Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
39 results about "Optical fluorescence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
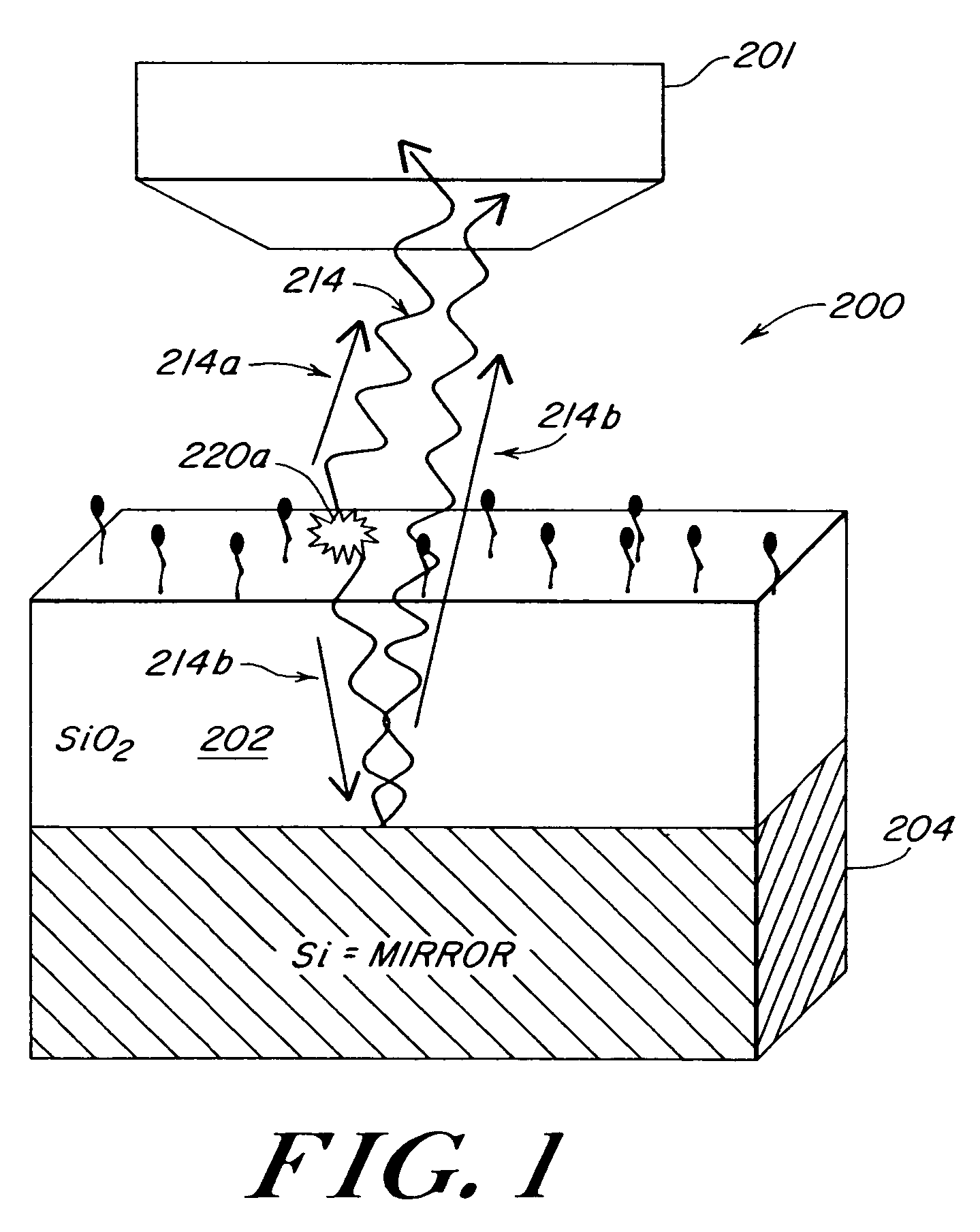
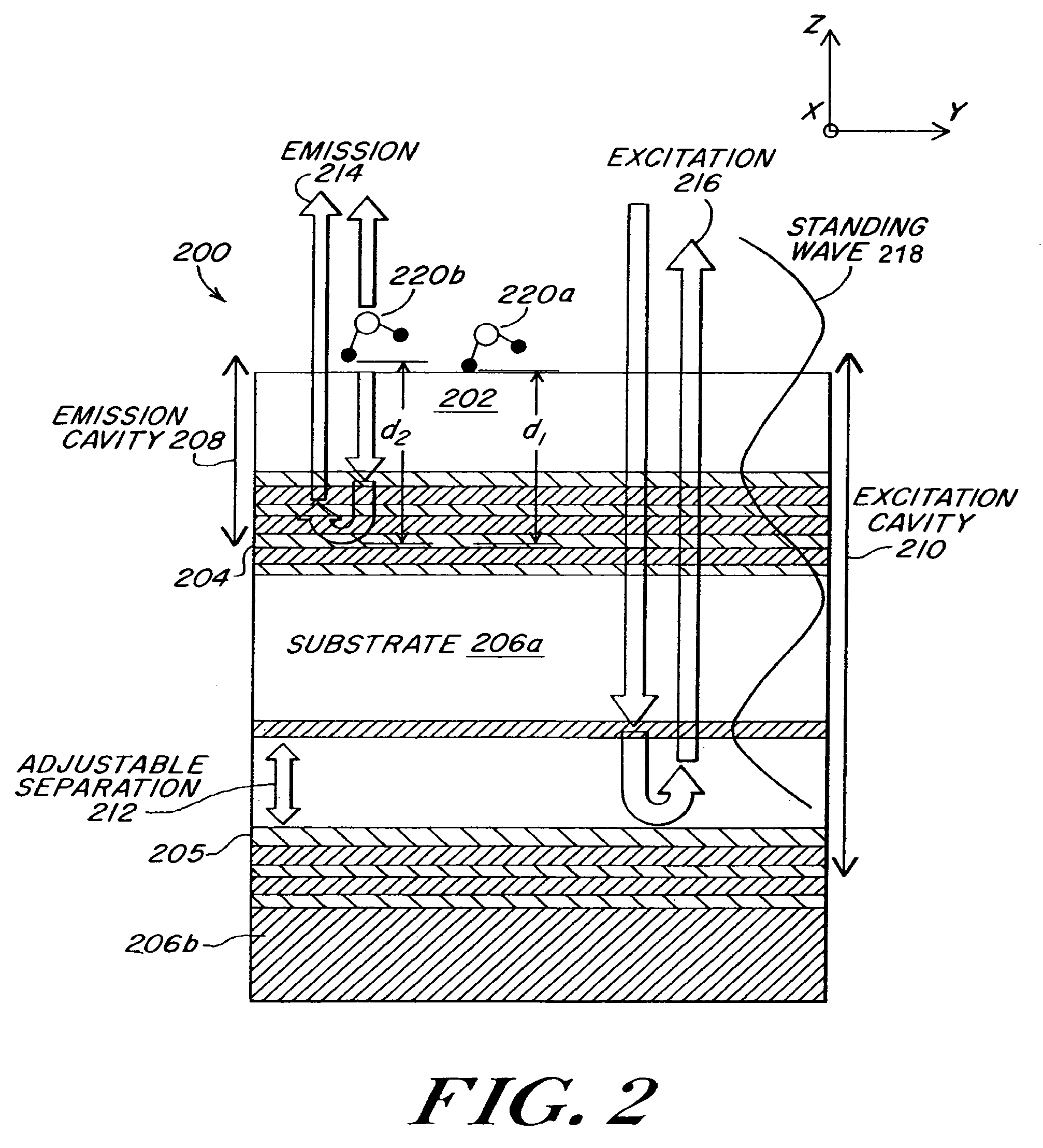
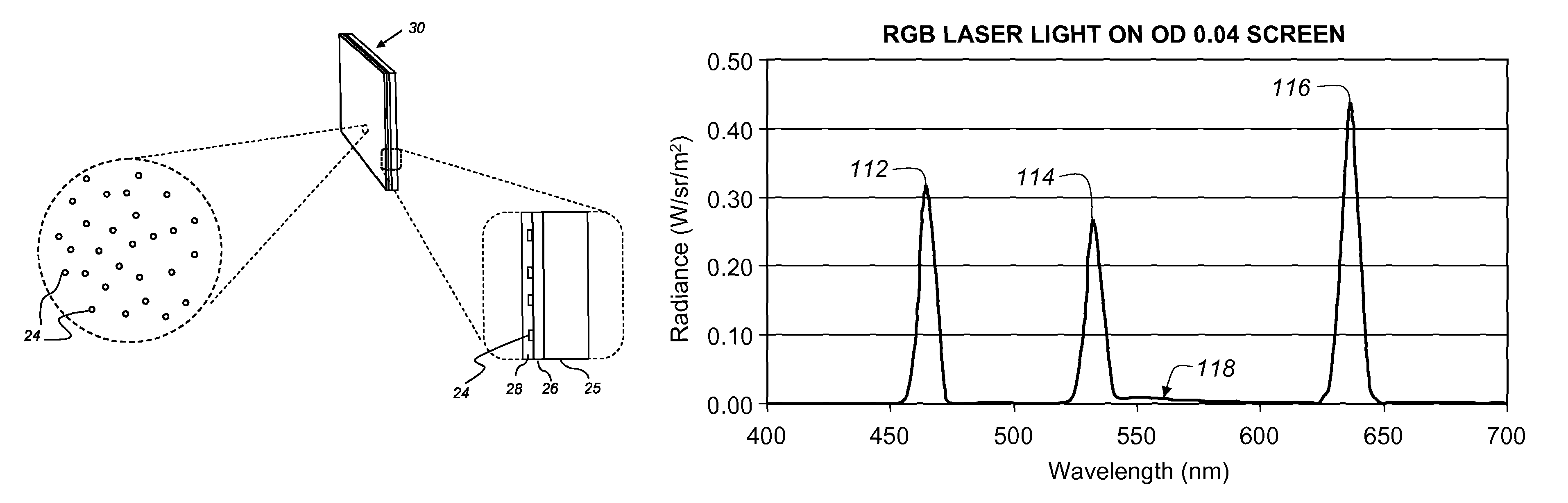
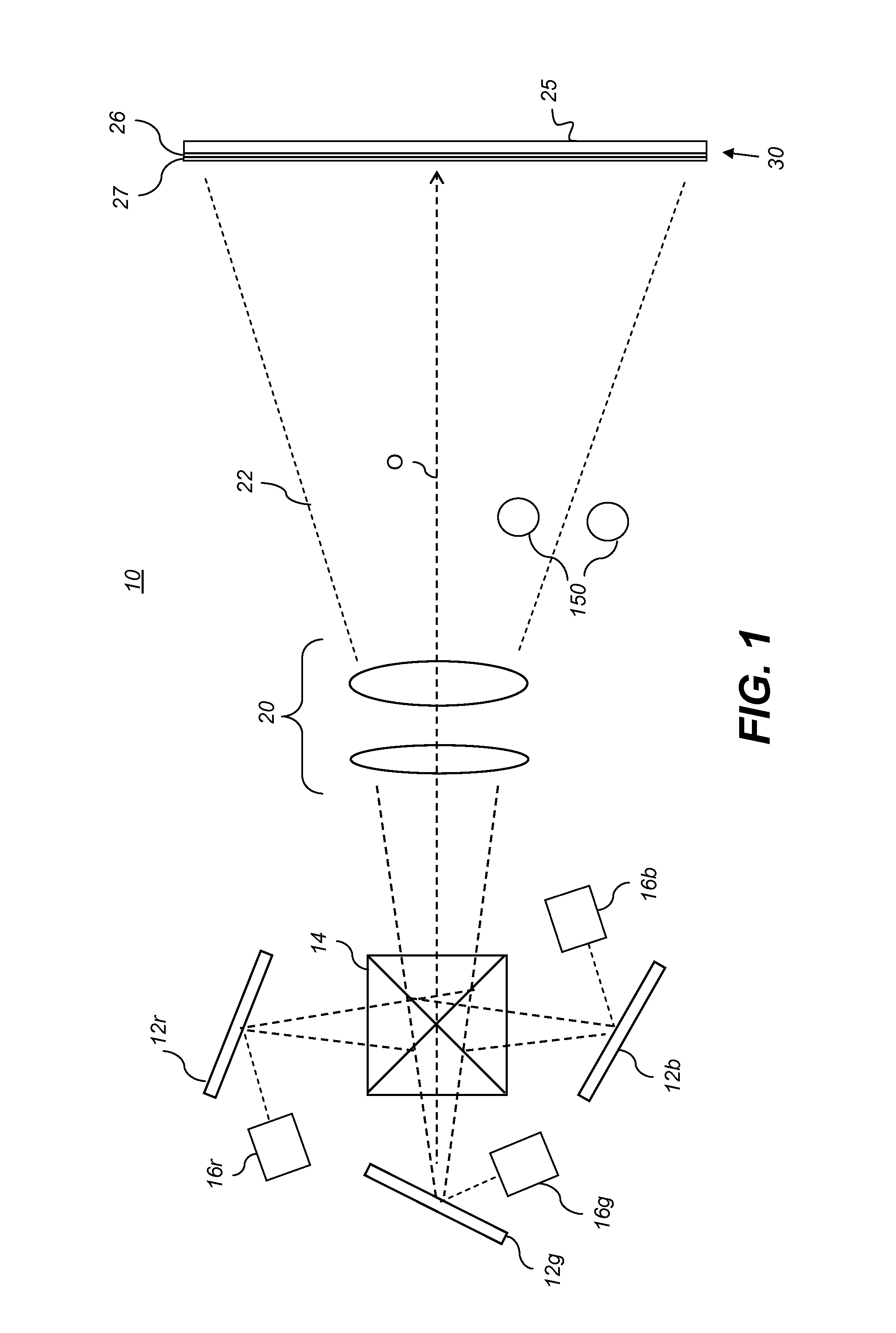
Optical fluorescence occurs when a molecule absorbs light at wavelengths within its absorption band, and then nearly instantaneously emits light at longer wavelengths within its emission band.
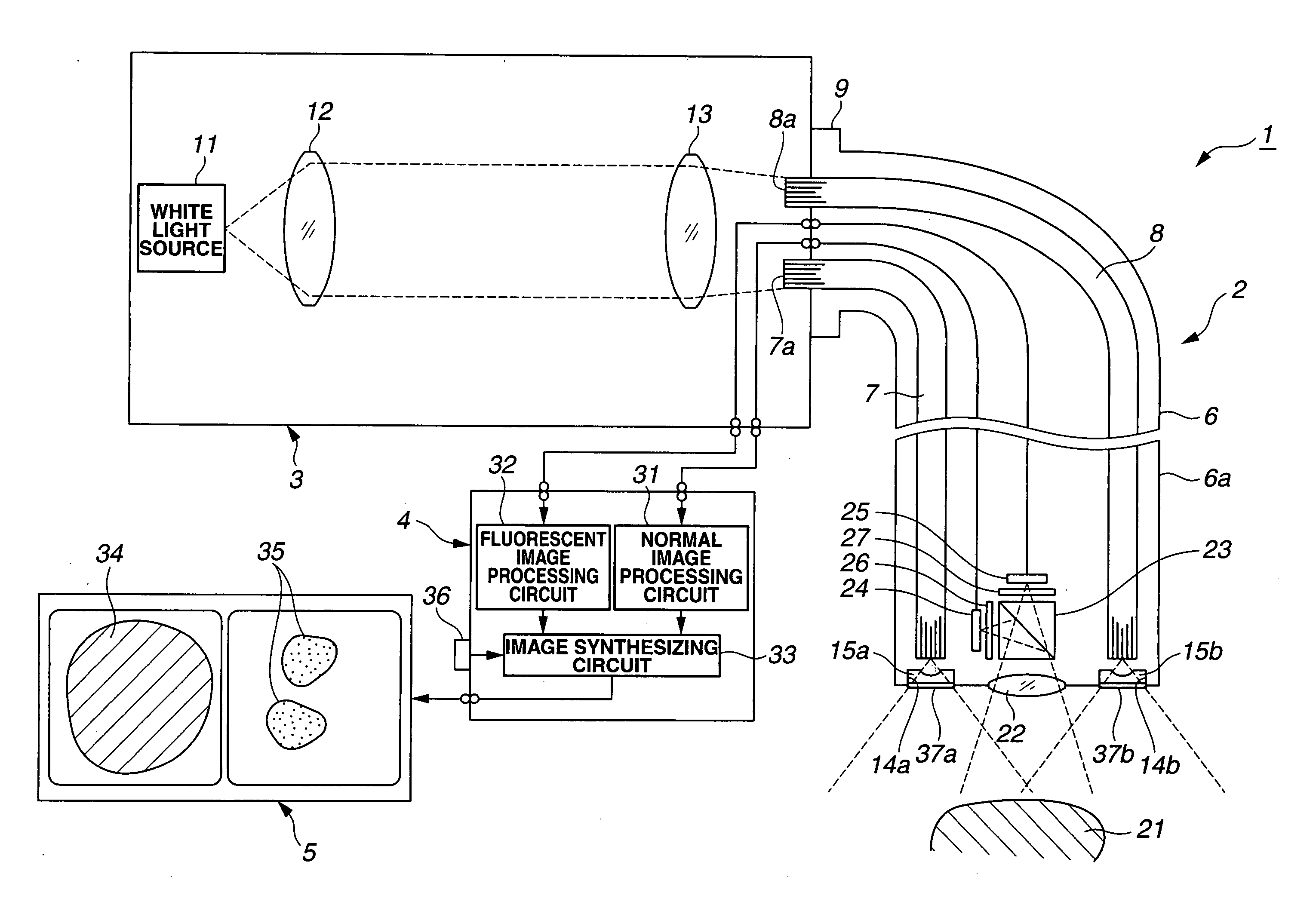
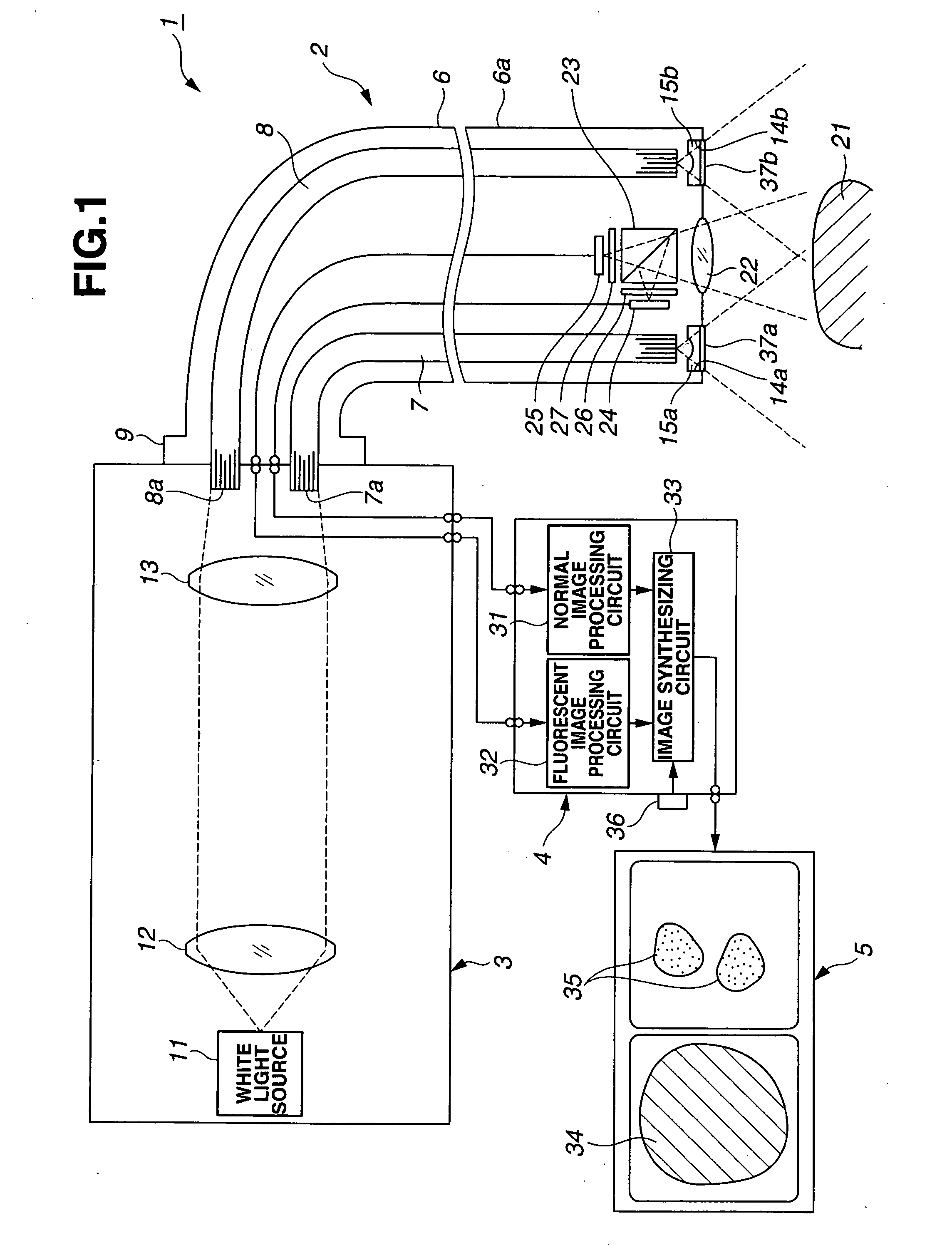
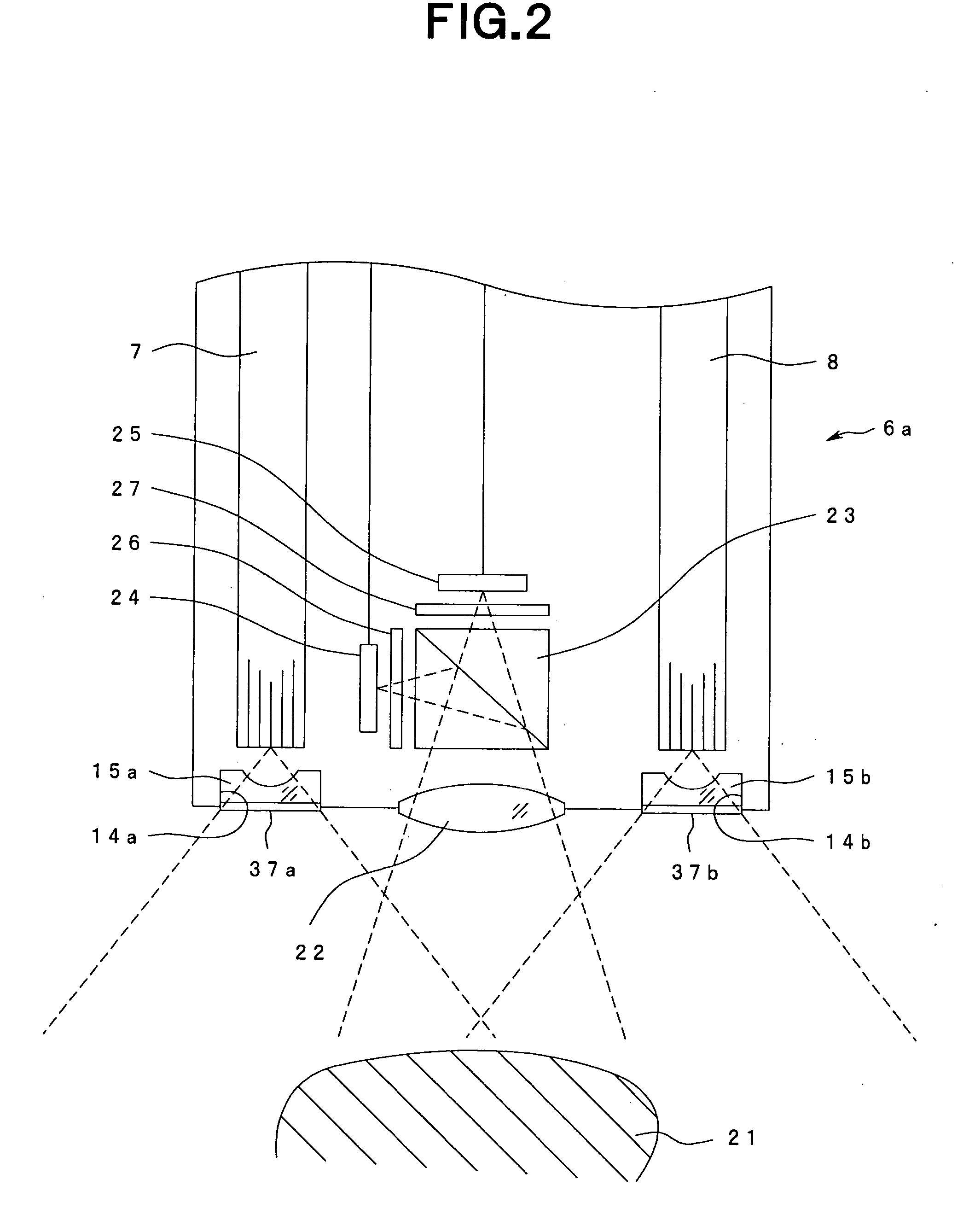
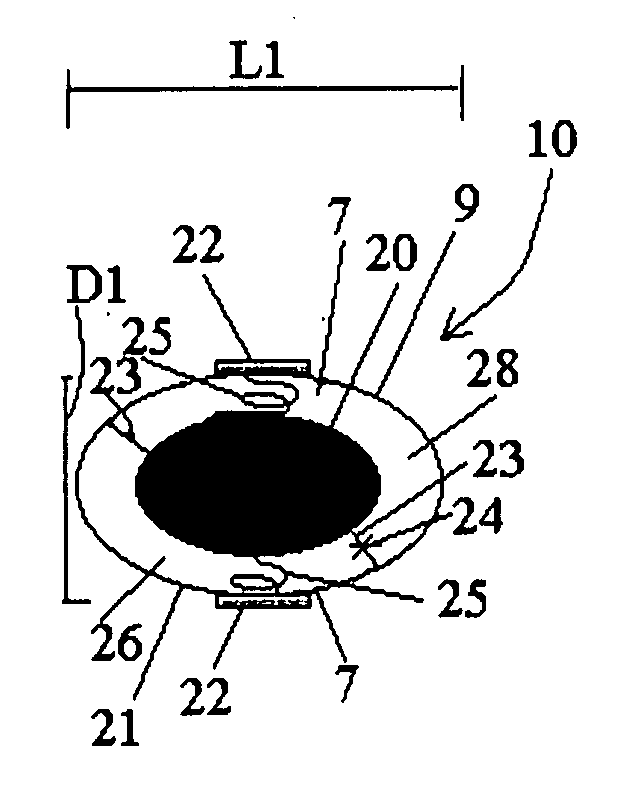
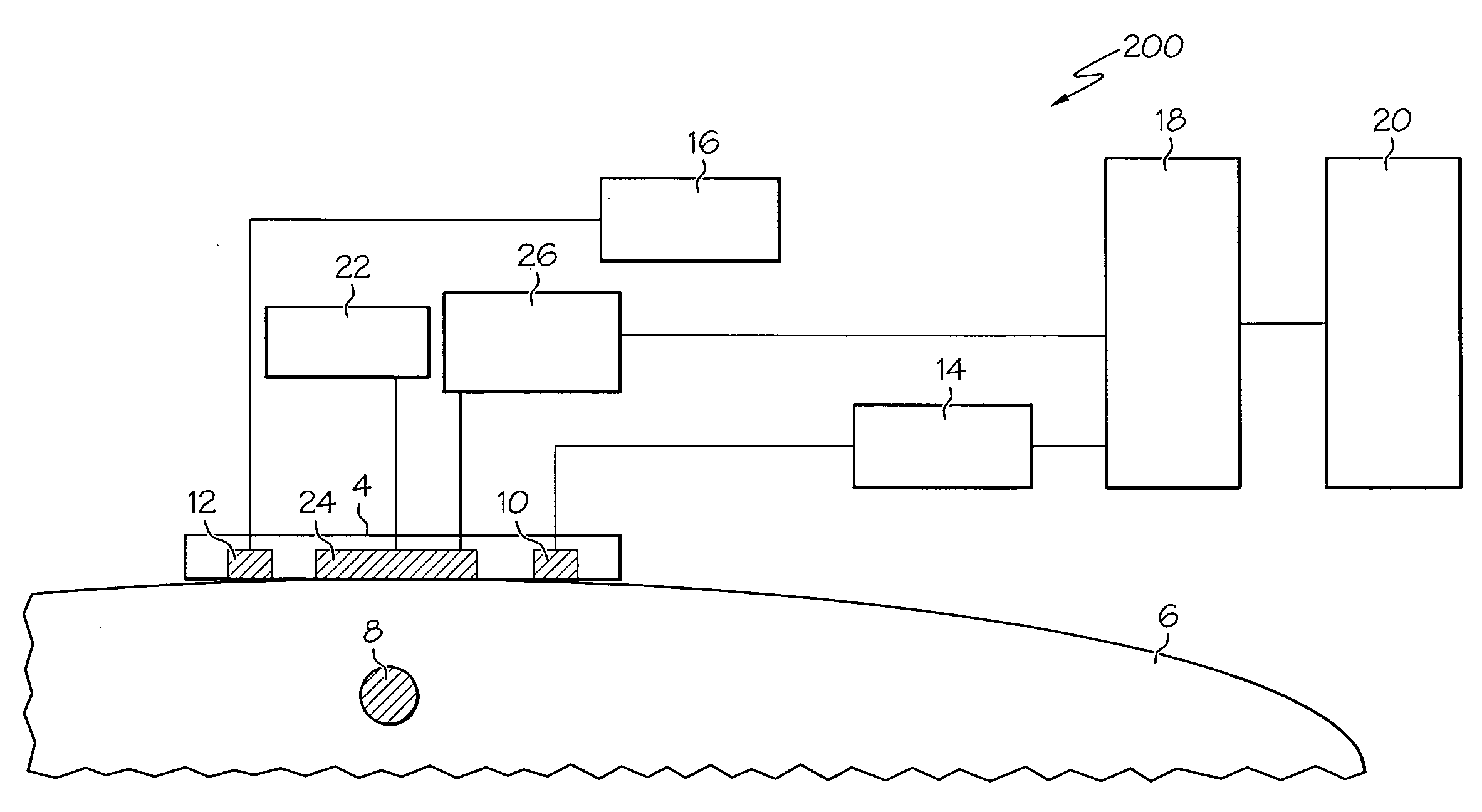
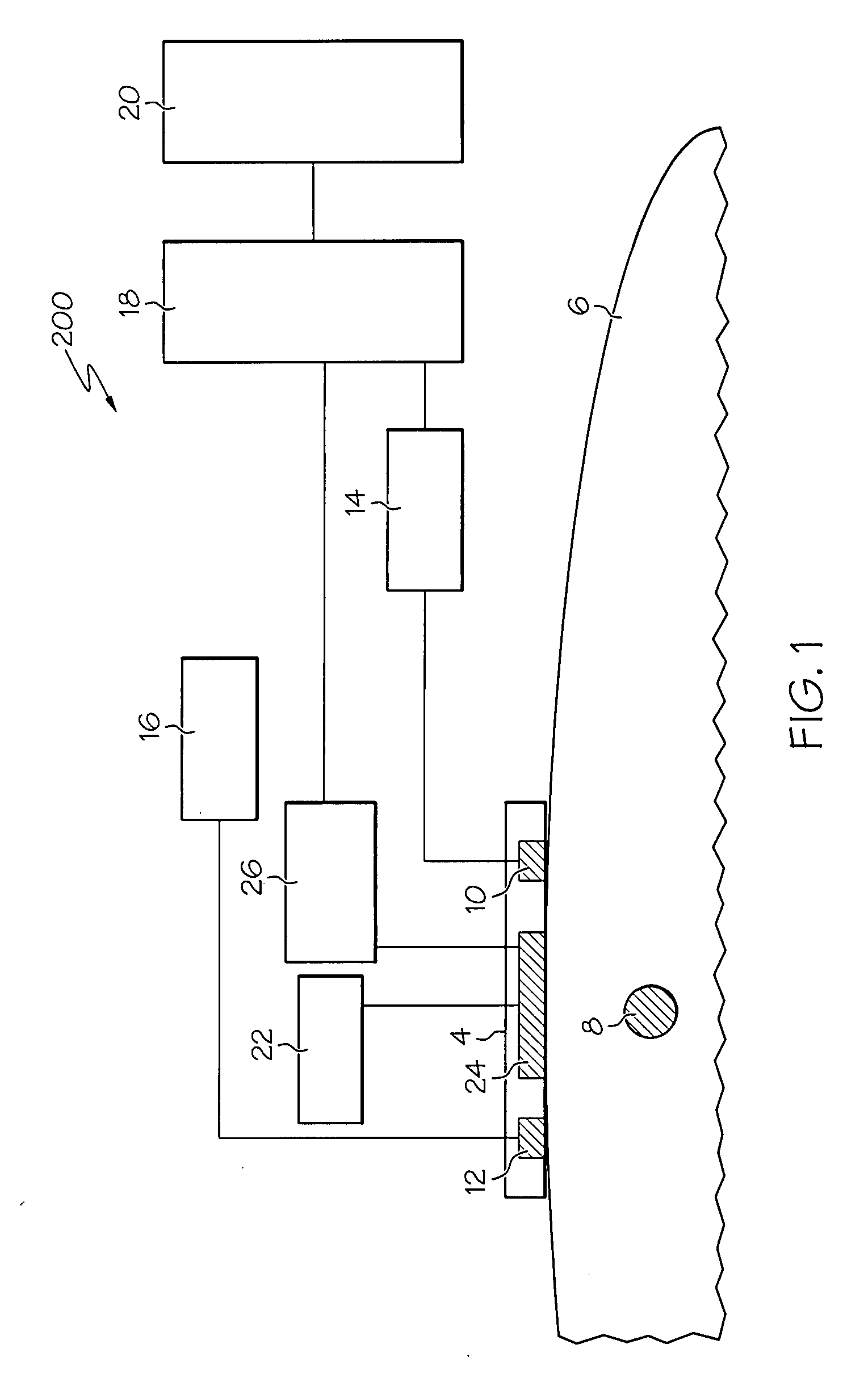
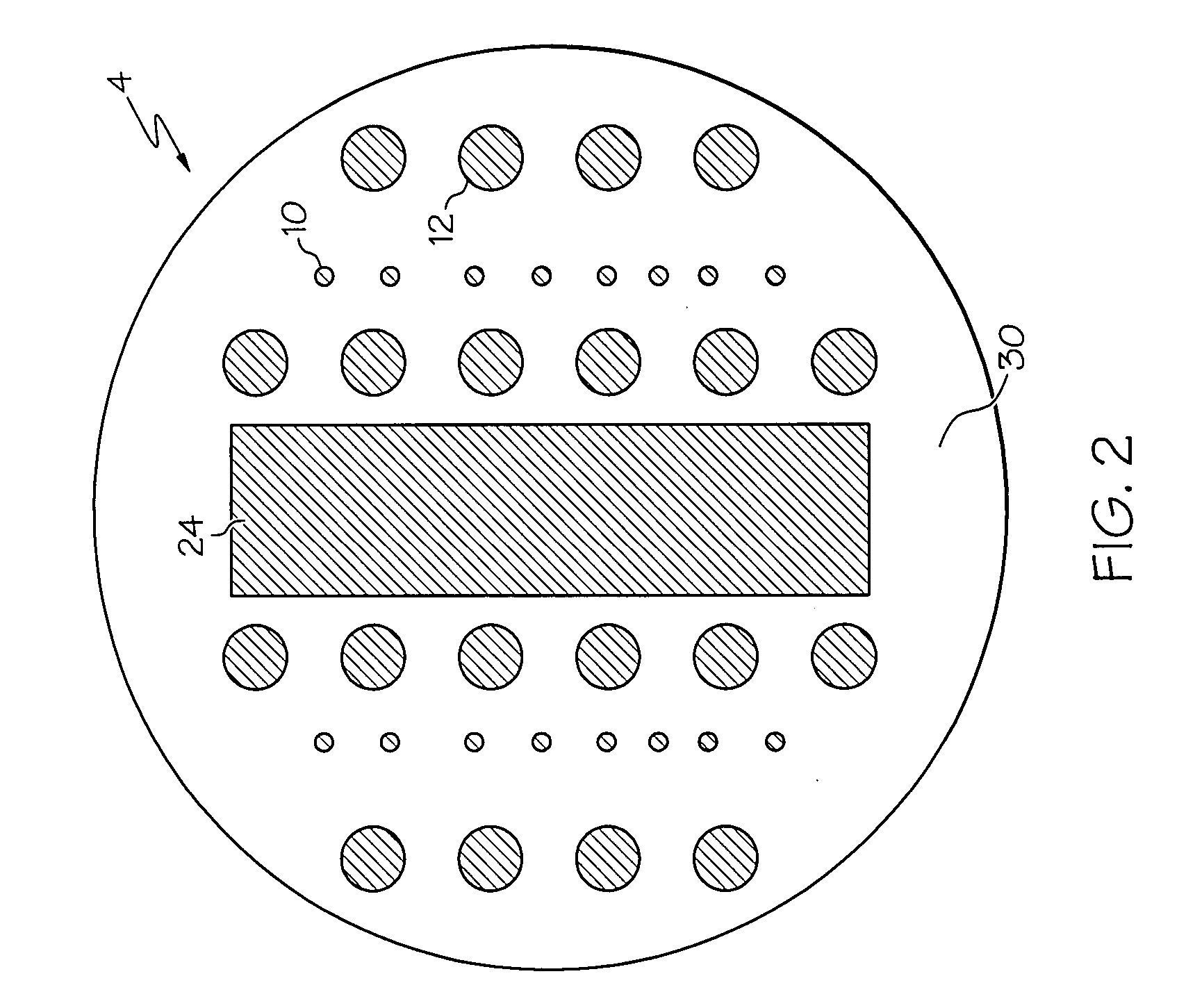
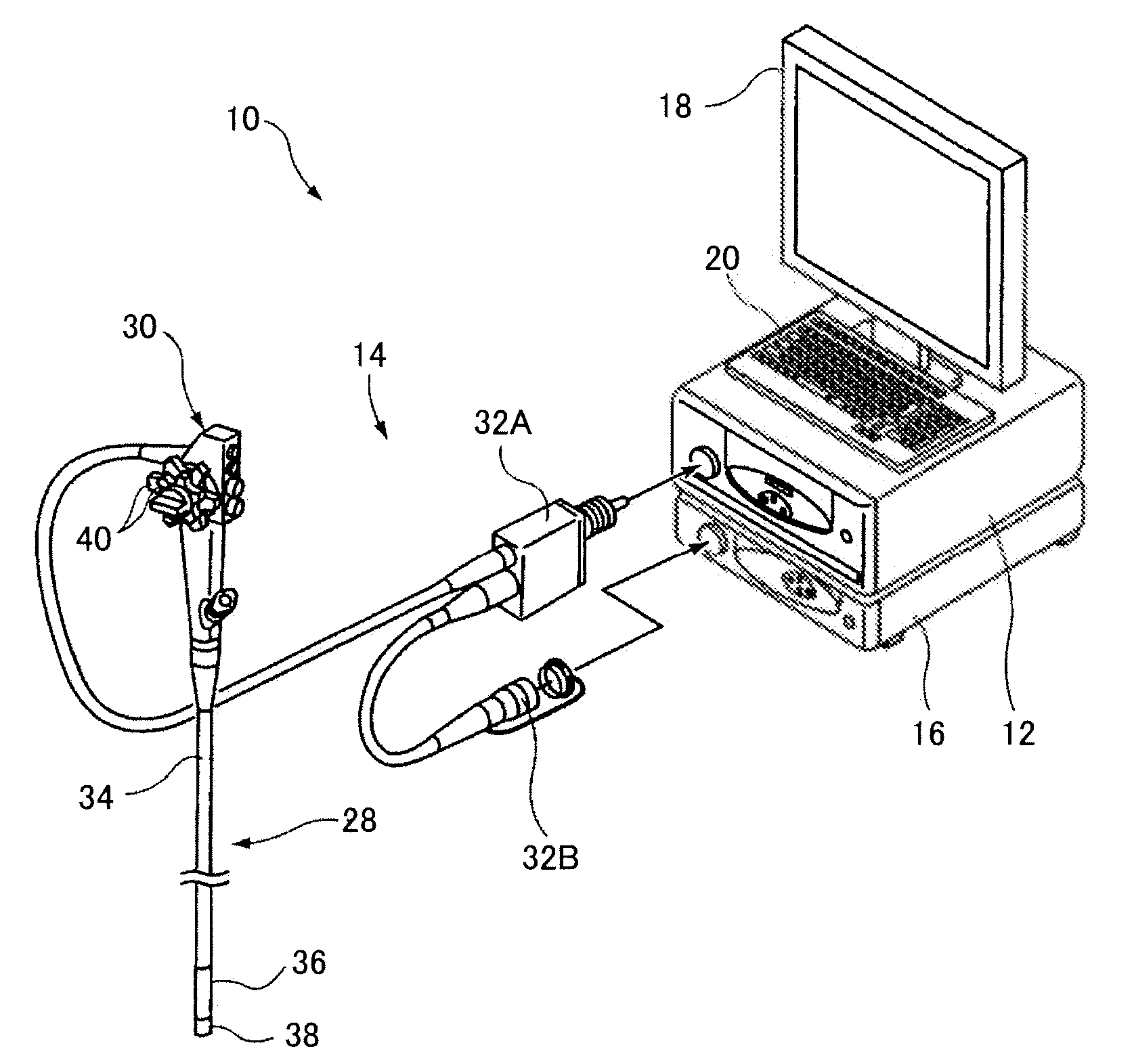
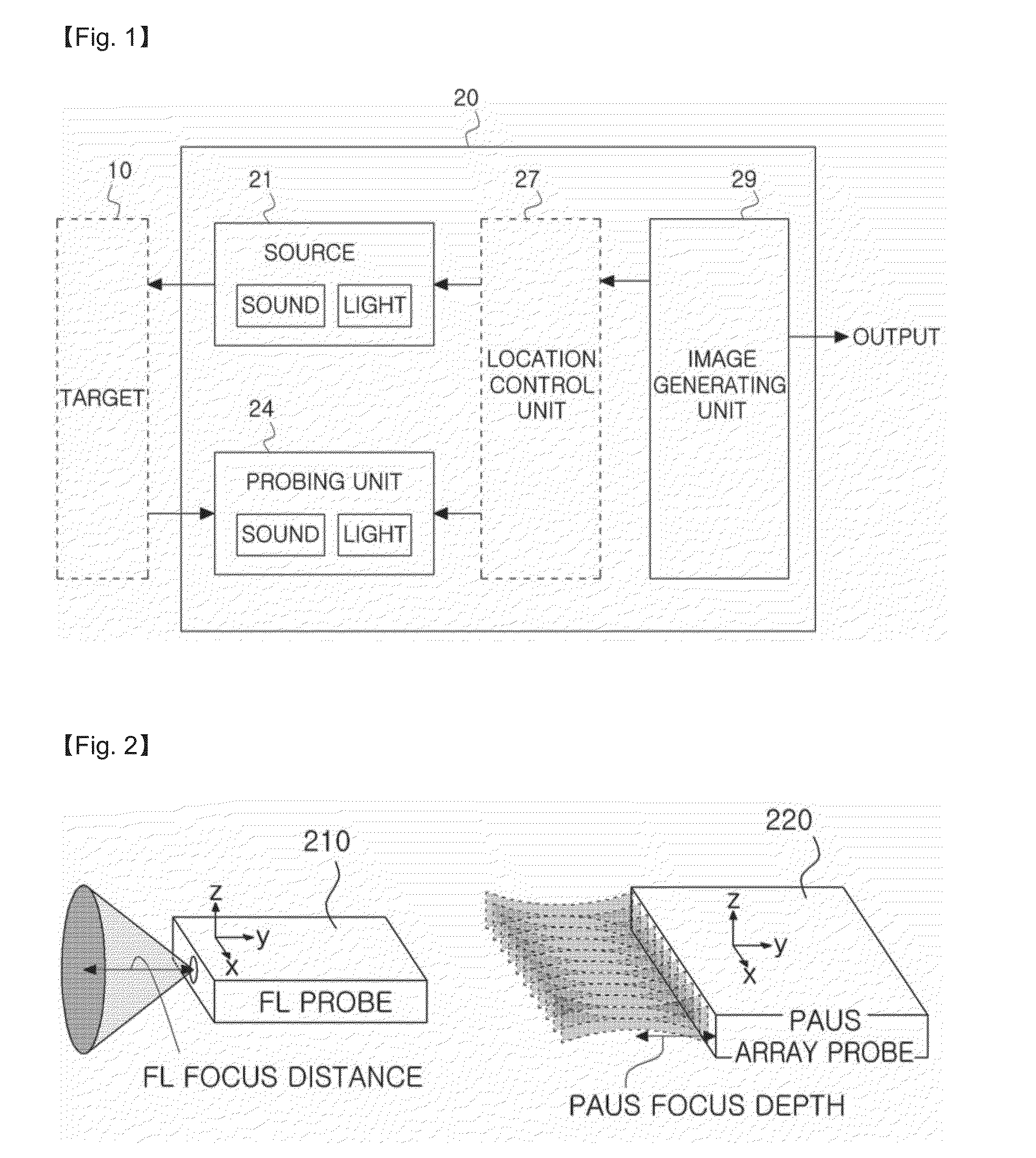
Optical imaging device
ActiveUS20070046778A1Reduce decreaseReduce lightSurgeryDiagnostics using spectroscopyOptical fluorescenceLight guide
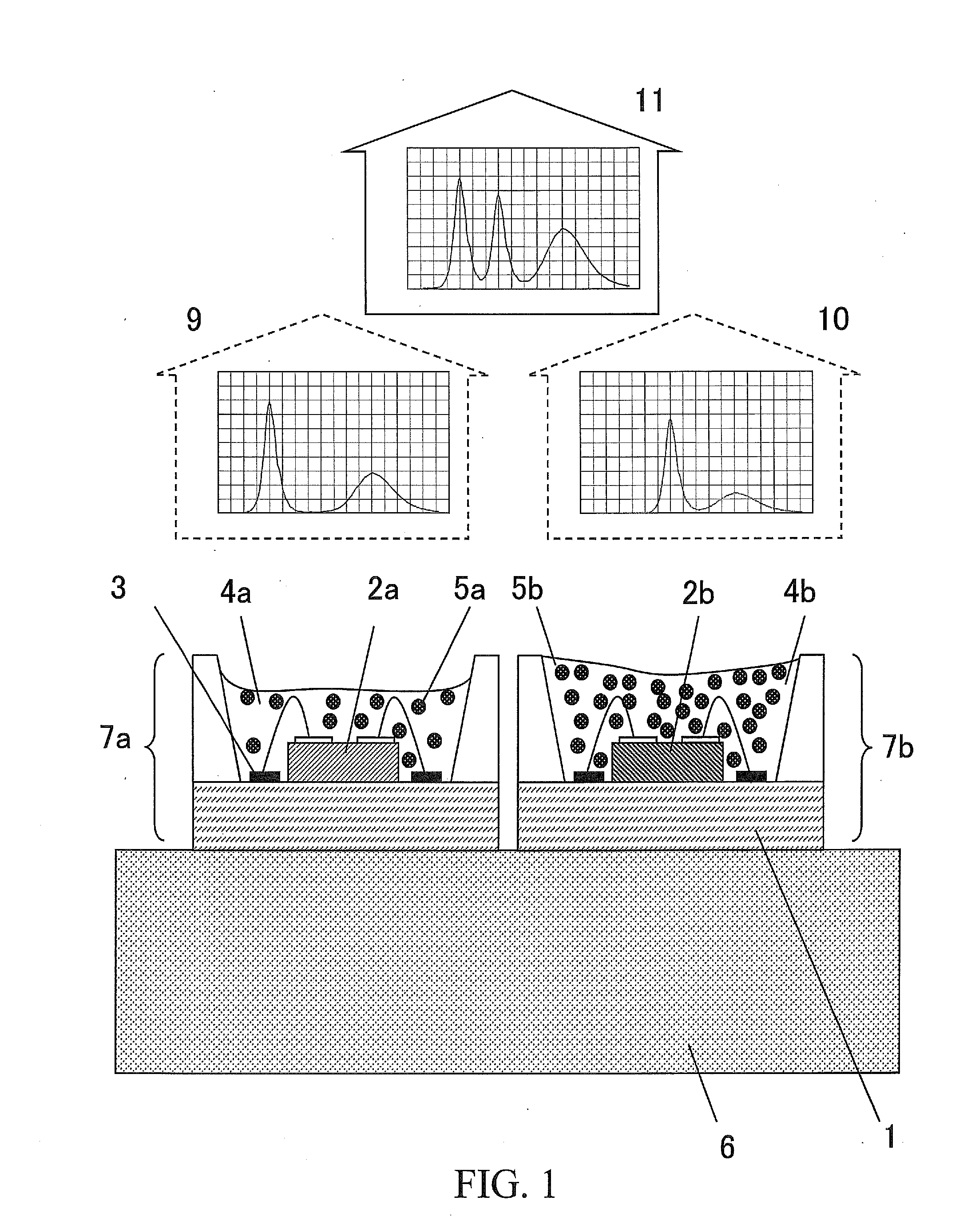
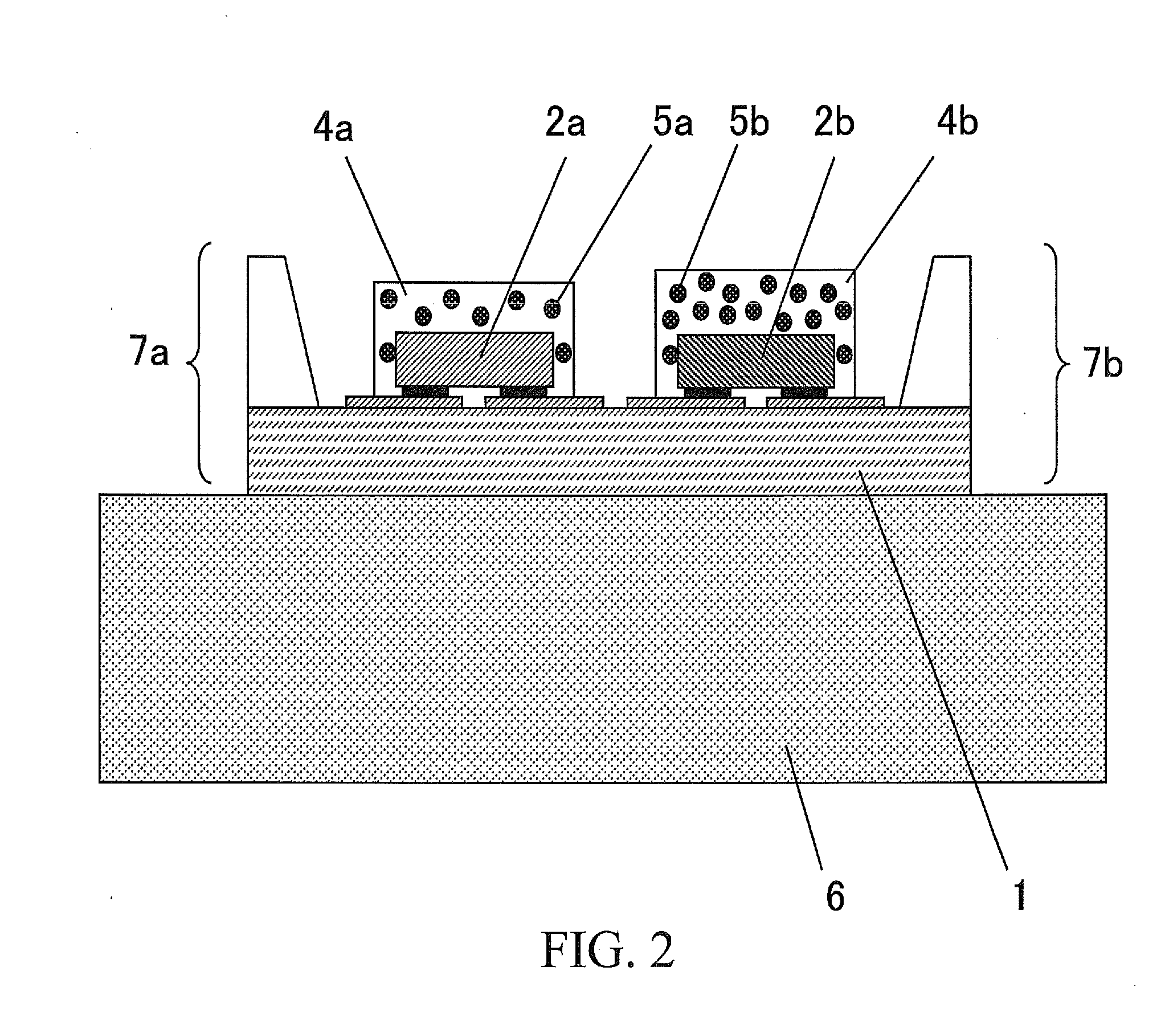
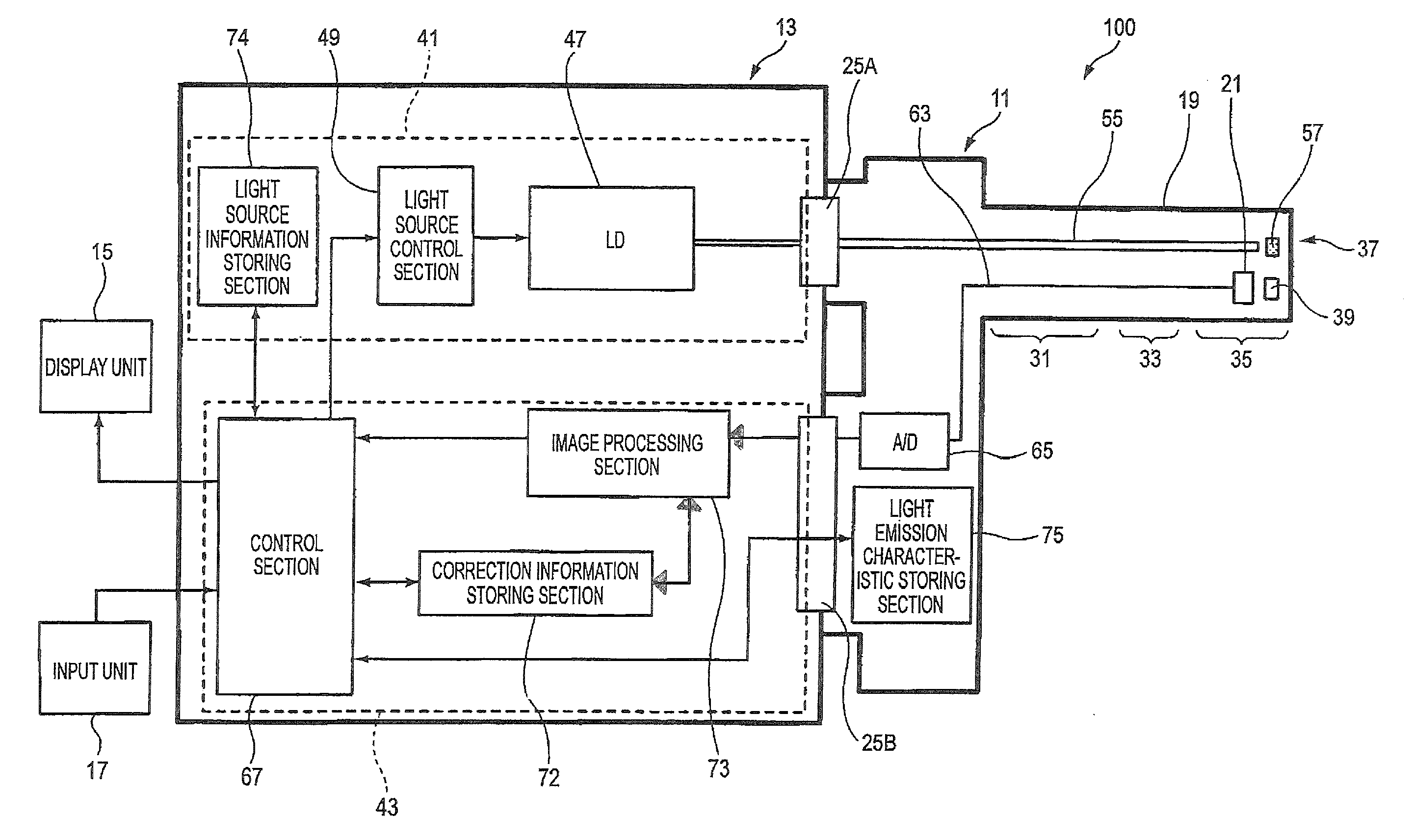
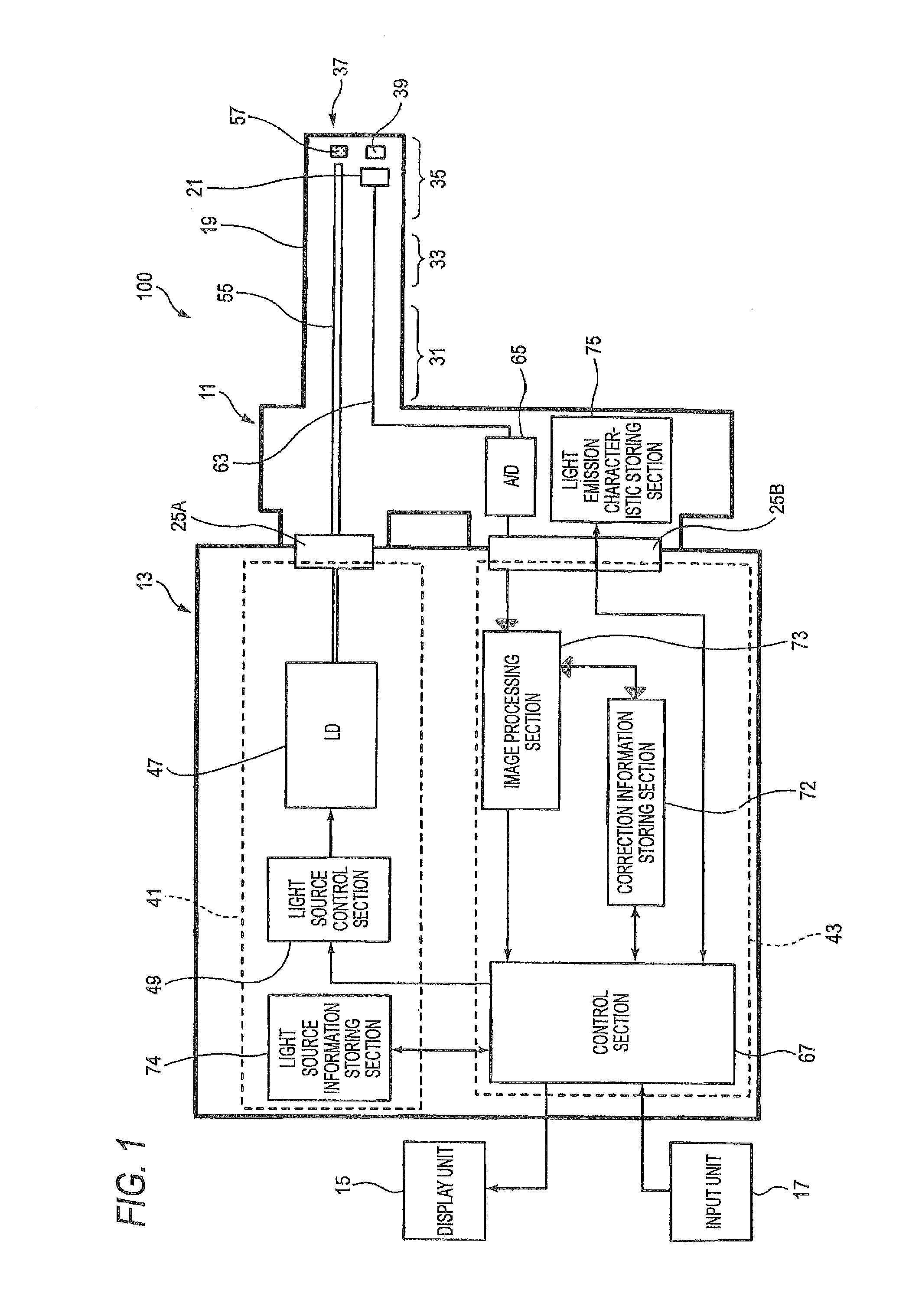
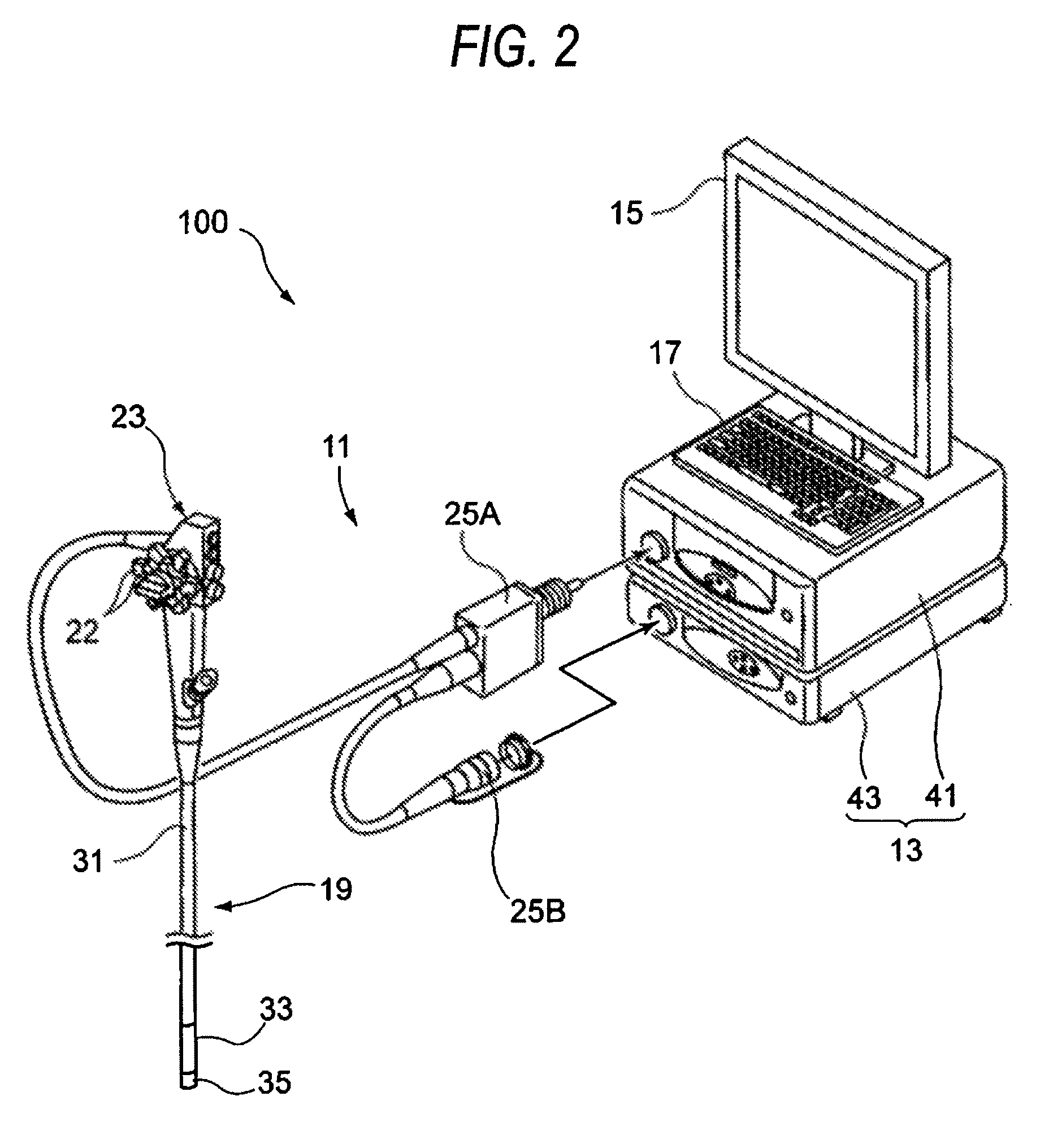
An optical imaging device of the present invention comprises: a light source device; a light guide and illumination lens, provided in an insertion section that can be inserted into a body cavity, for constituting an illumination light path for guiding an illumination light from the light source device to a subject; an objective lens for receiving return lights from the subject; an image capturing section for acquiring a visible light band image from the return light; an excitation light cut filter and image capturing section for acquiring a fluorescent image from the return lights; and an illumination light filter, provided on the illumination light path, for decreasing light in a band overlapping with the band of light of which image is captured by the image capturing section from the illumination light incident on.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
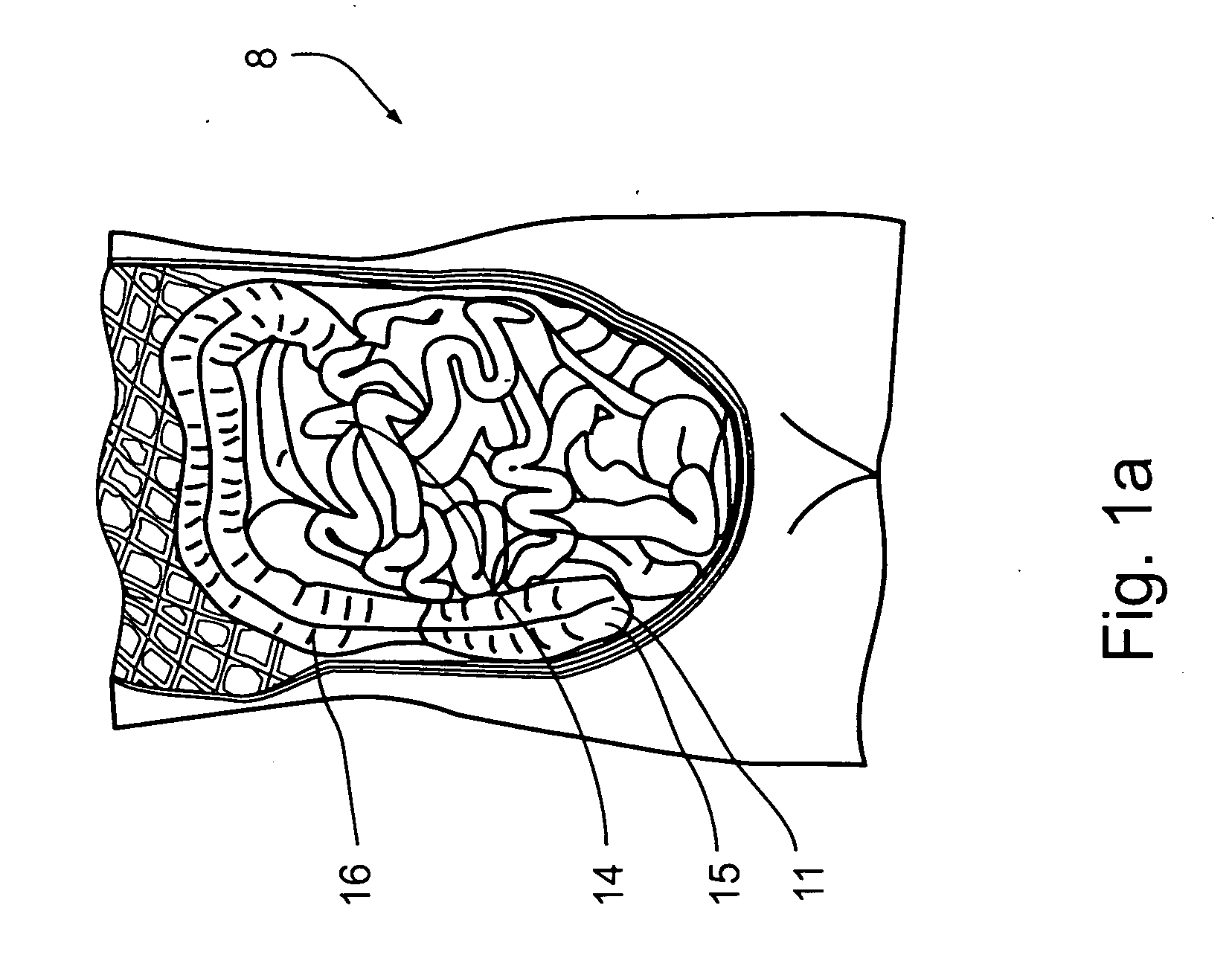
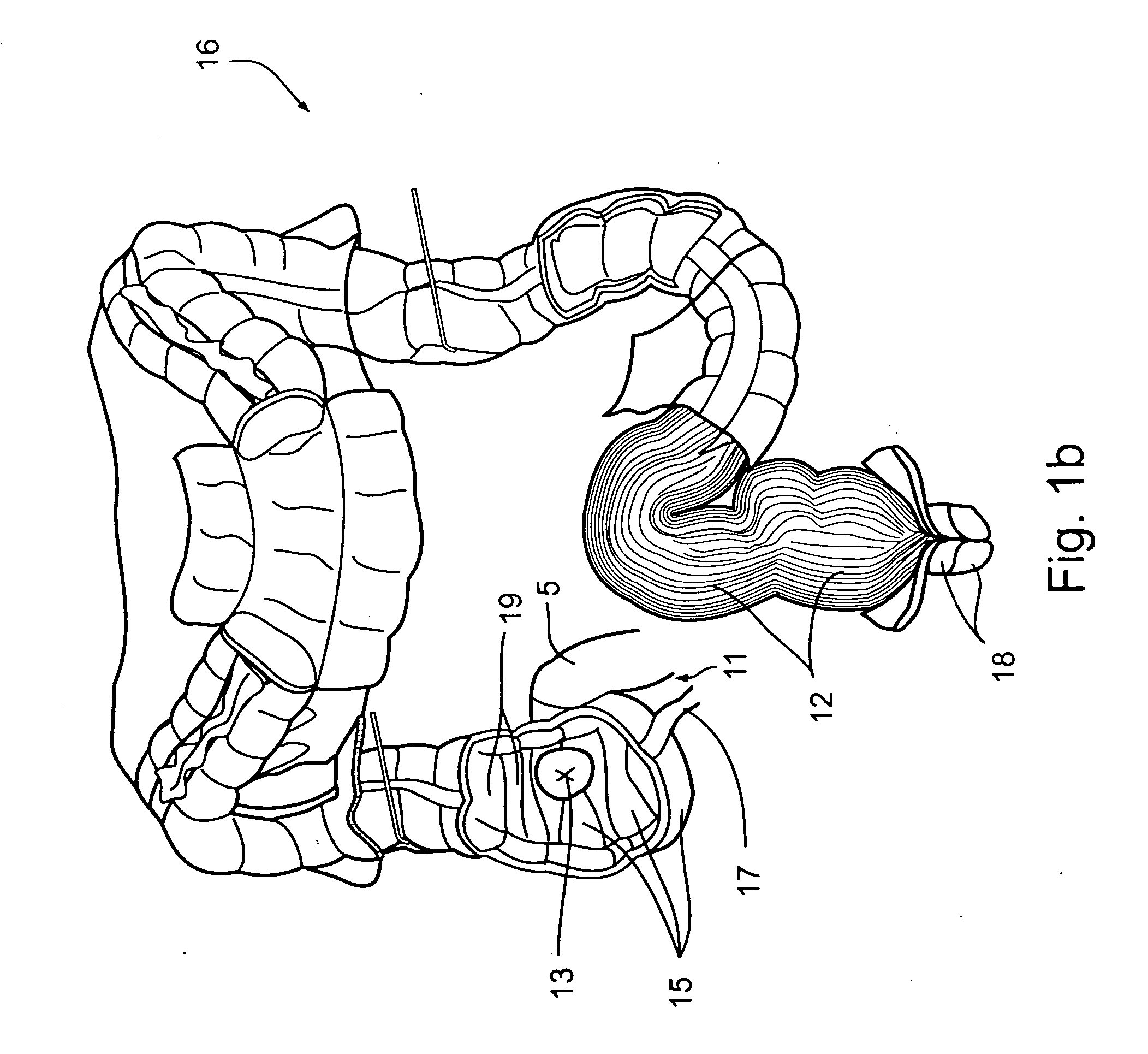
Ingestible device platform for the colon
ActiveUS20050266074A1Enhance the imageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryAbnormal tissue growthOptical fluorescence
An ingestible pill platform for colon imaging is provided, designed to recognize its entry to the colon and expand in the colon, for improved imaging of the colon walls. On approaching the external anal sphincter muscle, the ingestible pill may contract or deform, for elimination. Colon recognition may be based on a structural image, based on the differences in diameters between the small intestine and the colon, and particularly, based on the semilunar fold structure, which is unique to the colon. Additionally or alternatively, colon recognition may be based on a functional image, based on the generally inflammatory state of the vermiform appendix. Additionally or alternatively, pH, flora, enzymes and (or) chemical analyses may be used to recognize the colon. The imaging of the colon walls may be functional, by nuclear-radiation imaging of radionuclide-labeled antibodies, or by optical-fluorescence-spectroscopy imaging of fluorescence-labeled antibodies. Additionally or alternatively, it may be structural, for example, by visual, ultrasound or MRI means. Due to the proximity to the colon walls, the imaging in accordance with the present invention is advantageous to colonoscopy or virtual colonoscopy, as it is designed to distinguish malignant from benign tumors and detect tumors even at their incipient stage, and overcome blood-pool background radioactivity.
Owner:SPECTRUM DYNAMICS MEDICAL LTD
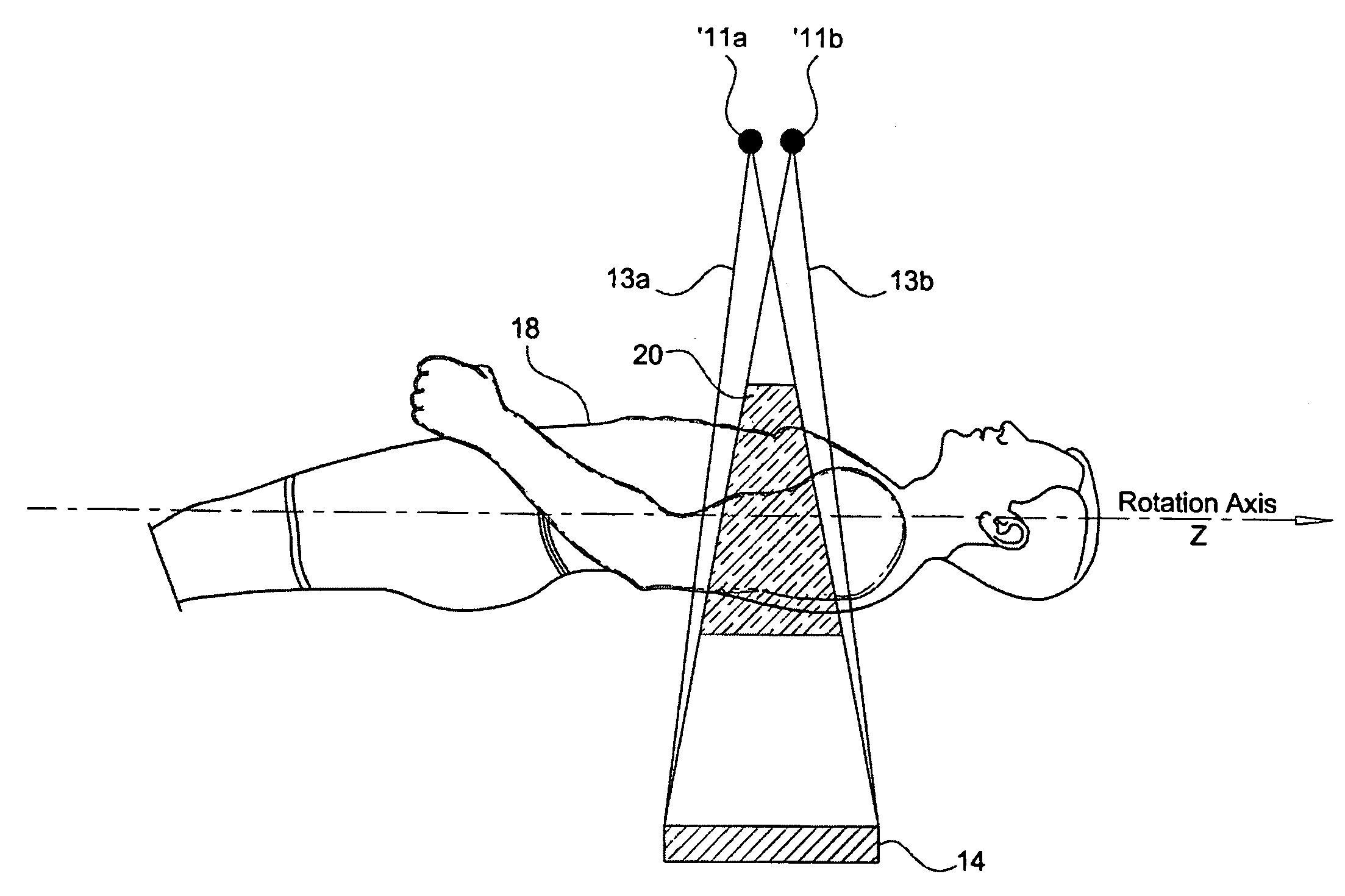
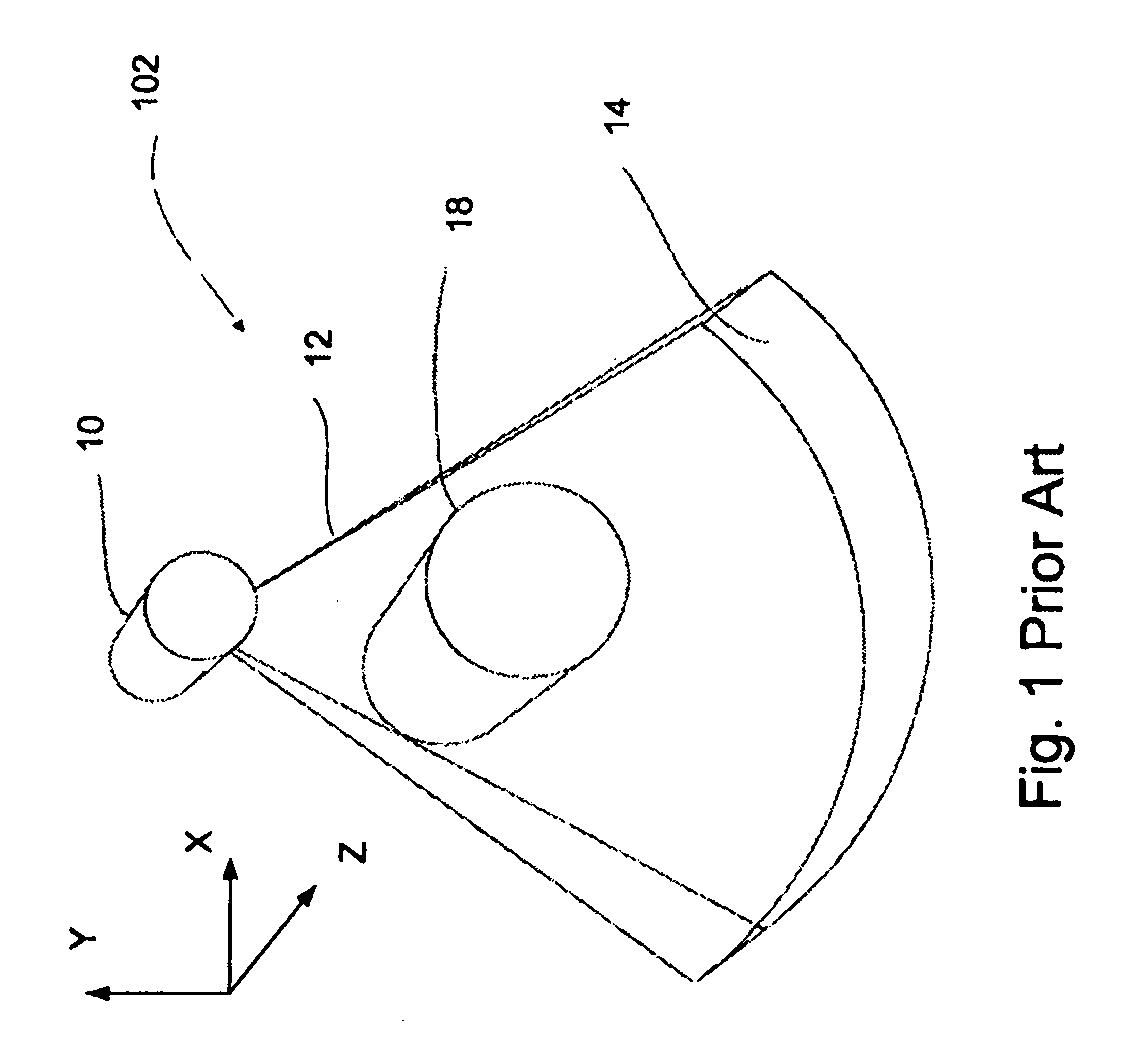
Apparatus and method for tracking feature's position in human body
ActiveUS20090257551A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingHuman bodyFluoroscopic image
A CT scanner for scanning a subject is provided, the scanner comprising: a gantry capable of rotating about a scanned subject; at least two cone beam X-Ray sources displaced from each other mounted on said gantry; at least one 2D detector array mounted on said gantry, said detector is capable of receiving radiation emitted by said at least two X-Ray sources and attenuated by the subject to be scanned; a first image processor capable of generating and displaying CT images of a volume within the subject; a second image processor capable of generating projection X-Ray images of said volume, wherein the images are responsive to X-Ray separately emitted by each of said at least two cone beam X-Ray sources; and a third image processor capable of generating and displaying fluoroscopic images composed of said projection X-Ray images, wherein said fluoroscopic images are spatially registered to said CT images.
Owner:ARINETA
Solid-state detector and optical system for microchip analyzers
InactiveUS6867420B2Easy to makeMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrophoresesOptical fluorescence
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC +1
Method and apparatus for medical imaging using near-infrared optical tomography and flourescence tomography combined with ultrasound
ActiveUS20080058638A1High qualityGreat frequencyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis by optical meansTissue volumeFluorescence
Methods and apparatus for medical imaging using diffusive optical tomography and fluorescent diffusive optical tomography are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method for medical imaging comprises, scanning a tissue volume with near-infrared light to obtain structural parameters, wherein the tissue volume includes a biological entity, scanning the tissue volume with near-infrared light to obtain optical and fluorescence measurements of the scanned volume, segmenting the scanned volume into a first region and a second region, and reconstructing an optical image and a fluorescence image of at least a portion of the scanned volume from the structural parameters and the optical and fluorescence measurements. In another embodiment an apparatus for medical imaging is disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Spectral imaging for vertical sectioning
InactiveUS7110118B2Efficient scanningRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometrySelf interferenceOptical fluorescence
A method and apparatus for performing optical microscopy in one to three dimensions employs a spectral self-interference fluorescent microscopy technique that includes providing at least one fluorescent microscopy sample, at least one objective lens, and at least one reflecting surface. The fluorescent sample is disposed between the objective lens and the reflecting surface, the distance from the sample to the reflecting surface being several to several tens times an excitation wavelength. Excitation light causes the fluorescent sample to emit light, at least a portion of which is reflected by the reflecting surface. The objective lens collects the reflected light and the light emitted directly by the fluorescent sample. The direct and reflected light interfere causing spectral oscillations in the emission spectrum. The periodicity and the peak wavelengths of the emission spectrum are spectroscopically analyzed to determine the optical path length between the fluorescent sample and the reflecting surface.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Projection display surface providing speckle reduction
ActiveUS8085467B1Speckle reductionImpact image qualityProjectorsColor photographyOptical fluorescenceReflective layer
A projection display surface for reducing speckle artifacts from a projector having at least one narrow band light source having an incident visible wavelength band, wherein the incident visible wavelength band has an incident peak wavelength and an incident bandwidth, comprising: a substrate having a reflective layer that reflects incident light over at least the incident visible wavelength band; and a fluorescent agent distributed over the reflective layer, wherein the fluorescent agent absorbs a fraction of the light in the incident visible wavelength band and emits light in an emissive visible wavelength band having an emissive peak wavelength and an emissive bandwidth; wherein return light from the projection display surface produced when incident light in the incident visible wavelength band is incident on the projection display surface contains light in both the incident visible wavelength band and emissive visible wavelength band, thereby reducing speckle artifacts.
Owner:IMAX THEATERS INT
Light emitting device, and illumination light source, display unit and electronic apparatus including the light emitting device
InactiveUS20110211336A1No lot-to-lot variationColor tone is easilySolid-state devicesIlluminated signsOptical fluorescencePeak value
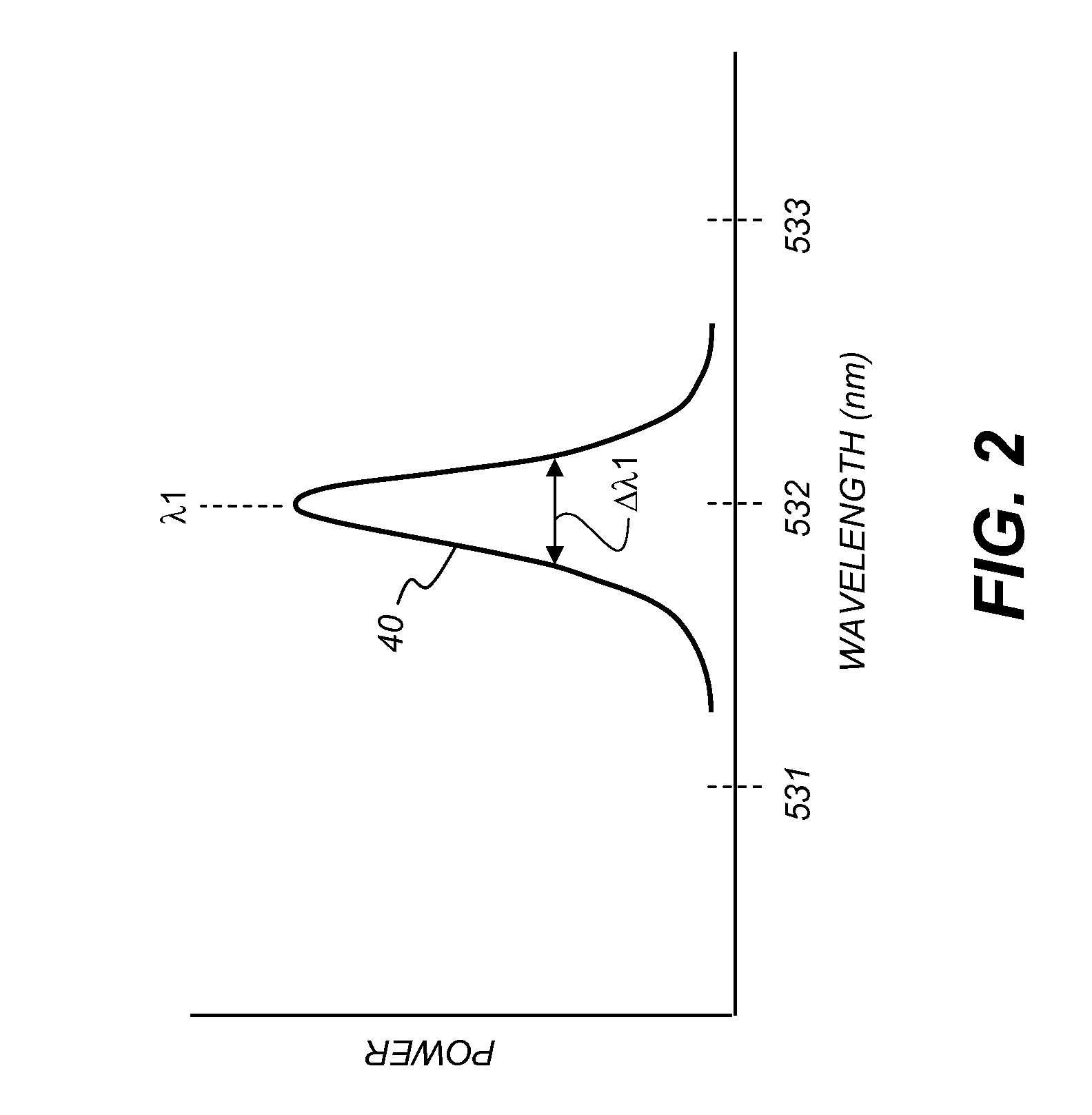
A light emitting device includes: a first semiconductor light emitting element having a solid-state blue light emitting element that emits blue light with a light emission peak in a wavelength range from 420 nm to less than 480 nm, and a first red phosphor layer that covers the solid-state blue light emitting element and includes a first red phosphor that emits red light with a light emission peak in a wavelength range from 600 nm to less than 680 nm; and a second semiconductor light emitting element having a solid-state green light emitting element that emits green light with a light emission peak in a wavelength range from 500 nm to less than 550 nm, and a second red phosphor layer that covers the solid-state green light emitting element and includes a second red phosphor that emits red light with a light emission peak in a wavelength range from 600 nm to less than 680 nm.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
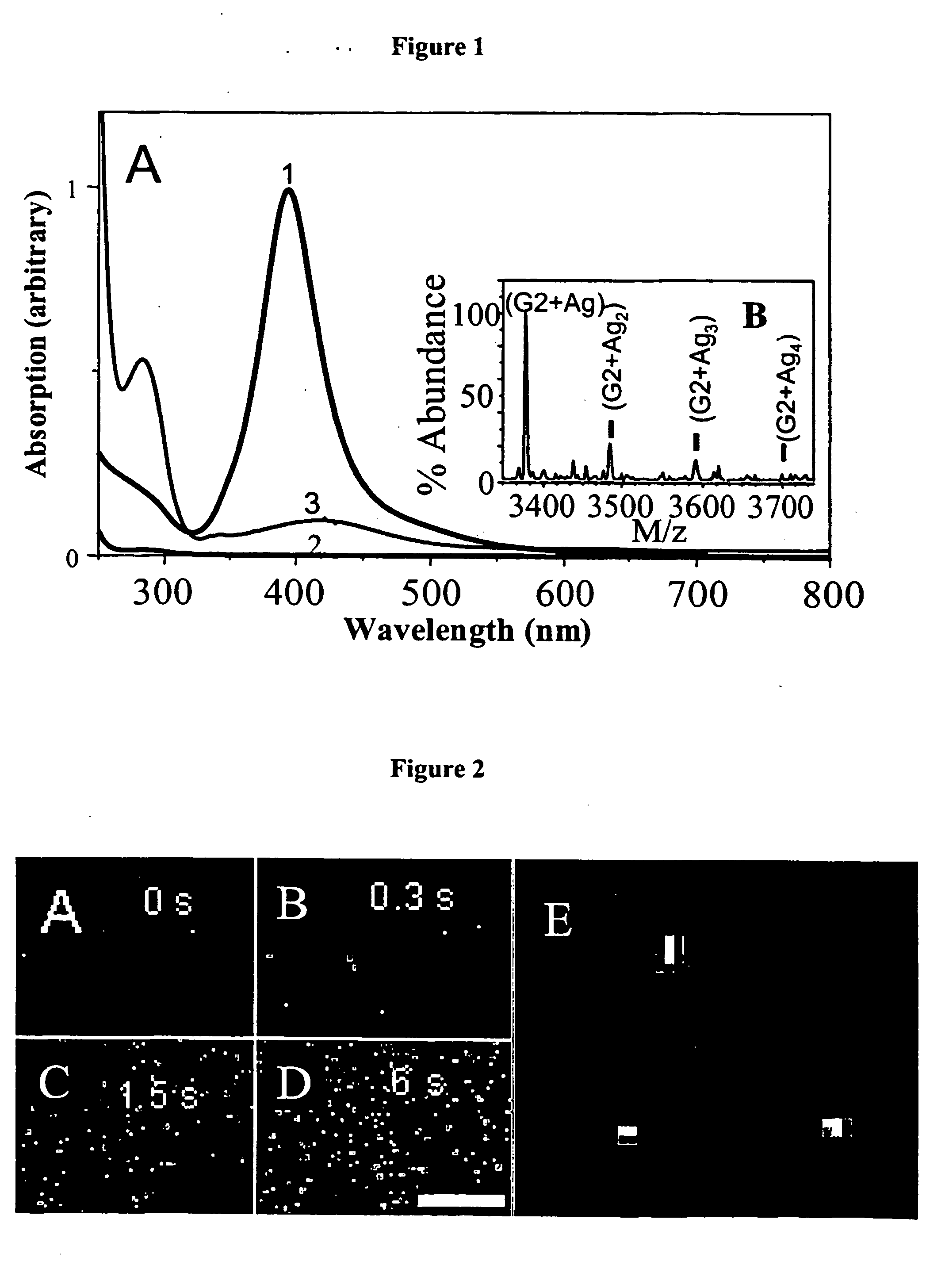
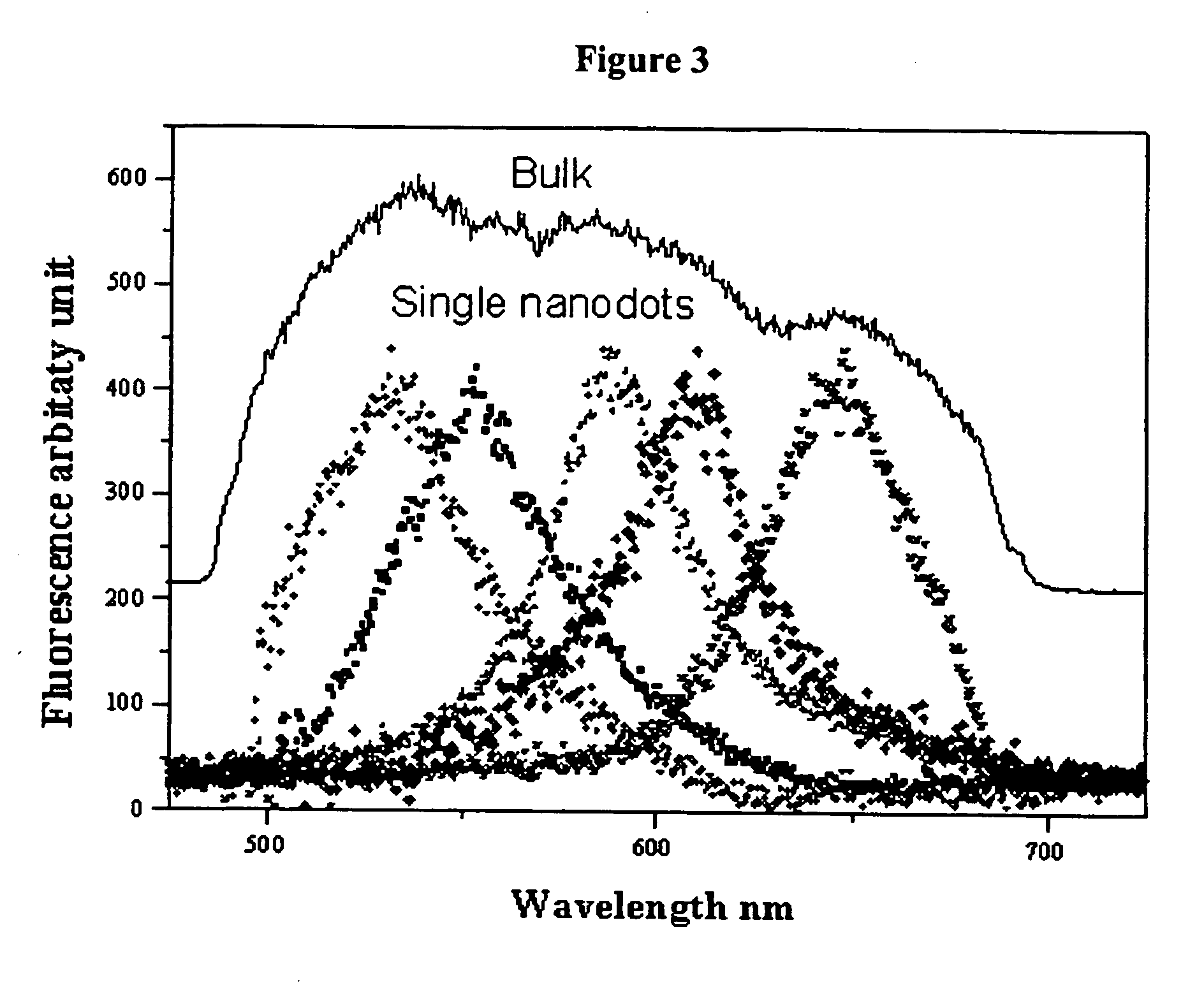
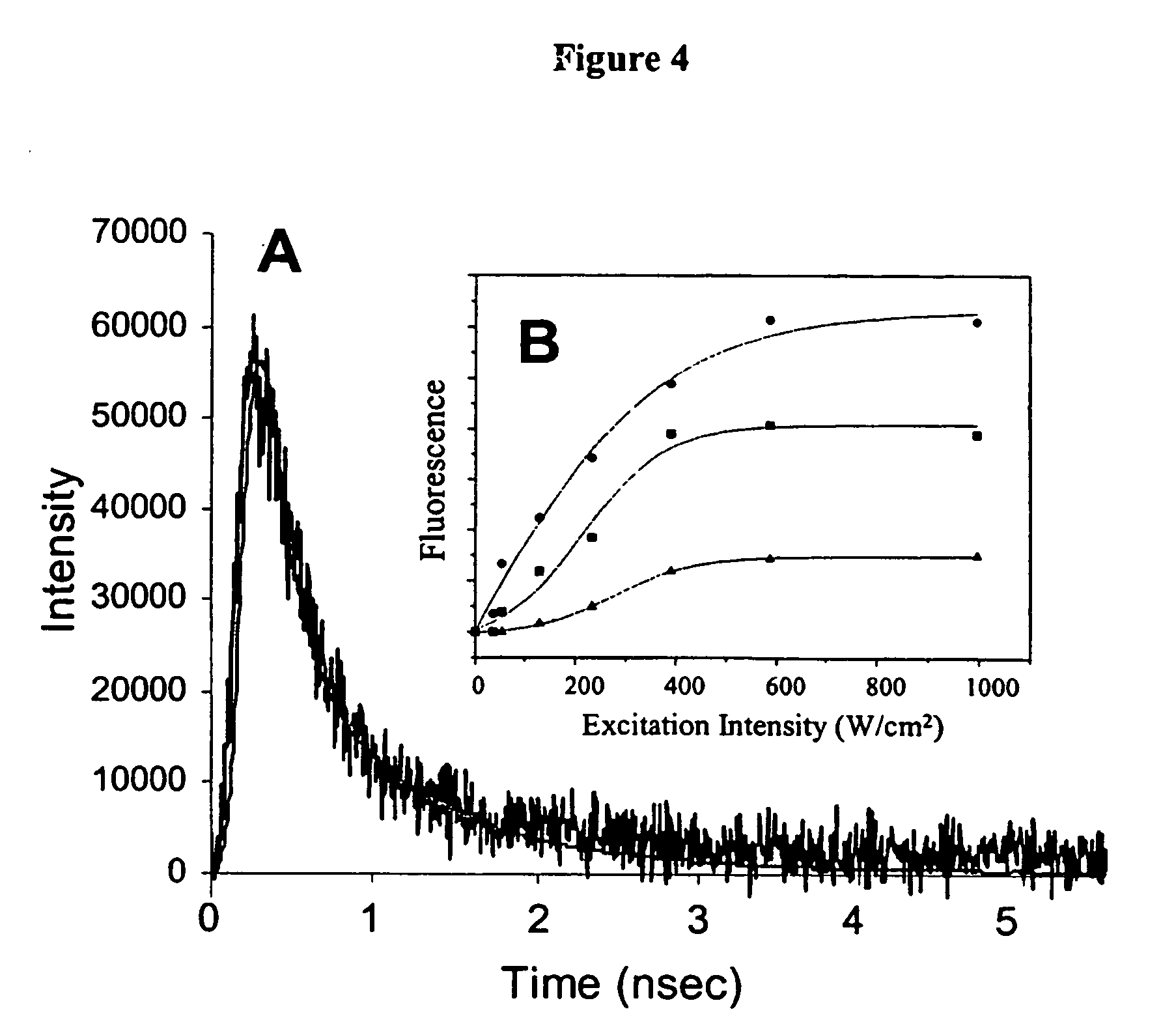
Nano-sized optical fluorescence labels and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060051878A1Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementDendrimerSpectral emission
A composition is disclosed which is capable of being used for detection, comprising an encapsulated noble metal nanocluster. Methods for preparing the encapsulated noble metal nanoclusters, and methods of using the encapsulated noble metal nanoclusters are also disclosed. The noble metal nanoclusters are preferably encapsulated by a dendrimer or a peptide. The encapsulated noble metal nanoclusters have a characteristic spectral emission, wherein said spectral emission is varied by controlling the nature of the encapsulating material, such as by controlling the size of the nanocluster and / or the generation of the dendrimer, and wherein said emission is used to provide information about a biological state.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Endoscopic diagnosis system
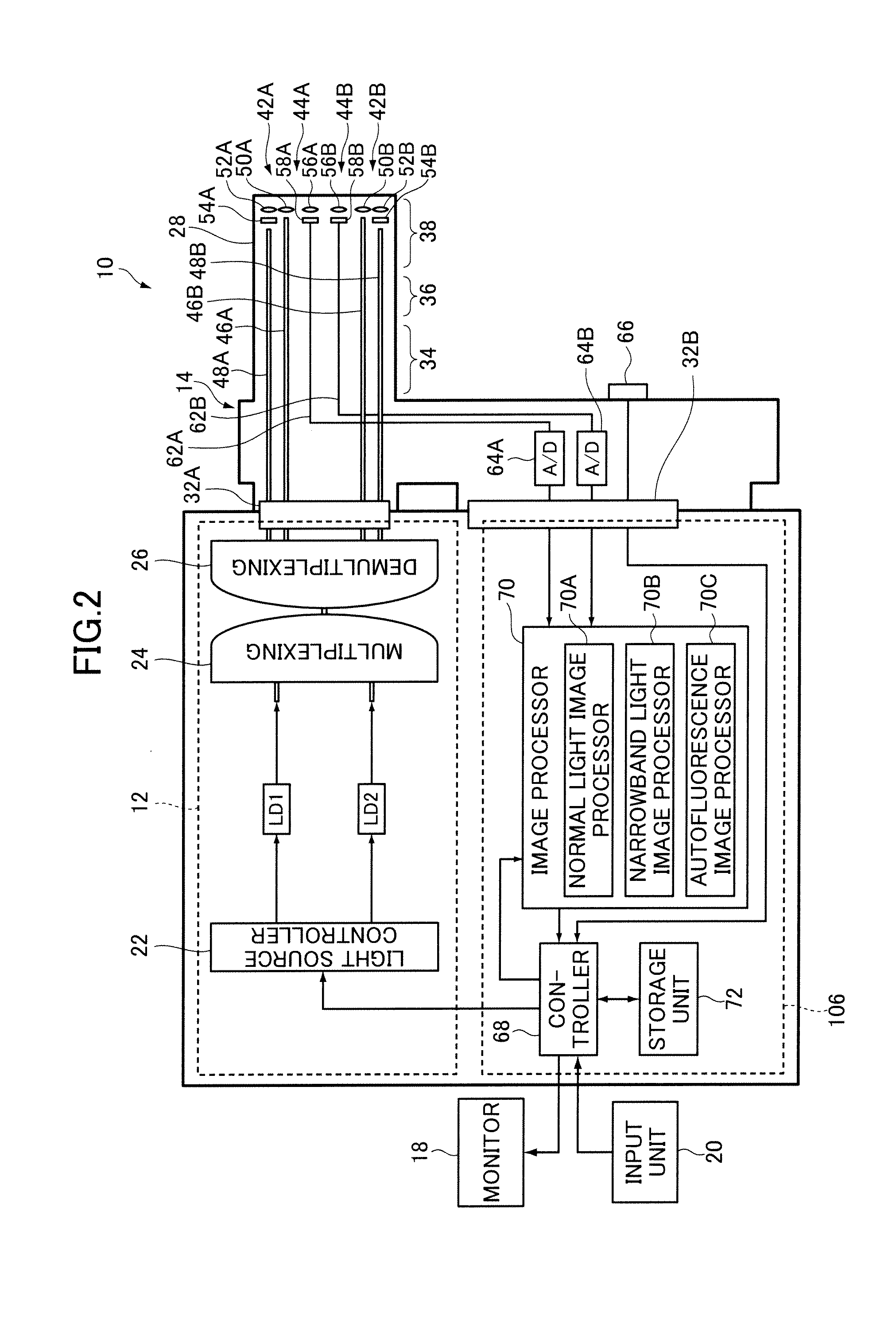
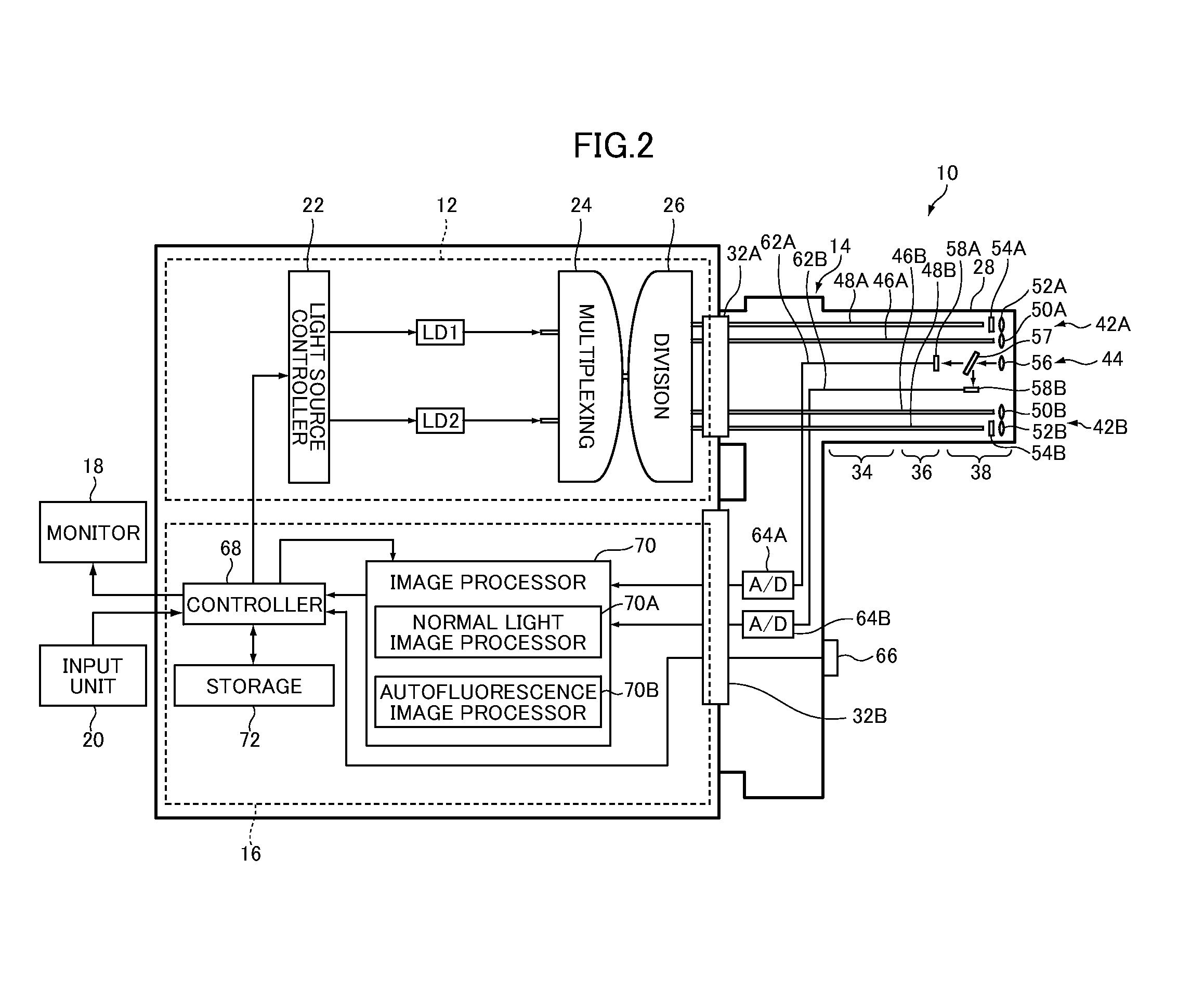
ActiveUS20120165627A1High quality imagingHigh-quality autofluorescenceSurgeryEndoscopesOptical fluorescenceEndoscope
An endoscopic diagnosis system includes first and second narrowband light sources for emitting respectively first and second narrowband lights having a wavelength range different from each other, a first image sensor for receiving reflected light of the first narrowband light illuminating a subject to acquire a narrowband light image in a narrowband light observation mode, a second image sensor for receiving first autofluorescence emitted from the subject as the first narrowband light illuminates the subject to acquire a first autofluorescence image in a first autofluorescence observation mode and receiving second autofluorescence emitted from the subject as the second narrowband light illuminates the subject to acquire a second autofluorescence image in a second autofluorescence observation mode, and a light source controller for increasing emission amounts of the first and the second narrowband light in the first and the second autofluorescence observation mode.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Projection display surface providing speckle reduction
ActiveUS20110310478A1Speckle reductionImpact image qualityProjectorsColor photographyOptical fluorescenceReflective layer
A projection display surface for reducing speckle artifacts from a projector having at least one narrow band light source having an incident visible wavelength band, wherein the incident visible wavelength band has an incident peak wavelength and an incident bandwidth, comprising: a substrate having a reflective layer that reflects incident light over at least the incident visible wavelength band; and a fluorescent agent distributed over the reflective layer, wherein the fluorescent agent absorbs a fraction of the light in the incident visible wavelength band and emits light in an emissive visible wavelength band having an emissive peak wavelength and an emissive bandwidth; wherein return light from the projection display surface produced when incident light in the incident visible wavelength band is incident on the projection display surface contains light in both the incident visible wavelength band and emissive visible wavelength band, thereby reducing speckle artifacts.
Owner:IMAX THEATERS INT
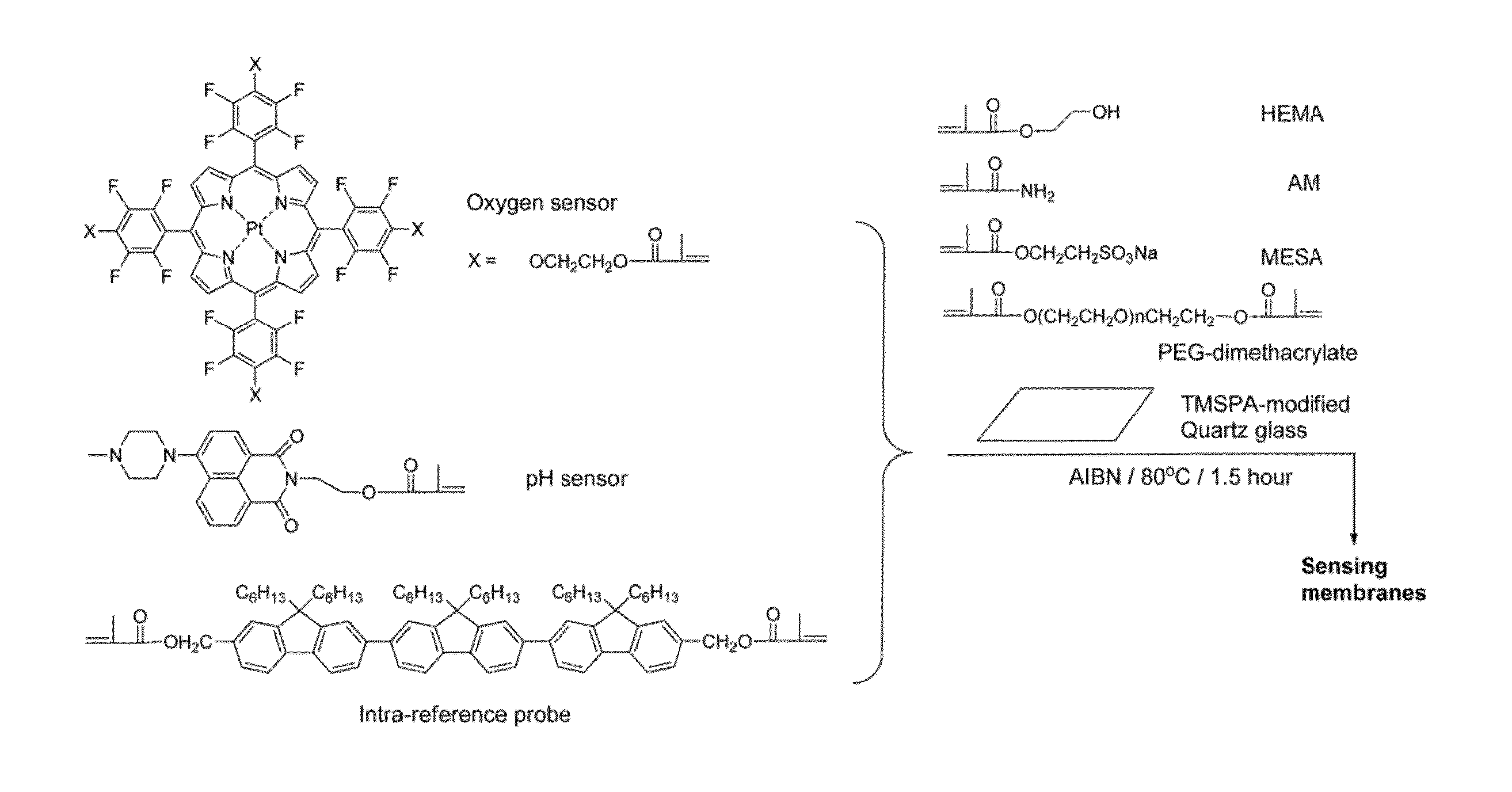
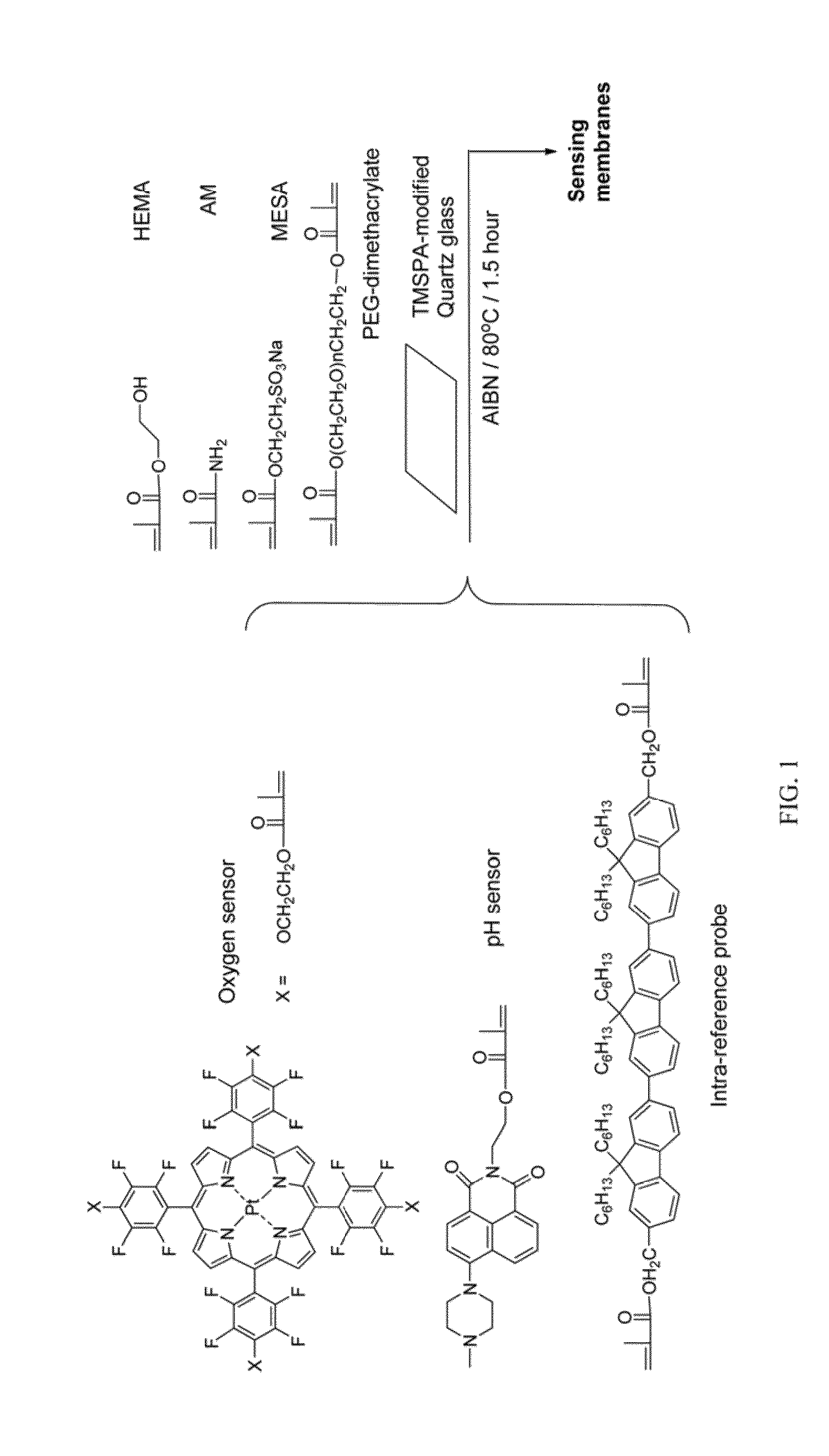
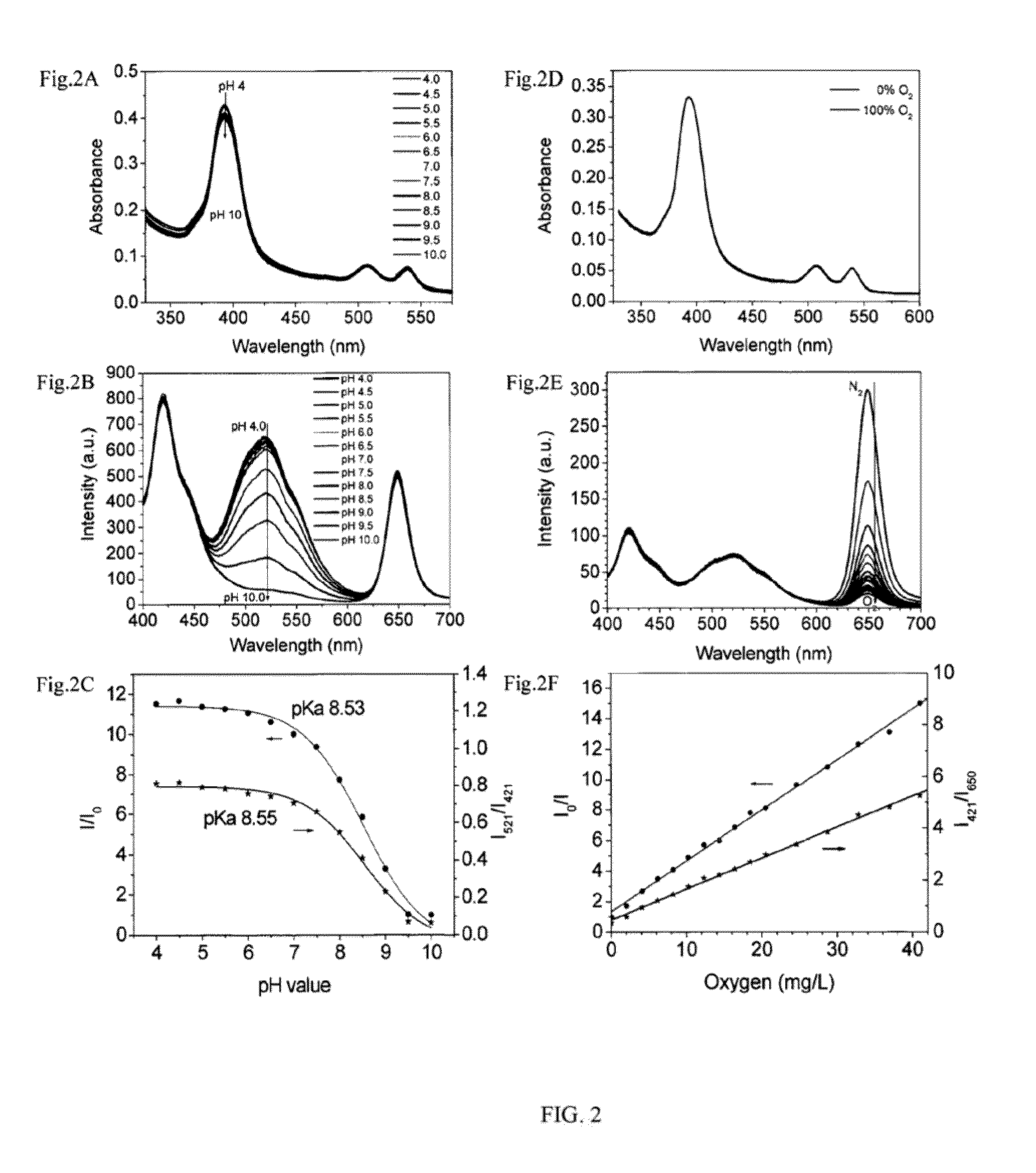
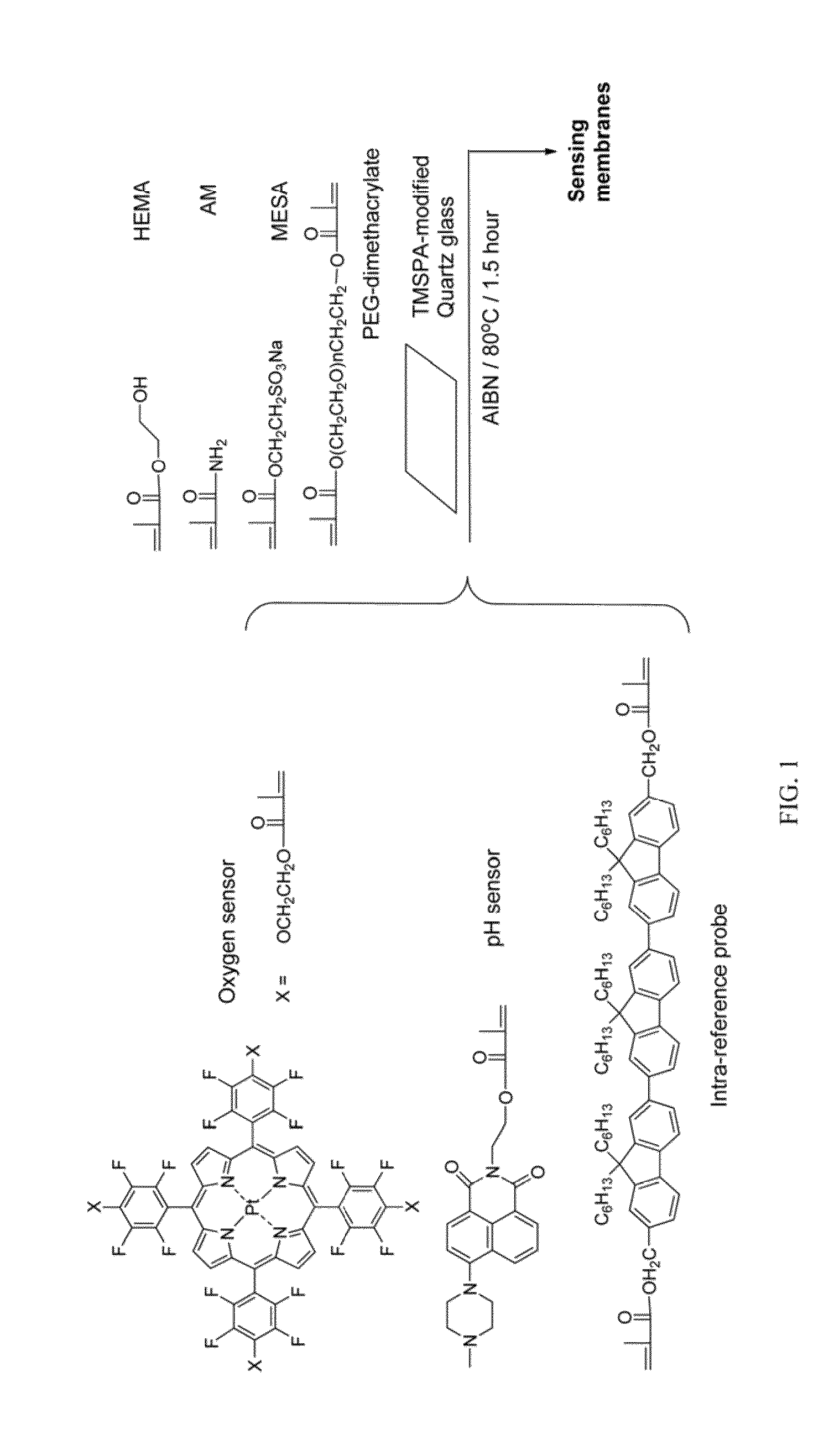
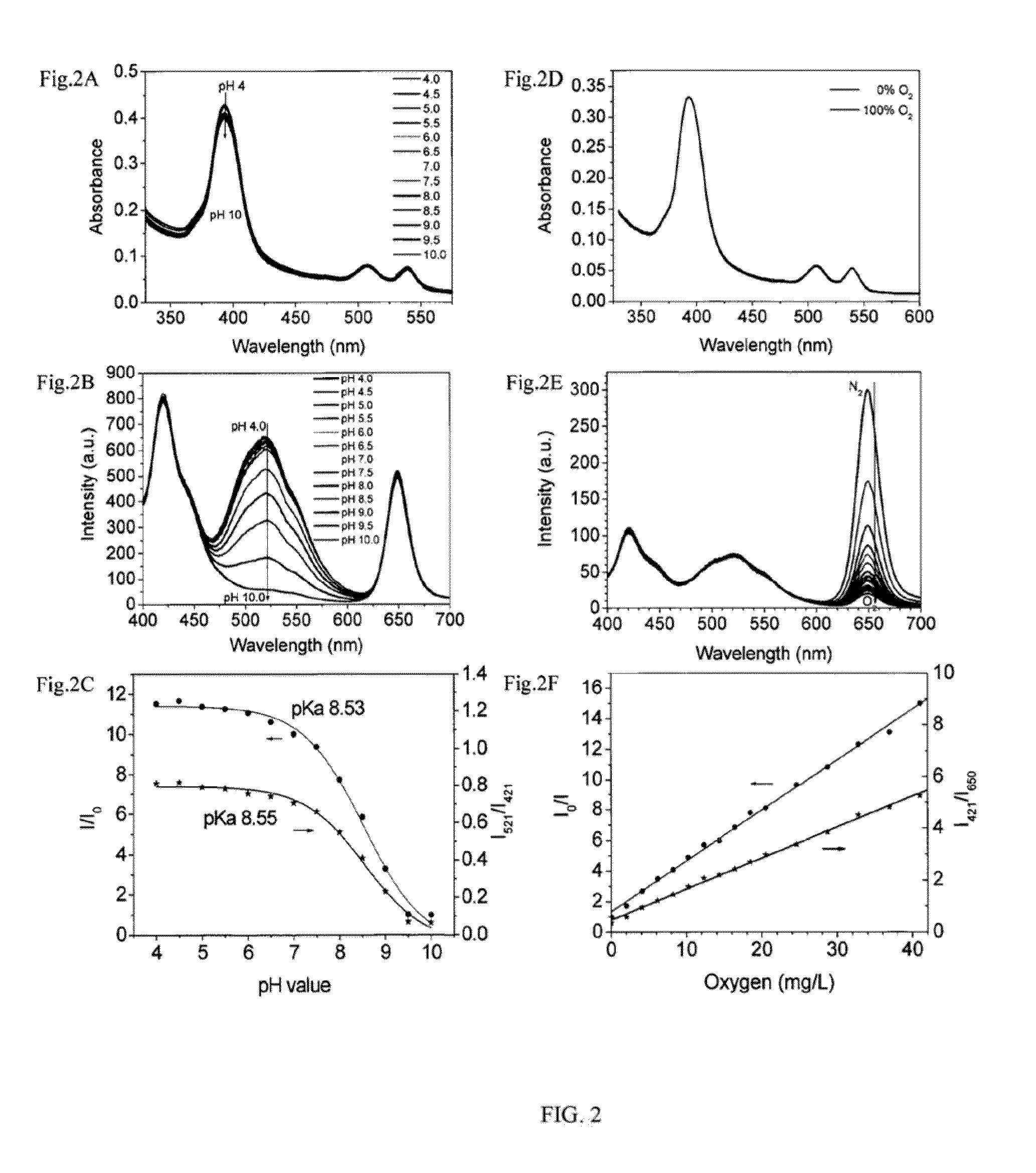
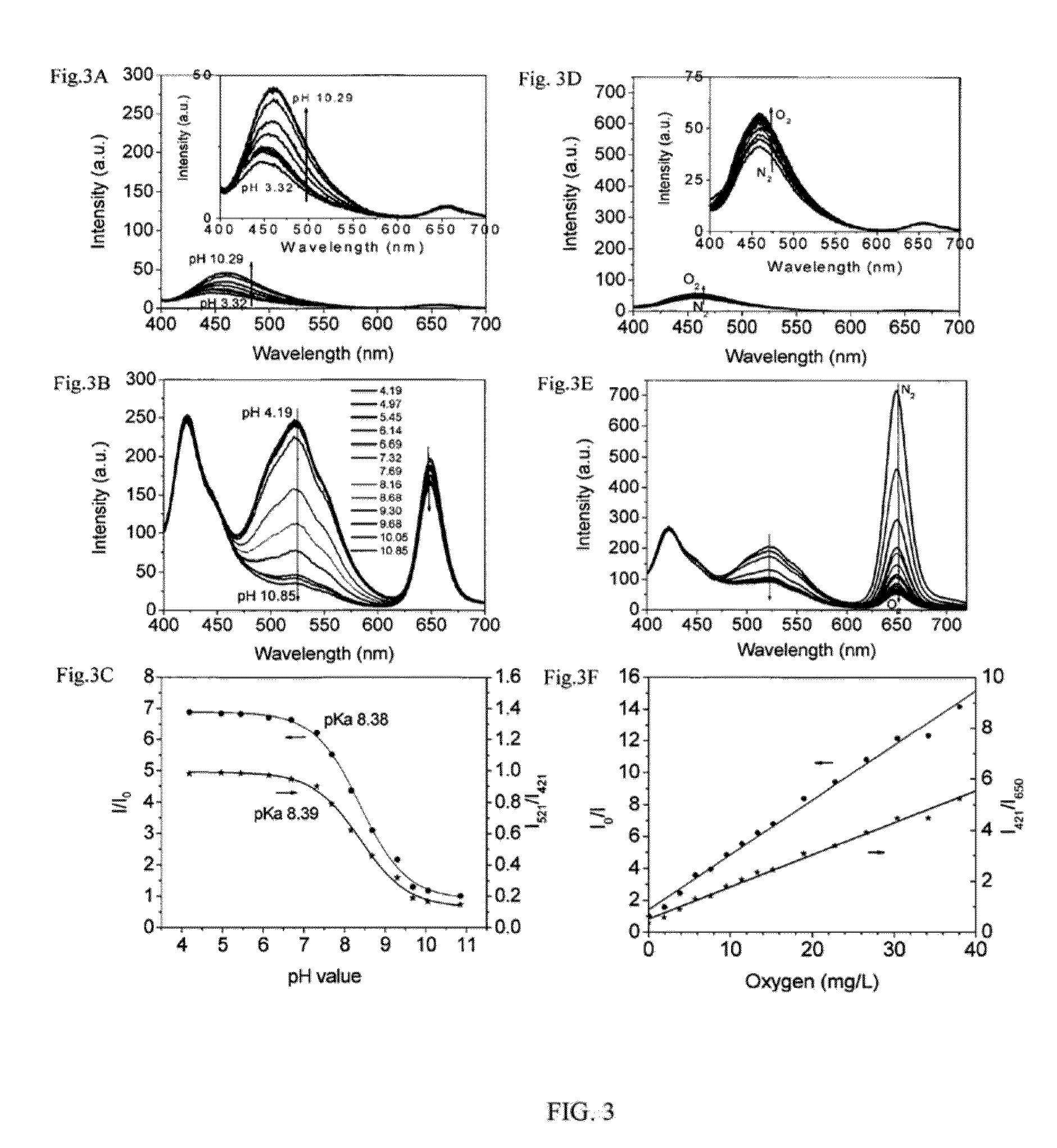
Optical fluorescence dual sensors and methods of preparing and using them
ActiveUS20130102024A1Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementOptical fluorescenceOxygen
The present invention relates to an optical fluorescence dual sensor comprising a probe for sensing pH, a probe for sensing oxygen, an intra-reference probe and a matrix. The present invention also relates to methods of preparing an optical fluorescence dual sensor and methods of using them.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
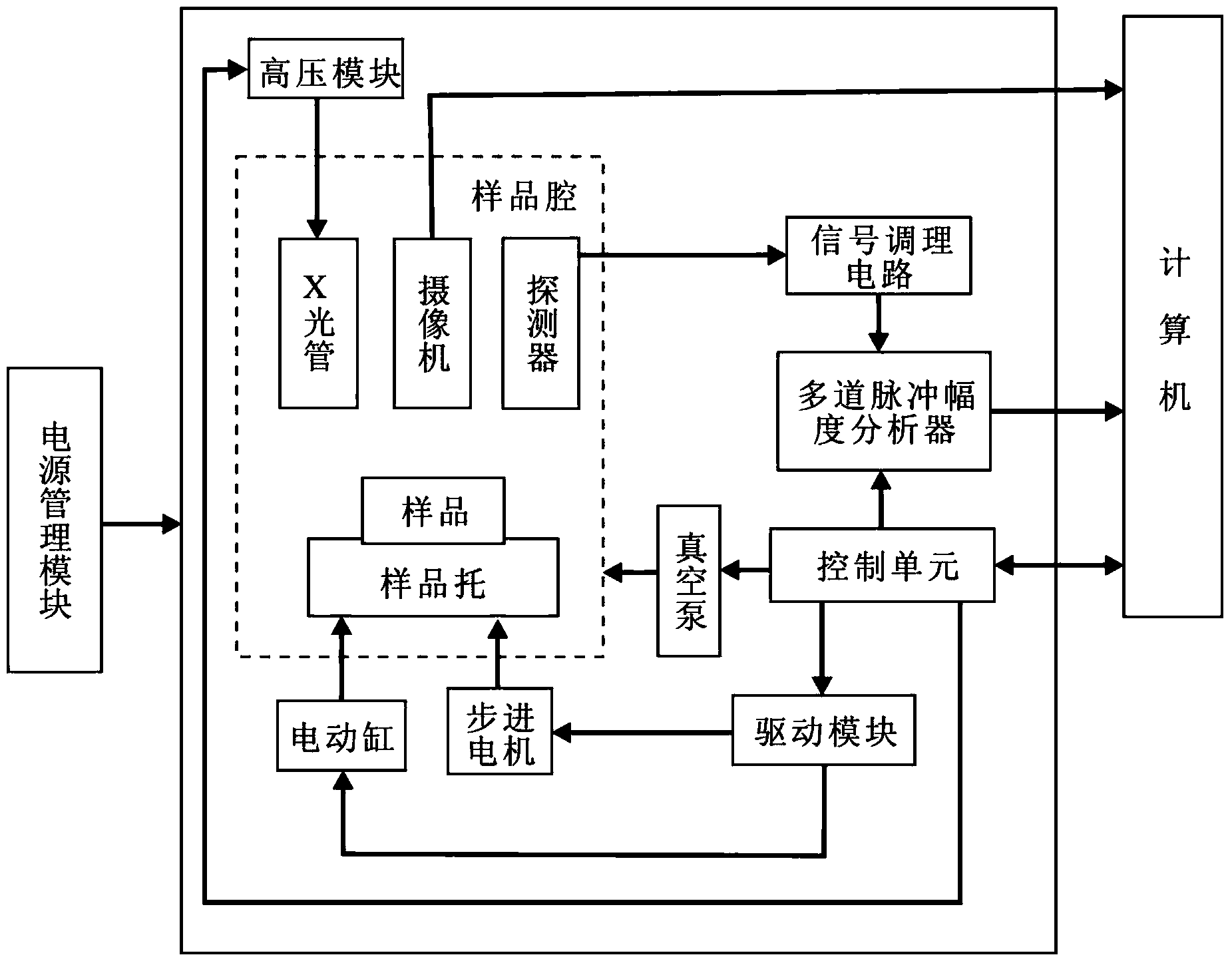
Automatic energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence analysis test platform
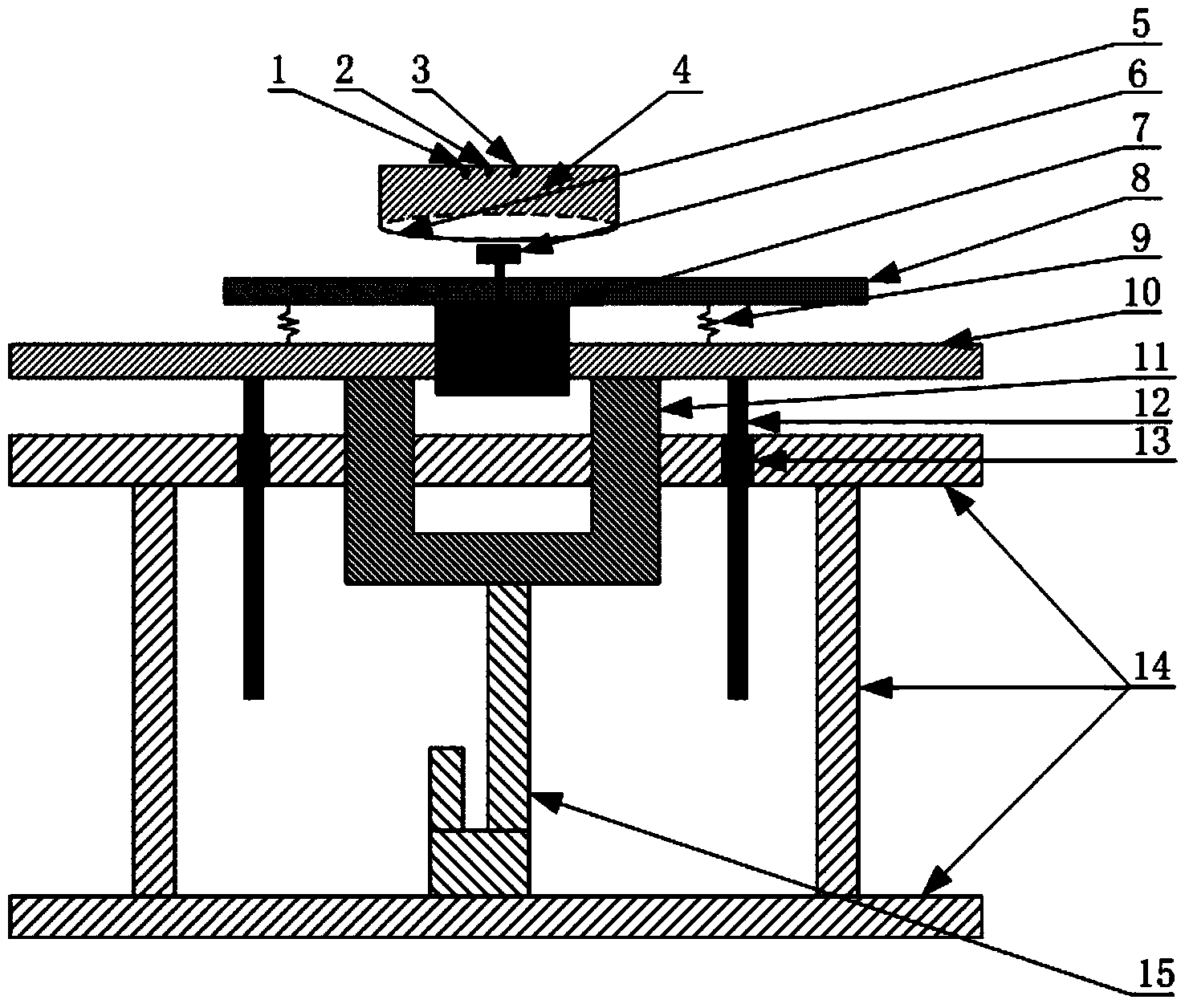
ActiveCN103472081AReduce measurement errorPrecise distance controlMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationObservational errorOptical fluorescence
The invention discloses an automatic energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence analysis test platform. The automatic energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence analysis test platform comprises a sample chamber, a stepping motor and an electric cylinder. The sample chamber and a seal plate form a closed chamber. The stepping motor is fixed to a tray. The tray is connected to a bracket. The bracket is connected to the electric cylinder. A rotation shaft of the stepping motor passes through the seal plate and enters into the closed chamber. The rotation shaft of the stepping motor is provided with a sample support. The sample chamber is provided with an X-ray pipe, a camera and a detector. The closed chamber is communicated with a vacuum pump. The camera is connected to a computer. The automatic energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence analysis test platform reduces measure errors, reduces detector-caused pollution, improves a light element detection capability and improves detection efficiency.
Owner:四川新先达测控技术有限公司
Endoscopic diagnosis system
InactiveUS20130053703A1Eliminate the effects ofIncrease or decreaseSurgeryEndoscopesOptical fluorescenceImage correction
An endoscopic diagnosis system includes a light source unit for emitting green and red light, blue and green light, or white light and excitation light having different central wavelengths for causing an autofluorescent substance to emit autofluorescence, an imaging unit for receiving reflected light from the observation region to acquire a reflected light image when the observation region is illuminated with the illumination light emitted, and receiving autofluorescence that is emitted from the autofluorescent substance, absorbed by blood, and decreases according to the amount of the blood to acquire an autofluorescence image when the observation region is irradiated with the excitation light emitted, and an image correction unit for correcting the autofluorescence image based on the reflected light image.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
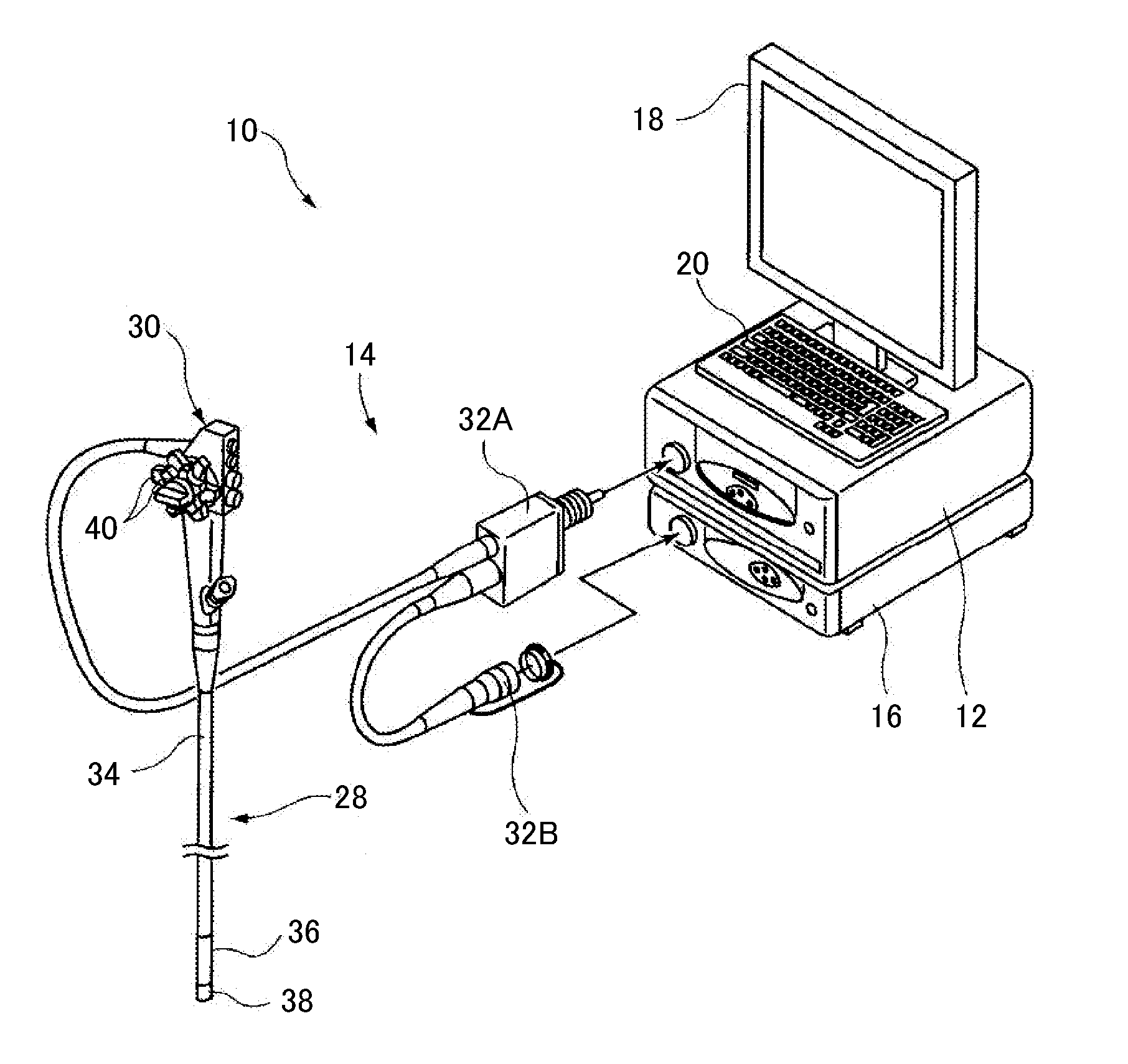
Mobile molecular diagnostics system with wireless communication
ActiveUS9901923B2Low costLow setHeating or cooling apparatusNanoparticle analysisPoint of careProtein detection
A mobile, self contained molecular diagnostics system is provided with a microfluidic chip, detection apparatus and an integrated or wireless control interface and imager. The system provides automated sample preparation and rapid optical detection of multianalyte nucleic acids and proteins. On chip PCR may be performed to improve the optical fluorescence signal for nucleic acid detections. Plasmonic protein detection is performed using a dark field smartphone microscope. Dark field illumination is based on an evanescent field generated by LED total internal reflection. The smartphone element may also be used as an interface to control the detection apparatus, acquire images, process data and for wireless communications with remote computers. The handheld automated system has low power requirements and is particularly suited for point of care and on demand diagnostics in resource limited settings.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Optical fluorescence dual sensors and methods of preparing and using them
ActiveUS8748192B2Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementOptical fluorescenceOxygen
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Device and method for acquiring fusion image
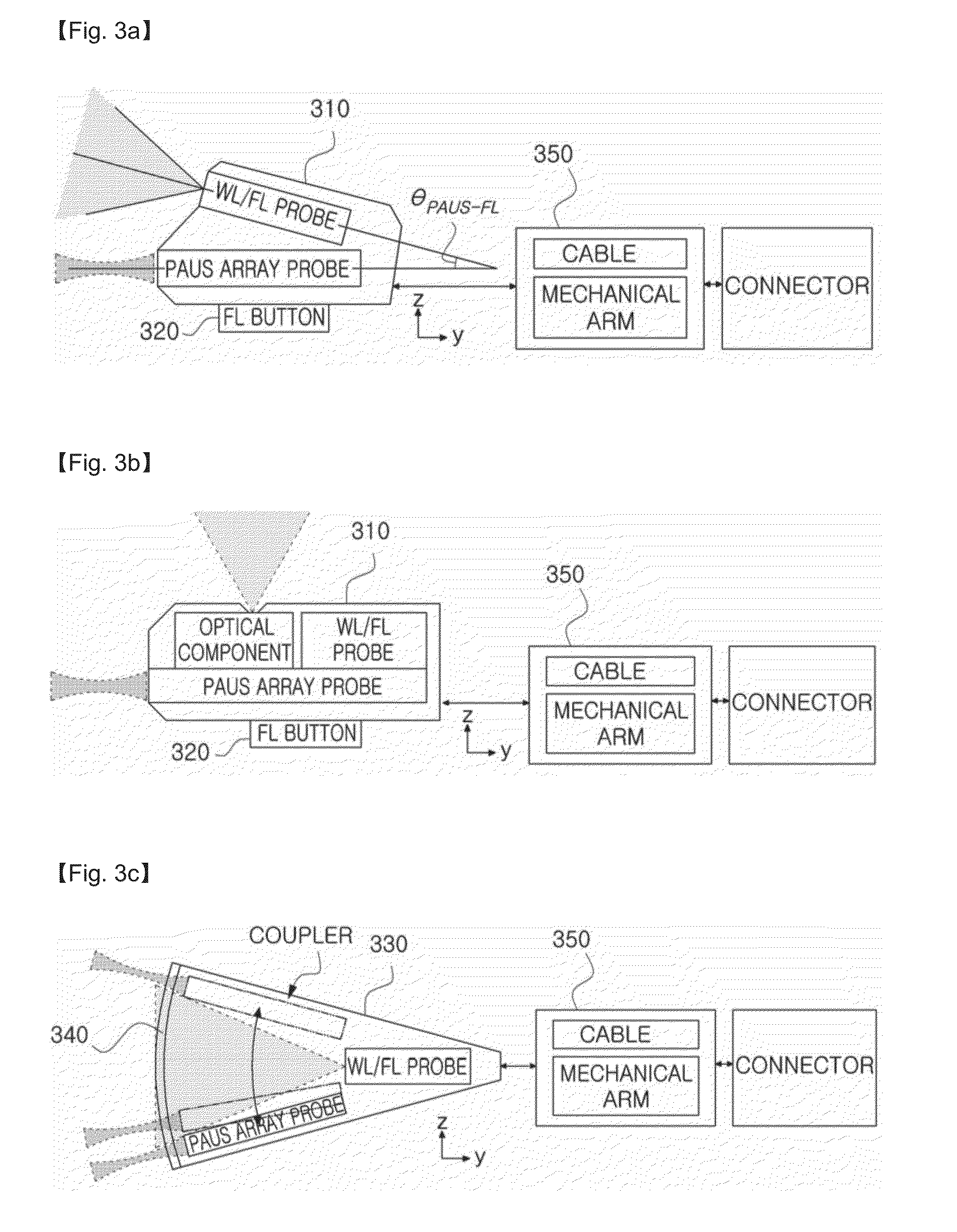
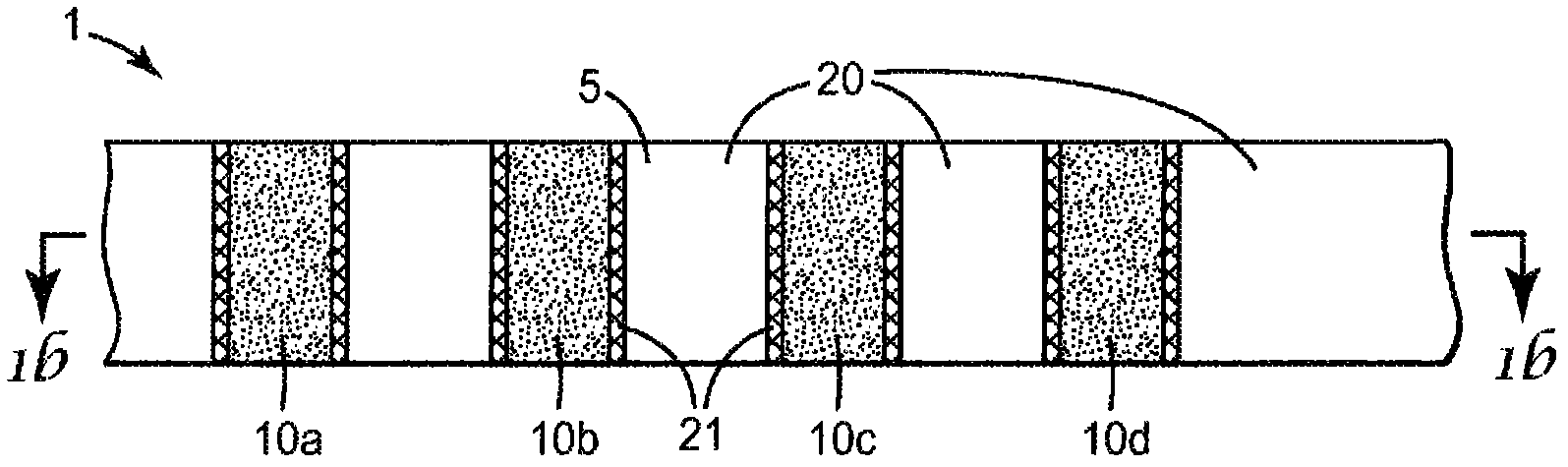
InactiveUS20160192840A1Easy to analyzeSimplify manipulationTelevision system detailsDiagnostics using lightOptical fluorescenceComputer vision
Disclosed is a device and method for acquiring a fusion image, which applies an ultrasound signal for an ultrasound image, an optical signal for a photoacoustic image and a fluorescent image to a target, receives an ultrasound signal, a photoacoustic signal and an optical signal from the target, and generates a fusion image including image information with different probing planes with respect to the target by using at least two signals of the received ultrasound signal, the received photoacoustic signal and the received optical signal.
Owner:SOGANG UNIV RES FOUND
Monitoring of frying oil quality using combined optical interrogation methods and devices
InactiveCN102007406AMethods to improve subjective measurements such as visual inspectionAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorOptical fluorescenceElectrical polarity
Herein are disclosed methods and devices for optically monitoring multiple parameters of an oil sample. In one embodiment, the methods and devices can be used for determining the quality of cooking or frying oil in terms of the free fatty acid content and total polar compound content of the oil. The methods use an optical absorbtive / reflective property in evaluating the free fatty acid content, and use optical fluorescence in evaluating the total polar compound content, with both measurements using a single sampling substrate and a single measuring device.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
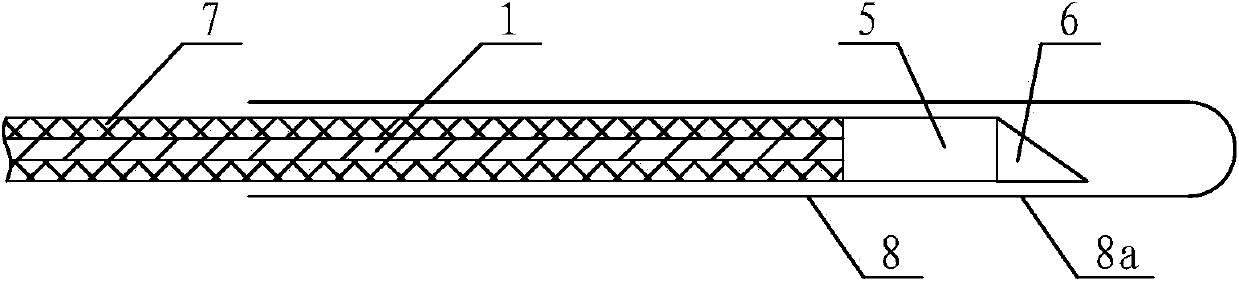
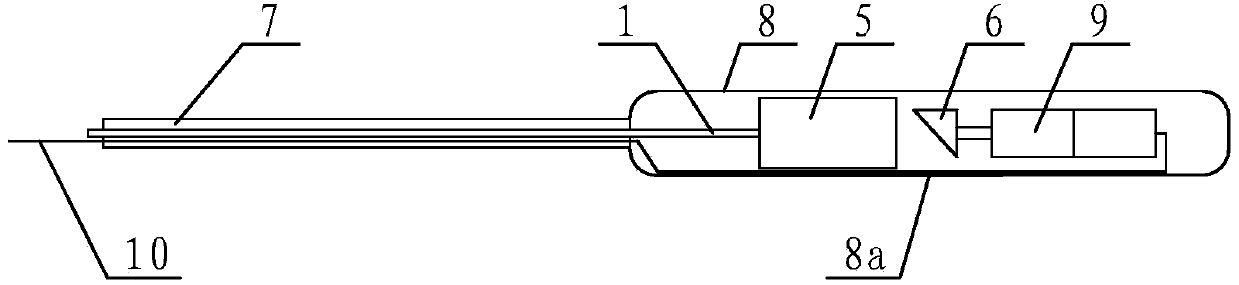
Endoscope
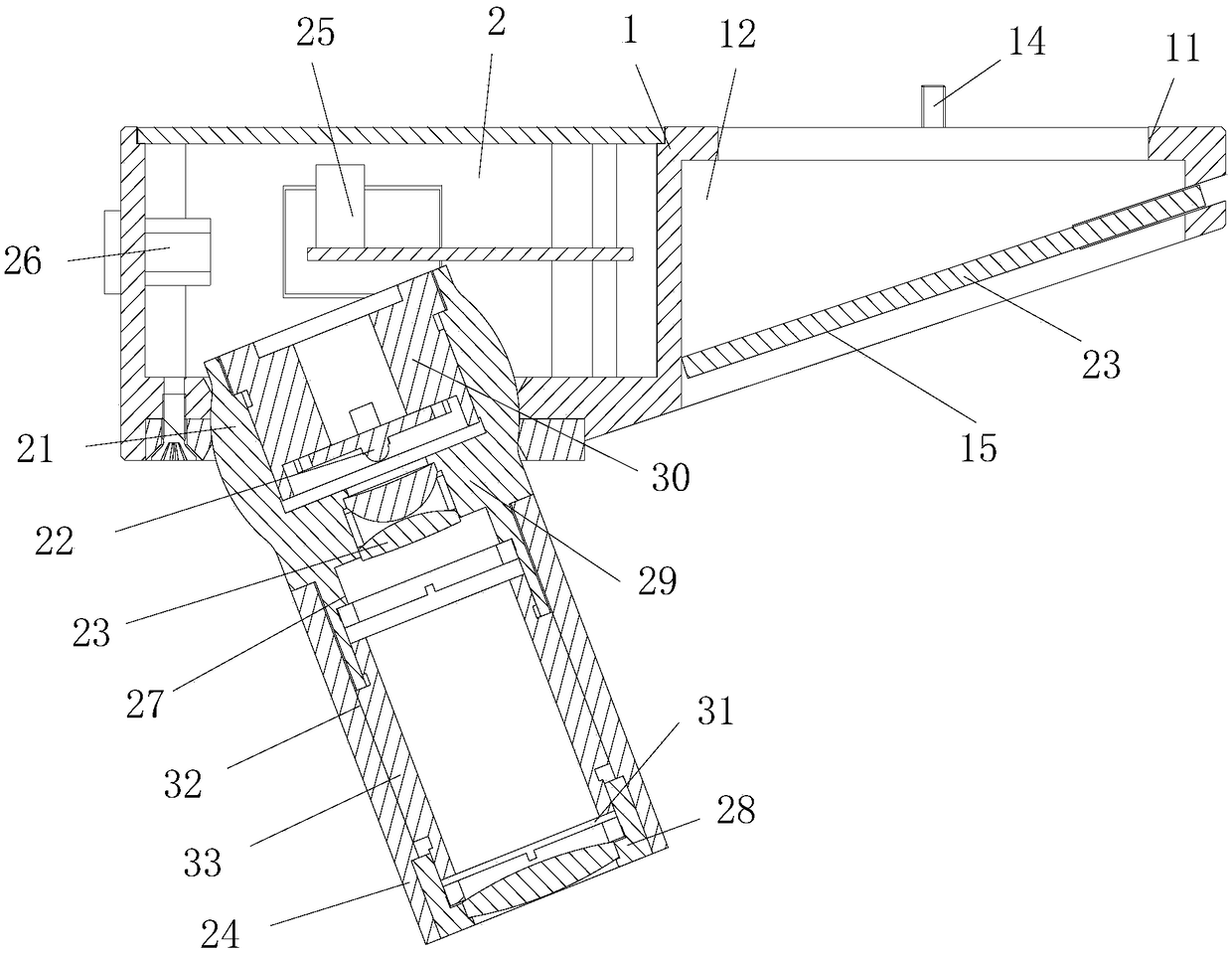
InactiveCN103767660AAchieving lateral imagingIncrease flexibilitySurgeryOptical fluorescenceBiochemical engineering
The invention provides an endoscope which comprises a connecting optical fiber, a self-focusing lens, a slant reflection mirror and a motor. The connecting optical fiber is connected with the tail portion of the self-focusing lens, the slant reflection mirror is opposite to the self-focusing lens, the rear end of the slant reflection mirror is fixed with one end of a rotary shaft, the other end of the rotary shaft is fixed with one end of a column magnet, a supporting sleeve is arranged outside of the rotary shaft, the column magnet, the rotary shaft, the slant reflection mirror and the self-focusing lens are coaxial, and a transparent sleeve is arranged outside the column magnet, the rotary shaft, the slant reflection mirror and the self-focusing lens, and the supporting sleeve and the self-focusing lens are both fixed with the transparent sleeve. A pair of plate magnets with opposite S poles and N poles is arranged on the power output end of the motor in the circumferential direction, a power output shaft of the motor is coaxial with the rotary shaft, and the plate magnets are adjacent to the column magnet. The endoscope is high in flexibility, the outer diameter of the transparent sleeve can be less than 1mm and even can reach micron dimension, and a use range is wide. The endoscope is applicable to an OCT system and imaging systems of optical scanning imaging, scanning fluorence imaging, B ultrasonic imaging and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Optical system with diffraction optical element used for mapping signal light onto a detector
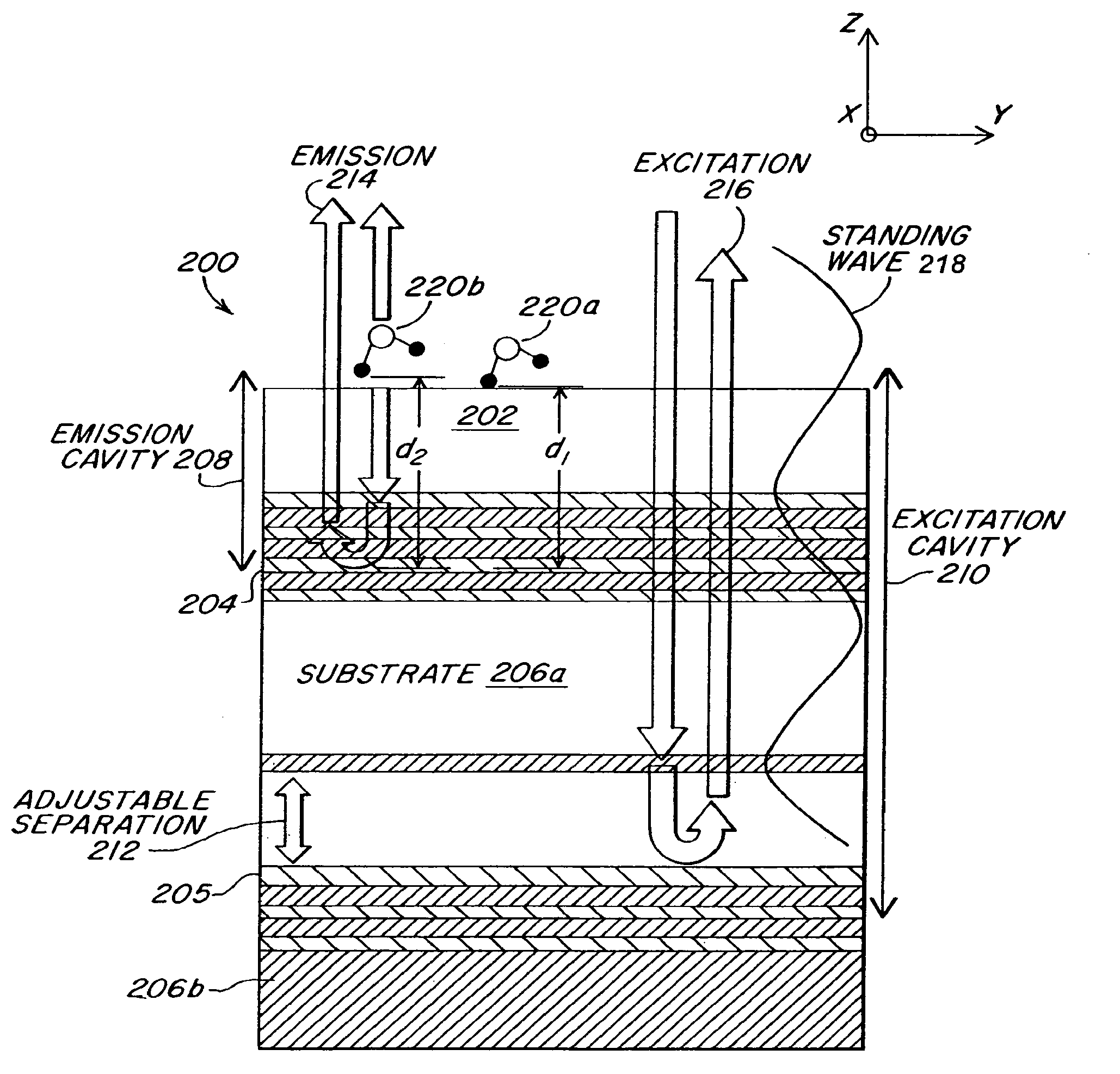
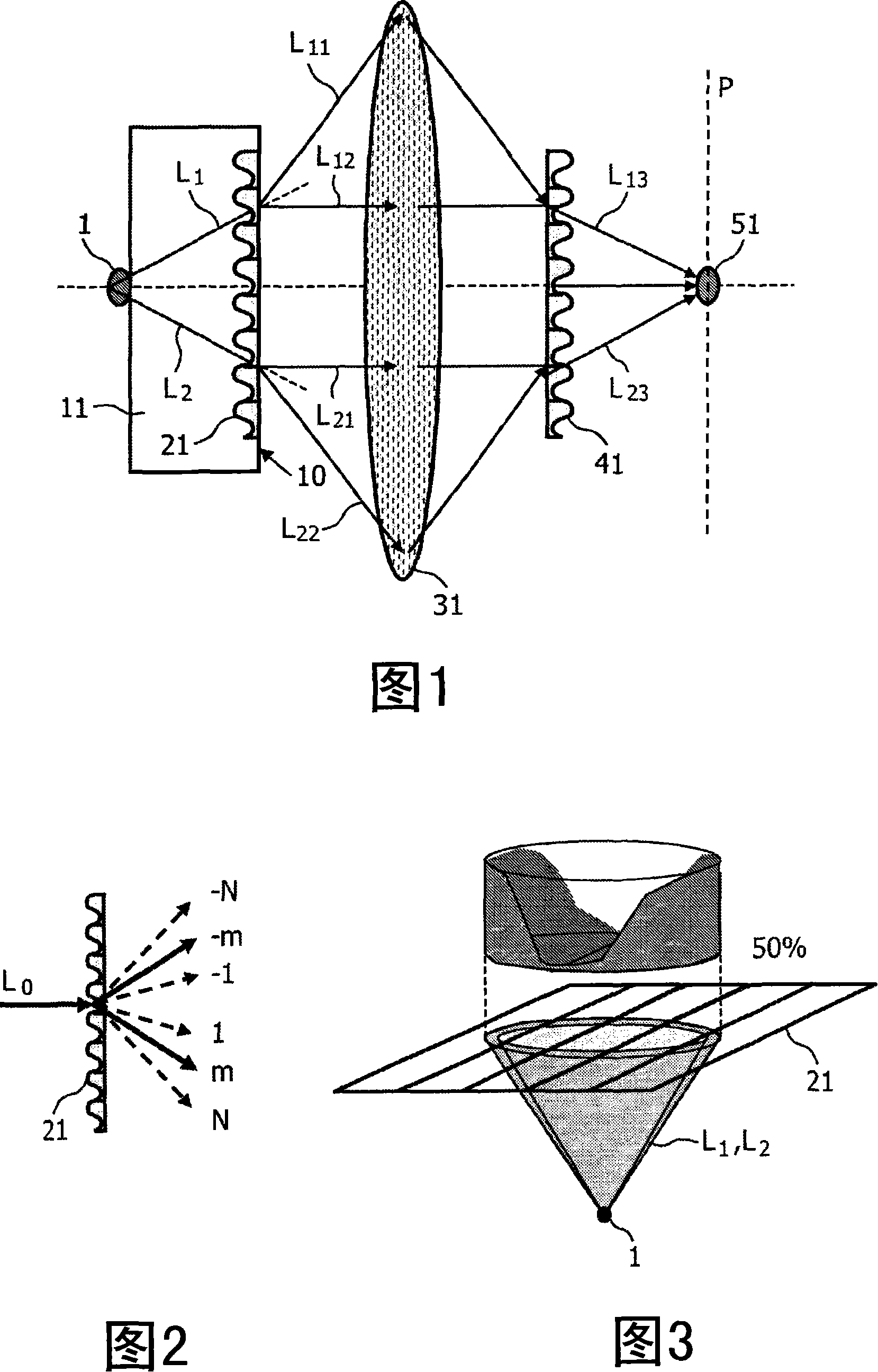
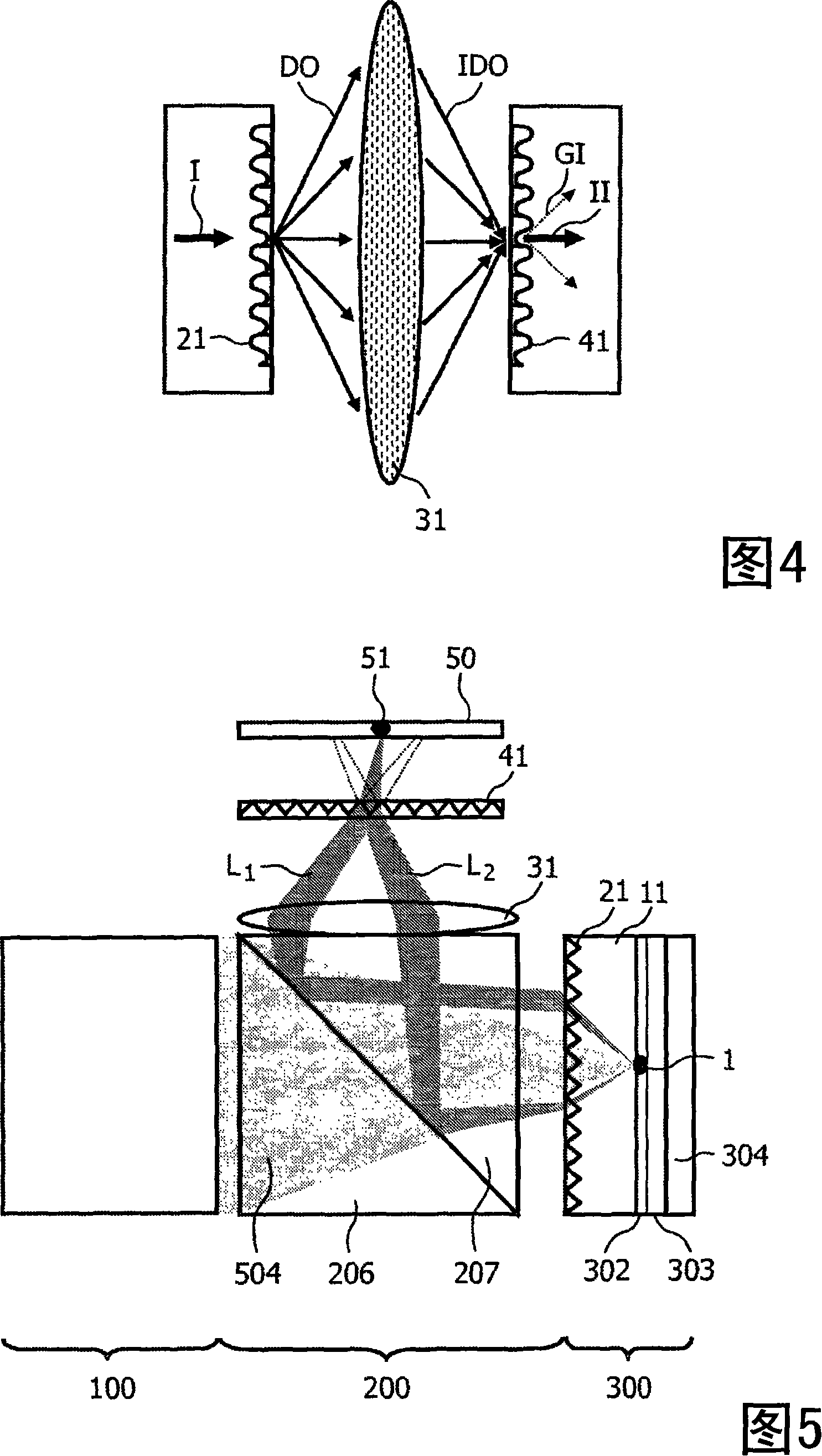
The invention relates to an optical system that particularly allows an improved detection of signal light propagating from a light source (1) through a flat glass substrate (11). SC-modes of this signal light that would normally be totally internally reflected at the backside (10) of the substrate (11) are coupled out by a first diffractive optical element DOE (21). To map all signal light leaving the substrate (11) onto a single target location (51), a focusing lens (31) and a second DOE (41) are disposed in the optical path behind the substrate (11). The DOEs (21, 41) may for example be a ID sinusoidal grating or a 2D blaze grating. The optical system may particularly be applied in an investigation apparatus for detecting multiple spots of a fluorescent sample material.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and Apparatus for Terahertz or Microwave Imaging
PendingUS20210389248A1Reduce image blurIncrease field strengthMaterial analysis using microwave meansFluorescence/phosphorescenceOptical fluorescenceMicrowave imaging
An apparatus and method for imaging using microwave or terahertz radiation are described. The apparatus (10) comprises: a cell (12) comprising a vapour of atoms; one or more laser beams (14) propagating through said cell (12), said one or more laser beams (14) defining a sensing region (15) in said cell (12); an imaging beam (16) for illuminating an object receiving area for receiving an object (18) to be imaged, said imaging beam (16) comprising microwave or terahertz radiation; an imaging system (20, 22) for focussing the imaging beam (16) to form, in use, an image of said object (18) at said sensing region (15) in said cell (12); wherein respective frequencies of said one or more laser beams (14) and said imaging beam (16) are such that at least some of said atoms, when subjected to radiation of both said one or more laser beams (14) and said imaging beam (16), are excited to a final excited state which decays to a lower energy state by emission of optical fluorescence (24).
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DURHAM
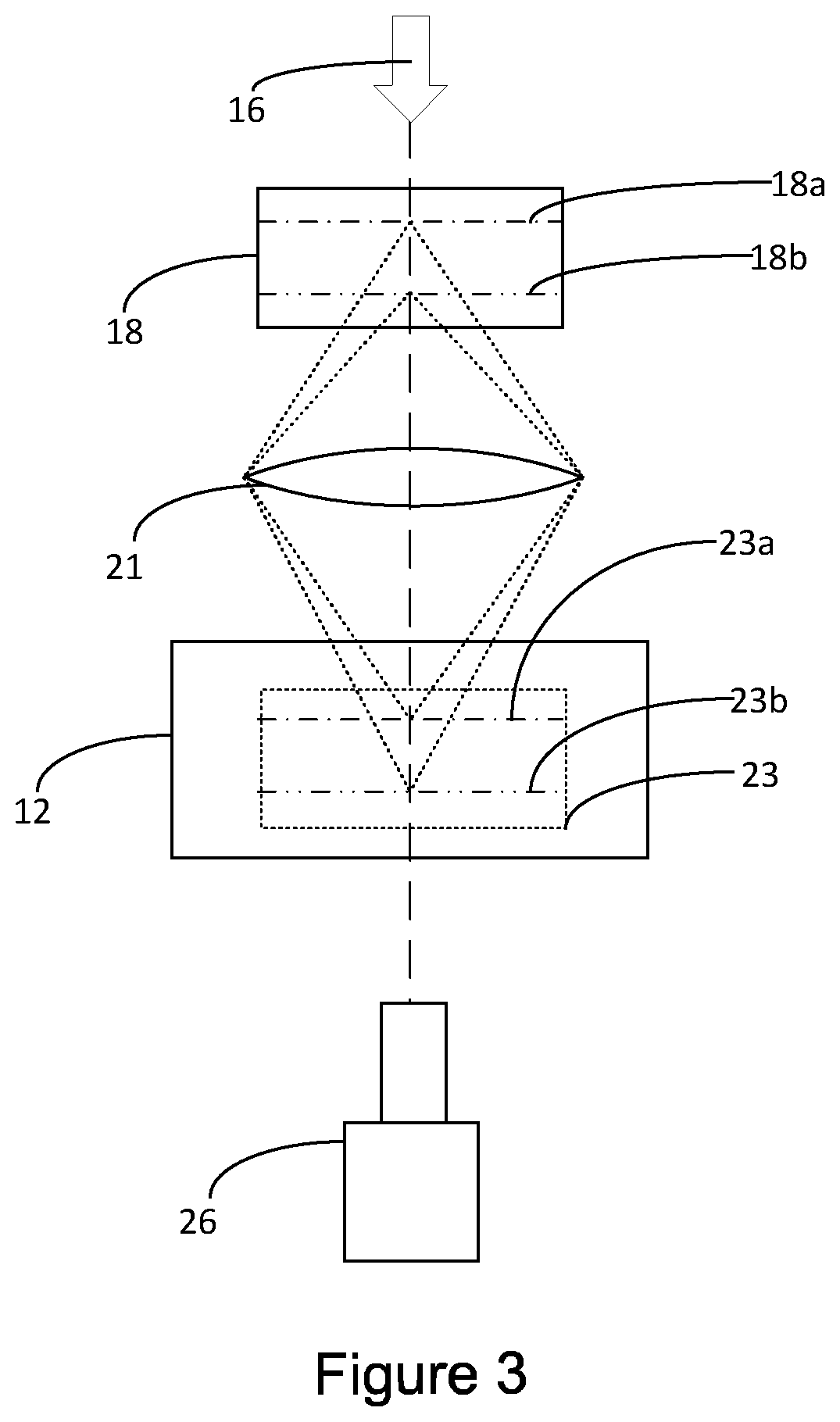
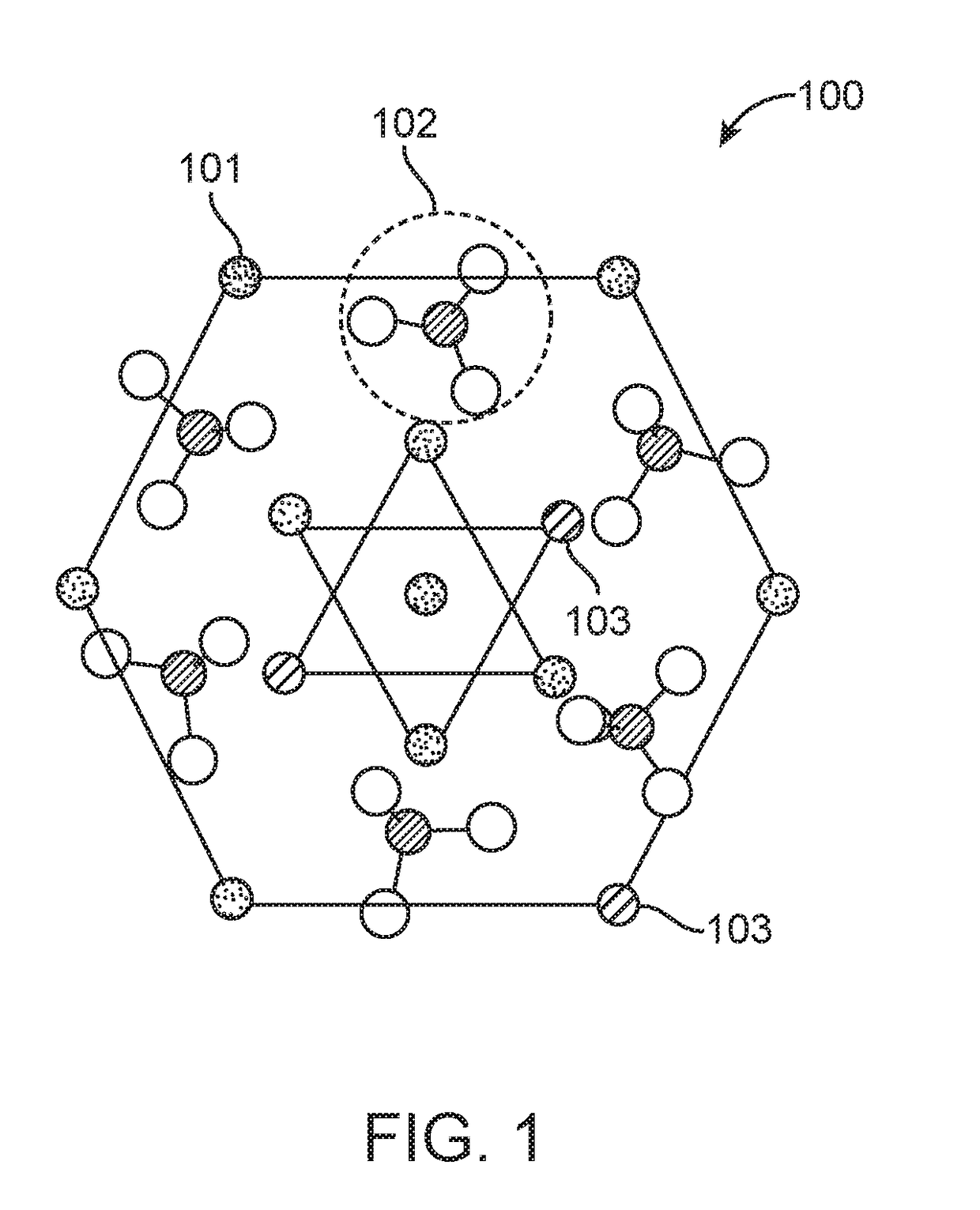
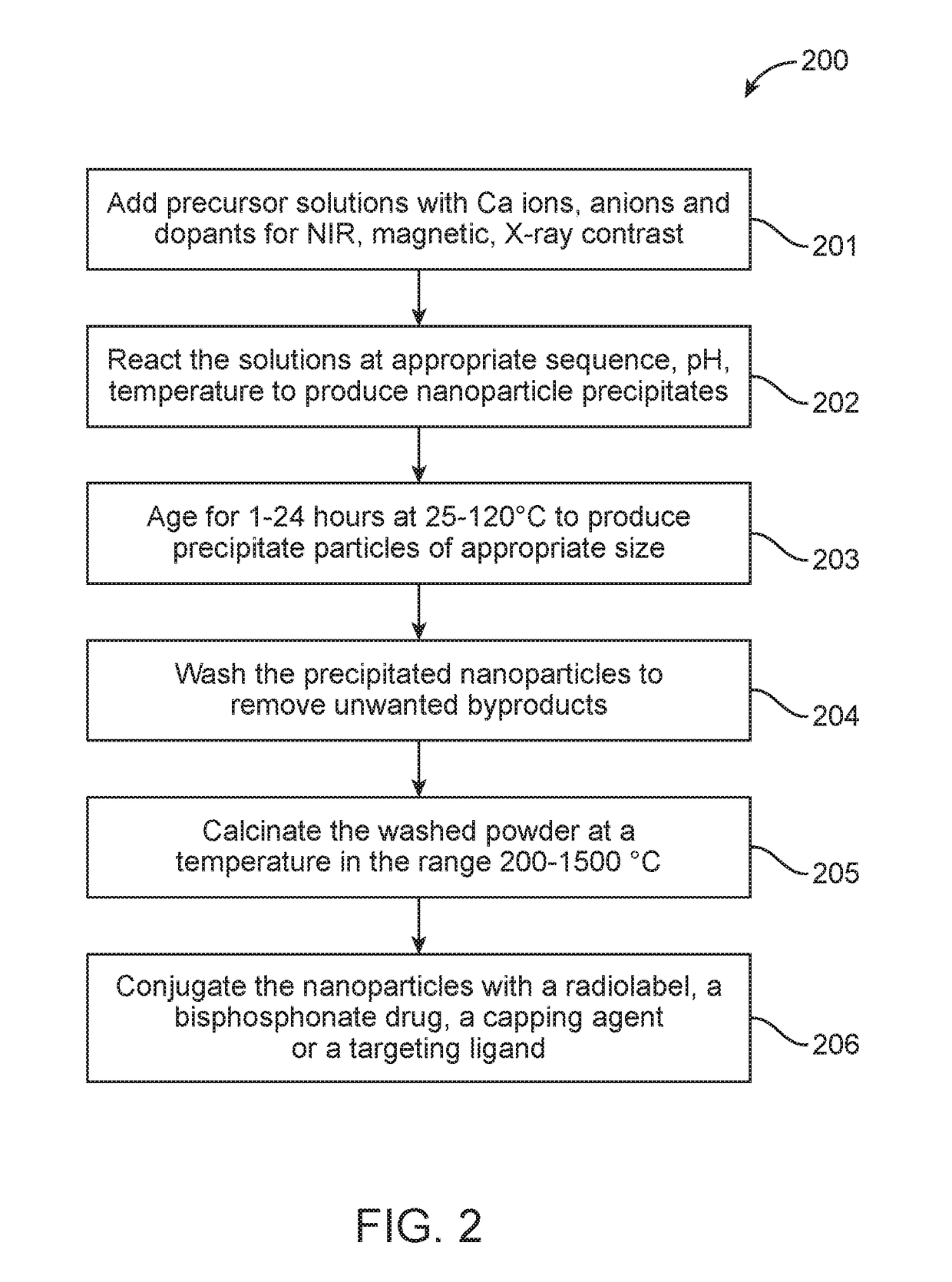
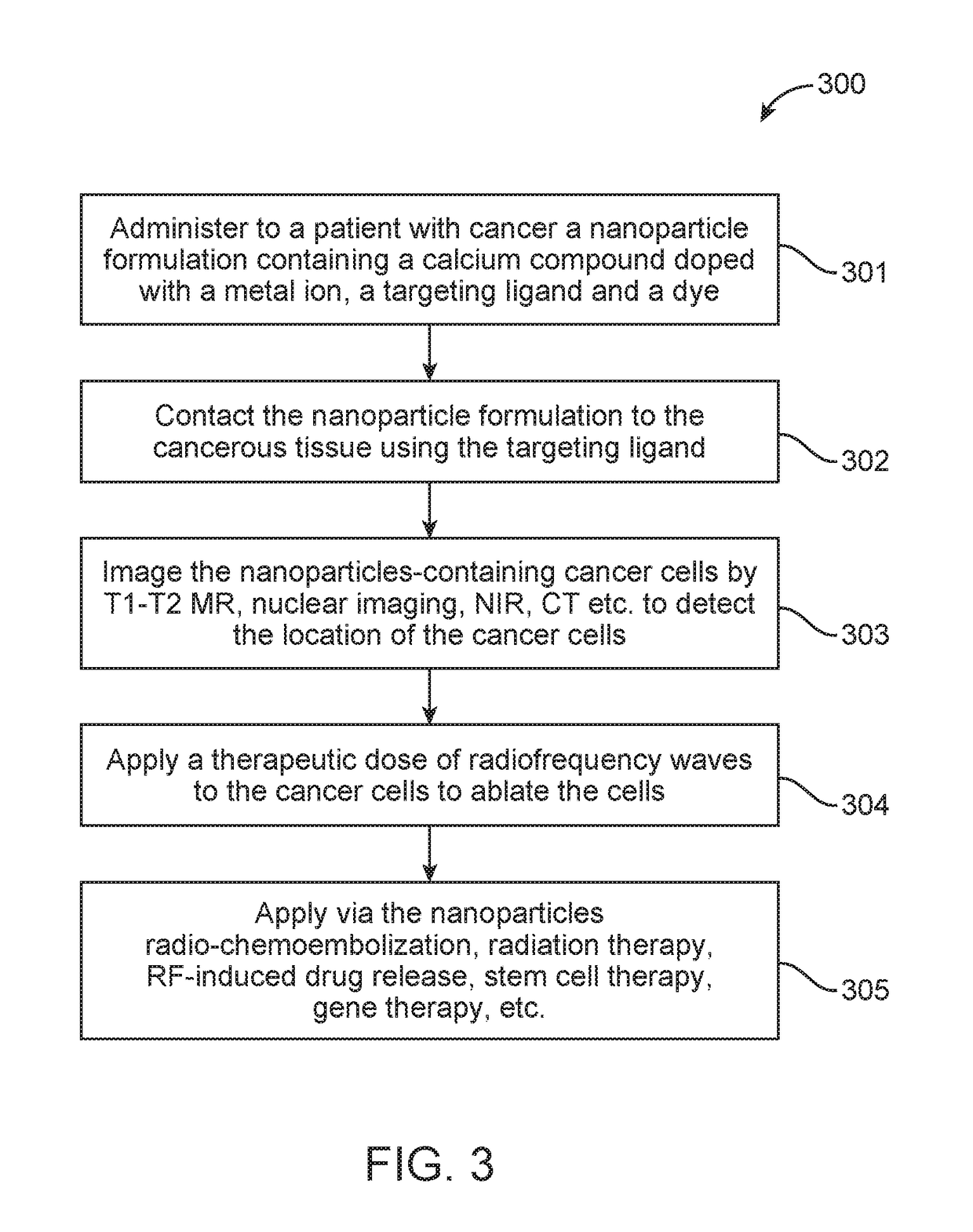
Radio-wave responsive doped nanoparticles for image-guided therapeutics
The invention discloses nanoparticles comprising compounds of calcium with anions such as phosphate, pyrophosphate, sulphate, silicate, carbonate, molybdate, or phosphosilicate that are doped with various ions. The nanoparticles are configured to produce heat (hyperthermia) under radio-wave (1 KHz-1000 GHz) exposure together with magnetism suitable for contrast imaging in MRI, X-ray absorption for computed tomography, near-infrared optical fluorescence for optical imaging, and / or radio-isotope emission for nuclear imaging or therapy. The nanoparticles can also be incorporated into micro-beads or other 3 dimensional scaffolds for image-guided (MRI, CT, NIR, nuclear) tissue regeneration, immunotherapy, vascular or tumor embolization, and / or chemo / radio-embolization.
Owner:AMRITA VISHWA VIDYAPEETHAM
Illumination apparatus and projection display apparatus using the same
An illumination apparatus includes an illumination optical system configured to illuminate a light modulation element; a plurality of light source units each including a fluorescent member, at least one light source, and a light-guiding optical system; and an optical-path combining system. A predetermined region in an area where light source images are formed by the illumination optical system using light beams from the optical-path combining system is defined as an effective region, and the number of the light source units is denoted by N. In this case, the light source images and N subregions obtained by dividing the effective region by N along a first side direction of the effective region or a second side direction orthogonal to the first side direction satisfy a predetermined relation.
Owner:CANON KK
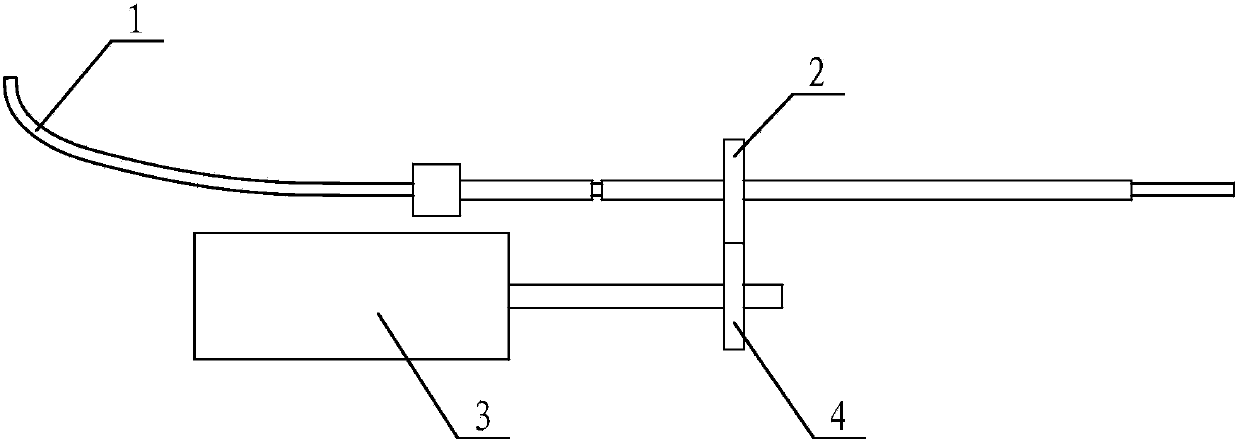
Twist-proof detecting optical fiber for intrinsic fluorescent diagnostic instrument
InactiveCN1709198ATorsion stress reliefGuaranteed service lifeEndoscopesOptical fluorescenceDiagnostic instrument
The present invention relates to an anti-twist detection optical fibre for inherent fluorescent diagnostic apparatus. It is formed from a first optical fibre and at least a second optical fibre. One end of first optical fibre is connected with medical optical fibre probe, its another end is equipped with a first collimator, and one end of second optical fibre is equipped with a second collimator, said first collimator is fixed in a tubular connecting member, and said second collimator is fixed in a column connecting member. Besides, said invention also provides its working principle and its advantages.
Owner:SHANGHAI LASER MEDICAL INSTR CO LTD
Endoscope system with color correction information
InactiveUS8665327B2Easy maintenance and operationReliable maintenanceSurgeryEndoscopesImaging processingOptical property
Provided is an endoscope system including an endoscope which includes an illumination optical system having a fluorescent substance and an imaging optical system having an imaging element; and a control device which is connected to the endoscope. The control device includes a light source unit having a semiconductor light emitting element generating excitation light used to excite the fluorescent substance, a storage section storing predetermined color correction information, and an image processing section creating captured image data by performing a calculation process on an image signal output from the imaging element on the basis of the color correction information. At least one of optical characteristics of the fluorescent substance and the semiconductor light emitting element is detected, and the color correction information stored in the storage section is corrected on the basis of the detected optical characteristic.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Fluorescent device for operating microscope
The invention discloses a fluorescent device for an operating microscope. The fluorescent device includes a light transmitting portion and an irradiation portion connected to the rear of the light transmitting portion, wherein an objective lens interface adapted to the objective lens of the operating microscope is arranged above the light transmission part, an optical path passage is arranged in the middle of the light transmitting part, a lens groove for placing a lens is provided at an optical path outlet of the optical path channel, the lower part of the irradiation part is provided with auniversal rotating head, the top of the universal rotary head is movably connected with the irradiation part, the lower part of the universal rotary head is provided with a UV lamp bead and a lens assembly in turn, the outer side of the lens assembly is provided with a light spot adjusting ring, the outer side of the irradiation part is provided with a power switch, and the power switch is connected with a UV lamp bead circuit. The fluorescent device for the operating microscope can not only effectively protect the objective lens of the operating microscope, but also provide ultraviolet lightaccording to actual needs, and has the characteristics of high integration level and convenient use.
Owner:广西奥顺仪器有限公司
Fluorescent emulsion
InactiveCN102170913ASuppress or even block spurious signalsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationEmulsion deliveryFluorescenceOil in water
The invention relates to a fluorescent emulsion, to its uses and to labelling reagents comprising it. The fluorescent emulsion of the invention is of the oil-in-water type, comprising at least one aqueous continuous phase in which droplets of at least one oil phase are dispersed, said oil phase droplets being stabilized by a surfactant layer, characterized in that it comprises at least one pair of labels, differing from one another, formed from a donor fluorescent label that absorbs at a wavelength lambda1 and emits at a wavelength lambda2 different from lambda1, and an acceptor label that absorbs at the emission wavelength lambda2 of the donor fluorescent label; in that the donor fluorescent label and the acceptor label are kept close together by the encapsulation of one of them in the oil phase droplets and either by linking the other of them to the oil phase droplet / aqueous phase interface, or by the encapsulation of the other of them in the oil phase droplets; and in that it comprises molecules of at least one amphiphilic surfactant and at least one solubilizing lipid. The fluorescent emulsion of the invention is applicable in the field of optical fluorescence imaging, in particular optical fluorescence biomedical imaging.
Owner:法国原子能与替代能源委员会
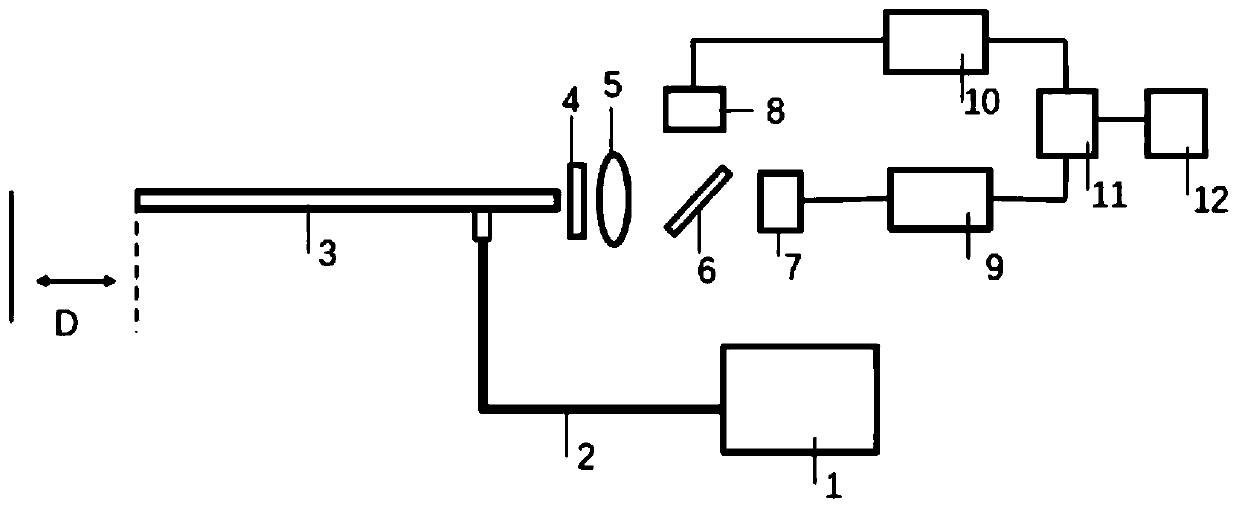
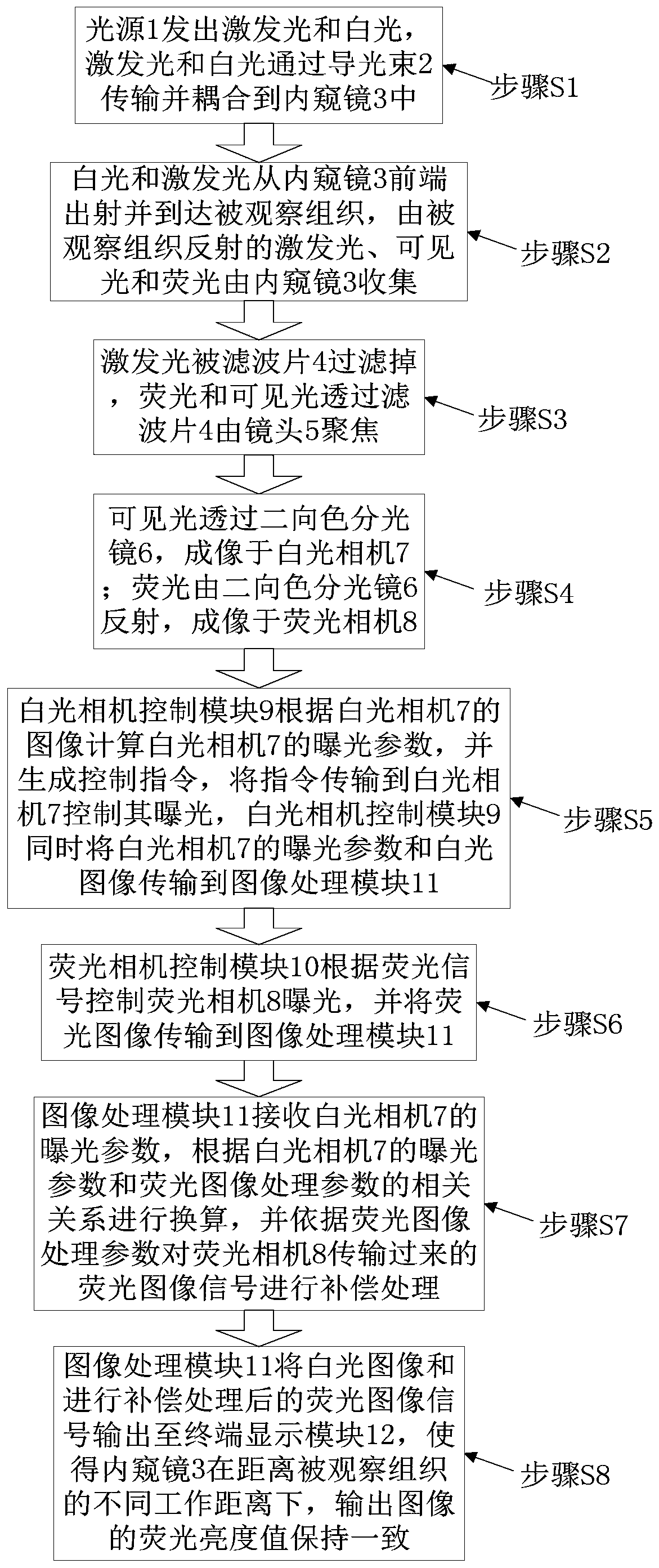
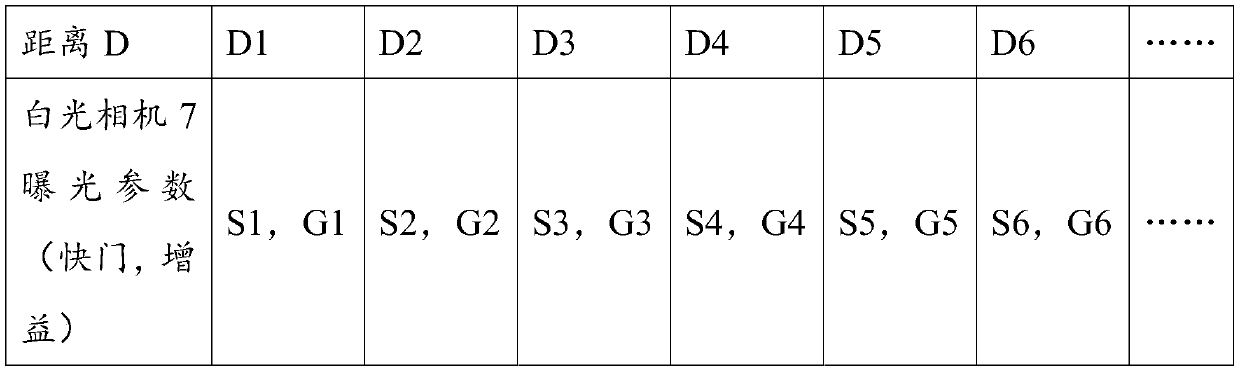
Exposure feedback type fluorescent navigation endoscope system and image processing and self-adjusting method
The invention discloses an exposure feedback type fluorescent navigation endoscope system and an image processing and self-adjusting method. By reading exposure parameters of a white-light camera in real time, image processing related parameters are calculated, original signals transmitted by a fluorescent camera are adjusted, and processed signals are output to a terminal to be displayed, so output fluorescent images are kept consistent in brightness under different imaging distances.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPTO MEDIC TECH CO LTD
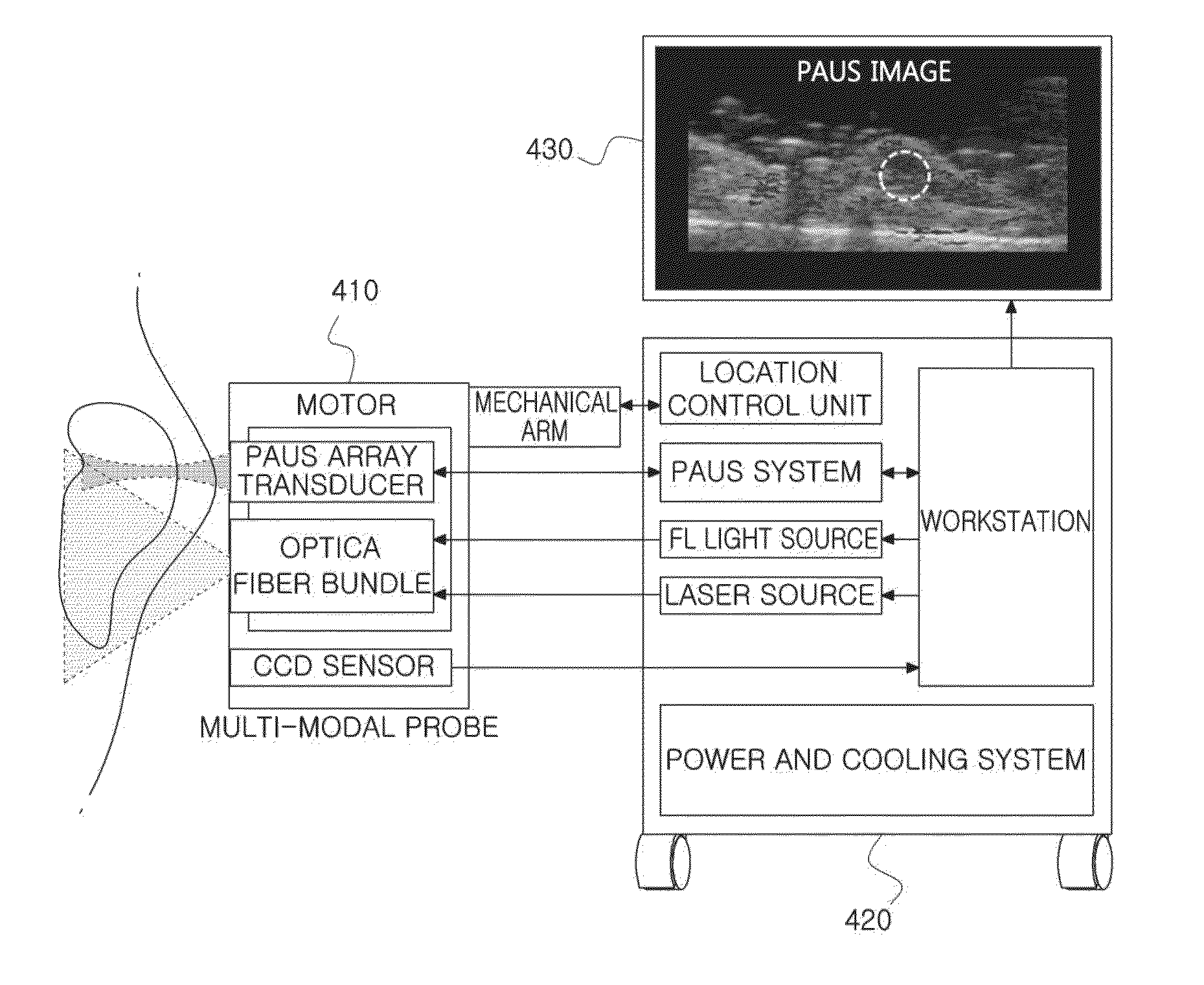
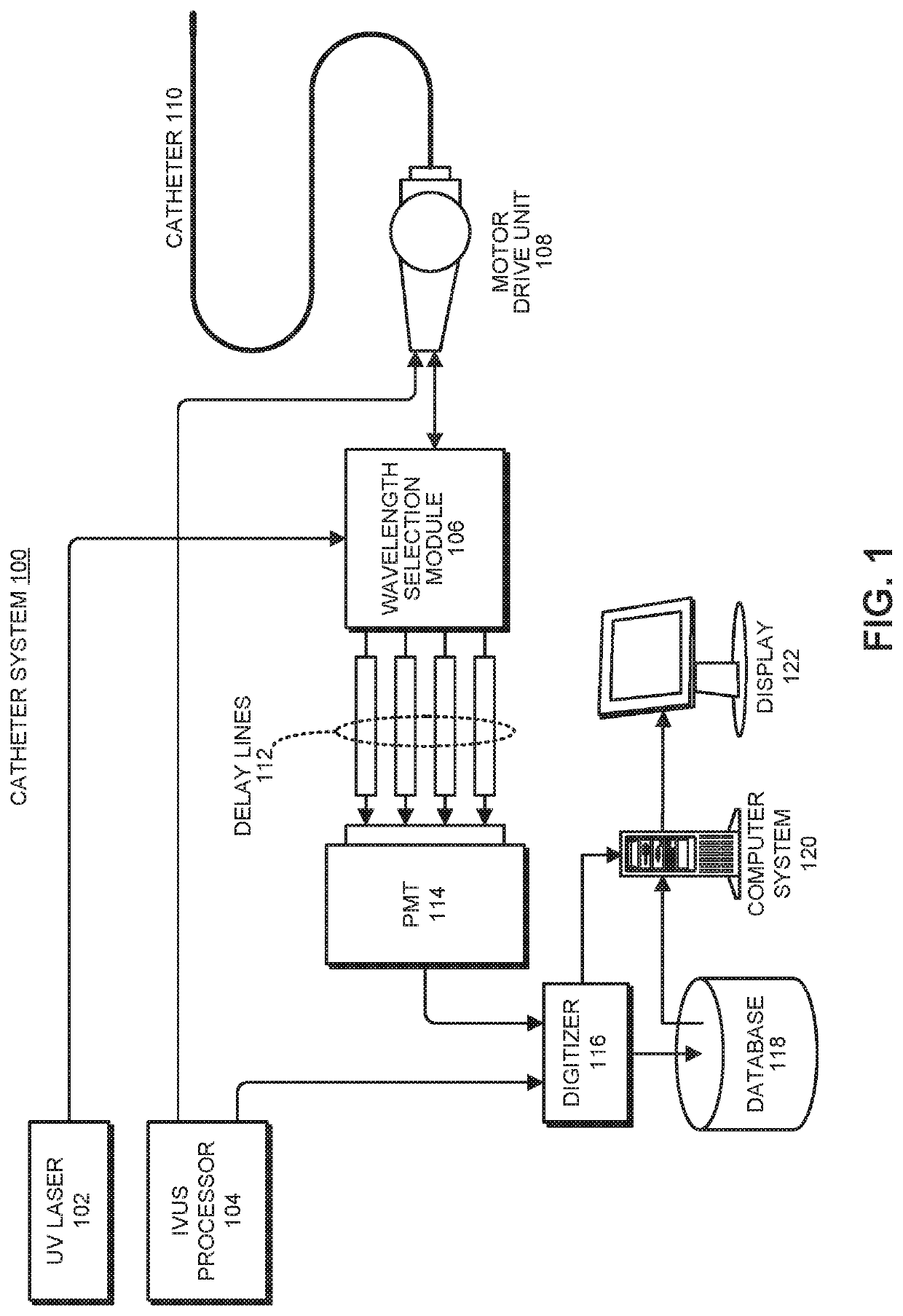
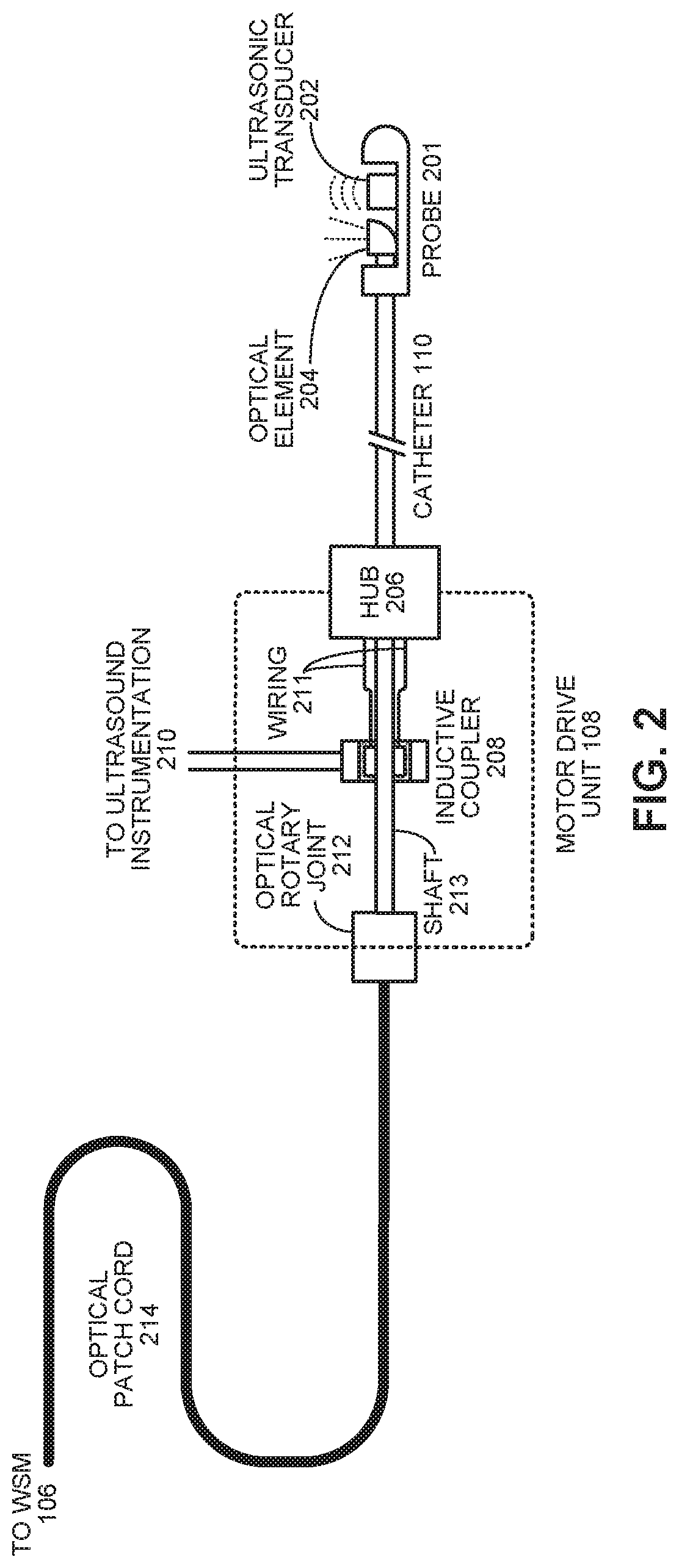
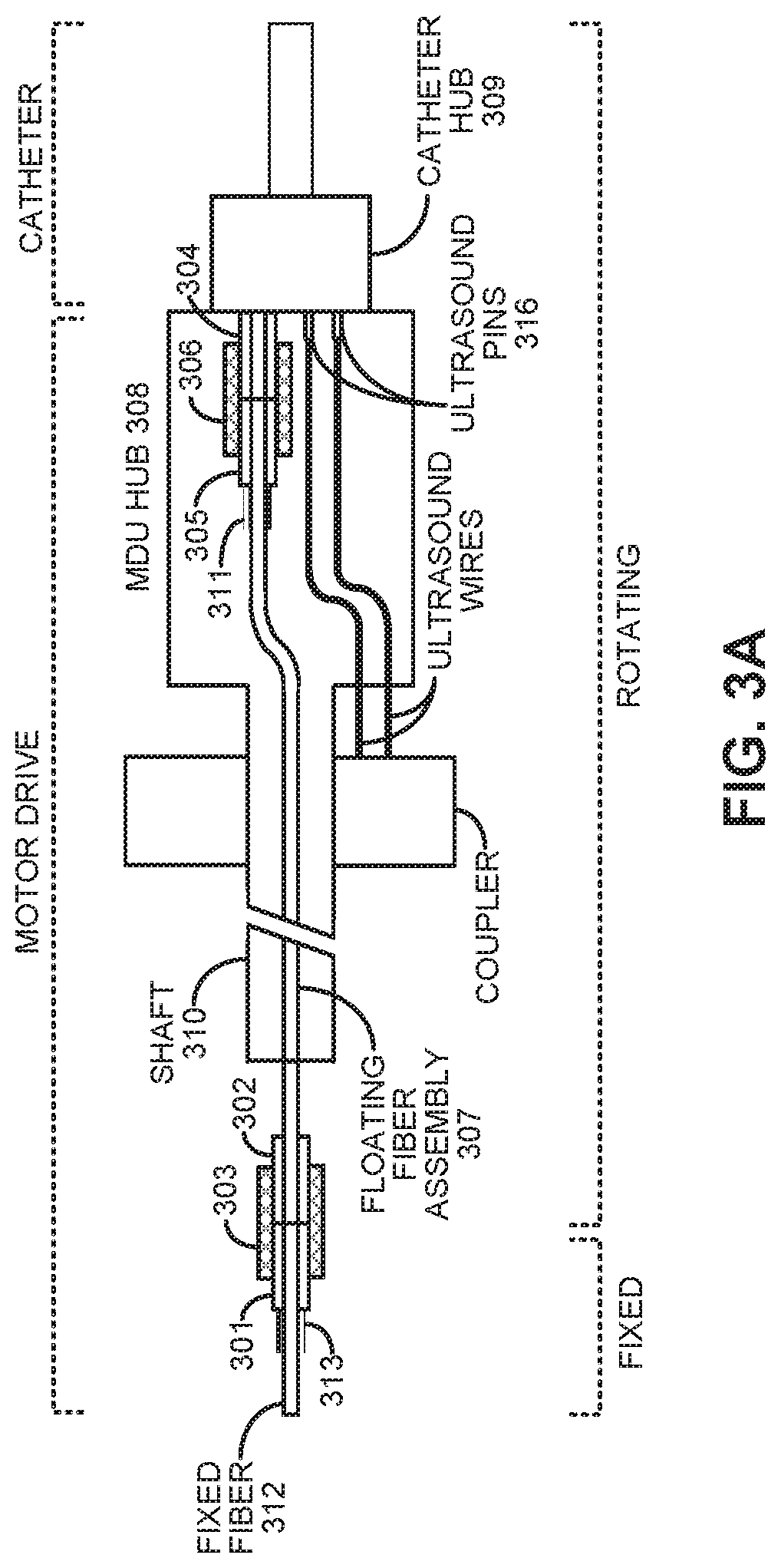
Single catheter system that provides both intravascular ultrasound and fluorescence lifetime imaging
ActiveUS20190374195A1Time resolutionOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryRotational axisUltrasonic sensor
A multimodal intravascular catheter system includes a catheter with an optical channel and an electrical channel. A distal end of the catheter includes an optical element and an ultrasonic transducer, which are oriented orthogonally to a rotational axis of the catheter. A motor drive unit (MDU) is coupled to a proximal end of the catheter and includes a drive motor to rotate the catheter. The optical channel directs light from a pulsed UV laser source to the optical element, and returns an optical fluorescence signal from the optical element. A photodetector converts the returned optical fluorescence signal into an electrical fluorescence signal. An intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) processor is coupled to the ultrasonic transducer through the electrical channel, wherein the IVUS processor generates a drive signal for the ultrasound transducer, and processes echo information returned from the ultrasound transducer. Finally, a digitizer samples the electrical fluorescence signal and associated echo information.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
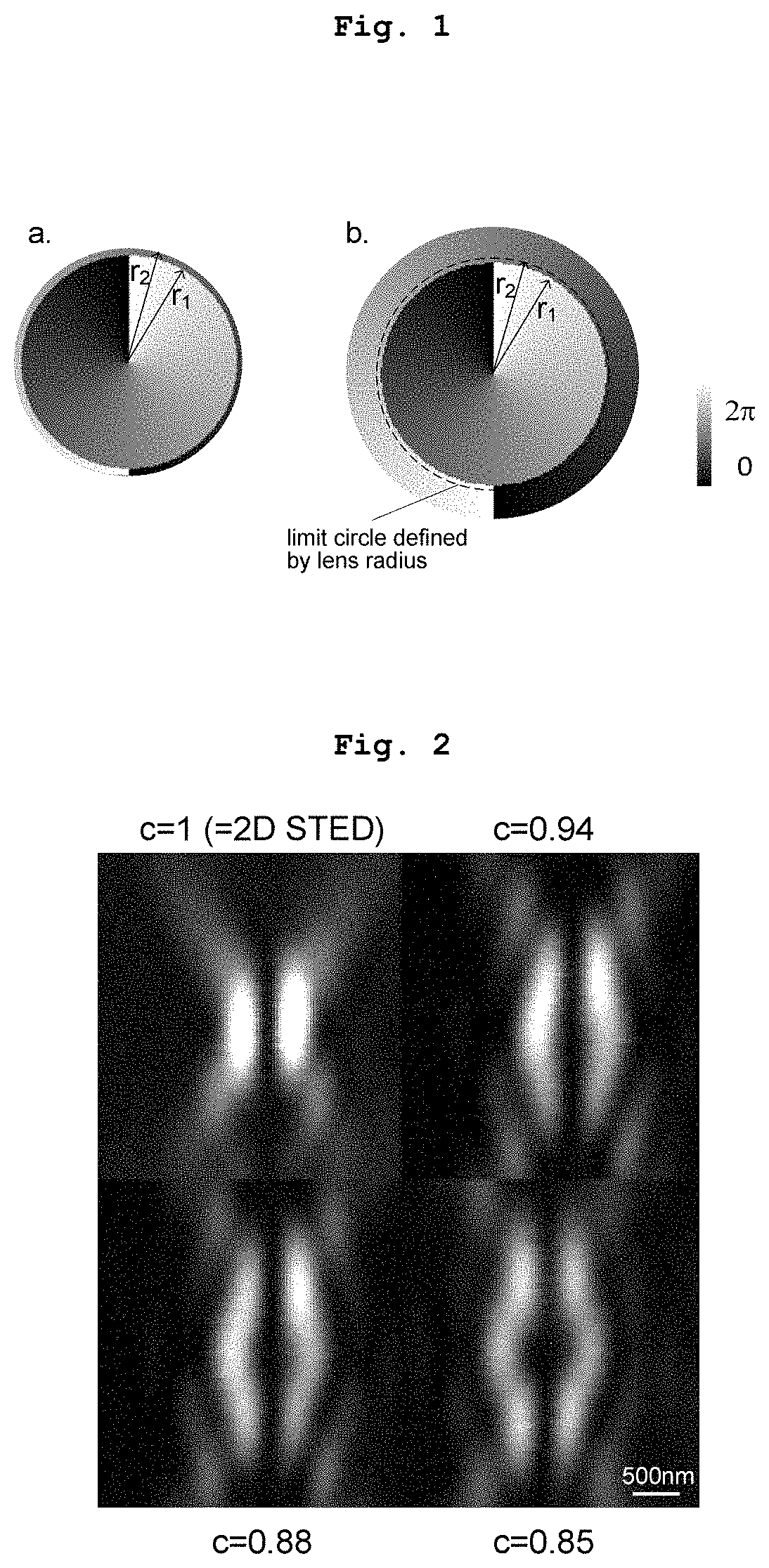
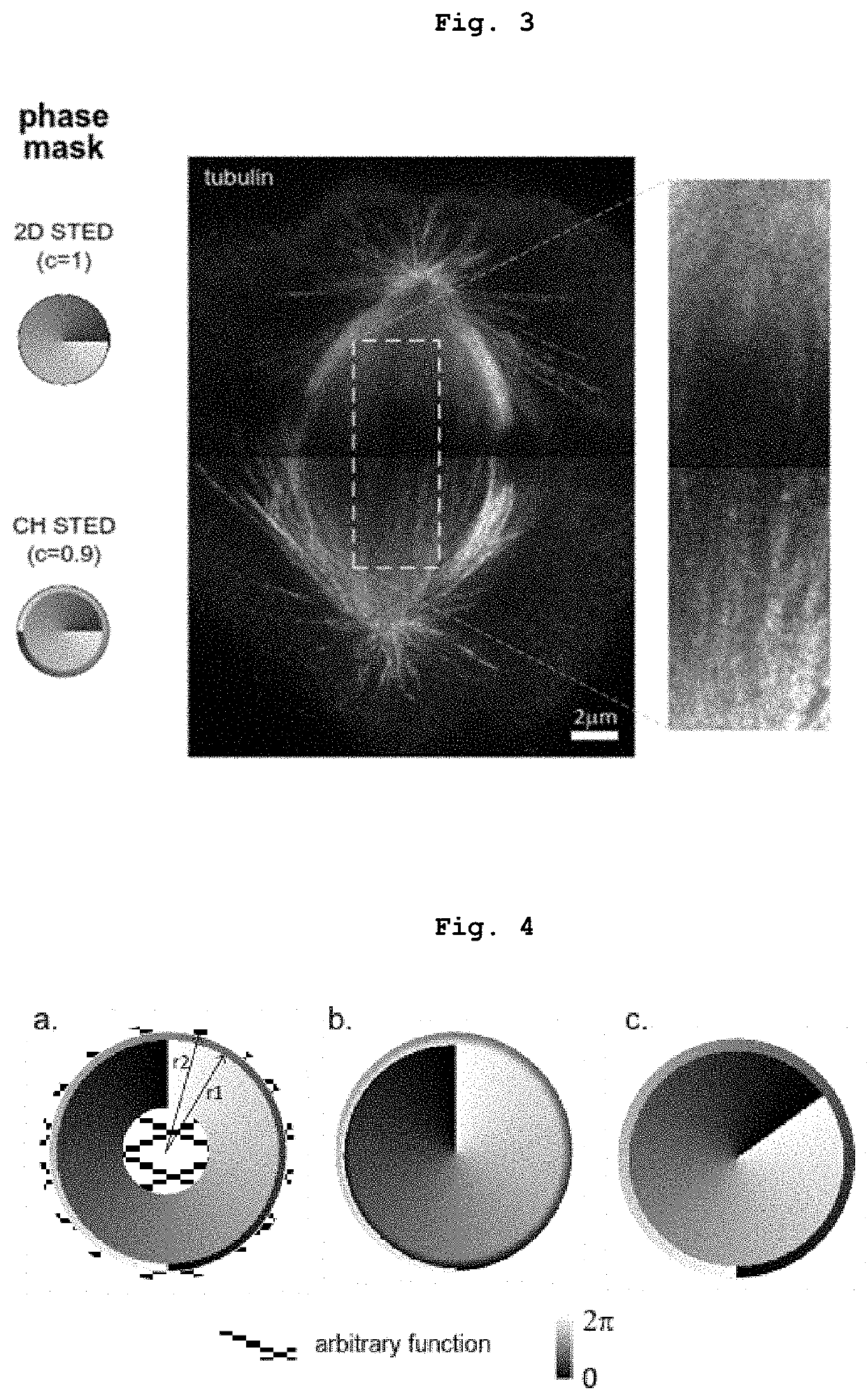
Device for improving performance in STED and RESOLFT microscopy using a single phase mask
ActiveUS11487098B2Degree of freedom is loweredLightweight strengthMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesSpatial light modulatorOptical fluorescence
Owner:INST DE BIOLOGIA MOLECULAR E CELULAR IBMC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com