Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
150results about How to "Reduce quantization noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
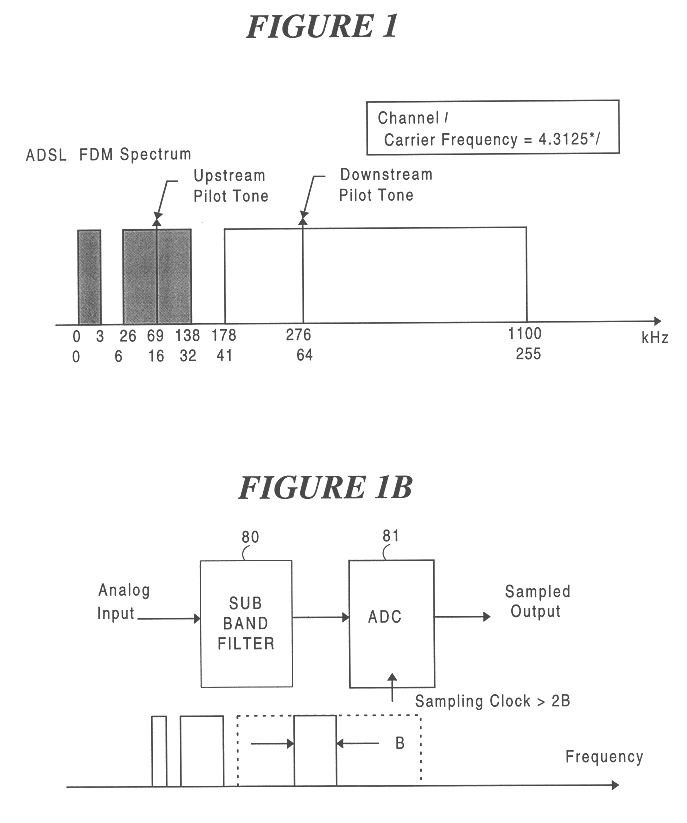
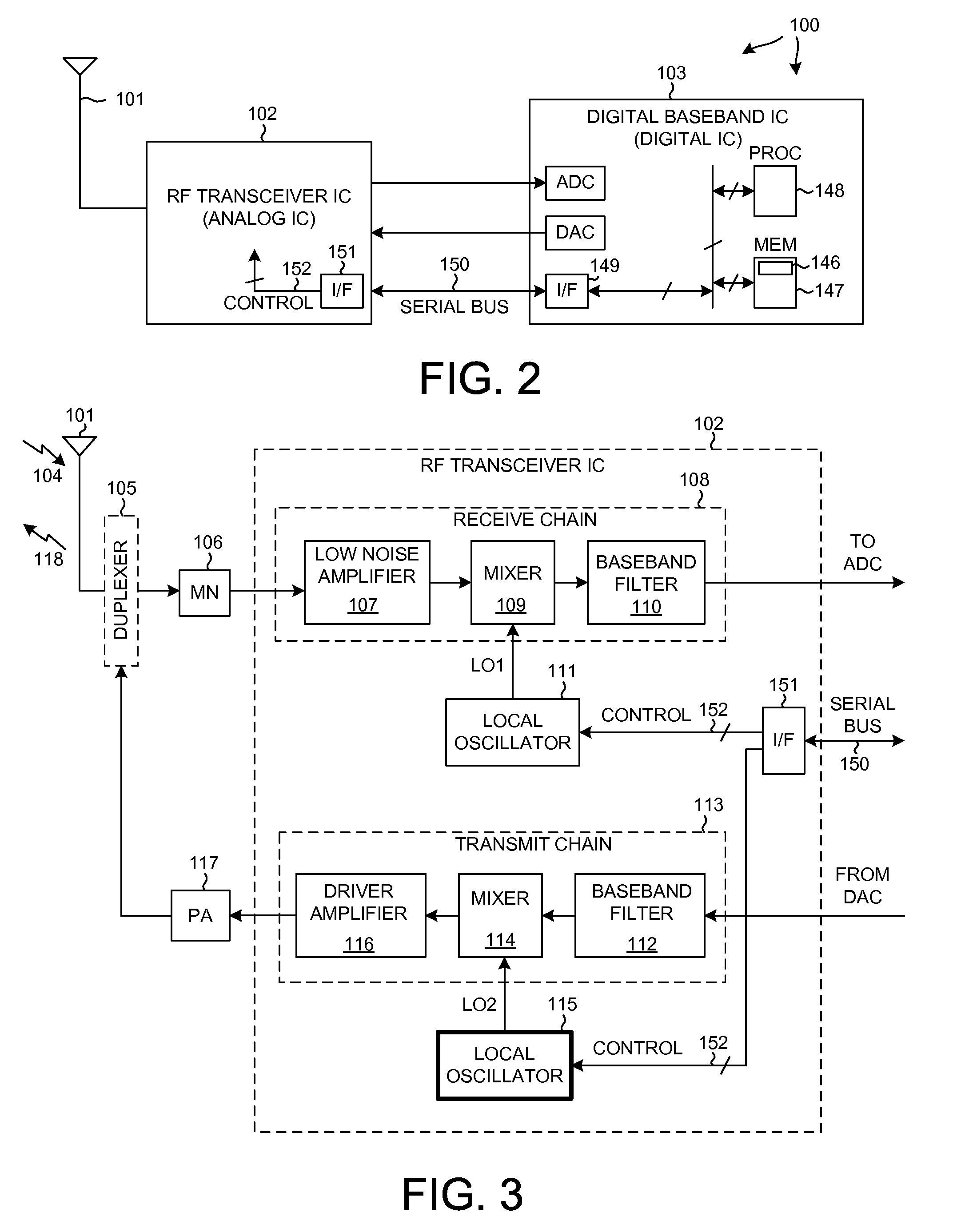
Multiple low speed sigma-delta analog front ends for full implementation of high-speed data link protocol
InactiveUS6442195B1Reduce quantization noiseReduce shapingTelephonic communicationSignal channelsModularityIntegrated circuit
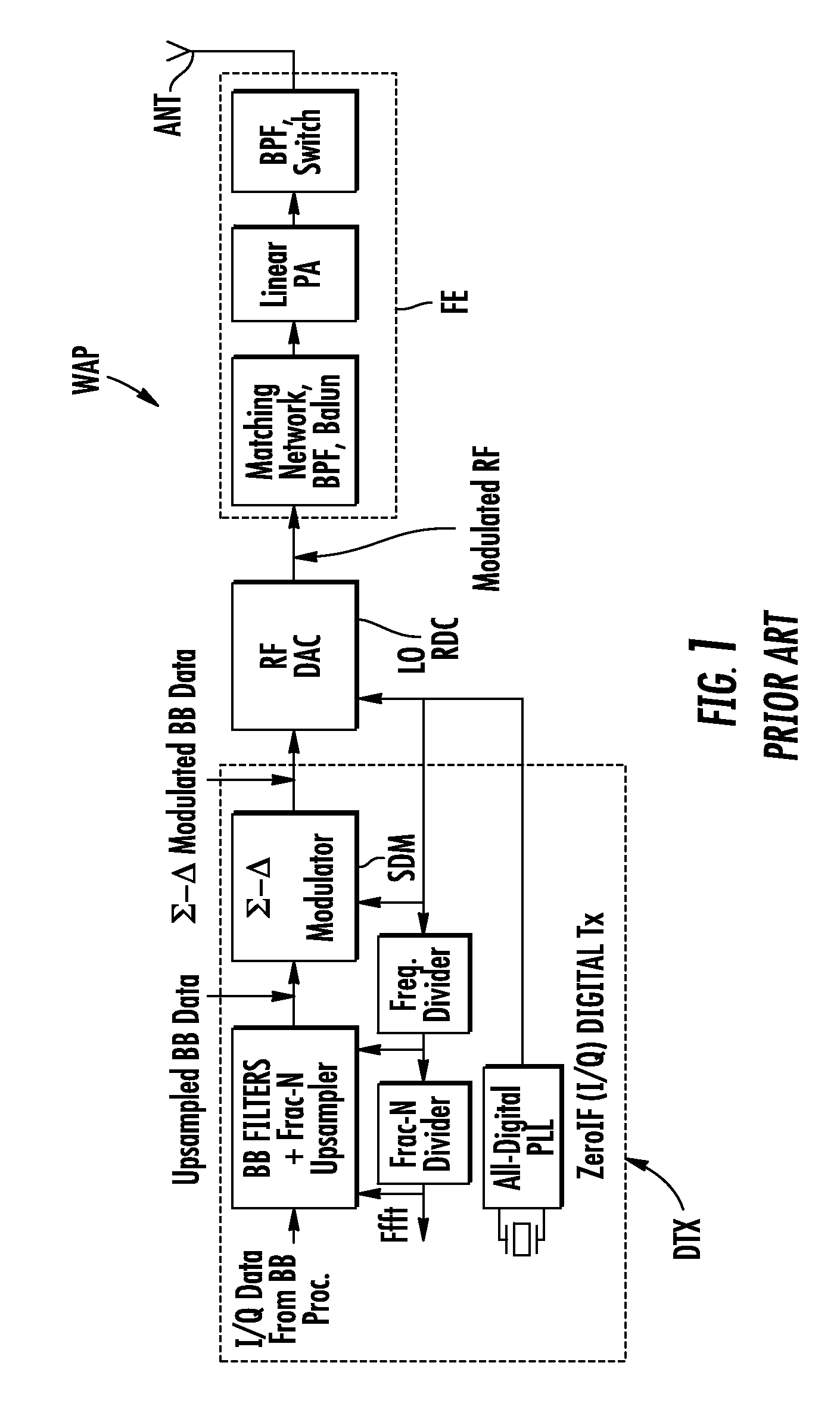
An analog front end (AFE) circuit used in a high-speed communications system is presented that includes multiple stages each including a bandpass filter, base band modulator, low pass filter and Sigma-Delta modulator. Each stage processes a fractional portion of the total frequency of a wide bandwidth analog signal. The number of such AFE stages is configurable in parallel to process the entire bandwidth of the received signal. The AFEs can be incorporated in a single integrated circuit or similar suitable manner so as to be modular, and easily replaceable / upgradeable. To achieve minimum quantization noise and reduce manufacturing costs, the Sigma-Delta modulators in each AFE are made to have identical characteristics. Because the wideband signal is broken down into smaller frequency portions, the sampling rate, and thus the complexity and cost associated with the AFEs, is reduced significantly. In a preferred embodiment, a number of such AFEs are used in an ADSL modem for processing separate but roughly equal portions of the wideband ADSL signal containing data carrying DMT sub-channels. The separated portions are re-combined in a DMT receiver logic circuit to reconstruct the original data stream.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP +1
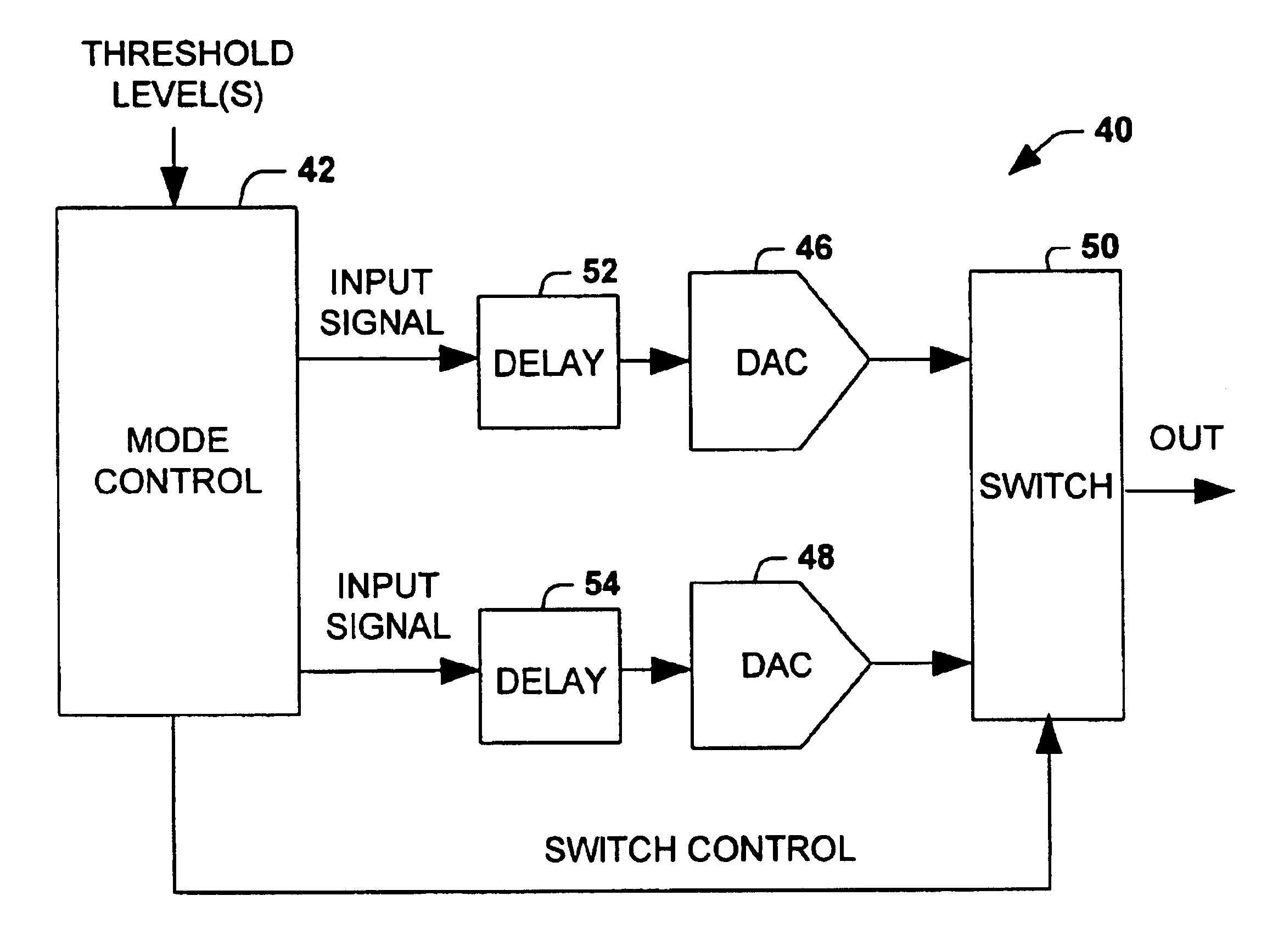
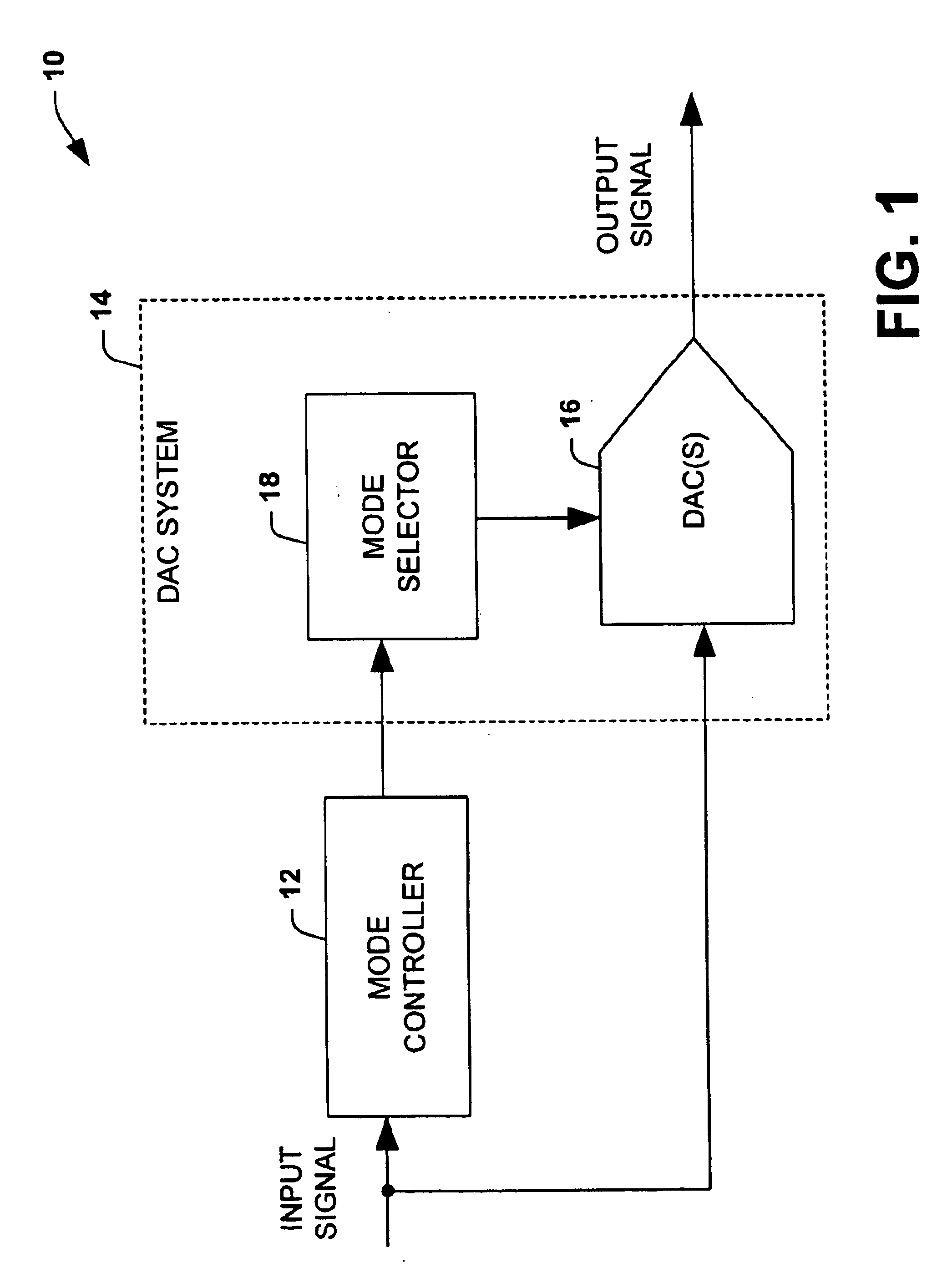
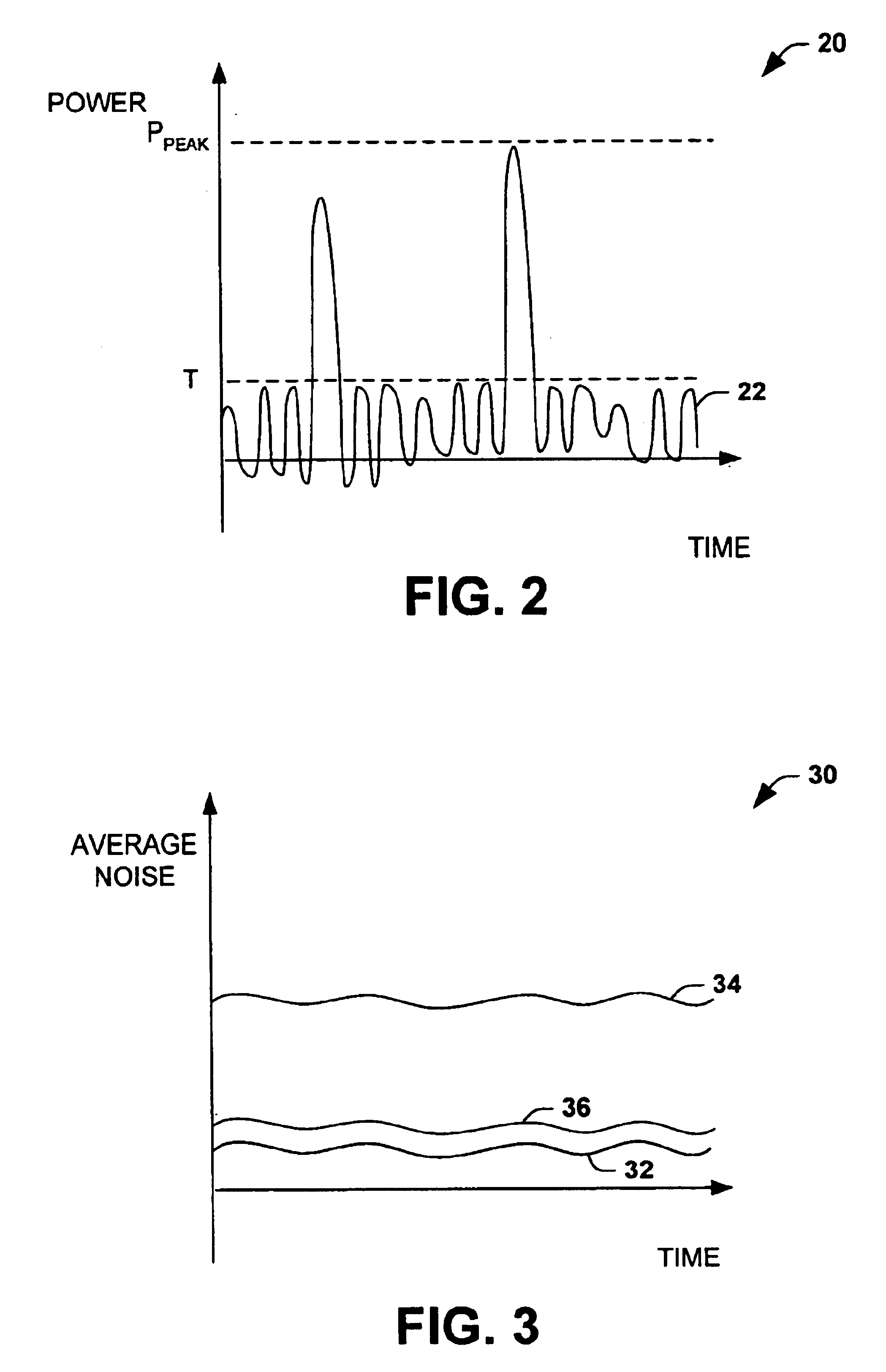
Extended range digital-to-analog conversion
InactiveUS6822595B1Reduce quantization noiseElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionDigital analog converterNoise level
A conversion system converts an input signal from a digital signal to an analog signal over an extended dynamic range. The system includes a DAC system and a mode selector. The mode selector selects a mode of operation for the digital-to-analog converter system from a plurality of modes. The mode selector selects a mode according to a characteristic of the input signal. Each of the modes is associated with an instantaneous dynamic range and quantization noise level of the DAC system. The ensemble of modes provides an improvement in total or effective dynamic range compared to any DAC component within the DAC system.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Adaptive spectral noise shaping to improve time to digital converter quantization resolution using dithering
ActiveUS20080068236A1High resolutionHigh frequency noiseElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionFrequency spectrumNoise shaping
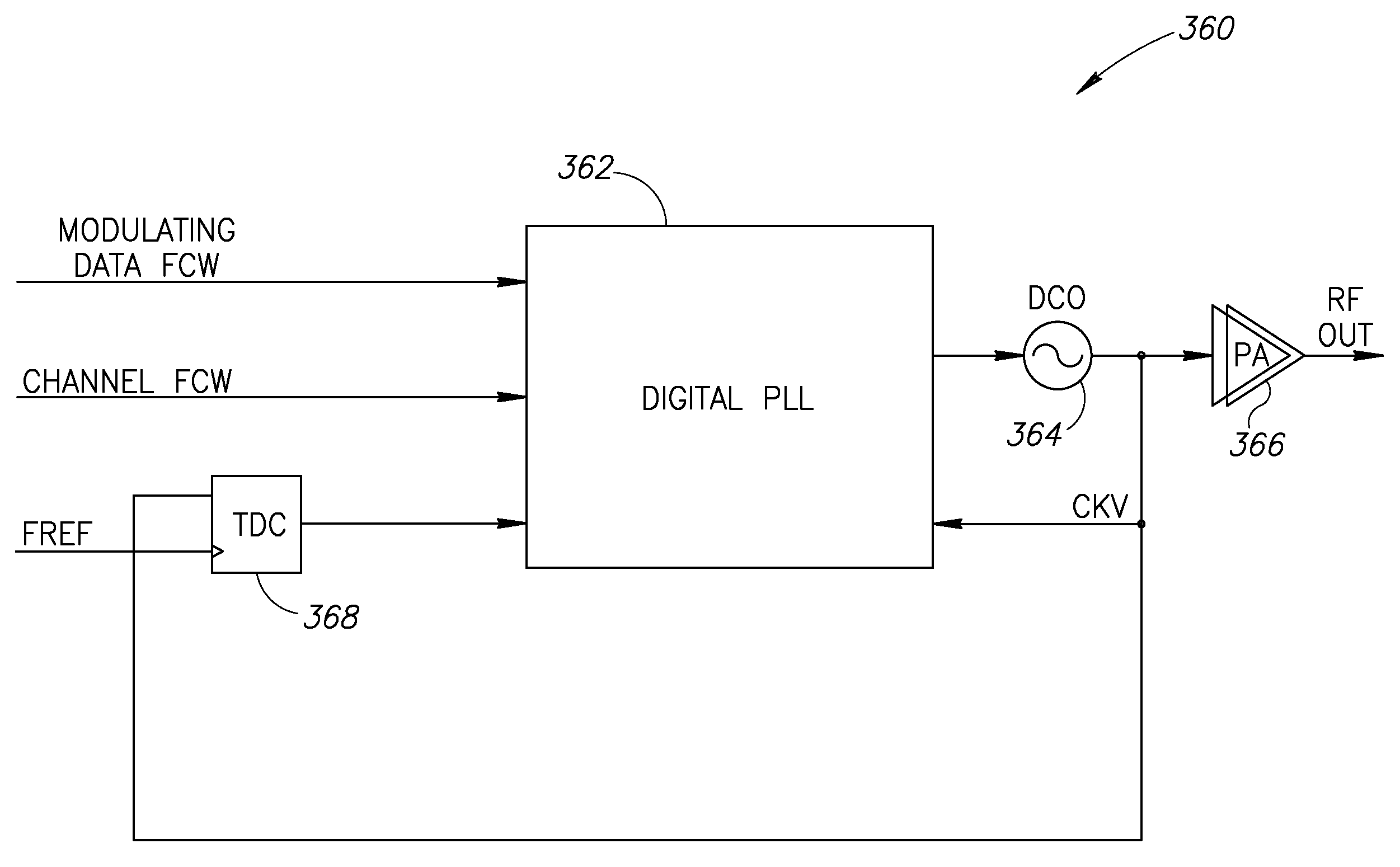
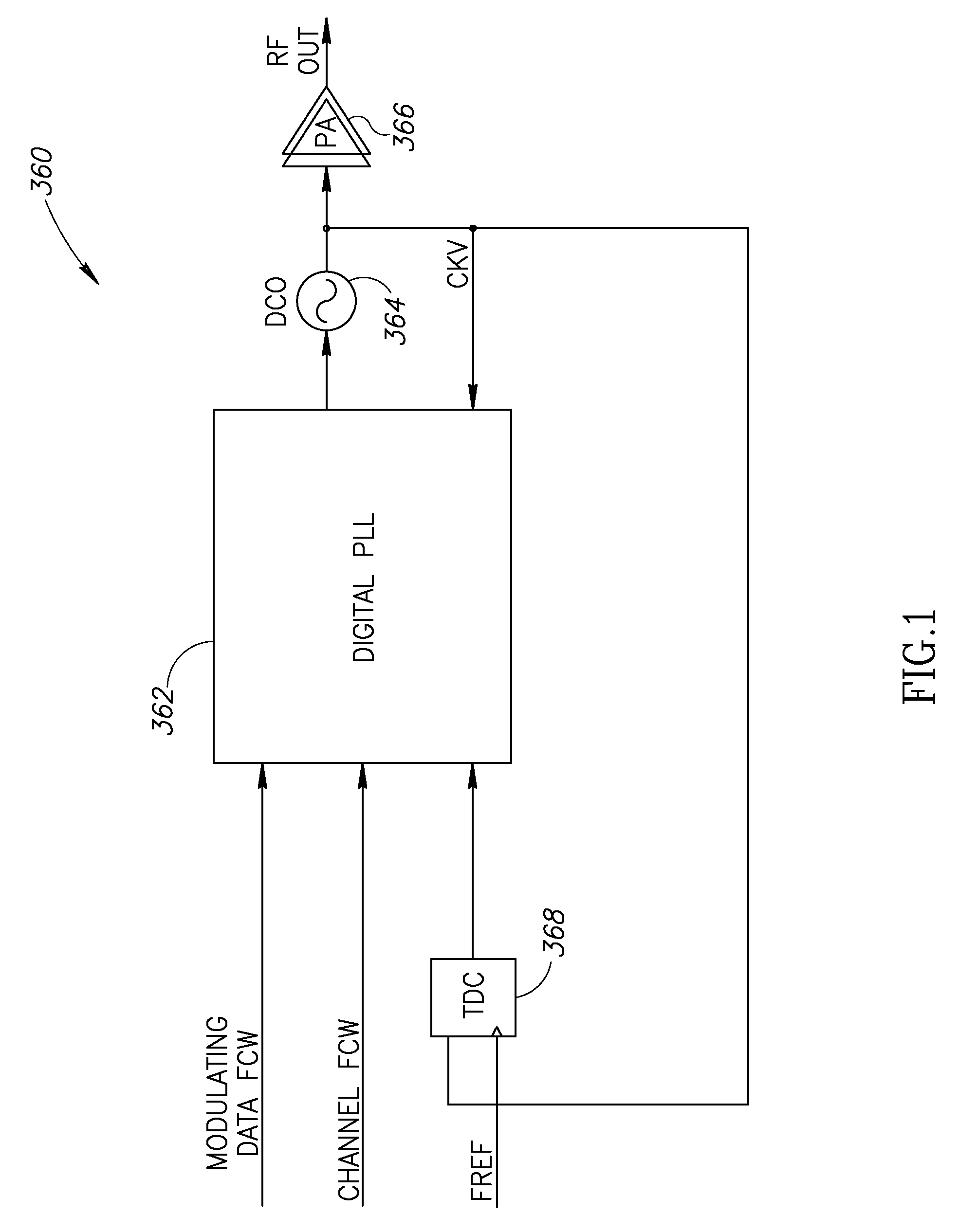
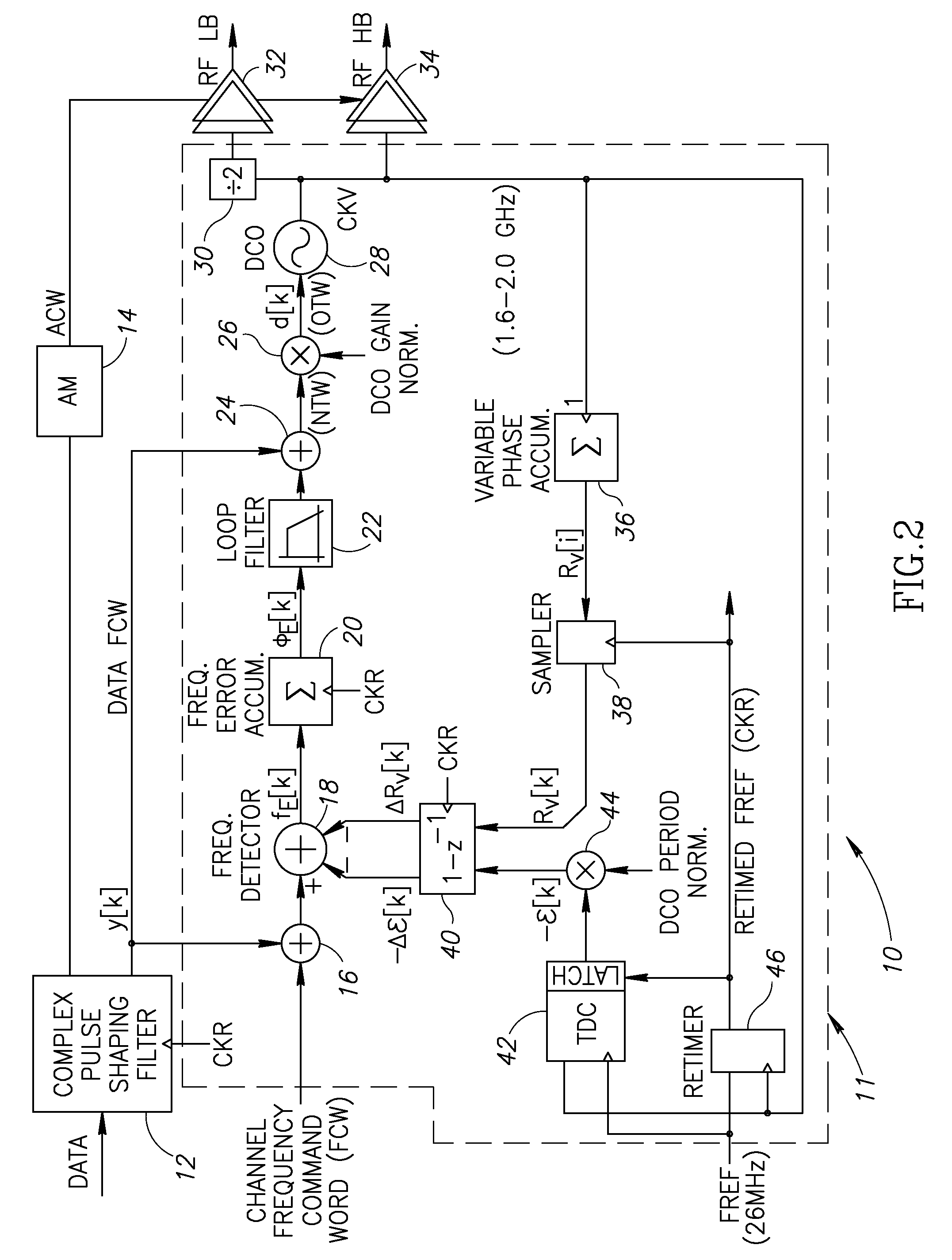
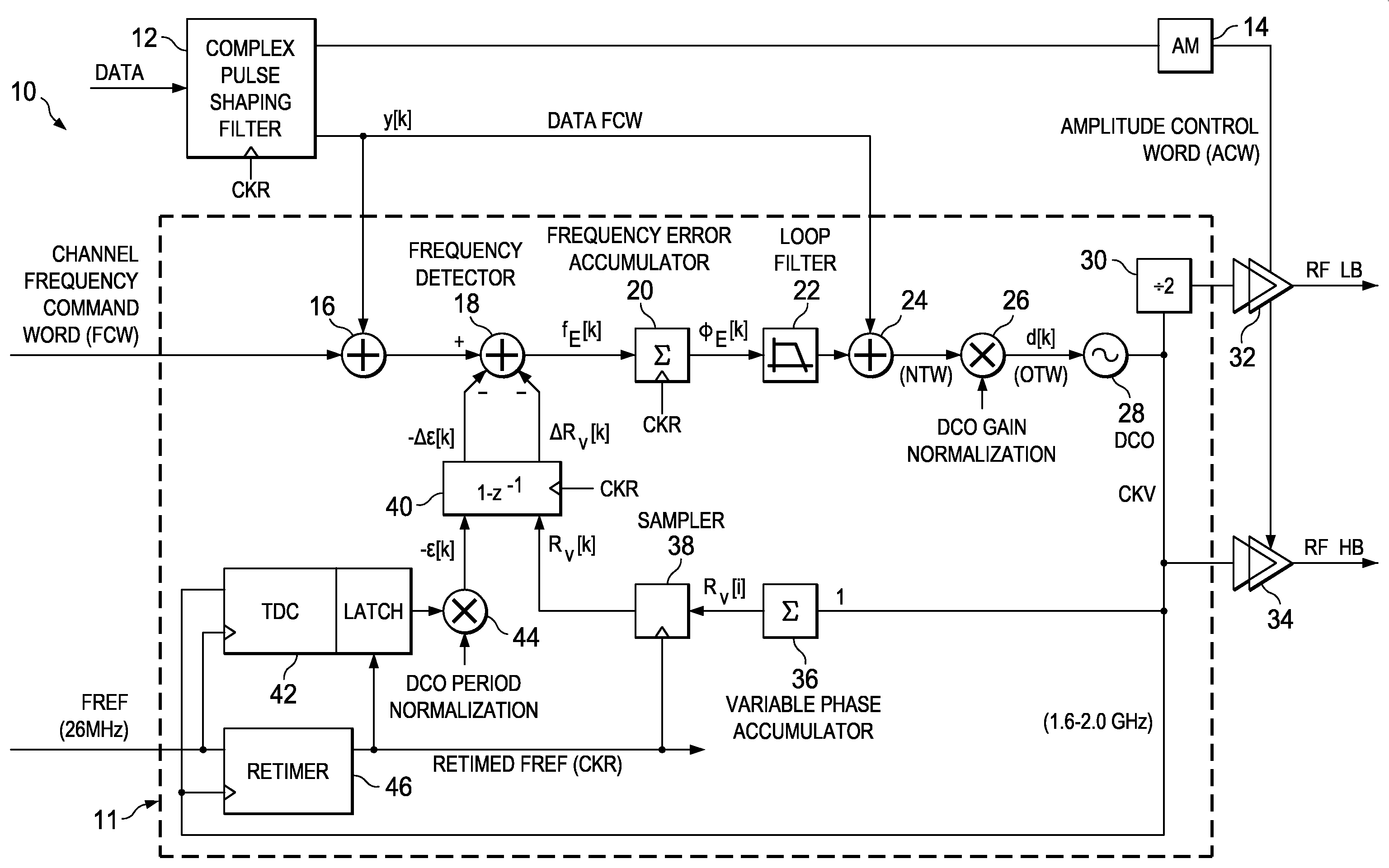
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of improving the quantization resolution of a time to digital converter in a digital PLL using noise shaping. The TDC quantization noise shaping scheme is effective to reduce the TDC quantization noise to acceptable levels especially in the case of integer-N channel operation. The mechanism monitors the output of the TDC circuit and adaptively generates a dither (i.e. delay) sequence based on the output. The dither sequence is applied to the frequency reference clock used in the TDC which adjusts the timing alignment between the edges of the frequency reference clock and the RF oscillator clock. The dynamic alignment changes effectively shape the quantization noise of the TDC. By shaping the quantization noise, a much finer in-band TDC resolution is achieved resulting in the quantization noise being pushed out to high frequencies where the PLL low pass characteristic effectively filters it out.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
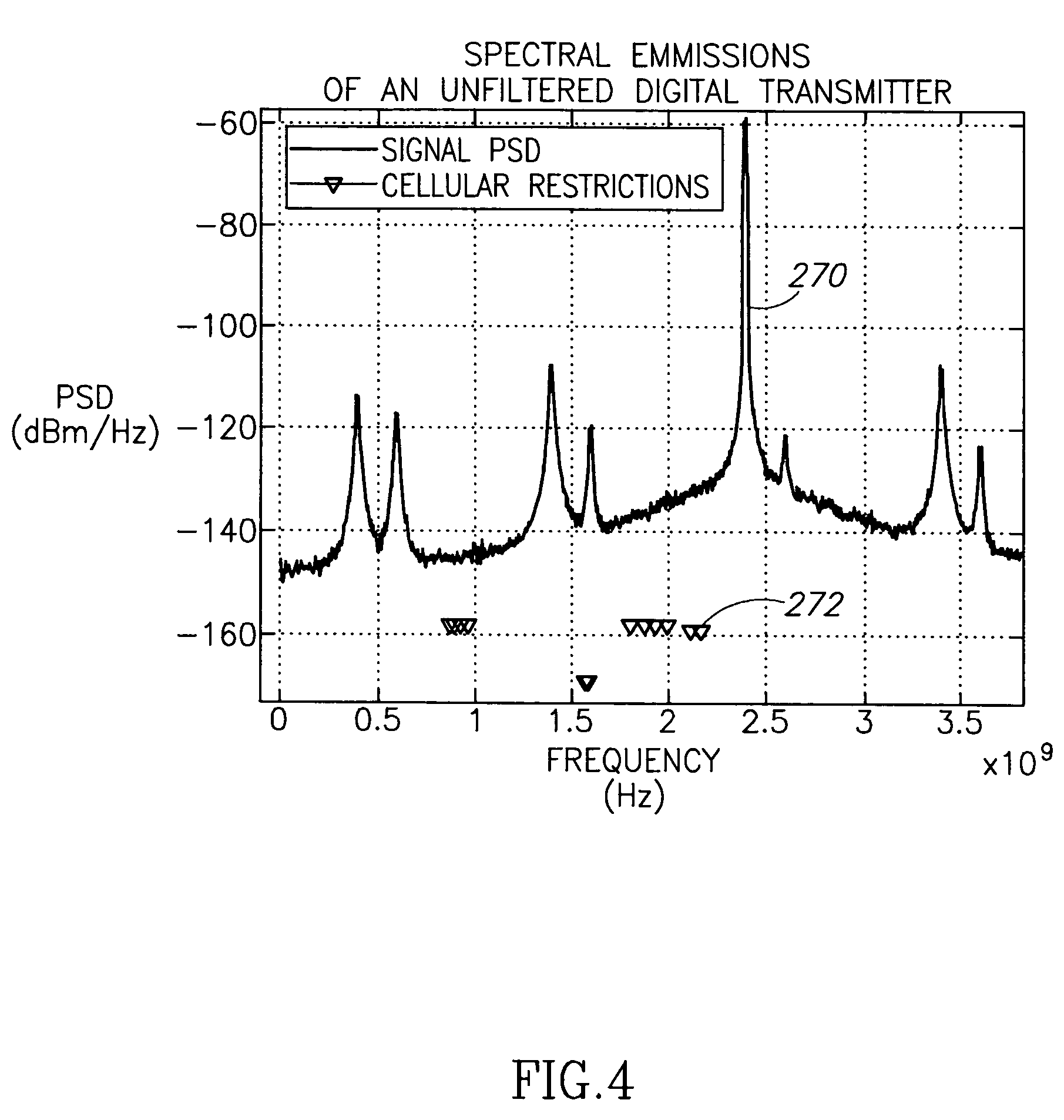
Transmitter for wireless applications incorporation spectral emission shaping sigma delta modulator
ActiveUS20060119493A1Sufficient attenuationDesired noise shapingAnalogue conversionSecret communicationSpectral emissionFrequency spectrum
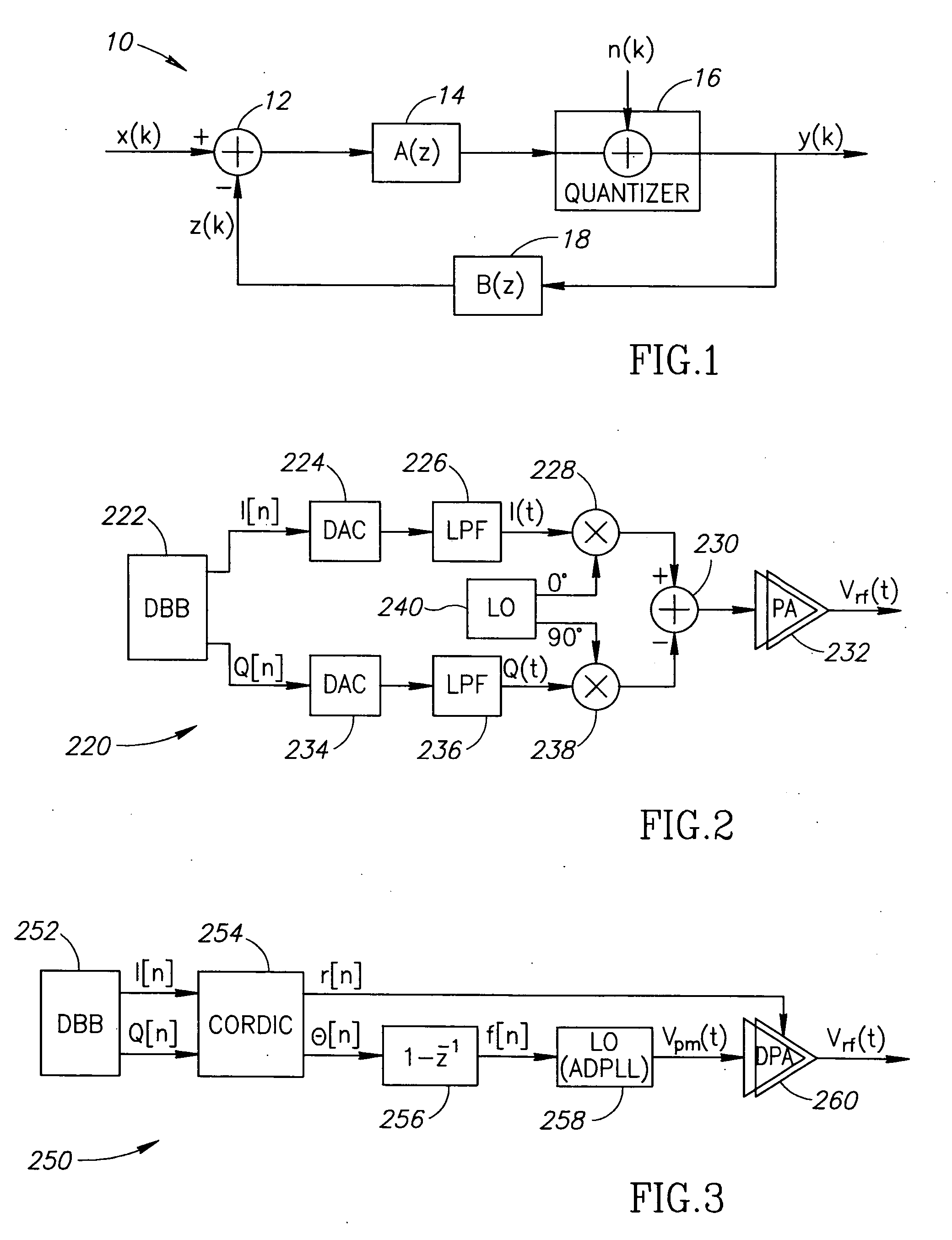
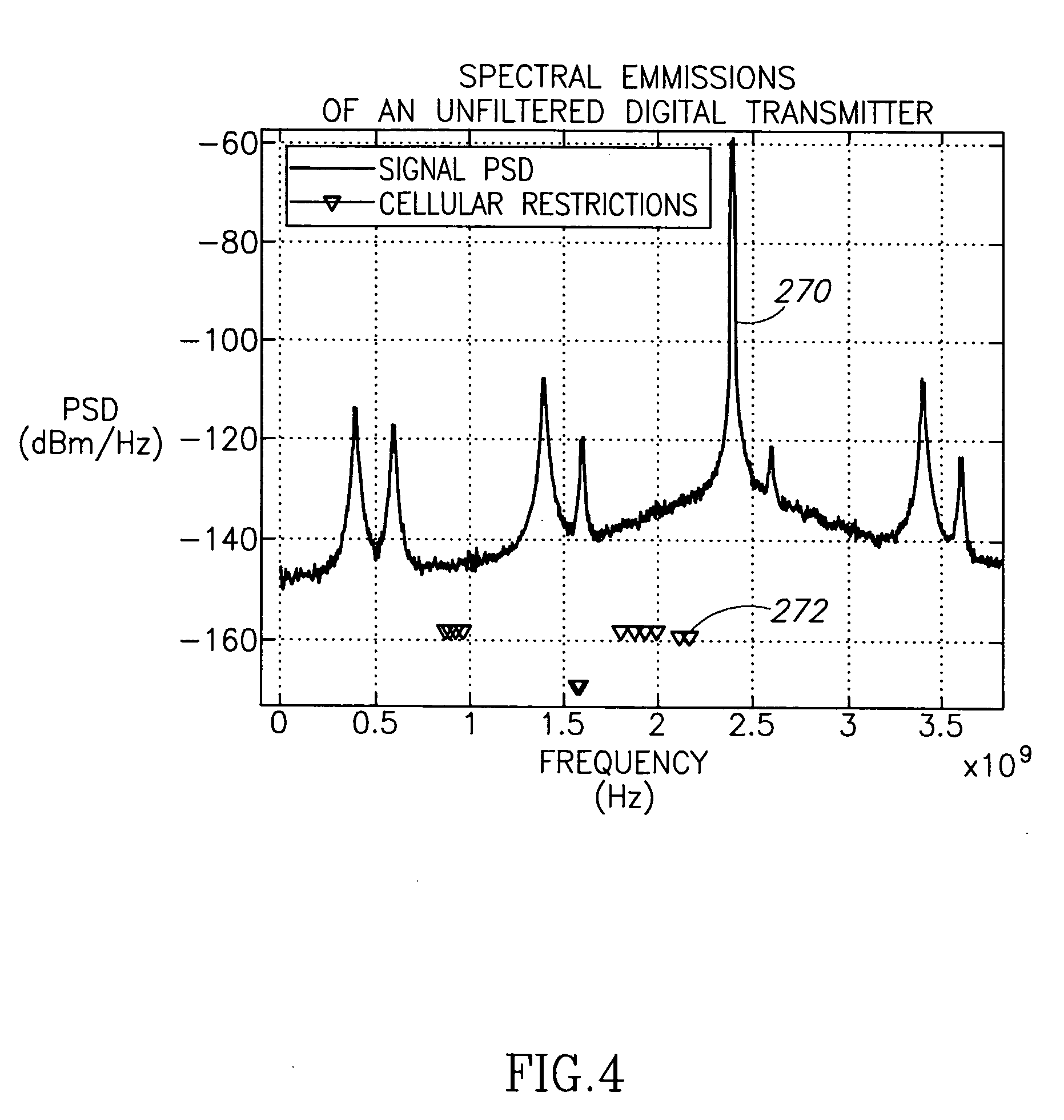
A transmitter employing a sigma delta modulator having a noise transfer function adapted to shift quantization noise outside at least one frequency band of interest. A technique is presented to synthesize the controllers within a single-loop sigma delta modulator such that the noise transfer function can be chosen arbitrarily from a family of functions satisfying certain conditions. Using the novel modulator design technique, polar and Cartesian (i.e. quadrature) transmitter structures are supported. A transmitter employing polar transmit modulation is presented that shapes the spectral emissions of the digitally-controlled power amplifier such that they are significantly and sufficiently attenuated in one or more desired frequency bands. Similarly, a transmitter employing Cartesian transmit modulation is presented that shapes the spectral emissions of a hybrid power amplifier such that they are significantly and sufficiently attenuated in one or more desired frequency bands.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
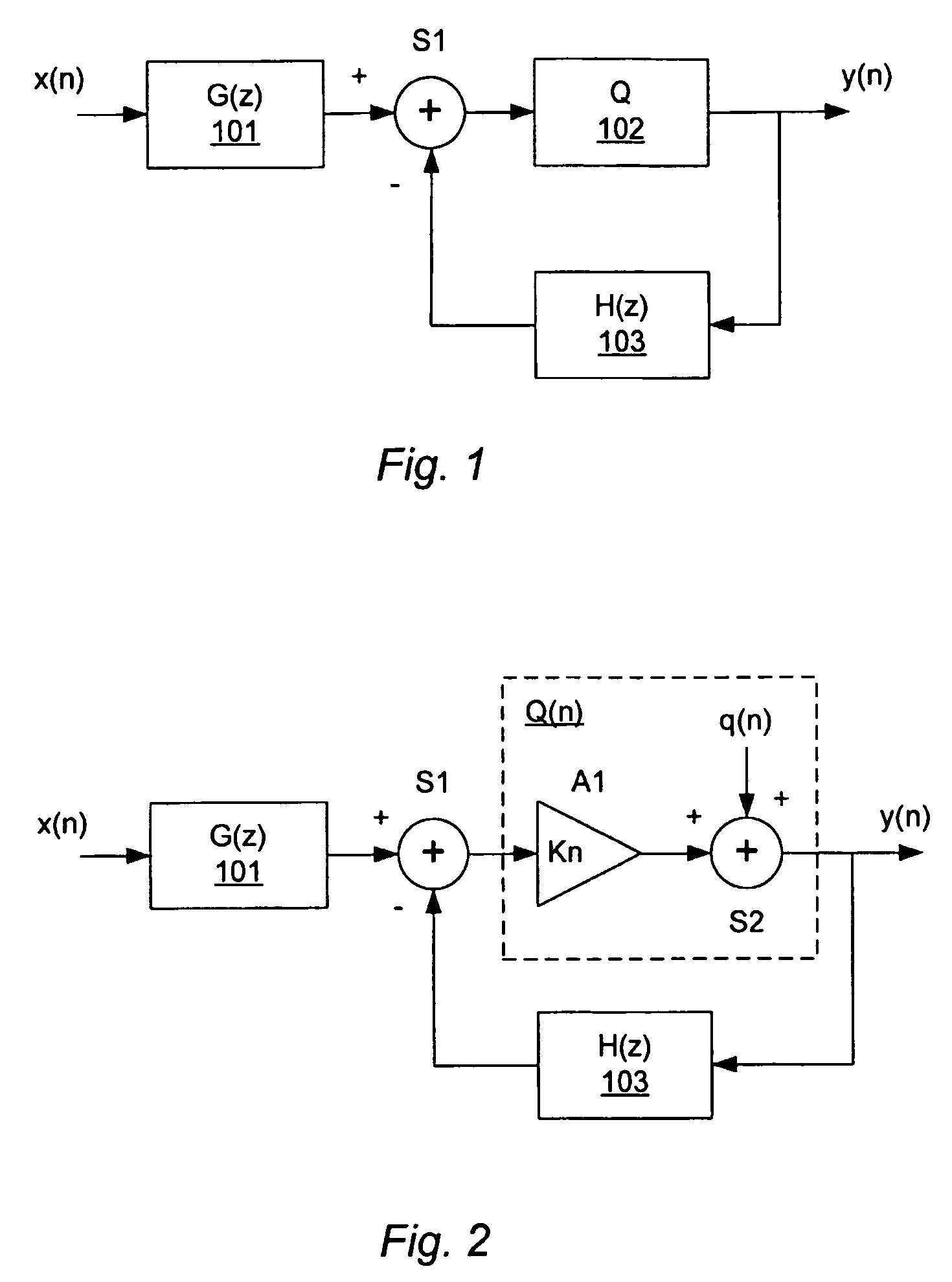
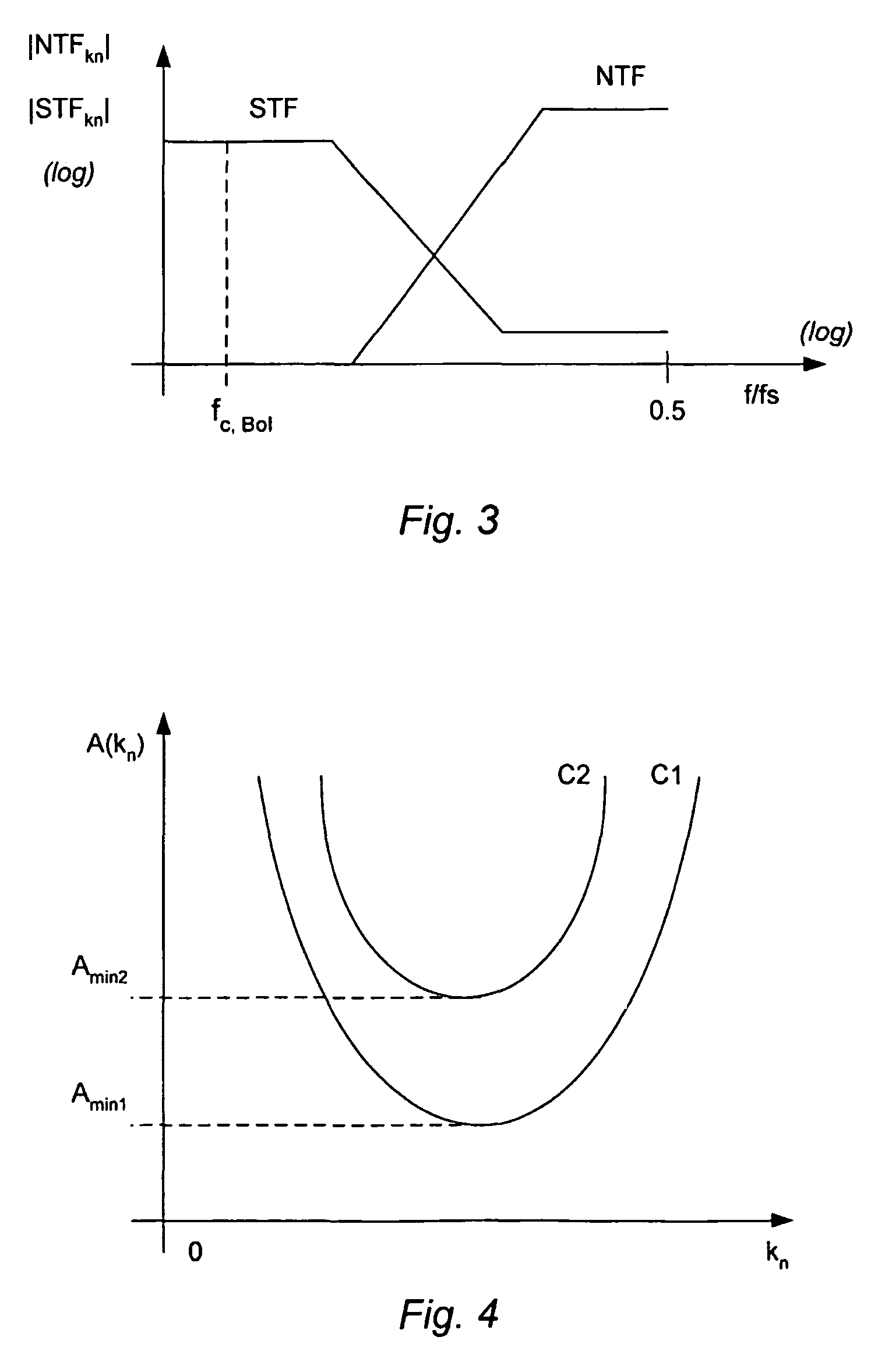
Sigma delta modulator
ActiveUS20090066549A1More freedomStable maintenanceDelta modulationDifferential modulationSignal transfer functionGreek letter sigma
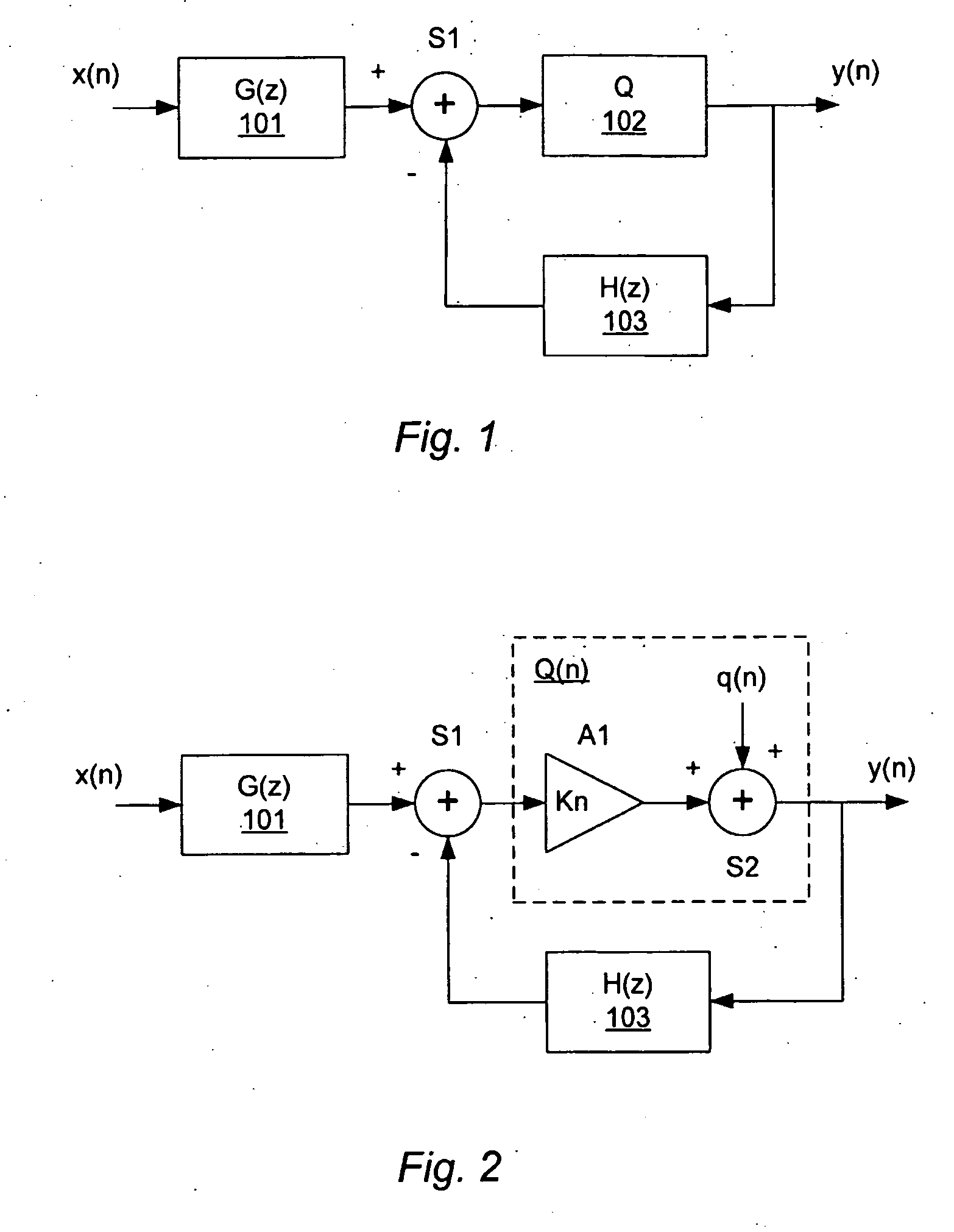
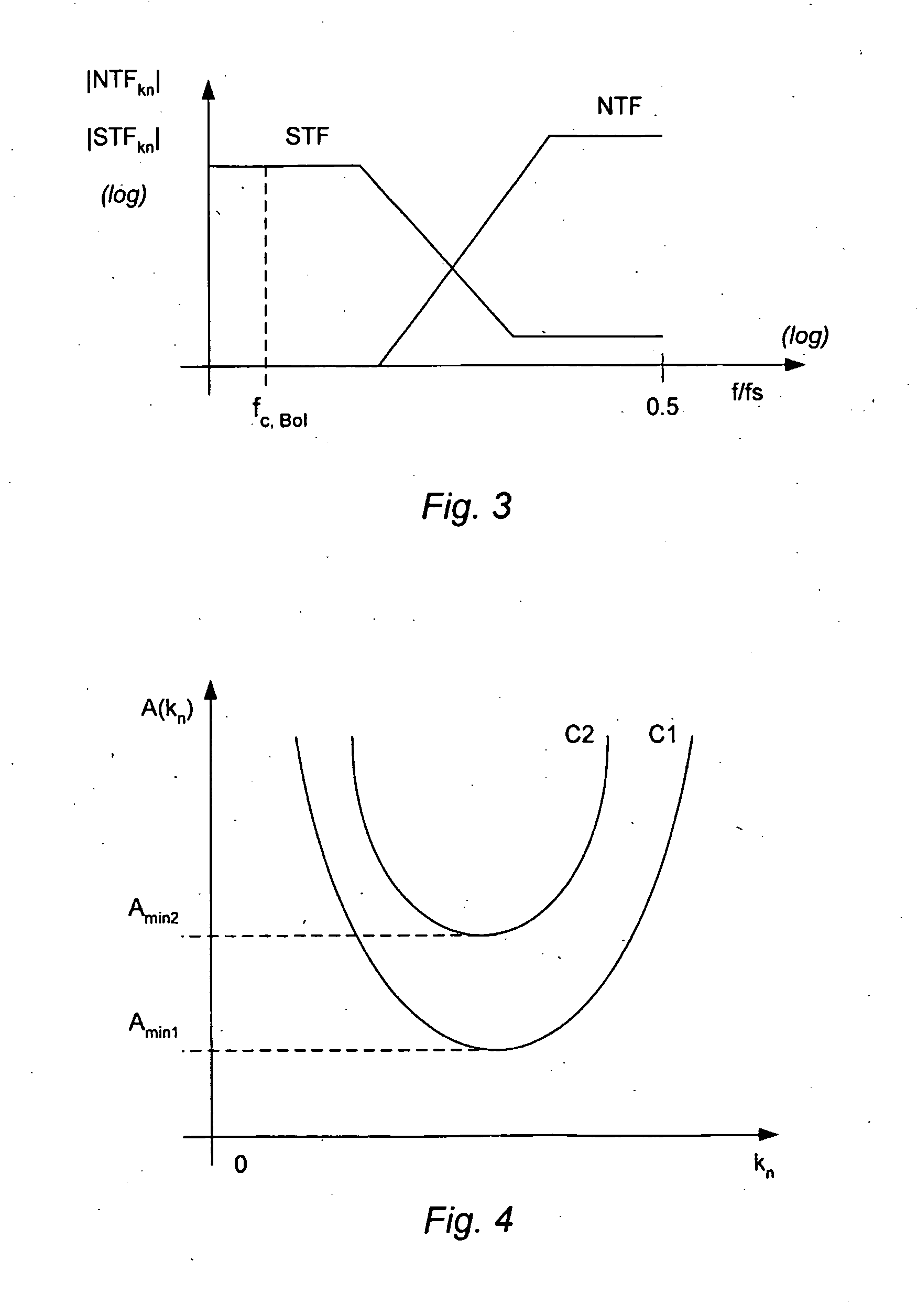
A method of controlling a sigma delta modulator with a loop which establishes a signal transfer function, STF, and a quantization noise transfer function, NTF, of the sigma delta modulator, wherein the sigma delta modulator receives an input signal, x(n), and provides a modulated output signal, y(n) in response to the input signal. The method is characterized in comprising the step of controlling the sigma delta modulator to change the quantization noise transfer function, NTF, in response to a signal feature, A(n), which is correlated with the input signal.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Method for notch filtering a digital signal, and corresponding electronic device
ActiveUS20090082006A1Reduce quantization noiseMore power consumptionElectric signal transmission systemsDigital technique networkDigital dataAnalog signal
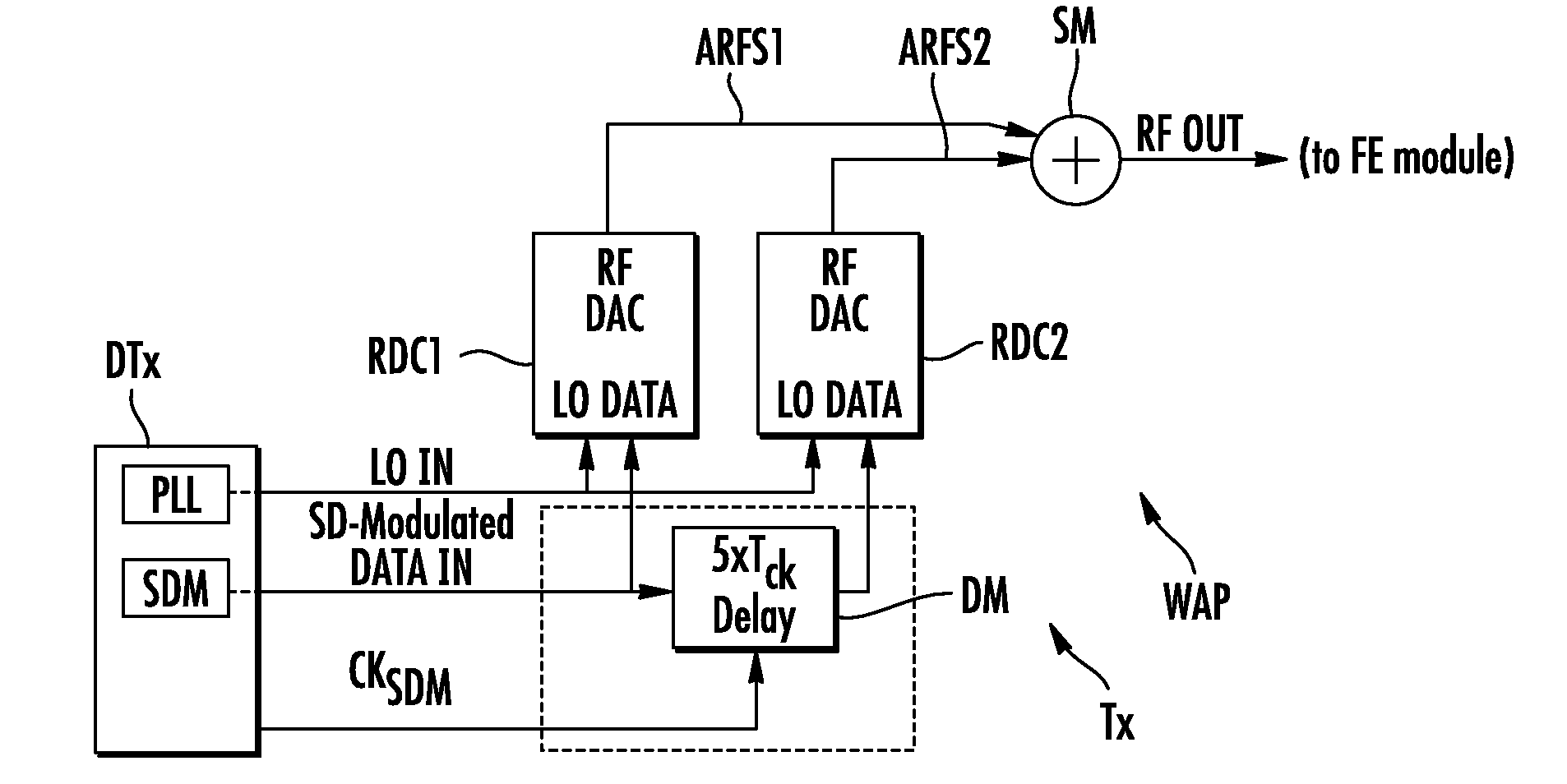
An electronic device, includes sigma-delta modulation circuit to operate with a clock signal and having output circuitry to deliver a digital data signal. First circuitry delivers a radiofrequency transposition signal. A notch filter includes radiofrequency digital-to-analog conversion blocks, having first input circuitry coupled to the output circuitry. Second input circuitry receives the radiofrequency transposition signal. Second output circuitry delivers a radiofrequency analog signal. Digital delay circuitry is controlled by the clock signal and includes a delay block between the two first input circuits. The frequency of a notch of the notch filter is related to the value of the delay from the delay block. Summation circuitry sums the radiofrequency signals.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
Adaptive spectral noise shaping to improve time to digital converter quantization resolution using dithering
ActiveUS7570182B2Quantization noise resolutionReduce noiseElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionFrequency spectrumNoise shaping
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Digital/Analogue conversion apparatus
ActiveUS20090110217A1Reduce out-of-band quantization noiseSignificantly increases in-band noise (Transversal filtersDigitally weighted transducing elementsImage resolutionAnalog signal
A digital / analog conversion apparatus for converting a digital signal into an analog signal. The digital / analog conversion apparatus can generate a high-quality analog signal, even when elements configuring the digital / analog conversion apparatus have variance, with high resolution and a small circuit size. The data conversion apparatus is provided with a first data converter for reducing the number of bits of an input signal, a second data converter for converting the format of the first output signal, and a third data converter for conversion into a code which corresponds to the history of the output from the second data converter.
Owner:TRIGENCE SEMICONDUCTOR INC
System and Method for Enhancing a Decoded Tonal Sound Signal
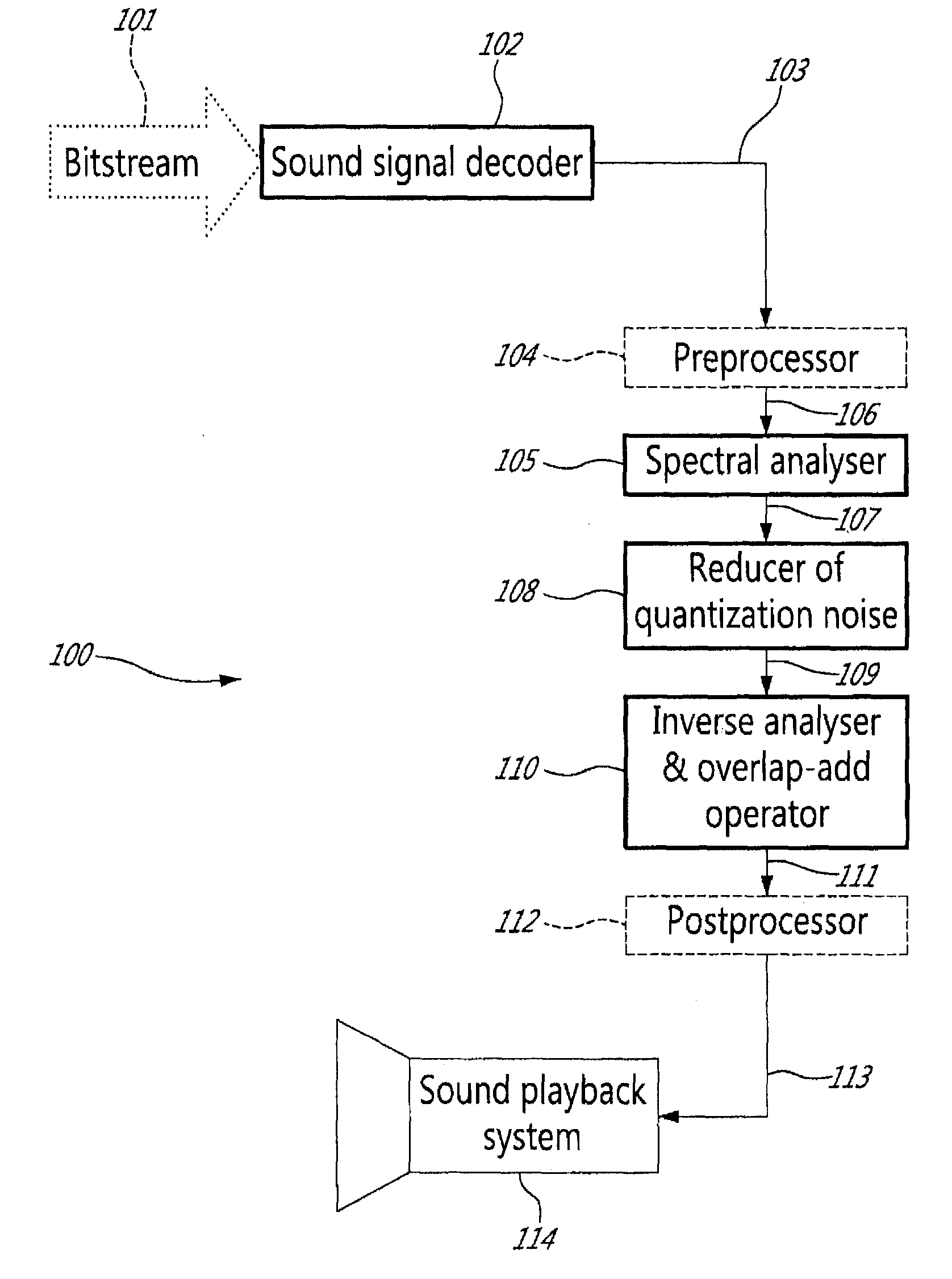
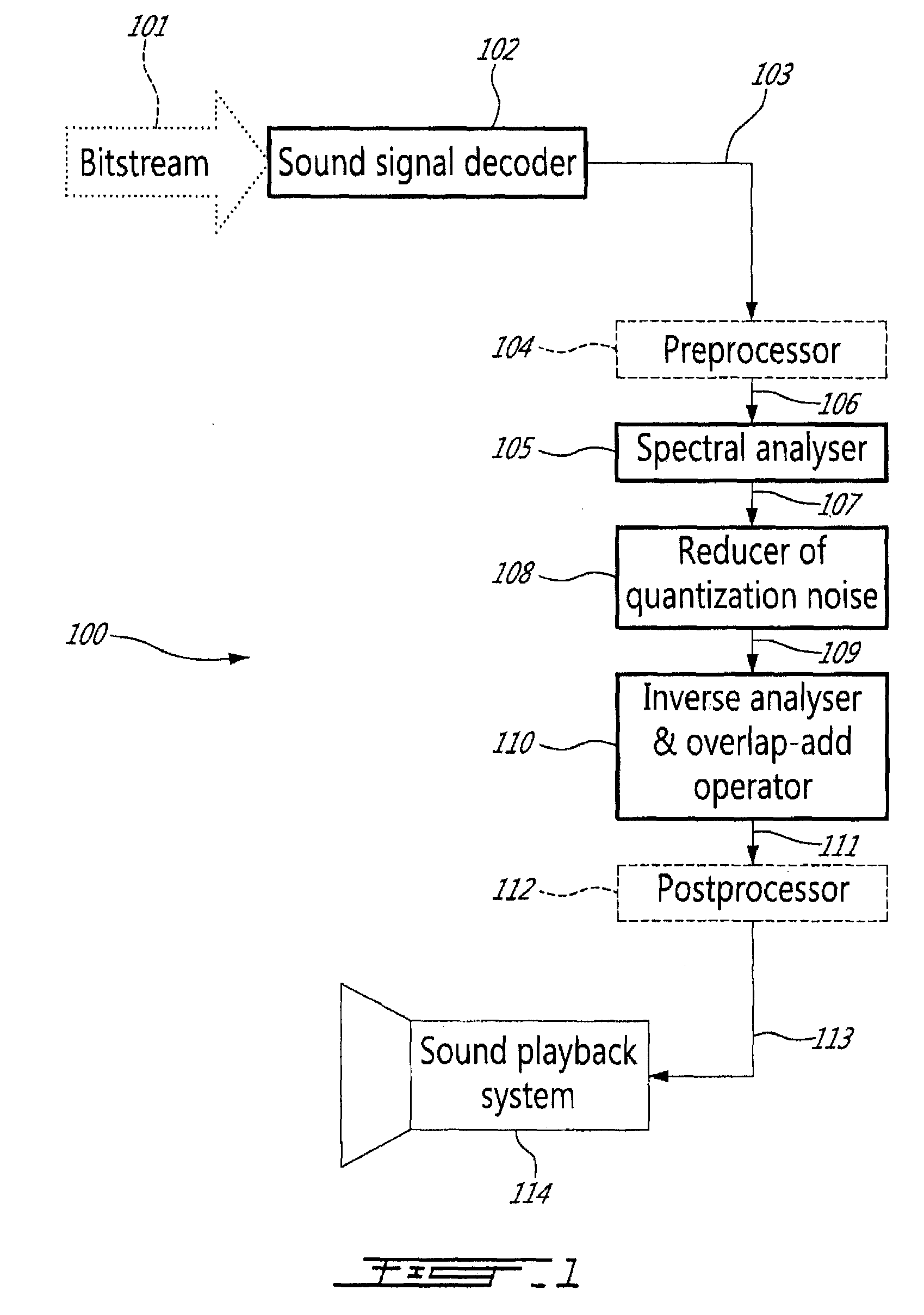
ActiveUS20110046947A1Enhanced signalReduce quantization noiseSpeech analysisTransmission noise suppressionFrequency spectrumSpectrum analyzer
A system and method for enhancing a tonal sound signal decoded by a decoder of a speech-specific codec in response to a received coded bit stream, in which a spectral analyser is responsive to the decoded tonal sound signal to produce spectral parameters representative of the decoded tonal sound signal. A quantization noise in low-energy spectral regions of the decoded tonal sound signal is reduced in response to the spectral parameters produced by the spectral analyser. The spectral analyser divides a spectrum resulting from spectral analysis into a set of critical frequency bands each comprising a number of frequency bins, and the reducer of quantization noise comprises a noise attenuator that scales the spectrum of the decoded tonal sound signal per critical frequency band, per frequency bin, or per both critical frequency band and frequency bin.
Owner:VOICEAGE EVS LLC
Digital switching amplifier
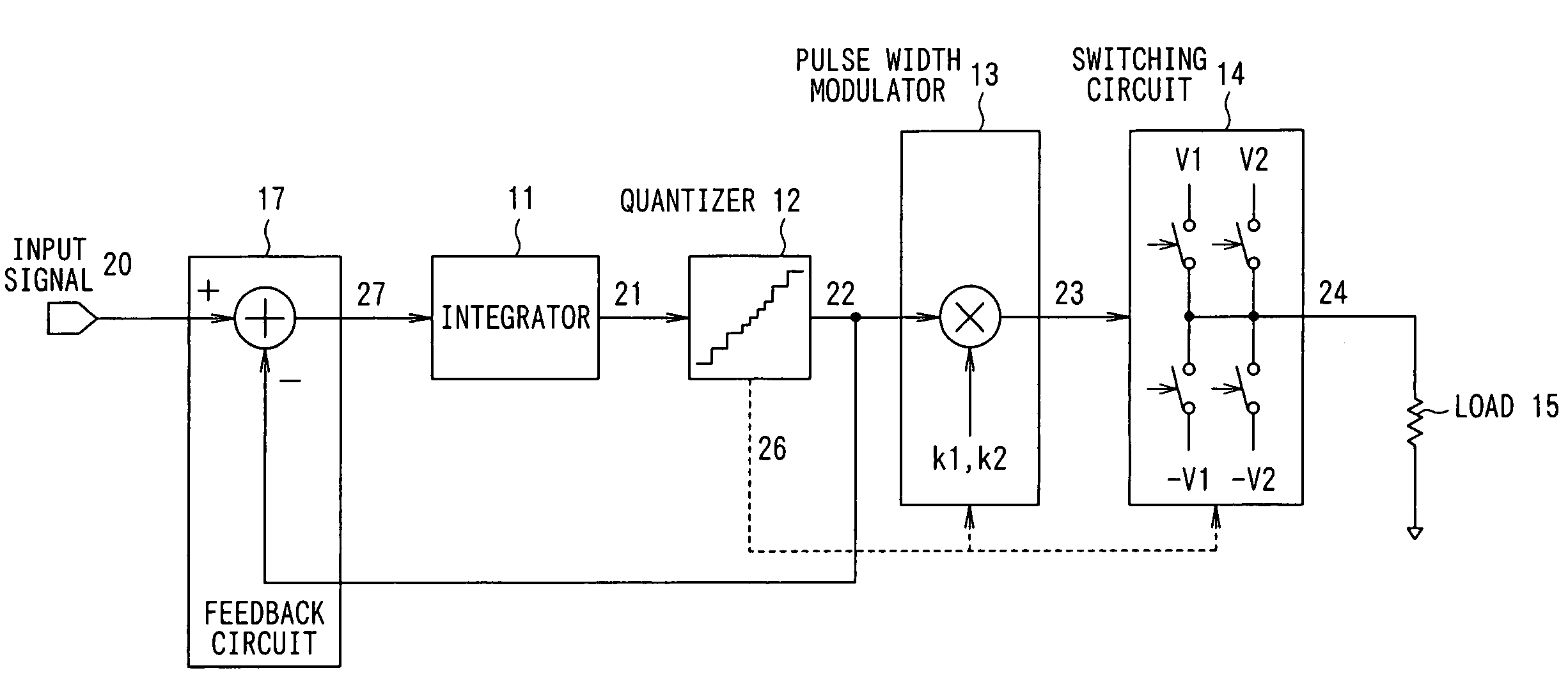
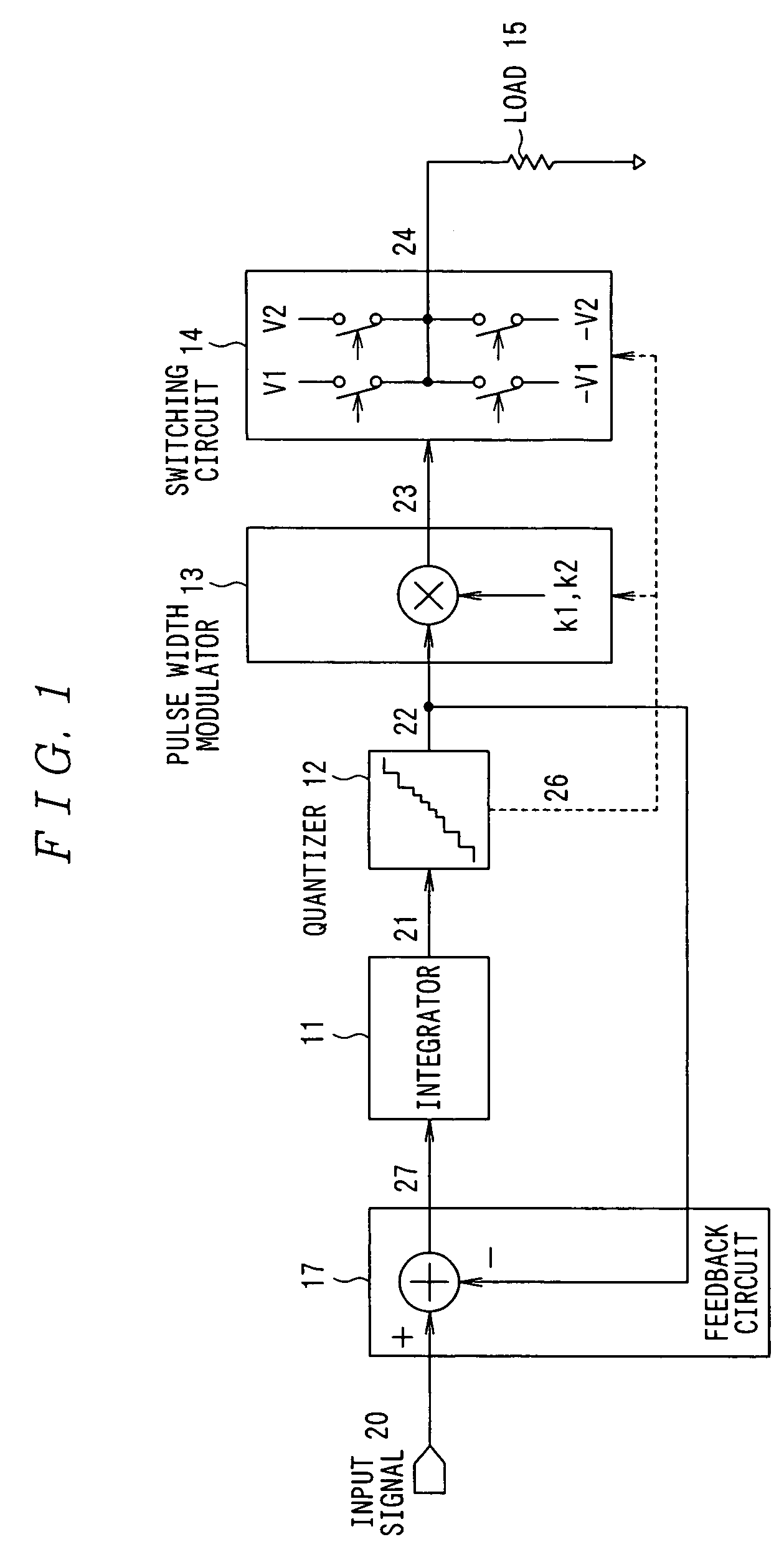
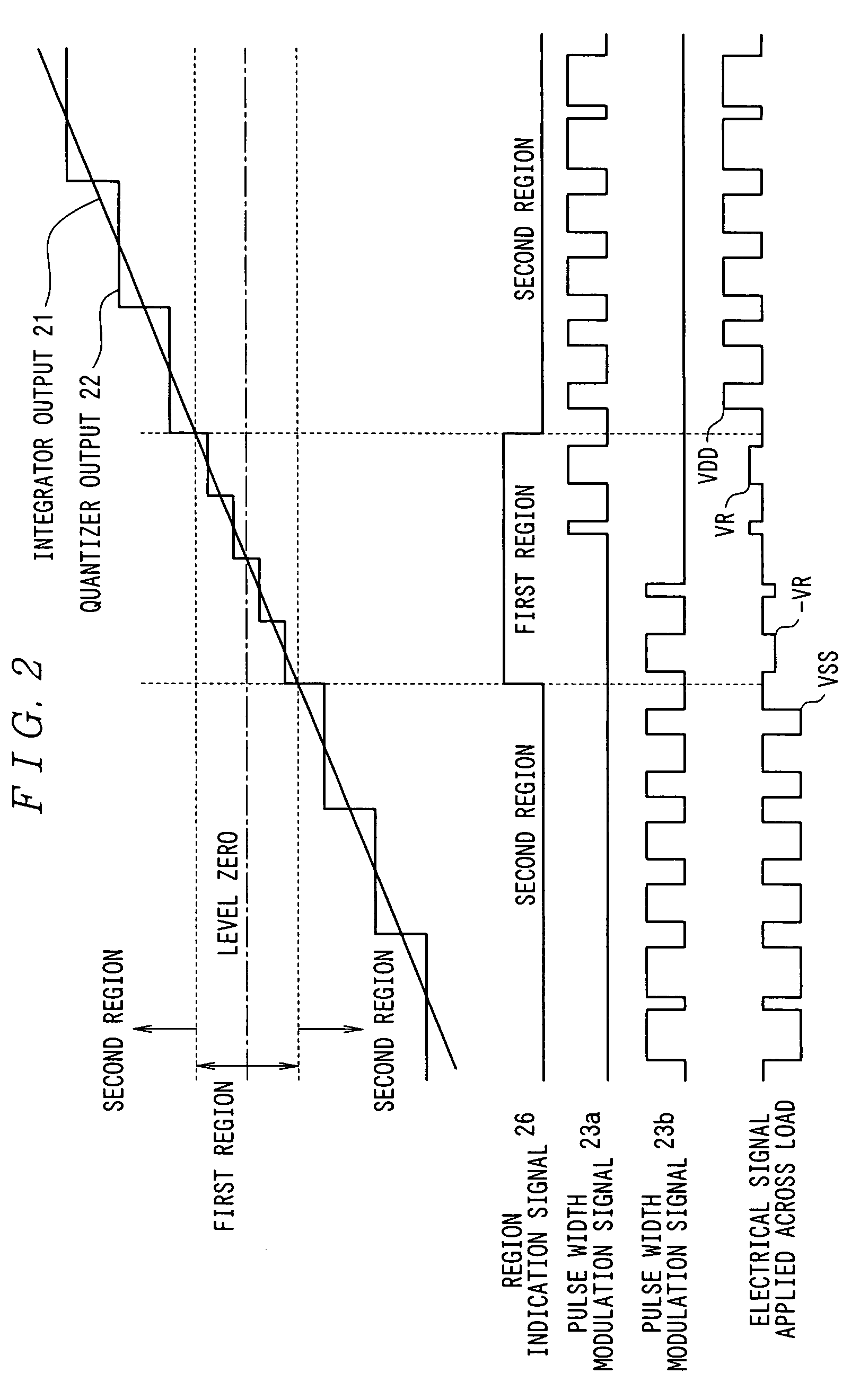
ActiveUS7330069B2Reduce quantization noiseImprove signal-to-noise ratioNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceIntegratorAudio power amplifier
There is provided a digital switching amplifier capable of enhancing an S / N ratio at the time of a small signal output and reducing current consumption and electromagnetic interference (EMI). The digital switching amplifier according to the present invention is provided with an integrator 11 for integrating an input signal, quantizer 12 for quantizing the output signal of the integrator 11 with resolutions different for each of the predetermined signal regions, pulse width modulator 13 for performing pulse width modulation for each of signals quantized with different resolutions by the quantizer 12 using different proportionality coefficients, switching circuit 14 for providing the load 15 with electrical signals different in value for each of pulse-width modulated signals with different proportionality coefficients by the pulse width modulator 13 in response to the pulse-width modulated signal, and feedback circuit 17 for negatively feeding back the output of the quantizer 12 to the input of the integrator 11.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI ELECTRONICS CO LTD
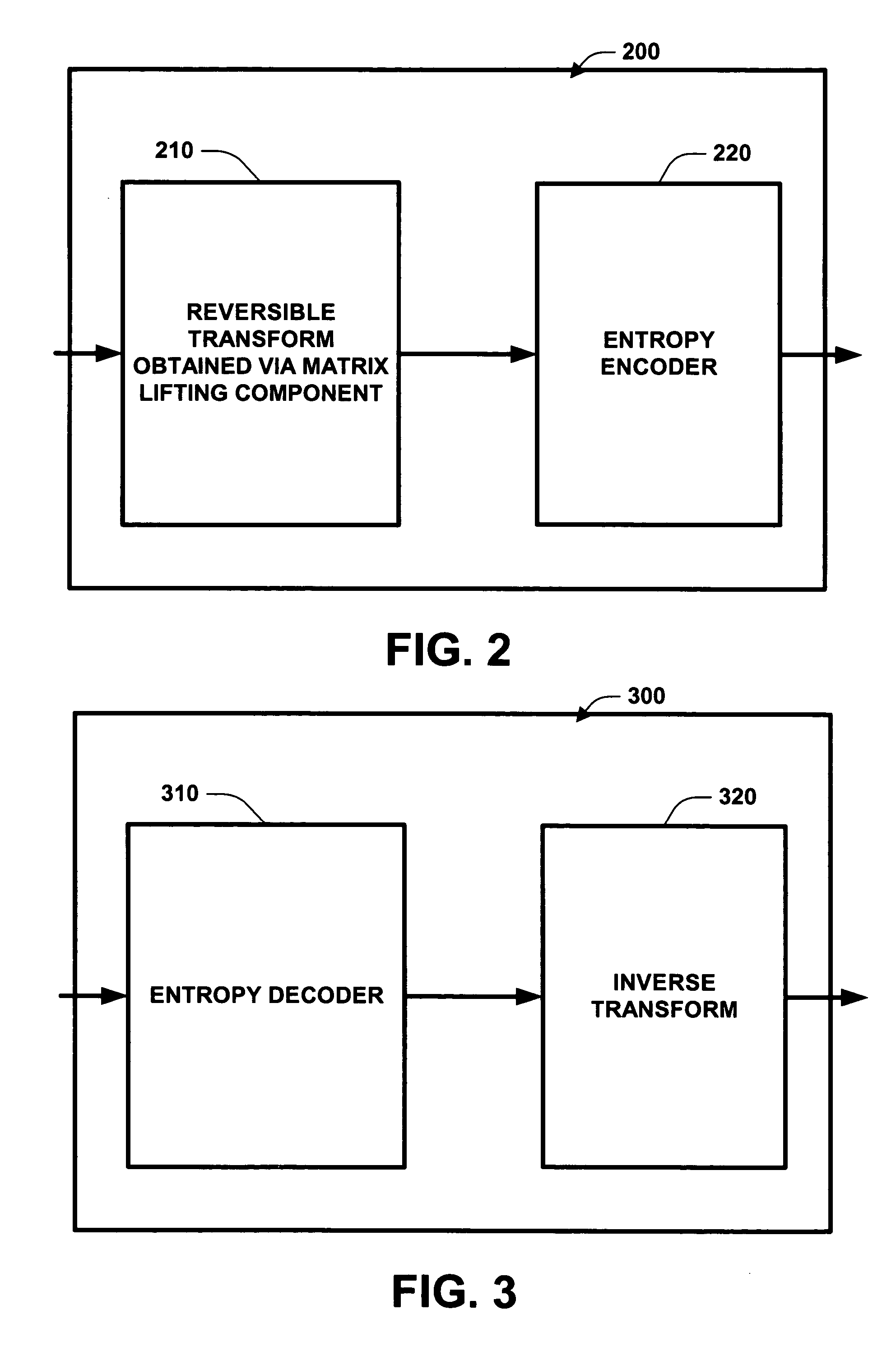
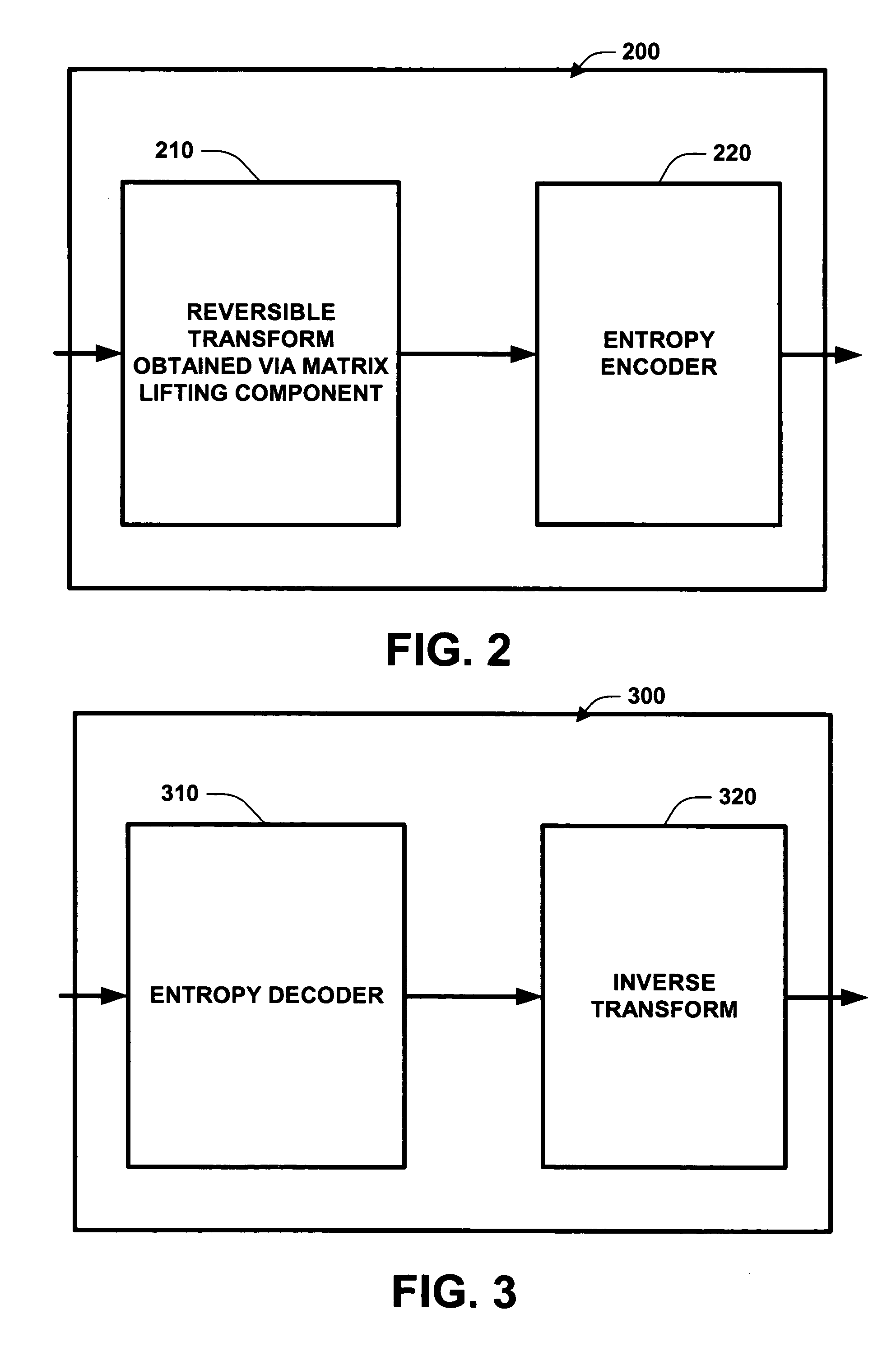
System and method for a media codec employing a reversible transform obtained via matrix lifting
InactiveUS20050083216A1Reduce quantization noiseLow noiseSpeech analysisCode conversionSpeech recognitionAudio signal
A system and method for encoding and / or decoding a signal, such as an audio signal, employing a reversible transform obtained via matrix lifting. This reversible transform not only converts integer input to integer output, but also reconstructs the exact input from the output. It is one of the key modules for lossless and progressive to lossless audio codecs. The system and method of the invention produces smaller quantization noise and better compression performance of lossless and progressive to lossless codecs previously known. A number of embodiments employing RMDCT solutions are described. Matrix lifting is used to implement a reversible fast Fourier transform (FFT) and a reversible fractional-shifted FFT, respectively, which are further combined with reversible rotations to form a RMDCT. A progressive-to-lossless embedded audio codec (PLEAC) employing RMDCT is implemented with superior results for both lossless and lossy audio compression.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for a media codec employing a reversible transform obtained via matrix lifting
InactiveUS7315822B2Reduce noiseReduce quantization noiseSpeech analysisCode conversionFast Fourier transformFourier transform on finite groups
A system and method for encoding and / or decoding a signal, such as an audio signal, employing a reversible transform obtained via matrix lifting. This reversible transform not only converts integer input to integer output, but also reconstructs the exact input from the output. It is one of the key modules for lossless and progressive to lossless audio codecs. The system and method of the invention produces smaller quantization noise and better compression performance of lossless and progressive to lossless codecs previously known. A number of embodiments employing RMDCT solutions are described. Matrix lifting is used to implement a reversible fast Fourier transform (FFT) and a reversible fractional-shifted FFT, respectively, which are further combined with reversible rotations to form a RMDCT. A progressive-to-lossless embedded audio codec (PLEAC) employing RMDCT is implemented with superior results for both lossless and lossy audio compression.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Solid-state radiation detector in which signal charges are reduced below saturation level
InactiveUS20010038076A1Great radiation absorptionReduce the amount requiredMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementFluorescent lightSaturation level
In a radiation detector: a CsI:Tl (or CsI:Na) scintillator receives a number X of radiation quantums for each pixel, and emits a number L of photons constituting fluorescent light in response to each radiation quantum; photoelectric converters containing Si (or Se) as a main component are arranged corresponding to respective pixels to receive the fluorescent light with an entrance efficiency T, and generate charges when the fluorescent light is detected; and a capacitor is connected to each photoelectric converter, and stores the charges generated by the photoelectric converter. When the radiation detector receives a 10 to 300 mR dose of the radiation, the numbers X and L, the entrance efficiency T, the fill factor F and the photoelectric conversion efficiency eta of each photoelectric converter, and the maximum storable charge amount Q of the capacitor satisfy a relationship X.L.T.F.eta<=Q.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Multi-rate digital phase locked loop
InactiveUS20100310031A1Reduce power consumptionReduce digital imagePulse transformerPulse automatic controlDigital tuningHigh rate
A Digital Phase-Locked Loop (DPLL) involves a Time-to-Digital Converter (TDC) that receives a DCO output signal and a reference clock and outputs a first stream of digital values. Quantization noise is reduced by clocking the TDC at a high rate. Downsampling circuitry converts the first stream into a second stream. The second stream is supplied to a phase detecting summer of the DPLL such that a control portion of the DPLL can switch at a lower rate to reduce power consumption. The DPLL is therefore referred to as a multi-rate DPLL. A third stream of digital tuning words output by the control portion is upsampled before being supplied to the DCO so that the DCO can be clocked at the higher rate, thereby reducing digital images. In a receiver application, no upsampling is performed and the DCO is clocked at the lower rate, thereby further reducing power consumption.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Solid-state radiation detector in which signal charges are reduced below saturation level
InactiveUS6515286B2Great radiation absorptionReduce the amount requiredSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansCapacitanceFluorescent light
In a radiation detector: a CsI:Tl (or CsI:Na) scintillator receives a number X of radiation quantums for each pixel, and emits a number L of photons constituting fluorescent light in response to each radiation quantum; photoelectric converters containing Si (or Se) as a main component are arranged corresponding to respective pixels to receive the fluorescent light with an entrance efficiency T, and generate charges when the fluorescent light is detected; and a capacitor is connected to each photoelectric converter, and stores the charges generated by the photoelectric converter. When the radiation detector receives a 10 to 300 mR dose of the radiation, the numbers X and L, the entrance efficiency T, the fill factor F and the photoelectric conversion efficiency eta of each photoelectric converter, and the maximum storable charge amount Q of the capacitor satisfy a relationship X.L.T.F.eta<=Q.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
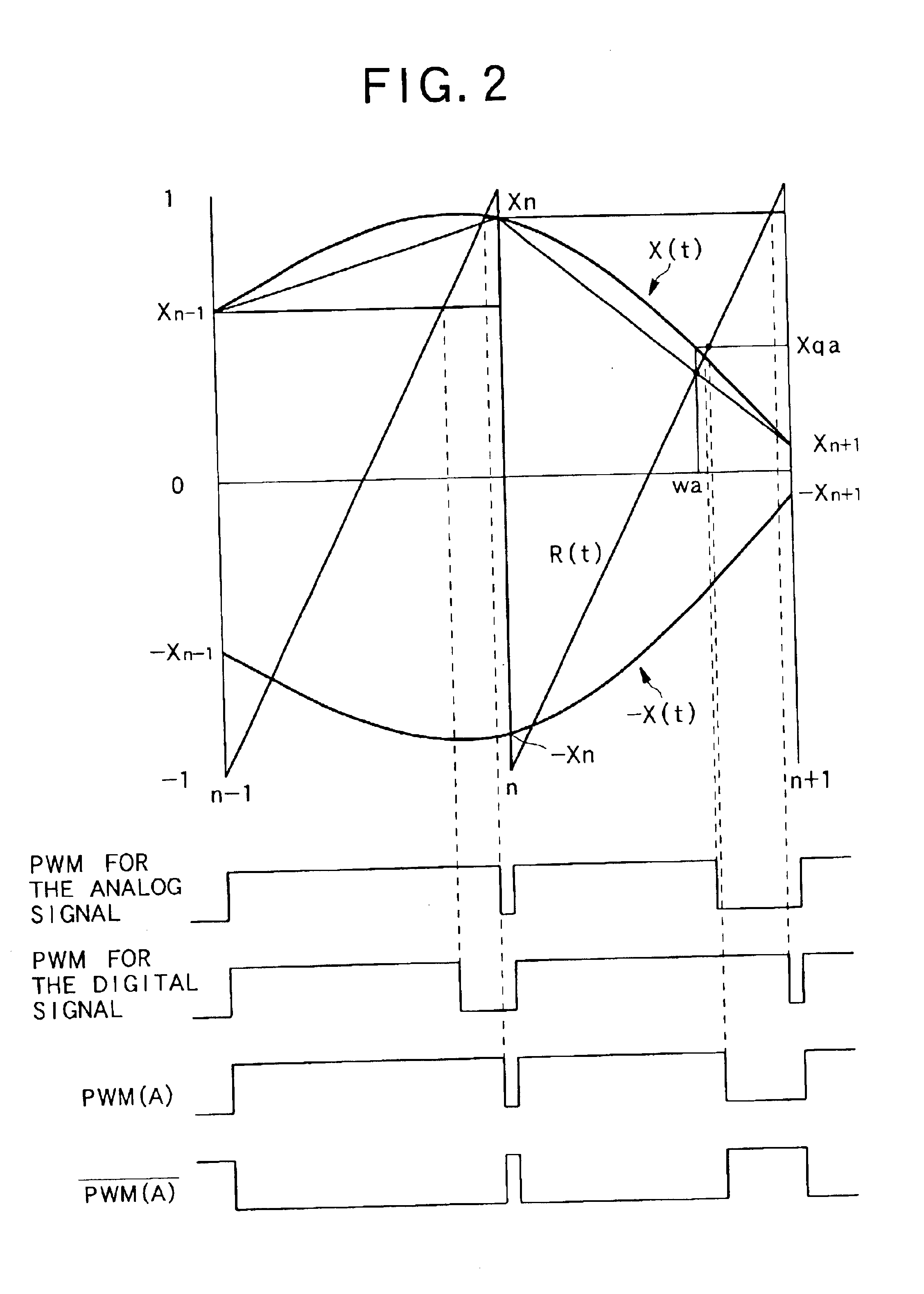
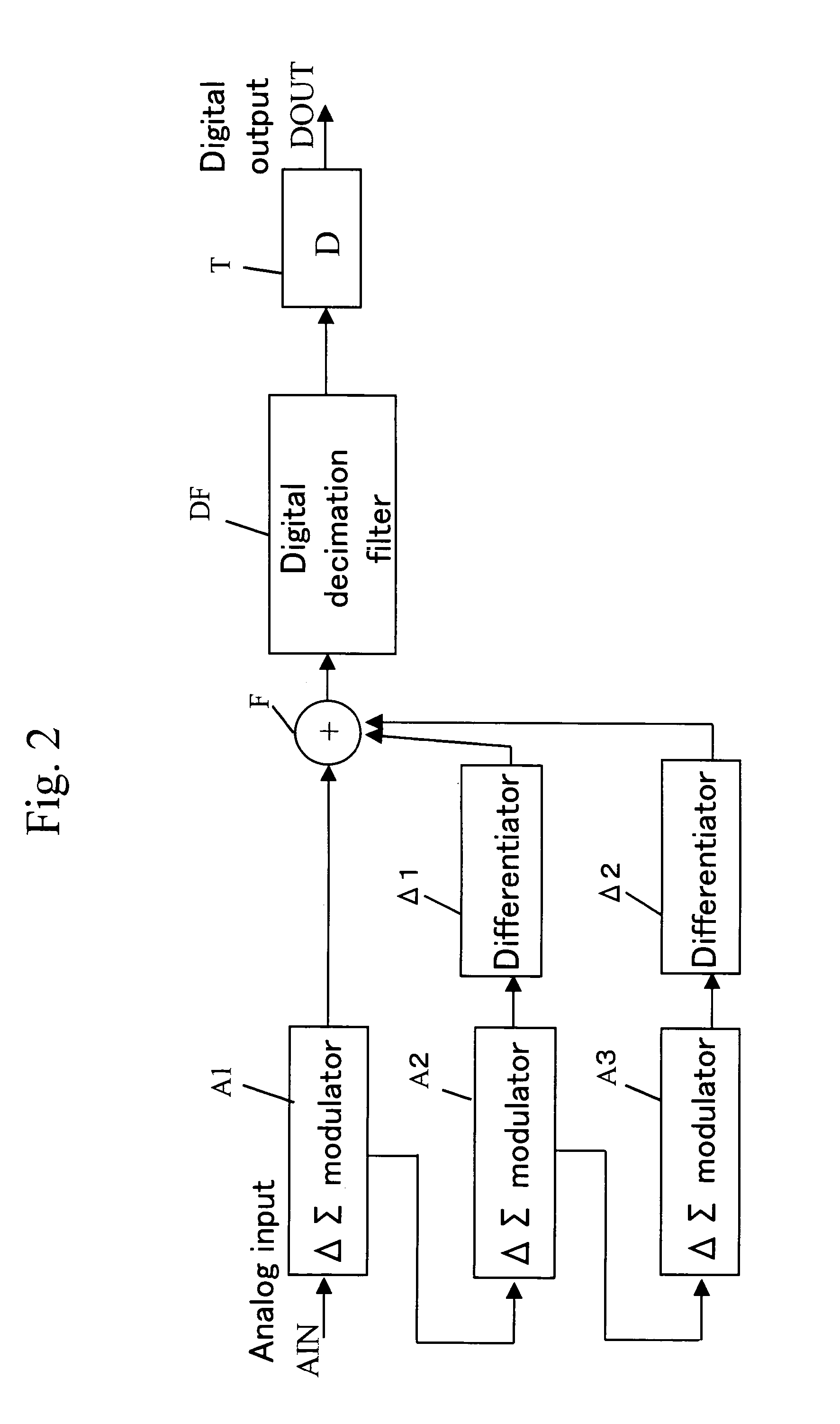
Digital signal conversion apparatus, digital signal conversion method, and computer-readable recording medium in which digital signal conversion program is recorded
InactiveUS6873275B2Reduce nonlinear distortionReduce quantization noiseElectric signal transmission systemsDuration/width modulated pulse demodulationNoise shapingEngineering
The digital signal conversion apparatus comprises: an over-sampling circuit that samples the input digital signal at high frequency; a polarity-inversion circuit that inverts the polarity of the sampled digital signal; interpolation circuit (A) and interpolation circuit (B) that perform interpolation of each respective digital signal; noise-shaping circuit (A) and noise-shaping circuit (B) that perform noise shaping on the interpolated signals; PWM conversion circuit (A) and PWM conversion circuit (B) that perform PWM conversion on the noise-shaped signals; and a switching circuit for driving a load based on the PWM signals from PWM conversion circuit (A) and PWM conversion circuit (B).
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Digital/analogue conversion apparatus
ActiveUS8423165B2Reduce quantization noiseImprove noiseTransversal filtersDigitally weighted transducing elementsImage resolutionEngineering
A digital / analog conversion apparatus for converting a digital signal into an analog signal. The digital / analog conversion apparatus can generate a high-quality analog signal, even when elements configuring the digital / analog conversion apparatus have variance, with high resolution and a small circuit size. The data conversion apparatus is provided with a first data converter for reducing the number of bits of an input signal, a second data converter for converting the format of the first output signal, and a third data converter for conversion into a code which corresponds to the history of the output from the second data converter.
Owner:TRIGENCE SEMICONDUCTOR INC
Phase locked loop with a modulator
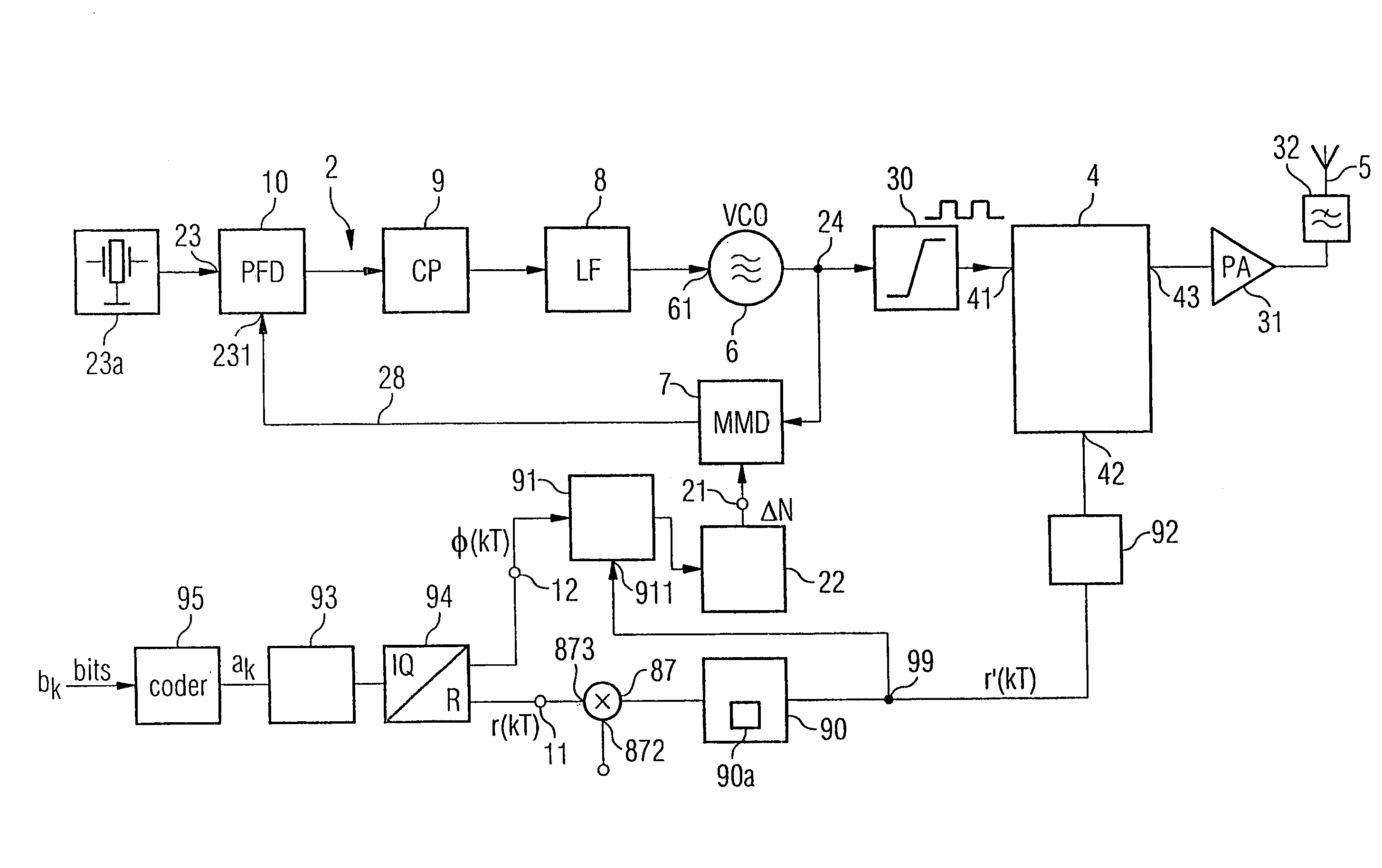
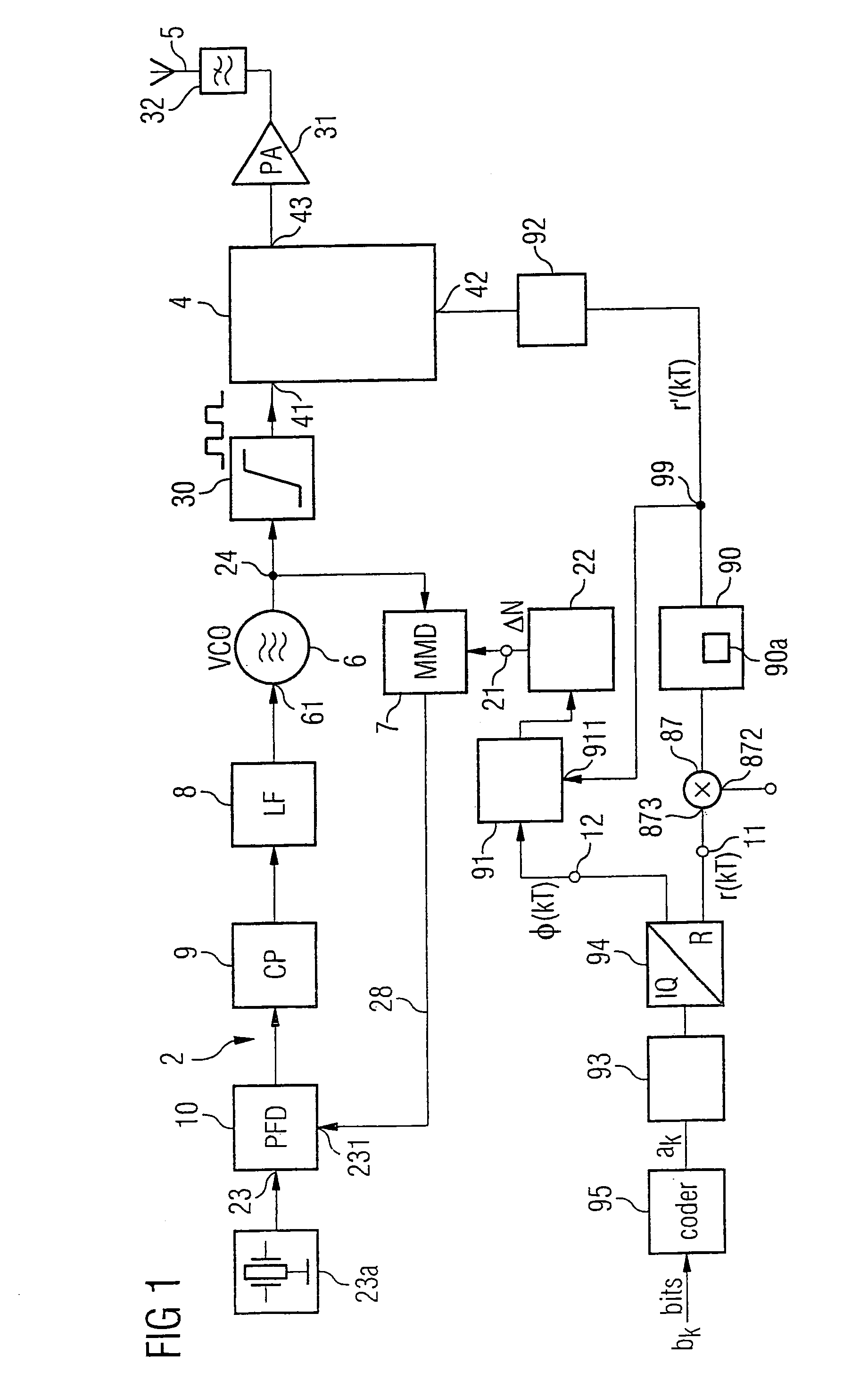
ActiveUS20050280473A1Reduce quantization noiseSmall step sizePulse automatic controlAngle modulation detailsModulation bandwidthMultiplexer
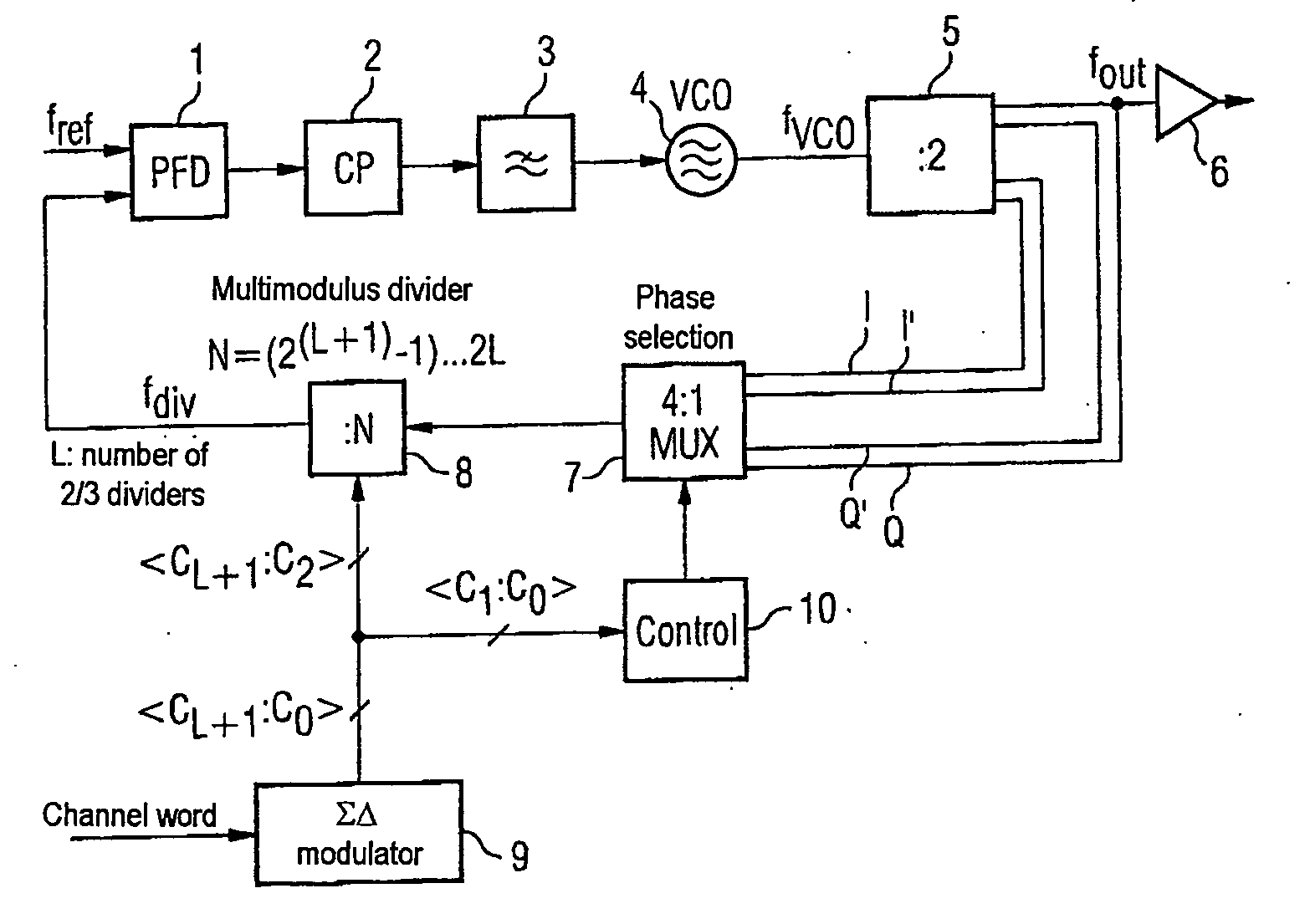
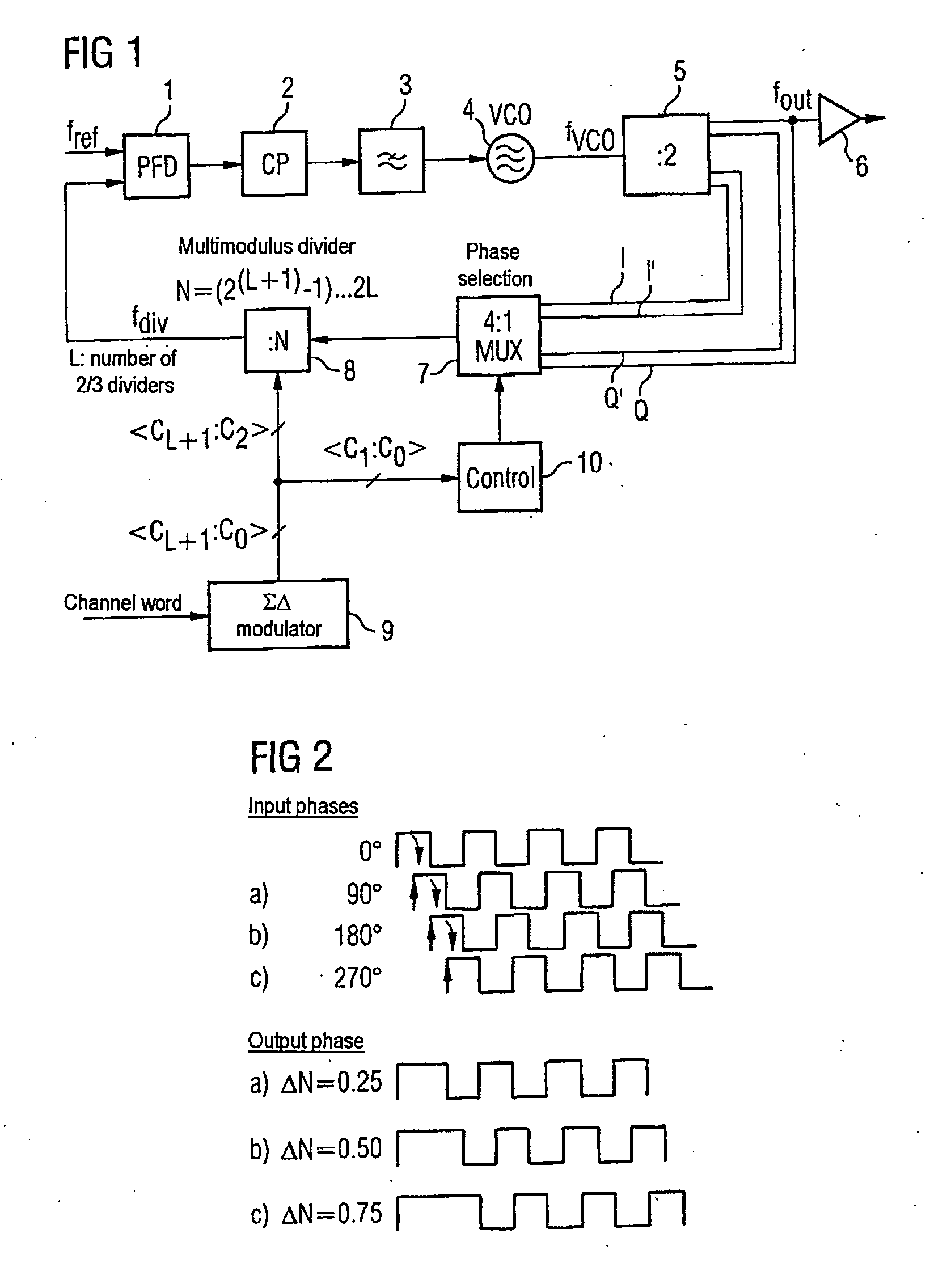
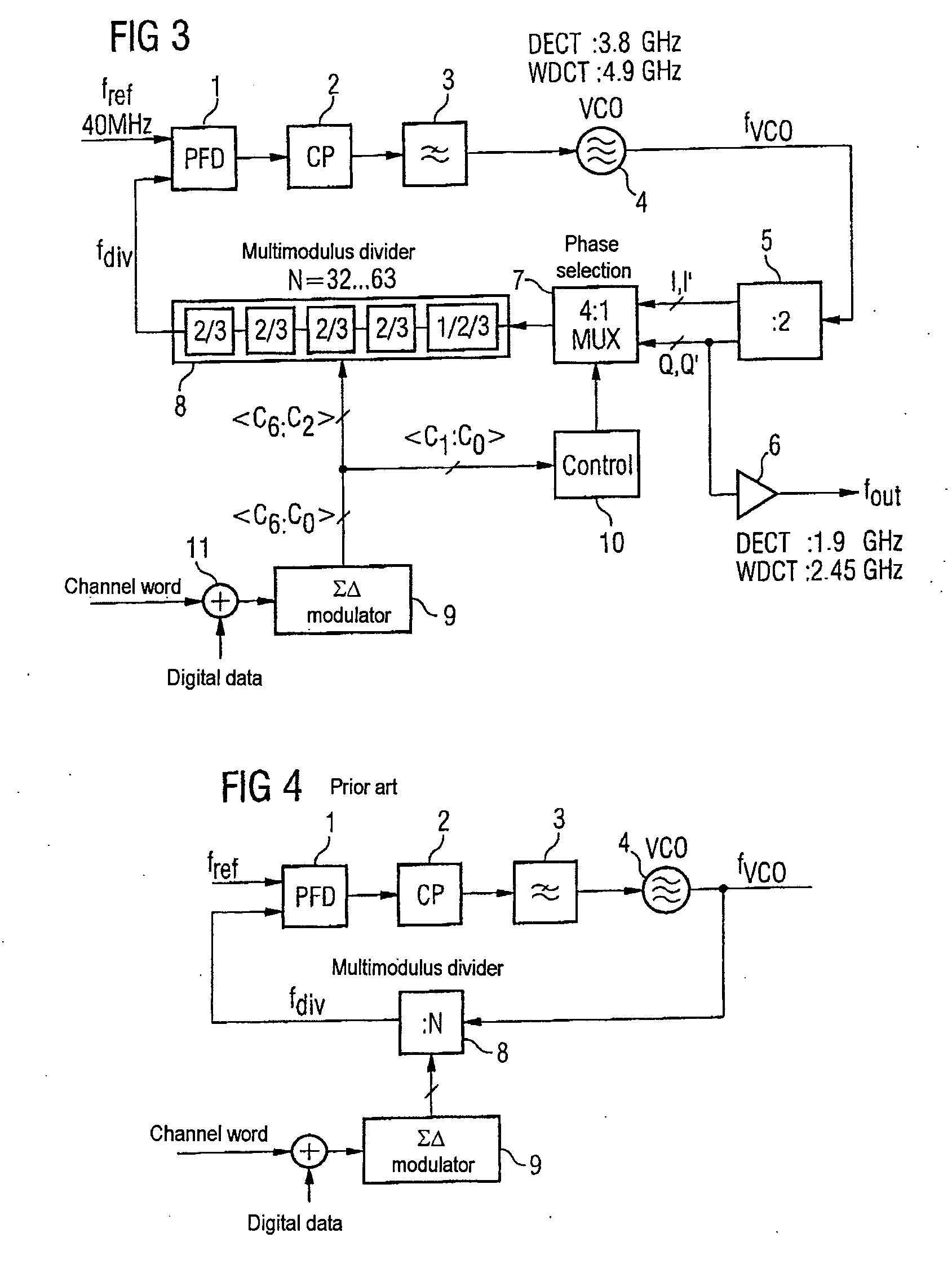
The invention provides a phase locked loop having a modulator which is based on a ΣΔ fractional N phase locked loop. In the forward path of the PLL, the output of the oscillator has an additional frequency divider which provides the output frequency of the PLL in a plurality of different phases. A multiplexer which is connected upstream of the multimodulus divider in the PLL's feedback path and which is actuated by the ΣΔ modulator, like the divider, selects the respective desired phase. This allows the minimum step size of the division factors to be reduced to values of less than 1 relative to the output frequency, which significantly reduces the quantization noise. The PLL bandwidth may therefore advantageously be the same size as the modulation bandwidth.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
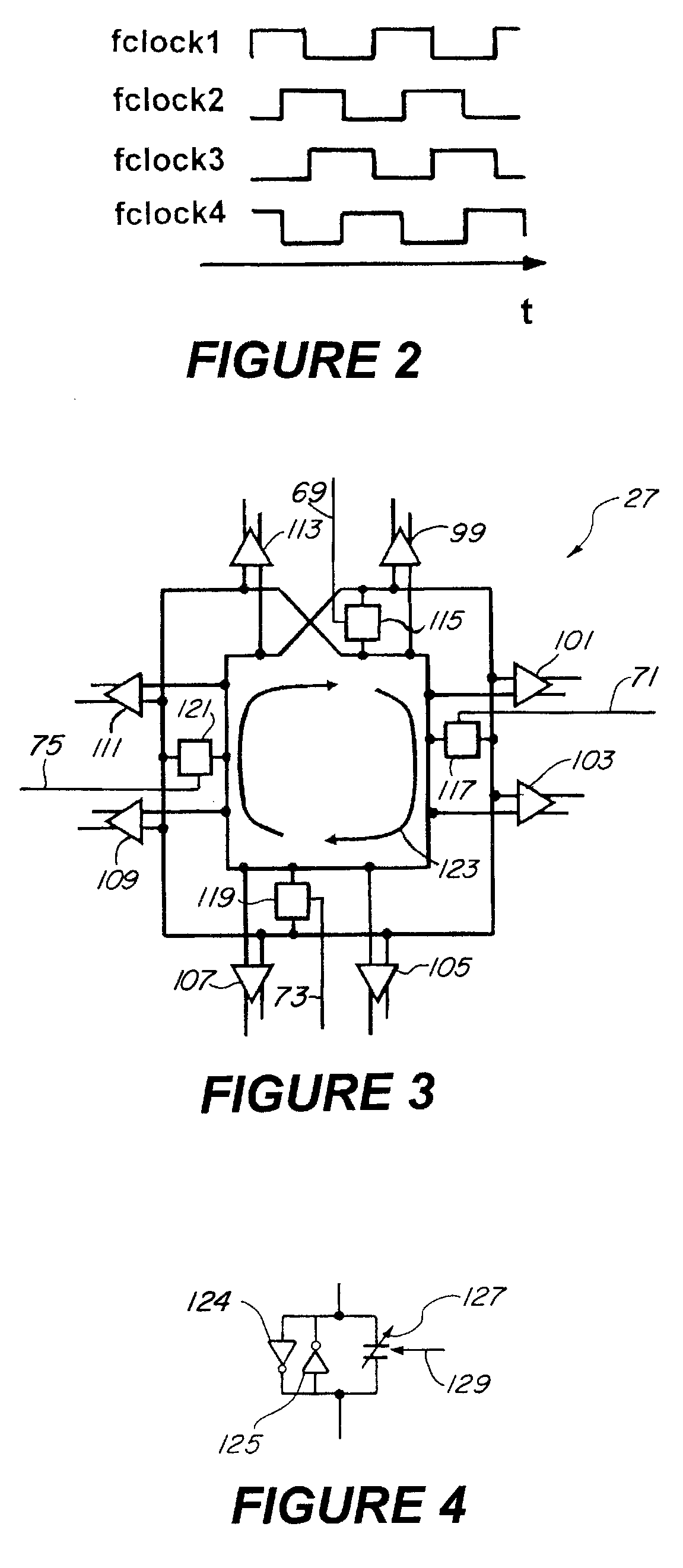
Phase lock loop with a multiphase oscillator
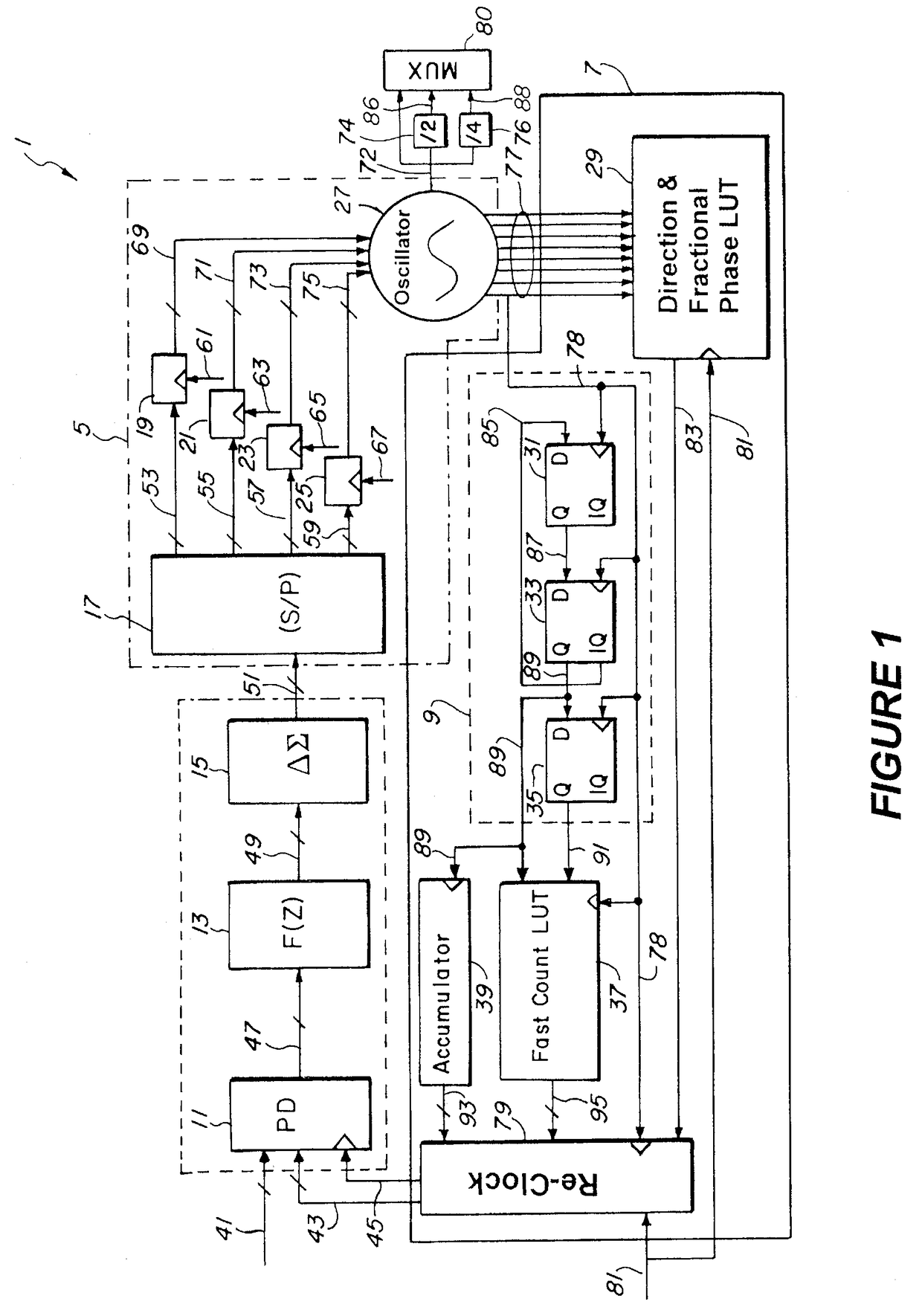
InactiveUS7907023B2Increase the oscillation frequencyHigh resolutionPulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsControl signalEngineering
A phase lock loop utilizes a multiphase oscillator having a plurality of digital inputs. A plurality of DQ flip-flops, offset in time from each other generate a plurality of control signals to remove control phase information from the oscillator in digital form. A DQ flip-flop connected between any two digital inputs on the oscillator determines direction of the traveling wave. The direction and phase information address a look-up table to determine the current fractional phase of the oscillator. A divide by N circuit is used to reduce the oscillator frequency. A total phase indicator signal for the oscillator is determined using the current fractional phase. The total phase is compared to a reference phase to produce a control signal for making adjustments to the oscillator. In a feed-forward path, frequency dividers divide a high frequency signal from the oscillator to a lower desired frequency, thereby increasing phase resolution.
Owner:III HLDG 12 LLC
Sigma delta modulator
ActiveUS7928876B2Stable maintenanceReduce quantization noiseDelta modulationDifferential modulationSignal transfer functionOptical transfer function
A method of controlling a sigma delta modulator with a loop which establishes a signal transfer function, STF, and a quantization noise transfer function, NTF, of the sigma delta modulator, wherein the sigma delta modulator receives an input signal, x(n), and provides a modulated output signal, y(n) in response to the input signal. The method is characterized in comprising the step of controlling the sigma delta modulator to change the quantization noise transfer function, NTF, in response to a signal feature, A(n), which is correlated with the input signal.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
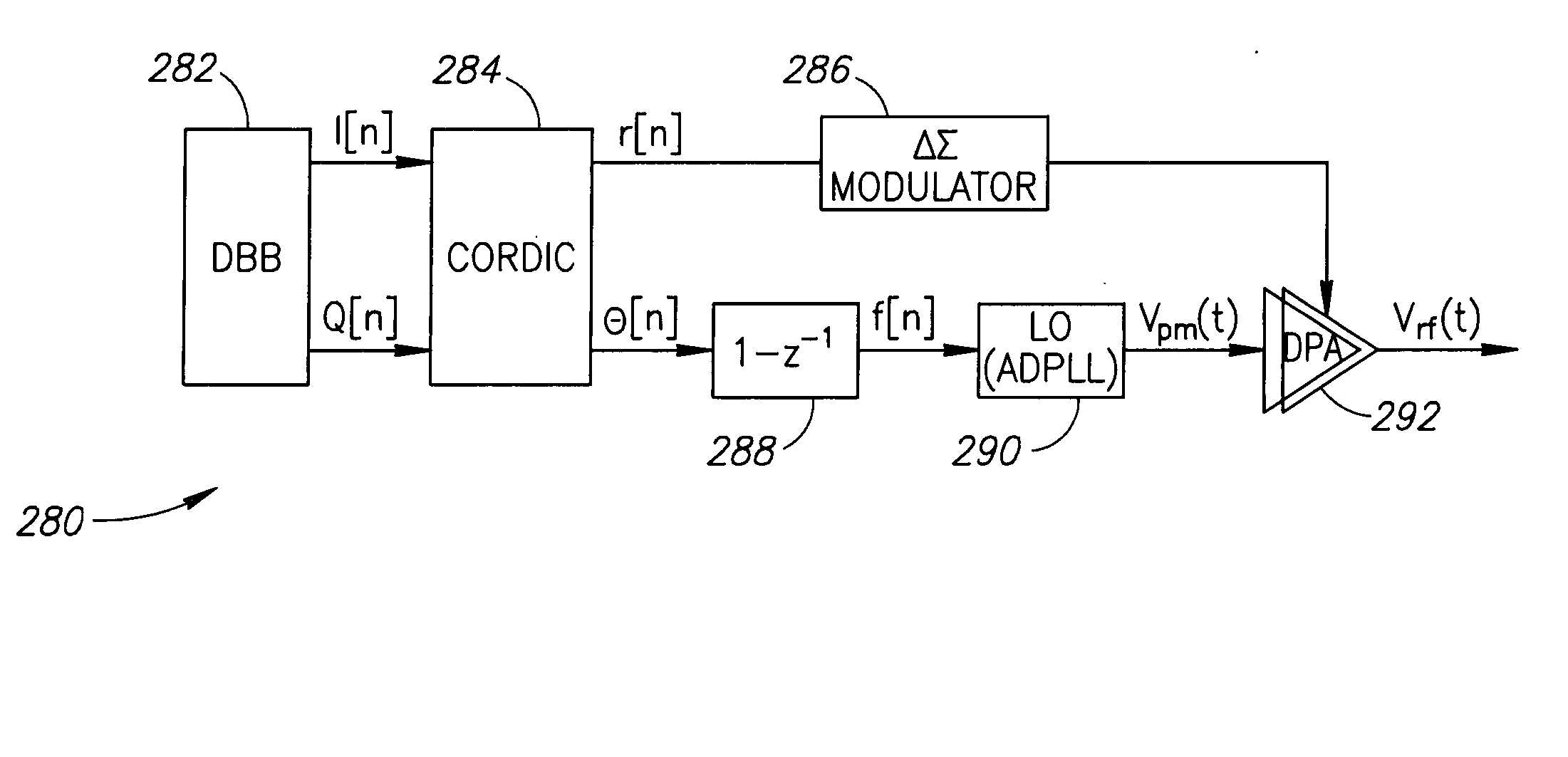
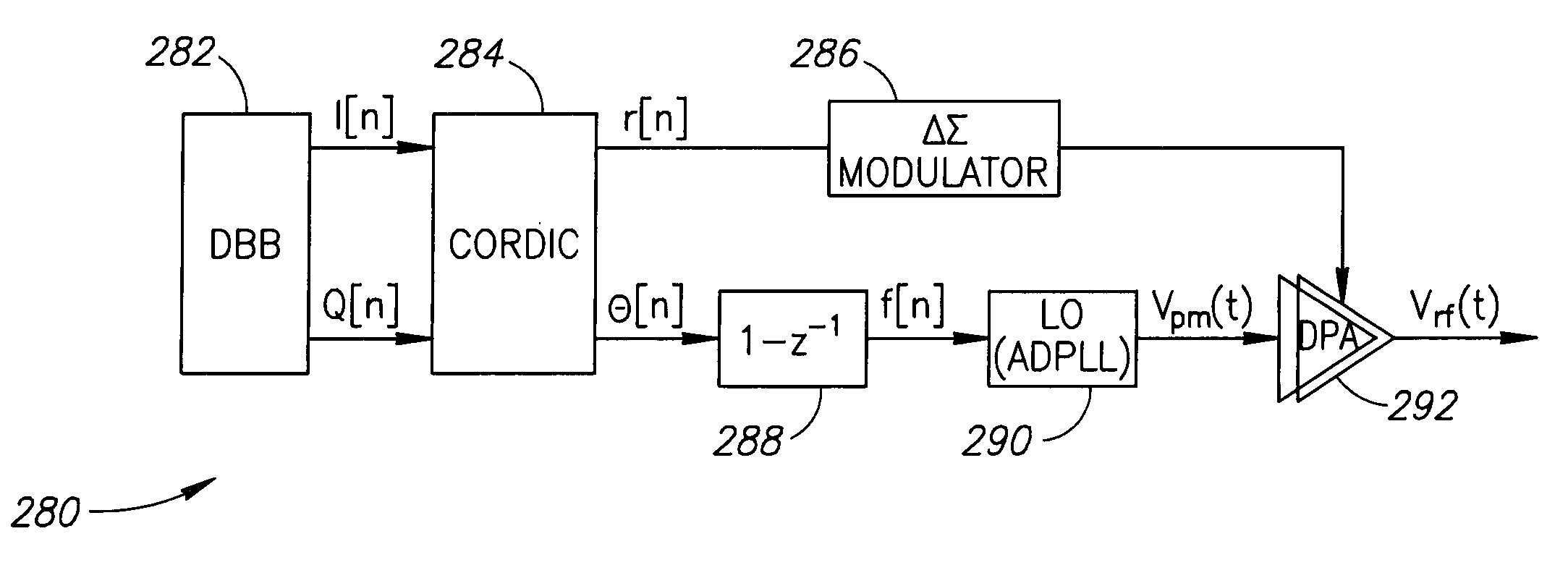
Polar modulator and a method for modulation of a signal
InactiveUS7289005B2Reduce power consumptionPrevent spurious data transmissionPower amplifiersModulation with suppressed carrierHarmonicRadio frequency signal
A polar modulator contains a phase locked loop which is designed to emit a radio-frequency signal at one frequency to one output, with the frequency being derived from the reference signal and from a phase modulation signal at a control input of the phase locked loop. The modulator additionally has a second signal input for supplying an amplitude modulation signal. The second signal input is connected to a control input of a pulse width modulator, one of whose signal inputs is coupled to the output of the phase locked loop. The pulse width modulator is designed to vary the duty ratio of a signal which is applied to the signal input, with this variation being adjustable via a regulation signal at the control input. A filter can be connected downstream from the output of the pulse width modulator and suppresses higher harmonic components in a signal which can be tapped off at the output of the pulse width modulator. The amplitude of an output signal is thus modulated by carrying out pulse width modulation and by subsequent suppression of higher-level frequency components.
Owner:INTEL CORP
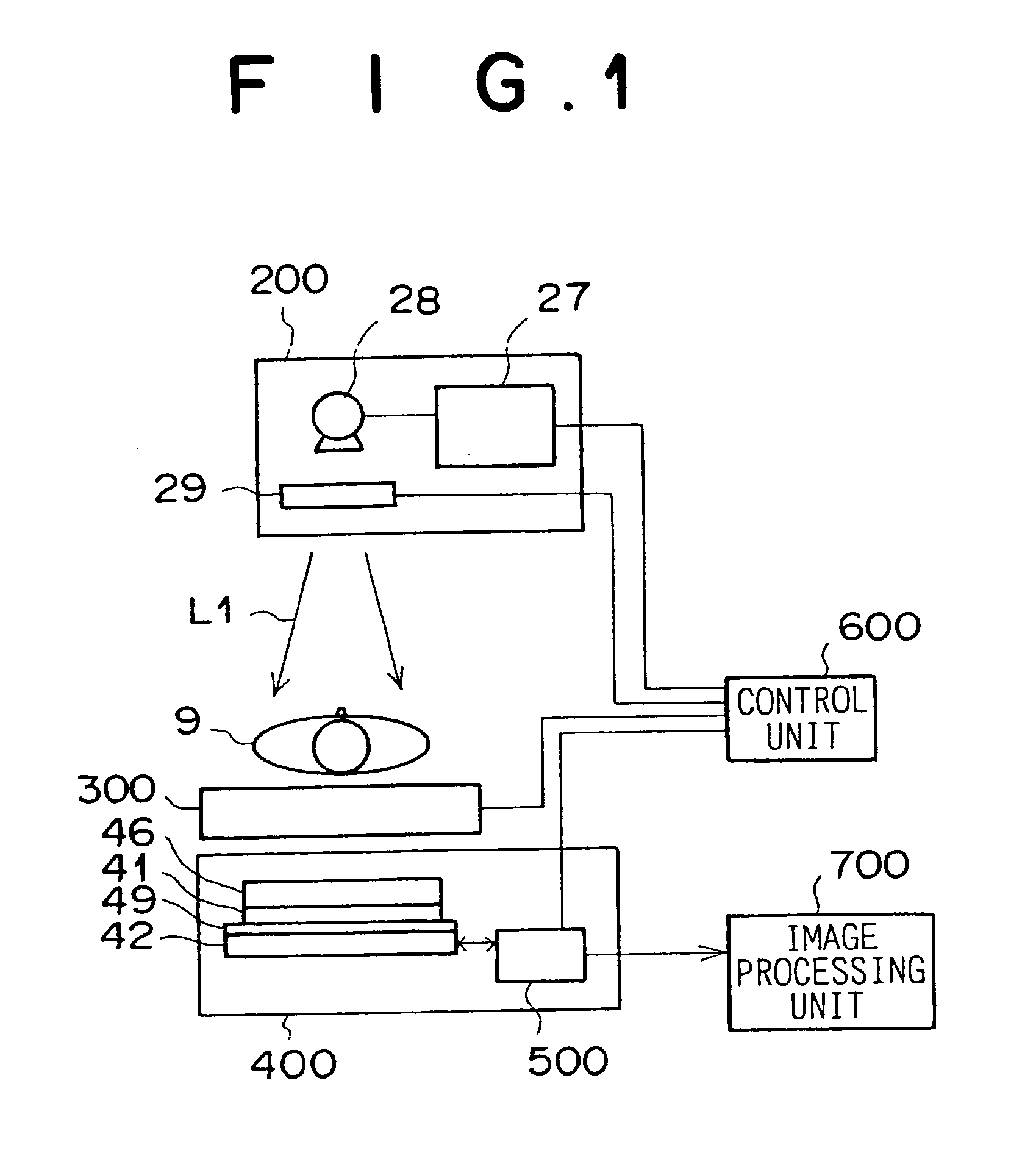
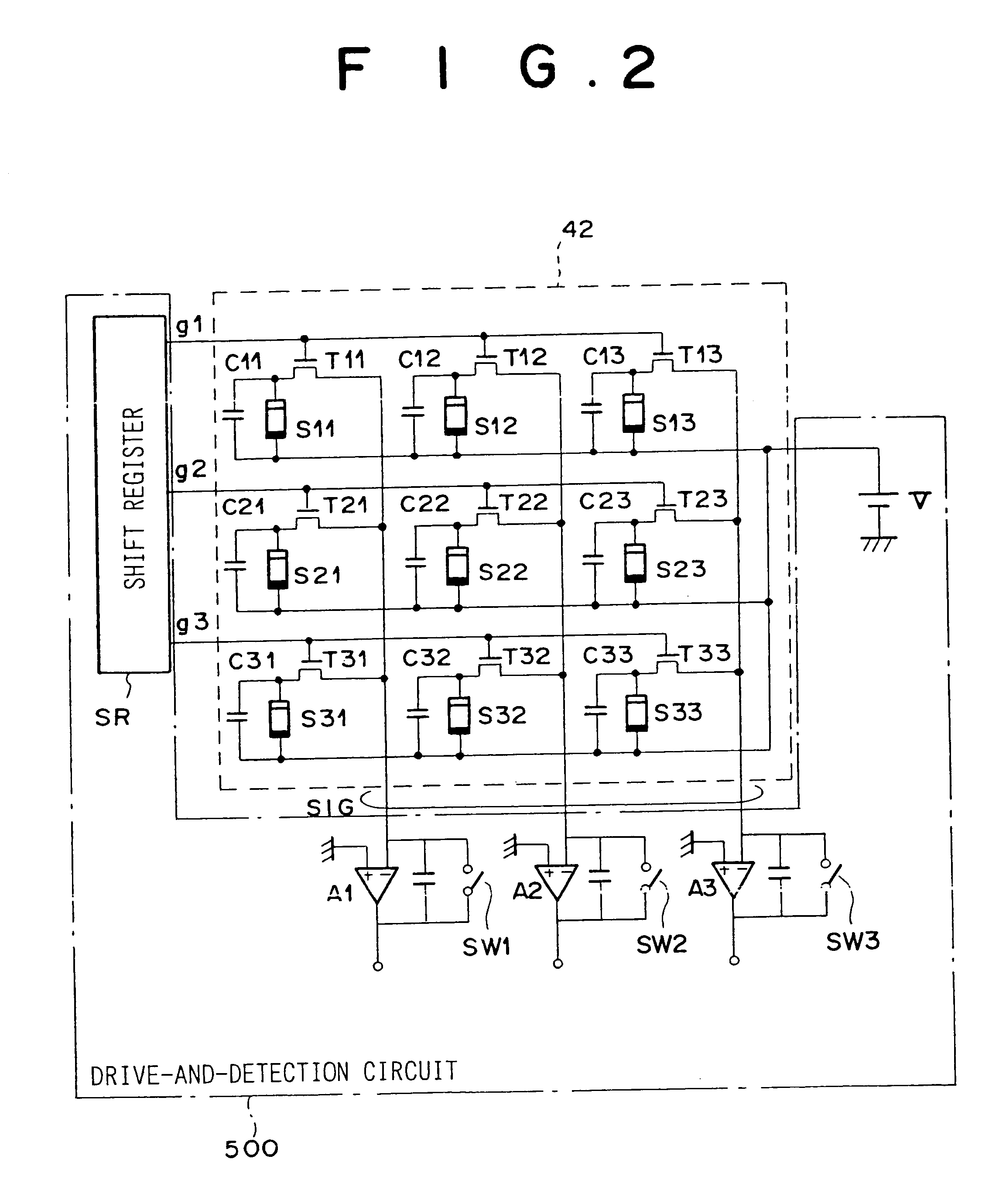
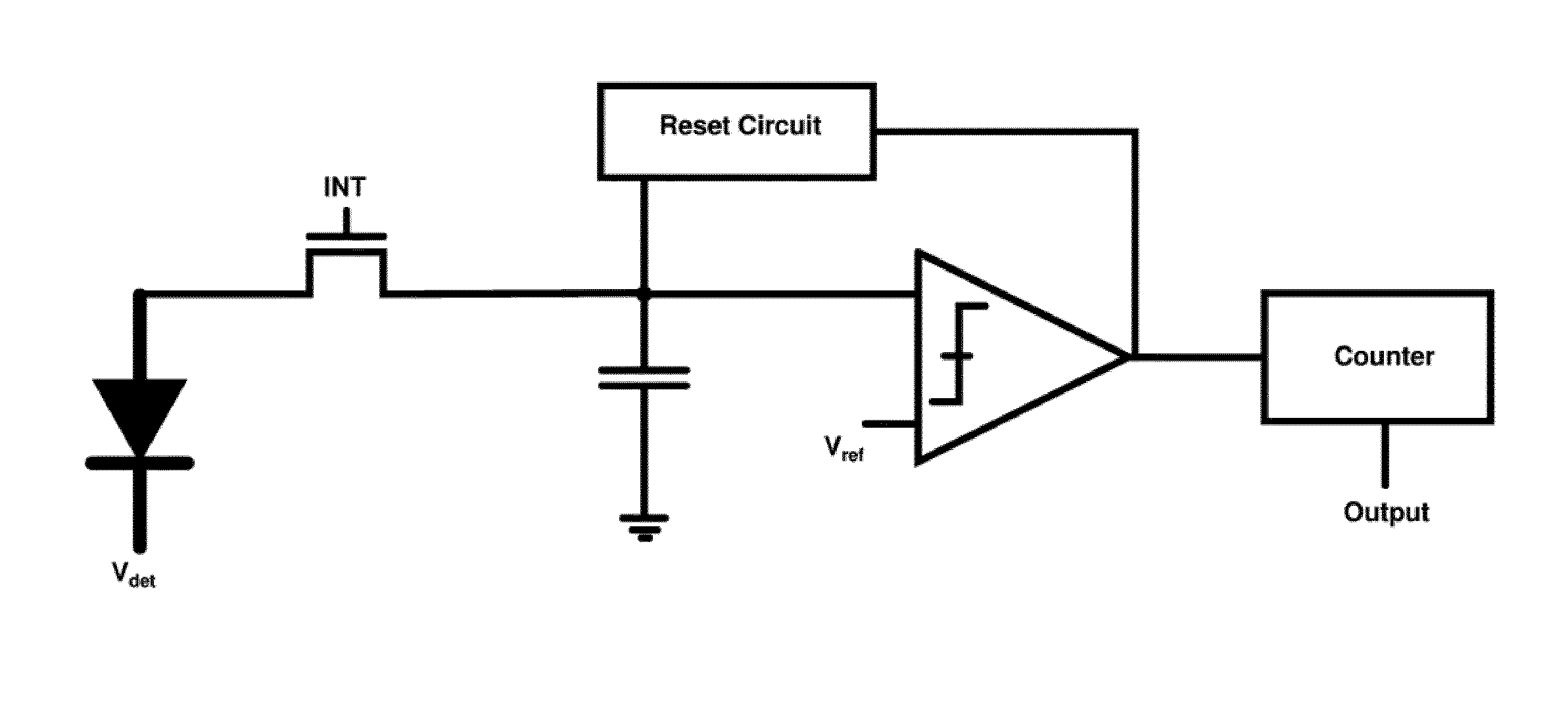
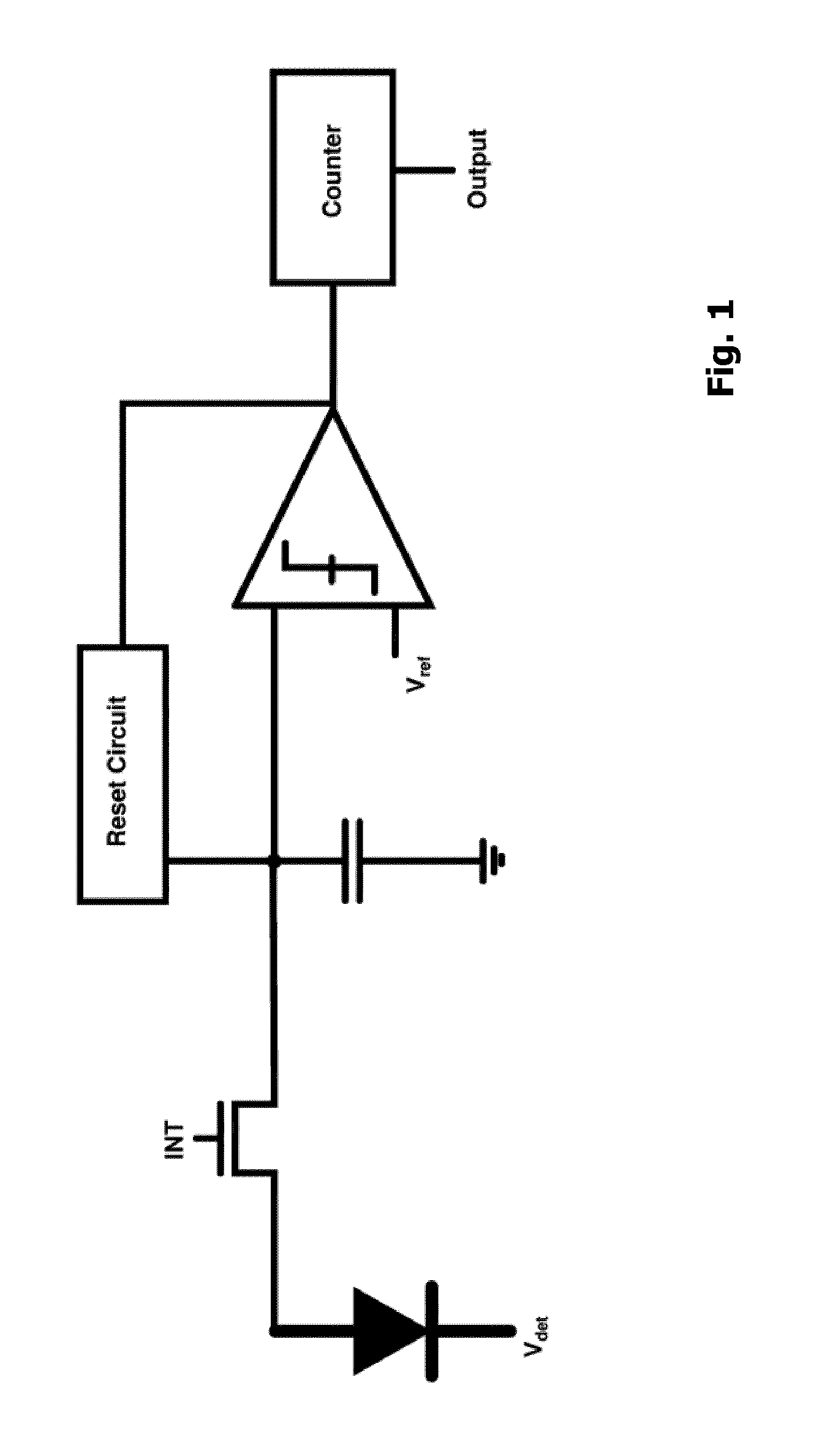
Self-reset asynchronous pulse frequency modulated droic with extended counting and having reduced quantization noise
InactiveUS20150015759A1Quantization noise is very lowLower frame rateTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOS sensorIntegrator
The present invention proposes a CMOS sensor pixel with a pulse frequency modulated digital readout integrated circuit (DROIC) comprising a photon sensitive element for receiving a plurality of photons and providing a charge signal indicative of the received photons, an integration capacitor connected to said photon sensitive element for determining a cumulative signal based on the charge signal for a certain integration time and producing an integrator output signal based on the cumulative signal and a comparator connected to the integrator for producing a comparator output signal. Each of said pixels further comprises a DAC that switches at each clock cycle following the end of an integration time and two counters respectively counting nunber of resets of said integration capacitor and voltage difference between an integrator output residue signal and a reference voltage of said comparator.
Owner:SABANCI UNIVERSITY
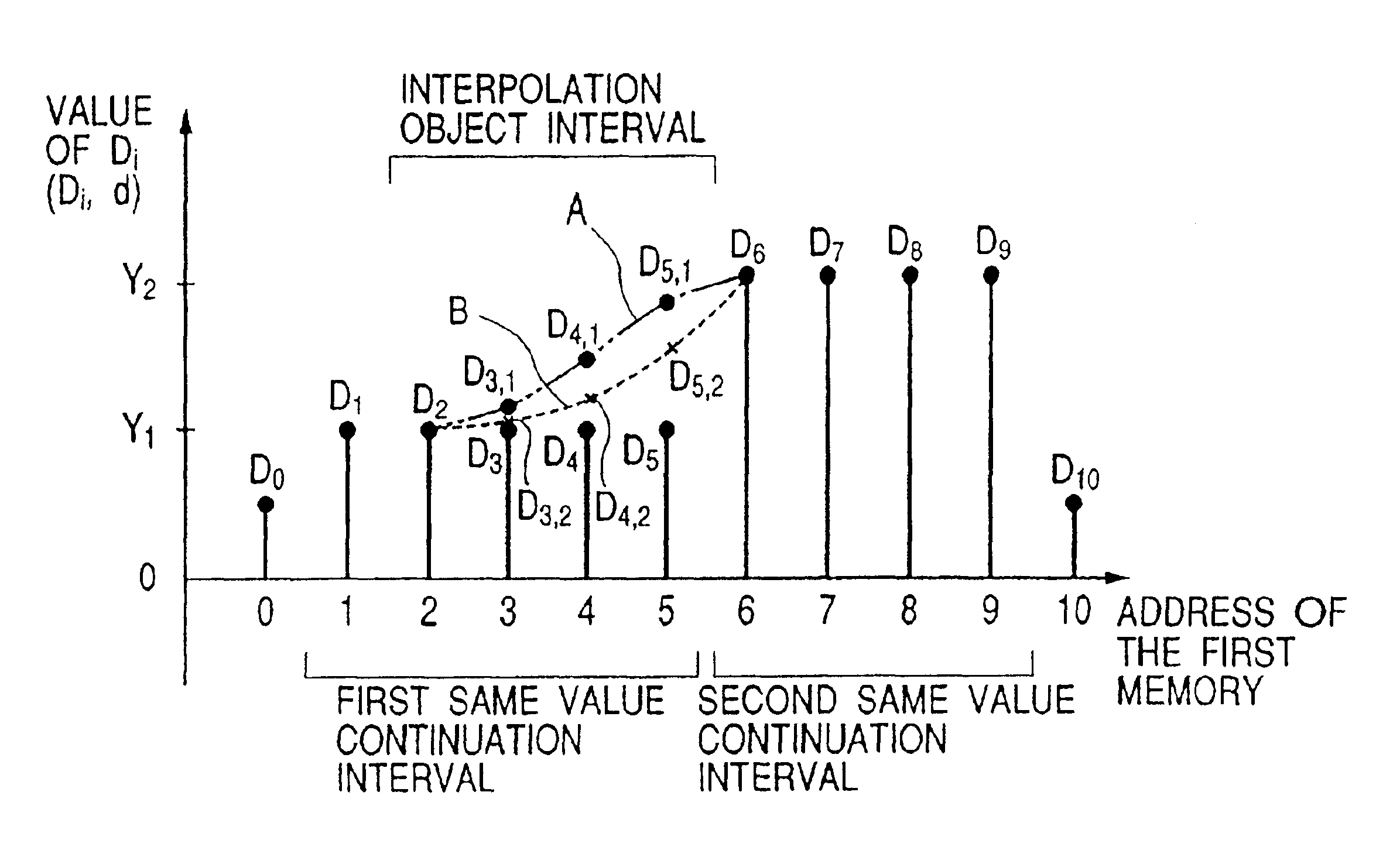
Method and apparatus for interpolating digital signal
InactiveUS6915319B1Easy to useImprove compression performanceDigital technique networkDigital video signal modificationDigital imageDigital audio signals
The present invention relates to an interpolation method and an interpolation apparatus for a digital audio signal or a digital image signal that has a predetermined sampling cycle and quantization bit length, and in particular, to an interpolation method and an interpolation apparatus that can effectively reduce quantization noise in a digital signal that is obtained by information compression. In the method and apparatus according to the present invention, it is made to perform interpolation processing of signal levels in a interpolation object interval in a given digital signal in accordance with a predetermined function curve, which monotonously changes, with the interpolation object interval including a discontinuous part that exists between one signal interval, where the same gradation levels continue, and another signal interval, which is adjacent to the one signal interval and in which the same gradation levels that are different continue.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
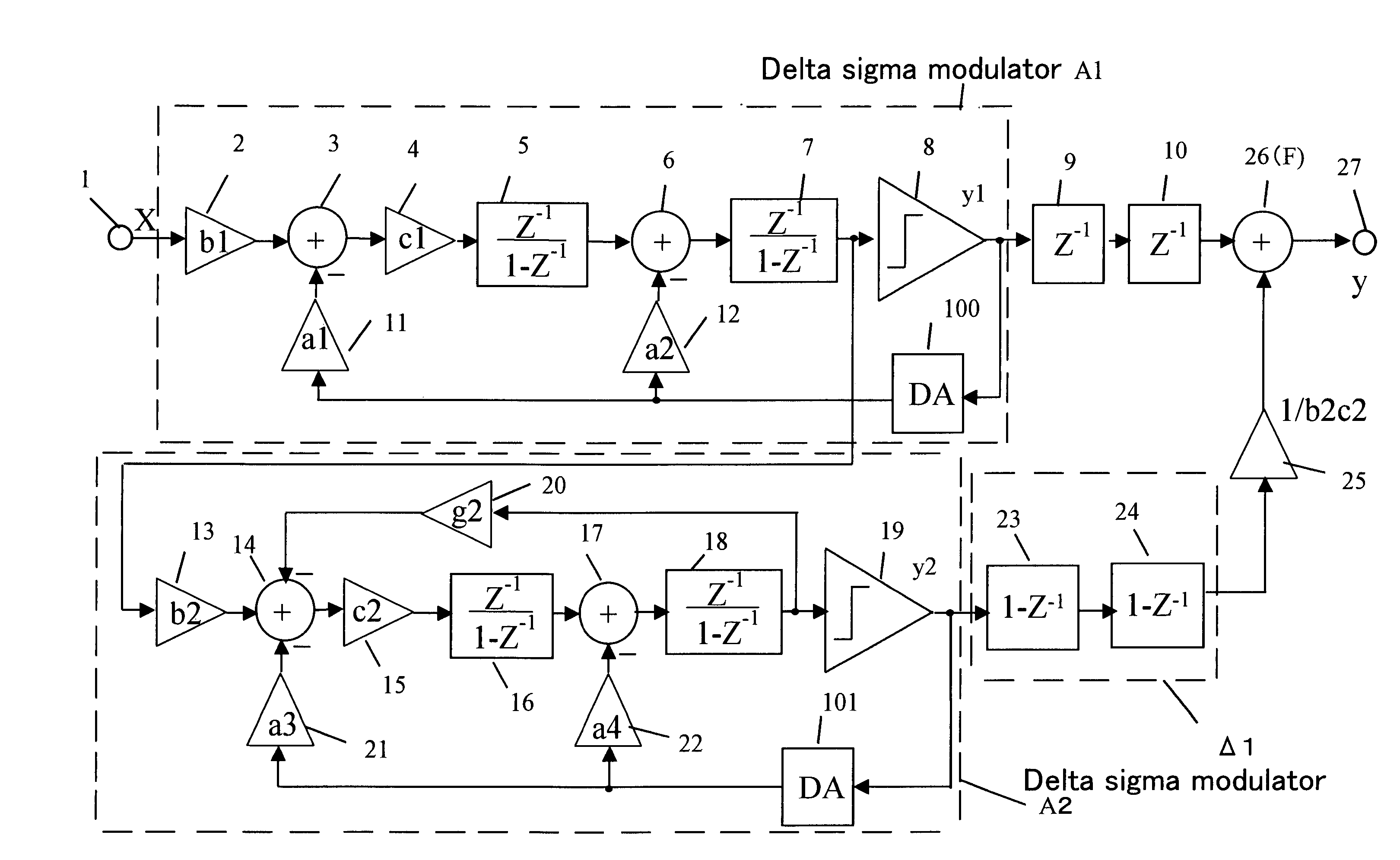
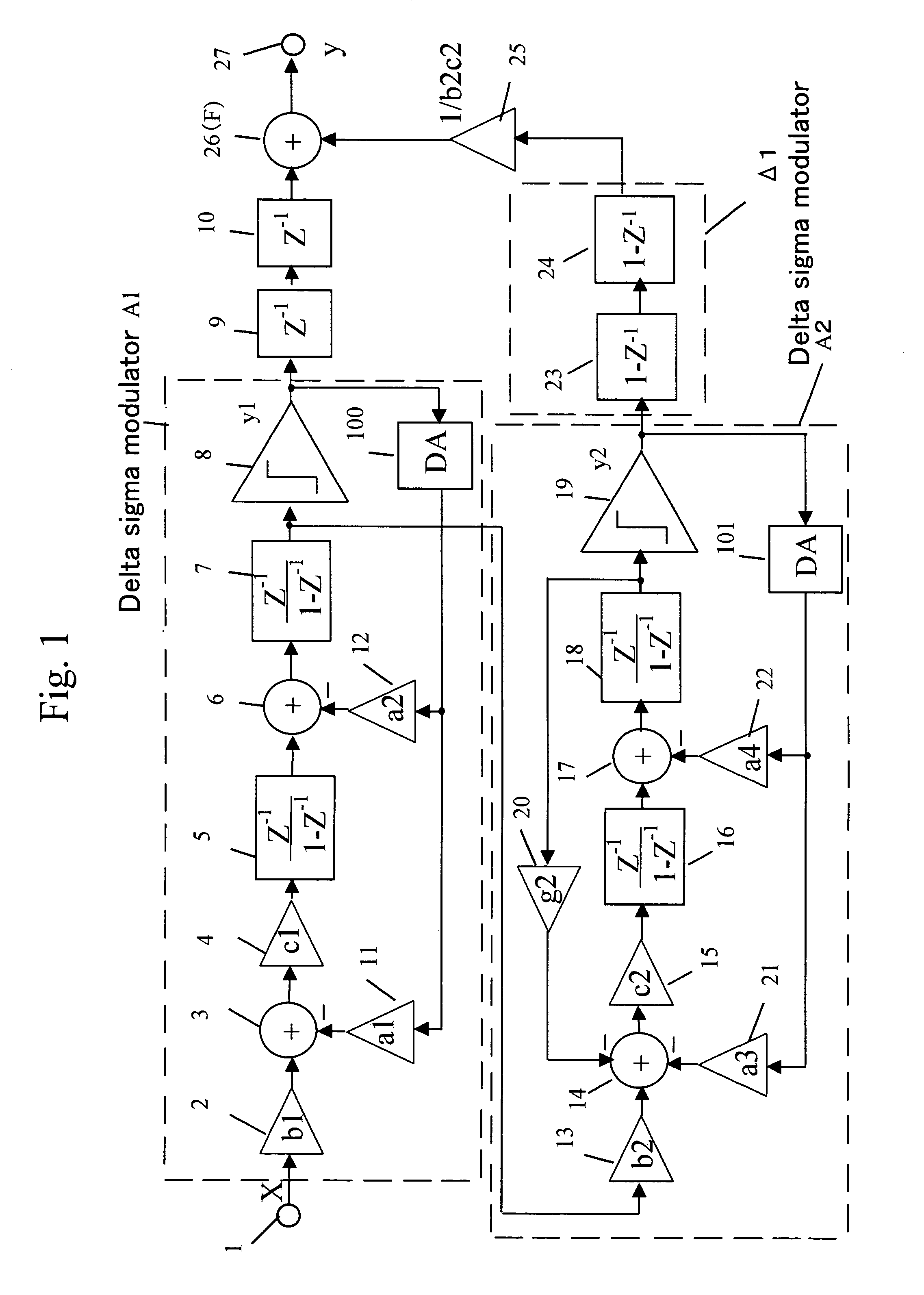
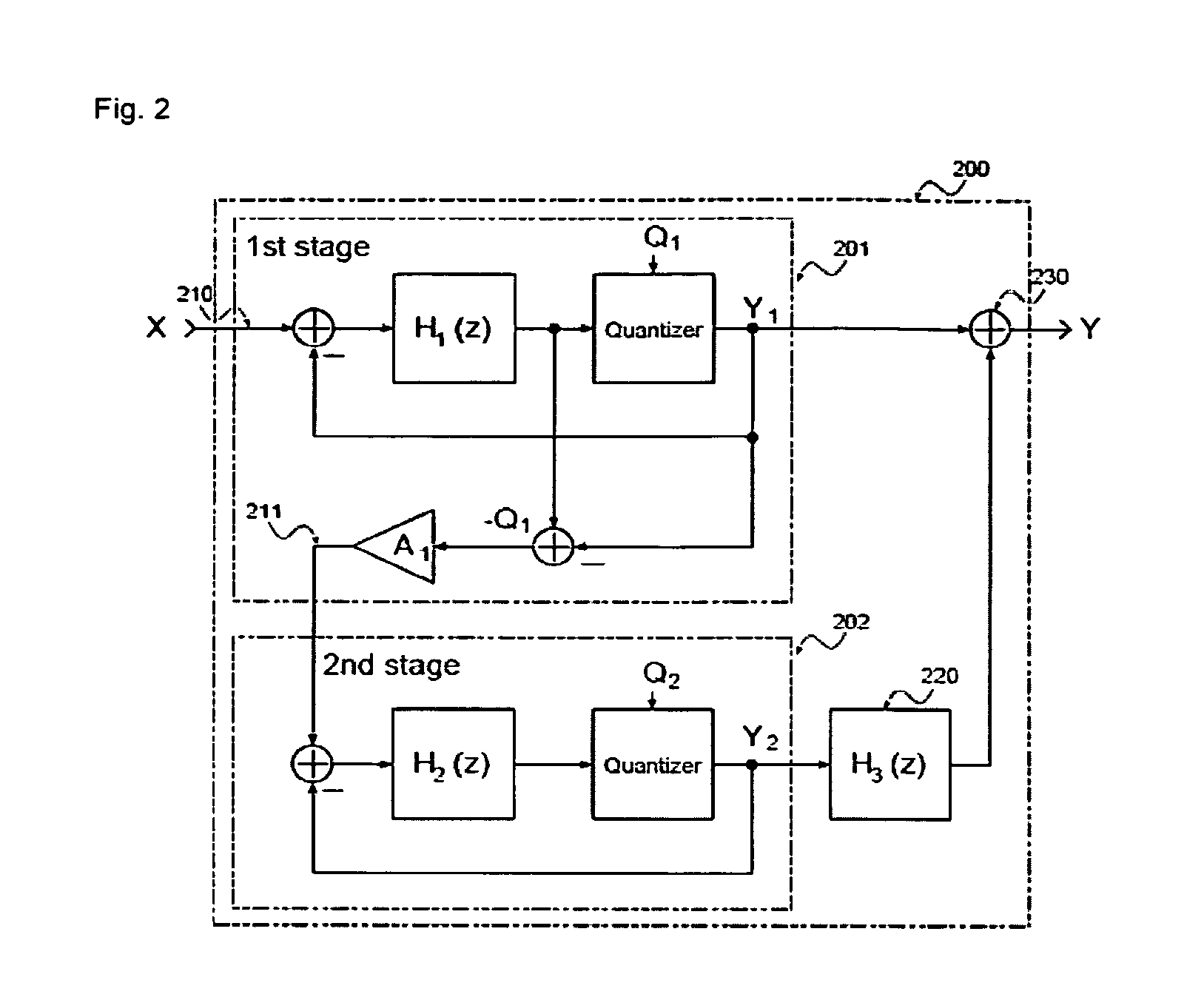
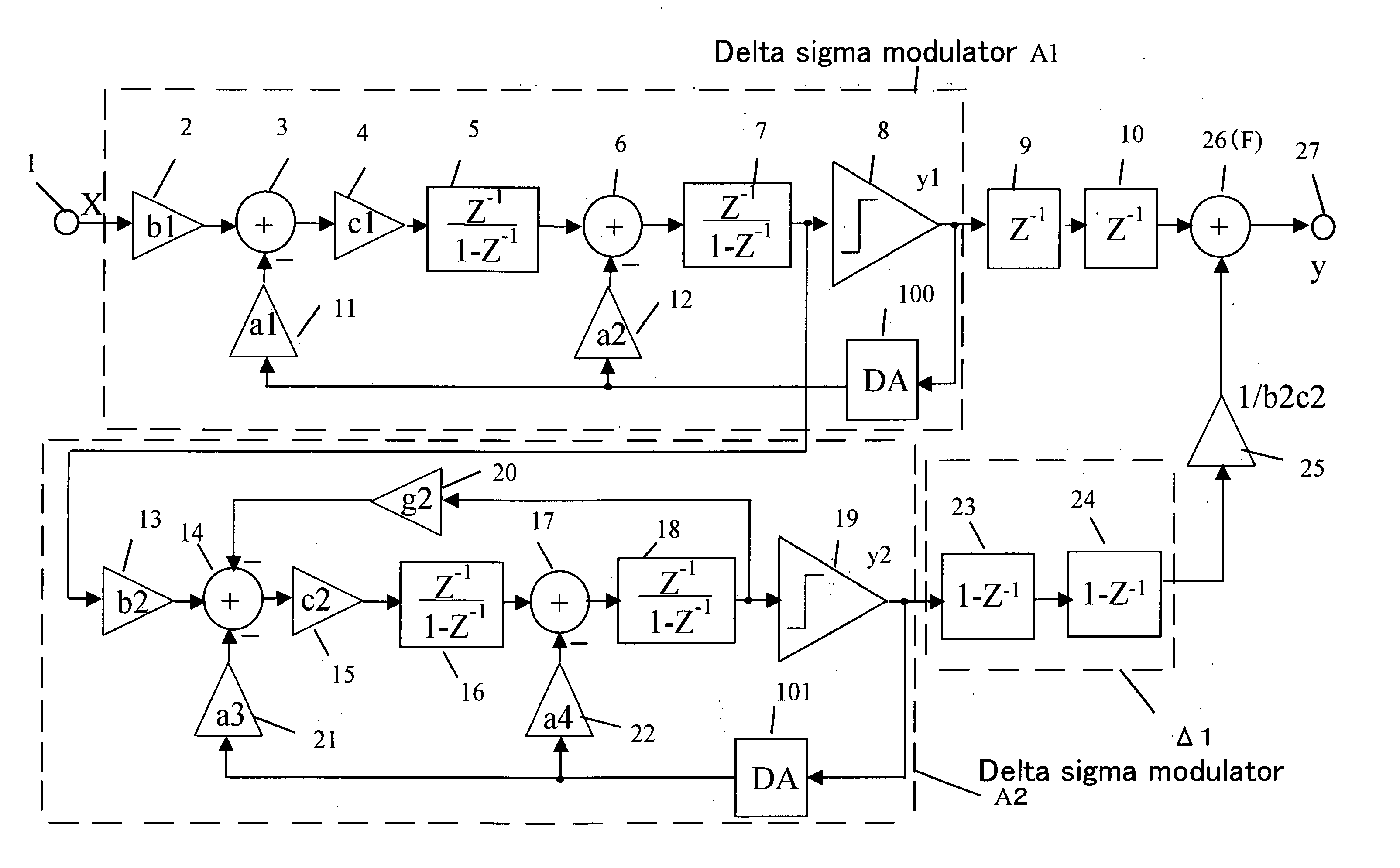
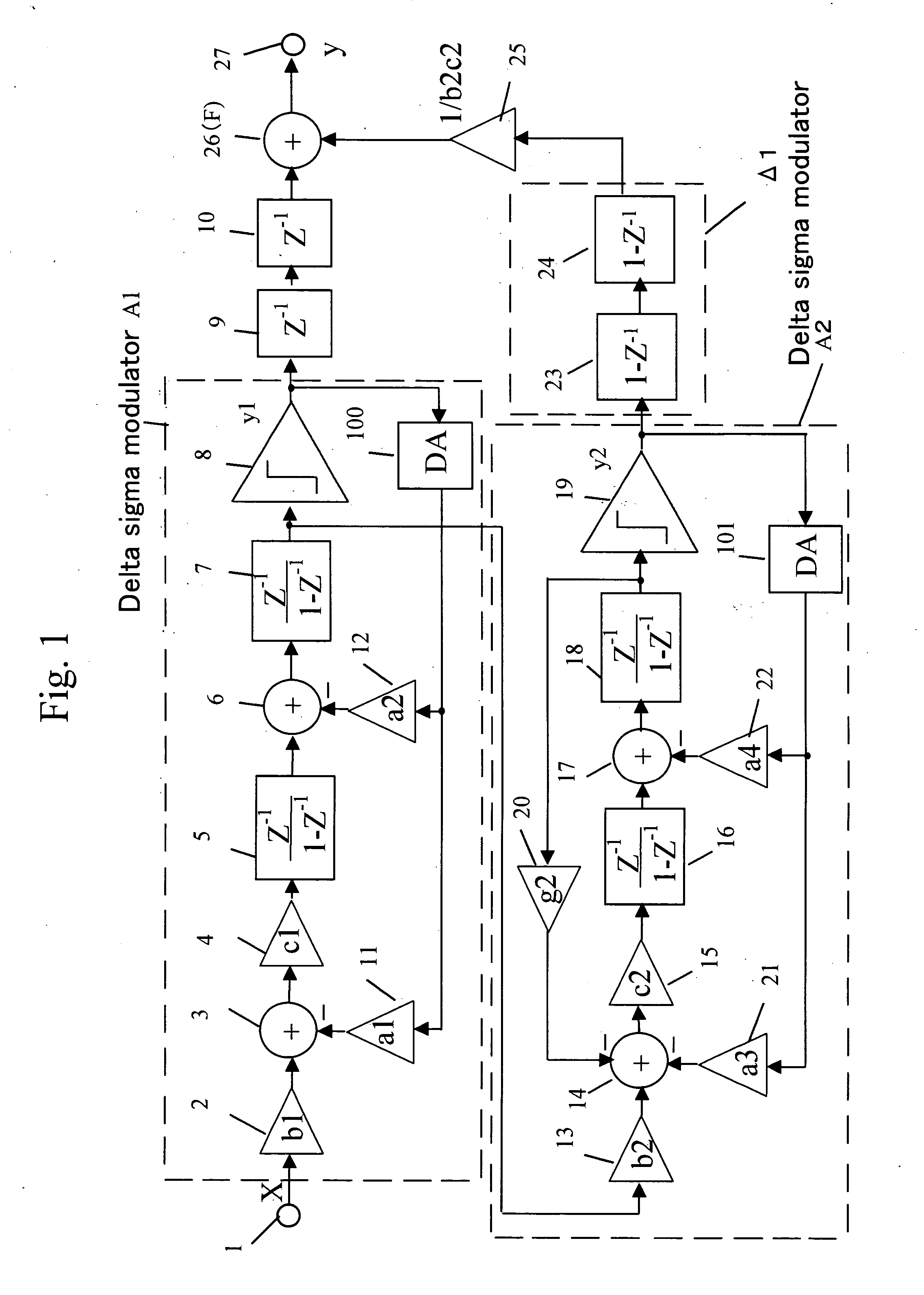
Delta sigma modulating apparatus
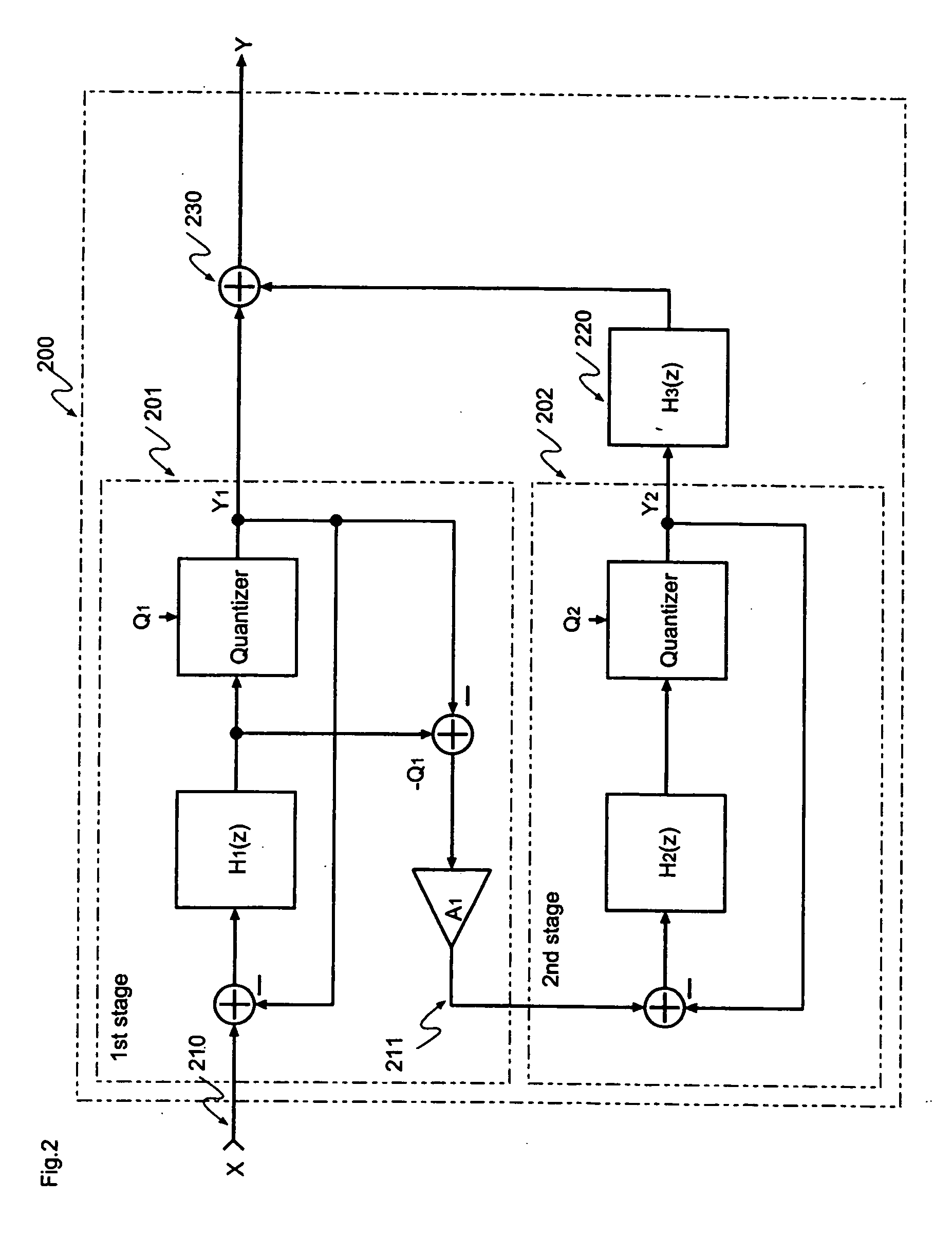
ActiveUS7084797B2Minimize quantization noiseNoise minimizationElectric signal transmission systemsDelta modulationElectrical and Electronics engineering
A first second- or higher-order delta sigma modulator and a second second- or higher-order delta sigma modulator having a notch characteristic are cascaded together, and a delayed signal of the output of the first delta sigma modulator and a differential signal of the output of the second delta sigma modulator are added together. The amount of feedback from the output portion to the input portion of the first delta sigma modulator and the amount of feedback from the output portion to the input portion of the second delta sigma modulator are made the same.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
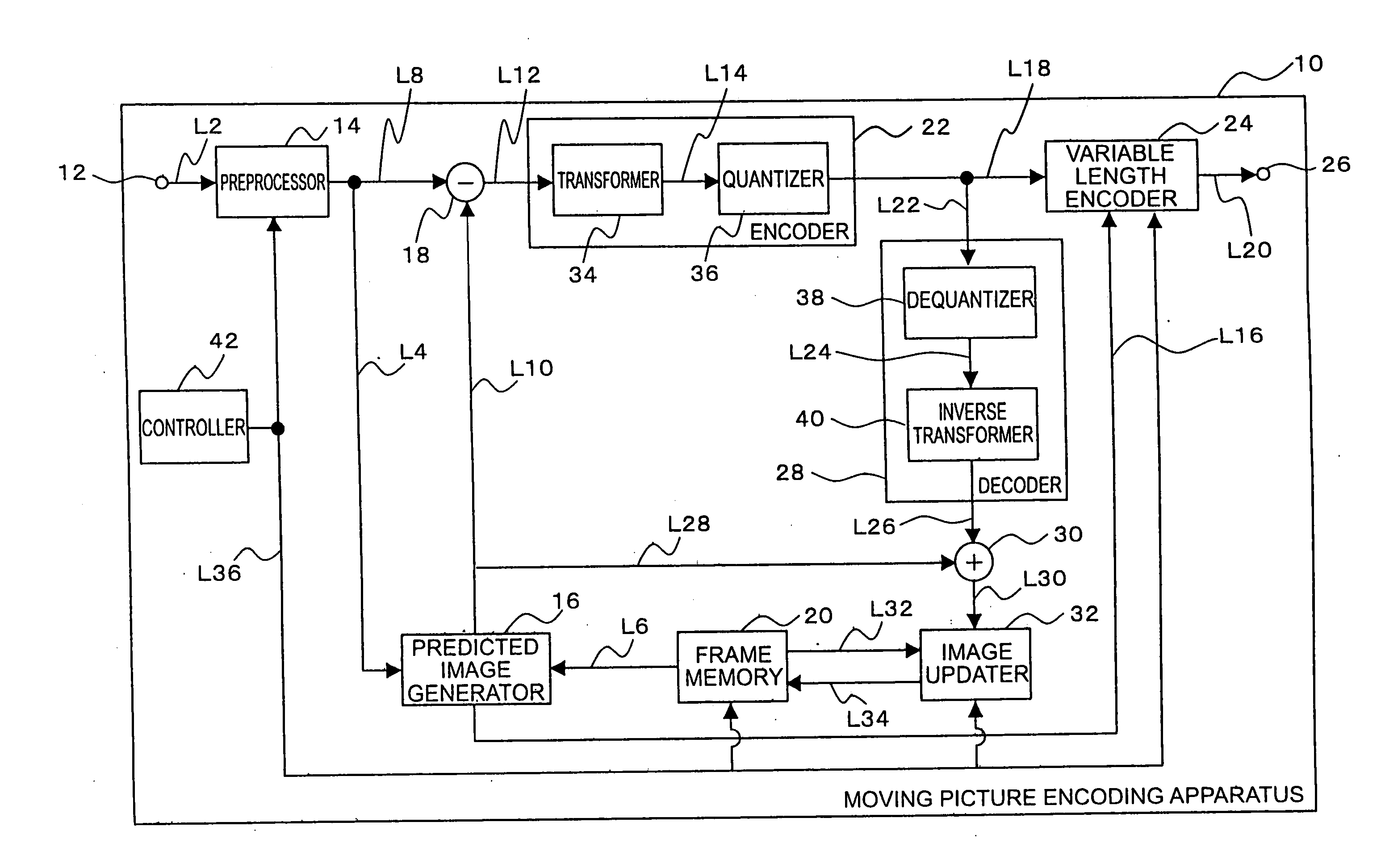
Moving picture encoding apparatus, moving picture encoding method, moving picture encoding program, moving picture decoding apparatus, moving picture decoding method, and moving picture decoding program
InactiveUS20050232500A1Reduce noiseEncoding efficiency can be improvedColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDecoding methodsReference image
In a moving picture encoding apparatus 10, as an embodiment of the present invention, a predicted image generator 16 generates a predicted image with respect to a target image, using a reference image stored in a frame memory 20. A difference image generator 18 performs a difference operation between the target image and the predicted image to generate a difference image. An encoder 22 encodes the difference image to generate an encoded difference signal. A decoder 28 decodes the encoded difference signal to generate a decoded difference image. A reproduced image generator 30 performs a summation of the decoded difference image and the predicted image to generate a reproduced image. An image updater 32 performs a weighted summation of a first image which is one of the reproduced image and the reference image, and a second image which is the other of the reproduced image and the reference image, to generate an updated image. The updated image is stored into the frame memory 20 to be used as a reference image in encoding of another target image.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Transmitter for wireless applications incorporation spectral emission shaping sigma delta modulator
ActiveUS7787563B2Sufficient attenuationDesired noise shapingAnalogue conversionSecret communicationSpectral emissionFrequency spectrum
A transmitter employing a sigma delta modulator having a noise transfer function adapted to shift quantization noise outside at least one frequency band of interest. A technique is presented to synthesize the controllers within a single-loop sigma delta modulator such that the noise transfer function can be chosen arbitrarily from a family of functions satisfying certain conditions. Using the novel modulator design technique, polar and Cartesian (i.e. quadrature) transmitter structures are supported. A transmitter employing polar transmit modulation is presented that shapes the spectral emissions of the digitally-controlled power amplifier such that they are significantly and sufficiently attenuated in one or more desired frequency bands. Similarly, a transmitter employing Cartesian transmit modulation is presented that shapes the spectral emissions of a hybrid power amplifier such that they are significantly and sufficiently attenuated in one or more desired frequency bands.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Digital/analogue conversion apparatus
InactiveUS20130156231A1Reduce quantization noiseImprove noiseTransversal filtersDigitally weighted transducing elementsImage resolutionAnalog signal
A digital / analog conversion apparatus to convert a digital signal into an analog signal. The digital / analog conversion apparatus can generate a high-quality analog signal, even when elements configuring the digital / analog conversion apparatus have variance, with high resolution and a small circuit size. The data conversion apparatus is provided with a first data converter to reduce the number of bits of an input signal, a second data converter to convert the format of the first output signal, and a third data converter for conversion into a code which corresponds to the history of the output from the second data converter.
Owner:TRIGENCE SEMICONDUCTOR INC
Fractional divider and fractional frequency-division phase locked loop
The invention discloses a fractional divider. The fractional divider comprises a conversion module, a phase selection module, a variable integer frequency division module and a D trigger, wherein the conversion module is used for generating a phase selection value and an integer frequency division value according to a fractional frequency division parameter; the phase selection module is used for selecting a phase clock corresponding to the phase selection value from M+1 equiphase clocks and transmitting the selected phase clock to the CK end of the D trigger; the variable integer frequency division module is used for transmitting a signal obtained by performing integer frequency division on a reference phase clock signal in the M+1 equiphase clocks to the D end of the D trigger according to the integer frequency division value; and the D trigger is used for generating a fractional frequency division signal from the Q end of the D trigger according to signals input at the CK end and the D end of the D trigger. Compared with a conventional technology for realizing the fractional frequency-division phase locked loop, the fractional divider has the advantages that quantization noise is not introduced, and the periodic jitter is relatively small.
Owner:SHANGHAI SUNPLUS TECH
Delta sigma modulating apparatus
ActiveUS20050088327A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioLow costElectric signal transmission systemsDelta modulationEngineeringGreek letter sigma
A first second- or higher-order delta sigma modulator and a second second- or higher-order delta sigma modulator having a notch characteristic are cascaded together, and a delayed signal of the output of the first delta sigma modulator and a differential signal of the output of the second delta sigma modulator are added together. The amount of feedback from the output portion to the input portion of the first delta sigma modulator and the amount of feedback from the output portion to the input portion of the second delta sigma modulator are made the same.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
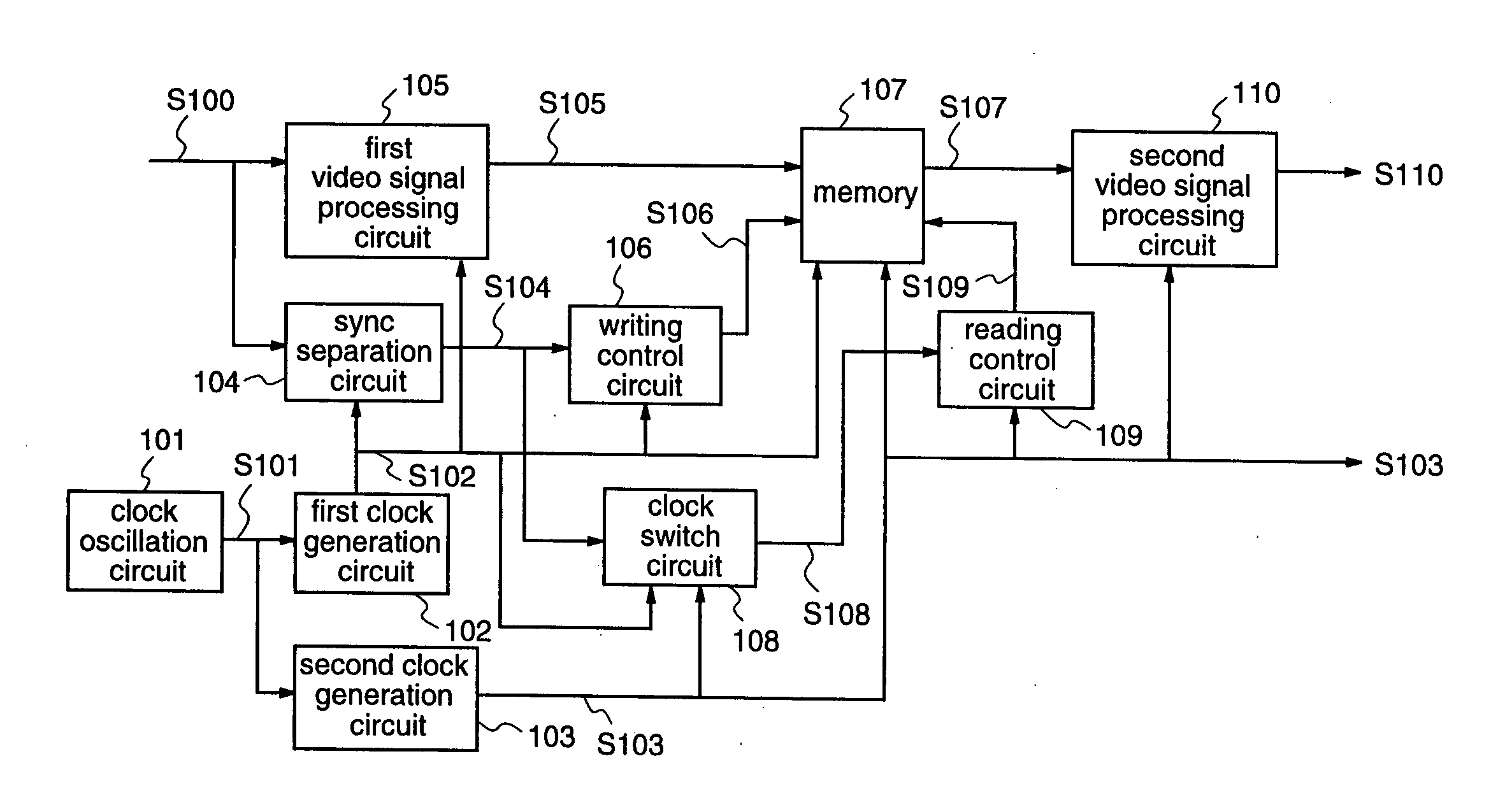
Video signal processing apparatus
InactiveUS20060187349A1Reduce quantization noisePromote generationTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsImage resolutionVideo processing
A video signal processing apparatus is provided with a first clock generation circuit for generating a first clock synchronized with an input signal; a second clock generation circuit for receiving a set value to be a reference of an output frequency, adding the set value for every reference clock, extracting data according to the cumulative value, converting the data into an analog signal, reducing quantization noise, and multiplying the analog signal, thereby to obtain a second clock; and a clock switch circuit for generating a sync signal that is switched to the second clock, by using a sync signal generated with the first clock; and video signal processing is carried out using the second clock that is generated according to the resolution of a pixel display.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com