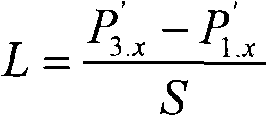Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1392 results about "Back projection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
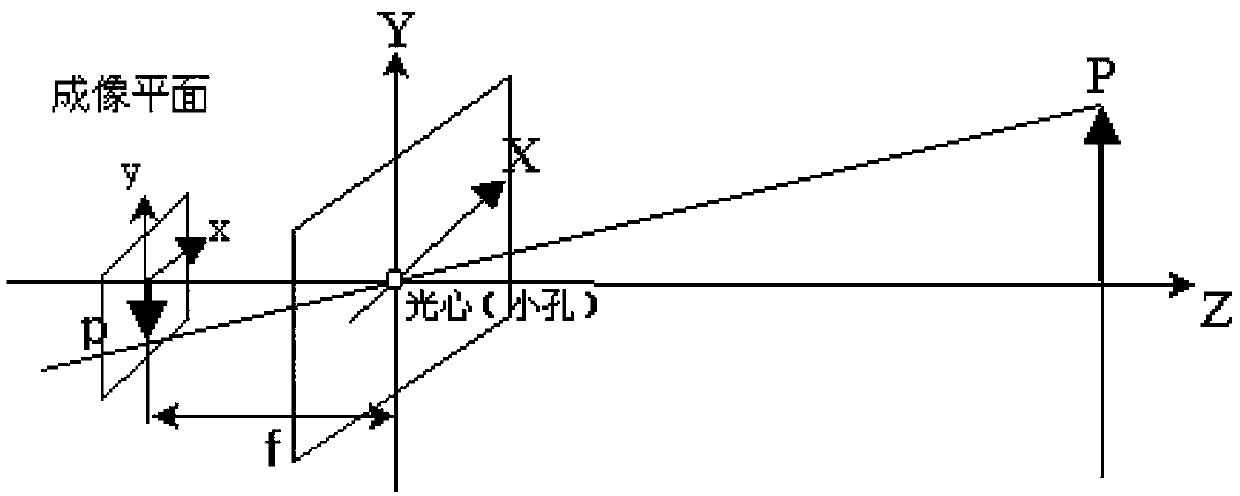
What is Back Projection?¶. Back Projection is a way of recording how well the pixels of a given image fit the distribution of pixels in a histogram model. To make it simpler: For Back Projection, you calculate the histogram model of a feature and then use it to find this feature in an image.
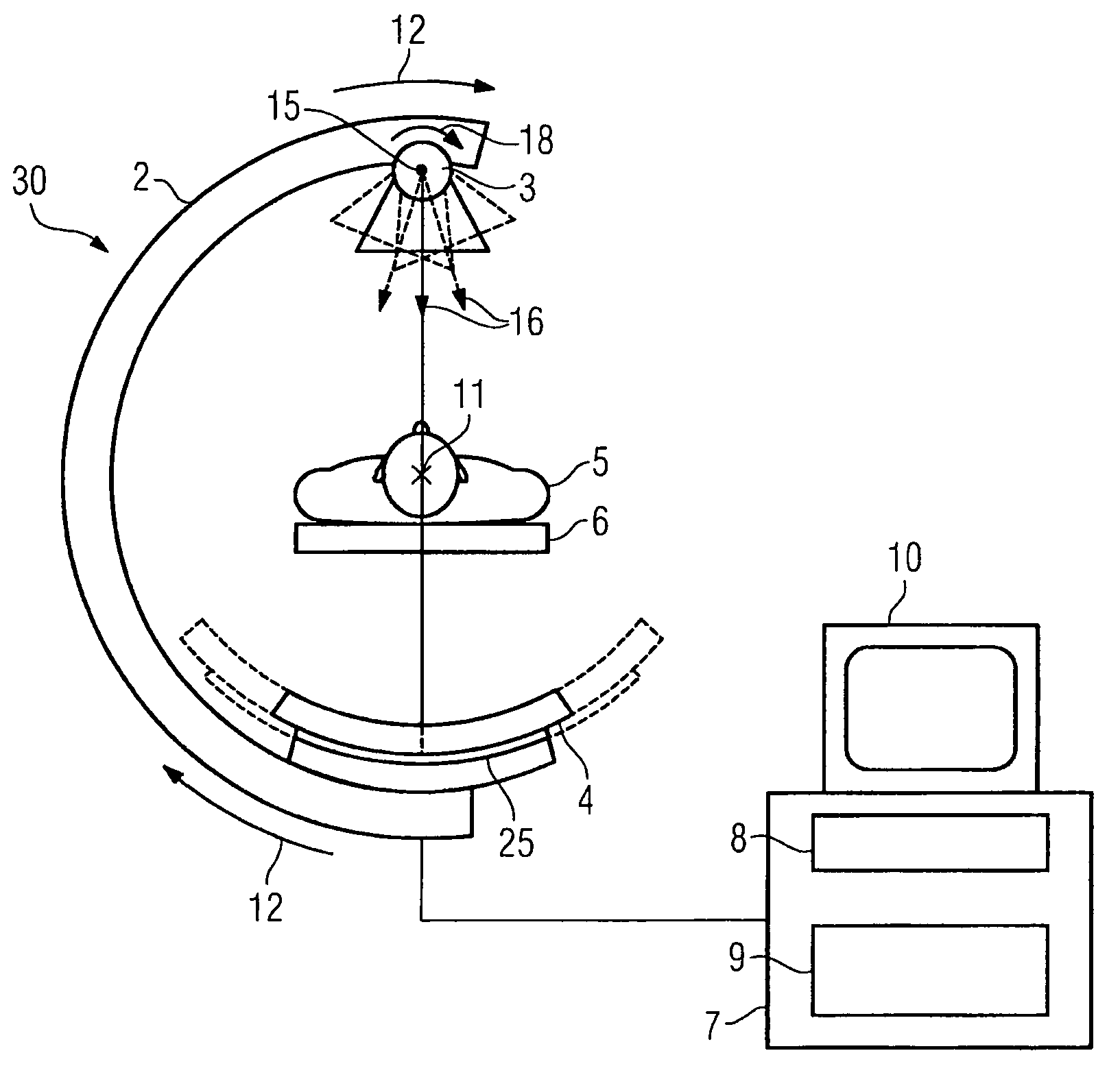
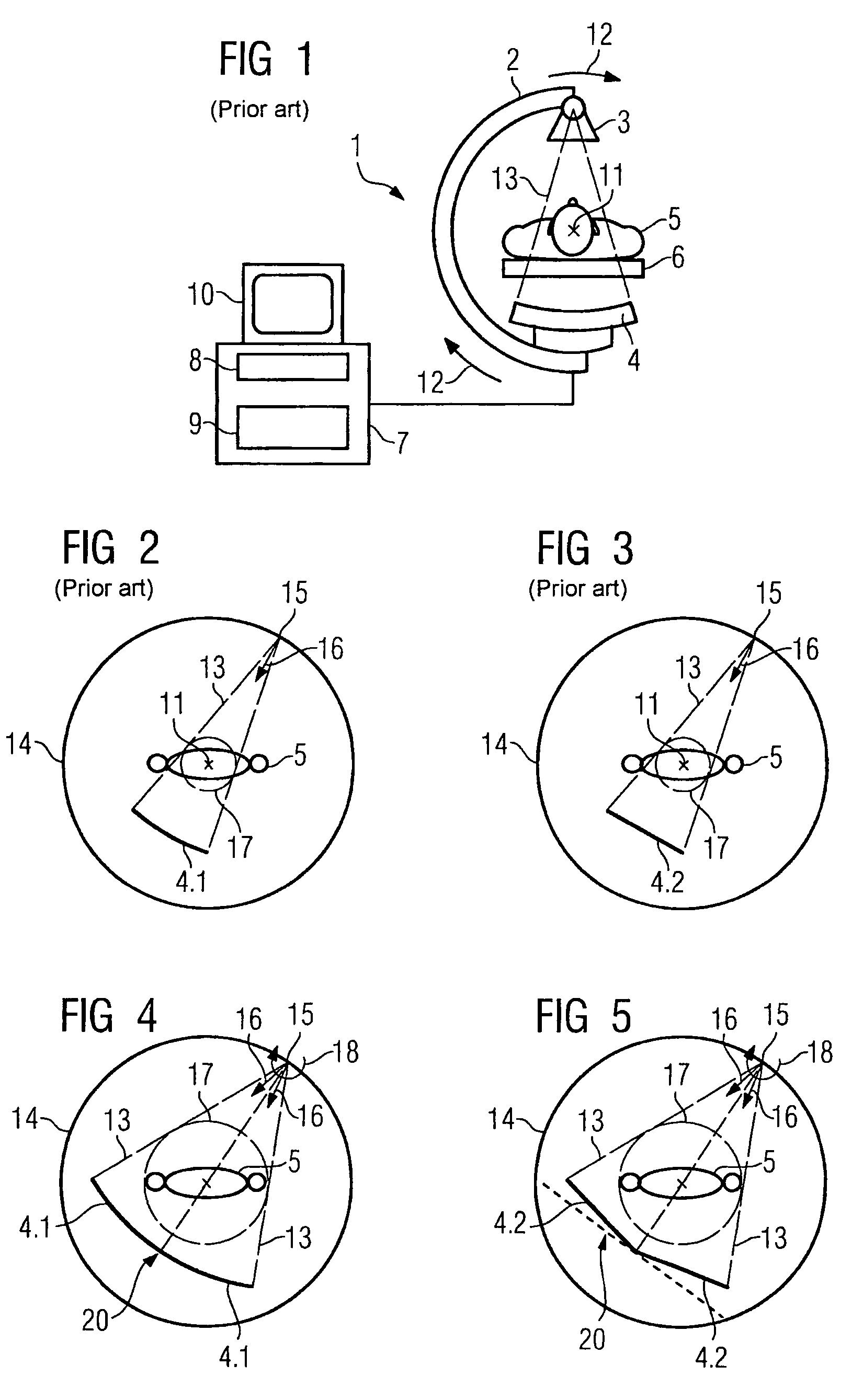
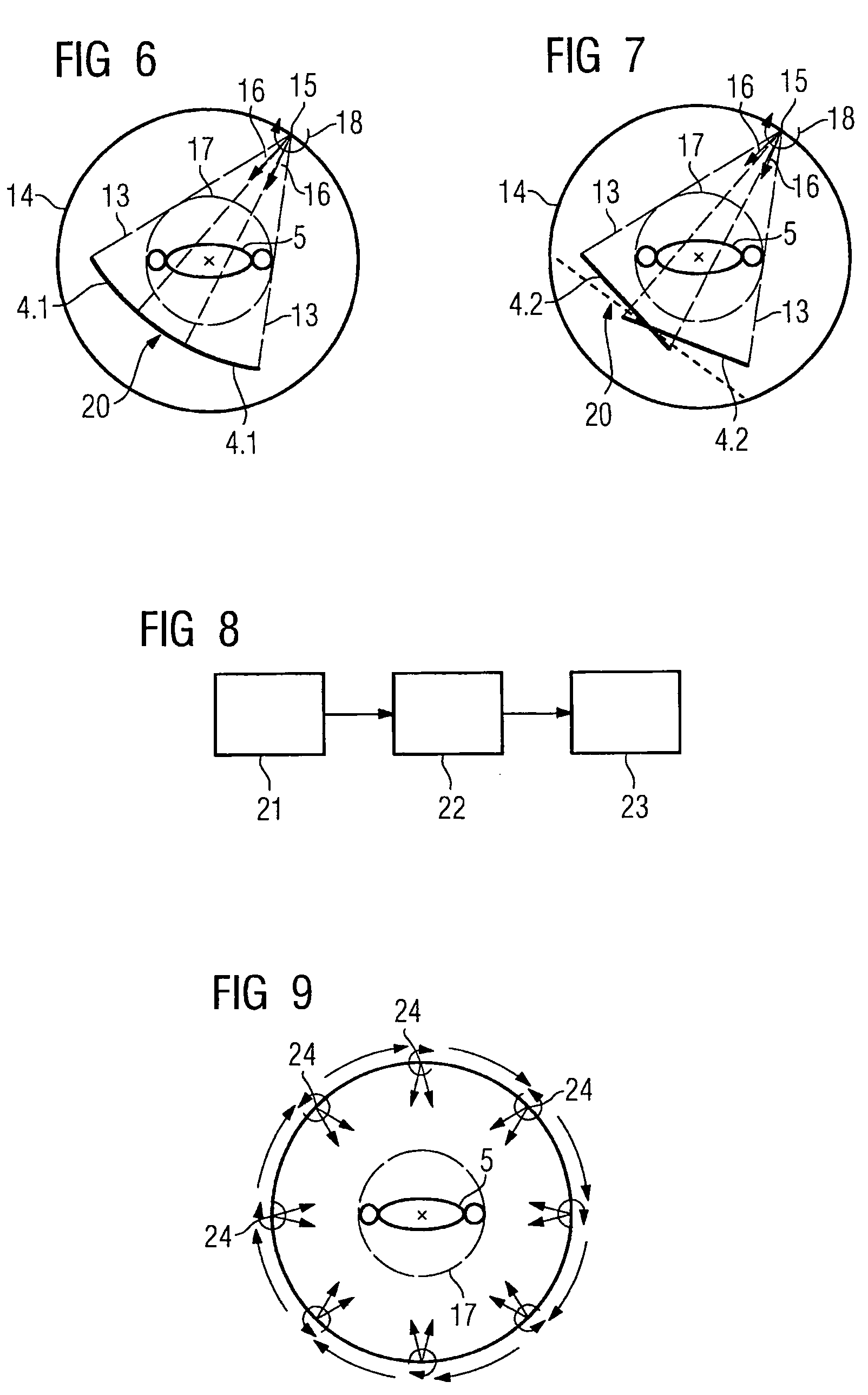
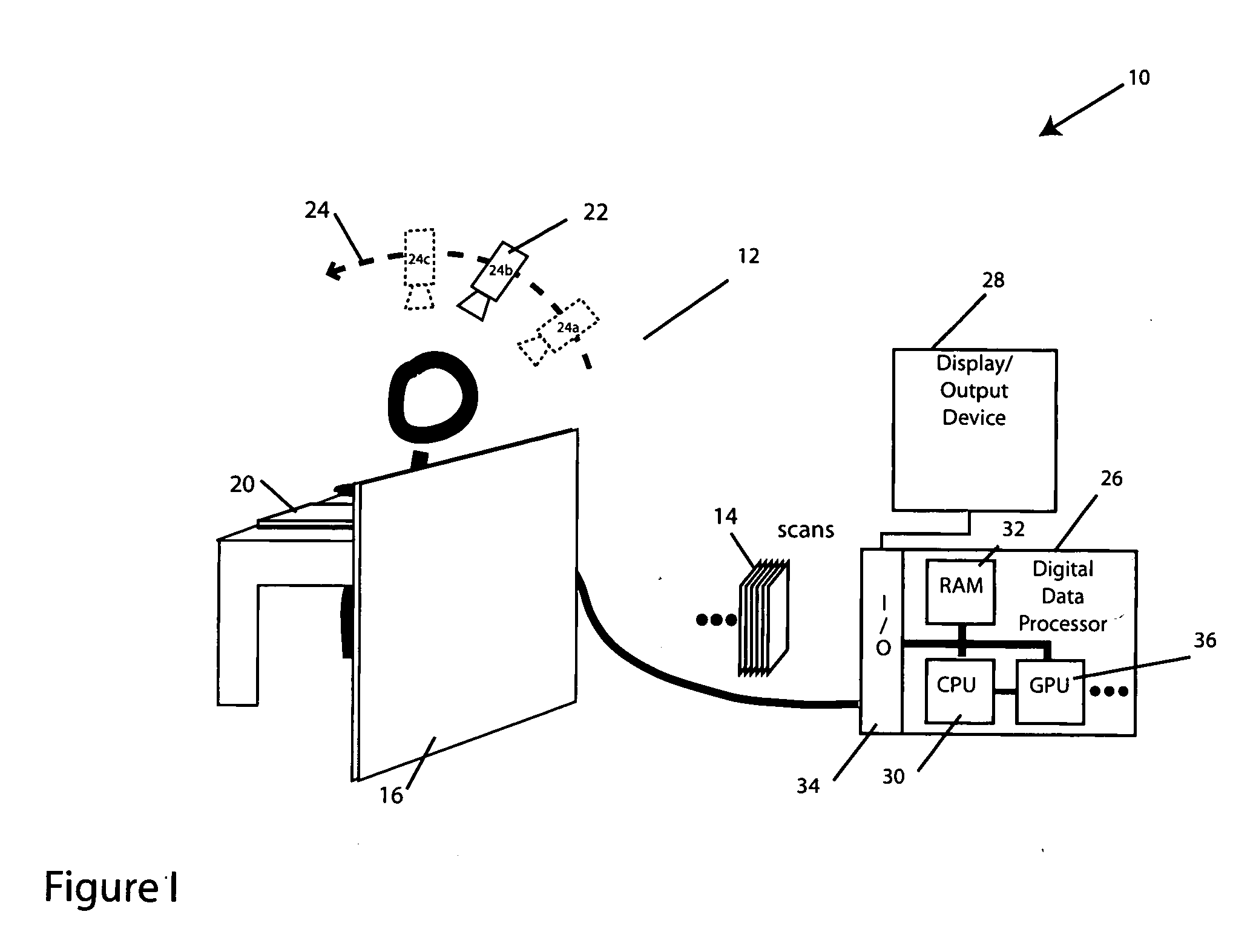
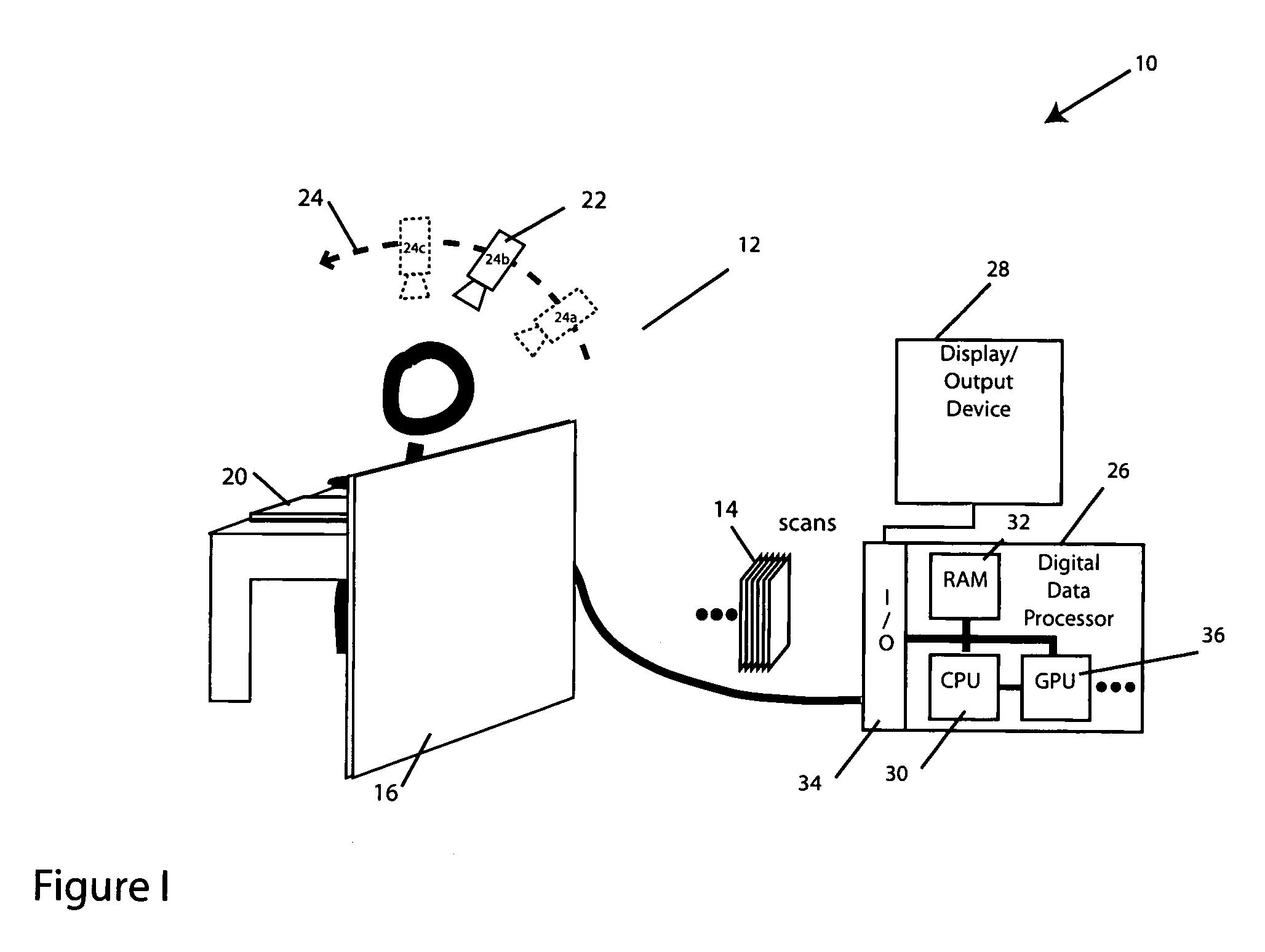
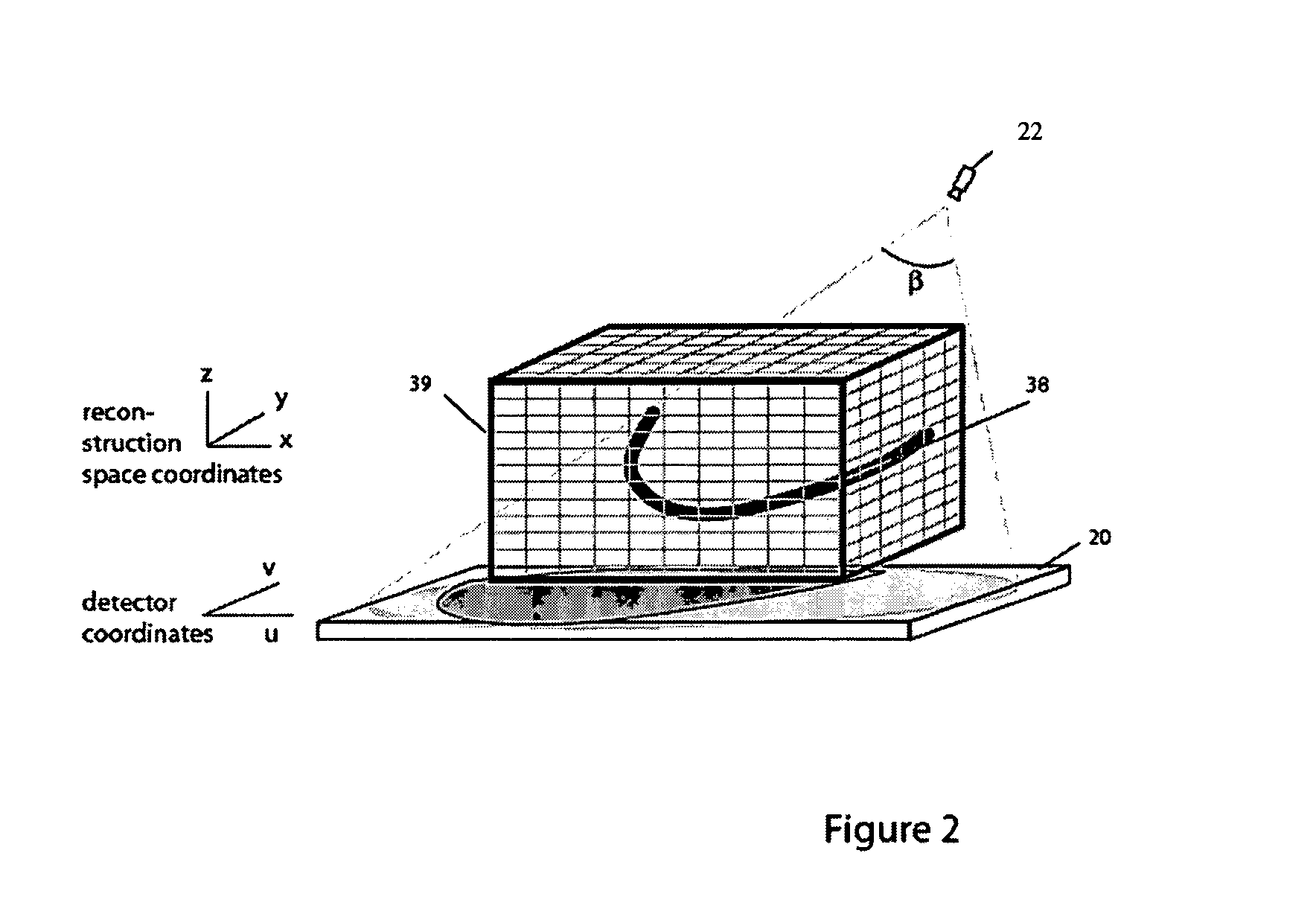
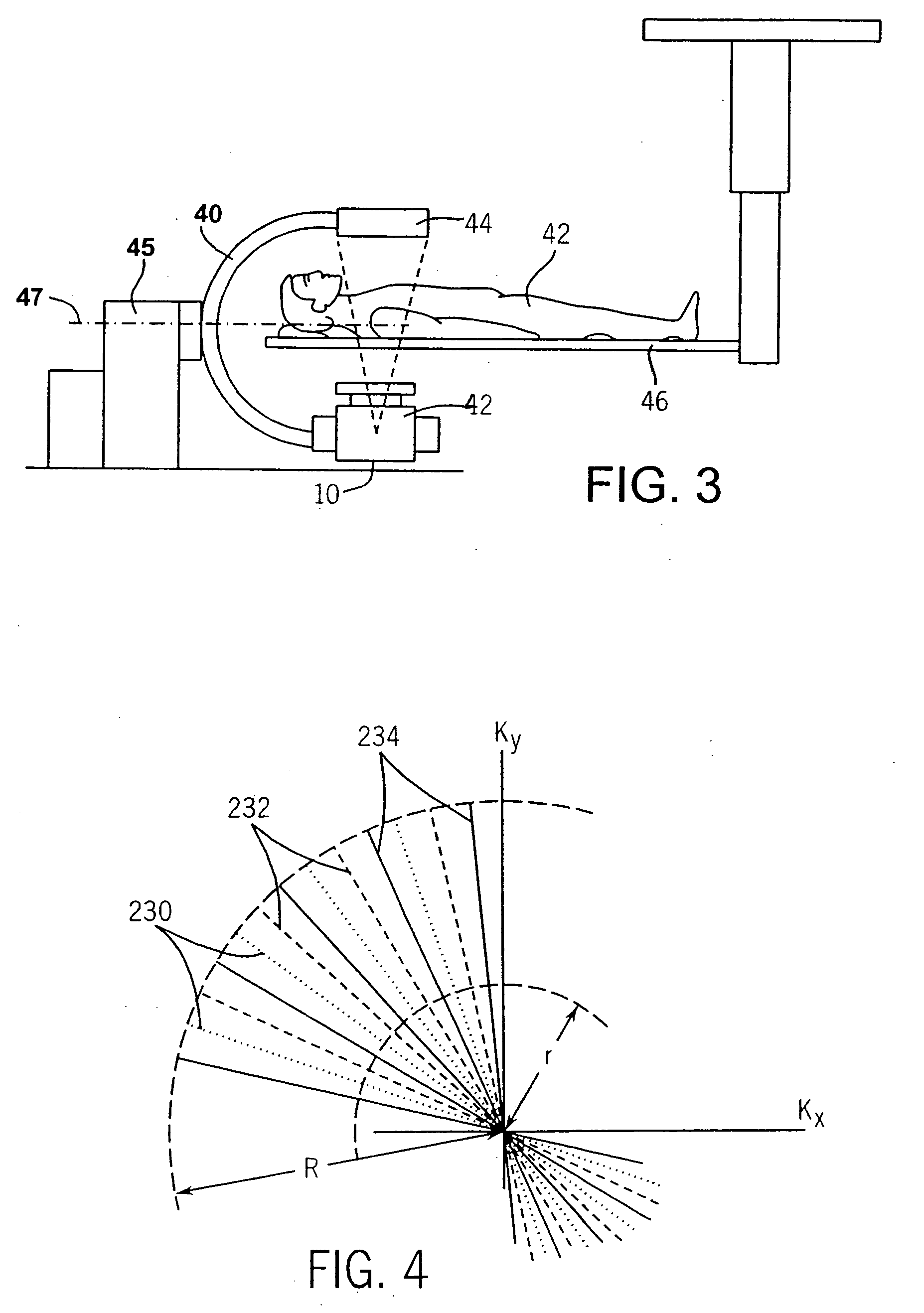
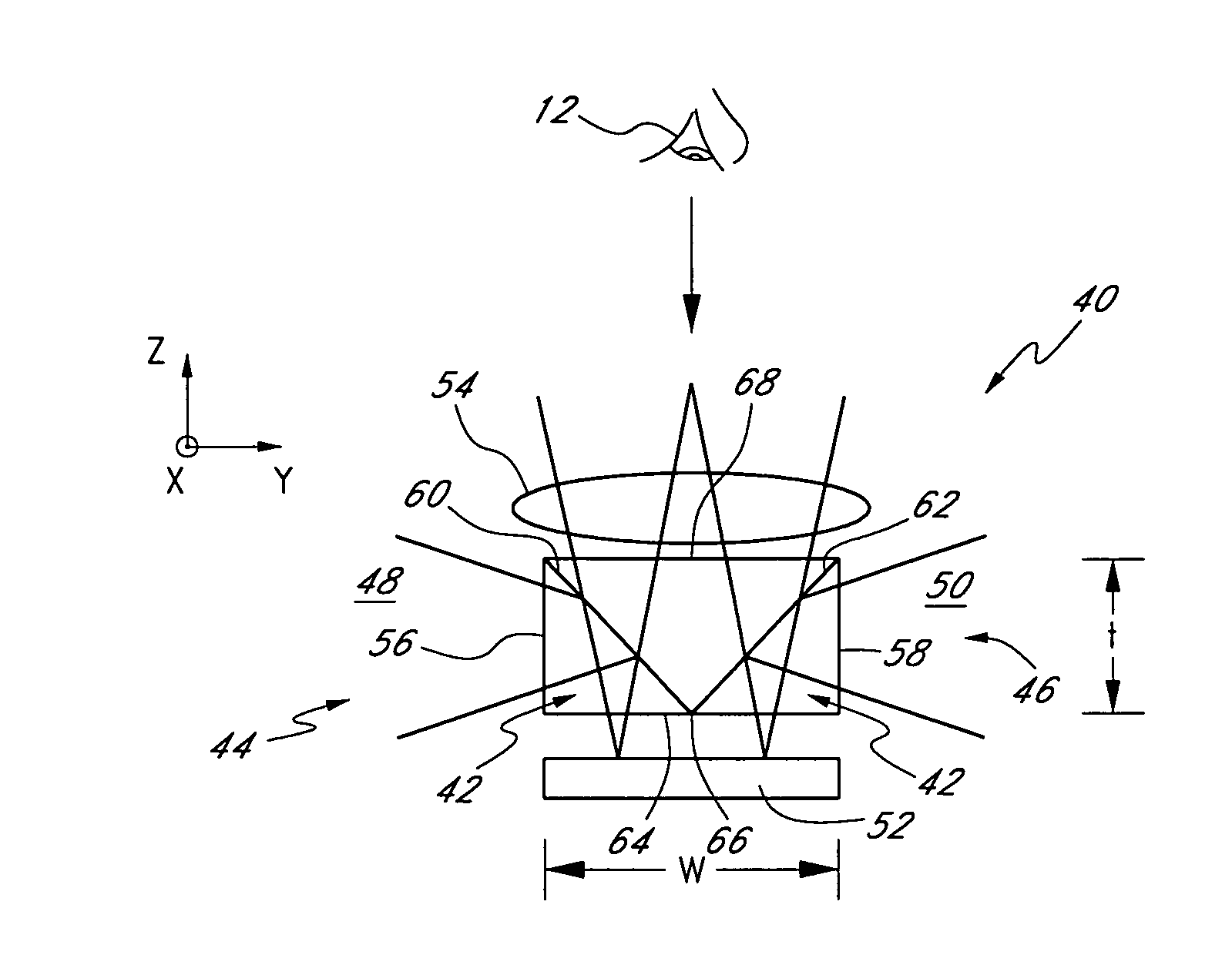
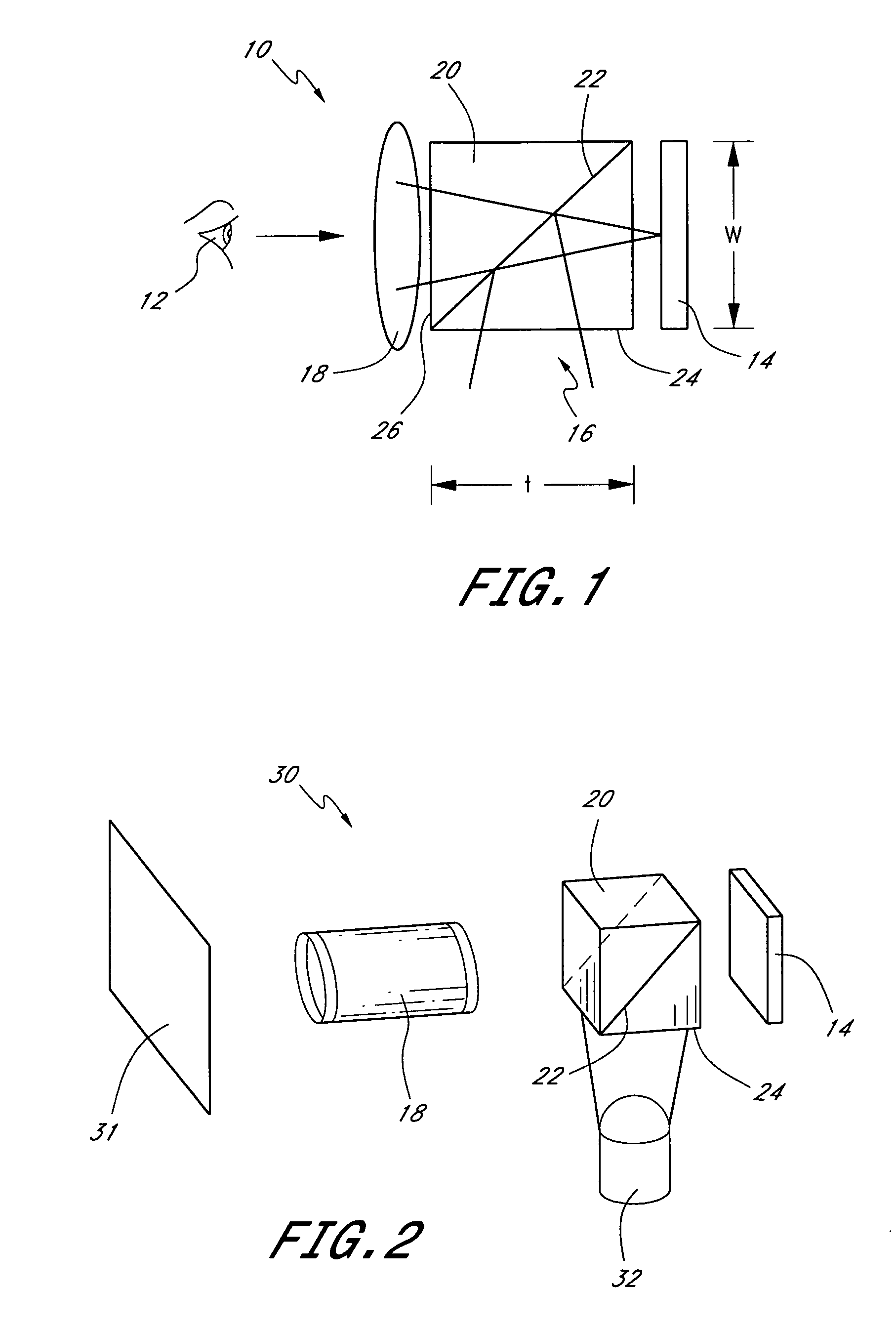
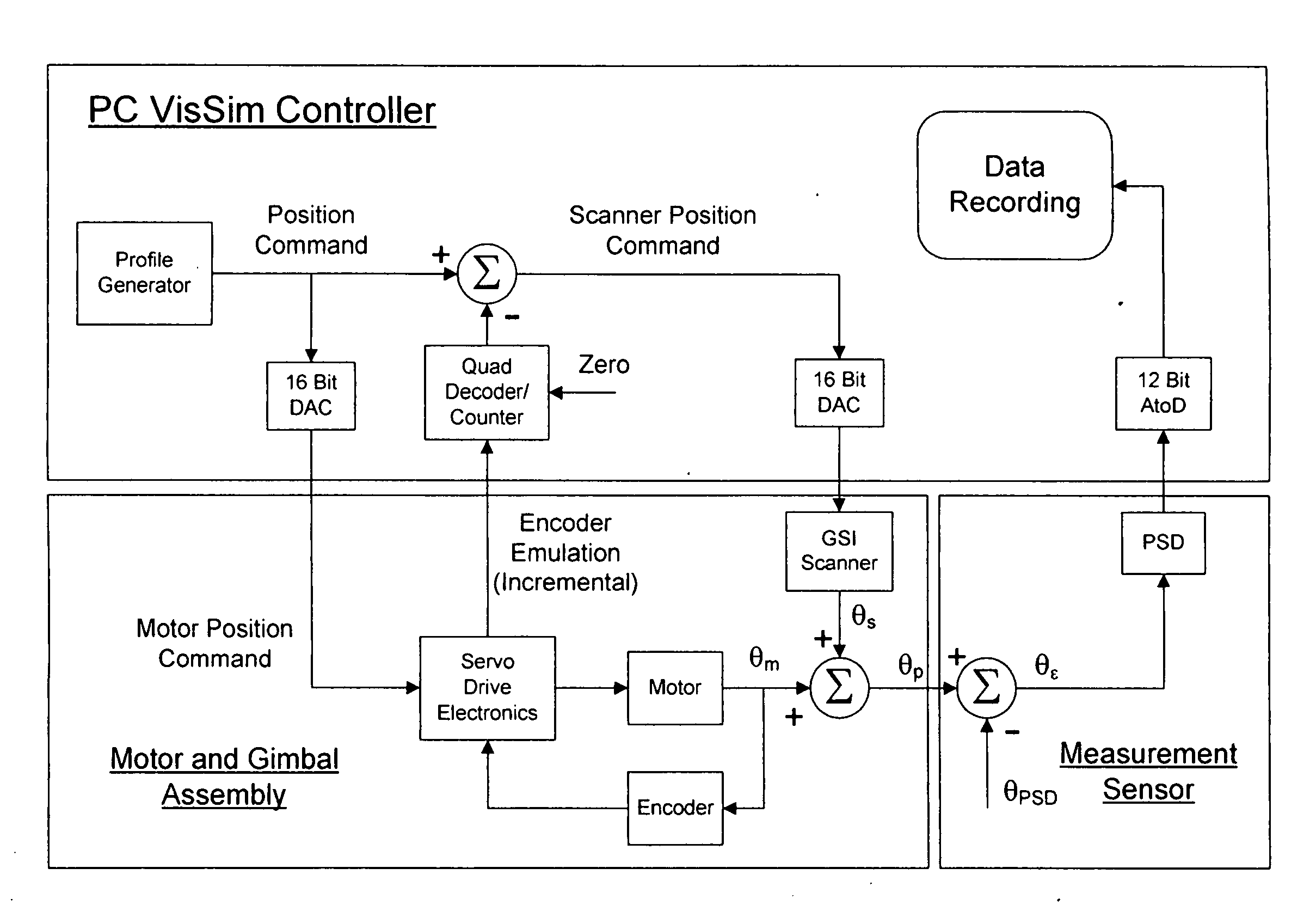
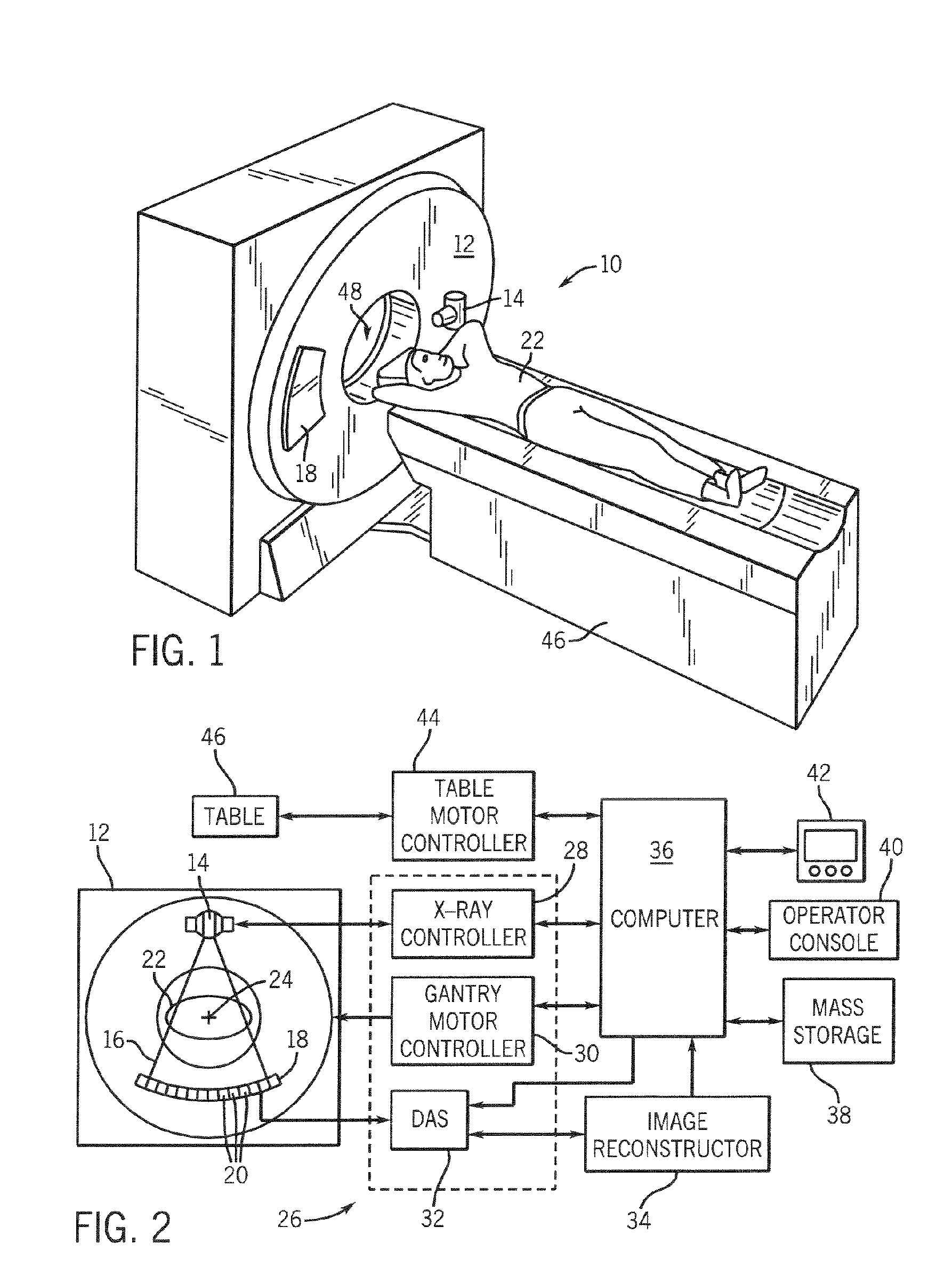
Method for reconstructing a three-dimensional image volume and x-ray devices
InactiveUS7711083B2Improve executionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingVoxelProjection image
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Three-dimensional photoacoustic imager and methods for calibrating an imager
InactiveUS20100249570A1Illuminating subjectUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesData acquisitionReconstruction algorithm
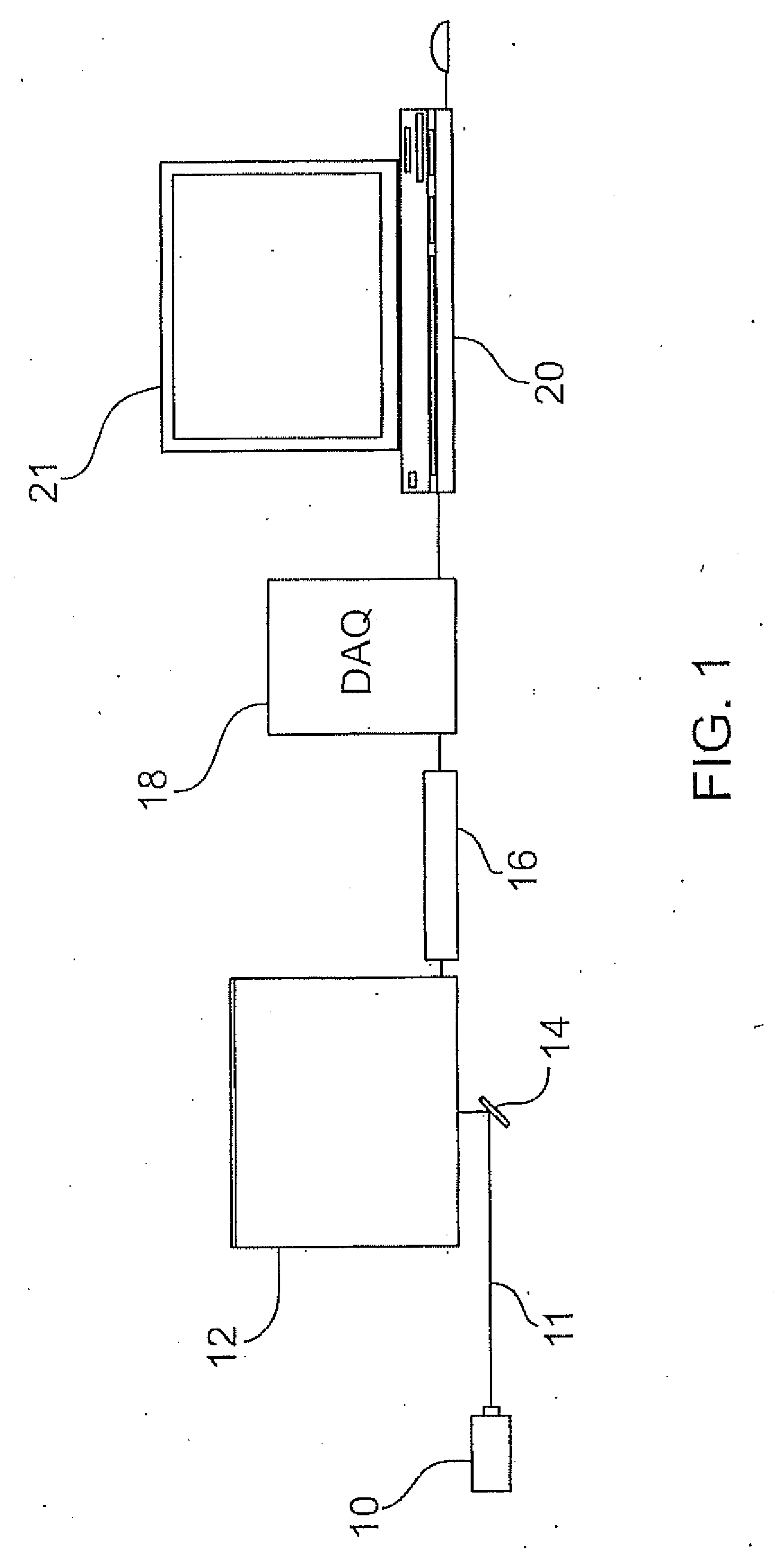
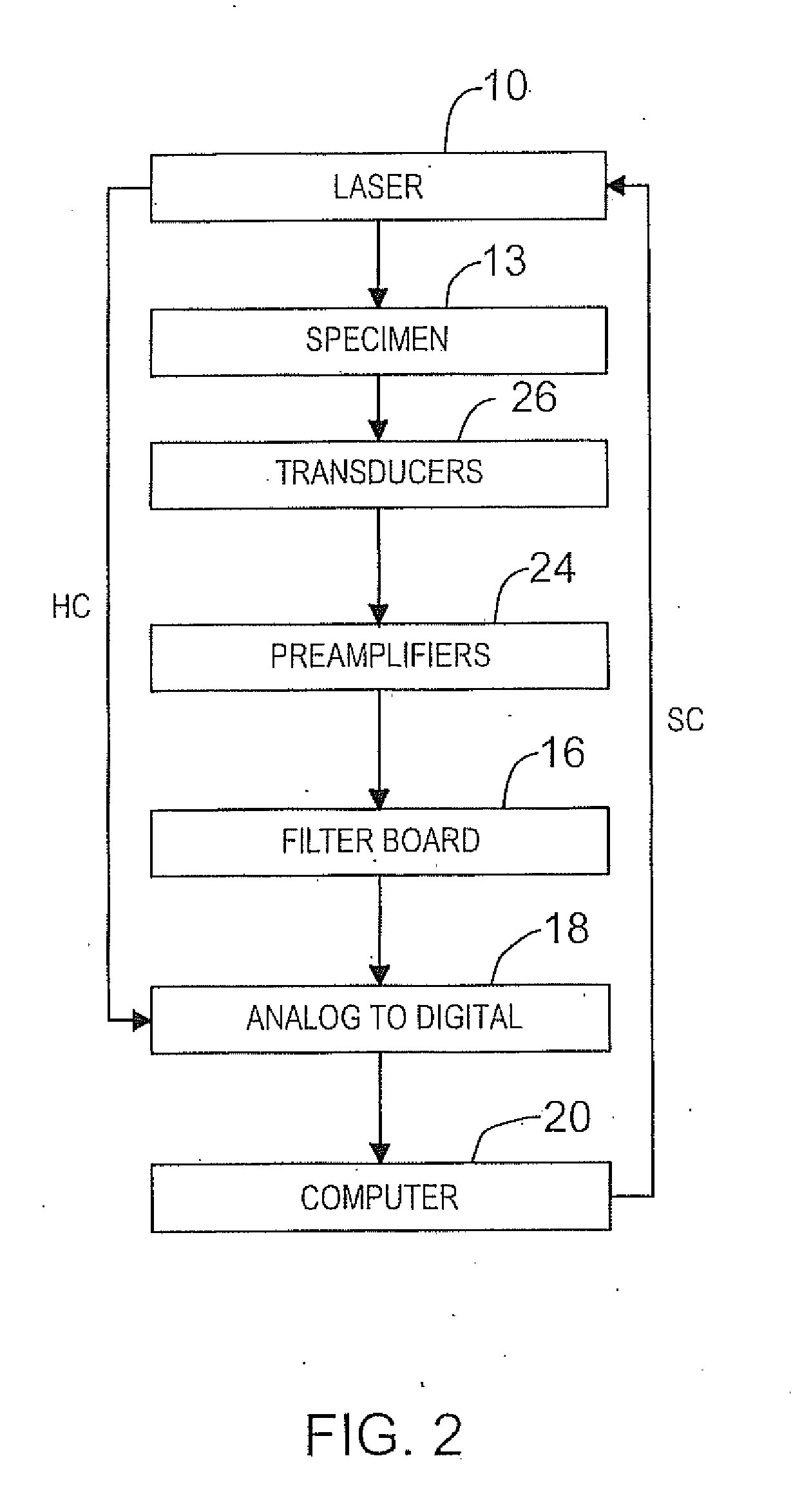
A photoacoustic imaging apparatus is provided for medical or other imaging applications and also a method for calibrating this apparatus. The apparatus employs a sparse array of transducer elements and a reconstruction algorithm. Spatial calibration maps of the sparse array are used to optimize the reconstruction algorithm. The apparatus includes a laser producing a pulsed laser beam to illuminate a subject for imaging and generate photoacoustic waves. The transducers are fixedly mounted on a holder so as to form the sparse array. A photoacoustic (PA) waves are received by each transducer. The resultant analog signals from each transducer are amplified, filtered, and converted to digital signals in parallel by a data acquisition system which is operatively connected to a computer. The computer receives the digital signals and processes the digital signals by the algorithm based on iterative forward projection and back-projection in order to provide the image.
Owner:MULTI MAGNETICS
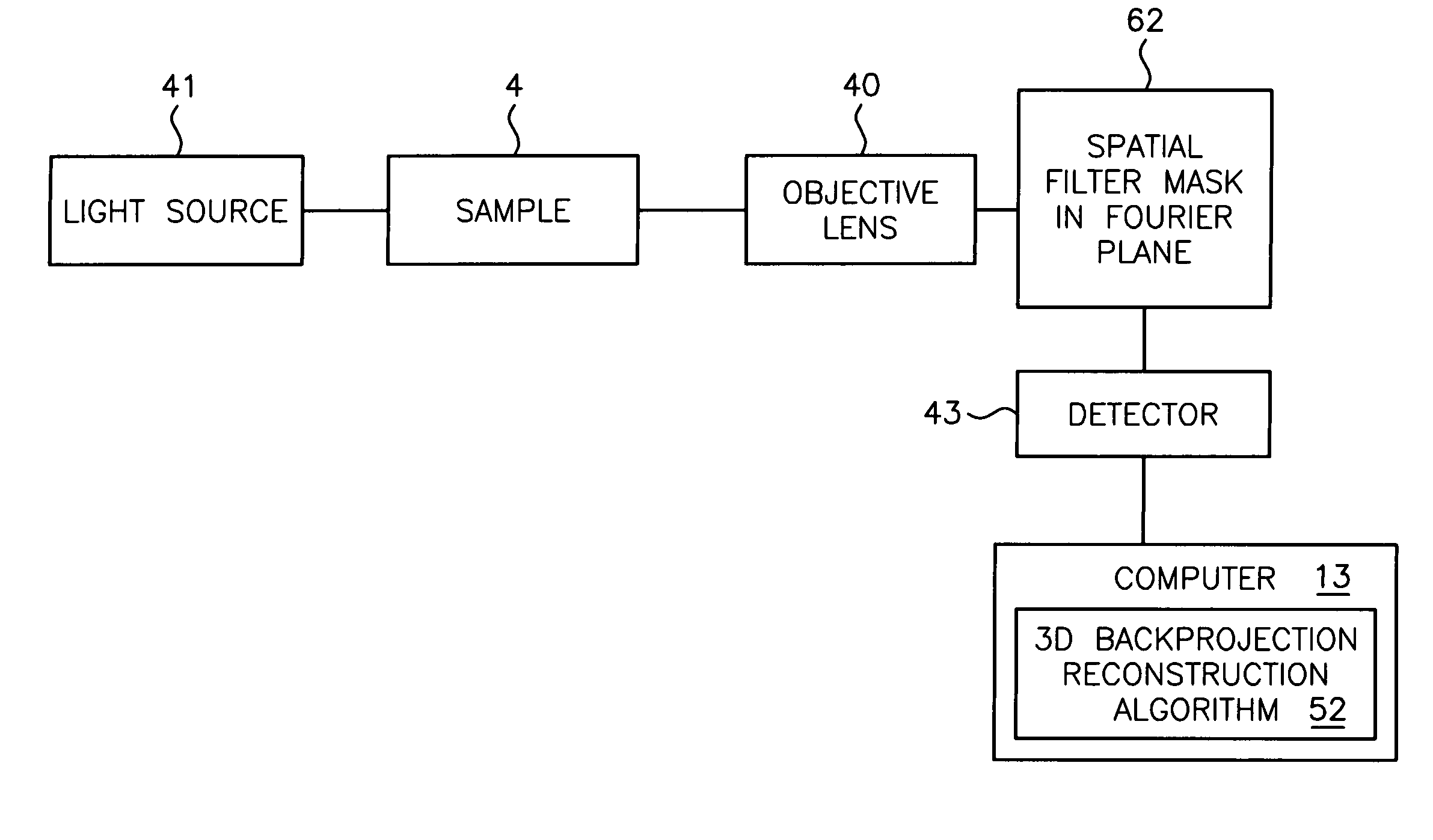
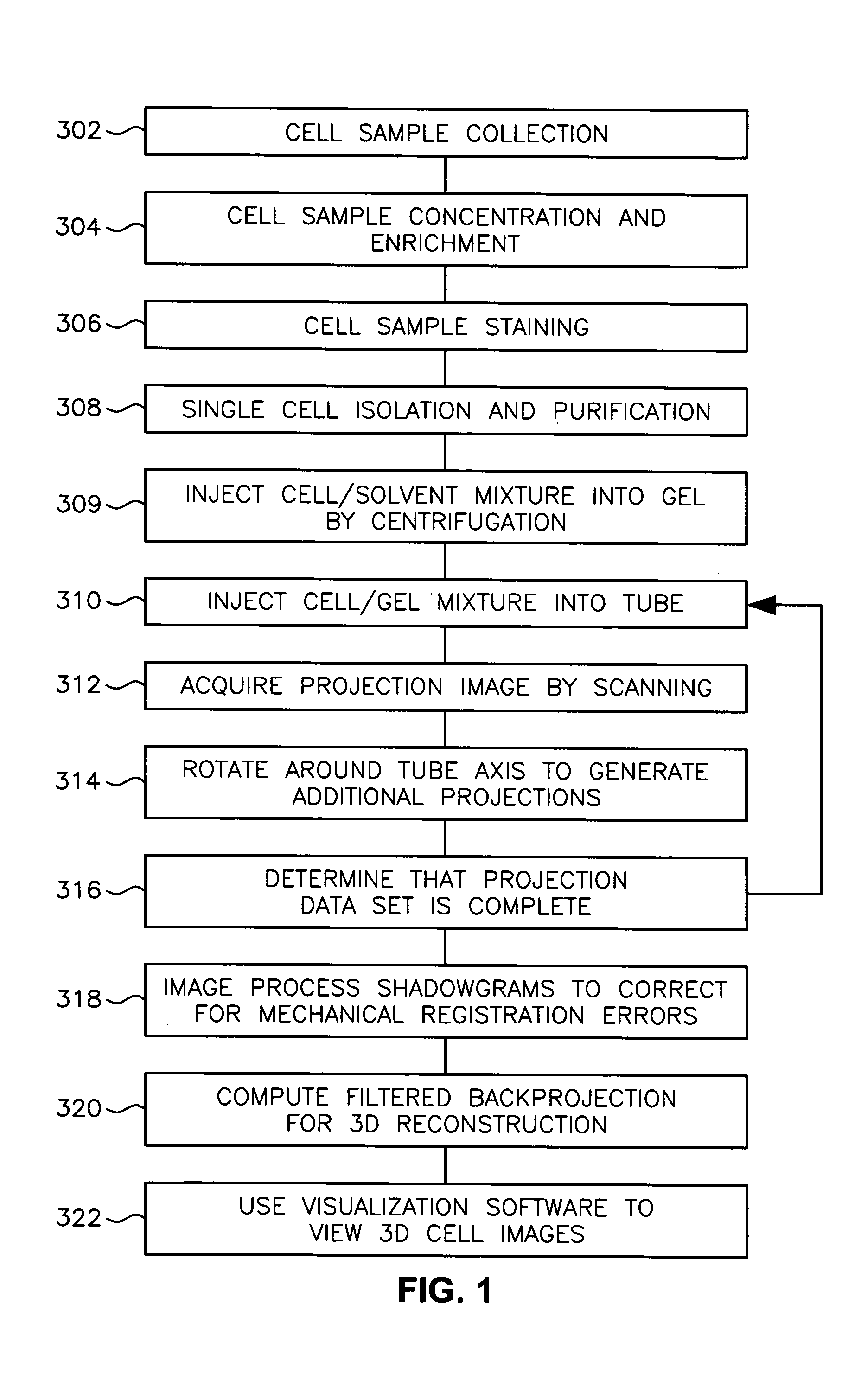
System and method for processing specimens and images for optical tomography
ActiveUS20050085721A1Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological cellOptical tomography
A scanning method for scanning samples of biological cells using optical tomography includes preparing, acquiring, reconstructing and viewing three-dimensional images of cell samples. Concentration and enrichment of the cell sample follows. The cell sample is stained. Cells are isolated from the cell sample and purified. A cell / solvent mixture is injected into a gel by centrifugation. A cell / gel mixture is injected into a capillary tube until a cell appears centered in a field of view using a step flow method. An optical imaging system, such as a fixed or variable motion optical tomography system acquires a projection image. The sample is rotated about a tube axis to generate additional projections. Once image acquisition is completed, the acquired shawdowgrams or image projections are corrected for errors. A computer or other equivalent processor is used to compute filtered backprojection information for 3D reconstruction.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
Image processing apparatus and method
ActiveUS7095432B2Small amount of calculationImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingProjection image
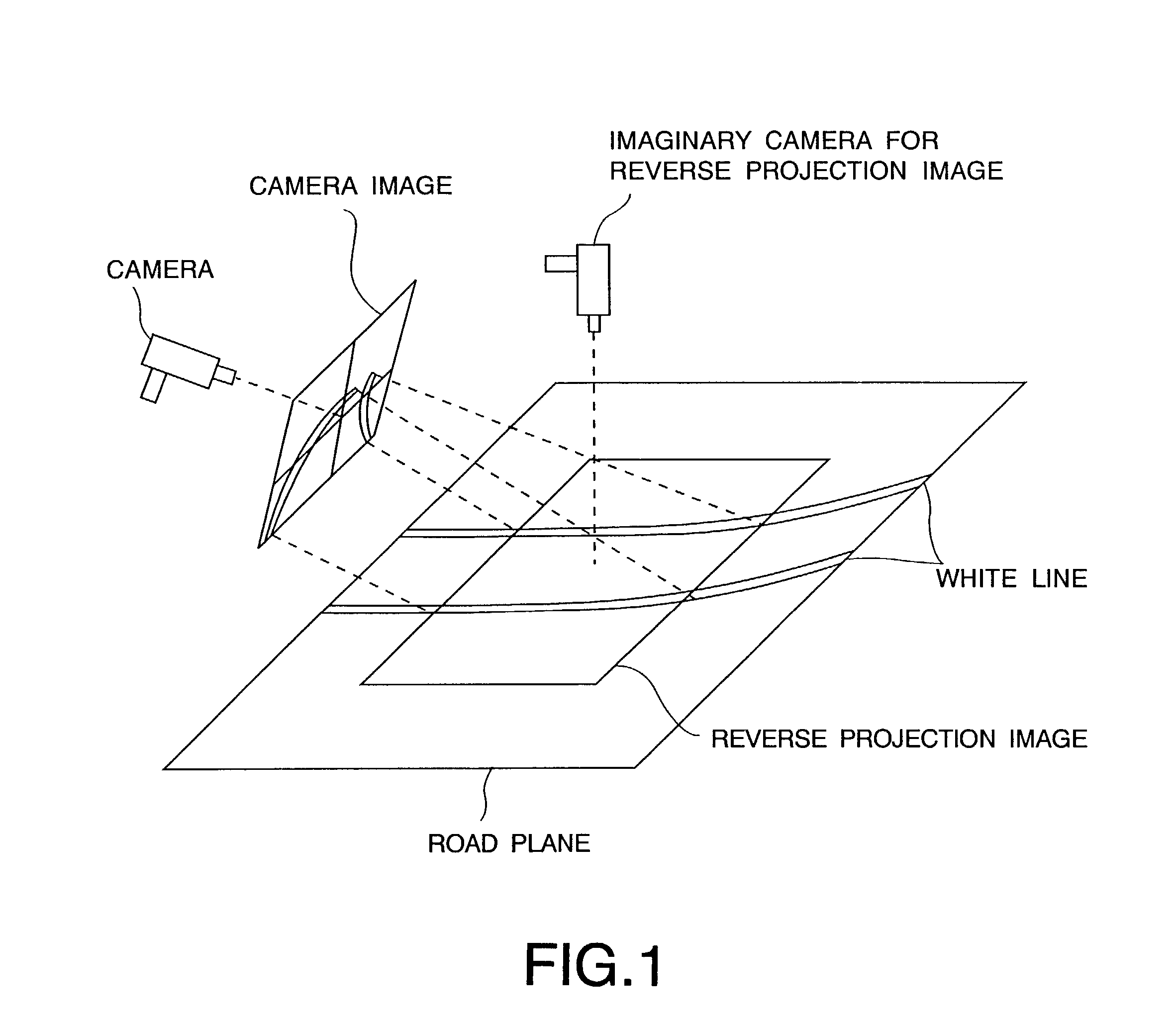
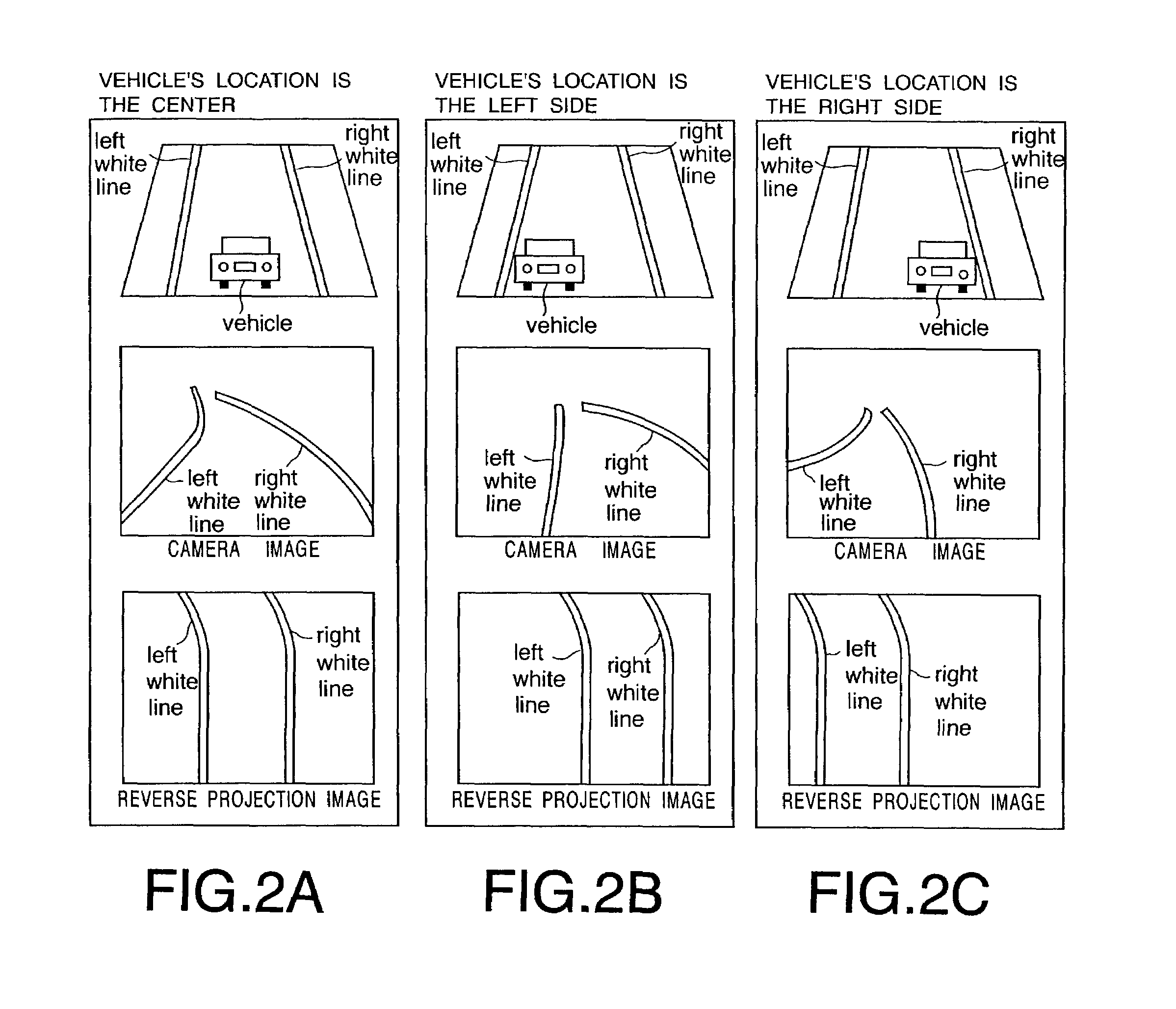
An image input unit inputs a plurality of images in a time series. Each input image includes a boundary line extending toward a vanishing point on a plane. A reverse projection image generation unit generates a reverse projection image of each input image by projecting information related to each input image onto the plane. A boundary line detection unit detects the boundary line from the reverse projection image by identifying a boundary line candidate on each reverse projection image.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Beamsplitting structures and methods in optical systems
ActiveUS7360899B2Improve uniformityTelevision system detailsDiffusing elementsFiberSpatial light modulator
Various embodiments involving structures and methods for illumination can be employed, for example, in projectors, head-mounted displays, helmet-mounted displays, back projection TVs, flat panel displays as well as other optical systems. Certain embodiments may include prism elements for illuminating, for example, a spatial light modulator. Light may be coupled to the prism in some cases using fiber optics or lightpipes. The optical system may also include a diffuser having scatter features arranged to scatter light appropriately to produce a desired luminance profile. Other embodiments are possible as well.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
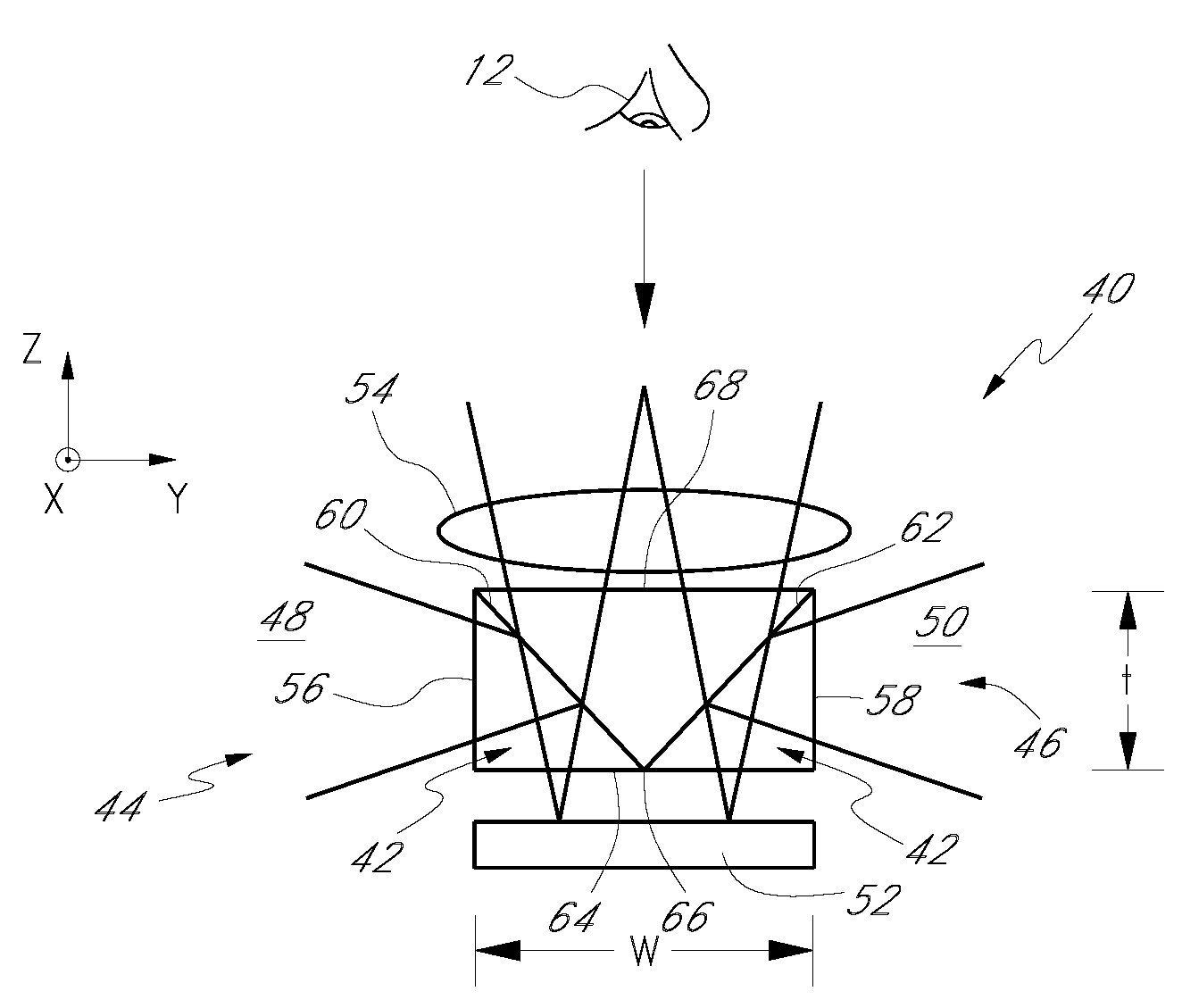
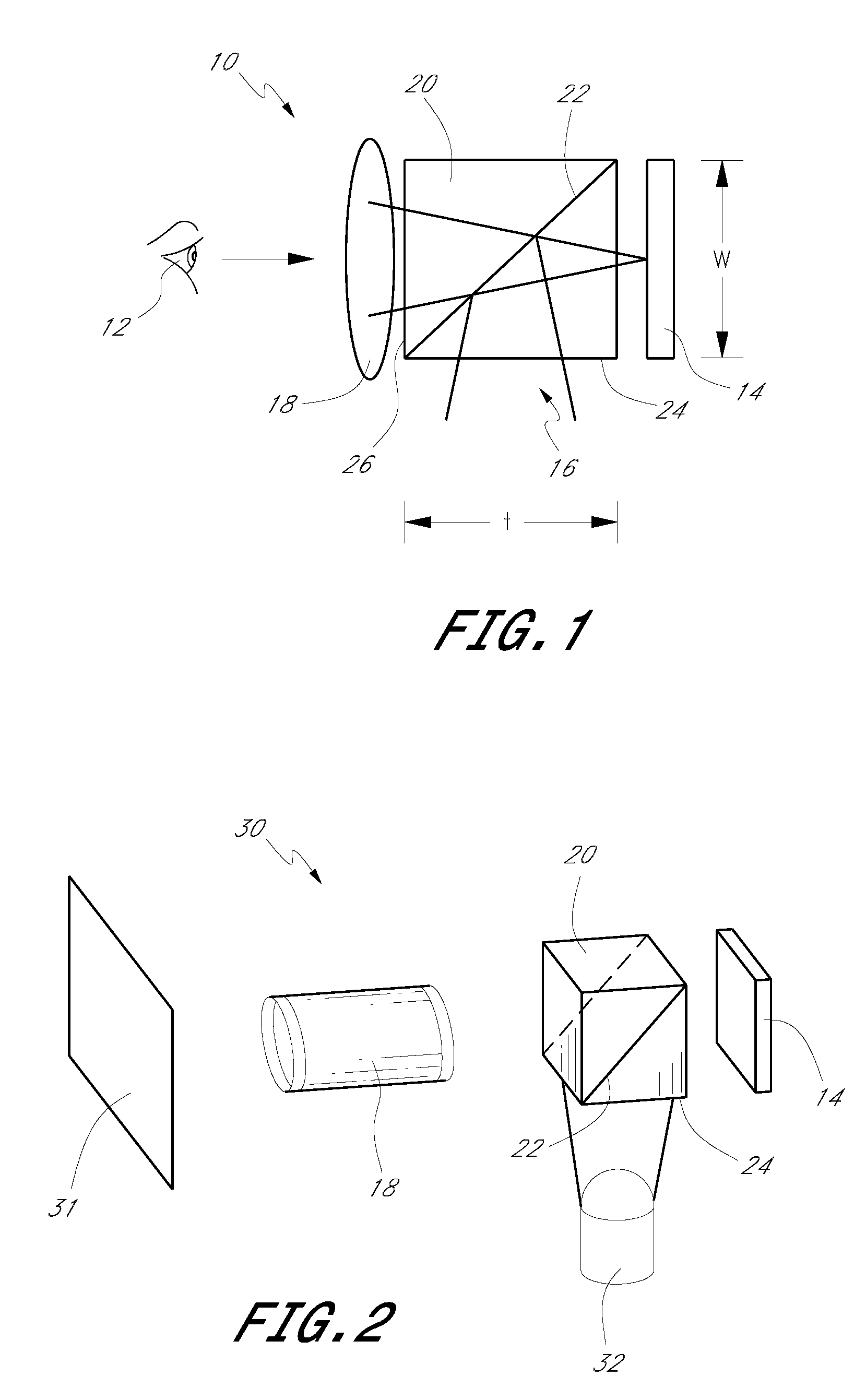
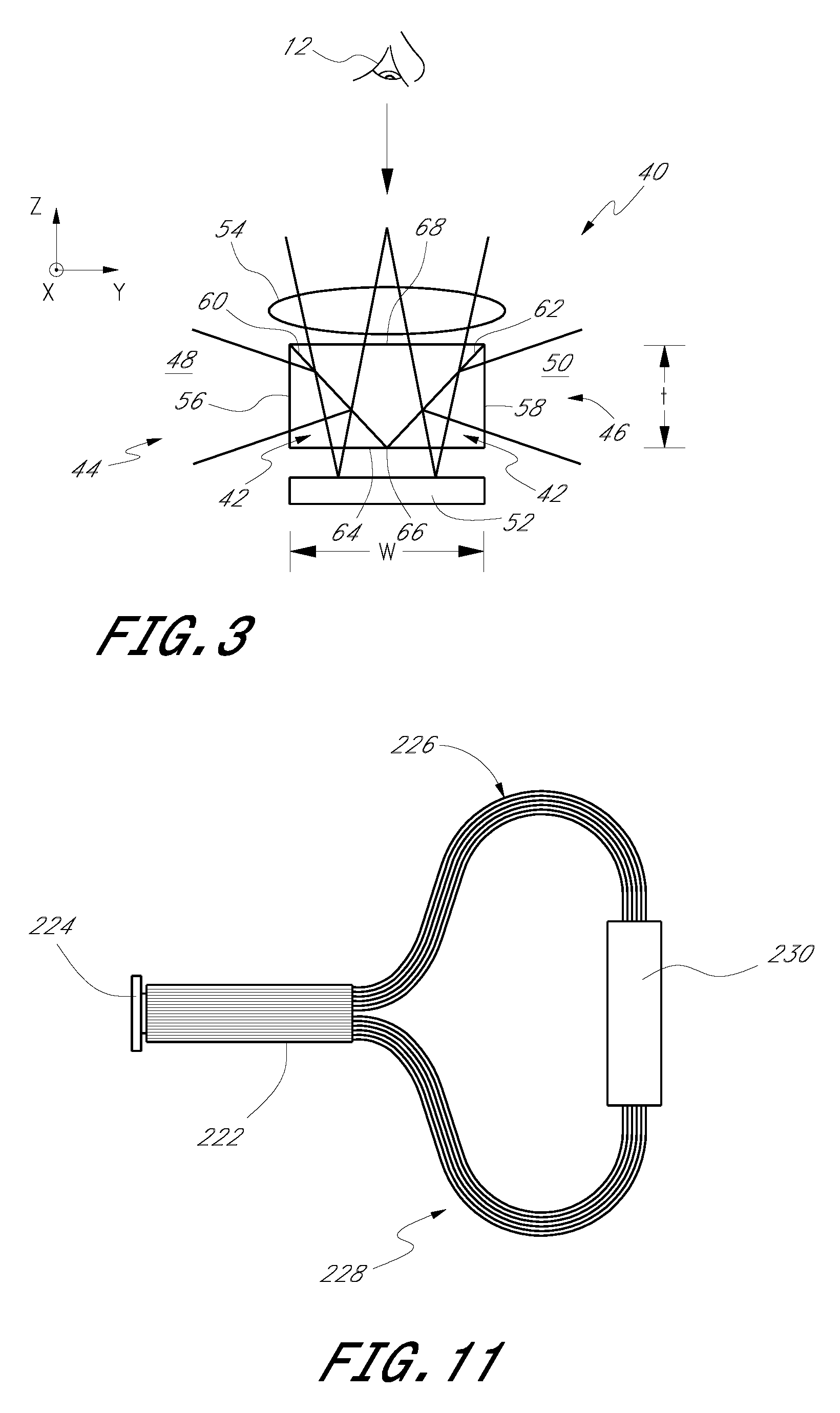
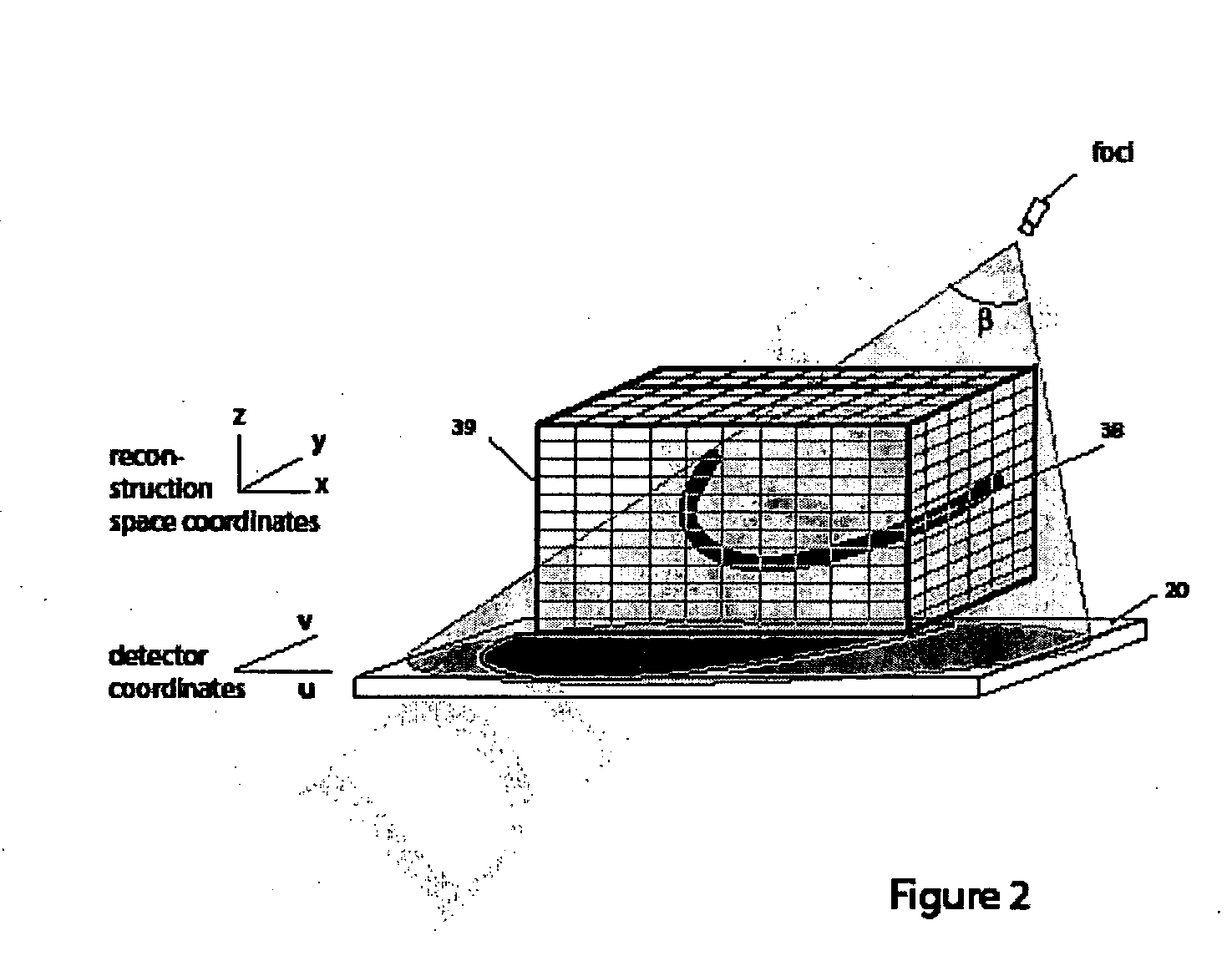
Methods and apparatus for back-projection and forward-projection
ActiveUS20050152590A1Few computational resourceAddressing slow performanceReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationVoxelProjection image
The invention provides improvements in reconstructive imaging of the type in which a volume is reconstructed from a series of measured projection images (or other two-dimensional representations) generated by projection of a point x-ray source (or other radiation source), positioned at a distinct focus, through the volume to a plane at which the respective projection image is acquired (“detector plane”). In one aspect, the improvements are with respect to back-projecting a two-dimensional representation lying in the detector plane (representing, for example, a difference between an originally-acquired measured projection image and a subsequently-generated estimate thereof) to generate three-dimensional representation (which can be used, for example, to update an estimate of the volume). According to this aspect, for each of one or more slices of the 3D representation parallel to the projection plane and for each distinct focus at which a projection is generated, the following steps are performed in connection with the back-projection: (i) warping the first 2D representation to generate a second 2D representation by applying to the first 2D representation a selected linear mapping, where that selected linear mapping would map, in order to match dimensions of the respective slice within the 3D representation, a region defined by projection, at the respective focus, of comers of that slice onto the detector plane, and (ii) incrementing values of each of one or more voxels of the respective slice by an amount that is a function of a value of a correspondingly indexed pixel of the second 2D representation. A related aspect provides improvements with respect to forward-projecting, as well as in iterative (and non-iterative) methodologies that incorporate both back-projection and forward-projection.
Owner:PME IP
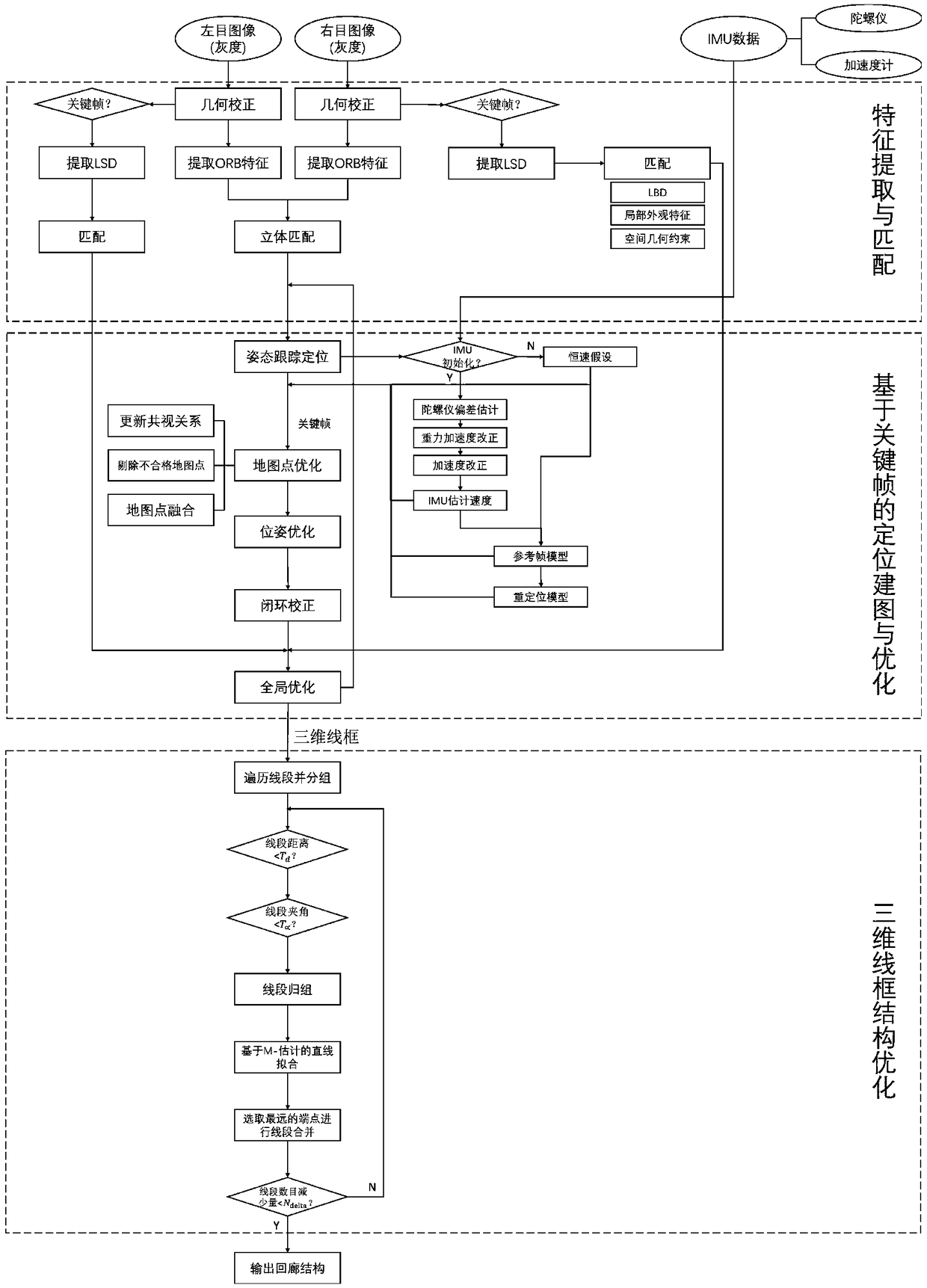
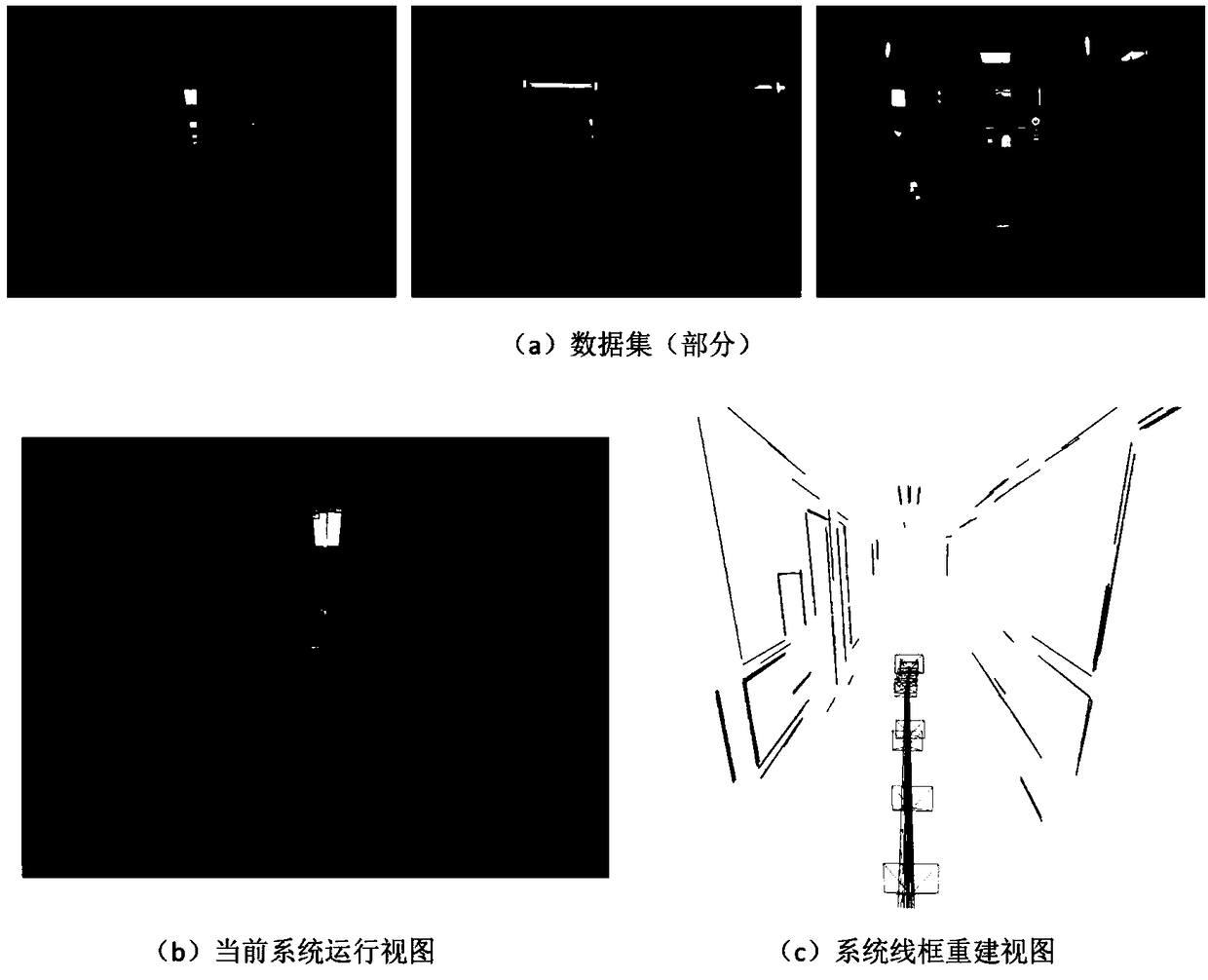
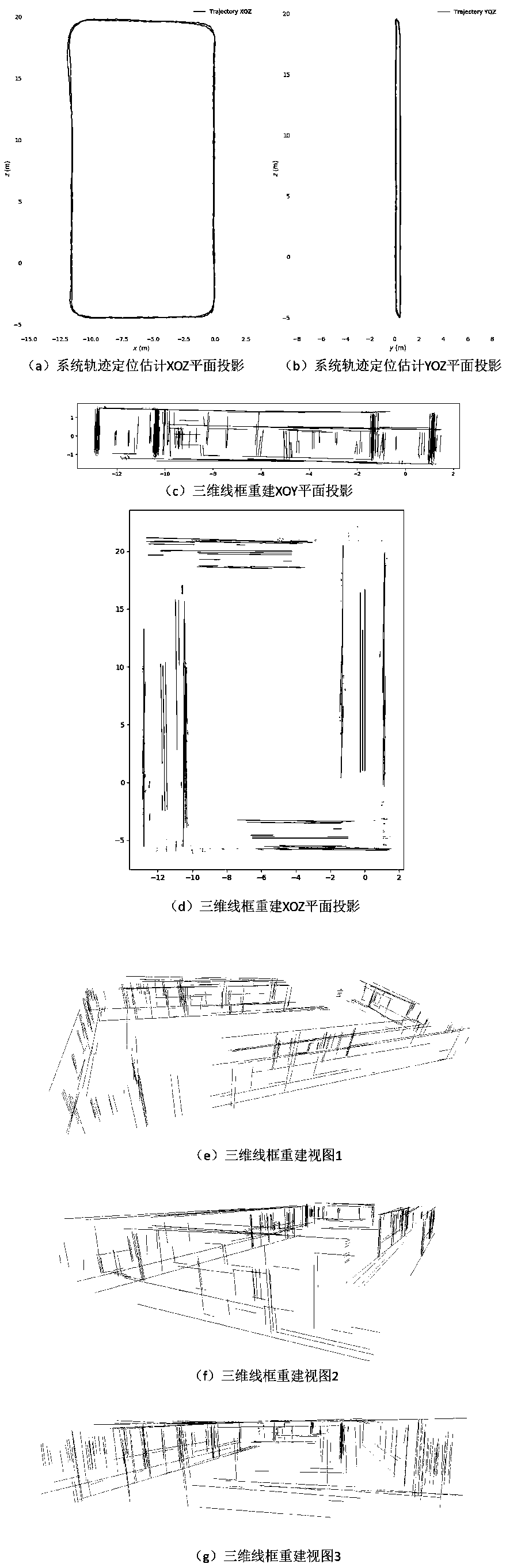
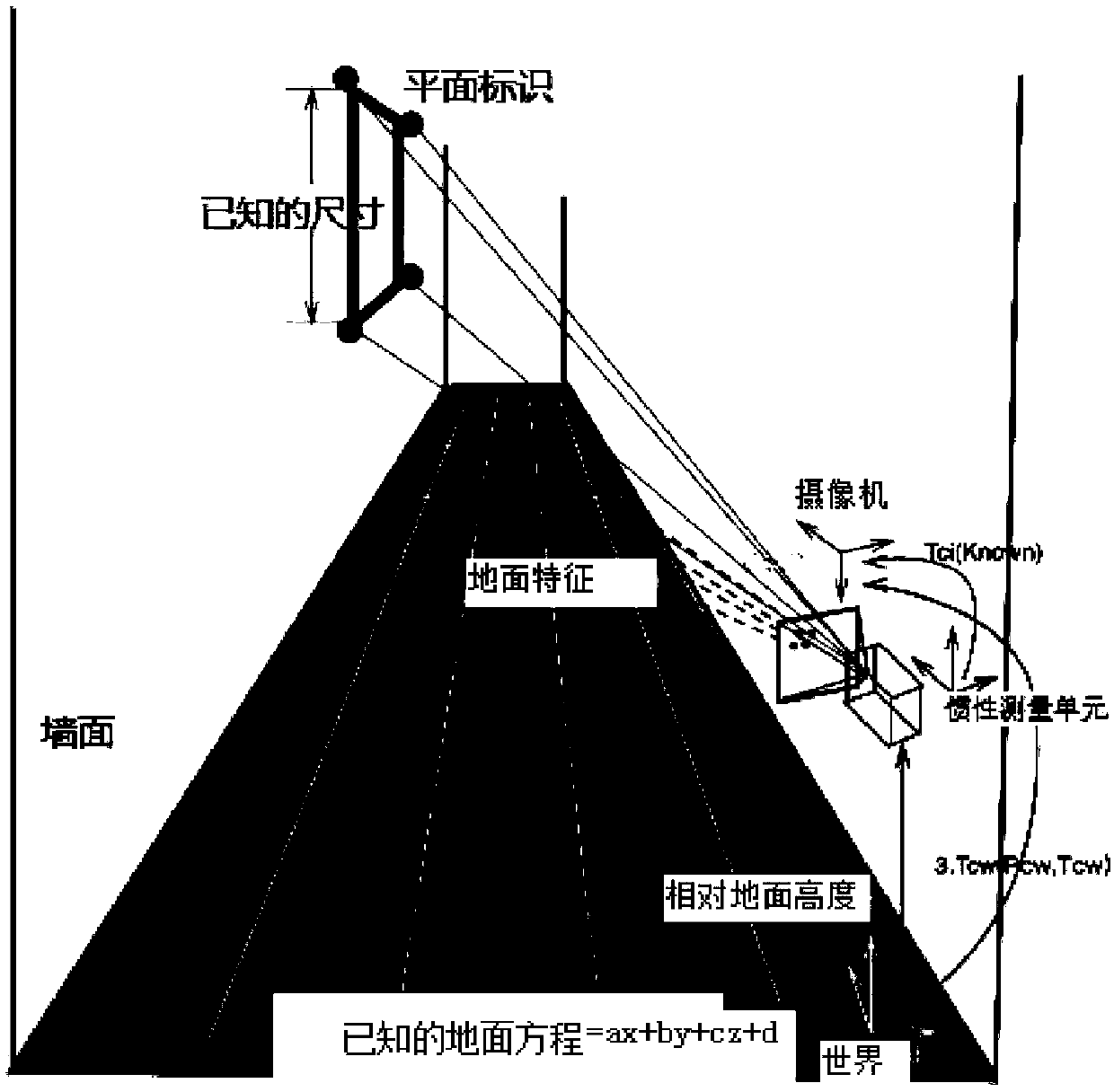
A three-dimensional wire frame structure method and system fusing a binocular camera and IMU positioning
ActiveCN109166149AGuaranteed uptimeImprove stabilityImage enhancementImage analysisThree-dimensional spaceDistance constraints
The invention relates to a three-dimensional wire frame structure method and system fusing a binocular camera and IMU positioning. On the basis of binocular vision, the invention initializes and fusesinertial measurement information by using a divide-and-conquer strategy, implements tracking, positioning and drawing, and can robustly run in indoor and outdoor environments and complex motion conditions. On the basis of accurate positioning, 3D wireframe reconstruction and iterative optimization are carried out based on the posture of the key frame. Linear segments are matched by local featuresand spatial geometric constraints and back-projected into three-dimensional space. Through the angle and distance constraints, the straight line segments are divided into different sets. Based on thegrouping results, the fitting region is determined and the straight line segments are merged. Finally, a 3-D wireframe structure is output. The invention fuses multi-source information to improve thestability and robustness of the system on the traditional vision-based positioning and mapping method. At the same time, line information is added to the key frame to sparsely express the structuralcharacteristics of the three-dimensional environment, which improves the computational efficiency.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
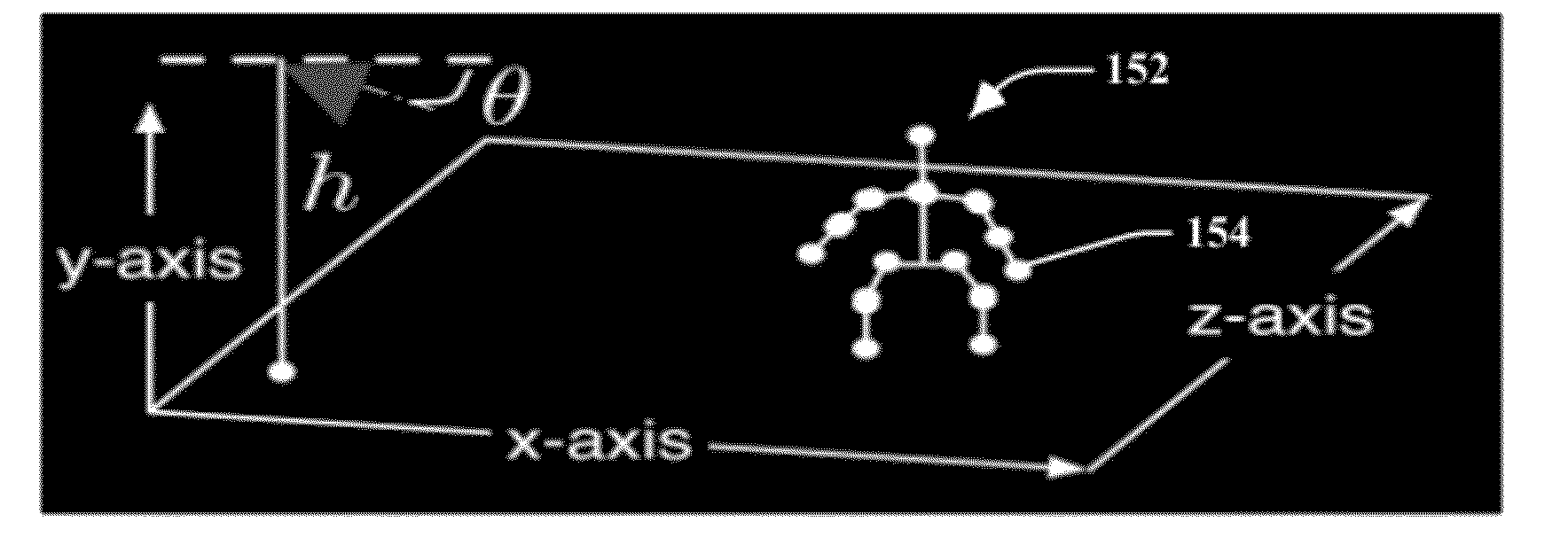
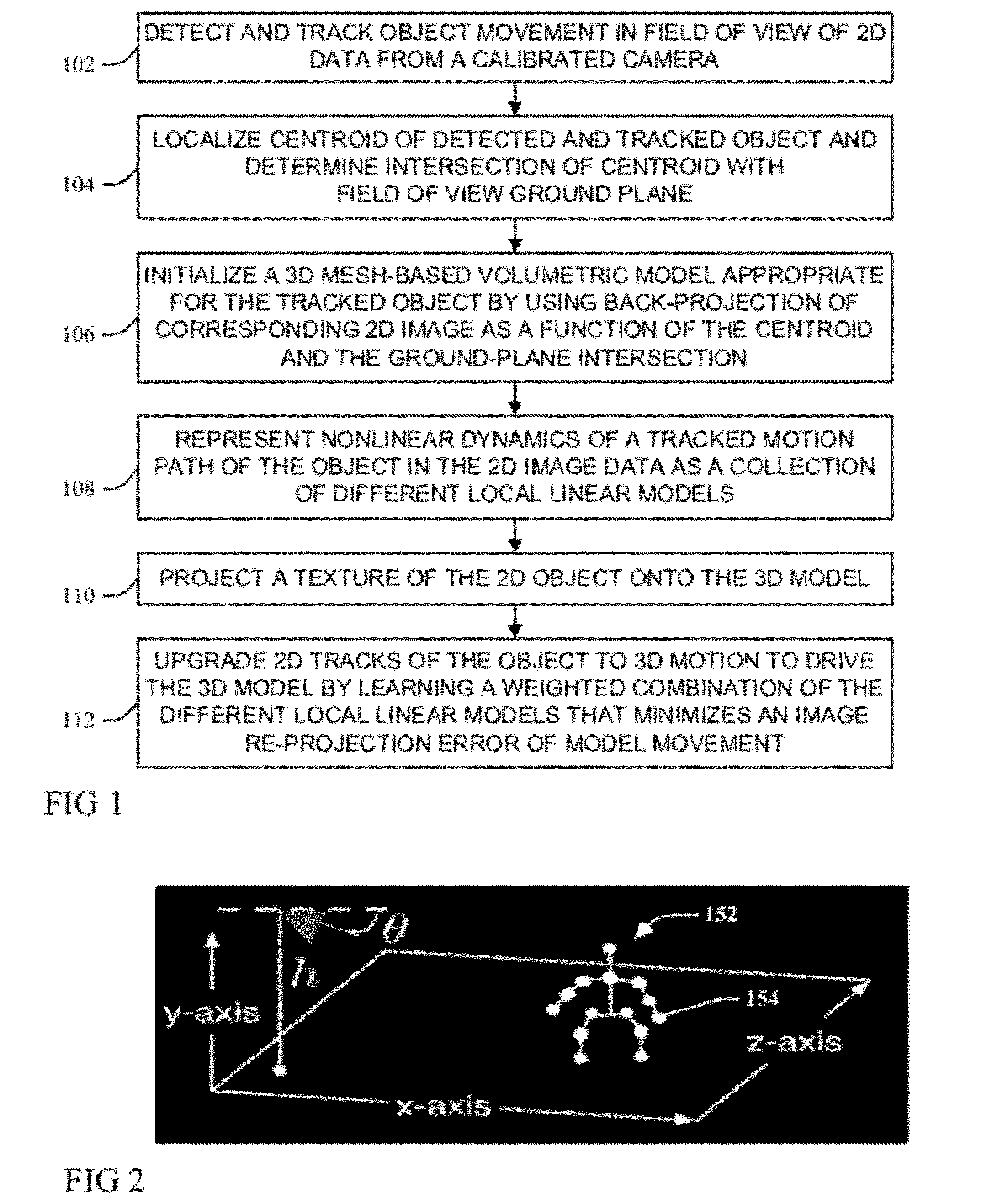
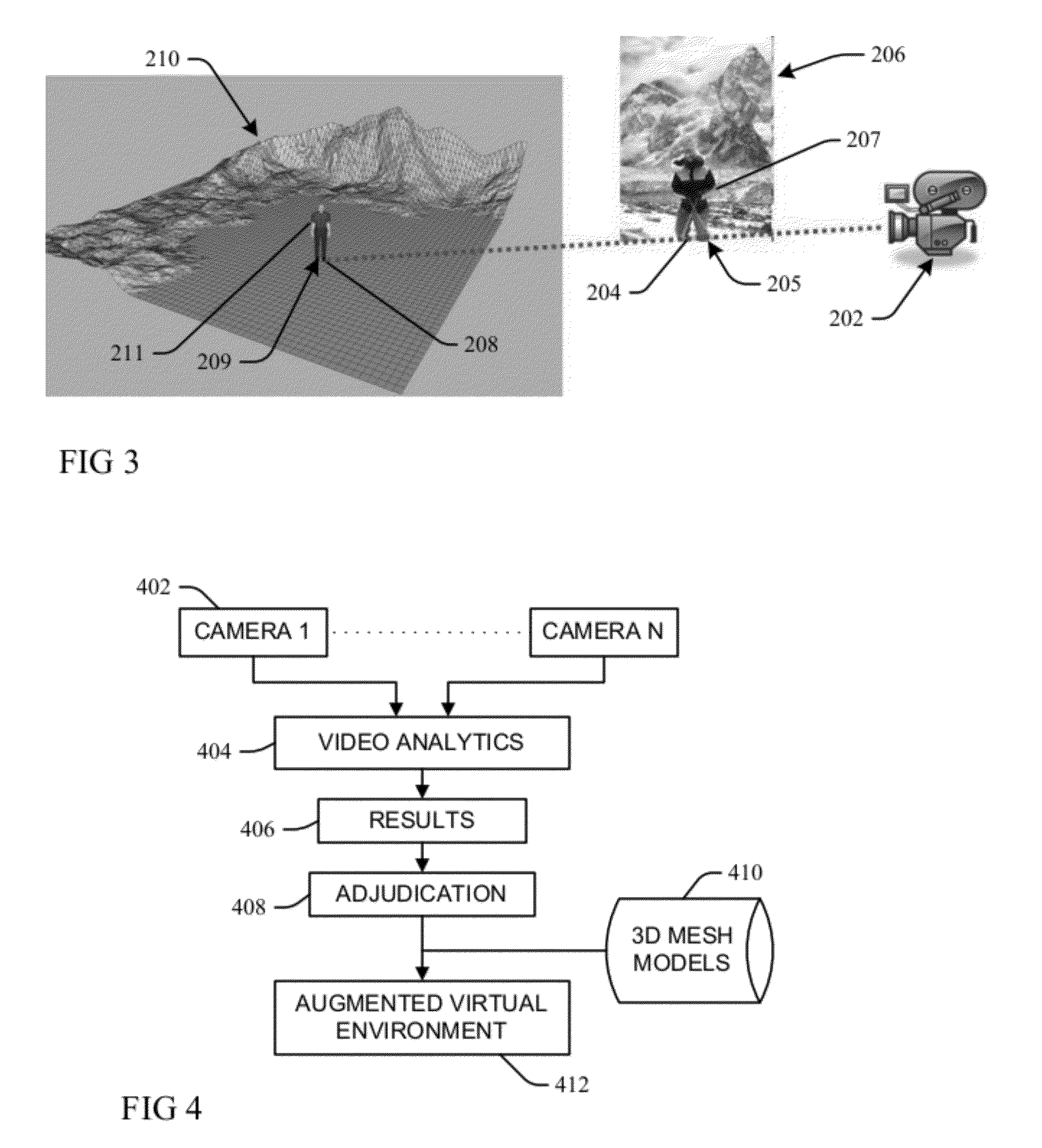
Incorporating video meta-data in 3D models
ActiveUS20120281873A1Minimizes an image re-projection error of model movementImaging errorTelevision system detailsImage analysisNon linear dynamicIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
A moving object detected and tracked within a field of view environment of a 2D data feed of a calibrated video camera is represented by a 3D model through localizing a centroid of the object and determining an intersection with a ground-plane within the field of view environment. An appropriate 3D mesh-based volumetric model for the object is initialized by using a back-projection of a corresponding 2D image as a function of the centroid and the determined ground-plane intersection. Nonlinear dynamics of a tracked motion path of the object are represented as a collection of different local linear models. A texture of the object is projected onto the 3D model, and 2D tracks of the object are upgraded to 3D motion to drive the 3D model by learning a weighted combination of the different local linear models that minimizes an image re-projection error of model movement.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
Image Reconstruction Methods Based on Block Circulant System Matrices
InactiveUS20090123048A1Minimized in sizeFast computerReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationIn planeLines of response
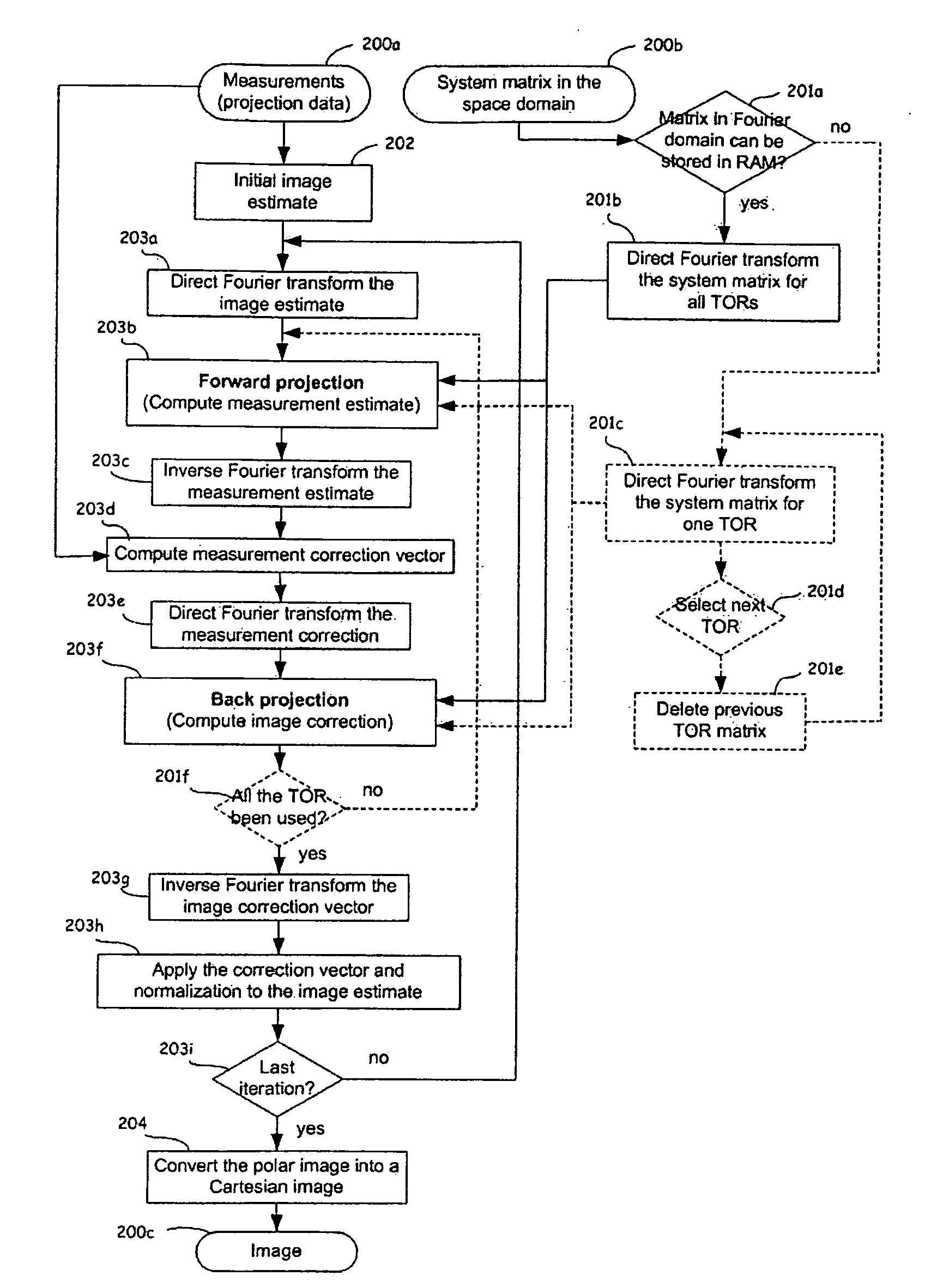
An iterative image reconstruction method used with an imaging system that generates projection data, the method comprises: collecting the projection data; choosing a polar or cylindrical image definition comprising a polar or cylindrical grid representation and a number of basis functions positioned according to the polar or cylindrical grid so that the number of basis functions at different radius positions of the polar or cylindrical image grid is a factor of a number of in-plane symmetries between lines of response along which the projection data are measured by the imaging system; obtaining a system probability matrix that relates each of the projection data to each basis function of the polar or cylindrical image definition; restructuring the system probability matrix into a block circulant matrix and converting the system probability matrix in the Fourier domain; storing the projection data into a measurement data vector; providing an initial polar or cylindrical image estimate; for each iteration; recalculating the polar or cylindrical image estimate according to an iterative solver based on forward and back projection operations with the system probability matrix in the Fourier domain; and converting the polar or cylindrical image estimate into a Cartesian image representation to thereby obtain a reconstructed image.
Owner:SOCPRA SCI SANTE & HUMAINES S E C
Methods and apparatus for back-projection and forward-projection
ActiveUS7120283B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationVoxelProjection image
The invention provides improvements in reconstructive imaging of the type in which a volume is reconstructed from a series of measured projection images (or other two-dimensional representations) generated by projection of a point x-ray source (or other radiation source), positioned at a distinct focus, through the volume to a plane at which the respective projection image is acquired (“detector plane”). In one aspect, the improvements are with respect to back-projecting a two-dimensional representation lying in the detector plane (representing, for example, a difference between an originally-acquired measured projection image and a subsequently-generated estimate thereof) to generate three-dimensional representation (which can be used, for example, to update an estimate of the volume). According to this aspect, for each of one or more slices of the 3D representation parallel to the projection plane and for each distinct focus at which a projection is generated, the following steps are performed in connection with the back-projection: (i) warping the first 2D representation to generate a second 2D representation by applying to the first 2D representation a selected linear mapping, where that selected linear mapping would map, in order to match dimensions of the respective slice within the 3D representation, a region defined by projection, at the respective focus, of corners of that slice onto the detector plane, and (ii) incrementing values of each of one or more voxels of the respective slice by an amount that is a function of a value of a correspondingly indexed pixel of the second 2D representation. A related aspect provides improvements with respect to forward-projecting, as well as in iterative (and non-iterative) methodologies that incorporate both back-projection and forward-projection.
Owner:PME IP
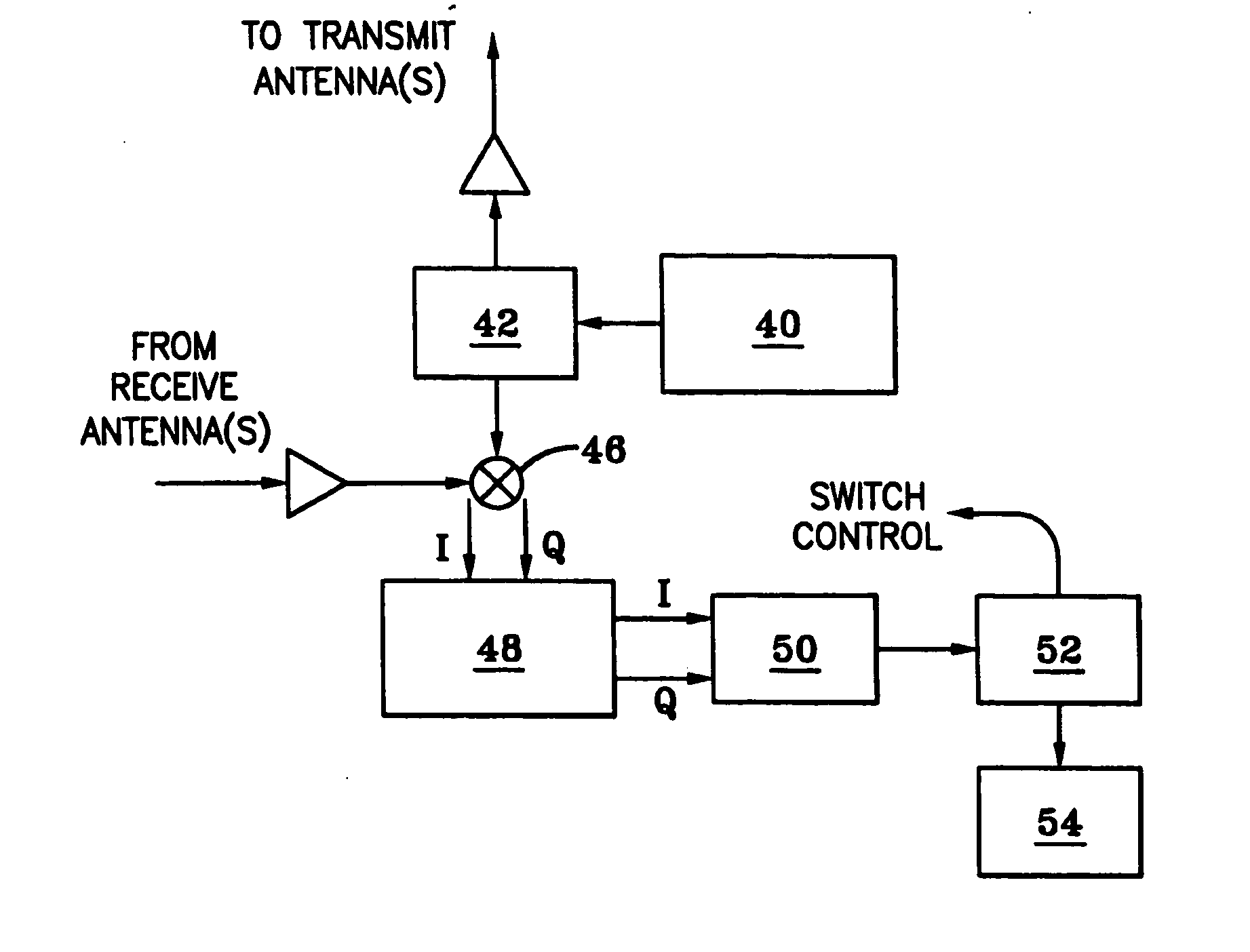
Vehicle obstacle warning radar
InactiveUS20060022866A1Position fixationIndividually energised antenna arraysDriver/operatorRadar systems
The present invention is a radar system for detecting the presence of obstacles. The radar system includes at least one transmitting antenna and at least one receiving antenna. The transmitting antenna receives an input signal and transmits an electromagnetic wave. The electromagnetic wave reflects off an obstacle back to the receiving antenna. The receiving antenna captures the reflected electromagnetic wave and produces an output signal. The output signal is then combined with the local reference signal in a quadrature mixer. The resulting in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) signals may be further processed and then transmitted to a processing system. The processing system uses a suitable algorithm, e.g., a back projection algorithm, to estimate the type and location of obstacles that reflected the electromagnetic wave. In an exemplary embodiment, the algorithm is adapted to discriminate between different sizes and locations of obstacles in order to determine if there is a hazard. Based on this information, the processing system then communicates with a visual and / or audible warning system in order to alert the driver about the obstacle if it has been determined to be a hazard.
Owner:OHIO STATE INNOVATION FOUND
Image capture device and image processing method
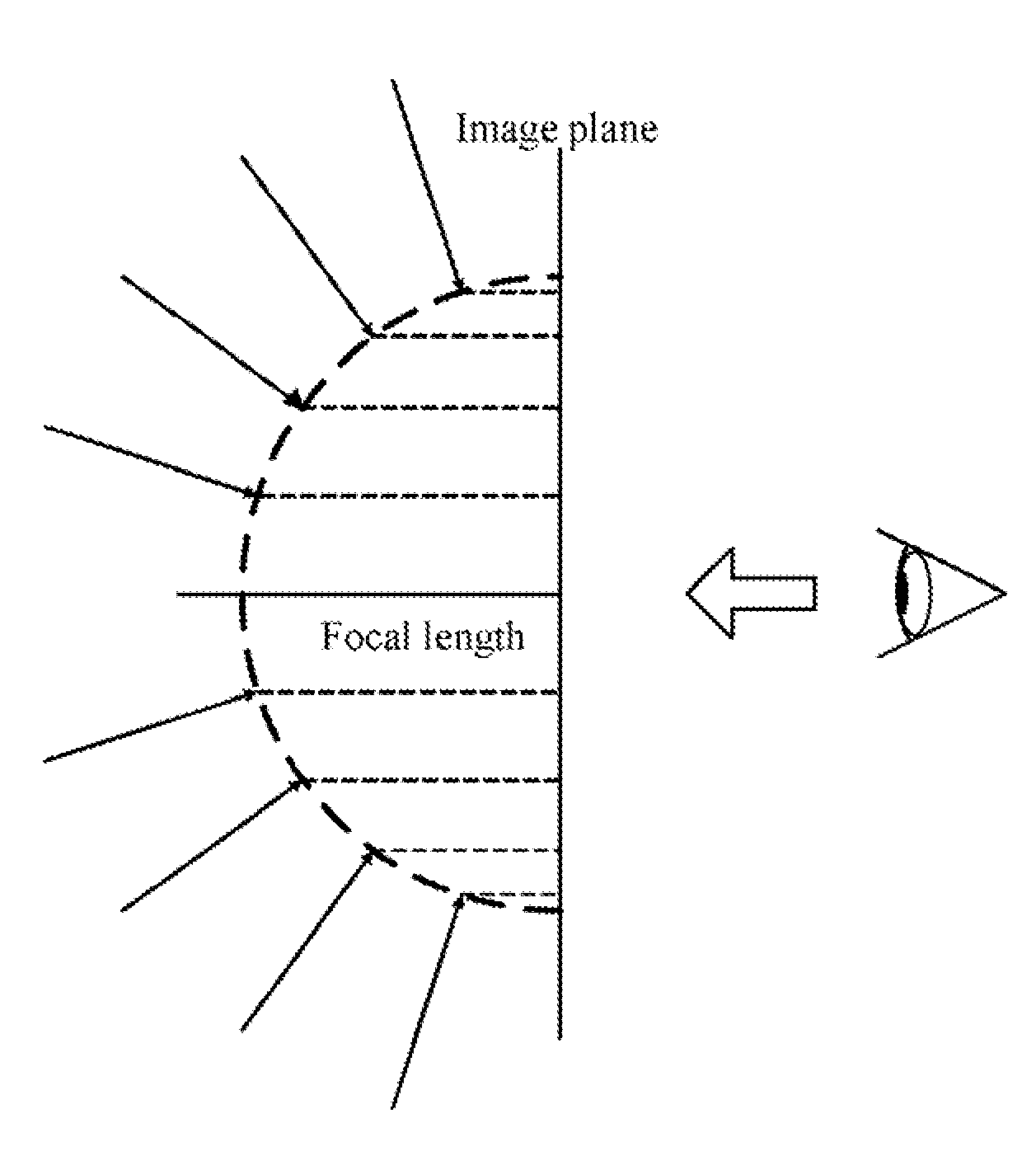
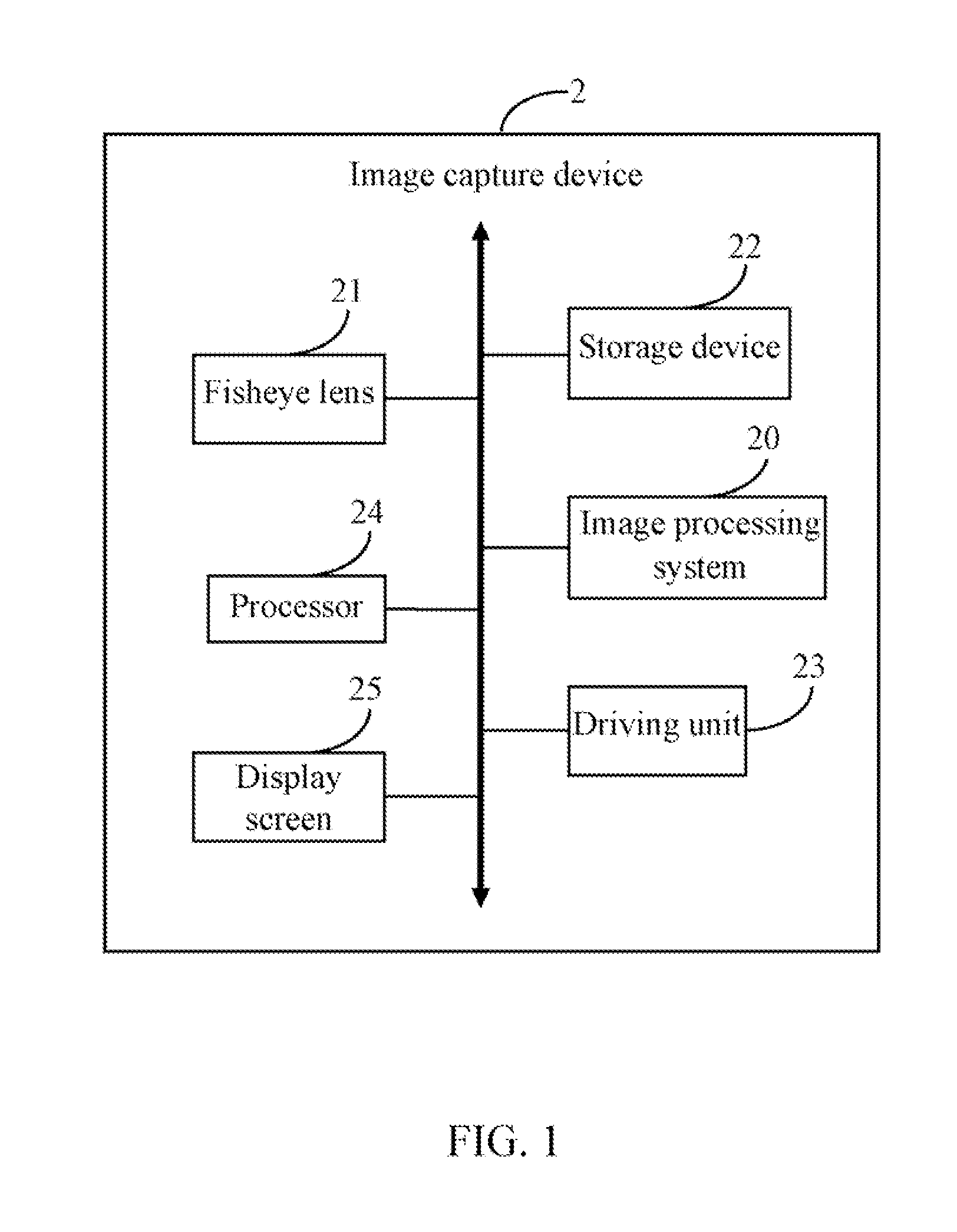
InactiveUS20120242782A1Television system detailsGeometric image transformationImaging processingFisheye lens
A method for processing an image captured by a fisheye lens of an image capture device. The method obtains a point (Px, Py) from an object plane of the fisheye lens, calculates a first projection point (Fx*, Fy*, Fz*) of the obtained point (Px, Py) on a first image plane of a virtual lens, calculates a second projection point (Fx, Fy) of the point (Fx*, Fy*, Fz*) on a second image plane of the fisheye lens, and obtains transforming formulae between (Px, Py) and (Fx, Fy). The method further obtains a back-projection point for each point of the captured image on the object plane of the fisheye lens according to the transforming formulae, and creates an updated image of the specified scene from the back-projection points.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
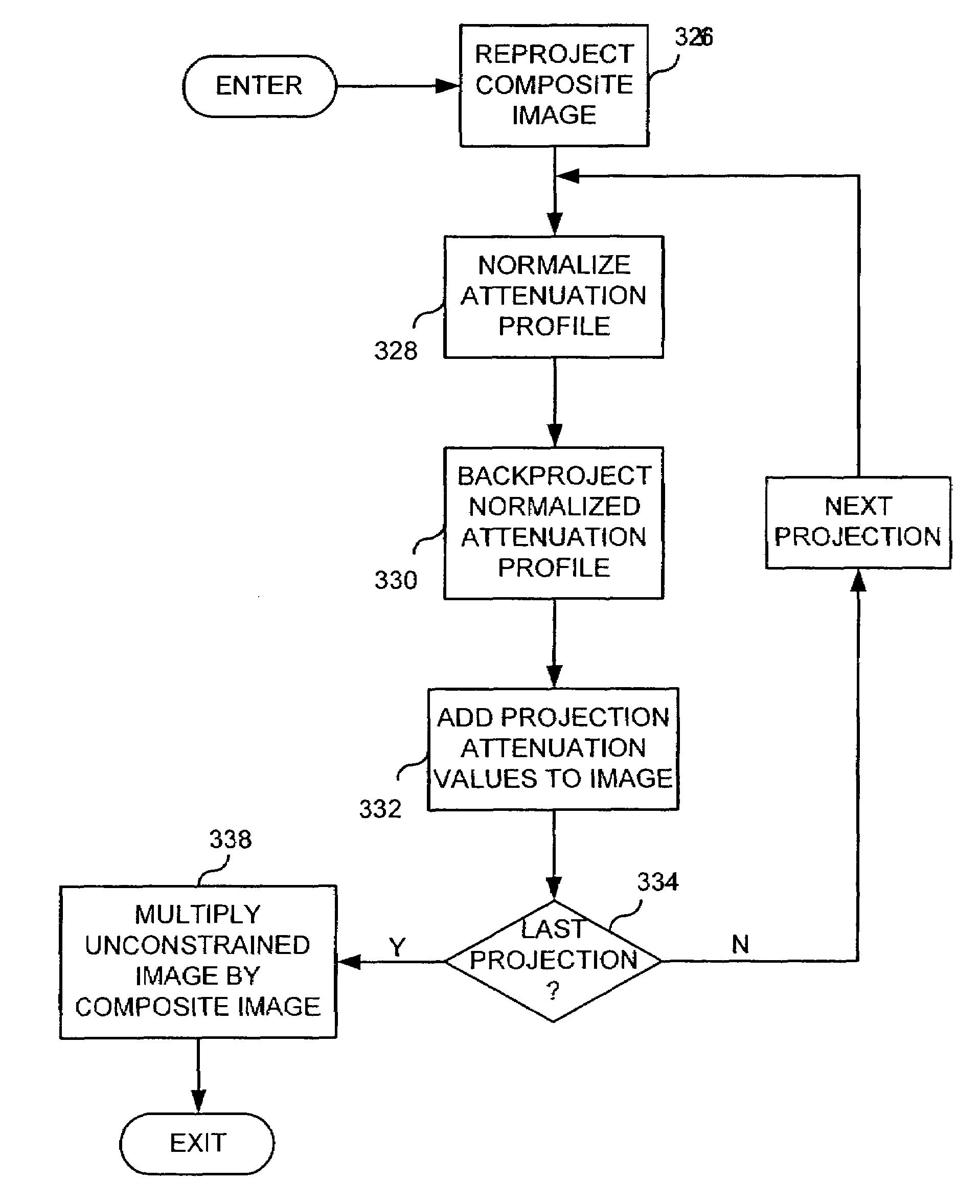
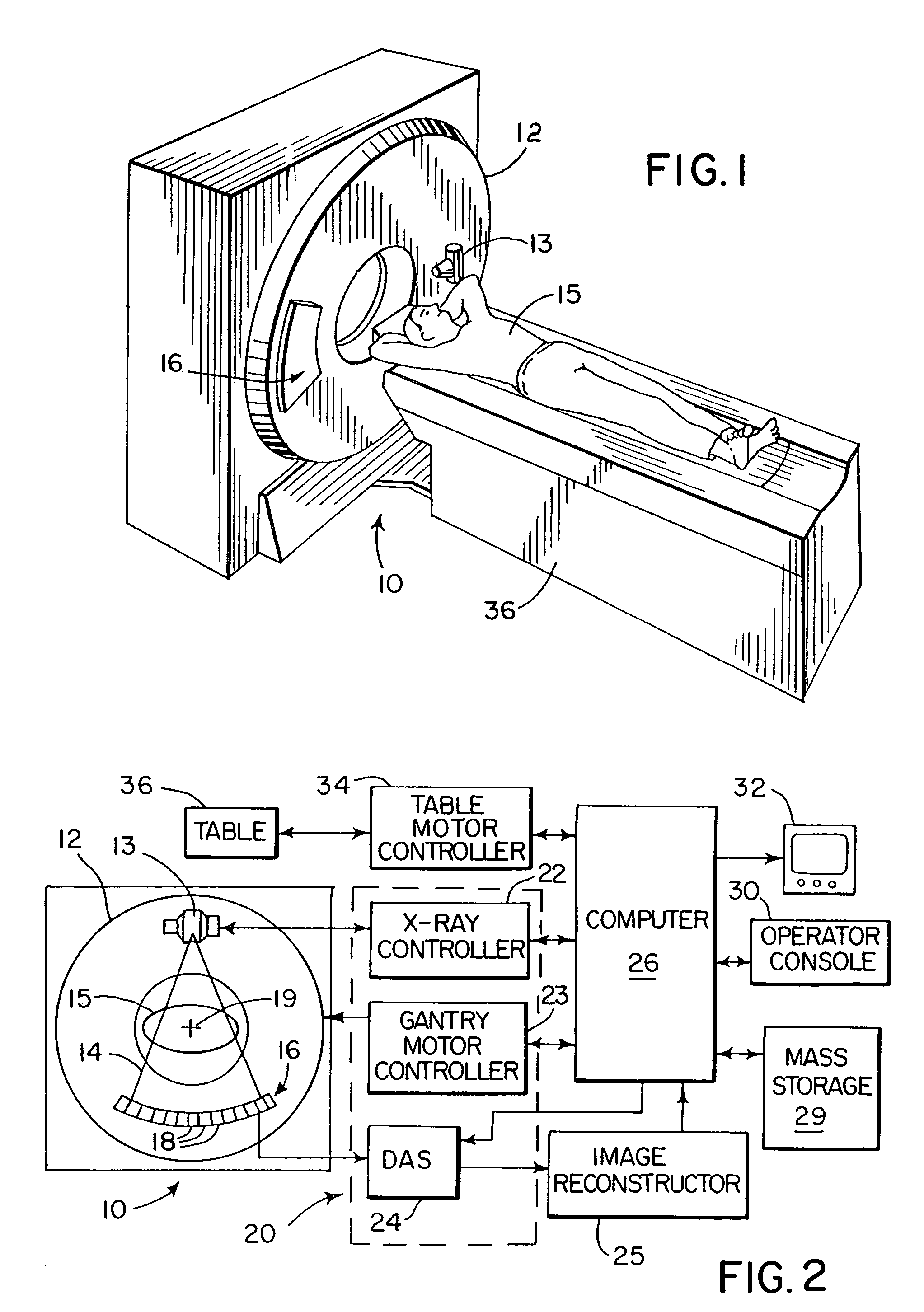
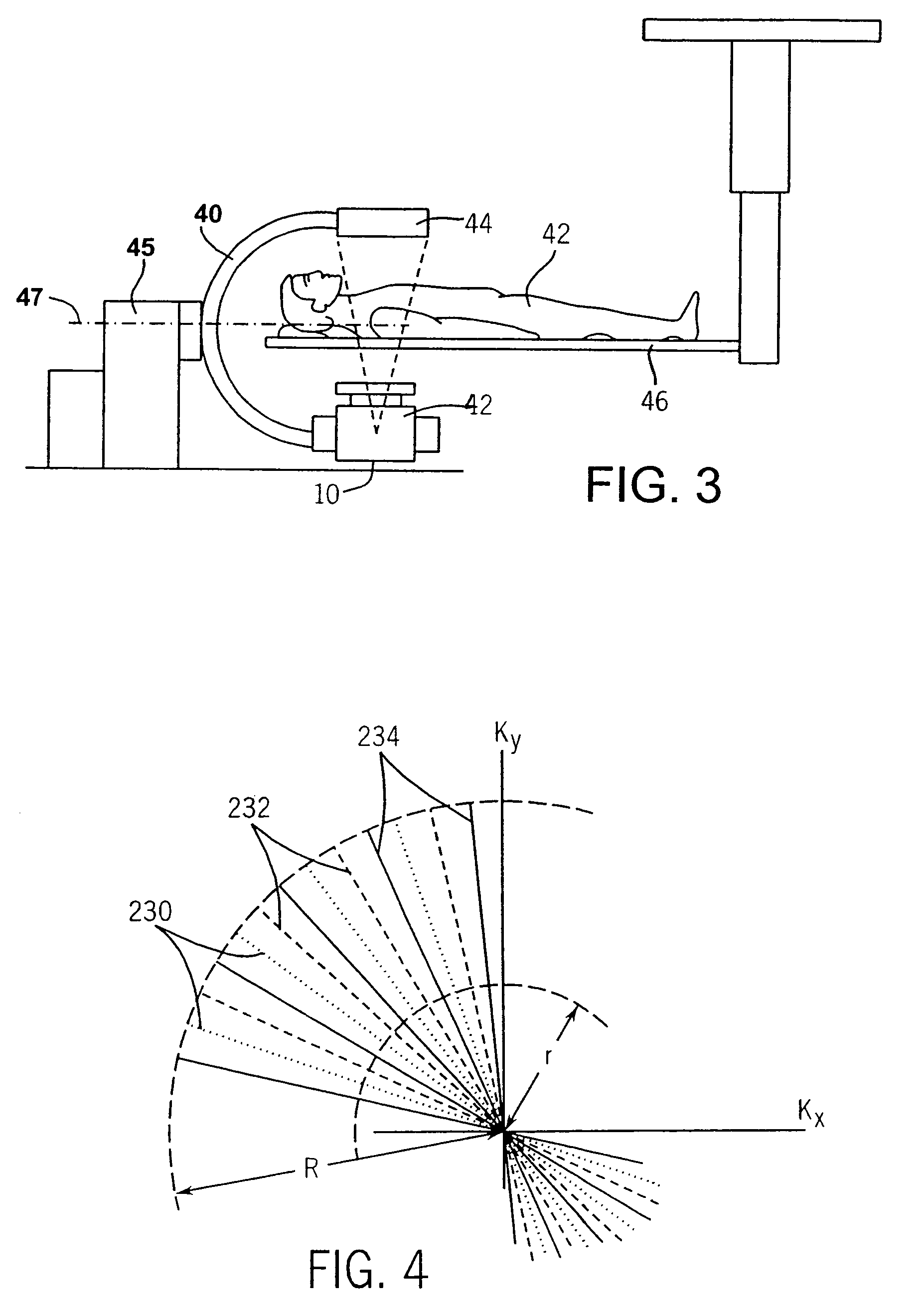
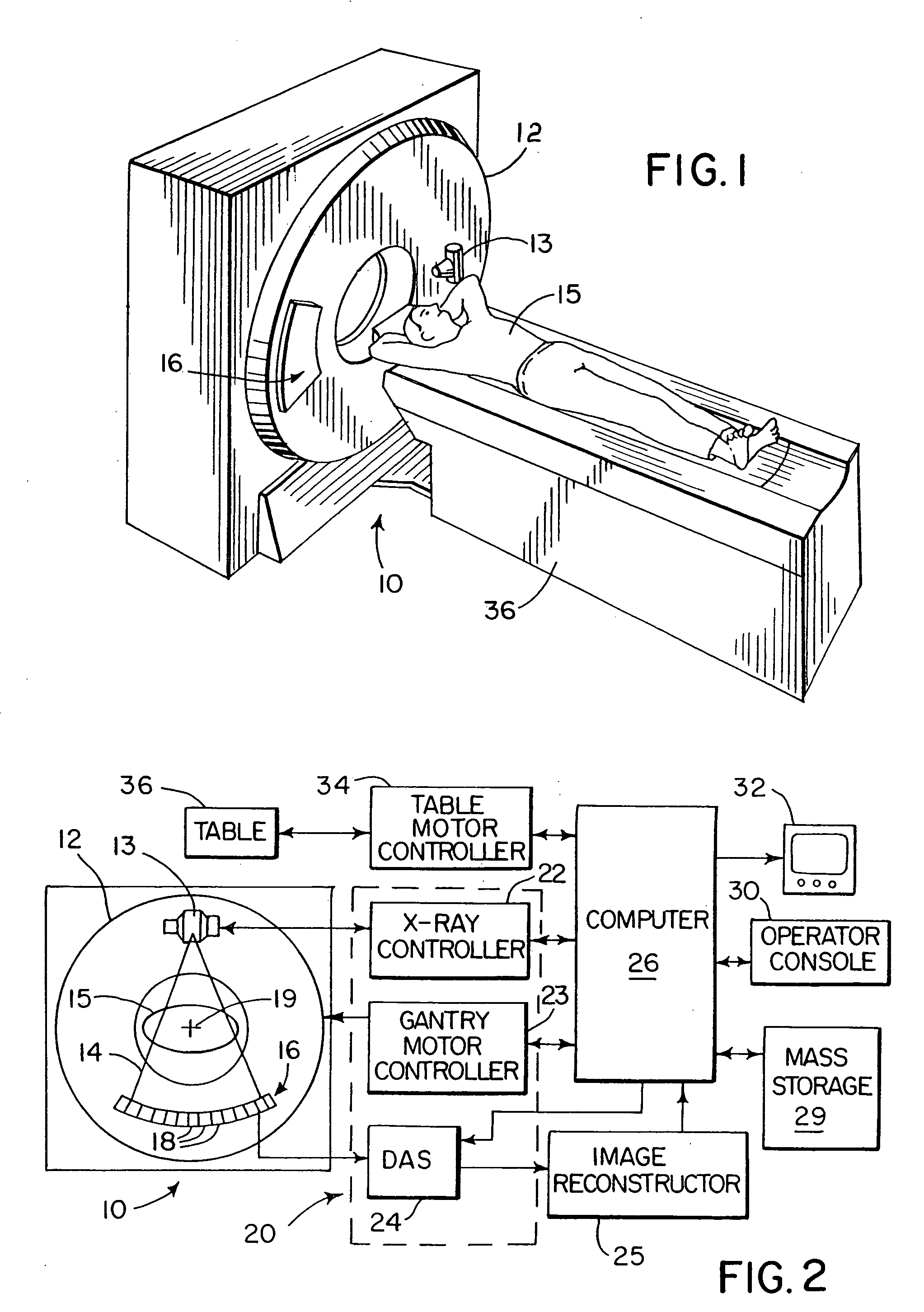
Backprojection reconstruction method for CT imaging
ActiveUS7545901B2Simple methodLower doseReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiologyBack projection
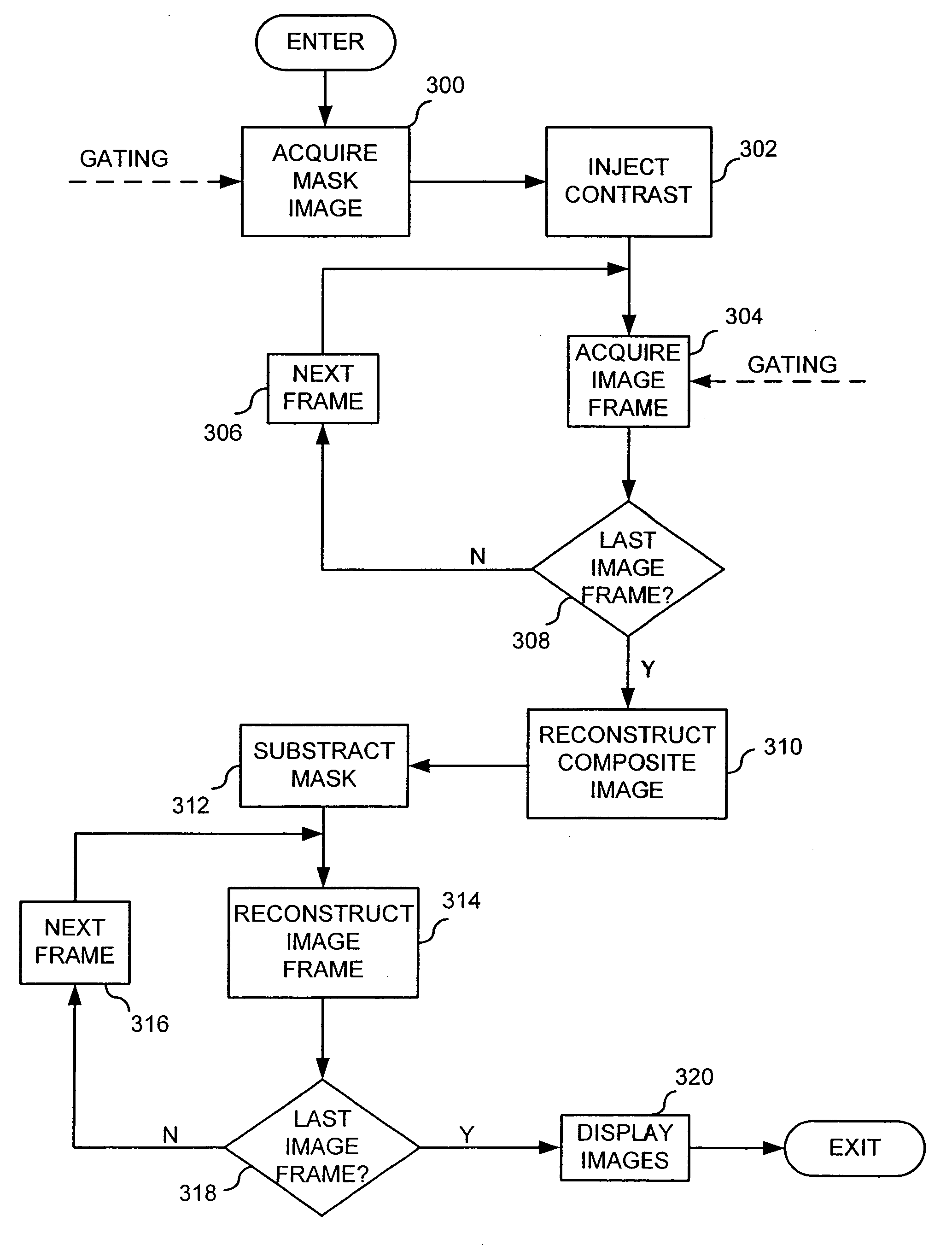
Two-dimensional or three-dimensional, time-resolved CT frame images are acquired during a dynamic study of a subject. A composite image is produced and this is used to reconstruct each CT frame image by weighting the backprojection of each projection view acquired for that image frame by the corresponding value in the composite image. This weighted backprojection enables artifact-free image frames to be produced with far fewer projection views of the subject. The composite image may be reconstructed from views acquired separately, or it may be produced by combining views acquired during the course of the dynamic study.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Backprojection reconstruction method for CT imaging
ActiveUS20070009080A1Improved image reconstructionImprove time resolutionReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiologyBack projection
Two-dimensional or three-dimensional, time-resolved CT frame images are acquired during a dynamic study of a subject. A composite image is produced and this is used to reconstruct each CT frame image by weighting the backprojection of each projection view acquired for that image frame by the corresponding value in the composite image. This weighted backprojection enables artifact-free image frames to be produced with far fewer projection views of the subject. The composite image may be reconstructed from views acquired separately, or it may be produced by combining views acquired during the course of the dynamic study.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Light distribution apparatus and methods for illuminating optical systems
ActiveUS20050018308A1Constant brightnessEasy to divergeDiffusing elementsColor television detailsFiberSpatial light modulator
Various embodiments involving structures and methods for illumination can be employed, for example, in projectors, head-mounted displays, helmet-mounted displays, back projection TVs, flat panel displays as well as other optical systems. Certain embodiments may include prism elements for illuminating, for example, a spatial light modulator. Light may be coupled to the prism in some cases using fiber optics or lightpipes. The optical system may also include a diffuser having scatter features arranged to scatter light appropriately to produce a desired luminance profile. Other embodiments are possible as well.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
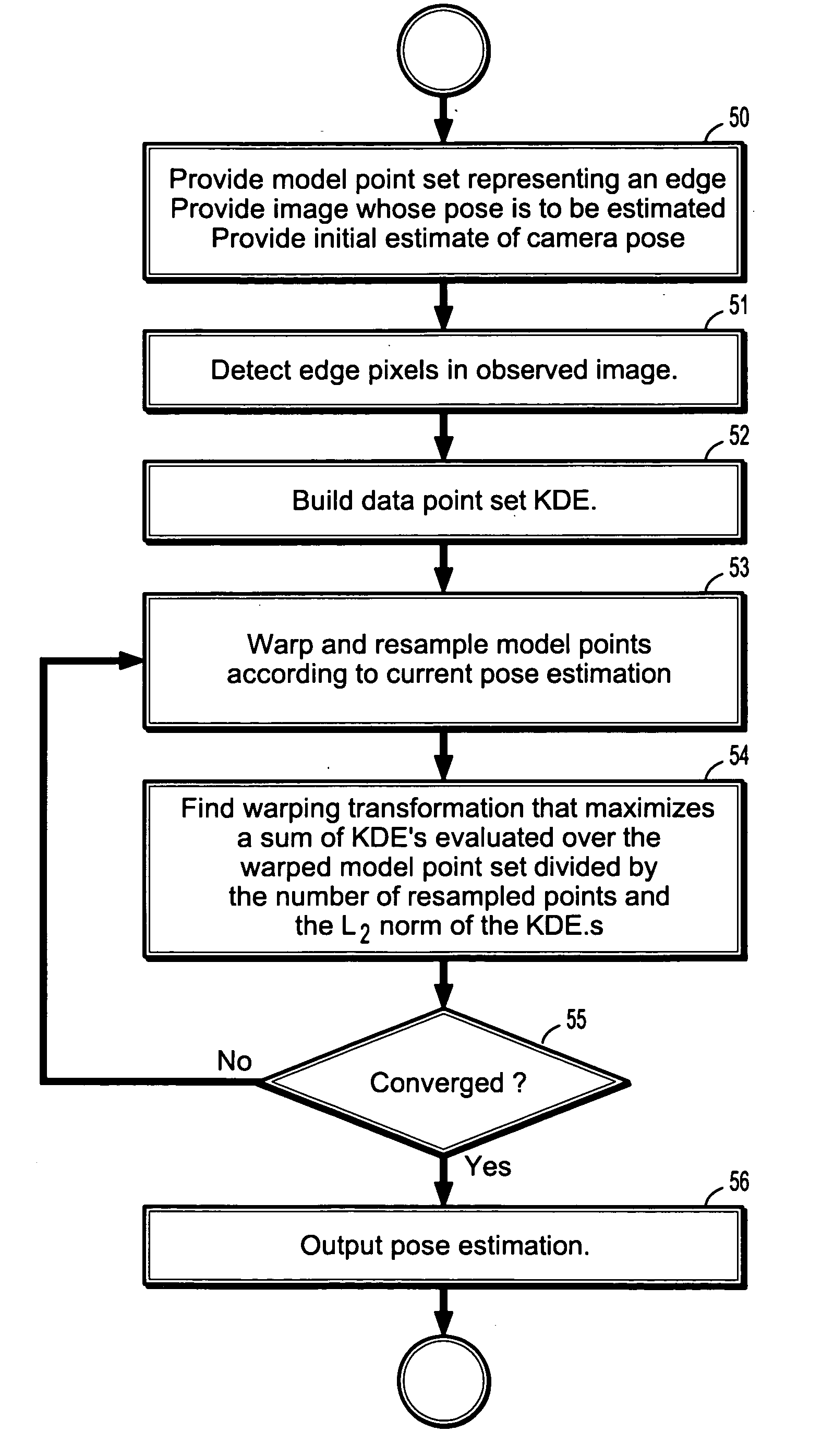
System and method for camera tracking and pose estimation
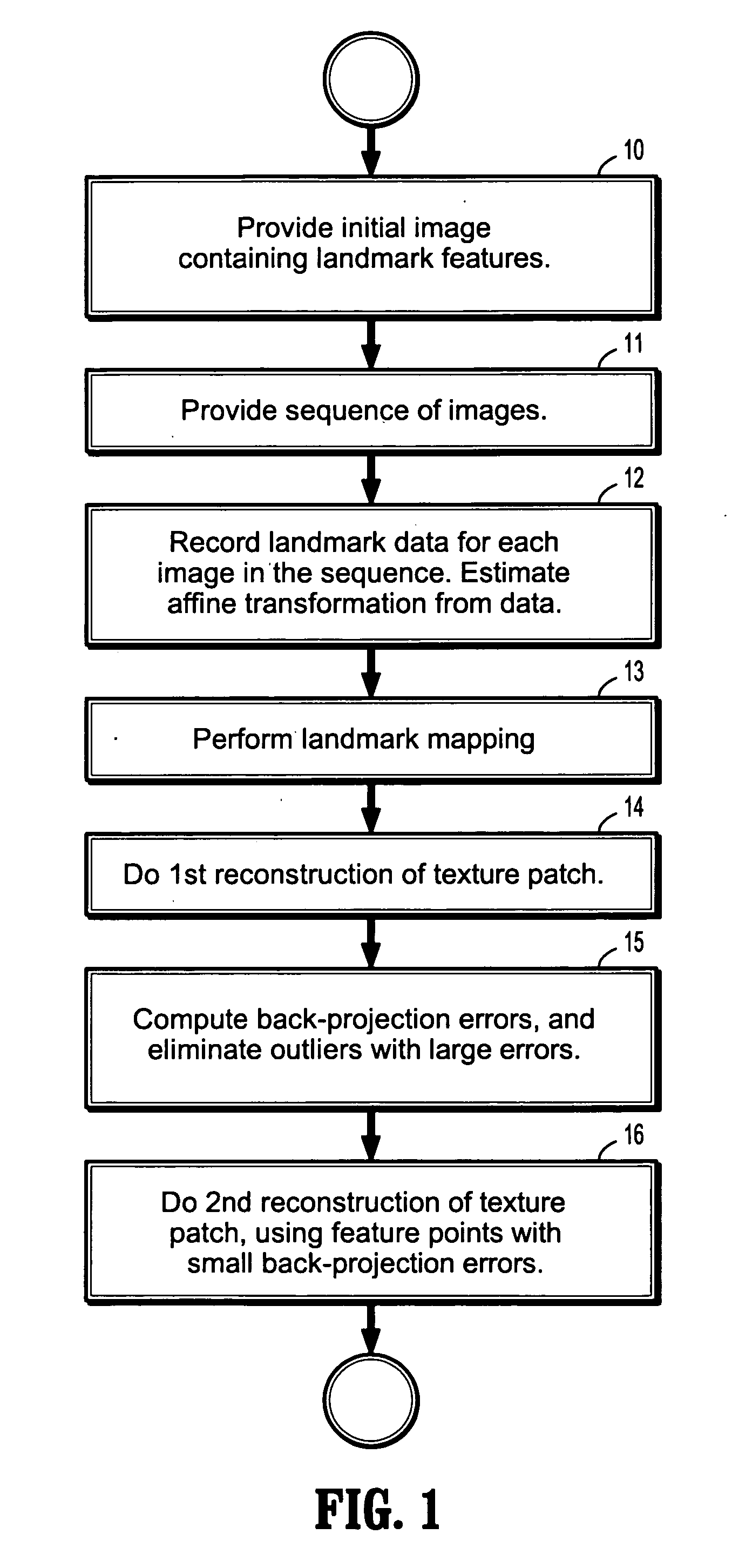
InactiveUS20060188131A1Promote reconstructionAvoid driftingImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionTriangulationBack projection
A method of tracking a pose of a moving camera includes receiving a first image from a camera, receiving a sequence of digitized images from said camera, recording, for each of said sequence of digitized images, the pose and 2D correspondences of landmarks, reconstructing a location and appearance of a 2-dimensional texture patch from 2D correspondences of the landmarks by triangulation and optimization, computing back-projection errors by comparing said reconstructed texture patch with said first received image; and reconstructing said location and appearance of said 2-dimensional texture patch from the 2D correspondences of the landmarks of said sequence of digitized images by triangulation and optimization after eliminating those landmarks with large back-projection errors.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
General-purpose aviation simulator based on virtual operation
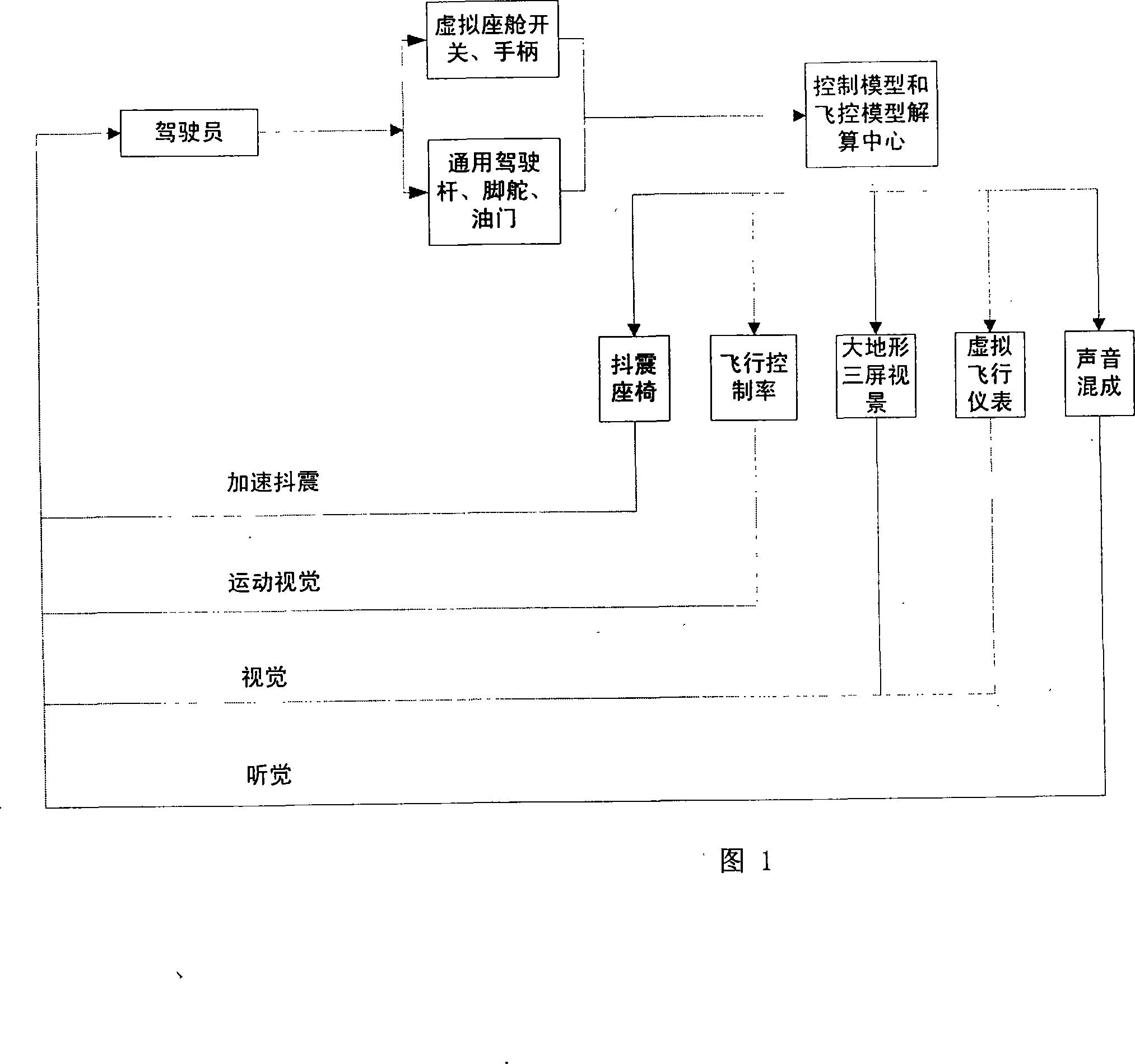
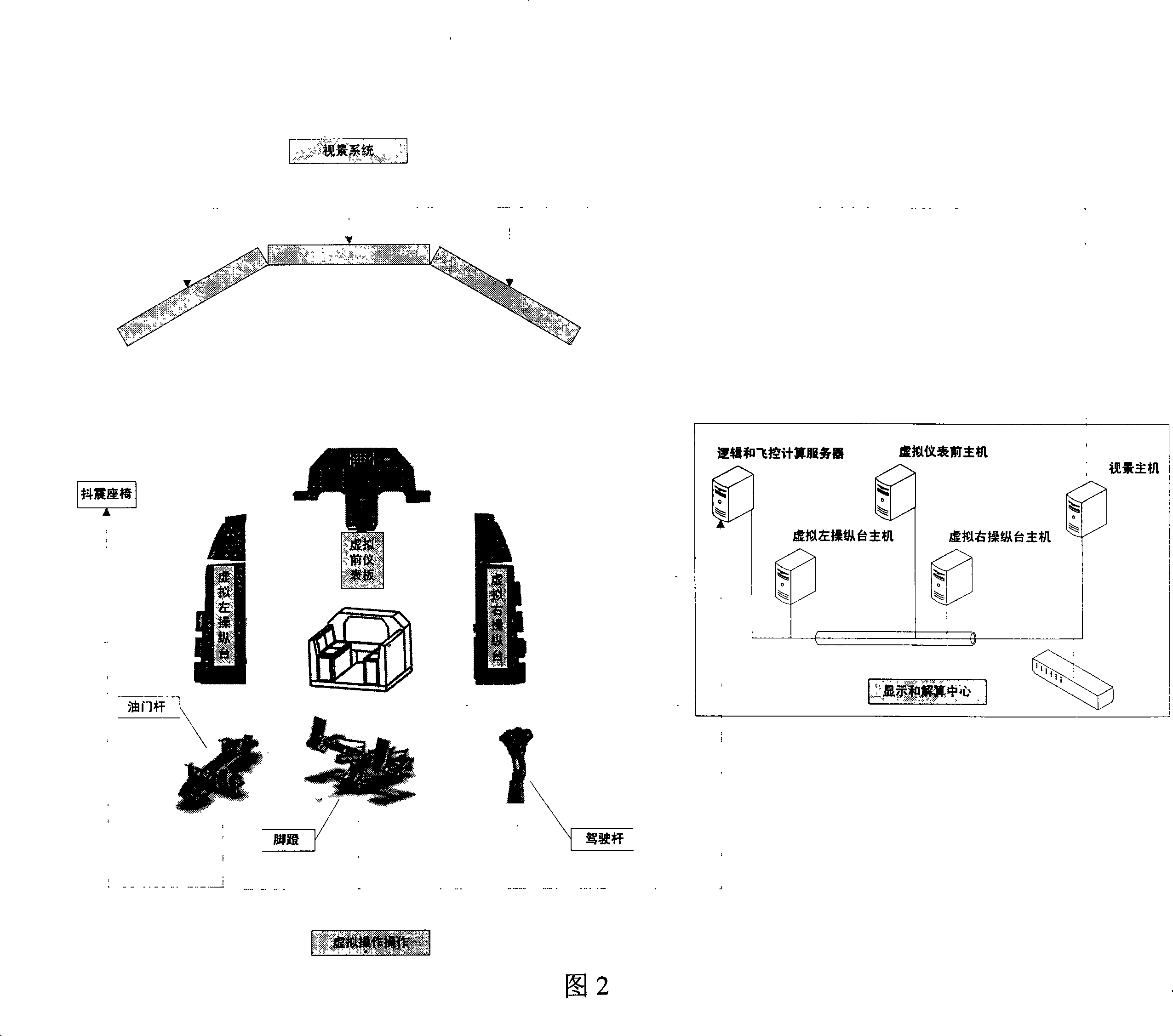
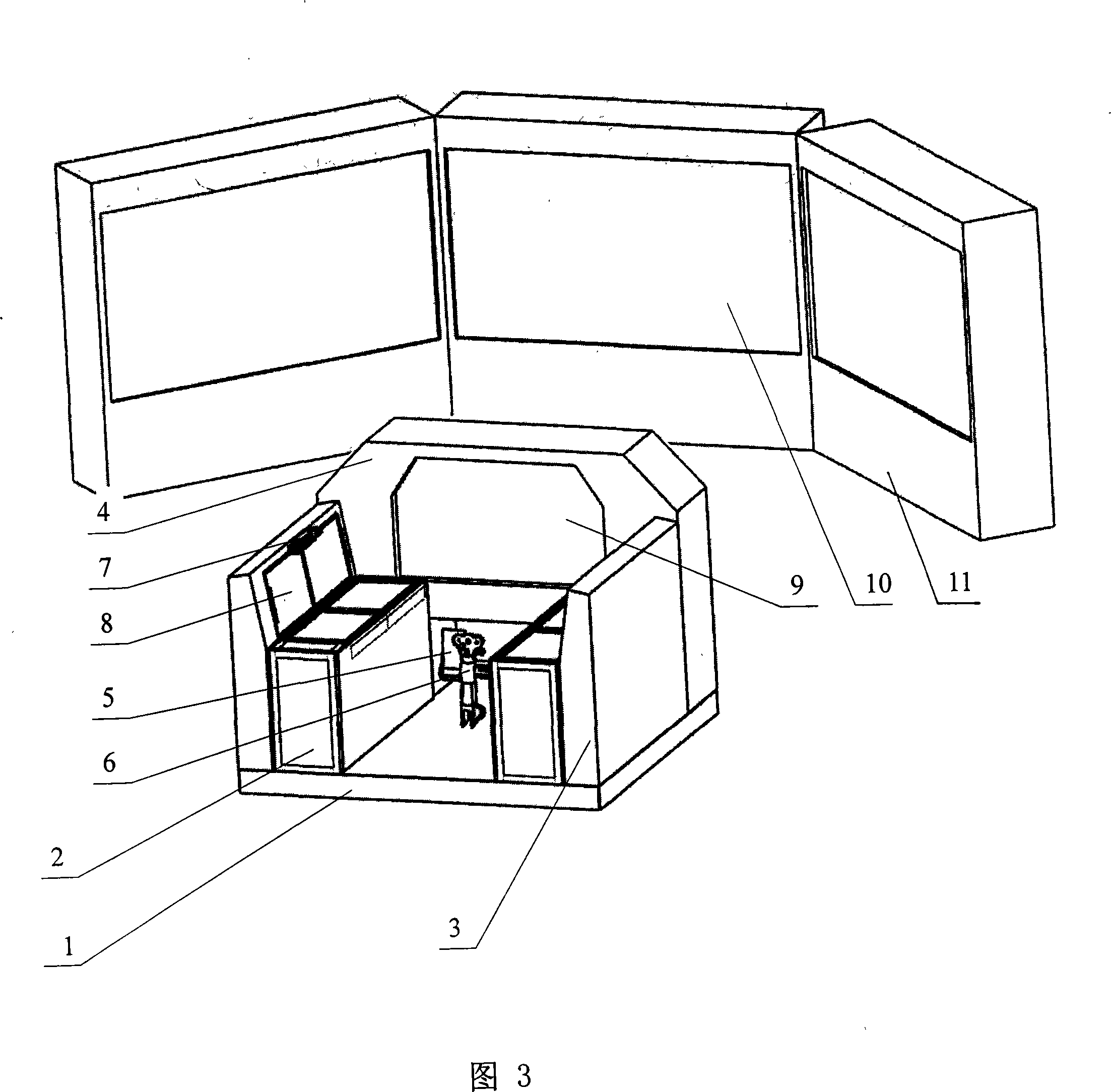
InactiveCN101251959AFlexible switchingReduce volumeCosmonautic condition simulationsVideo gamesAviationGeneral purpose
The invention relates to a universal flight simulator based on virtual operation, which comprises footstools, a throttle lever, a steering column and a sound blending box arranged in a universal concept cabin of the virtual operation; the universal concept cabin also comprises a sight display system consisting of a back projection system, a virtual switch, a knob and a virtual instrument operated by using a touch mode, a displaying and resolving center for model resolving, flight control resolving and acceleration resolving and a buffeting chair seated by a driver. The universal flight simulator based on virtual operation uses a virtual operation switch and the virtual instrument to replace a real physical hardware switch and an instrument and can flexibly switch the virtual switch, the instrument software and a flight control model into various models for flight training and games. The universal flight simulator is small in size, light in weight, convenient to disassemble and assemble and suitable for use under the ordinary office condition, has vivid simulation, low price and strong universality through switching models by software and can be combined to a simulator set with different models for confronting training and games after being connected to the Internet.
Owner:于辉
Method and apparatus for super-resolution of images
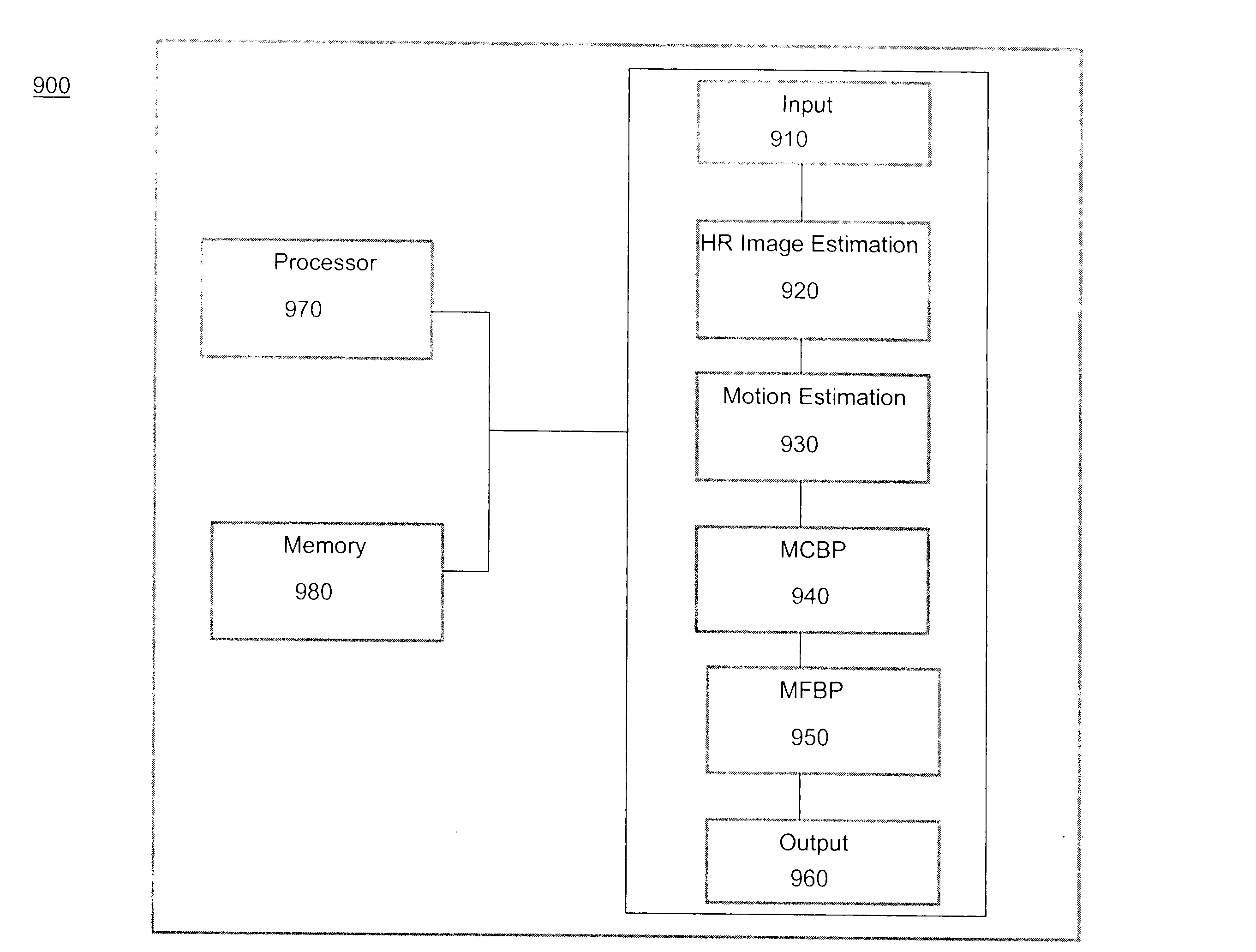
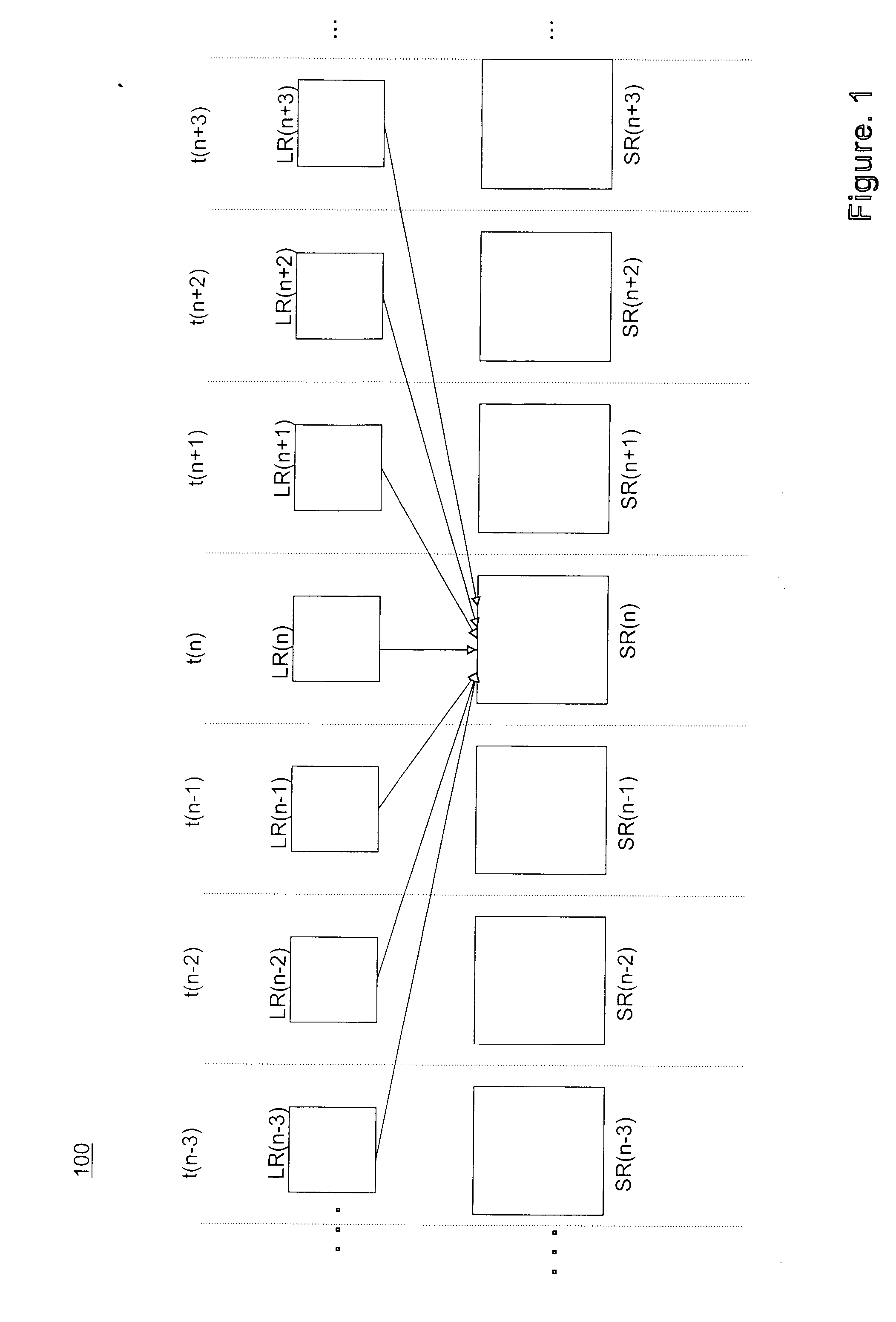
ActiveUS20090232213A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImage resolutionBack projection
A method to generate super-resolution images using a sequence of low resolution images is disclosed. The method includes generating an estimated high resolution image, motion estimating between the estimated high resolution image and comparison images from the sequence of low resolution images, motion-compensated back projecting, and motion-free back projecting that results in a super resolved image. A corresponding system for generating super-resolution images includes a high resolution image estimation module, a motion estimating module, a motion-compensated back projection module, a motion-free back projection module, an input interface, and an output interface.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
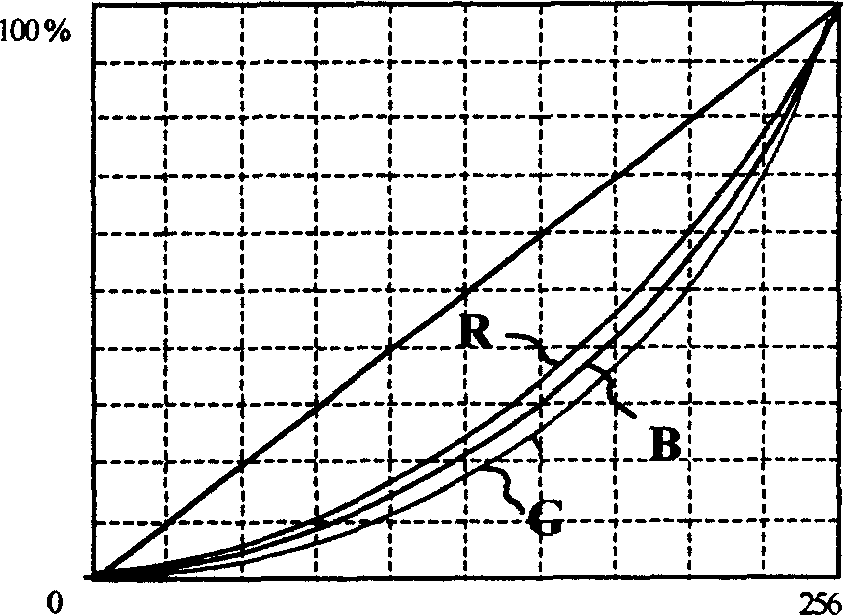
Automatic measurement and correction method and system for LCD GAMMA curve and color temperature
InactiveCN1845232AEasy CalibrationMiniaturizationStatic indicating devicesElectrical testingSystem configurationVideo image
The invention provides a GAMMA curvature correction and color-temperature automatic regulating method for liquid crystal display and the system. The said system consists of a system host-machine, a detector, a color analyzer, a video standard signal source, a data interface,and a system measure and correction software, which can perform GAMMA curvature correction and white balance adjustment for multi-purpose TV and computer display including LCD and high-resolution back projection and multi-structure liquid crystal display including TN, STN, DSTN and TFT to improve the videograph display quality of the liquid crystal display. The system host-machine connects multiple video signal sources, automatic measurement and correction software for GAMMA curvature and color-temperature and data interface together, the system parameter can be set manually or automatically, the system configuration is simple, GAMMA curvature correction and white balance adjustment software can be conveniently transferred, and can rapidly finish automatic measurement and correction for GAMMA curvature and color-temperature and can visually inspect the effect. The invention can be used in departments including scientific research, production, quality inspection and maintenance and can visually finish the GAMMA curvature correction and white balance adjustment for the LCD products with high accuracy and quick-speed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Display system for high-definition projectors
A display system is provided to surround a user with an out-the window scene. The system includes a screen structure that is a facetted back-projection dome made up of a polygonal polar top facet surrounded by trapezoidal facets angulated downward from it in an upper facet row. A middle row of facets extends angulated downward therefrom, and a lower row of trapezoidal facets extends down from them. Each facet has video projected thereon by a high definition projector, and to maximize resolution and efficiently use the projector output, the vertical height of each facet makes use of the full vertical field of pixels available from the associated projector. The facets are all tangent to a sphere about a design eyepoint of the dome. The projector resolutions and the size, position and material of the facets are such that the imagery visible on the inside of the dome on the facets is at resolution corresponding to a visual acuity of 20 / 50 or higher, preferably 20 / 20, and at or near eye-limiting resolution.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
Target acquisition and tracking system
InactiveUS20090260511A1Accurate informationImprove effective detection rateWeapon control systemsAiming meansBack projectionEngineering
A projectile tracking system for acquiring and precisely tracking a projectile in flight in order to reveal the source from which the projectile was fired. The source is revealed by the back projection of a 3-dimensional track file. In preferred embodiments the system is installed on a vehicle, such as an un-manned blimp or other aircraft, road vehicle or ship, for locating and destroying small arms fire directed at the vehicle. A kill system may also be included on the vehicle to destroy the source of the projectile.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Light distribution apparatus and methods for illuminating optical systems
InactiveUS7206133B2Increase illuminationIncrease the number ofDiffusing elementsColor television detailsFiberSpatial light modulator
Various embodiments involving structures and methods for illumination can be employed, for example, in projectors, head-mounted displays, helmet-mounted displays, back projection TVs, flat panel displays as well as other optical systems. Certain embodiments may include prism elements for illuminating, for example, a spatial light modulator. Light may be coupled to the prism in some cases using fiber optics or lightpipes. The optical system may also include a diffuser having scatter features arranged to scatter light appropriately to produce a desired luminance profile. Other embodiments are possible as well.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
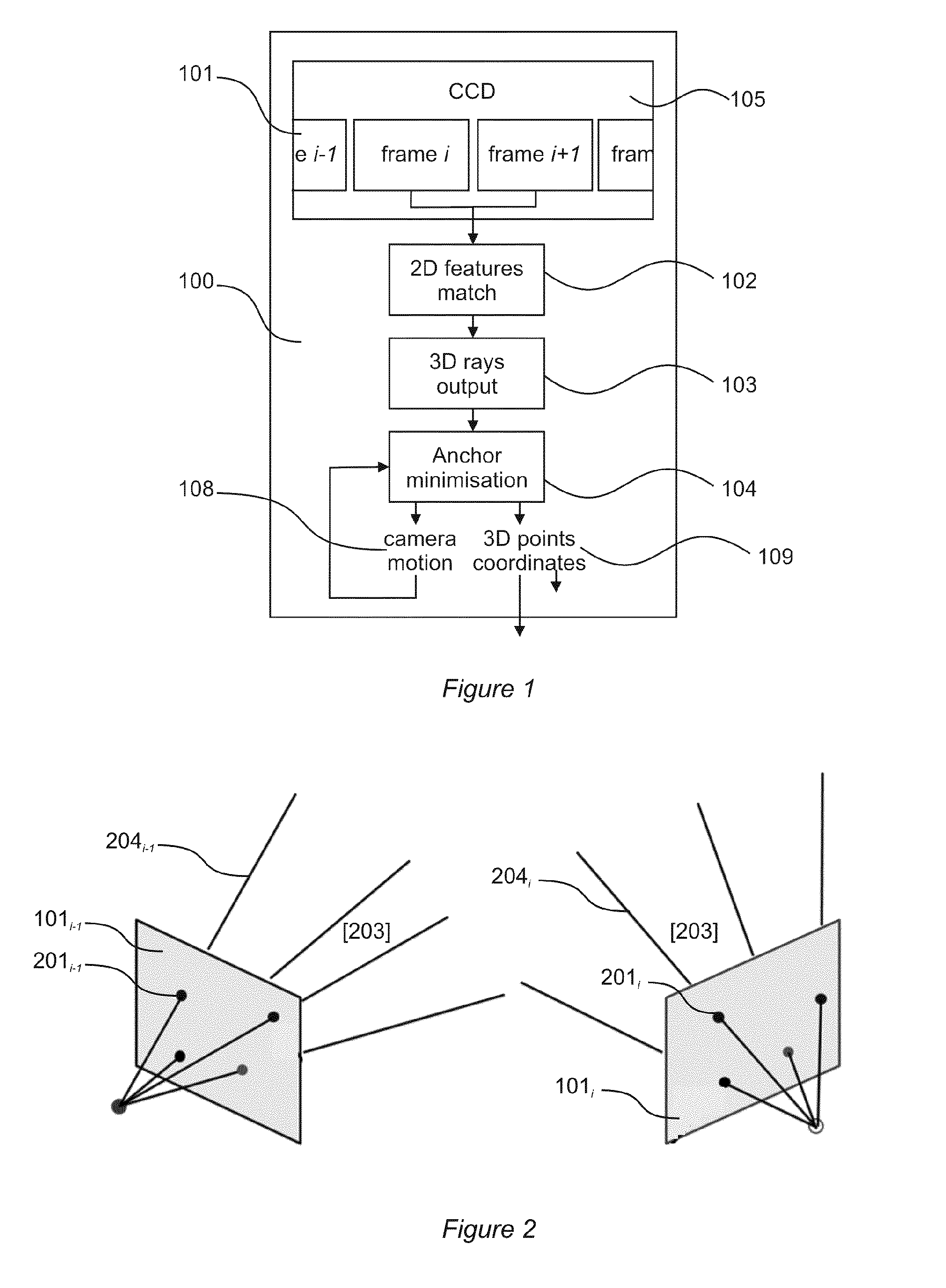
Method and System for Recovery of 3D Scene Structure and Camera Motion From a Video Sequence
InactiveUS20140147032A1Reduce processing loadEasy to useImage enhancementImage analysisBack projectionMotion parameter
An improved method and a system are disclosed for recovering a three-dimensional (3D) scene structure from a plurality of two-dimensional (2D) image frames obtained from imaging means. Sets of 2D features are extracted from the image frames, and sets corresponding to successive image frames are matched, such that at least one pair of matched 2D features refers to a same 3D point in a 3D scene captured in 2D in the image frames. A 3D ray is generated by back-projection from each 2D feature, and the generated 3D rays are subjected to an anchor-based minimization process, for determining camera motion parameters and 3D scene points coordinates, thereby recovering a structure of the 3D scene.
Owner:TRINITY COLLEGE DUBLIN
Apparatus and methods for illuminating optical systems
ActiveUS20050018309A1Balanced optical powerCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical elementsFiberSpatial light modulator
Various embodiments involving structures and methods for illumination can be employed, for example, in projectors, head-mounted displays, helmet-mounted displays, back projection TVs, flat panel displays as well as other optical systems. Certain embodiments may include prism elements for illuminating, for example, a spatial light modulator. Light may be coupled to the prism in some cases using fiber optics or lightpipes. The optical system may also include a diffuser having scatter features arranged to scatter light appropriately to produce a desired luminance profile. Other embodiments are possible as well.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Beamsplitting structures and methods in optical systems
ActiveUS20070252954A1Improve light uniformityImprove uniformityTelevision system detailsDiffusing elementsFiberSpatial light modulator
Various embodiments involving structures and methods for illumination can be employed, for example, in projectors, head-mounted displays, helmet-mounted displays, back projection TVs, flat panel displays as well as other optical systems. Certain embodiments may include prism elements for illuminating, for example, a spatial light modulator. Light may be coupled to the prism in some cases using fiber optics or lightpipes. The optical system may also include a diffuser having scatter features arranged to scatter light appropriately to produce a desired luminance profile. Other embodiments are possible as well.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Ground obstacle detection method based on binocular stereo vision of robot
ActiveCN101852609ASolve the real-time detection problemReduce loadImage analysisUsing reradiationParallaxBack projection
The invention discloses a ground obstacle detection method based on the binocular stereo vision of a robot, which belongs to the technical field of intelligent robots, and comprises the following steps that: according to the binocular baseline length and the focus, the ground parallax values of all rows in an image are analyzed through the geometrical configuration of the known image; based on the ground parallax values, a back projection model calculates the three-dimensional coordinates of a scene point corresponding to a pixel so as to initially judge whether the pixel belongs to an obstacle or a ground point; the obstacle and the ground point are respectively endowed with different colors; the results are post-processed and the false obstacle is removed; and three-dimensional errors are removed and a grid map is established. The method is applicable to various complicated indoor environments, can precisely identify various obstacles, has very high real-time performance, and provides very good preparation conditions for the robot to avoid obstacles.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
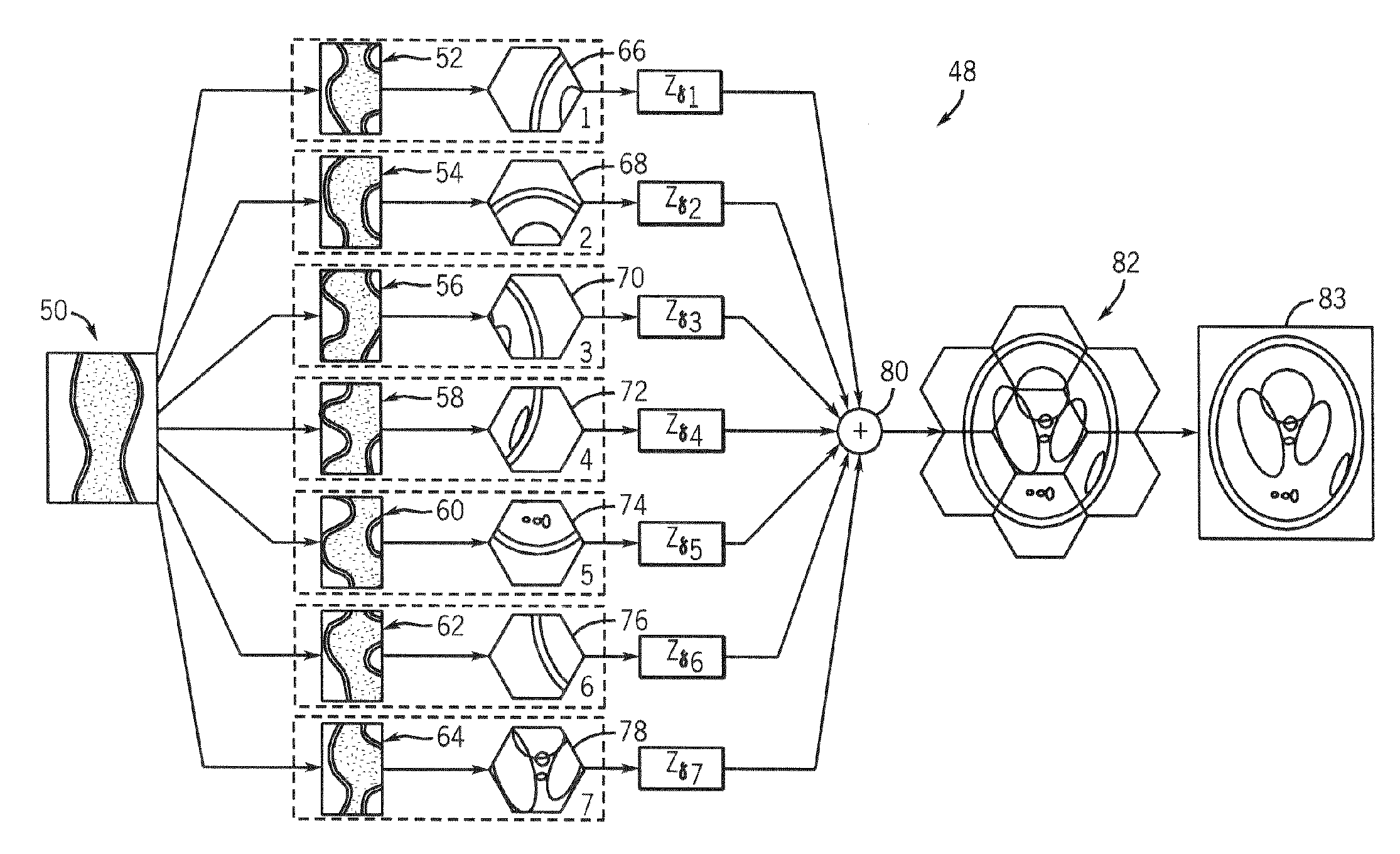
Fast backprojection/reprojection with hexagonal segmentation of image
InactiveUS7215731B1Reduce processing timeReduce in quantityReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
A reprojection / backprojection technique and apparatus for carrying out such a technique provides a hierarchical solution to speeding-up reprojection and backprojection of tomographic images. In the context of reprojection, a tomographic image is divided into a series of subimages. Each subimage is shifted to the origin, projected at a reduced number of views, and then up-sampled and shifted back (in the sinogram space). The resulting sinograms are then combined to provide a single sinogram. This process is applied one or more times recursively. In the context of backprojection, the above steps are transposed such that a sinogram is divided into a series of subsinograms. The subsinograms are then shifted and decimated by a given decimation factor. The decimated subsinograms are then backprojected onto hexagonal tiles whereupon the tiles are composited into a final image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and system for remote-sensing image and laser point cloud registration based on road features
InactiveCN104123730AFast automated registrationEasy to distinguishImage analysisTerminal pointHigh resolution
The invention provides a method and a system for high-resolution remote-sensing image and laser point cloud registration based on road features. The method includes the steps of 1, extracting point cloud road vector line according to laser point cloud; 2, preprocessing the orthoimage of a remote-sensing image to acquire binary segmented images; 3, back projecting the point cloud road vector line to the binary segmented images through initial exterior orientation elements and acquiring an image road center line by a rectangular global matching method; 4, taking a terminal point of the point cloud road vector line as a ground control point and taking a terminal point of the image road center line as an image point of the ground control point to realize registration of the laser point cloud and the remote-sensing image. The method and the system can realize rapid, automatic and precise registration between multi-source data to provide reference for surface feature extraction, three-dimensional reconstruction and change detection after fusion of the data.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Visual inertial navigation SLAM method based on ground plane hypothesis
ActiveCN108717712AGet real depth in real timeEliminate cumulative errorsImage analysisPoint cloudGround plane
The invention relates to a visual inertial navigation SLAM method based on ground plane hypothesis. According to the method, feature points are extracted from an image to perform IMU pre-integration,a camera projection model is established, and camera internal parameter calibration and external parameter calibration between an IMU and a camera are performed; a system is initialized, a visually observed point cloud and a camera pose are aligned to the IMU pre-integration, and a ground equation and the camera pose are restored; the ground is initialized to obtain a ground equation, the ground equation under the current camera pose is determined and back projected to an image coordinate system, and a more accurate ground region is acquired; and based on state estimation, all sensor observation models are derived, camera observation, IMU observation and ground feature observation are fused to do state estimation, a graph optimization model is used to do state estimation, and a sparse graph optimization and gradient descent method is used to realize overall optimization. Compared with previous algorithms, the precision of the method is greatly improved, estimation of the camera pose can be limited globally, and therefore accuracy is greatly improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method and system for iterative image reconstruction
InactiveUS20060072801A1Need be addressReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationComputed tomographyImage estimation
A method for iteratively reconstructing image data acquired by a computed tomography system is provided. The method comprises generating a calculated sinogram from an image estimate and generating an error sinogram based on the calculated sinogram and a measured sinogram. Then, one or more backprojections are performed, each based upon a reconstruction parameter. The reconstruction parameter impacts at least one of convergence speed and computational cost of each iterative step and corresponding reconstruction. A filtering step is performed prior to performing the one or more backprojections. Finally, the initial image is updated by adding corresponding results of the one or more backprojections to the image estimate to obtain the reconstructed image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com