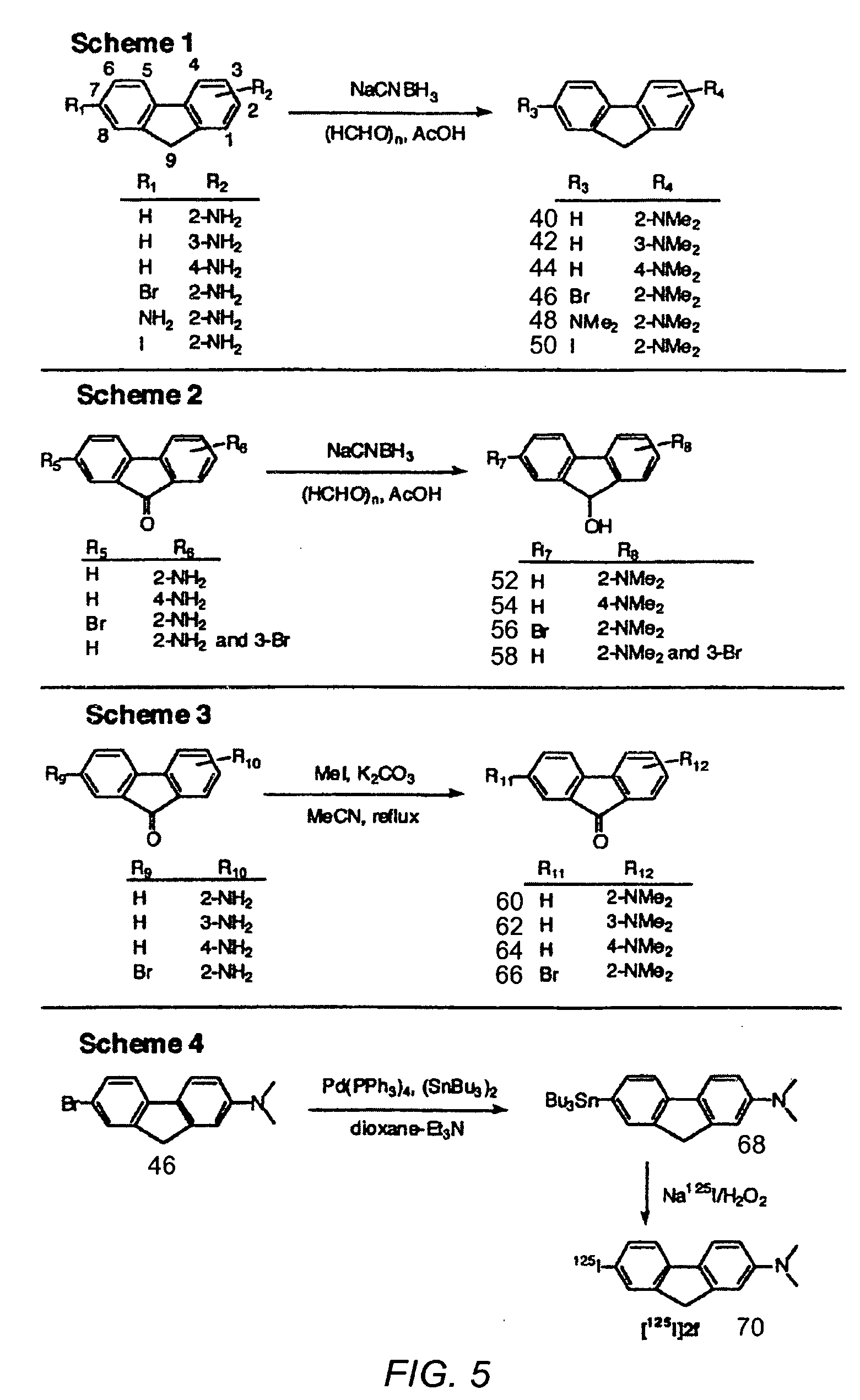
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
221 results about "Single-photon emission computed tomography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
<ul><li>The scanned images contain light or dark areas depending on how much radioactive tracer was absorbed.</li><li>The radiologist interprets the scan, reports the findings, and sends it over to the referring physician.</li><li>The report may provide information about which areas of the brain are more active, or if the heart is receiving an adequate blood flow.</li><li>It could show blockage in the coronary artery, and detect hidden bone fractures.</li></ul>
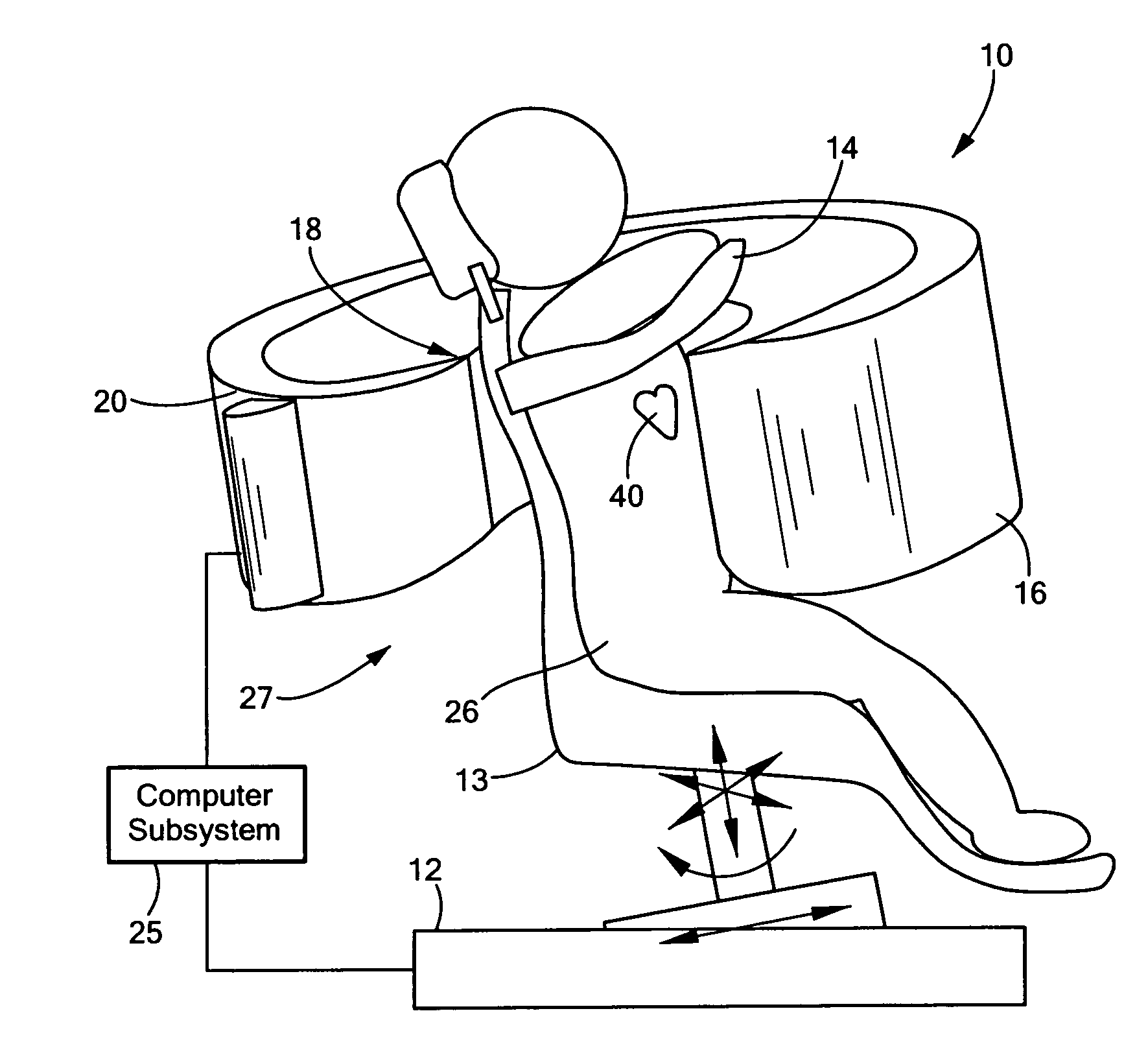
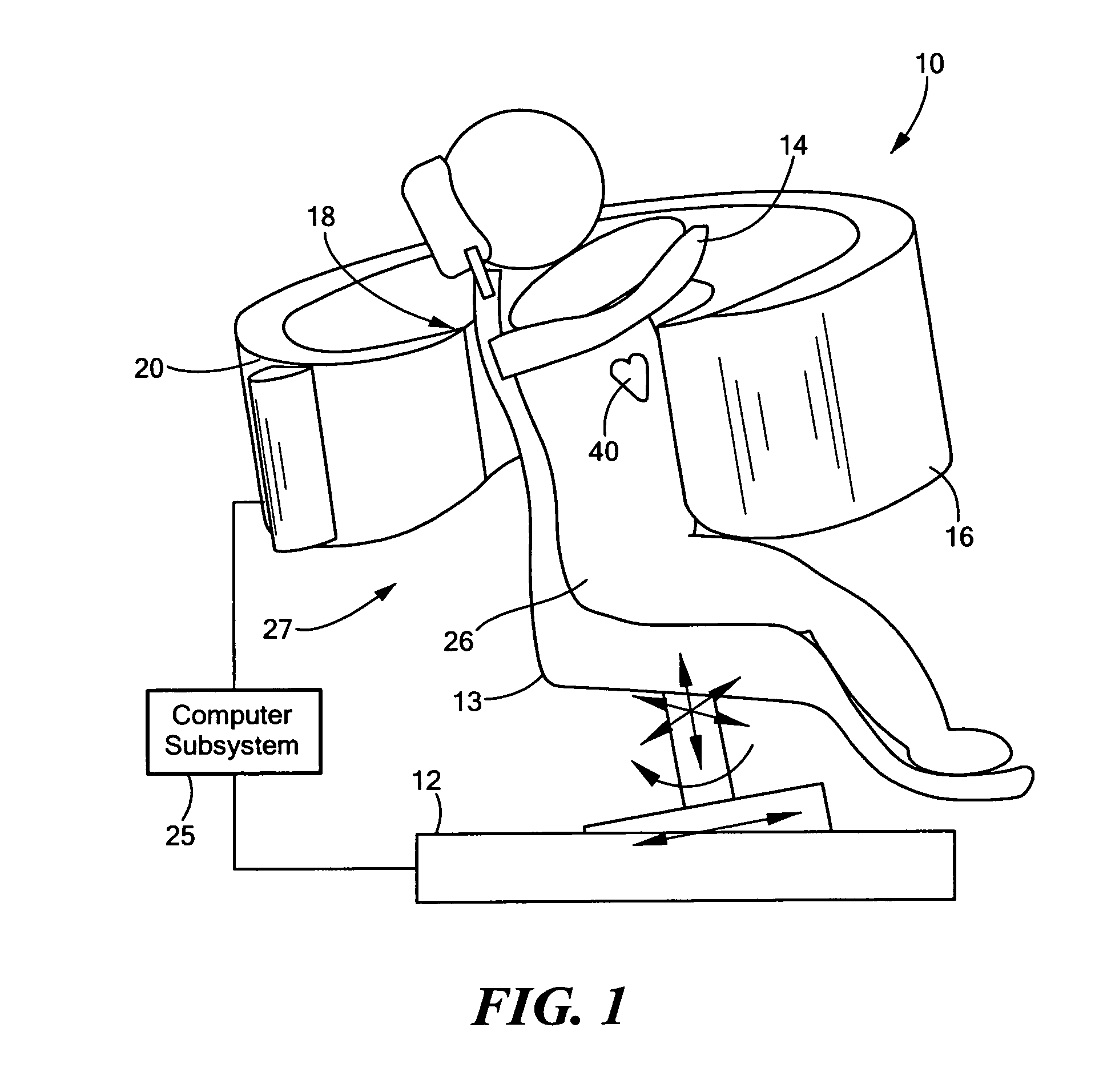
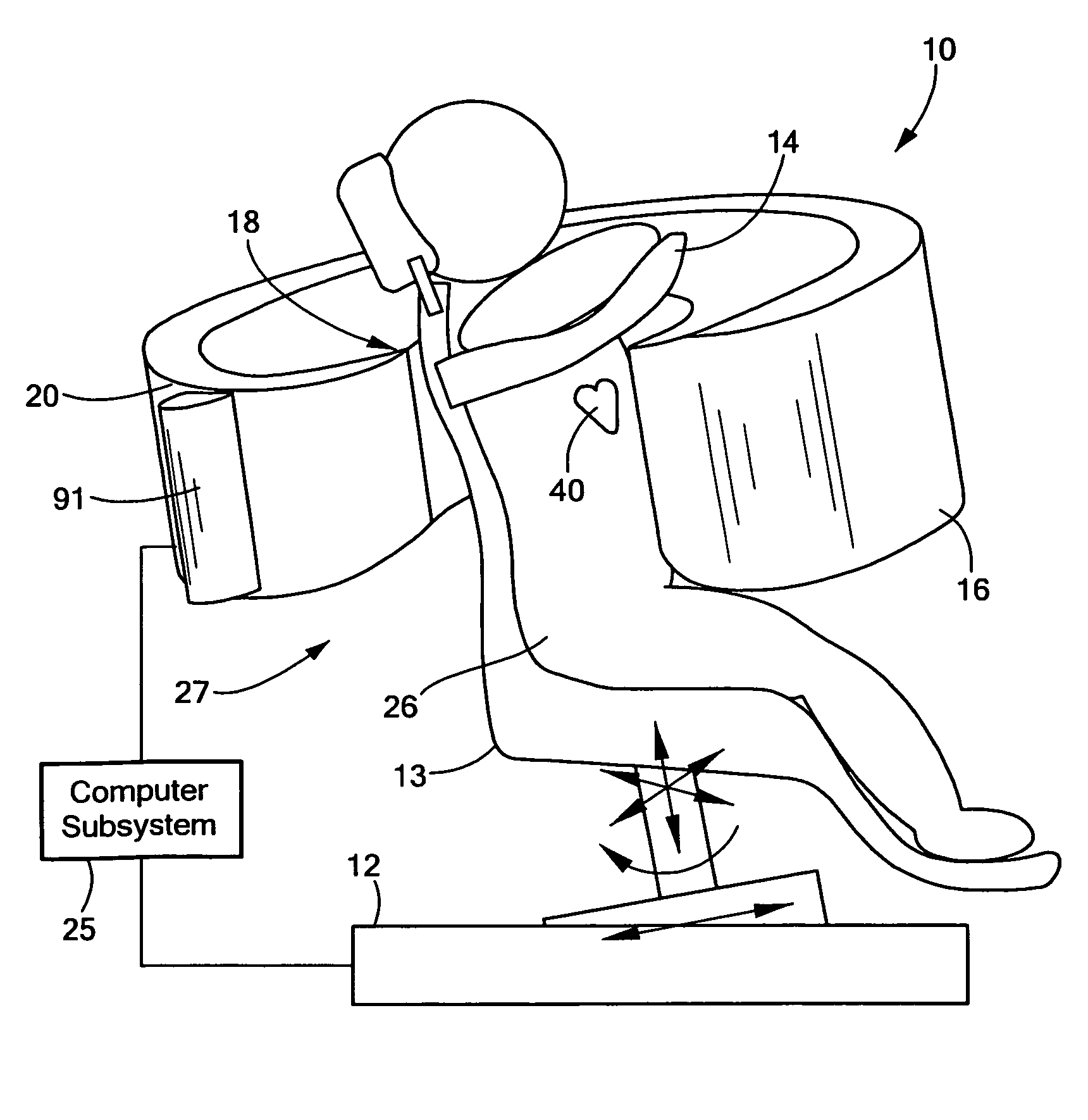
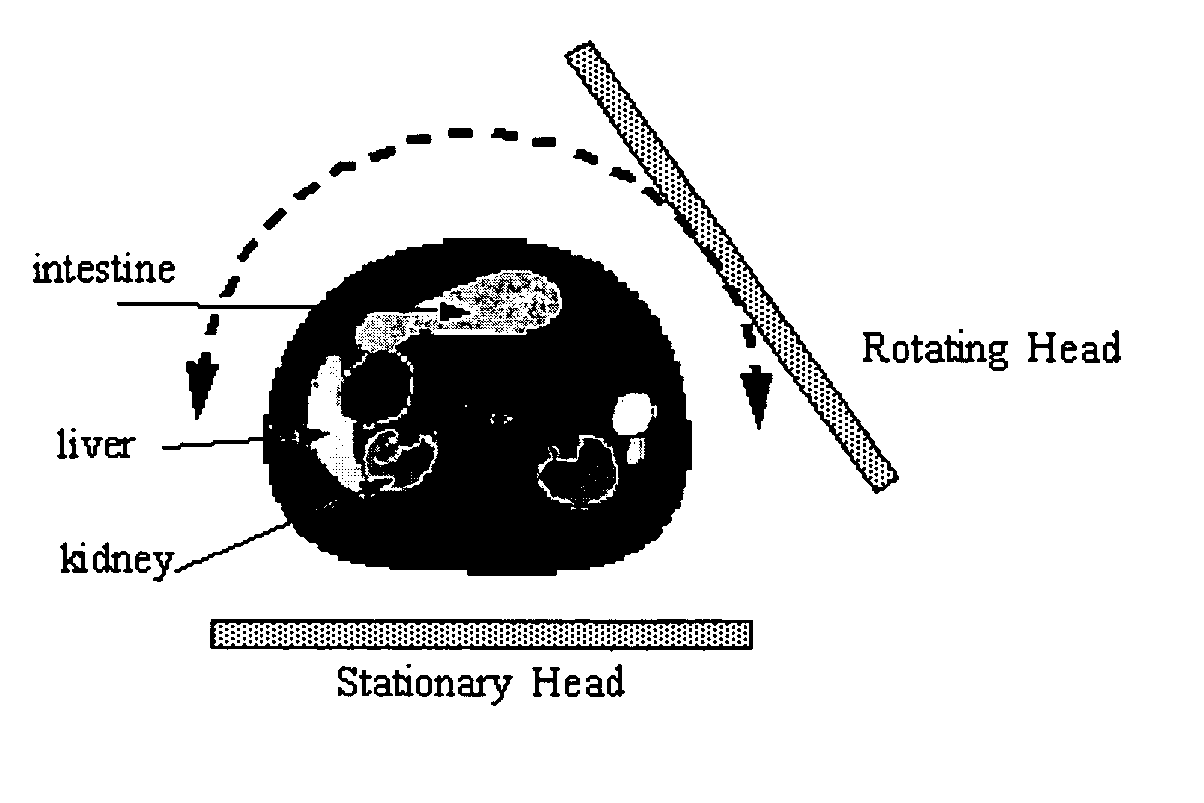
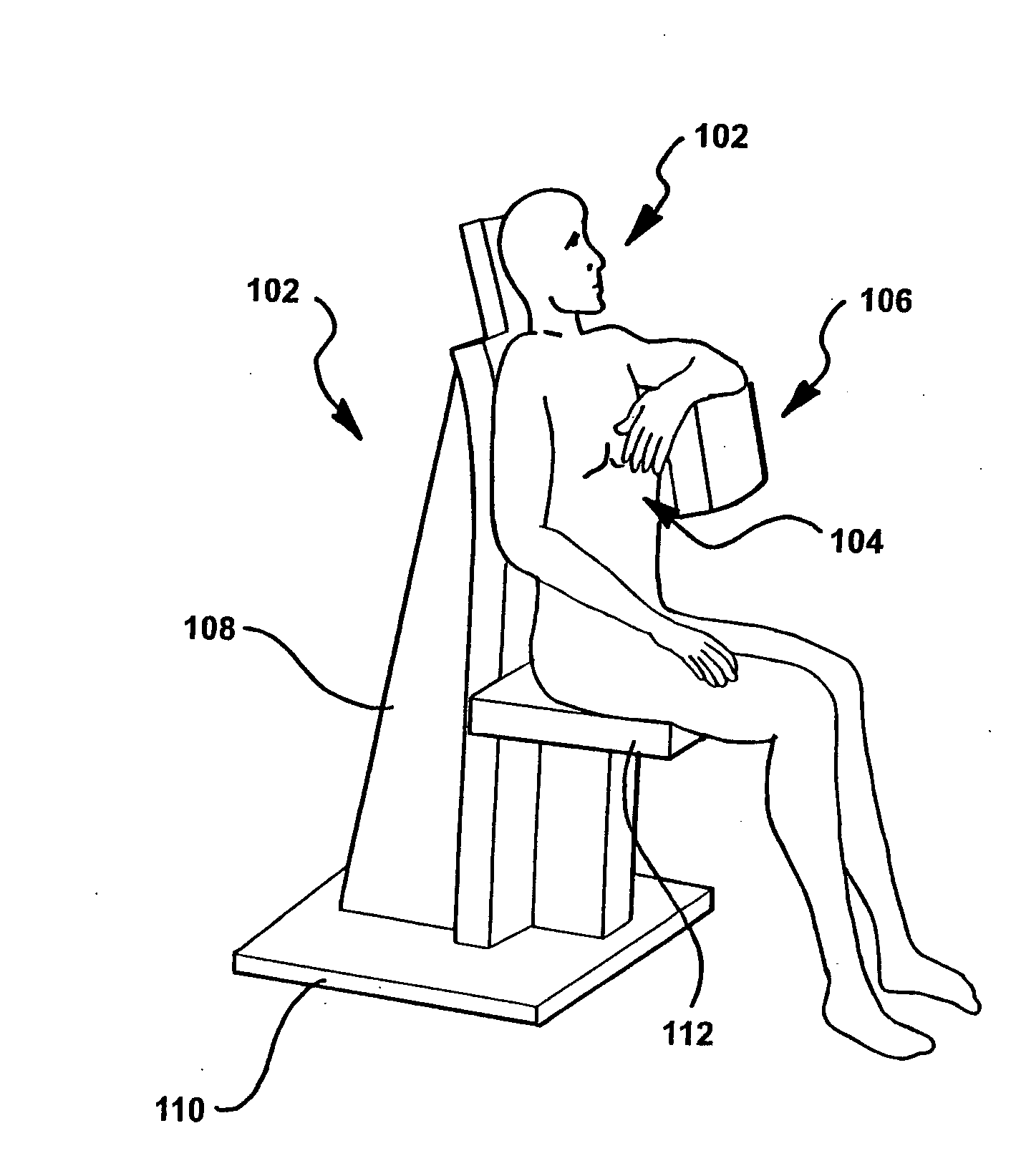
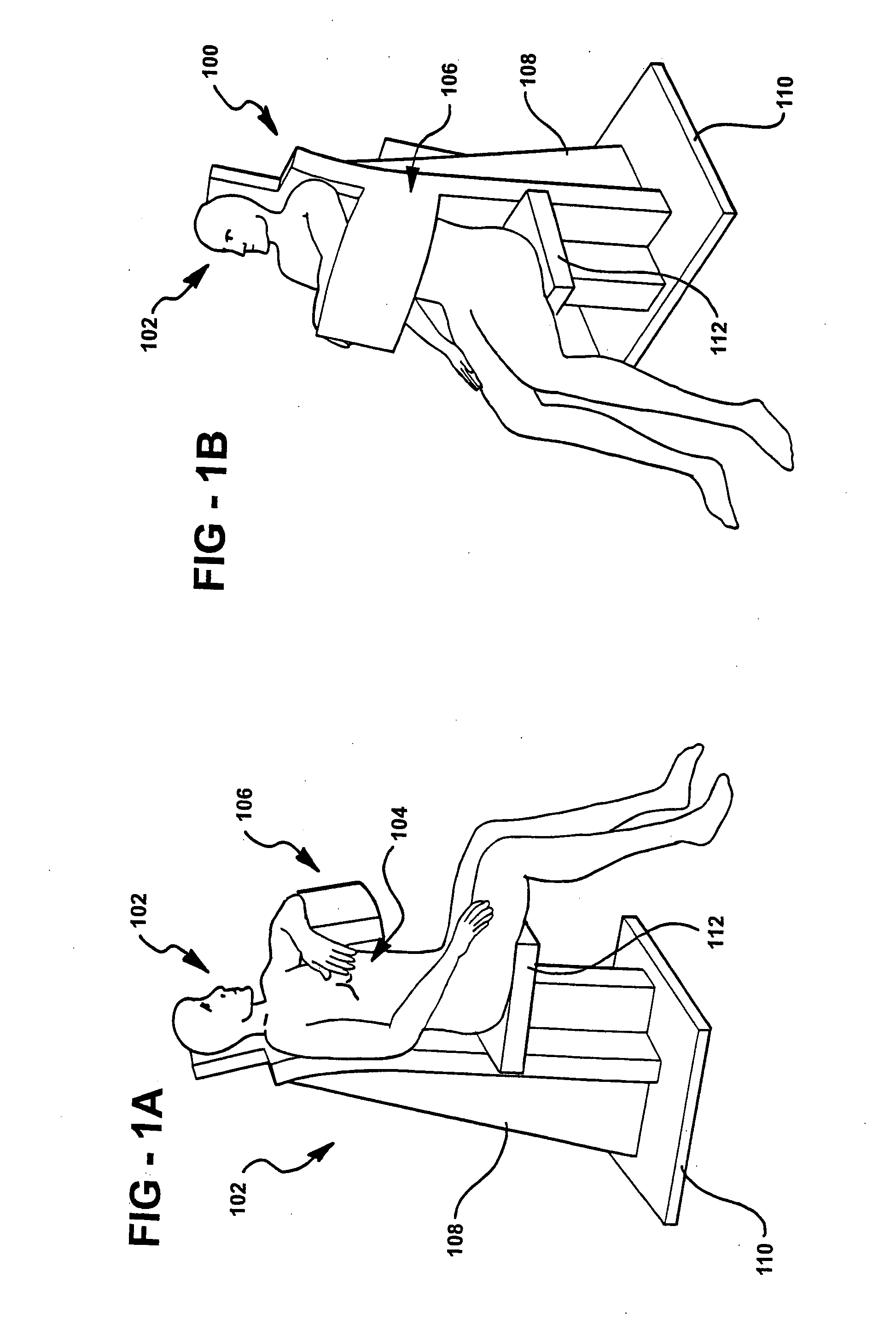
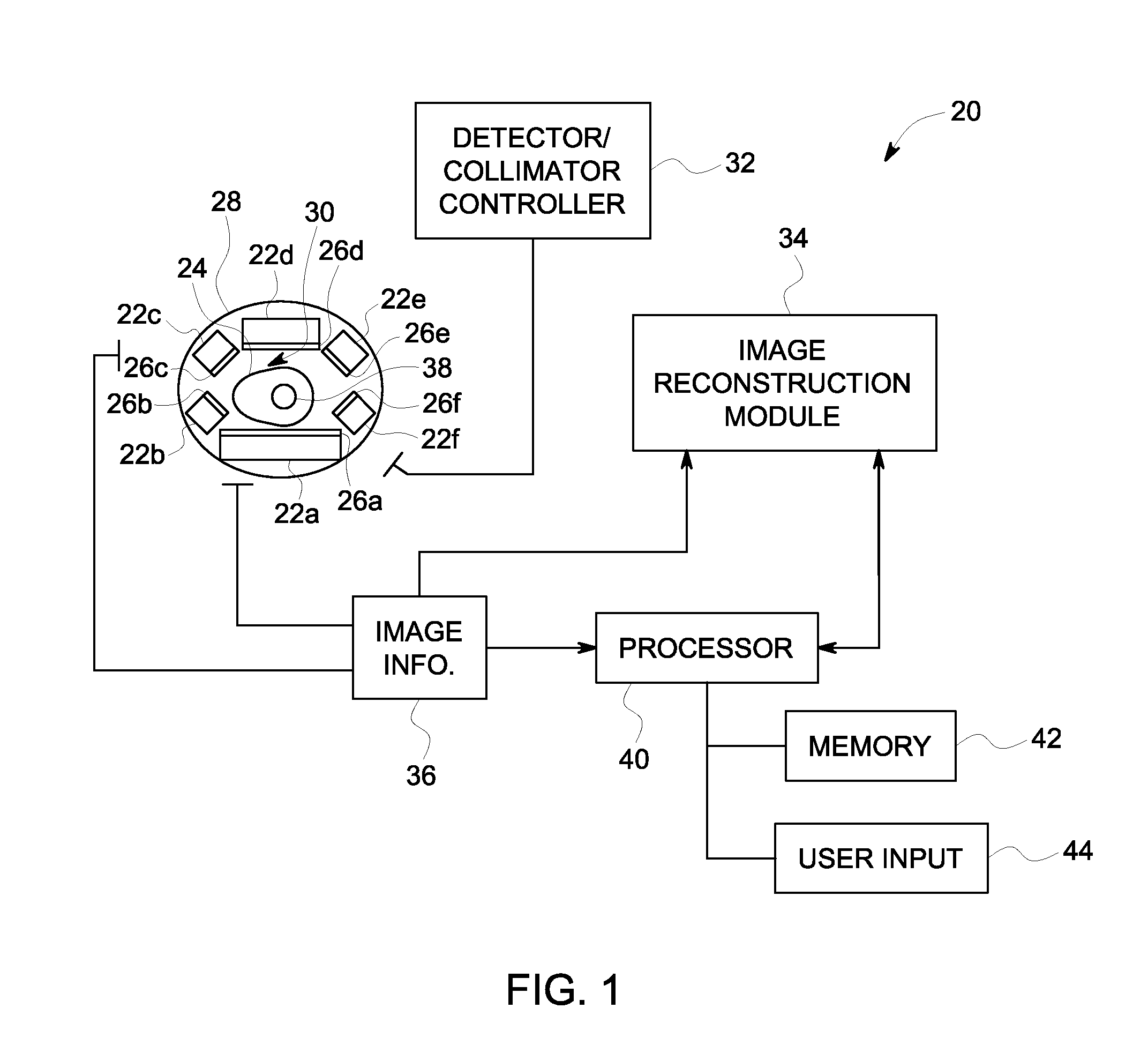
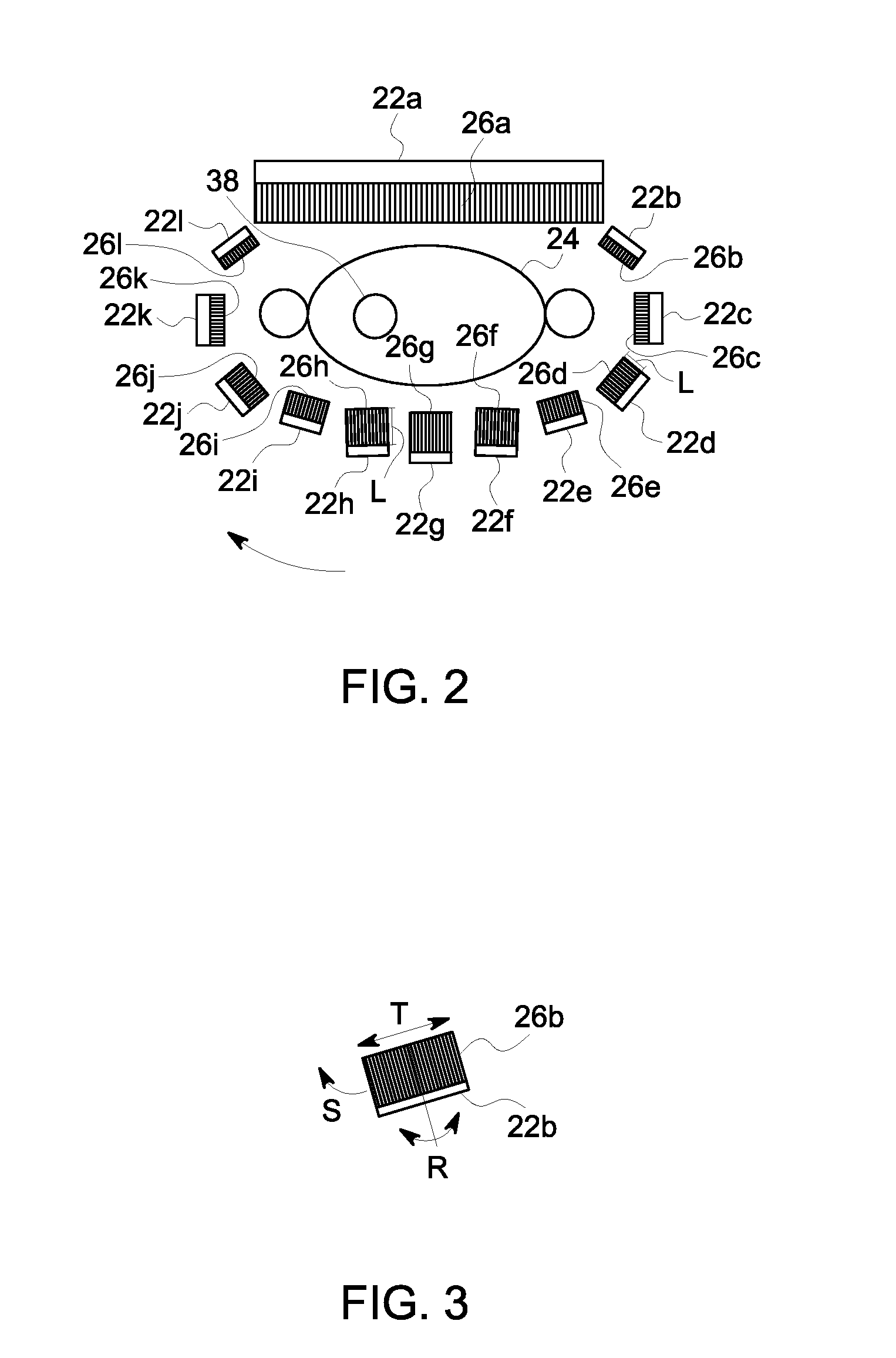
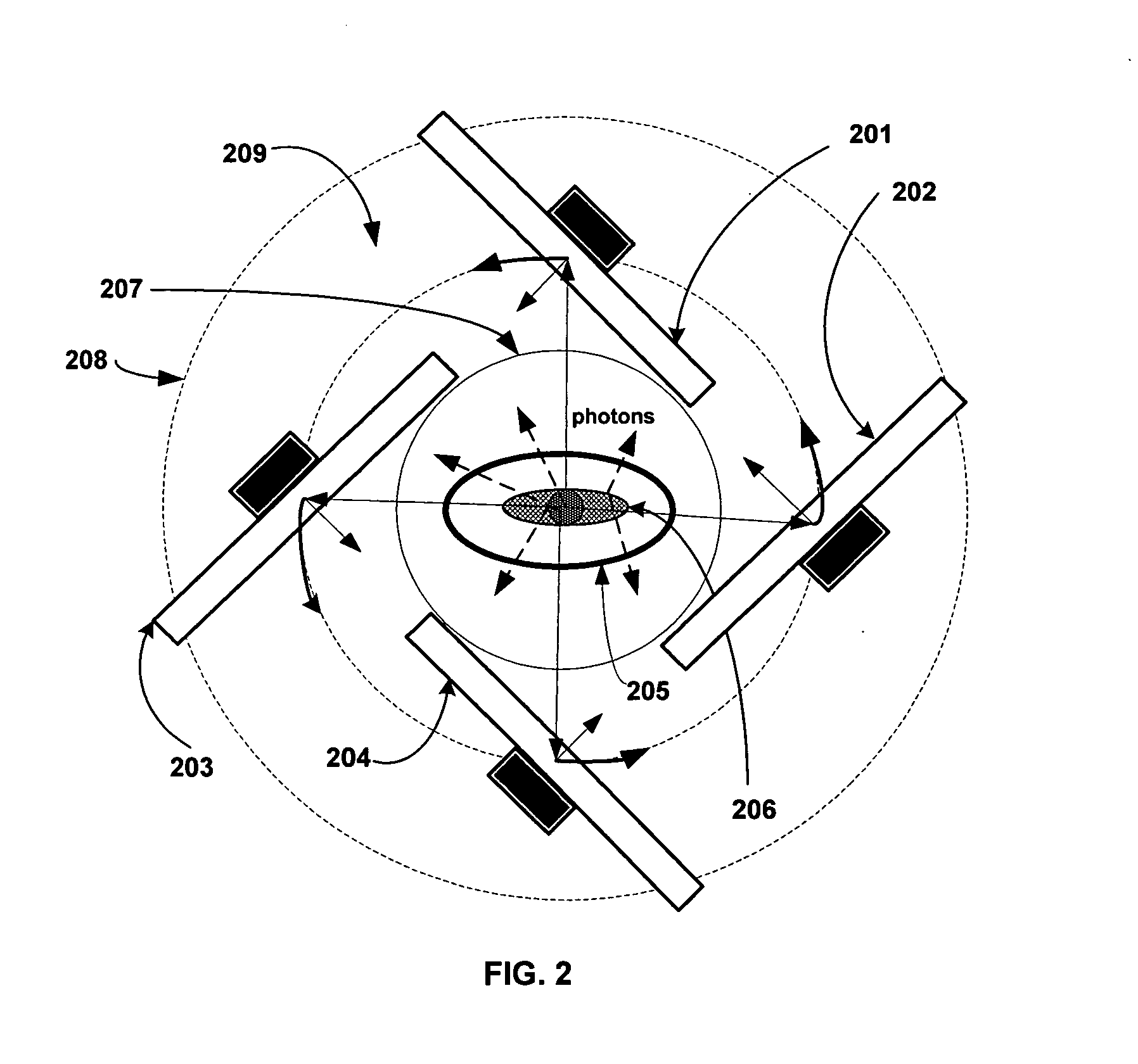
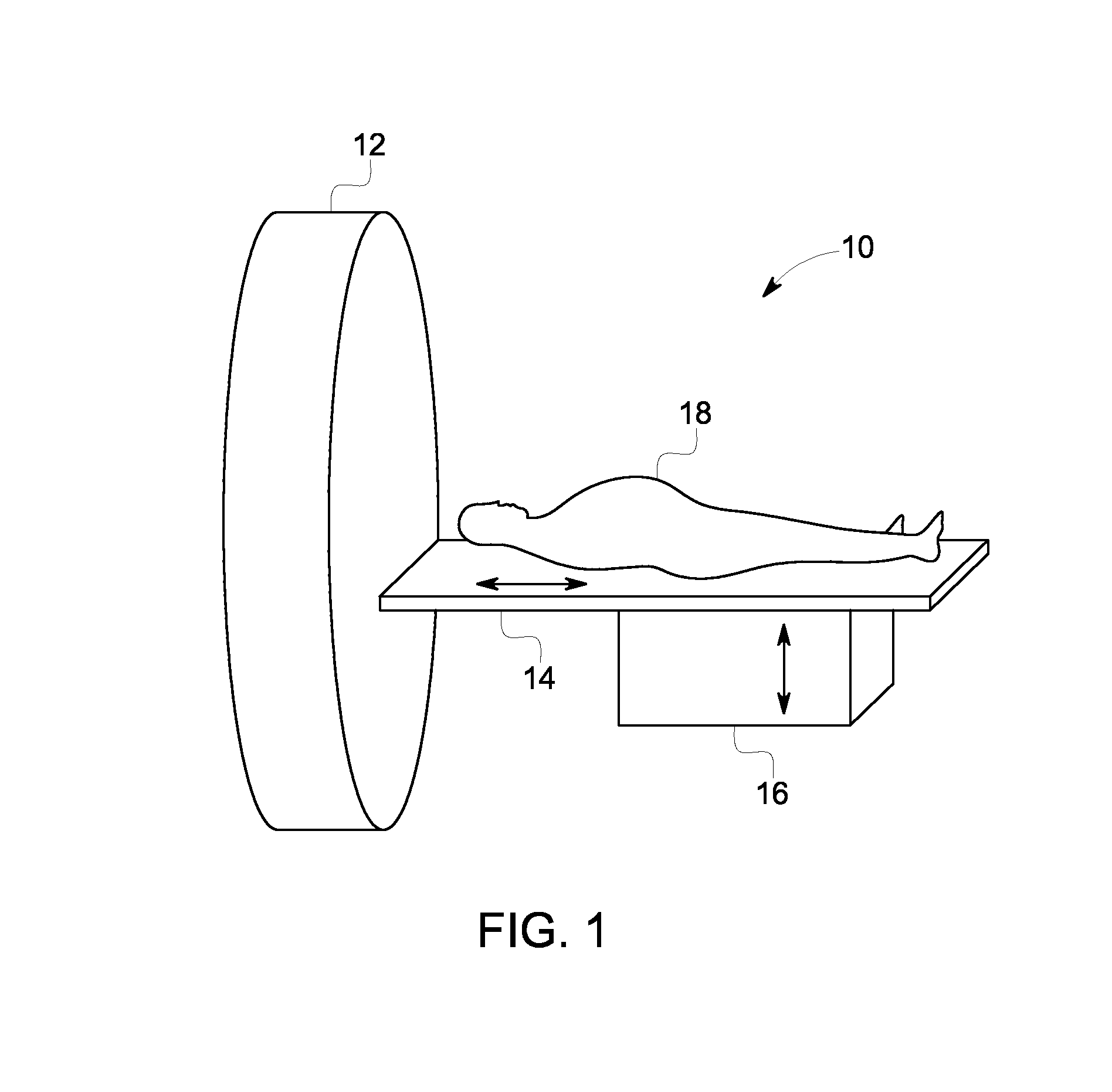
Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) system for cardiac imaging
ActiveUS7683331B2Optimize dataQuality improvementMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyGeometric efficiencyCardiac imaging
Owner:RUSH UNIV MEDICAL CENT
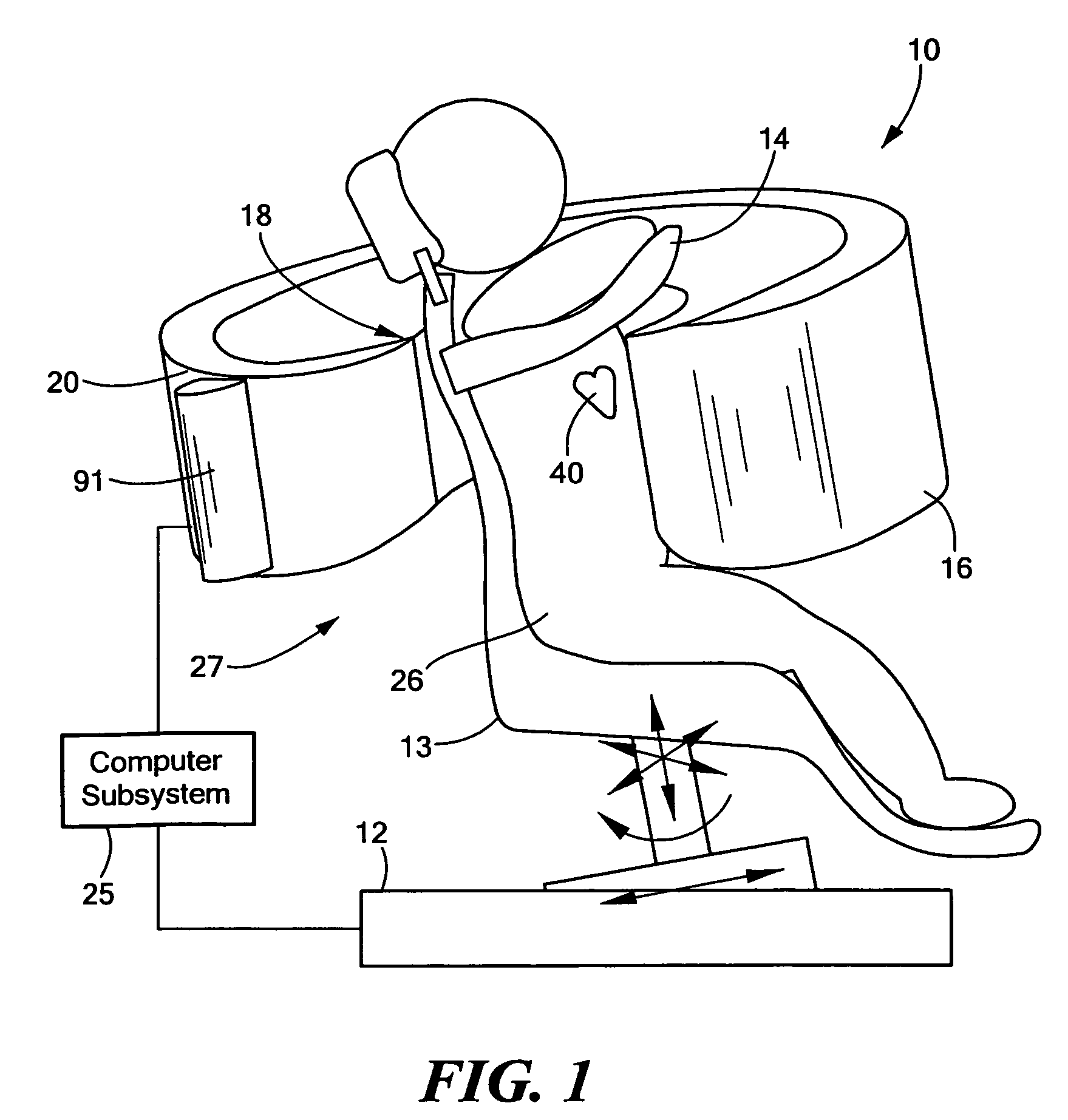
Integrated single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)/transmission computed tomography (TCT) system for cardiac imaging
ActiveUS7683332B2Improve image qualityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTransmission Computed TomographyPatients position
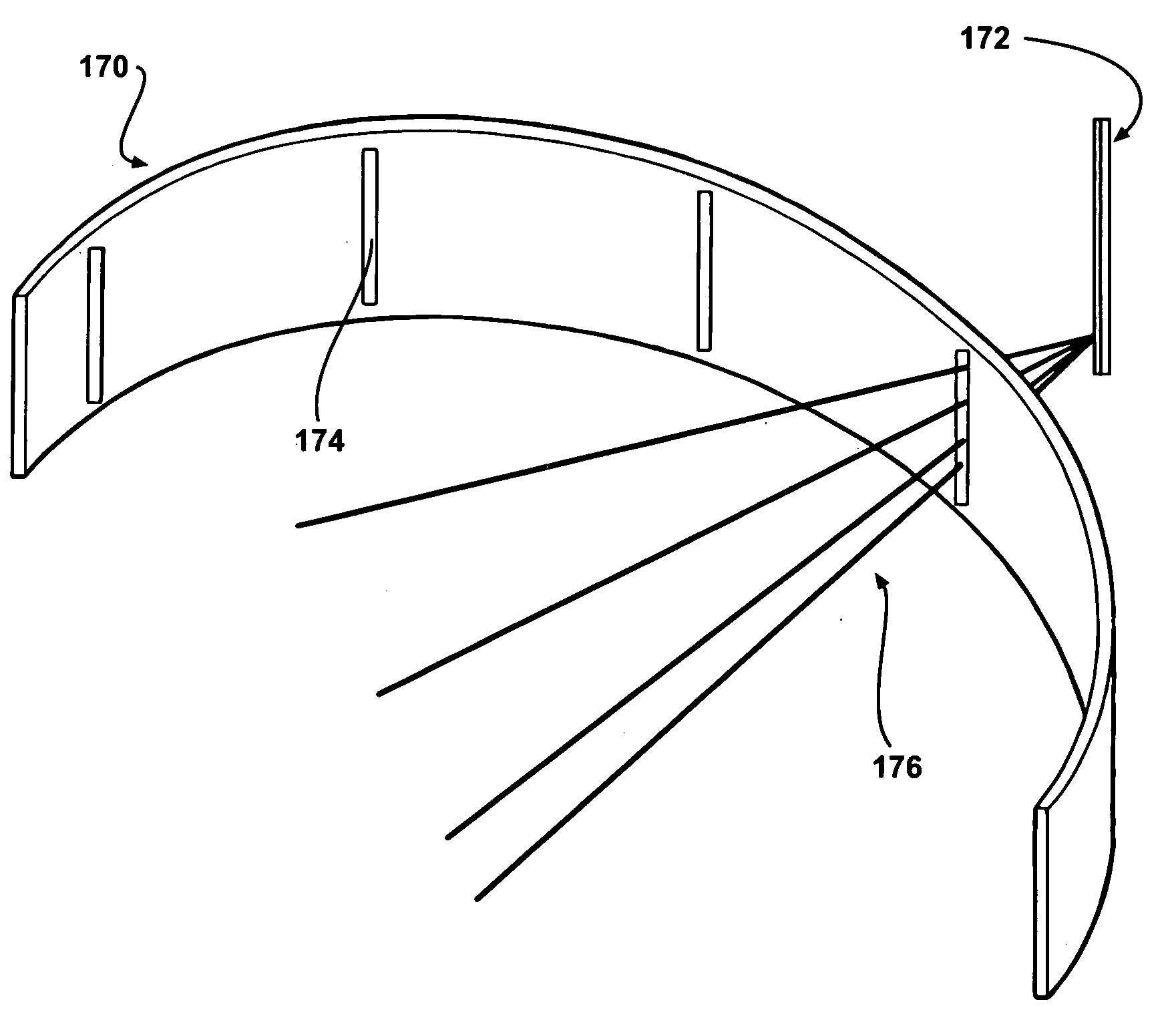
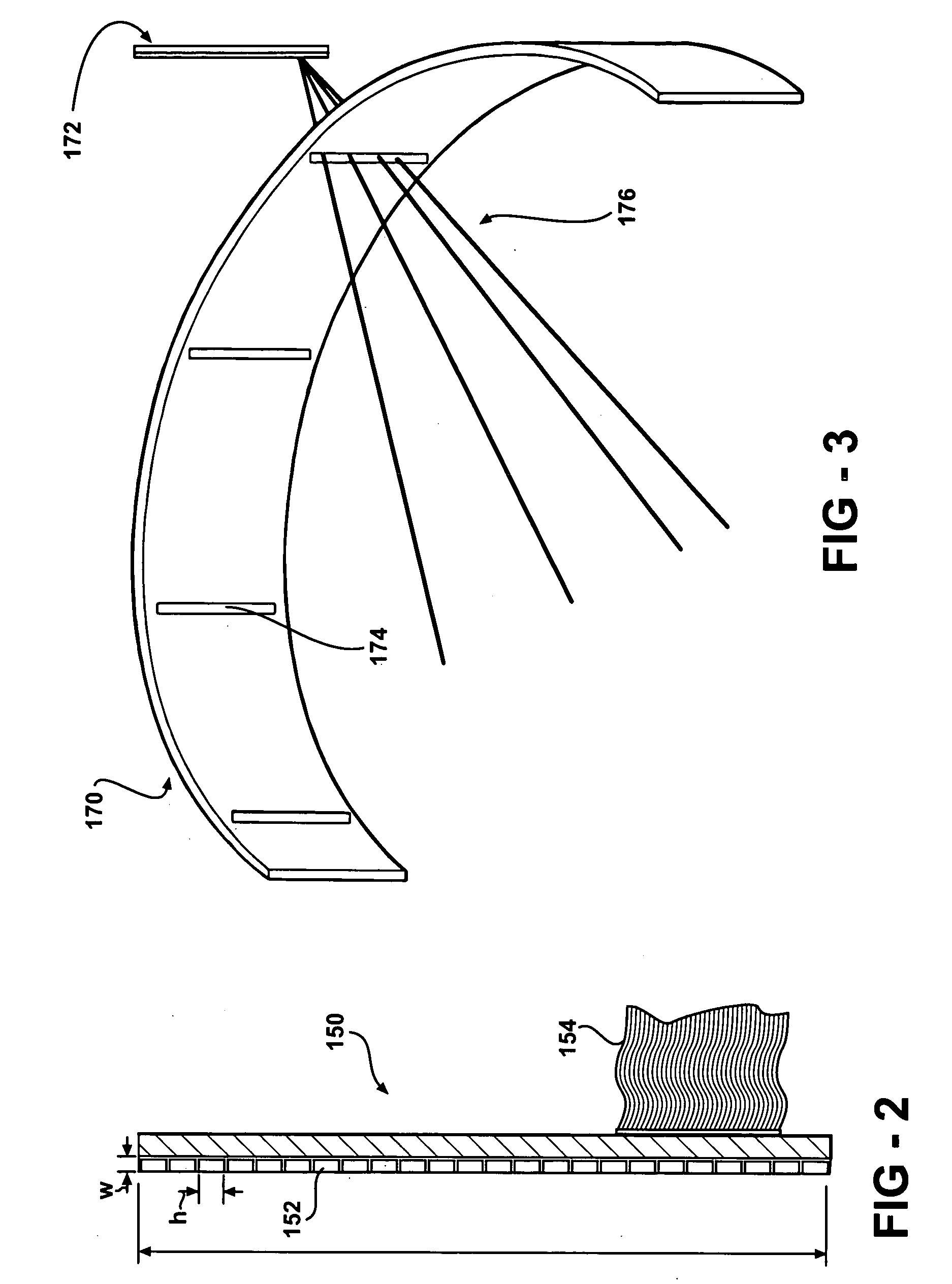
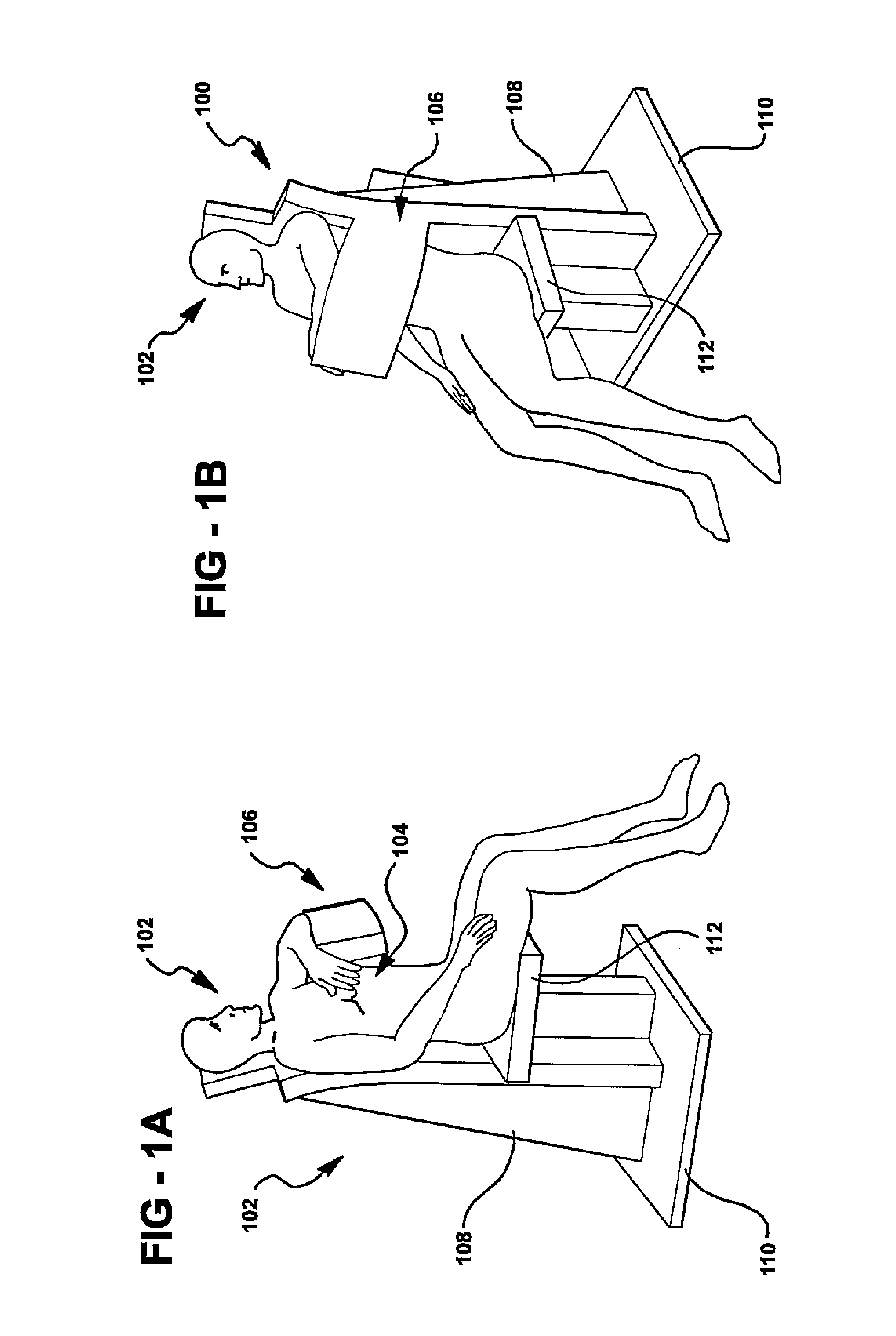
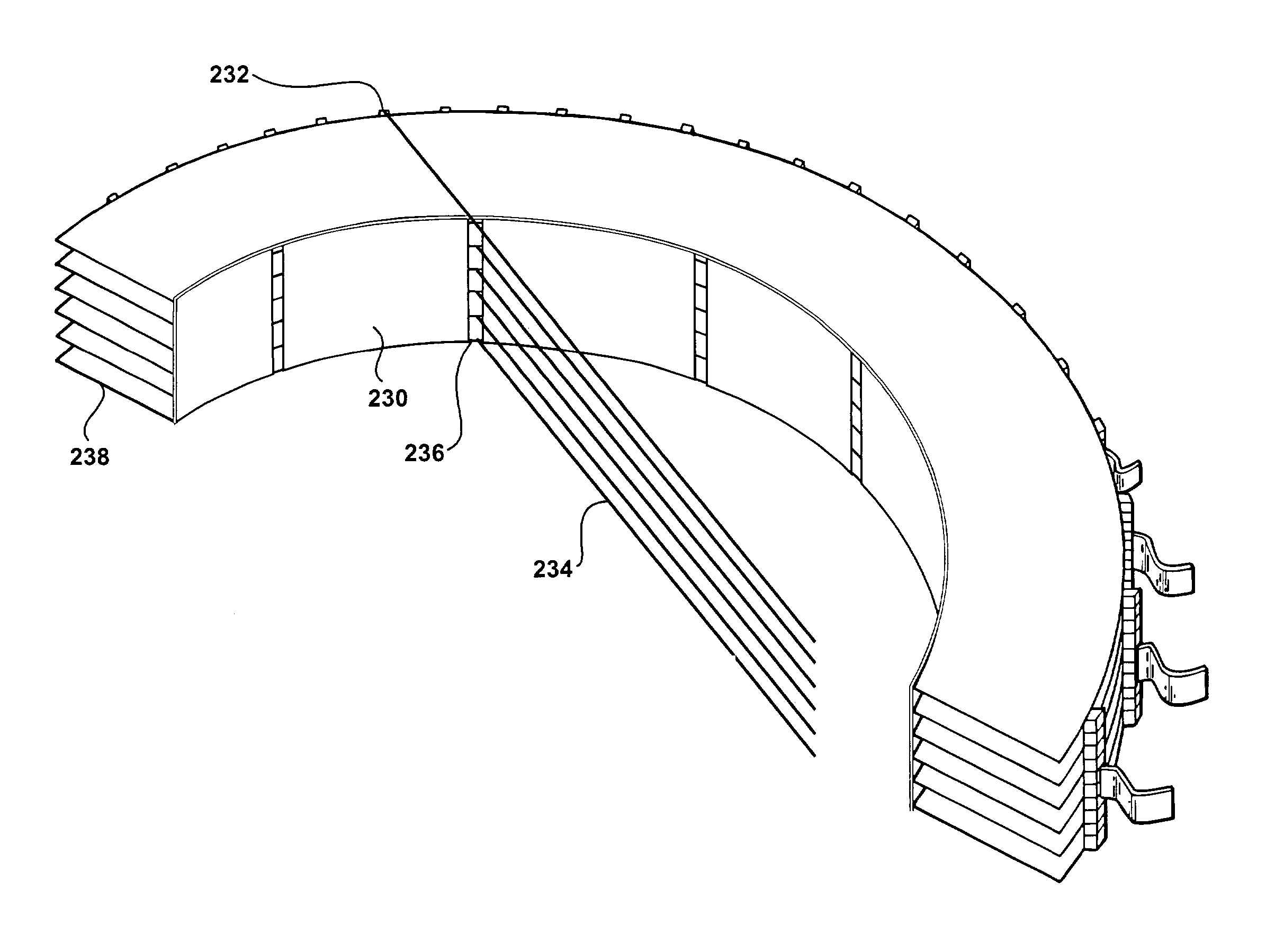
This invention features an integrated single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) / transmission computed tomography (TCT) system for cardiac imaging including an open arc-shaped frame. A collimator system is shaped to approximately match the thoracic contour of patients having different sizes and weights and shaped to surround and position the collimator closely proximate a heart of a patient of said patients encompassed by at least one predetermined image volume for optimizing collimation of radiation photons emitted from the heart. An arc-shaped detector system is coupled to the collimator subsystem having a shape closely matching the shape of the collimator subsystem for detecting collimated radiation photons from the collimator subsystem and generating output electrical signals. A patient positioning subsystem positions a patient to a predetermined central longitudinal axis of the three-dimensional imaging volume and for intermittently and incrementally rotating the patient about the predetermined central longitudinal axis for generating a plurality of TCT images.
Owner:RUSH UNIV MEDICAL CENT
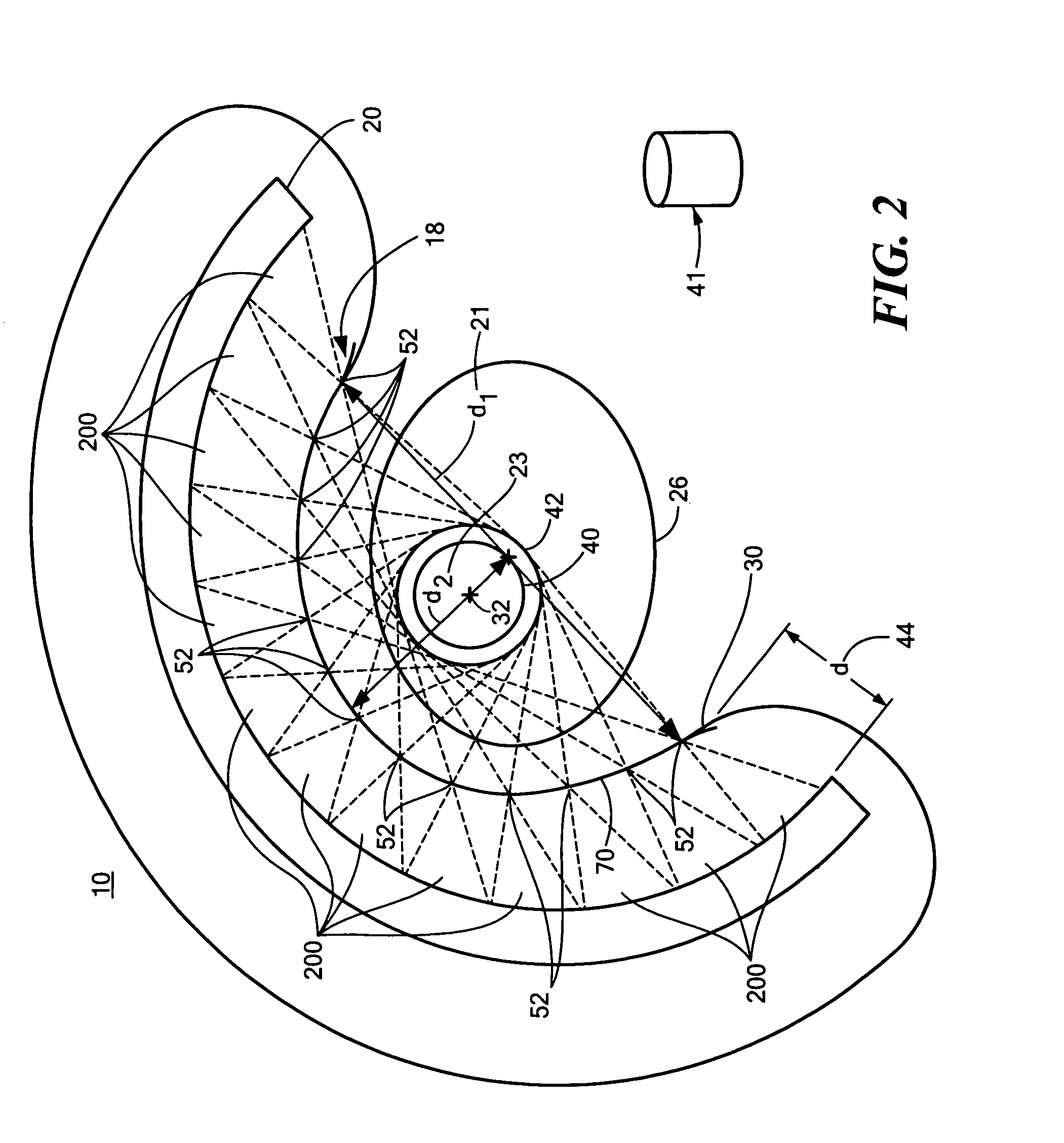
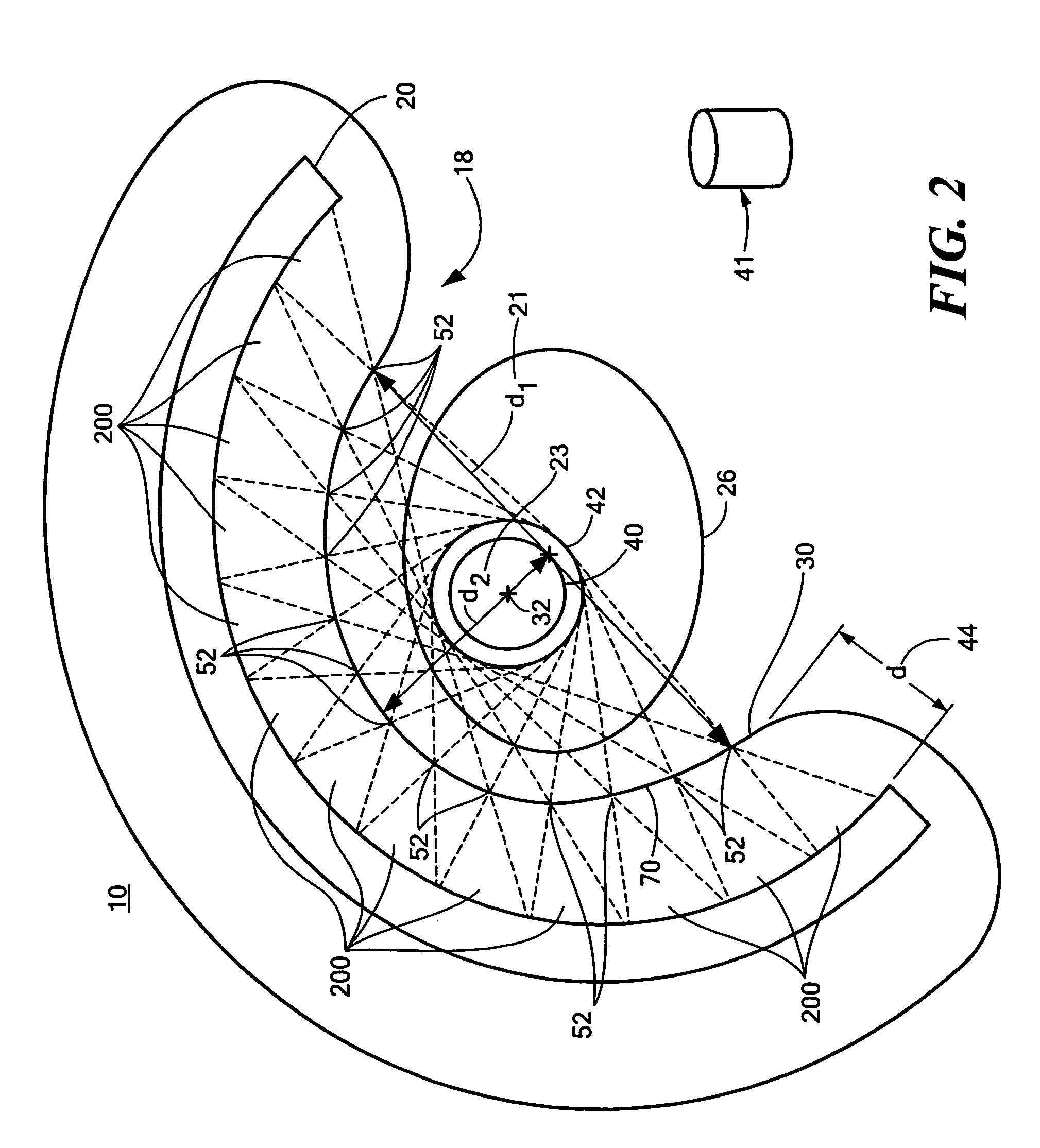
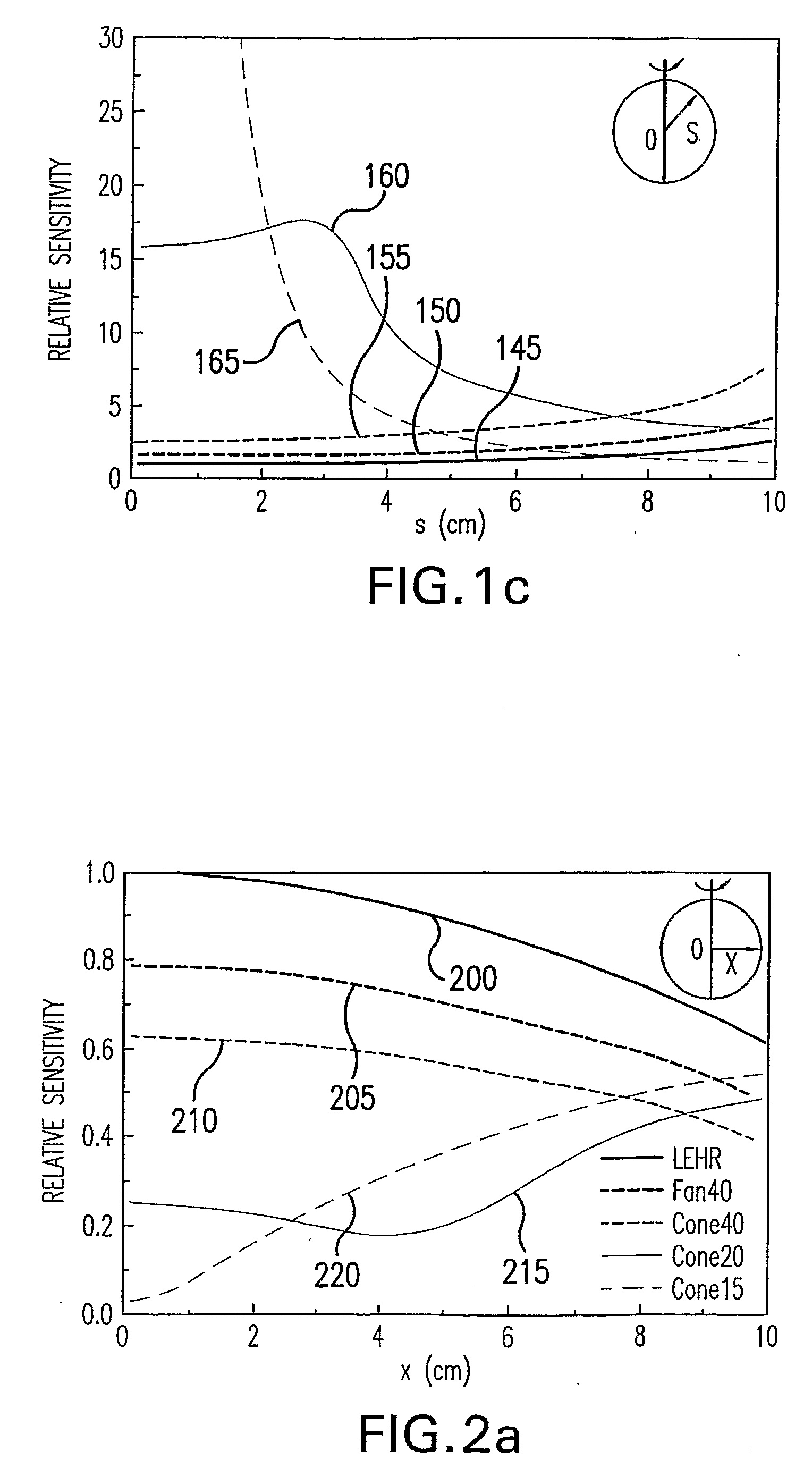
System and Method for Performing Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (Spect) with a Focal-Length Cone-Beam Collimation
InactiveUS20080302950A1Accurate estimateEasy to detectBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsRadiation/particle handlingBeam collimationField of view
A system and method are provided for obtaining data that may be used to generate images of a brain or other bodily organ. The system can include a pair of detecting arrangements and a collimating arrangement associated with each detecting arrangement. A first collimating arrangement can include a cone-beam collimating arrangement having a focal point located within the brain or other organ being imaged. A second collimating arrangement can include a fan-beam collimating arrangement having a focal length selected such that the organ being imaged lies within its field of view to ensure data sufficiency. Cone-beam collimating arrangements having improved hole geometries can also be utilized to provide further increases in imaging sensitivity.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
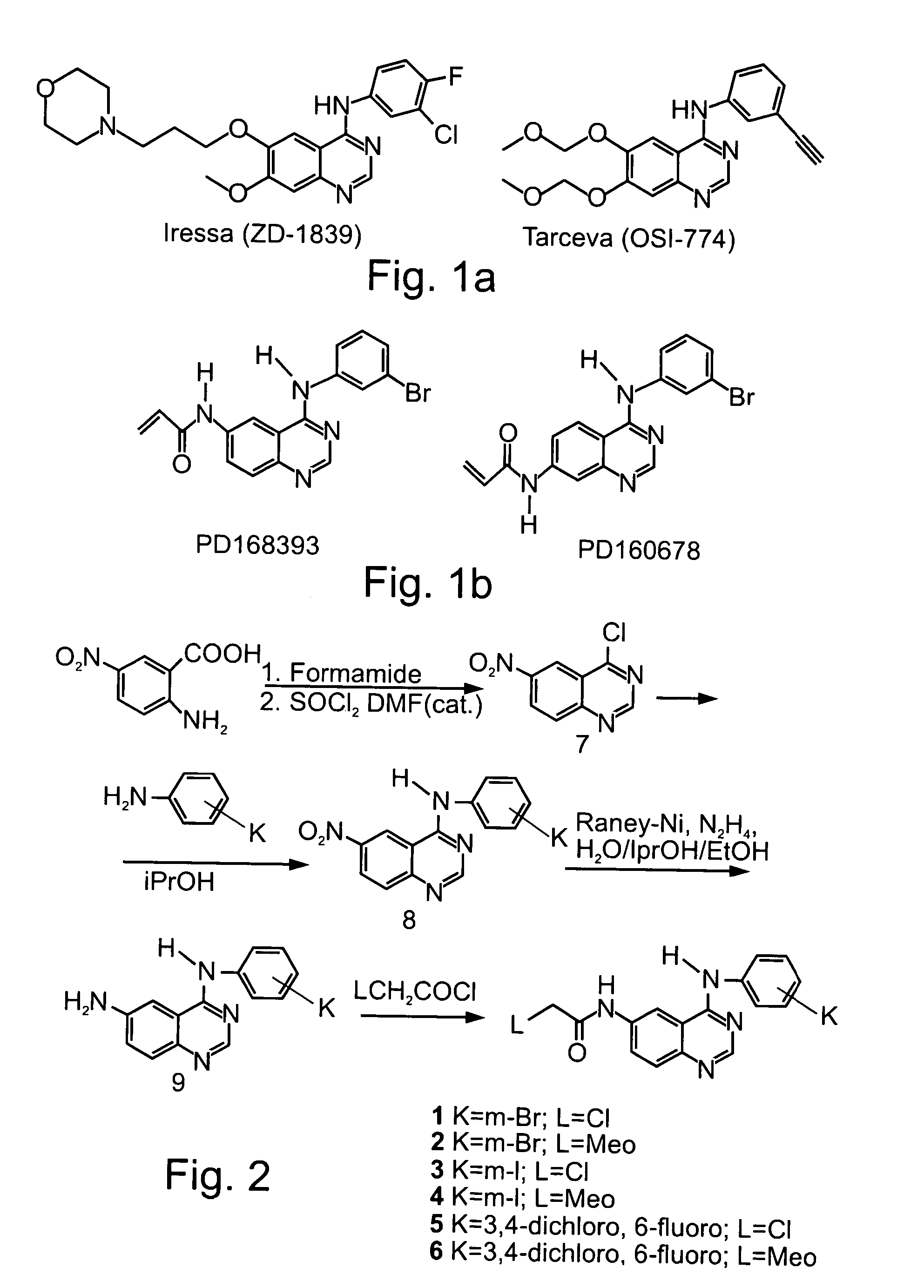
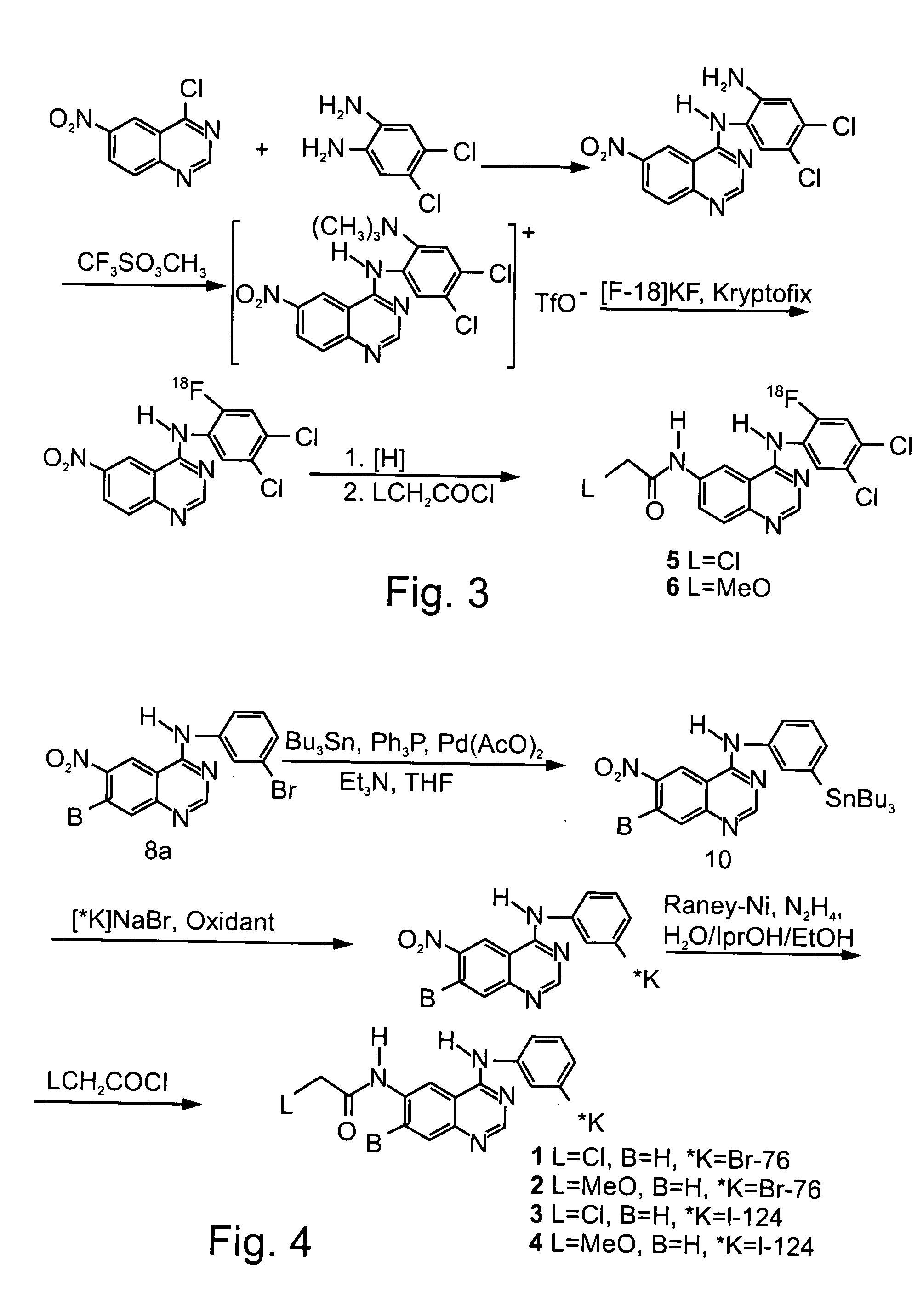
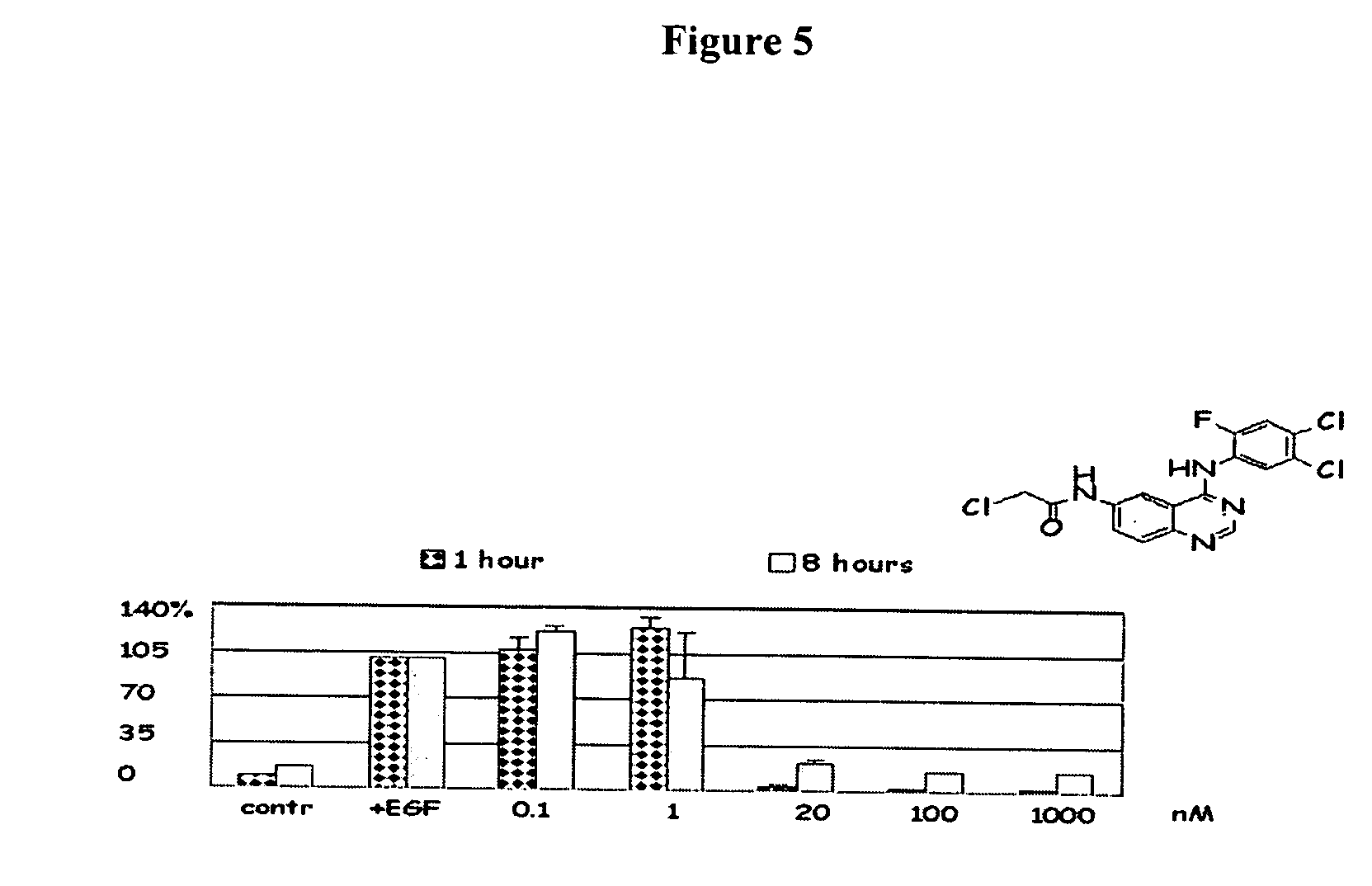
Radiolabeled irreversible inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase and their use in radioimaging and radiotherapy
InactiveUS6562319B2BiocideOrganic chemistryPositron emission tomographyEpidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD +1
Radiolabeled irreversible inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase and their use in radioimaging and radiotherapy
InactiveUS20020128553A1BiocideOrganic chemistryPositron emission tomographyEpidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase
Radiolabeled epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase (EGFR-TK) irreversible inhibitors and their use as biomarkers for medicinal radioimaging such as Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) and as radiopharmaceuticals for radiotherapy are disclosed.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD +1
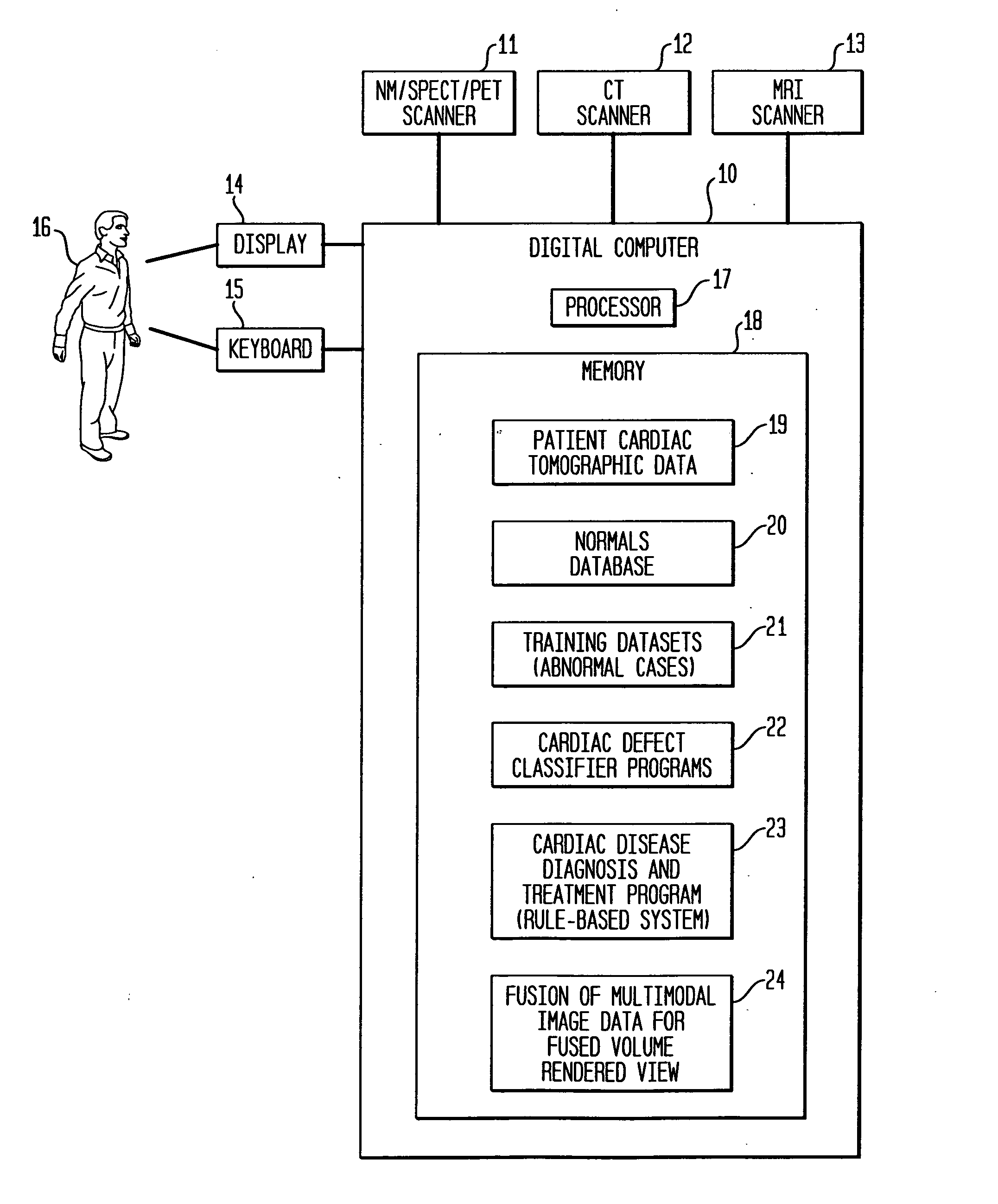
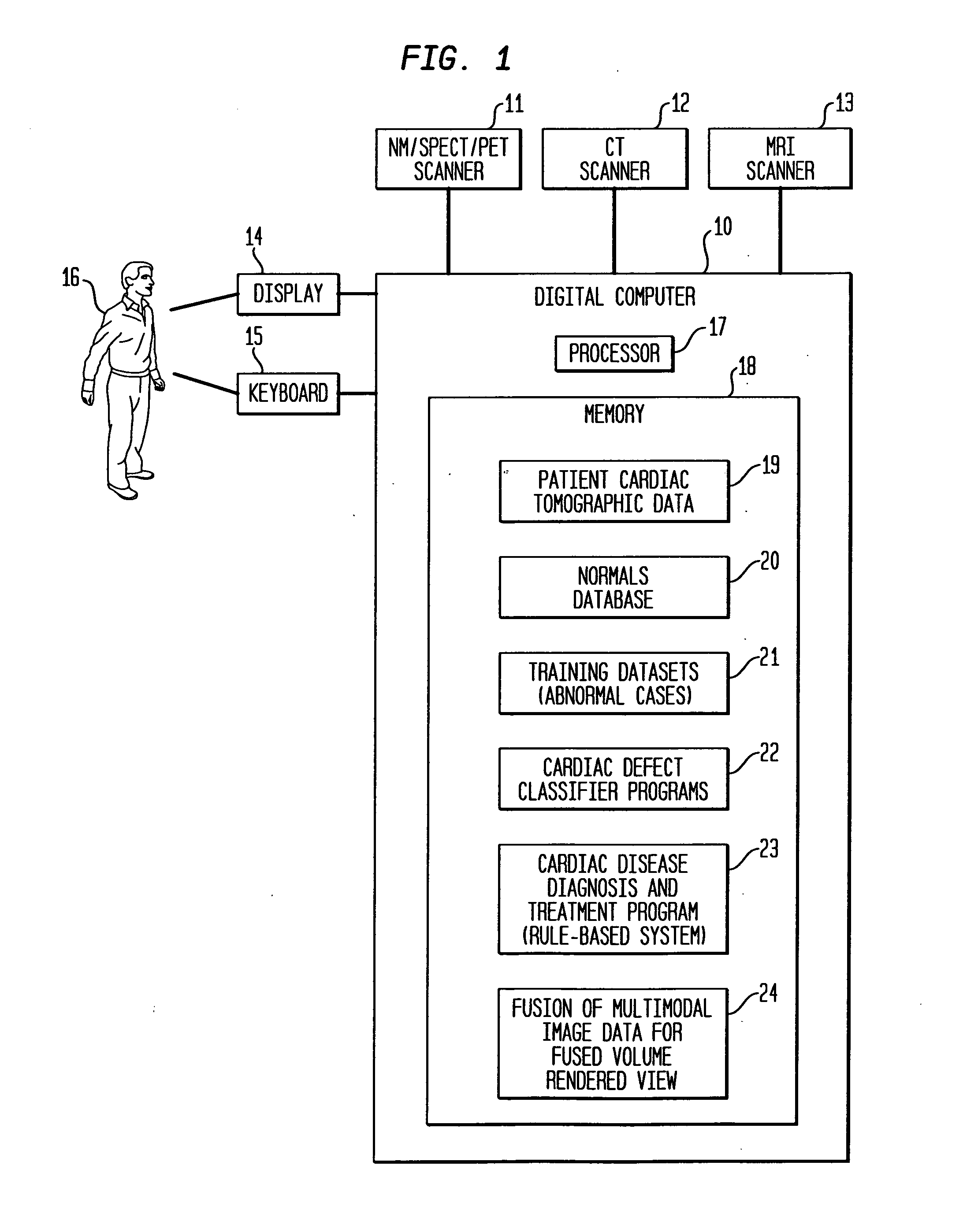
Dedicated display for processing and analyzing multi-modality cardiac data
For diagnosis and treatment of cardiac disease, images of the heart muscle and coronary vessels are captured using different medical imaging modalities; e.g., single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), positron emission tomography (PET), electron-beam X-ray computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or ultrasound (US). For visualizing the multi-modal image data, the data is presented using a technique of volume rendering, which allows users to visually analyze both functional and anatomical cardiac data simultaneously. The display is also capable of showing additional information related to the heart muscle, such as coronary vessels. Users can interactively control the viewing angle based on the spatial distribution of the quantified cardiac phenomena or atherosclerotic lesions.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
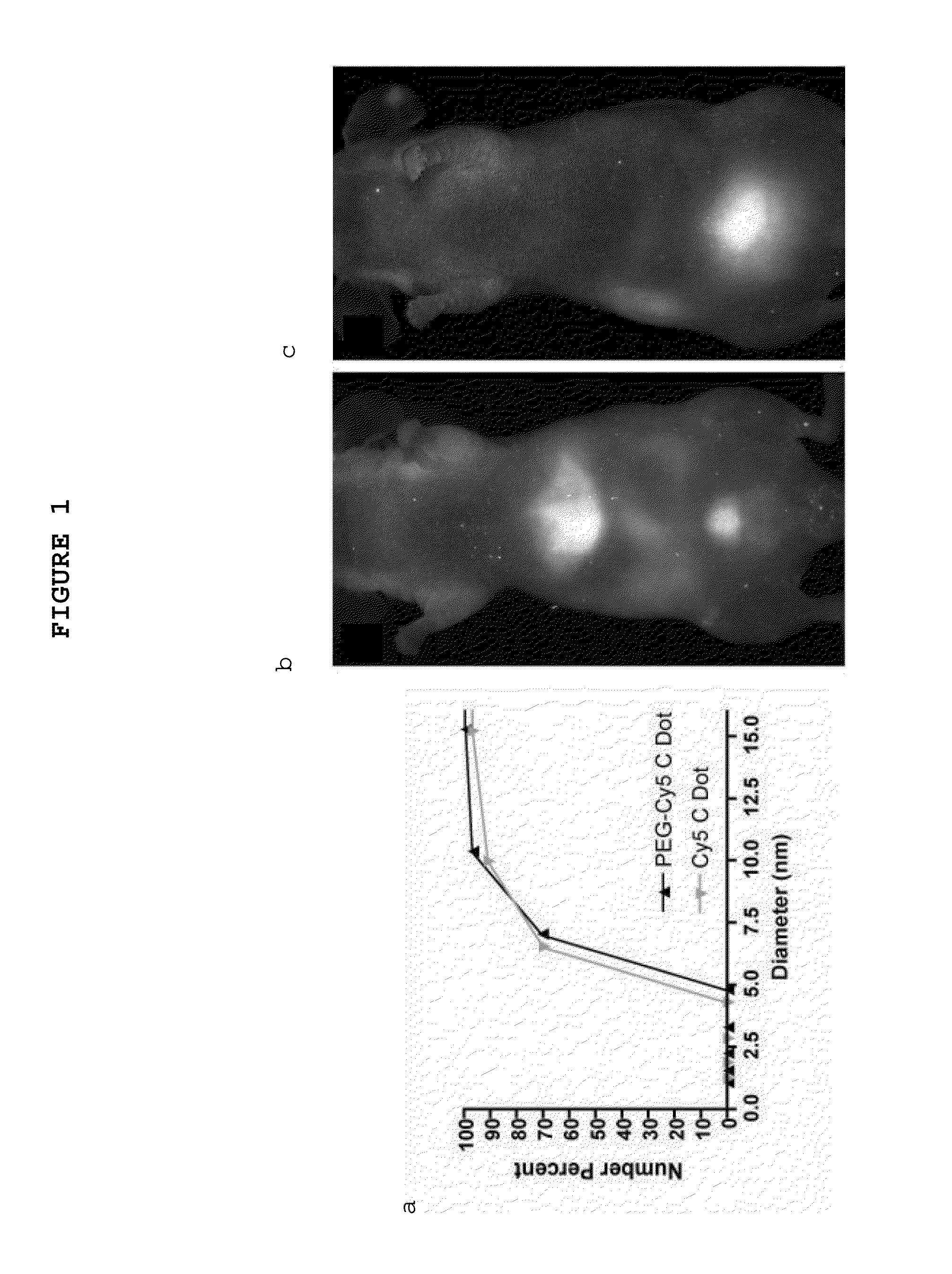
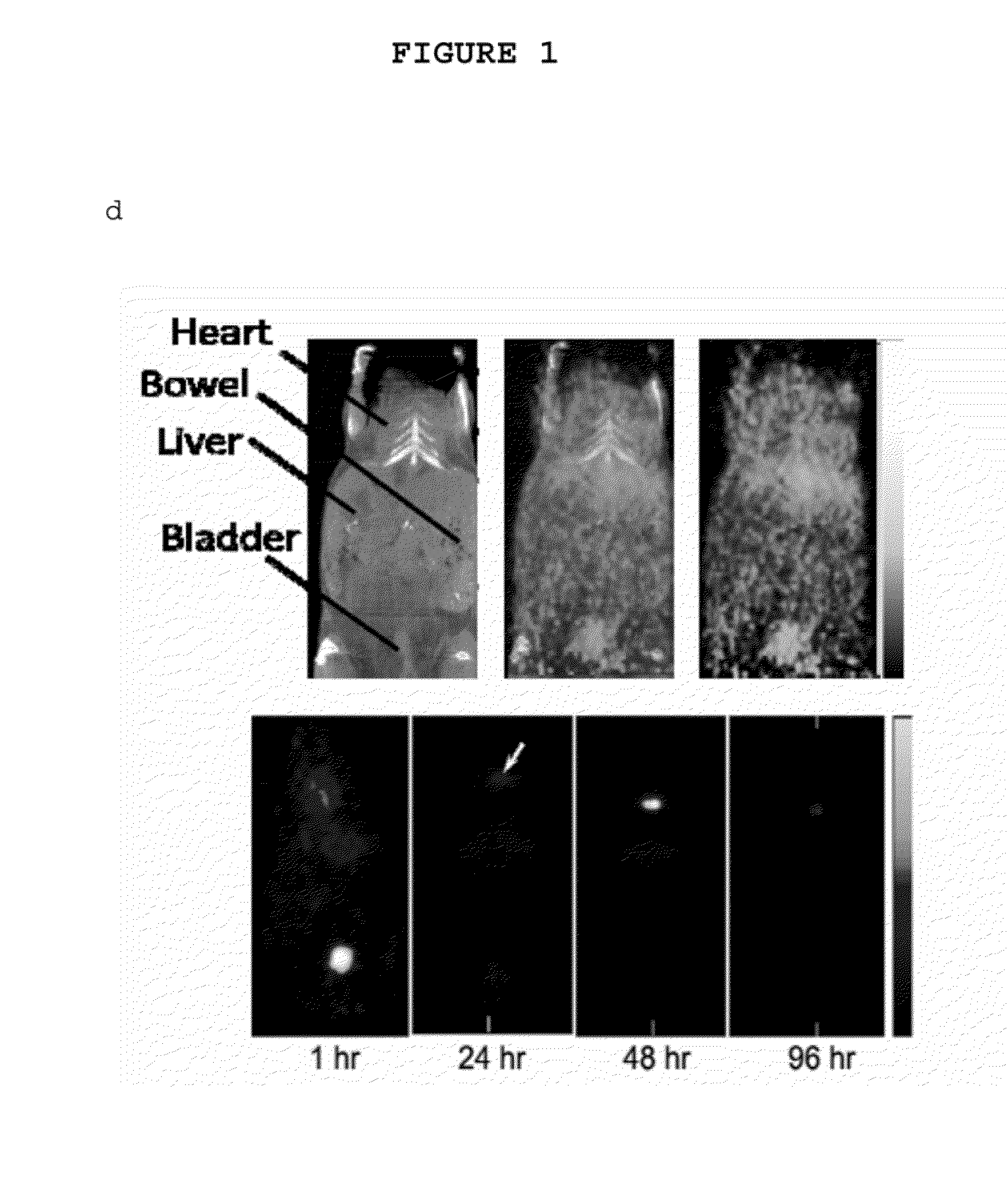
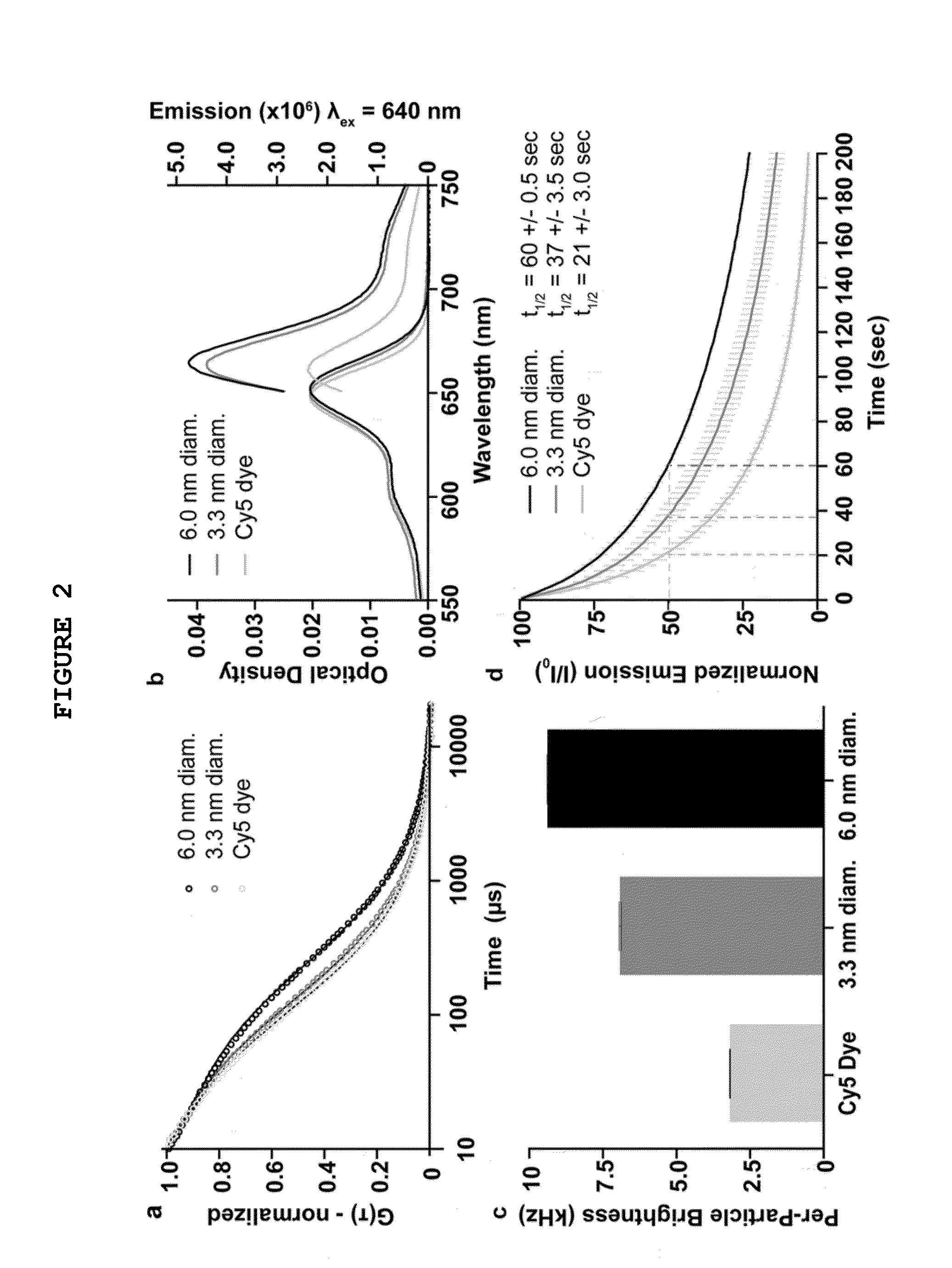
Multimodal silica-based nanoparticles
ActiveUS20140248210A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryCellular componentDisease
The present invention provides a fluorescent silica-based nanoparticle that allows for precise detection, characterization, monitoring and treatment of a disease such as cancer. The nanoparticle has a range of diameters including between about 0.1 nm and about 100 nm, between about 0.5 nm and about 50 nm, between about 1 nm and about 25 nm, between about 1 nm and about 15 nm, or between about 1 nm and about 8 nm. The nanoparticle has a fluorescent compound positioned within the nanoparticle, and has greater brightness and fluorescent quantum yield than the free fluorescent compound. The nanoparticle also exhibits high biostability and biocompatibility. To facilitate efficient urinary excretion of the nanoparticle, it may be coated with an organic polymer, such as poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG). The small size of the nanoparticle, the silica base and the organic polymer coating minimizes the toxicity of the nanoparticle when administered in vivo. In order to target a specific cell type, the nanoparticle may further be conjugated to a ligand, which is capable of binding to a cellular component associated with the specific cell type, such as a tumor marker. In one embodiment, a therapeutic agent may be attached to the nanoparticle. To permit the nanoparticle to be detectable by not only optical fluorescence imaging, but also other imaging techniques, such as positron emission tomography (PET), single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), computerized tomography (CT), bioluminescence imaging, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), radionuclides / radiometals or paramagnetic ions may be conjugated to the nanoparticle.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES +1
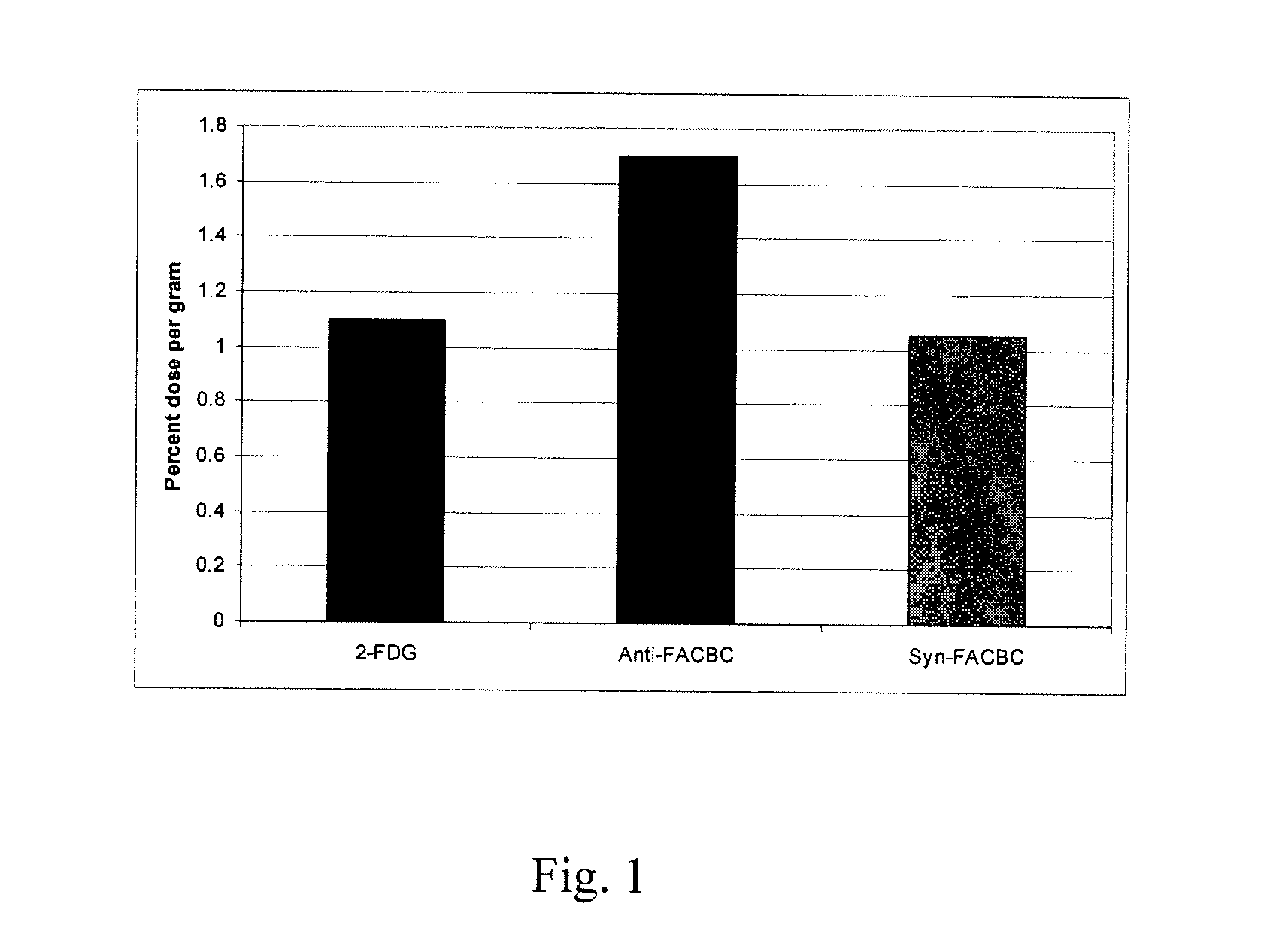
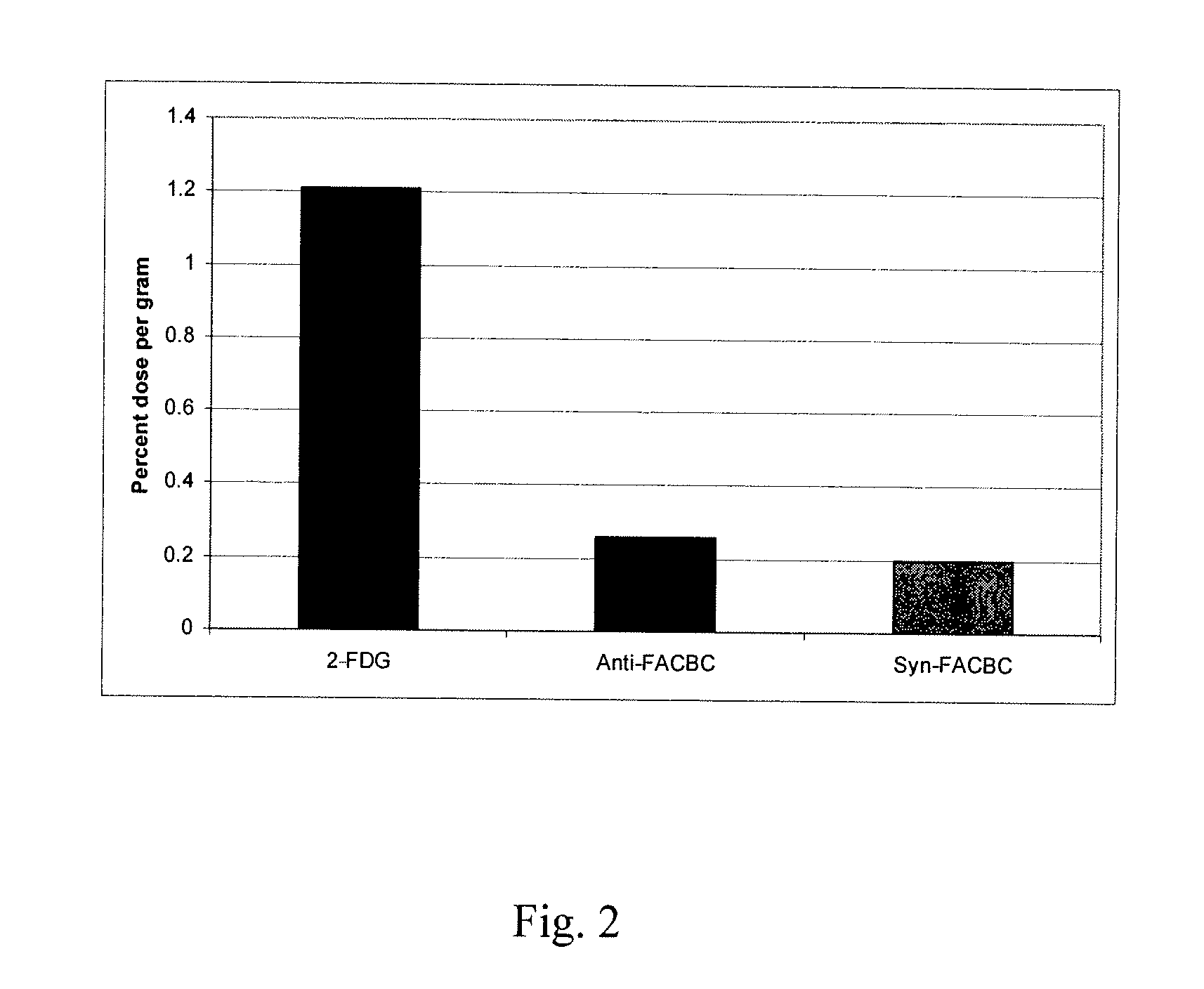
Stereoselective Synthesis of Amino Acid Analogs for Tumor Imaging
InactiveUS20060292073A1Maximum service lifeOrganic compound preparationSulfonic acid esters preparation1-amino-3-fluorocyclobutane-1-carboxylic acidCyclobutane
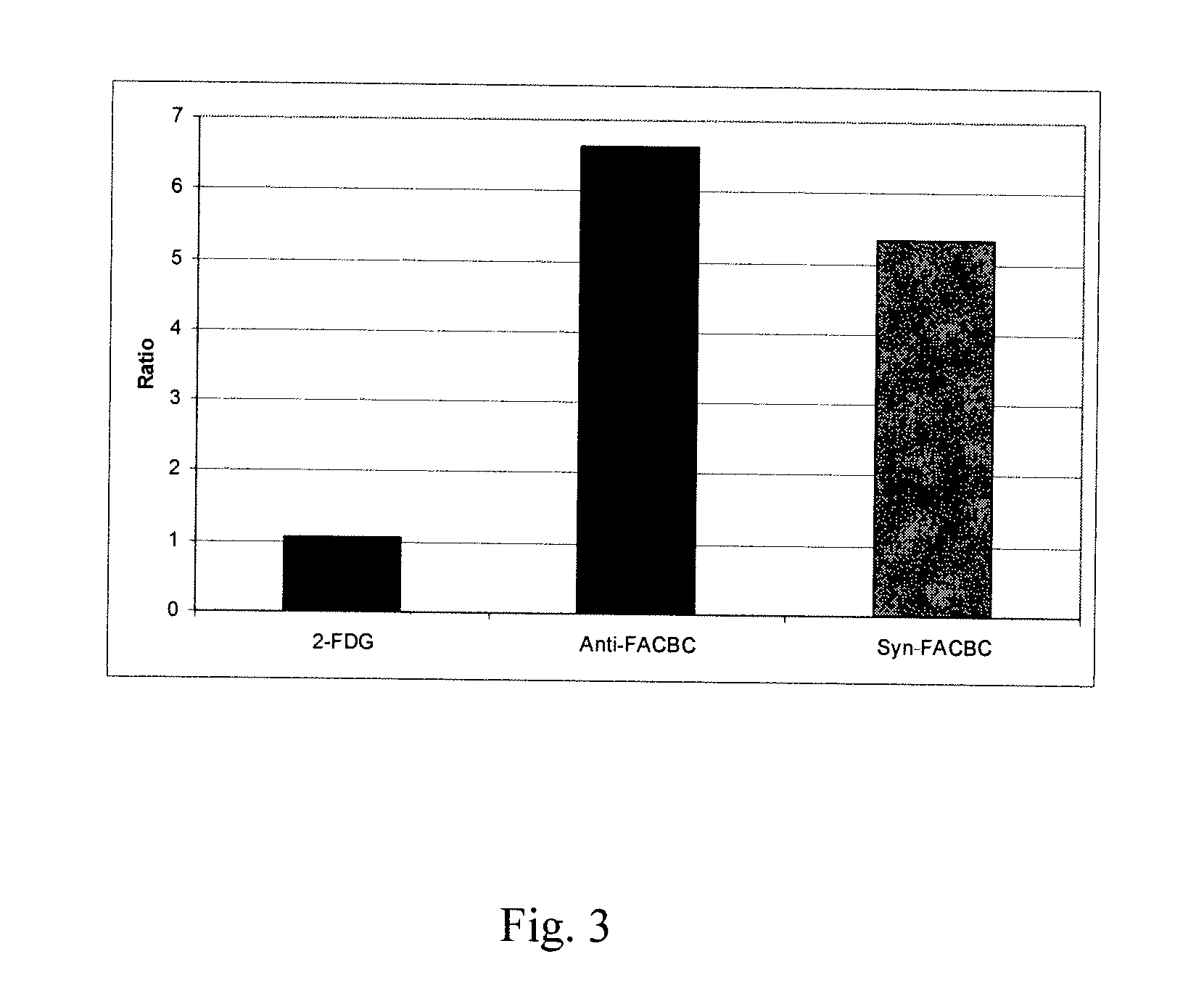
The radiolabeled non-natural amino acid 1-amino-3-cyclobutane-1-carboxylic acid (ACBC) and its analogs are candidate tumor imaging agents useful for positron emission tomography and single photon emission computed tomography due to their selective affinity for tumor cells. The present invention provides methods for stereo-selective synthesis of syn-ACBC analogs. The disclosed synthetic strategy is reliable and efficient and can be used to synthesize a gram quantity of various syn-isomers of the ACBC analogs, particularly, syn-[18F]-1-amino-3-fluorocyclobutane-1-carboxylic acid (FACBC) and syn-[123I]-1-amino-3-iodocyclobutane-1-carboxylic (IACBC) acid analogs.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
PSMA-binding agents and uses thereof
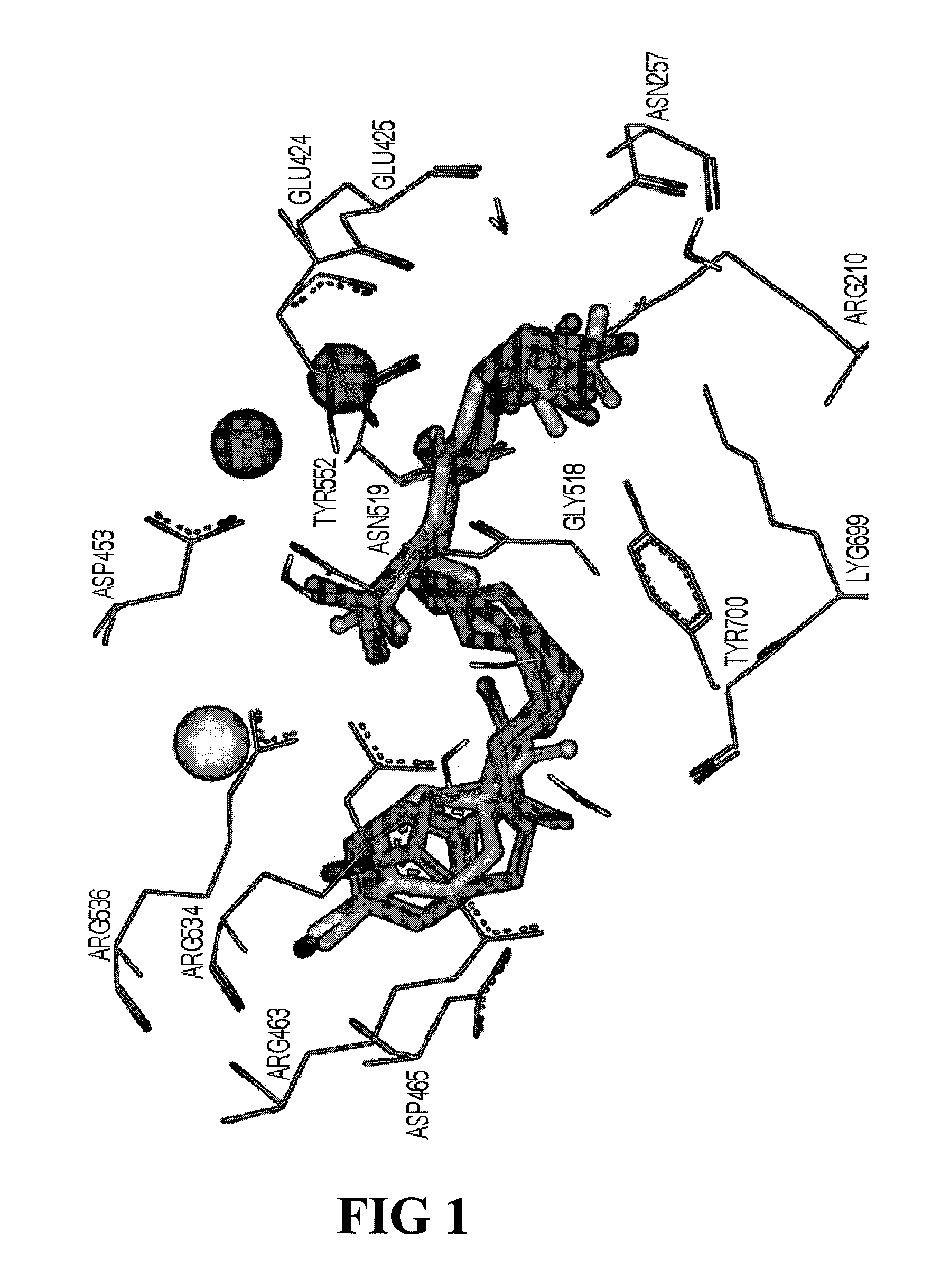
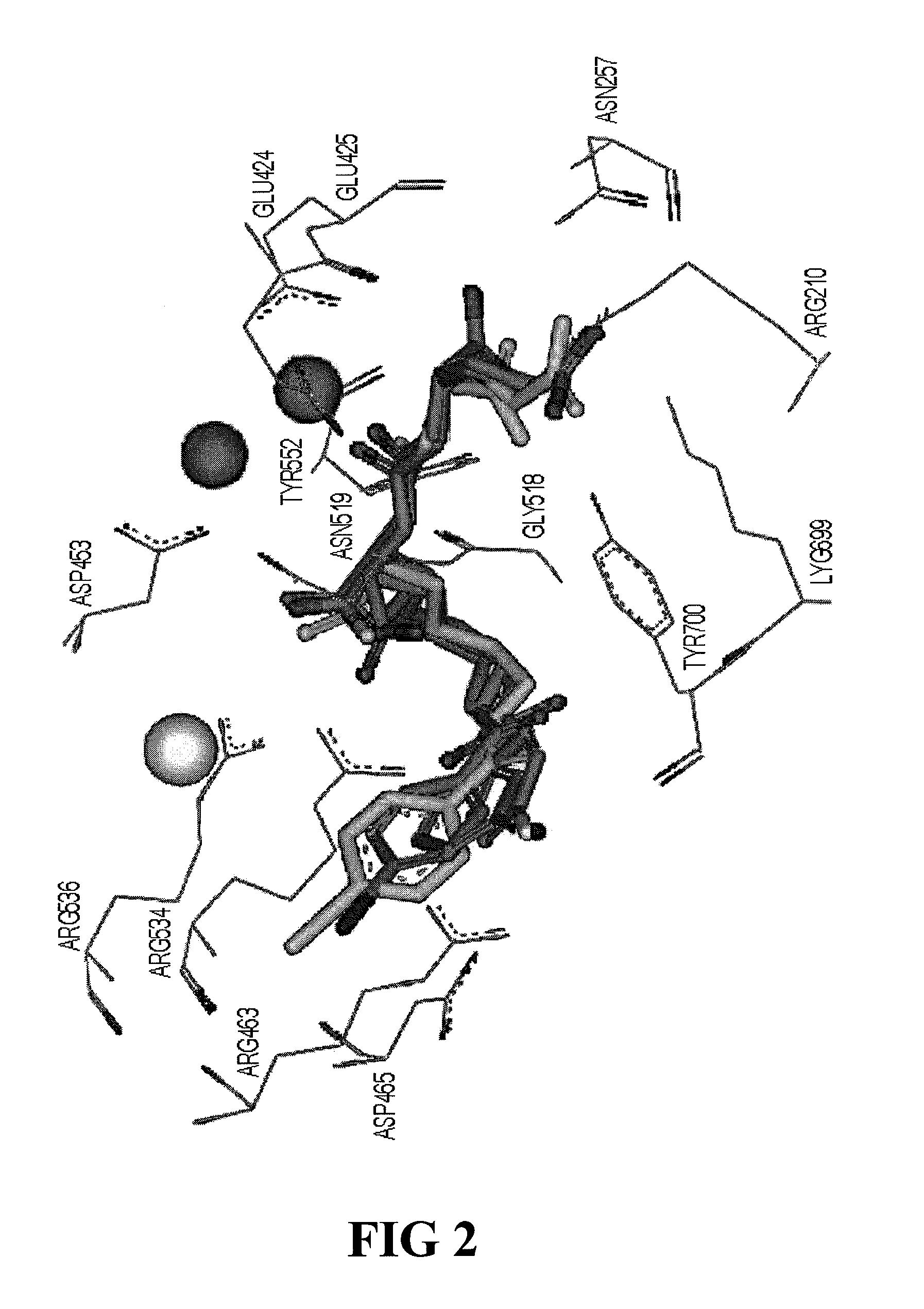
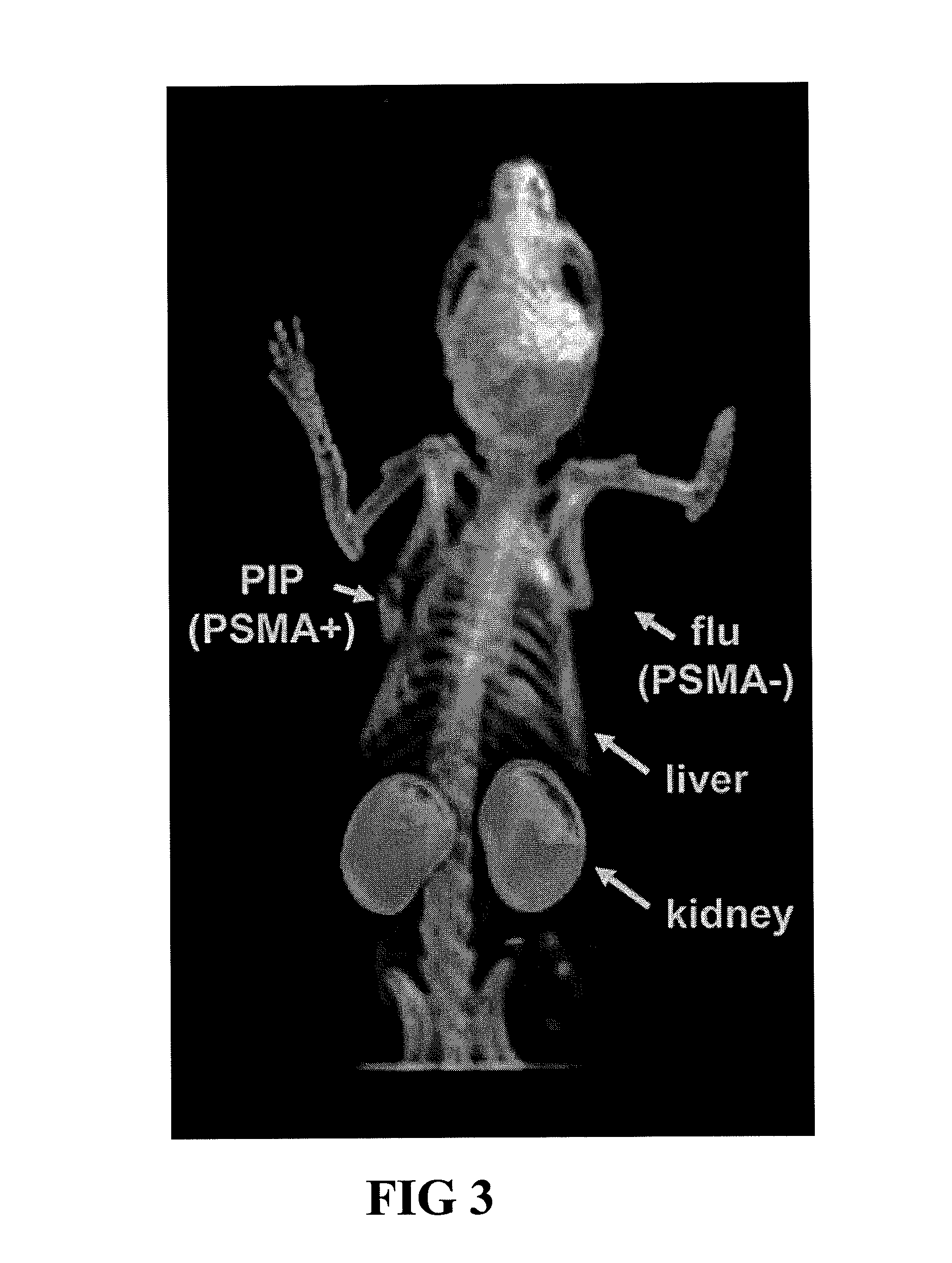
ActiveUS8778305B2Satisfies long standing and unmetSharp contrastGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsProstate cancer cellAntigen
Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) binding compounds having radioisotope substituents are described, as well as chemical precursors thereof. Compounds include pyridine containing compounds, compounds having phenylhydrazine structures, and acylated lysine compounds. The compounds allow ready incorporation of radionuclides for single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET) for imaging, for example, prostate cancer cells and angiogenesis.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
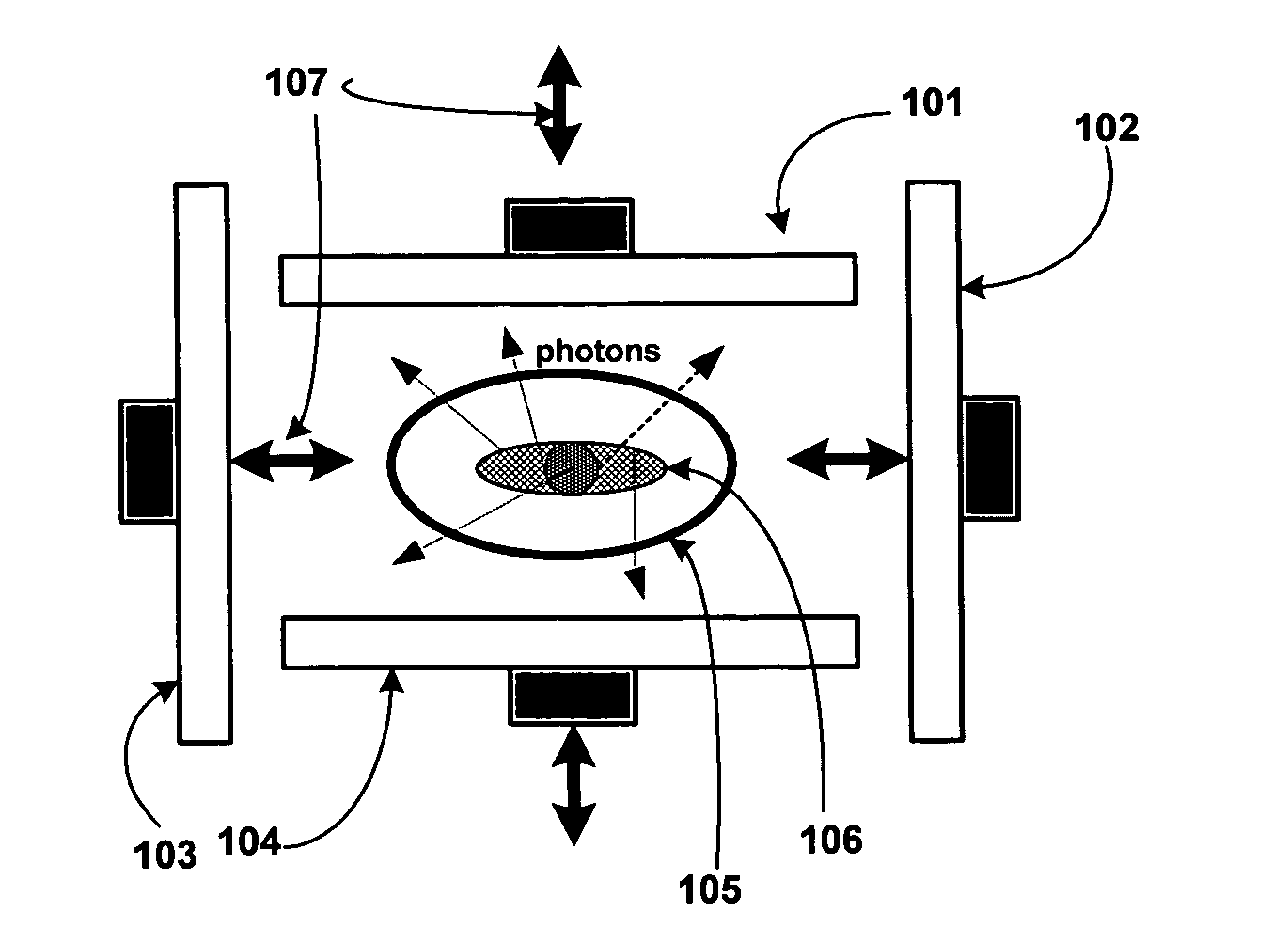
Single photon emission computed tomography system
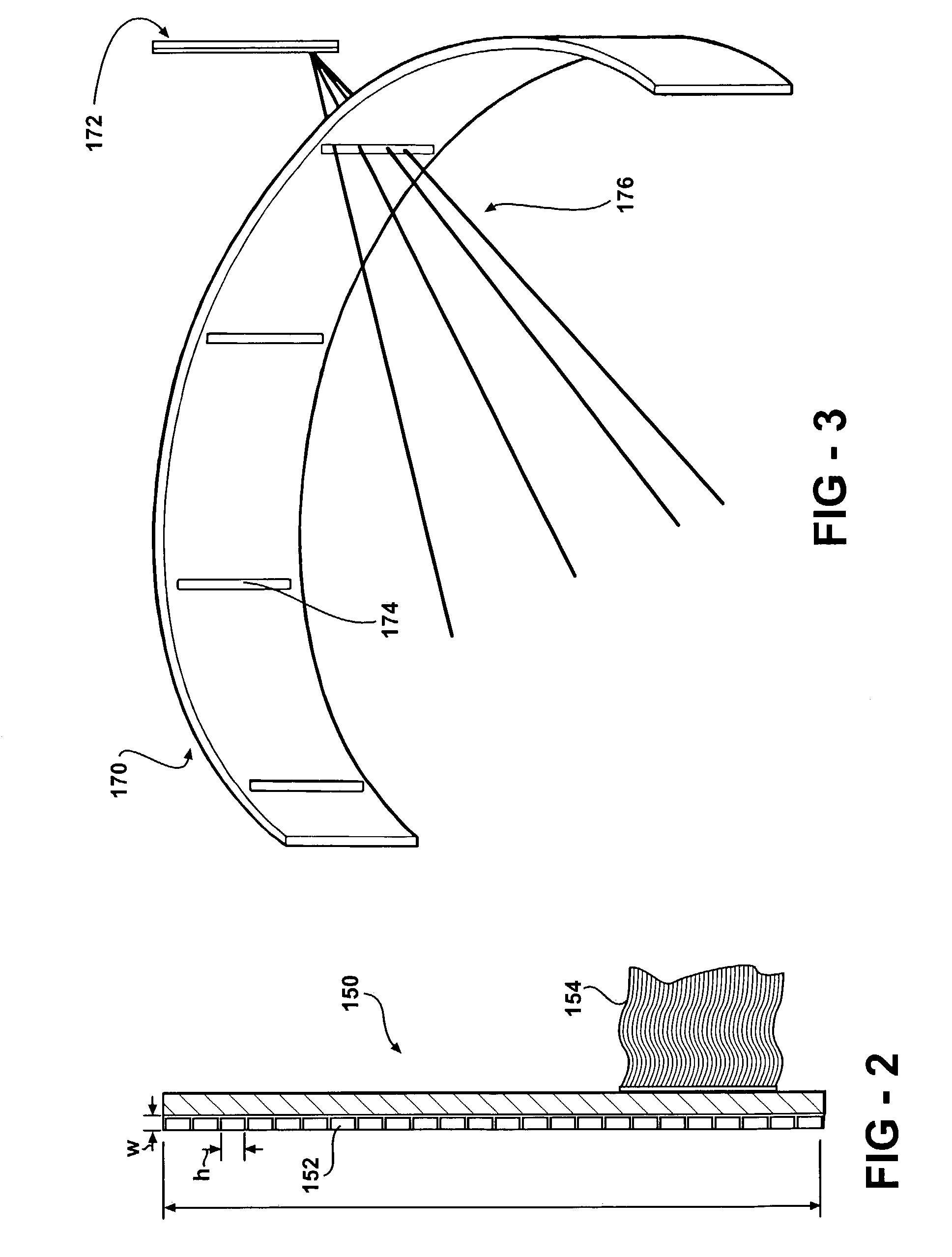
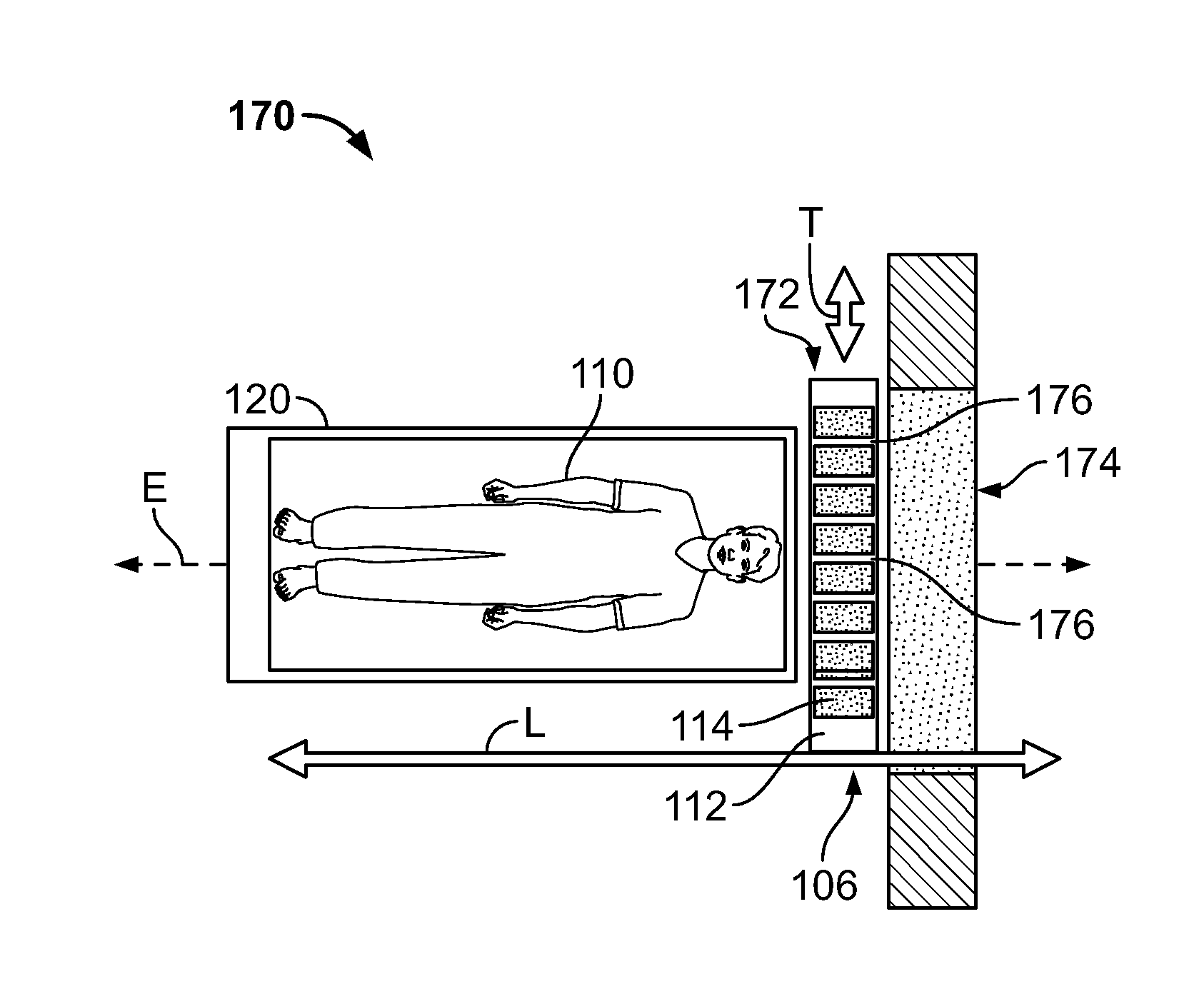
InactiveUS20050001170A1Handling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansPhoton attenuationField of view
A single photon emission computed tomography system includes a base for supporting a patient and a detector assembly adjacent the field of view. The detector assembly detects photon strikes from the field of view. A photon-blocking member is disposed between the field of view and the detector and has an aperture slot that allows passage of photons aligned with the slot. A collimating assembly includes a plurality of collimating vanes formed of photon-attenuating material. A support assembly supports the collimating assembly and includes a first support member and a second support member with the collimating assembly being disposed therebetween. An adjustment assembly includes a first adjuster operable to adjust a first distance between the collimating assembly and the first support member and a second adjuster operable to adjust a second distance between the collimating assembly and the second support member.
Owner:HIGHBROOK HLDG
Slit-slat collimation
ActiveUS7831024B2Handling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansImage resolutionSingle-photon emission computed tomography
This invention is directed to a collimator and collimation techniques. Specifically, the invention is directed to a collimator and method for collimation wherein the collimator combines the resolution and sensitivity properties of pinhole Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) imaging with the 2D complete-sampling properties of fan-beam collimators.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Fast dynamic imaging protocol using a multi-head single photon emission computed tomography system
ActiveUS7468513B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPhoton emissionData acquisition
An imaging system for acquiring multi-dimensional tomographic image data of an object, the imaging system having (1) a plurality of detectors to acquire image data, the detectors coupled to a supporting structure, wherein at least one of the detectors is adapted to move relative to the object during image data acquisition and wherein the detectors are adapted to rotate independently of each other, provided that image data from the detectors are collected concomitantly during a study time and (2) a data analyzer adapted to acquire and / or reconstruct the image data.
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
Psma-binding agents and uses thereof
ActiveUS20110142760A1Satisfies long standingSharp contrastUrea derivatives preparationGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsAntigenProstate cancer cell
Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) binding compounds having radioisotope substituents are described, as well as chemical precursors thereof. Compounds include pyridine containing compounds, compounds having phenylhydrazine structures, and acylated lysine compounds. The compounds allow ready incorporation of radionuclides for single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET) for imaging, for example, prostate cancer cells and angiogenesis.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
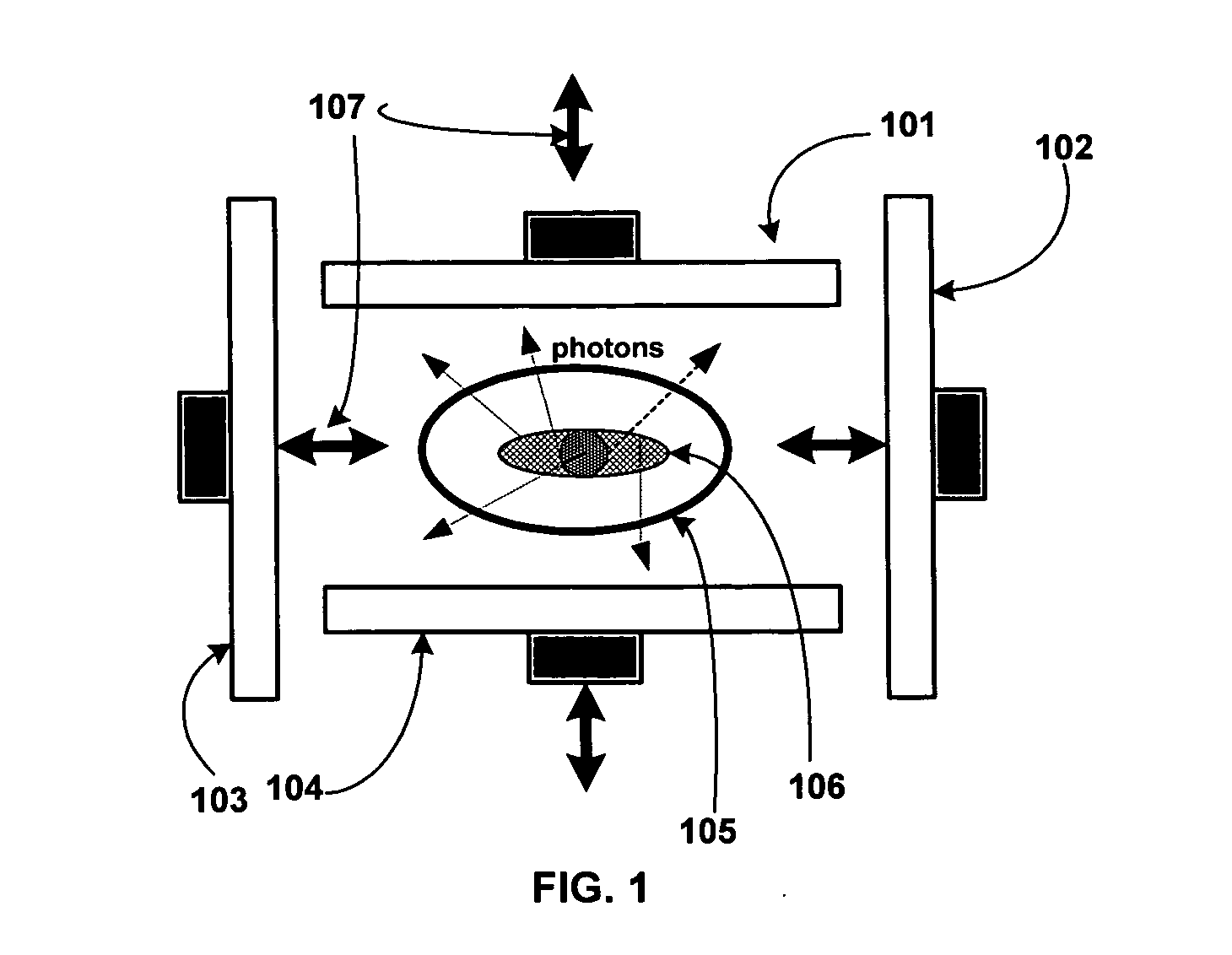
Single photon emission computed tomography system
InactiveUS20050056788A1Handling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansPhoton attenuationField of view
A single photon emission computed tomography system includes a base for supporting a patient and a detector assembly adjacent the field of view. The detector assembly detects photon strikes from the field of view. A photon-blocking member is disposed between the field of view and the detector and has an aperture slot that allows passage of photons aligned with the slot. A collimating assembly includes a plurality of collimating vanes formed of photon-attenuating material. A support assembly supports the collimating assembly and includes a first support member and a second support member with the collimating assembly being disposed therebetween. An adjustment assembly includes a first adjuster operable to adjust a first distance between the collimating assembly and the first support member and a second adjuster operable to adjust a second distance between the collimating assembly and the second support member.
Owner:HIGHBROOK HLDG
Multimodal imaging sources
A multimodal source for imaging with at least one of a gamma camera, a positron emission tomography (PET) scanner and a single-photon-emission computed tomography (SPECT) scanner, and at least one of a computed tomography (CT) scanner, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner and optical scanner. The multimodal source has radioactive material permanently incorporated into a matrix of material, at least one of a material that is a target for CT, MRI and optical scanning, and a container which holds the radioactive material and the CT, MRI and / or optical target material. The source can be formed into a variety of different shapes such as points, cylinders, rings, squares, sheets and anthropomorphic shapes. The material that is a target for gamma cameras, PET scanners and SPECT scanners and / or CT, MRI and / or optical scanners can be formed into shapes that mimic biological structures.
Owner:ISO SCI LAB
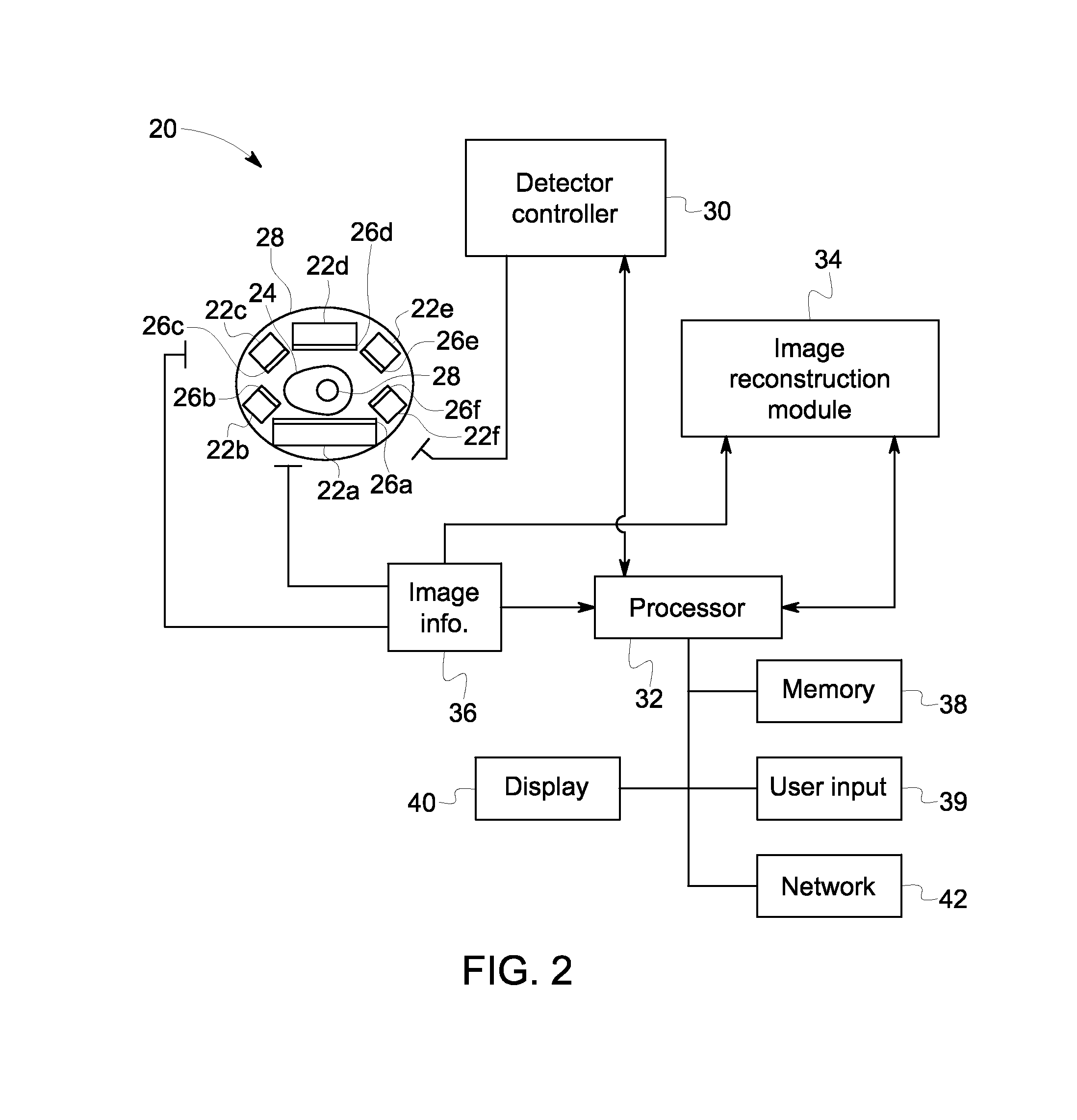
Nuclear medicine imaging system and method using multiple types of imaging detectors
ActiveUS20120248320A1Material analysis by optical meansTomographyHelical computed tomographyNuclear medicine imaging
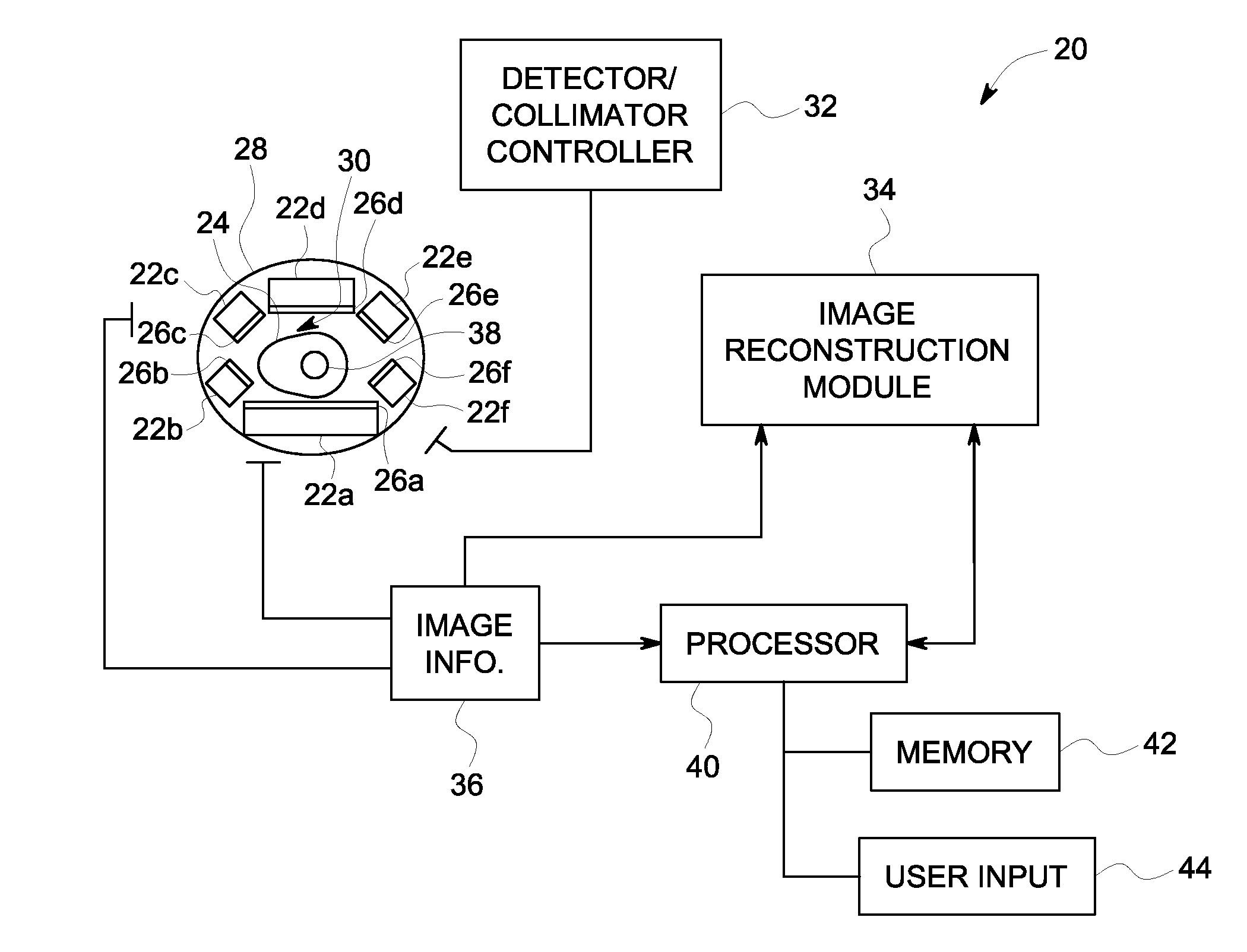
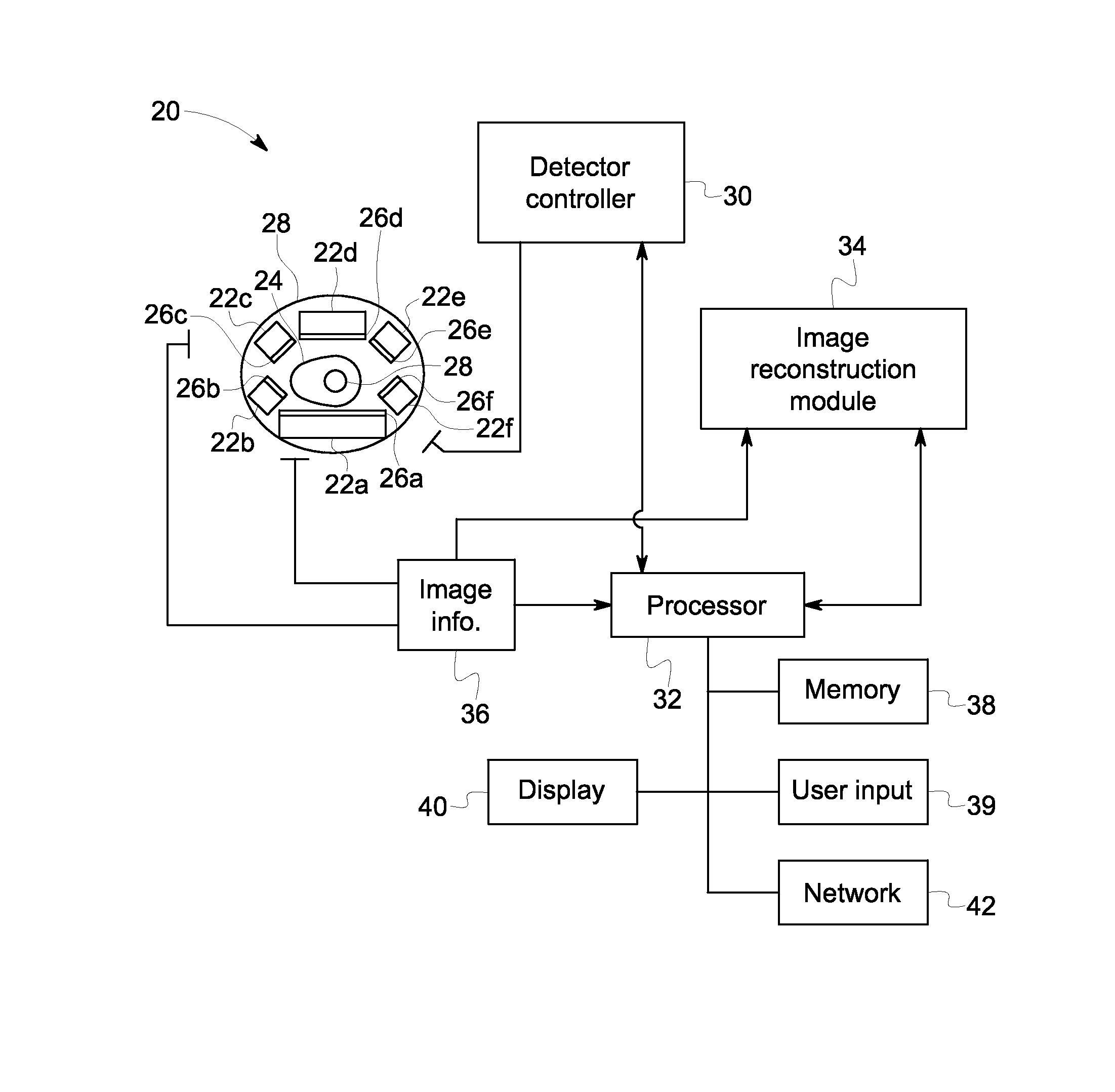
A Nuclear Medicine (NM) imaging system and method using multiple types of imaging detectors are provided. One NM imaging system includes a gantry, at least a first imaging detector coupled to the gantry, wherein the first imaging detector is a non-moving detector, and at least a second imaging detector coupled to the gantry, wherein the second imaging detector is a moving detector. The first imaging detector is larger than the second imaging detector and the first and second imaging detectors have different detector configurations. The NM imaging system further includes a controller configured to control the operation of the first and second imaging detectors during an imaging scan of an object to acquire Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) image information such that at least the first imaging detector remains stationary with respect to the gantry during image acquisition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for high-sensitivity Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography
ActiveUS20110073763A1Facilitates higher qualityAccurate clinical diagnosisMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPhoton emissionSystem matrix
A method and apparatus are disclosed for high-sensitivity Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT), and Positron Emission Tomography (PET). The apparatus includes a two-dimensional (2D) gamma detector array that, unlike a conventional SPECT machine, moves to different positions in a three-dimensional (3D) volume space near an emission source and records a data vector g which is a measure of gamma emission field. In particular, the 3D volume space in which emission data g is measured extends substantially along a radial direction r pointing away from the emission source, and unlike a conventional SPECT machine, each photon detector element in the 2D gamma detector array is provided with a very large collimator aperture. Data g is related to the 3D spatial density distribution f of the emission source, noise vector n, and a system matrix H of the SPECT / PET apparatus through the linear system of equations g=Hf+n. This equation is solved for f by a method that reduces the effect of noise.
Owner:SUBBARAO MURALIDHARA
Multi-mode little animal molecular image imaging device and imaging method
ActiveCN102764138AImage results are accurateImage results are reliableComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringDiagnostic Radiology ModalityData acquisition
The invention discloses a multi-mode little animal molecular image imaging device and an imaging method thereof. The device comprises an X-ray computer tomography (CT) system, a positron emission tomography (PET) system, a single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) system, a fluorescence molecular tomography (FMT) system, a rotating rack system, a little animal bed system, a data acquisition system and a computer, various imaging systems are sampled and stored by the data acquisition system through a data line into the computer, and various imaging systems share one little animal bed system and the same inspection shaft. According to the multi-mode little animal molecular image imaging device and the imaging method, various imaging systems share one little animal bed system and the same inspection shaft, an installing fusion molecular medicine image of four modes of X-ray CT, PET, SPECT and FMT can achieve complementary advantages of different image devices, and the obtained image result is accurate and reliable.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
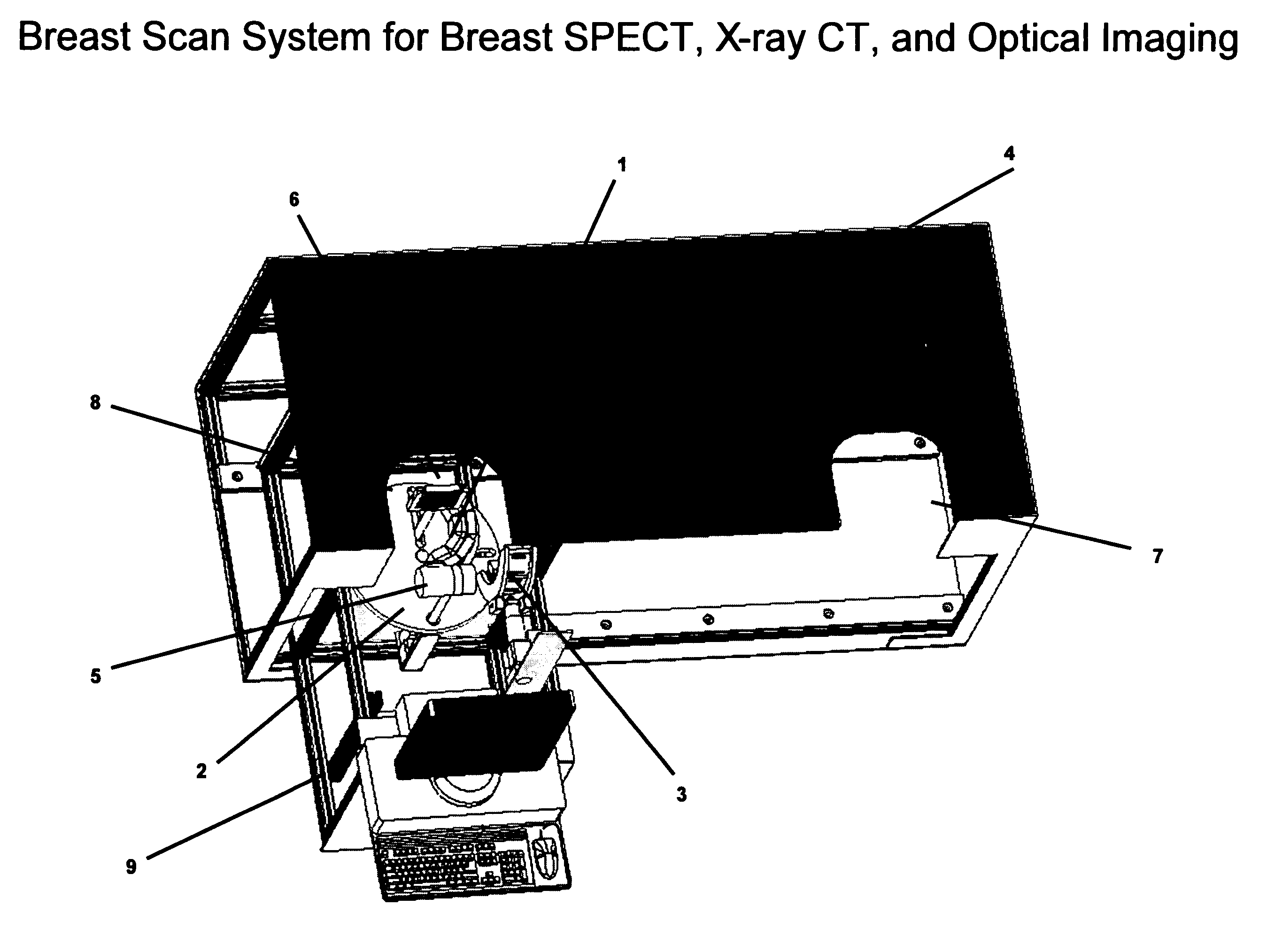
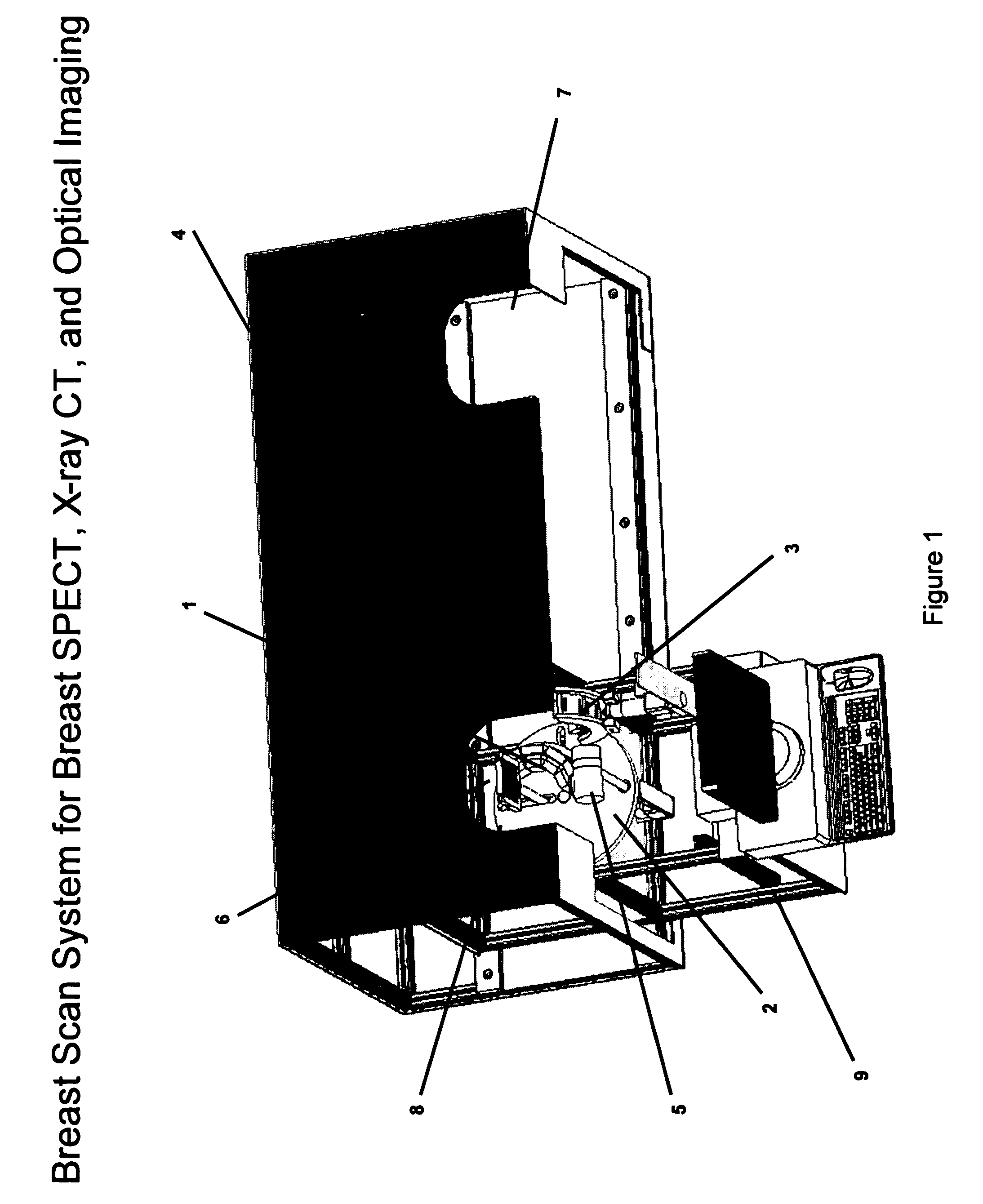
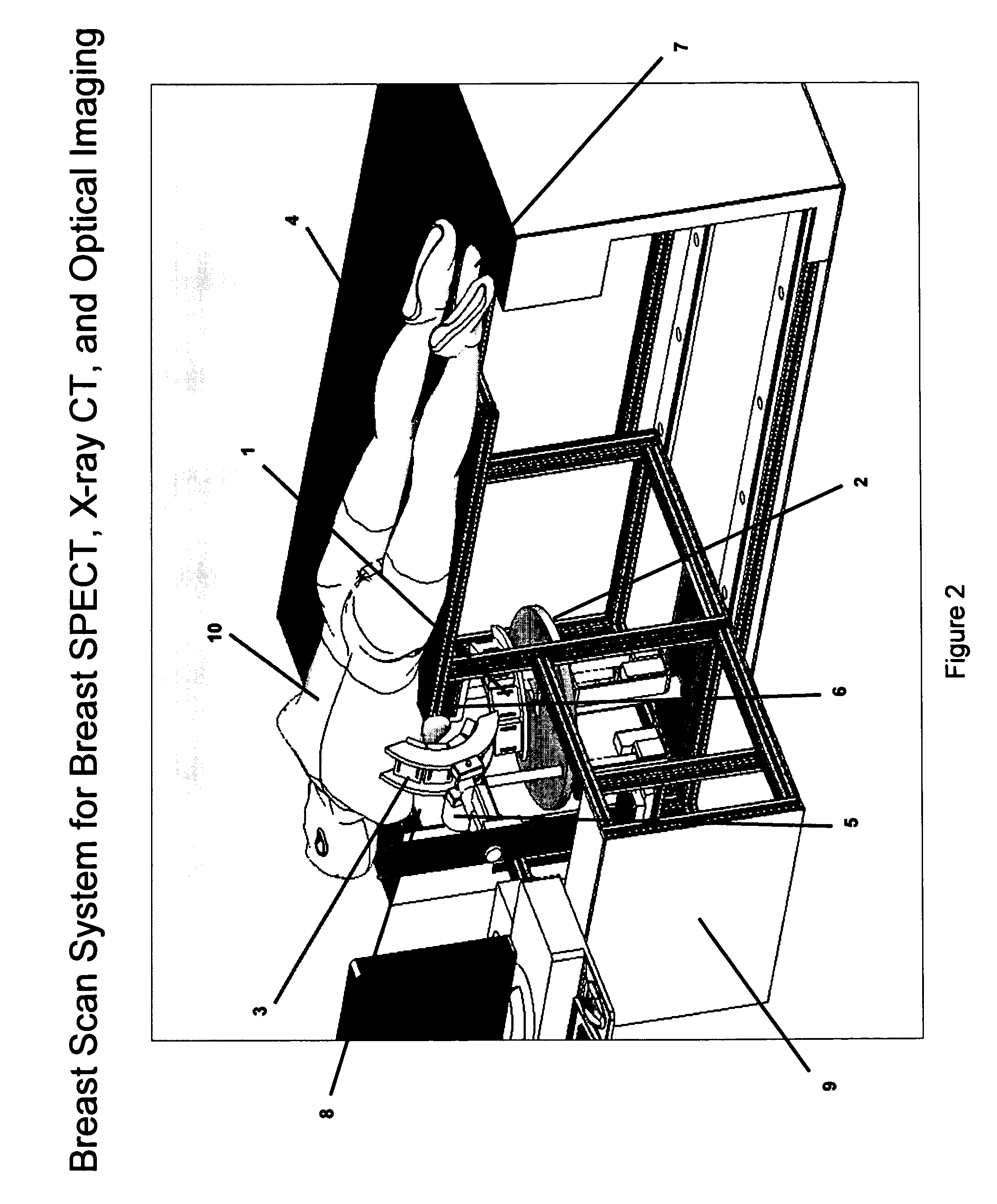
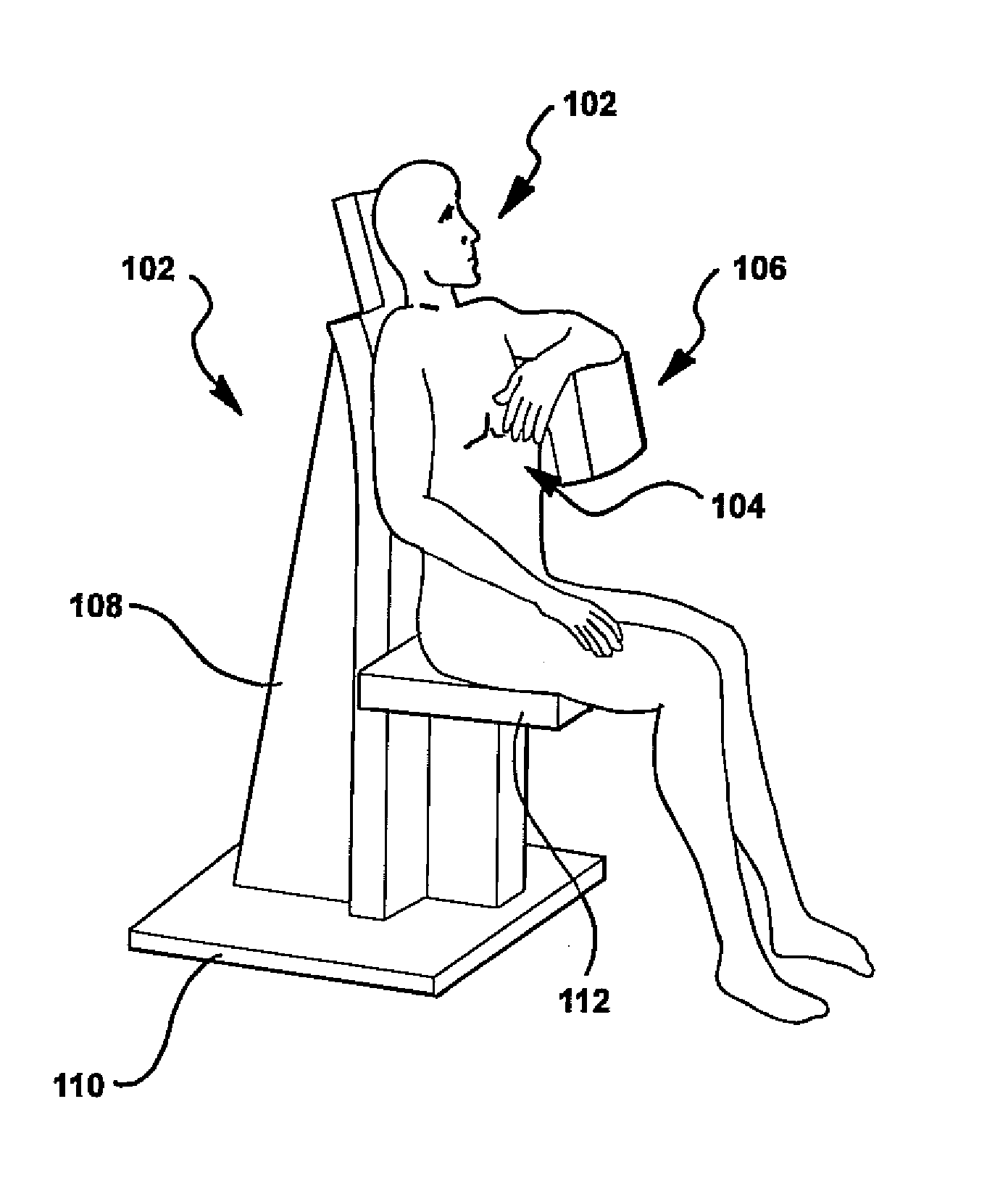
Breast diagnostic apparatus for fused SPECT, PET, x-ray CT, and optical surface imaging of breast cancer
InactiveUS20060239398A1Improve spatial resolutionImprove system capabilitiesDiagnostics using lightPatient positioning for diagnosticsOptical reflectionImage-Guided Therapy
A new method of breast imaging to improve the detection of cancer during early stages of development is disclosed. The system combines molecular images of radioisotope uptake in cancerous cells with three dimensional high resolution single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), positron emission tomography (PET), x-ray computed tomography (CT) and optical reflectance and emission (ORE) images of the breast. The system acquires data from nuclear isotopes within the breast and processes the data into three dimensional molecular tomographic images of cancerous cellular activity, morphological three dimensional x-ray density tomographic images and three dimensional optical surface images. These three sets of images or data are then combined to provide information as to the sensitivity and specificity as to the type of cancer present, three dimensional information as to the physical location of the cancer and reference information for radiologists, surgeons, oncologists and patients in order to plan stereo-tactic biopsy, minimally invasive surgery and image guided therapy, if necessary.
Owner:FUSED MULTIMODALITY IMAGING
Single photon emission computed tomography system
InactiveUS20070007455A1Material analysis by optical meansTomographyPhoton attenuationPhoton emission
A single photon emission computed tomography system includes a detector assembly adjacent a field of view and a collimating assembly disposed between the detector assembly and the field of view. The collimating assembly includes at least two spaced-apart collimating vanes of photon-attenuating material. The system further includes a photon-blocking member disposed between the field of view and the detector. The blocking member has an aperture defined therethrough. The system further includes a mask disposed adjacent the detector assembly having at least one aperture defined therethrough. A displacement actuator moves the photon-blocking member relative to the detector assembly.
Owner:HIGHBROOK HLDG
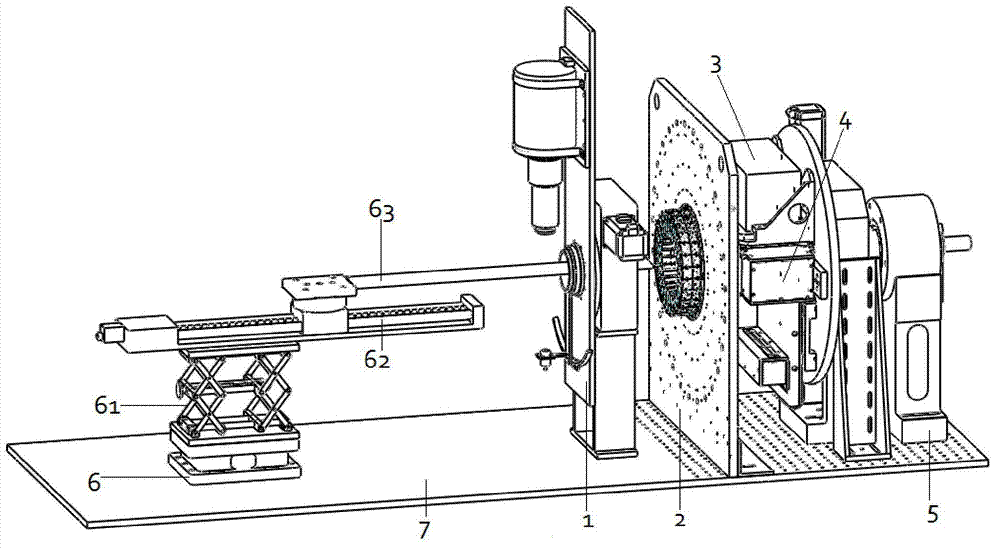
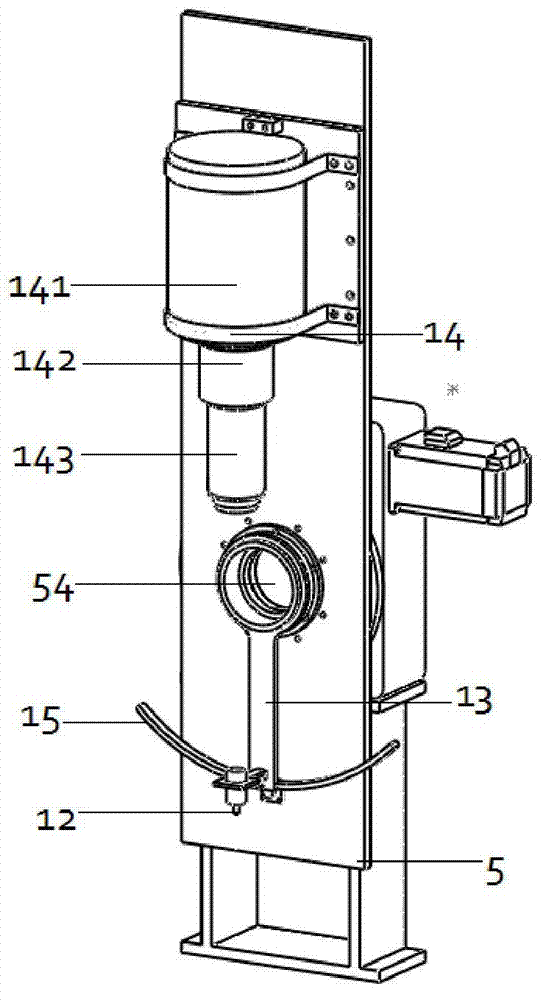
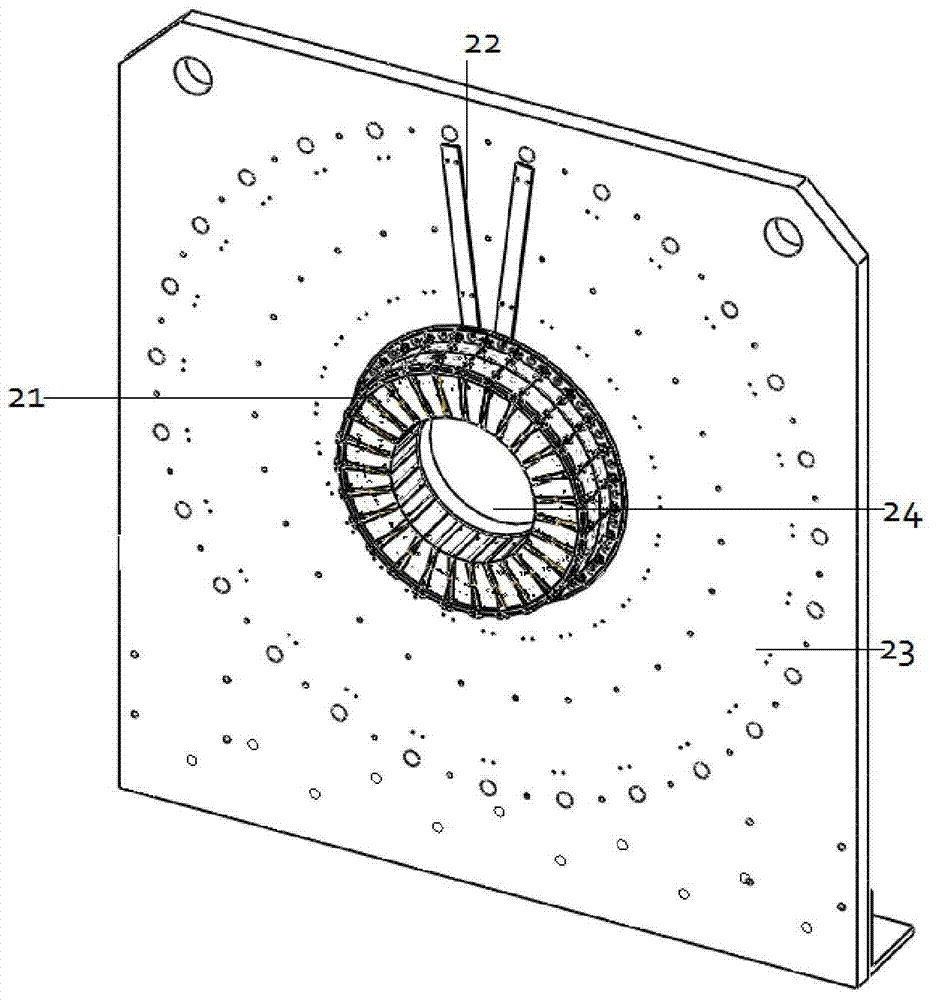
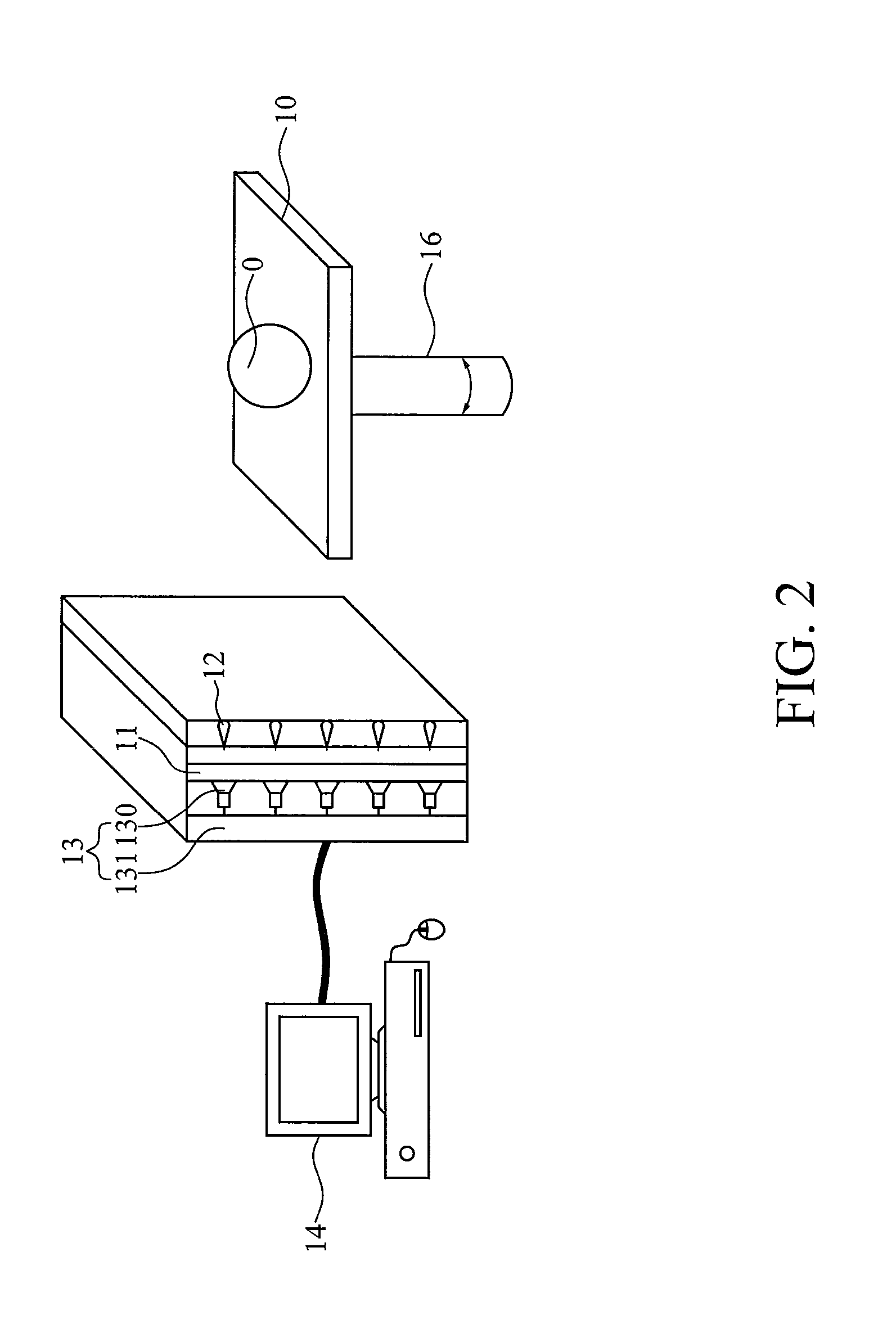
Single photon emission computed tomography instrument and the operating method thereof
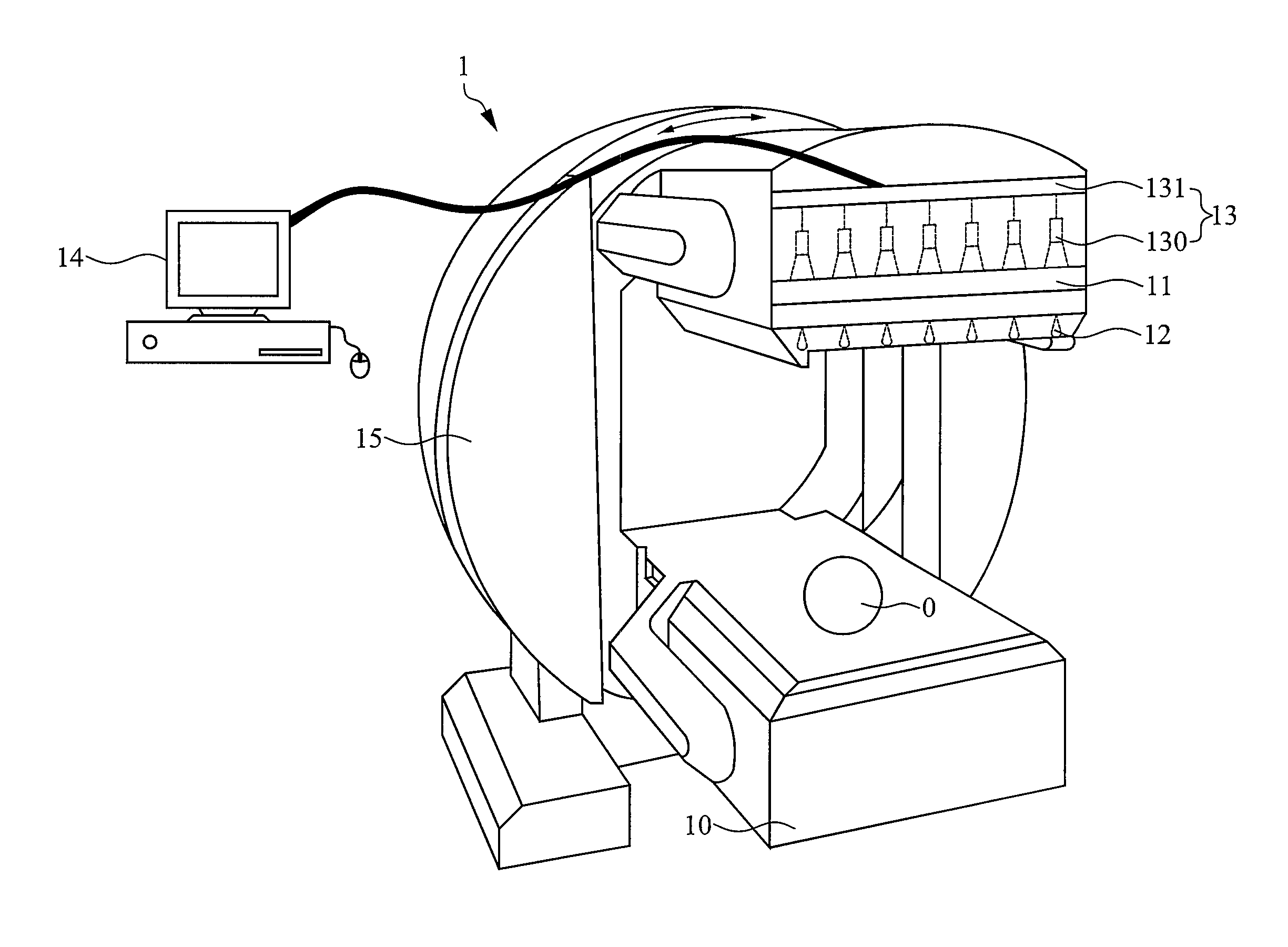
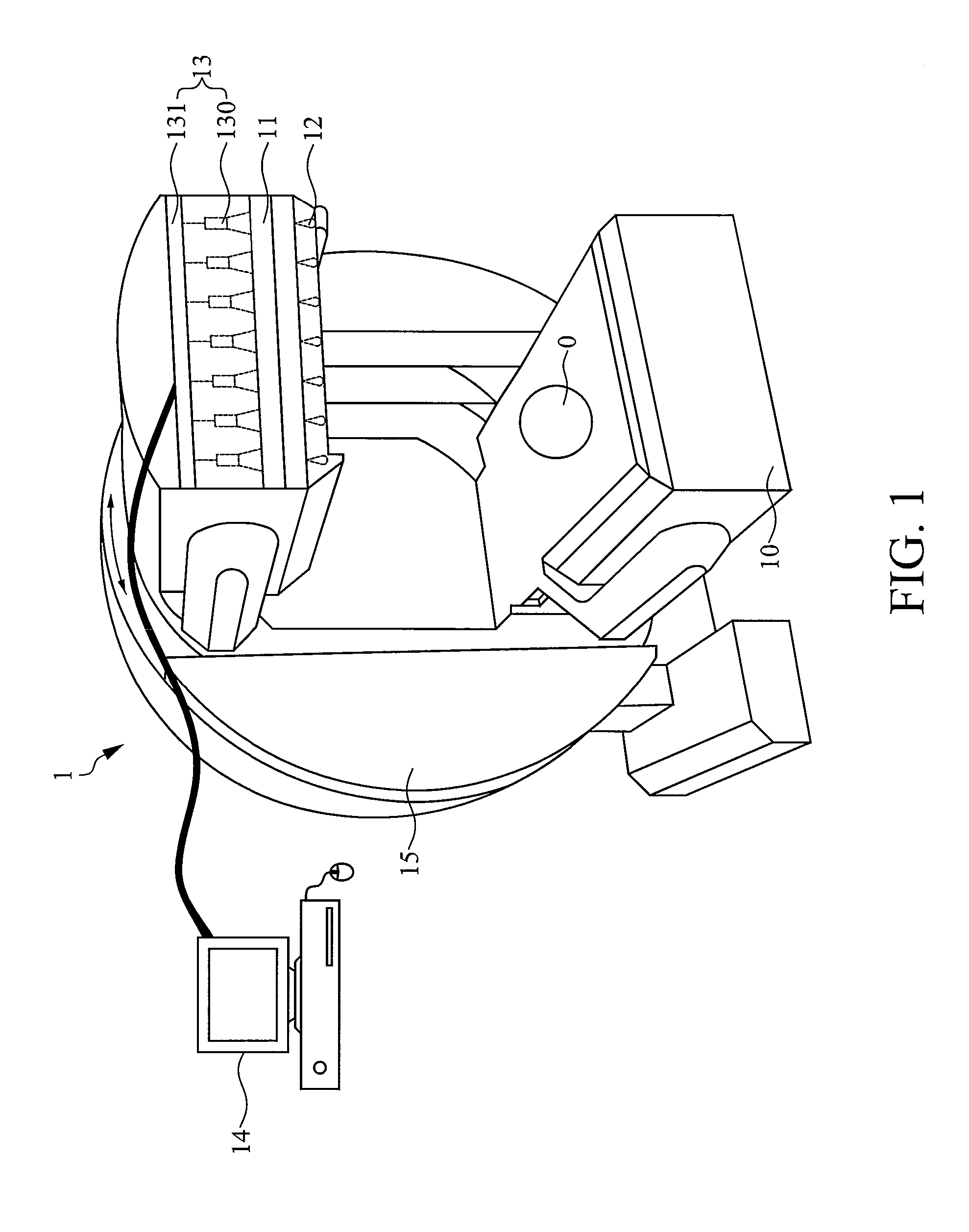
A single photon emission computed tomography instrument is provided, which has a platform, at least one detector, at least one beam stopper, a signal processing device and a computer. The at least one detector is disposed at one side of the platform, and the at least one beam stopper is disposed between the platform and the detector. The signal processing device is electrically communicated with the at least one detector, and the computer is electrically communicated with the signal processing device. The present disclosure further provides an operating method which the beam stopper is added or removed respectively while scanning an analyze by the single photon emission computed tomography instrument in different angles. The projection dataset emitted from the focus could be estimated by subtracting the projecting data without the beam stopper from that with the beam stopper, and high resolution image could be obtained by using image reconstruction program.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
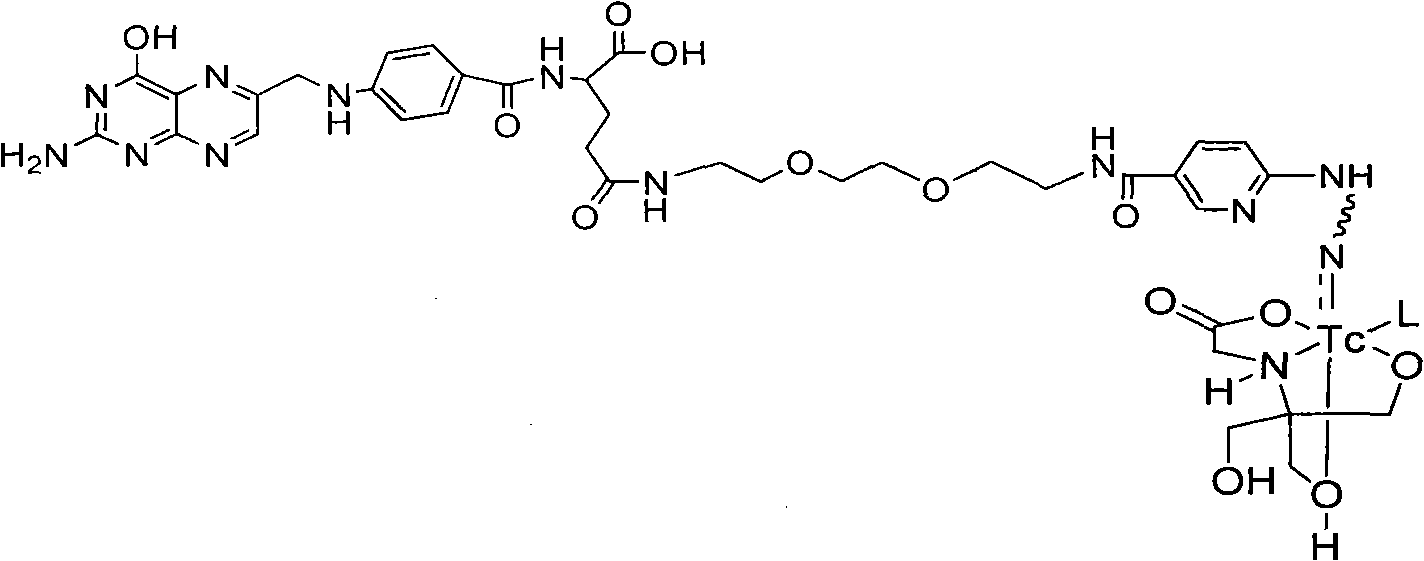
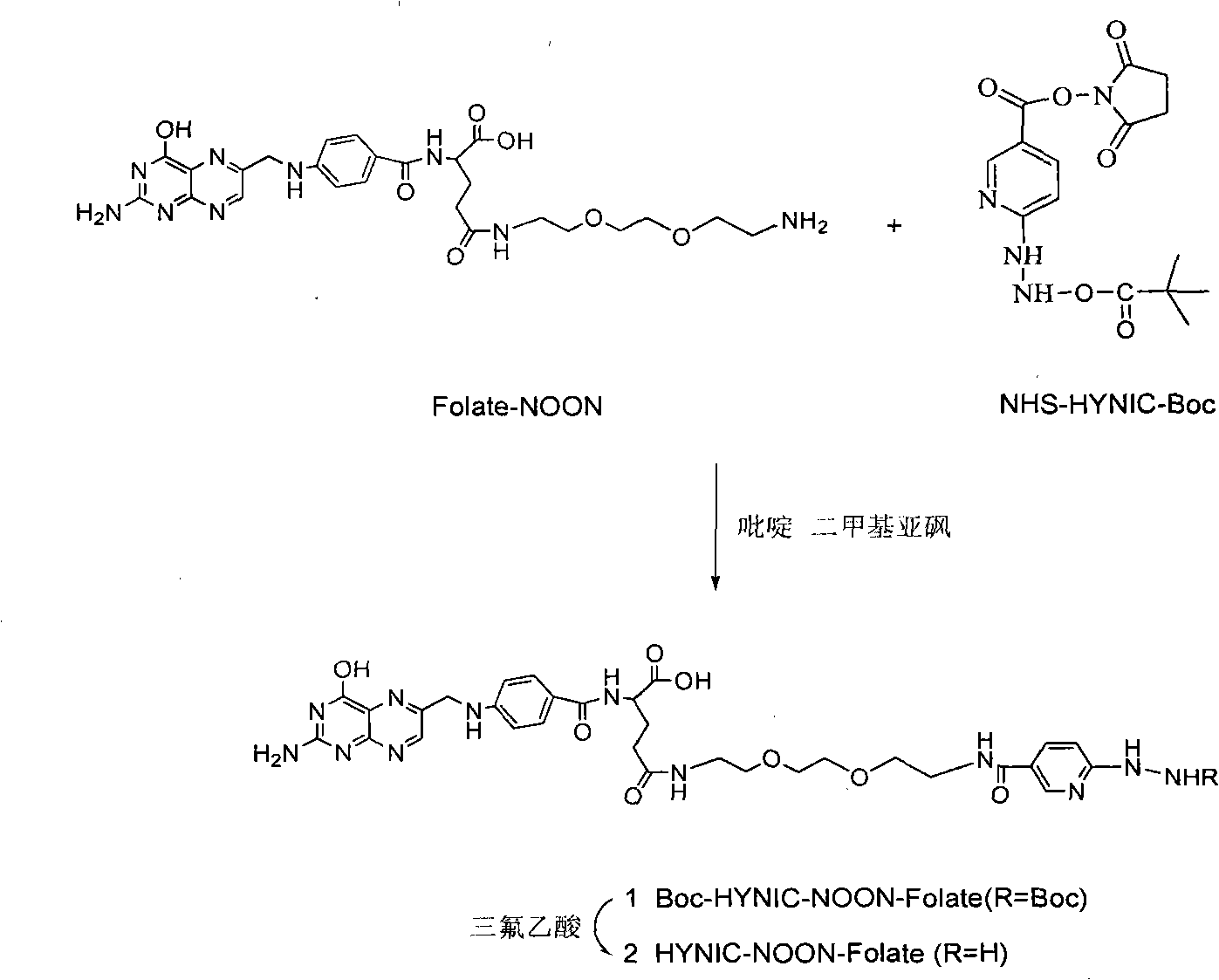
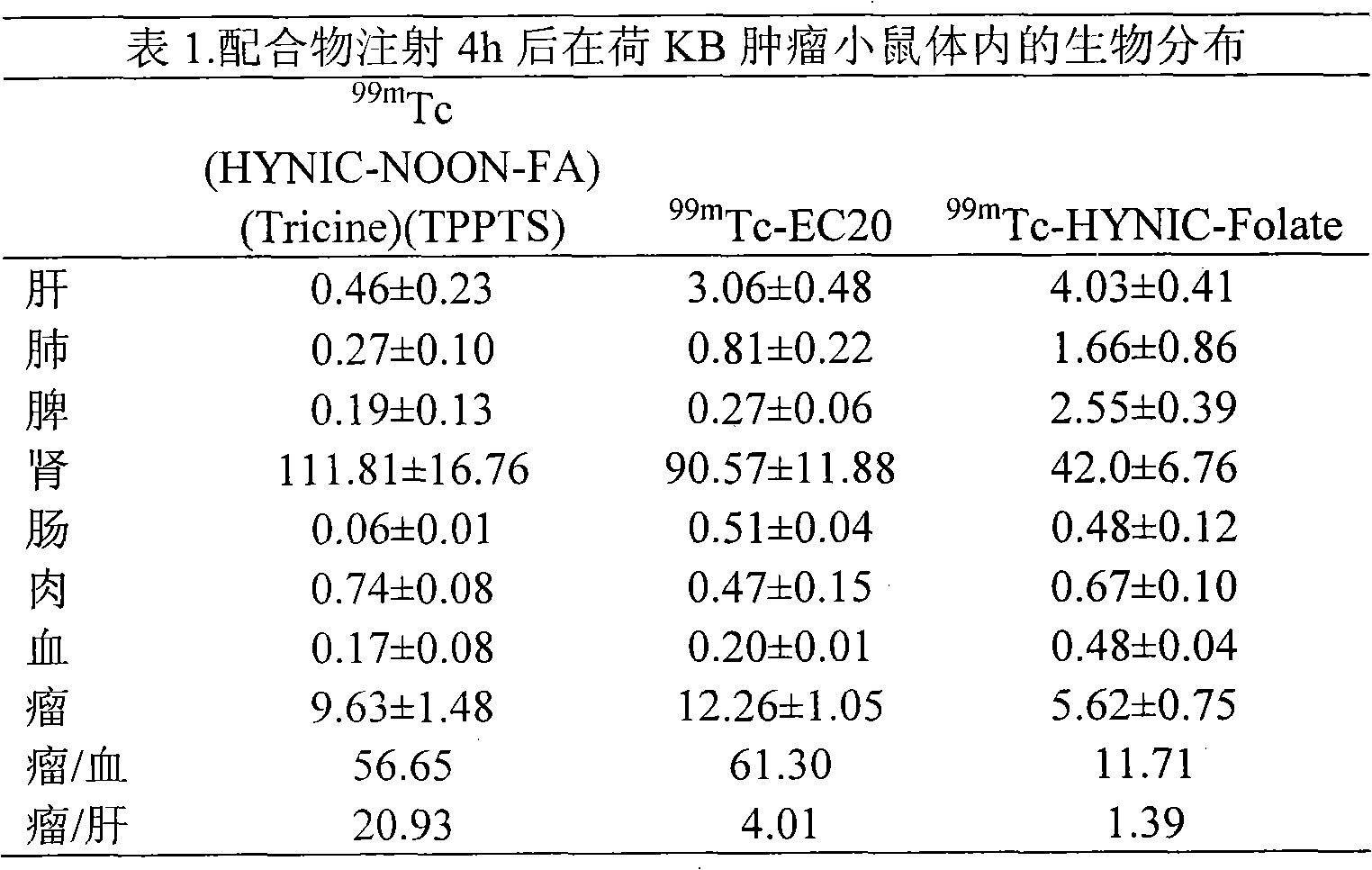
Labeled 99mTc hydrazino-nicotinamide-dioxodecoyl-folic acid coordination compound and preparation method
InactiveCN101863924AImprove performanceRadioactive preparation carriersGroup 7/17 element organic compoundsSodium phosphatesNiacin
The invention discloses a labeled 99mTc hydrazino-nicotinamide-dioxodecoyl-folic acid coordination compound with a general formula of 99mTc(HYNIC-NOON-FA)(Tricine)(L). In the structural formula, L is triphenyl sodium phosphate or triphenyl sodium photrisulfonic acid, wherein 1,8-diamido-3,6-octane dioxide is used as a connecting chain for generating a hydrazino-nicotinamide-3,6-dioxodecoyl-folic acid coupler respectively with folic acid and hydrazino-niacin through amido bonds and coordinating with oxygen atoms and phosphorus atoms in a co-ligand Tricine and an L molecule and 99mTc, and the 99mTc(HYNIC-NOON-FA)(Tricine)(L) coordination compound is obtained through two steps of: (a) synthesizing the hydrazino-nicotinamide-3,6-dioxodecoyl-folic acid coupler used as a ligand; and (b) labeling the 99mTc-hydrazino-nicotinamide-dioxodecoyl-folic acid coordination compound. The coordination compound has the advantages of high radiochemical purity, good stability, high tumor intake, good retention, low non-target organ background and clear tumor SPECT (Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography) development and can be prepared into a novel 99mTc labeled folic acid receptor tumor developer widely applied to the technical field of radioactive pharmaceutical chemistry and nuclear medicine.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Novel irreversible inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase and uses thereof for therapy and diagnosis
InactiveUS20060025430A1Improve bioavailabilityImprove biostabilityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsRadiation therapyPositron emission tomography
Novel epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase (EGFR-TK) irreversible inhibitors, pharmaceutical compositions including same and their use in the treatment of EGFR-TK related diseases or disorders are disclosed. Novel radiolabeled EGFR-TK irreversible inhibitors as their use as biomarkers for medicinal radioimaging such as Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) and as radiopharmaceuticals for radiotherapy are further disclosed.
Owner:T K SIGNAL
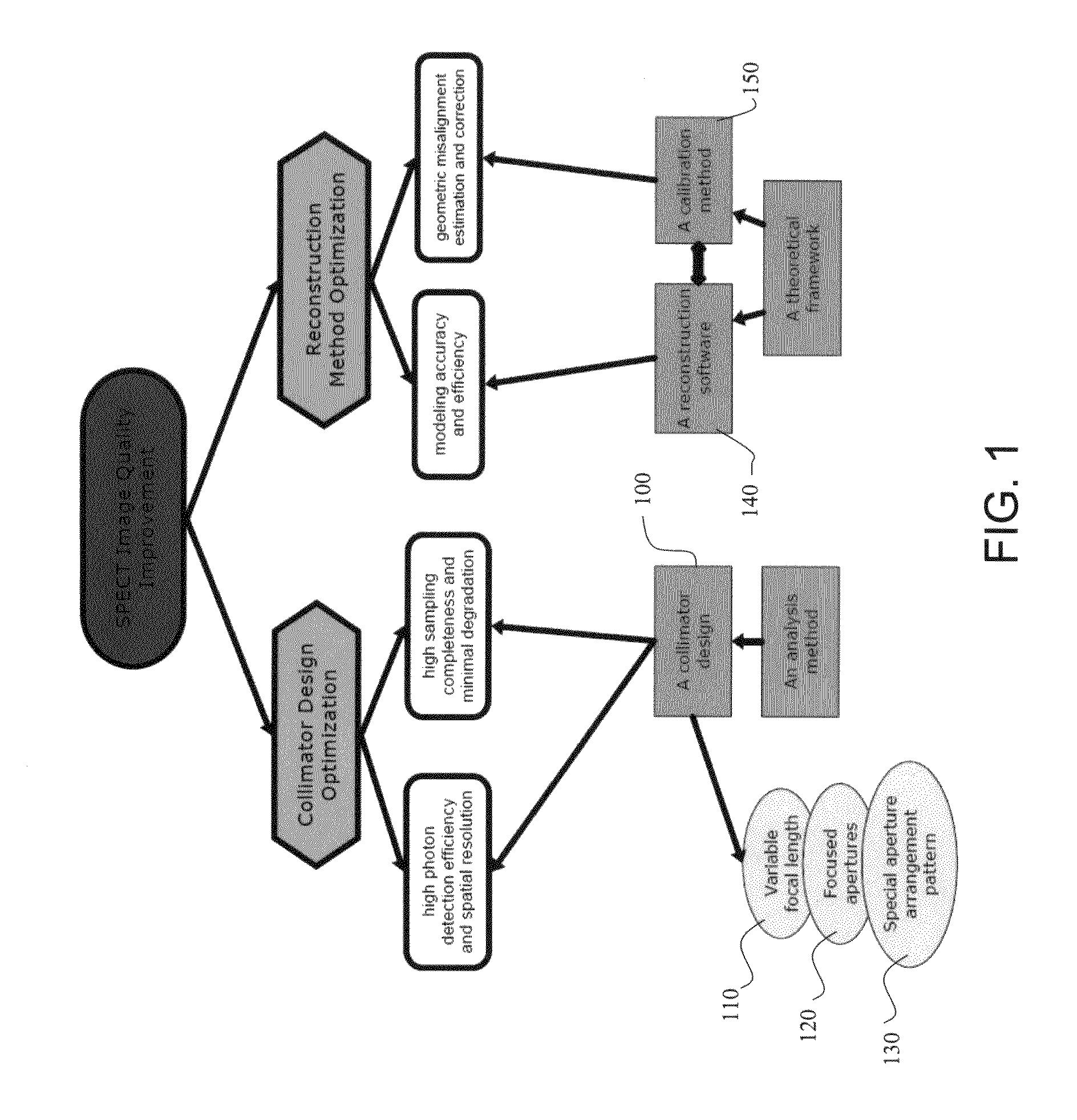
Geometric calibration method for SPECT (single photon emission computed tomography) system
ActiveCN104173074AImprove image qualityExact geometric parametersComputerised tomographsTomographySingle photon emission ctImaging quality
The invention discloses geometric calibration method for a SPECT (single photon emission computed tomography) system. The method comprises the steps as follows: a collimator is measured to obtain geometric parameters of a pinhole or a slot in the collimator; the collimator and a PET (position emission tomography) detector are assembled to form the SPECT system; the collimator is controlled to move, and the PET detector is used for measuring multi-group background coincidence events when the collimator moves to a plurality of target positions; and position coordinates of the collimator in the SPECT system are obtained according to the multi-group background coincidence events. According to the method, the geometric parameters of the SPECT system can be accurately calibrated, accurate geometric parameters are provided for image reconstruction of tomography, and accordingly, the imaging quality of the SPECT system is improved.
Owner:BEIJING NOVEL MEDICAL EQUIP LTD
In vivo imaging of amyloid plaques in glaucoma using intravenous injectable dyes
InactiveUS20050214222A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsLuminescence/biological staining preparationNervous systemFluorescence
In vivo imaging may be used to assess a condition (e.g., a state of glaucoma or a state of ocular hypertension) of an eye of a living animal. A dye may be intravenously injected into the living animal. The dye may bind to amyloid in the nervous system of the animal. Images may be taken of a retina, an optic nerve head, an optic nerve, the lateral geniculate nucleus, and / or the visual cortex. Images may be taken using methods such as fluorescent angiography, magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, positron emission tomography, and / or single photon emission computed tomography. The condition of the eye and / or retinal ganglion cells in the eye may be assessed from one or more of the images. The condition of the eye may be assessed based on the presence of amyloid in one or more of the images.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
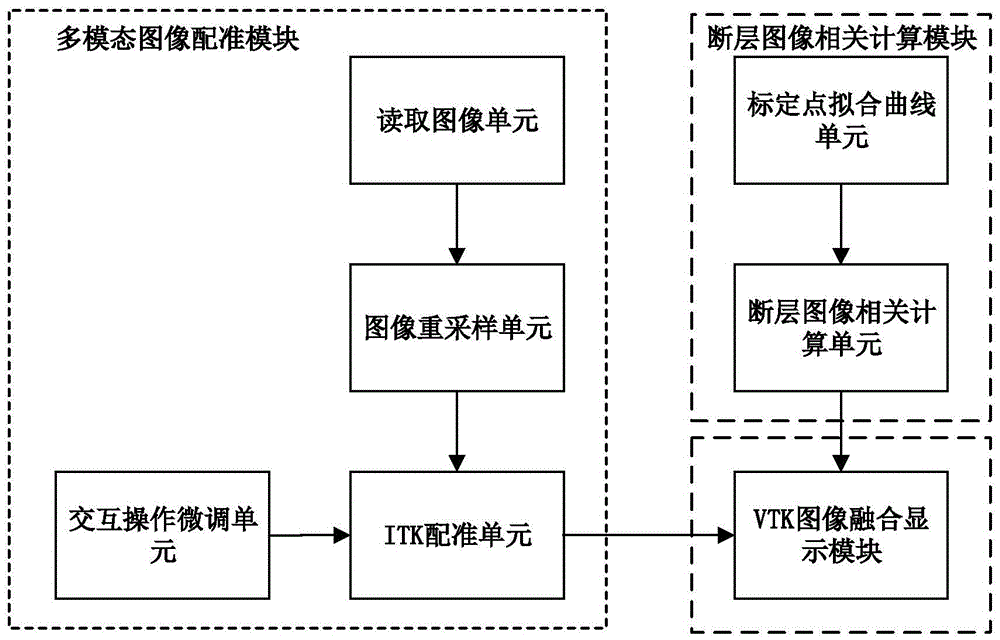
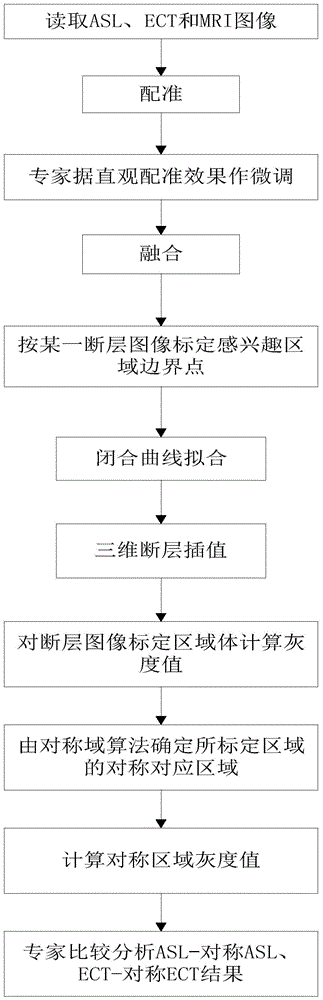
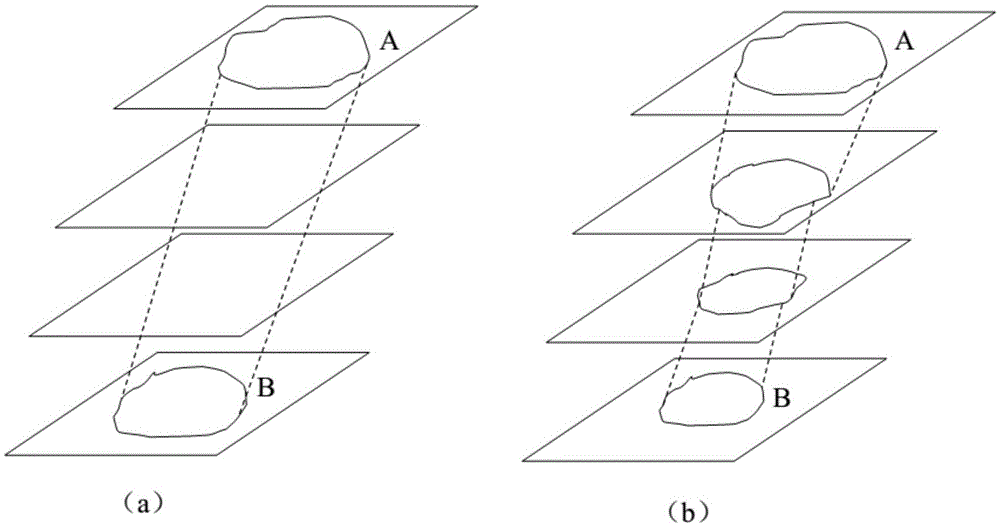
Brain ASL (Arterial Spin Labeling), SPECT (Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography) and MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) image registration and fusion conjoint analysis method and system
The invention discloses a brain ASL, SPECT and MRI image registration and fusion conjoint analysis method and system. Registration is respectively carried out to an ASL image and an MRI image by taking the MRI image as a standard; the ASL image and an SPECT image are fused according to different transparencies; a region to be computed is marked in the faultage of the SPECT image; a closed curve is obtained through carrying out a cubic spline interpolation to the ASL image; the volume and the gray value corresponding to the region to be computed and the gray value of an interesting region body through a circular truncated cone approach mode. According to the invention, the advantages of the ASL image reflected brain blood perfusion, the SPECT image reflected brain blood perfusion and the MRI provided brain structure change are combined; an interesting region is segmented and analyzed through providing interactive calibration operation a doctor and a medical expert; the judgement accuracy of a brain ischemic disease is improved; and iconography instructions are provided for a clinician to formulate a rational therapeutic schedule.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
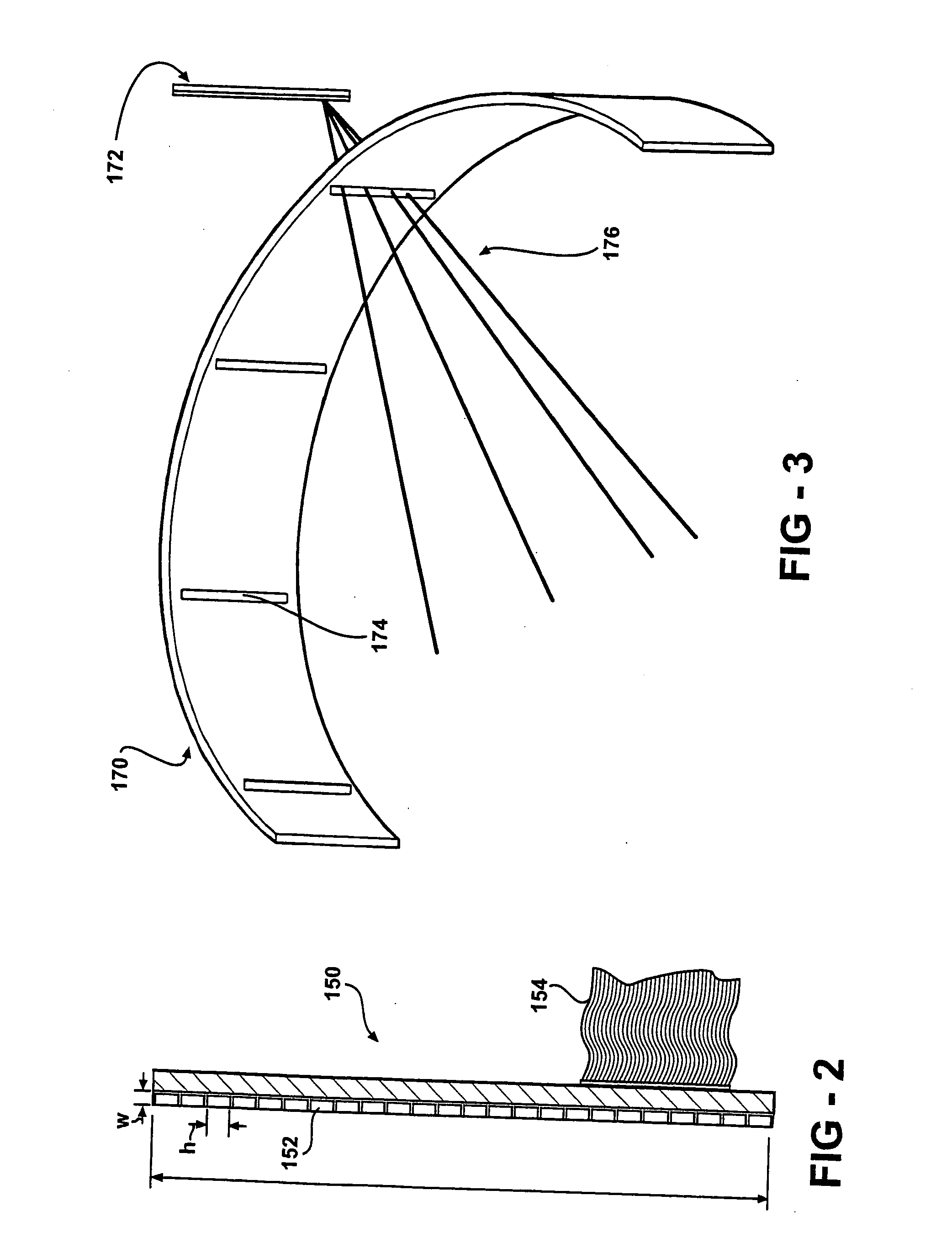
Single photon emission computed tomography system
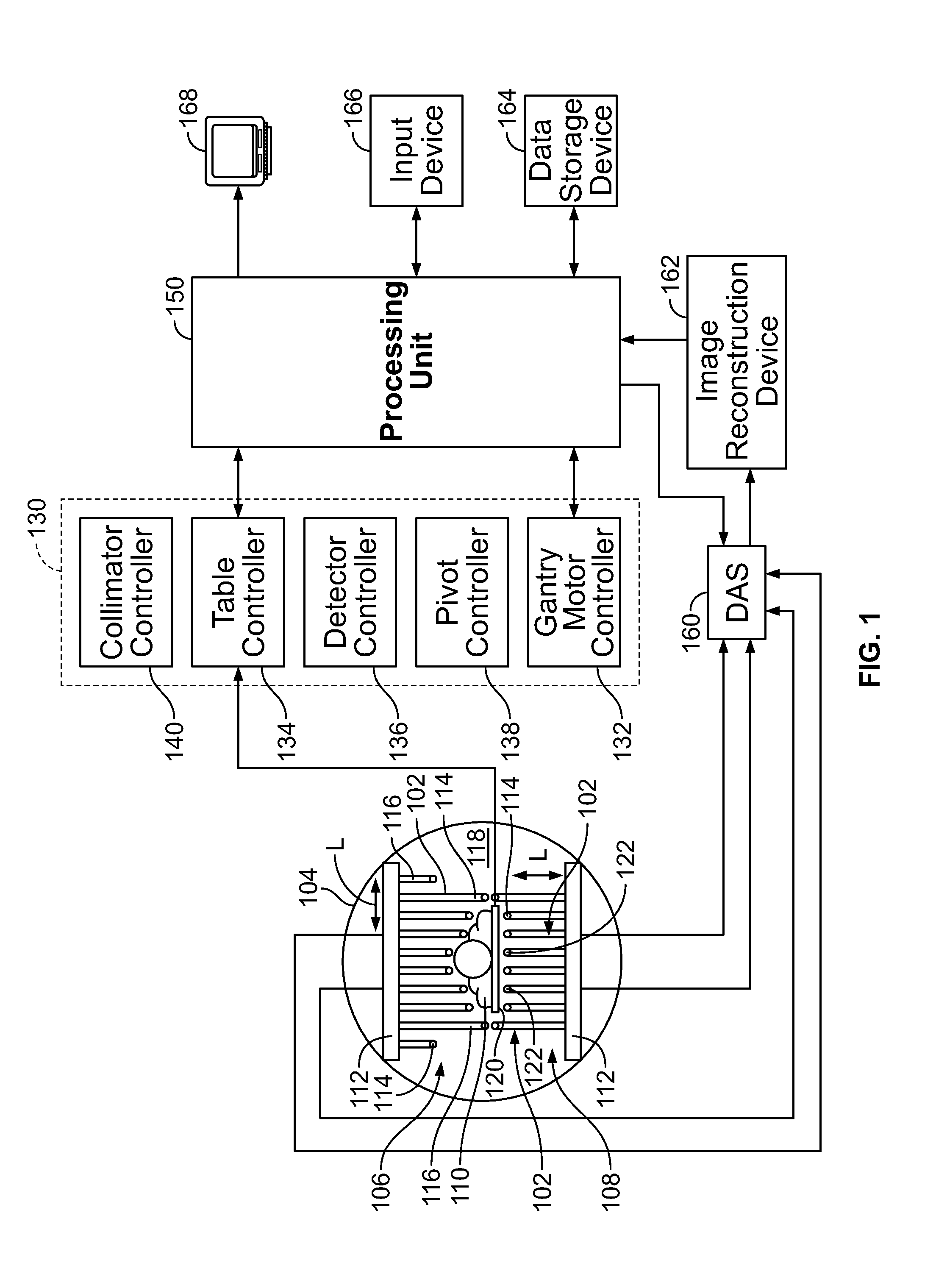
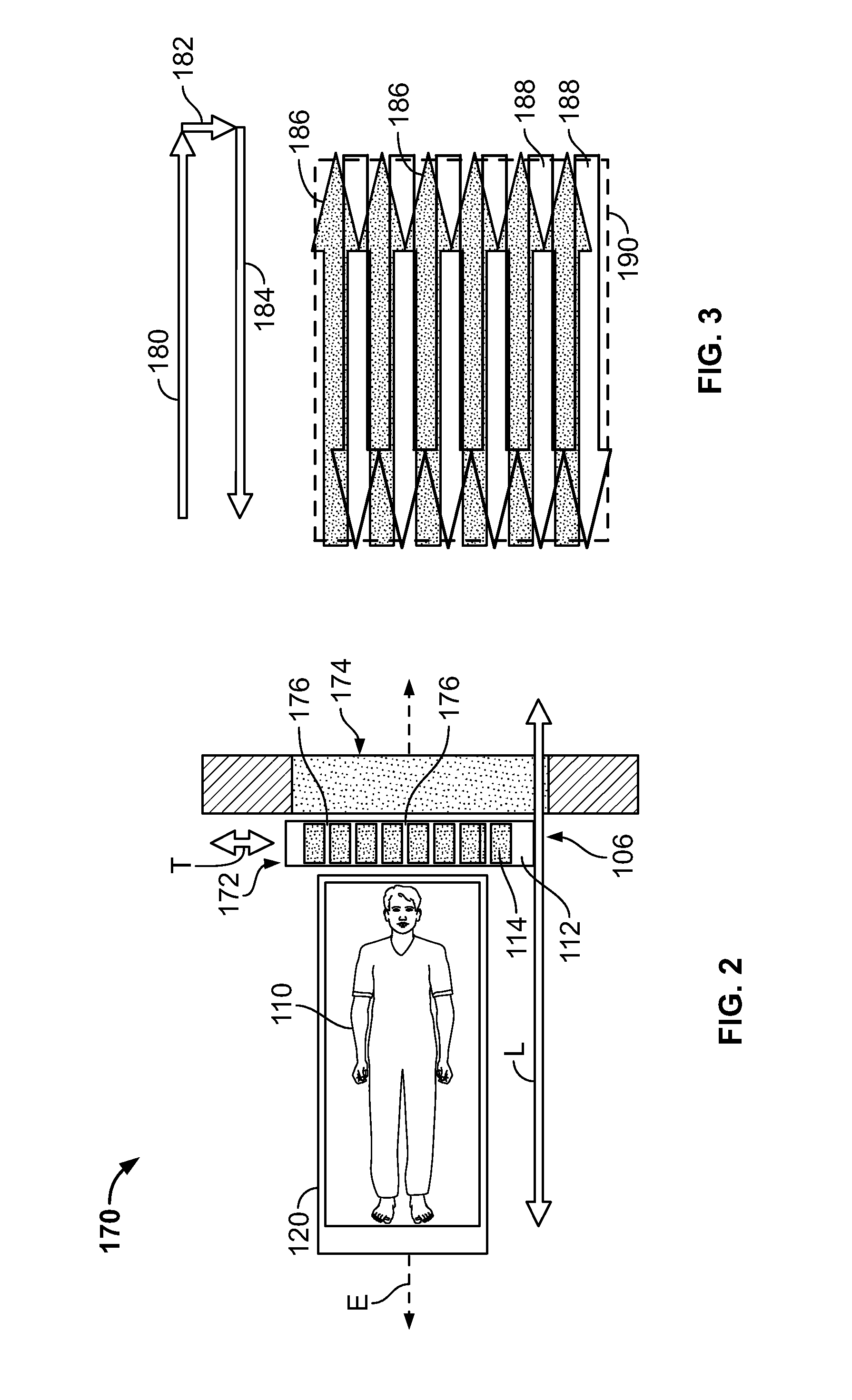
InactiveUS7015476B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by optical meansLines of responseFront edge
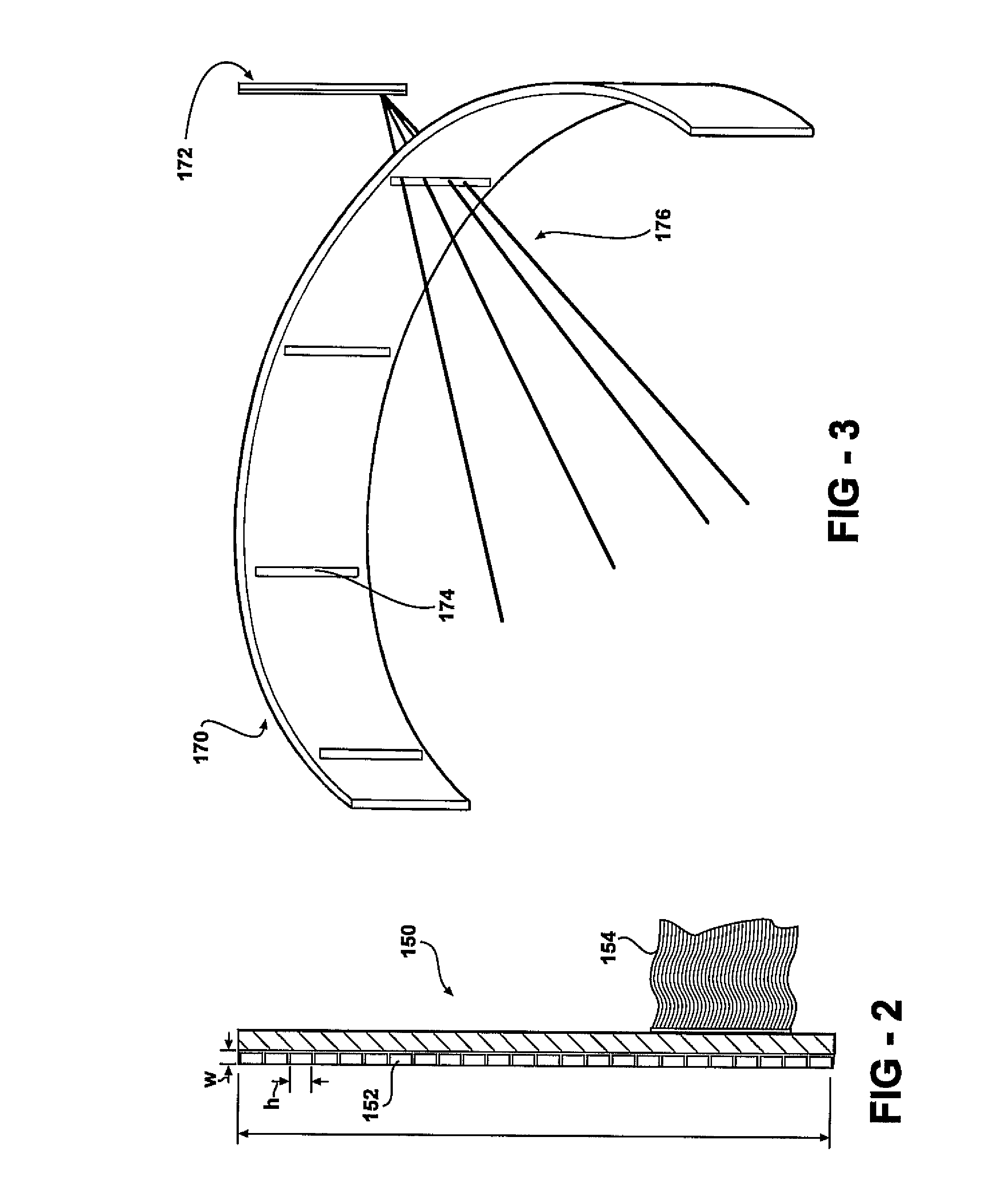
A single photon emission computed tomography system produces multiple tomographic images of the type representing a three-dimensional distribution of a photon-emitting radioisotope. The system has a base including a patient support for supporting a patient such that a portion of the patient is located in a field of view. A longitudinal axis is defined through the field of view. A detector module is adjacent the field of view and includes a photon-responsive detector. The detector is operable to detect if a photon strikes the detector. A photon-blocking member is positioned between the field of view and the detector. The blocking member has an aperture slot for passage of photons aligned with the aperture slot. A line of response is defined from the detector through the aperture. A collimating assembly includes a plurality of generally parallel collimating vanes formed of a photon attenuating material. The vanes are spaced apart so as to find a plurality of gaps, with the gaps each having a height. Each of the vanes has a front edge directed toward the field of view and a back edge directed towards the detector. The front-to-back depth of each of the vanes is greater than 10 times the height of the gaps. The plurality of vanes is disposed between the detector and the field of view such that only photons passing through one of the gaps can travel from the field of view to the detector. A displacement device moves either the detector module or the photon-blocking member relative to the other so that the aperture is displaced relative to the detector and the line of response is swept across at least a portion of the field of view.
Owner:HIGHBROOK HLDG
Imaging system using independently controllable detectors
ActiveUS9029791B1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by optical meansPhoton emissionTomography
A customizable and upgradable imaging system is provided. Imaging detector columns are installed in a gantry to receive imaging information about a subject. Imaging detector columns can extend and retract radially as well as be rotated orbitally around the gantry. The gantry can be partially populated with detector columns and the detector columns can be partially populated with detector elements. The system can automatically adjust an imaging operation based on installation information related to partial population or other factors such as scan type or subject specific information. This system can be a Nuclear Medicine (NM) imaging system to acquire Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) image information.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
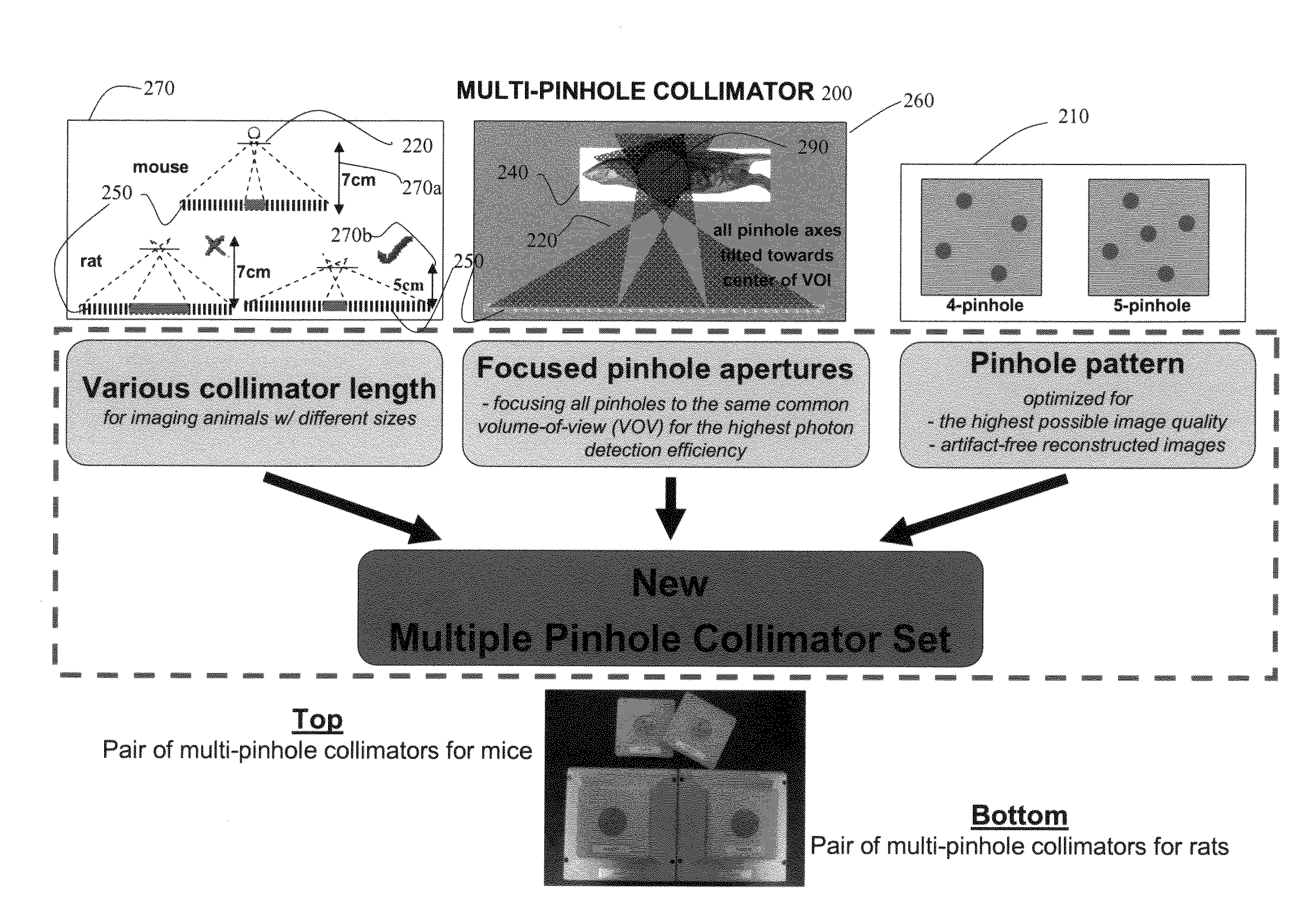
Multi-aperture single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20080116386A1Reduce image noiseSolve the low detection efficiencySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansResearch ObjectImaging quality
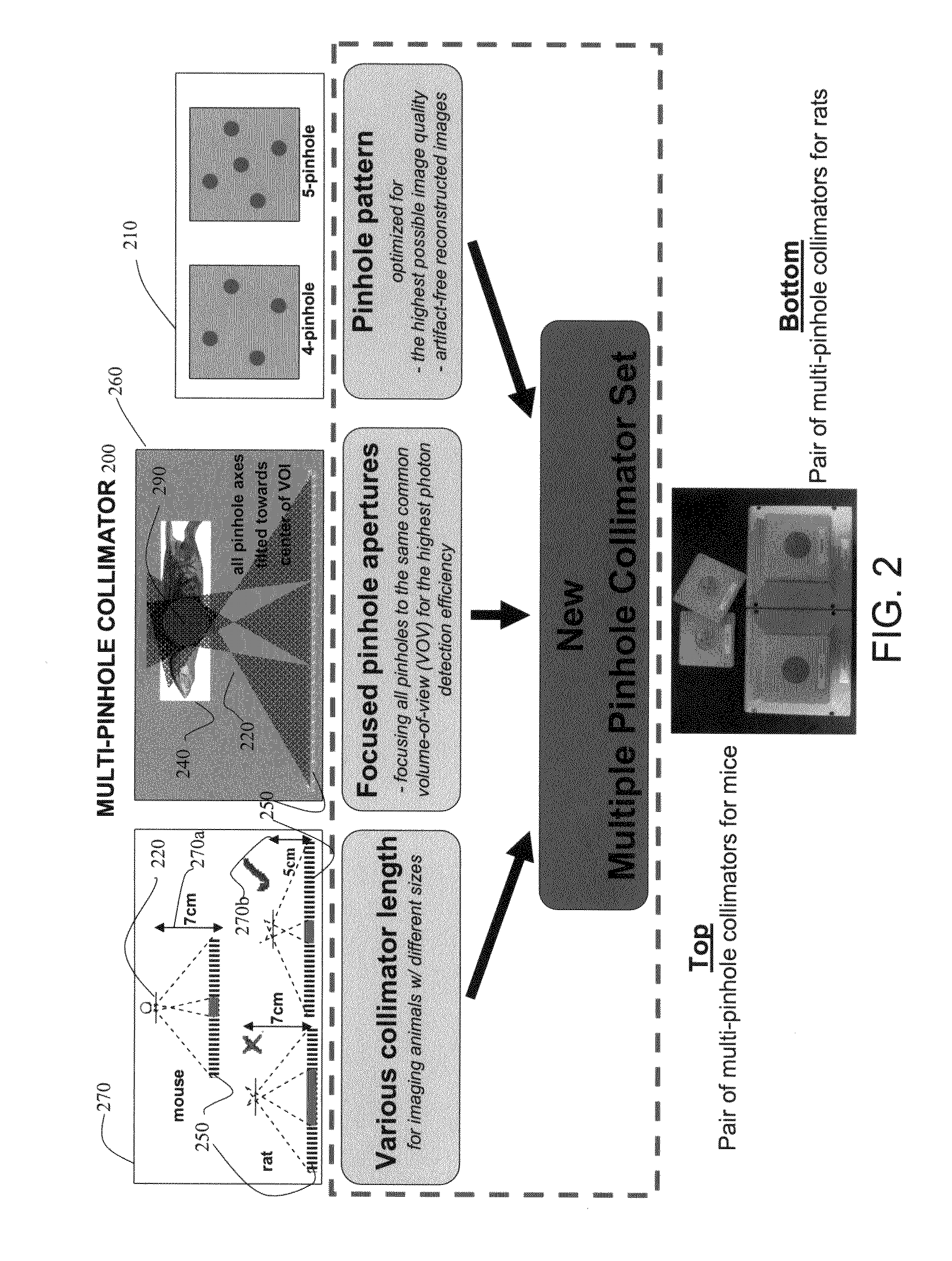
Methods and systems for improving image quality of single photon nuclear imaging systems, such as single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) systems for imaging of an object under study, such as small objects including small animals of different sizes using synthetic apertures. The methods and systems include processes and instrumentations for high-resolution, high detection efficiency leading to lower image noise and artifact-free synthetic aperture single photon nuclear images, such as SPECT images. Also, the method and systems provide design parameters, hardware settings, and data acquisition processes for optimal imaging of objects having different sizes.
Owner:GAMMA MEDICA IDEAS
Systems and methods for planar imaging with detectors having moving detector heads
ActiveUS20150094573A1Patient positioning for diagnosticsComputerised tomographsPhotonSingle-photon emission computed tomography
Systems and methods for planar imaging with detectors having moving heads are provided. One system includes a gantry having an opening therethrough, a patient table movable through the opening of the gantry along an examination axis, and a plurality of detector units mounted to the gantry and aligned in a row transverse to the examination axis. The plurality of detector units are spaced apart from each other, wherein the spacing forms gaps between adjacent detector units. The plurality of detector units are configured to acquire Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) data. The system further includes a controller configured to control movement of the patient table and the plurality of detector units to acquire two-dimensional (2D) SPECT data, wherein the plurality of detector units remain in a fixed relative orientation with respect to each other when acquiring the 2D SPECT data and move together to acquire the 2D SPECT data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com