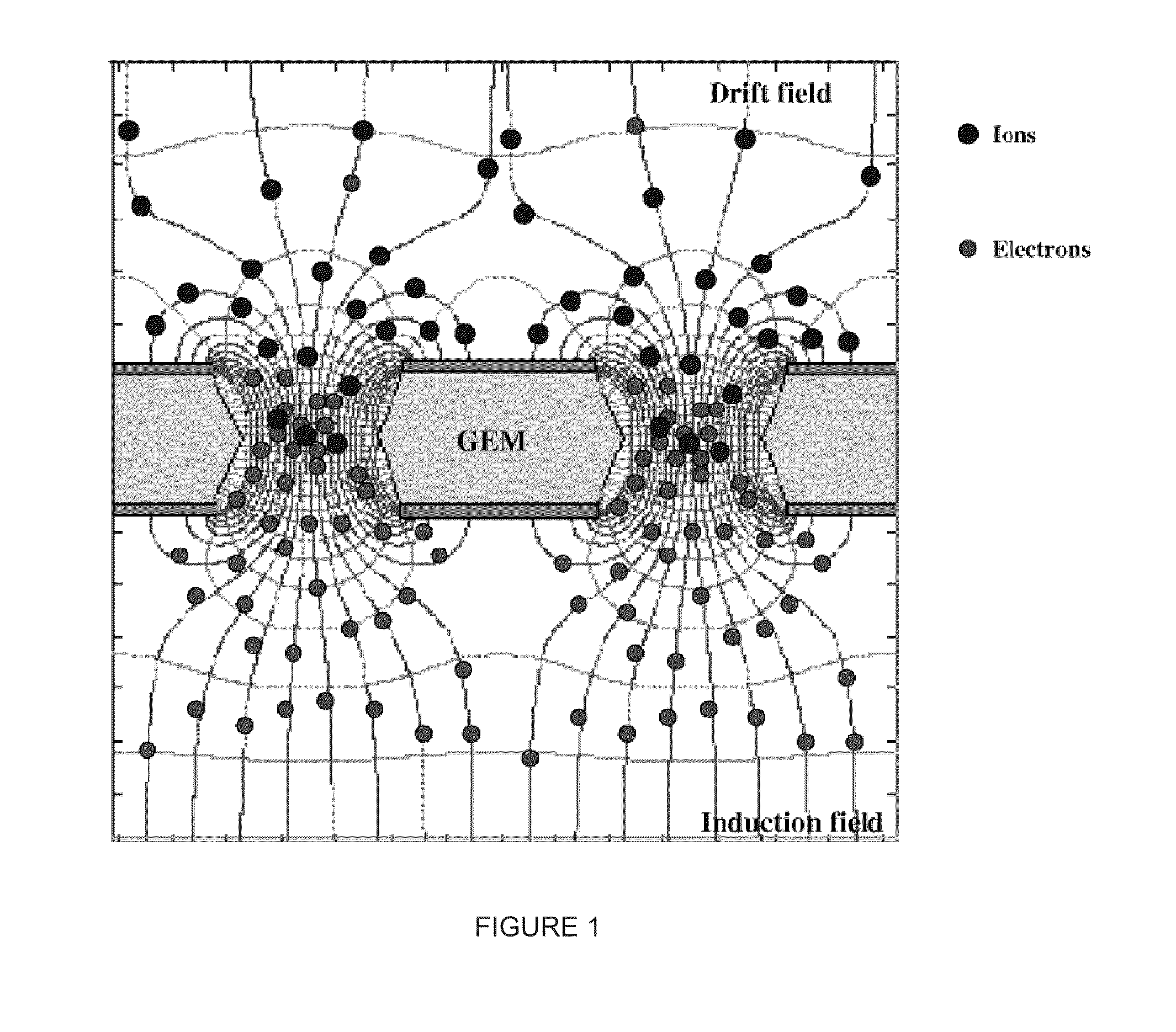
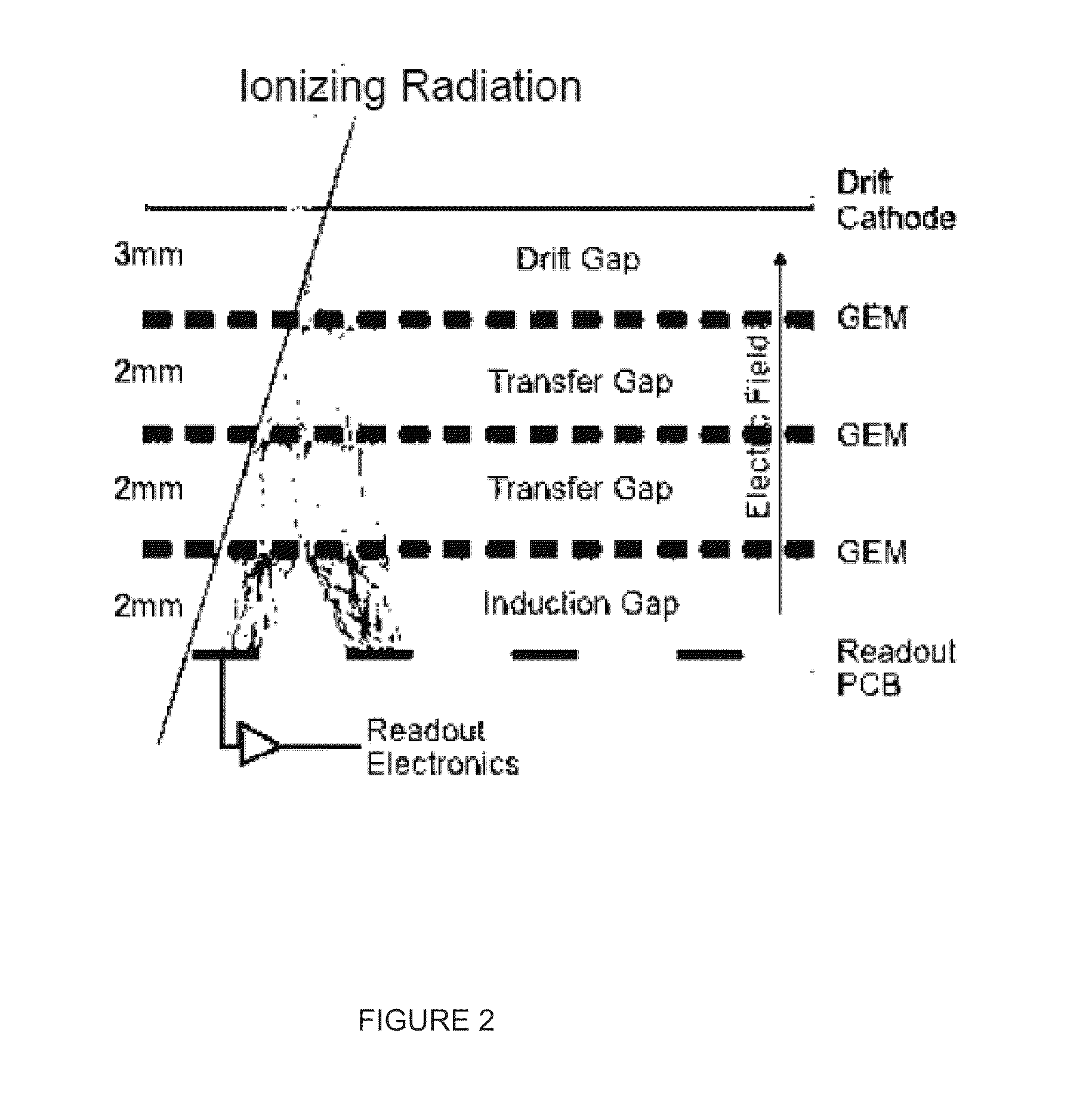
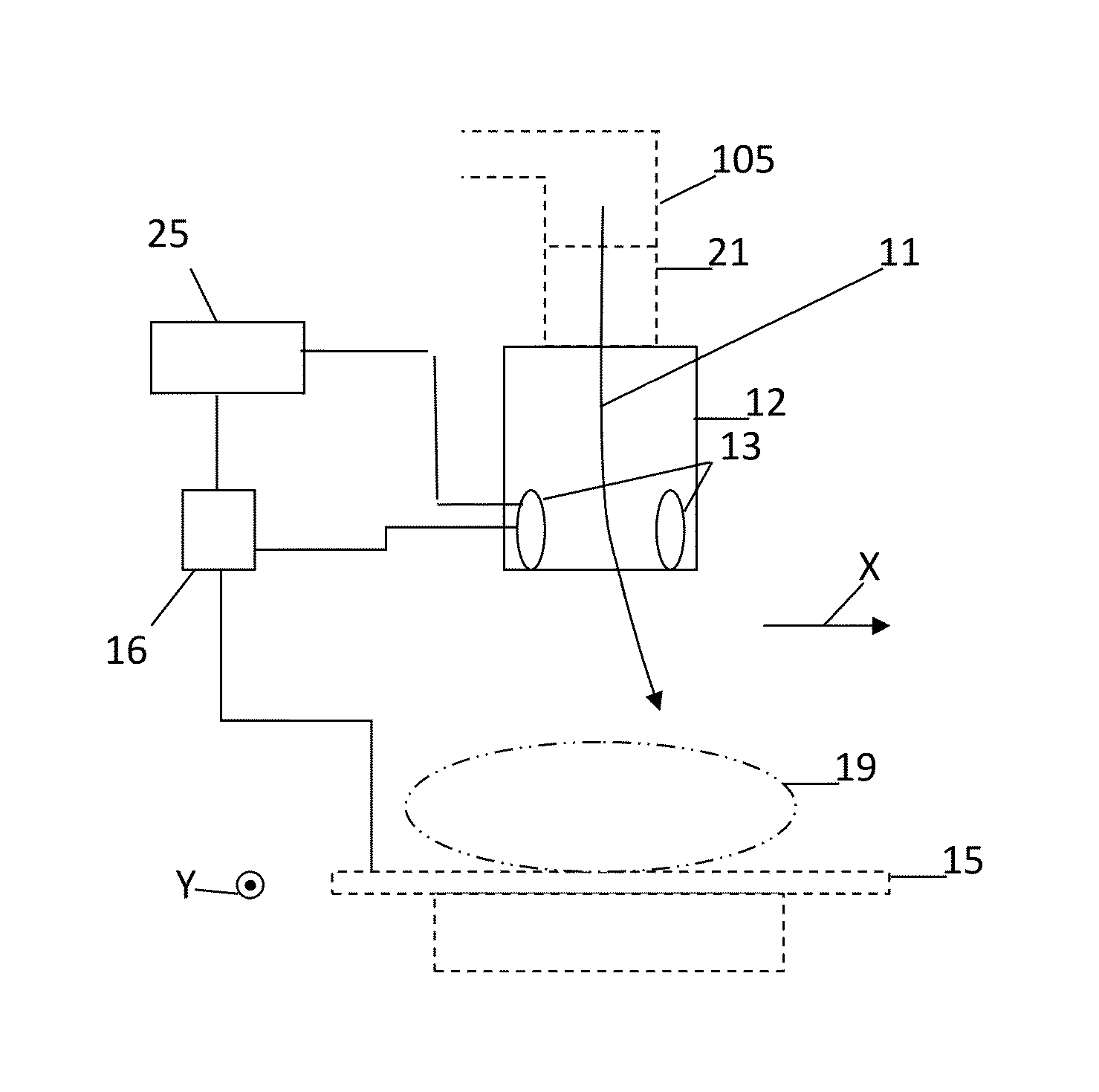
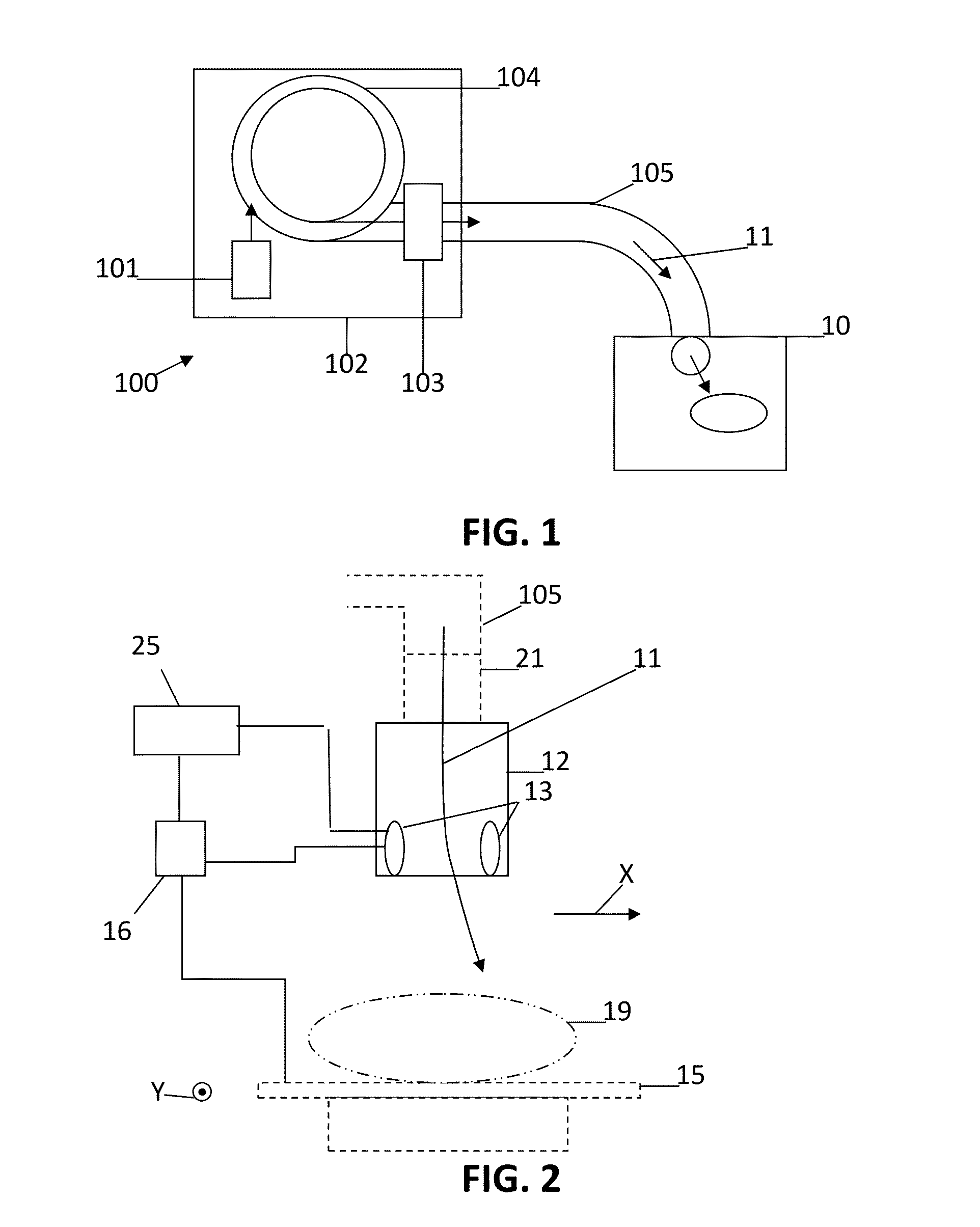
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43 results about "Hadron" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In particle physics, a hadron /ˈhædrɒn/ (Greek: ἁδρός, hadrós; "stout, thick") is a composite particle made of two or more quarks held together by the strong force in a similar way as molecules are held together by the electromagnetic force. Most of the mass of ordinary matter comes from two hadrons, the proton and the neutron.
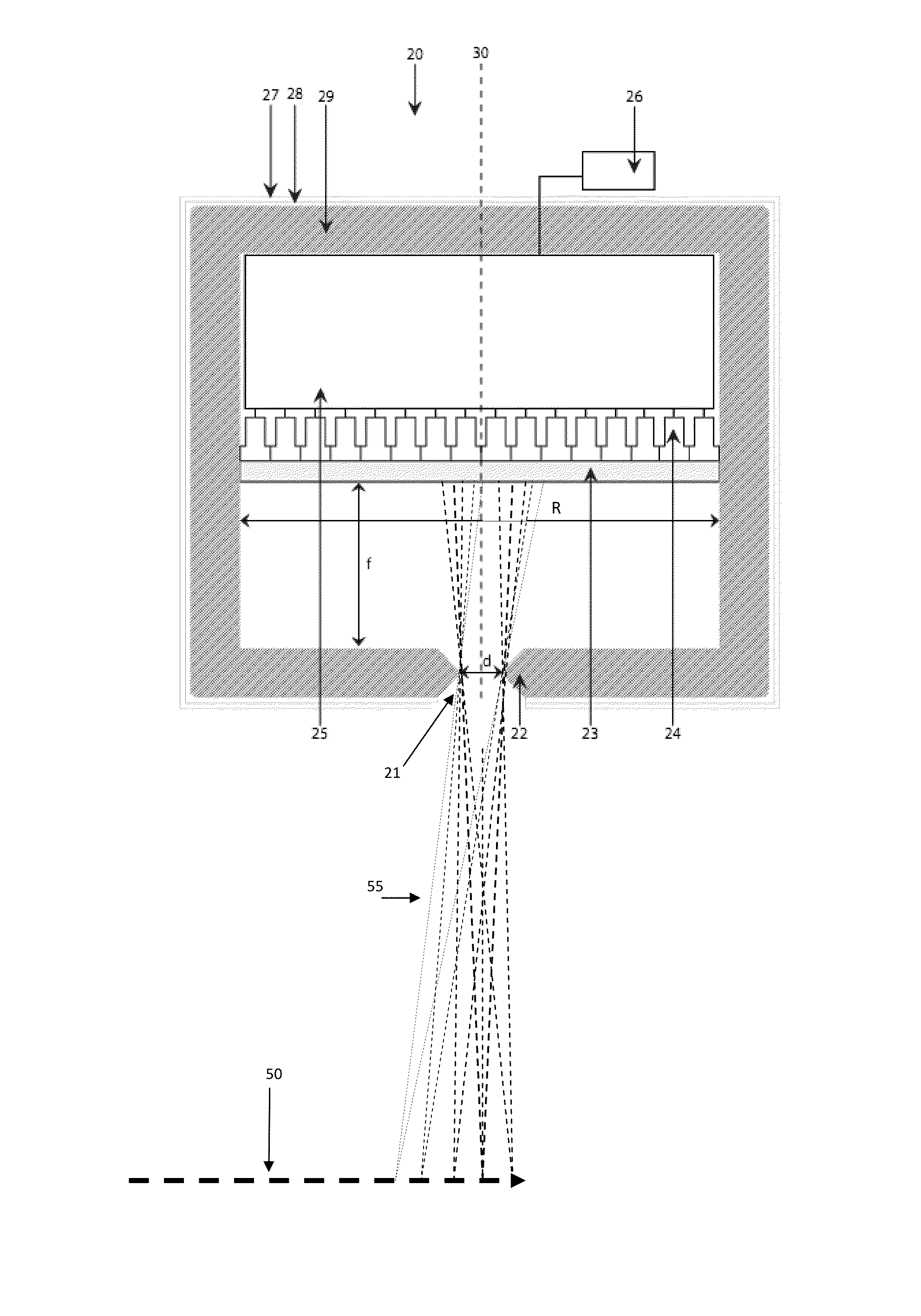
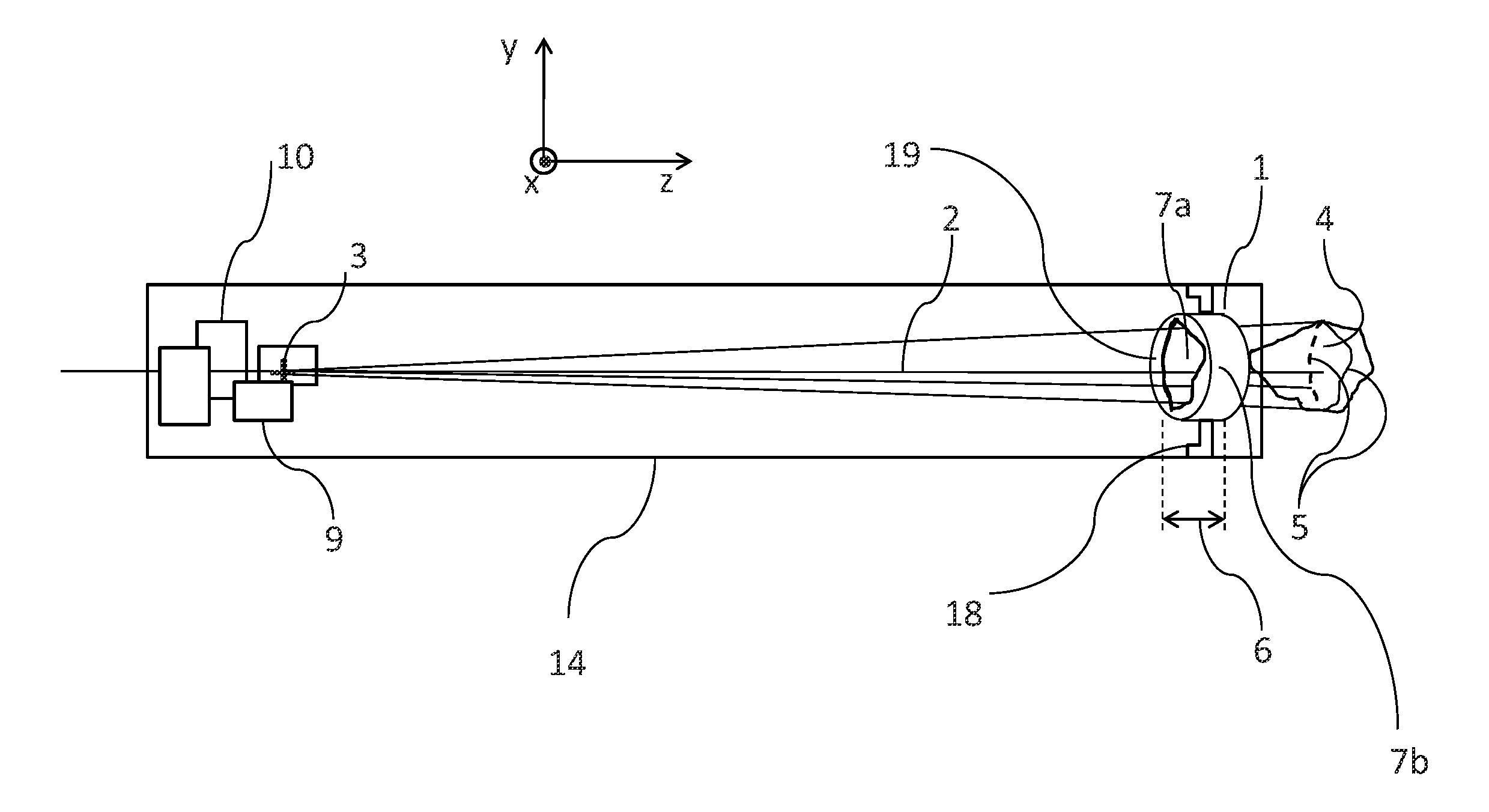
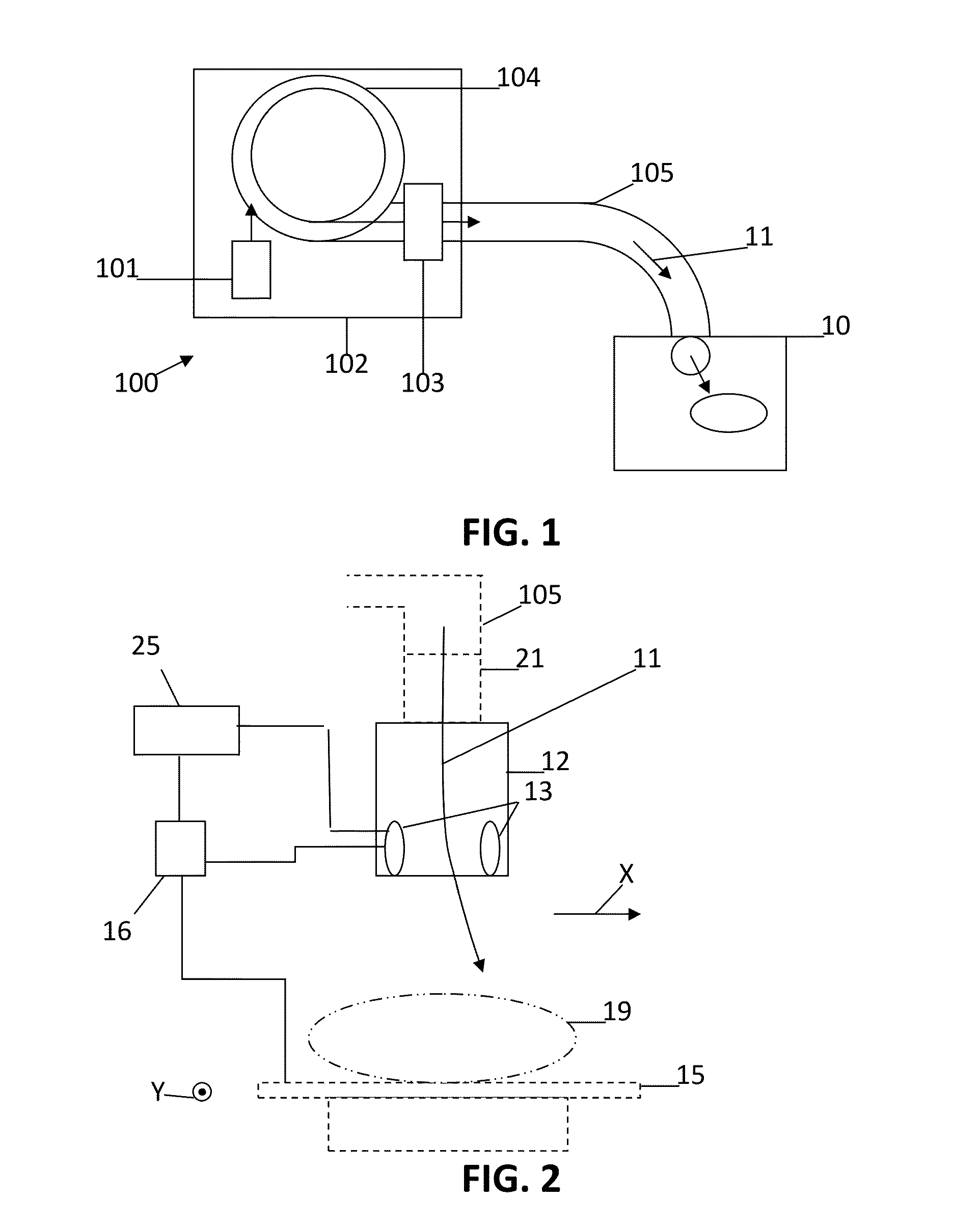
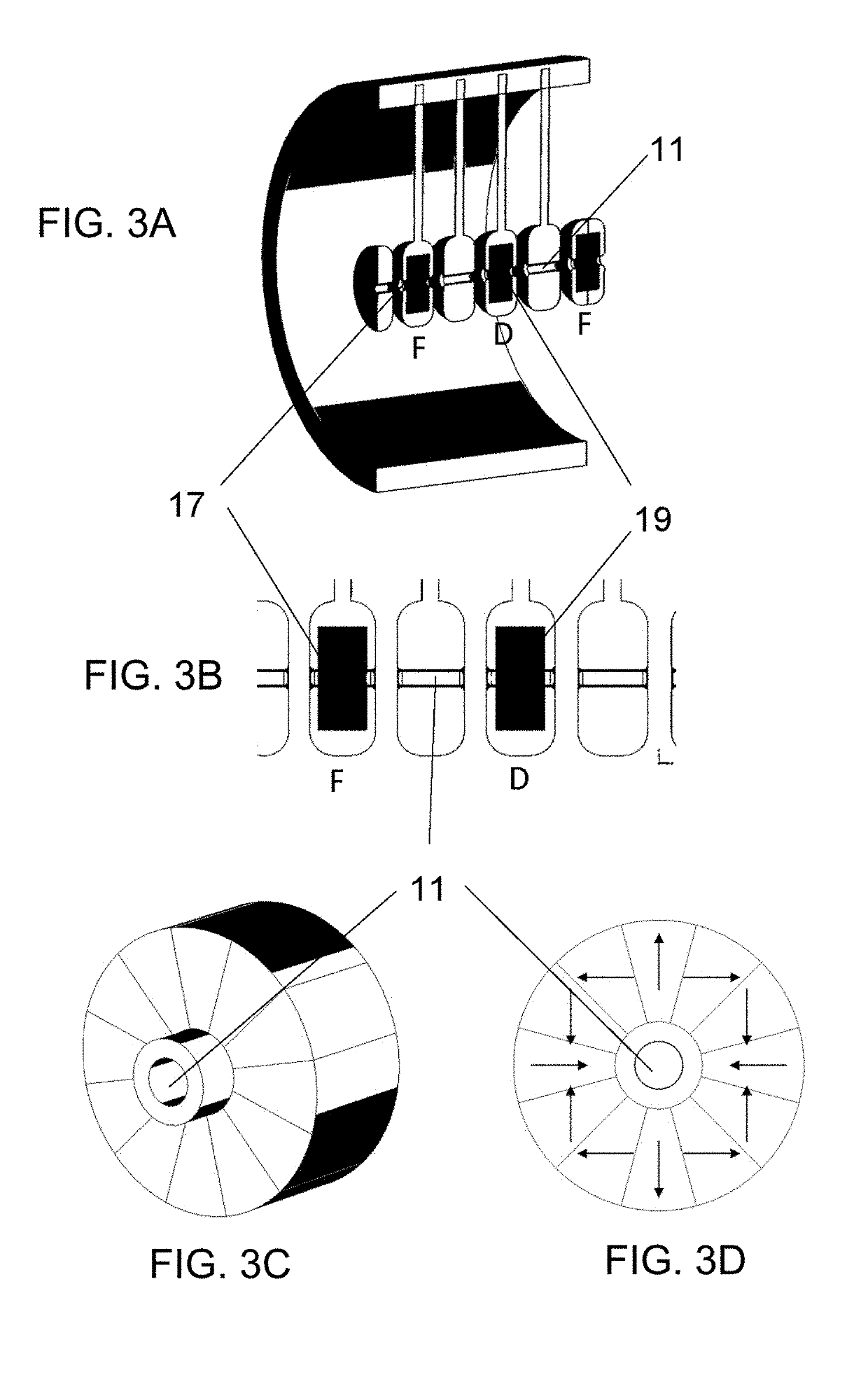
Apparatus, method and system for measuring prompt gamma and other beam-induced radiation during hadron therapy treatments for dose and range verification purposes using ionization radiation detection
InactiveUS20110284757A1Easy to detectElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansCritical structureGamma irradiation
An apparatus, method and system for measurement of radiation during or directly following hadron therapy treatment for dose and range verification purposes accomplished through measurement of prompt gamma and other beam-induced radiation. One example includes the measurement of secondary prompt gamma radiation during proton and carbon ion beam irradiation. The measurement can also be made of other beam-induced radiation results. The measurement of gamma radiation or other beam-induced radiation allows for optimization of radiation dose disposition to the target tissue, with improved sparing of surrounding critical structures and normal tissue. Adjustments to a radiation treatment may be made as needed based on actual and measured applied dosages.
Owner:HAMPTON UNIVERSITY
Charged hadron beam delivery
ActiveUS9283406B2Improve consistencyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyBeam scanningHadron therapy
A charged hadron therapy system for delivering charged hadron radiation to a target is provided. The system comprises a target positioning couch for supporting the target being moveable along a translation direction and a beam delivery system comprising a beam scanning means for scanning a hadron pencil beam over said target in a first scanning direction and a second scanning direction being substantially parallel with the translation direction. The beam scanning means is limited for providing a maximum scanning amplitude AY in the second scanning direction. The system comprises an irradiation controller configured for simultaneously and synchronously performing the moving of the couch and the scanning, so as to deliver charged hadron radiation to a target over a target size being larger in the Y direction than the maximum scanning amplitude AY.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Method and Apparatus for Monitoring a Charged Particle Beam
ActiveUS20140265823A1Line/current collector detailsSolid cathode detailsAmbient pressureEqualization
An ionization chamber with spatial distribution electrode for monitor hadron beam currents used for therapeutic treatment. Ionization chamber comprises humidity control, environmental sensing and real-time correction thereof. A flexible hermetic seal provide for ambient pressure equalization. X-Y electrode planes measure Gaussian distribution of incident particle beam. Methods described herein are suitable to fabricate highly accurate, low scattering electrodes with high spatial resolutions.
Owner:PYRAMID TECHN CONSULTANTS
Device and method for particle therapy verification
InactiveUS8481951B2Material analysis by optical meansHandling using diaphragms/collimetersHadron therapyStrong interaction
The invention is related to the field of charged Hadron Therapy, i.e. radiation therapy using strongly interacting particles. More particularly, the invention relates to a detector and method for measuring the beam range of a charged hadron beam in a target object as well as the particle dose distribution in the target object.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Apparatus For Particle Therapy Verification
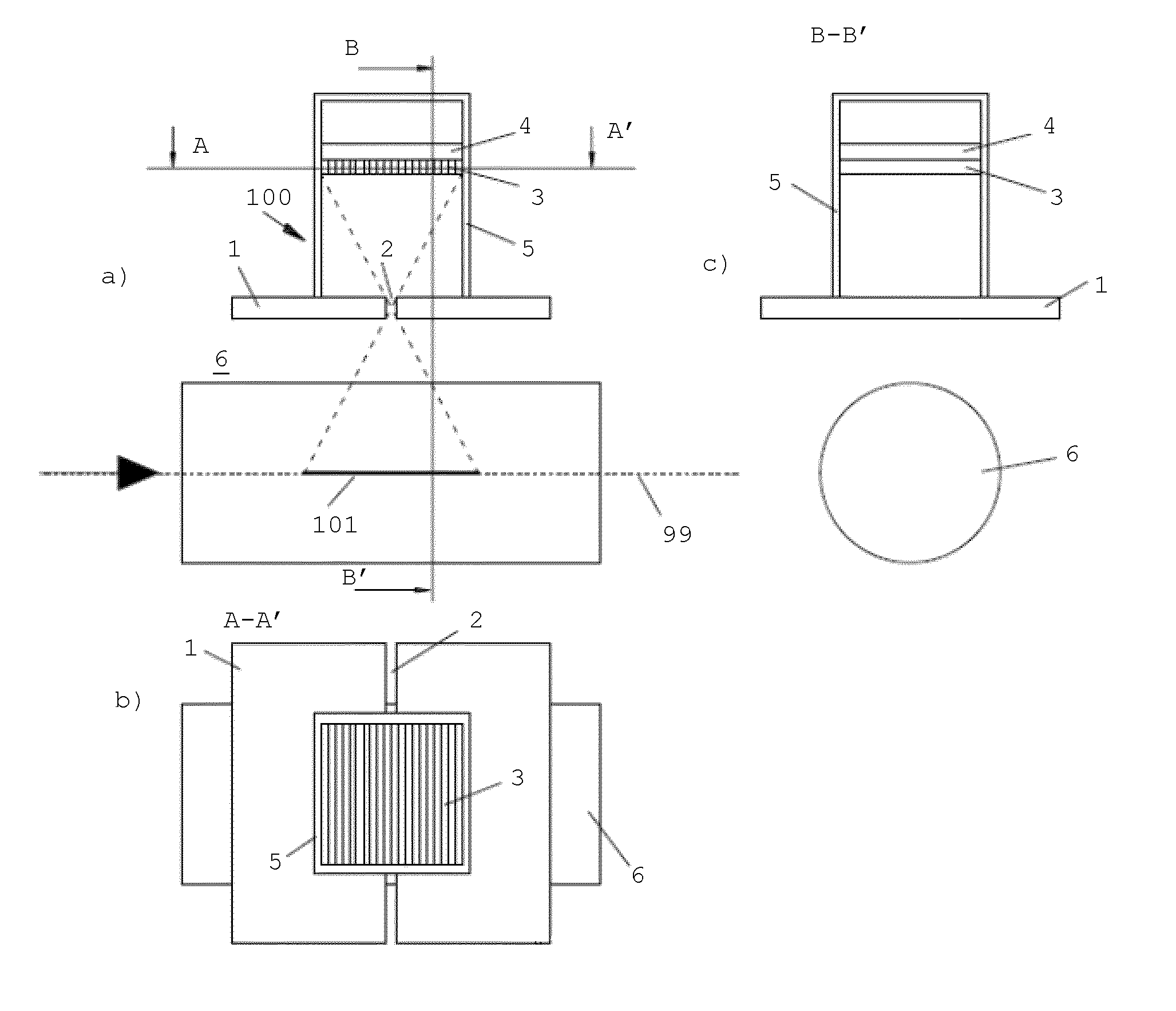
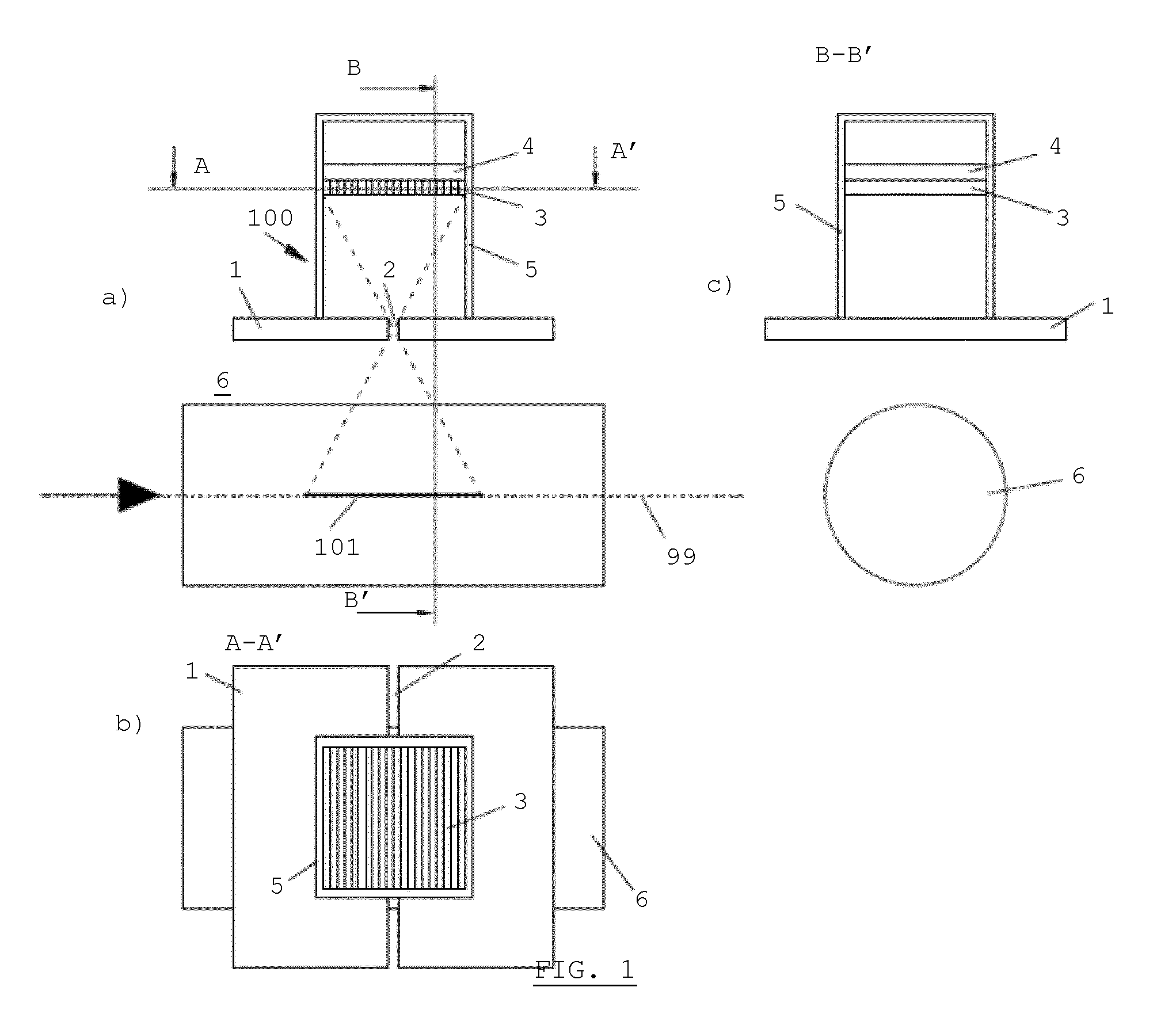
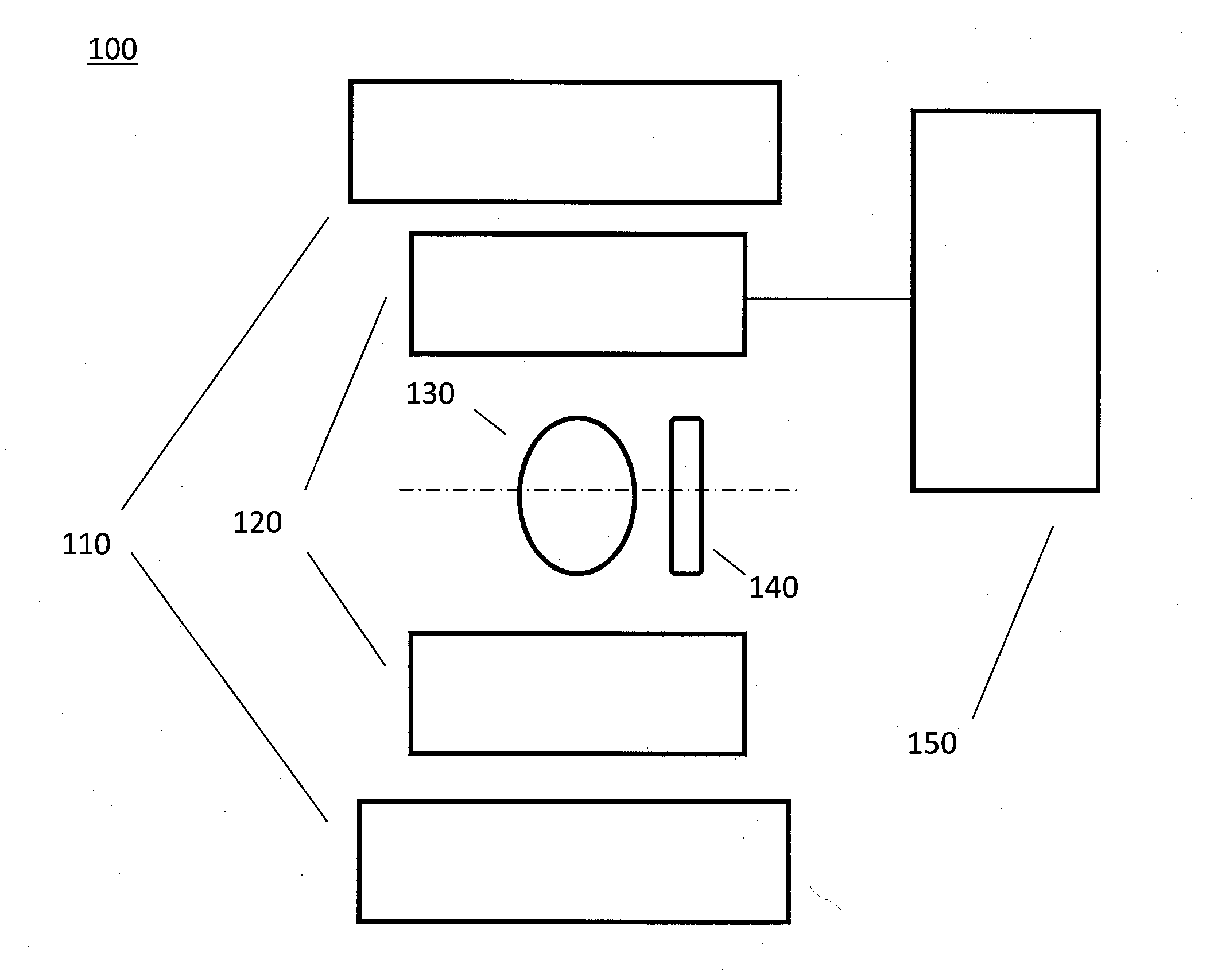
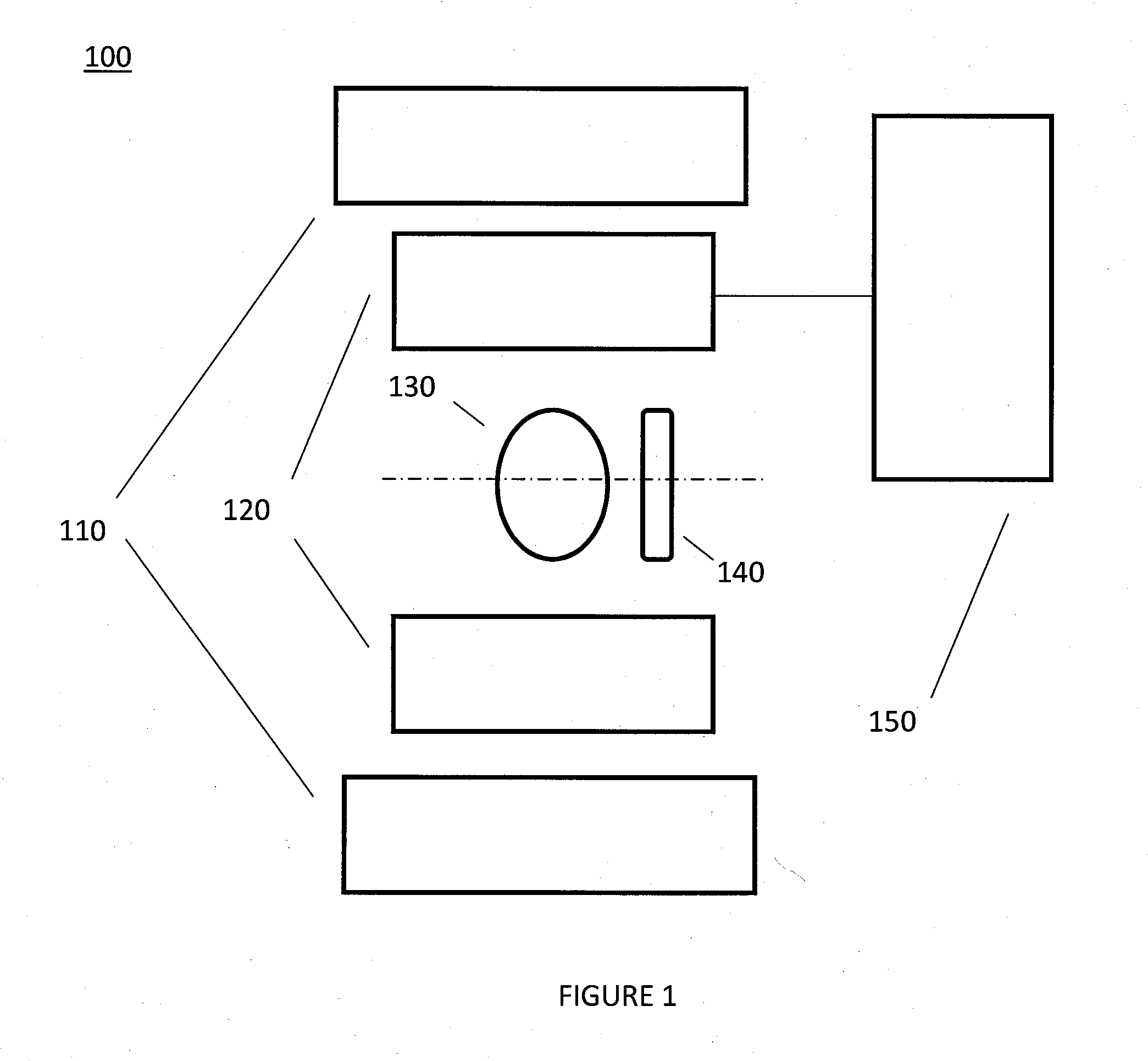
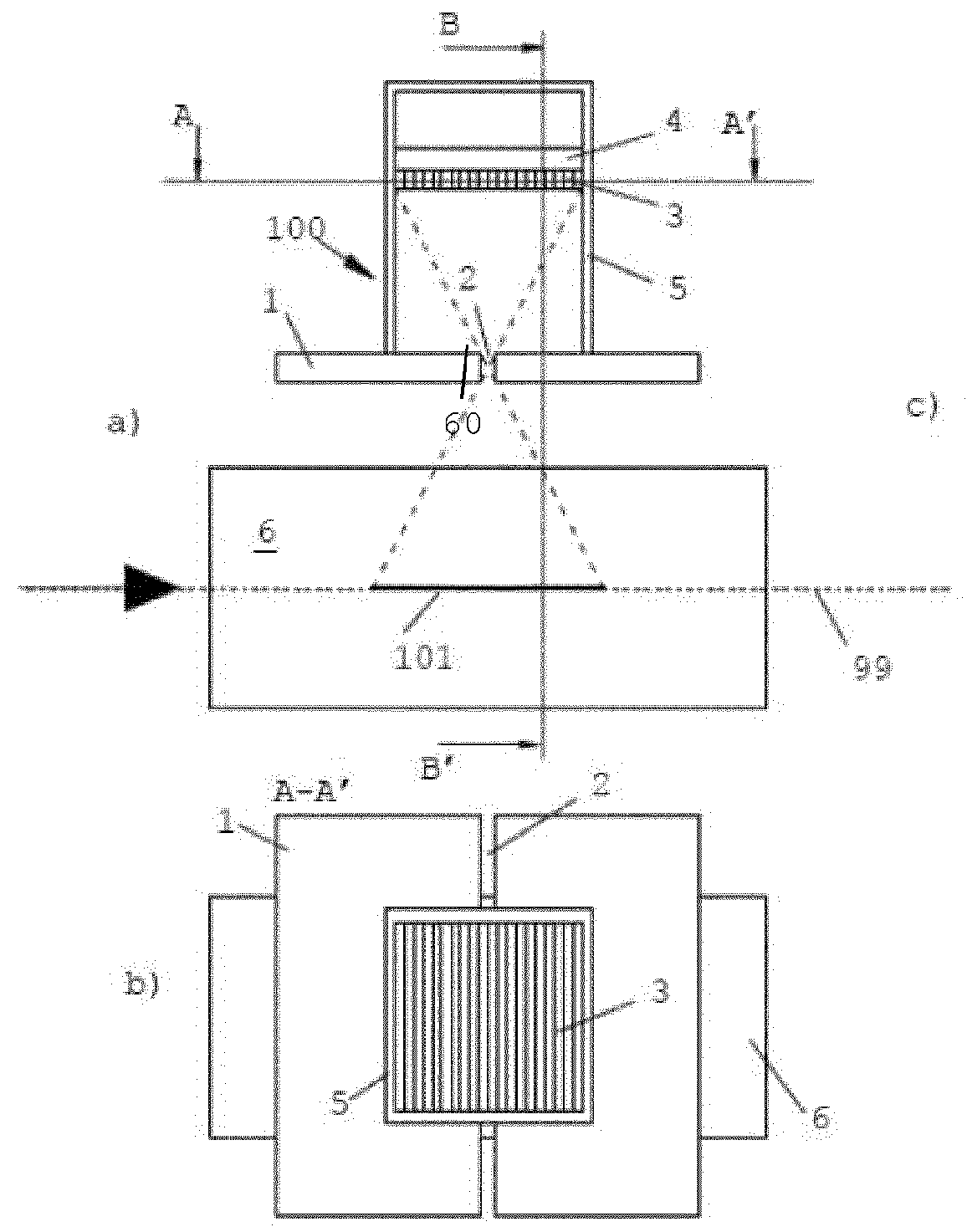
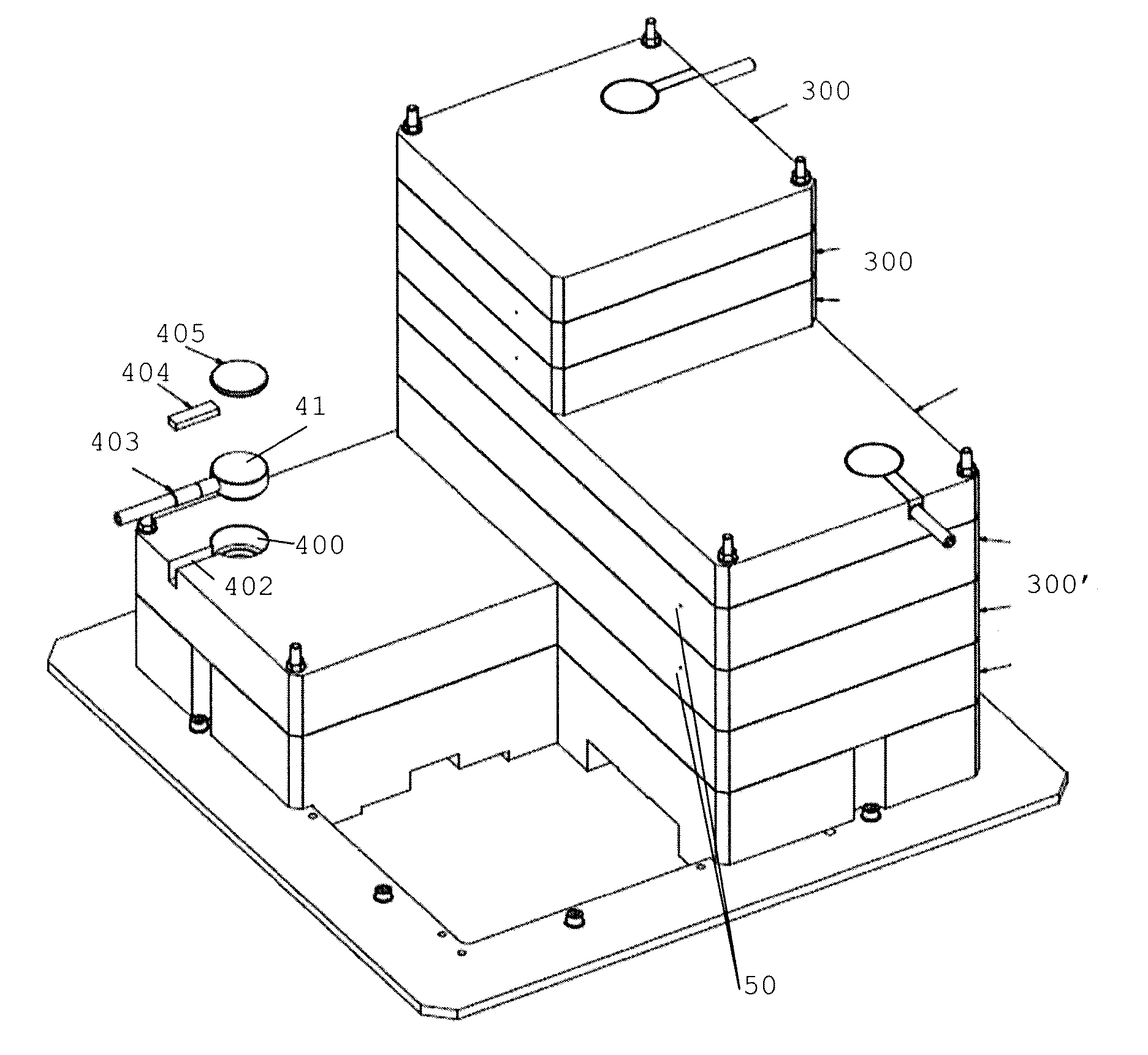
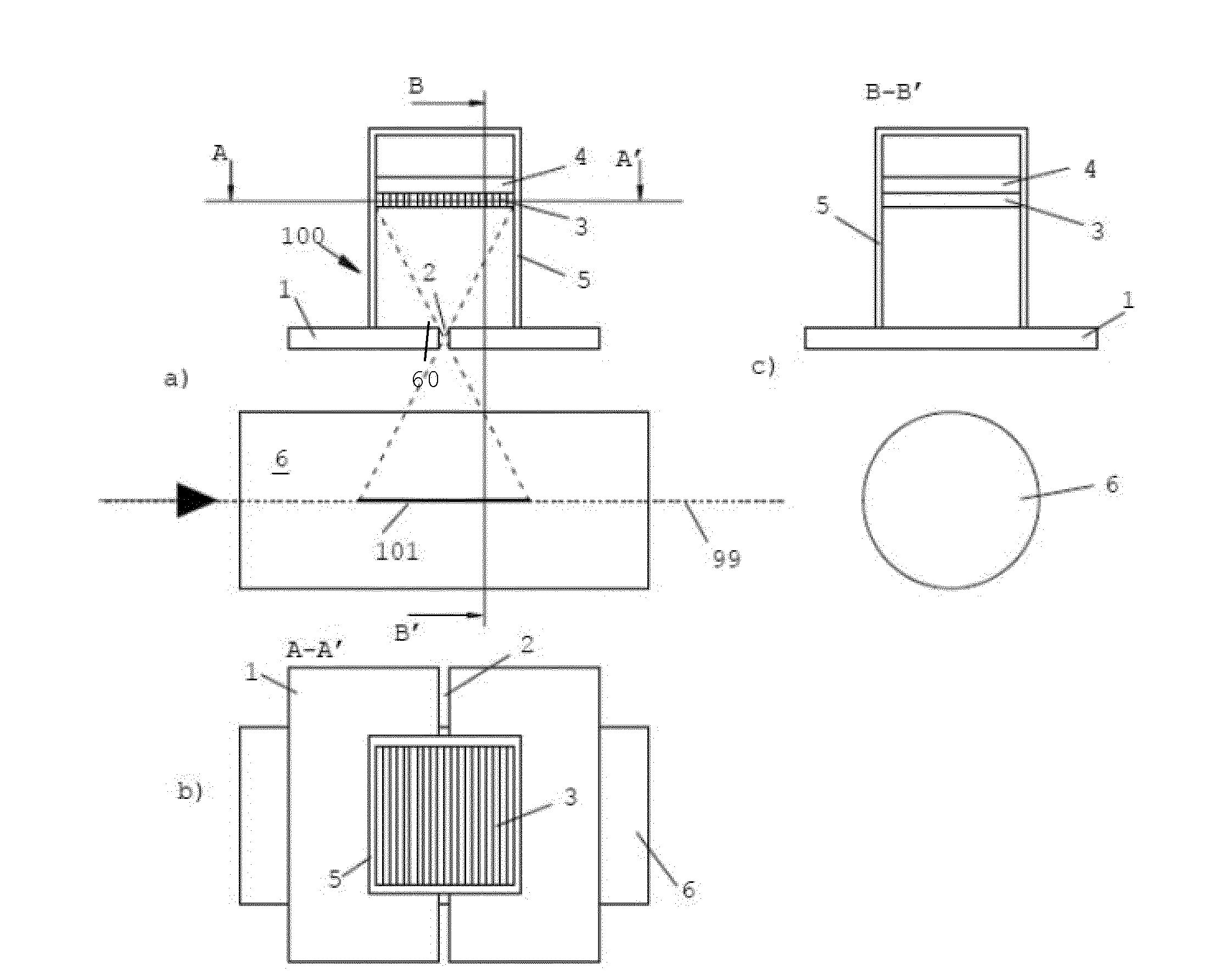
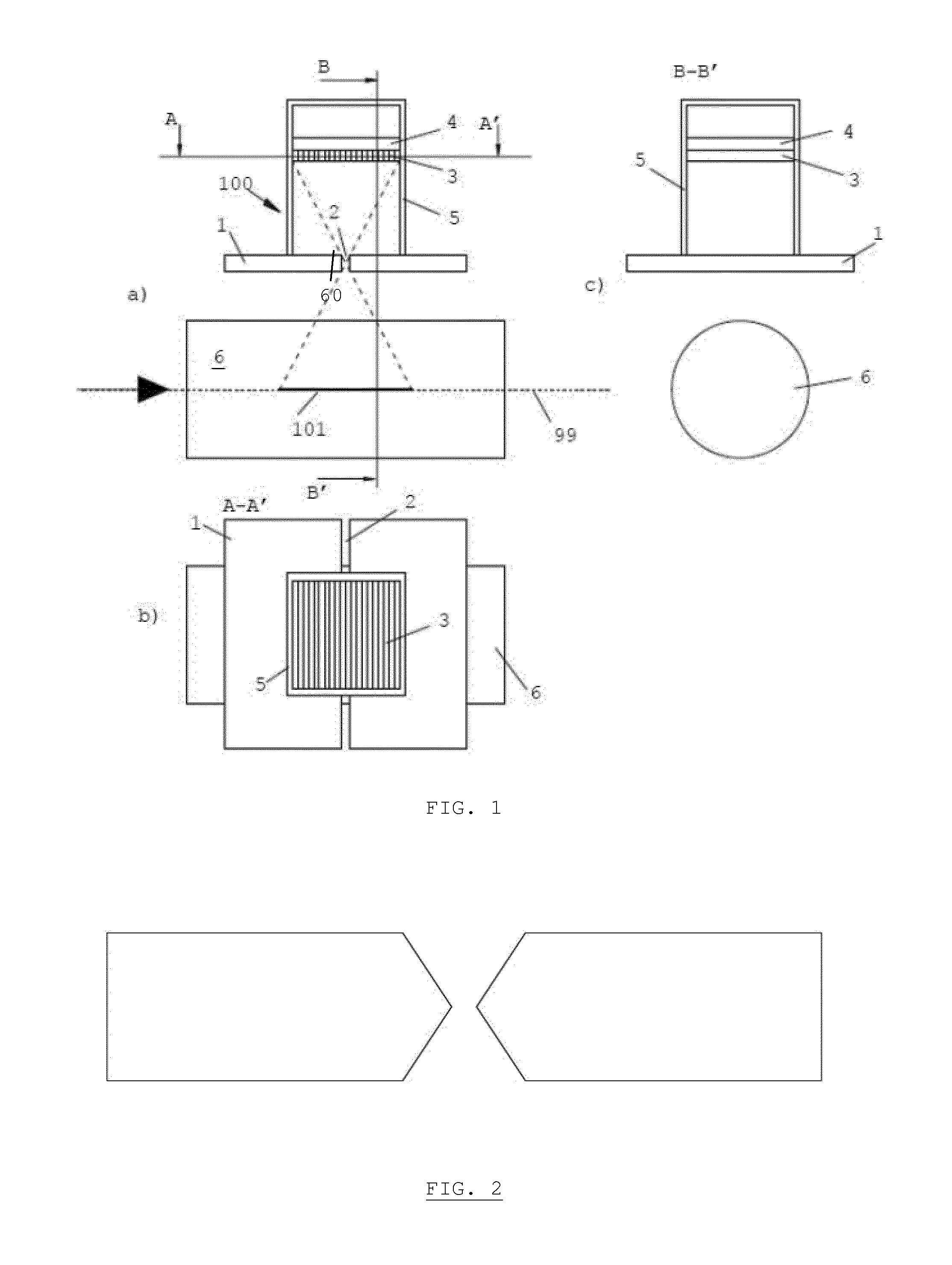
The invention is related to an apparatus and method for charged hadron therapy verification by detecting and / or quantifying prompt gammas produced when irradiating a target (6) with a charged hadron beam. The apparatus comprises a collimator (1) provided with a slit-shaped portion (2) configured to be arranged perpendicularly to the beam line and facing the target, a detection means (3,4) suitable for detecting said prompt gammas and a calculation and representation means. In the apparatus and method of the invention, the slit is configured to allow the passage of prompt gammas emitted from a range of depths in said target (6), said depths being measured in the direction of the charged hadron beam. Furthermore, said detection means is configured to detect prompt gammas emitted from each location within said range, and said calculation and representation means is configured to derive from a detected prompt gamma a value representative of the dose at the location from where said prompt gamma is emitted, and to represent a dose-related distribution for a plurality of locations within said range.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL +1
Hadron treatment planning with adequate biological weighting
ActiveUS20070228305A1Optimal biological effectivenessRadiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsDiseaseBragg peak
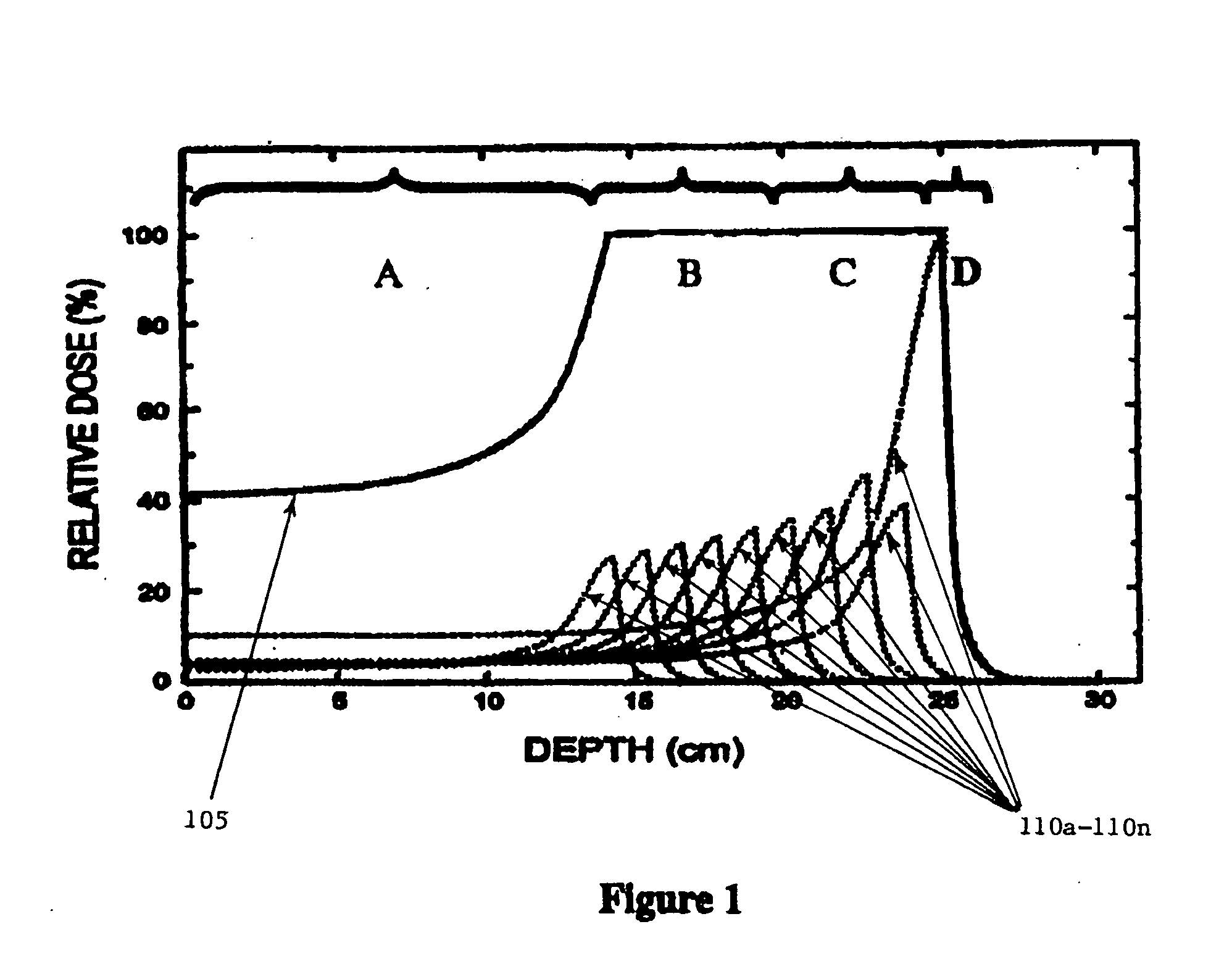
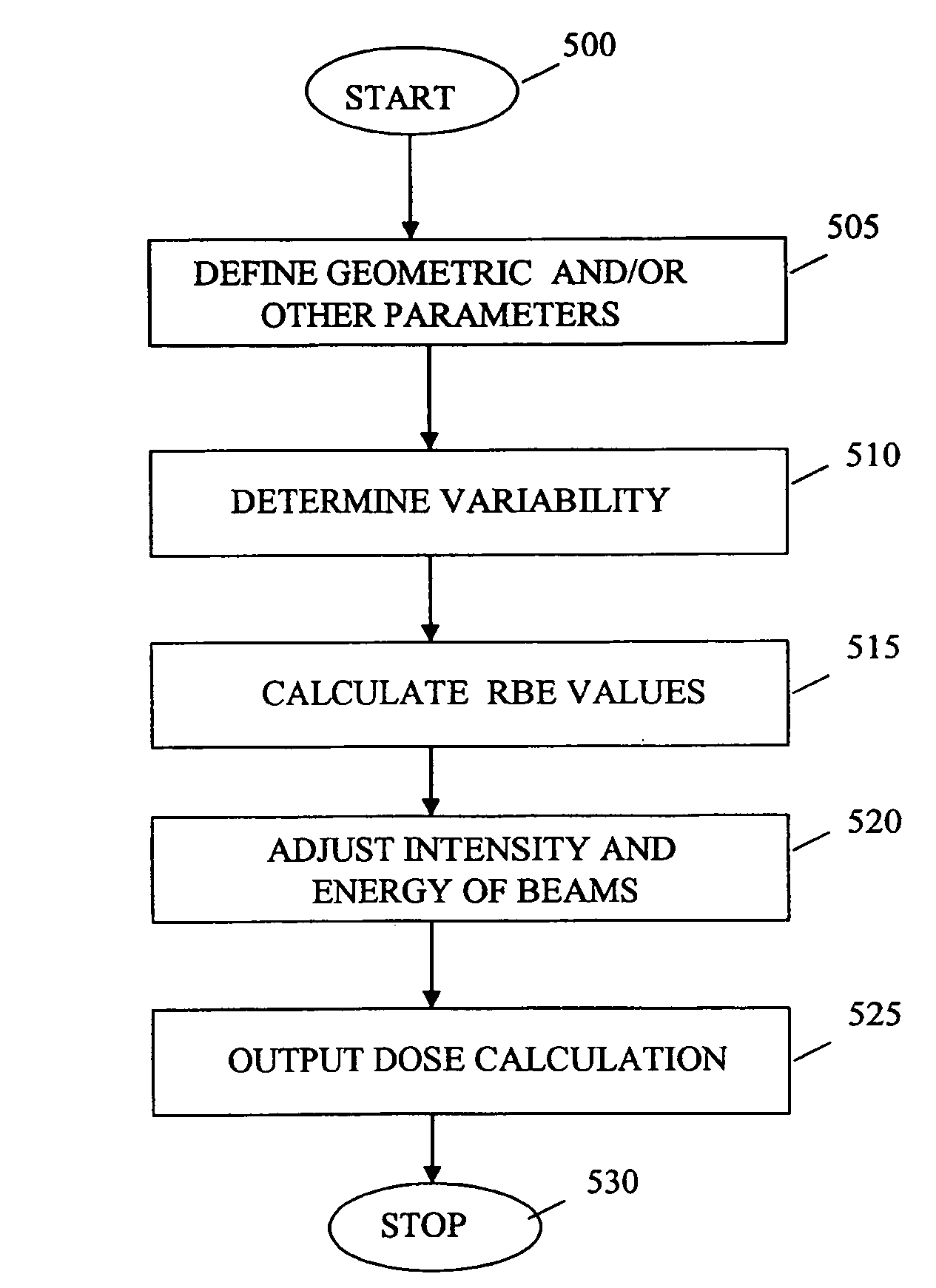
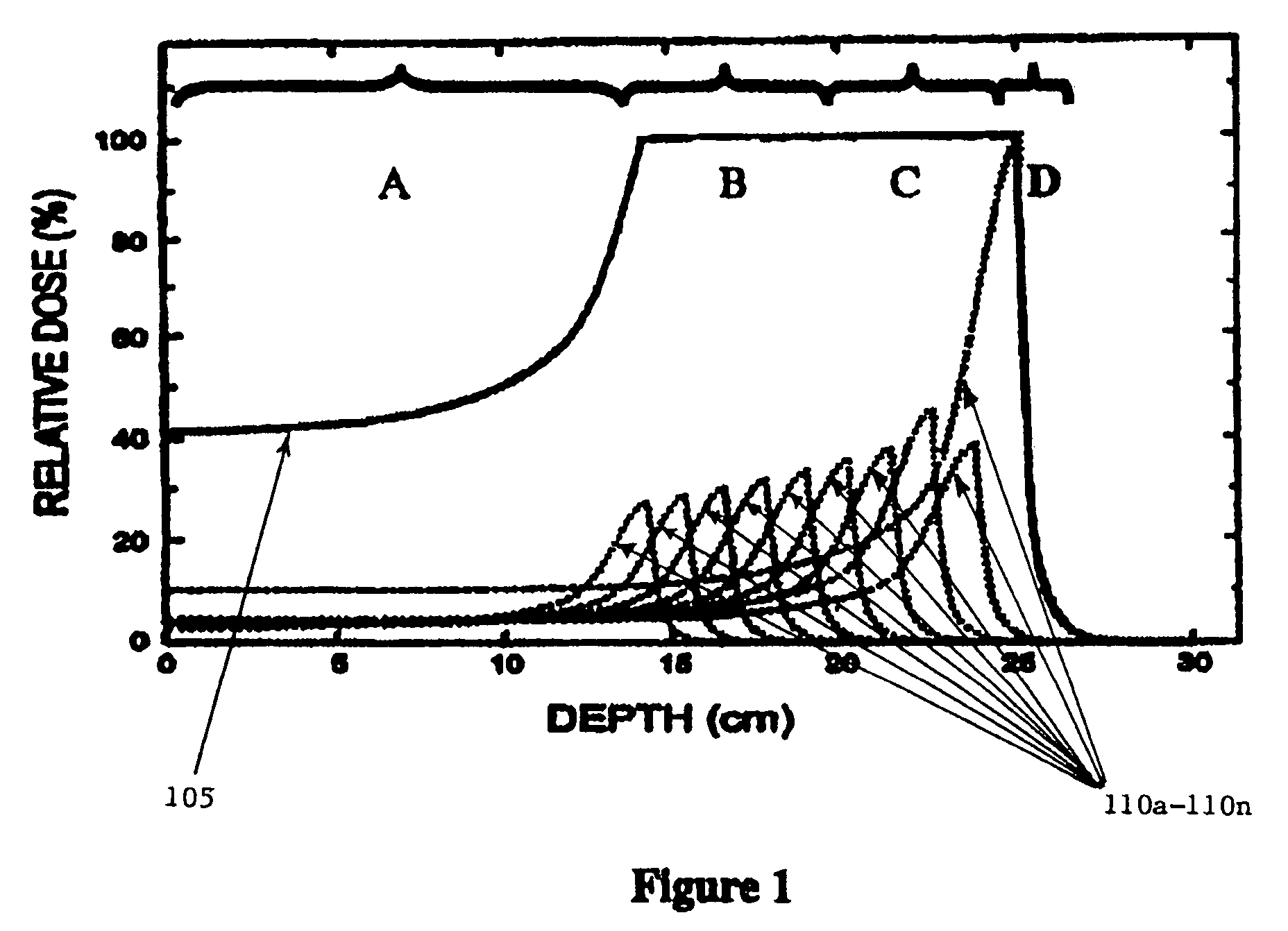
Treatment planning methods are provided that determine the variability of relative biological effectiveness (RBE) along a beam line and calculate, among other things, what intensity of hadron beam such as a proton or a carbon ion beam should be applied to achieve a desired biological dose at treatment site of a patient afflicted with a medical condition. Typically, three or four RBE values at three or four corresponding spacially-dispersed intervals along the beam line are calculated. In one embodiment, two RBE values for the spread-out Bragg peak (SOBP) region of the treatment site; one for the proximal section and one for the declining distal section is calculated. A third and different RBE value may be determined for the distal edge region of the SOBP. A fourth value may also be calculated for a pre-SOBP region.
Owner:HAMPTON UNIVERSITY
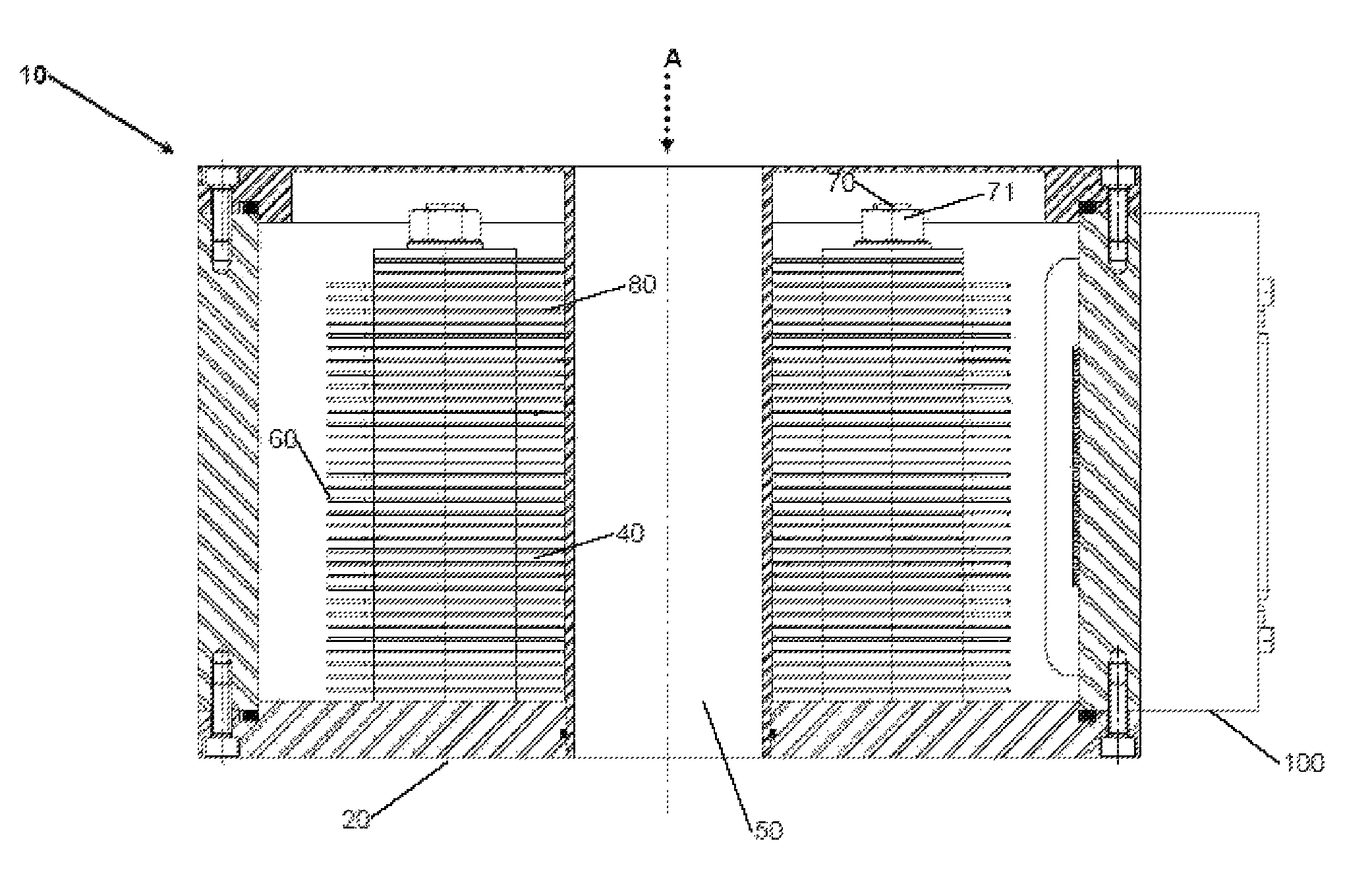
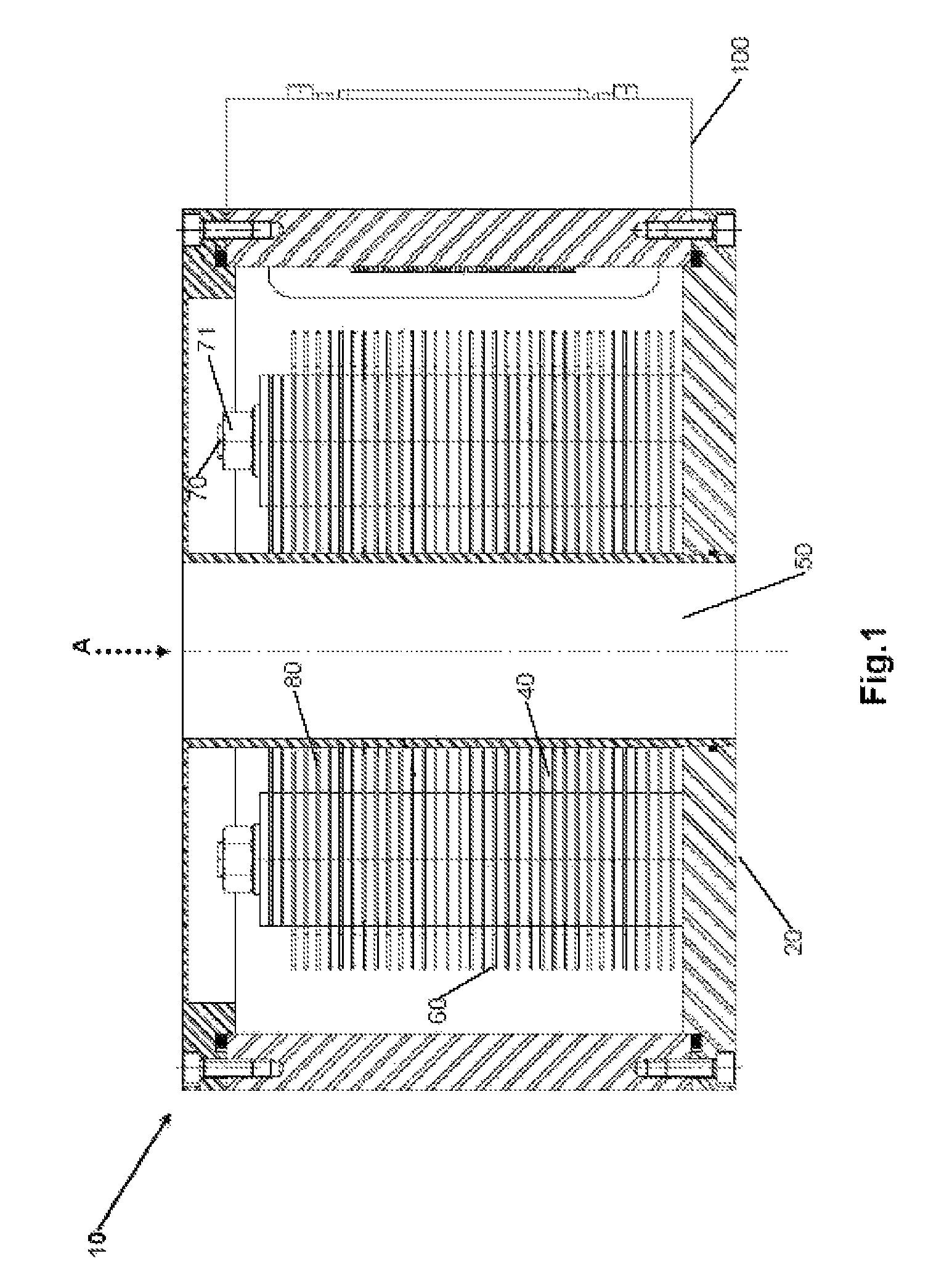
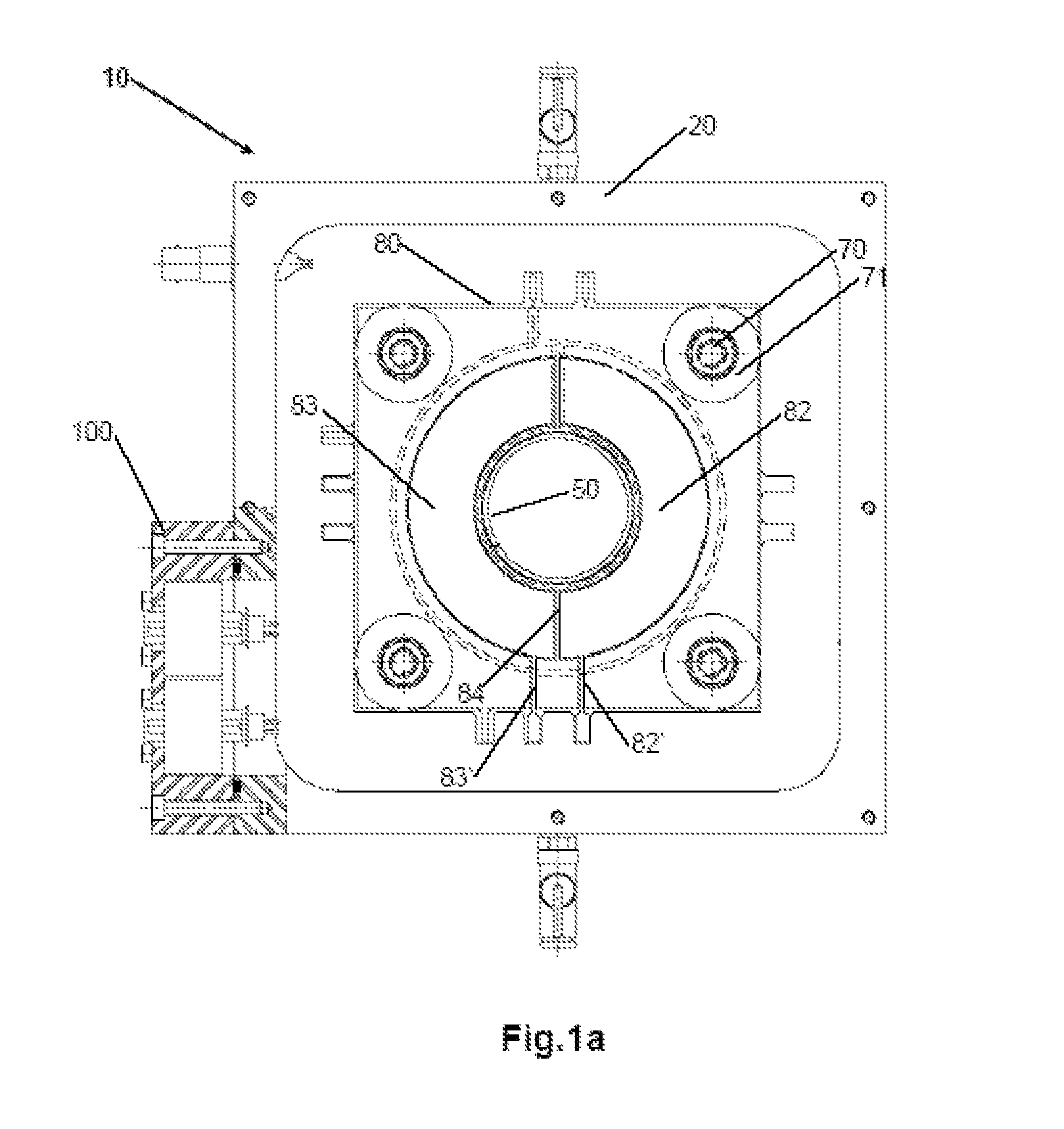
Device And Method For Monitoring A Hadron Beam
ActiveUS20120104270A1Reduce radiationElectric discharge tubesDosimetersIonization chamberEngineering
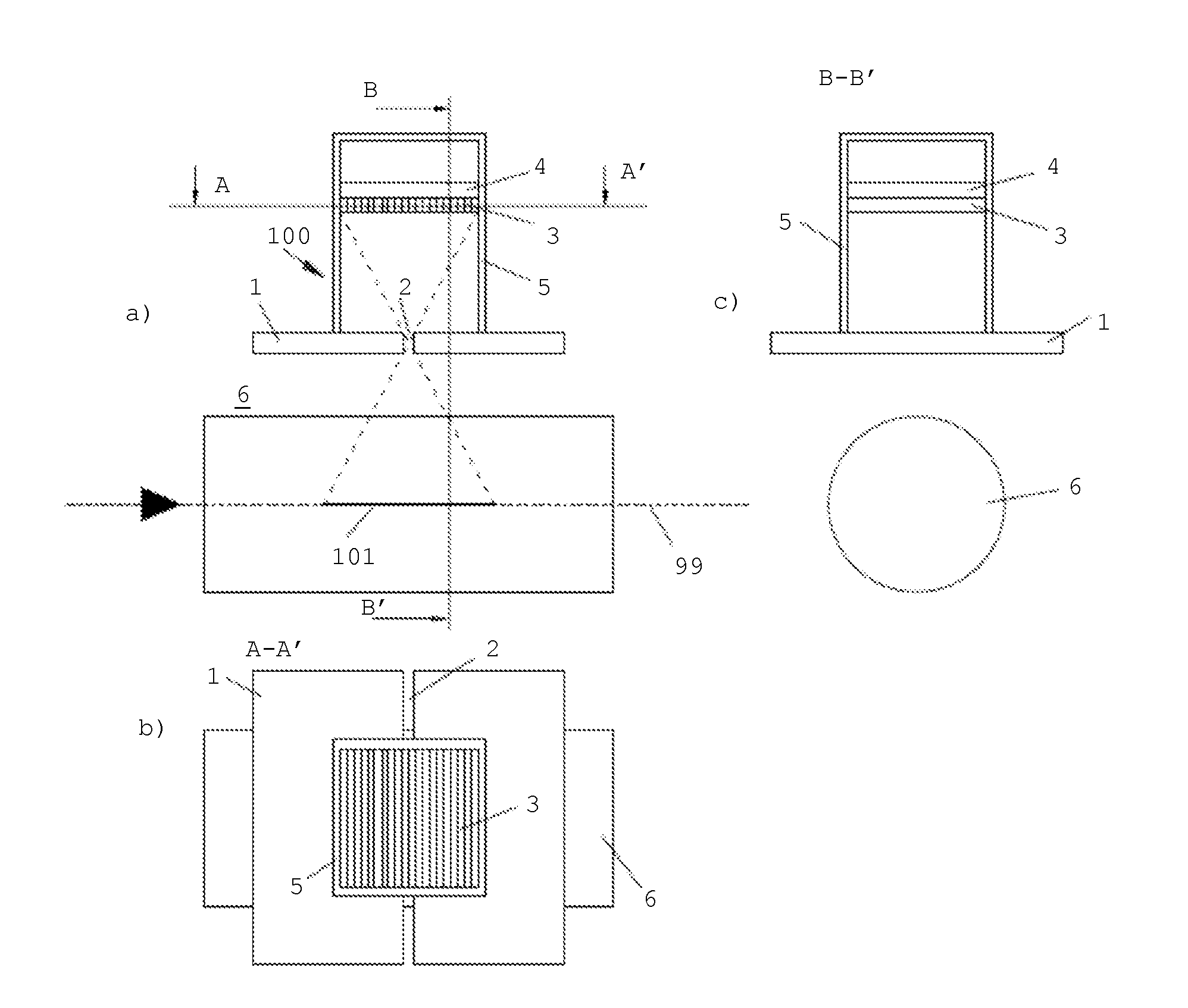
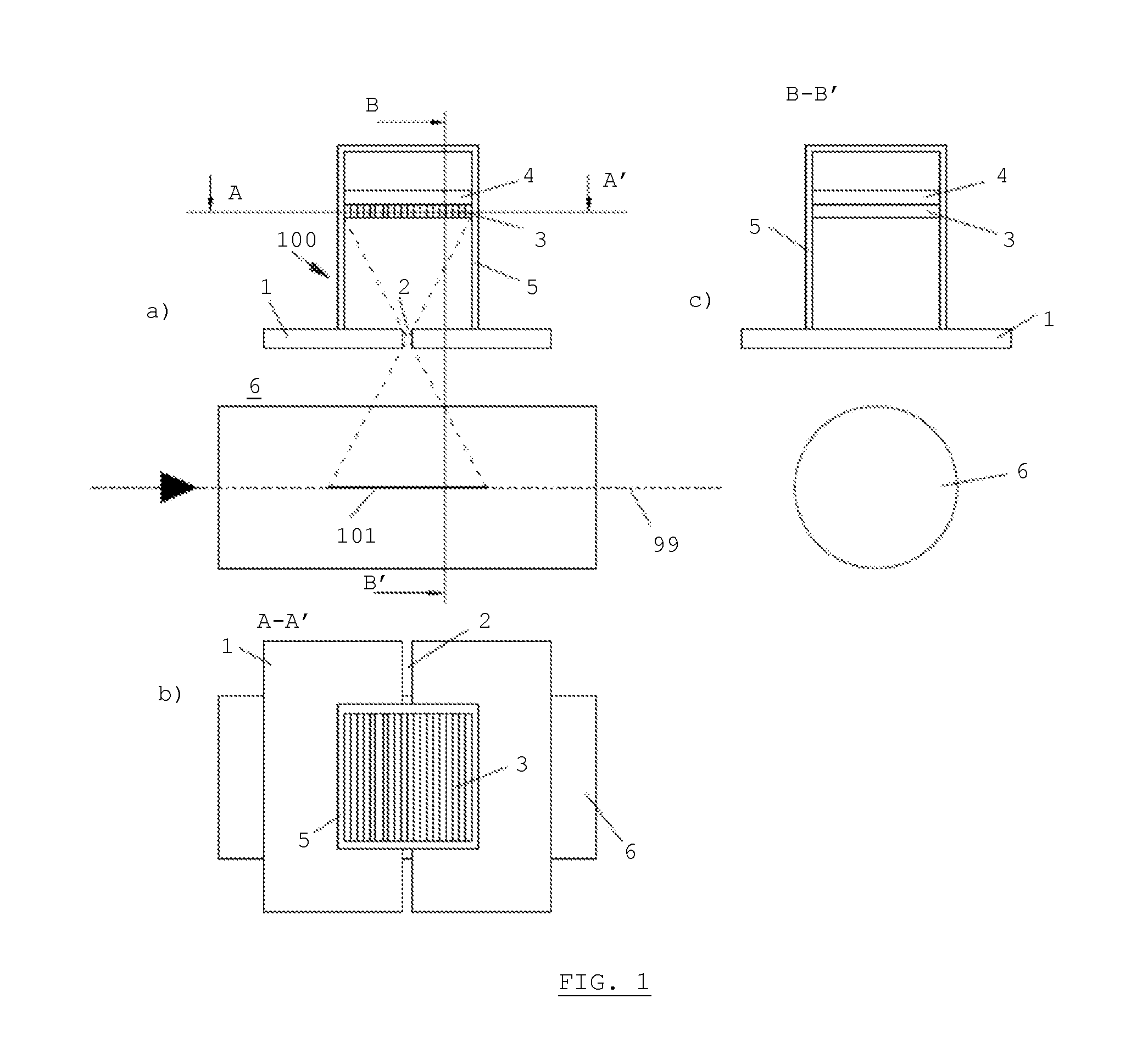
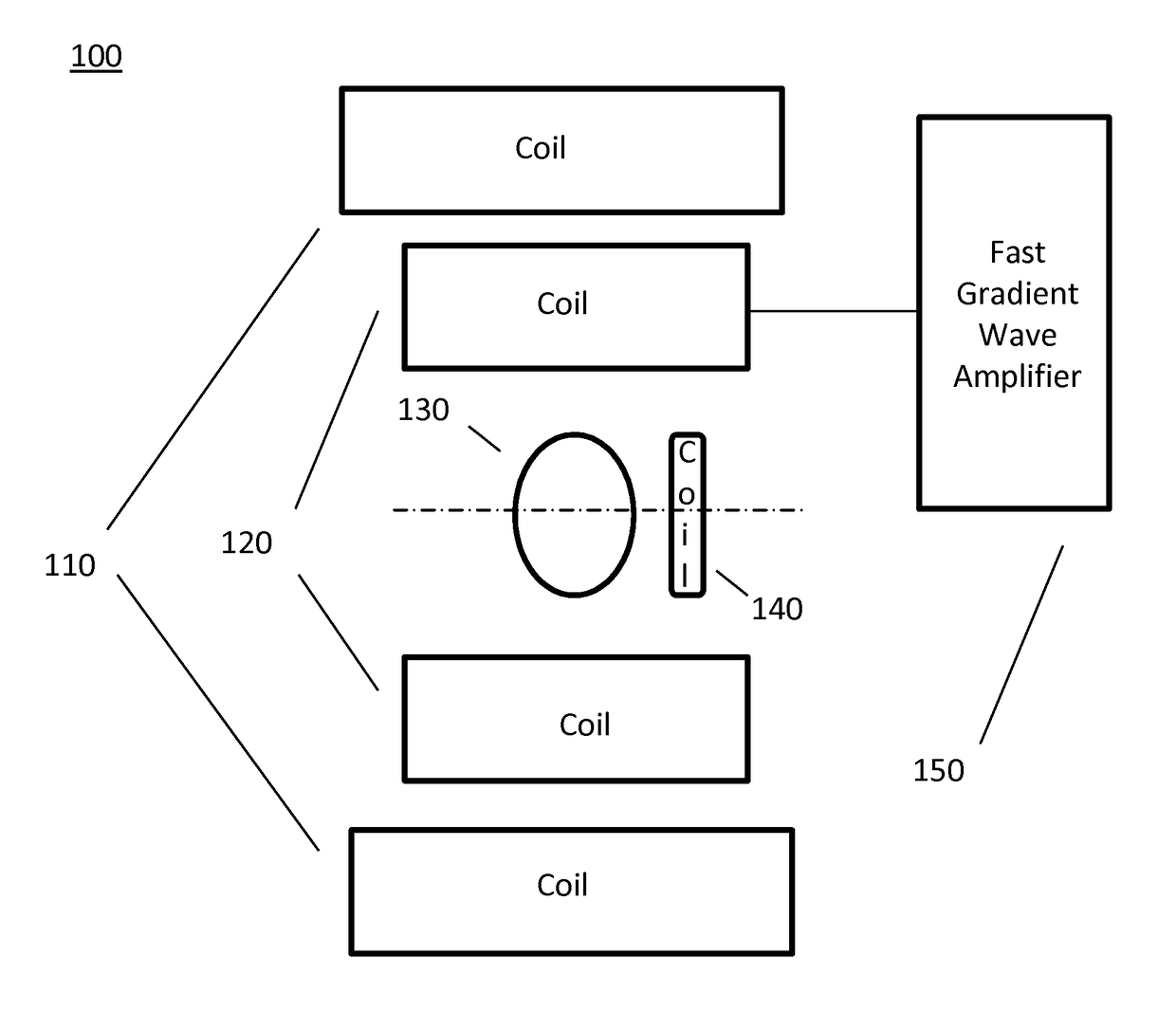
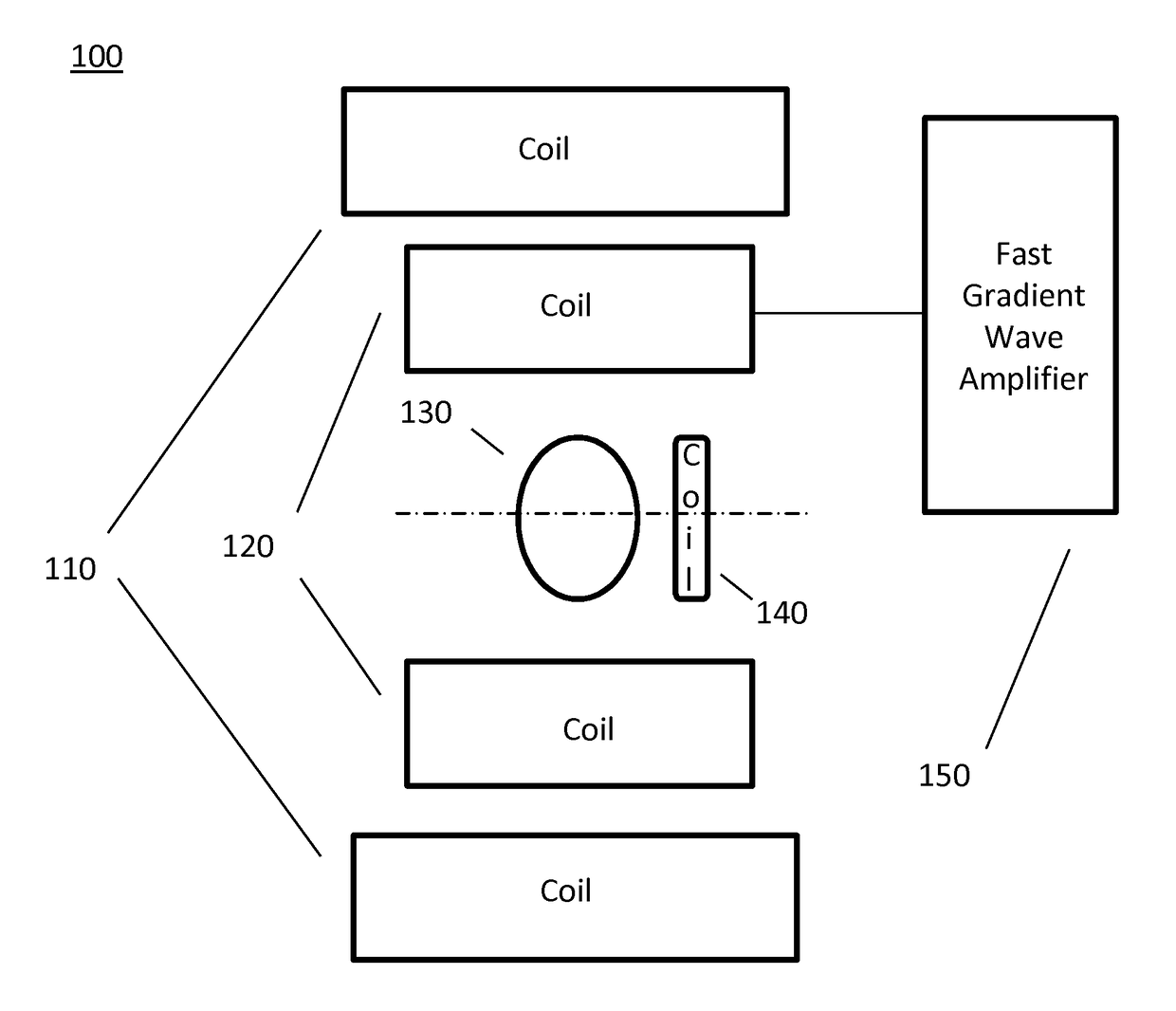
The present invention relates to a device for dosimetry monitoring of a hadron beam, comprising n successive ionization chambers i obtained by a serie or stack of n+1 parallel detector plates separated from each other by a gas filled gap, each detector plates having a collecting part comprising a collecting side insulated from a bias voltage part comprising a bias voltage side and ranged in a such way that the said collecting side is facing the said bias voltage side of a subsequent detector plate or inversely, each detector plate comprising m layers Lk of materials, the resulting assembly of these detector plates forming a plurality of ionization chamber cells, characterised in that: the thicknesses Ik and the choice of the materials of each layer Lk constituting each detector plate as well as the gap of an ionization chamber cell i have been selected in order to satisfy the equation (I) for each ionization chamber i, where lgi is the gas filled gap distance between two detector plates; Ik is the thickness of the corresponding layer Lk of a detector plate and; WETk is the water equivalent thickness (WET) of the corresponding layer Lk of a detector plate.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Ultra-fast magnetic field for electron paramagnetic resonance imaging used in monitoring dose from proton or hadron therapy
ActiveUS20120326722A1Measurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceElectric/magnetic detectionMedicineUltra fast
Owner:WEINBERG MEDICAL PHYSICS
Apparatus for particle therapy verification
The invention is related to an apparatus and method for charged hadron therapy verification by detecting and / or quantifying prompt gammas produced when irradiating a target (6) with a charged hadron beam. The apparatus comprises a collimator (1) provided with a slit-shaped portion (2) configured to be arranged perpendicularly to the beam line and facing the target, a detection means (3,4) suitable for detecting said prompt gammas and a calculation and representation means. In the apparatus and method of the invention, the slit is configured to allow the passage of prompt gammas emitted from a range of depths in said target (6), said depths being measured in the direction of the charged hadron beam. Furthermore, said detection means is configured to detect prompt gammas emitted from each location within said range, and said calculation and representation means is configured to derive from a detected prompt gamma a value representative of the dose at the location from where said prompt gamma is emitted, and to represent a dose-related distribution for a plurality of locations within said range.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL +1
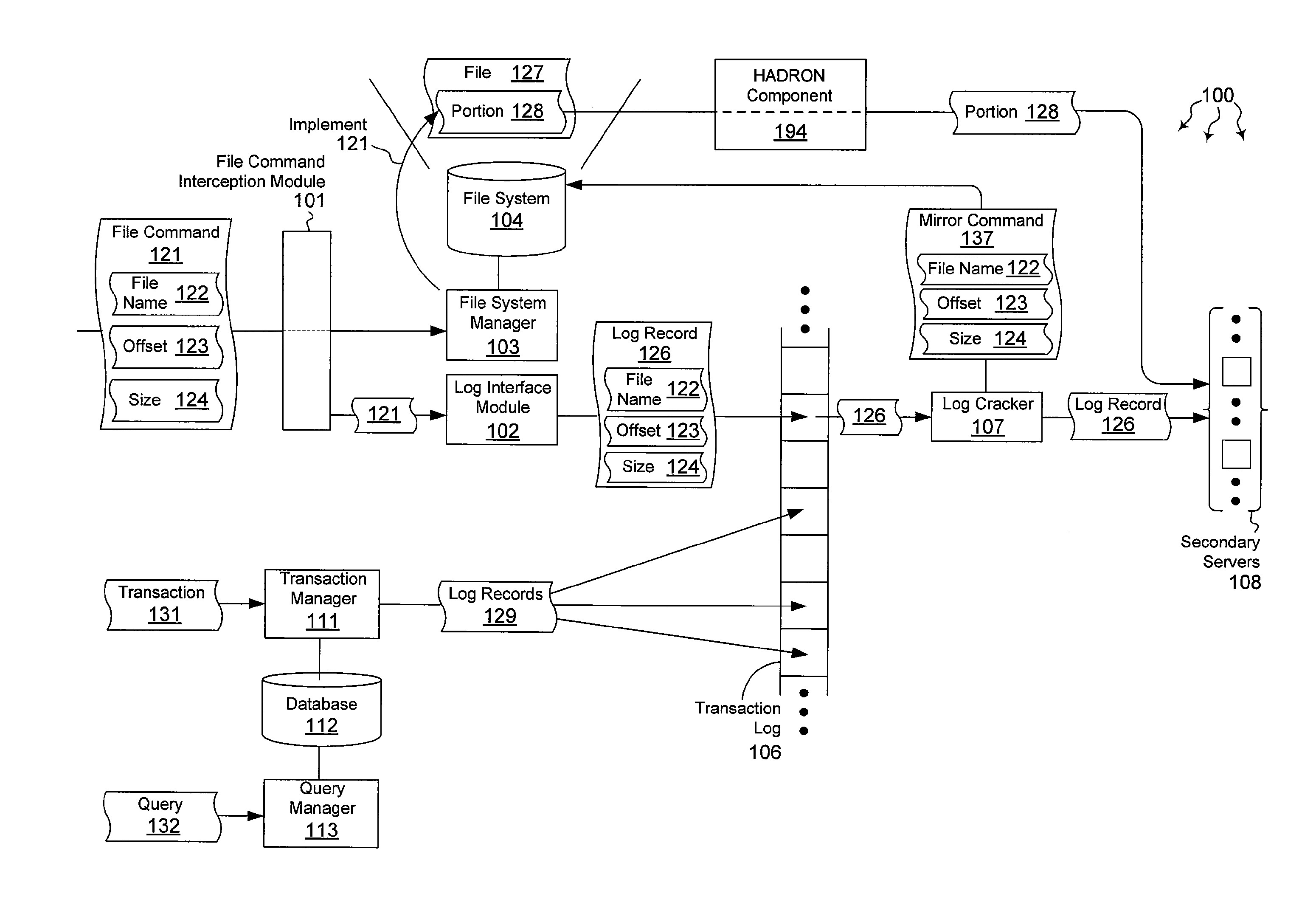
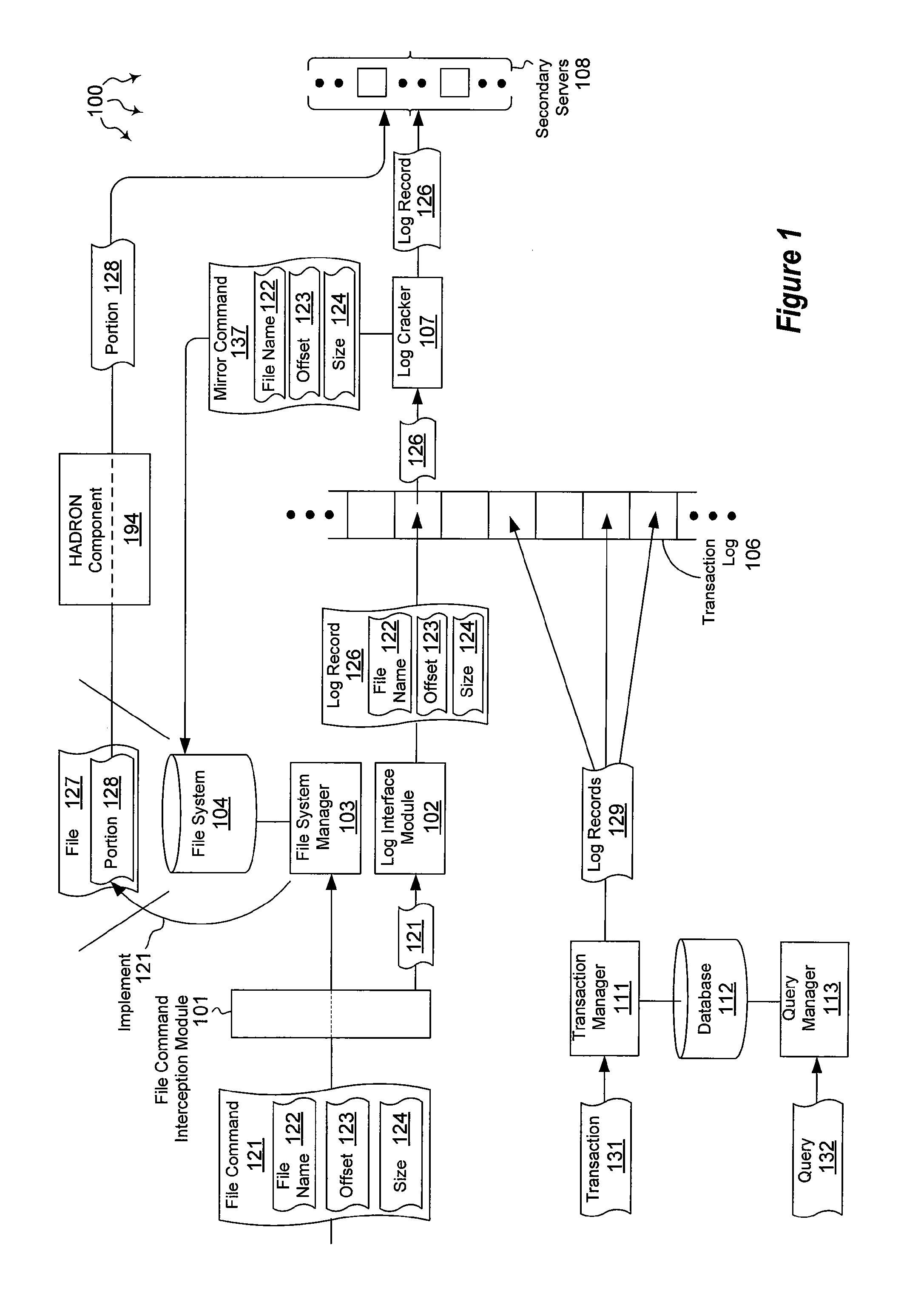
Mirroring file data
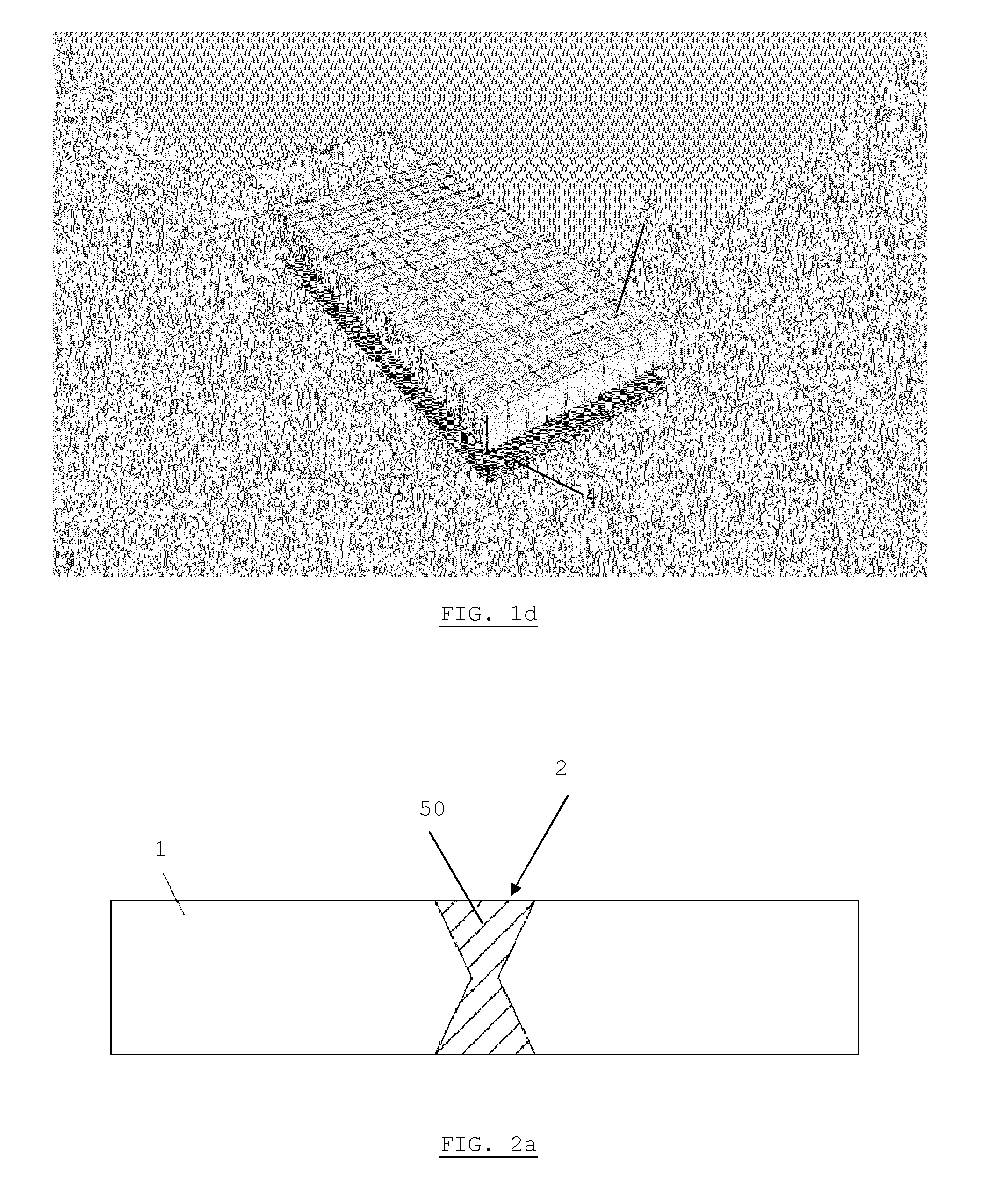
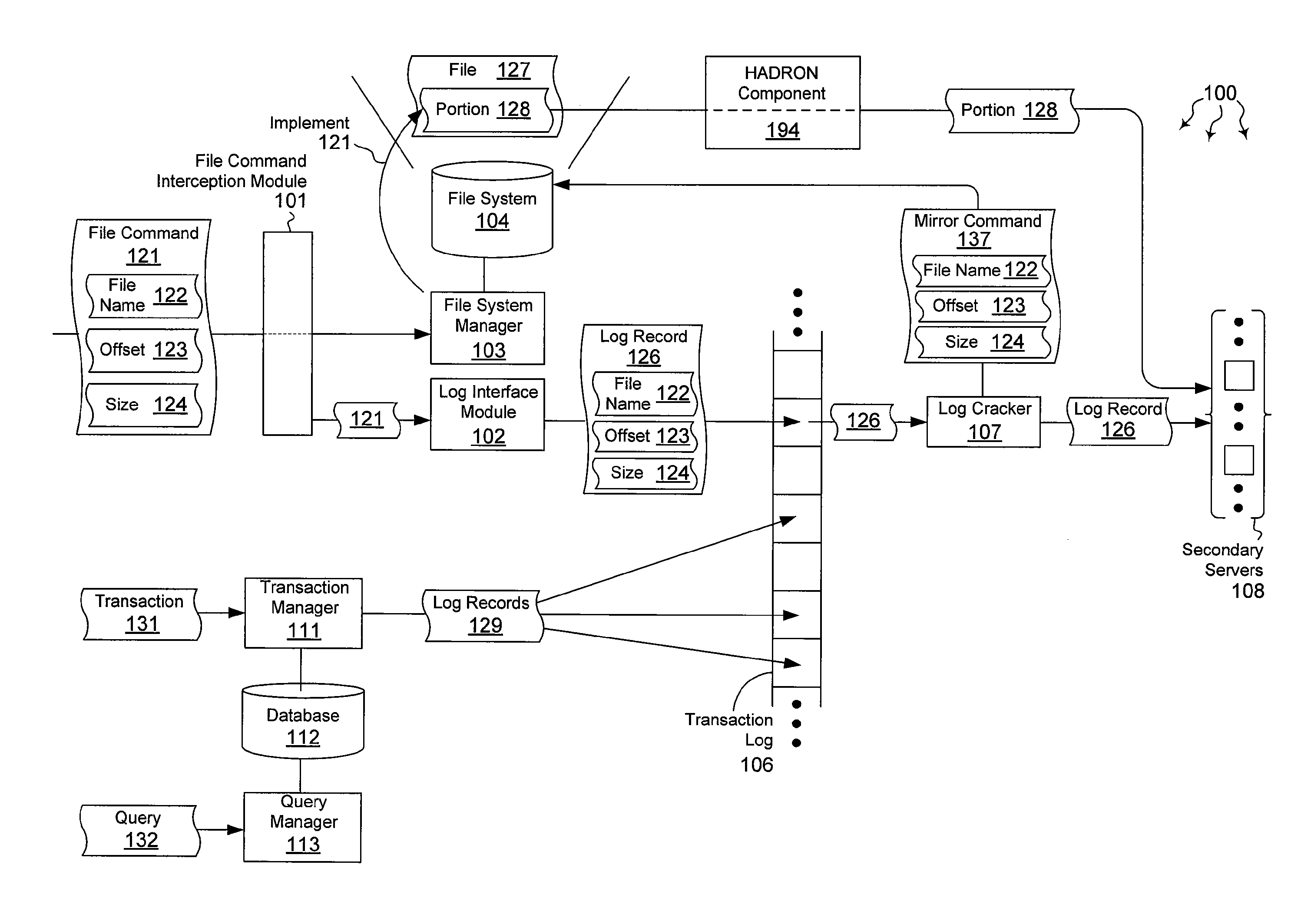
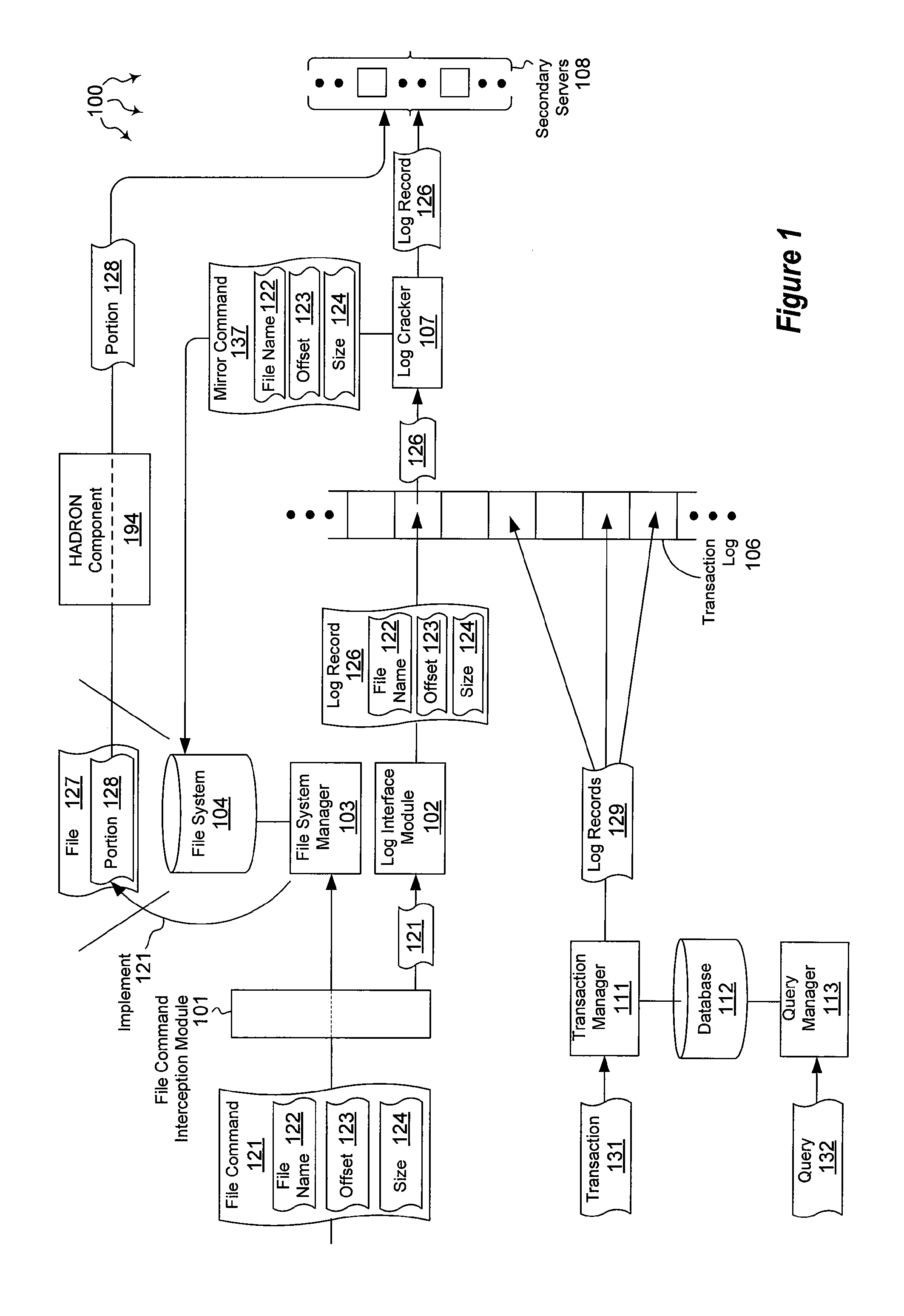
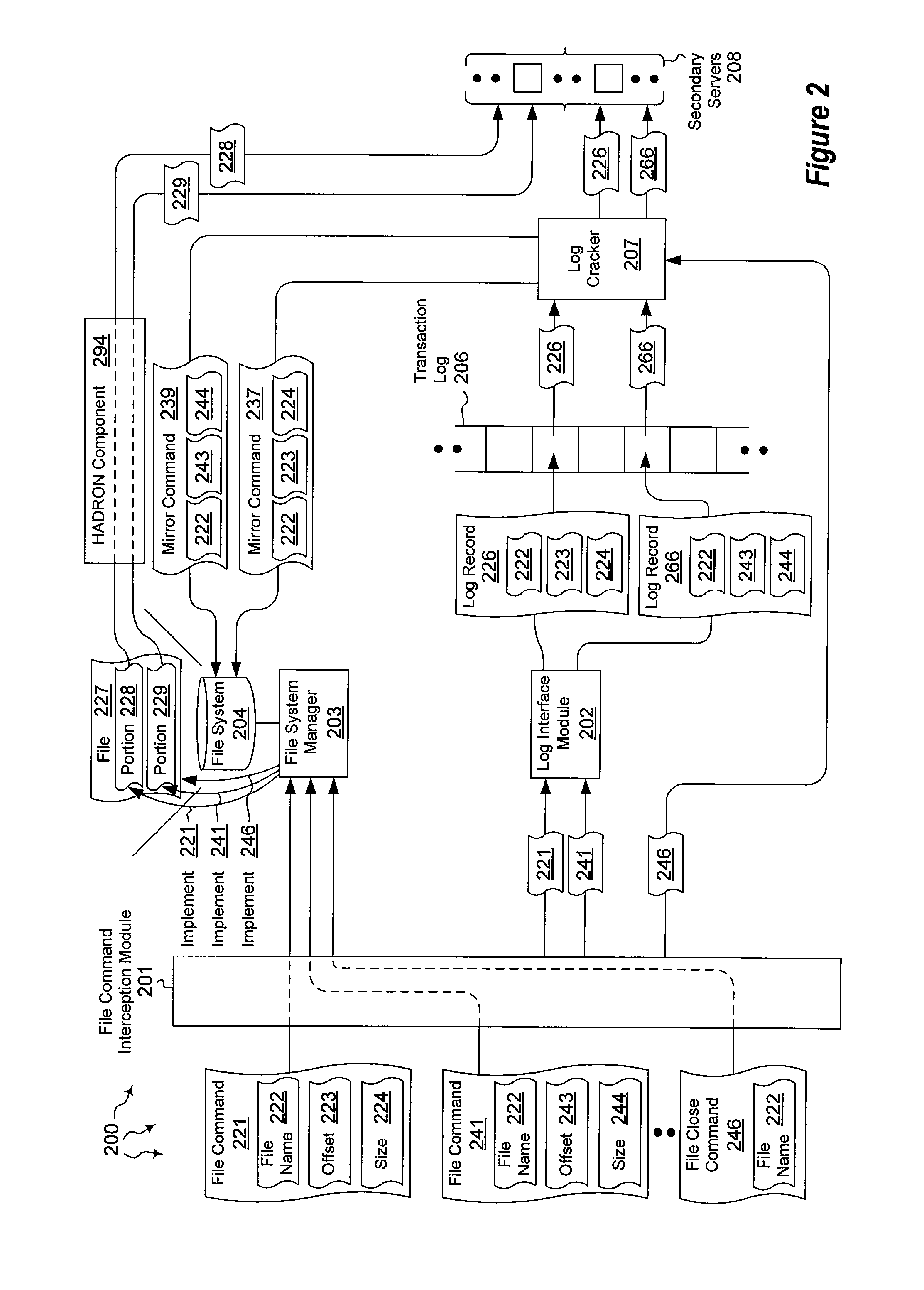
ActiveUS20120059798A1Well formedDigital data information retrievalMemory loss protectionHigh availabilityMirror image
The present invention extends to methods, systems, and computer program products for mirroring file data. Generally, high availability and disaster recovery (“HADRON”) is achieved within a database management system by detecting which parts of a file have changed and sending the changed parts to secondaries. Adjacent or partially overlapping parts of a file can coalesce to form larger chunks of changed data. Coalescing reduces the overall number of chunks that are tracked.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Shielding Device For An Irradiation Unit And Irradiation Method
InactiveUS20130043408A1Minimise any penumbraHandling using diaphragms/collimetersShieldingEngineeringIrradiation
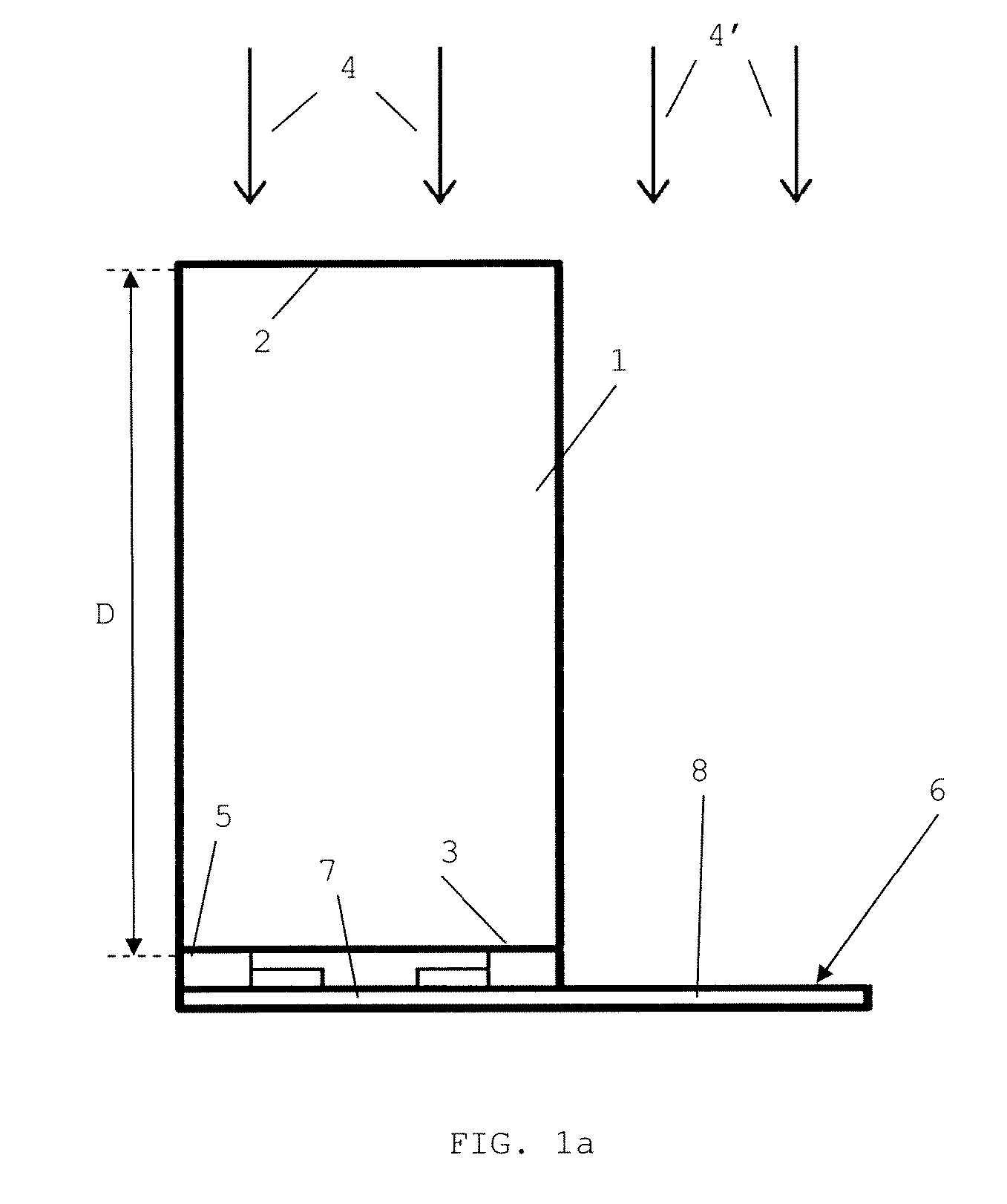
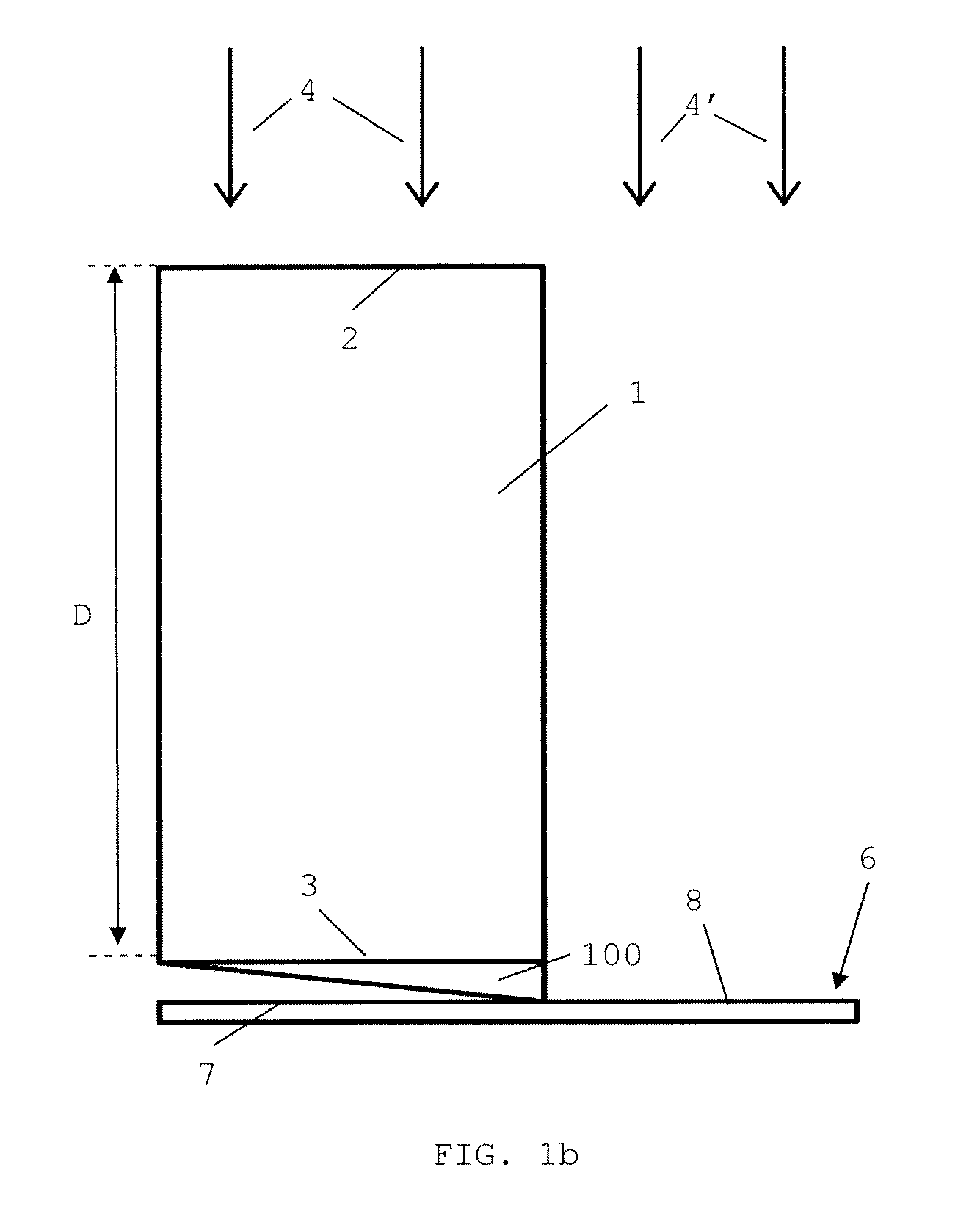
The present invention relates to a method for obtaining a shielding element for minimizing the penumbra of a beam of hadrons outside a target area, the hadron beam being guided in a longitudinal direction by an irradiation unit, and the beam having a width (σ). The method includes:(i) defining a closed or open contour of said target area;(ii) providing a block having a longitudinal thickness capable of blocking the passage of said beam and having a lateral surface perpendicular to said longitudinal thickness;(iii) forming an aperture of a shape similar to said contour and crossing said longitudinal thickness of said block for letting through said beam, said aperture forming a longitudinal internal surface; and(iv) trimming said block so as to form a longitudinal external surface around said longitudinal internals surface, said longitudinal internal and longitudinal external surfaces delimiting a side wall.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Charged hadron beam delivery
ActiveUS20150094517A1Well methodImprove consistencyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsIrradiation devicesBeam scanningHadron therapy
A charged hadron therapy system for delivering charged hadron radiation to a target is provided. The system comprises a target positioning couch for supporting the target being moveable along a translation direction and a beam delivery system comprising a beam scanning means for scanning a hadron pencil beam over said target in a first scanning direction and a second scanning direction being substantially parallel with the translation direction. The beam scanning means is limited for providing a maximum scanning amplitude AY in the second scanning direction. The system comprises an irradiation controller configured for simultaneously and synchronously performing the moving of the couch and the scanning, so as to deliver charged hadron radiation to a target over a target size being larger in the Y direction than the maximum scanning amplitude AY.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
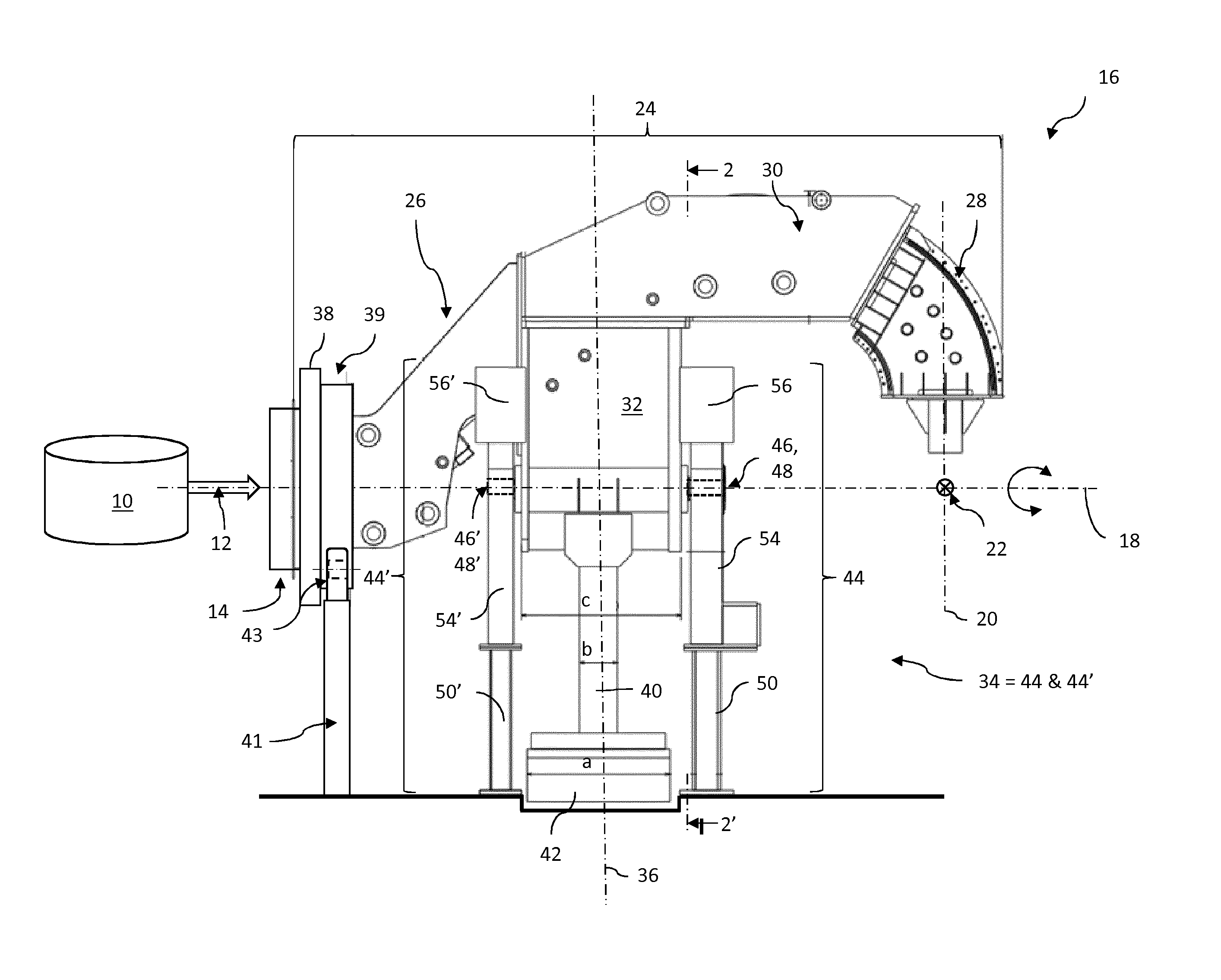
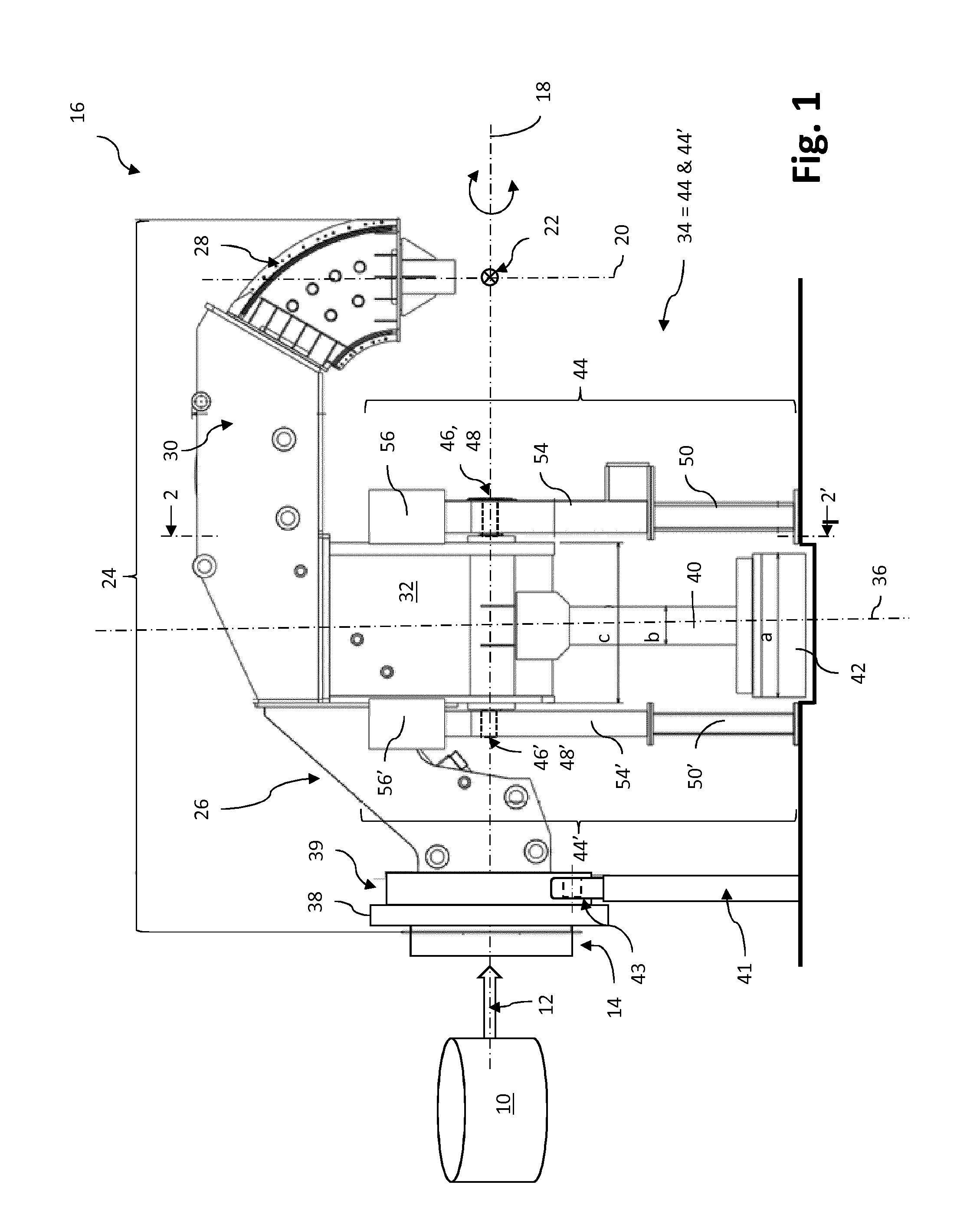
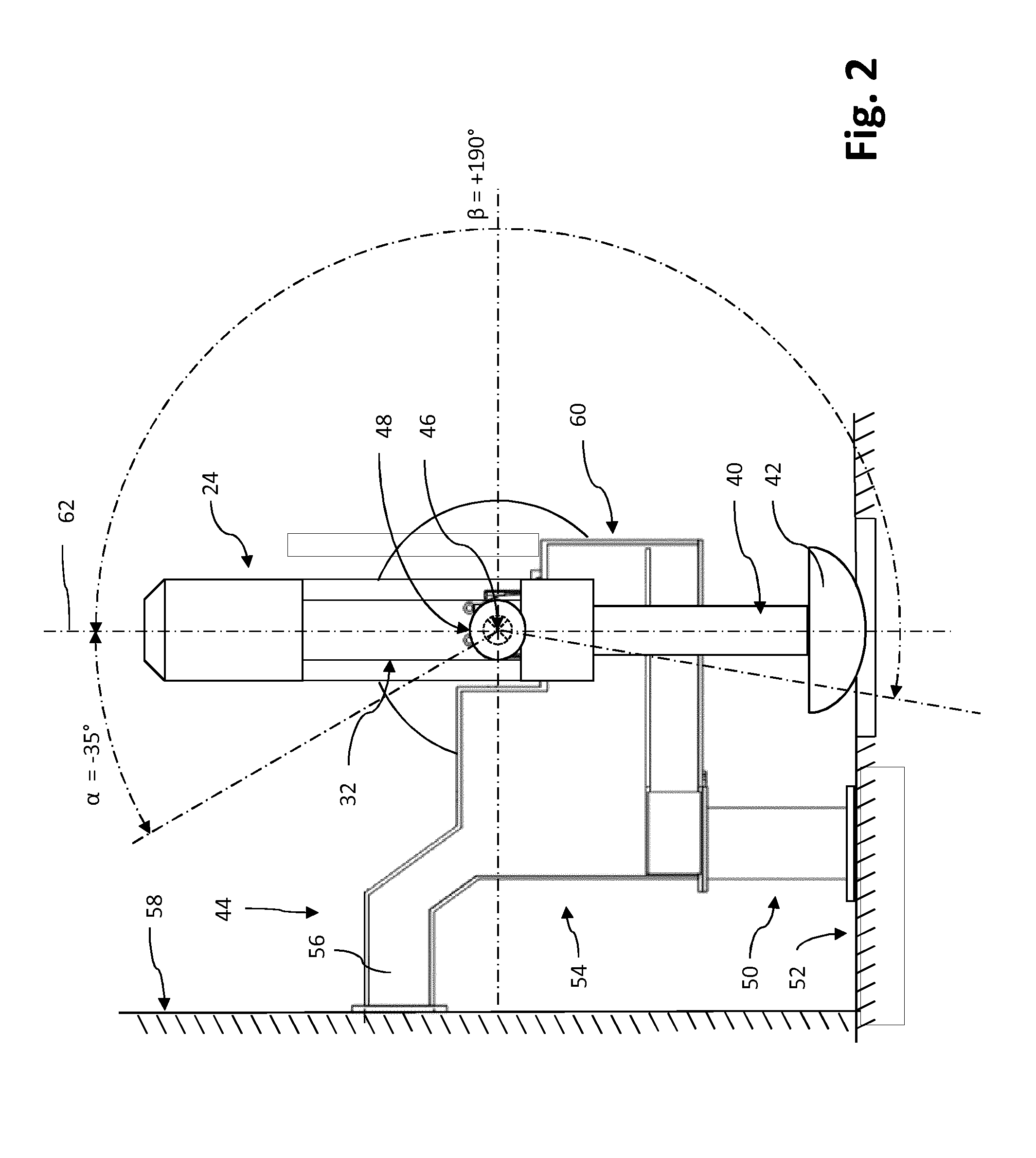
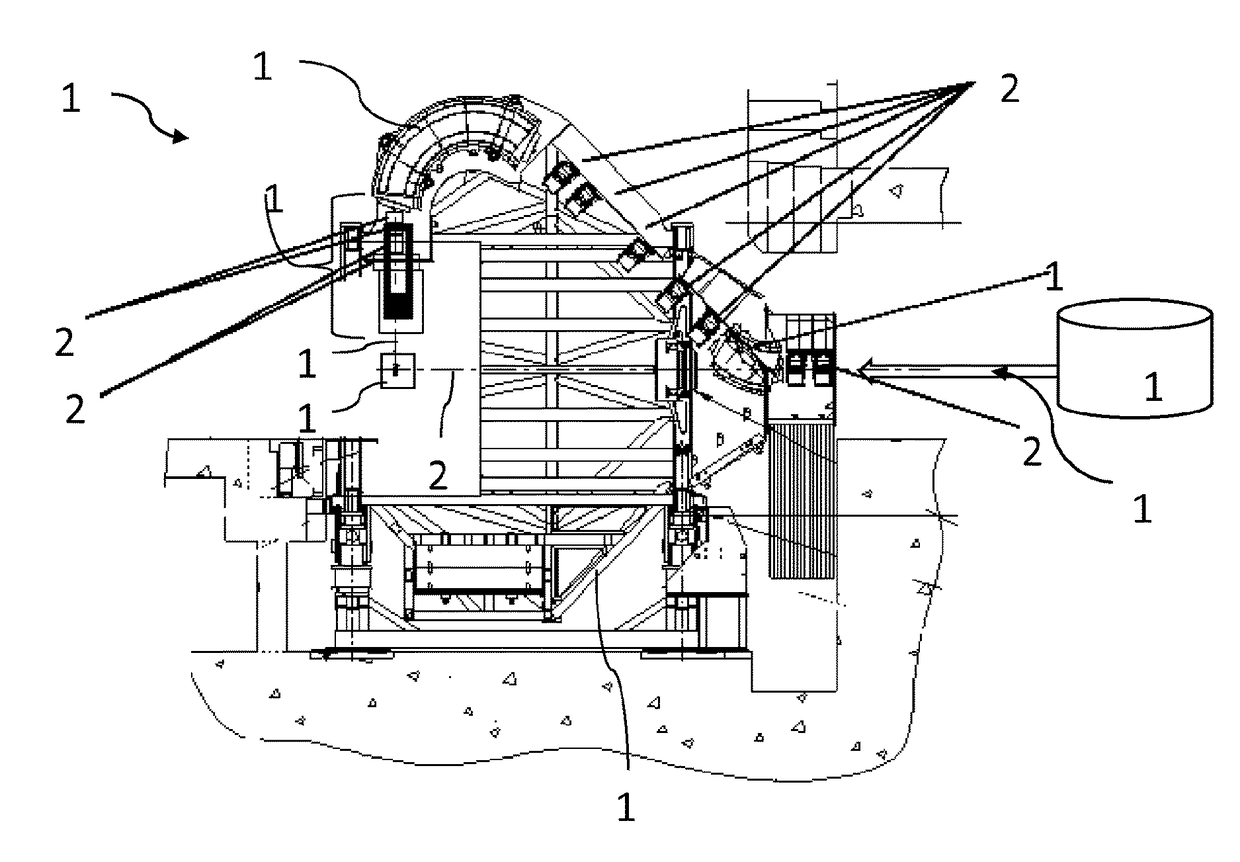
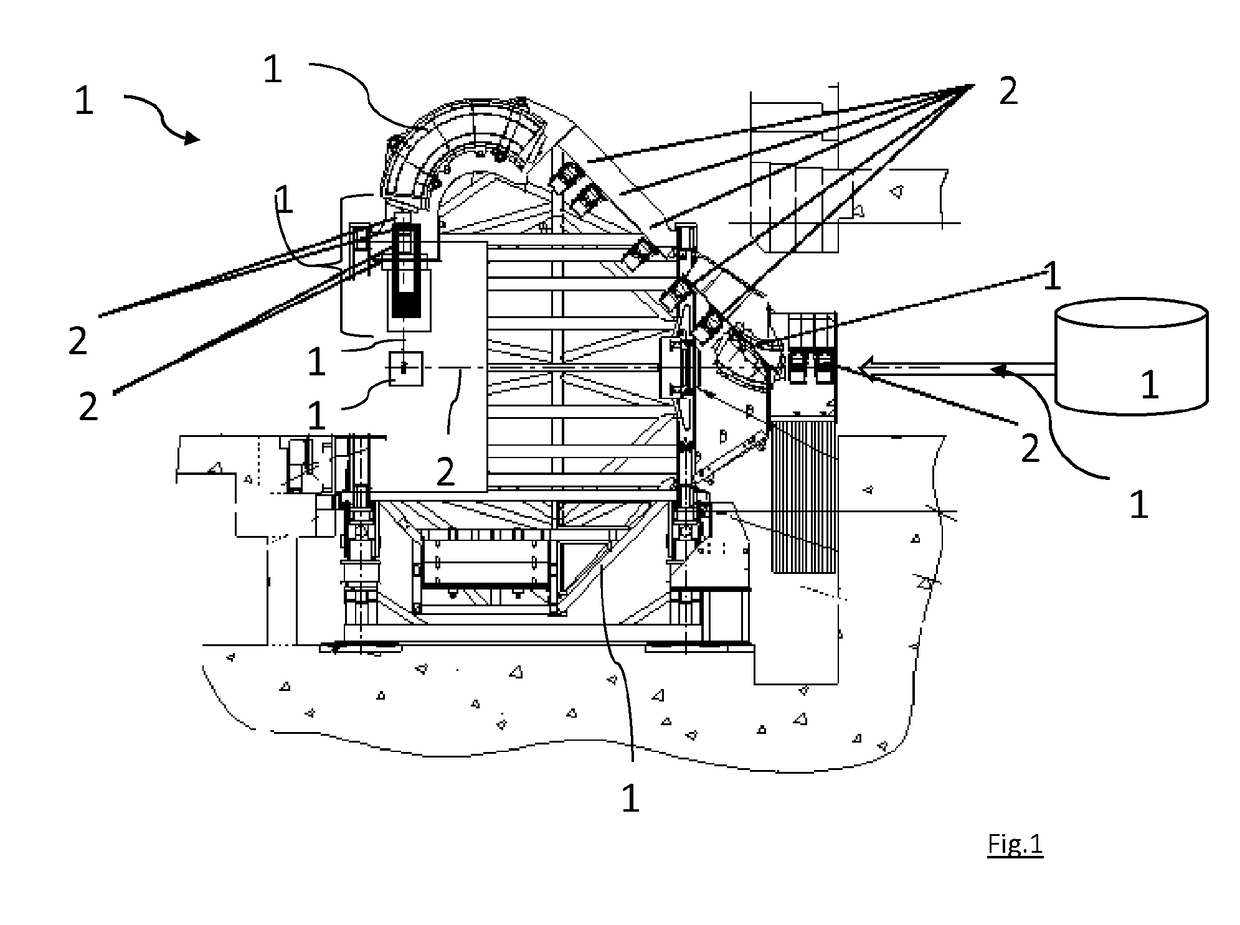
Gantry Structure For A Hadron Therapy Apparatus
ActiveUS20140357930A1Not bulkyEfficient integrationX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyLight beamEngineering
A gantry structure (16) designed for pivoting about an axis of rotation (18) and for delivering a hadron beam on a target comprises a beam delivery line (24) receiving the hadron beam in a direction essentially parallel to the axis of rotation (18), deviating it away from said axis of rotation (18) and delivering it so that the axis of the beam intersects the axis of rotation (18). The beam delivery line (24) is a self-supporting structure supported by a pivotable support arm (32) in proximity of the center of gravity of the beam delivery line (24). A counterweight (42) is supported by a support arm extension (40) on the other side of the axis of rotation (18) for compensating the moment of force due to the weight of the beam delivery line (24) and the support arm (32).
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
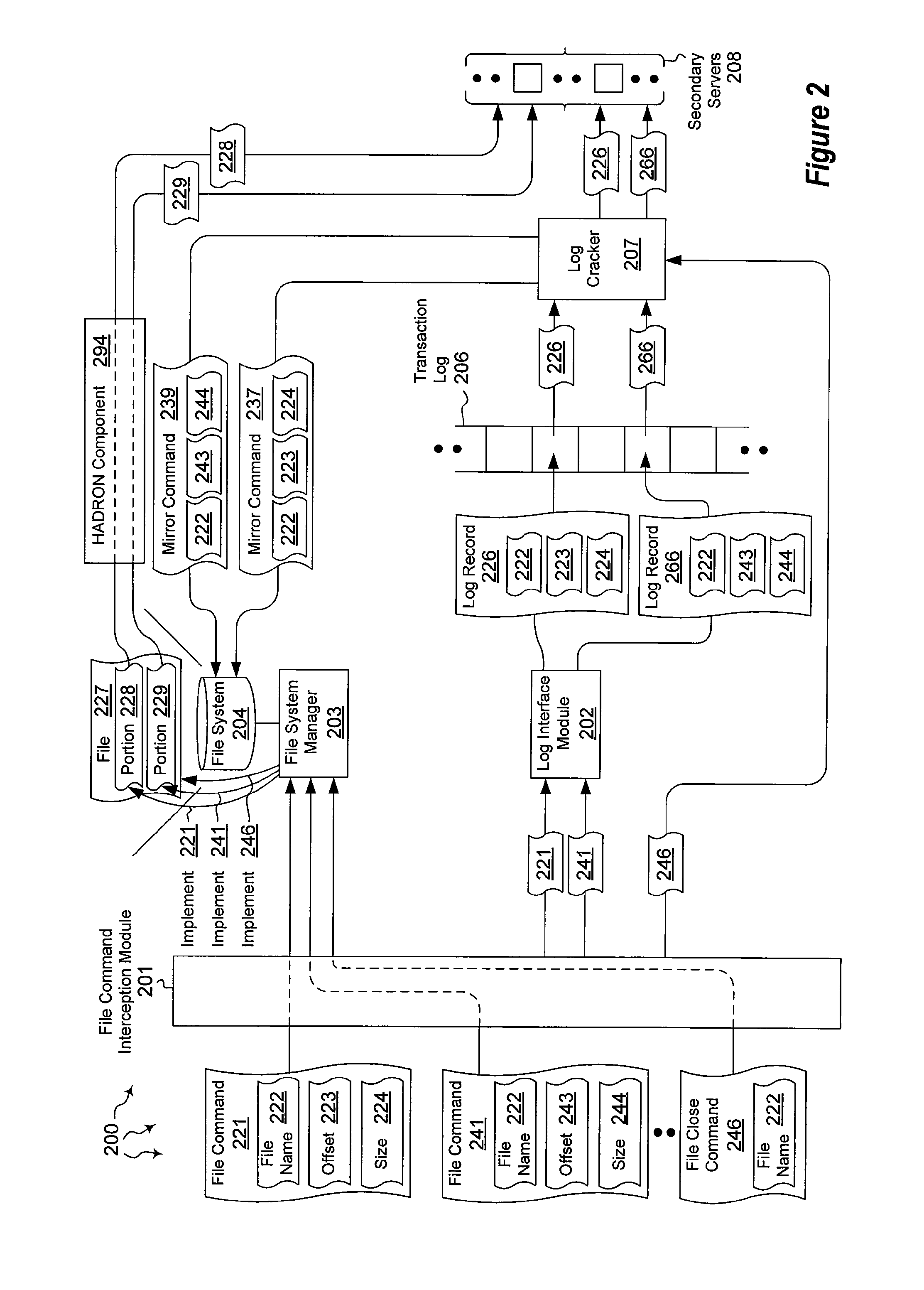
Mirroring file data
ActiveUS8401998B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsHigh availabilityMirror image
The present invention extends to methods, systems, and computer program products for mirroring file data. Generally, high availability and disaster recovery (“HADRON”) is achieved within a database management system by detecting which parts of a file have changed and sending the changed parts to secondaries. Adjacent or partially overlapping parts of a file can coalesce to form larger chunks of changed data. Coalescing reduces the overall number of chunks that are tracked.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Shielding device for an irradiation unit and irradiation method
InactiveUS8963111B2Electrode and associated part arrangementsHandling using diaphragms/collimetersLight beamEngineering
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Device and method for monitoring a hadron beam
The present invention relates to a device for dosimetry monitoring of a hadron beam, comprising n successive ionization chambers i obtained by a series or stack of n+1 parallel detector plates separated from each other by a gas filled gap, each detector plates having a collecting part comprising a collecting side insulated from a bias voltage part comprising a bias voltage side and arranged in a such way that the said collecting side is facing the said bias voltage side of a subsequent detector plate or inversely, each detector plate comprising m layers Lk of materials, the resulting assembly of these detector plates forming a plurality of ionization chamber cells, characterised in that: the thicknesses lk and the choice of the materials of each layer Lk constituting each detector plate as well as the gap of an ionization chamber cell i have been selected in order to satisfy the equation (I) for each ionization chamber i, where lgi is the gas filled gap distance between two detector plates; Ik is the thickness of the corresponding layer Lk of a detector plate and; WETk is the water equivalent thickness (WET) o f the corresponding layer Lk of a detector plate.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
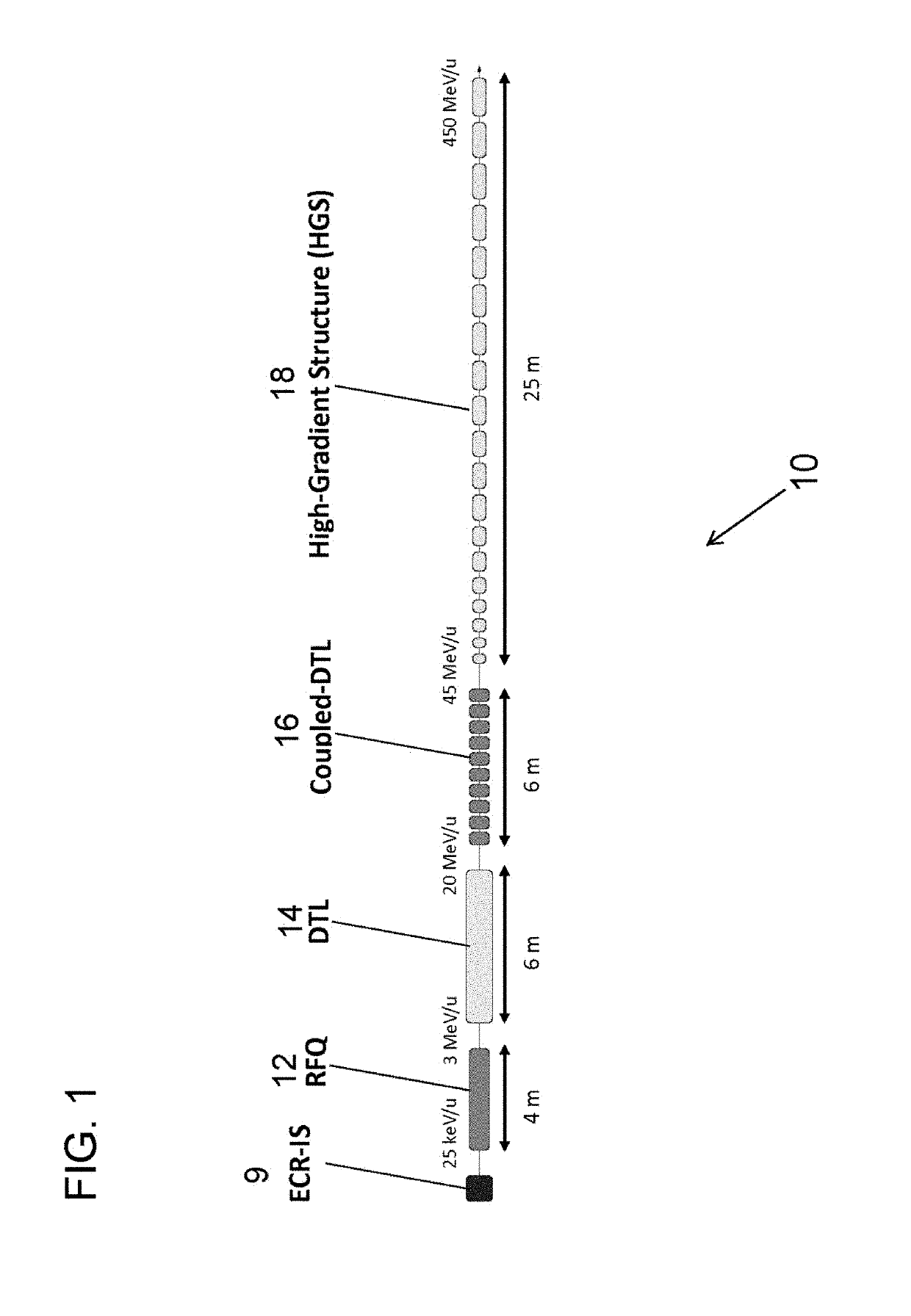
Compac carbon ion LINAC
ActiveUS10362666B2Improve efficiencyHigh frequencyMedical devicesLinear acceleratorsEnergy particleCarbon ion
The invention provides a method for accelerating protons and carbon ions up to 450 MeV / u in a very compact linac, the method comprising subjecting the particles to a radio frequency quadrupole field to accelerate the particles to at least 3 MeV / u, a drift tube linac (DTL) to an energy of 20 MeV / u, followed by a coupled DTL to 45 MeV / u and finally a high-gradient section made of CCL-type standing wave cavities or negative harmonic traveling wave cavities operating at S-band frequencies and capable of delivering voltage gradients of 40 to 60 MV / m. Focusing the accelerated particles while accelerated to higher energy is provided by appropriately placed constant field permanent magnets and electromagnetic quadrupoles. The compactness and power efficiency of the linac is enabled by using high-gradient structure in the S-band frequencies for lower energy particles than ever before. The low-intensity required for hadron therapy allows the use of small-aperture S-band structures and the operation at very high gradient compared to high-intensity machines for research. Operating with very short sub-microsecond pulses at repetition rates up to 400 Hz allows the fast and flexible beam energy and intensity tuning not provided by existing hadron therapy machines. The designed linac is capable of accelerating ions as heavy as neon to the full 450 MeV / u energy, therefore allowing fast beam switching if different ion sources are installed in the front-end of the linac.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Ultra-fast magnetic field for electron paramagnetic resonance imaging used in monitoring dose from proton or hadron therapy
ActiveUS9612308B2Measurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMedicineUltra fast
Instrumentation and methodologies are provided that enable the direct measurement of free radicals generated in patients as a result of radiation therapy through the use of proton beams and other forms of ionizing radiation. As a result, in accordance with at least one disclosed embodiment, the instrumentation and methodologies may be used in conjunction with radiation therapy to detect, monitor and / or control generation of free radicals in cancerous tissue during such radiation therapy.
Owner:WEINBERG MEDICAL PHYSICS
Method and apparatus for particle beam range verification
ActiveUS9358406B2Photometry using electric radiation detectorsX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentBragg peakBeam energy
The invention is related to a method and apparatus for verifying the beam range in a target irradiated with a charged hadron beam, such as a proton beam. The beam range is the location of the Bragg peak in the target, being the location where the largest portion of the dose is delivered. The method utilizes a prompt gamma camera provided with a slit-shaped opening, so as to be able to produced a 1-dimensional profile of the dose distribution along the beam line. The camera is mounted with the slit oriented perpendicularly to the beam line. The method comprises the steps of calculating a position of the camera with respect to a target, for a plurality of beam energies and spots to be irradiated. The method further comprises the steps of verifying the beam range for said plurality of spots, and delivering a value representative of the difference between the estimated beam range and the actual beam range. The apparatus of the invention is provided with a positioning module for positioning the camera.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Hadron treatment planning with adequate biological weighting
ActiveUS7550752B2Radiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsBragg peakDisease
Treatment planning methods are provided that determine the variability of relative biological effectiveness (RBE) along a beam line and calculate, among other things, what intensity of hadron beam such as a proton or a carbon ion beam should be applied to achieve a desired biological dose at treatment site of a patient afflicted with a medical condition. Typically, three or four RBE values at three or four corresponding spacially-dispersed intervals along the beam line are calculated. In one embodiment, two RBE values for the spread-out Bragg peak (SOBP) region of the treatment site; one for the proximal section and one for the declining distal section is calculated. A third and different RBE value may be determined for the distal edge region of the SOBP. A fourth value may also be calculated for a pre-SOBP region.
Owner:HAMPTON UNIVERSITY
Device and method for online quality assurance in hadron therapy
InactiveUS8859980B2Reduce leakageElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansDosimetry radiationQuality assurance
A device and method for on line dosimetry monitoring of a hadron beam generated from a source of radiation and delivered to a target, the device comprising a plurality of support plates arranged in parallel in a face-to-face relation, separated from each other by gas filled gaps and perpendicularly to the central axis of said hadron beam, and forming a plurality of ionization chambers, each support plate having on a first side one or more collecting electrodes and on a second side one or more high voltage electrode, arranged in such a way that each support plate has said first side substantially opposed to said second side of another support plate. Each support plate has an opening so as to form an inner cavity for allowing the undisturbed passage of a central portion of the hadron beam delivered to said target and a peripheral region for intercepting and measuring, by means of said plurality of ionization chambers, a peripheral portion of said hadron beam.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
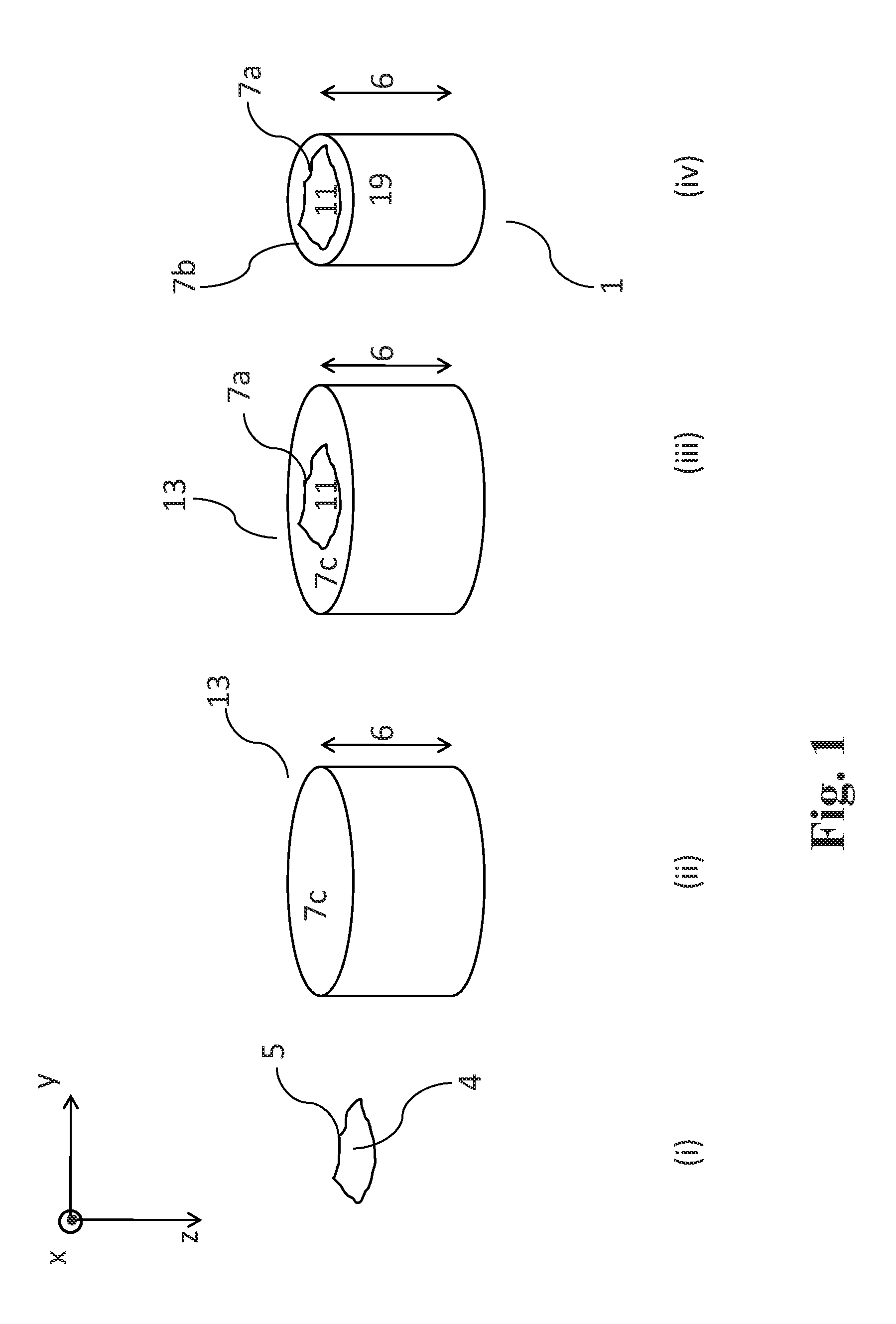
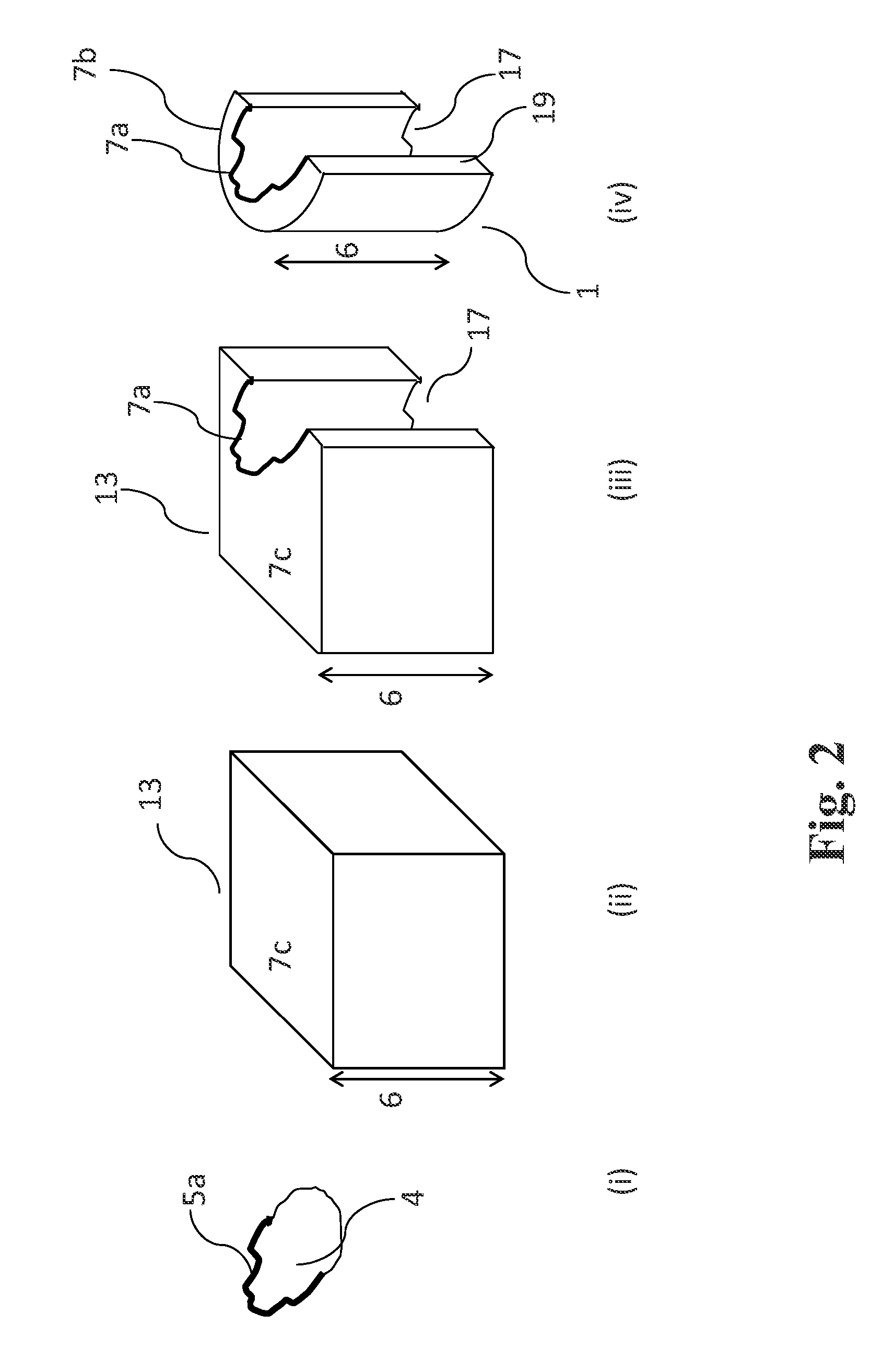
Apparatus and method for hadron beam verification
ActiveUS9192787B2High resolutionIrradiation devicesX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyLight beamHadron
The present invention is related to an apparatus and method for hadron beam verification. The apparatus allows to verify a number of different characteristics in a brief time span. The apparatus comprises at least one main degrader element and associated therewith a multiple thickness degrader element. The latter may comprise a number of patches of beam degrading material, the patches having constant but mutually different thicknesses. Alternatively, it may be a wedge-shaped element. By aiming a pencil beam at the various thicknesses, data points can be obtained which allow to make an estimation of the beam range. In addition to this, the apparatus comprises a zone where no degrader material is present, and where a measurement of the spot size can be obtained, without moving or replacing the apparatus.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Method And Apparatus For Particle Beam Range Verification
ActiveUS20140145088A1Material analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsBragg peakBeam energy
The invention is related to a method and apparatus for verifying the beam range in a target irradiated with a charged hadron beam, such as a proton beam. The beam range is the location of the Bragg peak in the target, being the location where the largest portion of the dose is delivered. The method utilizes a prompt gamma camera provided with a slit-shaped opening, so as to be able to produced a 1-dimensional profile of the dose distribution along the beam line. The camera is mounted with the slit oriented perpendicularly to the beam line. The method comprises the steps of calculating a position of the camera with respect to a target, for a plurality of beam energies and spots to be irradiated. The method further comprises the steps of verifying the beam range for said plurality of spots, and delivering a value representative of the difference between the estimated beam range and the actual beam range. The apparatus of the invention is provided with a positioning module for positioning the camera.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Enhancer signatures in the prognosis and diagnosis of cancers and other disorders
InactiveUS20100256008A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCell type specificEnhancer Elements
It has been discovered that enhancer signatures distinguish enhancer elements from other regulatory elements and that the characteristic enhancer signatures vary in a cell-type specific manner. These discoveries provide the basis for novel methods of predicting, diagnosing and monitoring of diseases, particularly cancer.
Owner:REN BING +3
Toroidal bending magnets for hadron therapy gantries
ActiveUS9711254B2Reduce system weightBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsRadiation/particle handlingBending magnetsSuperconducting Coils
Toroidal superconducting magnets can be used as lightweight rotating bending magnets in hadron therapy gantries. The toroidal bending magnets are self-shielded and do not require ferromagnetic material for field modification or shielding, decreasing both the magnet system weight, as well as overall gantry weight. Achromatic magnet can be made by combining two of these bending magnets. The simple geometry may allow the use of higher fields, making it attractive for carbon, as well as proton.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
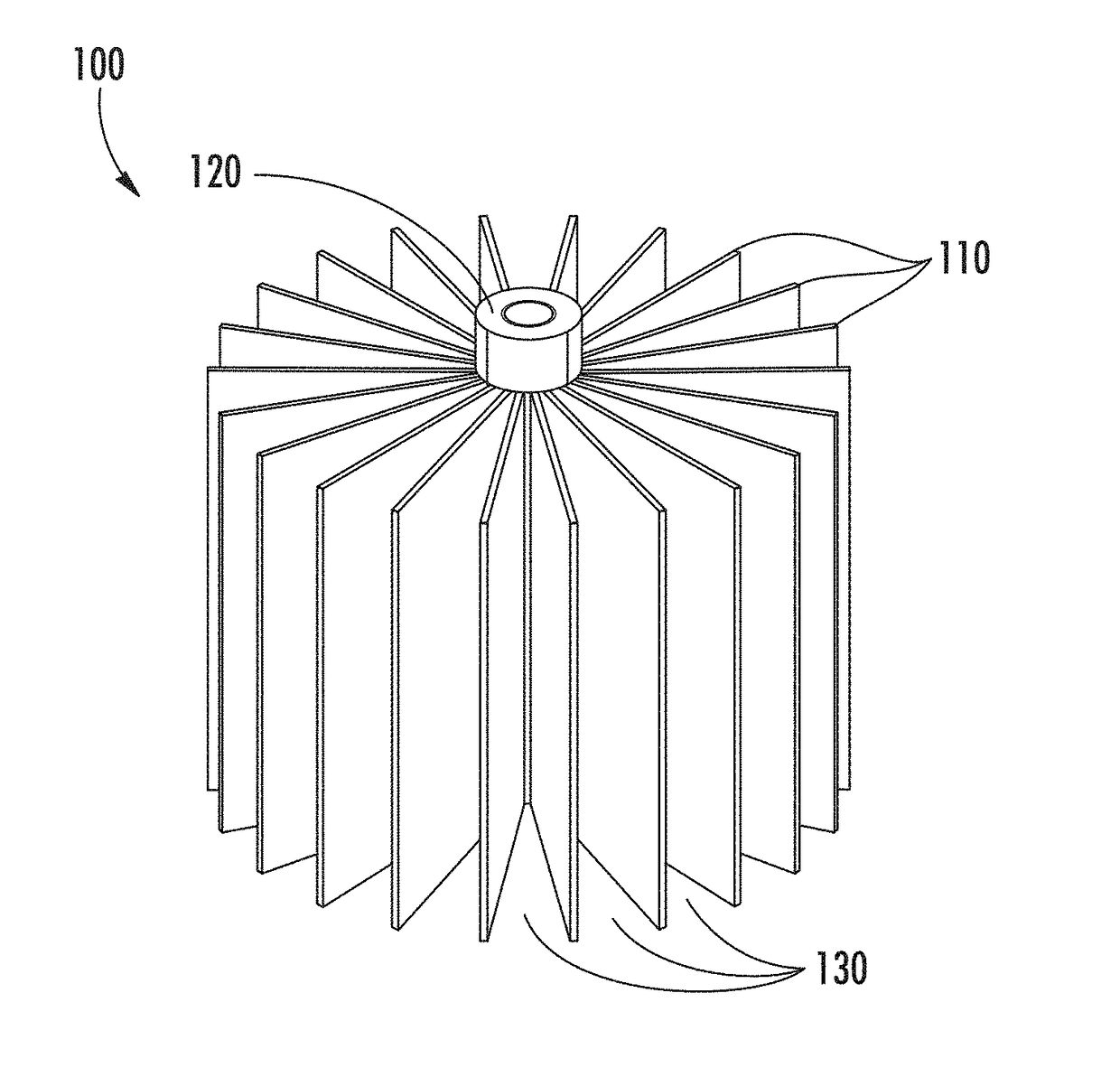
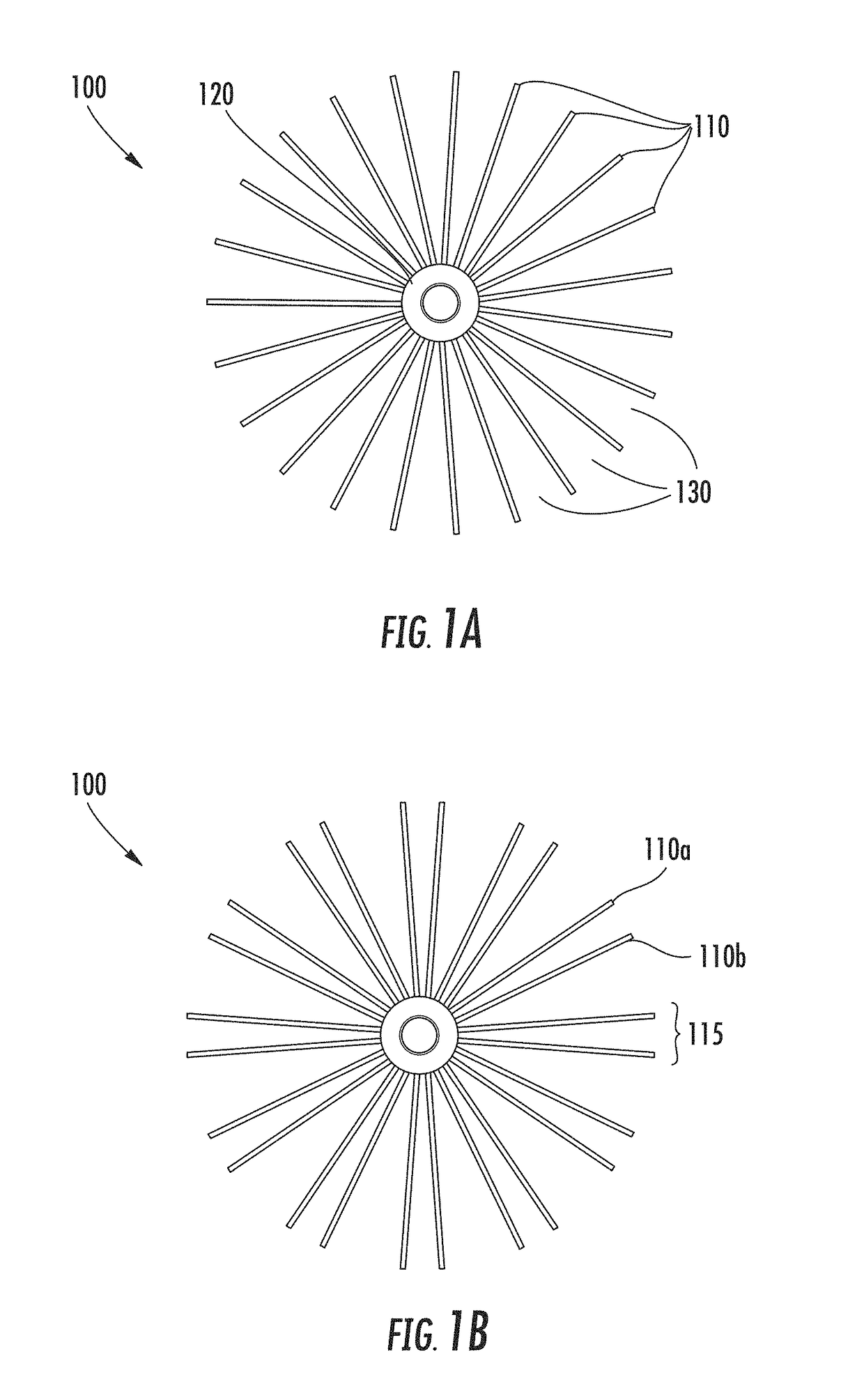
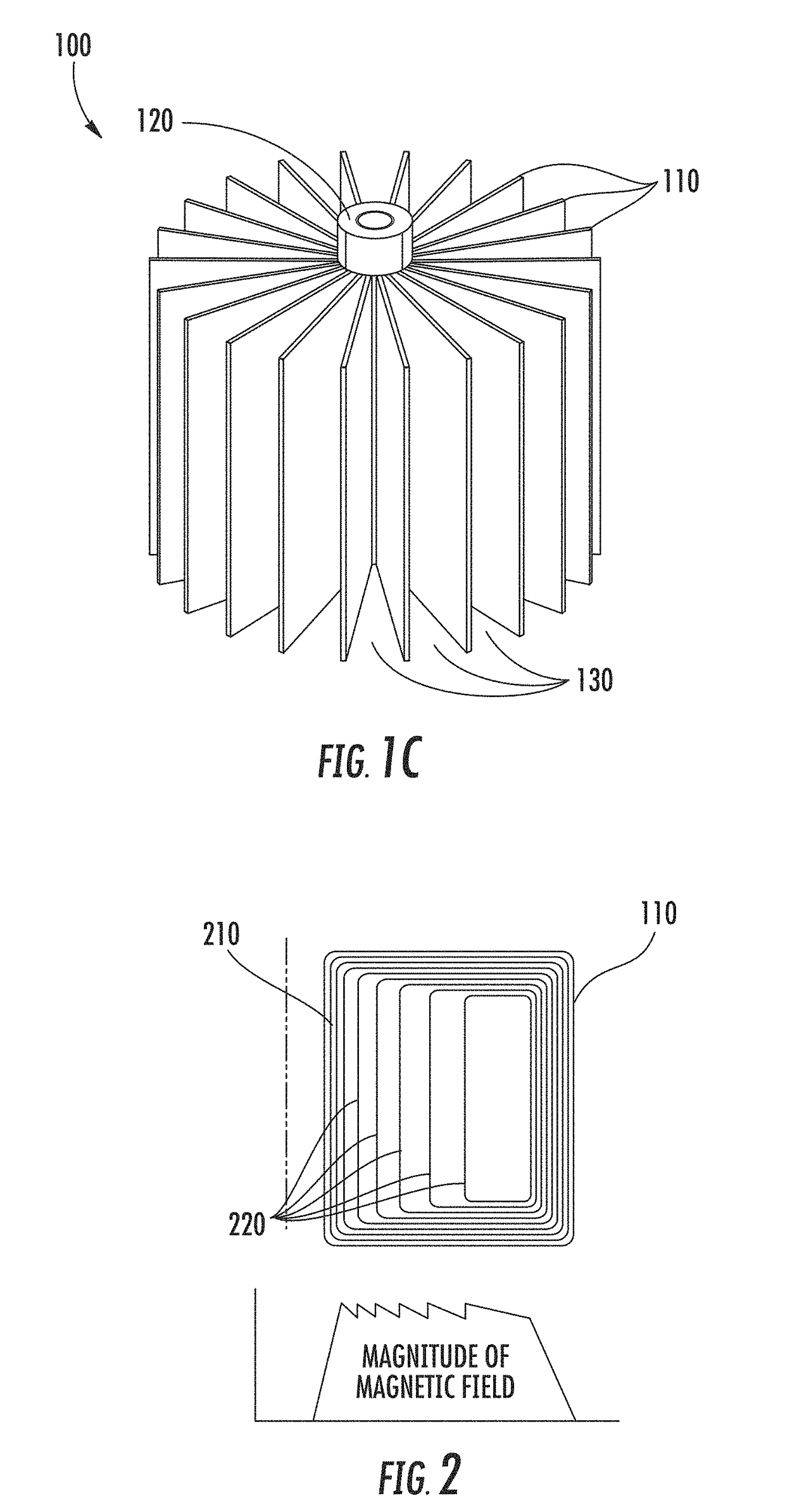
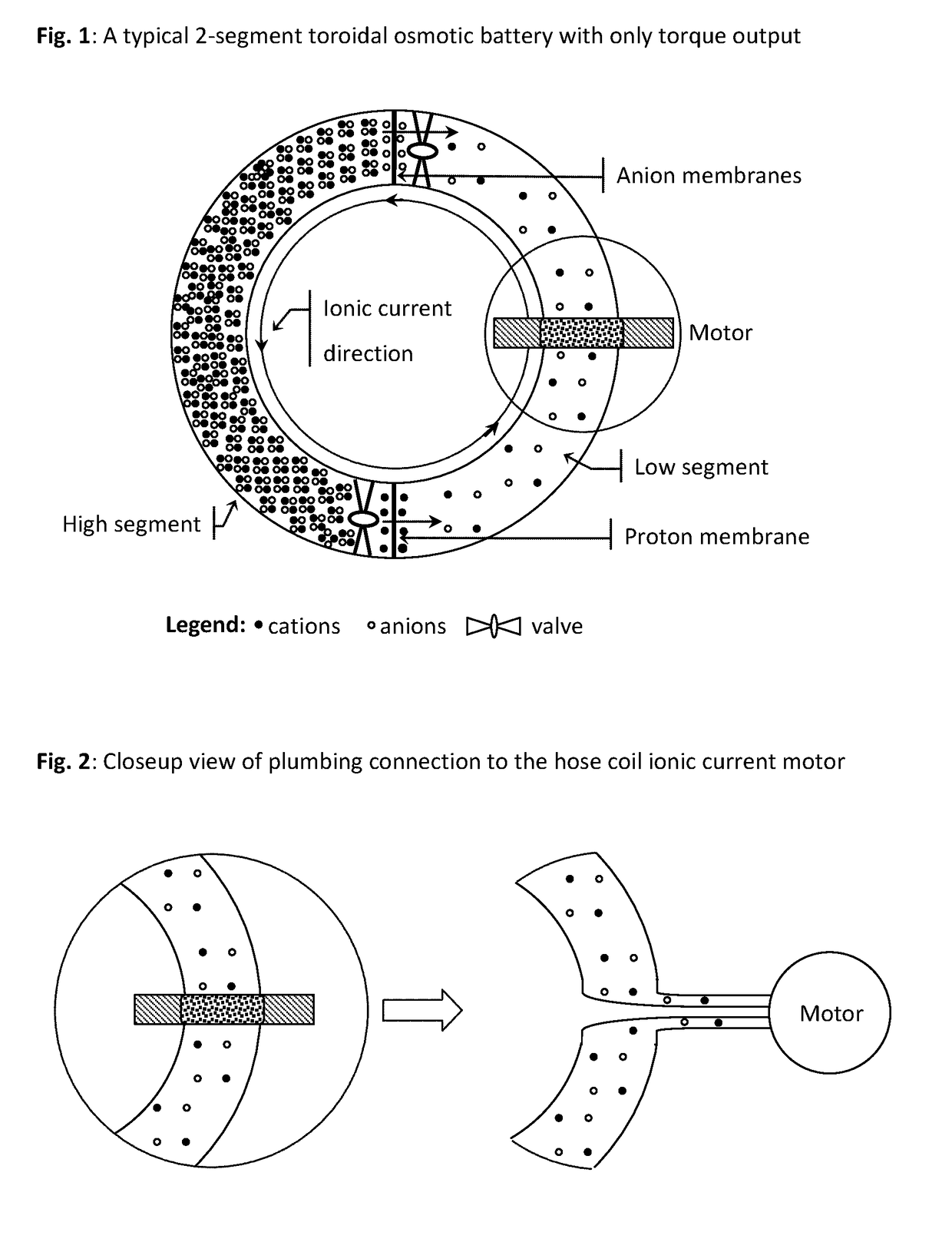
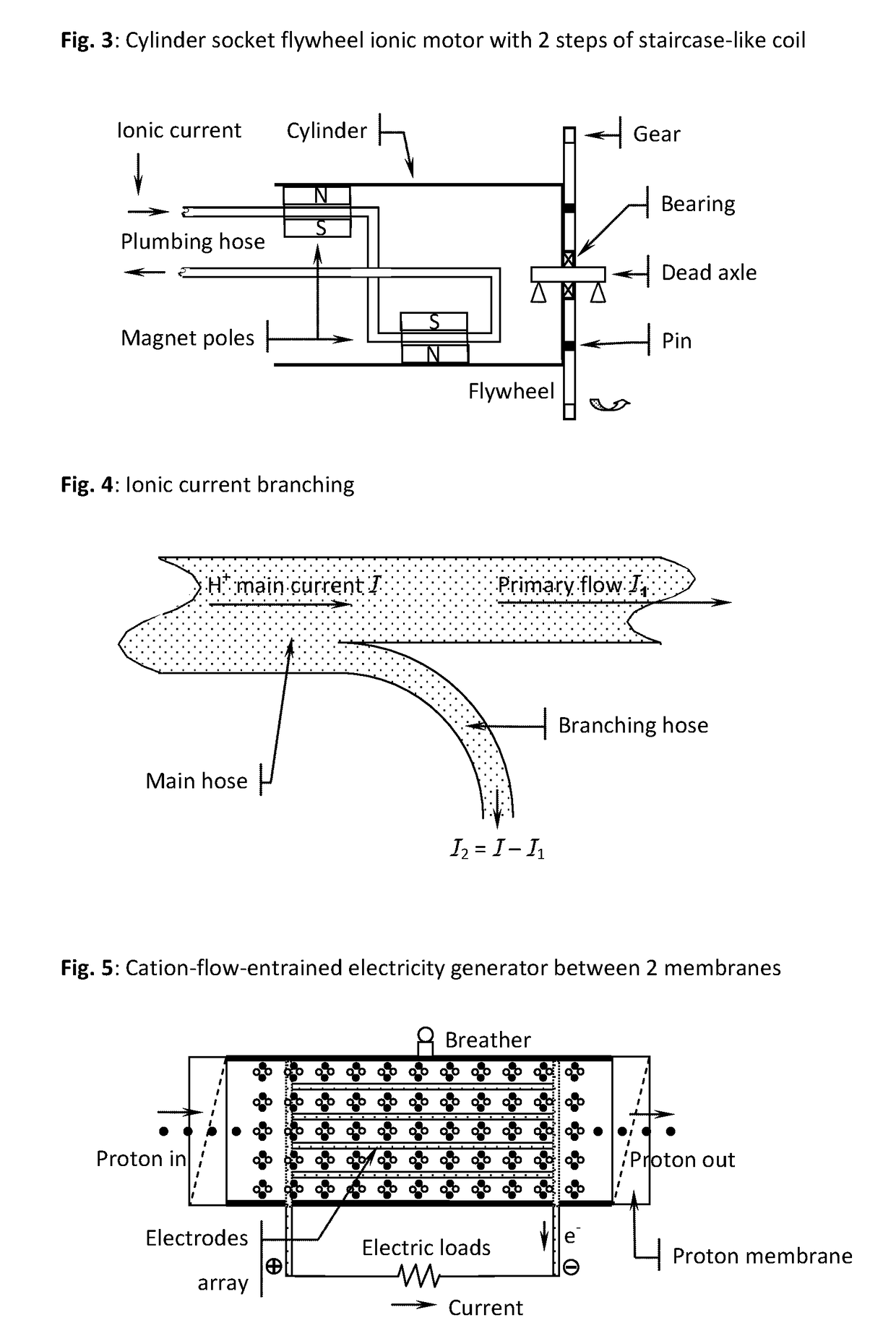
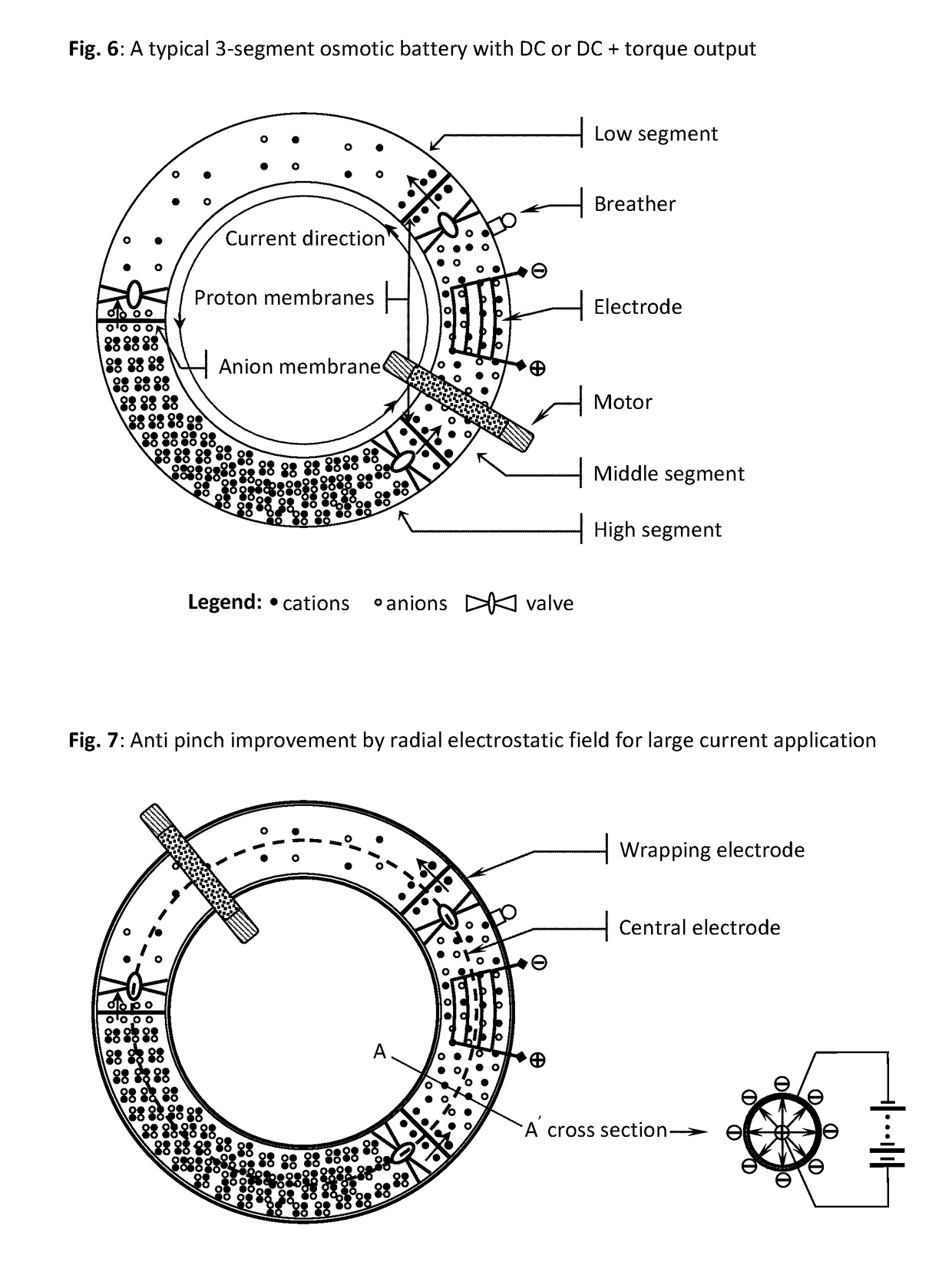
Osmosis battery & high magnetic field generator & superconducting ionic current loop
It is a battery, but electricity output not from electrochemistry, only ionic current loop and its induced high magnetic field ready for use. The power comes from osmotic pressure without any chemical reaction. Recharging the battery can be done by reverse osmosis, or replacement of liquid media. Electrolyte, 2 or 3 liquid segments, ion-exchange membranes and valves are needed. Only 3-segment system can output electricity by non-electrochemical method. Huge current can be generated in liquid-loop comprising different concentration compartments; it is not the regular invisible lepton electronic current, but pure hadron or baryon ionic current, up to millions amperes that can be far larger than any superconductor's capability. Protons and small anions are preferred, so as to reduce mass transfer & ion hammer effect.
Owner:WEI YANMING
Apparatus And Method For Hadron Beam Verification
The present invention is related to an apparatus and method for hadron beam verification. The apparatus allows to verify a number of different characteristics in a brief time span. The apparatus comprises at least one main degrader element and associated therewith a multiple thickness degrader element. The latter may comprise a number of patches of beam degrading material, the patches having constant but mutually different thicknesses. Alternatively, it may be a wedge-shaped element. By aiming a pencil beam at the various thicknesses, data points can be obtained which allow to make an estimation of the beam range. In addition to this, the apparatus comprises a zone where no degrader material is present, and where a measurement of the spot size can be obtained, without moving or replacing the apparatus.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
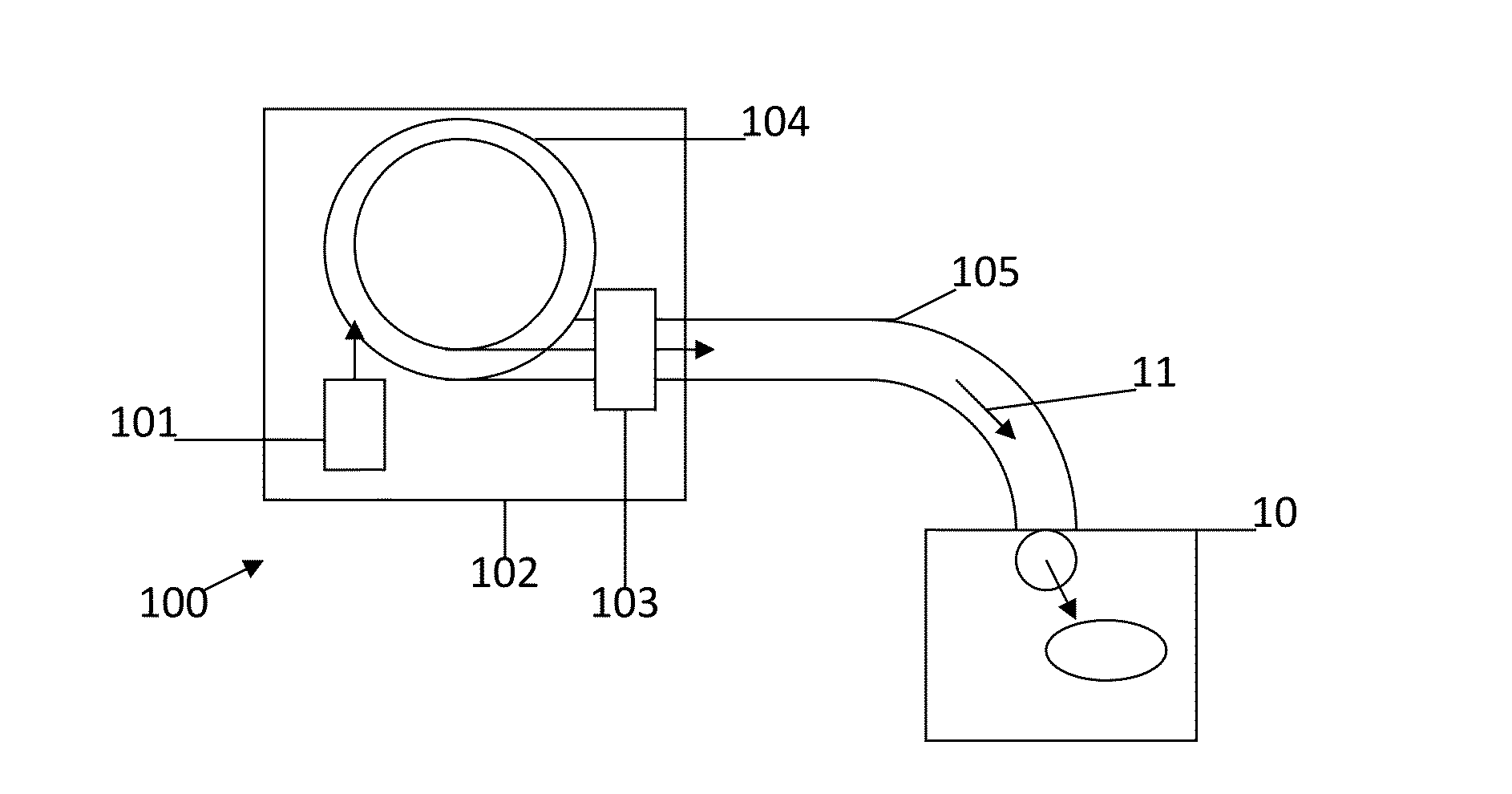
Hadron radiation installation and verification method
InactiveUS9707411B2Enhance optimize of and reliabilityEasy to installX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyValidation methodsControl system
A hadron radiation installation adapted to subject a target to irradiation by a hadron radiation beam includes a target support configured to support, preferably immobilize, a target; a hadron radiation apparatus adapted to emit a hadron radiation beam along a beam axis to irradiate the target supported by the target support, the radiation beam penetrating into the target. The radiation apparatus has a control system at least comprising a beam penetration depth control allowing at least to control and vary the penetration depth of the radiation beam into the target. The installation has a radiation beam range sensor device adapted to determine the penetration depth of said radiation beam into the target, where the range sensor device includes a gamma camera responsive to prompt gamma rays that are emitted while the hadron radiation beam penetrates into the target.
Owner:TECH UNIV DELFT
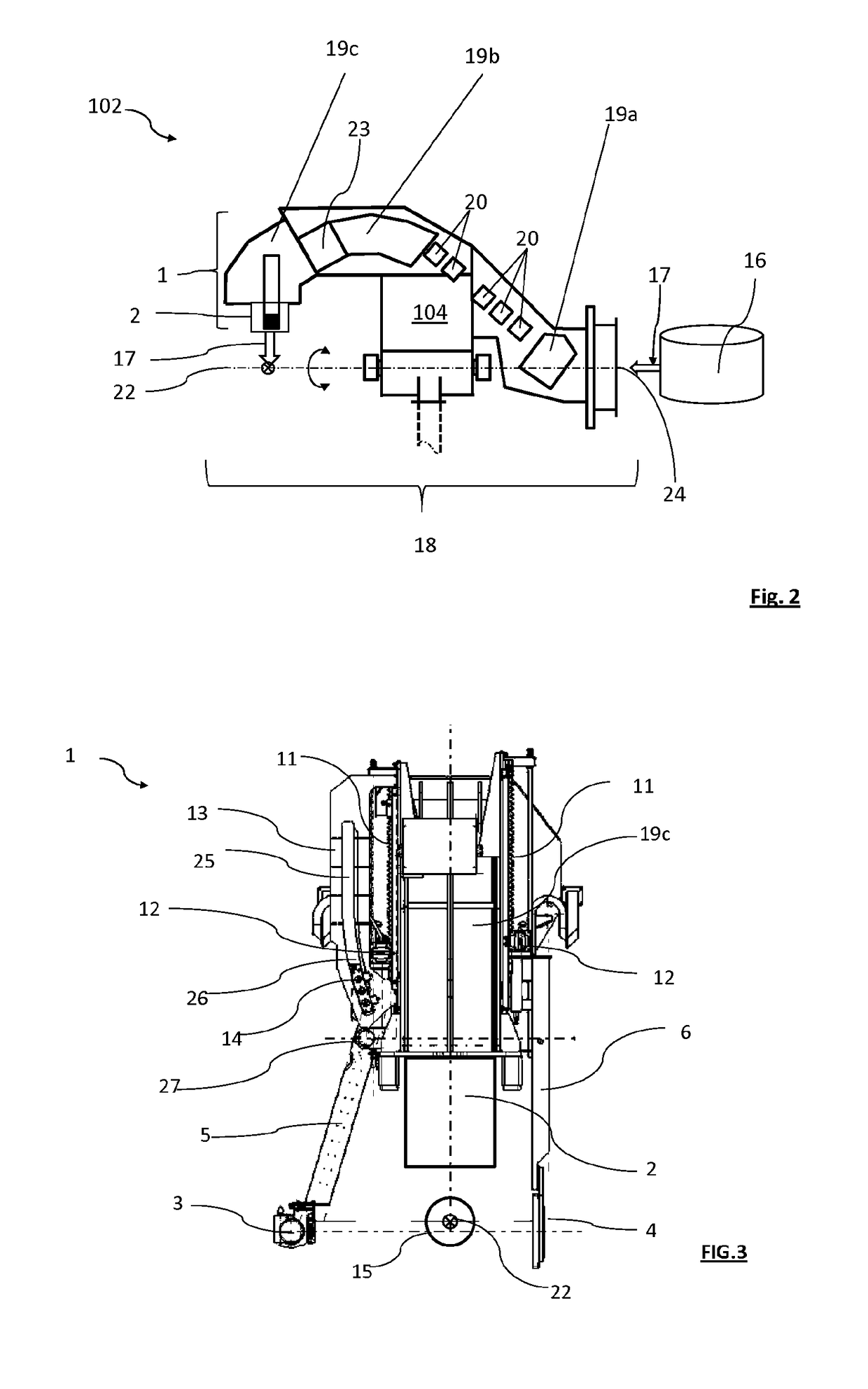
Hadron therapy installation comprising an imaging device
ActiveUS10124191B2Avoid accessEasy to viewComputerised tomographsTomographyFluoroscopic imagingEngineering
The invention relates to a hadron therapy installation that comprises an irradiation unit (1) supported by a rotary support structure, so as to be able to rotate around a target volume (15) centered on the axis of rotation (22), to deliver a treatment beam (17) from different angles on the target volume (15). An imaging device (3, 4) is secured in rotation with the irradiation unit (1) and translatable relative to the irradiation unit (1) between a retracted position at the irradiation unit (1) and a lateral deployed position relative to the target volume (15), such that in its deployed position, the imaging device (3, 4) can rotate around the target volume (15) together with the irradiation unit (1). Such an installation can be used for a cone beam computed tomography method and / or a fluoroscopic imaging method on a patient to be treated in the hadron therapy installation.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
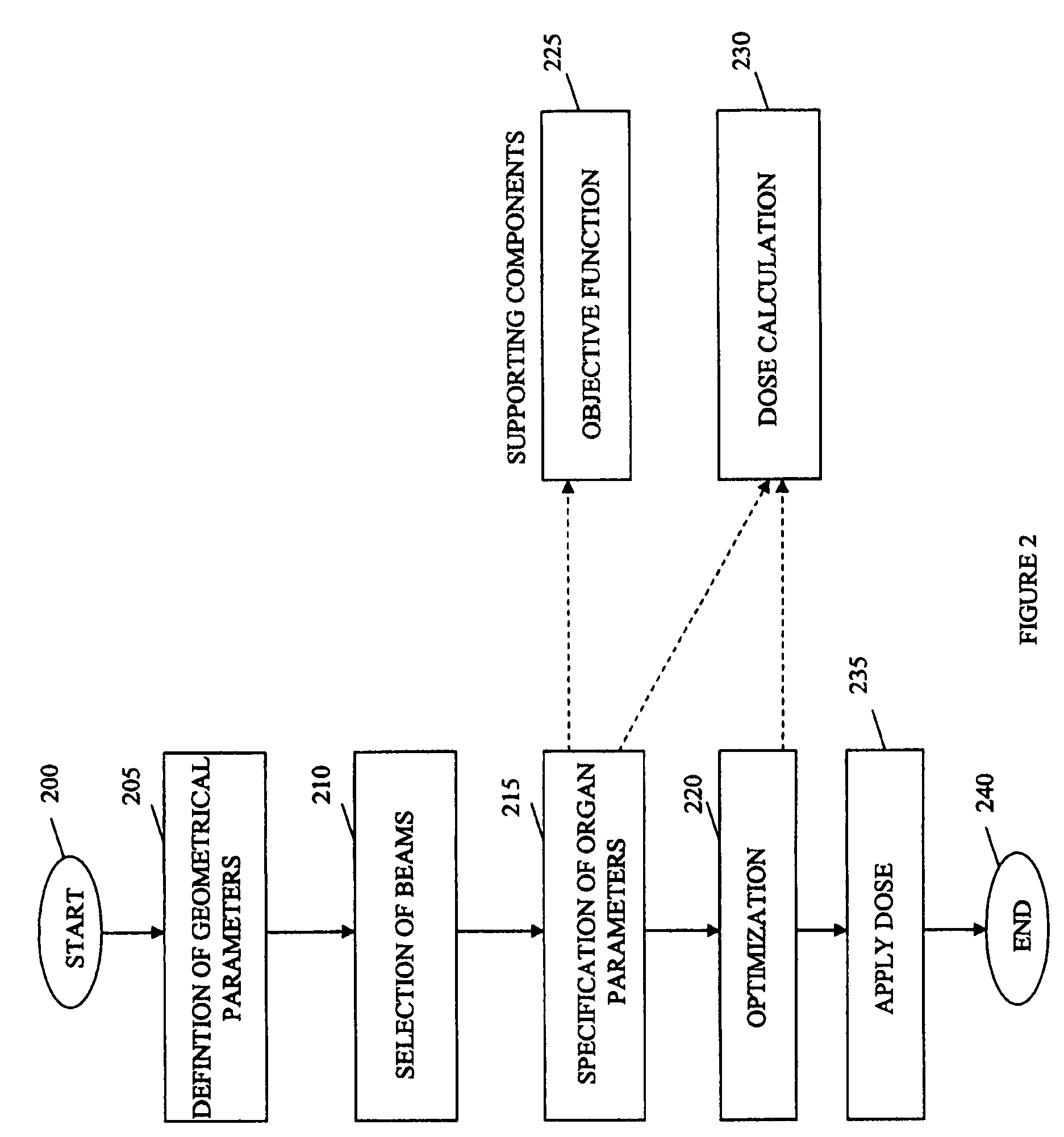
Method for quickly optimizing intensity-modulated sub-fields through grouping
ActiveCN104268437AReduce the number of hopsReduce optimization timeMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsThree dimensional shapeOrgan at risk
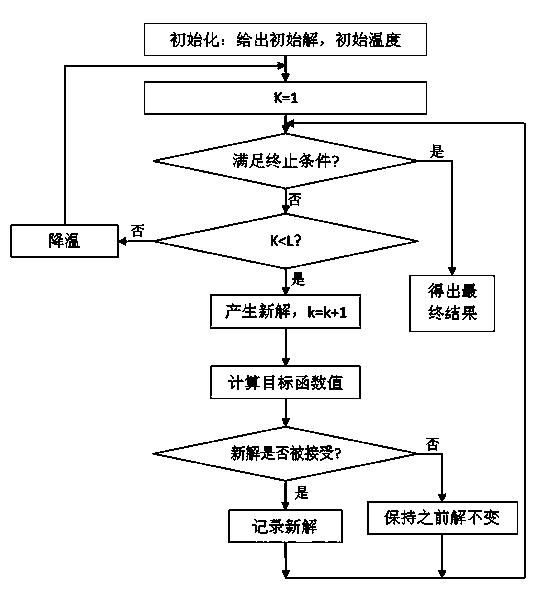
The invention discloses a method for quickly optimizing intensity-modulated sub-fields through grouping. The method for quickly optimizing intensity-modulated sub-fields through grouping solves the problems that the prior art needs multiple iterations, and the time is long. The method for quickly optimizing intensity-modulated sub-fields through grouping includes steps that (1) determining a blade needed for forming a field according to the anatomic relationship between the three-dimensional shape of a target region and the related organ at risk, and grouping the blade for forming the field; (2) using a simulated annealing method to judge the blade of each group. The method for quickly optimizing intensity-modulated sub-fields through grouping includes that grouping the blade before performing the simulated annealing, and using a CPU core to carry out optimal computation on each group; judging each sub-group through an independent target function, changing the blade position in the sub-group, calculating the target function, and judging whether the blade change can be accepted according to a solution accepting method. The method for quickly optimizing intensity-modulated sub-fields through grouping reduces the optimizing time based on reducing the sub-field number and monitor unit number and improving the implementation efficiency; the waste is lowered by means of the computation ability of the multi-core CPU.
Owner:成都奇林科技有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com