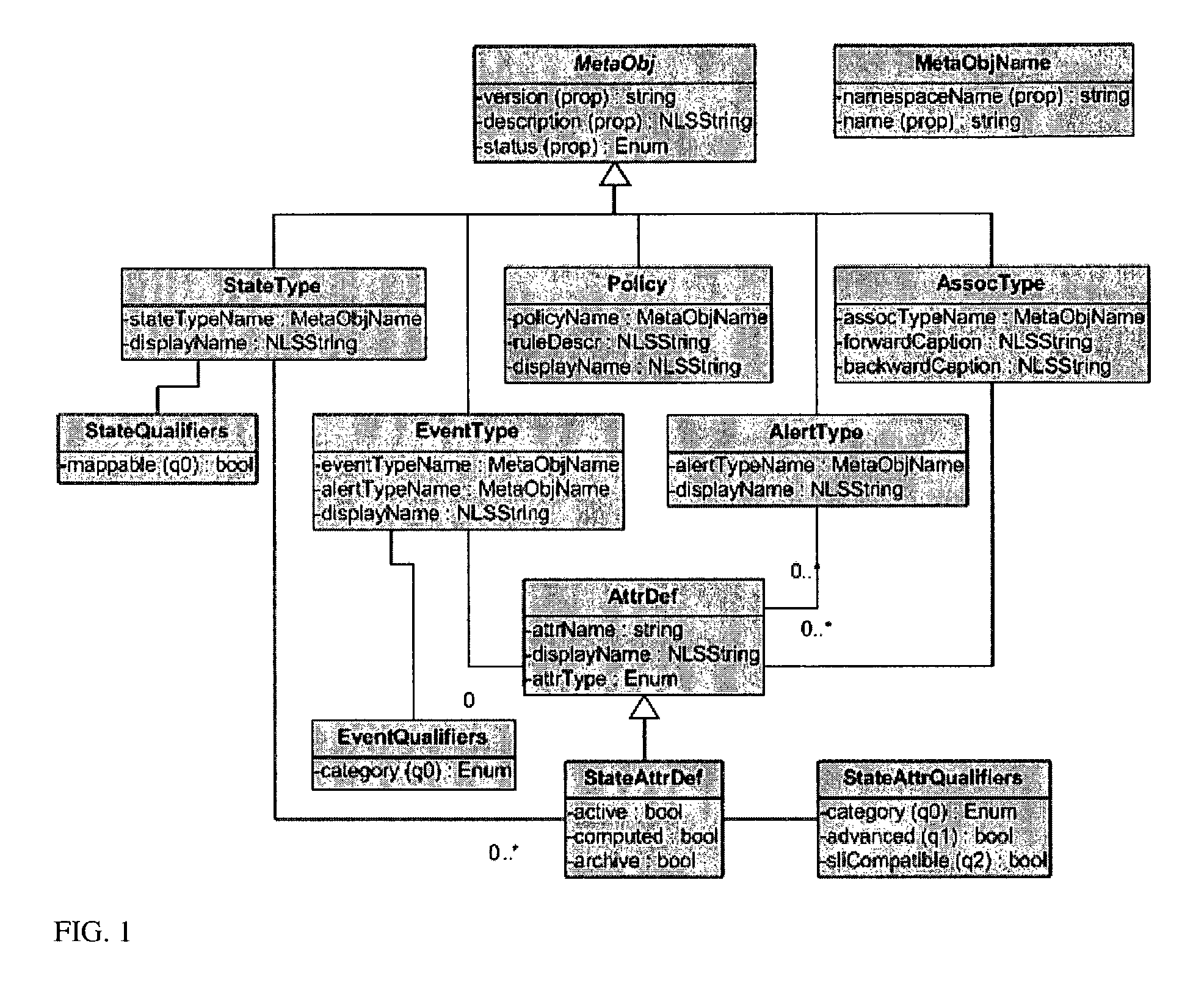
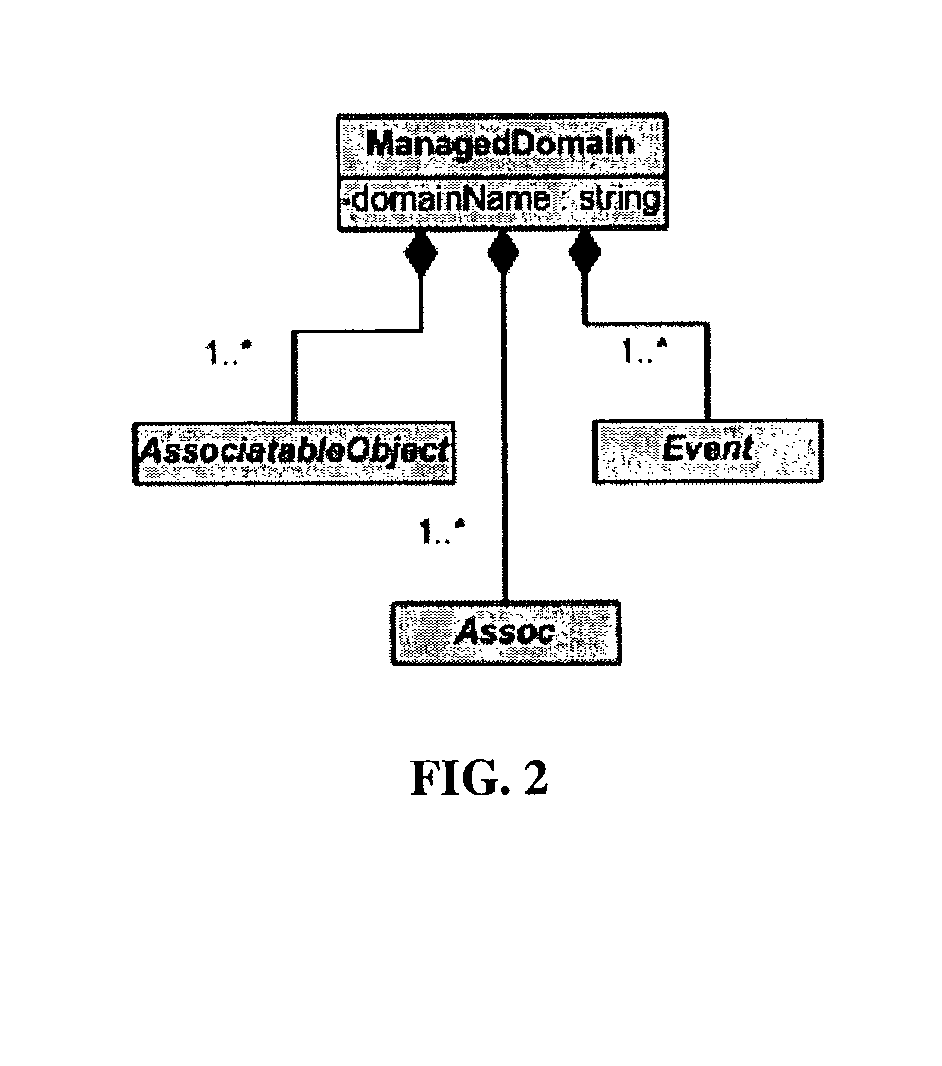
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1005 results about "Predicting performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
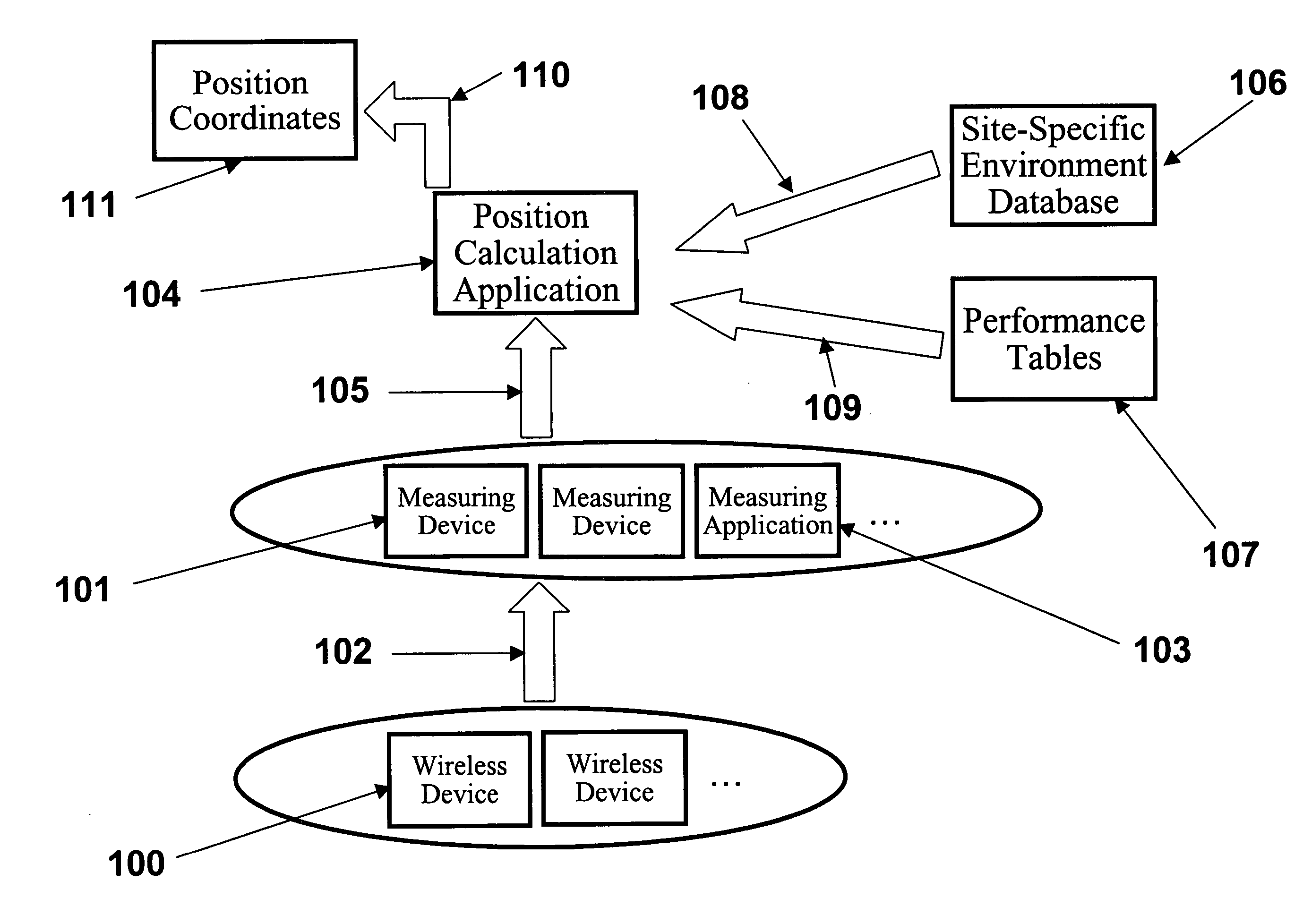
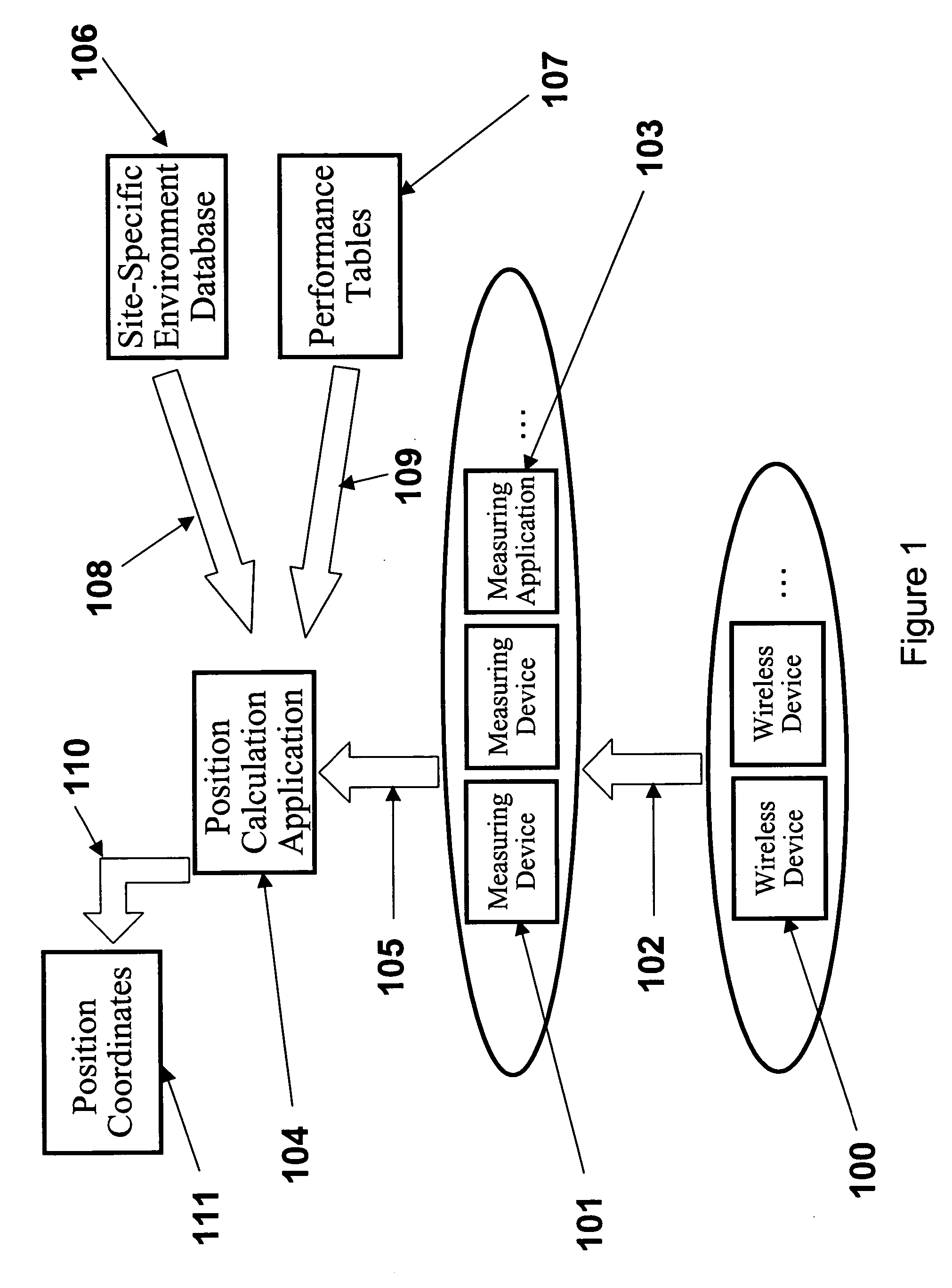
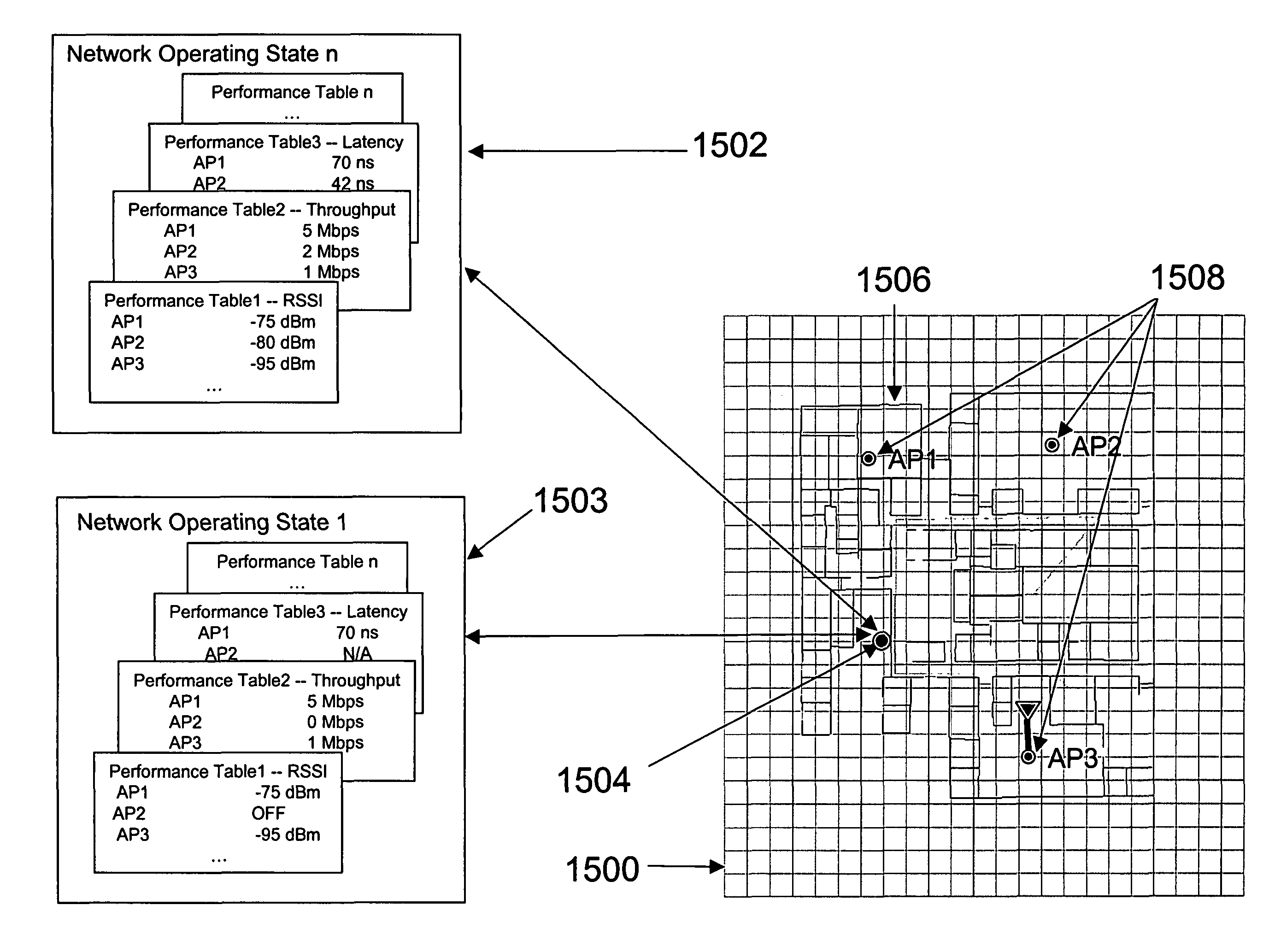
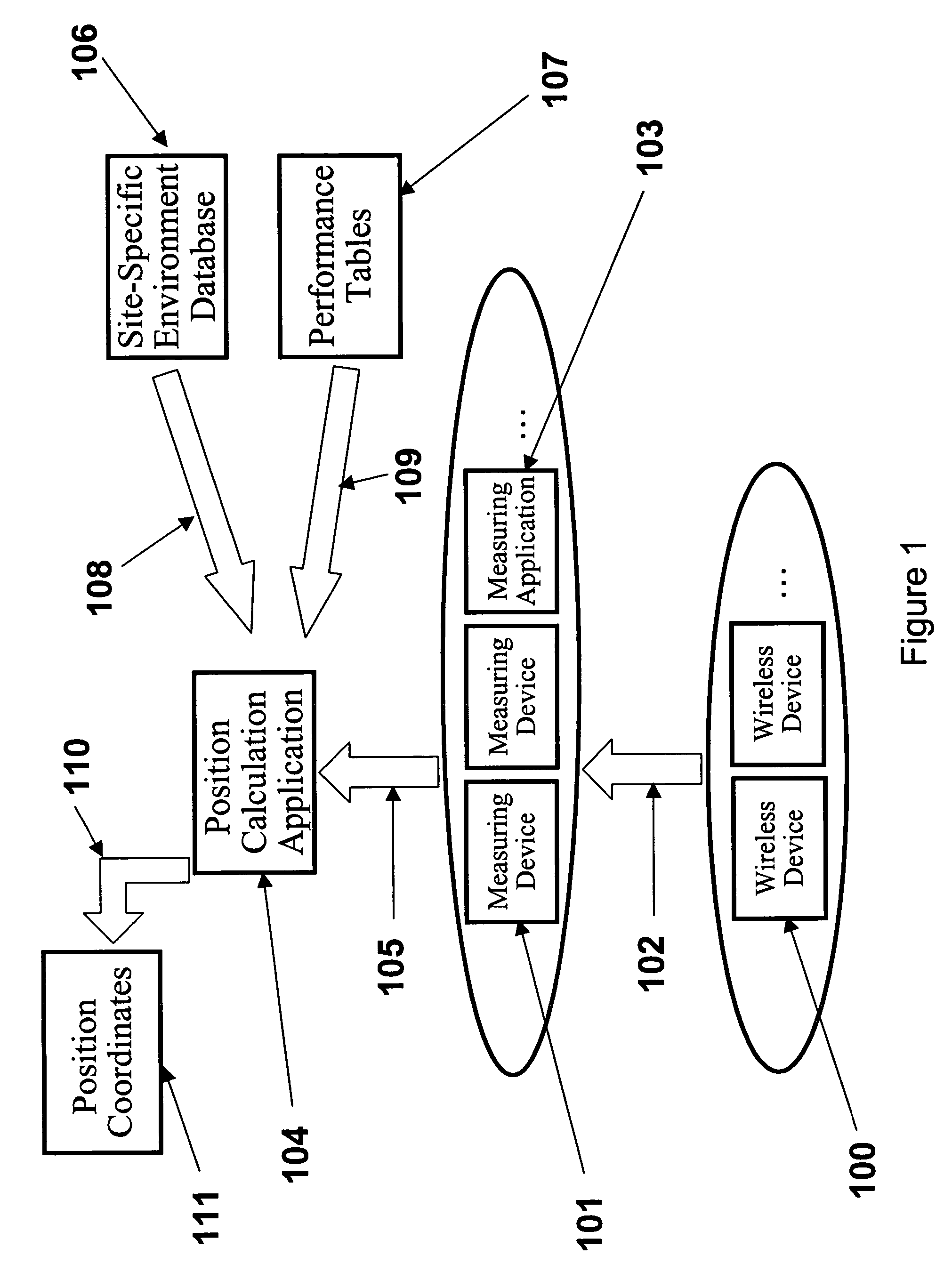
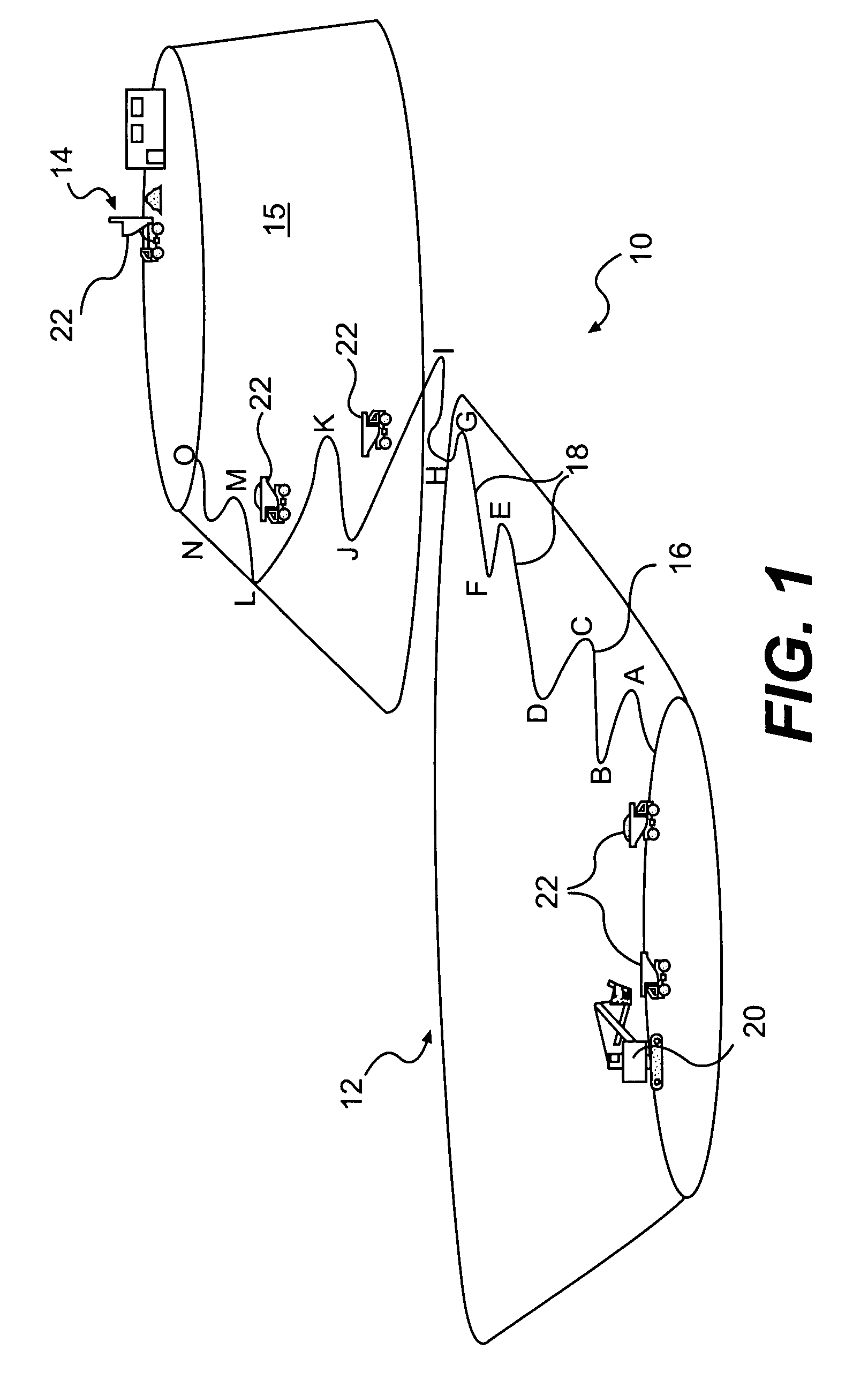
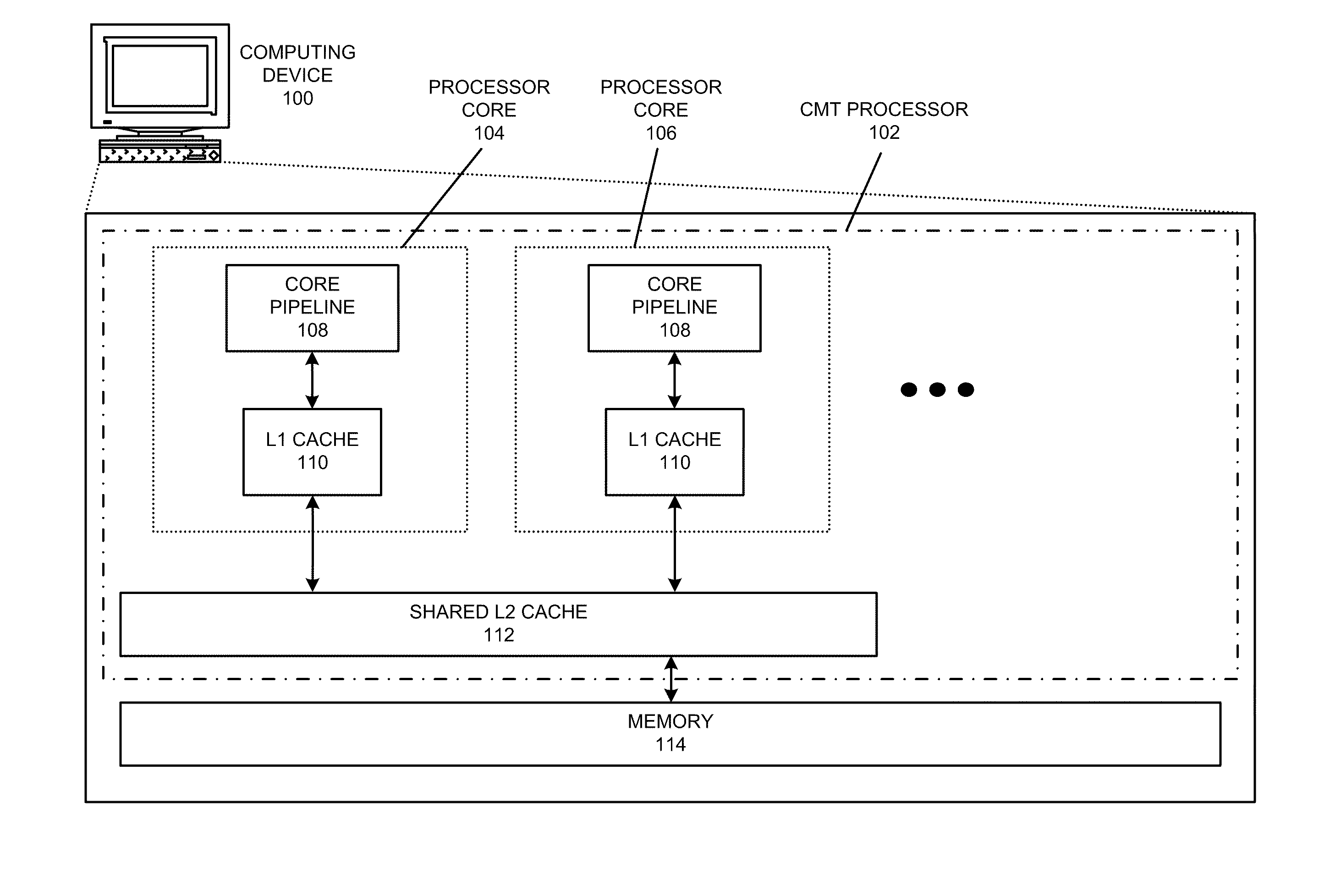
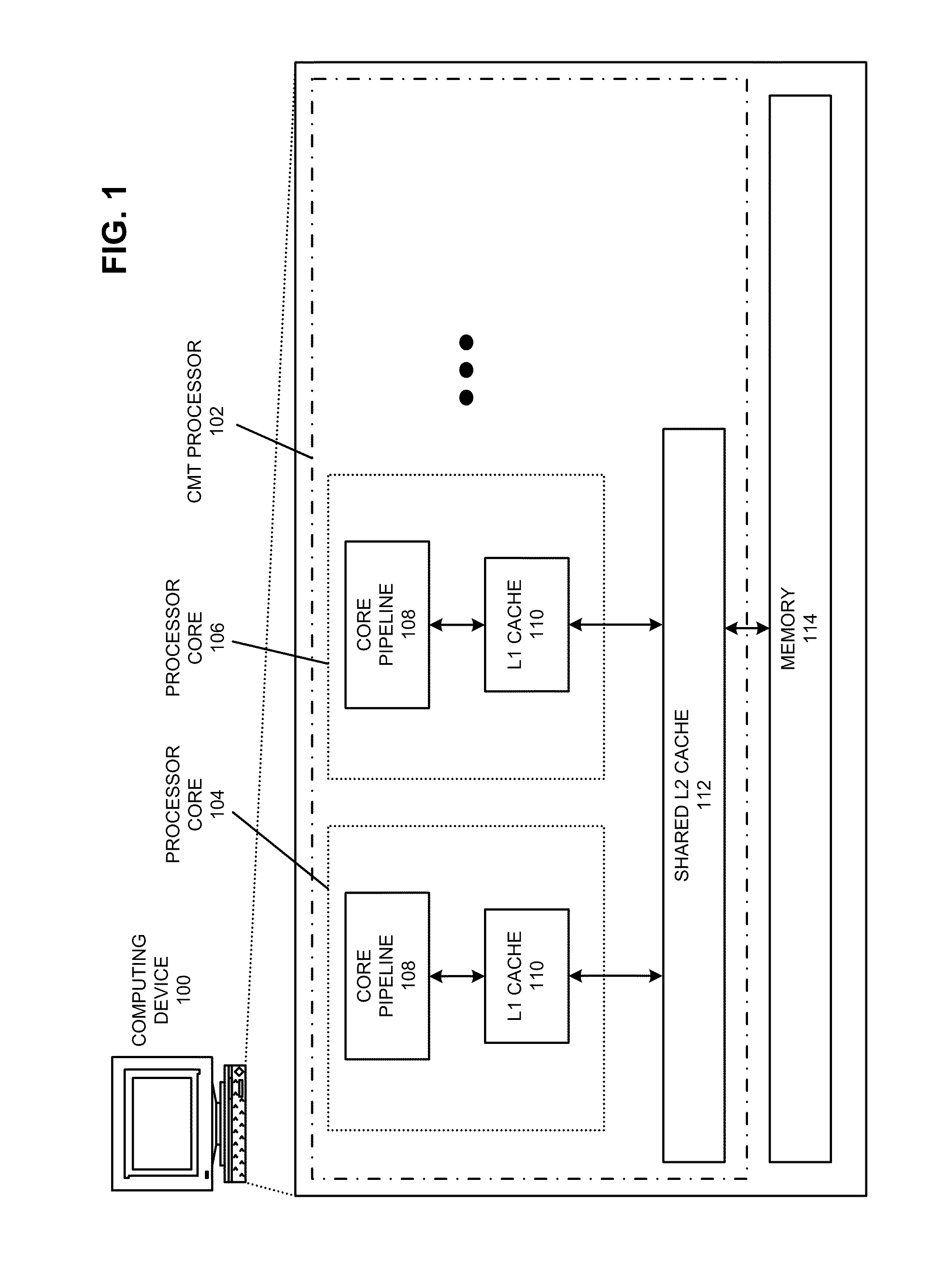
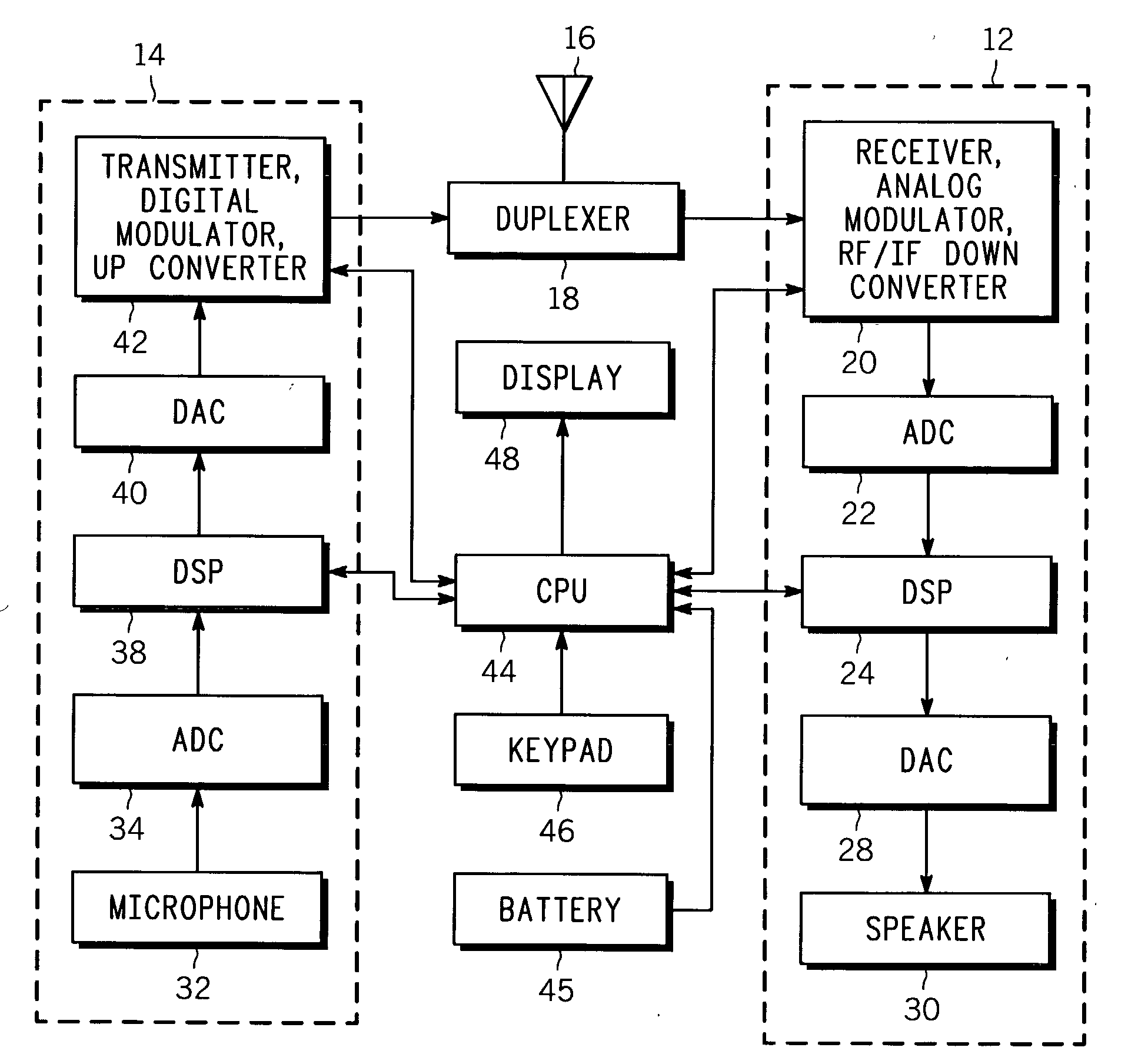
System, method, and apparatus for determining and using the position of wireless devices or infrastructure for wireless network enhancements
ActiveUS20060019679A1Increase network bandwidthHigh degreeDirection finders using radio wavesRoad vehicles traffic controlDevice typePredicting performance
A system and method for estimating the position of wireless devices within a wireless communication network combines measured RF channel characteristics for the wireless device with one or more predicted performance lookup tables, each of which correlates an RF channel characteristic to some higher order network performance metric and / or a position within an environmental model. Measured RF channel characteristics for wireless devices are compared against the performance lookup tables to determine the sent of lookup tables that most closely match the measured RF channel characteristics. The positions within the environmental model corresponding to the selected set of matching lookup tables are identified as possible locations for the wireless device. The performance lookup tables are uniquely constructed by site-specific location, technology, wireless standard, and equipment types, and / or the current operating state of the communications network.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
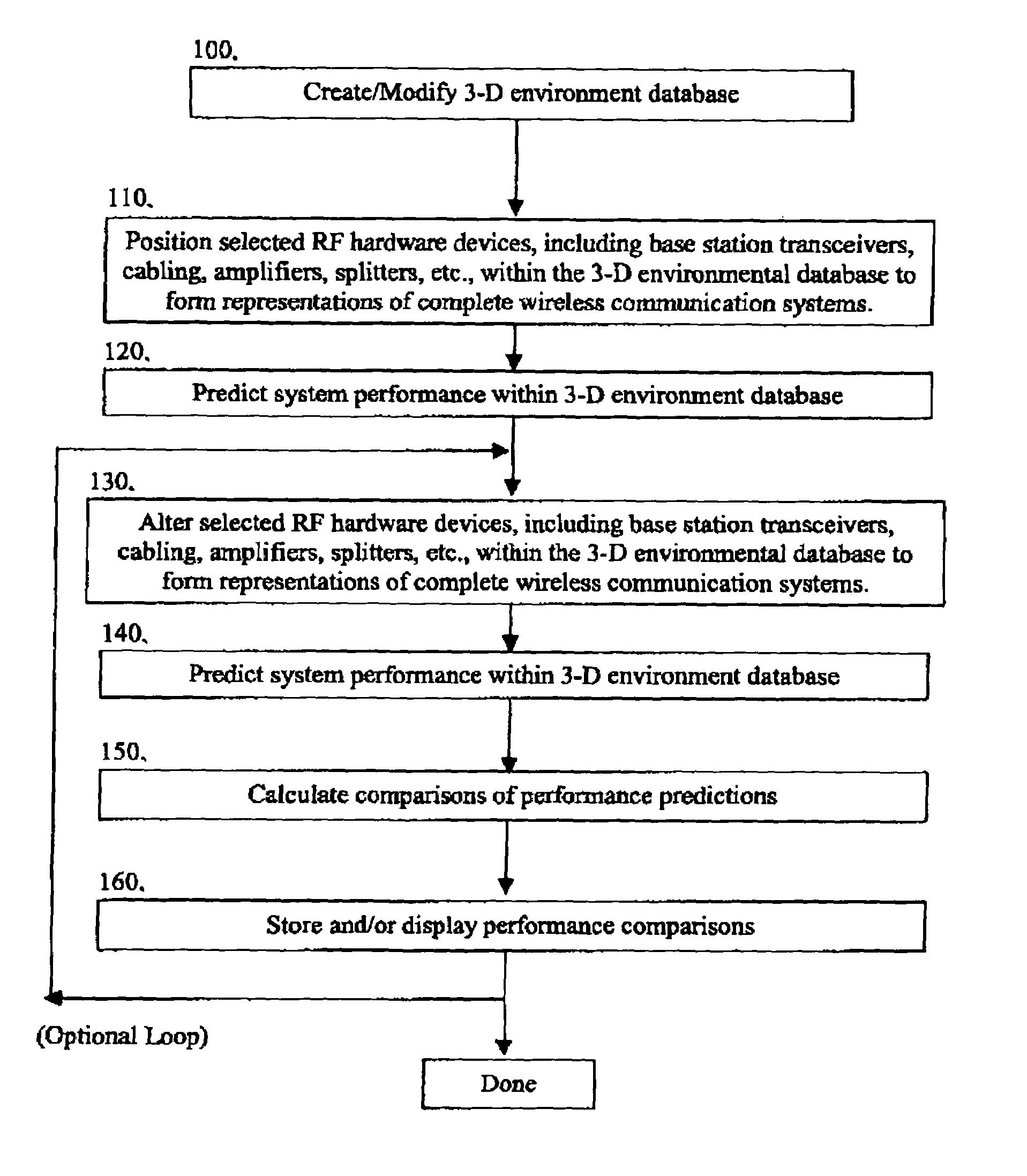
System and method for efficiently visualizing and comparing communication network system performance
InactiveUS7246045B1Easy to displayDrawing from basic elementsReceivers monitoringTerrainCommunications system
A method for visualizing and efficiently making comparisons of communication system performance utilizing predicted performance, measured performance, or other performance data sets is described. A system permits visualizing the comparisons of system performance data in three-dimensions using fluctuating elevation, shape, and / or color within a three-dimensional computer drawing database consisting of one or more multi-level buildings, terrain, flora, and additional static and dynamic obstacles (e.g., automobiles, people, filing cabinets, etc.). The method enables a design engineer to visually compare the performance of wireless communication systems as a three-dimensional region of fluctuating elevation, color, or other aesthetic characteristics with fully selectable display parameters, overlaid with the three-dimensional site-specific computer model for which the design was carried out.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
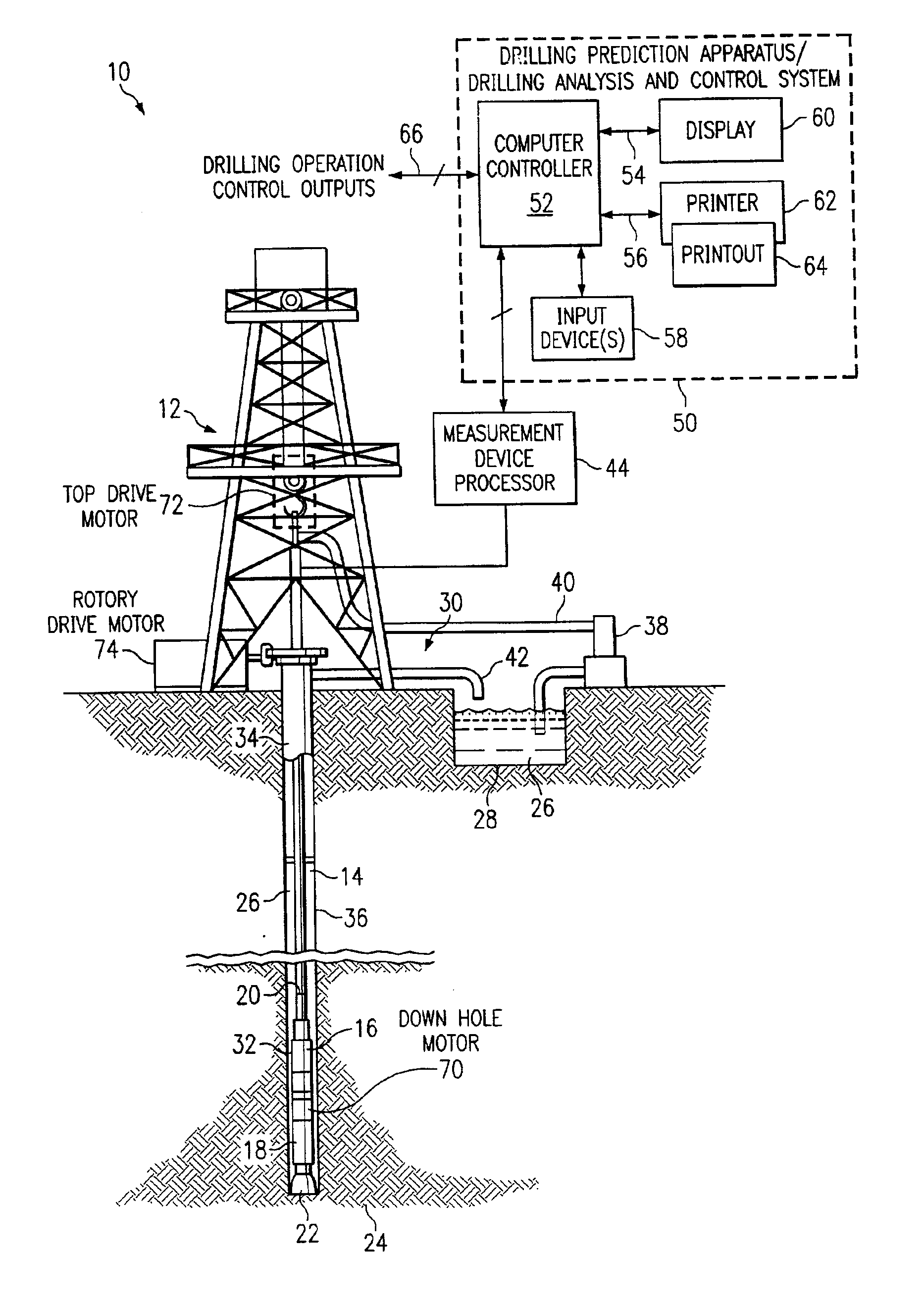
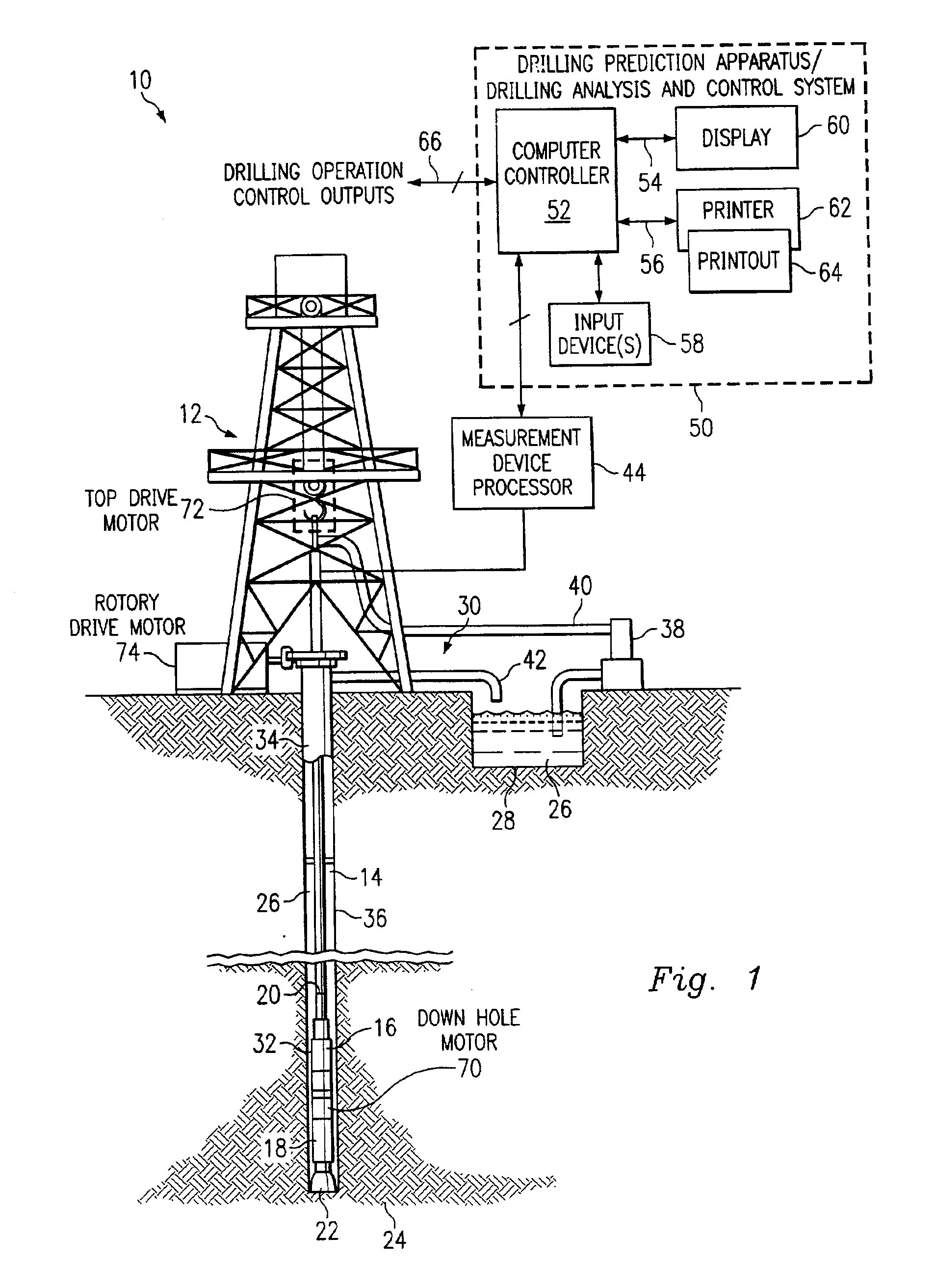
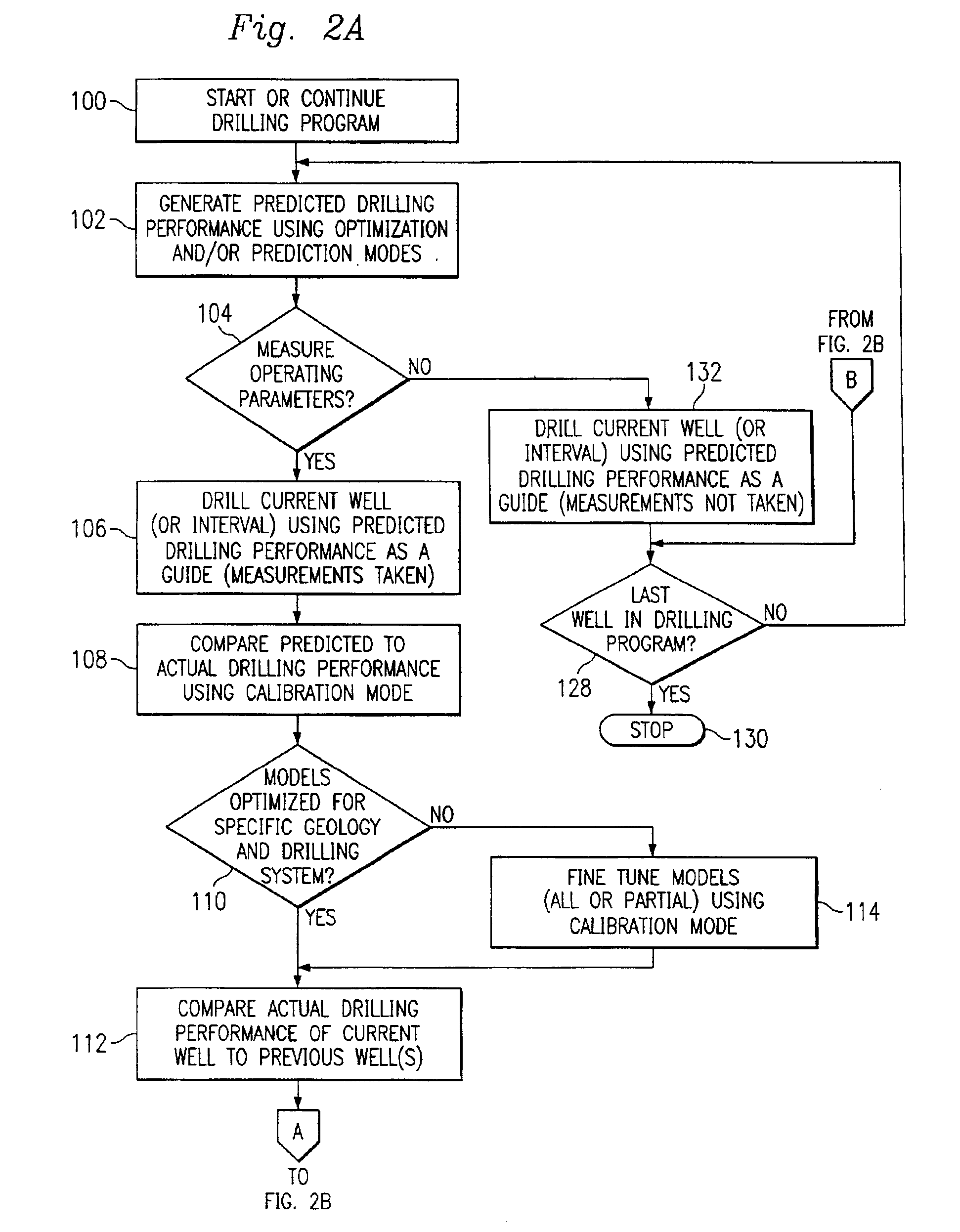
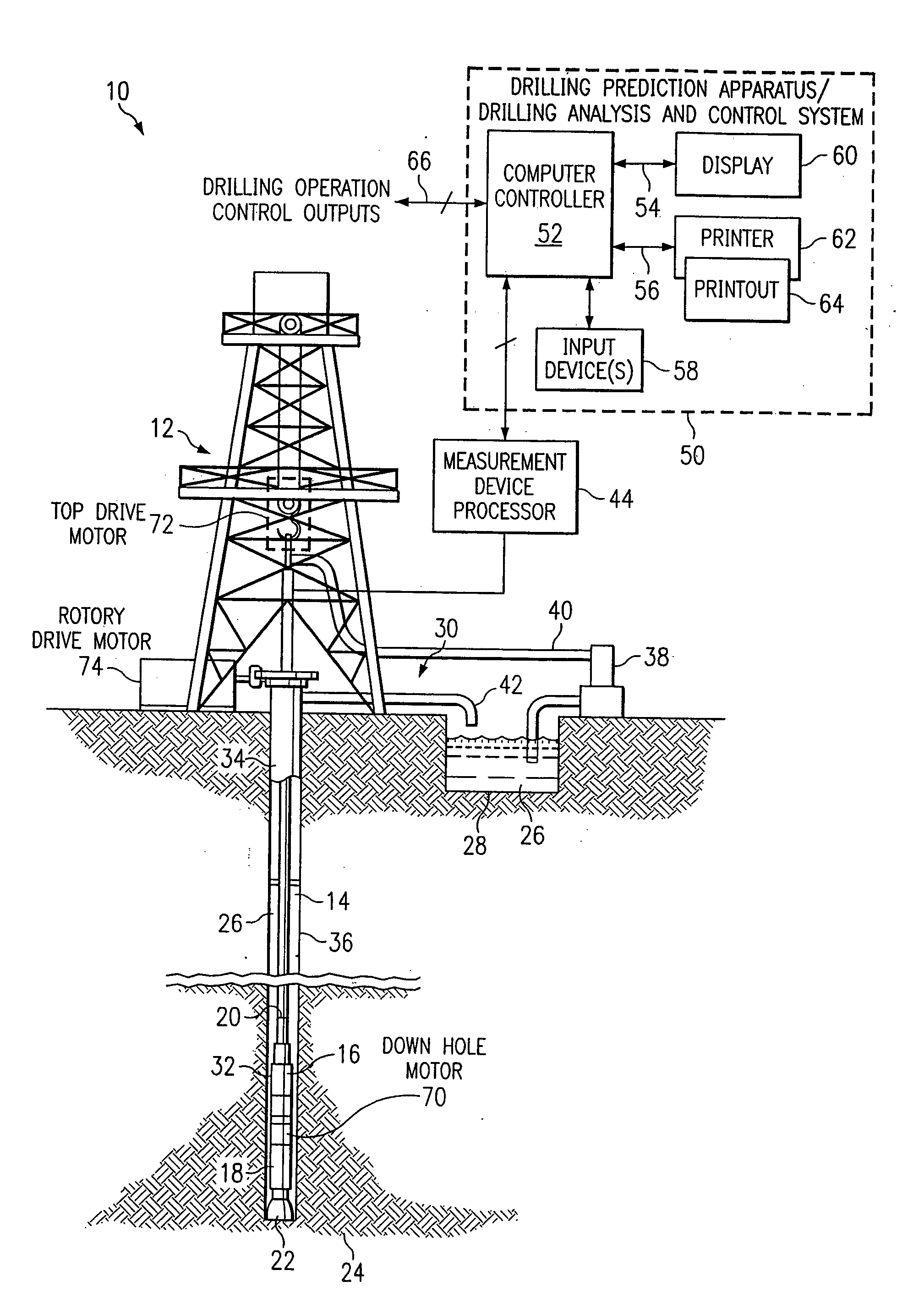
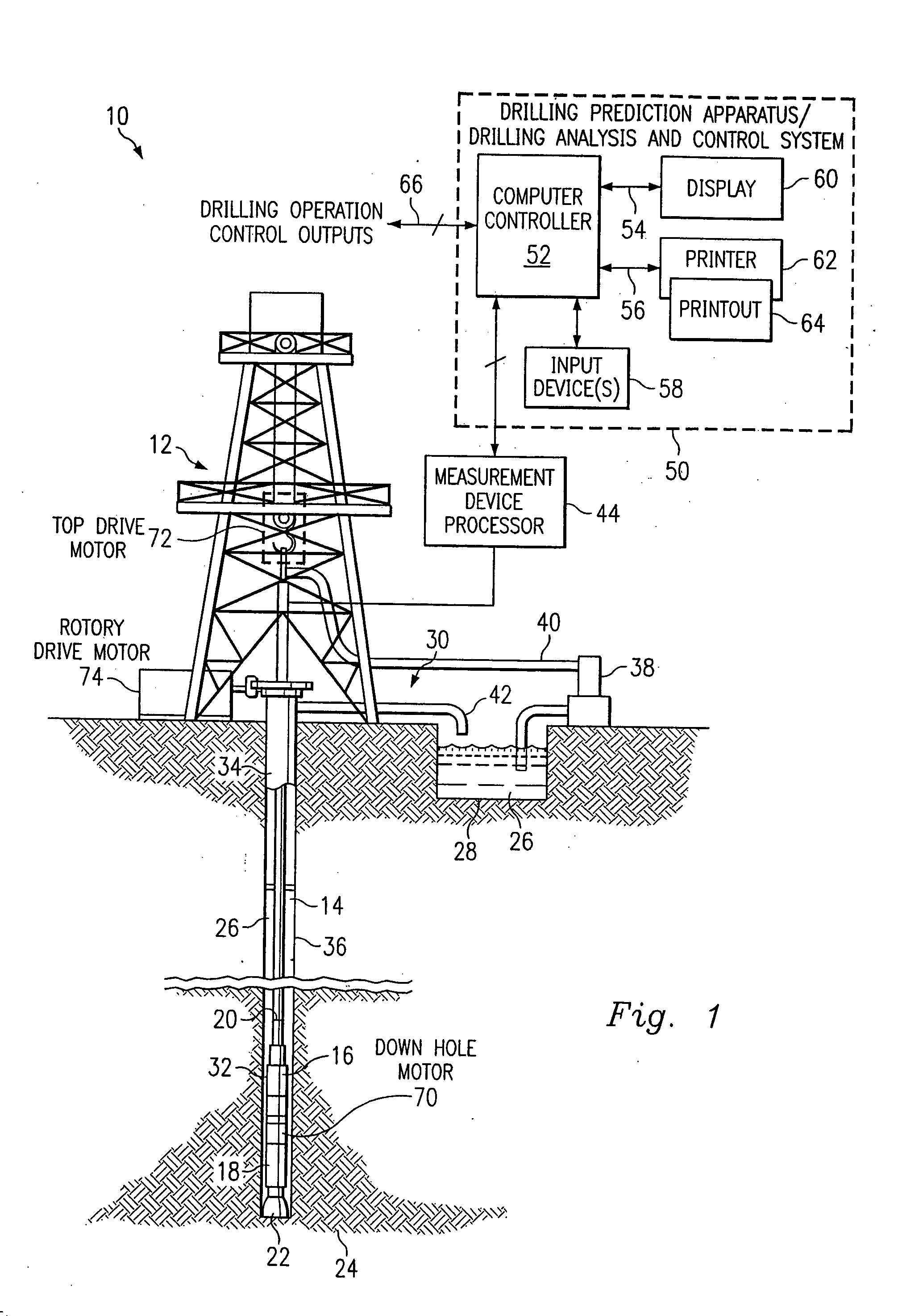
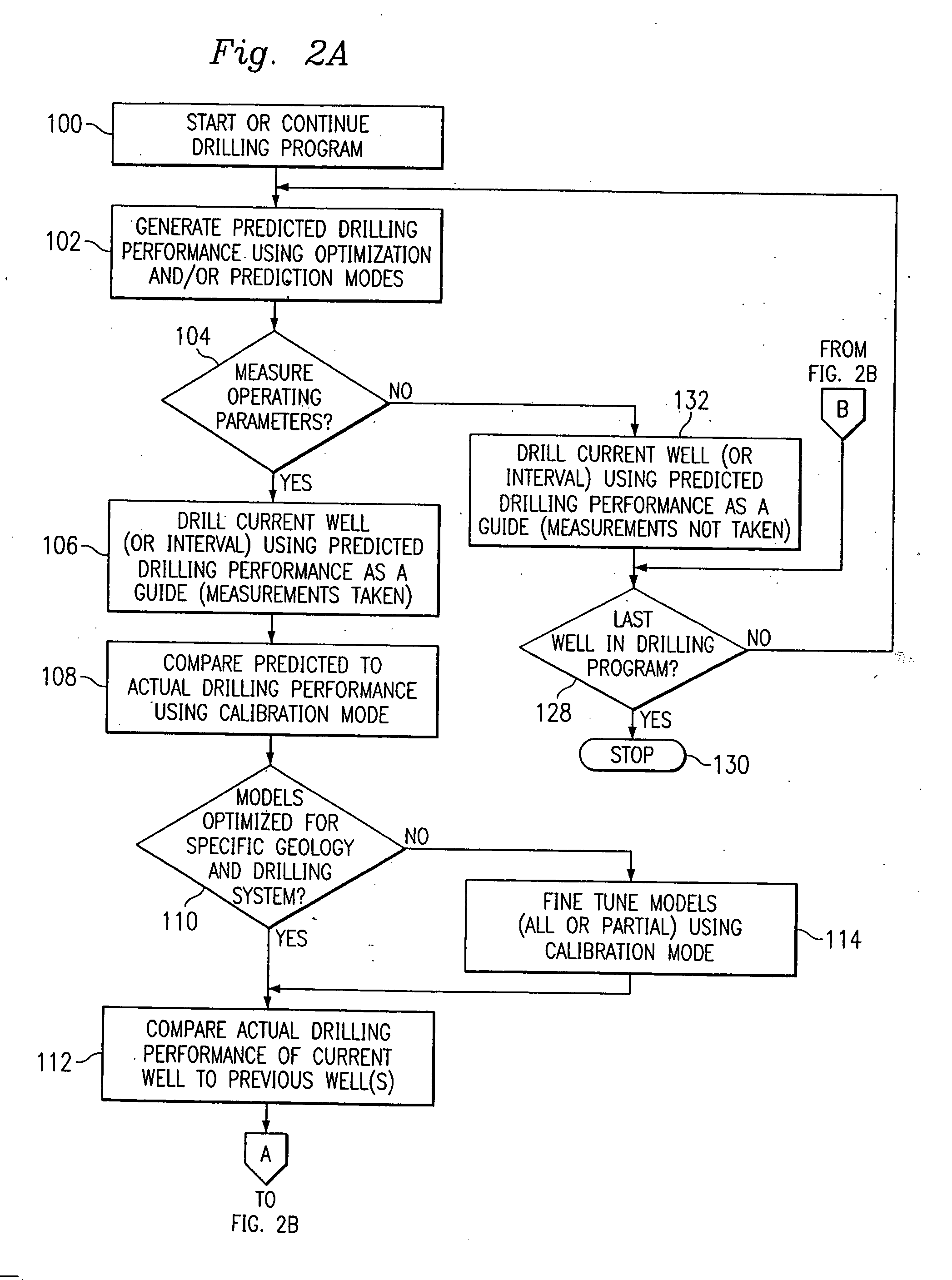
Method and system for predicting performance of a drilling system of a given formation
InactiveUS7032689B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingEarth drilling toolsComputer printingDisplay device
A method and apparatus for predicting the performance of a drilling system for the drilling of a well bore in a given formation includes generating a geology characteristic of the formation per unit depth according to a prescribed geology model, obtaining specifications of proposed drilling equipment for use in the drilling of the well bore, and predicting a drilling mechanics in response to the specifications as a function of the geology characteristic per unit depth according to a prescribed drilling mechanics model. Responsive to a predicted-drilling mechanics, a controller controls a parameter in the drilling of the well bore. The geology characteristic includes at least rock strength. The specifications include at least a bit specification of a recommended drill bit. Lastly, the predicted drilling mechanics include at least one of bit wear, mechanical efficiency, power, and operating parameters. A display is provided for generating a display of the geology characteristic and predicted drilling mechanics per unit depth, including either a display monitor or a printer.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
System and method for predicting performance of fantasy athletes
InactiveUS20060183548A1Apparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesAccess networkUser device
Disclosed is a system and method for predicting game play performance of a number of sports team players selected for fantasy game play where a winner of the fantasy game play is determined by a fantasy points value. The system includes a remote user device including a display, and a host system operatively coupled to the remote user device via an access network. The host system includes an application server and a database coupled to the application server where the application server is configured to provide a number of numerical performance indexes to a user of the remote user device based on sport team player performance data and game play data. The numerical performance indexes correspond to predicted game play performance of the sports team athletes, where the number of numerical performance indexes are utilized by the user to select a fantasy sports team for fantasy game play.
Owner:ASSISTANT GM
System, method, and apparatus for determining and using the position of wireless devices or infrastructure for wireless network enhancements
ActiveUS8019352B2High degreeHighly simplifiedDirection finders using radio wavesRoad vehicles traffic controlDevice typePredicting performance
A system and method for estimating the position of wireless devices within a wireless communication network combines measured RF channel characteristics for the wireless device with one or more predicted performance lookup tables, each of which correlates an RF channel characteristic to some higher order network performance metric and / or a position within an environmental model. Measured RF channel characteristics for wireless devices are compared against the performance lookup tables to determine the sent of lookup tables that most closely match the measured RF channel characteristics. The positions within the environmental model corresponding to the selected set of matching lookup tables are identified as possible locations for the wireless device. The performance lookup tables are uniquely constructed by site-specific location, technology, wireless standard, and equipment types, and / or the current operating state of the communications network.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
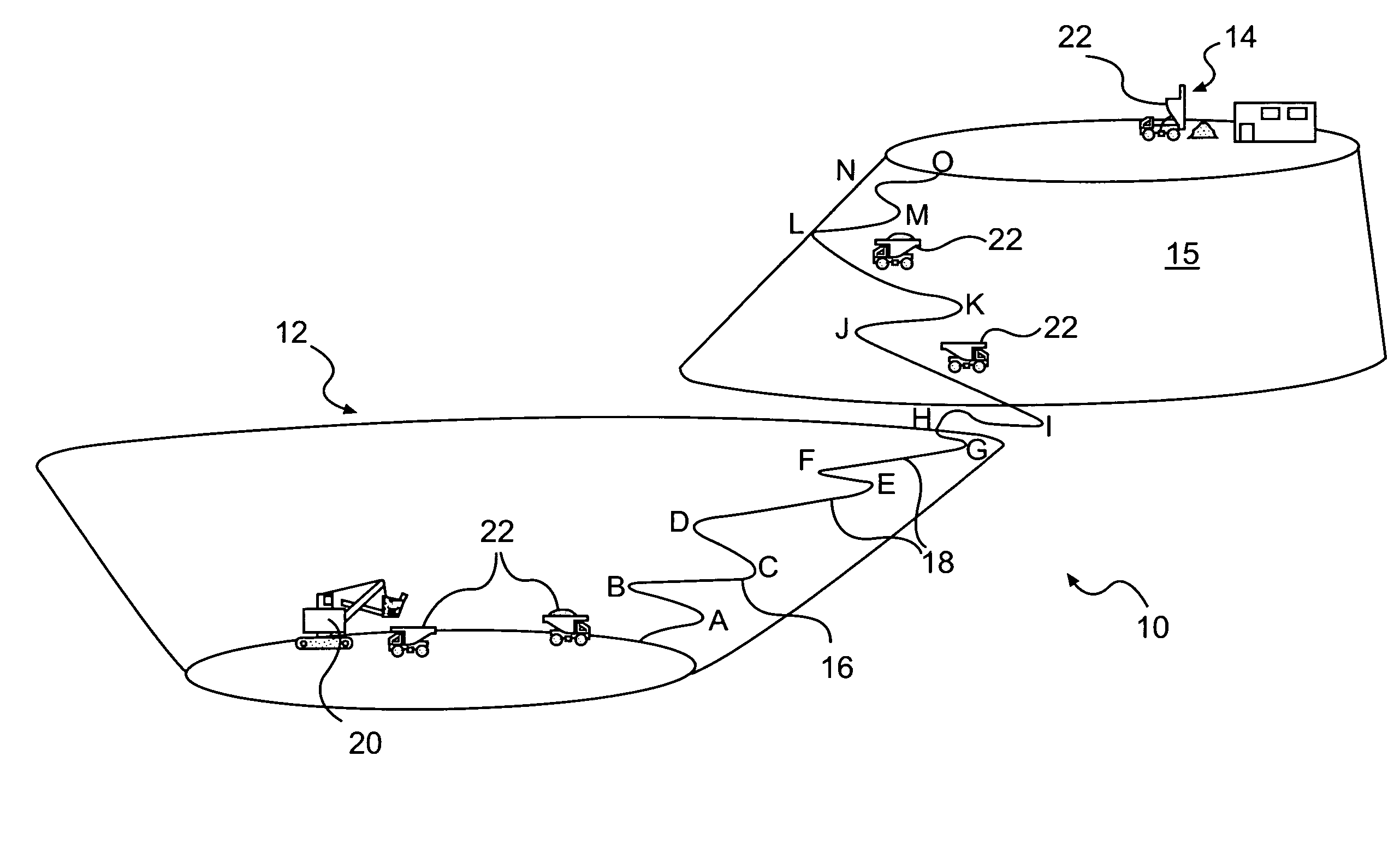
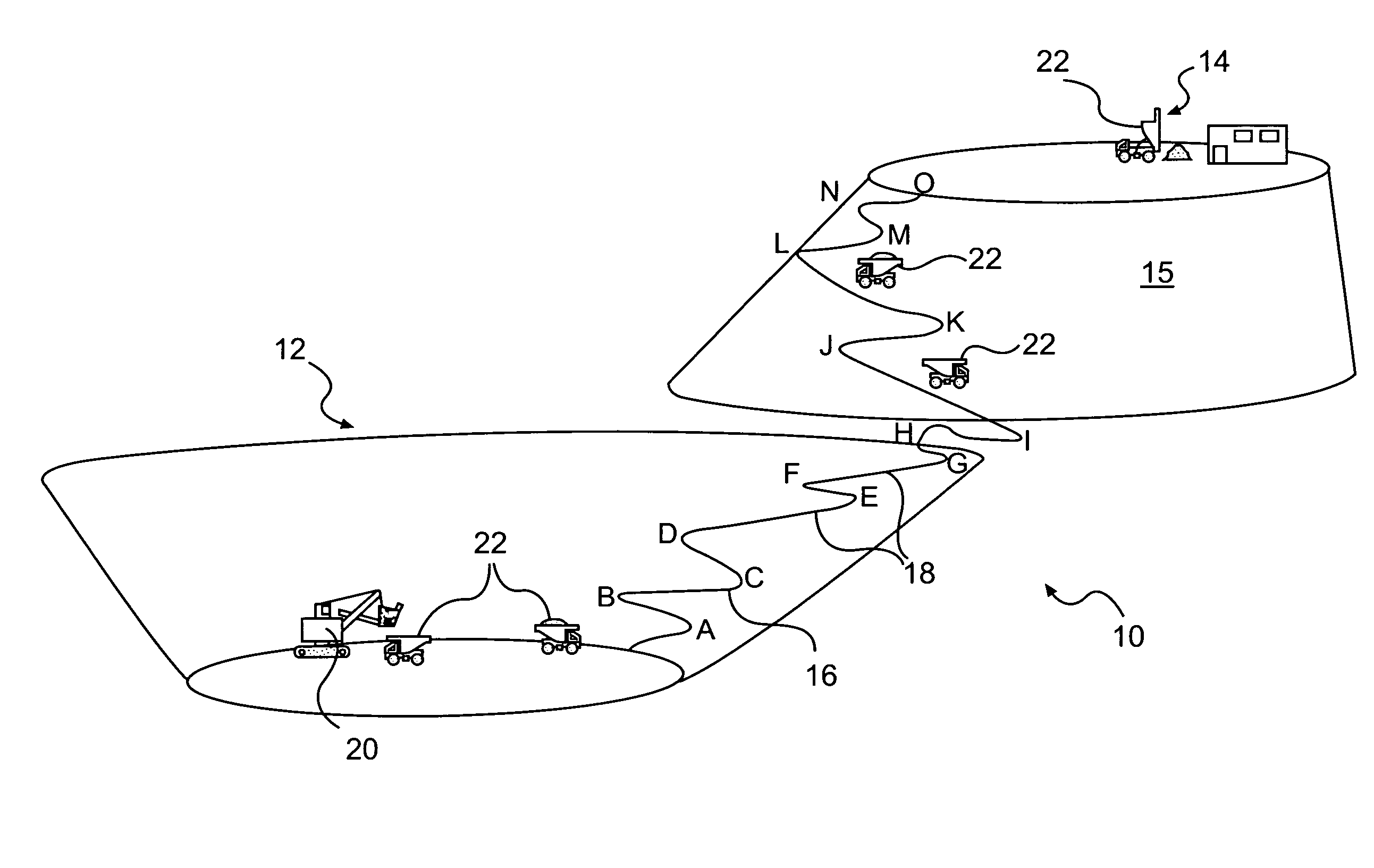
Method of determining a machine operation using virtual imaging
ActiveUS20080208415A1Instruments for road network navigationAnalogue computers for trafficPredicting performanceComputer science
A method of determining a machine for operating at an actual site includes establishing a three-dimensional geographical model representing the actual site, determining at least one operation characteristic relating to the operation of each of a set of machines in relation to the model, and predicting at least one performance characteristic for each machine based on the at least one operation characteristic and at least one respective characteristic of the different machines. The method further includes comparing the predicted performance characteristics for the different machines, and determining a target machine based on the comparison.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
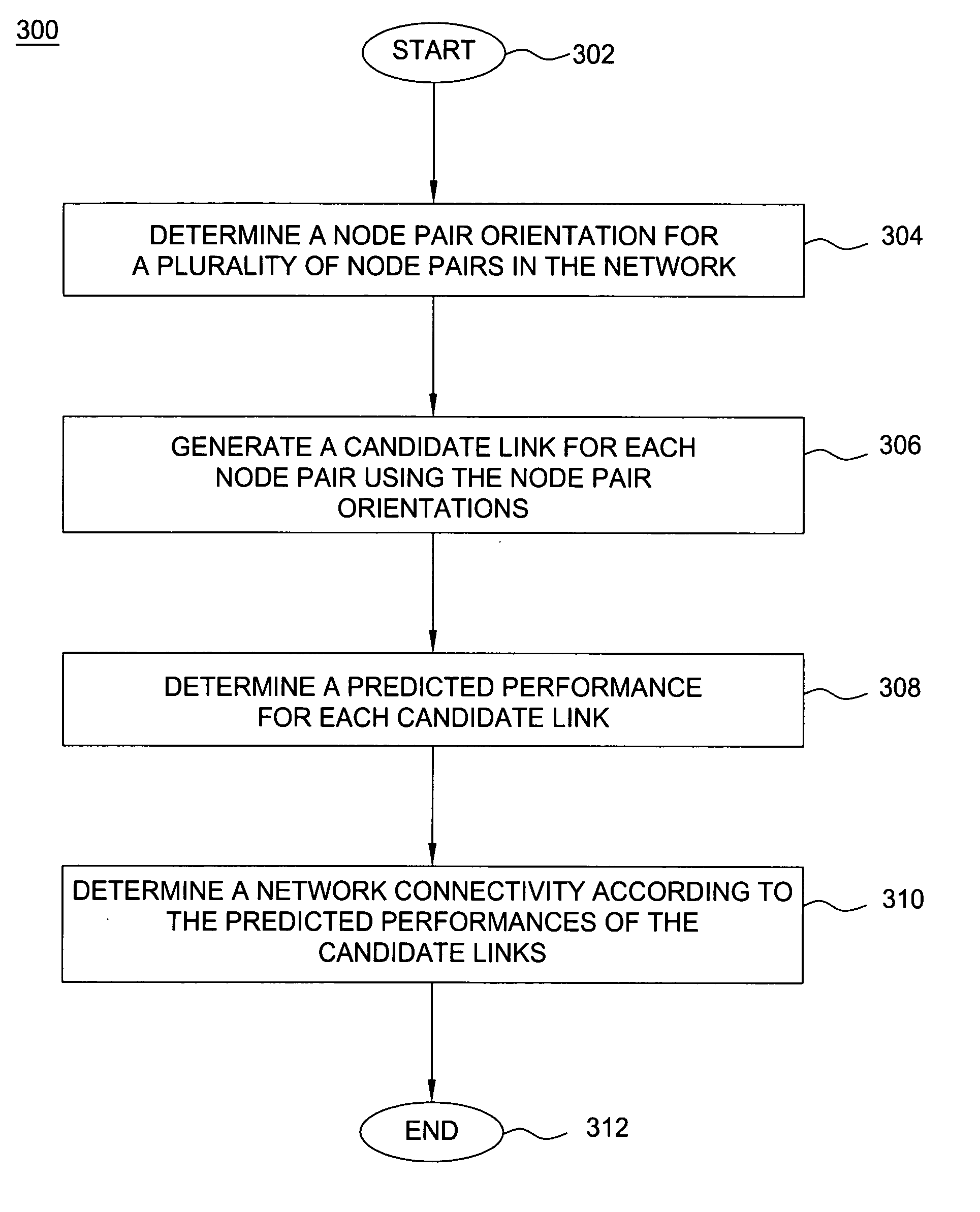
Method and apparatus for identifying network connectivity changes in dynamic networks
InactiveUS20070253341A1Minimize impactOn end-to-end network connectivityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPredicting performanceNetwork topology
The invention comprises a method and apparatus for determining a network connectivity in a network having a plurality of nodes. In particular, one embodiment of the method includes generating a candidate link for each of a plurality of node pairs, predicting a performance of each candidate link by evaluating an expected impact of at least one condition on each candidate link, and determining the network topology using the predicted performances of the candidate links. The performance of each candidate link may be predicted by identifying at least one condition, determining the expected impact of the at least one condition on the candidate link, and predicting the performance of the candidate link by adjusting an expected performance of the candidate link using the expected impact of the at least one condition on the candidate link.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
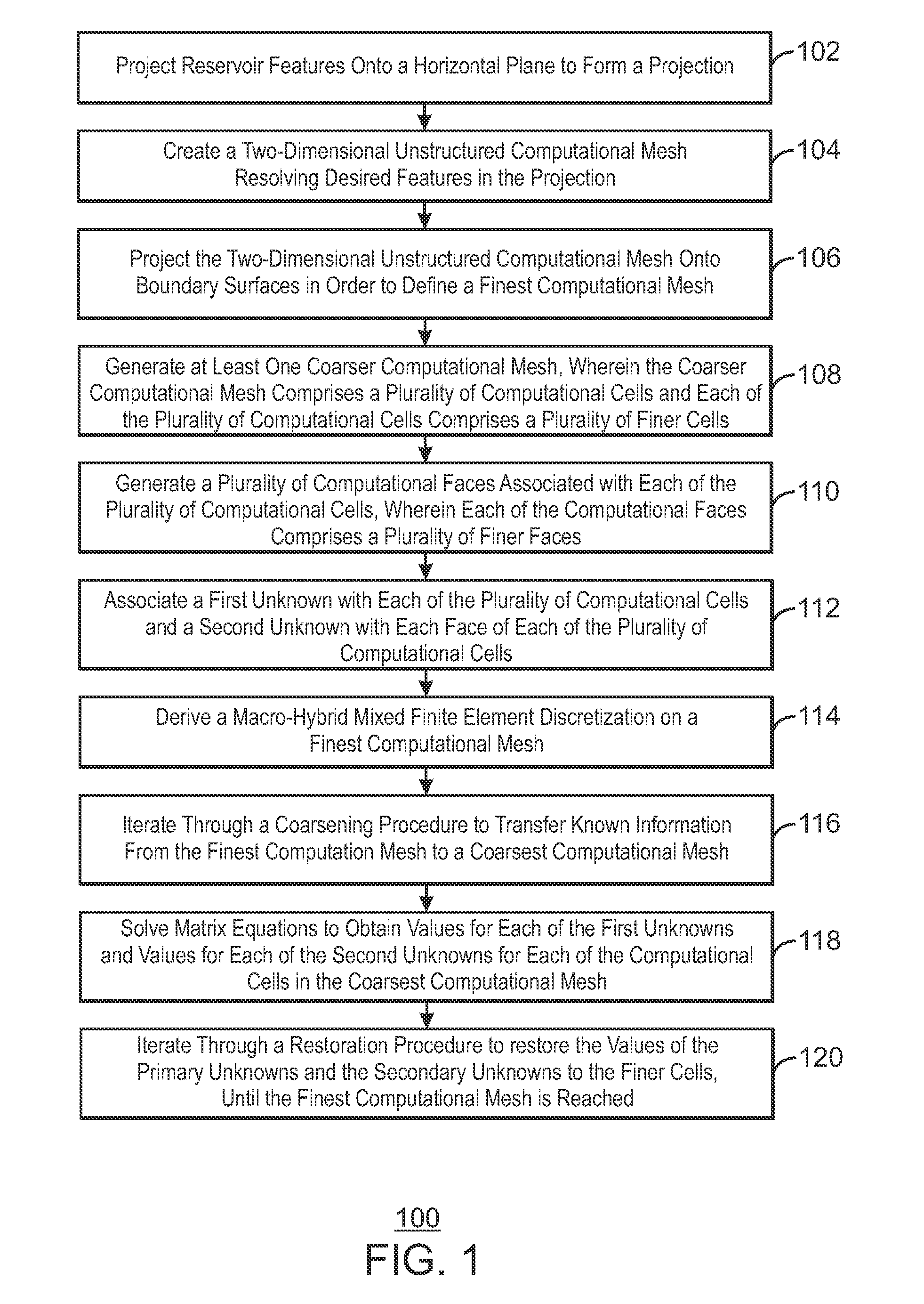
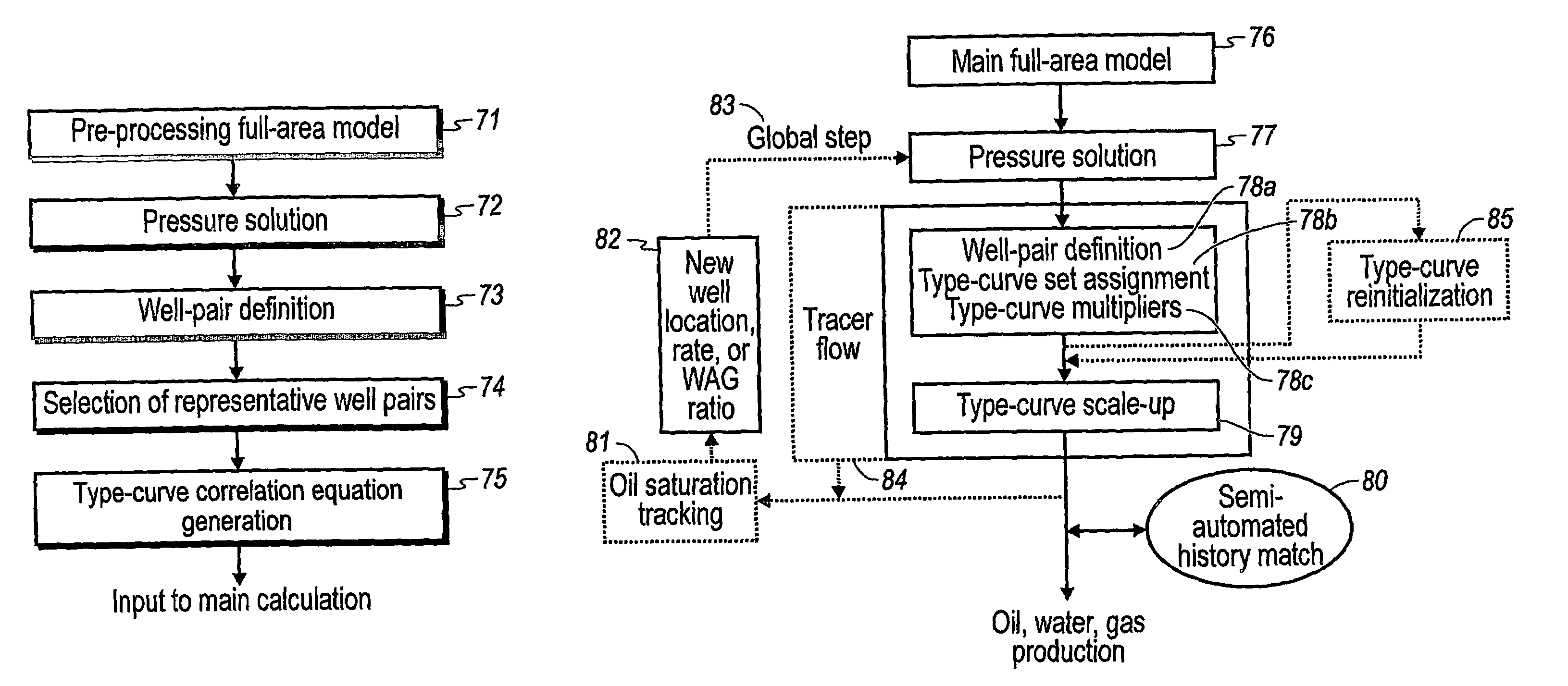
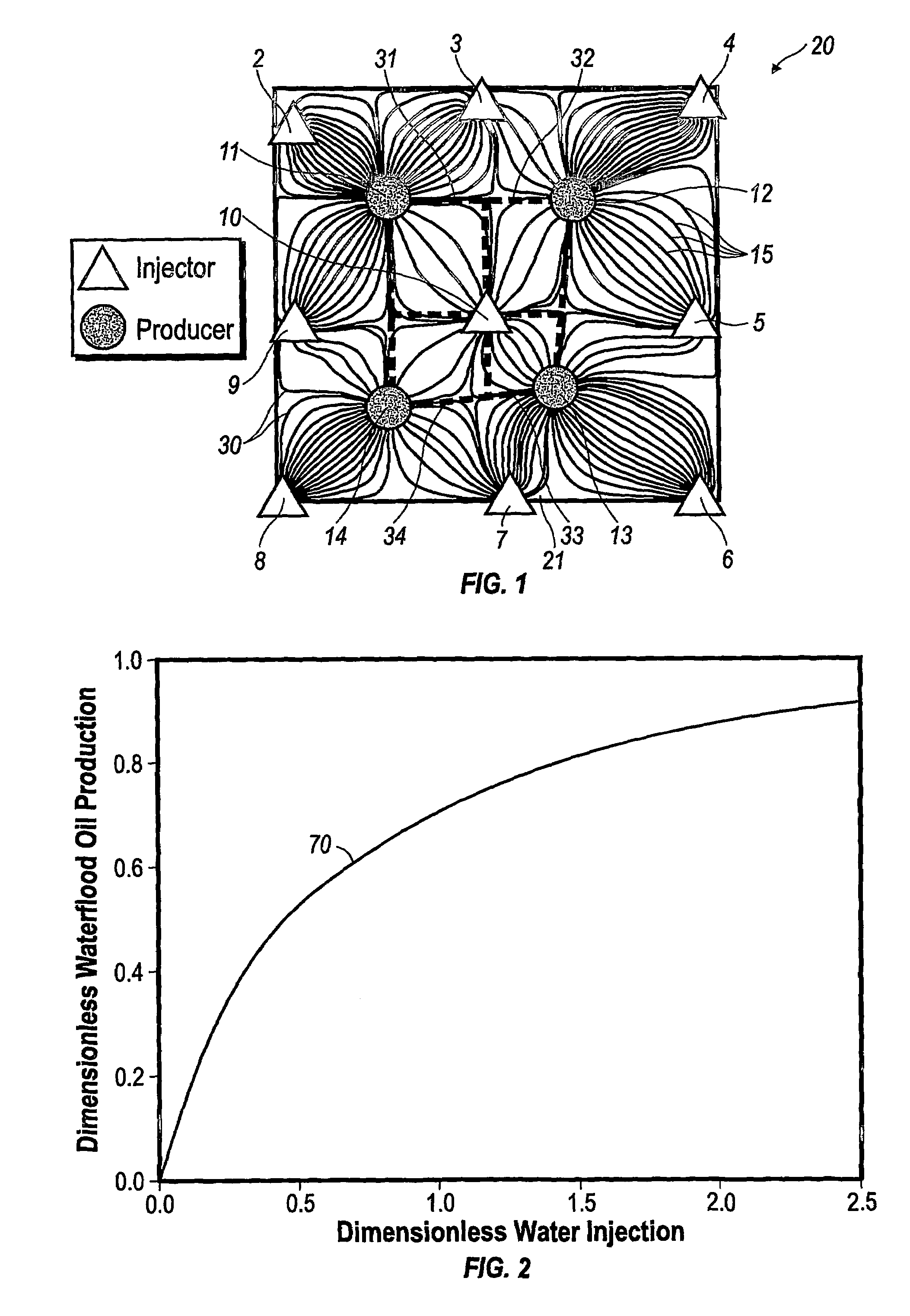
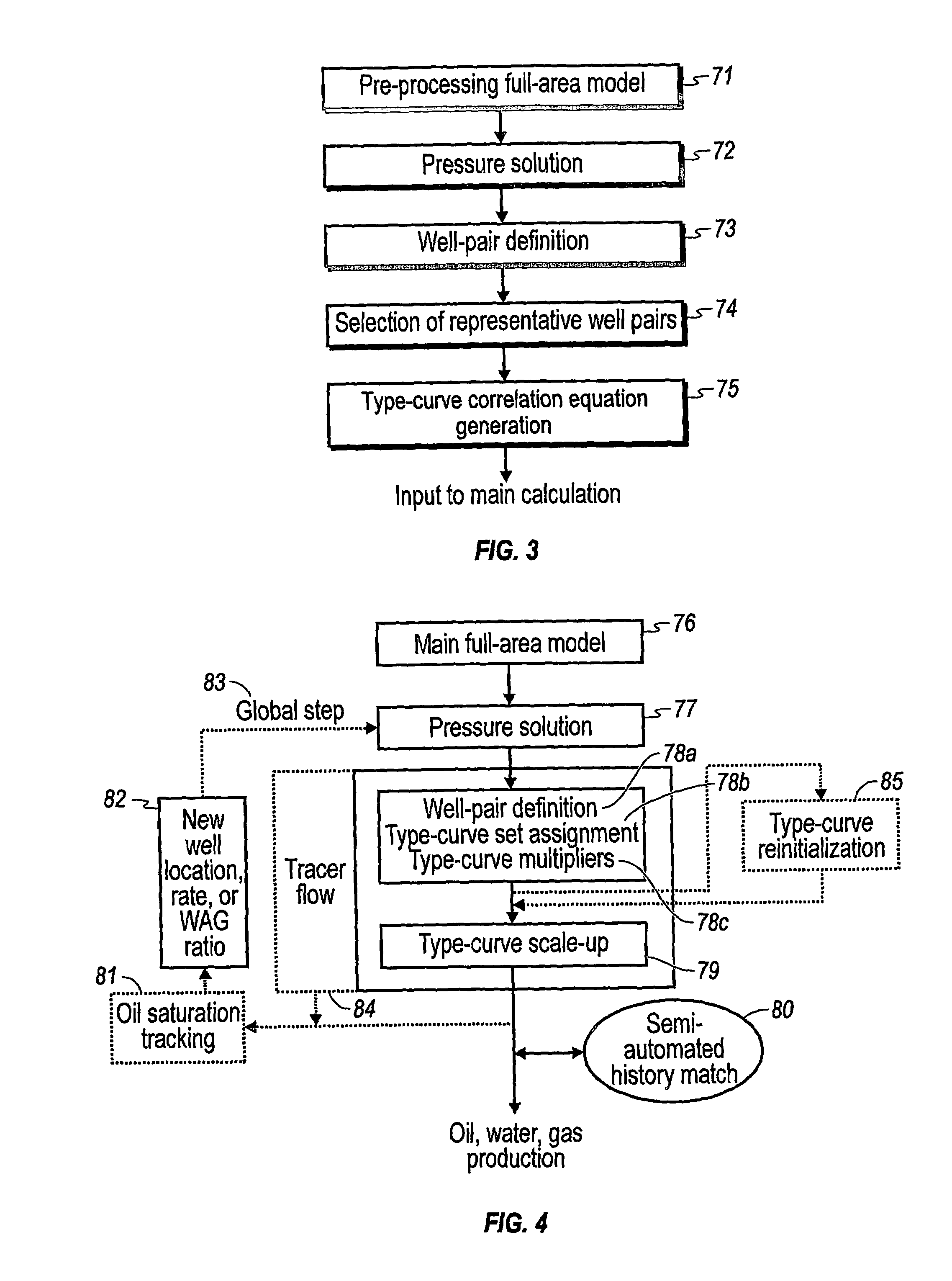
Performance prediction method for hydrocarbon recovery processes
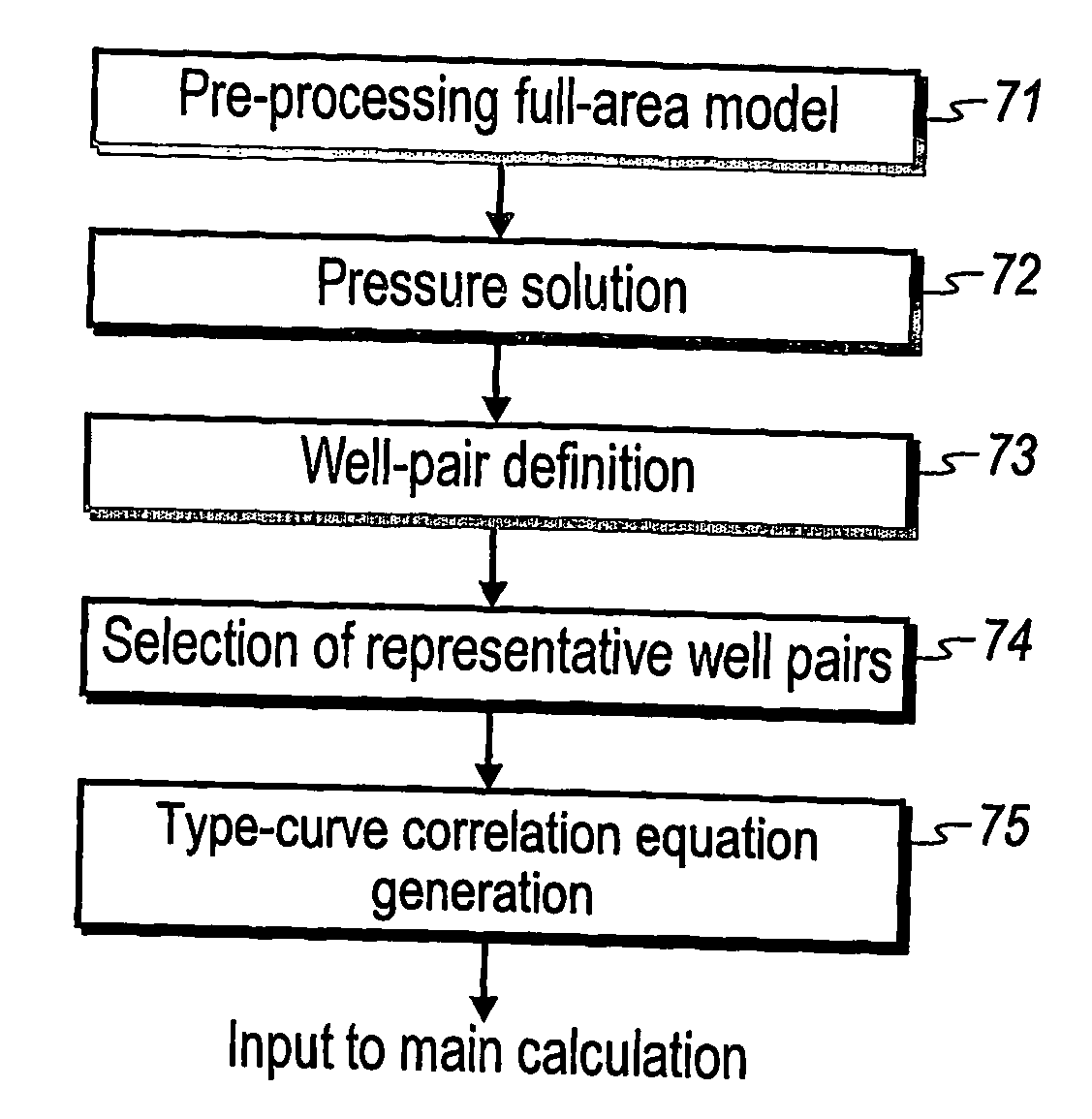
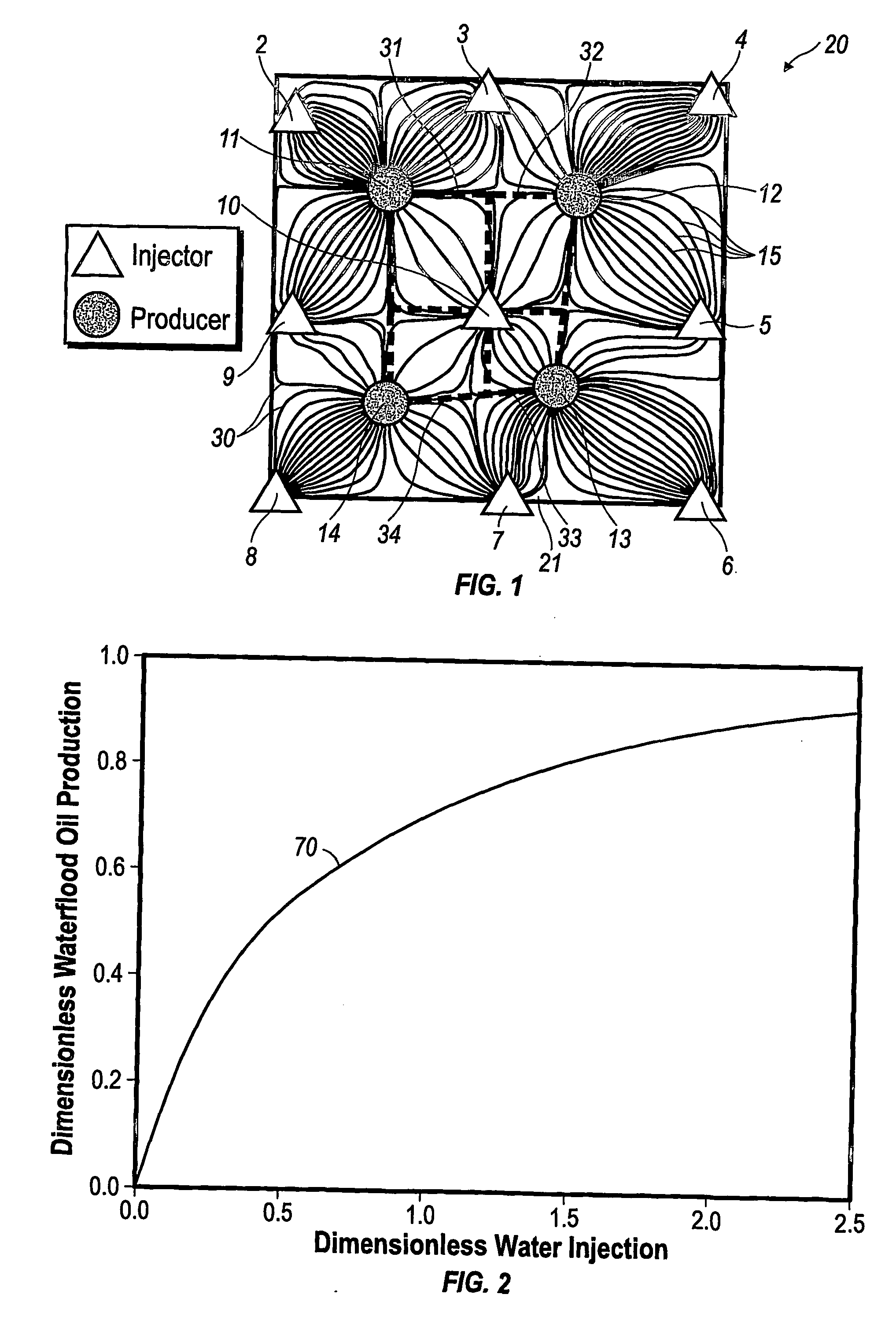
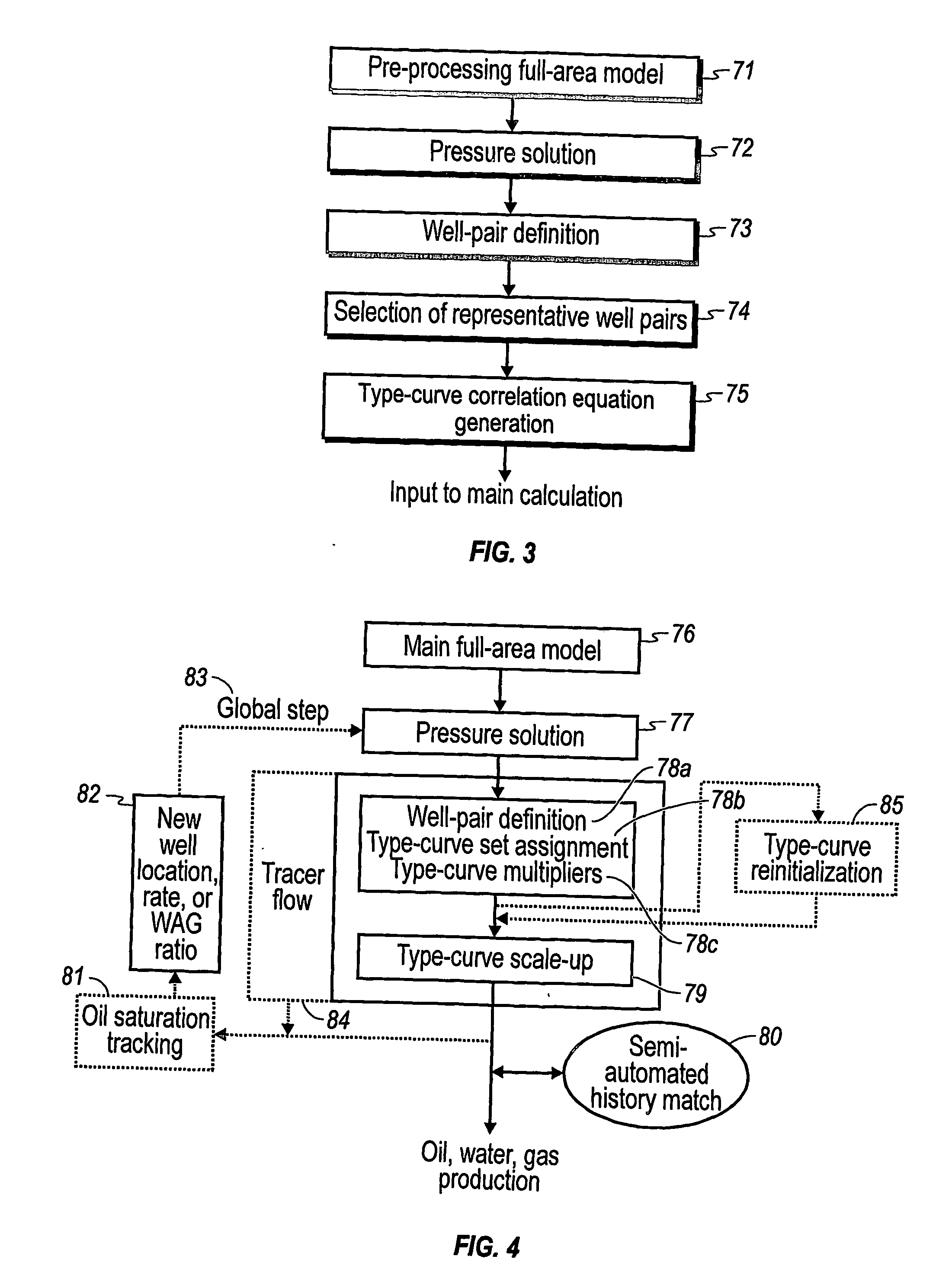
The invention relates to a method for predicting the performance of large-scale hydrocarbon-bearing reservoir floods. One embodiment of the invention includes a method for predicting performance of a patterned flooding process in a subterranean hydrocarbon-bearing formation, said formation being penetrated by a plurality of injector wells and producer wells, comprising the steps of: determining flow-based pairs of injector to producer wells [FIG. 4, item 78a] (first well pairs) using a geological model [item 76]; developing a connective pore volume distribution curve for each first well pair item [78b]; selecting at least two first well pairs (selected well pairs) that reflect narrow and wide connective pore volume distributions that correspond to high and lower oil recovery levels; developing a 3-D simulation model for each selected well pair, performing a reservoir simulation for each selected well pair for the corresponding flooding process; and generating prototype performance curves for each selected well pair. An alternate embodiment of the invention includes a method for predicting the performance of large-scale hydrocarbon-bearing reservoir floods where injection well location, production well location, a process parameter, or a well processing rate is modified.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
System and method for optimized task scheduling in a heterogeneous data processing system
InactiveUS20060168571A1Optimizing task throughputPerformance of was minimizedEnergy efficient ICTEnergy efficient computingData processing systemLoad Shedding
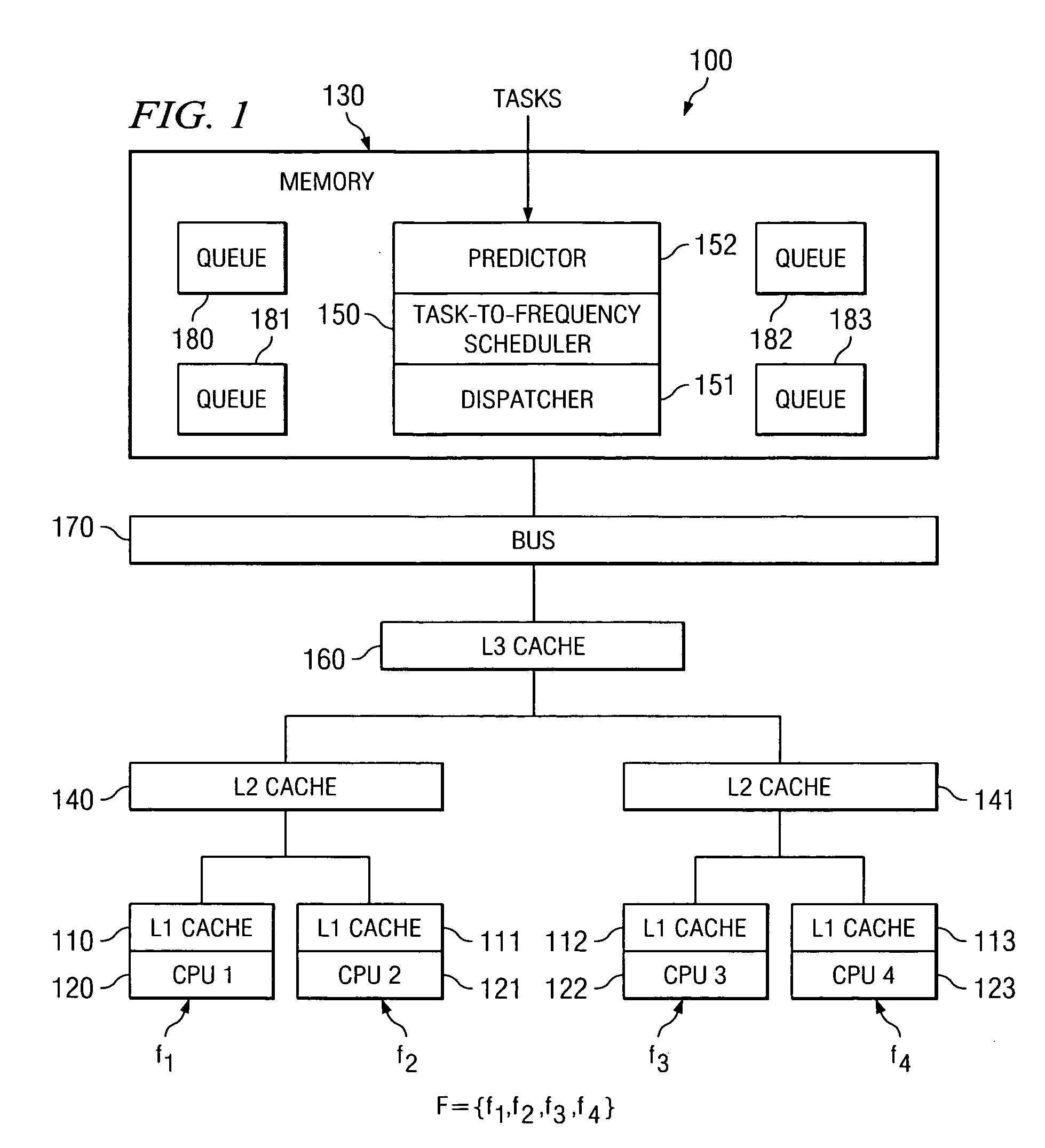
A method, computer program product, and a data processing system for optimizing task throughput in a multi-processor system. A performance metric is calculated based on performance counters measuring characteristics of a task executed at one of a plurality of processor frequencies available in the multi-processor system. The characteristics measured by the performance counters indicate activity in the processor as well as memory activity. A performance metric provides a means using measured data at one available frequency to predict performance at another processor frequency available in the multi-processing system. Performance loss minimization is used to assign a particular task to a particular frequency. Additionally, the present invention provides a mechanism for priority load balancing of tasks in a manner that minimizes cumulative performance loss incurred by execution of all tasks in the system.
Owner:IBM CORP
Enterprise management system for normalization, integration and correlation of business measurements with application and infrastructure measurements
A method is provided for monitoring, predicting performance of, and managing Business Operations by the simultaneous, real-time Integration, Normalization and Correlation of direct measurements at the Business Layer and other Layers of Business Operations. The other Layers considered, may include, for example, Application and Infrastructure Layers. The system enables the user to automate sophisticated management tasks by Correlating measurements of activity, performance and availability at all Layers of Business Operations. Significantly, the techniques described herein extend the domain of the Correlations across real-time measurements from all Layers of Business Operations, giving central importance to the measurements in the Business Layer within the Correlations.
Owner:COTAOFT
Method for simulation modeling of well fracturing
InactiveUS20060015310A1Reduce ambiguityRemove noiseGeometric CADFluid removalWell loggingModel system
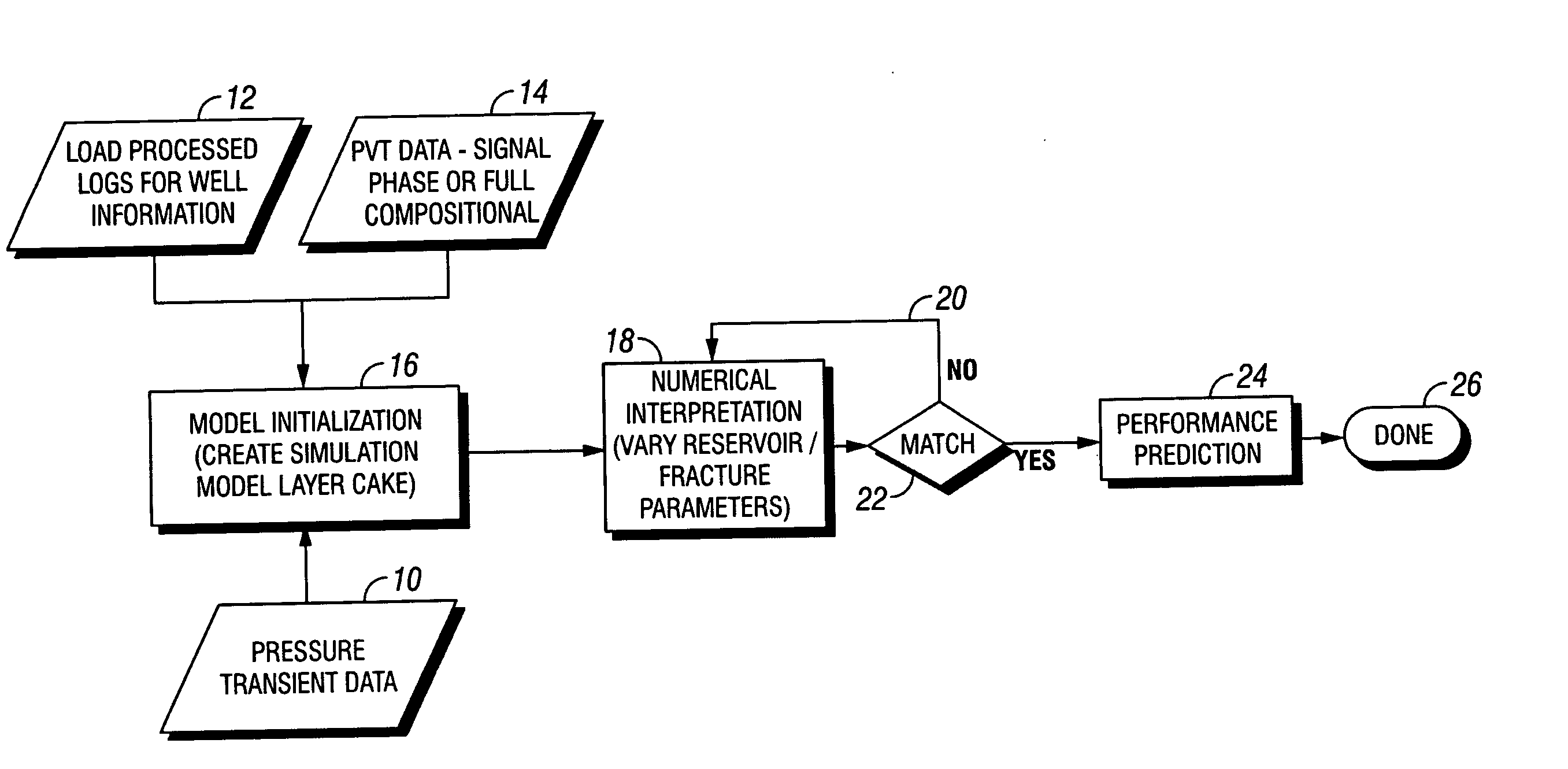
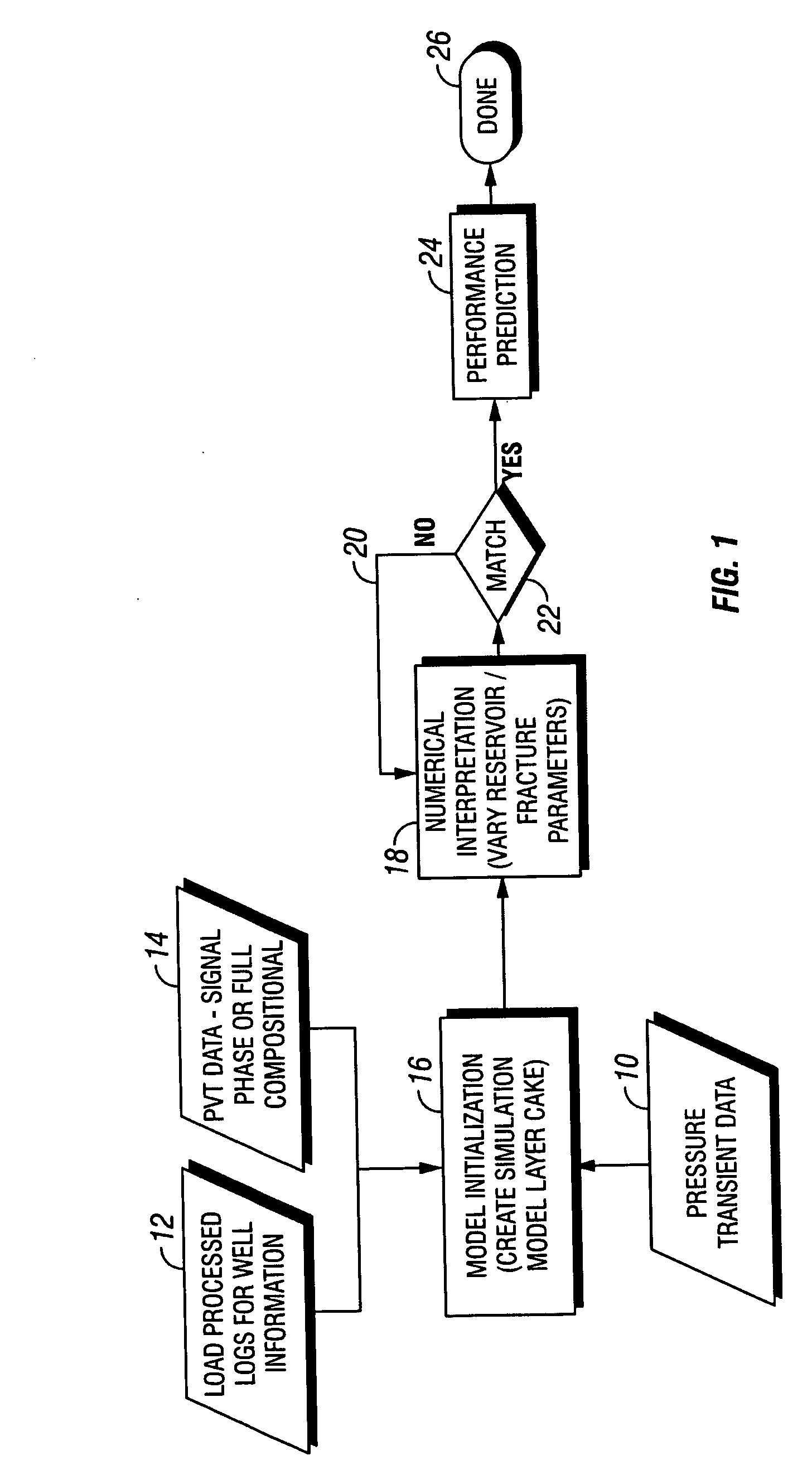
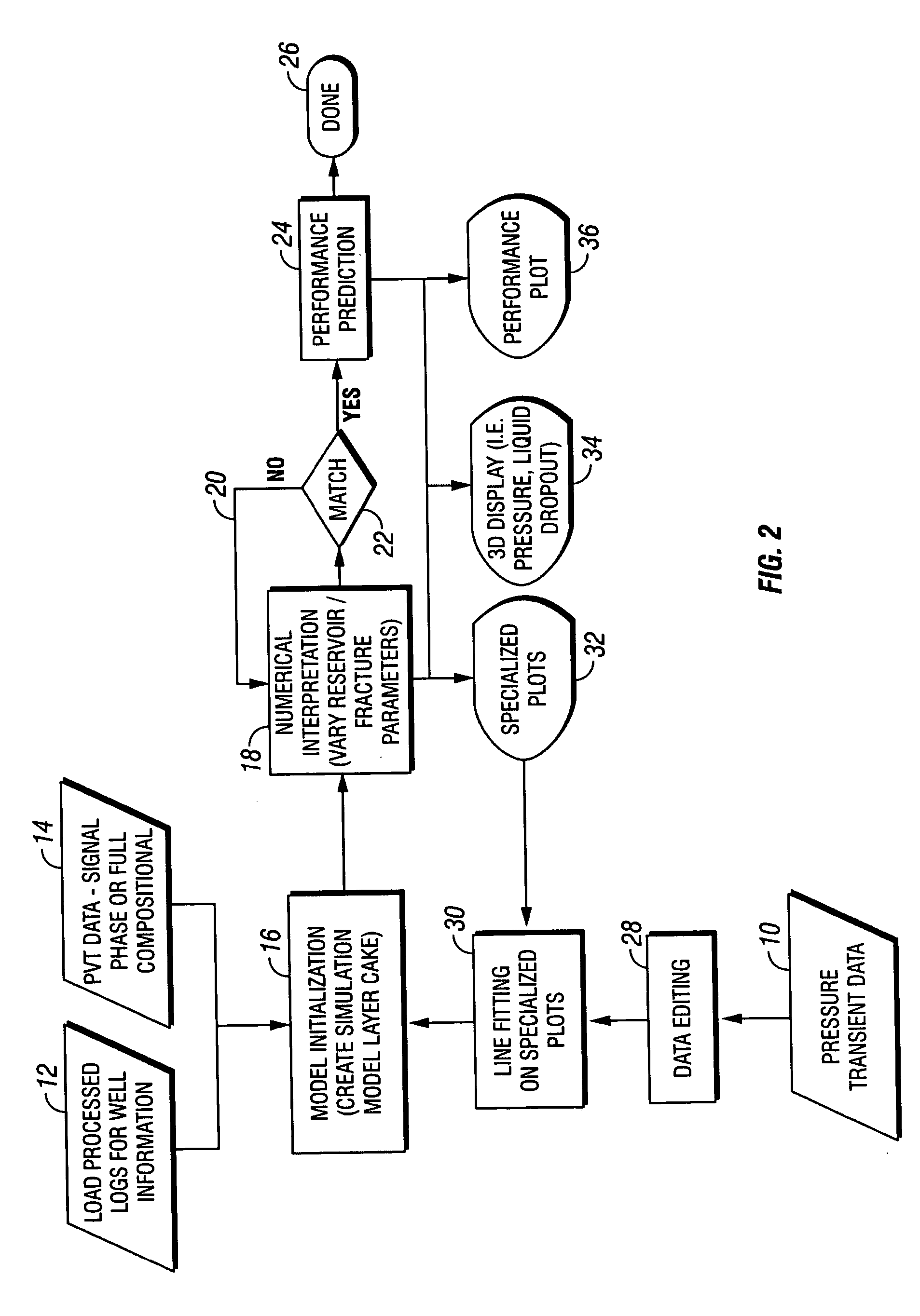
A model system for simulating the performance of a subterranean well, starts with a base model wherein input logging data, pressure transient data and PVT data is introduced into the base model. A numerical interpreter then calculates the predicted performance of the well. A match system compares actual performance data with calculated performance data based on the base model through reiterative loop for modifying the base model to provide a match between the actual performance data and the predicted performance data to optimize the base model. The method for generating the optimized performance data in accordance with the subject invention incorporates the steps of introducing known pressure transient data, well logging data and PVT data for the well into a base model and producing a performance prediction from the base model. These results are compared with actual performance data and the model is modified to generate a performance prediction that matches the actual performance for producing an optimized model. The method is particularly useful because it accounts for and adjusts the performance prediction based on non-Darcy factors effecting the fluid parameters in the well.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Artificial intelligence & knowledge based automation enhancement
ActiveUS20160078368A1Instantly leveragedDigital computer detailsMachine learningAnalysis dataArtificial general intelligence
This invention generally relates to a process, system and computer code for updating of computer applications based on collecting automation information related to a current application such as processing power, load, footprint, and performance attributes, determining a system automation profile; using an artificial intelligence based modeler for analyzing data, applying the data to an artificial intelligence model for training and predicting performance, adjusting the artificial intelligence model to achieve an updated automation criteria with optimal values, wherein the optimal values provide input to an automation criteria library for storing and updating a prior automation criteria, and exporting the upgraded automation criteria values for incorporation in a computer-to-be-updated, to achieve a reliable automatic update.
Owner:AUTOMATION ANYWHERE
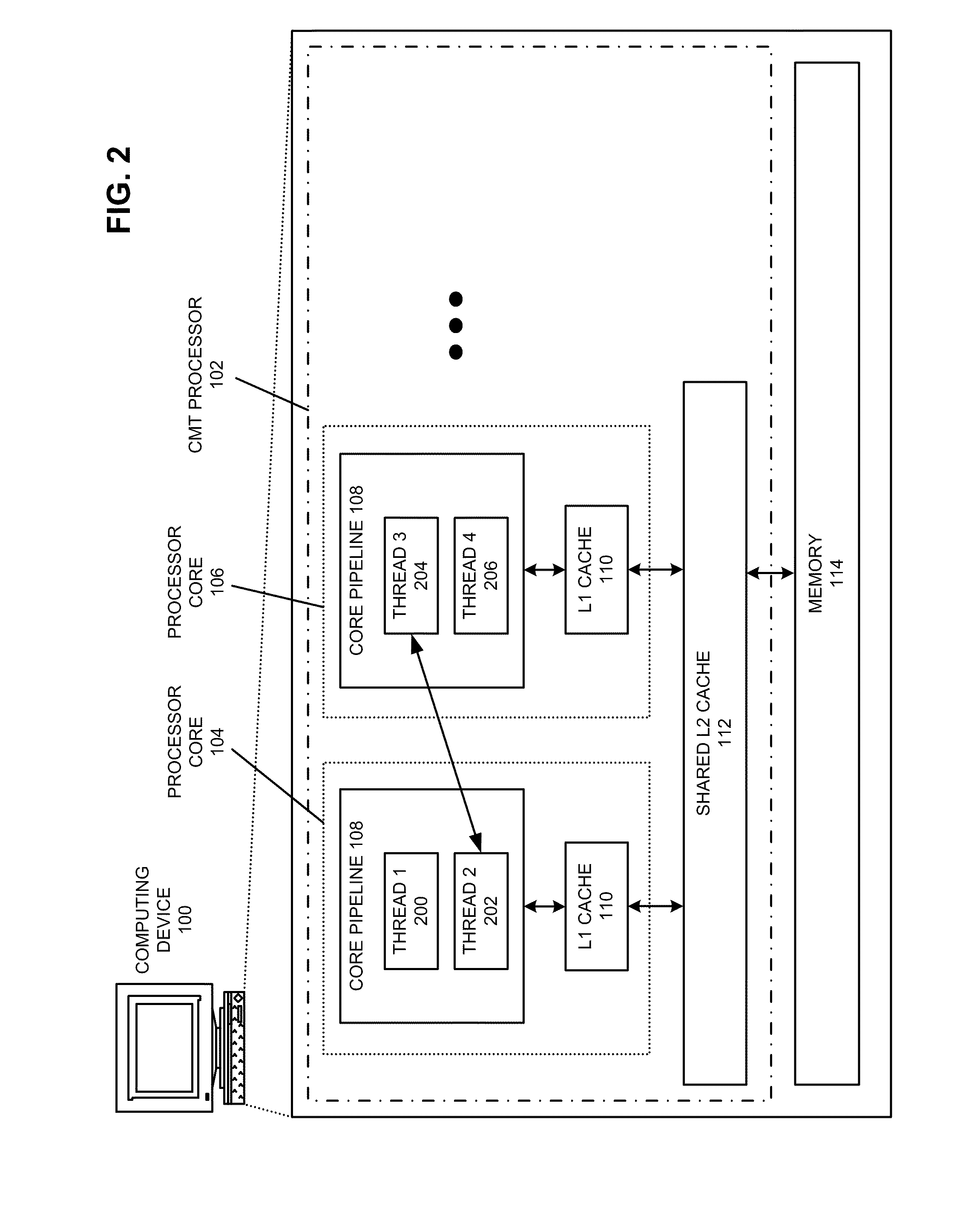
Cache-aware thread scheduling in multi-threaded systems
ActiveUS20110246995A1Facilitates predictively schedulingImprove performanceEnergy efficient ICTGeneral purpose stored program computerThread schedulingParallel computing
The disclosed embodiments provide a system that facilitates scheduling threads in a multi-threaded processor with multiple processor cores. During operation, the system executes a first thread in a processor core that is associated with a shared cache. During this execution, the system measures one or more metrics to characterize the first thread. Then, the system uses the characterization of the first thread and a characterization for a second, second thread to predict a performance impact that would occur if the second thread were to simultaneously execute in a second processor core that is also associated with the cache. If the predicted performance impact indicates that executing the second thread on the second processor core will improve performance for the multi-threaded processor, the system executes the second thread on the second processor core.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method of determining a machine operation using virtual imaging
ActiveUS8144245B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPredicting performanceComputer science
A method of determining a machine for operating at an actual site includes establishing a three-dimensional geographical model representing the actual site, determining at least one operation characteristic relating to the operation of each of a set of machines in relation to the model, and predicting at least one performance characteristic for each machine based on the at least one operation characteristic and at least one respective characteristic of the different machines. The method further includes comparing the predicted performance characteristics for the different machines, and determining a target machine based on the comparison.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
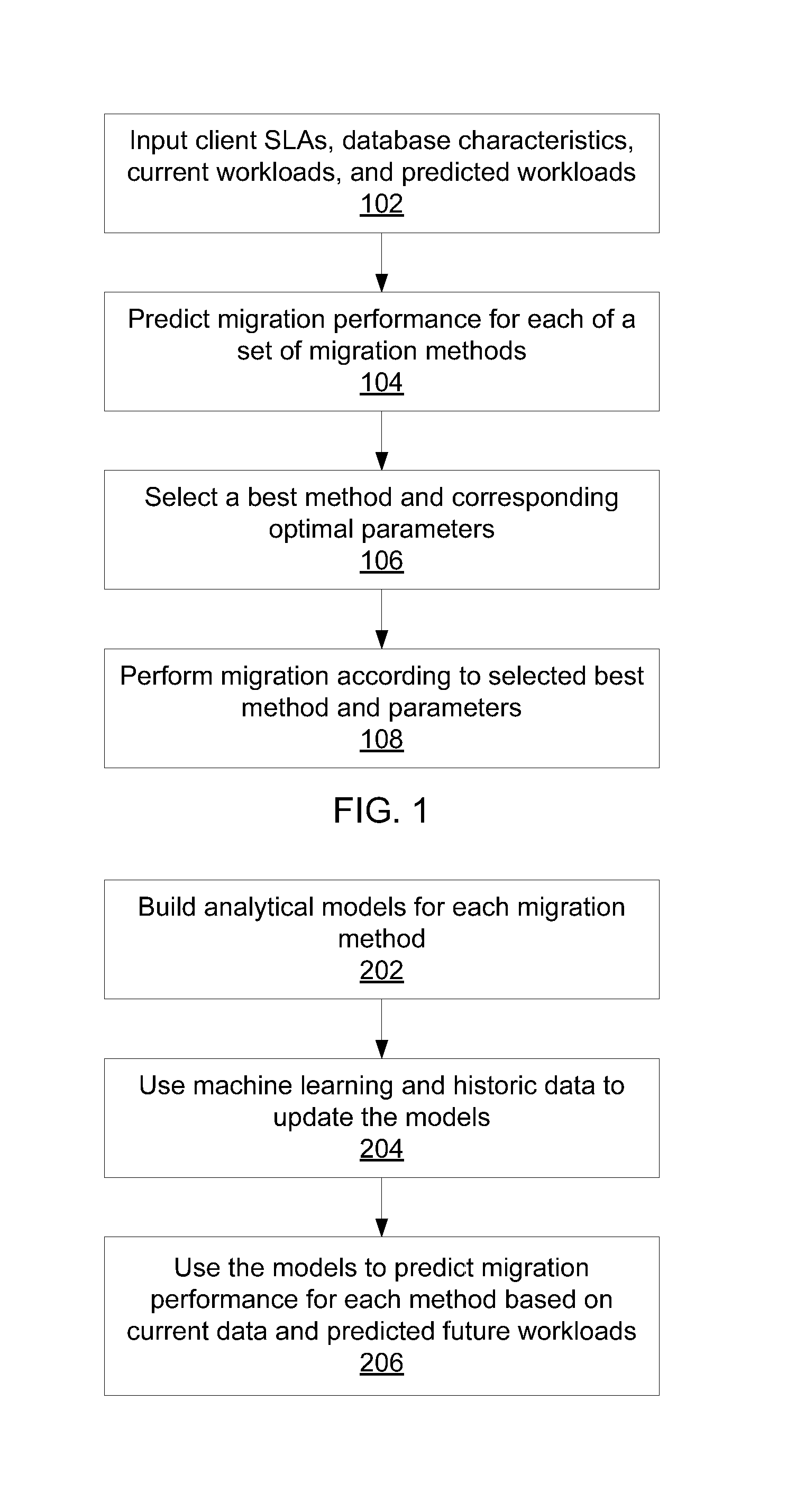
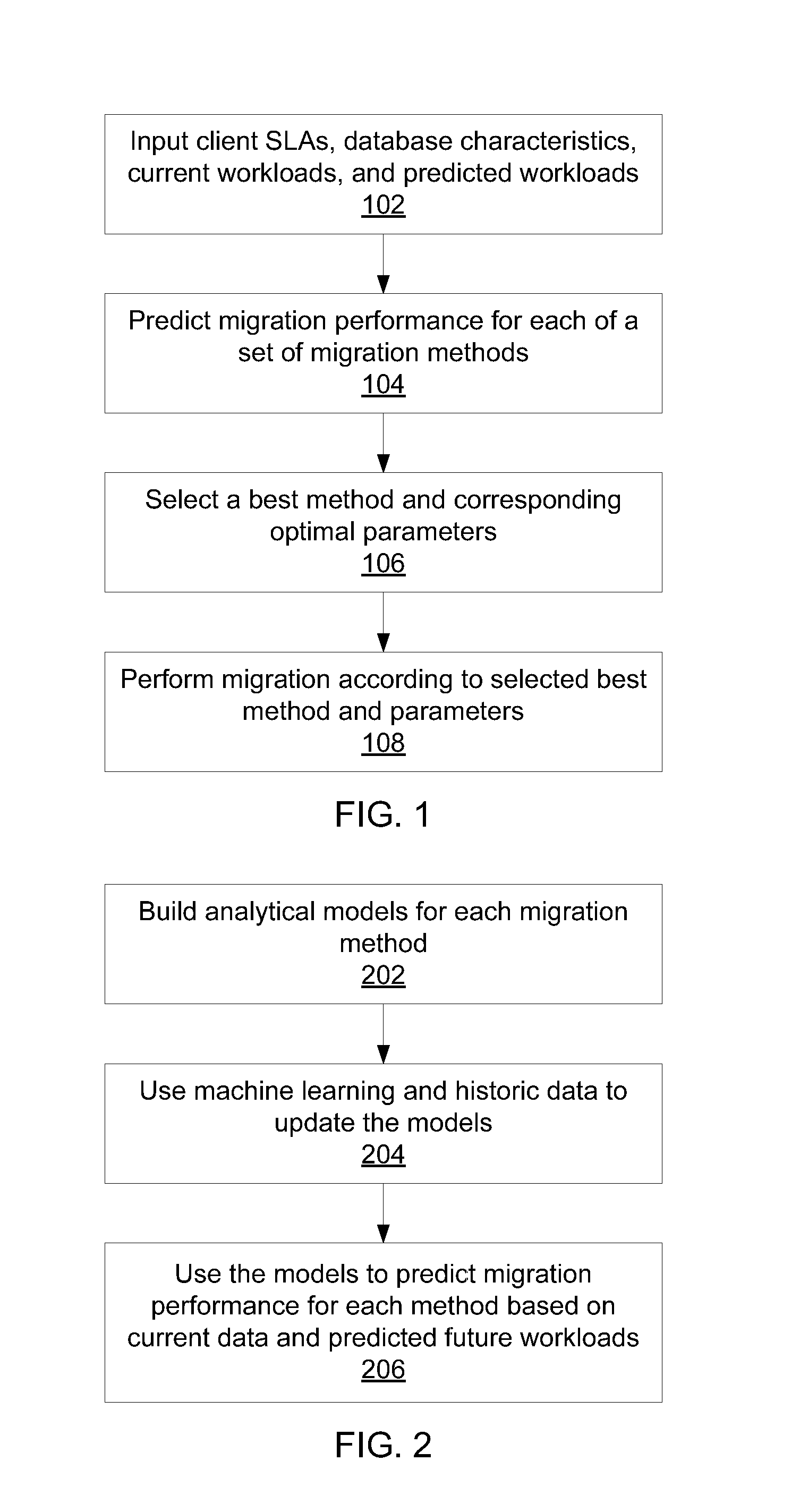
Service level agreement-aware migration for multitenant database platforms
InactiveUS20130085742A1Digital data information retrievalSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationService-level agreementPredicting performance
A method for migration from a multitenant database is shown that includes building an analytical model for each of a set of migration methods based on database characteristics; predicting performance of the set of migration methods using the respective analytical model with respect to tenant service level agreements (SLAs) and current and predicted tenant workloads, where the prediction includes a migration speed and an SLA violation severity; and selecting a best migration method from the set of migration methods according to the respective predicted migration speeds and SLA violation severities.
Owner:NEC LAB AMERICA
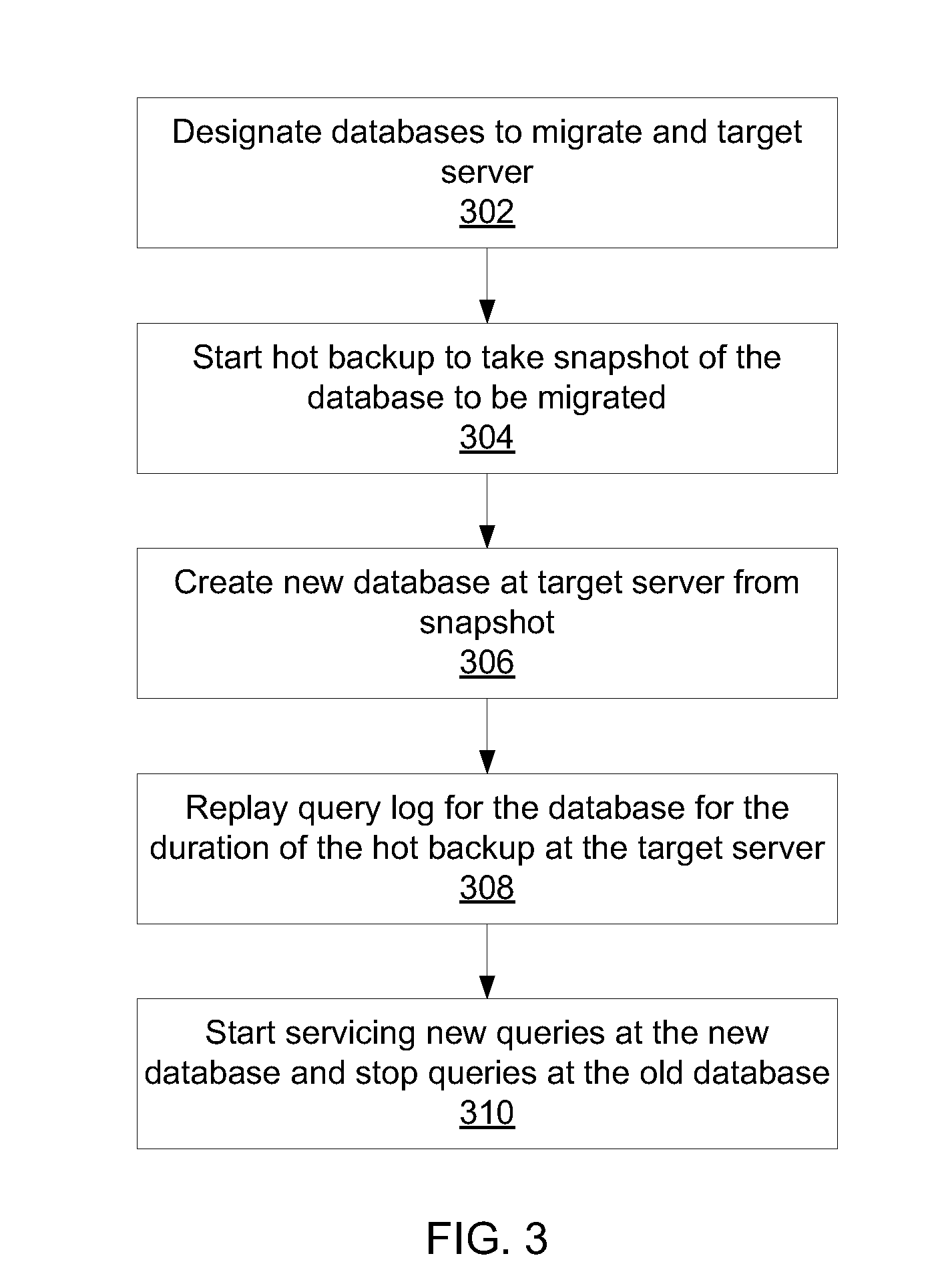
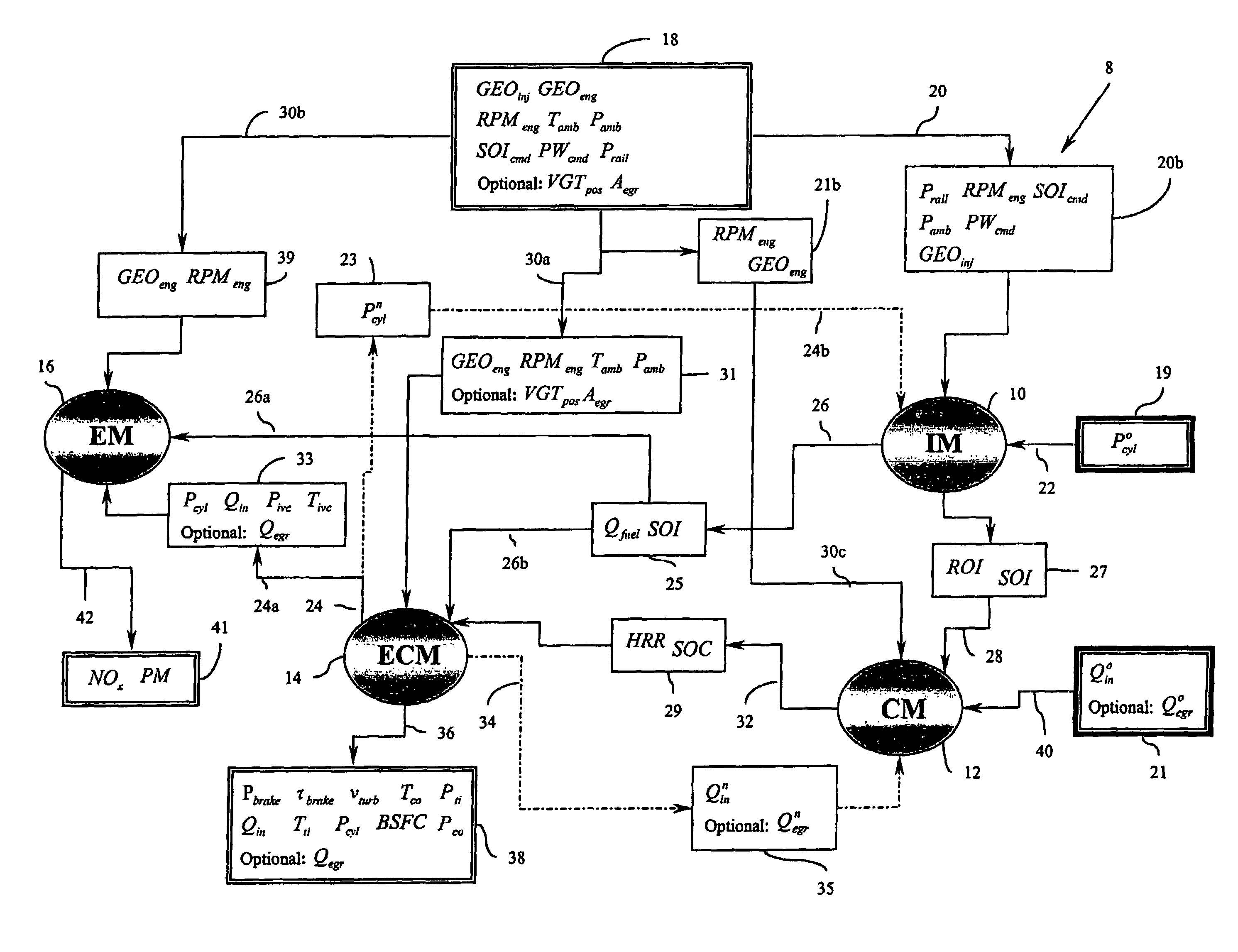
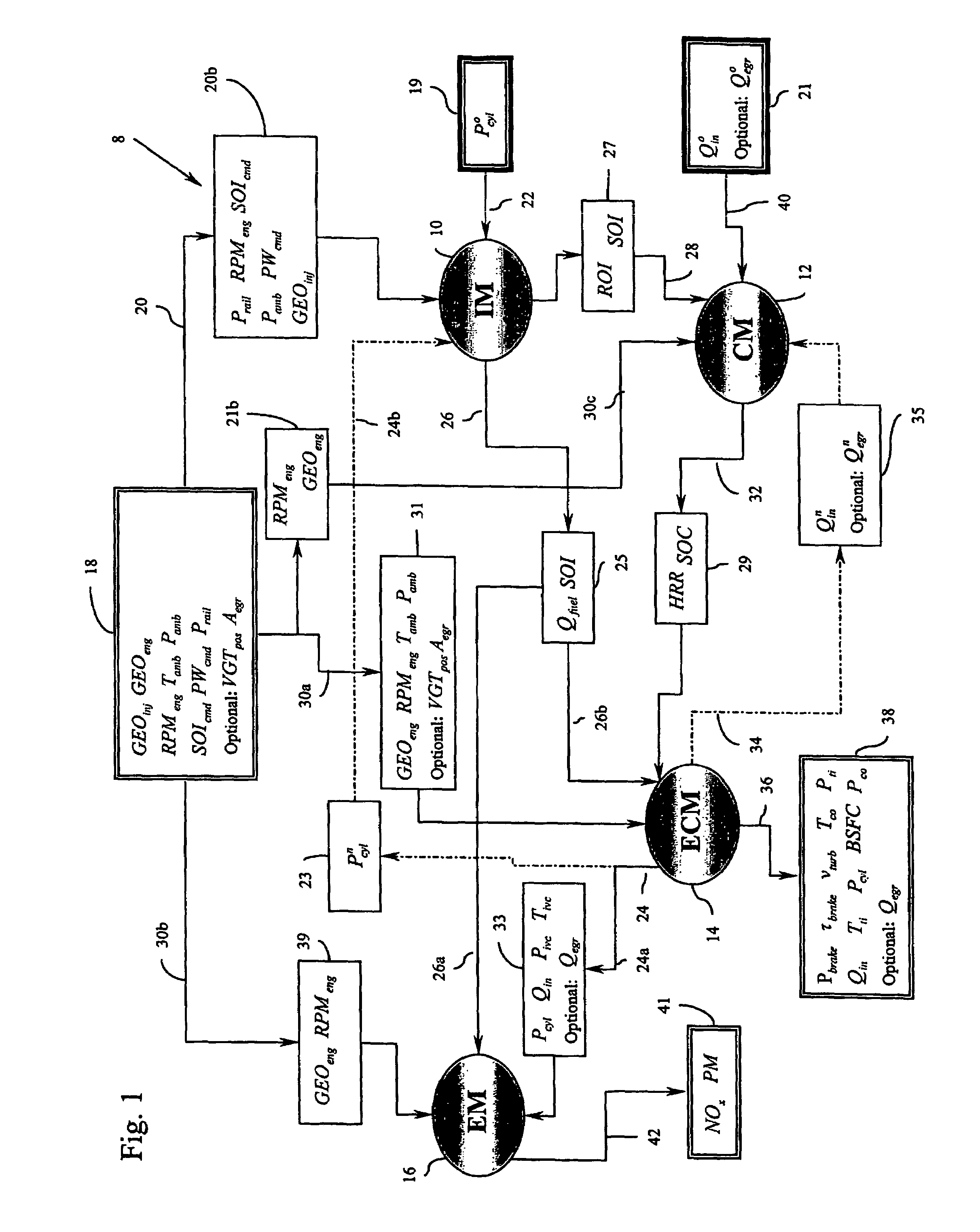
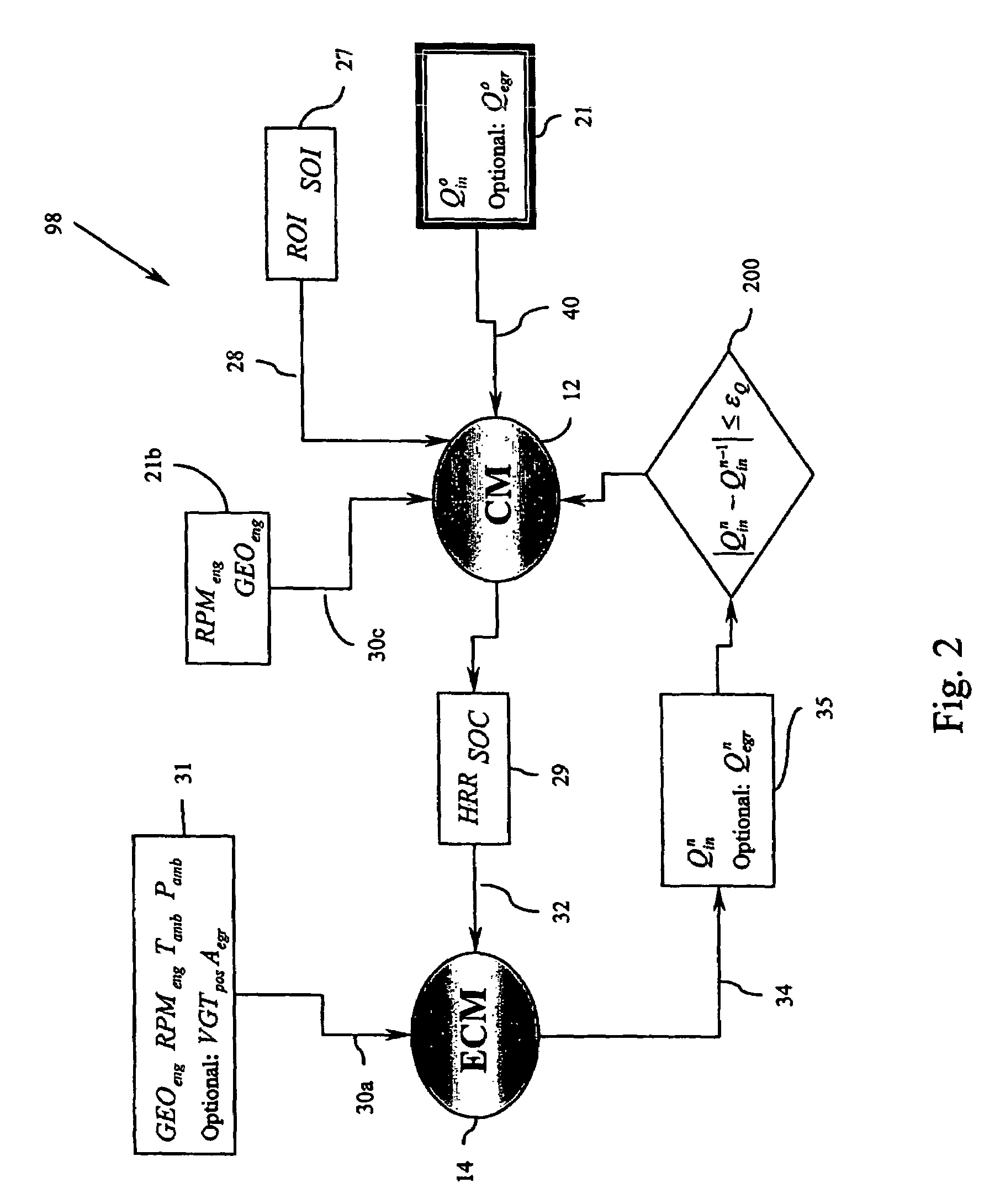
Method for controlling combustion in an internal combustion engine and predicting performance and emissions
InactiveUS7392129B2Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesBrake torqueBrake specific fuel consumption
Owner:WESTPORT POWER
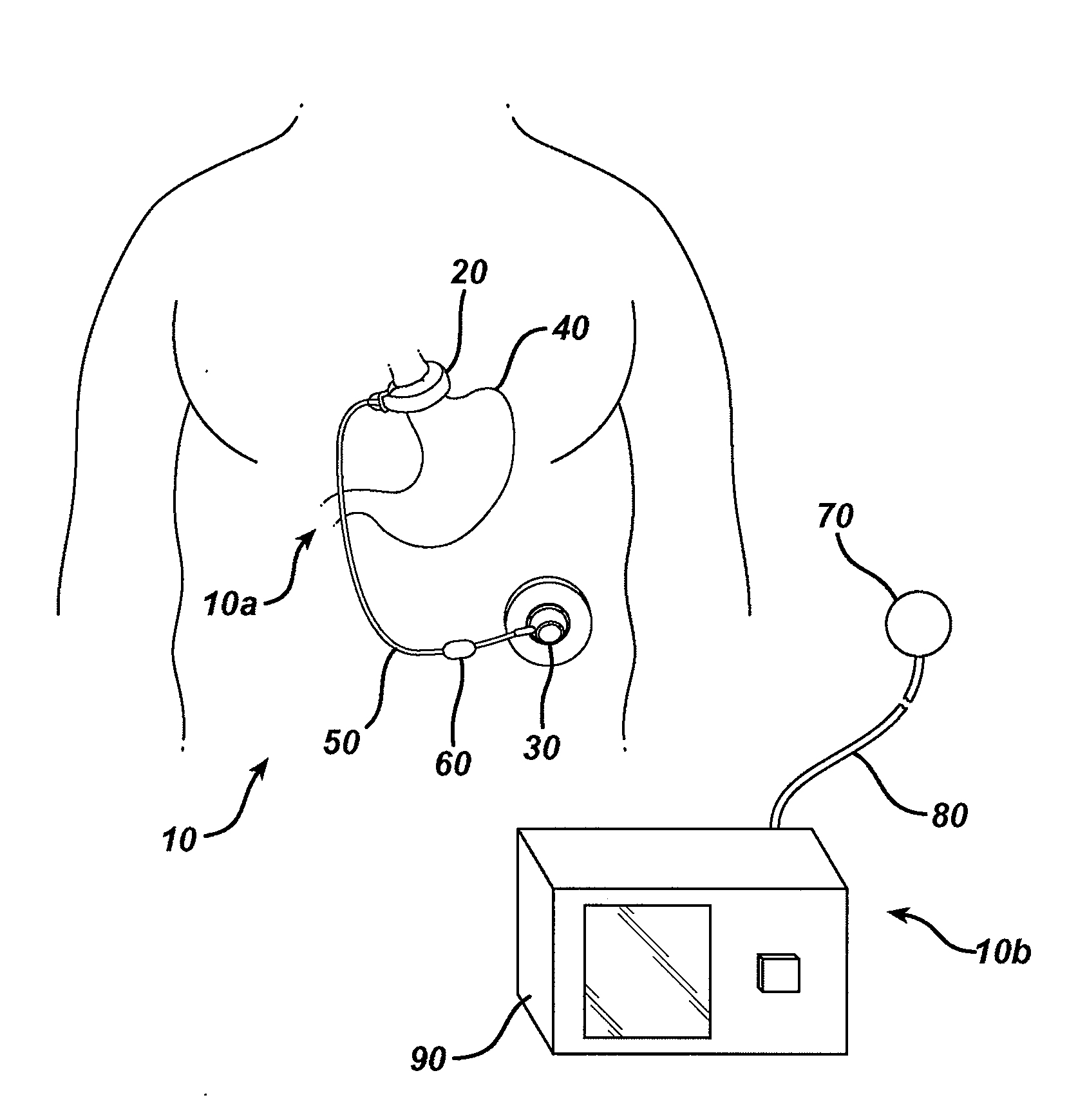
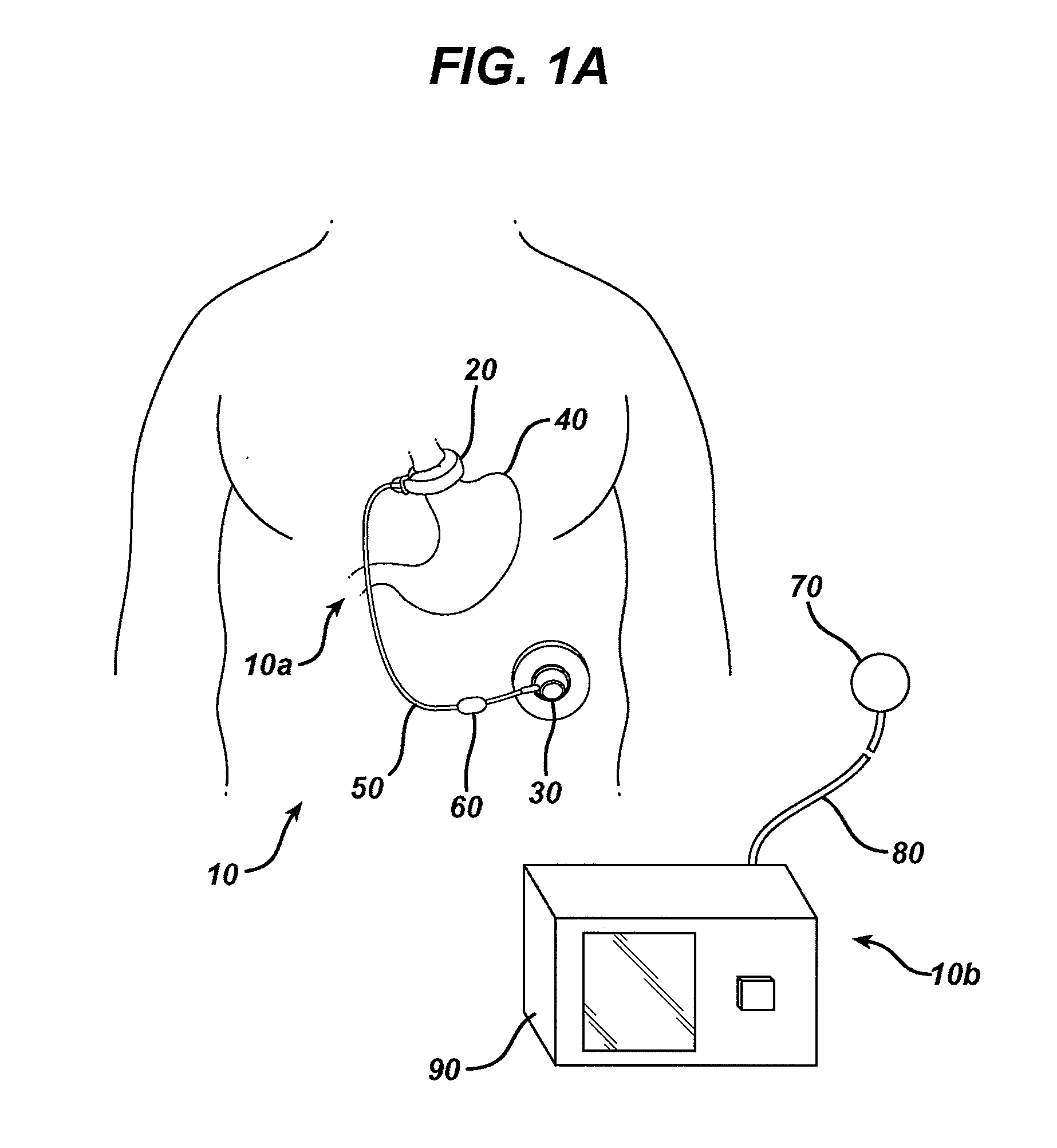
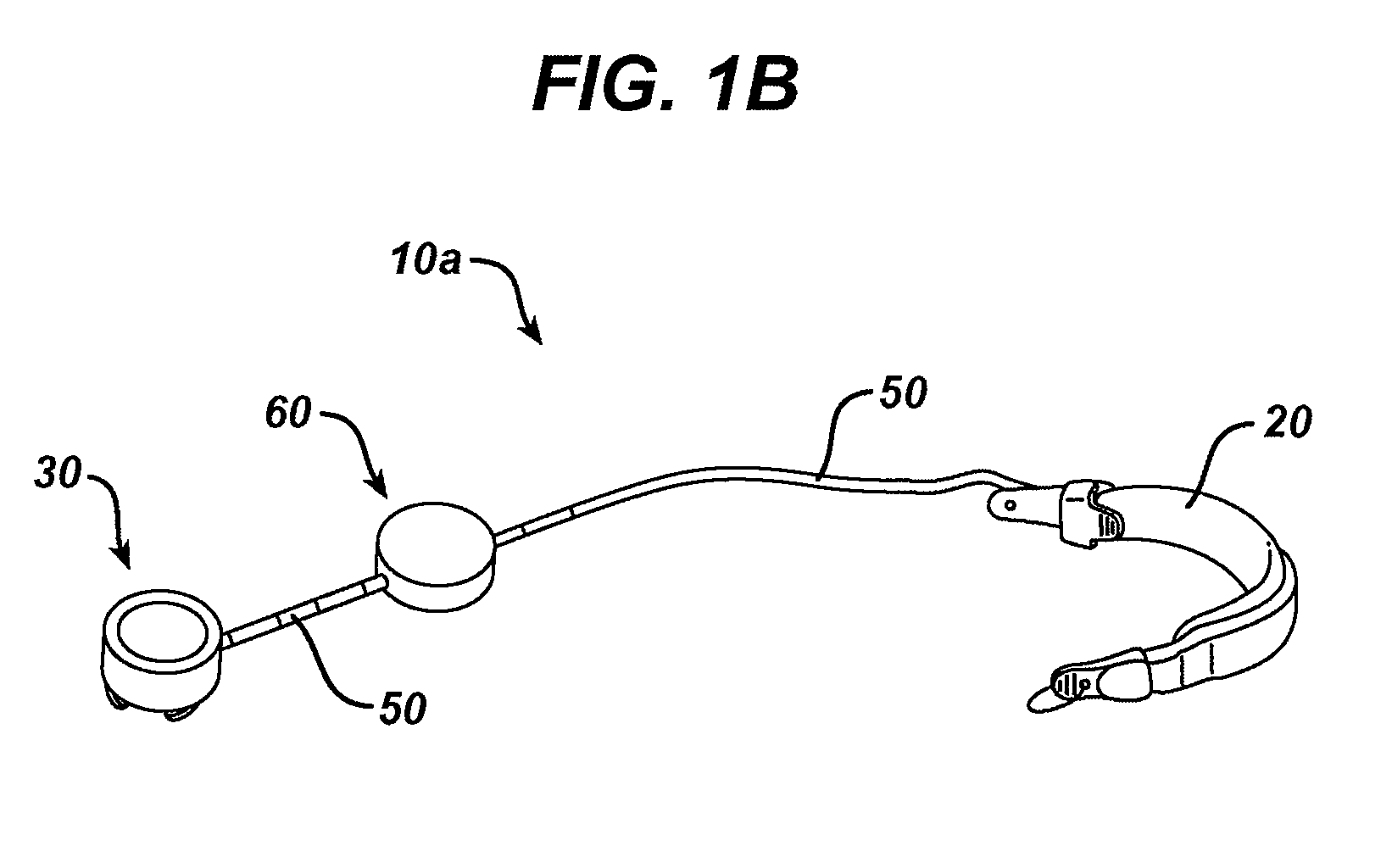
Methods and devices for predicting performance of a gastric restriction system
InactiveUS20090192541A1Medical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesGastric restrictionPredicting performance
Methods and devices are provided for predicting performance of a restriction system for a patient. In general, the methods and devices can allow detection and prediction of a trajectory of a particular patient attribute, such as weight loss. Using previously gathered data values, data values defining a future outcome can be predicted and compared with a desired future outcome. If the future outcome deviates from the desired future outcome, one or more corrective actions can be suggested to a patient and / or a health care provider to help align the patient's treatment plan with the desired future outcome rather than the currently predicted future outcome.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
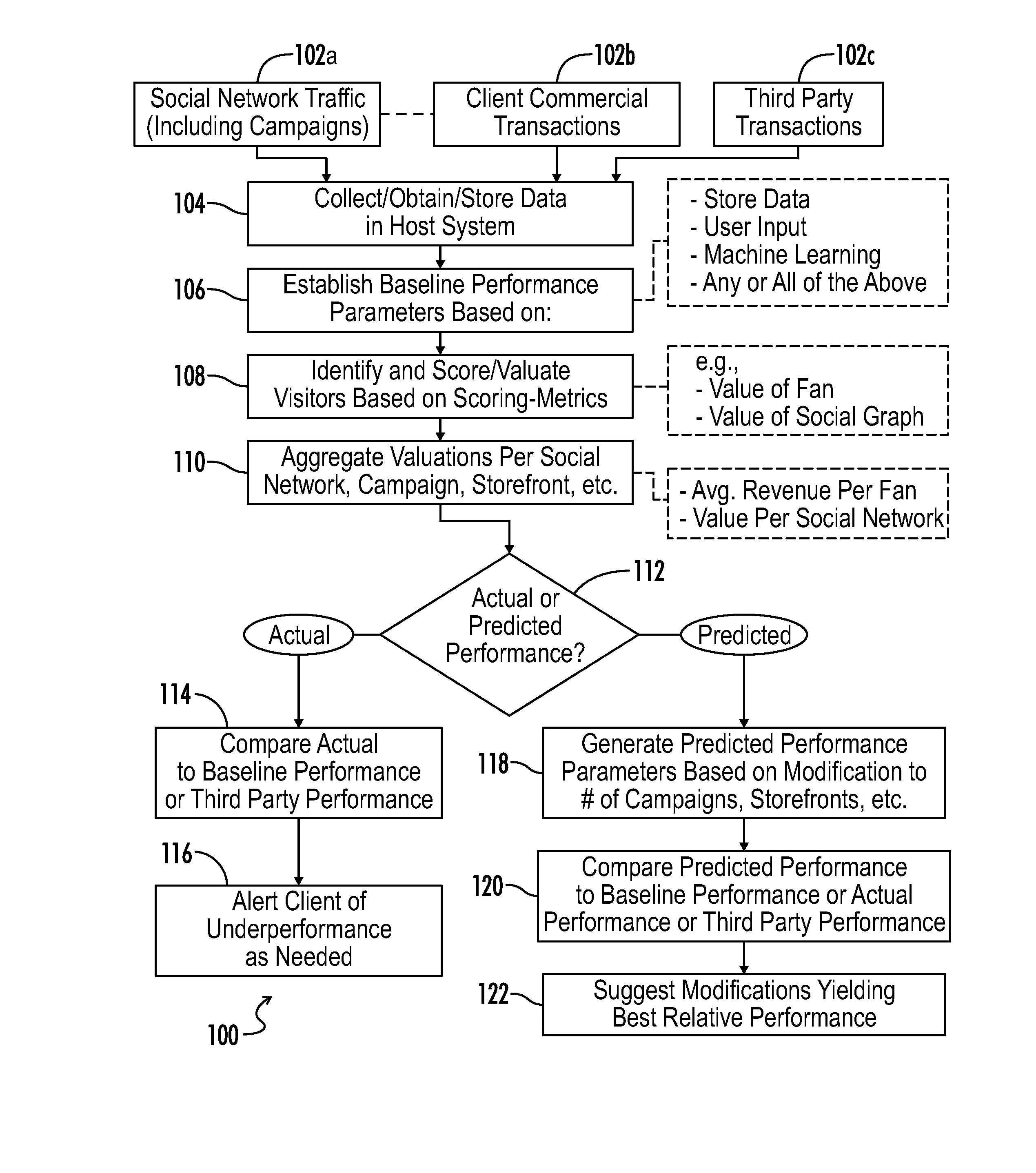
System and method of social commerce analytics for social networking data and related transactional data
A computer-implemented system and method is provided herein for social commerce analytics and optimization. A hosted platform collects and stores online visitor traffic data from social media platforms and from commercial platforms linked to social media campaigns operating on the social media platforms. Algorithms are executed to establish baseline performance parameters for the commercial platforms based on the stored data, and visitors of the social media campaigns and commercial platforms are identified and scored based on predetermined scoring metrics. The scores are aggregated with respect to the social media campaigns and / or the commercial platforms, and actual performances based on the aggregated scores are compared with the established baseline performance parameters. An interface may be generated for a client user associated with the commercial platform to represent one or more of the performance comparisons, and optionally provide alerts to underperformance or suggest future actions based on predicted performance.
Owner:MOONTOAST
System and method for efficiently visualizing and comparing communication network system performance
A method for visualizing and efficiently making comparisons of communication system performance utilizing predicted performance, measured performance, or other performance data sets is described. A system permits visualizing the comparisons of system performance data in three-dimensions using fluctuating elevation, shape, and / or color within a three-dimensional computer drawing database consisting of one or more multi-level buildings, terrain, flora, and additional static and dynamic obstacles (e.g., automobiles, people, filing cabinets, etc.). The method enables a design engineer to visually compare the performance of wireless communication systems as a three-dimensional region of fluctuating elevation, color, or other aesthetic characteristics with fully selectable display parameters, overlaid with the three-dimensional site-specific computer model for which the design was carried out.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
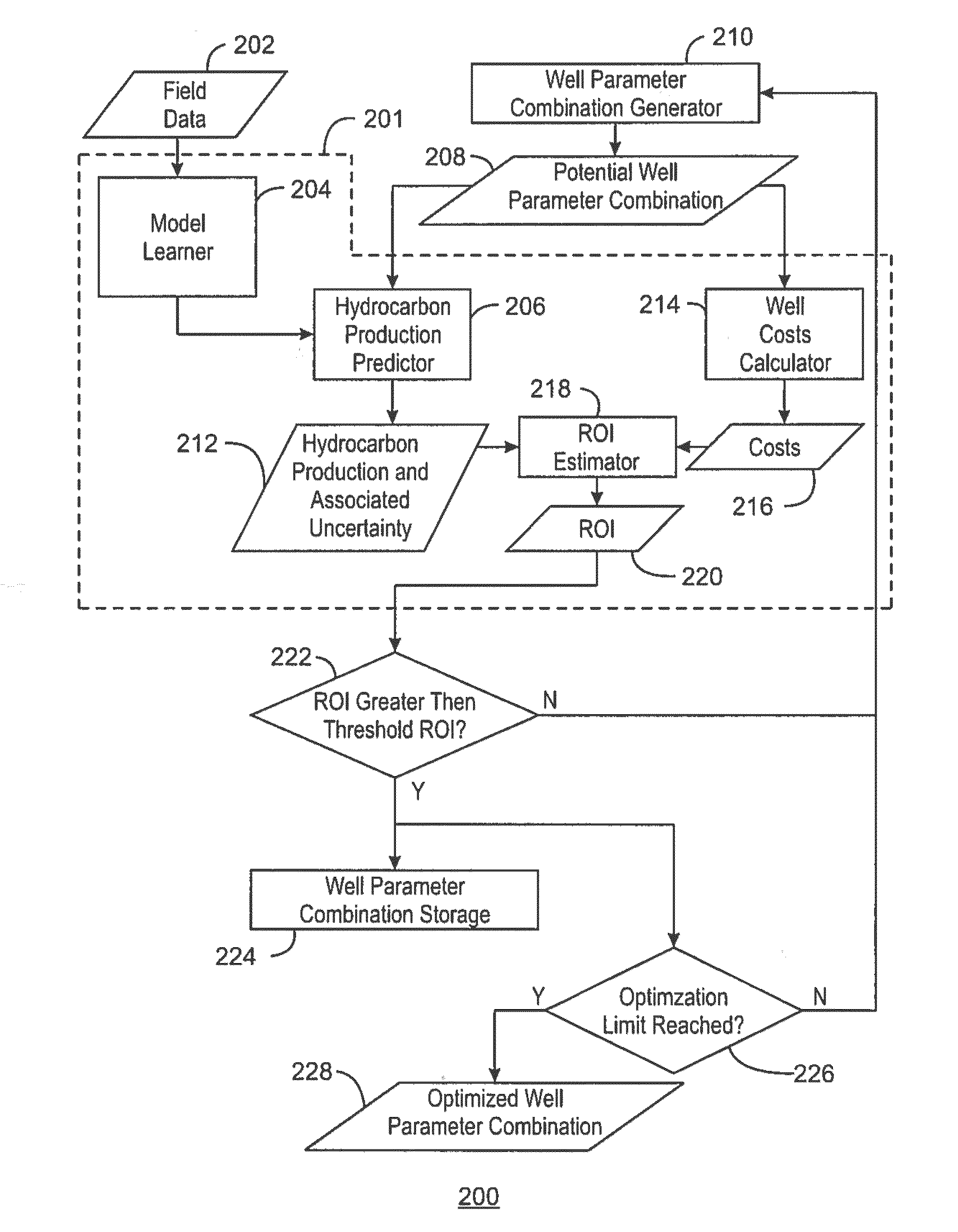
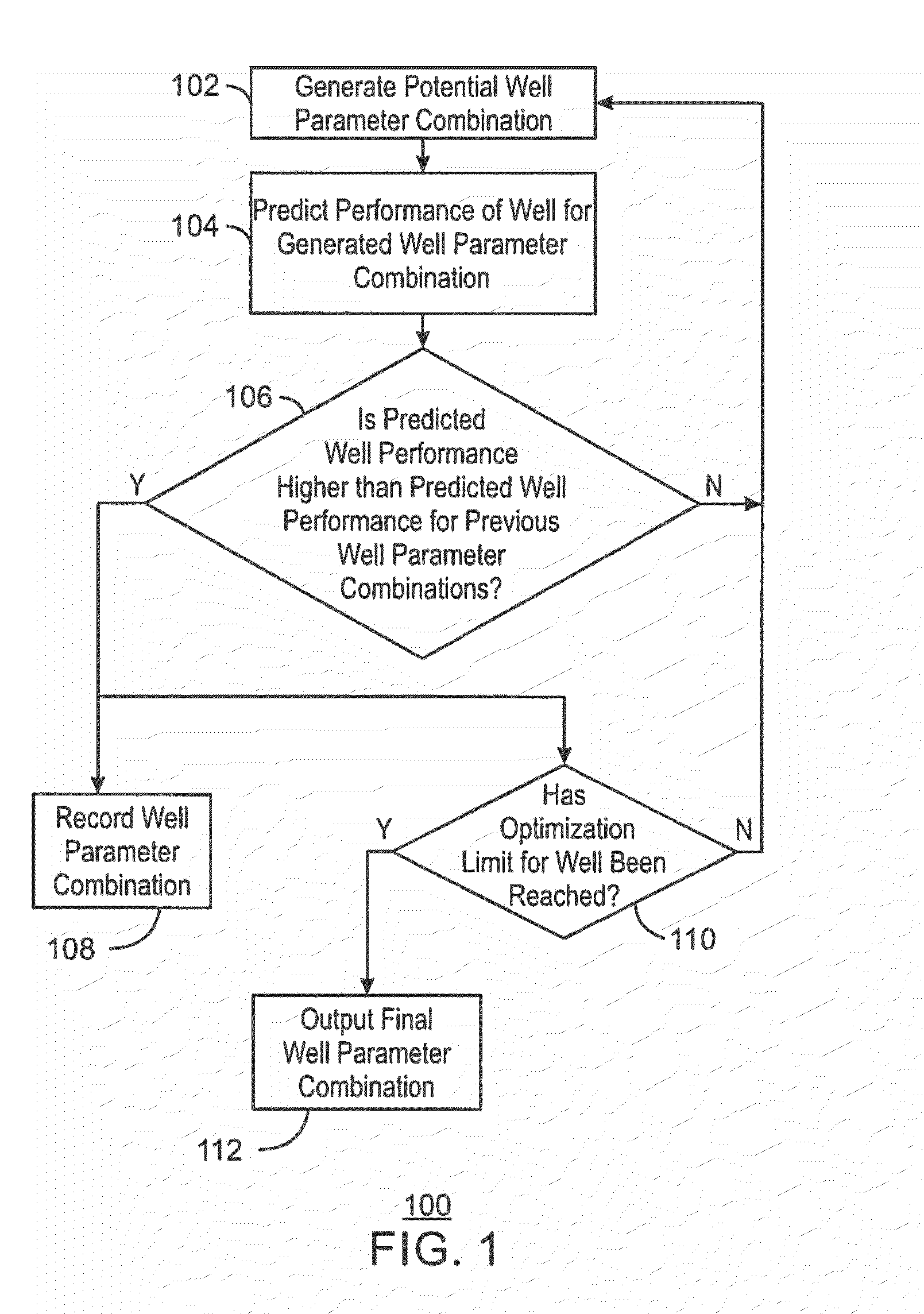
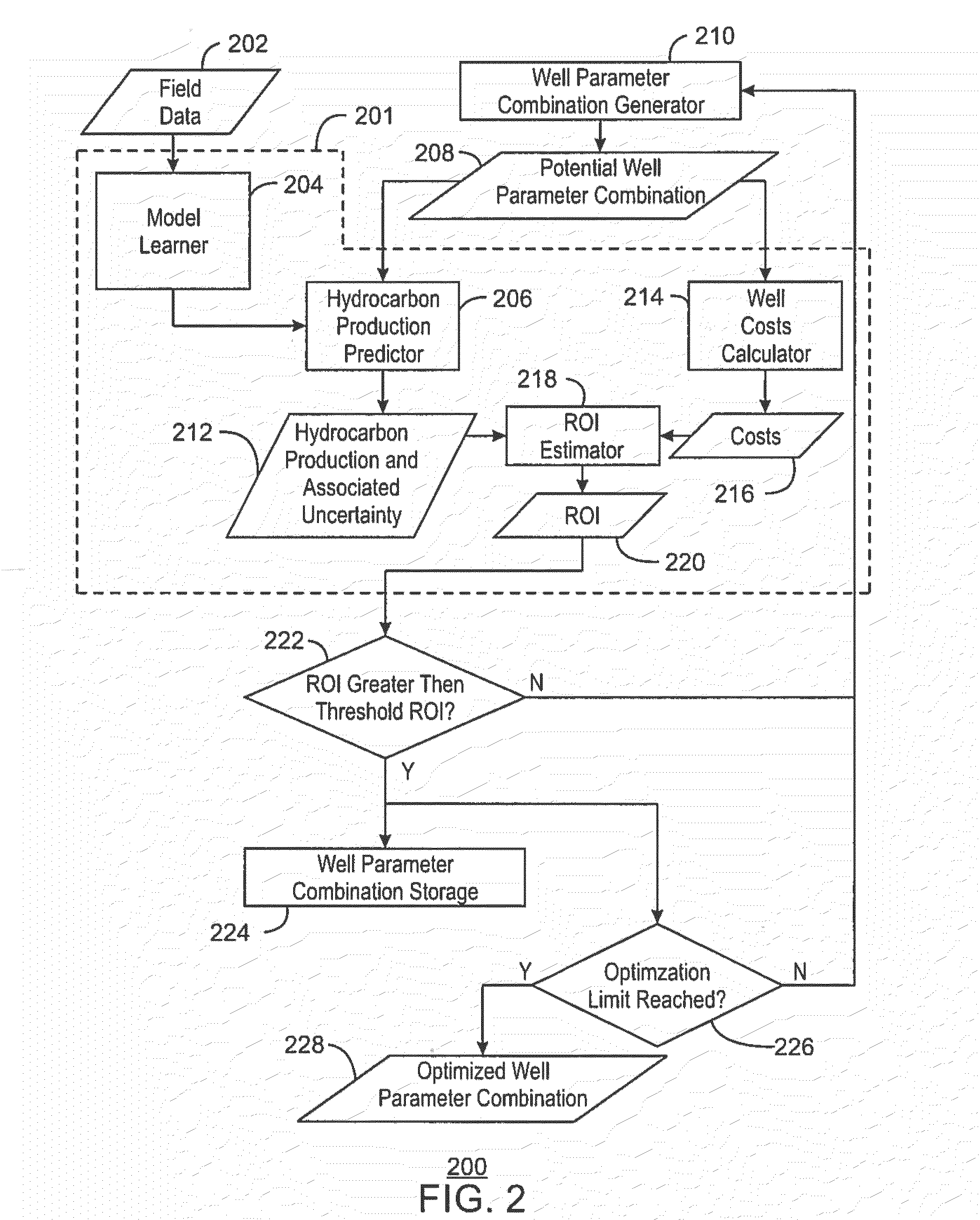
Determining Well Parameters For Optimization of Well Performance
ActiveUS20140365409A1Predictive performanceDigital computer detailsFluid removalPredicting performanceField data
Systems and methods for determining well parameters for optimization of well performance. The method includes training, via a computing system, a well performance predictor based on field data corresponding to a hydrocarbon field in which a well is to be drilled. The method also includes generating, via the computing system, a number of candidate well parameter combinations for the well and predicting, via the computing system, a performance of the well for each candidate well parameter combination using the trained well performance predictor. The method further includes determining, via the computing system, an optimized well parameter combination for the well such that the predicted performance of the well is maximized.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
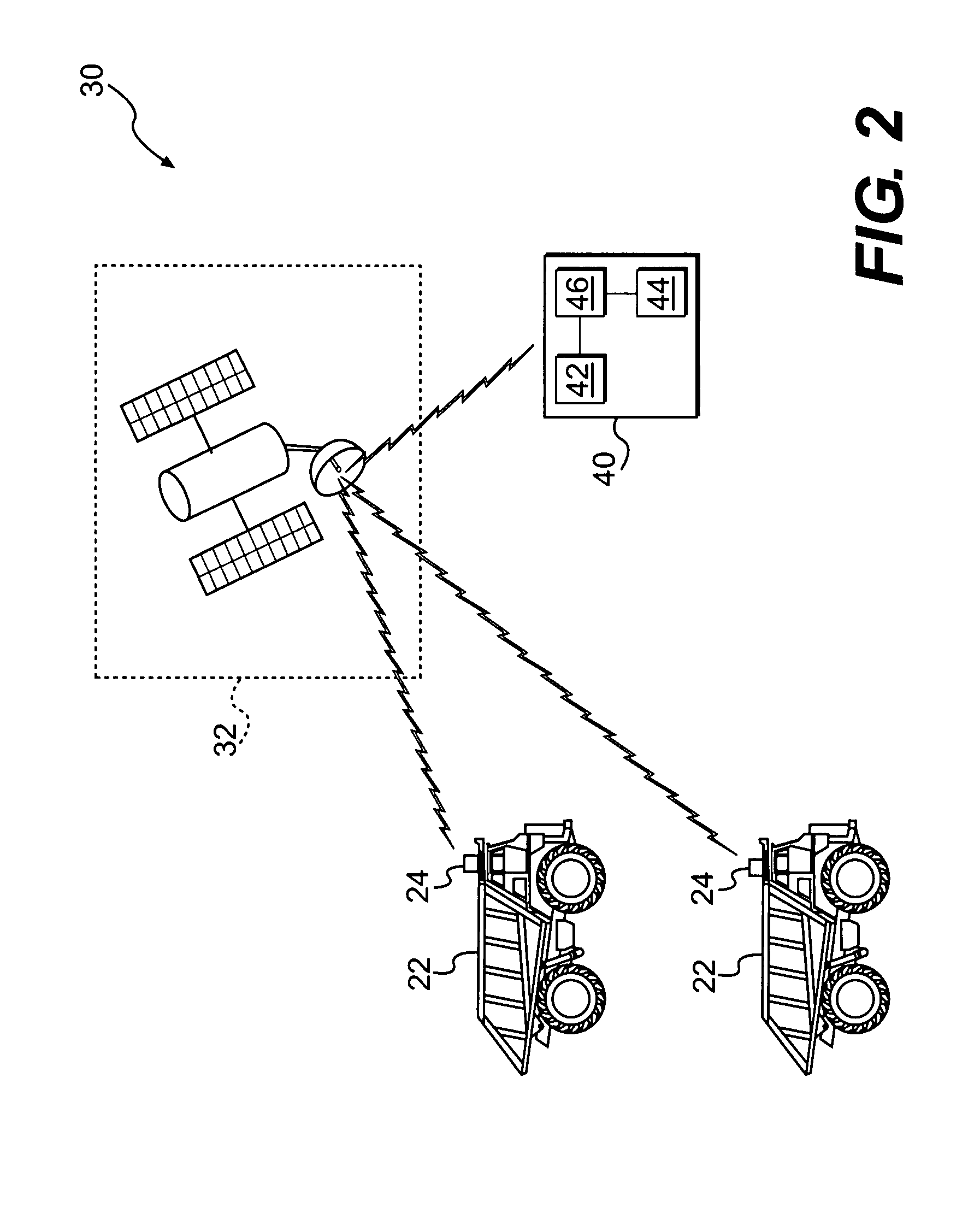
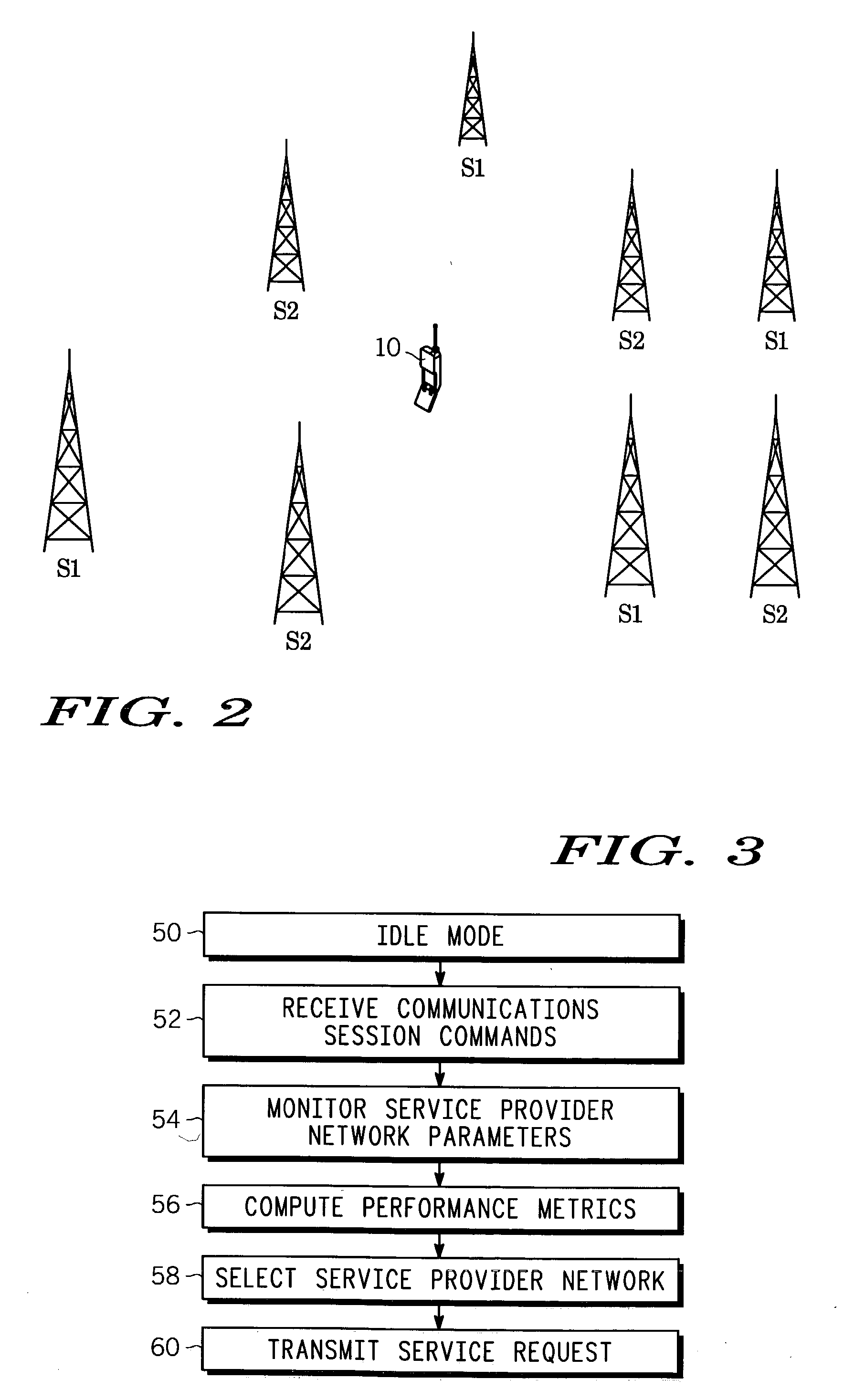
Subscriber device selection of service provider network based on predicted network capabilities
InactiveUS20040198360A1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionService provisionPredicting performance
Selection of a service provider network at a wireless subscriber device (10) includes monitoring service provider network parameters (54) of each of a plurality of available service provider networks (S1, S2), predicting performance capabilities of each of the plurality of available service provider networks (S1, S2), computing a performance metric (56) for each of the plurality of available service provider networks (S1, S2) based on desired performance parameters and on the predicting of performance capabilities of each of the plurality of available service provider networks (S1, S2), and selecting one of the plurality of available service provider networks (S1, S2) based on the computed performance metric (58). The subscriber device (10) is therefore capable of rapidly and autonomously identifying a service provider network that would best serve its current service needs based on the performance metric.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
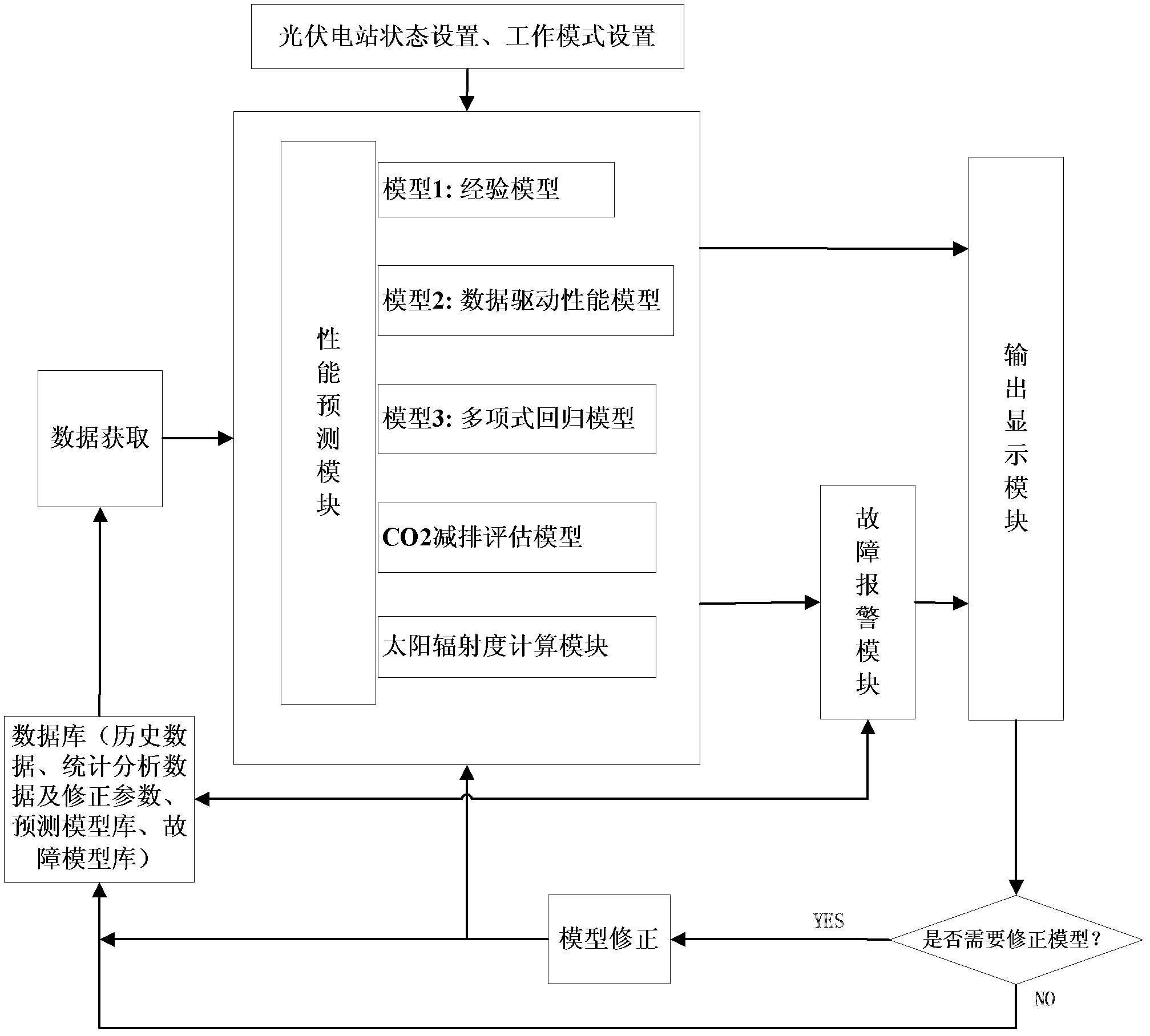
Performance prediction and fault alarm method for photovoltaic power station
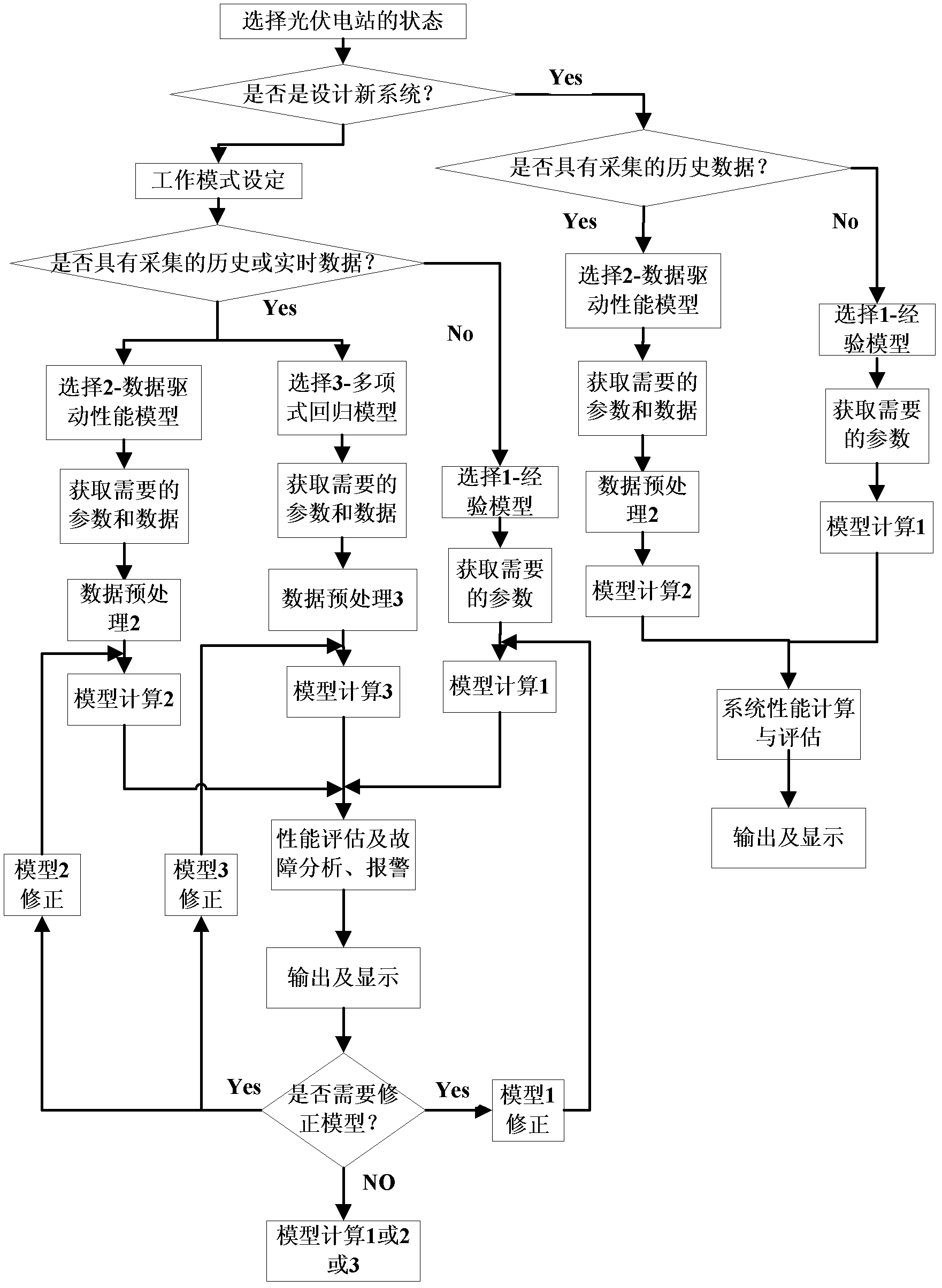
InactiveCN102566435AImprove accuracyEasy to troubleshootAdaptive controlReal-time dataPolynomial regression model
The invention discloses a performance prediction and fault alarm method for a photovoltaic power station. The method comprises the following steps of: a, setting the station of the power station; b, setting the operation mode of the power station; c, judging whether required real-time data or historical data exists or not; d, predicting the performance of the power station through an experience model if the state in the step a is that a new photovoltaic power station is required to be designed and the required real-time data or historical data in the step c does not exist, and predicting the performance of the power station through a data drive performance model if the required real-time data or historical data in the step c exists; e, predicting the performance of the power station through the data drive performance model or a polynomial regression model if the photovoltaic power station in the step a is operated and the required real-time data or historical data in the step c exists, and predicting the performance of the power station through the experience model if the required real-time data or historical data in the step c does not exist; f, comparing actual performance with the predicted performance, and performing fault alarm; and g, correcting the models on line by a Kalman filtering method and returning to the step c, and otherwise, directly returning to the step e. By the method, solar energy resources can be utilized to the maximum extent, and power utilization cost can be reduced; and the accuracy of performance prediction and fault diagnosis is improved.
Owner:AUTOMATION RES & DESIGN INST OF METALLURGICAL IND
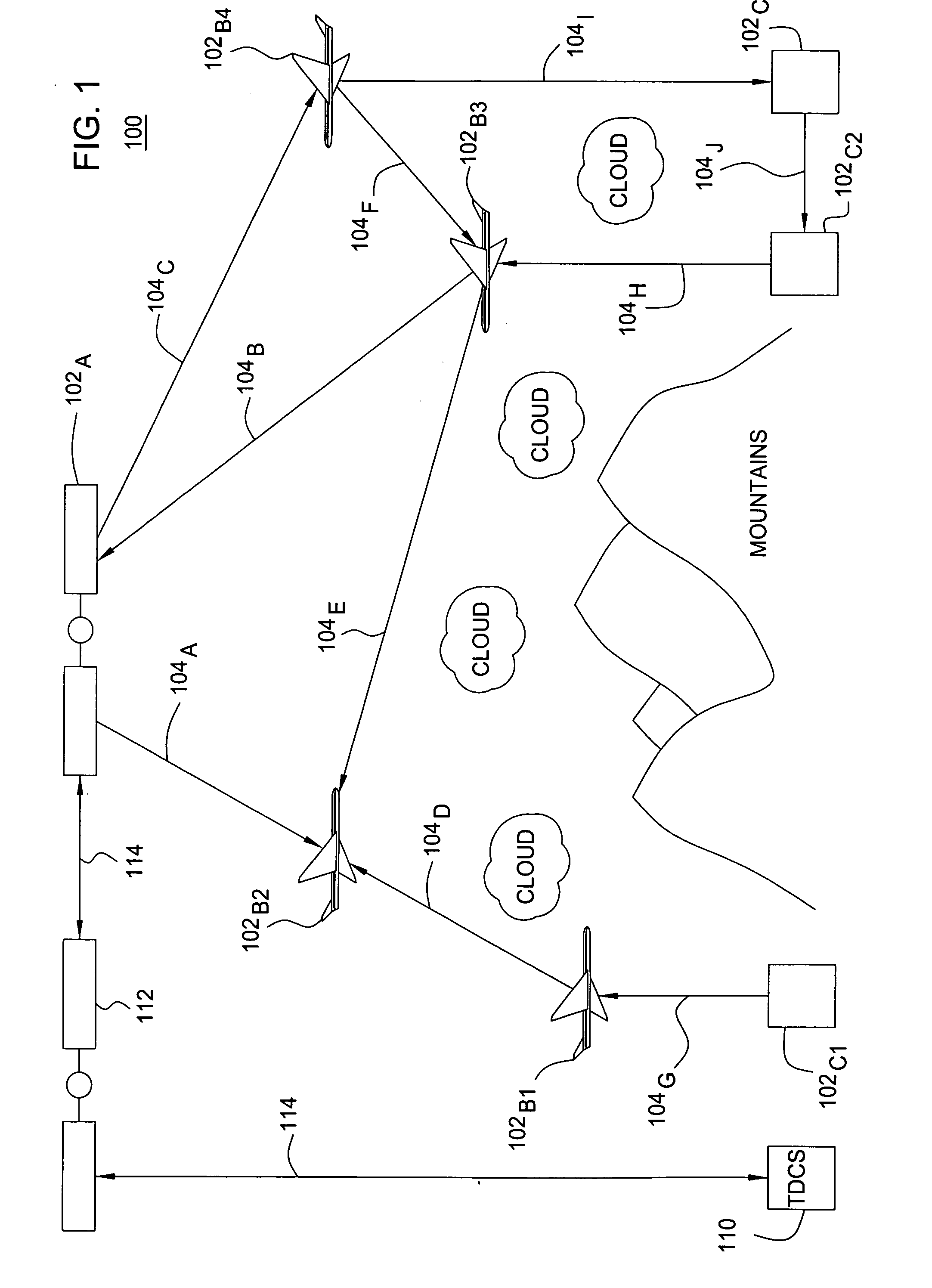
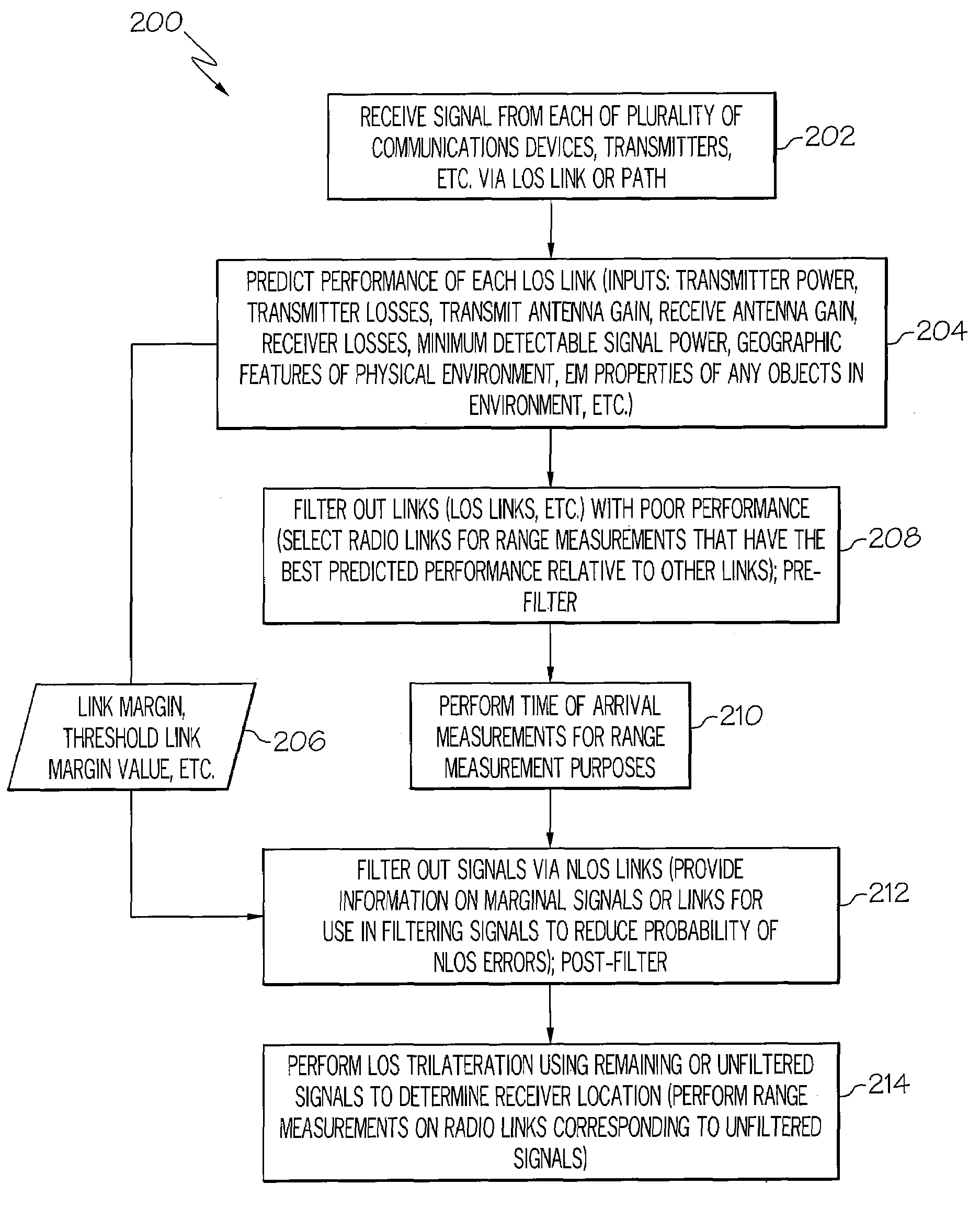
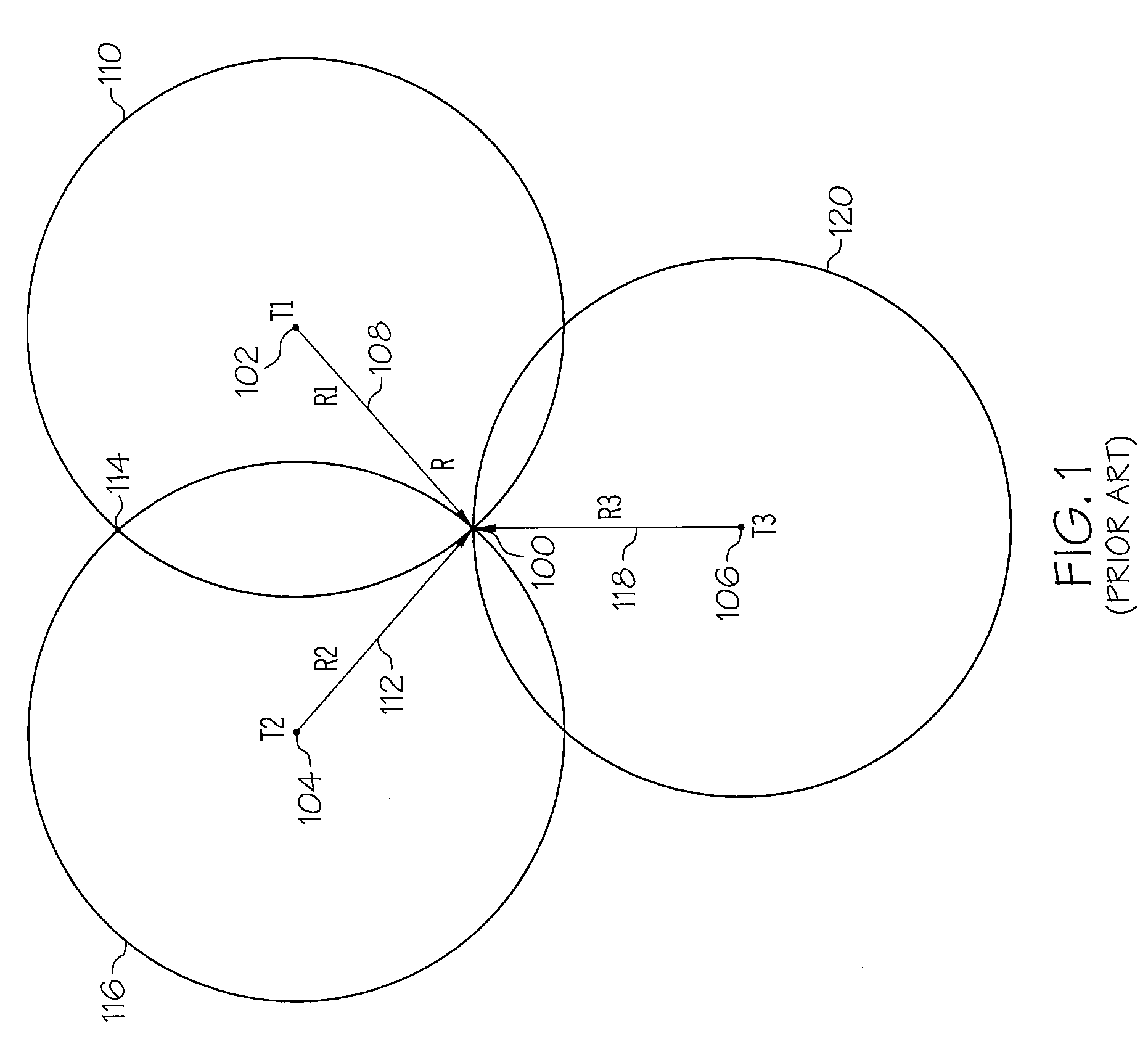
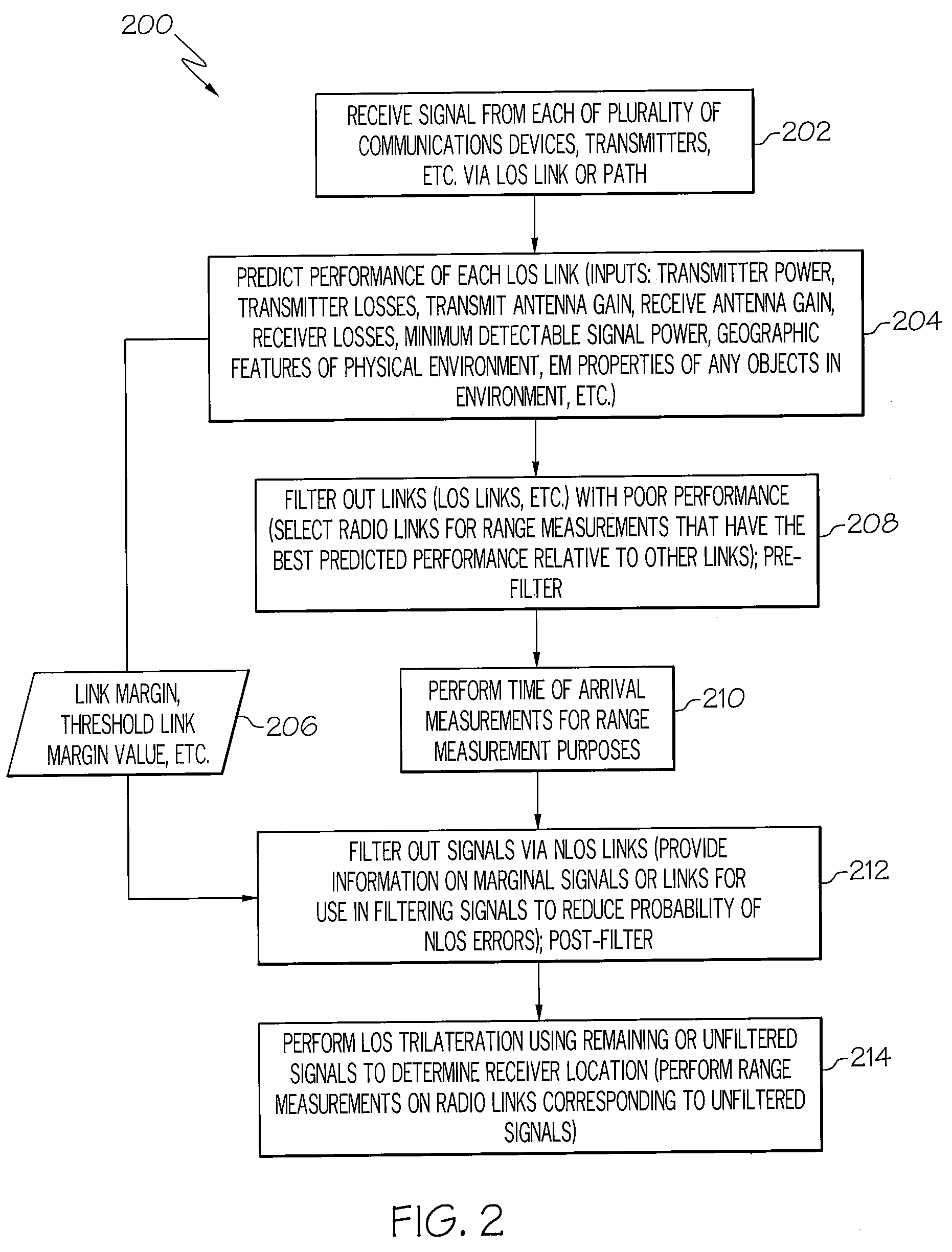
Method and device for trilateration using LOS link prediction and pre-measurement LOS path filtering
ActiveUS7468696B2Direction finders using radio wavesPosition fixationPredicting performanceElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method for trilateration may include receiving a signal via each of a plurality of LOS paths and predicting performance of each LOS path. The method may also include filtering out signals received via LOS paths with performance below a predetermined threshold value. The method may further include performing trilateration using unfiltered signals to substantially determine a location of a device.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Method and system for predicting performance of a drilling system for a given formation
InactiveUS20050284661A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingEarth drilling toolsWell drillingDisplay device
A method and apparatus for predicting the performance of a drilling system for the drilling of a well bore in a given formation includes generating a geology characteristic of the formation per unit depth according to a prescribed geology model, obtaining specifications of proposed drilling equipment for use in the drilling of the well bore, and predicting a drilling mechanics in response to the specifications as a function of the geology characteristic per unit depth according to a prescribed drilling mechanics model. Responsive to a predicted drilling mechanics, a controller controls a parameter in the drilling of the well bore. The geology characteristic includes at least rock strength. The specifications include at least a bit specification of a recommended drill bit. Lastly, the predicted drilling mechanics include at least one of bit wear, mechanical efficiency, power, and operating parameters. A display is provided for generating a display of the geology characteristic and predicted drilling mechanics per unit depth, including either a display monitor or a printer.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Method and System For Modeling Geologic Properties Using Homogenized Mixed Finite Elements
InactiveUS20120221302A1Computation using non-denominational number representationGeological measurementsDiffusionComputational science
Owner:LEWANDOWSKI JEROME +1
Performance prediction method for hydrocarbon recovery processes
The invention relates to a method for predicting the performance of large-scale hydrocarbon-bearing reservoir floods. One embodiment of the invention includes a method for predicting performance of a patterned flooding process in a subterranean hydrocarbon-bearing formation, said formation being penetrated by a plurality of injector wells and producer wells, comprising the steps of: determining flow-based pairs of injector to producer wells [FIG. 4, item 78a] (first well pairs) using a geological model [item 76]; developing a connective pore volume distribution curve for each first well pair item [78b]; selecting at least two first well pairs (selected well pairs) that reflect narrow and wide connective pore volume distributions that correspond to high and lower oil recovery levels; developing a 3-D simulation model for each selected well pair, performing a reservoir simulation for each selected well pair for the corresponding flooding process; and generating prototype performance curves for each selected well pair. An alternate embodiment of the invention includes a method for predicting the performance of large-scale hydrocarbon-bearing reservoir floods where injection well location, production well location, a process parameter, or a well processing rate is modified.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
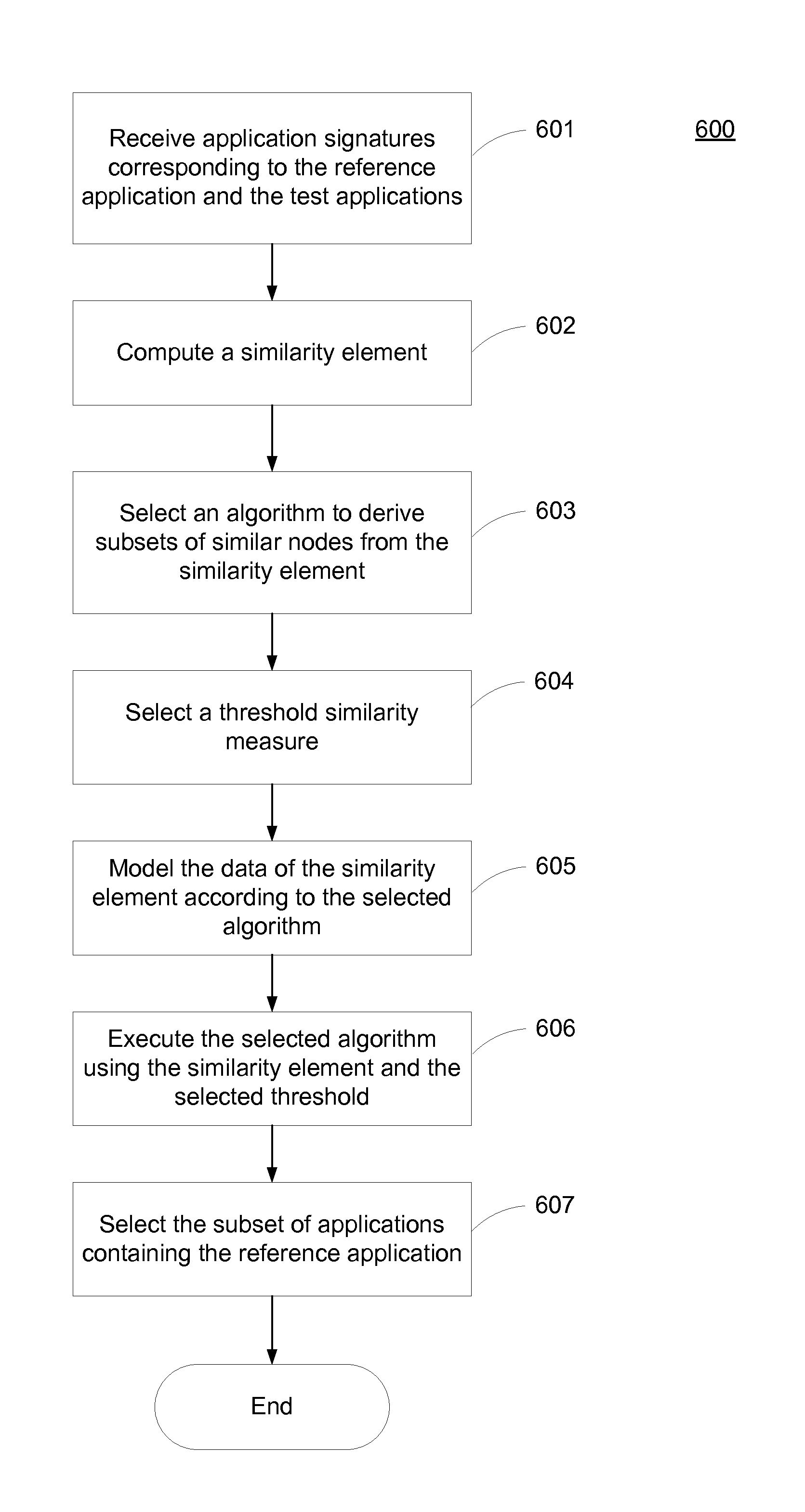
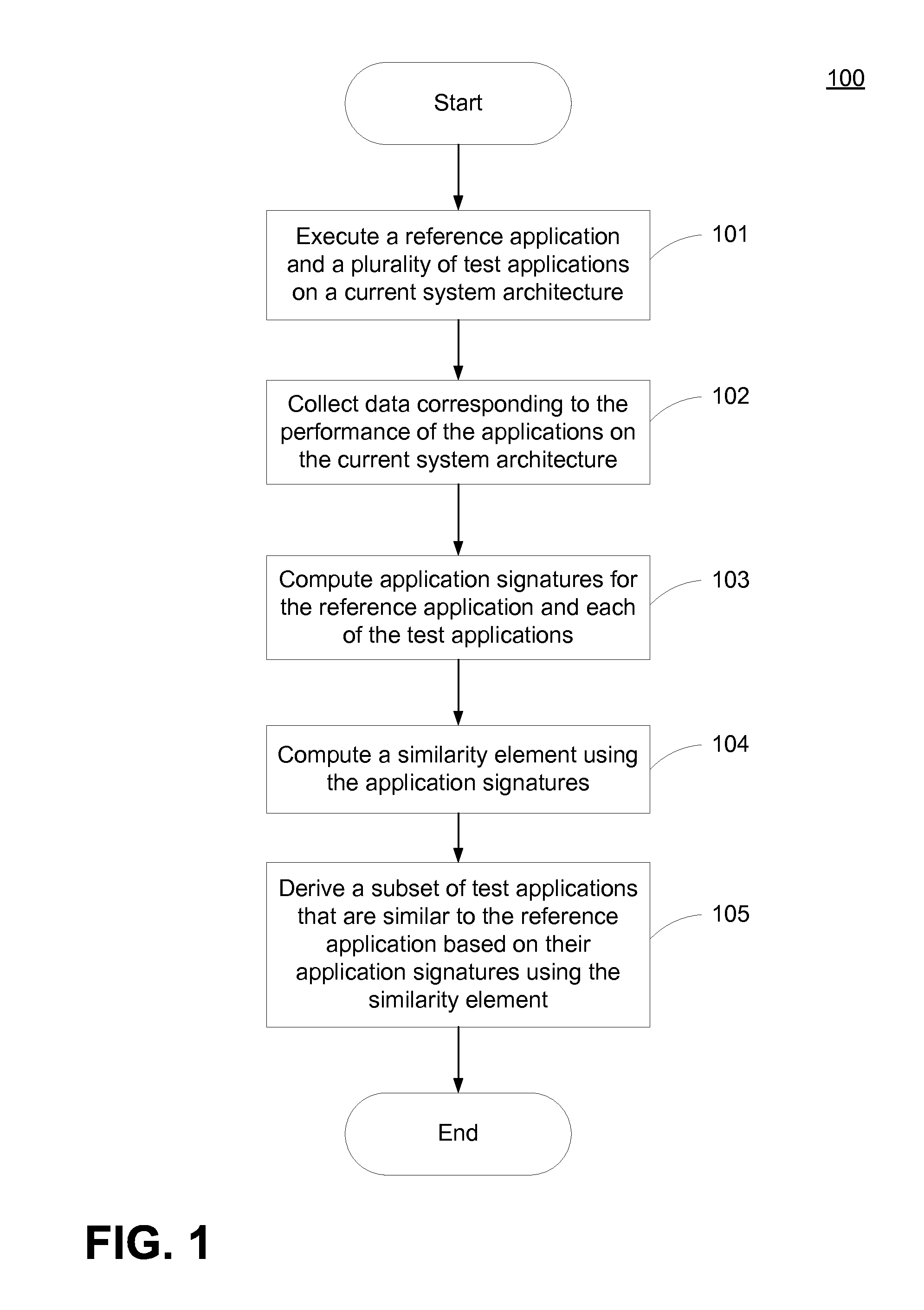
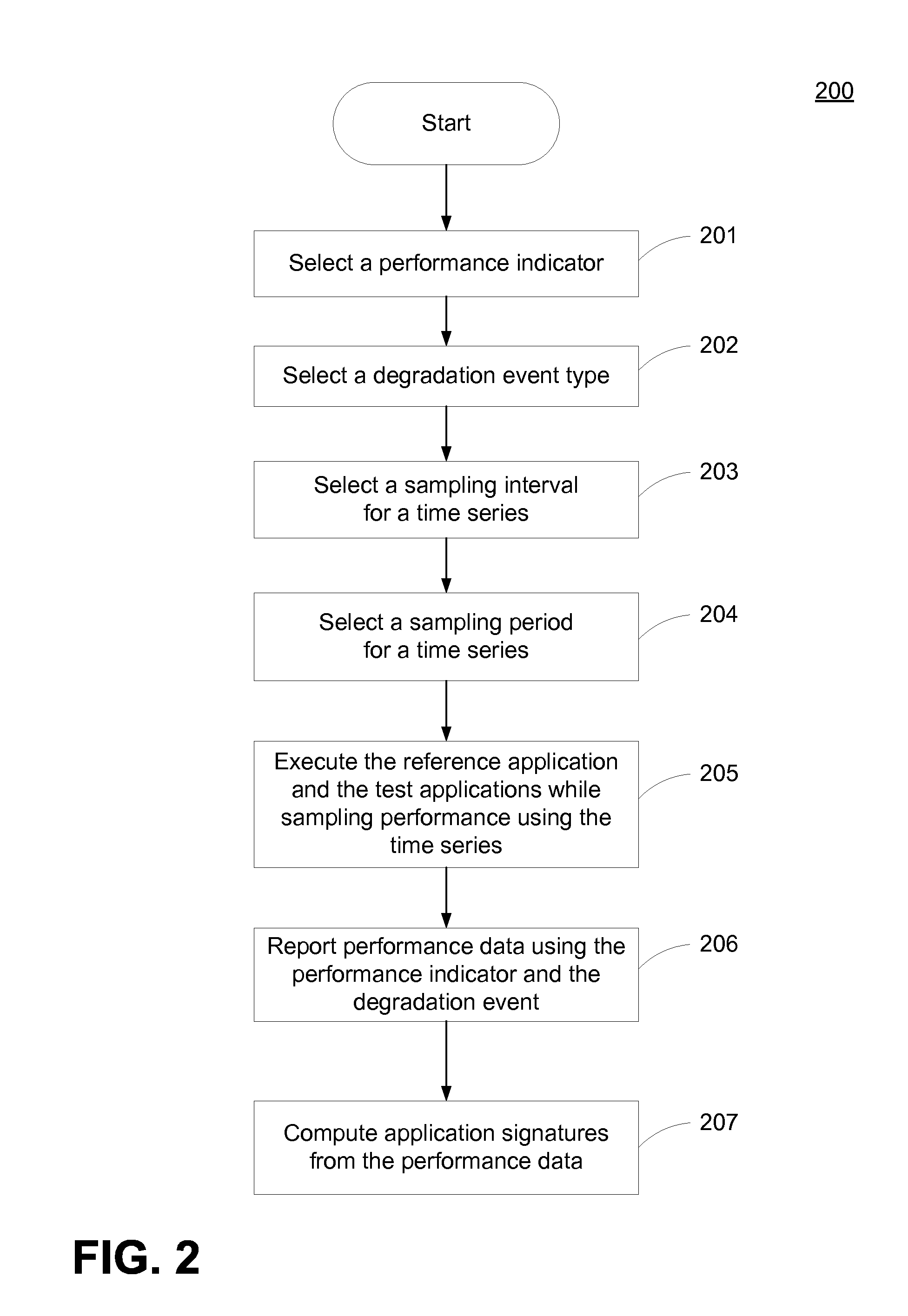
Method and System for Predicting Performance of Software Applications on Prospective Hardware Architecture
InactiveUS20120197626A1Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsHardware architectureParallel computing
A system and method for identifying optimal system architectures for a reference application are provided. The system and method comprise executing a reference application and a plurality of test applications on a current system architecture and sampling performance data for each of the applications. The performance data is used to compute an application signature for each application. A similarity element is derived from the application signatures that illustrates the similarity between each application and every other application. Using a similarity threshold and an algorithm, a subset of test applications that are similar to the reference application are derived.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
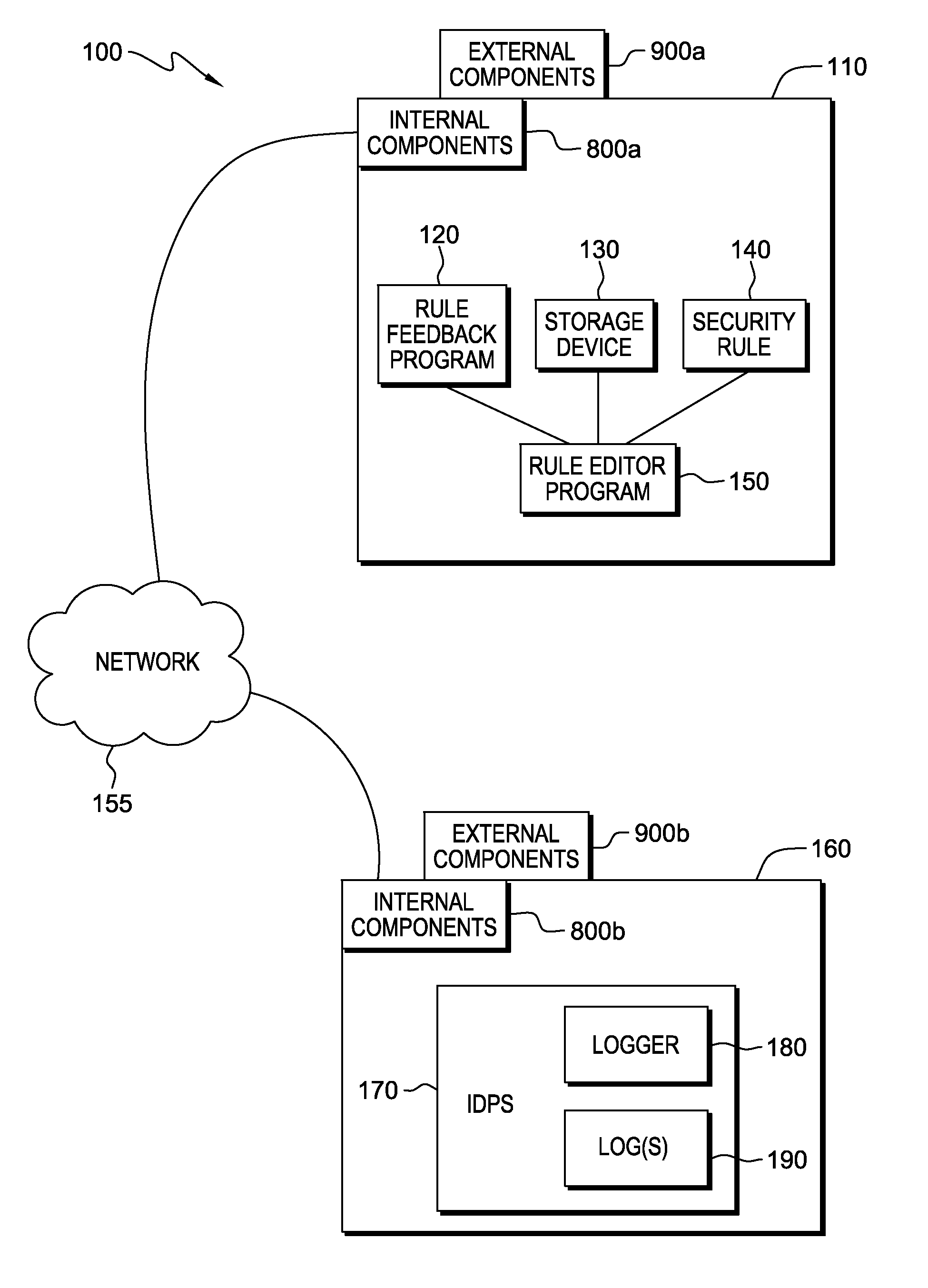
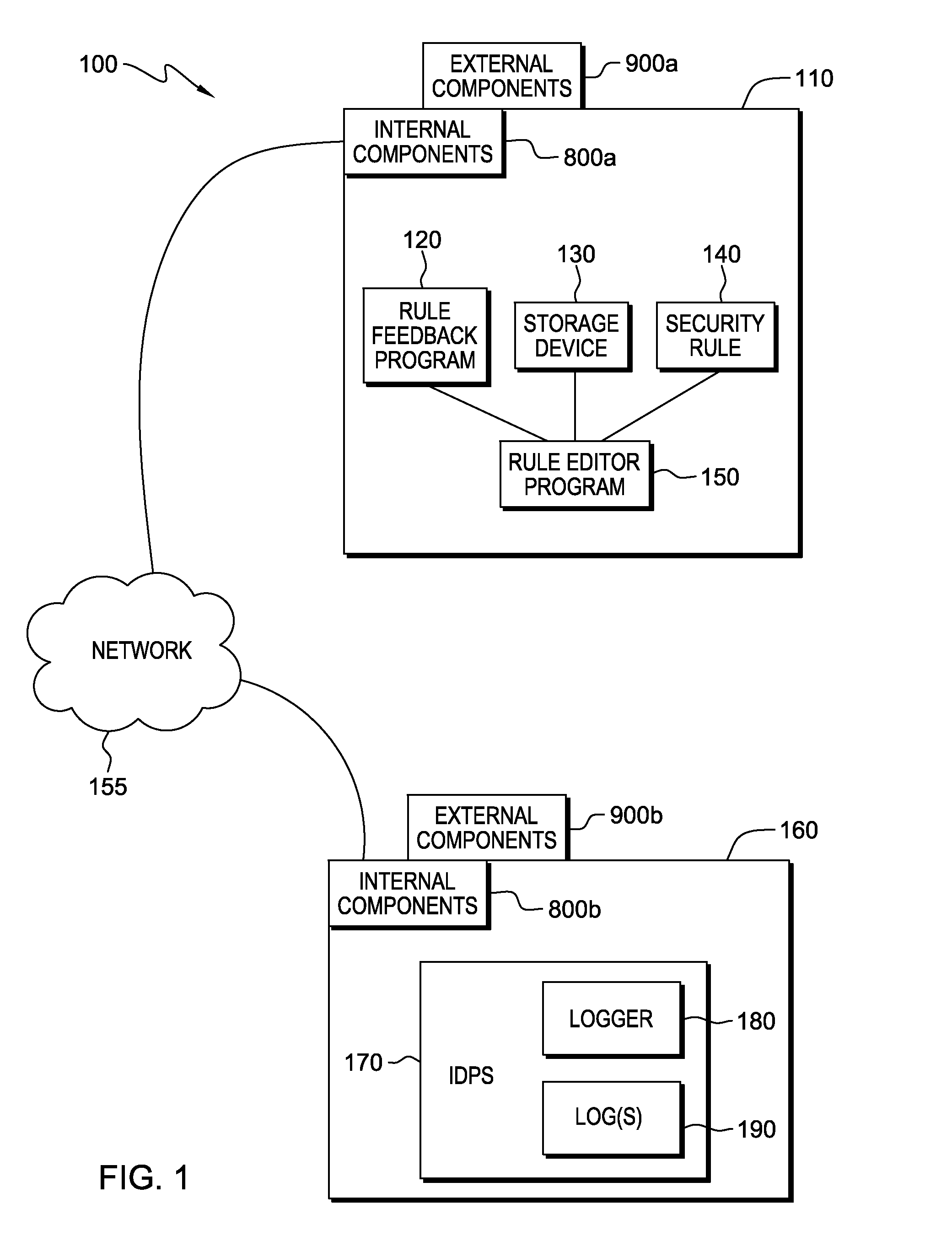
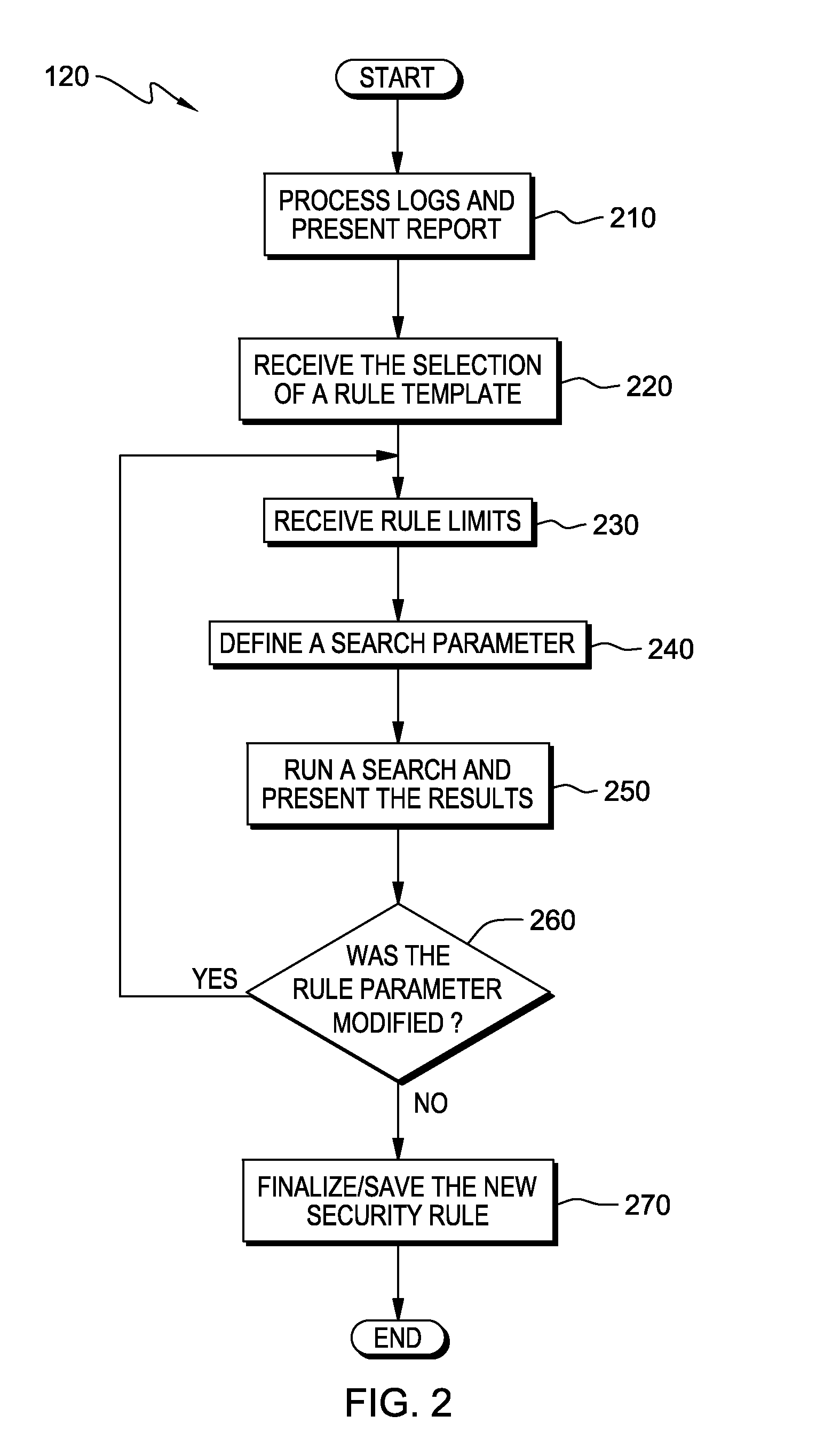
Automated feedback for proposed security rules
InactiveUS20140059641A1Desirable performanceComputer security arrangementsTransmissionEngineeringPredicting performance
A computer receives entry of a proposed security rule during a security rule entry or editing session and determines that the proposed security rule requires review of a type of security data. The number of matches of the proposed security rule to the logged security data is determined and a user is notified as to the number of matches. The computer searches the security data and applies the proposed security rule to the security data to determine the predicted performance of the proposed security rule. The computer generates a report that may include warnings, recommendations, and information correlated to the security data. The report is presented to a user during the rule editing session, and based on the report a modification to the proposed security rule can be made.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
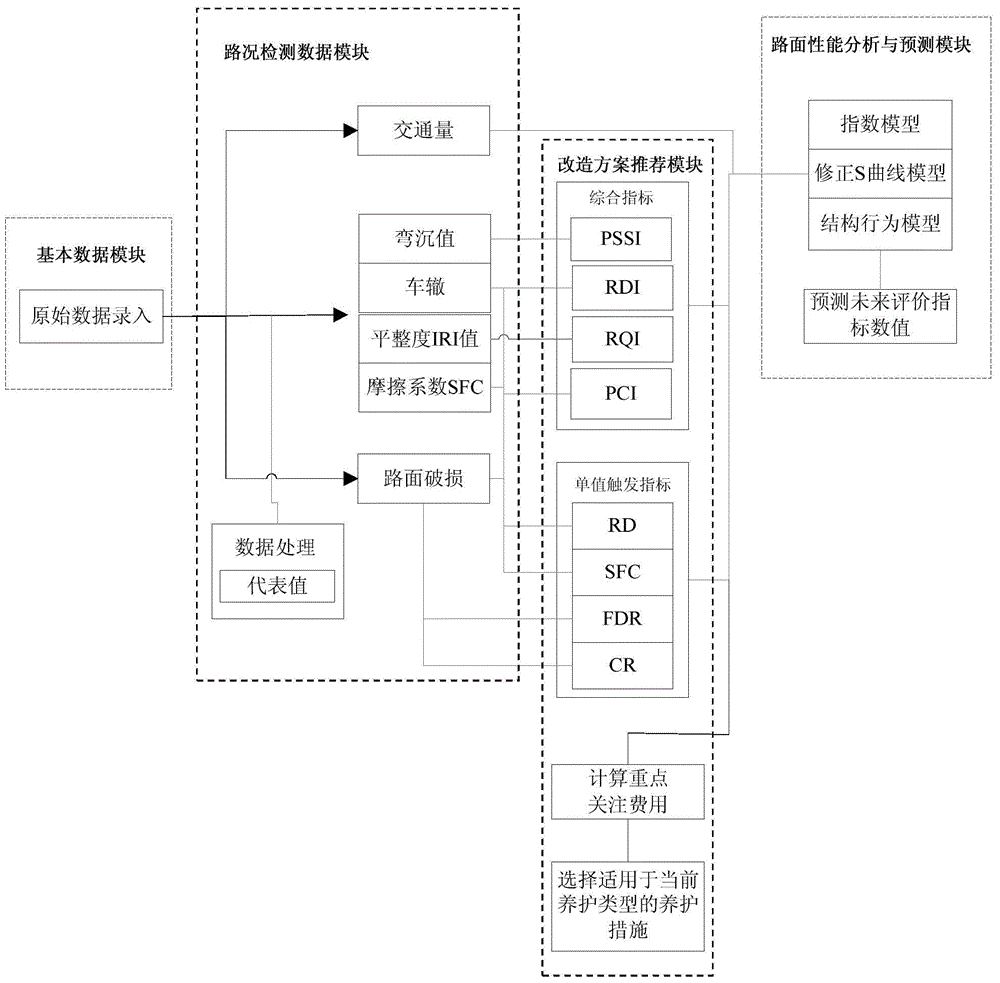
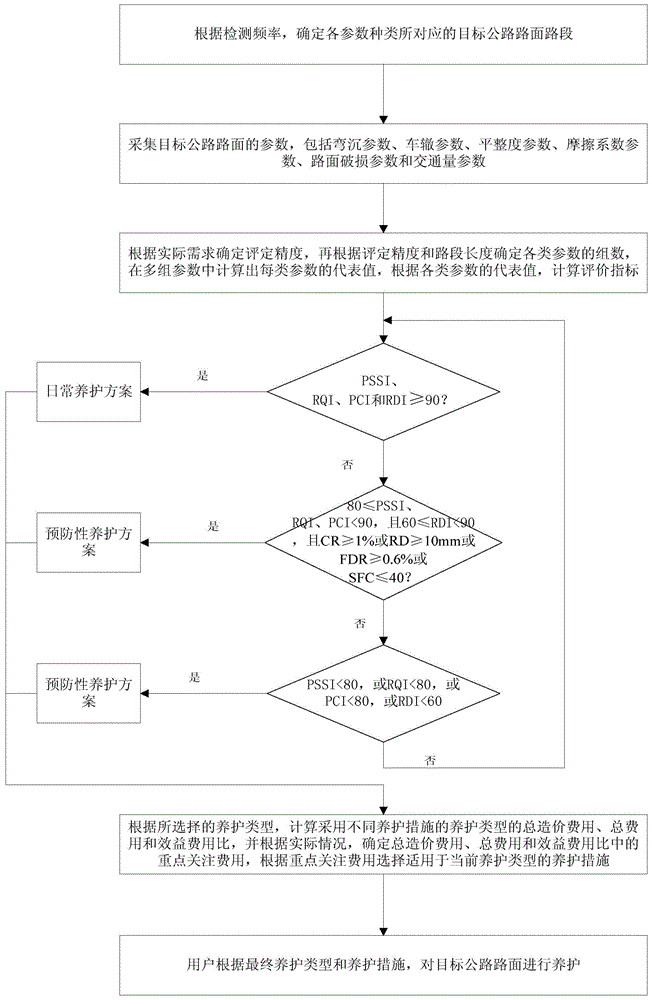
Modification scheme decision-making system and method for bituminous pavement
InactiveCN104463348AEasy to useSmall amount of calculationForecastingResourcesPavement maintenanceImage resolution
Owner:辽宁省交通科学研究院有限责任公司
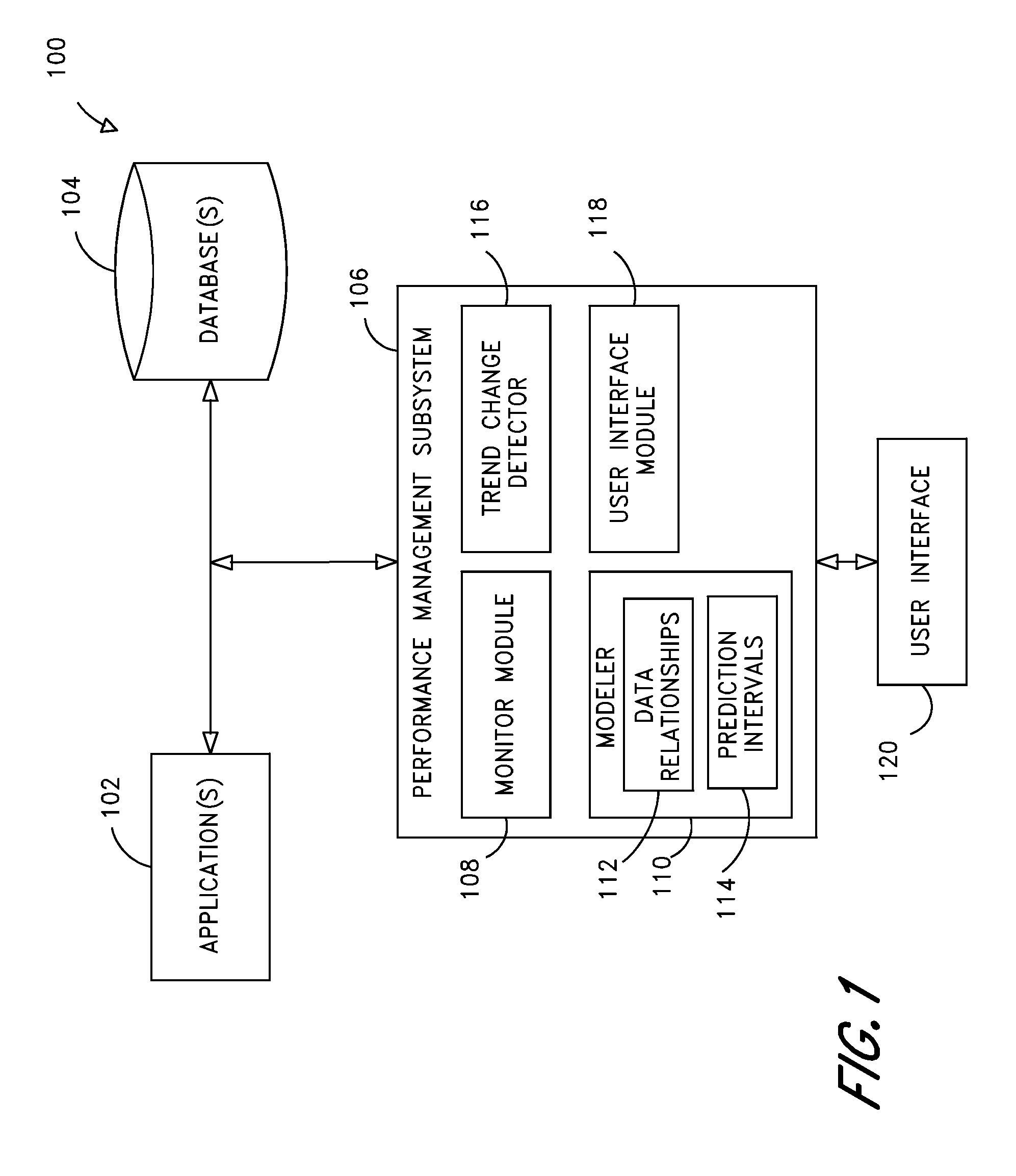
Computer systems and methods for predictive performance management of data transactions
ActiveUS8015454B1Improve performanceIncrease the amount of resourcesError detection/correctionSpecial data processing applicationsComputer moduleComputerized system
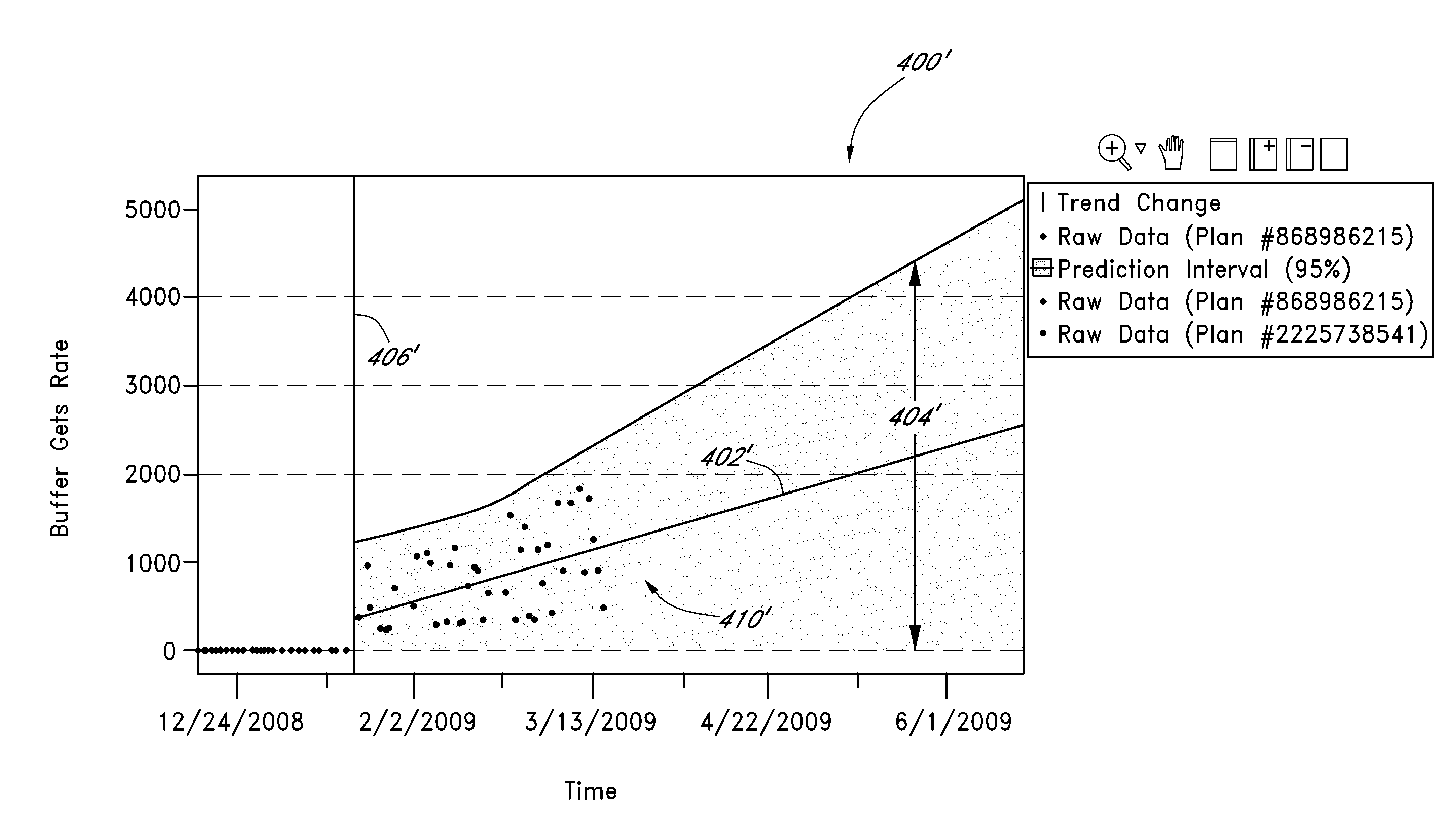
Systems and methods are disclosed for monitoring and managing data transactions, such as SQL transactions. In certain examples, a management subsystem generates an alert identifying degrading database transactions to facilitate preventative tuning or other maintenance. In particular, a monitor module tracks performance measurements (e.g., logical reads) of select transactions. A modeler correlates the performance measurements and assigns first performance model(s) to represent the performance measurements and predicted performance measurements of a particular transaction. A trend change module detects a significant change in a trend and / or variance of the performance measurements and can cause the modeler module to generate a second performance model to represent at least a portion of the performance measurements and the predicted performance measurements of the particular transaction. An interface module triggers an alert when the second performance model indicates that the predicted performance measurements of the particular transaction are degrading at or above a threshold rate.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com