Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
111 results about "Processor frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Frequency is the number times something occurs in a specific amount of time. In computing, frequency is used to measure processing speed, such as the clock speed of a CPU. For example, a 3.2 GHz processor has a frequency of 3.2 gigahertz, or 3,200,000,000 hertz. This means the processor performs 3,200,000,000 cycles each second.
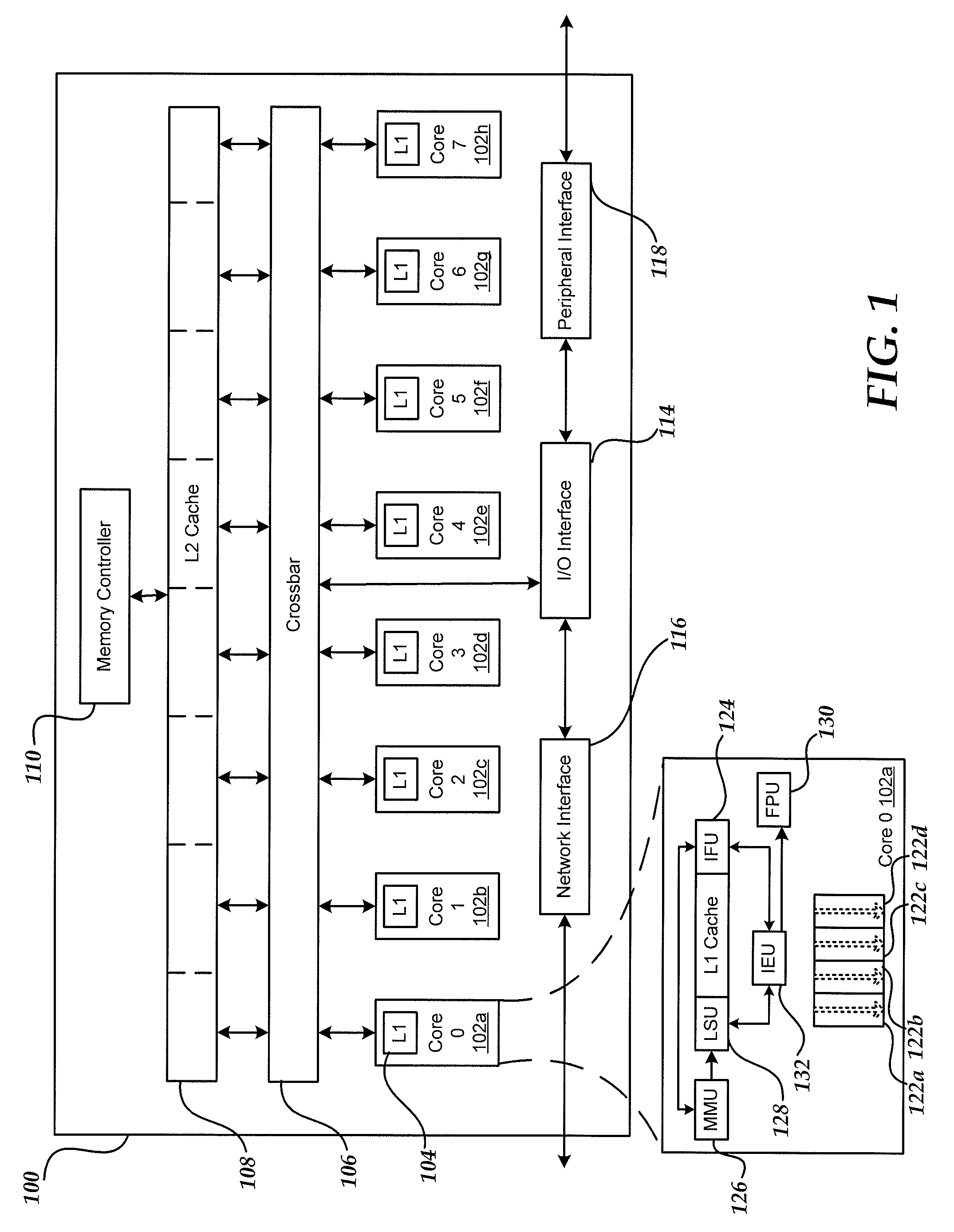
System and method for optimized task scheduling in a heterogeneous data processing system
InactiveUS20060168571A1Optimizing task throughputPerformance of was minimizedEnergy efficient ICTEnergy efficient computingData processing systemLoad Shedding
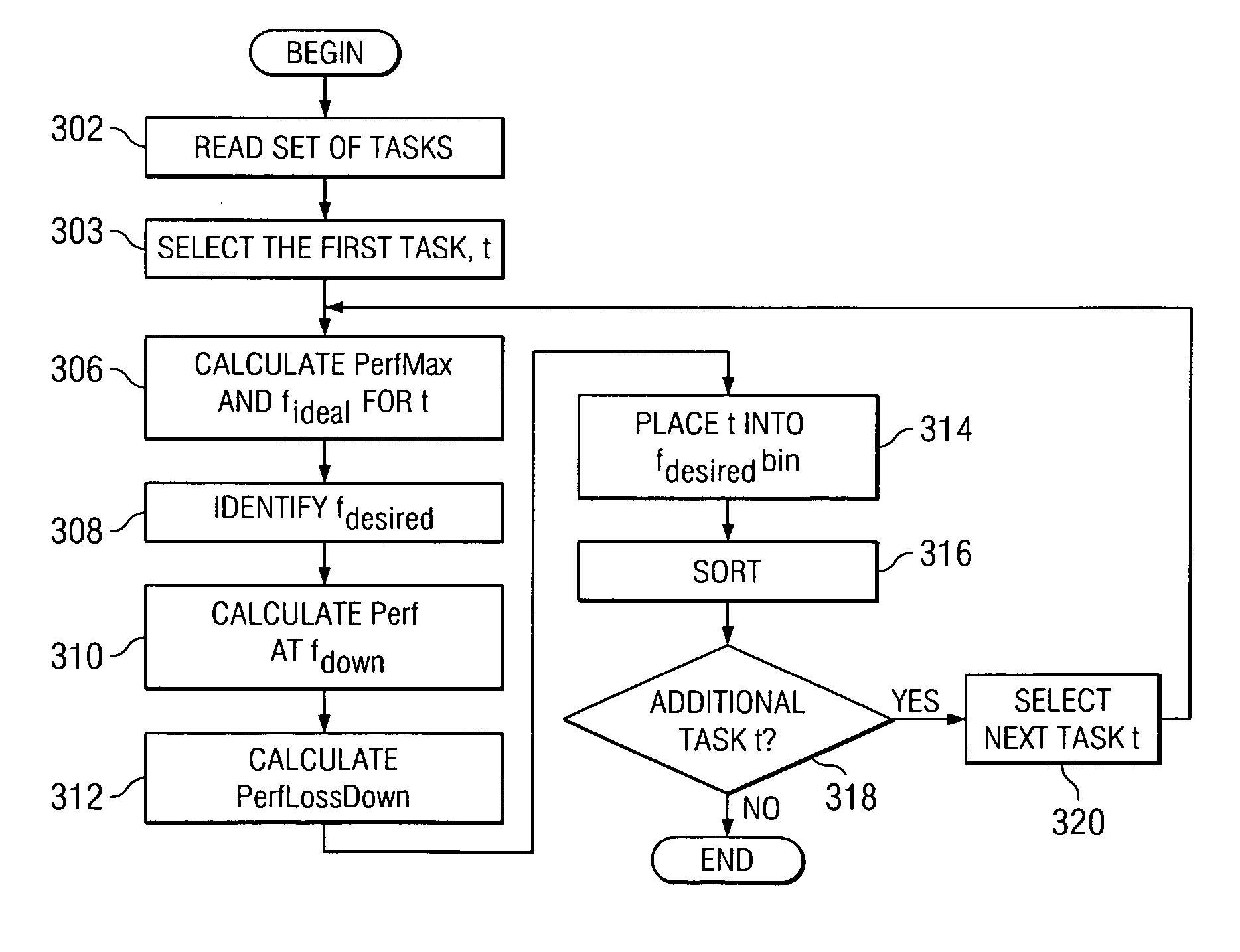
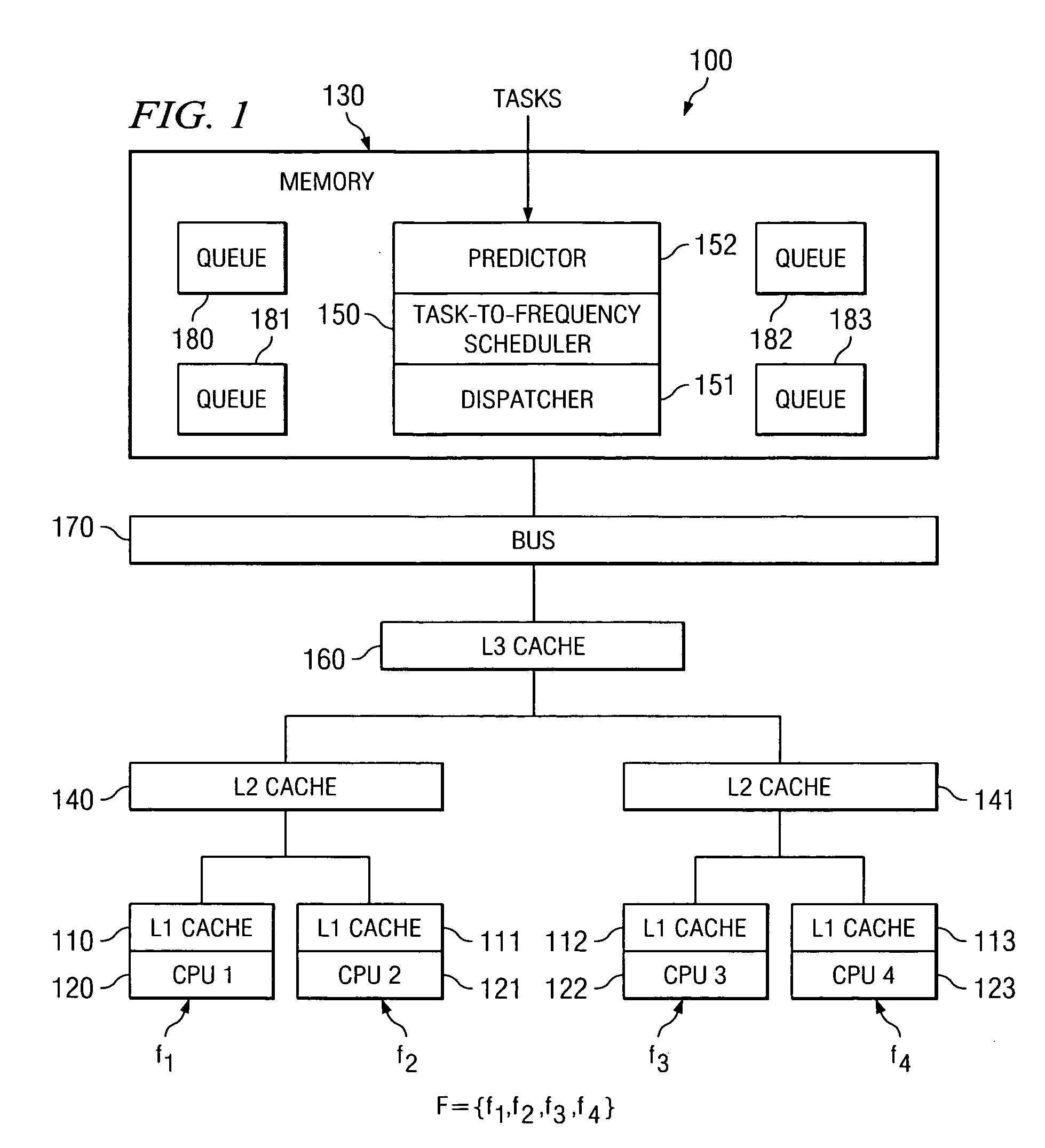
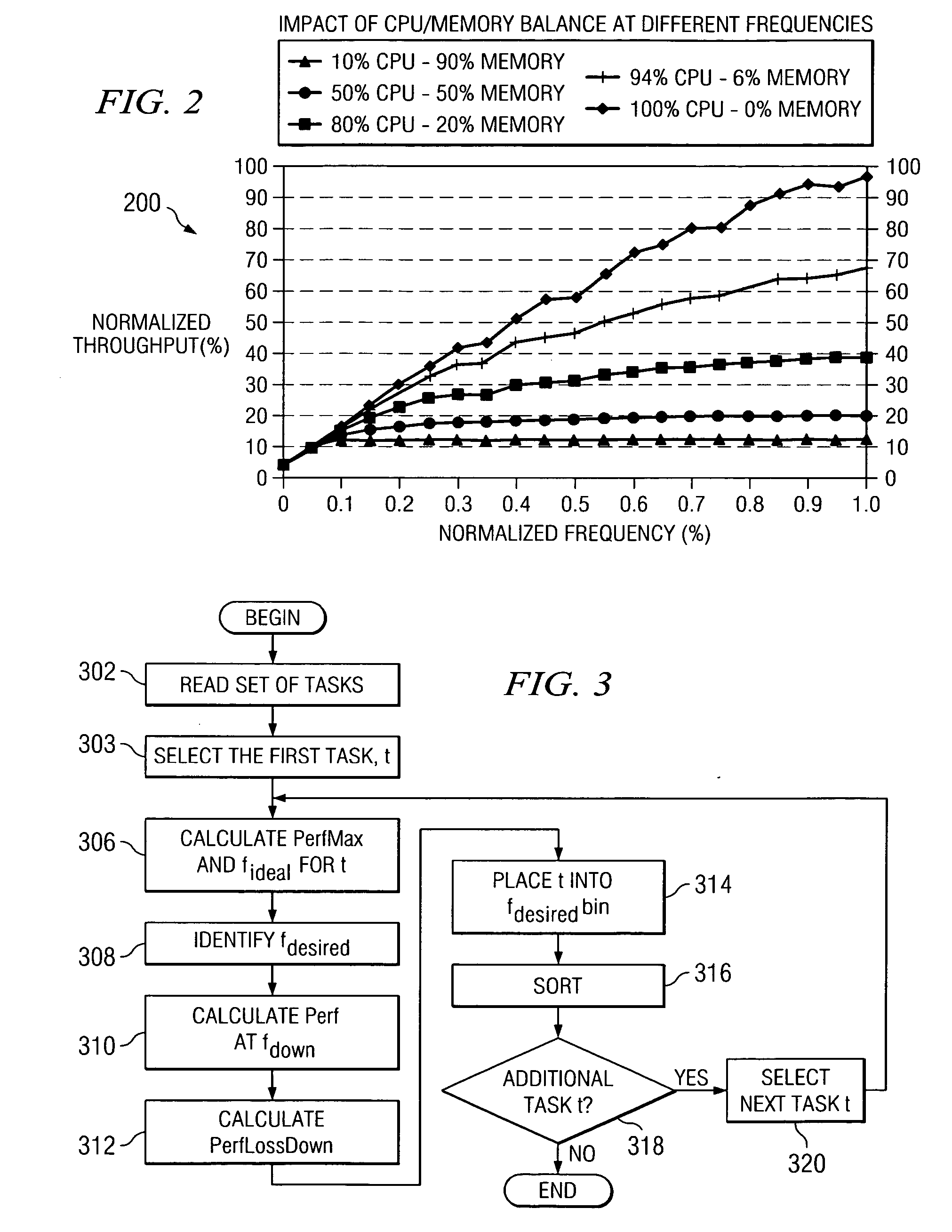
A method, computer program product, and a data processing system for optimizing task throughput in a multi-processor system. A performance metric is calculated based on performance counters measuring characteristics of a task executed at one of a plurality of processor frequencies available in the multi-processor system. The characteristics measured by the performance counters indicate activity in the processor as well as memory activity. A performance metric provides a means using measured data at one available frequency to predict performance at another processor frequency available in the multi-processing system. Performance loss minimization is used to assign a particular task to a particular frequency. Additionally, the present invention provides a mechanism for priority load balancing of tasks in a manner that minimizes cumulative performance loss incurred by execution of all tasks in the system.
Owner:IBM CORP
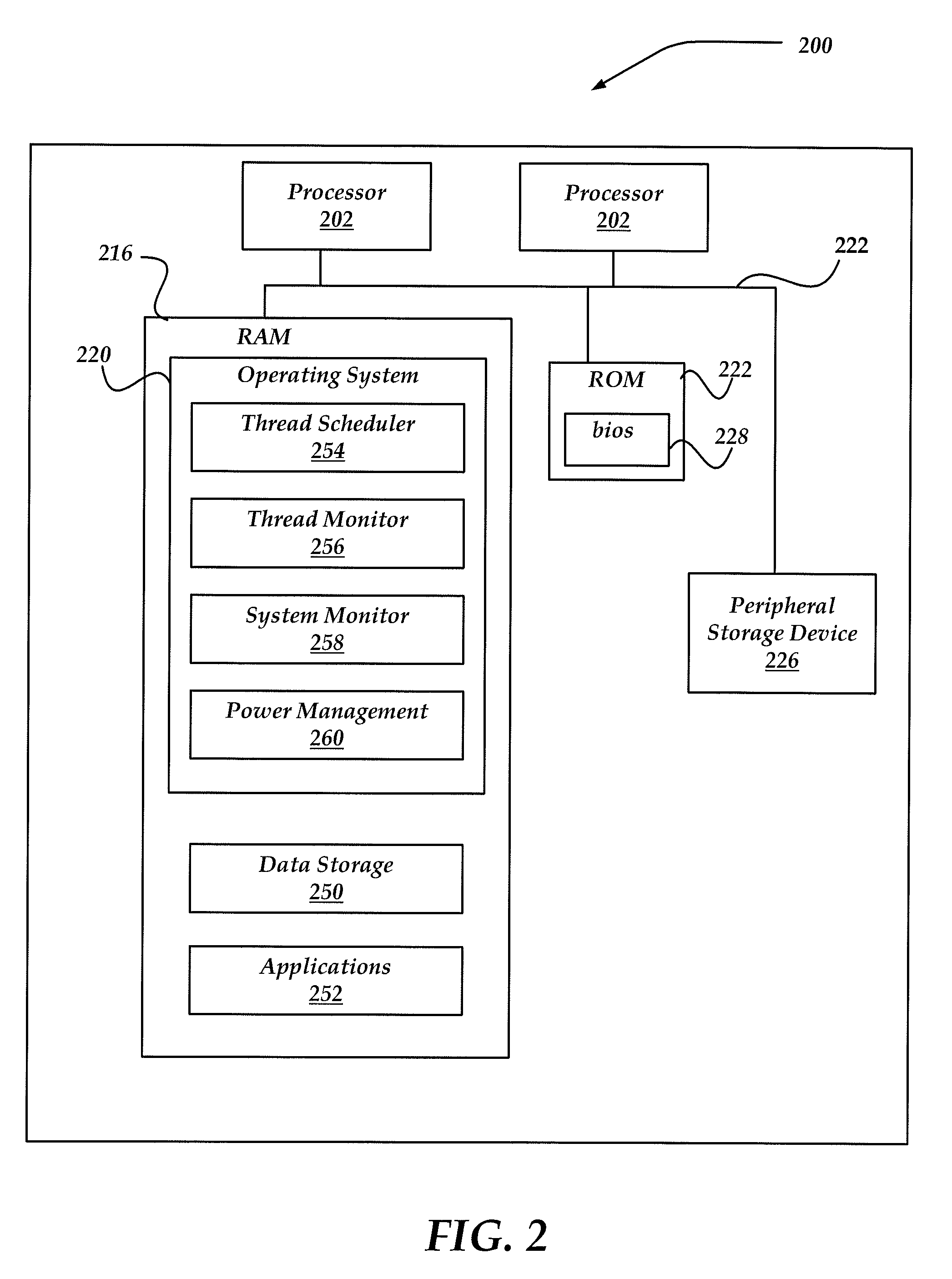
Use of cpi power management in computer systems
A device, system, and method are directed towards managing power consumption in a computer system with one or more processing units, each processing unit executing one or more threads. Threads are characterized based on a cycles per instruction (CPI) characteristic of the thread. A clock frequency of each processing unit may be configured based on the CPI of each thread assigned to the processing unit. In a system wherein higher clock frequencies consume greater amounts of power, the CPI may be used to determine a desirable clock frequency. The CPI of each thread may also be used to assign threads to each processing unit, so that threads having similar characteristics are grouped together. Techniques for assigning threads and configuring processor frequency may be combined to affect performance and power consumption. Various specifications or factors may also be considered when scheduling threads or determining processor frequencies.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
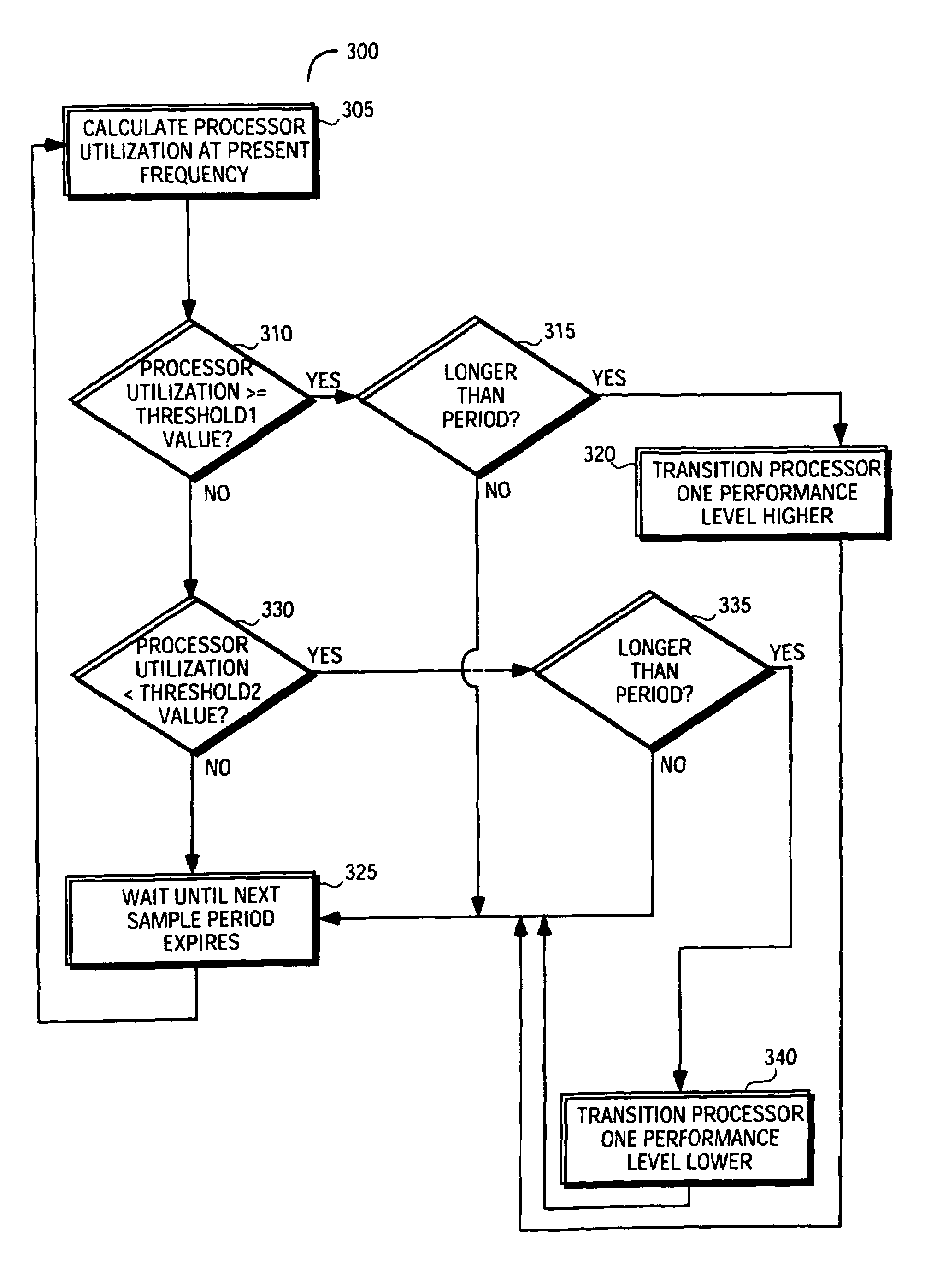
Power management system that changes processor level if processor utilization crosses threshold over a period that is different for switching up or down
InactiveUS7017060B2Energy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementParallel computingProcessor frequency
A method for automatically transitioning a processor to another performance level in a demand-based system. One embodiment of the invention provides for the automatic adjustment of processor frequency while preserving system responsiveness. The performance-level policy algorithm detects increased processor utilization quickly enough that transition to a higher performance level is comparable to maximum system performance. The performance-level policy algorithm delays processor transition to a lower performance level so that quick reversals in demand do not precipitate unnecessary transitioning.
Owner:INTEL CORP
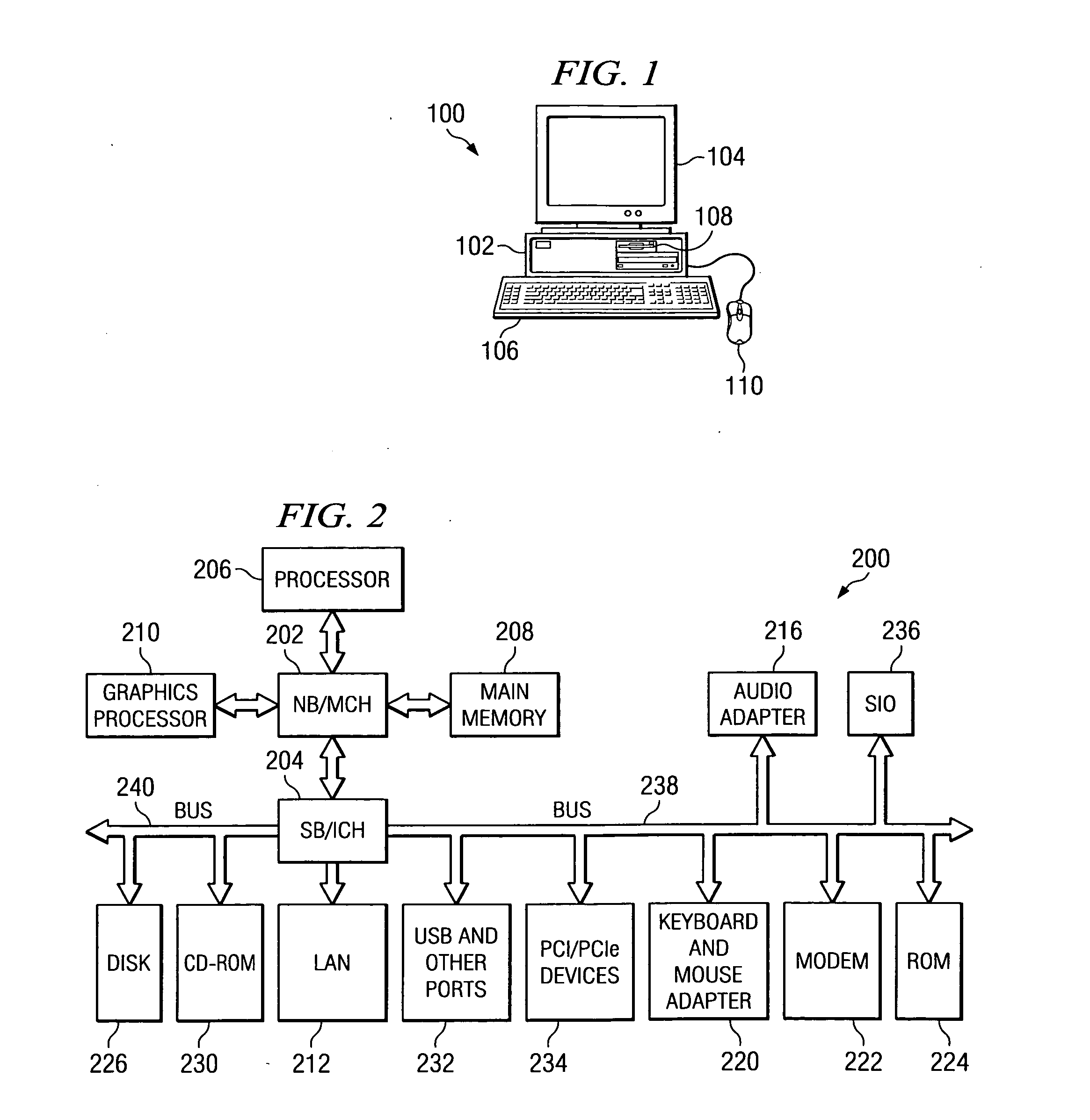
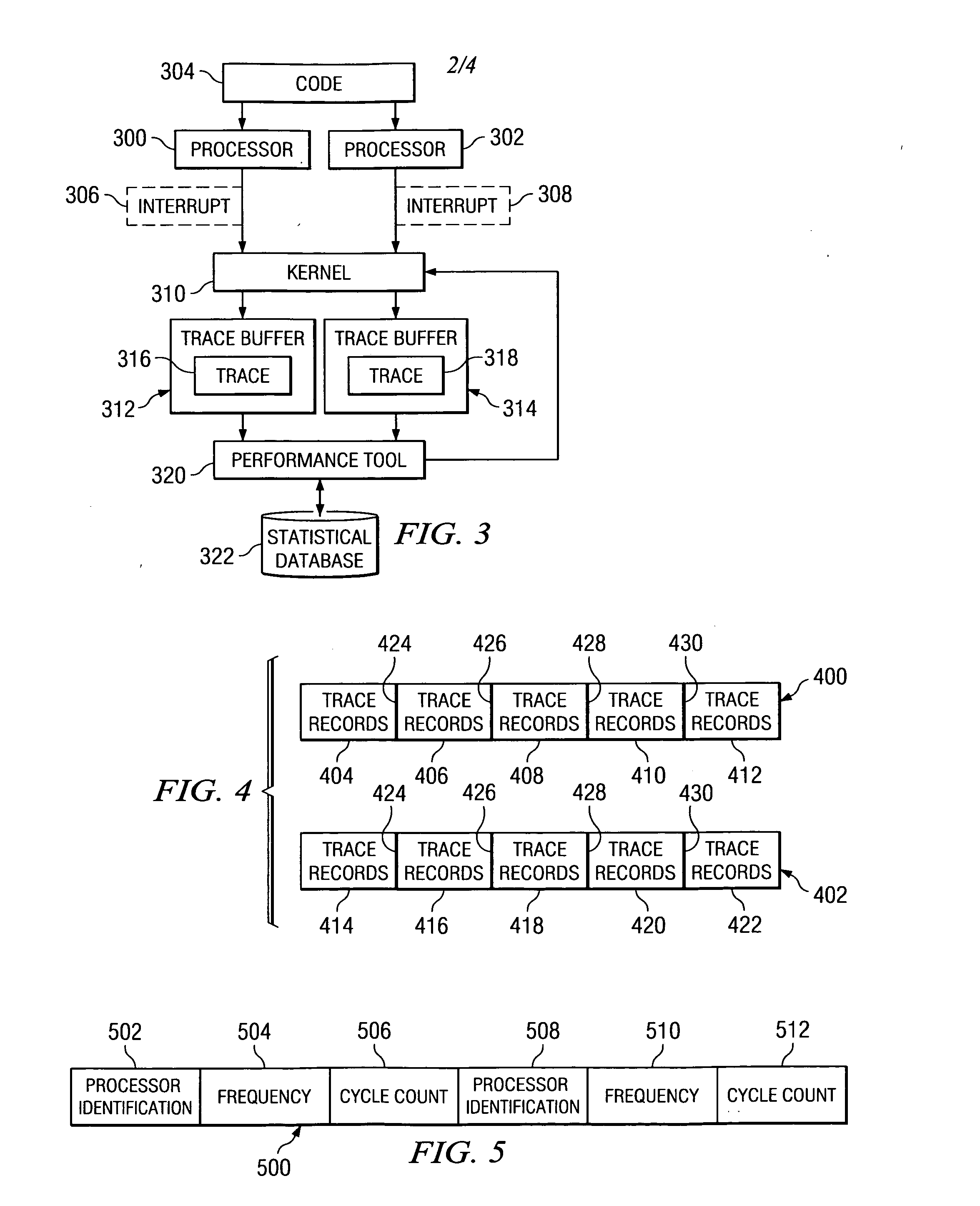
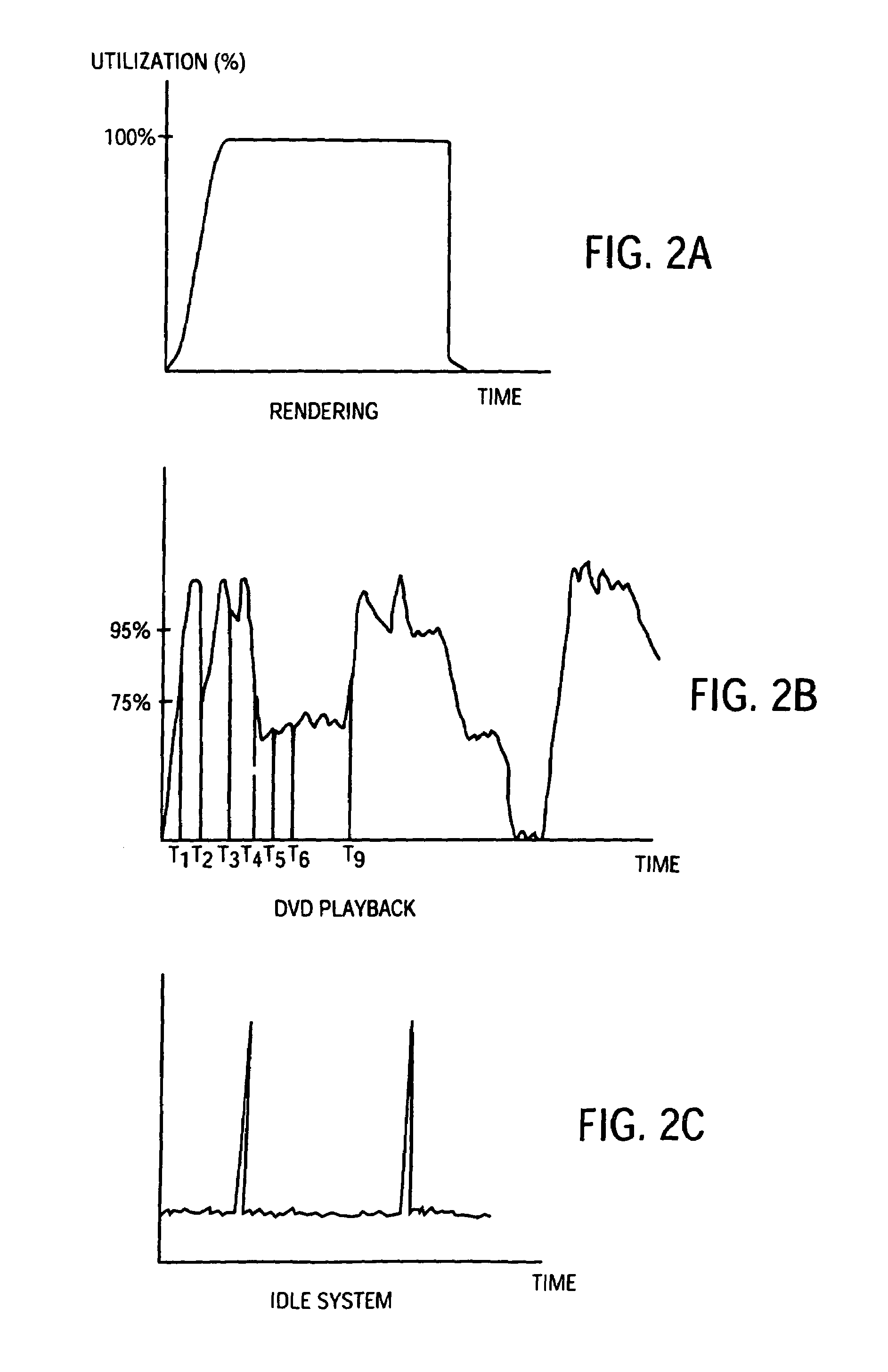
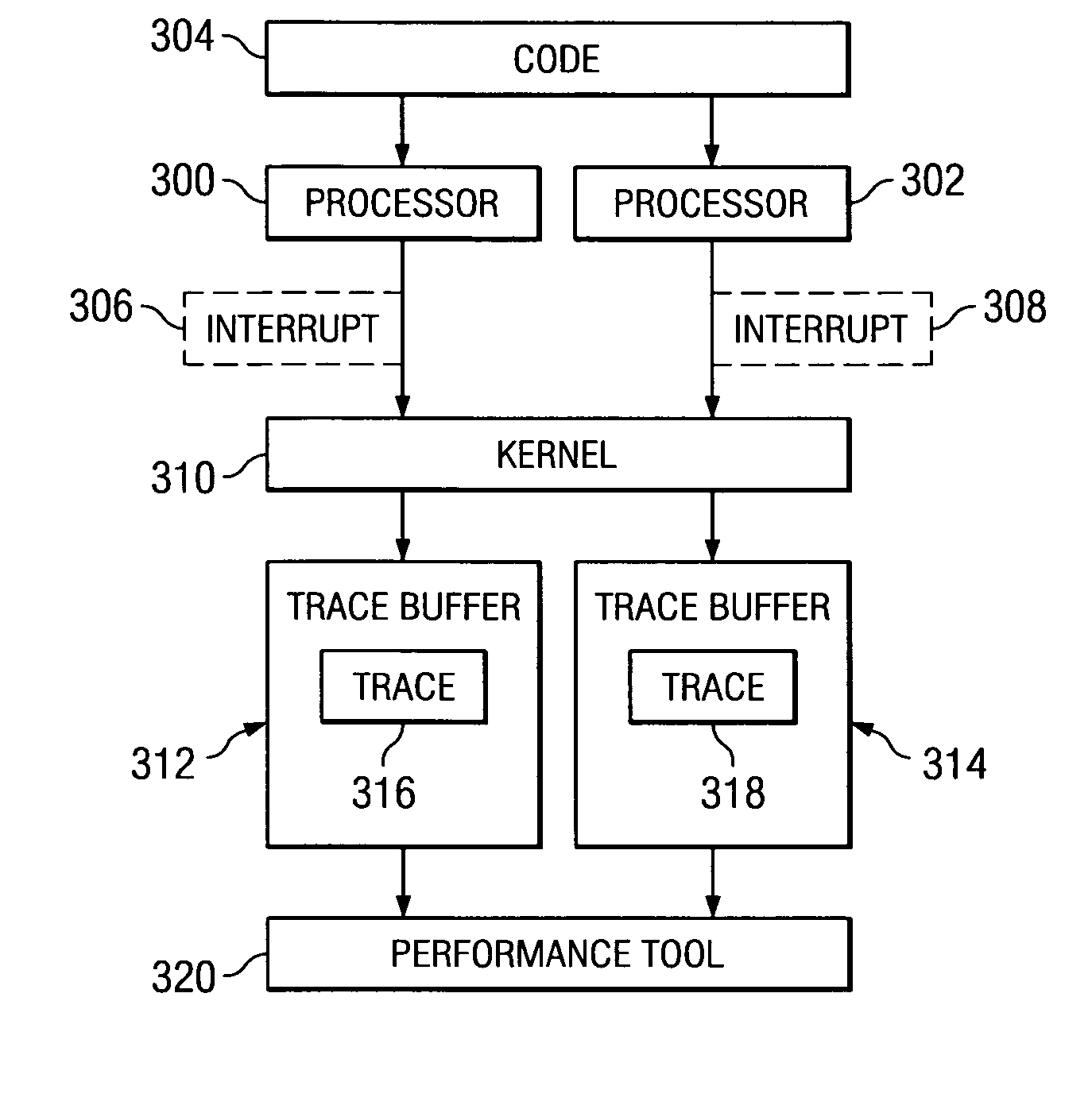
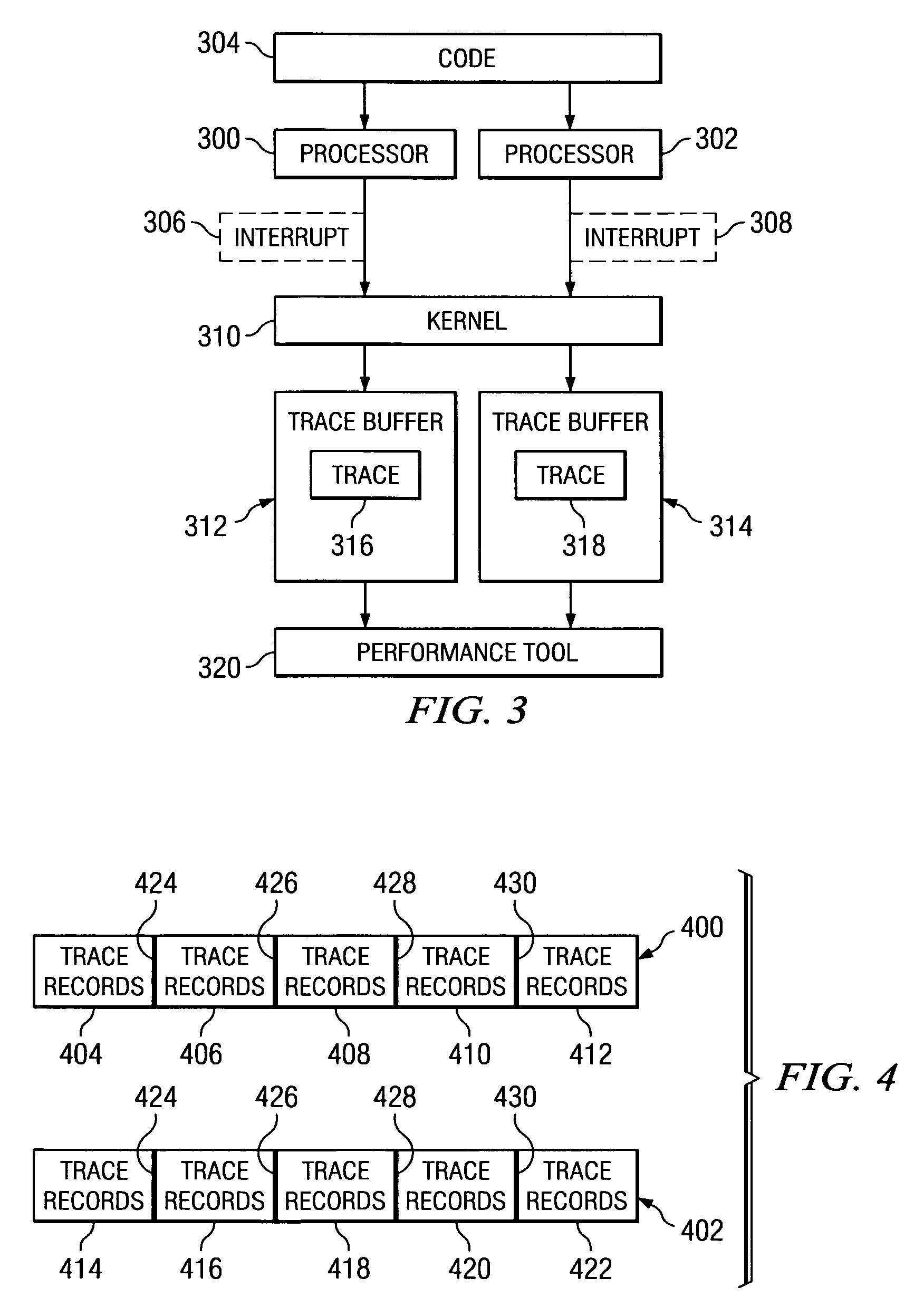
Method and apparatus for adaptive tracing with different processor frequencies
InactiveUS20070050174A1Digital computer detailsNuclear monitoringParallel computingProcessor frequency
A method, apparatus, and computer usable program code for managing trace records. A set of traces is generated for a set of processors. A trace is generated in the set of traces for each processor within the set of processors. A record of the frequency change is stored in the set of traces in response to a frequency change in a processor within the set of processors. Trace records are combined in the set of traces using the record of the frequency change to determine a correct order for the records.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for adaptive tracing with different processor frequencies
A method, apparatus, and computer usable program code for managing trace records. A set of traces is generated for a set of processors. A trace is generated in the set of traces for each processor within the set of processors. A record of the frequency change is stored in the set of traces in response to a frequency change in a processor within the set of processors. Trace records are combined in the set of traces using the record of the frequency change to determine a correct order for the records.
Owner:IBM CORP
Frequency scaling of processing unit based on aggregate thread CPI metric
A device, system, and method are directed towards managing power consumption in a computer system with one or more processing units, each processing unit executing one or more threads. Threads are characterized based on a cycles per instruction (CPI) characteristic of the thread. A clock frequency of each processing unit may be configured based on the CPI of each thread assigned to the processing unit. In a system wherein higher clock frequencies consume greater amounts of power, the CPI may be used to determine a desirable clock frequency. The CPI of each thread may also be used to assign threads to each processing unit, so that threads having similar characteristics are grouped together. Techniques for assigning threads and configuring processor frequency may be combined to affect performance and power consumption. Various specifications or factors may also be considered when scheduling threads or determining processor frequencies.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
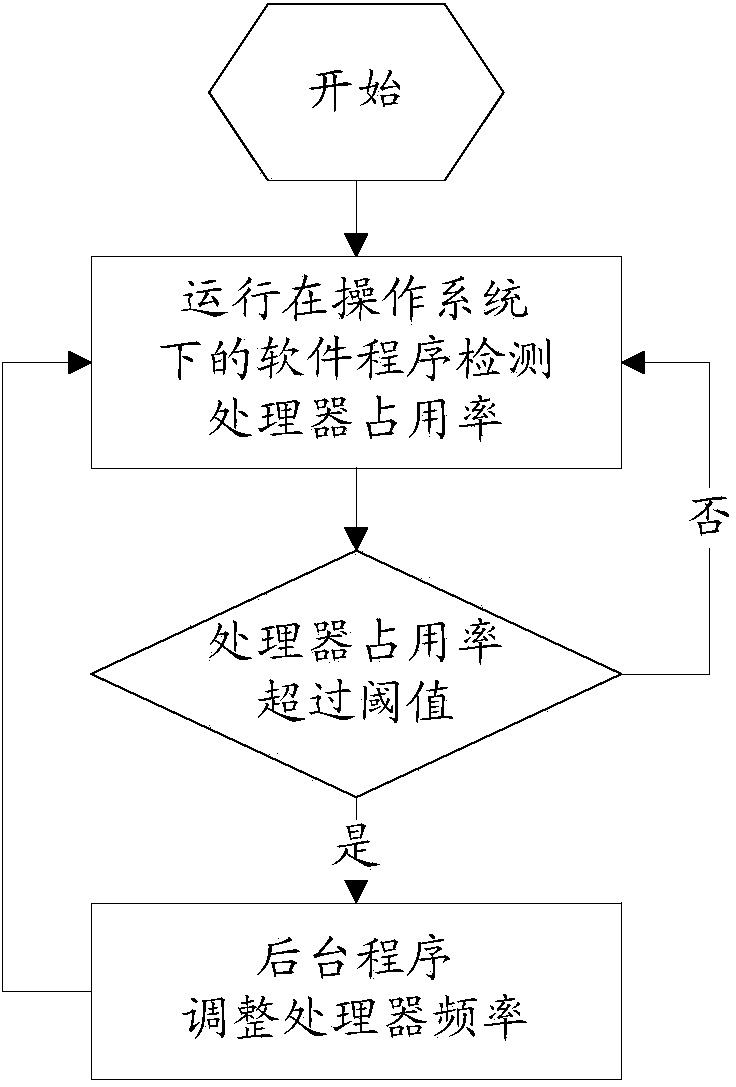
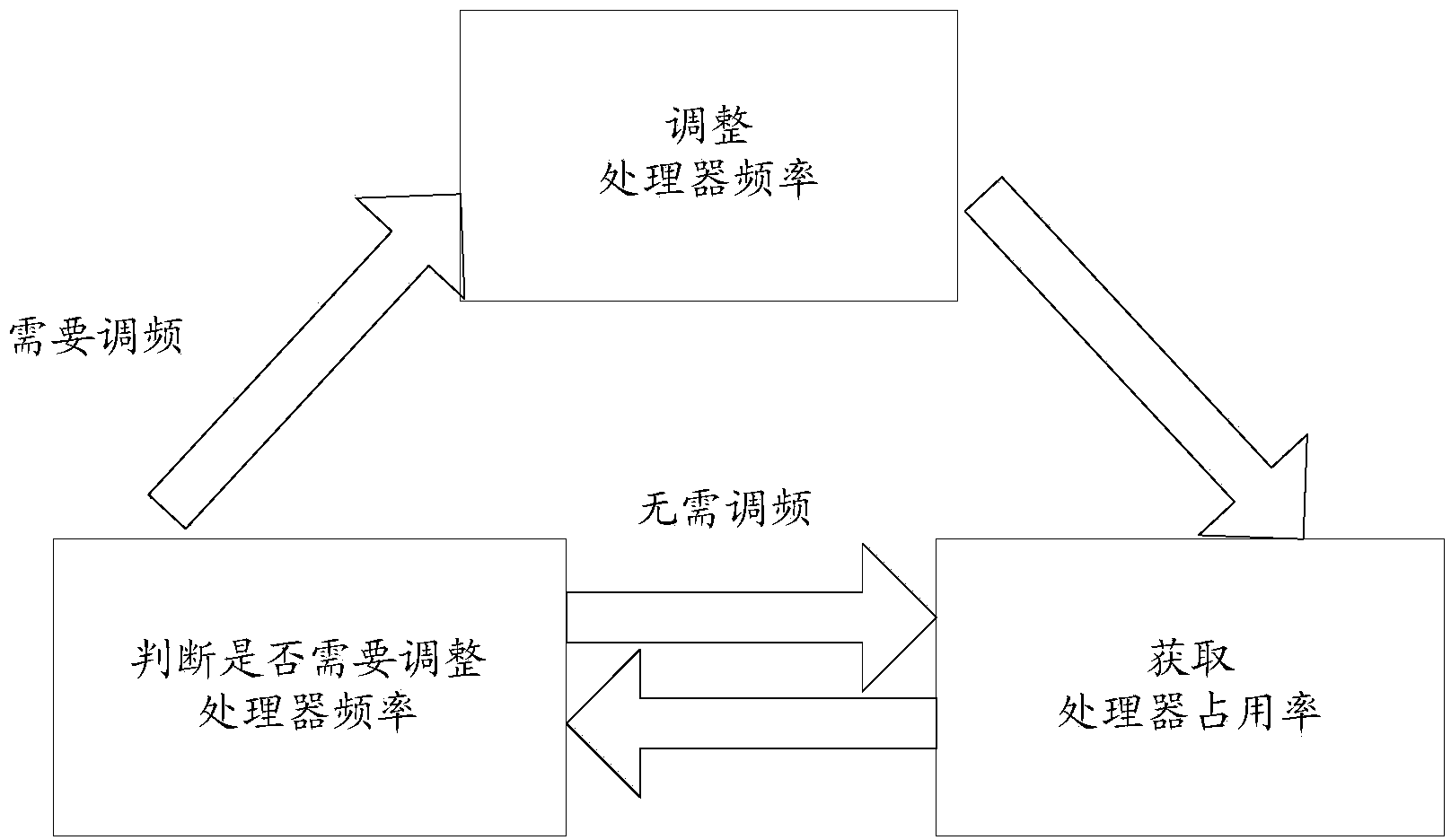
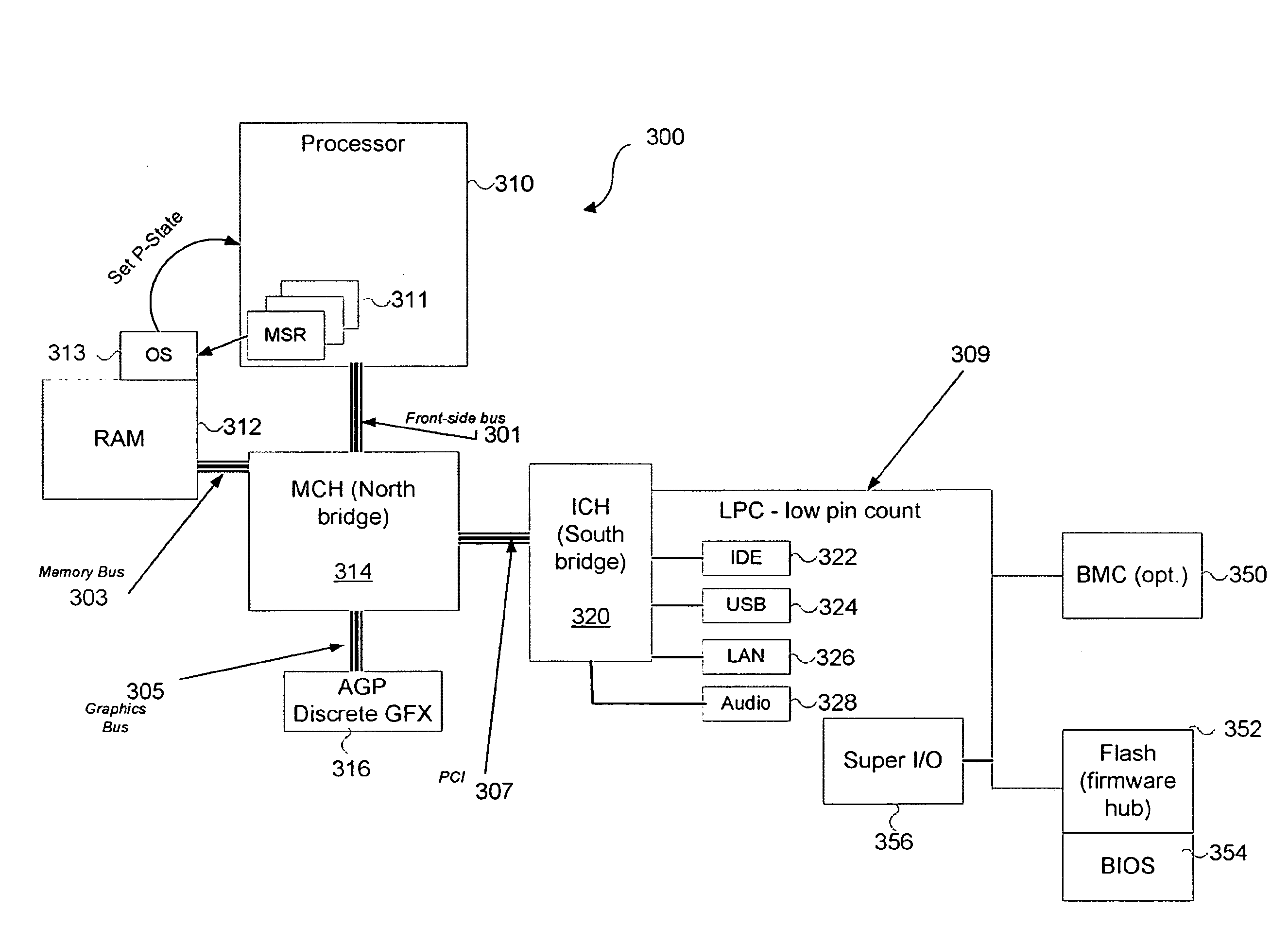
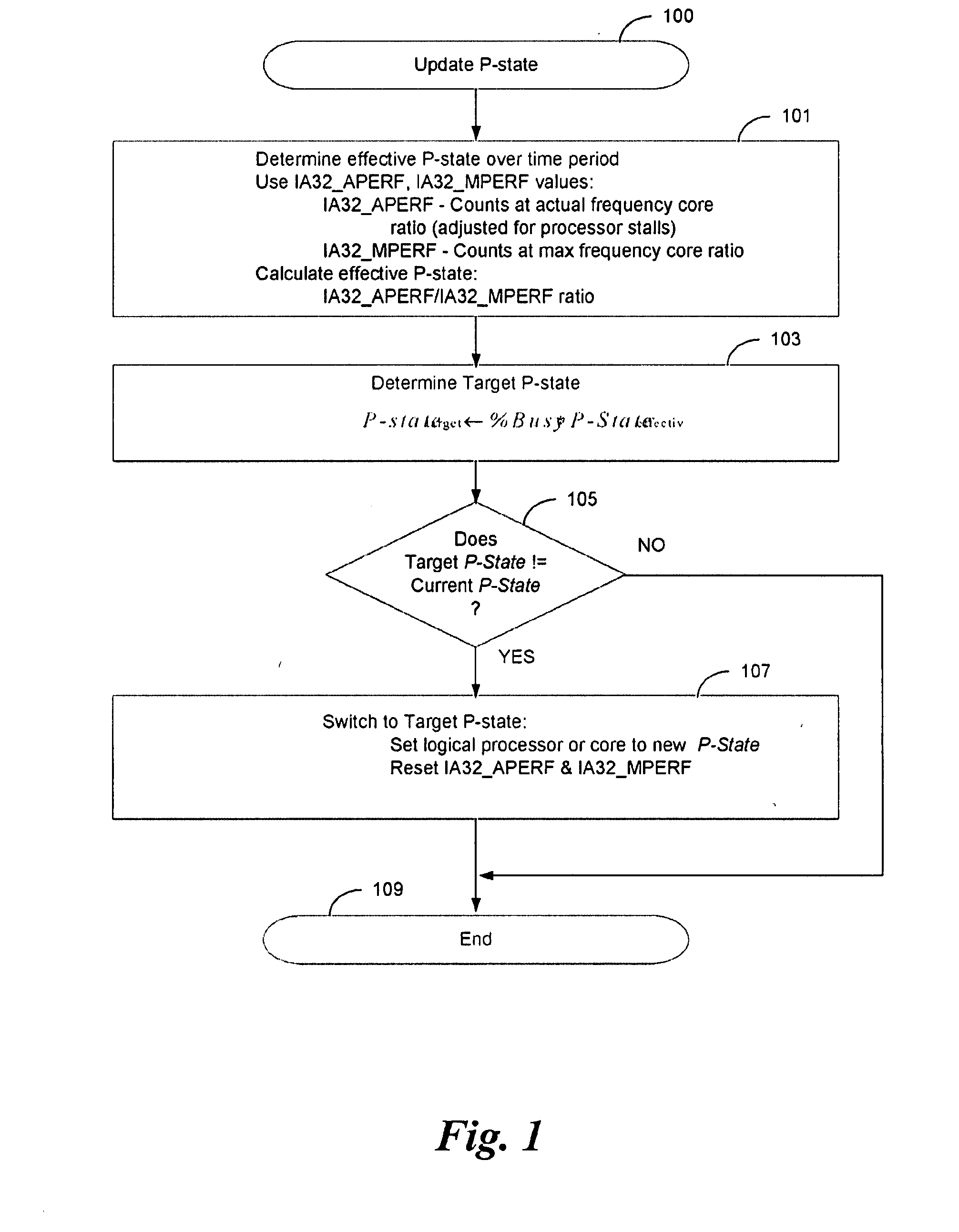
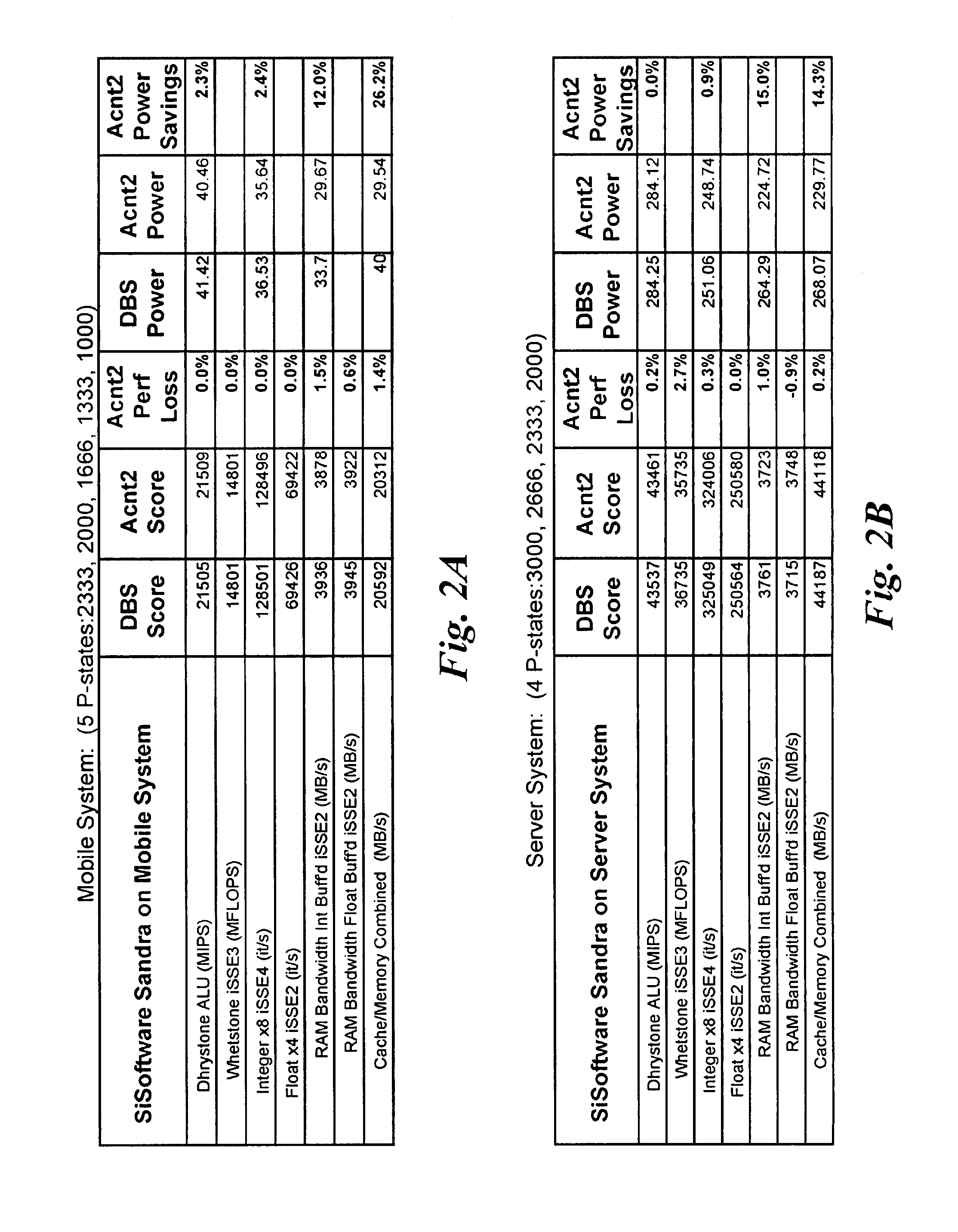
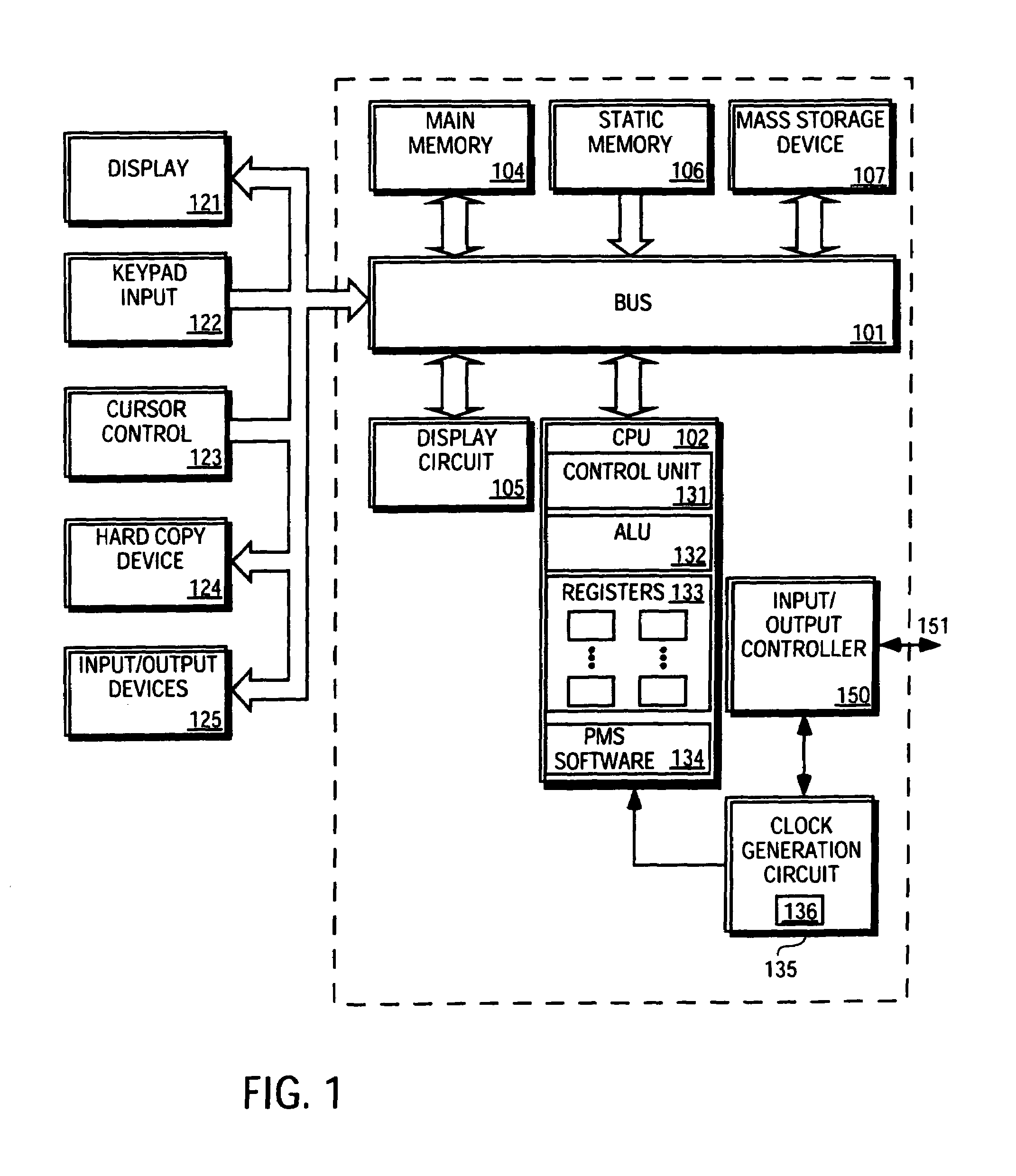
[method for dynamically adjusting CPU requency]
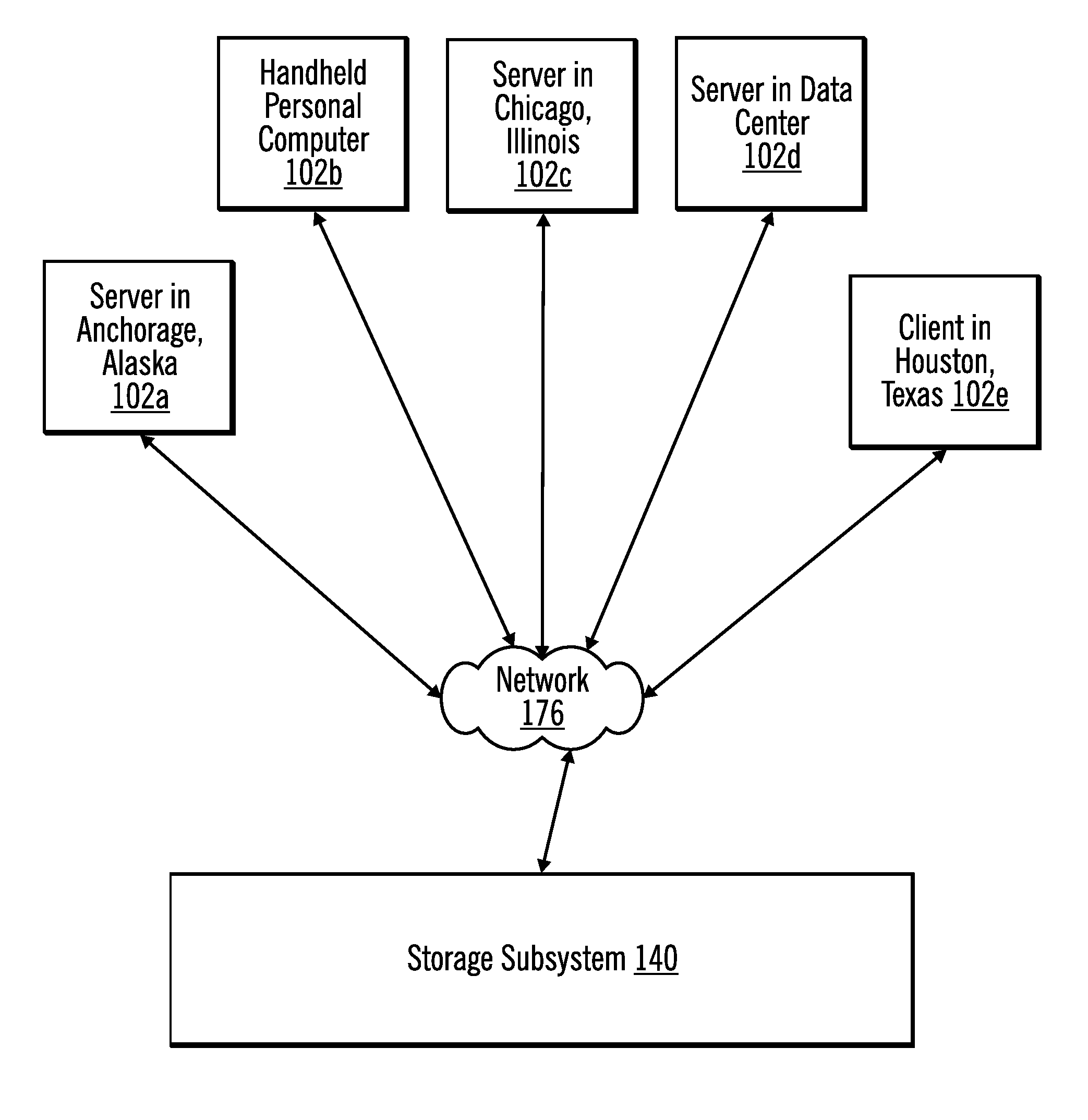
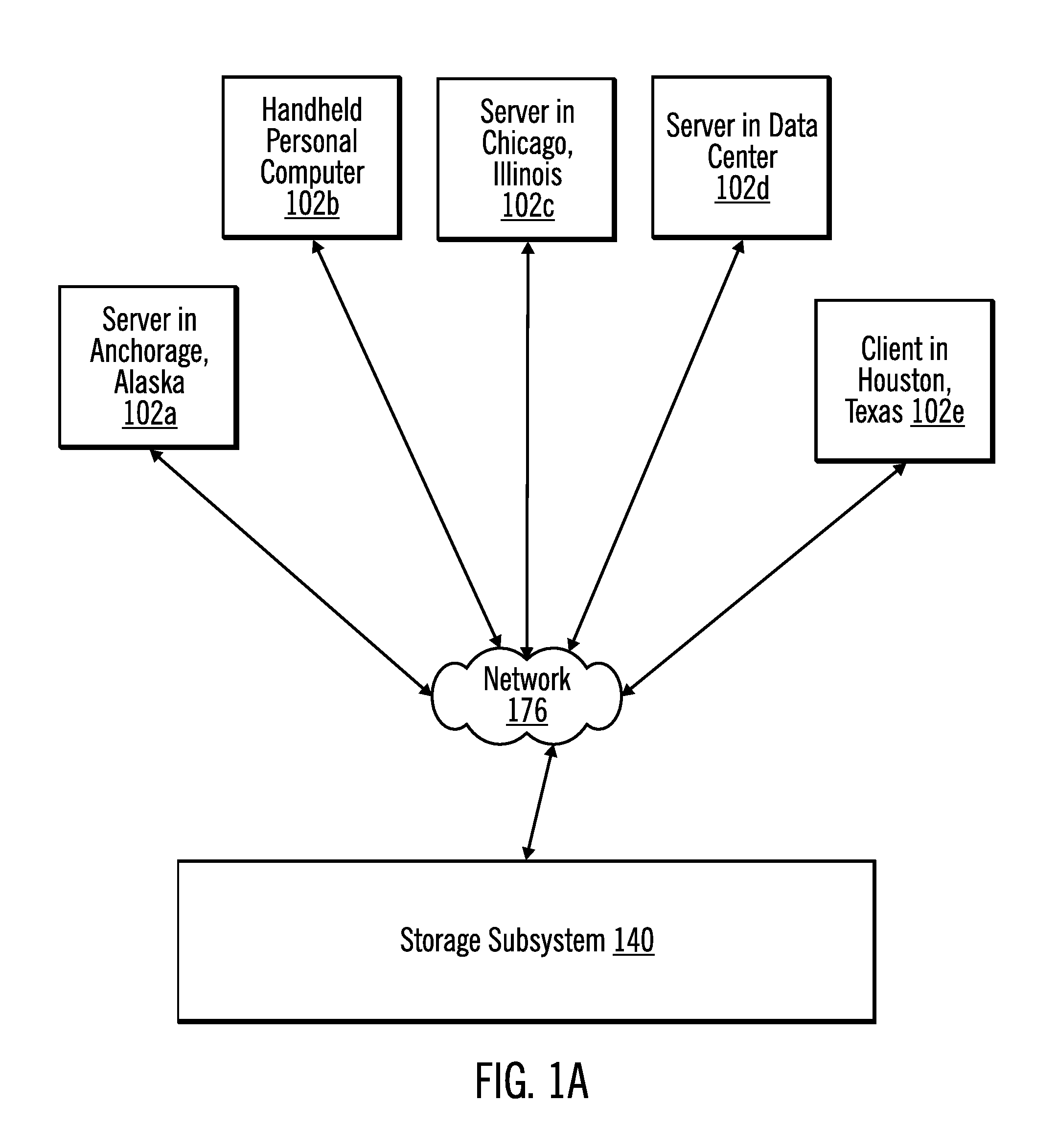
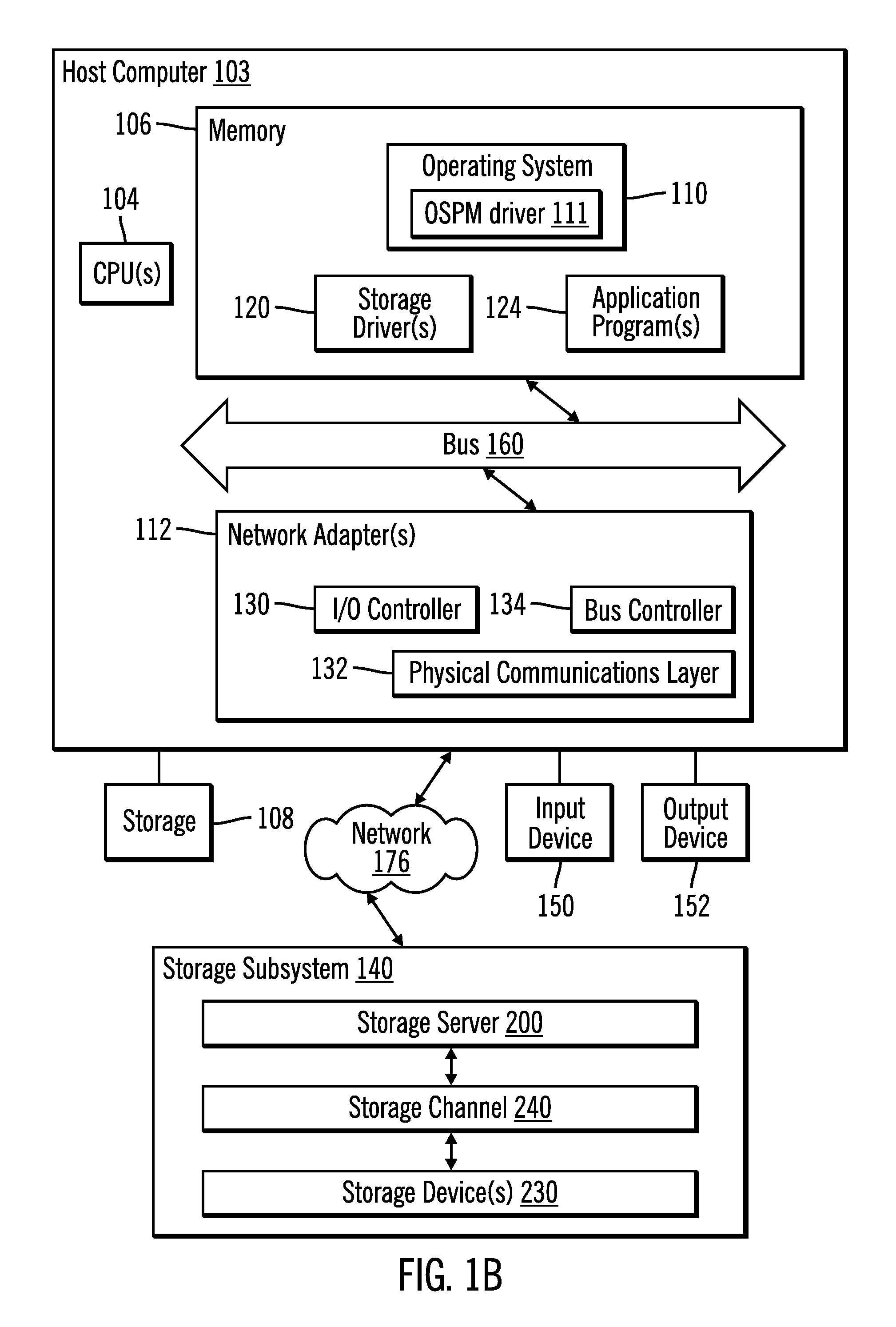
ActiveUS20050125705A1Save power consumptionProlong system operation timeEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementProcessor frequencyTranslation table
A method for dynamically adjusting central processing unit (CPU) frequency. Firstly, a translation table is provided between multilayer of CPU usage percentage and front-end bus operation frequency. Secondly, a current usage percentage of the CPU is obtained. Lastly, the operation frequency of the front-end bus is adjusted to a corresponding layer according to the current usage rage, so that the current usage rage is located within the range of CPU usage percentage that is defined by corresponding layer.
Owner:COMPAL ELECTRONICS INC
System and method for adjusting I/O processor frequency in response to determining that a power set point for a storage device has not been reached
InactiveUS7174471B2Energy efficient ICTInput/output to record carriersProcessor frequencyComputer science
Provided is a technique for power and performance management of one or more storage devices. With a power and performance management agent, a power change notification identifying a power set point is received and a power state of at least one storage device is adjusted.
Owner:INTEL CORP
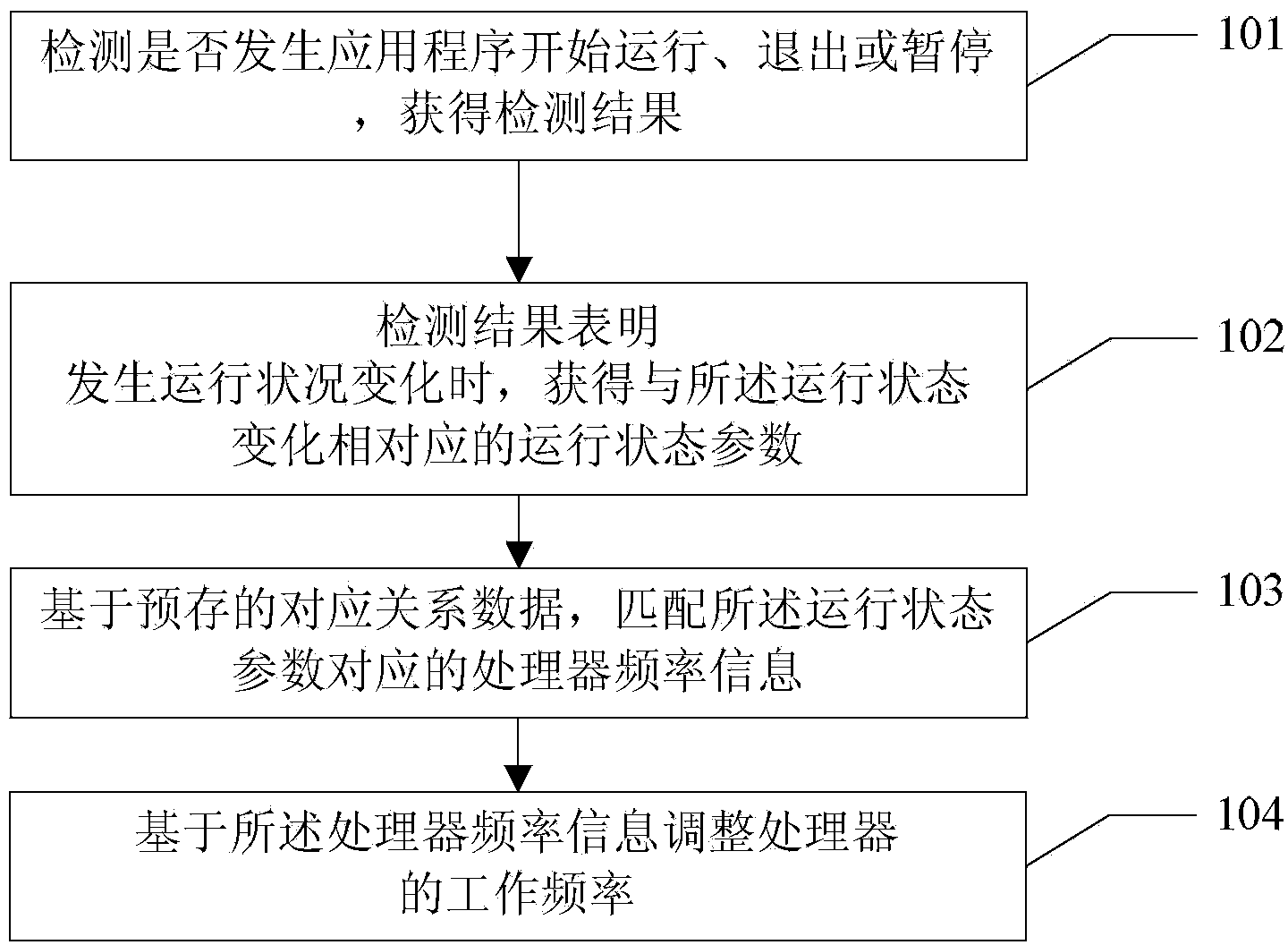
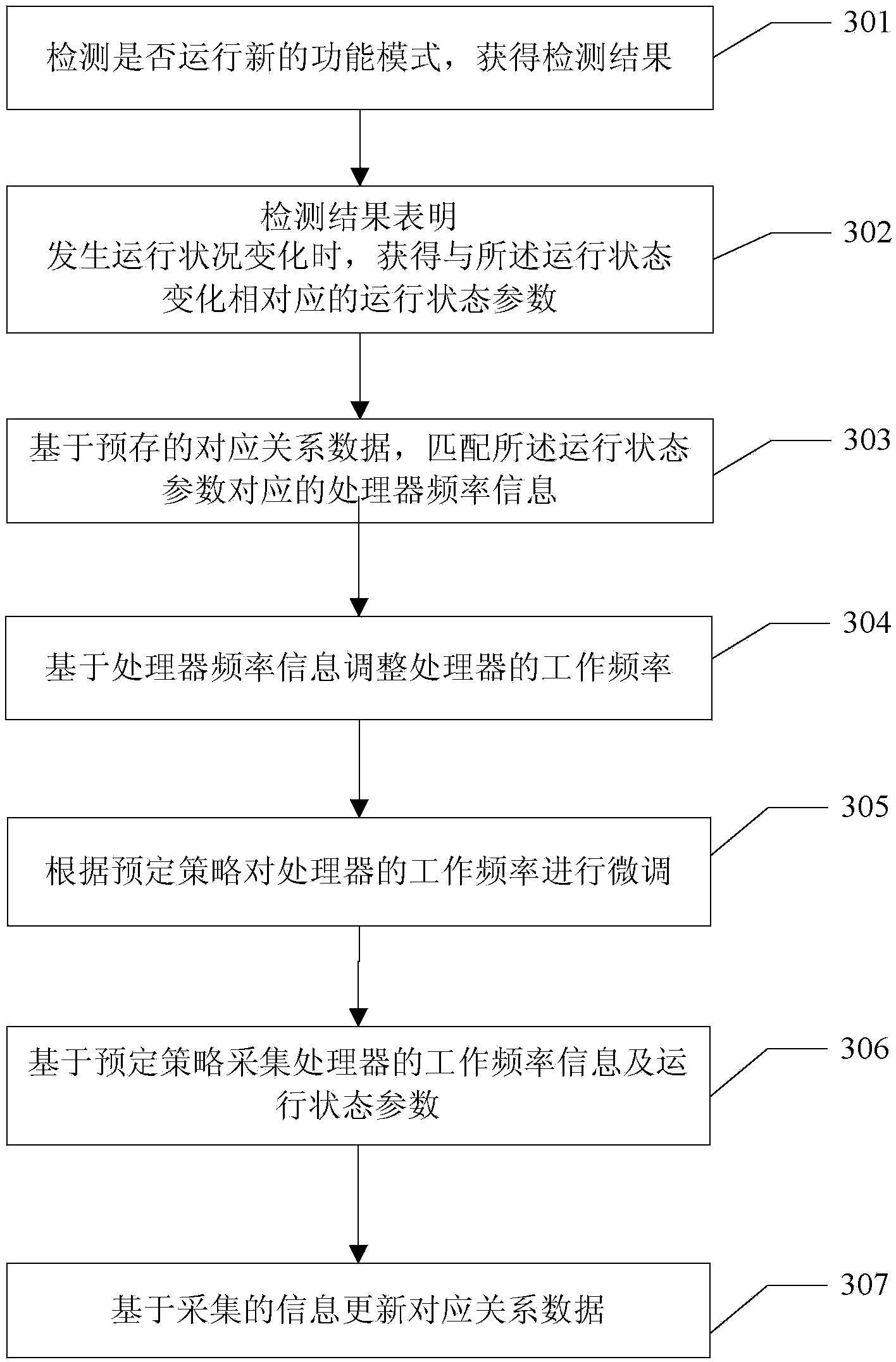
Processor frequency control method and electronic equipment
The invention relates to a processor frequency control method and electronic equipment. The method is applied to the electronic equipment. One or more applications can run in the electronic equipment, and the electronic equipment is provided with a processor. The method comprises the steps of detecting whether a running state change occurs to the one or more applications or not to obtain a detection result; when the detection result indicates that the running state change occurs to the one or more applications, obtaining a running state parameter corresponding to the running state change; matching processor frequency information corresponding to the running state parameter based on pre-stored corresponding relation data; regulating the working frequency of the processor based on the processor frequency information. According to the processor frequency control method and the electronic equipment, the system performance of the electronic equipment during running can be improved.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) CO LTD
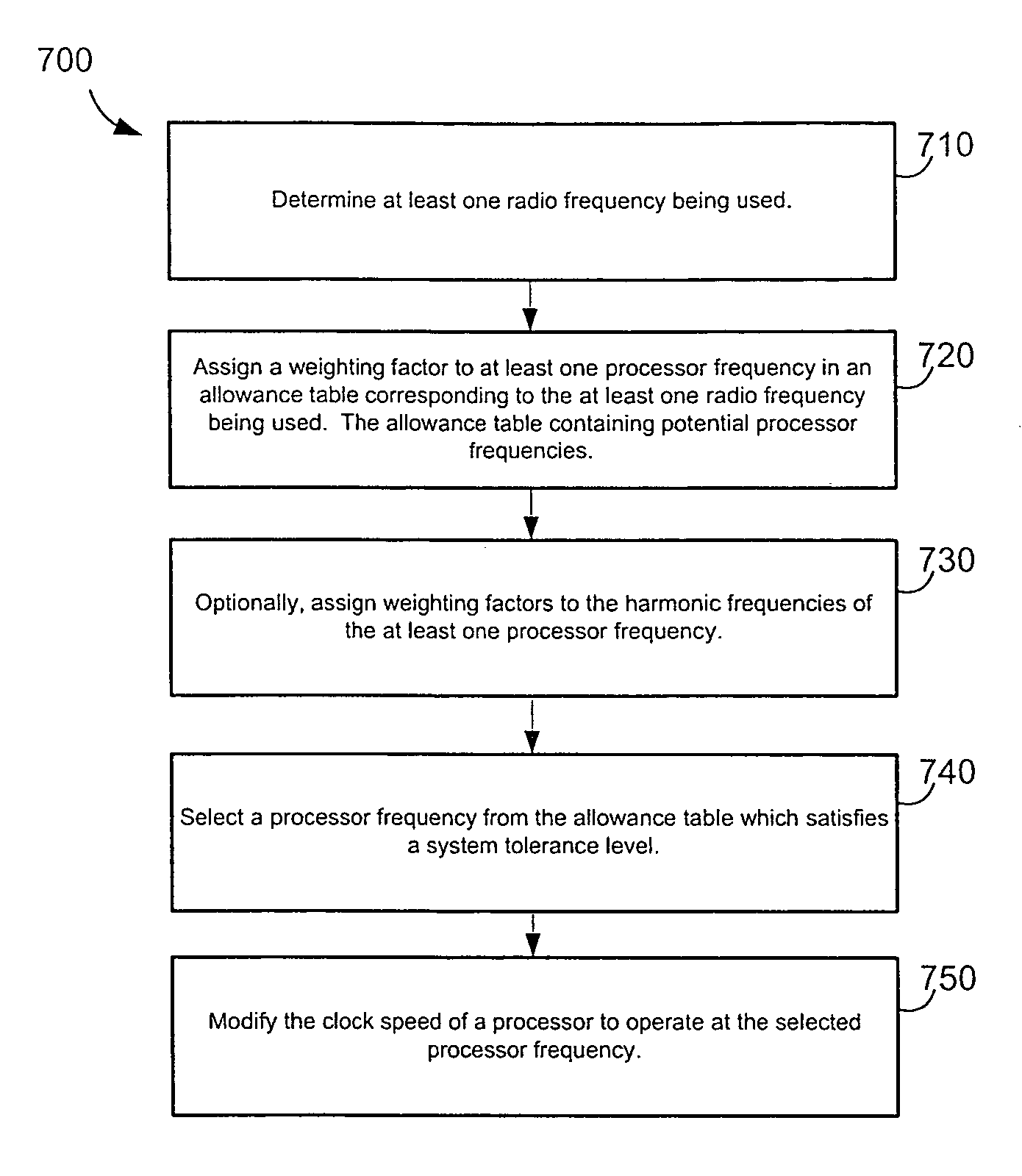
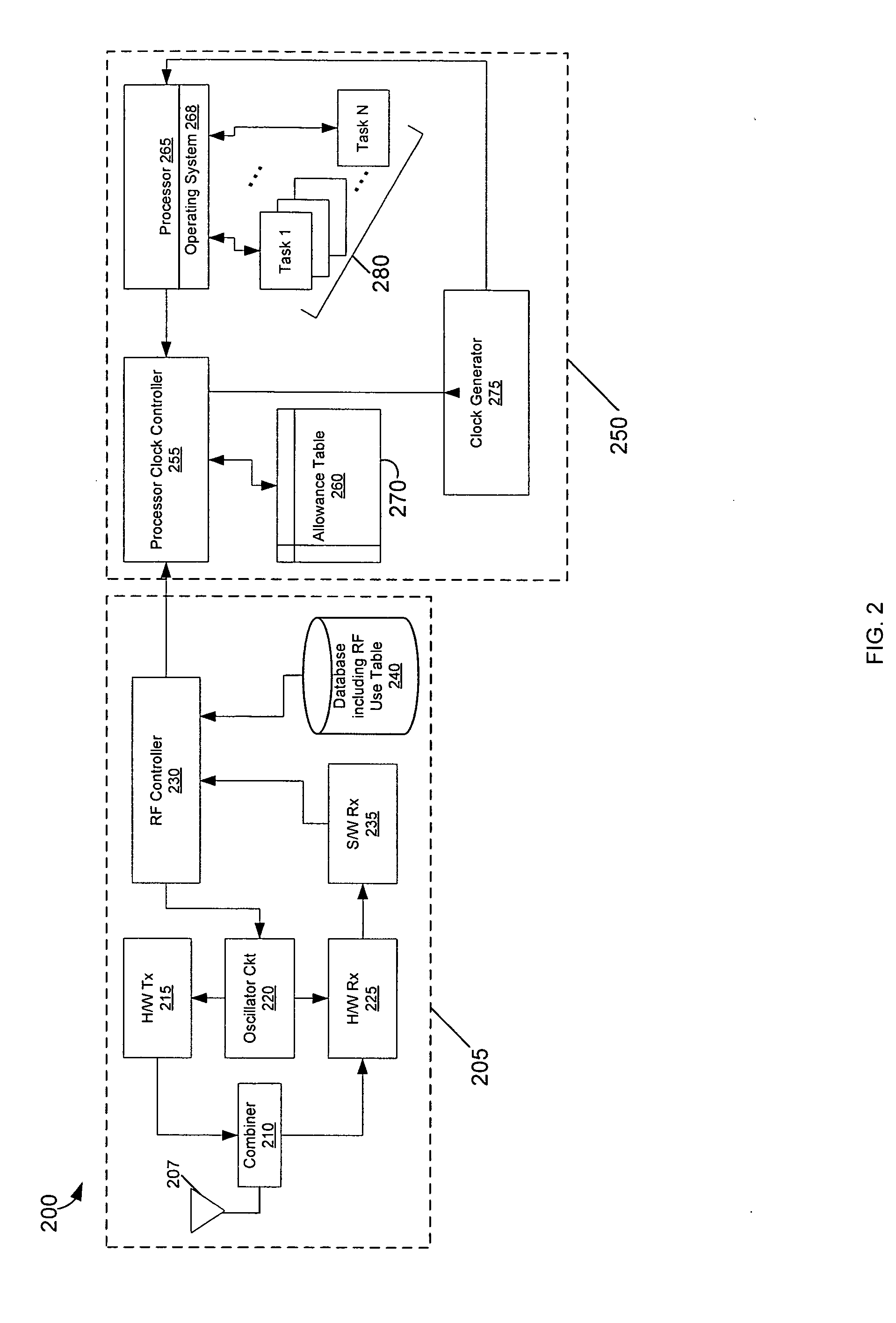
Methods and apparatus for radio frequency interference reduction
InactiveUS20070009067A1Reduce distractionsEasy to optimizeError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionInterference factorEngineering
Techniques for reducing interference on radio frequencies due to processor frequencies which control a processor in wireless device are disclosed. A method for reducing interference on radio frequencies includes the steps of determining at least one radio frequency used in the wireless device and assigning an interference factor to a potential processor frequency corresponding to at least one radio frequency used in the wireless device. The method further includes the step of selecting a first processor frequency other than the potential processor frequency to avoid interference with the at least one radio frequency.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
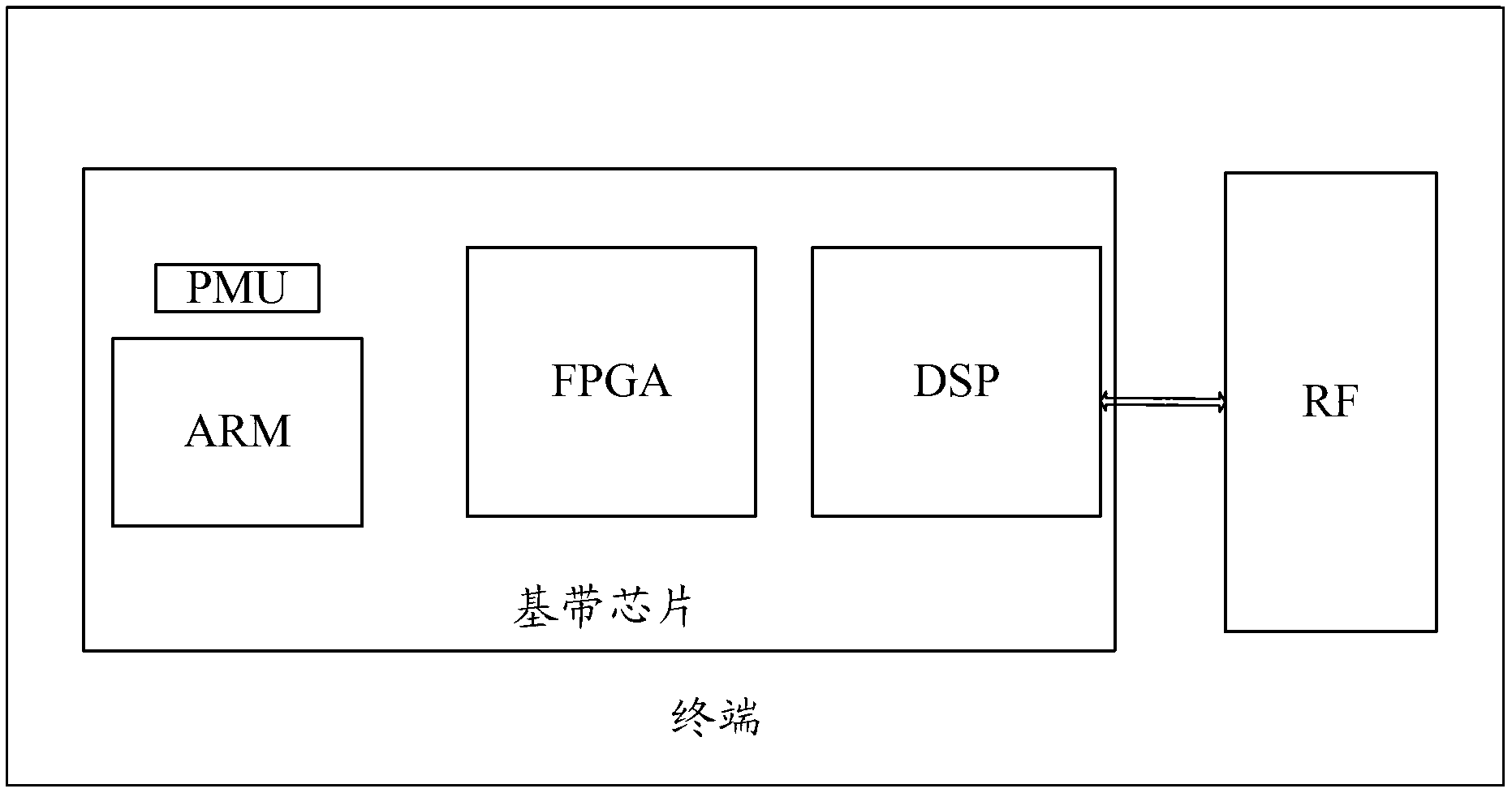
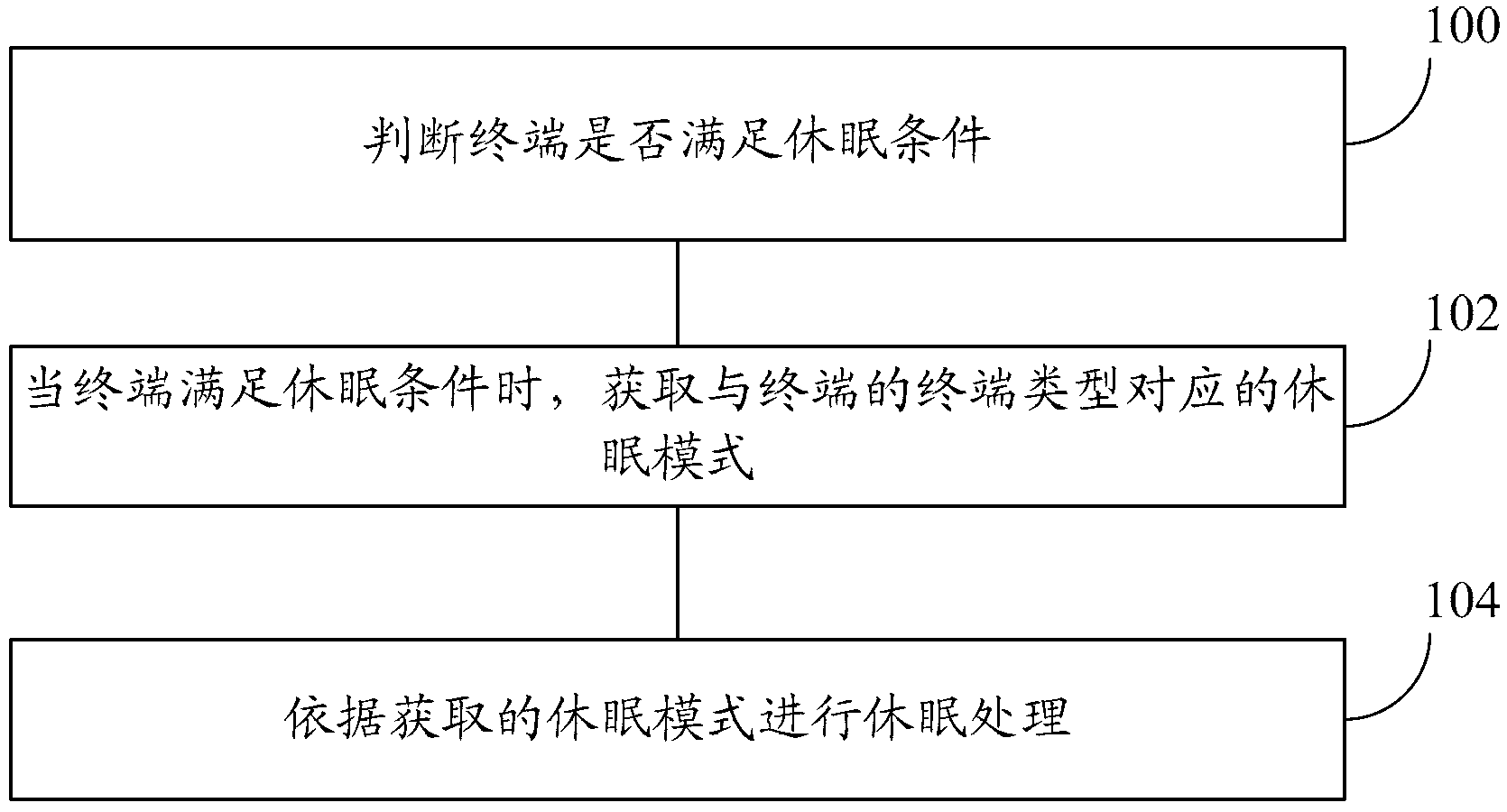
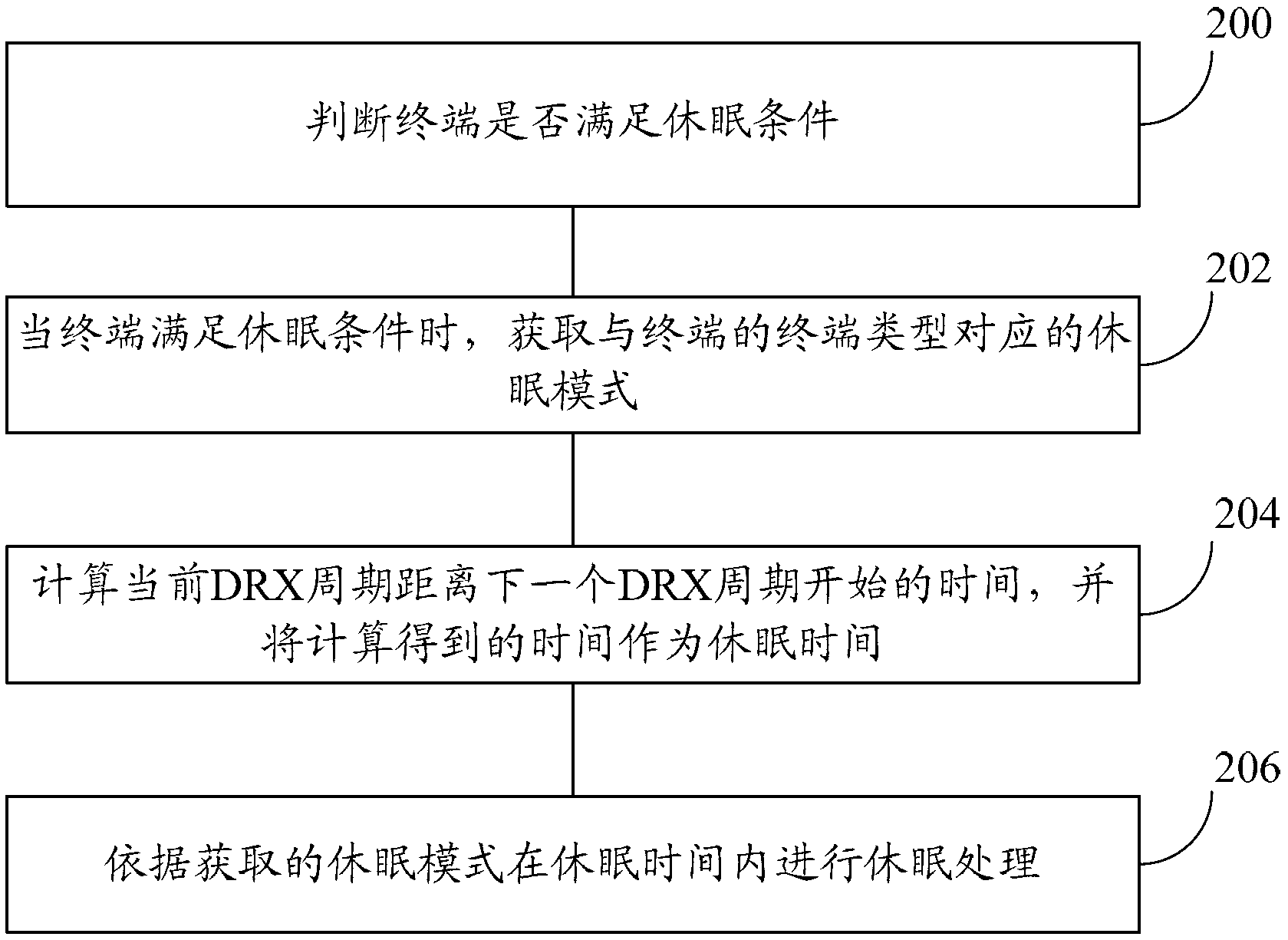
Terminal dormant method and terminal
ActiveCN103259939AReduce power consumptionExtend standby timeCurrent supply arrangementsHigh level techniquesProcessor frequencyComputer science
The invention provides a terminal dormant method and a terminal. The problems that a single dormant mode can not satisfy the requirements of LTE terminals of different types and the requirement for low power consumption in different application scenarios are solved. The terminal dormant method comprises the steps: whether the terminal satisfies dormant conditions or not is judged; when the terminal satisfies the dormant conditions, a dormant mode corresponding to the terminal type of the terminal is obtained; the terminal types comprise a single mode terminal, a first type multi-mode terminal and a second type multi-mode terminal, wherein the single mode terminal type corresponds to an electric mode under an advanced reduced instruction set processor, the first type multi-mode terminal corresponds to an advanced reduced instruction set processor frequency reducing mode, and the second type multi-mode terminal corresponds to an advanced reduced instruction set processor normal frequency mode; dormant processing is conducted according to the obtained dormant mode. According to the terminal dormant method and the terminal, the different dormant modes can be selected according to different terminal types, so that the dormant processing is conducted, and therefore the terminal dormant method and the terminal can satisfy the requirement for the low power consumption of the terminals of different types.
Owner:新奇点智能科技集团有限公司 +2
Method and apparatus for adjusting profiling rates on systems with variable processor frequencies
A computer implemented method, apparatus, and computer usable program code for adjusting rates at which events are generated or processed. In response to a frequency change in a processor, a frequency for the processor is identified. A rate at which samples of events generated by the processor are selected to meet a desired rate of sampling is adjusted in response to identifying the frequency change for the processor to form an adjusted rate.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and equipment for adjusting processor frequency
InactiveCN103488532AAdjust frequencyHigh precisionProgram initiation/switchingOccupancy rateProcessor frequency
The invention discloses a method and equipment for adjusting processor frequency, which are used for precisely acquiring the occupancy rate of a processor and adjusting the processor frequency. In the method provided by the embodiment of the invention, an out-band system reads the processor occupancy rate from the processor or determines the processor occupancy rate according to the specific parameter value returned from the processor after sending a command for reading a specific parameter value to the processor; the out-band system adjusts the processor frequency according to the obtained processor occupancy rate, wherein the out-band system comprises hardware operated by being independent from a user operation system in the equipment, and software operated on the hardware. After the method provided by the embodiment of the invention is adopted, the out-band system can directly obtain the processor frequency from the processor or determines the processor occupancy rate according to the specific parameter read from the processor, so the processor frequency is adjusted and the method and equipment have the advantage of high precision.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Dynamic capacity management of multiple parallel-connected computing resources
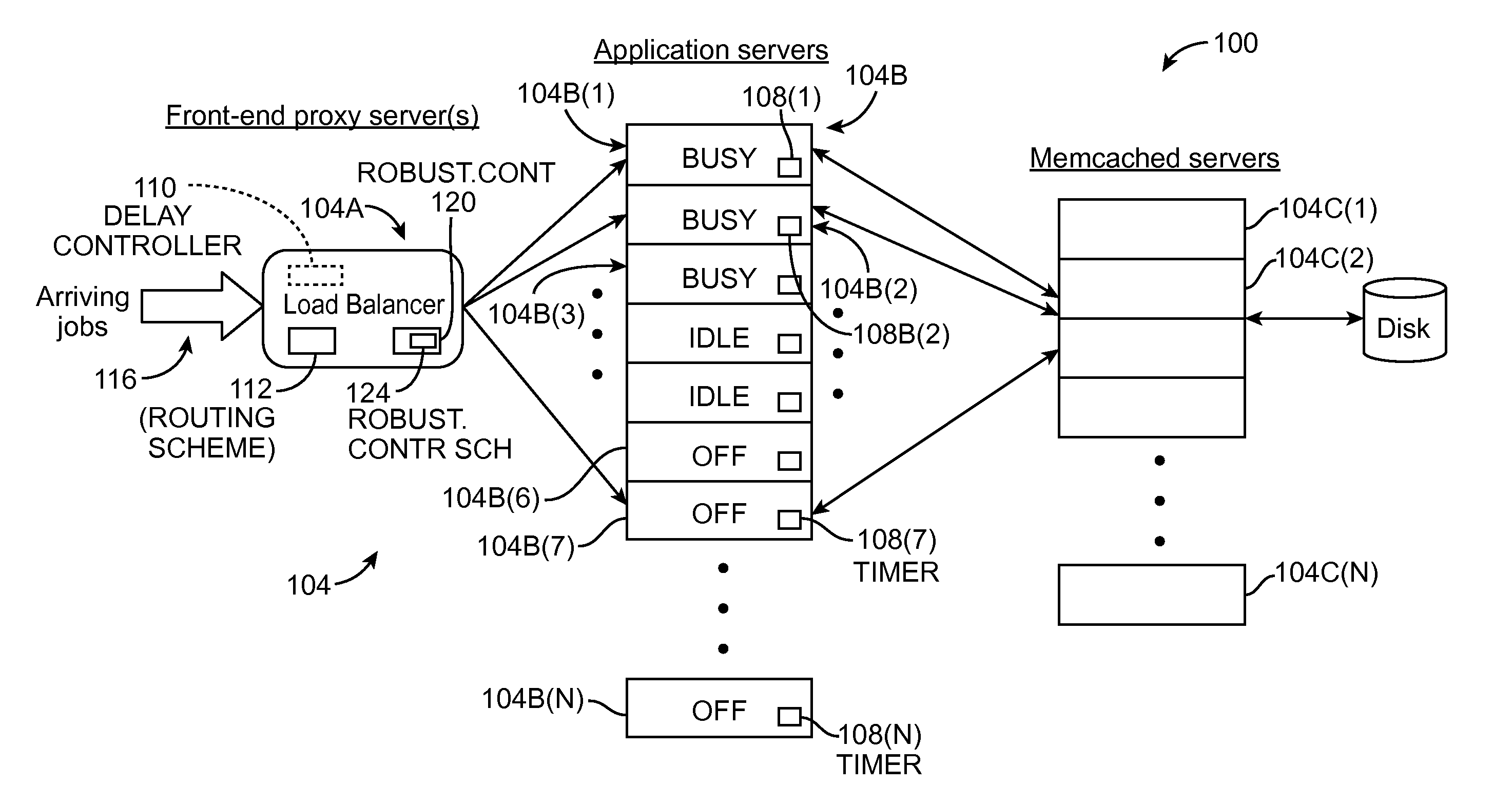
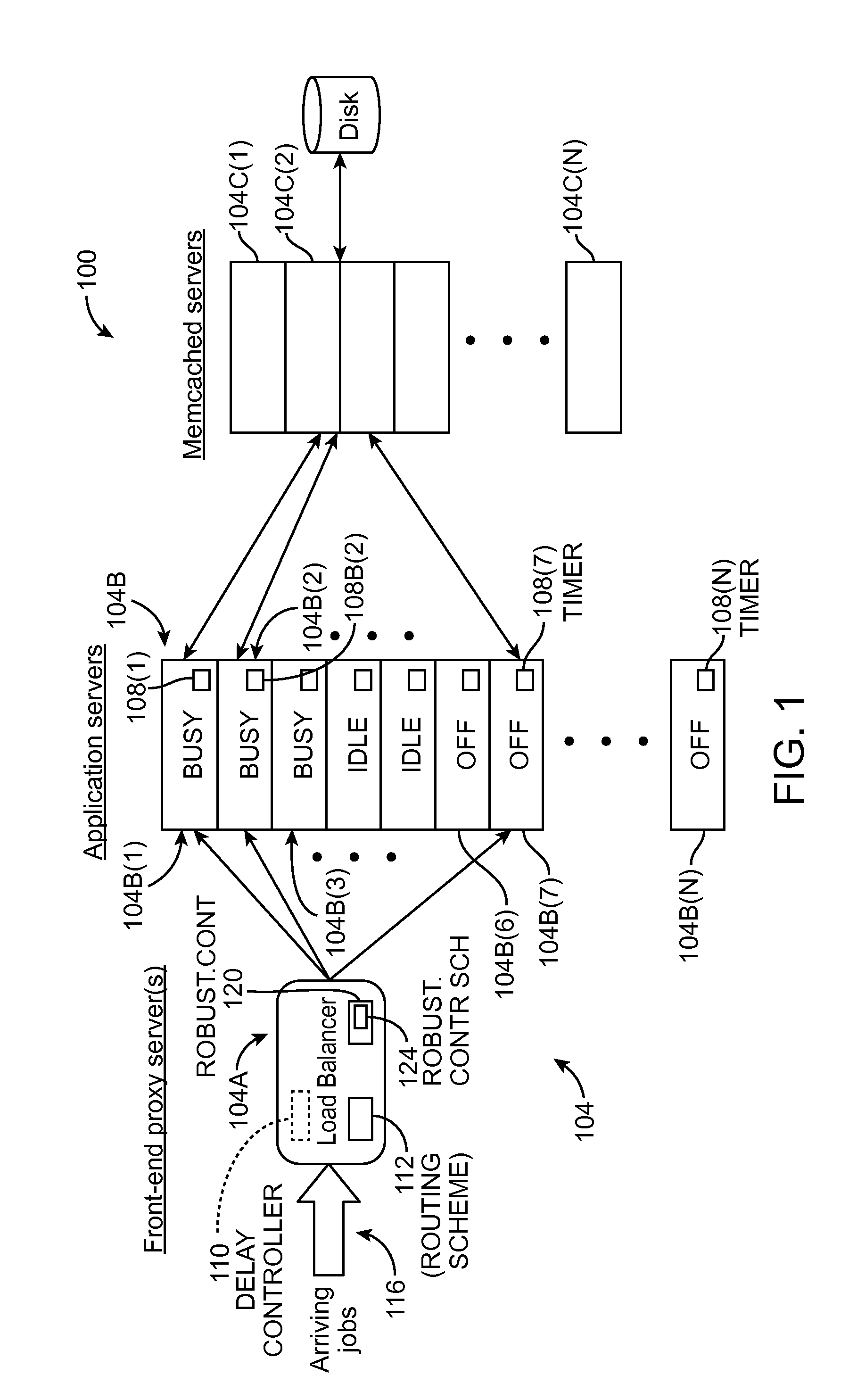
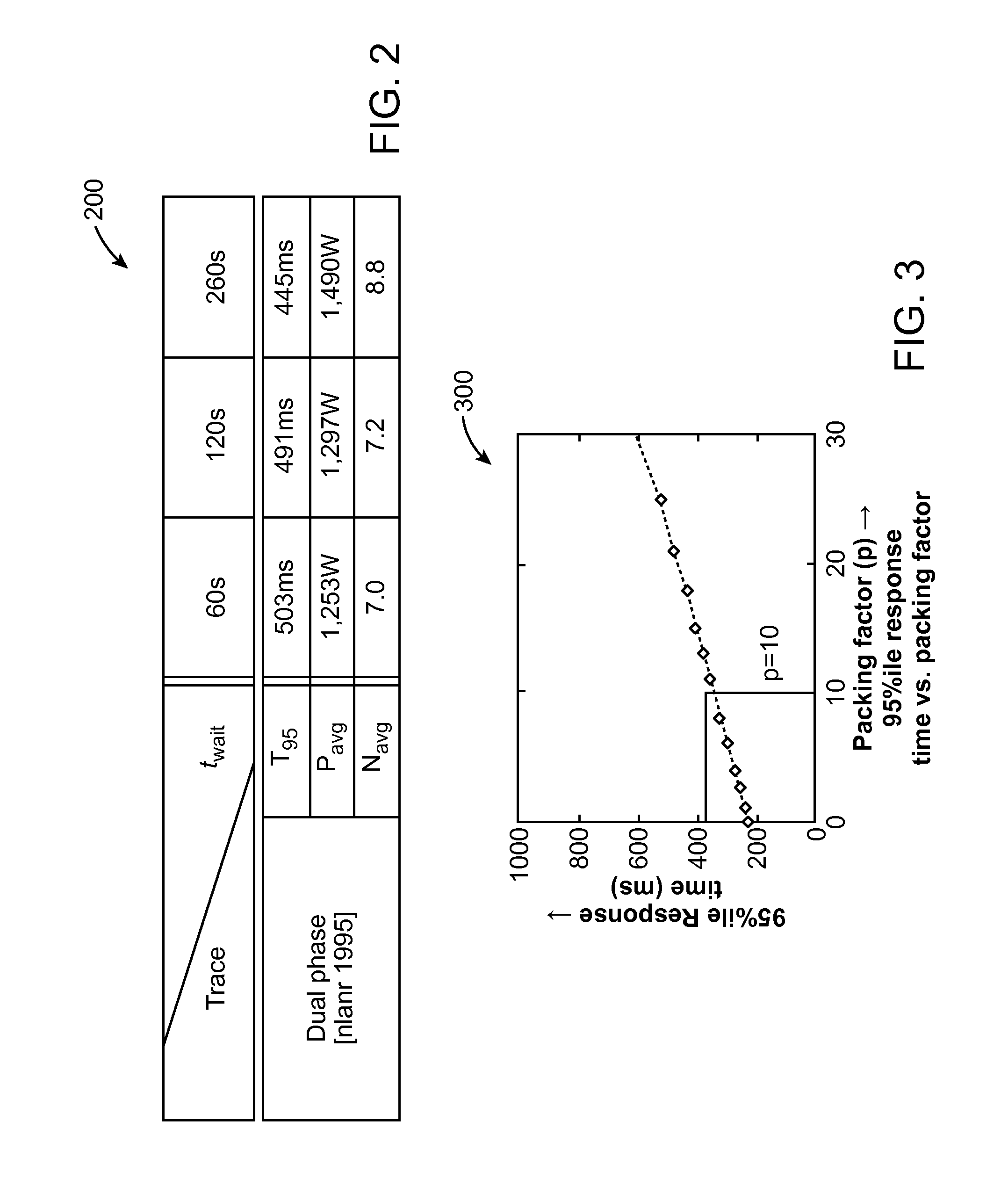
ActiveUS20120254444A1Program control using stored programsDigital computer detailsApplication serverProcessor frequency
A dynamic capacity management policy for multi-paralleled computing resources (e.g., application servers, virtual application servers, etc.) that includes one or more of a state-change component, a load-balancing component, and a robustness-control component. The state-change component delays the release (e.g., powering down of a physical server, removal from a virtual-server lease, etc.) of each computing resource for a set amount of time. The load-balancing component can work in conjunction with the state-change component to reduce the number of idle computing resources by distributing incoming requests in a manner that keeps the already-processing computing resources as full of requests as possible. The robustness-control component scales capacity as a function of the current number of requests within the system of computing resources to account for variations other than request rate, such as request size, reduced processor frequency, network slowdowns, etc., that affect processing capacity.
Owner:INTEL CORP +1
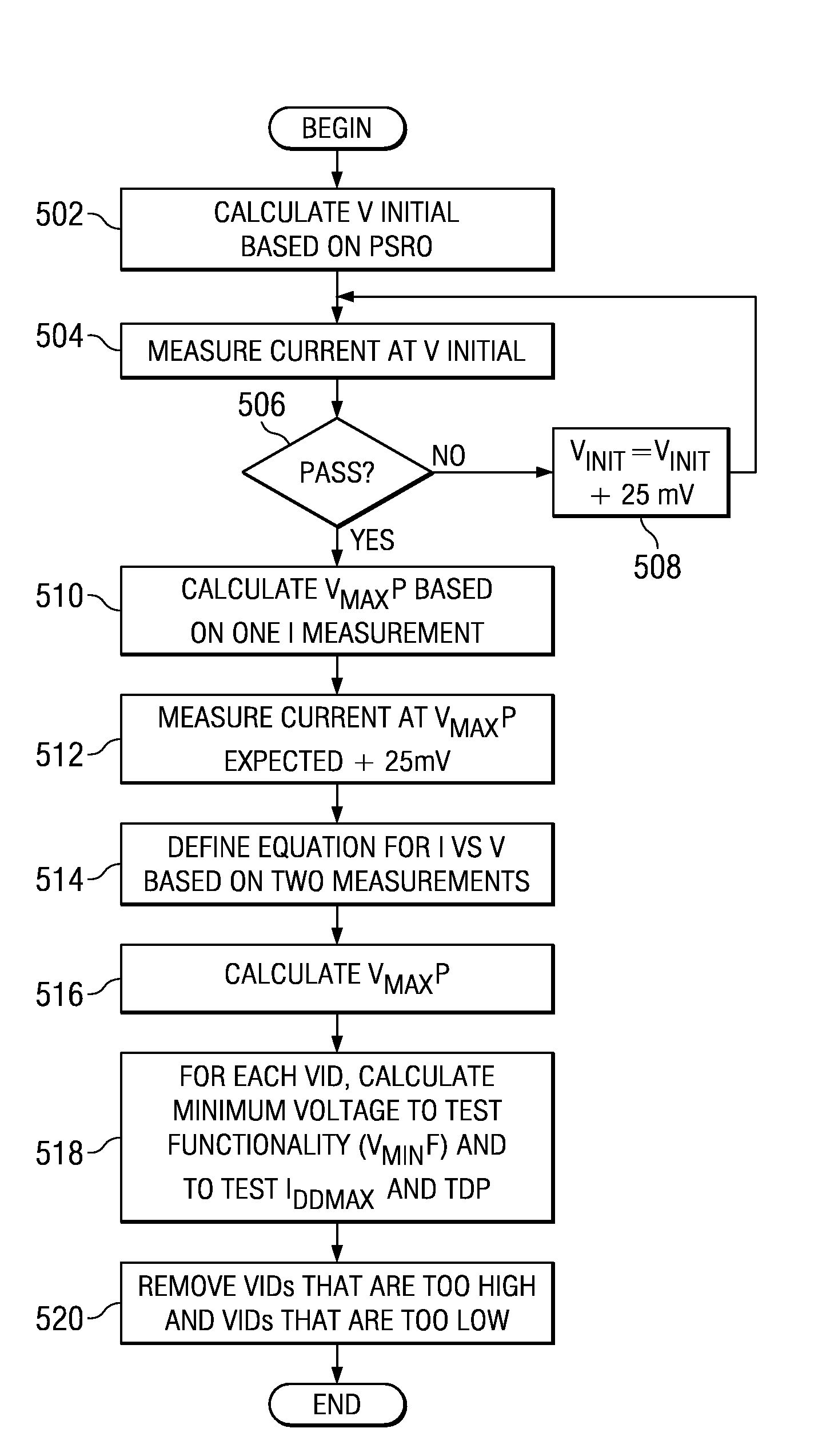
Voltage Identifier Sorting
A voltage identifier (VID) sorting system is provided that optimizes processor power and operating voltage guardband at a constant processor frequency. The VID sorting system determines a voltage versus current curve for the processor. The VID sorting system then uses the voltage versus current characteristics to calculate the power for each VID to determine an acceptable range of VIDs within the maximum power criteria. The VID sorting system then tests VIDs in the range and selects a VID from the range to optimize for minimum power and / or maximum voltage guardband at a constant processor frequency.
Owner:TWITTER INC
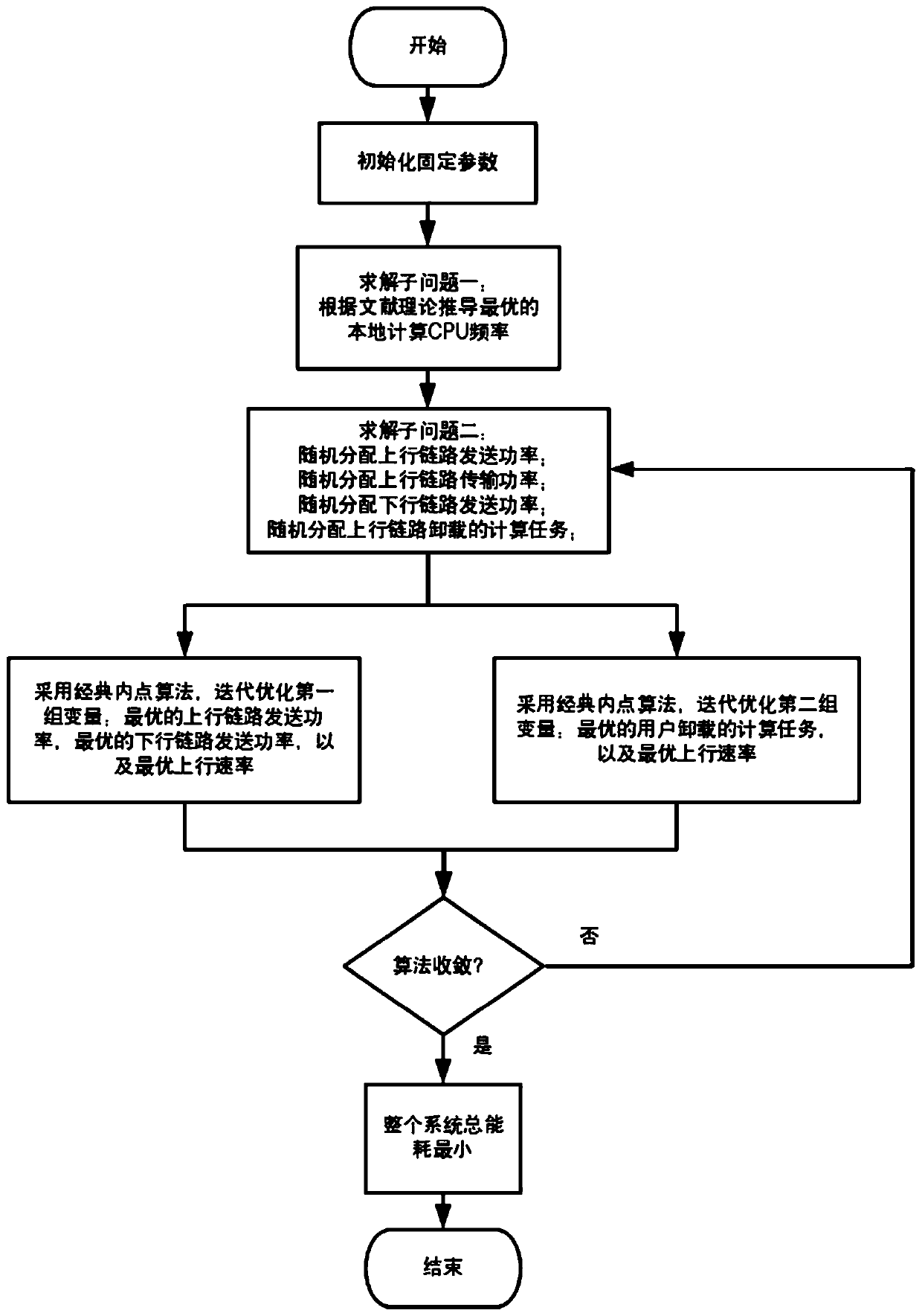
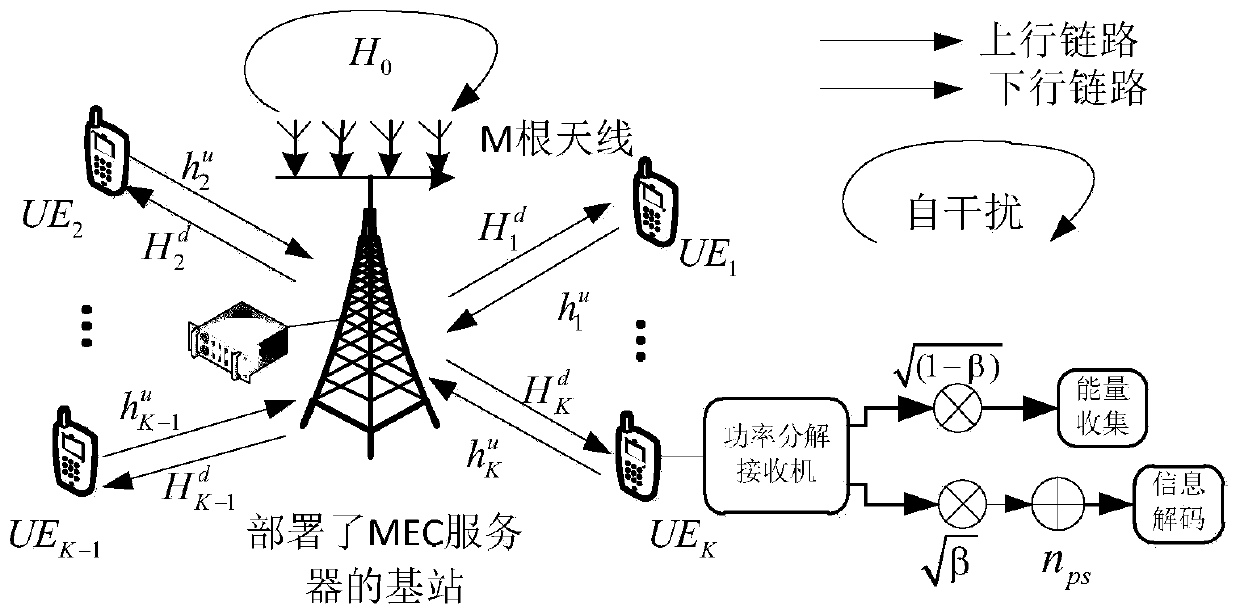
Communication processing method of full duplex mobile edge computing communication system
InactiveCN110545584AReduce energy consumptionReduce consumptionPower managementResource allocationCommunications systemMobile edge computing
The invention discloses a communication processing method of a full duplex mobile edge computing communication system. The full duplex mobile edge computing communication system comprises a pluralityof mobile devices and a base station with a mobile edge computing function server. A joint communication and computing resource optimization model is established and is divided into two sub-models tobe processed and solved respectively, and joint optimization allocation is carried out on two computing resources including an unloading task and processor frequency and two communication resources including sending power and a sending rate. The communication processing method provided by the invention has the advantage of remarkably reducing the energy consumption of the system on the premise ofensuring the system delay and the power constraint.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
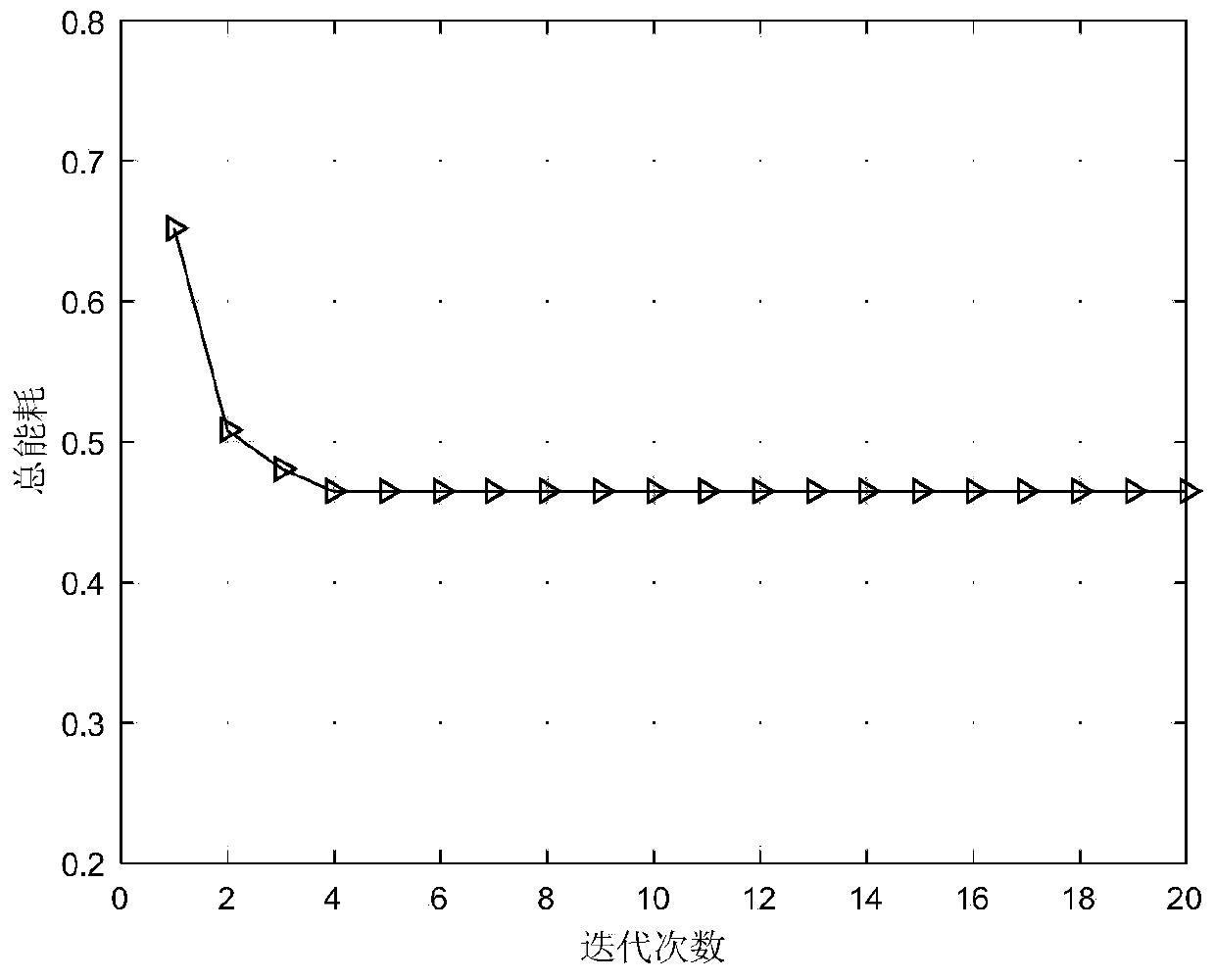
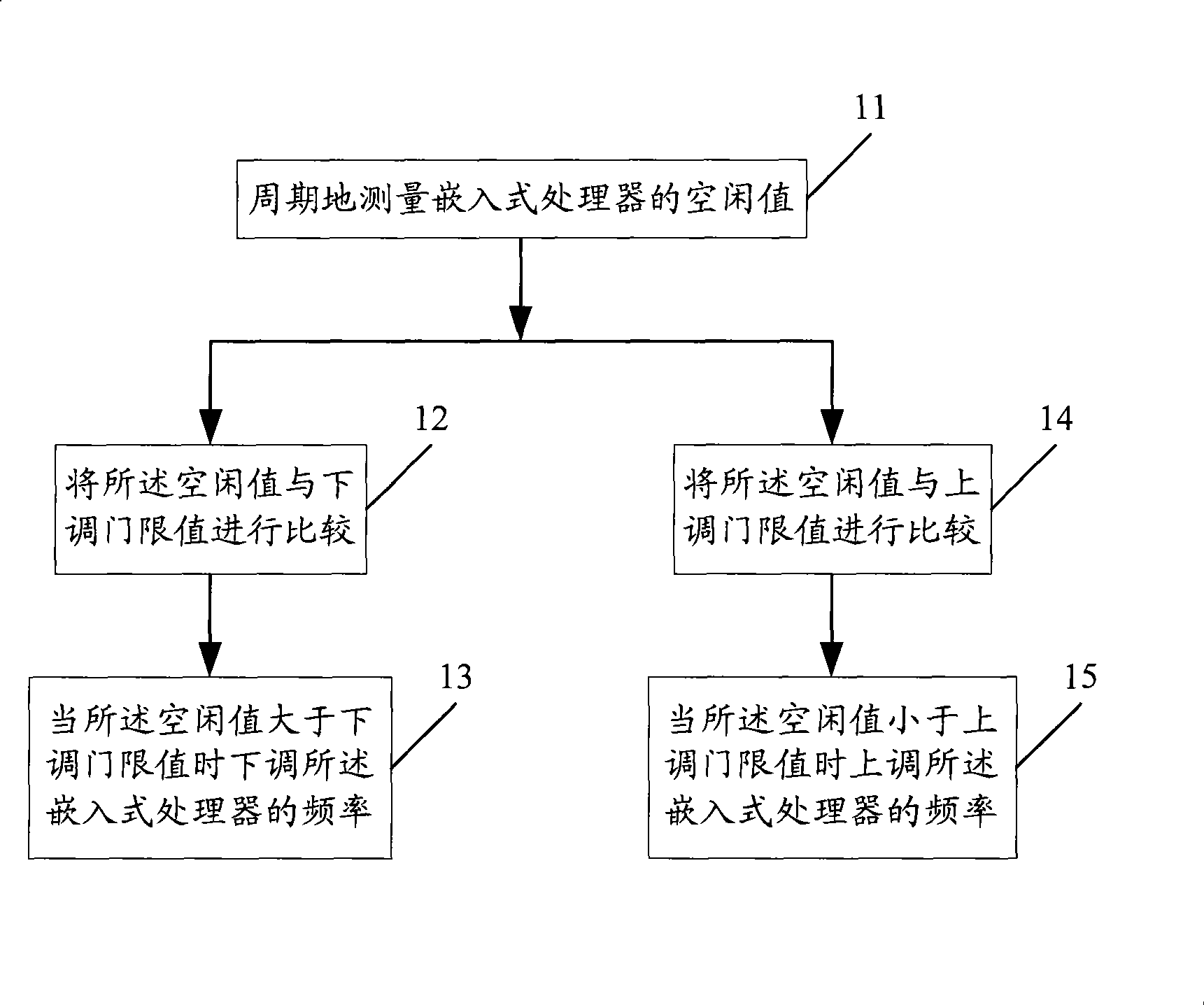
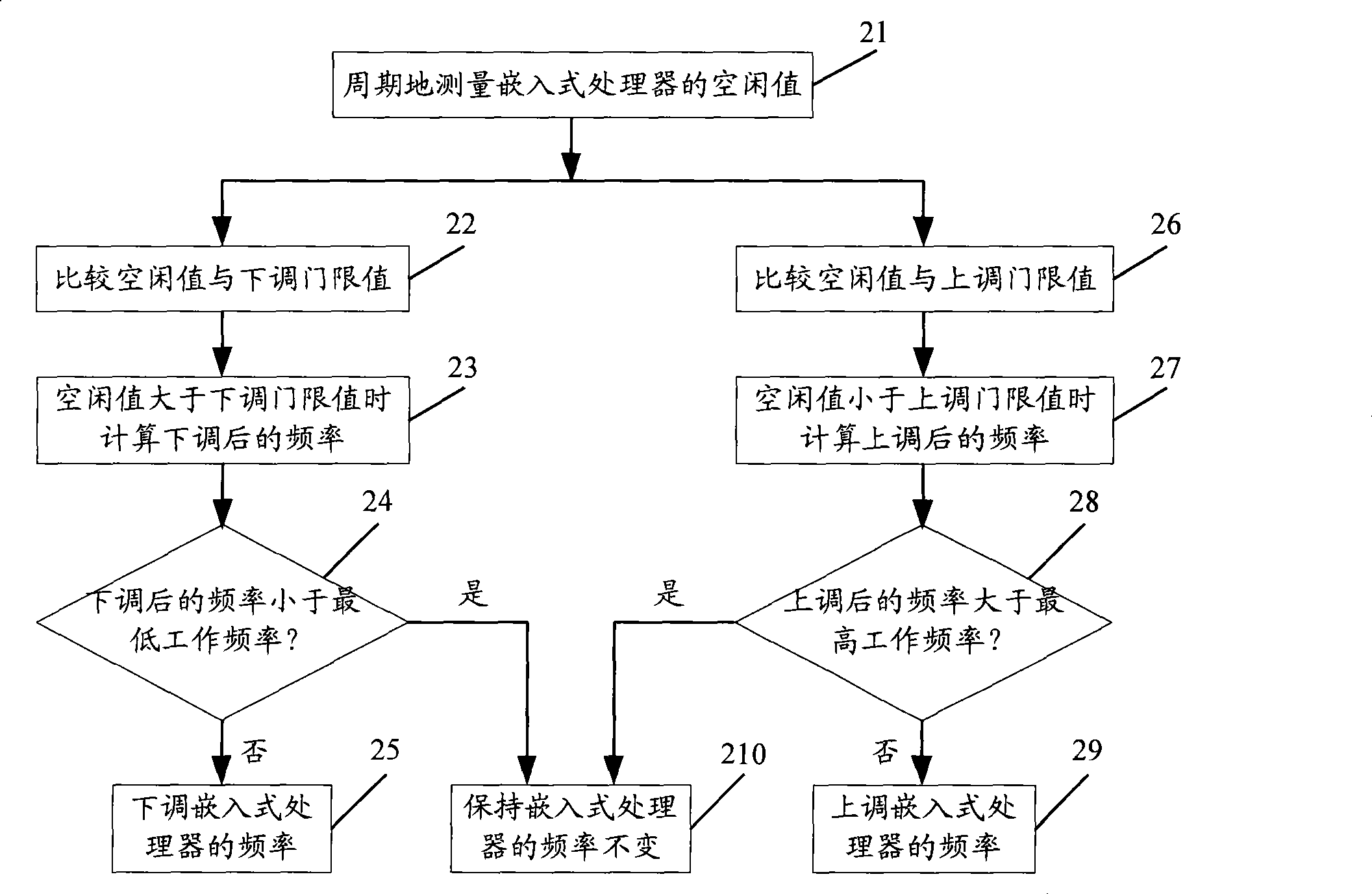
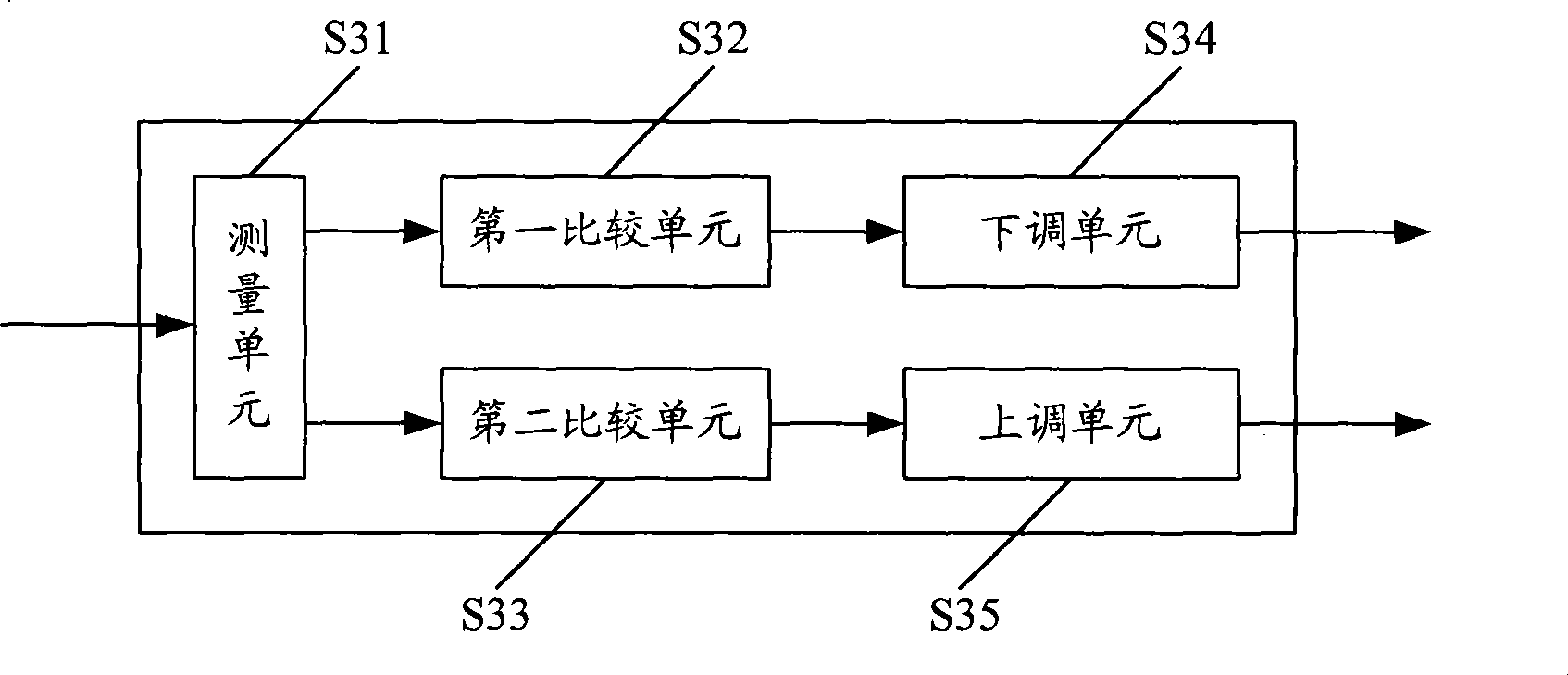
Method and apparatus regulating frequency of embedded processor and mobile terminal processor
InactiveCN101365192AGuaranteed uptimeReduce power consumptionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmissionProcessor frequencyEmbedded processing
The invention discloses a method for adjusting the frequency of an embedded processor. The method comprises the following steps: measuring the idleness value of the embedded processor; when the idleness value is higher than a first threshold value, reducing the frequency of the embedded processor; and when the idleness value is lower than a second threshold value, increasing the frequency of the embedded processor. The method can ensure that not only the embedded processor can operate various tasks normally, but also the embedded processor can operate at a lower frequency through regulating the frequency, thereby reducing the power consumption of the embedded processor, and further reducing the power consumption of portable devices which adopt the embedded processor, and prolonging the working time of the portable devices. The method further discloses an embedded processor frequency regulating device, and the corresponding method and device for regulating the frequency of a mobile terminal processor.
Owner:LEADCORE TECH
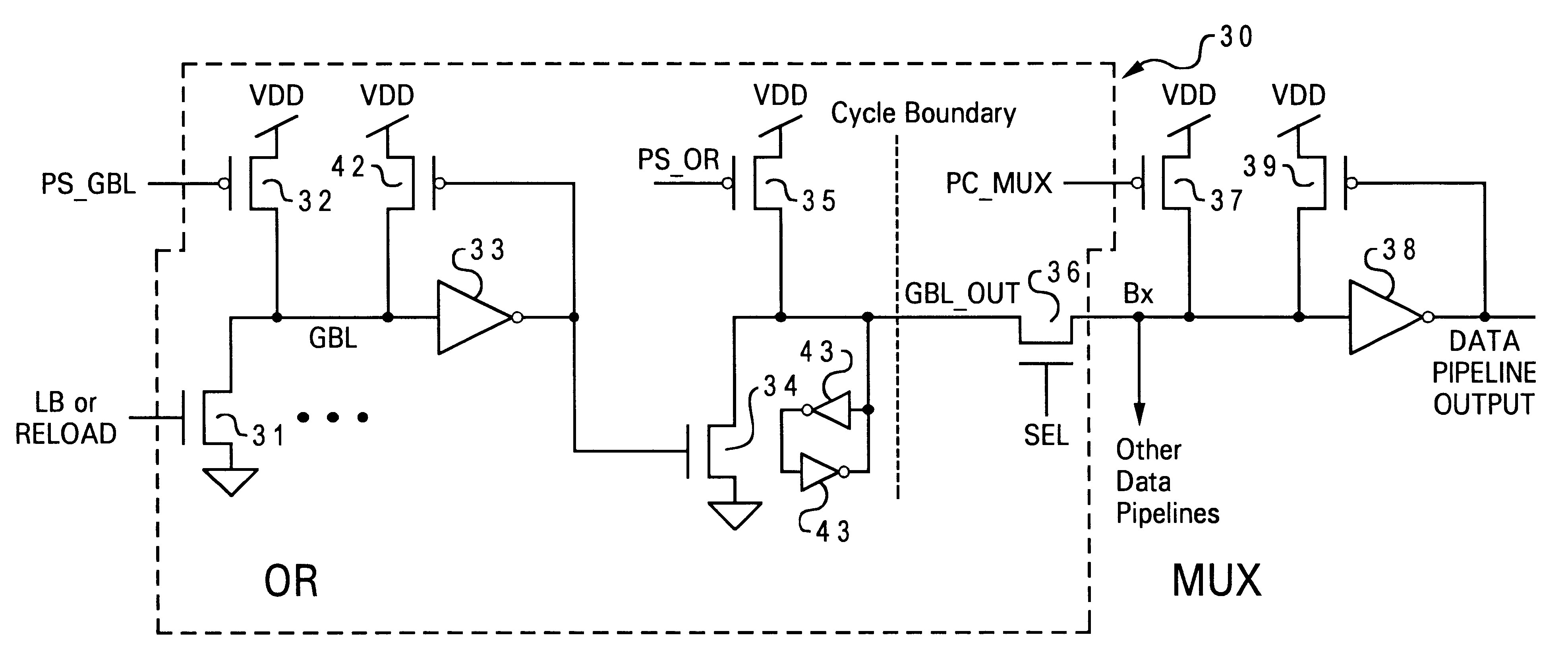
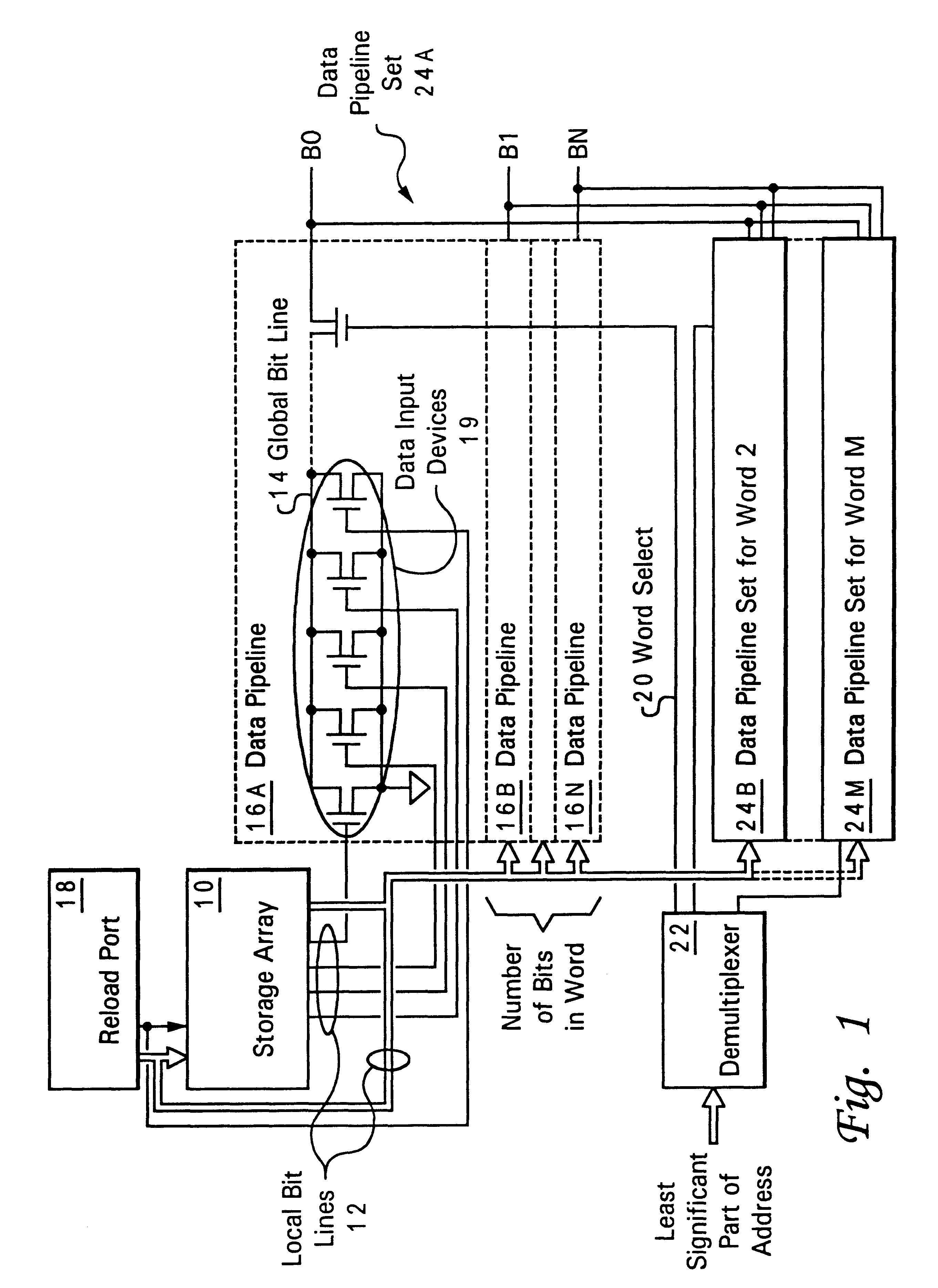
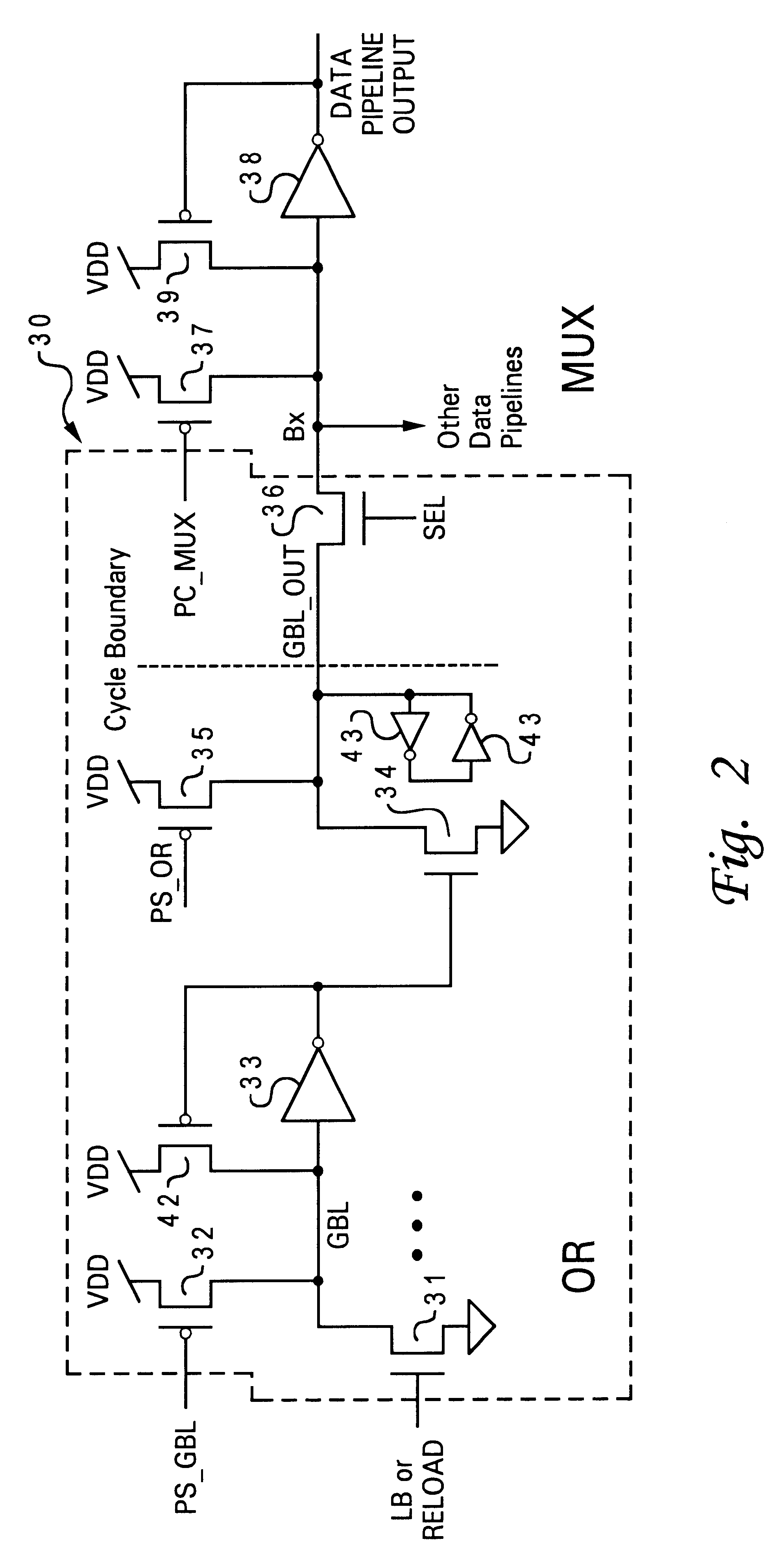
Processor cycle time independent pipeline cache and method for pipelining data from a cache
A processor cycle time independent pipeline cache and method for pipelining data from a cache provide a processor with operand data and instructions without introducing additional latency for synchronization when processor frequency is lowered or when a reload port provides a value a cycle earlier than a read access from the cache storage. The cache incorporates a persistent data bus that synchronizes the stored data access with the pipeline and can also utilize bypass mode data available from a cache input from the lower level when data is being written to the cache.
Owner:LINKEDIN
Method and apparatus for high accuracy distributed time synchronization using processor tick counters
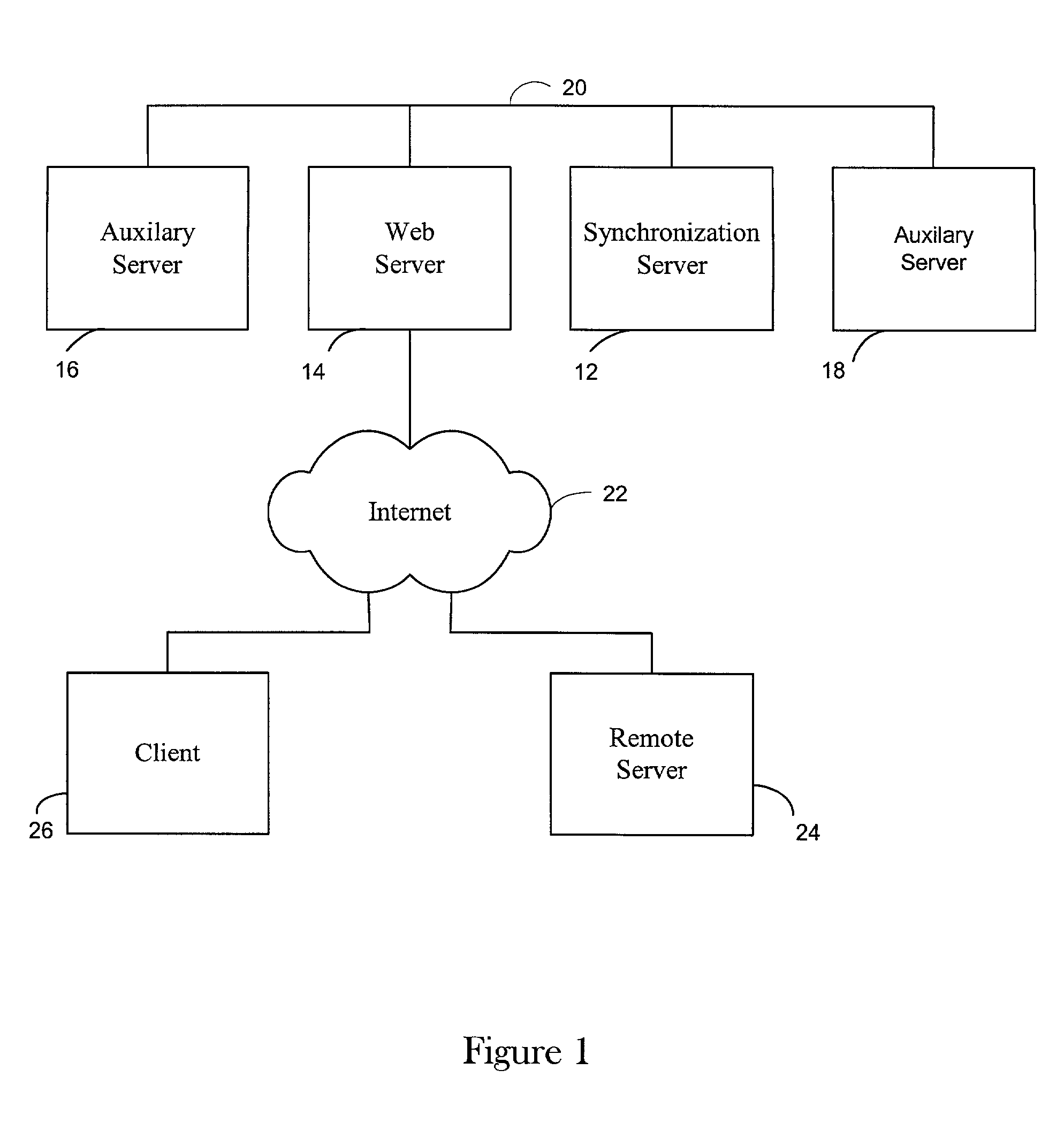
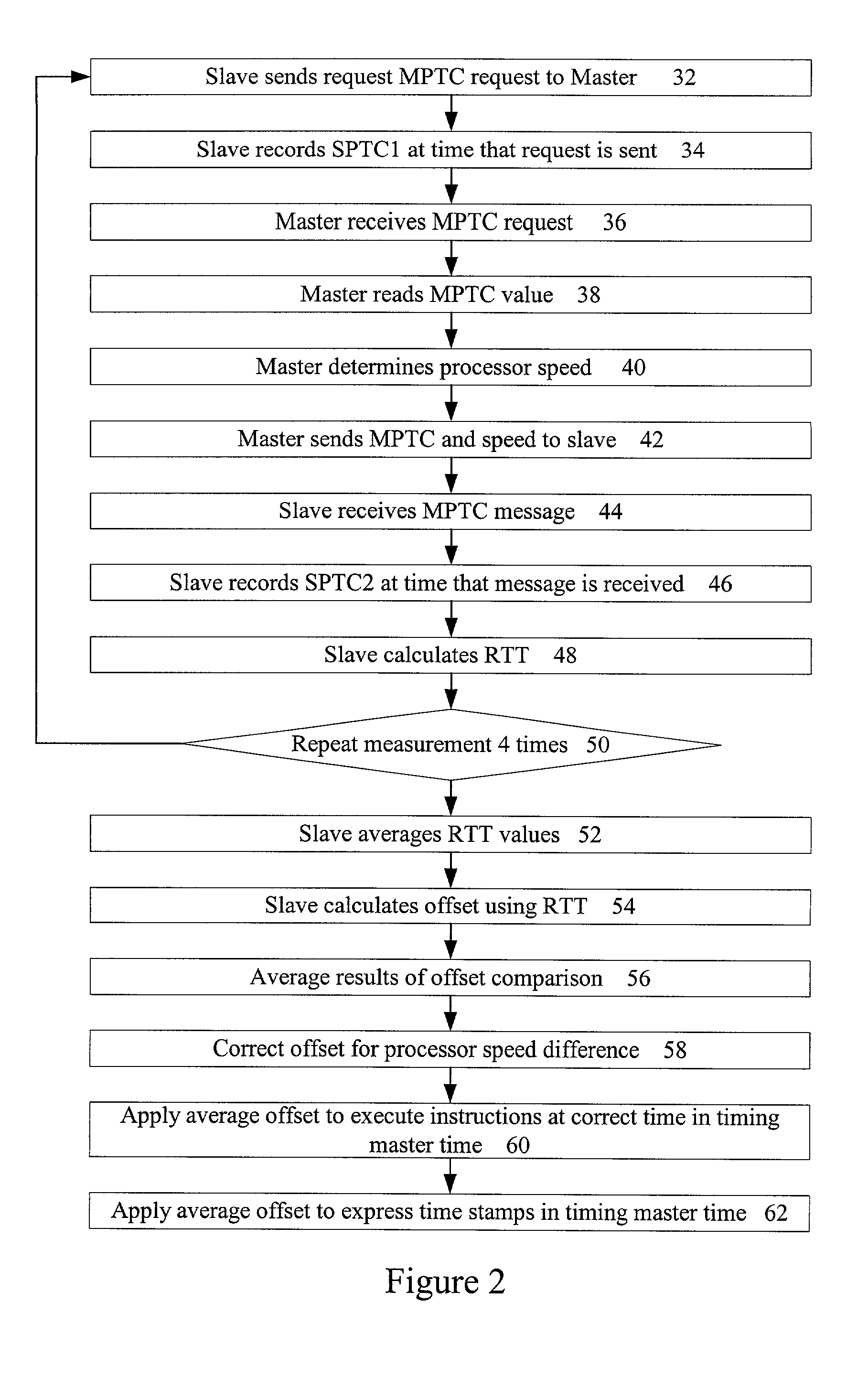
InactiveUS7194556B2Improve accuracyMinimal impact on network traffic loadsMultiple digital computer combinationsGenerating/distributing signalsComputer hardwareProcessor frequency
A method and apparatus are provided that allow processing engines to be synchronized to each other with high accuracy. In one embodiment, the invention includes obtaining a processor tick counter value from a first processing engine, comparing the obtained processor tick counter value to a processor tick counter value from a second processing engine and determining a timing offset for synchronizing the first processing engine and the second processing engine using the comparison. The invention may further include obtaining a processor tick counter value by sending a request message from the second processing engine to the first processing engine, and receiving a reply from the first processing engine at the second processing engine. The processor tick counter value at the second processing engine can be determined by recording the time at which the request message is sent and by recording the time at which the reply is received. The invention can further include obtaining a processor frequency from the first processing engine, obtaining a processor frequency from the second processing engine and correcting the timing offset for any difference between the first processing engine frequency and the second processing engine frequency.
Owner:INTEL CORP
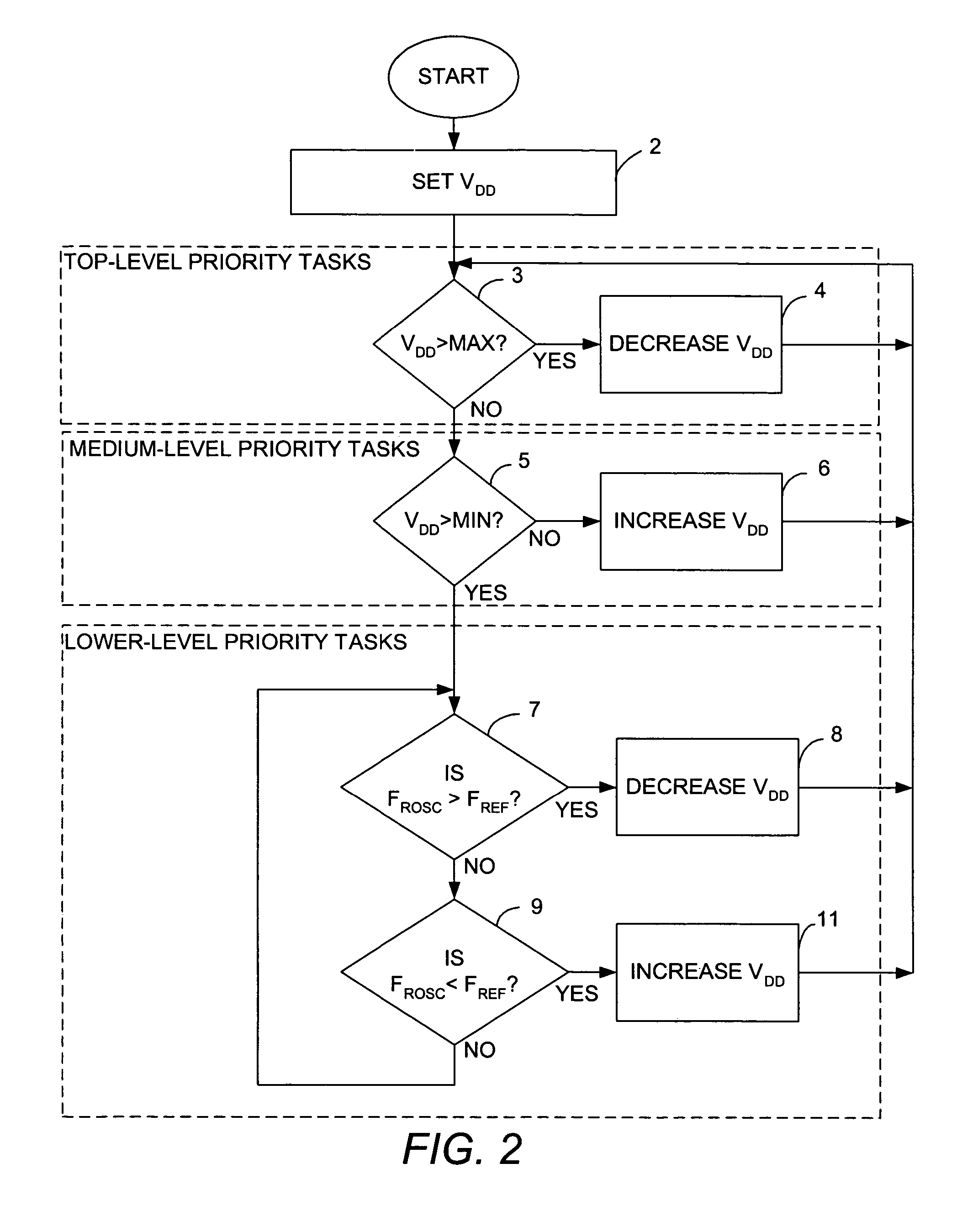
Method and apparatus for monitoring and controlling the thermal environment and operating conditions of an integrated circuit
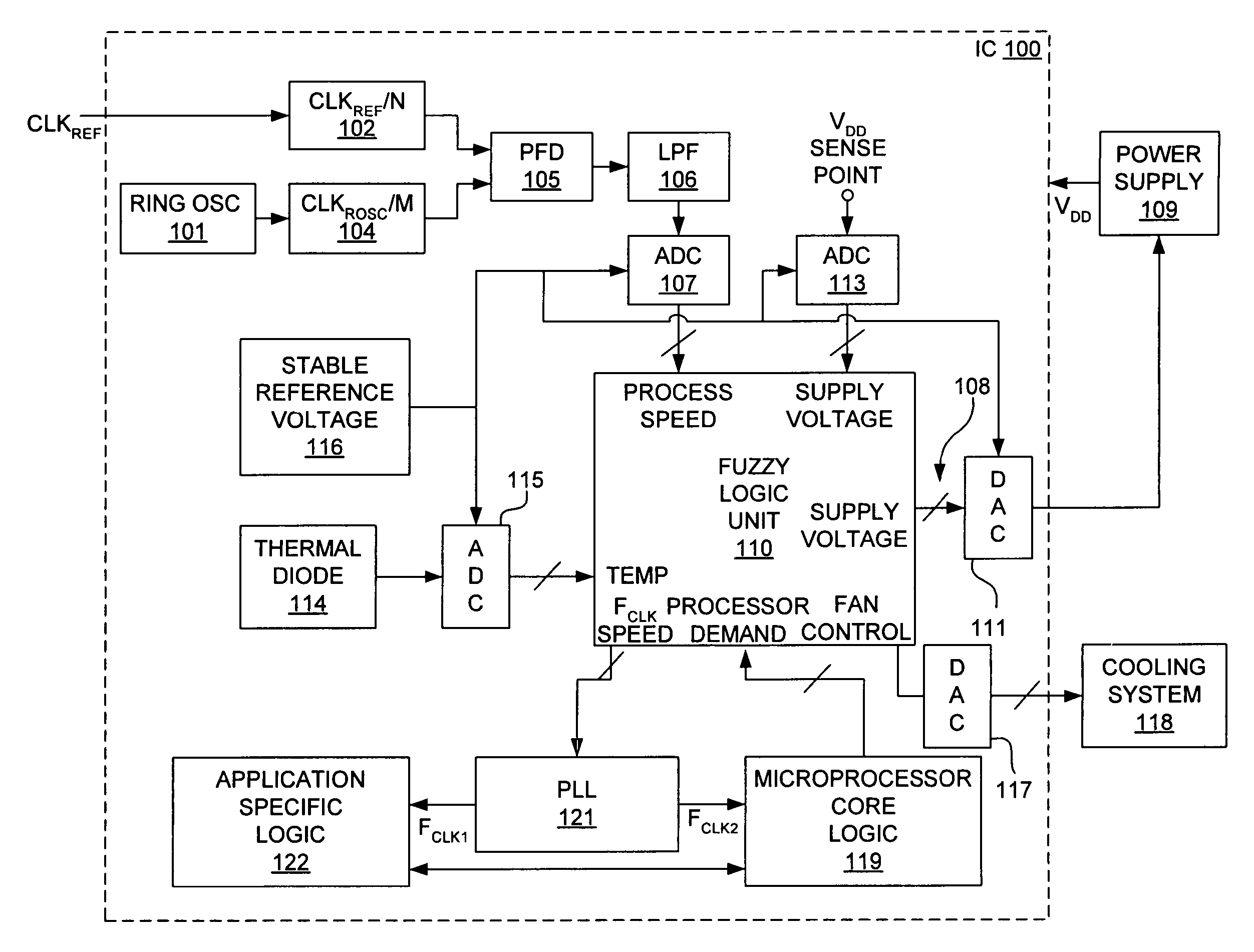
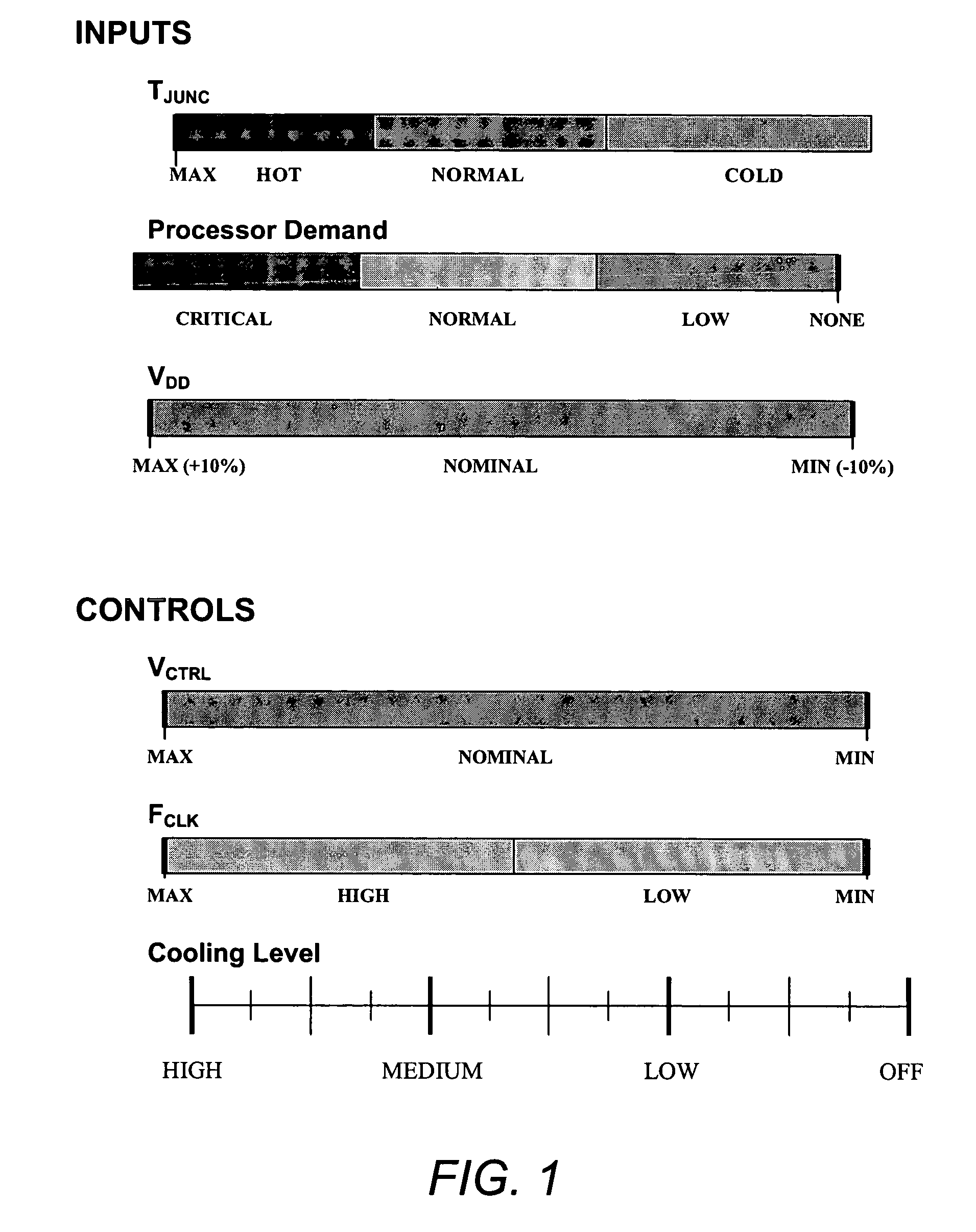
Logic included in an IC monitors values of parameters that may affect operation of the IC, such as, for example, supply voltage (VDD), junction temperature (TJUNC) and the frequency of a ring oscillator on the IC. In response to the monitored values, the logic in the IC changes, if necessary, one or more parameters such as VDD, processor frequency (FCLK), and / or cooling level to control the performance of the IC. Thus, the IC monitors its own environment and operating conditions and takes appropriate steps to control its environment and operating conditions to achieve certain goals.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
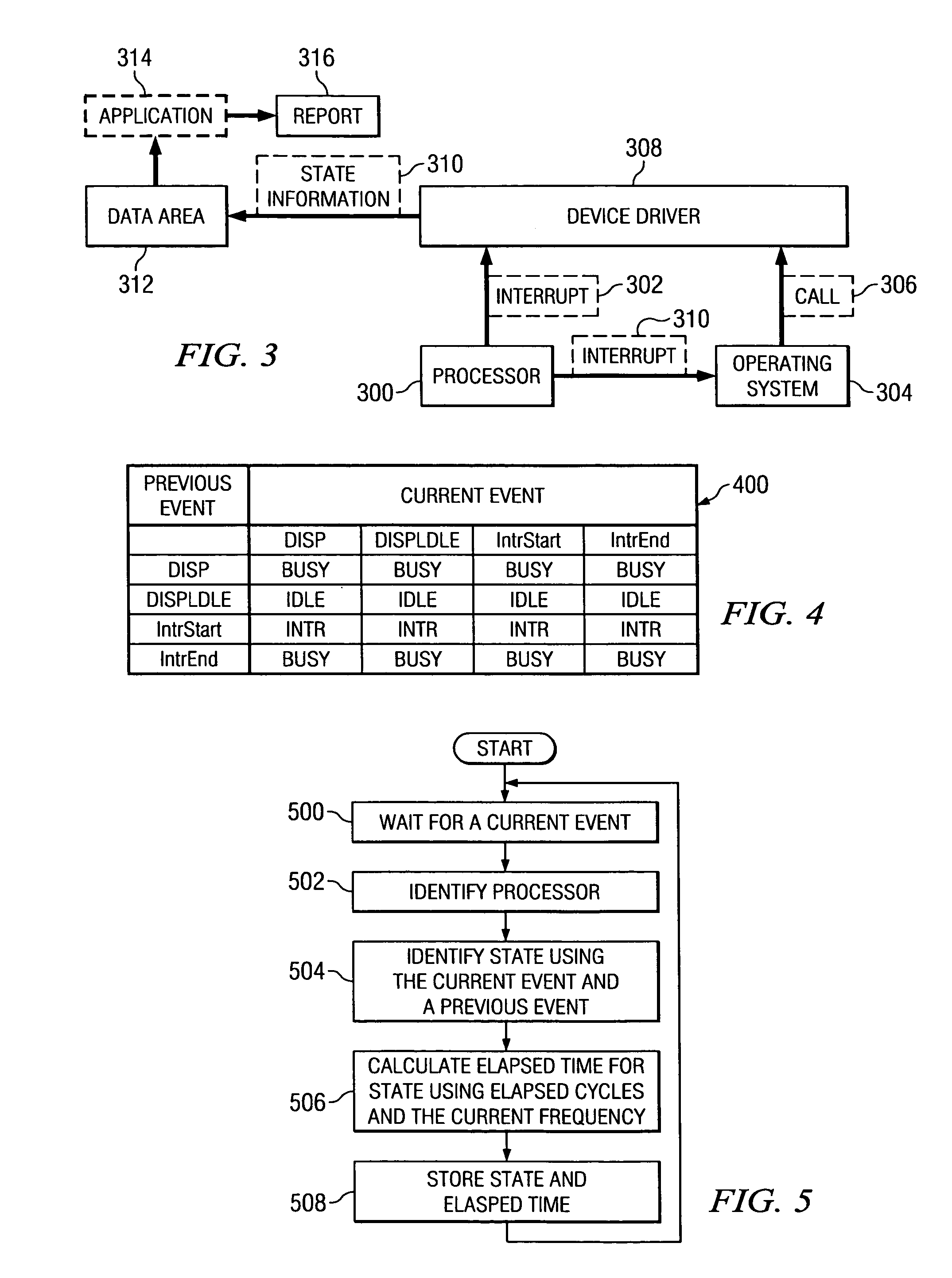
Adaptive processor utilization reporting handling different processor frequencies
InactiveUS20070061108A1Nuclear monitoringDigital computer detailsProcessor frequencyUtilization rate
A computer implemented method, apparatus, and computer usable code for identifying processor utilization. A current event is detected. A number of elapsed cycles for a processor since a previous event are identified in response to detecting the current event. An elapsed time using the number of elapsed cycles and a current frequency of the processor is calculated, wherein the elapsed time is used to identify the processor utilization.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for selecting optimal processor performance levels by using processor hardware feedback mechanisms
InactiveUS20090089598A1Energy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingParallel computingProcessor frequency
An embodiment of the present invention is a system and method relating to adaptive power management using hardware feedback to select optimal processor frequencies and reduce power / watt. In at least one embodiment, the present invention is intended to optimize processor frequency and power / watt usage based on the hardware feedback and processor stall behavior.
Owner:INTEL CORP
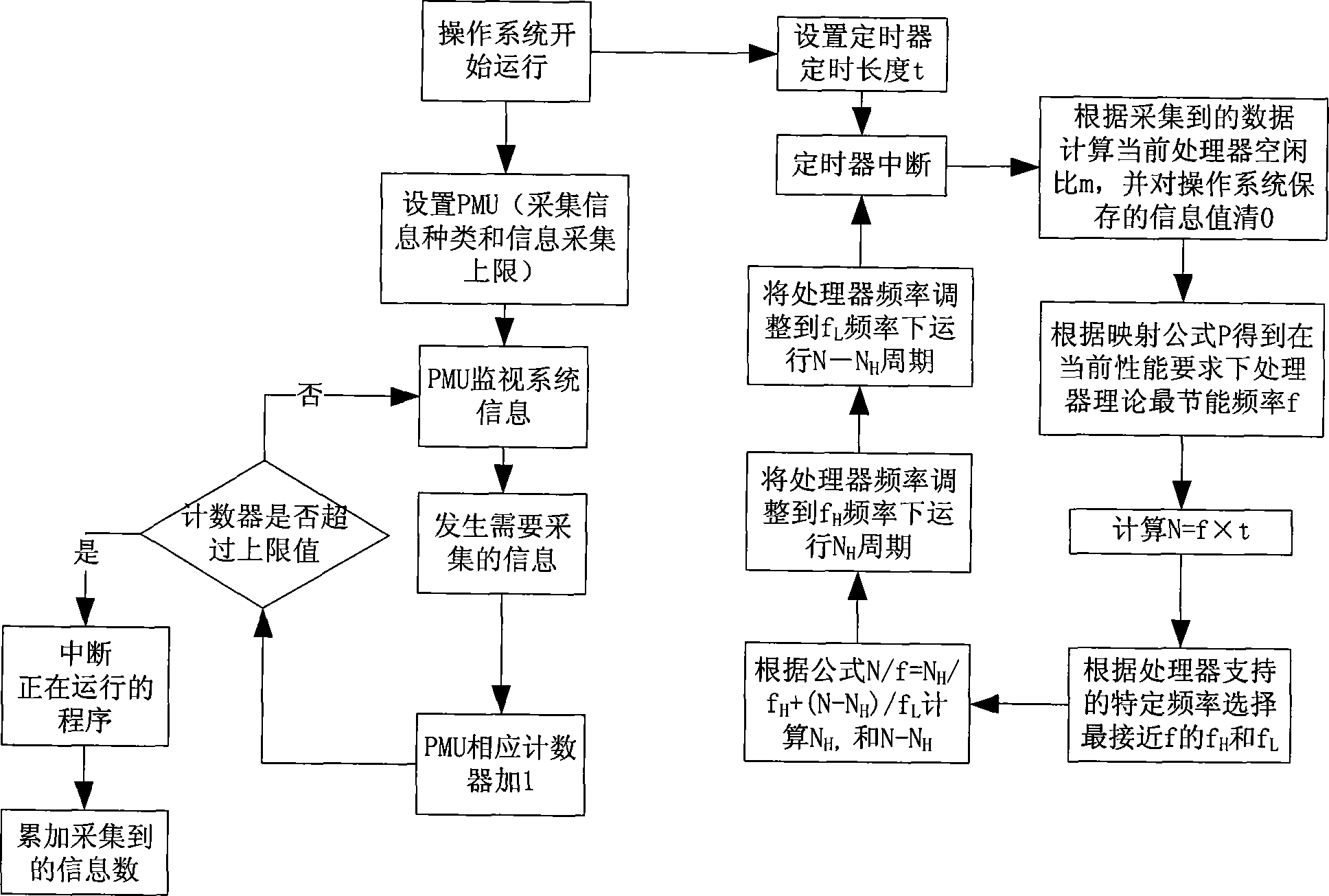
Embedded type low-power consumption operating system dynamic frequency regulation mapping method
InactiveCN101216727AGuaranteed performanceEnsure stabilityMultiprogramming arrangementsPower supply for data processingOperational systemProcessor frequency
The invention discloses a mapping method for adjusting the dynamic frequency in an imbedded low-power operating system and provides a new method and technology for modeling, addressing and optimizing the mapping issue during the dynamic adjustment of the processor frequency in an embedded low-power operating system. The invention uses the method that the operating frequency of the processor maps the most energy saving frequency of the theoretic processor upwards and downwards to the actual adjustable voltage in order to serve the energy saving purpose, and meanwhile to ensure the performance requirement for the system. The invention is based on a processor frequency mapping model, through which the most energy saving frequency of the theoretic processor is mapped to the actual adjustable processor frequency. When in operation, the operating system uses dynamic frequency and voltage modulation technology to determine the theoretically most energy saving operating frequency under current performance requirement according to the performance requirement and the operating status of the processor, and maps the most energy saving frequency to the actual processor frequency in order to serve the energy saving purpose.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
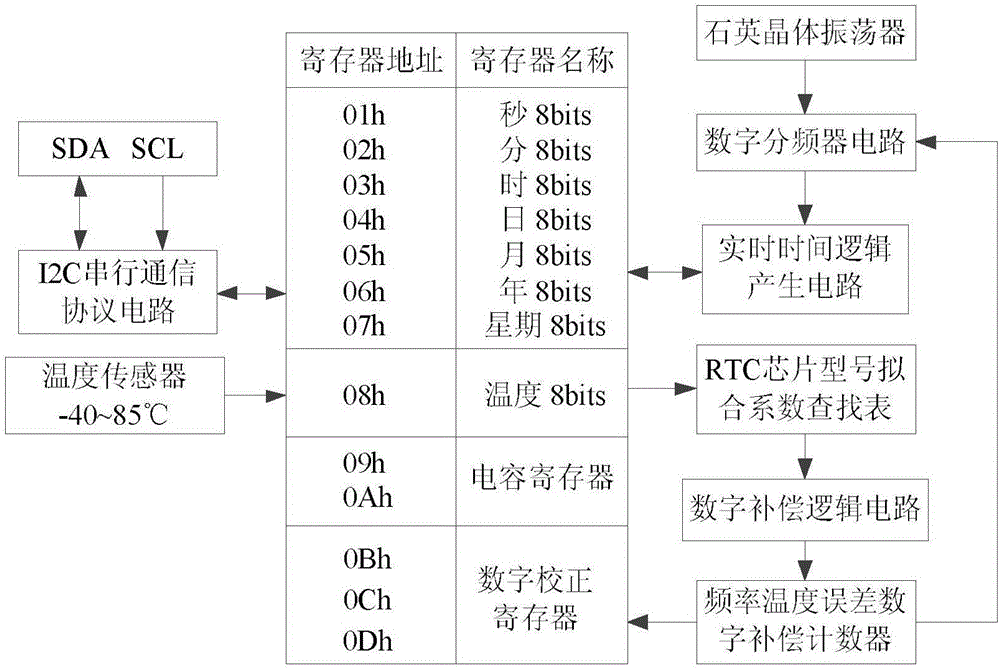
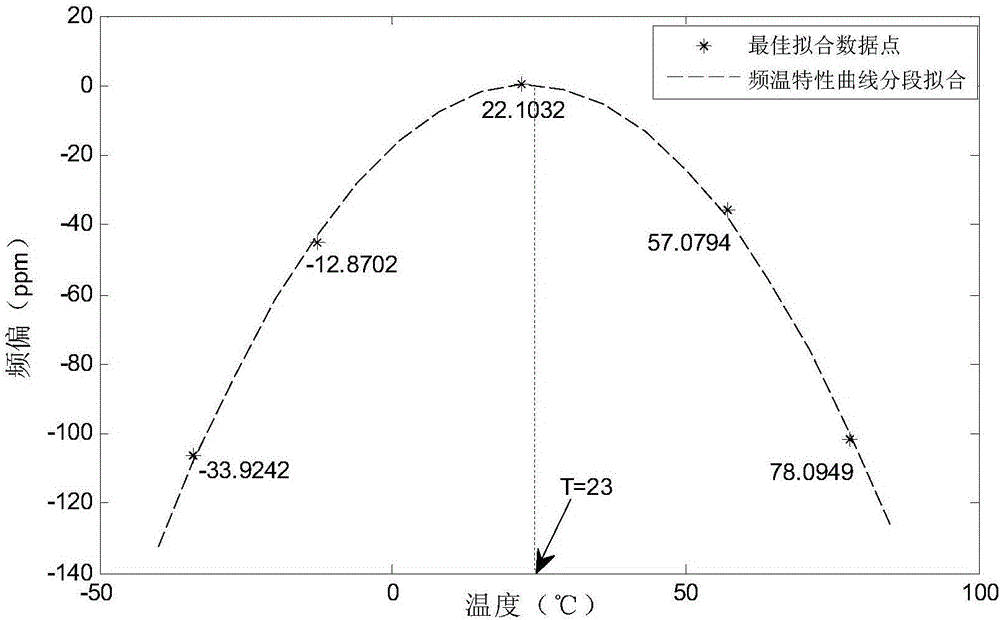
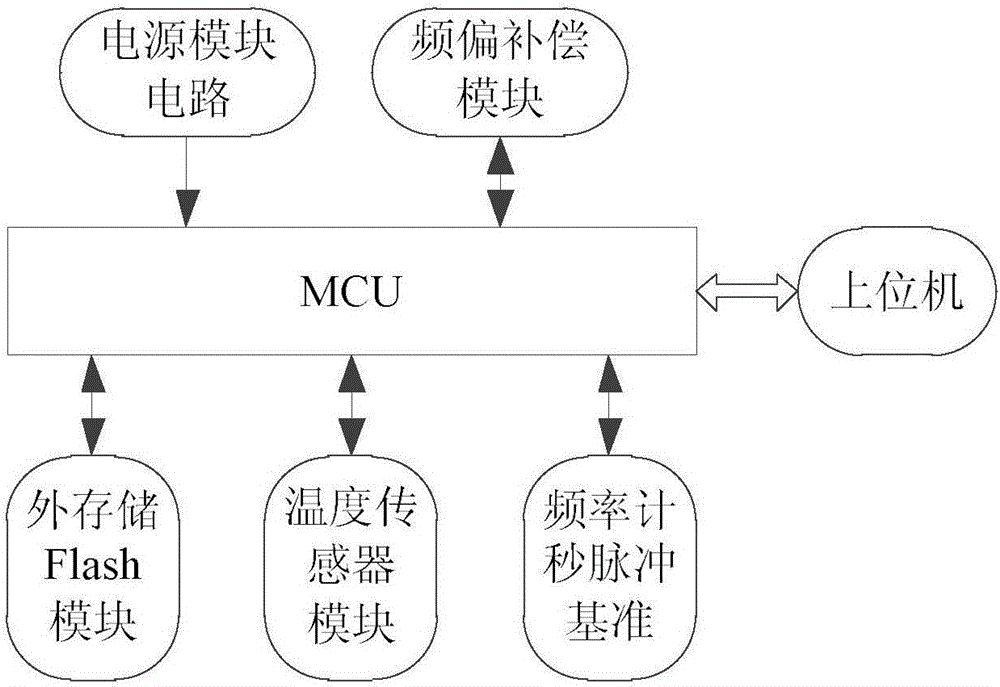
High-precision frequency deviation compensation method for RTC chip by combination of variable capacitance
ActiveCN106505996AAccurately find the frequency offset valueAccurately obtainedGenerator stabilizationCapacitanceReal-time clock
The invention discloses a high-precision frequency deviation compensation method for an RTC (Real-Time Clock) chip by combination of variable capacitance, and relates to a high-precision micro processor frequency deviation compensation method for the RTC chip by the combination of the variable capacitance. The high-precision frequency deviation compensation method comprises the following steps: building a mathematical model between temperature and a frequency deviation by adopting the least square method and a Lagrange interpolation algorithm through a piecewise function mode, and calculating an optimal fitting coefficient; then on the basis of the model, designing a high-precision capacitance compensation and accumulative error-based digital compensation combination frequency deviation compensation mode; and finally, completing corresponding compensation work under the control of an MCU module according to an actual temperature condition measured by a temperature sensor. The method provided by the invention can efficiently and intensively complete the frequency deviation compensation work of the RTC chip, and a design basis can be supplied to implementation of high-precision timekeeping of an intelligent electric meter in the field of electricity utilization of a power system.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
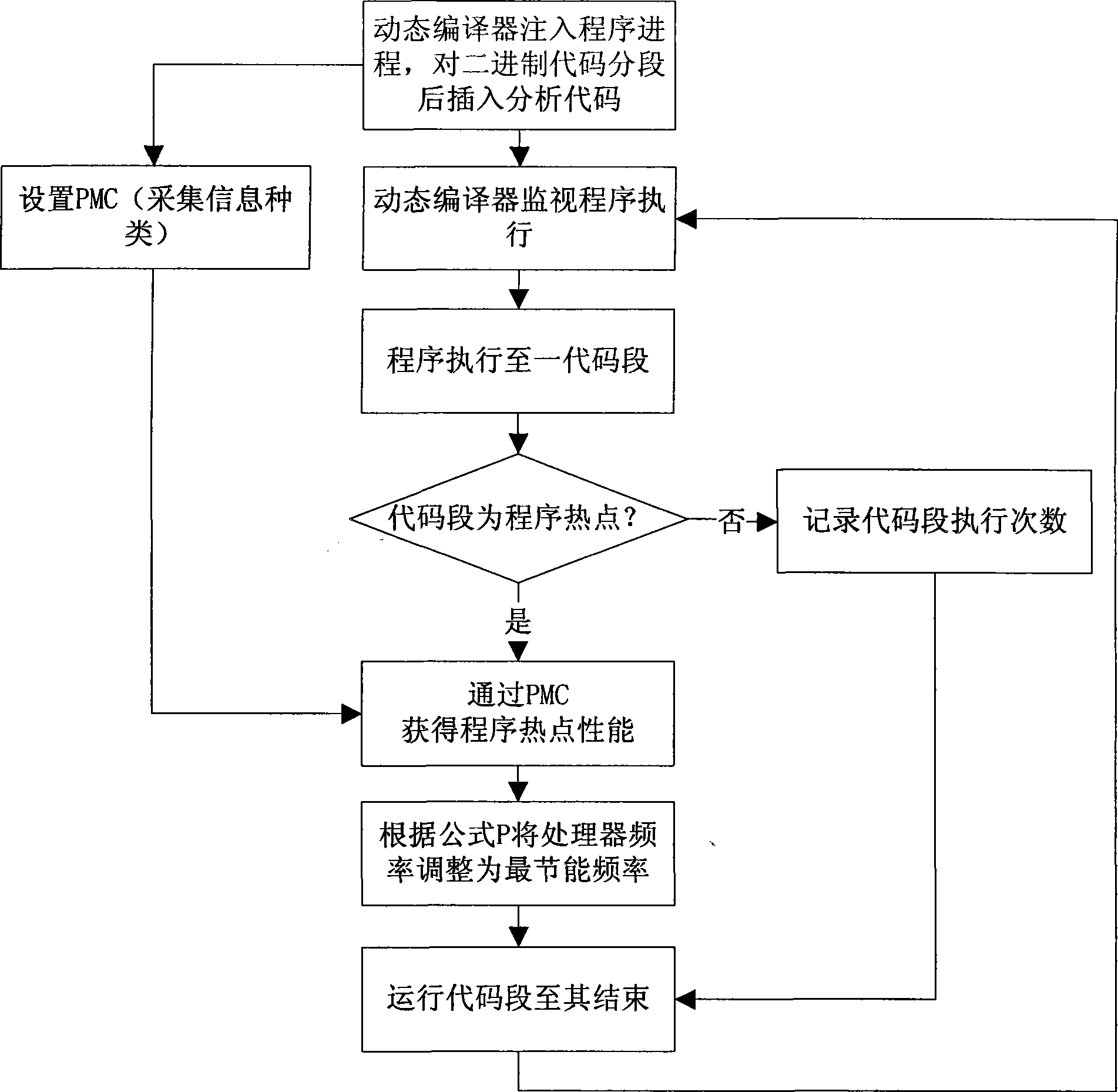
Method for controlling processor frequency when program operation by using dynamic compiler
InactiveCN101510115ATo achieve the purpose of energy savingGuaranteed Performance RequirementsEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingProcessor frequencyPerformance tuning
The invention relates to the field of the energy-saving technology based on system software and aims at providing a method which can control the frequency of a processor by using a dynamic compiler when a program runs. The method includes the following steps: an analysis code is inserted; a hotspot of the program is dynamically determined when the program runs; the performance of the hotspot of the program is acquired; and the frequency of the processor is adjusted according to the performance of the hotspot of the program. By dynamically analyzing the performance of the program and using the frequency-adjusting function of the processor, the best energy-saving frequency of the program theory processor is mapped to an actual-adjustable voltage when the program runs so as to achieve the purpose of energy conservation and simultaneously ensure the performance requirements of the system. The invention is characterized by transparency, stability and practicability and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
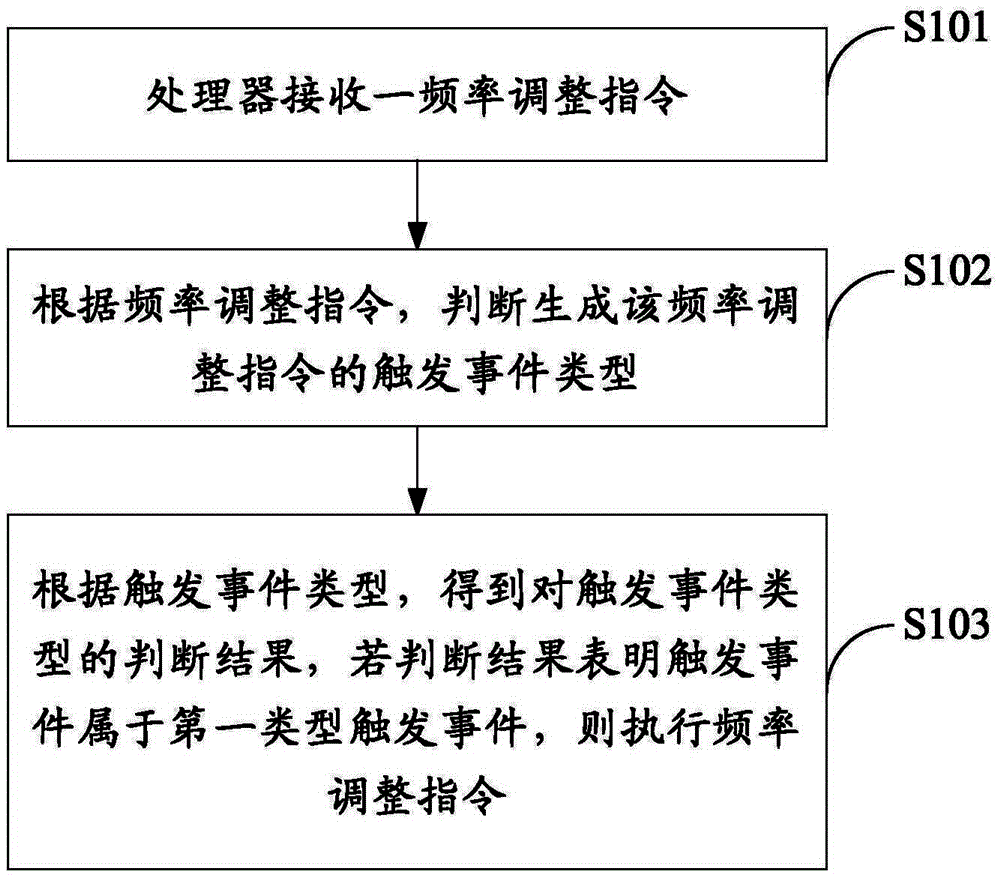
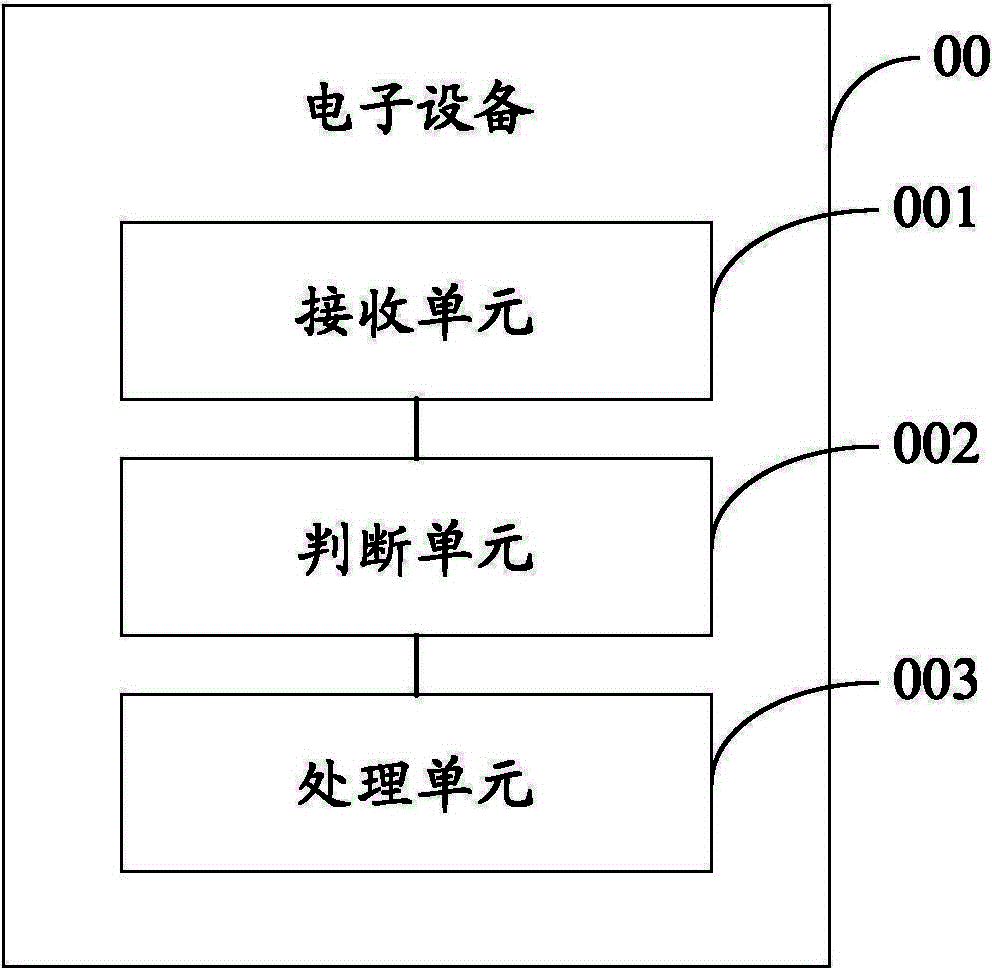
Processor frequency control method and electronic equipment
ActiveCN104423533AReduce power consumptionPower supply for data processingProcessor frequencyEmbedded system
The embodiment of the invention provides a processor frequency control method and electronic equipment, and relates to the technical field of electronics. Frequency adjusting instructions of a processor can be selectively executed according to the types of triggering events. The processor frequency control method comprises the following steps of according to one frequency adjusting instruction received by the processor, judging the type of the corresponding triggering event; according to the judging result, when the triggering event is a first-type triggering event, executing the frequency adjusting instruction. The processor frequency control method and the electronic equipment are used for controlling the frequency of the processor, and decreasing the power consumption of the electronic equipment.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) CO LTD
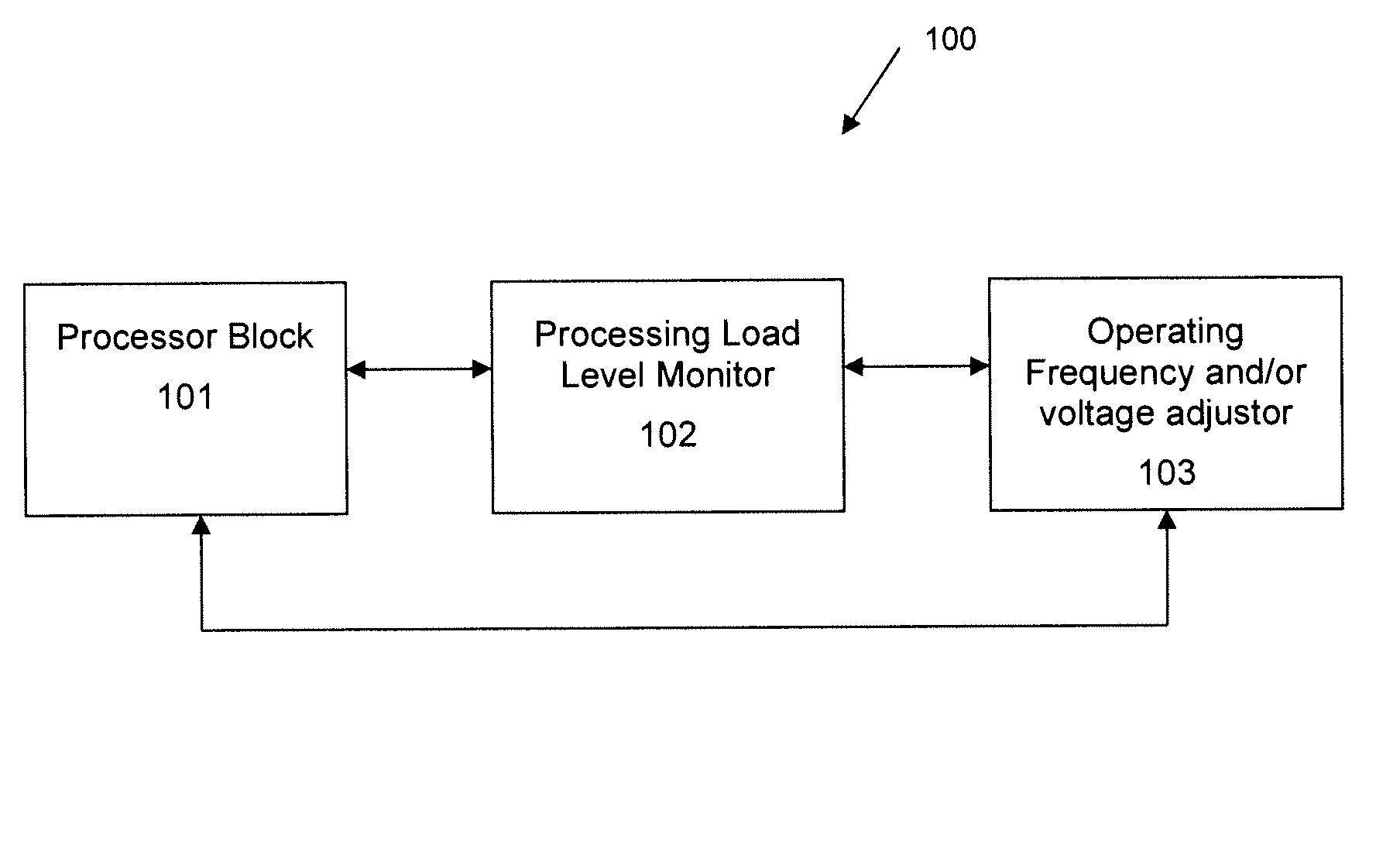
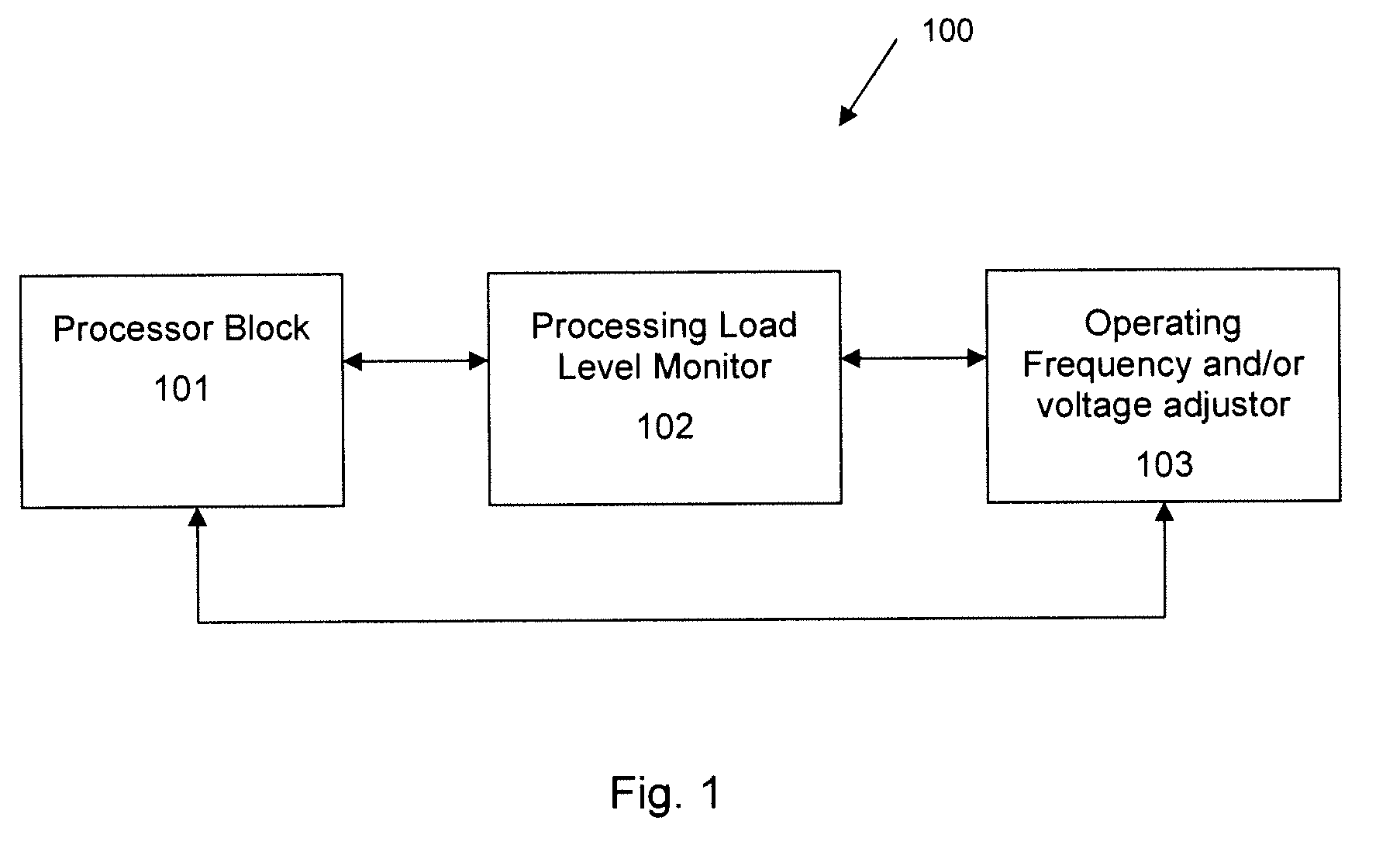
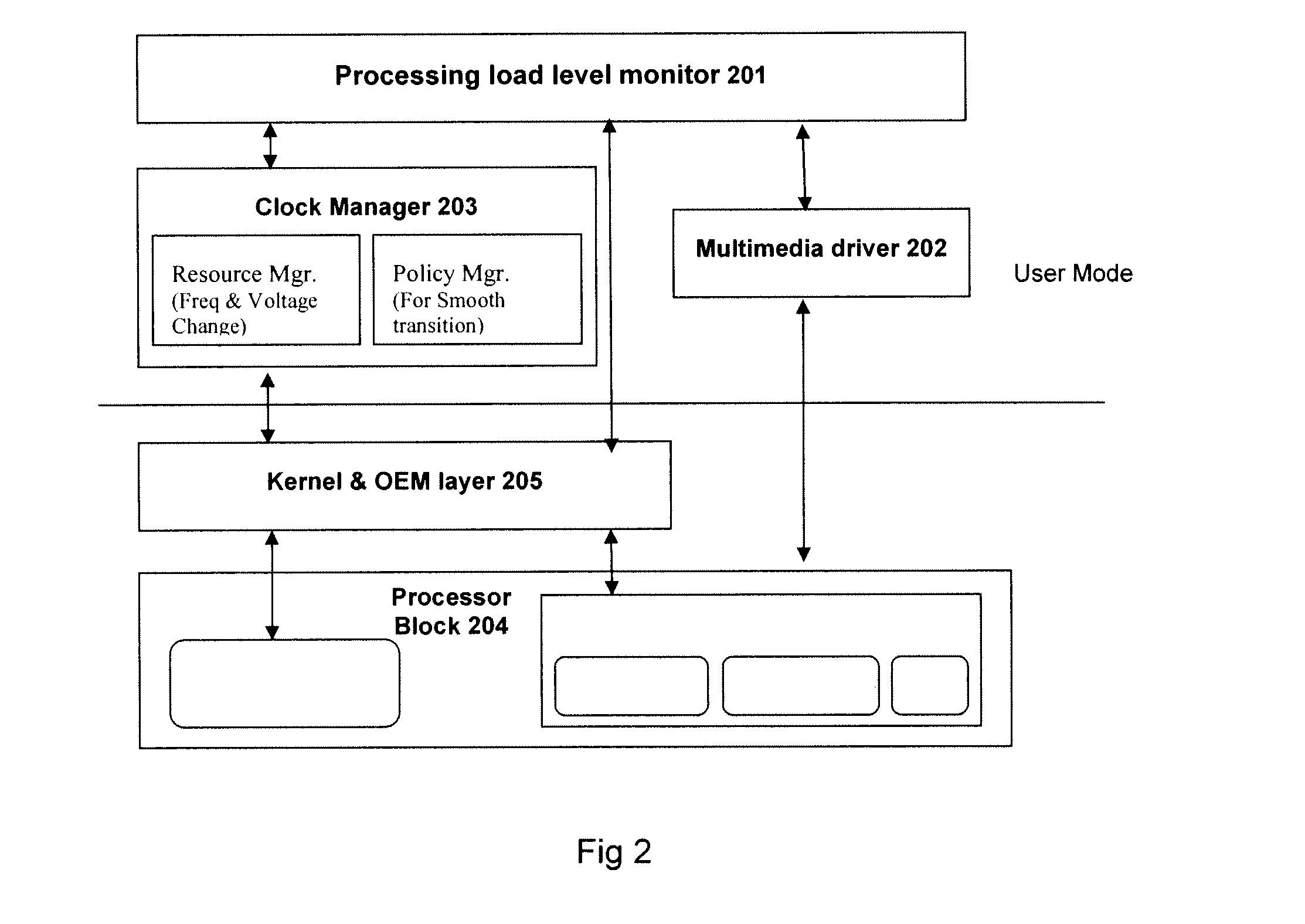
System and method for optimizing electrical power consumption
A system and a method for optimizing power in an electronic device are described. The system may be used to implement low power techniques to achieve maximum performance with low battery utilization. A processing load level monitor monitors load(s) on processors. Processor frequencies are updated through the driver until the load is close to 100%, which means that the core frequency is changed to the load processor around 100% at the minimum possible frequency.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
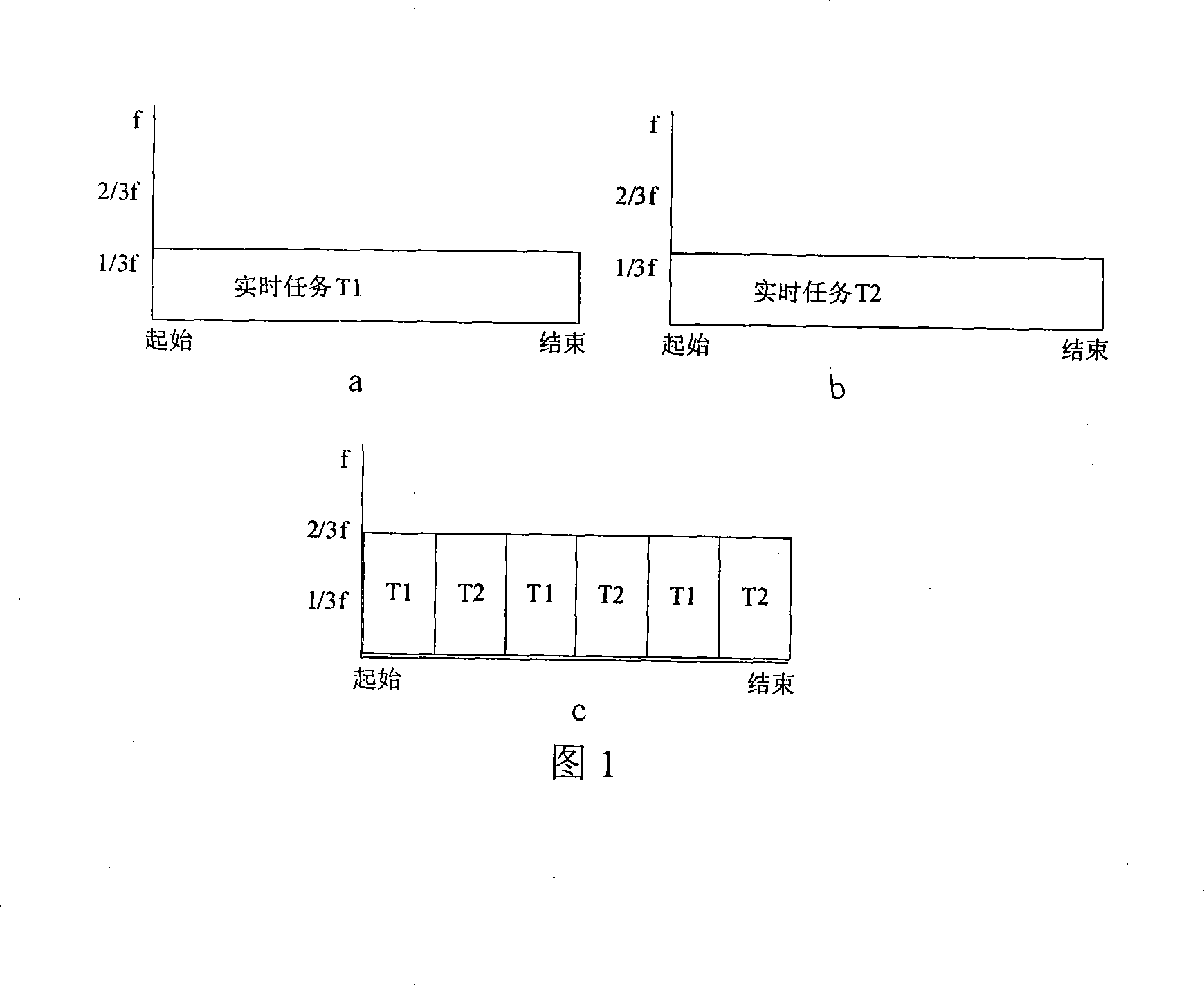
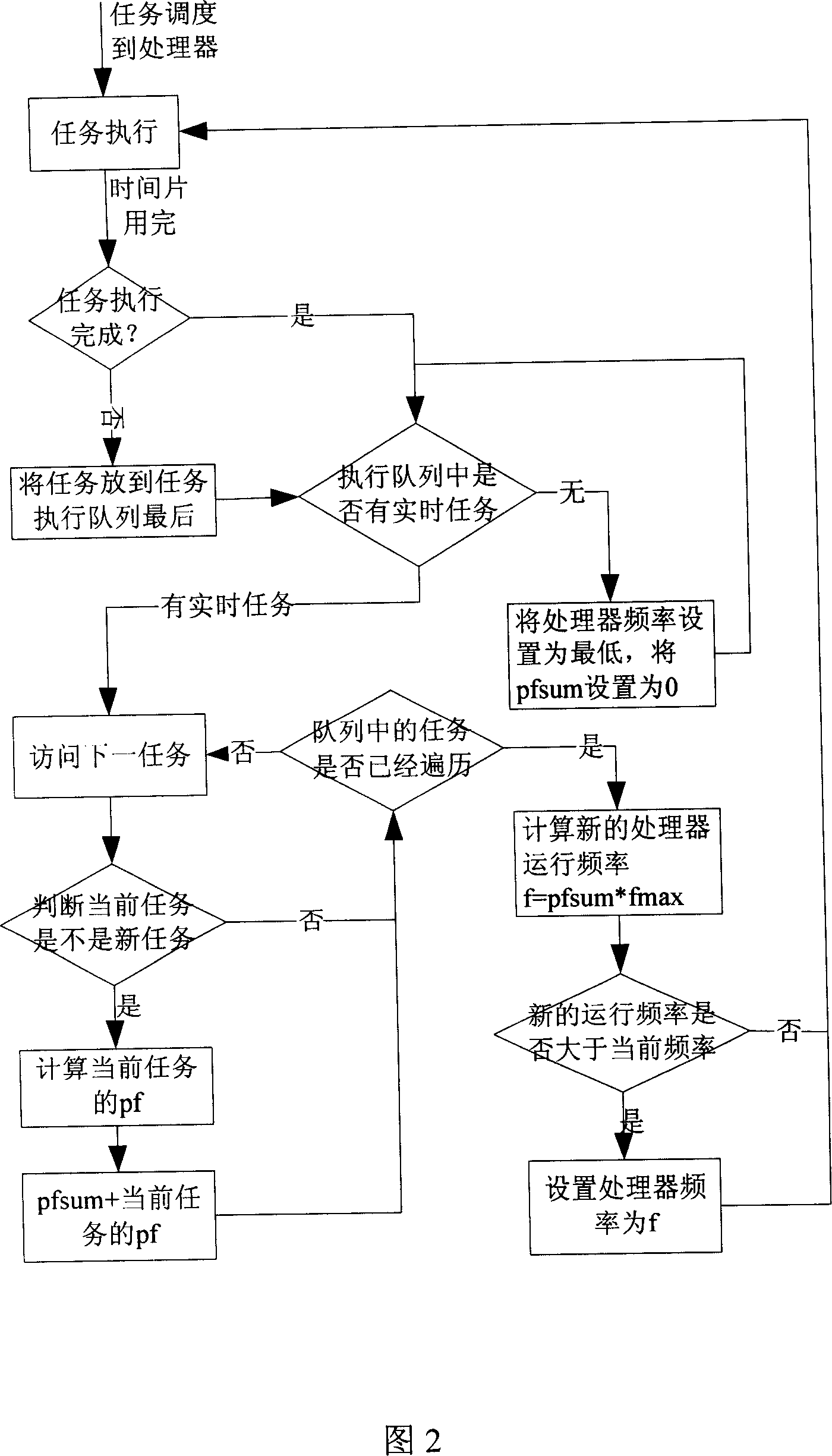
Simplifying method facing to embedded system low-power consumption real time task scheduling
InactiveCN101135927AExtended use timeReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTProgram initiation/switchingOperational systemProcessor frequency
The invention is used for optimizing the real-time task scheduling performance of the embedded system when it is running at low power consumption condition. It uses a real-time dynamical voltage-regulating and frequency-regulating technology and a real-time time flake cycle model to reach the real-time scheduling at low power consumption. Based on a time flake cycle task model, the invention adds a task real-time restrict to ensure the real-time capability of the task. Based on an original scheduling method, the invention adds a processor frequency controlling parameter to make the system get the lowest running frequency according to the real-time requirement of computing task.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
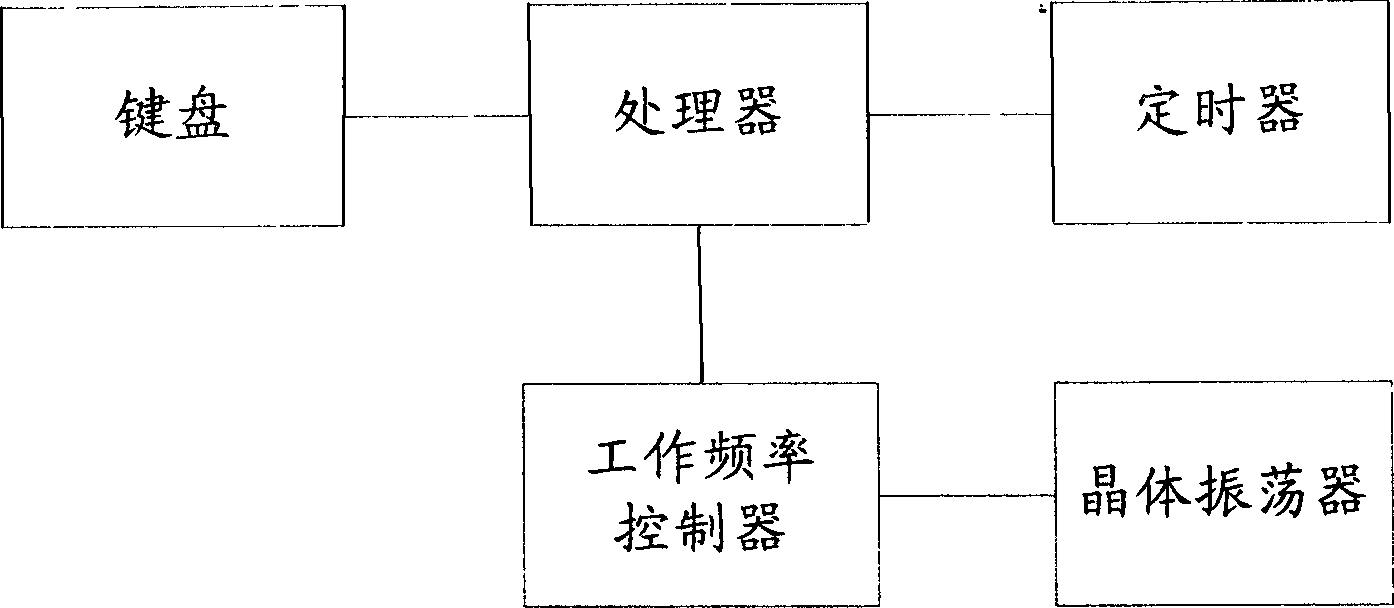
Method for reducing powder consumption of electronic equipment
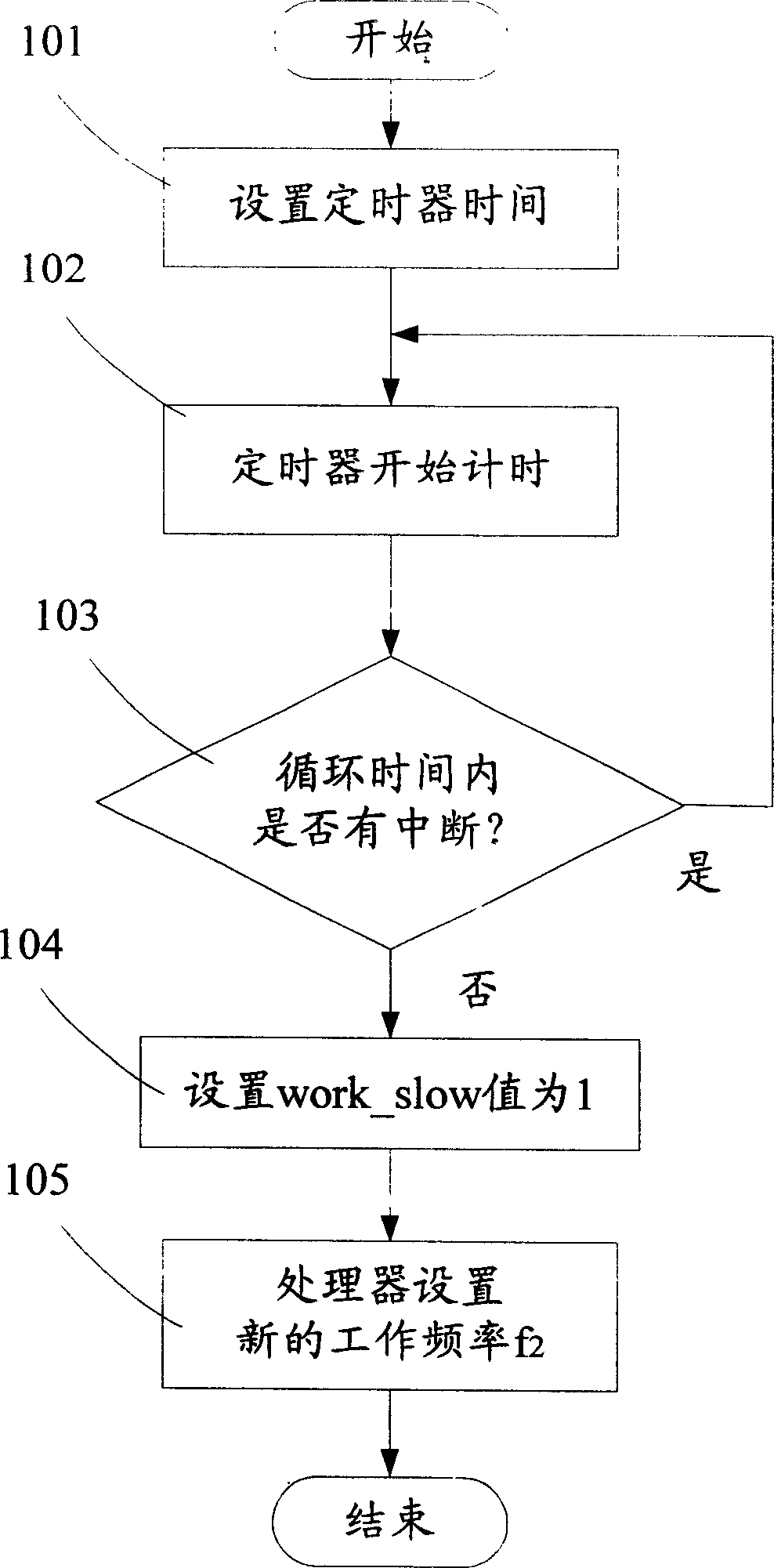
InactiveCN1716144AReduce power consumptionExtended run timePower supply for data processingGenerating/distributing signalsProcessor frequencyTimer
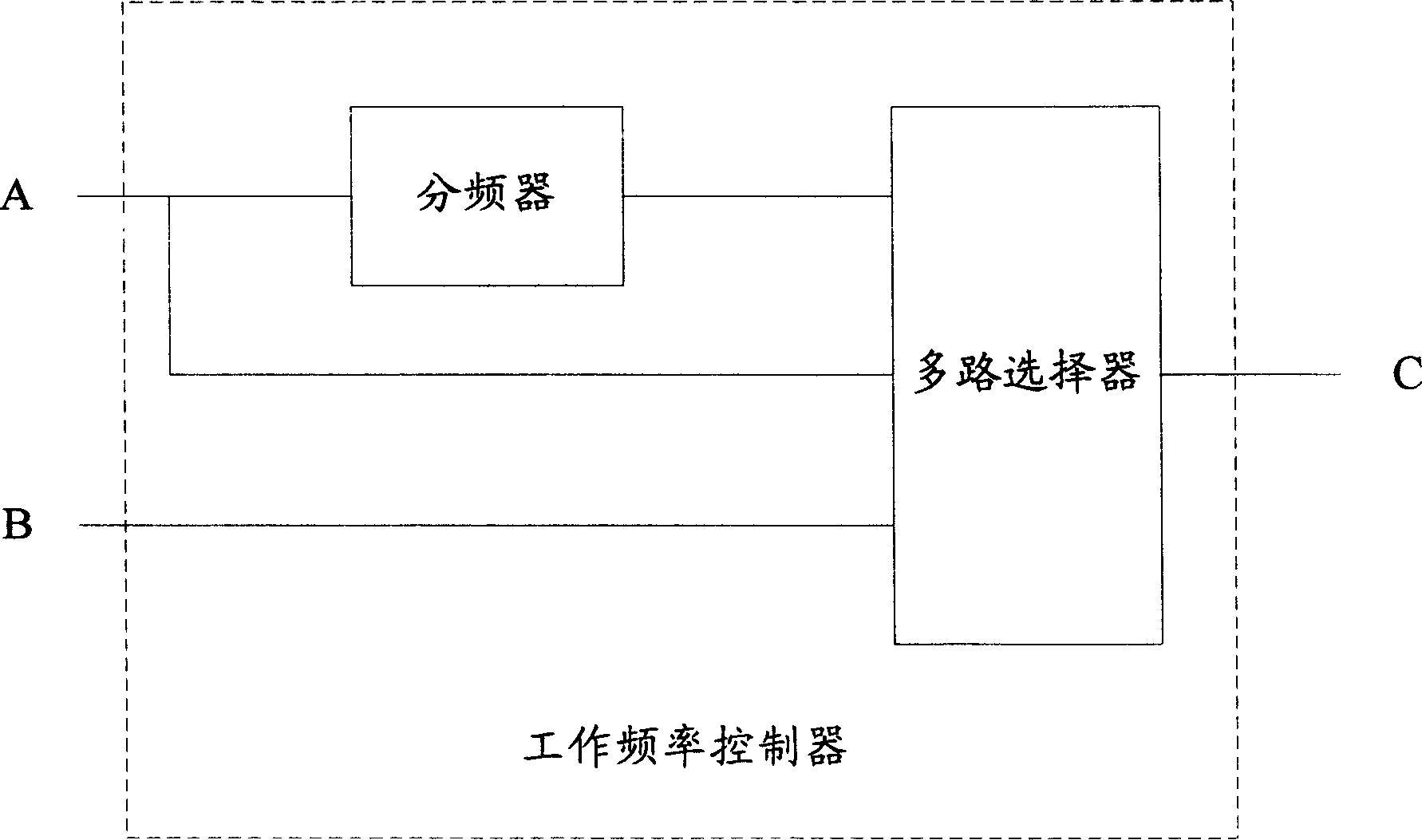
The method of reducing power consumption of electronic equipment includes the following steps: 1. for the timer to time; 2. to judge whether to have interruption during the time, and resetting the timer and retiming if there is interruption; and 3. if there is no interruption before reaching the set time, for the system to control the frequency of the processor via the work frequency controller, and for the clock signal the crystal vibrator outputs to pass through the frequency divider and the demultiplexer and for the demultiplexer to output signal as new input clock signal of the processor.
Owner:SHANGHAI DBTEL IND
Processor frequency control method, device and terminal
InactiveCN106210895AAvoid burnsPrevent discomfortSelective content distributionHigh surfaceProcessor frequency
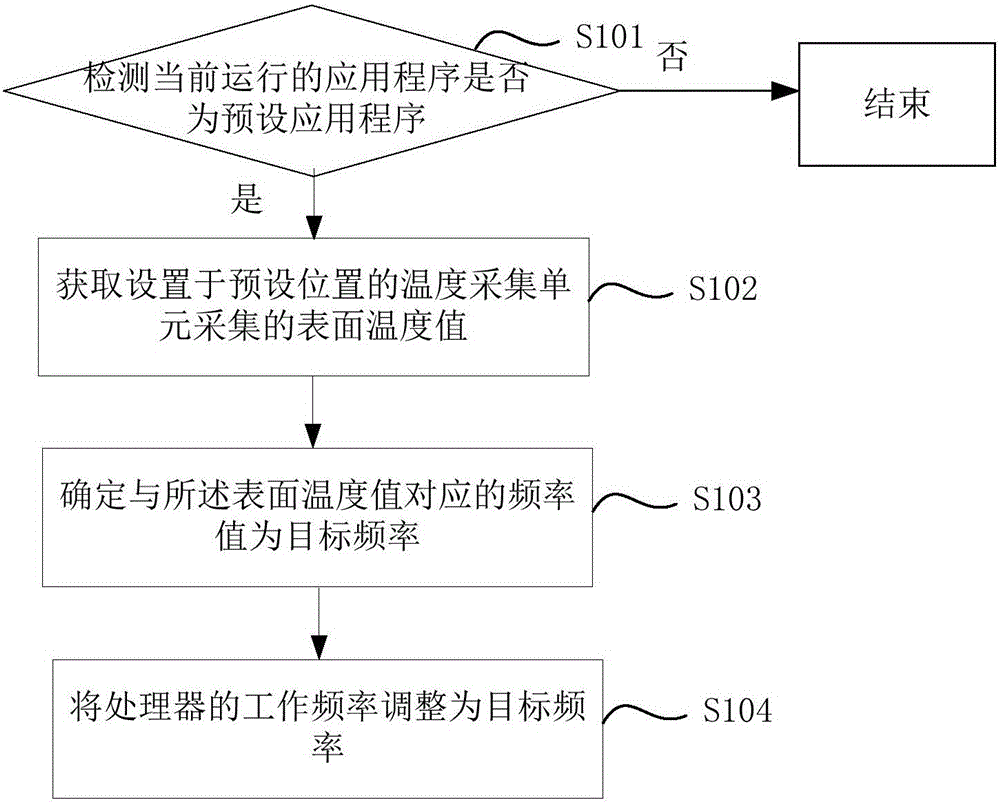
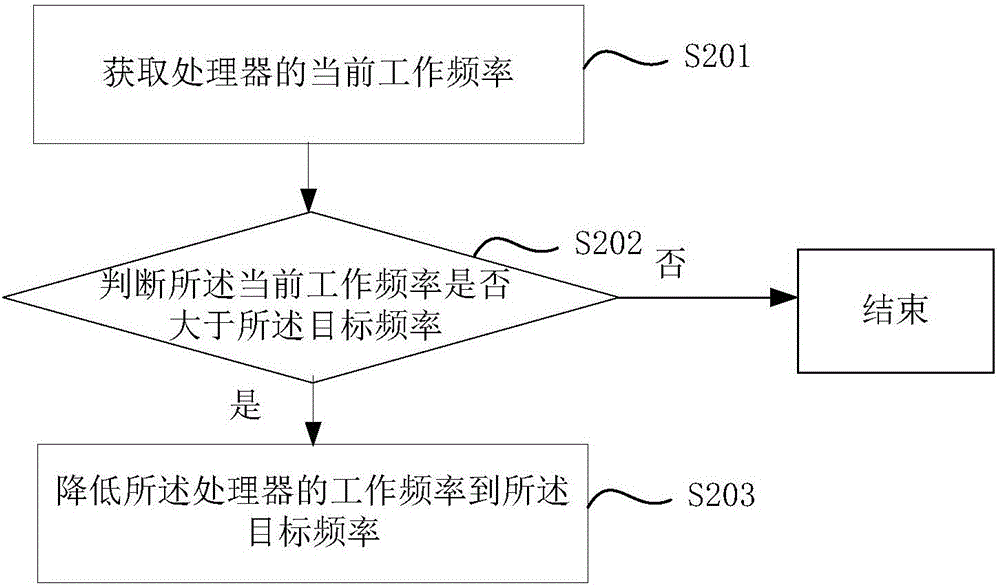
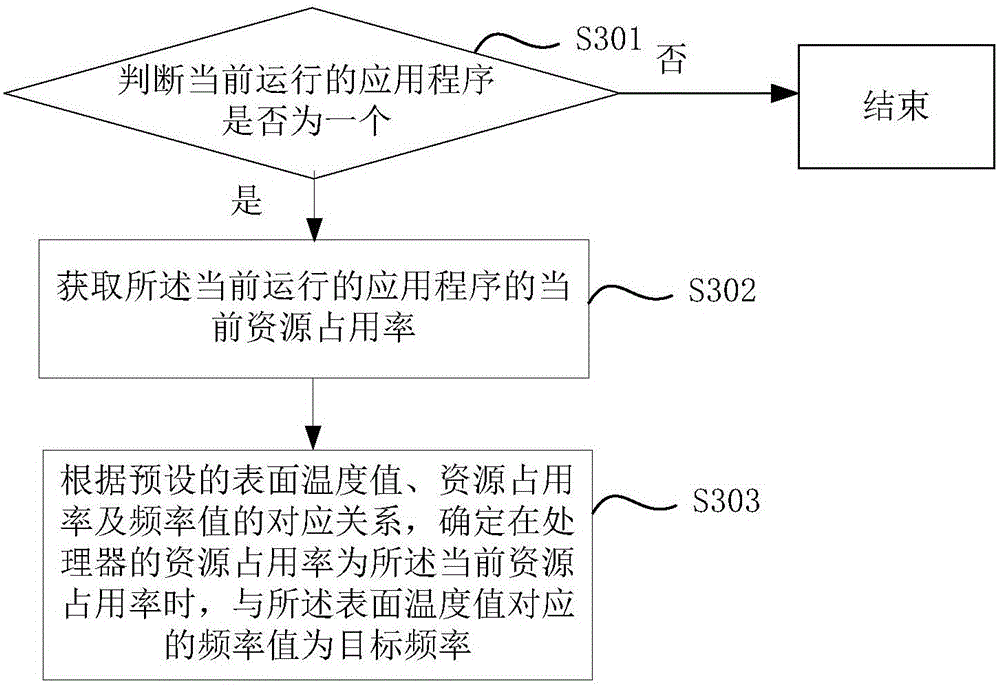
The embodiments of the invention provide a processor frequency control method, a processor frequency control device and a terminal. The method comprises the steps of: detecting whether the current running application program is a preset application program; when the current running application program is a preset application program, acquiring a surface temperature value acquired by a temperature acquisition unit arranged at a preset position; when the surface temperature value exceeds a preset temperature threshold, determining a frequency value corresponding to the surface temperature value as a target frequency; and adjusting the working frequency of a processor to the target frequency. The working frequency of the processor in the smart terminal can be automatically adjusted according to the surface temperature of the smart terminal, so that the surface temperature can be reduced by adjusting the working frequency of the processor when the surface temperature of the smart terminal is too high, to avoid the situation of scald or user discomfort caused by too high surface temperature of the smart terminal when a user unintentionally touches the smart terminal.
Owner:LETV HLDG BEIJING CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com







![[method for dynamically adjusting CPU requency] [method for dynamically adjusting CPU requency]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/5c651547-426c-417b-b45c-ce0a92af810f/US20050125705A1-20050609-D00000.png)
![[method for dynamically adjusting CPU requency] [method for dynamically adjusting CPU requency]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/5c651547-426c-417b-b45c-ce0a92af810f/US20050125705A1-20050609-D00001.png)
![[method for dynamically adjusting CPU requency] [method for dynamically adjusting CPU requency]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/5c651547-426c-417b-b45c-ce0a92af810f/US20050125705A1-20050609-D00002.png)