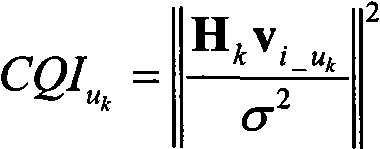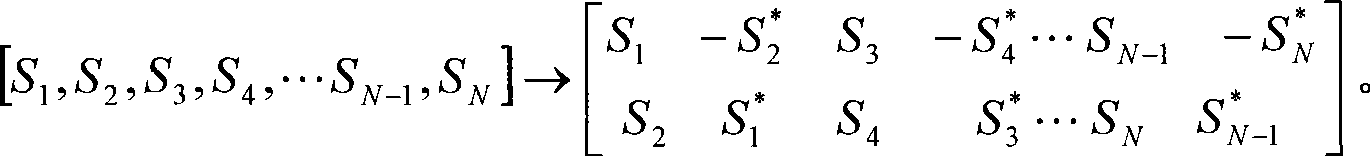Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
442 results about "Coding gain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
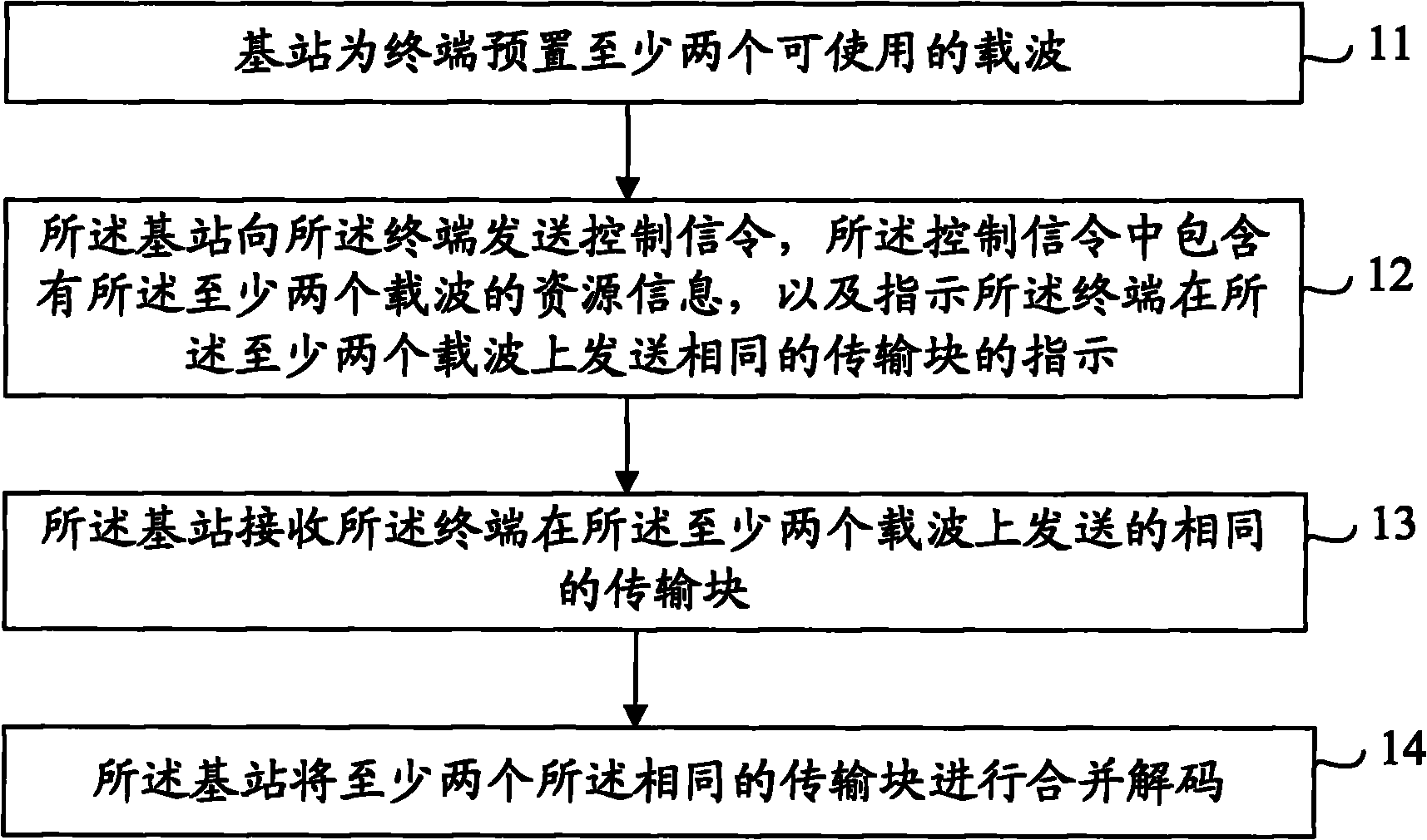
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
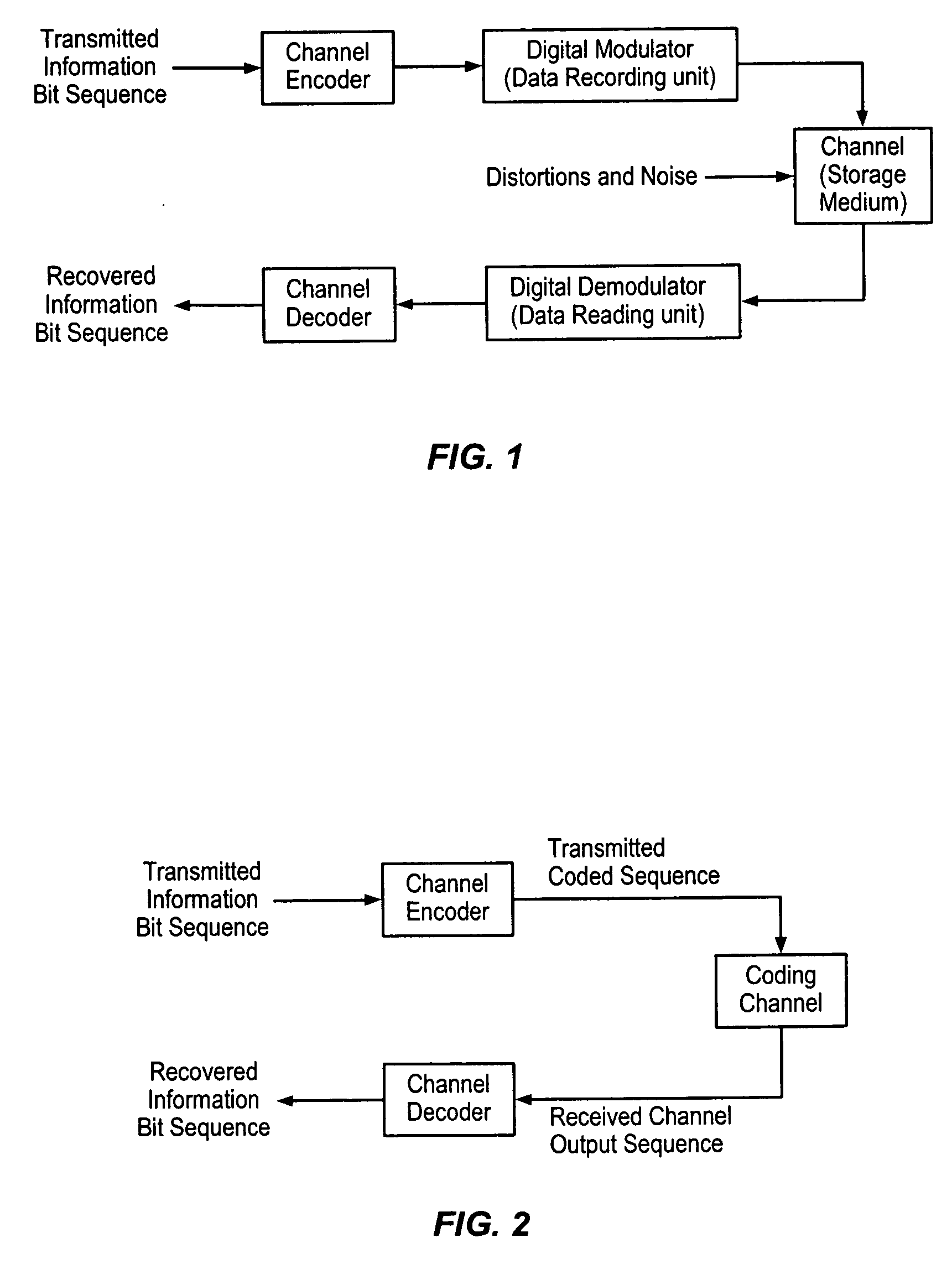
In coding theory and related engineering problems, coding gain is the measure in the difference between the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) levels between the uncoded system and coded system required to reach the same bit error rate (BER) levels when used with the error correcting code (ECC).
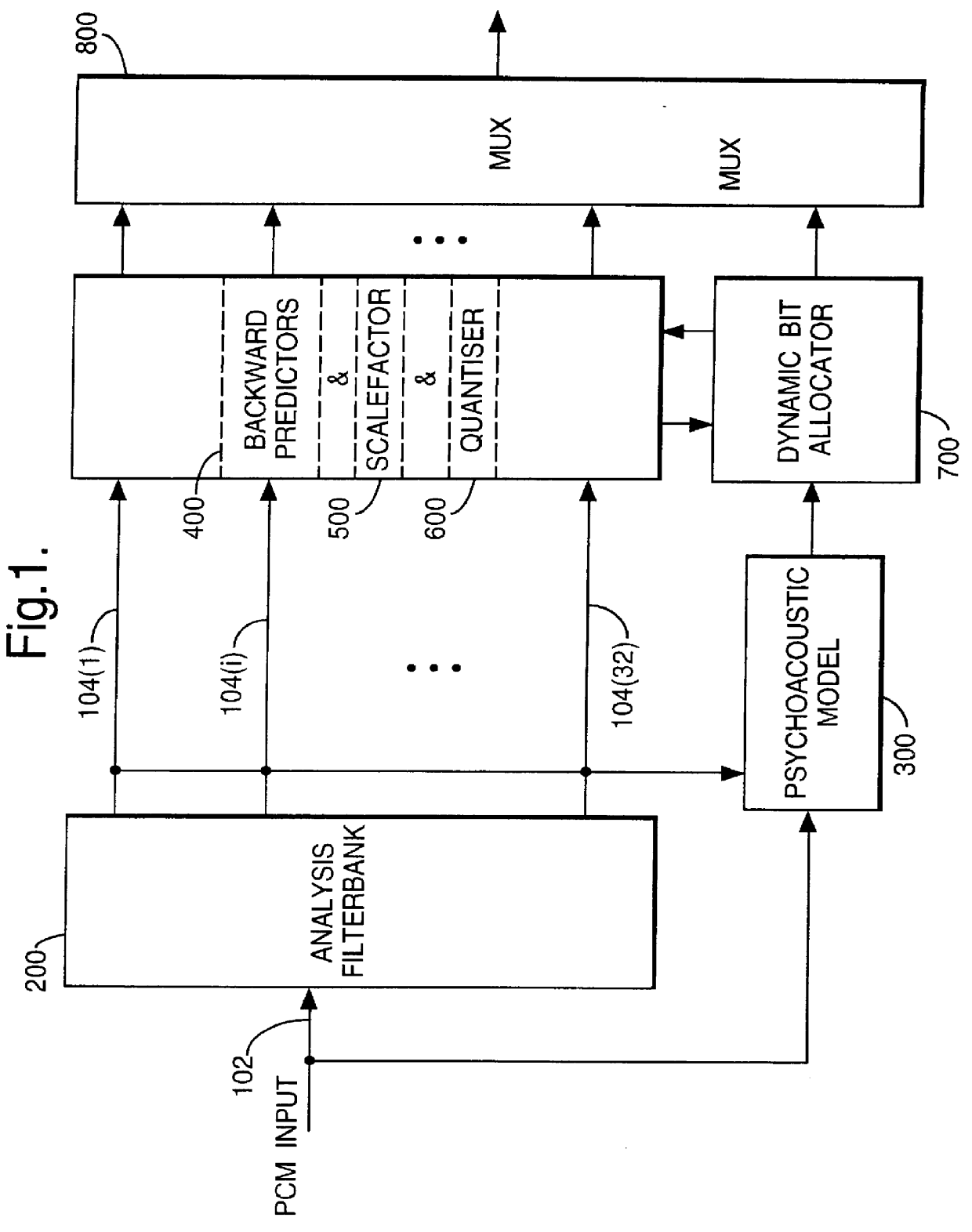
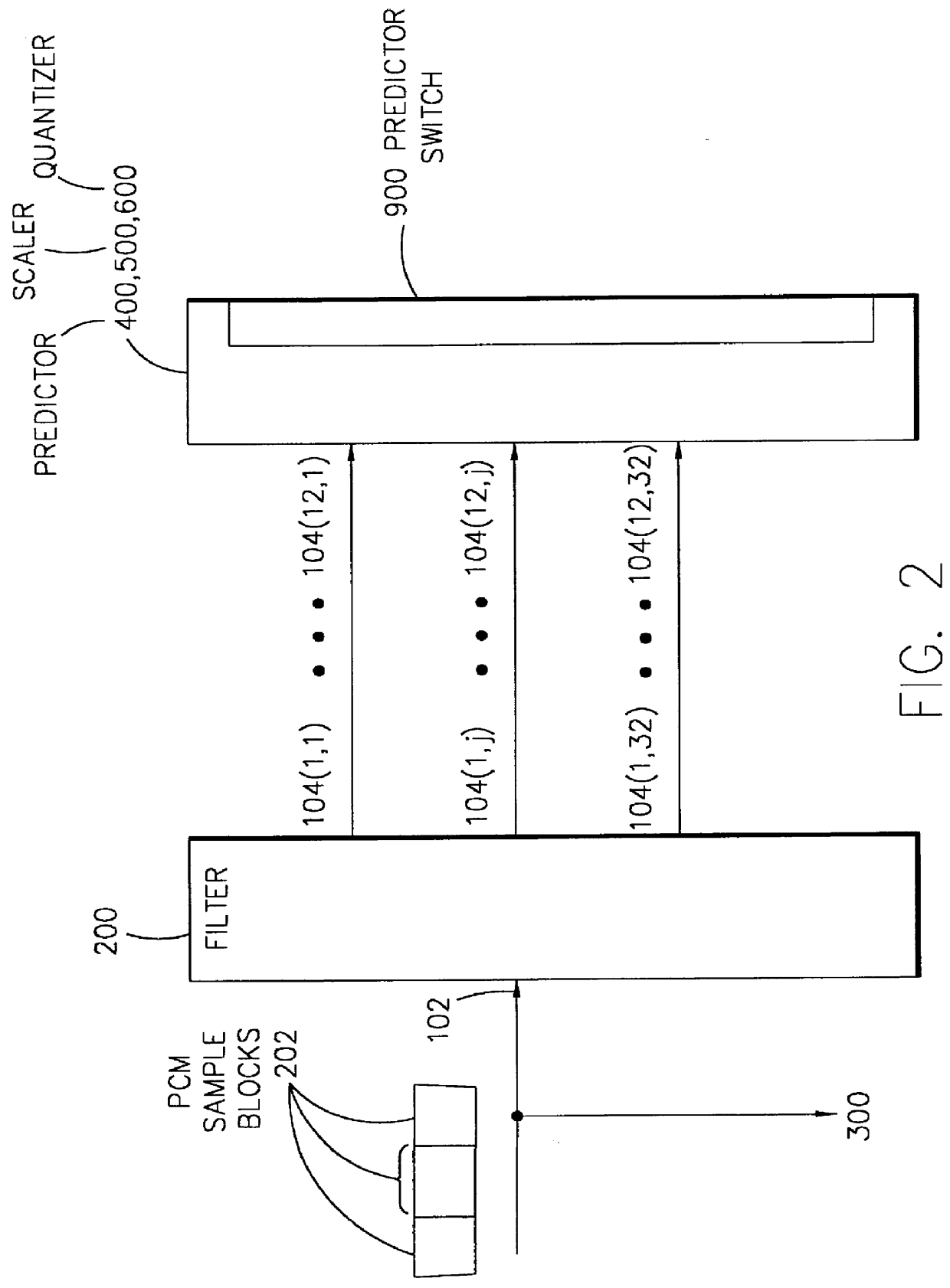
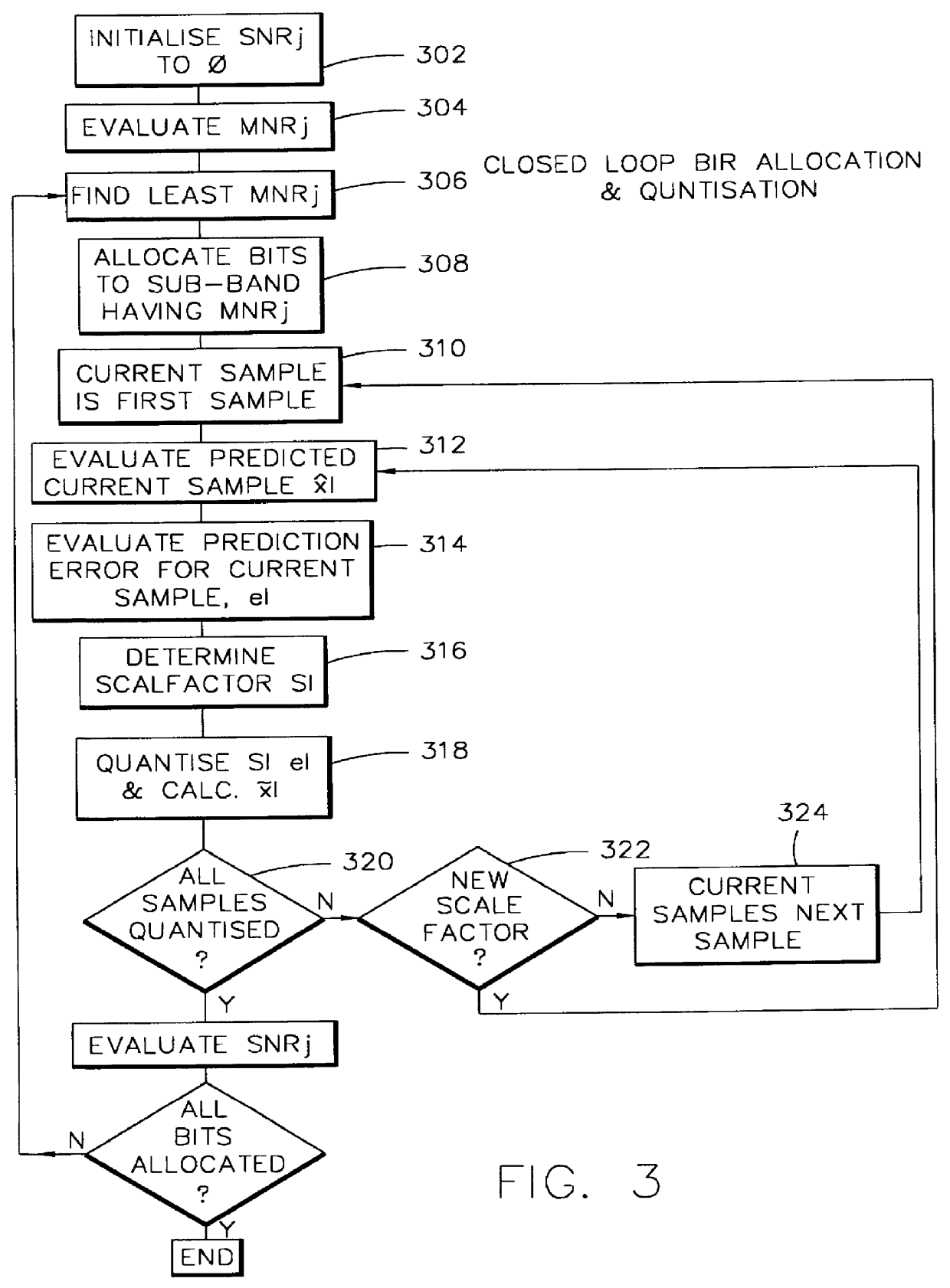
Audio coding with low-order adaptive prediction of transients
InactiveUS6104996AEasy to predictQuickly stabilises the predictorSpeech analysisSelf adaptiveAudio frequency
An encoder comprising predictive coding means for encoding electronic signals input thereto is disclosed. The predictive coding means is adapted to operate in a first high prediction order mode and in a second lower prediction order mode. The predictive coding means operates in the first and second modes in dependence on an input electronic signal comprising a transient signal. Preferably, the second mode comprises a transient recovery sequence of prediction orders. The transient signal detector determines predictive coding gain as well as a difference in predictive coding gain for a sequential input signal exceeding a threshold. The prediction orders are gradually increased for subsequent signals until the first mode (high) prediction order is attained. A transmission of electronics signals provides for an indication of initiation of a second mode for the predictive coding. Circuitry is included for reception of the second mode initiate signal. There is also disclosed a decoder for decoding signals encoded by the encoder.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
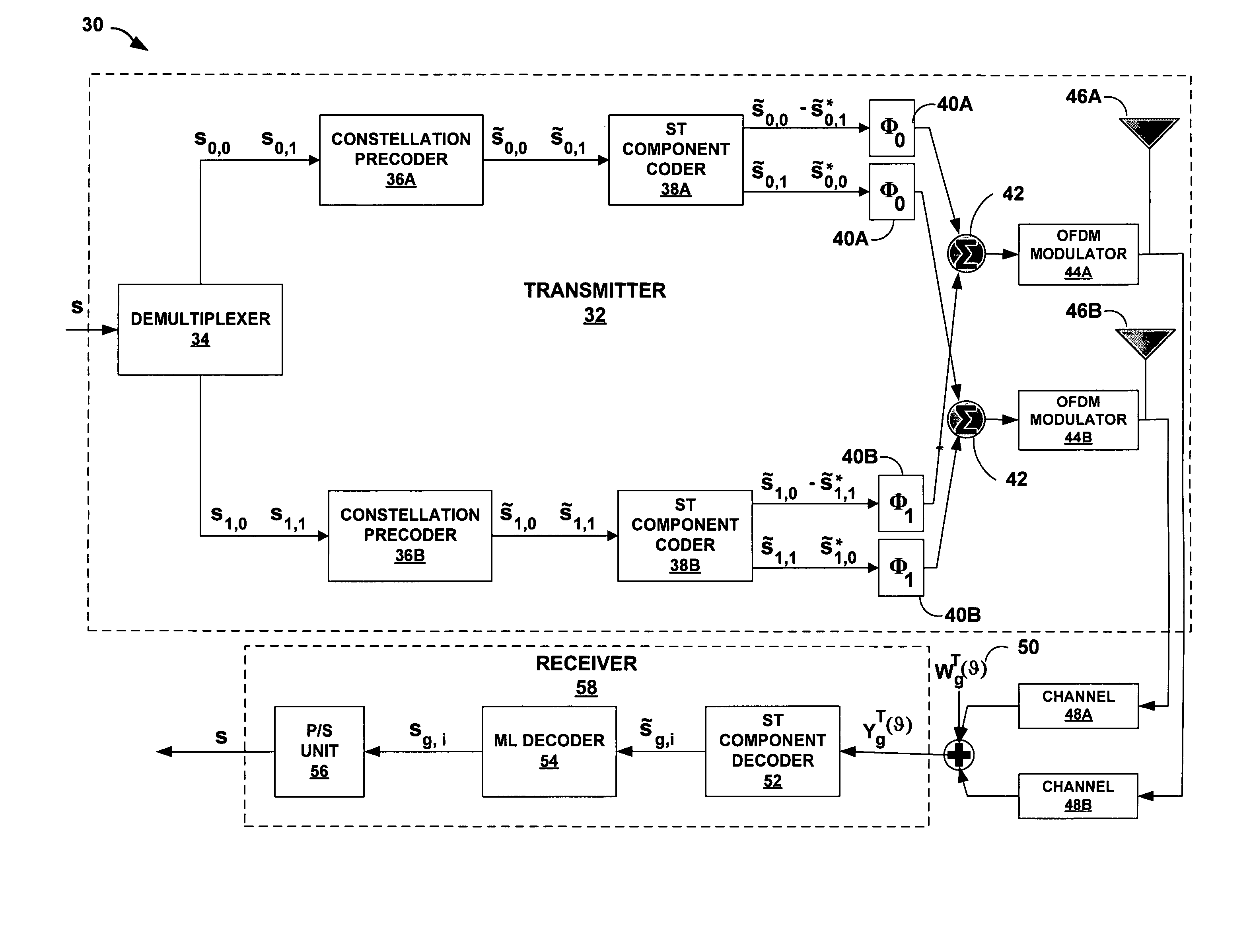
Space-time-frequency coded OFDM communications over frequency-selective fading channels
ActiveUS20050002325A1Maximal diversityHigh coding gainsTime-division multiplexFrequency-division multiplexComputer architectureCarrier signal
Techniques are described for space-time-frequency (STF) coding of multi-carrier transmissions over frequency-selective fading channels. In particular, techniques for STF coding of MIMO-OFDM systems are described that provide maximum diversity, high coding gains, and low decoding complexity are described. A set of generally correlated OFDM subcarriers are divided into groups of subcarriers creating a set of group STF (GSTF) subsystems, within which STF coding is applied to each GSTF subsystem. Subcarrier grouping preserves maximum diversity gains and simplifies both the code construction within each GSTF and decoding complexity. ST coding techniques are used in designing STF block (STFB) and STF trellis (STFT) codes which are applied within GSTF subsystems.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA +1
Parametric joint-coding of audio sources
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
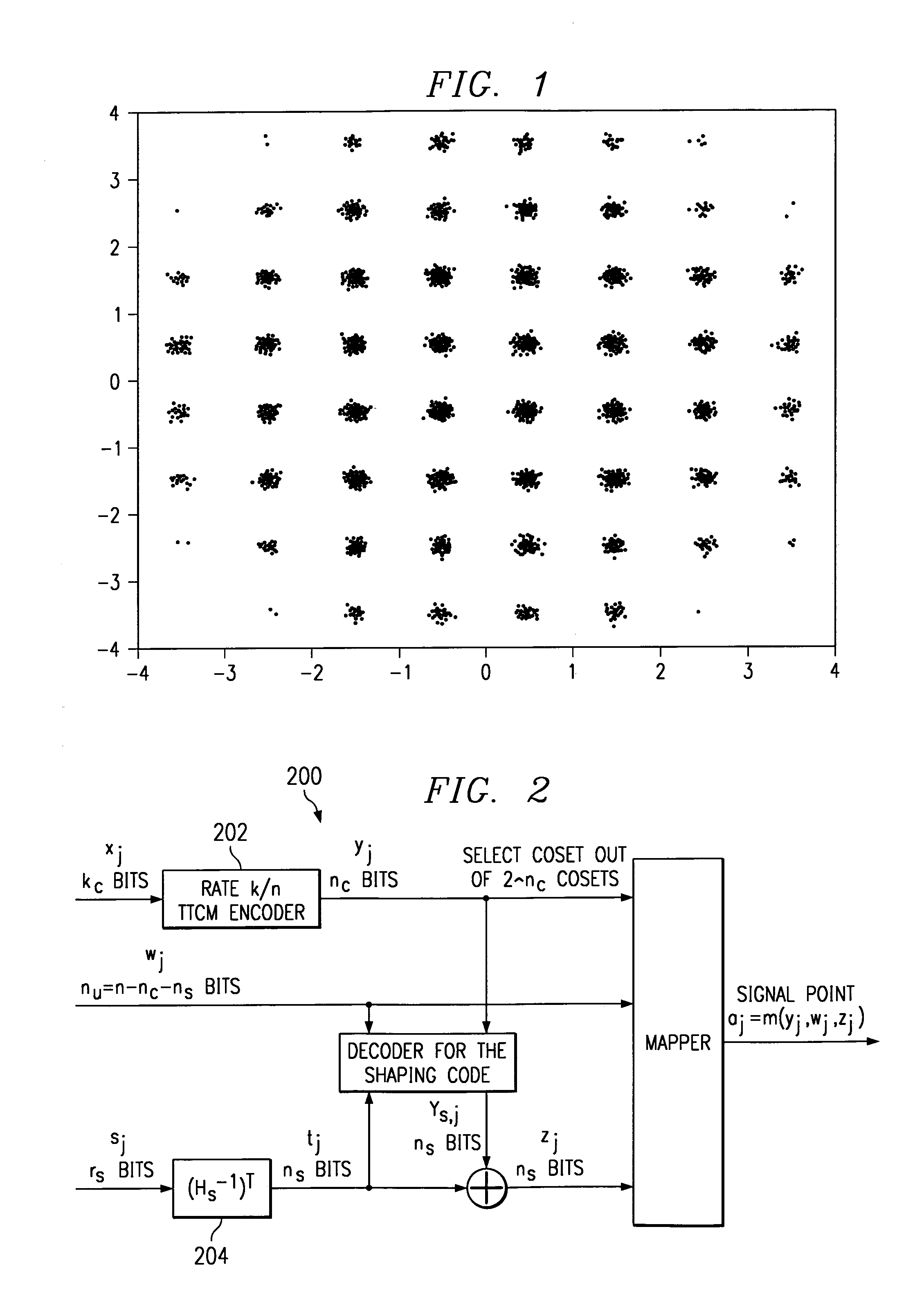
System and method of data communication using turbo trellis coded modulation combined with constellation shaping with or without precoding
InactiveUS7065147B2Improve performanceHigh coding gainsData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionPrecodingCommunications system
A technique that combines a turbo trellis coded modulation (TTCM) coding scheme with constellation shaping and precoding schemes to implement a binary coded communication system and method that can achieve high performance (high coding gains achieved in combination with shaping gain, and when necessary, also with high performance in ISI-channels via preceding).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
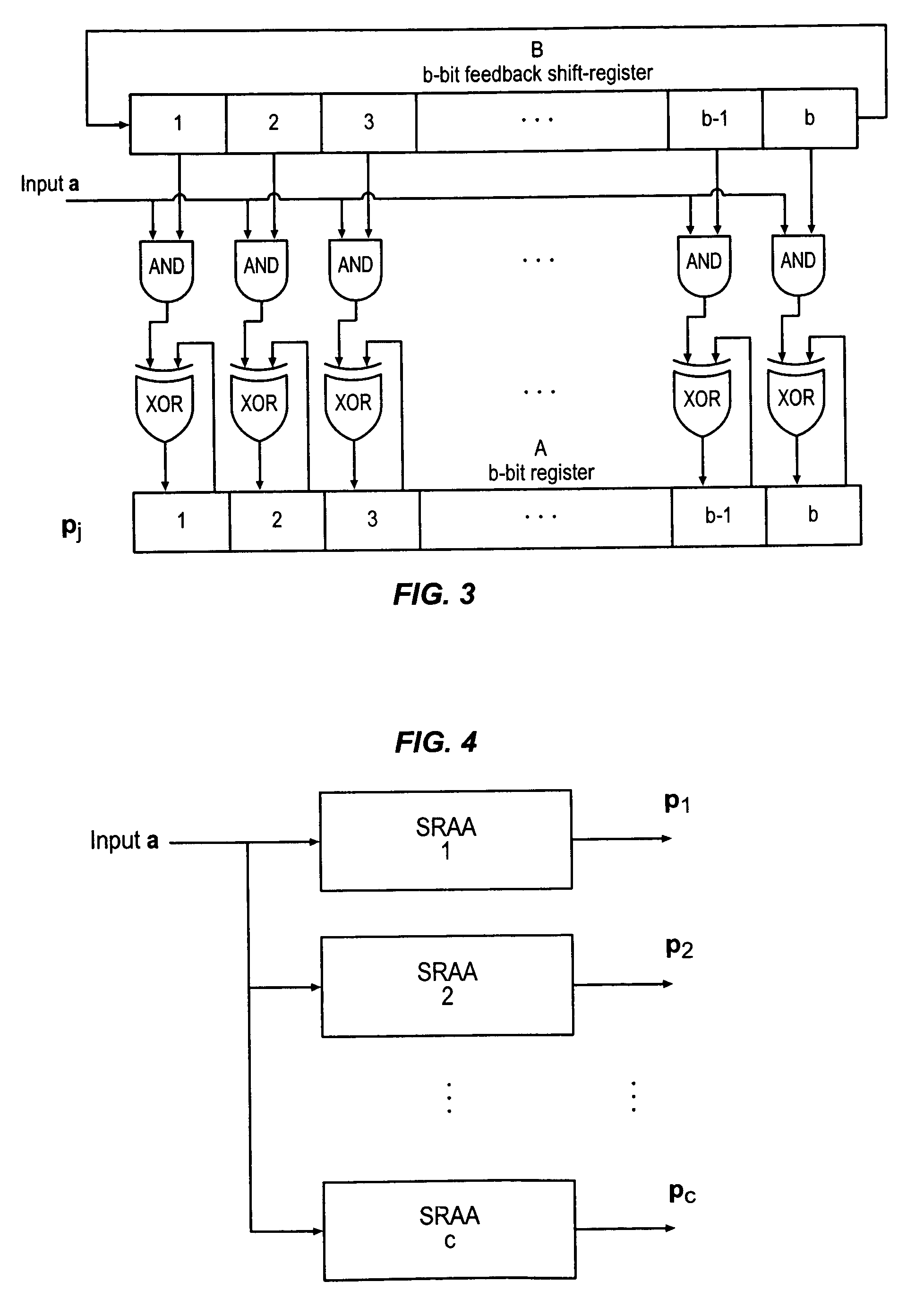
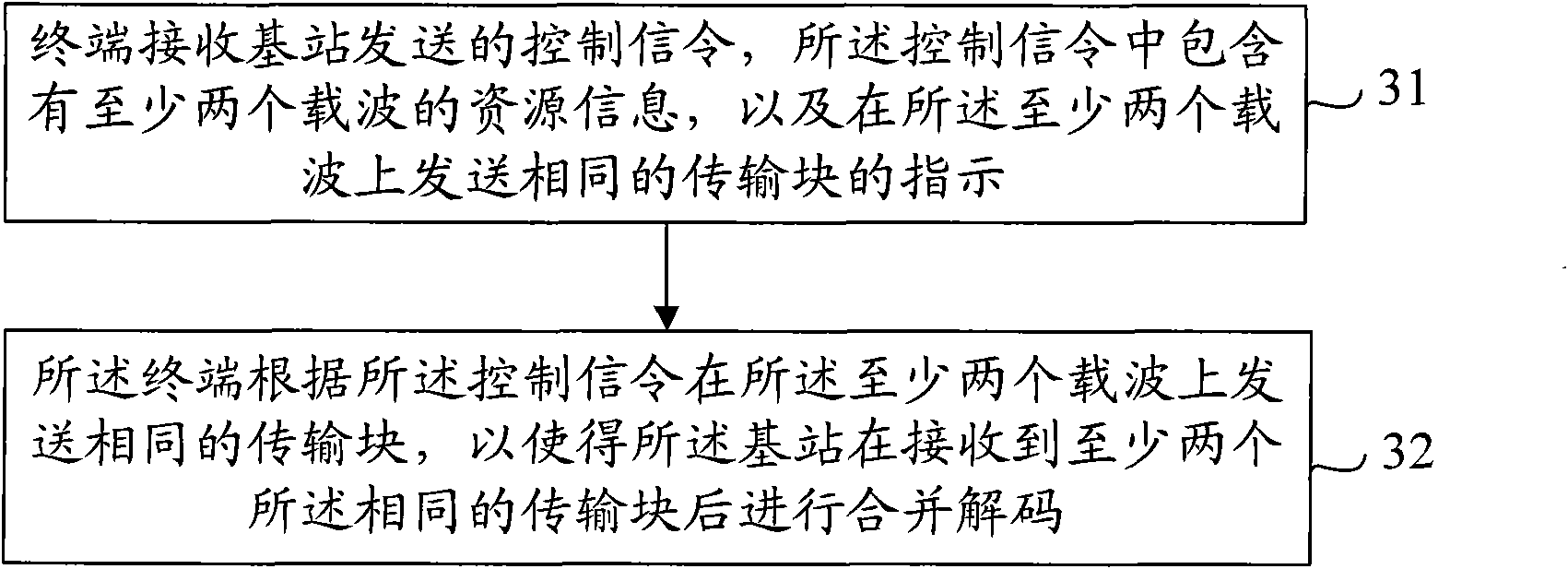
Universal error control coding system for digital communication and data storage systems
InactiveUS20080126908A1Reduce complexityReduce chip areaError detection/correctionCode conversionComputer architectureRound complexity
The universal forward error-correction coding system provides adjustable code rates and coding gains to greatly benefit the design of many modern digital communications (data storage) systems. The channel encoding and decoding methods are universal such that a single encoder and a single decoder can be used to implement all the forward error-correction codes of different code rates. This universal forward error-correction coding system also includes a novel systematic code generation procedure that has the capability of generating many classes of codes that provide the best balance between coding gain performance and implementation complexity.
Owner:COMM CODING
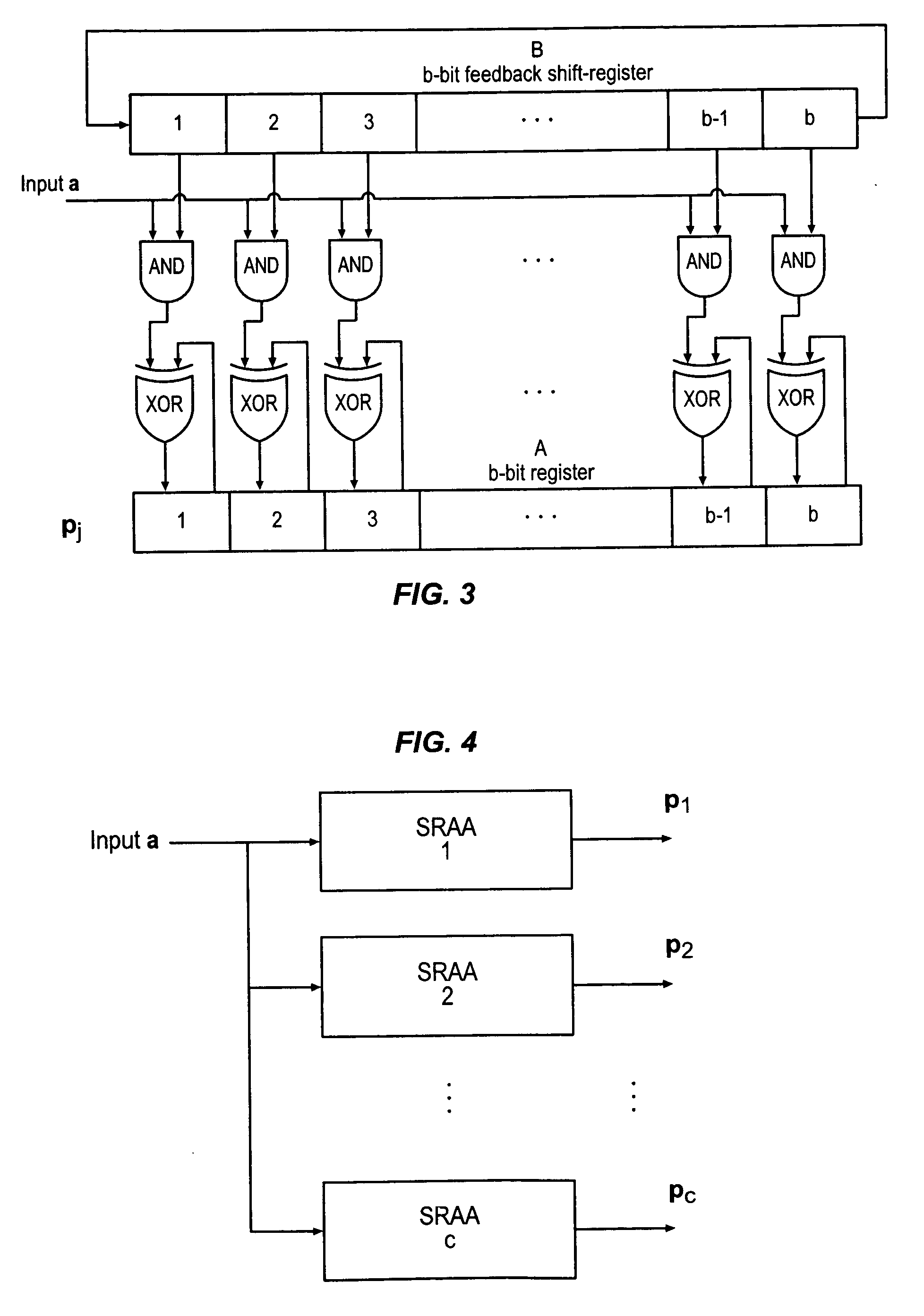
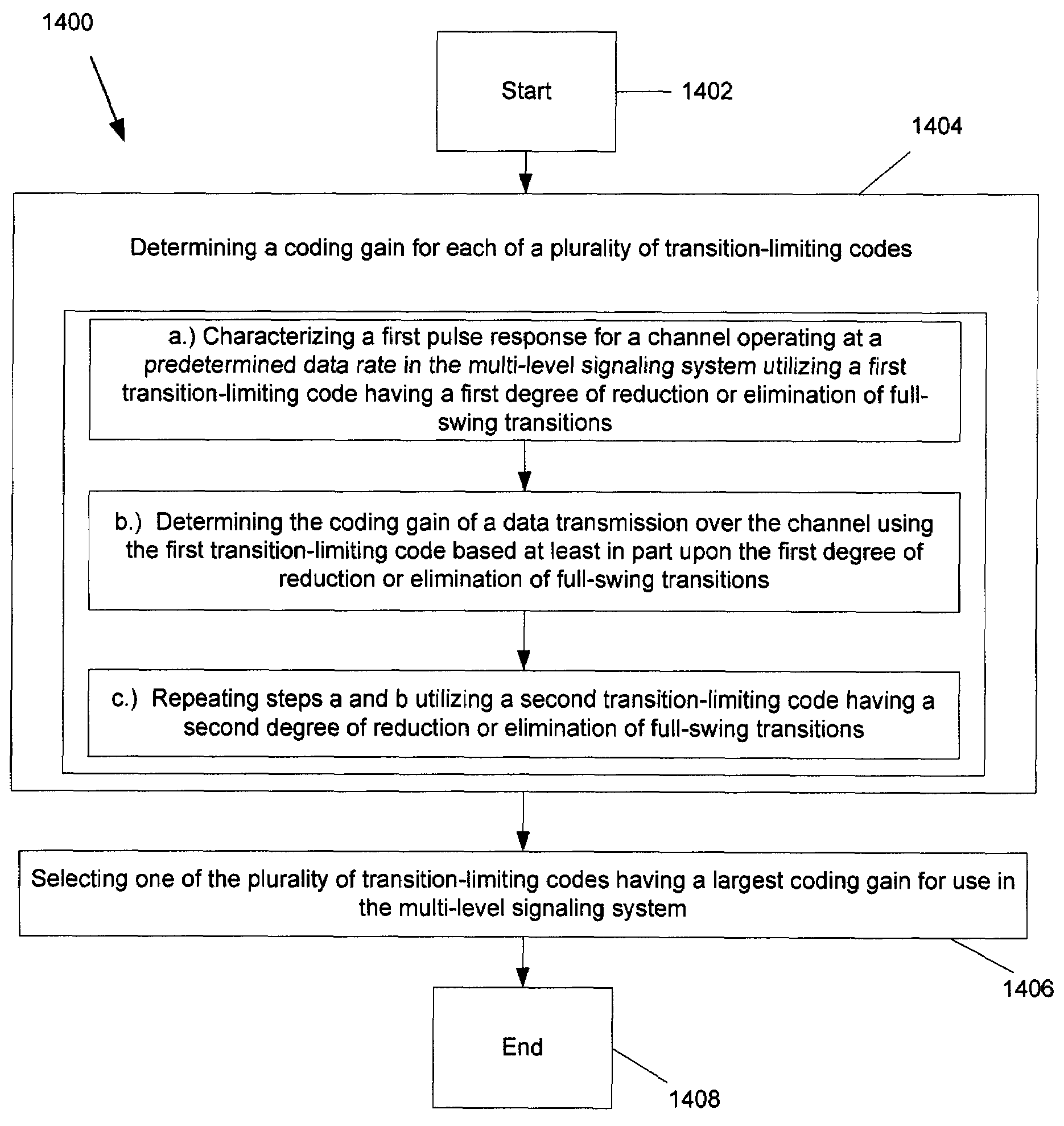
Technique for determining an optimal transition-limiting code for use in a multi-level signaling system
InactiveUS7620116B2Guaranteed maximum utilizationReduce eliminateModulated-carrier systemsIndividual digits conversionEngineeringSignaling system
A technique for determining an optimal transition-limiting code for use in a multi-level signaling system is disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the technique may be realized as a method for determining an optimal transition-limiting code for use in a multi-level signaling system. Such a method comprises determining a coding gain for each of a plurality of transition-limiting codes, and selecting one of the plurality of transition-limiting codes having a largest coding gain for use in the multi-level signaling system.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Method and device for rate matching of Polar code
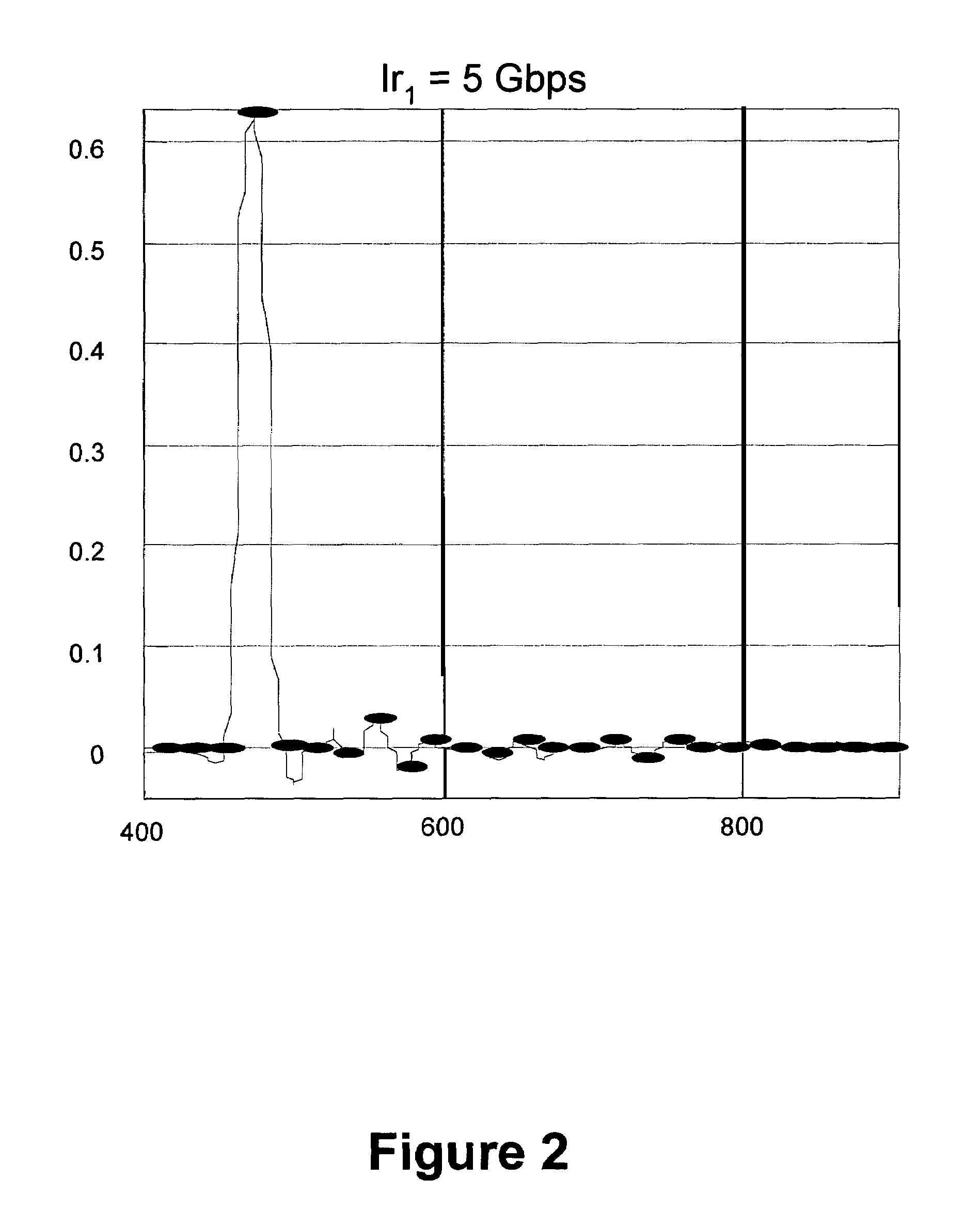
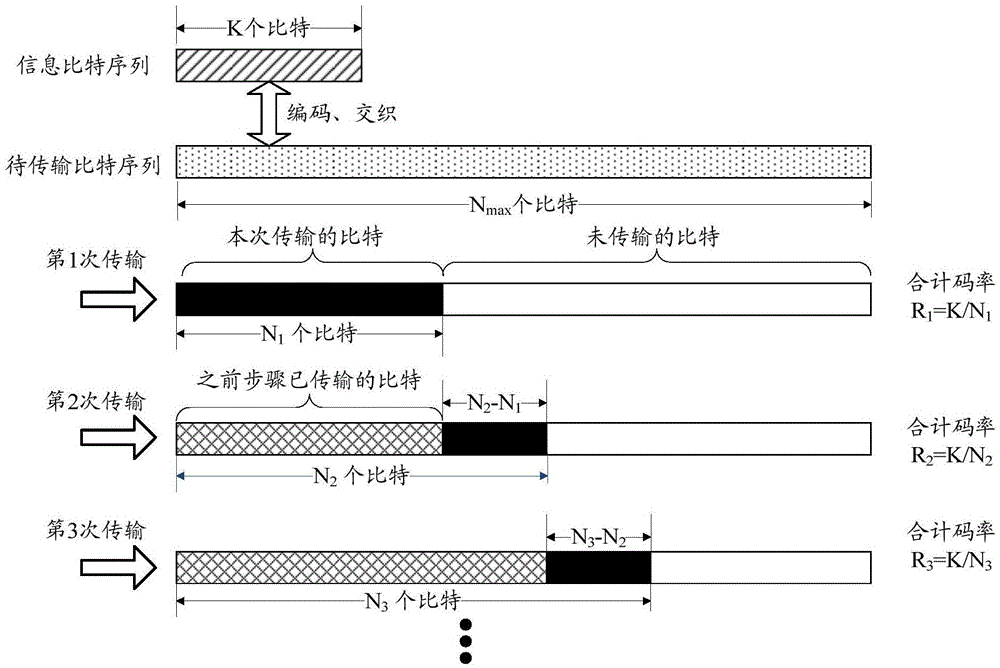
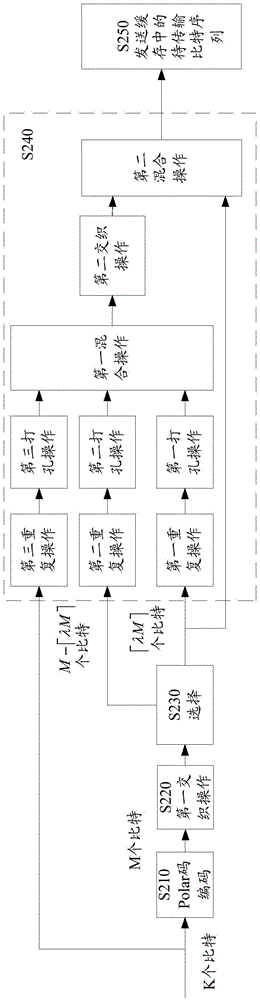
ActiveCN106817195AGood coding gainCode conversionChannel coding adaptationHybrid automatic repeat requestBit-length
The invention discloses a method and device for rate matching of Polar codes. The method comprises the steps of: performing Polar code encoding on an information bit sequence with a K-bit length, and generating an encoding bit sequence with an M-bit length; selecting Nmin bits from the encoding bit sequence as the first bit to Nmin-th bit of a bit sequence to be transmitted during a hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) process; and determining each bit of (Nmin+1)th bit to Nmax-th bit of the bit sequence to be transmitted from the information bit sequence and the encoding bit sequence, wherein each bit of the (Nmin+1)th bit to the Nmax-th bit of the bit sequence to be transmitted is determined according to a frame error rate of the bit sequence to be transmitted when each bit is added into the bit sequence to be transmitted. By adopting the method of the embodiment of the invention, HARQ transmission based on Polar code encoding can be achieved, and better encoding gain can be obtained.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Systems and methods for sparse code multiple access
InactiveCN104798317AModulated-carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSymbol mappingMulti dimensional
Coding gains can be achieved by encoding binary data directly to multi-dimensional codewords, which circumvents QAM symbol mapping employed by conventional CDMA encoding techniques. Further, multiple access can be achieved by assigning different codebooks to different multiplexed layers. Moreover, sparse codewords can be used to reduce baseband processing complexity on the receiver-side of the network, as sparse codewords can be detected within multiplexed codewords in accordance with message passing algorithms (MPAs).
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Transmitting device, receiving device, encoder, and encoding method
InactiveUS20100077276A1Improved error rate characteristicsCode conversionError correction/detection using block codesComputer scienceCoding gain
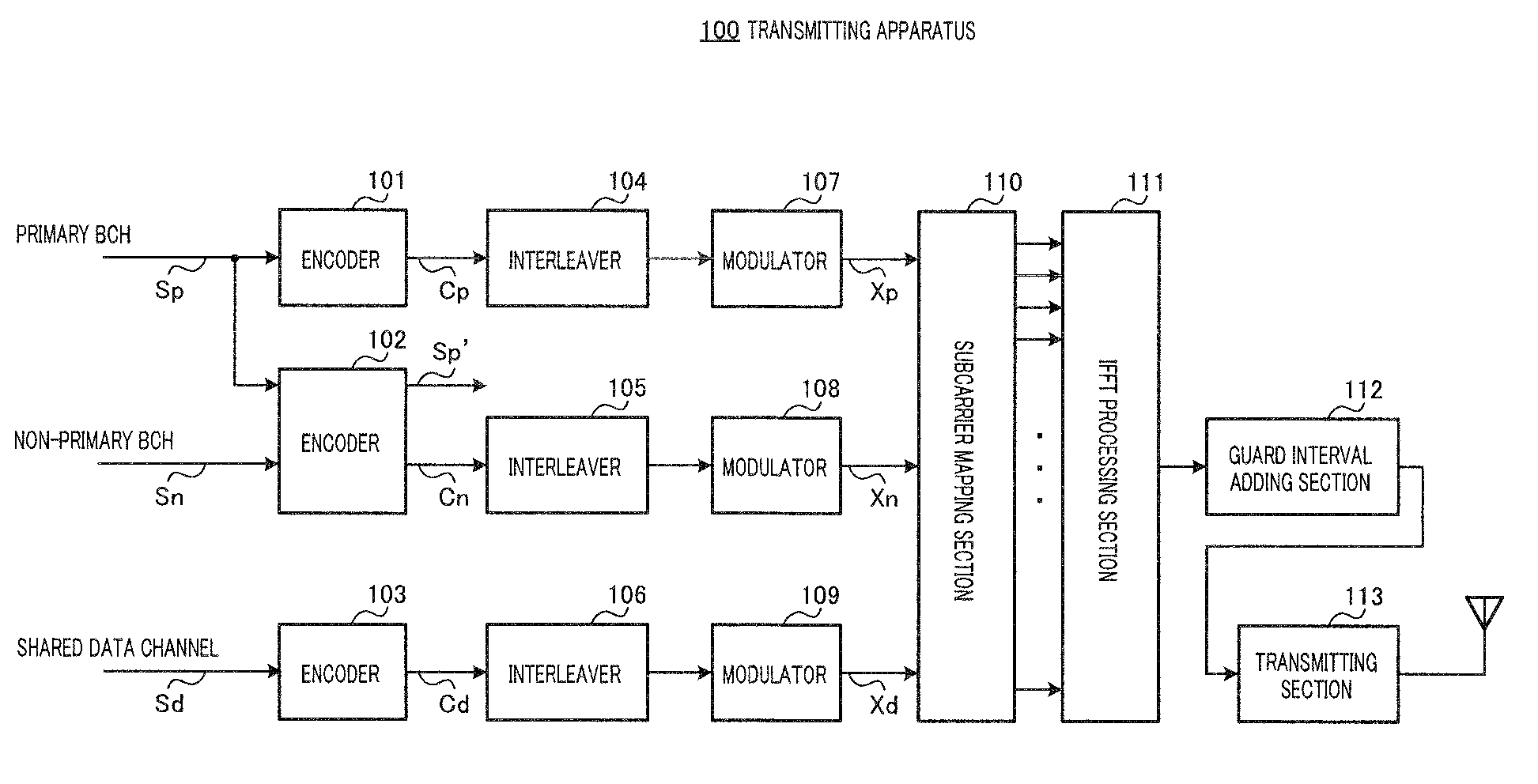
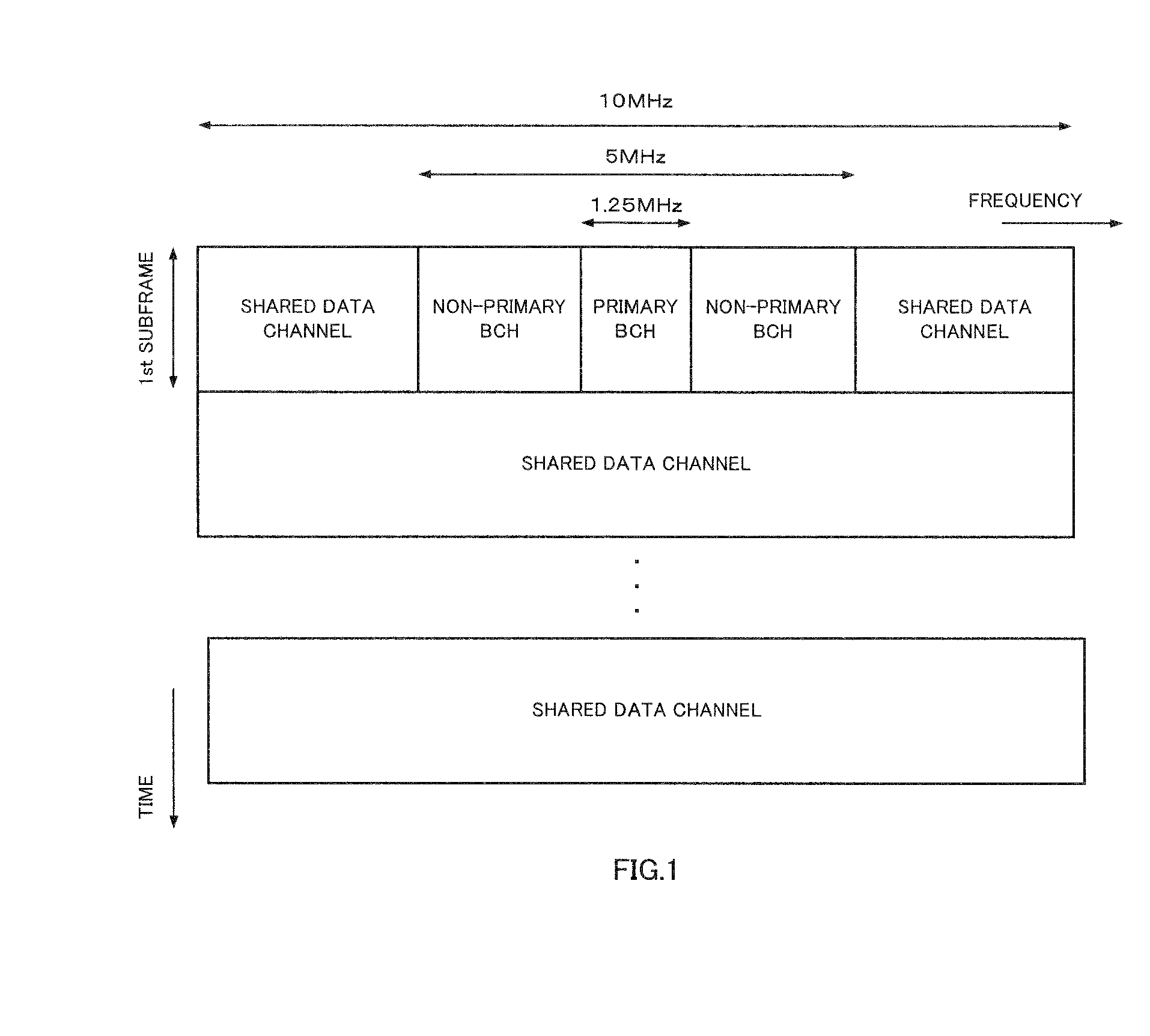
In such a relationship between information transmitted by a primary BCH, for example, and information transmitted by a non-primary BCH as a case of the transmission for a first information sequence that is easy to keep receiving quality and a second information sequence that is difficult to keep receiving quality, a transmitting device and a receiving device are disclosed for making it possible to improve an error rate of the second information sequence. In the devices, an encoder (102) encodes a non-primary BCH information sequence (Sn) with a long code length including a primary BCH information sequence (Sp). On the receiving side, a non-primary BCH information sequence is decoded with a long code length by using the received primary BCH value. With this, a higher encoding gain than encoding only with the non-primary BCH information can be obtained, so that a receiving characteristic of the non-primary BCH can be improved.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and apparatus using coordinate interleaving to increase diversity in a MIMO system
InactiveUS7409001B2Increase diversityModulated-carrier systemsPolarisation/directional diversityAs elementEngineering
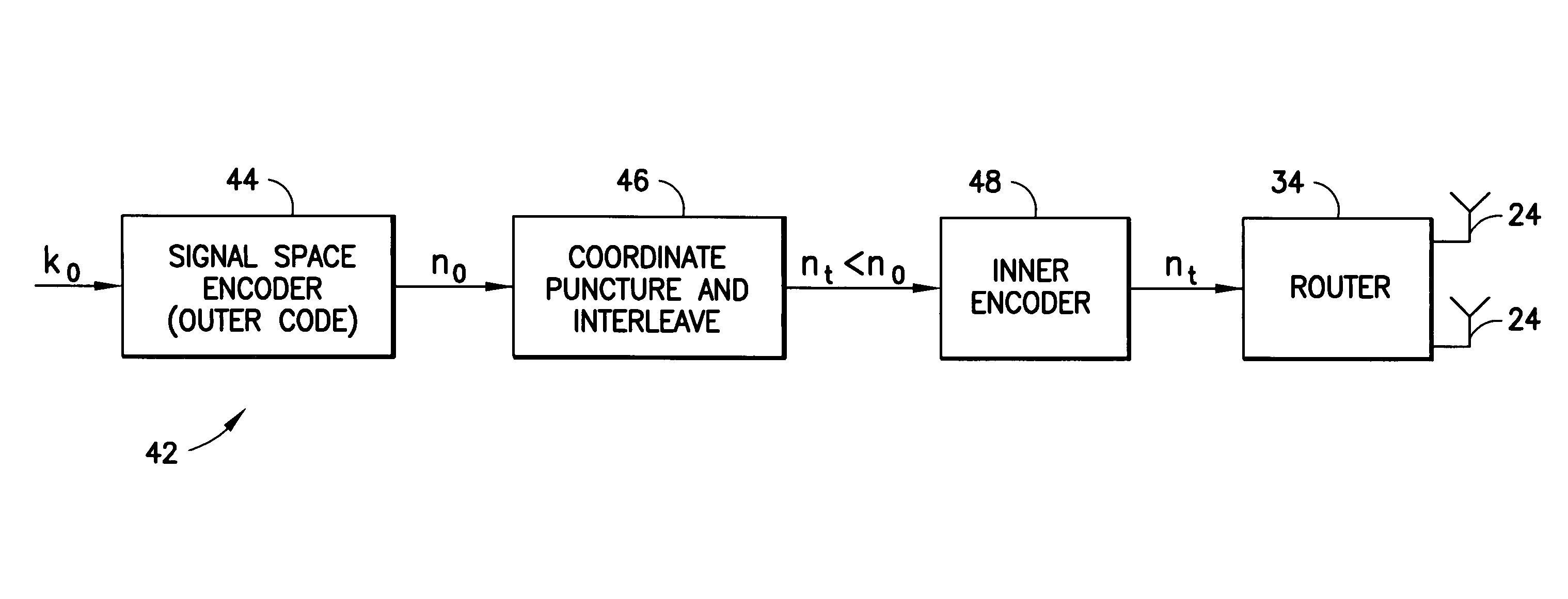
A method to increase diversity in MIMO fading channels interleaves coordinates of complex symbol(s) in a transmission frame after encoding and modulating. Specifically, an input signal is encoded and modulated into a codeword, jointly across at least two pipes, said pipes having space, time, frequency, or other nature, wherein the codeword spans a frame and is defined as at least one complex symbol whose complex values are all those to be transmitted during all channel uses covered by the frame. Each of the complex symbols have a first and second coordinate. After modulating, which may be combined with encoding in a signal space encoder, the coordinates are interleaved. In modulation, the complex symbols (typically two dimensional) may arise as elements of a multidimensional (typically greater than two dimensions) signal constellation, in which case those multidimensional constellation coordinates are the ones that are interleaved in the frame. The frame carrying the interleaved coordinates is transmitted by the first and at least second antennas, possible opposed sub-frames of the overall frame being transmitted separately by opposed antennas. A coset selector is used in some embodiments to maximize a minimum Hamming distance, and / or a minimum Euclidean distance, between coordinates within a coset to control diversity and / or coding gain. In some embodiments, the operation of the encoder and modulator is such as to maximize a minimum coordinate-wise Hamming distance, and / or a minimum Euclidean distance, between allowable codewords, and / or to provide additional structure for the allowable codewords. A method, transmitter, system, and mobile station are described.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Pre-coding method and system in MIMO system with multiple users
InactiveCN101286824AAvoid pairing failureAvoid the problem of pairing failureDiversity/multi-antenna systemsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionUnitary matrixComputer science
The embodiment of the invention discloses a precoding method which comprises the steps that: a first codebook and a second codebook are arranged at a base station and a user terminal, the second codebook is a set of unitary matrices generated by vectors in the first codebook and by making use of channel matrices, vectors that ensure that the user terminal obtains the maximum coding gain are respectively selected for every user terminal in the first codebook and corresponding CQI values are calculated; the base station determines the user terminal to be precoded and chooses a unitary matrix from the second codebook according to the vectors in the first codebook and corresponding CQI values corresponding to the user terminal to be precoded or chooses a unitary matrix from the second codebook and determines the user terminal to be precoded according to vectors in the first codebook and the corresponding CQI values corresponding to every user terminal; the unitary matrices or submatrices thereof are used as precoding matrices to carry out precoding towards the user terminal to be precoded. The embodiment of the invention also discloses a precoding system, and failure of matching among a plurality of user terminals can be avoided by the method and the system of the invention.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +1
Method and apparatus using coordinate interleaving to increase diversity in a MIMO system
InactiveUS20060034381A1Increase diversityPolarisation/directional diversityPhase-modulated carrier systemsAs elementEngineering
A method to increase diversity in MIMO fading channels interleaves coordinates of complex symbol(s) in a transmission frame after encoding and modulating. Specifically, an input signal is encoded and modulated into a codeword, jointly across at least two pipes, said pipes having space, time, frequency, or other nature, wherein the codeword spans a frame and is defined as at least one complex symbol whose complex values are all those to be transmitted during all channel uses covered by the frame. Each of the complex symbols have a first and second coordinate. After modulating, which may be combined with encoding in a signal space encoder, the coordinates are interleaved. In modulation, the complex symbols (typically two dimensional) may arise as elements of a multidimensional (typically greater than two dimensions) signal constellation, in which case those multidimensional constellation coordinates are the ones that are interleaved in the frame. The frame carrying the interleaved coordinates is transmitted by the first and at least second antennas, possible opposed sub-frames of the overall frame being transmitted separately by opposed antennas. A coset selector is used in some embodiments to maximize a minimum Hamming distance, and / or a minimum Euclidean distance, between coordinates within a coset to control diversity and / or coding gain. In some embodiments, the operation of the encoder and modulator is such as to maximize a minimum coordinate-wise Hamming distance, and / or a minimum Euclidean distance, between allowable codewords, and / or to provide additional structure for the allowable codewords. A method, transmitter, system, and mobile station are described.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
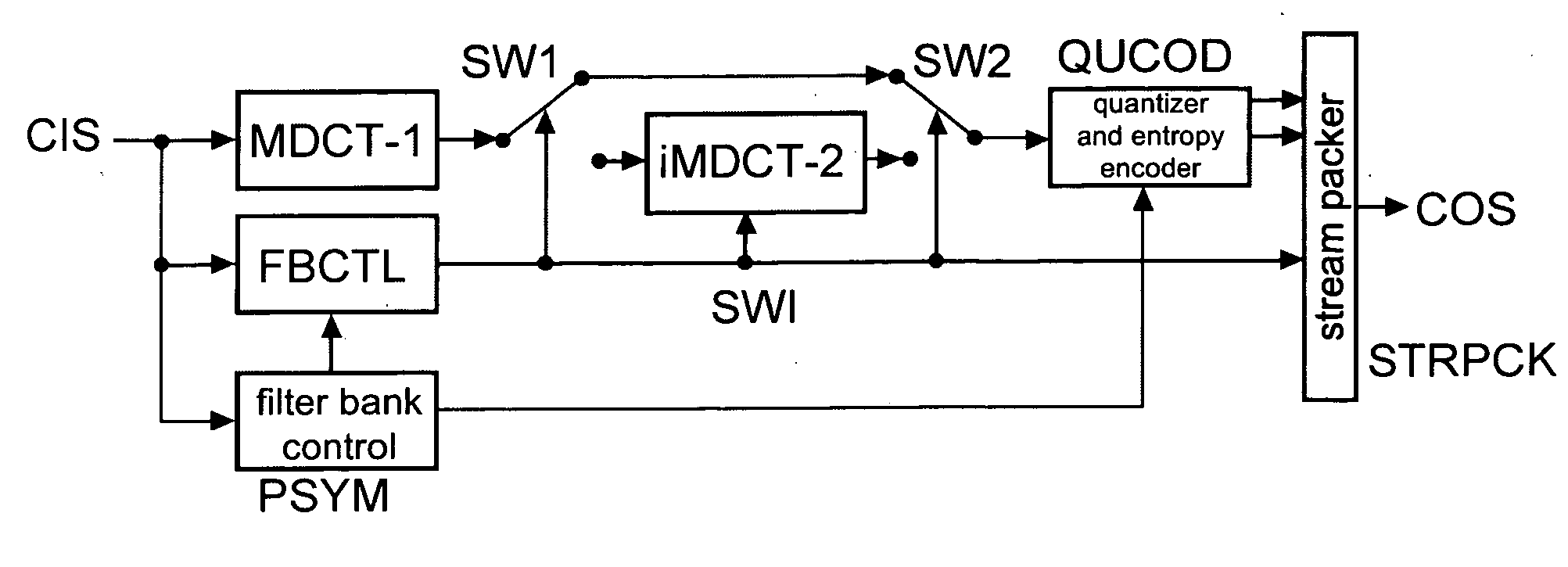
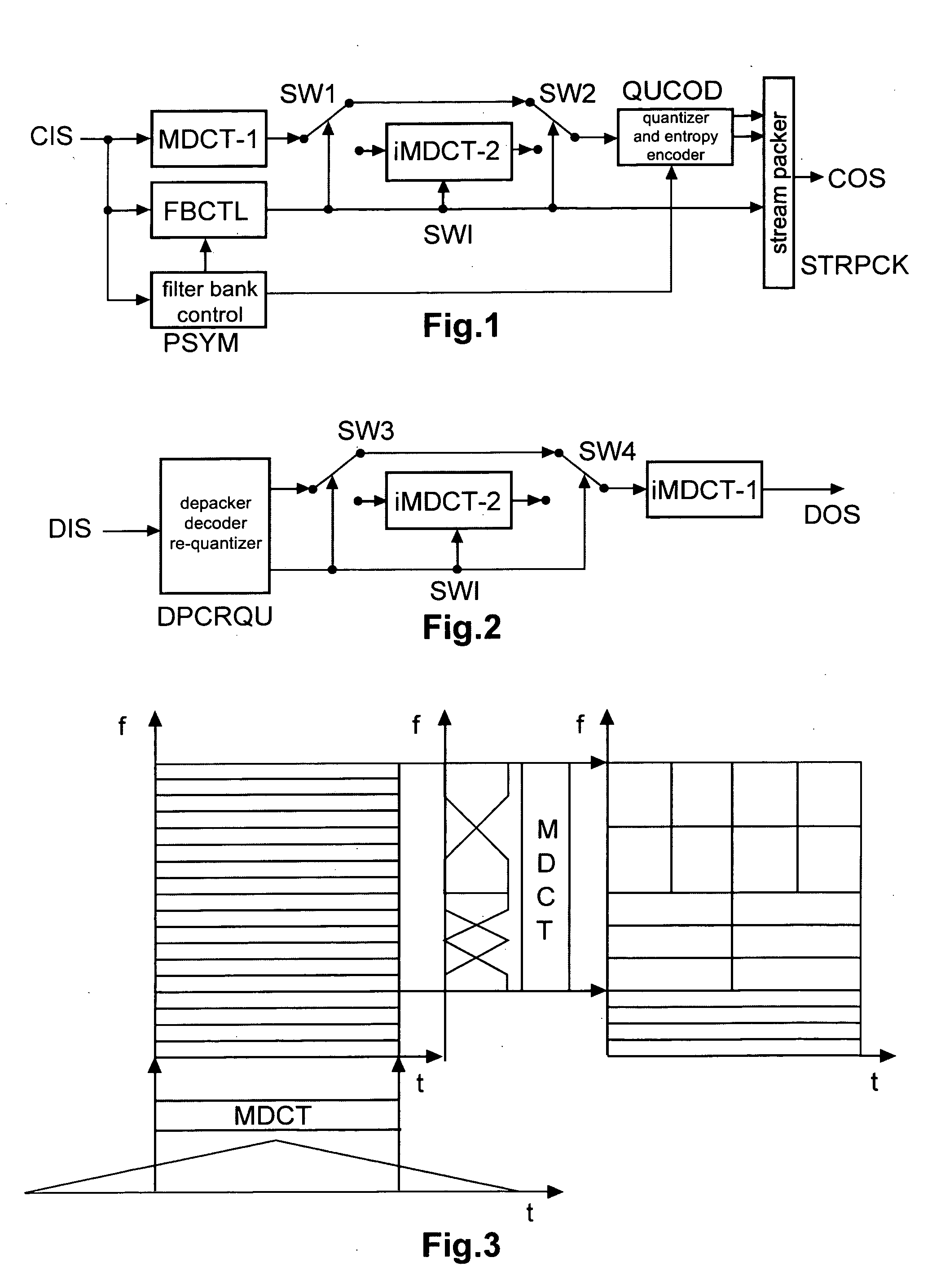
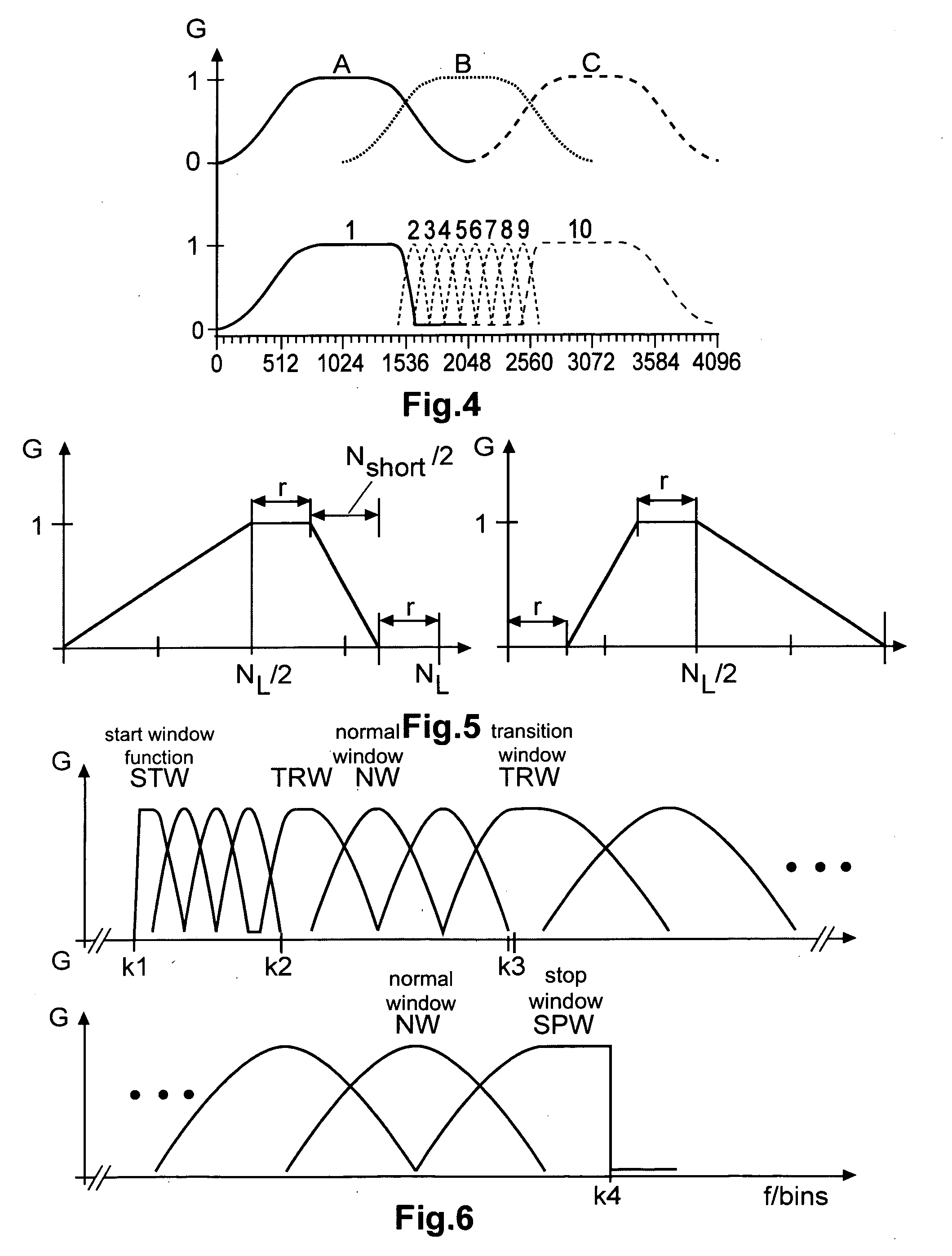
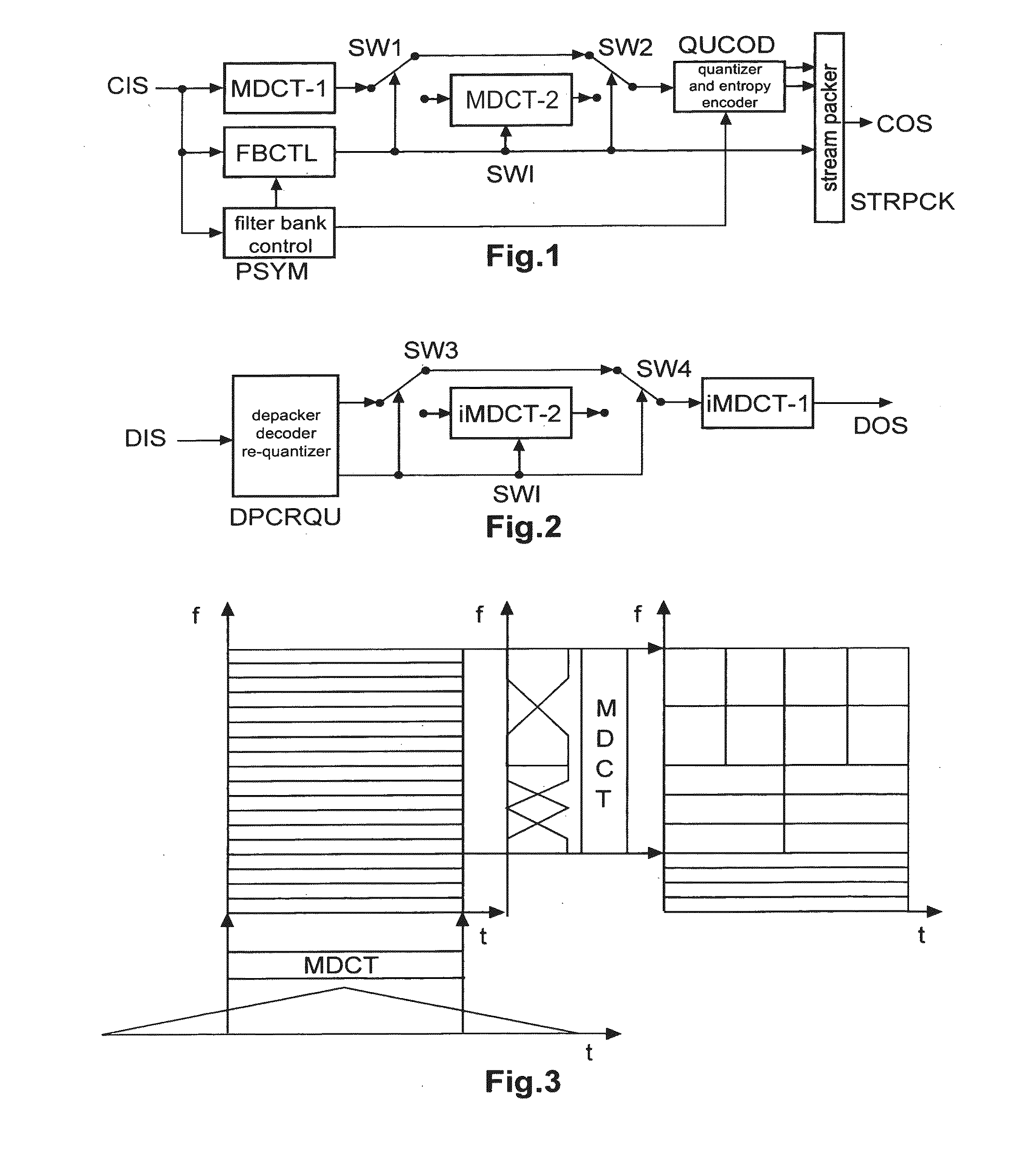
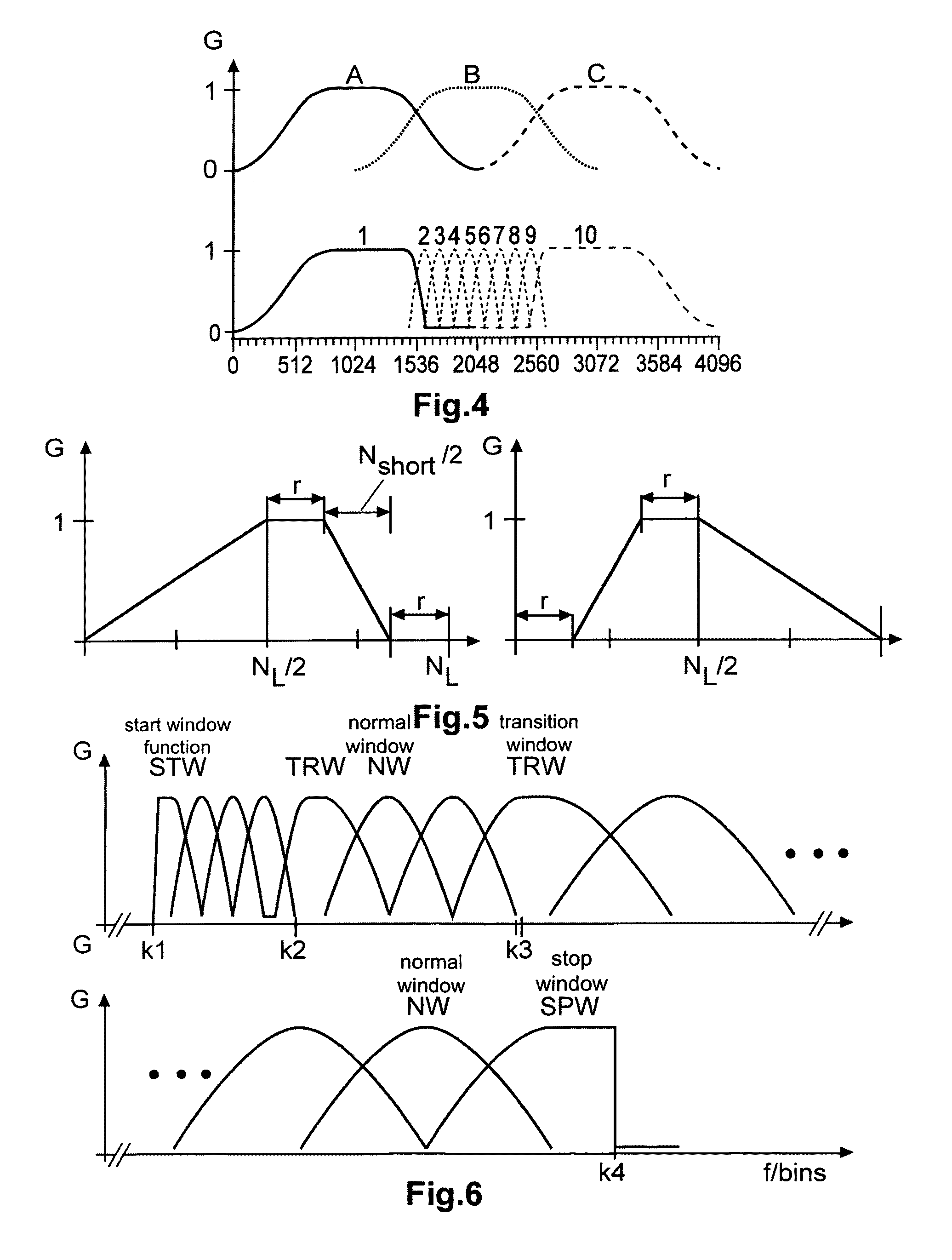
Method and apparatus for encoding and decoding an audio signal using adaptively switched temporal resolution in the spectral domain
ActiveUS20090012797A1Quality improvementReduce encoding delaySpeech synthesisTemporal resolutionFrequency spectrum
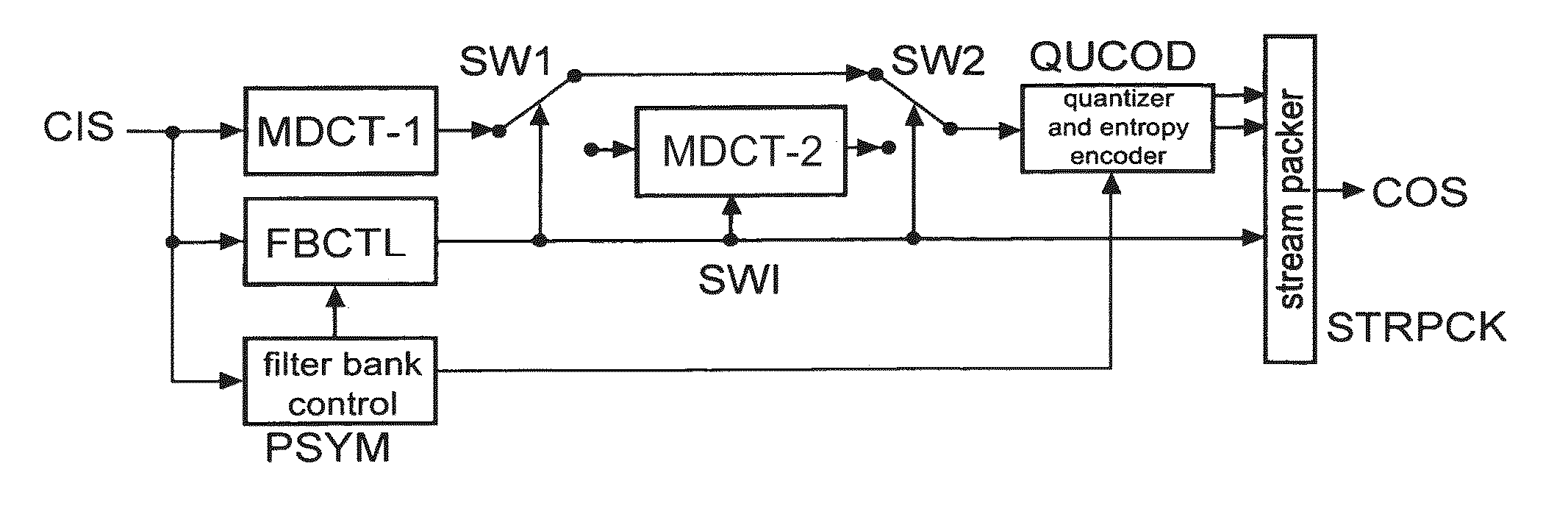
Perceptual audio codecs make use of filter banks and MDCT in order to achieve a compact representation of the audio signal, by removing redundancy and irrelevancy from the original audio signal. During quasi-stationary parts of the audio signal a high frequency resolution of the filter bank is advantageous in order to achieve a high coding gain, but this high frequency resolution is coupled to a coarse temporal resolution that becomes a problem during transient signal parts by producing audible pre-echo effects. The invention achieves improved coding / decoding quality by applying on top of the output of a first filter bank a second non-uniform filter bank, i.e. a cascaded MDCT. The inventive codec uses switching to an additional extension filter bank (or multi-resolution filter bank) in order to re-group the time-frequency representation during transient or fast changing audio signal sections. By applying a corresponding switching control, pre-echo effects are avoided and a high coding gain and a low coding delay are achieved.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Data transmission method and device
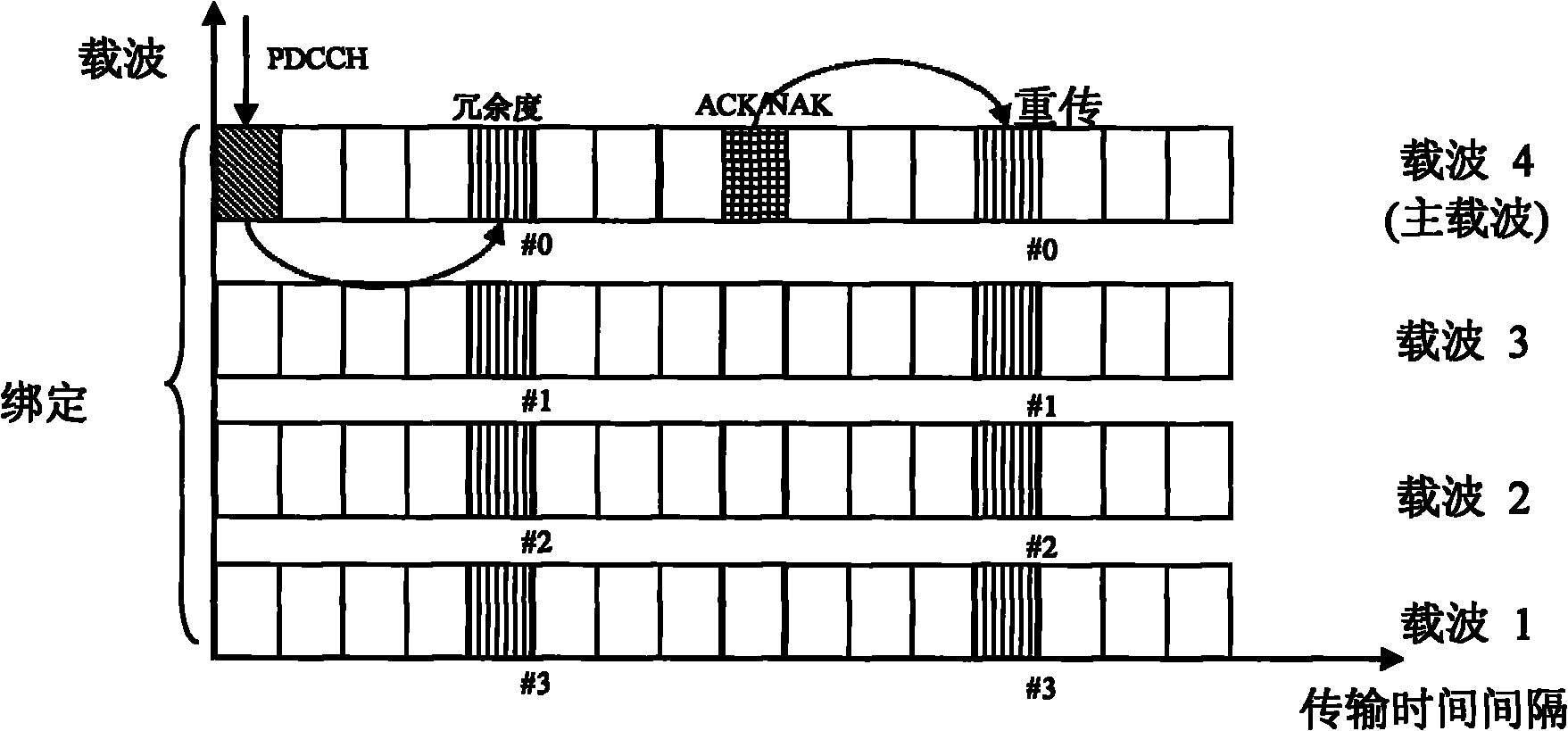
InactiveCN103378936ASolve the problem of relatively low coding gainIncrease coverageError prevention/detection by diversity receptionComputer hardwareData transmission
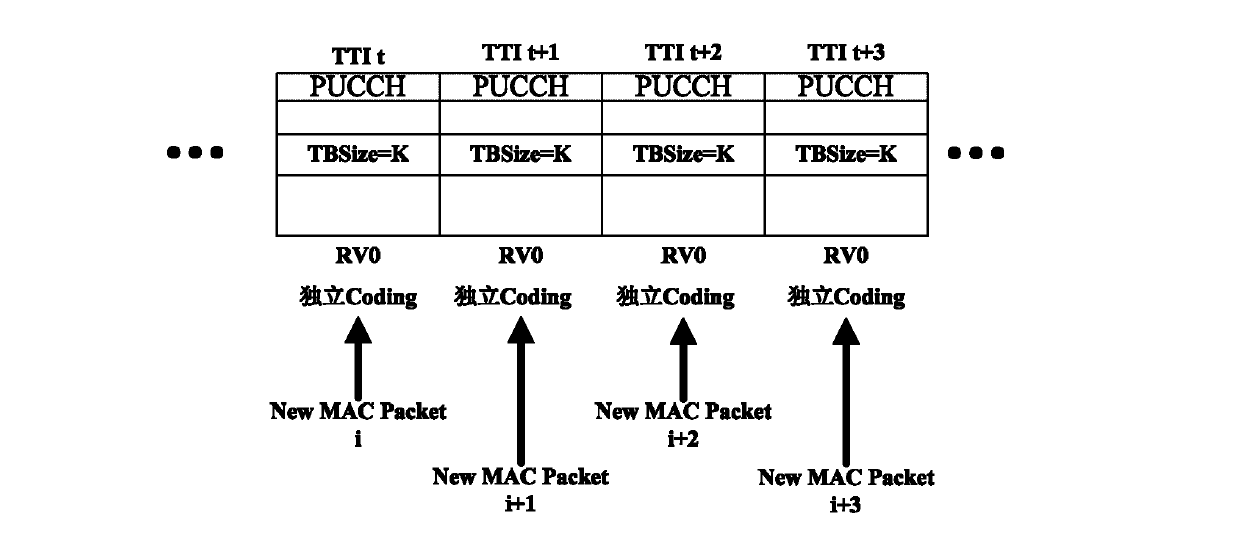
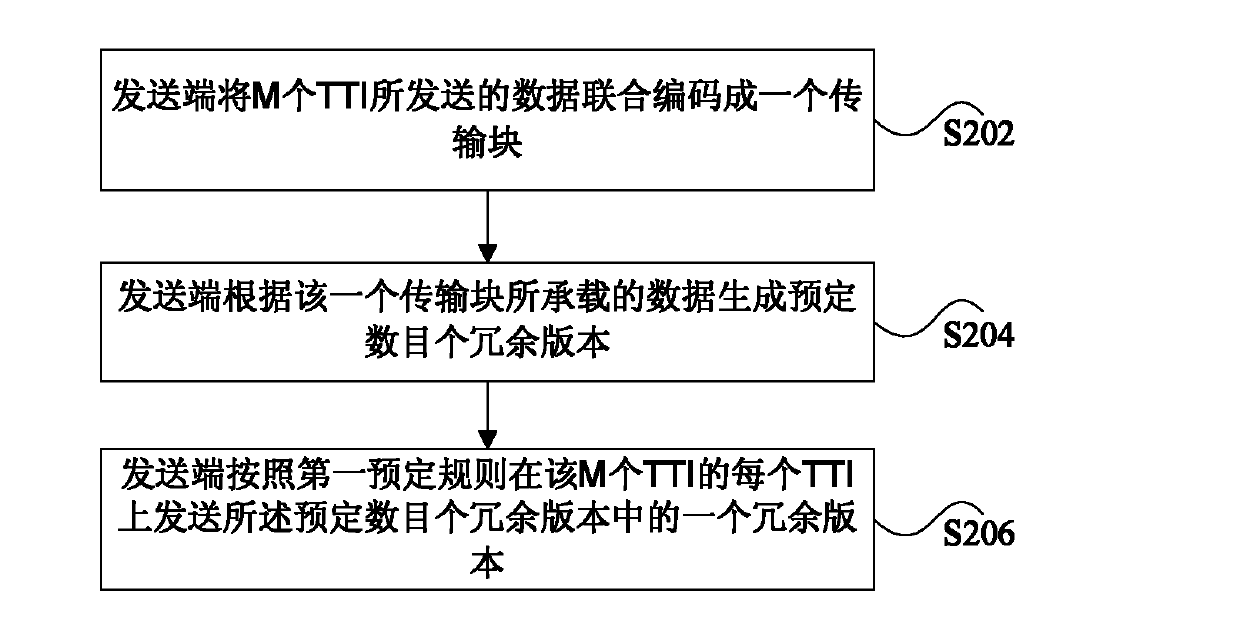
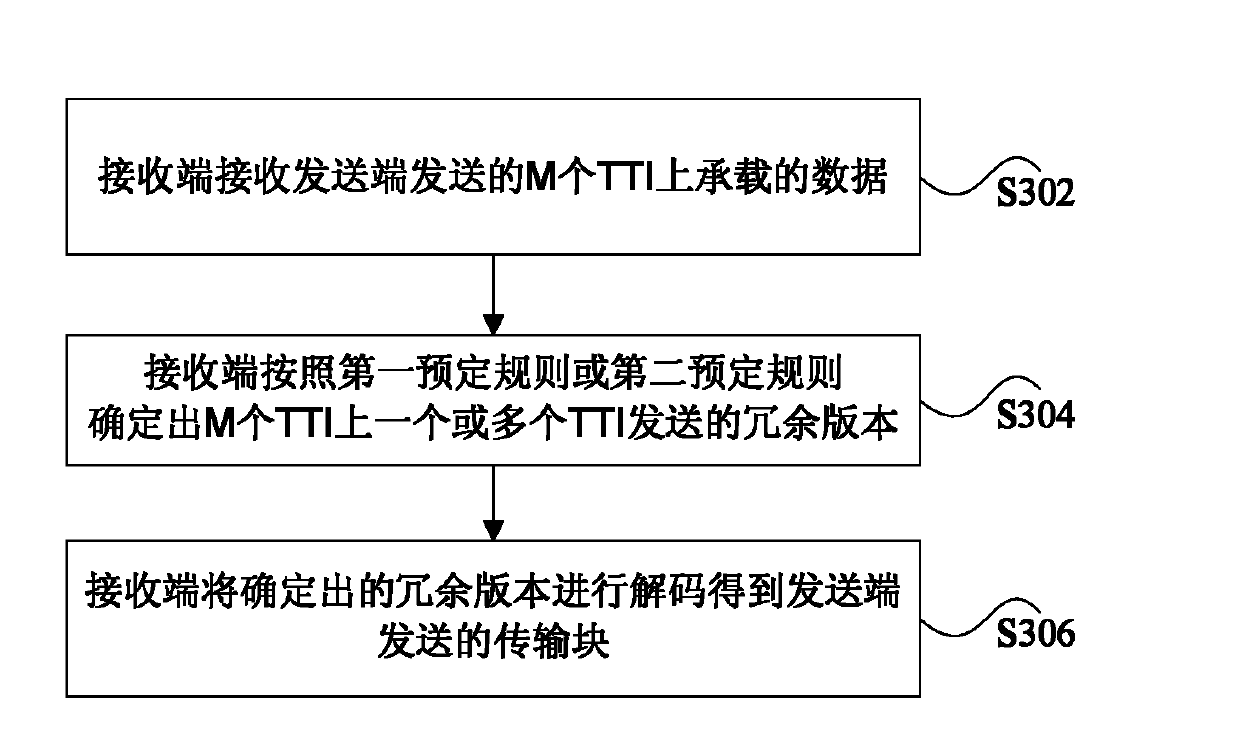
The invention discloses a data transmission method and device. The data transmission method comprises the following steps that data transmitted by M TTIs are encoded into a transmission block together by a transmitting terminal, wherein M is an integer larger than 1; a preset number of redundancy versions are generated by the transmitting terminal according to data carried by one transmission block; one redundancy version of the preset number of the redundancy versions is transmitted at each TTI of the M TTIs by the transmitting terminal according to a first predetermined rule. According to the data transmission method and device, the coverage range and coding gain of data transmission are improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method and apparatus for encoding and decoding an audio signal using adaptively switched temporal resolution in the spectral domain
ActiveUS8095359B2Quality improvementReduce encoding delaySpeech synthesisTemporal resolutionFrequency spectrum
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Universal error control coding system for digital communication and data storage systems
InactiveUS7831895B2Reduce complexity and chip area and chip power consumptionReduce complexityError detection/correctionCode conversionComputer architectureForward error correction
The universal forward error-correction coding system provides adjustable code rates and coding gains to greatly benefit the design of many modern digital communications (data storage) systems. The channel encoding and decoding methods are universal such that a single encoder and a single decoder can be used to implement all the forward error-correction codes of different code rates. This universal forward error-correction coding system also includes a novel systematic code generation procedure that has the capability of generating many classes of codes that provide the best balance between coding gain performance and implementation complexity.
Owner:COMM CODING
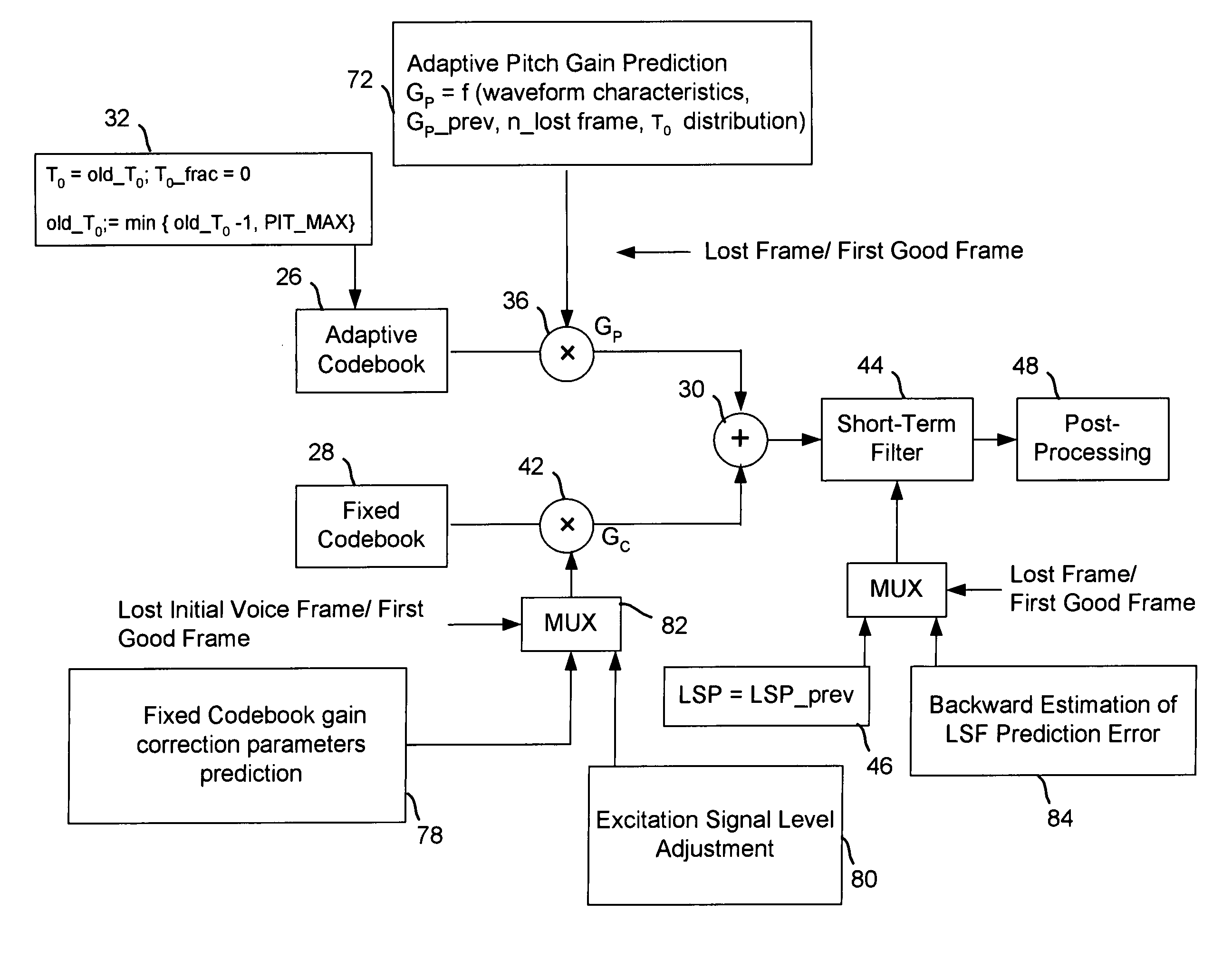
Packet loss concealment for a conjugate structure algebraic code excited linear prediction decoder
InactiveUS20070282601A1Speech analysisAlgebraic code-excited linear predictionClassification methods
A method to improve packet loss concealment for generation of a synthetic speech signal in a algebraic code excited linear prediction decoder for a voice over packet network. One method improves features for coding gains in the decoder and for post-filtering of the signals. An alternative method uses a classification method for the signal based on the bitstream in the decoder.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
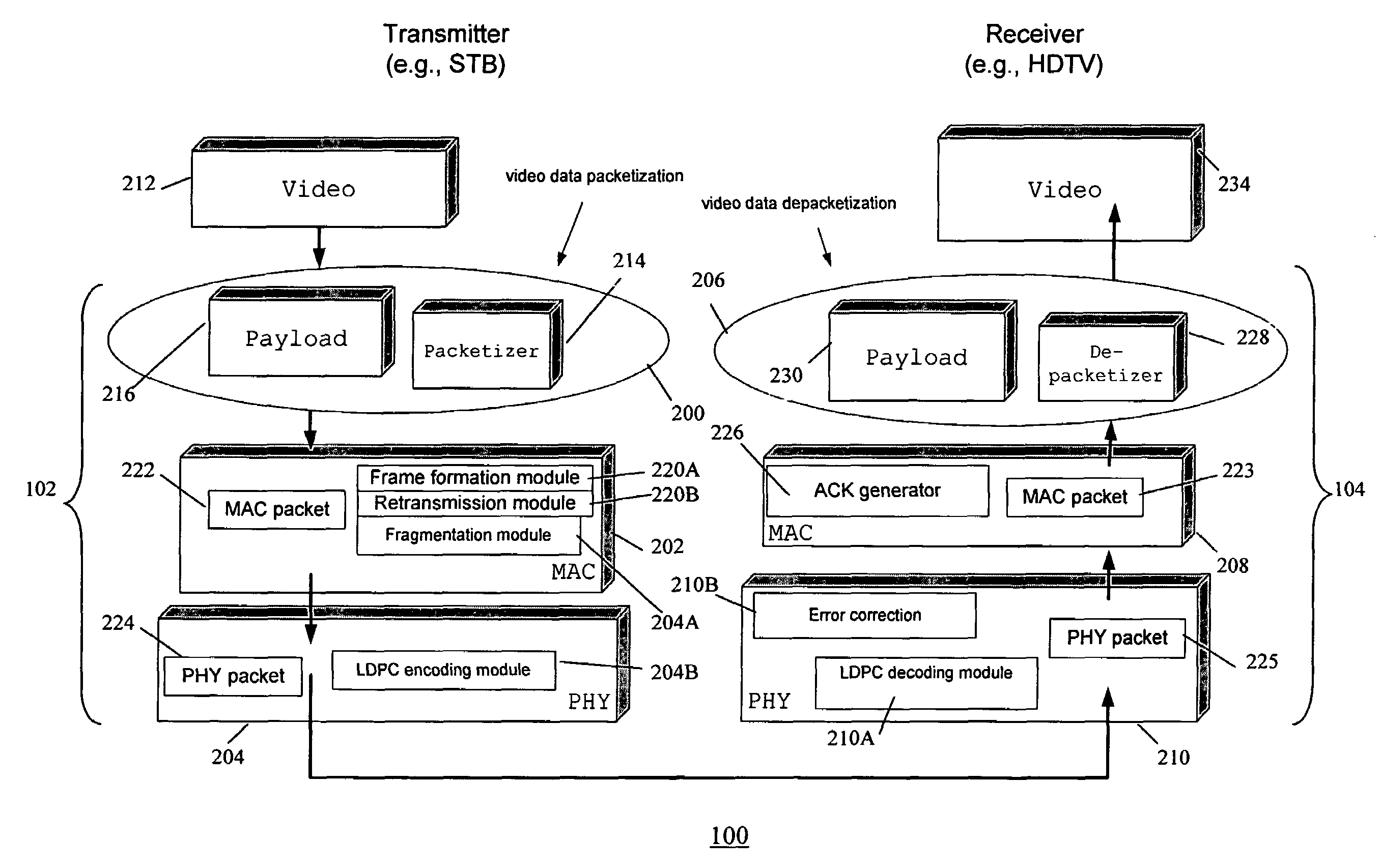
Method and system for unequal error protection with block codes for wireless transmission
A method and system for wireless data communication is provided, which involves constructing a data payload containing data, partitioning the data payload into fragments, performing block code encoding on each fragment, wherein at least one fragment is encoded at a different coding gain than another fragment, and transmitting the data payload including encoded fragments over a wireless channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Concatenated codes for holographic storage
ActiveUS20080163026A1Robust implementationGood flexibilityError preventionTransmission systemsComputer hardwareHolographic storage
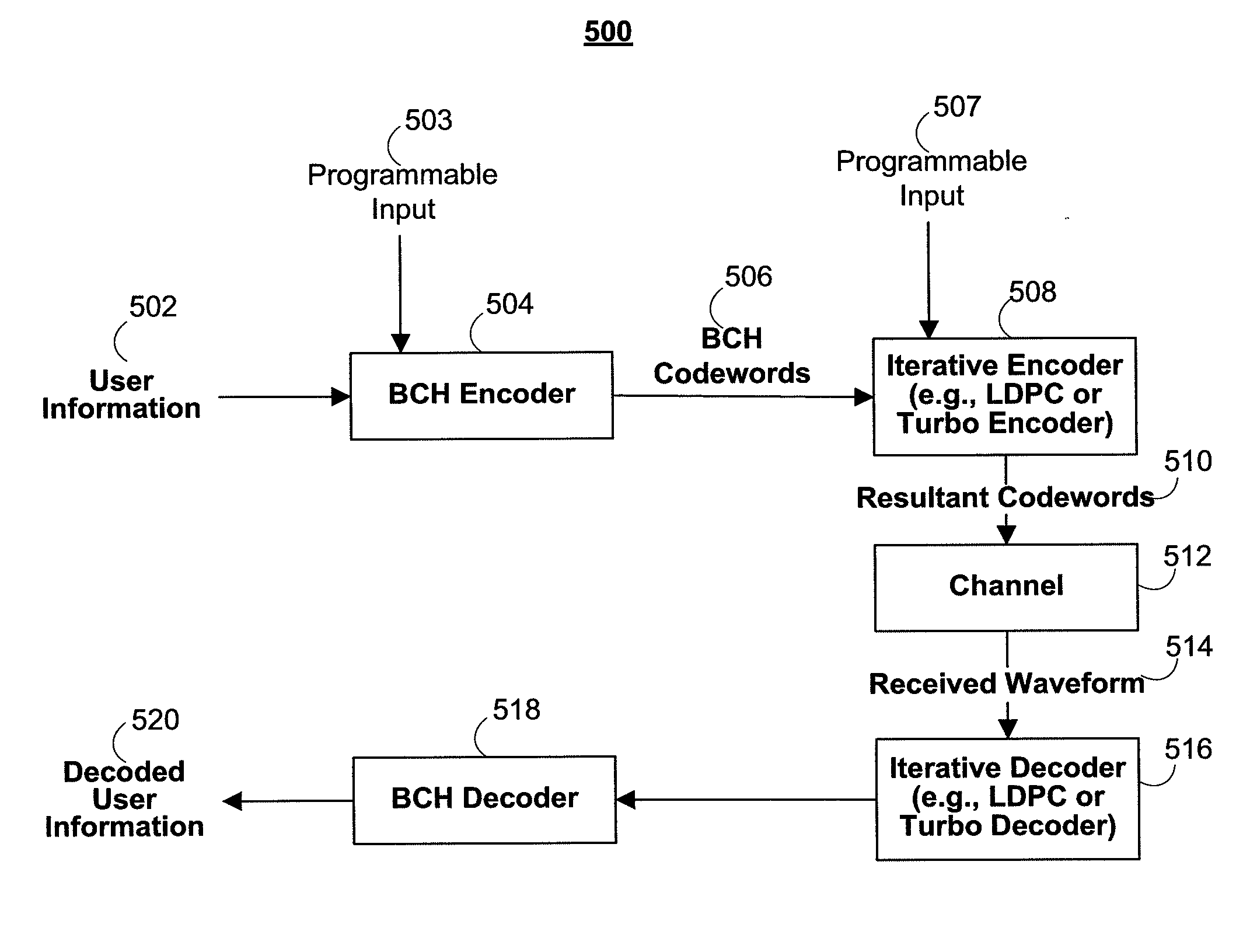
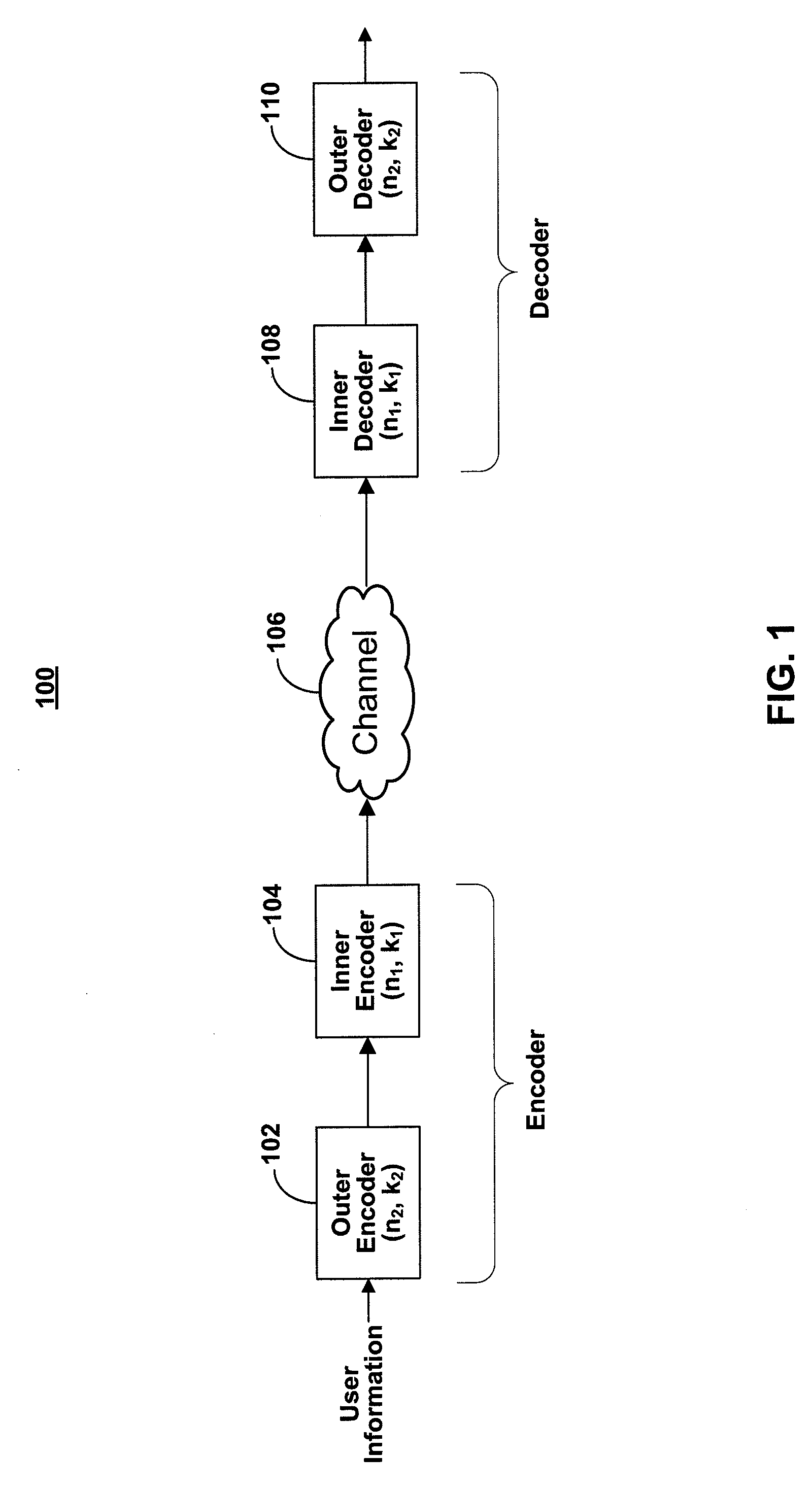
Systems and methods for constructing concatenated codes for data storage channels, such as holographic storage channels, are provided. The concatenated codes include an outer BCH code and an inner iteratively decodable code, such as an LDPC code or turbo code. The correction power and coding rate of one or both of the codes may be programmable based on the channel characteristics and the desired SNR coding gain. The correction power and / or coding rate of the inner and / or outer code may also be dynamically adjusted in real-time to compensate for time-varying error conditions on the channel.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Method for encoding/decoding error correcting code, transmitting apparatus and network
InactiveUS7024616B2Maximizing transmission distanceMaximize distanceError preventionCode conversionCoding blockByte
A client signal having a constant bit rate is segmented every a bytes to create code information blocks. The bit rate of the client signal is increased such that the client signal has the code information block and an empty area comprised of b bytes, and the ratio c / a is equal to or higher than 110% to create a code block 3 comprised of c bytes. The code information block in the code block is encoded such that an error correcting code is included therein to have an encoding gain of 6 dB or higher for a bit error ratio of 10−12. Associated check bits are placed in the empty area to eventually generate a super FEC signal.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
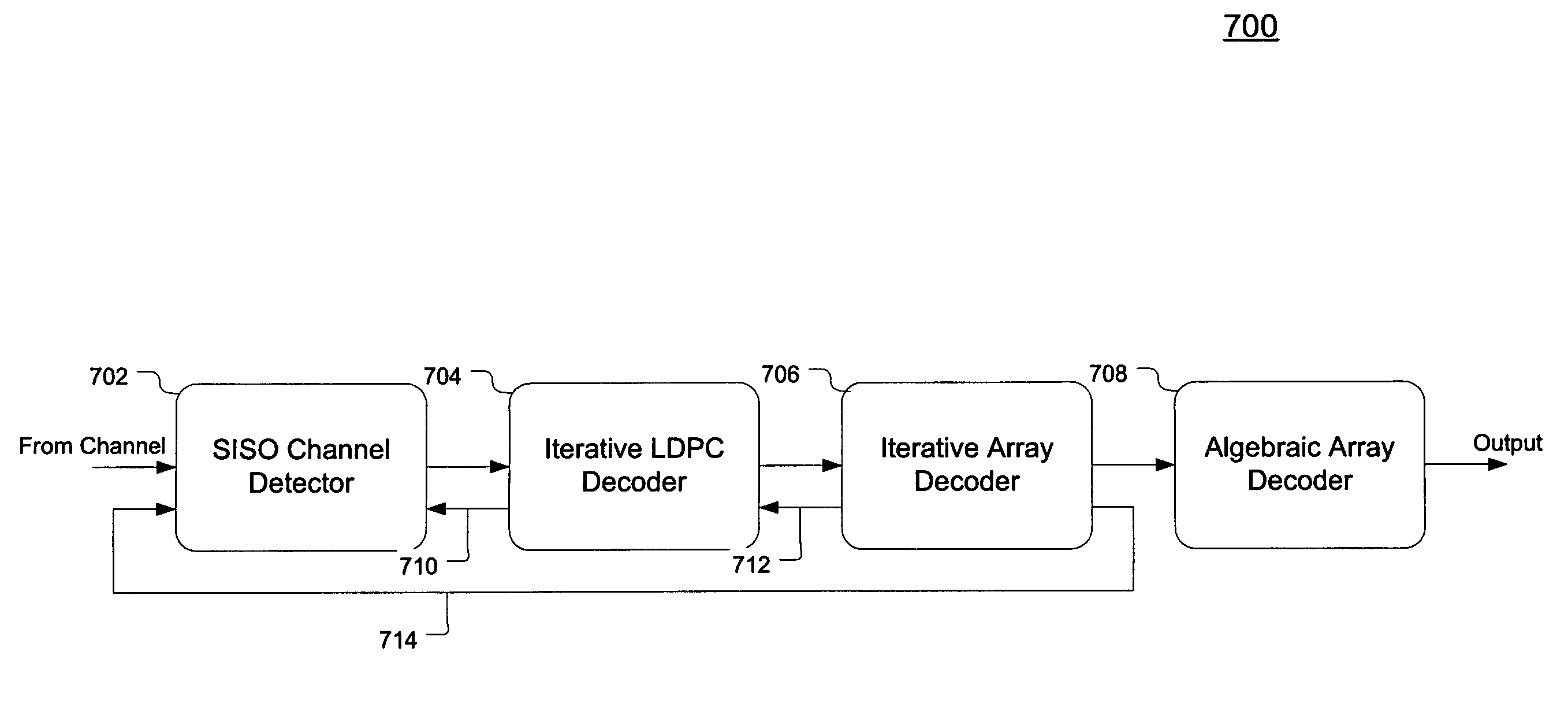
Concatenated iterative and algebraic coding
An apparatus for error-correction encoding information includes, in one embodiment, an outer encode that generates algebraically decodable data, the outer encoder operatively coupled to one or more inner encoders that generate iteratively decodable data. The outer encoder is adapted to encode a group of (q−r) original data symbols using r code symbols to produce q outer-encoded symbols, wherein the coding gain of the outer encoder provides for the correction of up to x symbol errors and (r−2x) symbol erasures where r is an integer greater than zero and x is an integer such that0≤x<r2.The one or more iterative EC-inner encoders are adapted to inner encode each of the q outer-encoded symbols or combinations of several outer-encoded symbols independently of the others, wherein each symbol is encoded with h additional code bits.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Methods and apparatus for efficient quantization of gain parameters in GLPAS speech coders
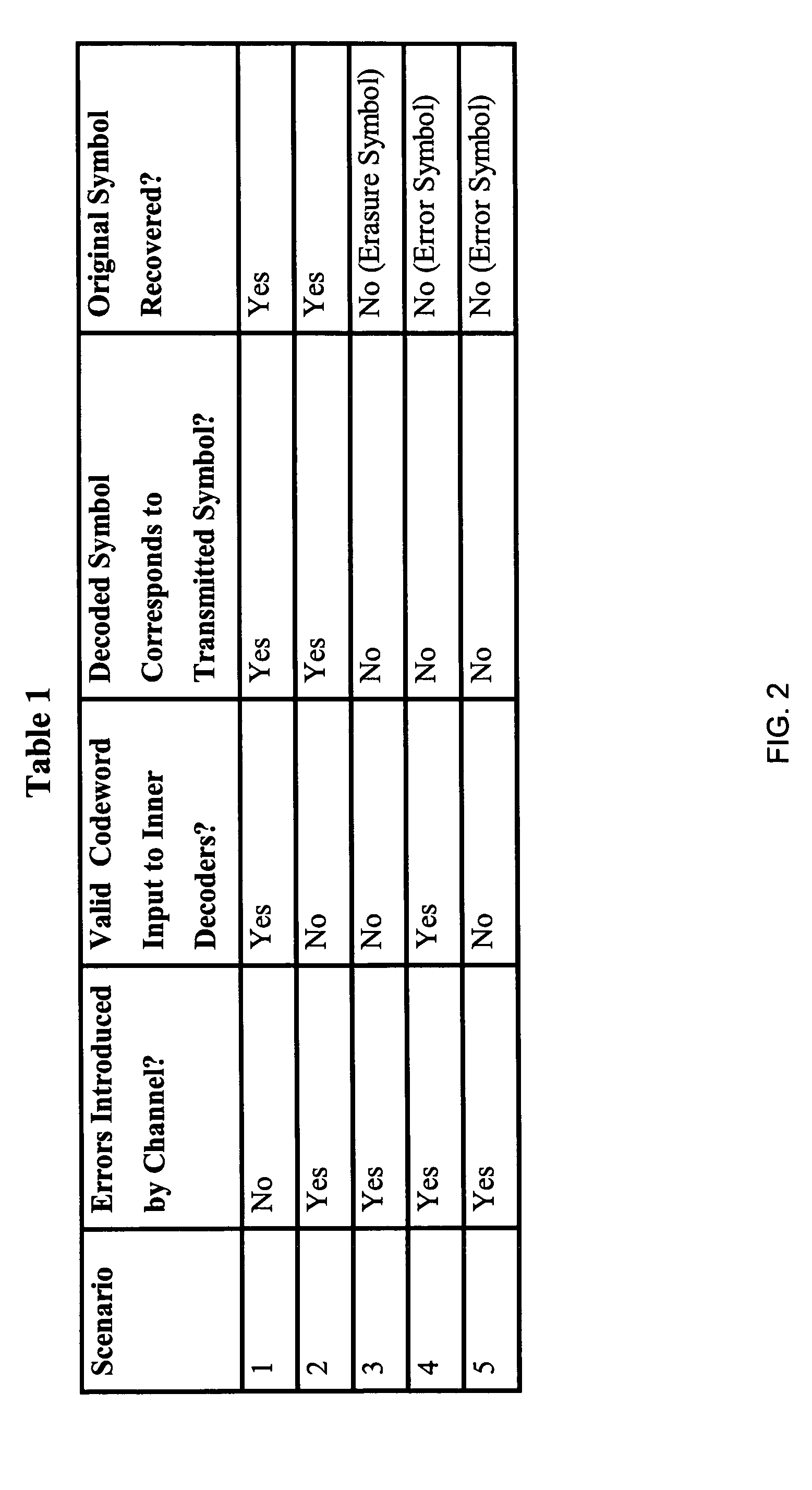
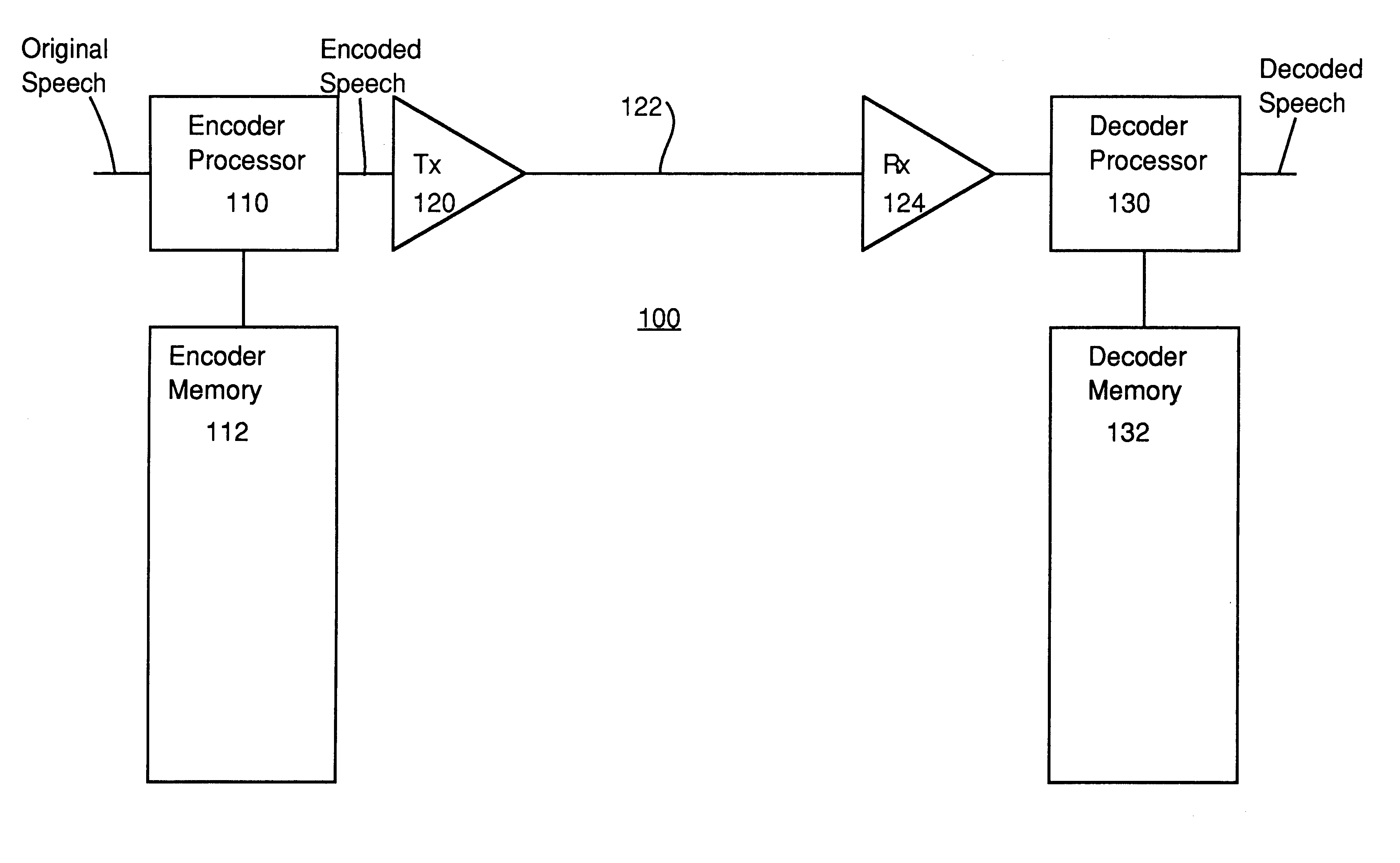
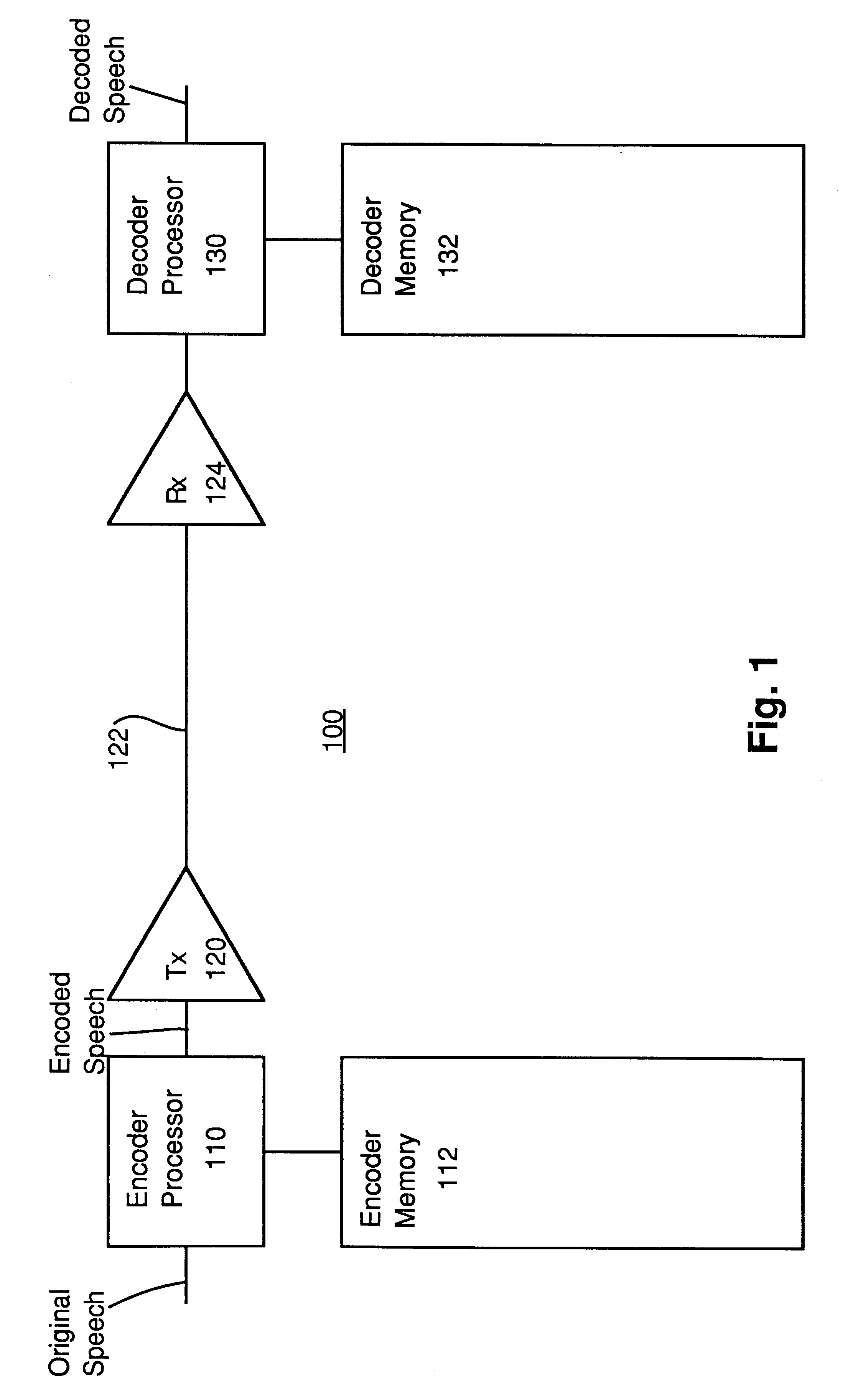
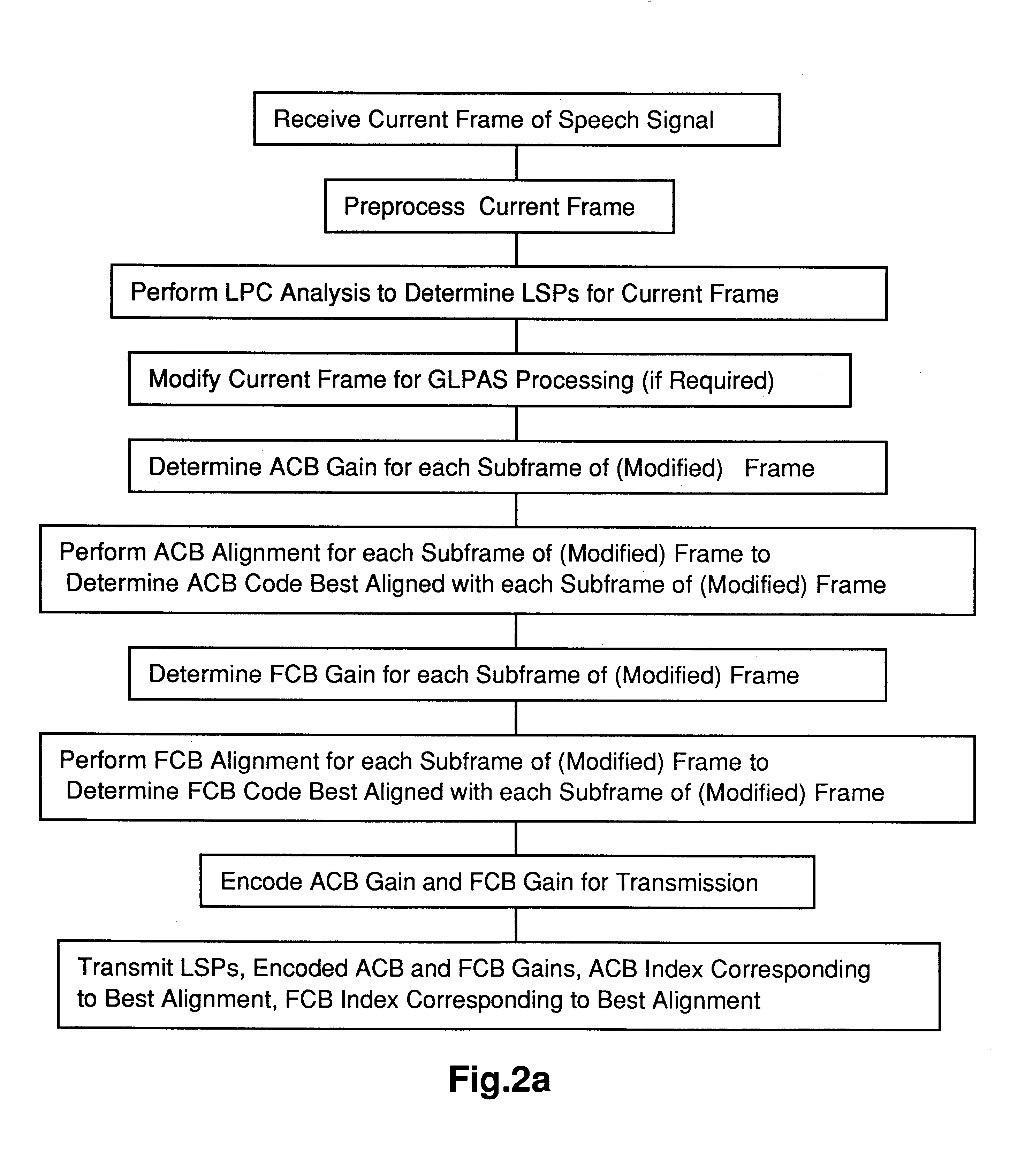
InactiveUS6240385B1Improve coding efficiencySpeech analysisFluid pressure measurementTrellis quantizationSpeech code
In methods and apparatus for encoding a gain parameter in a generalized linear predictive analysis-by-synthesis (GLPAS) coder, a subframe gain parameter is determined for each of a plurality of successive subframes of a frame, and a quantized frame gain parameter is determined for each frame using a delayed decision quantizer operating on the subframe gain parameters. The subframe gain parameters may be treated as components of a gain vector and the gain vector may be vector quantized to determine the quantized frame gain parameter. Encoder parameters are efficiently aligned with decoder parameters to ensure proper end-to-end operation. Alternatively, tree quantization or trellis quantization may be applied to the subframe gain parameters to determine the quantized frame gain parameter. The methods and apparatus are particularly applicable to low bit rate speech coding.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
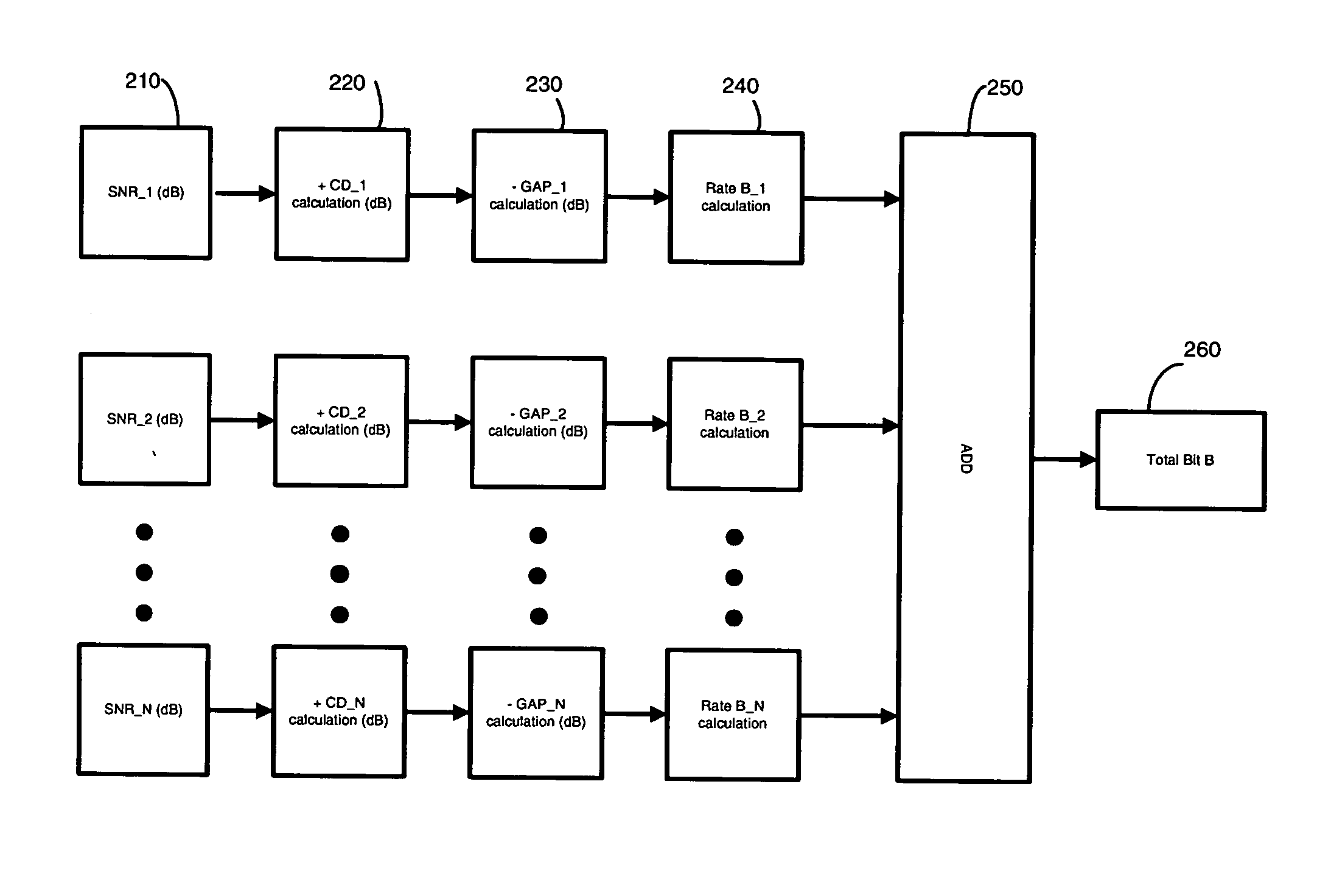
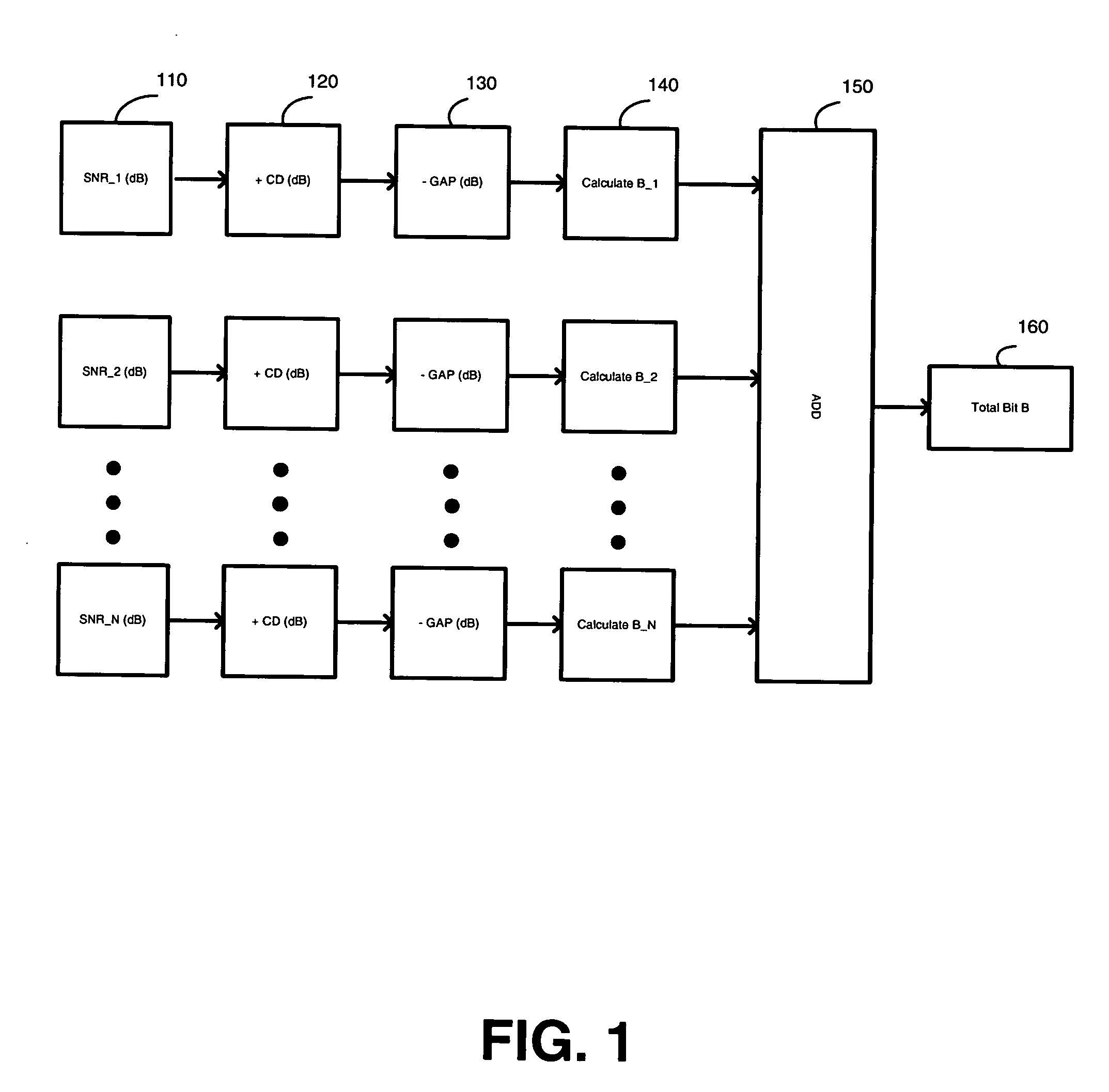
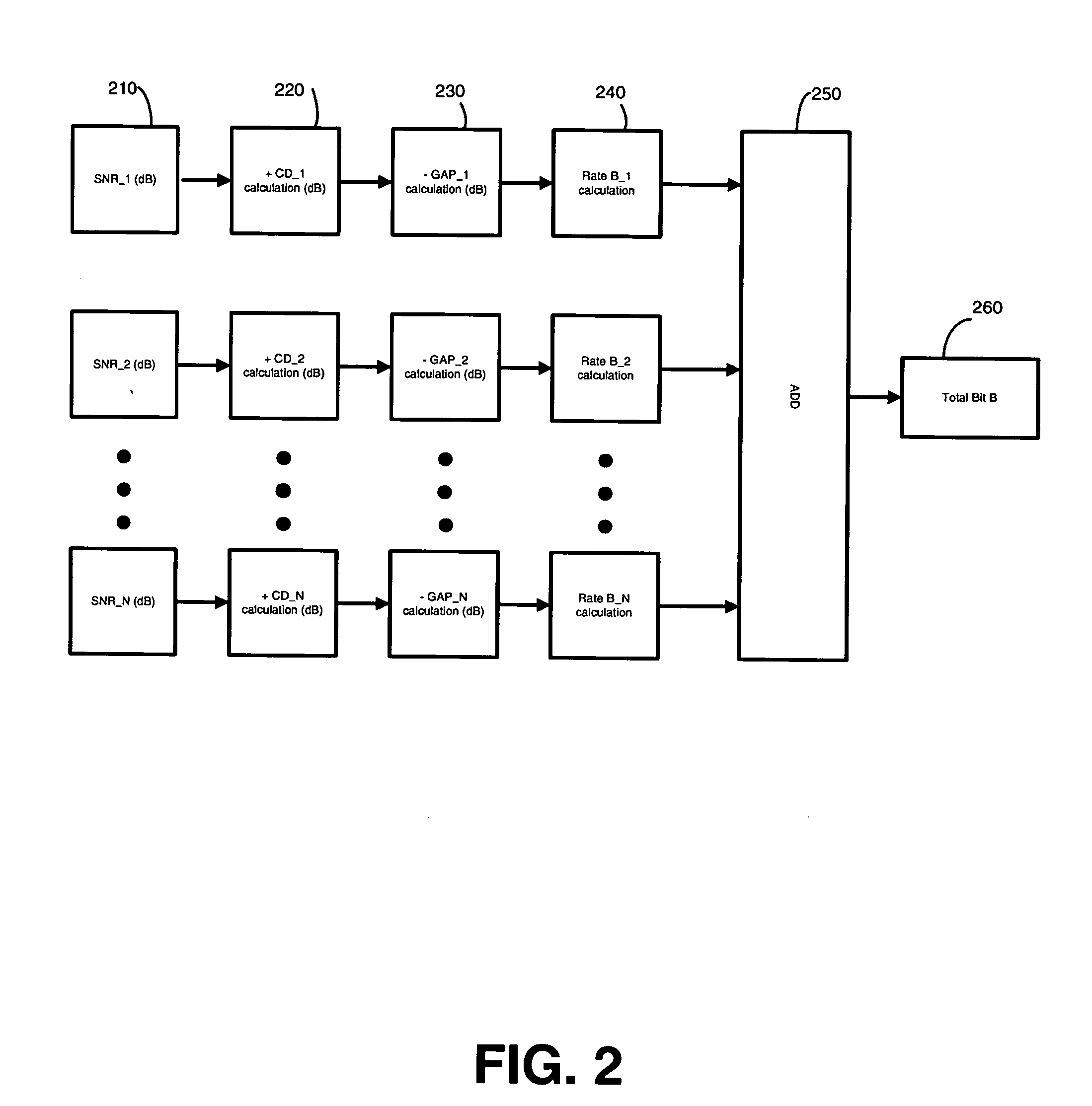
Bit-loading method and system for a DMT transceiver
InactiveUS20070147530A1Inhibition effectAvoid large gapsPower managementSecret communicationBit allocationComputer science
A system and method for a bit-loading algorithm based on an equal error rate principle for each sub-channel (bin) used in a discrete multi-tone modulation (DMT) system. The system and method of the present invention provides a bit-loading algorithm that provides long reach, high data rate and good error performance at a given condition. The bit-loading method and system depends on the Shannon channel capacity formula to allocate bits to different sub-channels. For DMT, the system and method tabulates different SNR GAP for different sub-channels (bins), and constructs a look-up table for the SNR GAP with different bits to achieve a better performance for the DMT system. In addition, Trellis coding across all the sub-channels are optionally supported in DMT, and likewise, the system and method creates another look-up table for variable coding gain provided for the Trellis coding gain in the bit-loading algorithm to further improve the system performance, knowing that the Trellis coding gain is different for different sub-channels with different bit allocation.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
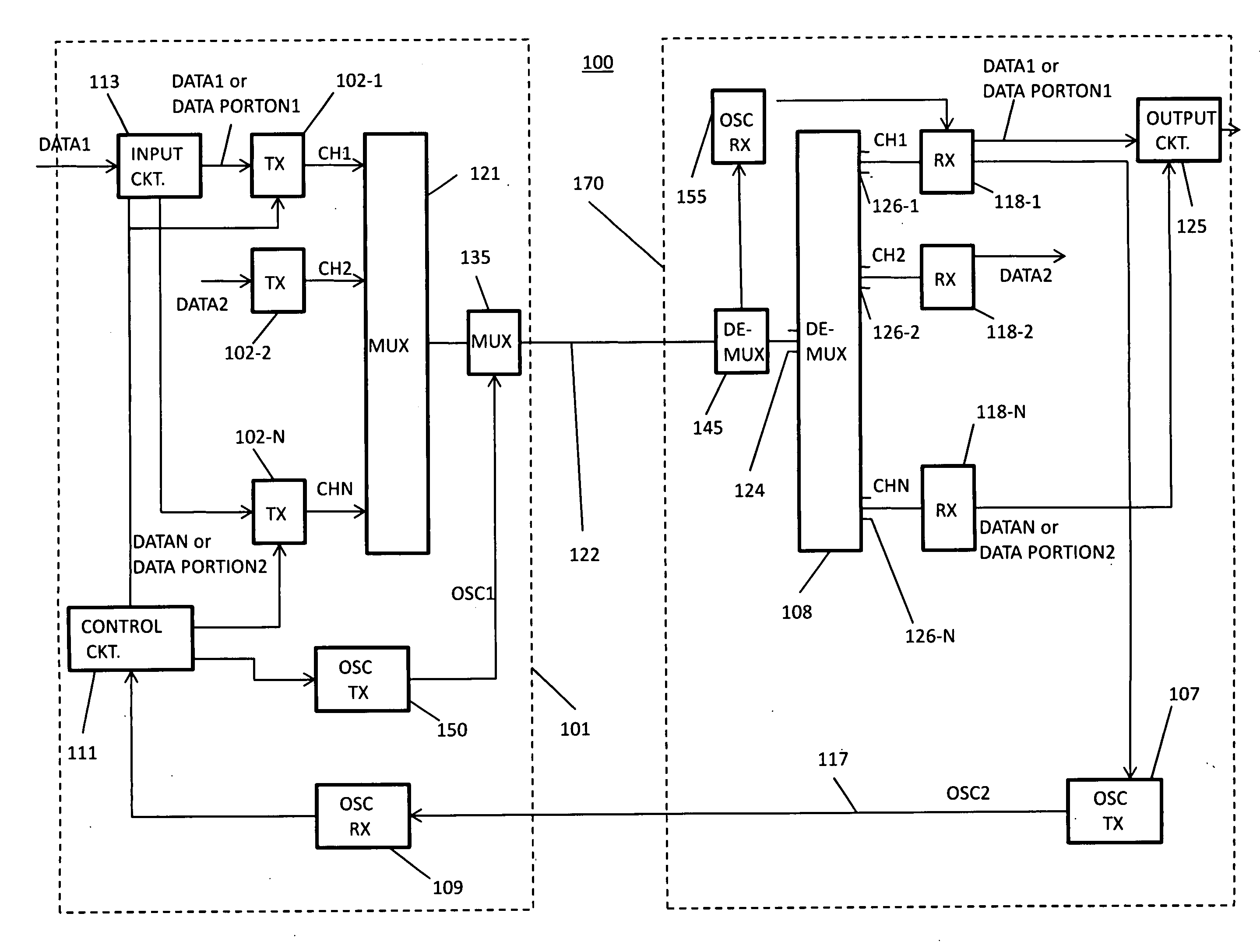
Degradation adaptation network
ActiveUS20100080562A1High overhead ratioTime-division optical multiplex systemsChannel coding adaptationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Noise level
Consistent with the present disclosure, based on system requirements or in response to an increase in optical signal-to-noise level of an optical channel, such as a WDM channel, additional FEC bits are inserted into and replace selected data payload bits in each frame carried by the channel. The replaced data payload bits may then be transmitted in subsequent frames on the same channel. As a result, the transmitted frames have a reduced data payload rate, but a higher coding gain. Alternatively, the replaced data payload bits may be included in frames transmitted on another optical channel. In that case, the frames carried by the two channels typically have the same bit length or number of bits and may thus be compliant with the frame length requirements of G.709, for example. Preferably, the number of coding bits may be changed dynamically to obtain different coding gains.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Method for encoding/decoding error correcting code, transmitting apparatus and network
A client signal having a constant bit rate is segmented every a bytes to create code information blocks. The bit rate of the client signal is increased such that the client signal has the code information block and an empty area comprised of b bytes, and the ratio c / a is equal to or higher than 110% to create a code block 3 comprised of c bytes. The code information block in the code block is encoded such that an error correcting code is included therein to have an encoding gain of 6 dB or higher for a bit error ratio of 10−12. Associated check bits are placed in the empty area to eventually generate a super FEC signal.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method, device and system for sending and receiving data
ActiveCN102006623AReduce transmission delayImprove accuracyError preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementPacket lossControl signal
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Transmission diversity method base on null-frequency encode
InactiveCN101378299ASimple designEasy to decodeSpatial transmit diversityMulti-frequency code systemsData streamEuclidean vector
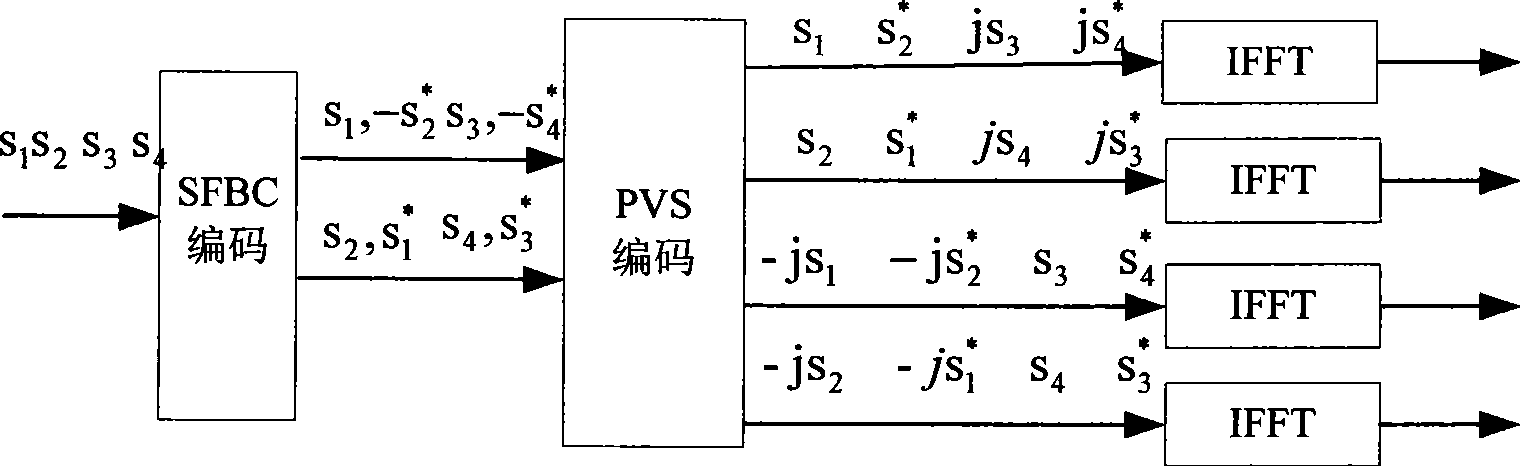
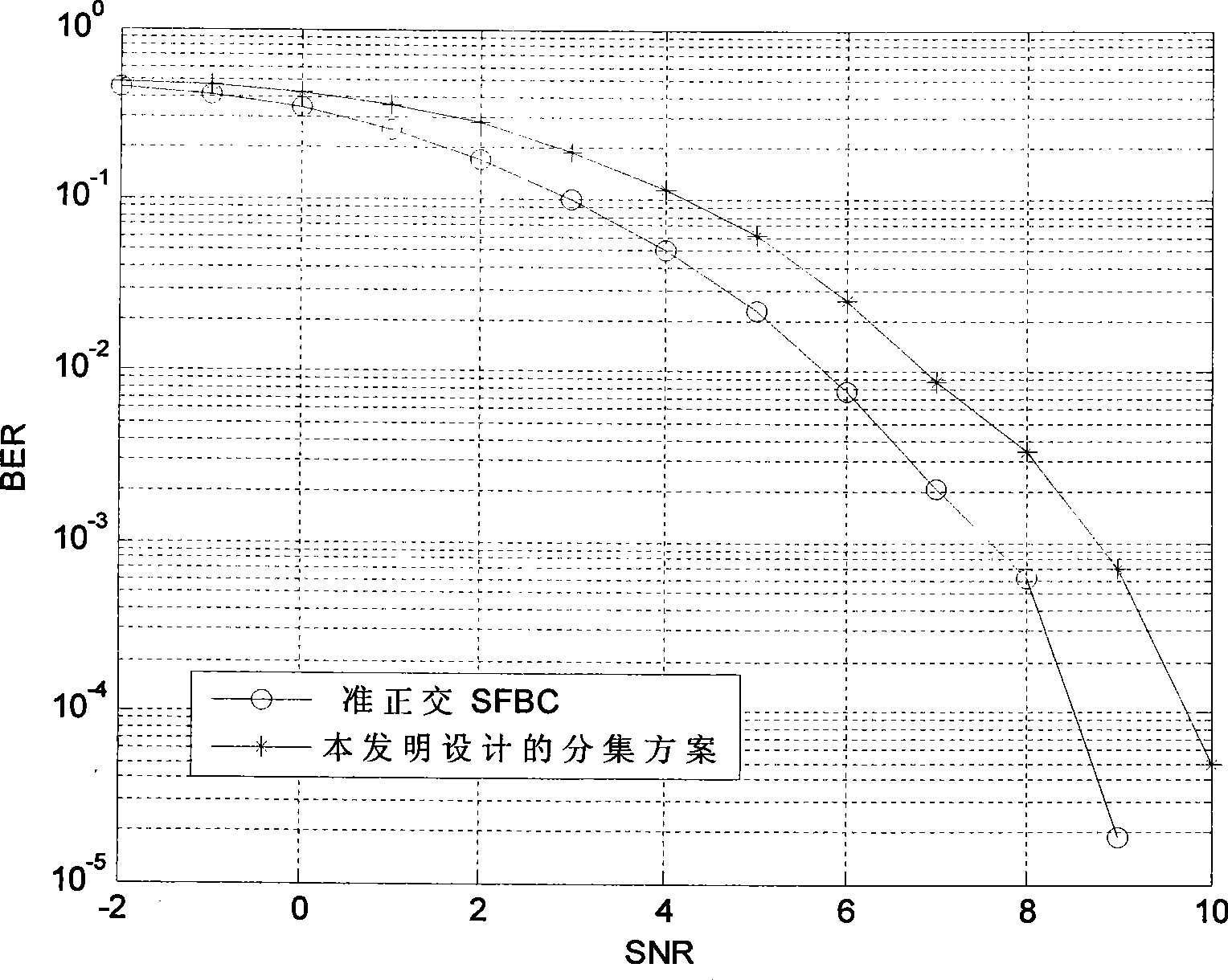
The invention discloses a transmission diversity method based on space-frequency coding, which is applicable to an MIMO-OPDM system with a sending antenna which is more than 2. The method takes a combination of the SFBC and pre-coding weighing switching as a diversity mode of SFBC+PVS, taking the objective factor into the account that the stronger the channel correlation is, the weaker the diversity effect is, and uses a weighted vector to remove the effect resulted by the inclination angle between antennae and the channel correlation between different antennae. The method comprises the following steps: step one, two paths of data streams are obtained by carrying out SFBC coding to an input bit stream; step two, two groups of pre-coding weighing vectors are selected; and step three, a coding matrix after pre-coding weighing switching is obtained after the pre-coding weighing vector is adopted to carry out weighing to an SFBC coding data block, and finally an in-time signal obtained by inverse fast Fourier transform is transmitted. By adopting the diversity method, the space diversity effect can be utilized better and the effect on coding gains can be reduced.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Apparatus and method for practical and efficient broadcast in mobile ad hoc networks
ActiveUS20080267106A1Reduce in quantityError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsBase codeTopology information
The present invention demonstrates how network-coding can be applied to a deterministic broadcast approach, resulting in significant reductions in the number of transmissions in the network. We propose two algorithms, that rely only on local two-hop topology information and make extensive use of opportunistic listening to reduce the number of transmissions: 1) a simple XOR-based coding algorithm and 2) a Reed-Solomon based coding algorithm that determines the optimal coding gain achievable for a coding algorithm that relies only on local information.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Systems and Methods for Improved Bit-Loading for Discrete Multi-Tone Modulated Multiple Latency Applications
InactiveUS20070110176A1Improved bit loadingReduce capacity lossSecret communicationChannel coding adaptationTransfer systemCarrier signal
Systems and methods for performing bit loading in a dual latency data transmission system. In a computer network, such as an XDSL-based network, carrier channels are allocated between two latency paths. Error sensitive information is transmitted over a latency path employing one or more forward error correction techniques. Latency sensitive information that is relatively more tolerant of errors is transmitted over the other latency path. Rather than employing the lowest coding gain for carrier channels having the two different latency paths, the highest coding gain for each path is used by applying different target S-N-R margins for carrier channels having different latency paths.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
Equipment and method for selecting matched data stream and corresponding precoding vectors
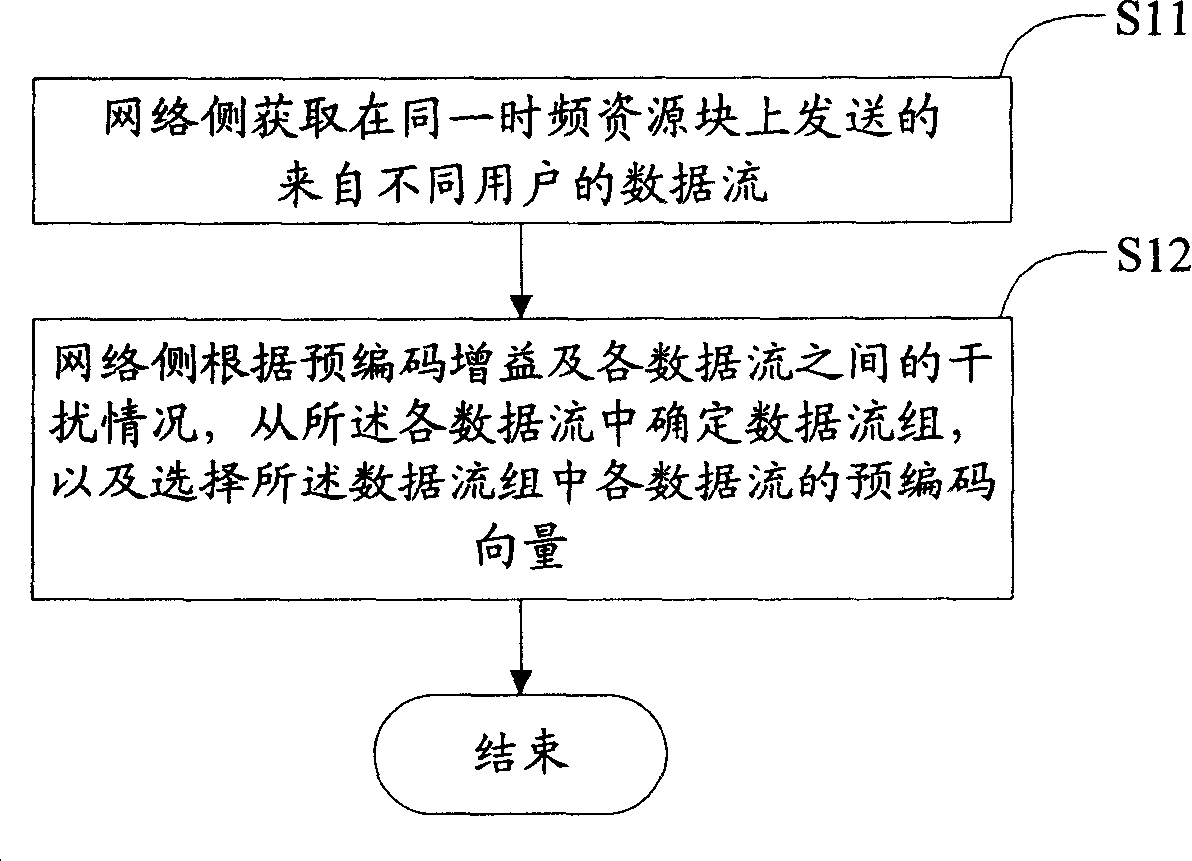
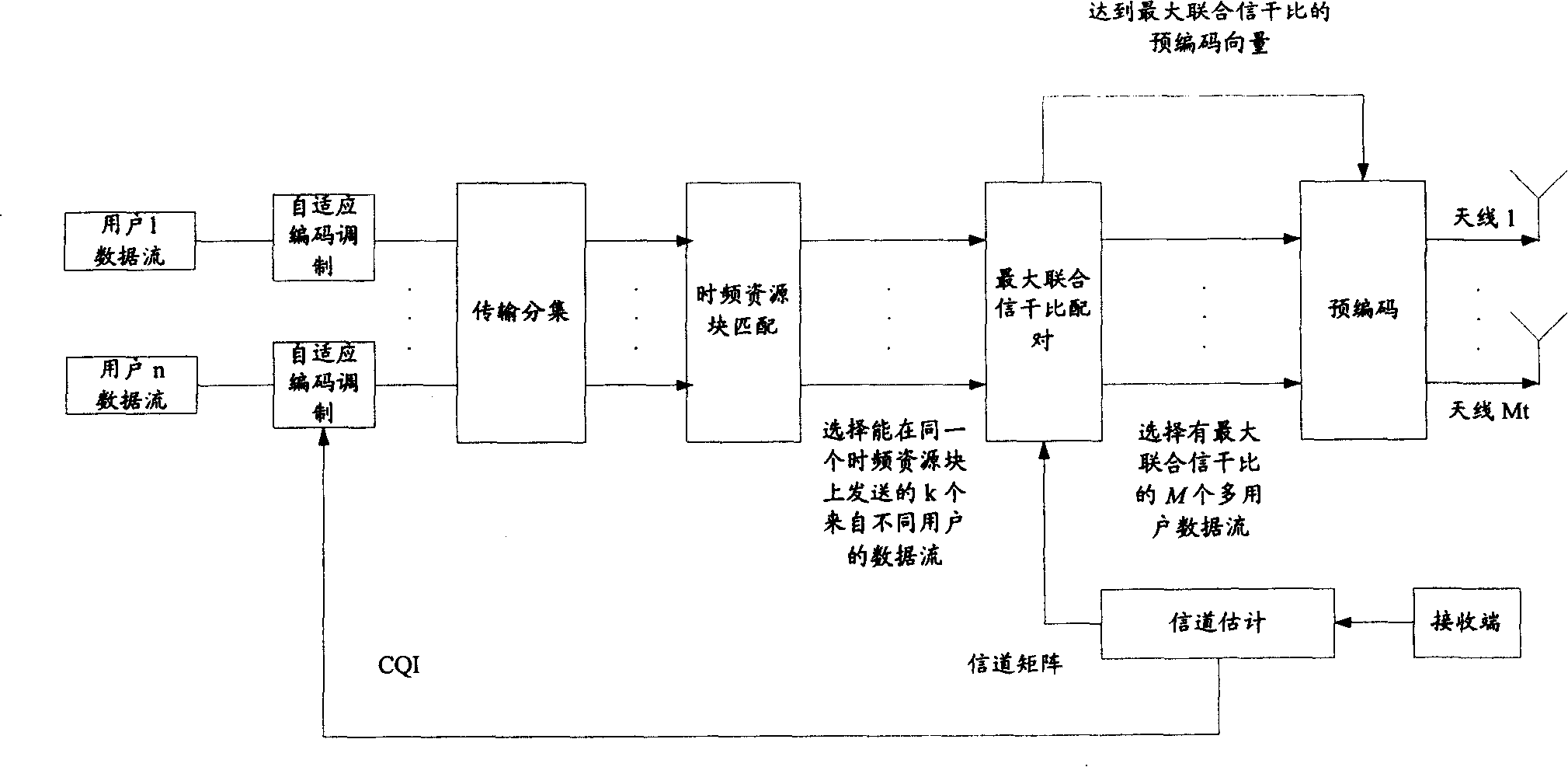
InactiveCN101232478AAvoiding problems with precoding vector selectionLarge capacitySpatial transmit diversityTime-division multiplexSystem capacityData stream
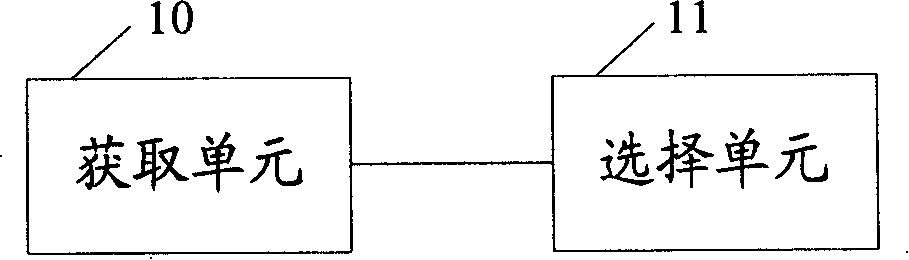
The invention discloses a method and a device for selecting matching data flow and the corresponding pre-coded vector, which can optimize the system and increase the system capacity. The method includes the following steps: the network accesses the data flows sent from different users in the same frequency resource block; the network identifies a data flow group from the data flows and selects the pre-coded vector of each data flow in the data flow group according to the pre-coding gain and the interference among data flows. The base station comprises an access unit for accessing the data flows sent from different users in the same frequency resource block; a selecting unit for identifying a data flow group from the data flows and selecting the pre-coded vector of each data flow in the data flow group according to the pre-coding gain and the interference among data flows.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com