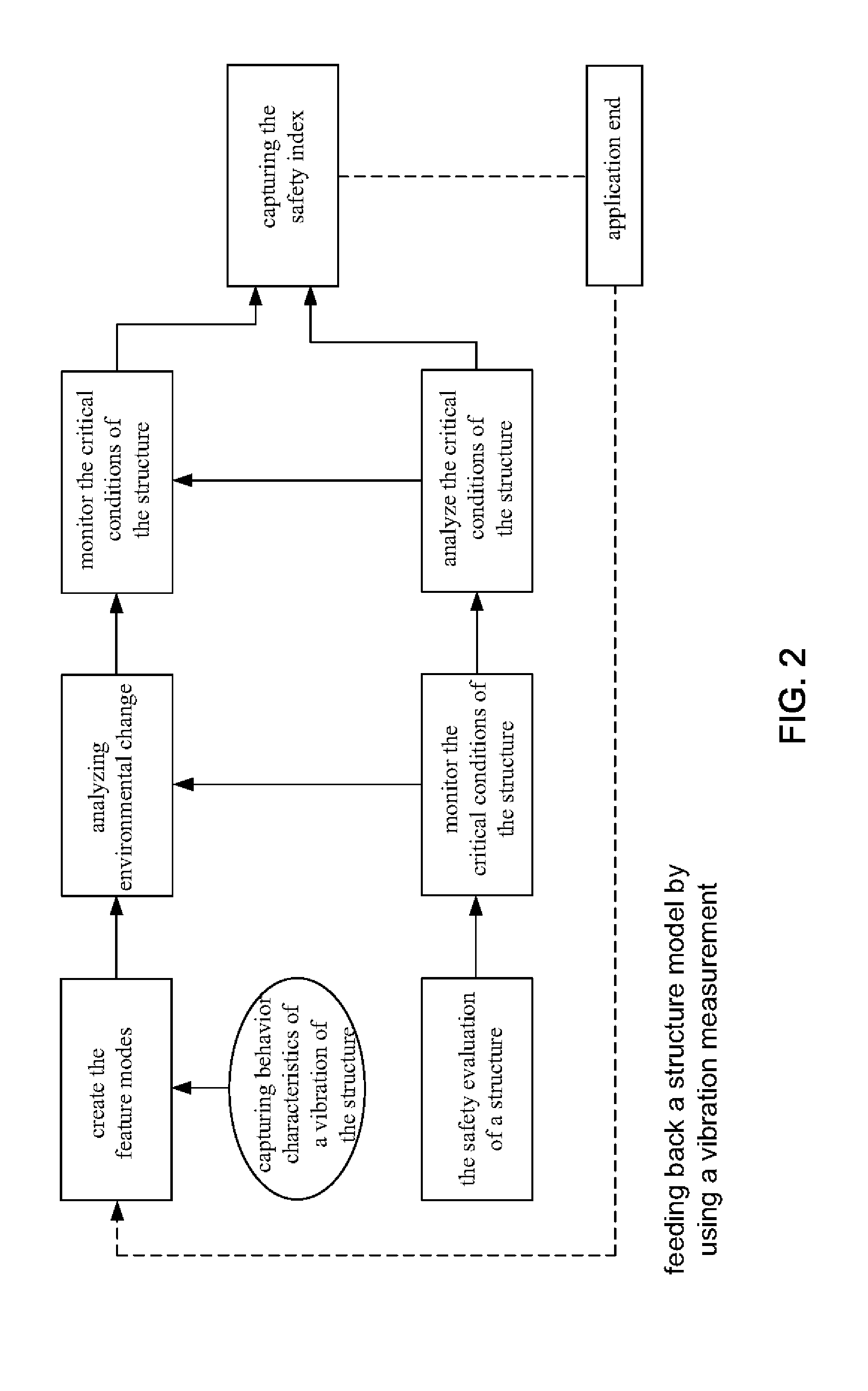
Method for analyzing structure safety
InactiveUS20120204646A1Guarantee structureMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial strength using single impulsive forceVibration measurementStability index
The present invention discloses a method for analyzing structure safety, and the method uses valid vibration measurement signals to obtain mutual feedbacks for a structural model analysis and a calibrated structural model to simulate a disaster situation to obtain the critical force exertion and deformation scale of a structure. The method is applied to capture the stability index of the structure to analyze the structure safety or applied for a structure safety evaluation or a health monitoring, or even for a structure multi-hazards safety determination.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
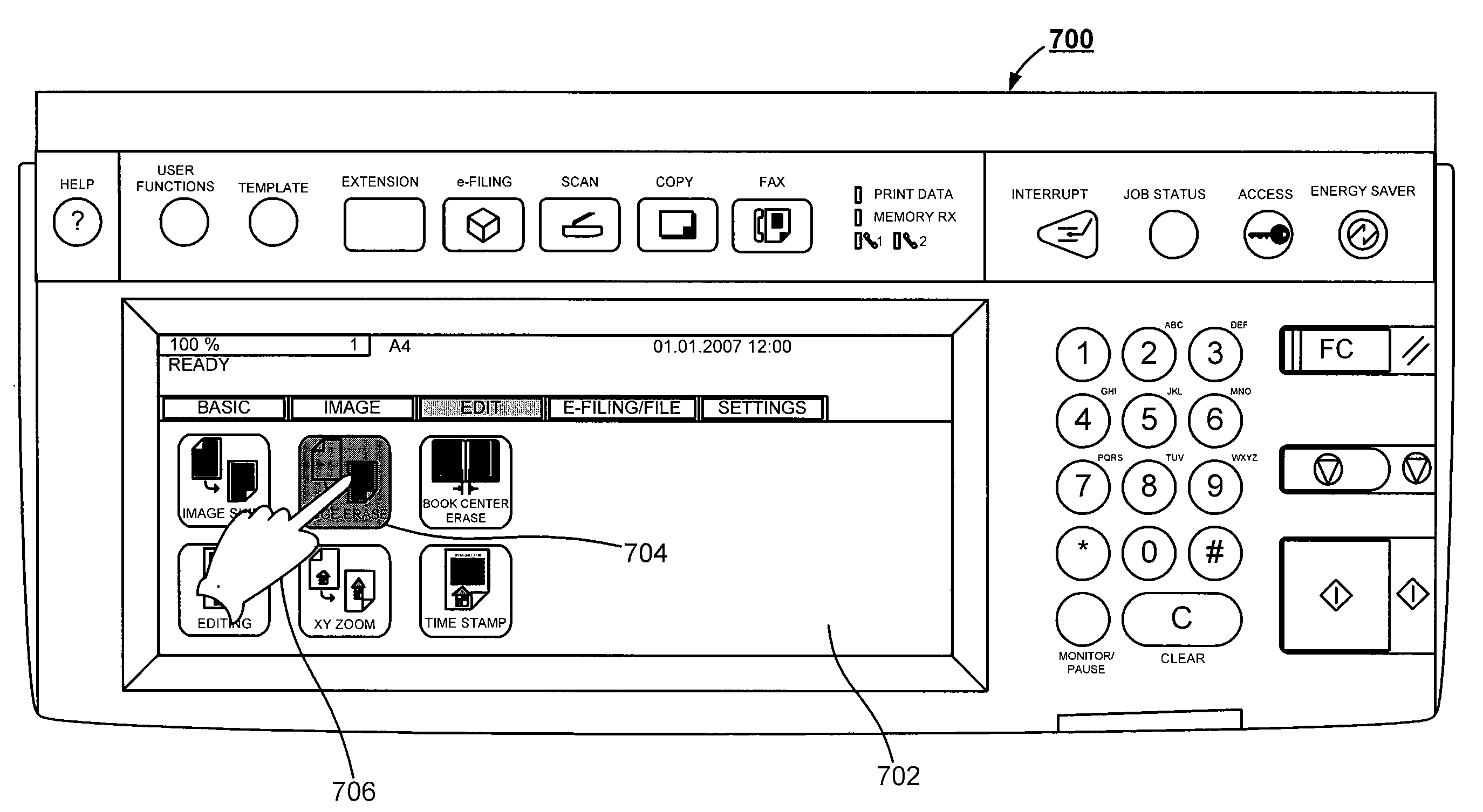
System and method for generating context sensitive help for a graphical user interface
InactiveUS20090158152A1Provided any assistanceElectrographic process apparatusExecution for user interfacesInformation processingGraphics
The subject application is directed to a system and method for generating context sensitive help for a graphical user interface. Display data corresponding to a plurality of indicia is first generated on an associated display, each indicia corresponding to a functionality of an associated information processing device. Selection data is then received corresponding to a selected indicia from those displayed. A touch down signal is then received corresponding to a tactile exertion of positive physical pressure. Duration data representing the duration of the exerted positive physical pressure is then received. A display of data associated with the functionality of the information processing device is subsequently triggered in accordance with the selected indicia corresponding to the received selection data and the received duration data.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
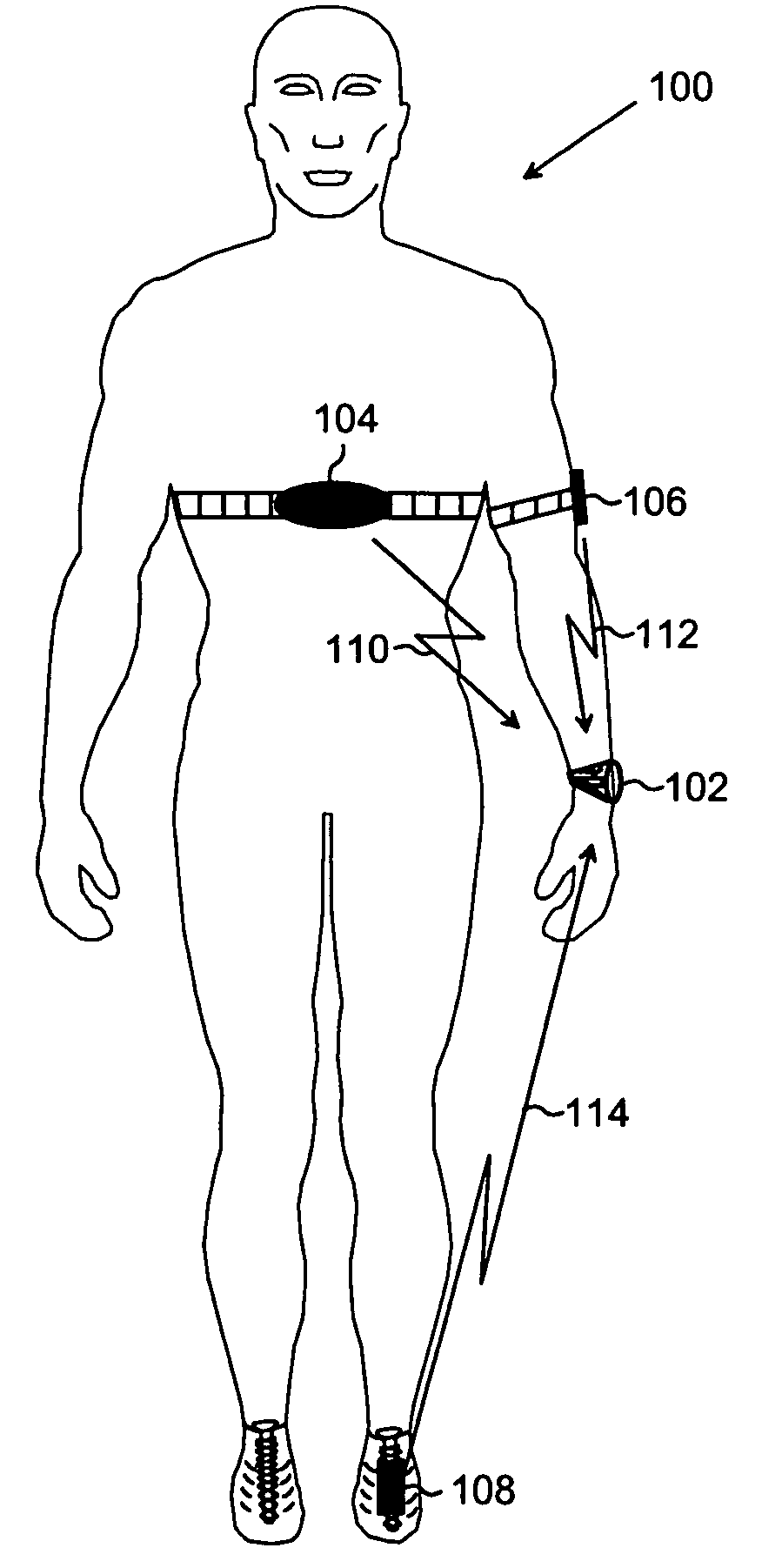
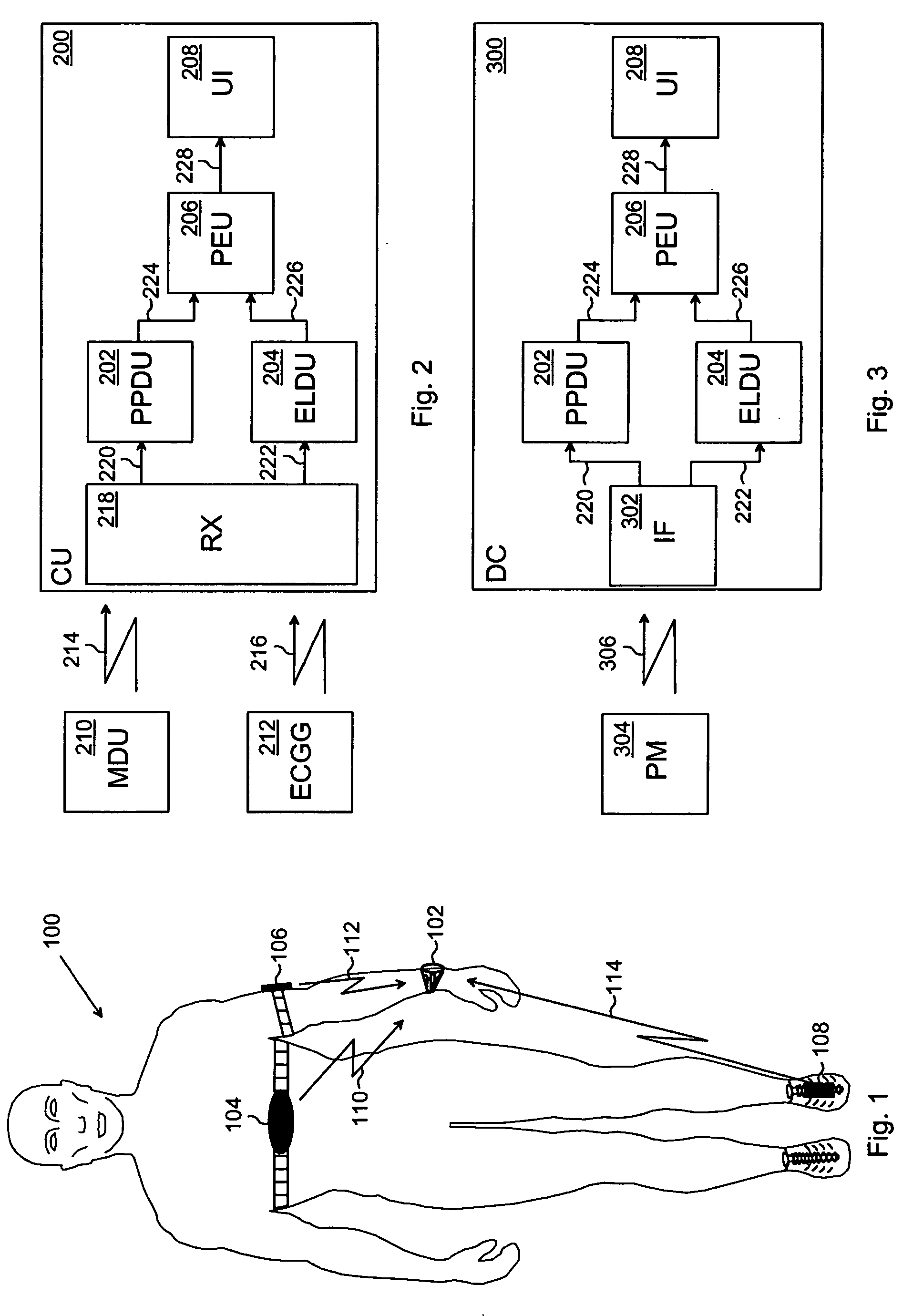
Method and apparatus for noninvasive physiologic monitoring
Intense environmental or working conditions can impede an individual's evaporative cooling mechanism normally responsible for thermoregulation during exercise or exertion. Non-invasive physiological monitoring capabilities are needed to more precisely define the cardiovascular responses and identify markers of impending failure of compensatory mechanisms prior to collapse or onset of irreversible pathology. The oxymetry method and system of the present invention provides non-invasive, continuous remote monitoring and analysis of cardiovascular and pulmonary function that overcomes accuracy and monitoring deficiencies of current oximetry systems.
Owner:SEKOS
Motorized garbage can and automatic lid opener
A remote controlled motorized garbage can that is capable of transferring material to the intended designation, in conjunction, an automatic lid opener apparatus to facilitate in the dispersing of material and the lid comprising a lock and sensor mechanism to prevent personal, financial and other such information readily accessible for unlawful inclinations. To transfer the container by a remote control, rather than manual exertion, provides an efficient, convenient and permits accessibility, in consideration, to almost all individuals of physical ability.
Owner:WILSON KRISTIE LYNN
Means and method for the detection of cardiac events
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
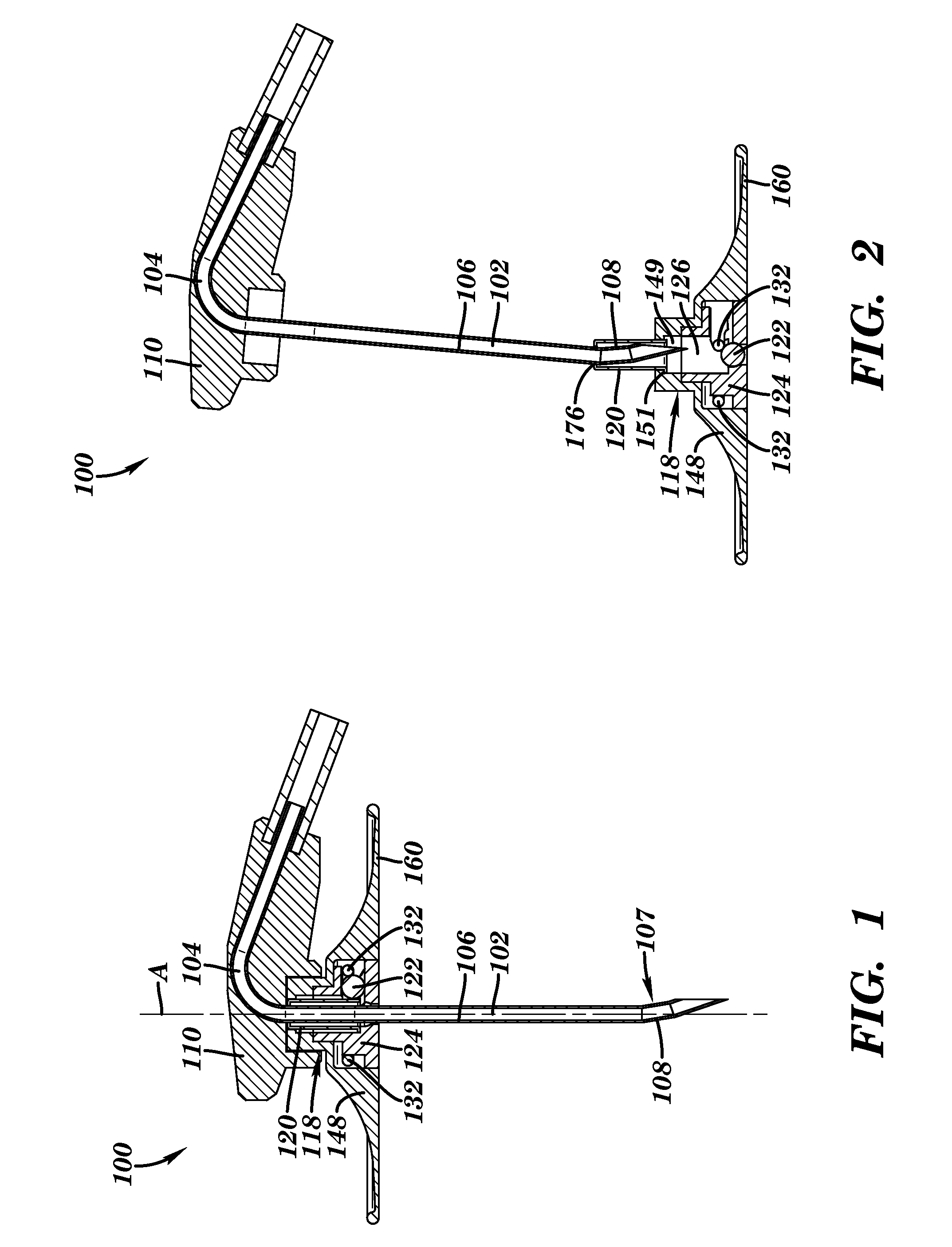
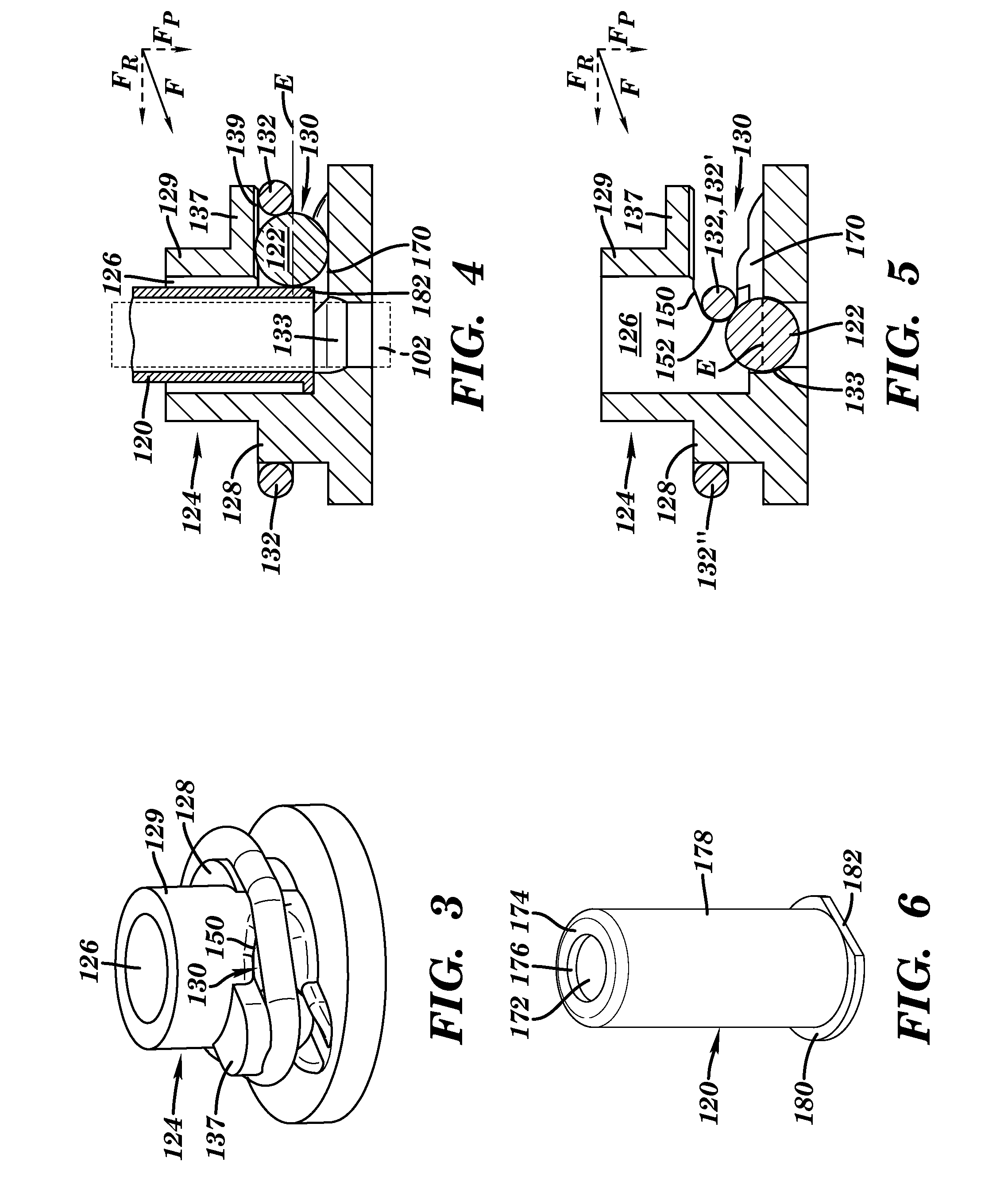
Needle-based medical device and related method
A needle-based medical device and a method for constructing it are disclosed. The medical device includes a needle blocking object movable from a non-blocking position offset from the longitudinal axis of the needle to a blocking position; a needle shield housing, the needle shield housing including: a lumen for accommodating at least part of the needle such that the needle shield housing; an opening for accommodating at least part of the needle blocking object; and a biasing member for applying a biasing force on the needle blocking object, the biasing force including a first component substantially perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the needle and a second component substantially parallel to the longitudinal axis of the needle. The needle blocking object moves by exertion of the biasing force to the blocking position, preventing the needle from emerging from the needle shield housing, in response to a triggering proximal movement of the needle.
Owner:ERSKINE MEDICAL LLC
Adjustable length breathing circuit
Owner:KING SYST
Adjustable length breathing circuit
A unilimb breathing circuit has a proximal end coupling member, a distal end coupling member, an expiratory tube extending between the proximal and distal end coupling members, and an inspiratory tube extending between the proximal and distal end coupling members. The expiratory tube is a corrugated expiratory tube that is expandable between a fully compressed rest position, and a fully expanded rest position, and has a plurality of intermediate rest positions. At the plurality of intermediate rest positions, the expiratory tube is capable of maintaining its rest length without the exertion of an external force. The inspiratory tube is a corrugated inspiratory tube having a length that is variable between a fully compressed rest position and a fully expanded rest position, and includes a plurality of intermediate rest positions between the fully expanded rest position and the fully compressed rest position. The inspiratory tube is also capable of maintaining these intermediate rest positions without the exertion of an external force.
Owner:KING SYST
360 degree rotator attachment for exercise equipment
InactiveUS20050085352A1Smooth rotationSmooth movementDumb-bellsMovement coordination devicesSports equipmentEngineering
Disclosed is a weight lifting apparatus having mechanism for assisting in adding a rotational element to the traditional front / back (or flexion and extension) activities during the lifting of weights or other athletic resistance activitiesl. This invention to provides an attachment apparatus that provides a weight holding means that is able to offer 360 degrees of smooth movement which allows complete rotational positionability for use with any stationary or moving resistive weight apparatus. This invention also provids an apparatus wherein the weight holding means also provides a safety measure which can limit the speed of rotation or even stop this motion in the event that the weight is dropped or rotational exertion limits are reached.
Owner:BAXTER BRENT ALAN
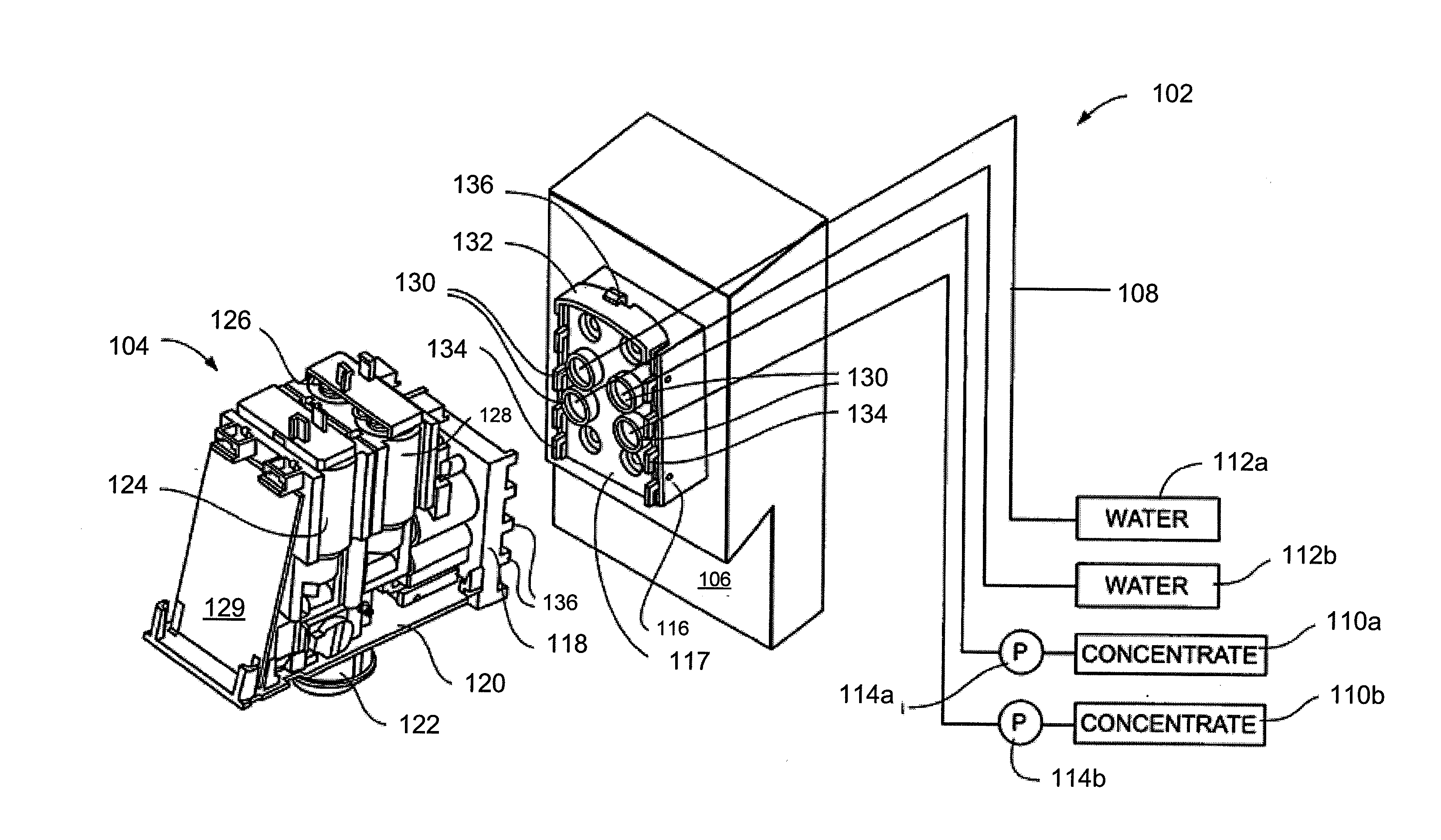
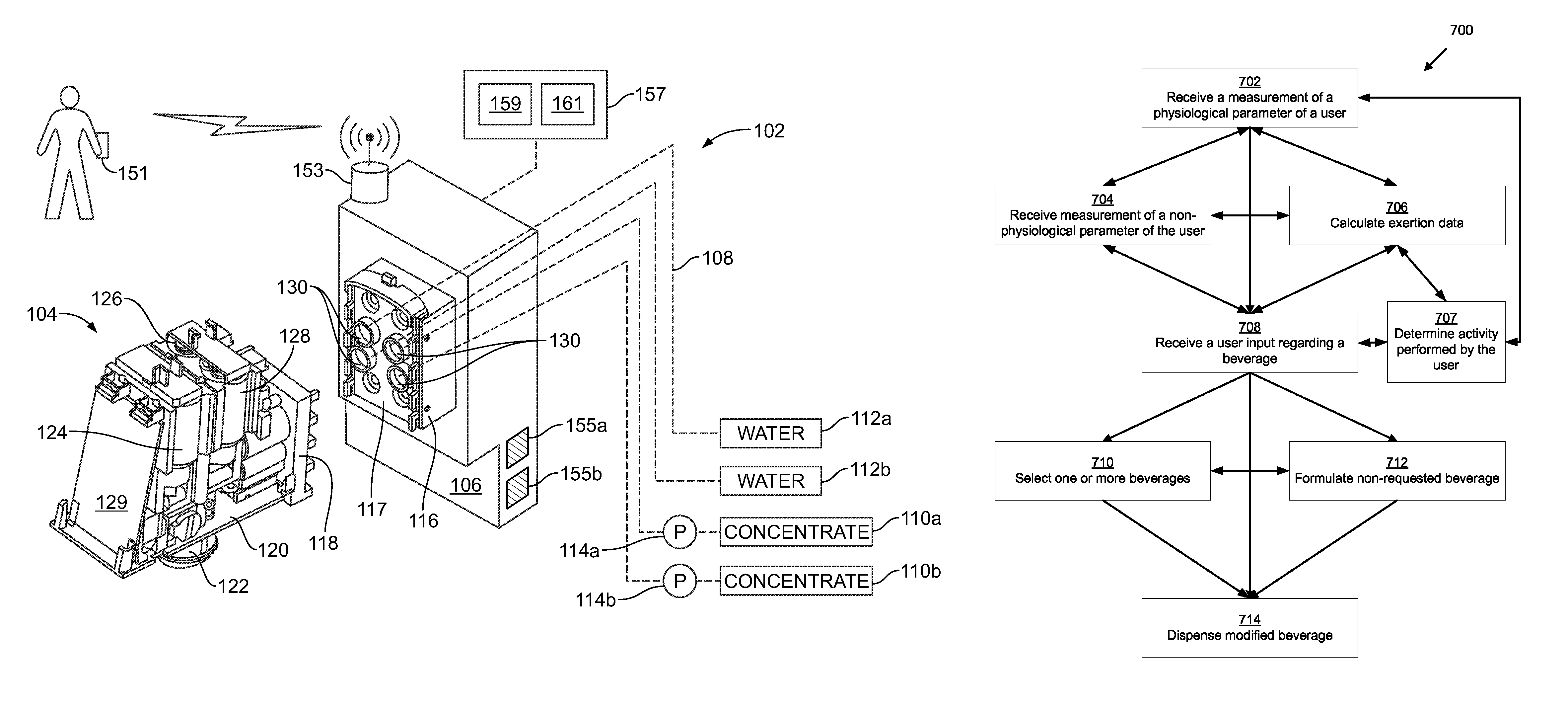
Beverage dispensing device
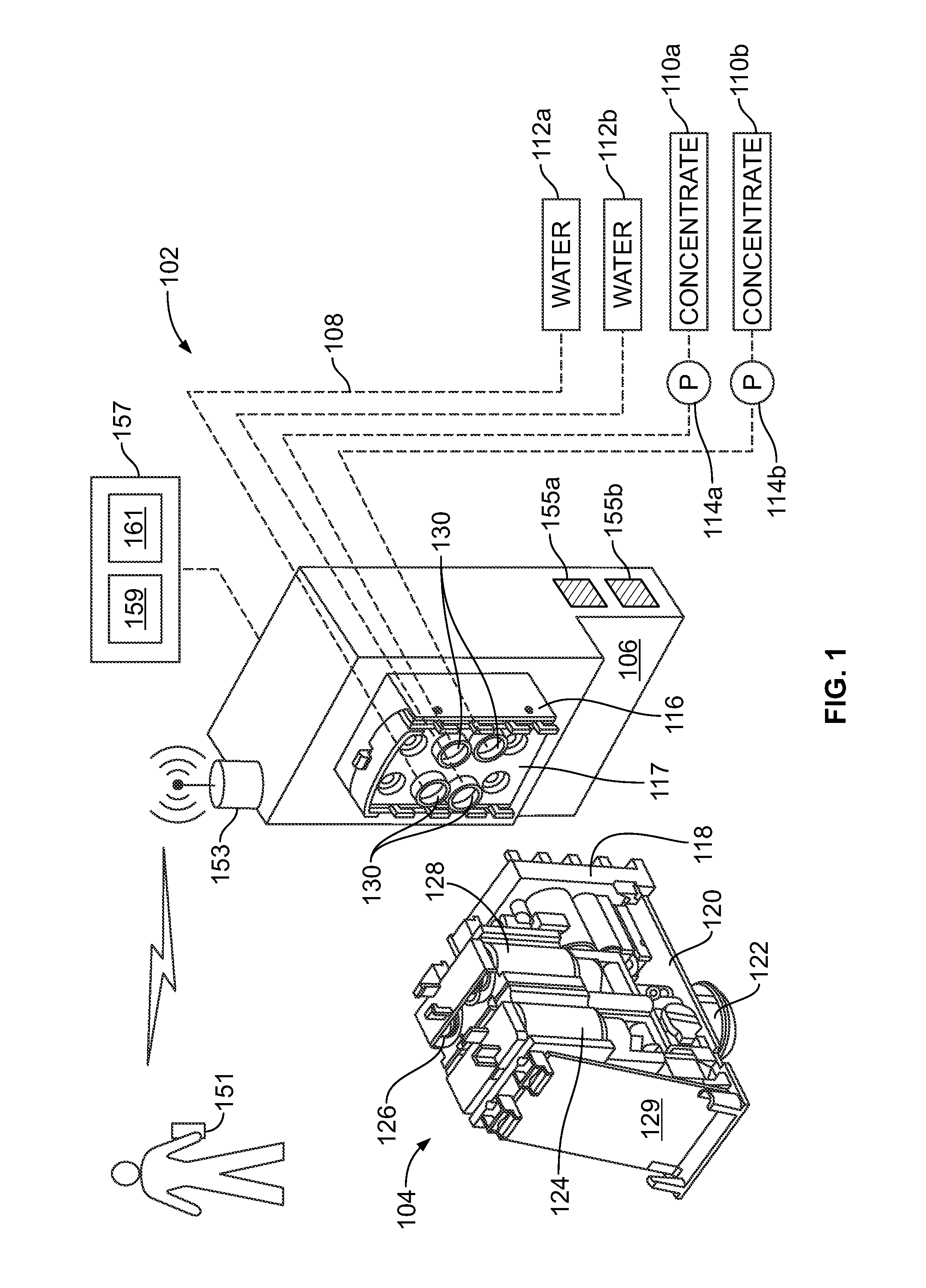
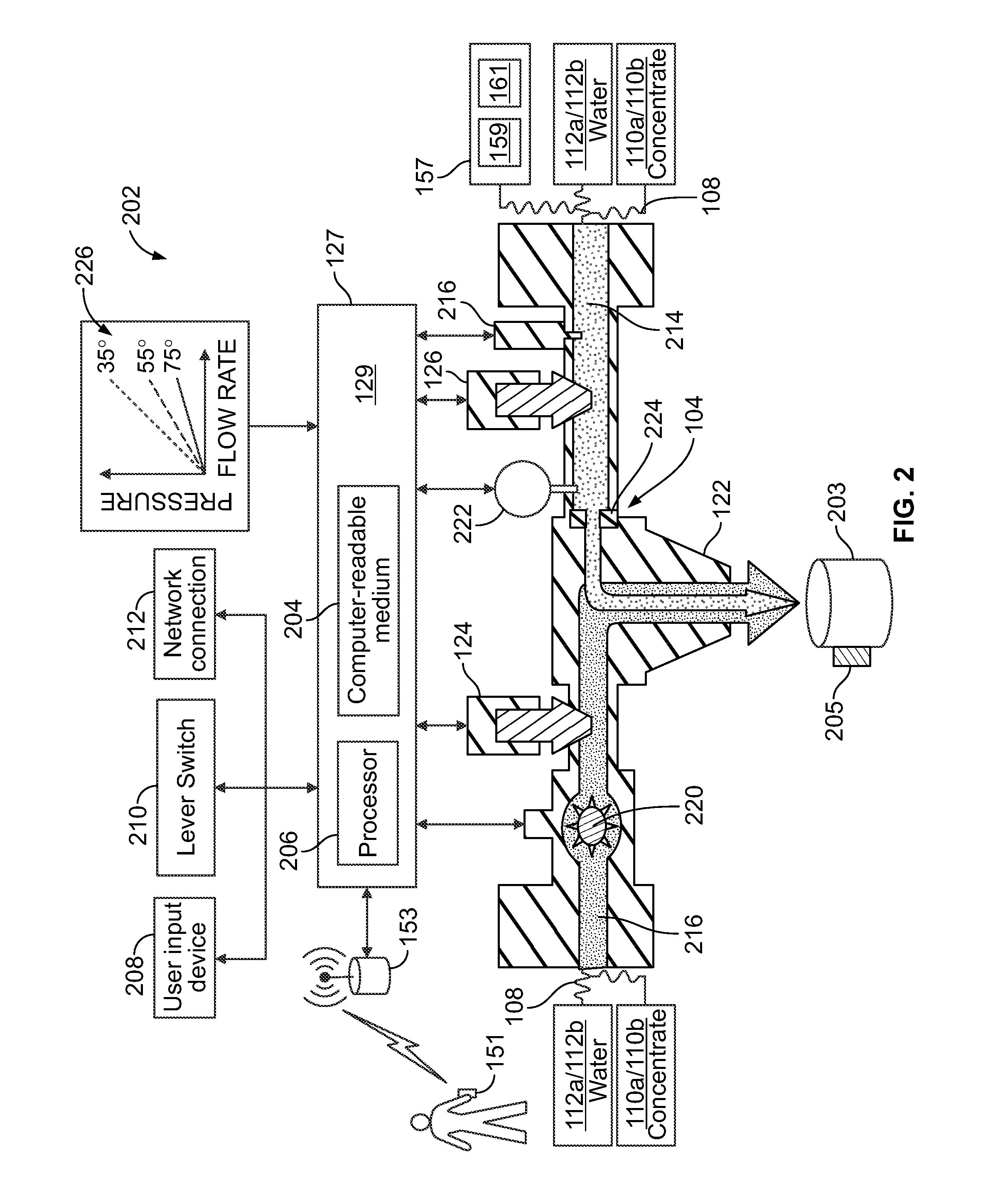
ActiveUS20110121032A1Accurate assessmentLow costLighting and heating apparatusFlow controlEngineeringExertion
Novel systems and methods for dispensing compositions, such as beverages, are provided. Novel beverage dispensers may be configured to receive one or more physiological parameters regarding a user, and in response, formulate at least one beverage recipe for dispensing. A beverage dispenser may wirelessly receive data from a biosensor. In certain embodiments, data from the biosensor may be used to alter the recipe to another existing beverage or a custom beverage. Non-physiological data may also be considered. In one embodiment, environmental and / or biographical data may be utilized. In another embodiment, exertion data may be calculated. The calculation of exertion data may receive inputs regarding at least one physiological parameter and / or non-physiological parameters to derive a second physiological parameter not being measured. Novel systems and methods may reduce costs associated with extra sensors and / or allow more accurate assessment of the user's exertion level.
Owner:PEPSICO INC
Method and apparatus for hemostasis
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in patients who have received skin-penetrating wounds to the periphery, including the head, arms, and legs. Such haemostatic packing devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery, or military setting. The devices utilize fluid impermeable barriers surrounded by exterior dams and pressure to achieve tamponade and hemostasis, primarily by exertion of force to hold the dams against the skin surrounding a wound. The devices are capable of serving as carriers for thrombogenic, antimicrobial or antipathogenic agents. The devices do not require the use of adhesives to work as they are attached to the patient using mechanical locking devices. Peripheral haemostatic packing devices include optional adhesive hemostatic barriers to attach at least a portion of the device to the skin or to assist with initial coupling of a hold-down strap to another strap using a more secure mechanical lock. The peripheral hemostatic packing system does not completely surround the extremity having the wound and therefore do not cause a tourniquet effect. The peripheral hemostatic packing system preferably is held against the skin surrounding a wound by a force that is generally unidirectional and substantially perpendicular to the plane in which the skin of the wound resides.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
Active assist for the ankle, knee and other human joints
InactiveUS20060142680A1Reduce the risk of injuryLower requirementNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSports activityKnee Joint
A human joint assist device that applies a torque at the joint to assist physiological exertion forces, that is the load carrying task of the joint and surrounding muscles, tendons, and ligaments. The application of this device reduces the physiological exertion force requirement, and may be adjusted with respect to assist level, to suit the issue associated with joint motion and is useful for joint rehabilitation and sports activities. Among other things, this results in a reduction of physiological exertion force in a fashion that makes it easier to extend the levers (long bones) associated with extension against a given resistance. For example, standing from a squatted position with the assist of this device reduces the stress on physiological members associated with joint articulation.
Owner:IAROCCI MICHAEL ANTHONY
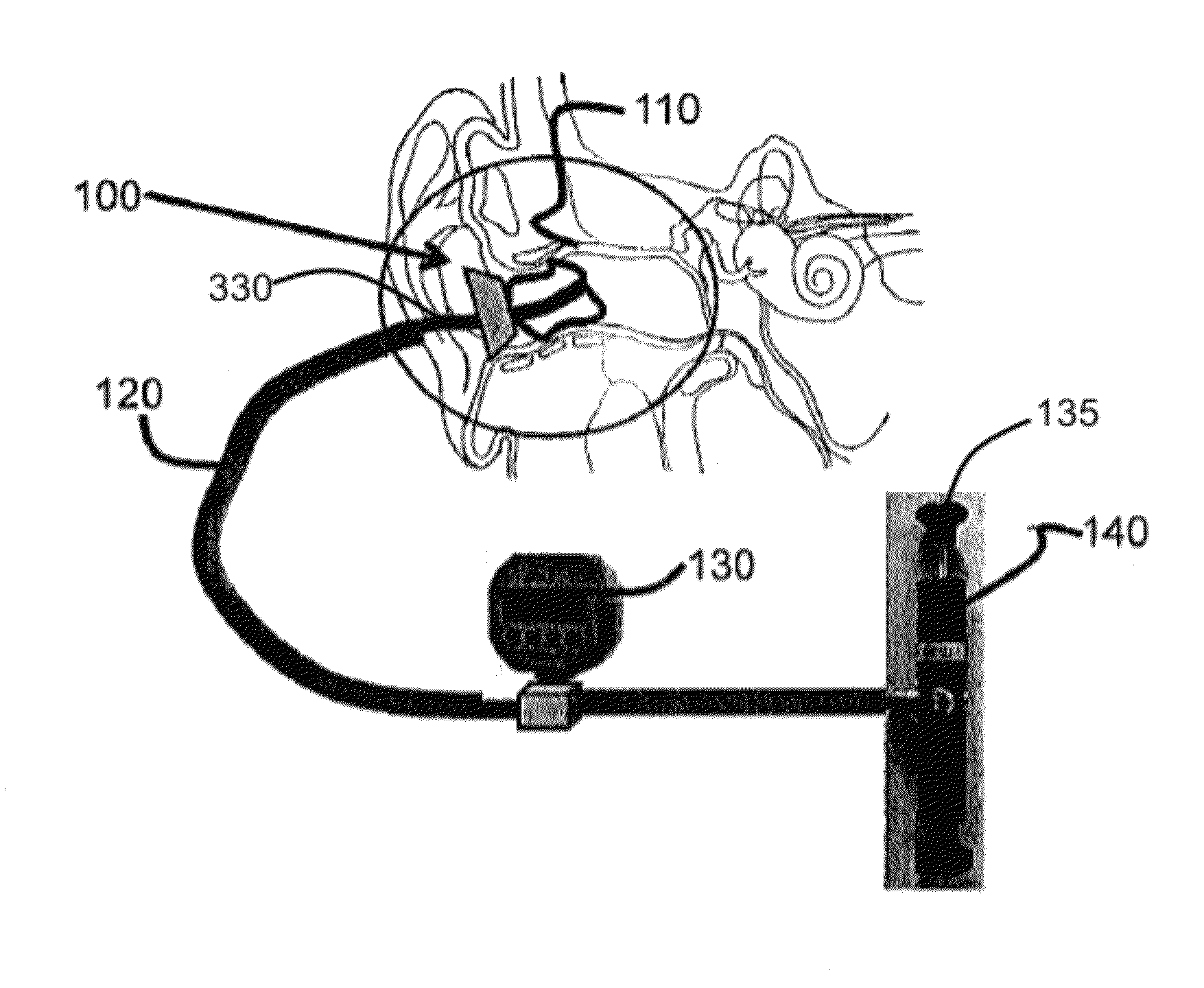
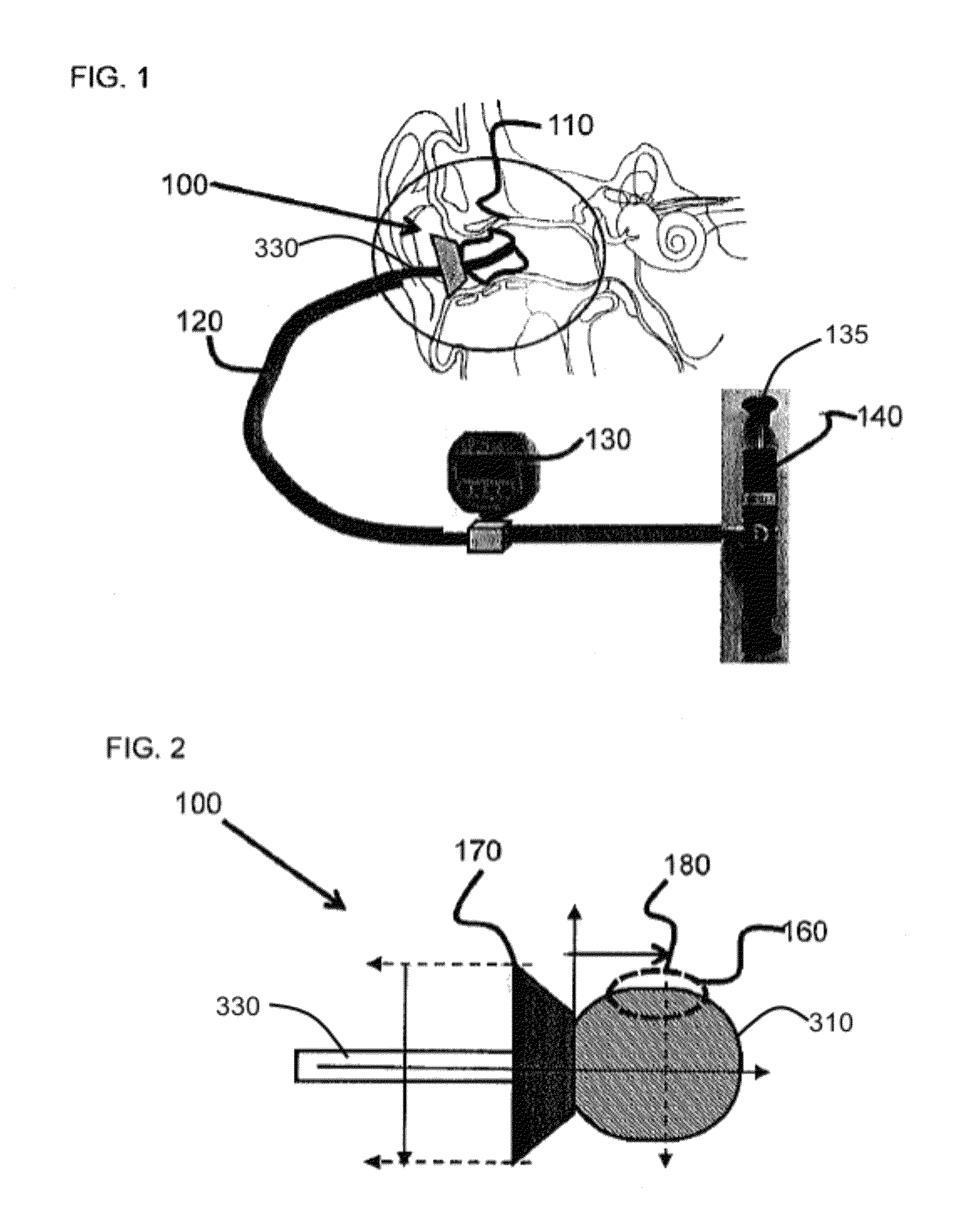
Device and method for radial pressure determination
Methods and apparatus for measuring ear canal wall pressure comfort level are provided. An expandable pressure exertion device is inserted into an orifice. The device is expanded inside the orifice in increments of pressure. A threshold level is saved where a user indicates that the pressure exerted against the walls of the orifice is becoming at least one of uncomfortable, painful, and noticeable.
Owner:STATON TECHIYA LLC
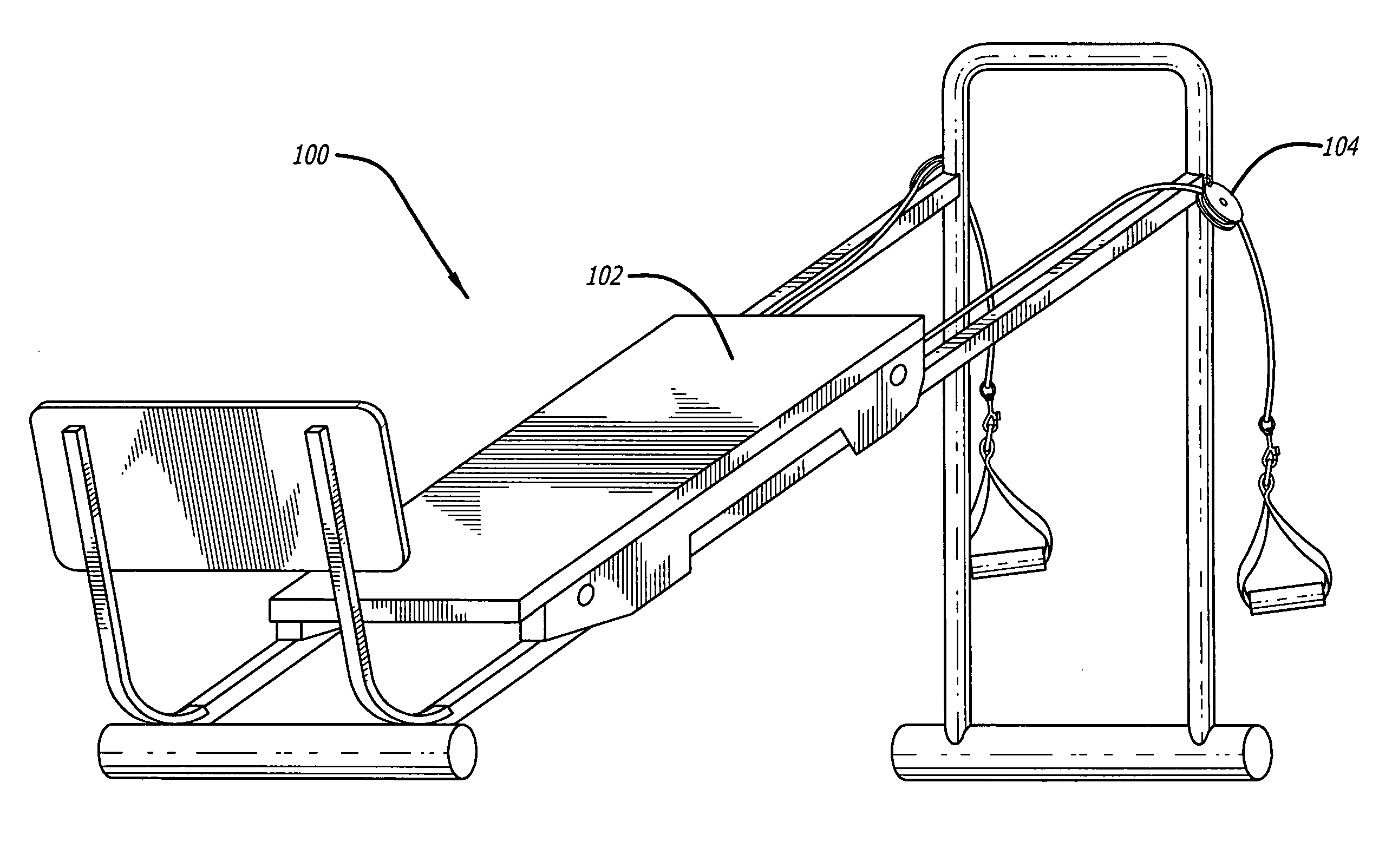
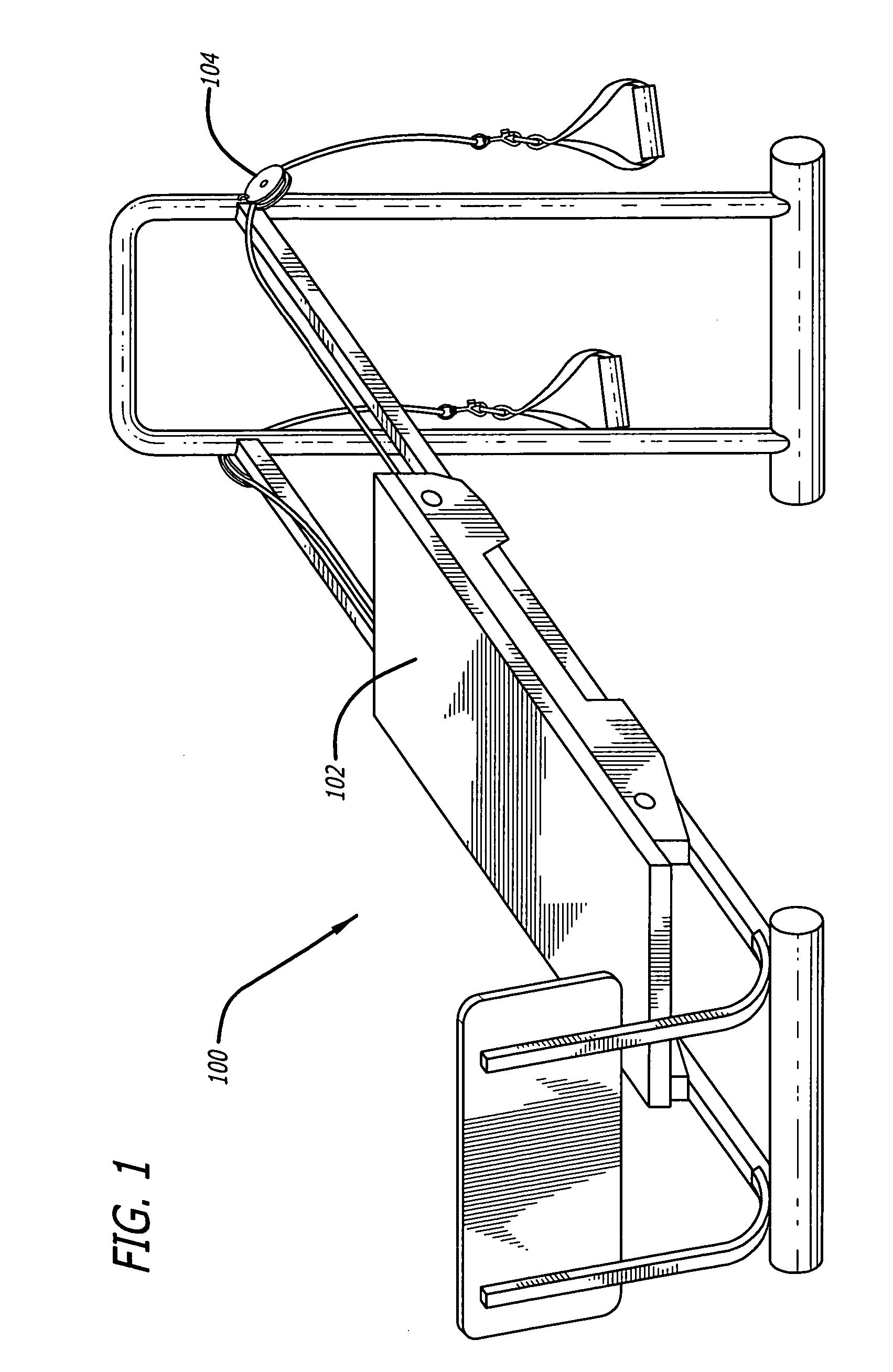
Networked exercise machine
Exercise machines are networked together to provide a user with an indication of the user's performance level compared to the performance levels of other users. Simulated characters corresponding to the users are shown on one or more displays viewable by the users. The simulated characters have a primary movement that may differ in type from the primary movement used in achieving the exercise by the corresponding user. Further, the primary movement used to achieve exercise by one user may differ from the primary movement used to achieve exercise by another user. Exertion transducers provide signals that are used in calculating parameters such as speed and acceleration. Biometric data may be measured from the users during exertion and displayed or uploaded onto the network.
Owner:SBC KNOWLEDGE VENTURES LP
Personalized beverage dispensing device
ActiveUS8490829B2Accurate assessmentLow costLighting and heating apparatusFlow controlPersonalizationExertion
Owner:PEPSICO INC
Resistance exercise method and system
InactiveUS20070093369A1Improves muscular strength and self-efficacyStiltsMovement coordination devicesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationExertion
A method for exercise by performing exercise sets in a sequence progressing from exertion of larger to smaller muscles, with the exercise movement performed using slow movements. Each exercise set is performed to a point of momentary failure. The slow movement is at a rate of less than about thirty degrees per second. The exercise sets are performed with as little rest between each exercise set as global or central fatigue will allow. Resistance is applied during each exercise set to produce muscle failure within a predefined time under tension parameter.
Owner:BOCCHICCHIO VINCENT J
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com