Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1628 results about "Junction temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
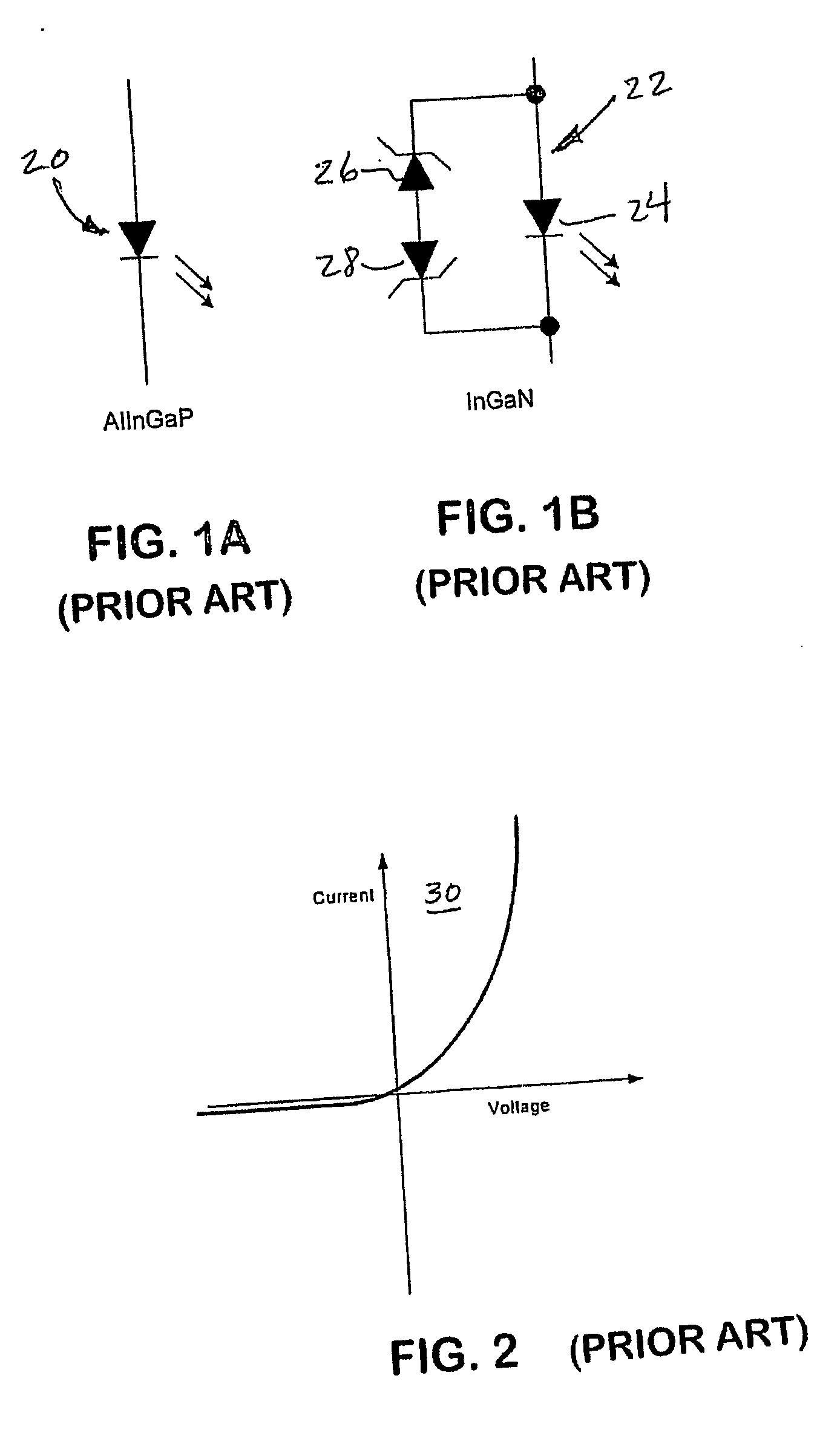
Junction temperature, short for transistor junction temperature, is the highest operating temperature of the actual semiconductor in an electronic device. In operation, it is higher than case temperature and the temperature of the part's exterior. The difference is equal to the amount of heat transferred from the junction to case multiplied by the junction-to-case thermal resistance.
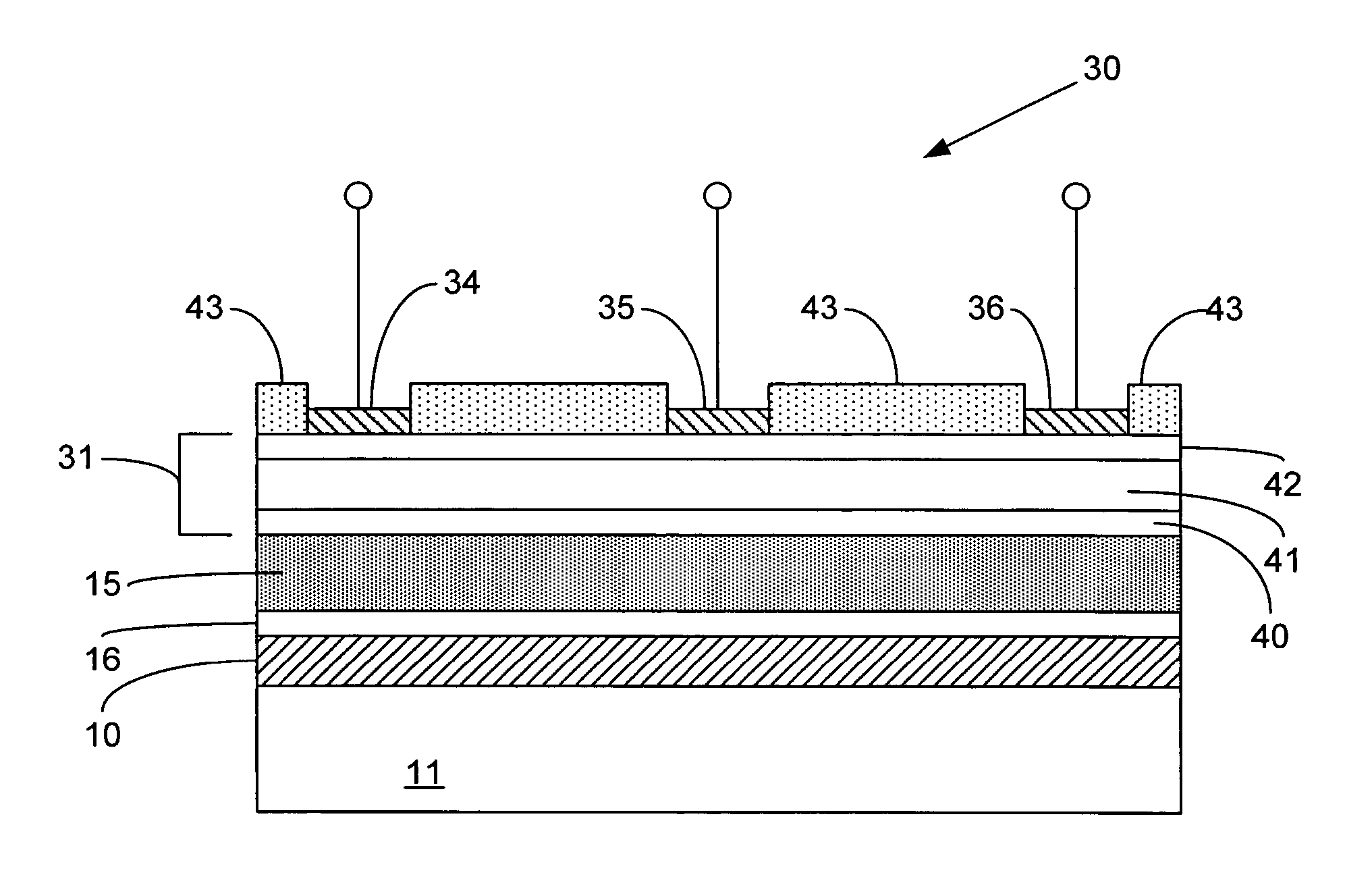
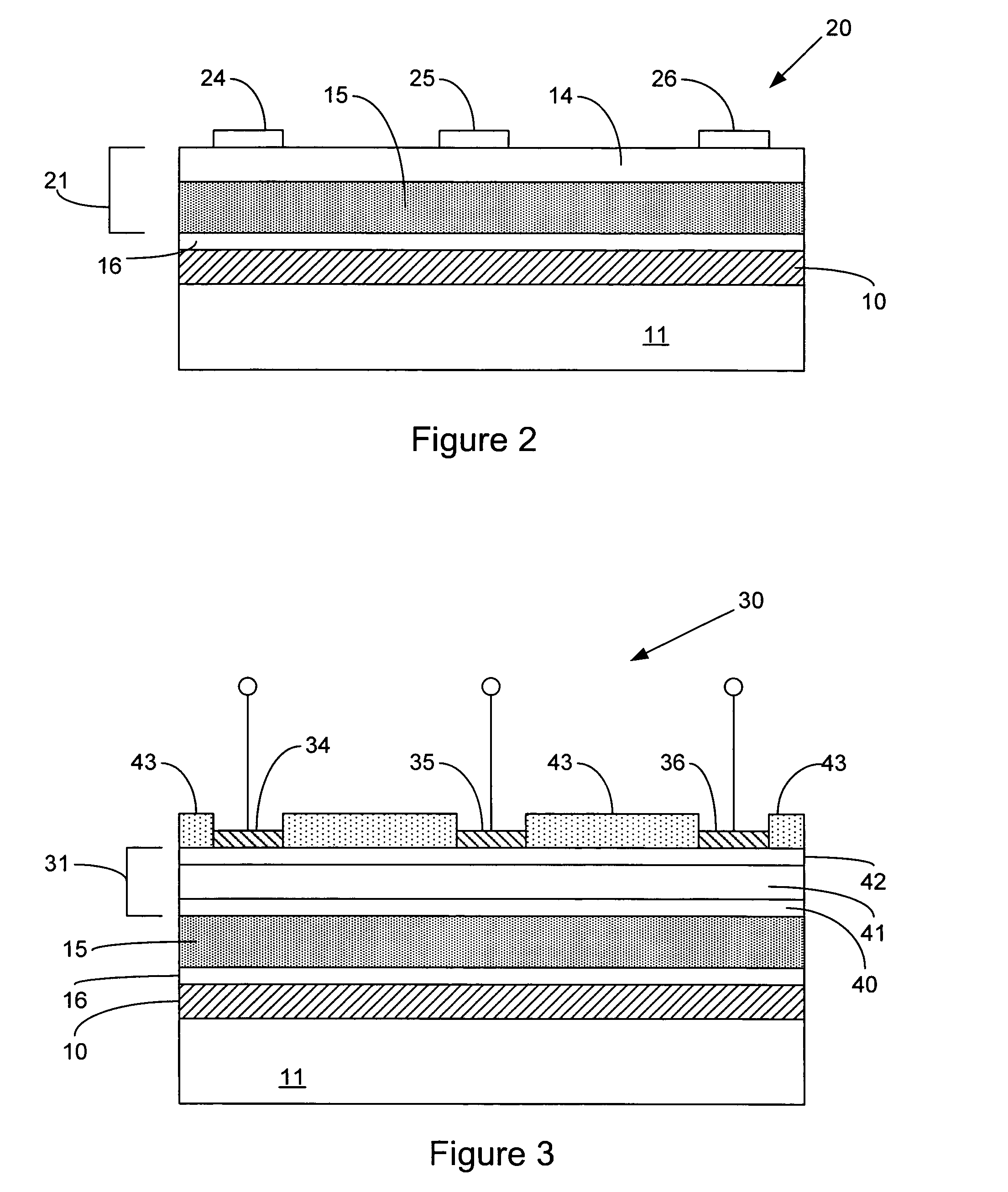
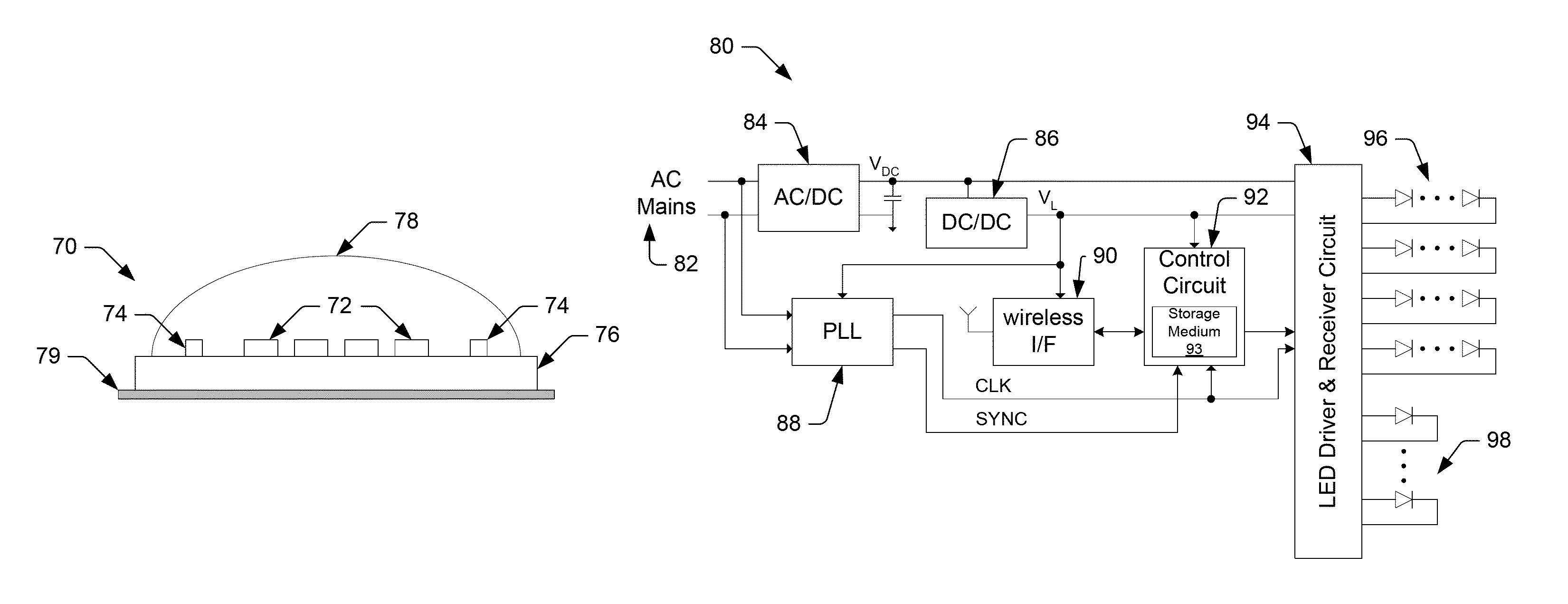
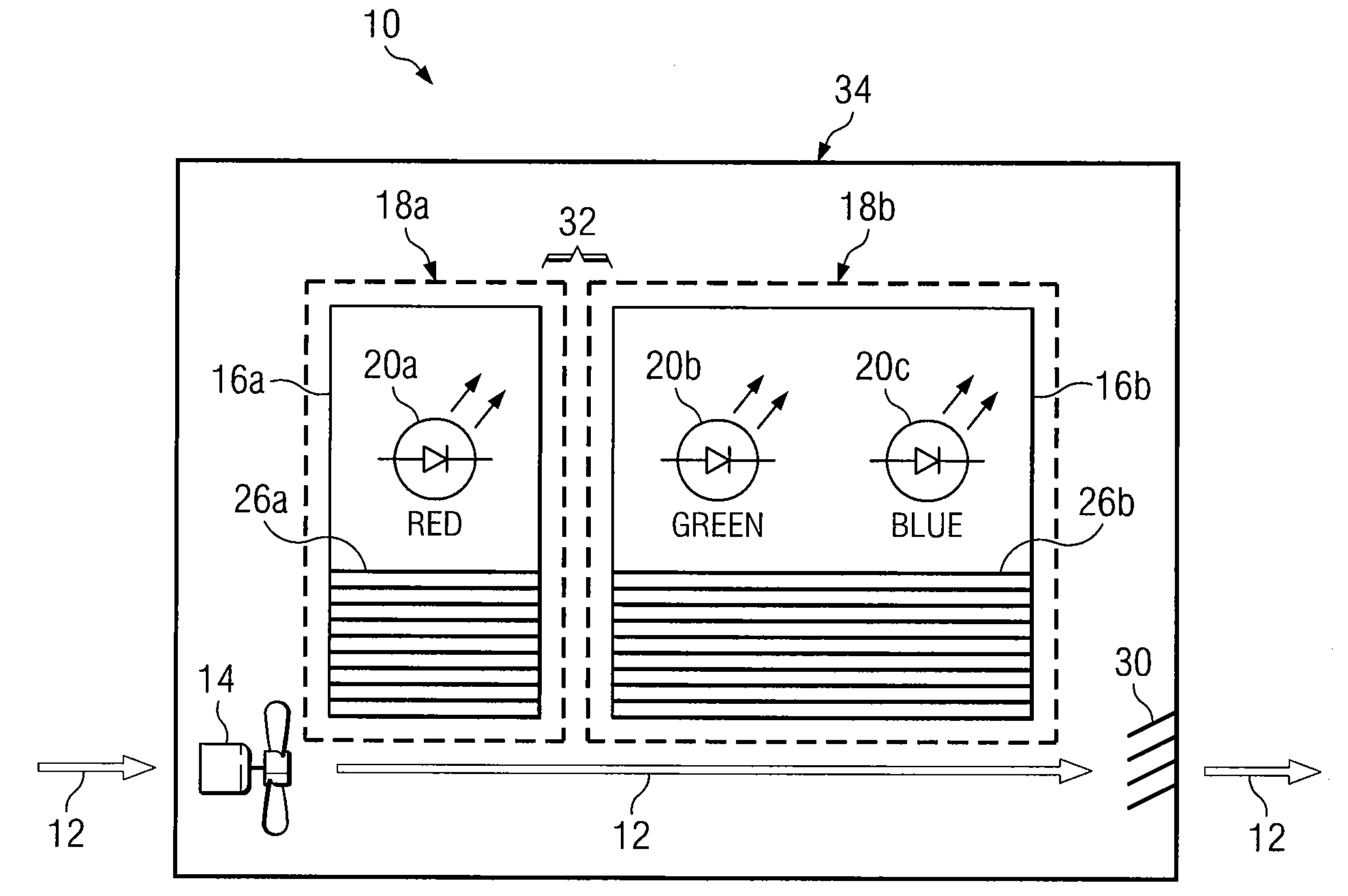
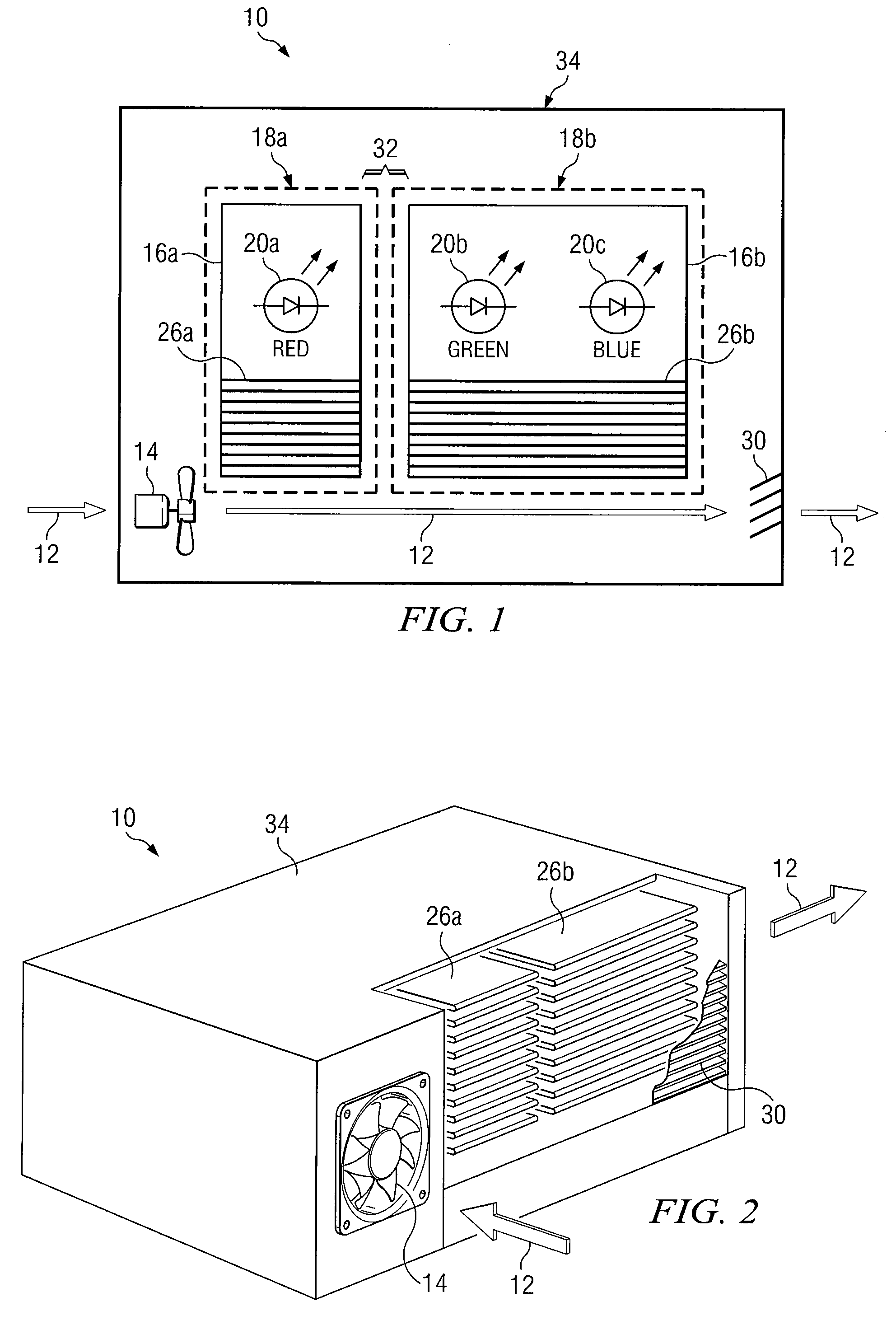
Digitally controlled luminaire system
InactiveUS20070040512A1Radiation pyrometryBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsJunction temperatureEngineering
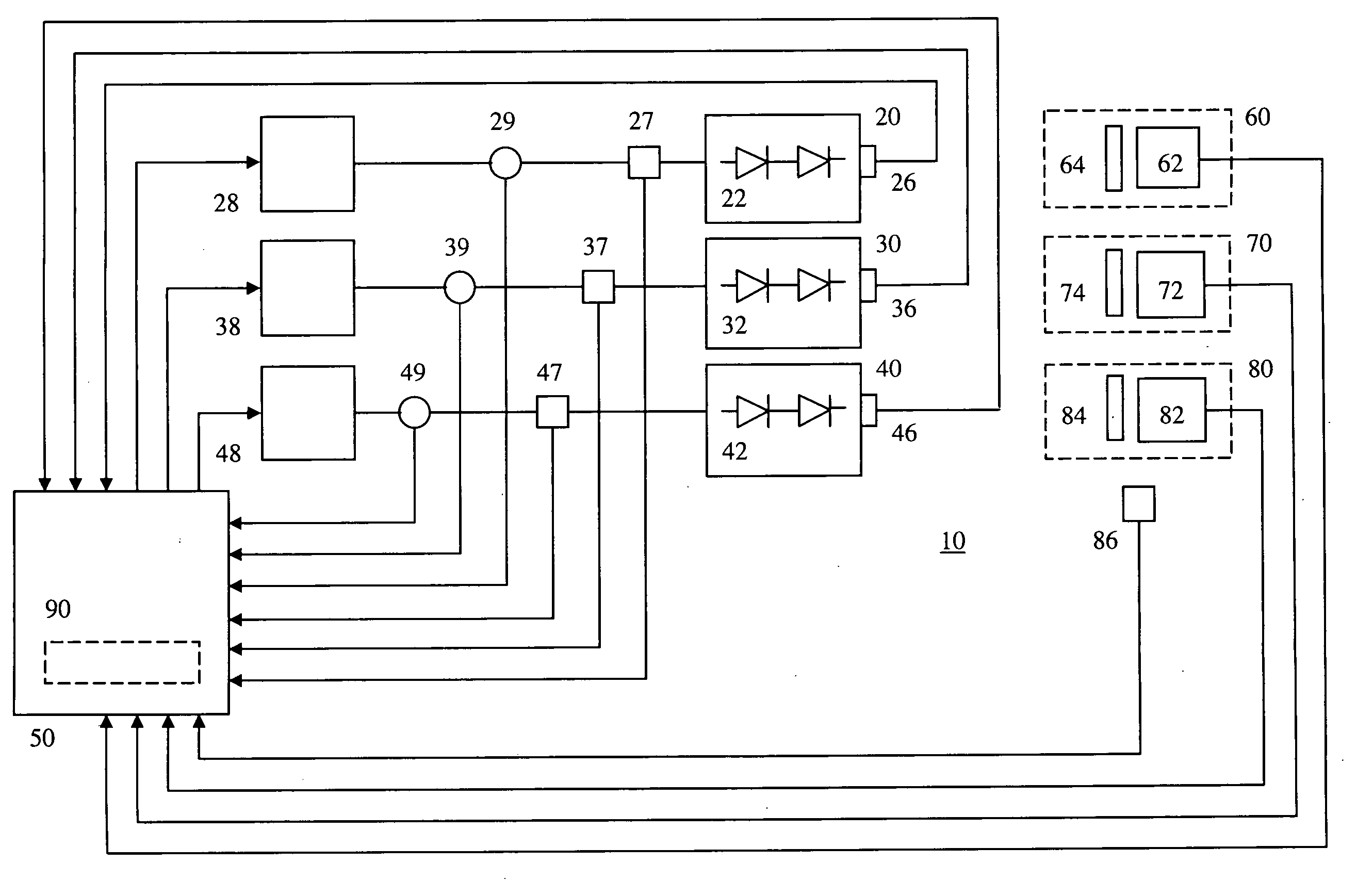
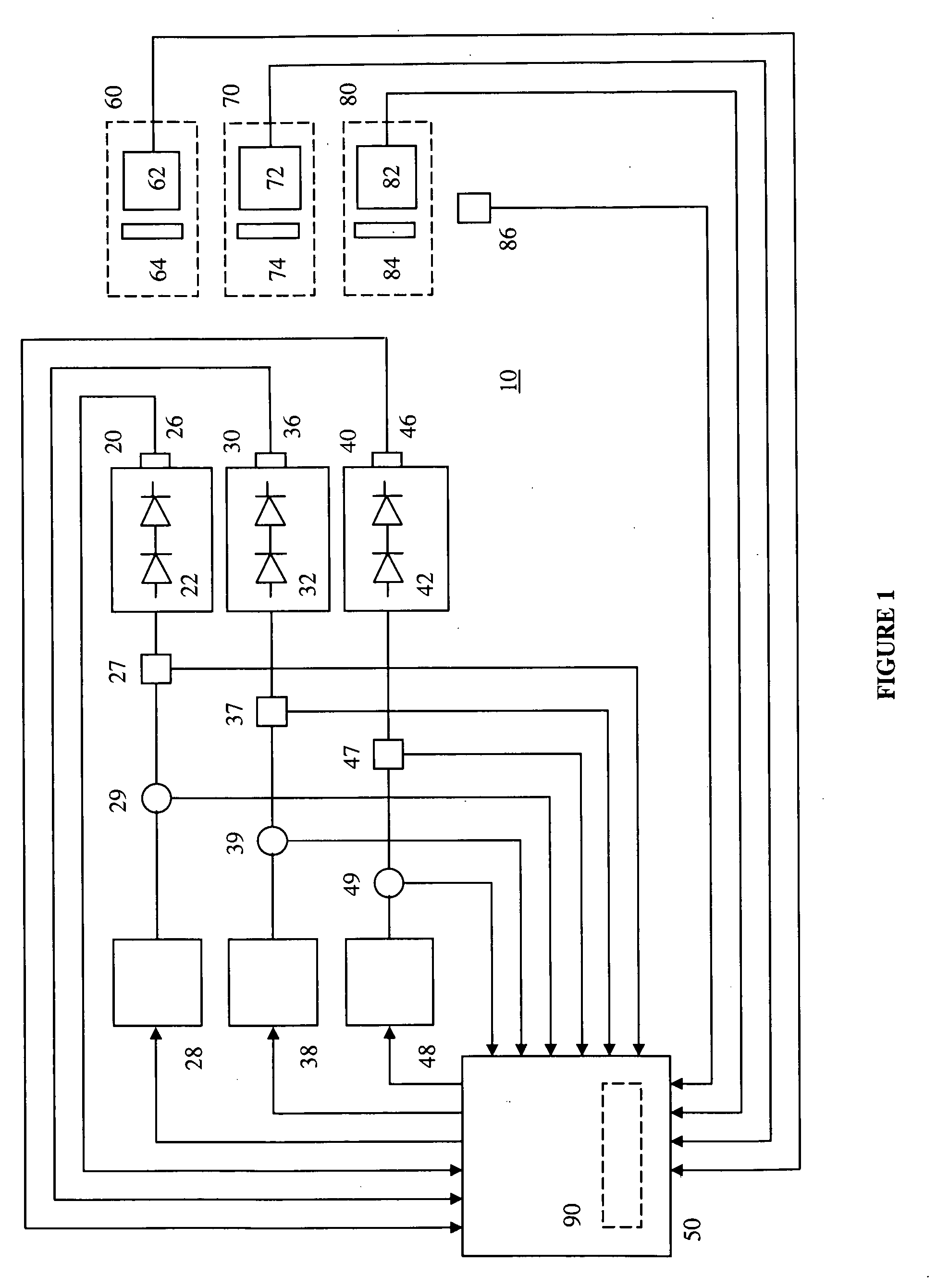
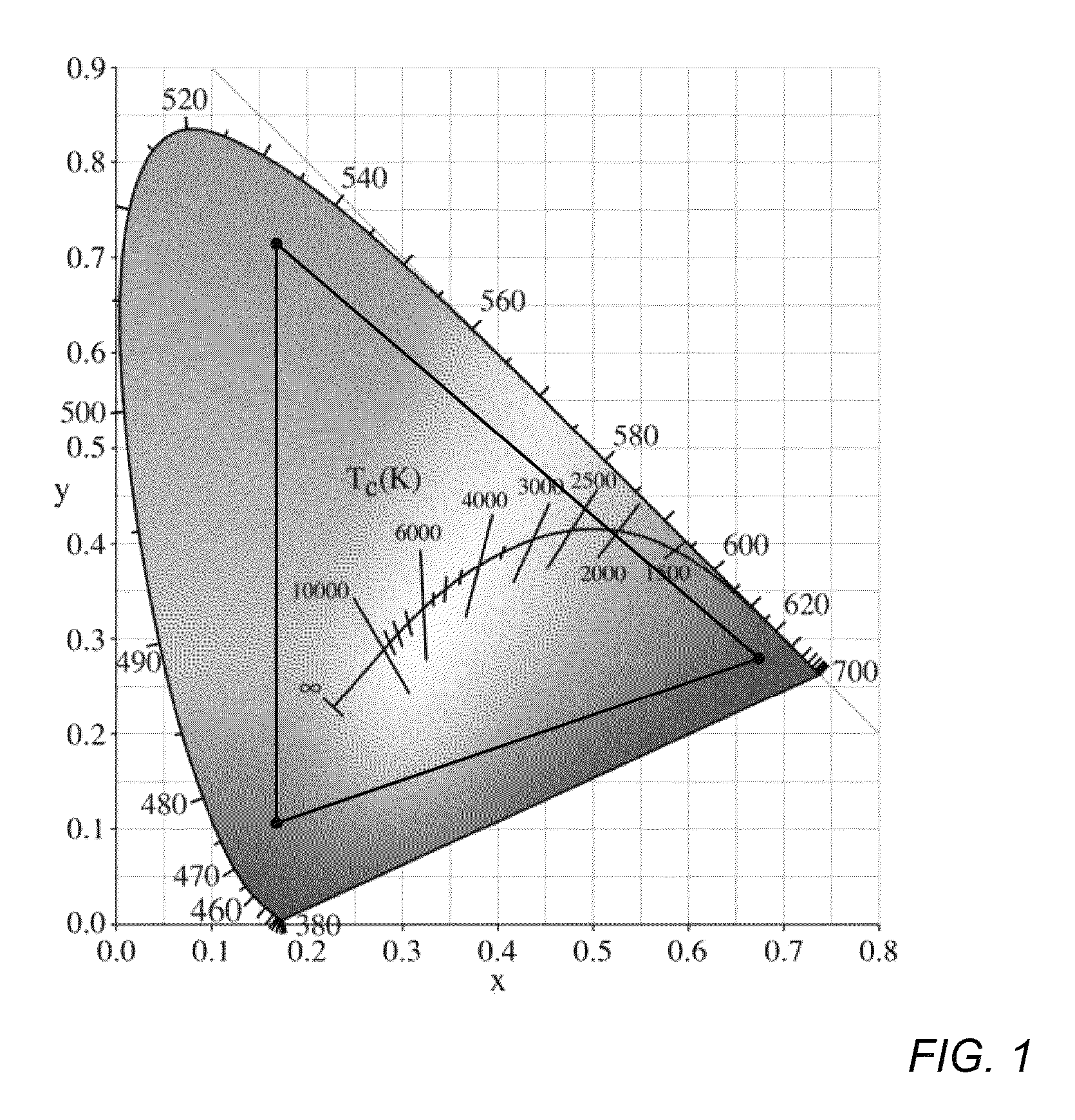
The present invention provides a luminaire system capable of generating light of a desired chromaticity and luminous flux output during continuous operation with varying ambient operating temperature. The luminaire system can be further capable of maintaining a desired correlated colour temperature during dimming of the luminaire. The luminaire system comprises one or more arrays of light-emitting elements for generating light with a current driver system coupled thereto for selectively supplying electrical drive current to each of the arrays, wherein the current driver system is responsive to drive signals received from a controller. The luminaire system further comprises an optical sensor system for generating optical signals representative of chromaticity and luminous flux output of the light. A heat sensing system is operatively coupled to the one or more arrays for generating signals representative of the junction temperatures of arrays of light-emitting elements during operation. The luminaire system further comprises a controller that is operatively connected to the current driver system, the optical sensor system and the heat sensing system for receiving the signals generated by each of these systems and is configured to generate one or more drive signals for transmission to the current driver system in response to the optical signals and thermal signals received from the optical system and the heat sensing system, respectively, thereby enabling a desired level of control of the output light.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
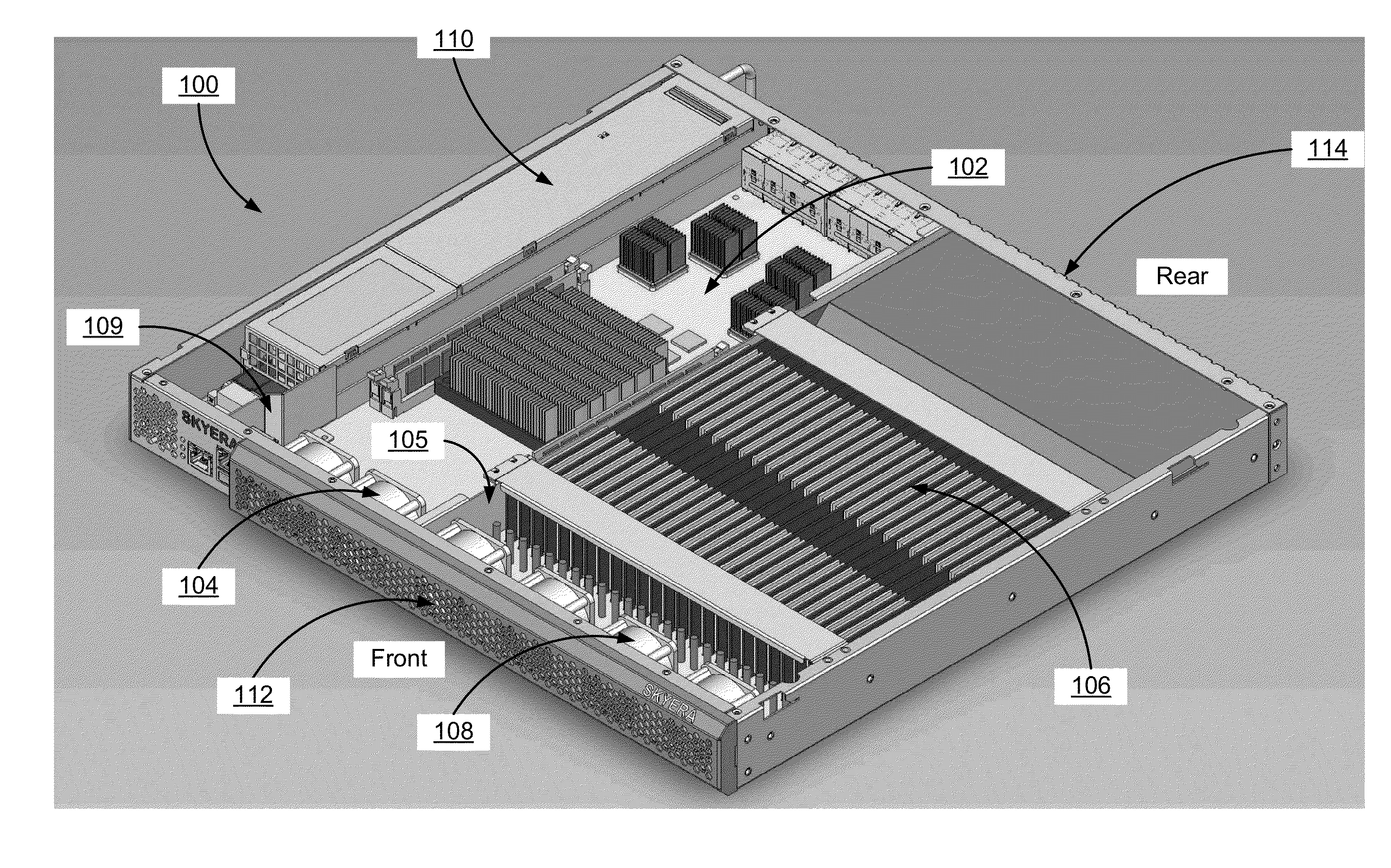
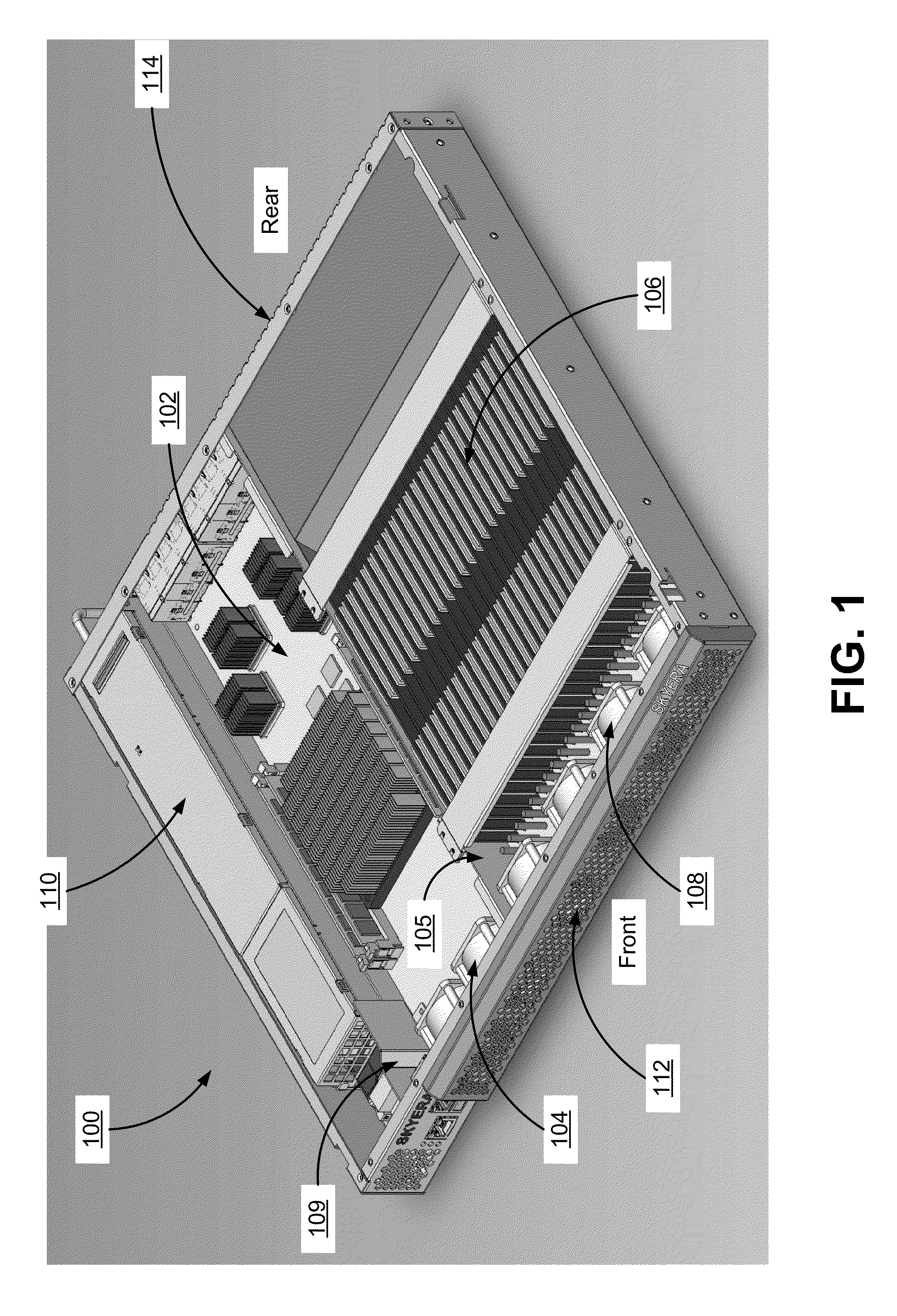
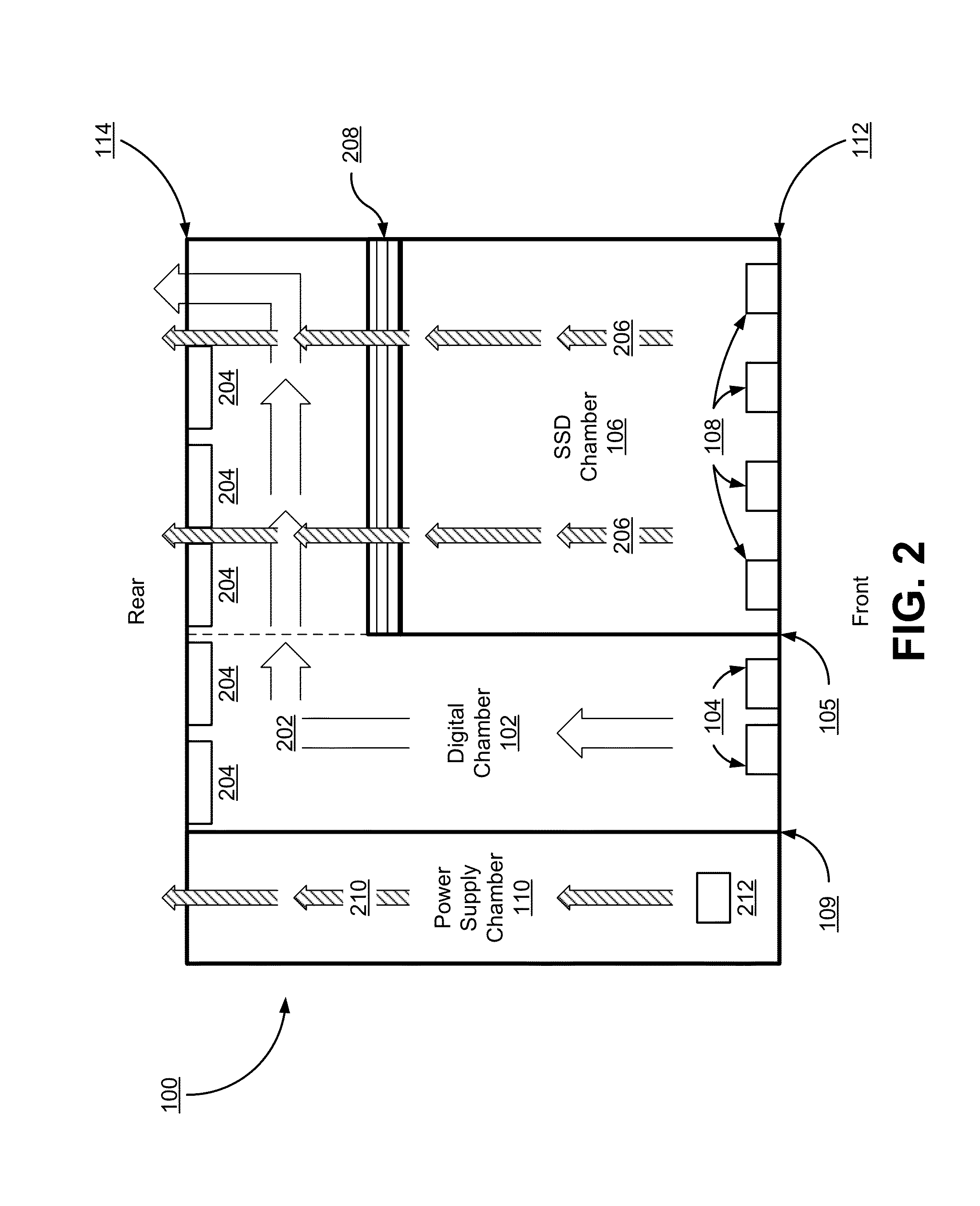
Chassis with separate thermal chamber for solid state memory
ActiveUS20140063721A1Extended service lifeServersTemperatue controlTemperature controlJunction temperature
A chassis for a network storage system contains a first thermal chamber that houses conventional electronic components and a second thermal chamber that houses non-volatile solid state memory such as flash memory. A cooling system keeps the electronics in first thermal chamber below their maximum junction temperature. Meanwhile, a temperature regulating system maintains the solid state memory in the second thermal chamber within a range of a preferred operating temperature selected to extend the lifetime and / or improve the reliability of the solid state memory. Thus, the chassis provides dual zone temperature control to improve performance of the network storage system.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Digitally controlled luminaire system
InactiveUS7319298B2Radiation pyrometryBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsJunction temperatureLuminous flux
The present invention provides a luminaire system capable of generating light of a desired chromaticity and luminous flux output during continuous operation with varying ambient operating temperature. The luminaire system can be further capable of maintaining a desired correlated colour temperature during dimming of the luminaire. The luminaire system comprises one or more arrays of light-emitting elements for generating light with a current driver system coupled thereto for selectively supplying electrical drive current to each of the arrays, wherein the current driver system is responsive to drive signals received from a controller. The luminaire system further comprises an optical sensor system for generating optical signals representative of chromaticity and luminous flux output of the light. A heat sensing system is operatively coupled to the one or more arrays for generating signals representative of the junction temperatures of arrays of light-emitting elements during operation. The luminaire system further comprises a controller that is operatively connected to the current driver system, the optical sensor system and the heat sensing system for receiving the signals generated by each of these systems and is configured to generate one or more drive signals for transmission to the current driver system in response to the optical signals and thermal signals received from the optical system and the heat sensing system, respectively, thereby enabling a desired level of control of the output light.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
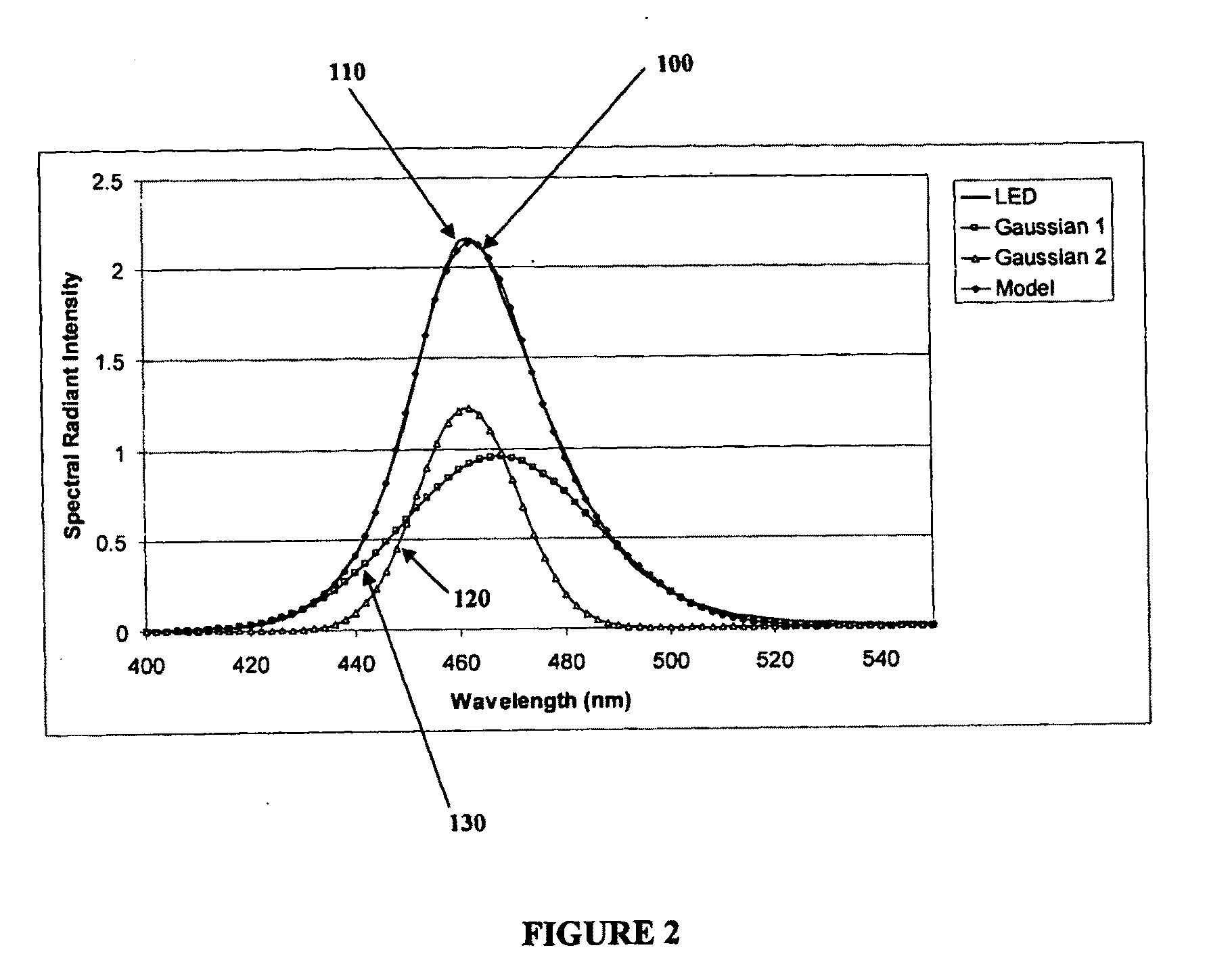
Wavelength conversion for producing white light from high power blue LED
InactiveUS20100289044A1Reduce energy consumptionElectroluminescent light sourcesGas discharge lamp usageFull width at half maximumJunction temperature
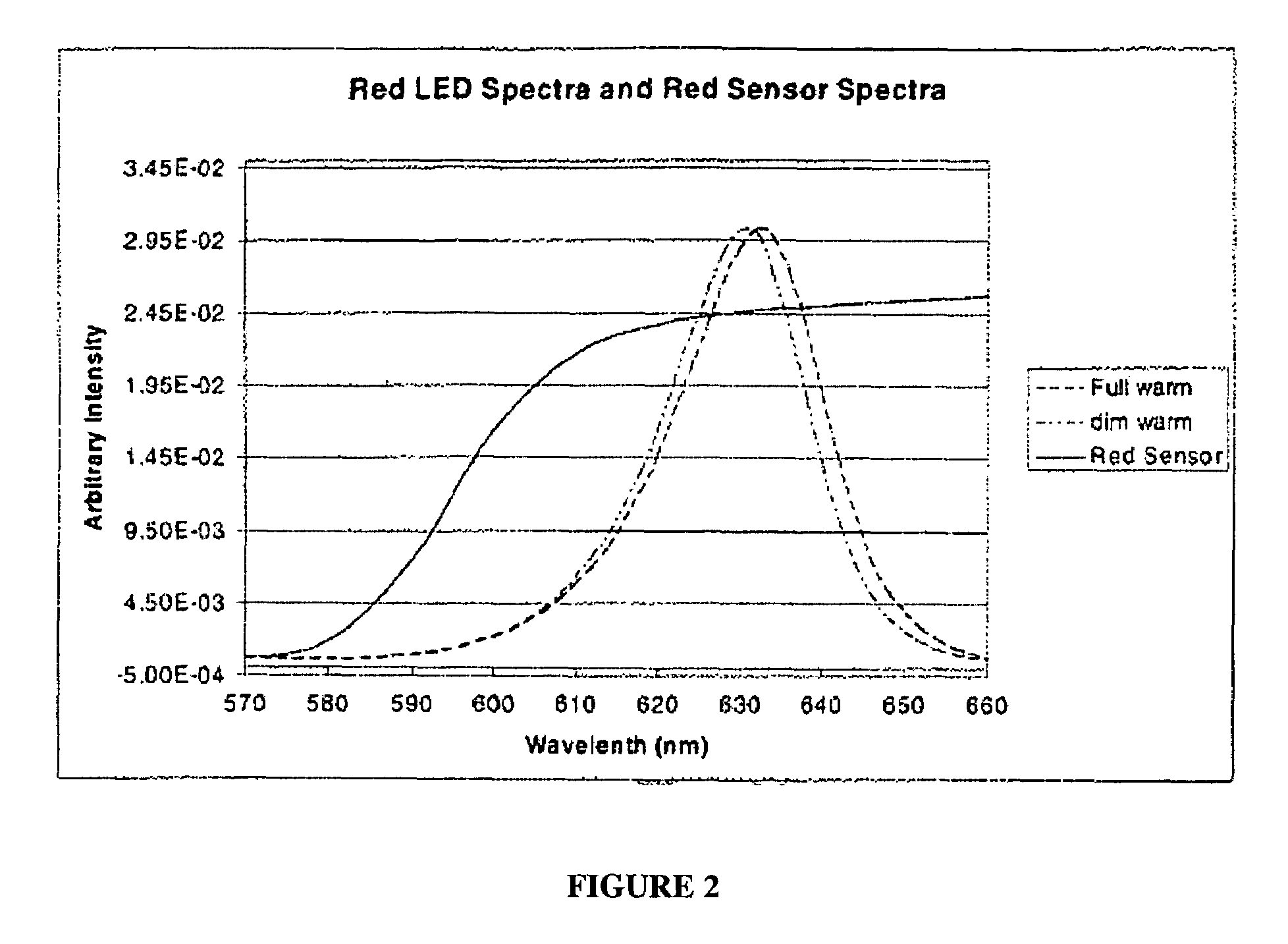
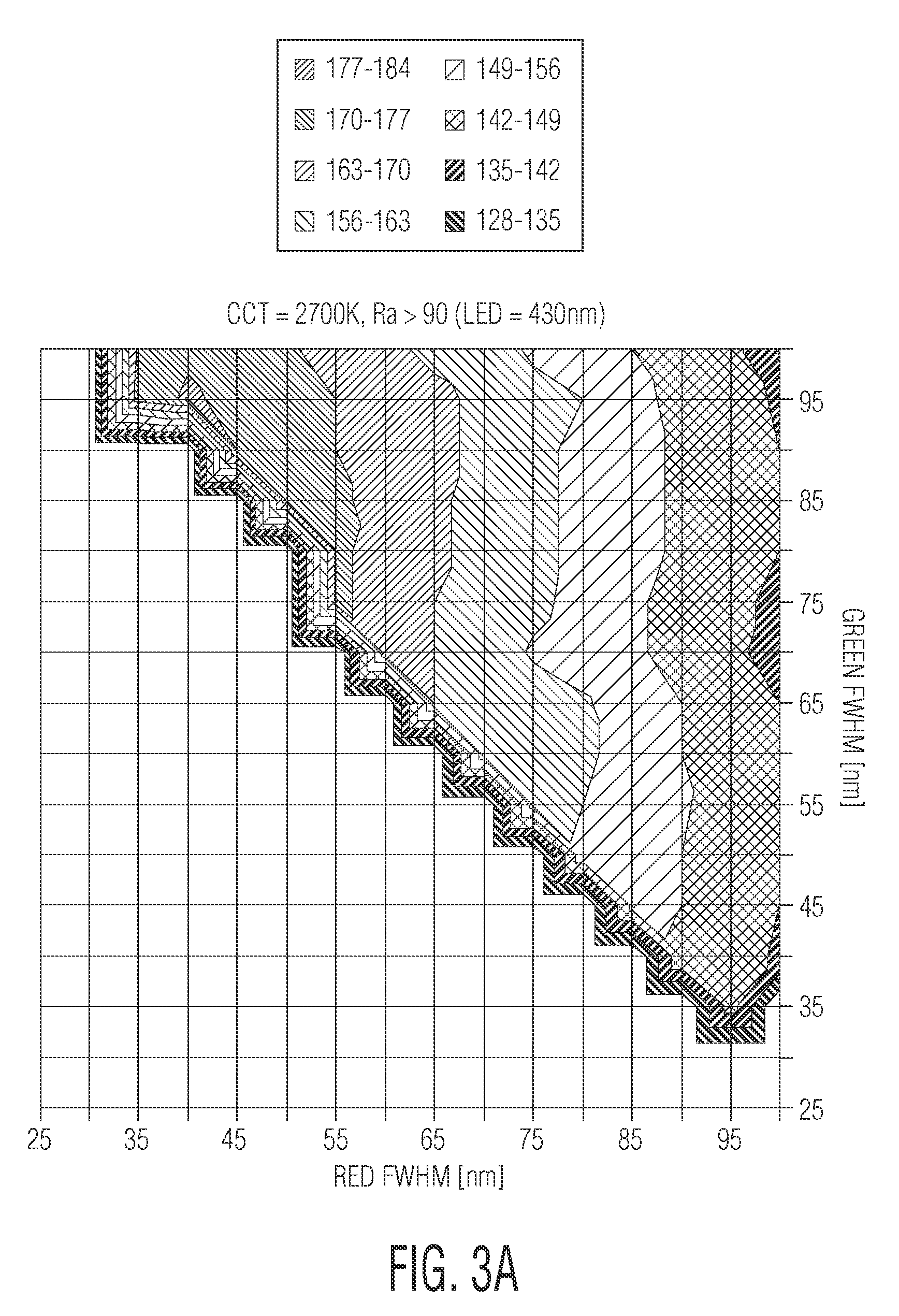
A white light LED is described that uses an LED die that emits visible blue light in a wavelength range of about 450-470 nm. A red phosphor or quantum dot material converts some of the blue light to a visible red light having a peak wavelength between about 605-625 nm with a full-width-half-maximum (FWHM) less than 80 nm. A green phosphor or quantum dot material converts some of the blue light to a green light having a FWHM greater than 40 nm, wherein the combination of the blue light, red light, and green light produces a white light providing a color rendering of Ra,8>90 and a color temperature of between 2500K-5000K. Preferably, the red and green converting material do not saturate with an LED die output of 100 W / cm2 and can reliably operate with an LED die junction temperature over 100 degrees C.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV +1
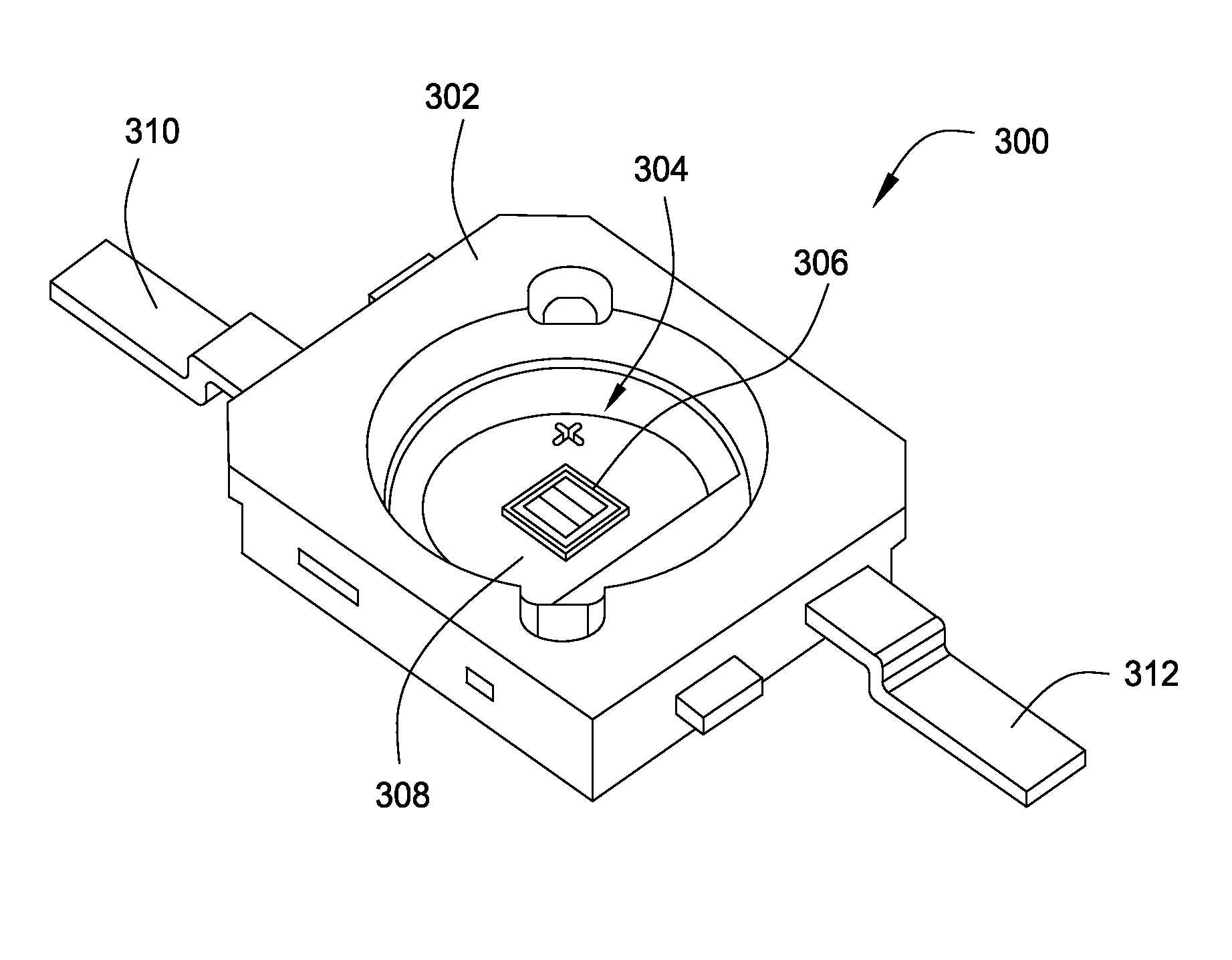
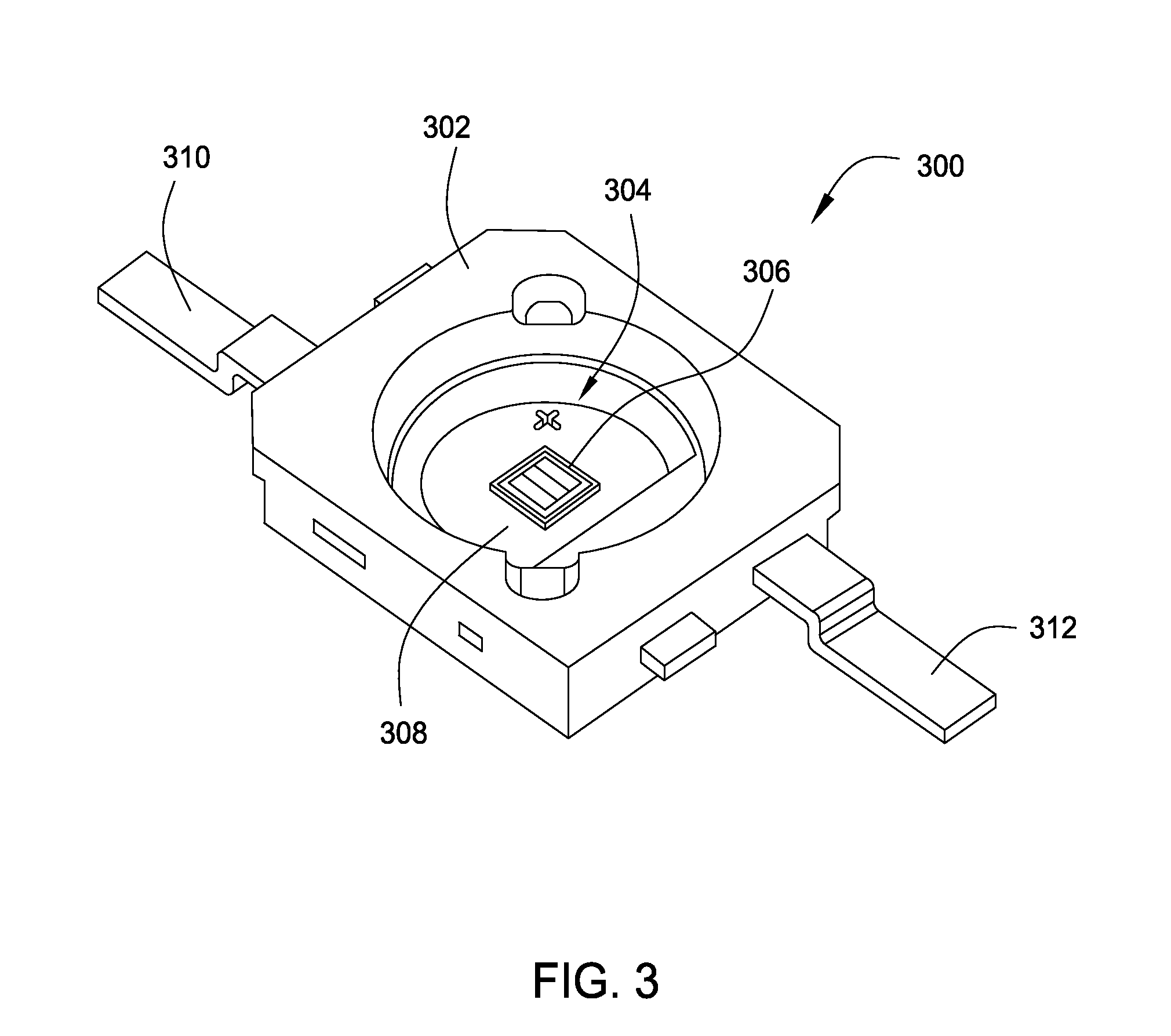
LED light module assembly
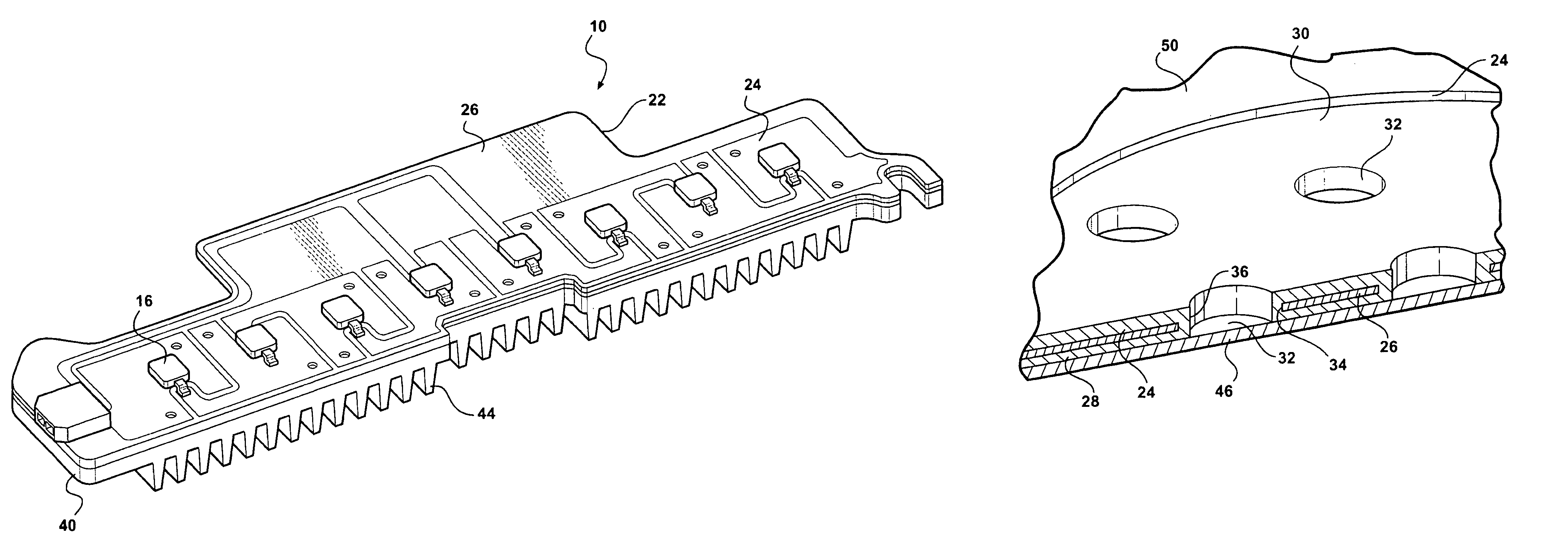
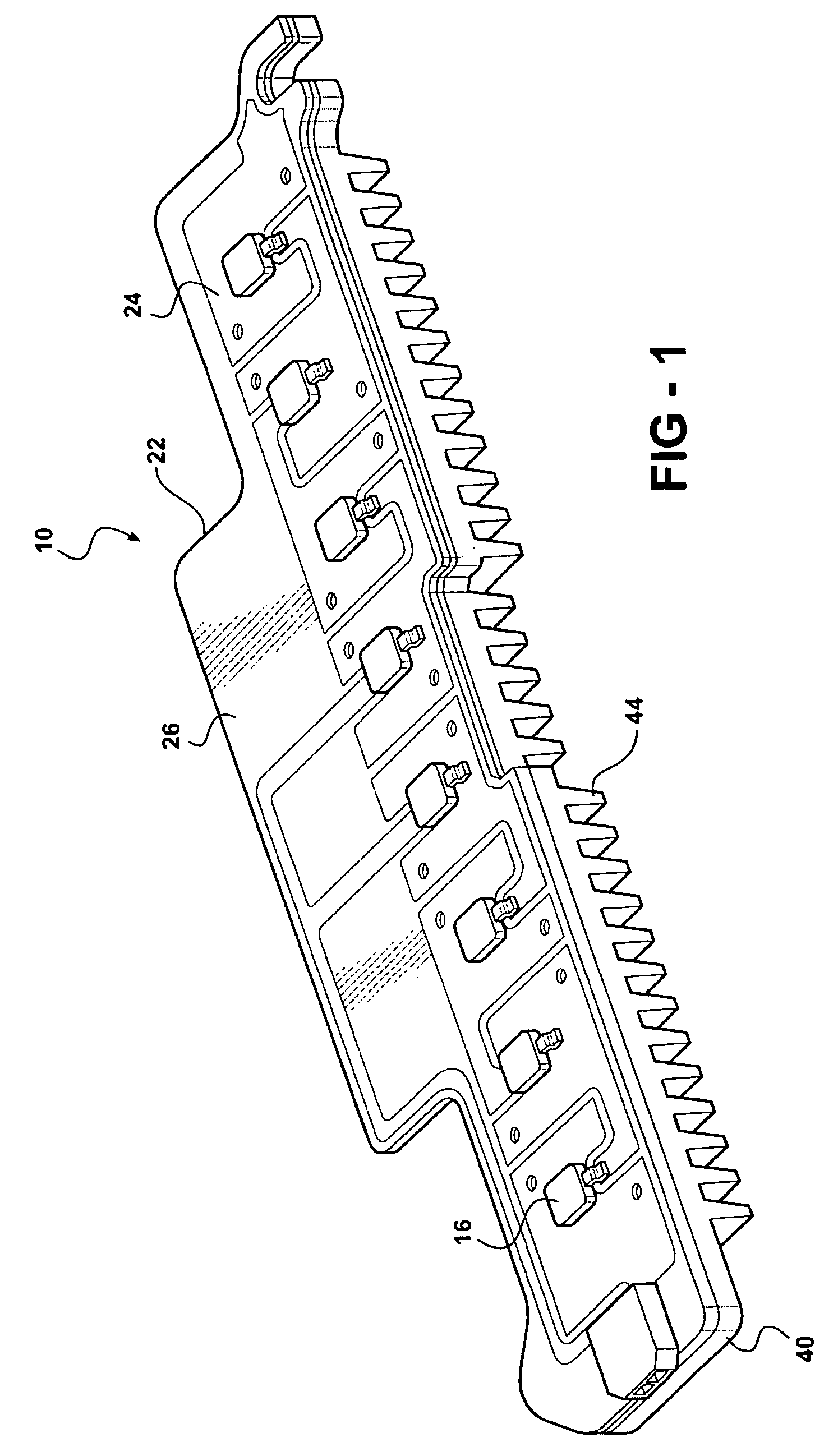
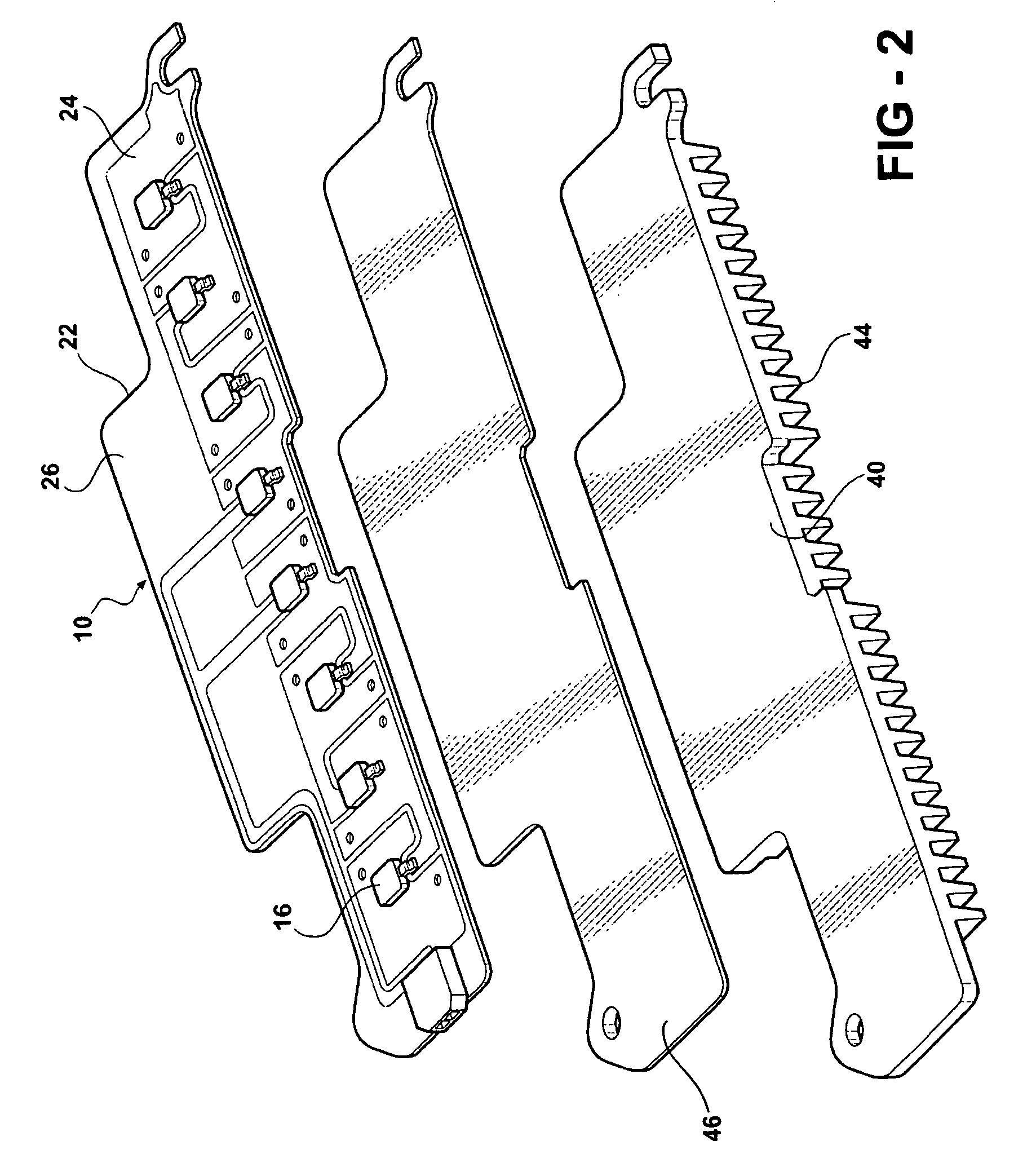
ActiveUS20060181878A1Point-like light sourceLighting heating/cooling arrangementsSurface mountingFlexible circuits
An LED light module assembly for use with high power, high light output LED's includes a thin flexible circuit board with surface mounted LED's and other electronic components which is attached to a metal heat sink using a layer of a thermally conductive adhesive, such as a thermally conductive epoxy adhesive. A conduction path is provided from the LED carrier through the flexible circuit board by the incorporation of one or more thermally conductive vias in the region of the attachment pad used to bond the LED to the flexible circuit board. These vias provide a conduction path from the back side of the LED carrier through the circuit board to the thermally conductive adhesive and heat sink. The LED light module assembly has the capacity to dissipate between about 10-14 W of power without exceeding a maximum LED junction temperature of about 125° C.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL WORLD WIDE LLC
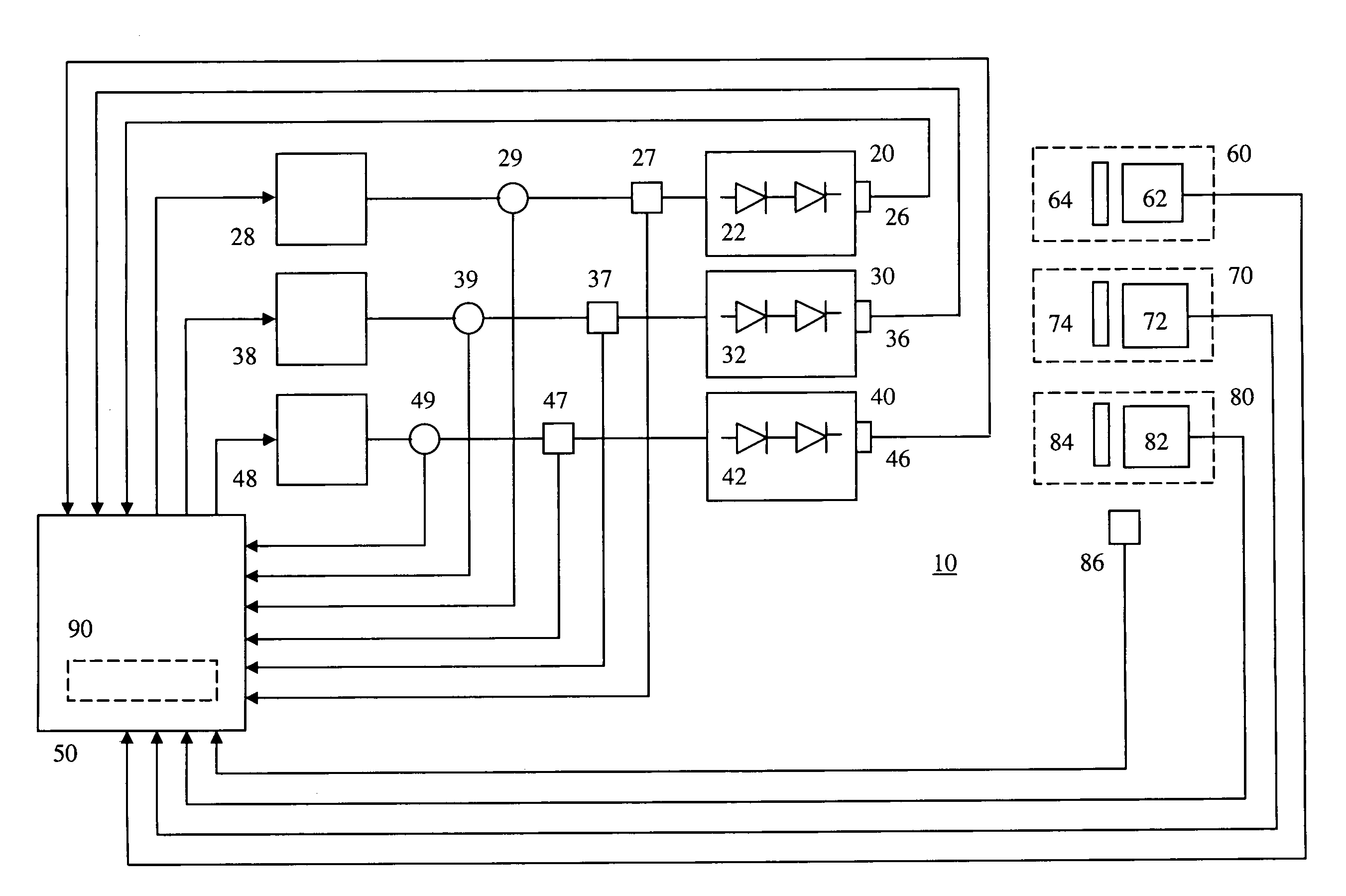
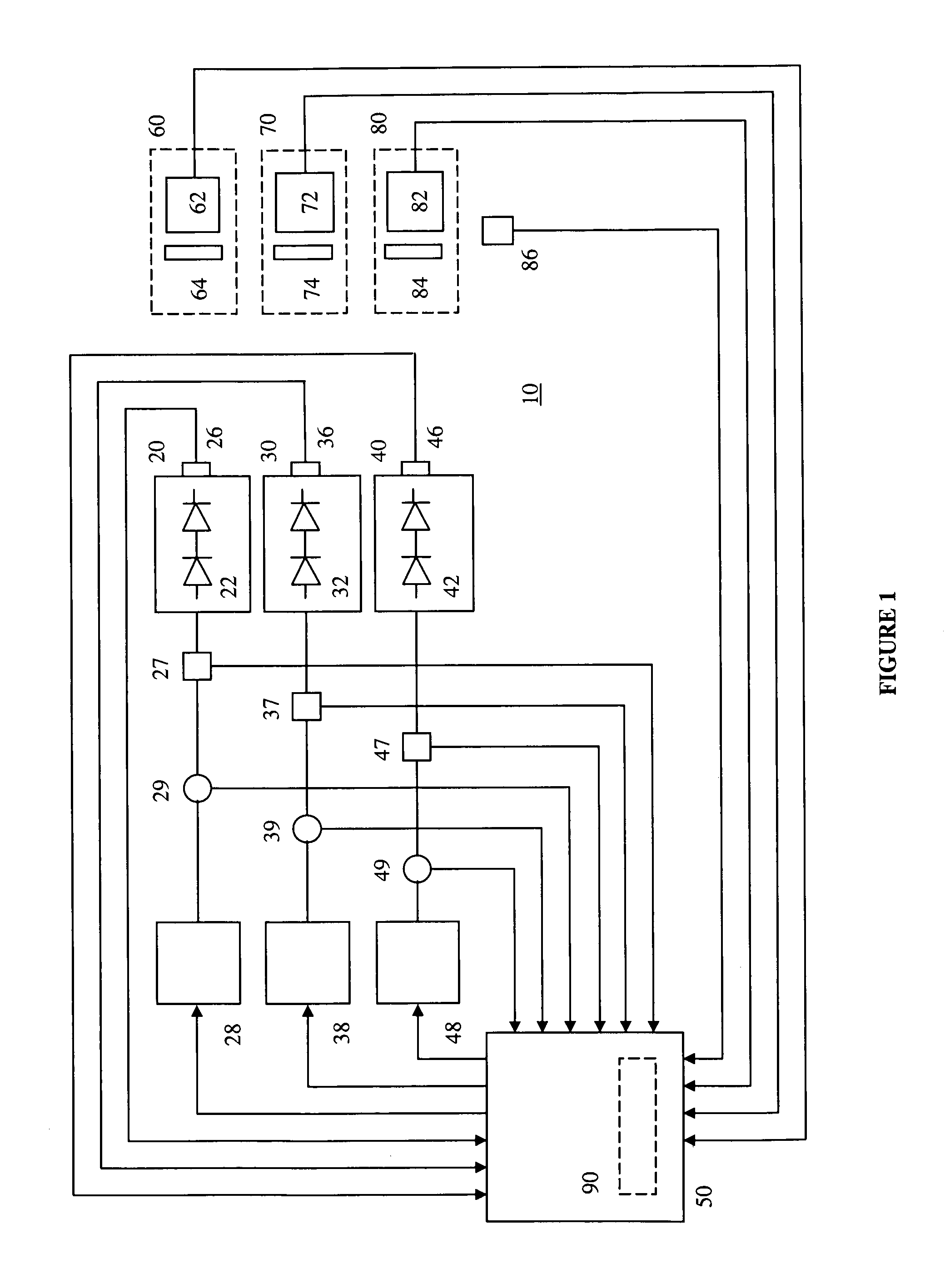
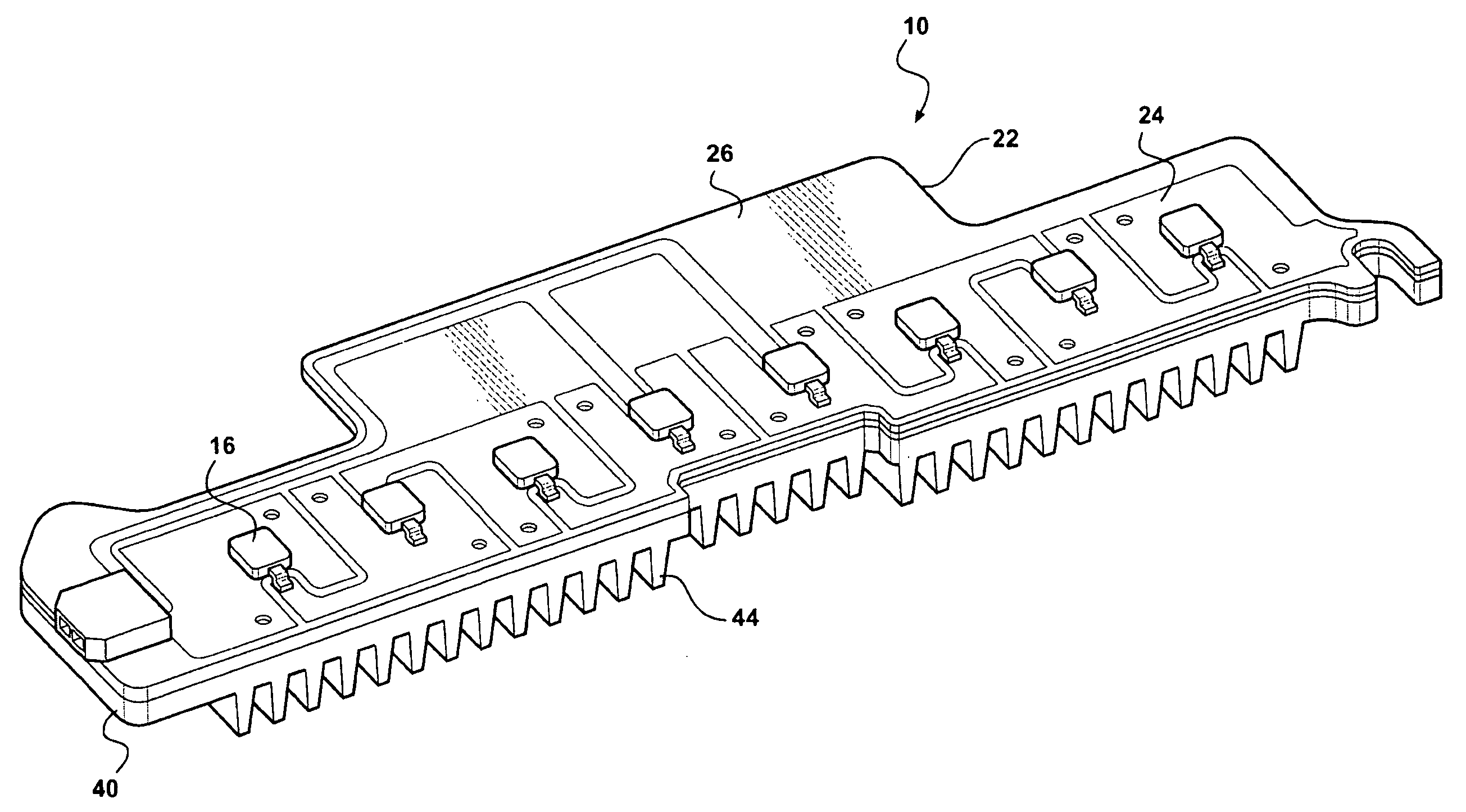
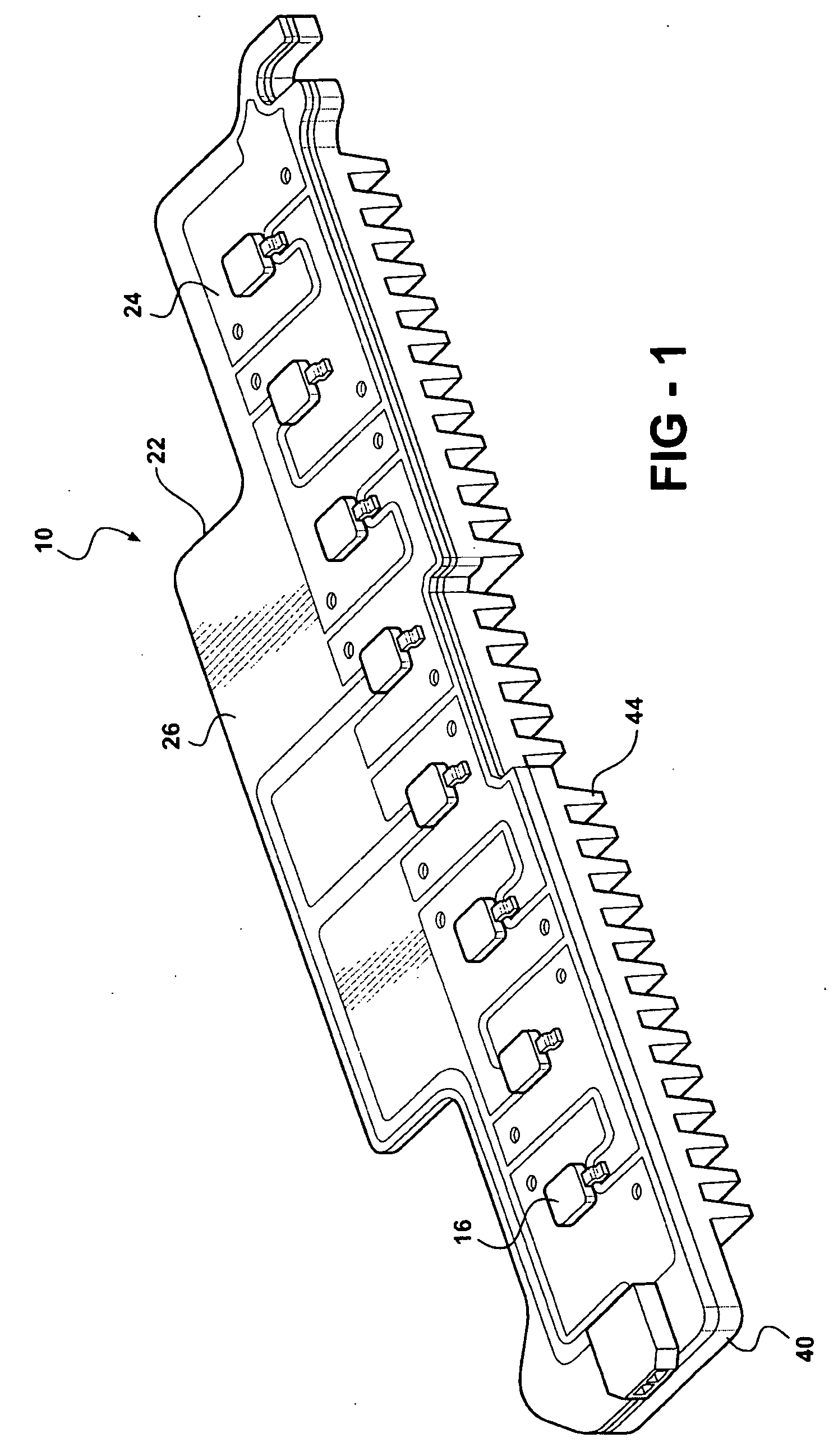
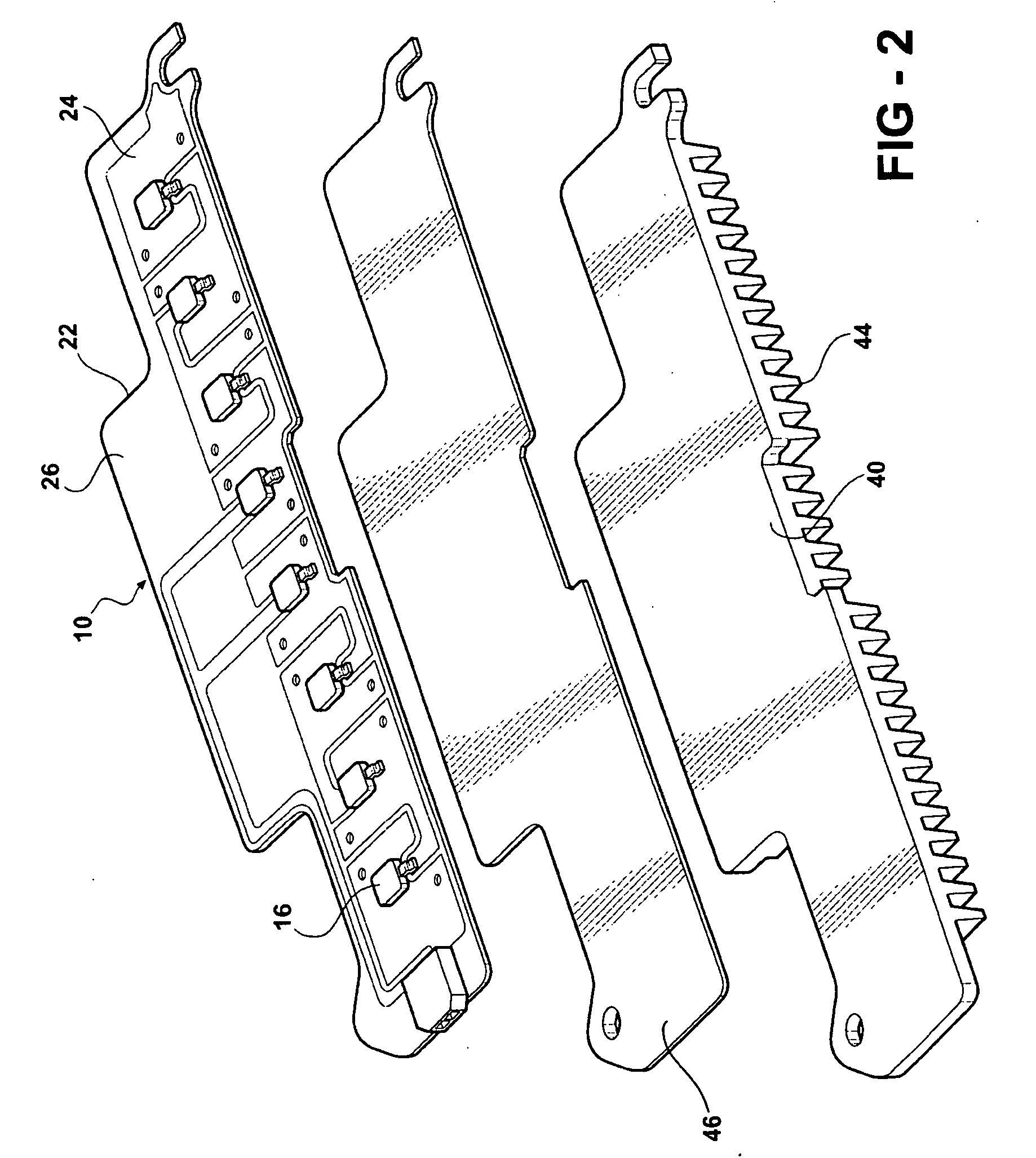
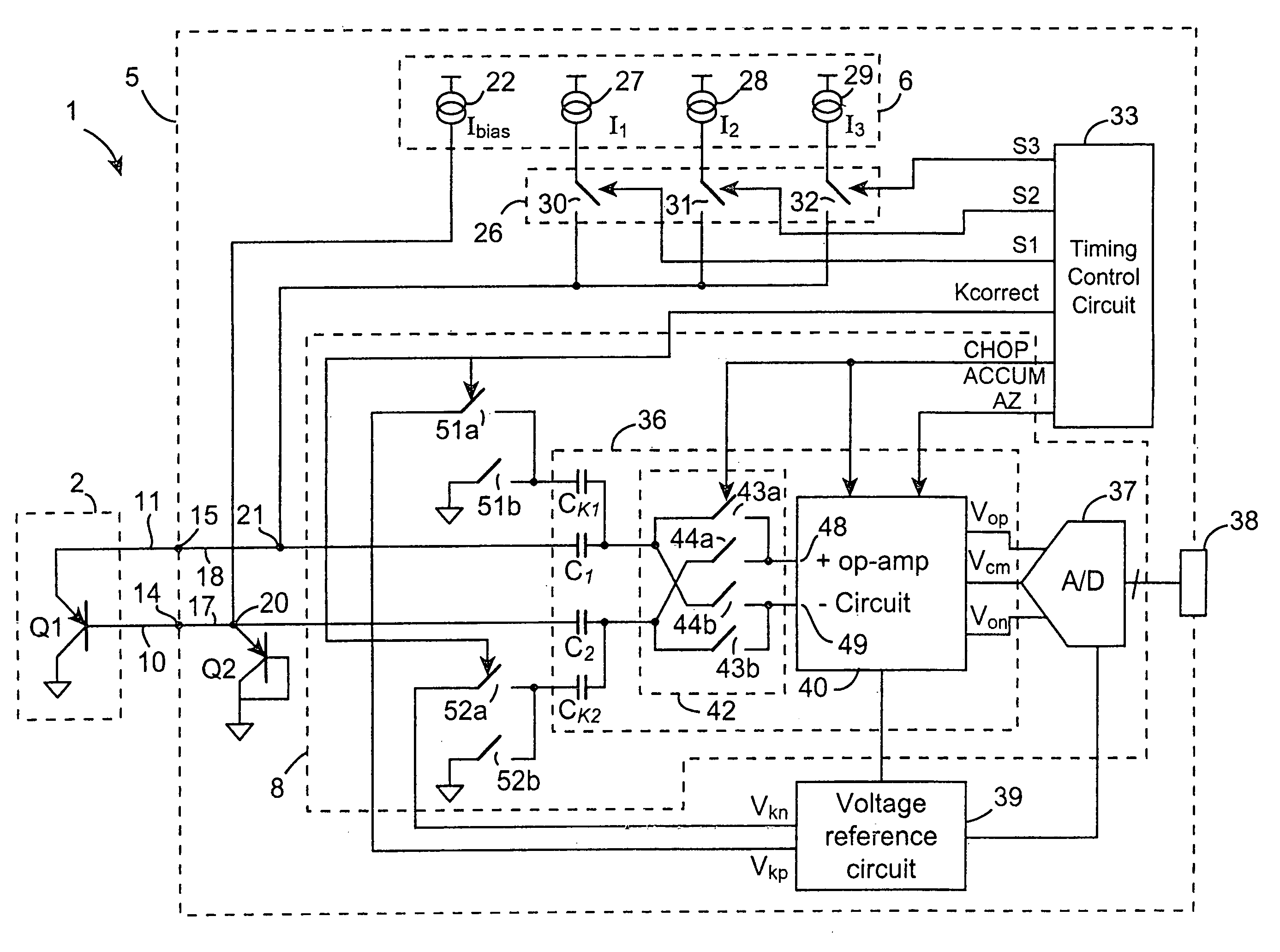
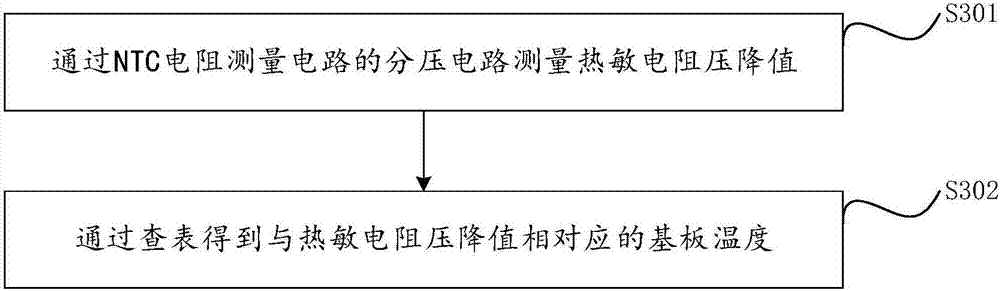
Method and a measuring circuit for determining temperature from a PN junction temperature sensor, and a temperature sensing circuit comprising the measuring circuit and a PN junction
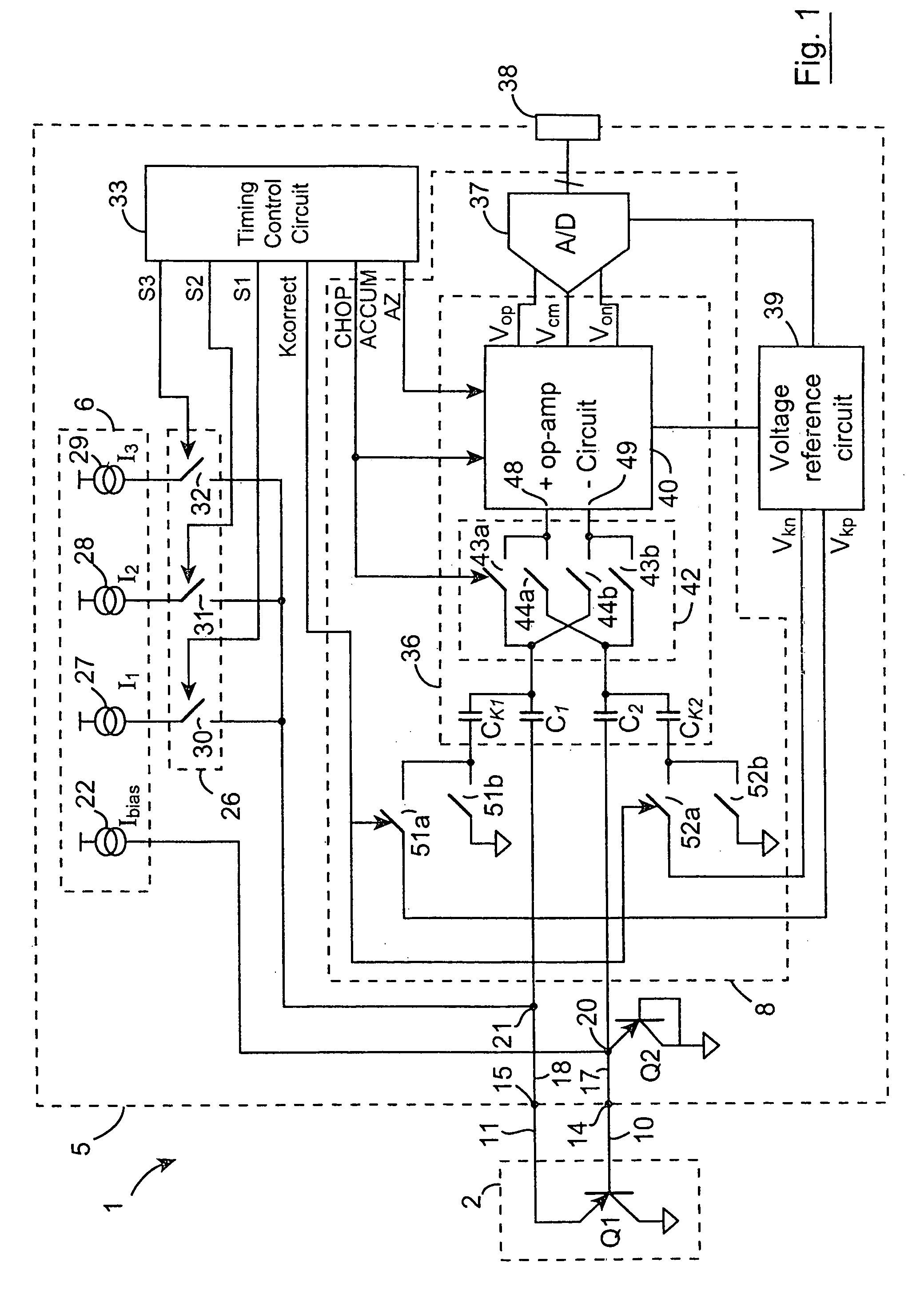
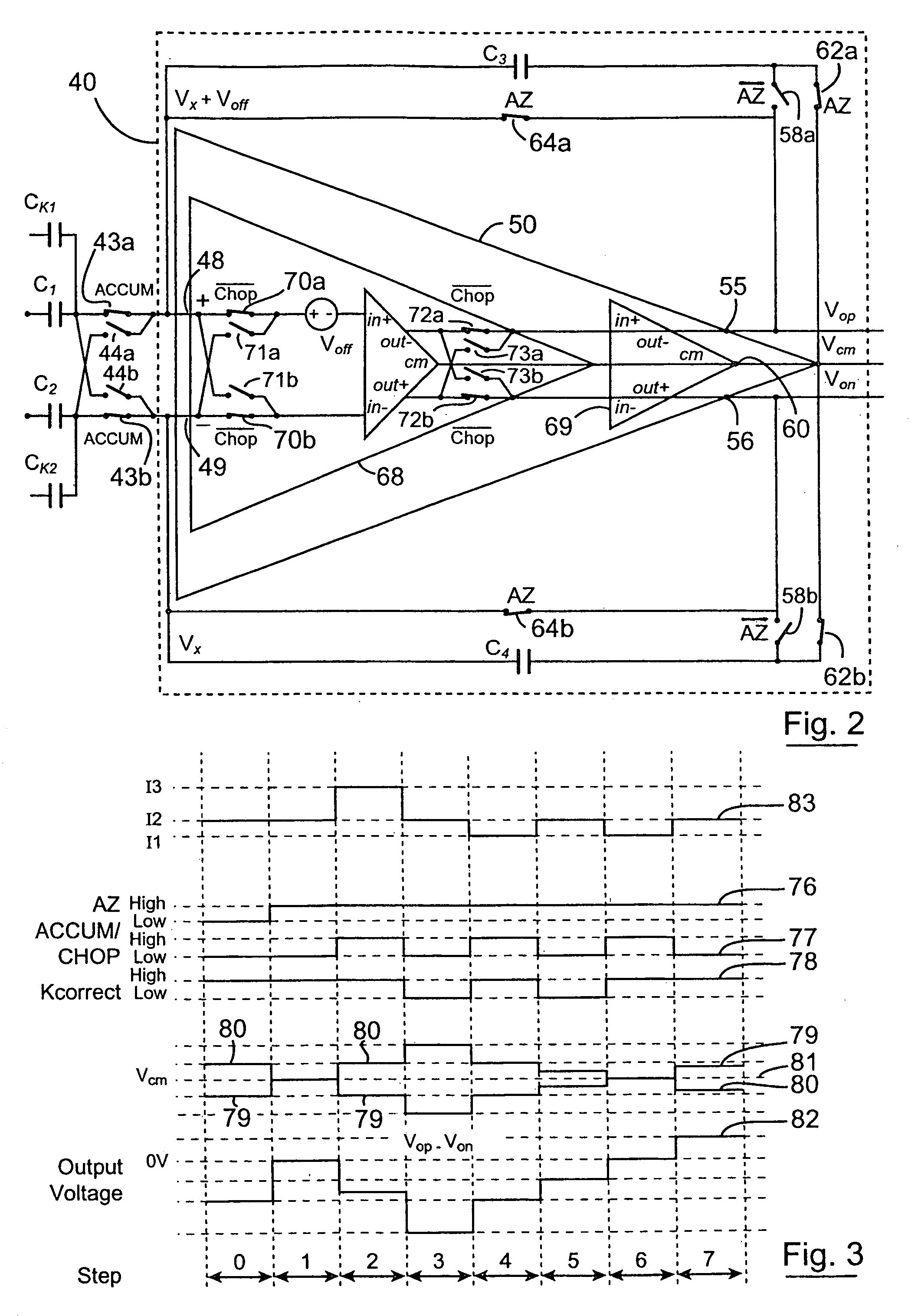
ActiveUS7010440B1Accurate representationEliminate the effects ofThermometer detailsThermometers using material expansion/contactionSwitched currentExcitation current
A switched current temperature sensing circuit (1) comprises a measuring transistor (Q1) which is located remotely of a measuring circuit (5) which applies three excitation currents (I1,I2,I3) of different values to the measuring transistor (Q1) in a predetermined current sequence along lines (10,11). Resulting base / emitter voltages from the measuring transistor (Q1) are applied to the measuring circuit (5) along the same two lines (10,11) as the excitation currents are applied to the measuring transistor (Q1). Voltage differences ΔVbe of successive base / emitter voltages resulting from the excitation currents are integrated in an integrating circuit (36) of the measuring circuit (5) to provide an output voltage indicative of the temperature of the measuring transistor (Q1). By virtue of the fact that the measuring transistor (Q1) is excited by excitation currents of three different values, the effect of current path series resistance in the lines (10,11) on the output voltage indicative of temperature is eliminated. The predetermined current sequence in which the excitation currents are applied to the measuring transistor (Q1) is selected to minimize the voltages in the integrating circuit (36) during integration of the voltage differences ΔVbe.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Light source intensity control system and method
InactiveUS20100259182A1Electroluminescent light sourcesElectric light circuit arrangementControl signalControl system
The light source comprises one or more first light-emitting elements for generating light having a first wavelength range and one or more second light-emitting elements for generating light having a second wavelength range. The first light-emitting elements and second light-emitting elements are responsive to separate control signals provided thereto. A control system receives a signal representative of the operating temperature from one or more sensing devices and determines first and second control signals based on the desired colour of light and the operating temperature. The light emitted by the first and second light-emitting elements as a result of the received first and second control signals can be blended to substantially obtain the desired colour of light. The desired colour of light generated can thus be substantially independent of junction temperature induced changes in the operating characteristics of the light-emitting elements.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
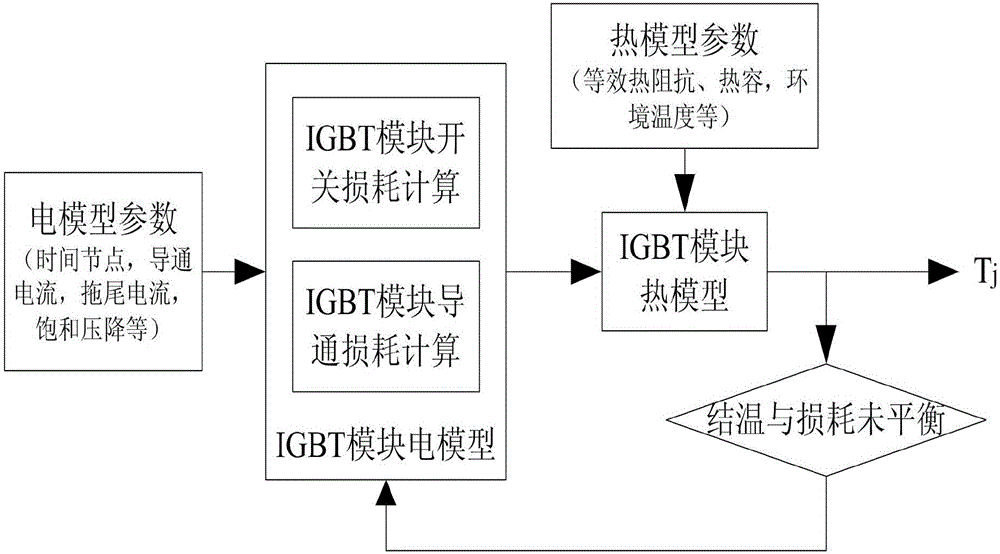
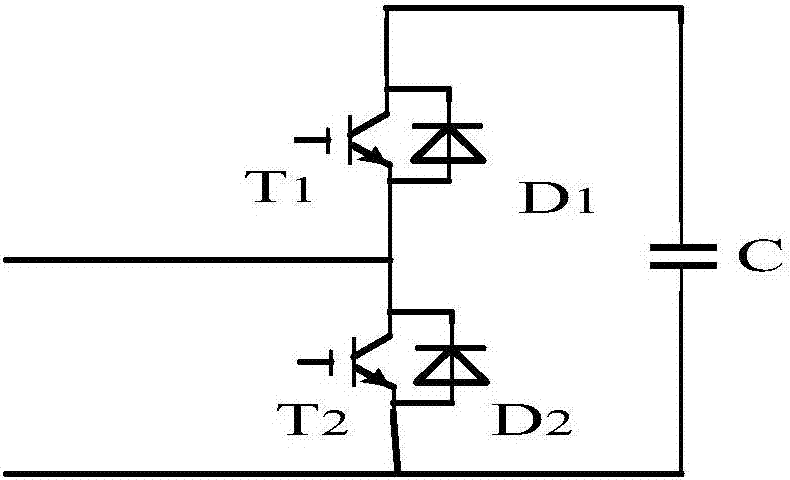
Electric-heat-aging junction temperature calculation model establishing method of IGBT module
ActiveCN106443400AImplement junction temperature prediction functionImproved thermal managementSemiconductor operation lifetime testingElectricityCoupling
The invention relates to an electric-heat-aging junction temperature calculation model establishing method of an IGBT module. The method is technologically characterized by comprising the following steps of testing electric heating parameters of the IGBT module in different aging degrees, acquiring a three-dimensional relation curved surface and establishing an electric heating data sheet in different aging degrees; establishing an electric model of the IGBT module and a thermal network model of the IGBT module, inputting a power loss which is calculated through the electric model of the IGBT module into the thermal network model of the IGBT module in a current source manner, performing real-time feedback of the junction temperature which is calculated by the thermal network model to the electric model, and finishing establishment of an electric-heat coupling model of the IGBT module; performing aging state evaluation on the IGBT module; and performing junction temperature calculation on the IGBT module. According to the electric-heat-aging junction temperature calculation model establishing method, the corresponding electric heating parameters for different aging processes are acquired and furthermore the electric heating parameters are input into the electric-heat coupling model for performing junction temperature calculation, namely the parameter of the electric-heat coupling model is dynamically changed in real time according to the aging degree of the model, thereby realizing a junction temperature prediction function for the module aging degree.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
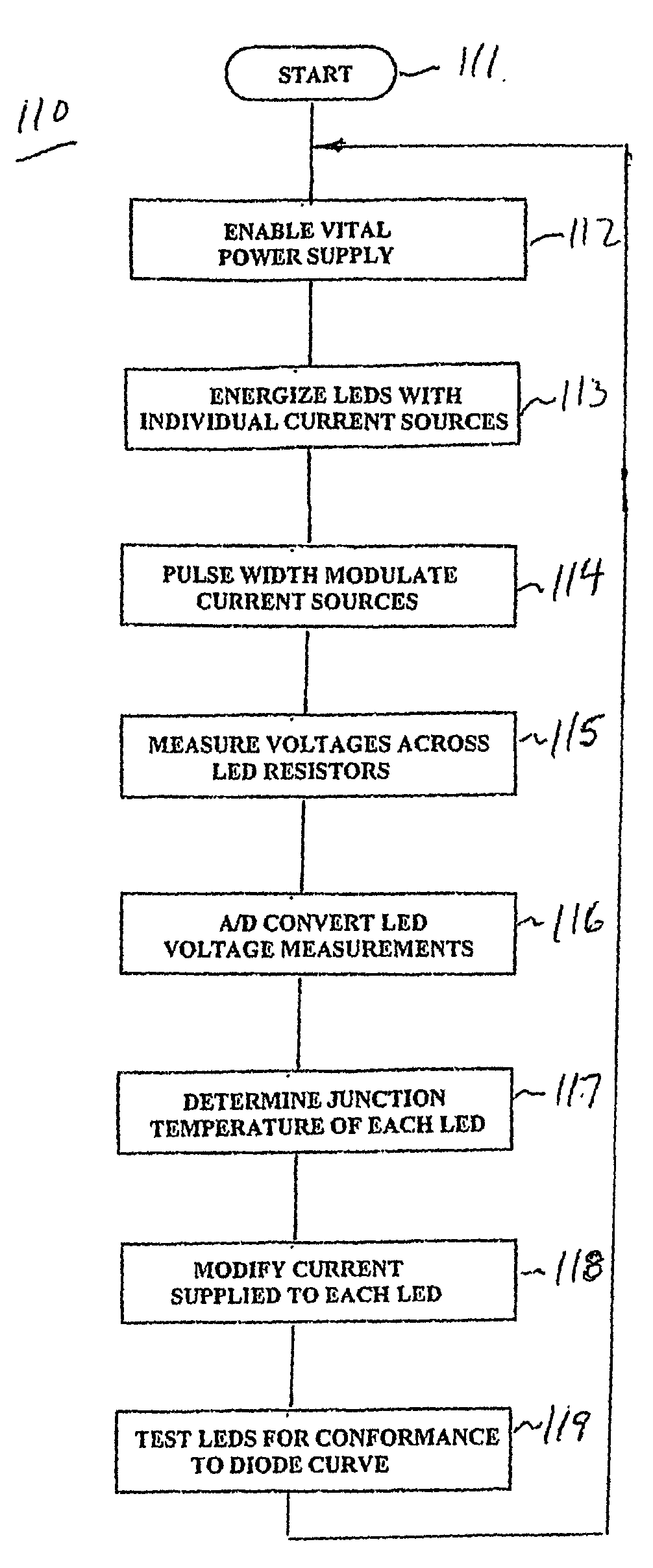
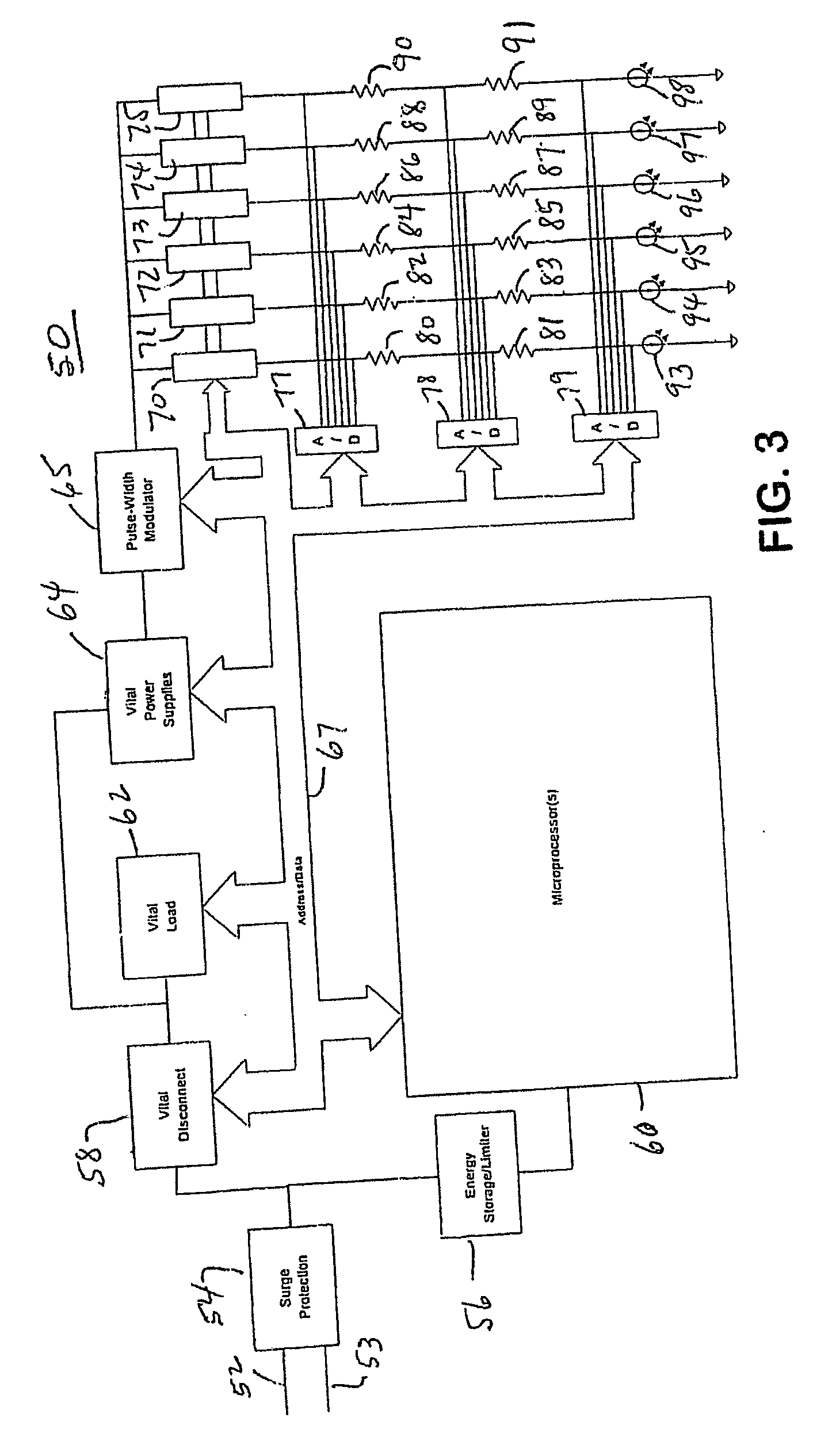
Wayside LED signal for railroad and transit applications
InactiveUS20050062481A1Sufficient energySufficient energy storageVisible signalsElectrical apparatusJunction temperatureData treatment
A LED signal lamp that monitors, controls and tests the operational status of a plurality of LEDs. A separate current source is provided for each LED and resistors are in series between the current sources and LEDs. Analog-to-digital converters monitor the voltages at the resistors and LEDs and convert the voltages to digital form for a data processor. The data processor determines the junction temperature of each LED, controls the amount of current supplied to each LED and tests the operational status of each LED by matching its characteristics to a known diode curve. A pulse-width modulator provides further control of the amount of power supplied to the current sources. The data processor further controls a vital disconnect and a vital load. An energy storage / limiter circuit stores energy for the data processor during the absence of normal power input. Related methods of monitoring, controlling and testing such an LED system are also disclosed.
Owner:SAFETRAN SYST CORP CORP
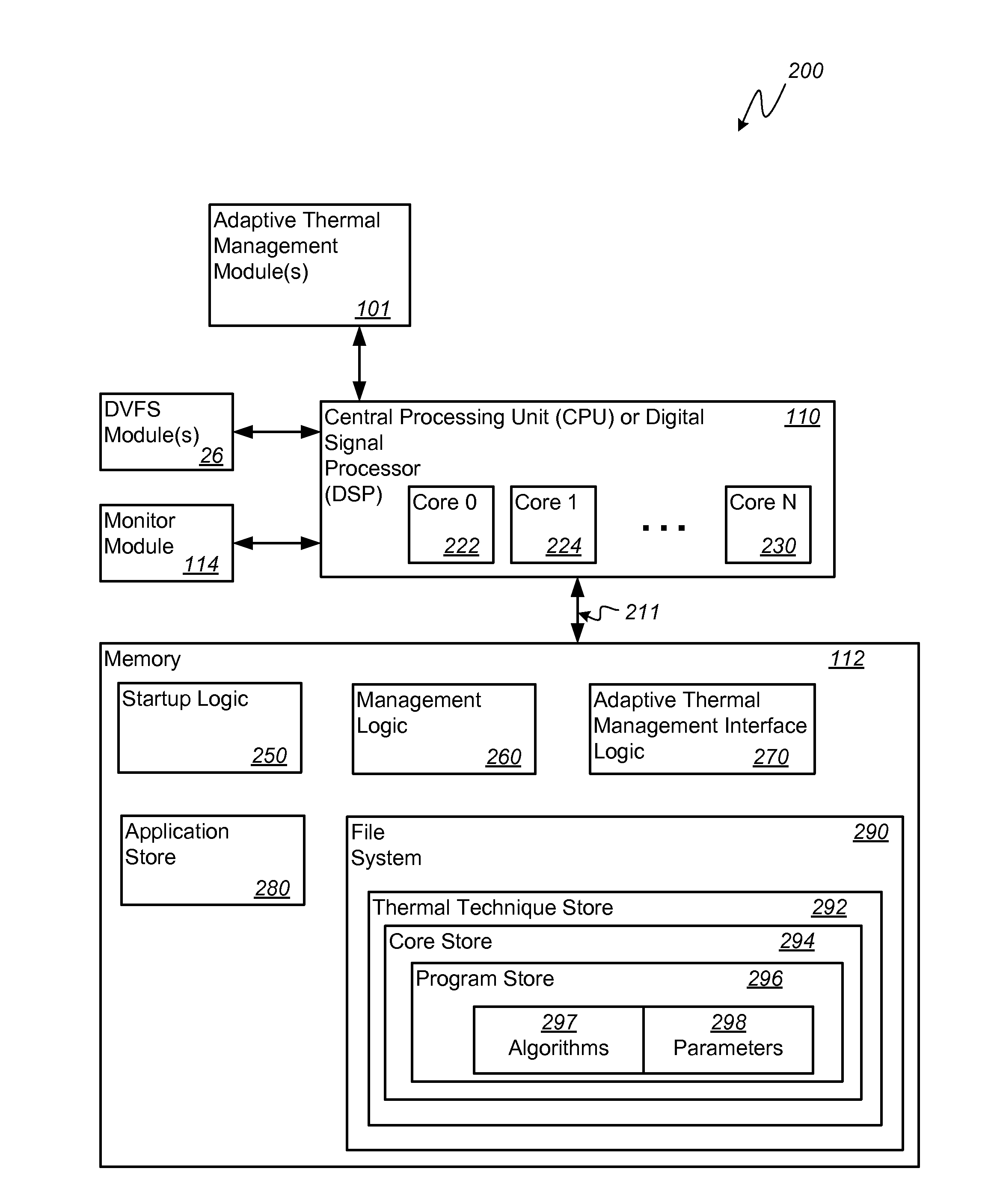
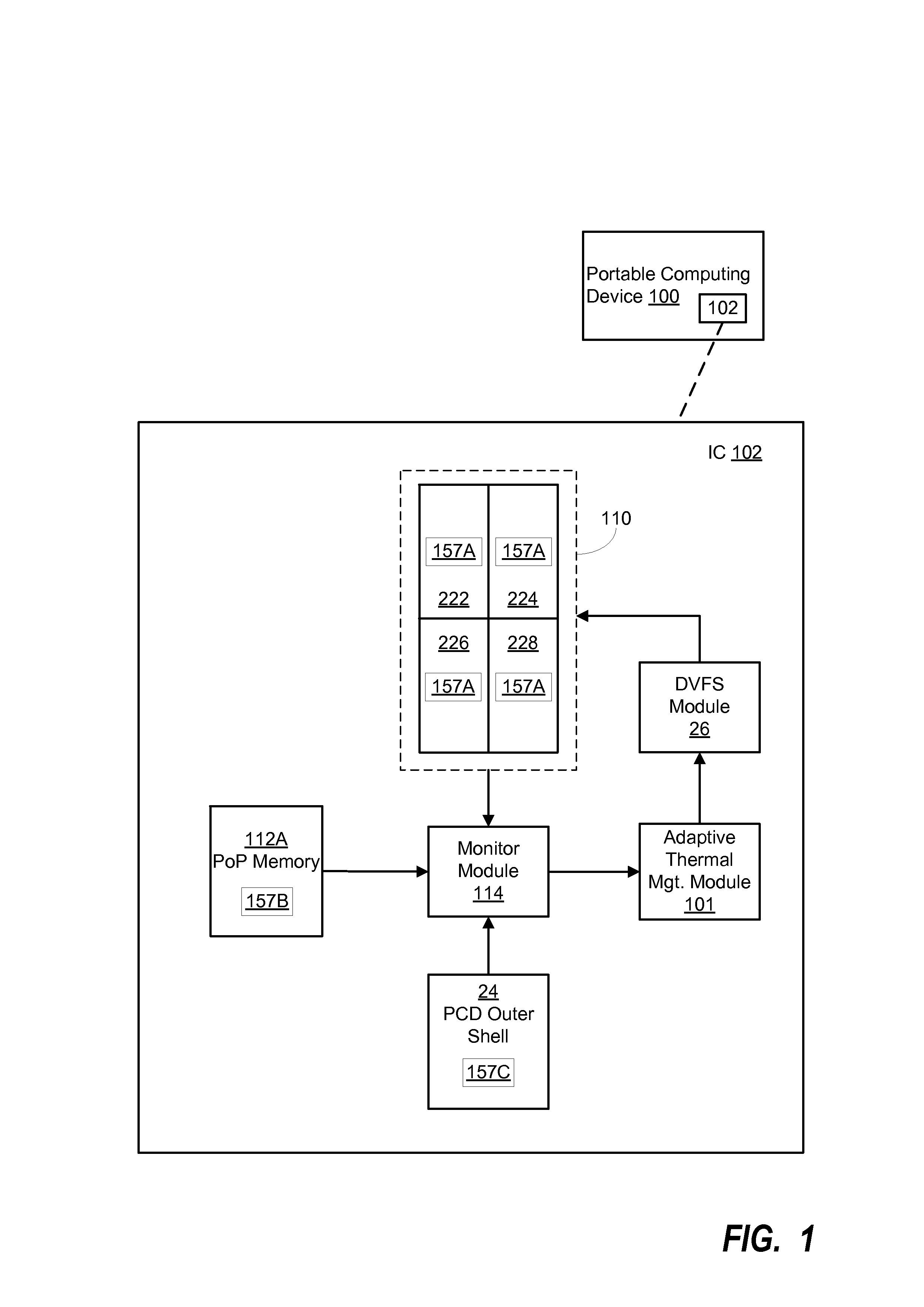
System and Method For Adaptive Thermal Management In A Portable Computing Device
ActiveUS20140006818A1Reduced performance levelLower performance requirementsVolume/mass flow measurementHardware monitoringJunction temperatureSelf adaptive
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
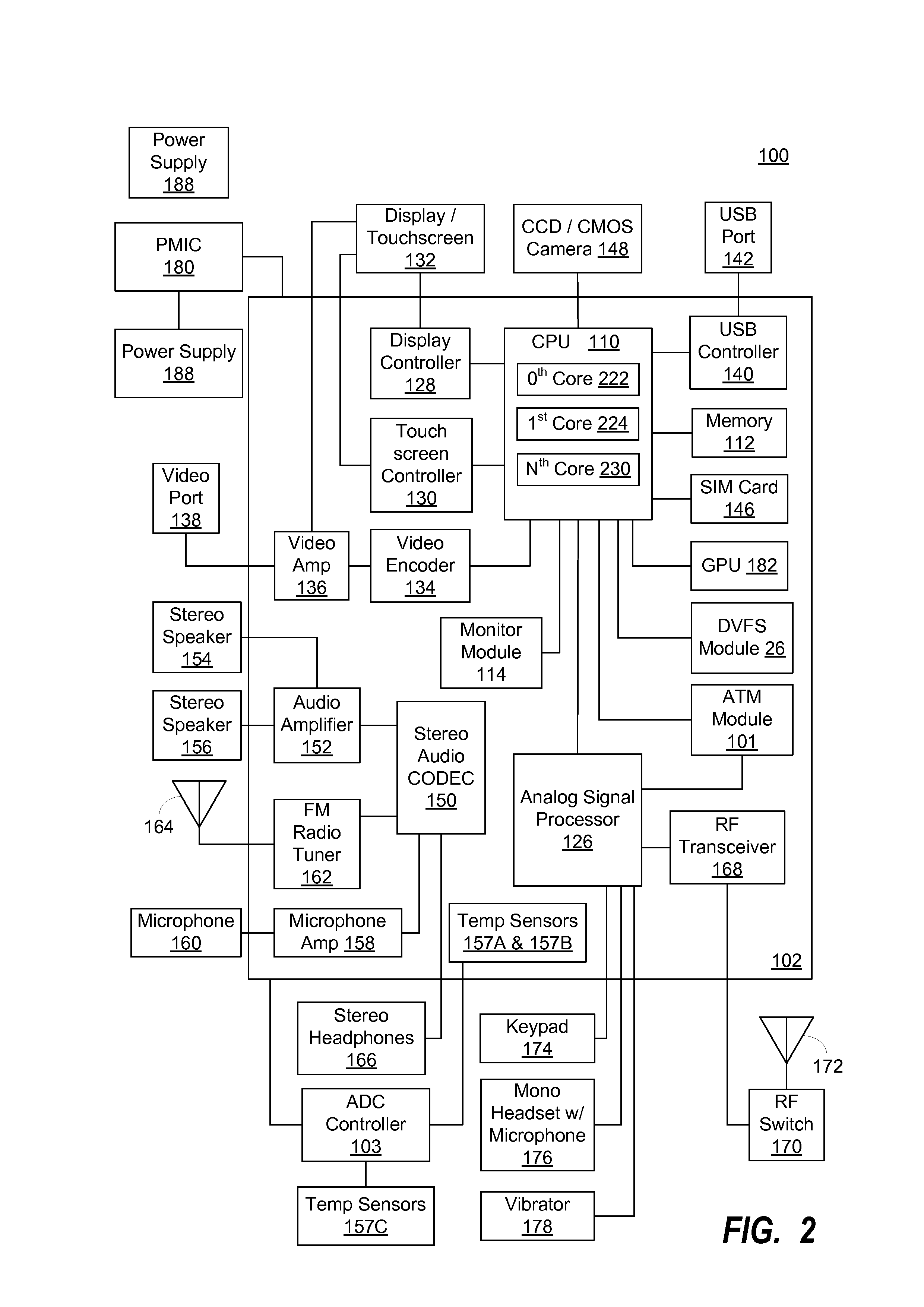
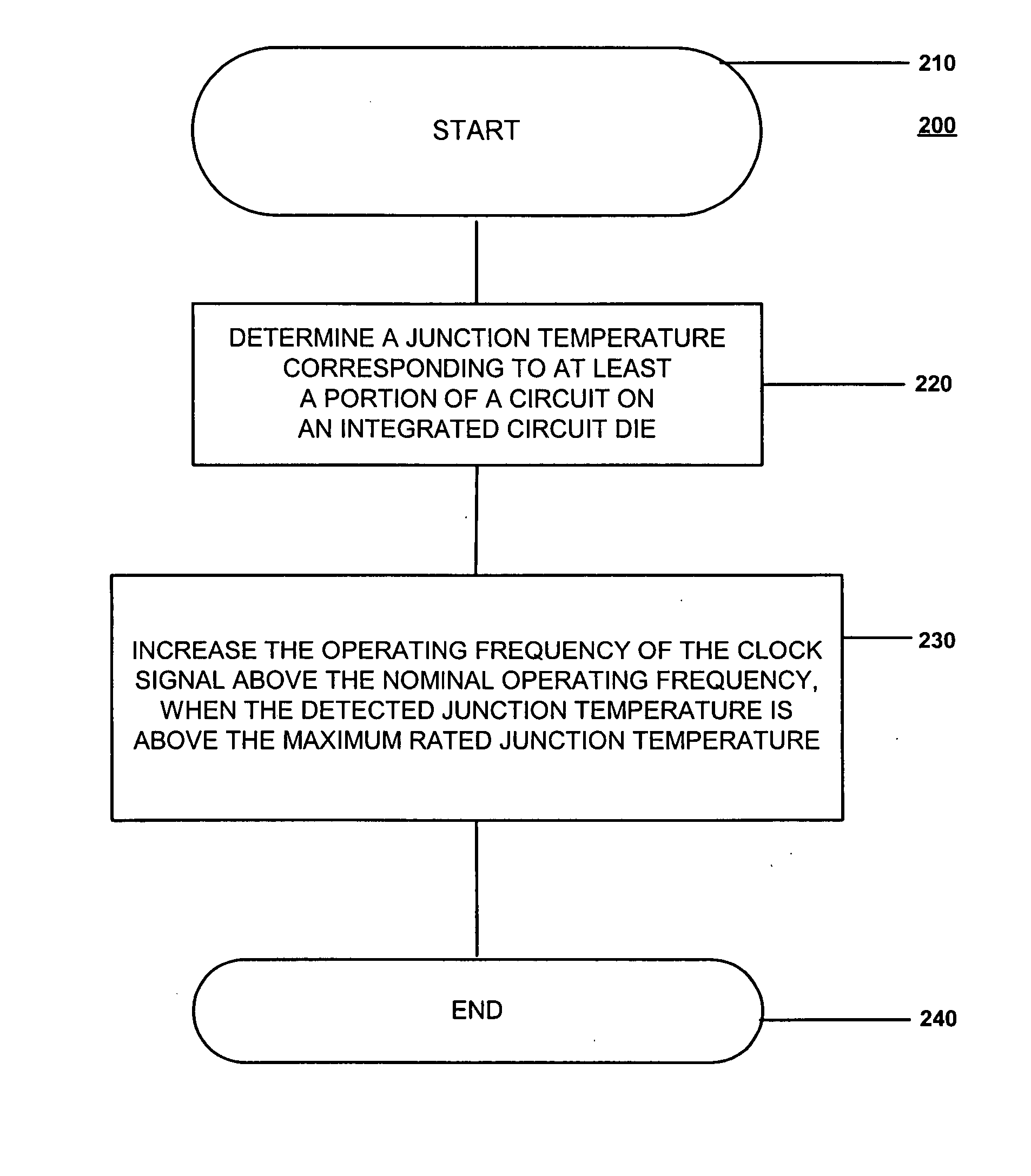
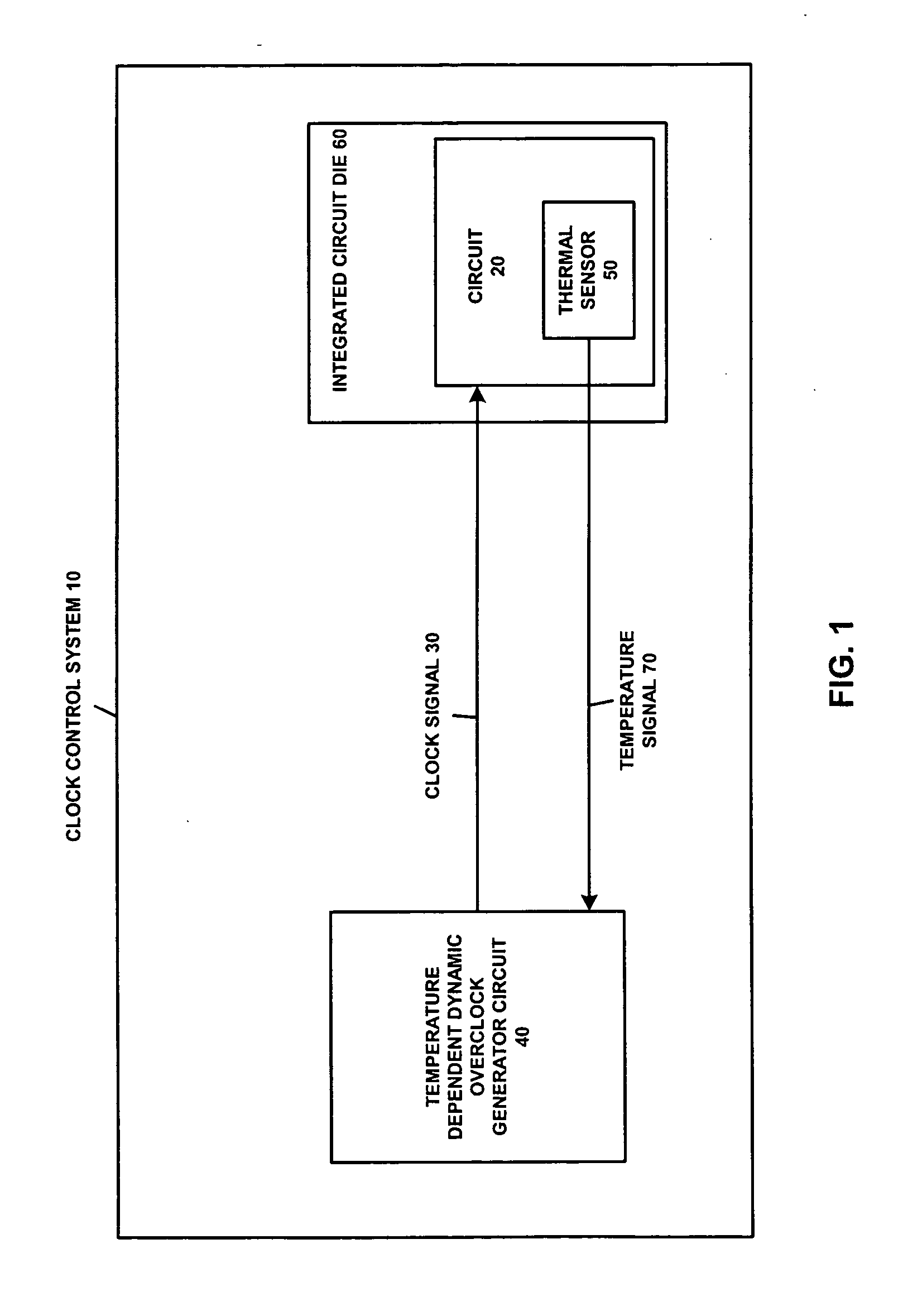
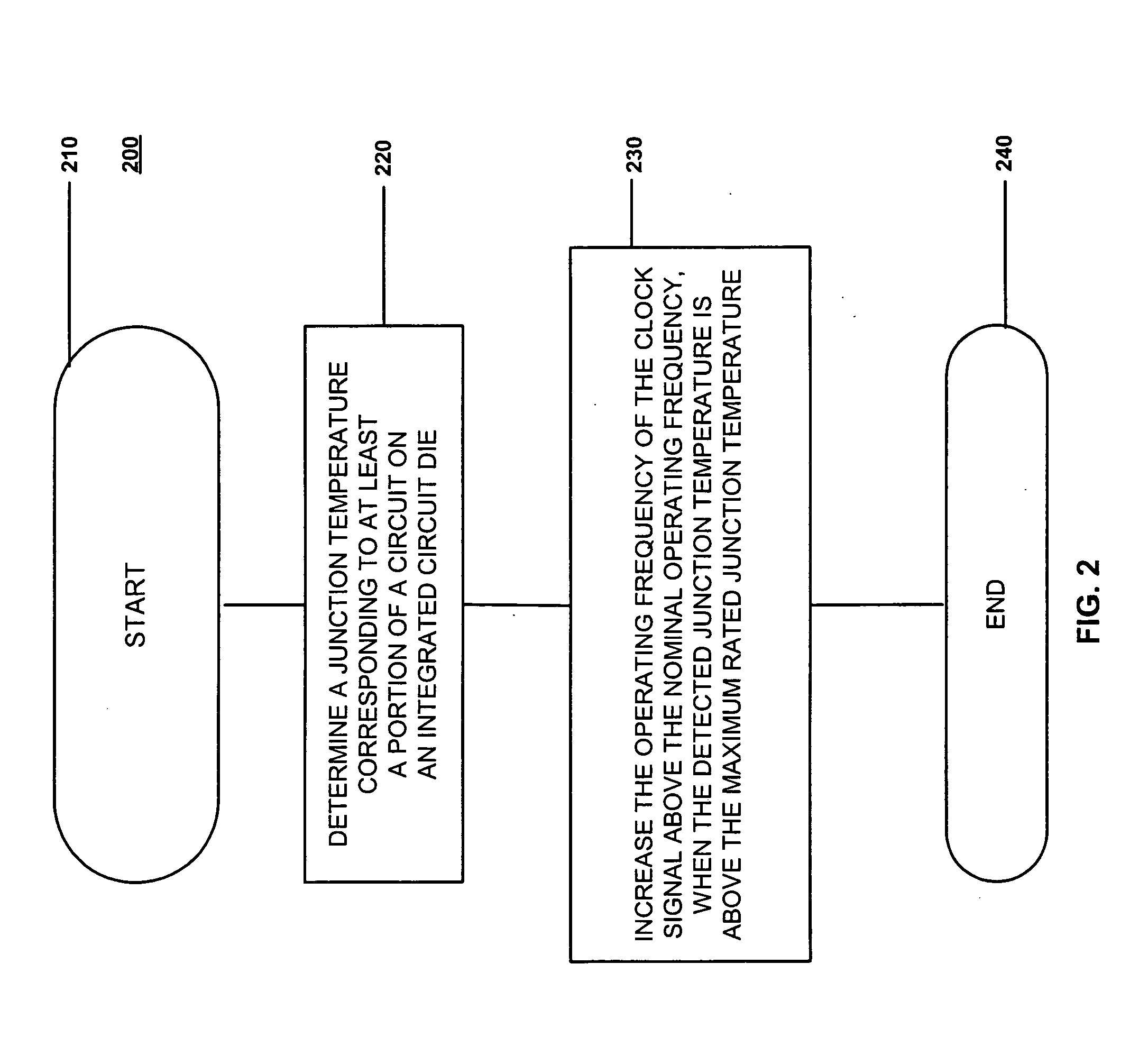
Adaptive temperature dependent feedback clock control system and method
An adaptive temperature dependent clock feedback control system and method for adaptively varying a frequency of a clock signal to a circuit such that the circuit may operate at a maximum safe operating clock frequency based on a circuit junction temperature. The clock control system includes a thermal sensor and a temperature dependent dynamic overclock generator circuit. The thermal sensor detects a junction temperature corresponding to at least a portion of the circuit on a semiconductor die. The temperature dependent dynamic overclock generator circuit varies the clock signal based on the semiconductor die junction temperature, such that the clock signal operates at the highest possible operating frequency associated with the detected junction temperature. The frequency of the clock signal is increased from a first frequency to at least a second frequency and a third frequency if the junction temperature is below a lower junction temperature threshold.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
Silicon Carbide on Diamond Substrates and Related Devices and Methods
ActiveUS20050164482A1Improve thermal conductivityReduce thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesWaferingSemiconductor structure
A method of forming a high-power, high-frequency device in wide bandgap semiconductor materials with reduced junction temperature, higher power density during operation and improved reliability at a rated power density is disclosed, along with resulting semiconductor structures and devices. The method includes adding a layer of diamond to a silicon carbide wafer to increase the thermal conductivity of the resulting composite wafer, thereafter reducing the thickness of the silicon carbide portion of the composite wafer while retaining sufficient thickness of silicon carbide to support epitaxial growth thereon, preparing the silicon carbide surface of the composite wafer for epitaxial growth thereon, and adding a Group III nitride heterostructure to the prepared silicon carbide face of the wafer.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
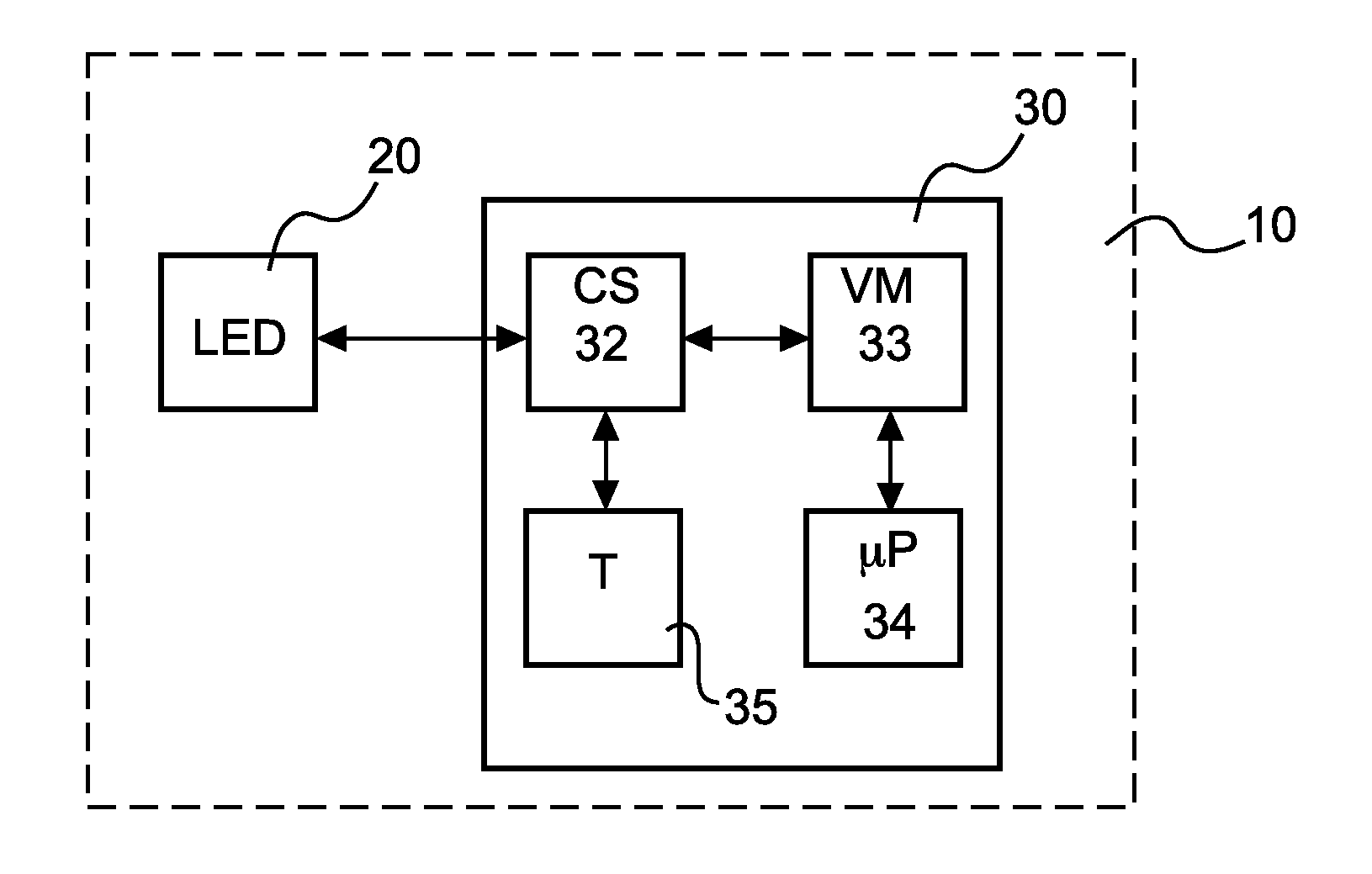
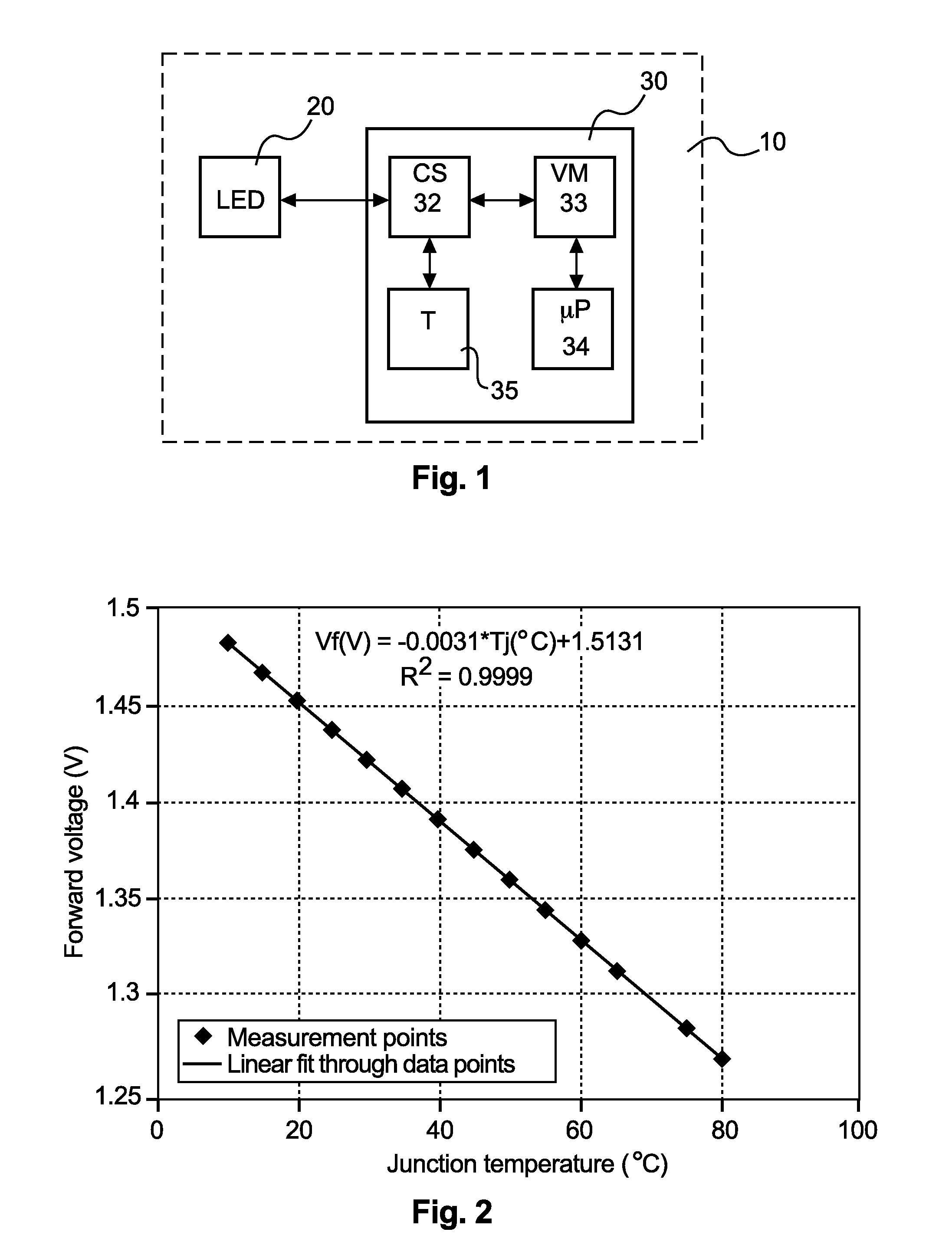
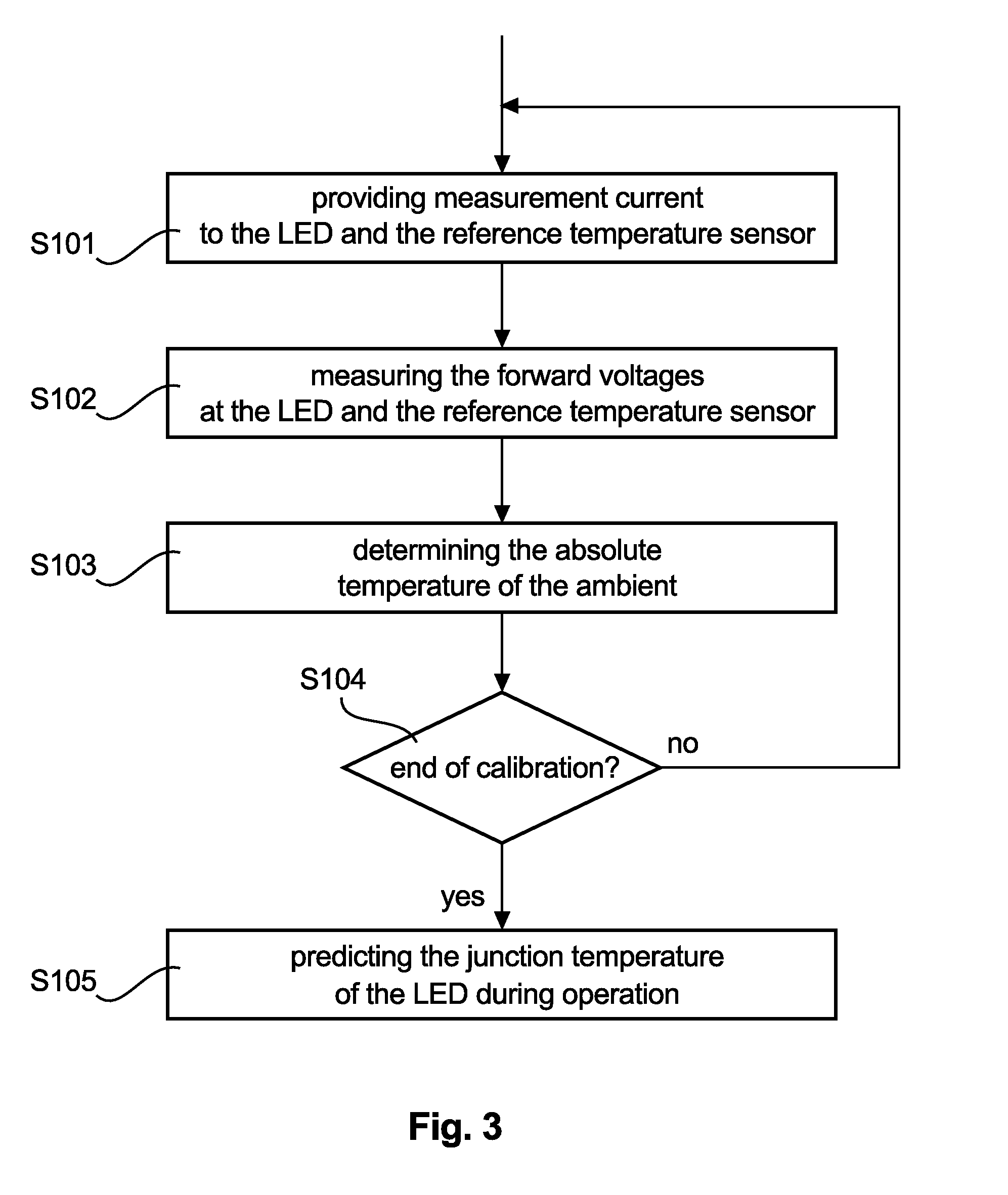
Self-calibration circuit and method for junction temperature estimation
InactiveUS20110150028A1Accurate and fast junction temperature measurementAccurate and fast junction temperatureThermometer detailsElectrical apparatusJunction temperatureEngineering
The present invention relates to a calibration circuit, computer program product, and method of calibrating a junction temperature measurement of a semiconductor element, wherein respective forward voltages at junctions of the semiconductor element and a reference temperature sensor are measured, and an absolute ambient temperature is determined by using the reference temperature sensor, and the junction temperature of the semiconductor element is predicted based on the absolute ambient temperature and the measured forward voltages.
Owner:NXP BV
LED light module assembly
ActiveUS7284882B2Point-like light sourceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsFlexible circuitsSurface mounting
An LED light module assembly for use with high power, high light output LED's includes a thin flexible circuit board with surface mounted LED's and other electronic components which is attached to a metal heat sink using a layer of a thermally conductive adhesive, such as a thermally conductive epoxy adhesive. A conduction path is provided from the LED carrier through the flexible circuit board by the incorporation of one or more thermally conductive vias in the region of the attachment pad used to bond the LED to the flexible circuit board. These vias provide a conduction path from the back side of the LED carrier through the circuit board to the thermally conductive adhesive and heat sink. The LED light module assembly has the capacity to dissipate between about 10-14 W of power without exceeding a maximum LED junction temperature of about 125° C.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL WORLD WIDE LLC
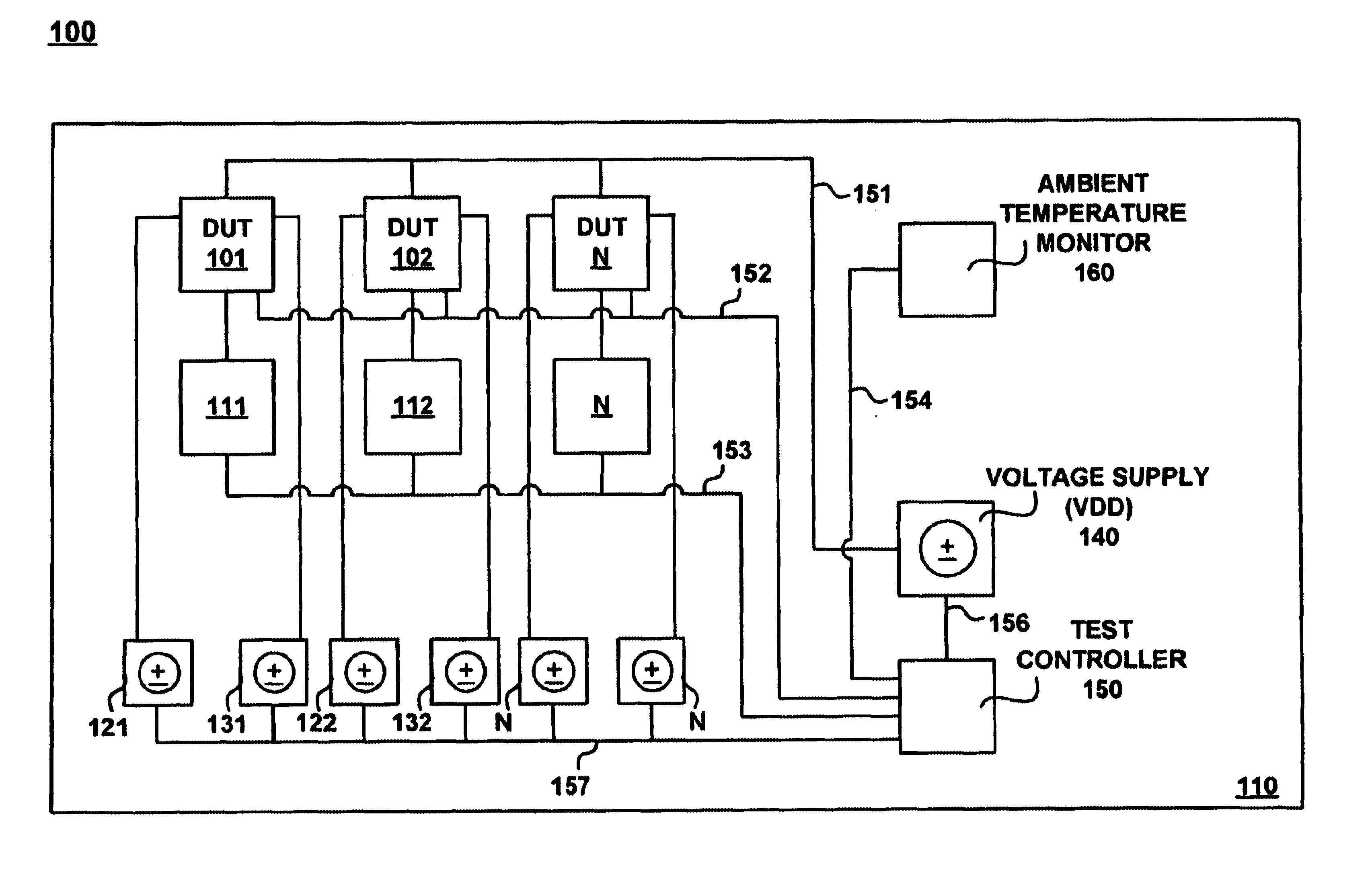
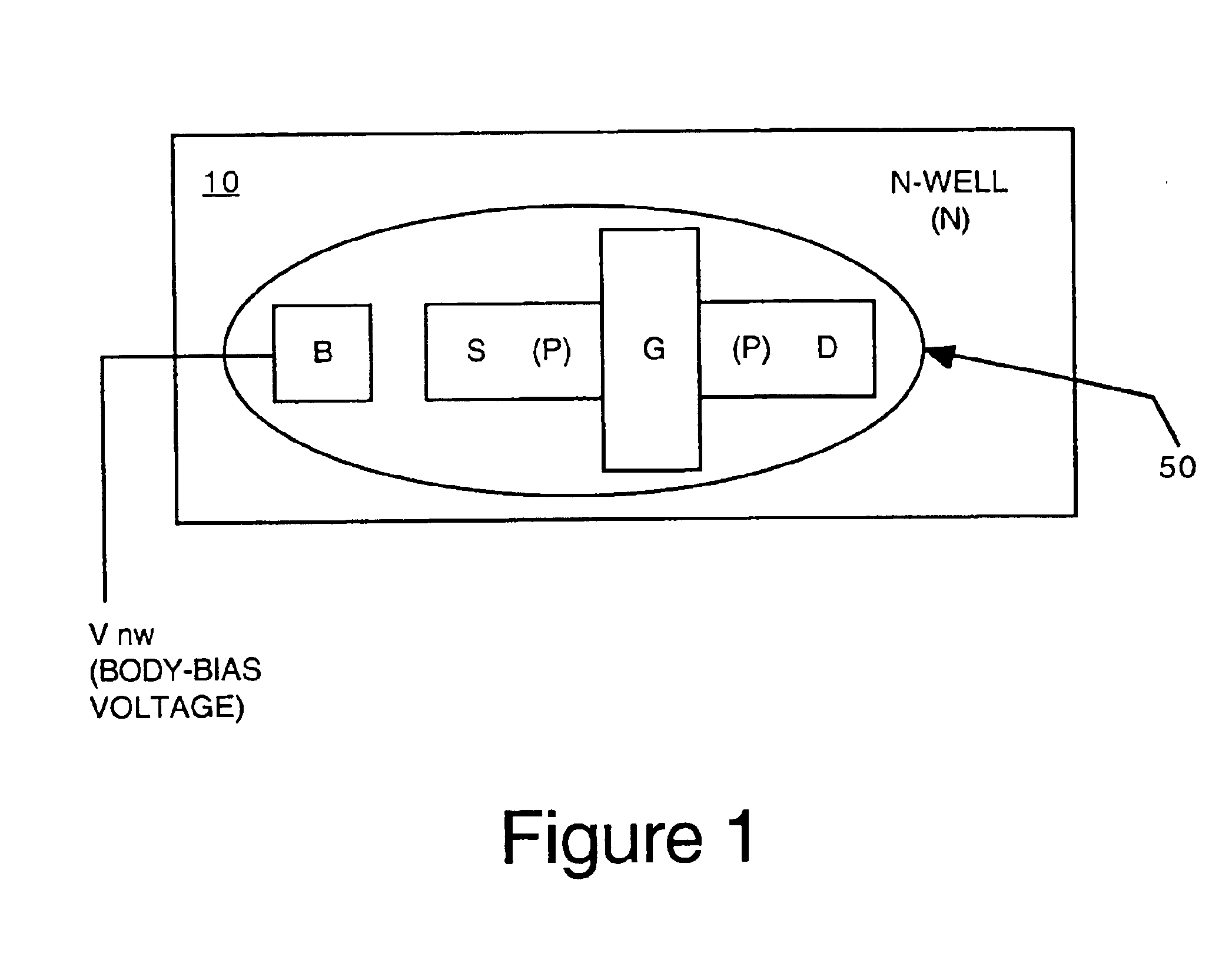
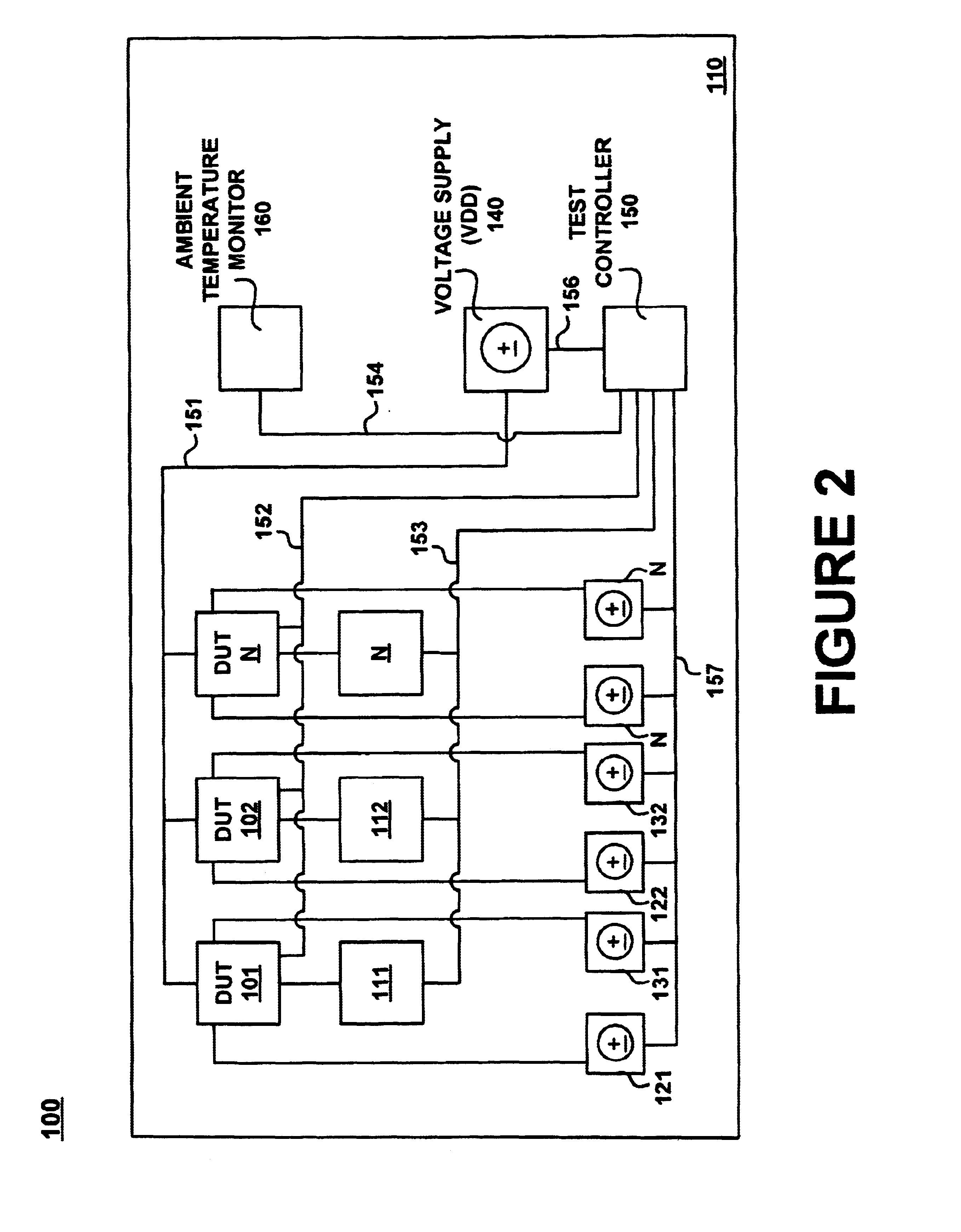
System and method for controlling temperature during burn-in
ActiveUS6900650B1Electronic circuit testingFault location by increasing destruction at faultJunction temperatureVoltage
Systems and methods for reducing temperature dissipation during burn-in testing are described. Devices under test are each subject to a body bias voltage. The body bias voltage can be used to control junction temperature (e.g., temperature measured at the device under test). The body bias voltage applied to each device under test can be adjusted device-by-device to achieve essentially the same junction temperature at each device.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
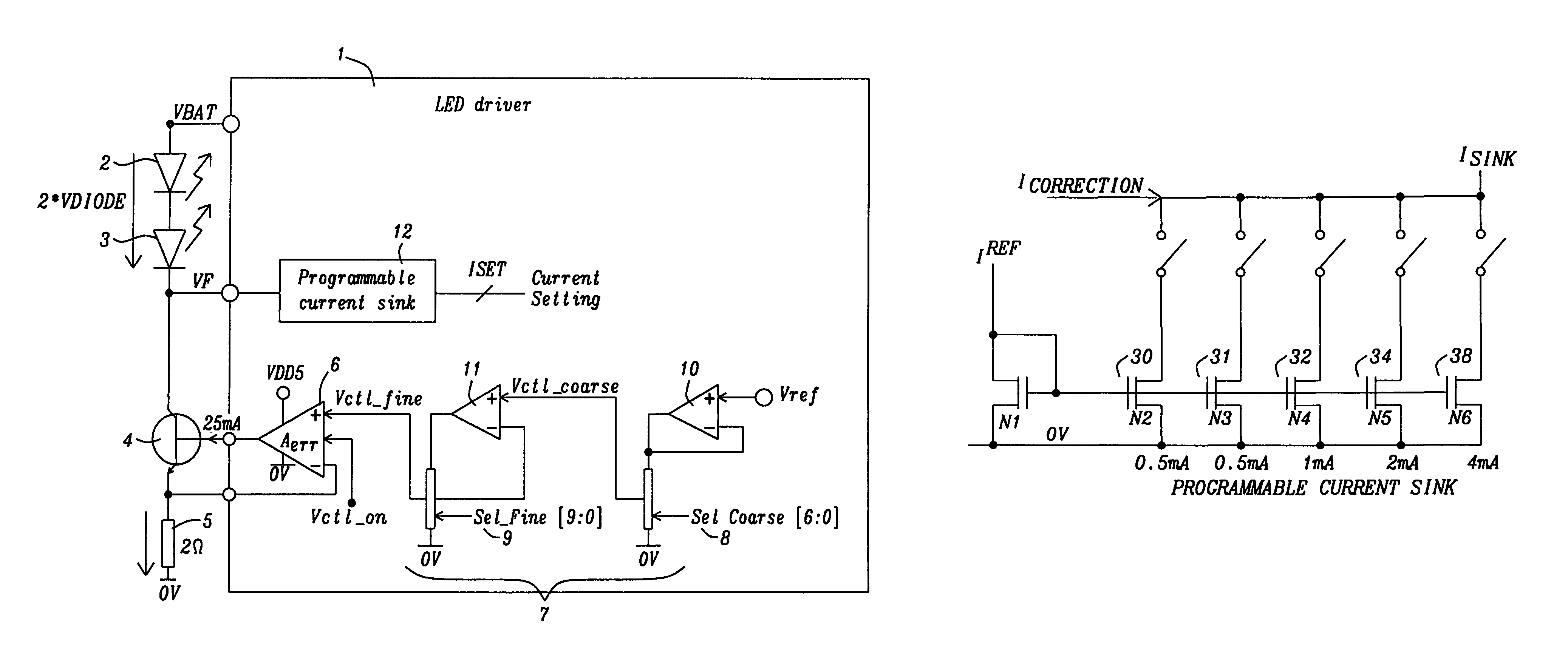
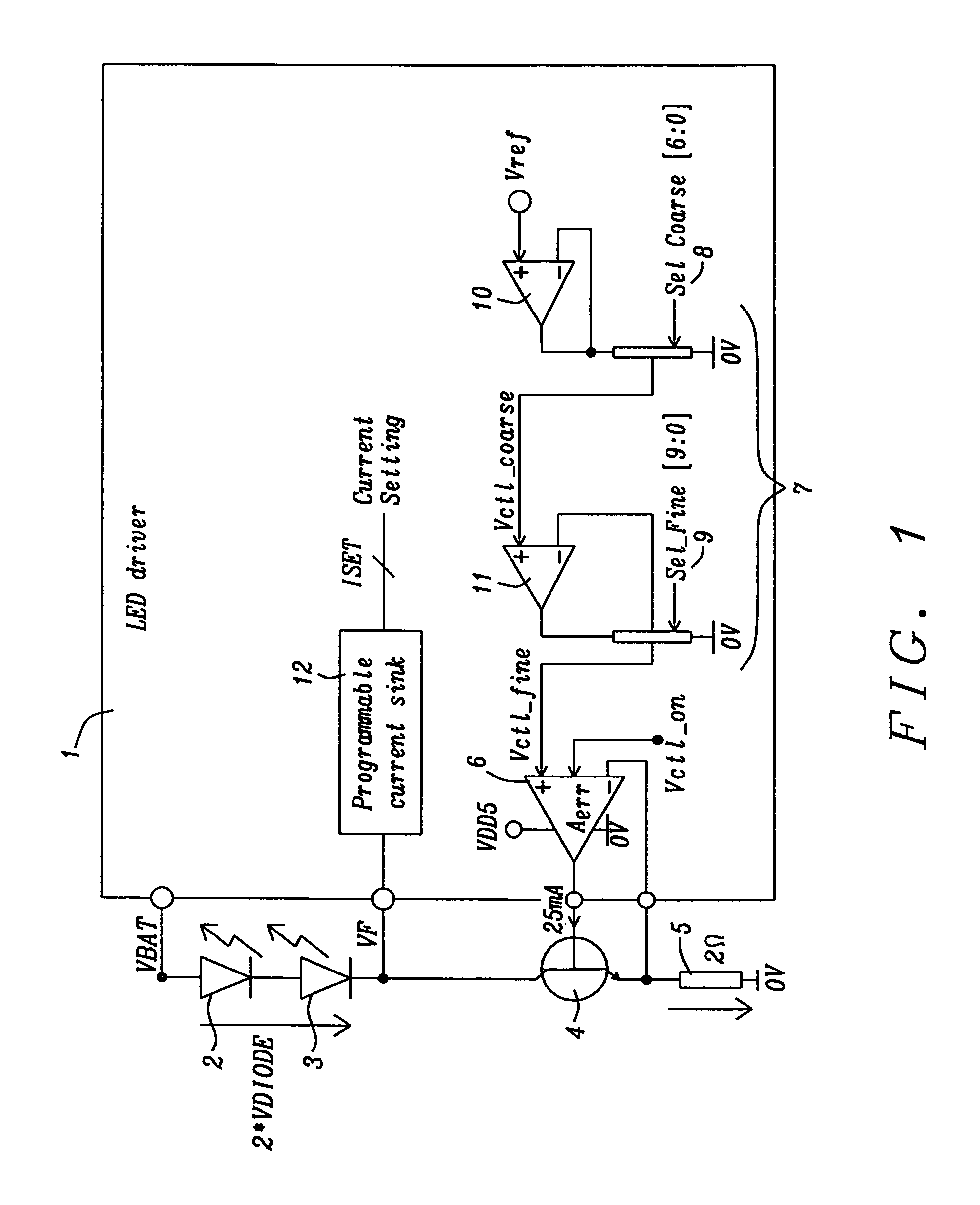
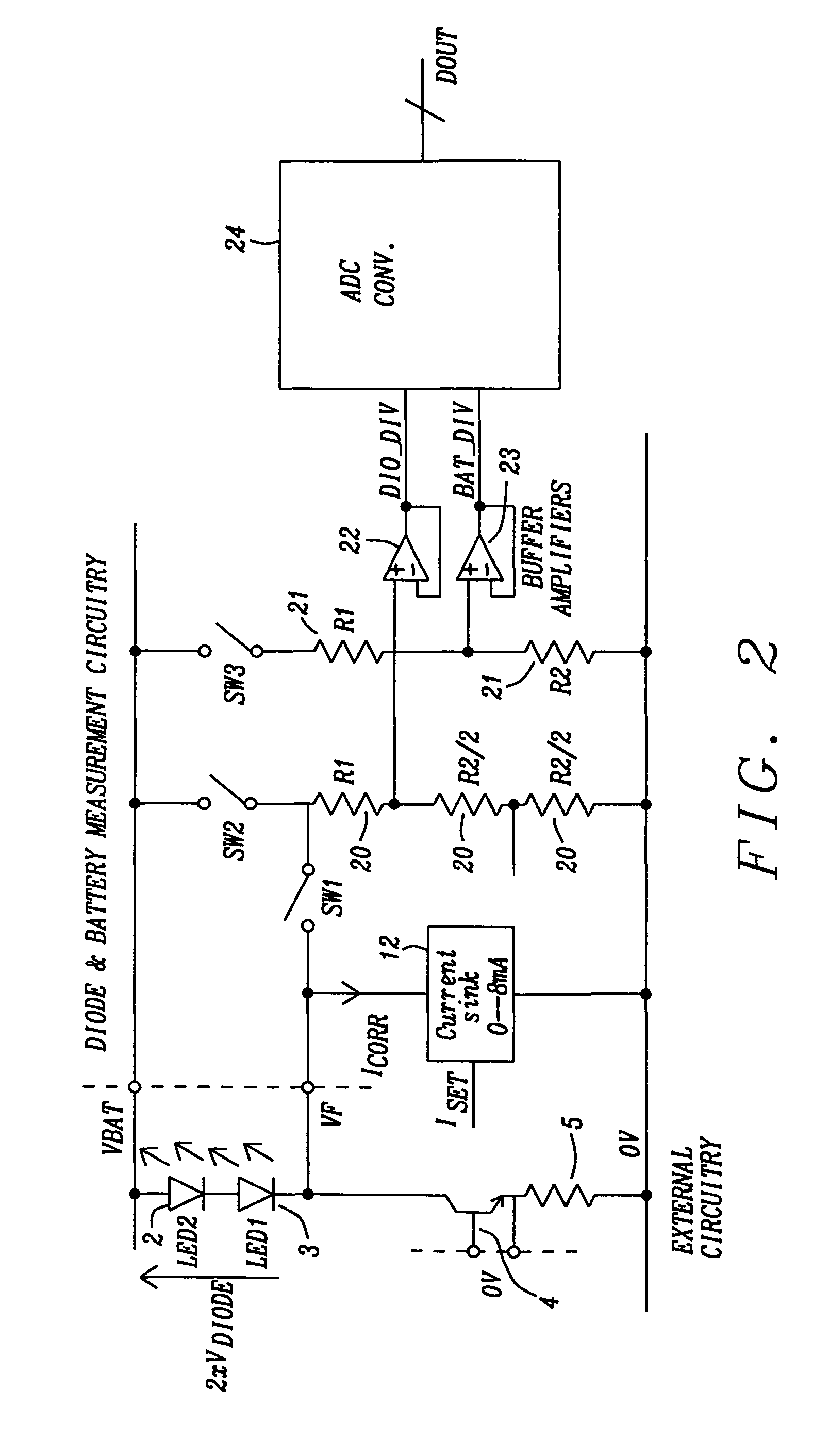
Circuit for driving an infrared transmitter LED with temperature compensation
ActiveUS8283876B2Eliminate currentElectroluminescent light sourcesElectric light circuit arrangementDriving currentJunction temperature
Systems and methods to achieve a circuit for driving one or more infrared transmitter LEDs with temperature compensation have been disclosed. In a preferred embodiment of the invention the circuit has been applied for a rain sensing system. The junction temperature of the LED is measured and compensated by adjusting the driver current of a voltage-to-current converter driving the LED. The LED junction temperature is measured by comparing the difference in the forward diode voltage at different current densities. This voltage difference is extracted when switching the drive currents between different constant values. The measurement results are converted to digital values, which are used by a buffered dual ladder resistive DAC structure to adjust the drive current to temperature variations.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
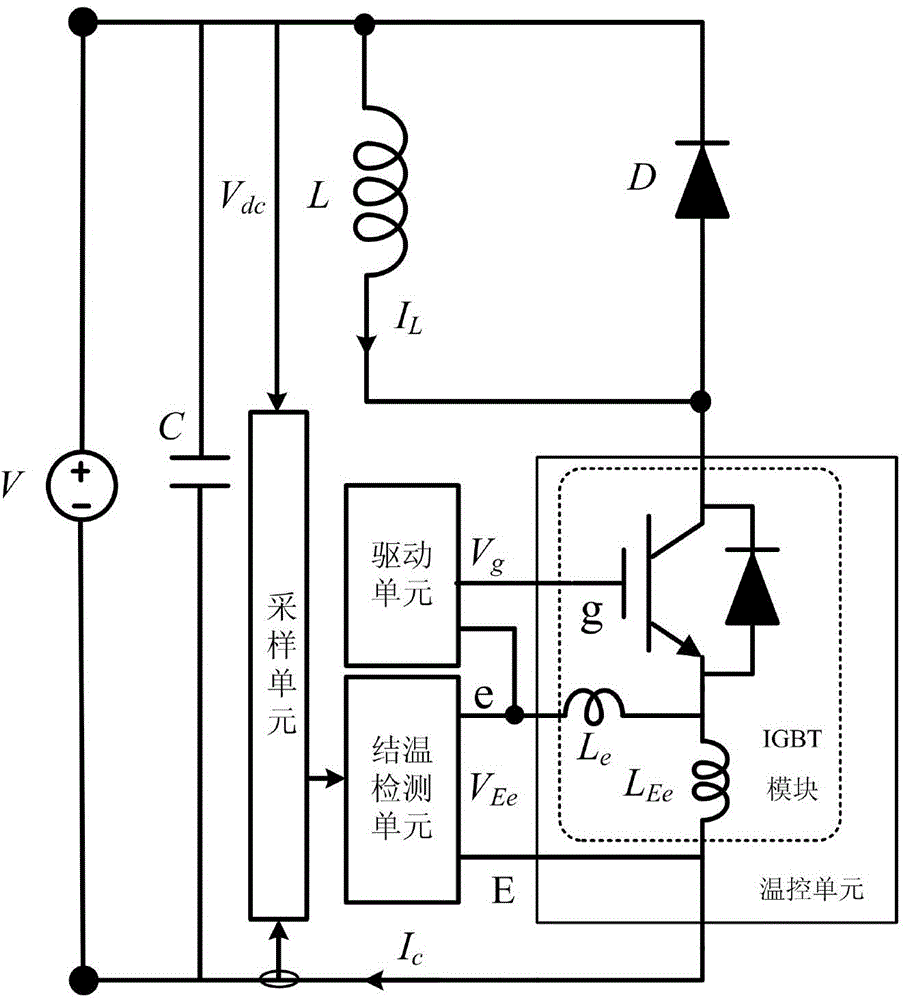
System and method for on-line detection of operating junction temperature of IGBT module
The invention discloses a system and a method for on-line detection of operating junction temperature of an IGBT module. Under an actually continuous on and off switching operate states of the IGBT module, changeable drive current and collector current generate induced voltage on stray inductance of the IGBT module; the induced voltage occurs twice voltage changes during turn-off, and the interval is recorded as the temperature-sensitive time which is closely related to the operating junction temperature of the IGBT module under a regular voltage and current turn-off condition. According to the system and the method, an IGBT test system is established to extract the temperature-sensitive time at different DC bus voltages, IGBT conducting currents and operating junction temperatures so as to establish an off-line reference database, voltage between a driving emitting electrode and a power emitting electrode of the IGBT module are monitored during the actual operation of an IGBT, and the temperature-sensitive time is extracted to calculate junction temperature on line. Compared with the conventional technology for monitoring the operating junction temperature of the IGBT, the method provided by the invention has higher real-time performance and integration.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Lighting device with one or more removable heat sink elements
ActiveUS20110074265A1Easy to removeEasy to replacePoint-like light sourceElectric discharge tubesShortest distanceJunction temperature
A lighting device comprising at least a first light source and at least one heat sink element that is removable, that comprises an first inner region and an first outer region, that is identical in shape to another heat sink element, that is in thermal contact with a trim element, that is stacked, that is in thermal contact with at least a first portion of a first surface of the trim element, that has a cross-sectional area at a first distance from an axis of a trim element that is larger than at a shorter distance, and / or that maintains a junction temperature of a lighting device at or below a recommended junction temperature. Also, a lighting device comprising at least a first light source, a trim element, a driver sub-assembly and a spacer element positioned between the trim element and the driver sub-assembly. Also, methods of dissipating heat.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
Devices And Methods For LED Life Test
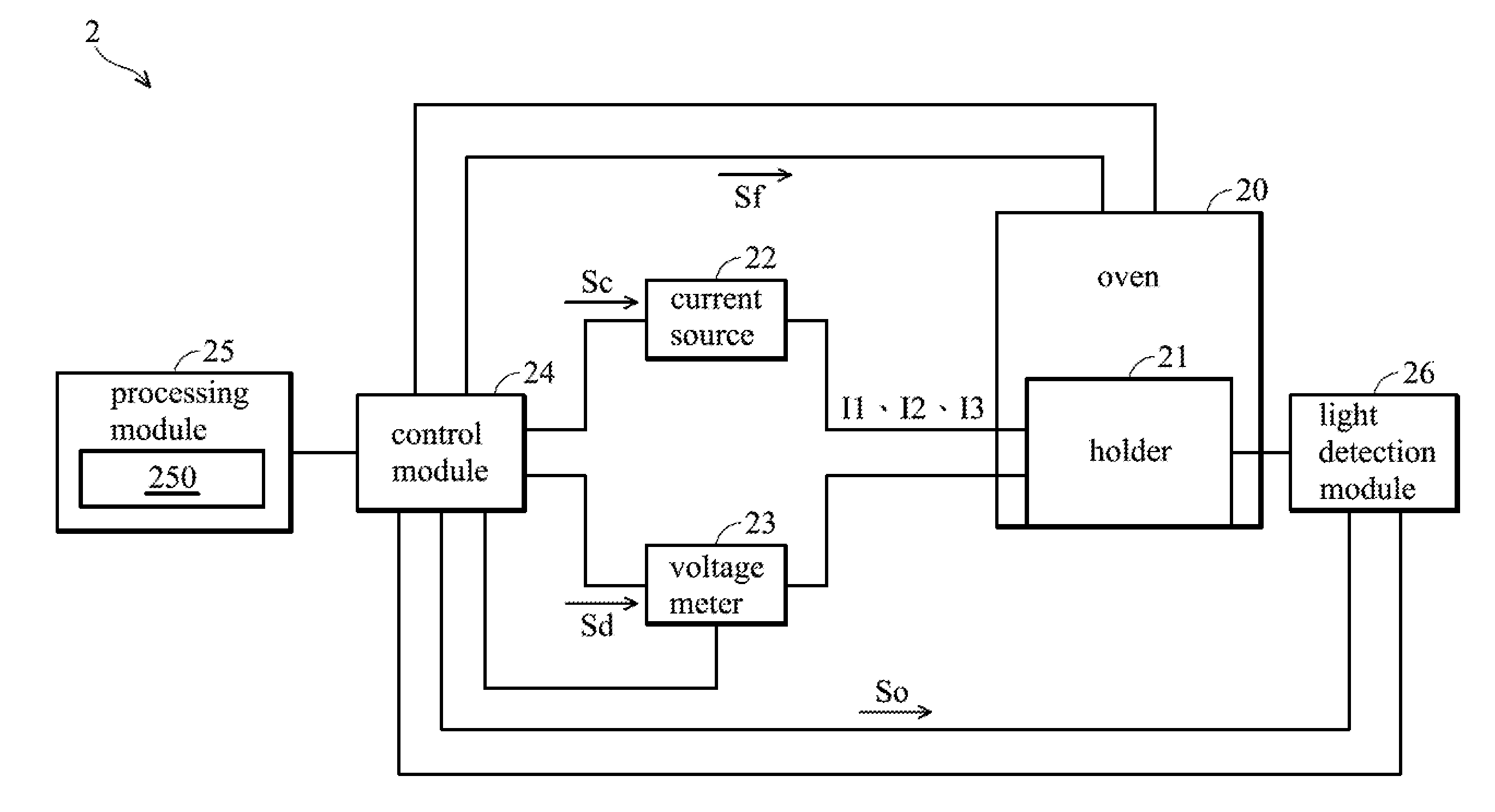
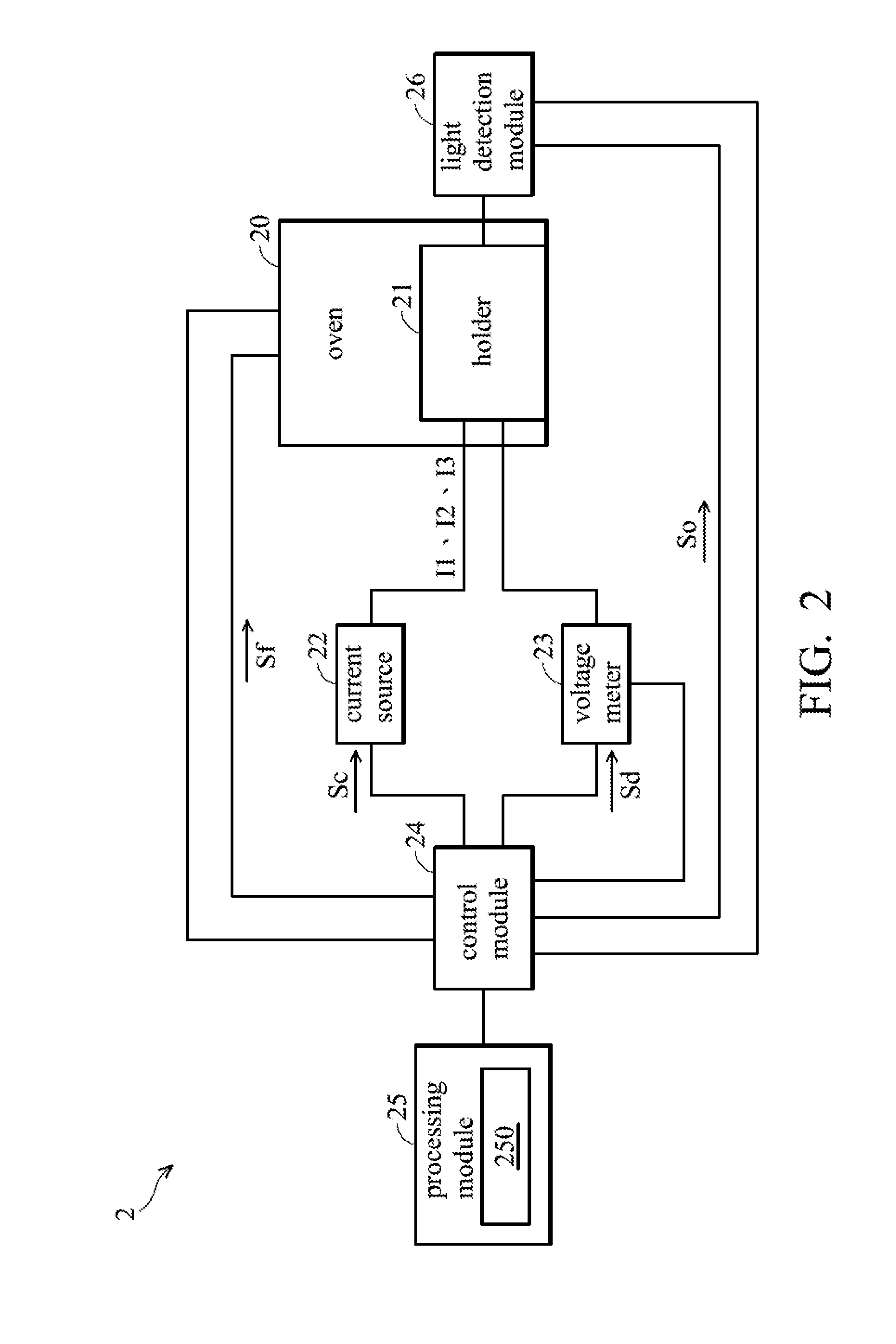
A life test device comprises an oven, a current source, a voltage meter, a control module, and a process module. A light-emitting diode (LED) is disposed in the oven. The temperature of the oven is gradually changed in a first period and remains at a set temperature in a second period. The current source provides a first current and a second current to the LED. The voltage meter measures forward voltages of the LED. The control module controls the current source to output the first or second current to the LED and controls the voltage meter to measure the forward voltages of the LED. The process module calculates a junction temperature of the LED according to the forward voltages and a variation relationship formula between the forward voltages and the temperature of the oven.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
LED illumination device and calibration method for accurately characterizing the emission LEDs and photodetector(s) included within the LED illumination device
ActiveUS9392660B2Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDriving currentPhotovoltaic detectors
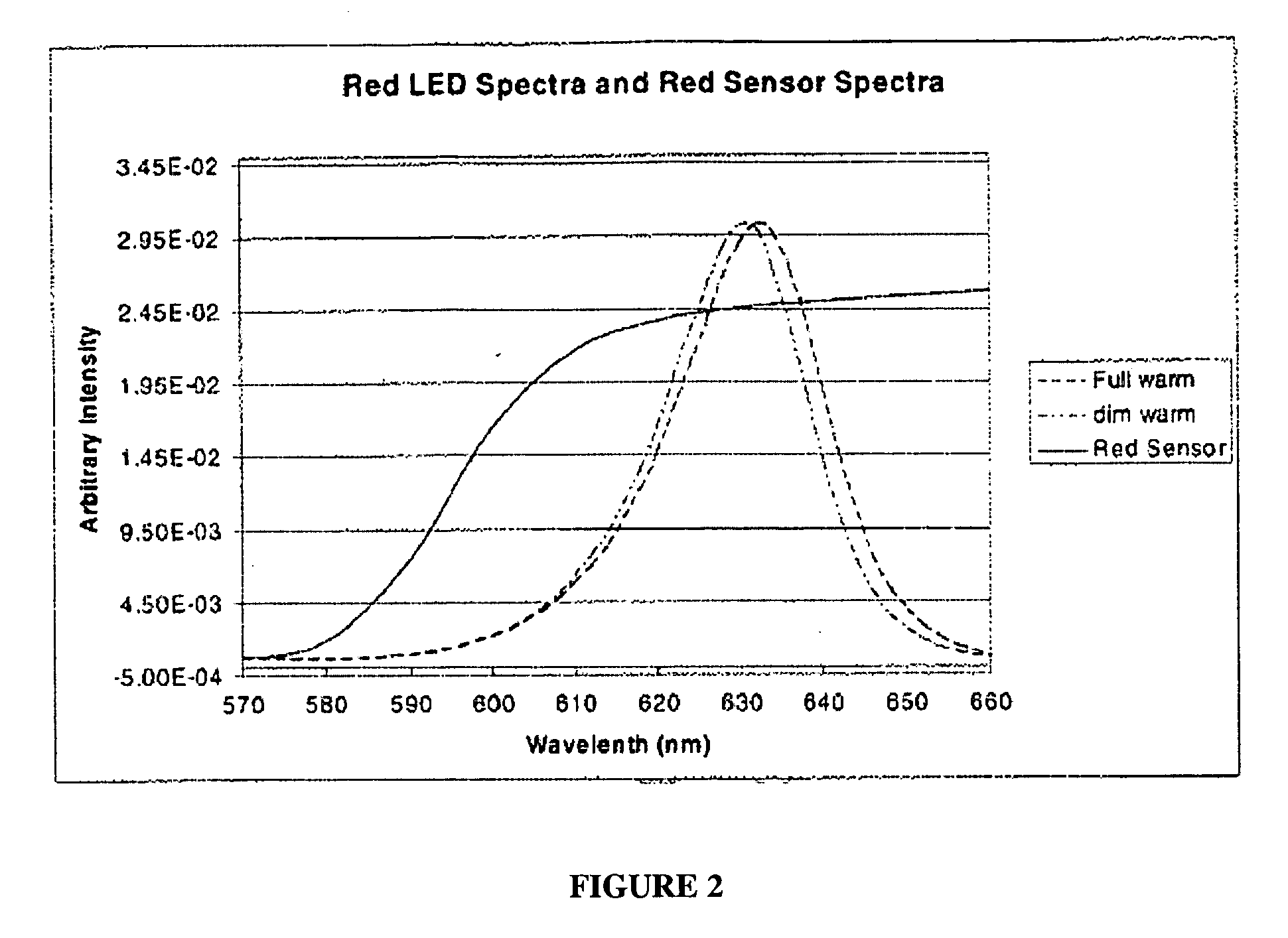
An illumination device and method is provided herein for calibrating individual LEDs and photodetector(s) included within the illumination device, so as to obtain a desired luminous flux and a desired chromaticity of the device over time as the LEDs age. Specifically, a calibration method is provided herein for characterizing each emission LED and each photodetector separately. The wavelength and intensity of the illumination produced by each emission LED is accurately characterized over a plurality of different drive currents and ambient temperatures, and at least a subset of the wavelength and intensity measurement values are stored with a storage medium of the illumination device for each emission LED. The responsivity of the photodetector is accurately characterized over emitter wavelength and photodetector junction temperature, and results of said characterization are stored with the storage medium.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Method and system for calculating transient junction temperature of IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Translator) module
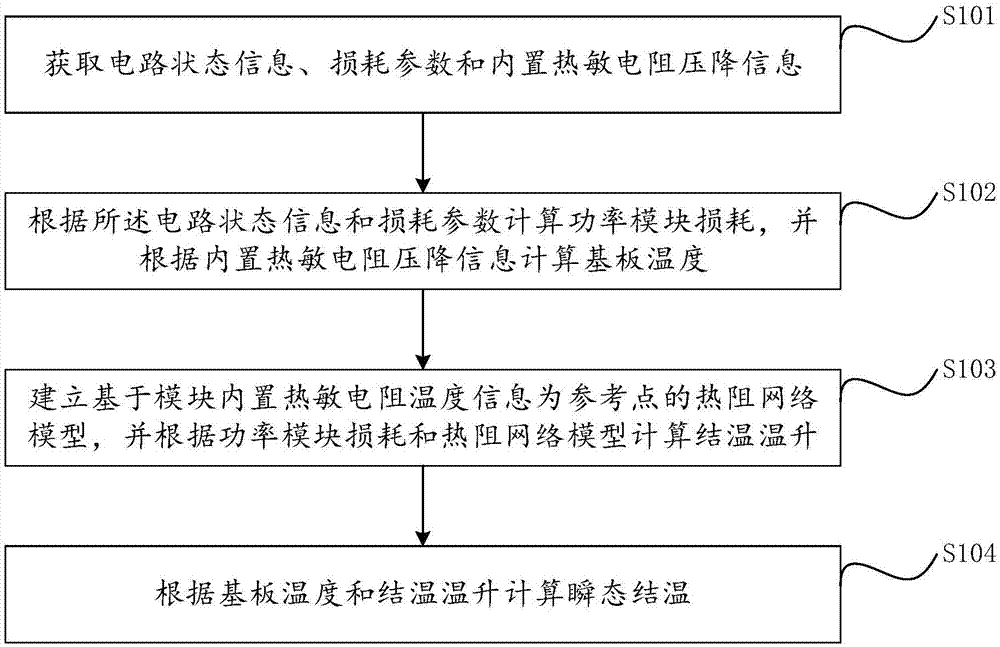
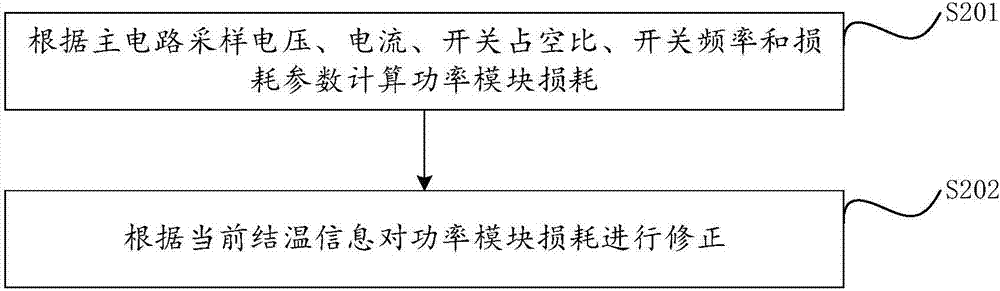
ActiveCN107219016AAccurate Junction Temperature InformationAchieve online accessThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansElectrical resistance and conductanceJunction temperature
The invention provides a method and a system for calculating the transient junction temperature of an IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Translator) module. The method comprises the steps of: acquiring circuit state information, loss parameter and internal thermistor voltage drop information; calculating power module loss according to the circuit state information and the loss parameter, and calculating substrate temperature according to the internal thermistor voltage drop information of the module; according to the temperature information provided by internal chips and the internal thermistor of the module as reference temperature, in consideration with thermal coupling between the internal chips of the power module at the same time, establishing a simpler IGBT module thermistor network model, and calculating a junction temperature rise according to the power module loss and the thermistor network model; and calculating the transient junction temperature according to the substrate temperature and the junction temperature rise, thus realizing on-line acquisition of the transient working junction temperature of the IGBT. By sufficiently utilizing the existing thermistor resource inside the power module, a junction temperature measurement system based on a power module electro-thermal coupling model is established, so that accurate power device junction temperature information is provided for security operation and health management of a converter system.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
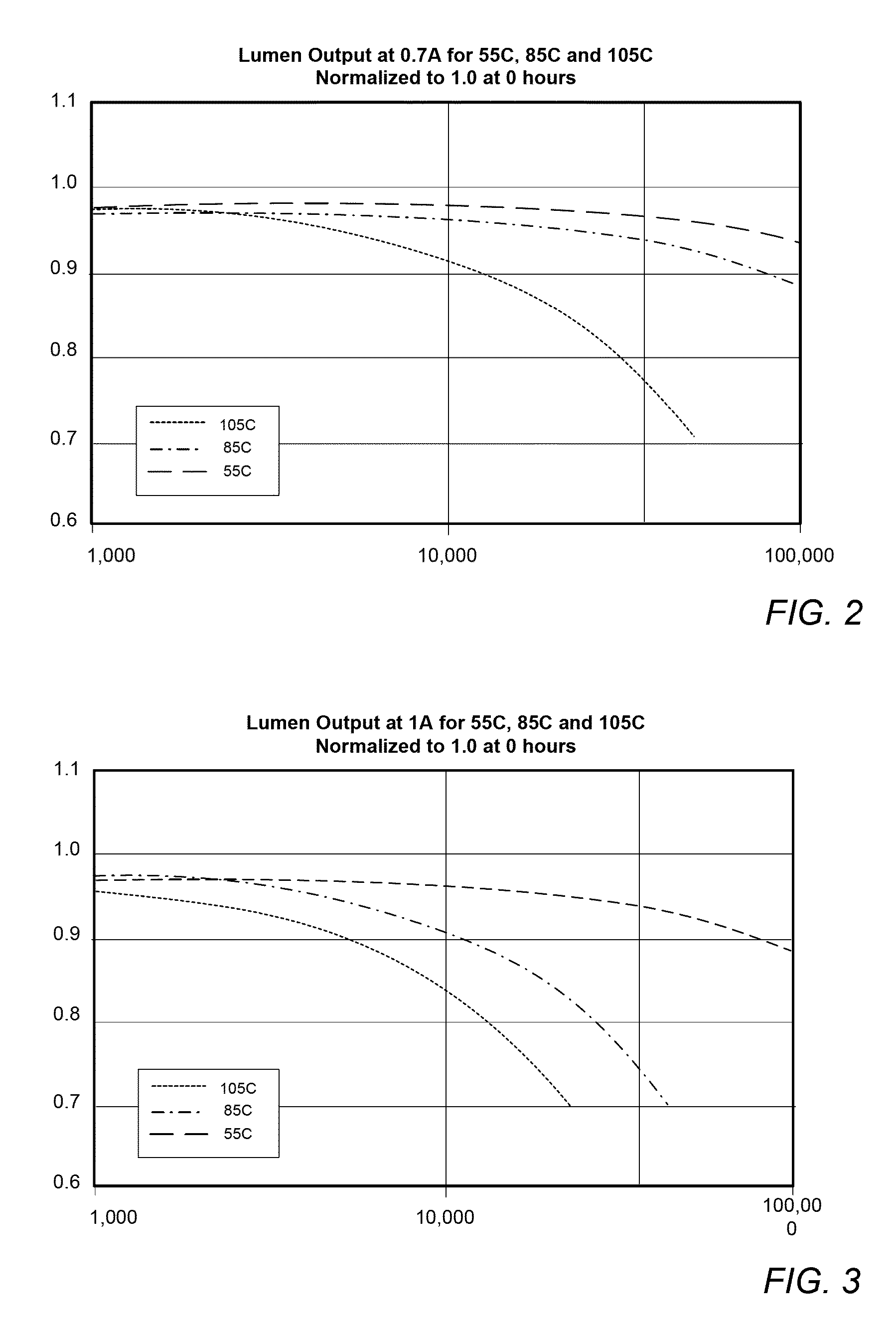
Power module life estimation fatigue function
A system and method for estimating a condition of a power module is provided. In accordance with an embodiment, a motor controller may be maintained by tracking a total proportion of power module life expended by a power module in a variable frequency motor controller based on a minimum junction temperature or a mean junction temperature and a junction temperature change, and indicating when the power module is estimated to fail.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
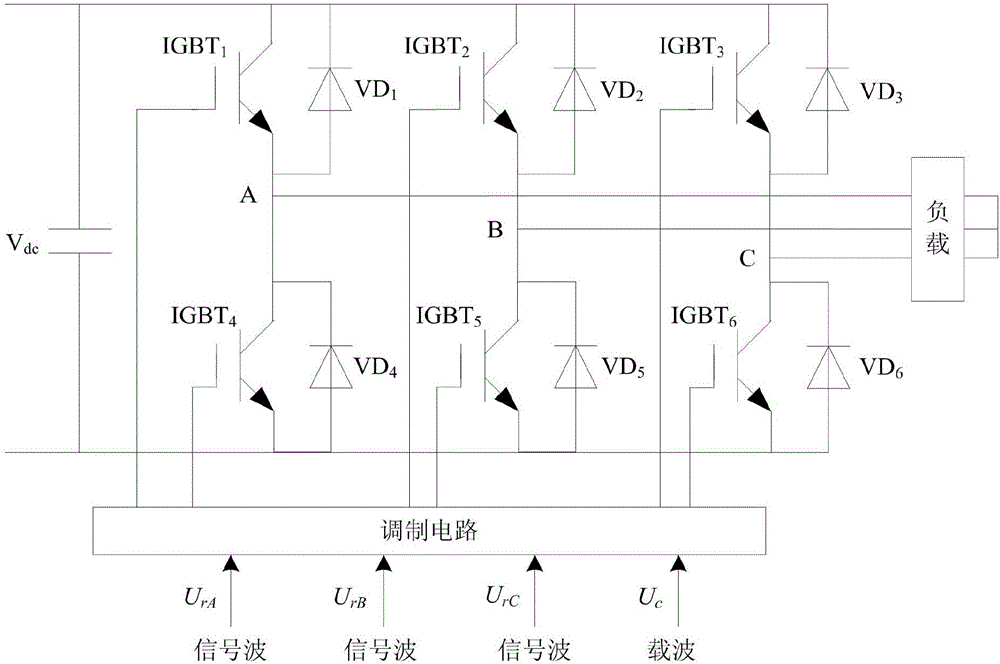
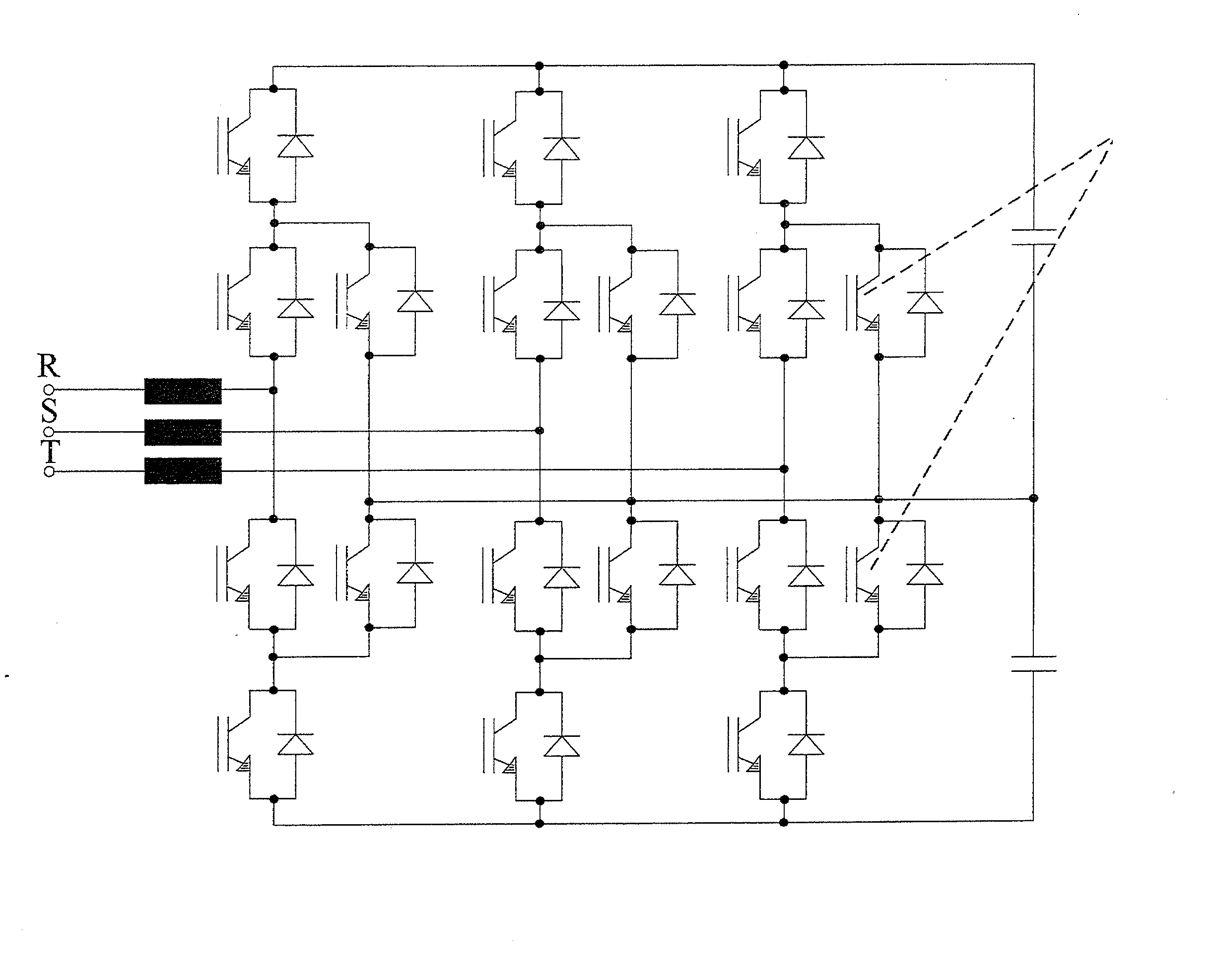
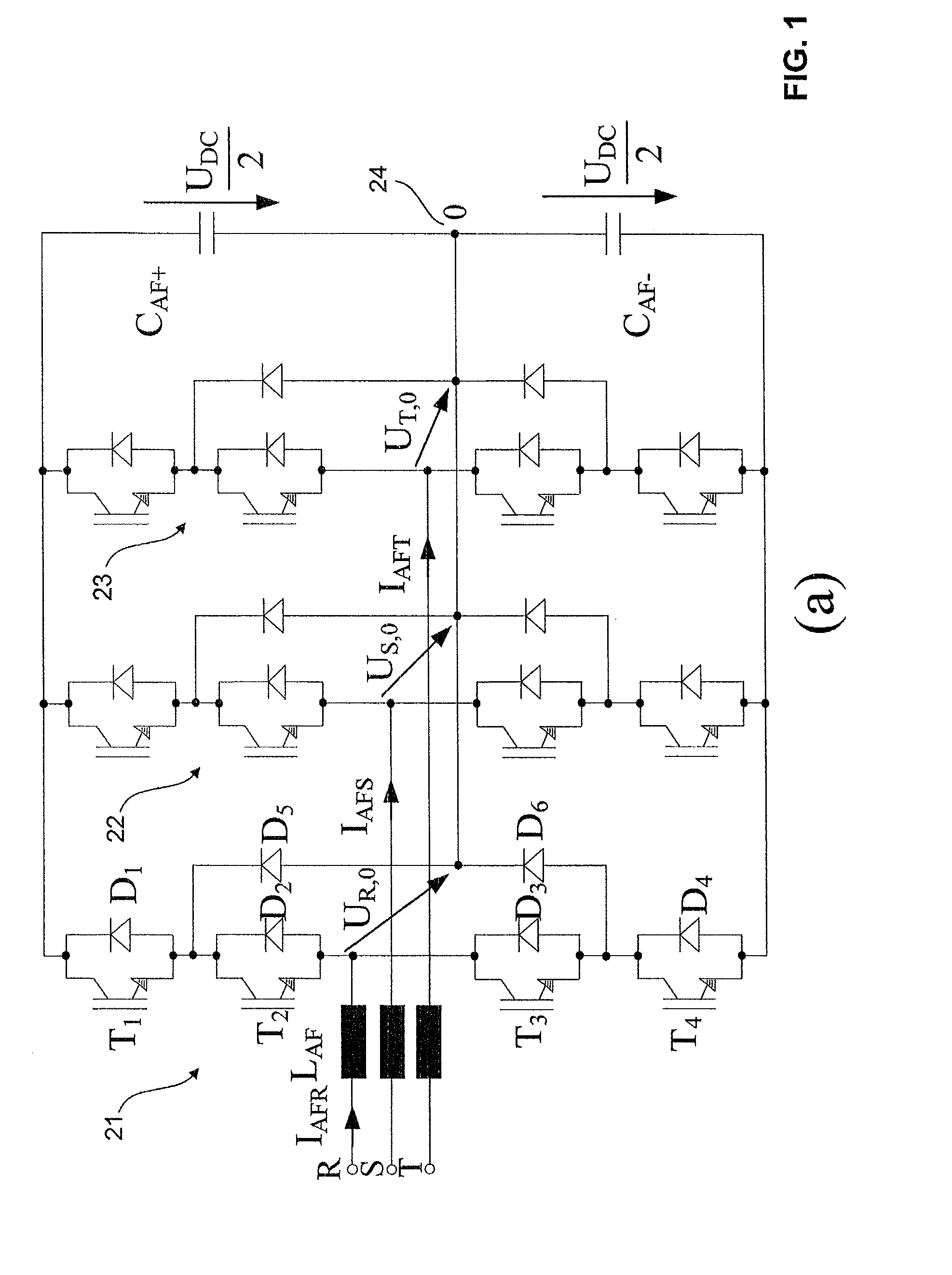
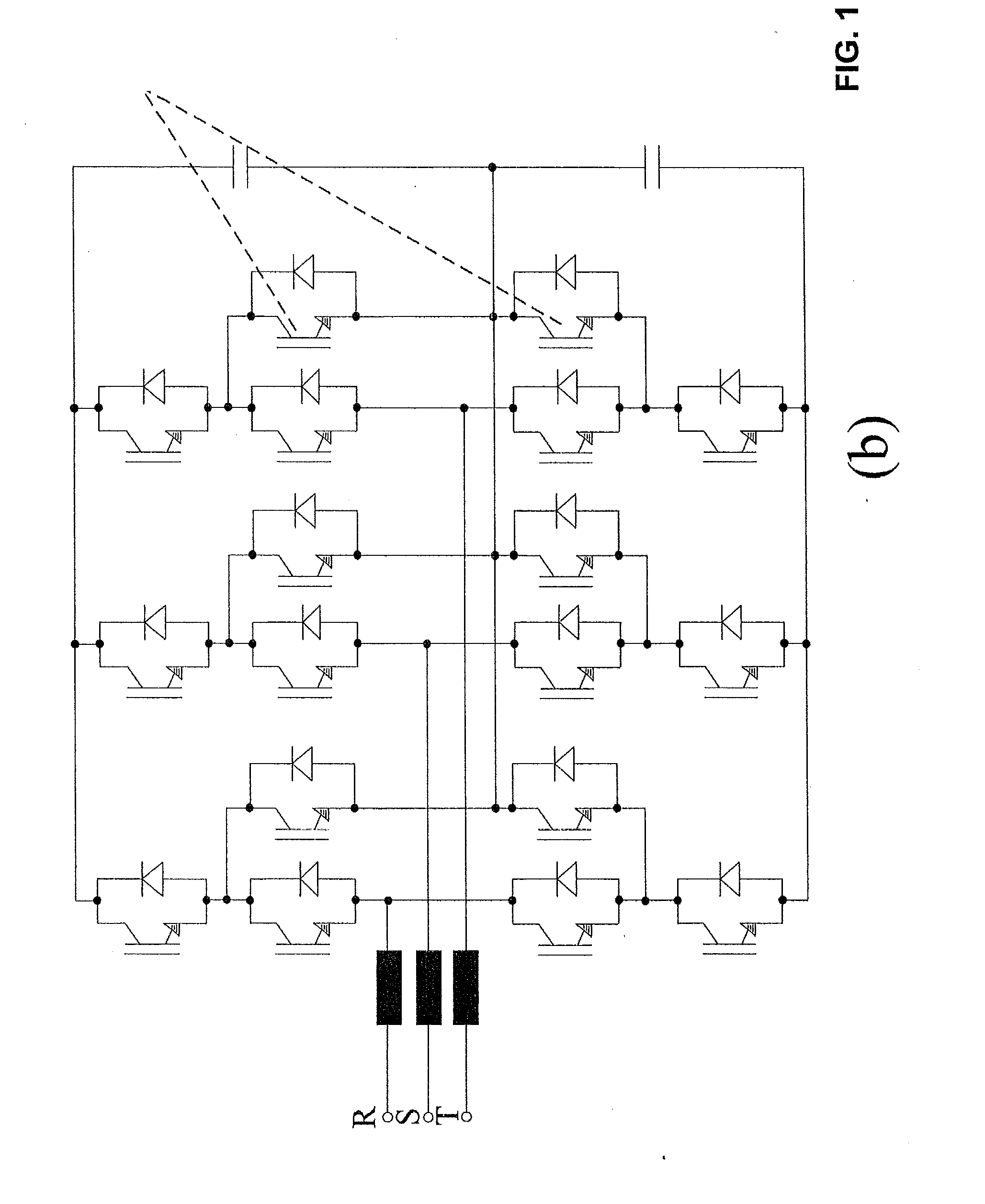
Method and device for determining a control scheme for an active power filter
ActiveUS20120300514A1Improve balanceReduce lossActive power filteringAc-dc conversion without reversalPhase shiftedJunction temperature
A method is provided for determining a control scheme for a neutral point clamped (NPC) voltage source converter (VSC) with at least 3 levels and a topology of three bridge legs between each of three phases of a grid and a neutral point. Each leg includes at least four active switches, and a clamping carrier modulator synchronized with the grid is provided for the control of no-switching intervals. The method includes: analyzing the waveform of the grid and / or a load voltage and determining windows defining an allowed period for no-switching of the corresponding bridge leg; operating or simulating the operation of the voltage source converter with different clamping carrier modulator frequencies, and then analyzing the balance in the operating junction temperatures and / or power losses across the active switches and also analyzing the total losses of the voltage source converter; comparing the balance and the total losses of different clamping carrier modulator frequencies and selecting either the clamping carrier modulator frequency according to showing, as primary criterion, the better balance and, as secondary criterion, the lower total losses; operating or simulating the operation of the voltage source converter with the selected clamping carrier modulator frequency, while iteratively changing at least one of the following operating parameters of the voltage source converter: switching frequency, DC-link voltage reference, duty cycle of clamping carrier modulator, phase shift of the clamping carrier modulator relative to the grid, and optimizing the balance in the operating junction temperatures and / or power losses across the active switches and the total losses of the voltage source converter as a function of the adjustment of these operating parameters until reaching optimum operation parameters for the control scheme.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
Silicon carbide on diamond substrates and related devices and methods
ActiveUS7033912B2Improve thermal conductivityReduce thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesWaferingSemiconductor structure
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
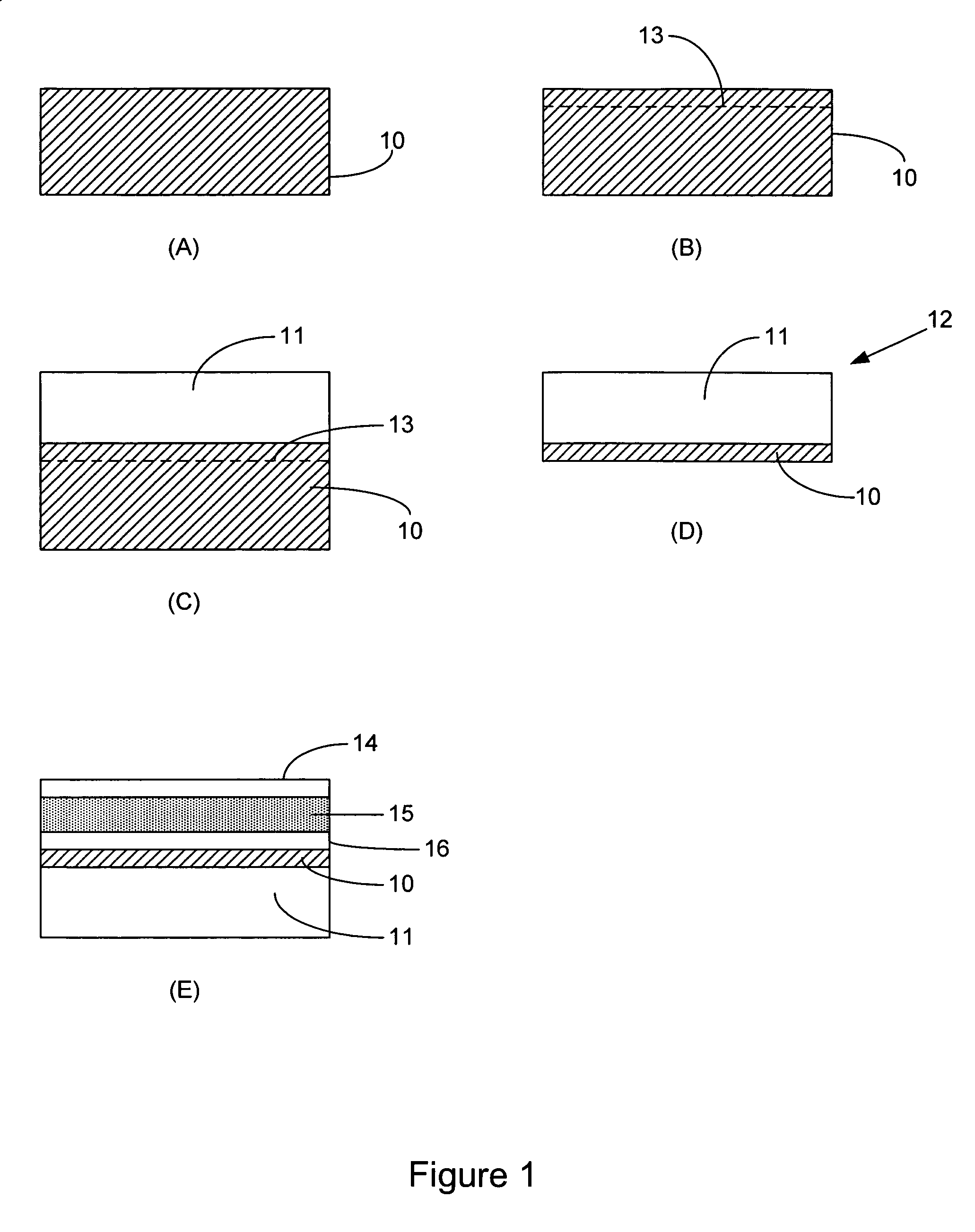
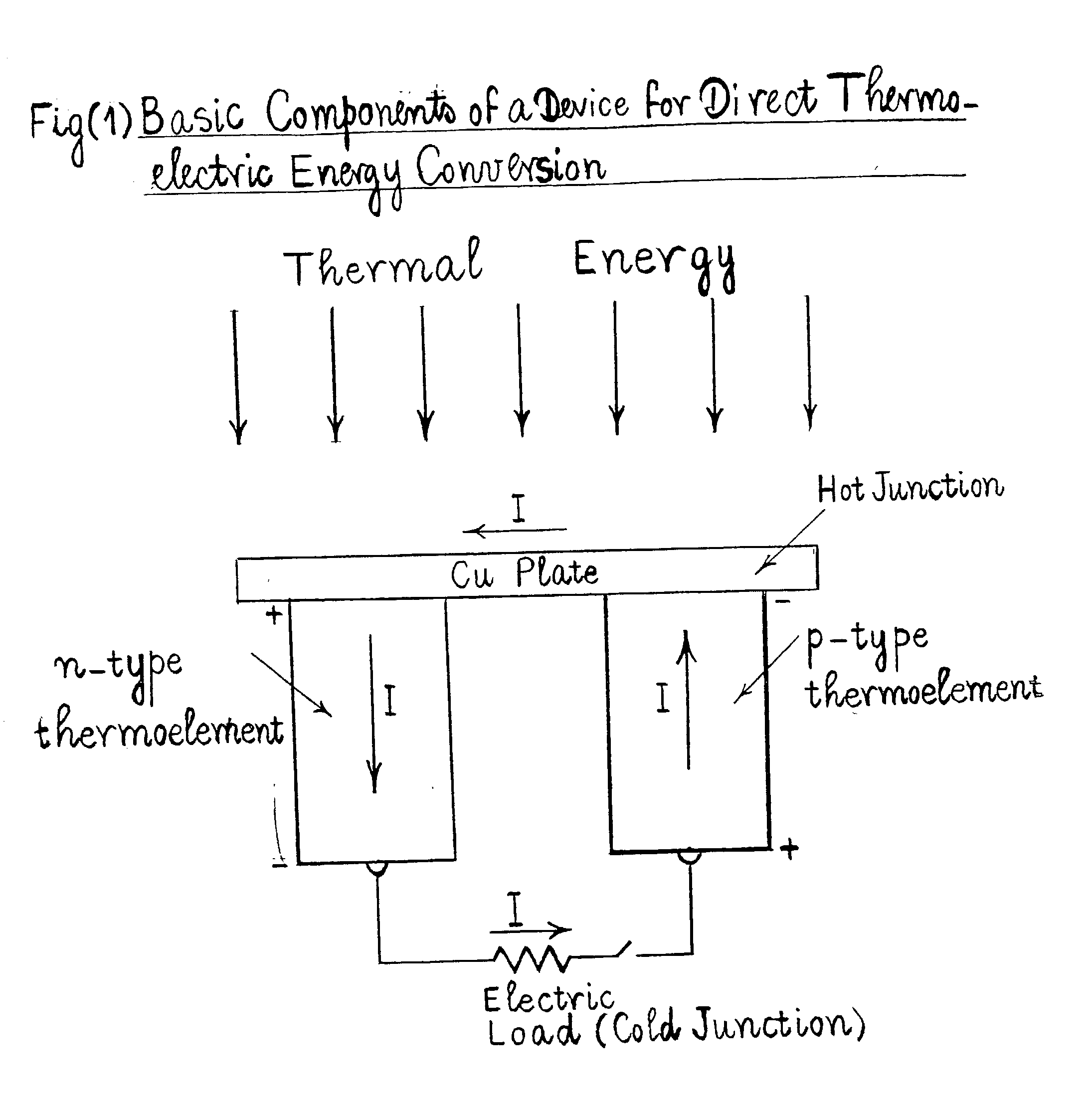
Method for producing a device for direct thermoelectric energy conversion
InactiveUS20030110892A1Polycrystalline material growthThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentJunction temperatureEngineering
In devices used for the direct conversion of heat into electricity, or vice versa, known in the art as thermoelectric power generators, thermoelectric refrigerators and thermoelectric heat pumps, the efficiency of energy conversion and / or coefficient of performance have been considerably lower than those of conventional reciprocating or rotary, heat engines and / or vapor-compression systems, employing certain refrigerants. The energy conversion efficiency of power generating devices, for example, aside from the hot and cold junction temperatures, also depends on a parameter known in the art as the thermoelectric figure of merit Z=S2sigma / k, where S is the thermoelectric power, sigma is the electrical conductivity and k is the thermal conductivity, of the material that constitutes the p-type, and / or n-type, thermoelements, or branches, of the said devices. In order to achieve a considerable increase in the energy conversion efficiency, a thermoelectric figure of merit of the order of 10-2 K-1, or more, is needed. It is reasonably expected that such an order of magnitude, for the figure of merit, can be realized with a composition of matter, comprising magnesium, silicon, lead and barium, and optionally comprising one, or more, additional doping materials.
Owner:NICOLOAU MICHAEL C
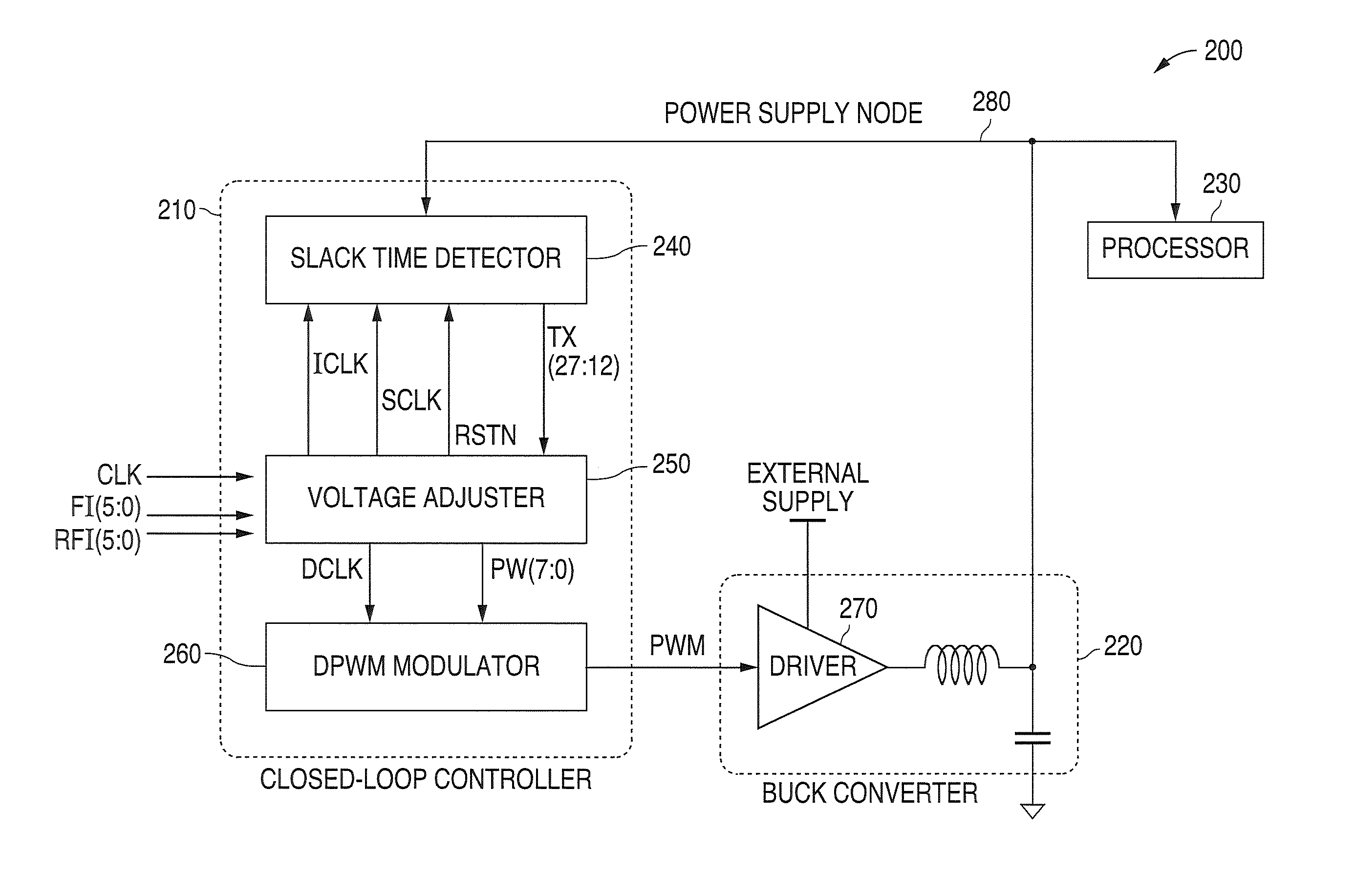
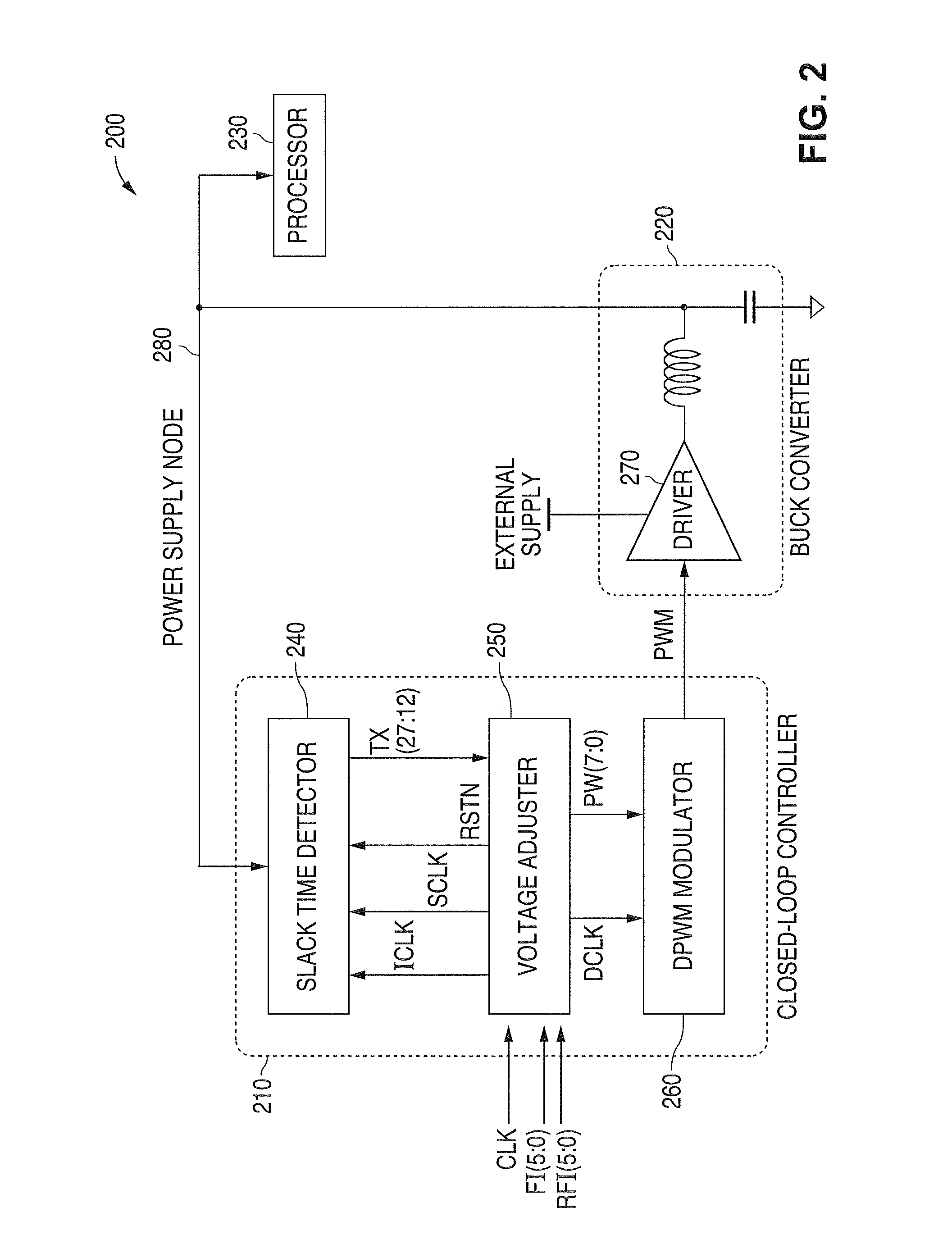
System and method for providing a digital self-adjusting power supply that provides a substantially constant minimum supply voltage with regard to variations of PVT, load, and frequency
A system and method is disclosed that provides a digital self-adjusting power supply for semiconductor digital circuits. The power supply provides a substantially constant minimum supply voltage with regard to process corner, junction temperature, external voltage source, load variation, and operating frequency. The system comprises a slack time detector, a voltage adjuster, and a digital pulse width modulation (PWM) modulator. The system supplies a minimum required voltage without the used of a band gap or reference voltage. A finite state machine is also used to minimize oscillations introduced by start-up, load transients, frequency changes, and the like, thereby eliminating the need for a proportional integrator differentiator (PID) circuit.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Heat Sinks for Cooling LEDS in Projectors
ActiveUS20090059582A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedProblems can be reduced eliminatedLighting elementsLighting heating/cooling arrangementsJunction temperatureEngineering
According to certain embodiments, an apparatus for cooling light emitting diodes (LEDs) in projectors includes one or more first LEDs, one or more first heat sinks, one or more second LEDs, and one or more second heat sinks. The first LEDs are configured to generate light, and each first LED has a first desired junction temperature. The first heat sinks are configured to dissipate heat generated by the first LEDs. The second LEDs are configured to generate light, and each second LED has a second desired junction temperature that is higher than the first desired junction temperature. The second heat sinks are configured to dissipate heat generated by the one or more second LEDs. A cooling fan directs air flow over the first heat sinks and the second heat sinks, and an exhaust vent enables the air flow over the first heat sinks and the second heat sinks.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
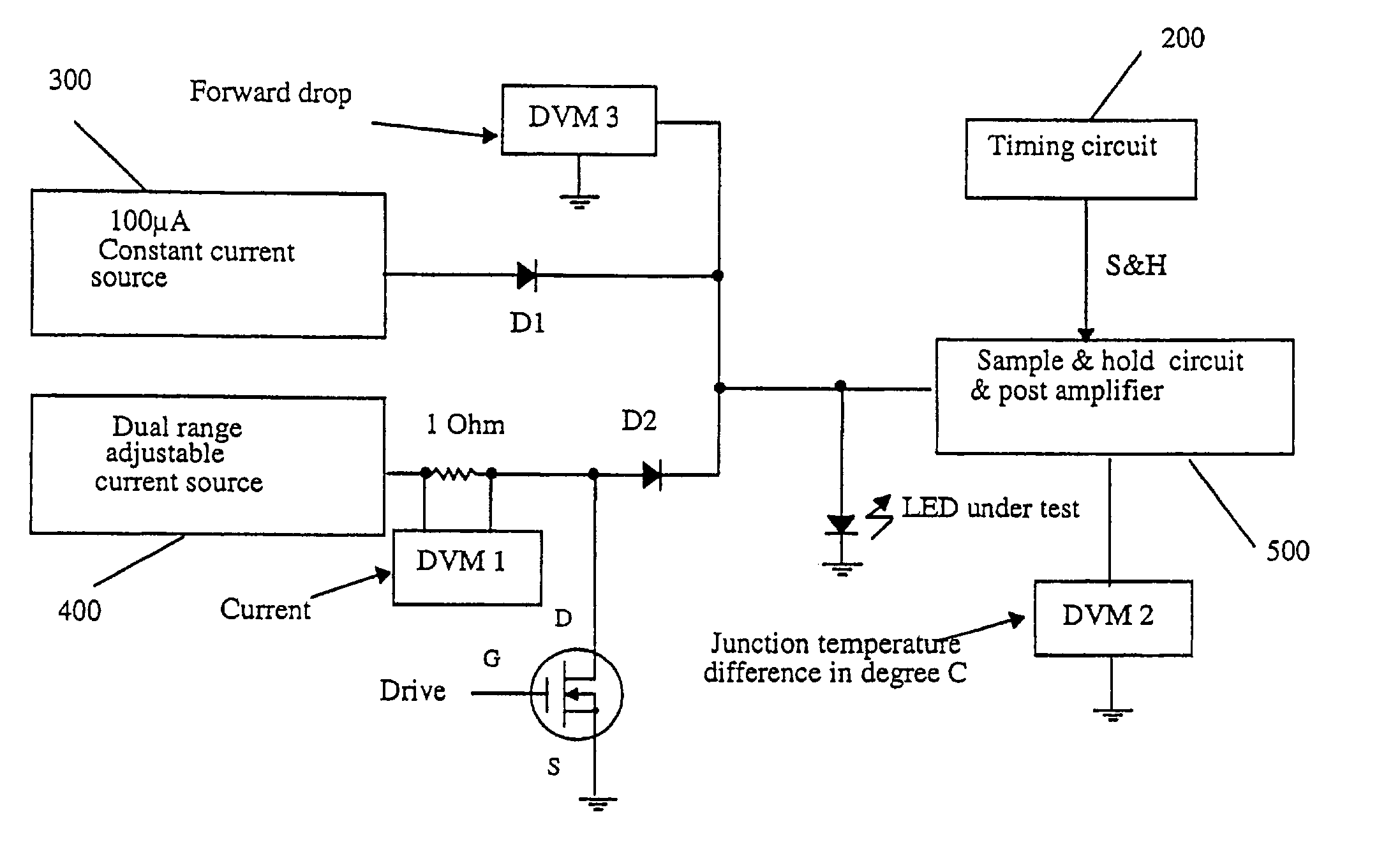
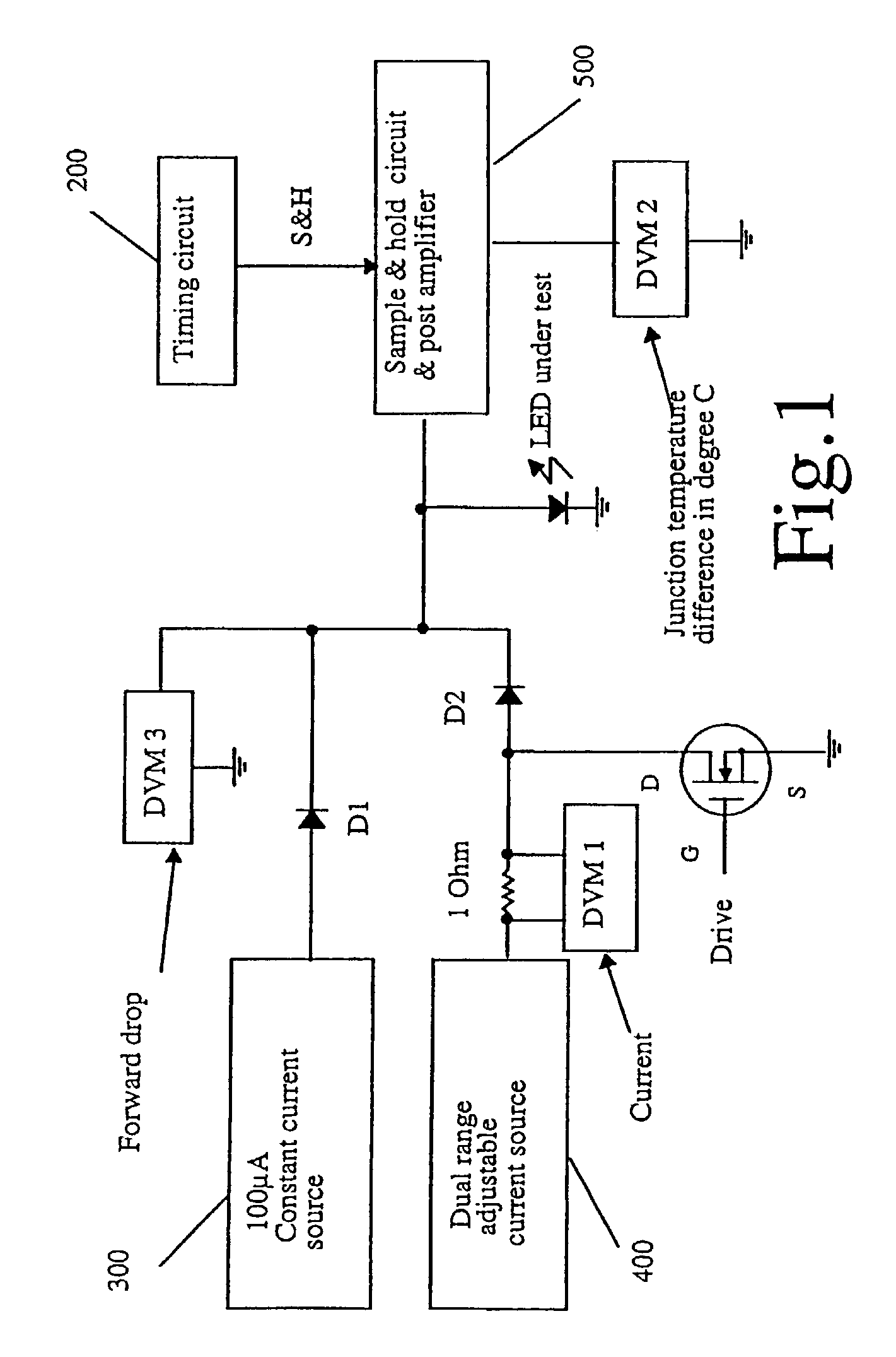
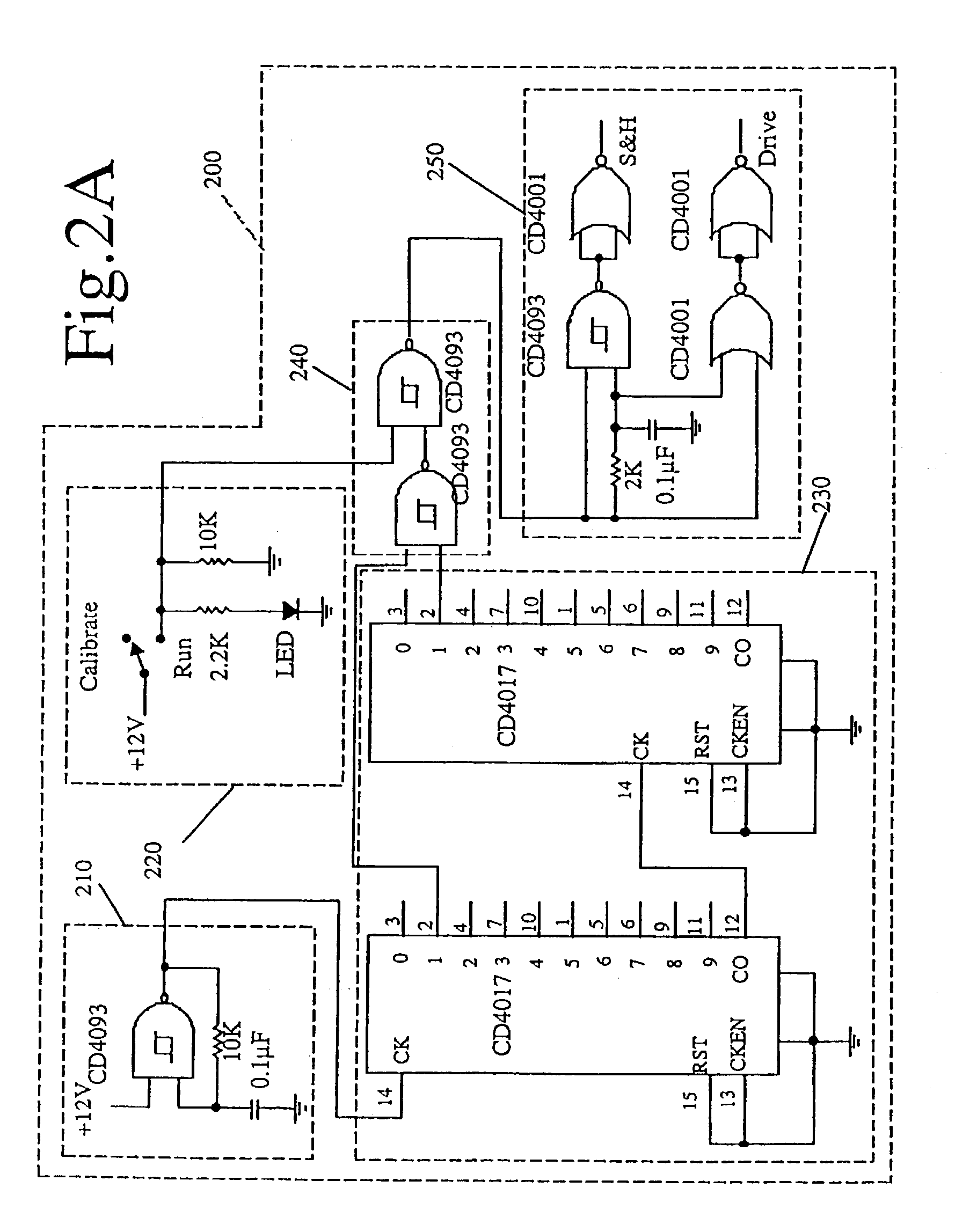
LED junction temperature tester
InactiveUS7052180B2Diode testingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsJunction temperatureLinear relationship
An instrument measures the LED junction temperature directly by taking advantage of the linear relationship between the forward current driven through the LED, the forward drop of the LED, and the junction temperature to determine the LED junction temperature.Calibration is conducted by placing two LEDs from the same family in ambient temperature and passing a small test current through each of the LEDs to obtain the forward drop of the LED at ambient temperature. The LED under test is then placed in an environmentally-controlled chamber where the temperature is raised a known amount above ambient temperature. Known low and high voltage values are associated with the ambient temperature and the environmental chamber temperature, causing the LED under test becomes a calibrated thermometer that can measure its own junction temperature due to the linear relationship between the forward drop and the junction temperature.
Owner:SHIH KELVIN
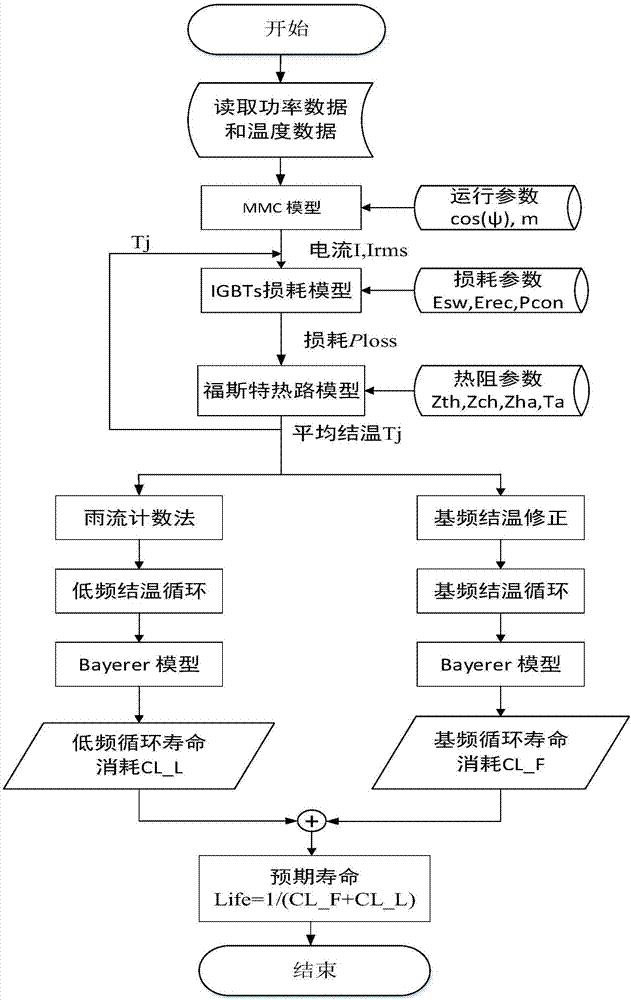
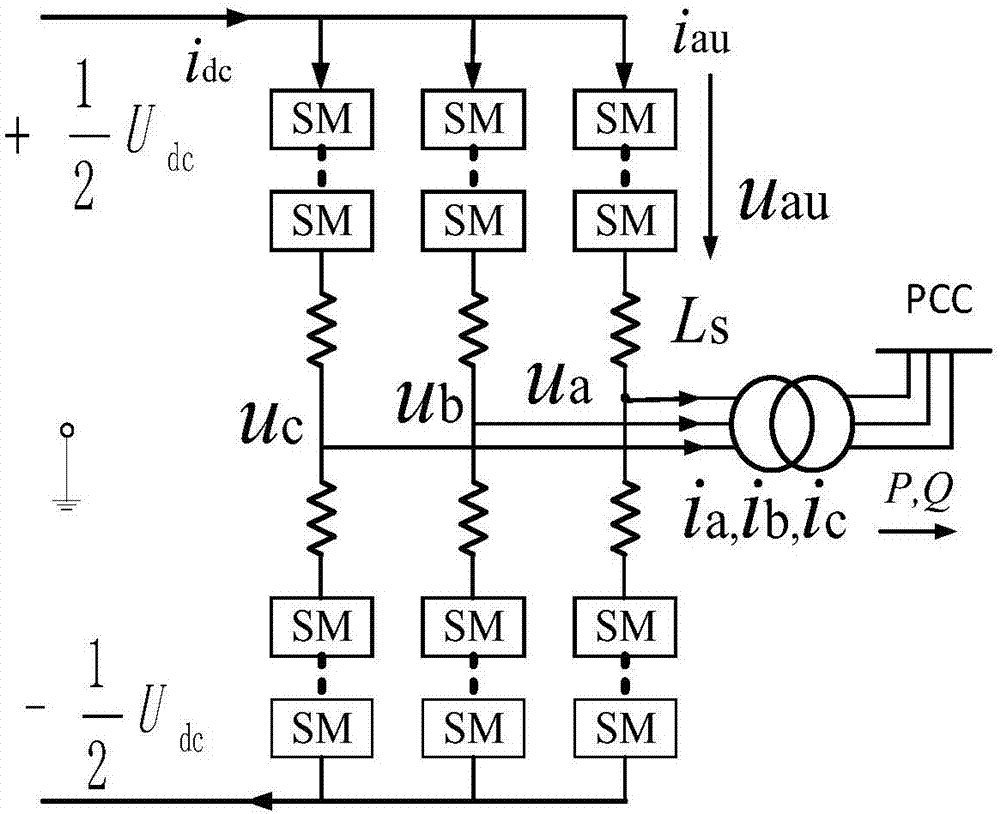
Life evaluation method for modular multilevel converter
ActiveCN107341326AFast operationImprove accuracyAc-dc conversionDesign optimisation/simulationJunction temperatureEngineering
The invention discloses a life evaluation method for a modular multilevel converter (MMC). The life evaluation method comprises the following steps: reading year-round temperature data of a running natural environment of the MMC and power data input into the MMC; performing analytic calculation on the average value and the effective value of the current of sub-modules IGBT and Diode of the MMC; calculating the average loss power Ploss,T and Ploss,D of the sub-modules IGBT and Diode of the MMC within the fundamental frequency period; calculating the average temperature rise Tja of a semiconductor device within the working frequency period by use of a Forster network model to obtain the average junction temperature value Tj of IGBT modules (IGBT modules, IGBTs, including IGBT and Diode); modifying fitting calculation of loss of the IGBTs according to the average junction temperature of the IGBTs; calculating the extreme values of the function temperature within the working frequency and counting the year-round fundamental frequency junction temperature cycle; counting fluctuation information of the year-round low-frequency junction temperature; and calculating the failure number Nf of the fundamental frequency and the low frequency of the semi-conductor device by use of a Bayerer life model, and obtaining the life of the MMC in combination with operation conditions. The life evaluation method can reliably forecast the life of the MMC, can effectively improve the forecasting calculation speed through obtaining an analytical expression of both current and the junction temperature, and has the characteristics of project operational capability and the like.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Solid state lighting system and maintenance method therein
A solid state light module incorporating light emitting diodes (LEDs) disposed on a metal substrate, a solid state lighting system employing such modules, and method of replacing LEDs of the light modules are provided. The metal substrate may allow for lower LED junction temperature and, hence, a longer device lifetime. In addition, the metal substrate may allow for the potential omission of a heat sink, which may reduce light module size, when compared to conventional solid state light emitters.
Owner:SEMILEDS OPTOELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com