Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
213 results about "Tamponade" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tamponade is the closure or blockage (as of a wound or body cavity) by or as if by a tampon, especially to stop bleeding. Tamponade is a useful method of stopping a hemorrhage. This can be achieved by applying an absorbent dressing directly into a wound, thereby absorbing excess blood and creating a blockage, or by applying direct pressure with a hand or a tourniquet.
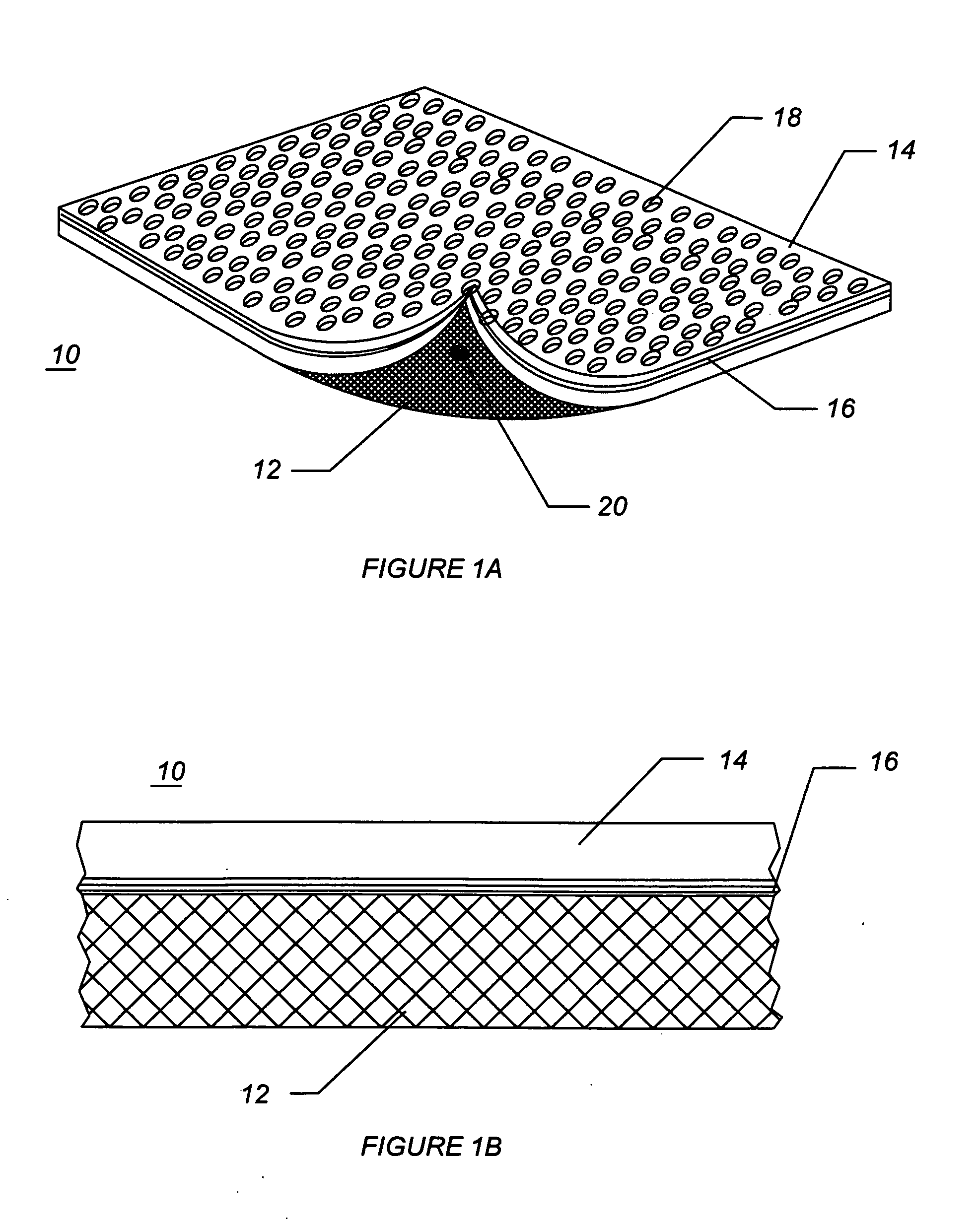
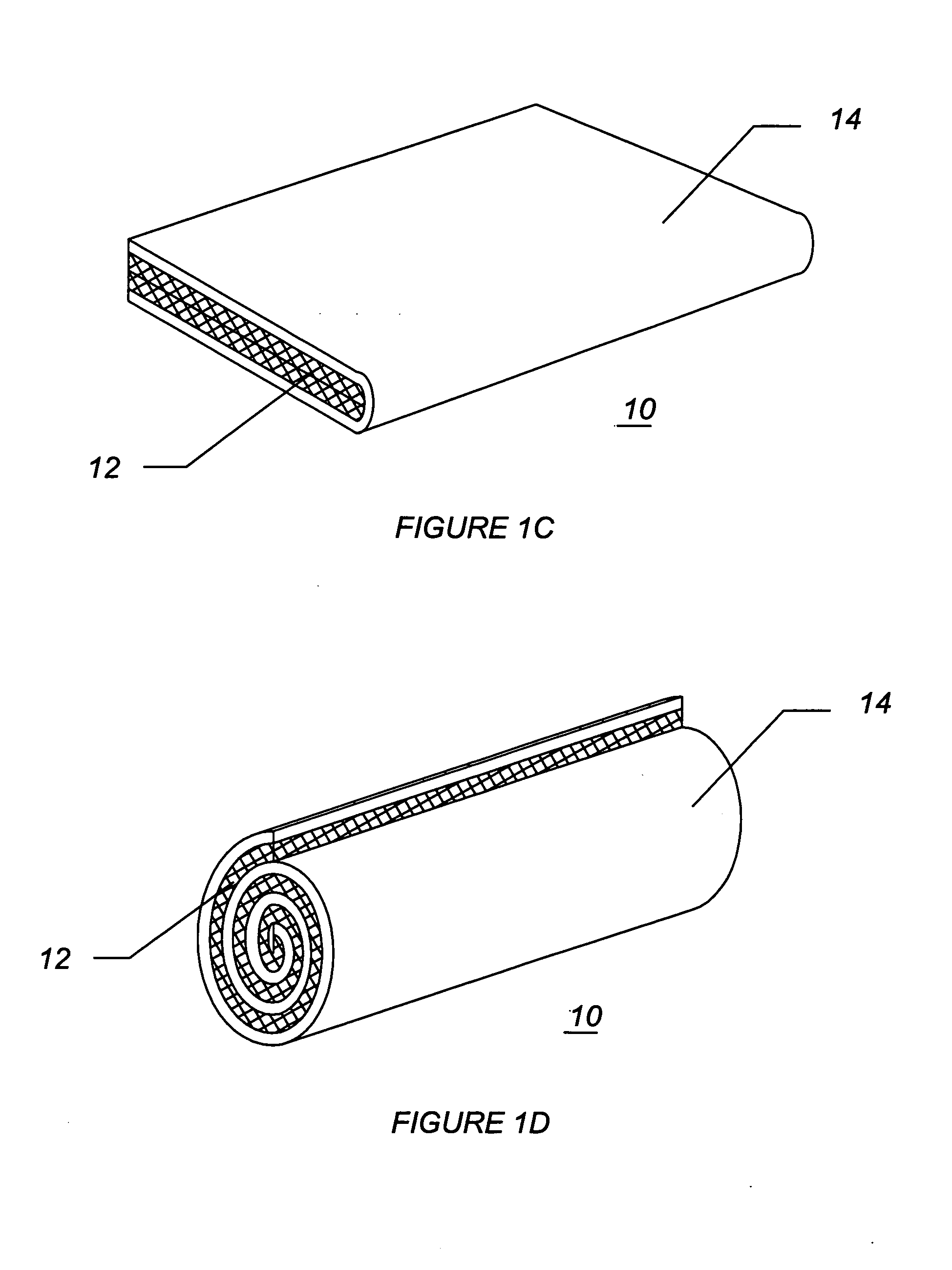
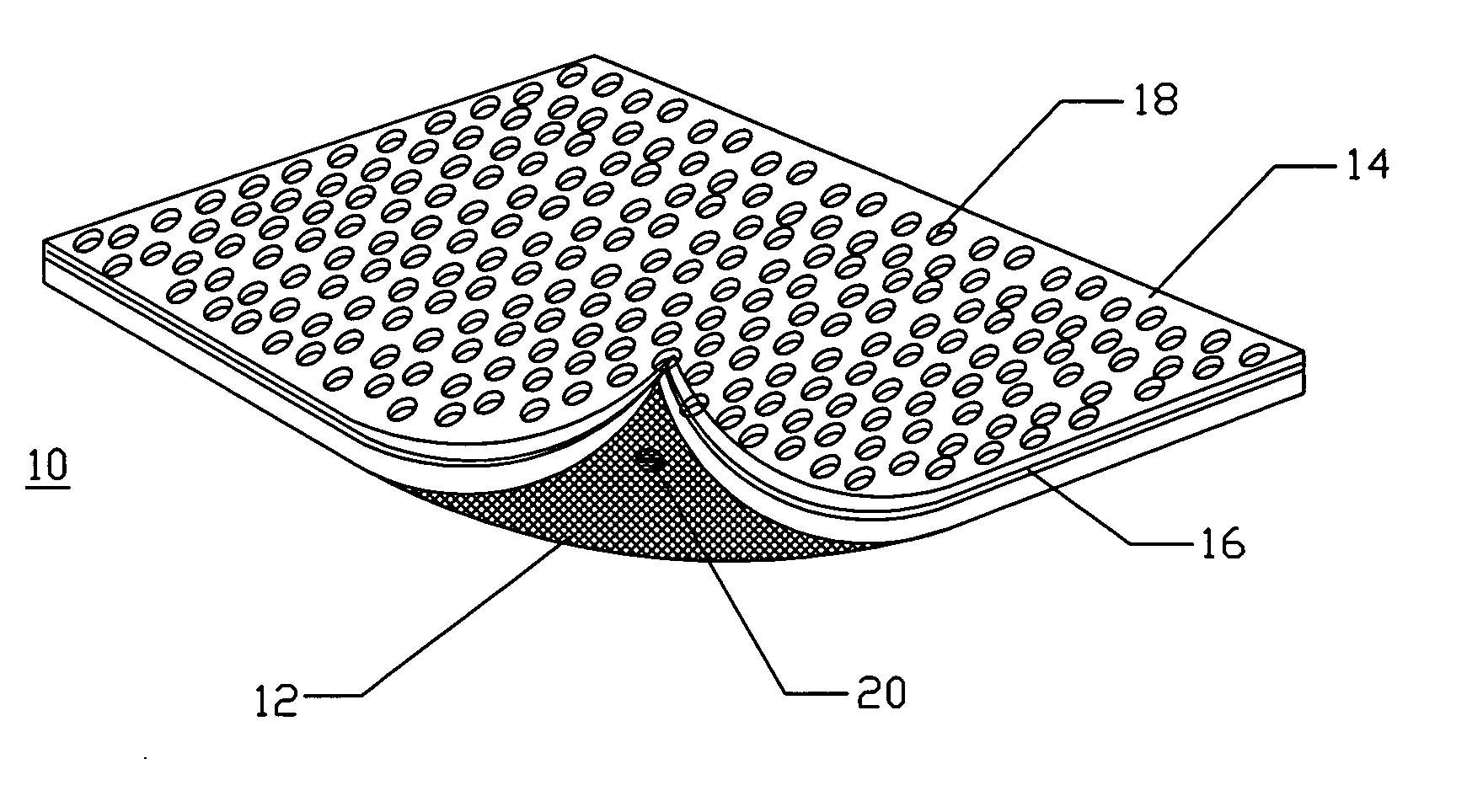
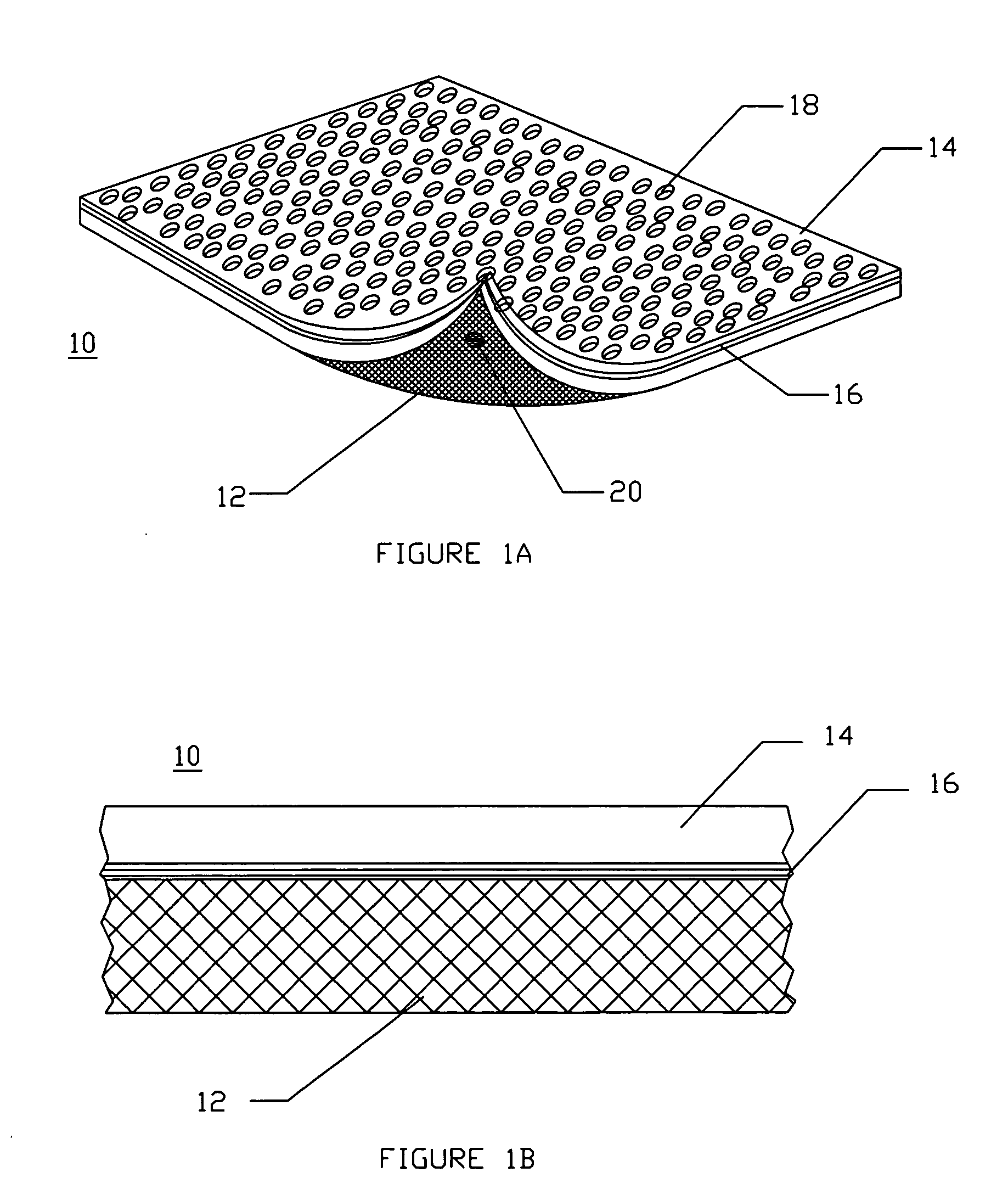
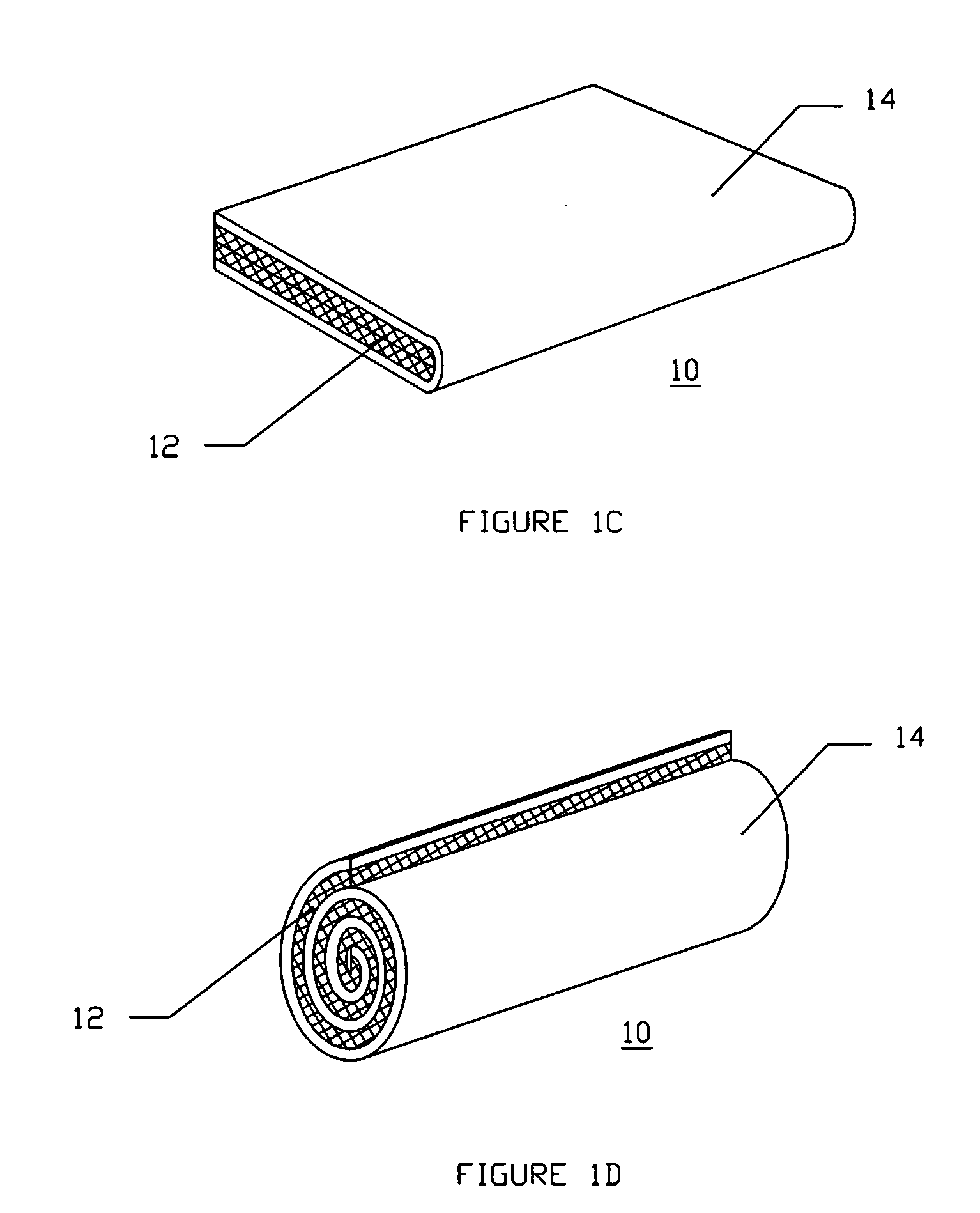
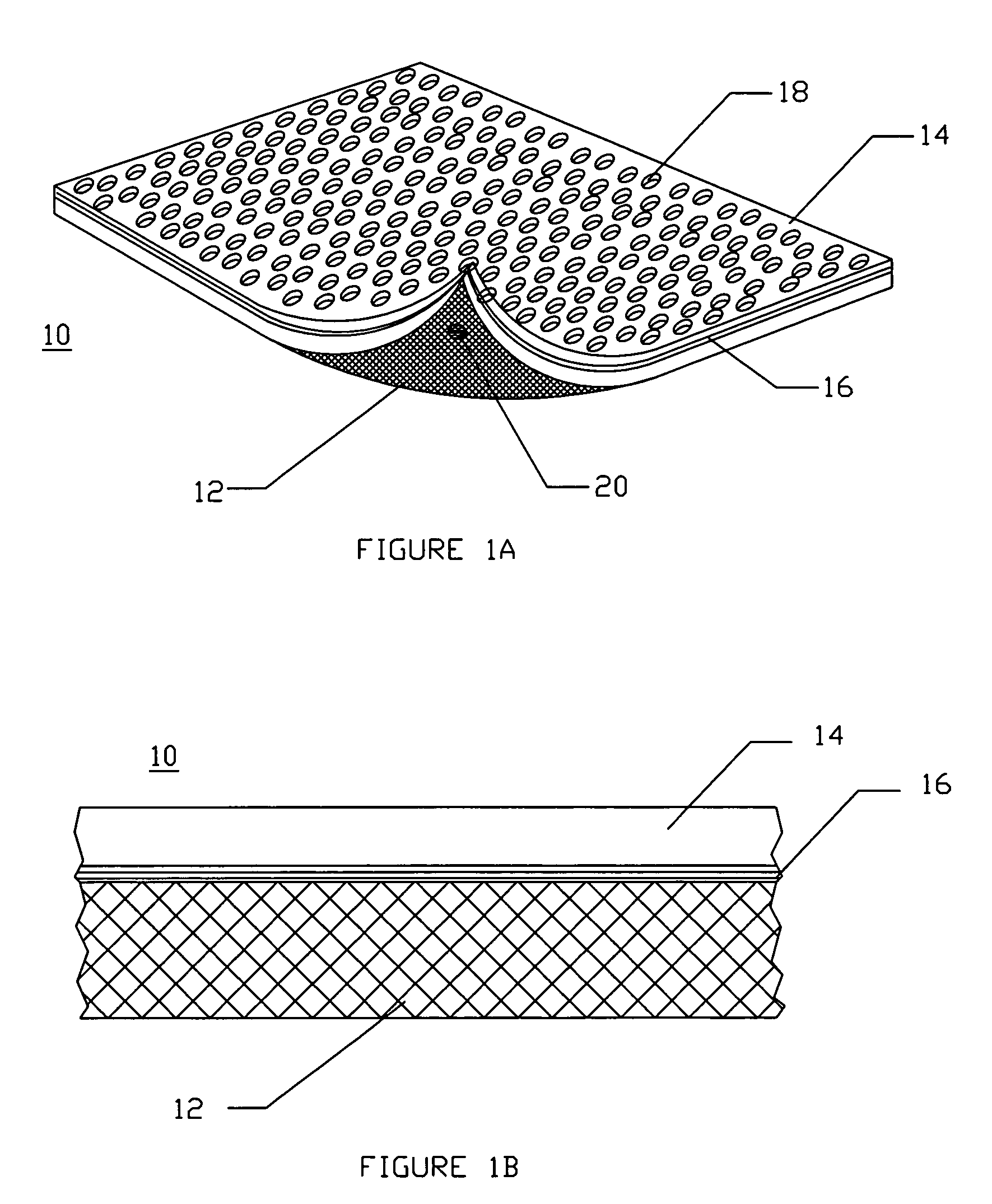
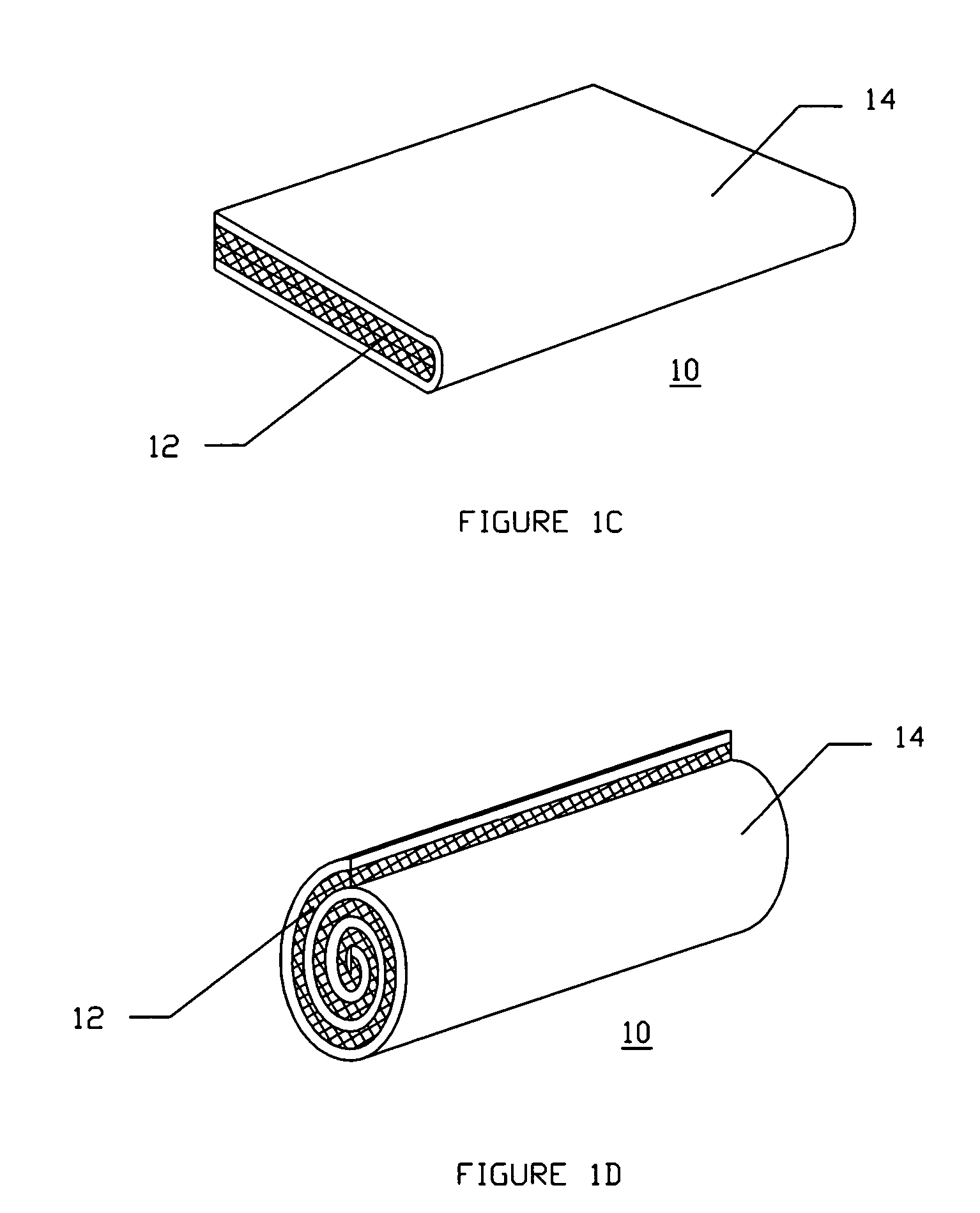
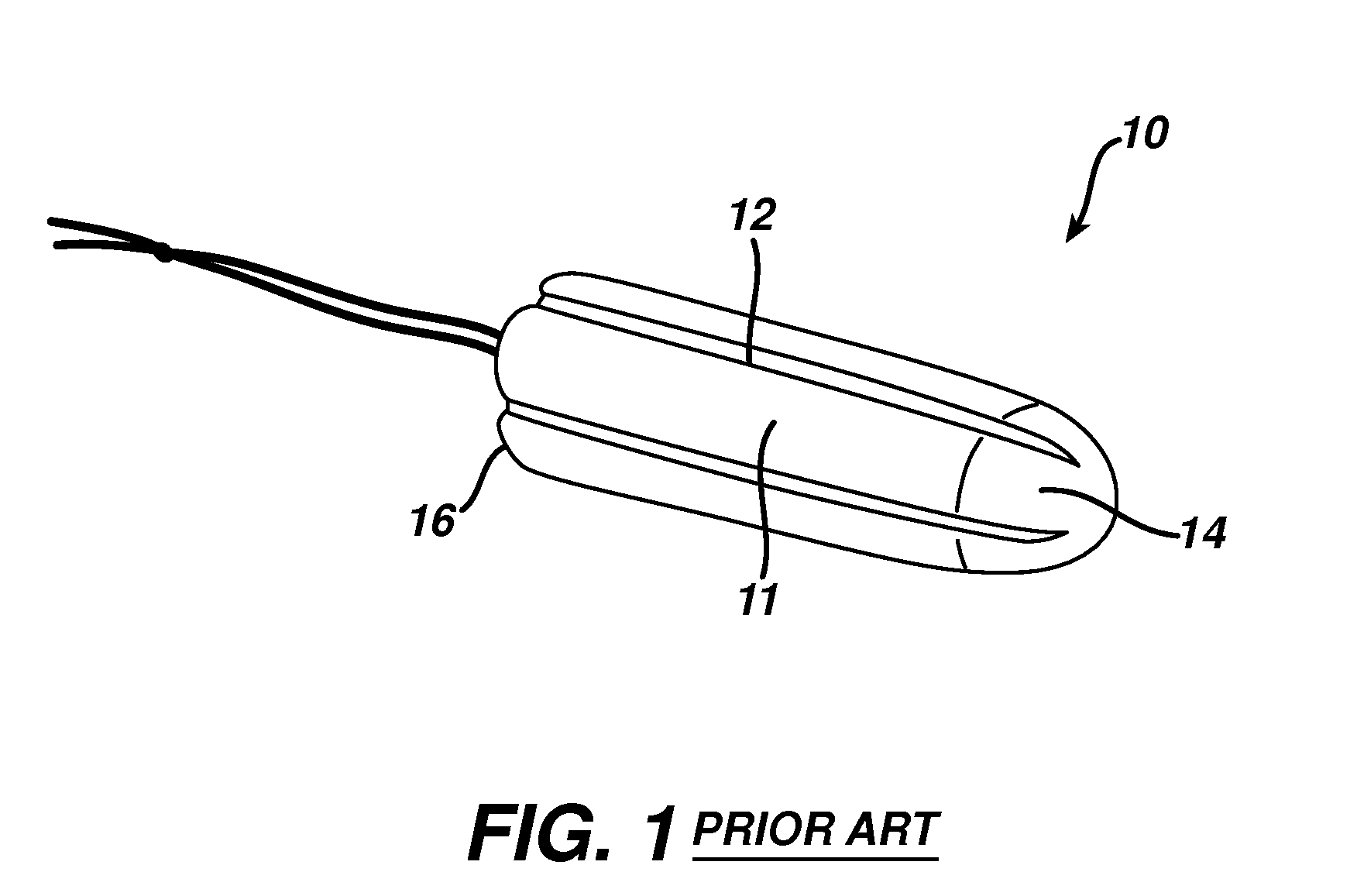
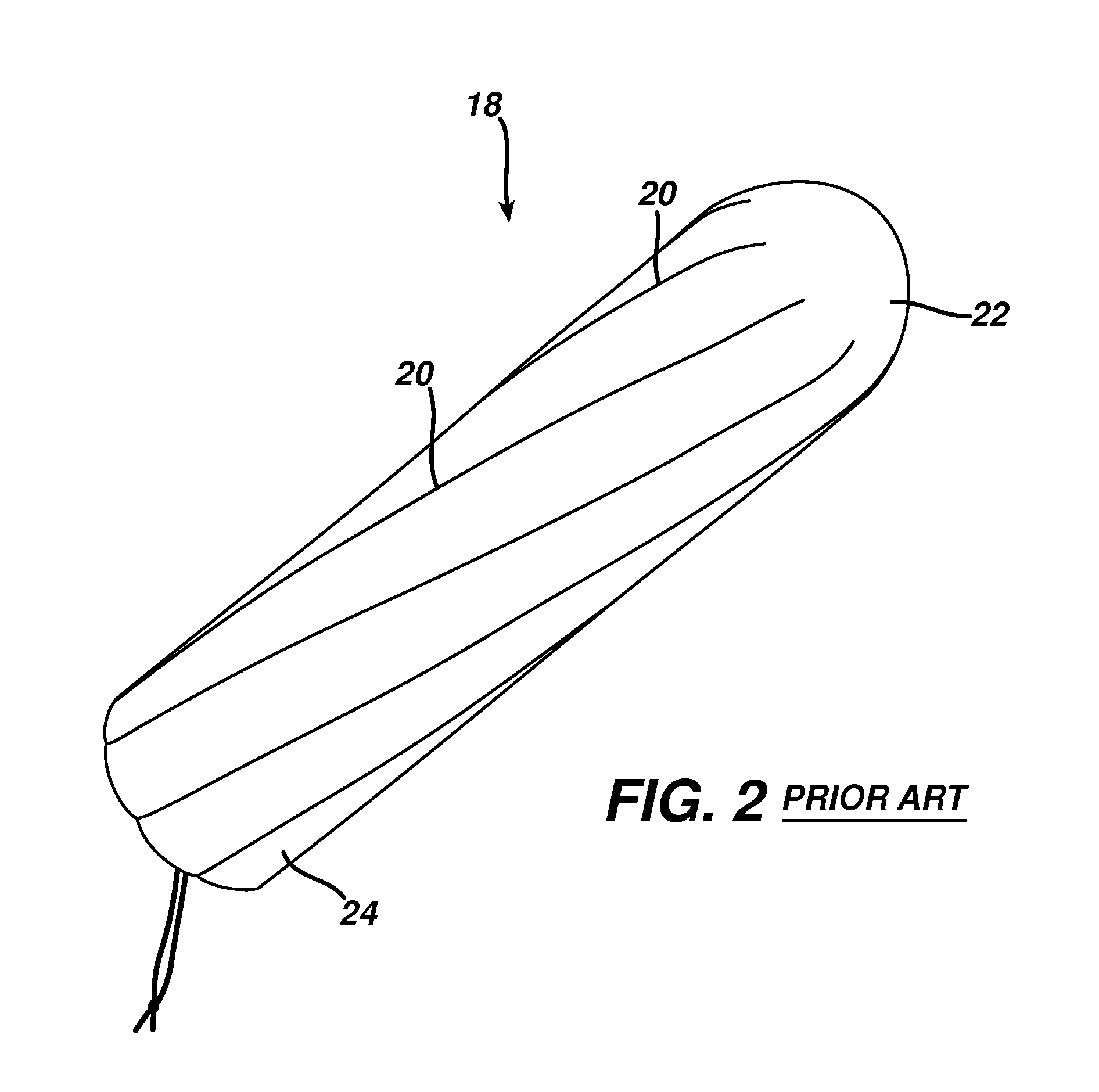
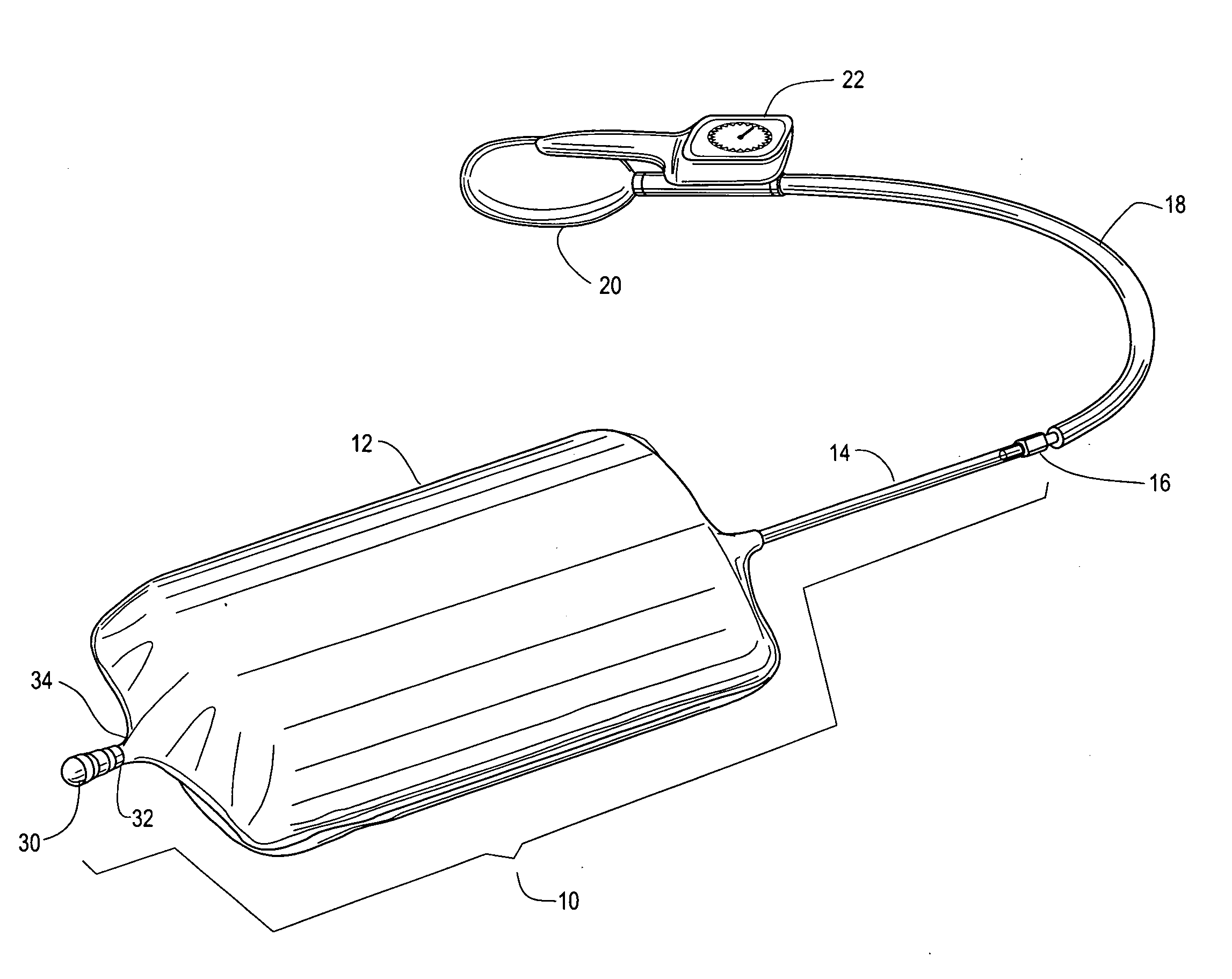
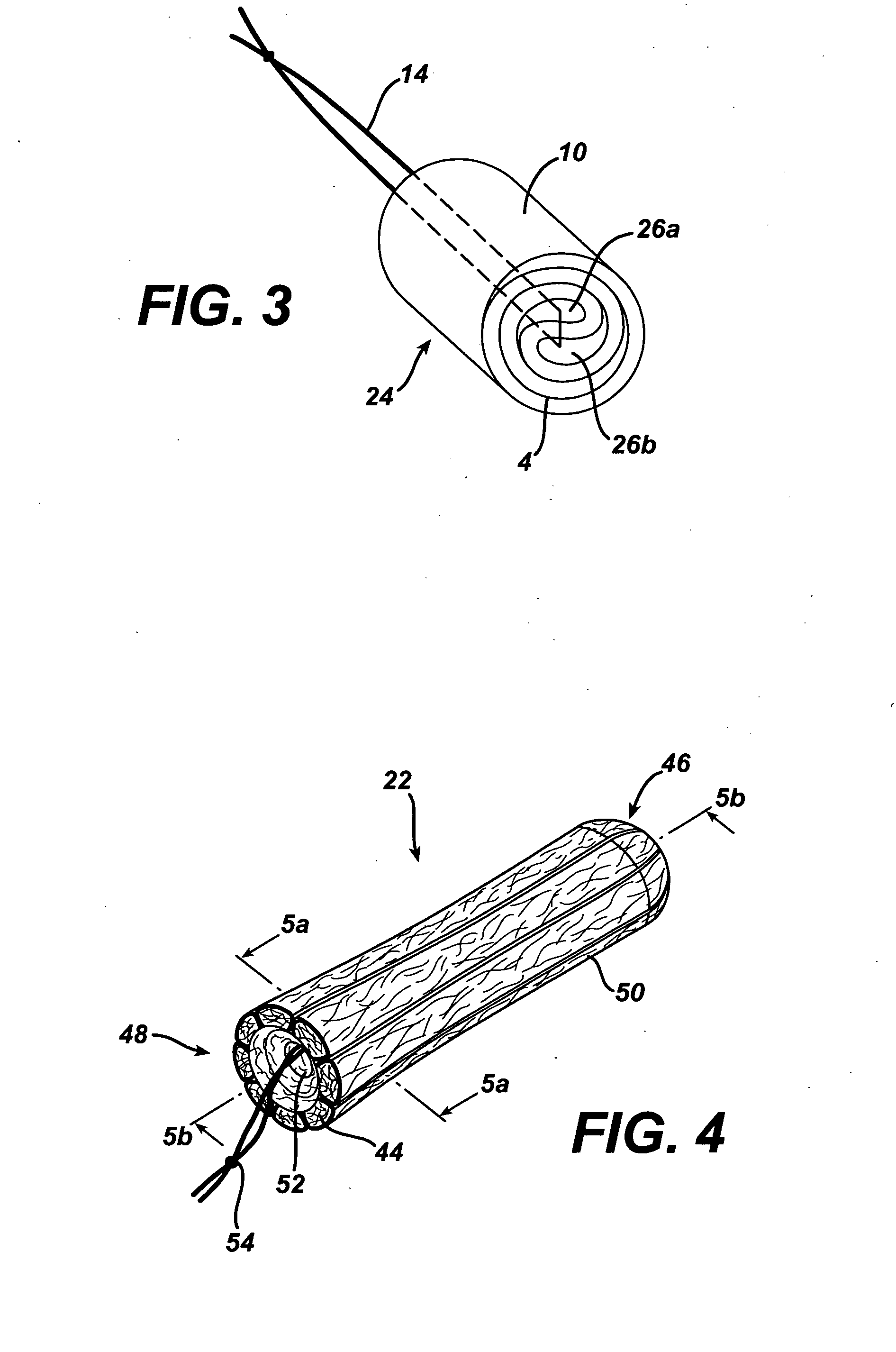
Method and apparatus for improved hemostasis and damage control operations
InactiveUS6998510B2Improved hemostatic packing in trauma careGood hemostasisPlastersBaby linensTamponadePERITONEOSCOPE
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in traumatized patients. The devices utilize fluid impermeable outer surfaces and distributed pressure to achieve tamponade and hemostasis, primarily by exertion of pressure. The devices are capable of serving as carriers for throabogenic or antipathogenic agents. Peripheral haemostatic packing devices include optional adhesive hemostatic barriers to cover the entire wound area over the hemostatic pack. The hemostatic packing devices may be placed and removed by open surgery or laparoscopic access without generating excessive re-bleeding, and may further comprise antimicrobial or thrombogenic regions.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
Absorbable implants and methods for their use in hemostasis and in the treatment of osseous defects
ActiveUS20050065214A1Stimulate bone healing processLower potentialBiocidePowder deliveryBarium saltTG - Triglyceride
Two (or more), -component, body-implantable, absorbable, biocompatible, putty, and non-putty hemostatic tamponades for use in surgery. Component 1 is a finely powdered bulking material, preferably less than 50 microns, e.g. the calcium, magnesium, aluminum, or barium salts of saturated or unsaturated carboxylic acids containing about 6 to 22 carbon atoms, hydroxyapatite, DBM, polyglycolide, polylactide, poldioxinones, polycaprolactones, absorbable glasses, gelatin, collagens, mono, and polysaccharides starches. Component 2, a dispersing vehicle, may be esters of C8-C18 monohydric alcohols with C2-C6 aliphatic monocarboxylic acids; C2-C18 monohydric alcohols with polycarboxylic acids; C8-C30 monohydric alcohols; tocopherol and esters thereof with C2-C10 aliphatic monocarboxylic acids or polycarboxylic acids; absorbable 10-14C hydrocarbons; free carboxylic acids such as oleic, capric, and lauric; dialkyl ethers and ketones; alkyl aryl ethers and ketones, polyhydroxy compounds and esters and ethers thereof; (ethylene oxide / propylene oxide copolymers), oils e.g. olive oil, castor oil and triglycerides.
Owner:ABYRX
Method and apparatus for hemostasis
InactiveUS20080132820A1Different compressibilityDifferent resilienceNon-adhesive dressingsPlastersTrauma surgeryTourniquet time
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in patients who have received skin-penetrating wounds to the periphery, including the head, arms, and legs. Such haemostatic packing devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery, or military setting. The devices utilize fluid impermeable barriers surrounded by exterior dams and pressure to achieve tamponade and hemostasis, primarily by exertion of force to hold the dams against the skin surrounding a wound. The devices are capable of serving as carriers for thrombogenic, antimicrobial or antipathogenic agents. The devices do not require the use of adhesives to work as they are attached to the patient using mechanical locking devices. Peripheral haemostatic packing devices include optional adhesive hemostatic barriers to attach at least a portion of the device to the skin or to assist with initial coupling of a hold-down strap to another strap using a more secure mechanical lock. The peripheral hemostatic packing system does not completely surround the extremity having the wound and therefore do not cause a tourniquet effect. The peripheral hemostatic packing system preferably is held against the skin surrounding a wound by a force that is generally unidirectional and substantially perpendicular to the plane in which the skin of the wound resides.
Owner:BUCKMAN ROBERT F +2
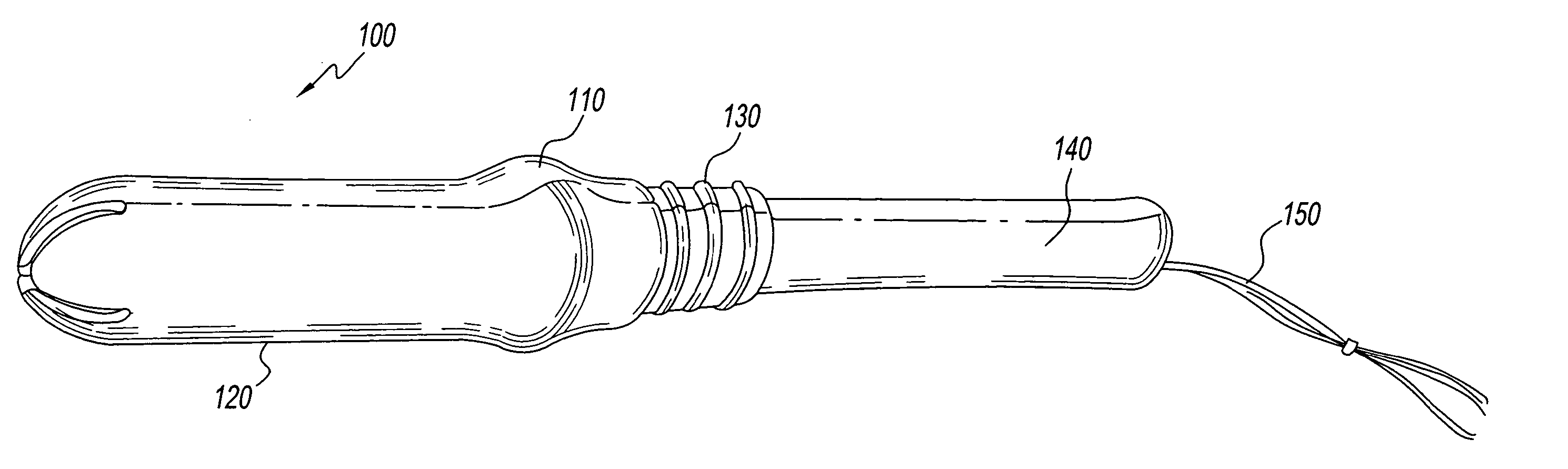
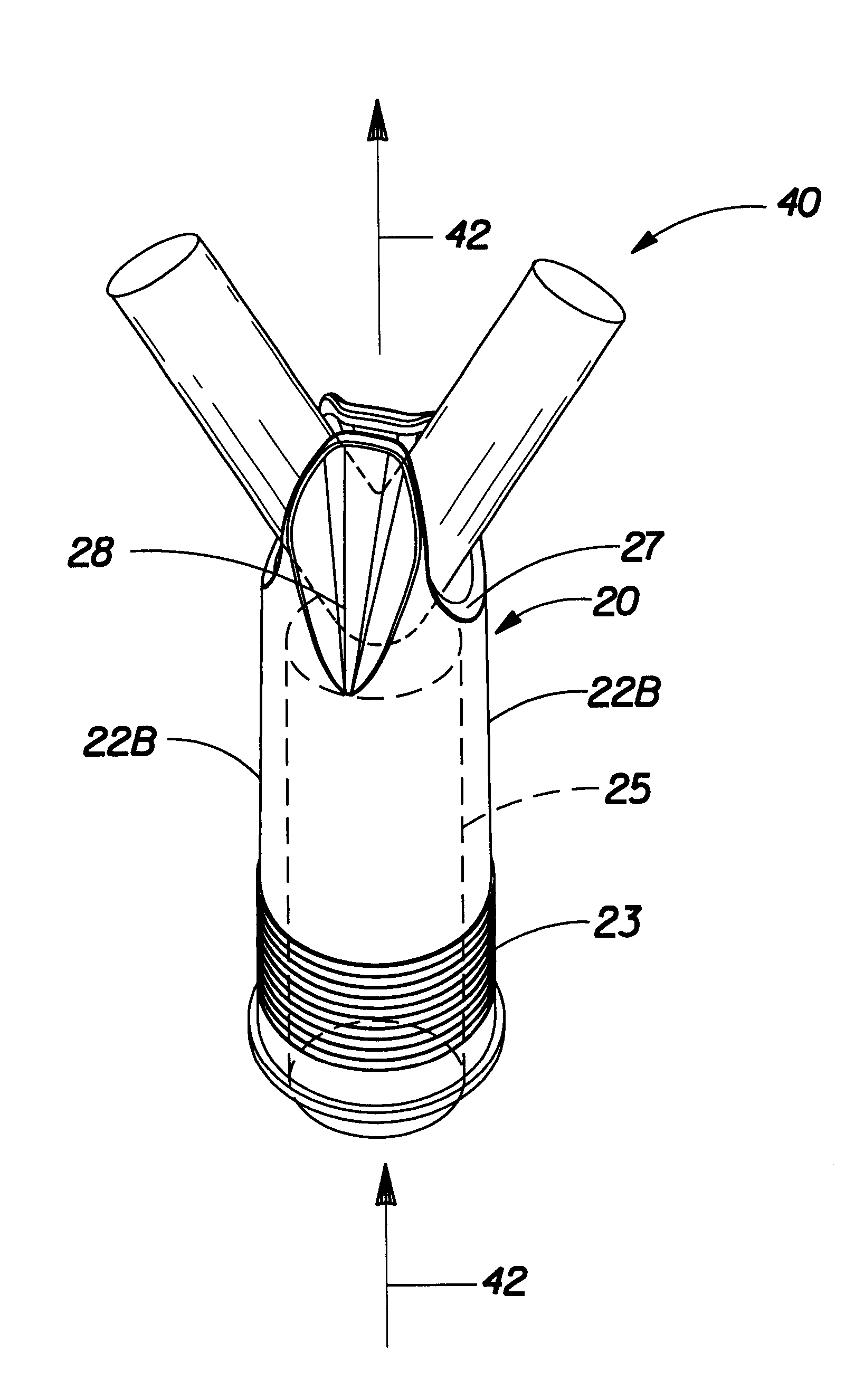
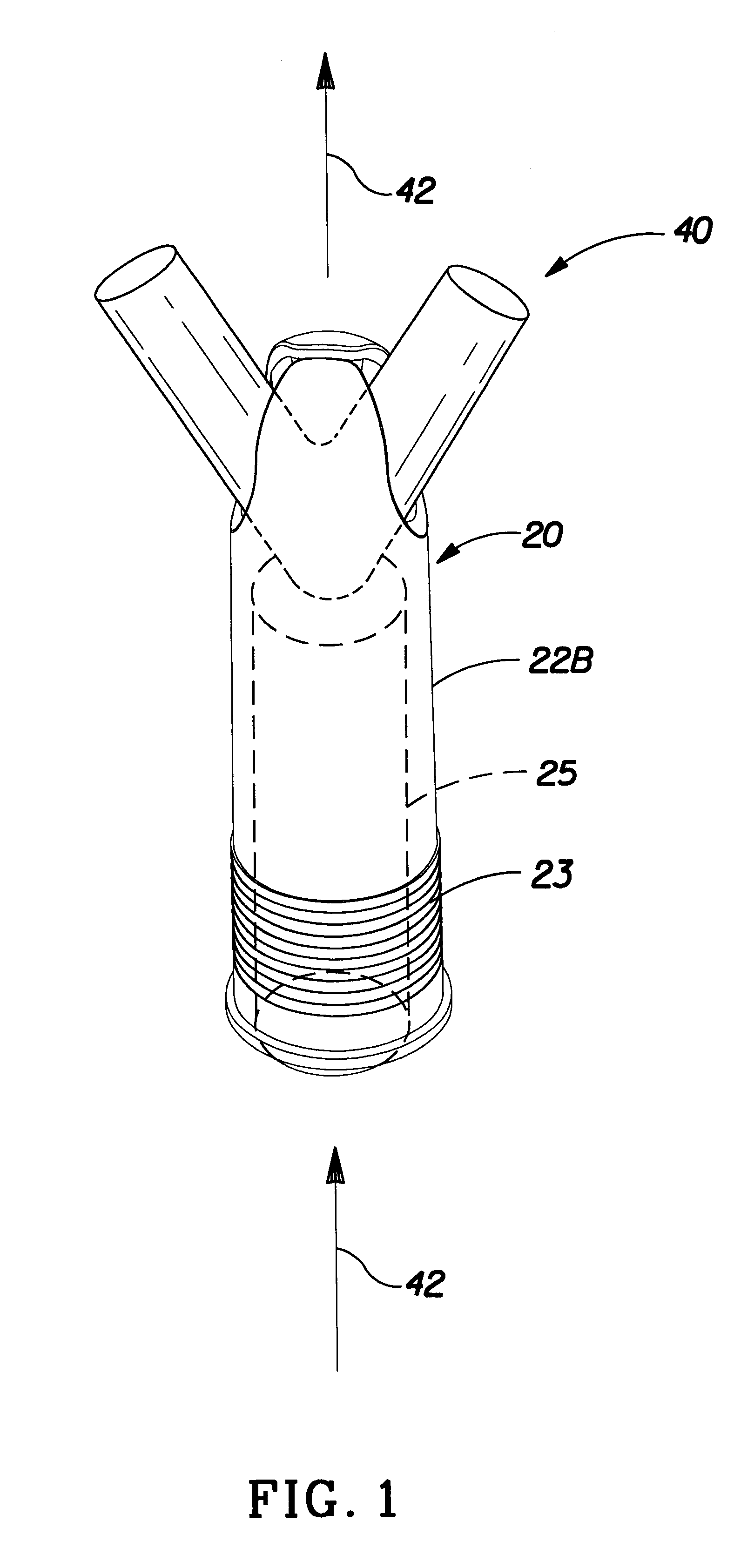
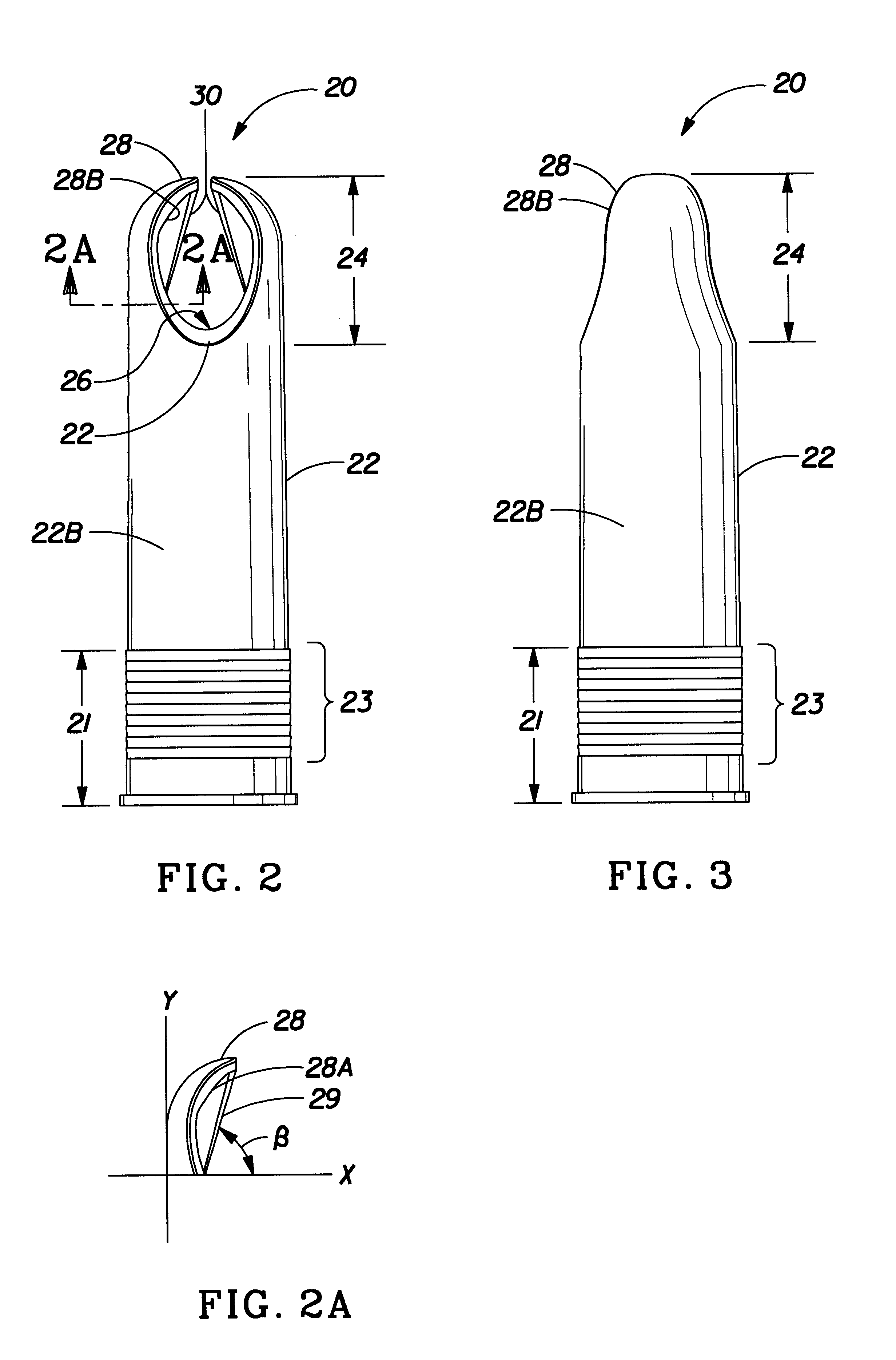
Insertion tool and insertion method for arterial tamponade device
InactiveUS20140074143A1Reduce bleedingReduce and eliminate blood flowDilatorsWound clampsTamponadeEngineering
An ergonomic insertion tool for insertion and retrieval of an arterial tamponade device which has an elongate connecting strut of resiliently deformable material and an arterial compressor at one end. The tool has a handle with a hand grip portion including an actuating trigger, and an elongate barrel. The barrel has a shaft and an outer sleeve telescopically engaged over the shaft. In a first position, a hooked distal end of the shaft protrudes from the sleeve to engage a bend between adjacent end portions of the connecting strut. On movement into a second position, the sleeve extends over the hooked end and compresses the deformable connecting strut into a deformed, U-shaped configuration to hold the device during insertion or retrieval. On movement back into the first position, the deformed device is released to spring out towards the expanded condition.
Owner:SINOCCLUSIVE
Absorbable implants and methods for their use in hemostasis and in the treatment of osseous defects
ActiveUS20060013857A1Lower potentialMinimally inhibit osteogenesis and subsequent bone healingSurgical adhesivesSkeletal disorderBarium saltApatite
Two (or more), -component, body-implantable, absorbable, biocompatible, putty, and non-putty hemostatic tamponades for use in surgery. Component 1 is a finely powdered bulking material, preferably less than 50 microns, e.g. the calcium, magnesium, aluminum, or barium salts of saturated or unsaturated carboxylic acids containing about 6 to 22 carbon atoms, hydroxyapatite, DBM, polyglycolide, polylactide, poldioxinones, polycaprolactones, absorbable glasses, gelatin, collagens, mono, and polysaccharides starches. Component 2, a dispersing vehicle, may be esters unsubstituted and N-substituted pyrrolidones of C8-C18 monohydric alcohols with C2-C6 aliphatic monocarboxylic acids; C2-C18 monohydric alcohols with polycarboxylic acids; C8-C30 monohydric alcohols; tocopherol and esters thereof with C2-C10 aliphatic monocarboxylic acids or polycarboxylic acids; absorbable 10-14C hydrocarbons; free carboxylic acids such as oleic, capric, and lauric; dialkyl ethers and ketones; alkyl aryl ethers and ketones, polyhydroxy compounds and esters and ethers thereof; (ethylene oxide / propylene oxide copolymers), oils e.g. olive oil, castor oil and triglycerides.
Owner:ABYRX
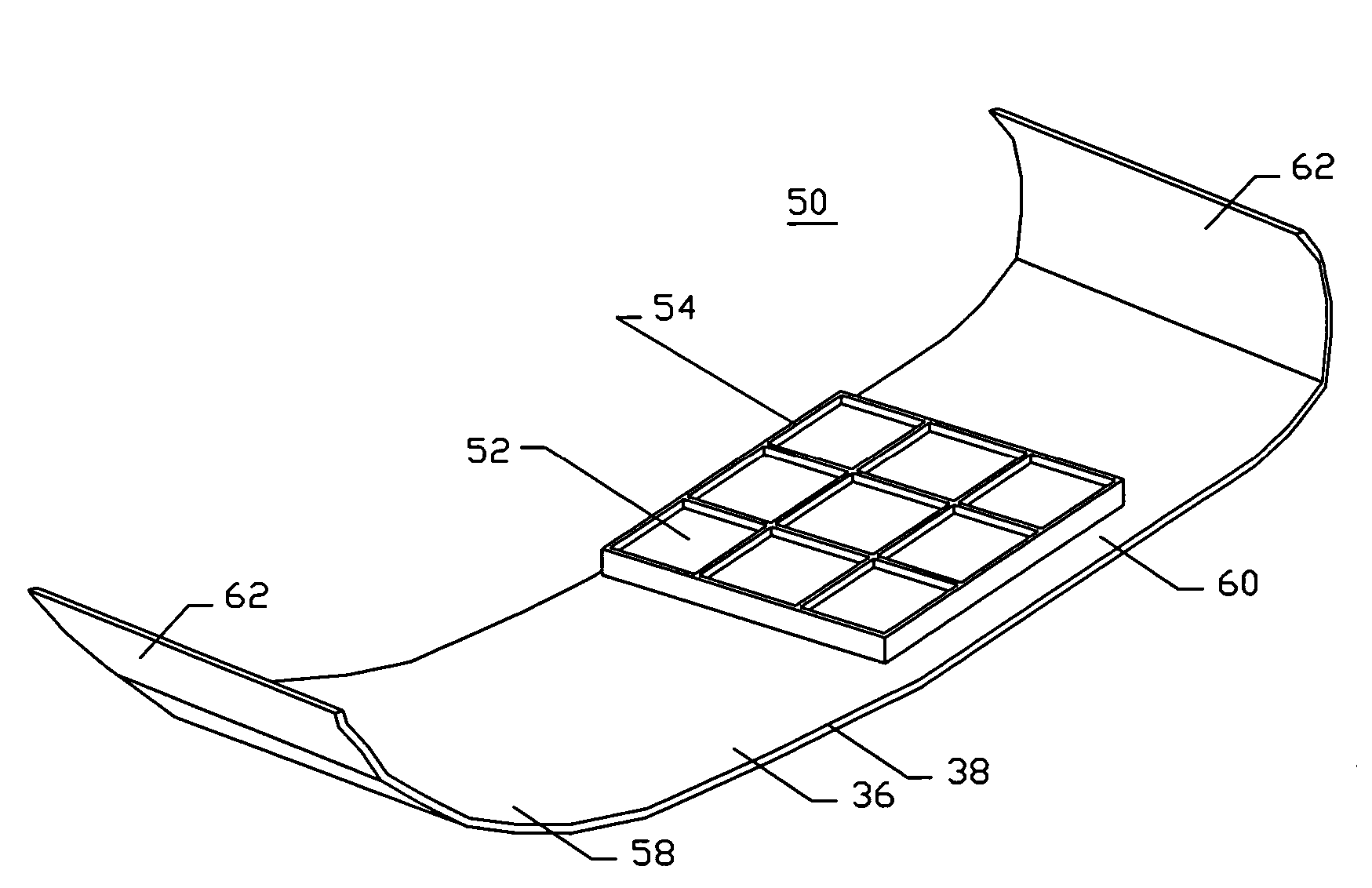
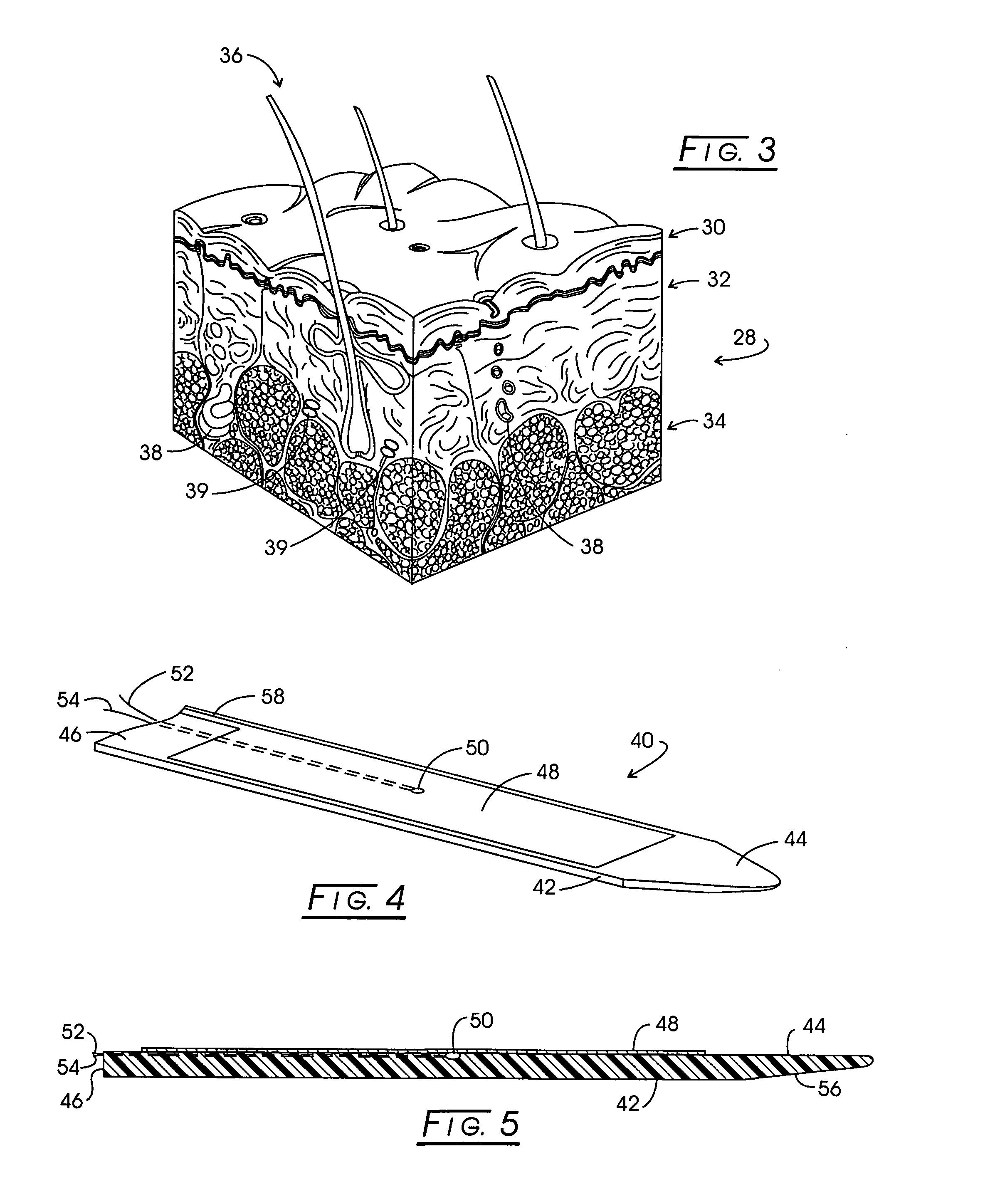
Gastro-esophageal reflux control system and pump
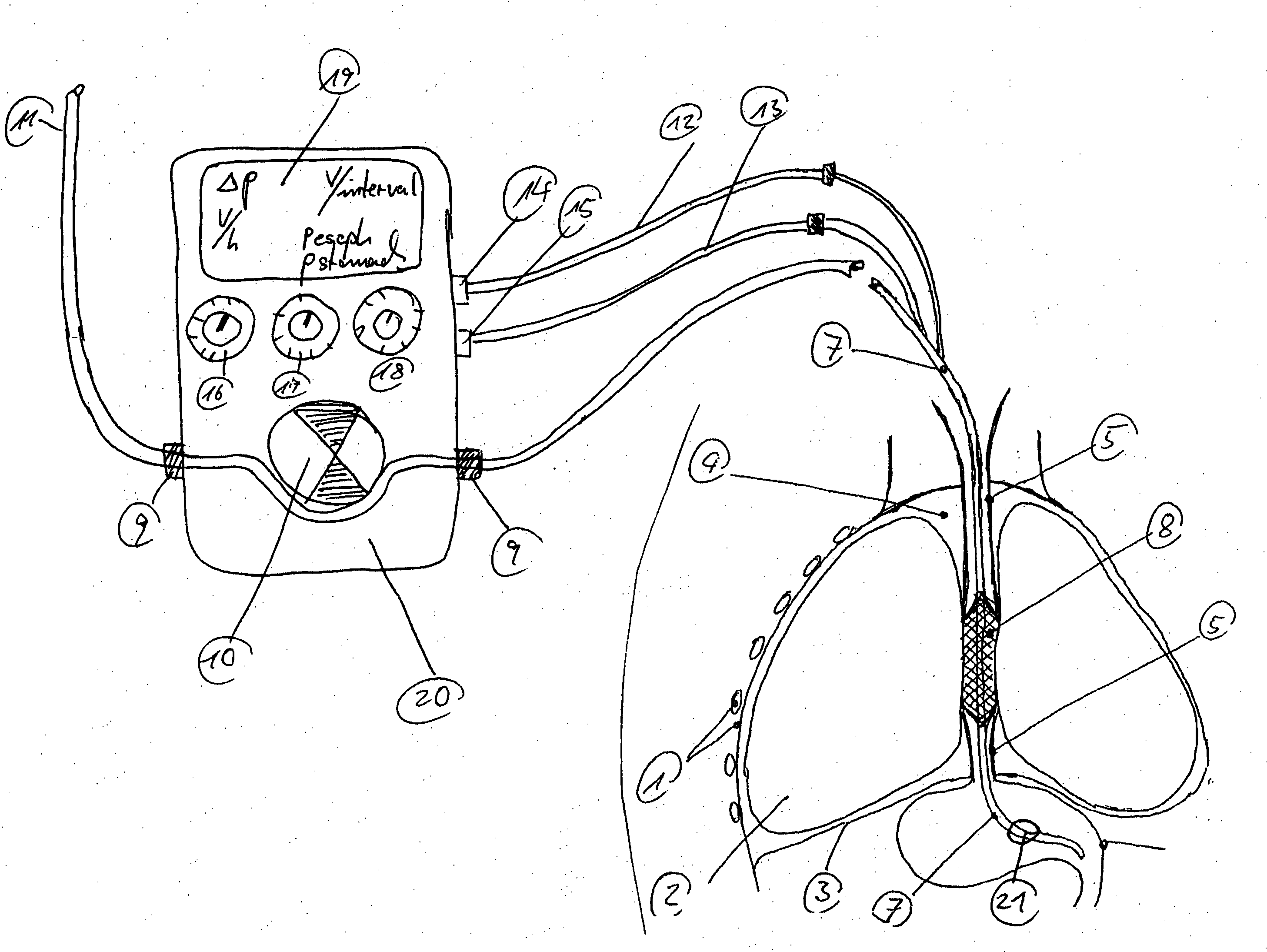
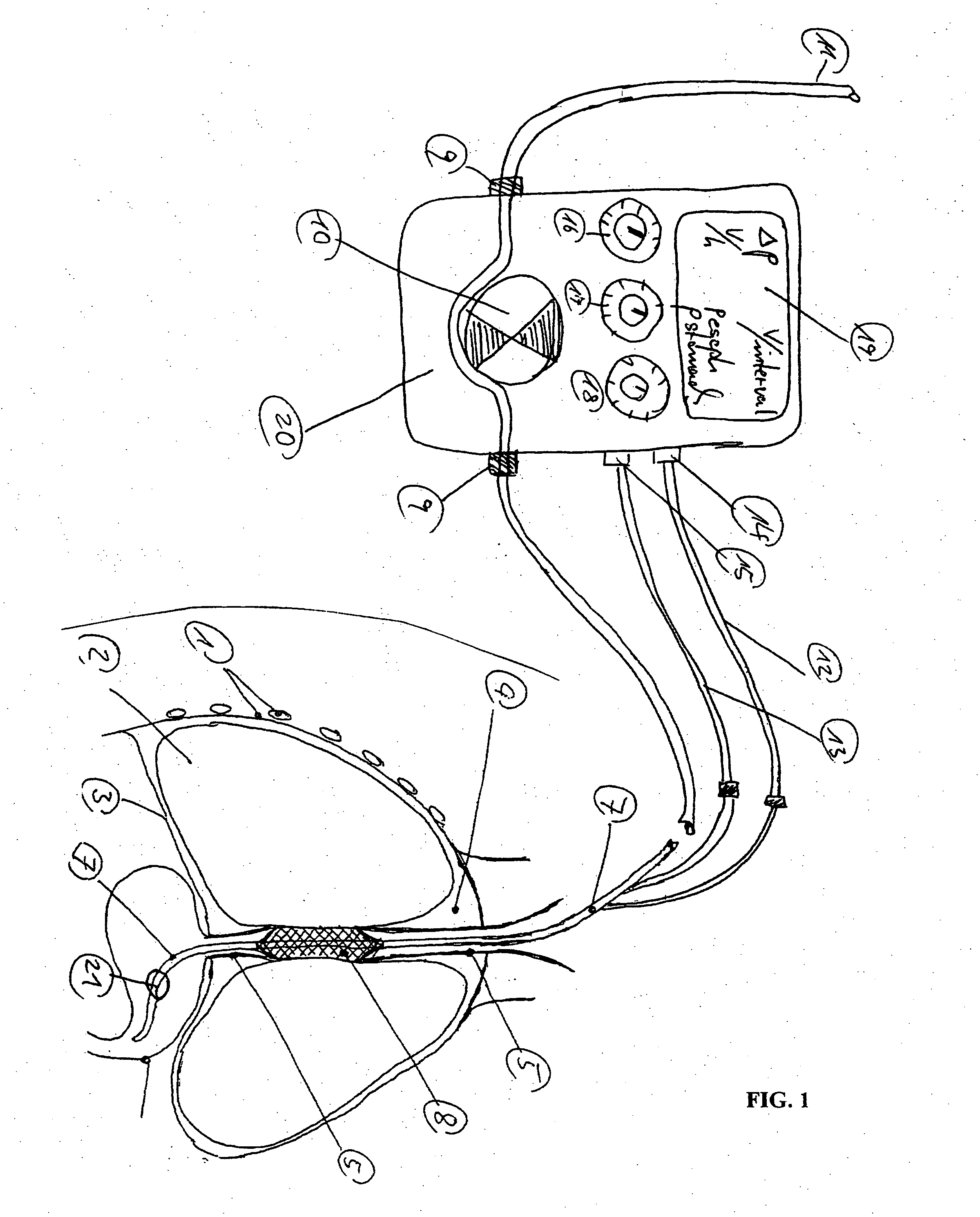
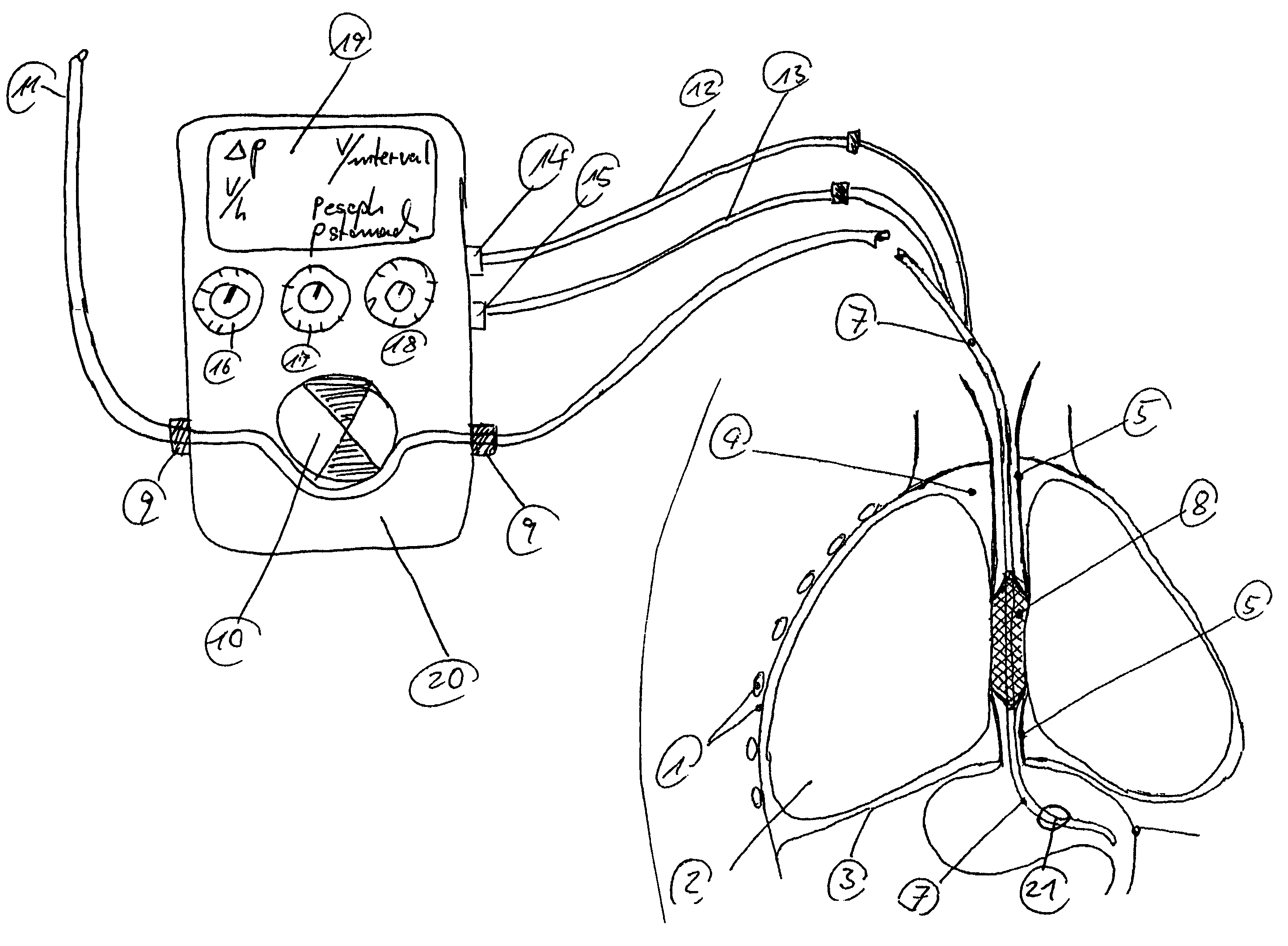
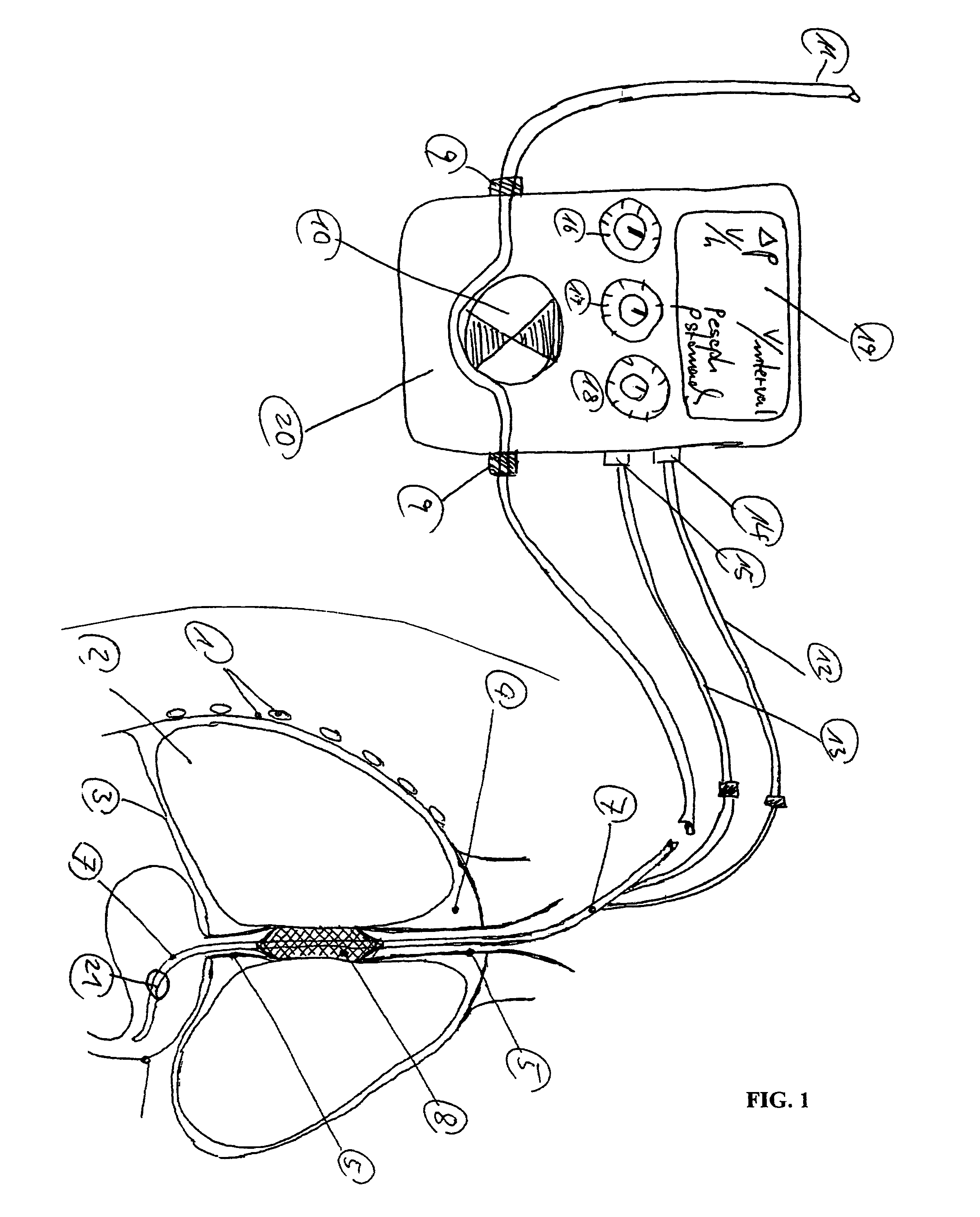
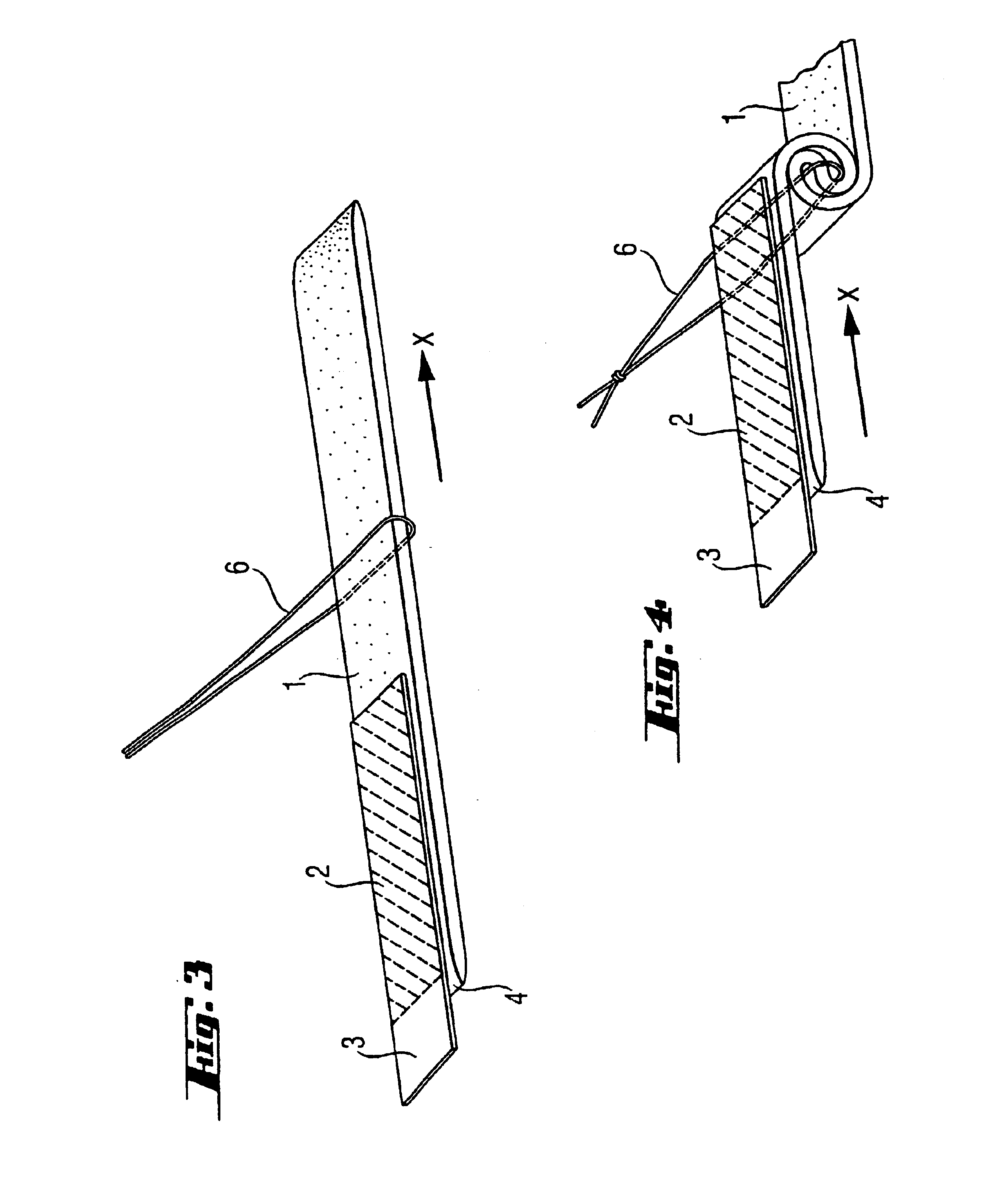
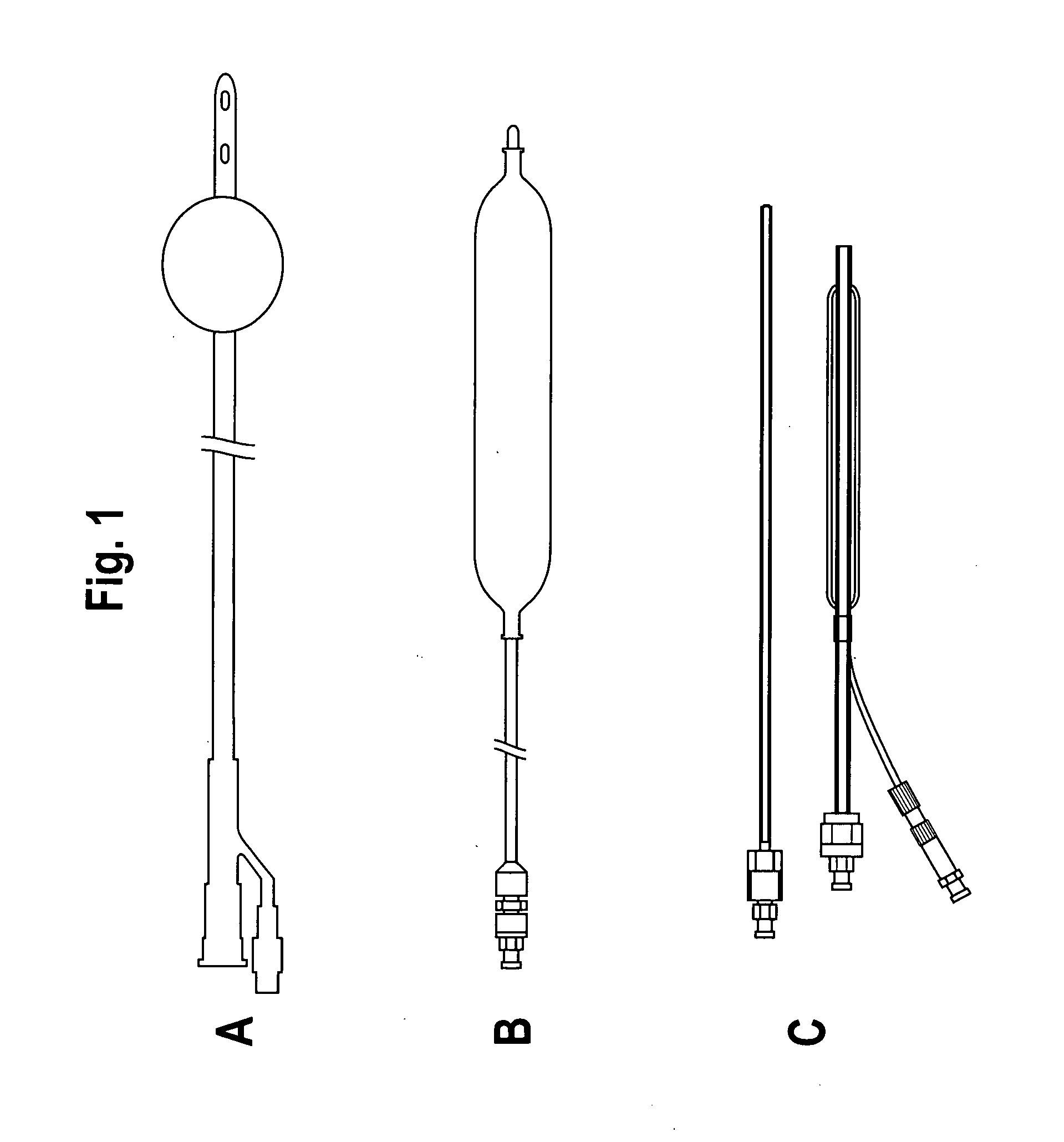
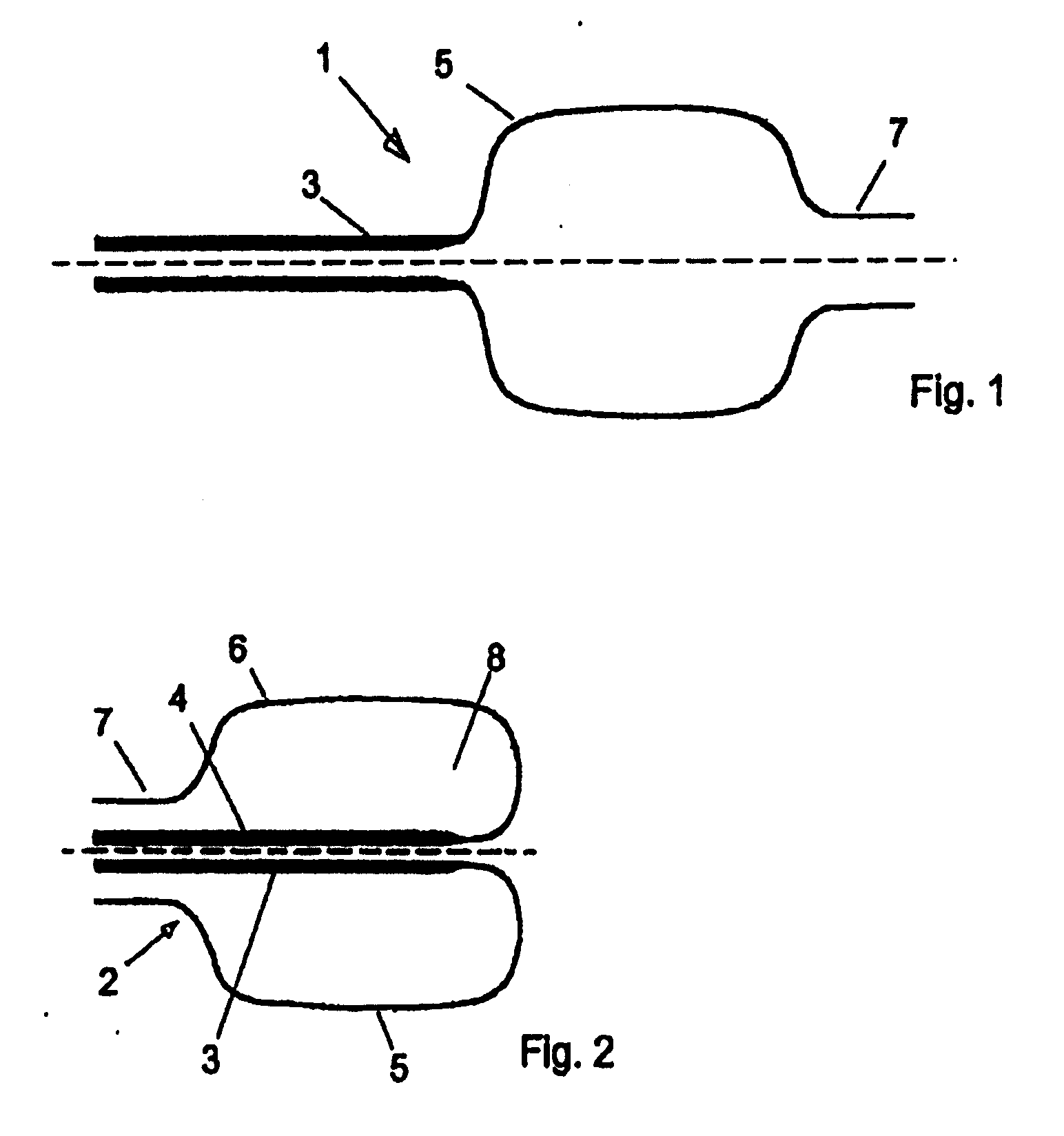
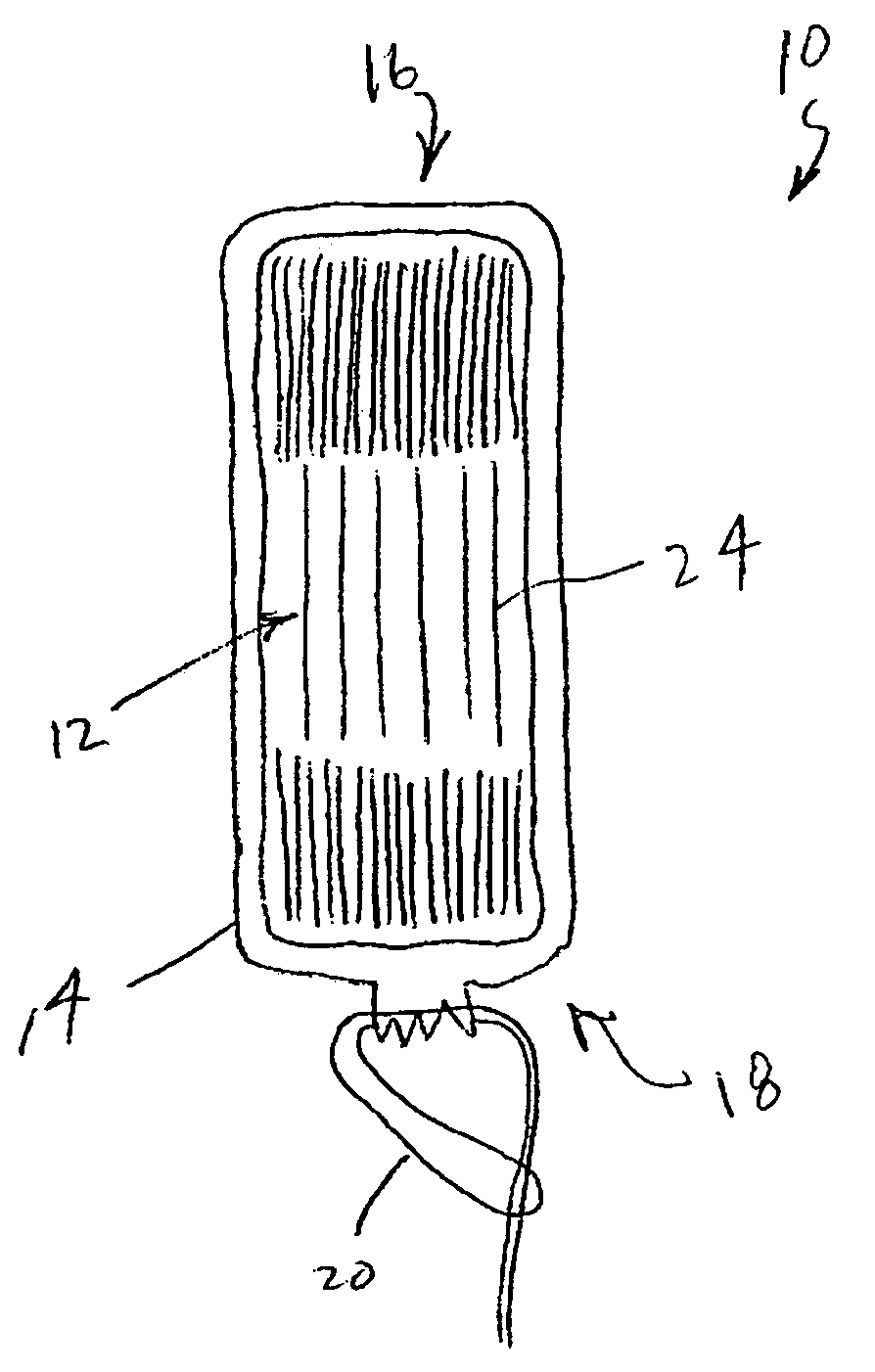
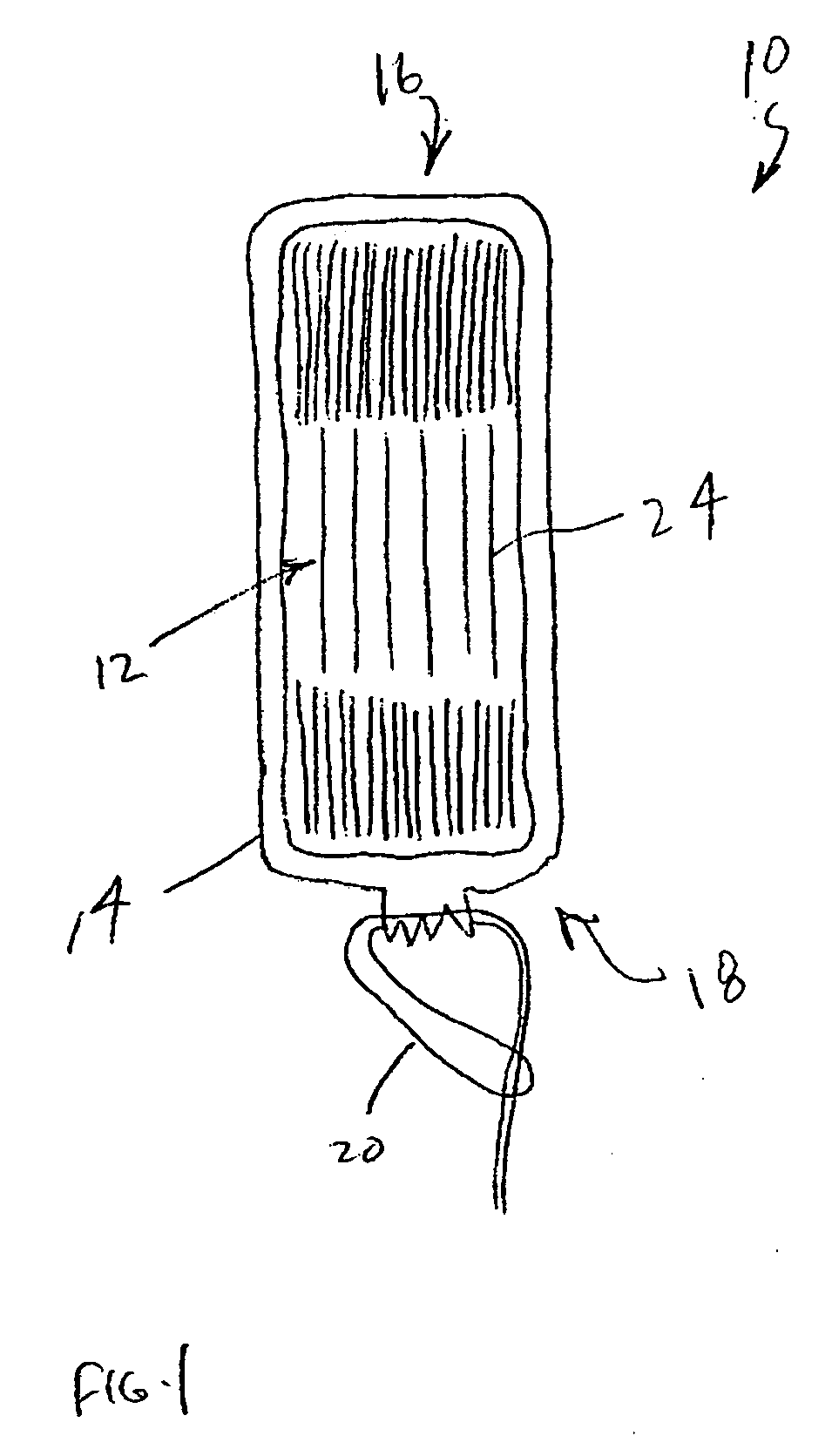
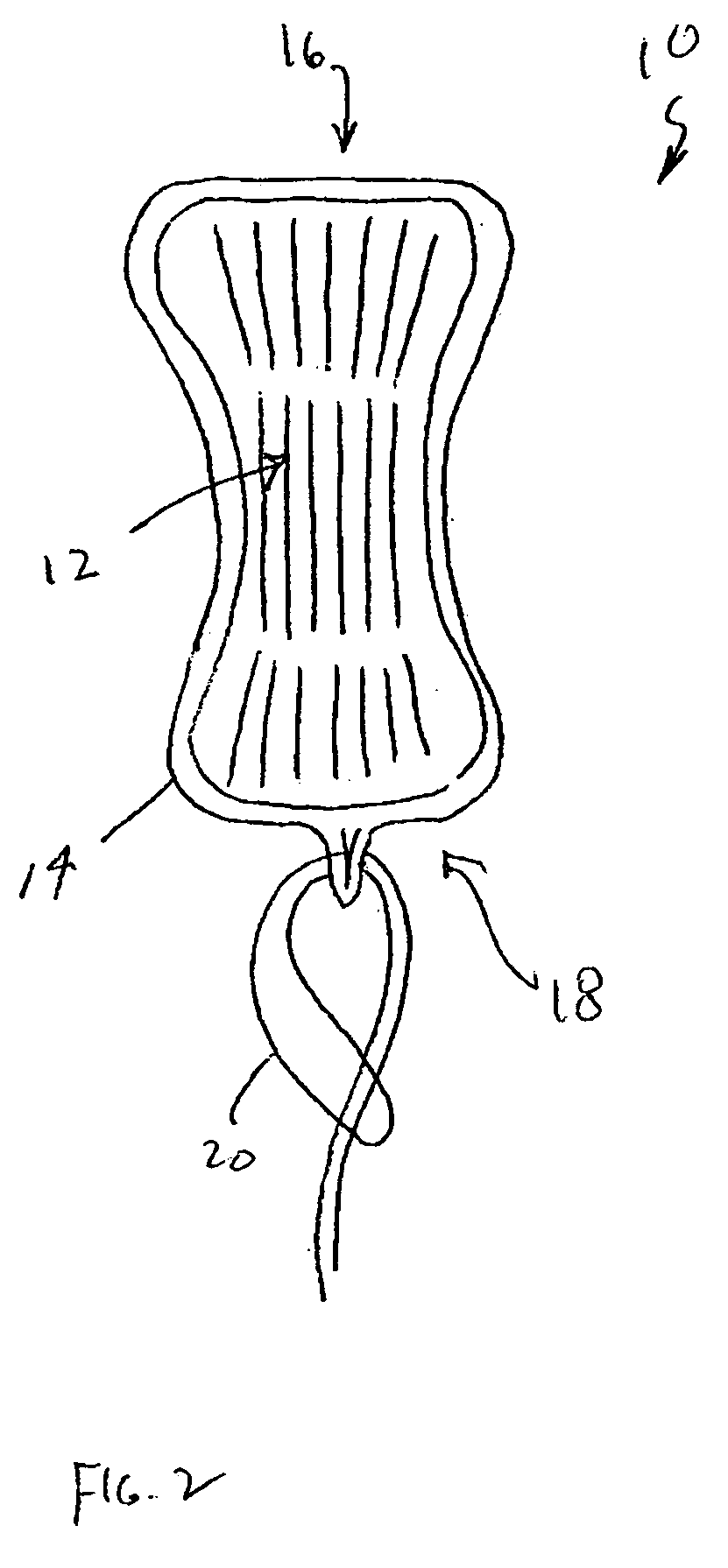
An enteral feeding unit or system that minimizes the occurrence of gastro-esophogeal-pharynegal reflux during feeding is described. The enteral feeding unit or device includes an automatable feeding pump with a feedback sensor for sensing a relative pressure in a patient's stomach and esophagus, and a regulator system for controlling or monitoring feeding rate to said patient as a function of said relative gastro-esophageal pressure. The system includes a stomach probe that has a fluid-tight closure of the esophagus. The stomach probe, according to the invention, is characterized by a tampon-bladder for watertight closure of the esophagus, in which the tampon-bladder forms from flexible and / or elastic material at least a closed inner cavity for the reception of a fluid medium, through a means (11) of establishing a prescribed pressure for the medium in the tampon-bladder (16) by an inner lumen forming the actual stomach probe, from which an outer hose-like lumen (18) extending to the tampon-bladder (16) is so arranged that between the outer lumen (18) and the inner lumen (17) a channel is formed connected to the inner cavity of the tampon-bladder (16) arranged on the outer lumen (18) by a number of openings (20), whereby the inner cavity of the tampon-bladder (16) is connected via the canal formed between the inner and outer lumina (17, 18) with the means of production of pressure in the tampon-bladder, that is, with a suitably graded reservoir or equalizing vessel (11) for the liquid medium situated above the tampon-bladder and outside the patient.
Owner:AVENT INC
Gastro-esophageal reflux control system and pump
An enteral feeding unit or system that minimizes the occurrence of gastro-esophogeal-pharynegal reflux during feeding is described. The enteral feeding unit or device includes an automatable feeding pump with a feedback sensor for sensing a relative pressure in a patient's stomach and esophagus, and a regulator system for controlling or monitoring feeding rate to said patient as a function of said relative gastro-esophageal pressure. The system includes a stomach probe that has a fluid-tight closure of the esophagus. The stomach probe, according to the invention, is characterized by a tampon-bladder for watertight closure of the esophagus, in which the tampon-bladder forms from flexible and / or elastic material at least a closed inner cavity for the reception of a fluid medium, through a means (11) of establishing a prescribed pressure for the medium in the tampon-bladder (16) by an inner lumen forming the actual stomach probe, from which an outer hose-like lumen (18) extending to the tampon-bladder (16) is so arranged that between the outer lumen (18) and the inner lumen (17) a channel is formed connected to the inner cavity of the tampon-bladder (16) arranged on the outer lumen (18) by a number of openings (20), whereby the inner cavity of the tampon-bladder (16) is connected via the canal formed between the inner and outer lumina (17, 18) with the means of production of pressure in the tampon-bladder, that is, with a suitably graded reservoir or equalizing vessel (11) for the liquid medium situated above the tampon-bladder and outside the patient.
Owner:AVENT INC
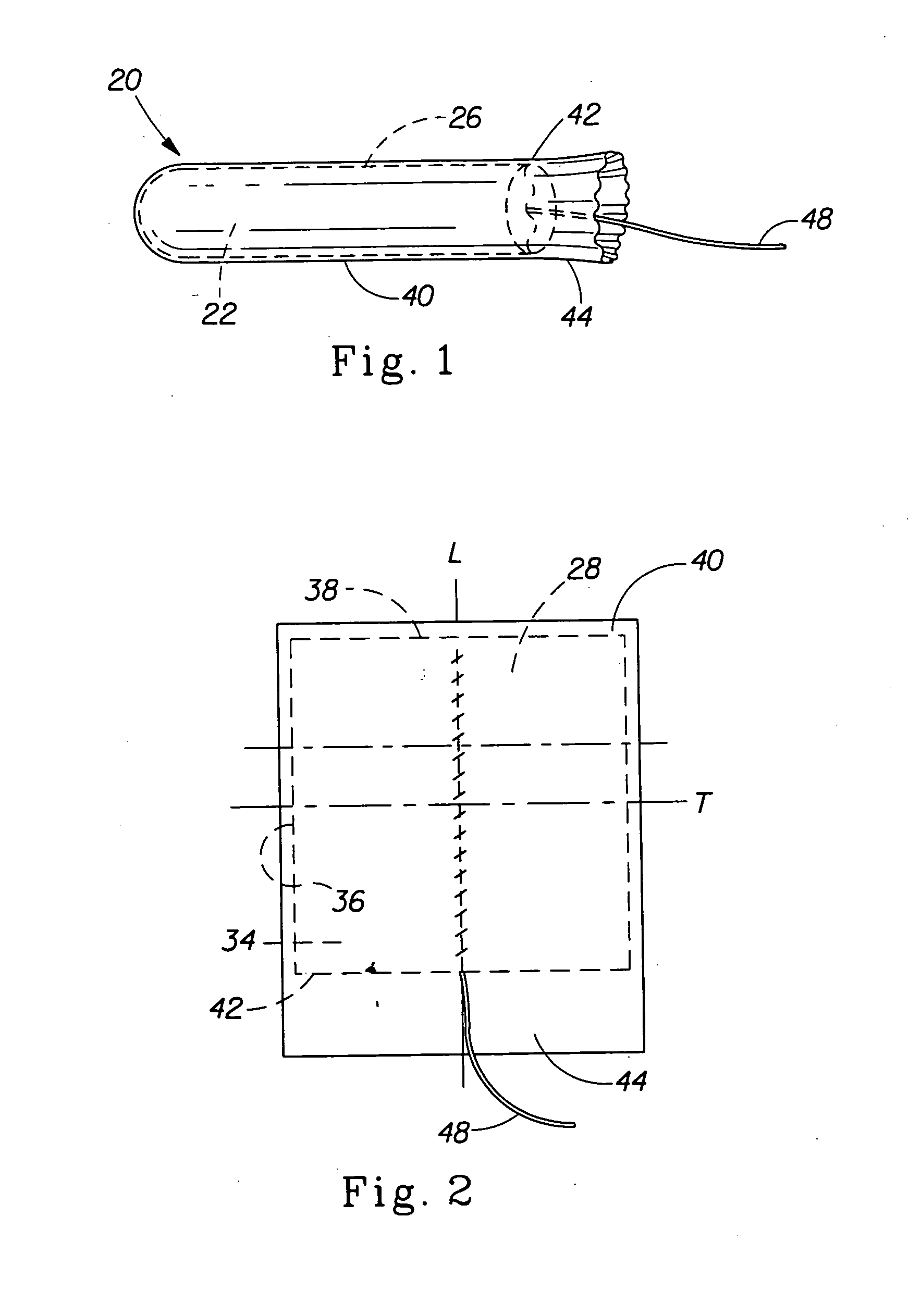
Tampon pledget for increased by-pass leakage protection
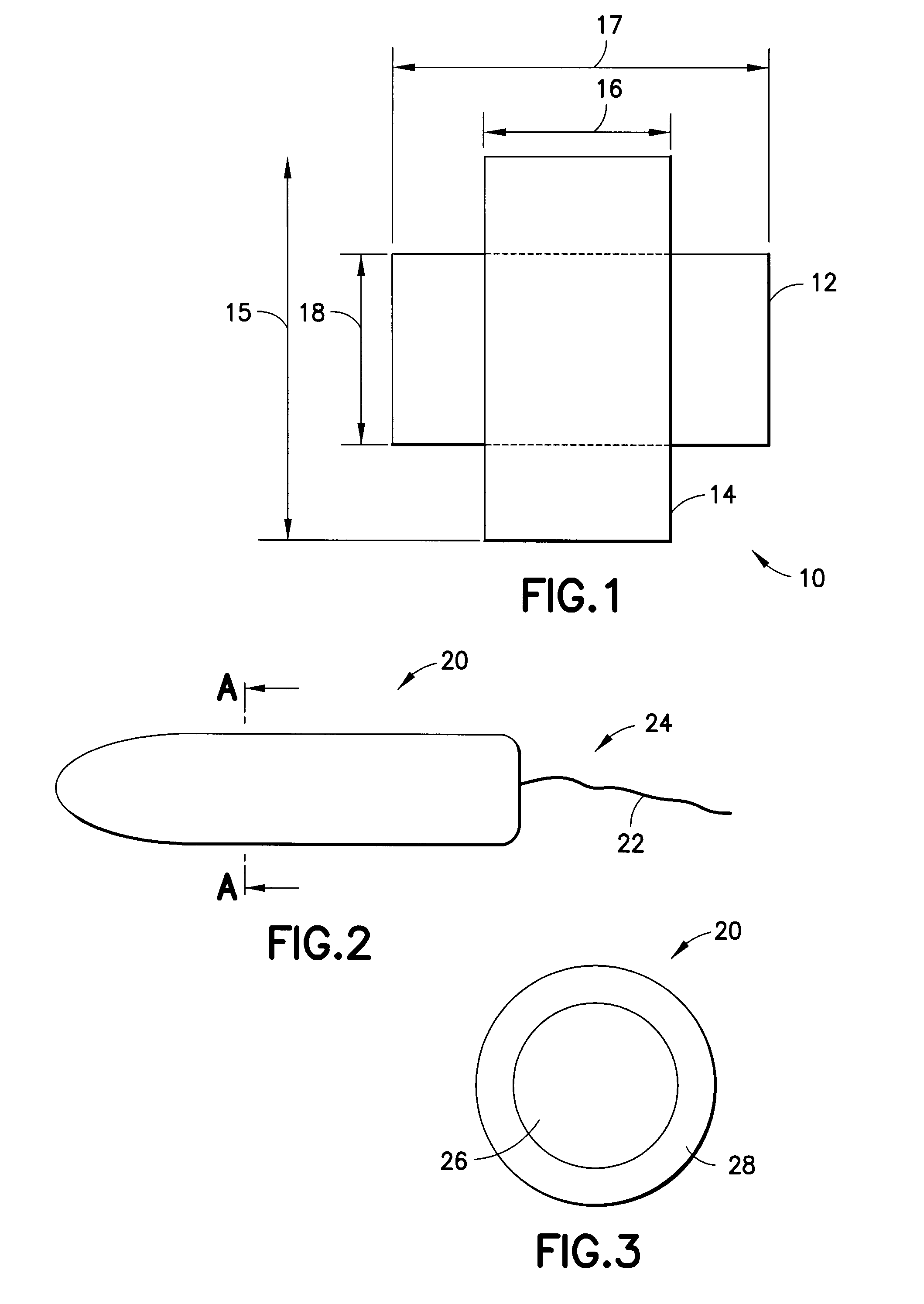
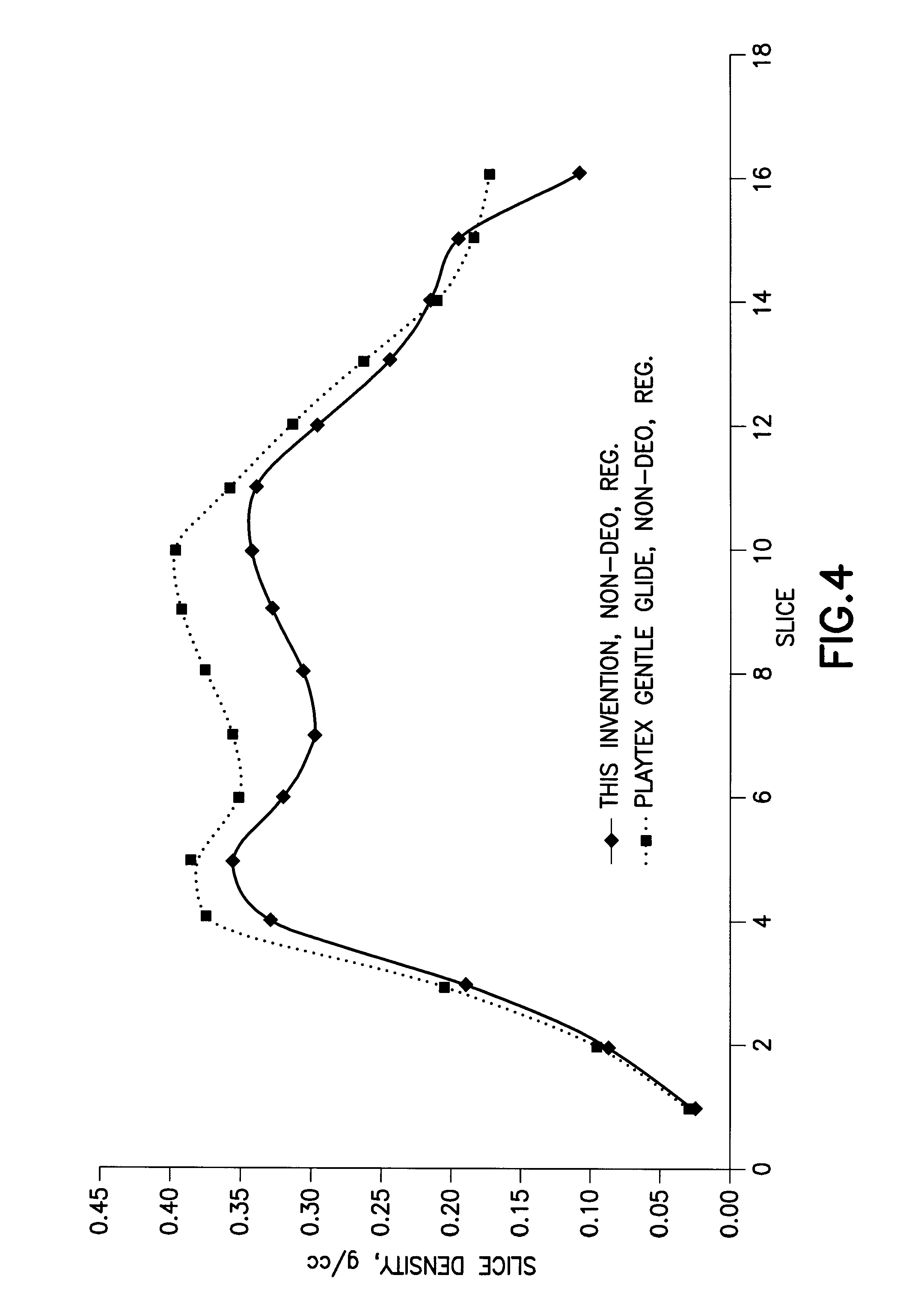
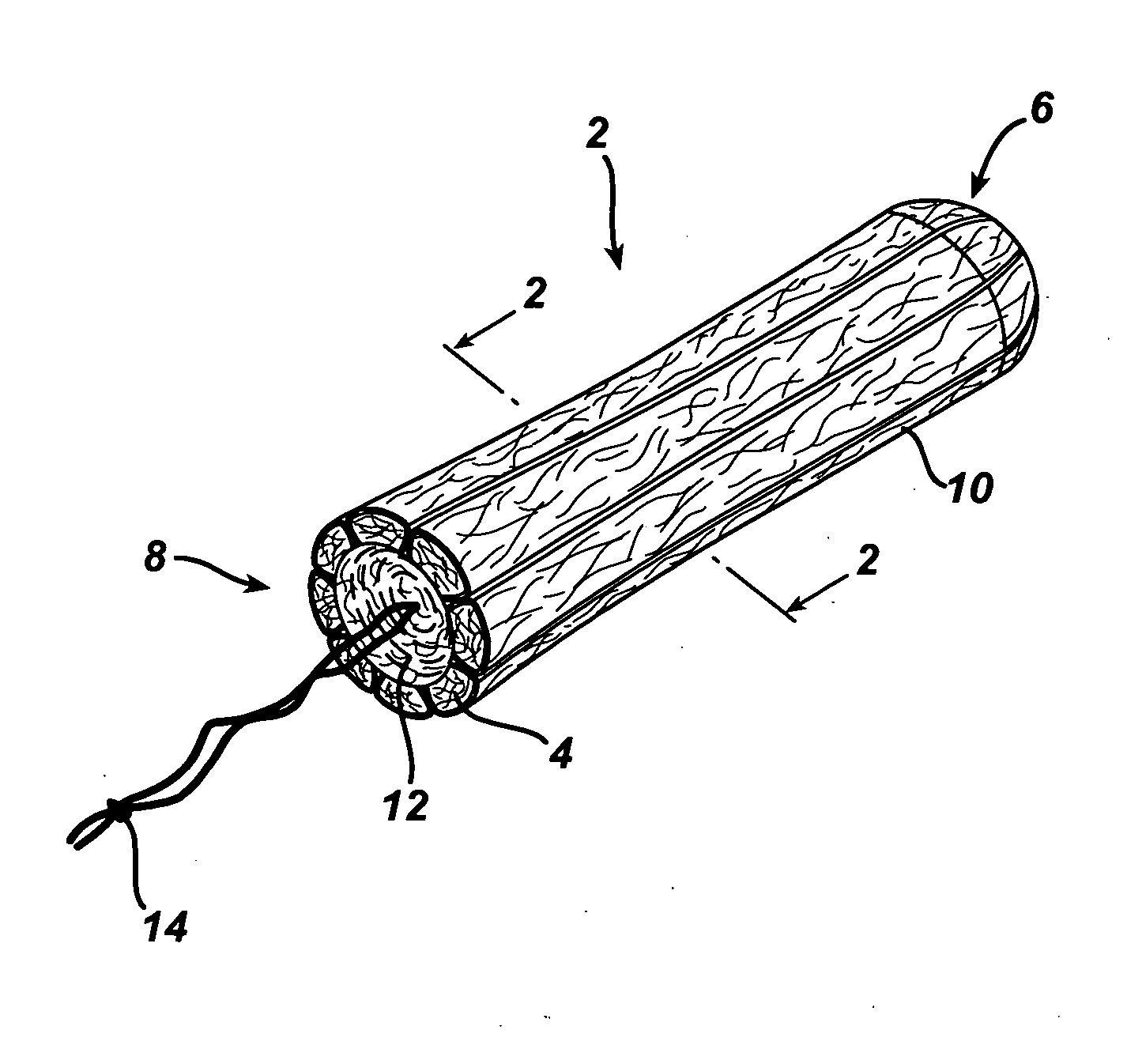
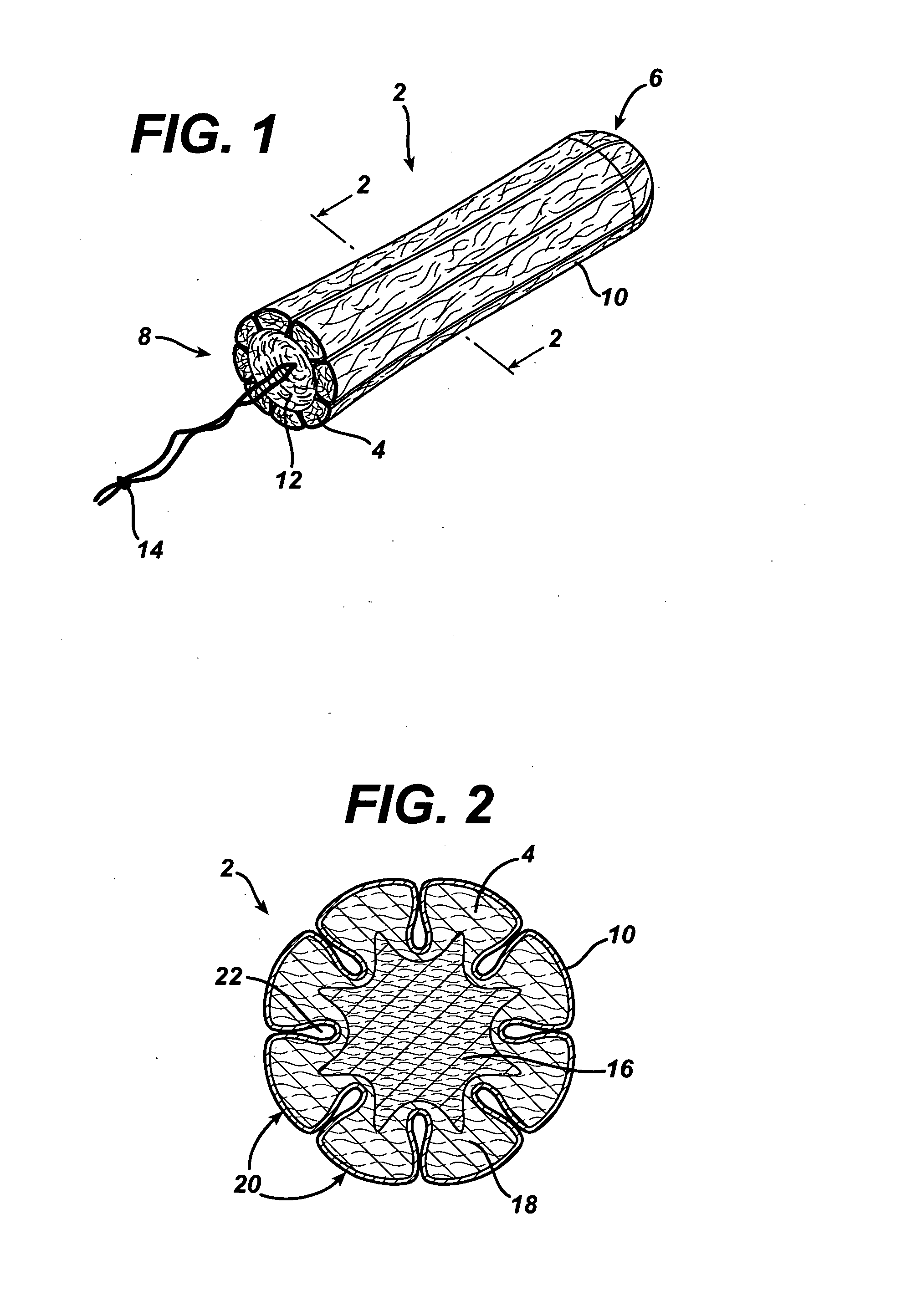
InactiveUS20080287902A1Increase in of absorbency capacityIncrease in rate of absorbencyBaby linensTamponsMedicineTamponade
The present invention provides a tampon pledget with one or more of the following properties: increased absorbency rate; high absorbent capacity and fluid retention; rapid expansion potential; and ease of ejection of the pledget from the applicator. Surprisingly, the one or more properties are achieved by using a modified dual cross-pad, folded, compressed tampon pledget design.
Owner:PLAYTEX PROD INC
Tampon having an oval form after expansion and process for producing the same
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Segmented tampon pledget
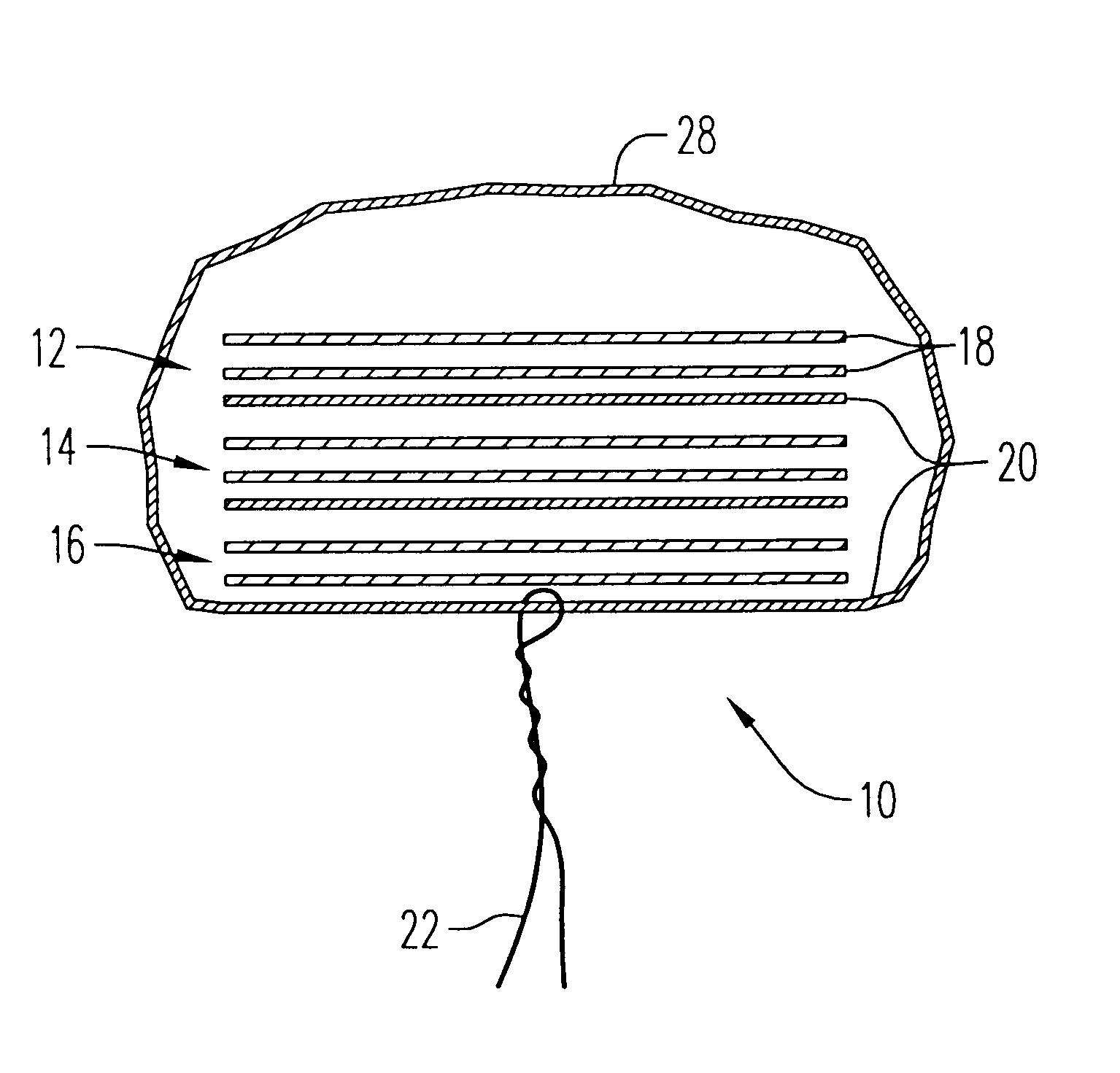
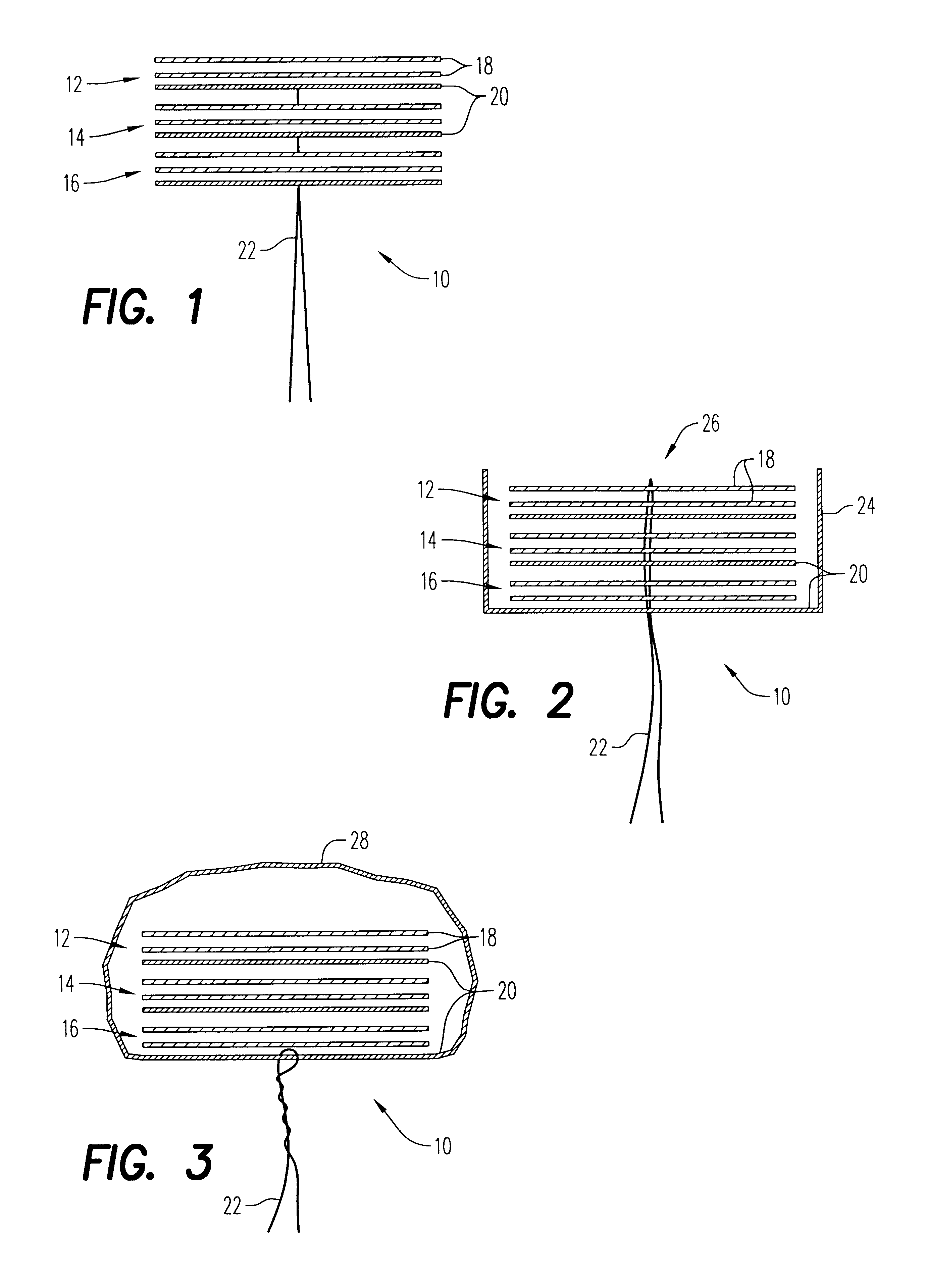
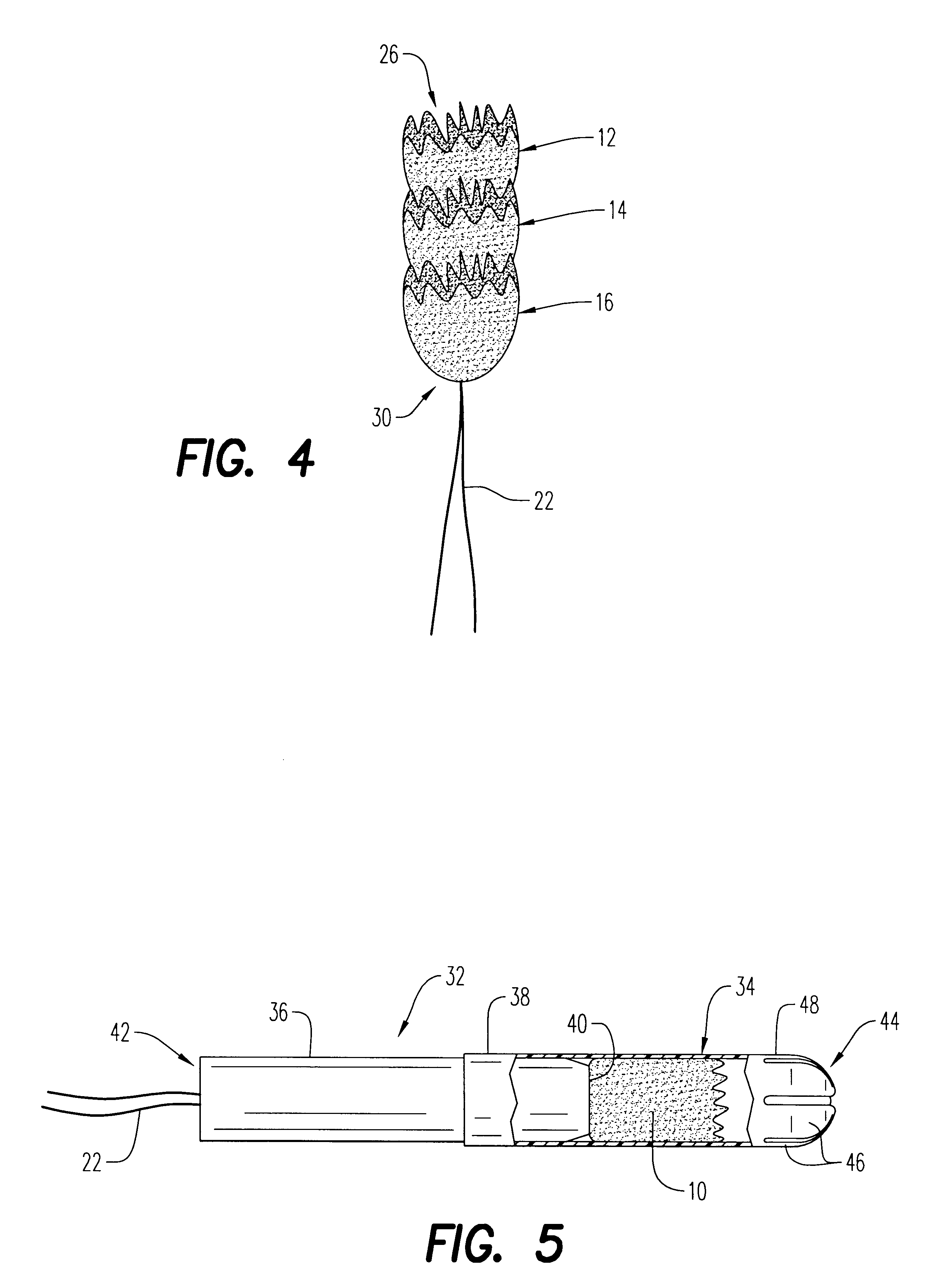
There is provided a tampon having a plurality of pledget segments with each segment having one or more layers of absorbent material and one or more layers of semipermeable material. The one or more semipermeable layers of each segment forms an absorption restriction boundary to the next adjacent segment that allows each segment to absorb and expand independently from the other segments. The plurality of pledget segments can be positioned in a coverstock bag.
Owner:EDGEWELL PERSONAL CARE BRANDS LLC
Method and apparatus for hemostasis
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in patients who have received skin-penetrating wounds to the periphery, including the head, arms, and legs. Such haemostatic packing devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery, or military setting. The devices utilize fluid impermeable barriers surrounded by exterior dams and pressure to achieve tamponade and hemostasis, primarily by exertion of force to hold the dams against the skin surrounding a wound. The devices are capable of serving as carriers for thrombogenic, antimicrobial or antipathogenic agents. The devices do not require the use of adhesives to work as they are attached to the patient using mechanical locking devices. Peripheral haemostatic packing devices include optional adhesive hemostatic barriers to attach at least a portion of the device to the skin or to assist with initial coupling of a hold-down strap to another strap using a more secure mechanical lock. The peripheral hemostatic packing system does not completely surround the extremity having the wound and therefore do not cause a tourniquet effect. The peripheral hemostatic packing system preferably is held against the skin surrounding a wound by a force that is generally unidirectional and substantially perpendicular to the plane in which the skin of the wound resides.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
Tampon assembly providing proper bodily placement of a pledget
Provided is a tampon applicator having one or more insertion indicators to gauge and / or control the insertion depth of a tampon. The one or more insertion indicators may be located on the tampon applicator barrel, plunger, tampon, removal string, or any combinations thereof. As a result of the one or more insertion indicators, a woman can adjust the insertion depth of the tampon to her body's requirements ensuring leakage protection, comfort, or both.
Owner:EDGEWELL PERSONAL CARE BRANDS LLC
Menstrual tampon
The disclosure concerns a compressed menstrual tampon including an elongated generally rod-shaped absorption body having an insertion end and a withdrawal end and having a withdrawal string extending from the withdrawal end. The absorption body has at least one wave-shaped compression line extending continuously from the insertion end to the withdrawal end.
Owner:ESSITY HYGIENE & HEALTH AB
System for transvaginal drug delivery
InactiveUS7004171B2Less amountPharmaceutical delivery mechanismBaby linensTamponadeAbsorbent material
A transvaginal drug delivery system comprising: (a) a deposition comprising an effective amount of said drug and, optionally, a wetting agent; and (b) a polymeric support on which said deposition is deposited. Also disclosed is a catamenial tampon for insertion in a human vagina comprising: (a) an inner core comprising an absorbent material; (b) an outer layer comprising a liquid-permeable material; and (c) a delivery system according to the invention. A method of transvaginal drug delivery is also described.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD +1
Method and apparatus for hemostasis
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in patients who have received skin-penetrating wounds to the periphery, including the head, arms, and legs. Such haemostatic packing devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery, or military setting. The devices utilize fluid impermeable barriers surrounded by exterior dams and pressure to achieve tamponade and hemostasis, primarily by exertion of force to hold the dams against the skin surrounding a wound. The devices are capable of serving as carriers for thrombogenic, antimicrobial or antipathogenic agents. The devices do not require the use of adhesives to work as they are attached to the patient using mechanical locking devices. Peripheral haemostatic packing devices include optional adhesive hemostatic barriers to attach at least a portion of the device to the skin or to assist with initial coupling of a hold-down strap to another strap using a more secure mechanical lock. The peripheral hemostatic packing system does not completely surround the extremity having the wound and therefore do not cause a tourniquet effect. The peripheral hemostatic packing system preferably is held against the skin surrounding a wound by a force that is generally unidirectional and substantially perpendicular to the plane in which the skin of the wound resides.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
Tampon with segmented grooves
An intravaginal tampon is formed of compressed material and has an outer surface, an insertion end, a withdrawal end, and a center portion formed between the insertion and withdrawal ends. The outer surface has at least two segmented grooves are formed therein, and each segmented groove is separated from and spaced at a distance from an adjacent segmented groove. Each segmented groove has at least one substantially longitudinal segment and at least one accumulator segment. The arrangement of the segments provides a pooling region to impede bodily fluid flow along the outer surface of the tampon.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES
Rapid expansion tampon pledget
There is provided a tampon pledget that expands without the aid of moisture or menses. The tampon pledget has a plurality of high resiliency, non-absorbent fibers and a plurality of absorbent fibers. The tampon pledget has improved comfort as compared to conventional fully compressed tampon pledgets.
Owner:EDGEWELL PERSONAL CARE BRANDS LLC +1
Absorbable putty-like implants and methods for their use for mechanical hemostasis of bone and for the treatment of osseous defects
ActiveUS20060002976A1Lower potentialImproved bone healingPowder deliverySurgical adhesivesBarium saltTG - Triglyceride
Two (or more), component, body-implantable, absorbable, biocompatible, putty-like surgical mechanical hemostatic tamponades for use in surgery. Component 1, a carboxylic acid salt bulking material preferably less than 50 micron, preferably the calcium, magnesium, zinc, aluminum, lithium or barium salts of saturated or unsaturated carboxylic acids containing about 6 to 22 carbon atoms. Component 2, a dispersing vehicle, may be esters of C8-C18 monohydric alcohols with C2-C6 aliphatic monocarboxylic acids; C2-C18 monohydric alcohols with polycarboxylic acids; C8-C30 monohydric alcohols; tocopherol and esters thereof with C2-C10 aliphatic monocarboxylic acids or polycarboxylic acids; absorbable 10-14C hydrocarbons; free carboxylic acids such as oleic, linoleic, caprylic, capric, and lauric; dialkyl ethers; alkyl aryl ethers; dialkyl ketones and alkyl aryl ketones; polyhydroxy compounds and esters and ethers thereof; oils such as olive oil and castor oil and triglycerides.
Owner:ABYRX
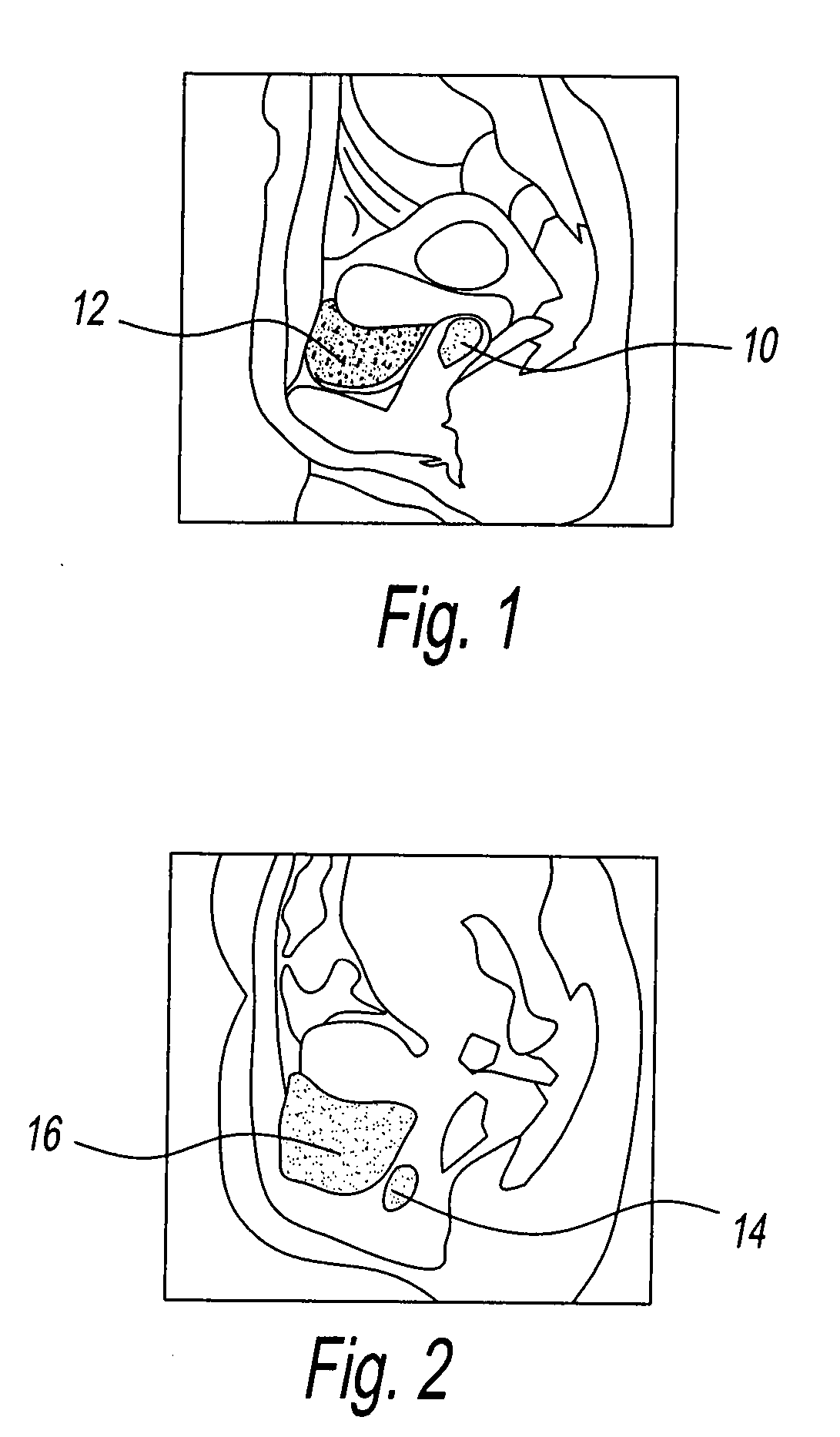
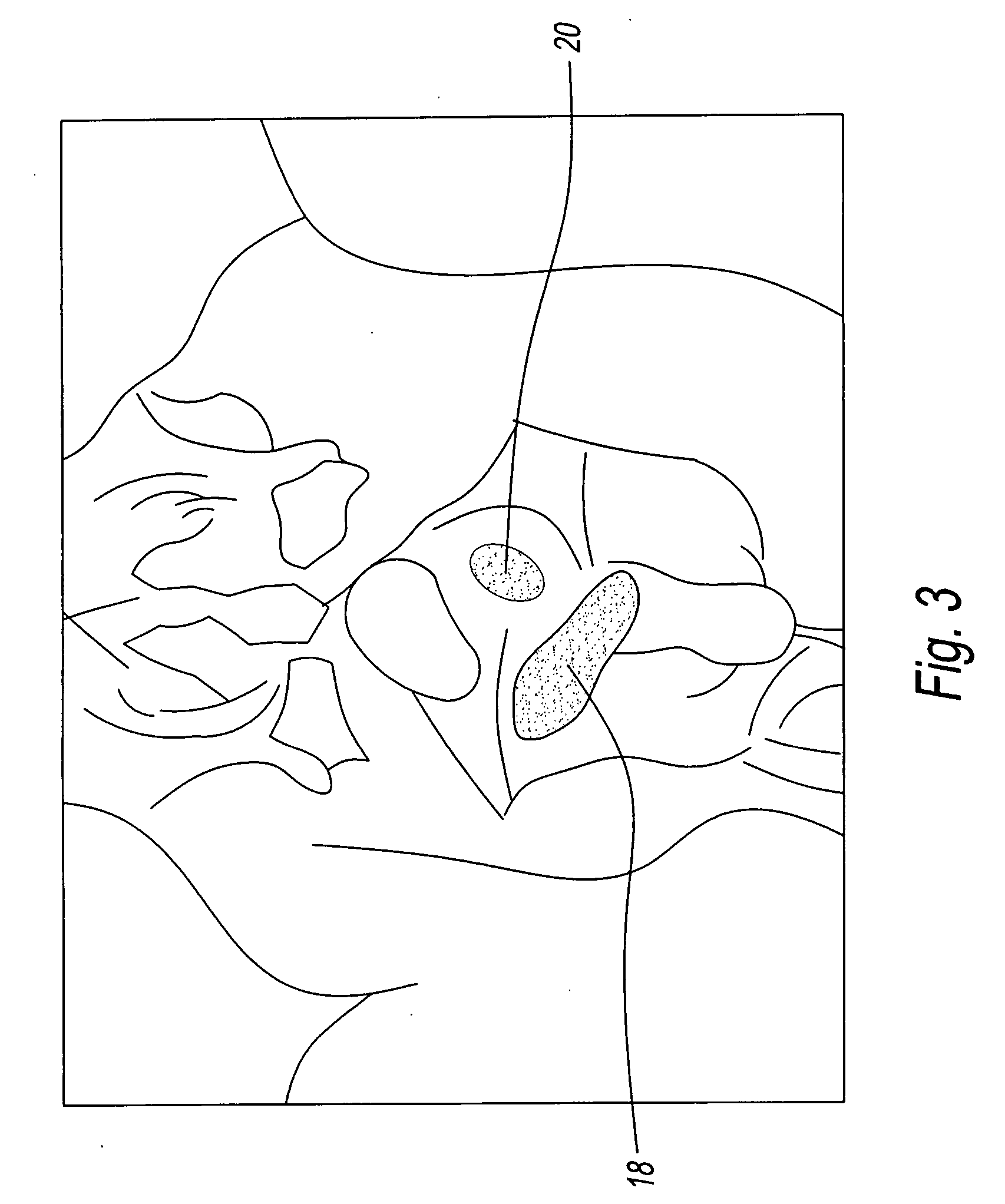
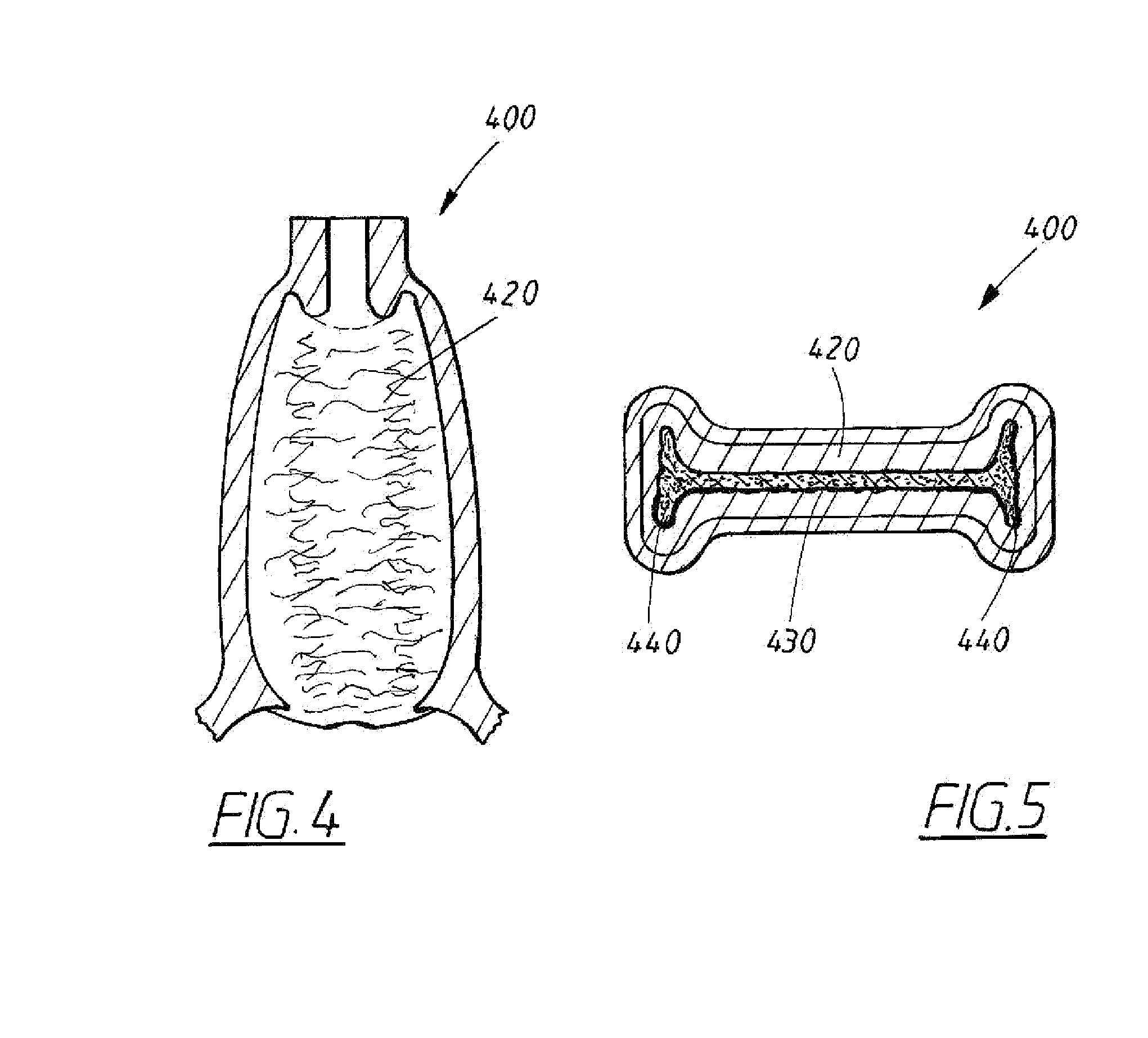
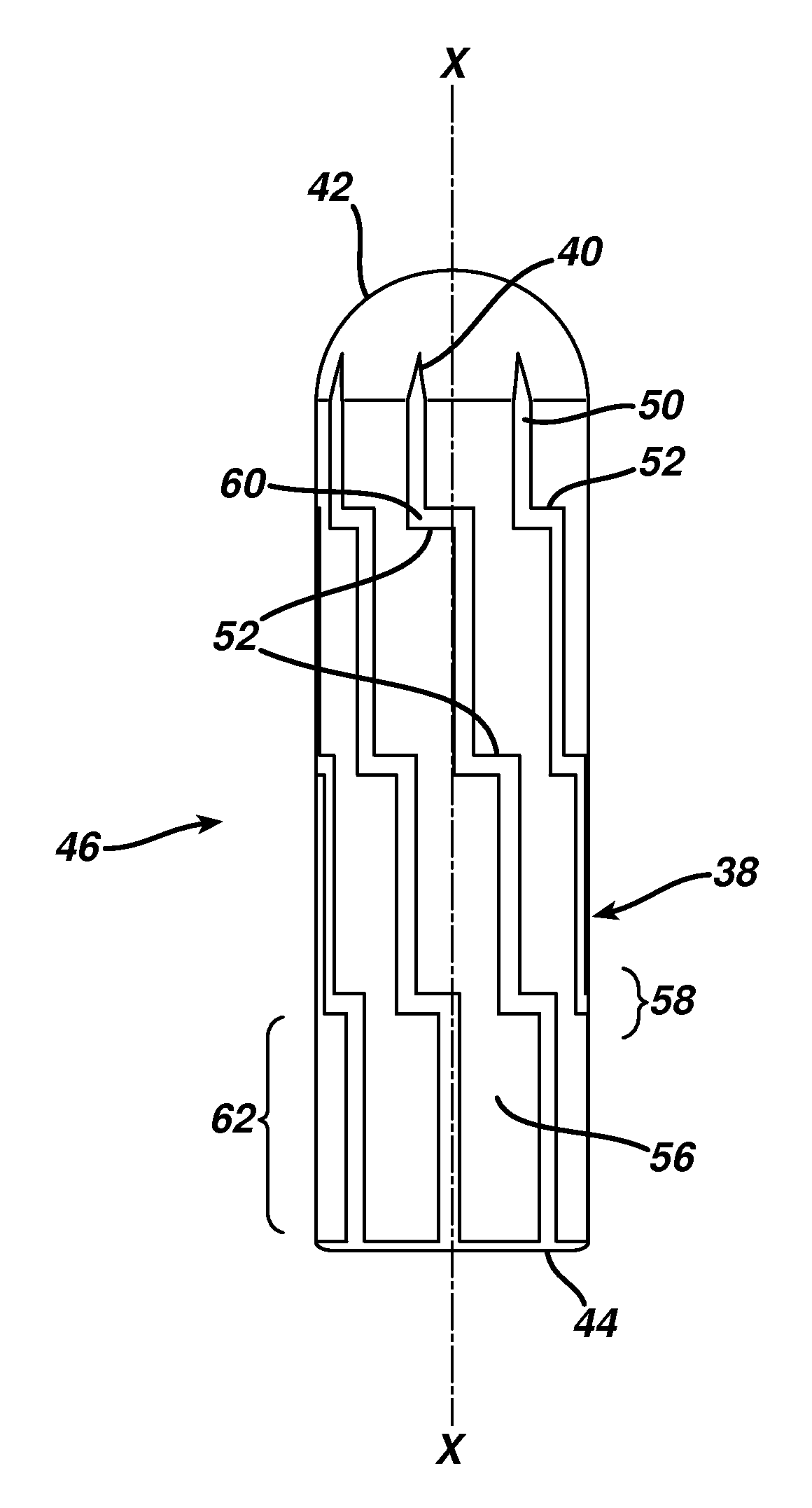
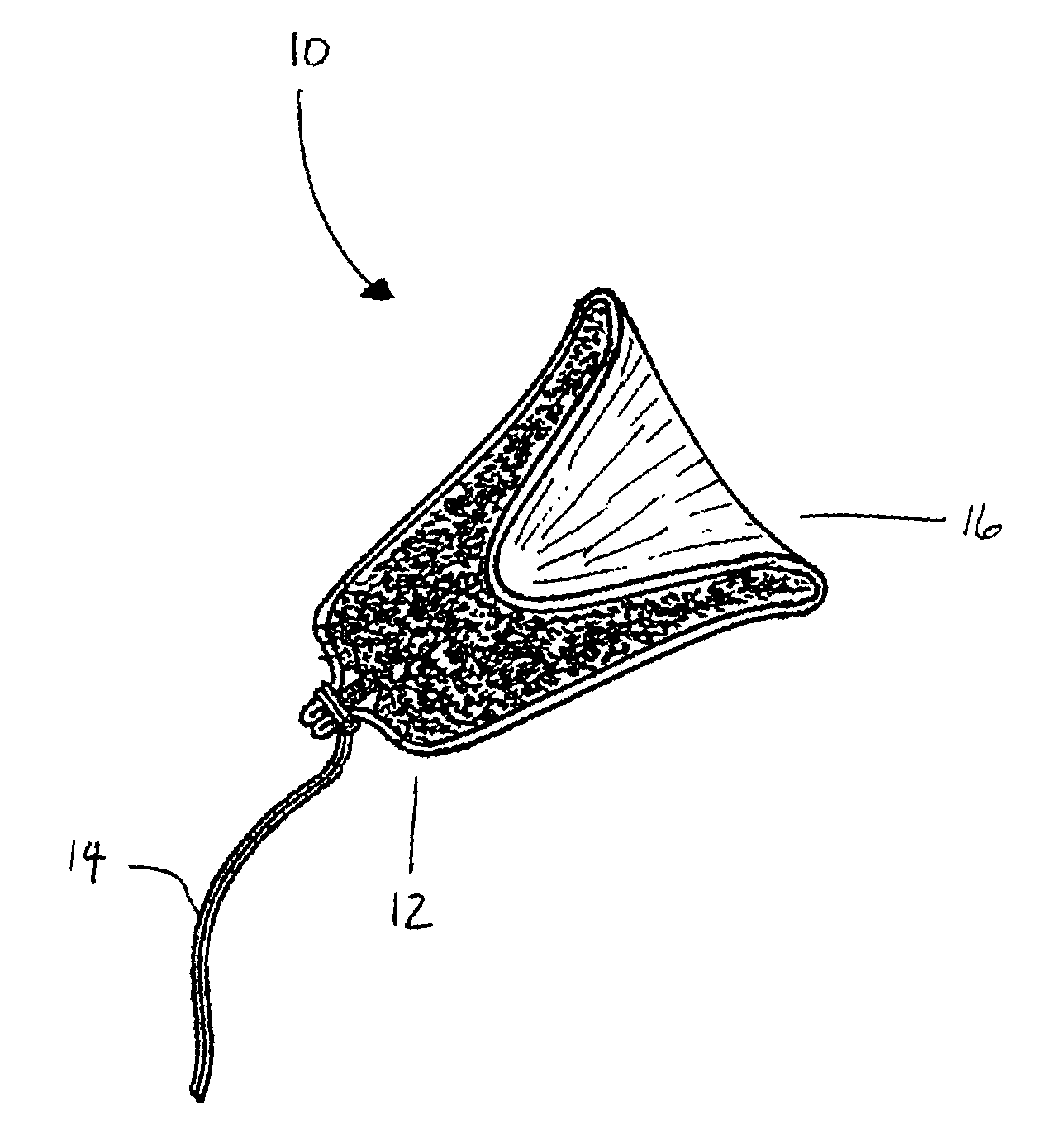
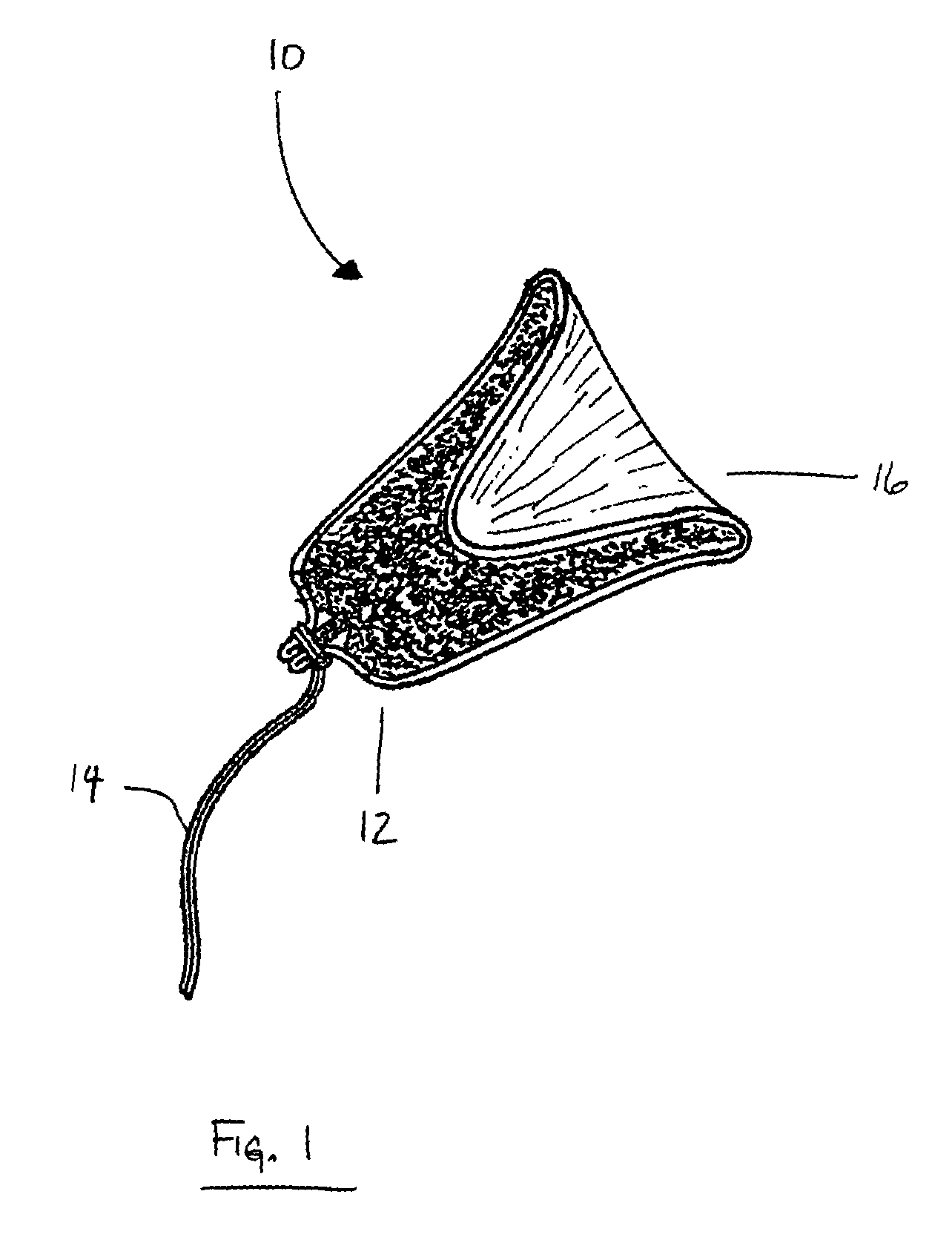
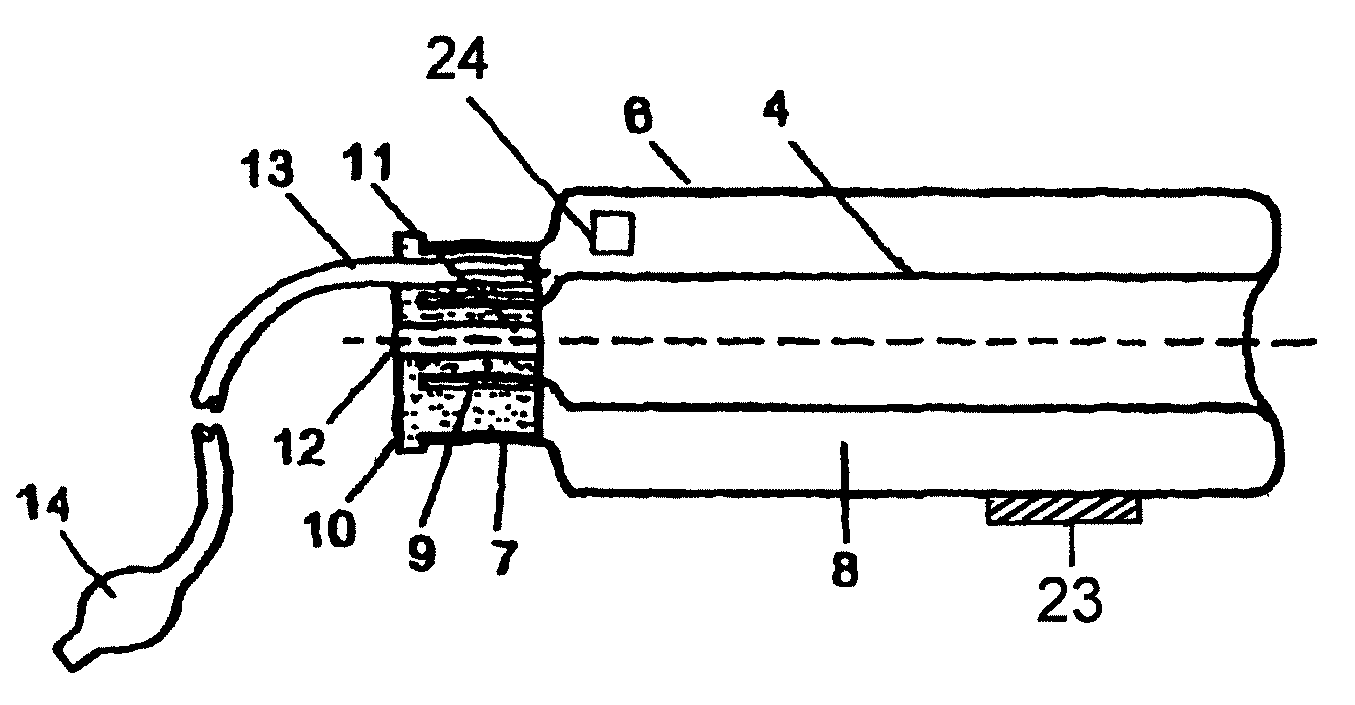
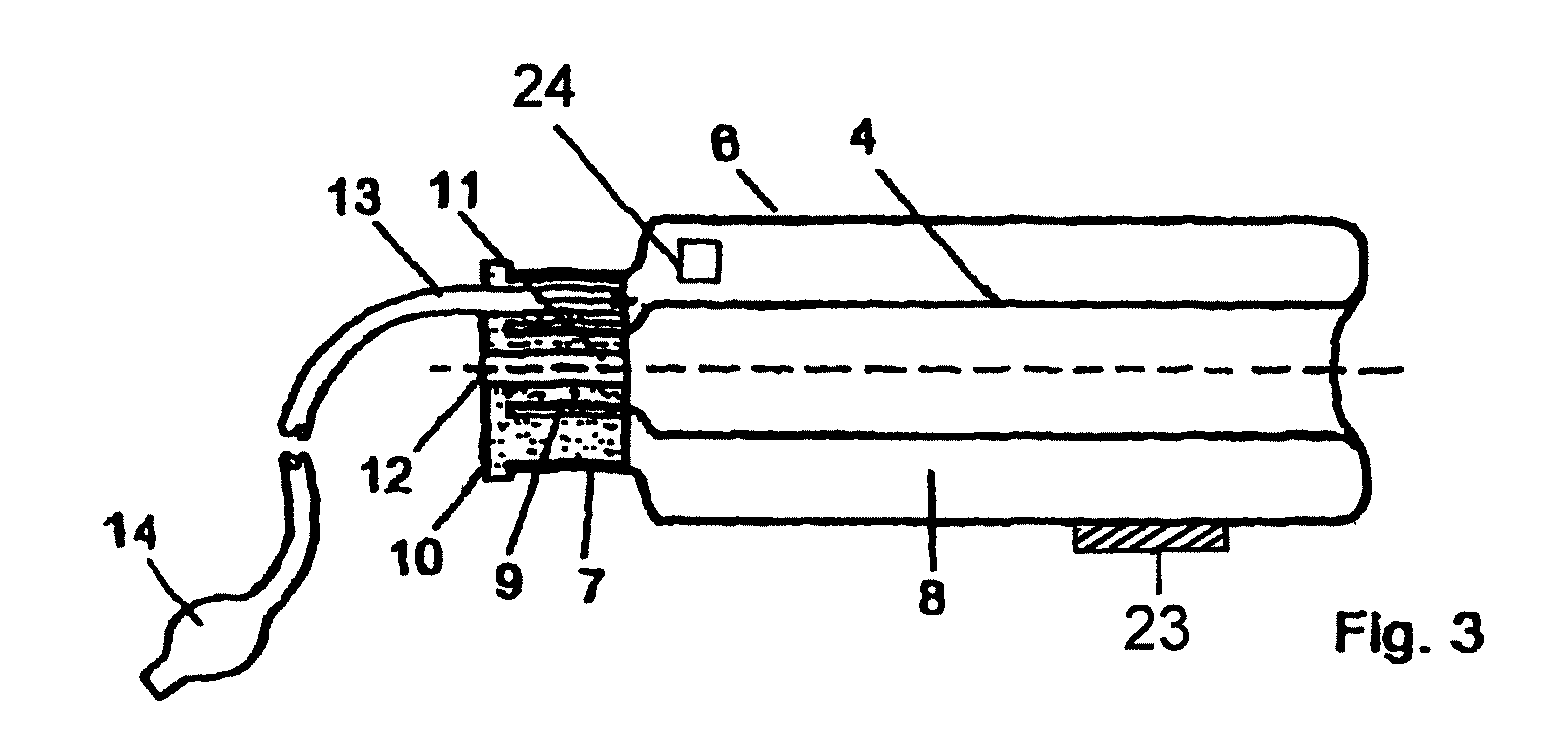
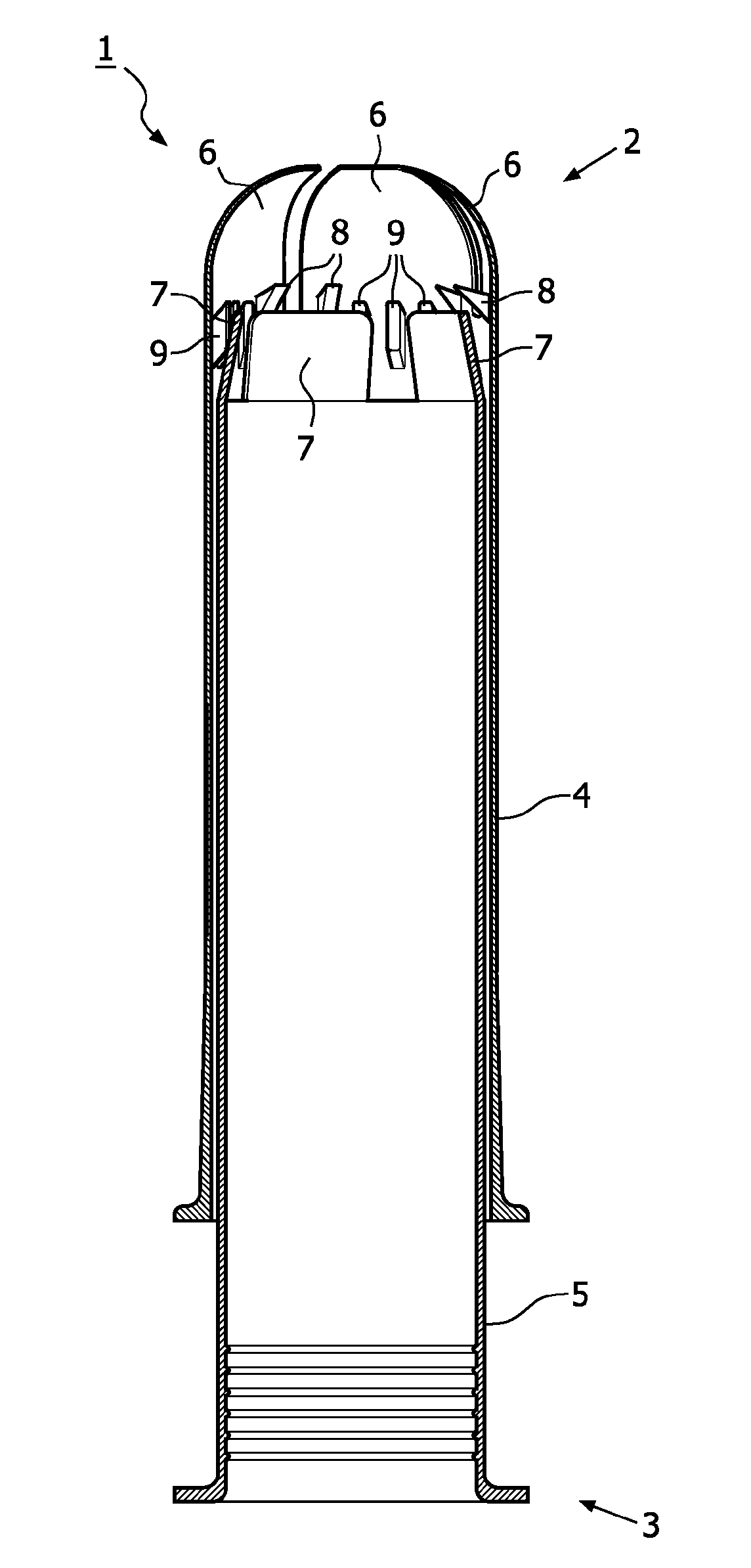
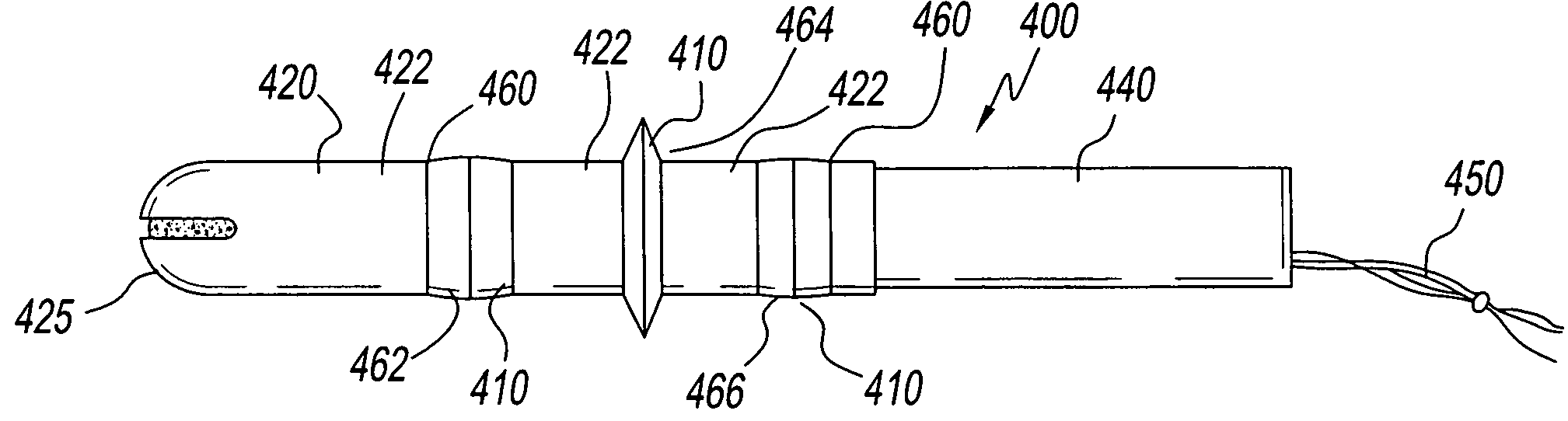
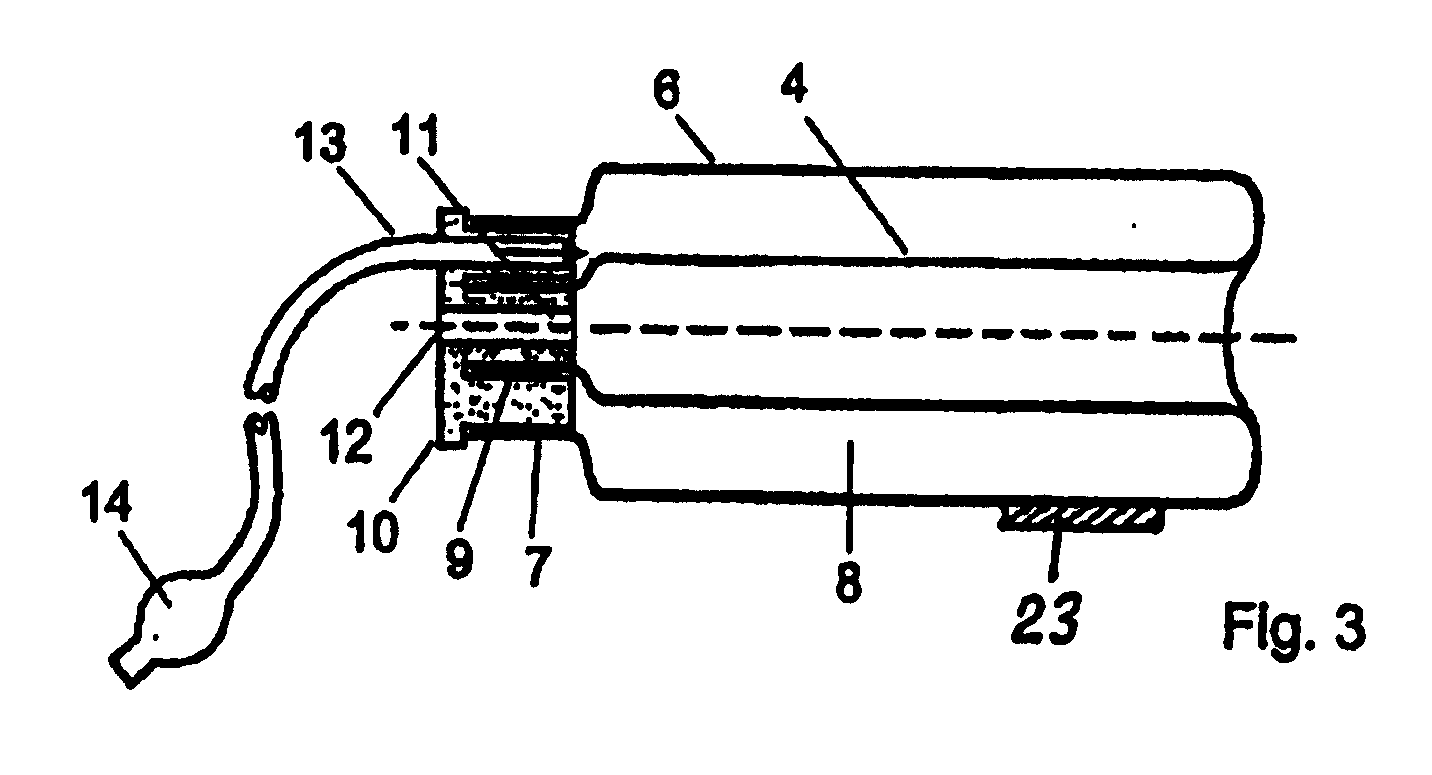
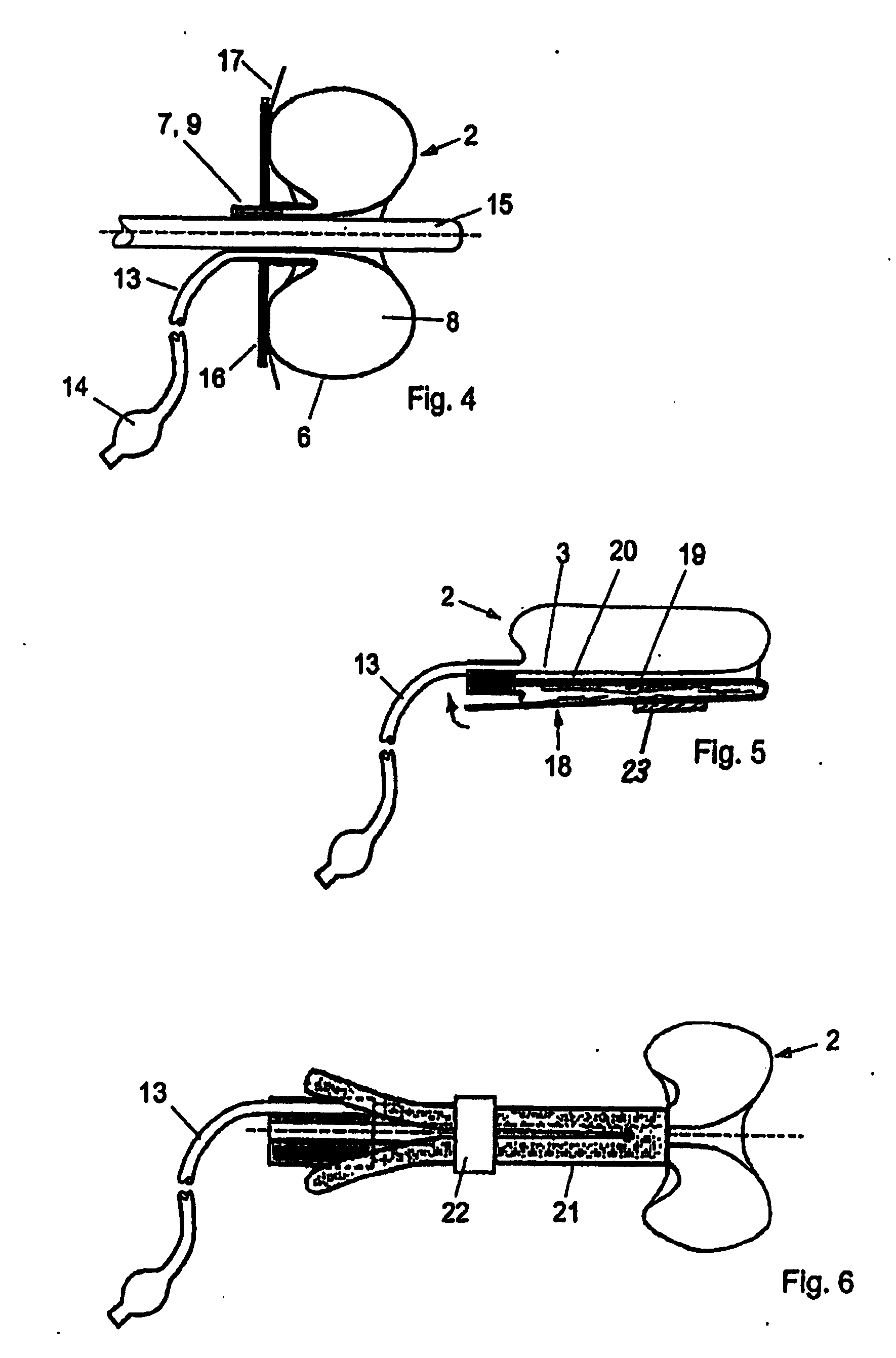
Device for tamponade of body cavities and mechanical anchoring of a catheter
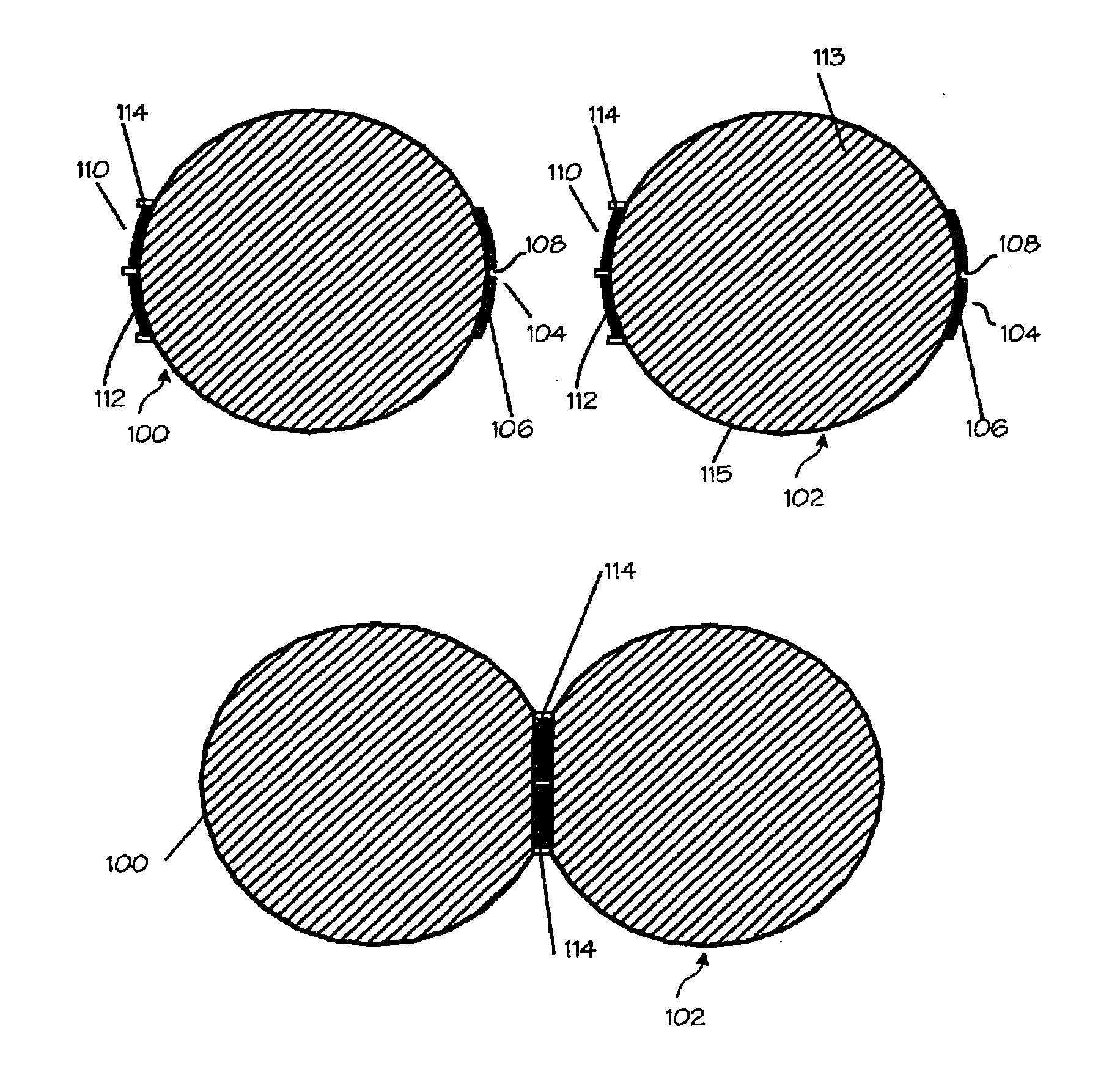
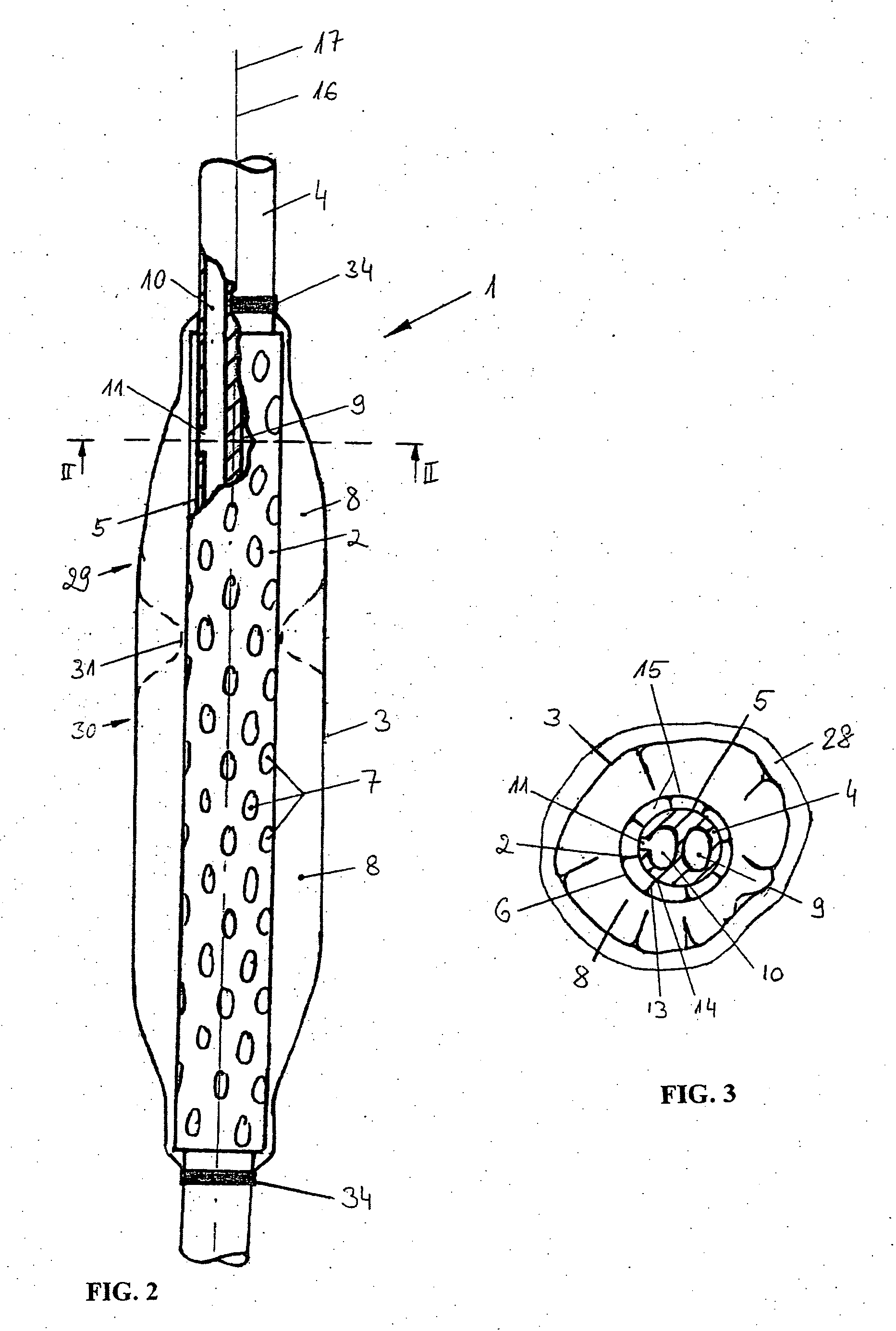
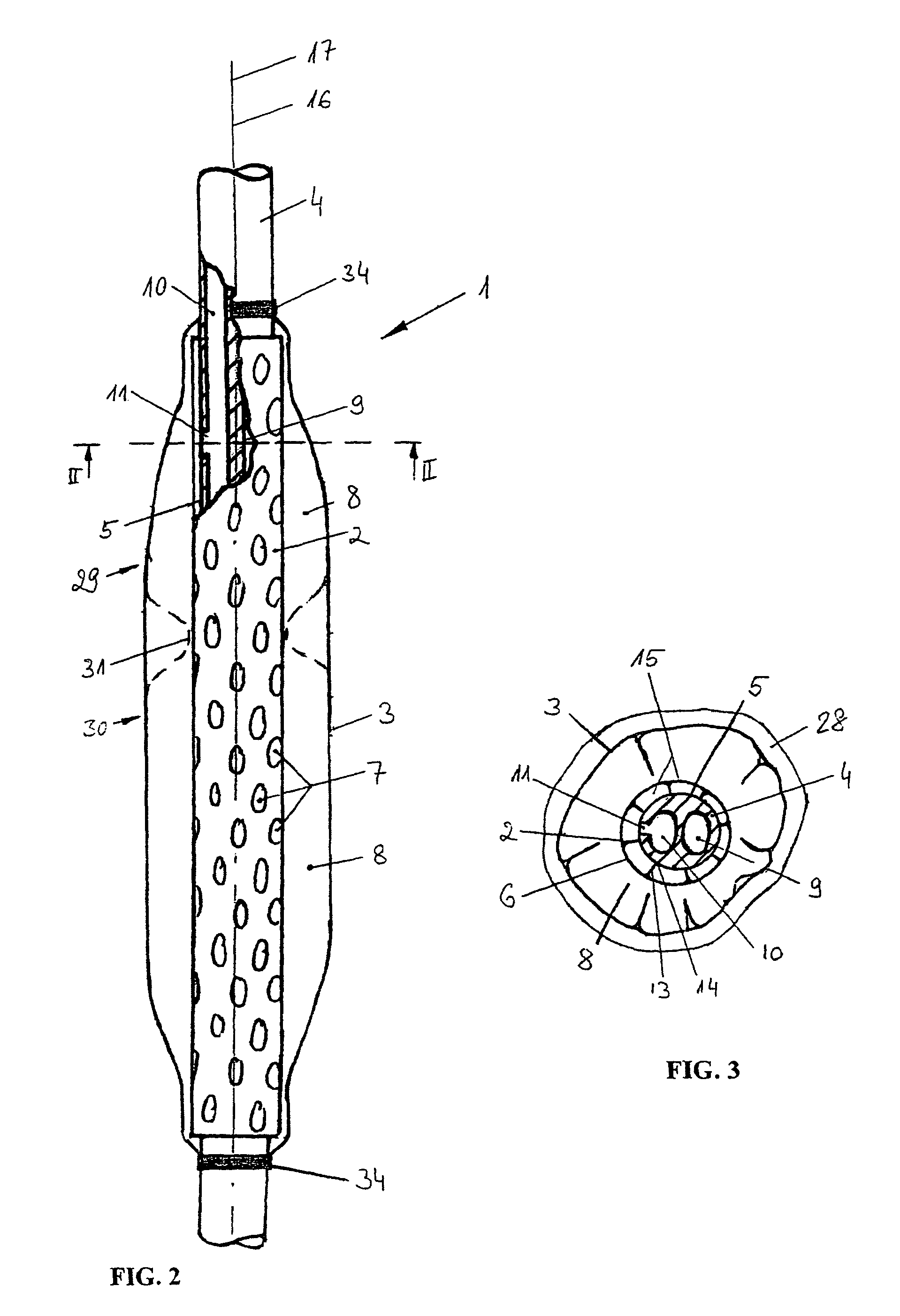
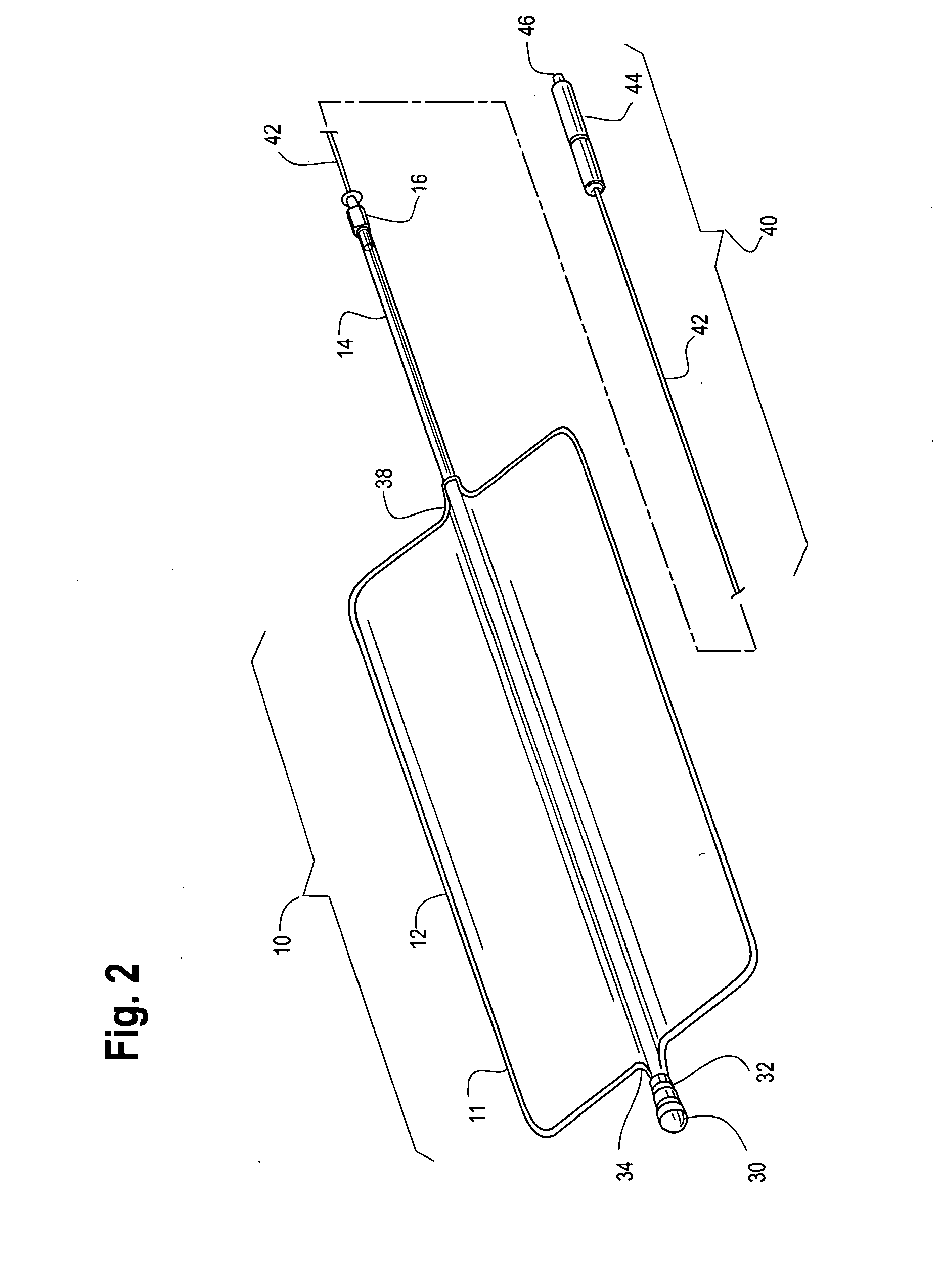
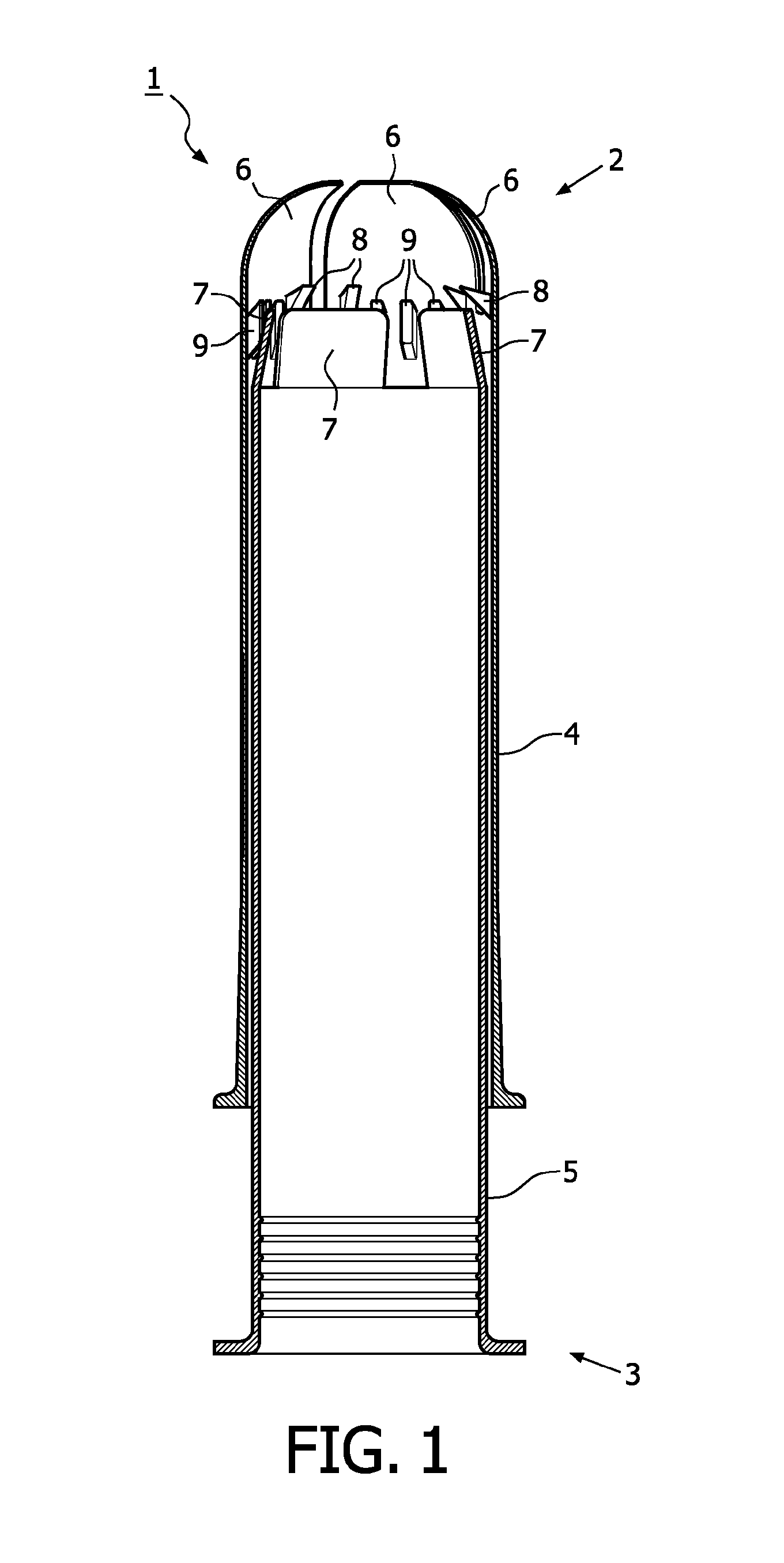
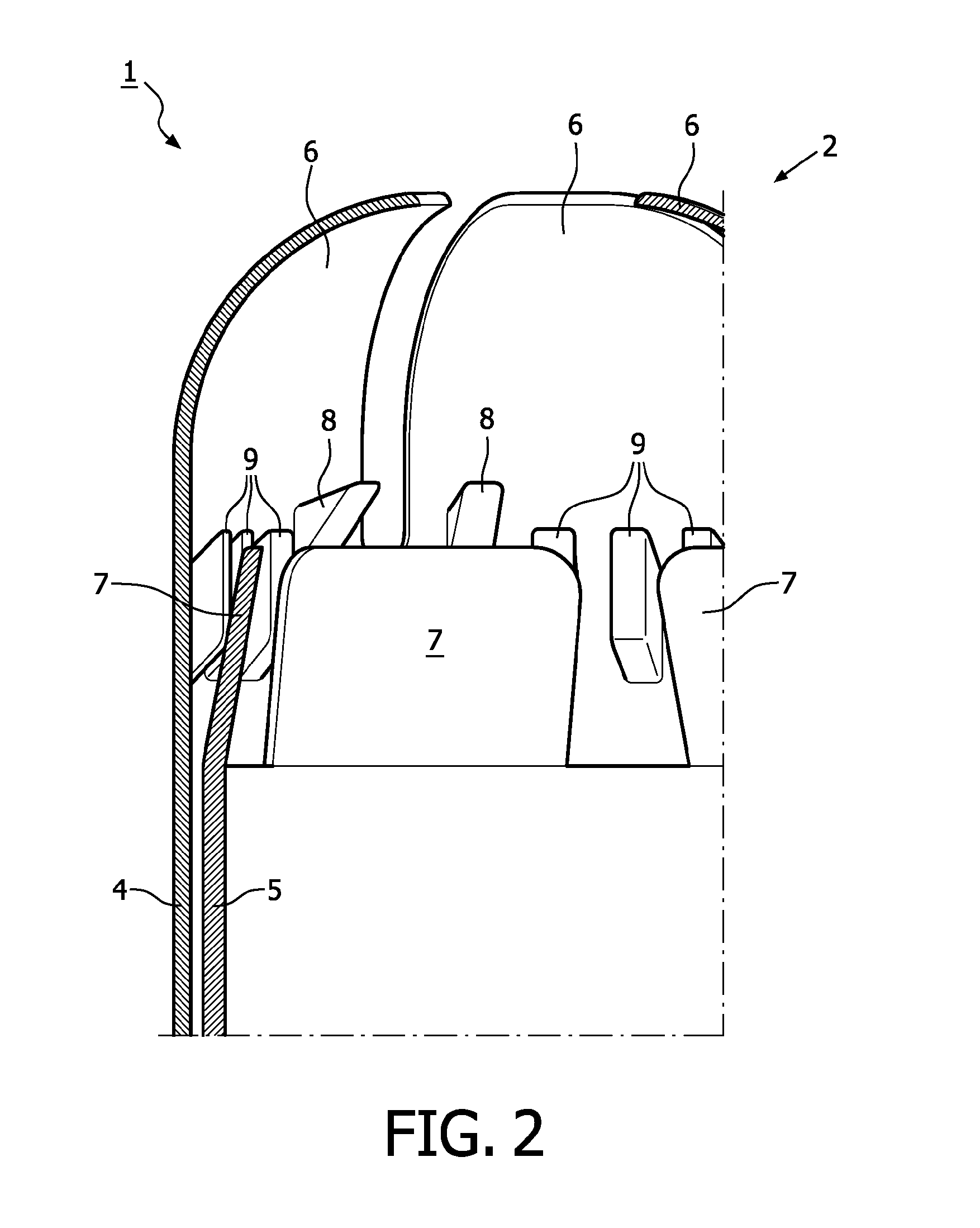
A device for tamponade of body cavities and for mechanical anchoring of a catheter, the device including a flexible tube segment (2) having an inner wall (4) and an outer wall (6) that surround an interior space (8), wherein the tube segment (2) is inflatable, and is configured without through-passing support bodies so that a displacement of tube wall material between the inner wall (4) and the outer wall (6) of the tube segment (2) is possible by inflation of the tube segment, wherein the tube segment is provided with two ends (7,9), which are fastened to a same closing element (10), configured so that a torus geometry is striven for as the inflatable tube segment (2) is inflated and the closing element (10) is a pipe nipple and the two ends (7,9) of the tube segment (2) are joined together fluid-tightly.
Owner:AVENT INC
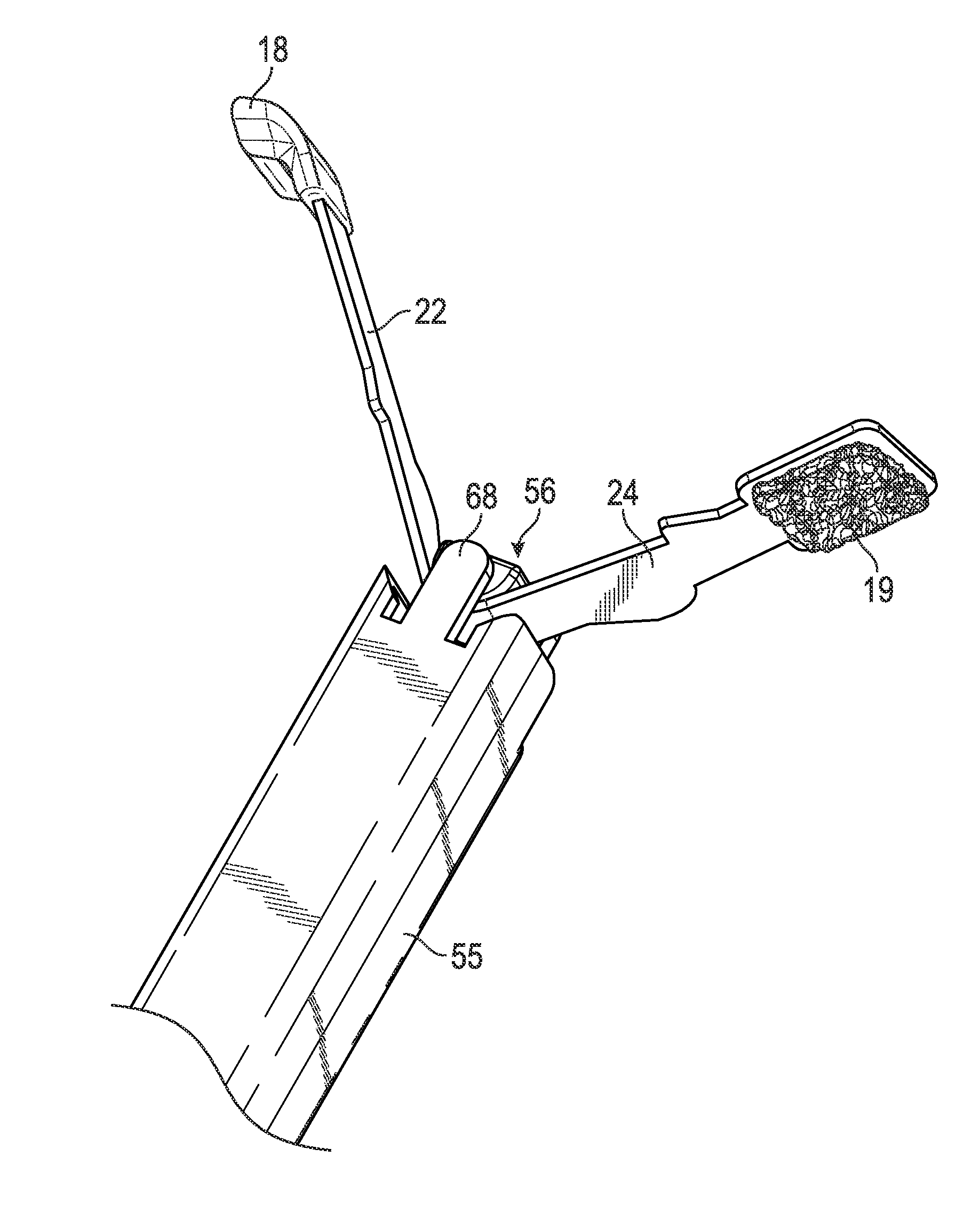
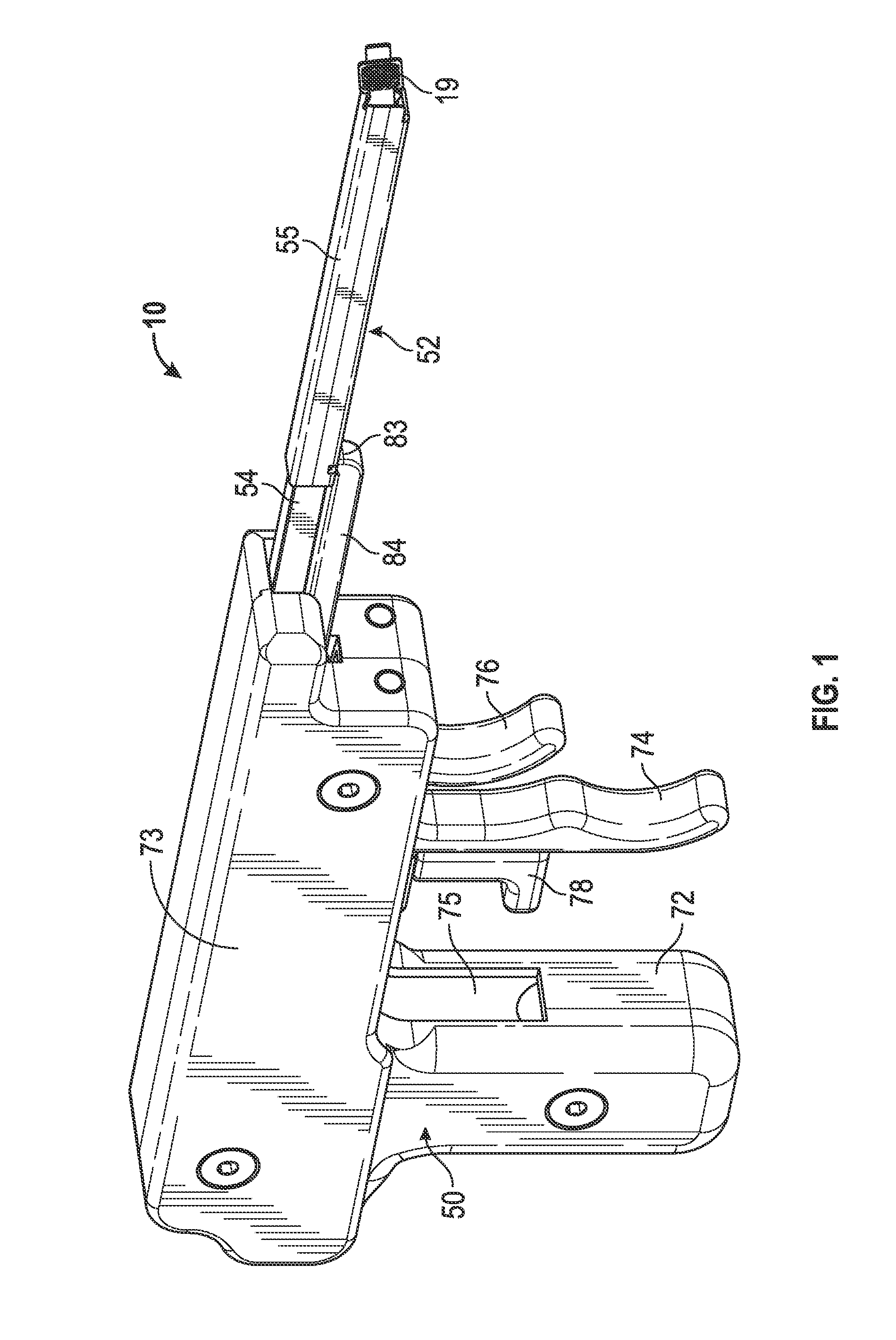
Enhanced system and method for wound track navigation and hemorrhage control
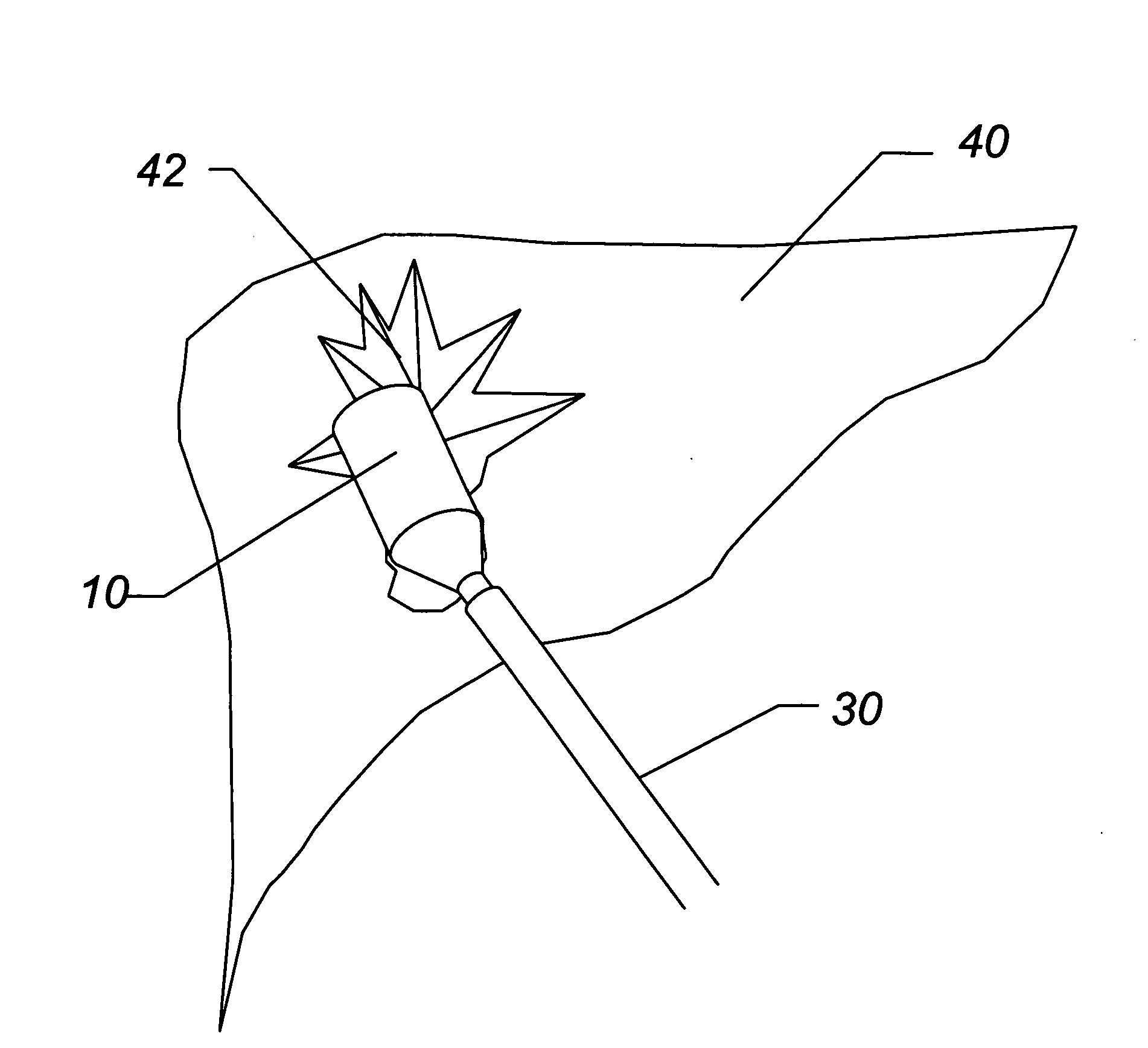
An internal compression tourniquet catheter system and method for wound track navigation for controlling hemorrhage from wounds. The preferred embodiments include an inflatable member constructed of thin, flexible, biocompatible, and puncture resistant material such that when deflated it lies flat and can be wrapped around the catheter shaft, which passes within and has a lumen to inflate it, to minimize overall diameter when deflated for insertion into the tissue track created by the wounding agent. The inflatable member is of large potential volume enabling full inflation with near zero internal pressure when unconstrained externally. When positioned within a wound track and inflated, the gas or liquid injected into the balloon lumen creates pressure because its expansion is constrained by the tissues of the wound, and that pressure is transmitted directly to the surrounding tissue of the wound track. The pressure exerted on the tissue can be precisely measured and controlled, automatically if appropriate, such that sufficient pressure is applied to tamponade bleeding, but not damage tissue. Since the balloon is of large potential volume, it can easily expand to fill and compress small, large, and irregular wound tracks and can successfully tamponade wounds that smaller, elastic balloon catheters would be unable to tamponade. The catheter system includes means to assist insertion into the wound track, including a rounded or bulbous exploring tip and an internal stylet. In it non-inflatable embodiments, the my devices are introduced into the wound track and deliver hemorrhage controlling agents or materials which are designed to promote clotting of the wound or to occupy space to assist in tamponade of the bleeding.
Owner:CARDIOCOMMAND
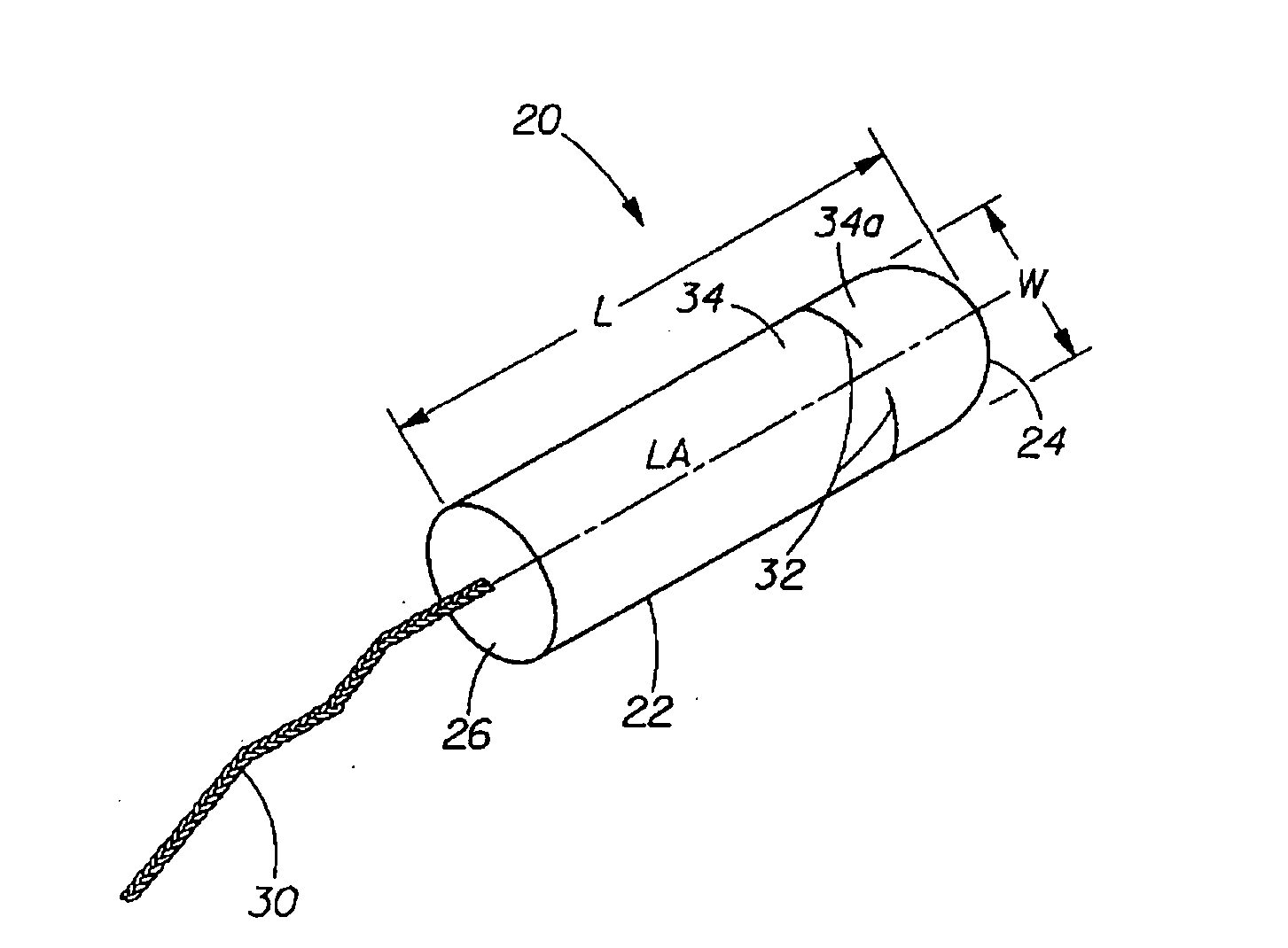
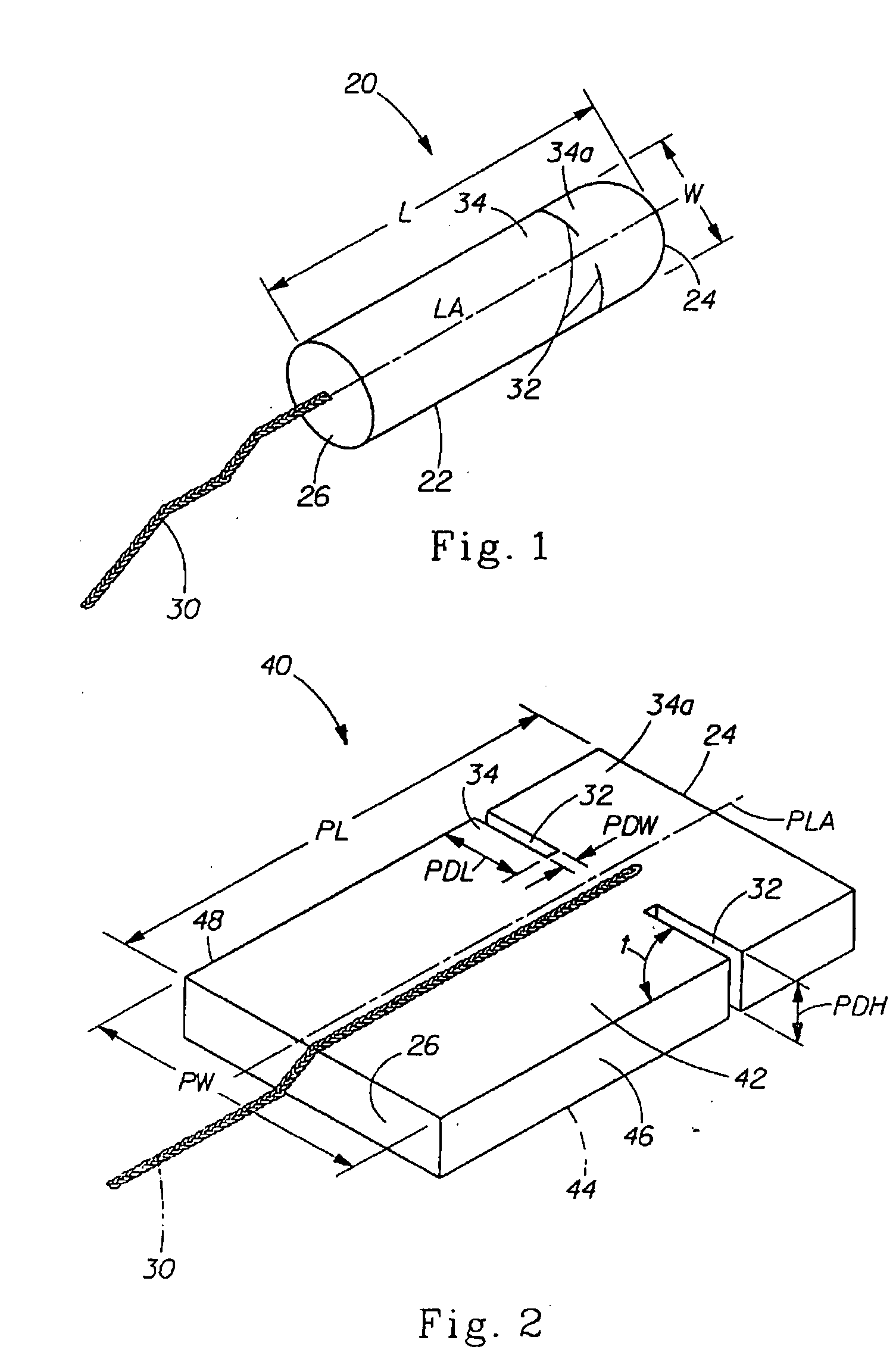
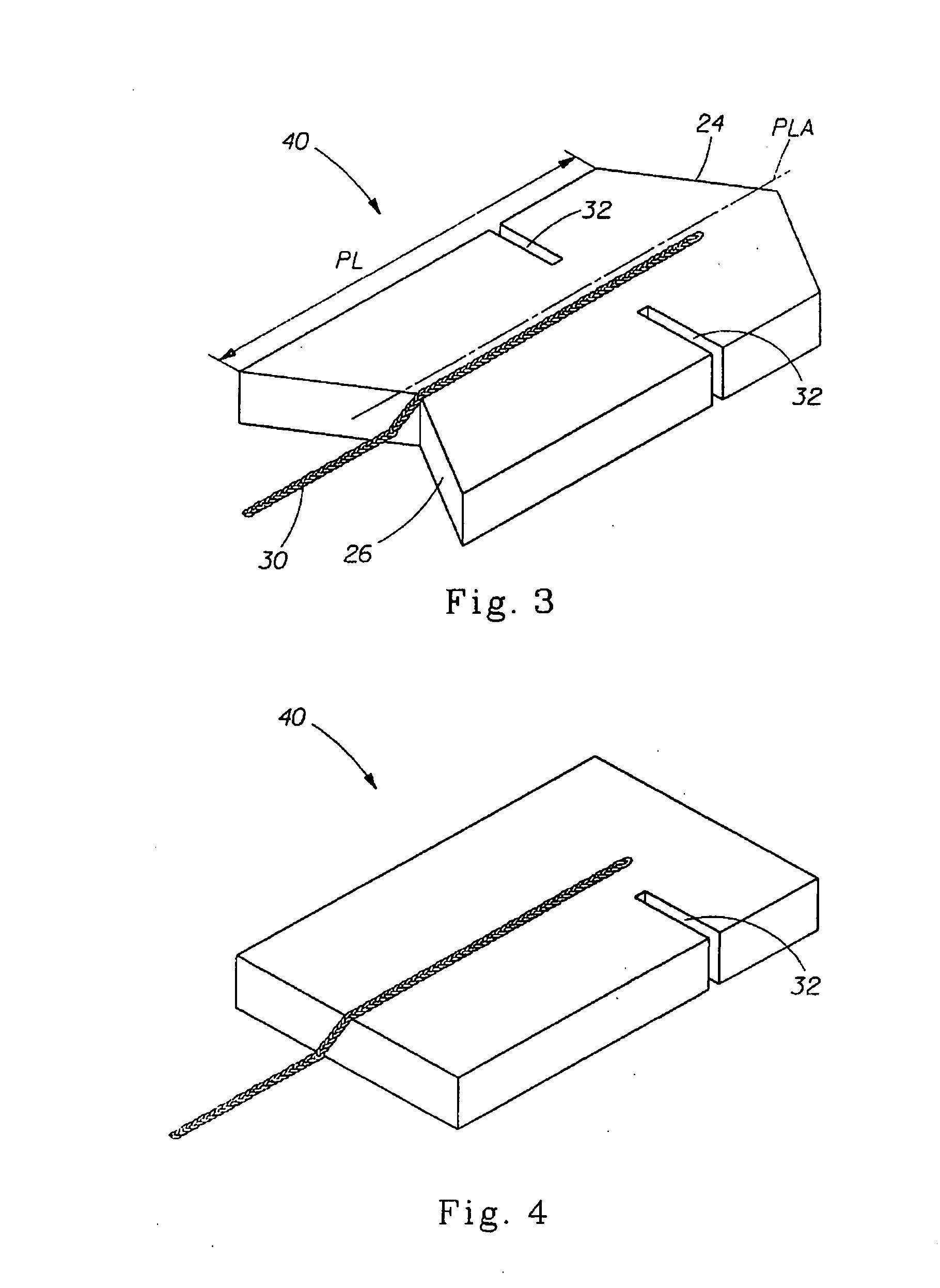
Absorbent Tampon Providing Clean Digital Insertion
A tampon has a generally uniform fiber distribution along its length, an insertion end, a withdrawal end, and a longitudinal axis. A finger recess having a depth of at least about 5 mm is formed into the withdrawal end. Nonetheless, a column strength of at least about 10 Newtons (N) can still be achieved. The tampon can be formed by winding an absorbent fibrous web around a winding mandrel; transferring the blank into a press; inserting a forming mandrel into one end of a tampon blank while the tampon blank is positioned in the press; moving a plurality of press jaws toward a central longitudinal press axis to compress the tampon blank and to form a compressed tampon having a finger recess formed into the one end of the tampon; and ejecting the compressed tampon from the press.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES
Tampon having at least one physical discontinuity
A tampon having at least one physical discontinuity is provided. The physical discontinuity, or physical discontinuities, are located in the compressed absorbent member and may be made in the tampon pledget before the pledget is compressed into the absorbent member. The physical discontinuities partially isolate a portion, or portions, of the tampon from the rest of the tampon. The partial isolation of a portion of the tampon reduces the amount of menses absorbed by that portion, which could be transported to the rest of the tampon through wicking. The concentration of menses absorption in a portion allows that portion have a higher level of expansion than the rest of the tampon to prevent menses from leaking out of the vaginal opening.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Tampon with a tampon applicator
A suitable tampon with a tampon applicator for expelling the tampon to provide side-to-side coverage and inserting the tampon into a body cavity is provided. The tampon applicator has a tampon holder tube having interior and exterior surfaces, a longitudinal axis, a hollow portion and an expulsion end dimensioned for insertion into the body cavity. The tampon holder tube has a feature for separating and spreading a tampon apart during expulsion of the tampon. A plunger may also be telescopically and slidably mounted in the tampon holder tube distal to the expulsion end and adapted to directionally expel the tampon from the tampon holder tube when a user expels the tampon from the tampon holder tube.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Tampon applicator
InactiveUS20110201992A1Reduce decreaseIncrease engagementHollow filament manufactureFilament/thread formingEngineeringTampon
A tampon applicator is described which comprises an ejector tube and an outer tube. The outer tube is dimensioned to fit closely and telescopically over the ejector tube. The outer tube has a distal discharge end. The distal end of the ejector tube is formed with one or more radially inwardly slanted fingers. The outer tube can comprise supporting means configured to restrict radially outward expansion of the fingers of the ejector tube when the tampon applicator is in telescopically compacted position.
Owner:ONTEX HIGIENEARTIKEL DEUT GMBH
Method and apparatus for carrying out the controlled heating of tissue in the region of dermis
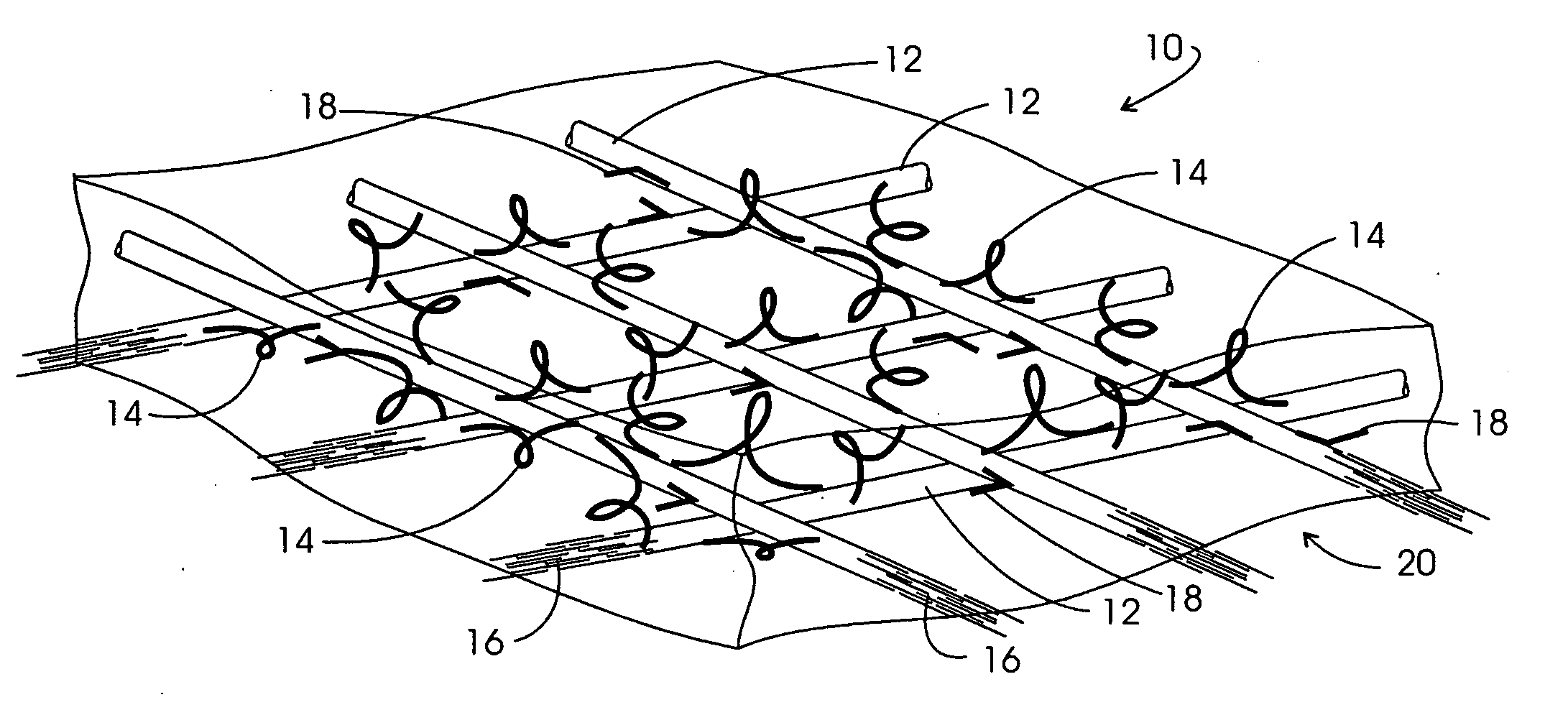
InactiveUS20080097557A1Improve protectionImprove electrical performanceSurgical needlesSurgical instrument detailsAdjuvantTamponade
Implant apparatus and method for effecting a controlled heating of tissue within the region of dermis of skin. The heater implants are configured with a thermally insulative generally flat support functioning as a thermal barrier. One surface of this thermal barrier carries one or more electrodes within a radiofrequency excitable circuit as well as an associated temperature sensing circuit. The implants are located within heating channels at the interface between skin dermis and the next adjacent subcutaneous tissue layer such that the electrodes are contactable with the lower region of dermis. During therapy a conformal heat sink is positioned against the skin above the implants and a slight tamponade is applied through the heat sink to assure uniform dermis contact with electrode surfaces. An adjuvant may be employed to infiltrate dermis to significantly lower the thermal threshold transition temperature for dermis or dermis component shrinkage.
Owner:APSARA MEDICAL
Tampon assembly providing proper bodily placement of a pledget
Provided is a tampon applicator having one or more insertion indicators to gauge and / or control the insertion depth of a tampon. The one or more insertion indicators may be located on the tampon applicator barrel, plunger, tampon, removal string, or any combinations thereof. As a result of the one or more insertion indicators, a woman can adjust the insertion depth of the tampon to her body's requirements ensuring leakage protection, comfort, or both.
Owner:EDGEWELL PERSONAL CARE BRANDS LLC
Method and apparatus for carrying out the controlled heating of tissue in the region of dermis
InactiveUS20070135880A1Improve protectionIncrease heatSurgical instrument detailsTherapeutic coolingAdjuvantCapillary malformation
Owner:APSARA MEDICAL
Tampon having indicator enclosed in a tampon applicator
An array of disposable absorbent articles. The array has a first absorbent article and a second absorbent article. The first absorbent article is enclosed in a first tampon applicator having i.) an outer surface wherein the outer surface has an outer surface area and ii.) a first identifier having a first surface area. The first identifier is disposed on the first absorbent article and corresponds to a first absorbency. The first identifier is disposed on the first absorbent article. A second absorbent article is enclosed in a second tampon applicator having i.) an outer surface wherein the outer surface has an outer surface area and ii.) a second identifier having a second surface area. The second identifier is disposed on the second absorbent article and corresponds to a second absorbency. The first surface area is different than the second surface area.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Device to be used in healing processes
ActiveUS20060184109A1Facilitates targeted treatmentEasy to prevent inadvertent secondary injuryBalloon catheterCannulasInterior spaceTamponade
A device for tamponade of body cavities and for mechanical anchoring of a catheter, the device including a flexible tube segment (2) having an inner wall (4) and an outer wall (6) that surround an interior space (8), wherein the tube segment (2) is inflatable, and is configured without through-passing support bodies so that a displacement of tube wall material between the inner wall (4) and the outer wall (6) of the tube segment (2) is possible by inflation of the tube segment, wherein the tube segment is provided with two ends (7,9), which are fastened to a same closing element (10), configured so that a torus geometry is striven for as the inflatable tube segment (2) is inflated and the closing element (10) is a pipe nipple and the two ends (7,9) of the tube segment (2) are joined together fluid-tightly.
Owner:AVENT INC
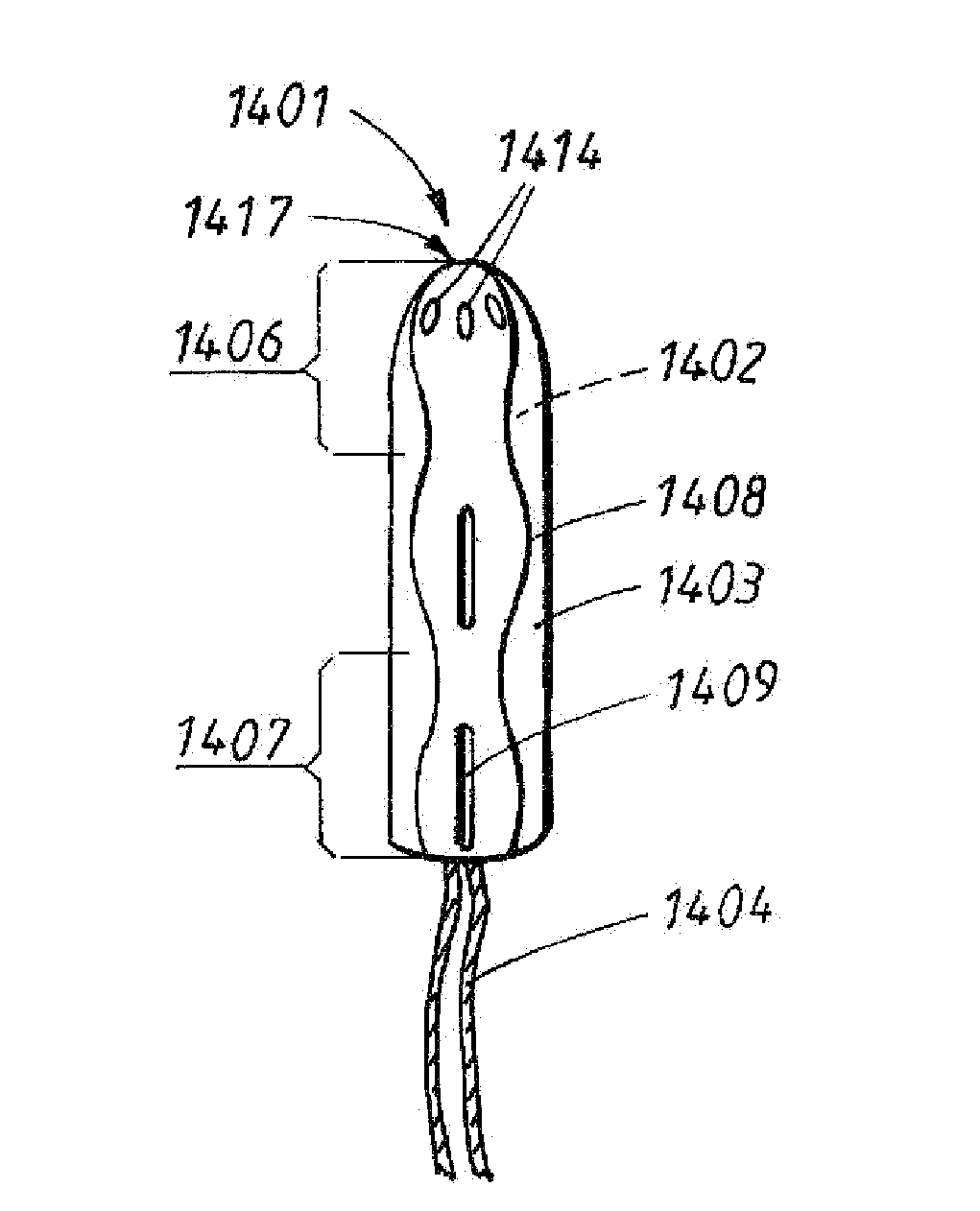
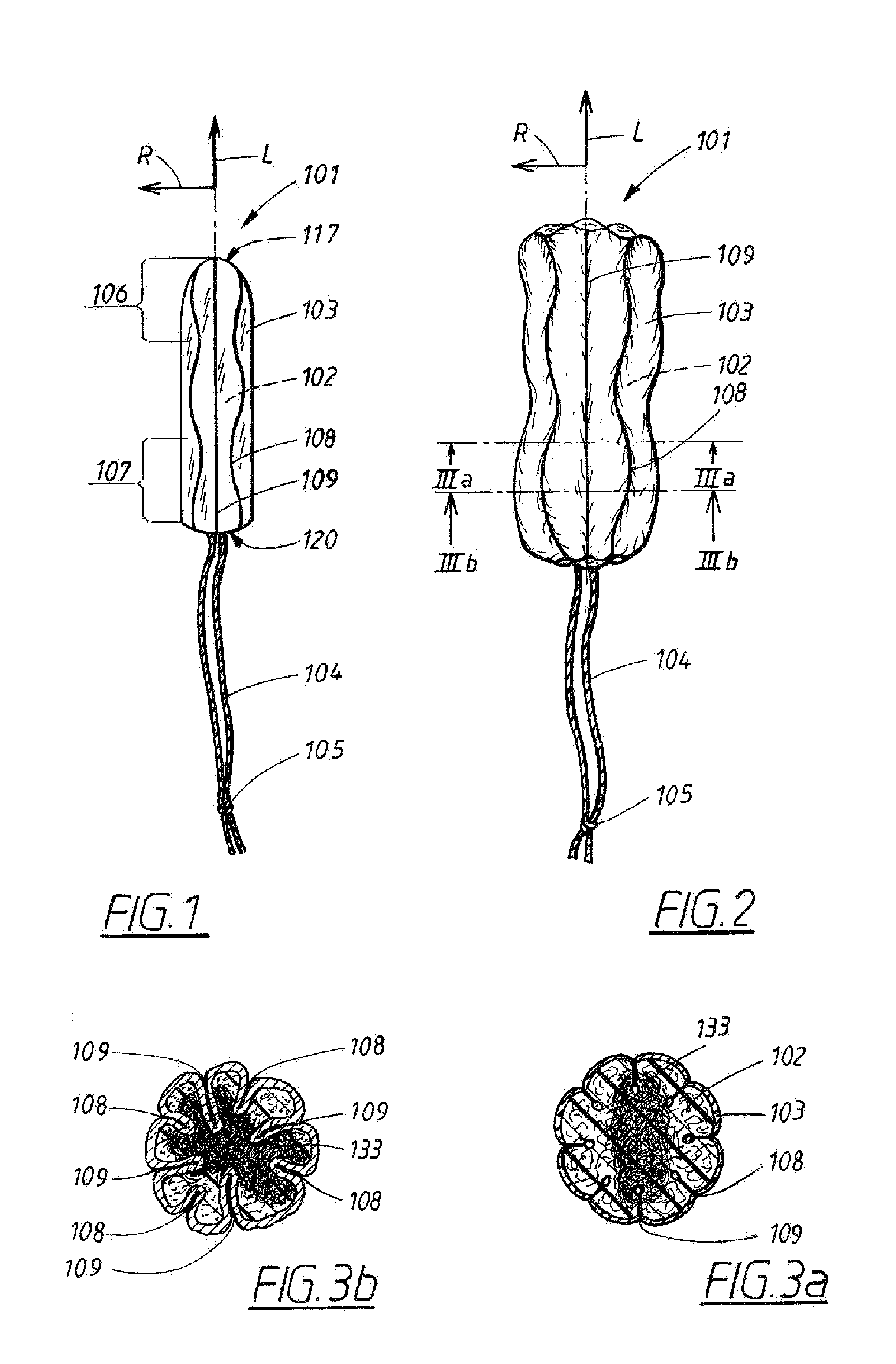
Anthroprometrically expandable tampon pledget
InactiveUS20090036859A1Improve comfortReduce leakageBaby linensTextiles and paperTamponadeAbsorbent material
A tampon pledget has an absorbent mass of material and a withdrawal string located at one end thereof. During use, the tampon pledget expands to take on a geometric configuration that approximates the shape of the vagina into which the tampon pledget is inserted. An anthroprometrically expandable tampon pledget has an absorbent mass of material that is defined by a first end having a first density, a second end having a second density, and a portion intermediate the first and second ends. The material expands at different rates upon being contacted by body fluids, thereby allowing the tampon pledget to conform to the shape of a vagina. A method of making an expandable tampon pledget includes the steps of providing an absorbent material, attaching a string thereto, and compressing the material into a cylindrical shape such that a density gradient is realized over a length of the compressed material.
Owner:EVEREADY BATTERY CO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com