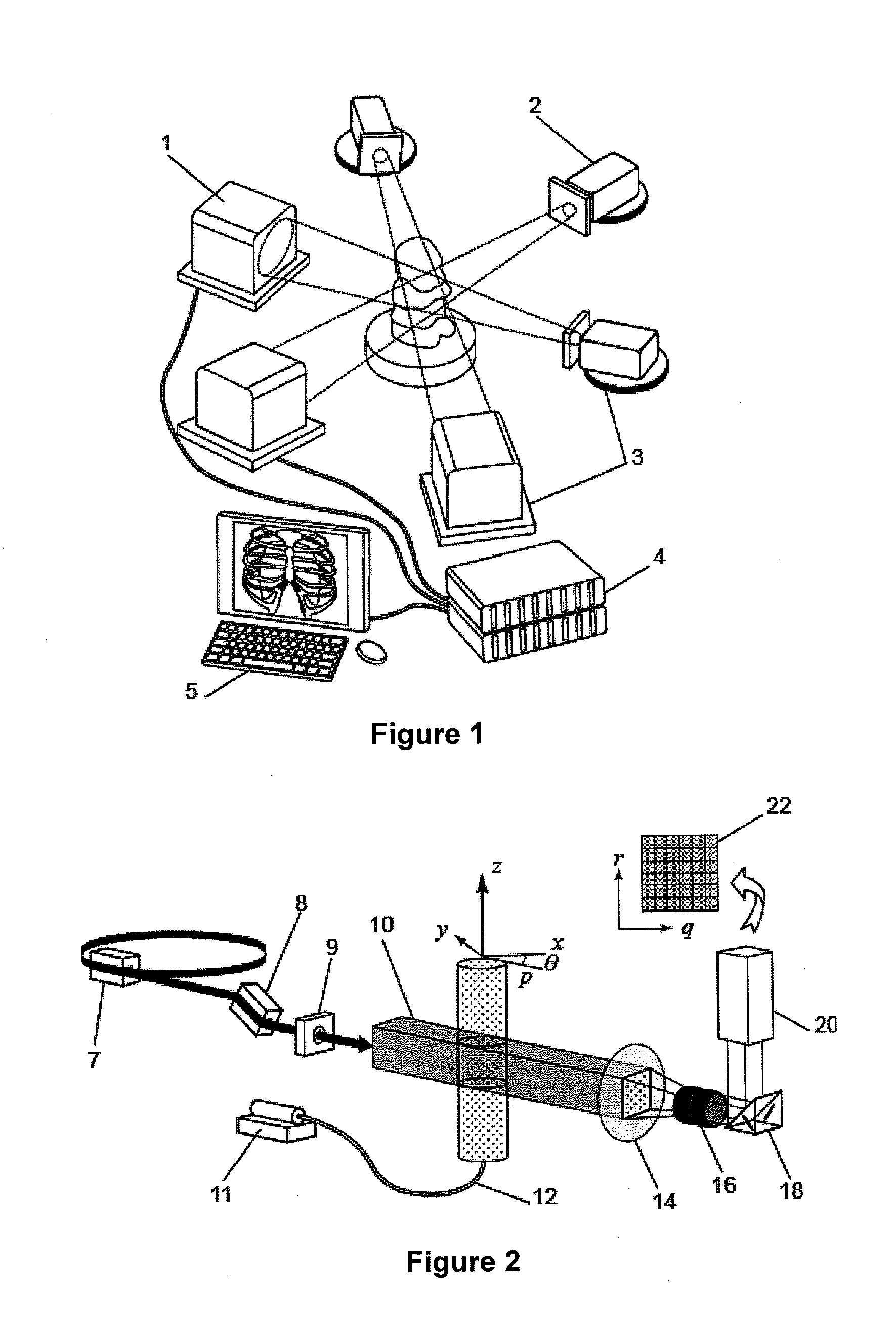
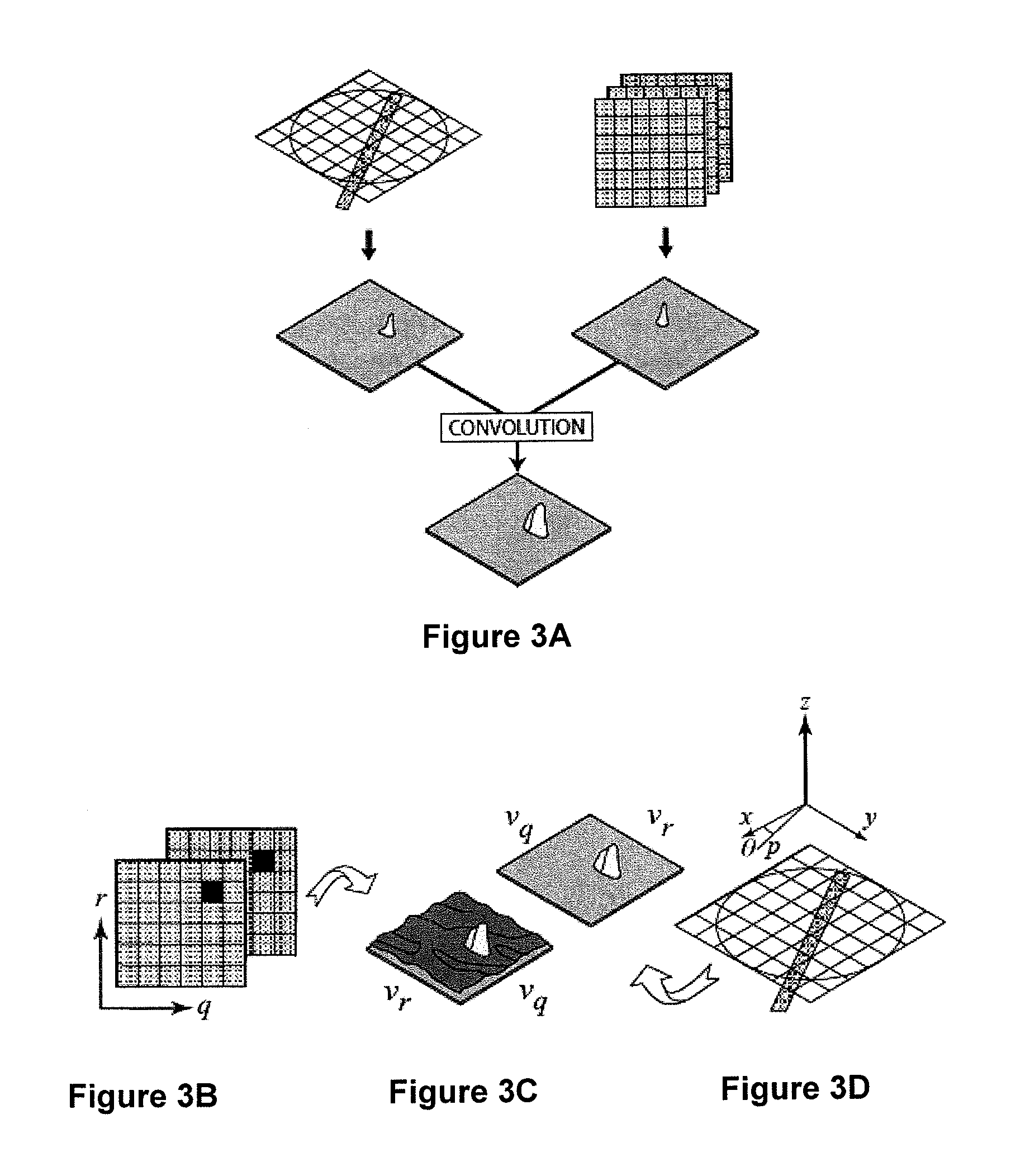
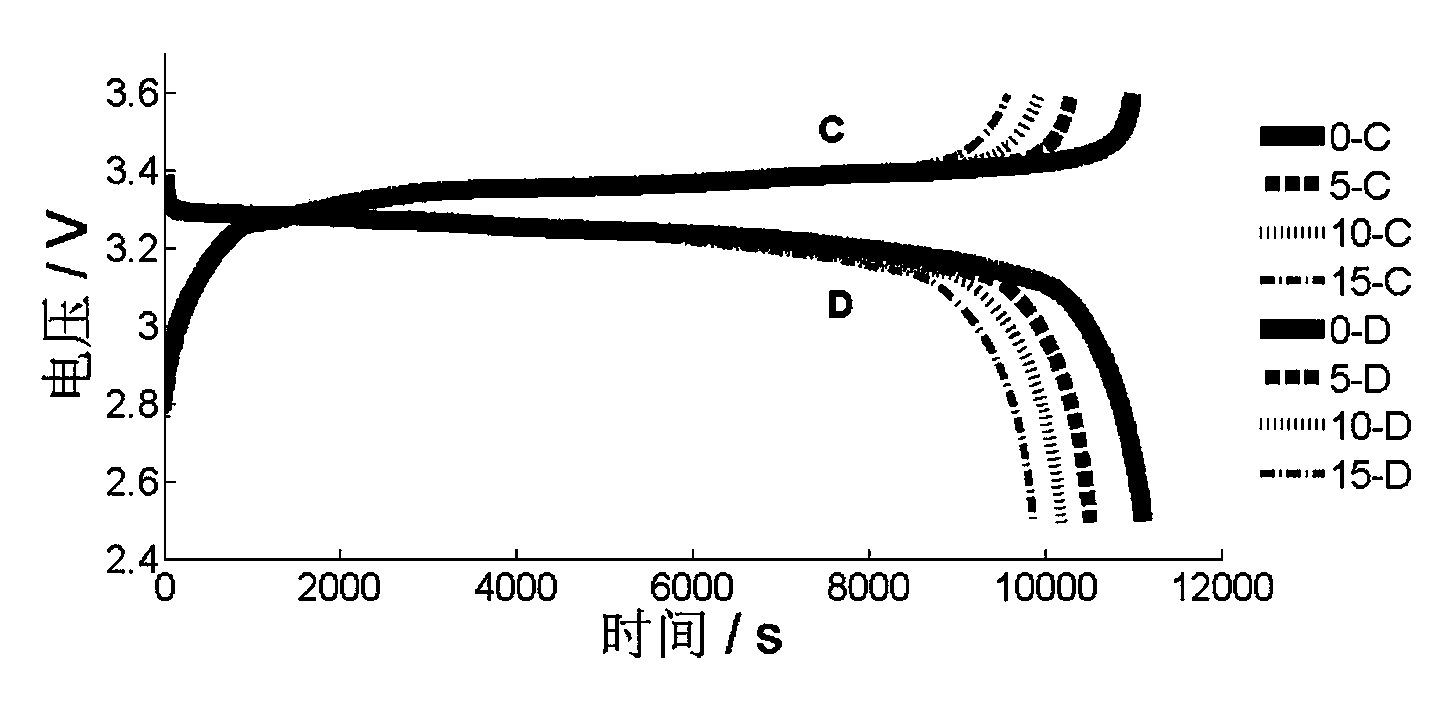
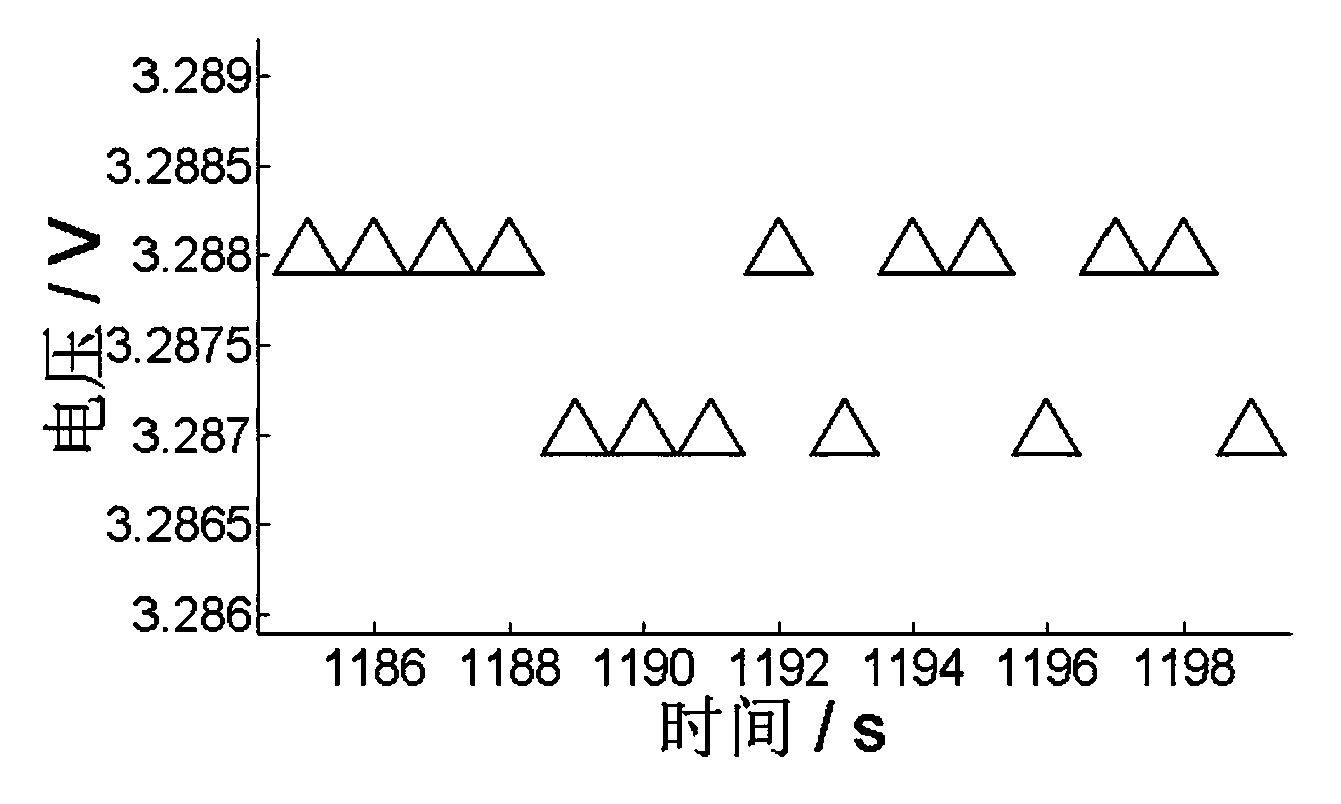
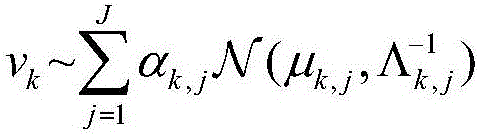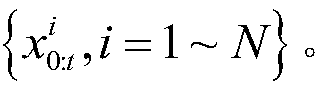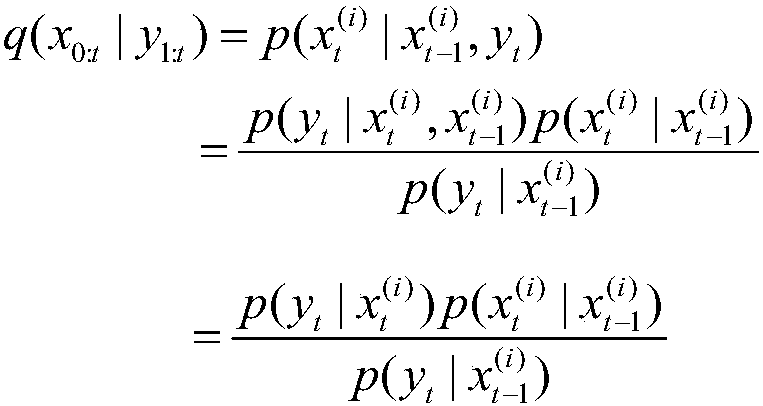Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1705 results about "Normal density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
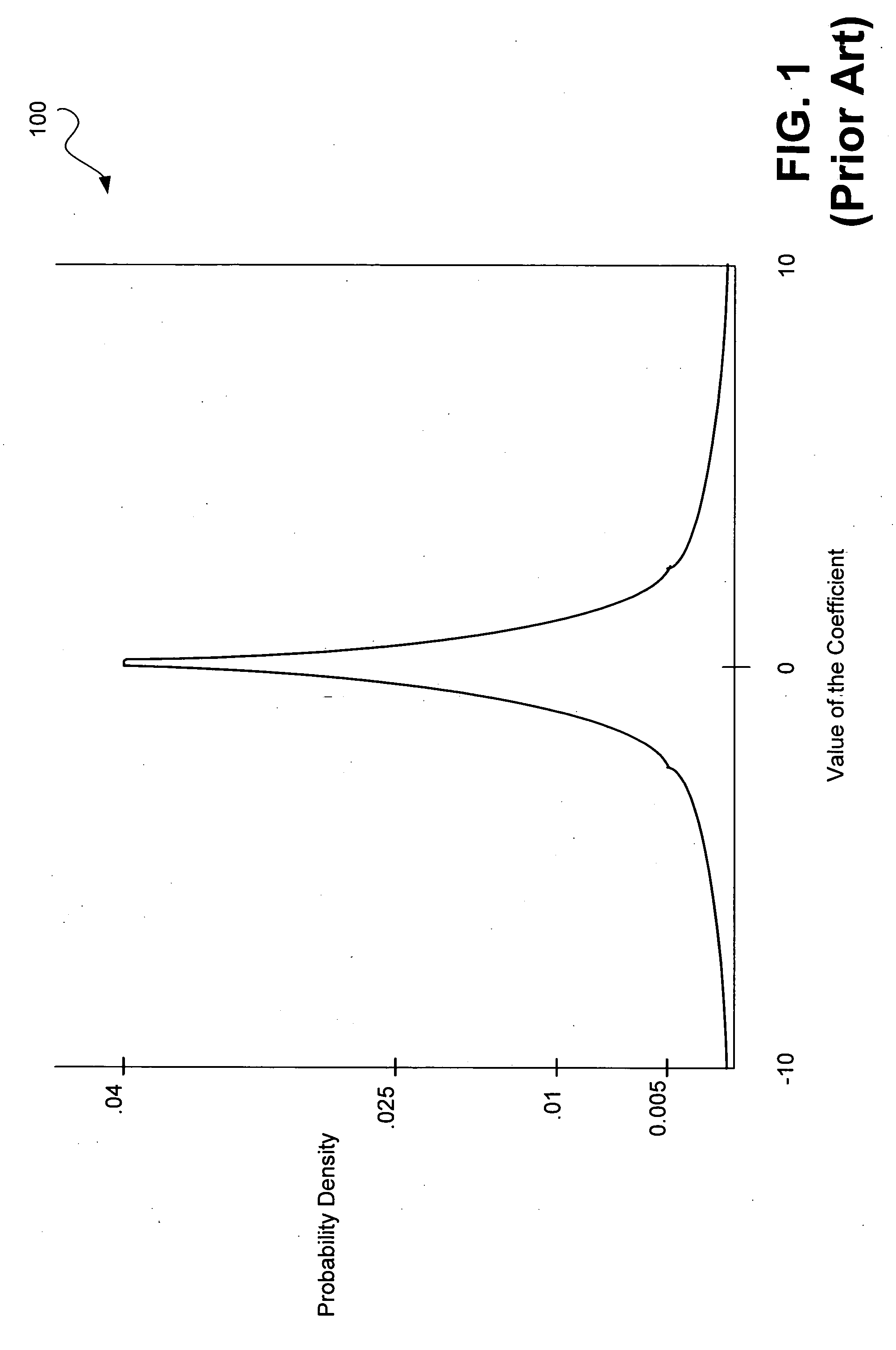
Unlike a probability, a probability density function can take on values greater than one; for example, the uniform distribution on the interval [0, ½] has probability density f(x) = 2 for 0 ≤ x ≤ ½ and f(x) = 0 elsewhere. The standard normal distribution has probability density.
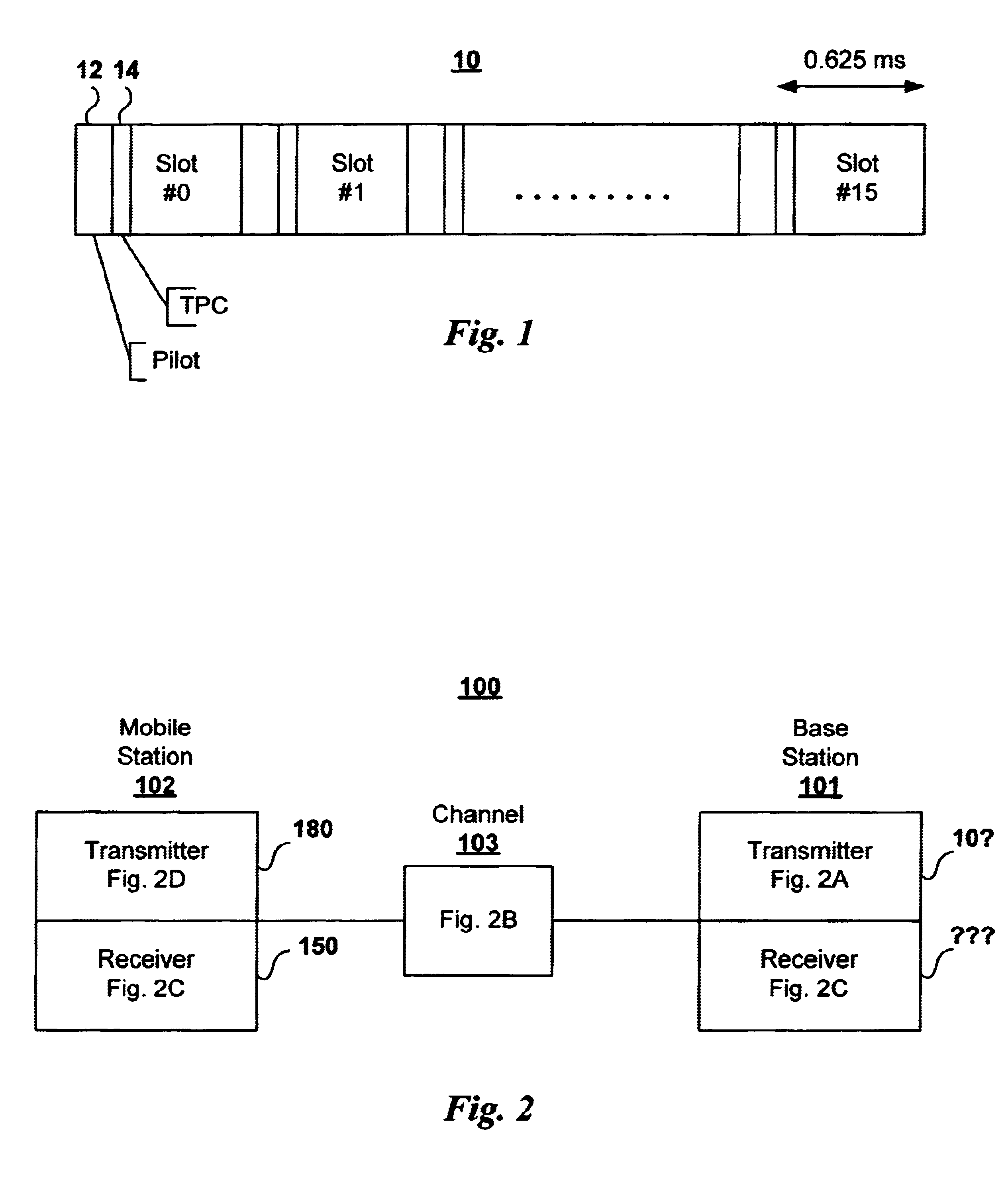
Adaptive power control in wideband CDMA cellular systems (WCDMA) and methods of operation
InactiveUS6690652B1Maintain conductivityMaximizes controlEnergy efficient ICTFrequency-division multiplex detailsChannel powerControl signal
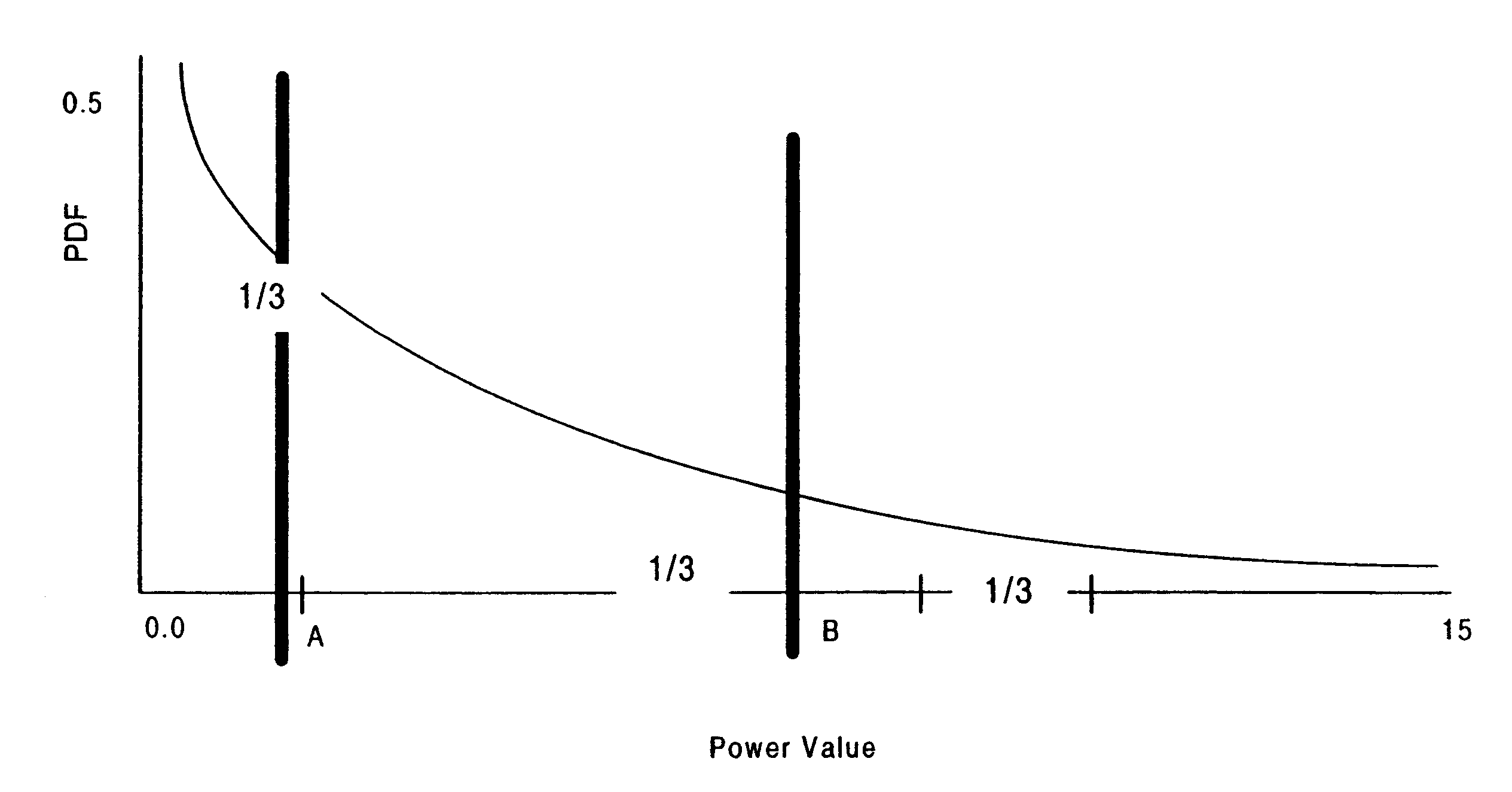
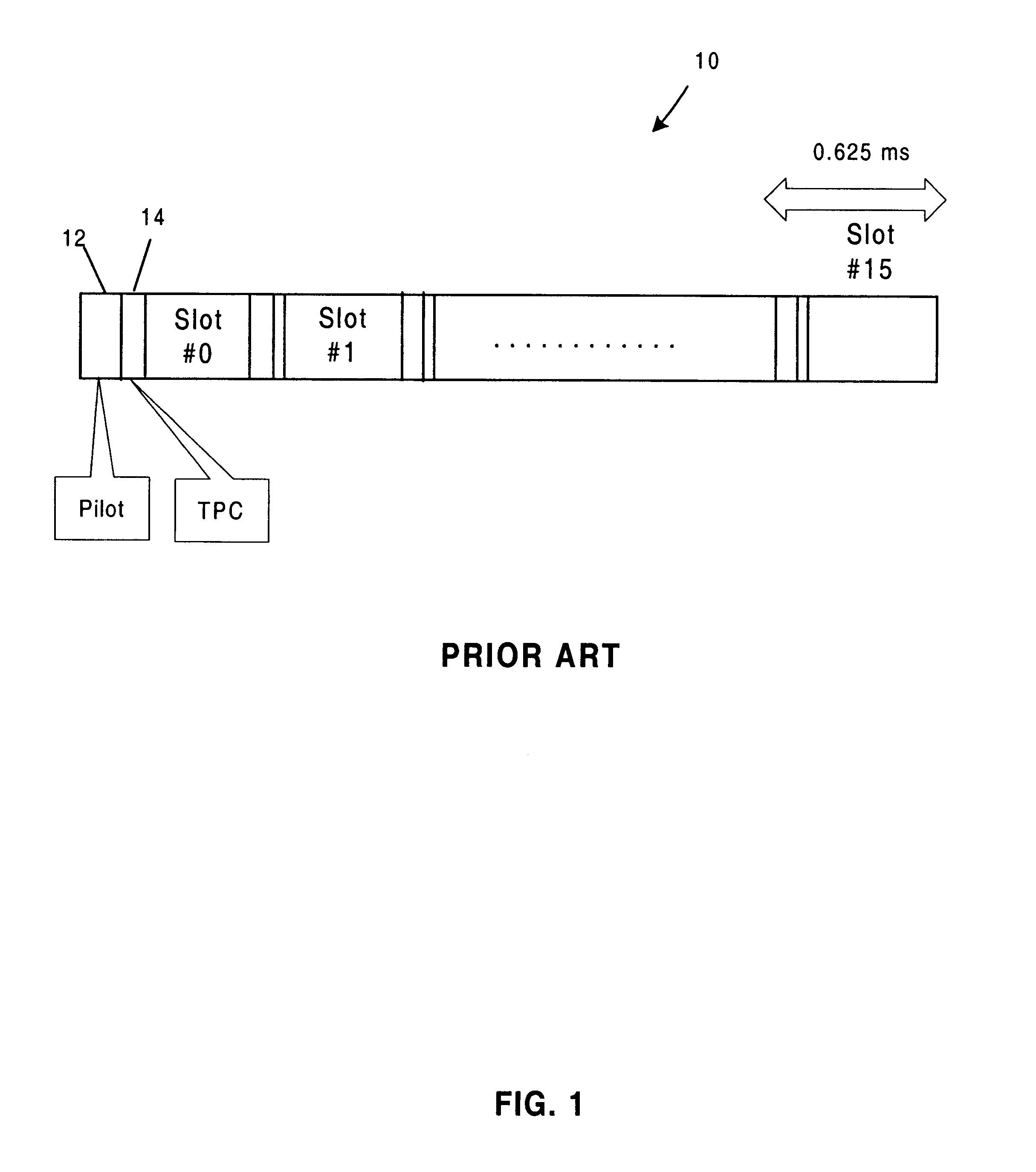
A WCDMA system includes a Base Station (BS) transmitter, or forward transmitter and a pilot channel that transmits control signals between the BS and a Mobile Station (MS) to reconfigure their transmitter / receiver. Reconfiguration is performed according to the prediction of the channel attenuation and the threshold set at the BS or MS based on its channel power probability density function separated into three distinct equal probable regions. In one embodiment, Seamless Rate Change (SRC) / Transmitter Power Control (TPC) logic uses the predicted channel attenuation to signal both the transmitter and the receiver in a channel to reconfigure their transmit power level according to the power density function (pdf) of the channel power and threshold level. A transmission rate is reduced when the power level is below the threshold and increased when the channel power is above threshold. The pilot channel is used to signal the mobile station and the base station.
Owner:IBM CORP
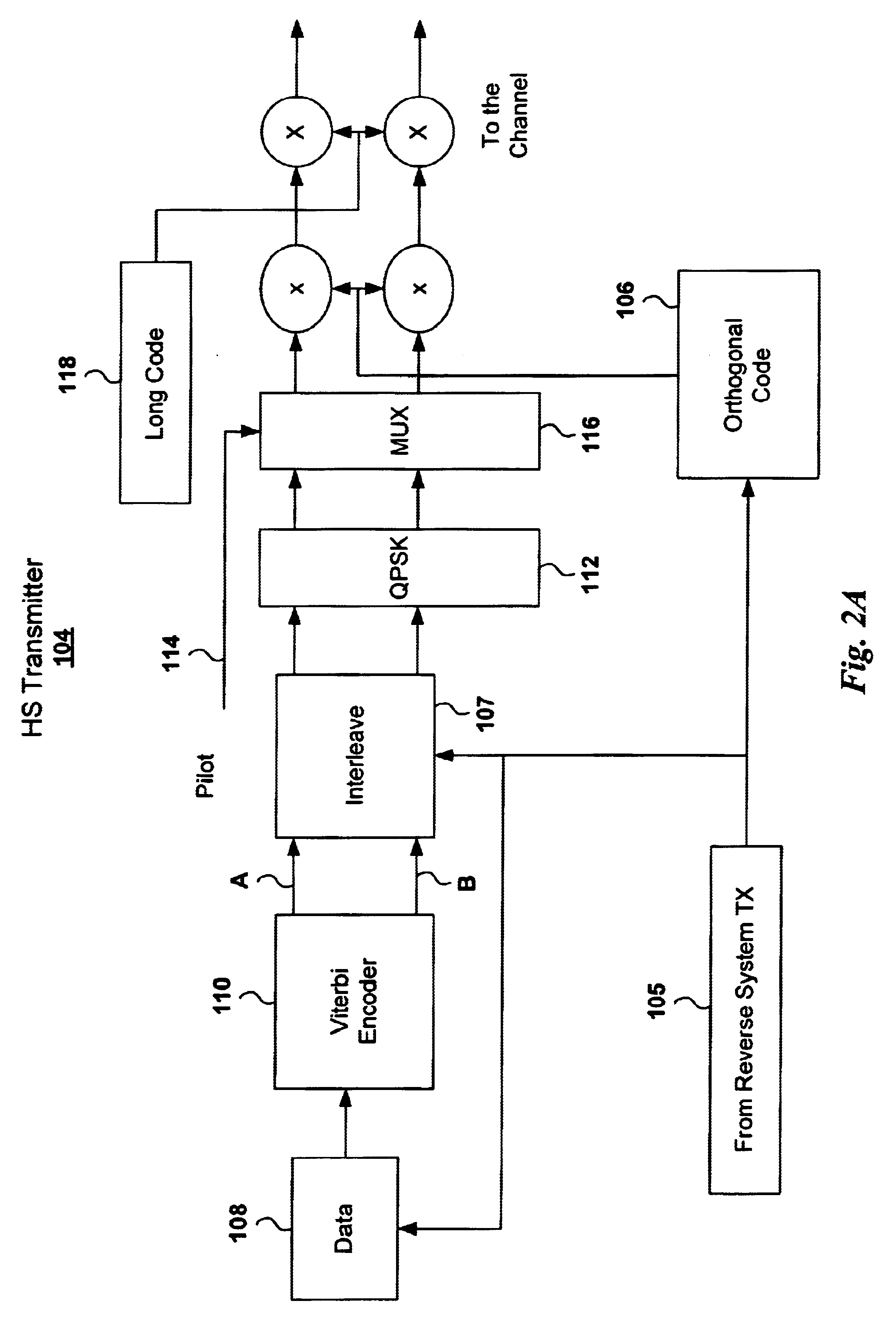
Adaptive power control based on a rake receiver configuration in wideband CDMA cellular systems (WCDMA) and methods of operation
InactiveUS6621808B1Maximizes controlMaximize throughputPower managementTransmission control/equalisingChannel powerOperational system
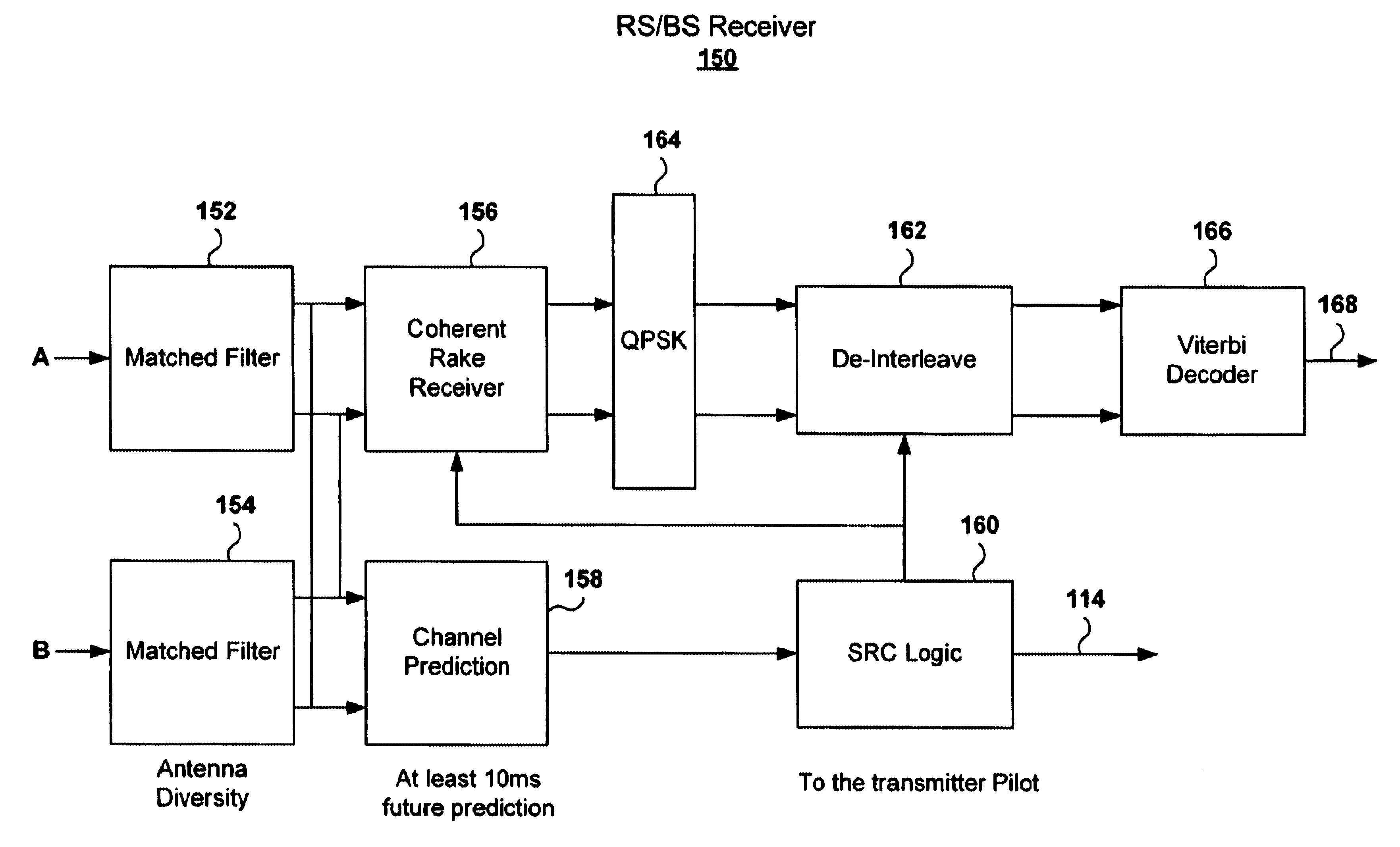
A WCDMA system includes a Base Station (BS) or forward transmitter and a pilot channel that transmits control signals between a Mobile Station (MS) and BS to reconfigure their transmitter / receiver according to the prediction of the channel power and channel power probability density function separated into three distinct equal probable regions. Data signals are encoded using a one-half Viterbi encoder and interleaved. The interleaved data bits are modulated using Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK) modulation. The QPSK data is multiplexed with the pilot channel and spread by an appropriate code in an OFDM transmitter modified by a long code. Output of the transmitter may be provided to two diverse antennas for reliable communications to the receiver. Data may be received at two diverse antennas. The outputs are provided to match filters coupled to a coherent rake receiver and a channel prediction system. The future attenuation of the channel coefficients and power are determined by the prediction system for several milliseconds. The power levels of each finger in the Rake receiver can be predicted and the strongest ones used in determining the optimum transmitter power or rate control for operating the system transmitters and receivers based on computing a long range power prediction of each finger of a rake receiver.
Owner:WISTRON CORP
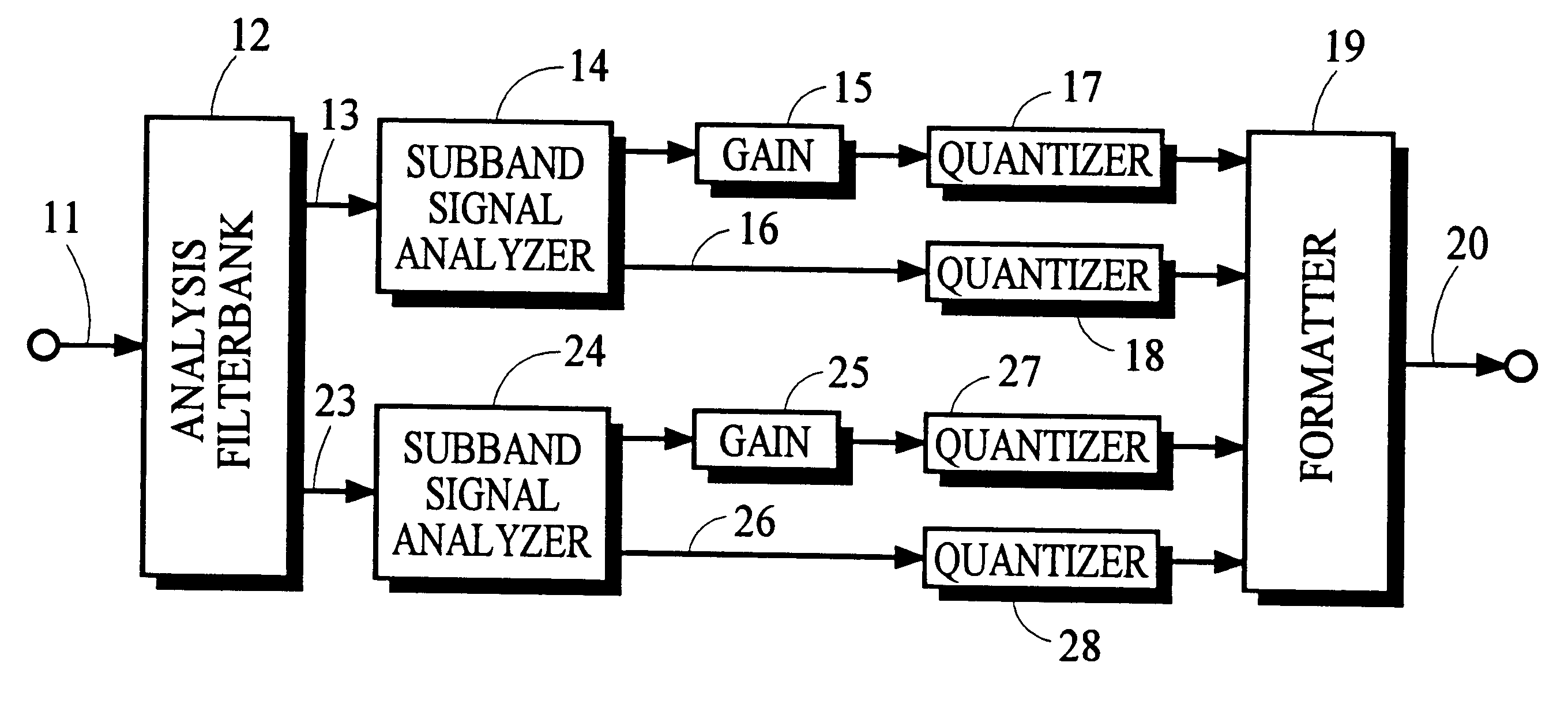
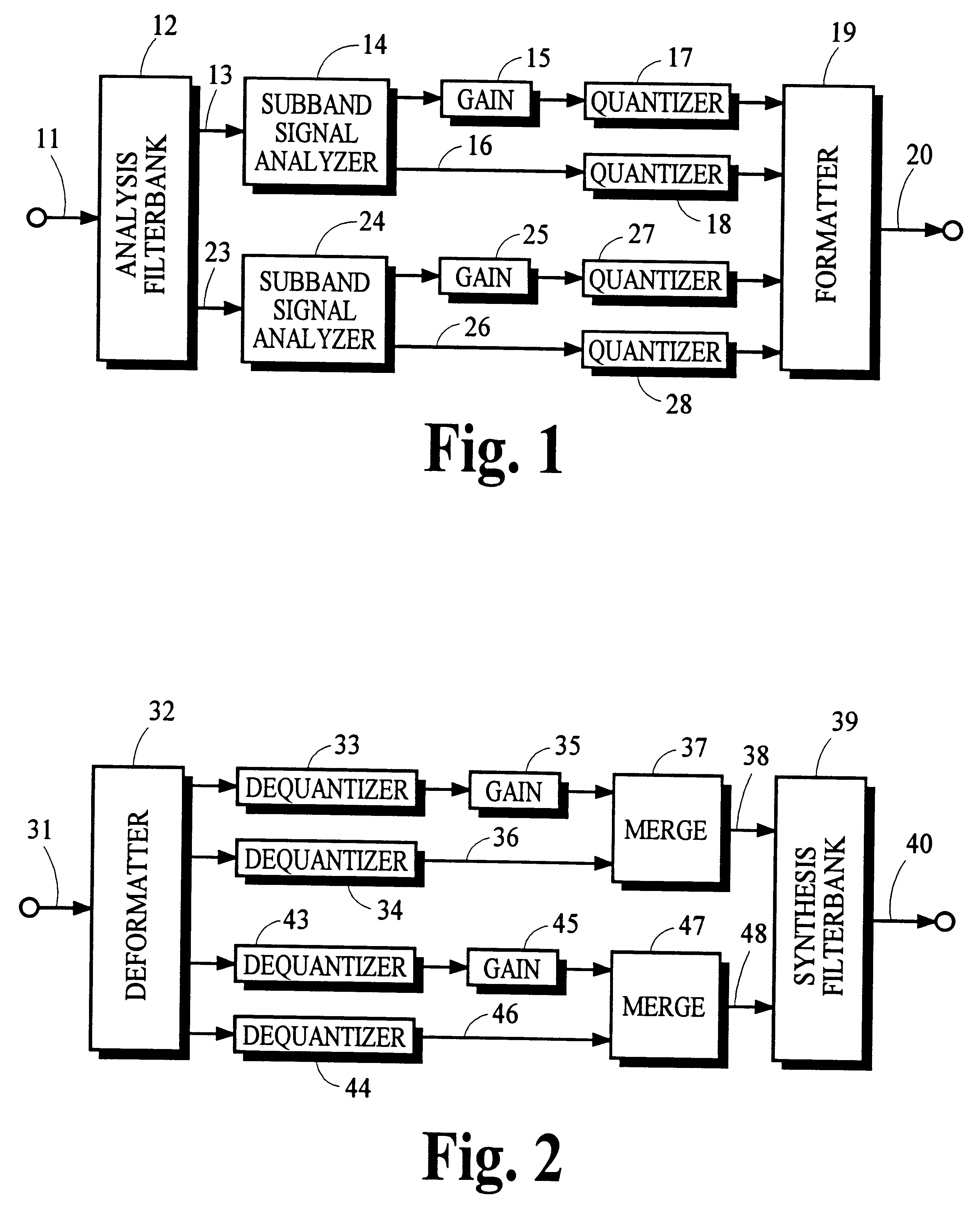
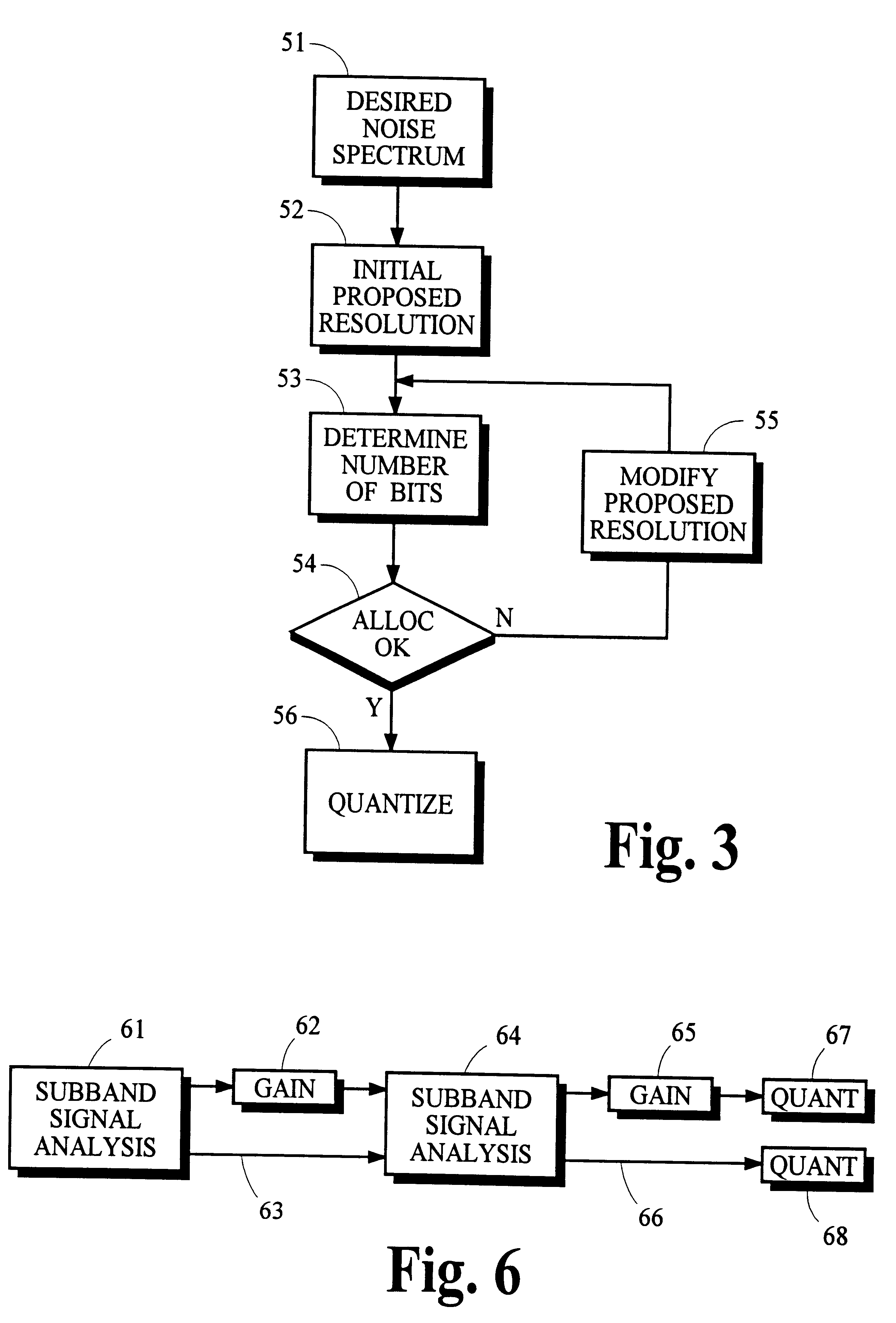
Using gain-adaptive quantization and non-uniform symbol lengths for improved audio coding
InactiveUS6246345B1Good coding gainEfficient executionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionNormal densityIntra-frame
Techniques like Huffman coding can be used to represent digital audio signal components more efficiently using non-uniform length symbols than can be represented by other coding techniques using uniform length symbols Unfortunately, the coding efficiency that can be achieved by Huffman coding depends on the probability density function of the information to be coded and the Huffman coding process itself requires considerable processing and memory resources. A coding process that uses gain-adaptive quantization according to the present invention can realize the advantage of using non-uniform length symbols while overcoming the shortcomings of Huffman coding. In gain-adaptive quantization, the magnitudes of signal components to be encoded are compared to one or more thresholds and placed into classes according to the results of the comparison. The magnitudes of the components placed into one of the classes are modified according to a gain factor that is related to the threshold used to classify the components. Preferably, the gain factor may be expressed as a function of only the threshold value. Gain-adaptive quantization may be used to encode frequency subband signals in split-band audio coding systems. Additional features including cascaded gain-adaptive quantization, intra-frame coding, split-interval and non-overloading quantizers are disclosed.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Density evolution based polarization code constructing method and polarization code coding and decoding system
ActiveCN105811998AImprove decoding performanceReduced characteristicsError correction/detection using linear codesComputation complexityDensity based
The invention discloses a density evolution based polarization code constructing method and polarization code coding and decoding system. According to the invention, the code length N and the information bit length K of an information code to be processed are obtained, an expectation value set of a log-likelihood ratio probability density function of N bit channels, K bit channels are selected as the information bit channels according to the expectation value set and information bit information index vector quantity is generated; an information bit sequence and a fixed bit sequence are mixed and the mixed bit vector quantity is multiplied by a polarization code for generating a matrix so as to output an encoding sequence; the encoding sequence is modulated and input into a transmission channel and the sequence output by the transmission channel is subjected to decoding operation by adopting a polarization code decoding algorithm, bit error probability and frame error rate of the decoded code are calculated and a design signal to noise ratio is changed, the above operation is repeated until the bit error probability and frame error rate become the minimum. The method and system provided by the invention are suitable for general binary system memoryless channels, the bit error probability and frame error rate are low, the calculation complexity is low and the communication performance of a communication system is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
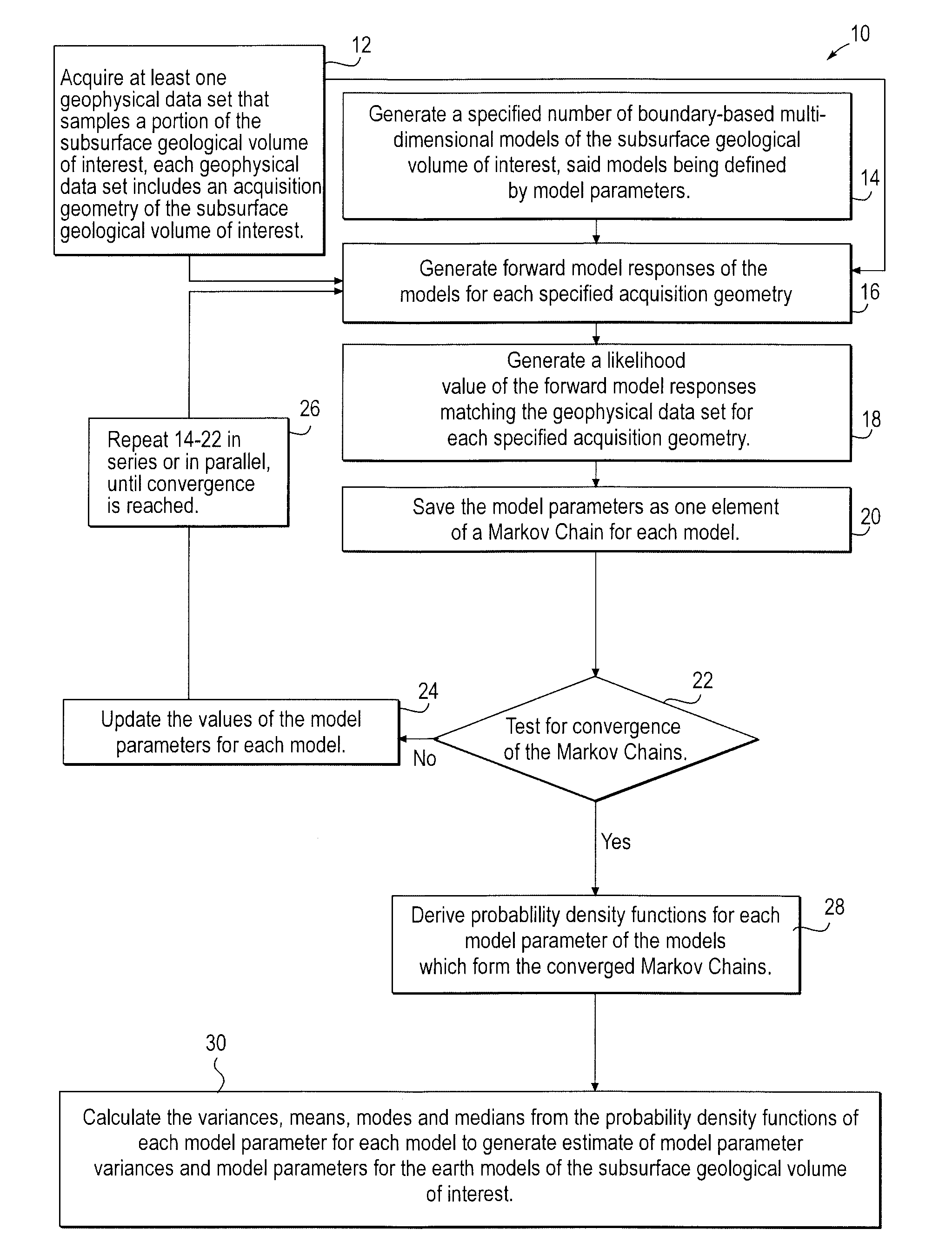
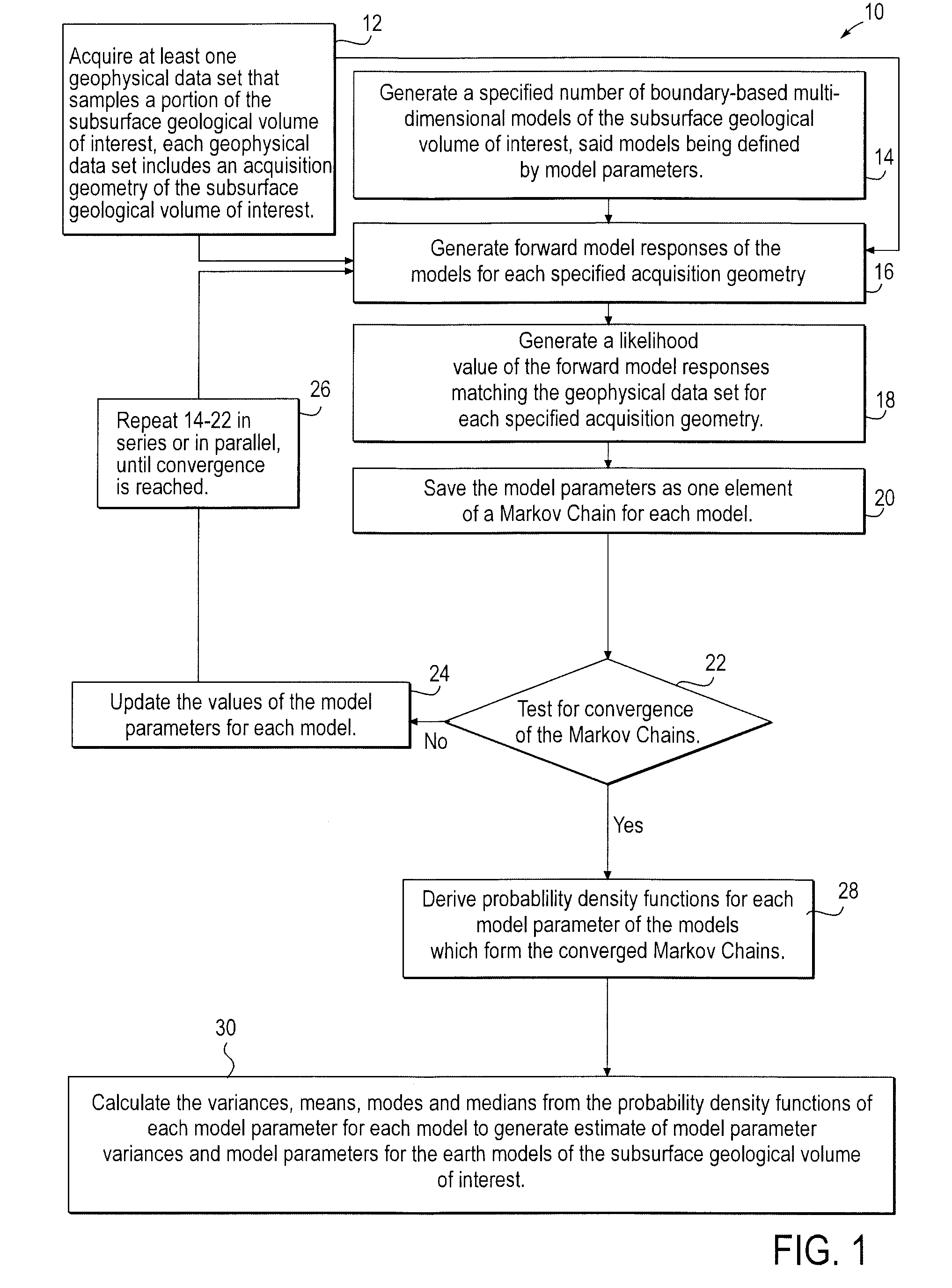
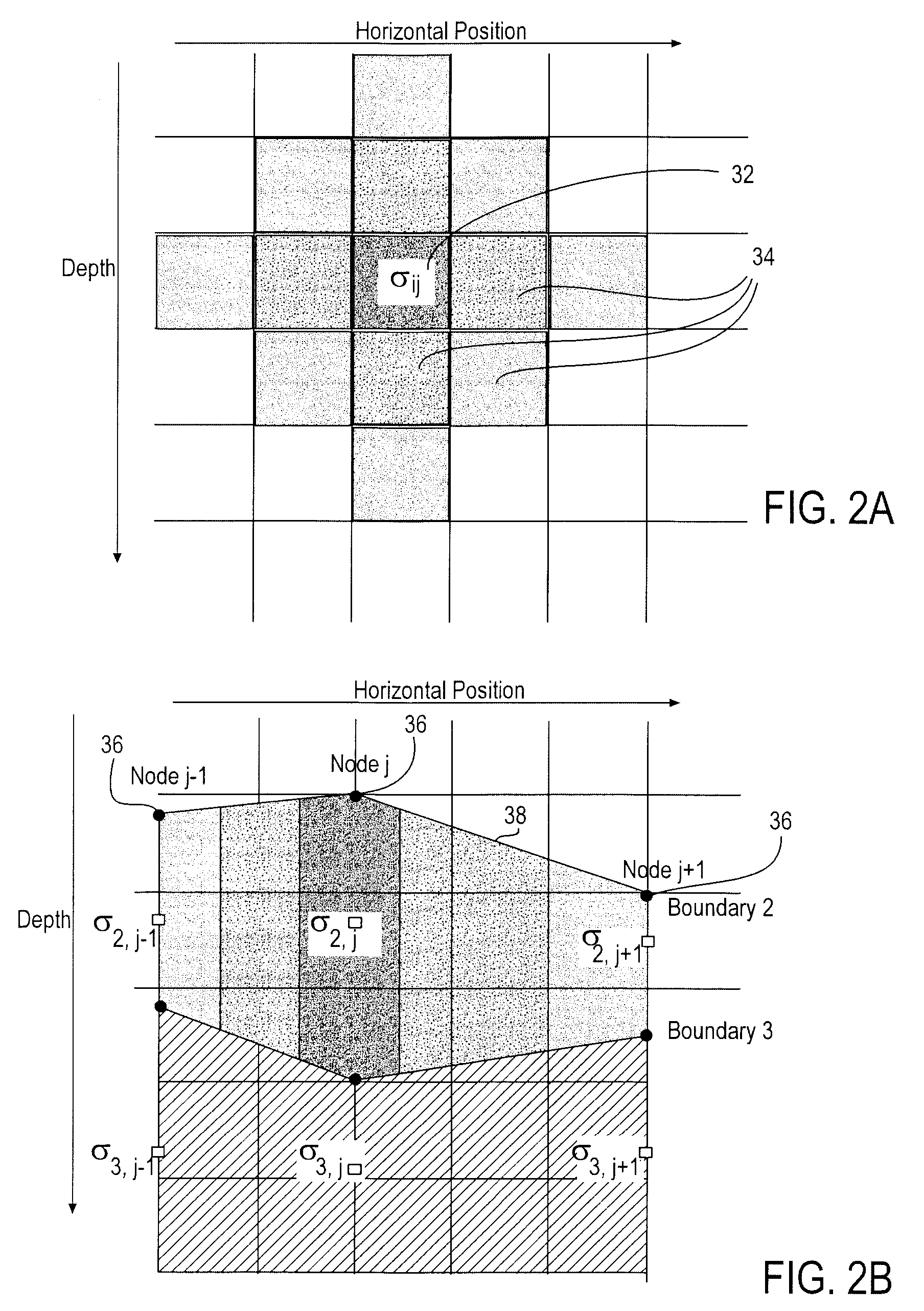
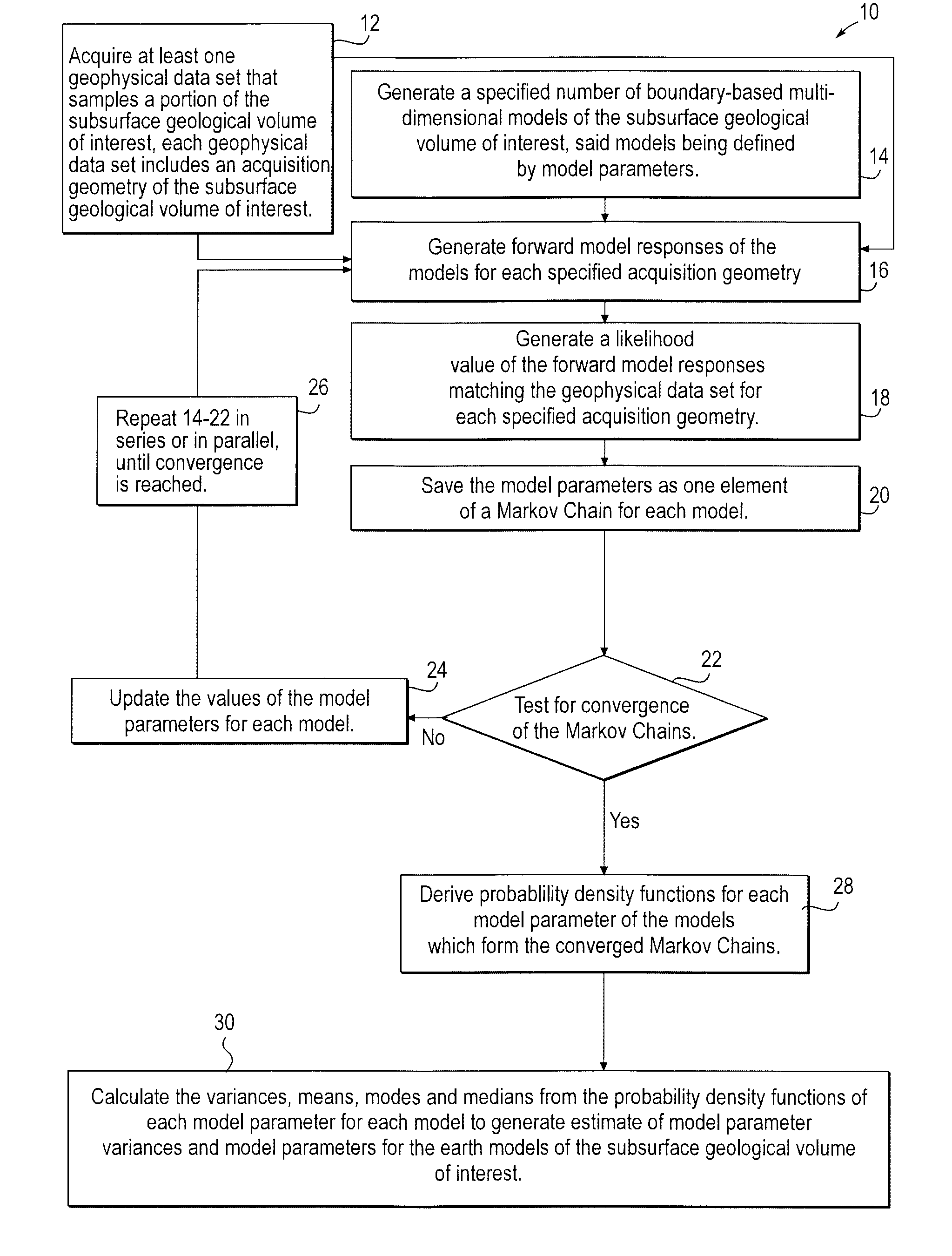
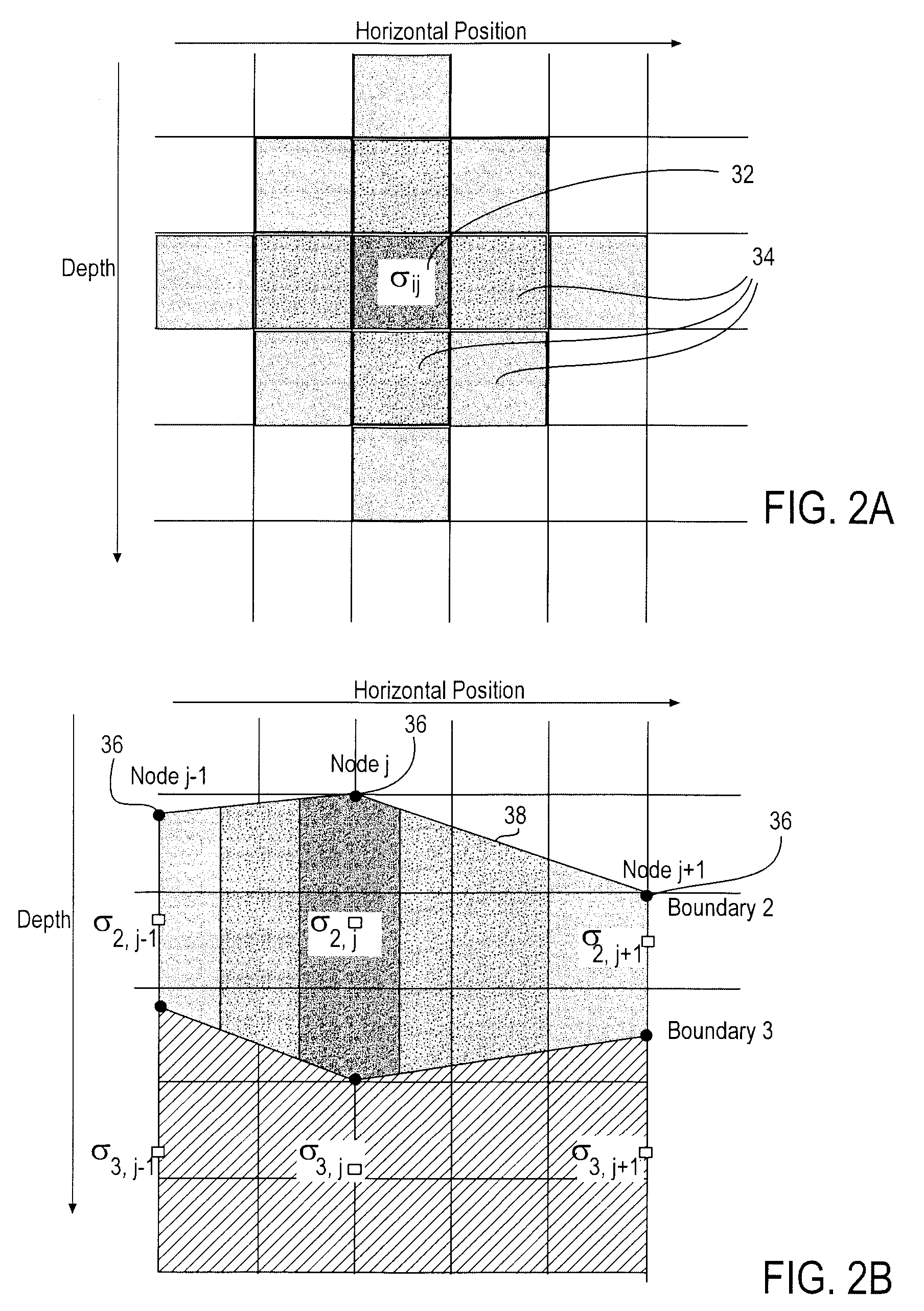
Stochastic inversion of geophysical data for estimating earth model parameters
A computer implemented stochastic inversion method for estimating model parameters of an earth model. In an embodiment, the method utilizes a sampling-based stochastic technique to determine the probability density functions (PDF) of the model parameters that define a boundary-based multi-dimensional model of the subsurface. In some embodiments a sampling technique known as Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) is utilized. MCMC techniques fall into the class of “importance sampling” techniques, in which the posterior probability distribution is sampled in proportion to the model's ability to fit or match the specified acquisition geometry. In another embodiment, the inversion includes the joint inversion of multiple geophysical data sets. Embodiments of the invention also relate to a computer system configured to perform a method for estimating model parameters for accurate interpretation of the earth's subsurface.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
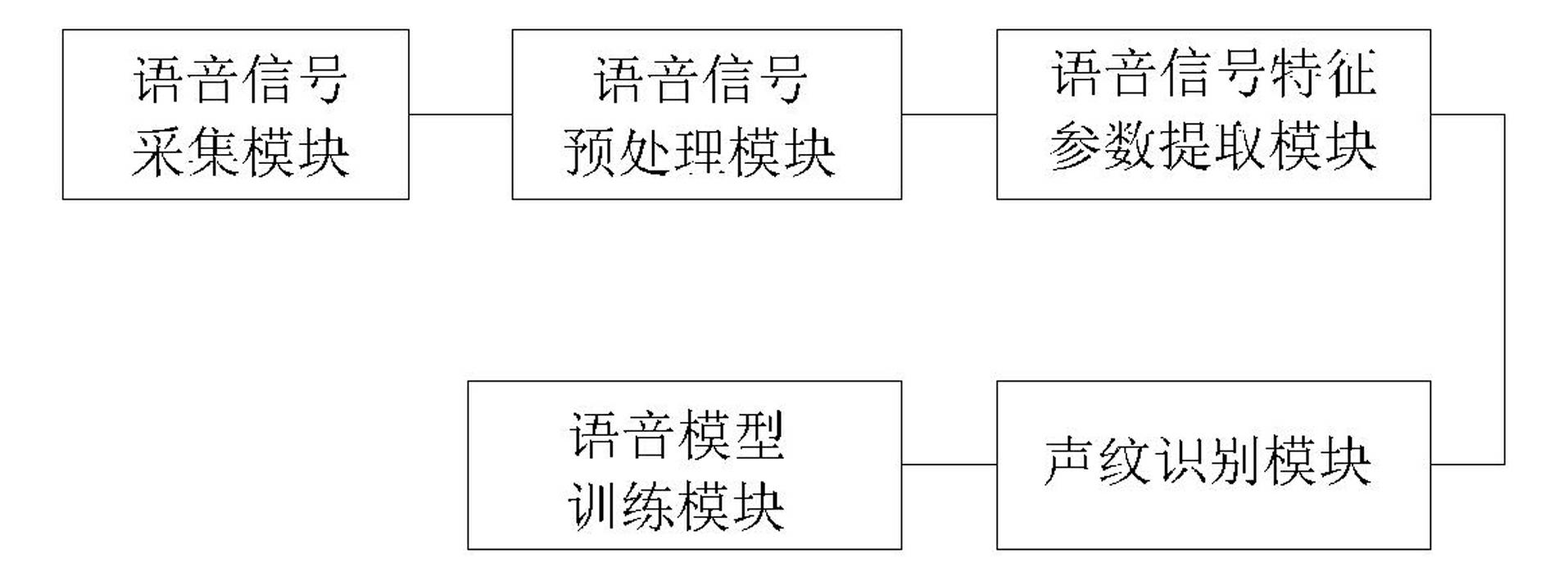
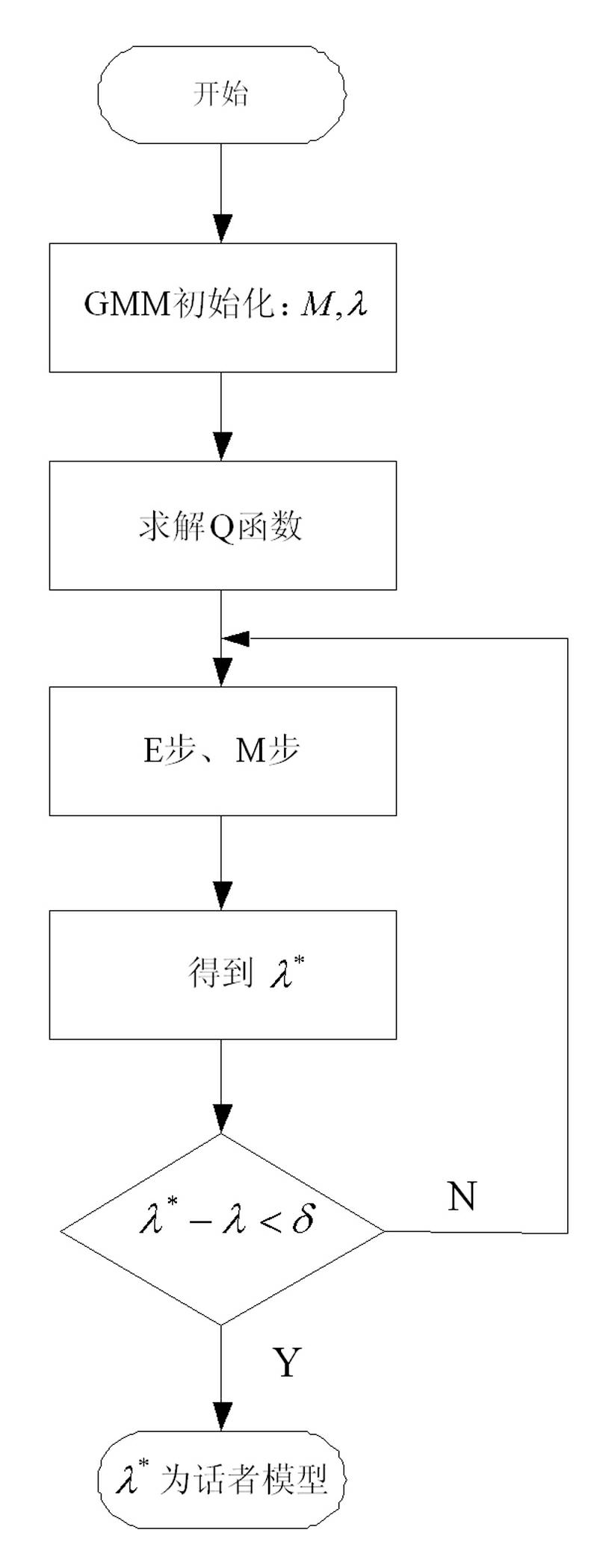
Voiceprint identification method based on Gauss mixing model and system thereof
InactiveCN102324232AGood estimateEasy to trainSpeech recognitionMel-frequency cepstrumNormal density
The invention provides a voiceprint identification method based on a Gauss mixing model and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps: voice signal acquisition; voice signal pretreatment; voice signal characteristic parameter extraction: employing a Mel Frequency Cepstrum Coefficient (MFCC), wherein an order number of the MFCC usually is 12-16; model training: employing an EM algorithm to train a Gauss mixing model (GMM) for a voice signal characteristic parameter of a speaker, wherein a k-means algorithm is selected as a parameter initialization method of the model; voiceprint identification: comparing a collected voice signal characteristic parameter to be identified with an established speaker voice model, carrying out determination according to a maximum posterior probability method, and if a corresponding speaker model enables a speaker voice characteristic vector X to be identified to has maximum posterior probability, identifying the speaker. According to the method, the Gauss mixing model based on probability statistics is employed, characteristic distribution of the speaker in characteristic space can be reflected well, a probability density function is common, a parameter in the model is easy to estimate and train, and the method has good identification performance and anti-noise capability.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
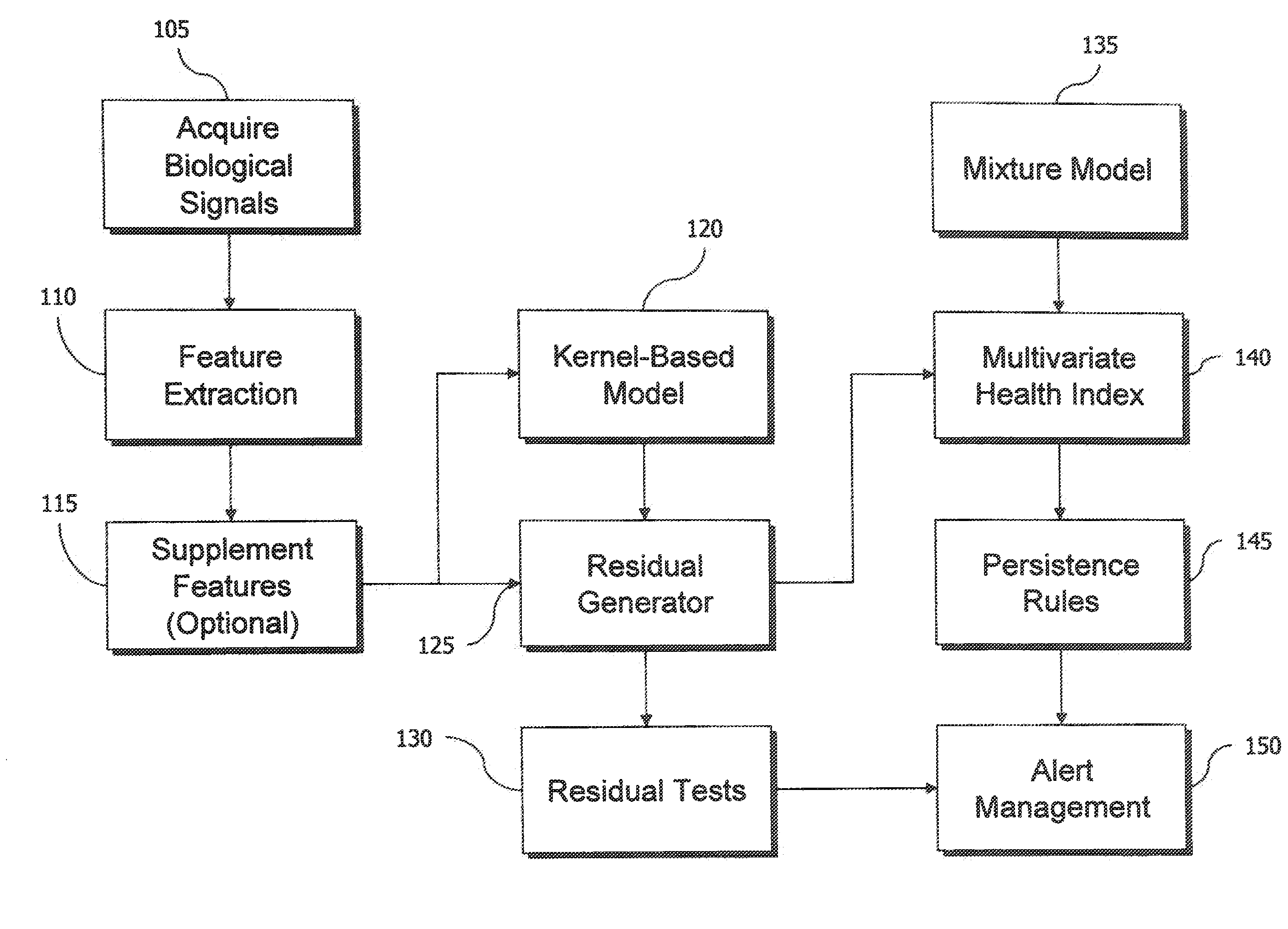
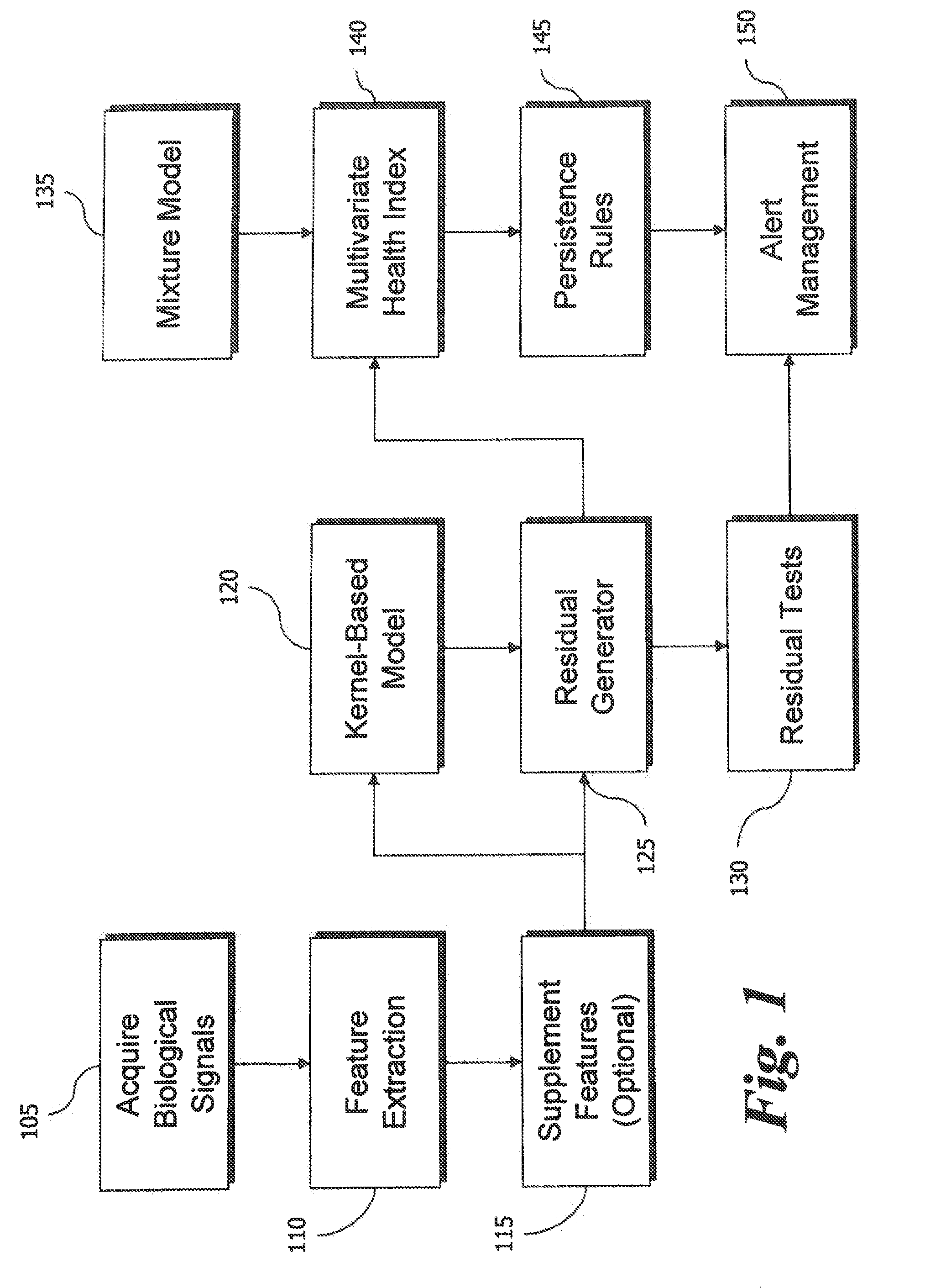
Multivariate Residual-Based Health Index for Human Health Monitoring
ActiveUS20110172504A1Early detectionMedical simulationHealth-index calculationNormal densityHealth index
Ambulatory or in-hospital monitoring of patients is provided with early warning and prioritization, enabling proactive intervention and amelioration of both costs and risks of health care. Multivariate physiological parameters are estimated by empirical model to remove normal variation. Residuals are tested using a multivariate probability density function to provide a multivariate health index for prioritizing medical effort.
Owner:PHYSIQ
Illumination optimization for specific mask patterns
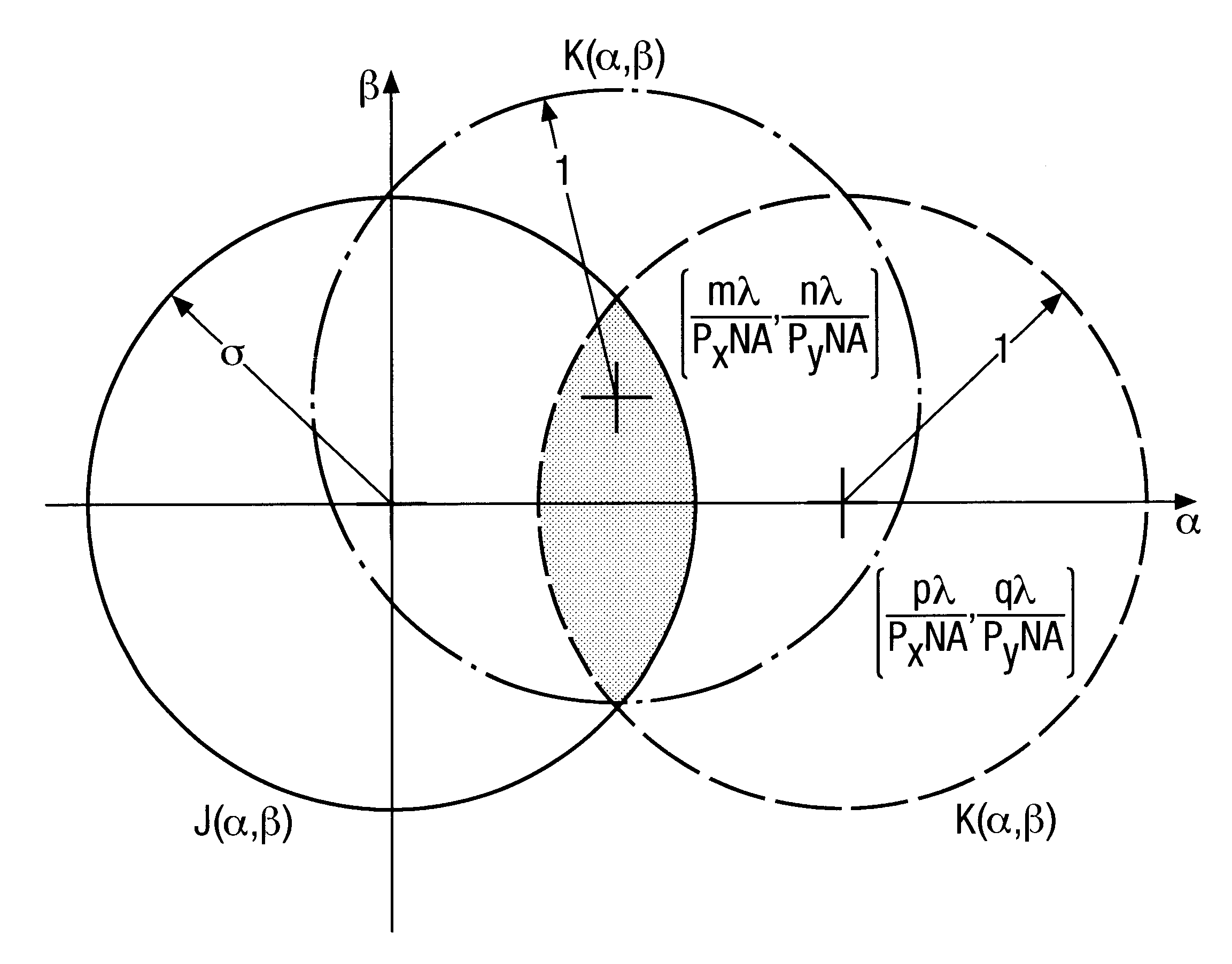
InactiveUS6871337B2Reduce in quantityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProjection opticsDiffraction order
A method and apparatus for microlithography. The method and apparatus include optimizing illumination modes based on characteristics of a specific mask pattern. The illumination is optimized by determining an appropriate illumination mode based on diffraction orders of the reticle, and the autocorrelation of the projection optic. By elimination of parts of the illumination pattern which have no influence on modulation, excess DC light can be reduced, thereby improving depth of focus. Optimization of mask patterns includes addition of sub-resolution features to reduce pitches and discretize the probability density function of the space width.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
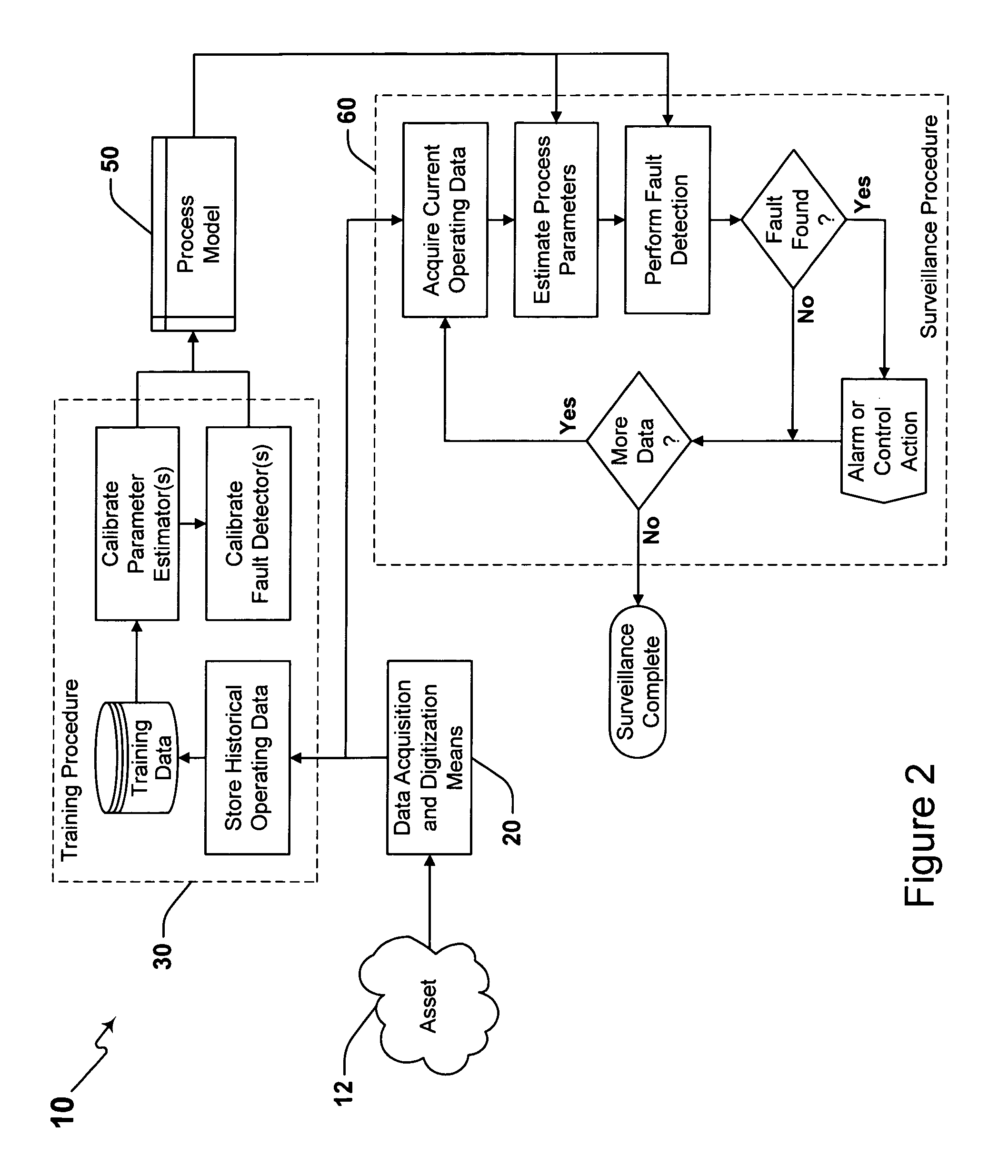
Surveillance system and method having an adaptive sequential probability fault detection test
InactiveUS7082379B1Performance trade-offSolve the high false alarm rateTime indicationSynchronous motors for clocksNormal densityHypothesis
System and method providing surveillance of an asset such as a process and / or apparatus by providing training and surveillance procedures that numerically fit a probability density function to an observed residual error signal distribution that is correlative to normal asset operation and then utilizes the fitted probability density function in a dynamic statistical hypothesis test for providing improved asset surveillance.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL ASSETAB
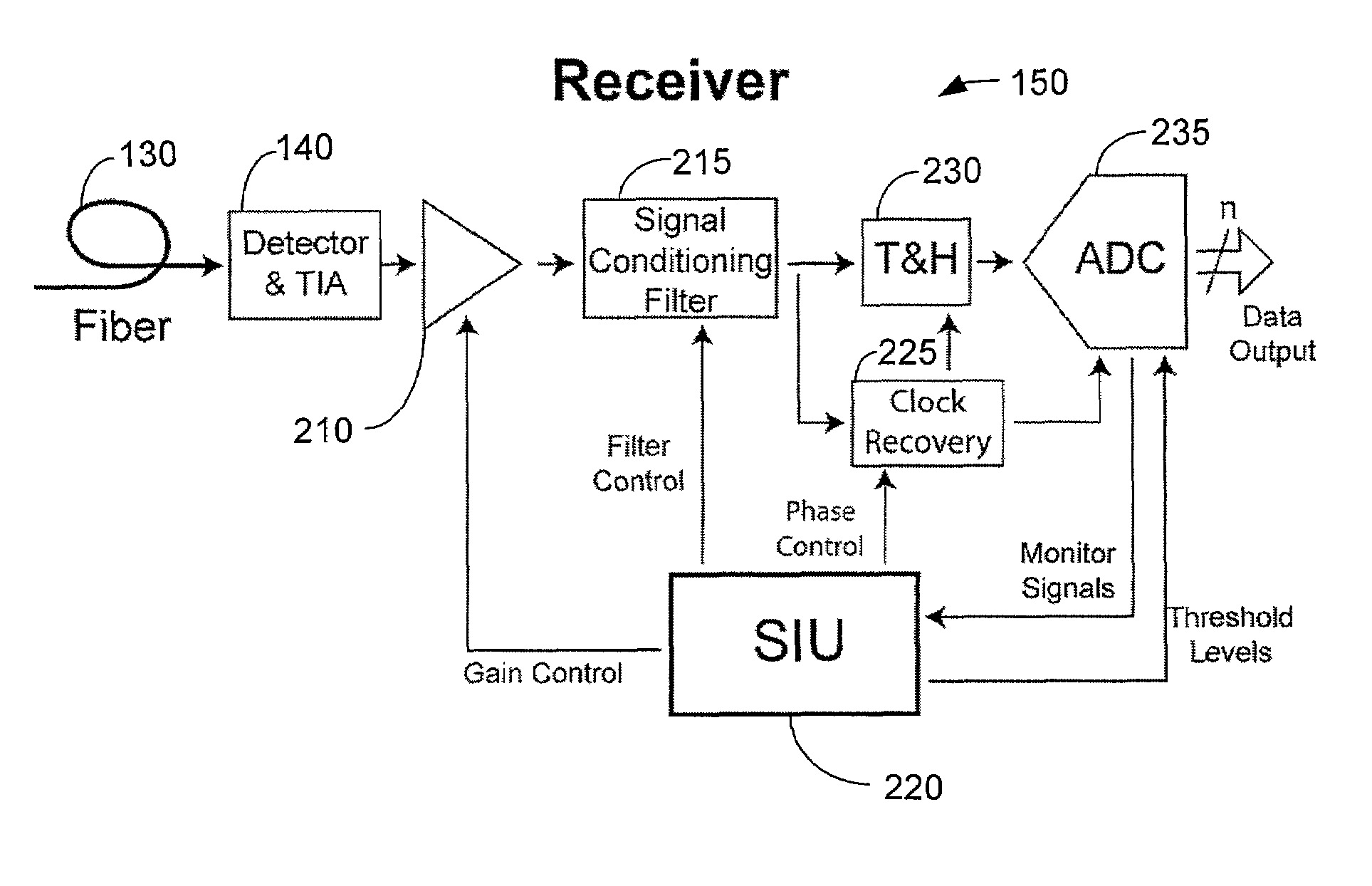
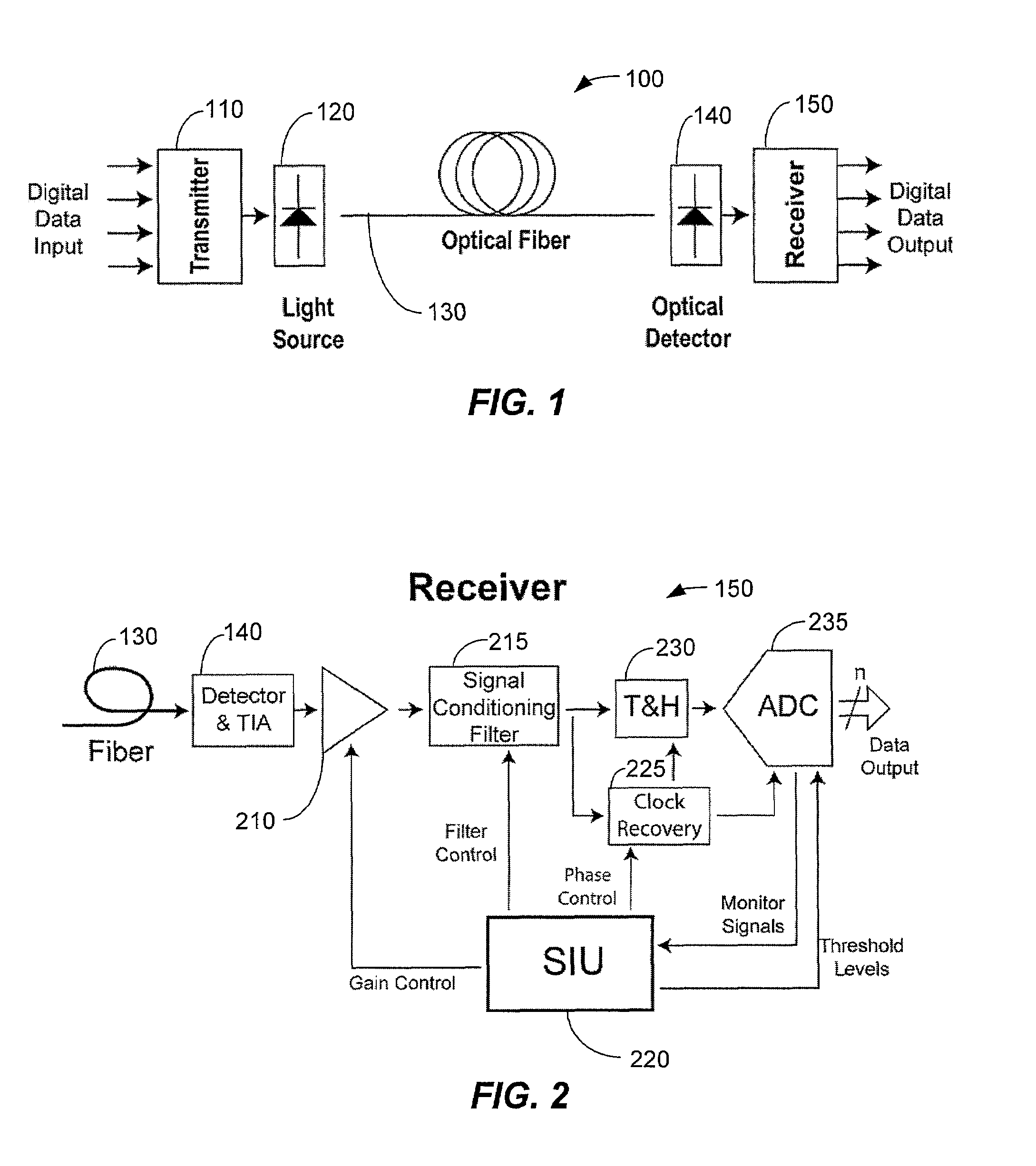
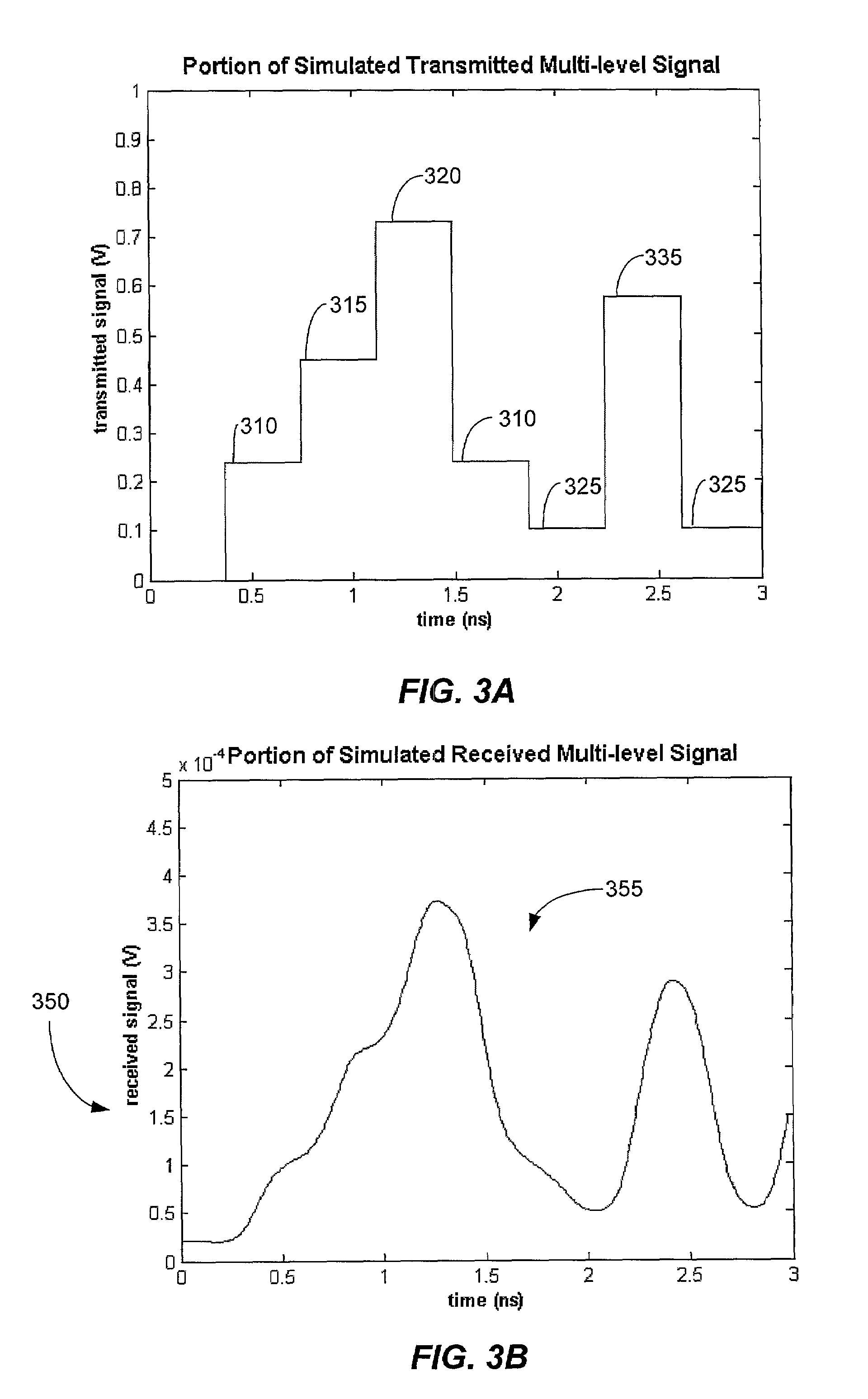
Method and system for decoding multilevel signals
ActiveUS7215721B2Efficient processingMinimizes average error probabilityRepeater/relay circuitsDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionNormal densityAutomatic control
A multilevel optical receiver can comprise a plurality of comparators that generally correspond with the number of levels in a multilevel data stream. Each comparator can be individually controlled and fed a decision threshold in order to decode a multilevel signal. The multilevel optical receiver can generate a statistical characterization of the received symbols in the form of a marginal cumulative distribution function (CDF) or probability density function (pdf). This characterization can be used to produce a set of ε-support estimates from which conditional pdfs are derived for each of the transmission symbols. These conditional pdfs may then be used to determine decision thresholds for decoding the received signal. The conditional pdfs may further be used to continuously estimate the fidelity or error rate of the received signal without the transmission of a testing sequence. The ε-supports may further be used to automatically control the gain on the receiver.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
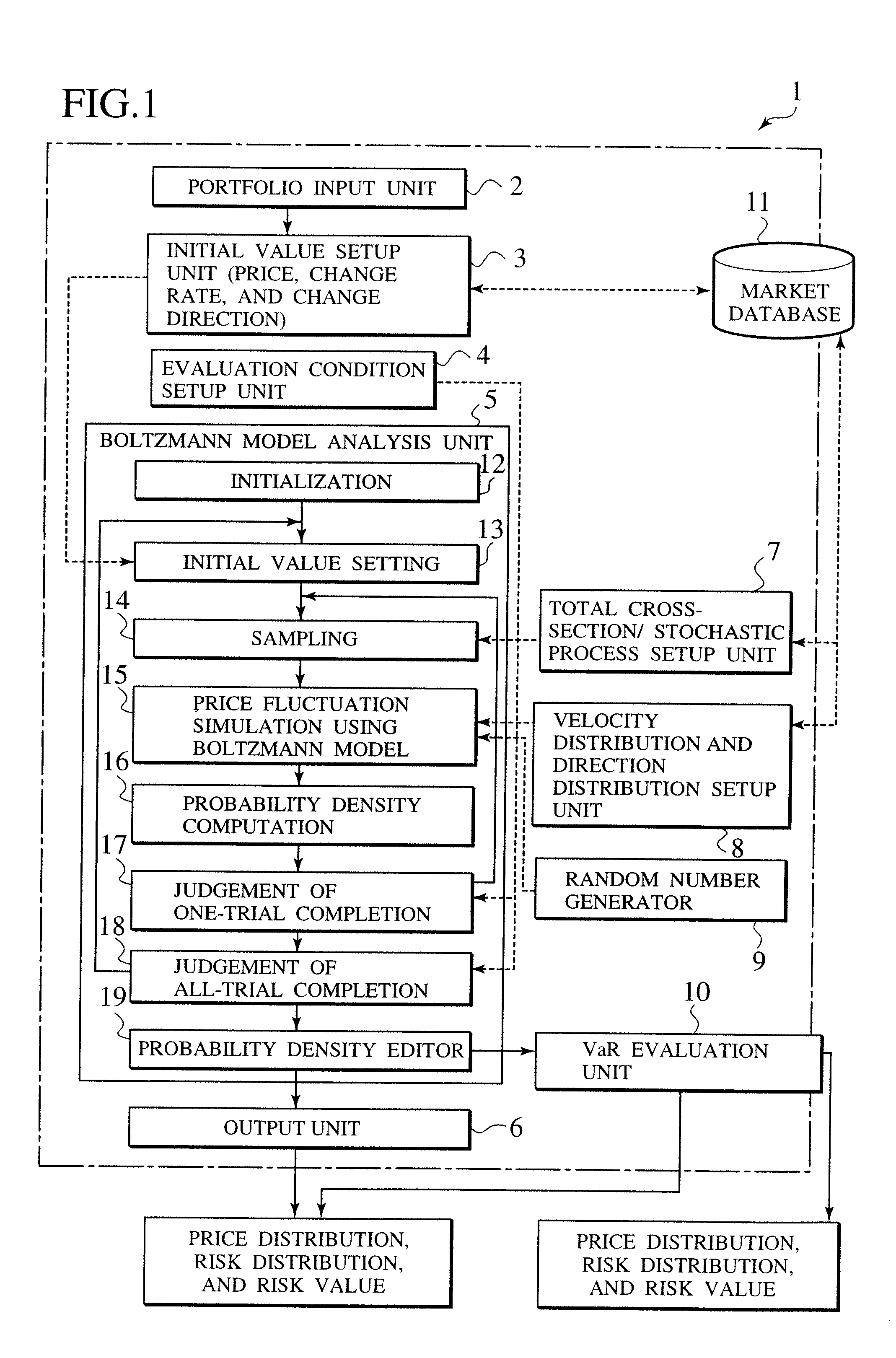
Price and risk evaluation system for financial product or its derivatives, dealing system, recording medium storing a price and risk evaluation program, and recording medium storing a dealing program
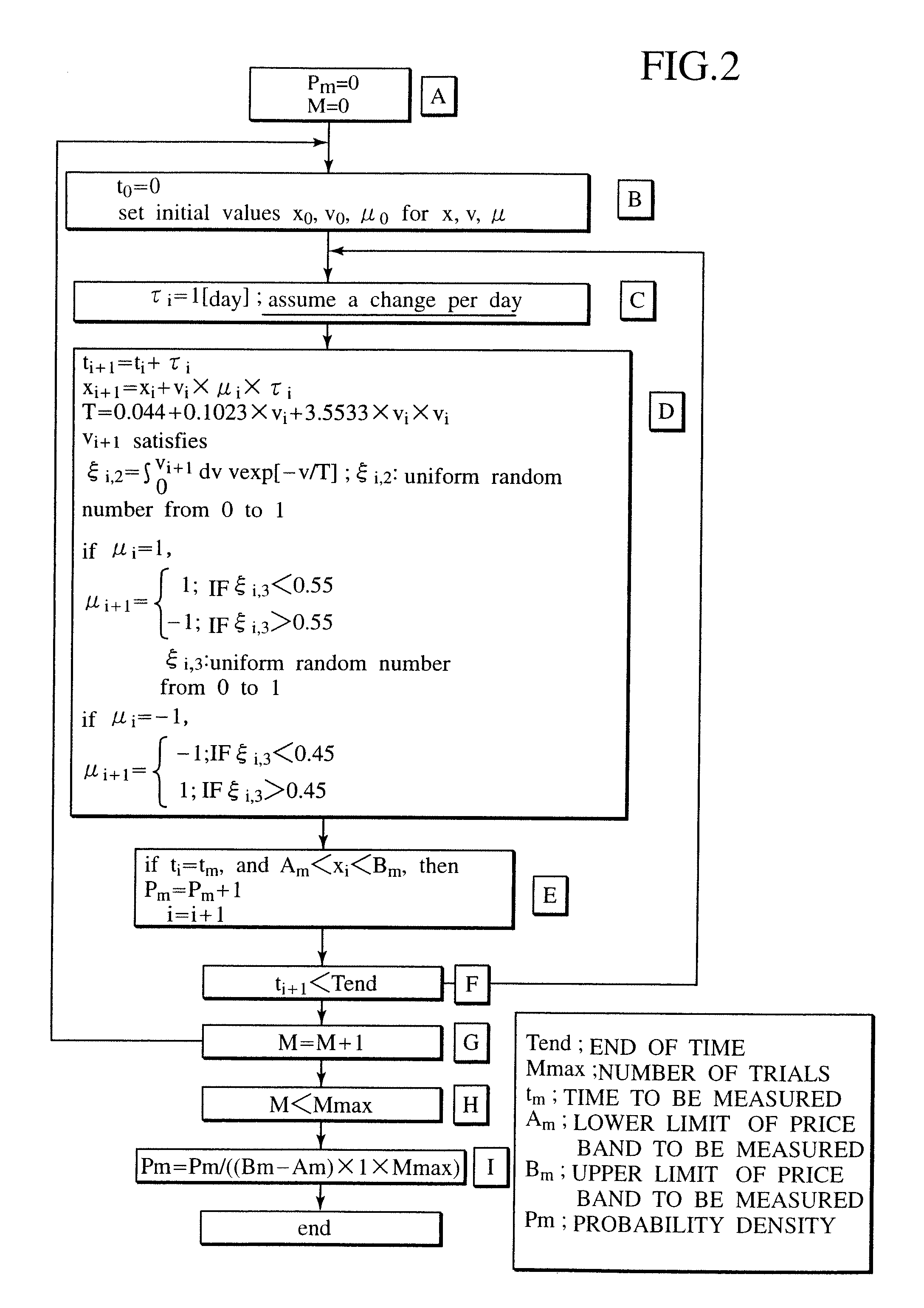
A system for correctly evaluating a price distribution and a risk distribution for a financial product or its derivatives introduces a probability density function generated with a Boltzmann model at a higher accuracy than the Gaussian distribution for a probability density. The system has an initial value setup unit and an evaluation condition setup unit. Initial values include at least one of price, price change rate, and the price change direction of a financial product. The evaluation conditions include at least time steps and the number of trials. The Boltzmann model analysis unit receives the initial values and the evaluation conditions, and repeats simulations of price fluctuation, based on the Boltzmann model using a Monte Carlo method. A velocity / direction distribution setup unit supplies the probability distributions of the price, price change rate, and the price change direction for the financial product to the Boltzmann model analysis unit. A random number generator for a Monte Carlo method employed in the analysis by the Boltzmann model, and an output unit displays the analysis result. A dealing system applies the financial Boltzmann model to option pricing, and reproduces the characteristics of Leptokurcity and Fat-tail by linear Boltzmann equation in order to define risk-neutral and unique probability measures. Consequently, option prices can be evaluated in a risk-neutral and unique manner, taking into account Leptokurcity and Fat-tail of a price change distribution.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and system for integrated uncertainty analysis
InactiveUS20050004833A1Efficient analysisSimulator controlComputation using non-denominational number representationNormal densityComputer architecture
A system and a method are provided for performing an integrated uncertainty analysis on a system having interacting modules. The interaction of the modules includes data transfer between the modules with the output of one module being indicative of the input of another module. An uncertainty analysis is performed on each module based on given probability density functions of each input to the module. The uncertainty analysis may include developing a deterministically equivalent model for one or more modules. Data may be provided from one module to another in a uniform format. Thus, two or more modules may be integrated with uncertainties in the inputs of one module being effectively propagated to the inputs of another module. A plurality of modules may thus be modeled as a single integrated system. The integrated system may be replaced with a deterministically equivalent model, preferably of a further reduced order. In this manner, key uncertainties in particular inputs may be isolated. Once these inputs are identified, resources may be effectively allocated to minimize the impact of those inputs on the variability of the results.
Owner:REACTION DESIGN
Cauchy-distribution based coding system and method
InactiveUS20050031034A1Digital variable displayPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDistortionNormal density
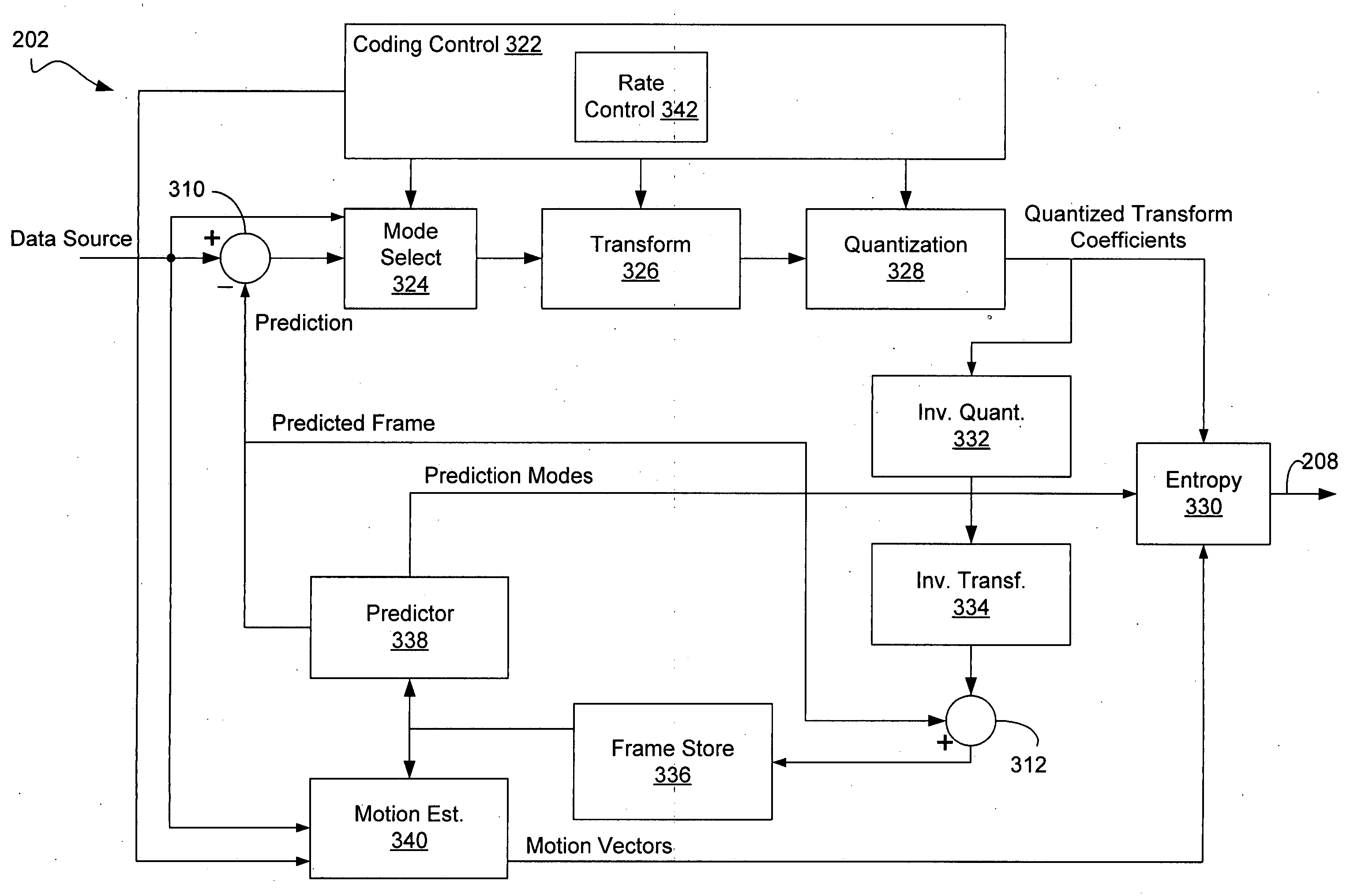
Embodiments of a coding system and method are disclosed. One method embodiment includes determining a Cauchy-based probability density function fit to a statistical distribution of coefficients generated from a transformed image frame block that are to be quantized, and estimating rate and distortion of quantized coefficients based on the Cauchy-based probability density function.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
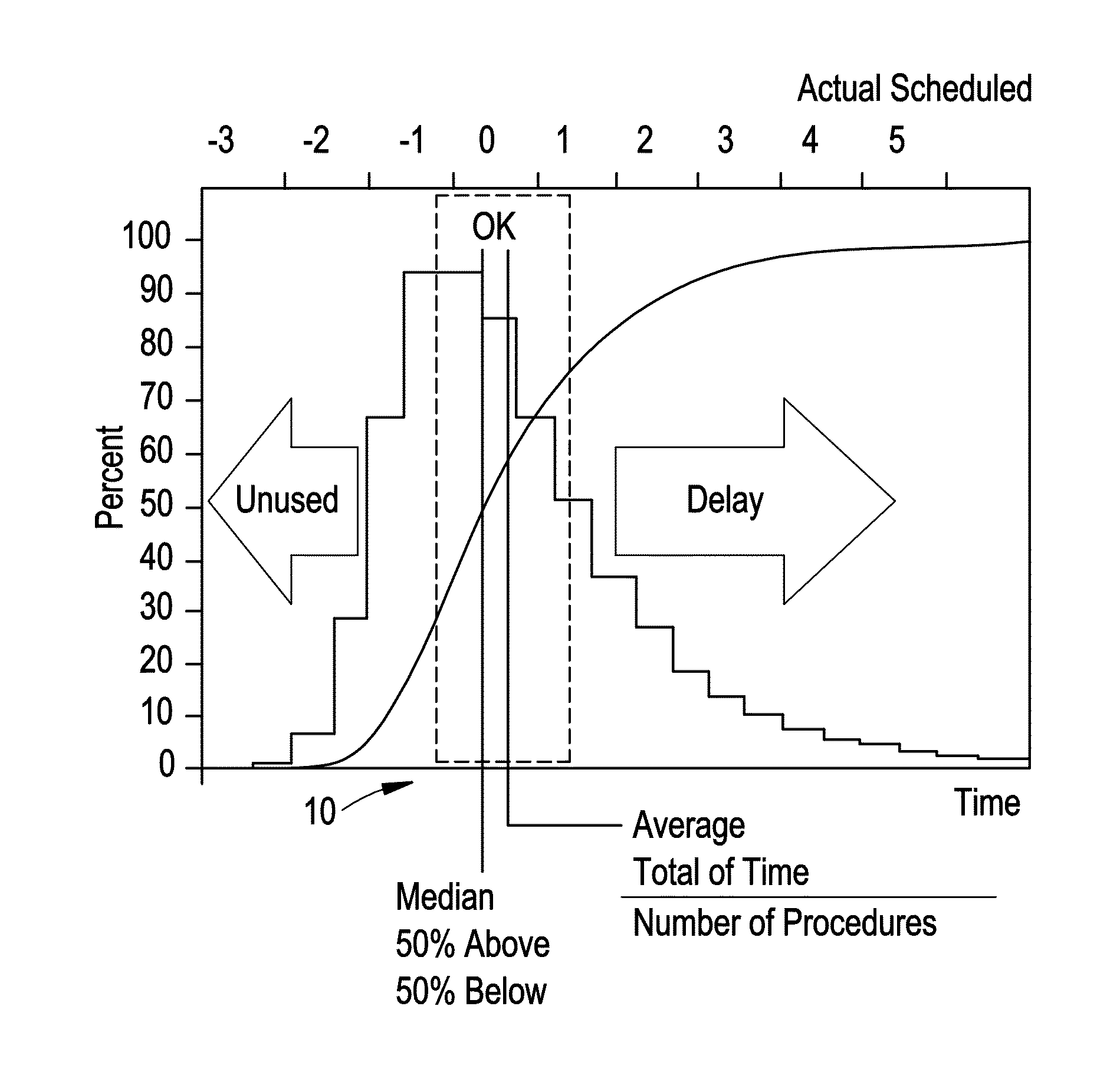
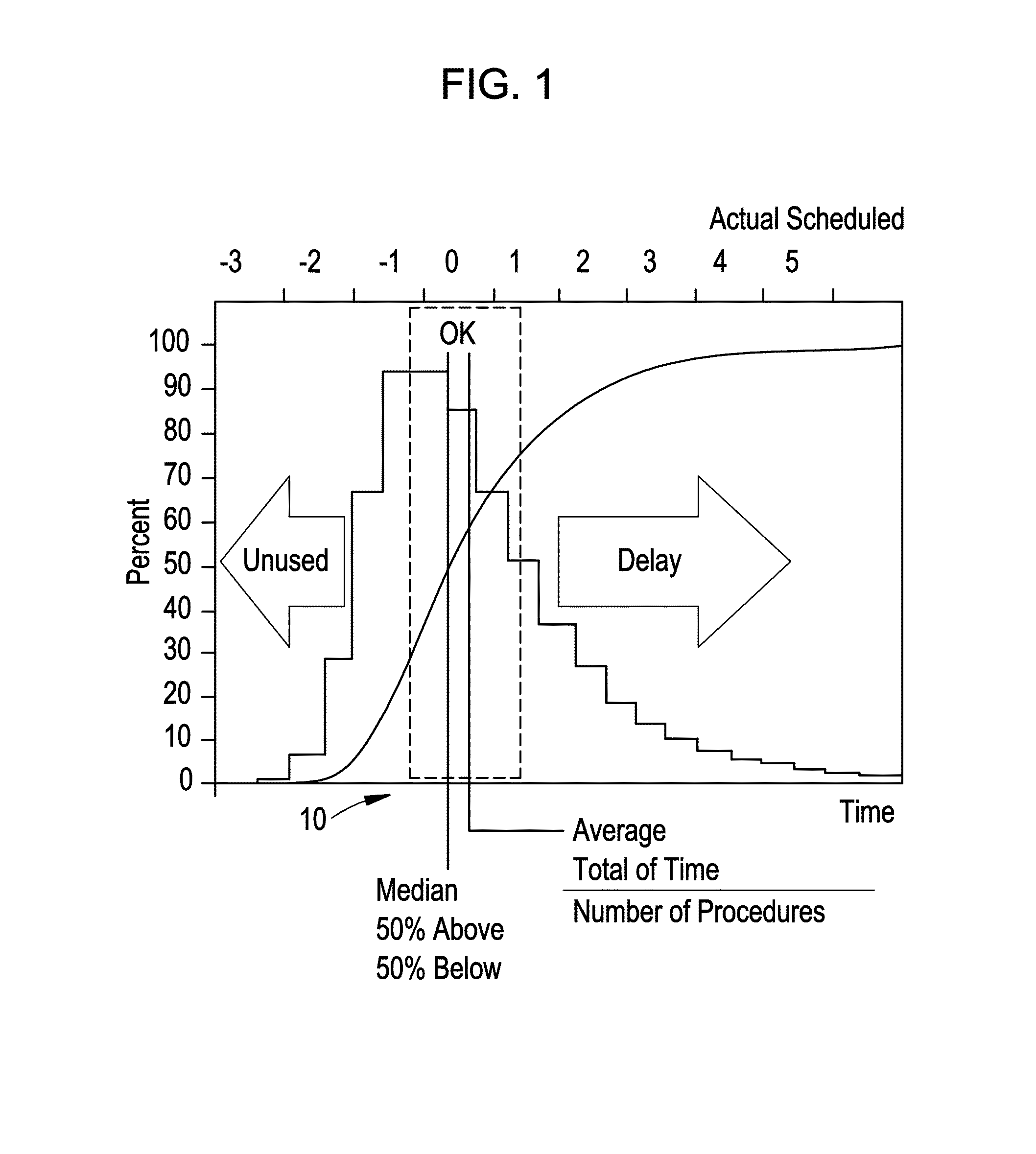
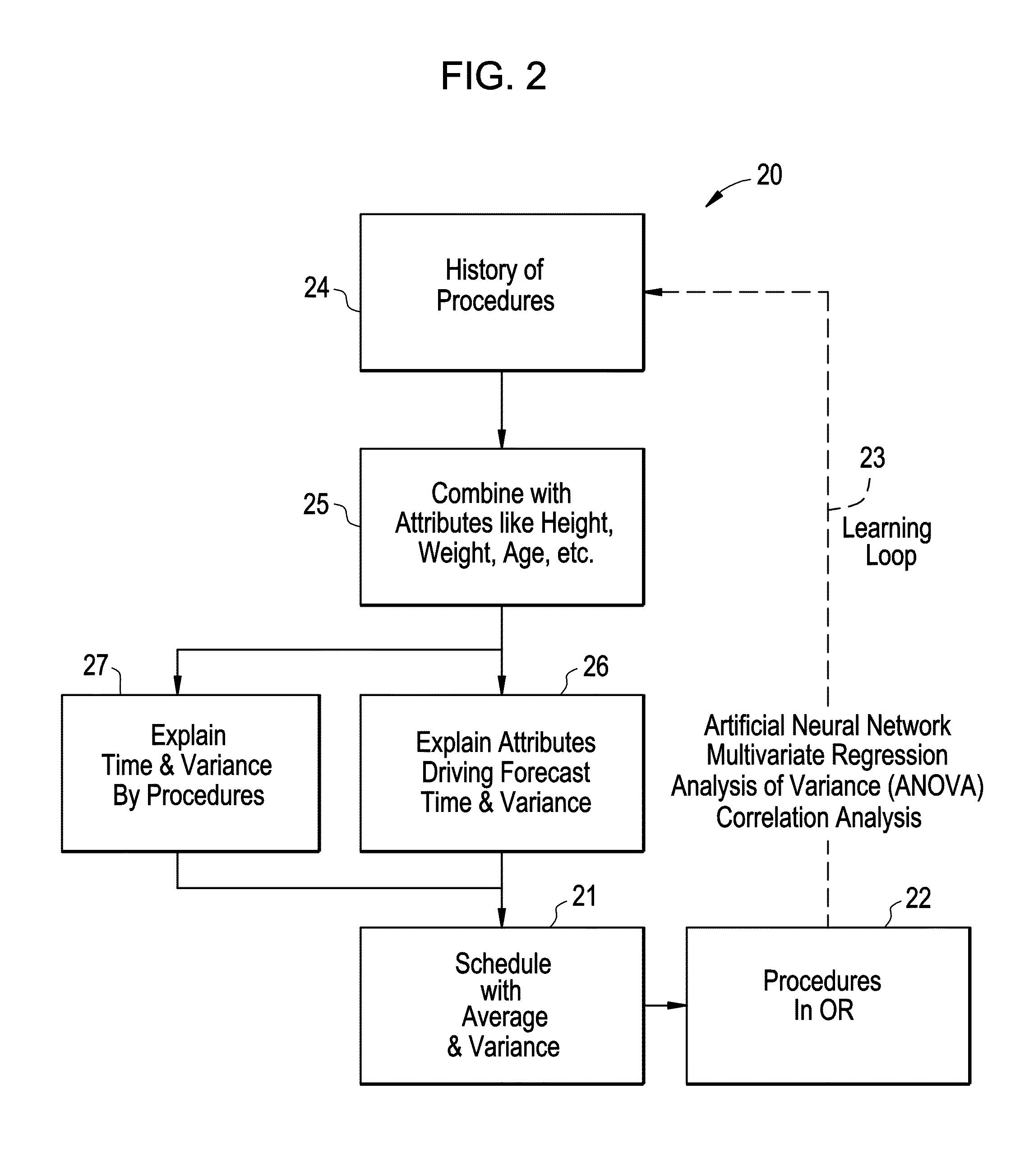
Optimizing state transition set points for schedule risk management
ActiveUS20160063192A1Quick scanGreat advantageHospital data managementResourcesNormal densityState dependent
Systems, methods, and apparatus to dynamically manage interdependent, variable scheduled procedures are provided. An example method includes calculating a cumulative distribution function (CDF) for task(s) in a healthcare protocol based on a probability density function associated with task duration(s) for the task(s). The method includes determining a plurality of schedule risk states for each task in a healthcare protocol, each schedule risk state associated with an upper specification limit (USL) and a lower specification limit (LSL) along the CDF. The method includes identifying, within USL and LSL for each schedule risk state, setpoint(s) associated with probability(-ies) along the CDF. The method includes monitoring execution of task(s) in the healthcare protocol to identify a transition in schedule risk state according to USL and LSL. The method includes triggering an action to react to an actual or upcoming change in schedule risk state based on setpoint(s) associated with the schedule risk state.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
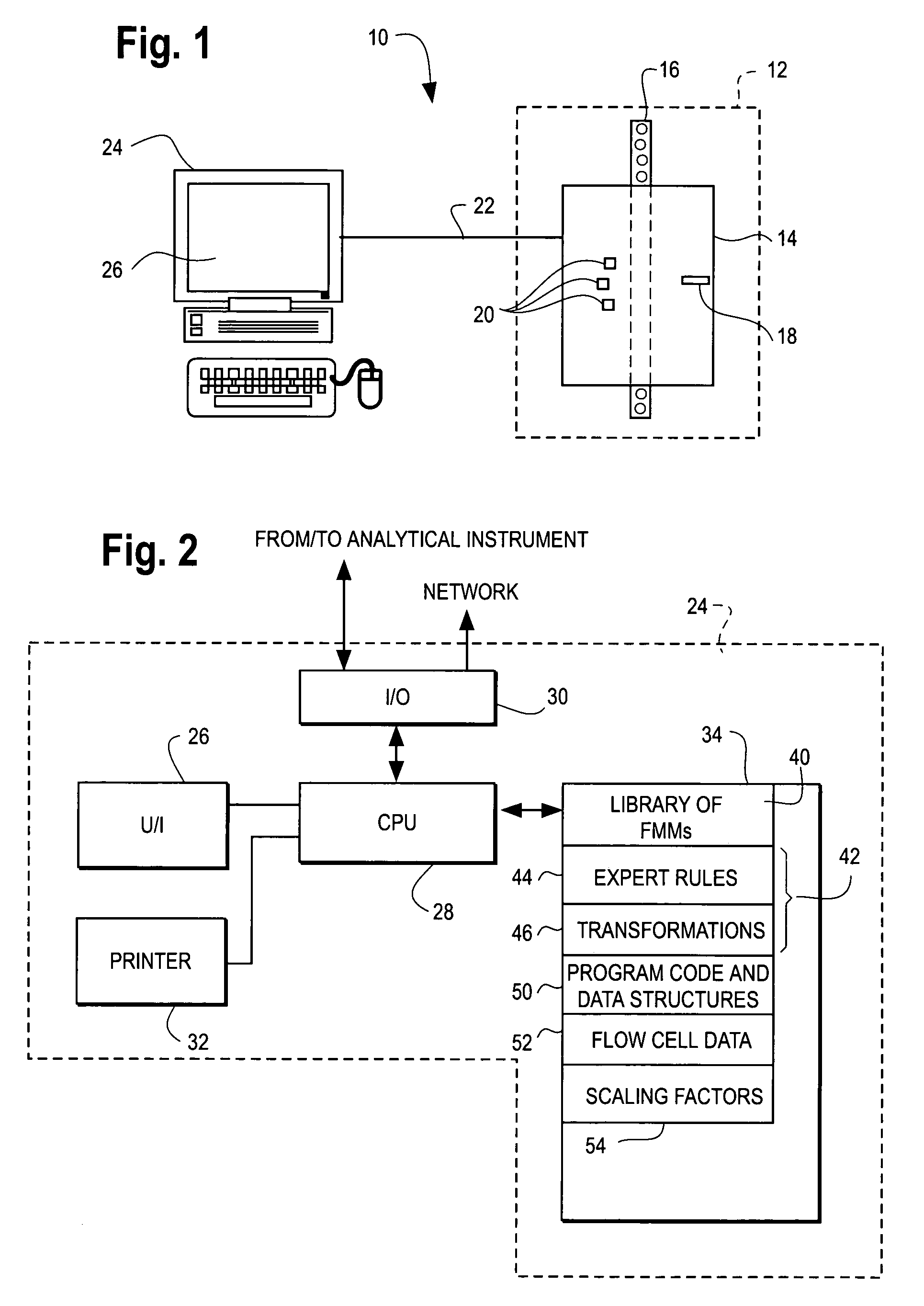
Methods for identifying discrete populations (e.g., clusters) of data within a flow cytometer multi-dimensional data set
InactiveUS20070118297A1Accurate classificationRobust and accurateMedical data miningBiological particle analysisData transformationData set
Systems and methods for identifying populations of events in a multi-dimensional data set, e.g., seven dimensional flow cytometry data of a blood sample. The populations may, for example, be sets or clusters of data representing different white blood cell components in the sample. The methods use a library consisting of one or more one finite mixture models, each model component comprising parameters representing multi-dimensional Gaussian probability density functions, one density for each population of events expected in the data set. The methods further use an expert knowledge set comprising one or more data transformations for operation on the multi-dimensional data set and one or more logical statements. The transformations and logical statements encode a priori expectations as to the relationships between different event populations in the data set. The methods further use program code comprising instructions by which a processing unit such as a computer may operate on the multi-dimensional data, a finite mixture model selected from the library, and the expert knowledge set to thereby identify populations of events in the multi-dimensional data set.
Owner:IDEXX LABORATORIES
Adaptive contrast enhancement method for video signals based on time-varying nonlinear transforms
InactiveUS7221408B2Increase contrastEnhanced output signalImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionNormal density
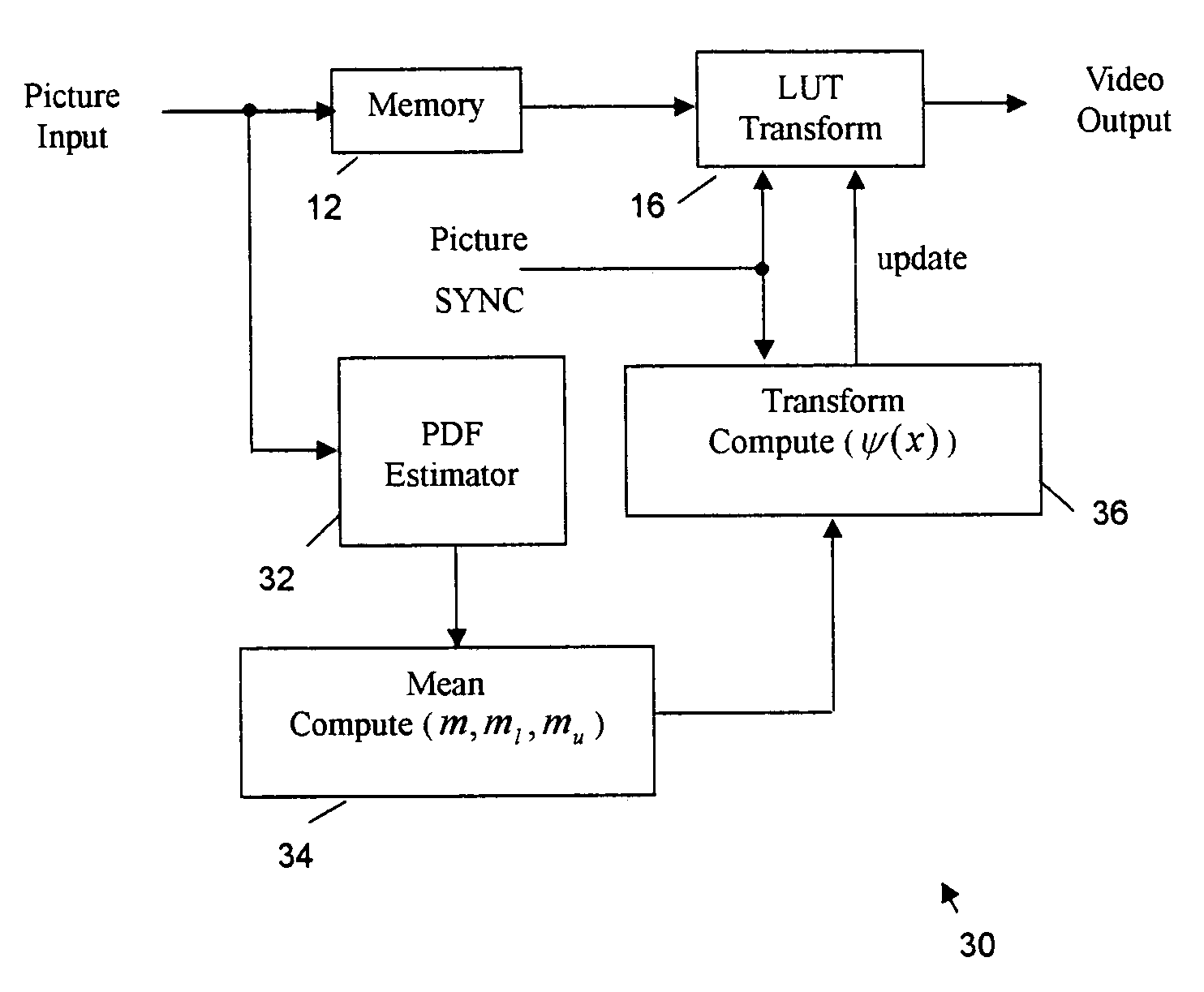
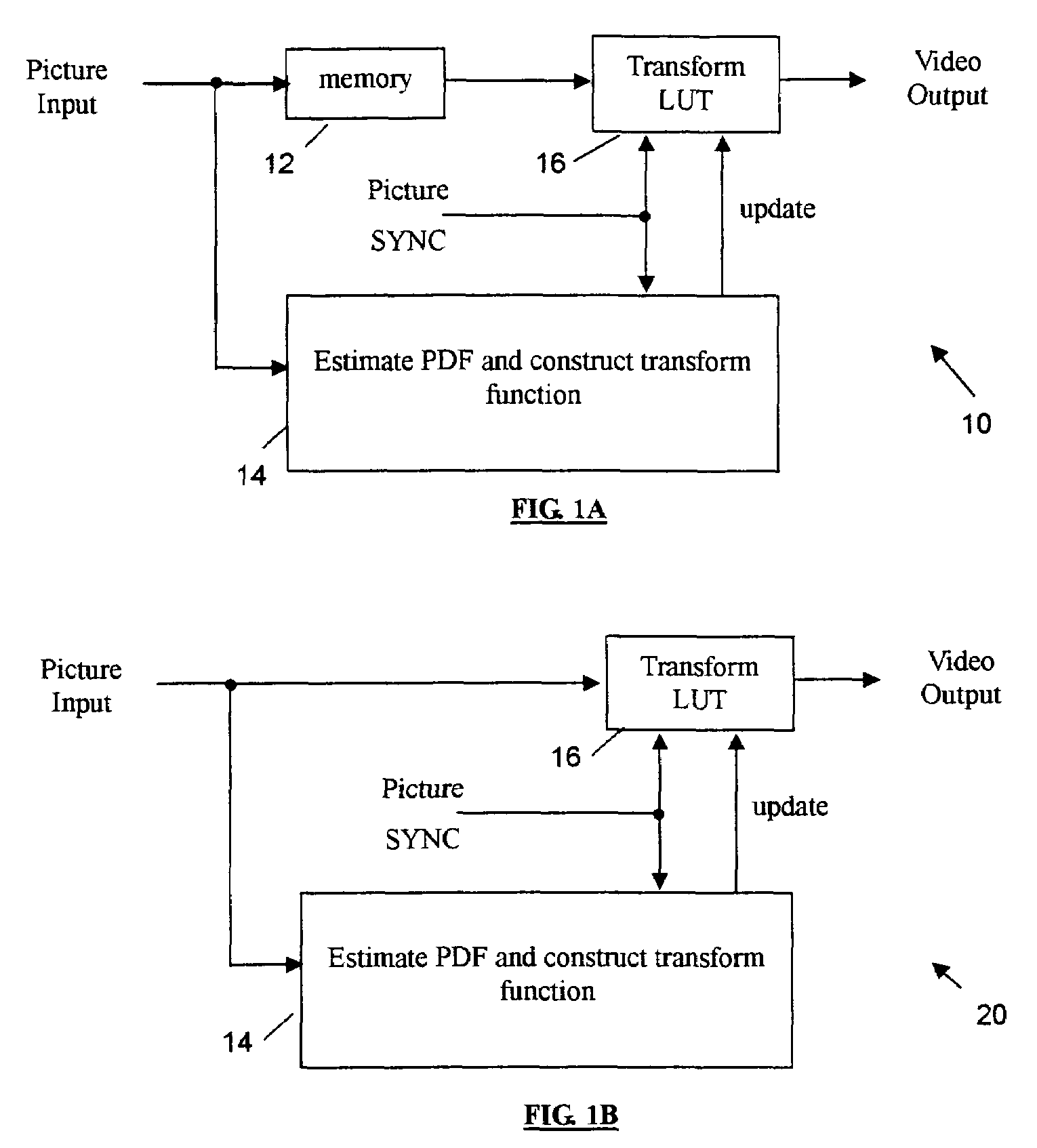
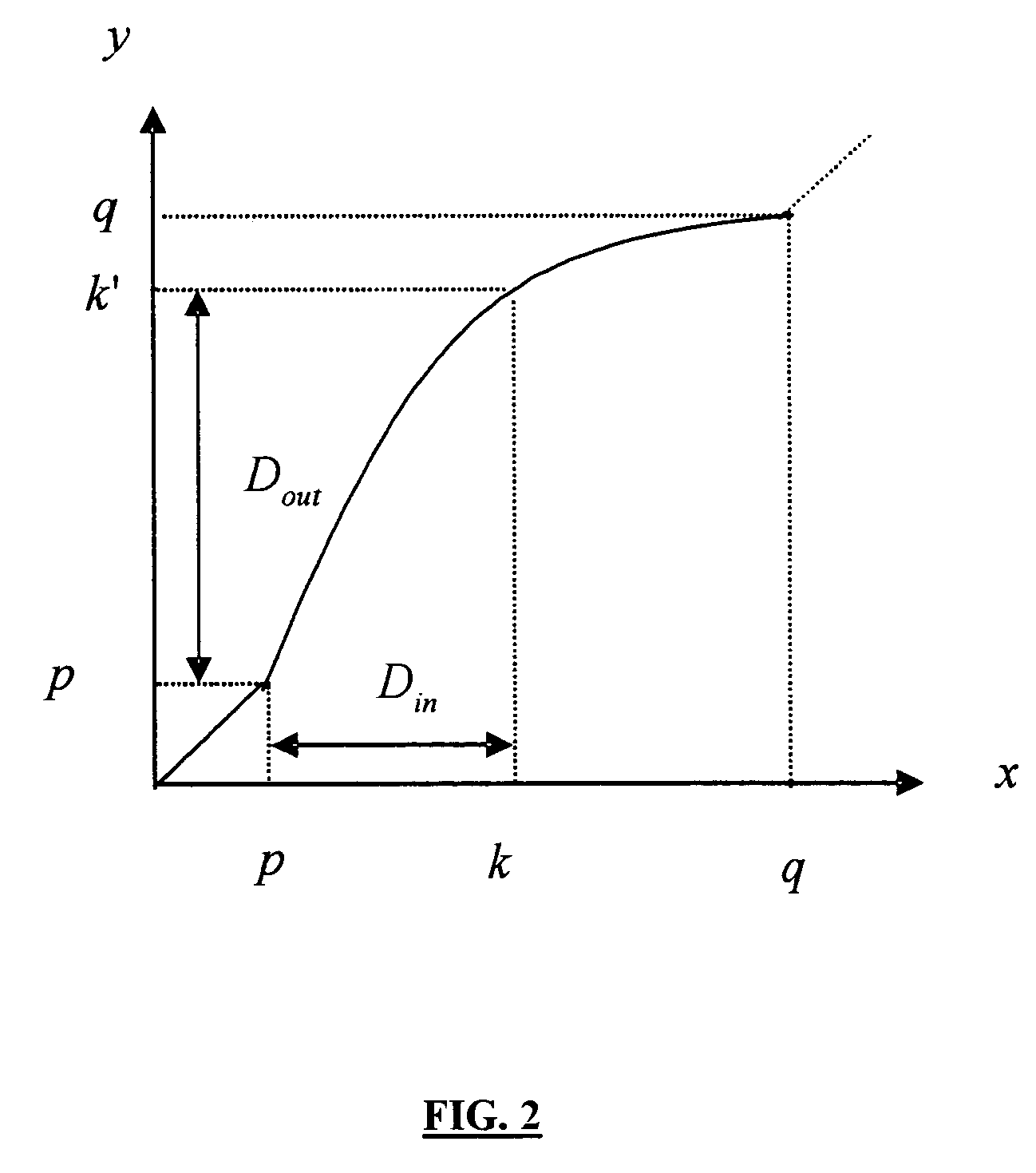
An adaptive contrast enhancement (ACE) method and apparatus provide a natural enhancement in accordance with the time-varying characteristics of a video sequence. Characteristics of a time varying video sequence are specified and a nonlinear transform over the input video sequence is performed to enhance mainly the contrast of the input. A probability density function (PDF) of a time varying input video sequence is computed and then some predetermined video parameters relating to contrast is extracted from the PDF. Based upon the extracted video parameters, a nonlinear transform function is then constructed and updated as a look up table (LUT), which is synchronized with the associated video picture or field SYNC signal. The transform LUT is then applied to the input video to provide an enhanced video output signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for early warning of sensitive client electric energy experience quality under voltage dip disturbance
InactiveCN103487682AReduce the risk of electricity supply and useAccurately monitor power quality disturbancesElectrical testingNormal densitySvm classifier
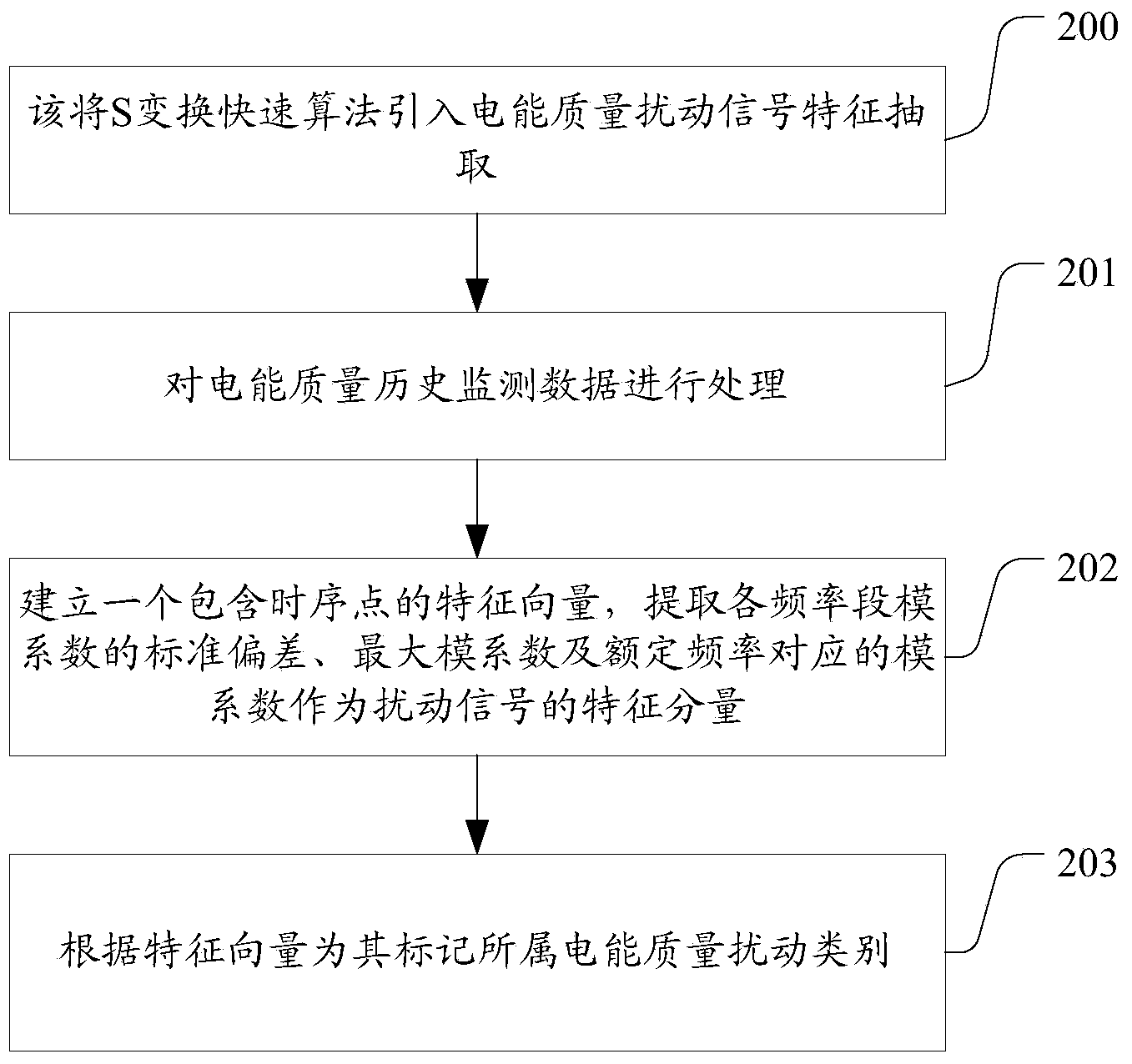
The invention provides a method for early warning of sensitive client electric energy experience quality under the voltage dip disturbance. The method comprises the steps that based on the S conversion rapid algorithm and an increment SVM classifier, voltage dip disturbances of sensitive clients are automatically identified; based on identification results of the voltage dip disturbances, voltage tolerance curves of devices corresponding to multiple types of sensitive clients at different load levels are determined; historical monitoring data of the voltage dip disturbances serve as samples, the samples are converted into sample values of a voltage dip amplitude ponderance index MSI and a lasting time ponderance index DSI, a probability density function of the MSI and the DSI is determined on the basis of the maximum entropy principle, the sensitive device fault probability is evaluated, and the probabilities of the sensitive devices corresponding to the sensitive clients at the voltage dip level are obtained. By the adoption of the method for early warning of sensitive client electric energy experience quality under the voltage dip disturbance, the electric energy quality disturbance condition can be accurately monitored, whether a client load is influenced by the disturbance or not is determined according to the load sensitivity degree of each client, and potential risks of load operation are found.
Owner:SHENZHEN POWER SUPPLY BUREAU +1
Method for uncertainty quantifiation in the performance and risk assessment of a carbon dioxide storage site
ActiveUS20100299126A1SeismologyComputation using non-denominational number representationCarbon dioxideRisk assessment
A CO2 sequestration site is evaluated by incorporating a consistent petrophysical framework having uncertainties expressed in the form of probability density functions of wellbore measurements, by systematically propagating the uncertainties in generating probability density functions or cumulative distribution functions of the parameters used in a reservoir simulation, by using the reservoir simulation to transform the first set of parameters into output variables with uncertainties, and by using the output variables and uncertainties to generate an answer product from which uncertainty levels of performance metrics can be ascertained.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Partical image velocimetry suitable for x-ray projection imaging
ActiveUS20130070062A1Enhance the imageImprove overall utilizationTelevision system detailsTomographyX-rayDynamic speckle
A 2D or 3D velocity field is reconstructed from a cross-correlation analysis of image pairs of a sample, without first reconstructing images of the sample spatial structure. The method can be implemented via computer tomographic x-ray particle image velocimetry, using multiple projection angles, with phase contrast images forming dynamic speckle patterns. Estimated cross-correlations may be generated via convolution of a measured autocorrelation function with a velocity probability density function, and the velocity coefficients iteratively optimised to minimise the error between the estimated cross-correlations and the measured cross-correlations. The method may be applied to measure blood flow, and the motion of tissue and organs such as heart and lungs.
Owner:4DX LTD
Method for evaluating state of health battery in real time
ActiveCN103675702ASolve common problemsBreak through the difficulty of estimating battery state of health (SOH) onlineElectrical testingNormal densityInternal resistance
The invention provides a method for evaluating state of health of a battery in real time and belongs to the technical field of batteries. By the method, realtime estimation of the state of health of the battery is realized, shared problems of a charging and discharging method, a voltage differential method / capacity increment method and an internal resistance measuring method are solved, the difficulty in online estimating the SOH (state of health) of the battery is overcome, and an advanced algorithm is provided for an electromobile battery management system. As shown in an abstract drawing, the algorithm includes two stages, the first stage is a test and calibration stage which is similar to MAP graph calibration of an internal combustion engine and is generally performed in a laboratory, and a probability density function (PDF) is used in the first stage; the second stage is an online estimation stage which is an implementation process of an online estimation algorithm of the SOH of the battery. In an embodiment of the invention, realtime estimation error of the algorithm is smaller than 2% in most circumstances.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
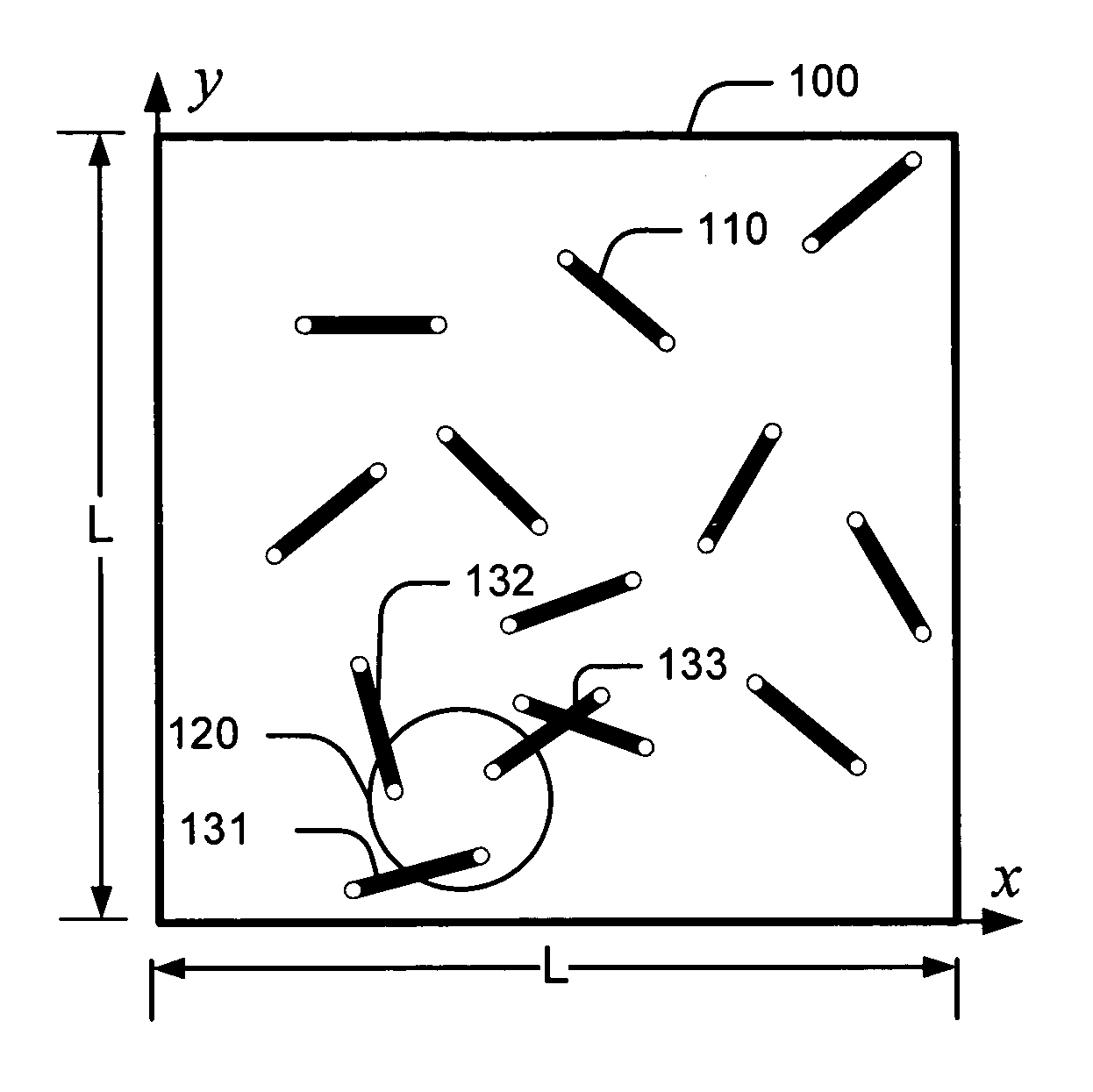
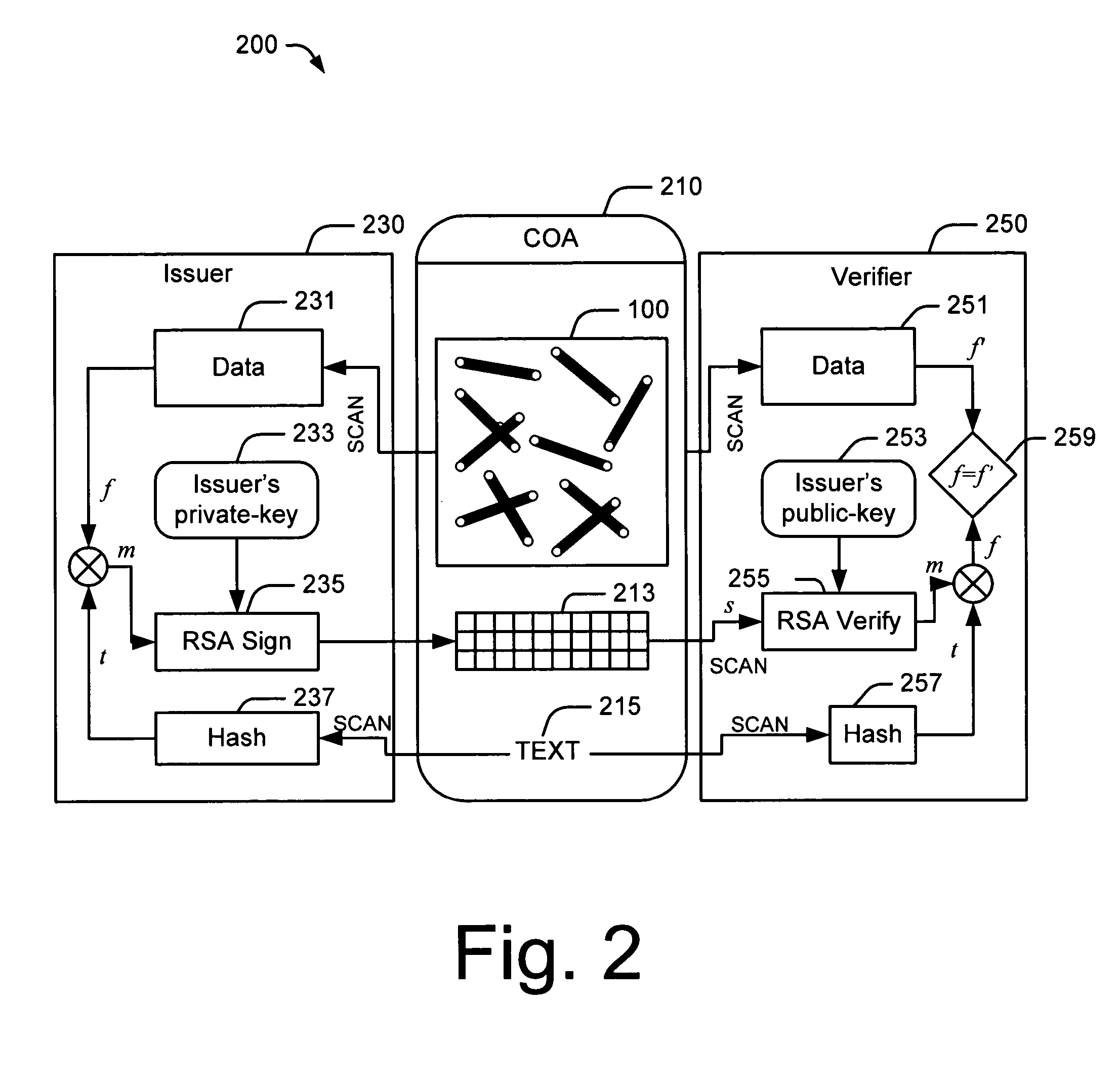
Systems and methods for encoding randomly distributed features in an object
The described systems and methods described are directed at encoding randomly distributed features in an object. Randomly distributed features in an authentication object are determined. Data representing the randomly distributed features is compressed and encoded with a signature. A label is created and includes the authentication object and the encoded data. The data may be compressed by determining a probability density function associated with the authentication object. Vectors associated with the randomly distributed attributes are determined based, at least in part, on the probability density function. The vectors are encoded using an arithmetic coding algorithm.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
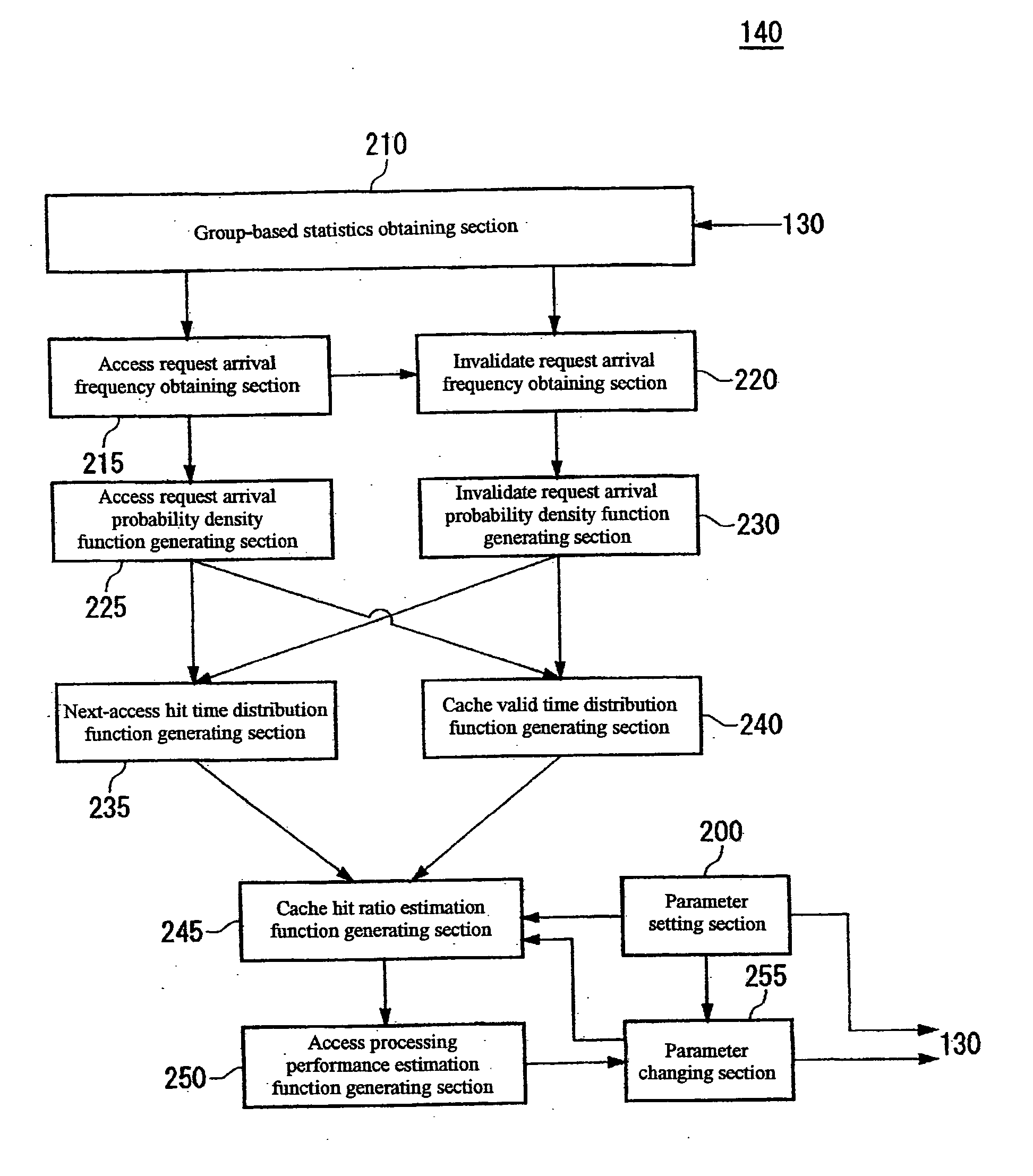
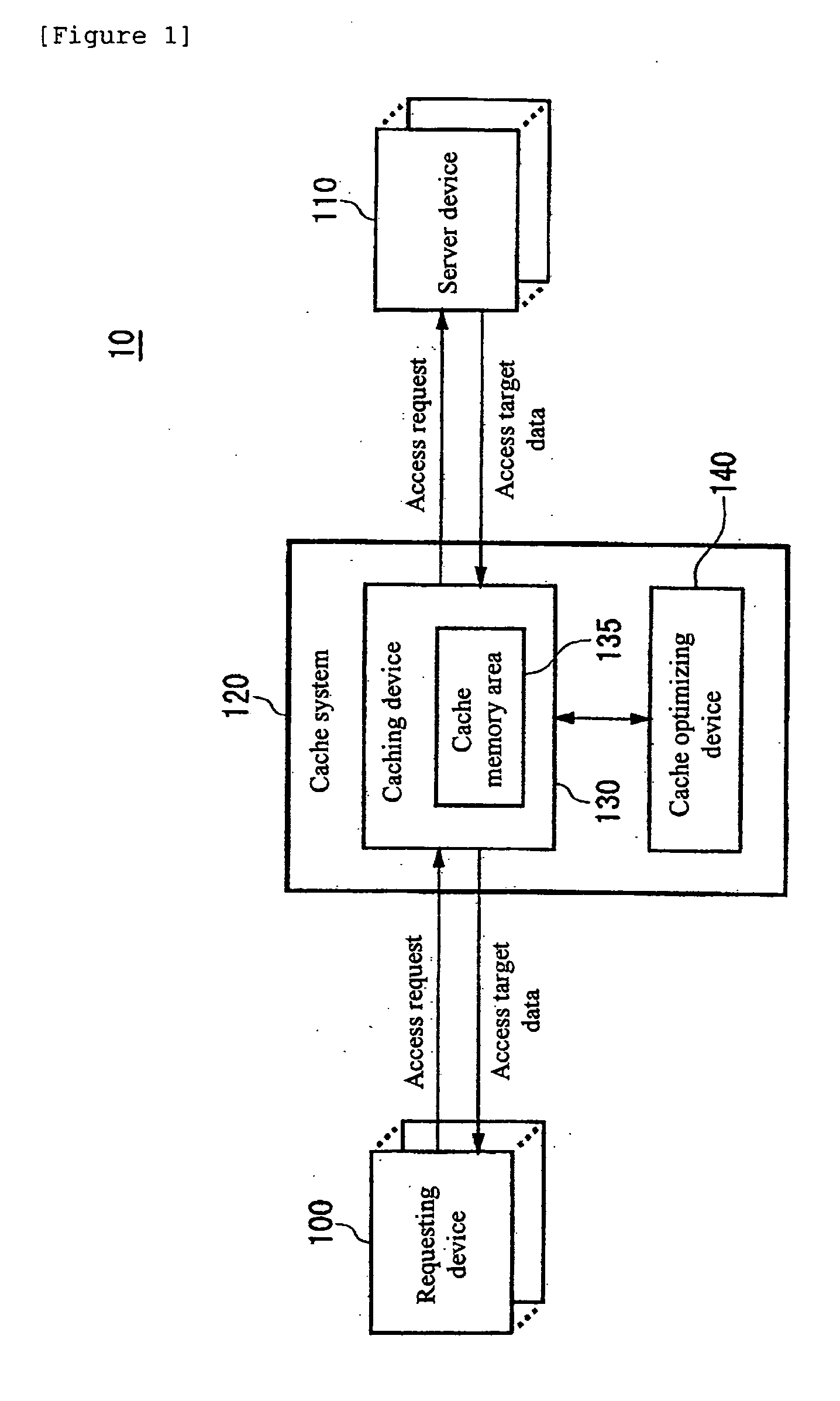
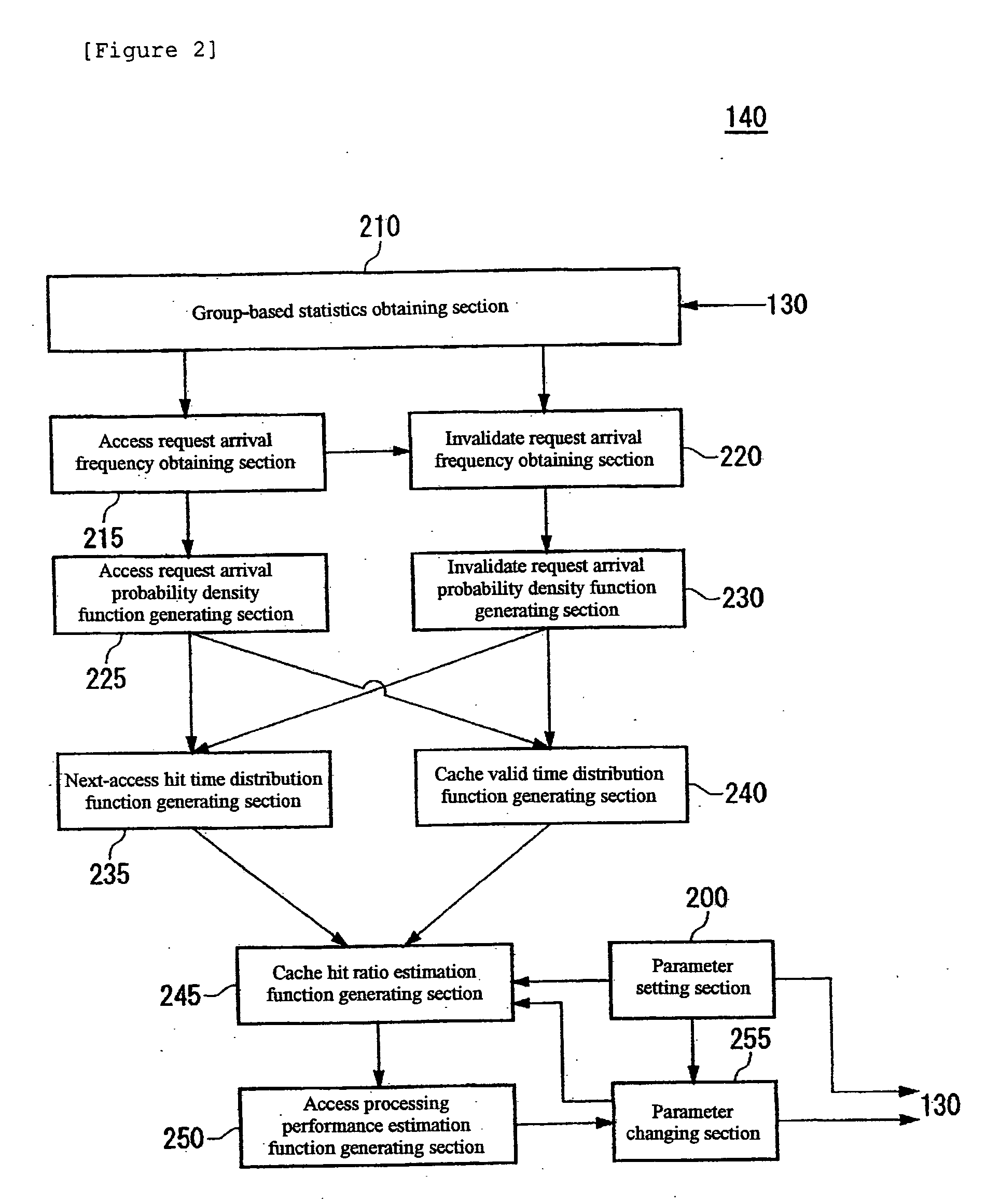
Cache hit ratio estimating apparatus, cache hit ratio estimating method, program, and recording medium
InactiveUS20050268037A1Improve accuracyEasy to processInput/output to record carriersError detection/correctionCache accessNormal density
Determining a cache hit ratio of a caching device analytically and precisely. There is provided a cache hit ratio estimating apparatus for estimating the cache hit ratio of a caching device, caching access target data accessed by a requesting device, including: an access request arrival frequency obtaining section for obtaining an average arrival frequency measured for access requests for each of the access target data; an access request arrival probability density function generating section for generating an access request arrival probability density function which is a probability density function of arrival time intervals of access requests for each of the access target data on the basis of the average arrival frequency of access requests for the access target data; and a cache hit ratio estimation function generating section for generating an estimation function for the cache hit ratio for each of the access target data on the basis of the access request arrival probability density function for the plurality of the access target data.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
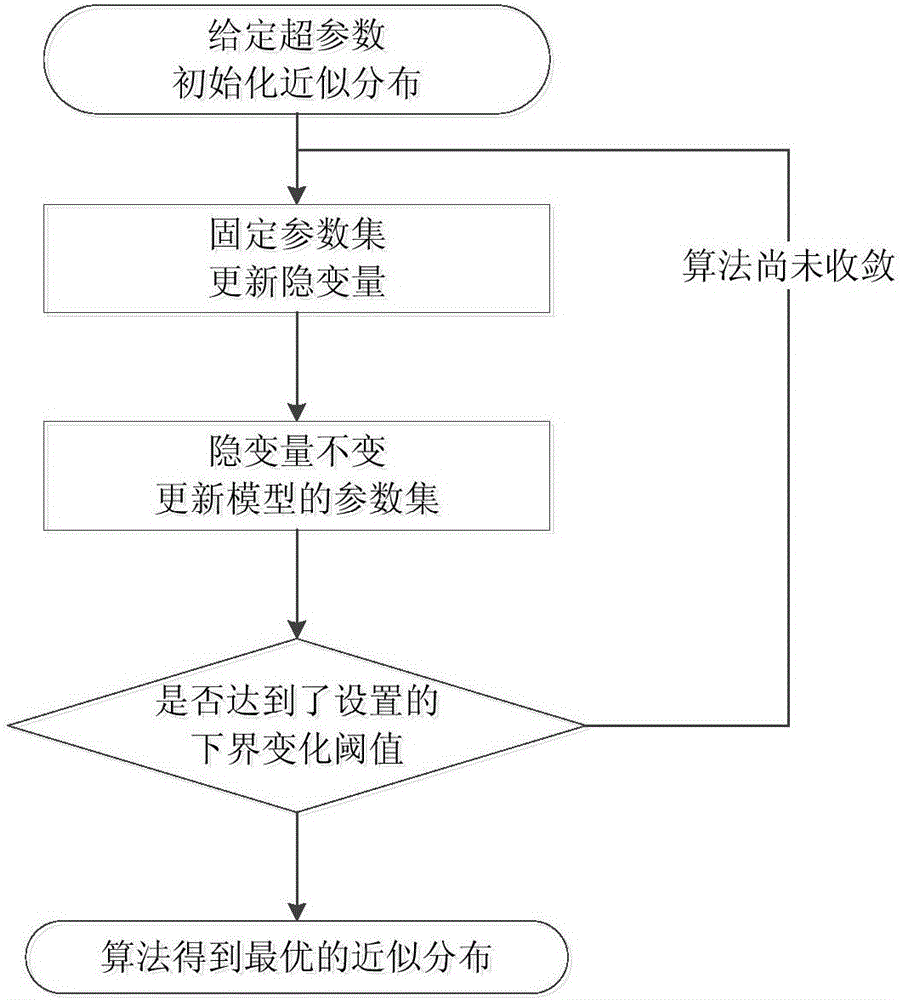
Particle filtering method based on Gaussian mixture model and variational Bayes
The invention discloses a particle filtering method based on a Gaussian mixture model and variational Bayes, comprising the following steps: (1) modeling observation noise using a Gaussian mixture model, and initializing the initial state; (2) randomly generating N initial particles based on the probability density function of the initial state; (3) initializing the super parameters of the unknown parameters in the Gaussian mixture model of observation noise; (4) generating sampling particles from a chosen importance reference function; (5) updating measurement, and calculating the particle weights according to the latest observation value and a particle weight iteration formula; (7) using a variational Bayesian method to get the distribution of the unknown parameters in the Gaussian mixture model by means of loop iteration; and (7) normalizing the particle weights, and re-sampling a particle set in view of particle degradation. Through the scheme, the filtering precision and the target state estimation performance are improved effectively.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
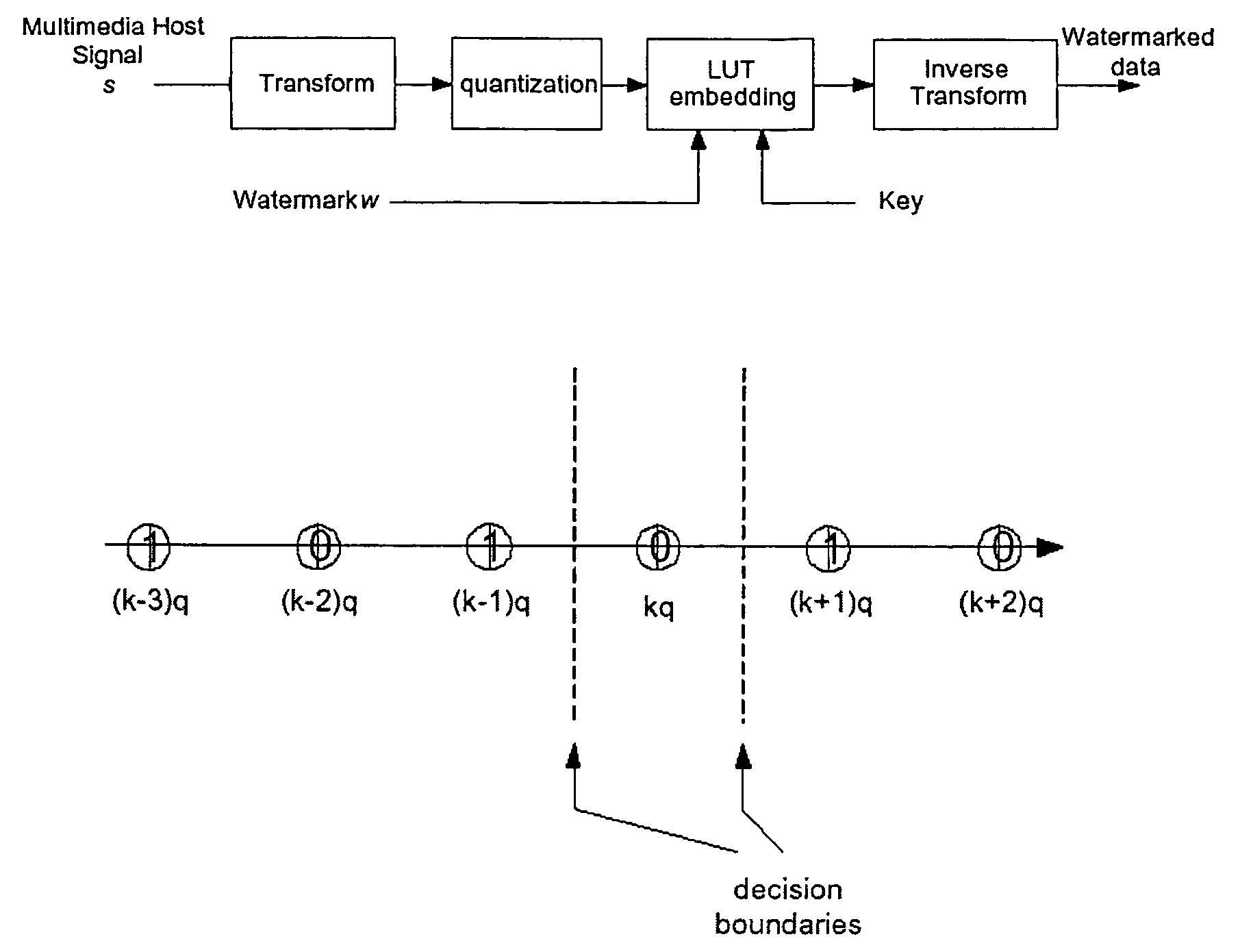
Watermark embedding and detecting methods, systems, devices and components
InactiveUS7693297B2Character and pattern recognitionImage data processing detailsNormal densityAlgorithm
Method determining lookup table (“LUT”) for embedding watermark. For each quantization cell, calculating probabilities that signal point falls into cell. Selecting cell by probabilities. Setting LUT value to watermark value with largest probability, subject to run constraint. For remaining cells, repeating selecting and setting steps. Other method determining quantization ensemble by calculating probability density function for signal points where the watermark value to be embedded. Distortion and robustness functions are formulated. Given robustness or distortion is selected. Functions optimized, and ensemble of quantizers determined with parameters that comply. Other method quantizing in association with lossy compression. Strength of compression determined. Adapting strength of watermark with strength of compression by a mapping. Other method selecting points for embedding watermark. Determine threshold between large and small signal points using statistical method. Select signal points for embedding according to threshold. Also, processors, computer programs, and systems.
Owner:ZHANG XIAO PING +1
Method of producing a two-dimensional probability density function (PDF) eye diagram and Bit Error Rate eye arrays
InactiveUS20060018374A1Noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementError preventionNormal densityPortable document format
A method of producing of a two-dimensional probability density function eye diagram and Bit Error Rate eye arrays generates a two-dimensional PDF array of a correlated waveform record of a data pattern under test which is convolved with a two-dimensional probability density function (PDF) array of the uncorrelated jitter and noise in the data pattern under test. The resulting aggregate two dimensional PDF array of the correlated waveform record pattern with uncorrelated jitter and noise is divided into unit intervals and the unit intervals are summed to generated a two-dimensional PDF eye diagram array. The two-dimensional PDF eye diagram is processed to generate a two-dimensional Bit Error Rate eye array.
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
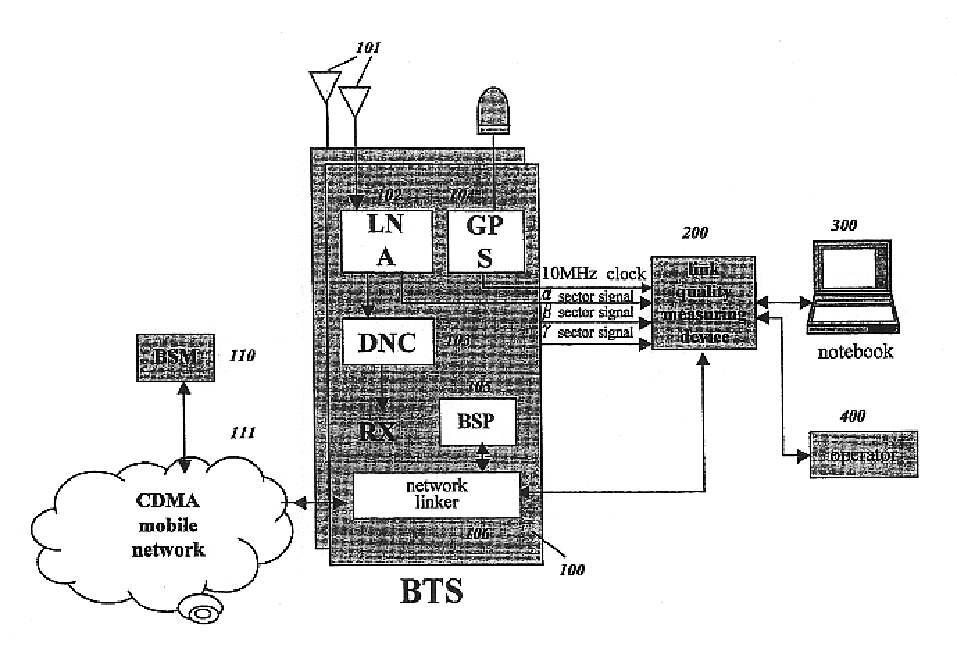
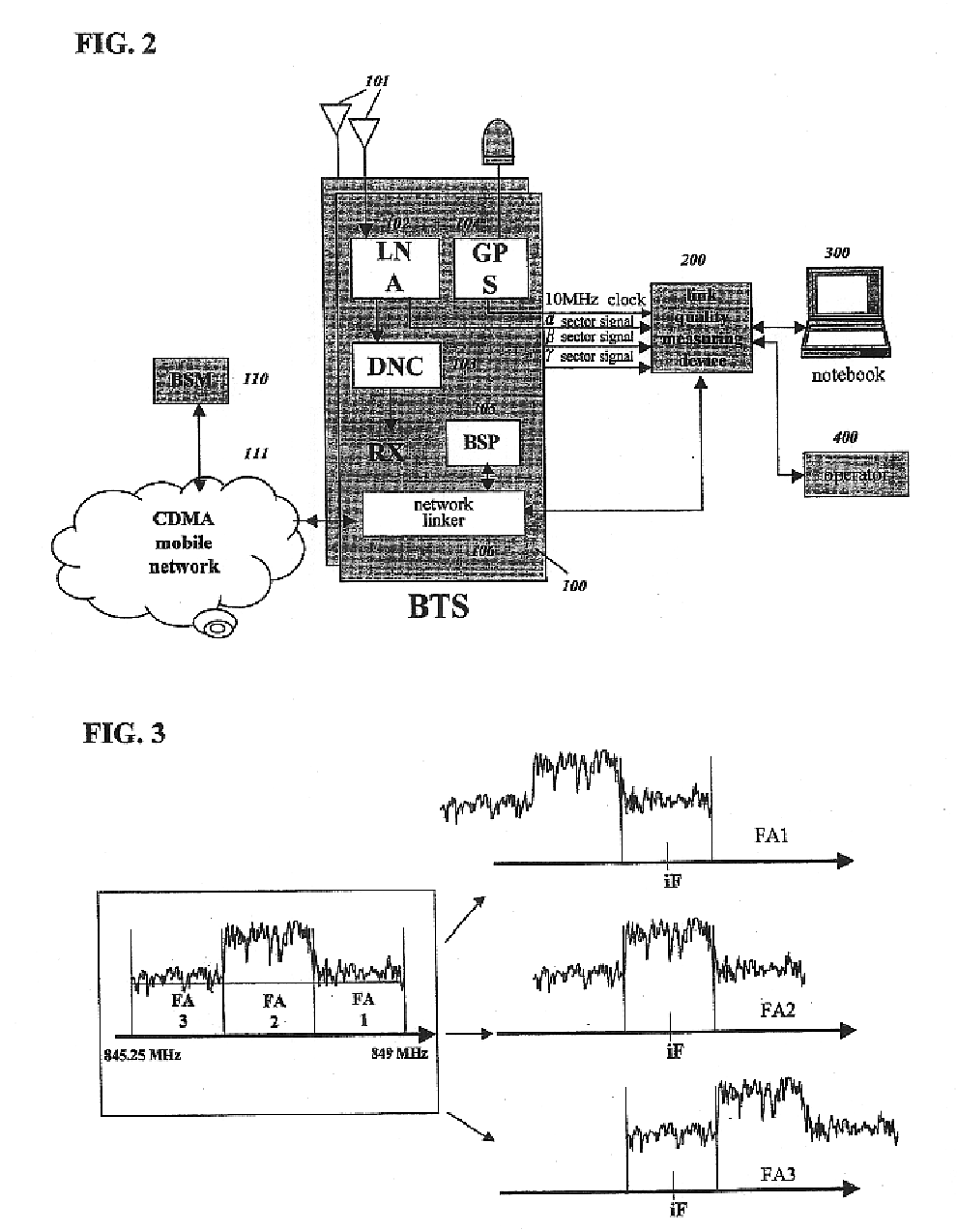
Apparatus and method for measuring quality of a reverse link in a CDMA system
InactiveUS6760567B1Load accuratelyAccurate qualityReceivers monitoringError preventionNormal densityMobile station
An apparatus and method for measuring the quality of a reverse link and the load of a base station (BTS) in a CDMA mobile telecommunication system. The apparatus and method periodically detect the power of a receiving signal from a mobile station to a BTS, constructs a practical statistical distribution curve for a power ratio of signal to interference, compares the practical distribution curve with the theoretical distribution curve pre-constructed based upon the parameter condition of a BTS, and determines the quality of a reverse link based upon the difference between the distribution curves. The link-quality measuring device has a power detecting unit for detecting the power of signals received by a BTS; a converter for digitizing the detected power; a controlling unit constructing a PDF (Probability Density Function) and / or a CDF (Cumulative Distribution Function) for a ratio of a received power to a background noise power using the digitized data, comparing the constructed function with the theoretical PDF and / or CDF for the ratio which is pre-calculated based upon various values of input parameters, and acquiring the traffic load according to the compared result; and data entering unit for receiving the values for the input parameters provided from an operator or an external device.
Owner:SK TELECOM CO LTD
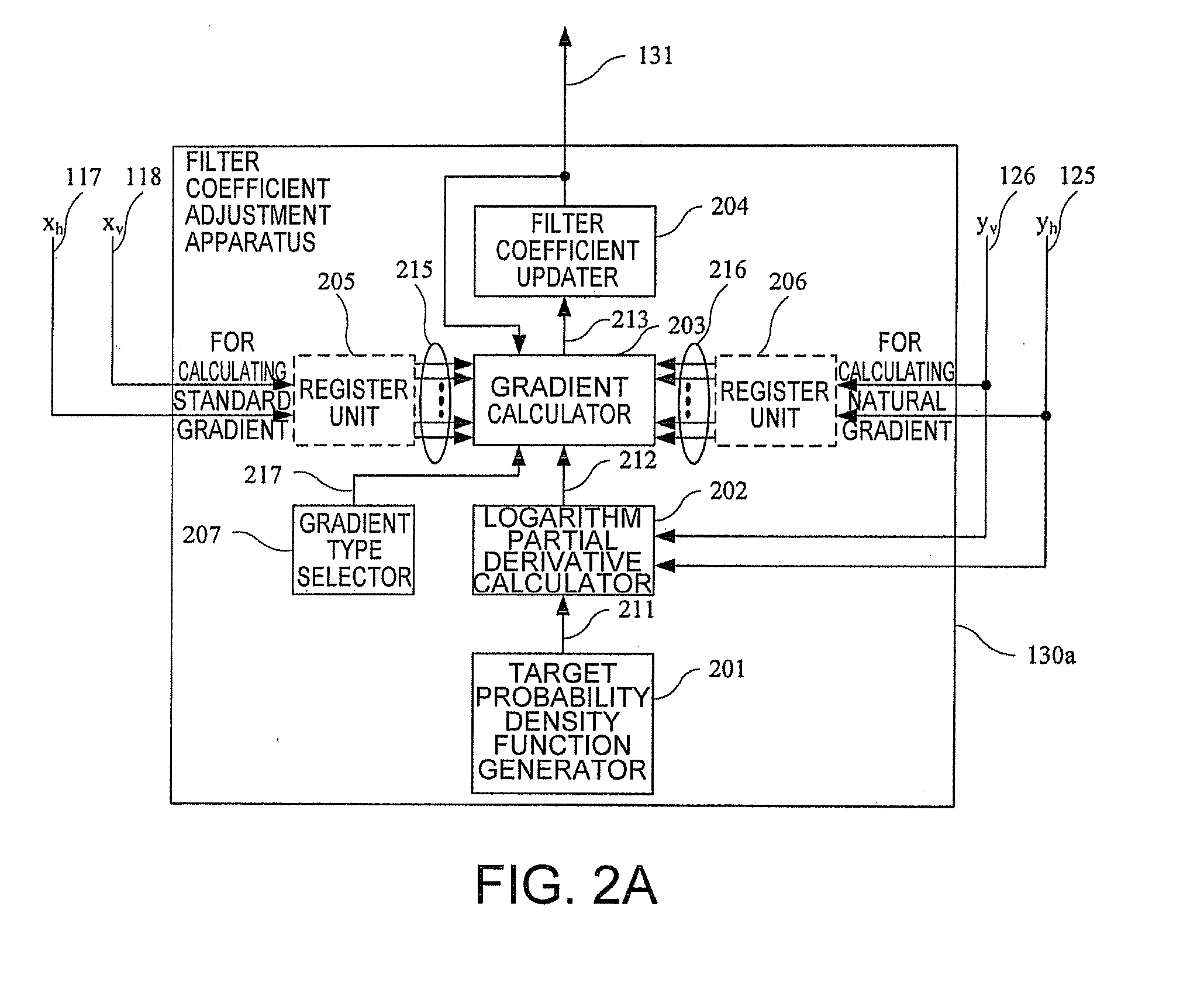
Filter coefficient adjustment apparatus
ActiveUS20100003028A1Avoid violationsMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsMultiplexingNormal density
In present invention, a filter coefficient adjustment apparatus is used in a polarization demultiplexer which demultiplexes the input signals by using filters to obtain demultiplexed output signals, said filter coefficient adjustment apparatus being used for adjusting the coefficients of the filters, wherein said filter coefficient adjustment apparatus comprises: an logarithm partial derivative calculation unit for calculating the logarithm partial derivative value of a target probability density function of the demultiplexed output signals when its self-variable value is the present demultiplexed output signal value; a gradient calculation unit for calculating the gradient of a target optimizing function for optimizing the distribution of the multiplexed output signals based on the logarithm partial derivative value calculated by the logarithm partial derivative calculation unit; and a filter coefficient updating unit for updating the coefficients of the filters based on the gradient calculated by the gradient calculation unit.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Stochastic inversion of geophysical data for estimating earth model parameters
A computer implemented stochastic inversion method for estimating model parameters of an earth model. In an embodiment, the method utilizes a sampling-based stochastic technique to determine the probability density functions (PDF) of the model parameters that define a boundary-based multi-dimensional model of the subsurface. In some embodiments a sampling technique known as Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) is utilized. MCMC techniques fall into the class of “importance sampling” techniques, in which the posterior probability distribution is sampled in proportion to the model's ability to fit or match the specified acquisition geometry. In another embodiment, the inversion includes the joint inversion of multiple geophysical data sets. Embodiments of the invention also relate to a computer system configured to perform a method for estimating model parameters for accurate interpretation of the earth's subsurface.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
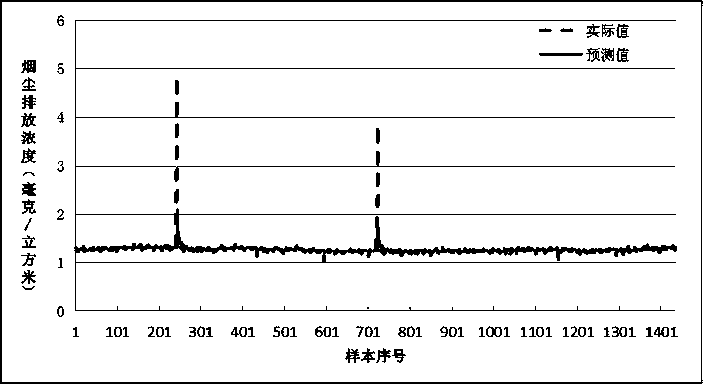
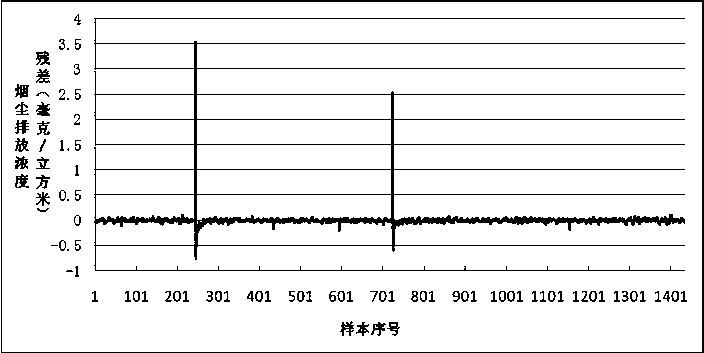
Residual error posterior-based abnormal value online detection and confidence degree assessment method
ActiveCN107092582AImprove accuracyImprove reliabilityComplex mathematical operationsNormal densityState model
The invention discloses a residual error posterior-based abnormal value online detection and confidence degree assessment method. The method comprises the steps of collecting data, establishing time series data, performing linear fitting on the time series data to obtain a linear combination formula of data at a current moment and p pieces of previous data, and predicting a data value of subsequent time; comparing the predicted data value with an actually detected data value to obtain a predicted residual error series; determining a probability density function of the predicted residual error series by adopting a KDE (Kernel Density Estimation) method; performing posterior ratio check on the predicted residual error series, and judging whether the data at the current moment is an abnormal point or not; and by taking the time series data as an input, building an SOM state model, obtaining state series and state transition probability matrixes, defining an abnormal scoring function, and outputting an abnormal score. By comparing the probability that the data is the abnormal point with the probability that the data is a normal point, the abnormal value in the pollutant discharge concentration time series data is identified online, so that the accuracy and reliability of abnormal value judgment are improved.
Owner:JIANGSU FRONTIER ELECTRIC TECH +2
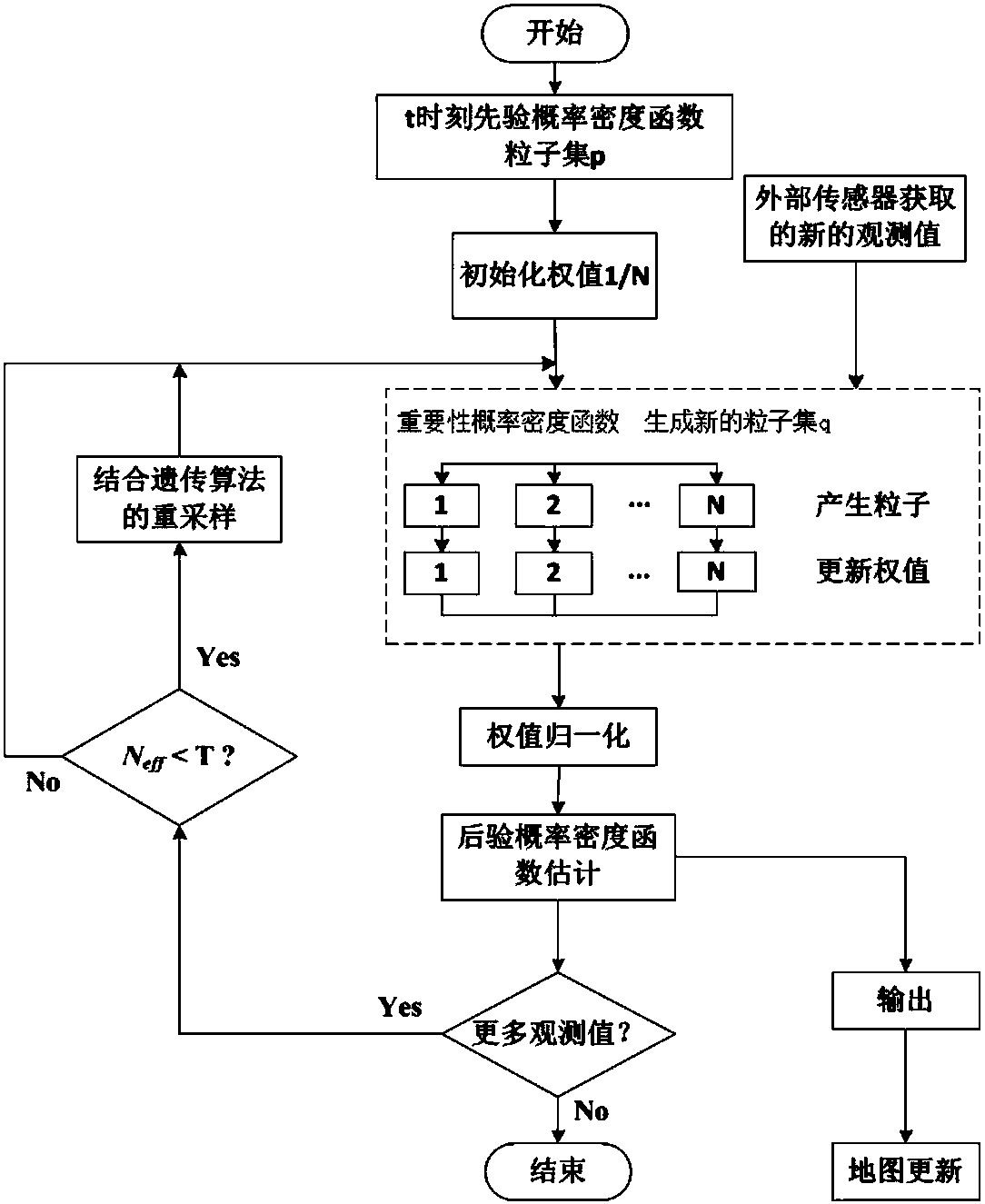
Method for simultaneous localization and mapping of mobile robot based on improved particle filter
InactiveCN107246873AEasy to keepReduce the impactNavigational calculation instrumentsPosterior probability densitySimultaneous localization and mapping
The invention discloses a method for simultaneous localization and mapping of a mobile robot based on an improved particle filter. The method comprises the following steps: initializing an initial-moment pose of a robot; obtaining a t-moment prior probability density function according to the pose information at a t-1 moment, and generating a sampling particle set p; initializing the weights of particles; selecting an importance probability density function, generating a new sampling particle set q, calculating the weights of particles, updating the weights of the particles, and normalizing the weights; calculating the weighted sum of random sample particles at current moment t to express posterior probability density, and obtaining the moving pose and environmental map information; judging whether a new observed value is input; if so, returning; otherwise, ending the cycle; before returning, judging whether resampling is needed or not. According to the difference of the system state, a dynamic threshold is set for judgment, and a genetic algorithm is combined. According to the method disclosed by the invention, influence of a problem of particle degeneration on SLAM is reduced, and the calculated amount of the SLAM problem is reduced.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com