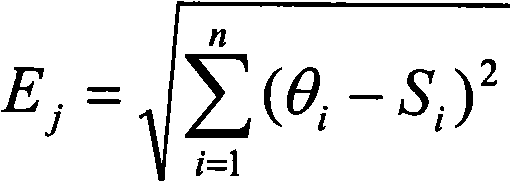Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
177 results about "Trilateration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
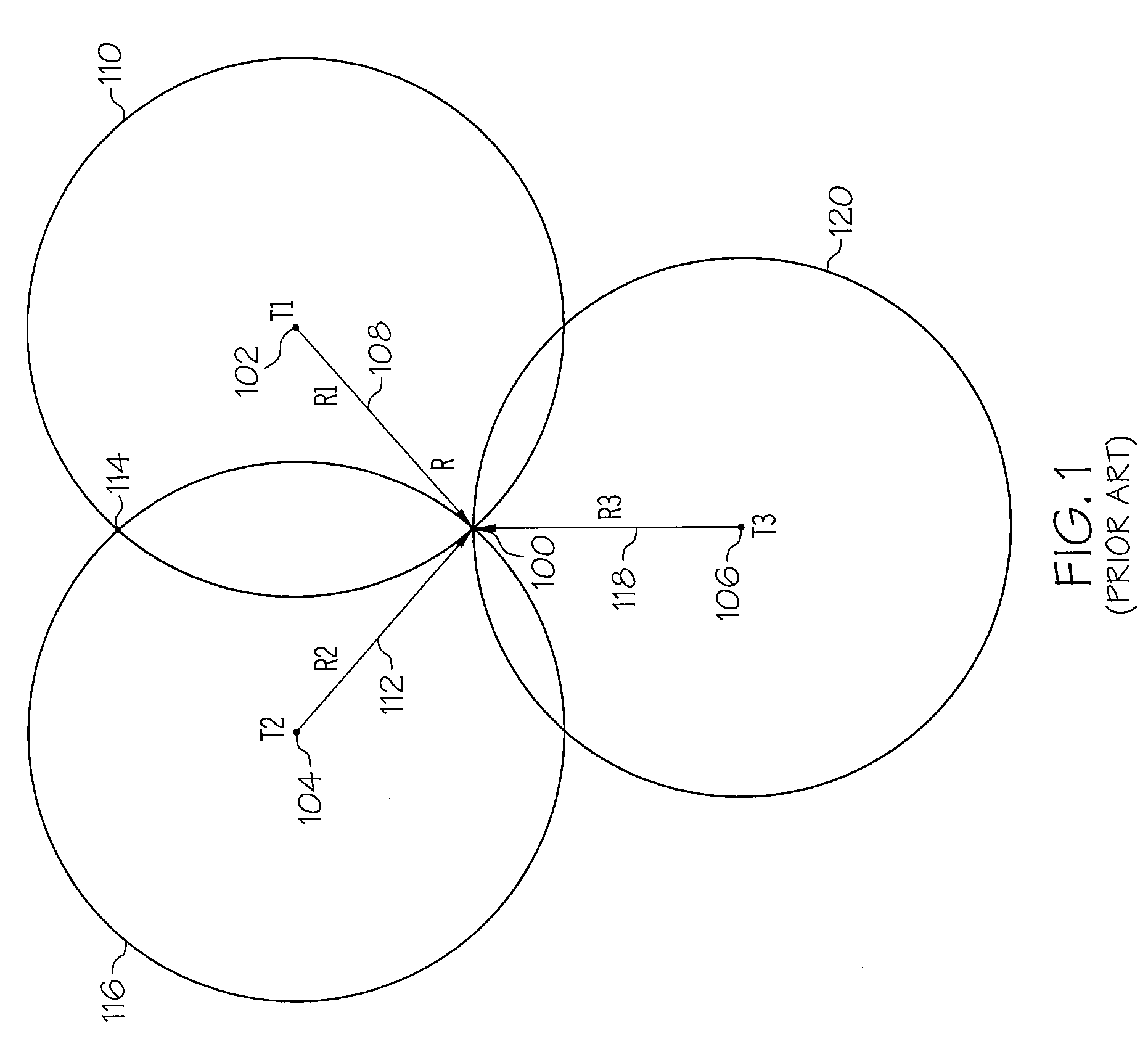
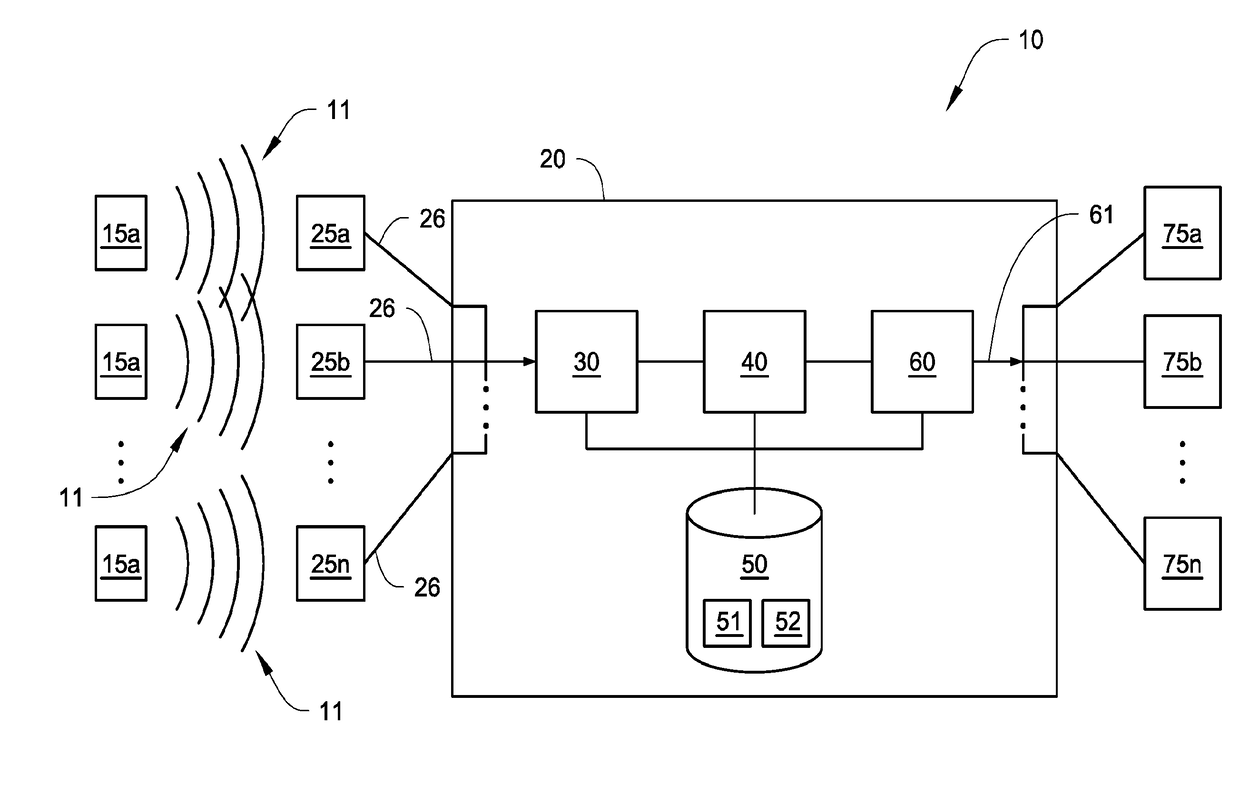
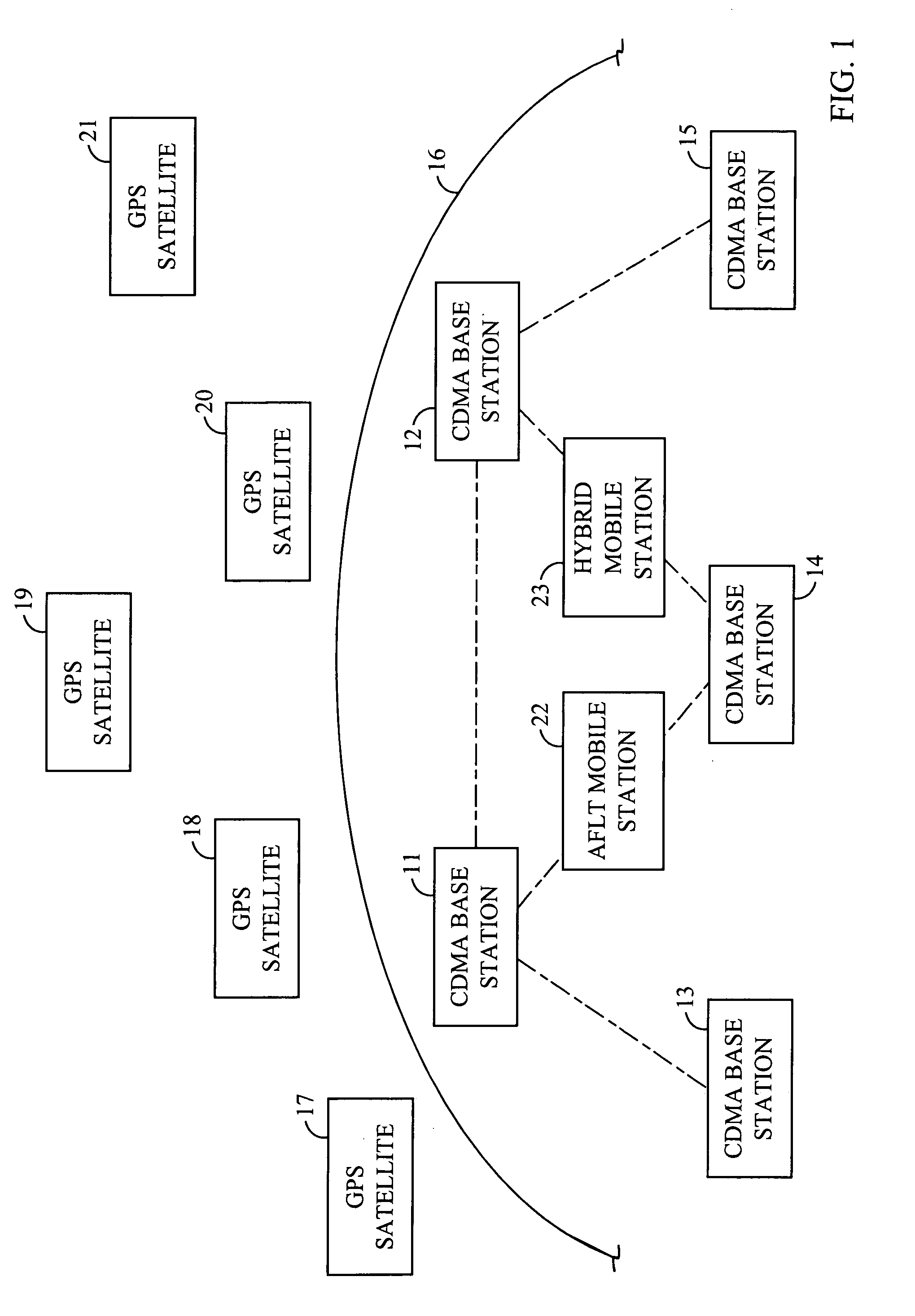
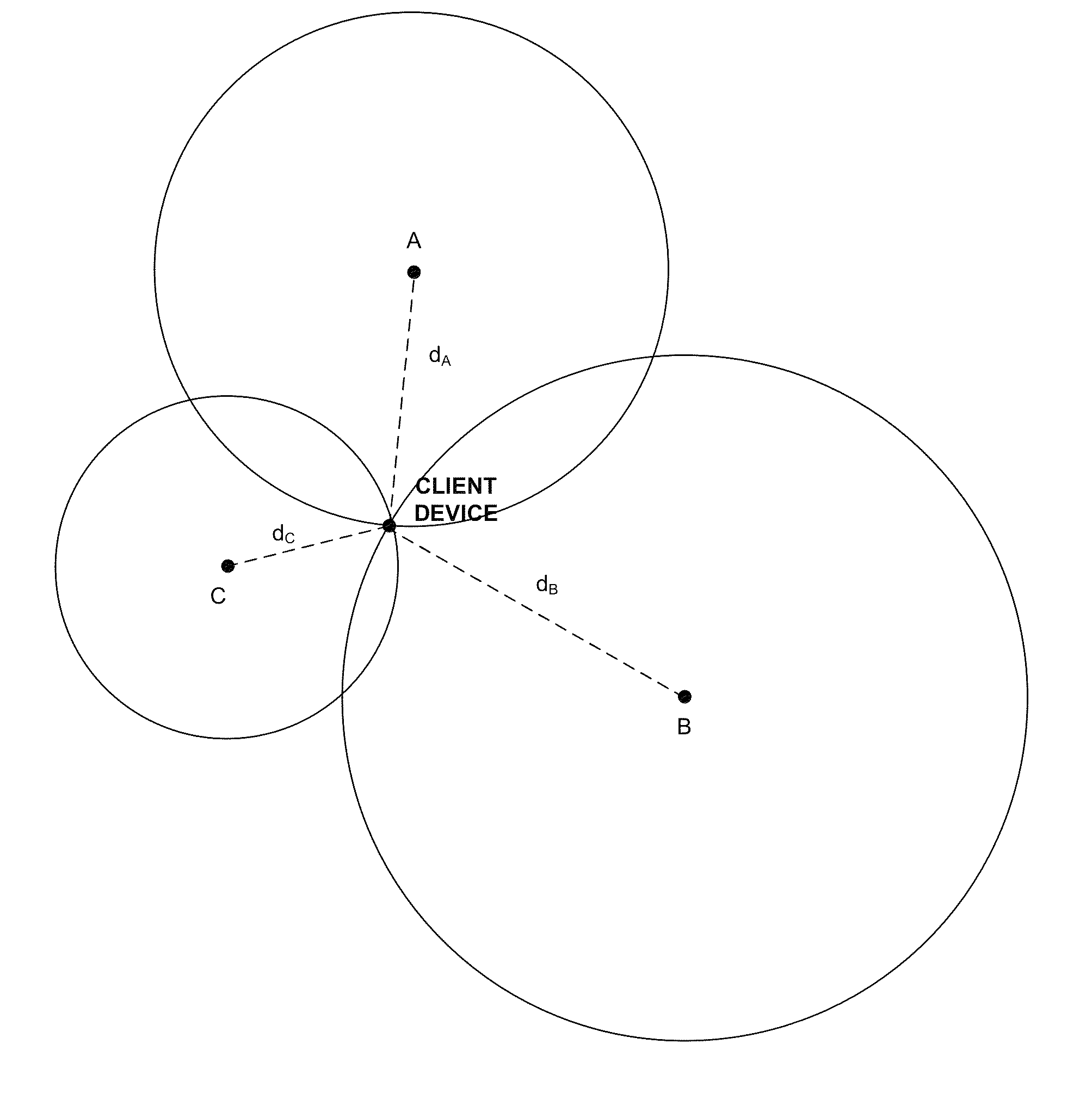
True range multilateration is a method to determine the location of a movable vehicle or stationary point in space using multiple ranges (distances) between the vehicle/point and multiple spatially-separated known locations (often termed 'stations'). True range multilateration is both a mathematical topic and an applied technique used in several fields. A practical application involving a fixed location is the trilateration method of surveying. Applications involving vehicle location are termed navigation when on-board persons/equipment are informed of its location, and are termed surveillance when off-vehicle entities are informed of the vehicle's location.
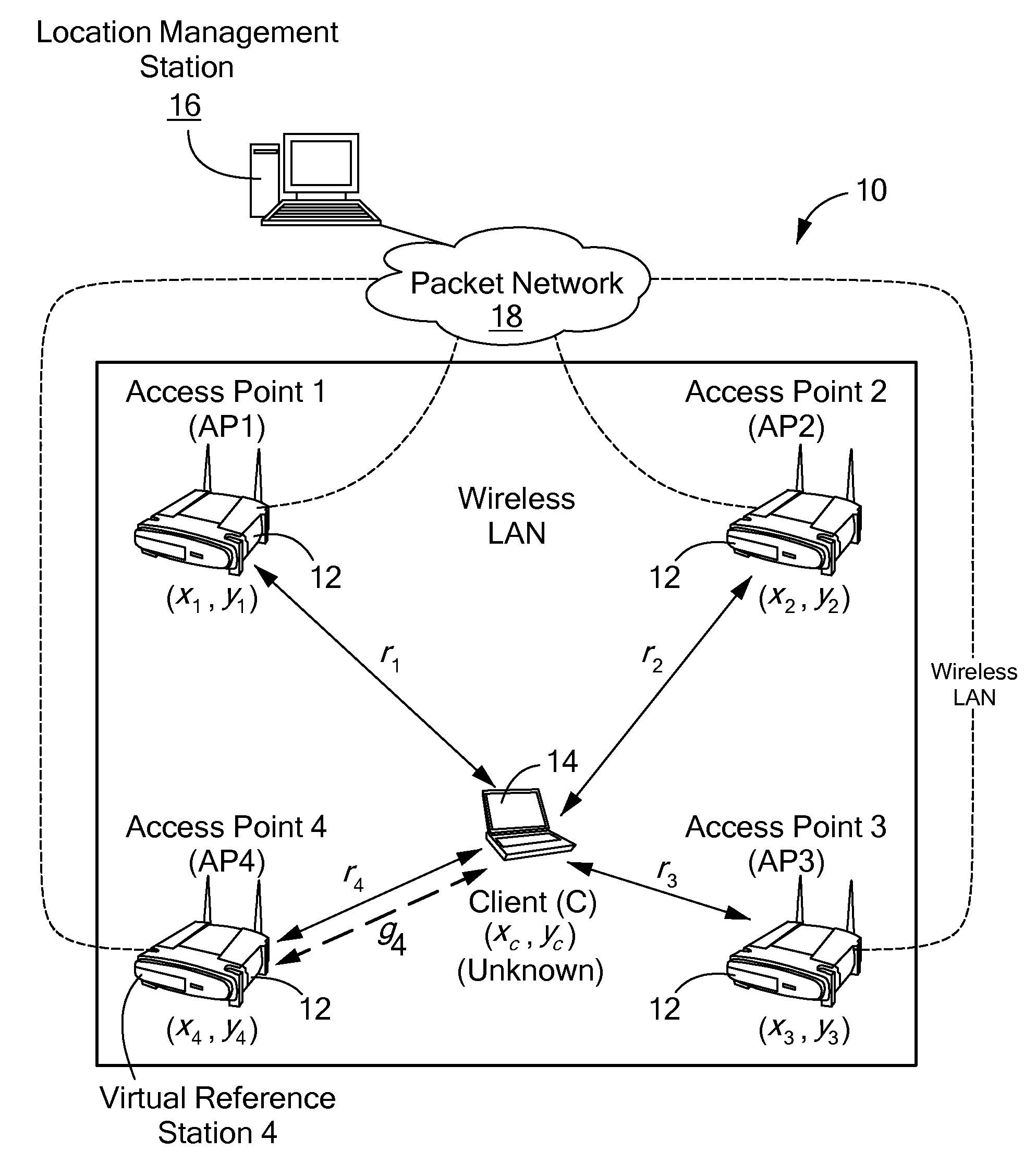
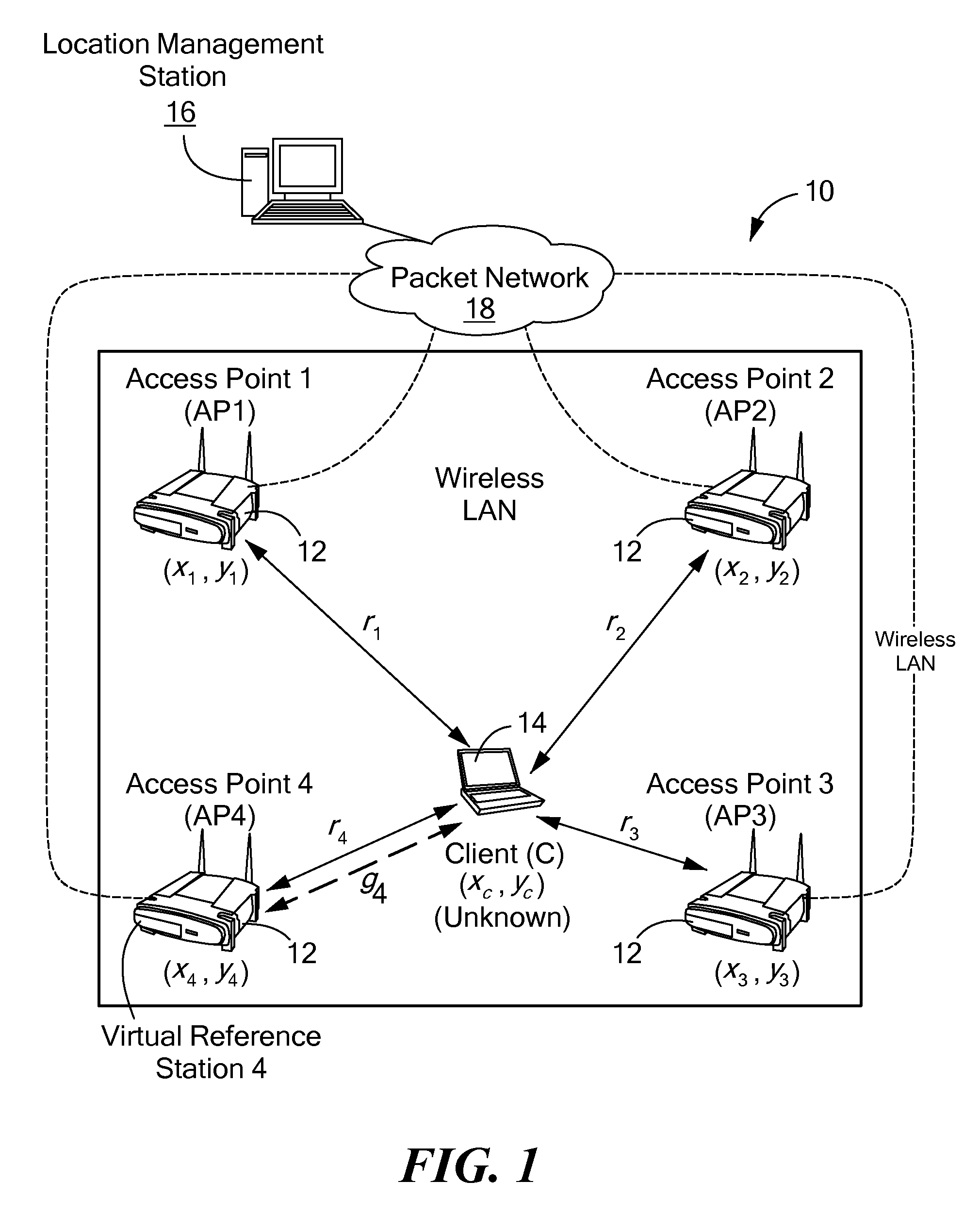
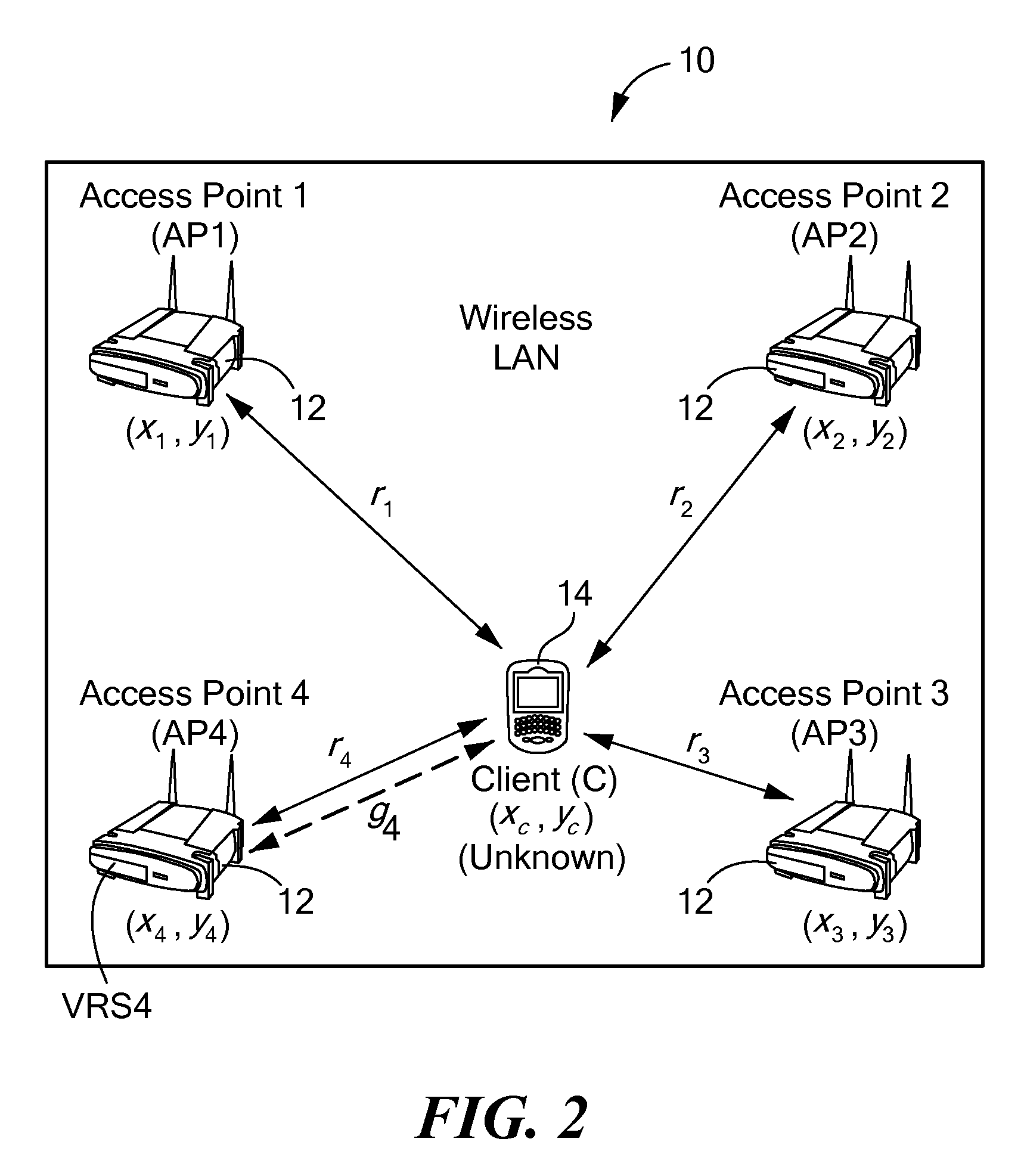
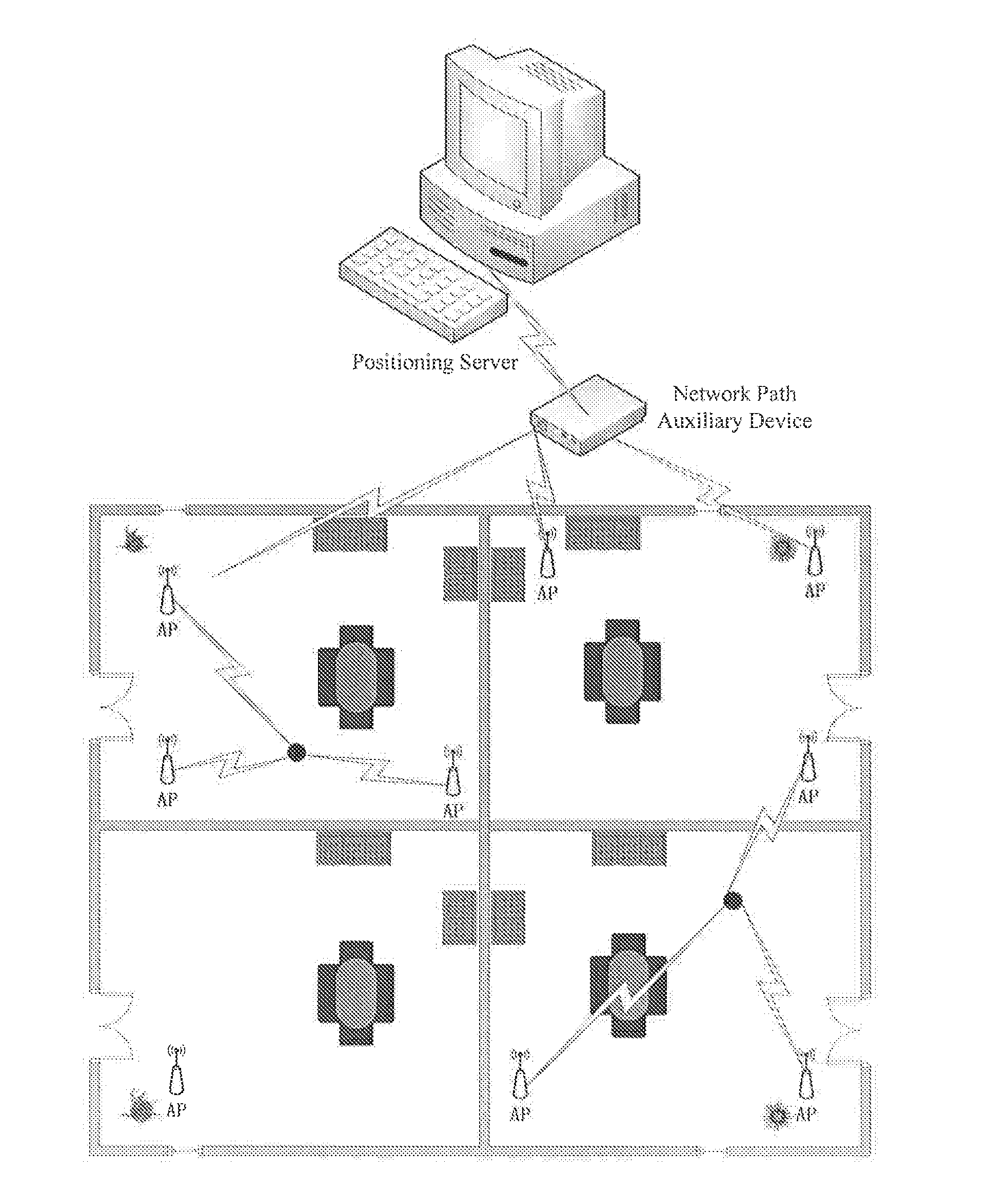
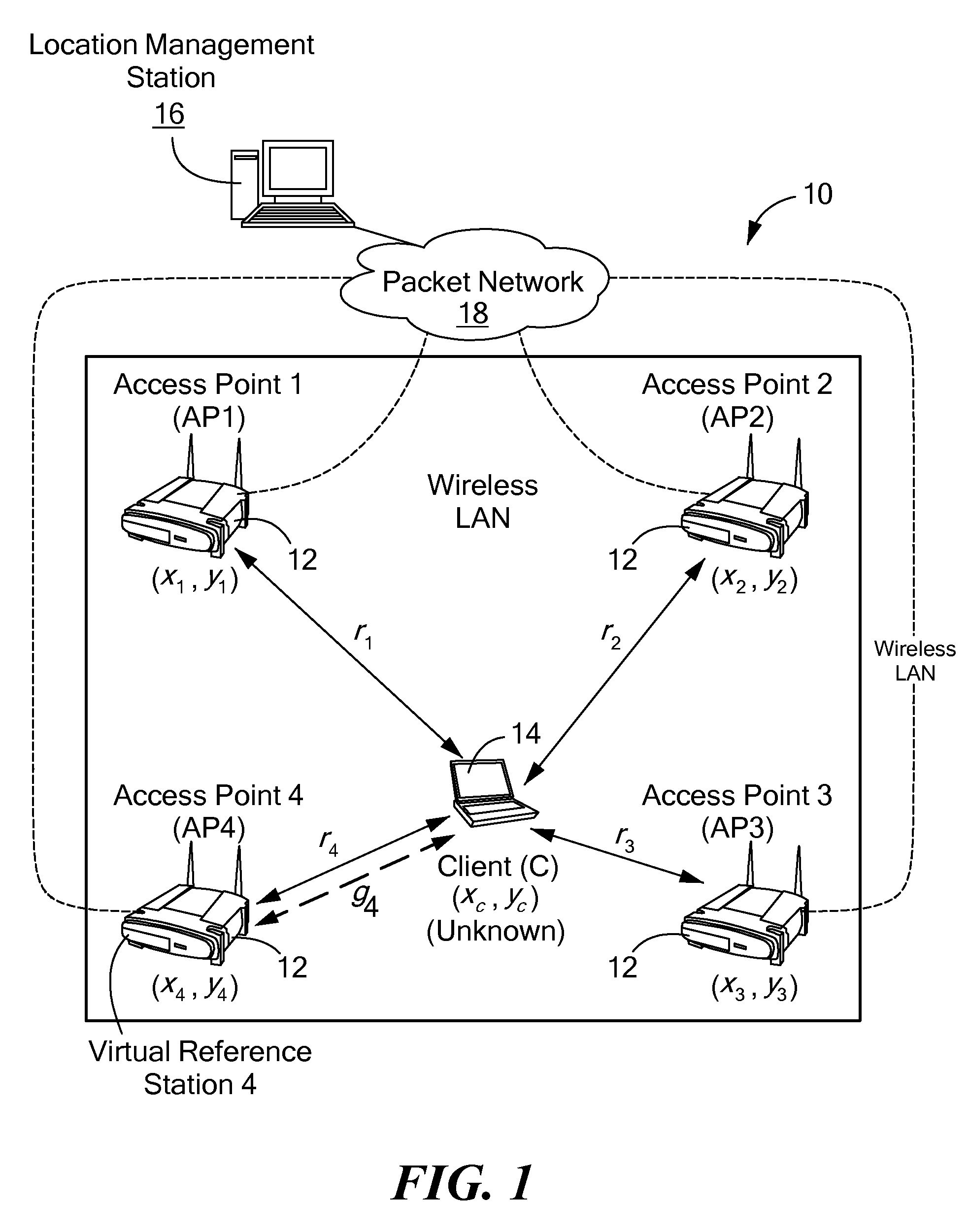
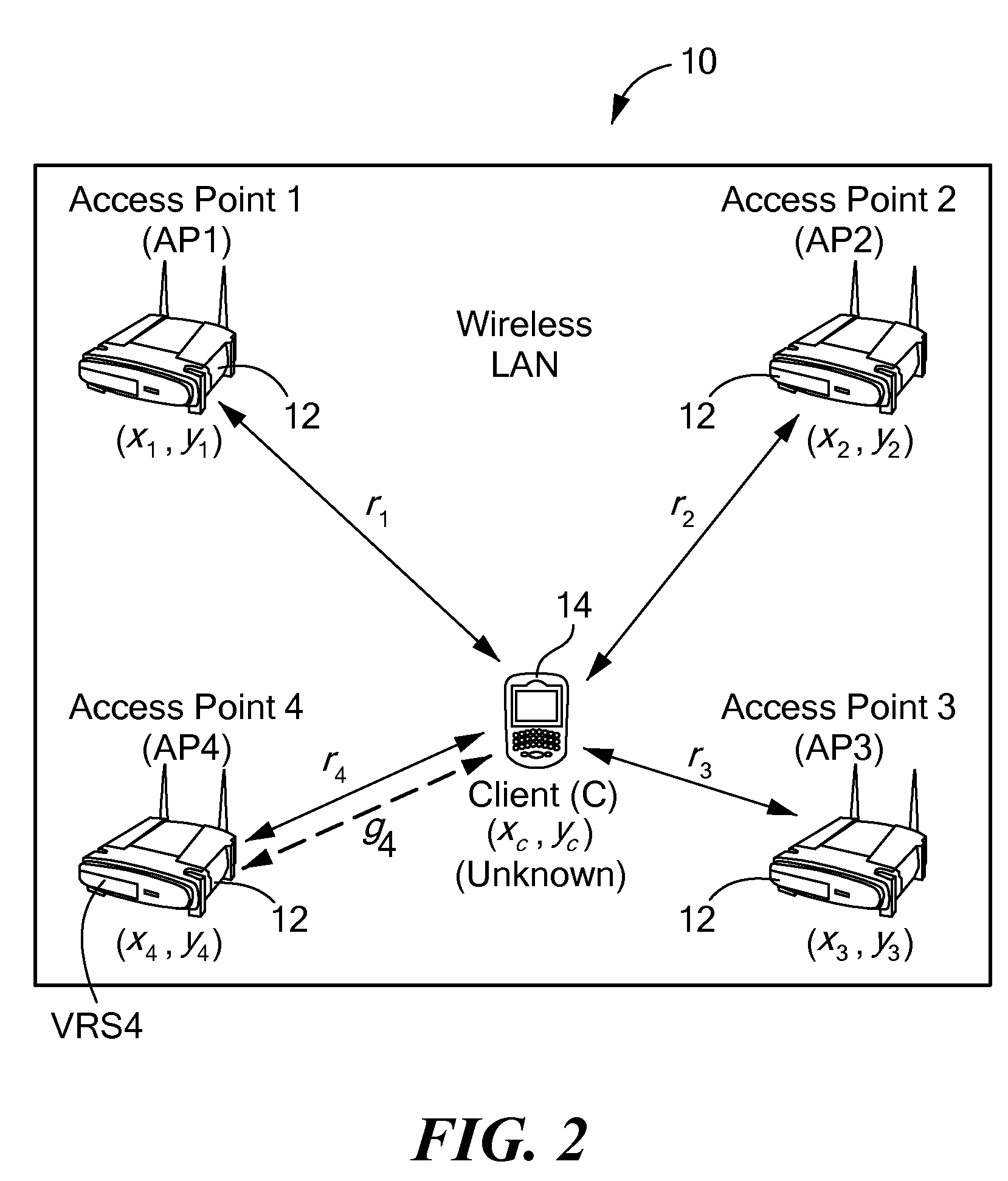
Method and system for wireless lan-based indoor position location
A method and system for position location of clients in wireless local area networks. (WLANs). The position location technique utilizes time-of-flight (TOF) measurements of signals transmitted from a client to a number of wireless access points (APs) or vice versa to determine distances. Round-trip time (RTT) measurement protocols are used to estimate TOF and distances between the client at an unknown position and the WLAN APs. The method and system improves positioning accuracy by identifying and mitigating non-line-of sight (NLOS) errors such as multipaths. Trilateration algorithms are utilized in combination with median filtering of measurements to accurately estimate the position of the client.
Owner:AVAYA INC +1
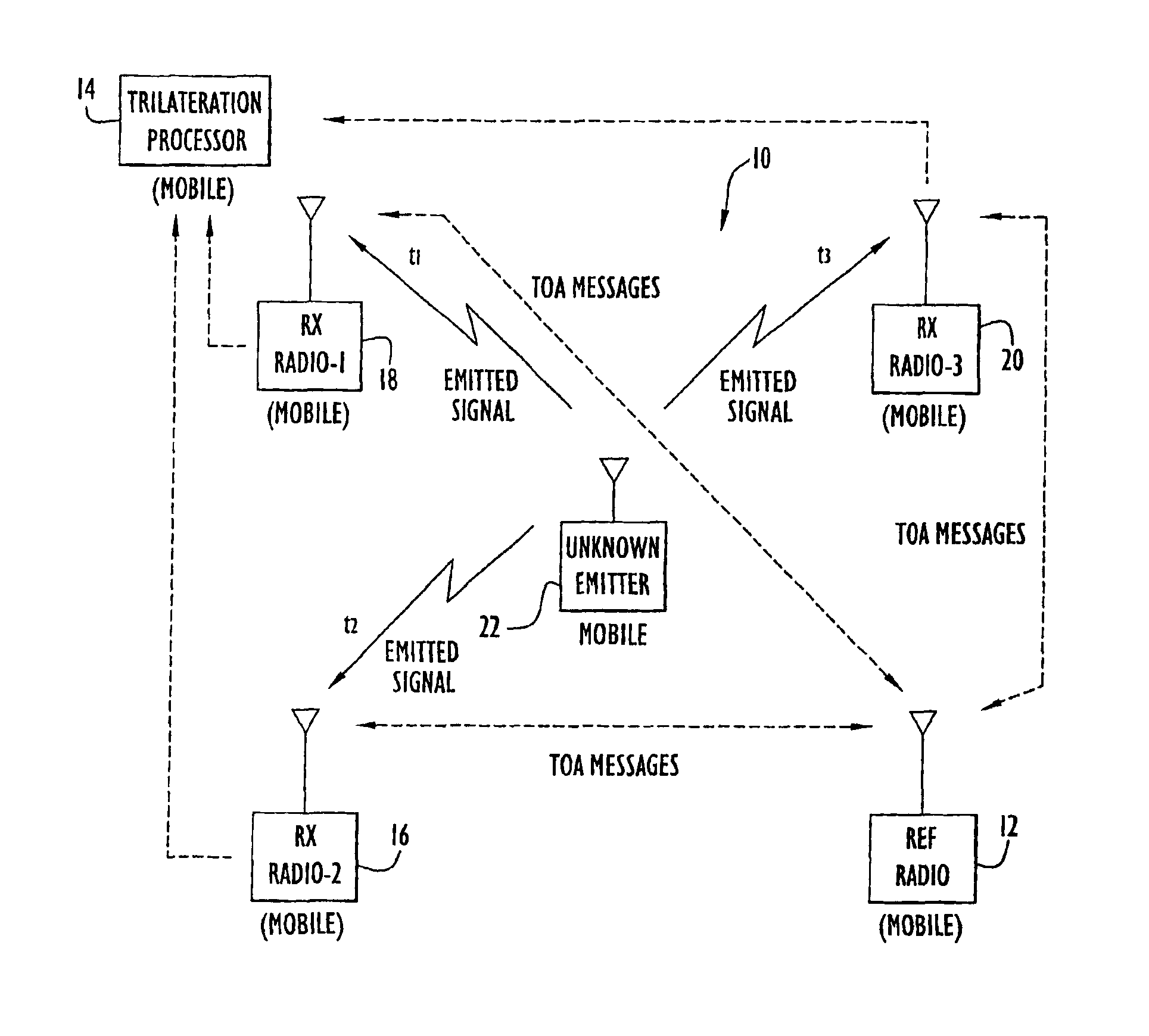
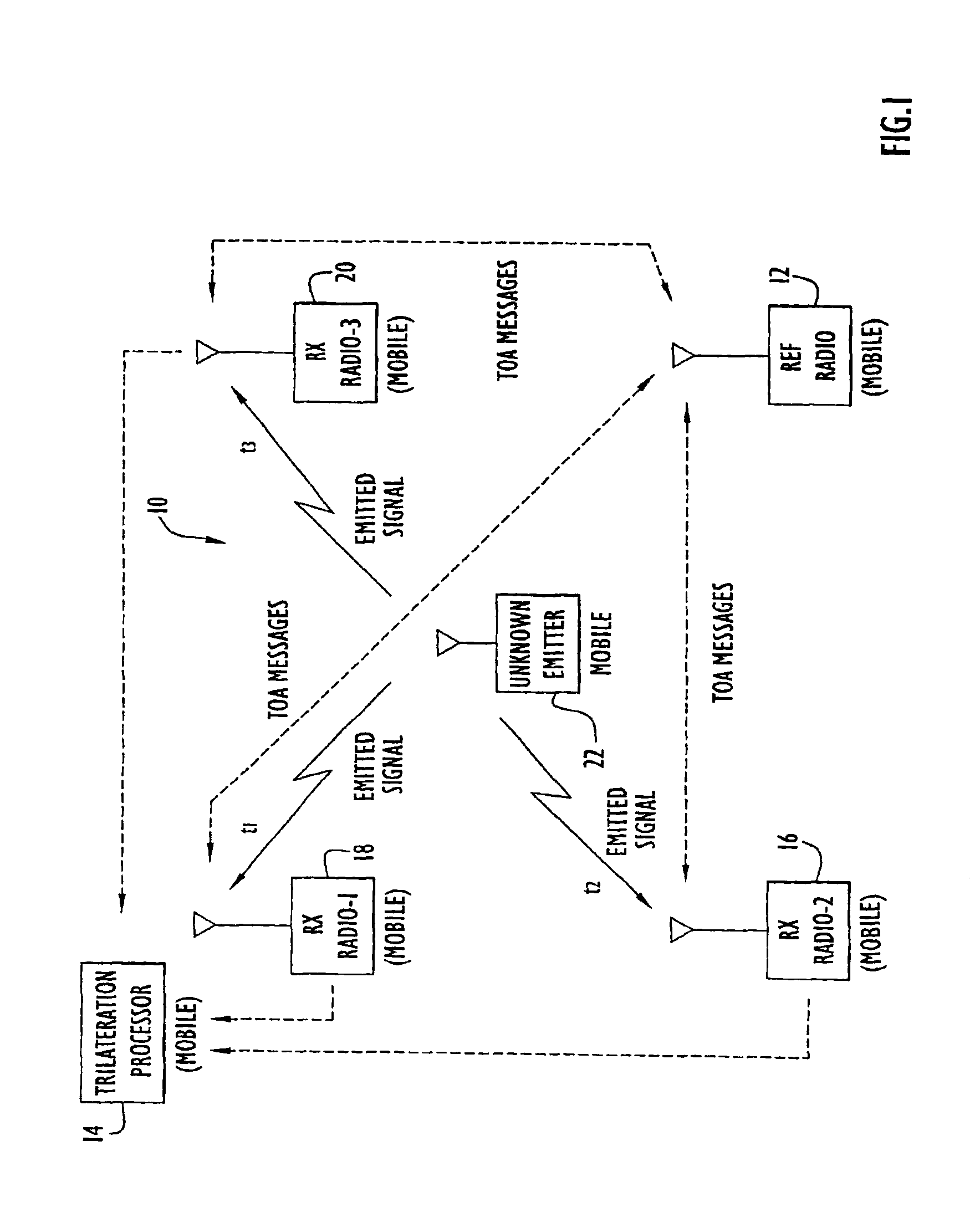
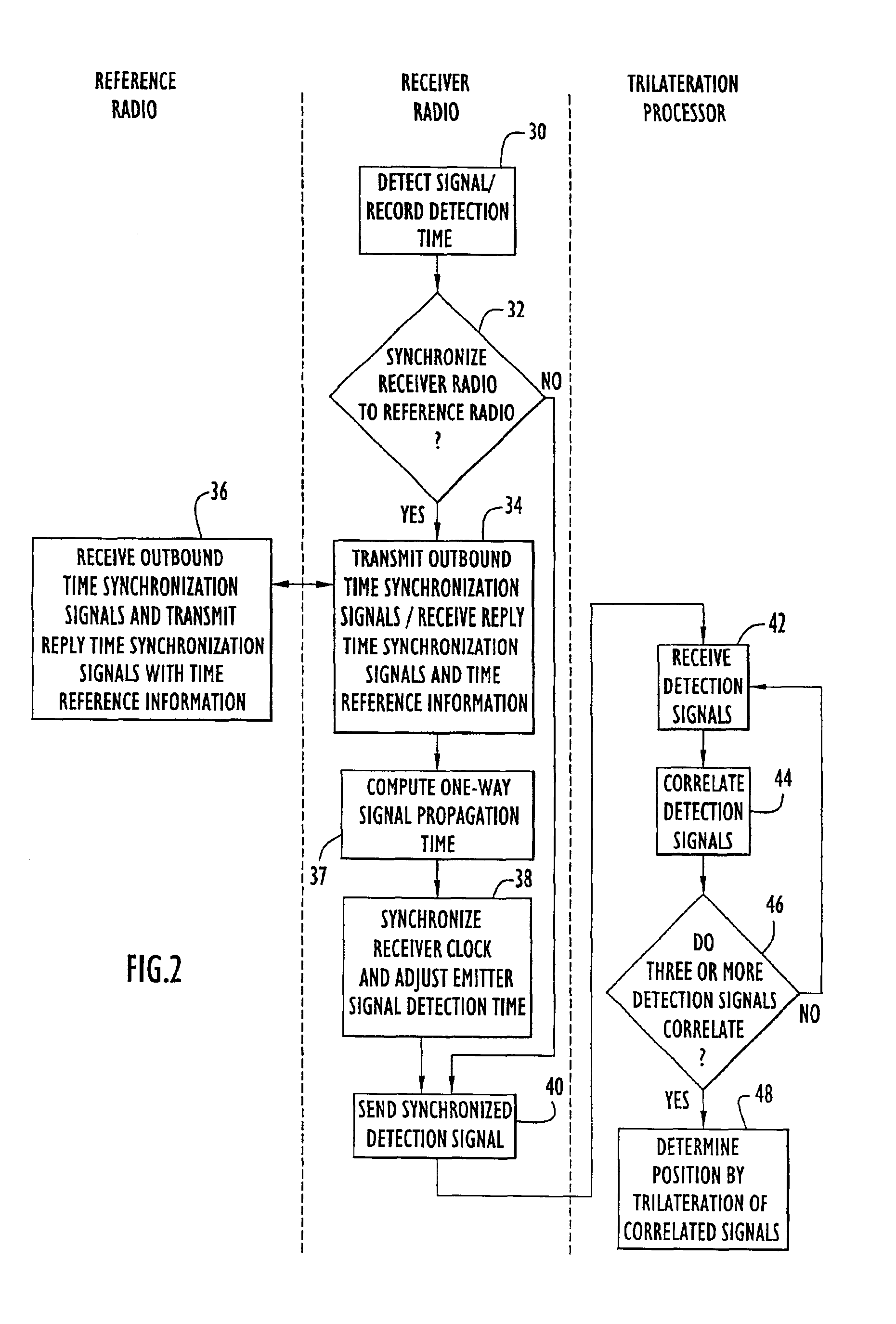
System for determining position of an emitter
InactiveUS6861982B2Improve accuracyMinimizes designDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationPropagation timeExchange time
The position of a non-cooperating emitter is determined by detecting a signal from the emitter at three or more receiver communication devices positioned at different locations. The receiver communication devices determine respective detection times of the emitted signal in respective local time reference frames. To establish a common time reference frame for the emitted signal detections, each receiver communication device exchanges time synchronization signals with a reference communication device. Since any of the receiver communication devices and the reference communication device may be mobile, the signal exchange allows each receiver communication device to accurately determine the signal propagation time between itself and the reference communication device and factor the signal propagation time into an accurate adjustment of the local time reference frame. Using trilateration, the position of the emitter is determined from known positions of the receiver communication devices and the emitted signal detection times from the receiver communication devices.
Owner:EXCELIS INC
Reverse infrastructure location system and method
InactiveUS20060071790A1Good precisionVoting apparatusRoad vehicles traffic controlTransceiverTransmitted power
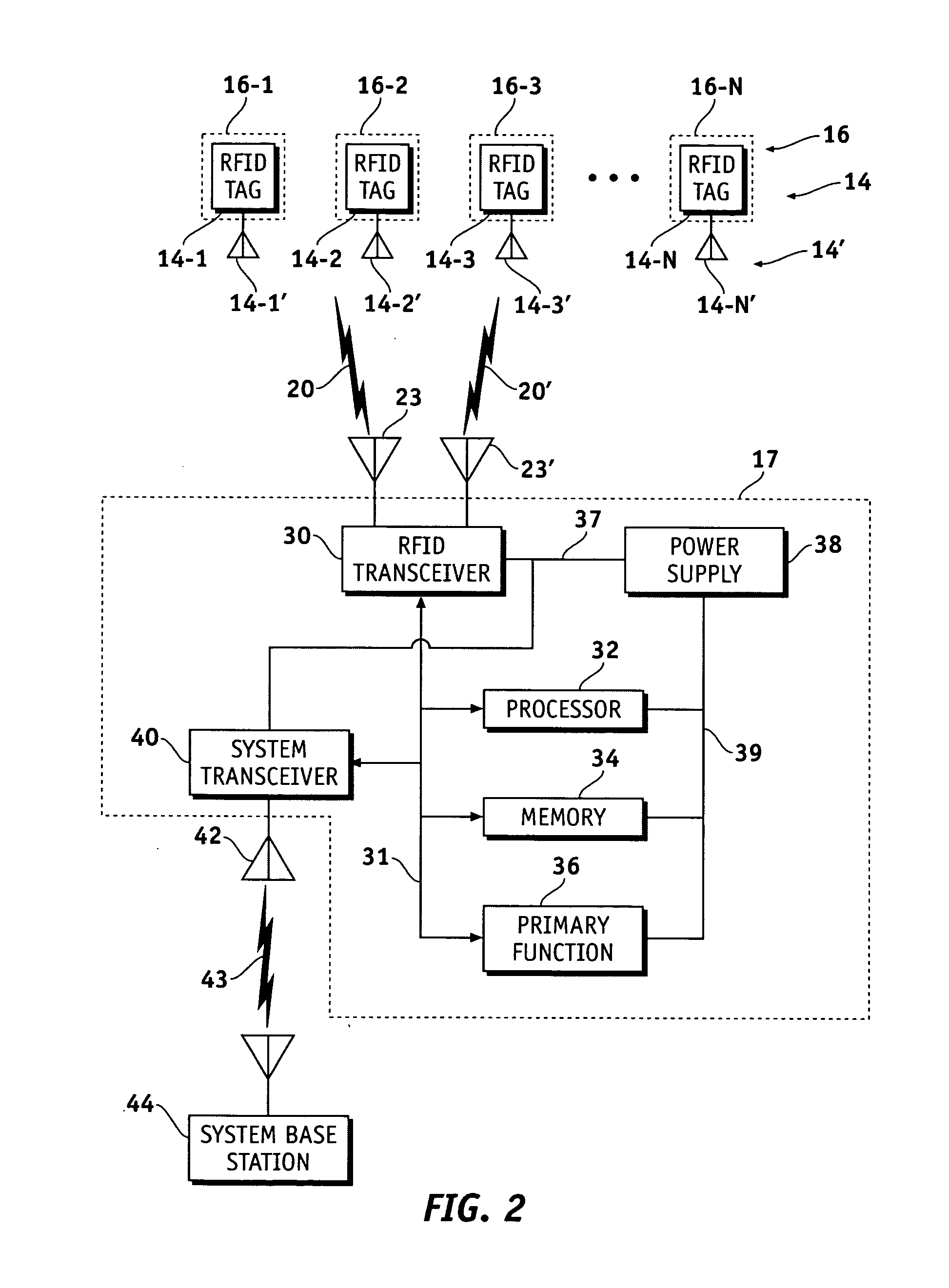
Methods and apparatus are provided to locate a terminal within a workspace. Radio frequency identification (RFID) tags are provided in known locations, preferably in, on or adjacent the light fixtures or other workspace infrastructure. The terminal comprises an RFID tag interrogation transceiver, processor and memory. The transceiver interrogates the tags which respond with information correlatable with their unique locations. The terminal determines its locations relative to the known locations of responding tags by, for example, varying its transmit power and / or receiver sensitivity and / or by trilateration using, for example, phase or time difference of arrival measurements on the tag response signals. Once it has determined its own location it may transmit or otherwise announce its location as desired by the user. In a preferred embodiment, the natural electromagnetic radiation and / or RADAR cross section backscatter from fluorescent type fixtures, modulated with their position information, acts as the RFID infrastructure beacon.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
Local Alignment and Positioning Device and Method
InactiveUS20140293266A1Accurate measurement rangeAccurate measurementOptical rangefindersWeapon control systemsTerrainVoxel
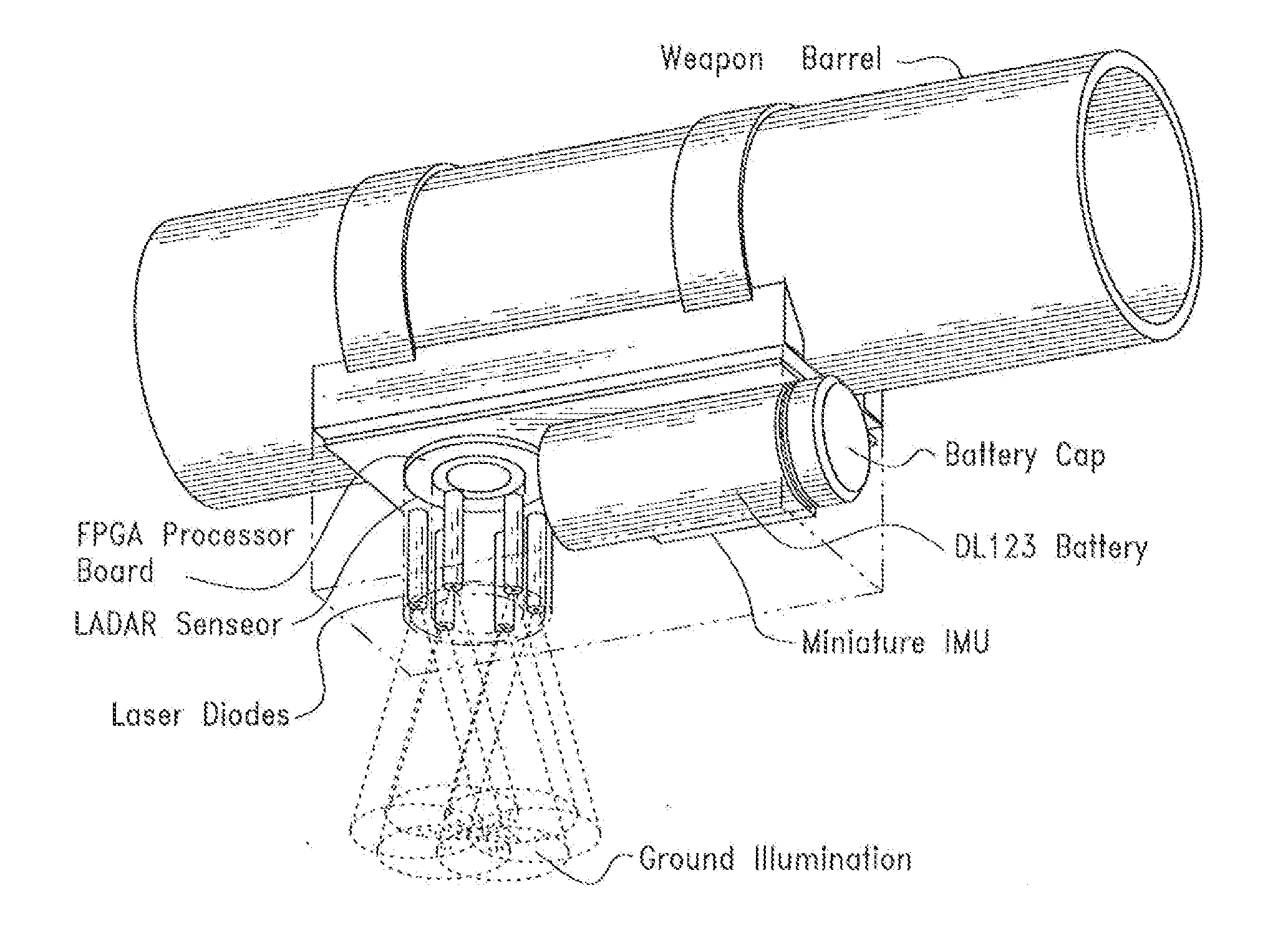
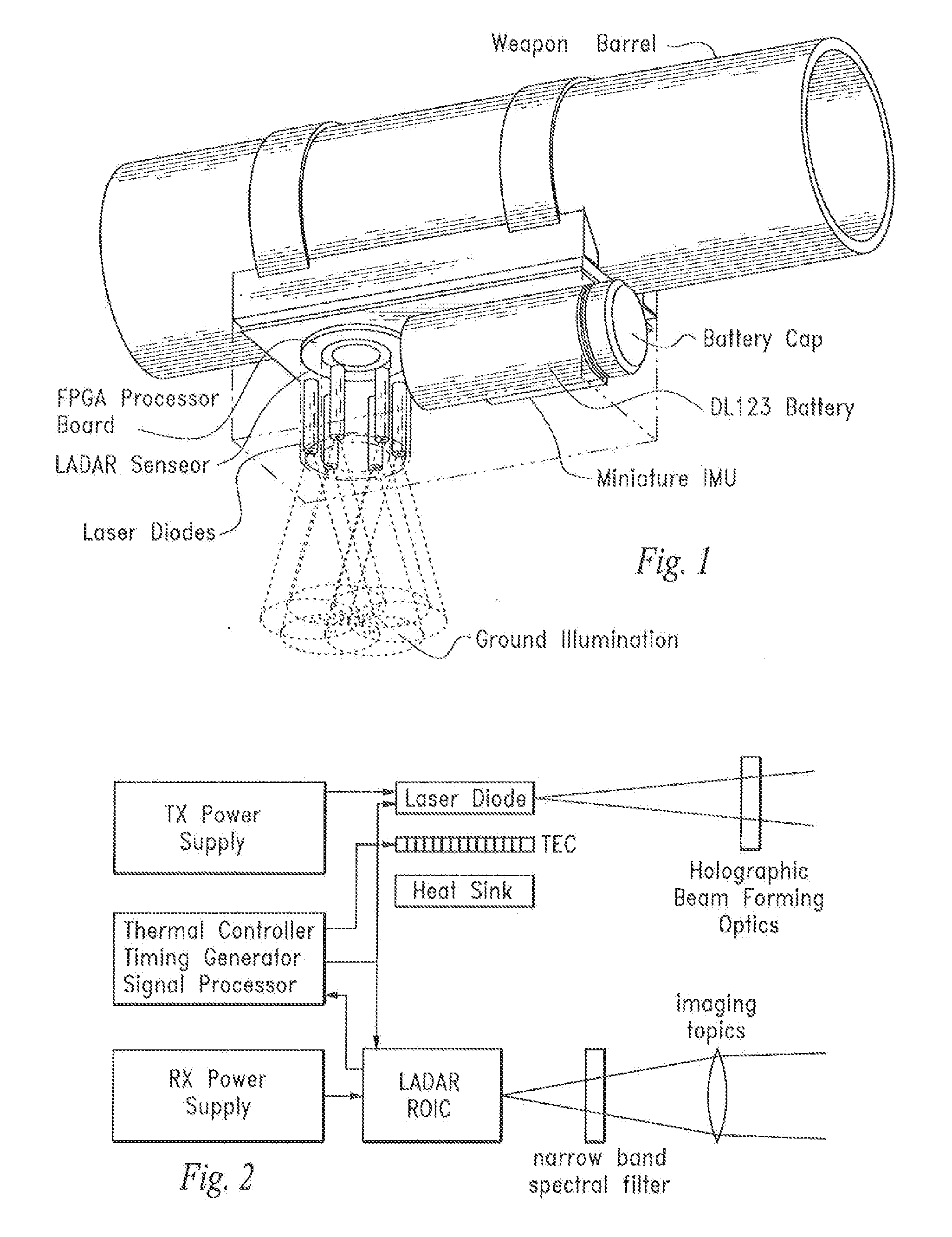
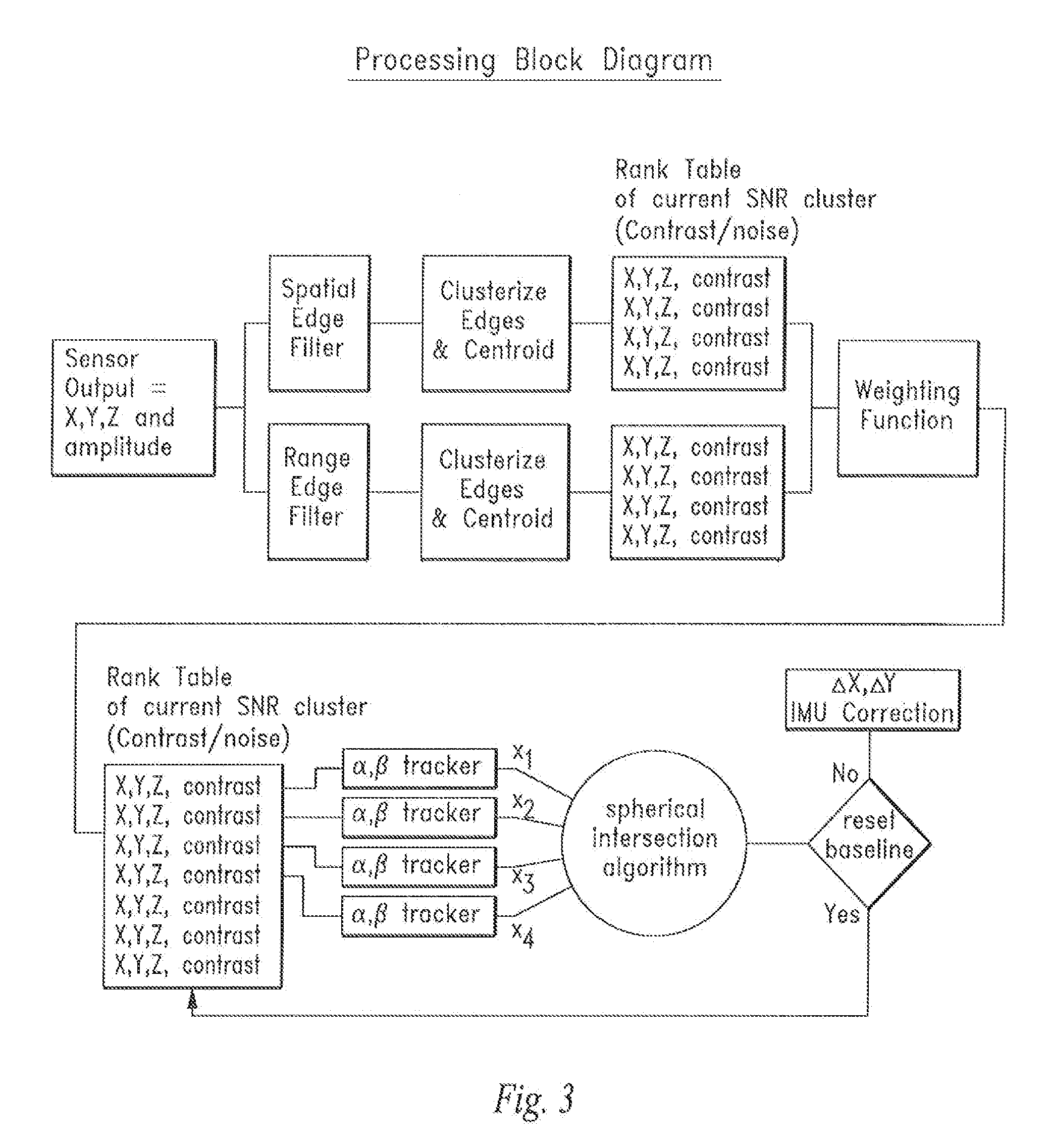
A device and method that uses terrain features having one or more predetermined characteristics or weights in an electronic image date frame or set of frames such as a LIDAR voxel set of image data frames for use as system reference points which are, in turn, used in one or more trilateration calculations performed in electronic circuitry to determine a position or ego-motion of the device.
Owner:PFG IP
Indoor/Outdoor Personal Security System
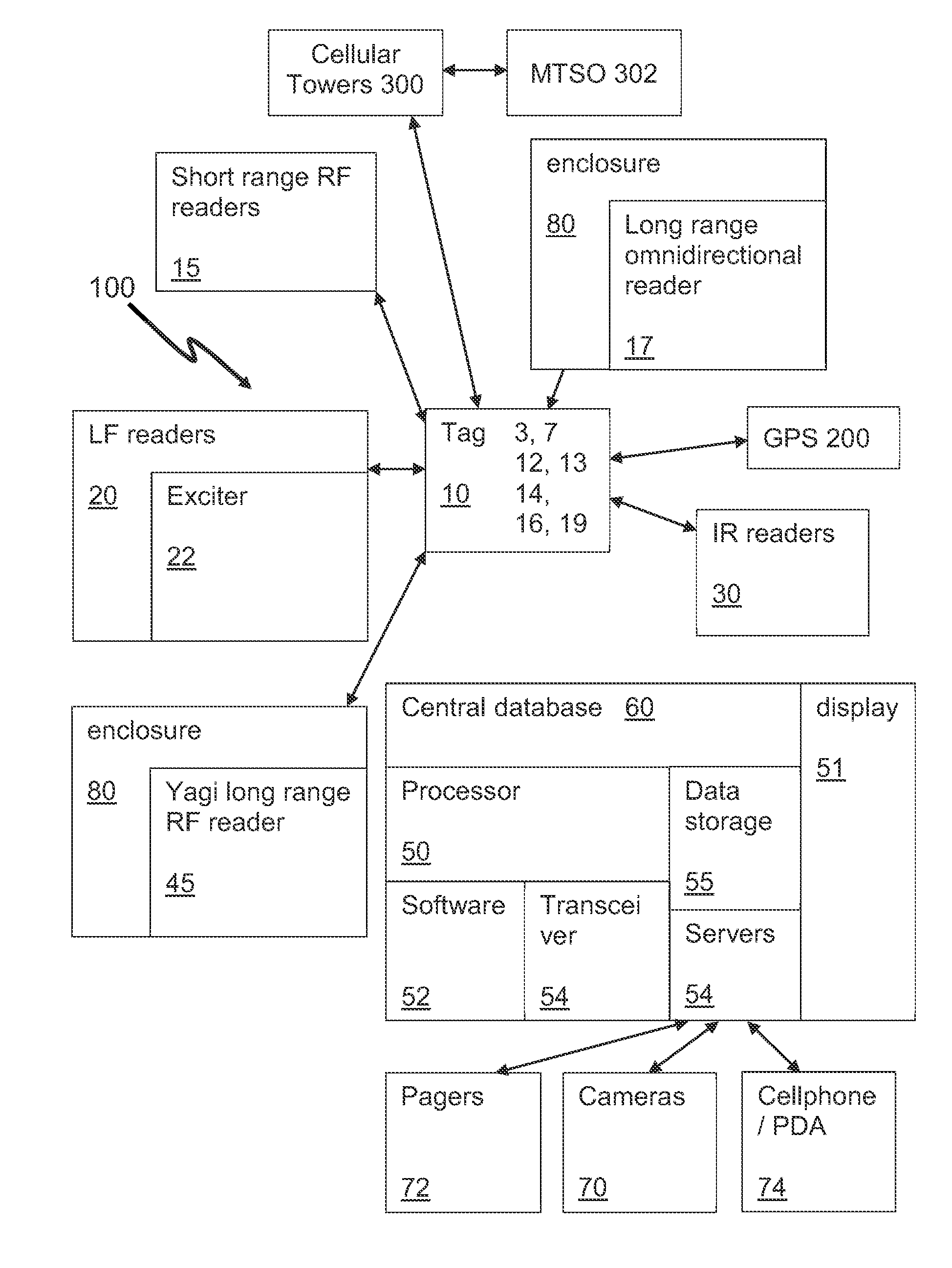
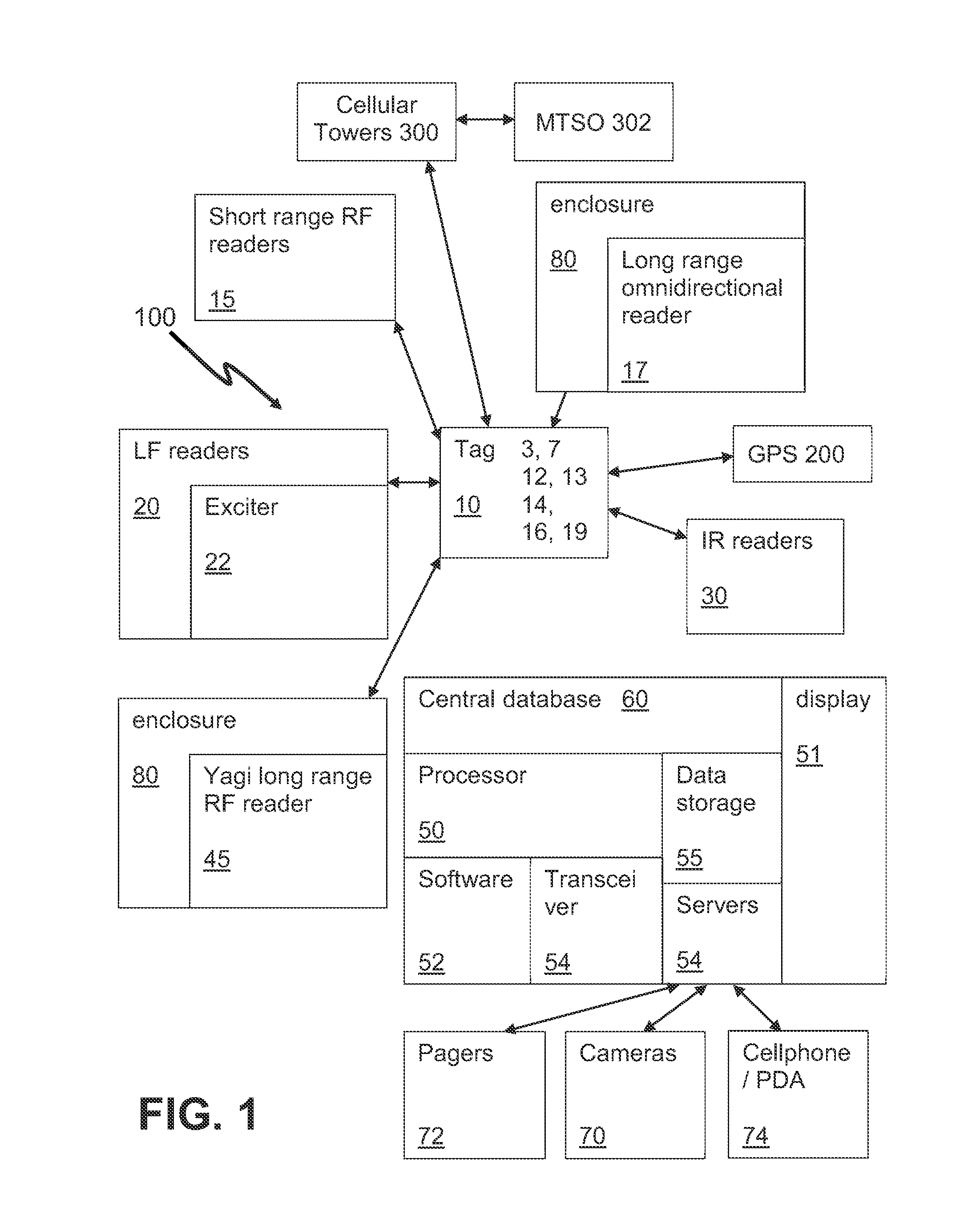
InactiveUS20140206307A1Provide securityEmergency connection handlingTelephonic communicationTriangulationCentral database
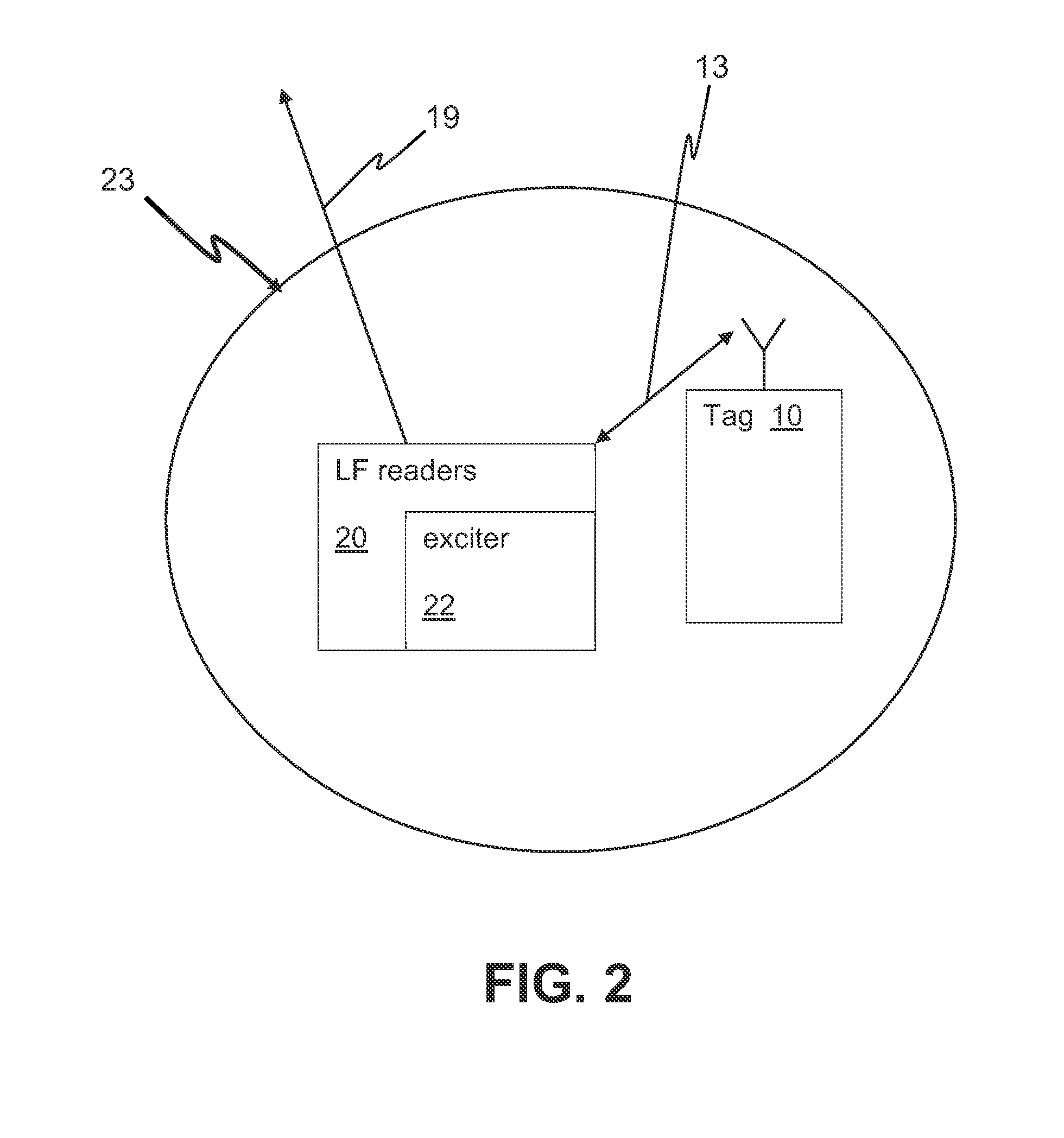
A security system uses tags that are able to receive time signals sent from the GPS satellites or the broadcasting radio signals from the cell towers and transmit the identification and location information or signals to the central database and server for triangulation / trilateration periodically or in the event of an emergency. A security system uses tags that are able to transmit RF signals to readers located around a college campus. The tags may transmit signals periodically or in the event of an emergency. Certain locations use LF readers with exciters that trigger a signal from the tag. The security system may provide quick identification and location of individuals in danger.
Owner:MAURER MICHAEL +5
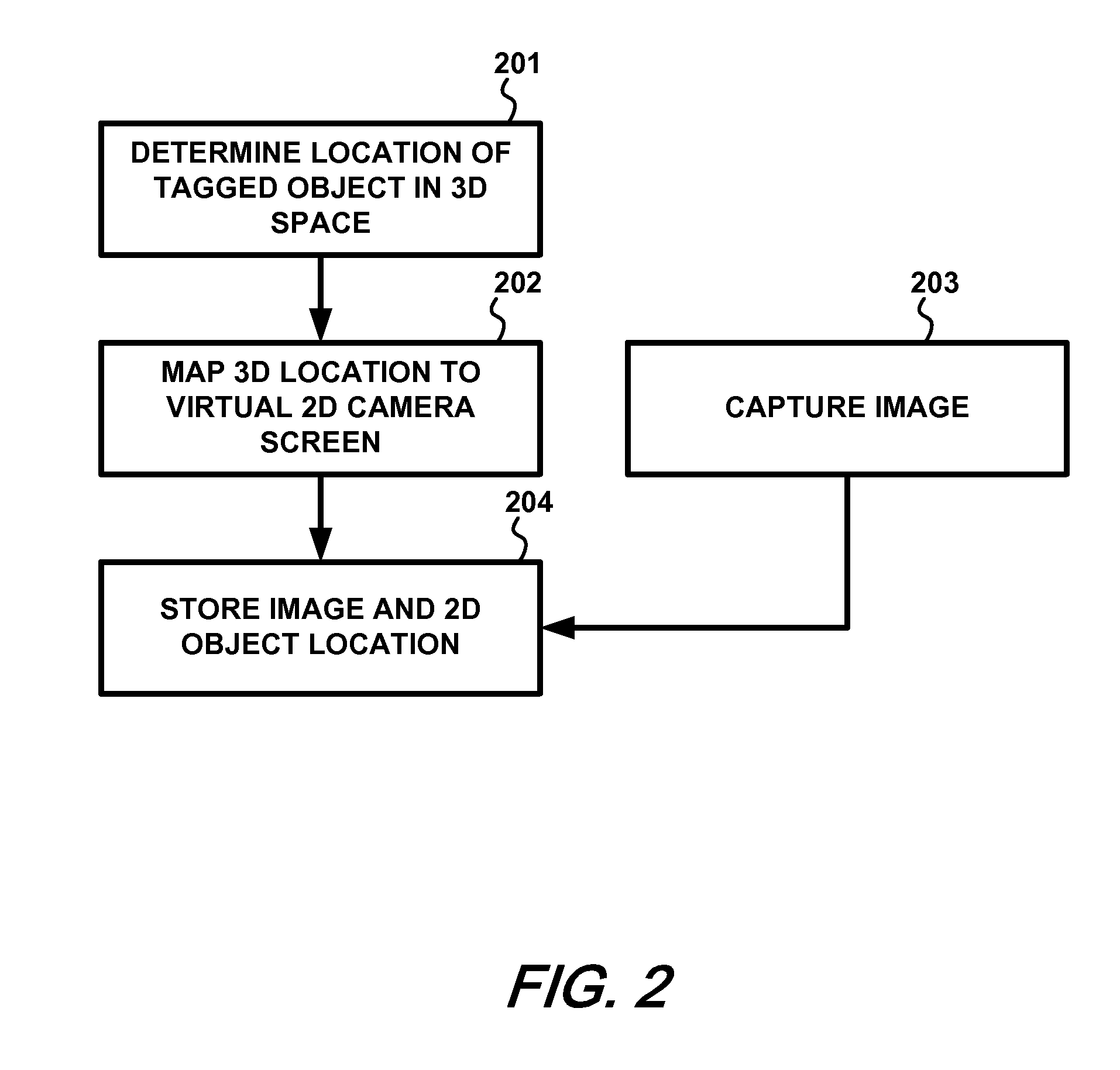
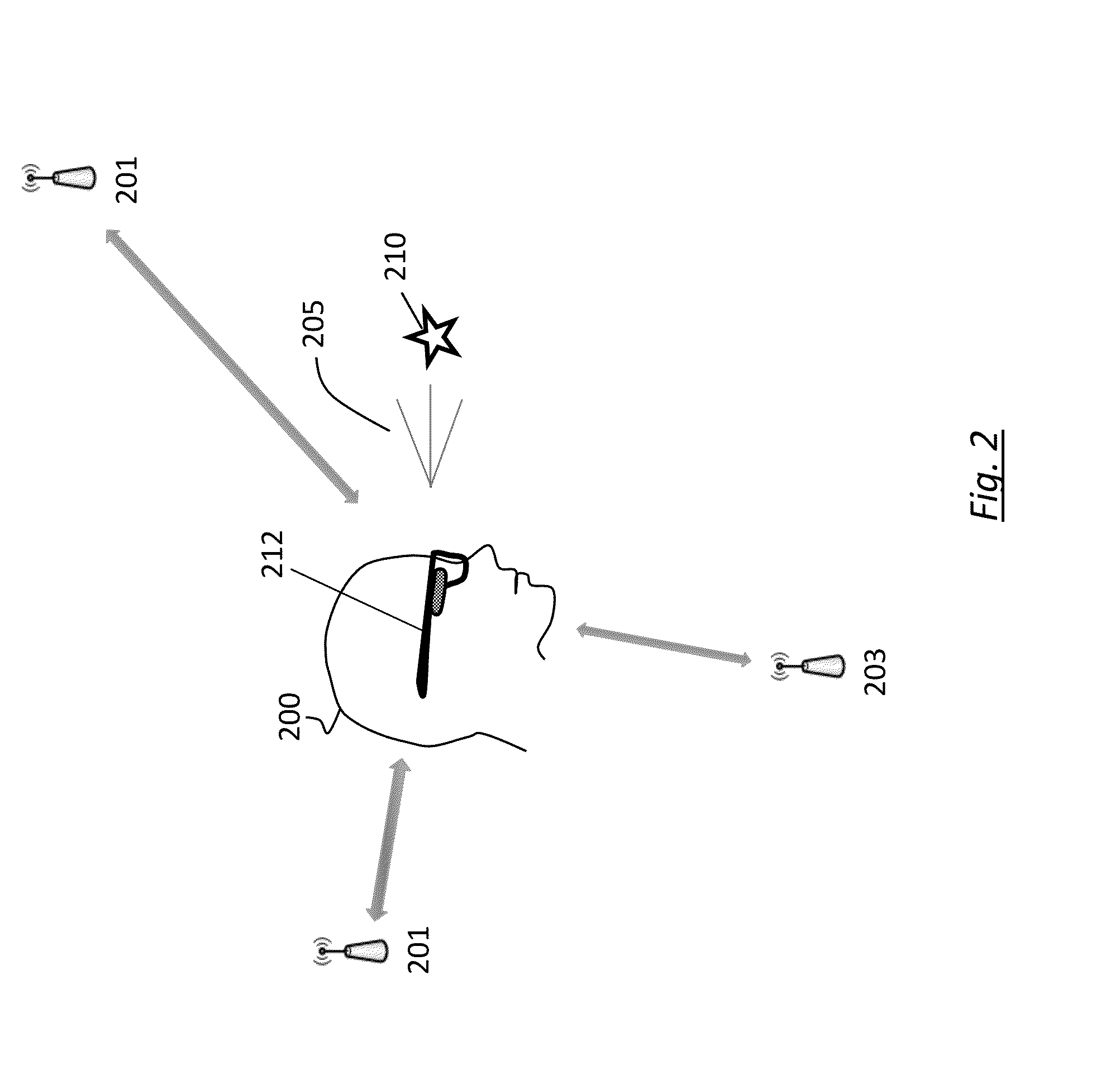
Real time object tagging for interactive image display applications
InactiveUS20100103173A1Enhanced informationTelevision system detailsTwo-way working systemsRadio equipmentComputer graphics (images)
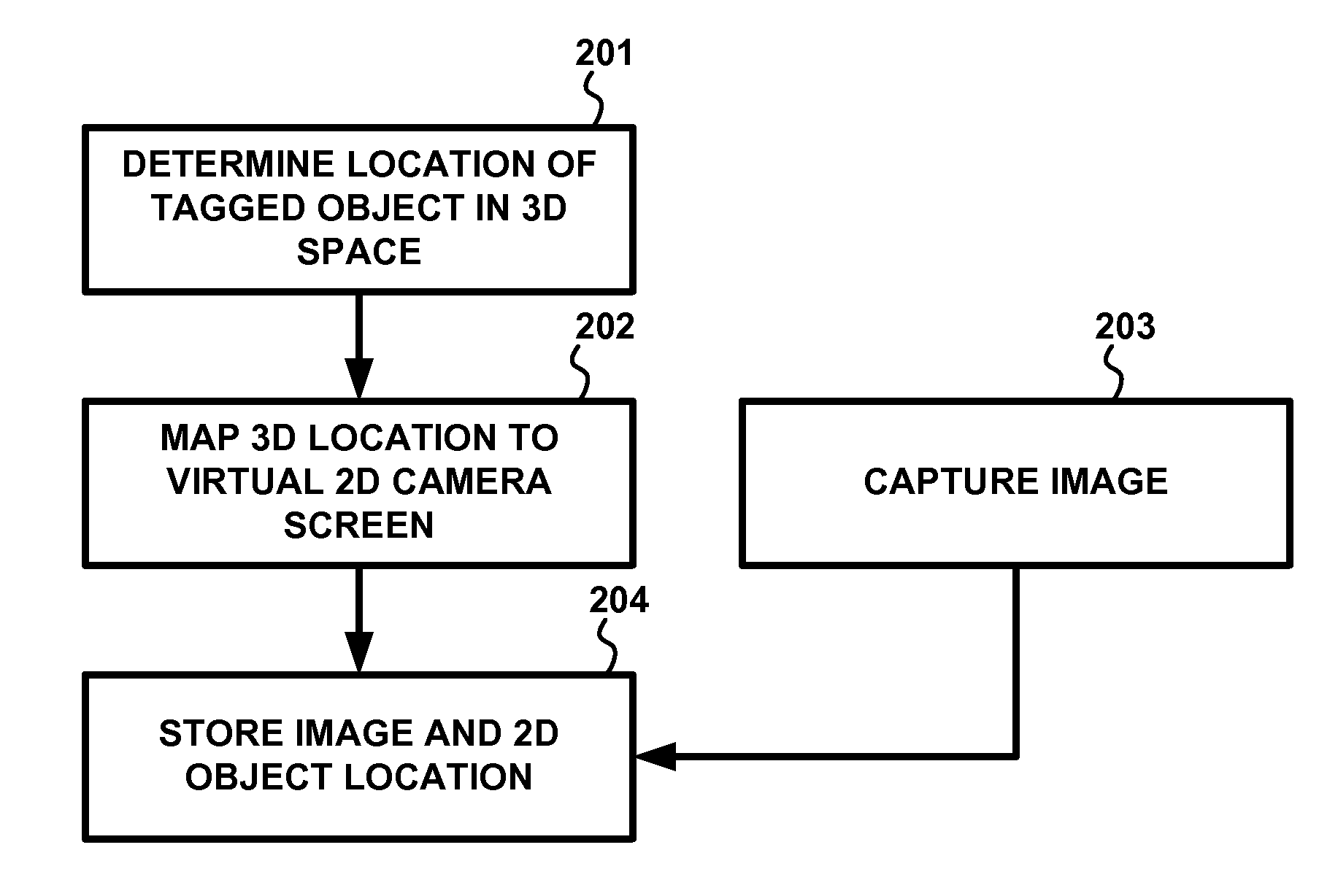
Apparatus and methods that track the location of an object within a video image at the time of capture of the video image are described. The location of the object within each frame can be recorded as meta-data for the video image so that when the video image is played back, a viewer can select the object using suitable interaction means and be linked through to a source of additional information about the object, such as a product website or the like. A device emitting radio frequency (RF) signals is attached to an object that is to be identified and tracked within a video image. Using an RF receiver with multiple antennas and applying trilateration techniques, the object's location within the video image is determined in real time and recorded as the video image is recorded. Where multiple objects are to be tracked, each object is provided with a radio device having a unique ID and the location of each device within the video image is recorded. The described solution automates an otherwise manual, error-prone and time-consuming process.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
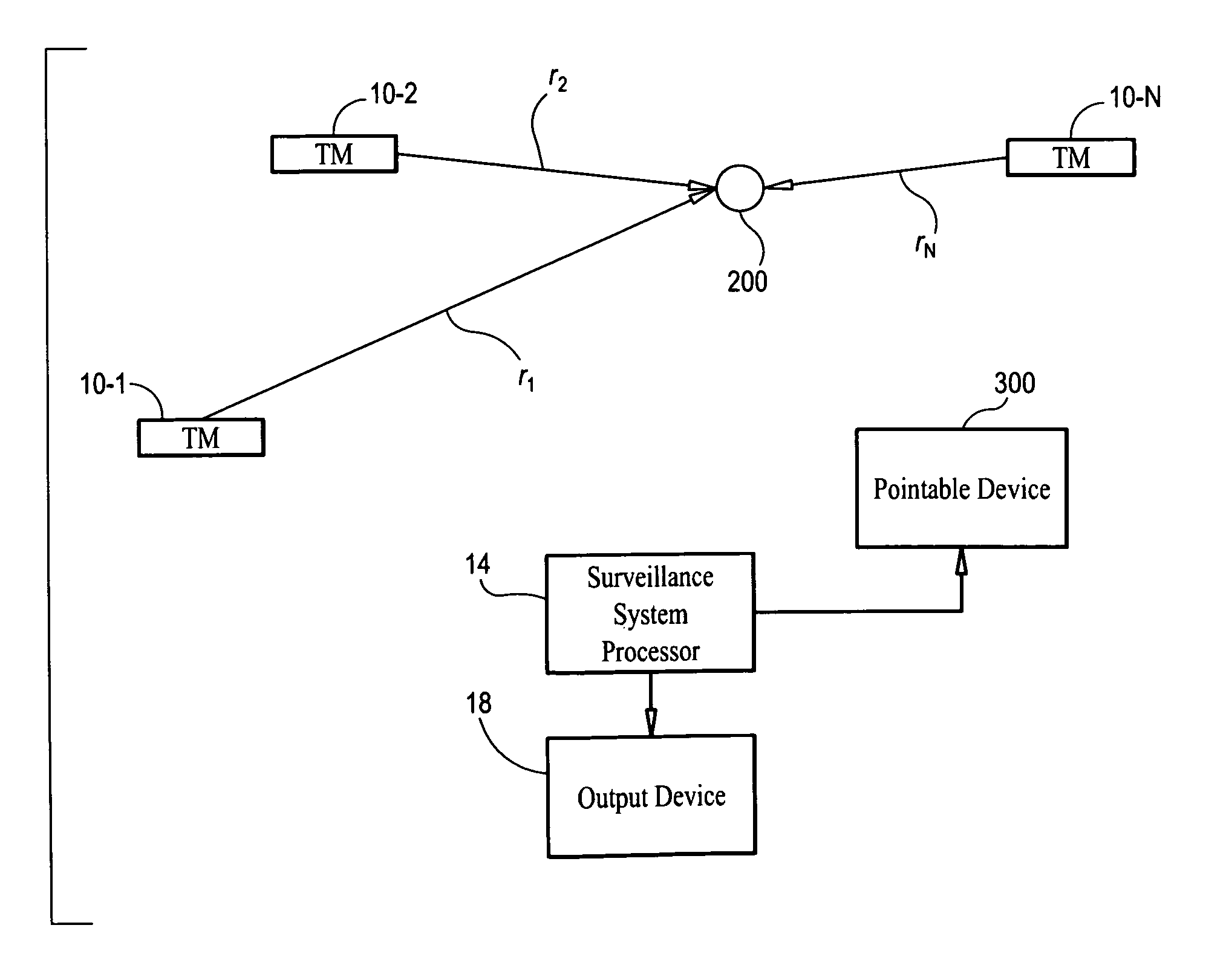
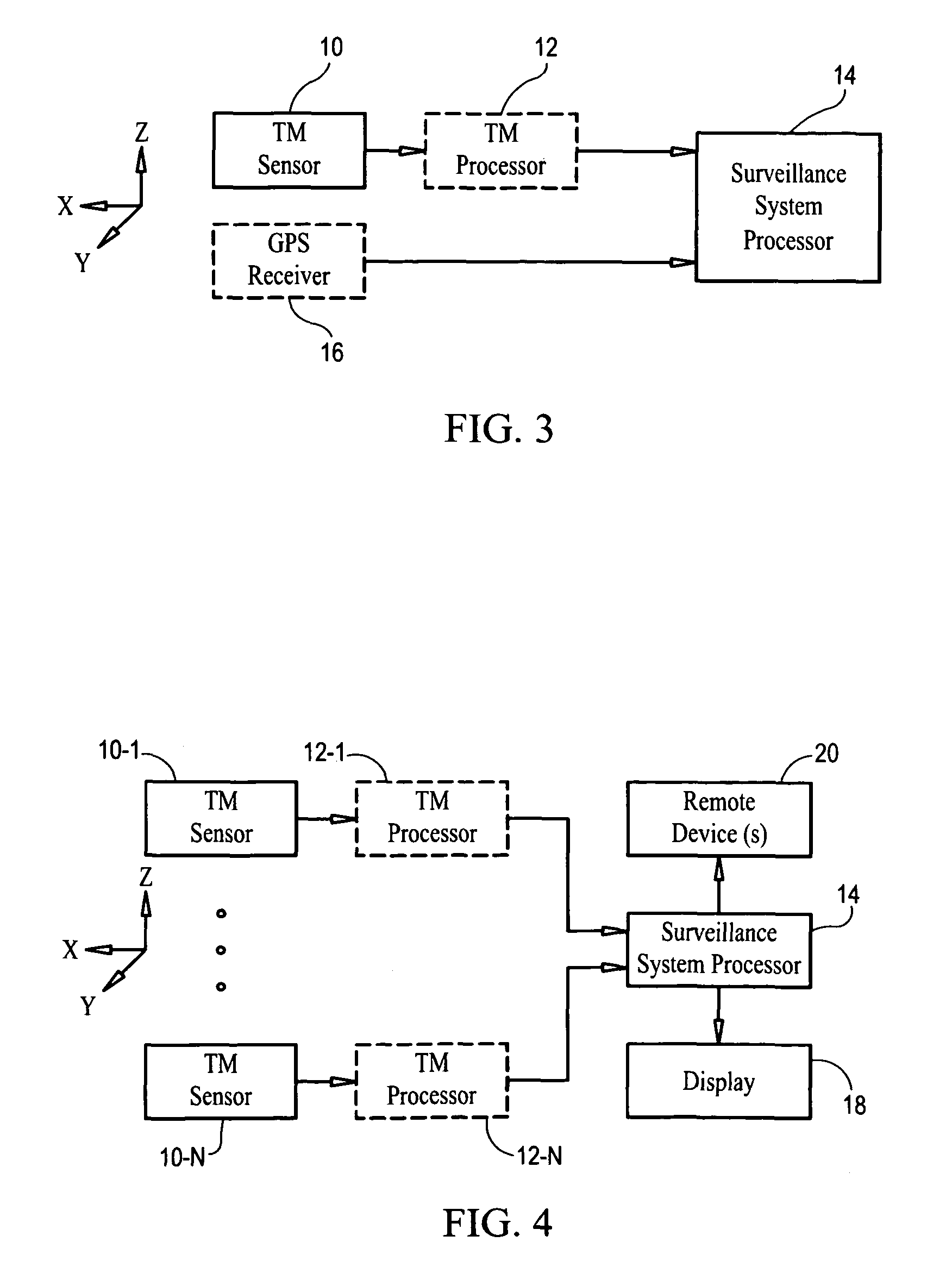
Magnetic anomaly surveillance system using spherical trilateration
InactiveUS8575929B1Digital computer detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsOutput deviceMagnetic anomaly
A magnetic anomaly surveillance system includes triaxial magnetometer (TM) sensors arranged at known locations in an array. A processor coupled to the TM sensors generates a scalar magnitude of a magnetic anomaly field measured at each of the TM sensors. The scalar magnitude is indicative of a spherical radius centered at the known location associated with a corresponding one of the TM sensors. The processor also generates a comparison between each scalar magnitude and a threshold value. The processor then determines at least one magnetic anomaly location in the coordinate system via a spherical trilateration process that uses each spherical radius and each scalar magnitude associated with selected ones of the TM sensors for which the threshold value is exceeded. One or more output devices coupled to the processor output data indicative of the one or more magnetic anomaly locations.
Owner:USA REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY
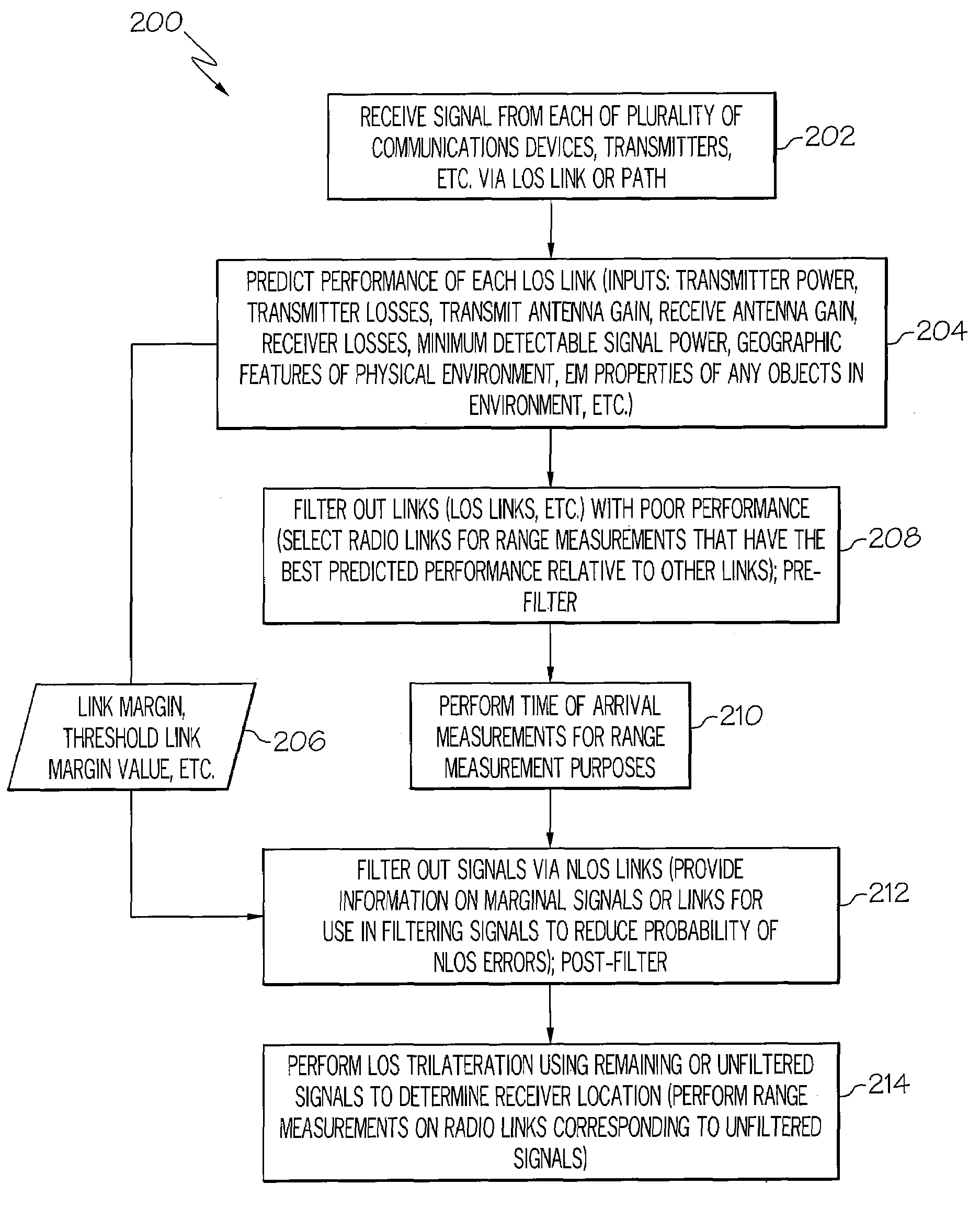
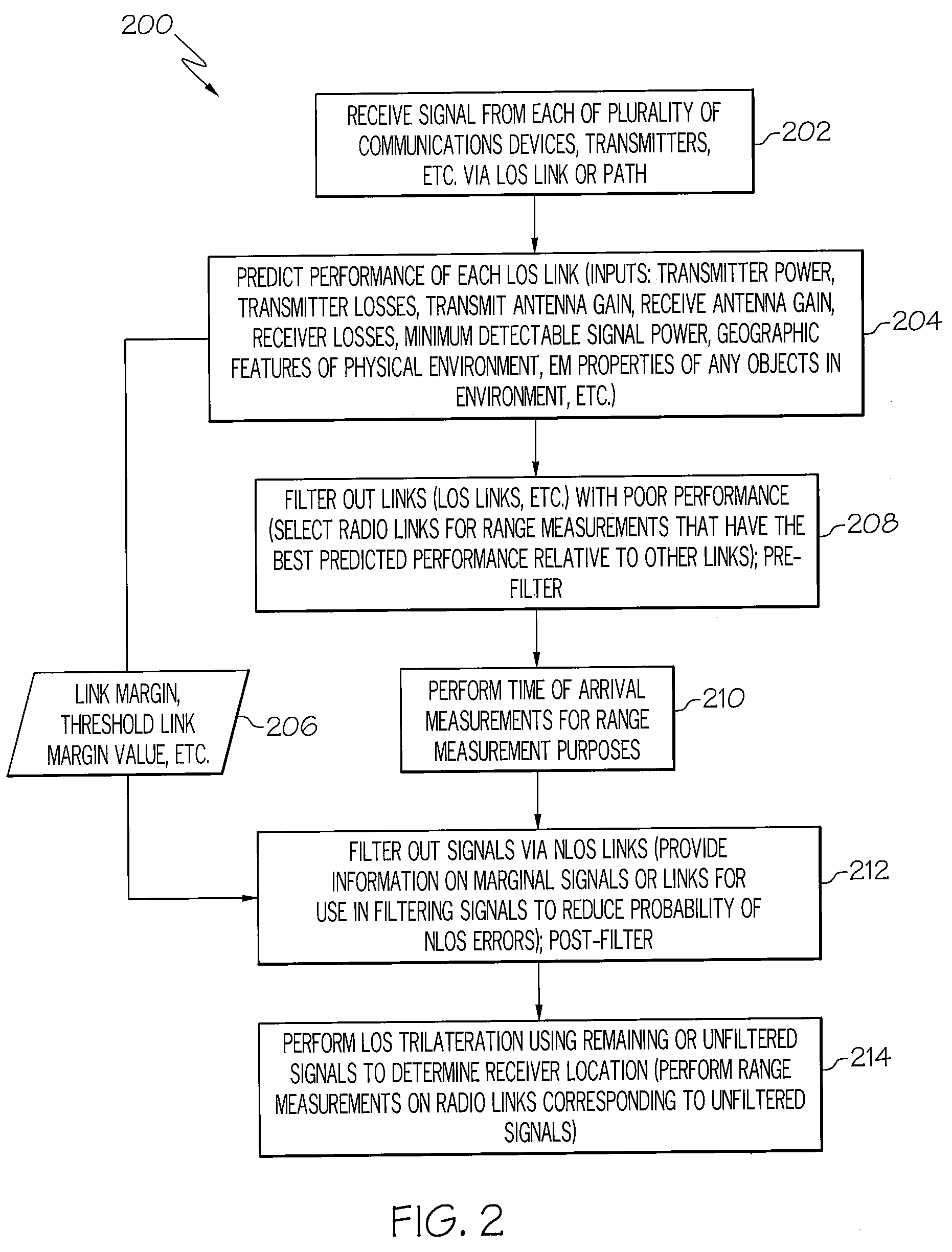
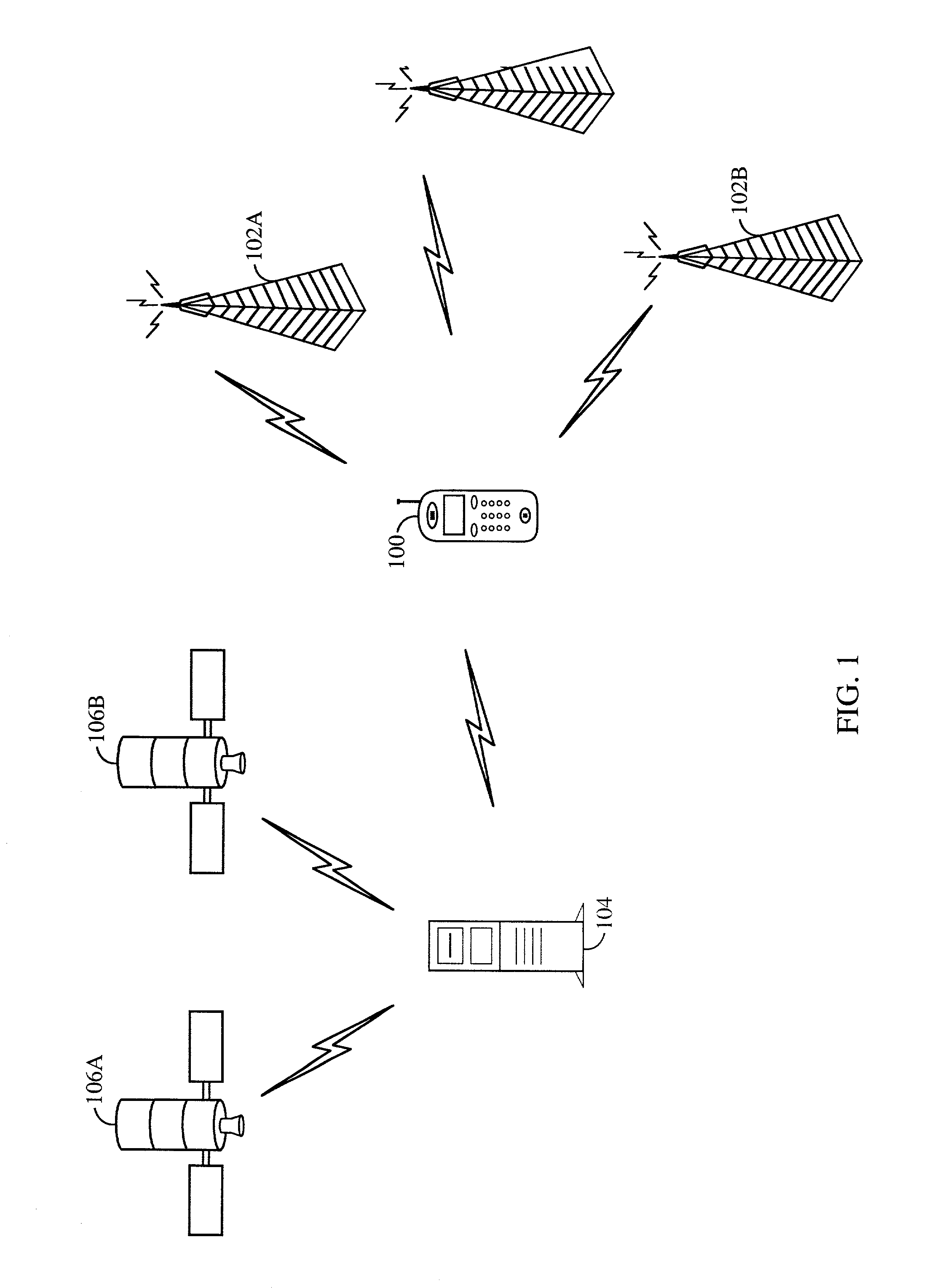
Method and device for trilateration using LOS link prediction and pre-measurement LOS path filtering
ActiveUS7468696B2Direction finders using radio wavesPosition fixationPredicting performanceElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method for trilateration may include receiving a signal via each of a plurality of LOS paths and predicting performance of each LOS path. The method may also include filtering out signals received via LOS paths with performance below a predetermined threshold value. The method may further include performing trilateration using unfiltered signals to substantially determine a location of a device.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
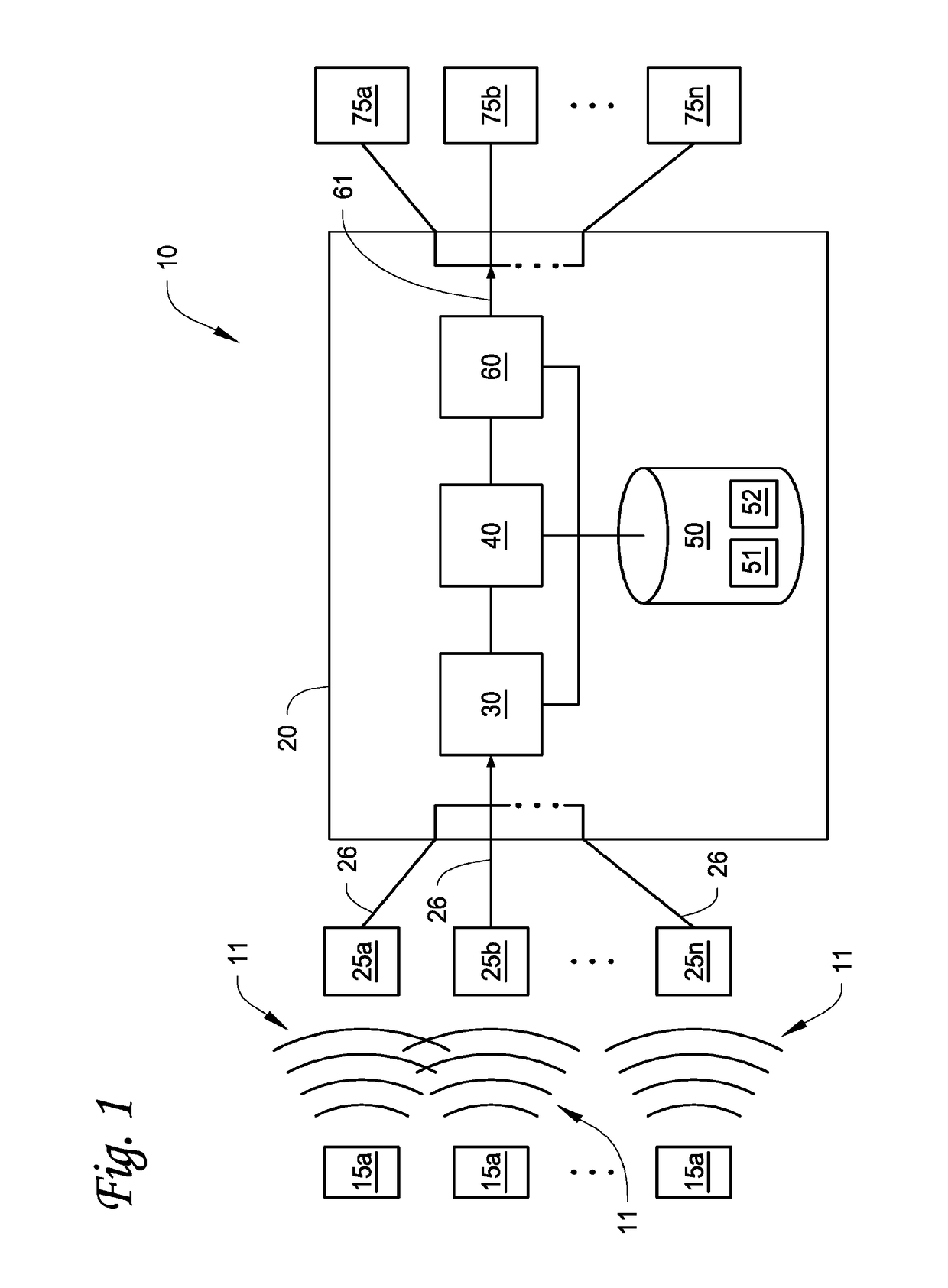
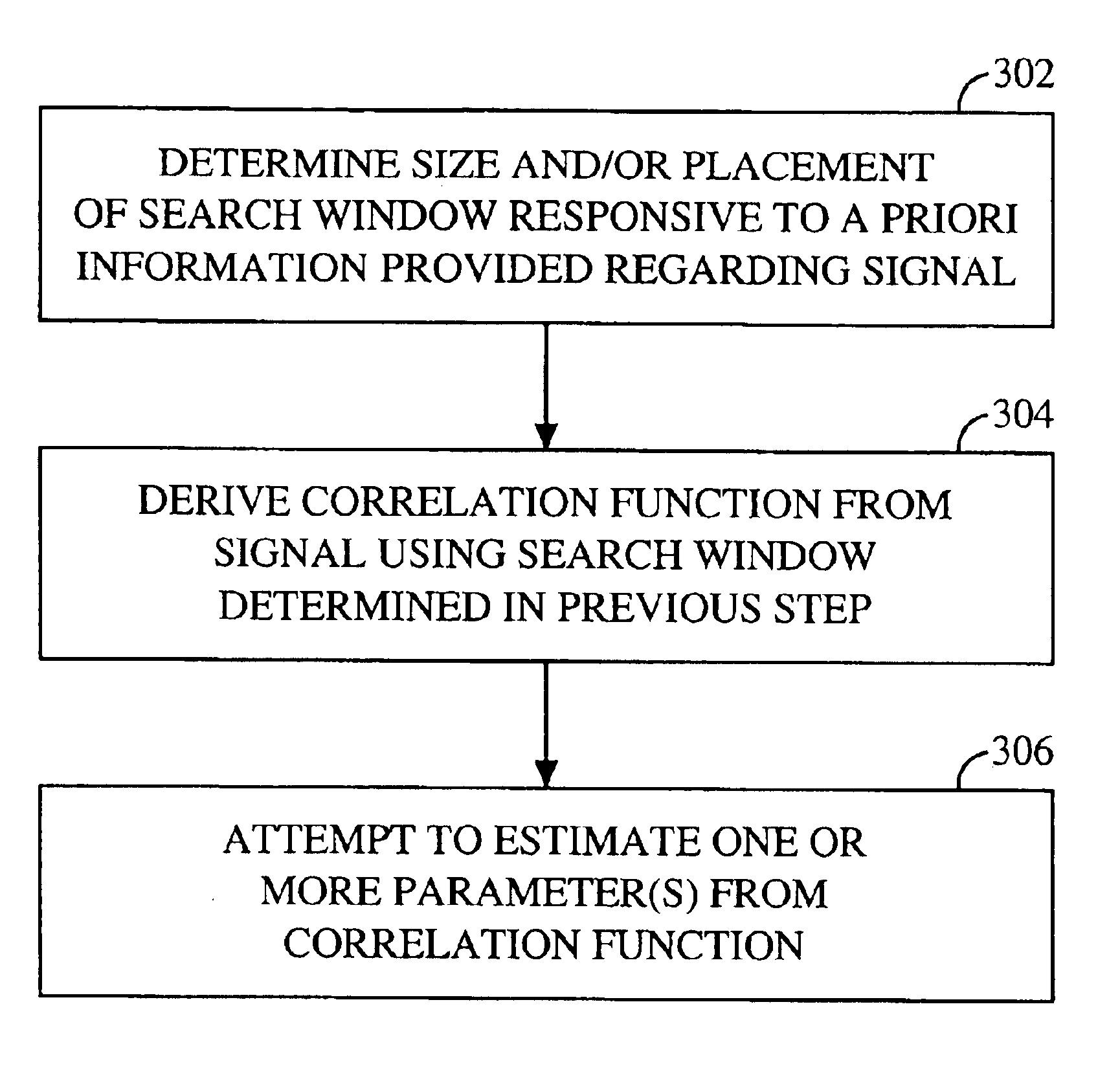
Parameter estimator with dynamically variable search window size and/or placement
InactiveUS20030086512A1Improve performanceShorten cycle timePosition fixationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemCorrelation function
A parameter estimator for estimating one or more parameter(s) from a correlation function derived from a signal using a dynamically variable search window is described. The parameter estimator may be employed in a subscriber station to estimate the time of arrival of one or more base station pilot signals in a wireless communication system. This information may be utilized in an overall advanced forward link trilateration (AFLT) process for estimating the location of the subscriber station.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Occupancy sensing and building control using mobile devices
Apparatus, systems and methods for ascertaining the occupancy of a building are presented. The building is divided into one or more control zones which correspond to physical areas of the building associated with controllable modules, such as HVAC units, lighting, irrigation, or other environmental features such as fountains, music, video, and the like. Zone parameters define how zone devices shall react to the number of occupants located in the particular zone. A building control system detects individual mobile devices in and around the building, and determines the locations of each device by using trilateration and / or location services. The identified mobile devices act as proxies for building occupants. The locations of these devices are correlated with the locations of the zones in the building, and the building control system then adjusts the operating parameters of the zone based on the number of devices present in the zone.
Owner:TRANE INT INC
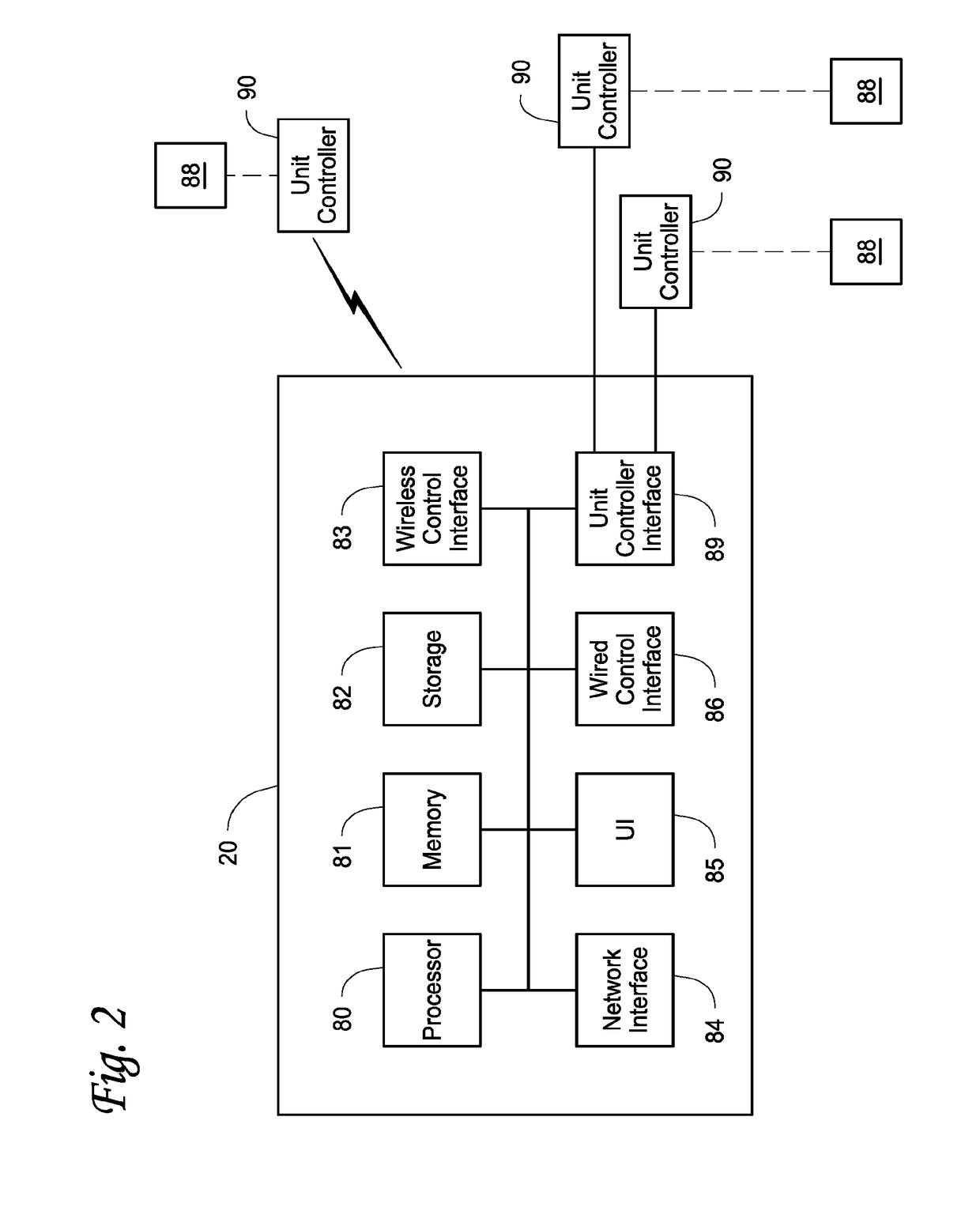
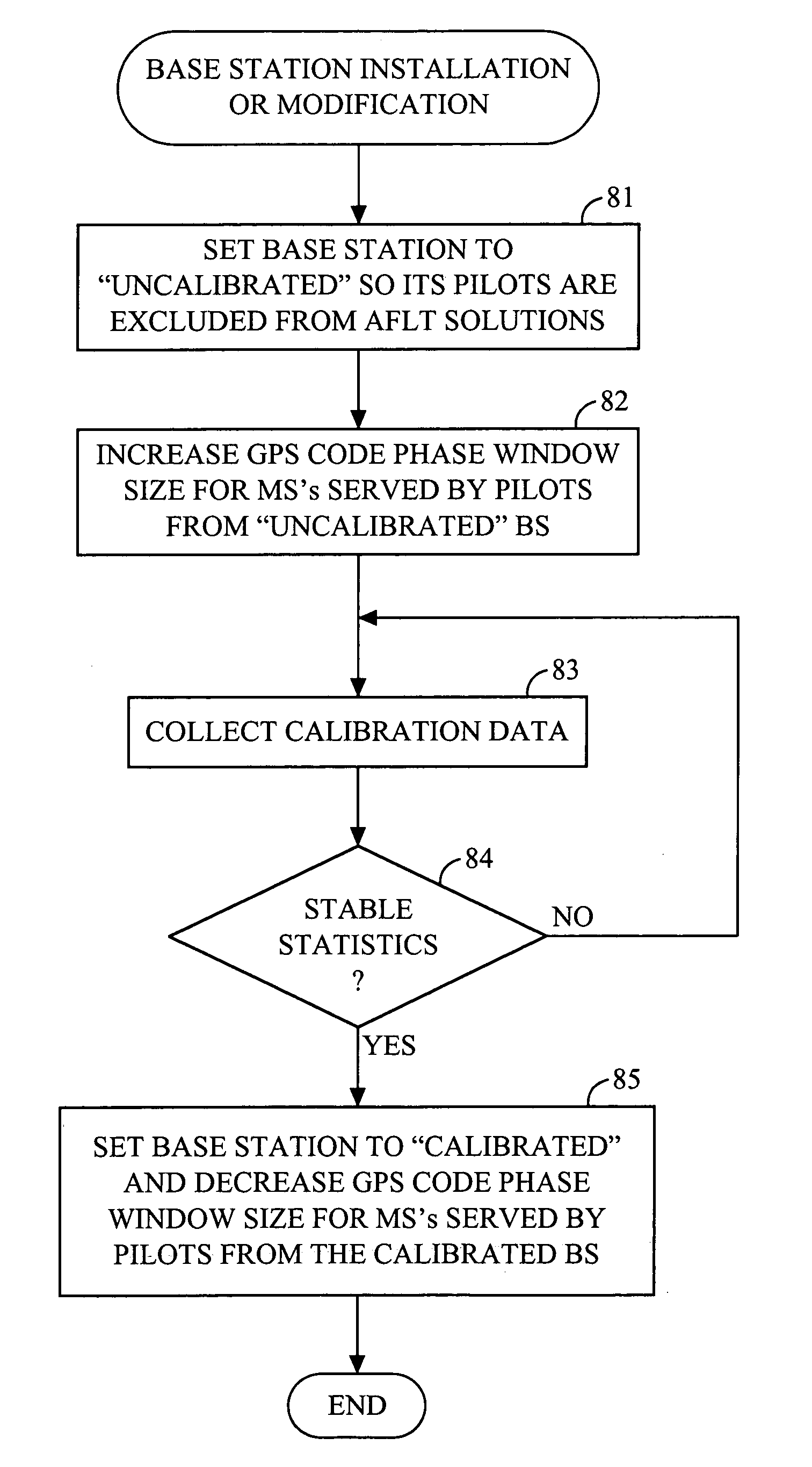
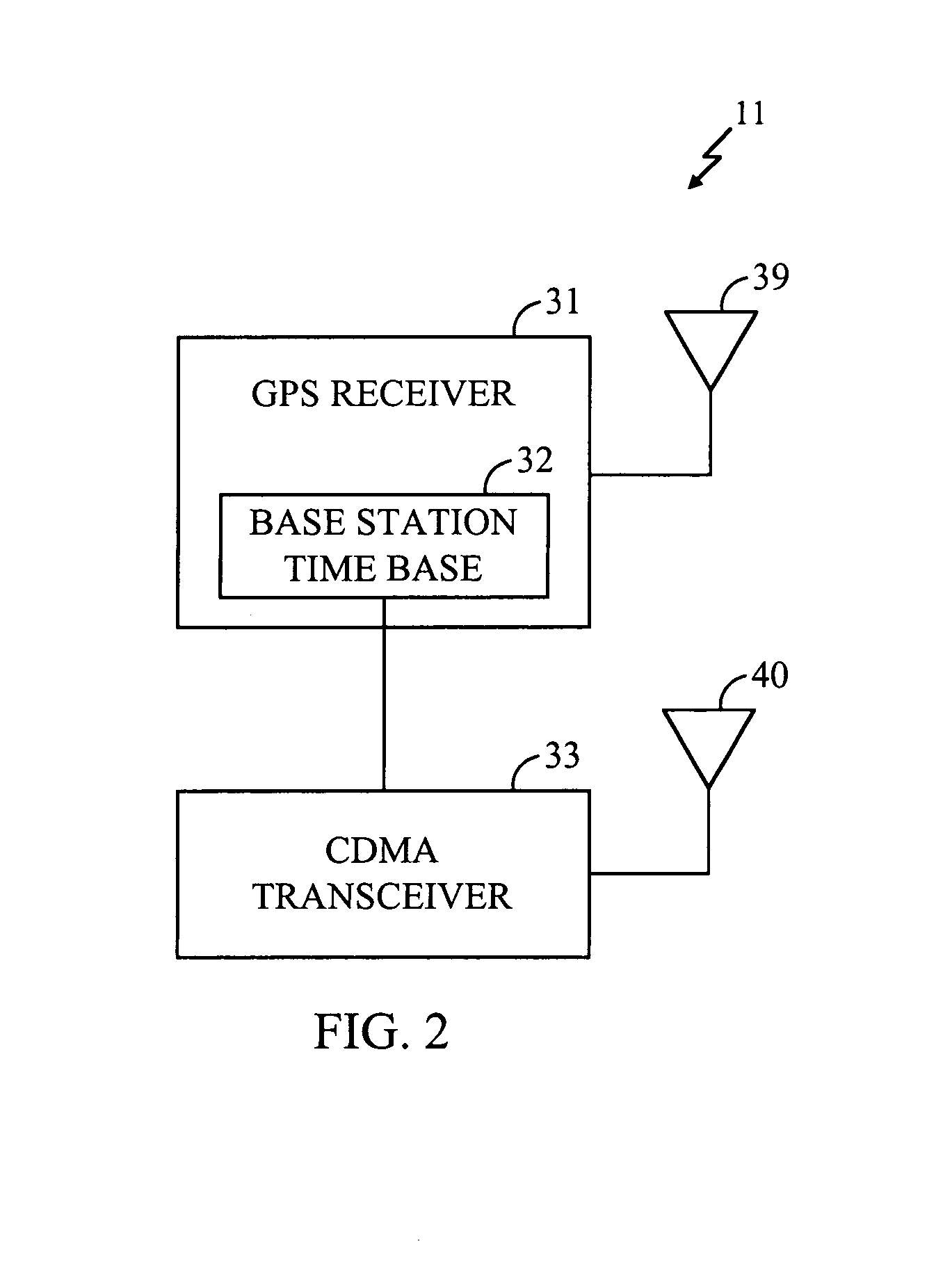
Base station time calibration using position measurement data sent by mobile stations during regular position location sessions
InactiveUS7006834B2Beacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationTelecommunications networkCode division multiple access
Base stations in a wireless telecommunications network are calibrated to GPS system time by using position measurement data obtained from one or more hybrid mobile stations during regular position location sessions. Therefore, the calibration data need not be obtained externally from a calibration instrument, and the calibration may occur on a continuous basis to compensate for any disturbances or drift in the base stations. Privacy concerns are alleviated by using regular position location sessions that occur only when the operator of the hybrid mobile station places or answers a wireless telephone call. In a preferred implementation, the network uses Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA), and the hybrid mobile stations may provide Advanced Forward Link Trilateration (AFLT) or GPS position location data to the network.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and system for hybrid location detection
InactiveUS20160183057A1Position fixationLocation information based serviceLocation detectionMobile device
The disclosure generally relates to a method and apparatus for hybrid location detection. The disclosed embodiments enable location determination for a mobile device in communication with one or more Access Points (APs) and an optical camera capable of measuring distance to a known object. In an exemplary embodiment, the camera is used to determine distance form a known object or a known location (i.e., anchor). In addition, using Wi-Fi infrastructure, round-trip signal propagation time may be used to determine one or more ranges from known access points (APs) connected. Round-trip signal propagation time may be measured, for example, by using a Time-Of-Flight algorithm. Additionally, trilateration algorithms may be used to determine a course location for the mobile device relative to the APs. Using a combination of optical distance measurement and the course location, the exact location of the mobile device may be determined.
Owner:INTEL CORP
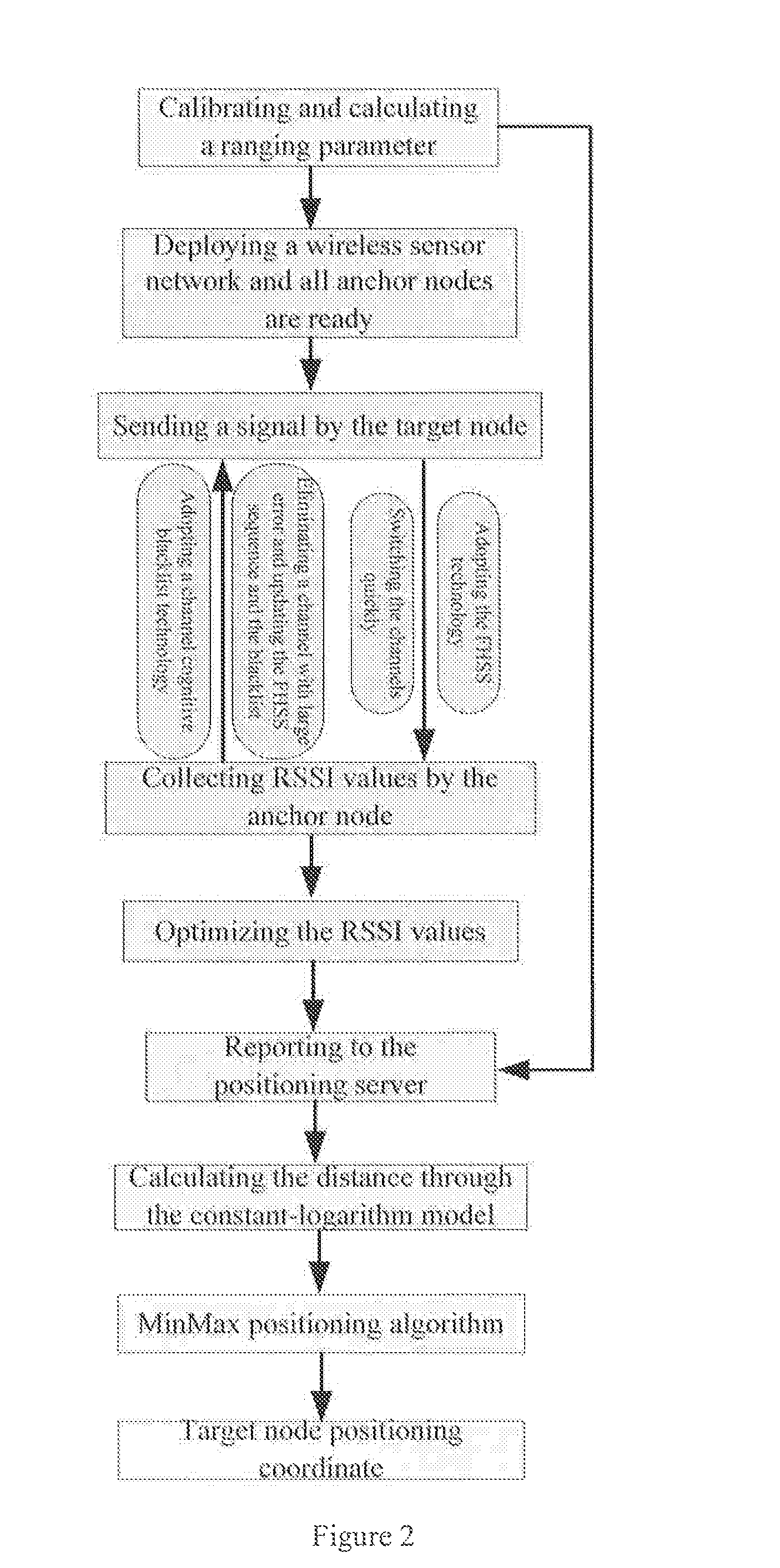
RSSI positioning method based on frequency-hopping spread spectrum technology
ActiveUS20160187460A1Reduce the impactIncrease coordinate calculating precisionBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationFrequency-hopping spread spectrumEngineering
An RSSI positioning method based on frequency-hopping spread spectrum technology, comprising: calibration stage: measuring the RSSI values of a plurality of channels at fixed points, and recording and calculating the ranging parameters in an RSSI ranging model; system preparation: deploying a positioning anchor node, and realizing synchronization between a target node and the anchor node; conducting communication on the target node by respectively utilizing a plurality of channels to obtain the RSSI values; signal processing stage: processing the RSSI into signal strength amplitude and performing optimization; and positioning stage: calculating a distance and the target node position on a positioning server according to each of the signal strength. The present invention solves the problem that low RSSI positioning precision cannot satisfy the actual requirements because a traditional RSSI positioning method is limited to factors such as multipath signal transmission, co-channel interference, obstacle interference and low coordinate calculation precision of a trilateration method.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
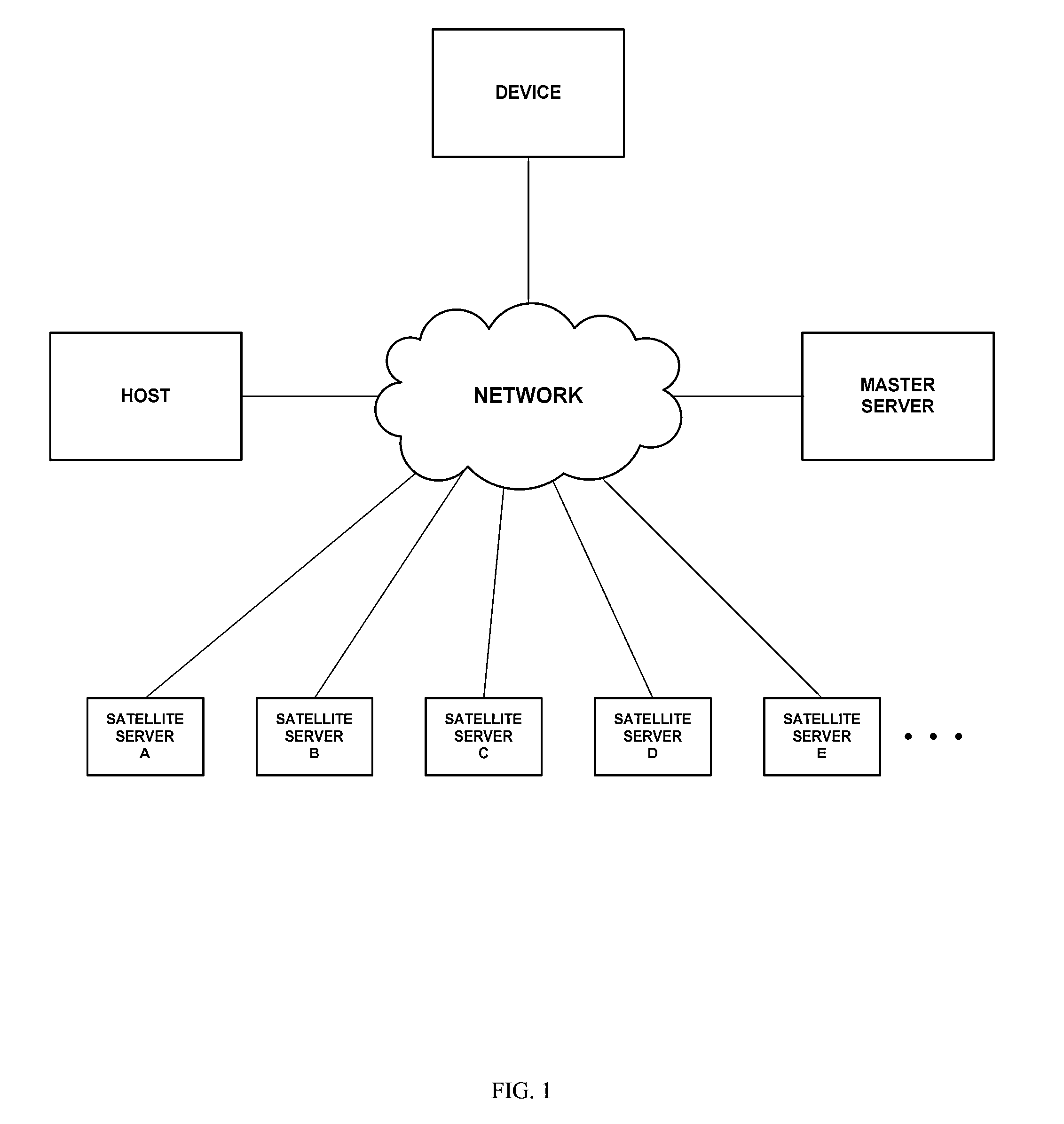
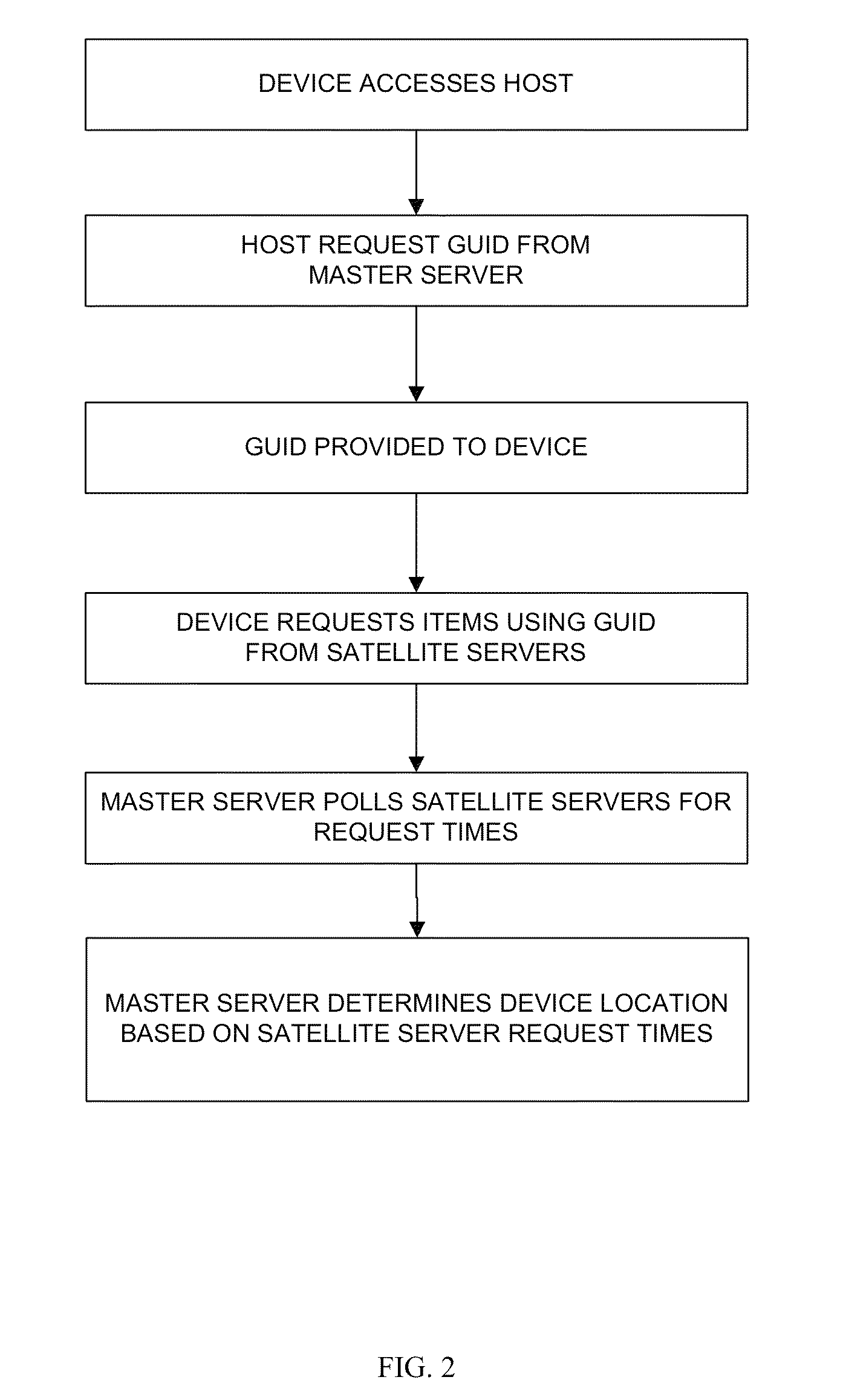
2D web trilateration
The invention provides systems and methods of locating a network device based on the time latency between a request by a user device and the receipt of the request by a plurality of satellite servers provided at different locations. Preferably three or more satellites may be employed. The request may be for an item, which may have a known file size, and which may or may not exist. Triangulation techniques may be utilized to determine the location of the device relative to the satellite servers.
Owner:THE 41ST PARAMETER
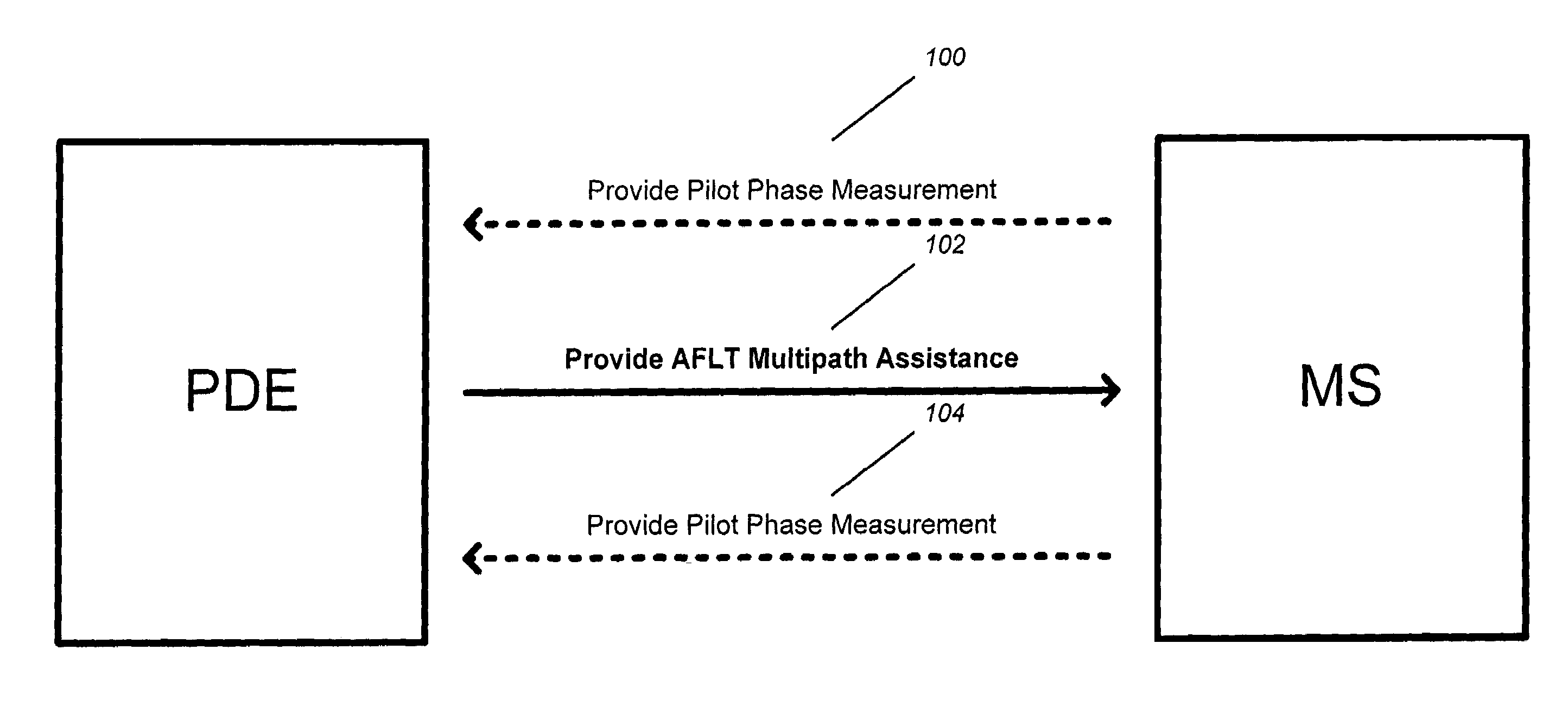
Multipath assistance for pilot phase measurement processes
ActiveUS6999778B2Improve accuracyImprove stabilityAssess restrictionRadio transmissionStatistical databaseGeographic regions
A method for enhancing the accuracy of Advanced Forward Link Trilateration (AFLT) position location calculations is disclosed. A position determination entity (PDE) constructs a statistical database of pilot phase measurements reported by mobile stations (MSs) located in a geographic region about a reference base station (BS). When a MS's location is to be calculated, the MS reports a set of PN phase offsets to the PDE. Using only that set of PN phase offsets, the PDE determines a rough estimate of the MS's location using conventional AFLT and also determines the region within which the MS is located. If the PDE determines that the MS did not report one or more earlier arriving PN phase offsets but reported a delayed multipath component, the PDE sends a message to the MS to look for an earlier arriving PN phase offset at a certain time prior to the reported PN phase offset.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Method and system for wireless LAN-based indoor position location
A method and system for position location of clients in wireless local area networks. (WLANs). The position location technique utilizes time-of-flight (TOF) measurements of signals transmitted from a client to a number of wireless access points (APs) or vice versa to determine distances. Round-trip time (RTT) measurement protocols are used to estimate TOF and distances between the client at an unknown position and the WLAN APs. The method and system improves positioning accuracy by identifying and mitigating non-line-of sight (NLOS) errors such as multipaths. Trilateration algorithms are utilized in combination with median filtering of measurements to accurately estimate the position of the client.
Owner:AVAYA INC +1
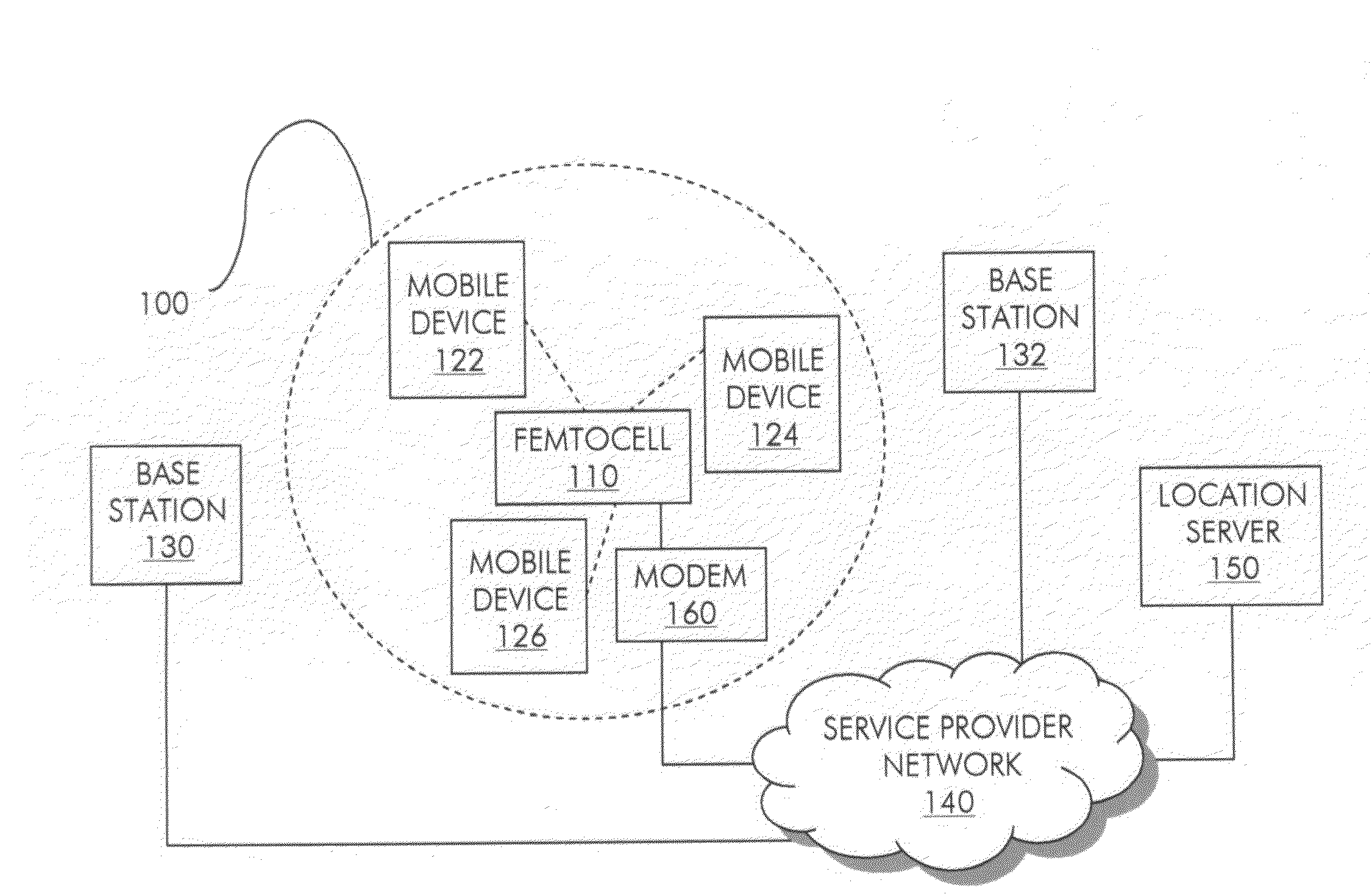
Methods and systems for determining the location of a femtocell
A femtocell acquires its geographic location using location samples reported by mobile devices that are communicatively coupled with the femtocell. The estimated location may be calculated as an arithmetic mean of reported location samples, a weighted mean of reported location samples, or by using reported location samples in conjunction with estimated distances and trilateration. The estimated location may be applied in geographic license checks, network interference checks and / or emergency call registration, for example.
Owner:SHARP LAB OF AMERICA INC
Positioning method based on wireless radio frequency recognition technology
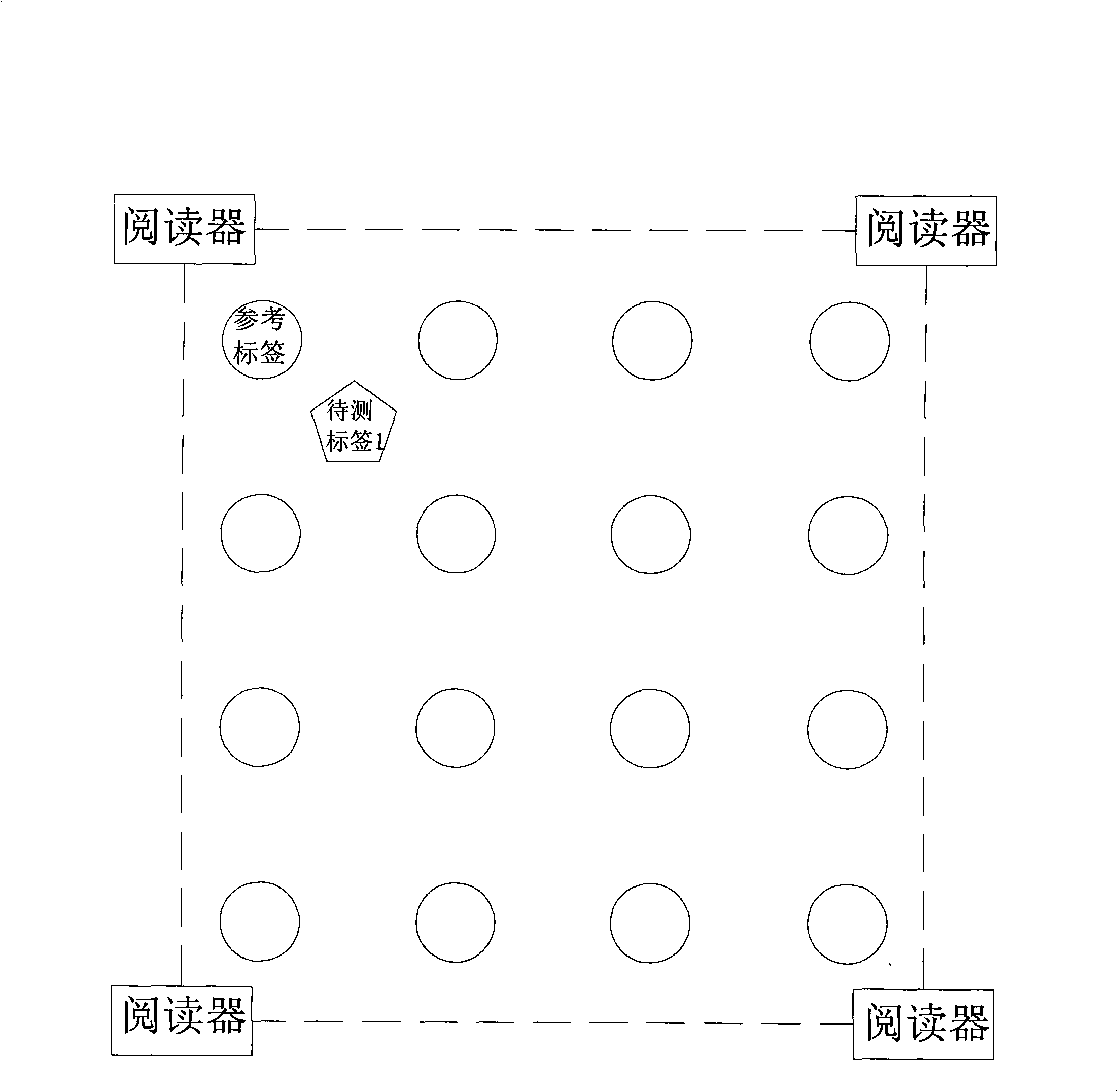
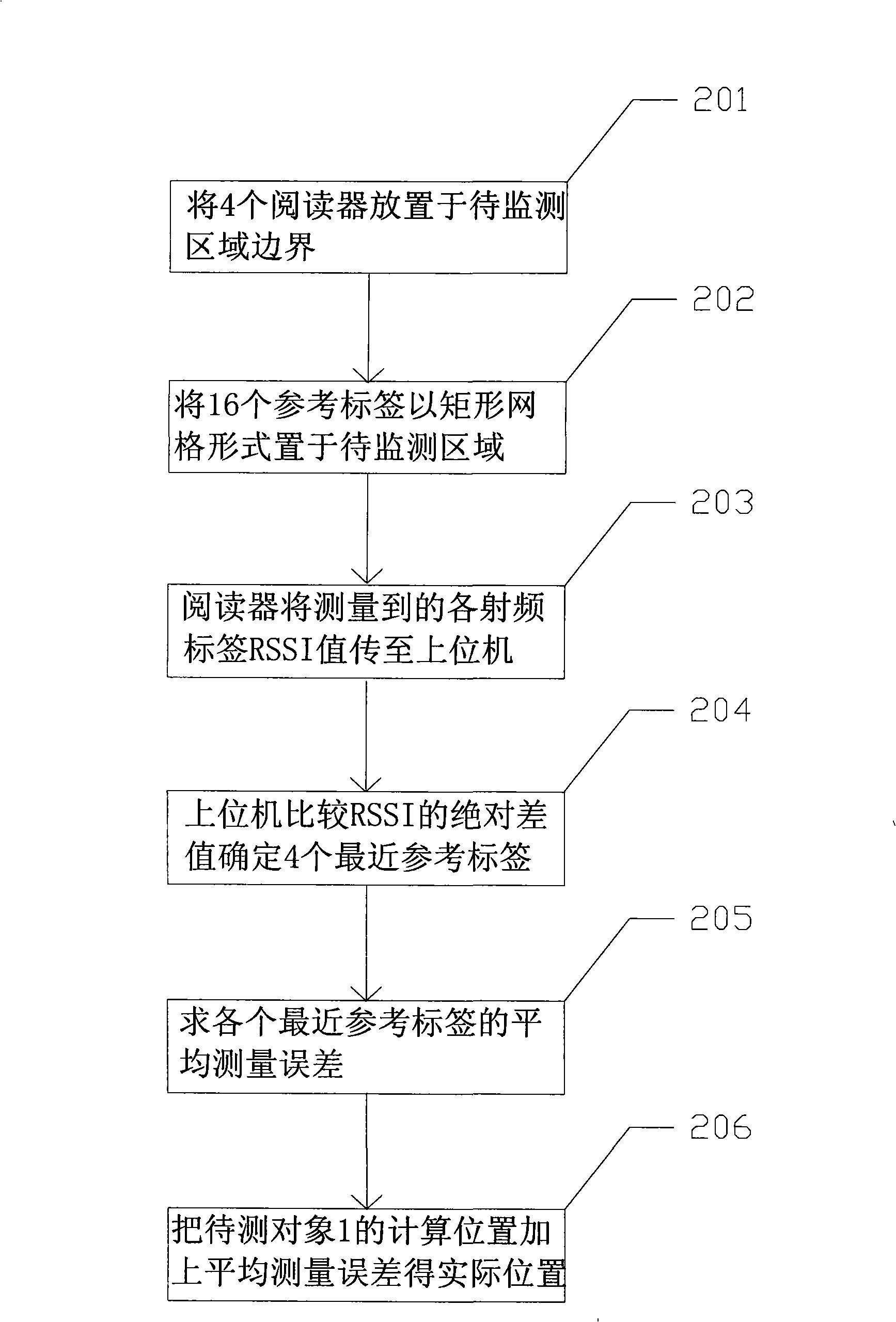
InactiveCN101320092ALow costAdapting to dynamicsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAbsolute differenceRadio frequency signal
A positioning method which is based on the wireless radio frequency identification technology comprises the steps that readers are arranged at the boundary of a zone to be monitored; reference tags are fixed at an indoor zone to be monitored in a rectangular grid type; when an object to be monitored with radio-frequency tags is arranged in the zone to be monitored, each of the readers detects the electromagnetic wave of each radio-frequency tag through the antenna of each of the readers, the radio-frequency signal intensity values of the reference tags which are obtained by the measurement and the tags of the object to be tested are sent to an upper computer; the upper computer compares the absolute difference values of the radio-frequency signal intensity of each of the reference tags and the tags of the object to be tested to determine a plurality of nearest reference tags of the object to be tested; each nearest reference tag and the calculated position of the object to be tested are obtained through the trilateration method, and the average measurement error of a system is obtained by comparing the calculated positions and the actual positions of the nearest reference tags; the calculated positions of the object to be tested adds the average measurement error to obtain the position coordinates of the object to be tested. By utilizing the method of the invention, a positioning system has good accuracy and real-time in the aspect of position induction.
Owner:黄以华
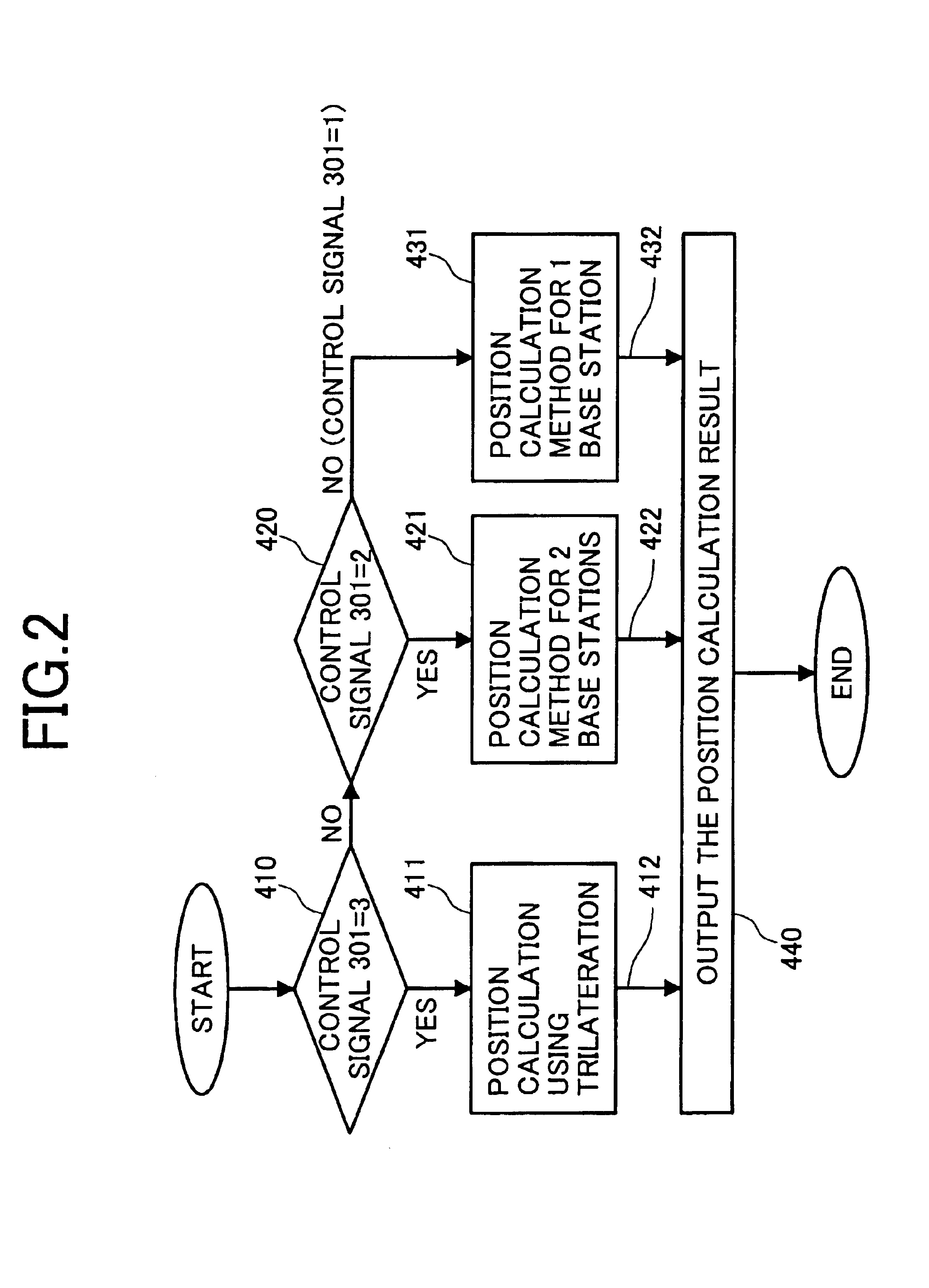
Equipment for the calculation of mobile handset position
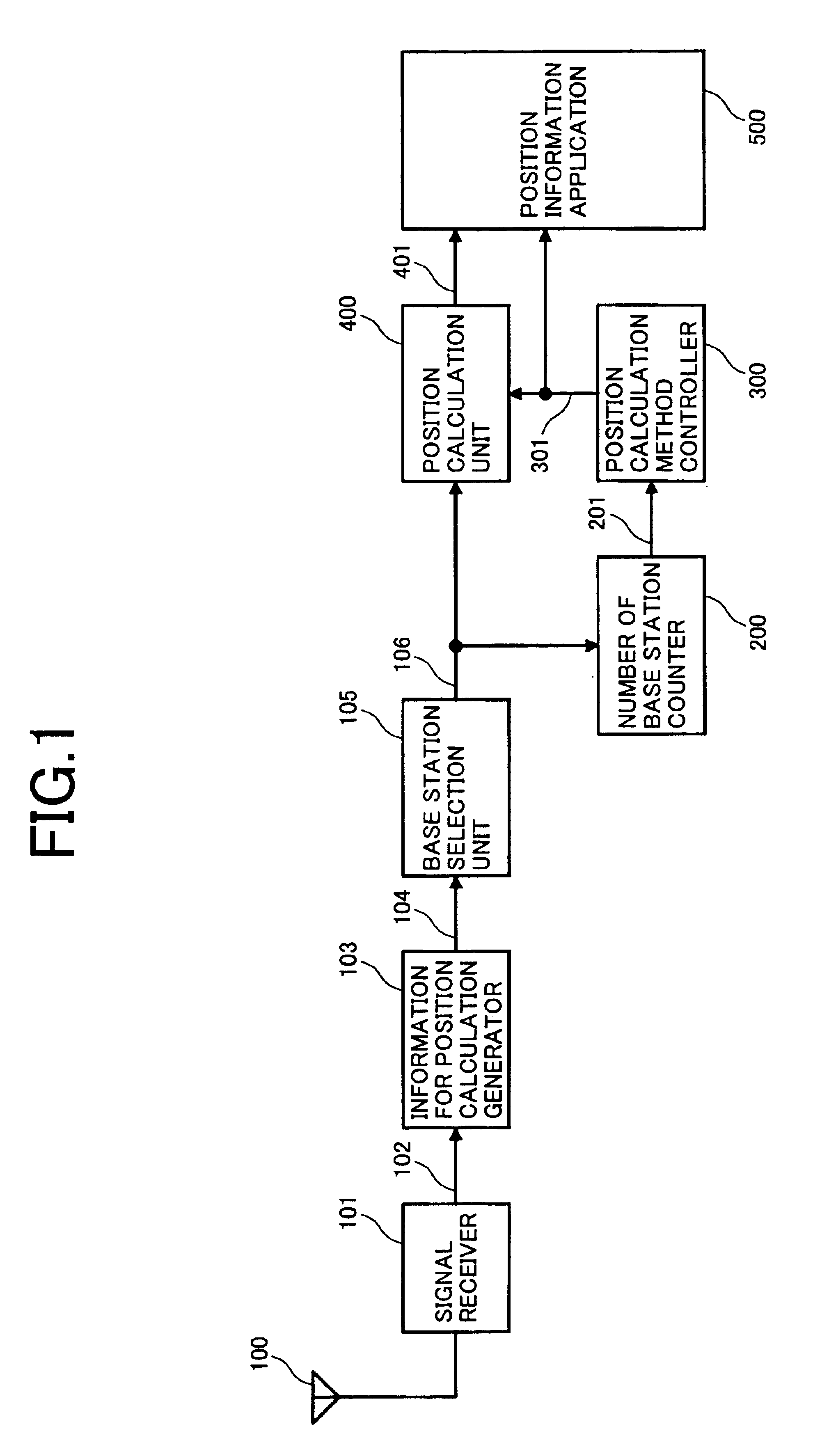
ActiveUS6990351B2Reduce operating positionsReduce stepsPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsComputer scienceCalculation methods
Even in areas where signals from only two or less base stations are available for position calculation, the mobile handset position can be calculated, expanding the position information service area and improving the usefulness. When the number of base stations available for position calculation is three or more, the position calculation is performed based on trilateration. When the number of available base stations is two or one, the position calculation is performed by using a two-station-based position calculation method or a one-station-based position calculation method according to the number of available base stations.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Parameter estimator with dynamically variable search window size and/or placement
InactiveUS6738438B2Improve performanceShorten cycle timePosition fixationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemCorrelation function
A parameter estimator for estimating one or more parameter(s) from a correlation function derived from a signal using a dynamically variable search window is described. The parameter estimator may be employed in a subscriber station to estimate the time of arrival of one or more base station pilot signals in a wireless communication system. This information may be utilized in an overall advanced forward link trilateration (AFLT) process for estimating the location of the subscriber station.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
A signal positioning system and a positioning method thereof
ActiveCN103592622AExpand the range of realizable applicationsVariable Positioning AccuracyPosition fixationTriangulationComputer science
The invention discloses a signal positioning system comprising at least one signal emission unit used for emitting wireless signals, at least one signal receiving unit used for measuring the wireless signals to obtain signal measurement data, at least one processing unit connected to the signal receiving unit and used for receiving and processing the signal measurement data, and a database unit connected to the processing unit and used for storing information needed by a storage positioning algorithm. According to the signal positioning system and the positioning method thereof of the invention, through a signal area positioning method, a realizable application scope of the existing positioning system is enlarged, and the accuracy and feasibility are improved. Furthermore, according to demands of practical application, variable positioning accuracy degrees are provided, so that the operation efficiency is raised. According to the signal positioning system and the positioning method thereof of the invention, dependence on trilateration or triangulation in the prior art are eliminated. The application scope is enlarged and the operation efficiency is raised. The invention also brings forward a positioning method of the signal positioning system.
Owner:佰路得信息技术(上海)有限公司
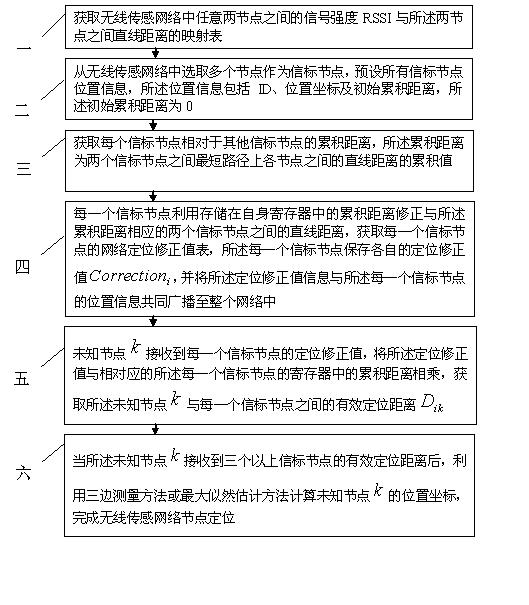
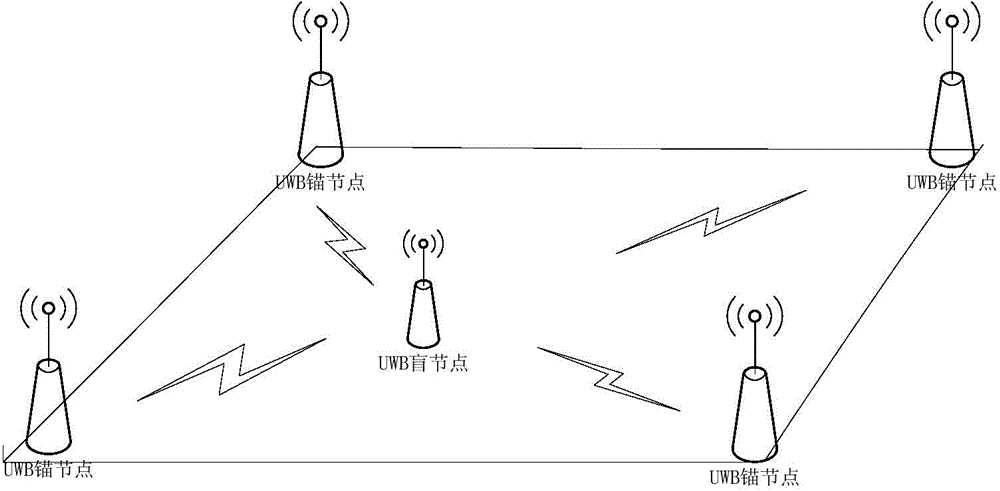
Wireless sensor network node positioning method based on distance assistance
InactiveCN101835259AReduce physical location differencesHigh positioning accuracyNetwork topologiesEstimation methodsPositioning technology
The invention relates to a wireless sensor network node positioning method based on distance assistance, relating to the technology of wireless sensor network positioning and solving the problem of great error of positioning of traditional wireless sensor network positioning methods. The wireless sensor network node positioning method comprises the following steps of: firstly establishing a mapping table relative to signal strength and distance, then receiving the signal strength of beaconing nodes, and querying the mapping table according to the signal strength of the beaconing nodes to further obtain the cumulative distance of other nodes; calculating the positioning correction value of the beaconing nodes, and further obtaining the effective positioning distance between an unknown nodeand the beaconing node; and finally utilizing a trilateration method or a maximum likelihood estimation method to calculate the position coordinates of the unknown node to complete wireless sensor network node positioning. The invention is suitable for wireless sensor network positioning.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
OFDM position location signaling utilizing mutually exclusive subsets of subcarriers
Position location signaling system, apparatus, and method are disclosed. Position location beacons can each be configured to transmit a frequency interlaced subset of orthogonal frequencies spanning substantially an entire channel bandwidth. The orthogonal frequencies can be pseudorandomly or uniformly spaced, and each beacon can be allocated an equal number of orthogonal frequencies. Each frequency of the interlaced subset of orthogonal frequencies can be modulated with an element of a predetermined data sequence. A mobile device can receive one or more of the beacon signals and determine a position using a position location algorithm that determines position in part on an arrival time of the beacon signal. Where the mobile device can receive three or more beacon signals, the mobile device can perform position location by trilateration to the beacon positions based, for example, on a time difference of arrival.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Parameter estimator configured to distinguish between peaks and sidelobes of correlation function
A parameter estimator for estimating one or more parameter(s) from a signal is described. A correlation function is derived from the signal, and the correlation function analyzed to determine if one or more first peak(s) are present, and, if so, distinguishable from the sidelobe(s) of a second peak. If the one or more first peak(s) are present and distinguishable from the sidelobe(s) of the second peak, the one or more parameter(s) are estimated from the one or more first peak(s). If the one or more first peak(s) are not present, or, if present, are not distinguishable from the sidelobe(s) of the second peak, the one or more parameter(s) are estimated from the second peak. The parameter estimator may be employed in a subscriber station to estimate a parameter such as the time of arrival of one or more base station or sector pilot signals in a wireless communication system. This information may be utilized in an overall advanced forward link trilateration (AFLT) process for estimating the location of the subscriber station.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
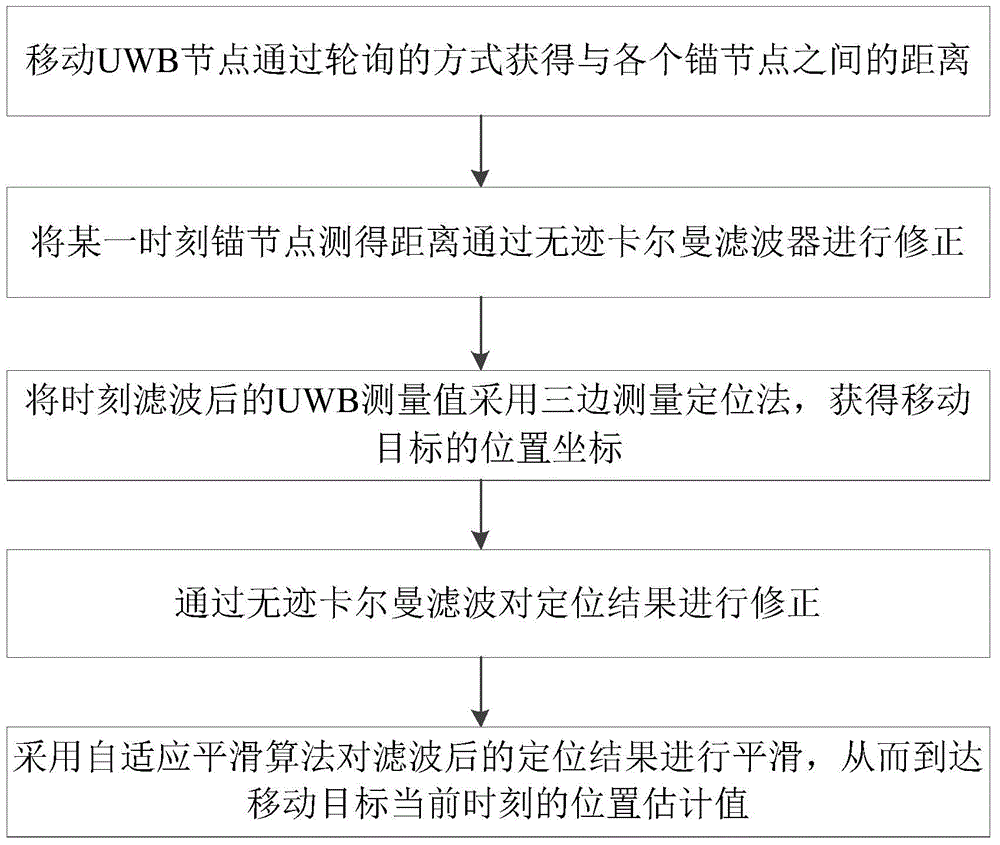
Indoor moving target positioning method based on trajectory smoothing
The invention puts forward an indoor moving target positioning method based on trajectory smoothing, comprising the following steps: (1) a mobile UWB (Ultra Wideband) node acquires the distance between the node and each anchor node through polling; (2) the distance measured by each anchor node at a moment is corrected by an unscented Kalman filter; (3) the position coordinate of a moving target is acquired through a trilateration positioning approach based on the filtered UWB measured value at the moment; (4) the positioning result is corrected by the unscented Kalman filter; and (5) the filtered positioning result is smoothed by an adaptive smoothing algorithm so as to reach the position estimated value of the moving target at the current moment. According to the invention, the measured values and estimated values at the current moment and at a previous moment are fully utilized, an unscented Kalman filtering mode is adopted, so the influence of environment, device and other factors on the measurement result is reduced, and the positioning accuracy of the trilateration approach is improved; and the positioning result is filtered secondarily and smoothed adaptively, and the positioning accuracy is further improved.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +5
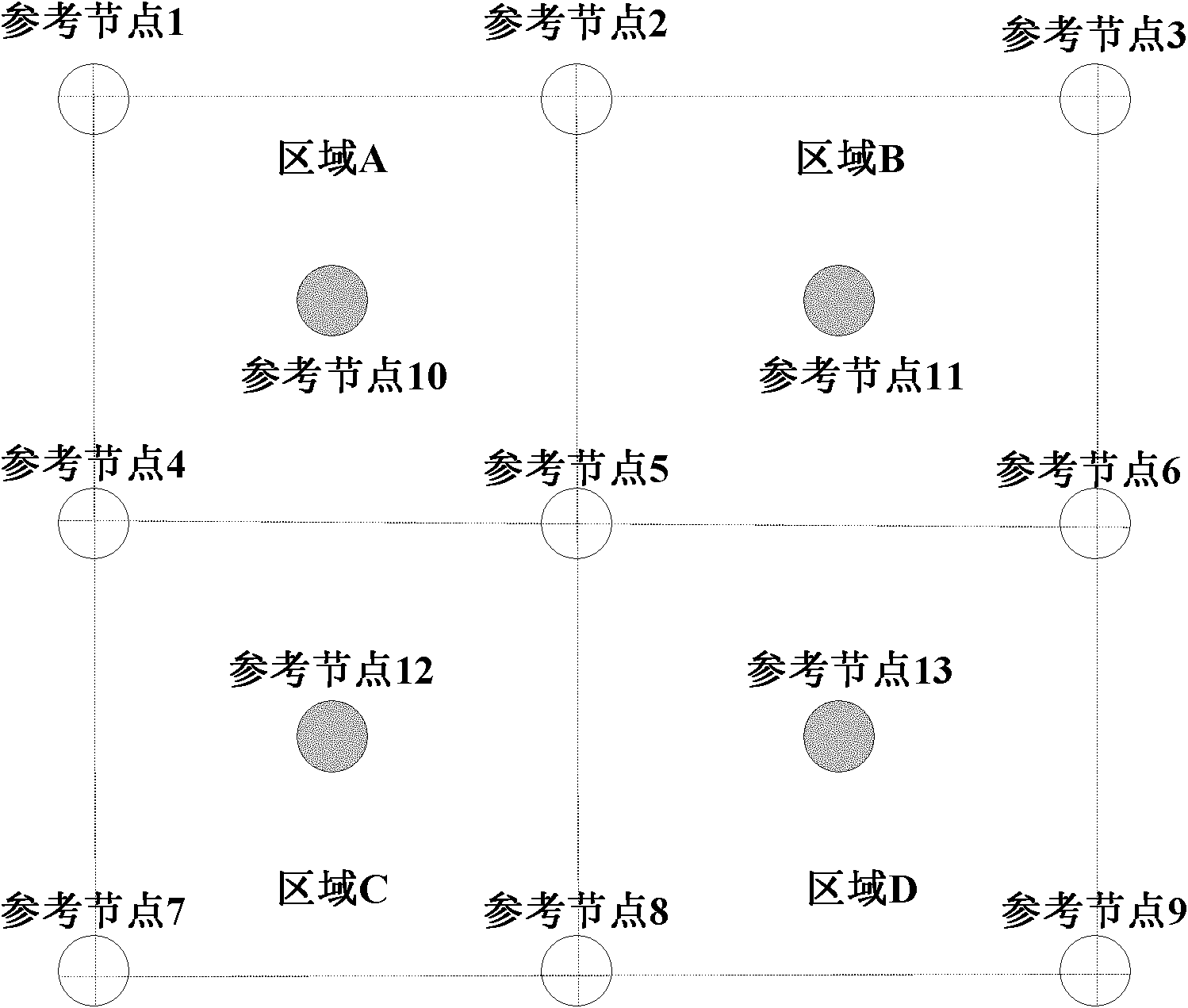
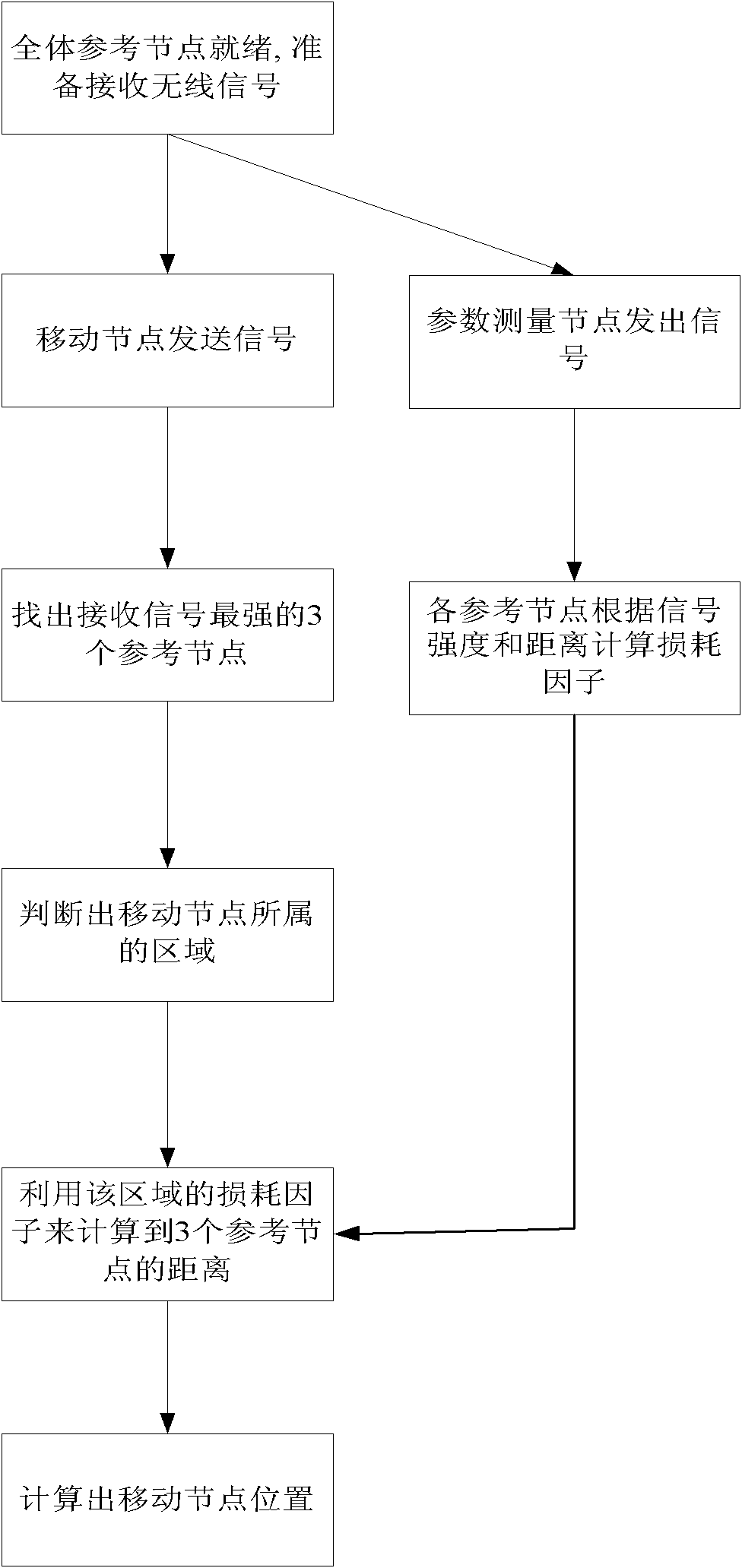
Environment adaptive RSSI local positioning system and method
ActiveCN102014489AEasy to implementHigh precisionTransmission monitoringWireless communicationEngineeringPositioning system
The invention provides an environment adaptive received signal strength indicator (RSSI) local positioning system and an environment adaptive RSSI local positioning method. The system and the method implement positioning based on signal energy strength, wherein the signals can be radio-frequency signals or underwater acoustic signals. The method comprises the following positioning steps of: in the positioning process, measuring reference node path loss factors of each corresponding area in real time by using reference nodes, and updating a database of the loss factors according to the set frequency; when the signal of a movable node is received, determining the area of the movable node by using three nodes with strongest signals; calculating the distance from the movable node to the threereference nodes by using the loss factors of the reference nodes of the corresponding area; and calculating the position of the movable node by using a trilateration method. The positioning technology has the advantage of overcoming the defect of low precision of the conventional RSSI positioning technology due to environmental change in a variable environment, for example, a warehouse where goods are frequently delivered.
Owner:58TH RES INST OF CETC
Location implementation method based on RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) indoor positioning device
InactiveCN103399295AOvercome the problems of complex positioning method and low positioning accuracyLow costPosition fixationElectrical and Electronics engineeringTime of arrival
The invention relates to the field of location and particularly relates to a location implementation method based on an RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) indoor positioning device. Position coordinates of three known RFID beacons are respectively (x1, y1), (x2, y2) and (x3,y3). The location implementation method comprises the following steps of setting current position coordinates of a first RFID reader to be (x, y) and the distances between the first RFID reader and the three RFID beacons to be d1, d2 and d3, and calculating the values of d1, d2 and d3 by adopting a distance computing method based on time of arrival (TOA); and calculating the position coordinates of the RFID reader by adopting a trilateration method according to the distances d1, d2 and d3 between the first RFID reader and the three RFID beacons, and further carrying out indoor location. The location implementation method is applied to the fields of position management of schools for students, position service of convention centers for exhibits and the like and can also realize anti-theft monitoring for indoor articles by slight improvement.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
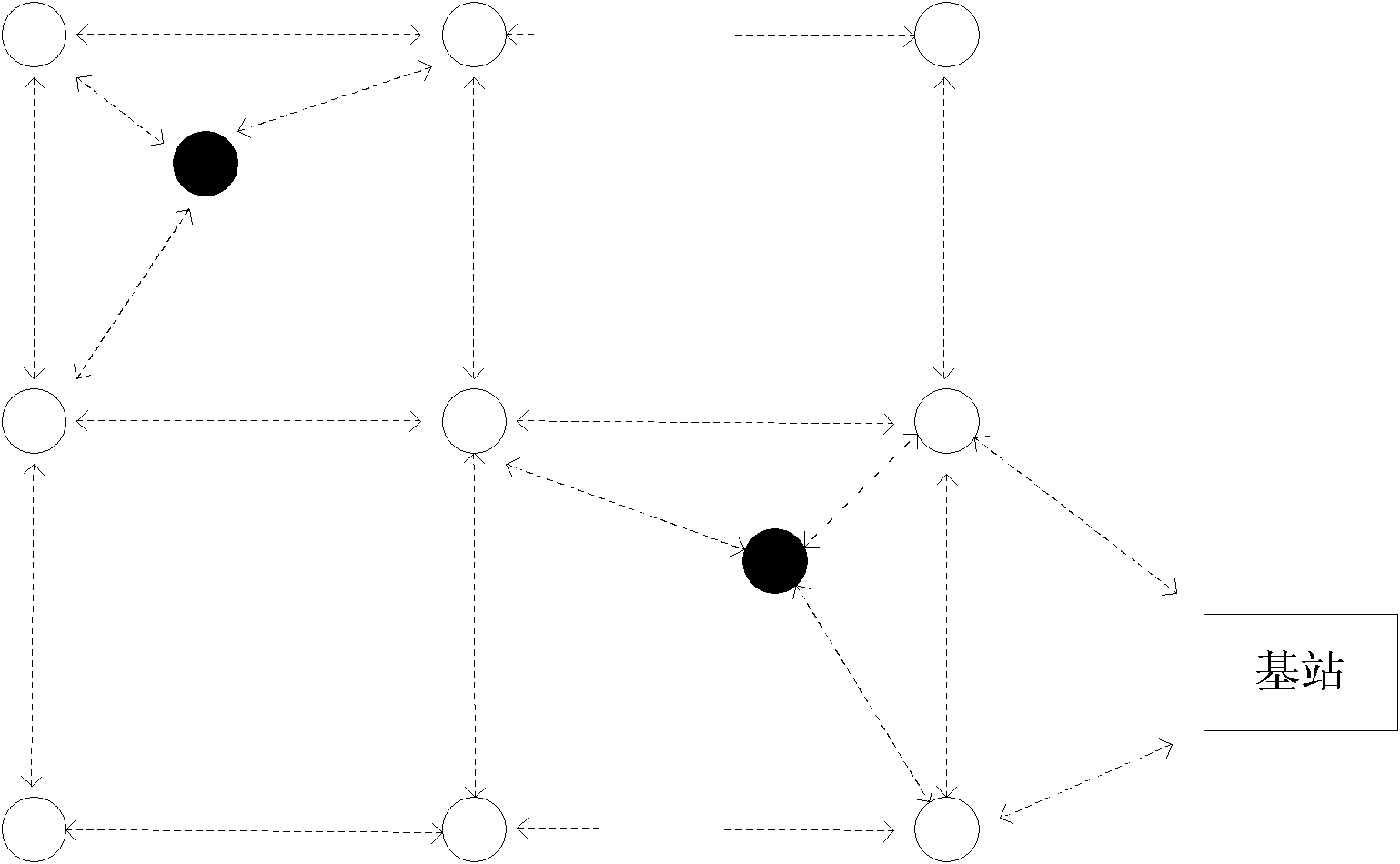
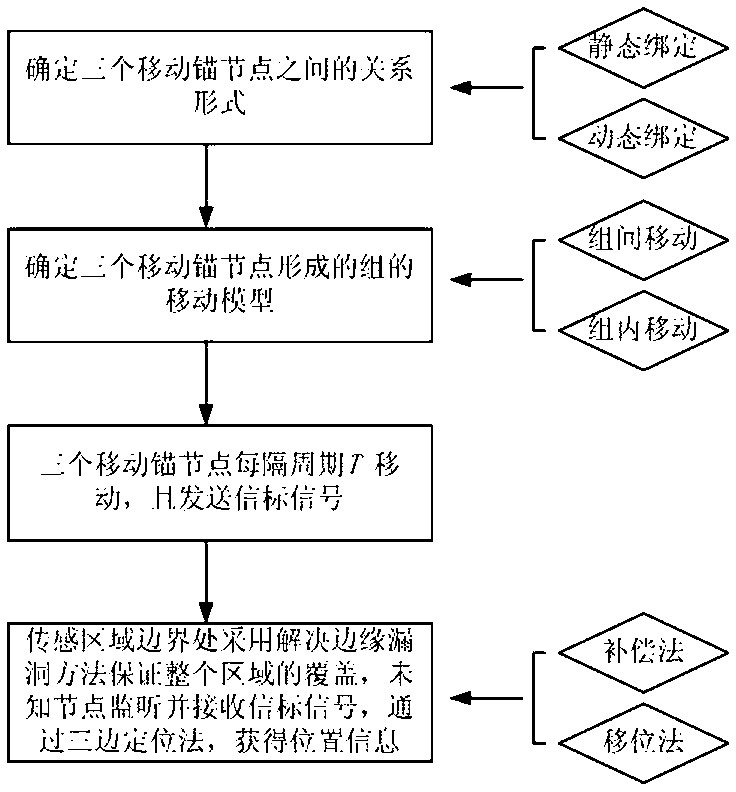
Method for planning moving path of multi-anchor-node set of wireless sensor network
ActiveCN103327607AThe effect of assisted positioning has no effectMeet application needsNetwork planningMobile wireless sensor networkWireless mesh network
The invention relates to a method for planning a moving path of a multi-anchor-node set of a wireless sensor network. The wireless sensor network comprises a plurality of static unknown nodes and three movable anchor nodes. The method comprises the steps that a dynamic binding relationship and a static binding relationship exist among the three movable anchor nodes and a relationship mode among the three movable anchor nodes is firstly determined; a moving model of the multi-anchor-node set is determined according to environment application requirements, the relationship mode of the three movable anchor nodes, and the positions of the three anchor nodes and energy surplus of the three anchor nodes in a zone; the three movable anchor nodes are located on the peak portions of an equilateral triangle respectively, beacon signals are moved and sent every period T according to the determined moving model, covering of the whole zone is guaranteed by means of the adoption of two kinds of margin loophole solution methods when the beacon signals move to the boundary of the sensing zone, beacon information is continuously monitored and received by the unknown nodes, and position information is obtained through a trilateration method. The method is capable of effectively assisting in location and improving the location accuracy and the location covering rate.
Owner:深圳宏安通信科技有限公司
Method and System for Providing Enhanced Location Based Information for Wireless Handsets
ActiveCN104025677AEmergency connection handlingDevices with GPS signal receiverLocation based informationGlobal Positioning System
Methods, devices and systems for generating enhanced location information on or about a mobile device may include hybrid lateration and / or trilateration solutions in which the mobile device performs location determination calculations with or without the aid or support of network components or global positioning systems (GPS). Mobile devices may automatically form groups based on proximity and / or may be grouped together via a network server. Mobile devices in a group may share computed location information and / or information collected from internal sensors with other grouped mobile devices. Information shared between grouped mobile devices may be used to enhance the location information computed on each mobile device. For example, each mobile device may supplement and / or augment previously computed location information based on the received location information and / or relative positions of other mobile devices in the same group. Each mobile device may also utilize local sensors to further enhance their location information.
Owner:RIVADA RES
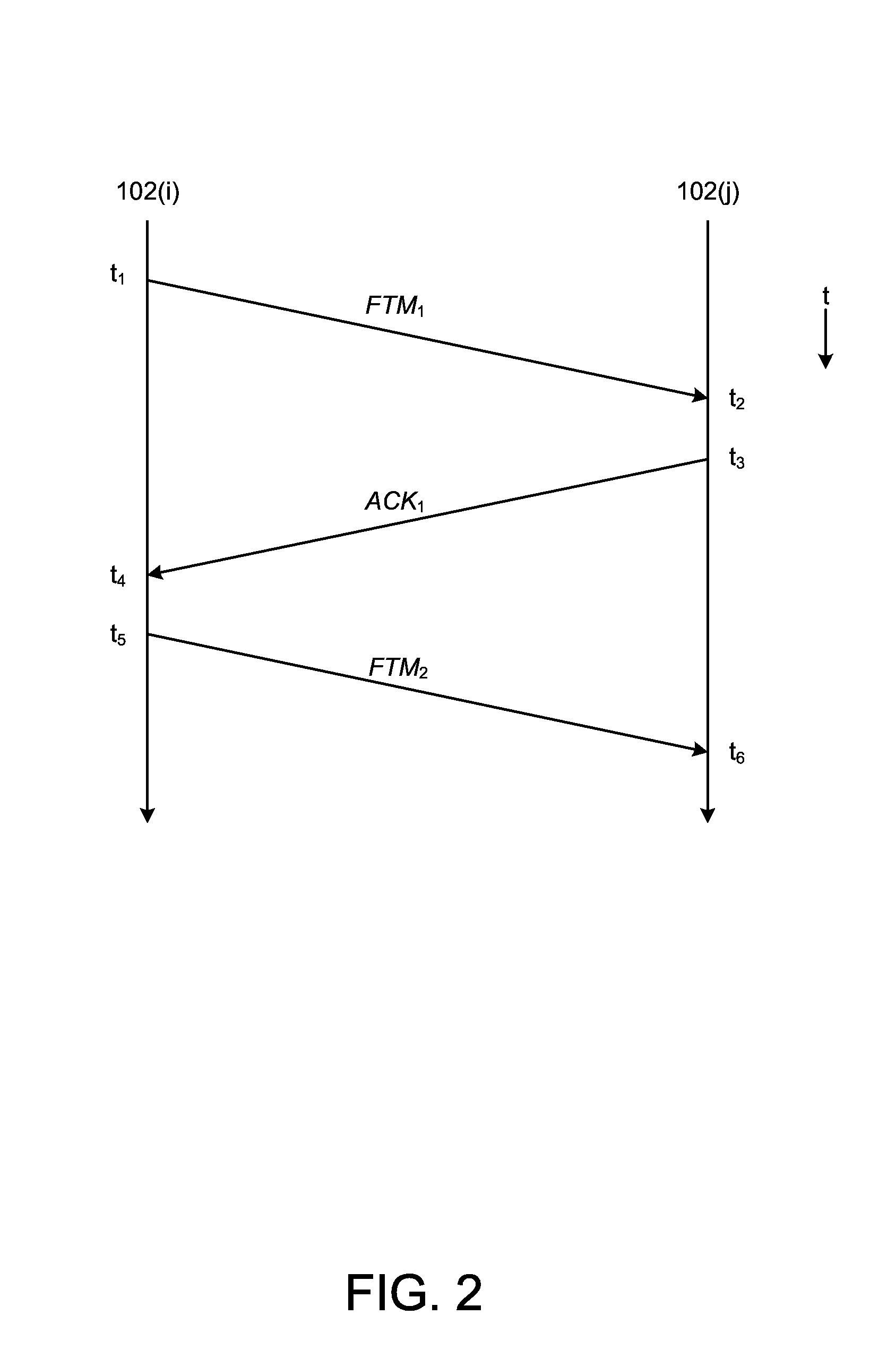
Location determination of wireless stations using one-to-many communication techniques
Certain embodiments herein relate to efficient location determination by wireless stations using one-to-many communication techniques. Location determination can be facilitated by using one-to-many communication techniques to provide for efficient timing message exchange between an initiating wireless station and one or more responding wireless stations. Based at least in part on the time-of-flight of the exchanged messages, the initiating wireless station can determine its distances from the respective one or more responding wireless stations. Based at least in part on the determined distances, the wireless initiating station can determine its location using trilateration or multilateration techniques.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com