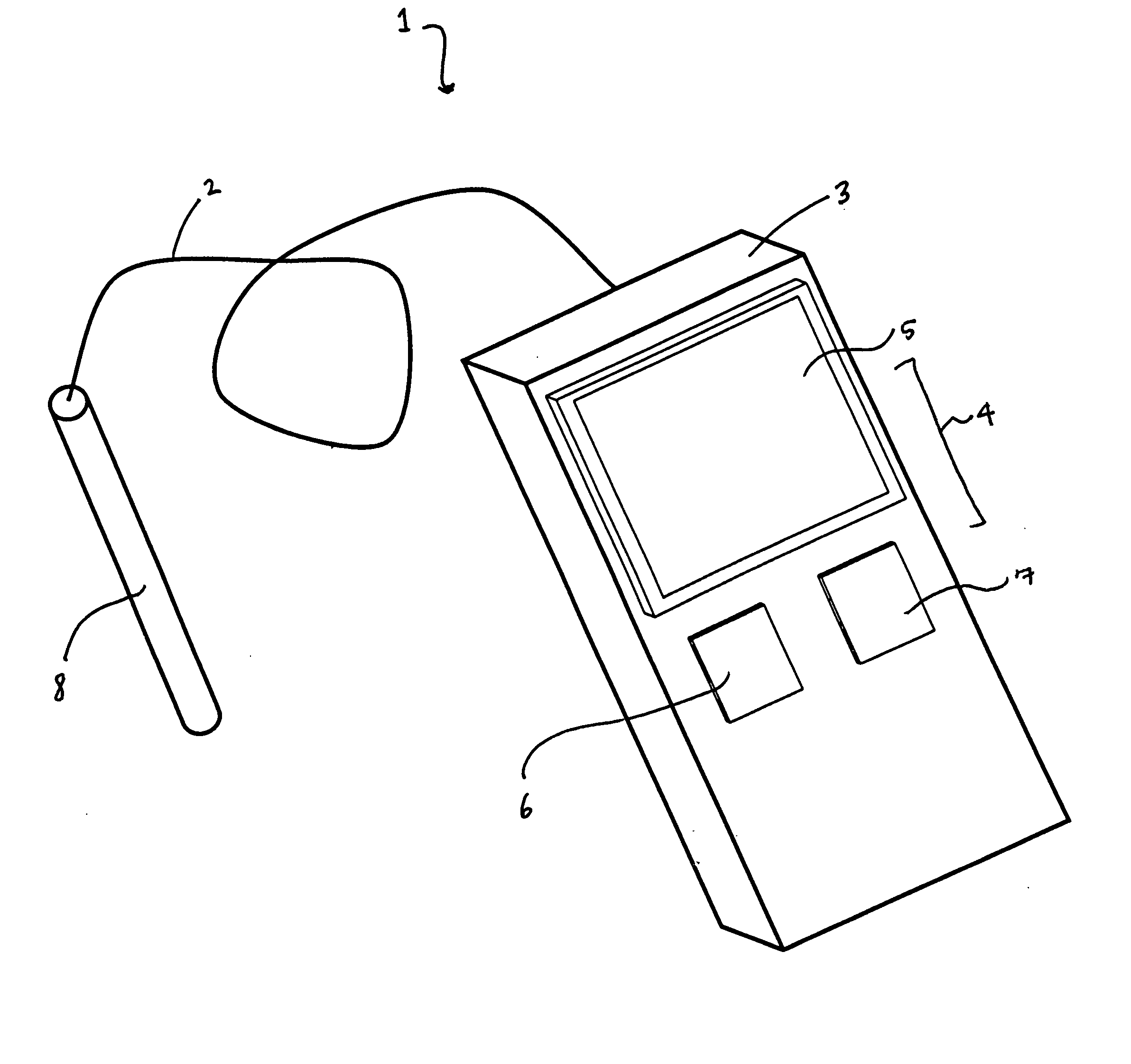
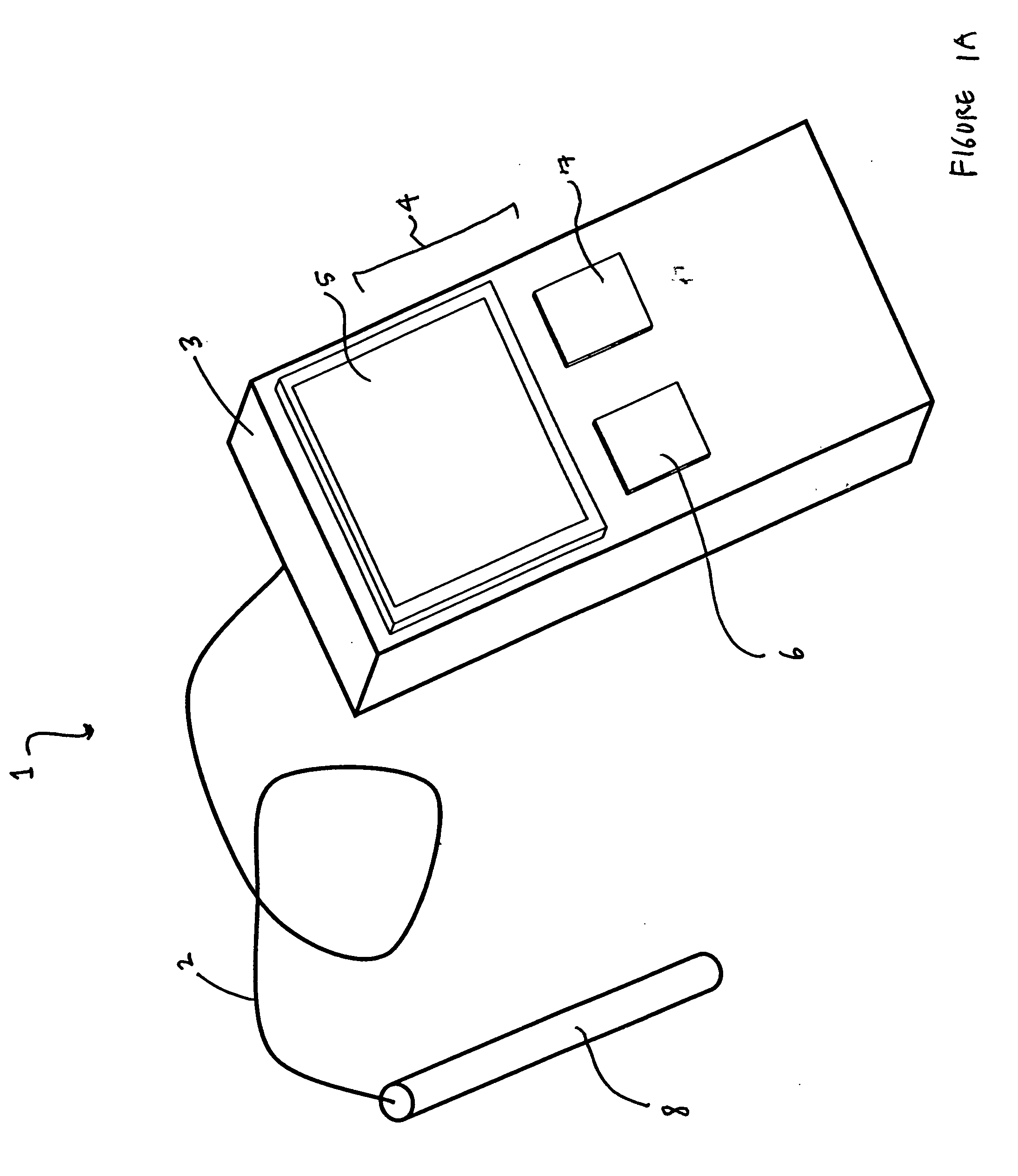
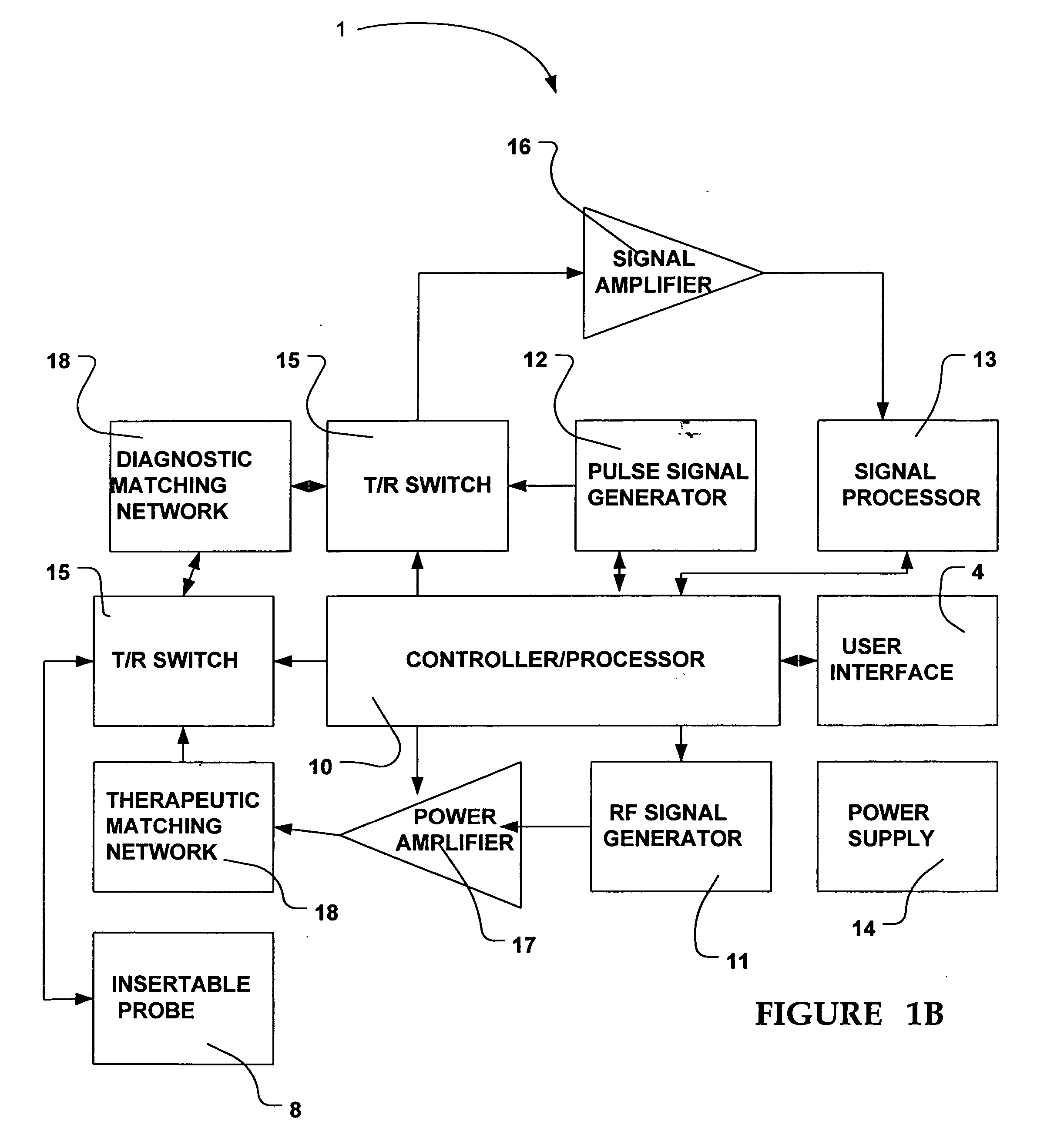
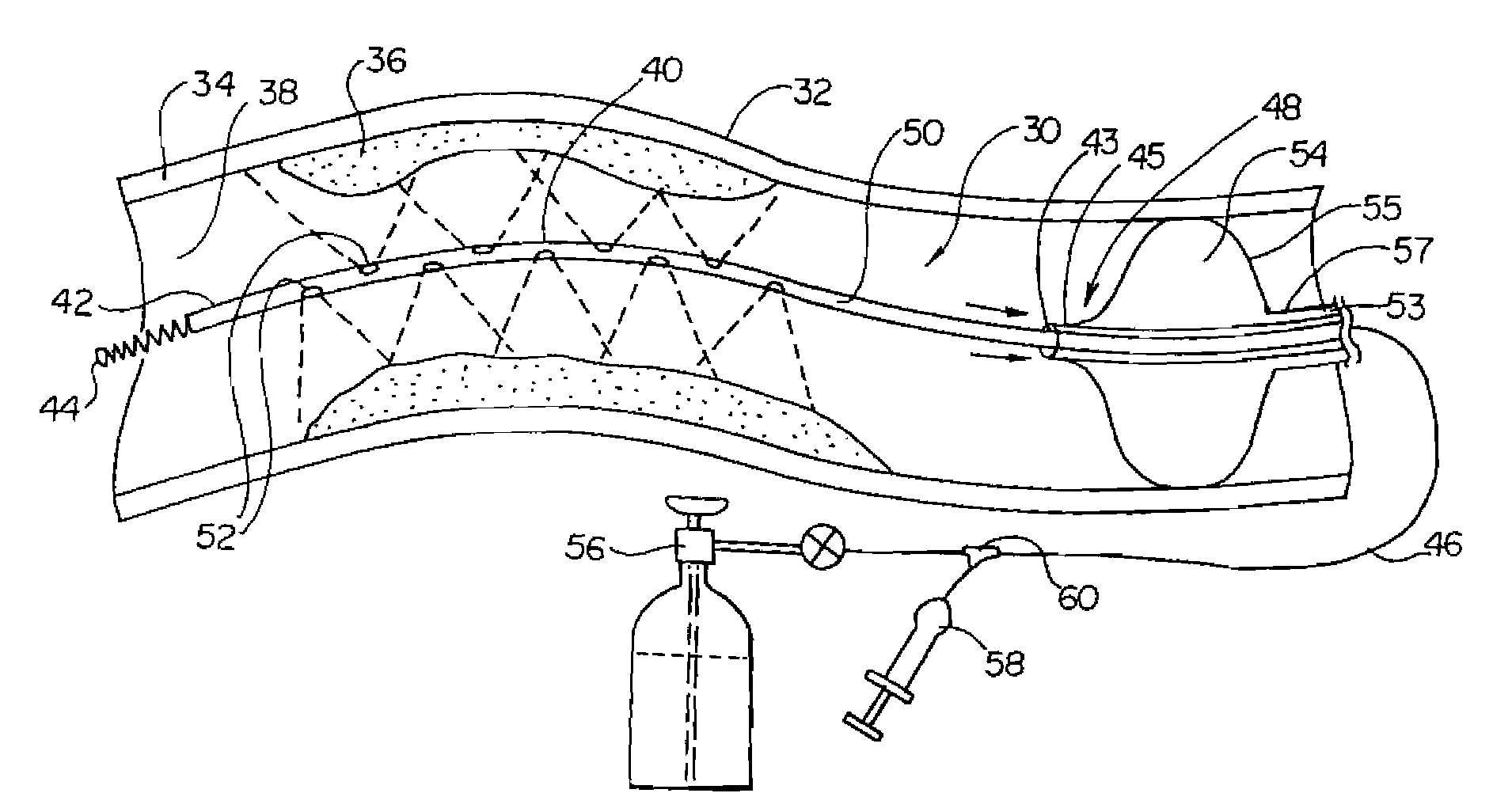
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5565 results about "Ultrasound probe" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An ultrasound probe, also known as a transducer, is a medical diagnostic device that emits ultrasound waves into a patient's body and transmits data to a computer to produce an internal image of the body, known as a sonogram.
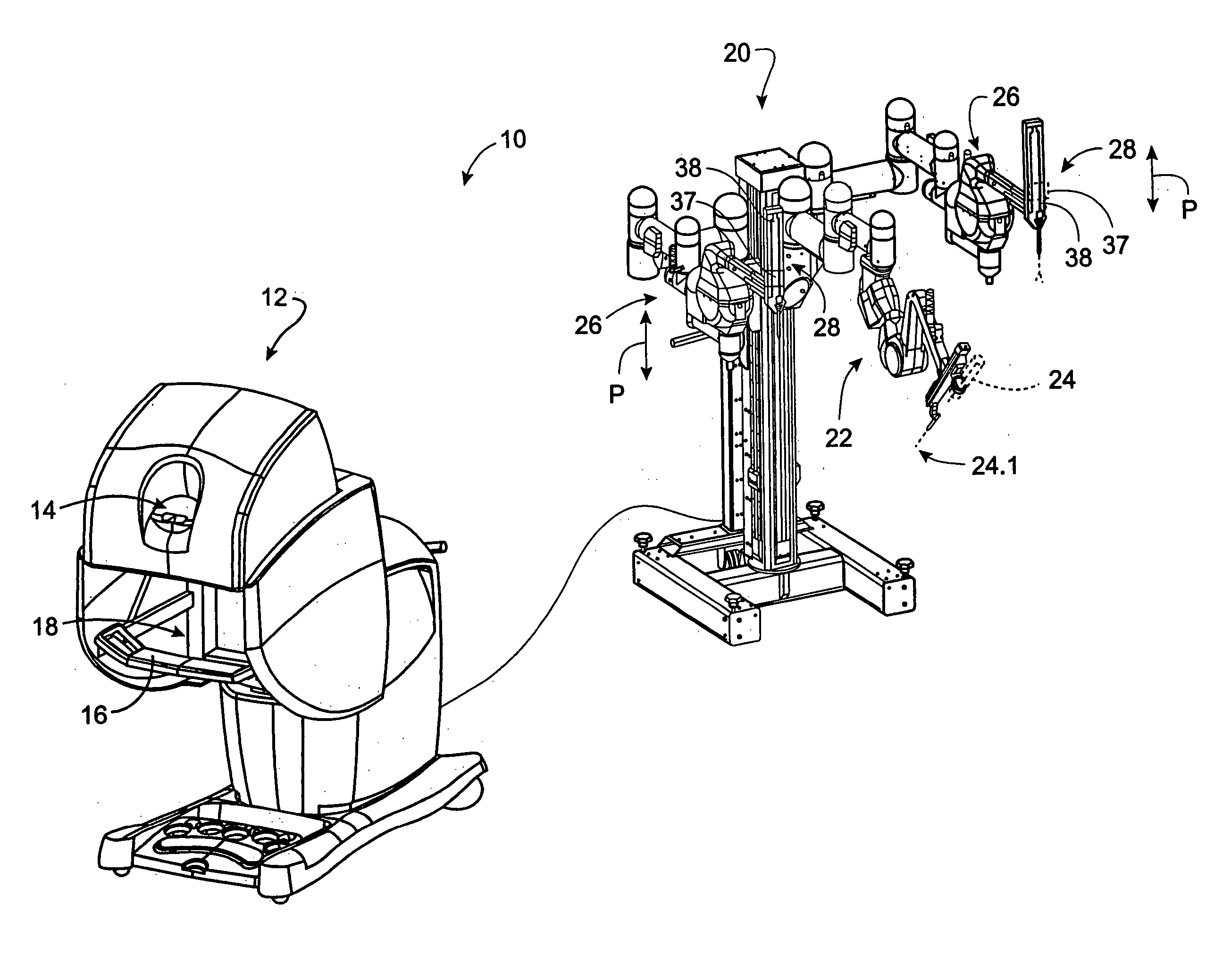
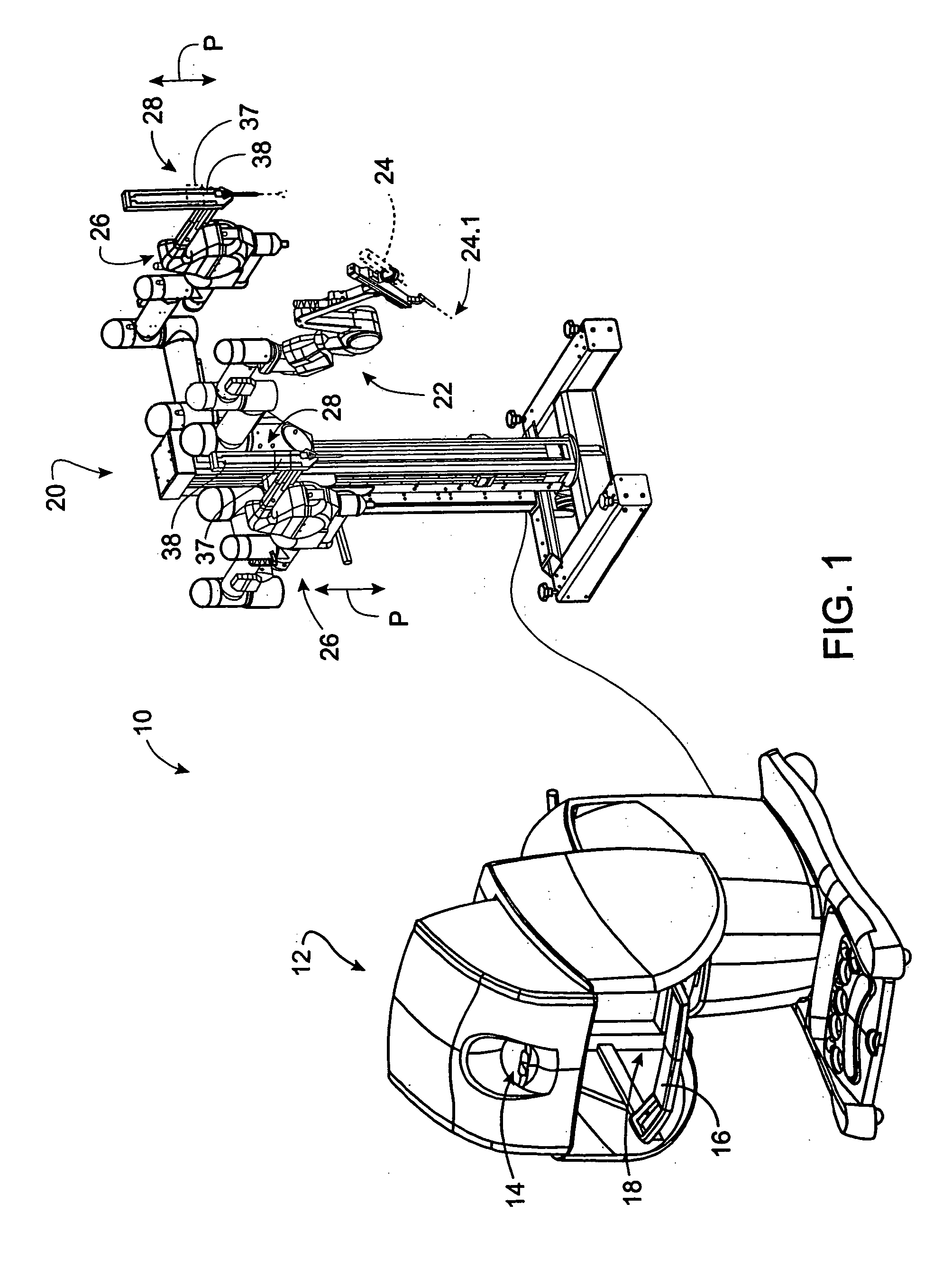
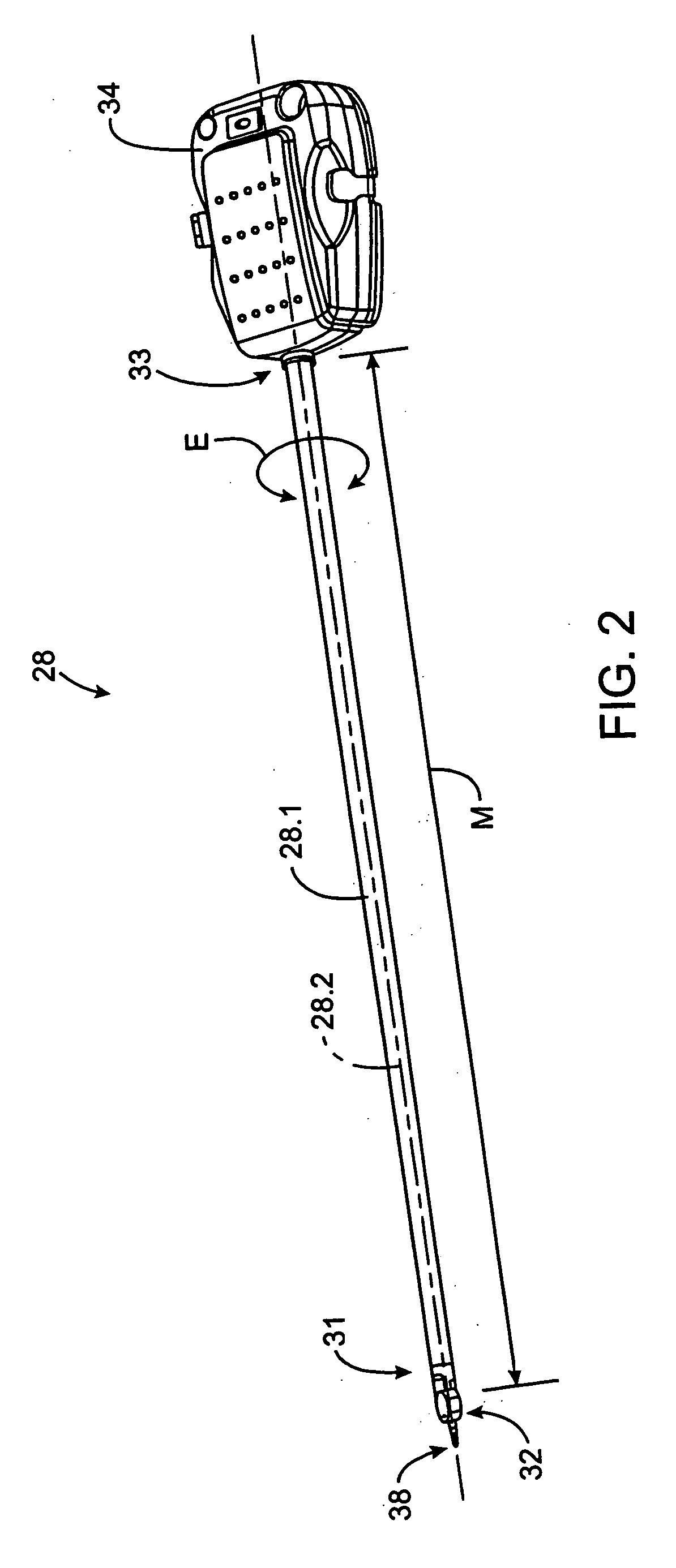
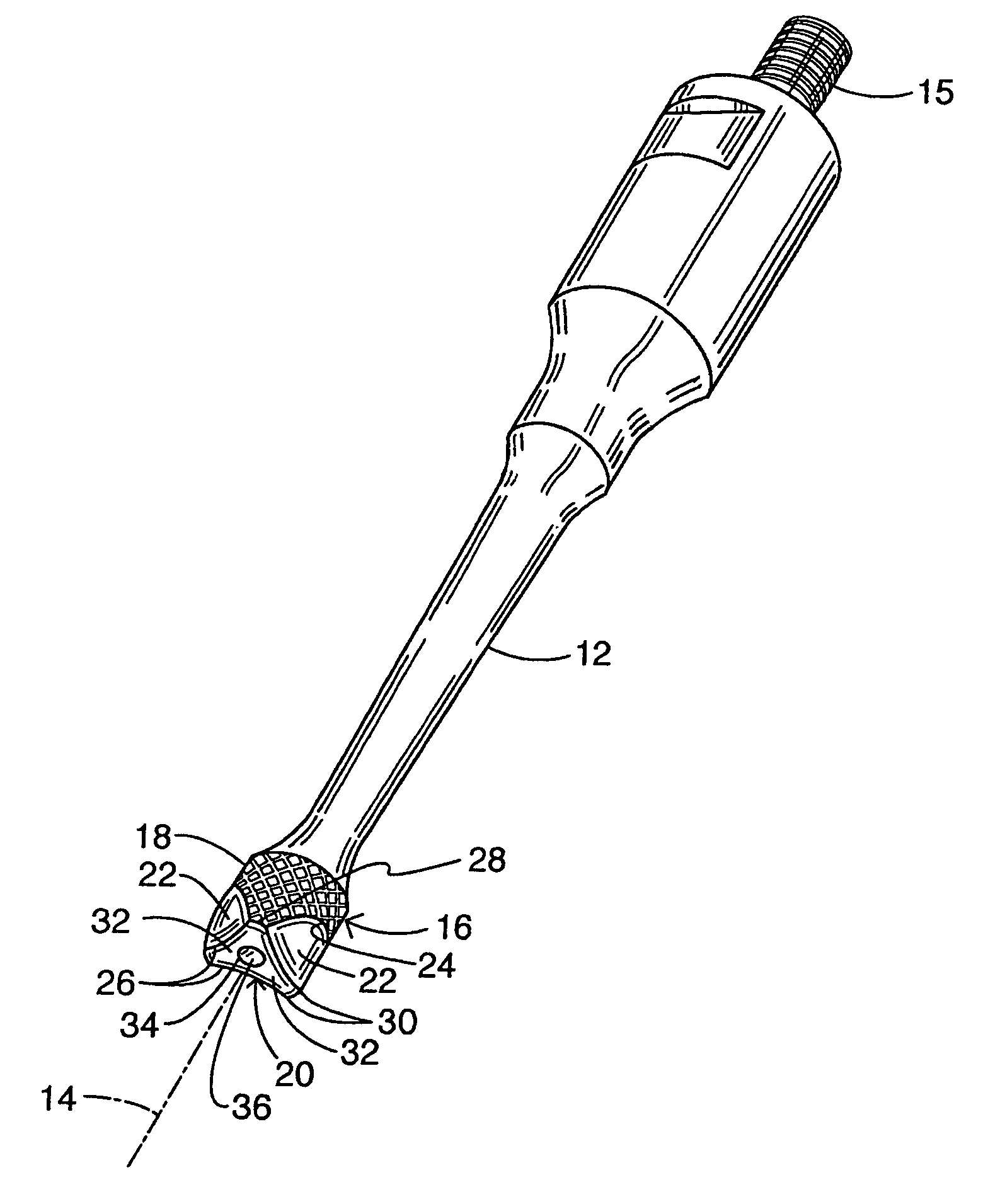
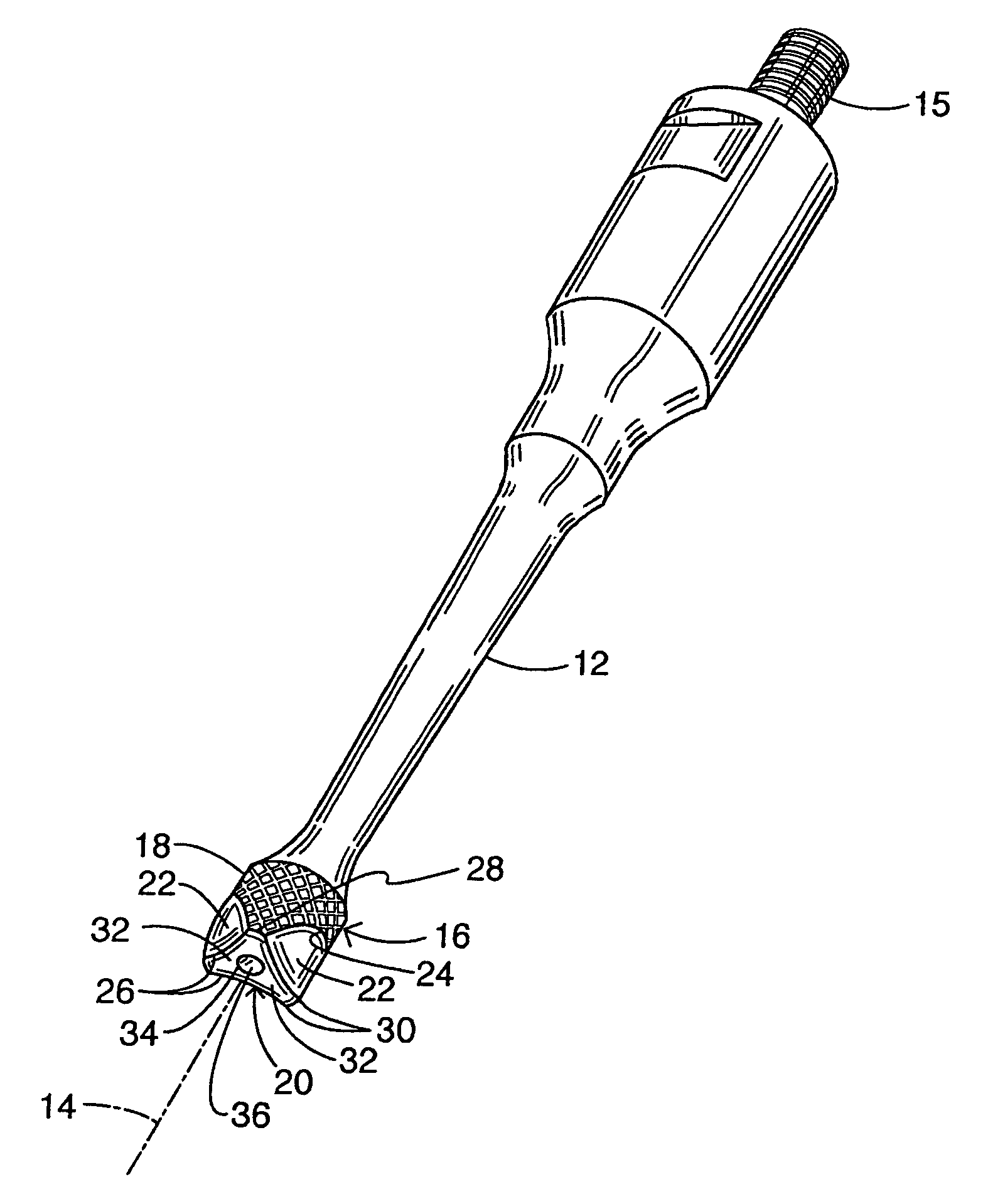
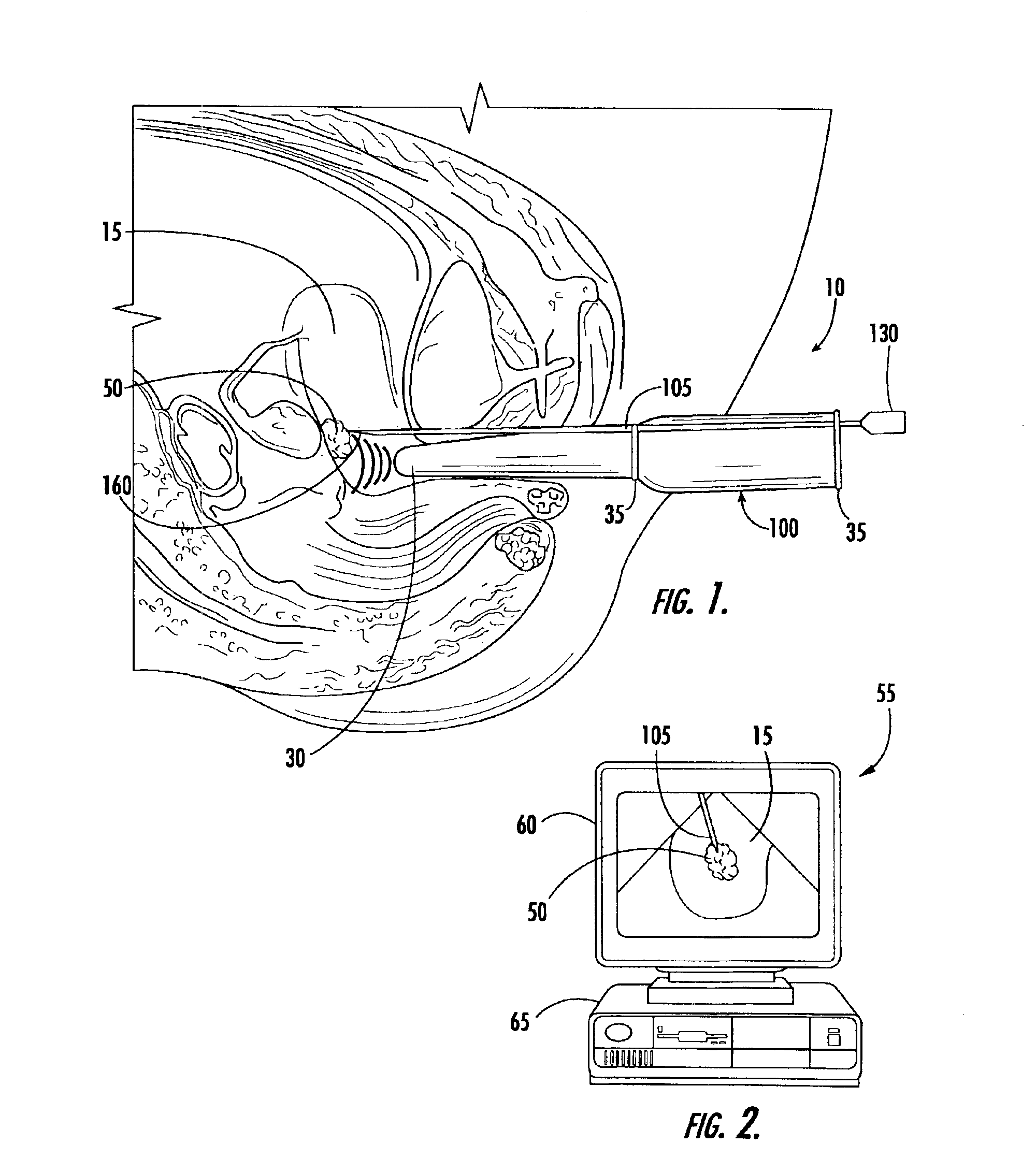
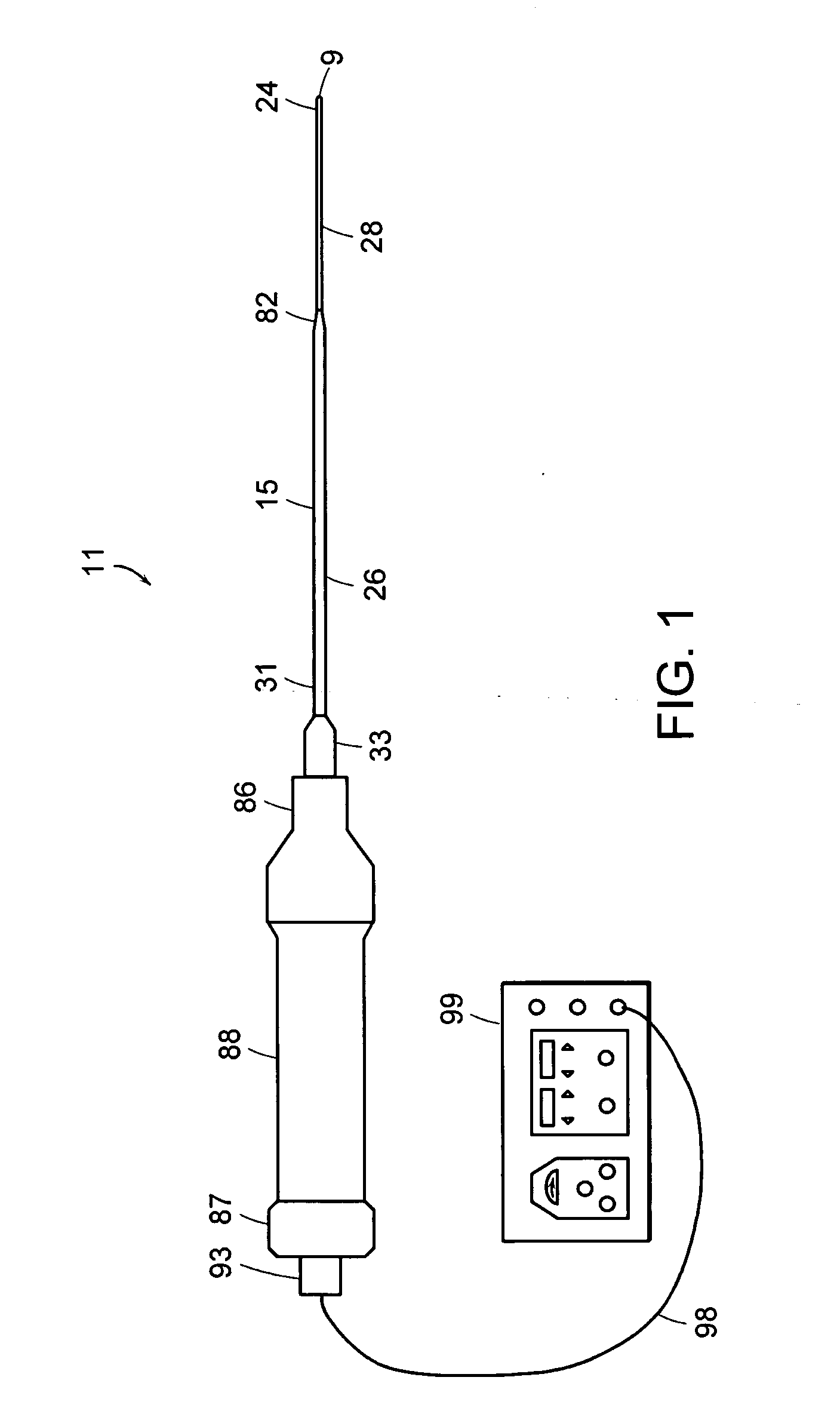
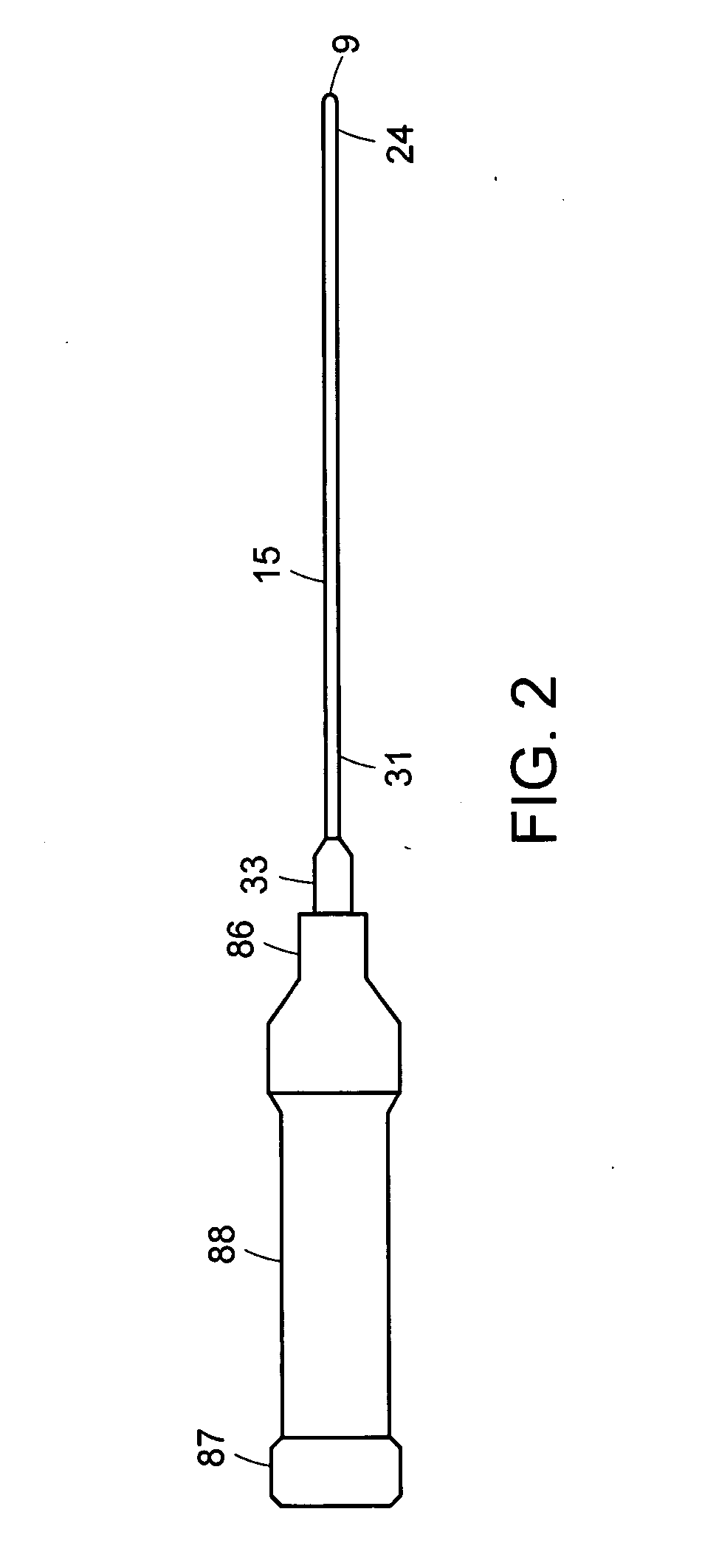
Robotic surgical tool with ultrasound cauterizing and cutting instrument
InactiveUS20050021018A1Enhancing robotic surgeryPrecise positioningUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSurgical siteActuator
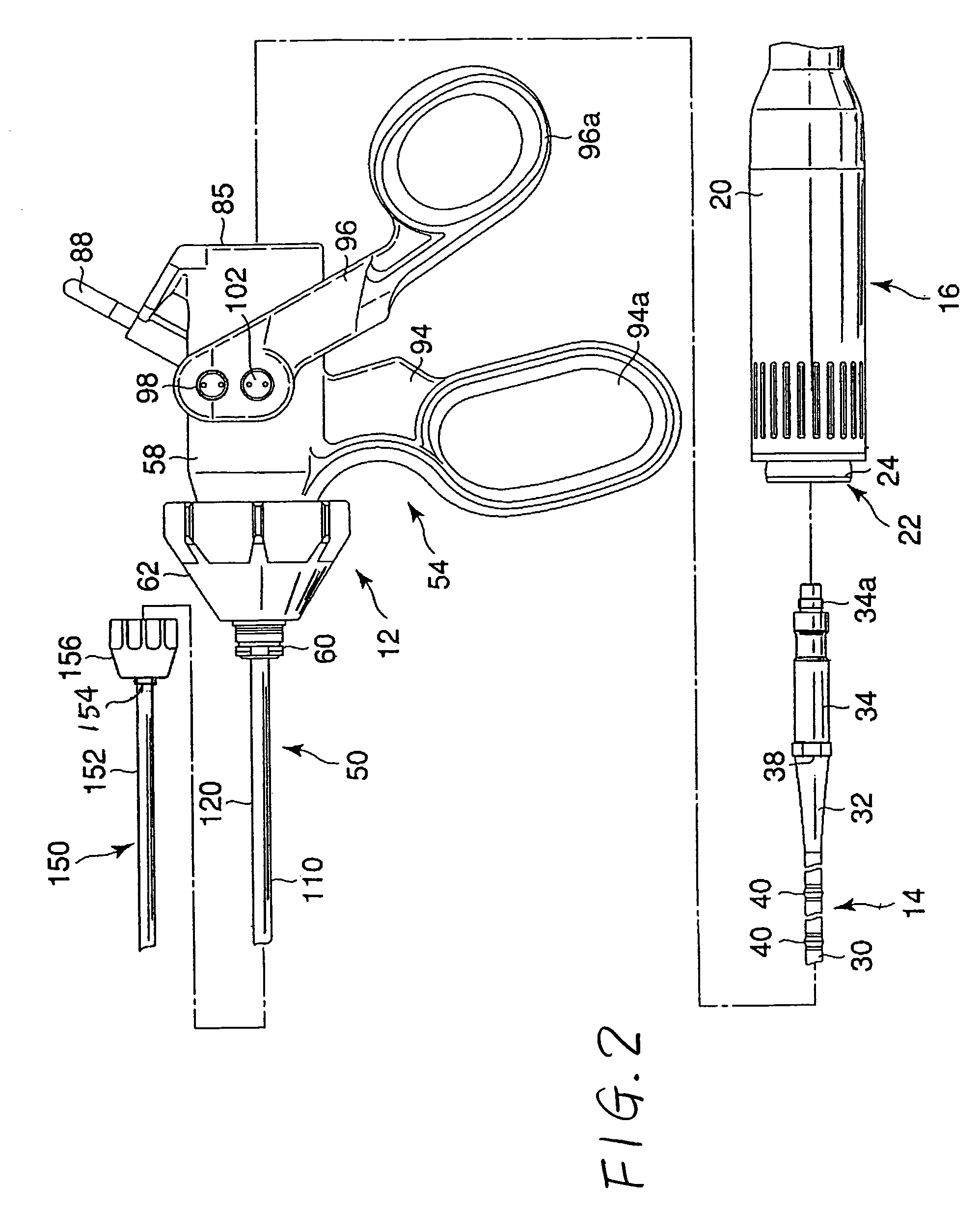
A surgical instrument for enhancing robotic surgery generally includes an elongate shaft with an ultrasound probe, an end effector at the distal end of the shaft, and a base at the proximal end of the shaft. The end effector includes an ultrasound probe tip and the surgical instrument is generally configured for convenient positioning of the probe tip within a surgical site by a robotic surgical system. Ultrasound energy delivered by the probe tip may be used to cut, cauterize, or achieve various other desired effects on tissue at a surgical site. In various embodiments, the end effector also includes a gripper, for gripping tissue in cooperation with the ultrasound probe tip. The base is generally configured to removably couple the surgical instrument to a robotic surgical system and to transmit forces from the surgical system to the end effector, through the elongate shaft. A method for enhancing robotic surgery generally includes coupling the surgical instrument to a robotic surgical system, positioning the probe tip in contact with tissue at a surgical site, and delivering ultrasound energy to the tissue.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL
Ultrasound system with stereo image guidance or tracking
ActiveUS20150148664A1Prevent movementOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgical navigation systemsDisplay deviceStereo image
An image-guided ultrasound system may include an ultrasound probe, a display configured to communicate with the ultrasound probe to receive ultrasound signals to display images from the ultrasound probe, and an imaging device that may be attached to or integral with the ultrasound probe and configured to communicate with the display to display information derived from images from the imaging device. The imaging device may include a stabilization assembly, an imaging device assembly physically coupled to the stabilization assembly, a plurality of light-sensitive devices physically coupled to the stabilization assembly, and a memory unit physically coupled to the imaging device assembly, the memory unit configured to store calibration or usage information for the image-guided ultrasound system.
Owner:CLEAR GUIDE MEDICAL
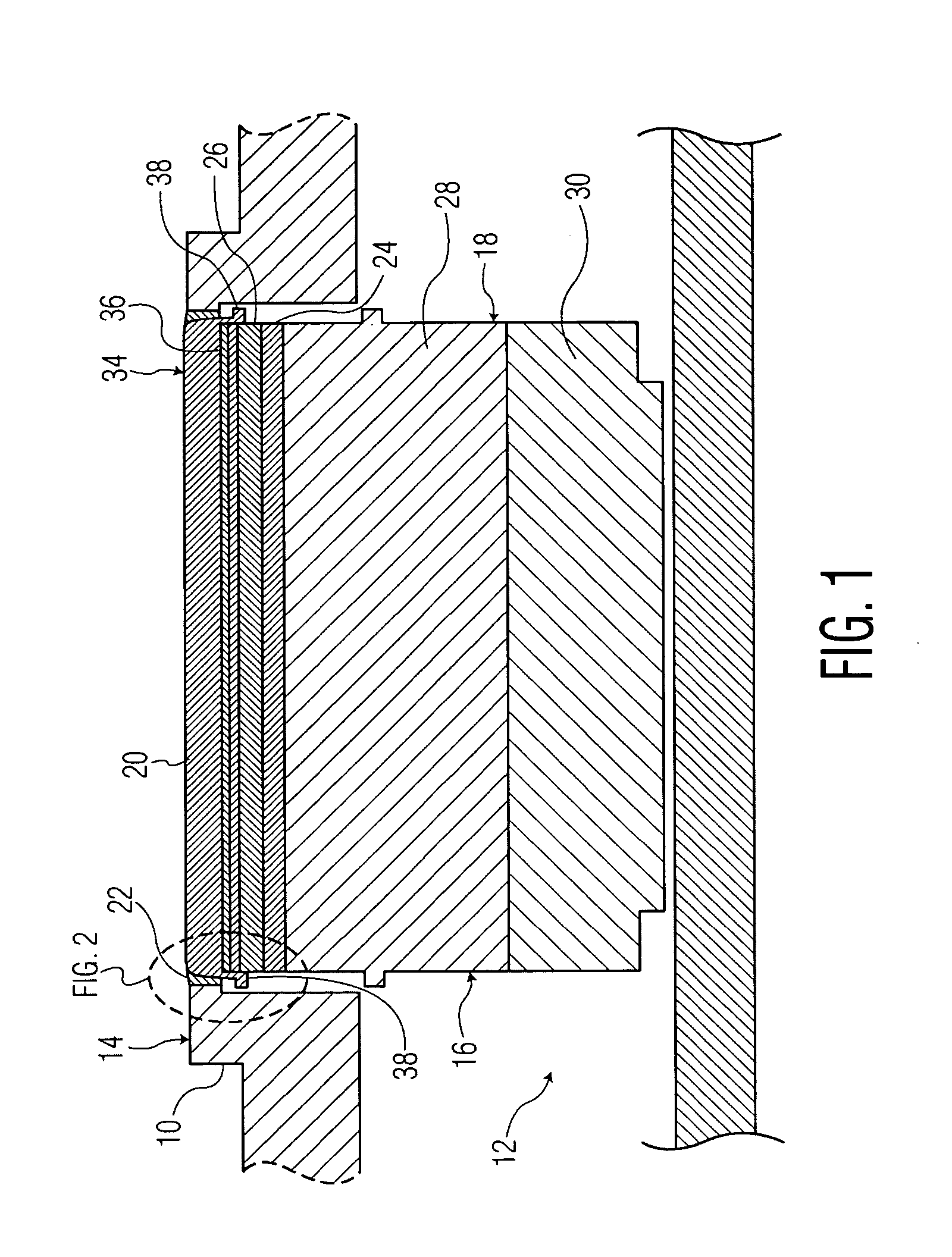
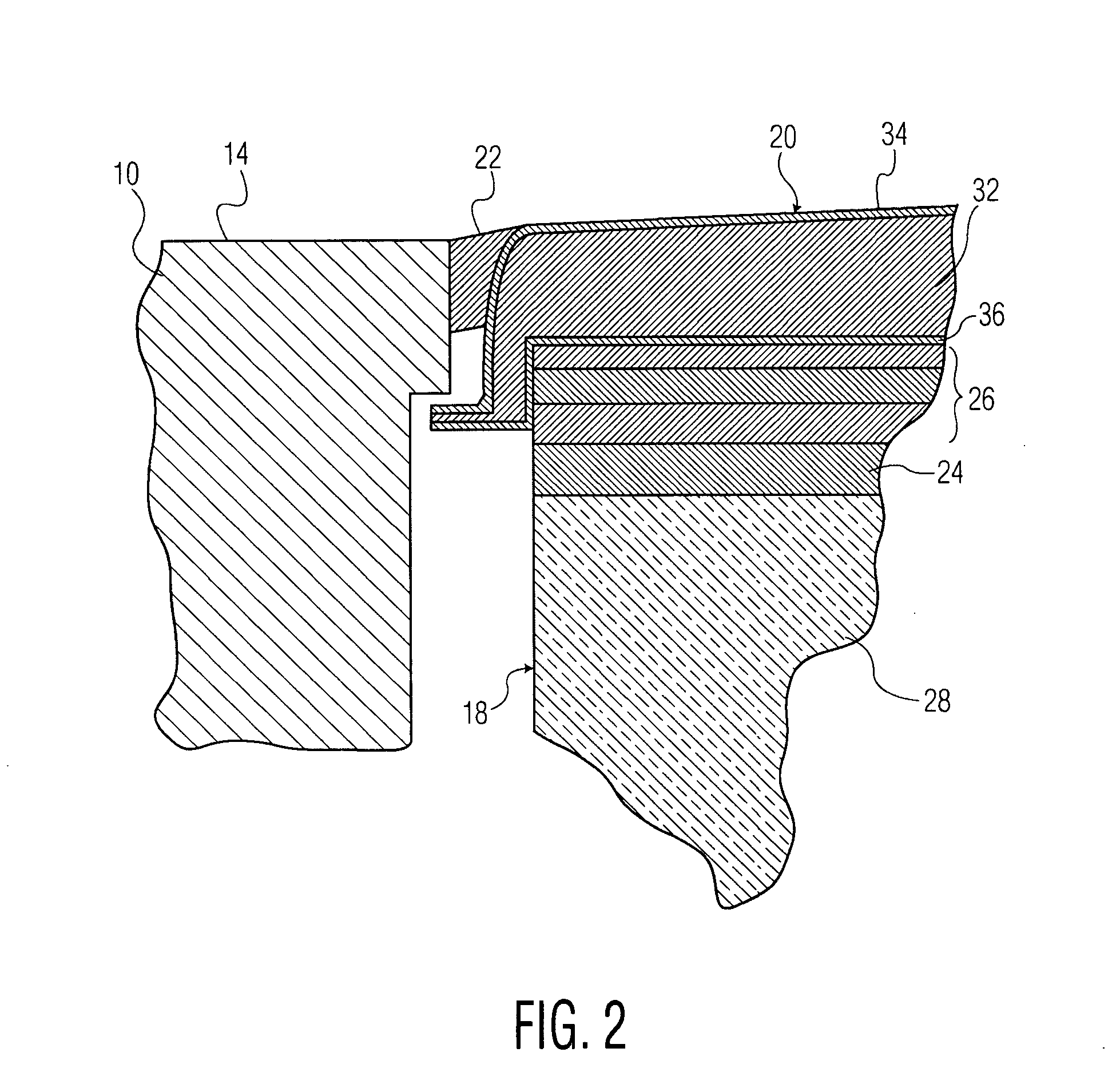
Ultrasonic probe deflection sensor
An ultrasonic surgical instrument having a deflection detection circuit is disclosed. The instrument includes an ultrasonic probe configured to conduct electricity and positioned a predetermined distance from one or more tubes. The ultrasonic probe is adapted to be operatively connected to an ultrasonic generator for vibration. The instrument also includes a deflection detection circuit having a secondary power source and an indicator, the power source is configured to supply electrical current to the tube, the probe, and the indicator, wherein the circuit is configured to close in response to the probe contacting the tube when the probe is deflected toward the tube thereby activating the indicator.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Surgical instrument
InactiveUS20090270771A1Efficiently conductedUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesBiological bodyPower flow
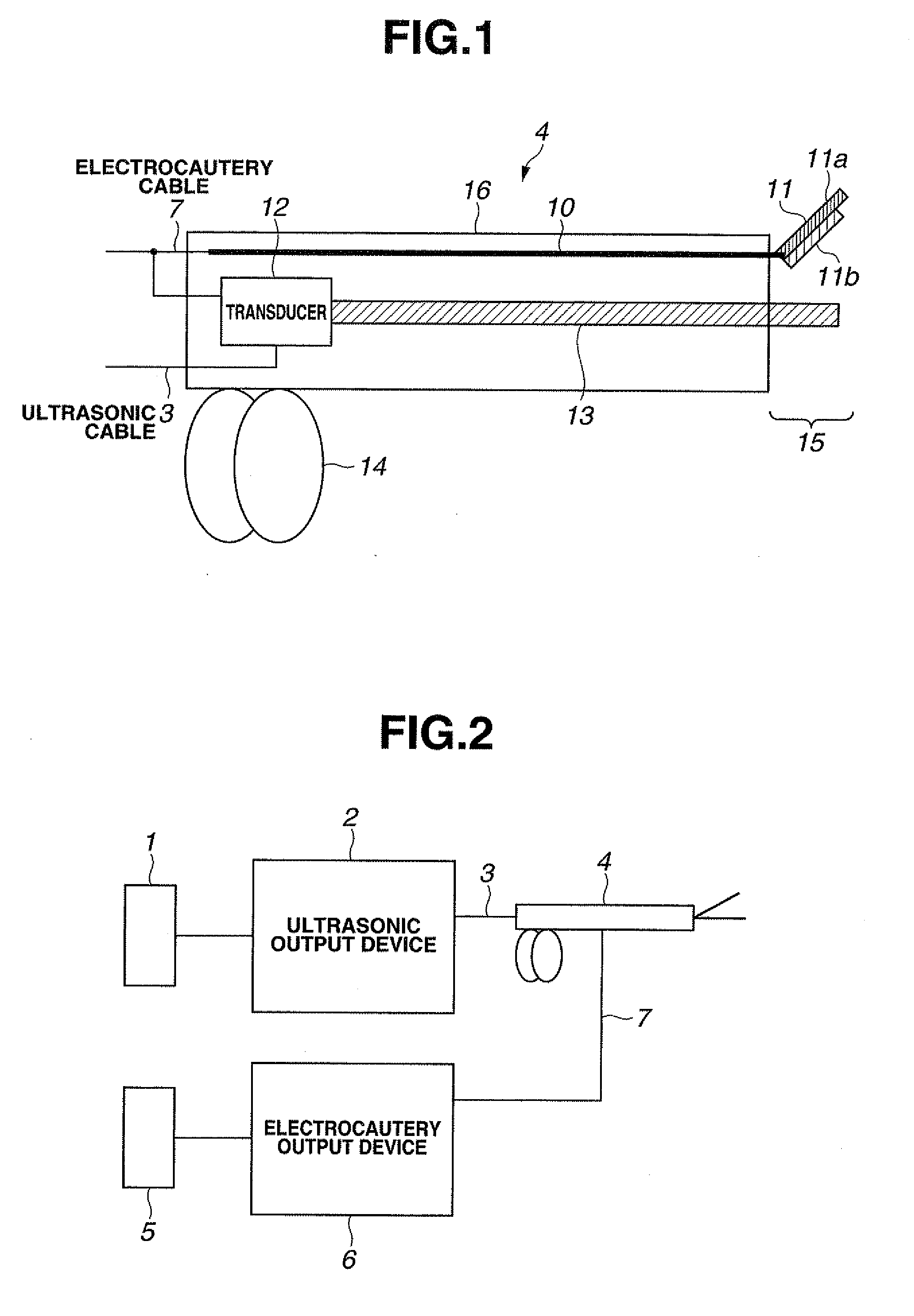
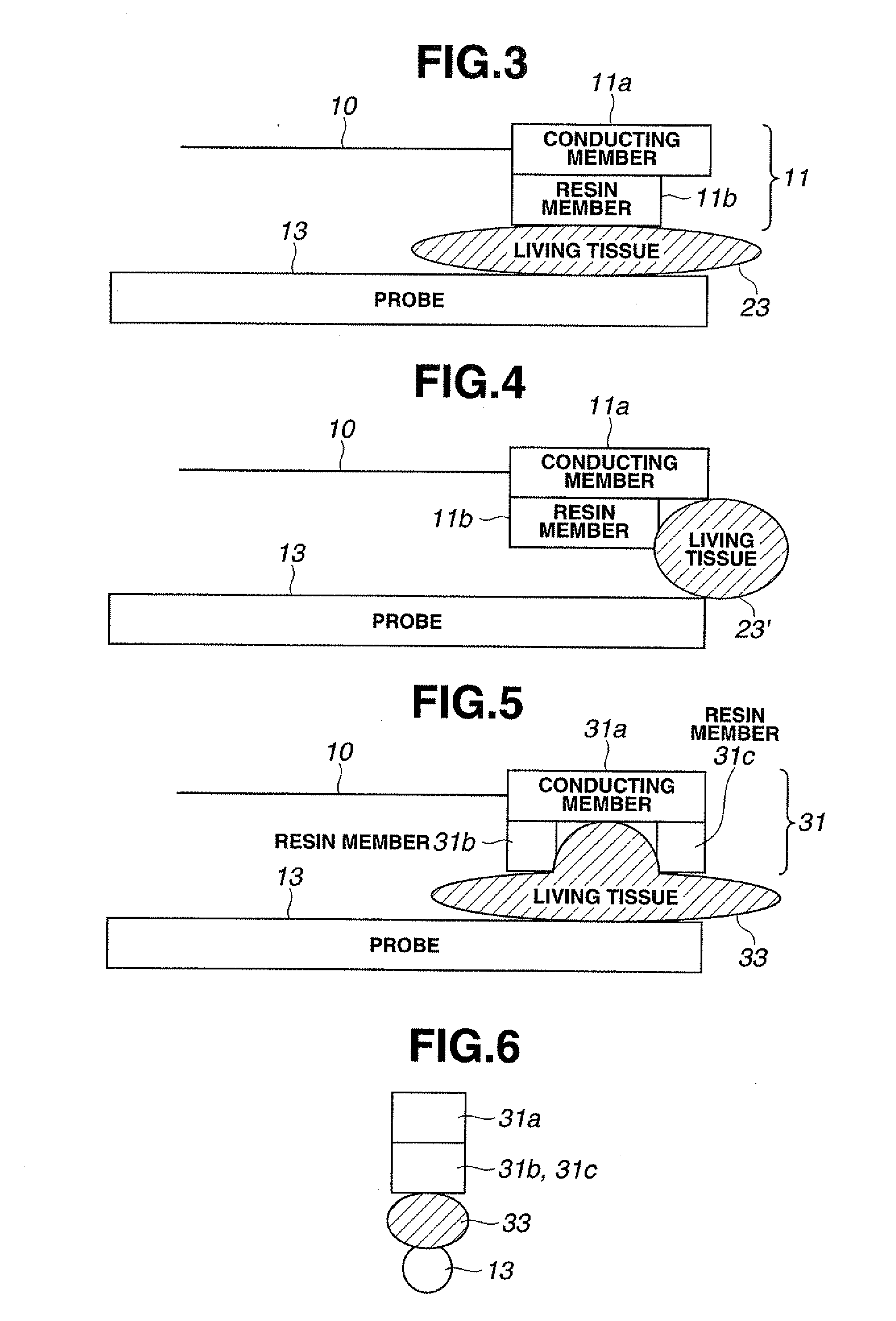
A surgical instrument is provided including: an ultrasonic transducer for generating ultrasonic vibration; an ultrasonic probe for transmitting the ultrasonic vibration generated by the ultrasonic transducer to a distal end portion; a grasping member capable of grasping a living tissue as an object to be treated between the grasping member and a distal end portion of the ultrasonic probe by moving between positions close to and distant from the distal end portion of the ultrasonic probe; a conductive member configured of a conductive material for supplying high-frequency current to the living tissue, the conductive member being provided to the grasping member; and a non-conductive member configured of a non-conductive material and formed in a shape for blocking a contact between the conductive member and the ultrasonic probe and exposing a part of one surface of the conductive member on the ultrasonic probe side, the non-conductive member being provided to the grasping member so as to be located between the conductive member and the ultrasonic probe, thereby allowing high-frequency current to be effectively conducted to a living tissue.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Treatment apparatus and treatment device for surgical treatments using ultrasonic vibration
ActiveUS7799045B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSurgical treatmentTransducer
An ultrasonic treatment device comprises a transducer unit, probe unit, and a main unit. The transducer unit comprises an ultrasonic transducer generating ultrasonic vibration in response to supply of power. The probe unit has a treatment member at a distal end thereof. The probe unit is detachably loaded to the transducer unit, and is equipped with an ultrasonic probe transmitting the ultrasonic vibration to the distal end of the treatment member when the transducer unit is loaded to the probe unit. The main unit is manually grasped by an operator. The probe unit with the transducer unit loaded thereto is detachably loaded to the main unit. The main unit has a cylindrical insert through which the ultrasonic probe is inserted to have the treatment member protruded outwardly when the probe unit is loaded. The main unit further has an outer sheath detachably covering an outer surface of the insert.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
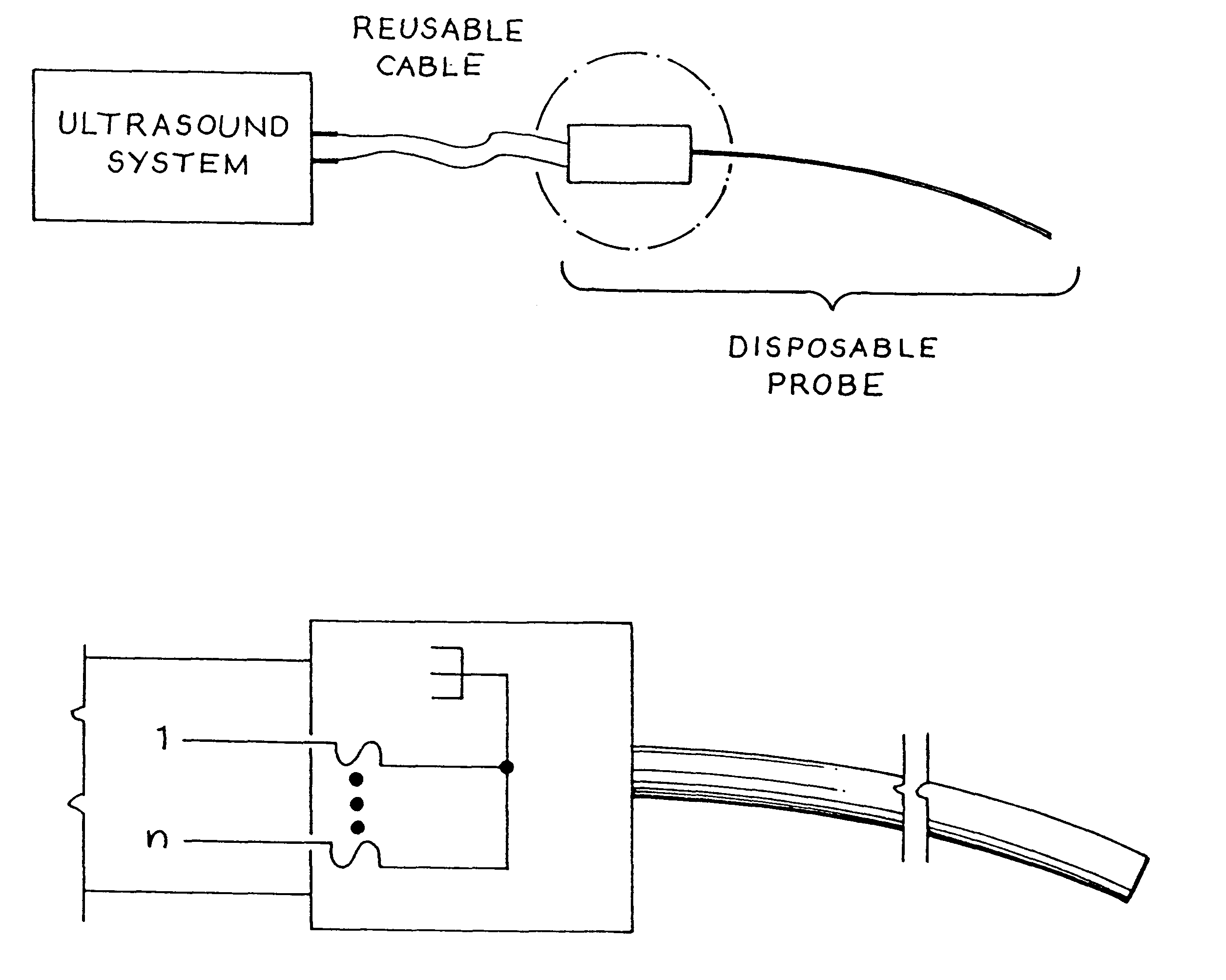
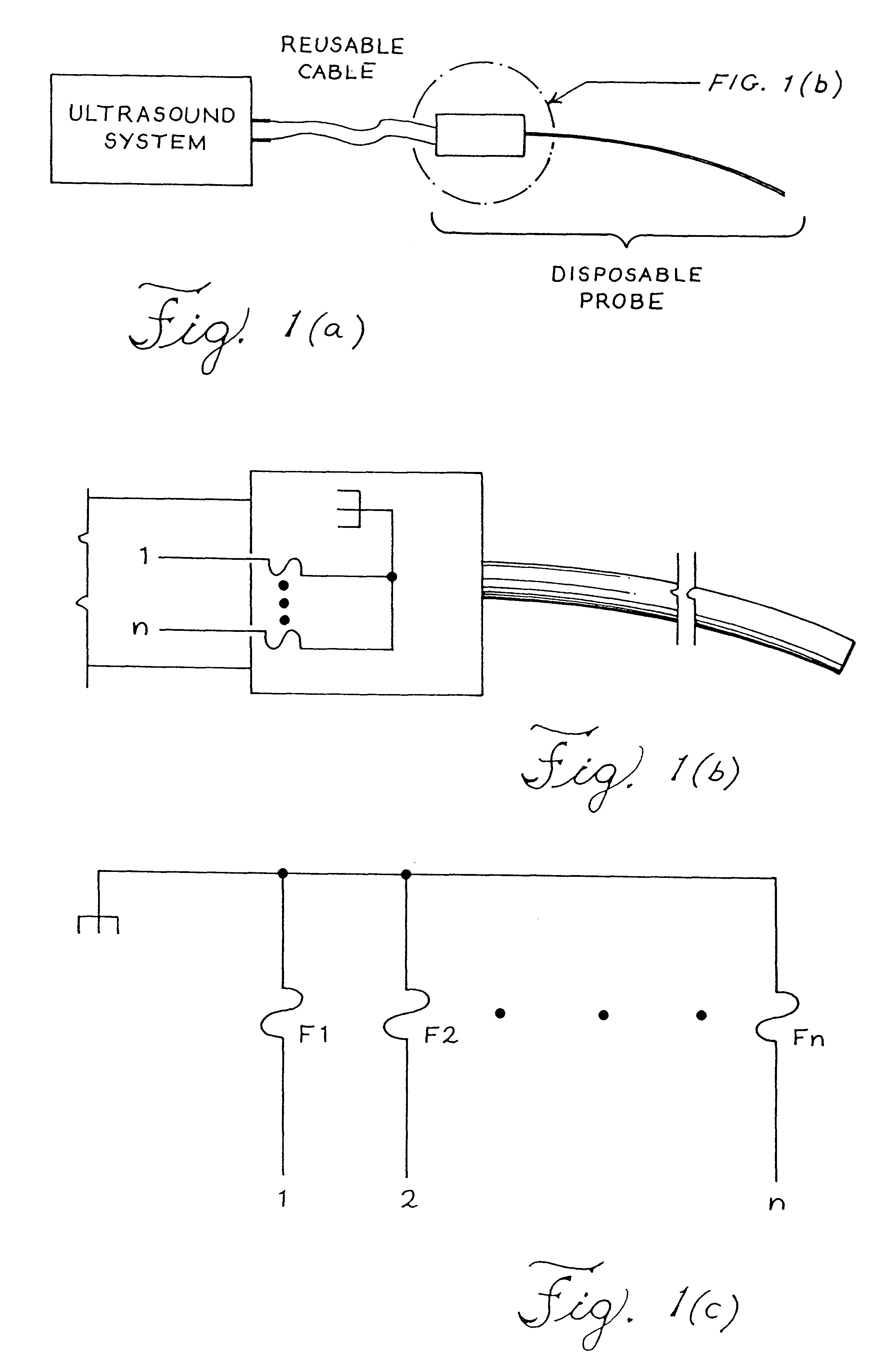
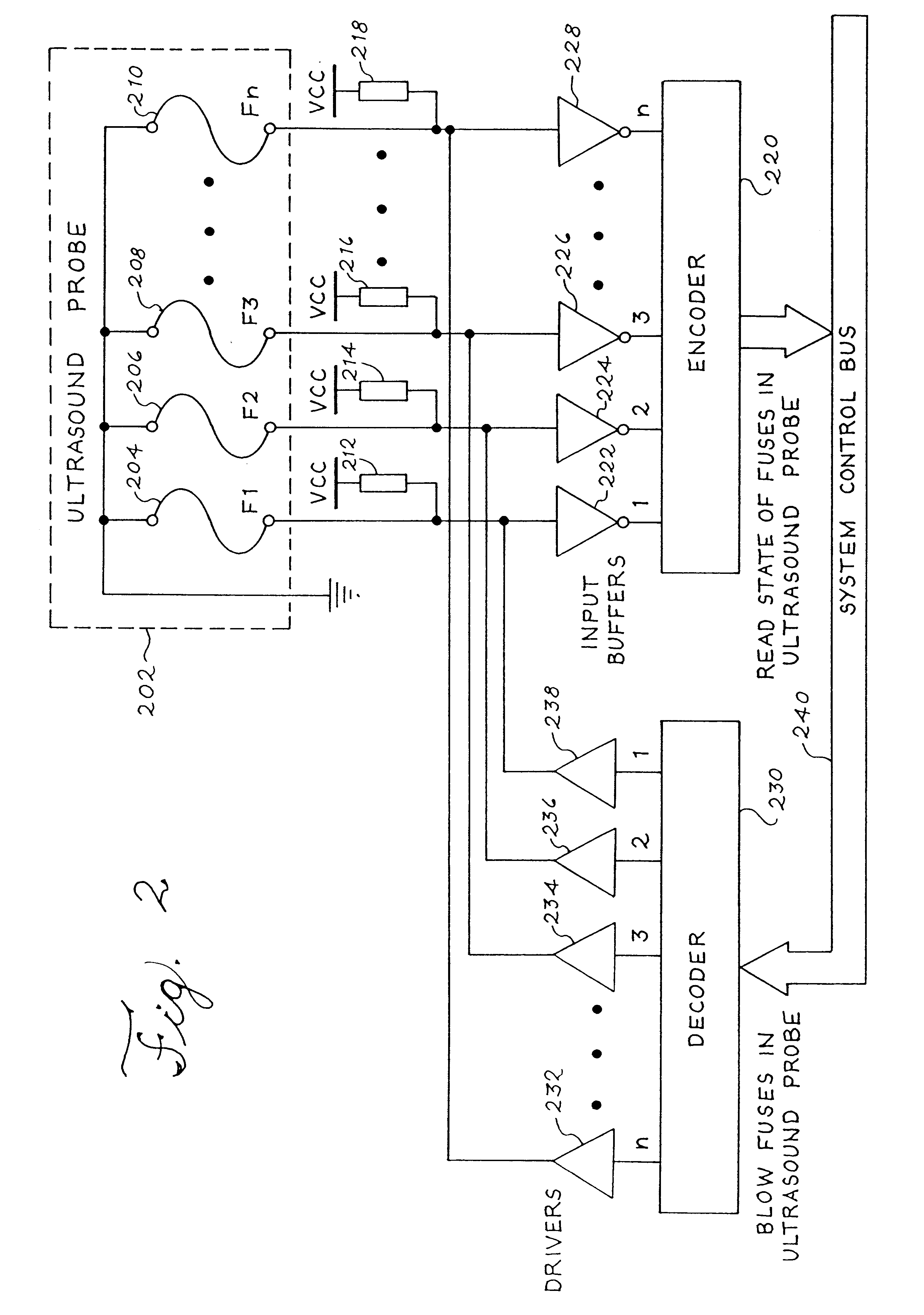
Apparatus and method to limit the life span of a diagnostic medical ultrasound probe
An ultrasound probe for diagnostic medical ultrasound imaging, including an ultrasound transducer and a circuit having a plurality of states to limit the use of the ultrasound probe. Ultrasound probe use can be limited based on a unique identification number (e.g., selected by means of electrically programmable fuses) assigned to each ultrasound probe. Alternatively, the ultrasound system software monitors and updates the number of times that the ultrasound probe has been used. Another aspect of the invention is directed to an ultrasound system, including an ultrasound probe with multiple states, a circuit to program and to receive state data from the ultrasound probe and interpret the state data, and a cable to communicate state data between the ultrasound probe and the processor. Another aspect of the invention is directed to a method for using a limited use ultrasound probe, including the steps of determining the state of a circuit in the limited use ultrasound probe and determining if the ultrasound probe can be used.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Insertable ultrasound probes, systems, and methods for thermal therapy
InactiveUS20050240170A1Increase temperatureUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyThermal energyTransducer
Disclosed herein are methods and systems for producing hemostasis, tissue closure, or vessel closure by inserting a thermal delivery probe into a passageway and emitting thermal energy from the probe to produce the hemostasis or tissue closure. These methods and systems may be used following a percutaneous medical procedure that creates a passageway in tissue of patient, such as is caused by introduction of an access device into the patient. The thermal delivery probe may have one or more ultrasound transducers positioned in an elongated shaft.
Owner:OTSUKA MEDICAL DEVICES +1
Cryotreatment device and method
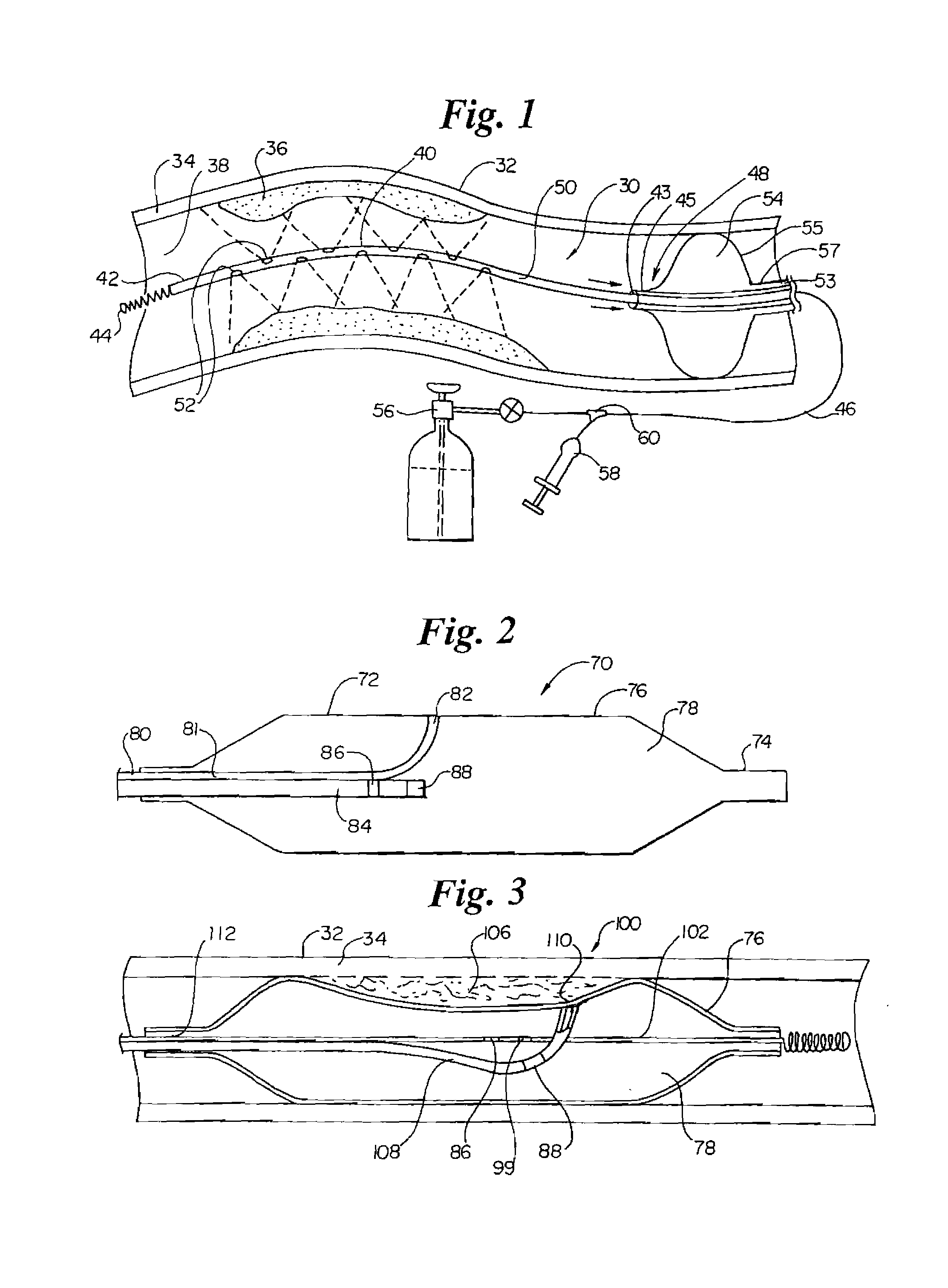
InactiveUS7220257B1Reduce adverse reactionsReduced responseStentsOther blood circulation devicesCoronary artery angioplastyPercent Diameter Stenosis
Devices and methods for cooling vessel walls to inhibit restenosis in conjunction with medical procedures such as coronary artery angioplasty. Stenosed vessel walls can be cooled prior to angioplasty, after angioplasty, or both. The invention is believed to inhibit restenosis through cooling to a temperature near freezing, preferably without causing substantial vessel wall cell death. One catheter device includes a distal tube region having coolant delivery holes radially and longitudinally distributed along the distal region. In some devices, holes spray coolant directly onto the vessel walls, with the coolant absorbed into the blood stream. In other embodiments, a balloon or envelope is interposed between the coolant and the vessel walls and the coolant returned out of the catheter through a coolant return lumen. Some direct spray devices include an occlusion device to restrict blood flow past the region being cooled. Pressure, temperature, and ultrasonic probes are included in some cooling catheters. Pressure control valves are included in some devices to regulate balloon interior pressure within acceptable limits. In applications using liquid carbon dioxide as coolant, the balloon interior pressure can be maintained above the triple point of carbon dioxide to inhibit dry ice formation. Some cooling catheters are coiled perfusion catheters supporting longer cooling periods by allowing perfusing blood flow simultaneously with vessel wall cooling. One coiled catheter is biased to assume a coiled shape when unconstrained and can be introduced into the body in a relatively straight shape, having a stiffening wire inserted through the coil strands.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
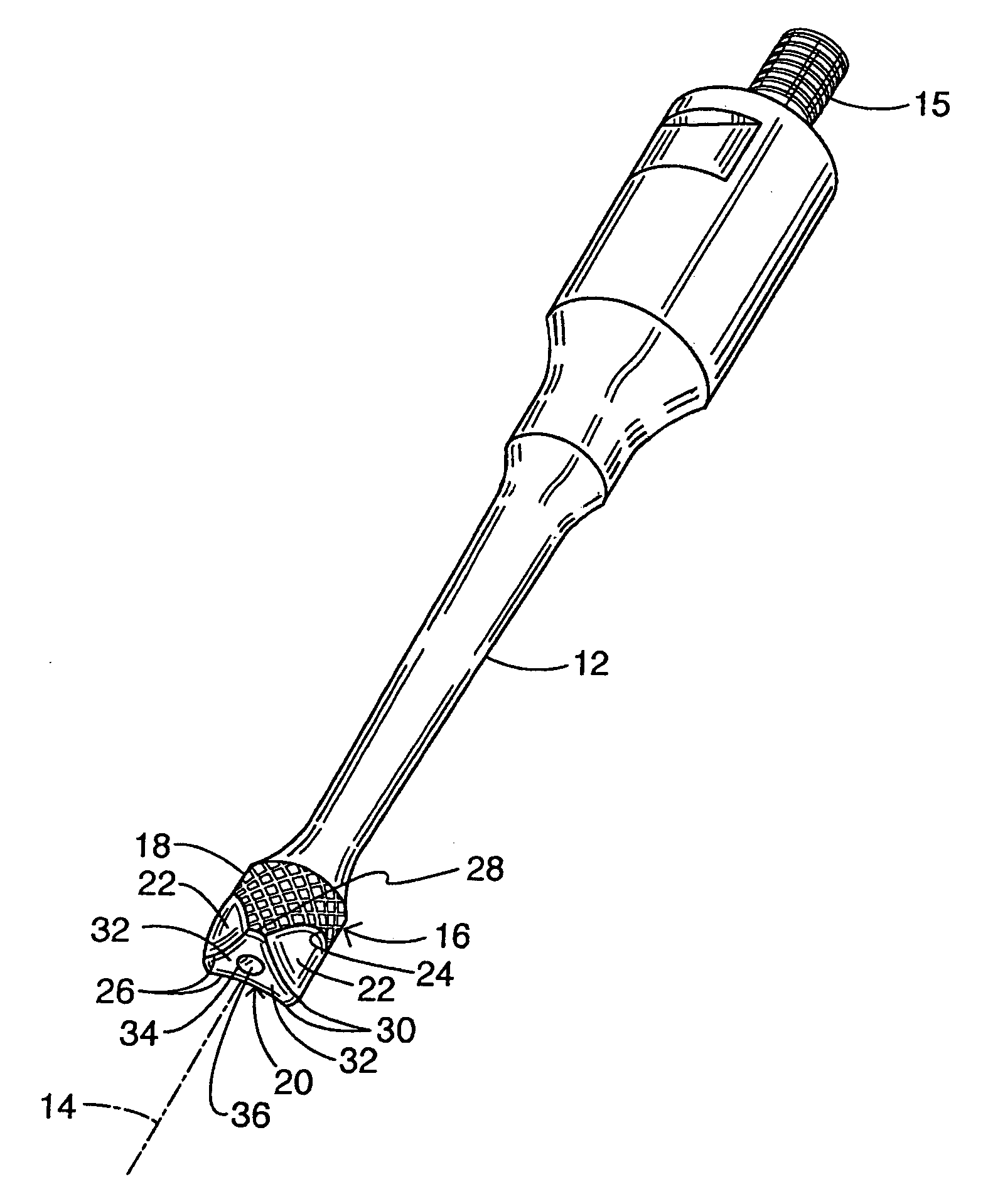
Ultrasonic wound debrider probe and method of use
An ultrasonic probe includes a shaft having a longitudinal axis and a head disposed at a distal end of the shaft. The head has a cylindrical lateral surface and an end face oriented perpendicularly to the axis. The head has three shaping surfaces at a distal end of the cylindrical surface, each shaping surface extending at an acute angle to the axis. Each of the shaping surfaces intersects or is contiguous with both the cylindrical surface and the end face.
Owner:MISONIX INC
Method and apparatus for calibration, tracking and volume construction data for use in image-guided procedures
An apparatus that collects and processes physical space data while performing an image-guided procedure on an anatomical area of interest includes a calibration probe that collects physical space data by probing a plurality of physical points, a tracked ultrasonic probe, a tracking device that tracks the ultrasonic probe in space and an image data processor. The physical space data provides three-dimensional coordinates for each of the physical points. The image data processor includes a computer-readable medium holding computer-executable instructions. The executable instructions include determining registrations used to indicate position in both image space and physical space based on the physical space data collected by the calibration probe; using the registrations to map into image space, image data describing the physical space of the tracked ultrasonic probe used to perform the image-guided procedure and the anatomical area of interest; and constructing a three-dimensional volume based on the ultrasonic image data on a periodic basis.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
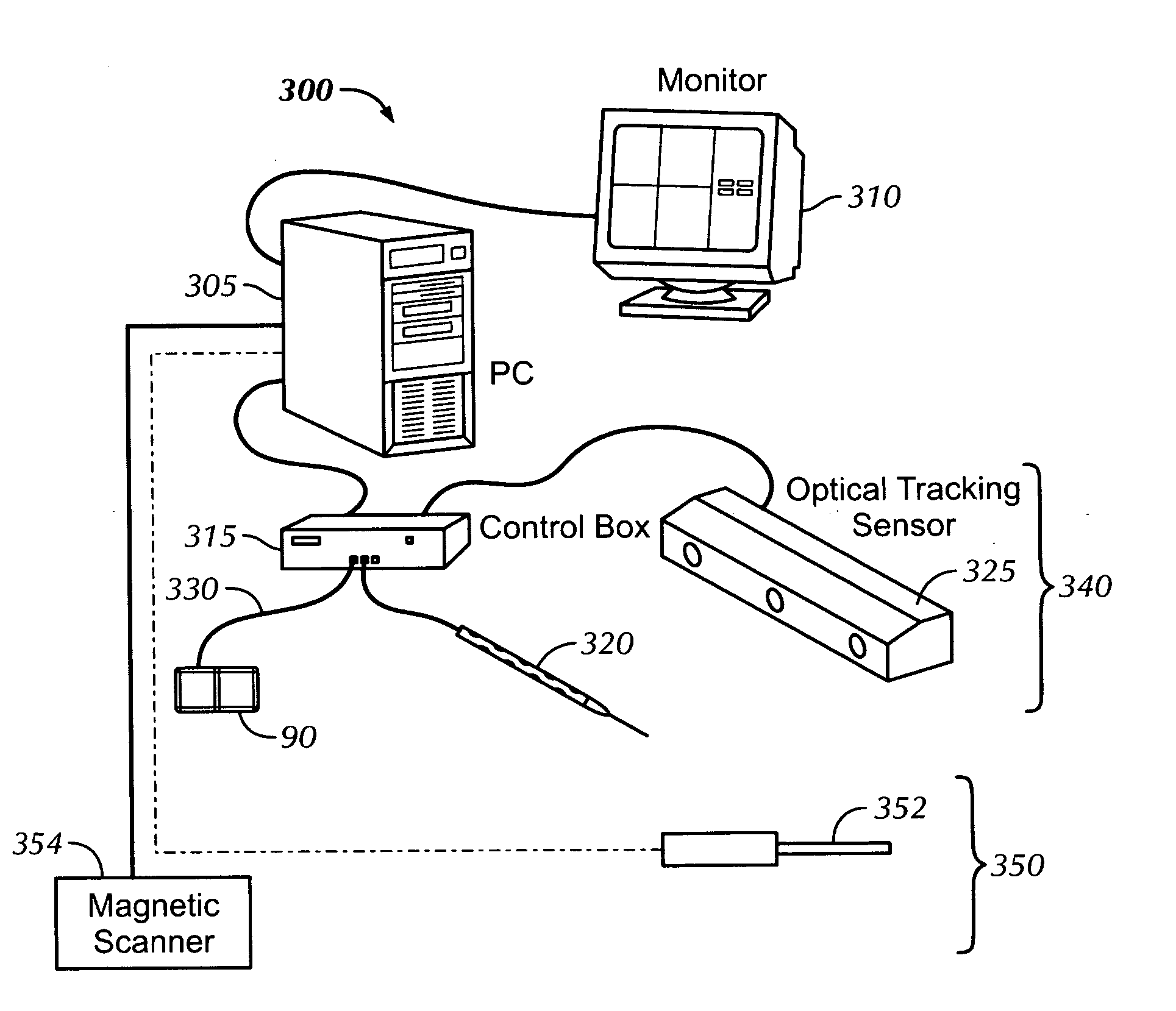
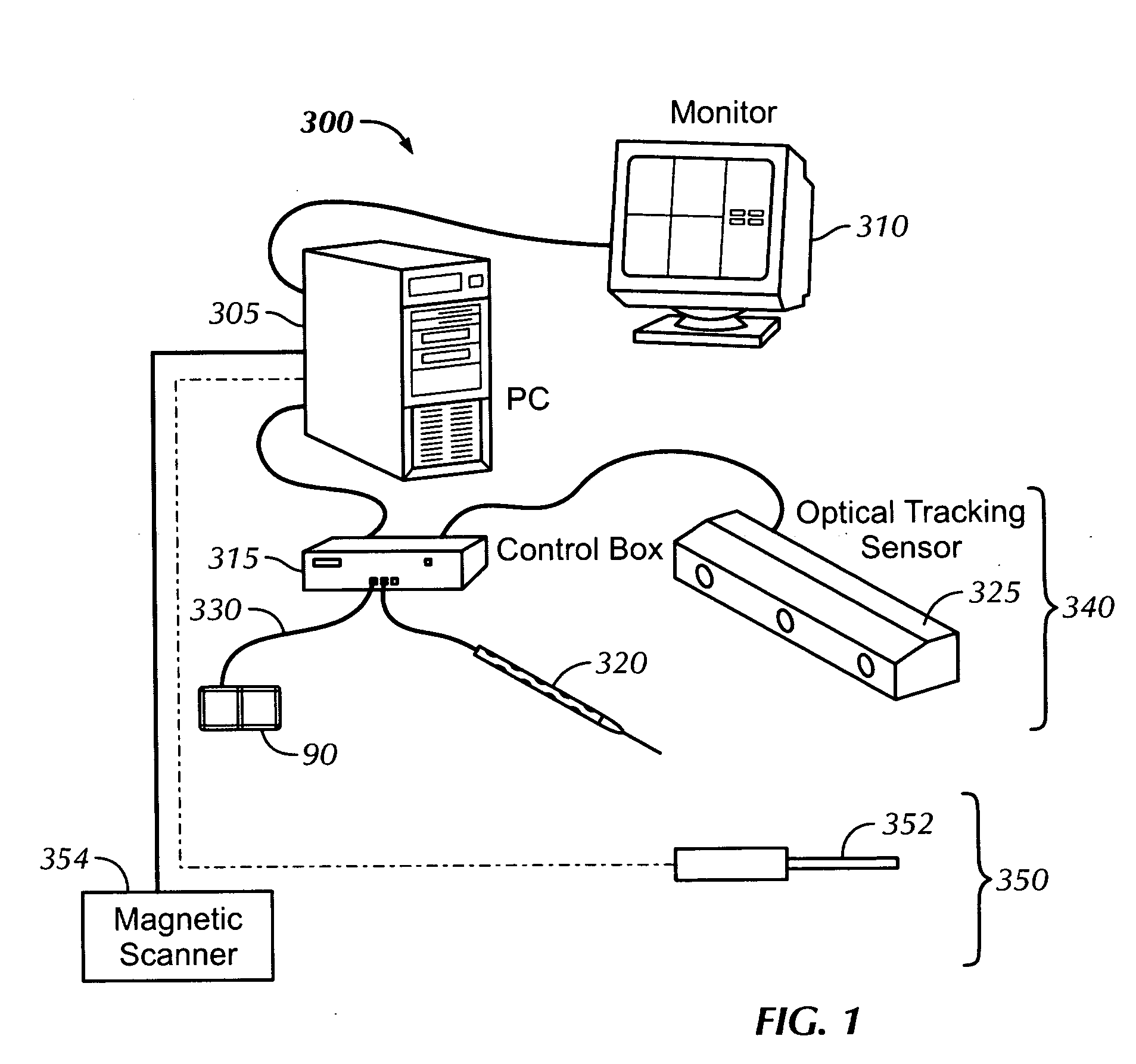
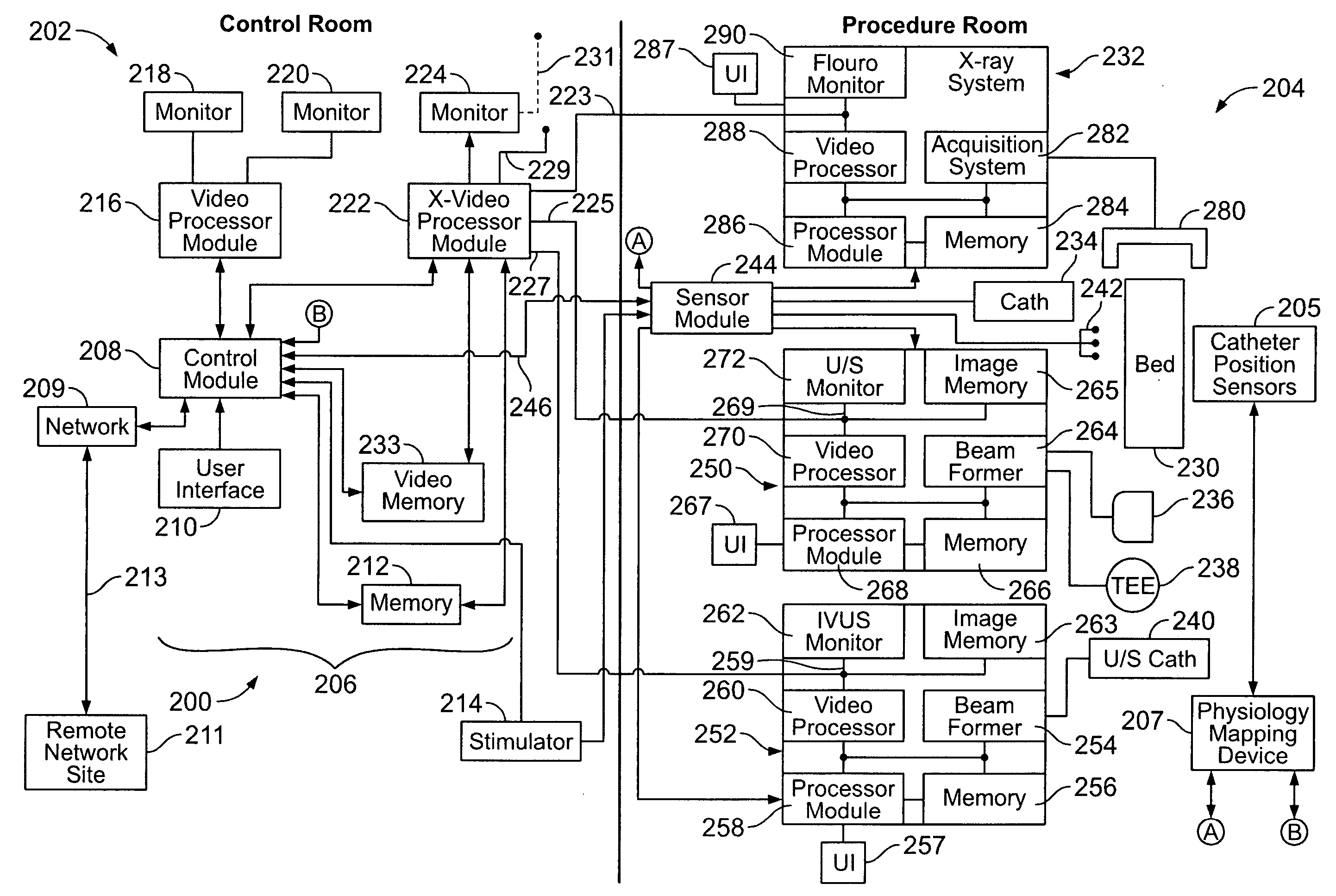
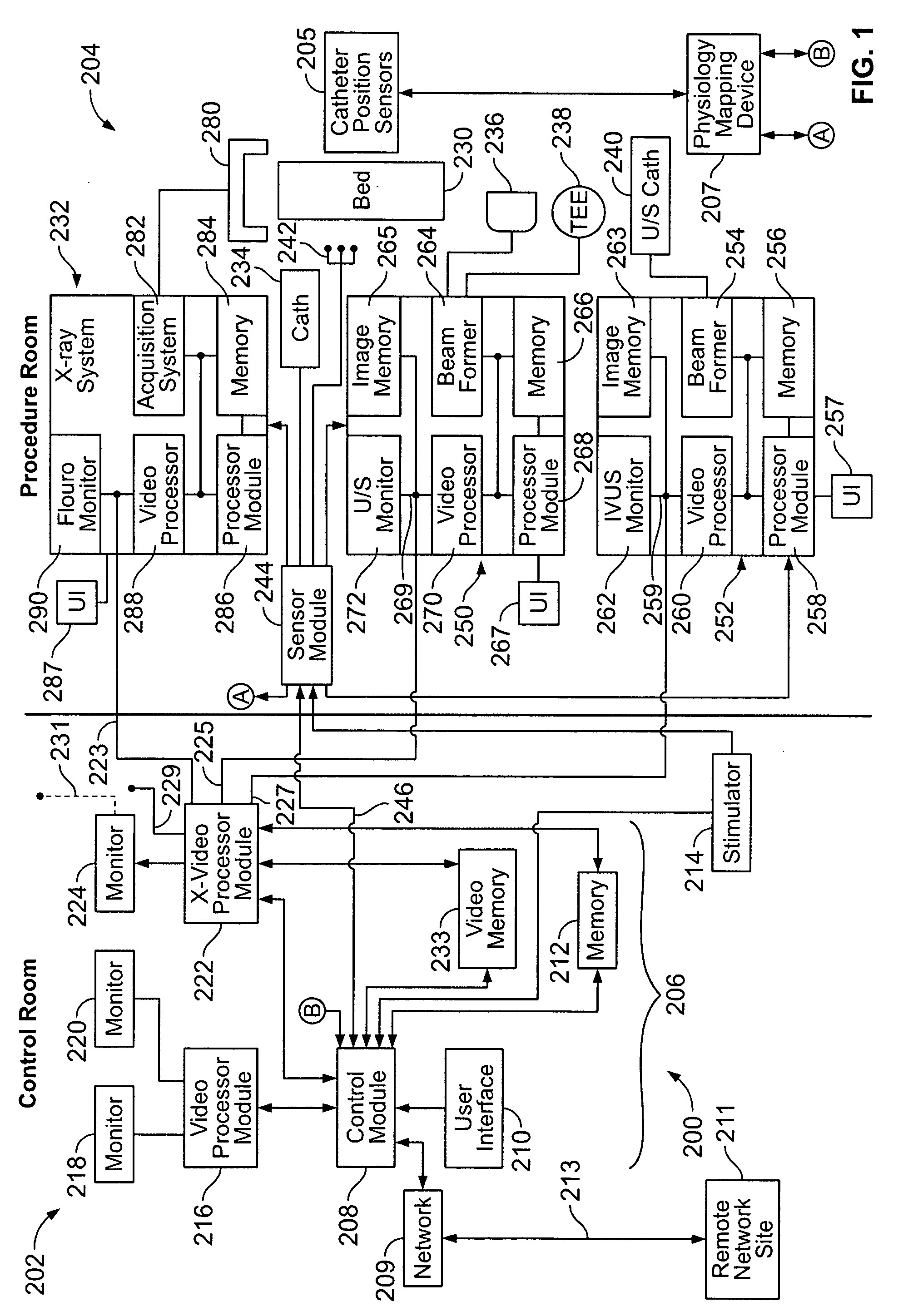
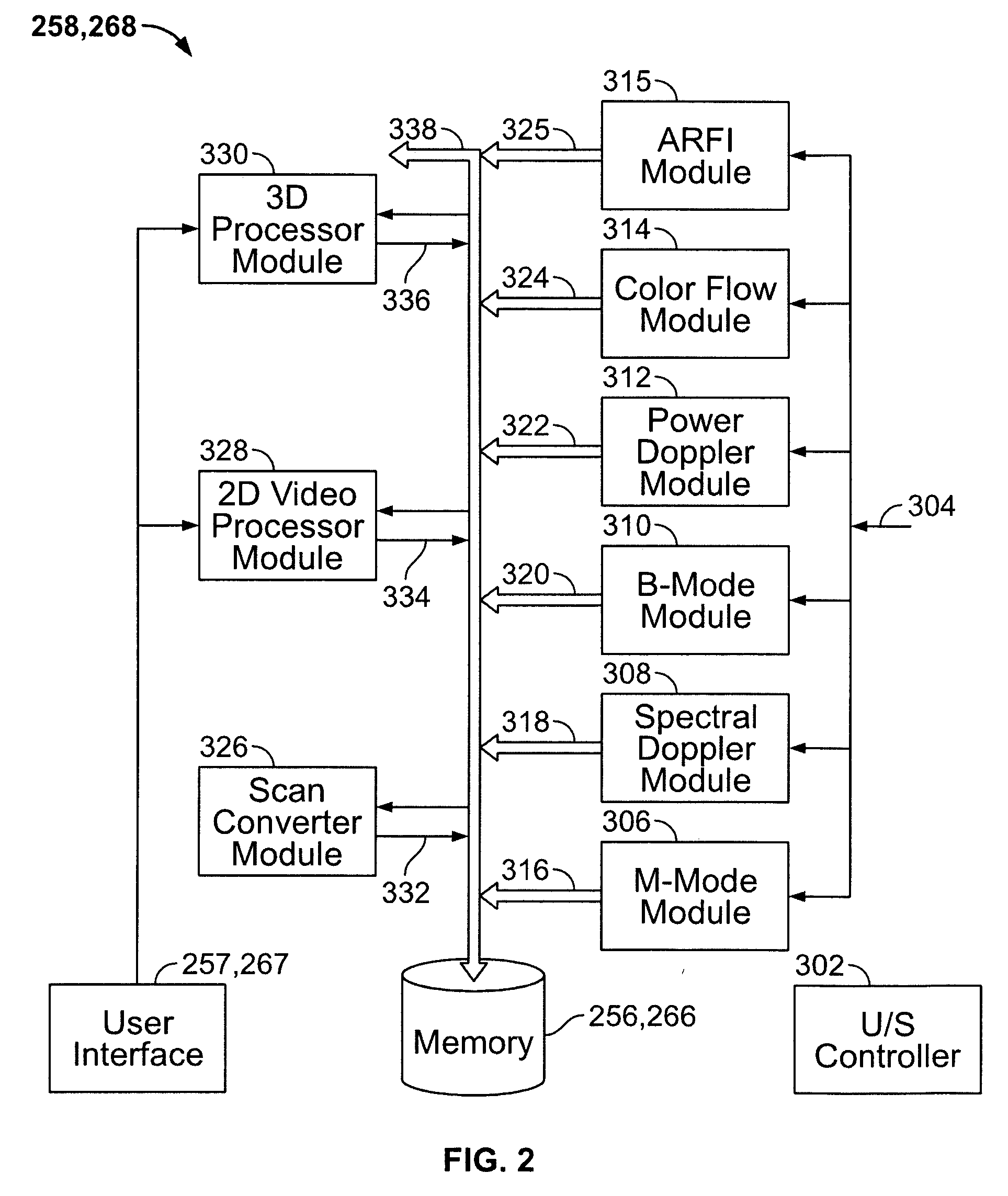
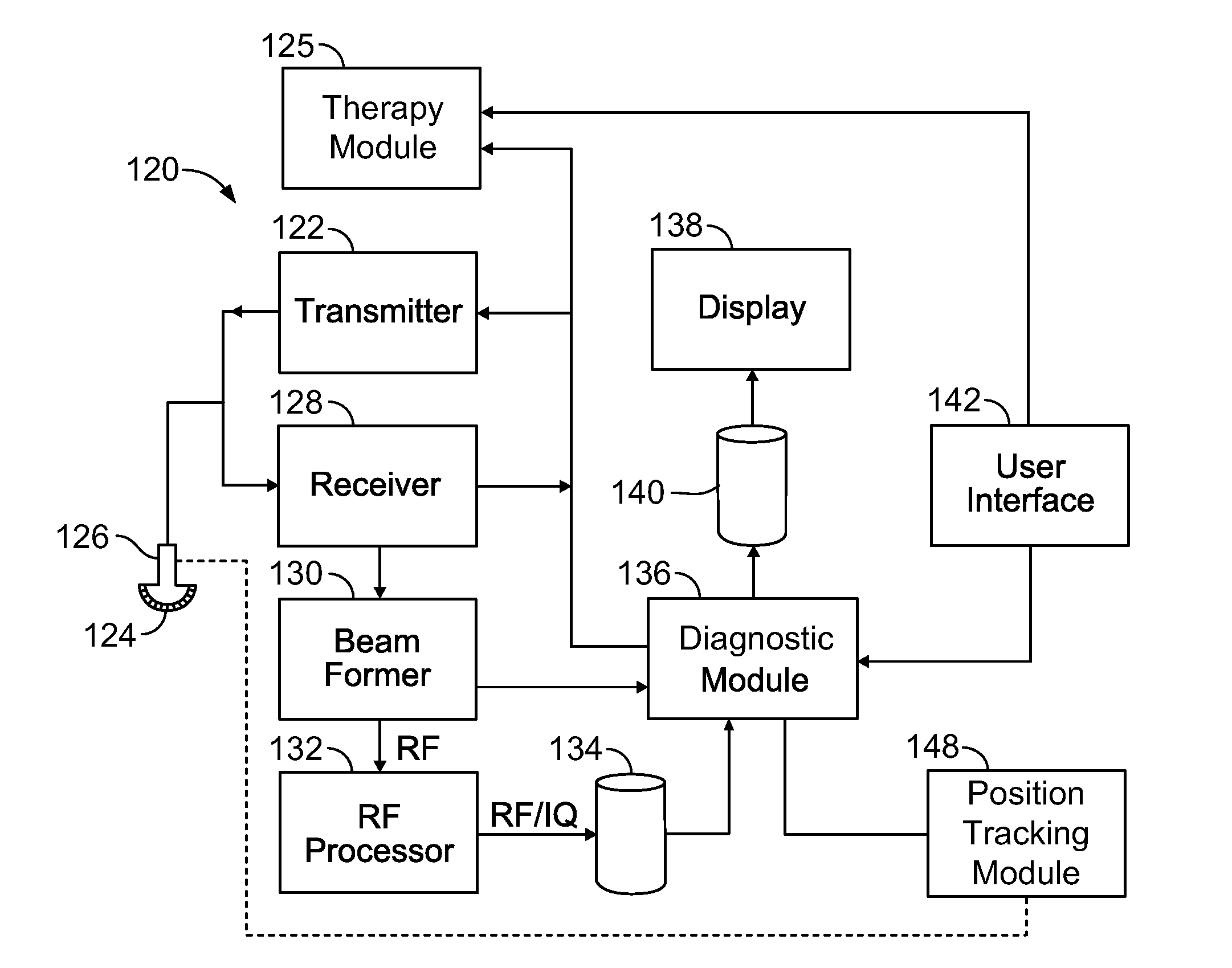
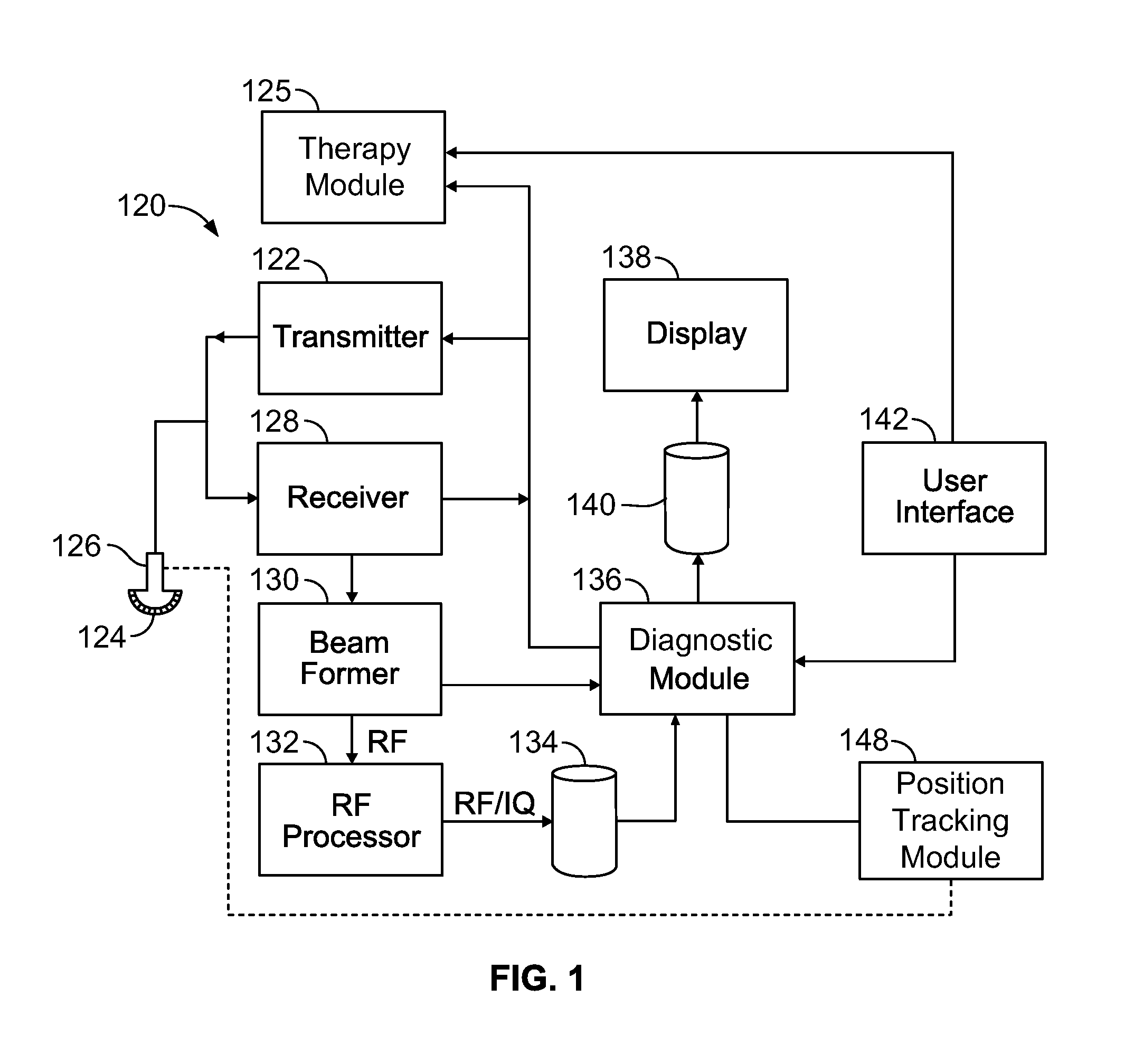
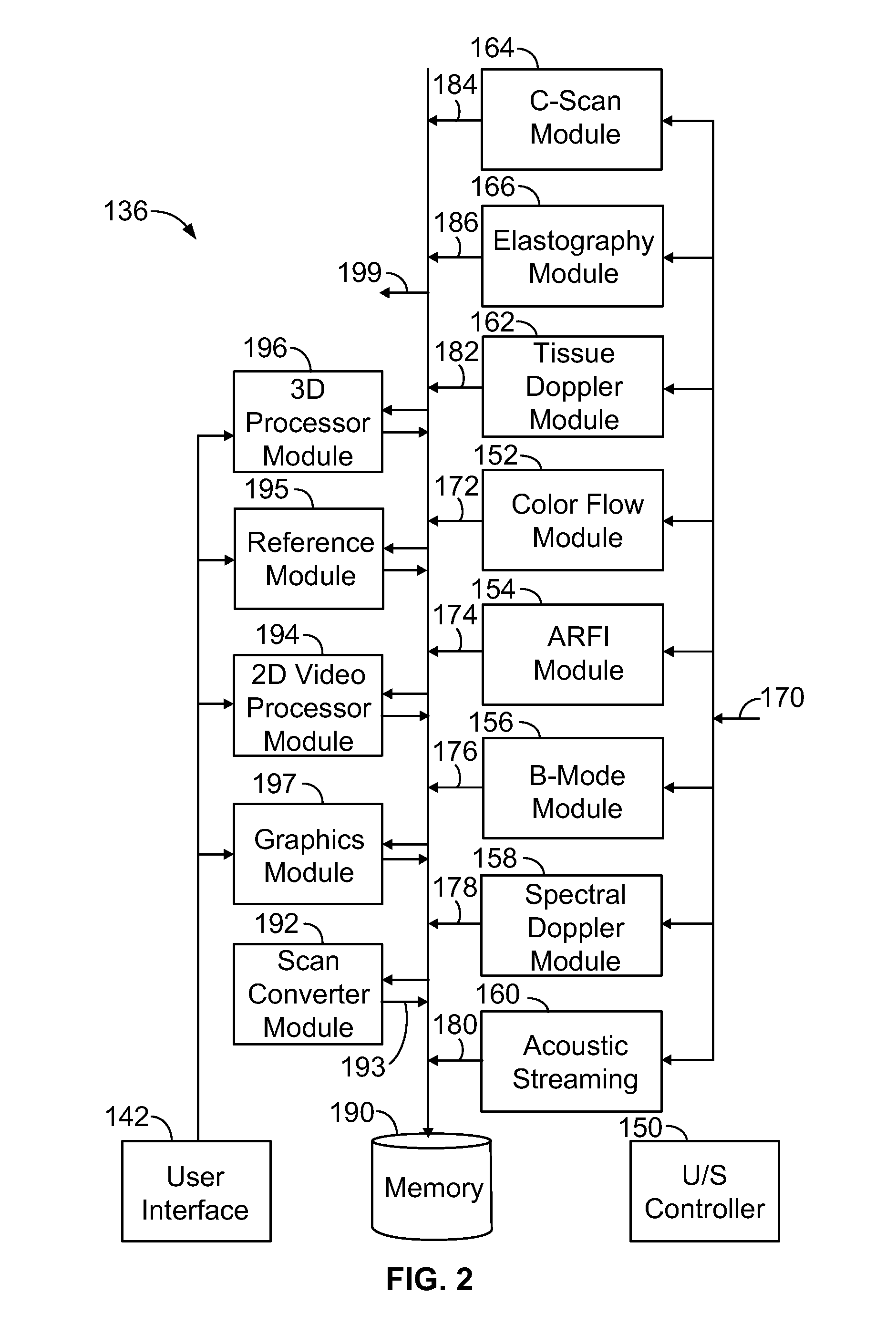
Physiology workstation with real-time fluoroscopy and ultrasound imaging
A physiology workstation is provided that comprises an physiology input configured to receive physiology signals from at least one of an intracardiac (IC) catheter inserted in a subject and surface ECG leads provided on the subject. The physiology signals are obtained during a procedure. A video input is configured to receive image frames, in real-time during the procedure. The image frames contain diagnostic information representative of data samples obtained from the subject during the procedure. A control module controls physiology operations based on user inputs. A display module is controlled by the physiology control module. The display module displays the physiology signals and the image frames simultaneously, in real-time, during the procedure. Optionally, the workstation may include a video processor module that formats the physiology signals into a display format. The video processor module may include an video processor and an external video processor that receive and control display of the physiology signals and image frames, respectively. The image frames may include at least one of ultrasound images obtained from a surface ultrasound probe, intravenous ultrasound images obtained from an ultrasound catheter and fluoroscopy images obtained from a fluoroscopy system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
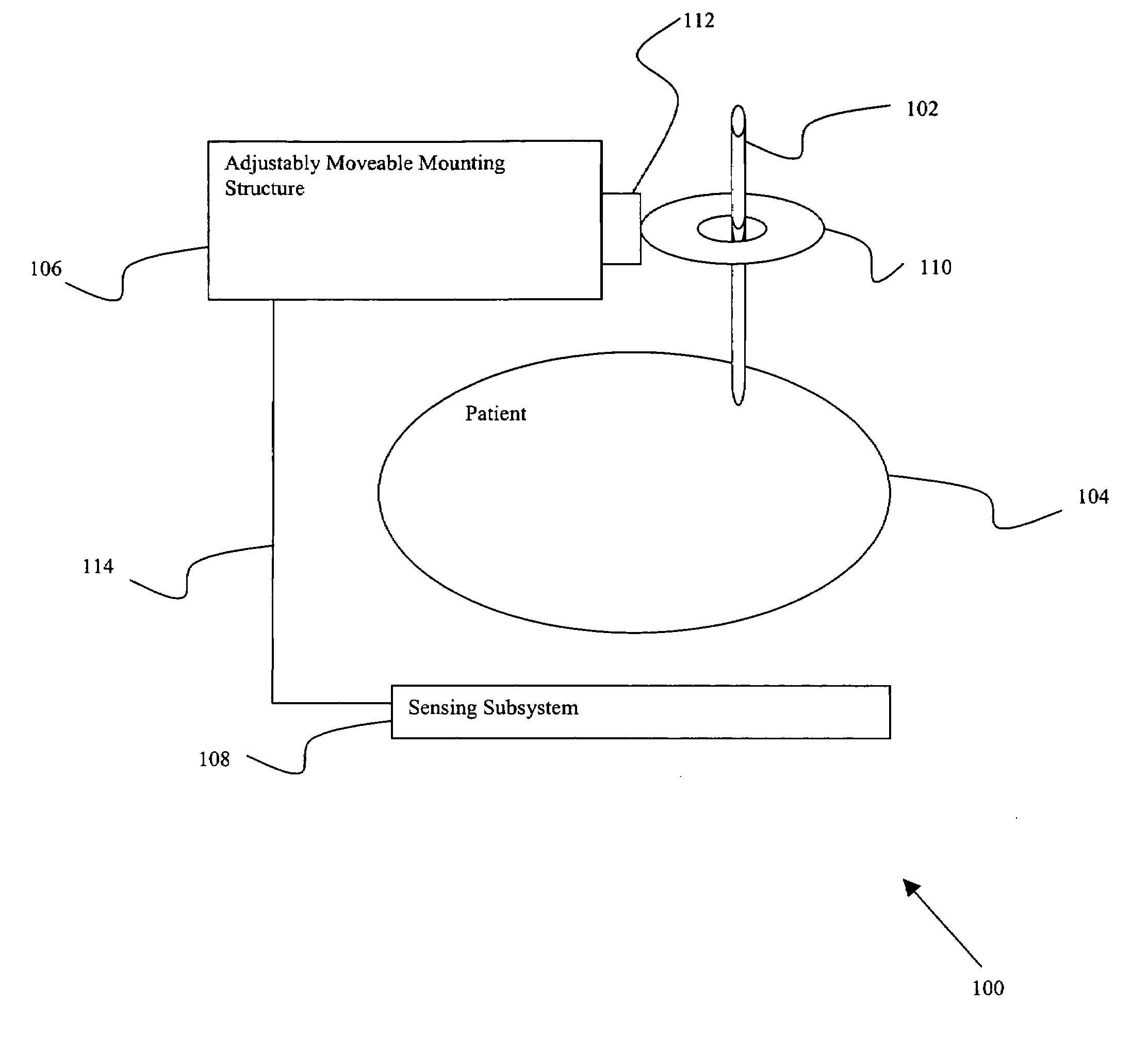
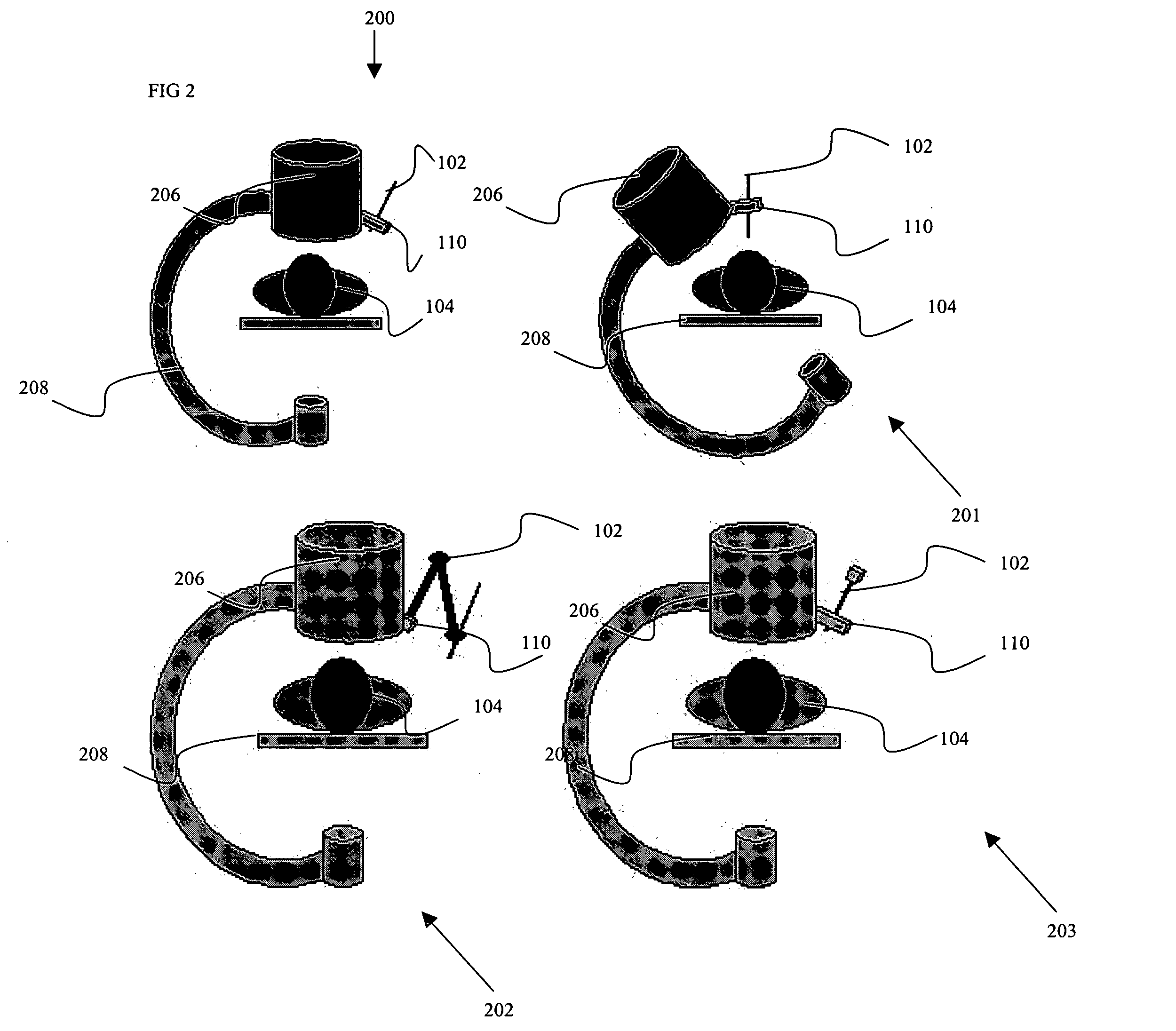
Surgical tool guide
InactiveUS20080004523A1Precise positioningDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFluoroscopic imagingEngineering
Certain embodiments of the present invention provide n system for orienting a surgical tool with respect to a patient including: a tool guide for facilitating orientation of the surgical tool with respect to the patient, the tool guide including a mounting portion and a tool receiving portion, wherein the tool guide is capable of being integrated with at least a portion of a radiological imaging subsystem including an adjustably moveable mounting structure. In an embodiment, the tool receiving portion is capable of receiving an end-effector. In an embodiment the at least a portion of the radiological imaging subsystem comprises a C-arm. In an embodiment the radiological imaging subsystem comprises a fluoroscopic imaging subsystem. In an embodiment, the end-effector comprises at least one of: an aperture, a cutting device, a drilling device, a clamp, a sleeve, a mounting surface, a ring, a rail, a threaded shaft, a clasp, a bayonet mount, an imaging device, an ultrasound probe, a surgical tool, a catheter, a pin, a screw, a plate, a drill, an awl, and a probe. In an embodiment, the tool guide further comprises an end-effector. In an embodiment, a position of the surgical tool is capable of being adjusted by automatically moving the adjustably movable mounting structure. In an embodiment, the system further comprises at least one position sensing subsystem for ascertaining a position of the surgical tool with respect to the patient.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Ultrasonic probe
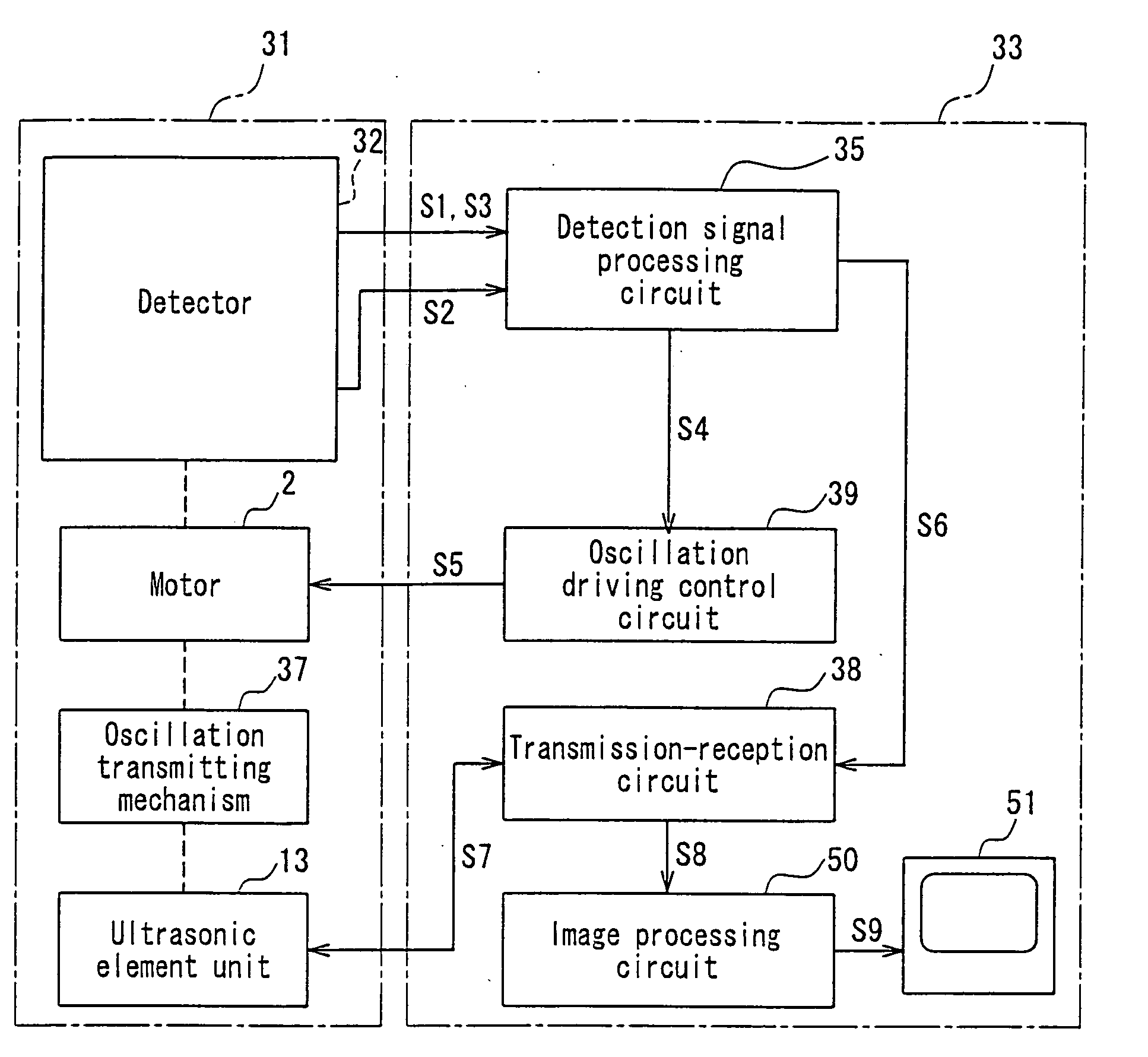
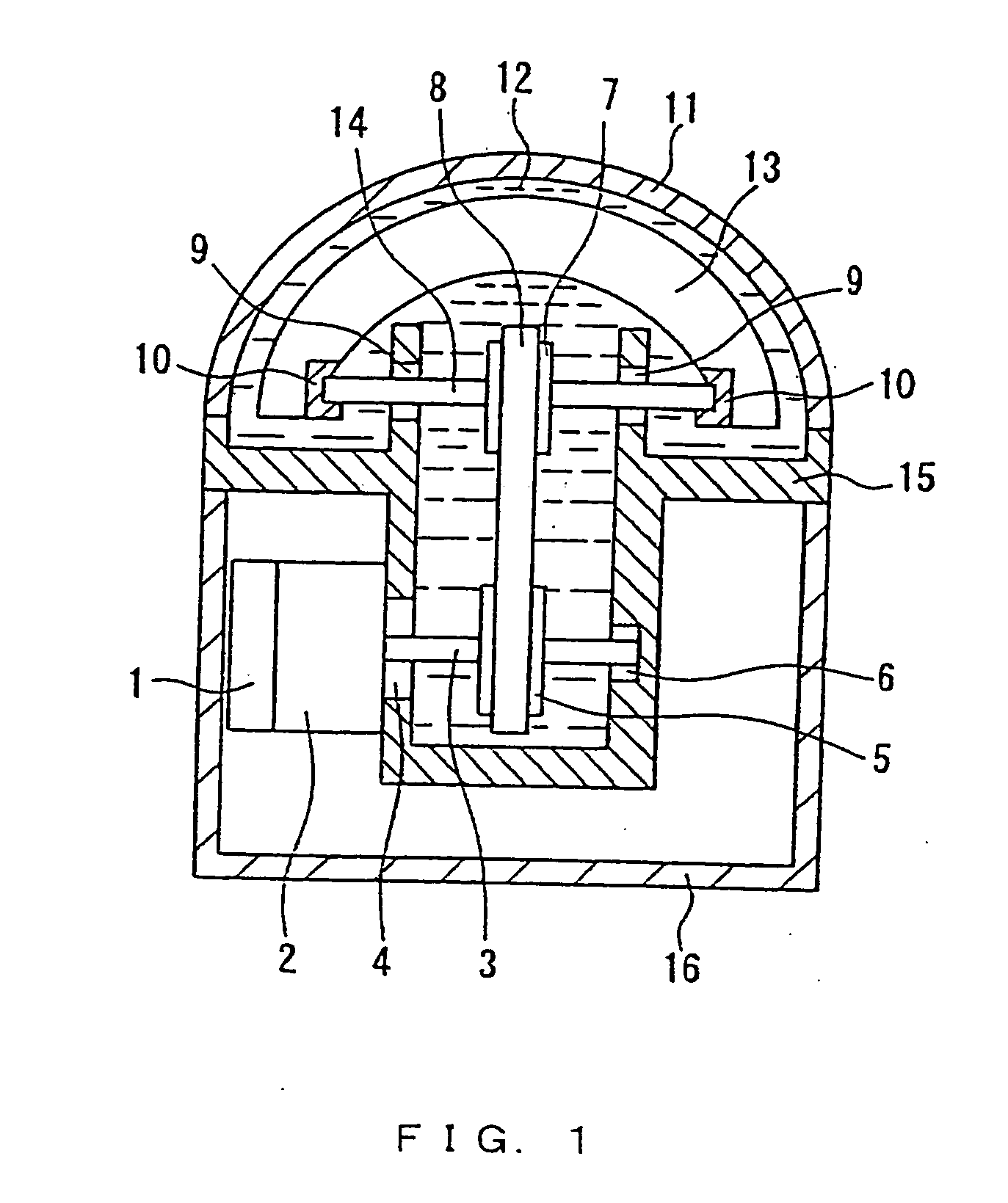
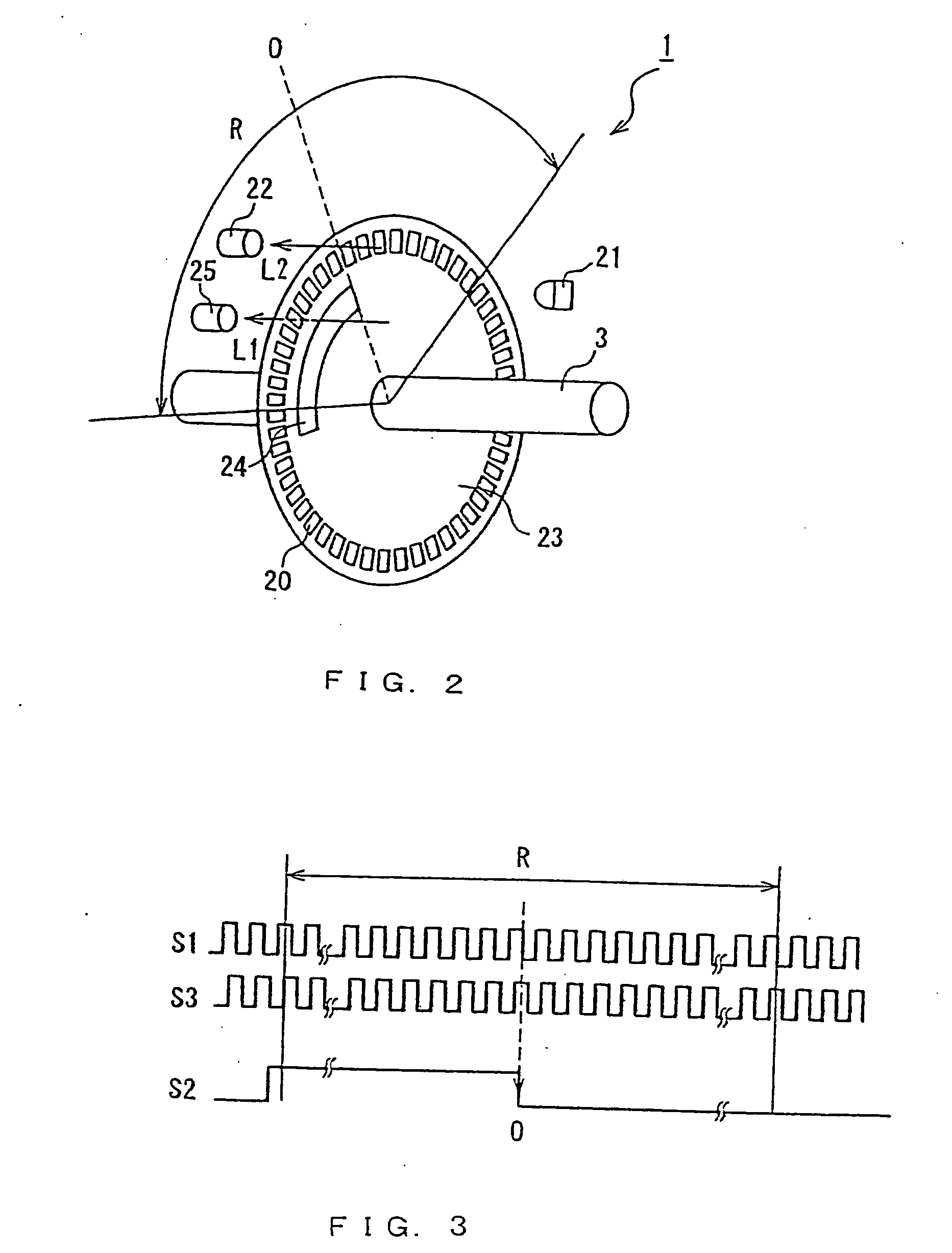
InactiveUS20060173329A1Easy to controlEasy to returnAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsUltrasound probe
The ultrasonic probe of the present invention includes an ultrasonic element unit for transmitting and receiving ultrasonic waves, an oscillation mechanism for causing oscillation to the ultrasonic element unit and a detector for detecting the oscillation of the ultrasonic element unit. The detector detects the oscillation angle and the oscillation origin of the ultrasonic element unit, and when the oscillation range of the ultrasonic element unit is divided at its oscillation origin into two regions of a positive region and a negative region, the detector detects in which area the ultrasonic element unit is located. In use of the ultrasonic probe, a control of origin return for returning the ultrasonic element unit to its oscillation origin is performed on the basis of the result of the detection by the detector.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Ultrasonic wound debrider probe and method of use
An ultrasonic probe includes a shaft having a longitudinal axis and a head disposed at a distal end of the shaft. The head has a cylindrical lateral surface and an end face oriented perpendicularly to the axis. The head has three shaping surfaces at a distal end of the cylindrical surface, each shaping surface extending at an acute angle to the axis. Each of the shaping surfaces intersects or is contiguous with both the cylindrical surface and the end face.
Owner:MISONIX INC
Ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus
ActiveUS20050090742A1Easy to detectOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgical needlesDisplay deviceDiagnostic ultrasound
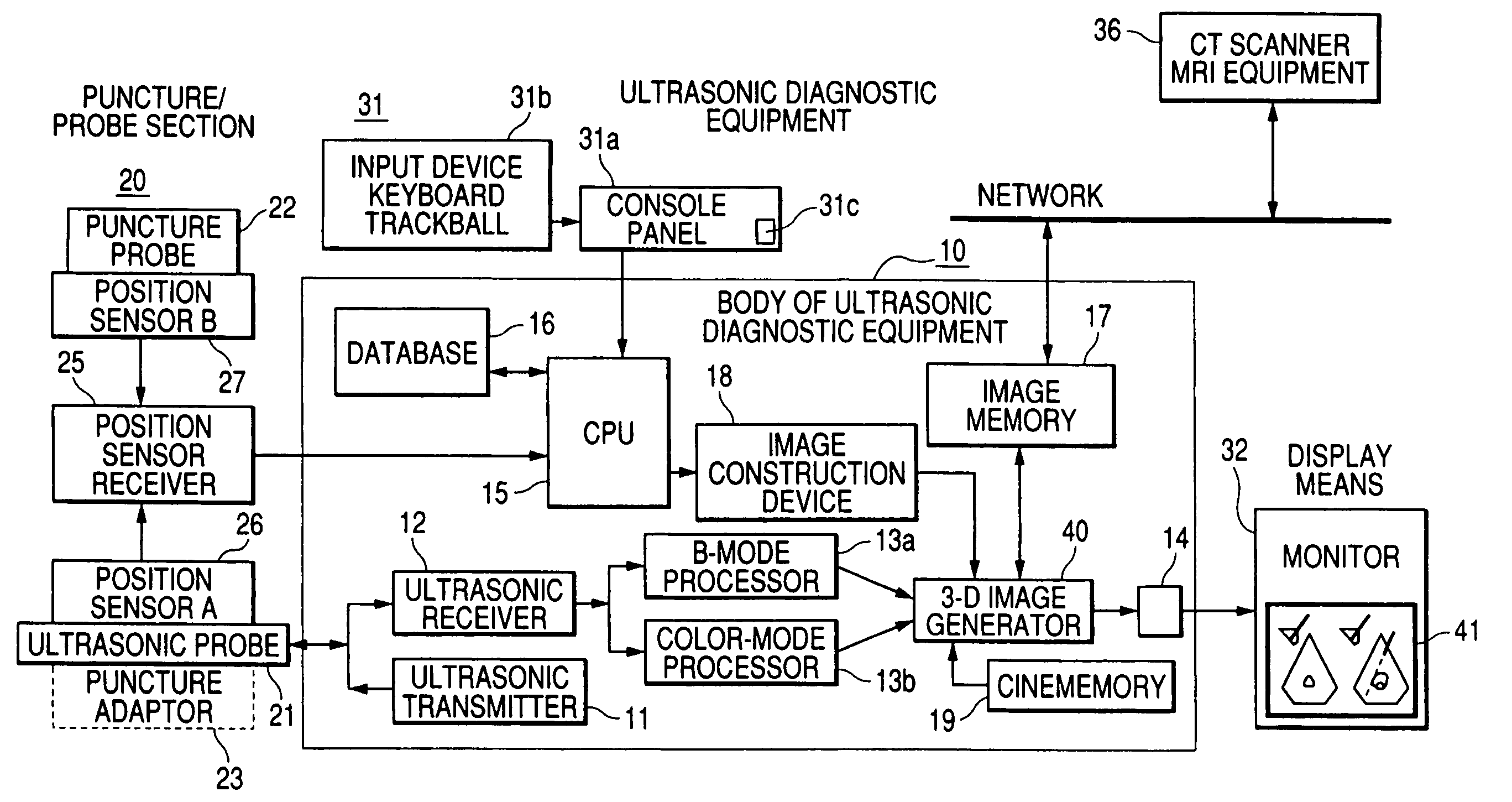
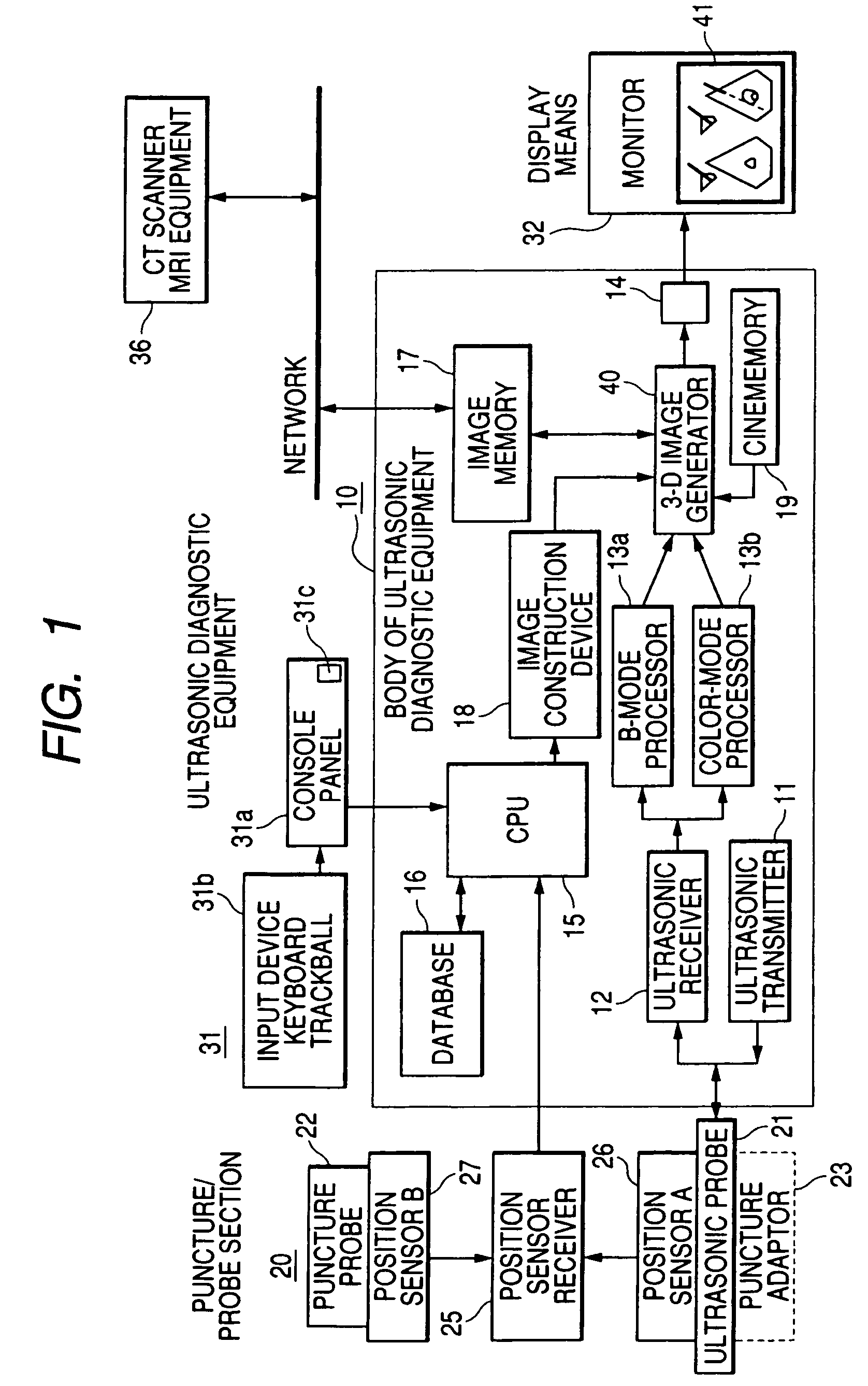
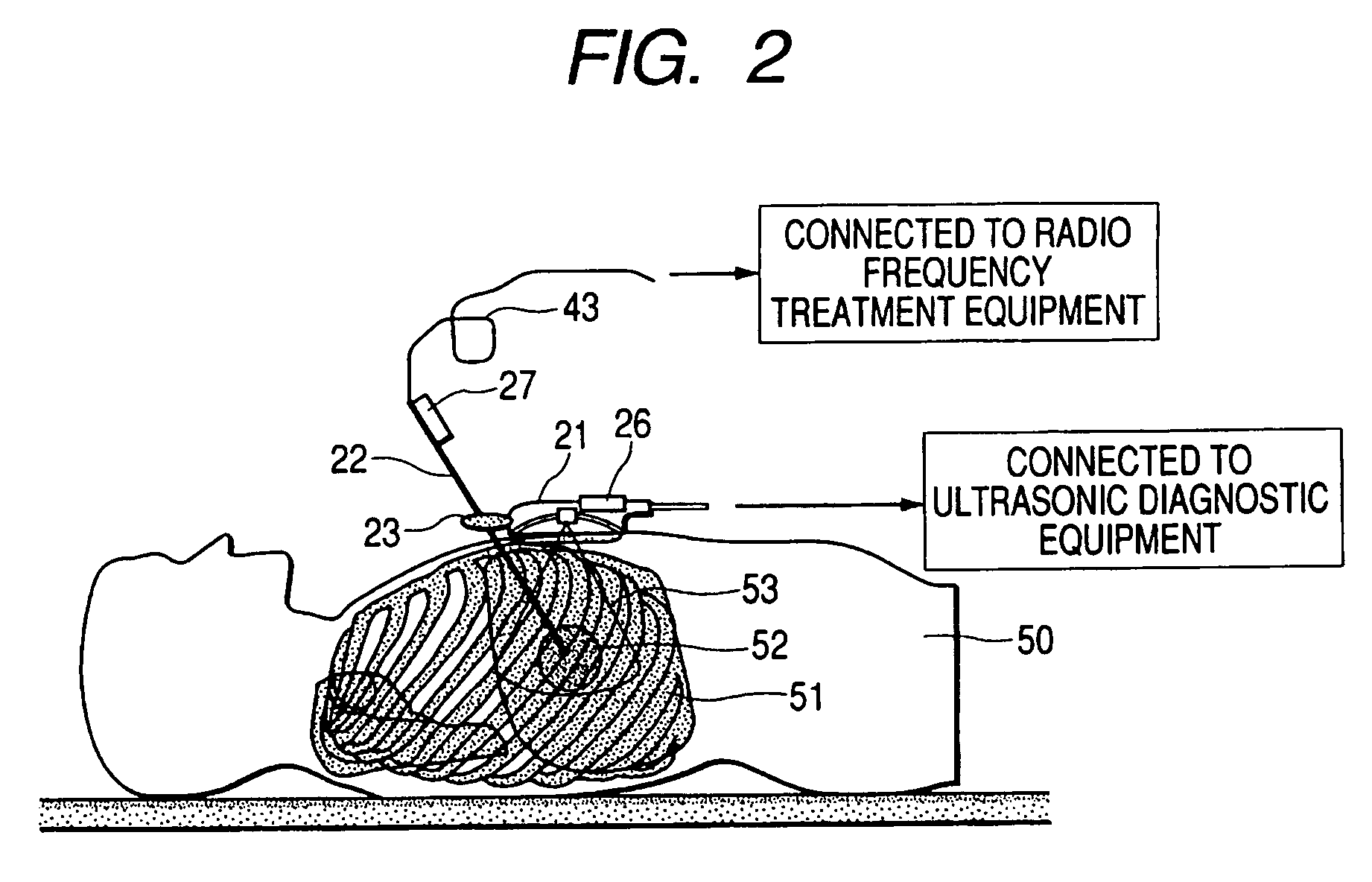
Ultrasonic diagnostic equipment is equipped with an ultrasonic probe that transmits / receives ultrasound to / from an examined body, a probe position sensor that detects the position and the direction of the ultrasonic probe, an image generator that generates image data based upon the output of the ultrasonic probe, a probe position sensor that detects the position and the direction of a puncture probe inserted into the examined body, a display image generator that generates the data of a display image in which the end position of the puncture probe is fixed to a specific position in an image display area according to the position and the direction of the ultrasonic probe and the position and the direction of the puncture probe based upon the image data and a display for displaying the display image in the image display area.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
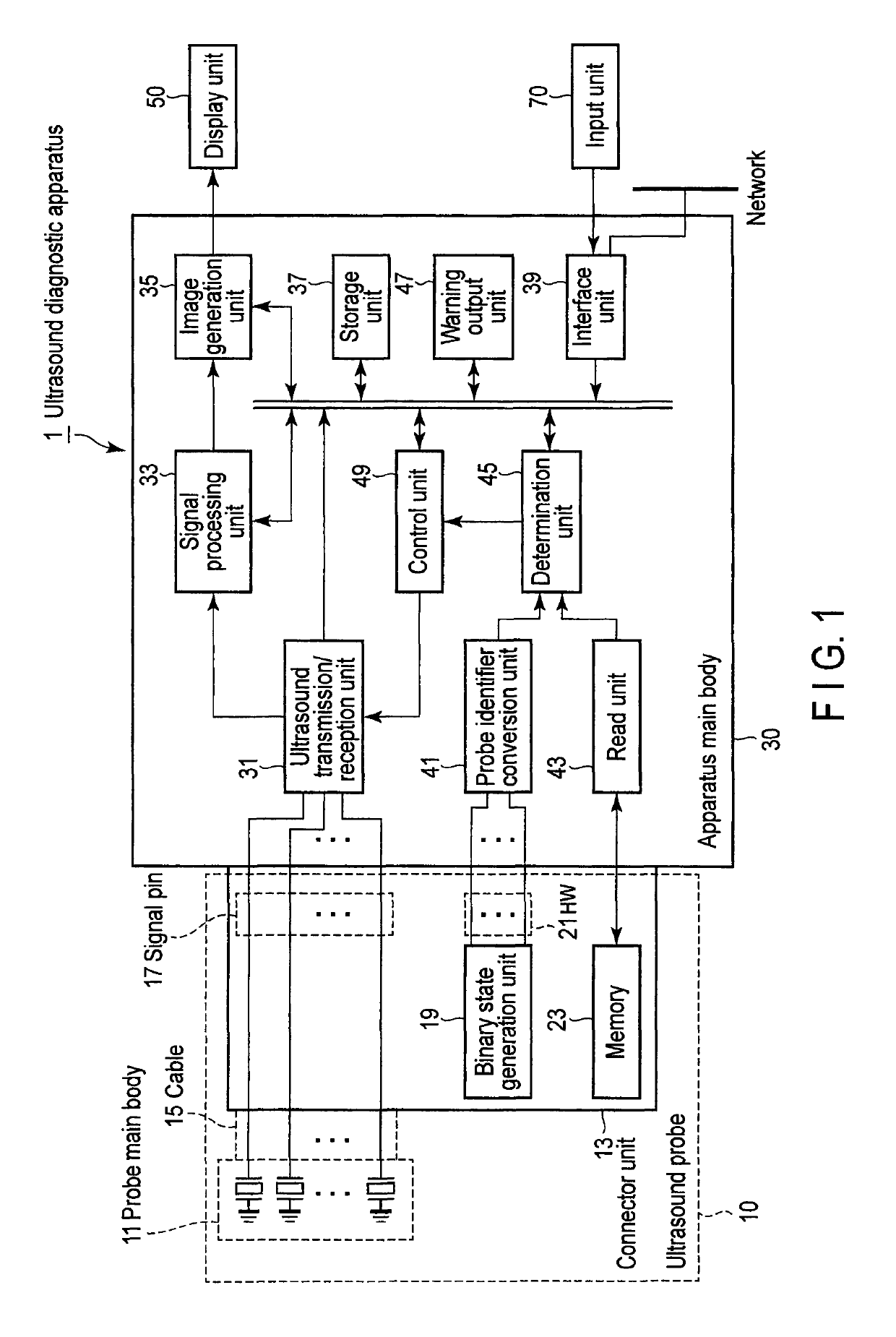
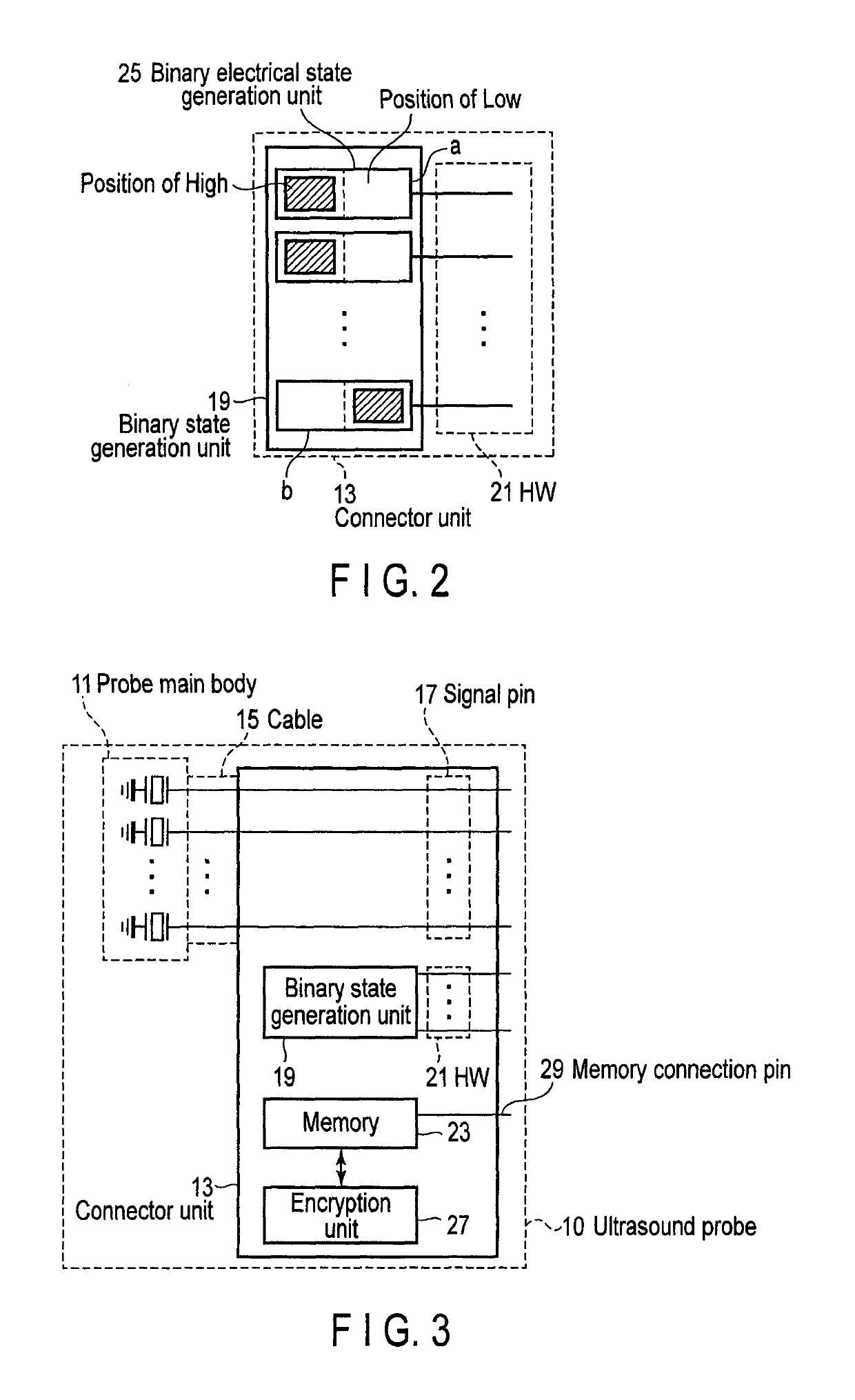
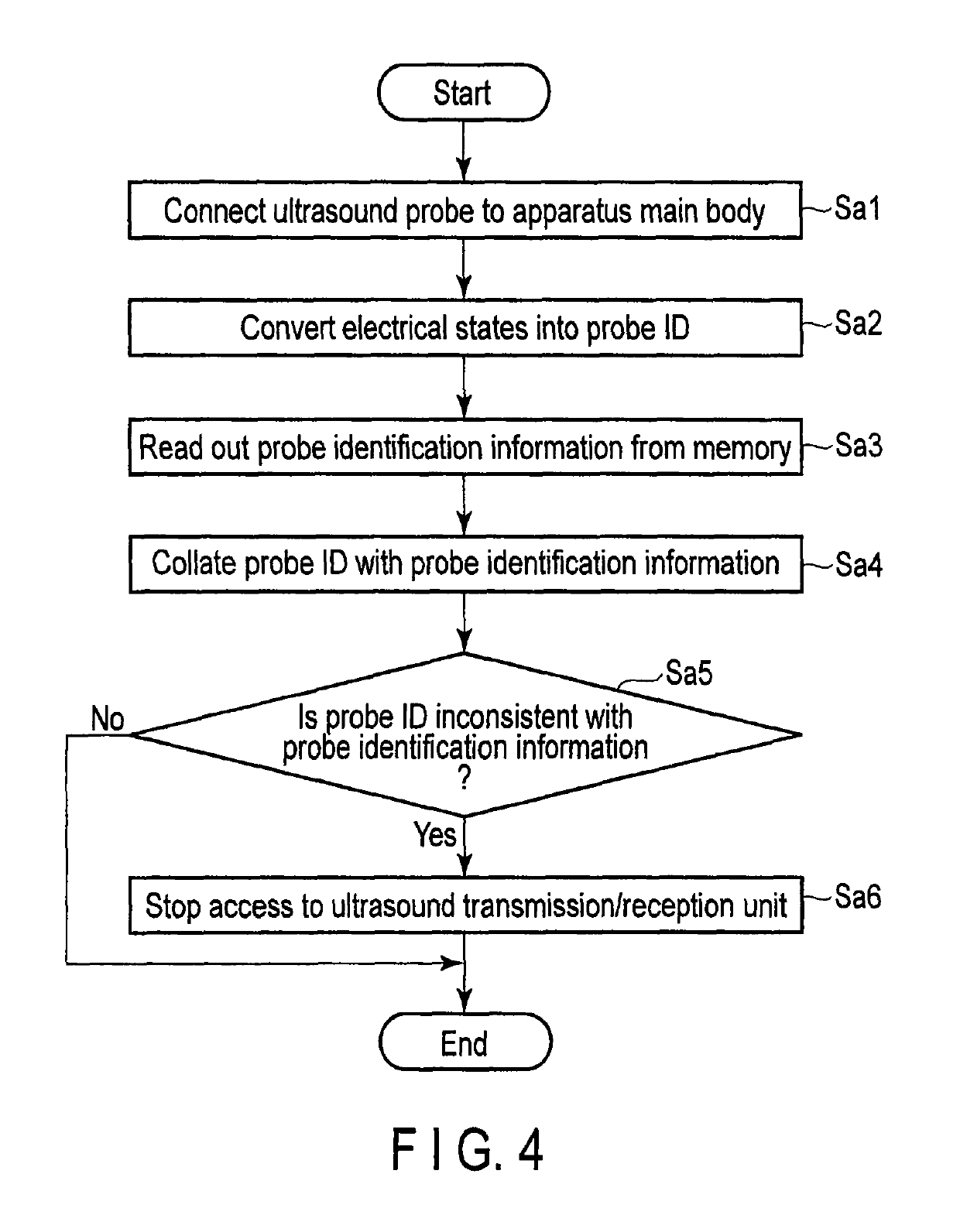
Ultrasound diagnostic apparatus and ultrasound probe
An ultrasound diagnostic apparatus includes an ultrasound probe with transducers, memory storing probe identification information and binary state generation unit generating a binary electrical state corresponding to a probe identifier, probe identifier conversion unit converting the electrical state into the probe identifier, read unit reading the probe identification information from the memory, determination unit determining consistency between the probe identifier after conversion and the probe identification information read from the memory, and warning output unit outputting a predetermined warning if the probe identifier is inconsistent with the probe identification information.
Owner:CANON MEDICAL SYST COPRPORATION
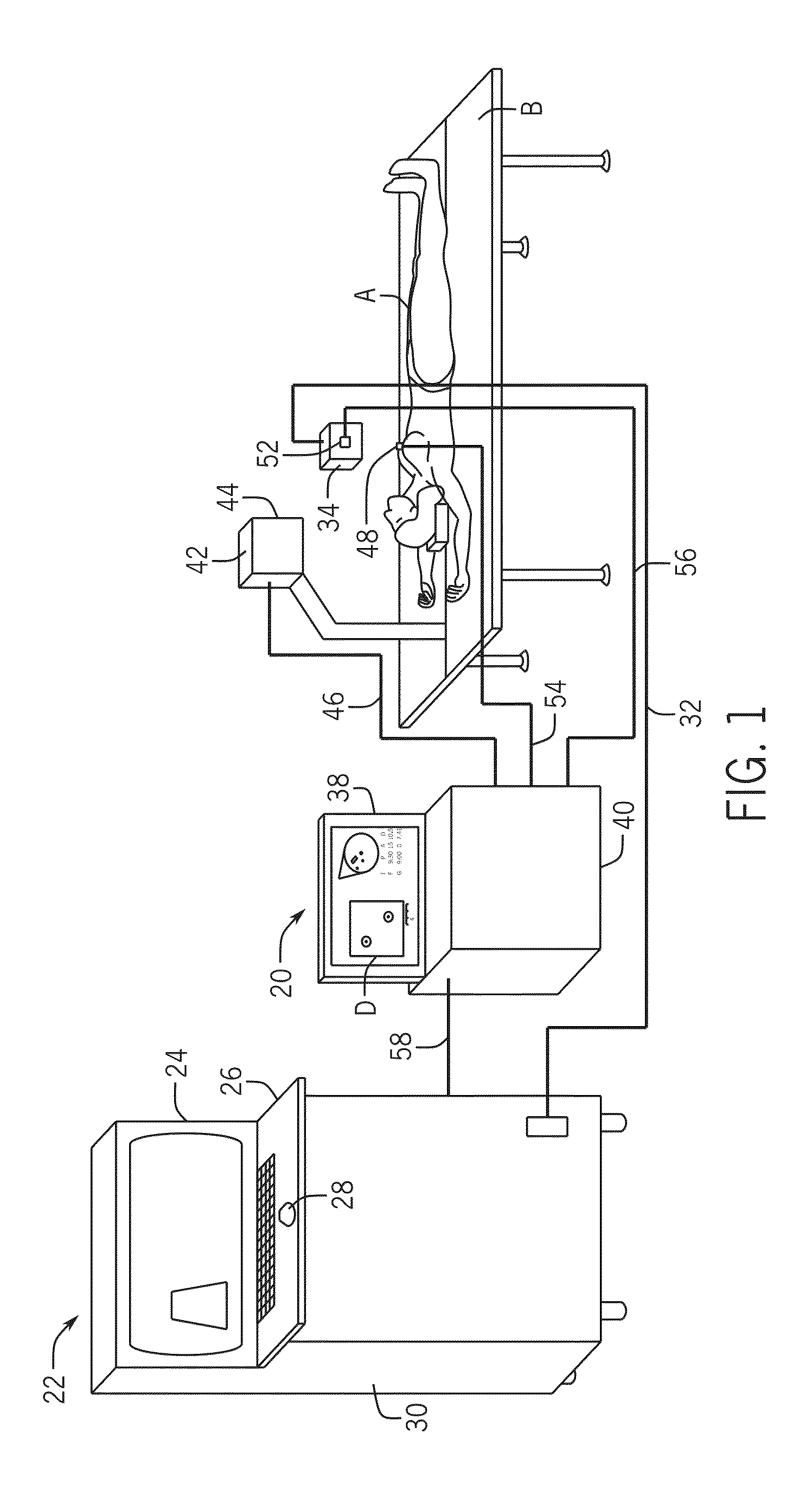
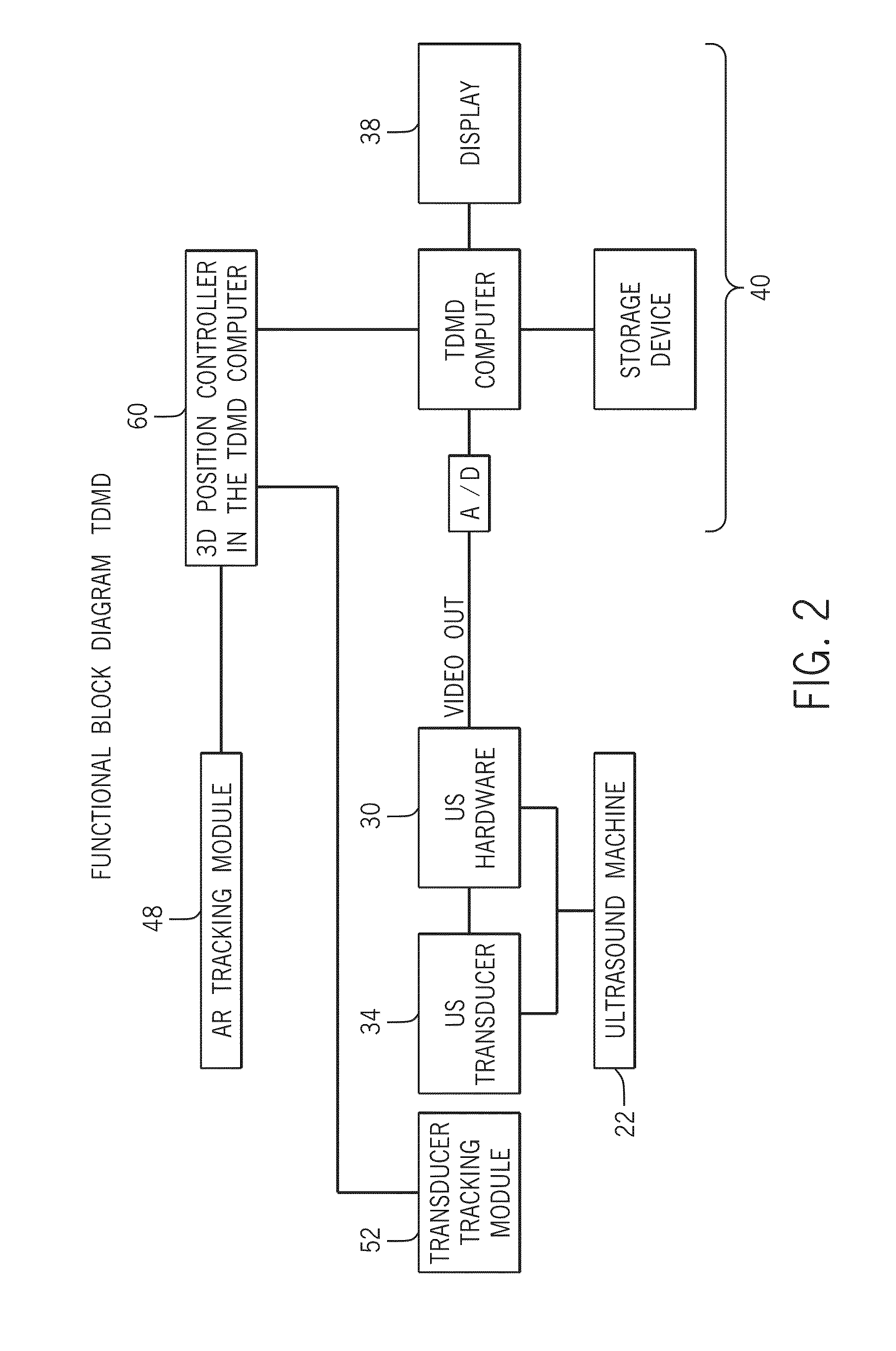
Three Dimensional Mapping Display System for Diagnostic Ultrasound Machines
ActiveUS20150051489A1Shorten the timeTime-consuming to eliminateOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationImaging interpretation
An automated three dimensional mapping and display system for a diagnostic ultrasound system is presented. According to the invention, ultrasound probe position registration is automated, the position of each pixel in the ultrasound image in reference to selected anatomical references is calculated, and specified information is stored on command. The system, during real time ultrasound scanning, enables the ultrasound probe position and orientation to be continuously displayed over a body or body part diagram, thereby facilitating scanning and images interpretation of stored information. The system can then record single or multiple ultrasound free hand two-dimensional (also “2D”) frames in a video sequence (clip) or cine loop wherein multiple 2D frames of one or more video sequences corresponding to a scanned volume can be reconstructed in three-dimensional (also “3D”) volume images corresponding to the scanned region, using known 3D reconstruction algorithms. In later examinations, the exact location and position of the transducer can be recreated along three dimensional or two dimensional axis points enabling known targets to be viewed from an exact, known position.
Owner:METRITRACK
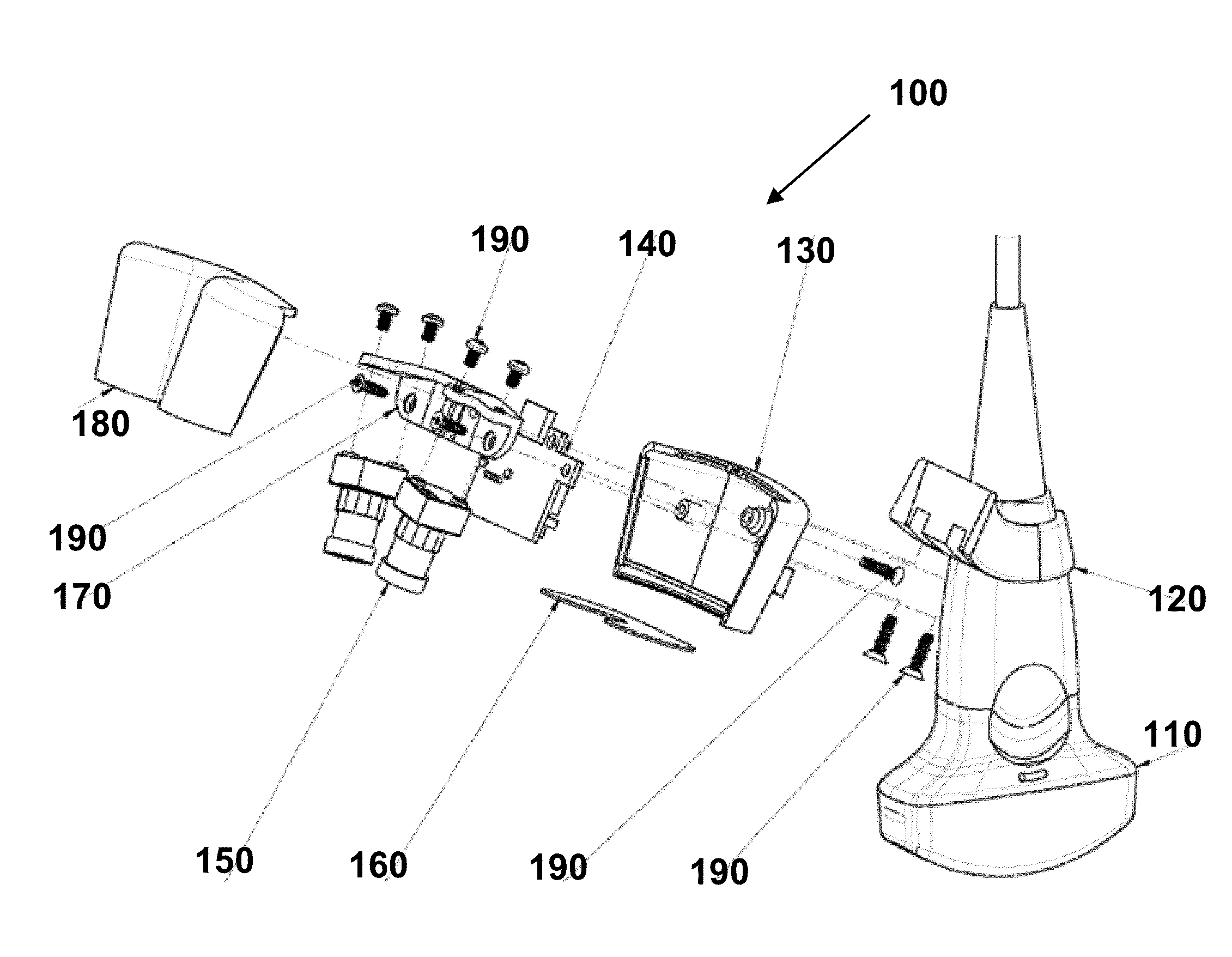
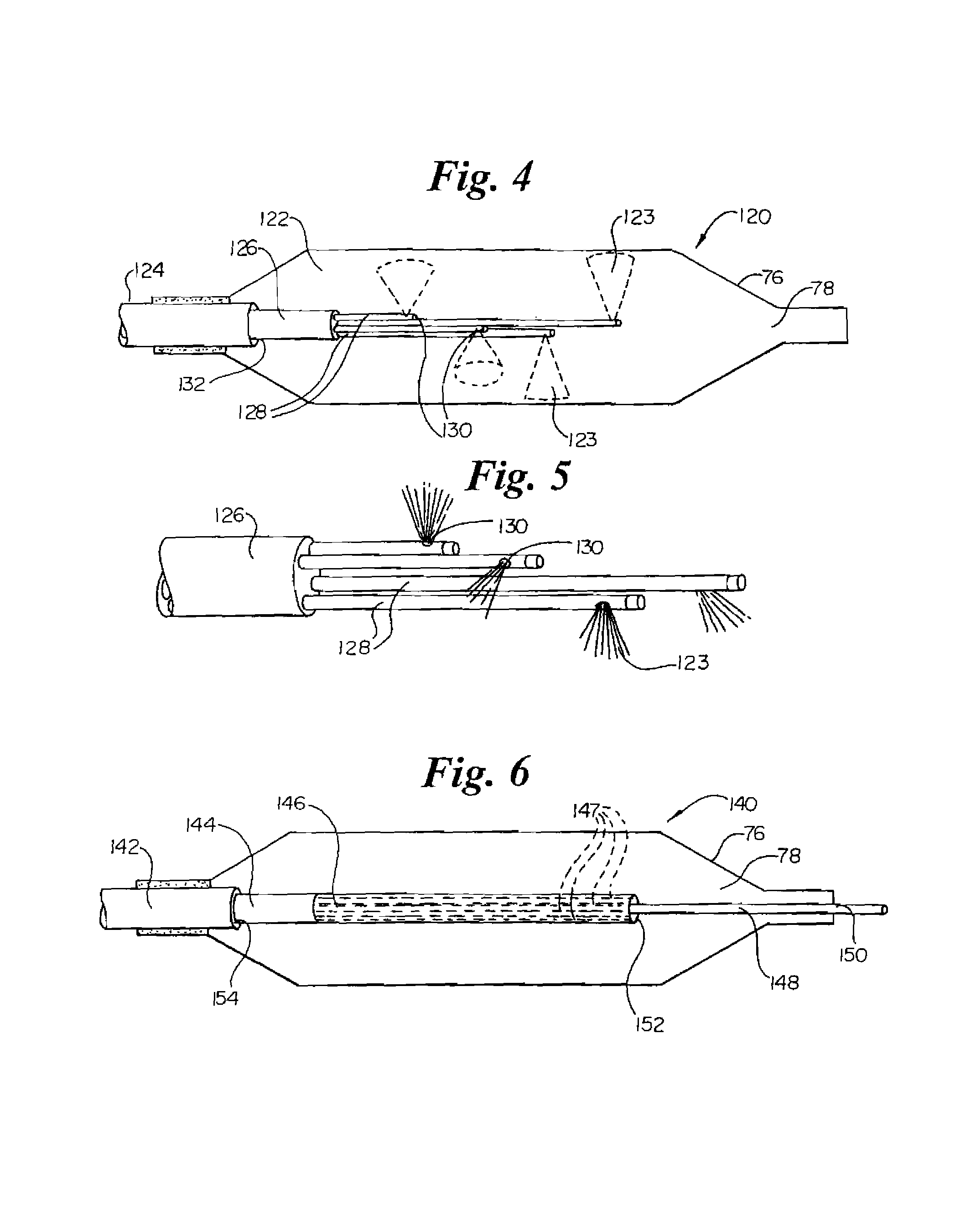
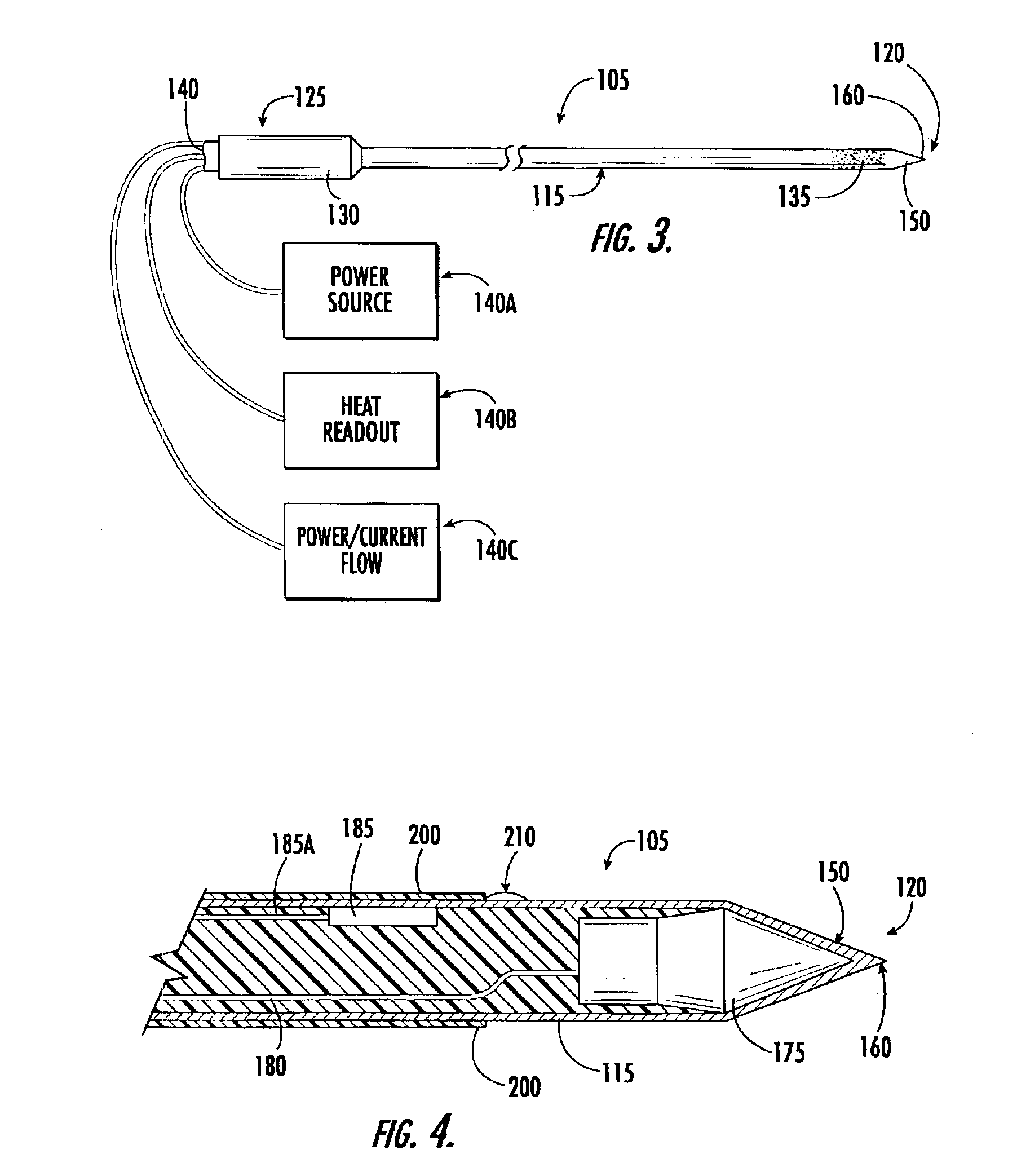
Method of manufacture of catheter tips, including mechanically scanning ultrasound probe catheter tip, and apparatus made by the method
InactiveUS20070167824A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsTransducerActuator
A method to fabricate a catheter tip that encapsulates a mechanically actuated ultrasound transducer assembly is provided. In a representative procedure, the steps include providing an ultrasound transducer assembly (100) adapted for use with a catheter (300), the ultrasound transducer assembly (100) comprising a proximal end (102) and a distal end (104), a drive linkage (132) to an actuator (130), and a transducer array (110), the transducer array (110) electrically connected to an interconnect (120) adapted for passage to or through a body of the catheter (300), connecting the actuator (130), adapted for use with the ultrasound transducer assembly (100), to the drive linkage (132); and inserting the ultrasound transducer assembly (100) and the actuator (132) into a polymer or a plastic type or reinforced polymer sheath (140) comprising an acoustically transparent section, a closed end (142) at its distal end and an open end (144) at its proximal end, wherein the polymer sheath (140) provides a defined rigidity.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
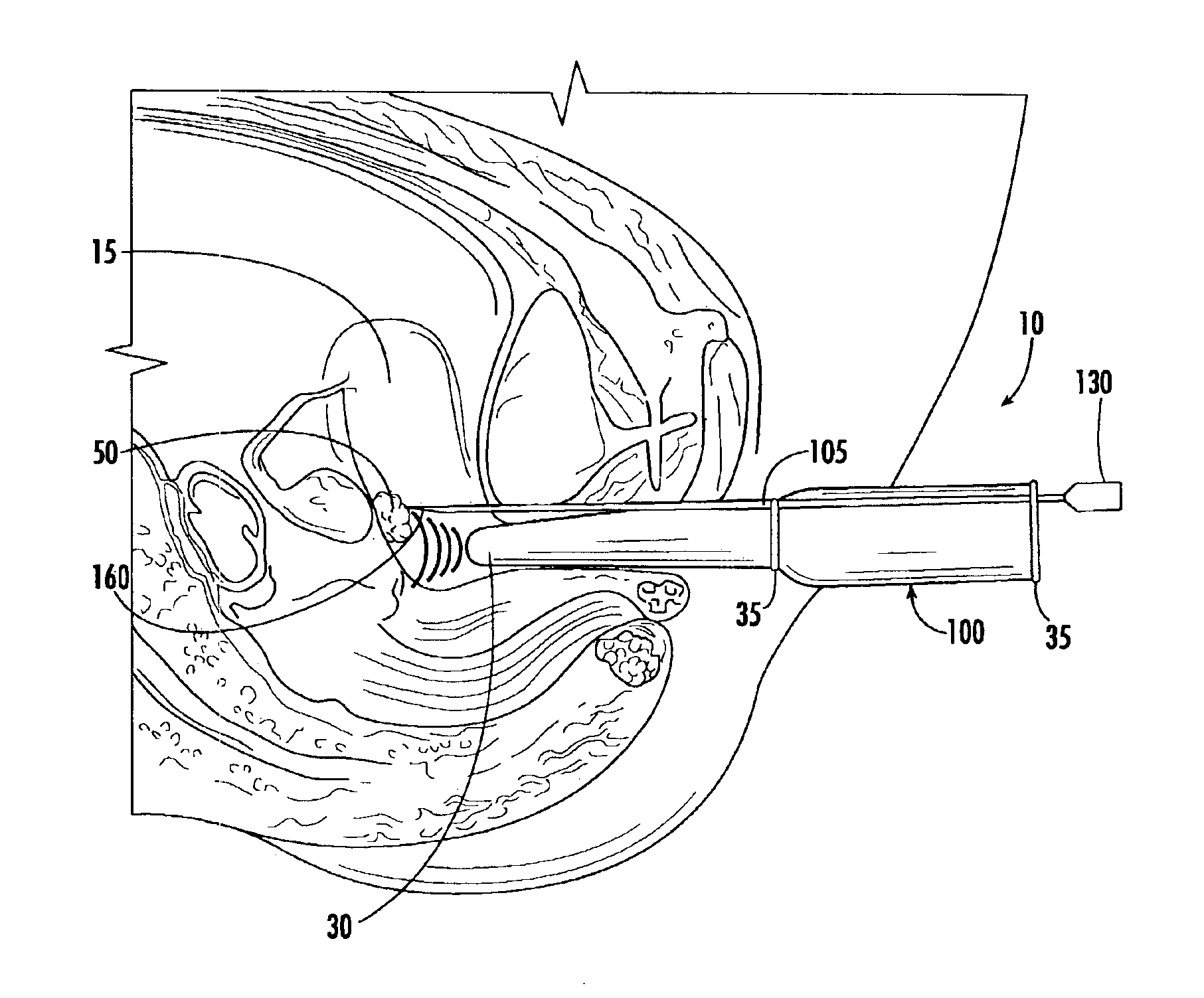
Echogenic needle for transvaginal ultrasound directed reduction of uterine fibroids and an associated method
InactiveUS6936048B2Increase awarenessImprove gripUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesVascular supplyRadio frequency
The invention is a transvaginal ultrasound probe having an attached echogenic needle that is useful in the treatment of uterine fibroids. The echogenic needle has an echogenic surface near its tip that allows the physician to visualize its location using ultrasound imaging. In one embodiment, the needle has an active electrode at its distal end. The active electrode supplies radio frequency energy to a fibroids causing necrosis of the targeted fibroid or by destroying the fibroid's vascular supply. The radio frequency needle preferably has a safety device that shuts-off energy if the needle punctures the uterine wall. In a second embodiment, the needle has a cryogen supply tube and cryogen supply. This embodiment destroys fibroid tissue by freezing it or its vascular supply when the tissue comes in contact with the needle's frozen distal end. The invention further includes the method of using the ultrasound probe with the attached needle.
Owner:GYNESONICS
Ultrasound system and method to deliver therapy based on user defined treatment spaces
InactiveUS20100286518A1Facilitates userUltrasound therapyOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasound imagingSonification
An ultrasound imaging and therapy system is provided that includes an ultrasound probe and a diagnostic module to control the probe to obtain diagnostic ultrasound signals from a region of interest (ROI) of the patient. The ROI includes adipose tissue and the diagnostic module generates a diagnostic image of the ROI based on the ultrasound signals obtained. The system also includes a display to display the image of the ROI and a user interface to accept user inputs to designate a treatment space within the ROI that corresponds to the adipose tissue. The display displays the treatment space on the image. The system also includes a therapy module to control the probe to deliver, during a therapy session, a therapy to a treatment location based on a therapy parameter. The treatment location is within the treatment space defined by the user inputs.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Ultrasound guided optical coherence tomography, photoacoustic probe for biomedical imaging
ActiveUS20110098572A1High resolution imagingEasy accessUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterDiagnostic Radiology ModalityHigh resolution imaging
An imaging probe for a biological sample includes an OCT probe and an ultrasound probe combined with the OCT probe in an integral probe package capable of providing by a single scanning operation images from the OCT probe and ultrasound probe to simultaneously provide integrated optical coherence tomography (OCT) and ultrasound imaging of the same biological sample. A method to provide high resolution imaging of biomedical tissue includes the steps of finding an area of interest using the guidance of ultrasound imaging, and obtaining an OCT image and once the area of interest is identified where the combination of the two imaging modalities yields high resolution OCT and deep penetration depth ultrasound imaging.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
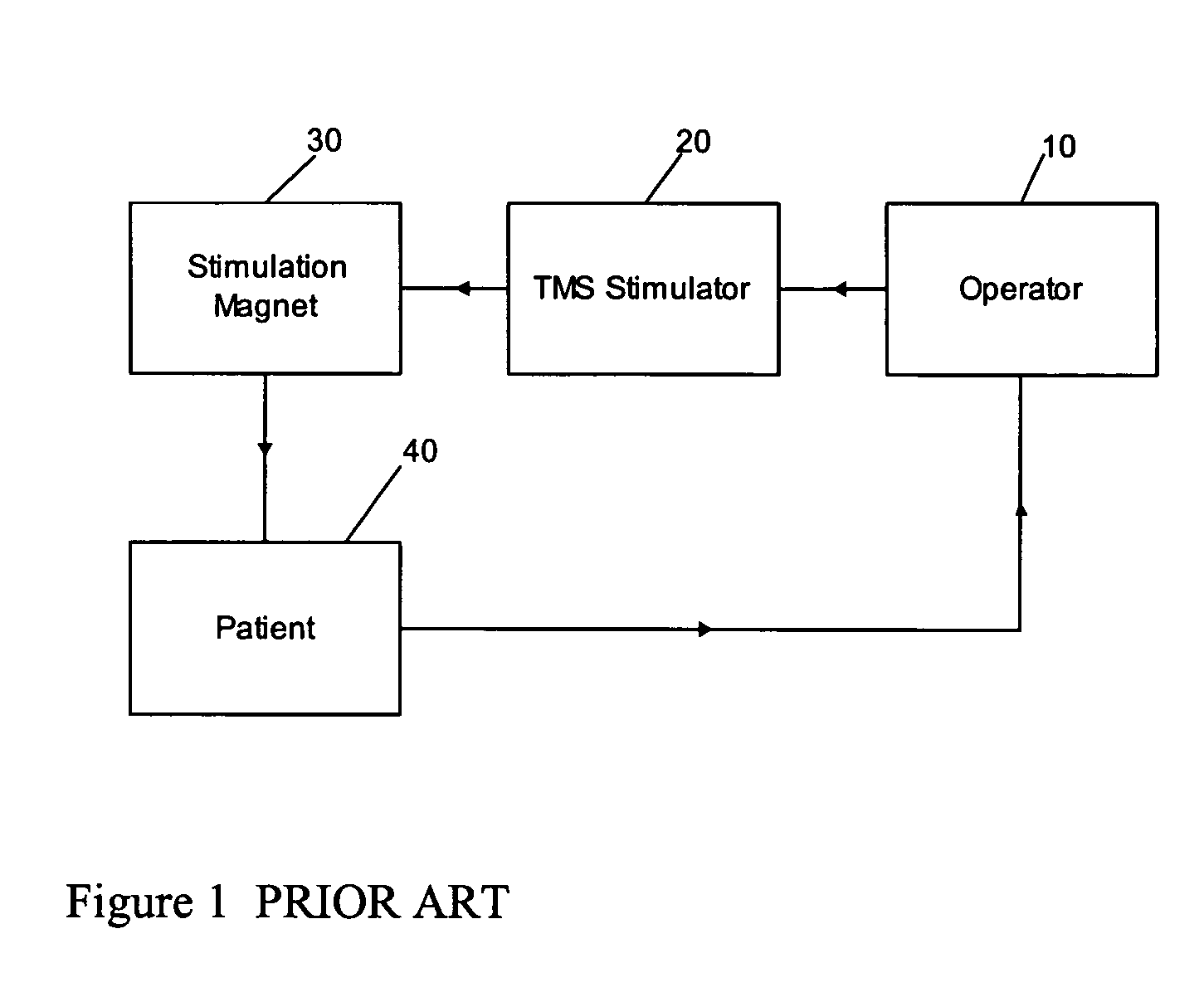
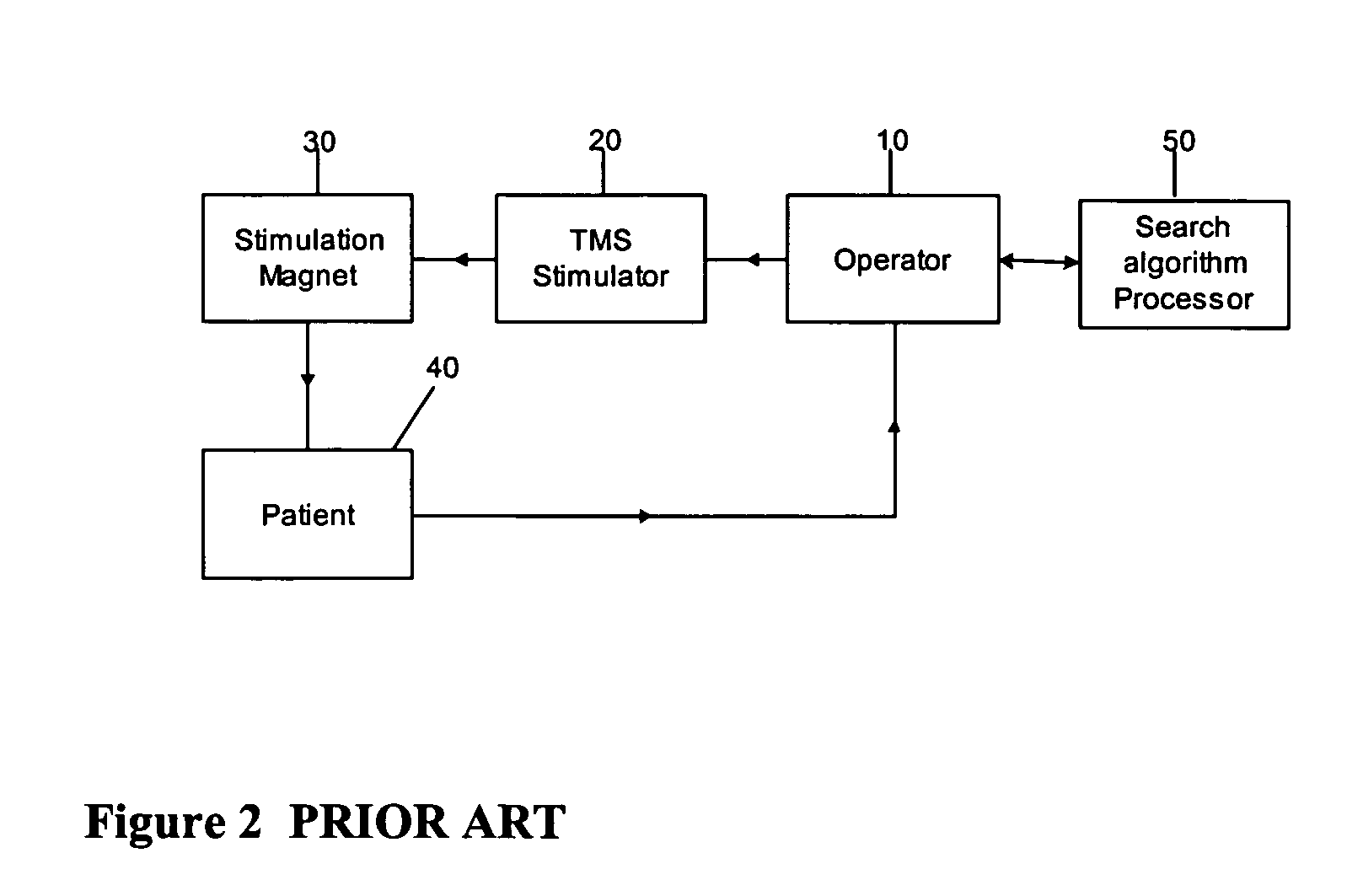
Determining stimulation levels for transcranial magnetic stimulation
ActiveUS7104947B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrotherapyMotion detectorREFLEX DECREASE
Owner:NEURONETICS
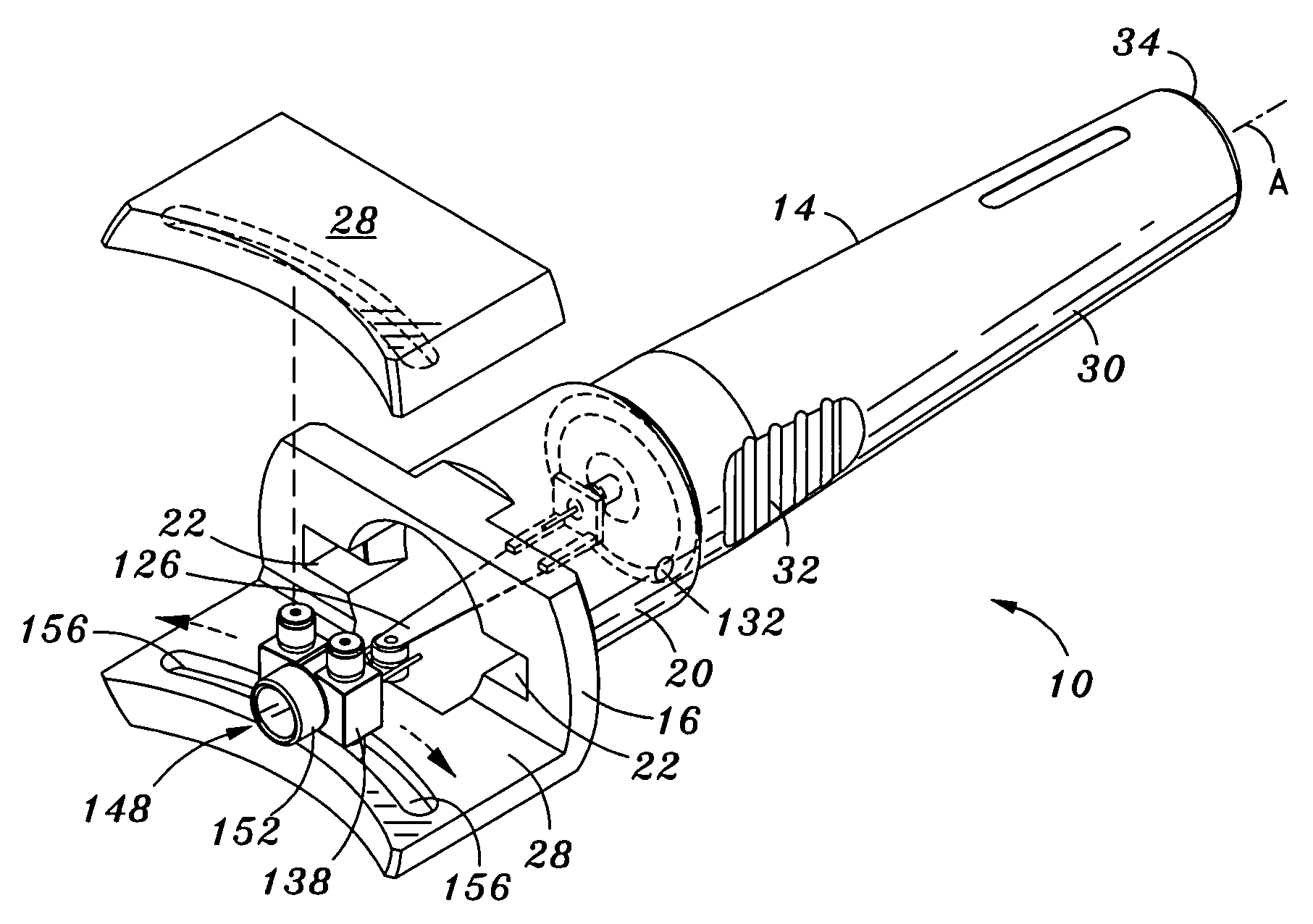
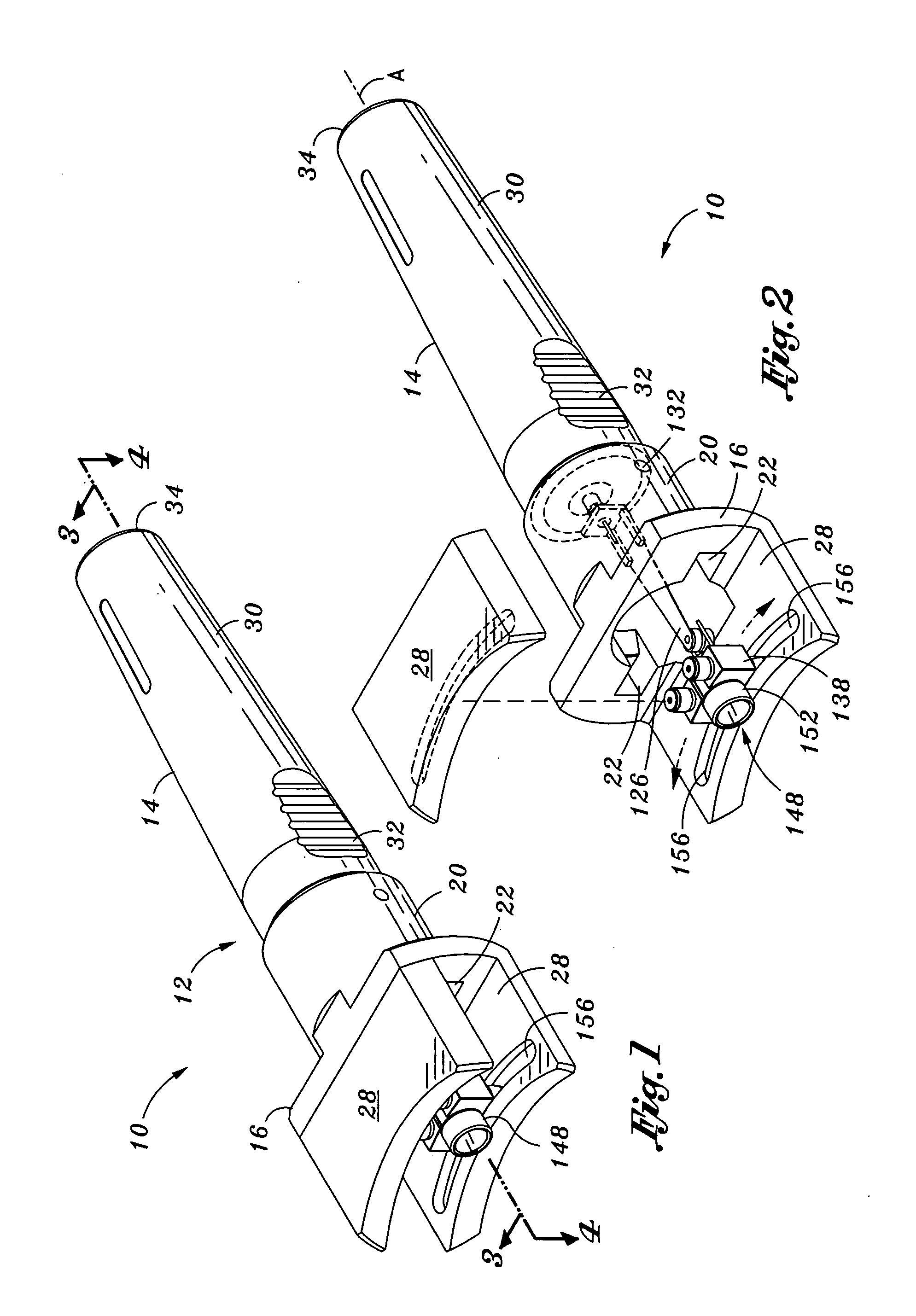
Ultrasonic probe with detachable slidable cauterization forceps
ActiveUS20050187512A1Function increaseImprove visualizationSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsSurgical operationForceps
A surgical device for ultrasonic ablation and RF cauterization includes a forceps member having at least one prong, the prong being formed as an electrode. At least one electrical connector is provided on the forceps member for operatively connecting the prong to an electrical power source. The surgical device further includes a mechanical connector attached to the forceps member for removably fastening the forceps member to a housing of an ultrasonic probe. The forceps member can thus function to carry out a cauterization procedure during a surgical operation utilizing the probe for ultrasonic ablation.
Owner:MISONIX INC
Ophthalmic ultrasound probe assembly
InactiveUS20080097214A1Accurate imagingMinimizes oblique reflectionMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesInfrasonic diagnosticsAnatomical structuresReciprocating motion
An ultrasonic probe assembly comprises a housing defining a longitudinal axis and having a linear motor assembly, a swivel base, and an extension arm disposed therewithin. An imaging transducer is mounted on a free end of the extension arm and is specifically adapted to be moved along an arcuate path as a result of mechanical interconnection of the swivel base to the linear motor assembly. The swivel base upon which the extension arm is mounted is configured to be pivotable about a pivot axis oriented transversely relative to the longitudinal axis such that reciprocative motion of the linear motor assembly is converted in swiveling motion of the swivel base and oscillating translation of the transducer along an arcuate path such that the transducer axis is oriented generally perpendicularly relative to an anatomical structure having a convexly shaped outer surface.
Owner:CAPISTRANO LABS
Apparatus and method for controlling an ultrasound system based on contact with an ultrasound probe
InactiveUS20100191120A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringTransducerEngineering
An ultrasound probe comprises a probe housing that has an inner surface and an outer surface. An array of transducer elements are within the probe housing. At least one sensor is formed between the inner and outer surfaces of the probe housing. The at least one sensor is configured to detect at least one parameter associated with an object in contact with the outer surface proximate the at least one sensor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Ultrasound probe with replaceable head portion
InactiveUS20100249598A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrical transducersTransducerEngineering
An ultrasound probe includes a transducer comprising an array of transducer elements removably disposed in a head portion. At least one or more stages of electronic circuit units is removably coupled to the transducer and configured to excite the transducer. A handle portion is detachably coupled to the head portion. The head portion and the handle portion are disposed enclosing the at least one or more stages of electronic circuit units. The ultrasound probe is used for one dimensional applications, two dimensional applications, and volumetric applications.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus and method for an ultrasonic medical device operating in torsional and transverse modes
InactiveUS20050187513A1Effective timeSimple, user-friendlySurgeryChiropractic devicesCavitationTransducer
The present invention provides an apparatus and a method for an ultrasonic medical device operating in a torsional mode and a transverse mode. An ultrasonic probe of the ultrasonic medical device is placed in communication with a biological material. An ultrasonic energy source is activated to produce an electrical signal that drives a transducer to produce a torsional vibration of the ultrasonic probe. The torsional vibration produces a component of force in a transverse direction relative to a longitudinal axis of the ultrasonic probe, thereby exciting a transverse vibration along the longitudinal axis causing the ultrasonic probe to undergo both a torsional vibration and a transverse vibration. The torsional vibration and the transverse vibration cause cavitation in a medium surrounding the ultrasonic probe to ablate the biological material.
Owner:CYBERSONICS
Devices for covering ultrasound probes of ultrasound machines
InactiveUS20080139944A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsAcousticsBiomedical engineering
Preferred embodiments of devices for covering an ultrasound probe can include a membrane, such as a sheath, having one or more ultrasonic couplers attached thereto for transferring ultrasonic energy between the ultrasound probe and a body surface of a patient.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Transducer assembly for ultrasound probes
InactiveUS20050165313A1Avoid shockAvoid enteringUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsElastomerNose
Transducer assembly for an ultrasound probe including a transducer array having transducer elements and an acoustic window attached directly to the transducer array such that the transducer array and the acoustic window form an integral unit. The acoustic window includes a layer of elastomer optionally covered on upper and lower surfaces by impervious polymer layers. An ultrasound probe, such as a transesophageal echocardiographic probe, a transnasal probe, a transthoracic probe, an intracavity probe and an intraoperative probe, including the transducer assembly in a cavity of the housing or nose is also disclosed.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Cryotreatment device and method
InactiveUS20070250050A1Reduce adverse reactionsReduced responseStentsOther blood circulation devicesCoronary artery angioplastyPercent Diameter Stenosis
Devices and methods for cooling vessel walls to inhibit restenosis in conjunction with medical procedures such as coronary artery angioplasty. Stenosed vessel walls can be cooled prior to angioplasty, after angioplasty, or both. The invention is believed to inhibit restenosis through cooling to a temperature near freezing, preferably without causing substantial vessel wall cell death. One catheter device includes a distal tube region having coolant delivery holes radially and longitudinally distributed along the distal region. In some devices, holes spray coolant directly onto the vessel walls, with the coolant absorbed into the blood stream. In other embodiments, a balloon or envelope is interposed between the coolant and the vessel walls and the coolant returned out of the catheter through a coolant return lumen. Some direct spray devices include an occlusion device to restrict blood now past the region being cooled. Pressure, temperature, and ultrasonic probes are included in some cooling catheters. Pressure control valves are included in some devices to regulate balloon interior pressure within acceptable limits. In applications using liquid carbon dioxide as coolant, the balloon interior pressure can be maintained above the triple point of carbon dioxide to inhibit dry ice formation. Some cooling catheters are coiled perfusion catheters supporting longer cooling periods by allowing perfusing blood flow simultaneously with vessel wall cooling. One coiled catheter is biased to assume a coiled shape when unconstrained and can be introduced into the body in a relatively straight shape, having a stiffeninig wire inserted through the coil strands.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com