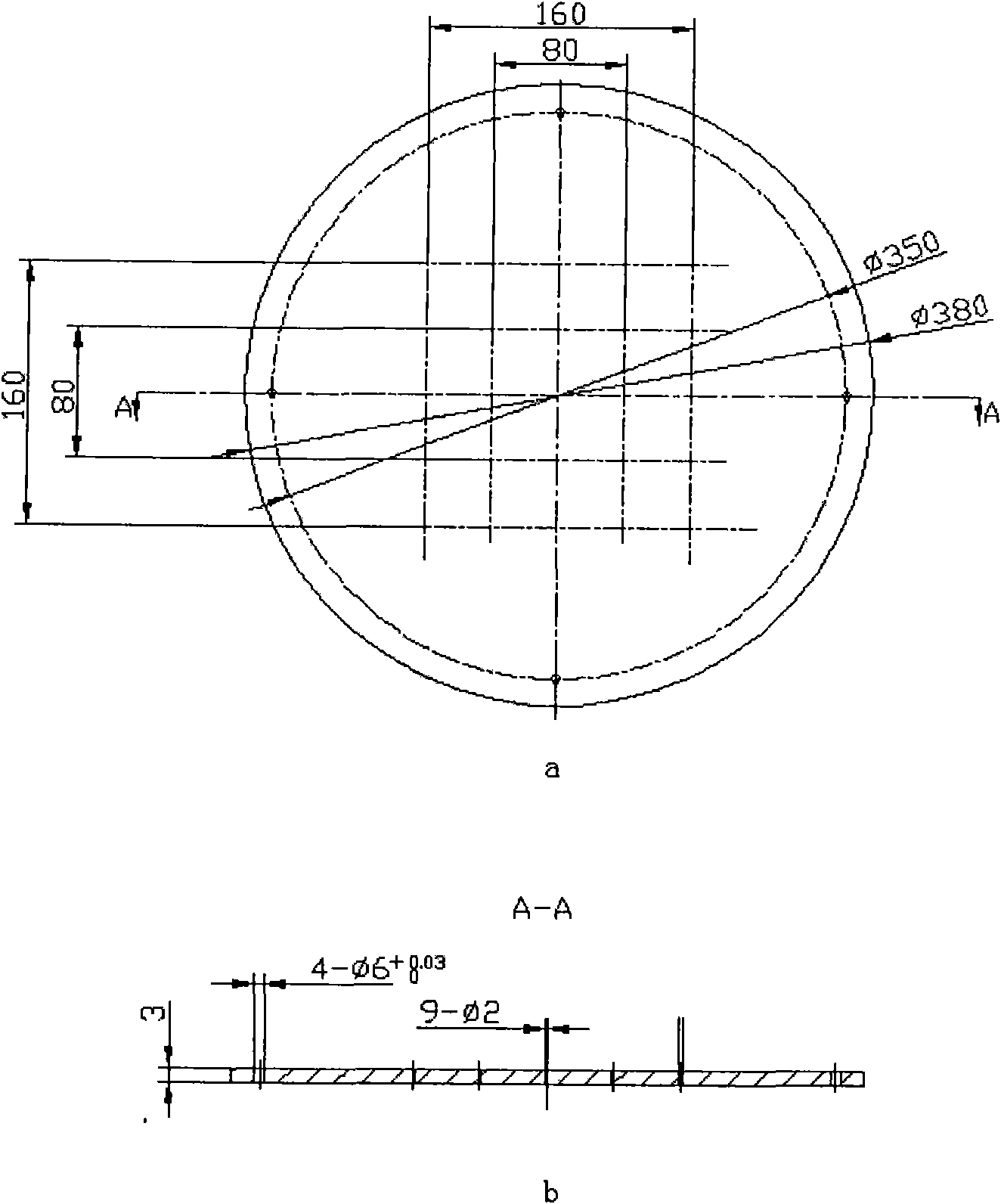
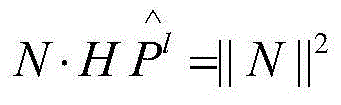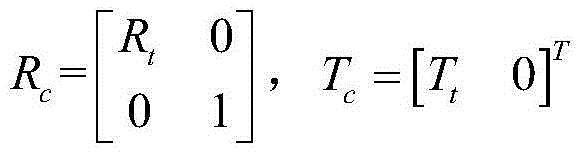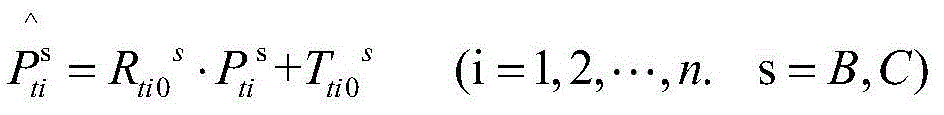Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
188 results about "Fluoroscopic imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
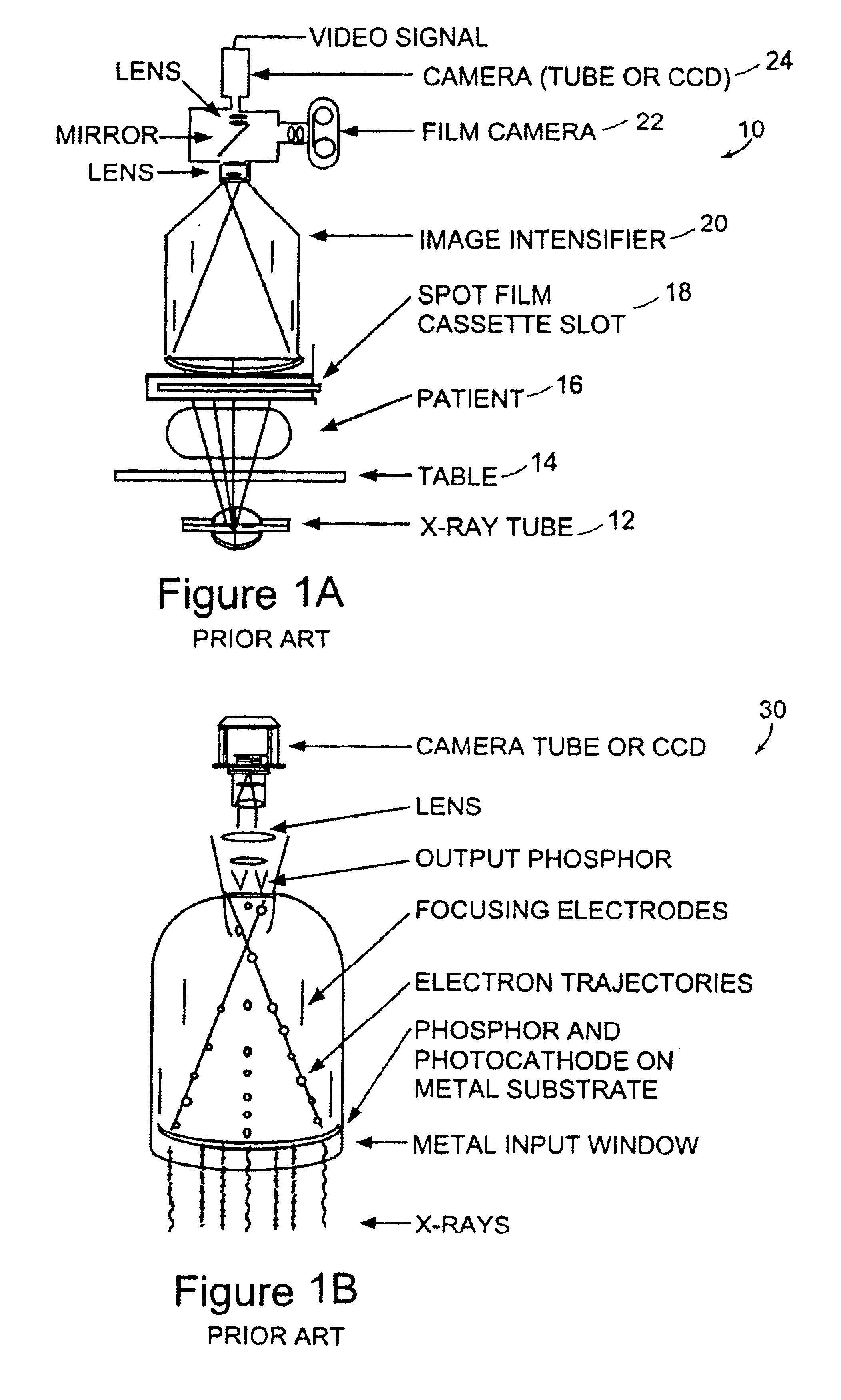
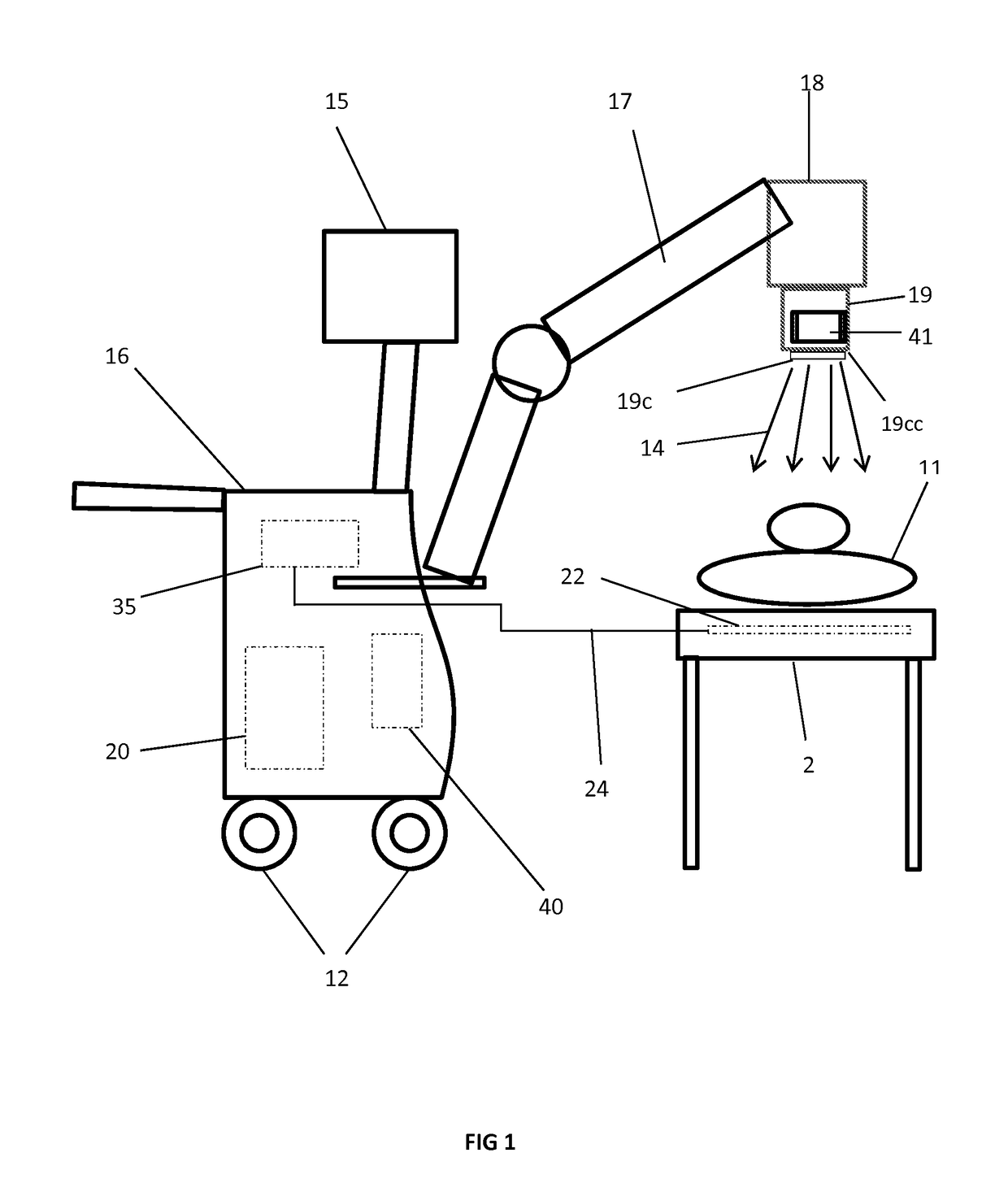
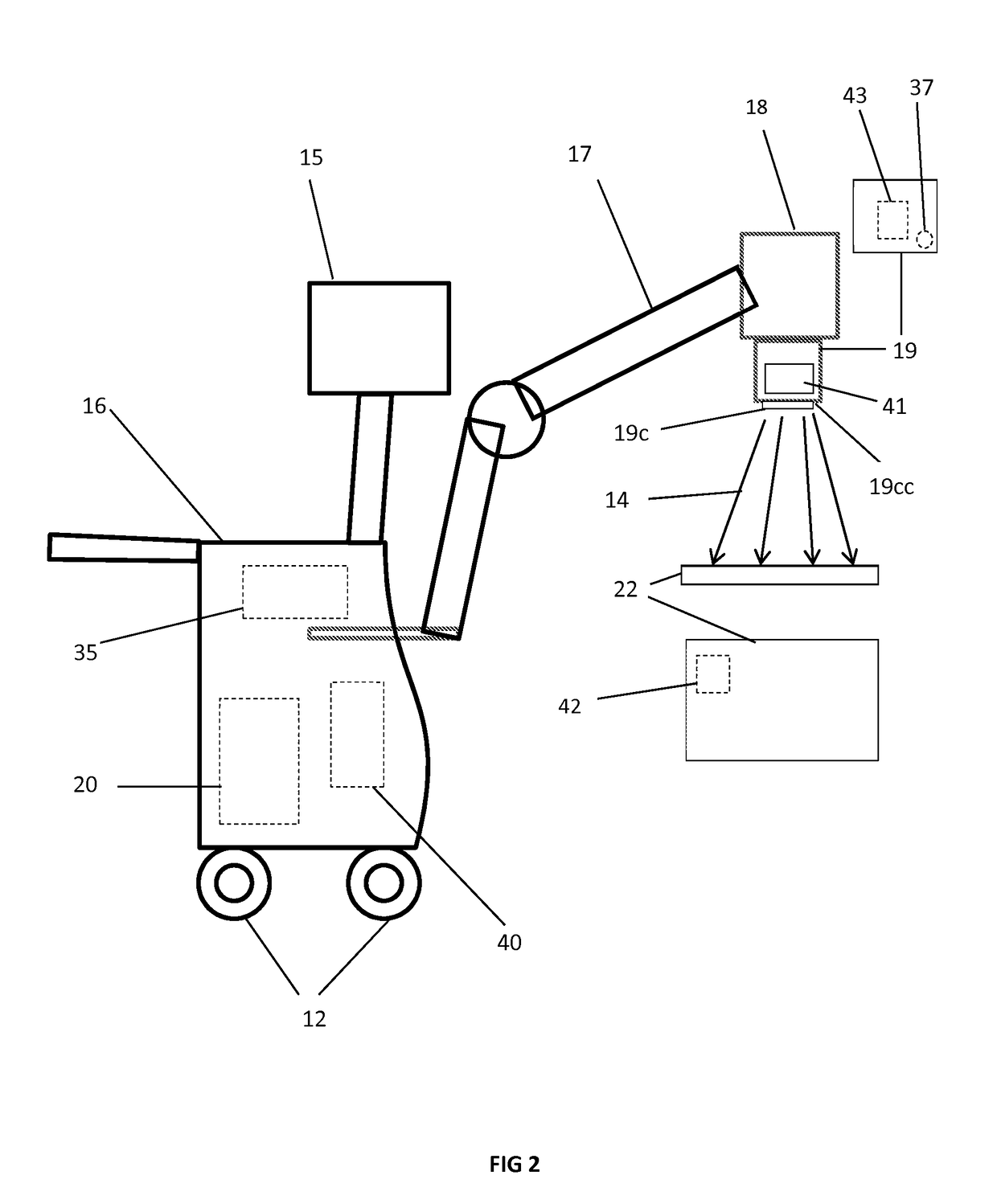
Fluoroscopy is an imaging technique that takes real time (live) moving images of patients’ internal structures using X-rays (radiation). The fluoroscope is a flat table with a camera that pulls over the patient and creates a tunnel. The radiologist or technologist will move the camera up and down to best see the area being examined.
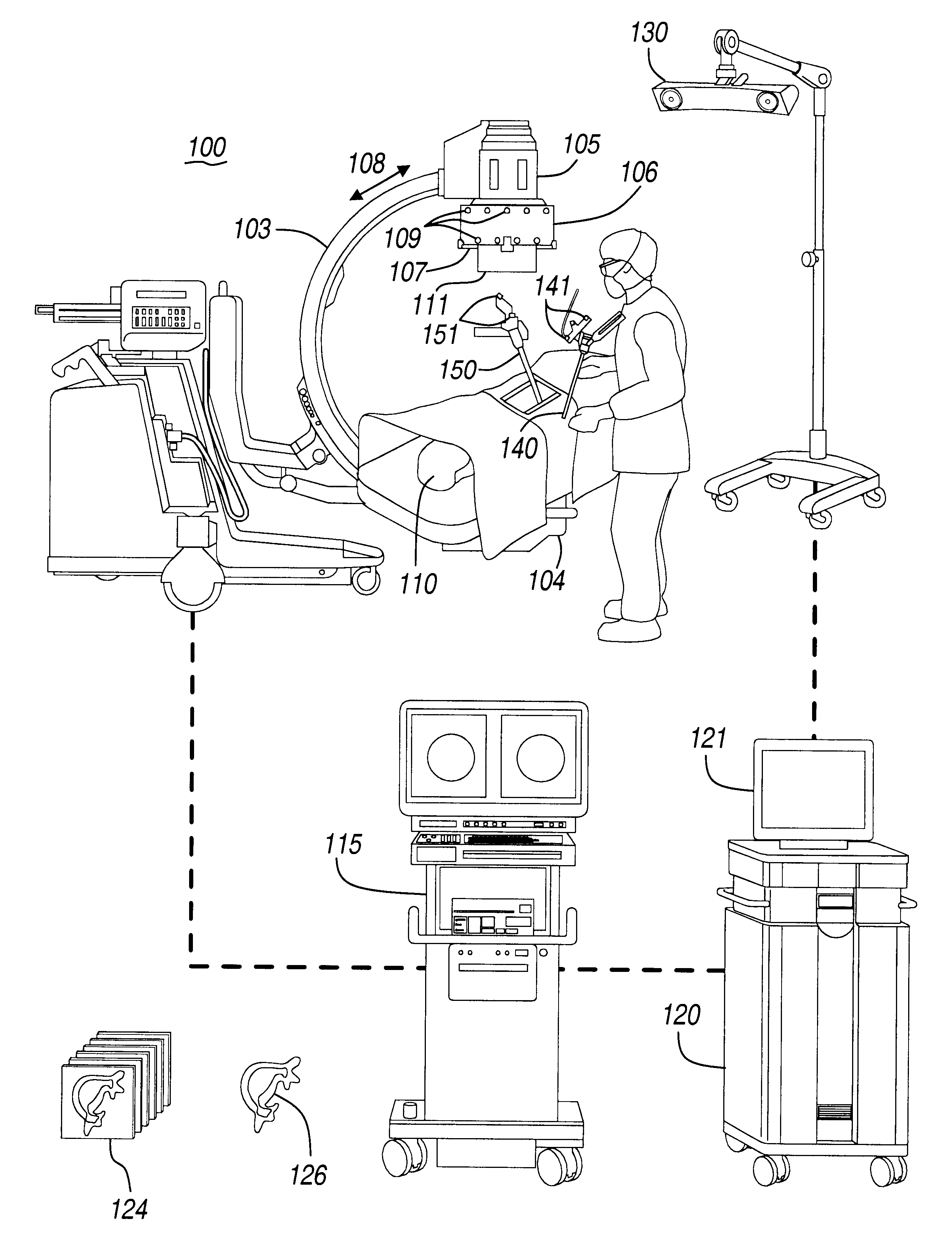
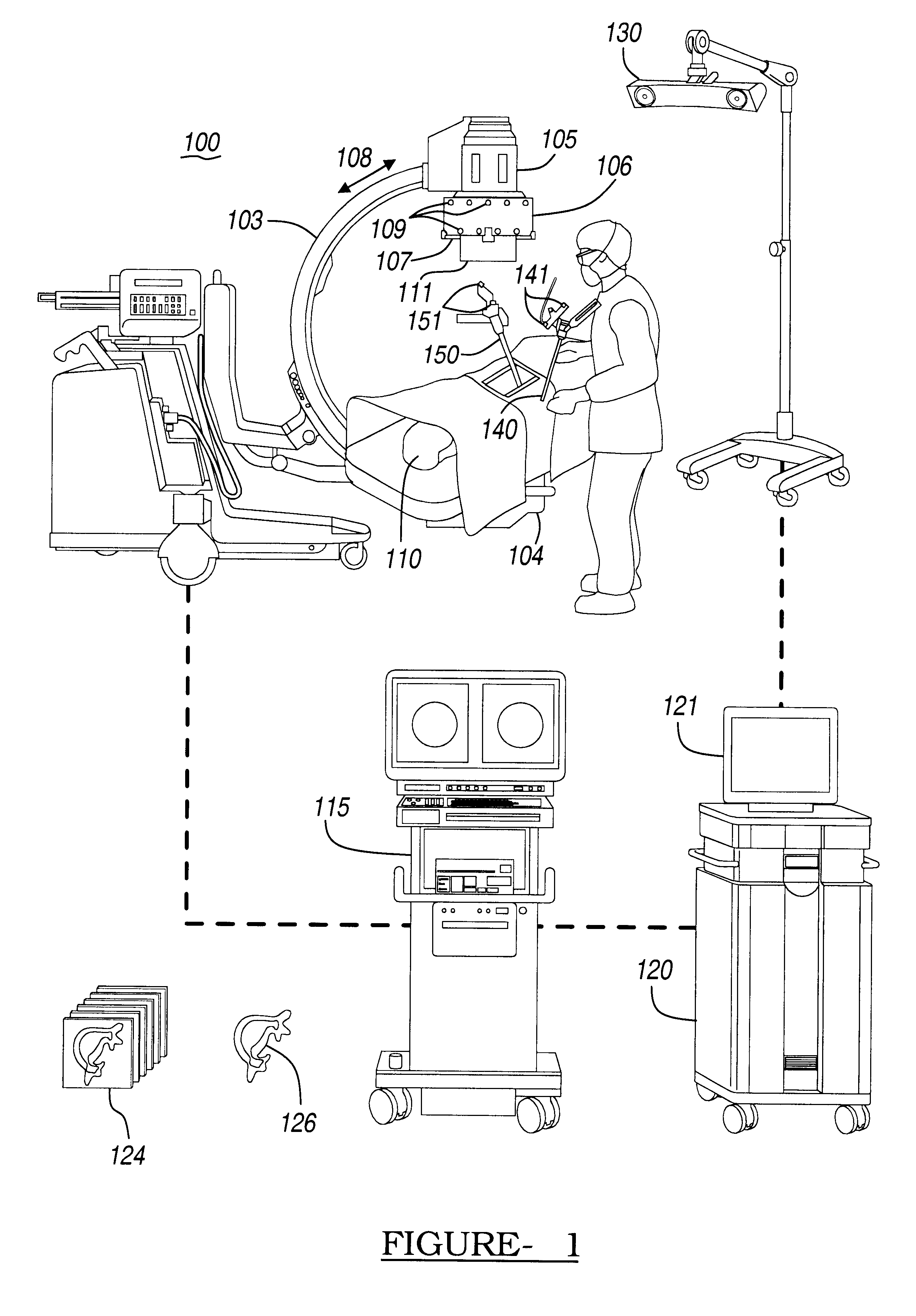
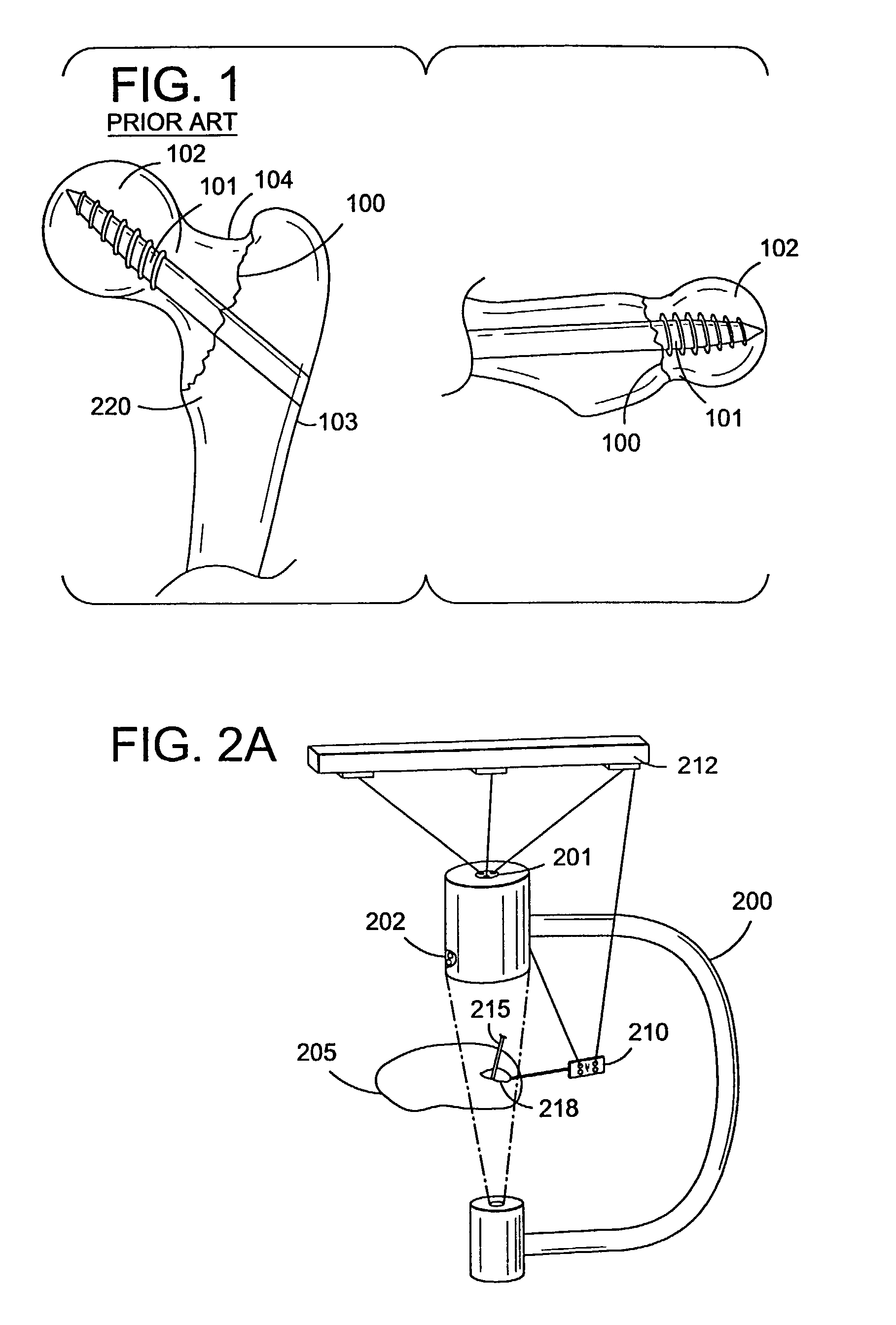
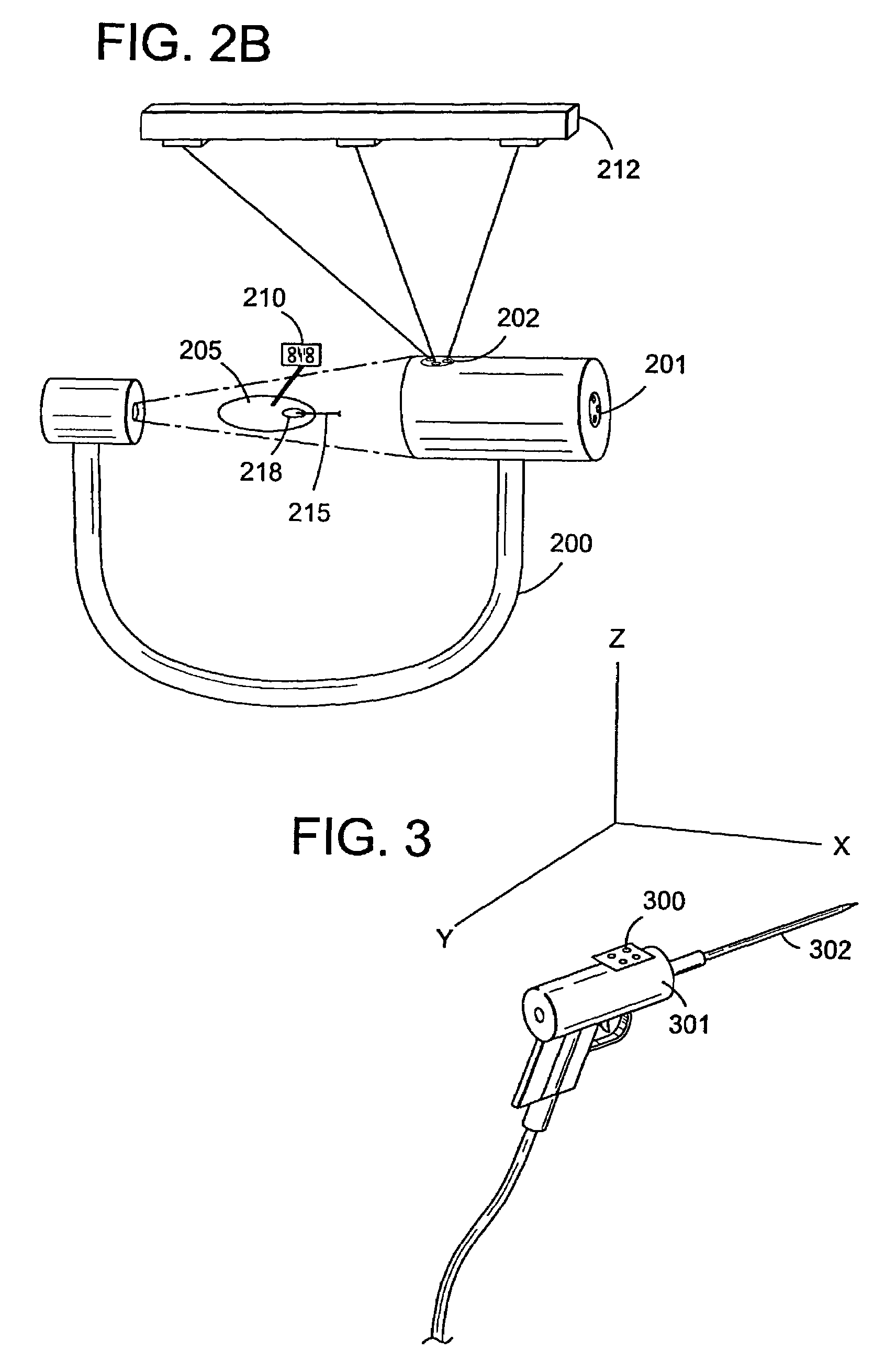
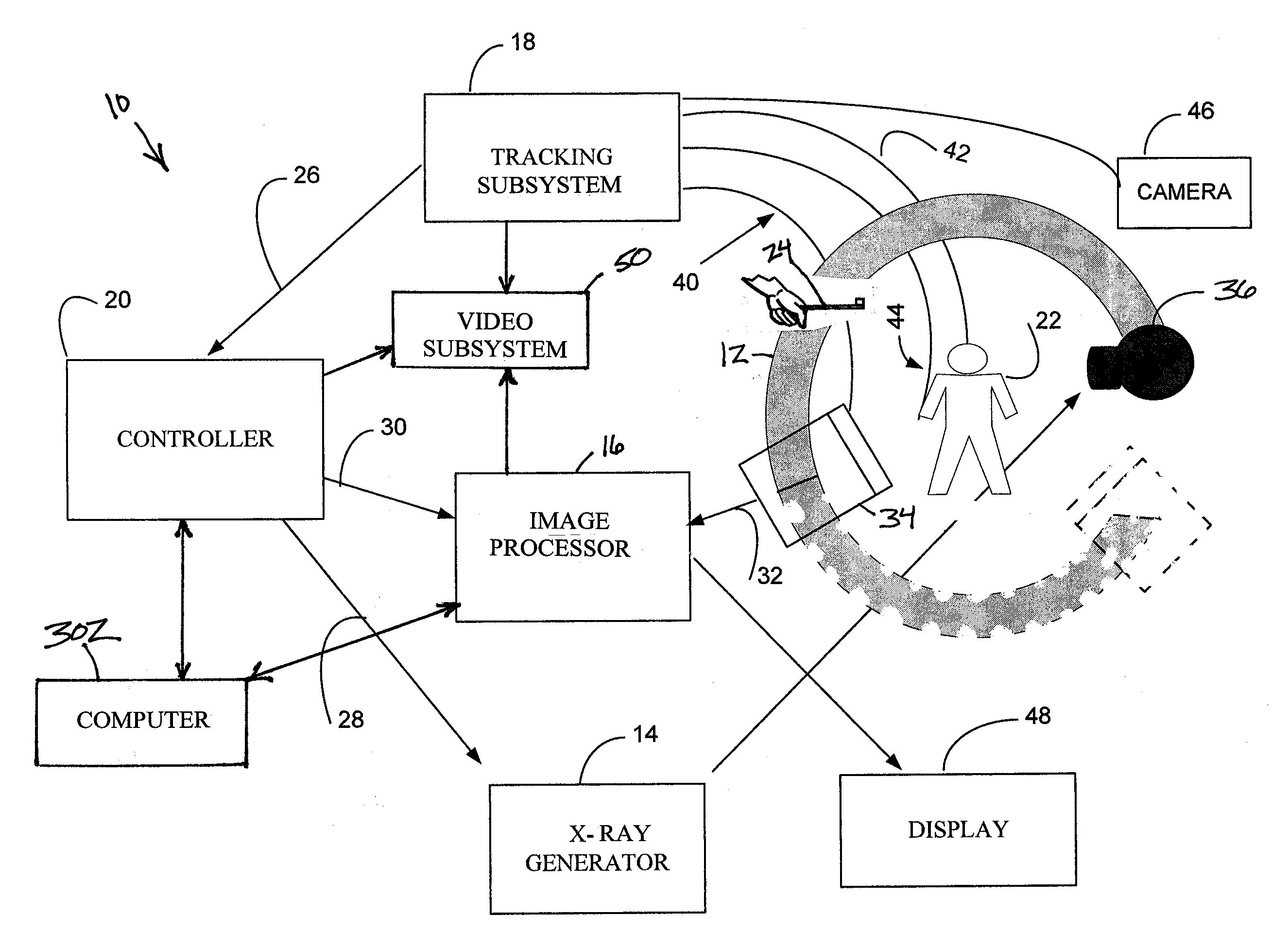
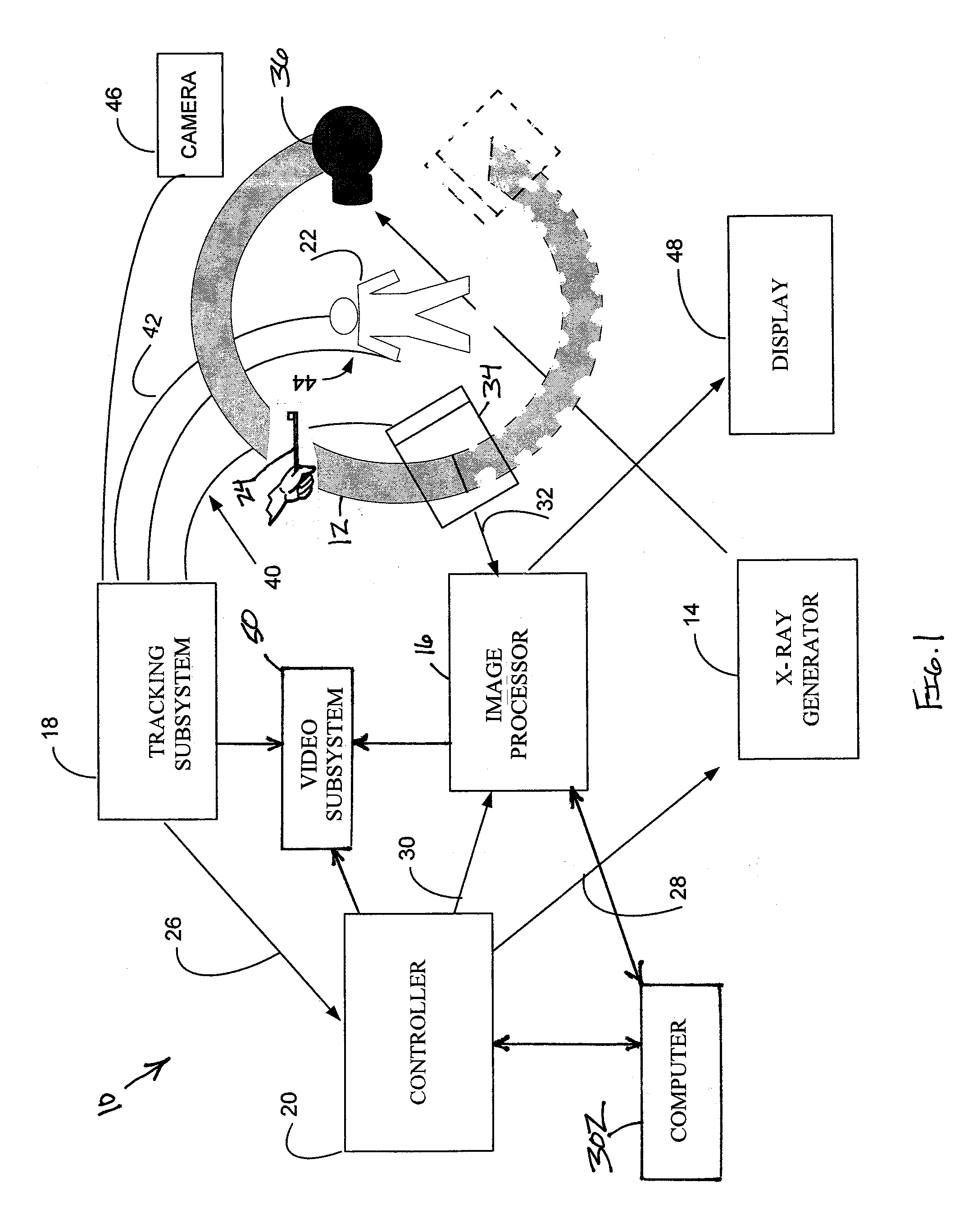
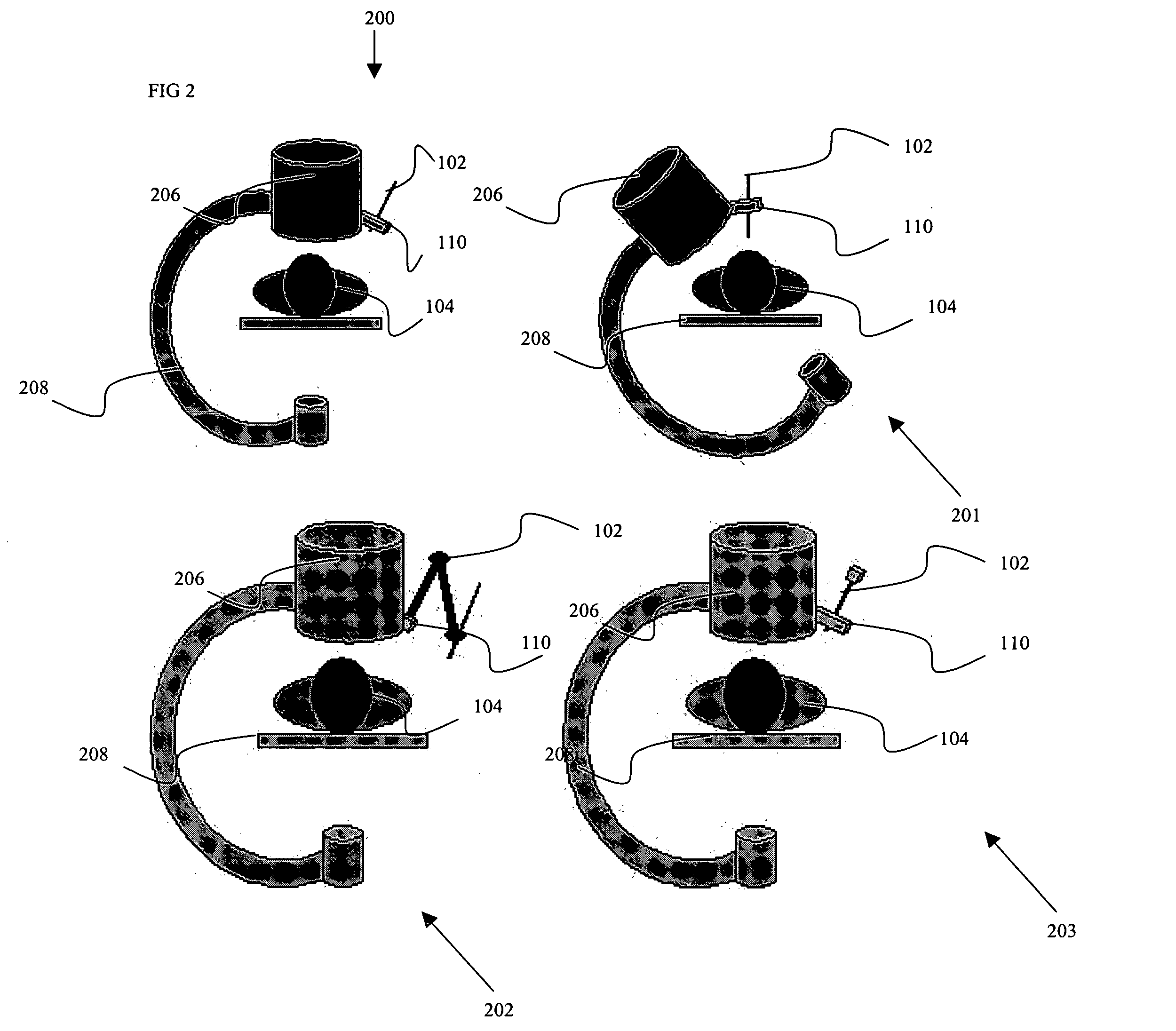
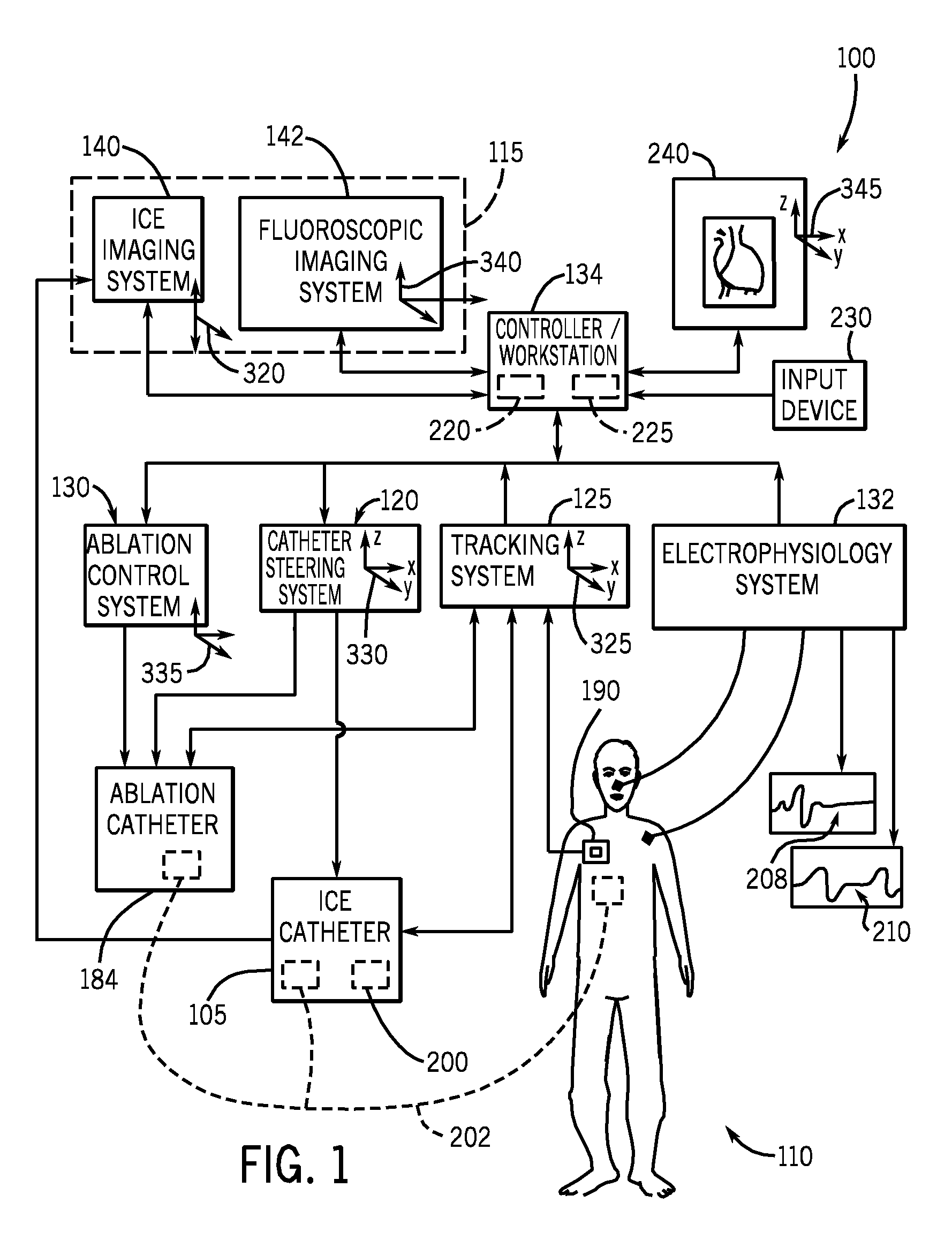
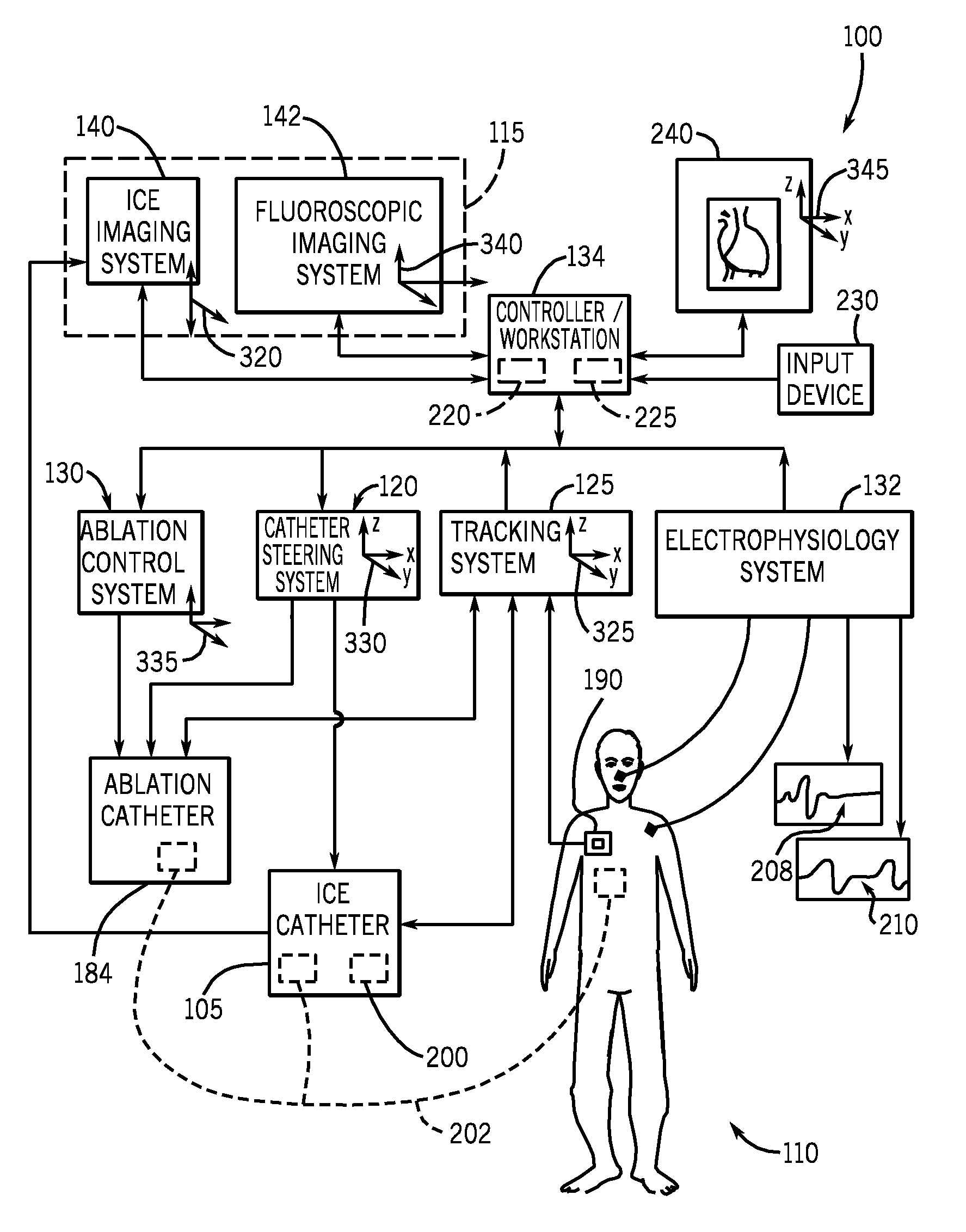
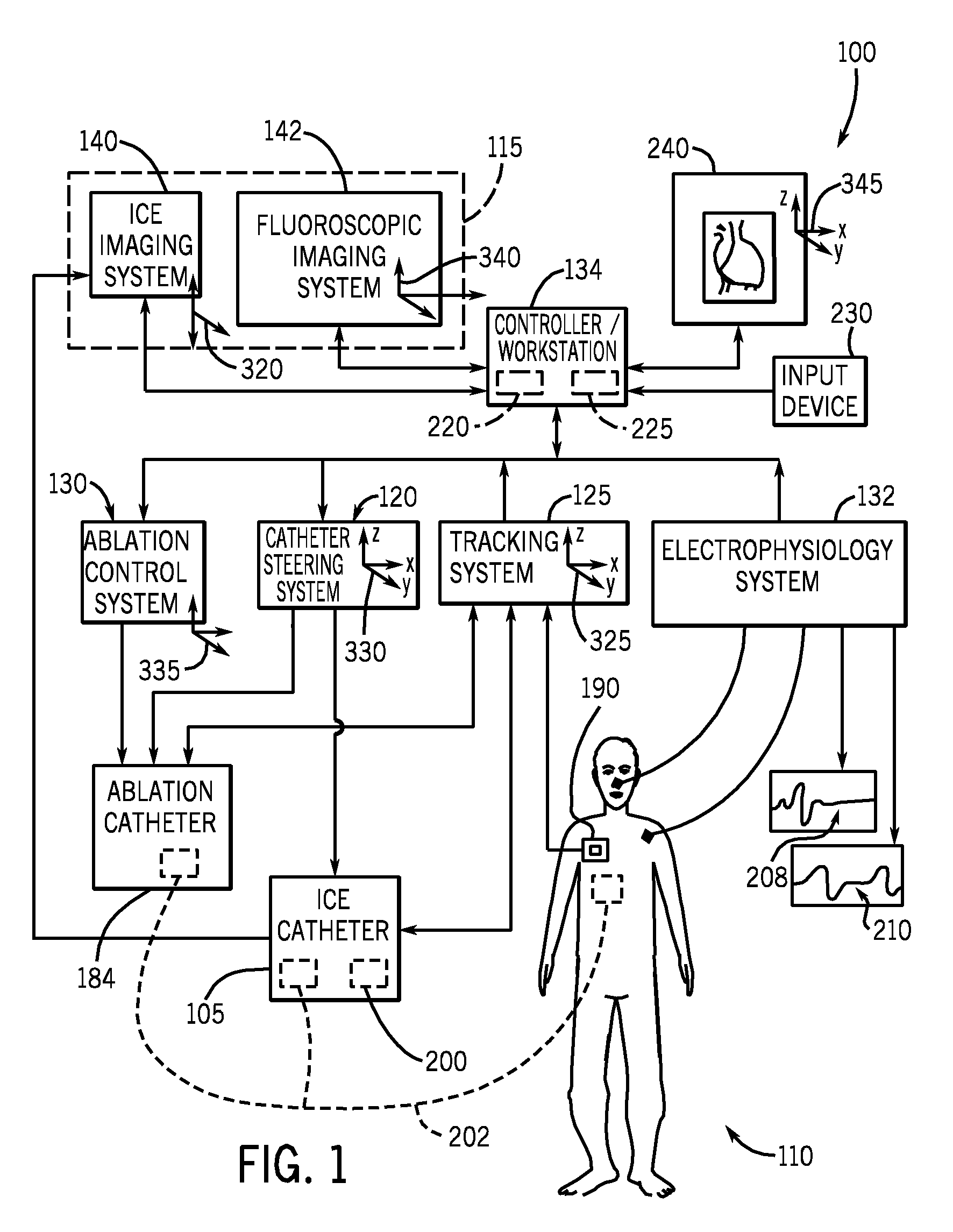
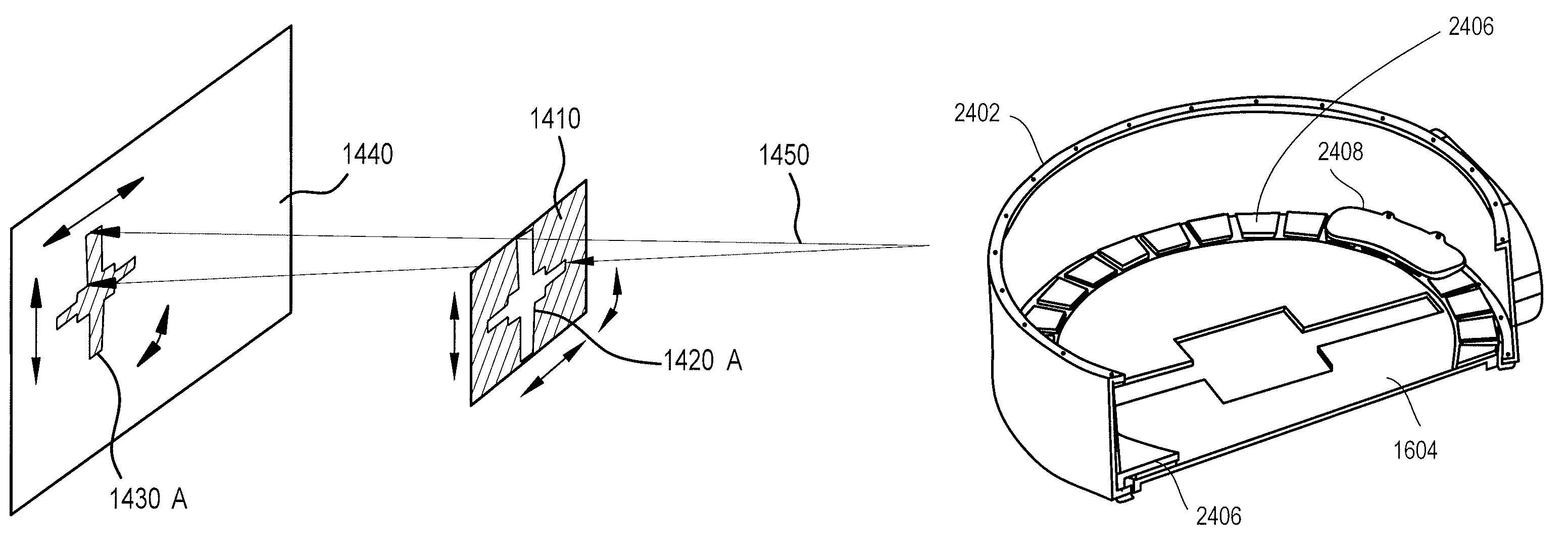
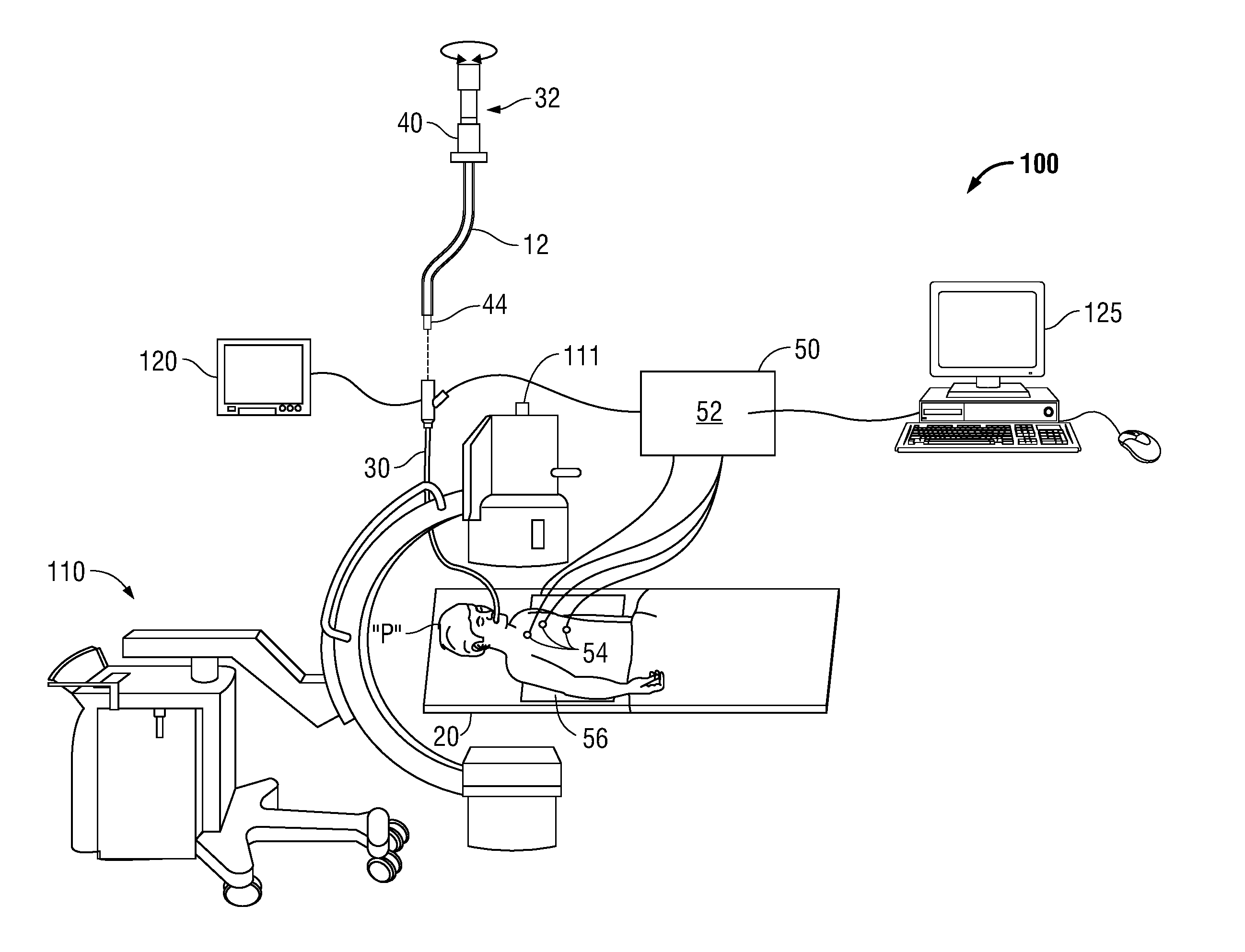
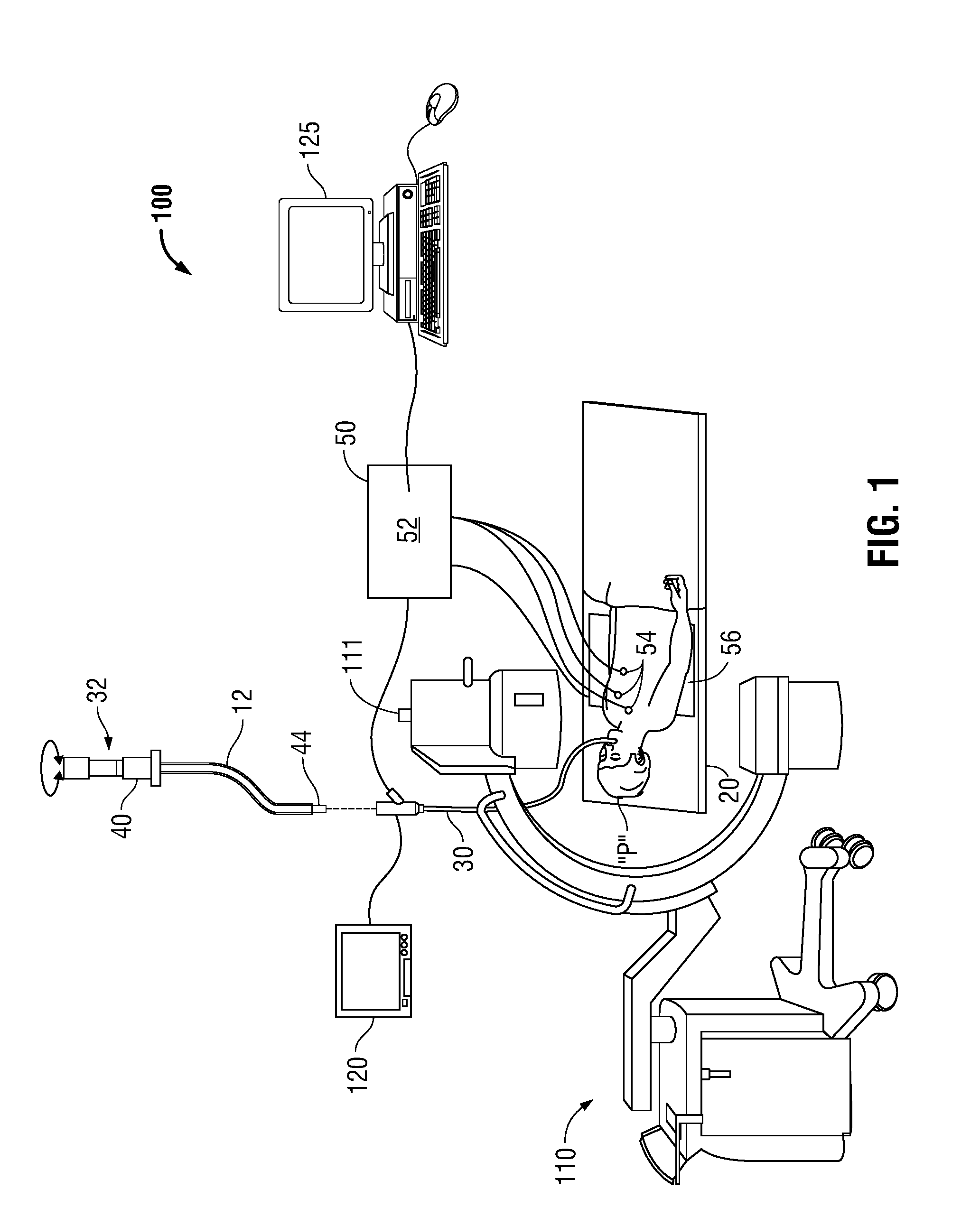
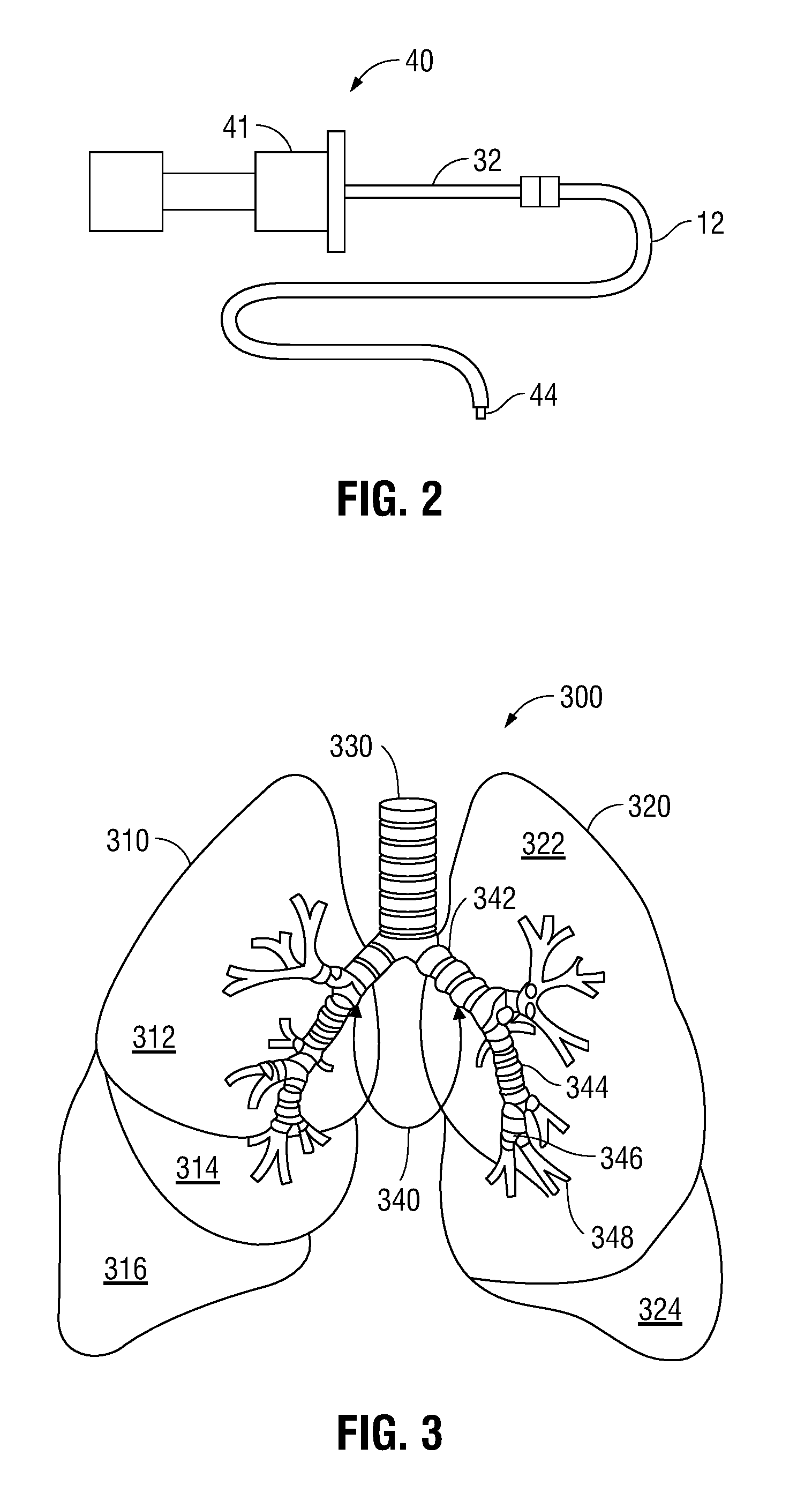
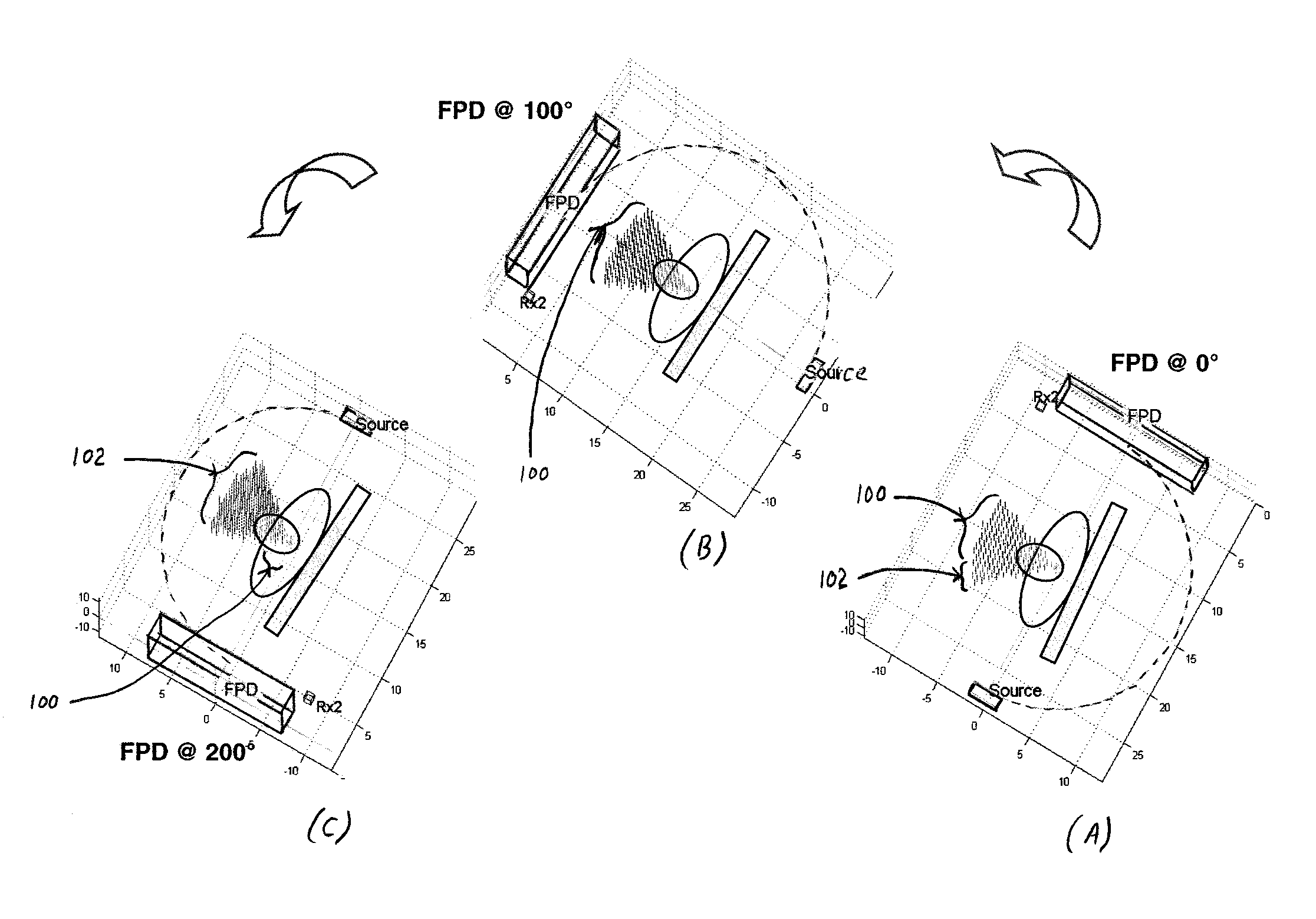
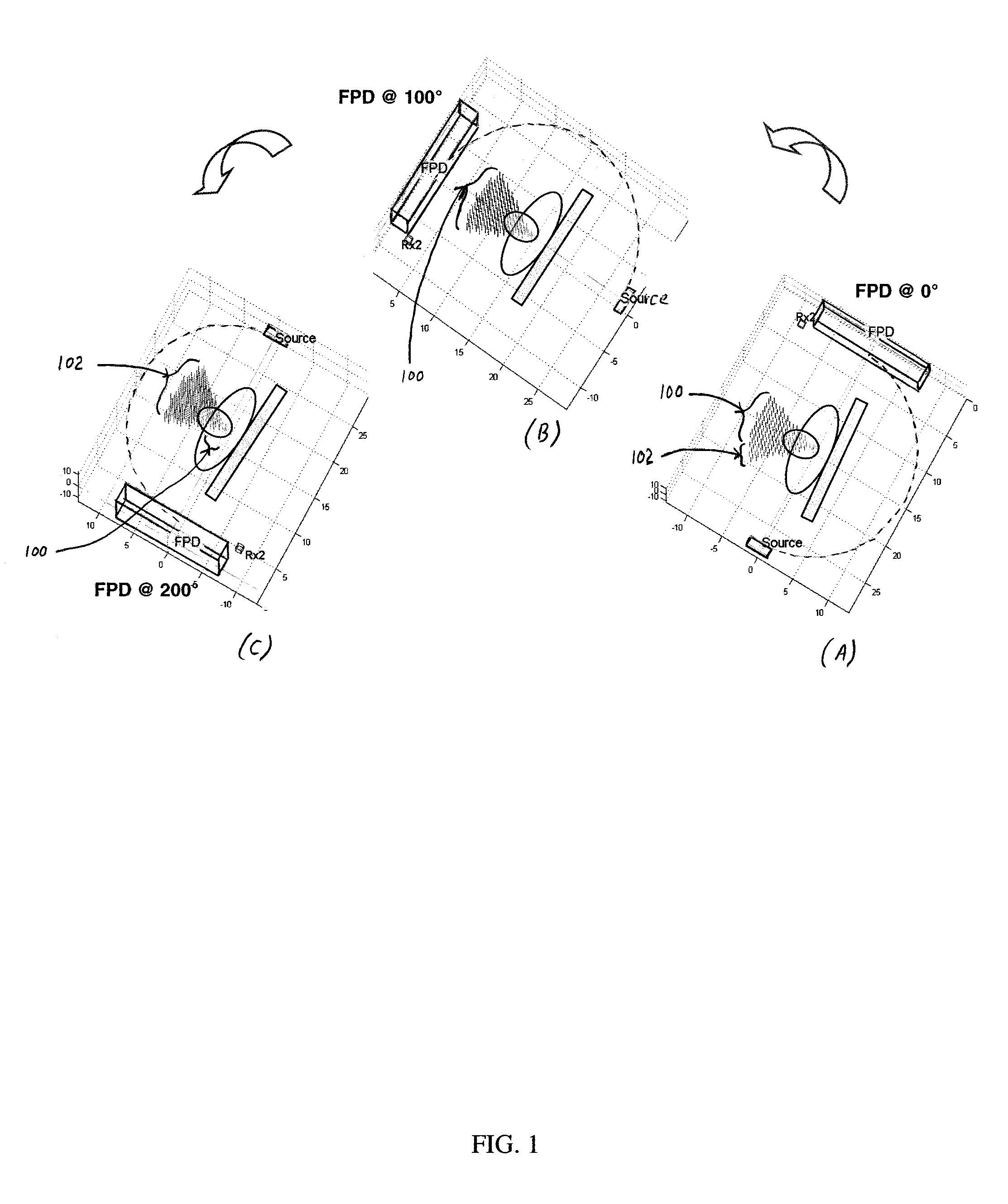
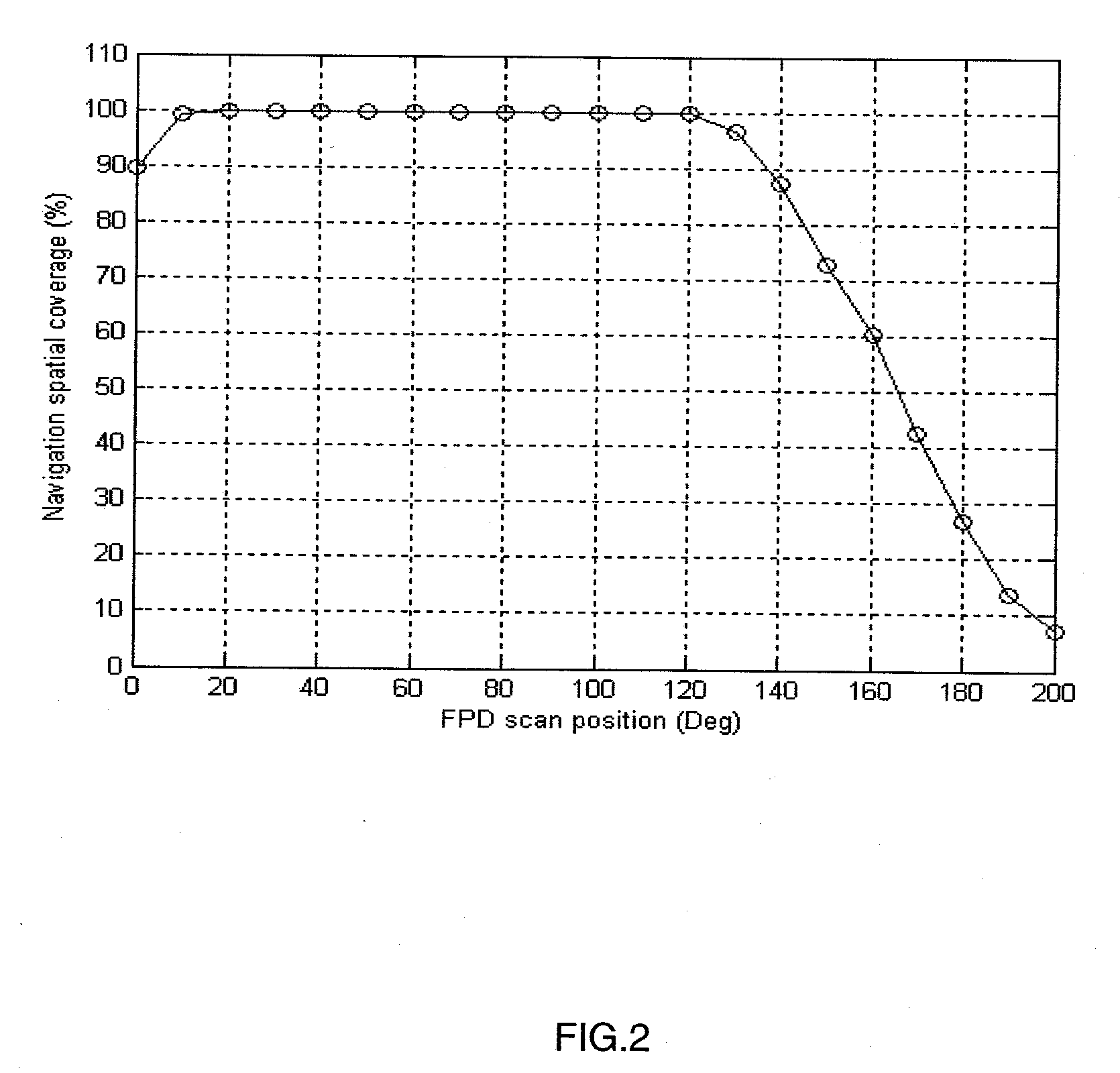
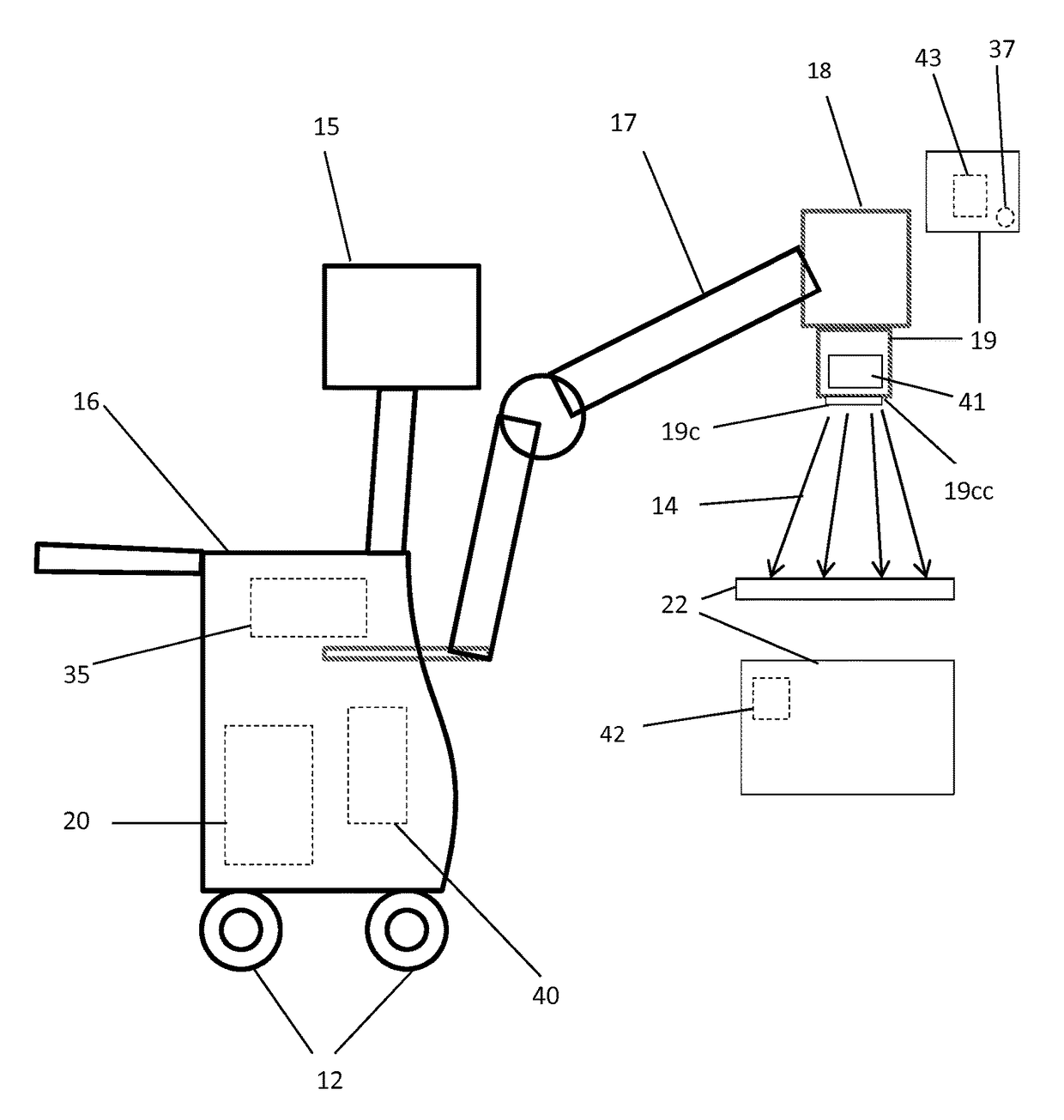
Navigational guidance via computer-assisted fluoroscopic imaging
Digital x-ray images taken before a surgical procedure by a fluoroscopic C-arm imager are displayed by a computer and overlaid with graphical representations of instruments be used in the operating room. The graphical representations are updated in real-time to correspond to movement of the instruments in the operating room. A number of different techniques are described that aid the physician in planning and carrying out the surgical procedure.
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION
Fluoroscopic image guided orthopaedic surgery system with intraoperative registration
InactiveUS7130676B2Safely determineCheck the accuracy of the procedureSurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringFluoroscopic imagingFluoroscopic image
A fluoroscopic image guided surgery system, comprising a C-arm fluoroscope for obtaining fluoroscopic images of an object bone, the C-arm fluoroscope including at least one set of emitters; a reference bar capable of attaching to an object bone, the reference bar including emitters; a surgical instrument for performing an operation, the instrument including emitters; a digitizer system in communication with the at least one set of emitters of the C-arm fluoroscope, the emitters of the reference bar, and the emitters of the surgical instrument so that the digitizer system can determine a position of each of the C-arm fluoroscope, the reference bar, and the surgical instrument; and a single fiducial marker for attachment to an object bone, the single fiducial marker being visible in the fluoroscopic images for determining a position of an object bone relative to the digitizer system.
Owner:SOFAMOR DANEK PROPERTIES
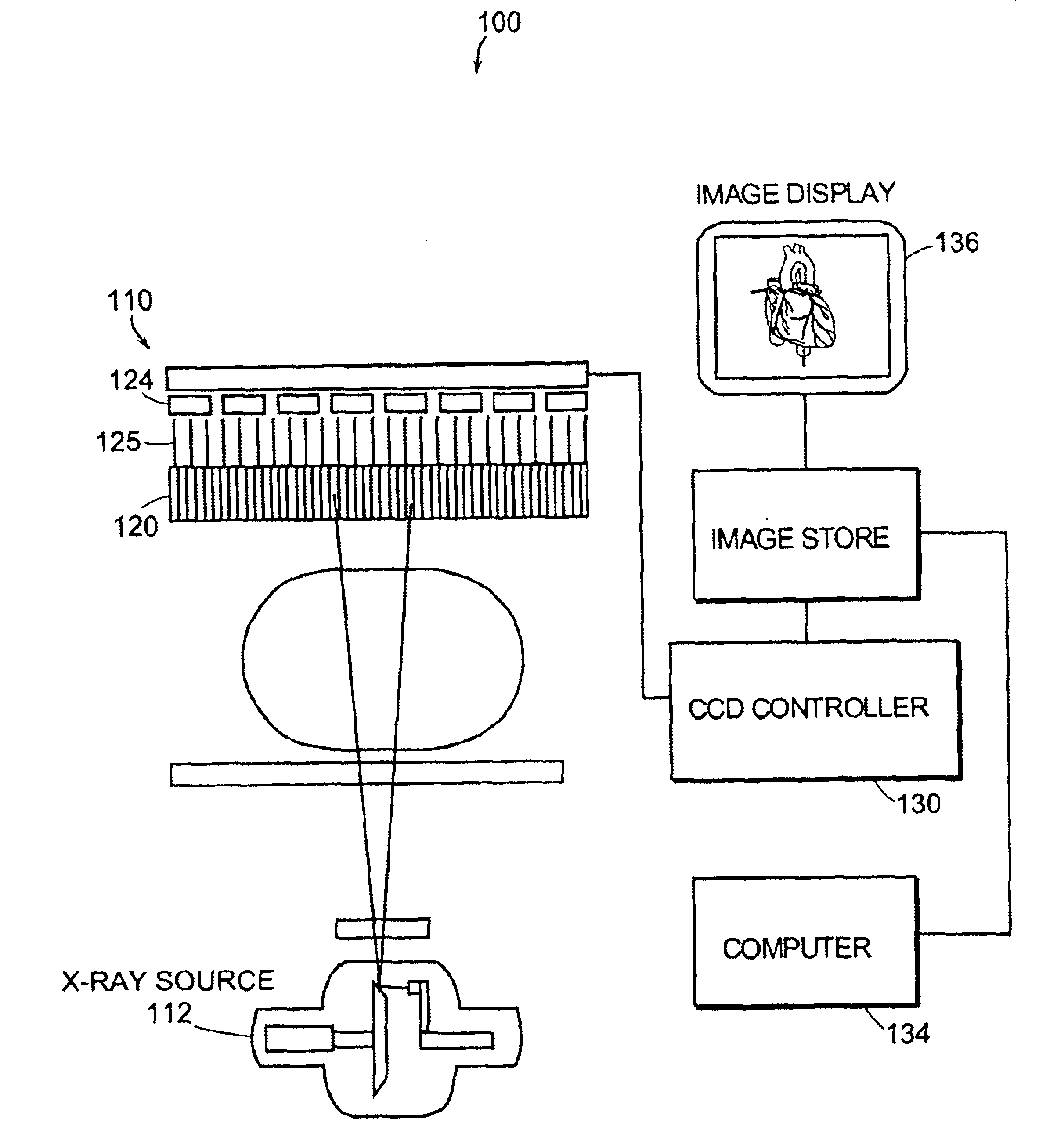
System and method for x-ray fluoroscopic imaging
InactiveUS6895077B2Increase frame rateAccurate imagingTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesFluorescenceX-ray
A system for x-ray fluoroscopic imaging of bodily tissue in which a scintillation screen and a charge coupled device (CCD) is used to accurately image selected tissue. An x-ray source generates x-rays which pass through a region of a subject's body, forming an x-ray image which reaches the scintillation screen. The scintillation screen re-radiates a spatial intensity pattern corresponding to the image, the pattern being detected by the CCD sensor. In a preferred embodiment the imager uses four 8×8-cm three-side buttable CCDs coupled to a CsI:T1 scintillator by straight (non-tapering) fiberoptics and tiled to achieve a field of view (FOV) of 16×16-cm at the image plane. Larger FOVs can be achieved by tiling more CCDs in a similar manner. The imaging system can be operated in a plurality of pixel pitch modes such as 78, 156 or 234-μm pixel pitch modes. The CCD sensor may also provide multi-resolution imaging. The image is digitized by the sensor and processed by a controller before being stored as an electronic image. Other preferred embodiments may include each image being directed on flat panel imagers made from but not limited to, amorphous silicon and / or amorphous selenium to generate individual electronic representations of the separate images used for diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS MEDICAL CENT
Navigational guidance via computer-assisted fluoroscopic imaging
ActiveUS20030073901A1Local control/monitoringSurgical navigation systemsFluoroscopic imagingGraphics
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION INC
System and method for video capture for fluoroscopy and navigation
InactiveUS20080144906A1Television system detailsDiagnostics using lightFluoroscopic imagingImage resolution
Systems and methods are provided in some embodiments for recording, storage and replay of captured video from a surgical navigation system, a fluoroscopic imaging system, or an integrated fluoroscopy and navigation system. In some embodiments, full resolution video data is captured in an acquisition buffer and is available for replay and storage.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Surgical tool guide
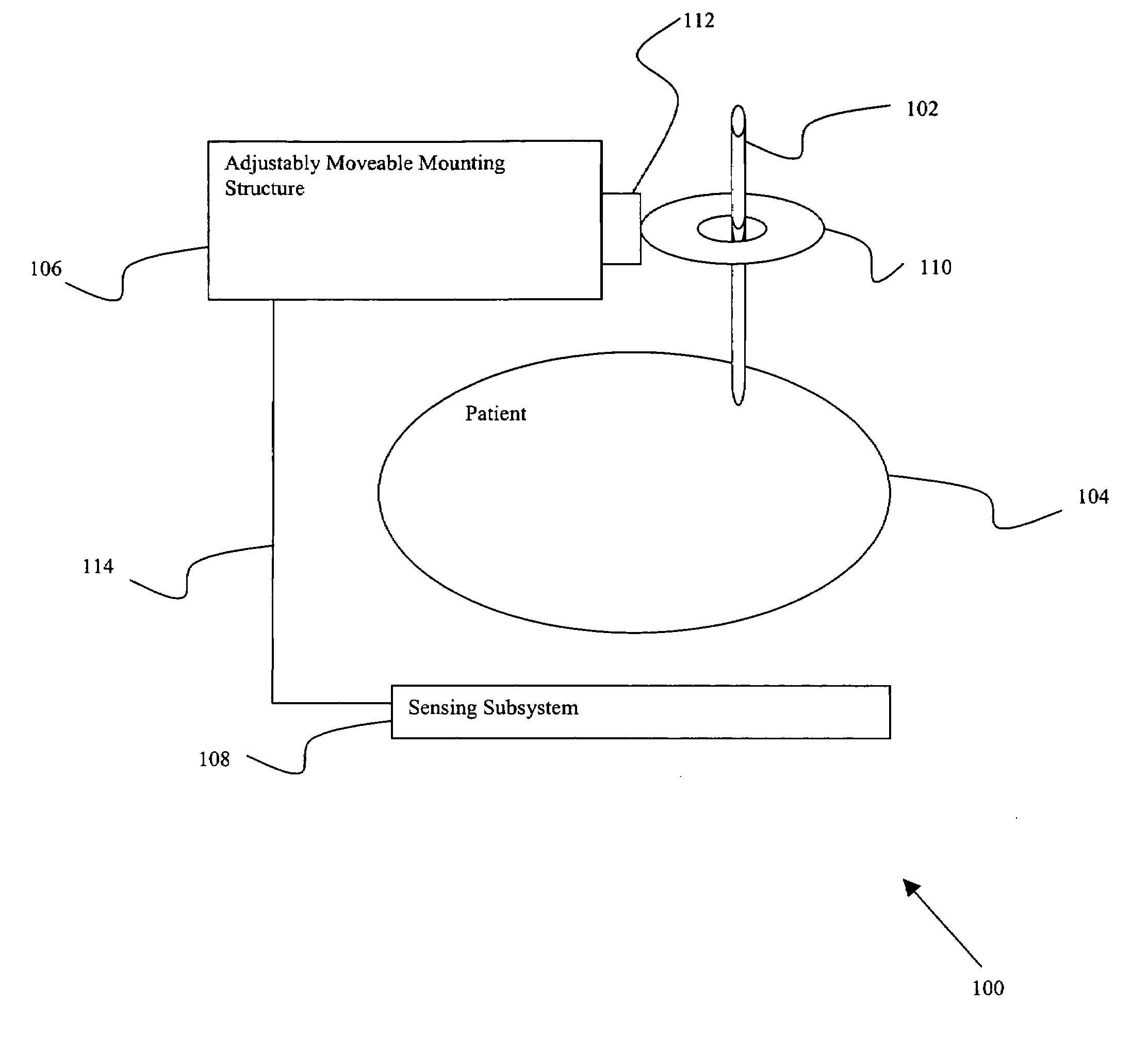
InactiveUS20080004523A1Precise positioningDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFluoroscopic imagingEngineering
Certain embodiments of the present invention provide n system for orienting a surgical tool with respect to a patient including: a tool guide for facilitating orientation of the surgical tool with respect to the patient, the tool guide including a mounting portion and a tool receiving portion, wherein the tool guide is capable of being integrated with at least a portion of a radiological imaging subsystem including an adjustably moveable mounting structure. In an embodiment, the tool receiving portion is capable of receiving an end-effector. In an embodiment the at least a portion of the radiological imaging subsystem comprises a C-arm. In an embodiment the radiological imaging subsystem comprises a fluoroscopic imaging subsystem. In an embodiment, the end-effector comprises at least one of: an aperture, a cutting device, a drilling device, a clamp, a sleeve, a mounting surface, a ring, a rail, a threaded shaft, a clasp, a bayonet mount, an imaging device, an ultrasound probe, a surgical tool, a catheter, a pin, a screw, a plate, a drill, an awl, and a probe. In an embodiment, the tool guide further comprises an end-effector. In an embodiment, a position of the surgical tool is capable of being adjusted by automatically moving the adjustably movable mounting structure. In an embodiment, the system further comprises at least one position sensing subsystem for ascertaining a position of the surgical tool with respect to the patient.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method And System For Dynamic Low Dose X-ray Imaging
InactiveUS20080118023A1Reduce decreaseReduce detectionTomosynthesisHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-rayX ray dose
A method and system for performing fluoroscopic imaging of a subject has high temporal and spatial resolution in a center portion of the captured dynamic images. The system provides for reduced X-ray dose to the patient associated with that part of the X-ray beam associated with a peripheral portion of the captured images although temporal, and in some embodiments spatial, resolution is reduced in the peripheral portion of the image. The system uses a rotating collimator to produce an X-ray beam having narrow wing portions associated with the peripheral portions of the image, and a broader central region associated with the high resolution center portion of the images.
Owner:FOREVISION IMAGING TECH LLC
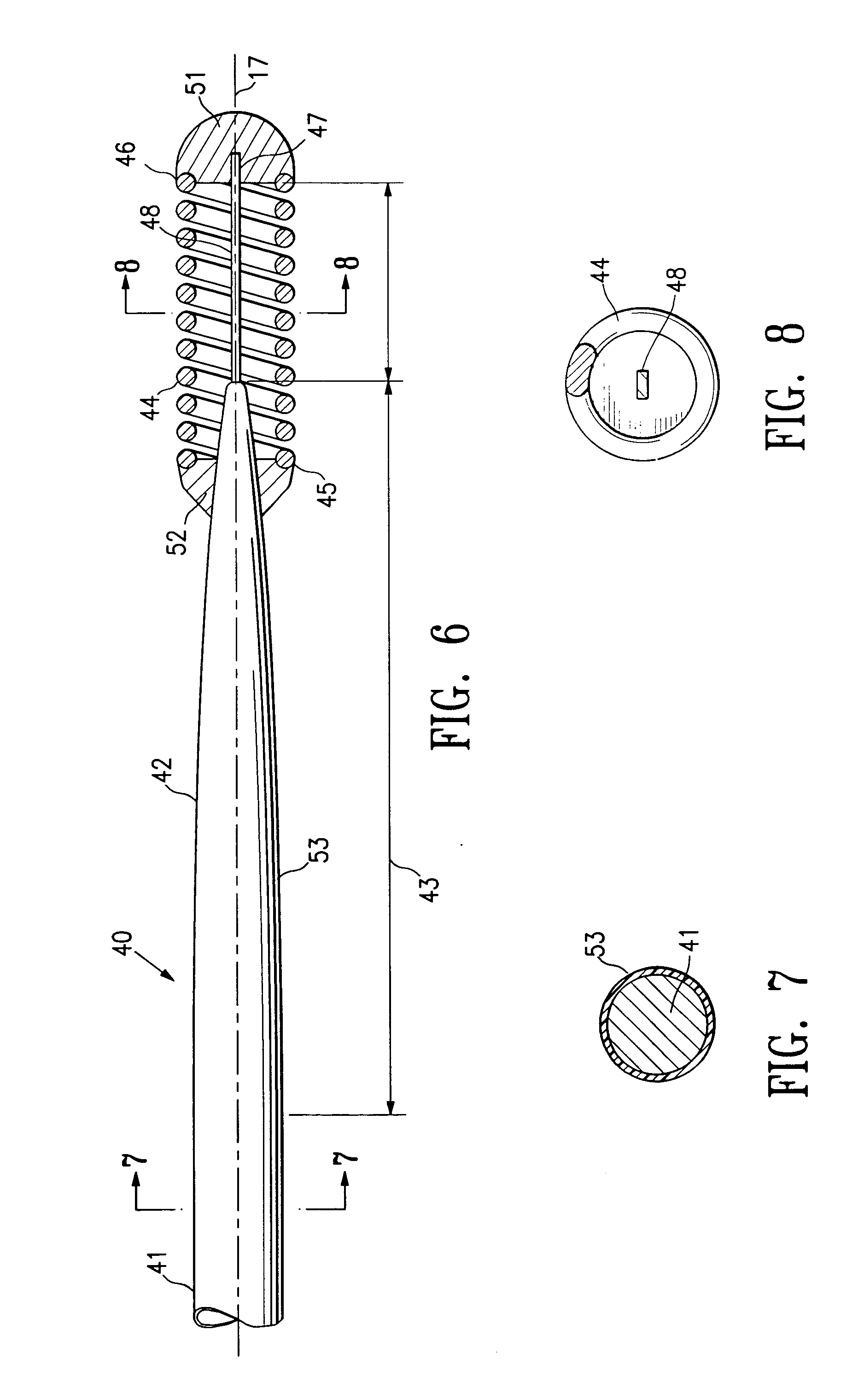
Polymer coated guidewire
InactiveUS7494474B2Enhanced distal and proximal supportImprove maneuverabilityGuide wiresSurgeryFluoroscopic imagingGuide wires
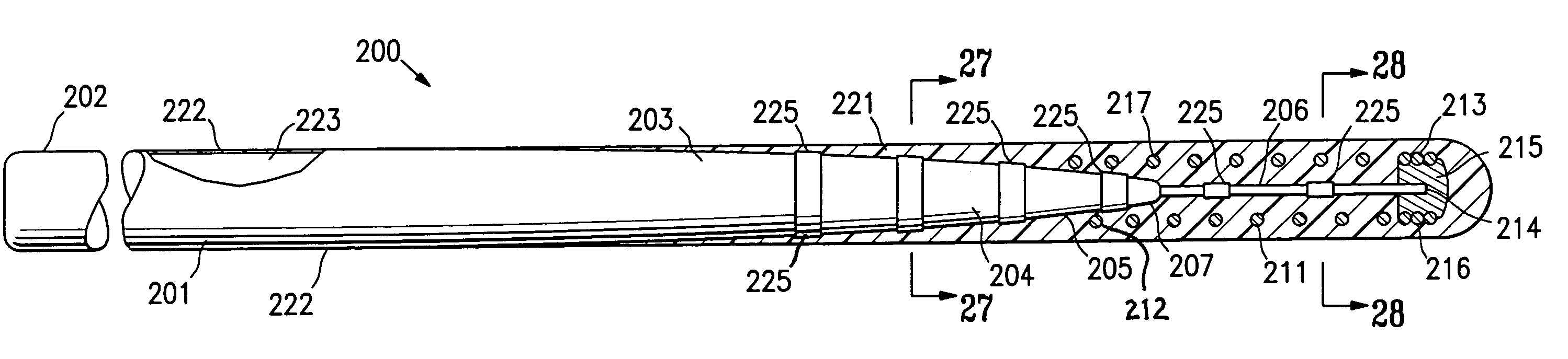
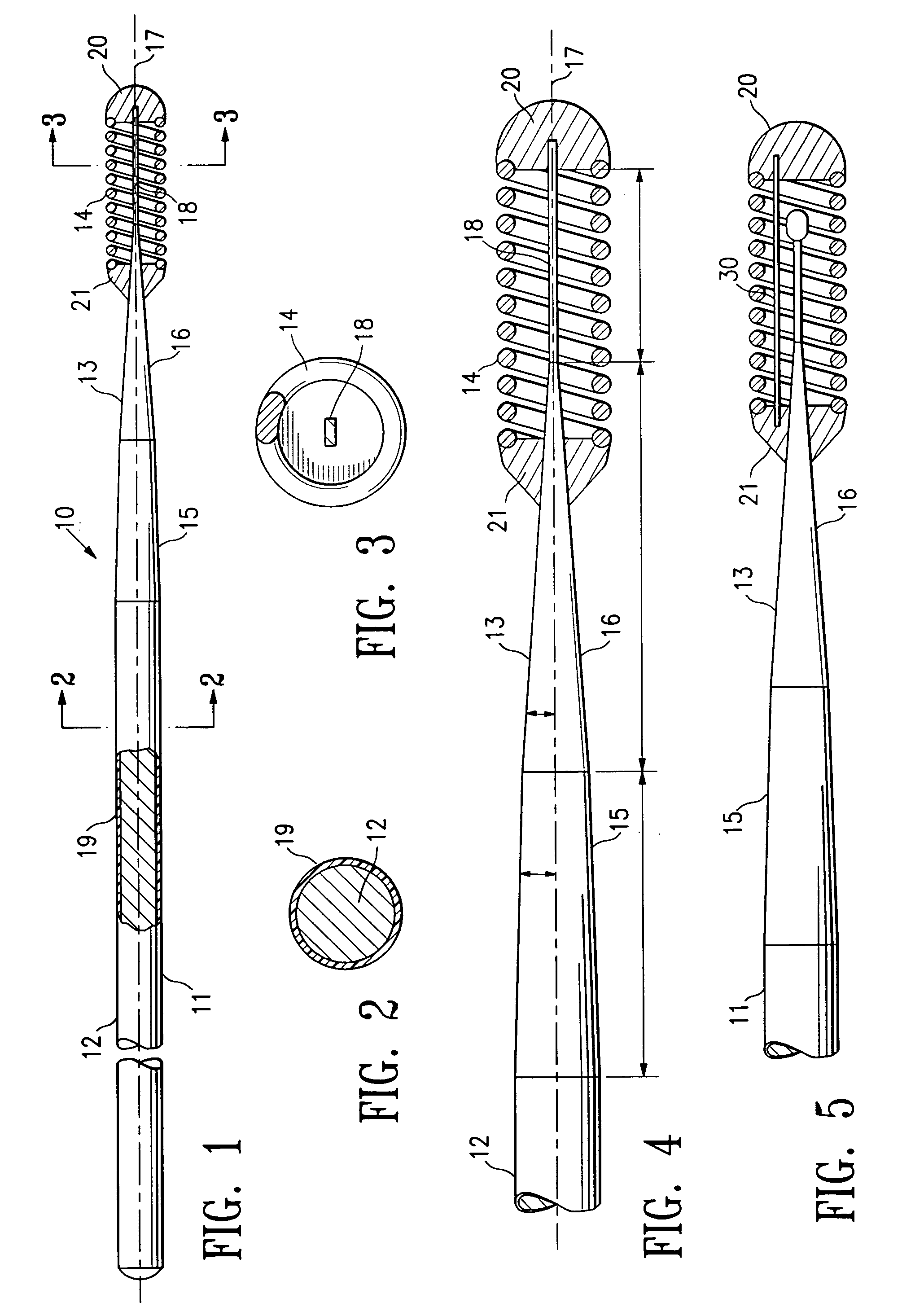
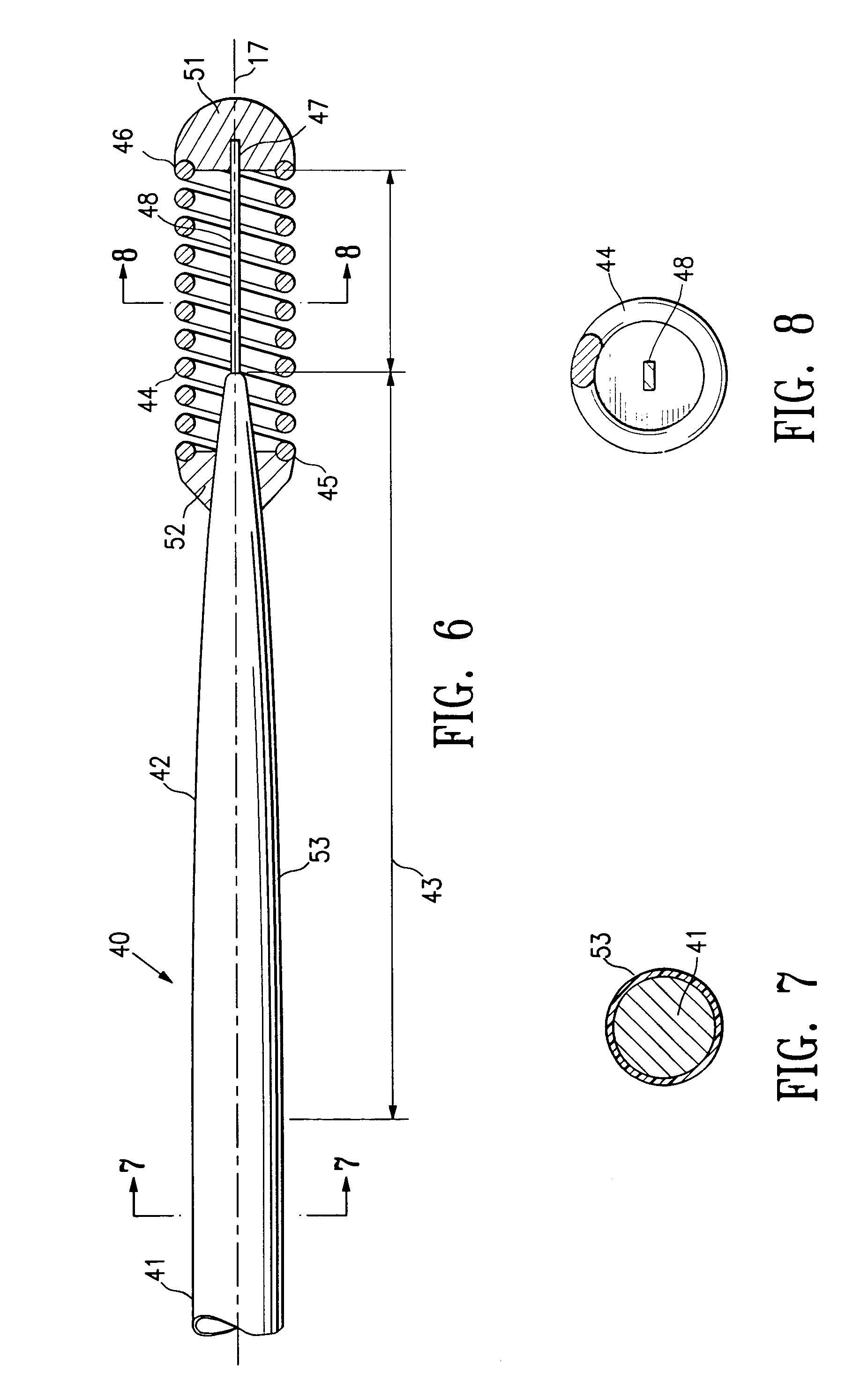
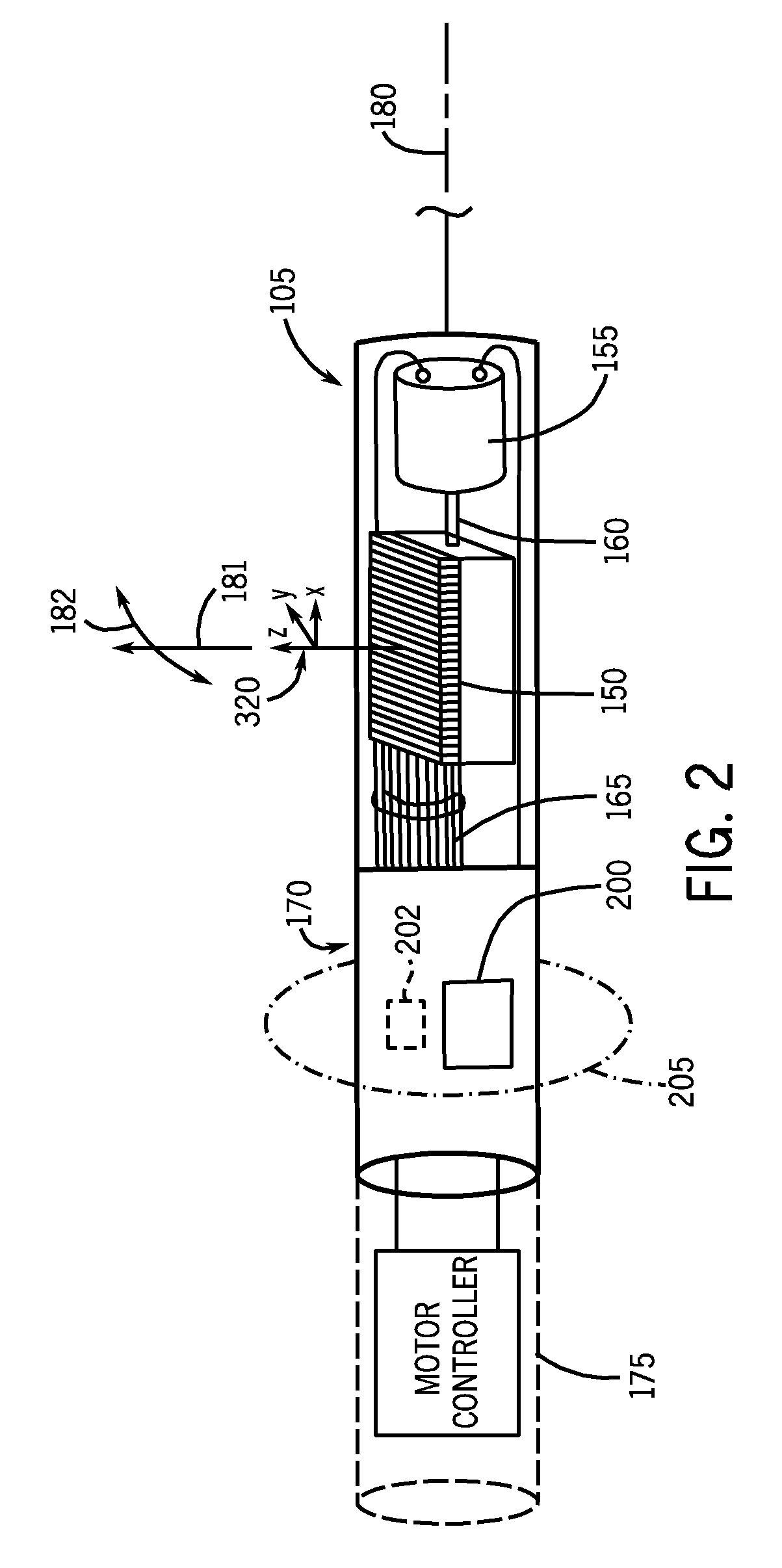
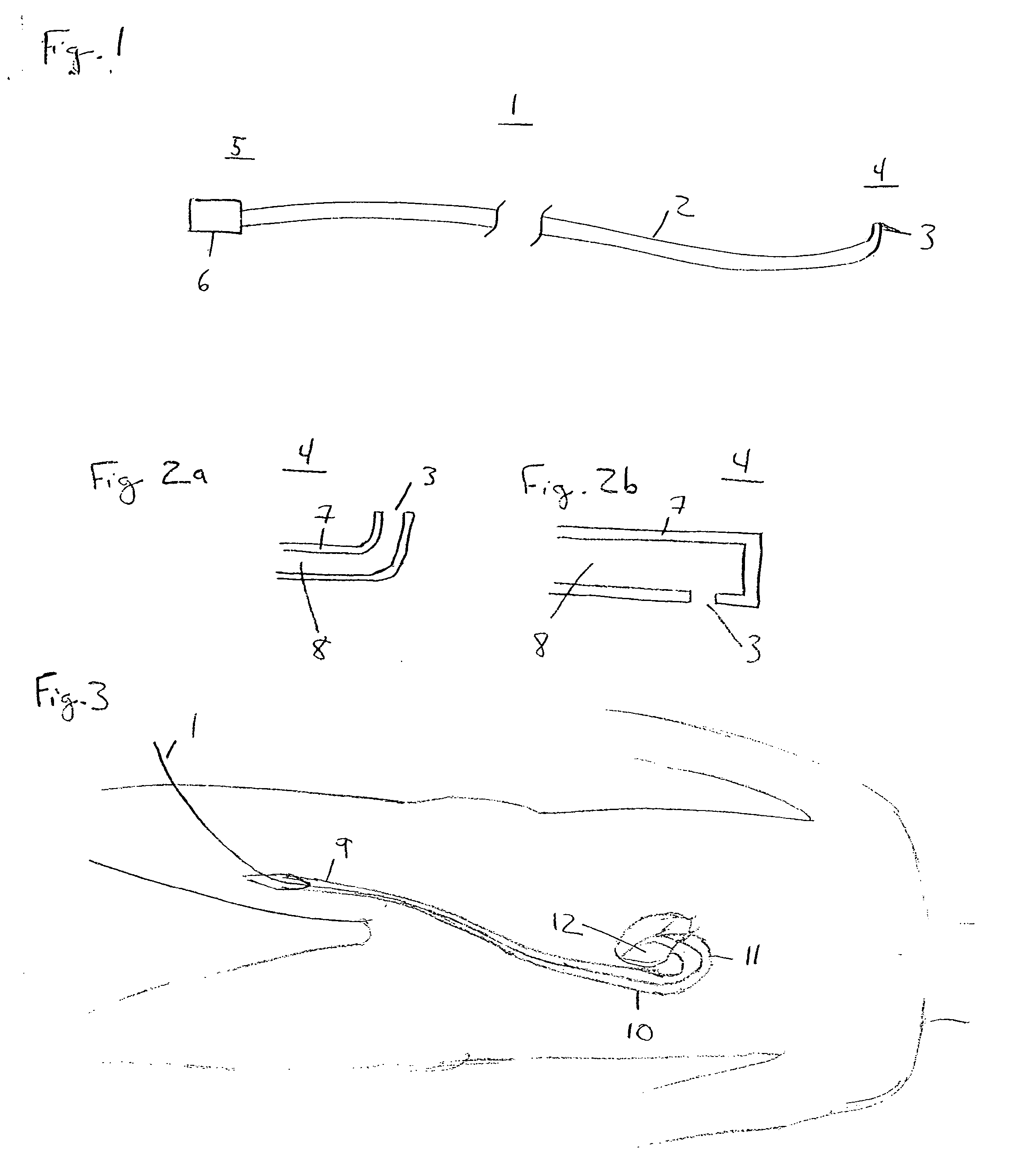
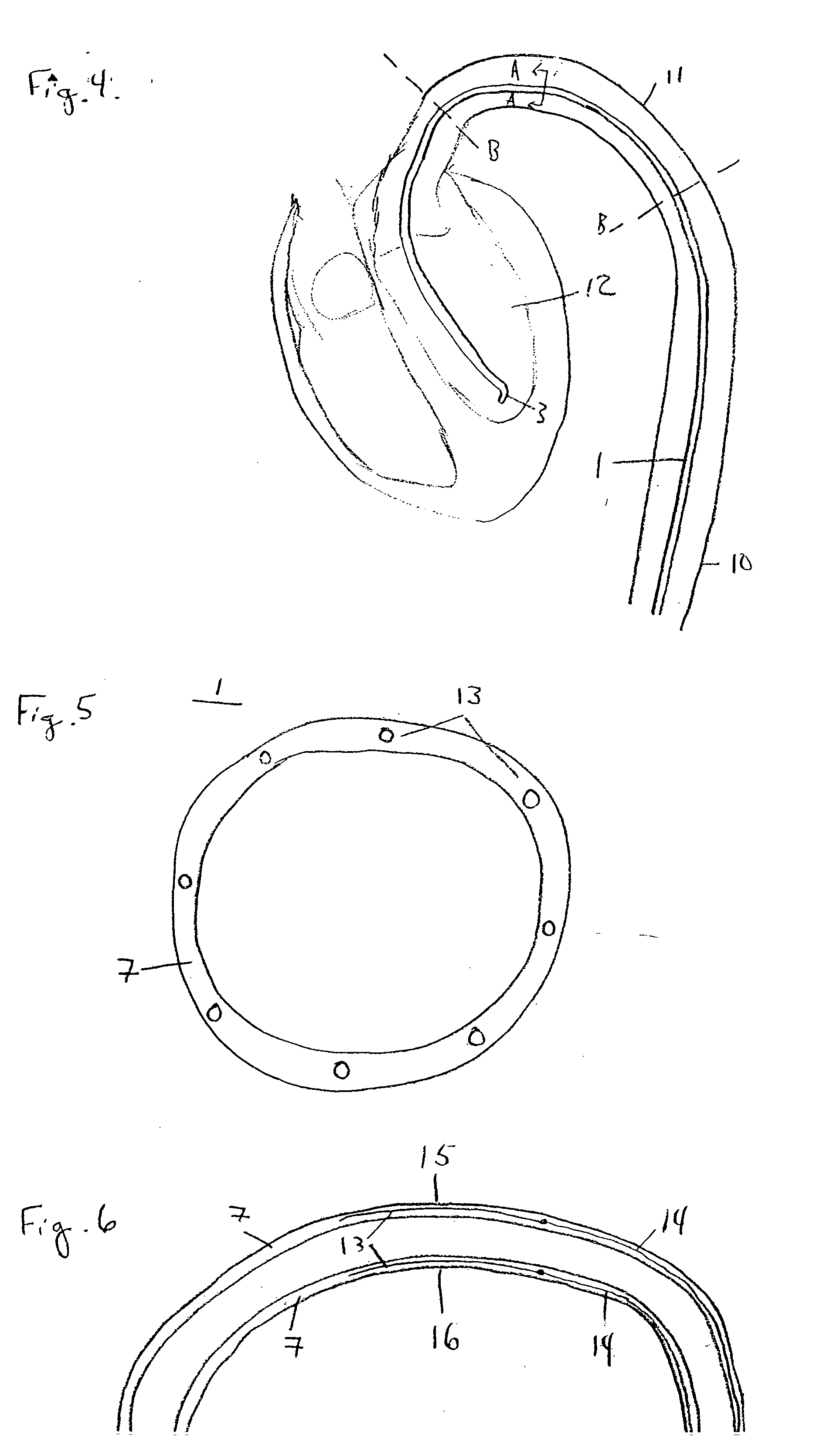
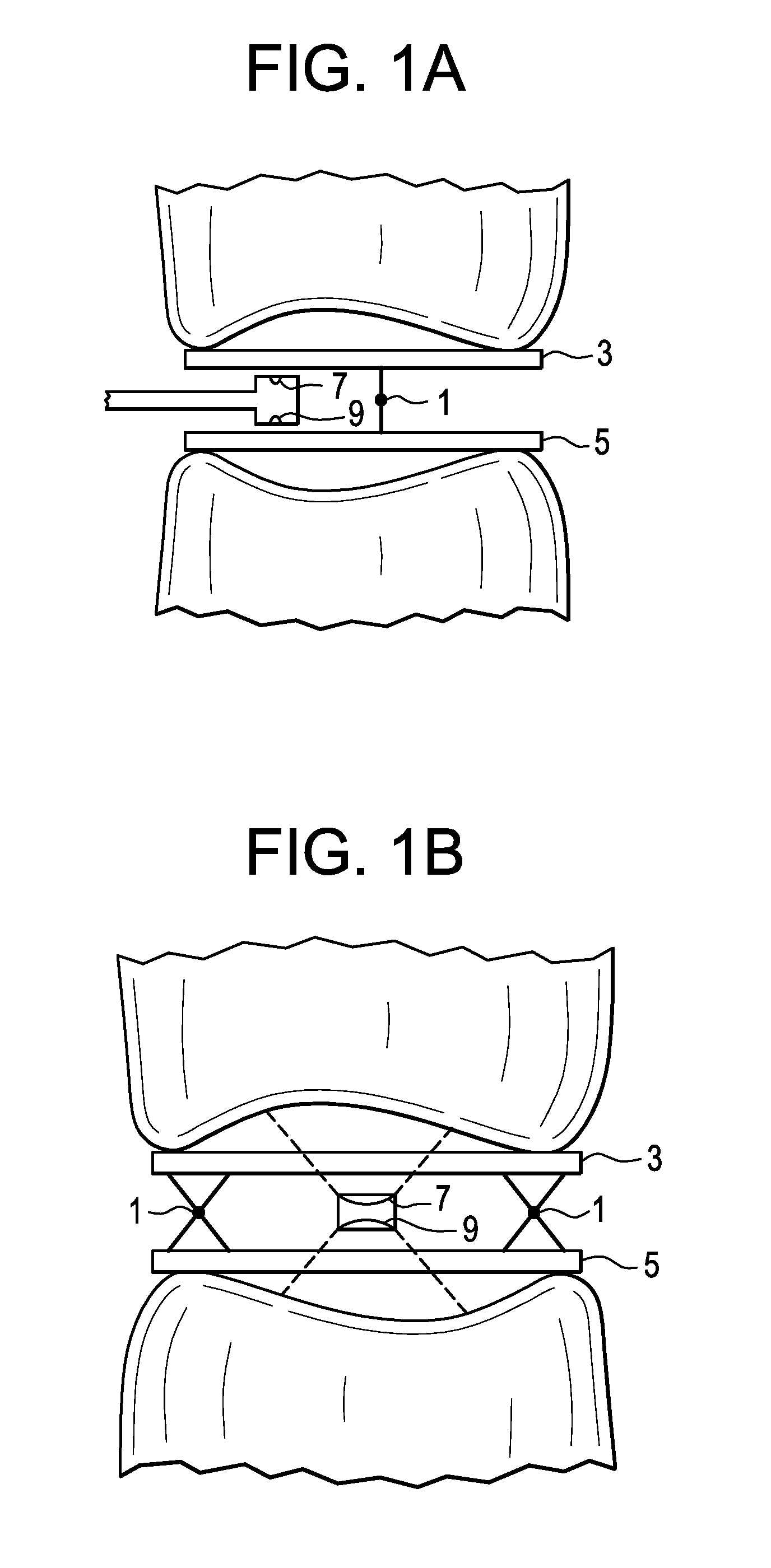
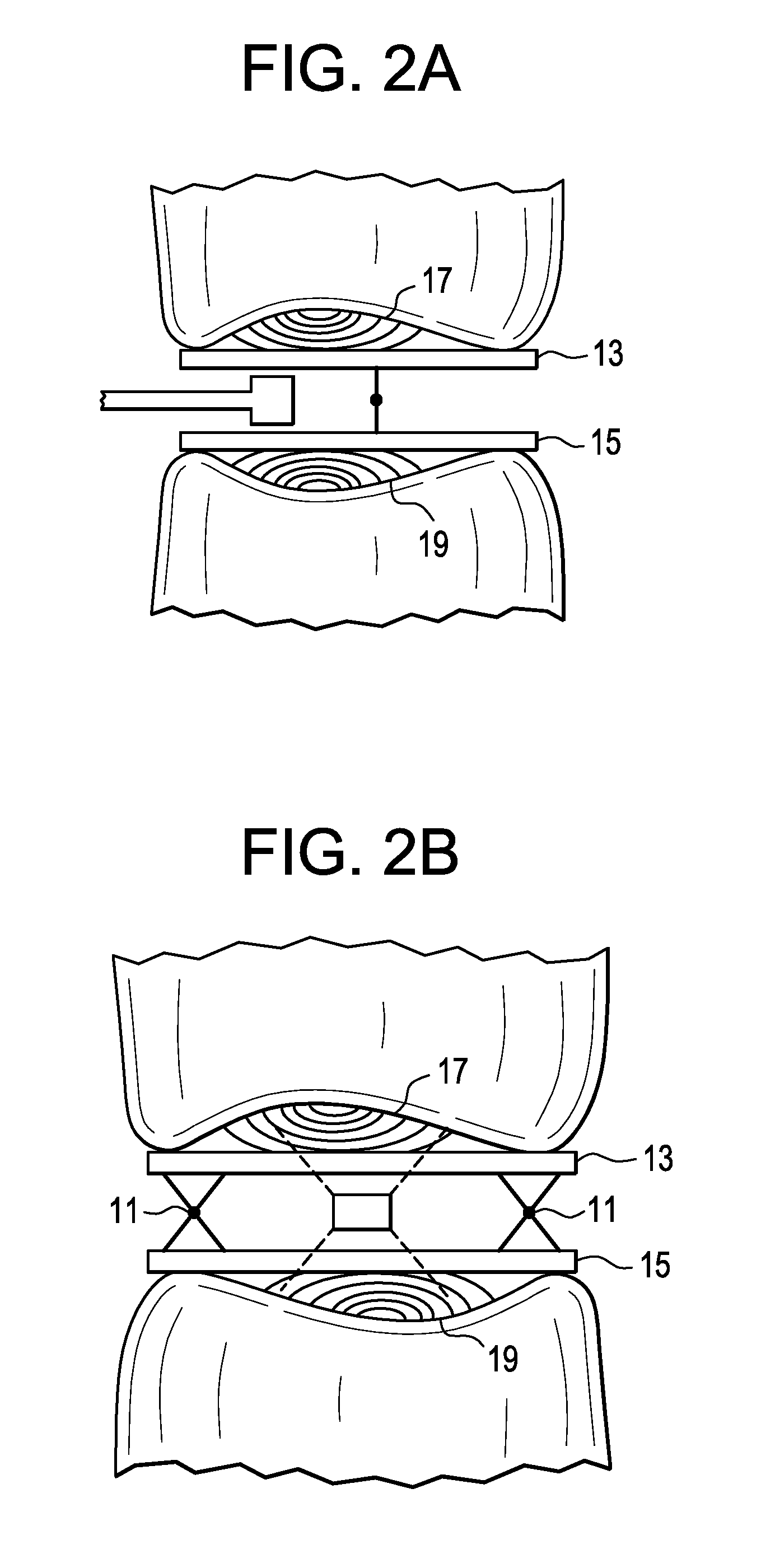
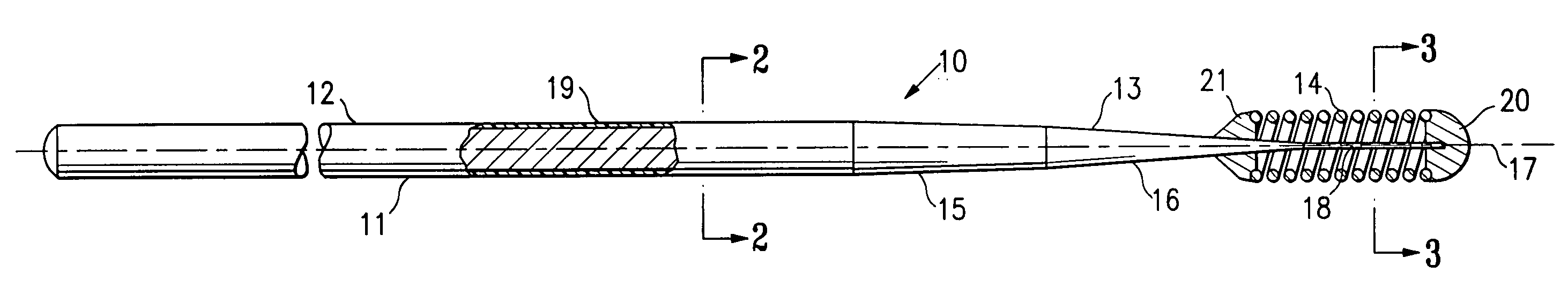
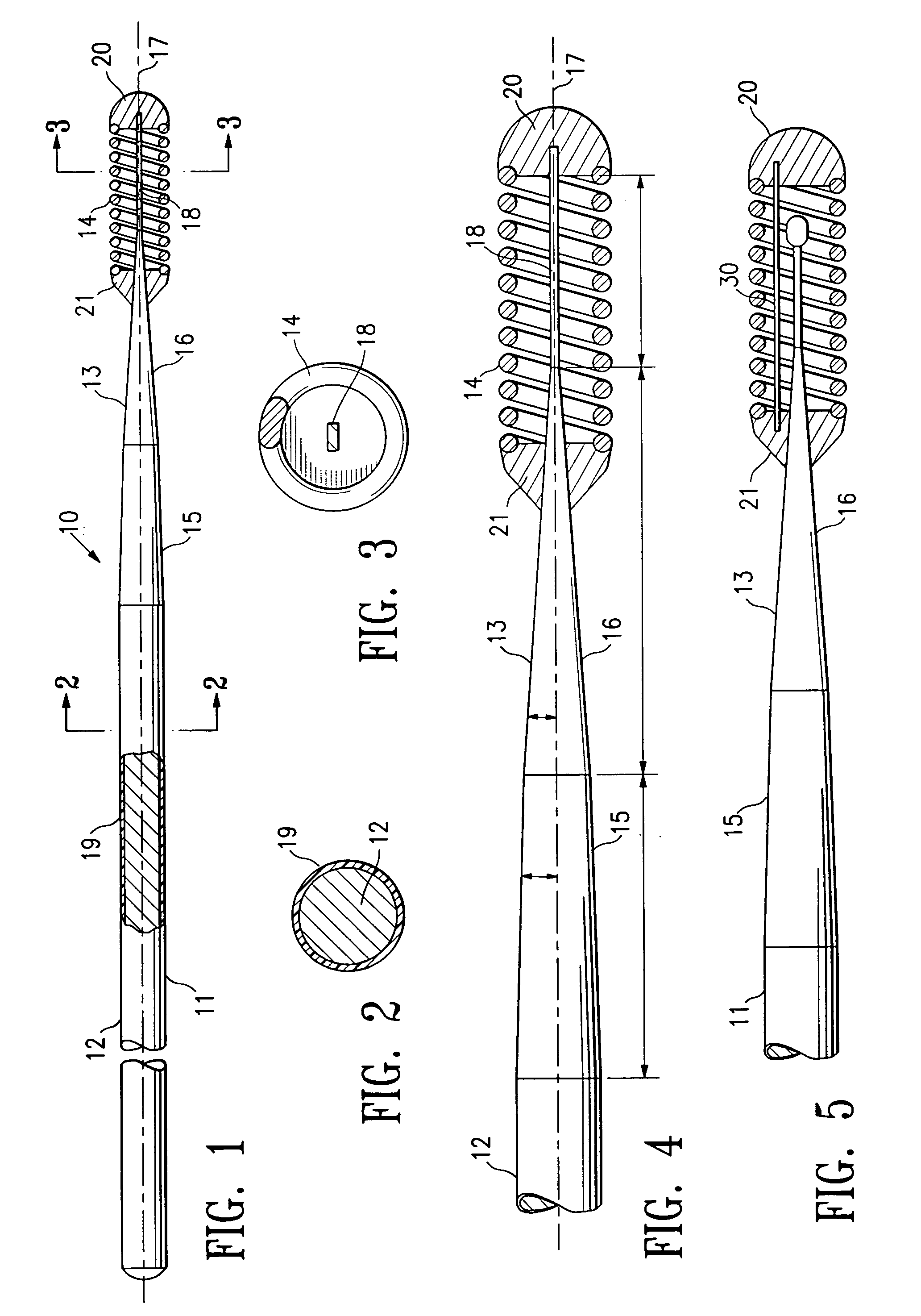
A guidewire or section thereof, that has a core member or the like with a plurality of contiguous tapered segments having taper angles that are configured to produce a linear change in stiffness over a longitudinal portion of the device. The device may also have a core section with a continuously changing taper angle to produce a curvilinear profile that is configured to produce a linear change in stiffness of the core over a longitudinal portion of the device. An embodiment has a plurality of radiopaque elements that may be intermittent, continuous or in the form of a helical ribbon for scaled measurement of intracorporeal structure under fluoroscopic imaging. Another embodiment has at least one layer of polymer over the distal end of the device.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
System and method of combining ultrasound image acquisition with fluoroscopic image acquisition
ActiveUS20080283771A1Enhancement in monitoring and treatingEasy to placeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsLuminescent dosimetersUltrasound imagingFluoroscopic imaging
A system and method to image an imaged subject is provided. The system comprises an ultrasound imaging system including an imaging probe operable to move internally and acquire ultrasound image data of the imaged subject, a fluoroscopic imaging system operable to acquire fluoroscopic image data of the imaged subject during image acquisition by the ultrasound imaging system, and a controller in communication with the ultrasound imaging system and the fluoroscopic imaging system. A display can be illustrative of the ultrasound image data acquired with the imaging probe in combination with a fluoroscopic imaging data acquired by the fluoroscopic imaging system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method of combining ultrasound image acquisition with fluoroscopic image acquisition
ActiveUS8364242B2Easy to monitorEnhancement of placement and guidanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsLuminescent dosimetersUltrasound imagingFluoroscopic imaging
A system and method to image an imaged subject is provided. The system comprises an ultrasound imaging system including an imaging probe operable to move internally and acquire ultrasound image data of the imaged subject, a fluoroscopic imaging system operable to acquire fluoroscopic image data of the imaged subject during image acquisition by the ultrasound imaging system, and a controller in communication with the ultrasound imaging system and the fluoroscopic imaging system. A display can be illustrative of the ultrasound image data acquired with the imaging probe in combination with a fluoroscopic imaging data acquired by the fluoroscopic imaging system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
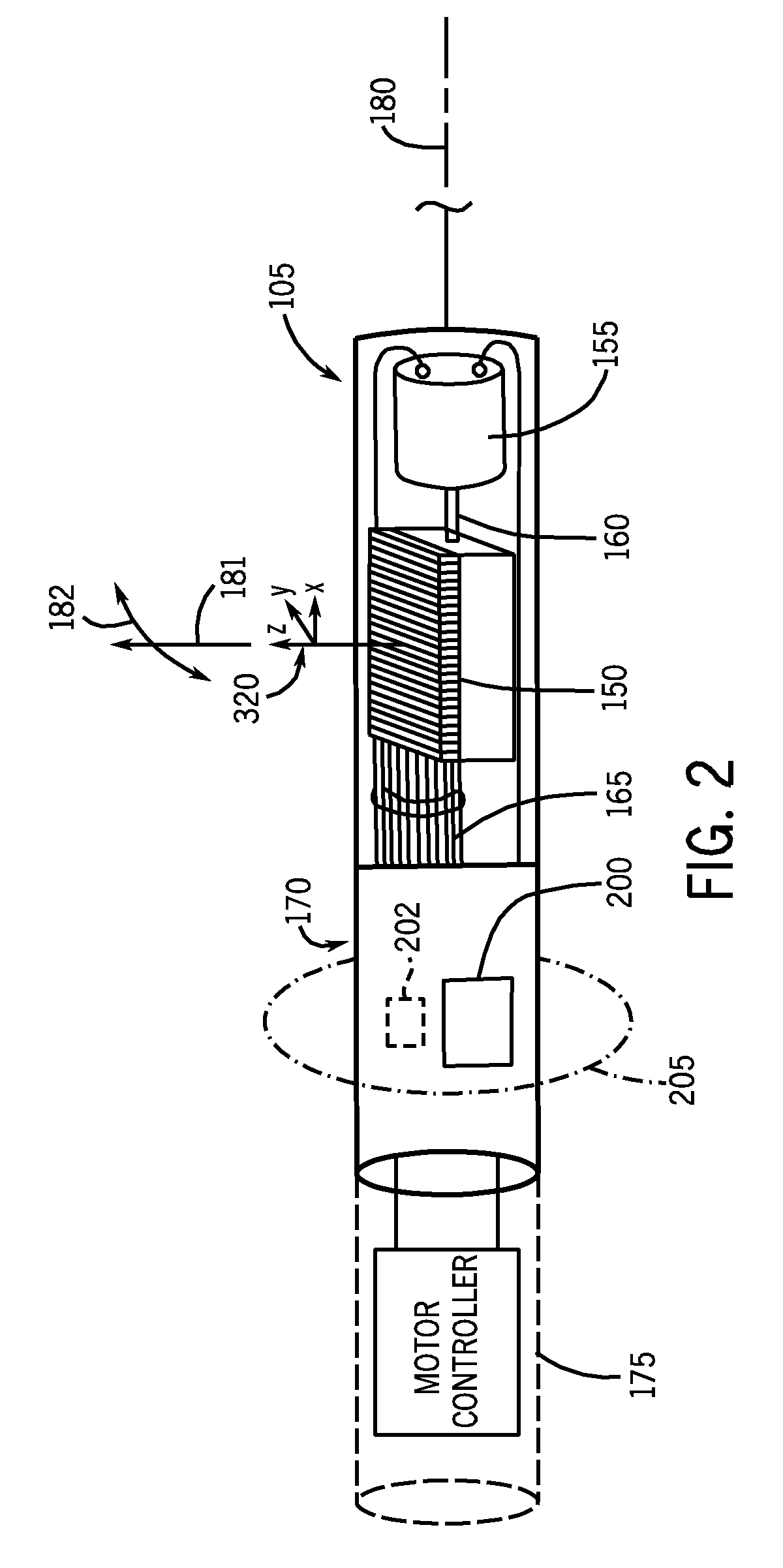
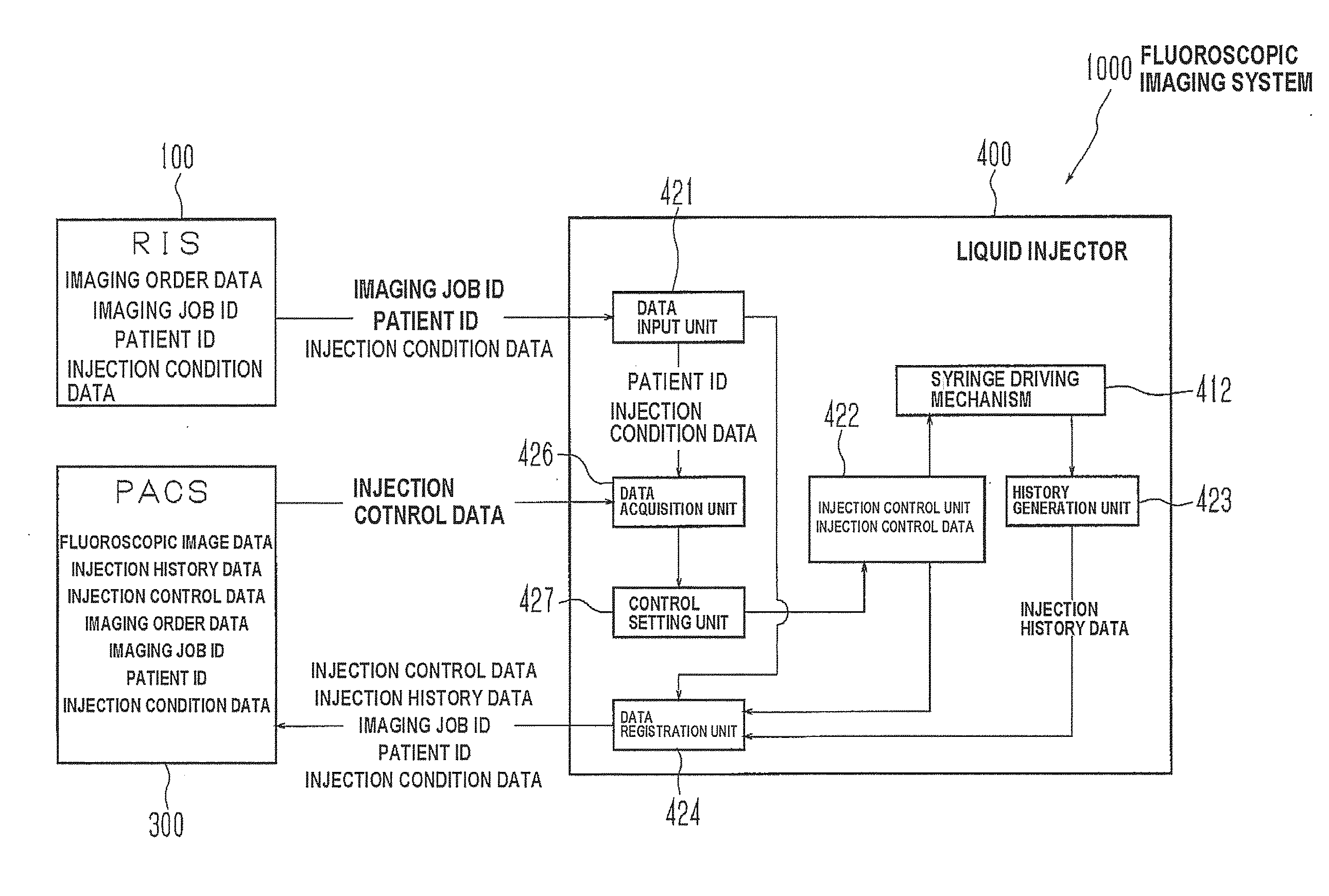
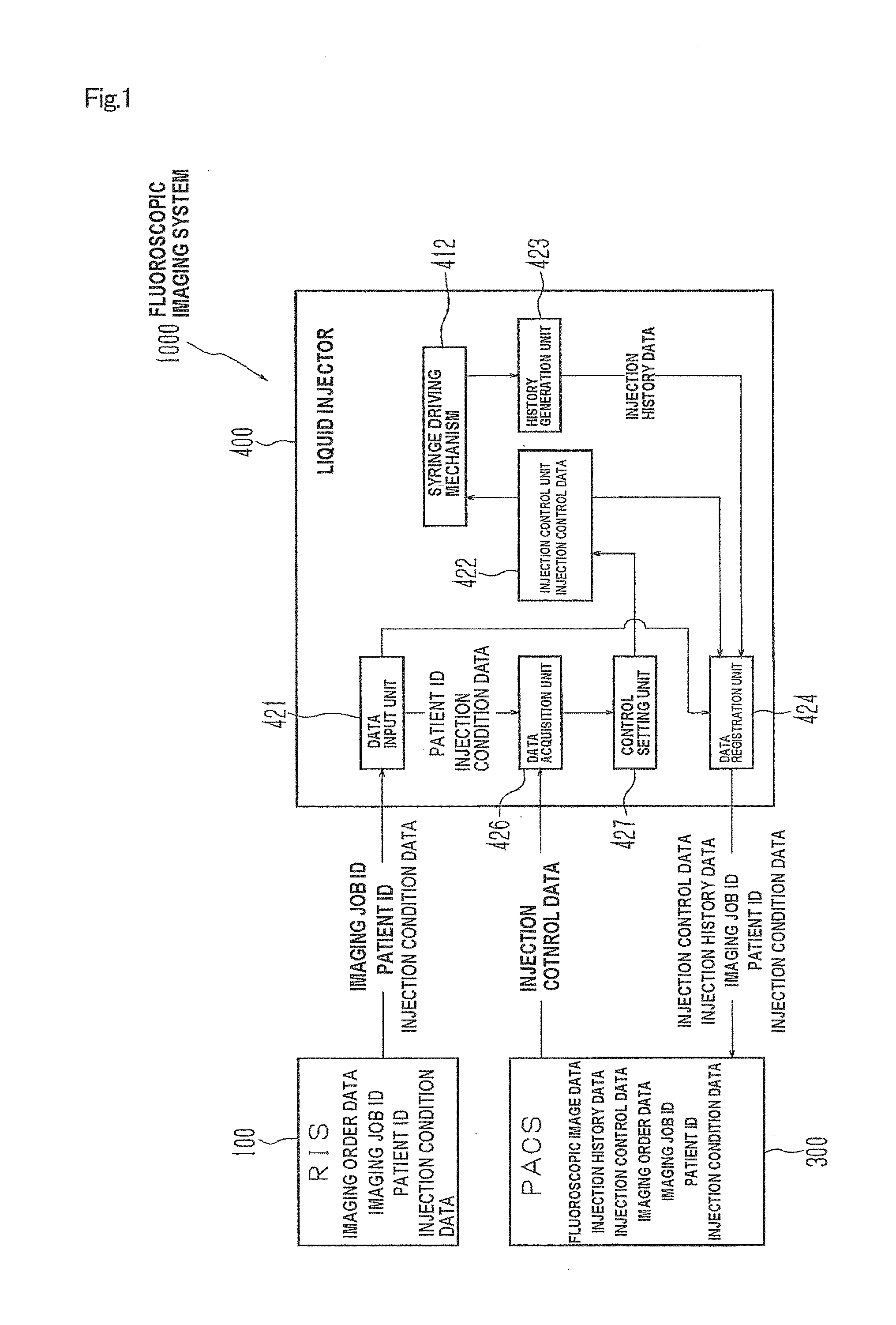
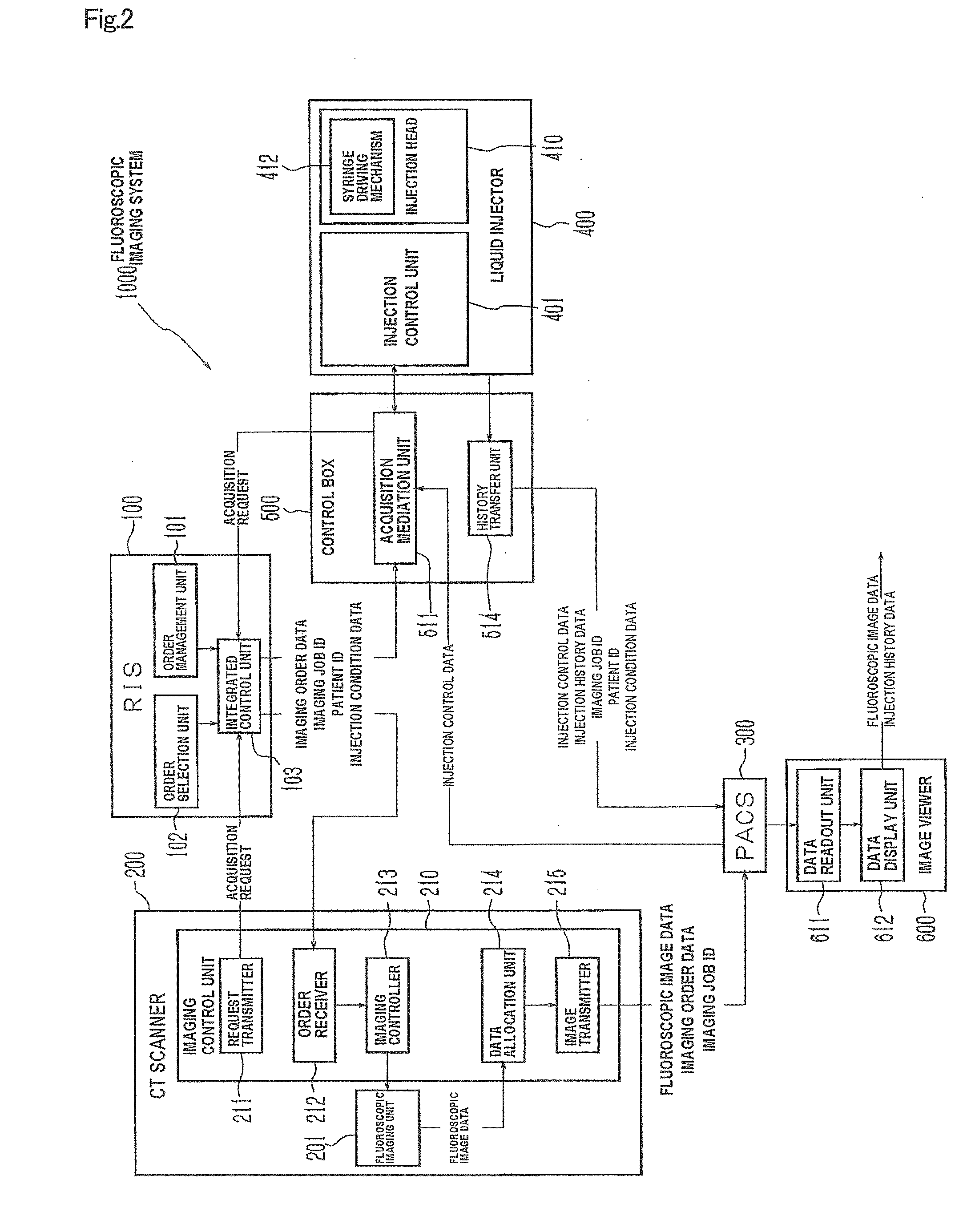
Liquid injector, fluoroscopic imaging system, and computer program
InactiveUS20100174181A1Easy to set upEliminate needData processing applicationsDrug and medicationsFluoroscopic imagingControl data
Once a patient ID and injection control data are input to a liquid injector and liquid injection is executed, the injection control data and injection history data are registered with the patient ID in a PACS. When the same patient is to undergo the second or subsequent liquid injection, the previous injection control data and injection history data are acquired by inputting the patient ID, and set as renewed injection control data. Such arrangement eliminates the need to input the same injection control data for the patient. Further, since the injection control data of each patient is registered and acquired utilizing the patient ID as index, erroneous setting of inappropriate injection control data can be automatically prevented, when the patient undergoes the injection. The liquid injector allows, therefore, easily setting the injection control data, and yet prevents liquid injection based on inappropriate injection control data.
Owner:NEMOTO KYORINDO KK
Device and methods for delivery and transfer of temporary radiopaque element
ActiveUS20110009818A1Accurate placementMinimal complicationBalloon catheterHeart valvesFluoroscopic imagingProsthetic valve
A device for the transfer of radiopaque material within the body comprises a valvuloplasty or other balloon coated with the radiopaque material. The balloon is inflated in the aortic valve for marking the site of an aortic annulus to enable accurate placement of prosthetic valves under fluoroscopic imaging.
Owner:GOFF THOMAS G
Medical device guidance from an anatomical reference
ActiveUS20050080429A1Rapid reliable determinationLow costEar treatmentSurgeryFluoroscopic imagingFluoroscopic image
A system and method for simply and reliably determining the location and orientation of a medical device within a patient's body. A medical device, such as a catheter, has bending indicators on or imbedded in its wall, and passes through an anatomical reference of known orientation relative to a target site within the patient. Information from the tube bending indicators permits determination of the orientation of a feature, such as an orifice, at the distal end of the medical device relative to the anatomical reference. From the known orientation of the anatomical reference, and information on the location and orientation of the distal end of the medical device obtained from fluoroscopic imaging from a single direction, the physician may reliably determine the orientation of the distal feature relative to the target site, eliminating the need for imaging from multiple directions.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
C-type arm image correction method based on perspective imaging model calibration
InactiveCN101582161AImprove the correction effectOptimization of internal and external parameter valuesImage enhancementImage analysisFluoroscopic imagingImaging processing
A C-type arm image correction method based on perspective imaging model calibration comprises the following four steps: step 1, designing a calibration panel calibrated by a C-type arm system; step 2, obtaining distortion coordinates of marked points by image processing on distorted images; step 3, calibrating the C-type arm system, including system calibration of three dimensional coordinates of marked points on the calibration panel, perspective imaging models, distortion models and distortion coordinates to obtain perspective imaging parameters; step 4, correcting images, namely, the calibrated perspective imaging models are used for correcting the distorted images. In the method, the C-type arm system calibration and the C-type arm X-ray distorted projected image correction are considered as a whole on line, and the C-type arm system is calibrated and the C-type arm X-ray distorted projected image is corrected based on the perspective imaging model of the camera, thereby changing the traditional method that image correction is first carried out off line and then linear calibration is carried out and ensuring concise and convenient system steps an easy on-line use.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Perspective imaging method based on laser scanning distance measuring instrument and multiple cameras
InactiveCN104156972AEasy accessRapid Fluoroscopy ResultsImage analysisFluoroscopic imagingPoint cloud
The invention relates to a perspective imaging method based on a laser scanning distance measuring instrument and multiple cameras. A traditional method that only an image sensor is adopted is abandoned. The laser scanning distance measuring instrument is introduced to obtain point cloud data of a scene on the basis that the image sensor is used for obtaining image information, the depth information of the scene is obtained according to the point cloud data, focus depth selection is carried out according to the depth information, and time complexity is reduced. Meanwhile, the depth information of the scene is utilized, obtained projection points can be screened, and the definition of a perspective imaging result can be improved. Due to the fact that the image information of the scene is obtained through the panorama cameras, and a multi-view angle image is obtained, the multi-view perspective imaging result can be obtained. The test is carried out on a self-established database, and the test result shows that by means of the method, a clearer multi-view perspective imaging result can be rapidly and effectively obtained.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method and system for dynamic low dose X-ray imaging
A method and system for performing fluoroscopic imaging of a subject has high temporal and spatial resolution in a center portion of the captured dynamic images. The system provides for reduced X-ray dose to the patient associated with that part of the X-ray beam associated with a peripheral portion of the captured images although temporal, and in some embodiments spatial, resolution is reduced in the peripheral portion of the image. The system uses a rotating collimator to produce an X-ray beam having narrow wing portions associated with the peripheral portions of the image, and a broader central region associated with the high resolution center portion of the images.
Owner:FOREVISION IMAGING TECH LLC
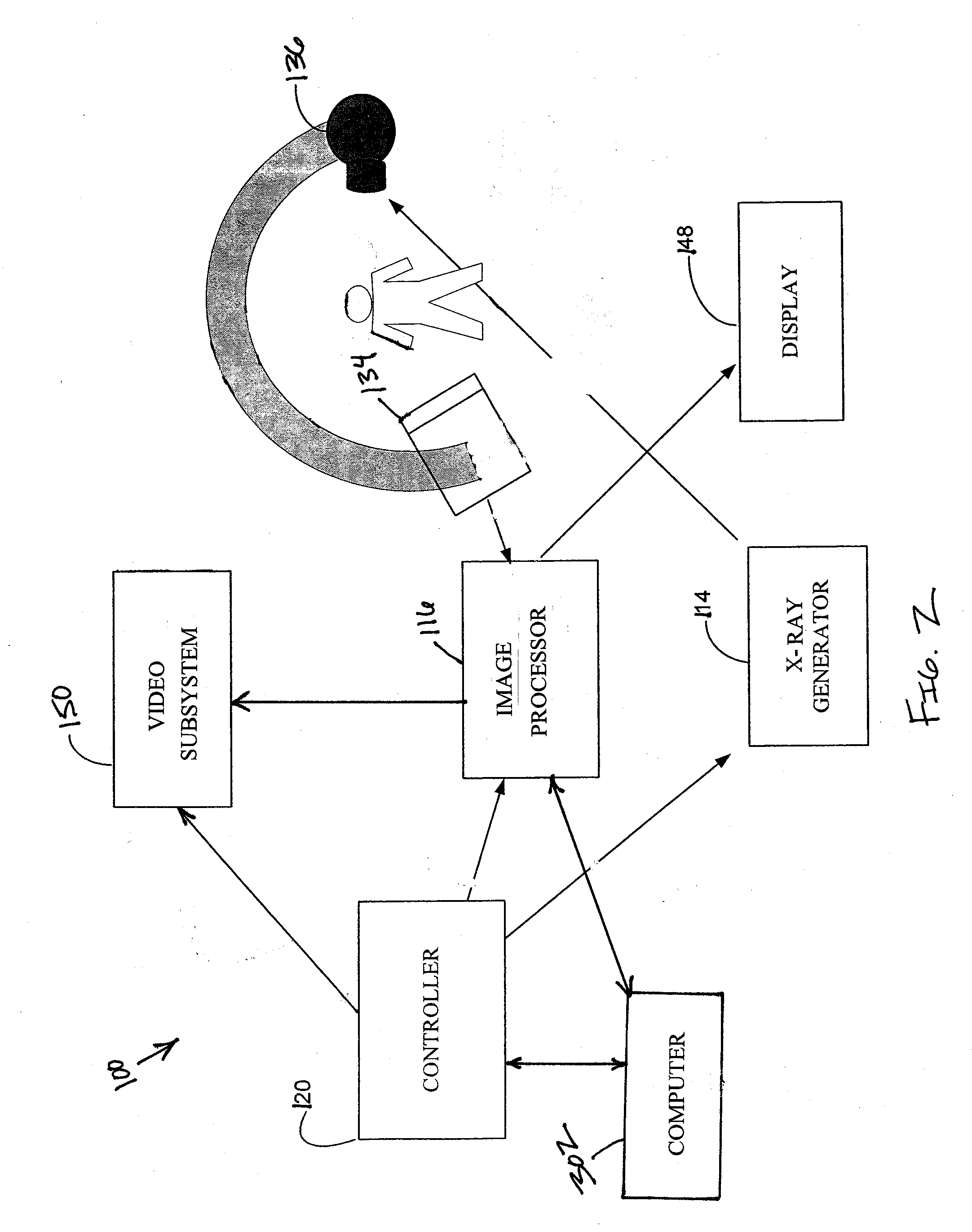
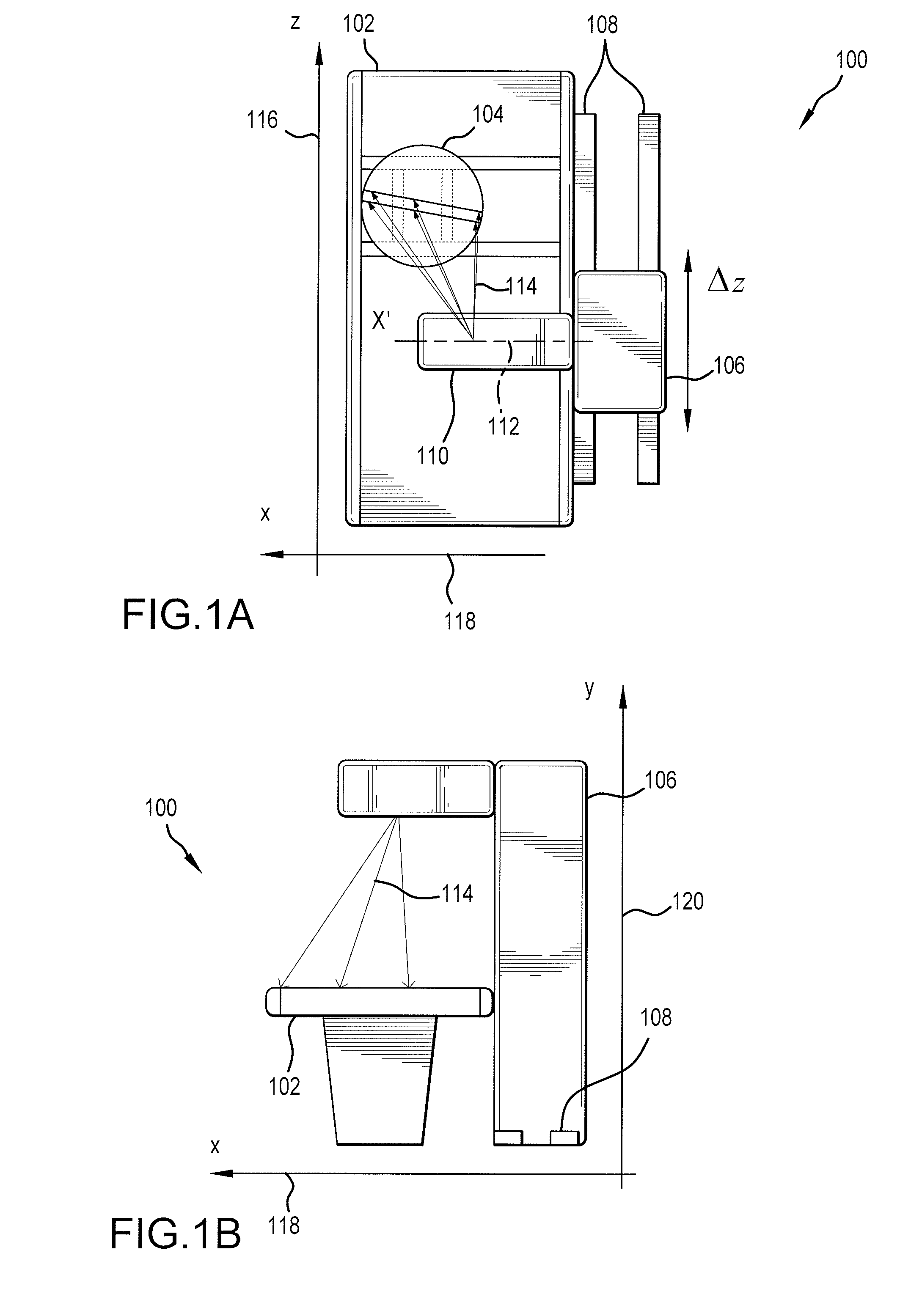
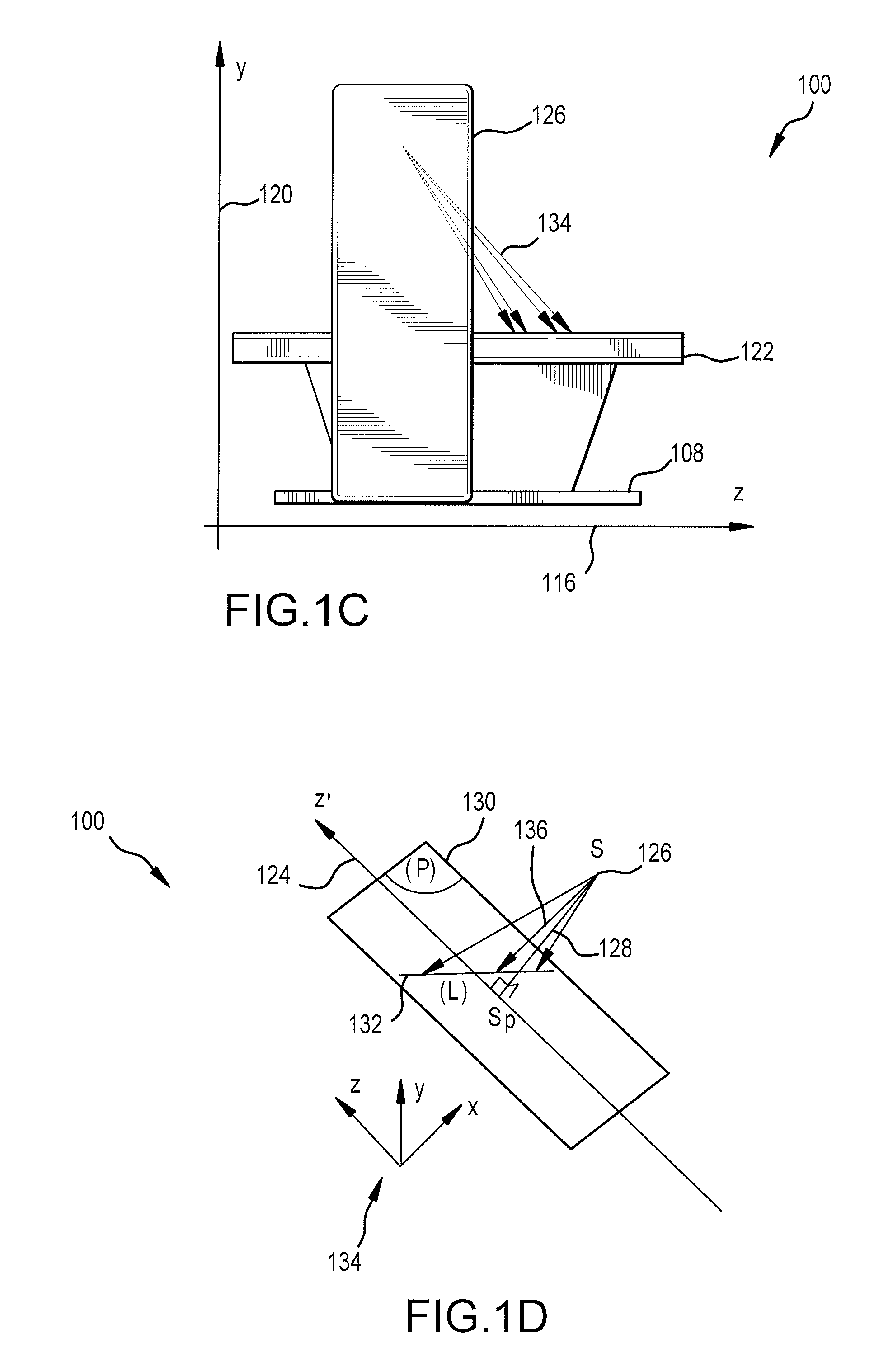
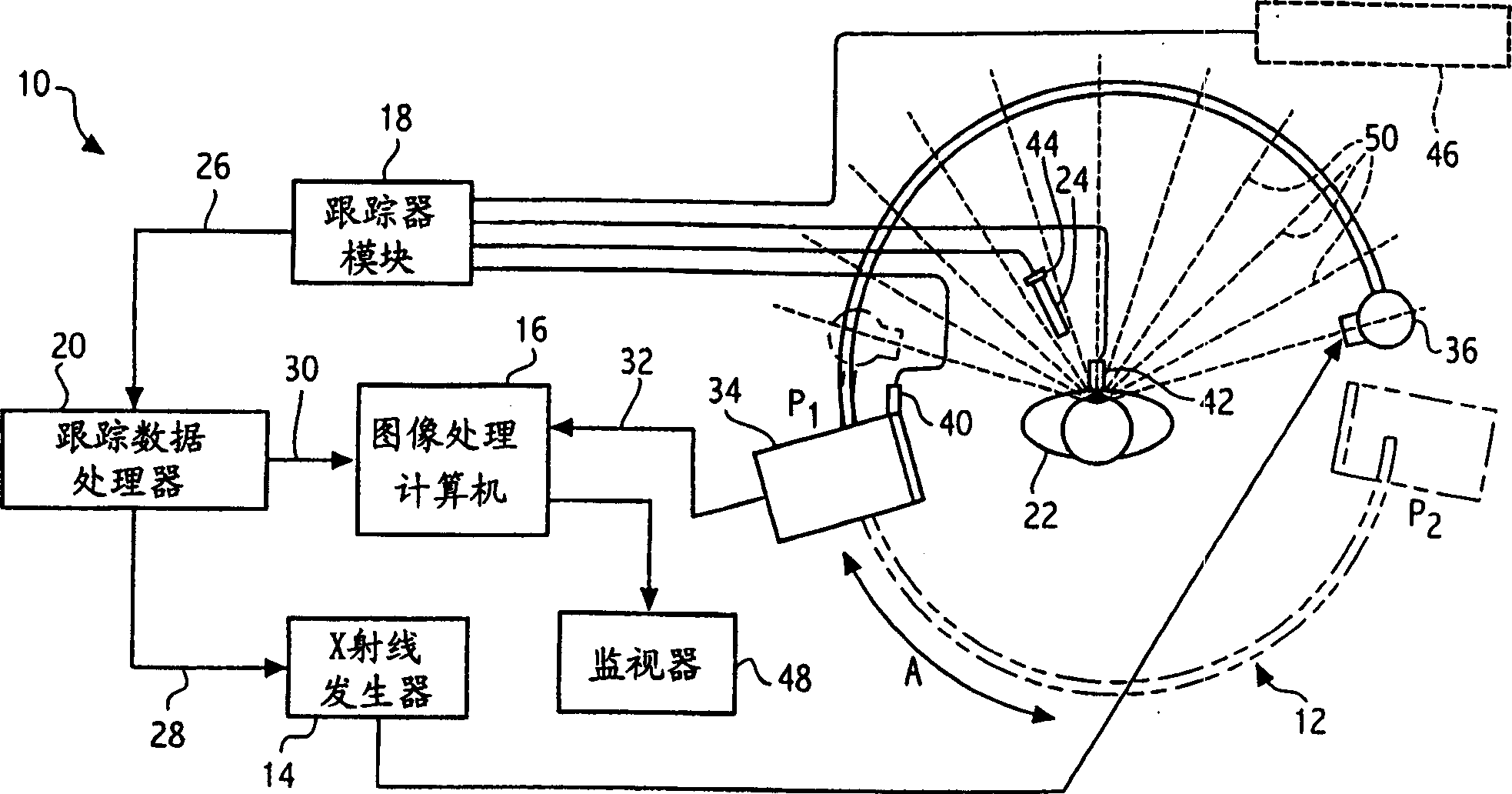
Method and apparatus for obtaining and displaying computerized tomography images by fluoroscopic imaging system
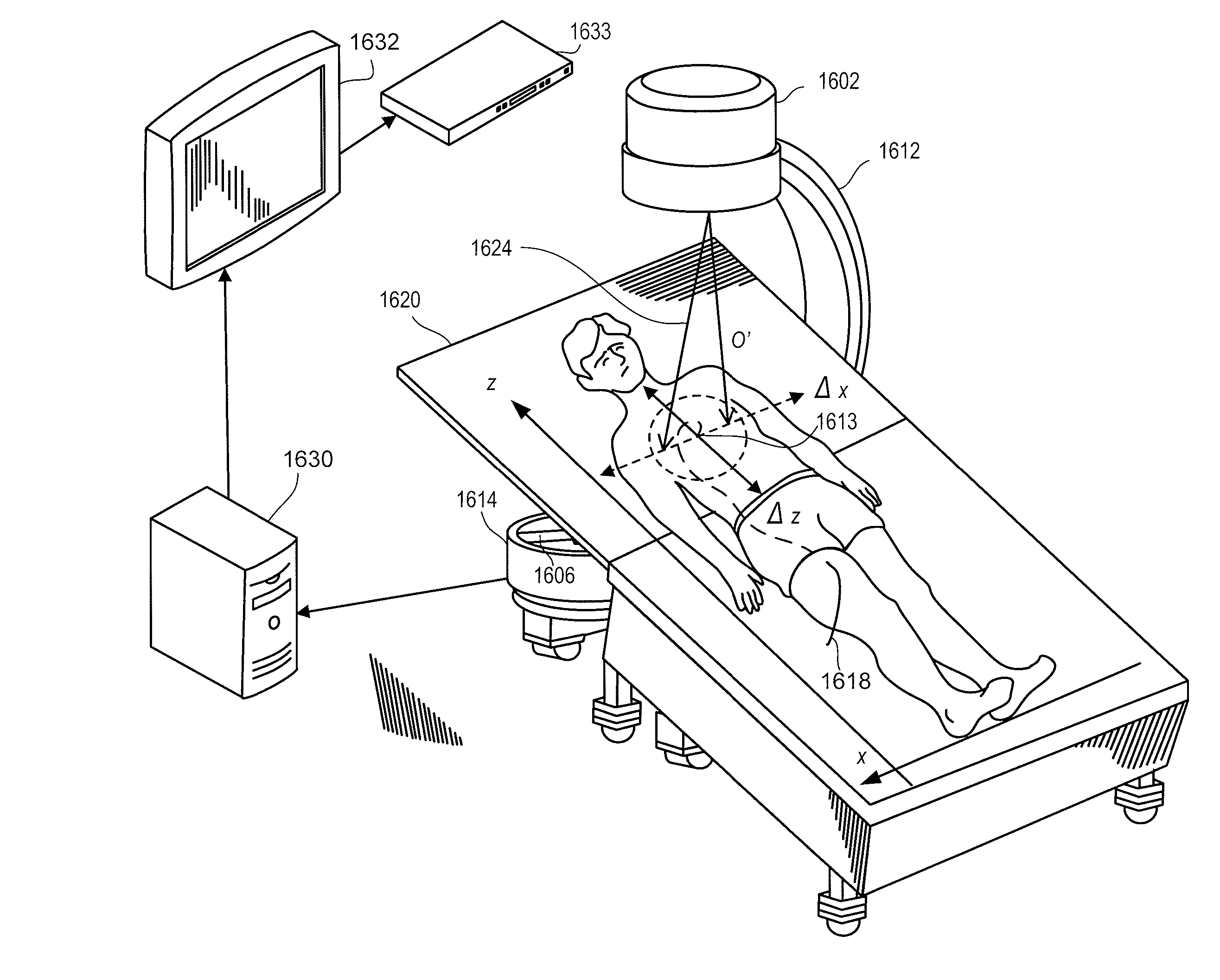
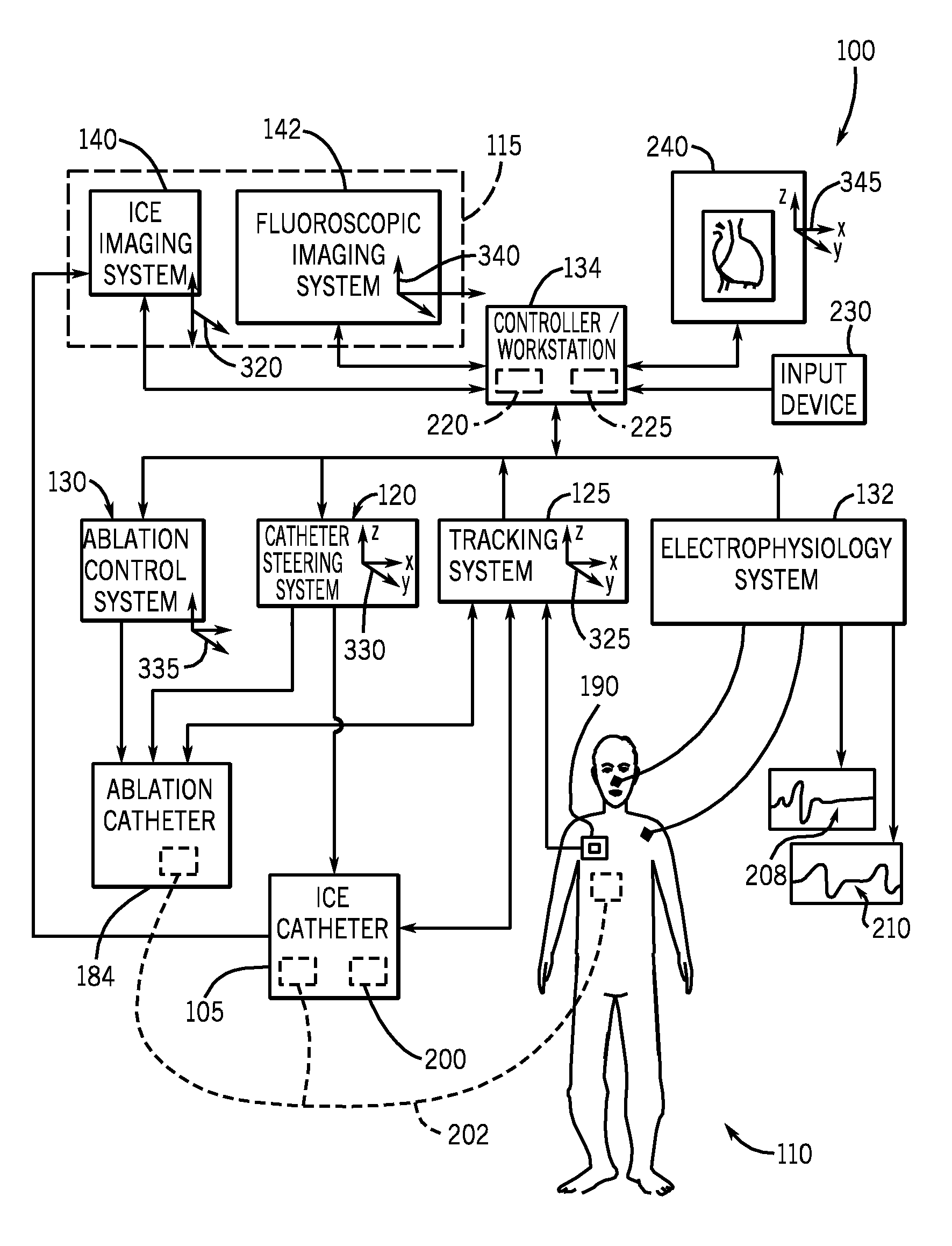
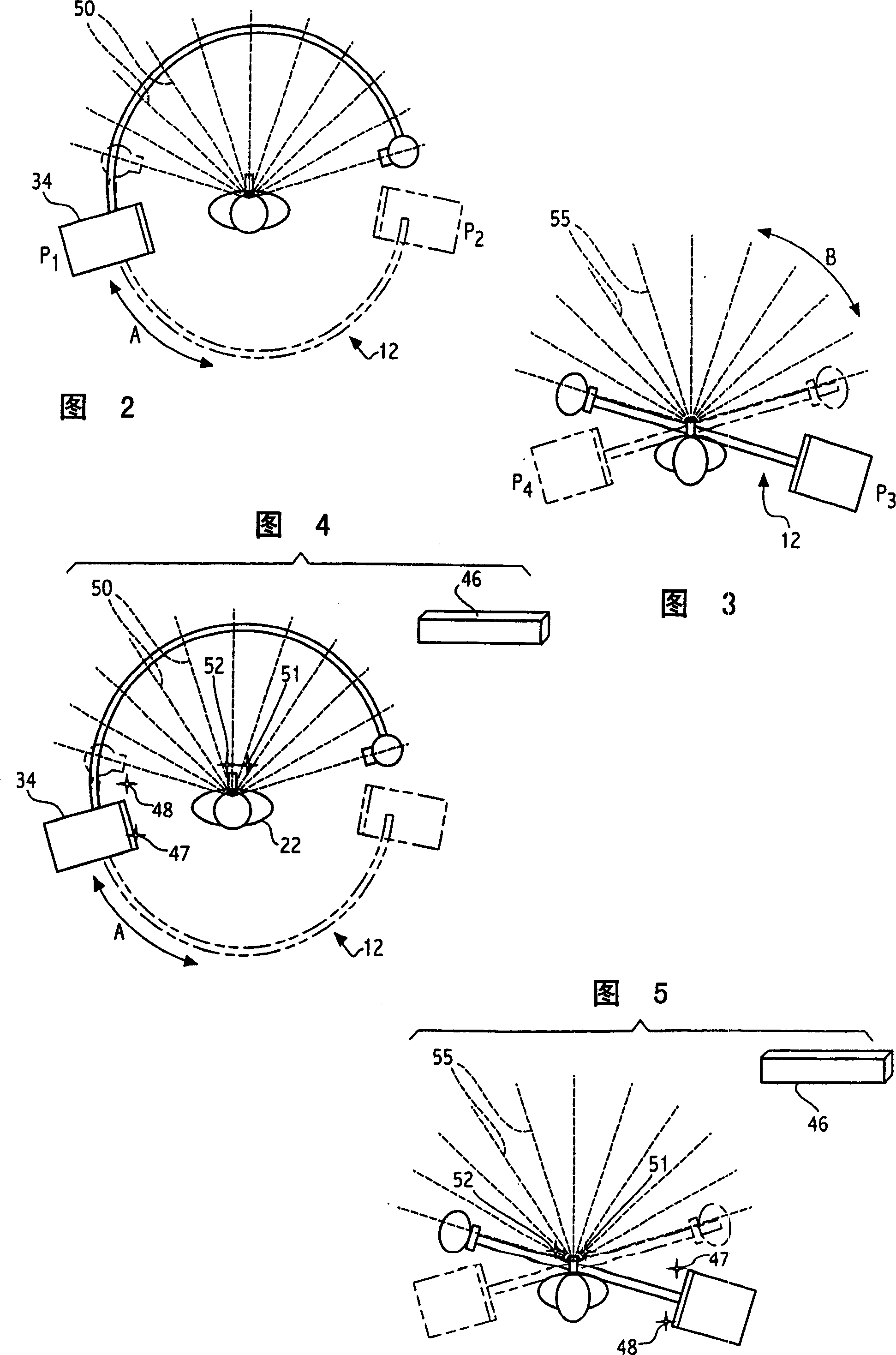
A medical imaging system is provided for diagnostic and interventional procedures. The system includes a C-arm having an x-ray source and a receptor for obtaining fluoroscopic images of a patient. The C-arm is moved through an image acquisition path (A, B), along which at least first and second images are obtained. An acquisition module obtains multiple 2-D fluoroscopic images at desired positions along the image acquisition path and an image processor constructs a 3-D volume of object data based on the 2-D fluoroscopic images. Patient information is displayed based upon the 3-D volume of patient information. A position tracking system is included to track the position of the receptor, patient and (if included) a surgical instrument. The position information is used to control the time at which exposures are obtained and (if included) to superimpose instrument graphical information on a display with patient information.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
System and method for navigating to target and performing procedure on target utilizing fluoroscopic-based local three dimensional volume reconstruction
ActiveUS20170035380A1Easy to navigateImprove navigation accuracyRadiation diagnosis data transmissionSurgical navigation systemsFluoroscopic imagingFluoroscopic image
A system and method for navigating to a target using fluoroscopic-based three dimensional volumetric data generated from two dimensional fluoroscopic images, including a catheter guide assembly including a sensor, an electromagnetic field generator, a fluoroscopic imaging device to acquire a fluoroscopic video of a target area about a plurality of angles relative to the target area, and a computing device. The computing device is configured to receive previously acquired CT data, determine the location of the sensor based on the electromagnetic field generated by the electromagnetic field generator, generate a three dimensional rendering of the target area based on the acquired fluoroscopic video, receive a selection of the catheter guide assembly in the generated three dimensional rendering, and register the generated three dimensional rendering of the target area with the previously acquired CT data to correct the position of the catheter guide assembly.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Dental fluoroscopic imaging system
ActiveUS20110150185A1X-ray/infra-red processesRadiation diagnostics for dentistryFluorescenceDental examination
The dental fluoroscopic imaging system includes a flat panel detector comprised by a gamma-rays or x-rays converter, a plate, a collector, a processing unit and a transmitter suitable for 2D intraoral / extraoral and 3D extraoral dental fluoroscopy. The x-ray converter contains a material capable of transforming the low dose gamma rays or x-rays beam received from an emitter after going through the dental examination area into electrical signals or a light image consequent with the radiographed image. The plate transmits the electric signals or light image to a collector which amplifies it and sends it to a processing unit and then to transmitter designed to transfer digital images sequentially to a host computer and software which can acquire, process, transform, record, freeze and enhance 2D and 3D images of video frame rates. Two dimensional images are obtained while using a C-arm / U-arm configuration while 3D images are obtained while using the O-arm configuration.
Owner:REAL TIME IMAGING TECH
Minimally invasive, direct delivery methods for implanting obesity treatment devices
A method includes selecting a template from a plurality of different sizes of templates based on measurements of the abdominal cavity of a patient; orienting the template on the patient at a location overlying the abdominal cavity to select an appropriate size implant using fluoroscopic imaging; marking an incision location and an indicator of an angle of approach; and removing the template from the patient, wherein marks made by the marking remain on the patient. Methods apparatus, instruments and implants for treating a patient are provided.
Owner:RESHAPE MEDICAL LLC
Patient-Specific Spinal Fusion Cage and Methods of Making Same
ActiveUS20150305878A1Maximize contact areaReduce subsidenceMusculoskeletal system evaluationCatheterSpinal columnFluoroscopic imaging
A method of determining disc space geometry with the use of an expandable trial having endplate-mapping capabilities. An expandable trial is inserted into the disc space and its height is adjusted to obtain the desired decompression and spinal alignment (which is typically confirmed with the use of CT or Fluoroscopic imaging). The endplate dome / geometry dome is then determined by one of the following three methods:a) direct imaging through the trial,b) balloon moldings filled with flowable in-situ fluid (for example, silicon, polyurethane, or PMMA) from superior / inferior endplates orc) light-based imaging through superior & inferior balloons.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Polymer coated guidewire
InactiveUS20080146967A1Sufficient radiopacityAllow useGuide wiresSurgeryFluoroscopic imagingGuide wires
A guidewire or section thereof, that has a core member or the like with a plurality of contiguous tapered segments having taper angles that are configured to produce a linear change in stiffness over a longitudinal portion of the device. The device may also have a core section with a continuously changing taper angle to produce a curvilinear profile that is configured to produce a linear change in stiffness of the core over a longitudinal portion of the device. An embodiment has a plurality of radiopaque elements that may be intermittent, continuous or in the form of a helical ribbon for scaled measurement of intracorporeal structure under fluoroscopic imaging. Another embodiment has at least one layer of polymer over the distal end of the device.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Patient-Specific Spinal Fusion Cage and Methods of Making Same
ActiveUS20170354510A1Maximize contact areaReduces expulsionMusculoskeletal system evaluationSurgeryFluoroscopic imagingDirect imaging
A method of determining disc space geometry with the use of an expandable trial having endplate-mapping capabilities. An expandable trial is inserted into the disc space and its height is adjusted to obtain the desired decompression and spinal alignment (which is typically confirmed with the use of CT or Fluoroscopic imaging). The endplate dome / geometry dome is then determined by one of the following three methods:a) direct imaging through the trial,b) balloon moldings filled with flowable in-situ fluid (for example, silicon, polyurethane, or PMMA) from superior / inferior endplates orc) light-based imaging through superior & inferior balloons.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
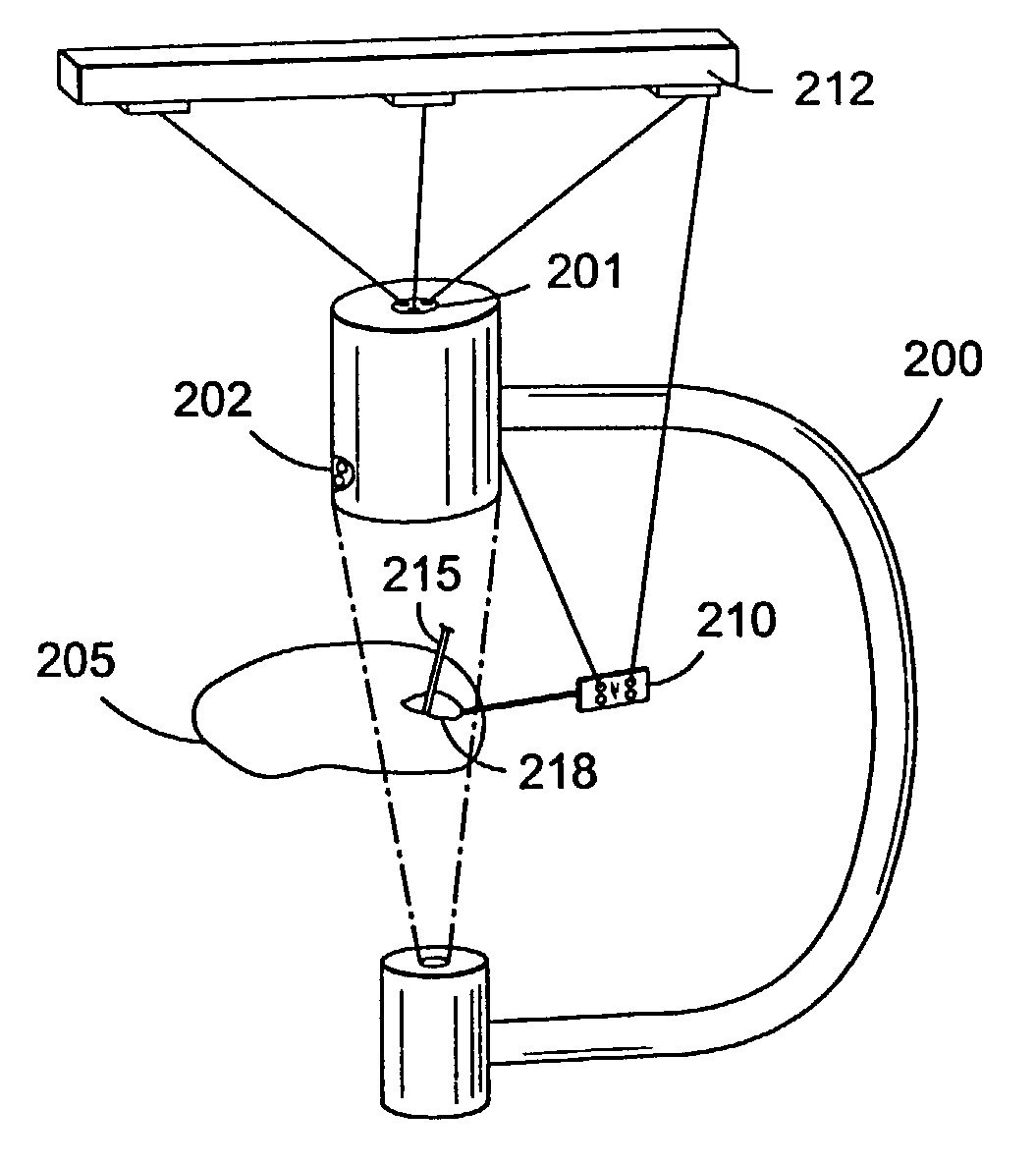
Method and system for restoration of a navigation data loss in image-guided navigation
ActiveUS7933730B2Testing/calibration apparatusDirection finders using radio wavesFluoroscopic imagingRestoration method
A method for restoring navigation failure information in a fluoroscopy-based imaging system is disclosed. The method includes obtaining a plurality of receiver navigation information using a calibration target rigidly attached to a supporting member of the imaging system. The calibration target may include a plurality of receivers providing navigation information and the supporting member may be a C-arm. The method identifies a navigation failure and corresponding to the navigation failure a calibrated receiver navigation information is generated. The calibrated receiver navigation information is generated using a calibration information and a C-arm imaging position obtained during navigation failure. A receiver navigation information corresponding to the navigation failure is estimated using the calibrated receiver navigation information, and a transmitter navigation information. Also disclosed is a restoration unit for restoring navigation failure information in a fluoroscopy-based imaging system and a fluoroscopic imaging system using the restoration unit.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
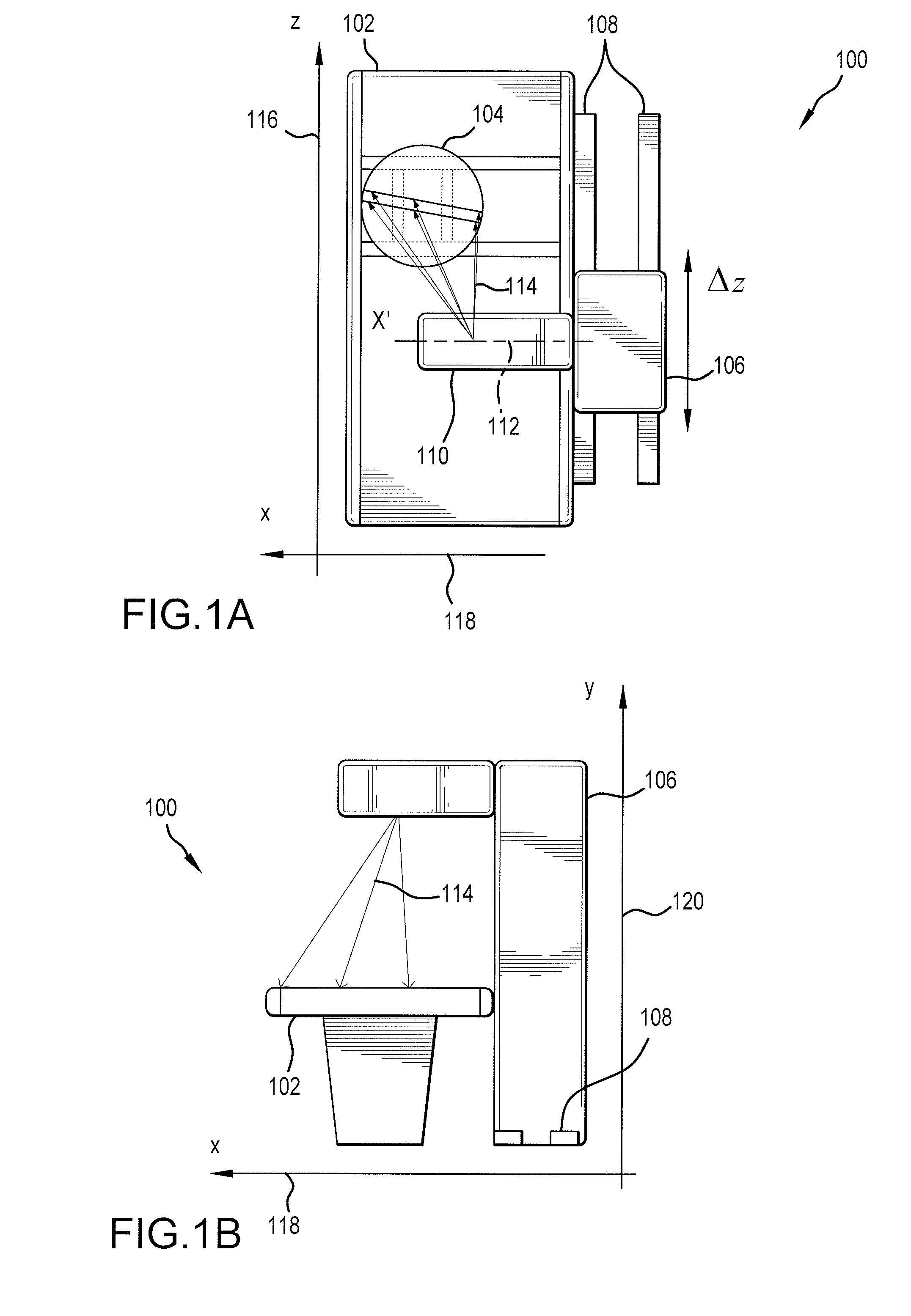
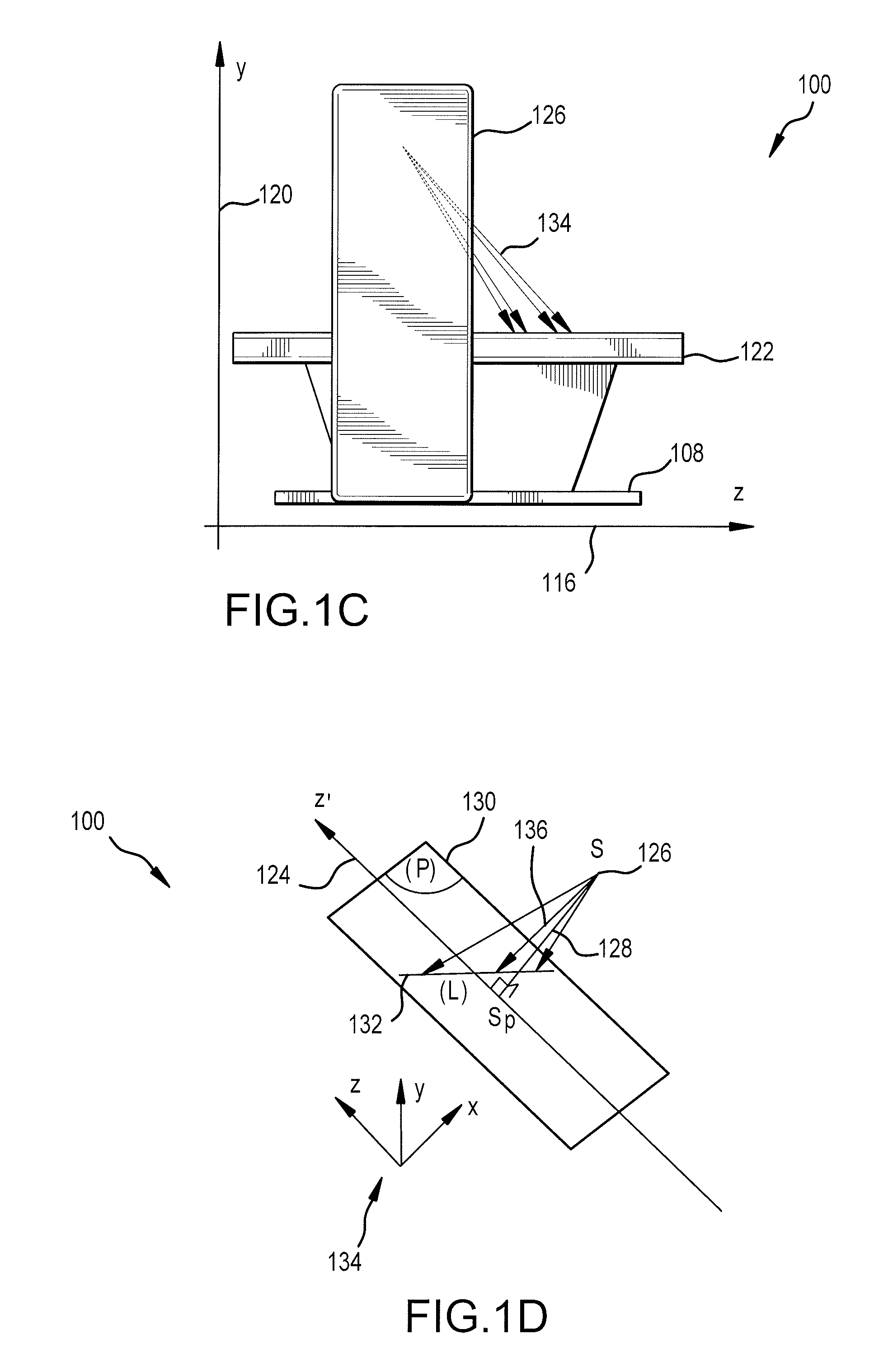
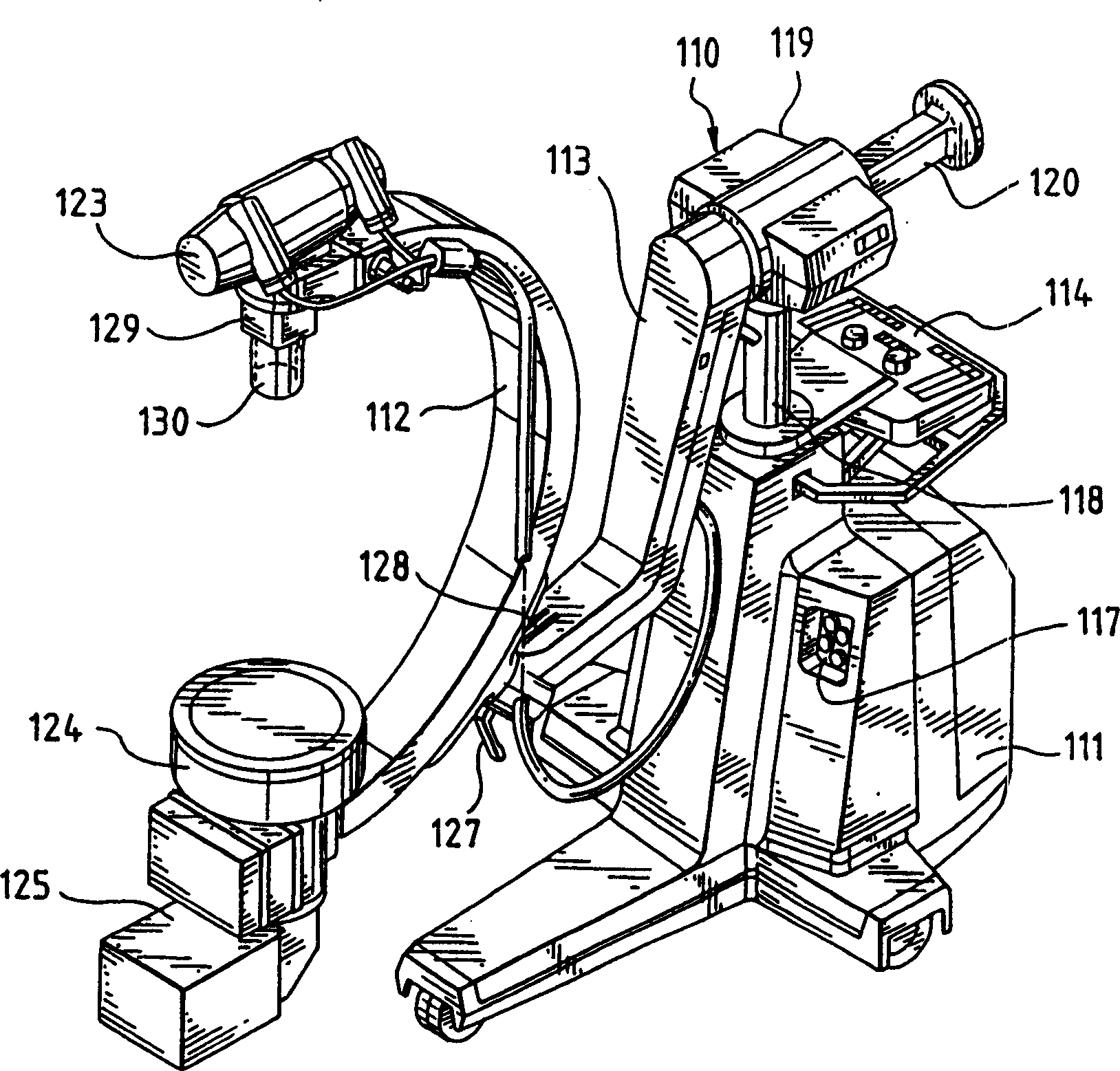
Mobile imaging system and method
ActiveUS9693746B2Easy alignmentHighly effectiveRadiation safety meansRadiation beam directing meansFluoroscopic imagingFluorescence
A mobile fluoroscopic imaging system having a portable radiation source capable of emitting radiation in both single and, alternatively, pulse emissions and adapted to move in all degrees of freedom; a portable detector operable to detect radiation from the radiation source, wherein the detector is adapted to move independently of the radiation source in all degrees of freedom; the radiation source and detector each comprises an alignment sensor in communication with a computer; the computer is in communication with the radiation source and the detector; the position, distance and orientation of the radiation source and the detector are established by the computer; and the computer sends an activation signal to the radiation source to indicate when radiation may be emitted. Preferably, the radiation source is prevented from emission of radiation until the detector and the radiation source have achieved predetermined alignment conditions.
Owner:PORTAVISION MEDICAL
Patient-specific spinal fusion cage and methods of making same
ActiveUS9757245B2Maximize contact areaReduces expulsionMusculoskeletal system evaluationInternal osteosythesisSpinal columnFluoroscopic imaging
A method of determining disc space geometry with the use of an expandable trial having endplate-mapping capabilities. An expandable trial is inserted into the disc space and its height is adjusted to obtain the desired decompression and spinal alignment (which is typically confirmed with the use of CT or Fluoroscopic imaging). The endplate dome / geometry dome is then determined by one of the following three methods:a) direct imaging through the trial,b) balloon moldings filled with flowable in-situ fluid (for example, silicon, polyurethane, or PMMA) from superior / inferior endplates orc) light-based imaging through superior & inferior balloons.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
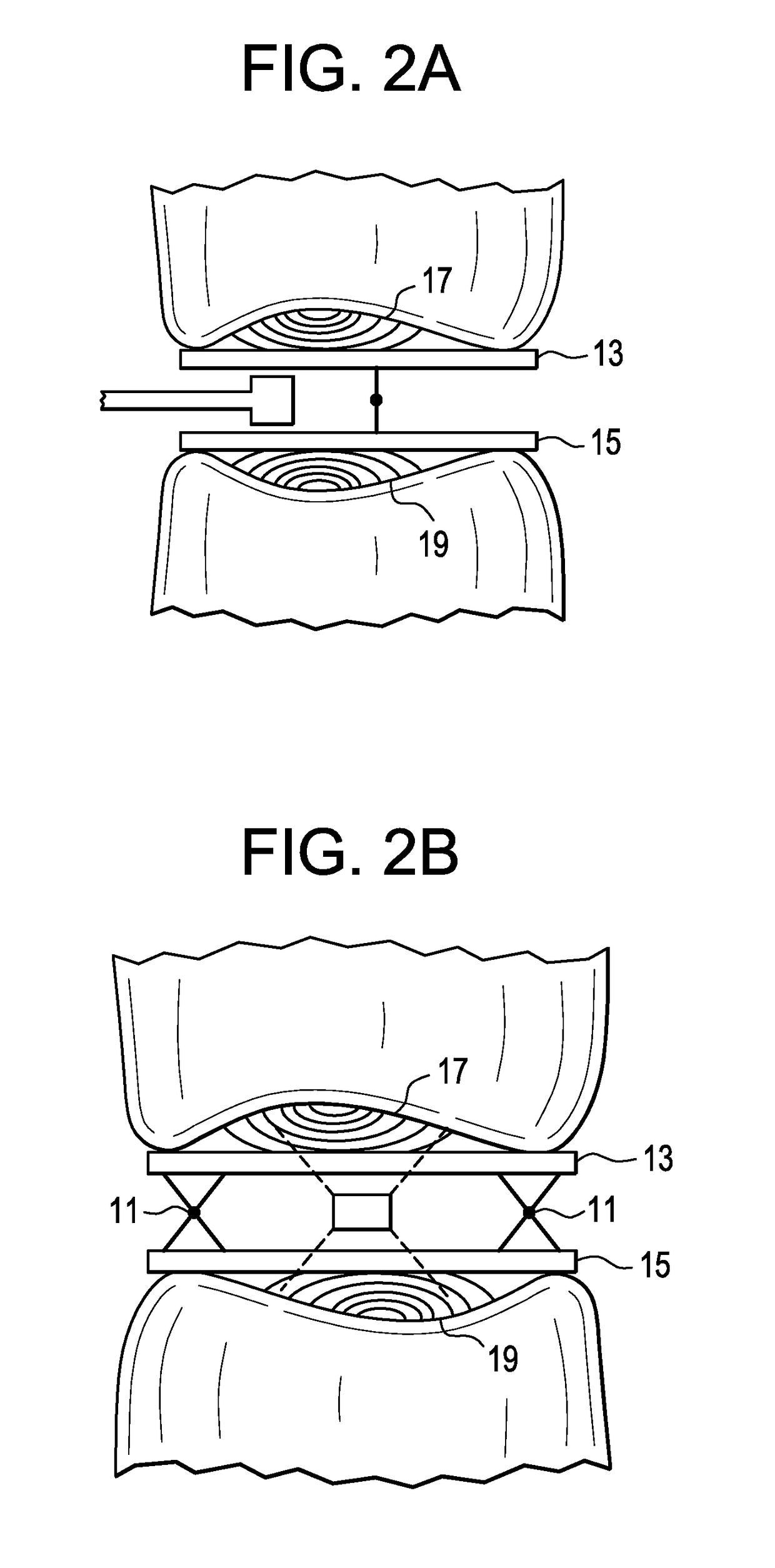
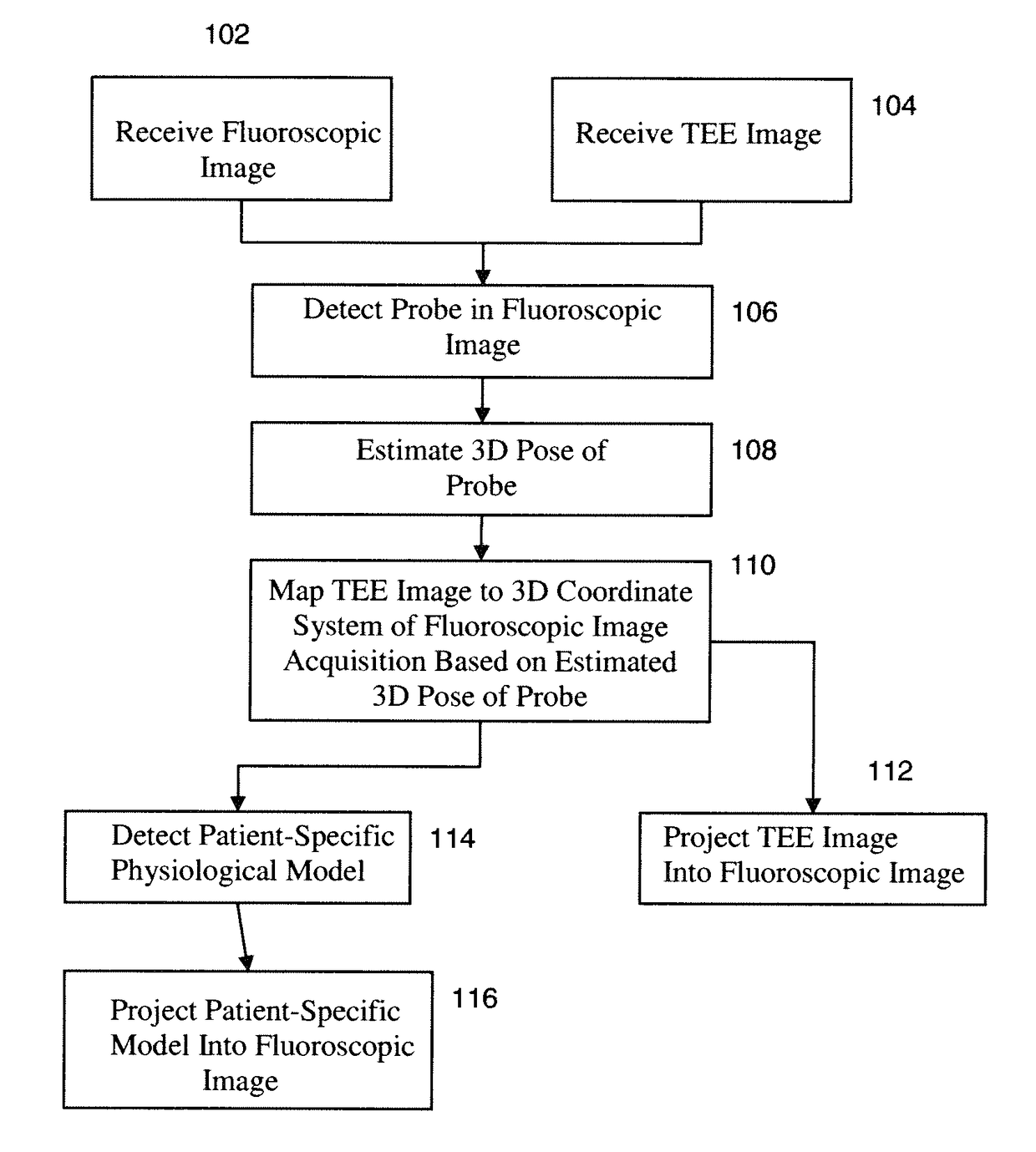
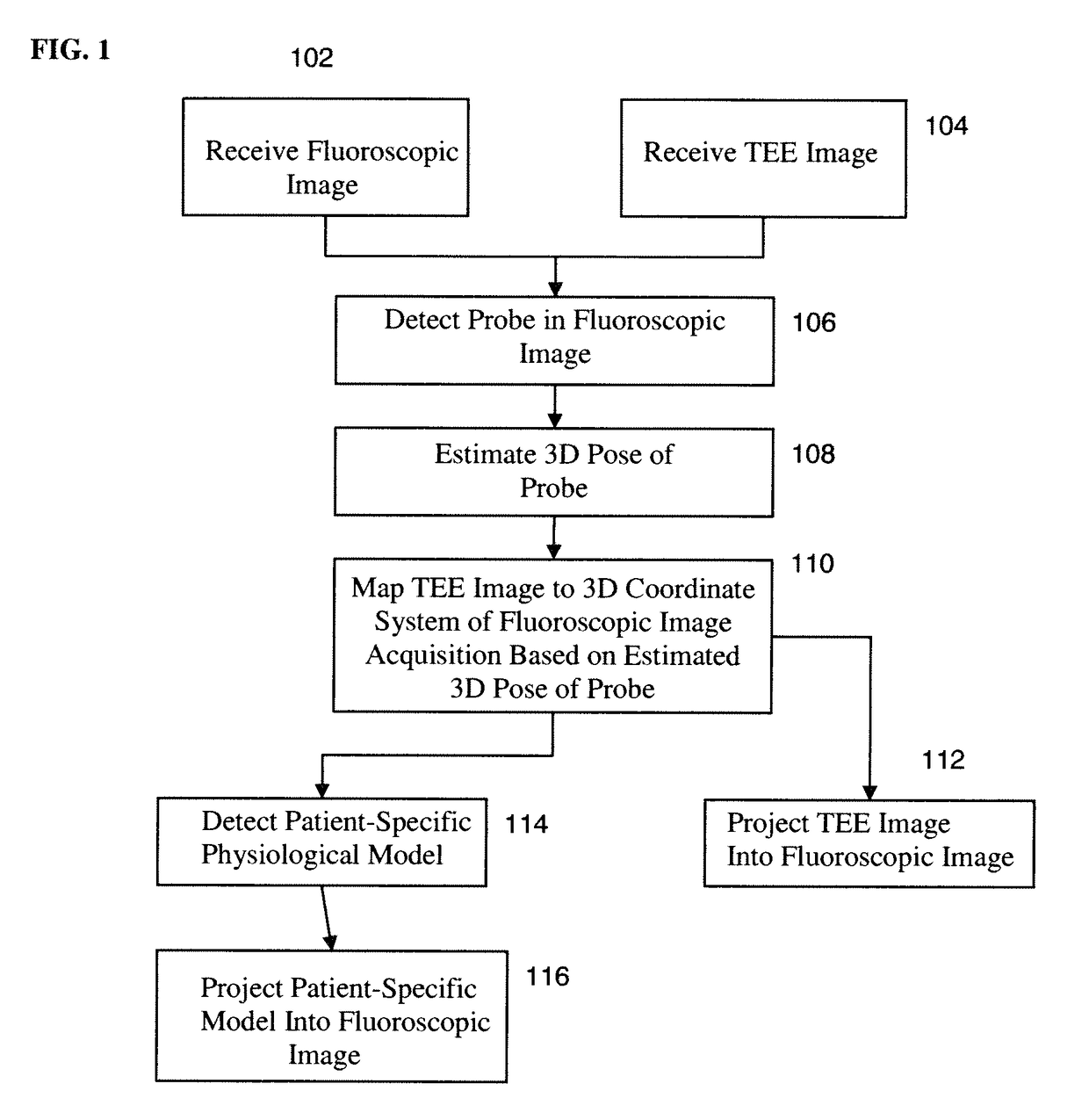
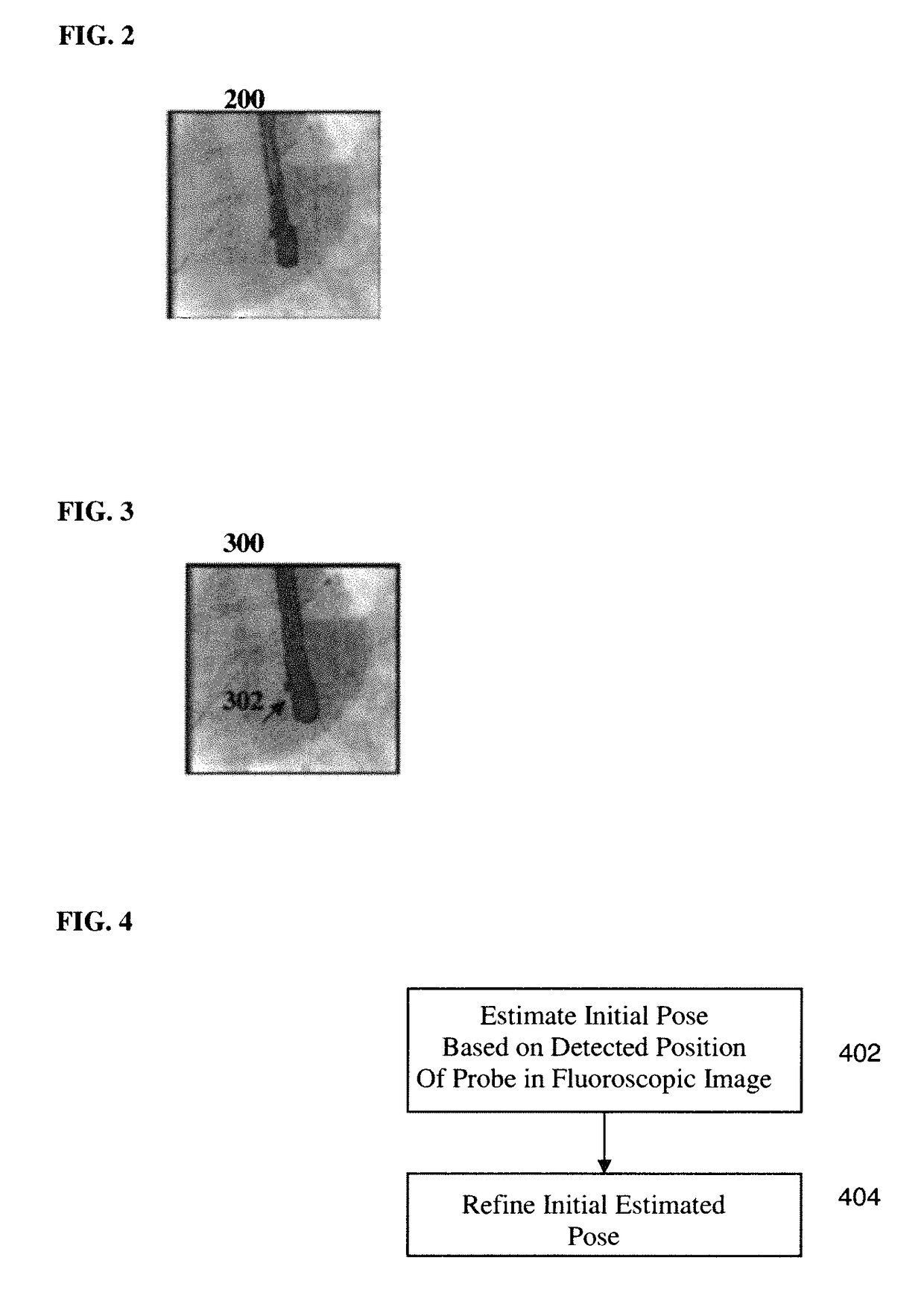
Method and system for registration of ultrasound and physiological models to X-ray fluoroscopic images
A method and system for registering ultrasound images and physiological models to x-ray fluoroscopy images is disclosed. A fluoroscopic image and an ultrasound image, such as a Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE) image, are received. A 2D location of an ultrasound probe is detected in the fluoroscopic image. A 3D pose of the ultrasound probe is estimated based on the detected 2D location of the ultrasound probe in the fluoroscopic image. The ultrasound image is mapped to a 3D coordinate system of a fluoroscopic image acquisition device used to acquire the fluoroscopic image based on the estimated 3D pose of the ultrasound probe. The ultrasound image can then be projected into the fluoroscopic image using a projection matrix associated with the fluoroscopic image. A patient specific physiological model can be detected in the ultrasound image and projected into the fluoroscopic image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and method for x-ray based assessment of aneurysm pulsation
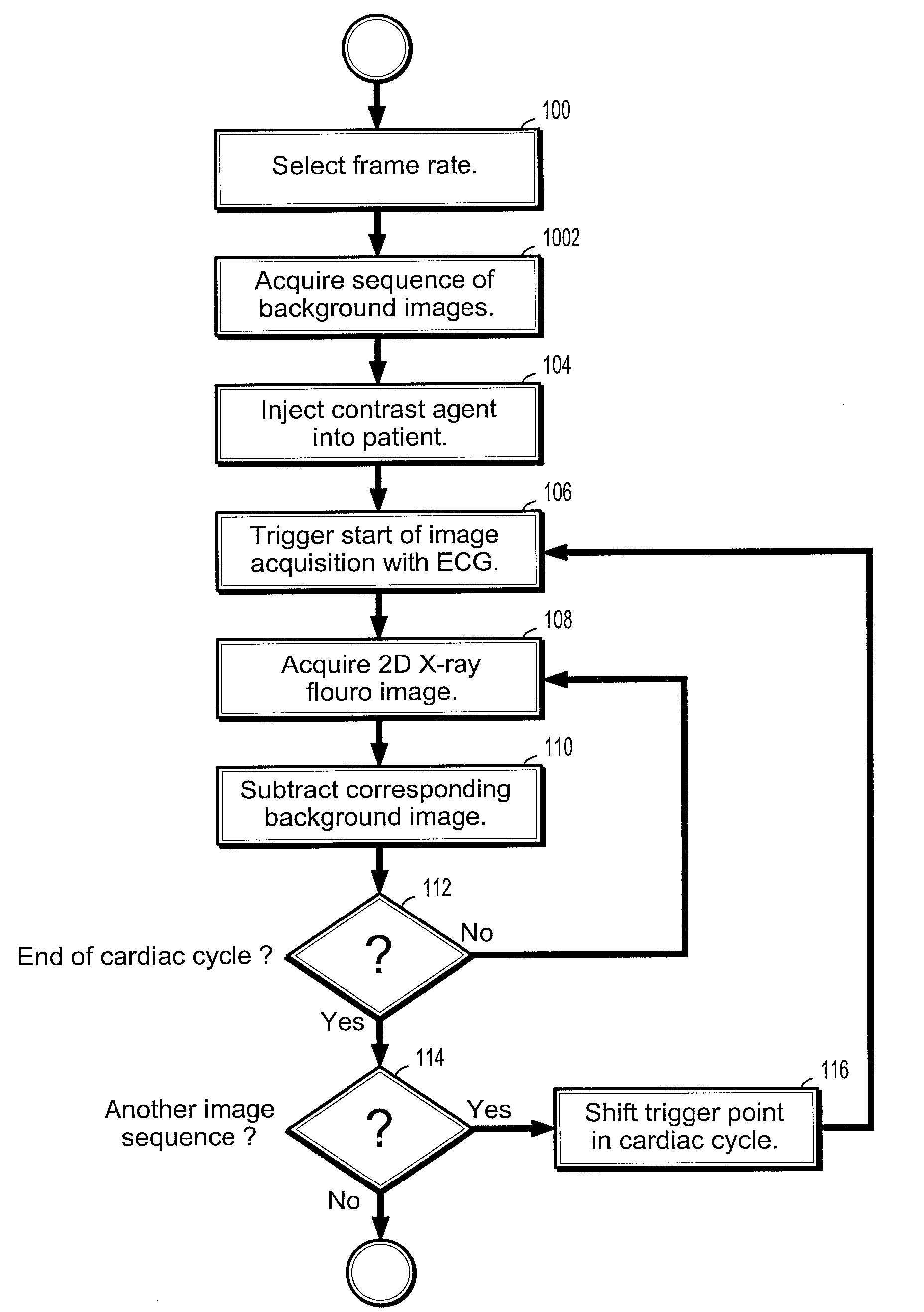
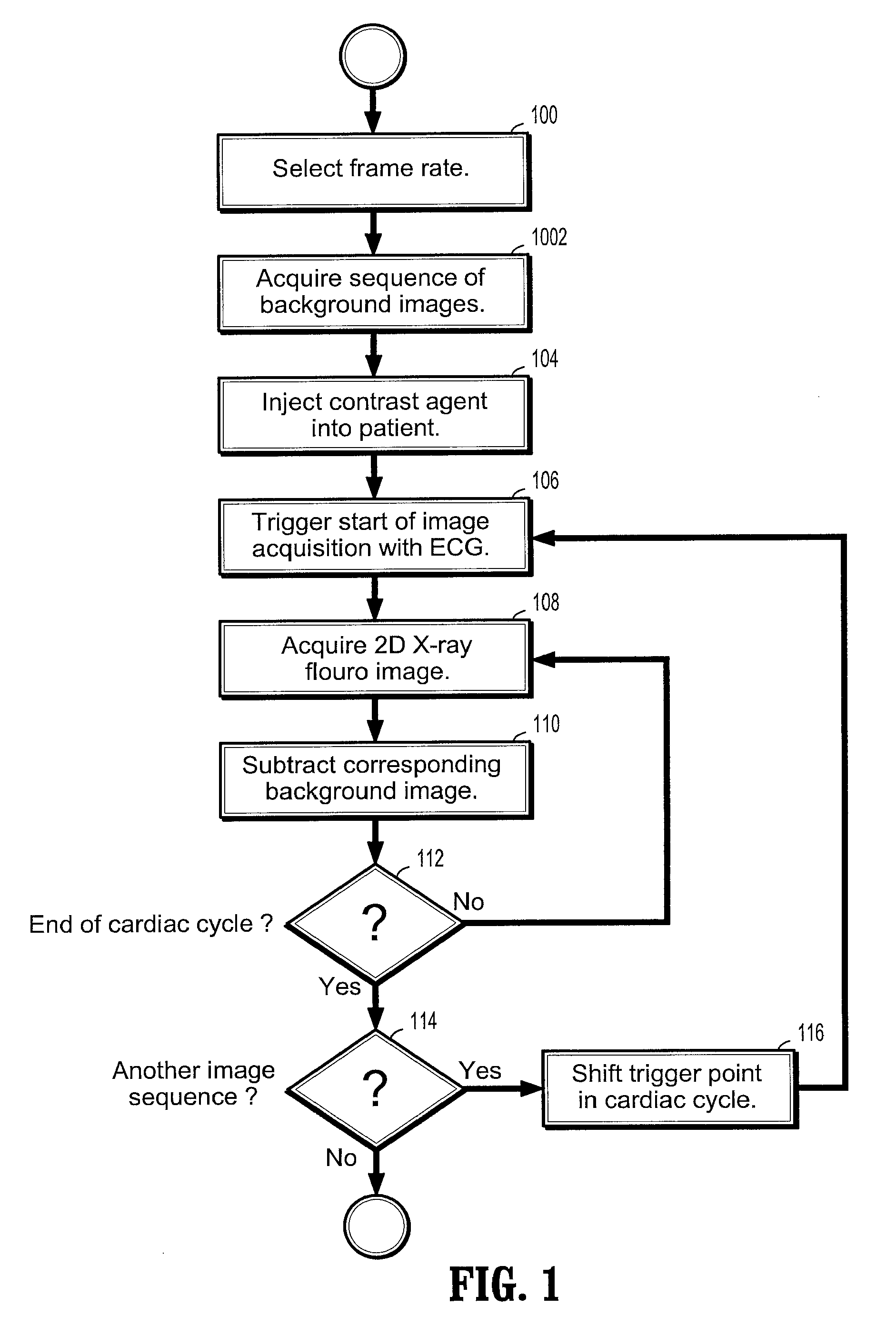
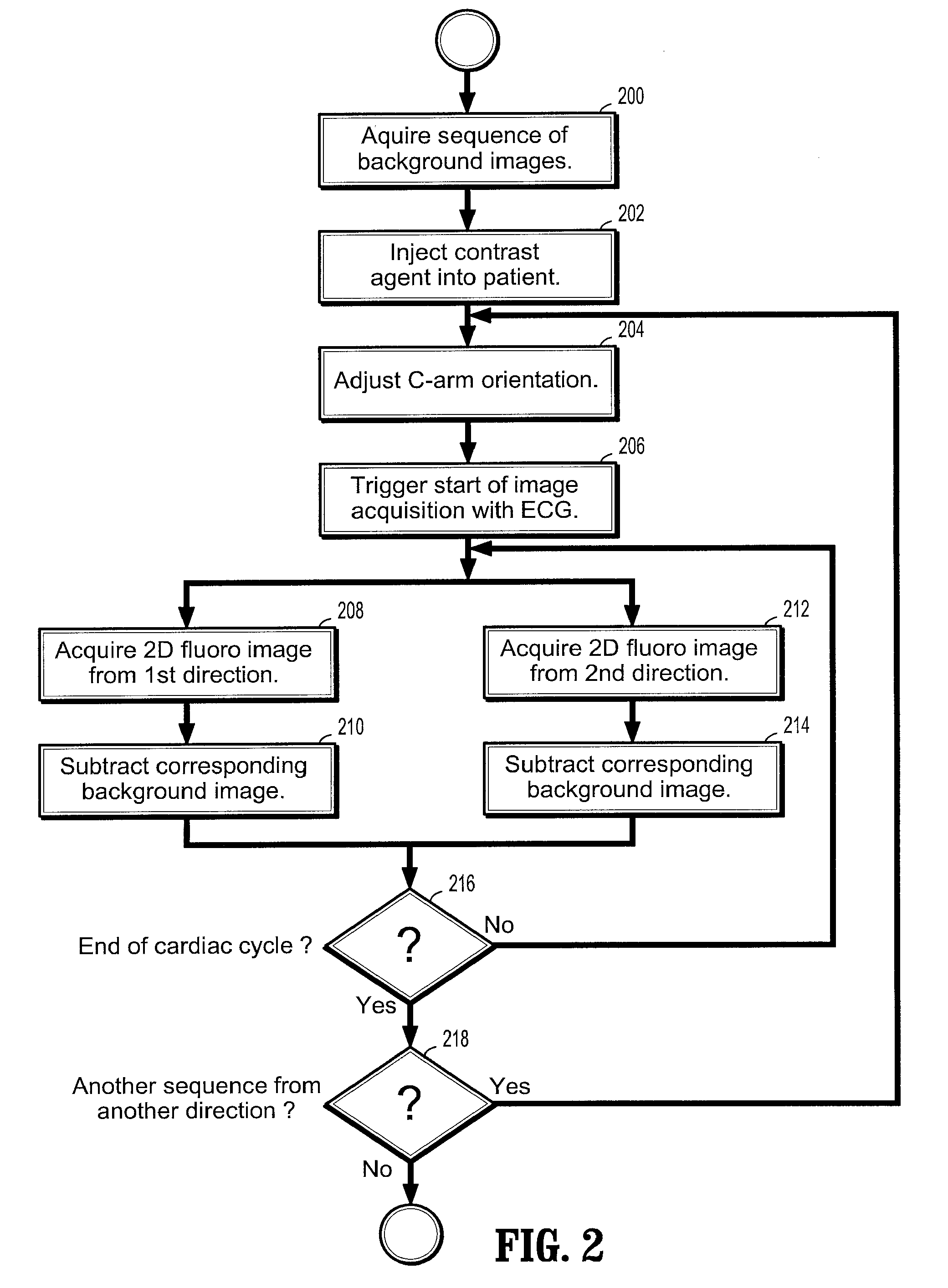
A method of assessing rupture risk of an aneurysm from time-resolved images includes injecting a contrast enhancing agent into a patient with an aneurysm, using an electrocardiogram (ECG) signal to trigger an image acquisition run, wherein a sequence of 2D X-ray fluoroscopic images is acquired along with a corresponding ECG signal value, rotating a C-arm attaching the X-ray fluoroscopic imaging apparatus during said image acquisition run, wherein the images in said X-ray fluoroscopic image sequence are acquired from a rotating viewpoint, sorting the images in said X-ray fluoroscopic image sequence into time windows of the cardiac cycle based on the ECG signal, and constructing one or more 3-dimensional (3D) angiography image volumes of said aneurysm from said 2D fluoroscopic image sequence.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Micro-focus X-ray precise perspective imaging detection equipment
ActiveCN102338756AImprove detection accuracyMeet the requirements of fine testingMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationAviationImage detection
The invention relates to micro-focus X-ray precise perspective imaging detection equipment applied in the field of electronic and micro-electronic assembly, belonging to nondestructive full-automatic detection equipment and comprising a micro-electronic X-ray source, a ray image receiver, an X-ray emitting source, a multi-angle rotating three-dimensional detection device of a receiver, a four-axis mobile platform of a detected object, a computer and a layering control system, wherein the multi-angle rotating three-dimensional detection device and the four-axis mobile platform of the detected object are assembled into a mobile bracket body; the detected object is arranged on the four-axis mobile platform; the micro-electronic X-ray source and the ray image receiver are respectively arranged at the two ends of a bracket of the multi-angle rotating three-dimensional detection device; and the computer and the layering control system finish real-time mobile control and real-time image acquisition and processing. The invention is a new-generation nondestructive detection equipment which is especially applied in detection of electronic and micro-electronic products and production detection of various fine industries, thus being applied in the fields such as aviation, aerospace, military and industry.
Owner:SHANGHAI MODERN TECH
Apparatus for rapidly correcting installation position of panoramic vision measuring system
InactiveCN102080969AAchieve correctionSimple structureUsing optical meansCamera lensFluoroscopic imaging
The invention provides an apparatus for rapidly correcting an installation position of a panoramic vision measuring system. The apparatus comprises a viewing module, a perspective imaging module and a protection module, wherein the viewing module comprises a hyperboloid reflector installed in a protective glass tube and a hyperboloid reflector connector arranged on the top of the protective glass tube; the perspective imaging module comprises a scientific grade camera with a high frame frequency, and a perspective lens; and the protective module comprises a protective glass tube. The viewing module is connected with the protection module through a connector; the perspective imaging module is installed in the protection module by a support; and the top of the hyperboloid reflector is a circular plane whose center is the original summit of the hyperboloid reflector, wherein the circular plane is in parallel with the bottom of the hyperboloid reflector. The apparatus provided by the invention has a simple structure and a good adaptability and needs no external auxiliary measures; the apparatus can realize high-precision correction of the installation position of the panoramic vision measuring system, therefore possessing a high practical value.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com