Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
363 results about "Patients position" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
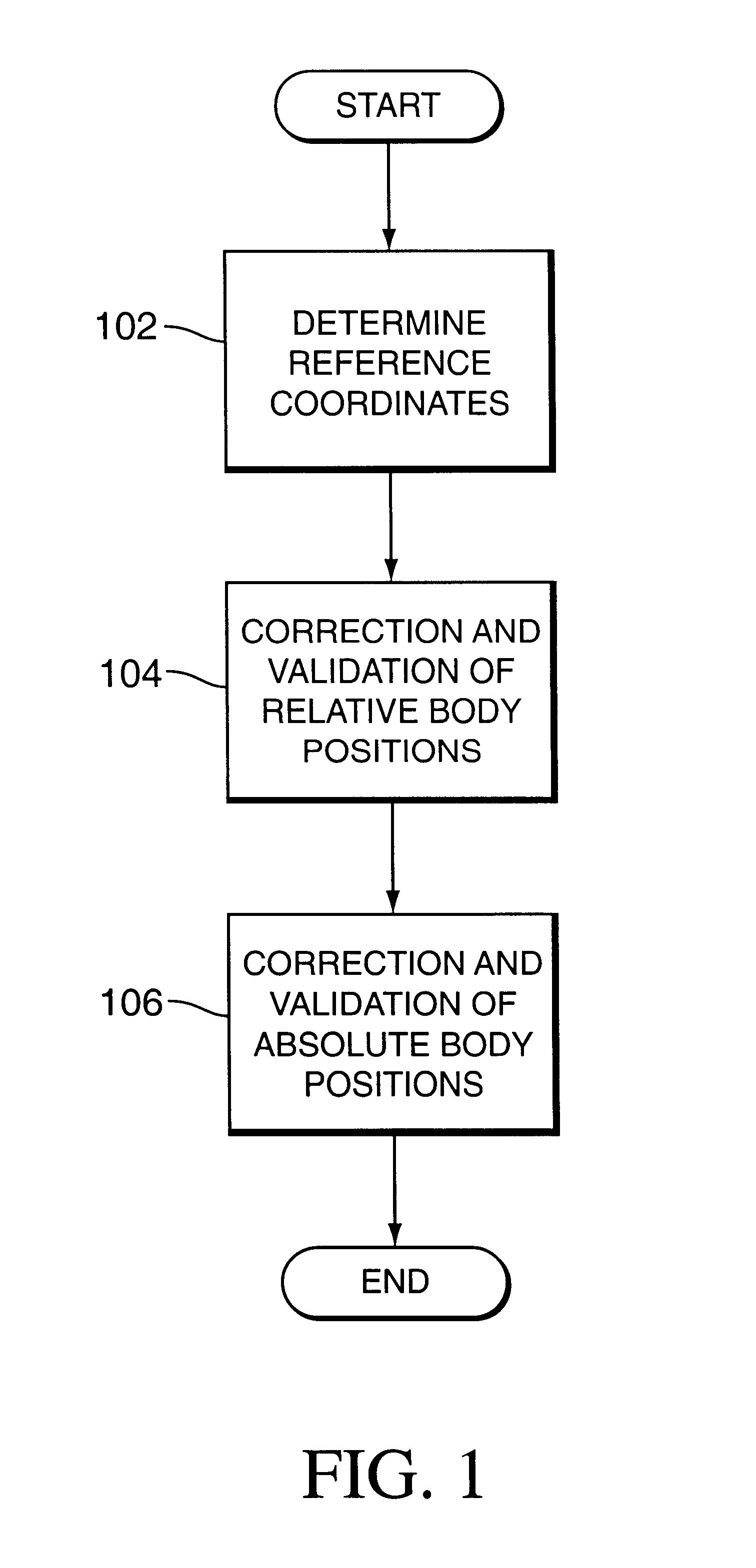
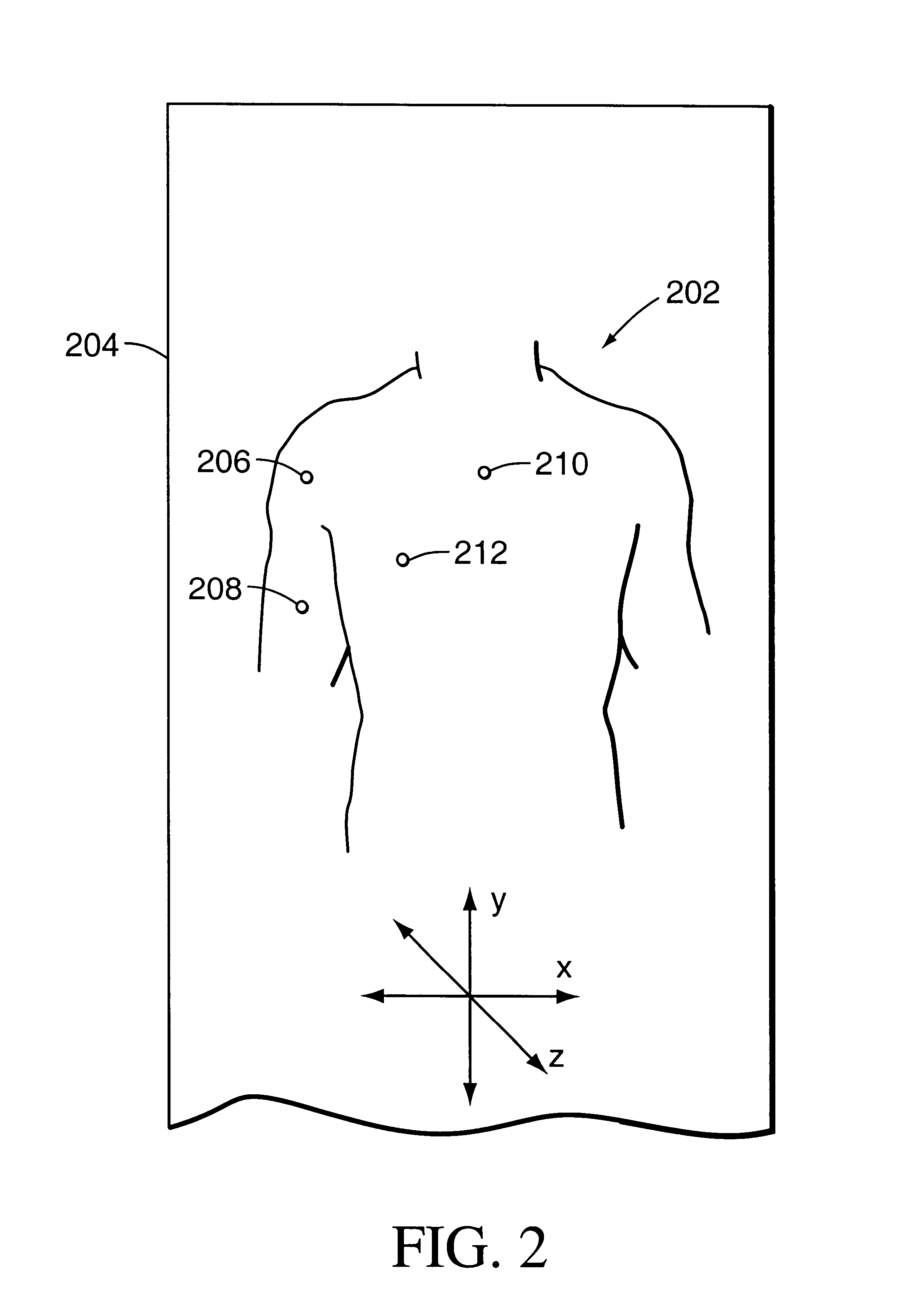
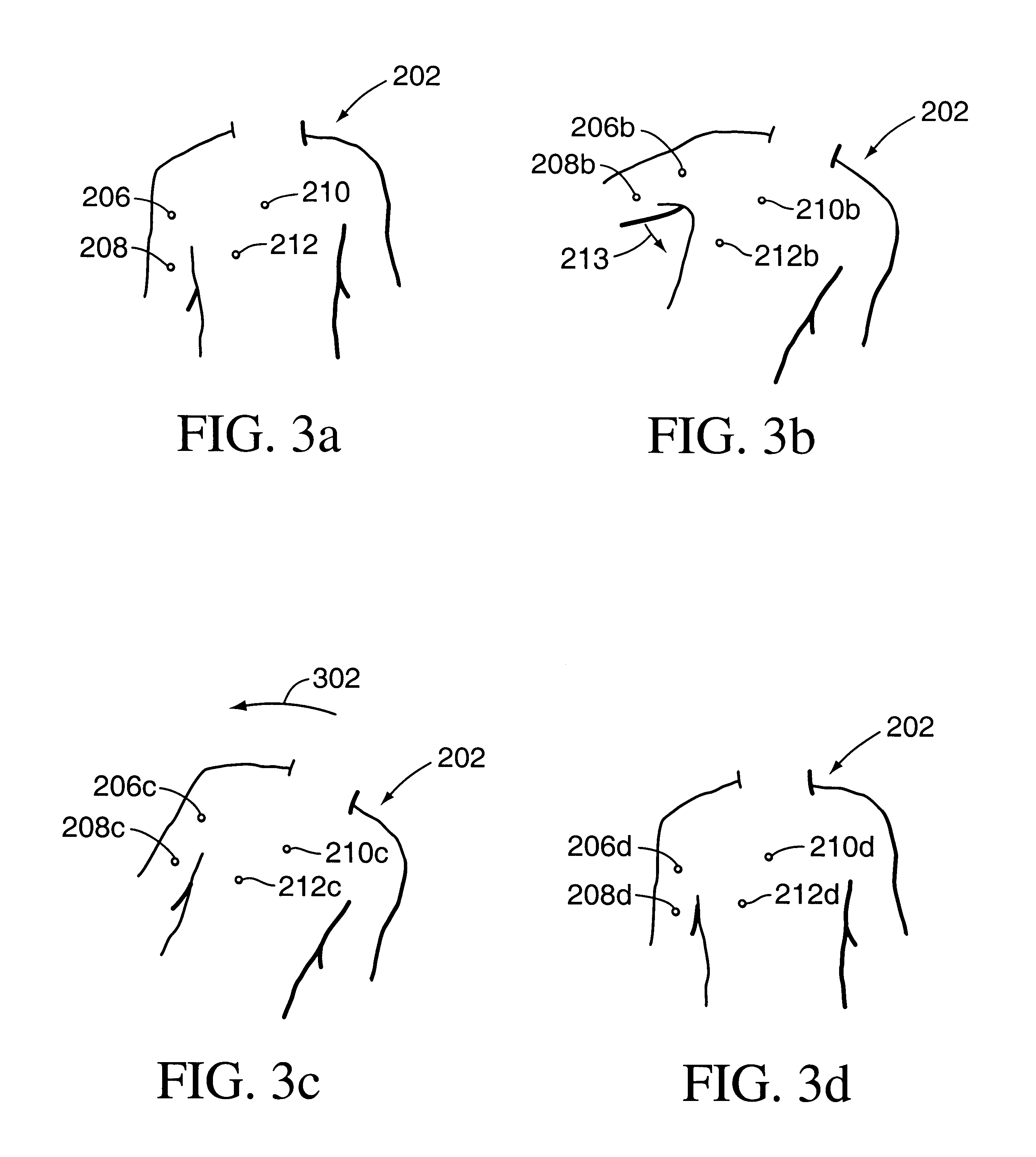
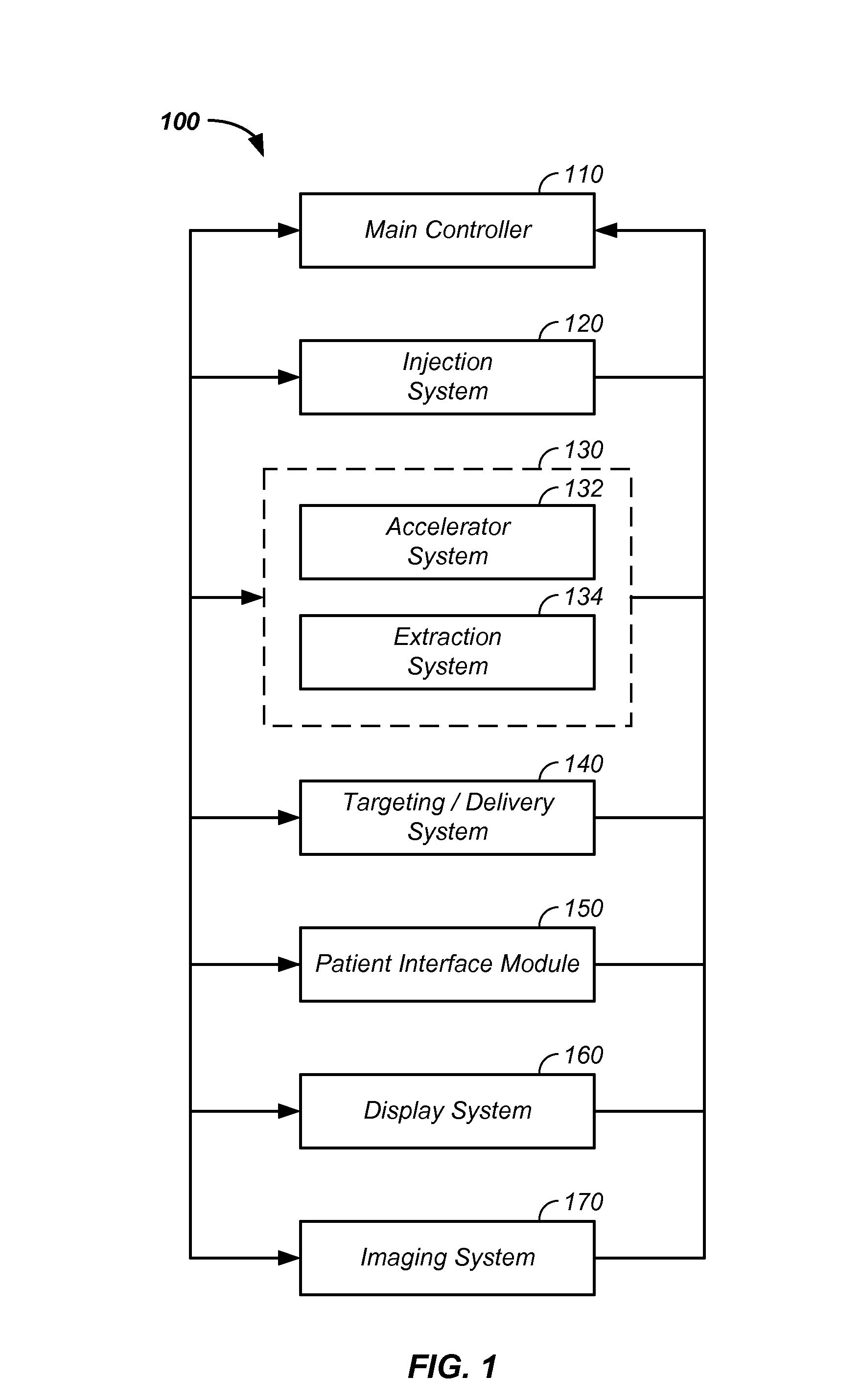
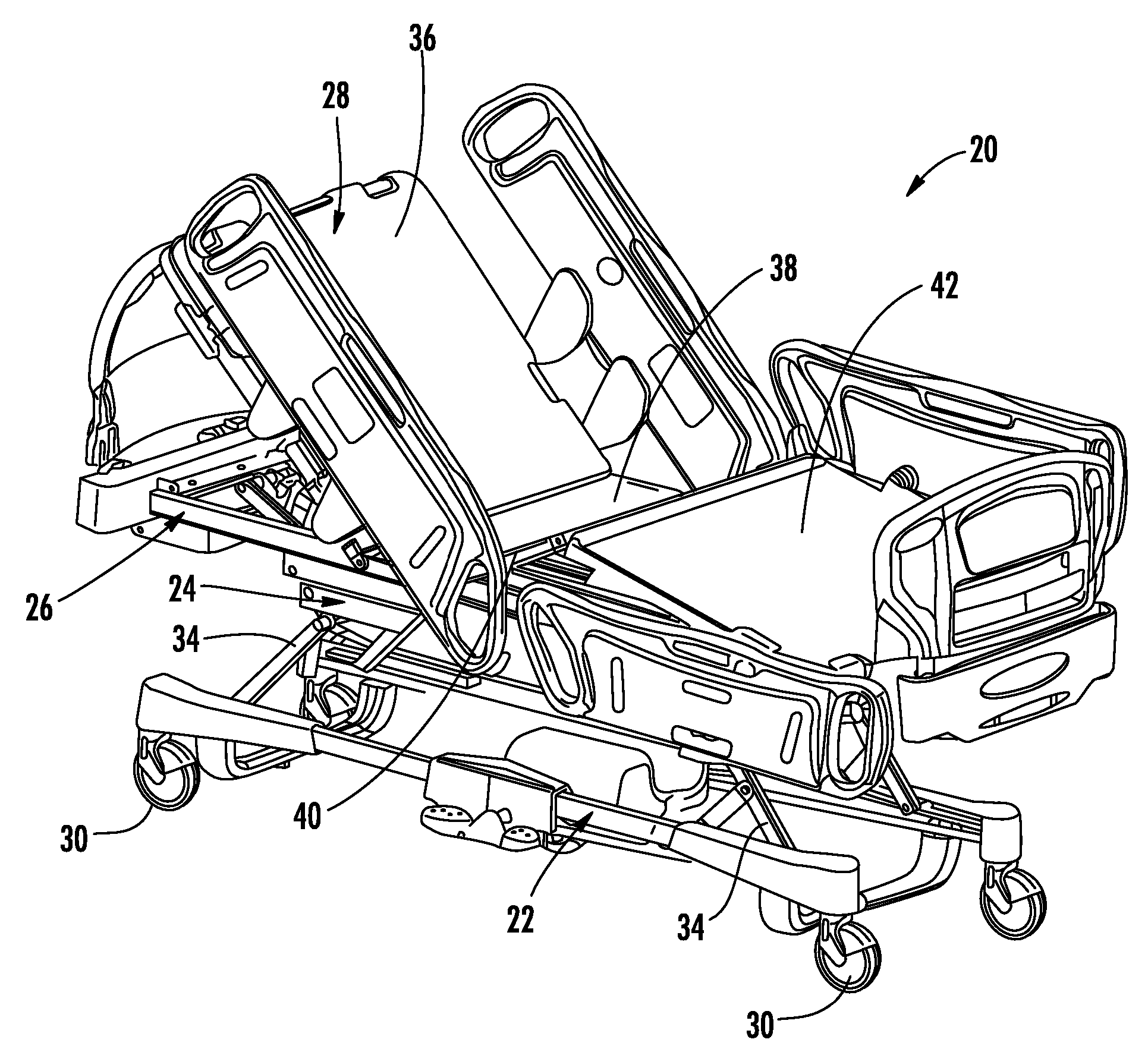
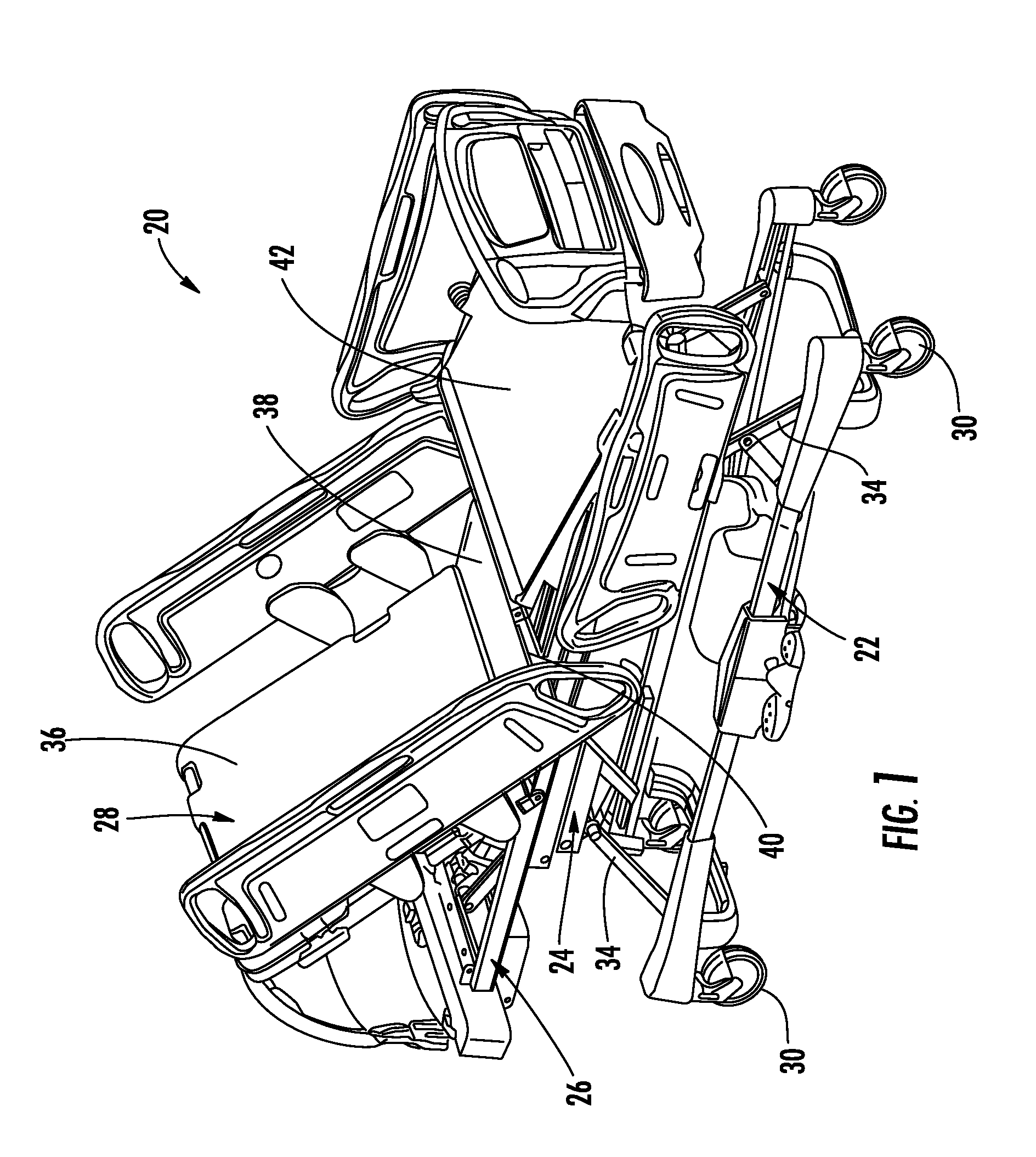
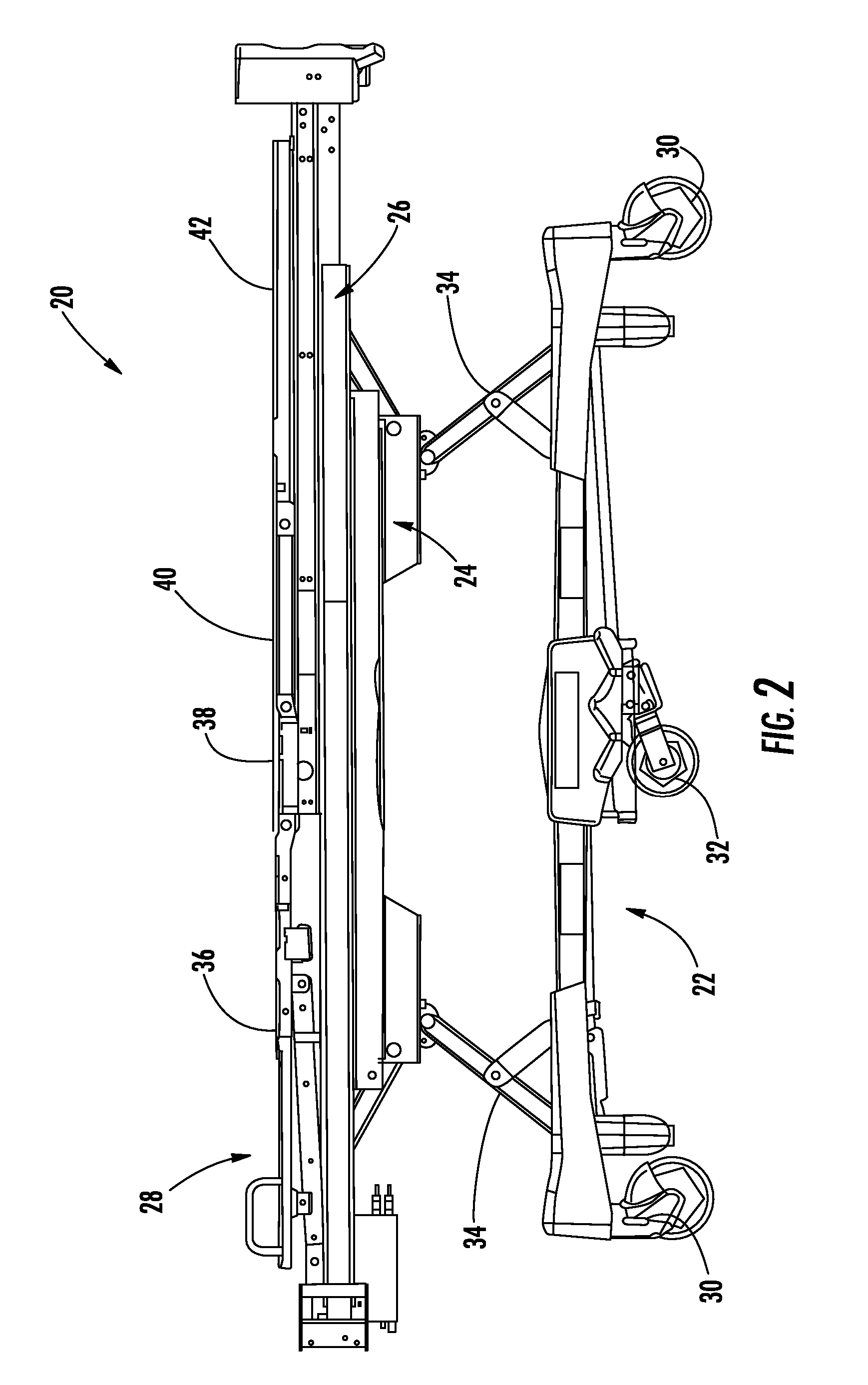
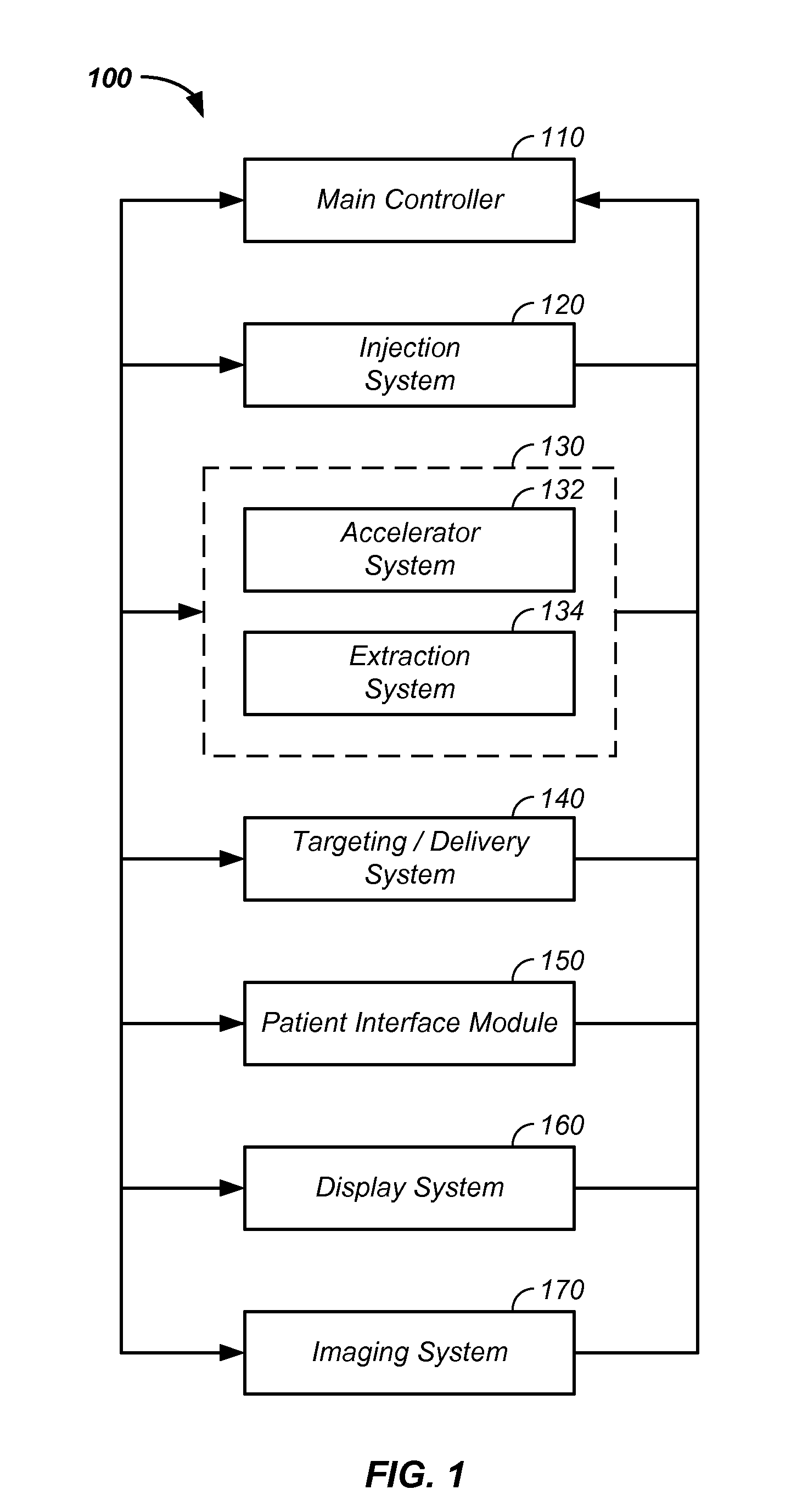
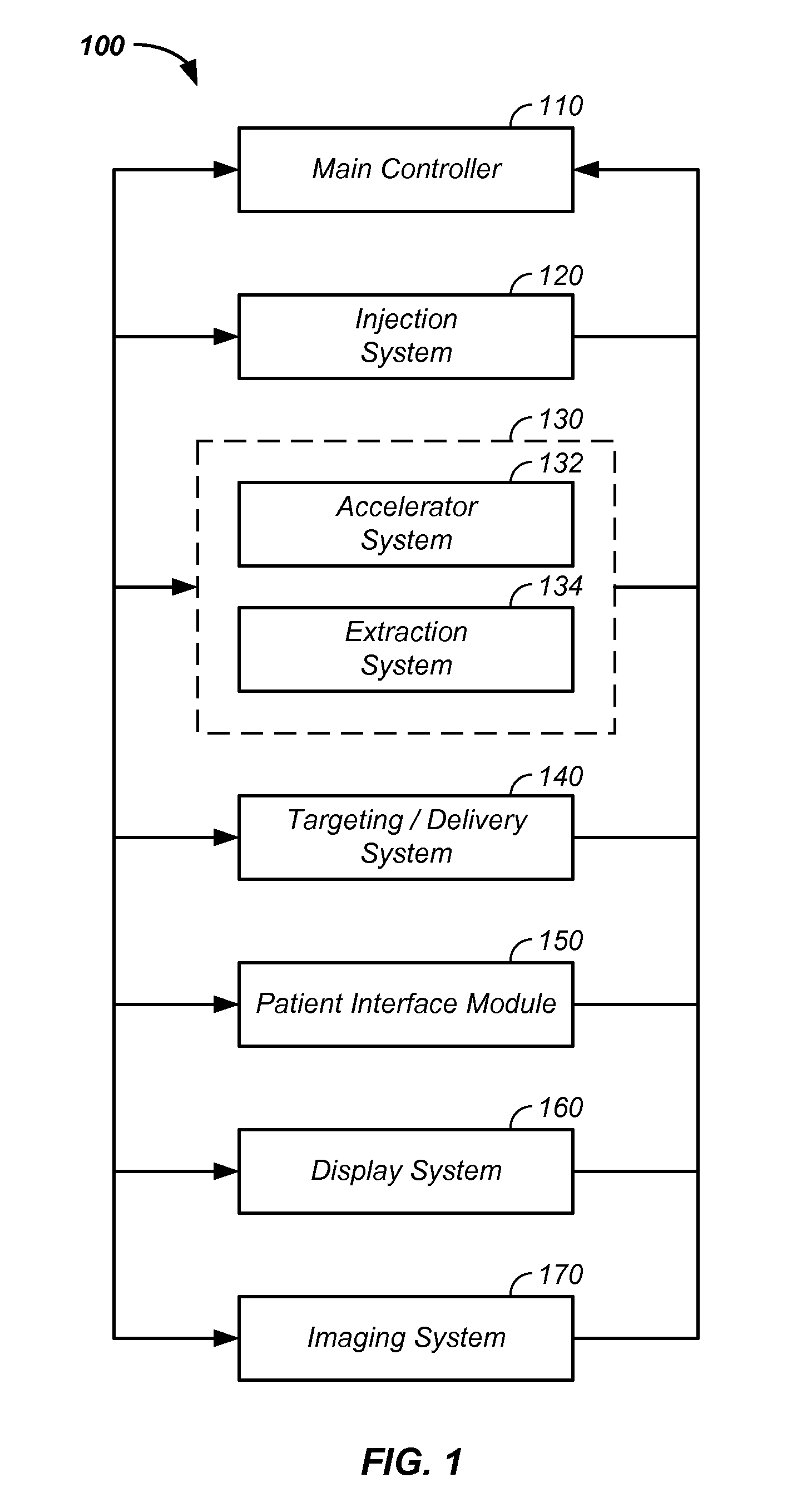
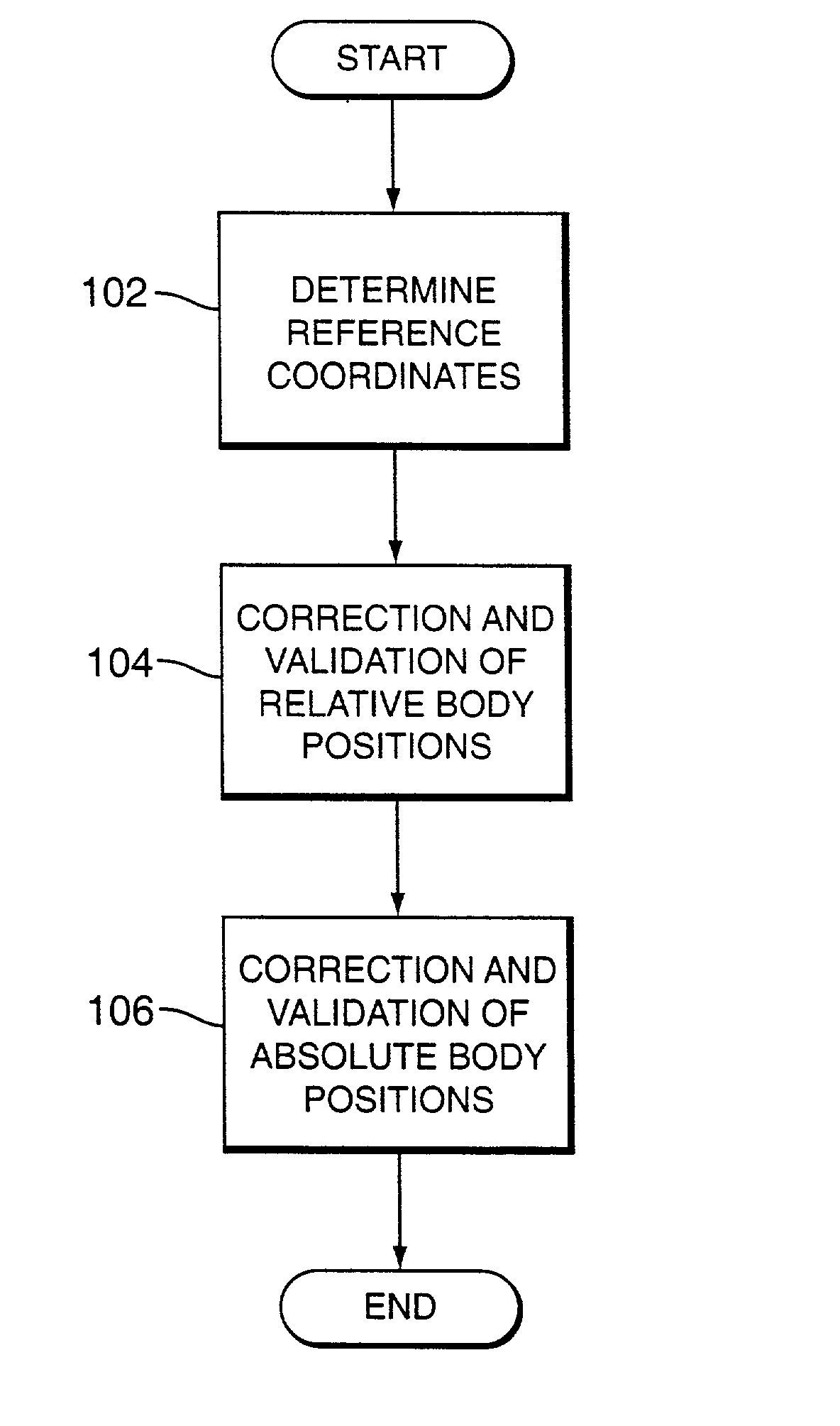
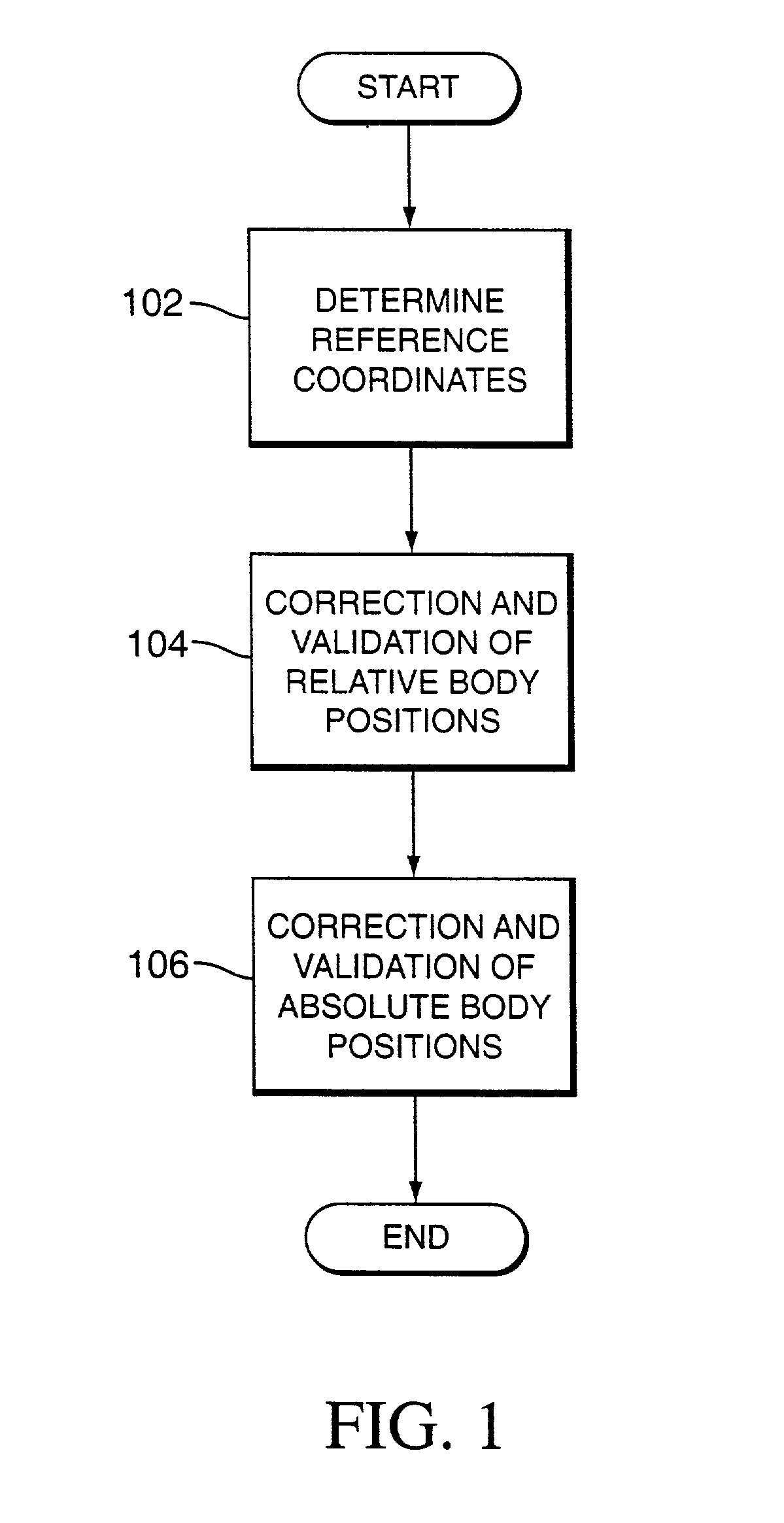
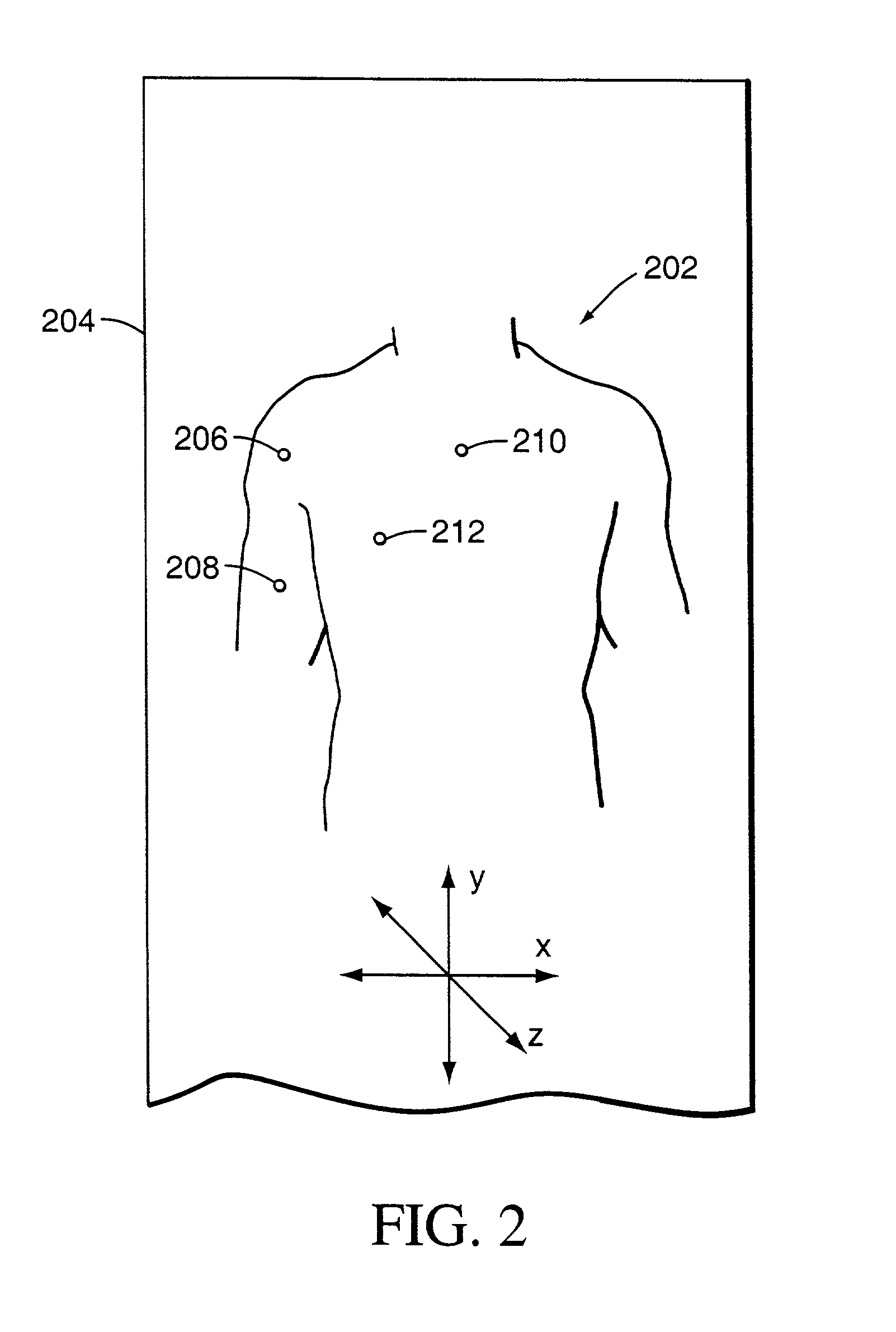
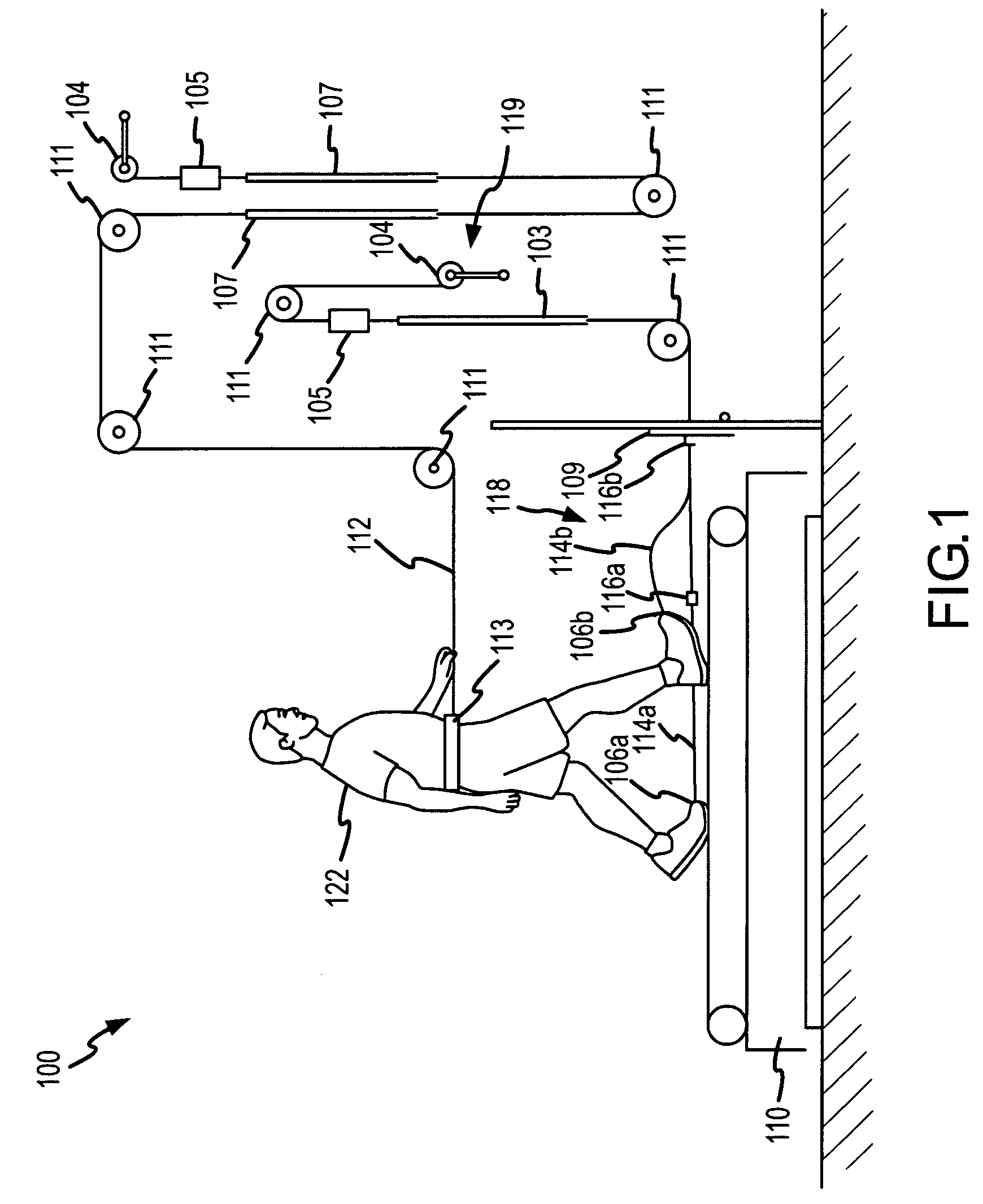
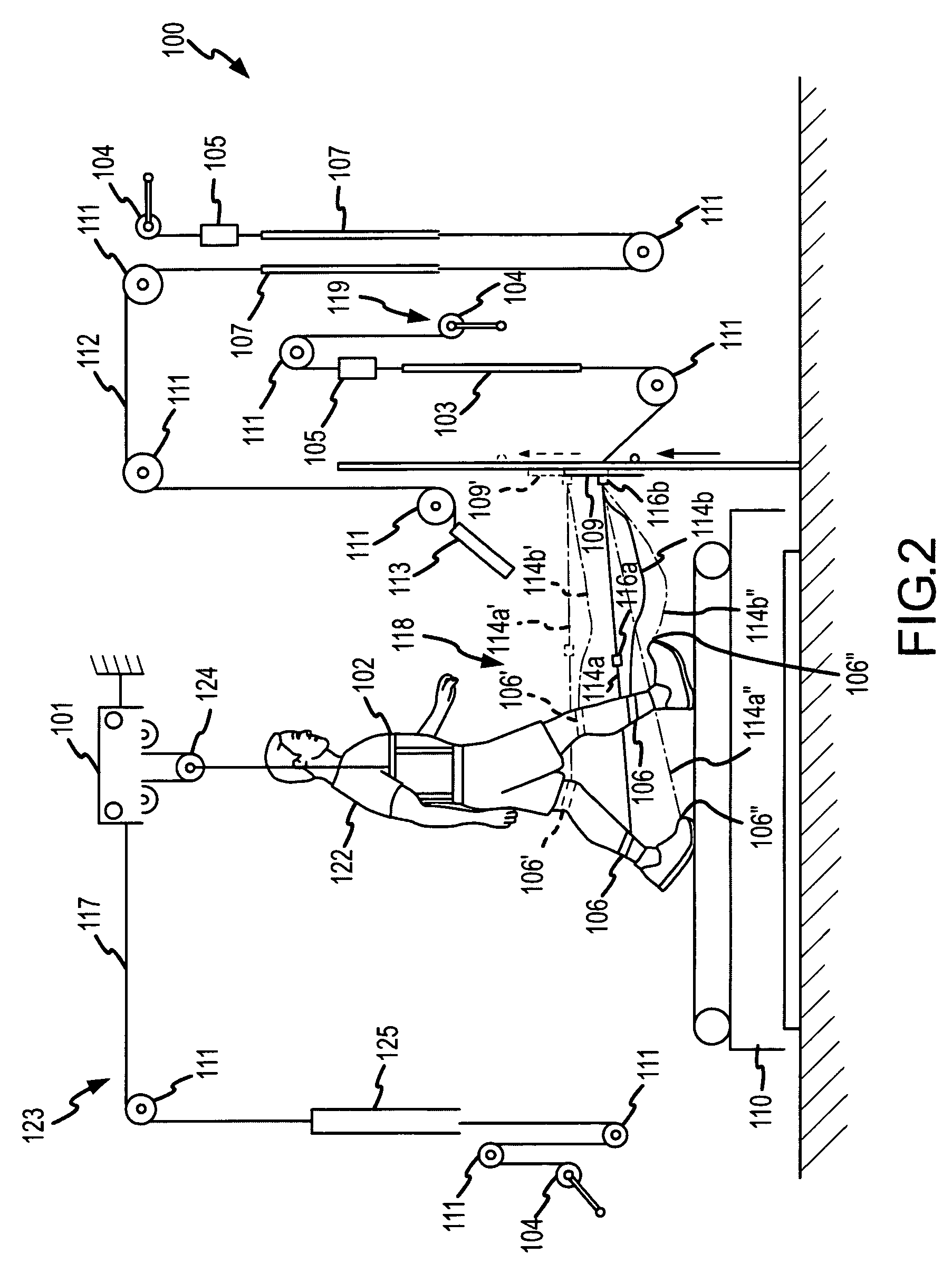
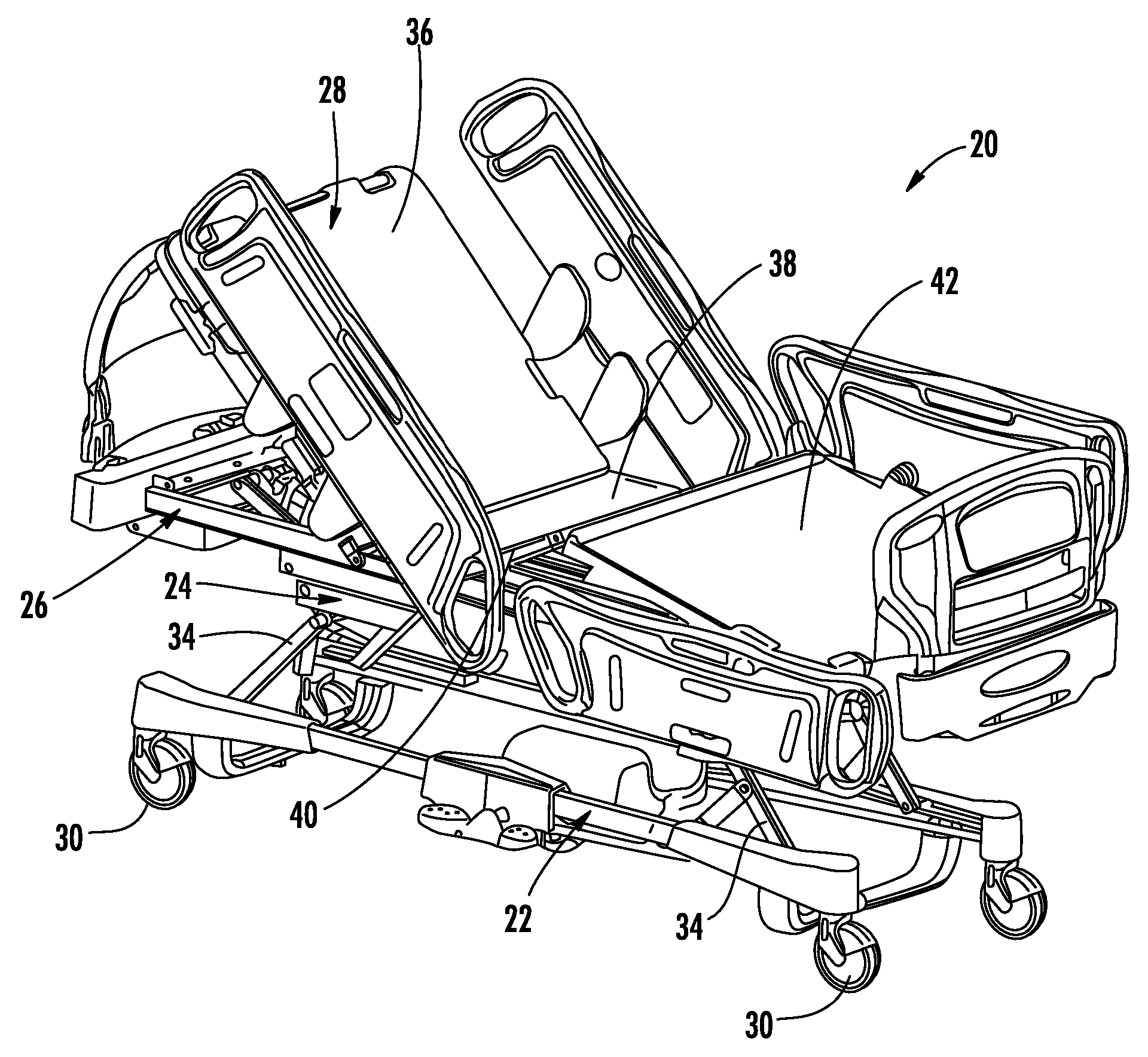
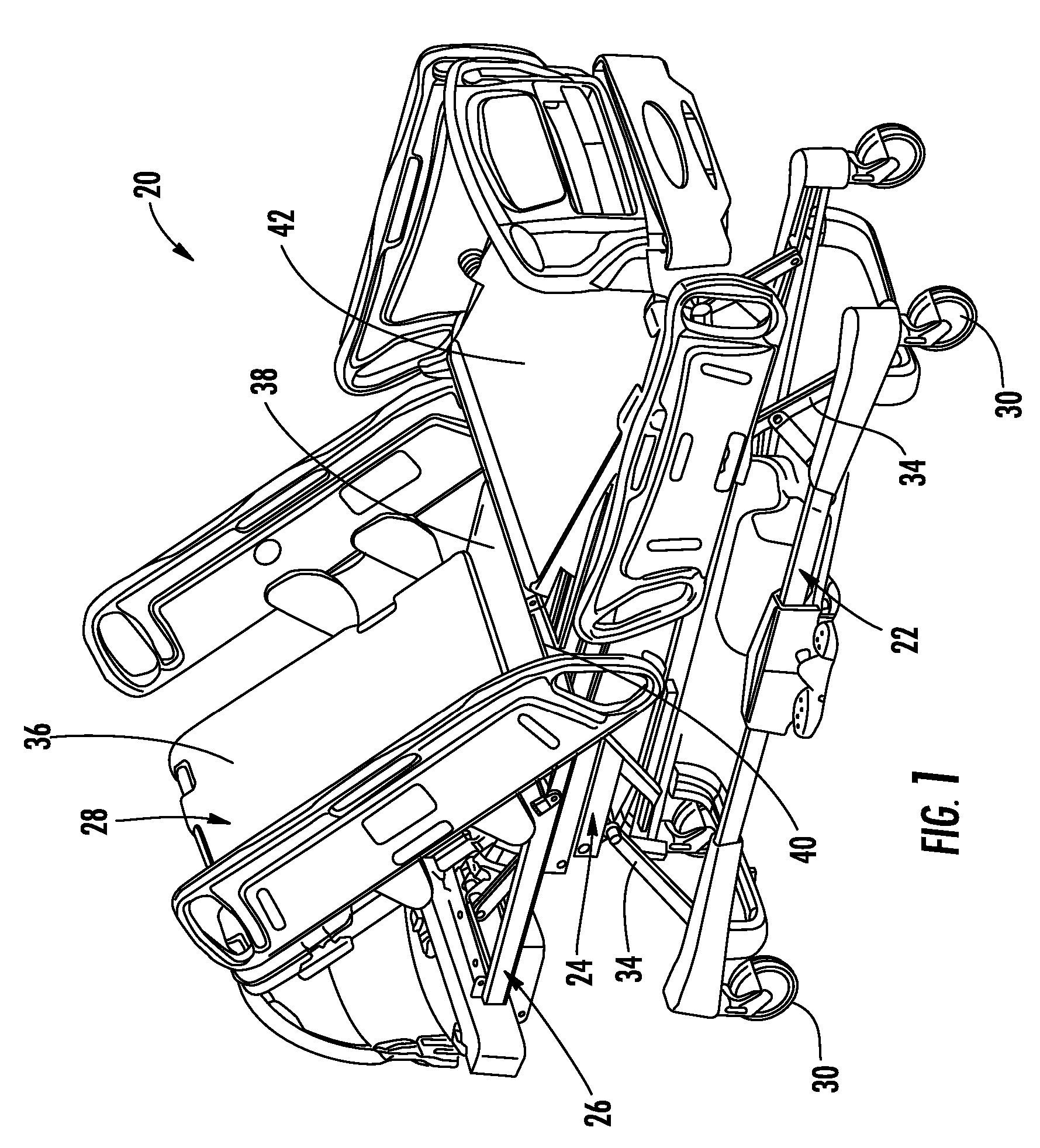
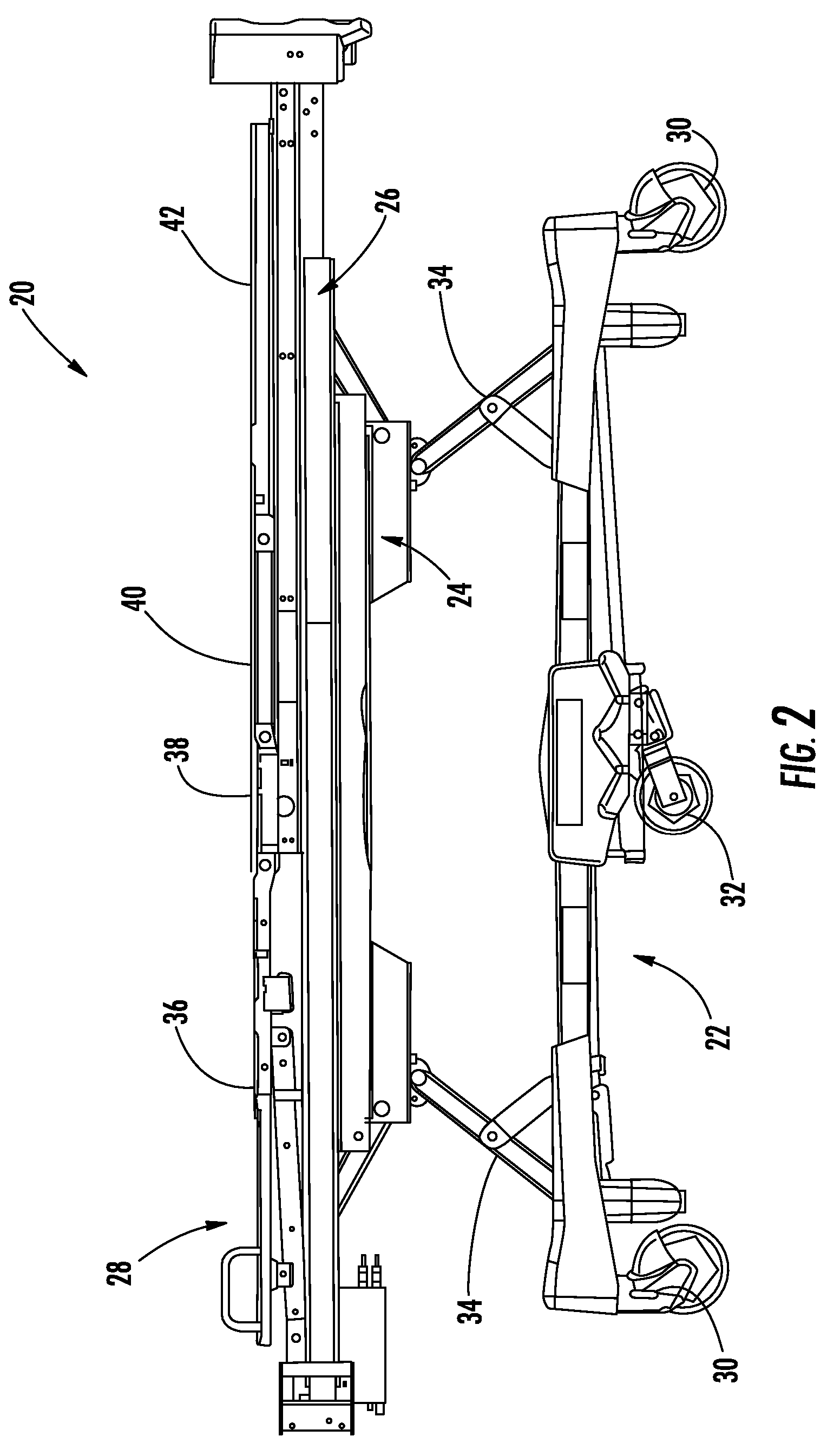
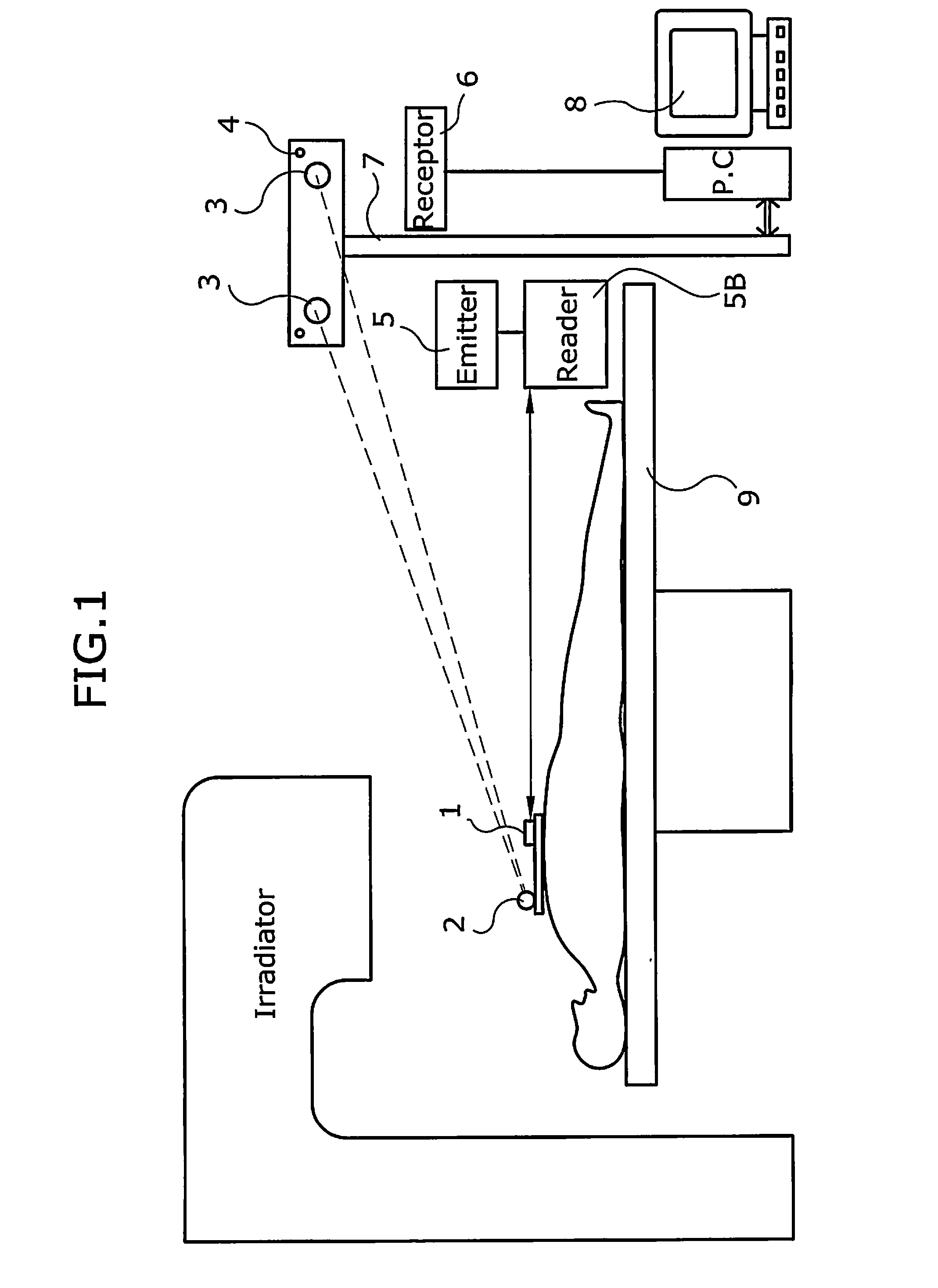
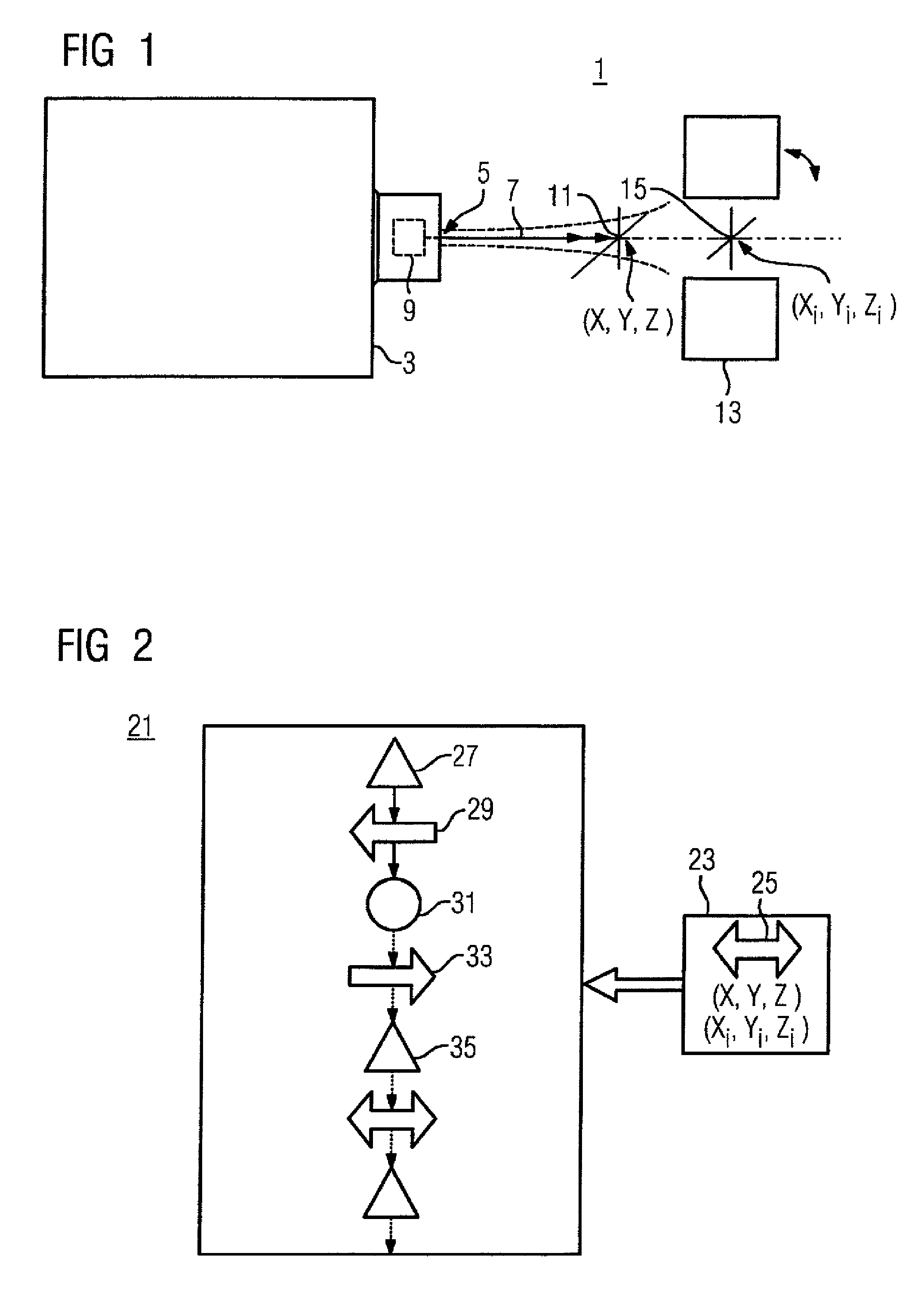
Method and system for positioning patients for medical treatment procedures
A system and method for measuring and correcting the position of a patient are disclosed. According to an aspect of the invention, reference coordinates for particular body locations on the patent are determined. At a later treatment session, the relative positioning of the patient's body locations are adjusted to match the relative positioning of the reference coordinates. The entire body of the patient can thereafter be moved as a single unit to match the patient's body location with the absolute location of the reference coordinates.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
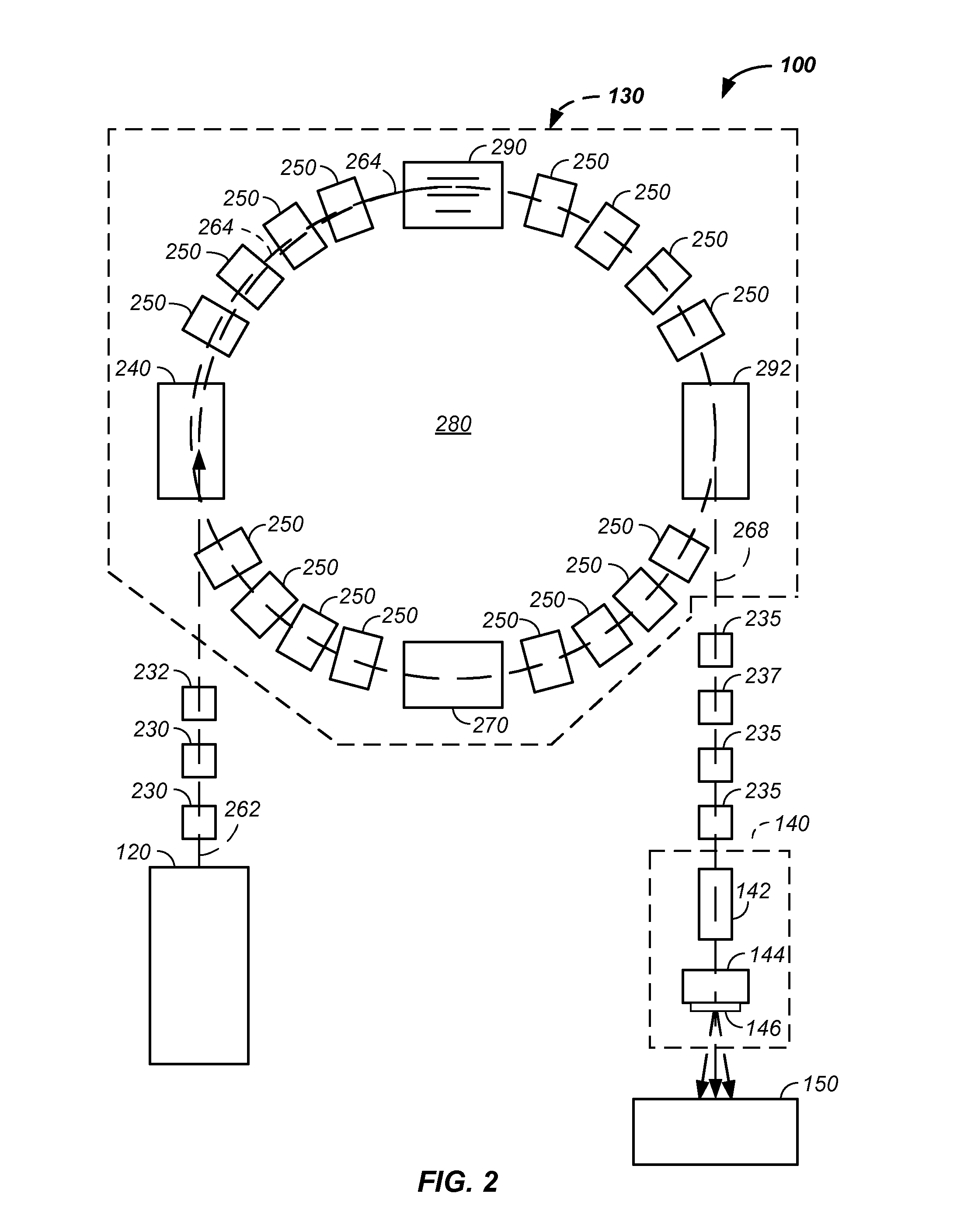
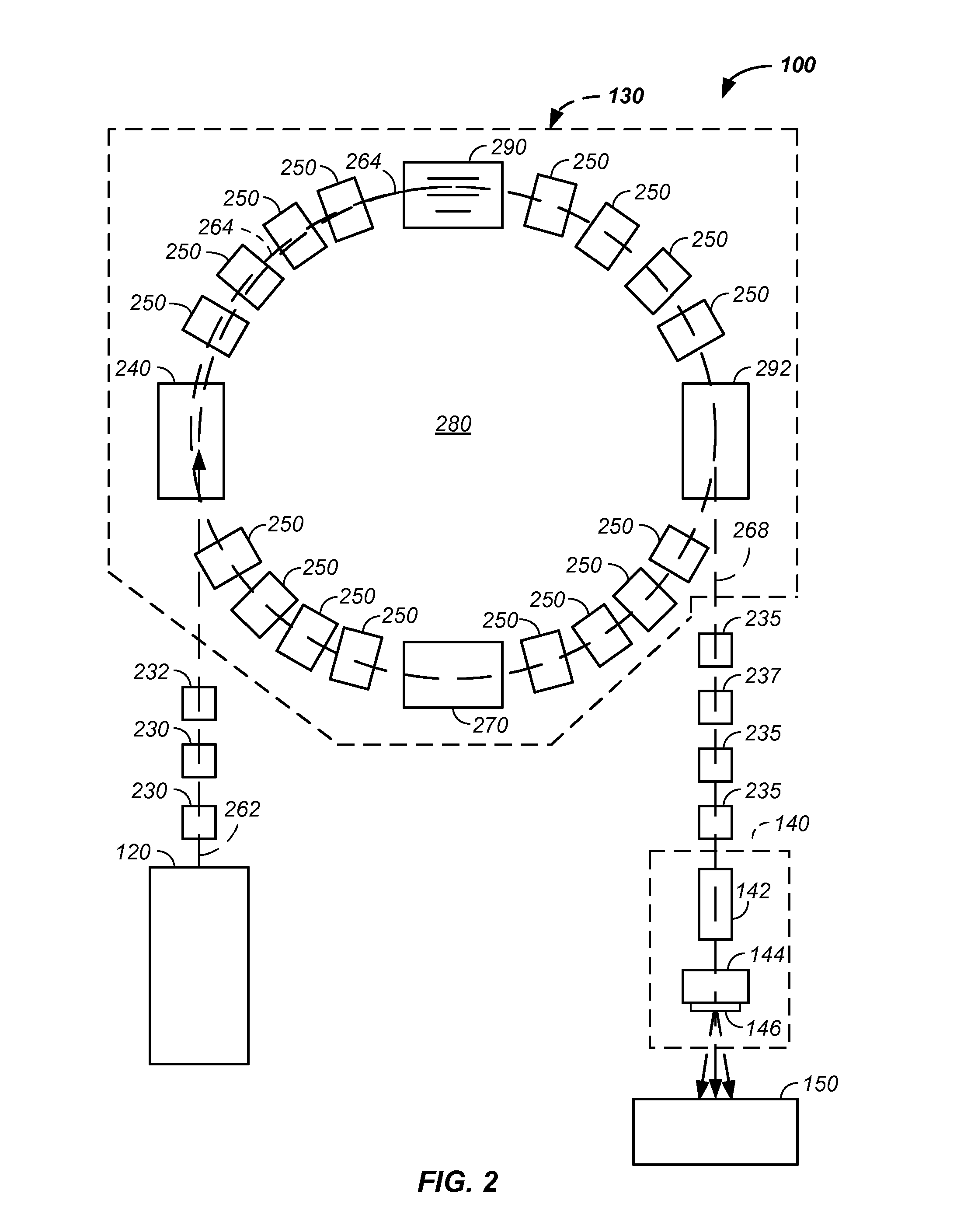
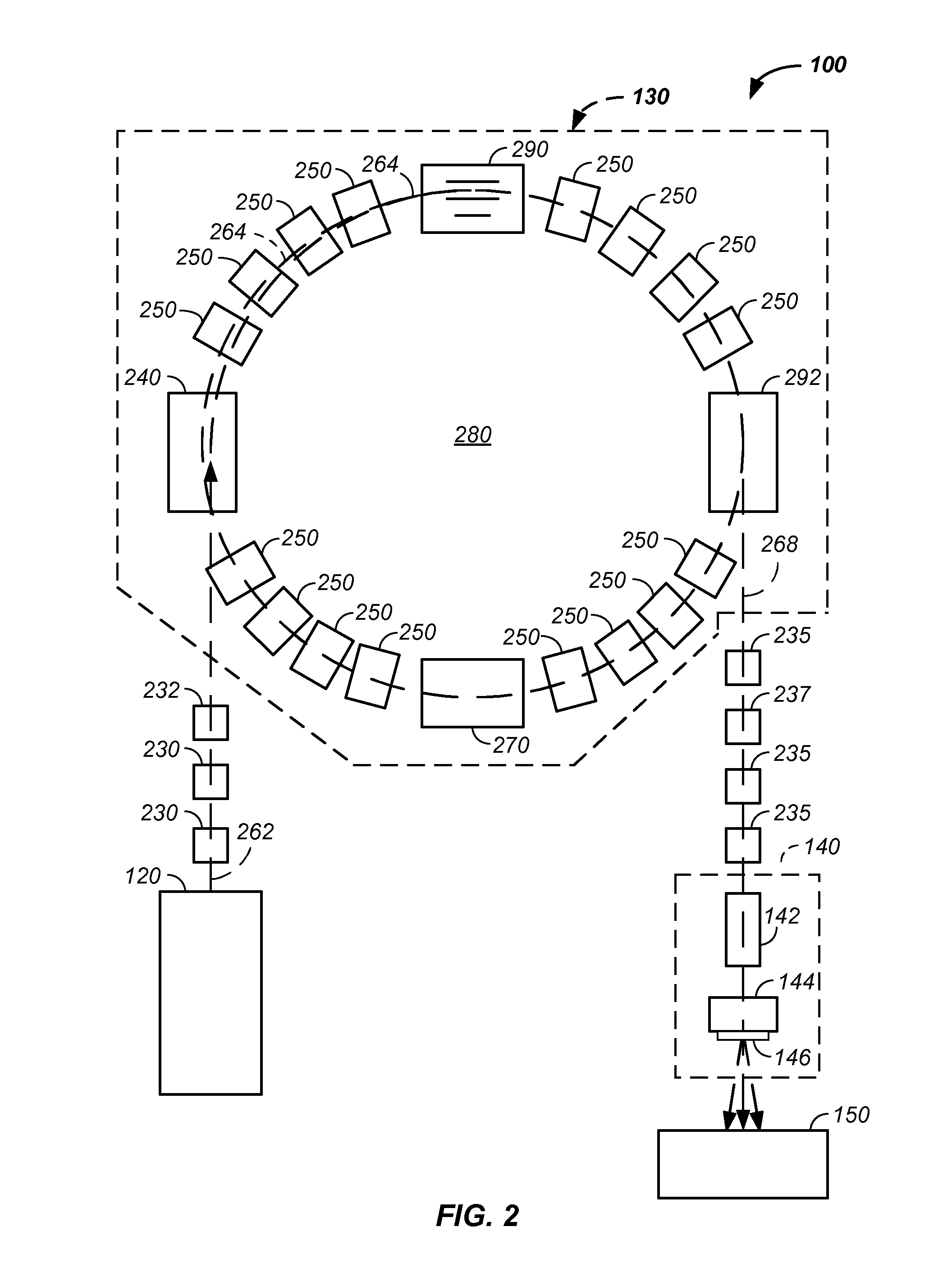
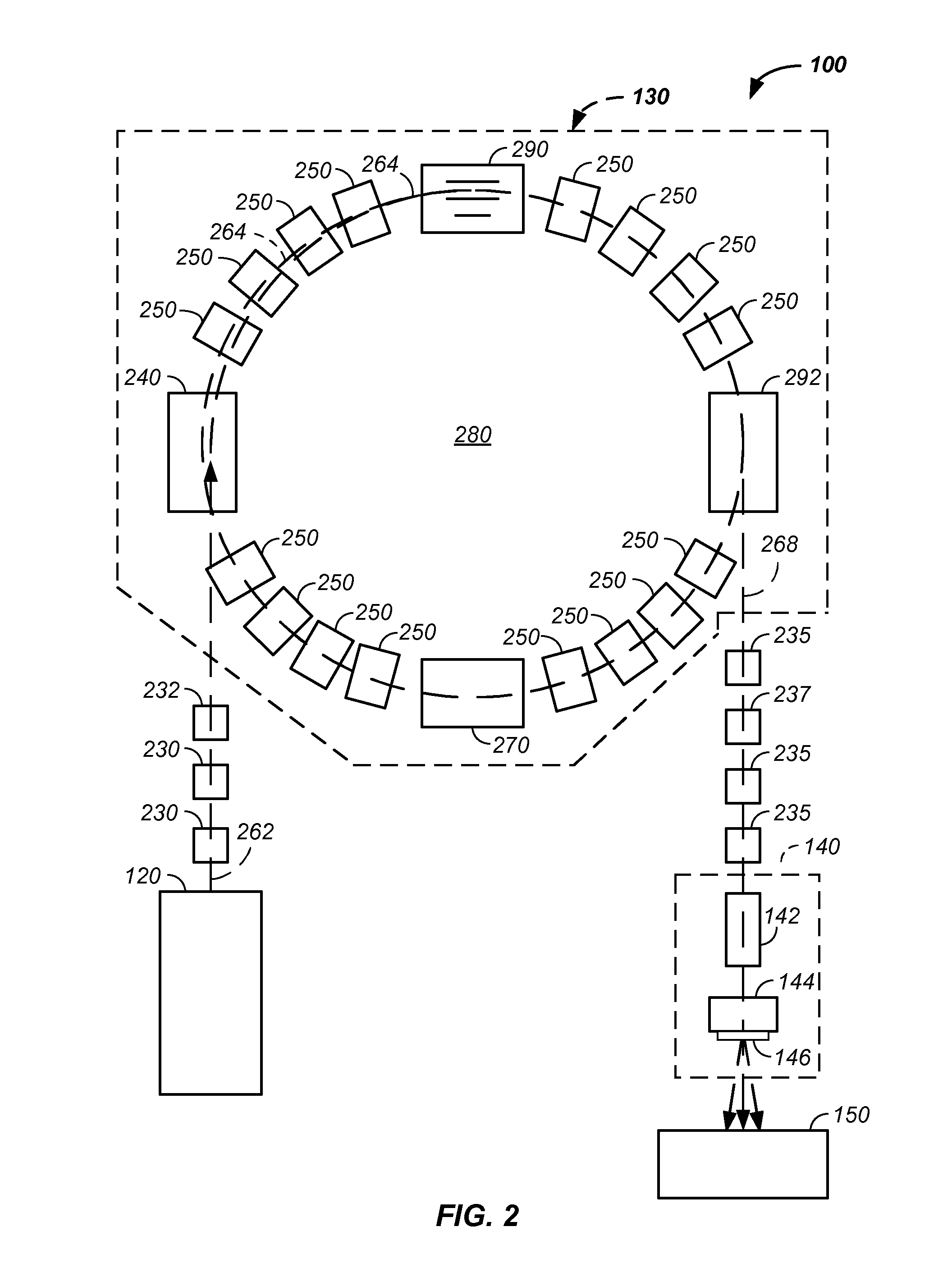
Synchronized x-ray / breathing method and apparatus used in conjunction with a charged particle cancer therapy system
ActiveUS20100128846A1Cathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingMagnetic resonance acceleratorsX-raySynchrotron
The invention comprises an X-ray system that is orientated to provide X-ray images of a patient in the same orientation as viewed by a proton therapy beam, is synchronized with patient respiration, is operable on a patient positioned for proton therapy, and does not interfere with a proton beam treatment path. Preferably, the synchronized system is used in conjunction with a negative ion beam source, synchrotron, and / or targeting method apparatus to provide an X-ray timed with patient respiration and performed immediately prior to and / or concurrently with particle beam therapy irradiation to ensure targeted and controlled delivery of energy relative to a patient position resulting in efficient, precise, and / or accurate noninvasive, in-vivo treatment of a solid cancerous tumor with minimization of damage to surrounding healthy tissue in a patient using the proton beam position verification system.
Owner:BALAKIN ANDREY VLADIMIROVICH +1
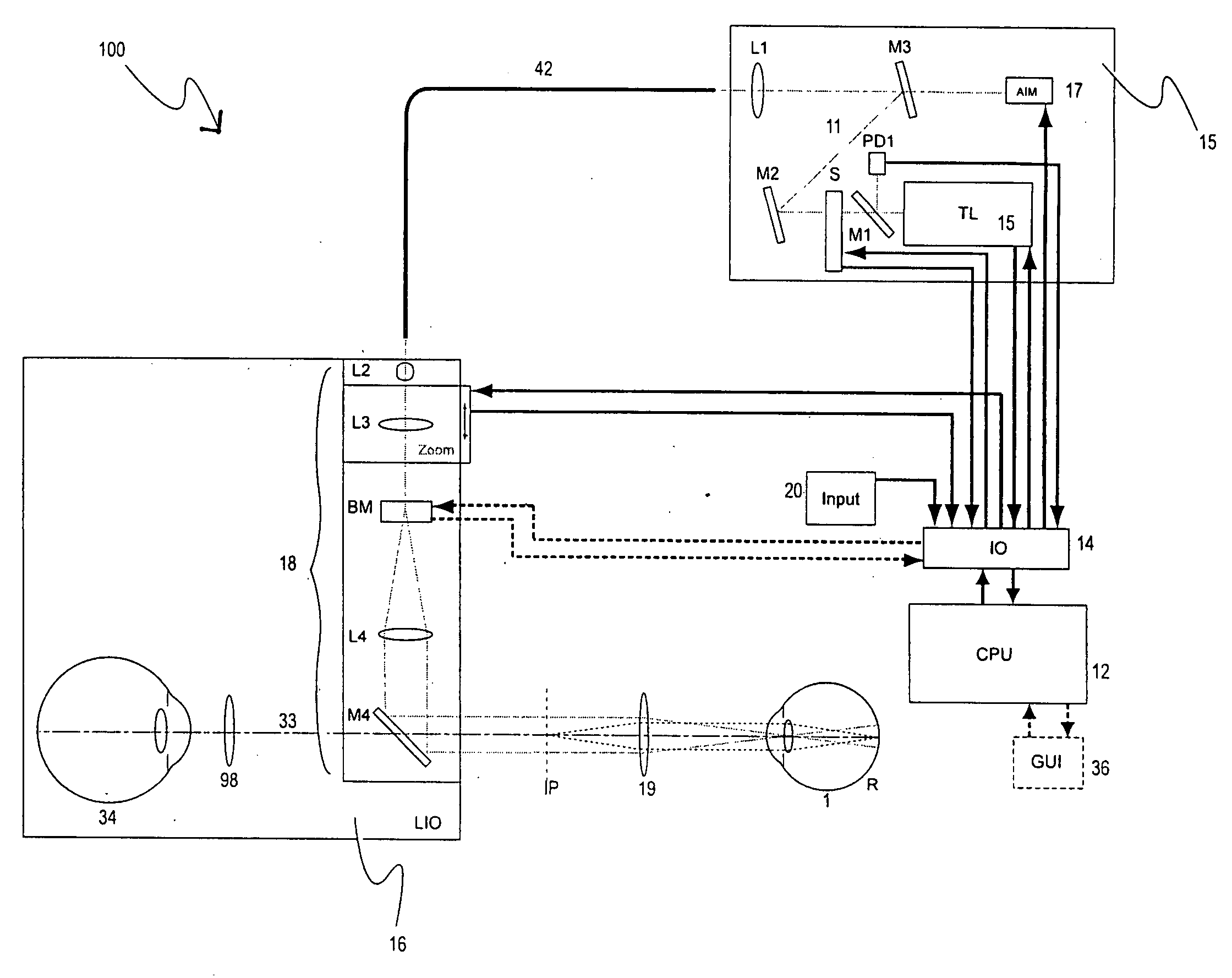
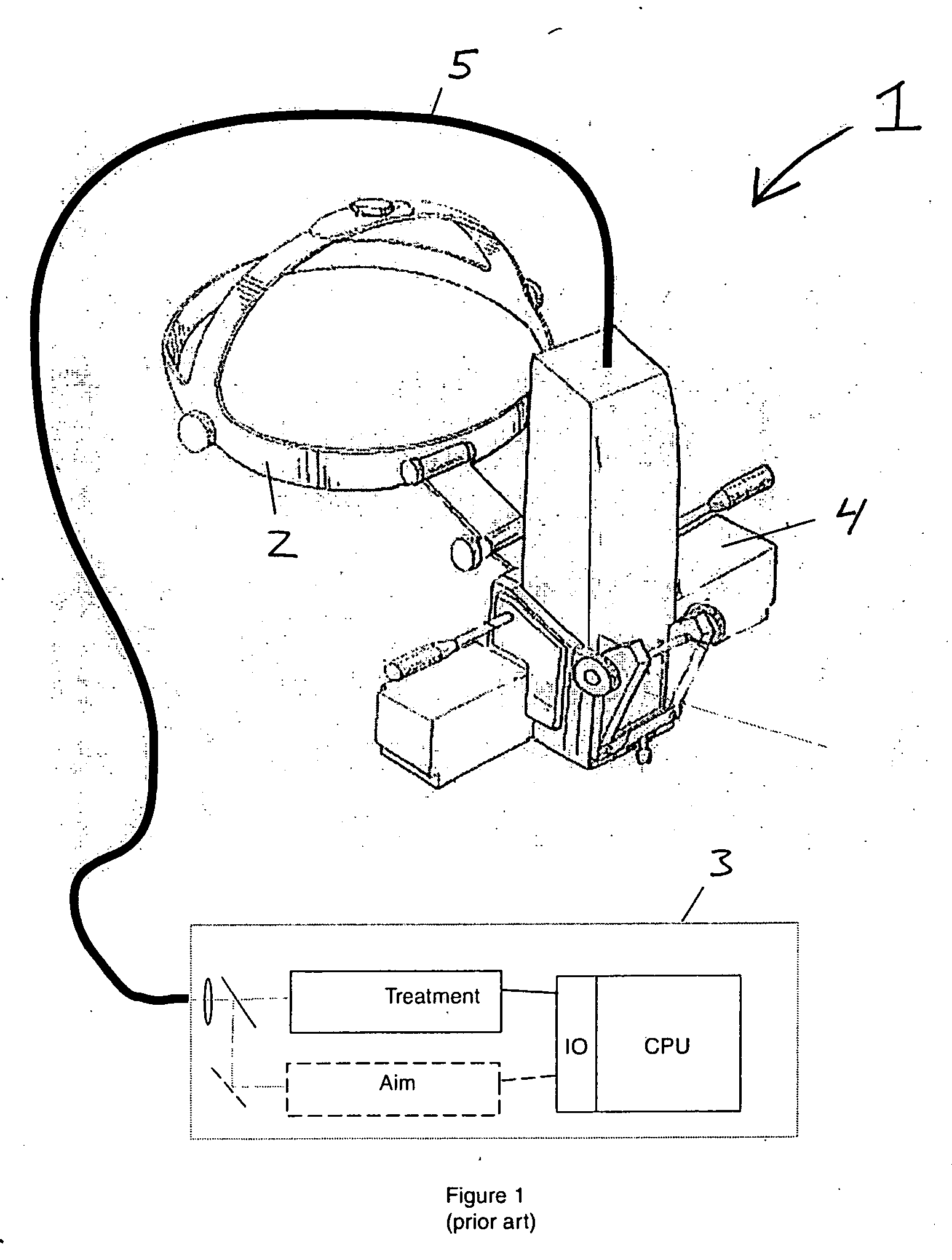
Multiple spot photomedical treatment using a laser indirect ophthalmoscope
A laser indirect ophthalmoscope (LIO) apparatus for photomedical treatment and / or diagnosis is presented. The LIO apparatus allows multiple spot ophthalmic surgery to be performed in a wider range of patient positions and less intrusively than currently available methods. The LIO apparatus utilizes a separate or integral beam multiplier that generates one or more optical beams via spatial and / or temporal separation, and an optical system that conditions and directs the one or more optical beams to a target to form a pattern. The LIO apparatus includes a headset, and is therefore wearable by the user (e.g., a physician).
Owner:TOPCON MEDICAL LASER SYST INC
Integrated single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)/transmission computed tomography (TCT) system for cardiac imaging
ActiveUS7683332B2Improve image qualityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTransmission Computed TomographyPatients position
This invention features an integrated single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) / transmission computed tomography (TCT) system for cardiac imaging including an open arc-shaped frame. A collimator system is shaped to approximately match the thoracic contour of patients having different sizes and weights and shaped to surround and position the collimator closely proximate a heart of a patient of said patients encompassed by at least one predetermined image volume for optimizing collimation of radiation photons emitted from the heart. An arc-shaped detector system is coupled to the collimator subsystem having a shape closely matching the shape of the collimator subsystem for detecting collimated radiation photons from the collimator subsystem and generating output electrical signals. A patient positioning subsystem positions a patient to a predetermined central longitudinal axis of the three-dimensional imaging volume and for intermittently and incrementally rotating the patient about the predetermined central longitudinal axis for generating a plurality of TCT images.
Owner:RUSH UNIV MEDICAL CENT
System for detecting and monitoring vital signs
ActiveUS20080005838A1Simple systemCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationFast Fourier transformPhysical therapy
A system and method for determining and monitoring various characteristics of a patient positioned on a patient support apparatus, such as a bed, stretcher, or cot, is disclosed. The system and method involve monitoring the forces exerted by the patient on one or more force sensors, which may be load cells on the support apparatus. These force sensors will detect vibrations that correspond to various conditions of the patient, including the patient's heart rate, breathing rate, and / or the seizure status of a patient. These vibrations may be analyzed, such as by Fast Fourier Transforms, in order to determine the various conditions of the patient.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Synchronized X-ray / breathing method and apparatus used in conjunction with a charged particle cancer therapy system
ActiveUS7953205B2Cathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingMagnetic resonance acceleratorsX-rayIn vivo
The invention comprises an X-ray system that is orientated to provide X-ray images of a patient in the same orientation as viewed by a proton therapy beam, is synchronized with patient respiration, is operable on a patient positioned for proton therapy, and does not interfere with a proton beam treatment path. Preferably, the synchronized system is used in conjunction with a negative ion beam source, synchrotron, and / or targeting method apparatus to provide an X-ray timed with patient respiration and performed immediately prior to and / or concurrently with particle beam therapy irradiation to ensure targeted and controlled delivery of energy relative to a patient position resulting in efficient, precise, and / or accurate noninvasive, in-vivo treatment of a solid cancerous tumor with minimization of damage to surrounding healthy tissue in a patient using the proton beam position verification system.
Owner:BALAKIN ANDREY VLADIMIROVICH +1
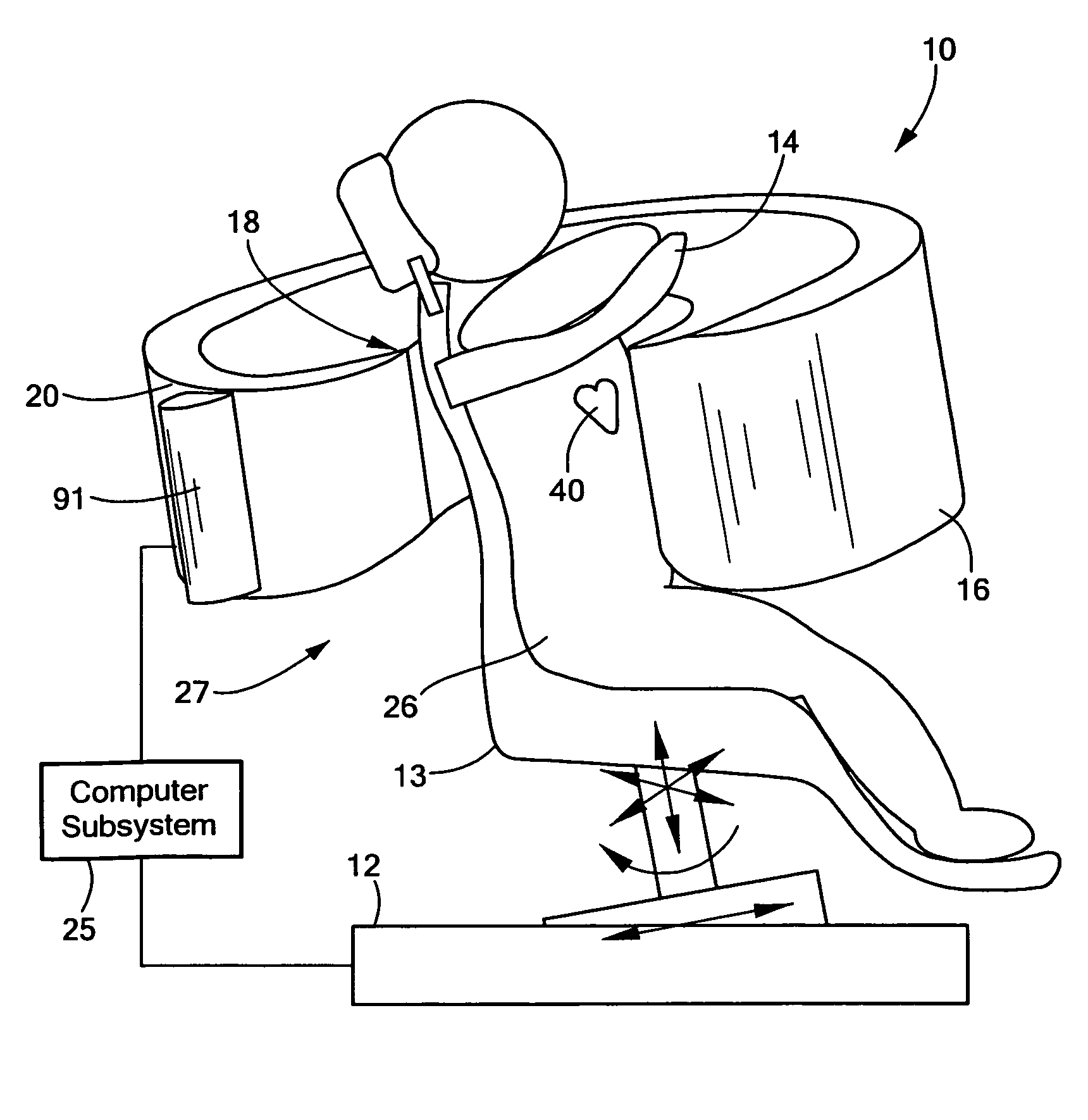
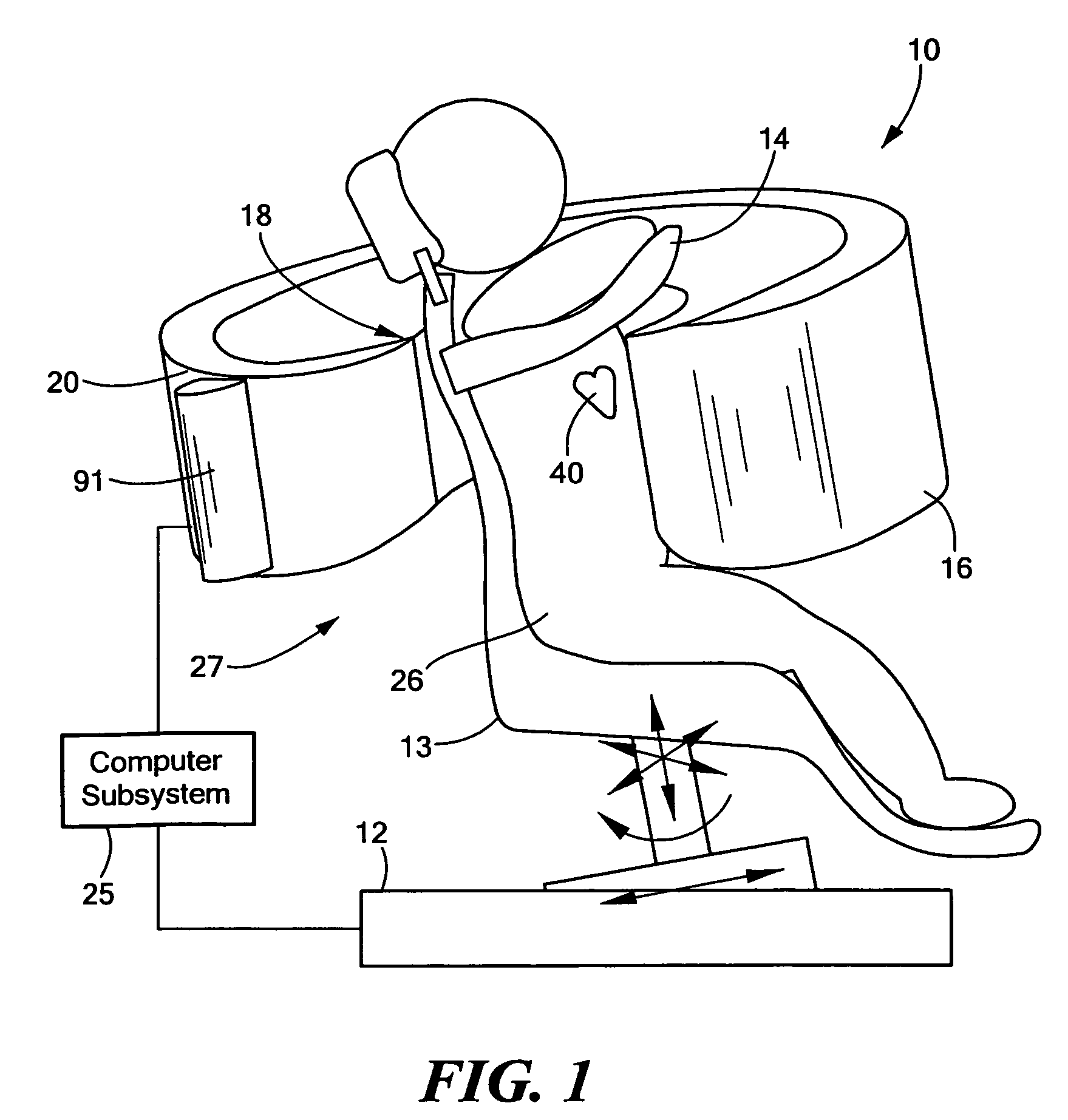
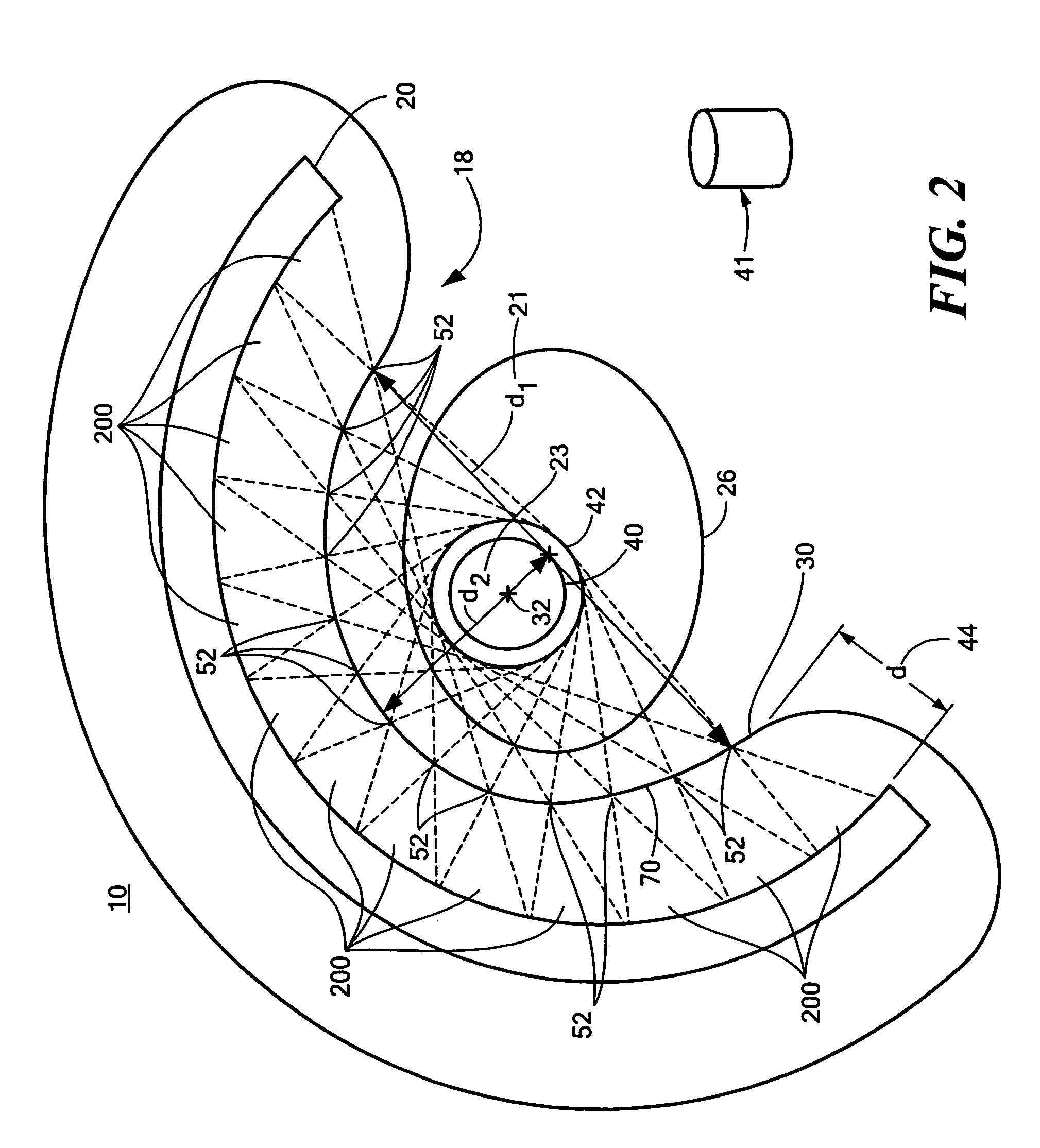
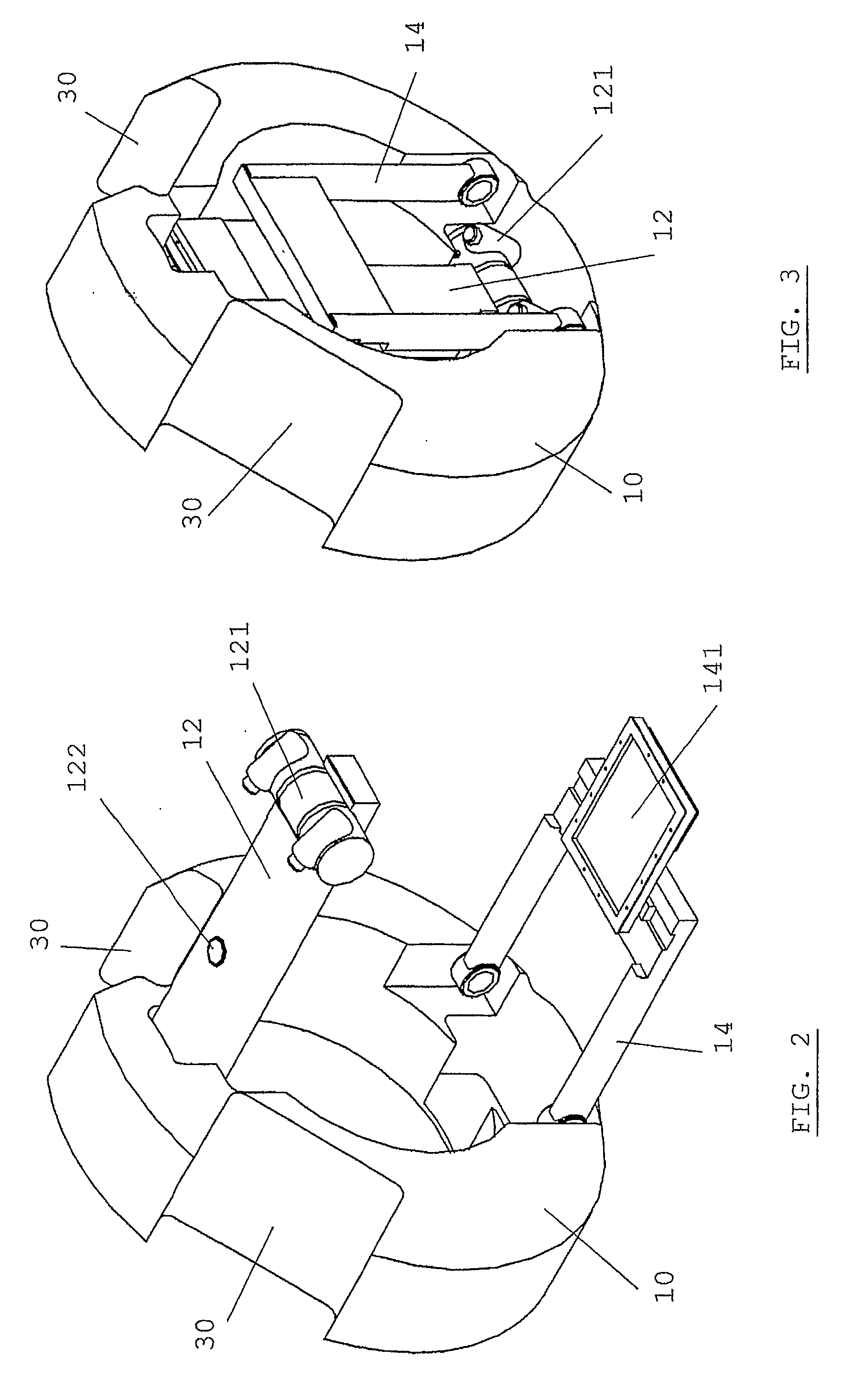
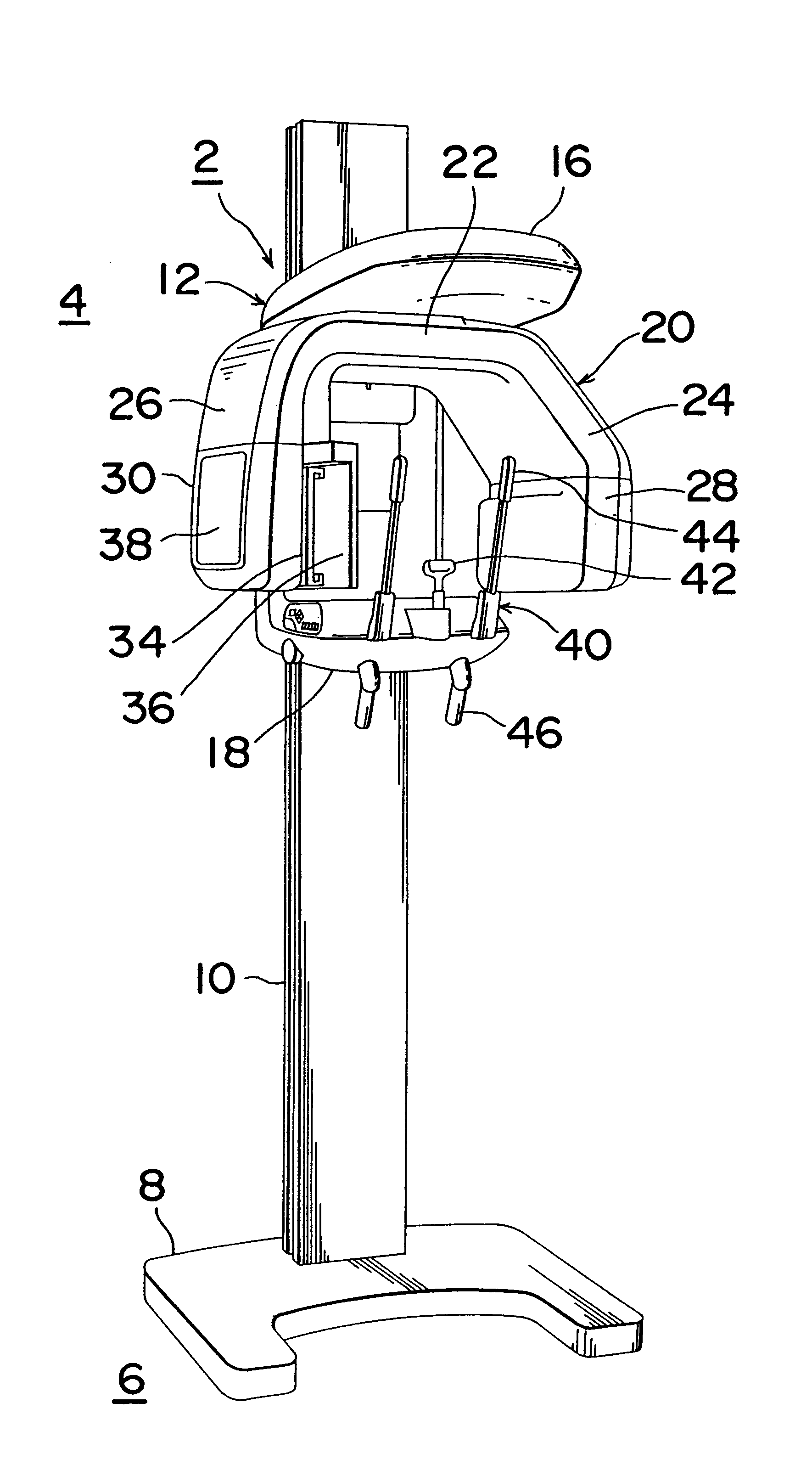
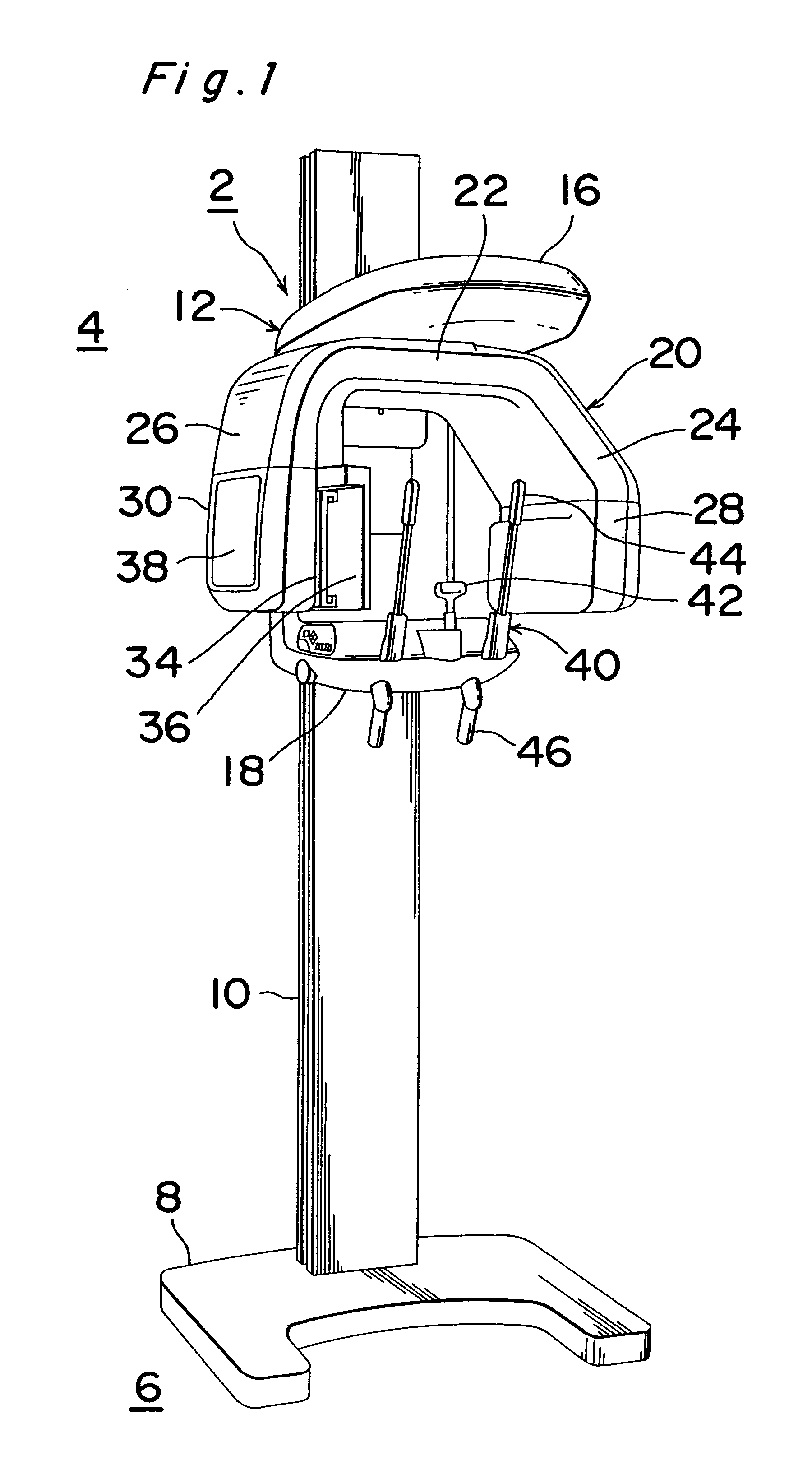
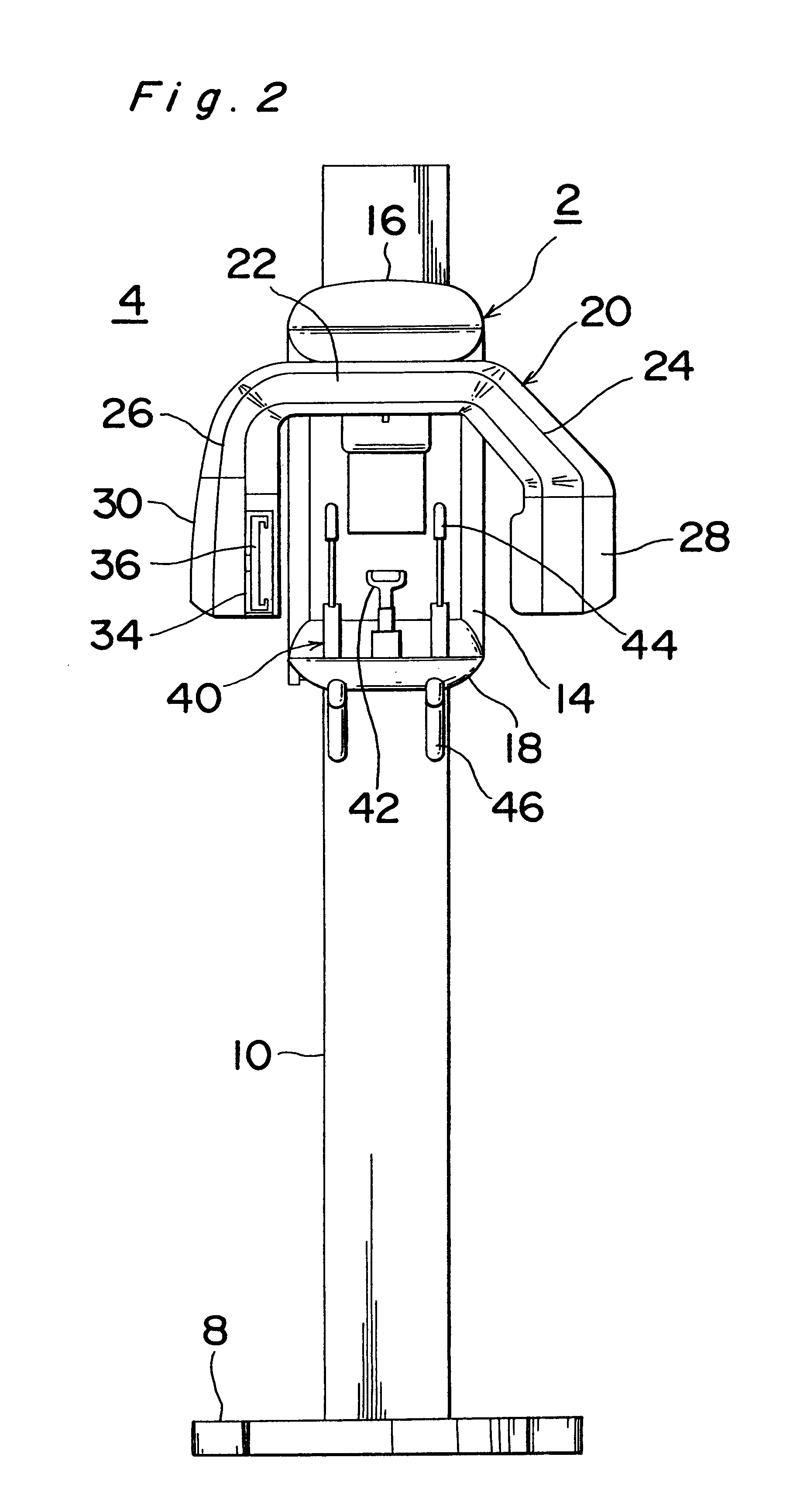
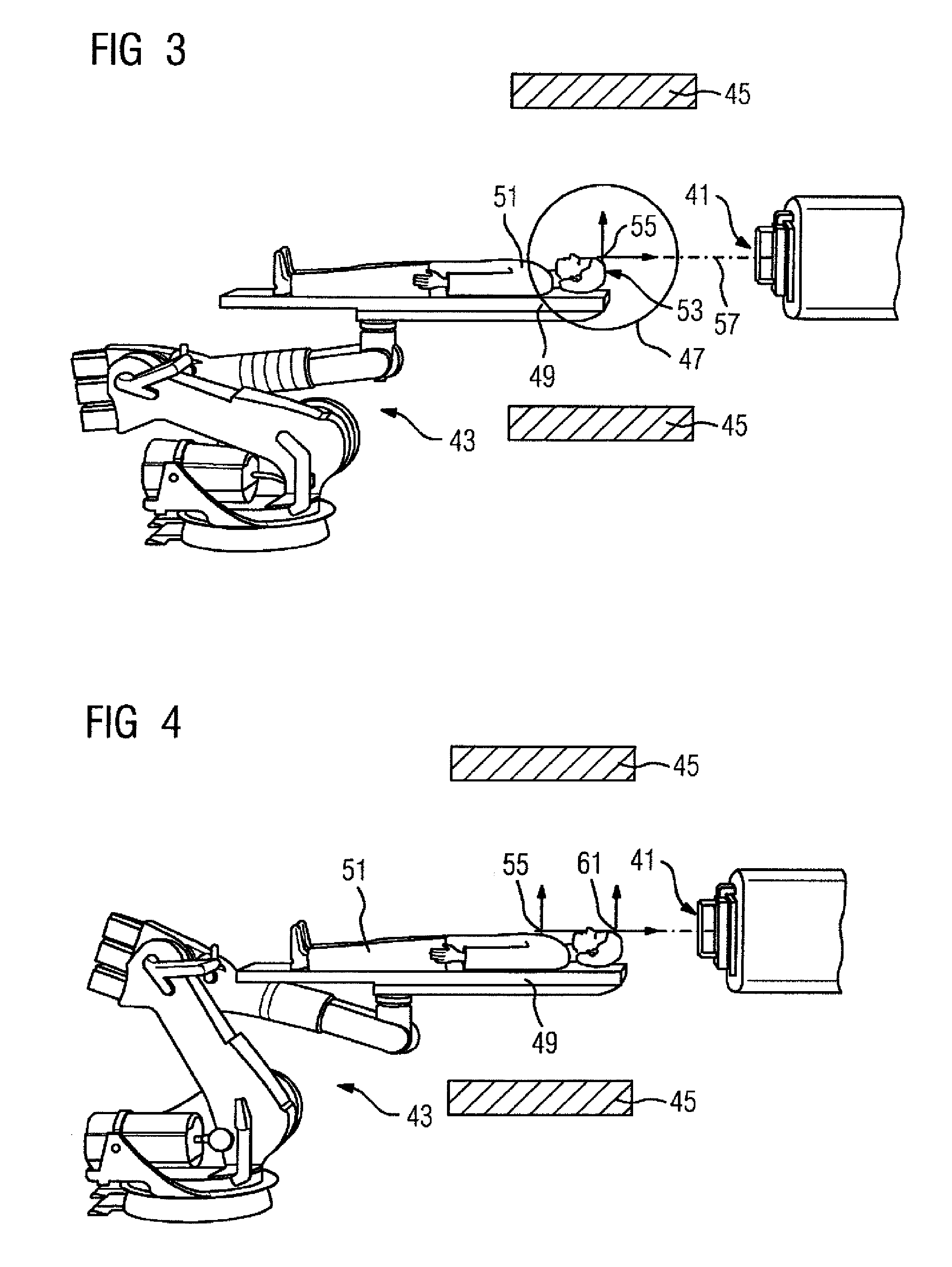
Patient positioning imaging device and method
InactiveUS20090304153A1Smooth foldingSmooth positioningMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingRotational axisBeam source
The present invention is related to a patient positioning imaging device for positioning a patient in a hadron therapy device provided with a rotatable gantry (20). The patient positioning imaging device comprises a rotatable structure (10) provided with an extensible arm or foldable pivoting arm (12) arranged for connecting an imaging beam source (121) and an extensible structure or foldable pivoting structure (14) arranged for carrying an imaging beam receiver (141). The rotatable structure (10) is arranged for taking CBCT shots of the patient while the patient is located in an offset position with respect to an isocentre of the hadron therapy device, said offset position being in the direction of a rotational axis of the rotatable gantry (20). The rotatable structure (10) is arranged for being rotated while the rotatable gantry (20) remains fixed, and while the extensible or pivoting arm (12) and the extensible or pivoting structure (14) are in extended or unfolded position.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
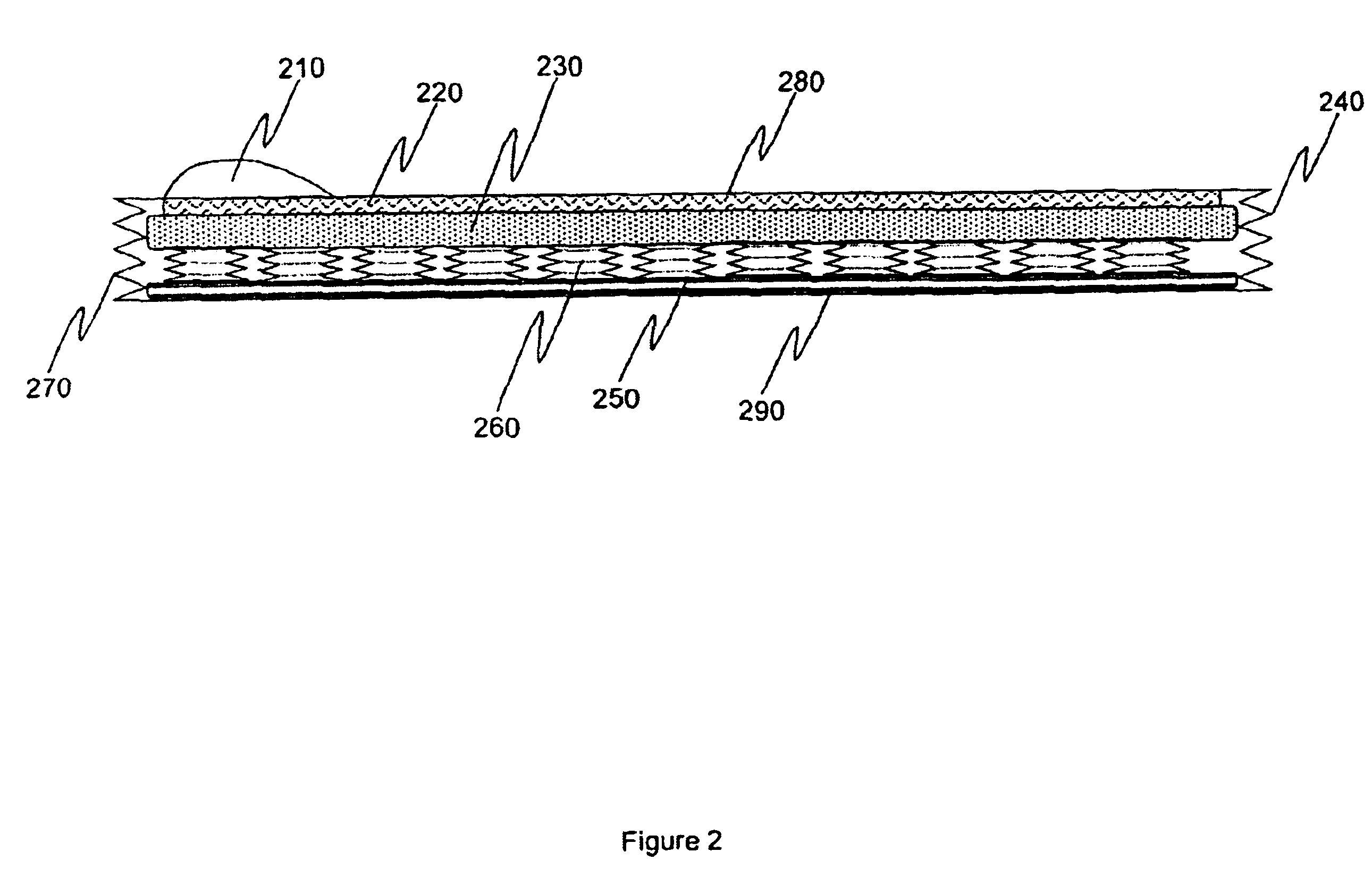
System and methods for detecting ischemia with a limited extracardiac lead set
Disclosed is a system for detecting pathophysiological cardiac conditions from a reduced number of extracardiac leads. A right side lead measures the electrical signal between the middle superior chest region over the heart and inferior right torso position. A left side lead measures the electrical signal between the left precordial chest region and an inferior left lateral or posterior torso position. The lead montage is preferably chosen so that, regardless of patient position (e.g. supine, upright), negative ST segments and / or T waves are used to detect right coronary or left circumflex ischemia. Also, in these positions, reduced slope of the final deflection in the QRS can be used to detect these types of ischemia. To detect transmural ischemia, the system examines changes in QRS slopes, ST segment, T wave and the difference between the J point and the PQ potentials. In addition, for transmural ischemia associated with the left anterior descending artery, a proxy for the propagation time across the front of the heart is examined by comparing QRS features of the right side lead with QRS features of the left side lead. Histogram profiles, trends, and statistical summaries, especially running averages, of all of the above mentioned features, corrected for heart rate, are maintained.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
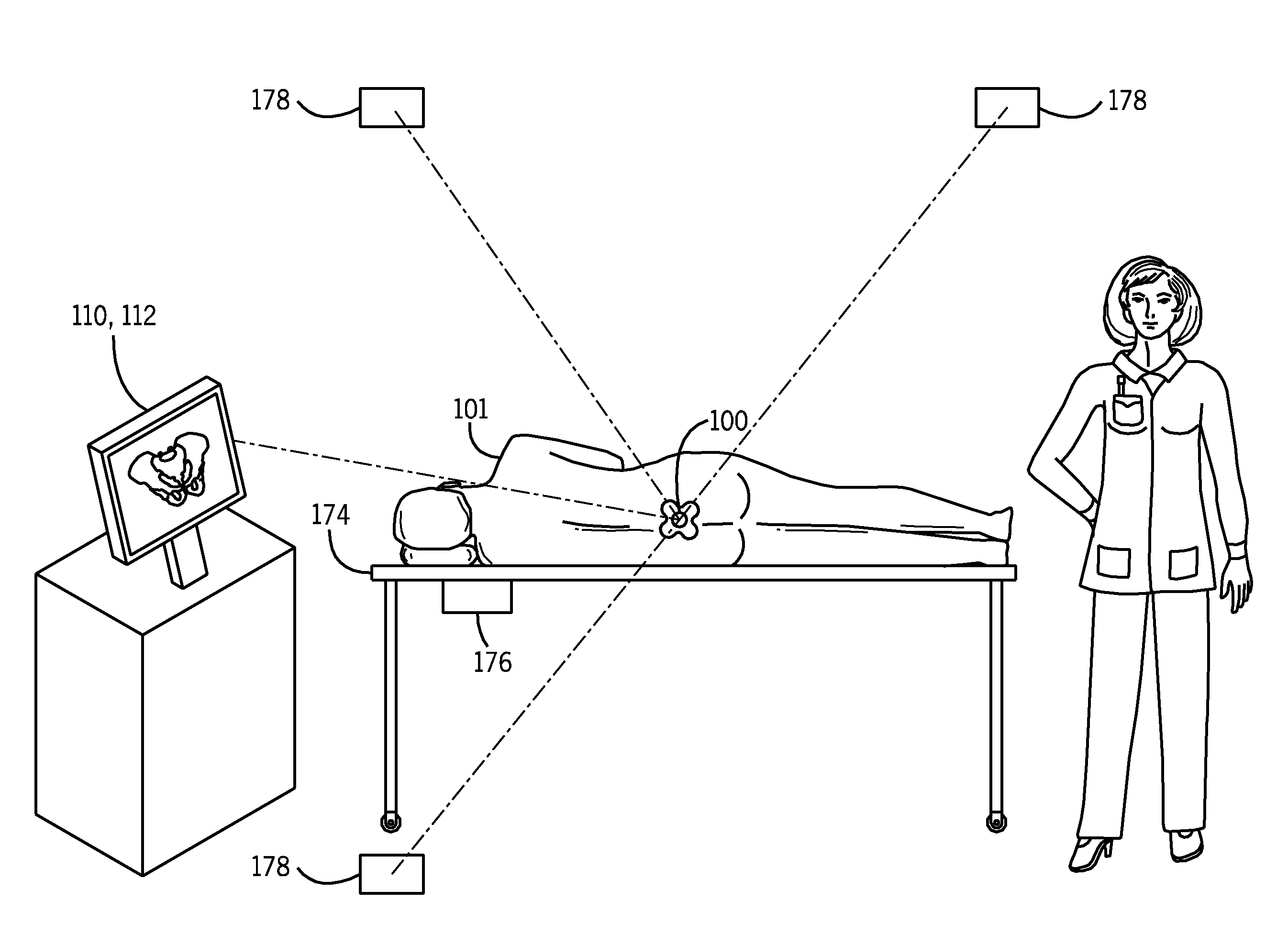
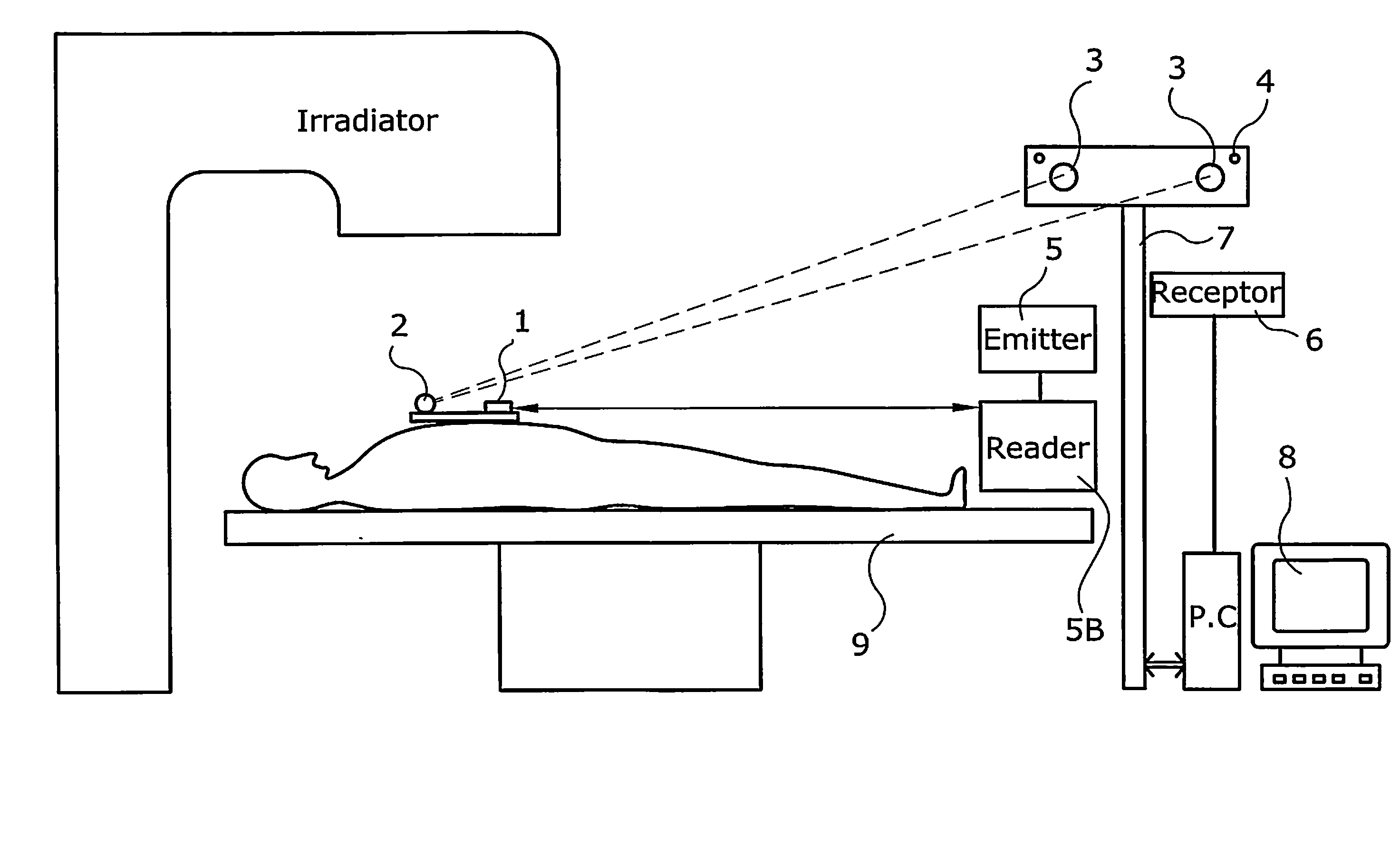
Registration of three dimensional image data with patient in a projection imaging system
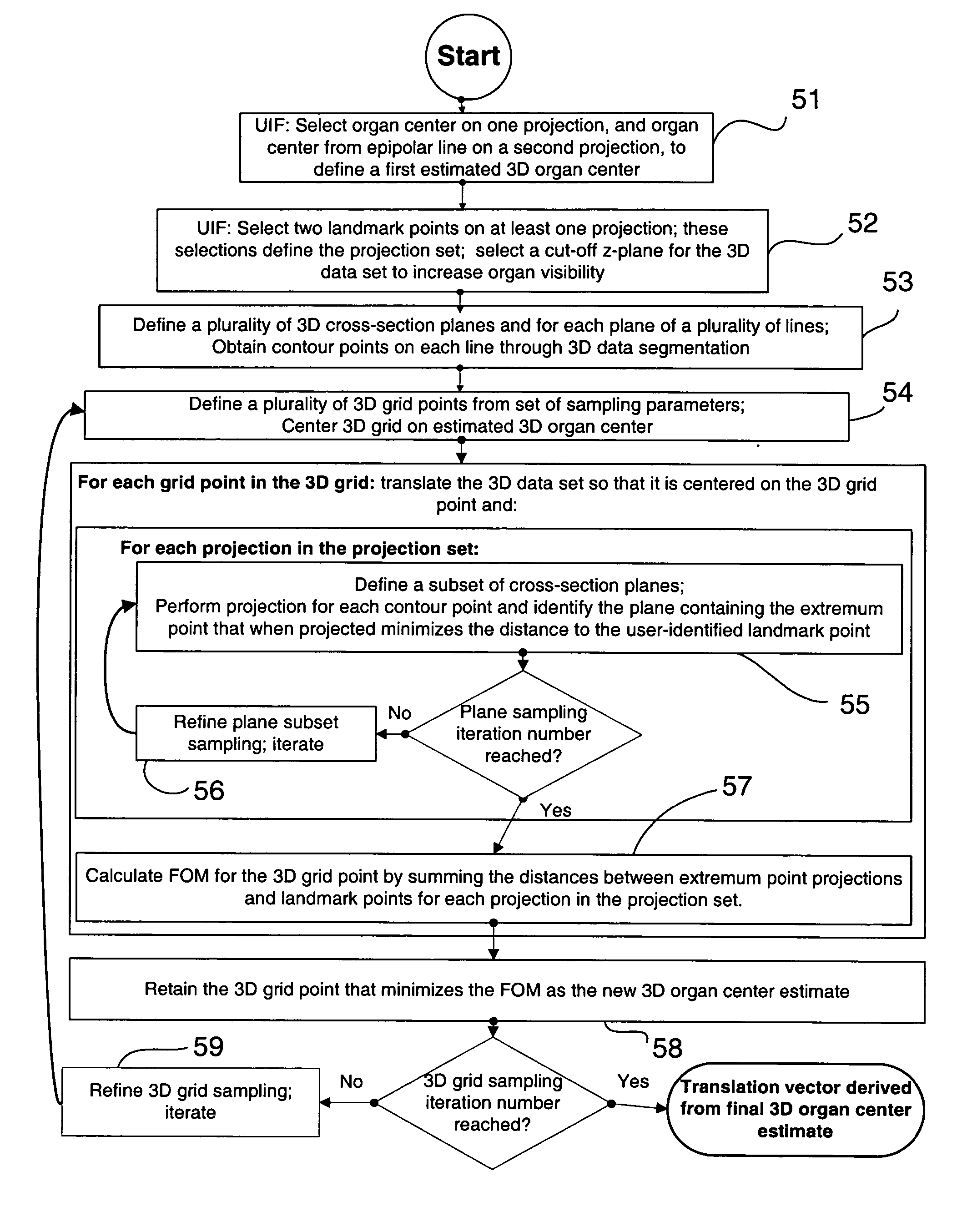
A method for determining a translation of a three-dimensional pre-operative image data set to obtain a registration of the three-dimensional image data with a patient positioned in a projection imaging system. In one embodiment the user identifies an initial three-dimensional organ center from projections and extreme contour landmark points of the object on a set of projections. A set of contour points for the image object in each of a plurality of three-dimensional cross-section planes; is obtained and the points projecting nearest to the user-identified landmark points are selected. A three-dimensional grid having a predetermined number of intervals at a predetermined interval spacing centered at the user-identified organ center is defined. The three-dimensional image data contour points as centered onto each grid point are projected for evaluation and selection of the grid point leading to contour points projecting nearest to the user-identified landmark points. This selection leads to the iterative definition of a series of improved estimated three-dimensional organ centers, and associated translation vectors. Registration of a three dimensional image data to the patient positioned in a projection imaging system will allow, among other things, overlay of a visual representation of a pre-operative image object onto a projection image plane that can serve as a visual tool and a surgical navigation aid. In particular, the position and orientation of a medical device can be shown with respect to the three-dimensional image data and thus enable quicker, safer, and less invasive navigation of the medical device to and within an organ of interest.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
Synchronized x-ray / breathing method and apparatus used in conjunction with a charged particle cancer therapy system
The invention comprises an X-ray system that is orientated to provide X-ray images of a patient in the same orientation as viewed by a proton therapy beam, is synchronized with patient respiration, is operable on a patient positioned for proton therapy, and does not interfere with a proton beam treatment path. Preferably, the synchronized system is used in conjunction with a negative ion beam source, synchrotron, and / or targeting method apparatus to provide an X-ray timed with patient respiration and performed immediately prior to and / or concurrently with particle beam therapy irradiation to ensure targeted and controlled delivery of energy relative to a patient position resulting in efficient, precise, and / or accurate noninvasive, in-vivo treatment of a solid cancerous tumor with minimization of damage to surrounding healthy tissue in a patient using the proton beam position verification system.
Owner:BALAKIN ANDREY VLADIMIROVICH +1
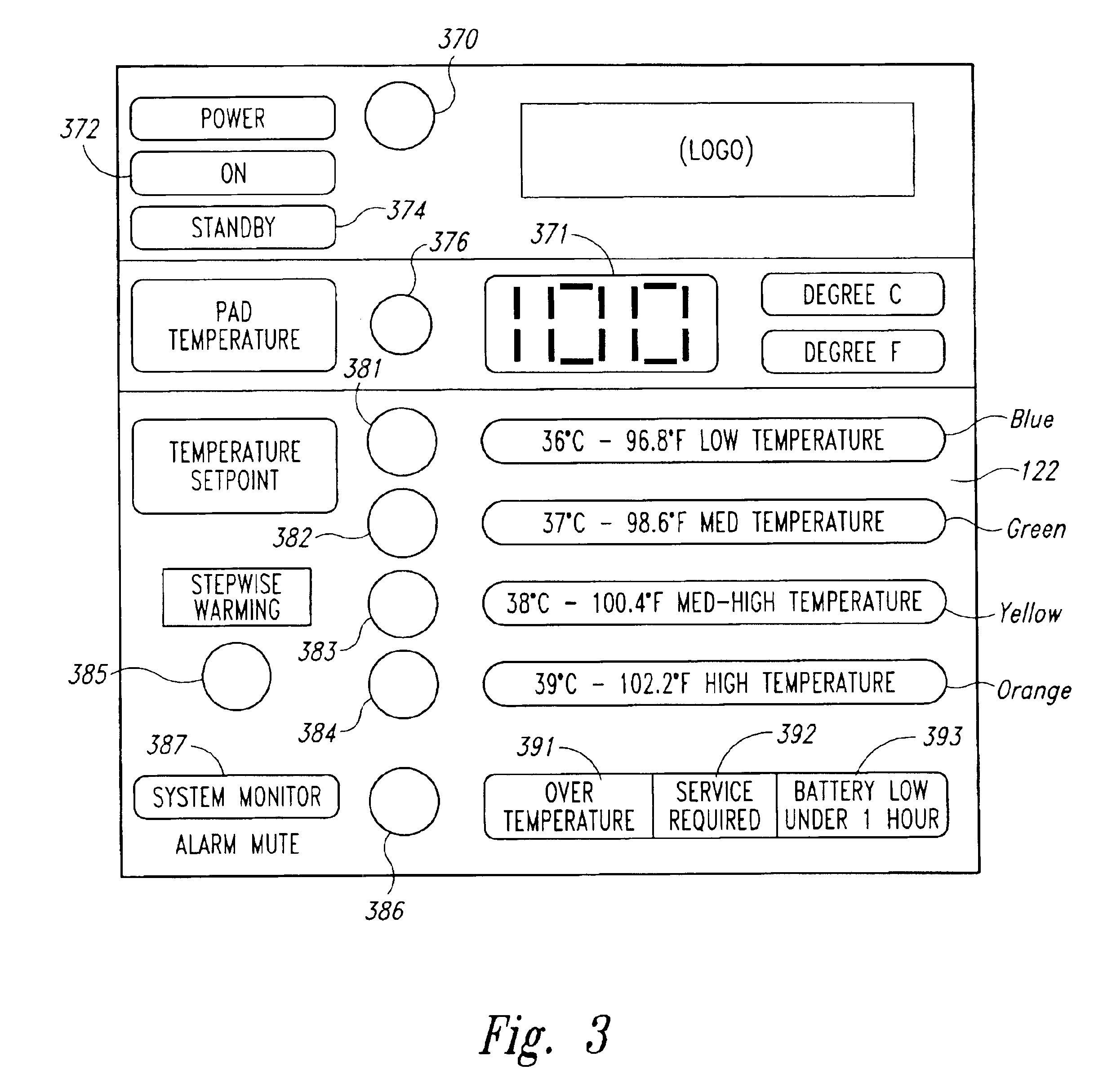
Personal warming systems and apparatuses for use in hospitals and other settings, and associated methods of manufacture and use
Personal warming systems and apparatuses for use in hospitals and other settings. In one embodiment, a heating mattress or pad for warming a patient during a hospital procedure can include a heating element positioned between a first foam portion and a second foam portion. The heating element and the foam portions can be at least partially enclosed in a fluid-resistant cover. The heating element can be operably connected to a control unit that allows an operator to select between a plurality of temperature options for the heating pad. In another embodiment, the heating pad can include one or more radiolucent, or at least generally radiolucent, features that will not appreciably obscure x-ray images taken of a patient positioned on the heating pad. In one aspect of this embodiment, the radiolucent features can include one or more of a carbon-based heating element, an optical temperature sensing device, and / or a thermally responsive state-changing device.
Owner:MEDLINE IND LP
Surgical navigation apparatus and method for same
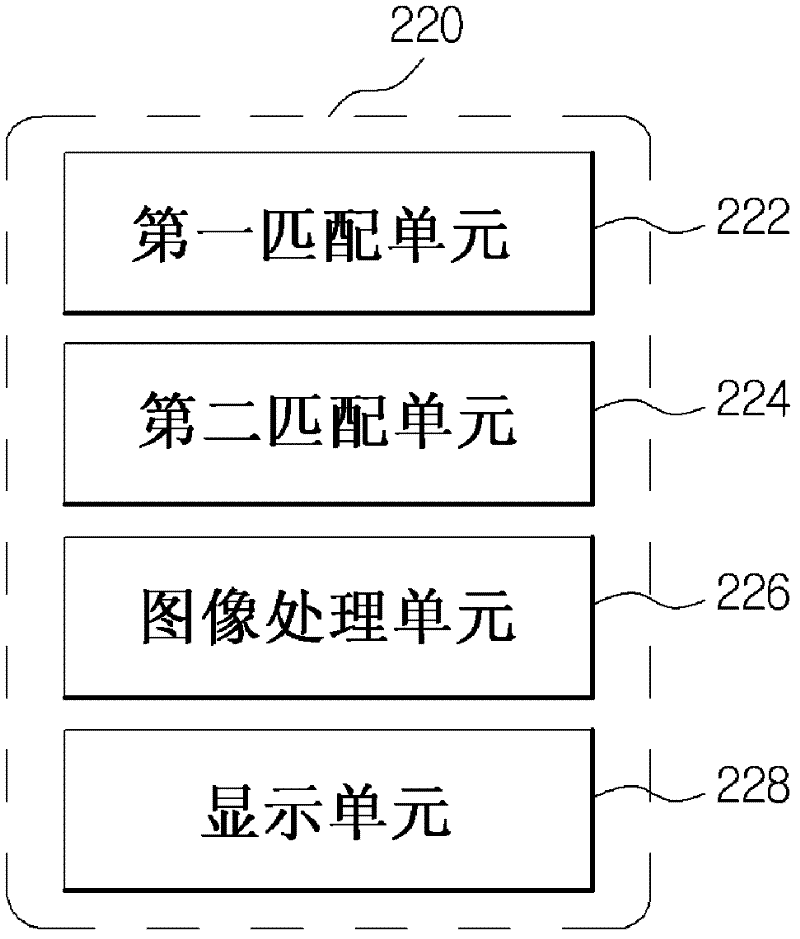
ActiveCN102316817ASurgical precisionSuture equipmentsImage enhancementImaging processingReference image
A surgical navigation apparatus and a method for same are disclosed. The surgical navigation apparatus according to the present invention comprises: a first matching unit which matches the position of a patient and reference image data, using the reference image data of the patient photographed prior to a surgery and patient position data; a second matching unit which matches, on a real-time basis, the patient position data and comparative image data received from a photographing unit; and an image-processing unit which matches, on a real-time basis, the comparative image data and the reference image data using the patient position data. The apparatus of the present invention enables images photographed during the surgery to be provided on a real-time basis, and to be compared with the images photographed prior to the surgery, and enables the provided images, including the current position of an endoscope and peripheral structure, to be outputted in a 3D format, thus increasing convenience for a surgeon.
Owner:EATON CORP
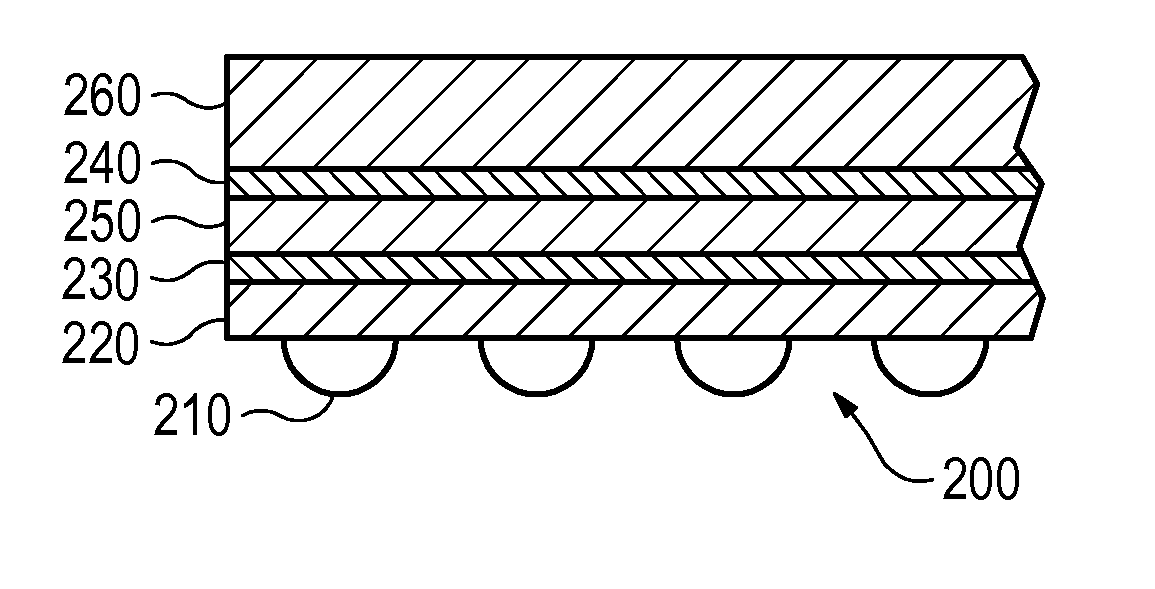
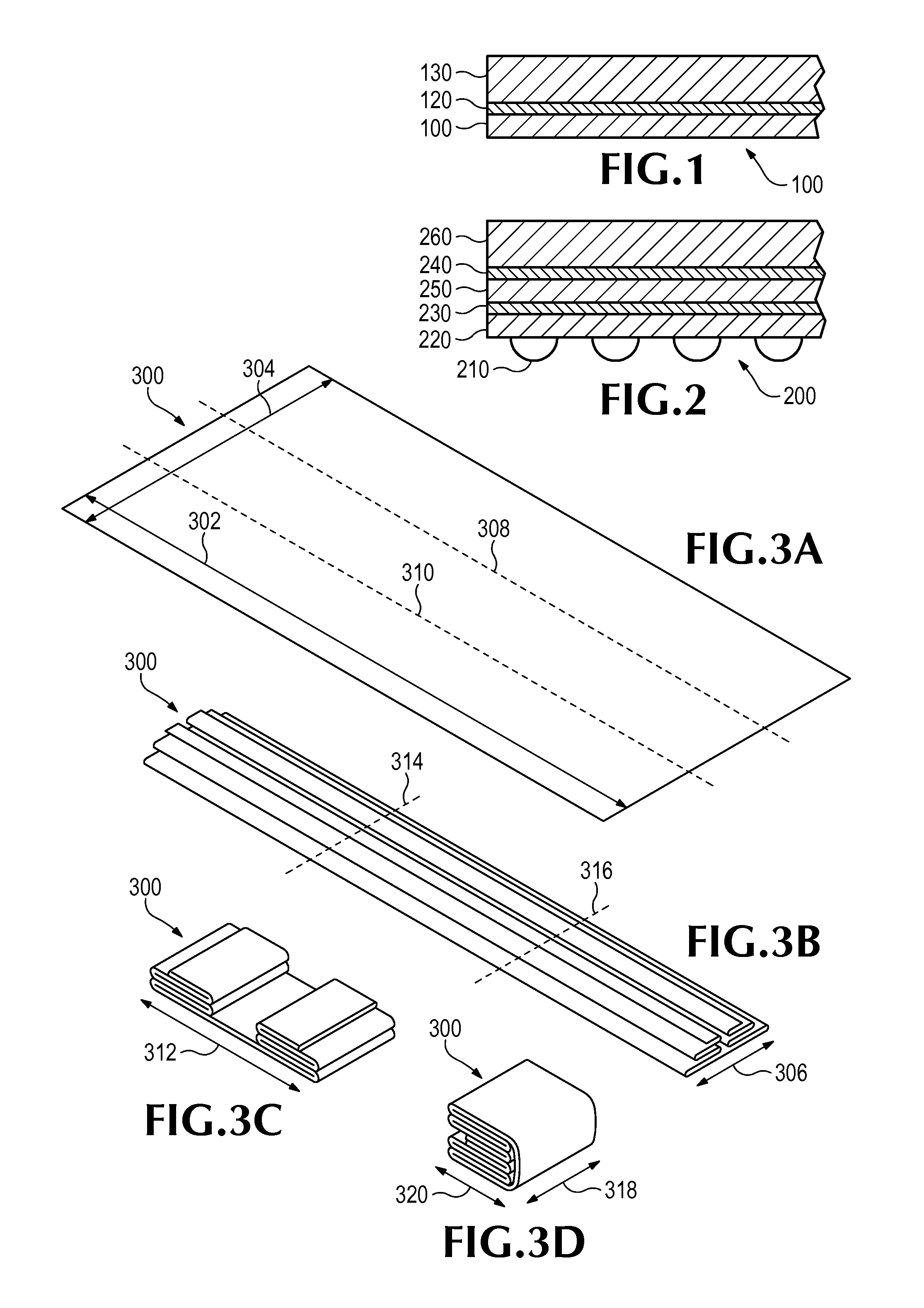
Method and system for positioning patients for medical treatment procedures
A system and method for measuring and correcting the position of a patient are disclosed. According to an aspect of the invention, reference coordinates for particular body locations on the patent are determined. At a later treatment session, the relative positioning of the patient's body locations are adjusted to match the relative positioning of the reference coordinates. The entire body of the patient can thereafter be moved as a single unit to match the patient's body location with the absolute location of the reference coordinates.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST TECH
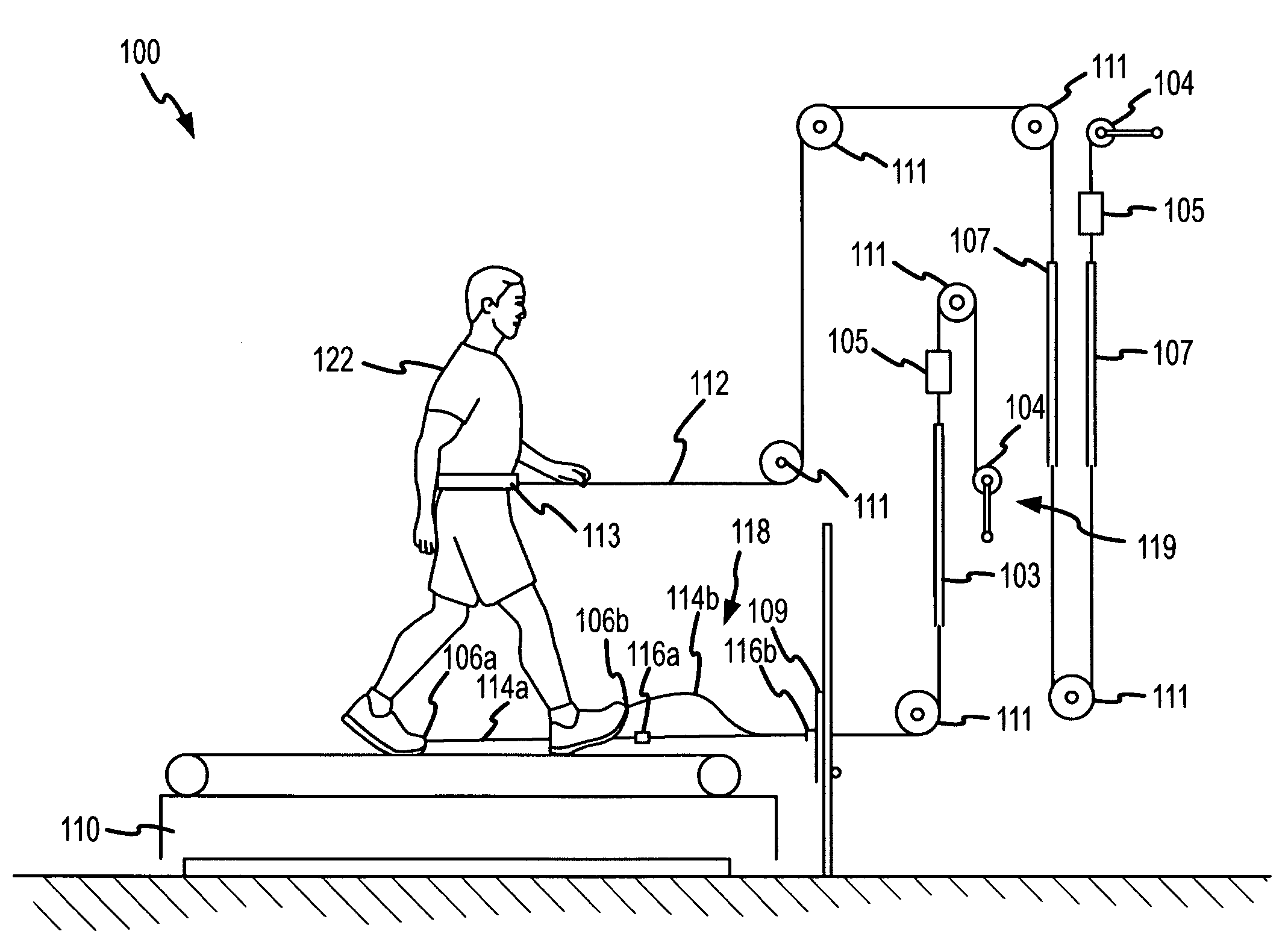
Force assistance device for walking rehabilitation therapy
InactiveUS7998040B2Resilient force resistorsChiropractic devicesPhysical therapy devicePatients position
A physical therapy apparatus for use in conjunction with a treadmill provides an assistive force to a forward movement of the legs. A force assistance device is adapted to attach to the feet or legs of a patient positioned on a motorized treadmill to assist in walking therapy by providing an assistive force to a forward movement of the patient's feet or legs. An adjustment device may vary an interface of attachment, for example, the height or direction, between the force assistance device and the patient's feet or legs. A force arresting device may arrest the assistive force provided by the force assistance device during the forward movement of the patient's feet or legs. The force assistance device provides a substantially constant assistance force during the forward movement of the patient's feet or legs. The physical therapy device may also include a force adjustment device connected with the force assistance device to vary the magnitude of the assistive force.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Overlay mattress
InactiveUS6859967B2Reduce riskEasy to useStuffed mattressesDiagnosticsDistribution systemEngineering
An overlay mattress has a plurality of internal elevating means, such as inflatable bladders, for raising selected portions of the mattress to achieve a wide range of patient positions. A fluid such as air may be supplied from a conventional surgical room air supply, a compressed canister, or a compressor to inflate the bladders. A fluid distribution system controls the flow of fluid to desired bladders. The overlay mattress may be used in conjunction with conventional surgical tables and mattresses. A thermal control means is also included in the overlay mattress to regulate a patient's body temperature. A pressure shifting means is also included to reduce the risk of bedsore formation.
Owner:NIMED
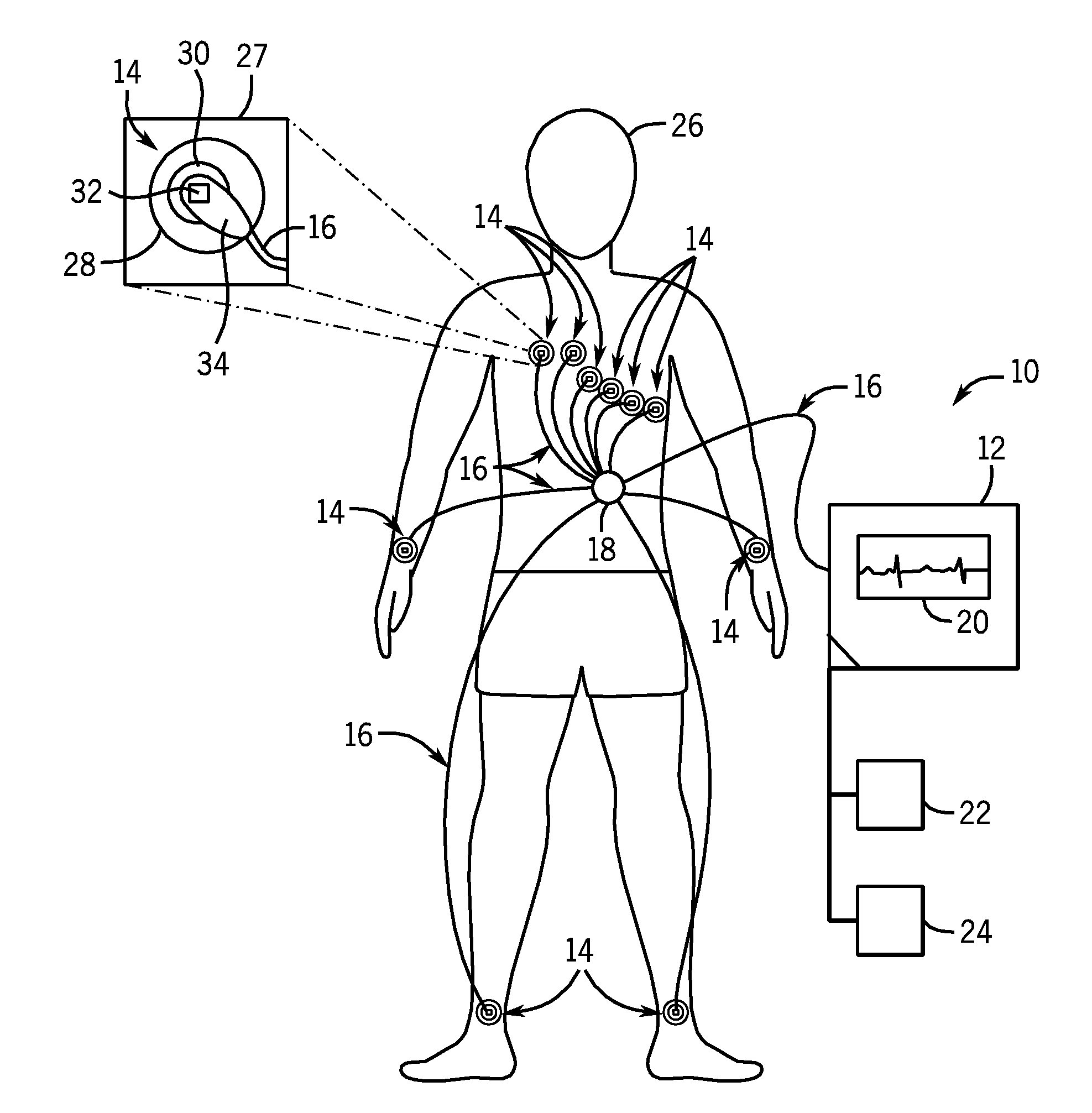
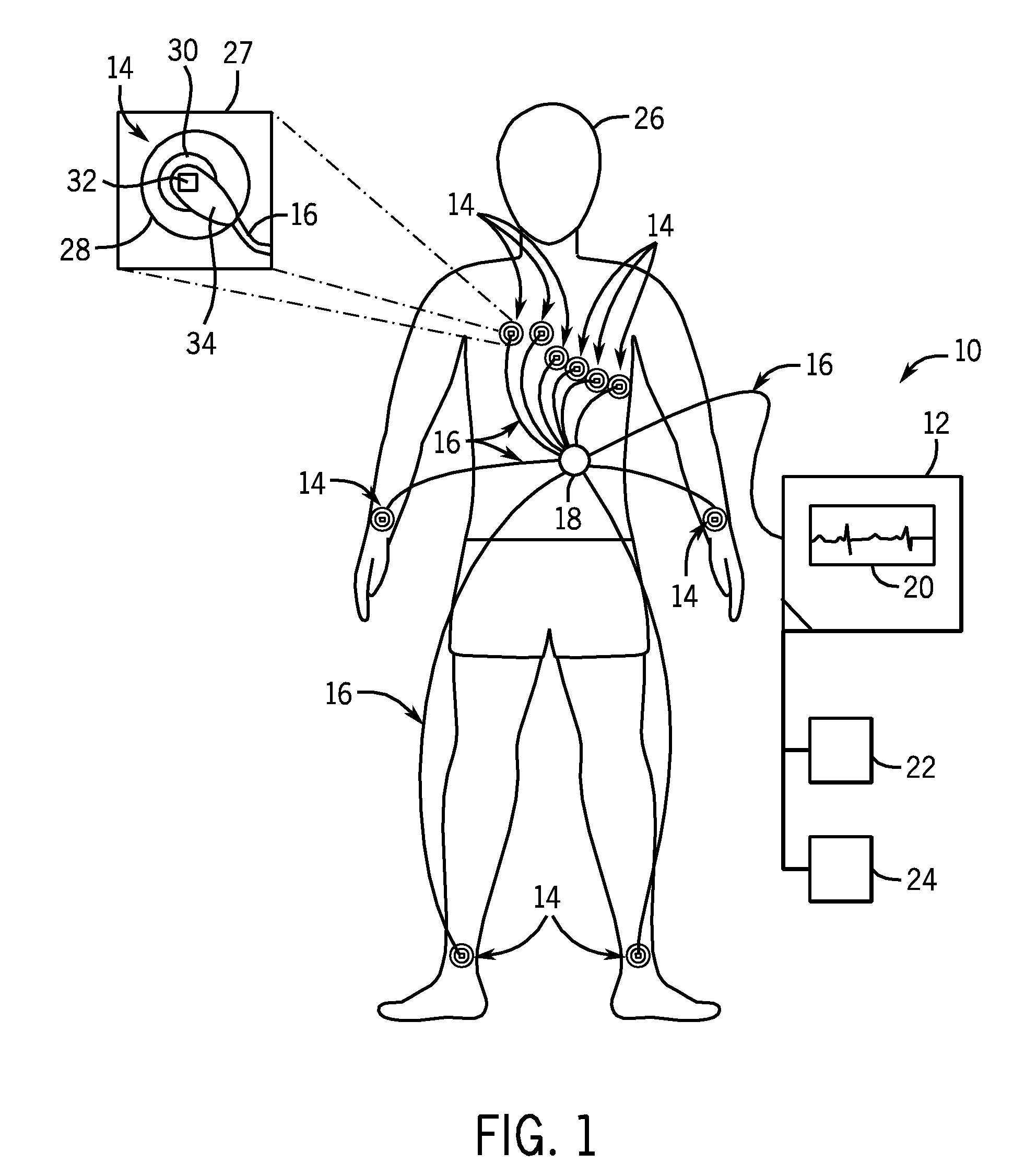
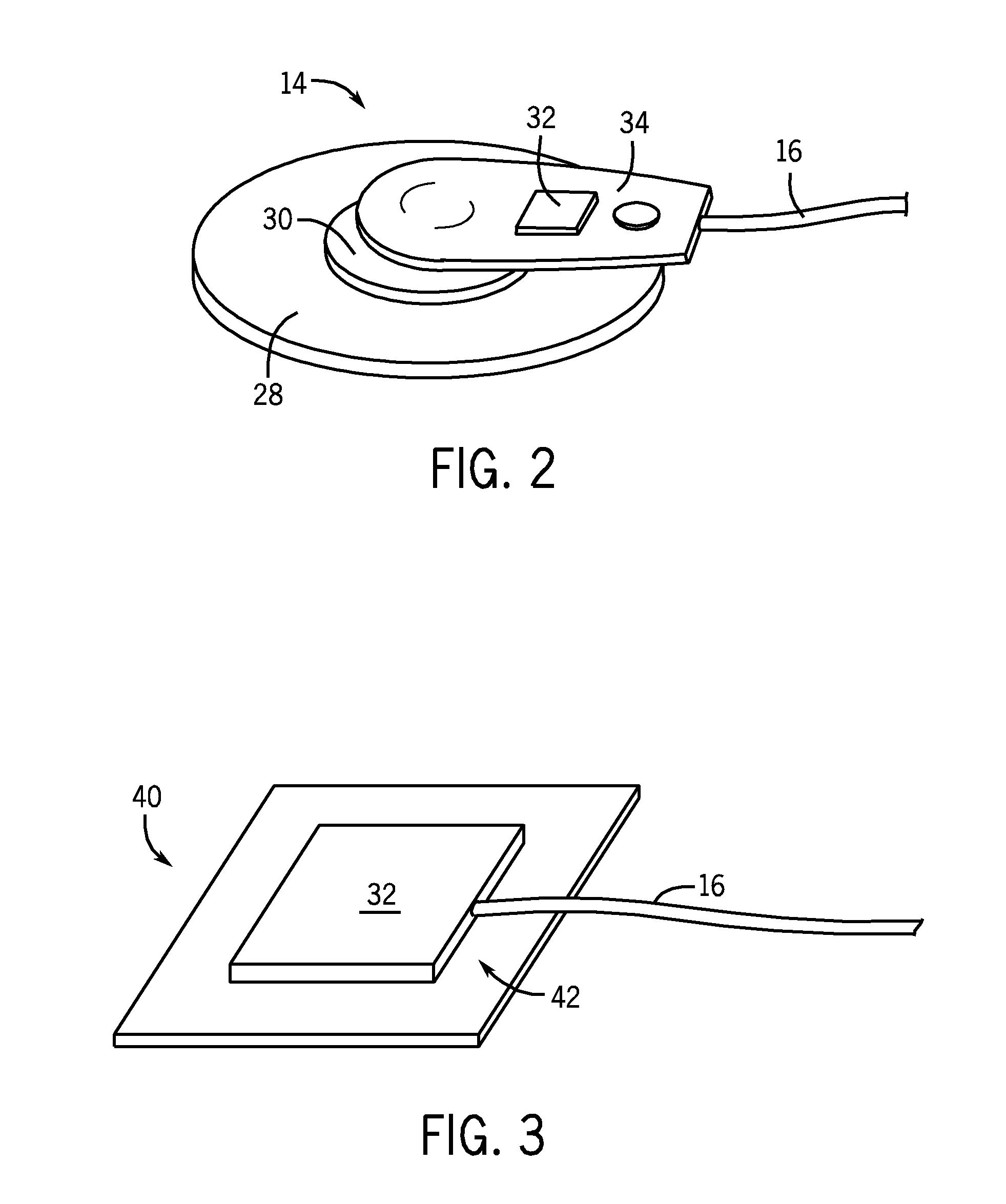
System and method of performing electrocardiography with motion detection
A system in accordance with present embodiments includes an electrocardiograph, a plurality of sensors communicatively coupled with the electrocardiograph, wherein each of the plurality of sensors comprises an electrode capable of detecting electrical impulses generated by a patient's body and transmitting signals indicative of detected electrical impulses to the electrocardiograph. In one embodiment, the system also includes a motion detection feature communicatively coupled with the electrocardiograph, wherein the motion detection feature is capable of detecting movement of the patient's body and providing signals indicative of detected movement to the electrocardiograph, and wherein the electrocardiograph is capable of detecting a particular type of patient motion and / or patient position based on the signals indicative of the detected motion, capable of providing output based on the signals indicative of the detected electrical impulses, and capable of providing output based on the signals indicative of the detected movement.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
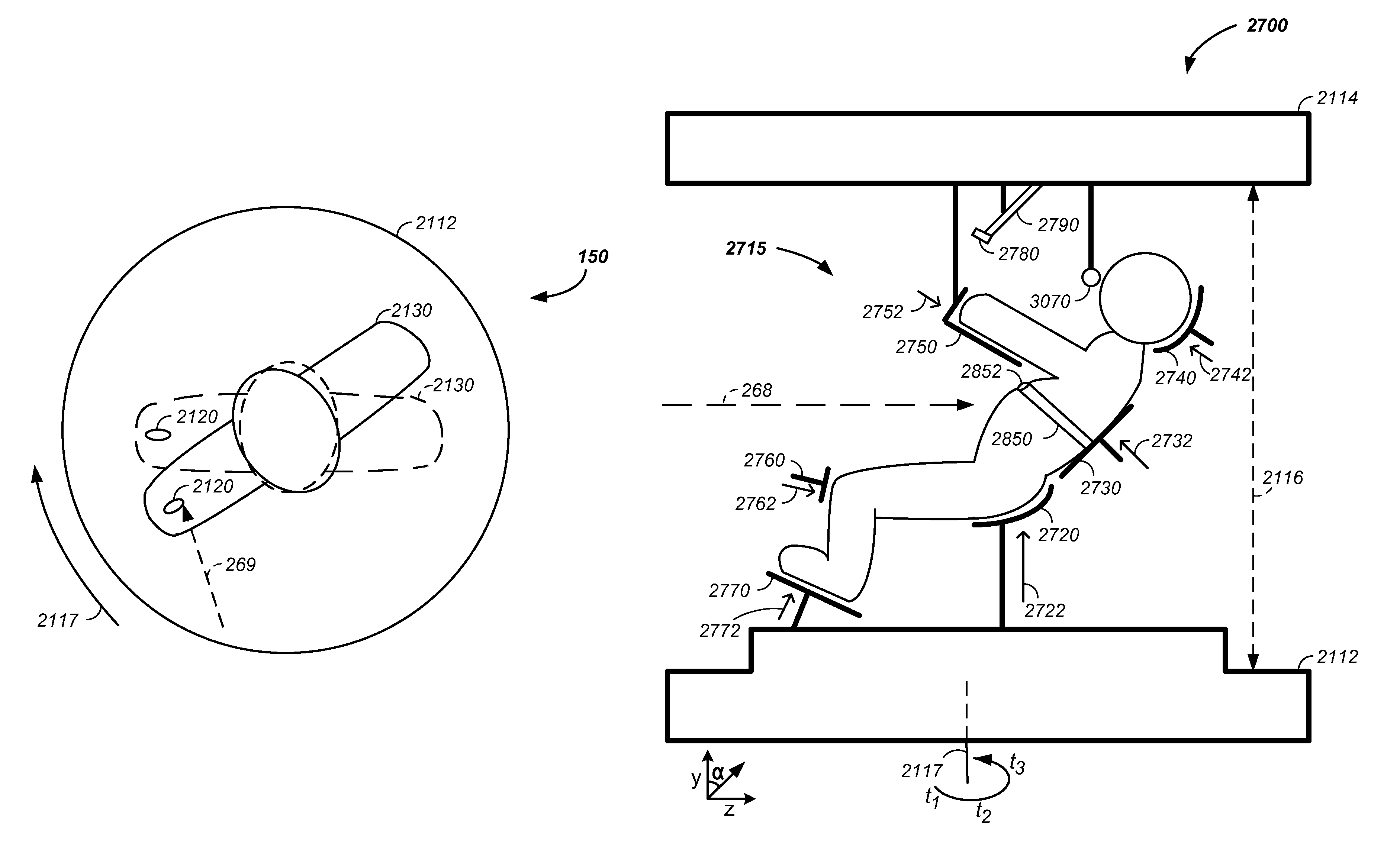
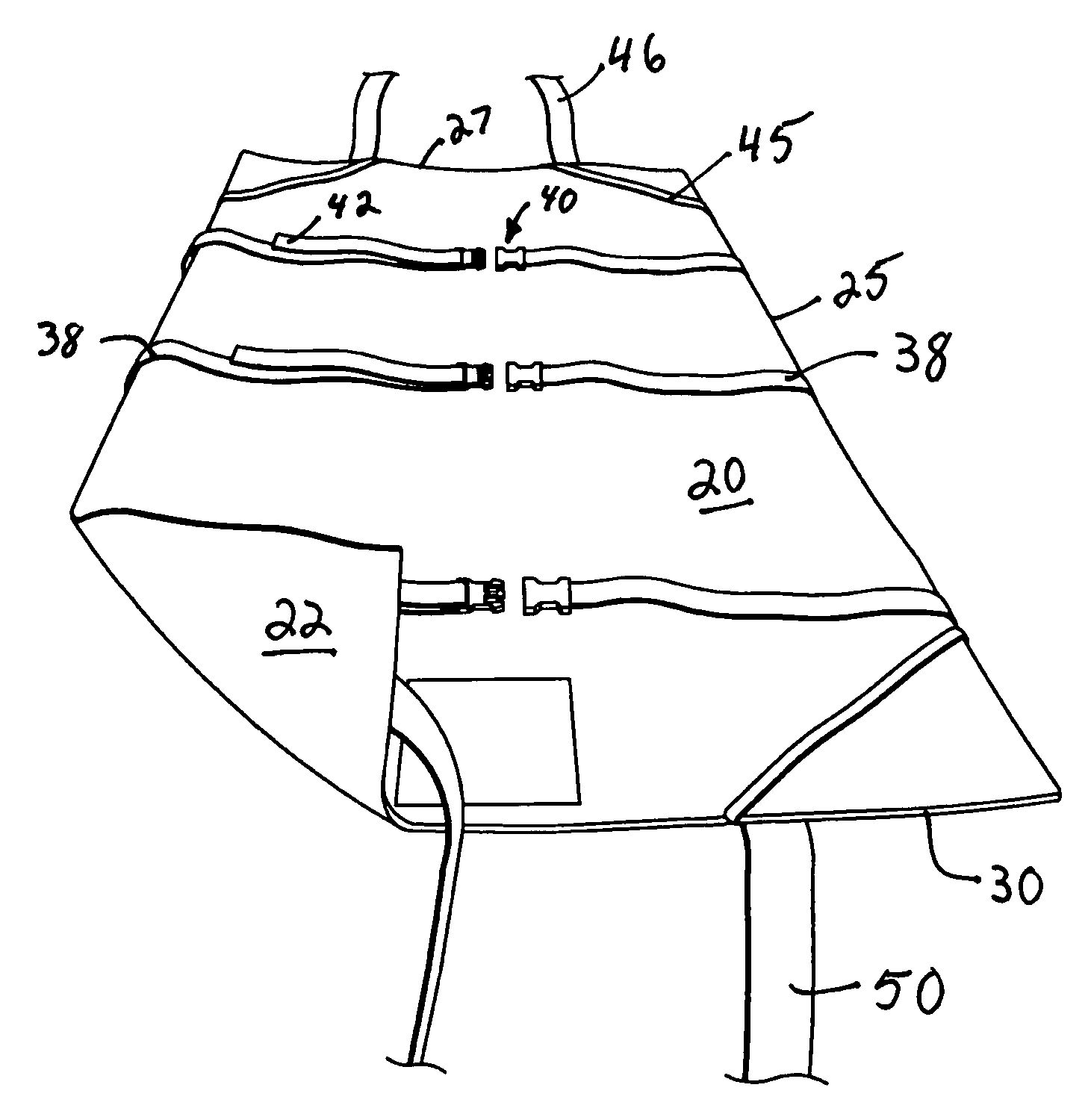
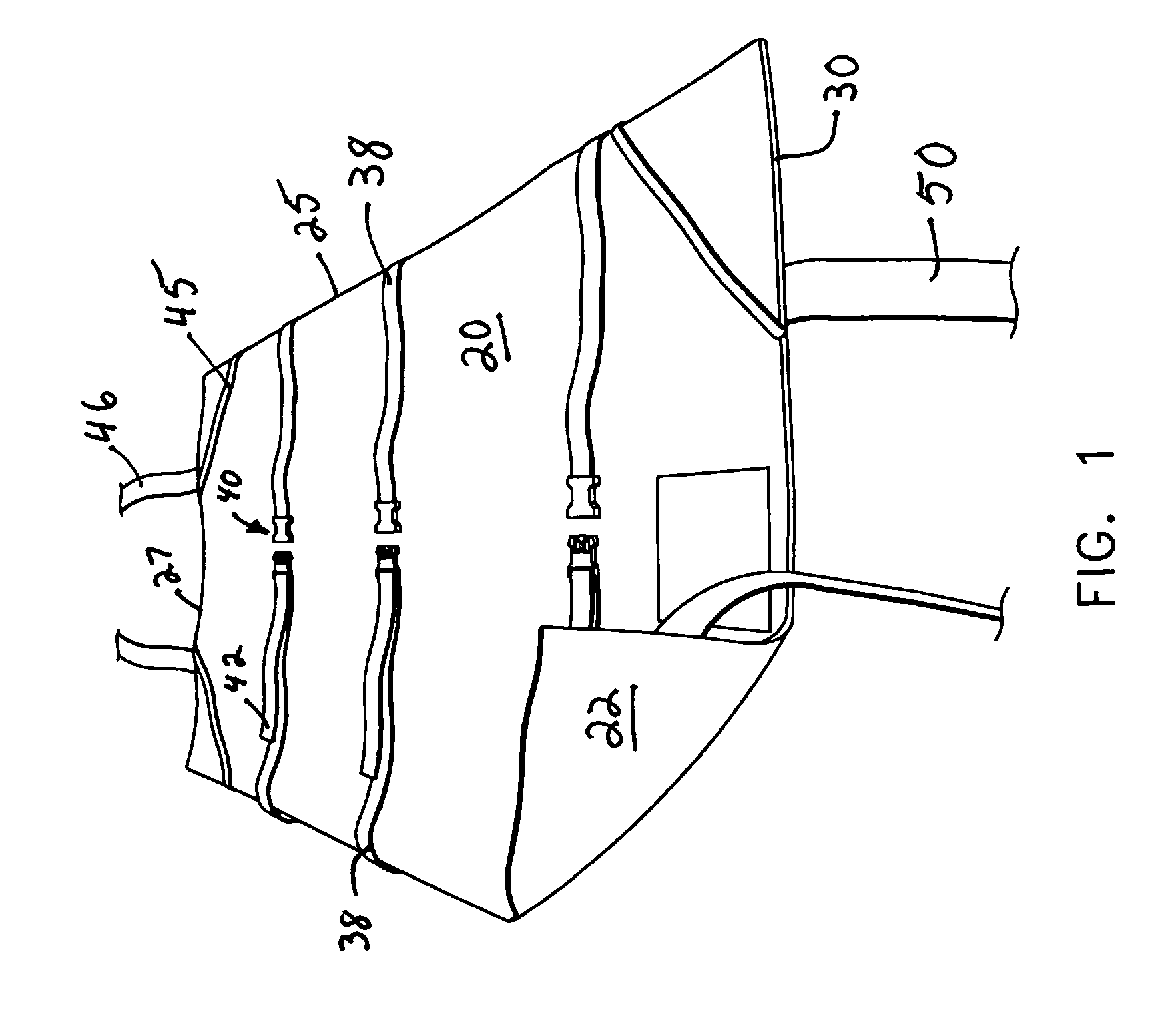
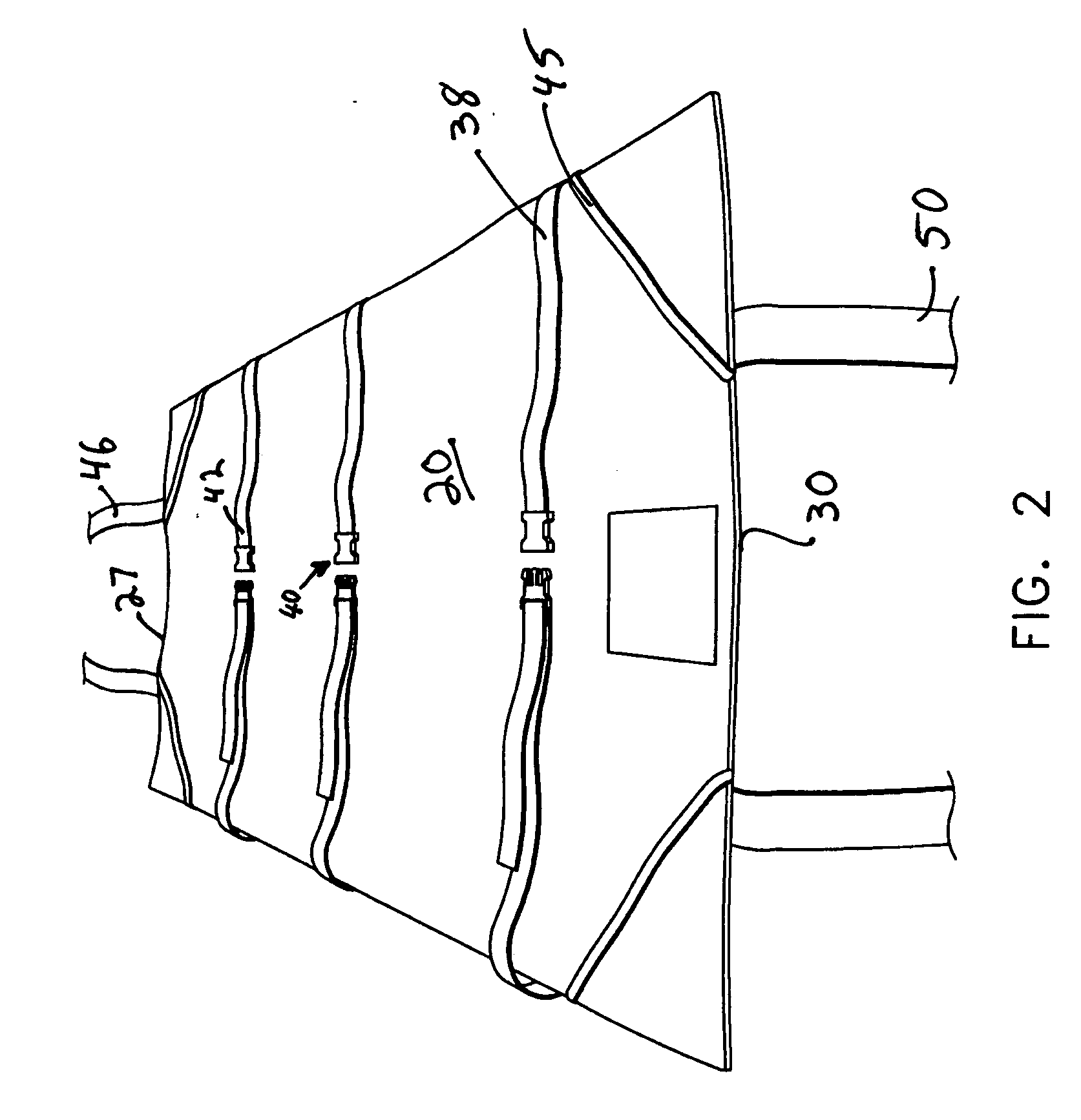
Operating table patient positioner and method
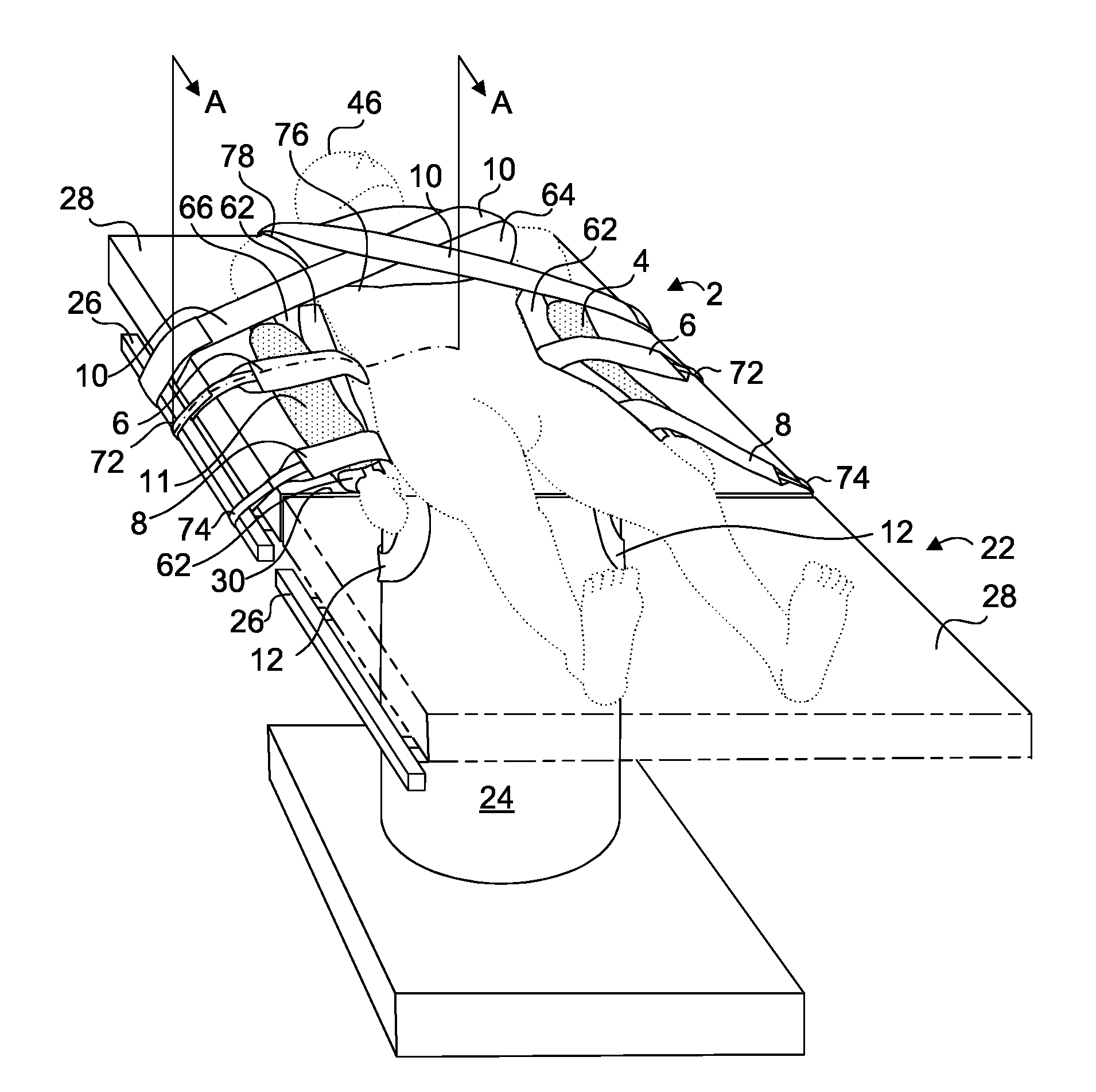
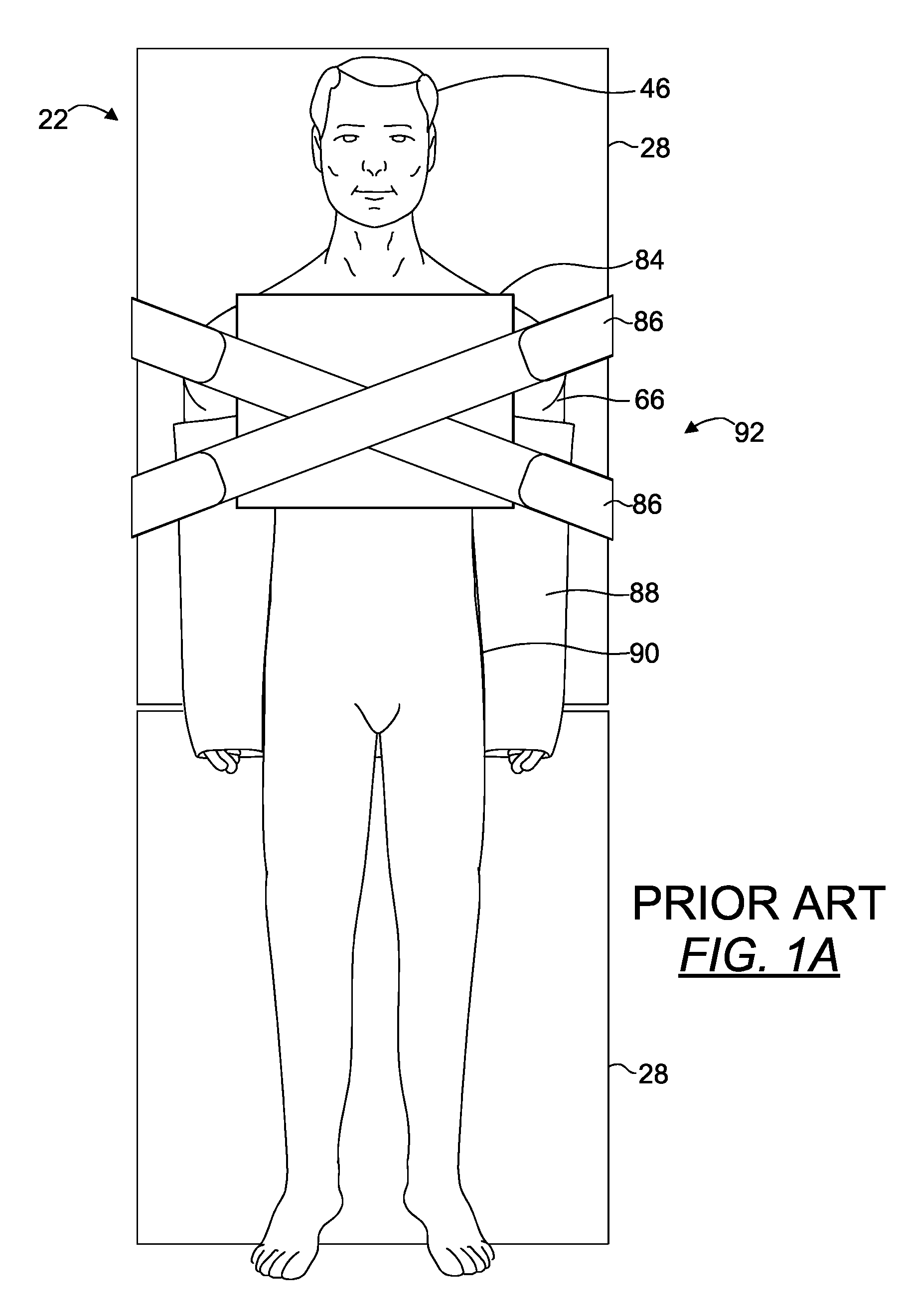
ActiveUS20100275377A1Effective maintenanceHigh likelihood of successOperating tablesDiagnosticsTorsoMedical procedure
A patient positioner for maintaining a patient's position during a medical procedure is provided. The patient positioner includes a generally rectangular body anchoring portion having a longitudinally disposed head and tail ends and two transversely disposed opposing side ends, placeable atop an operating table. There are a pair of spaced apart chest straps, a pair of spaced apart support base straps, a pair of upper arm straps, and a pair of wrist straps. There is a generally rectangular substrate backing having a longitudinally disposed head and tail ends and two transversely disposed opposing side ends, substantially concentrically disposed on and fixedly attached to the body anchoring portion. In one embodiment, an extender strap is further provided to facilitate securement of the support base straps to a support structure. In use, the body anchoring portion is positioned under the patient's torso with the substrate backing side ends wrapped over the arms while the chest straps are brought over the patient's shoulders and criss-crossed over the patient's chest and secured on an opposing side rail while the upper arm and wrist straps are brought from underneath the patient's torso and wrapped over the patient's arms. The support base straps are placed through a break of the operating table and brought around the support base and secured to each other to prevent the patient from sliding toward the head end of the operating table in the Trendelenburg position.
Owner:WEST TAMRA
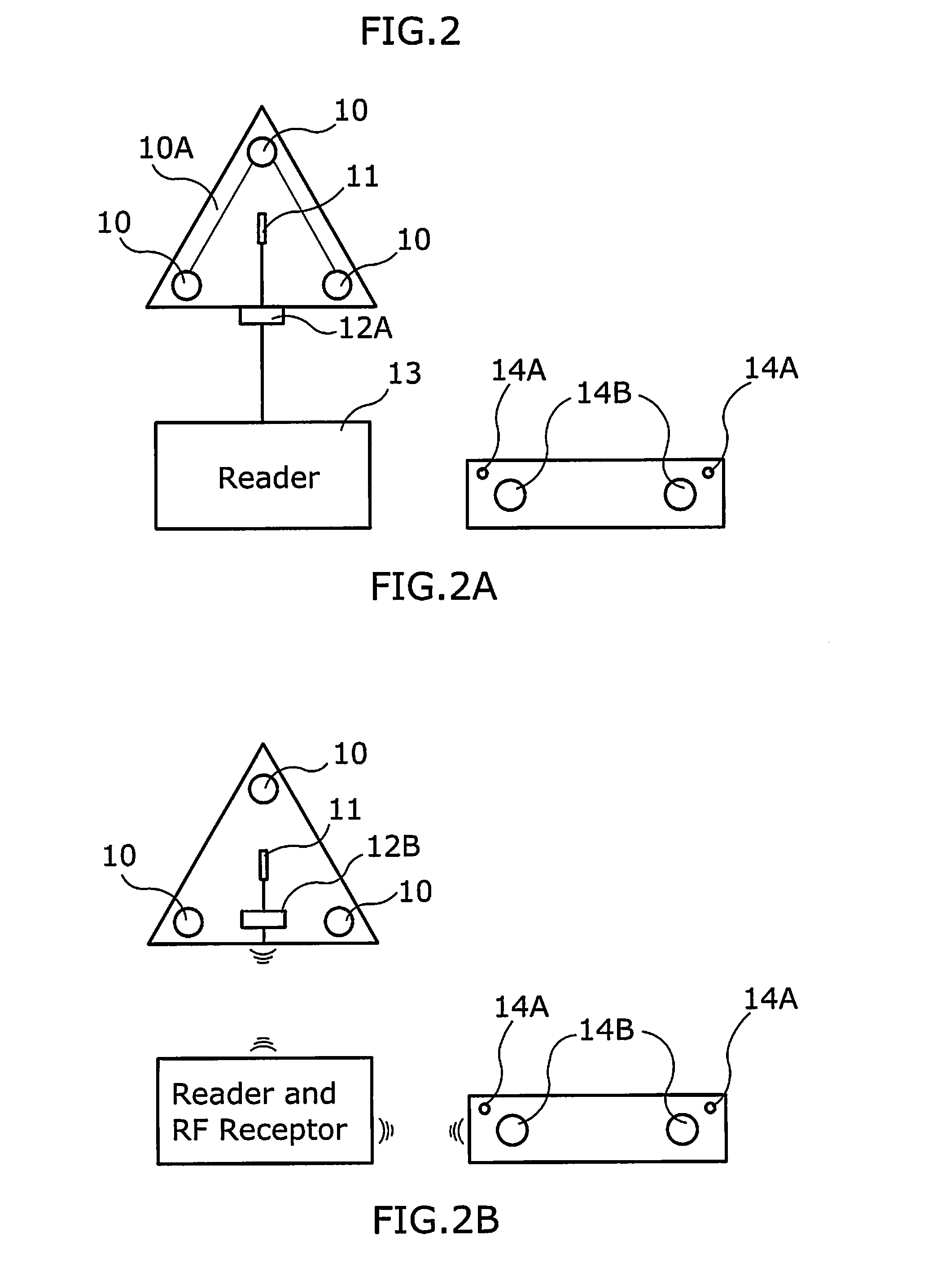
Patient Positioning Systems and Methods
ActiveUS20120203140A1Precise positioningSimple “eyeballingSurgical navigation systemsPerson identificationPhysical therapyPatients position
Systems and methods provide patient position information to a user. A patient positioning device is placed on a patient in a predefined location. The patient positioning device determines a relative patient position with respect to at least one known reference axis. The patient positioning device communicates patient position information including or with reference to the at least one known reference axis. The communicated patient position information allows the user to position the patient and / or a surgical tool using the communicated patient position information.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Synchronized X-ray / breathing method and apparatus used in conjunction with a charged particle cancer therapy system
Owner:BALAKIN ANDREY VLADIMIROVICH +1
Patient position monitoring device
InactiveUS6847301B1Withstand constant daily usageMinimize the possibilityContact operating partsDiagnostic recording/measuringCaregiver personWheelchair
The disclosed invention is a patient monitoring system that employs a pressure sensitive pad. The pad is placed beneath a patient who is lying in bed or sitting in a chair. When weight is removed from the pad, an alarm is given. The pad comprises an upper layer of circuitry and a lower layer of circuitry. When the respective layers of circuitry are in contact, the alarm remains off, but when the layers of circuitry become separated, the alarm is given. This invention is generally for use in hospitals and nursing homes to alert caregivers when a patient falls out of a bed or a wheelchair; or if a patient otherwise leaves a bed or chair against the wishes of the caregiver. This situation is of special concern with elderly patients, post operational patients, and / or at night when nursing staffs are reduced.
Owner:PROFESSIONAL SECURITY CORP
System for detecting and monitoring vital signs
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Radiation dosimeter with localization means and methods
InactiveUS20130033700A1Radiation measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansDosimeterPatients position
A apparatus for accurately measuring radiation beams during treatment which comprises a dosimeter which is used to measure the radiation; an optical marker which is used to determine the patient position; and said dosimeter and said optical marker are connected to one another used to provide and display simultaneously a radiation dose reading and a measurement of the patient's movements during treatment.
Owner:HALLIL ABDELBASSET
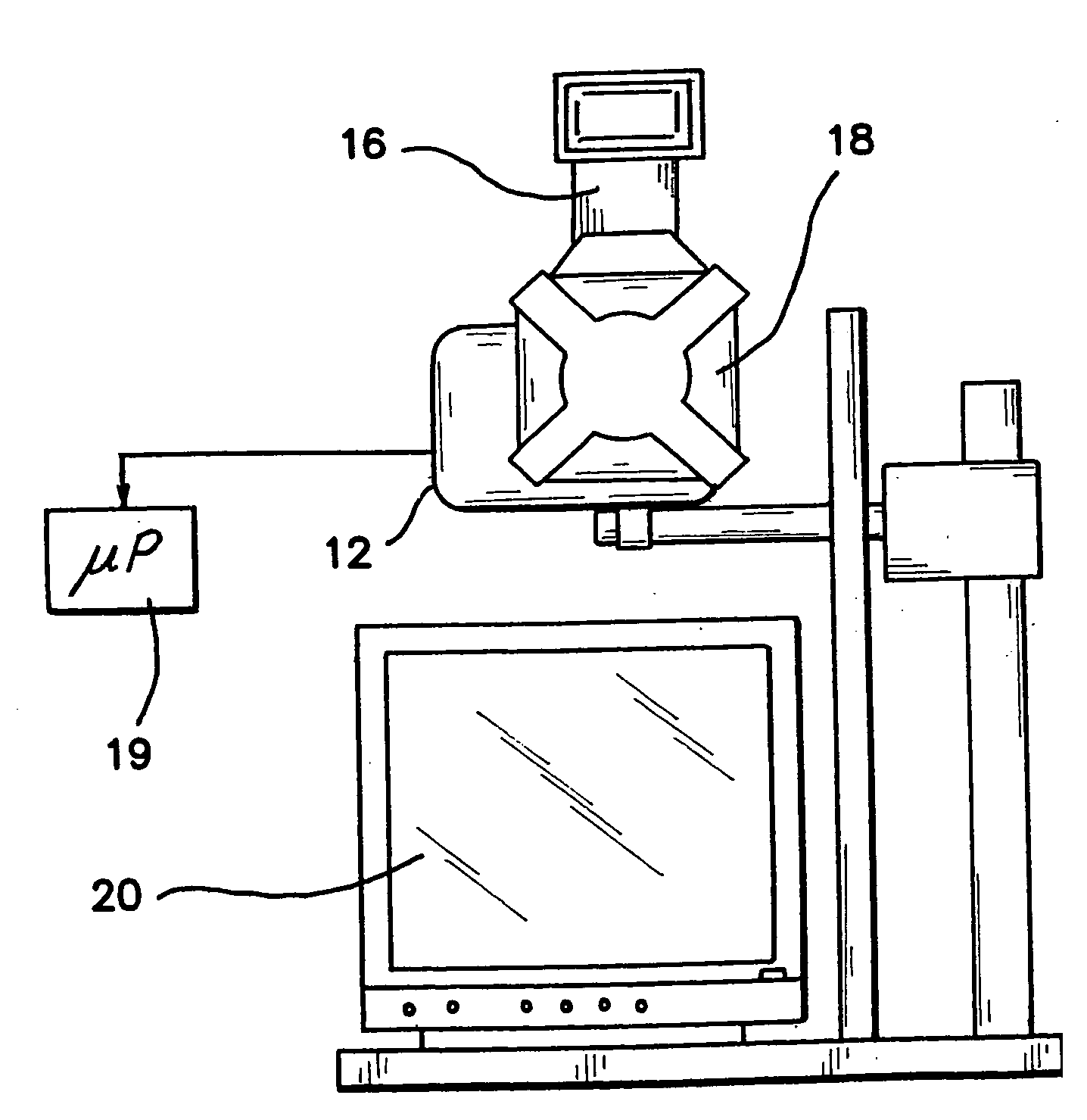
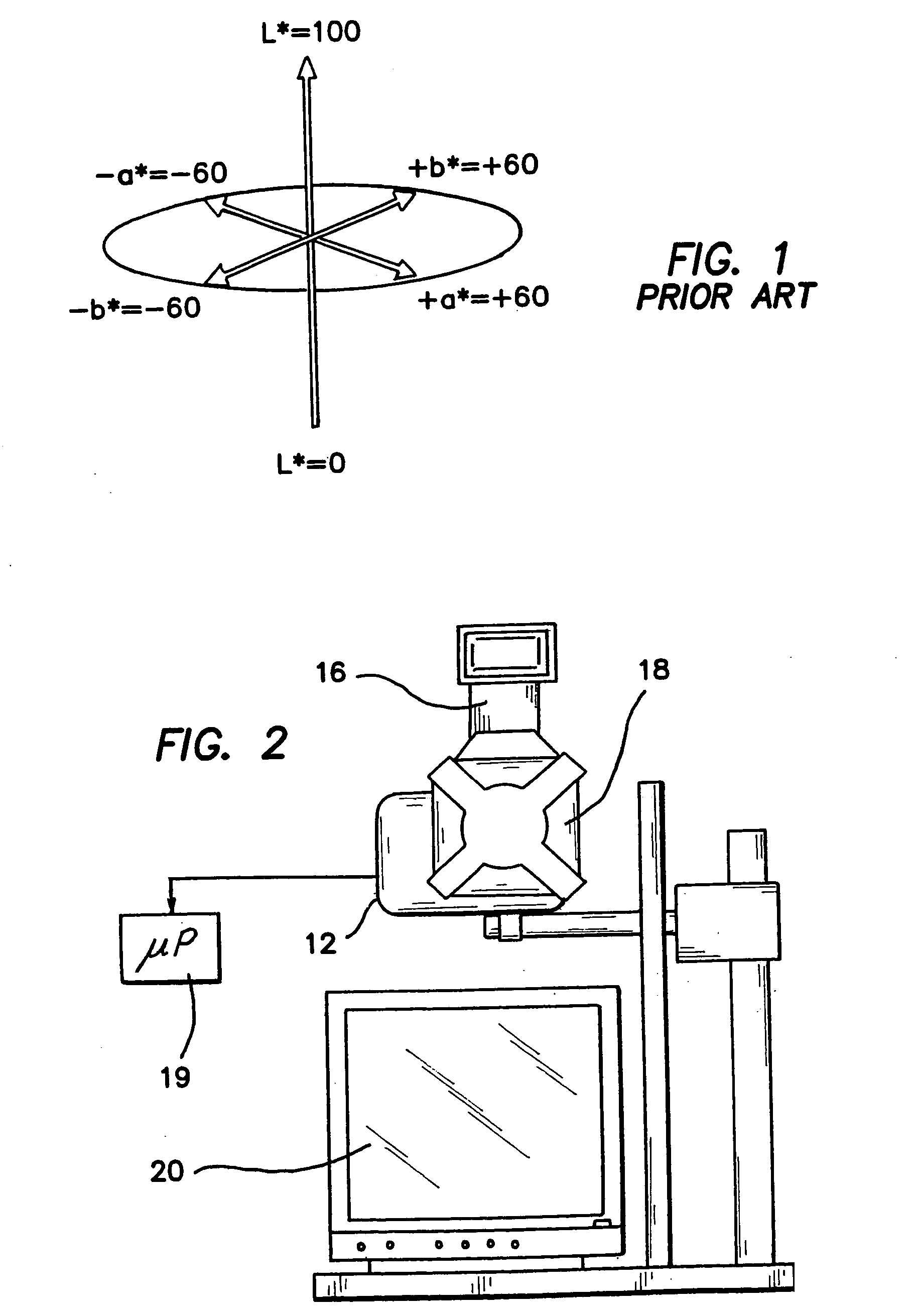
Method and apparatus for characterization of chromophore content and distribution in skin using cross-polarized diffuse reflectance imaging
ActiveUS20050030372A1Rapidly and quantitatively characterizesReduce reflected lightDiagnostics using lightCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital imagingSkin color
A digital imaging system provides color information of an entire port wine stain or other skin condition with a single image in CIE L*a*b* color space (L*, a*) derived from RGB pixel data (R, G, B). Cross-polarization optics produce marked reduction in specularly reflected light in the images. A patient positioning device allows for repeatable positioning of the patient's head or body portion. The digital nature of the system provides a near real-time mapping of melanin and erythema or other skin chromophore metrics. The cross-polarized diffuse reflectance color digital imaging system obtains subsurface skin color information and acquisition of facial images in a reproducible fashion at a fixed distance from an illumination source at optimized angles of view depending on the region of interest being imaged.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
X-ray apparatus with improved patient access
InactiveUS6169780B1Improve approachPrecise positioningTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPatients positionVisual perception
An X-ray device for generating a panoramic tomogram is designed so that a revolving arm can move between a first position, where an X-ray generator and an X-ray receiver that are both supported by the revolving arm oppose each other through the head of a patient positioned in a patient positioning station, and a second position, where an operator of the X-ray device can look at the patient's head from a side view, thereby allowing the operator to properly position the patient in the patient positioning station. The incorporation of a second X-ray receiver additionally allows for the generation of a cephalogram. The incorporation of a blind prevents the patient from visually or physically interacting with selected components of the apparatus.
Owner:MORITA MFG CO LTD
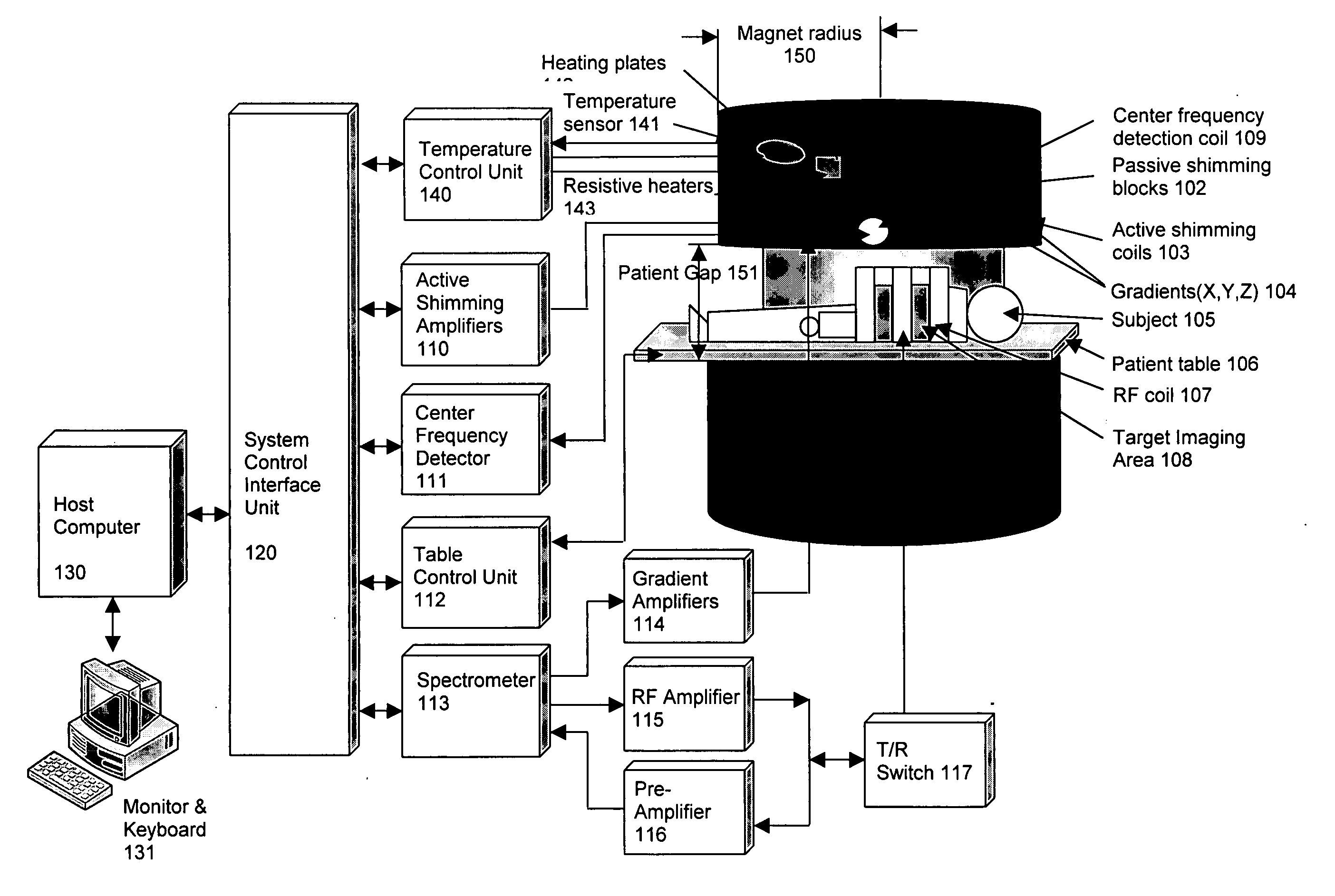
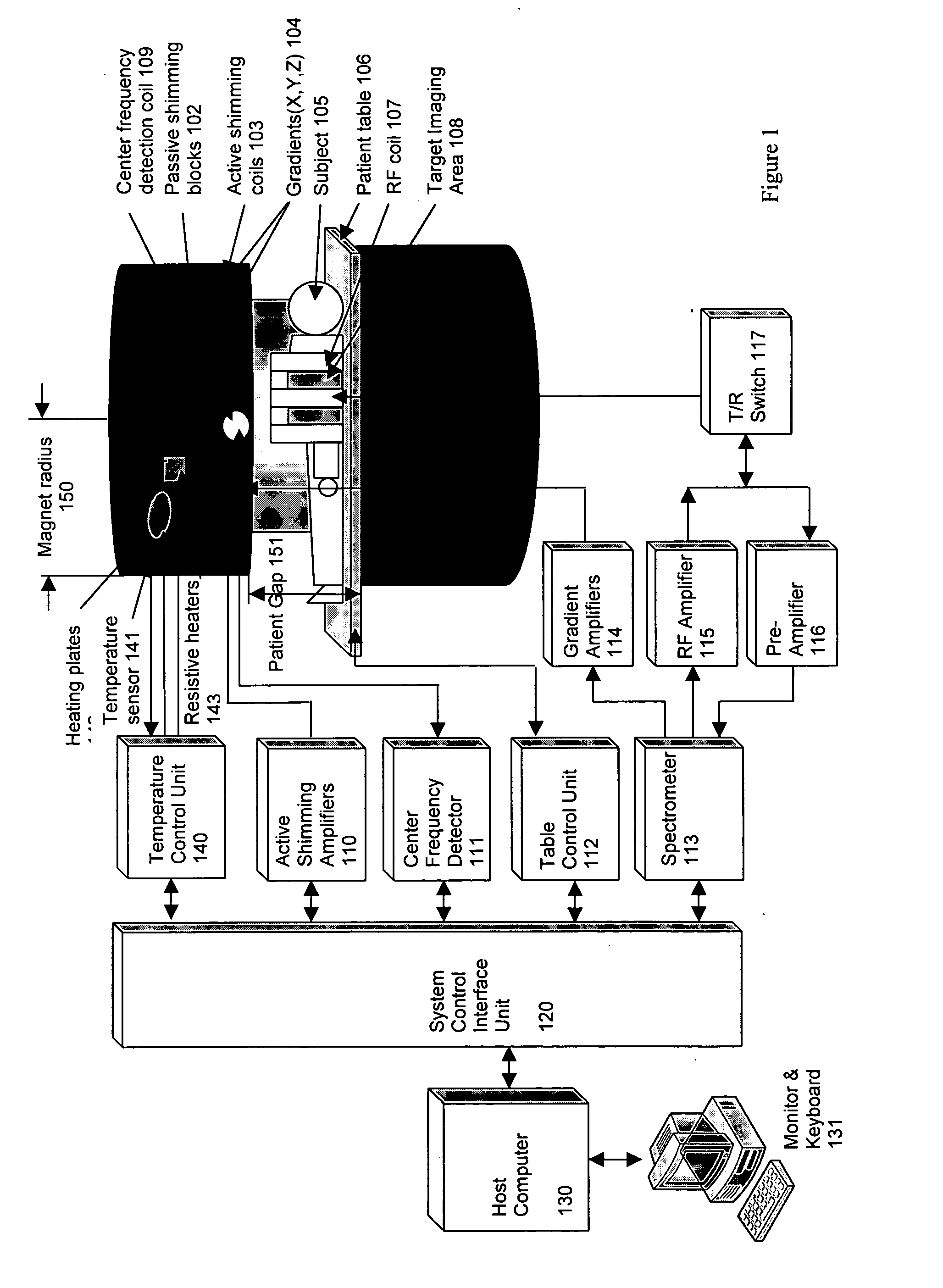
Method of using a small MRI scanner
InactiveUS20050154291A1Close accessMore accessDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCost effectivenessWhole body
Multiple methods of performing whole body scans using a cost-effective small magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system are disclosed. High magnetic field homogeneity of an open, small MRI is obtained by a combination of passive shimming and high order active shimming. A dynamic shimming while imaging (DSWI) method is provided to dynamically optimize field homogeneity for each scanned slab (slice) during imaging. Also provided is a method that scan a large subject volume only using a limited optimal imaging region of a magnet by continuously adjusting patient position and orientations with a 6 degrees of freedom patient table.
Owner:ZHAO LEI +2
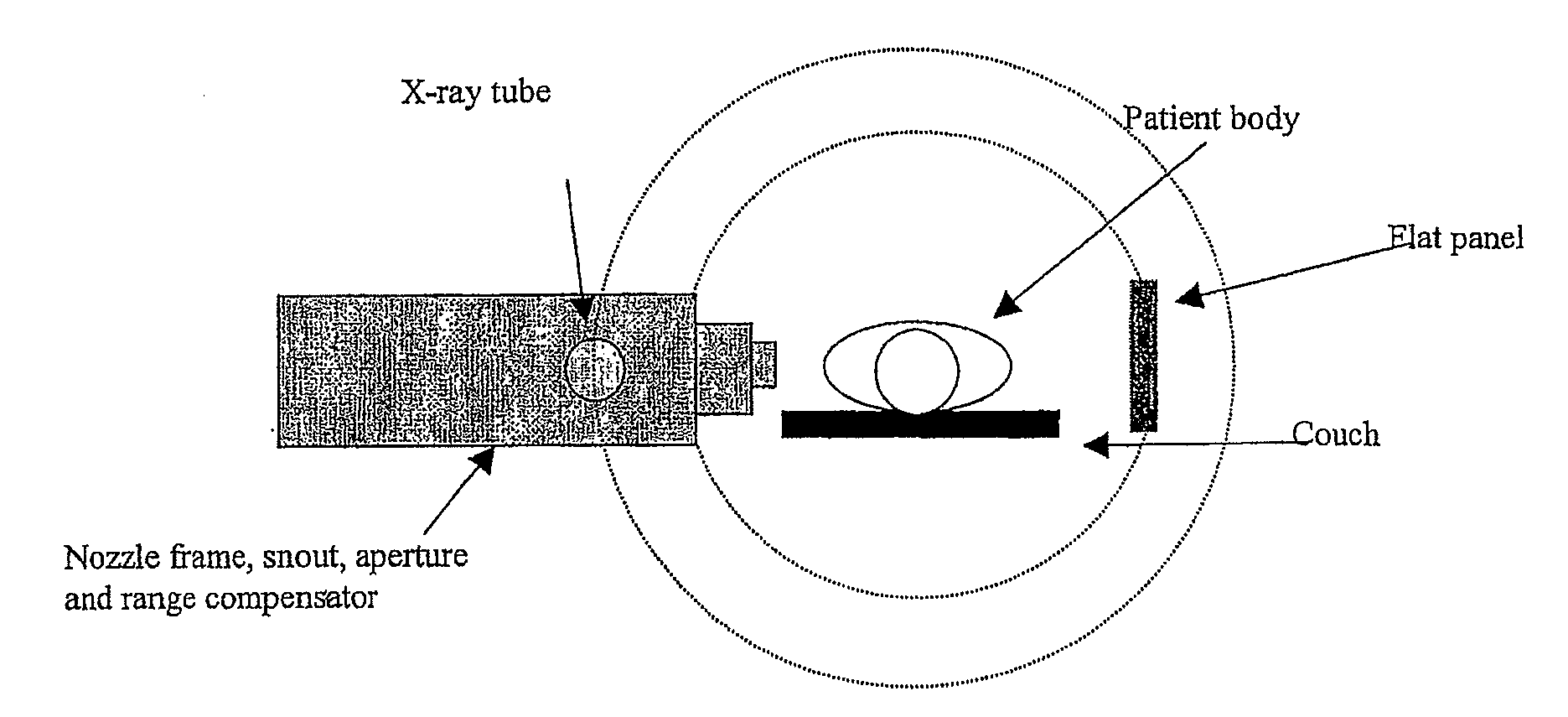
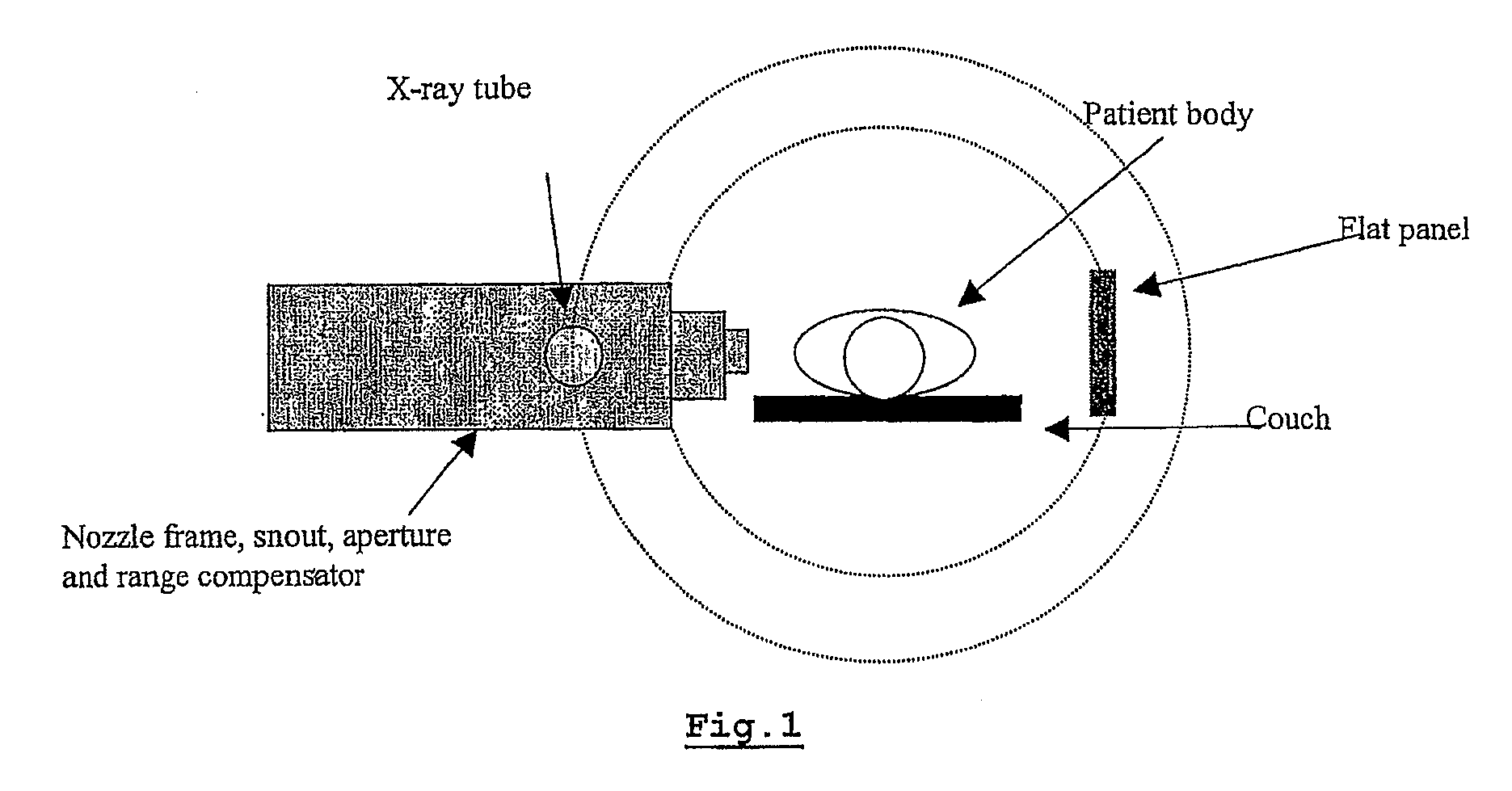
Particle therapy system
InactiveUS7834334B2Weighing apparatus using fluid action balancingMicrowave therapyParticle beamHigh energy
A particle therapy system for irradiating a volume of a patient to be irradiated with high-energy particles is provided. The system includes a radiation outlet of a radiation delivery and acceleration system from which a particle beam exits in order to interact with the patient positioned in an irradiation position; an imaging device for verifying the position of the volume to be irradiated in relation to the particle beam; and a patient-positioning device with which the patient can be brought into the irradiation position for irradiation. The imaging device checks the position of the volume to be irradiated in an imaging position of the patient that is spatially remote from the irradiation position, and the patient-positioning device automatically changes position between imaging position and irradiation position.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
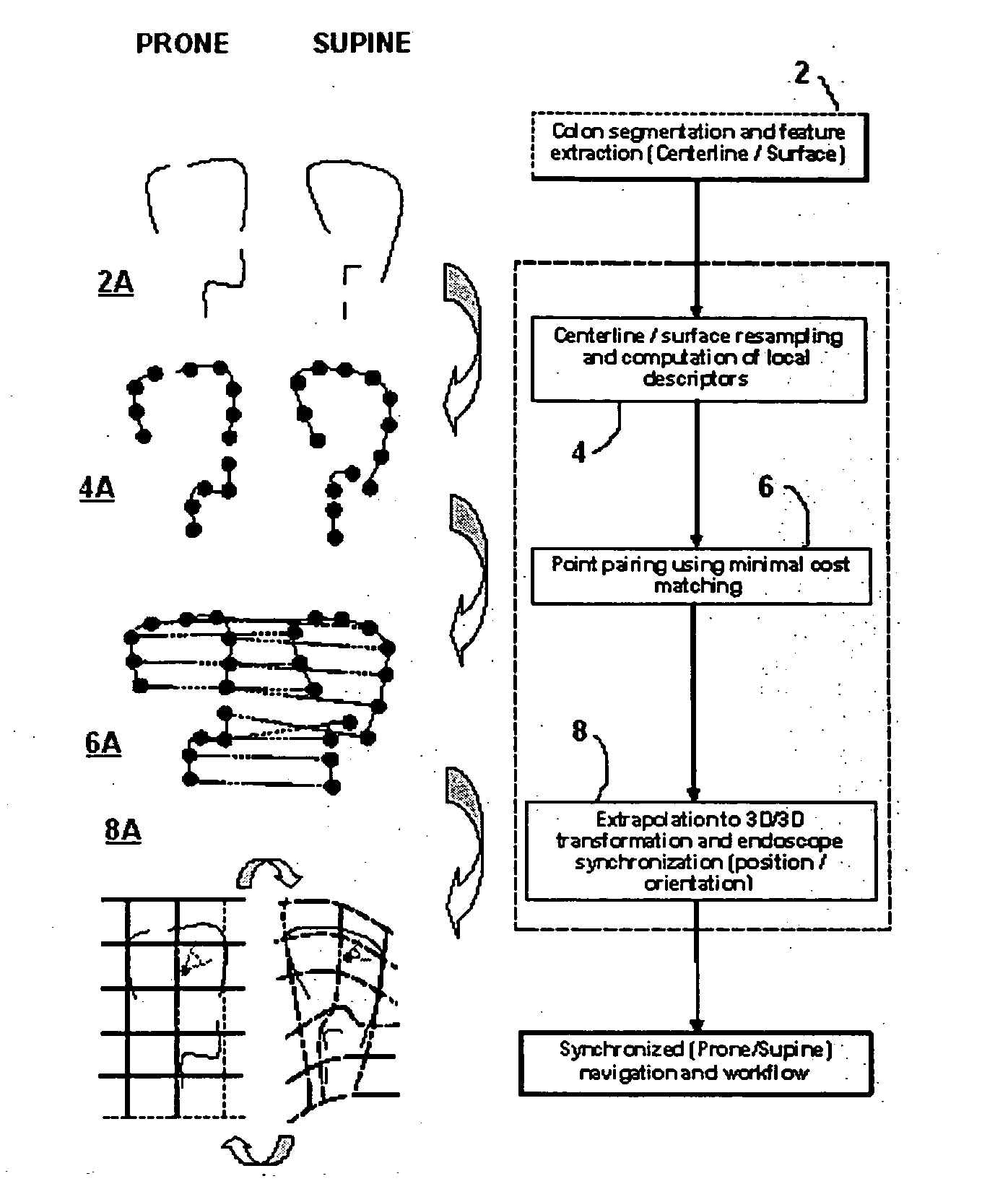
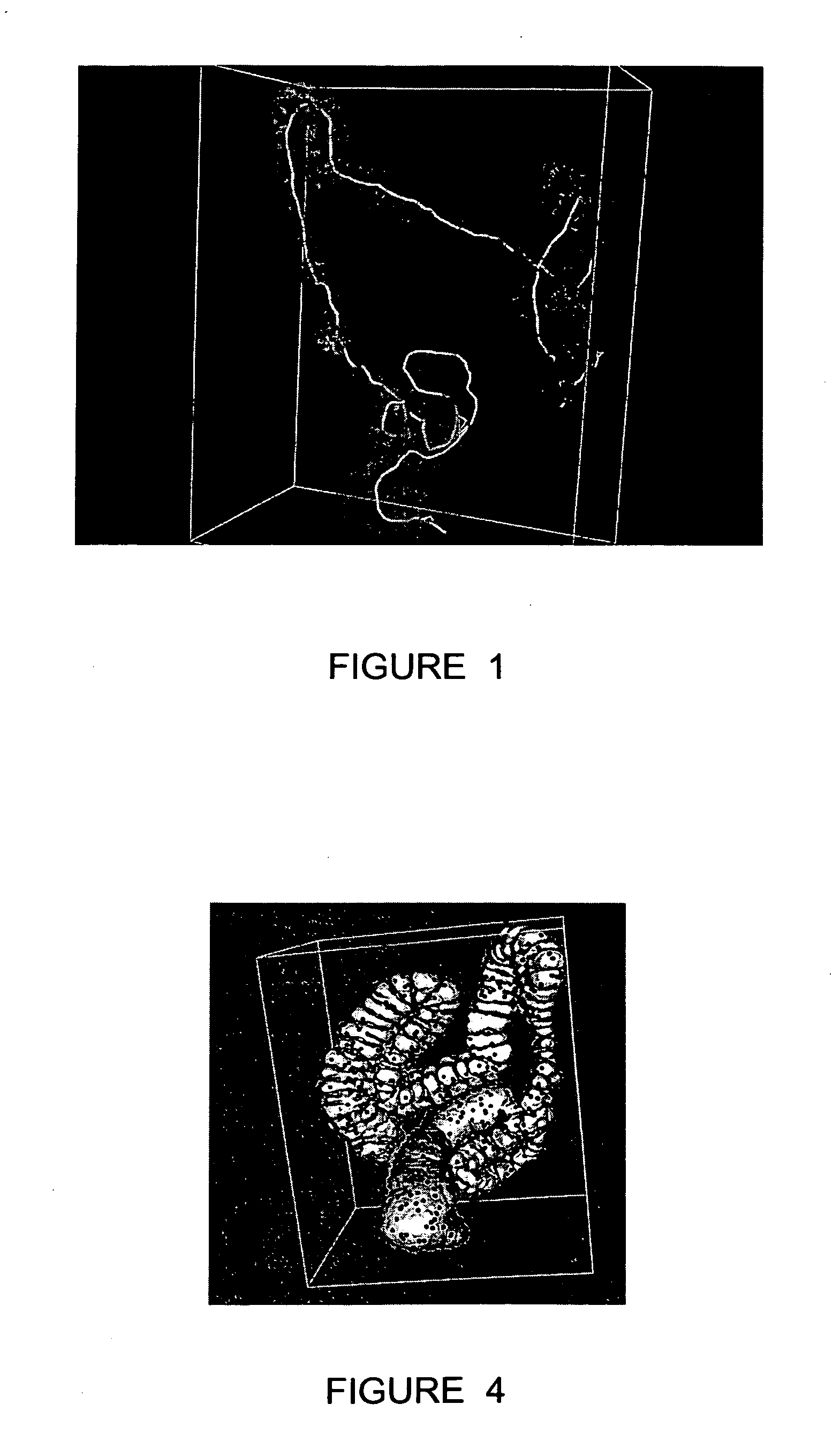
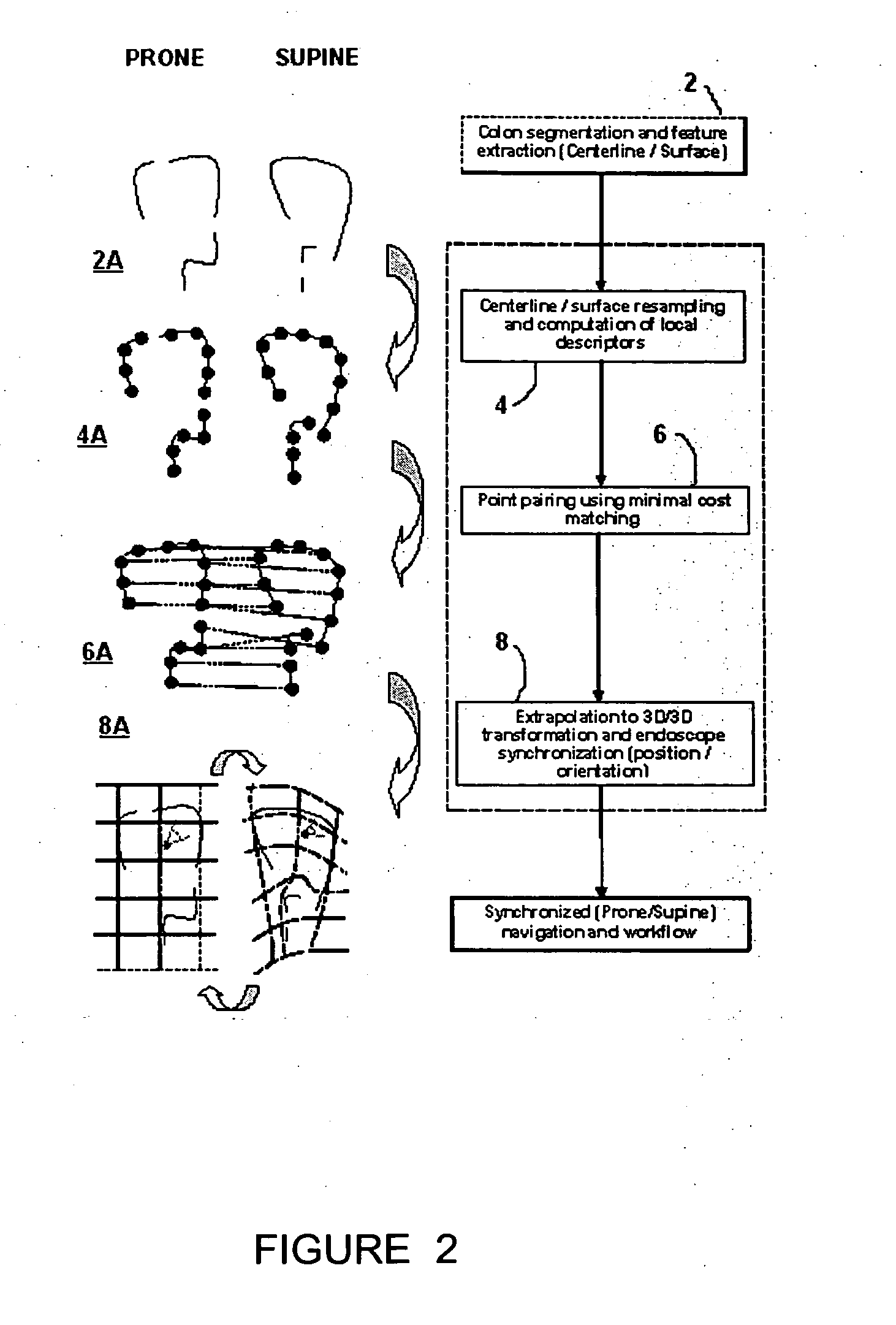
Method and apparatus for registration of virtual endoscopic images
InactiveUS20050048456A1Minimal cost matchingImage enhancementImage analysisFeature extractionReference frame
A method for registration of virtual endoscopy images in first and second patient positions comprises performing colon segmentation and feature extraction, including centerline and colon surface data for each of the images; resampling the centerline and colon surface data; computing respective local descriptors; pairing point correspondences on the centerlines between the first and second images by minimal cost matching; extrapolating the centerline point correspondences to a 3-dimensional / 3-dimensional (3D / 3D) transformation between the first and second images. The method also includes selecting a position for a virtual endoscope in one of the images; associating an orthogonal reference frame with the virtual endoscope; and applying the 3D / 3D transformation to the orthogonal reference frame so as to derive a corresponding transformed reference frame for the virtual endoscope in the other of the images.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Mattress sled
InactiveUS20060213010A1Reduce coefficient of frictionBreathing protectionStretcherEngineeringPatients position
A system for transporting an nonambulatory patient including a mattress having longitudinal sides and a bottom surface and a panel having longitudinal side edges, a head end edge, and a bottom surface coated with a low coefficient of friction coating. The panel is positioned below the bottom surface of the mattress, and includes a plurality of side straps extending outwardly from the longitudinal side edges in spaced relation to one another. A handle is located along at least one edge of the panel. The side straps are wrapped around the mattress so as to cause the mattress to curl so that the longitudinal sides are moved upwardly to thereby form a central longitudinal pocket suitable for cradling a patient positioned upon the mattress. The head end handle is then pulled to drag the curled mattress and the panel along a surface upon the low coefficient of friction coating.
Owner:DAVIS DAVID T
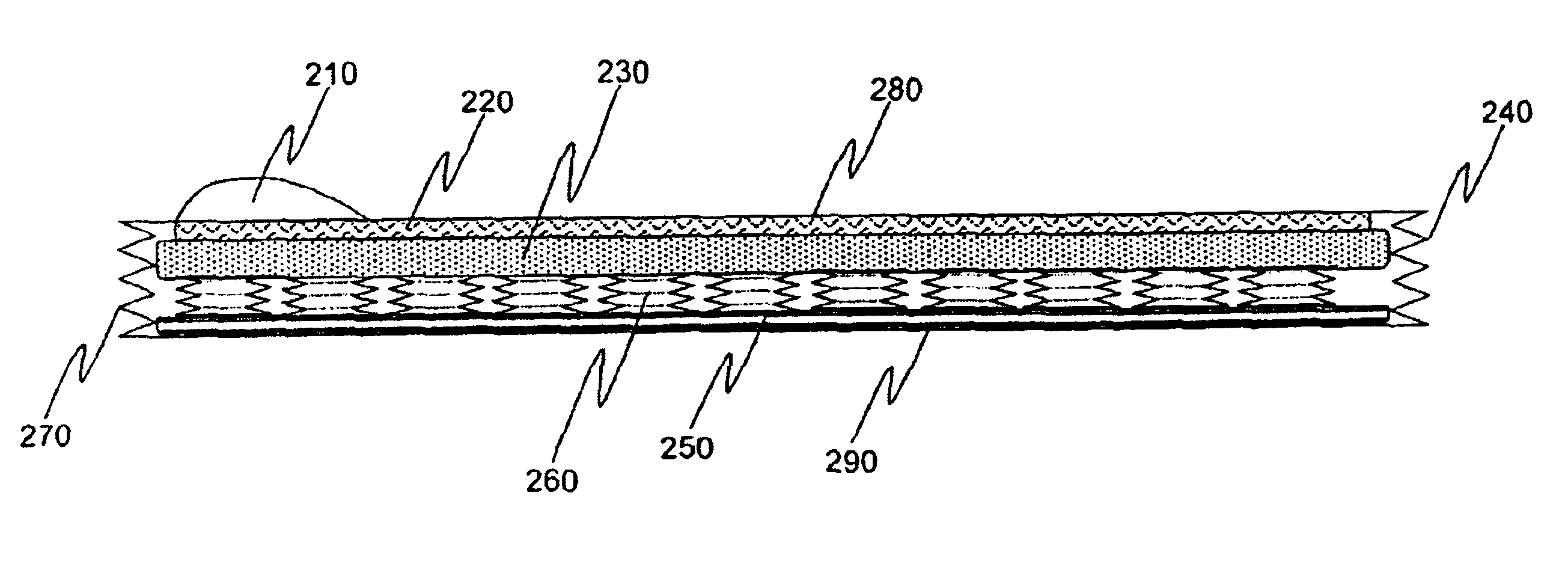
Medical protective table sheets
A disposable slip-resistant and preferably absorbent protective medical table sheet for protecting a medical table, such as an operating table or an examination table, from contamination due to contact with bodily fluids or other contaminants associated with a patient positioned upon the table sheet covering the medical table, and for resisting slippage between the patient and the table sheet and between the table sheet and the medical table and, if a lift sheet is used, between the table sheet and the lift sheet. The table sheet preferably includes an impermeable layer with a slip-resistant and absorbent layer of foam material on its upper side and a distribution of slip-resistant material on its lower side. The lower side of the impermeable layer may itself be comprised of slip-resistant material. The table sheet is preferably fan-and-book-foldable into a compact yet rapidly unfoldable table sheet.
Owner:TRIMOUNTAIN MEDICAL RESOURCES
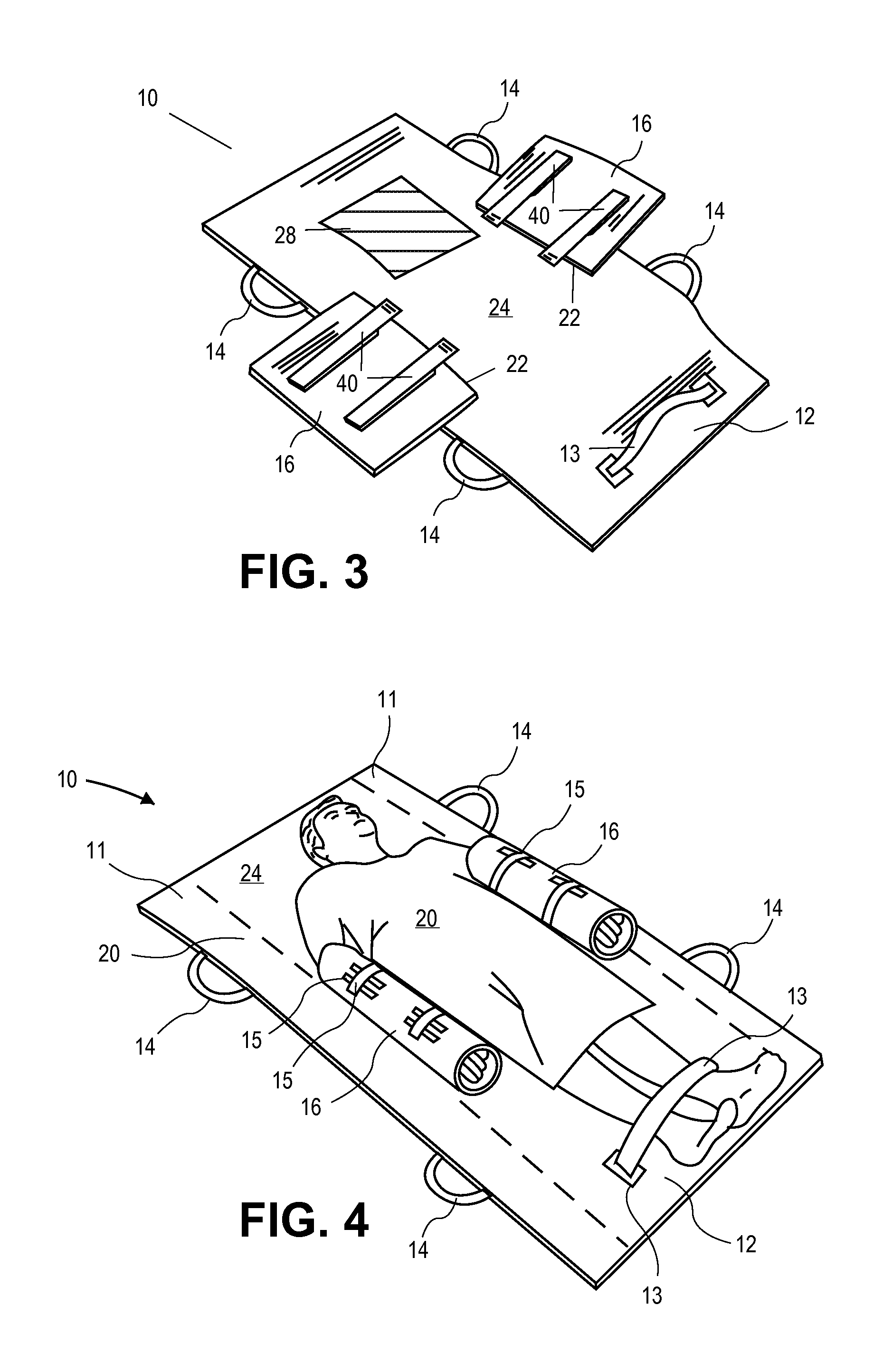
Patient Positioning Device
A patient positioning device provided to position, protect and secure a patient on a support surface for transfer to another support surface or for preparation for surgery. The positioning device includes a sheet with a first and second flexible substrate coupled to the sheet's top surface. The first and second flexible substrates may be padded. These substrates are capable of wrapping around an adjacent arm of the patient creating a wrapped engagement. This wrapped engagement may pad, protect, secure and elevate the arms from injury caused by pressure imparted thereon during surgery or transport. This positioning device may be lifted or slid from one support surface to another. Optionally, a third and fourth flexible substrate capable of wrapping around an adjacent arm of the patient creating a second wrapped engagement may be used for additional securing. Optionally, an inflatable support may be used with the device to aid when sliding or translating the device 10 with the patient thereon.
Owner:BCG MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com