Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
224results about "Differential modulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
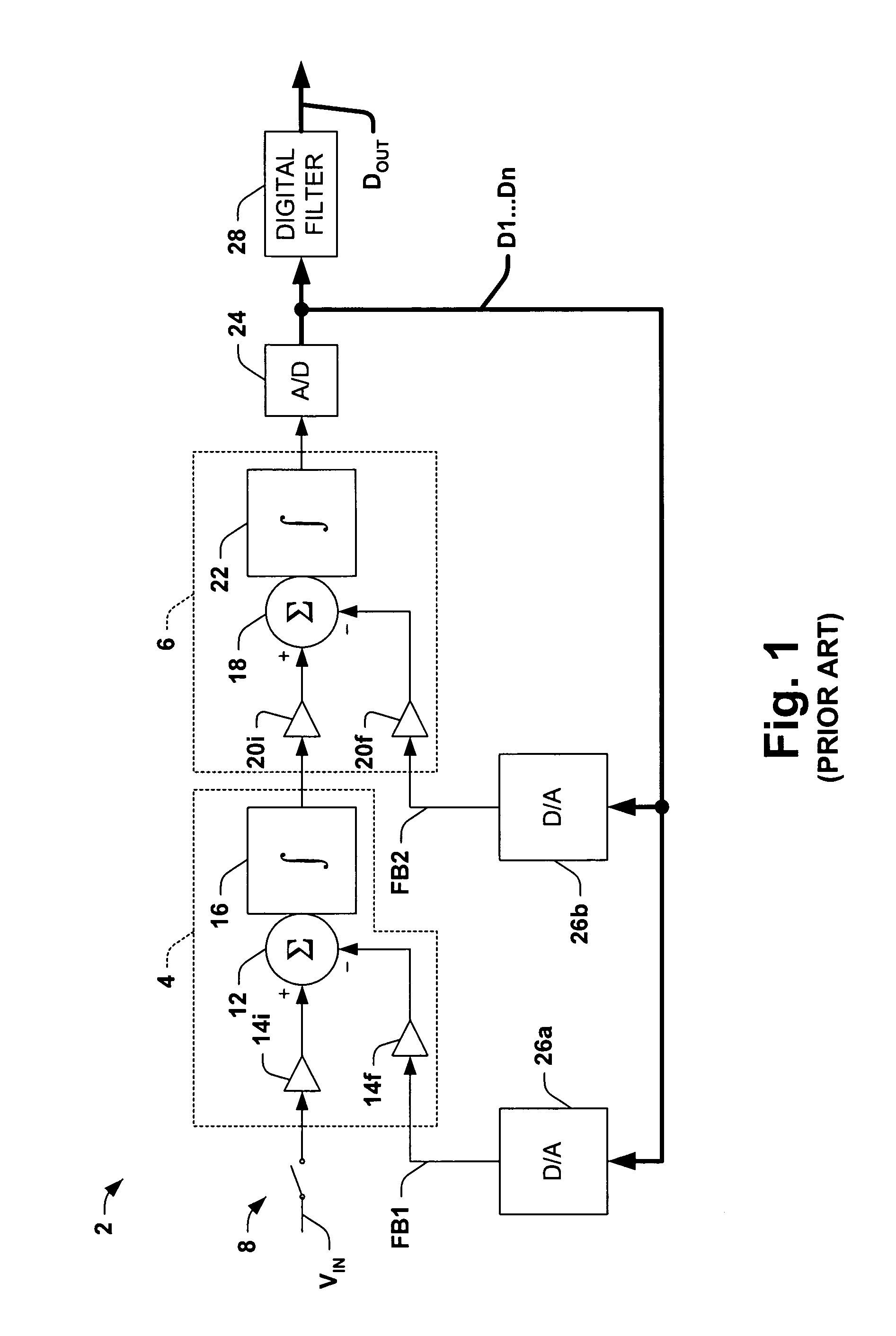
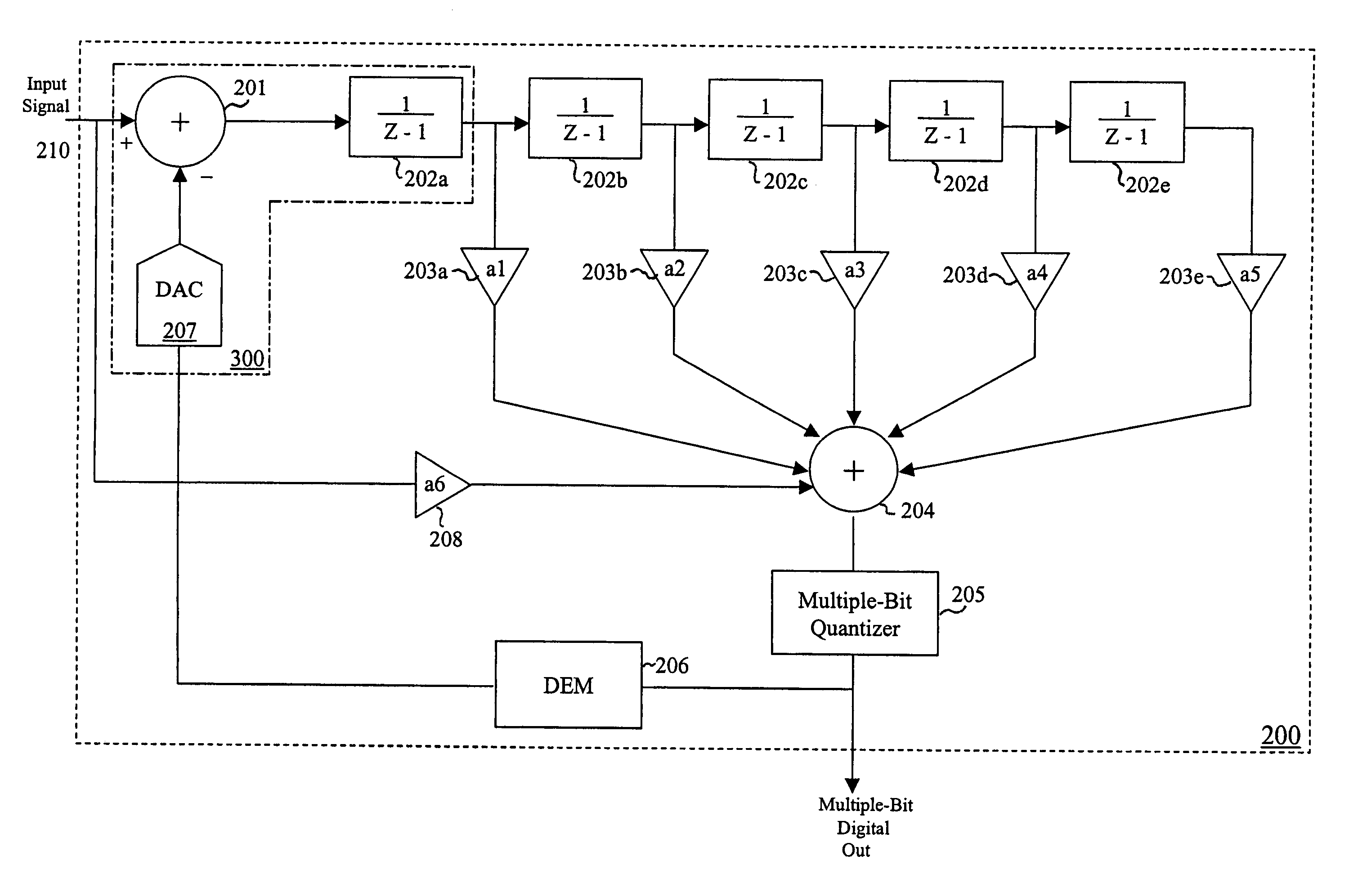
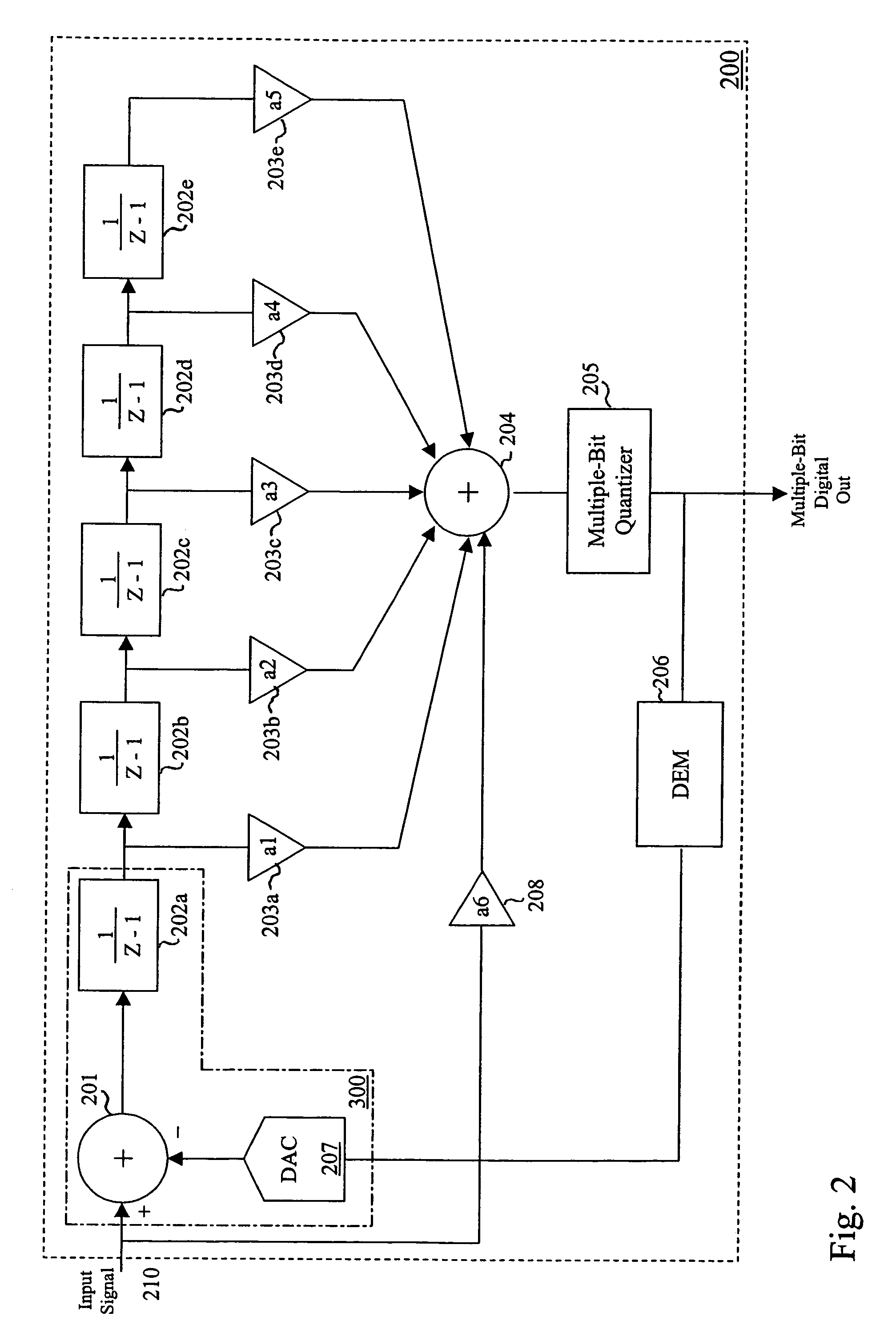
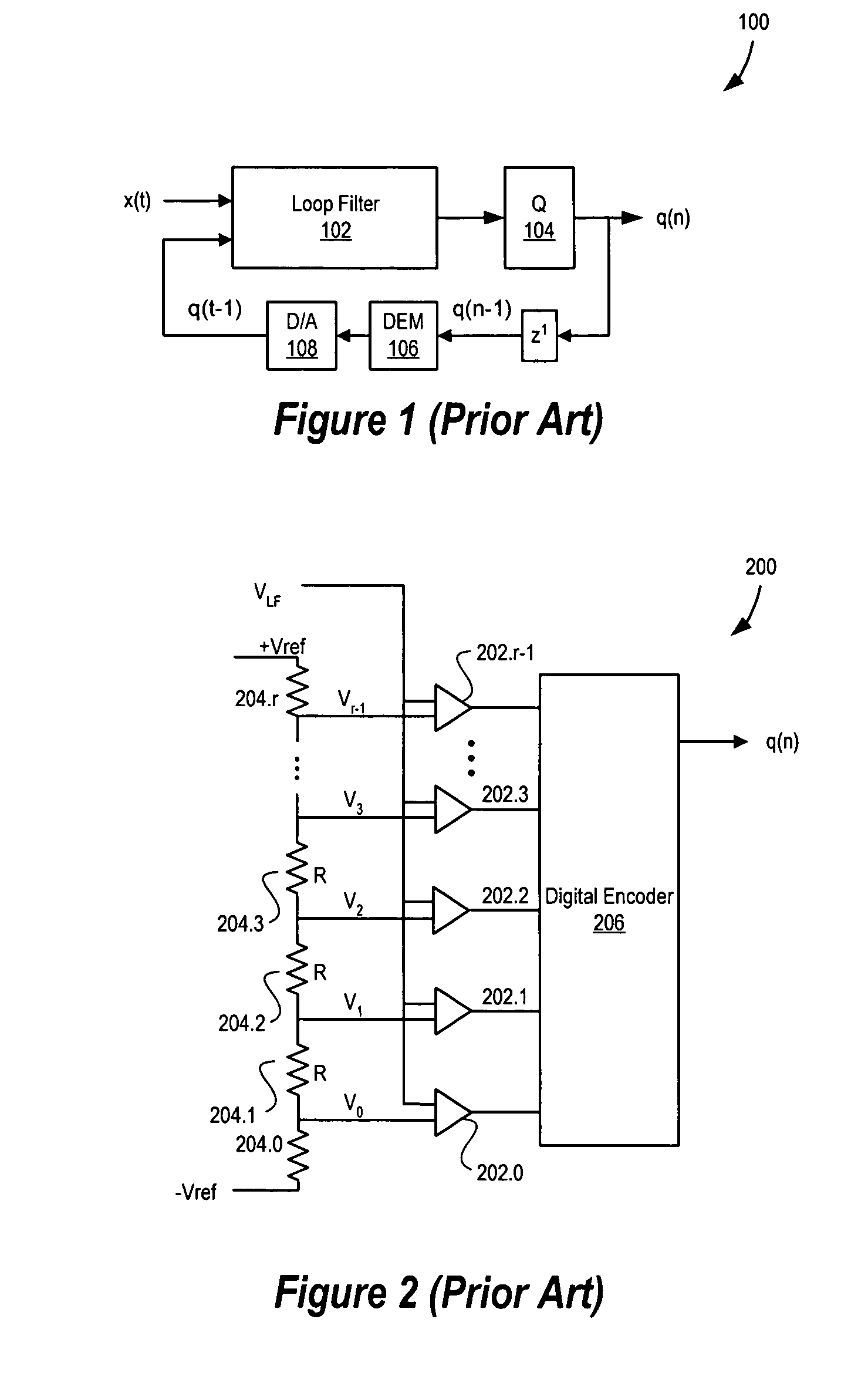
Delta-sigma A/D converter
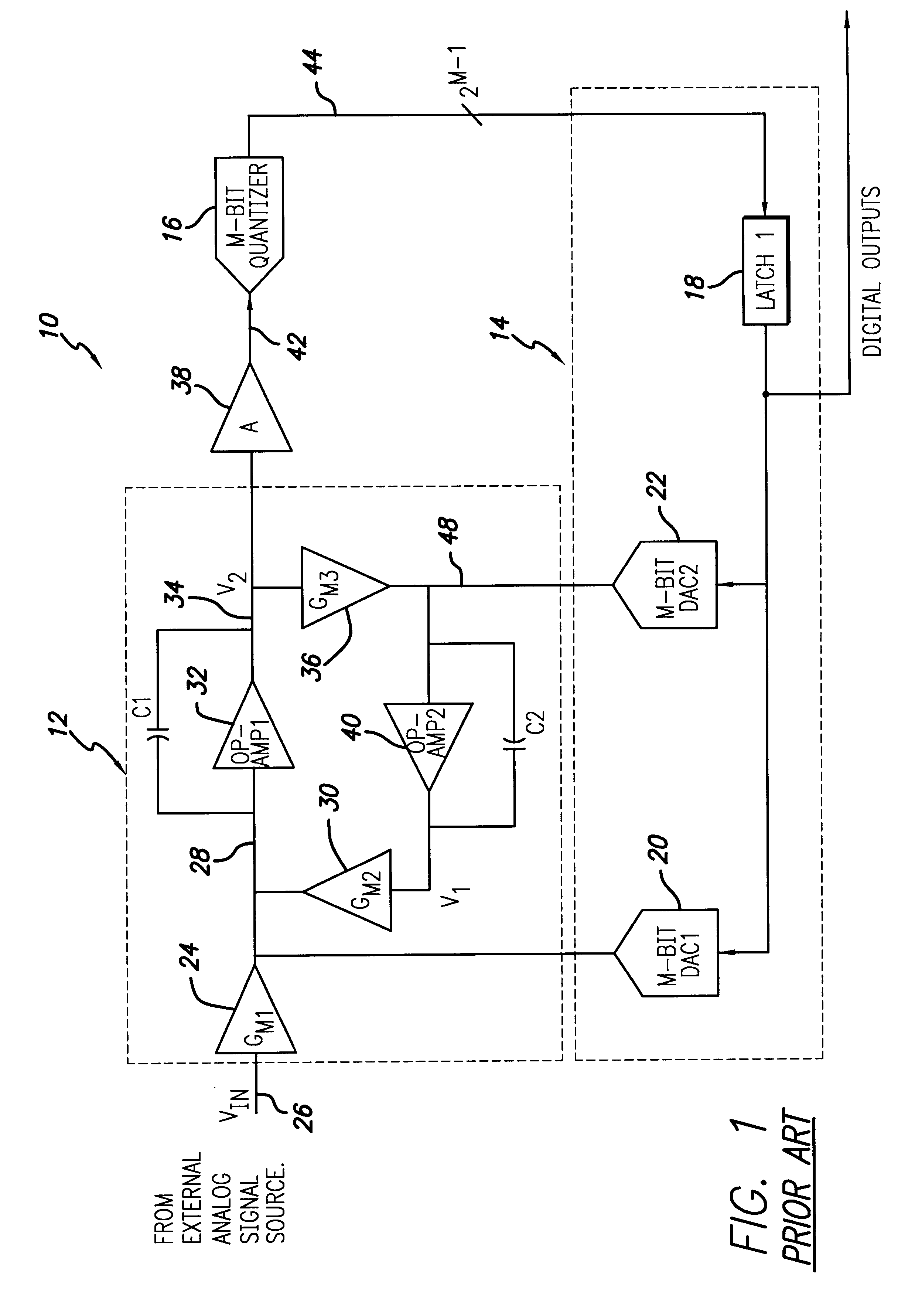
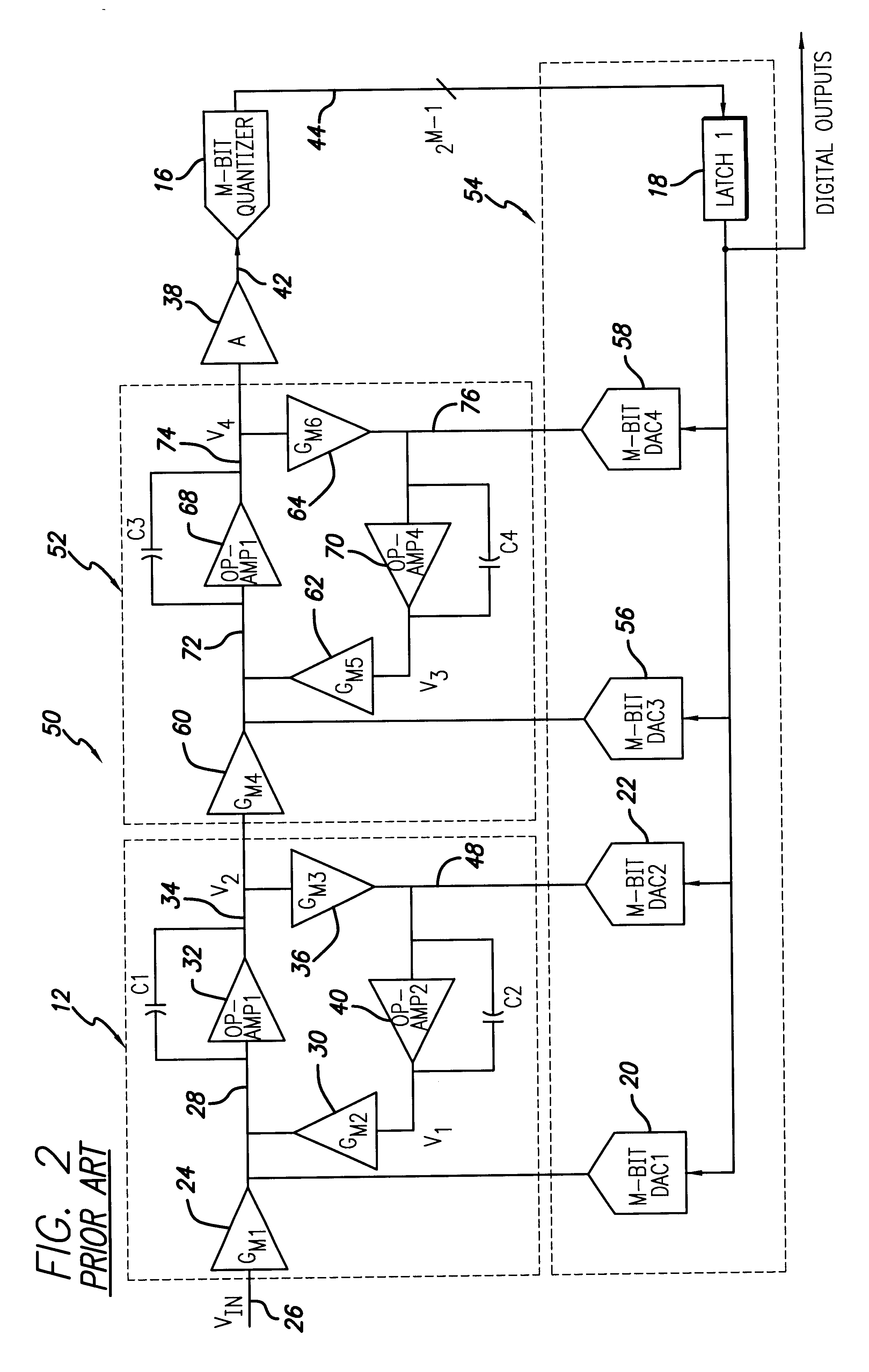
InactiveUS6271782B1Without compromising the modulator's stabilityTo overcome the large delayElectric signal transmission systemsDifferential modulationLoop filterAnalog feedback
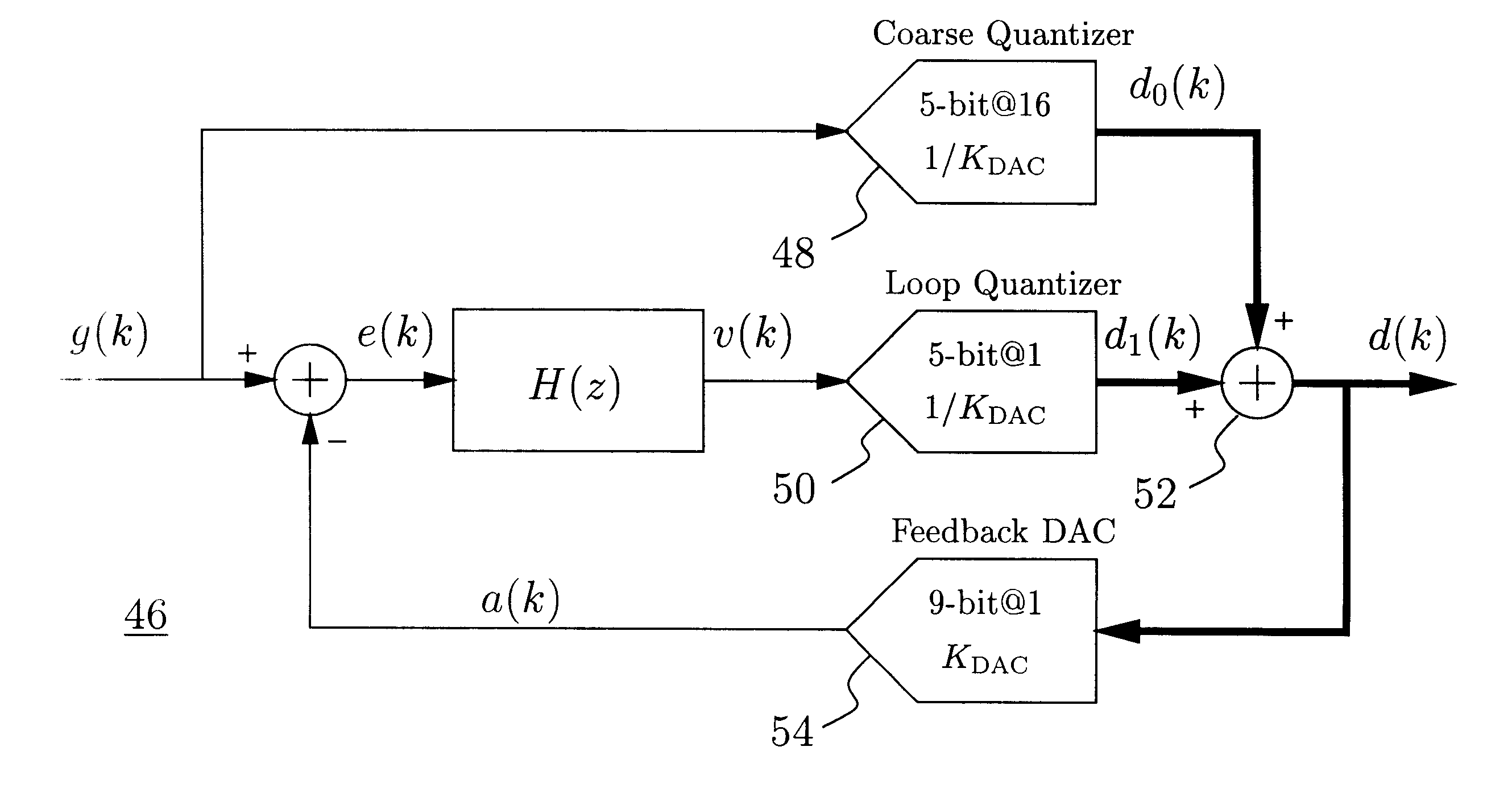
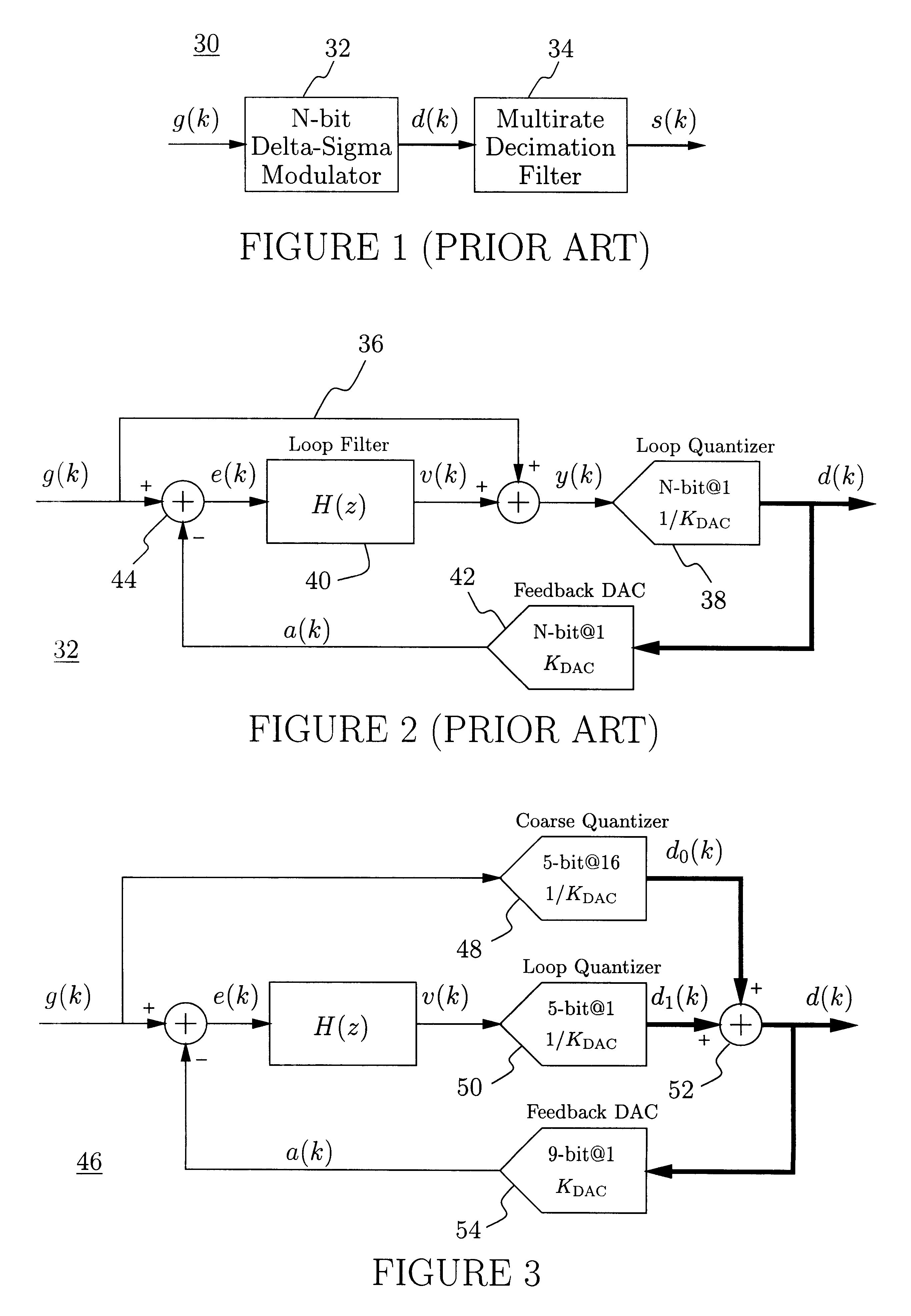
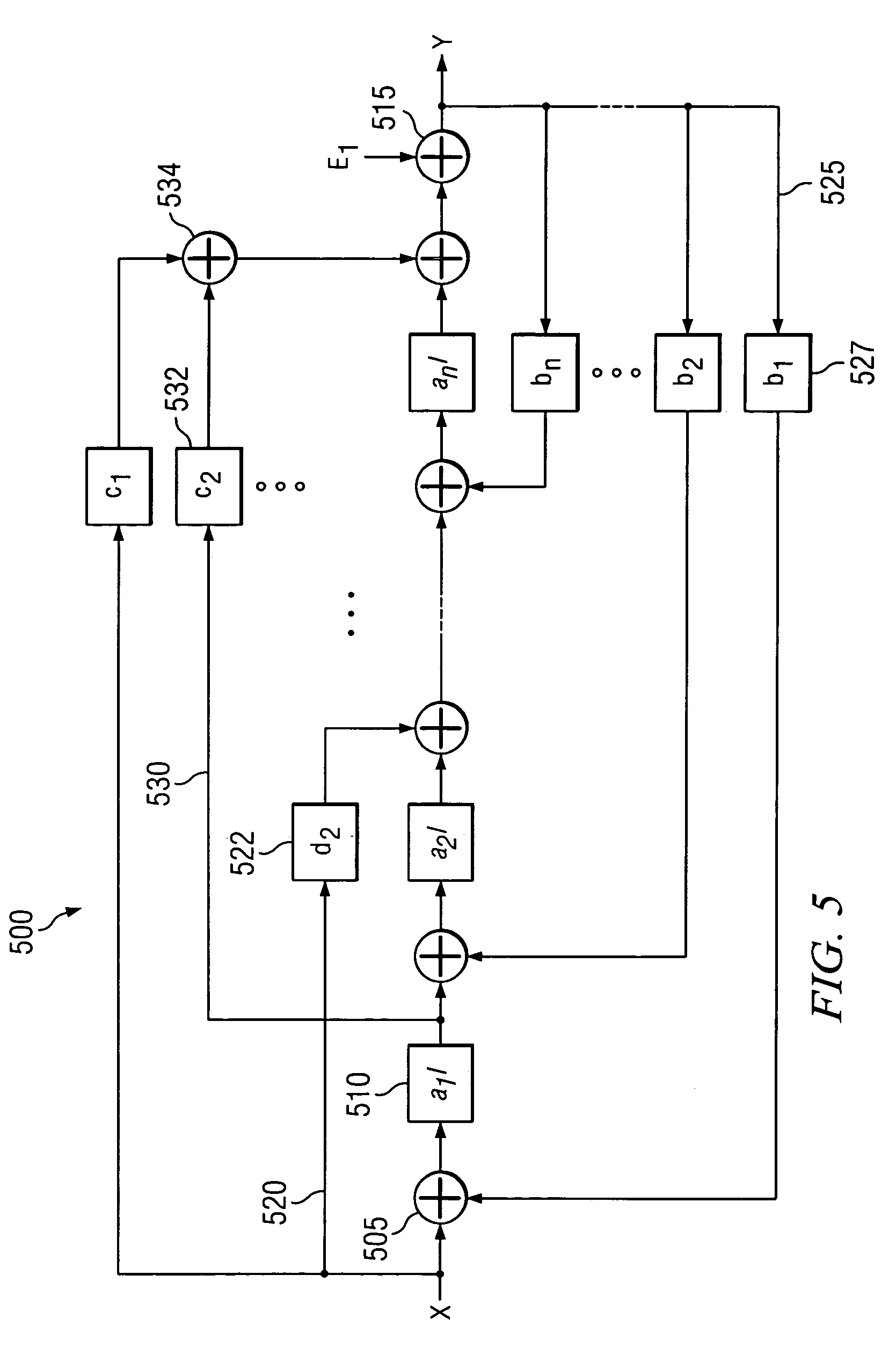
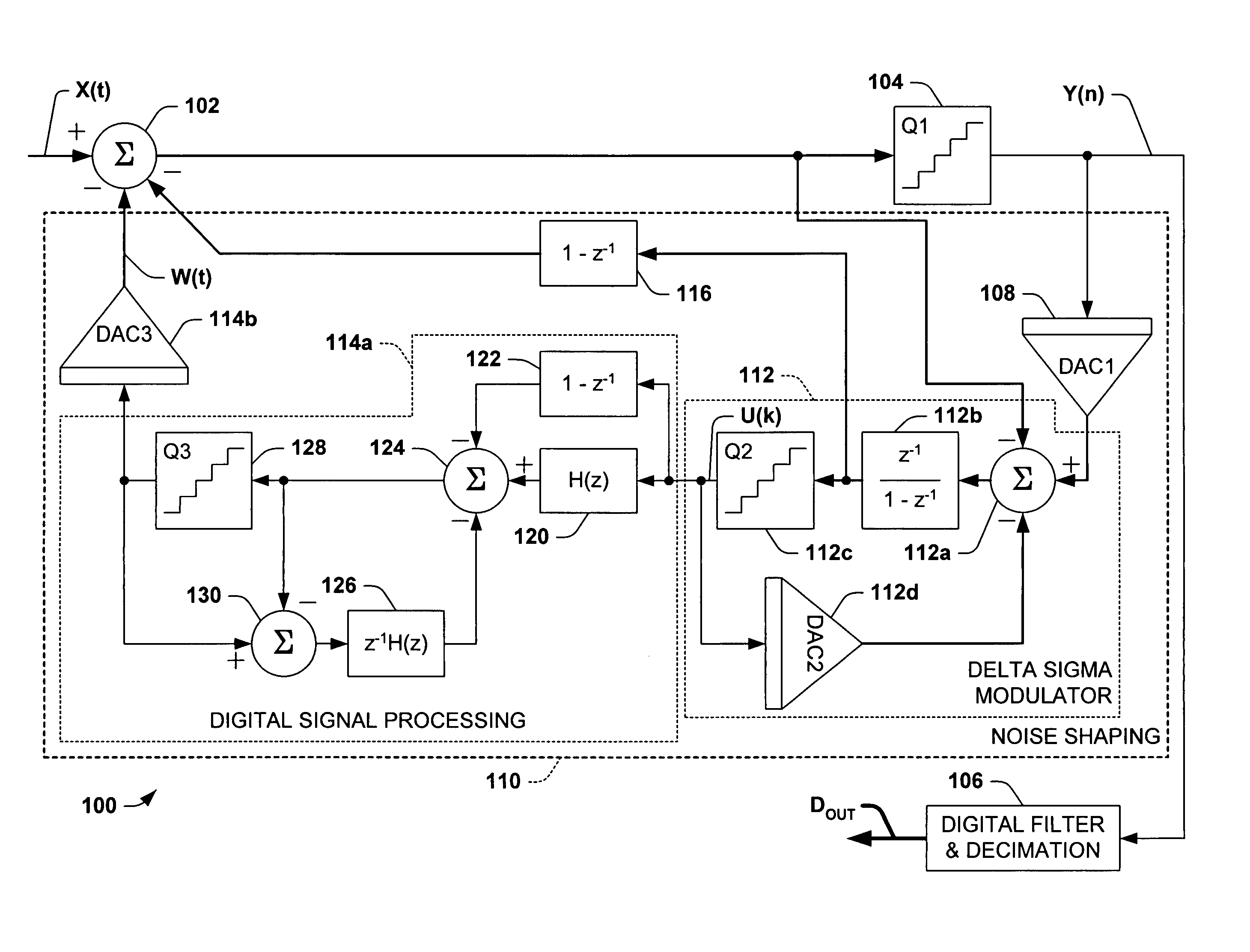
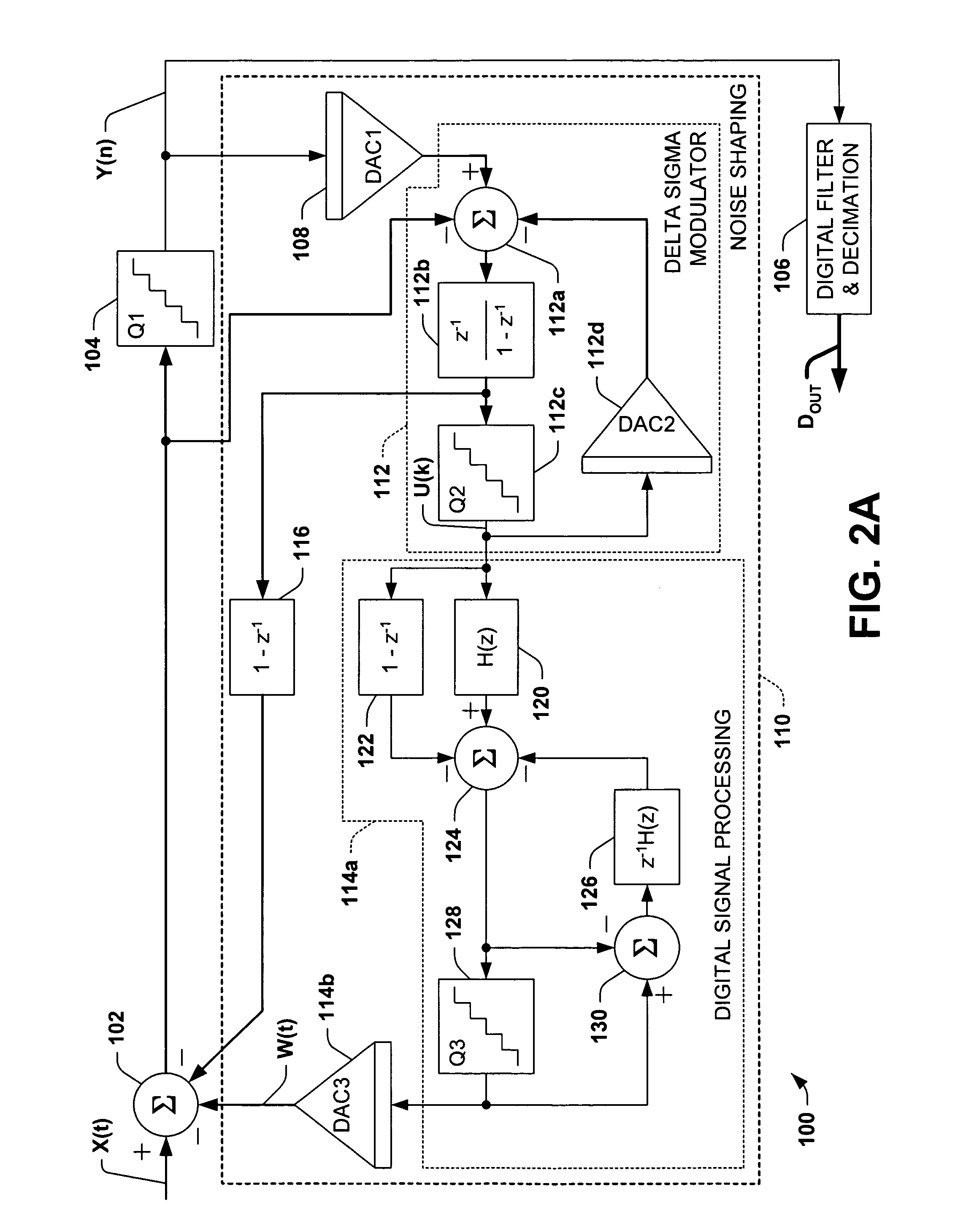
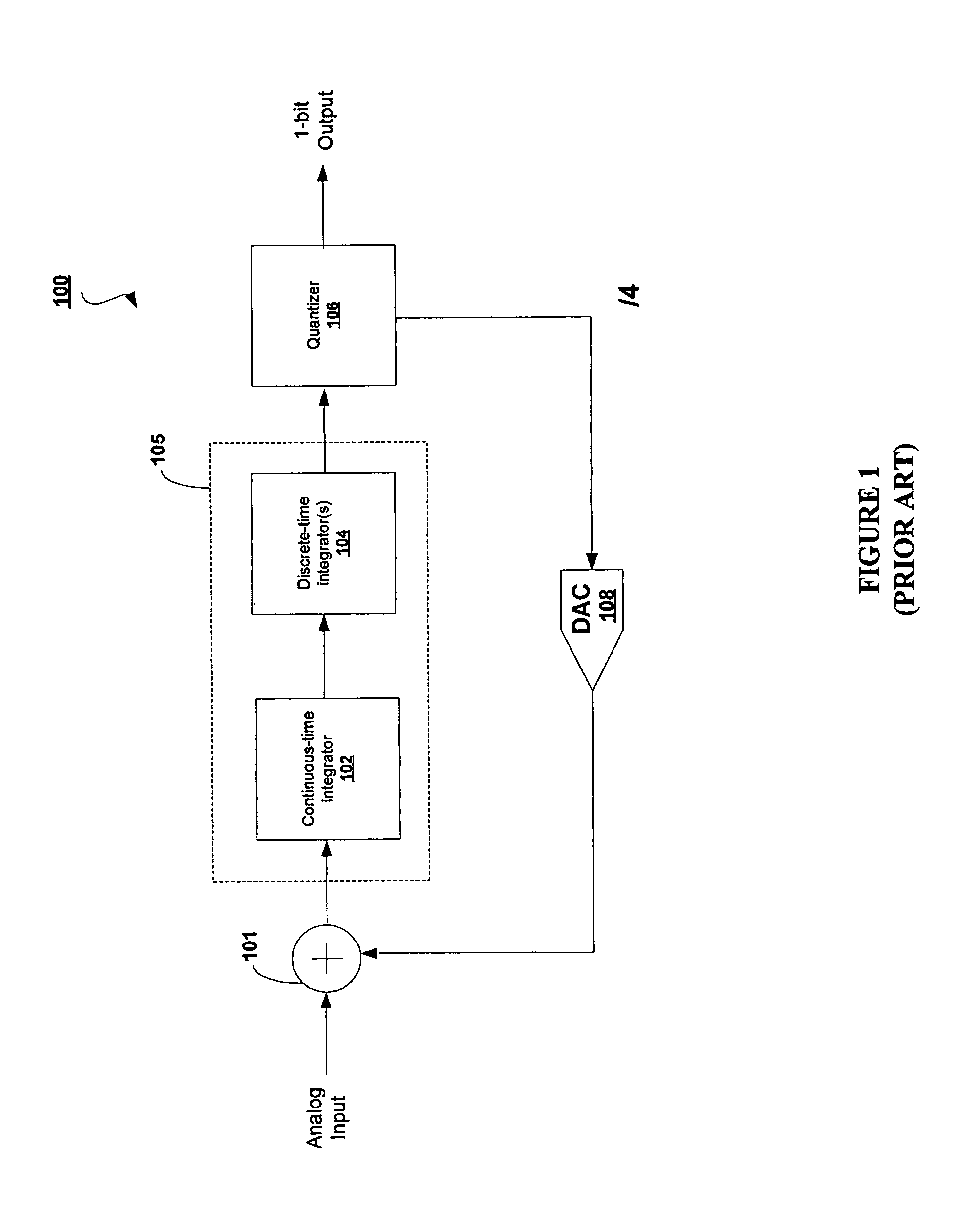
A delta-sigma modulator comprising a first quantizer providing a first digital signal d0(k) representing the input signal g(t); a loop filter with input signal paths; a loop quantizer providing a corrective digital signal d1(k) representing the loop filter's output signal y(t); an array of feedback DACs D / A converting the sum d(k)=df(k)=d0(k)+d1(k) of the first and the corrective digital signals and injecting feedback signals into the loop filter.The loop filter's input node is applied the difference of the input signal g(t) and the global analog feedback signal a3(t). The global feedback signal a3(t) is delayed several clock cycles with respect to the digital output signal d(k). The delay is used to carry out mismatch-shaping and deglitching algorithms in the feedback DACs. The feedback DACs' different delays and gain coefficients are designed such that the modulator is stable. The filter's input signal paths and the compensating DAC are designed such that the gain from the input signal g(t) to the loop quantizer is small, ideally zero. Thus, the loop quantizer's resolving range can be a fraction of the first quantizer's resolving range, whereby the output signal's d(k) resolution can be much higher than the individual resolutions of d0(k) and d1(k).The delta-sigma modulator is well suited for the implementation of high-resolution wide-bandwidth A / D converters. Important applications include digital communication systems.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES BV
Residue-compensating A/D converter
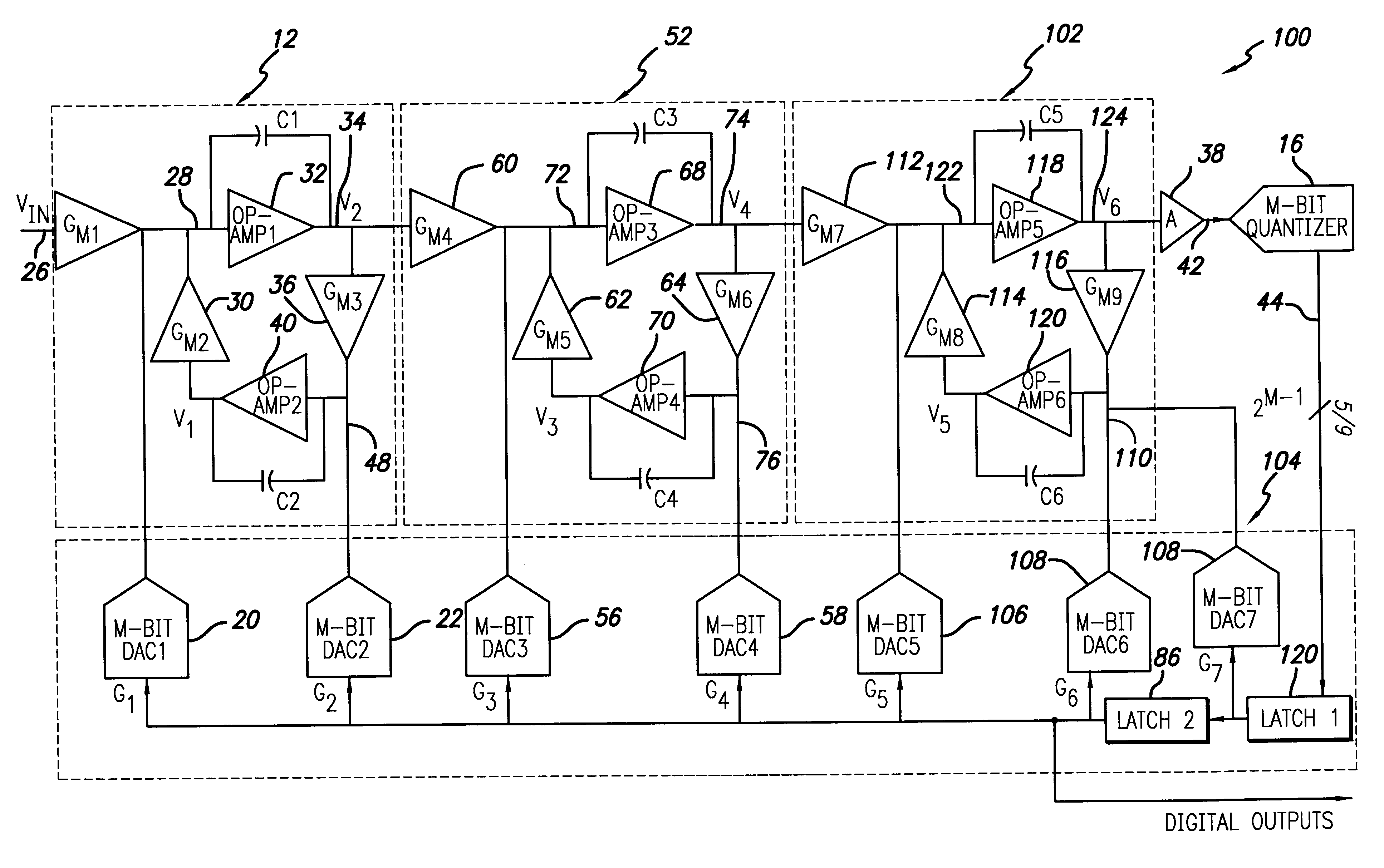
InactiveUS6556158B2Low-cost highly-linearSuitable for useElectric signal transmission systemsDifferential modulationModem deviceFrequency spectrum
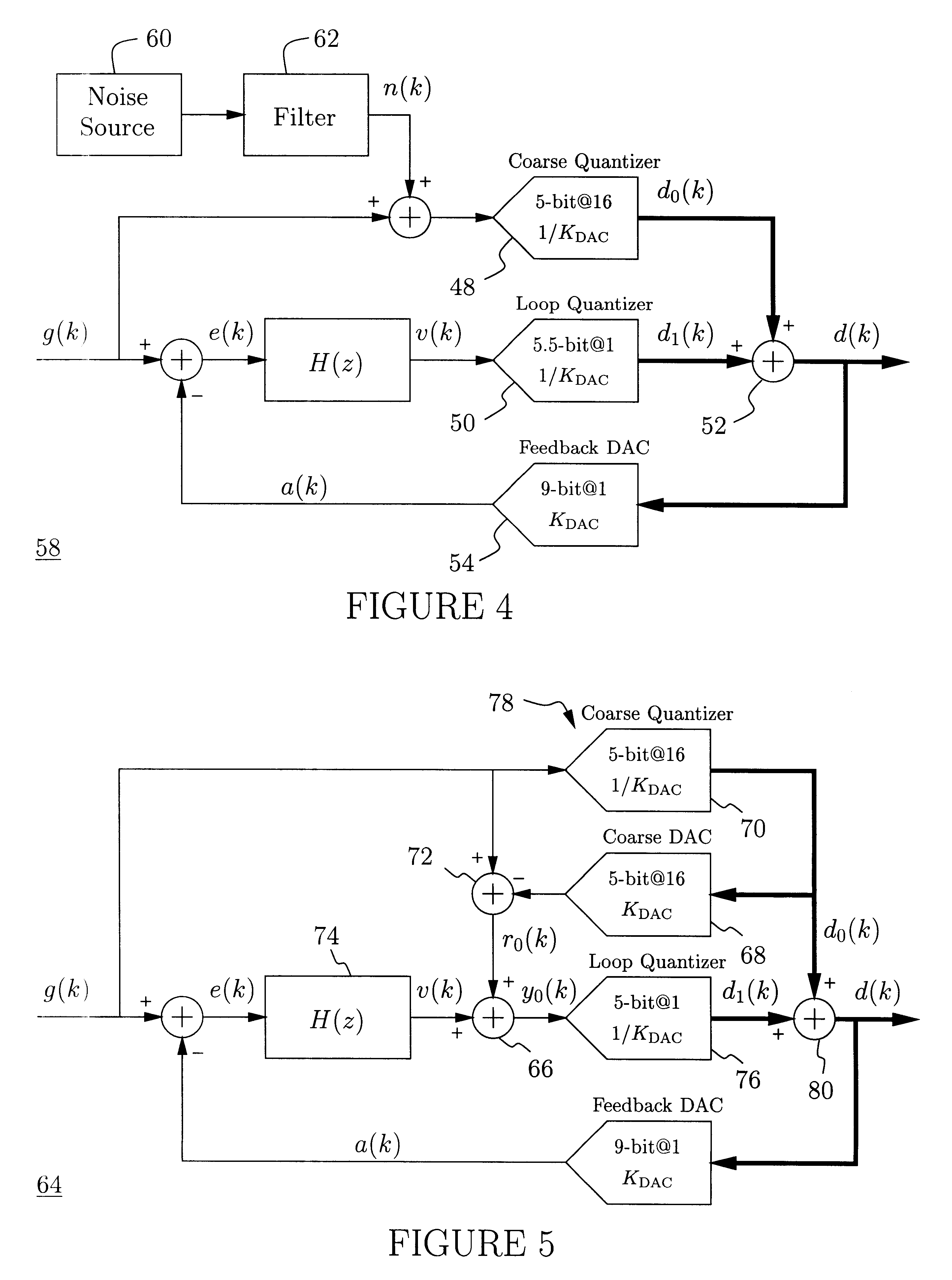
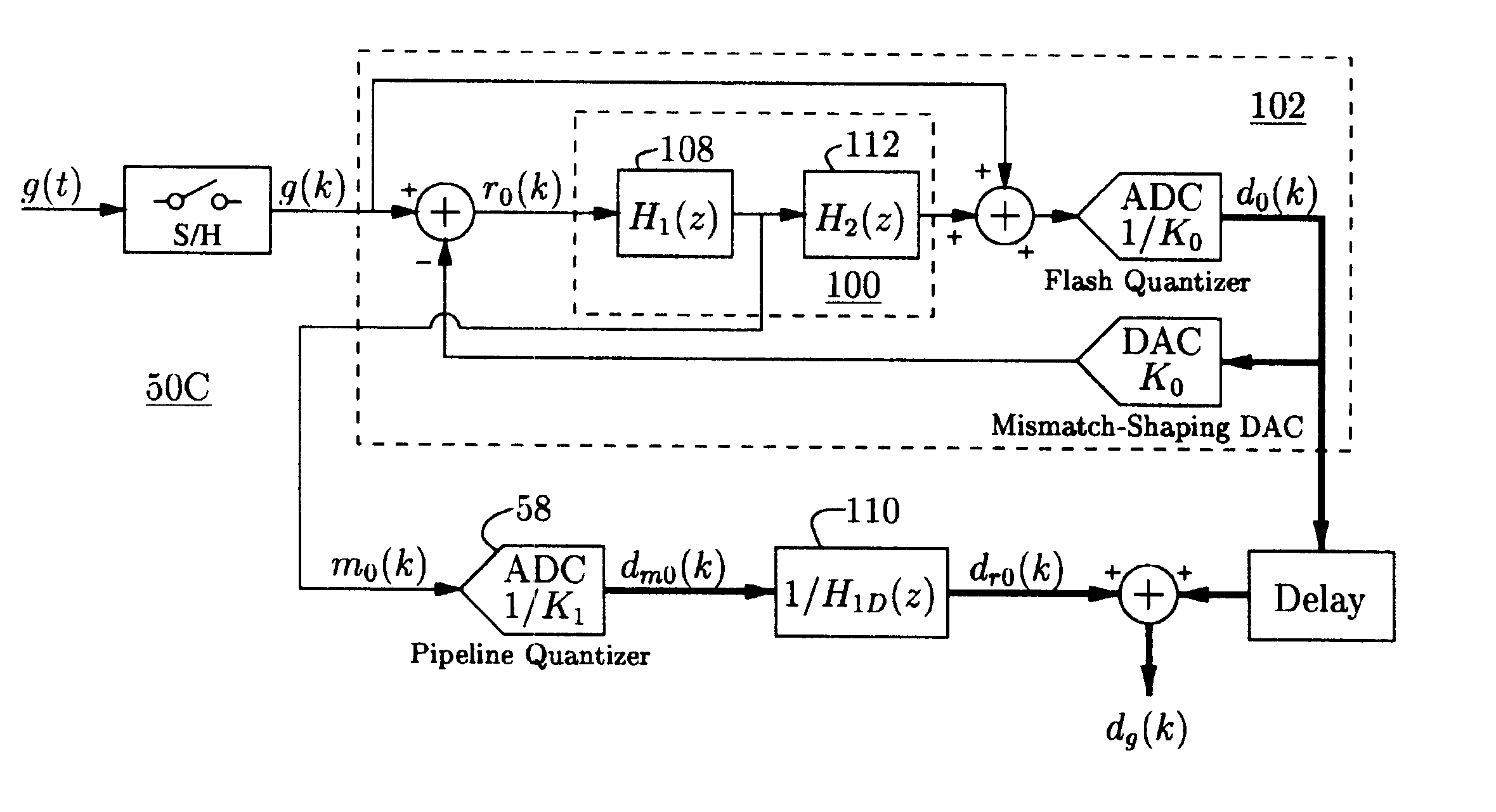
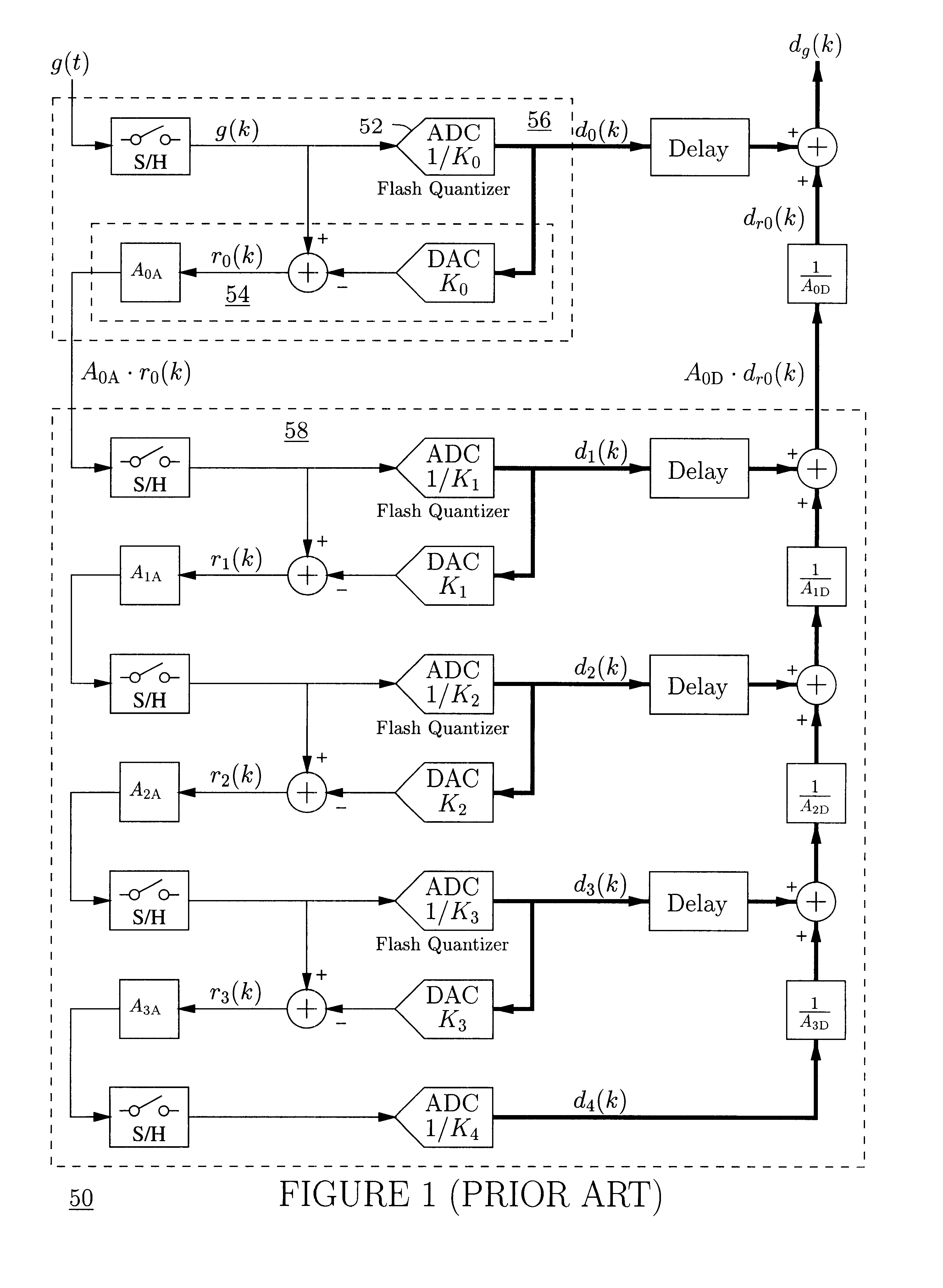
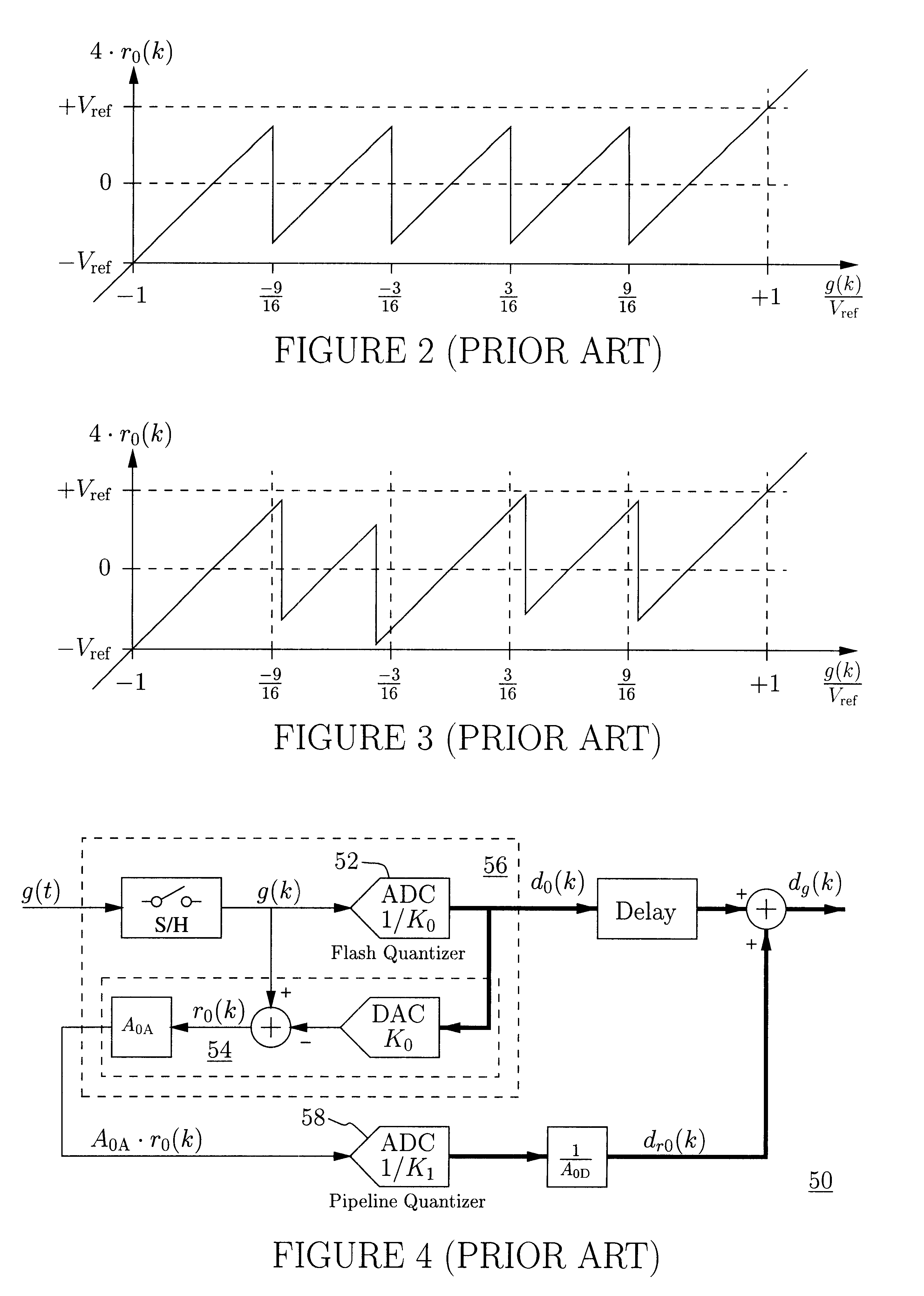
An analog-to-digital converter system [50D] processing an input signal, g, which can be either a discrete-time or a continuous-time signal. A first quantizer [154] generates a first digital signal, d0(k), representing the sum of the input signal, g, and a dithering signal, y0. A digital-to-analog converter [156] generates an analog feedback signal, alpha, representing accurately the first digital signal, d0(k). The DAC [156] may be linearized by the use of mismatch-shaping techniques. A filter [158] generates the dithering signal, y0, by selectively amplifying in the signal band the residue signal, r0, defined as the difference of the input signal, g, and the analog feedback signal, alpha. Optional signal paths [166][168] are used to minimize the closed-loop signal transfer function from g to y0, which ideally will be zero. An analog compensation signal, m0, which is described by a well-controlled relationship to the residue signal, r0, is extracted from the filter [158]. Ideally, the closed-loop signal transfer function from g to m0 will be zero, or at least small in the signal band. A second quantizer [160] converts the analog compensation signal, m0, into a second digital signal, dm0(k). The two digital signals, d0(k) and dm0(k), are filtered individually and then added to form the overall output signal, dg(k). The second digital filter [164] has a low signal-band gain, which implies that the sensitivity to signal-band errors caused by the second quantizer [160] will be low. The output signal, dg(k), is a highly-accurate high-resolution representation of the input signal, g. Circuit imperfections, such as mismatch, gain errors, and nonlinearities, will cause only noise-like errors having a very low spectral power density in the signal band.The invention facilitates the implementation of uncalibrated highly-linear high-resolution wide-bandwidth A / D converters [50D], e.g., for use in digital communication systems, such as xDSL modems and other demanding consumer-market products for which low cost is of the essence.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES BV
Continuous time bandpass delta sigma modulator ADC architecture with feedforward signal compensation
InactiveUS6396428B1Reduce system complexityInherent errorElectric signal transmission systemsDifferential modulationSignal transfer functionOptical transfer function
A continuous time Bandpass Delta Sigma (DELTASIGMA) Modulator architecture with feedforward and feedback coefficients to completely specify both the signal transfer function (STF) and the noise transfer function (NTF) for a stable modulator ADC system.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Method for reducing DAC resolution in multi-bit sigma delta analog-to digital converter (ADC)
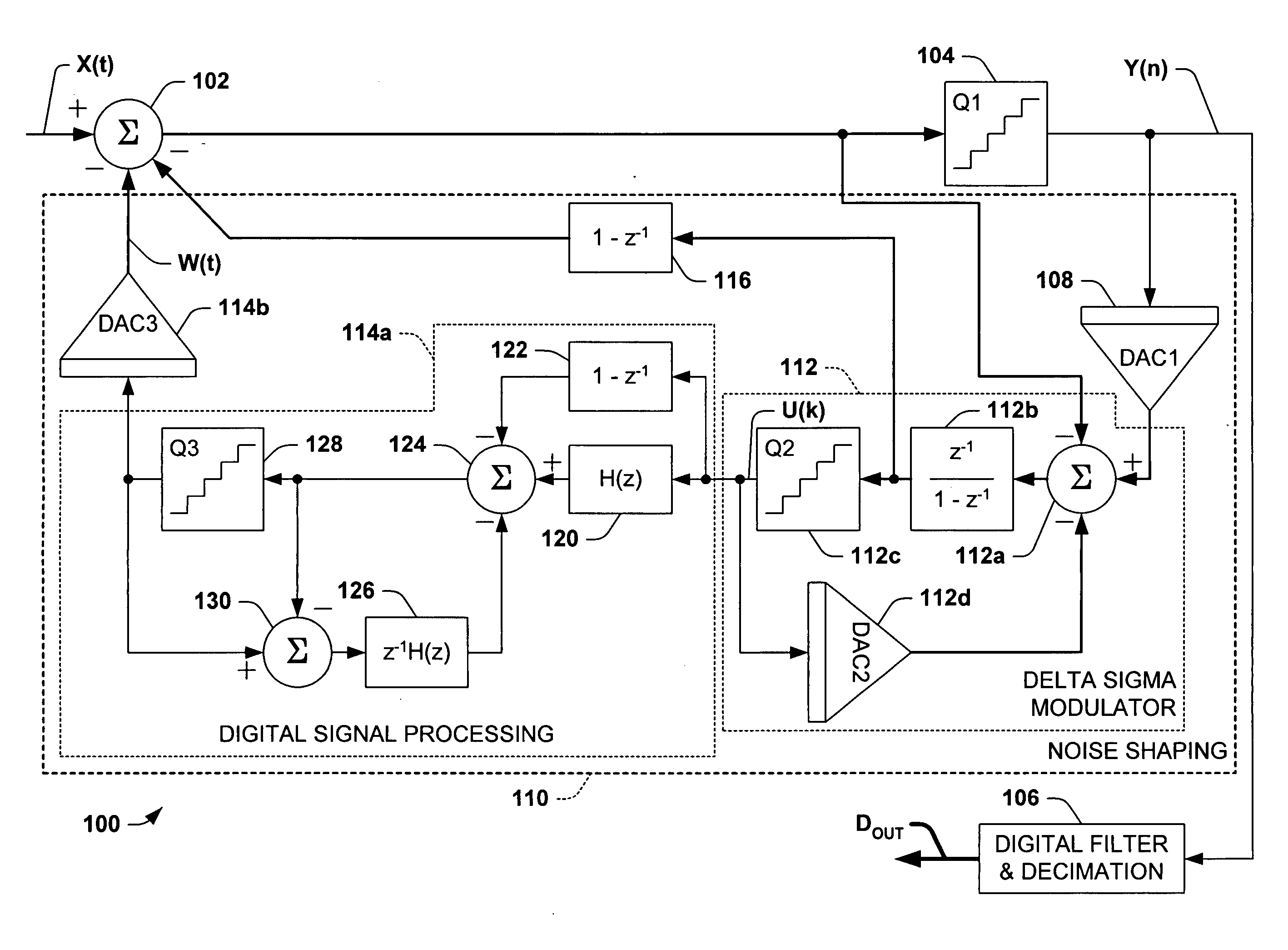
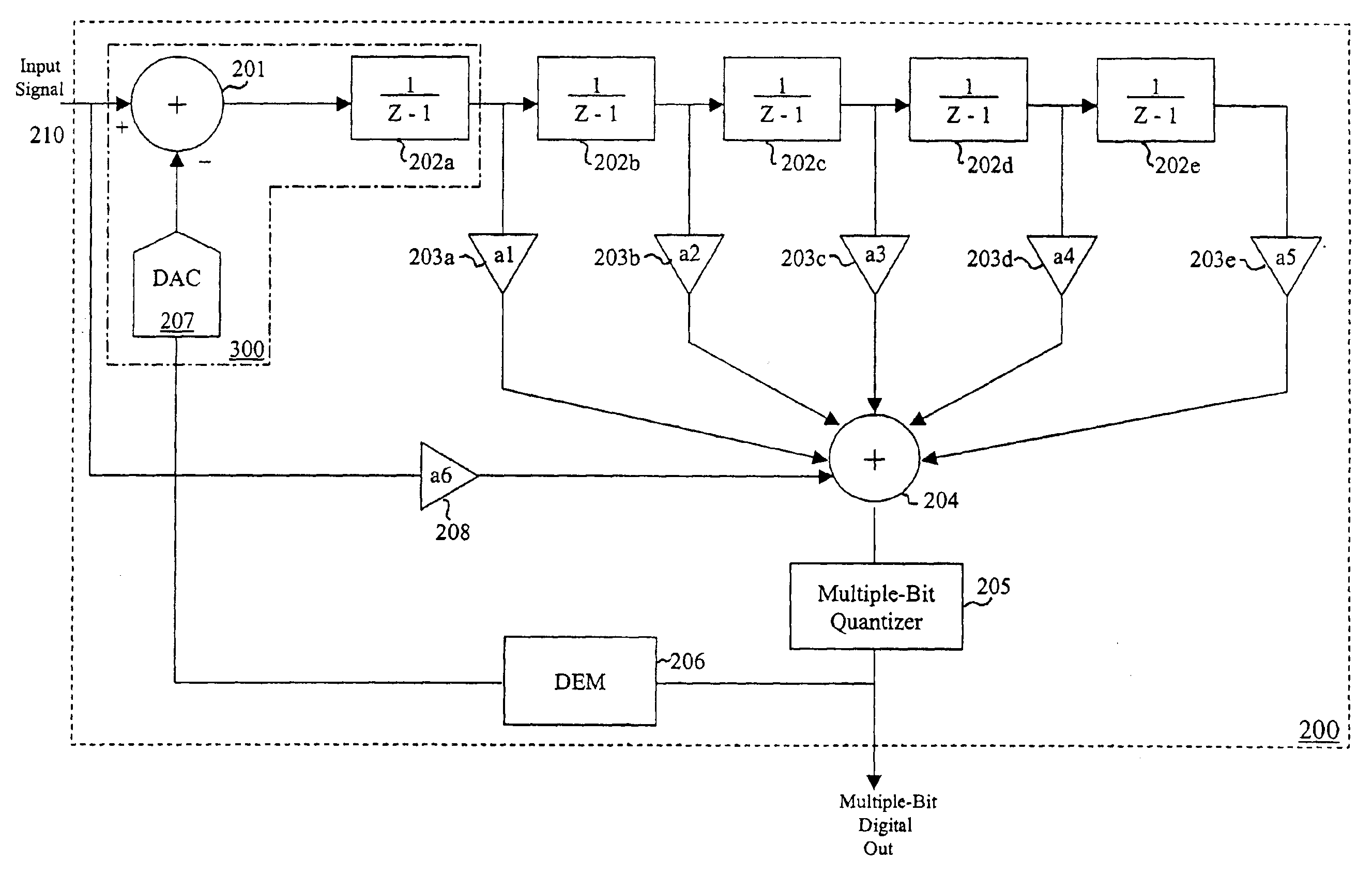
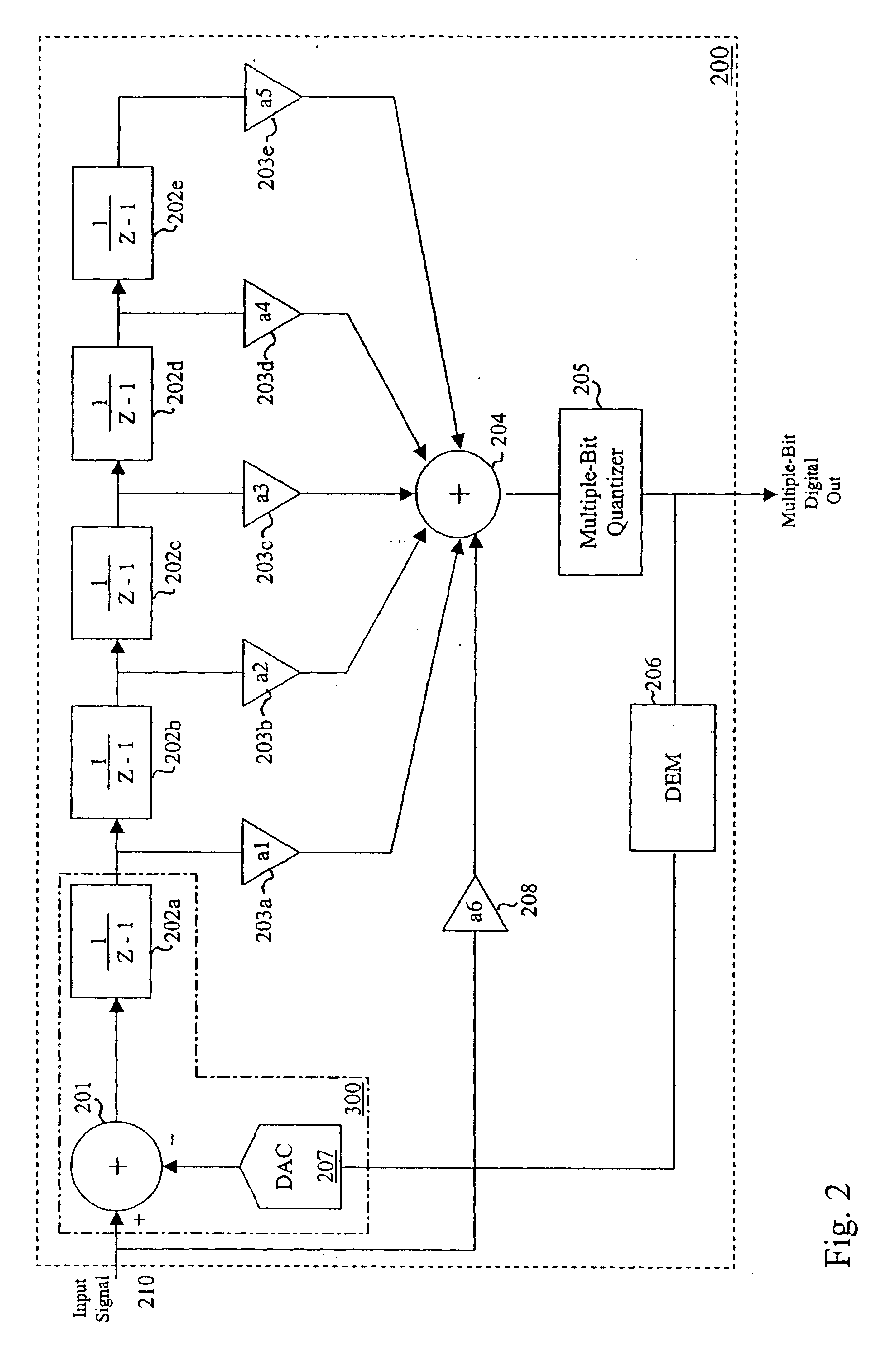
A method for reducing the resolution of a digital-to-analog converter in a multi-bit sigma-delta ADC is described. With the addition of digital sigma-delta modulators in the feedback path of a sigma-delta ADC, the truncation errors between the digital word output of the multi-bit sigma-delta ADC to the DAC input can be shaped to higher order than that of the quantization error. Thus, the DAC resolution can be reduced and the implementation of DEM for multi-bit DAC can be avoided. A preferred embodiment comprises selecting an outermost feedback loop in a sigma-delta ADC that has not been replaced and replacing it with a circuit with an equivalent transfer function. The circuit can be further enhanced with an additional term if the order of the noise shaping of the circuit is less than the order of the noise shaping of the sigma-delta ADC.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
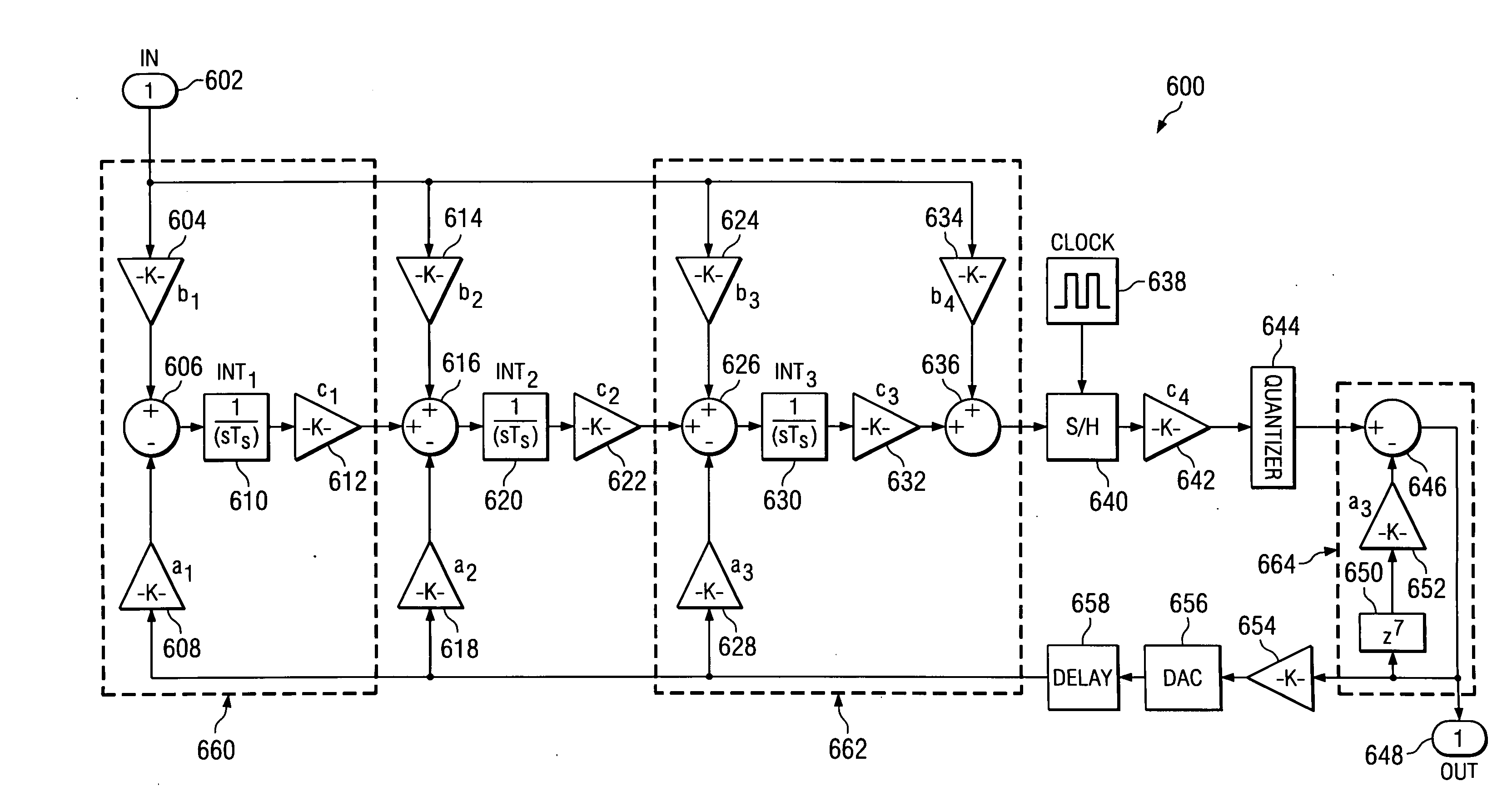
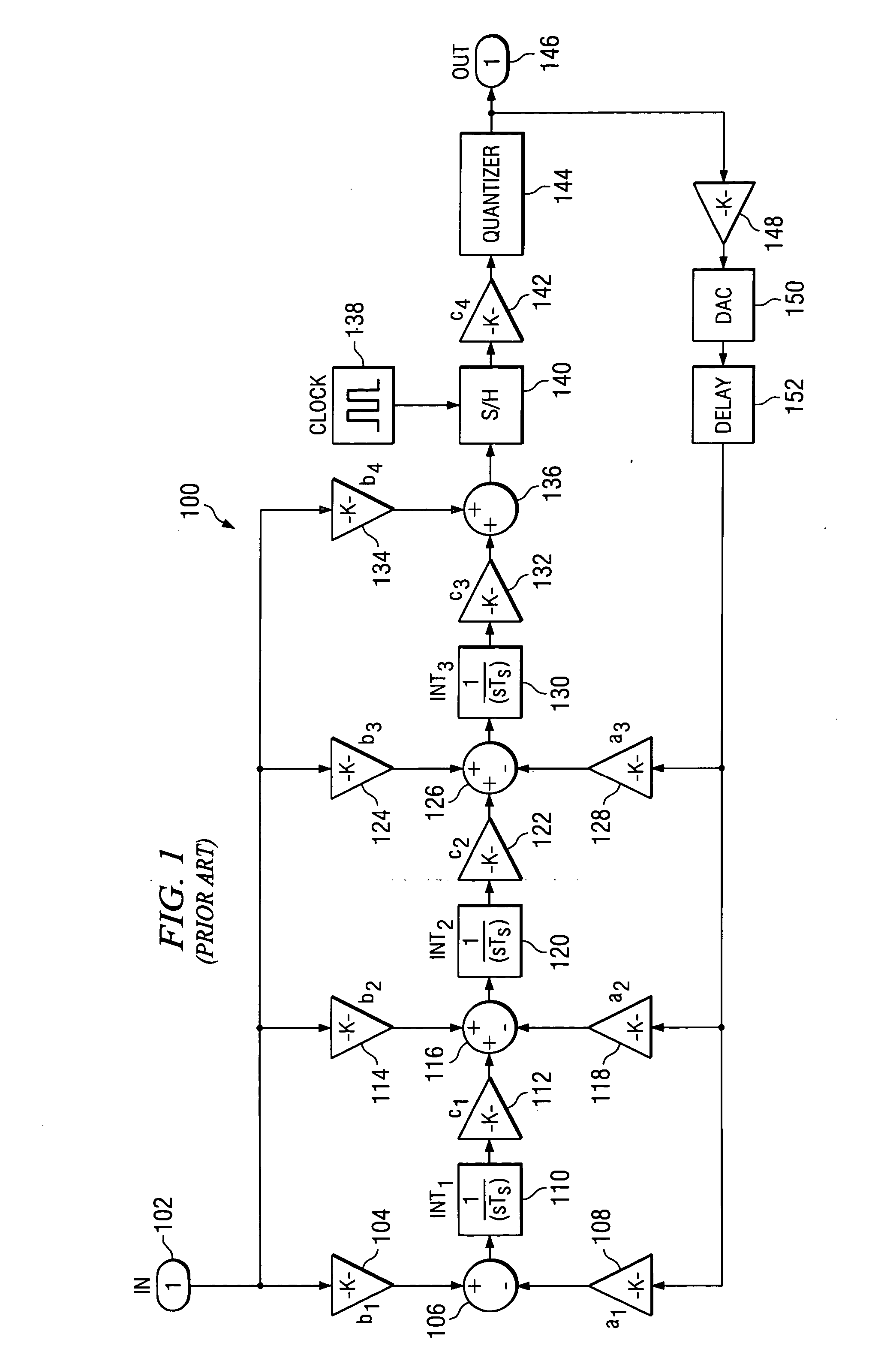
Excess delay compensation in a delta sigma modulator analog-to-digital converter
InactiveUS6414615B1Electric signal transmission systemsDelta modulationDigital analog converterAnalog signal
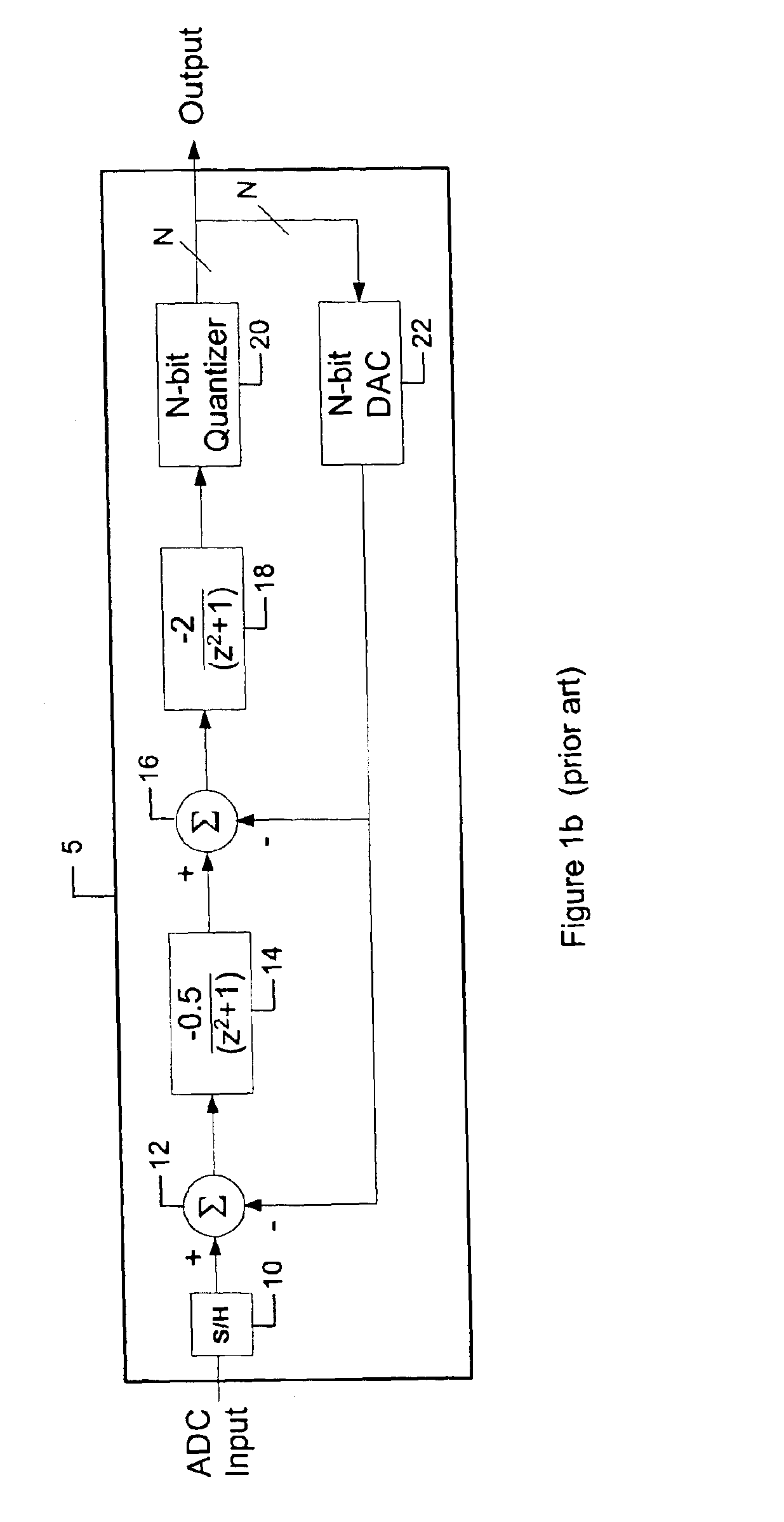
A high-performance delta sigma analog-to-digital converter. The high-performance delta sigma analog-to-digital converter includes a first mechanism for converting an input analog signal to a digital output signal. The first mechanism is characterized by a transfer function that is altered relative to an ideal transfer function. A second mechanism compensates for the alteration in the transfer function via a single additional digital-to-analog converter. In a specific embodiment, the alteration includes an additional pole and an additional zero induced by feedback delays in the first mechanism. The feedback delays include signal dependent jitter delay and feedback digital-to-analog converter cell switching delays. The second mechanism includes an additional latch that compensates for the signal dependent jitter delay. The first mechanism includes a resonator and a quantizer. The second mechanism includes a feedback path from an output of the quantizer to the resonator. The feedback path includes a first latch positioned between an output of the quantizer and the additional digital-to-analog converter. The additional latch is positioned at an output of the first latch and eliminates signal dependent jitter delay in the analog-to-digital converter. The additional feedback digital-to-analog converter is a non-return-to-zero digital-to-analog converter, an output of which is connected to the resonator.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
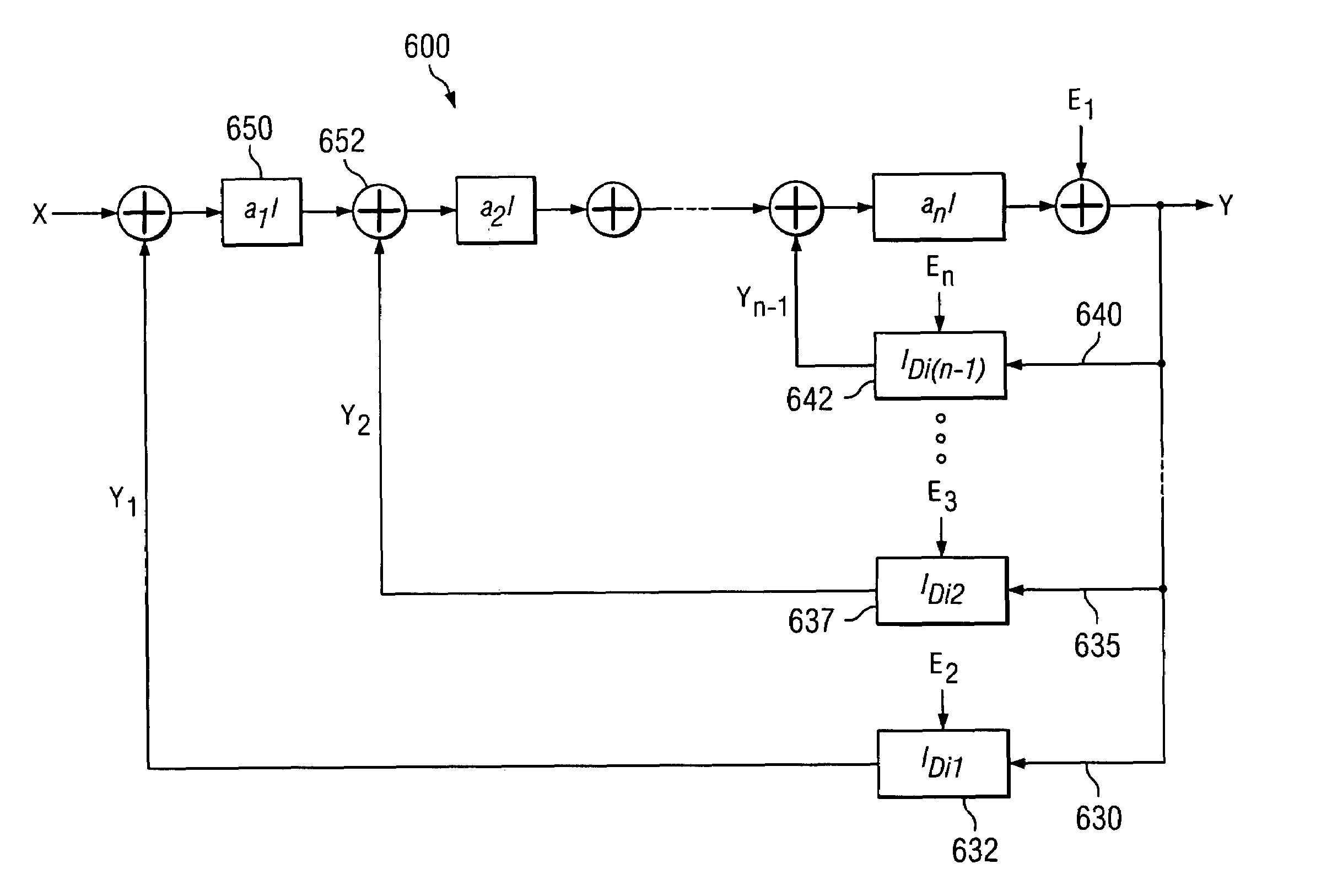
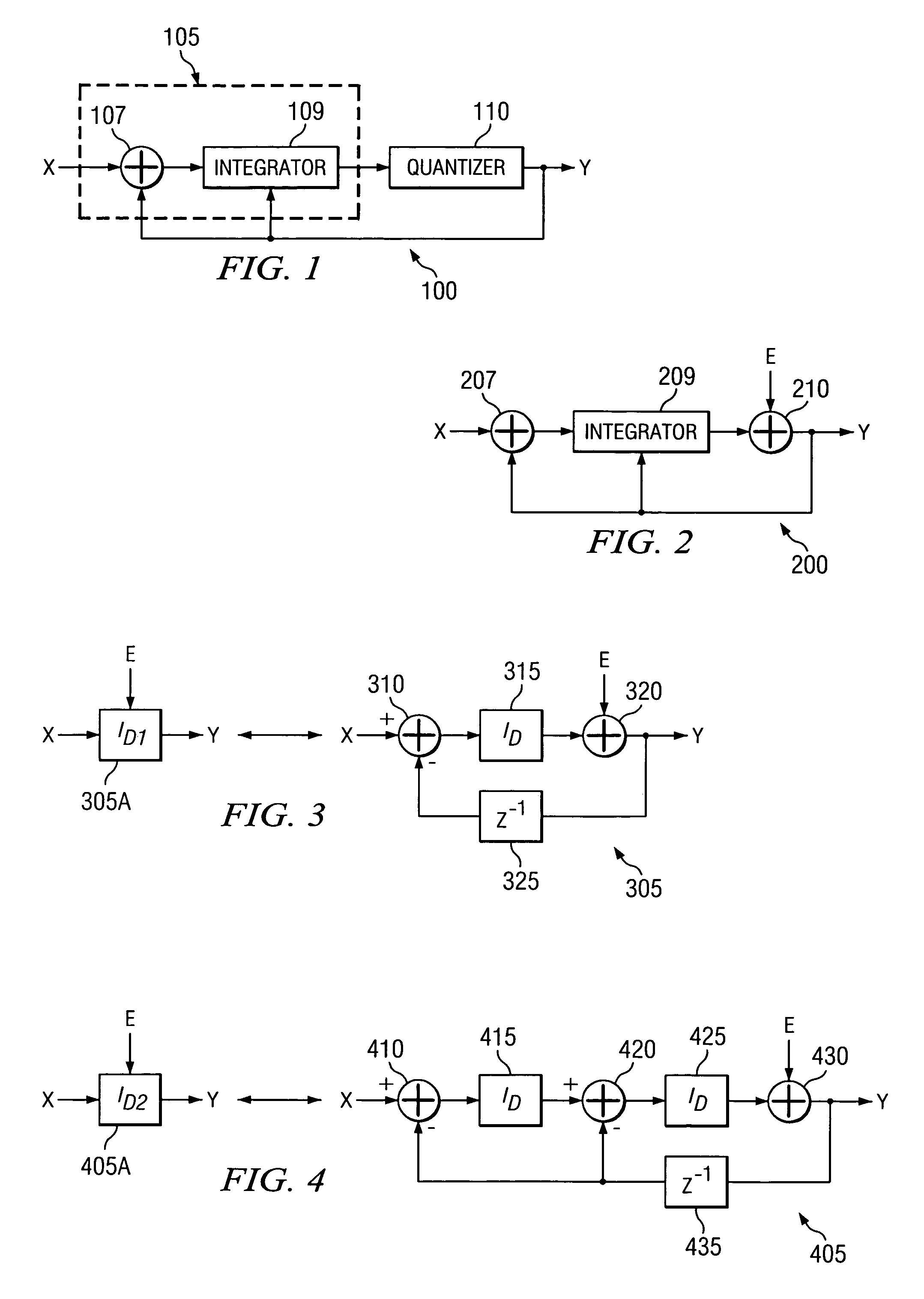
Sigma-delta analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with truncation error cancellation in a multi-bit feedback digital-to-analog converter (DAC)
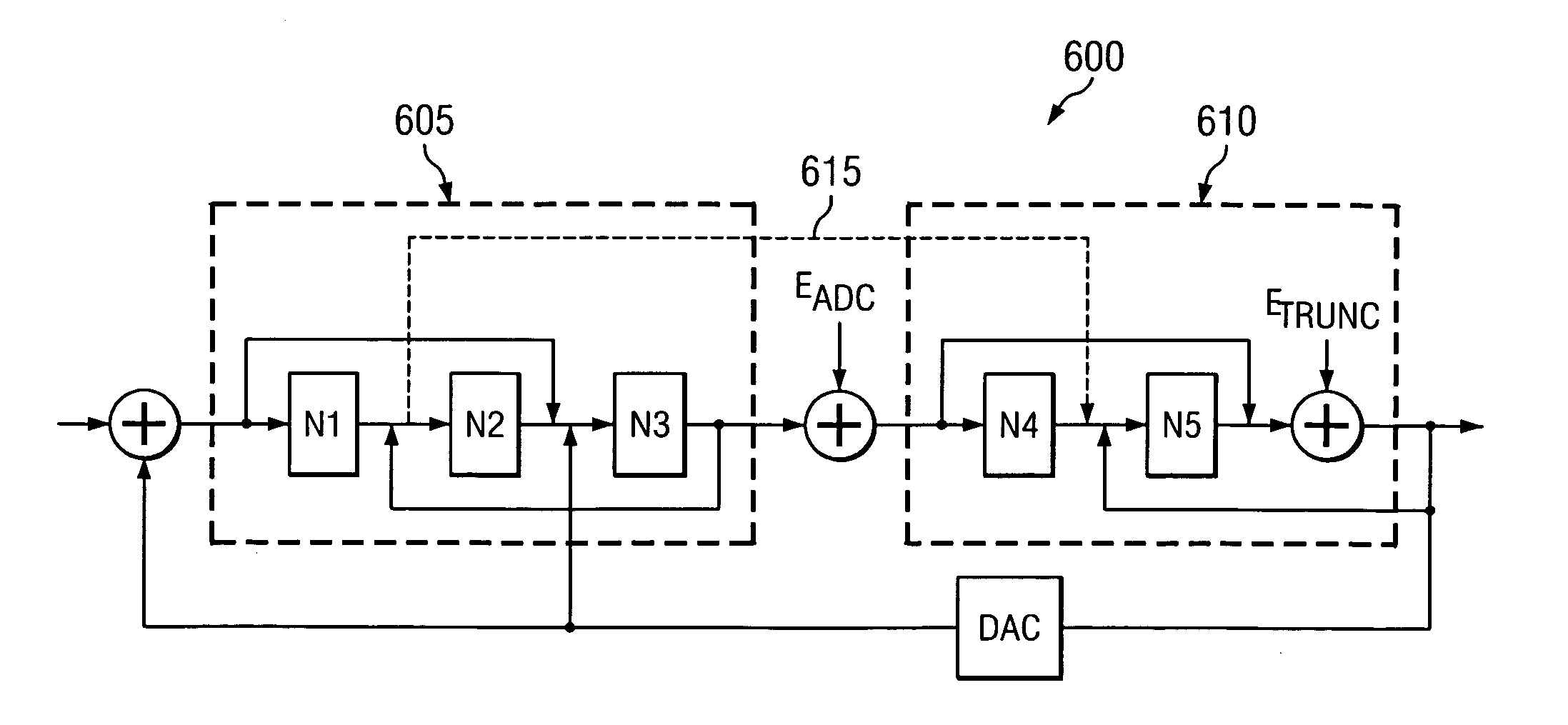
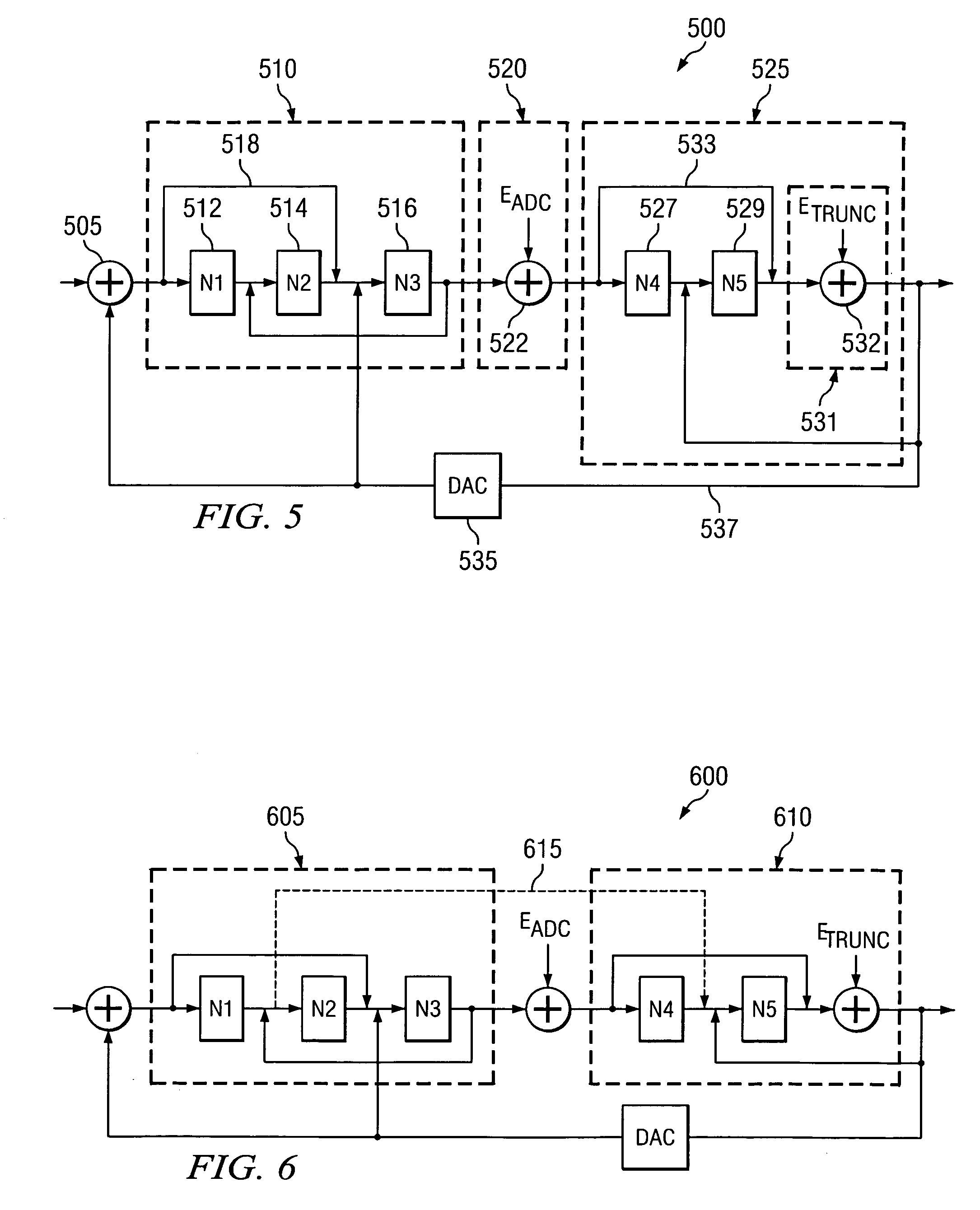
ActiveUS6967608B1Reduce complexityCancel out truncation errorDifferential modulationDigital analog converterImage resolution
A method for reducing the complexity of a multi-bit DAC in a sigma-delta ADC. The DAC resolution can be made to be less than that of the quantizer by canceling truncation error present in multi-bit DACs. Truncation errors are introduced by differences between the digital output word of the quantizer and the digital input word of the feedback DAC(s). The truncation error(s) can be cancelled and eliminated from the system transfer function. A preferred embodiment comprises expanding all feedback loops in the ADC, adding an adjusted truncation error for each feedback loop to an inner feedback loop, and then calculating a correction term for each adjusted truncation error. The correction term can be calculated by zeroing all signals except for the adjusted truncation error being canceled and then calculating a truncation error transfer function.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Sigma delta modulator
ActiveUS20090066549A1More freedomStable maintenanceDelta modulationDifferential modulationSignal transfer functionGreek letter sigma
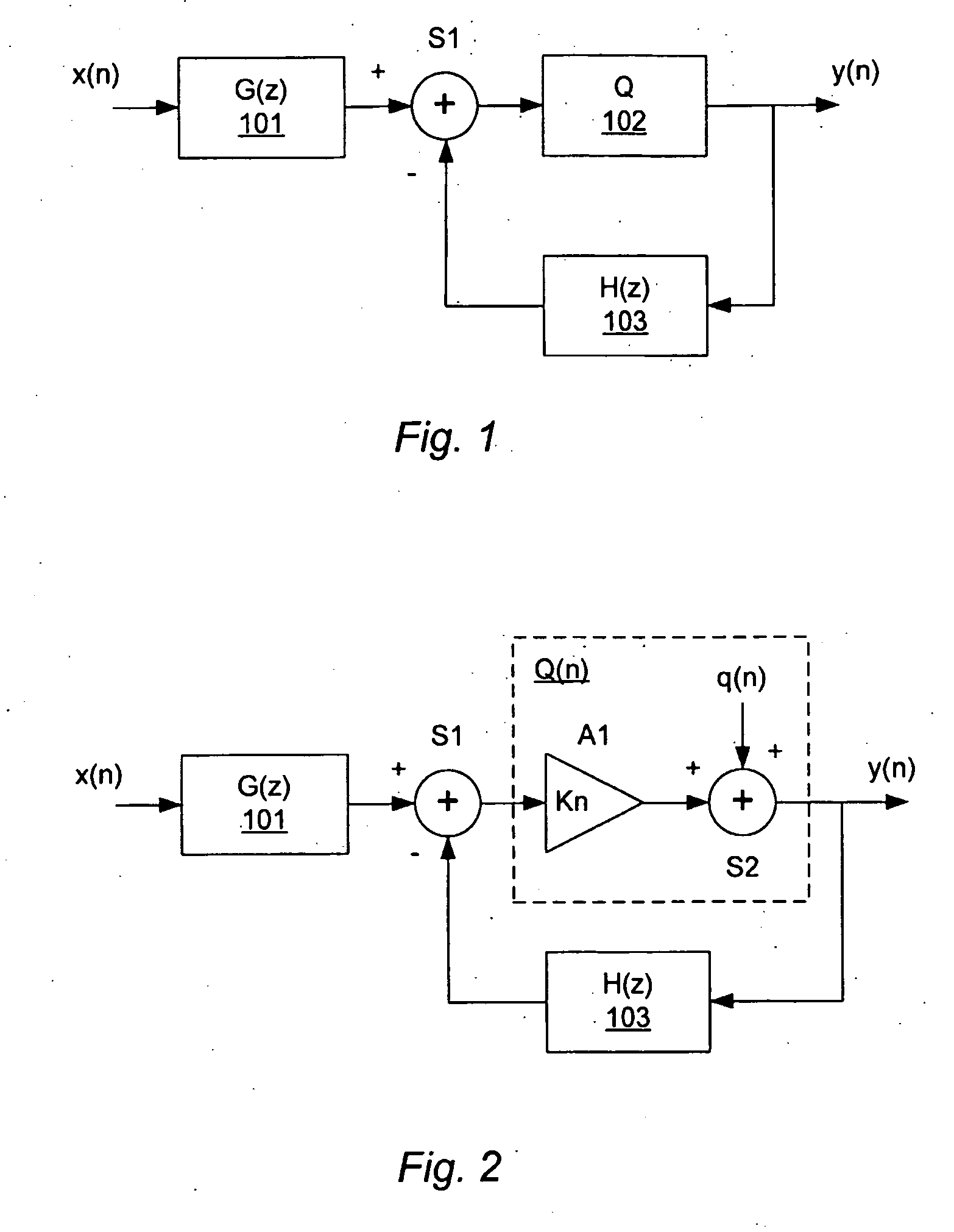
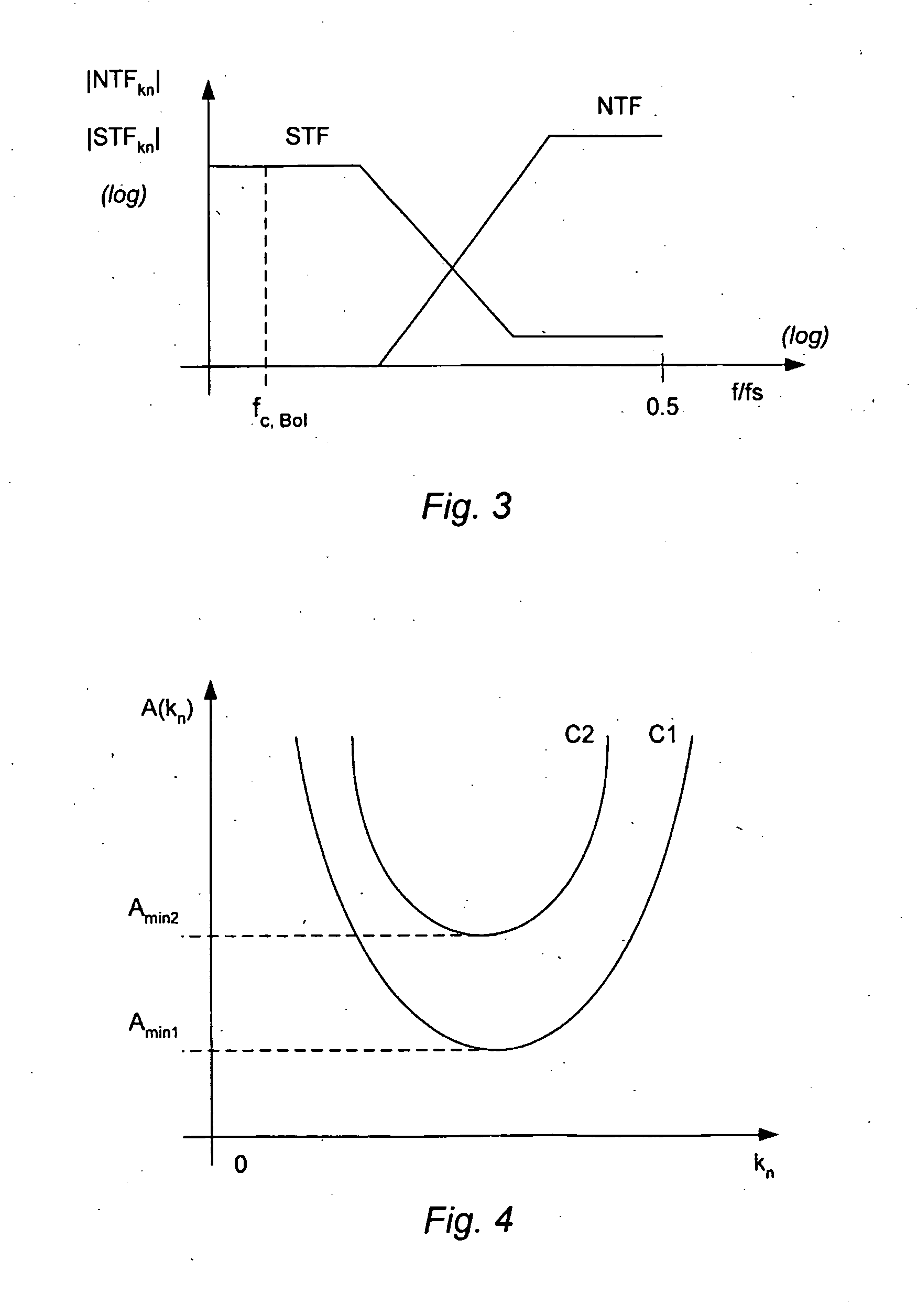
A method of controlling a sigma delta modulator with a loop which establishes a signal transfer function, STF, and a quantization noise transfer function, NTF, of the sigma delta modulator, wherein the sigma delta modulator receives an input signal, x(n), and provides a modulated output signal, y(n) in response to the input signal. The method is characterized in comprising the step of controlling the sigma delta modulator to change the quantization noise transfer function, NTF, in response to a signal feature, A(n), which is correlated with the input signal.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Analog-to-digital conversion system with second order noise shaping and a single amplifier
ActiveUS20050093726A1Well formedElectric signal transmission systemsDifferential modulationDigital signal processingIntegrator
A analog-to-digital converters and second order noise shaping systems are presented for providing a noise shaped analog feedback signal to a A / D converter in an analog-to-digital conversion system. The noise shaping system comprises a first order integrator having a single amplifier, and a digital error feedback system comprising a digital signal processing system, in which the digital error feedback system provides an analog feedback signal to the A / D converter with second order noise shaping with respect to a quantization error associated with the A / D converter.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
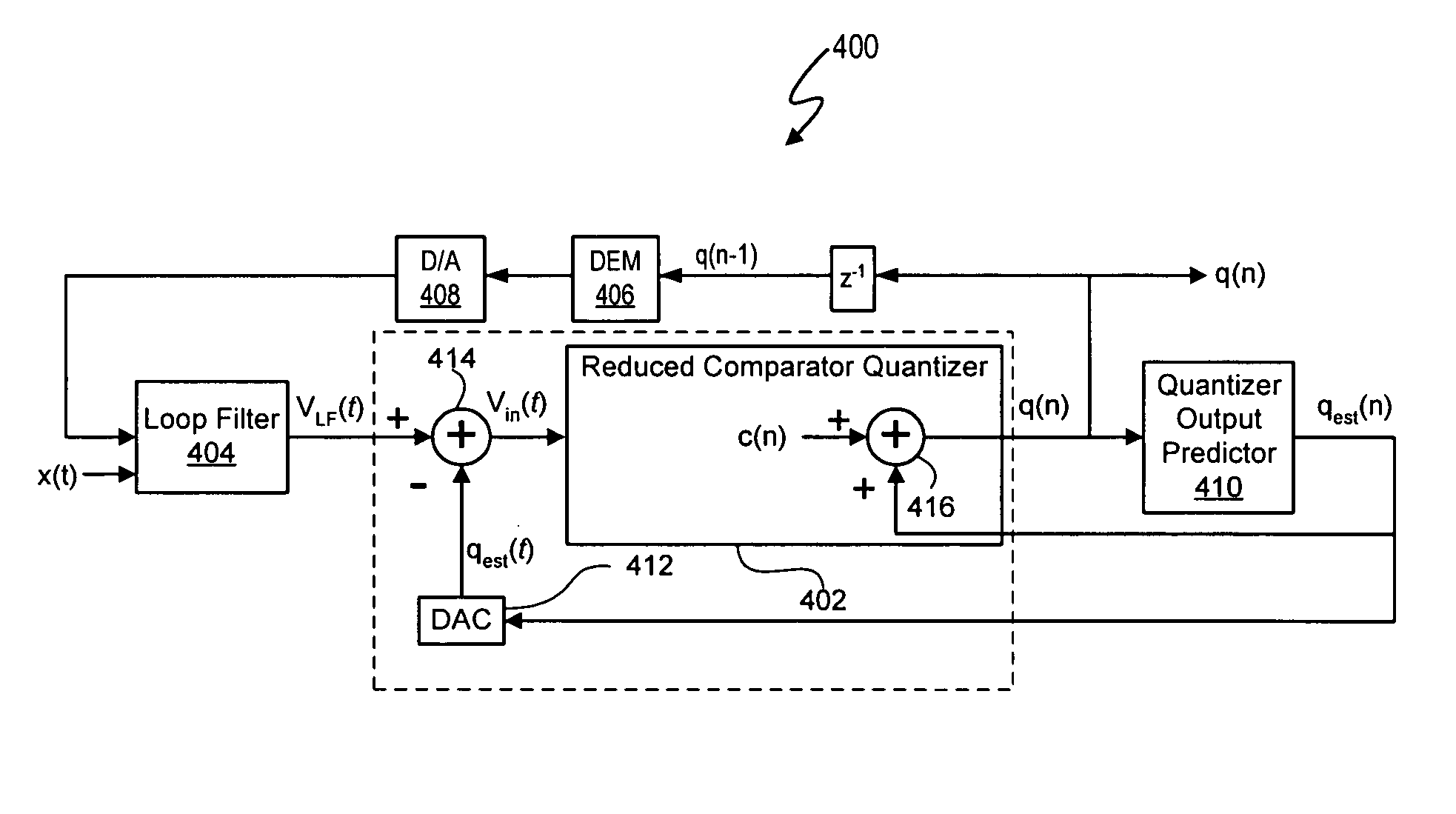
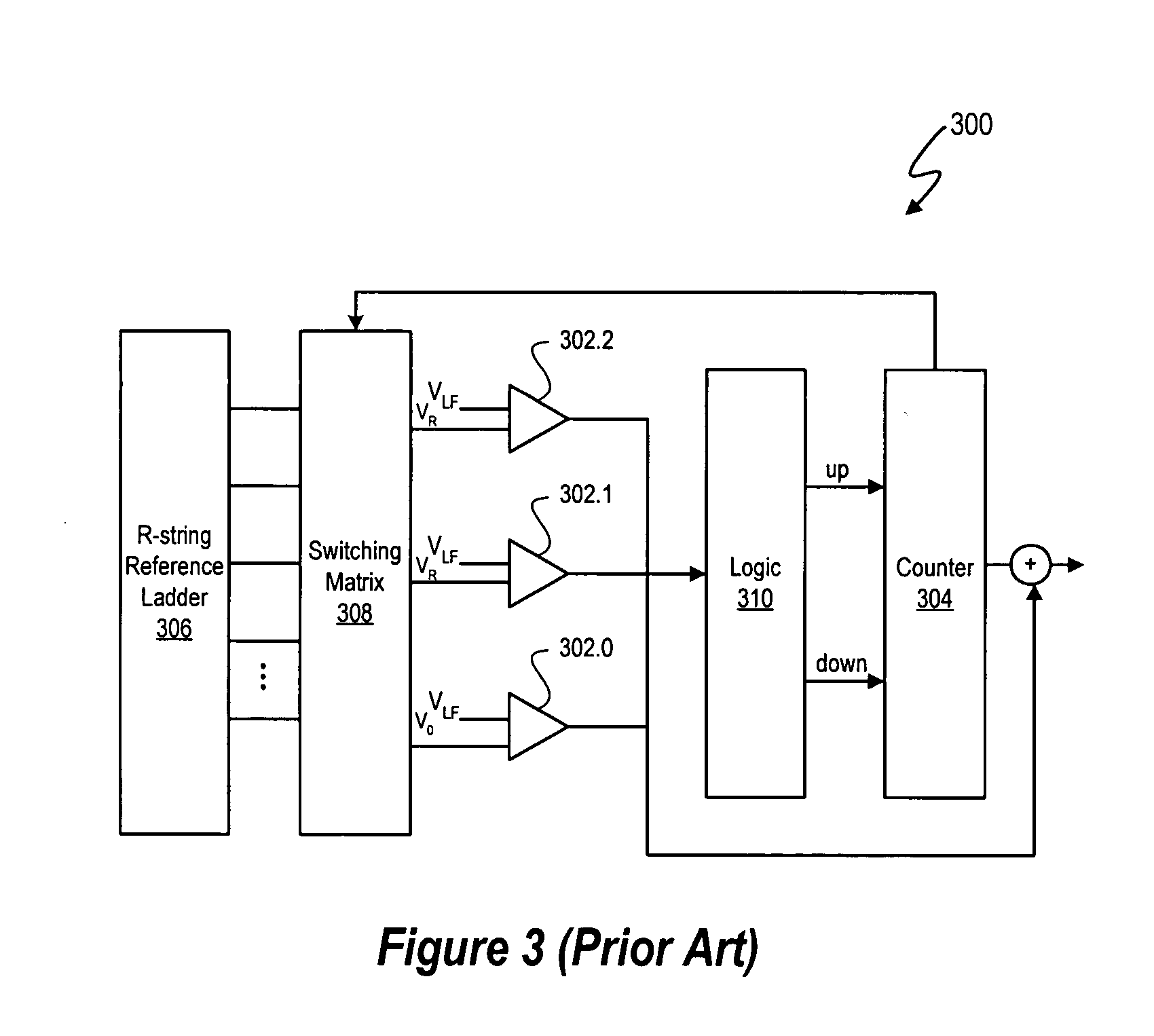
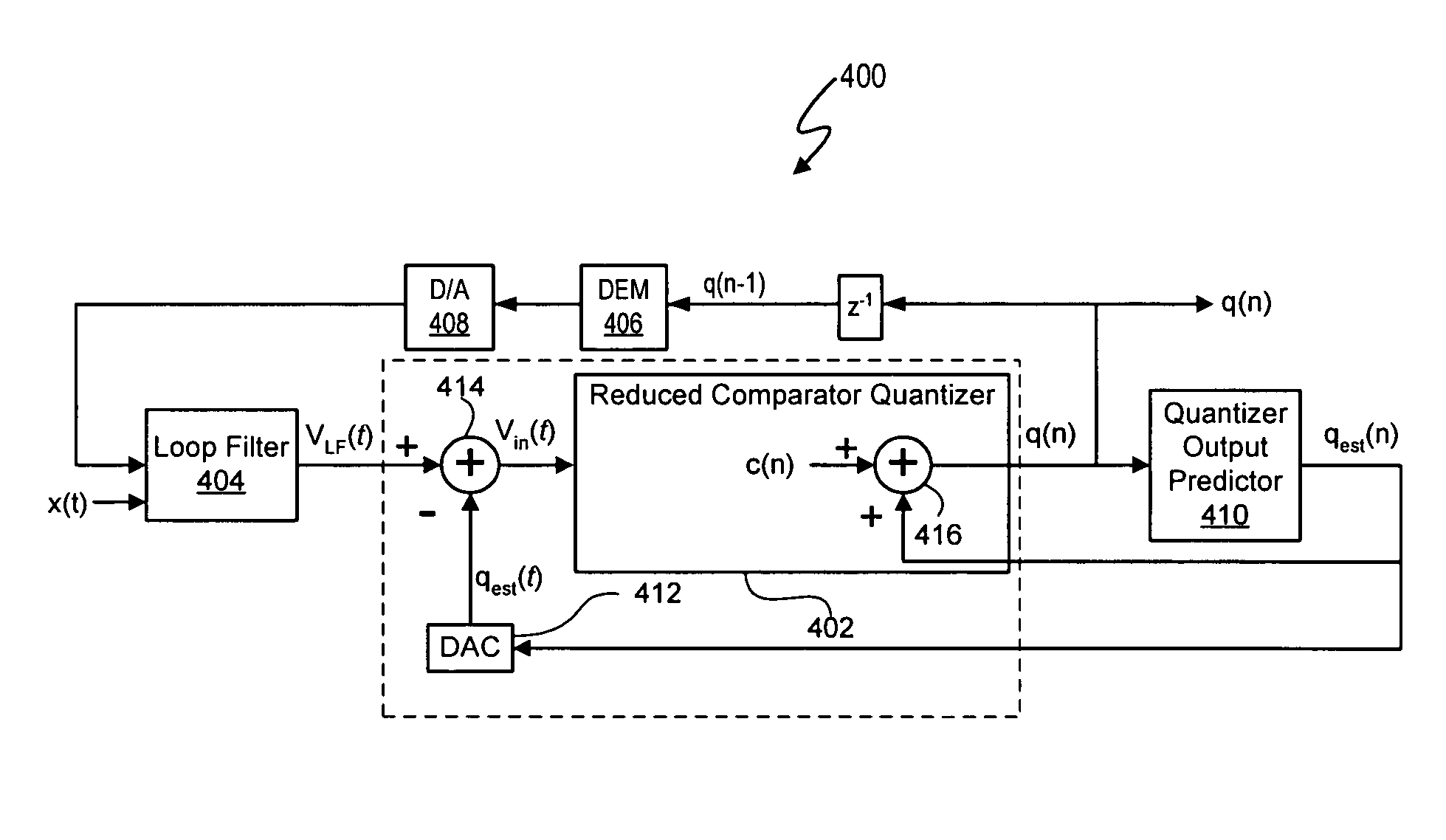
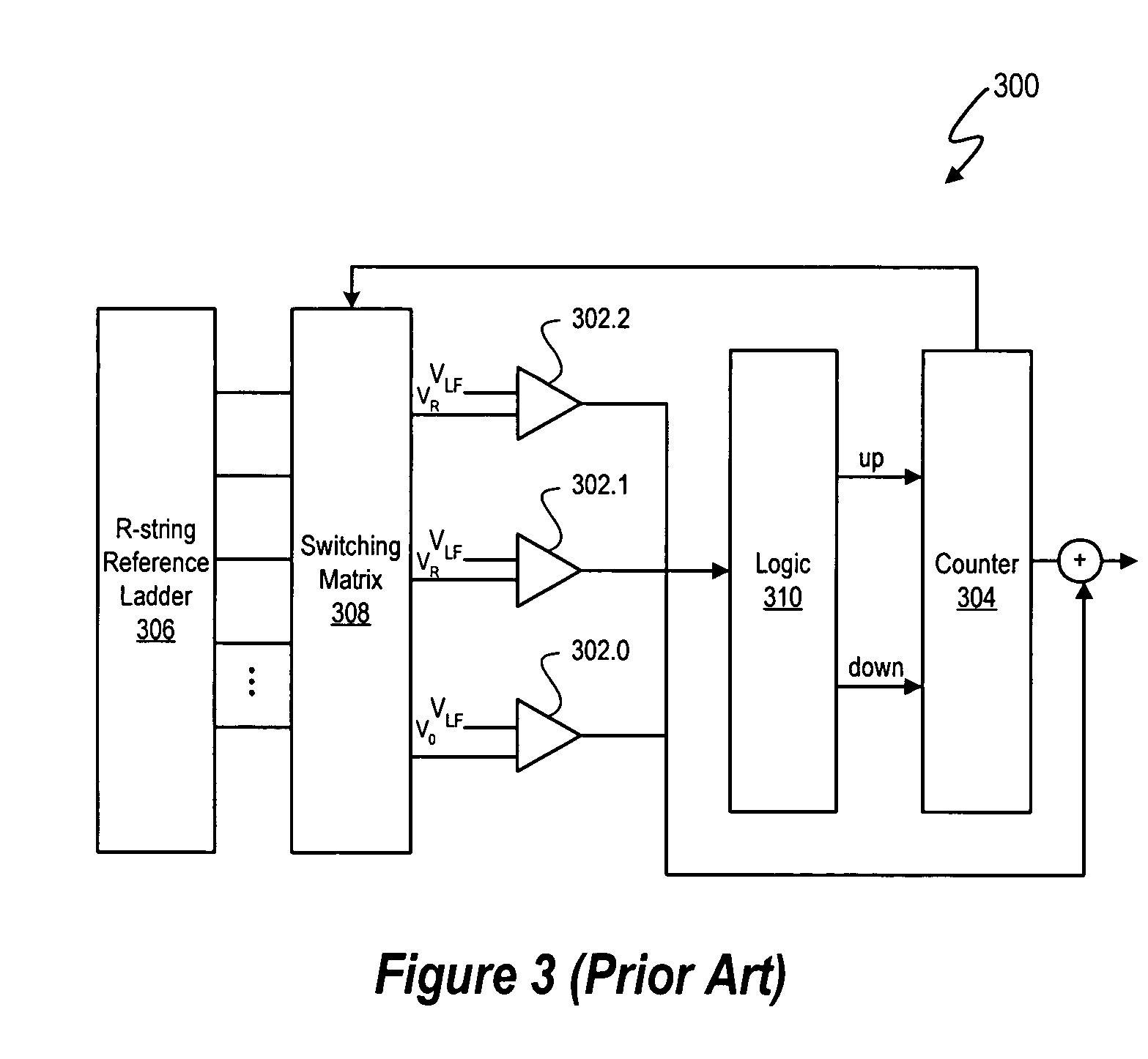
Delta sigma modulator analog-to-digital converters with quantizer output prediction and comparator reduction
ActiveUS20070222656A1Reduce settingsElectric signal transmission systemsSpeech analysisLoop filterA d converter
The quantizers of delta sigma modulators in the signal processing systems described herein use a reduced set of comparators for quantization by predetermining and maintaining a maximum per cycle deviation d between a loop filter output signal VLF(t) and a predicted quantizer output signal qest. In at least one embodiment, a maximum quantizer level deviation d is defined in terms of a number of quantization levels. Thus, the number of comparators in a quantizer needed to quantize the quantizer input signal Vin(t) is based on the maximum quantizer level deviation d. In addition to using fewer comparators than available quantization output levels N, the quantizers can use an even number of comparators M, in contrast to comparable conventional reduced comparator ADC tracking quantizer designs using M+1 number of comparators, where N and M are integers and M<N.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
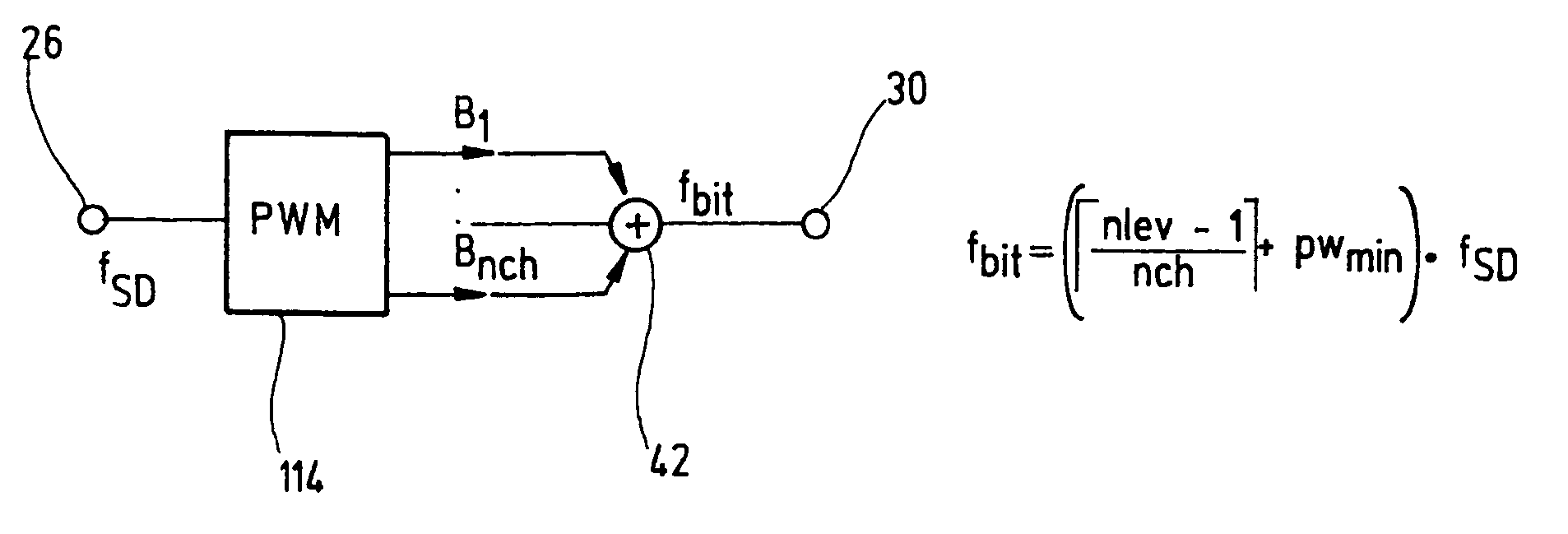
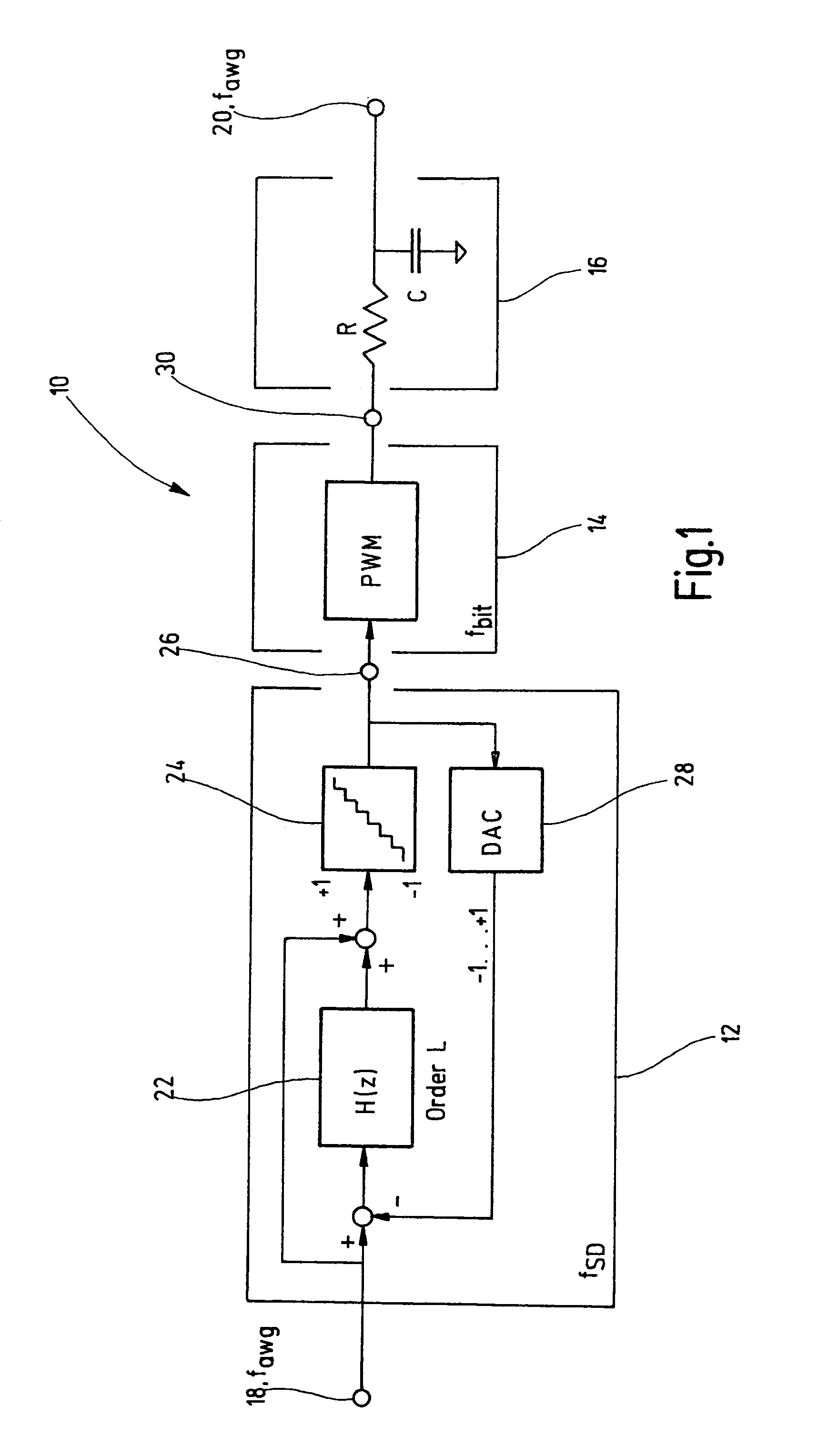
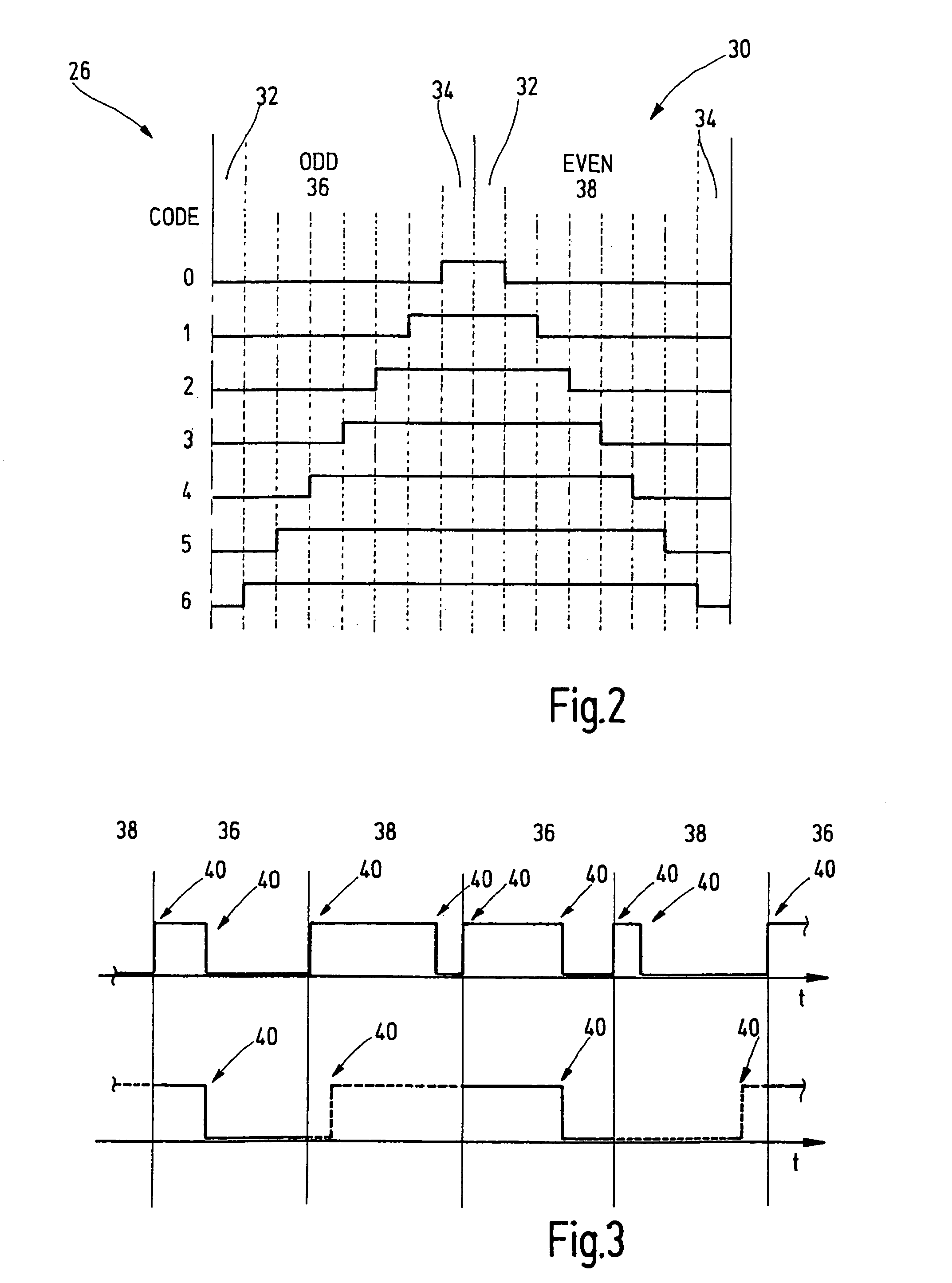
Sigma-delta modulator with PWM output
ActiveUS6972704B2Optimize timingHigh frequency ATE bit rateElectric signal transmission systemsDigital circuit testingQuantum electrodynamicsSigma delta modulation
The present invention relates to a method for providing an improved generated arbitrary waveform using a sigma-delta modulator with pulse width modulation, said method comprising the steps of sigma-delta modulation of said generated arbitrary waveform, and pulse width modulation of the output signal of said sigma-delta modulator, introducing a minimum pulse width (pwmin) during said pulse width modulation.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
Digital compensation of excess delay in continuous time sigma delta modulators
InactiveUS20050068213A1Minimizing excess loop delaySmall and simple and cost-effective approachDifferential modulationIntegratorA d converter
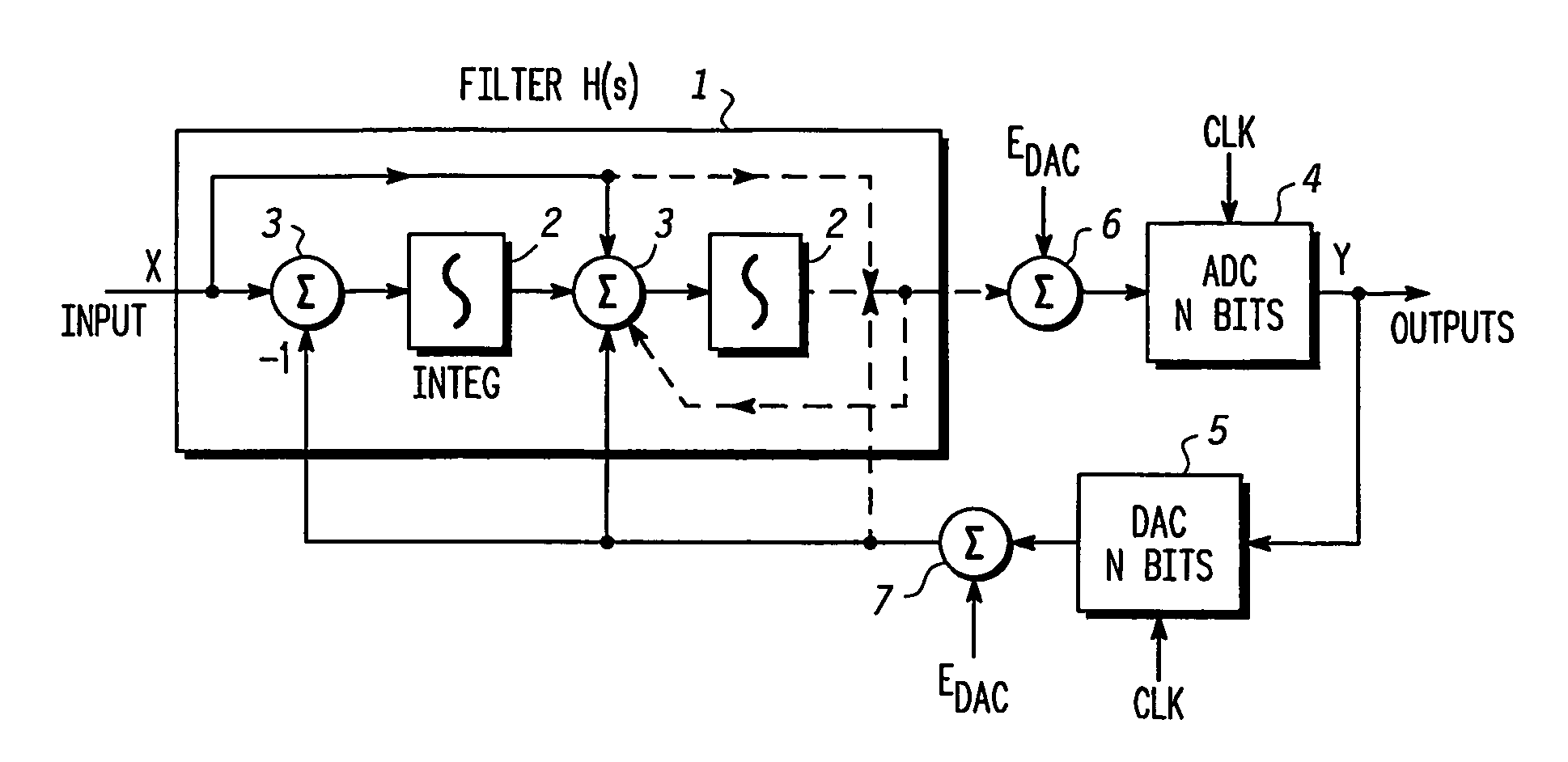
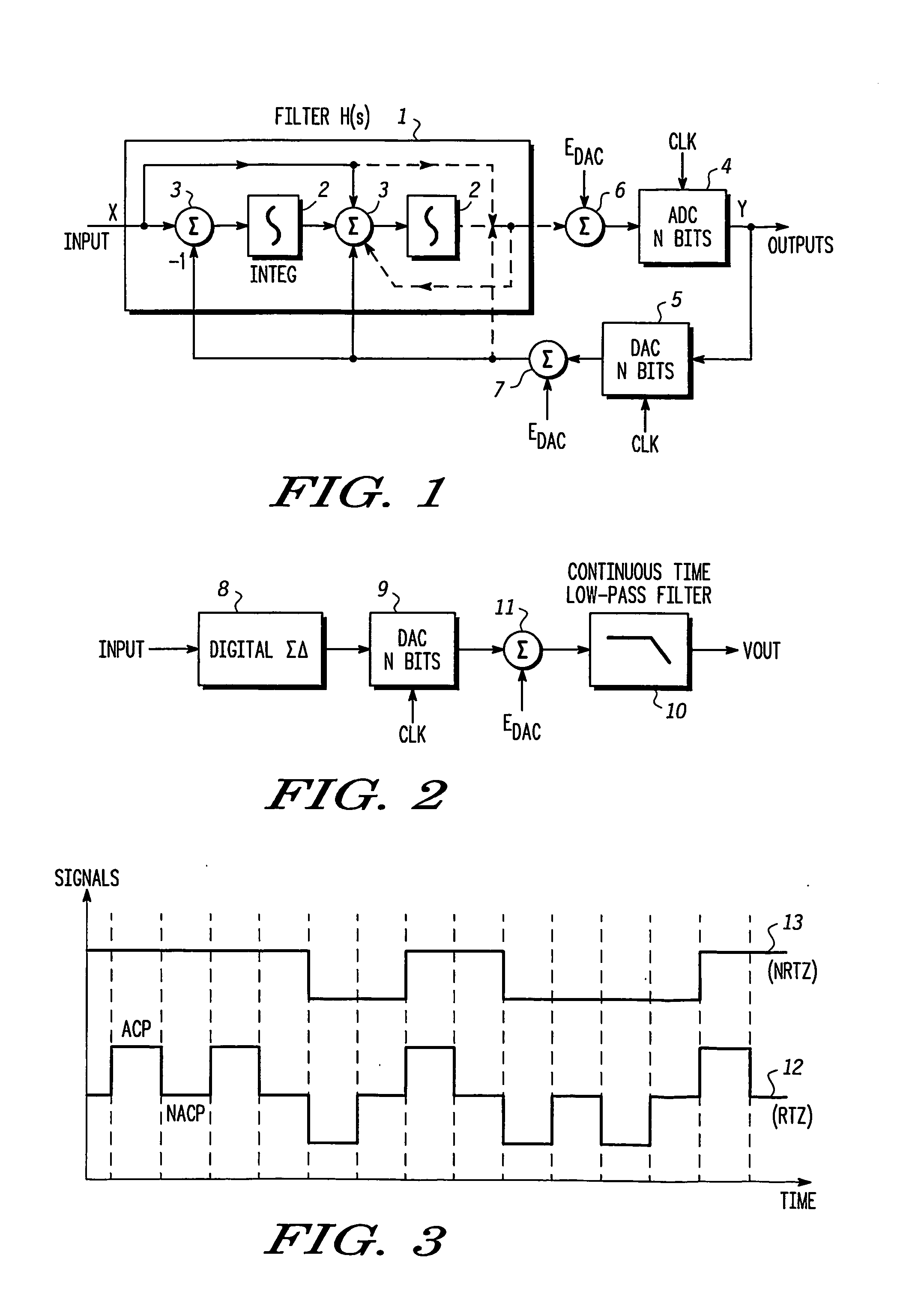
A continuous time sigma delta modulator having minimal excess loop delay. The continuous-time sigma delta modulator in accordance with the present invention includes at least one integrator stage coupled to receive an input signal and a resultant integrator output signal from a previous stage for providing a resultant integrator output. At least one output stage connects to the at least one integrator stage to receive the resultant integrator output signal from the previous integrator stage for providing a resultant integrator output. A sample and hold circuit connects to receive the second integrator input signal. A multiplier connects to the sample and hold circuit to provide a resultant sampled signal. An analog-to-digital converter quantizer couples to receive the resultant sampled signal and to produce a quantized output signal. A digital modulation loop circuit connects to the analog-to-digital converter quantizer to generate a resultant quantized output signal for correcting excess loop delay in the continuous time sigma delta modulator. A fourth feedback multiplier coupled to receive the resultant quantized output signal and produce a second resultant quantized output signal. A digital-to-analog converter coupled to receive the second resultant quantized output signal to produce a modulation feedback signal. A delay connects to the digital-to-analog converter to receive the modulation feedback signal and provide the resultant modulation feedback signal
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
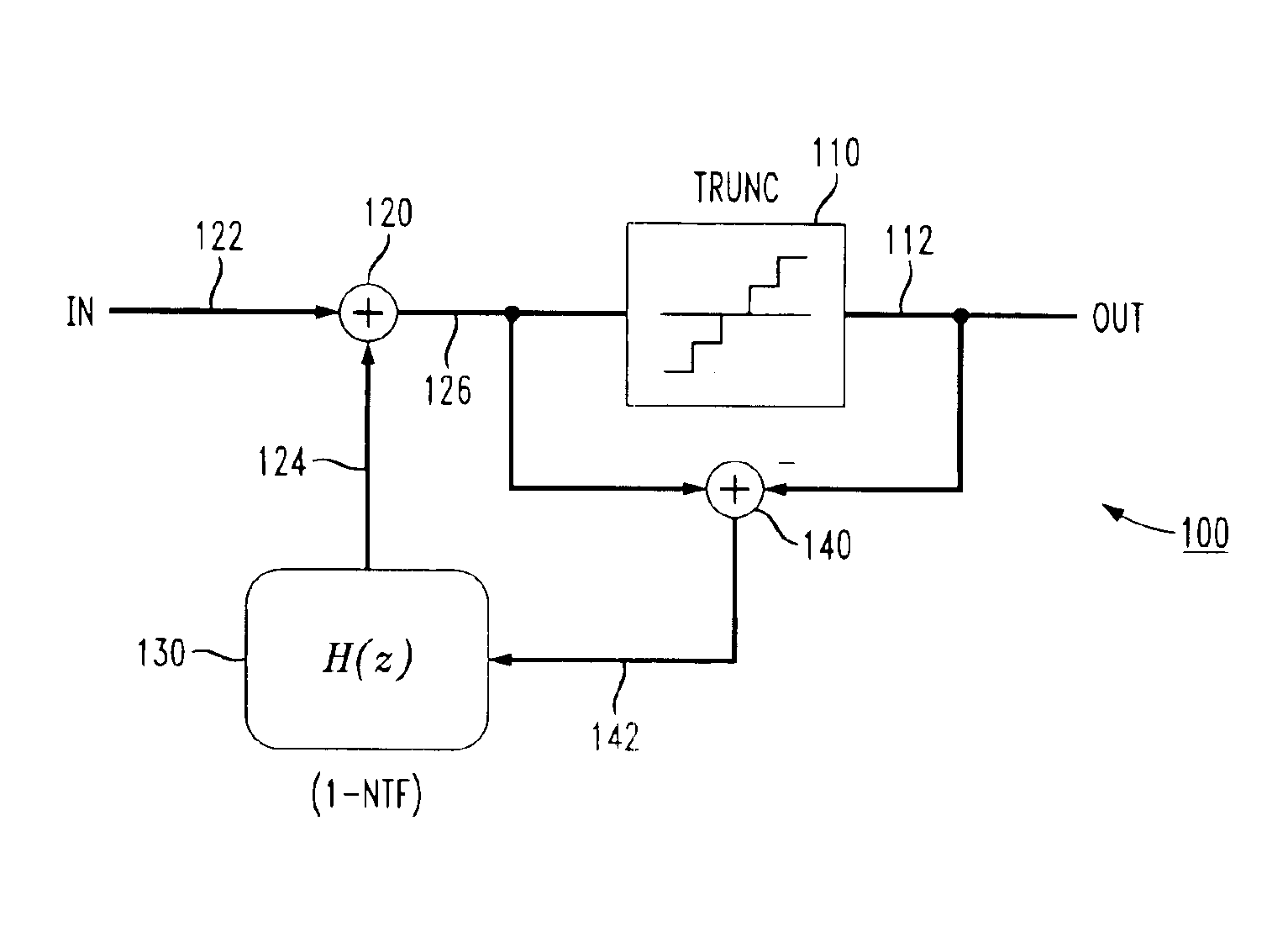
Stable high-order delta-sigma error feedback modulators, and noise transfer functions for use in such modulators
ActiveUS6888484B2Guaranteed smooth progressElectric signal transmission systemsAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesDigital analog converterSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Stable, robust, and high-resolution delta-sigma error feedback modulators, such as those used in digital-to-analog converters and phase-locked loops, include an L-order noise transfer function that is provided with L+1 high-order bits from a truncation element. The stability of such delta-sigma error feedback modulators is independent of the input signal. Moreover, the out-of-band gain of the noise transfer function need not be limited, which improves the resolution and the signal-to-noise ratio of the in-band signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Highly accurate switched capacitor DAC
ActiveUS6924760B1Minimize even-order errorReducing even-order errorElectric signal transmission systemsDifferential modulationCompact dimensionCapacitance
In one set of embodiments the invention comprises a highly accurate, low-power, compact size DAC utilizing charge redistribution techniques. Two complementary conversions may be performed and added together to form a final DAC output voltage by performing charge redistribution a first time, and again a second time in a complementary fashion, followed by a summing of the two charge distributions, in effect canceling the odd order capacitor mismatch errors. By canceling all odd order mismatch errors the accuracy of the DAC may become a function of the square of the mismatch of the two capacitors, resulting in greatly increased accuracy. When performing the complementary conversions for multiple bits, the sequence in which each of the two capacitors is charged may be determined to minimize the even-order errors, especially second-order errors. The DEM technique may be applied, in conjunction with the complementary conversions, with less oversampling than required by current DEM implementations, resulting in even-order errors being substantially reduced in addition to all odd-order errors being eliminated.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Analog-to-digital conversion system with second order noise shaping and a single amplifier
InactiveUS6940436B2Electric signal transmission systemsDifferential modulationDigital signal processingAudio power amplifier
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Programmable bandpass analog to digital converter based on error feedback architecture
ActiveUS6864818B1Improve programmabilityReduce circuit sizeDifferential modulationNoise shapingEngineering
A delta sigma modulator based analog to digital converter is presented, having a first quantizer and a digital error feedback system comprising a second quantizer and a digital bandpass noise shaping system. The second quantizer provides a second quantized output to the noise shaping system according to the first quantized output, the system analog input, and the noise shaped feedback signal. The digital noise shaping system provides a feedback signal to the first quantizer according to the second quantized output, where the feedback signal is bandpass noise shaped with respect to a quantization error of the first quantizer.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Signal processing system having an ADC delta-sigma modulator with single-ended input and feedback signal inputs
ActiveUS6972705B1Electric signal transmission systemsDifferential modulationAnalog feedbackEngineering
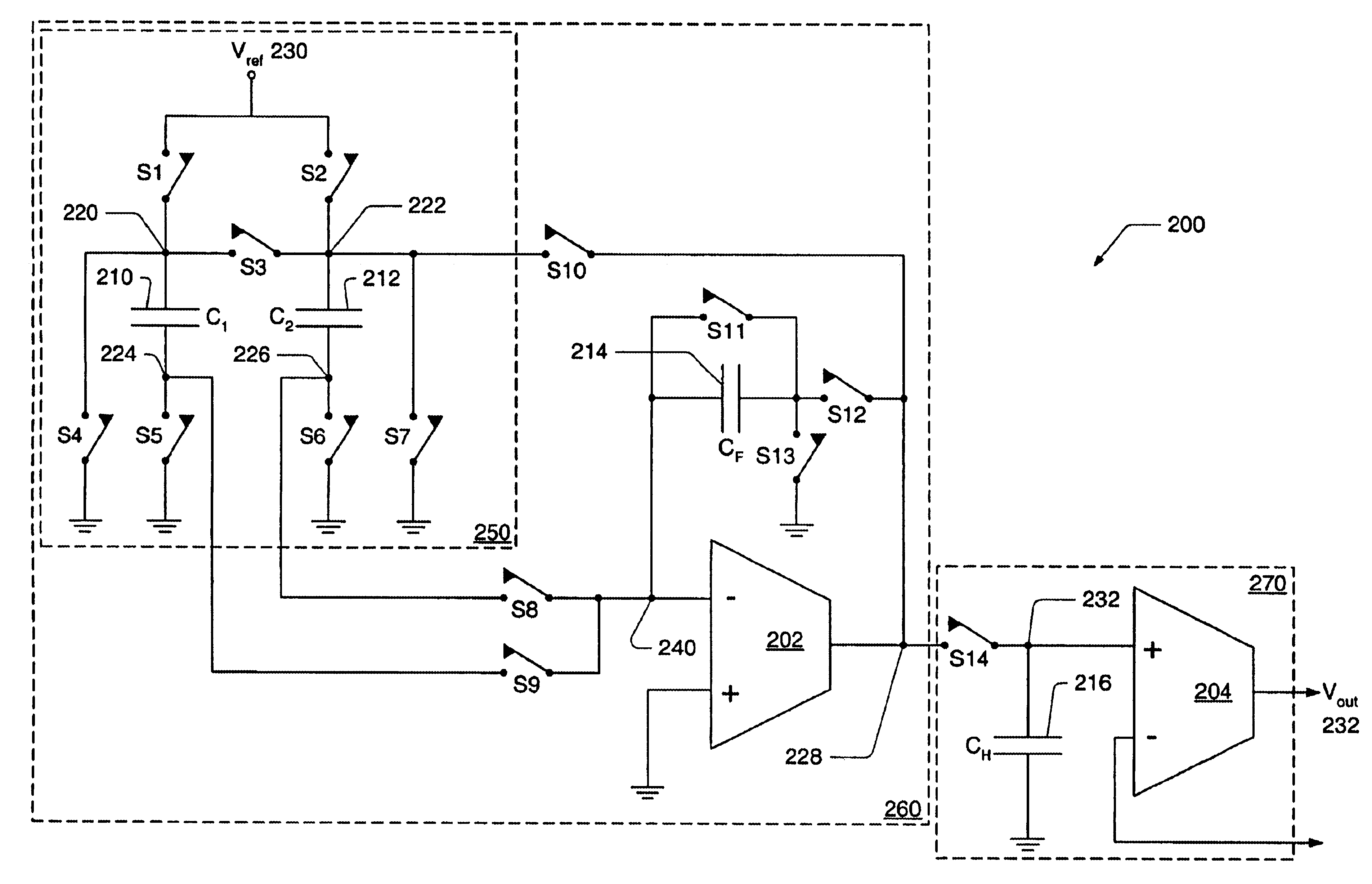
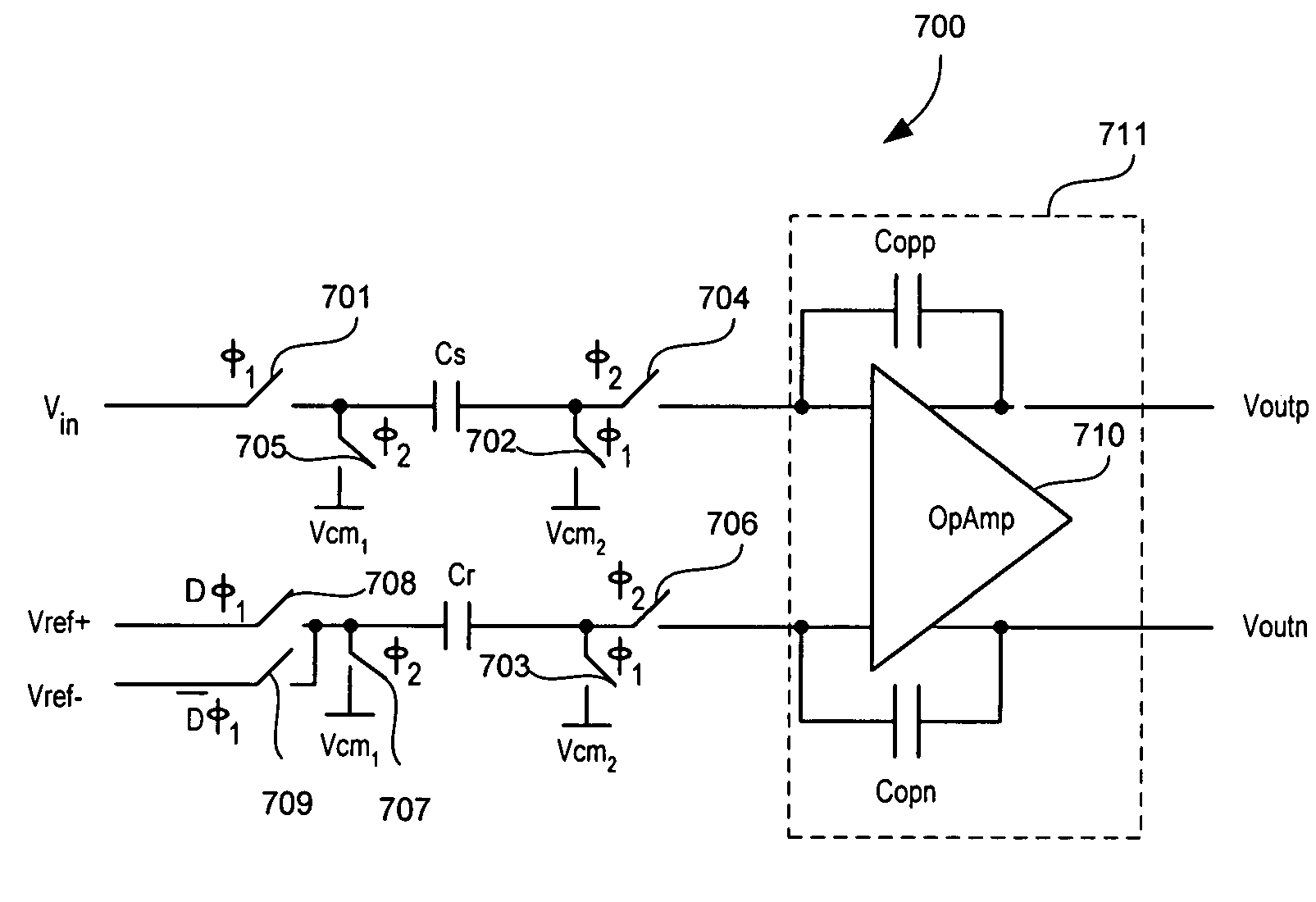
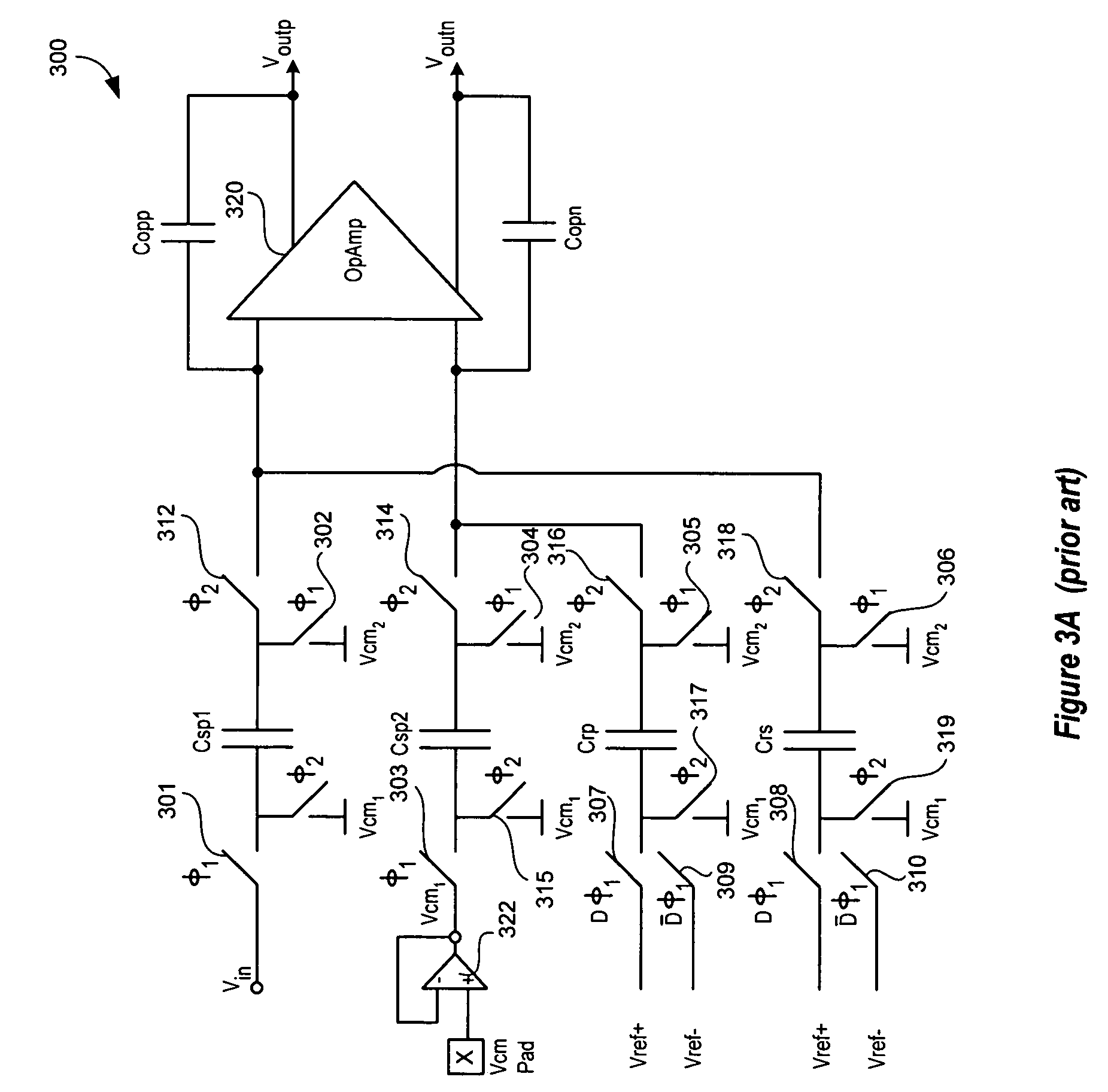
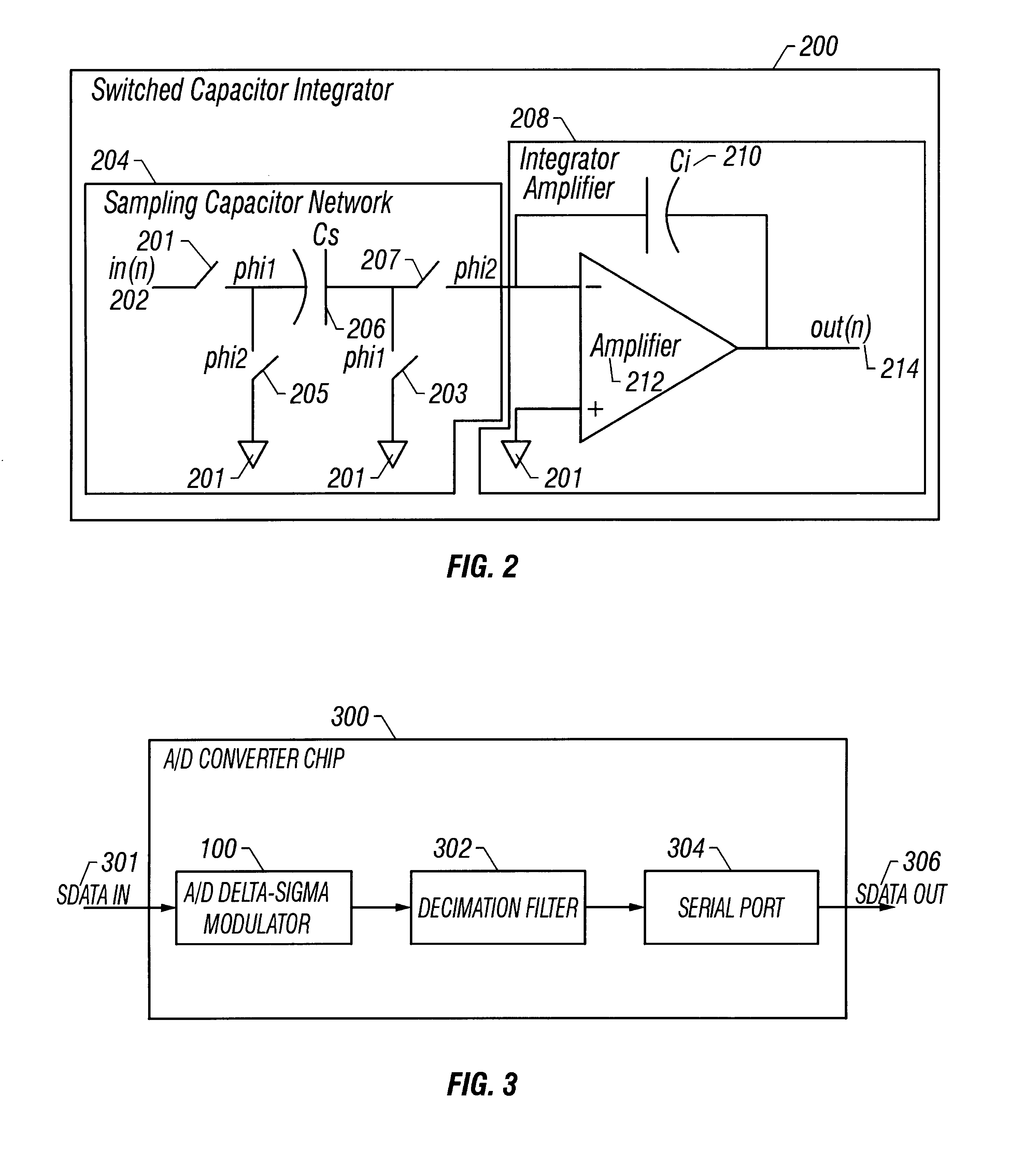
Signal processing systems described herein include an analog-to-digital delta sigma modulator to process a single-ended input signal using a single-ended analog feedback reference signal. The delta sigma modulator includes a switched capacitor circuit that integrates a difference between the single-ended input signal and the single-ended analog feedback signal derived from a quantization output of the delta sigma modulator. Embodiments of the switched capacitor circuit allow the delta sigma modulator to be implemented with fewer switches, less complicated reference signal generators, and smaller capacitors relative to conventional counterparts. Thus, embodiments of the delta sigma modulator described herein can cost less to build and use less power. Embodiments of the signal processing systems can be implemented in single and multi-bit delta sigma modulators and various sampling topologies, including single and double sampling topologies.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Multi-bit sigma-delta analog to digital converter with a variable full scale
InactiveUS6567025B2Analogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsLoop filterAnalog feedback
A multi-bit sigma-delta analog to digital converter has a quantizer, a loop filter circuit, and a digital to analog feedback circuit. The quantizer, loop filter, and digital to analog feedback circuit have a loop gain associated therewith. The quantizer and loop filter have a combined gain associated therewith. The full-scale of the digital to analog feedback circuit is varied. The combined gain of the quantizer and loop filter is also varied. More specifically, the combined gain of the quantizer and loop filter is varied in inverse proportion to the full-scale of the digital to analog feedback circuit to maintain the loop gain at a substantially constant level.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Delta-sigma analog-to-digital converter
ActiveUS6842129B1Electric signal transmission systemsDifferential modulationDigital analog converterDigital down converter
Systems and methods are provided for providing feedback to a delta-sigma analog-to-digital converter assembly. A noise shaper preprocesses an analog input signal according to an analog feedback signal and an associated transfer function. A quantizer converts the preprocessed analog input signal into a digital output signal. A delta-sigma modulator shapes noise within a sample of the digital output signal. A digital-to-analog converter converts the shaped digital signal into an analog signal to provide the analog feedback signal.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
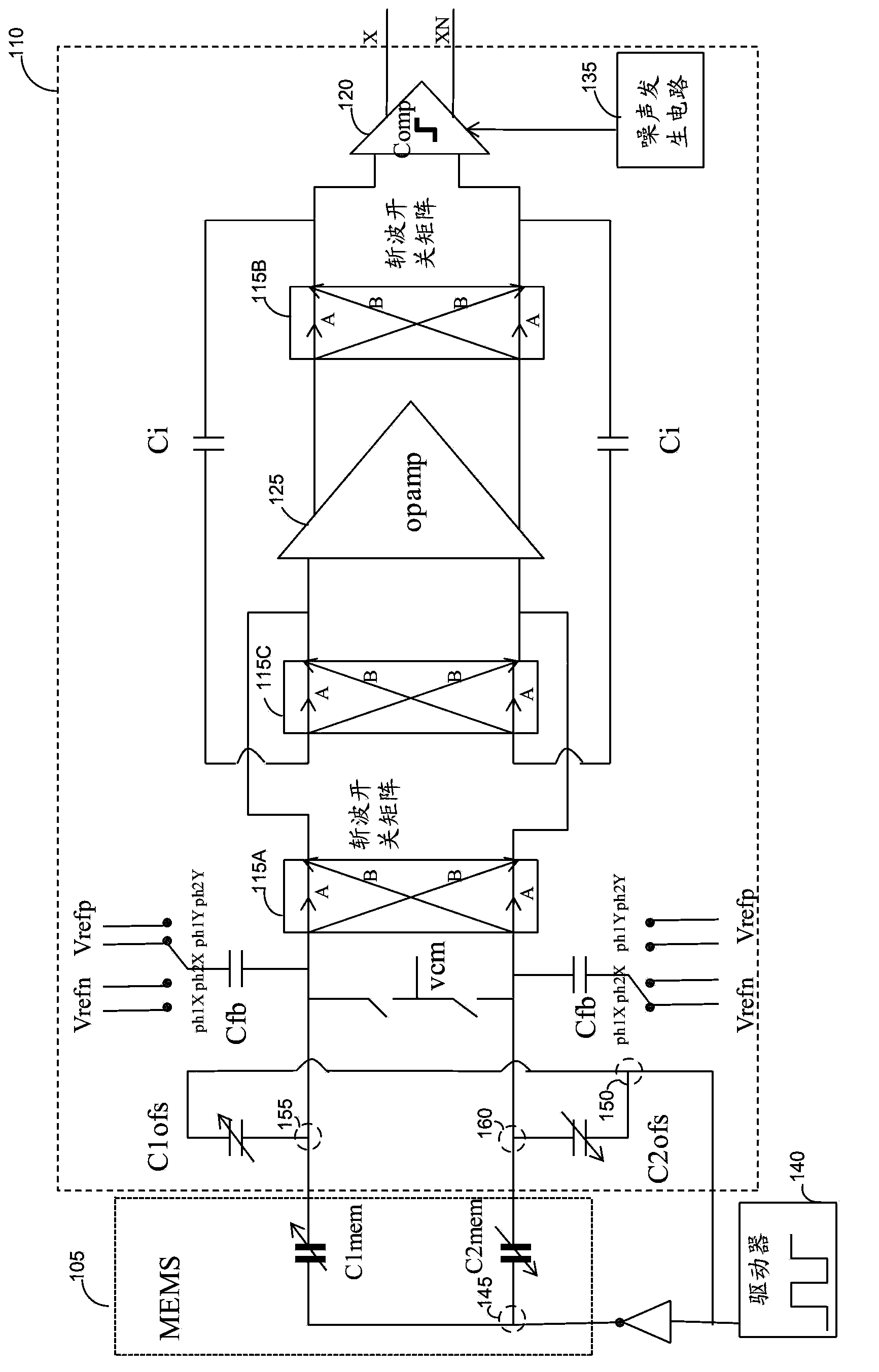
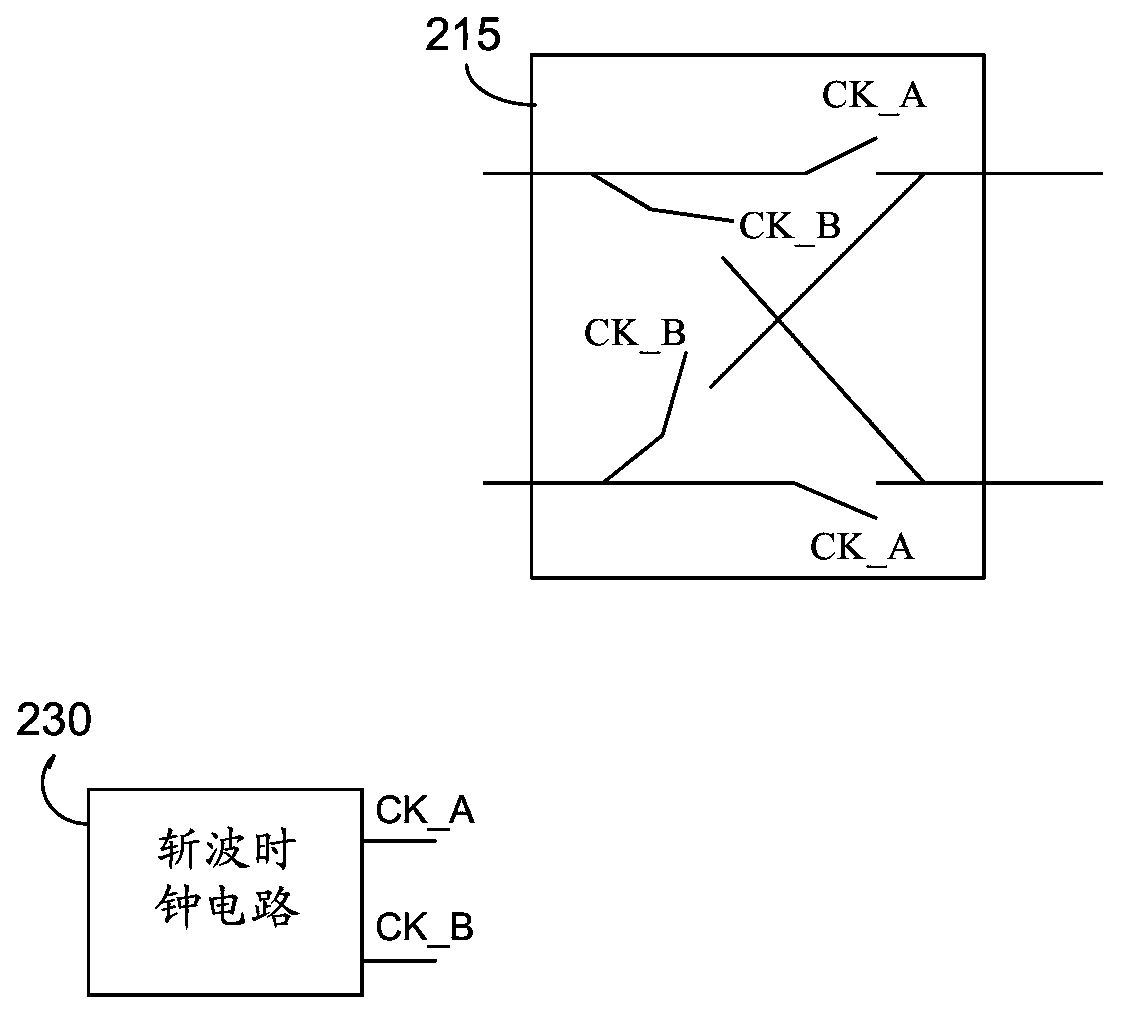
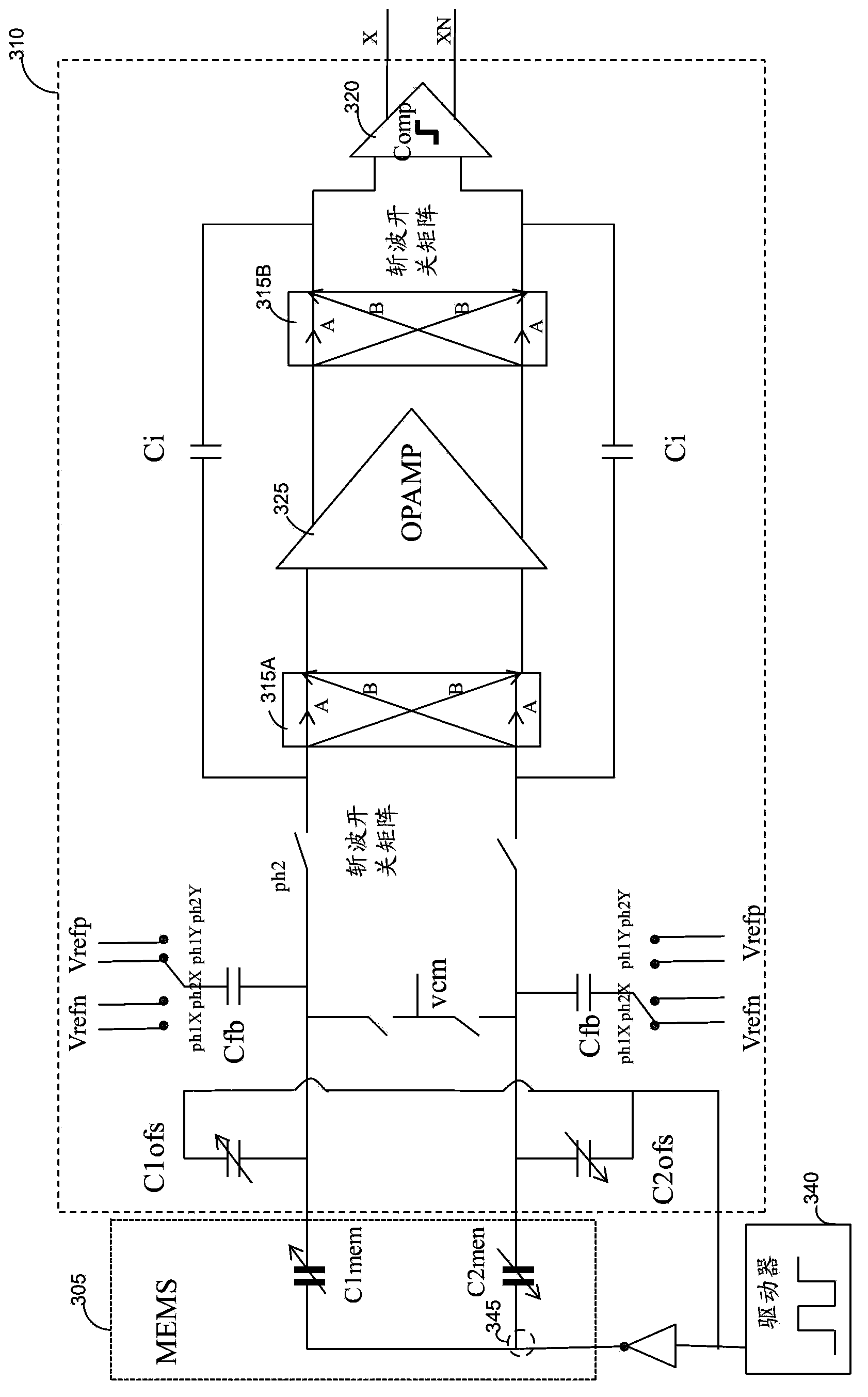
Noise reduction method and electronic cirucit based on merged MEMS accelerometer sensor chopping
The invention dislcoses a noise reduction method and an electronic cirucit based on merged MEMS accelerometer sensor chopping. An apparatus includes a capacitance-to-voltage converter circuit configured to be electrically connected to a micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) sensor circuit. The capacitance-to-voltage converter circuit includes a differential chopping circuit path configured to receive a differential MEMS sensor output signal and invert a polarity of the differential chopping circuit path, and a differential sigma-delta analog to digital converter (ADC) circuit configured to sample the differential MEMS sensor output signal and provide a digital signal representative of a change in capacitance of the MEMS sensor.
Owner:QST CORP
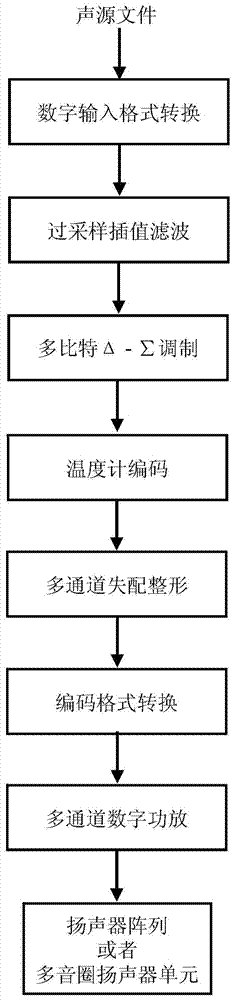
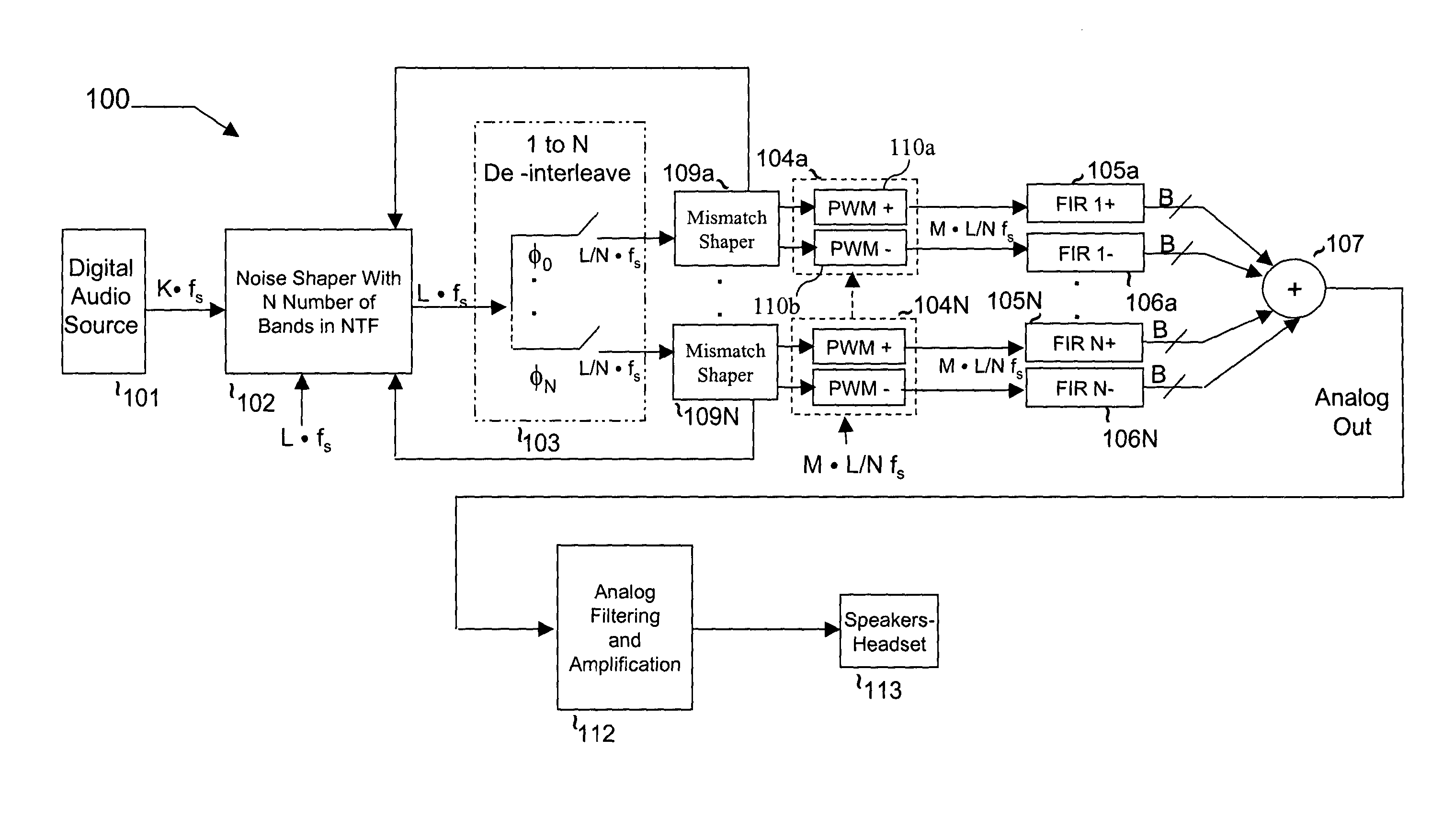
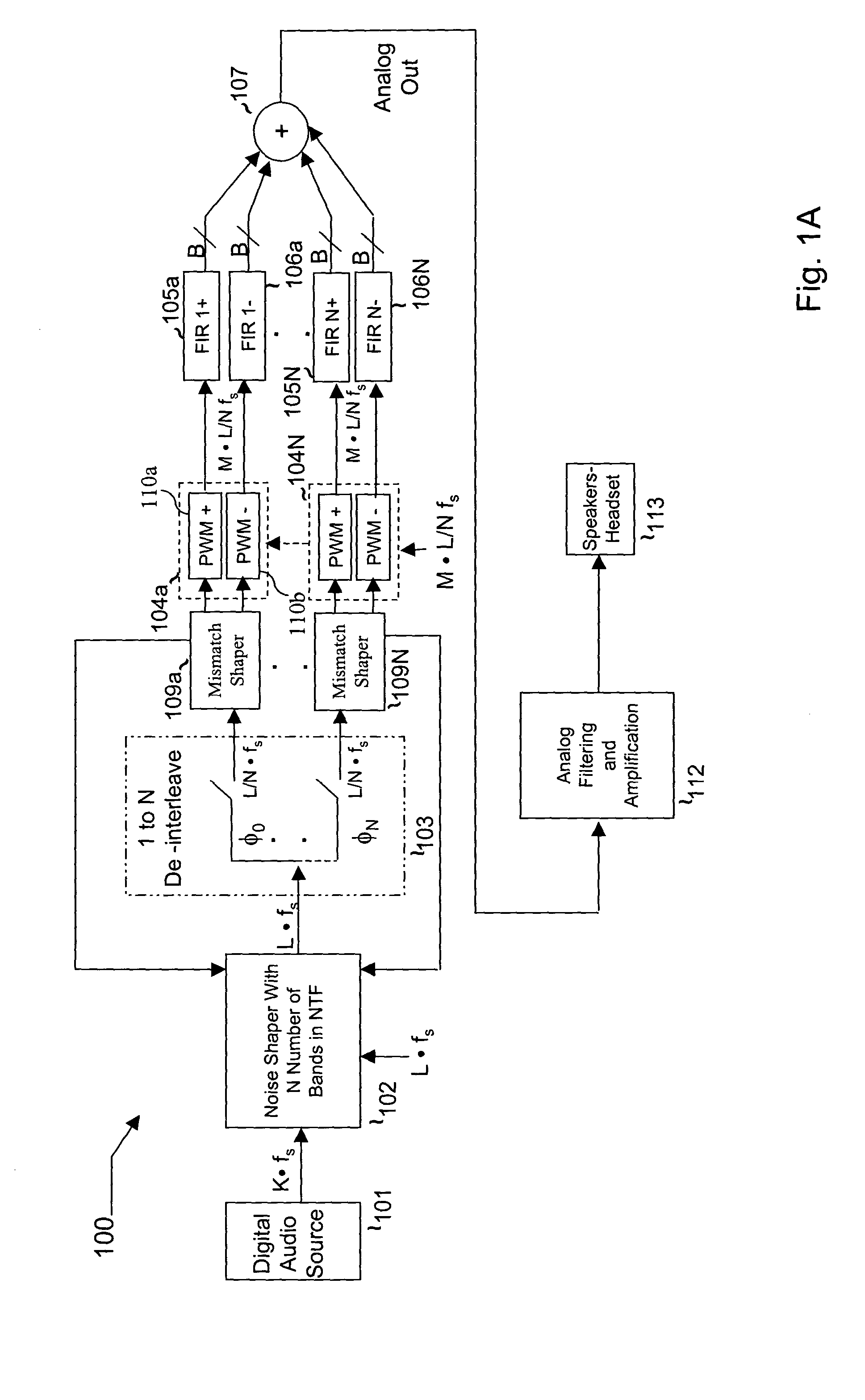
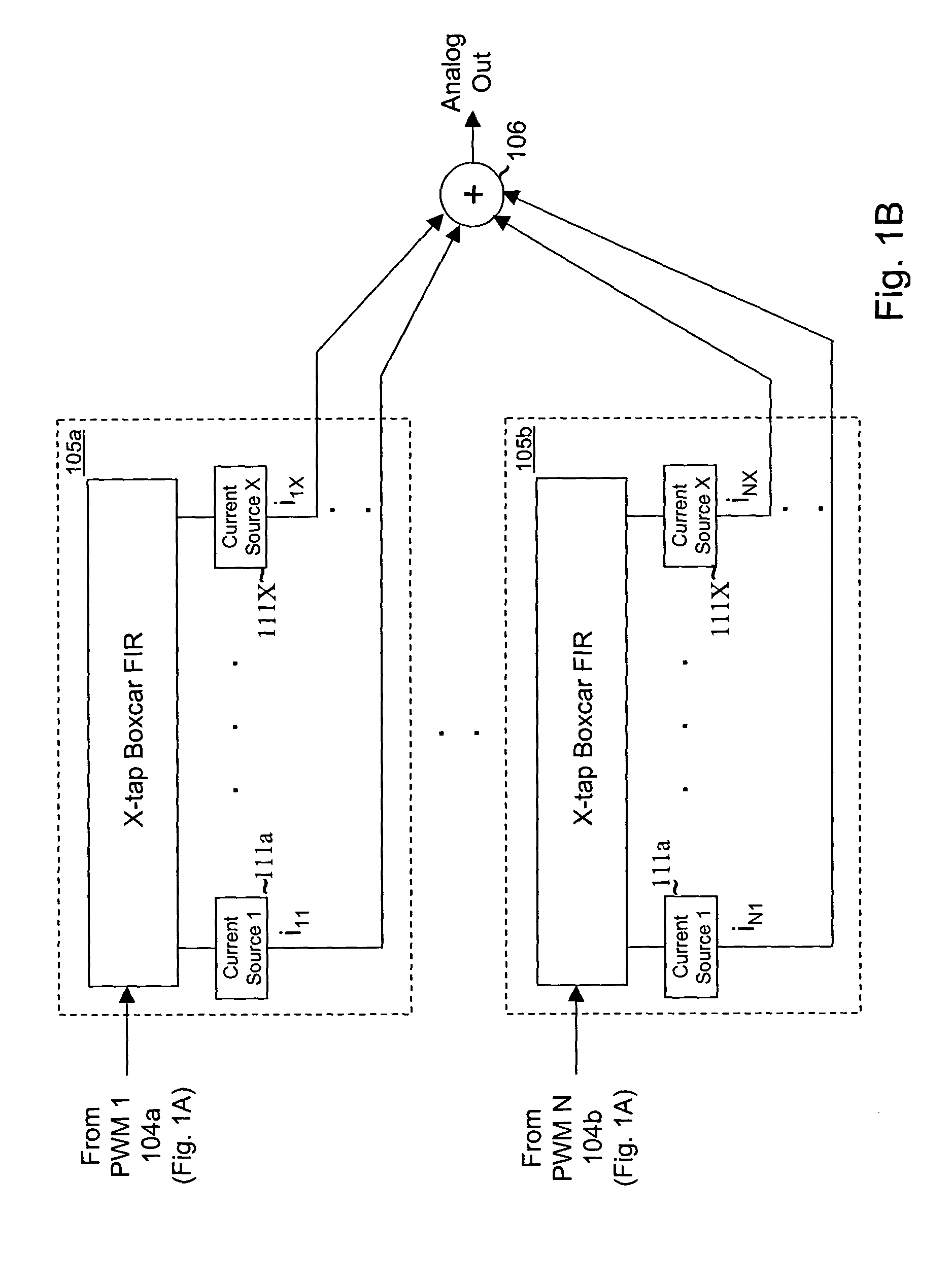
Multi-bit Delta-Sigma modulation-based digital speaker system implementation method and device
ActiveCN103701465AImprove battery lifeSave electricityDigitally weighted transducing elementsPower amplifiersLow voltageGreek letter sigma
The invention discloses a multi-bit Delta-Sigma modulation-based digital speaker system implementation method and device. The method comprises the following steps: 1) converting digital input formats; 2) performing oversampling interpolation filtering; 3) performing multi-bit Delta-Sigma modulation; 4) encoding a thermometer; 5) performing multi-channel mismatch-shaping; 6) converting encoding formats; 7) performing multi-channel digital power amplification; 8) driving a speaker array or a multi-voice coil speaker unit to phonate. The device comprises a digital input interface, an oversampling interpolation filter, a multi-bit Delta-Sigma modulator, a thermometer encoder, a multi-channel mismatch-shaper, an encoding format converter, a multi-channel digital amplifier, and a speaker array or multi-voice coil speaker unit which are sequentially connected. By adopting the method and the device, the high-power output under low-voltage power supply can be realized; the power consumption is reduced; the single chip integration of a multi-channel playback system is realized; the volume weight and the implementation cost of the system are reduced; the quality of playback voice is improved.
Owner:SUZHOU SONAVOX ELECTRONICS
Low distortion band-pass analog to digital converter with feed forward
ActiveUS6954159B1Improve toleranceReduces in-band noise degradationElectric signal transmission systemsDifferential modulationLow distortionDigital down converter
A low-distortion band-pass delta-sigma analog-to-digital converter (ADC), including an odd-phase sample and hold circuit coupled to a even-phase resonator, improves tolerance to mismatches between analog circuit components. The low-distortion ADC includes a feed-forward signal path that reduces, or eliminates, the input signal beyond the first summation point. In this way, the dynamic range and matching accuracy required of the resonator is reduced. An odd-phase sample and hold circuit shifts S / H spurious signals out-of-band. A two-phase resonator reduces in-band noise degradation caused by any mismatches between the resonator components.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Clock pulse generator apparatus with reduced jitter clock phase
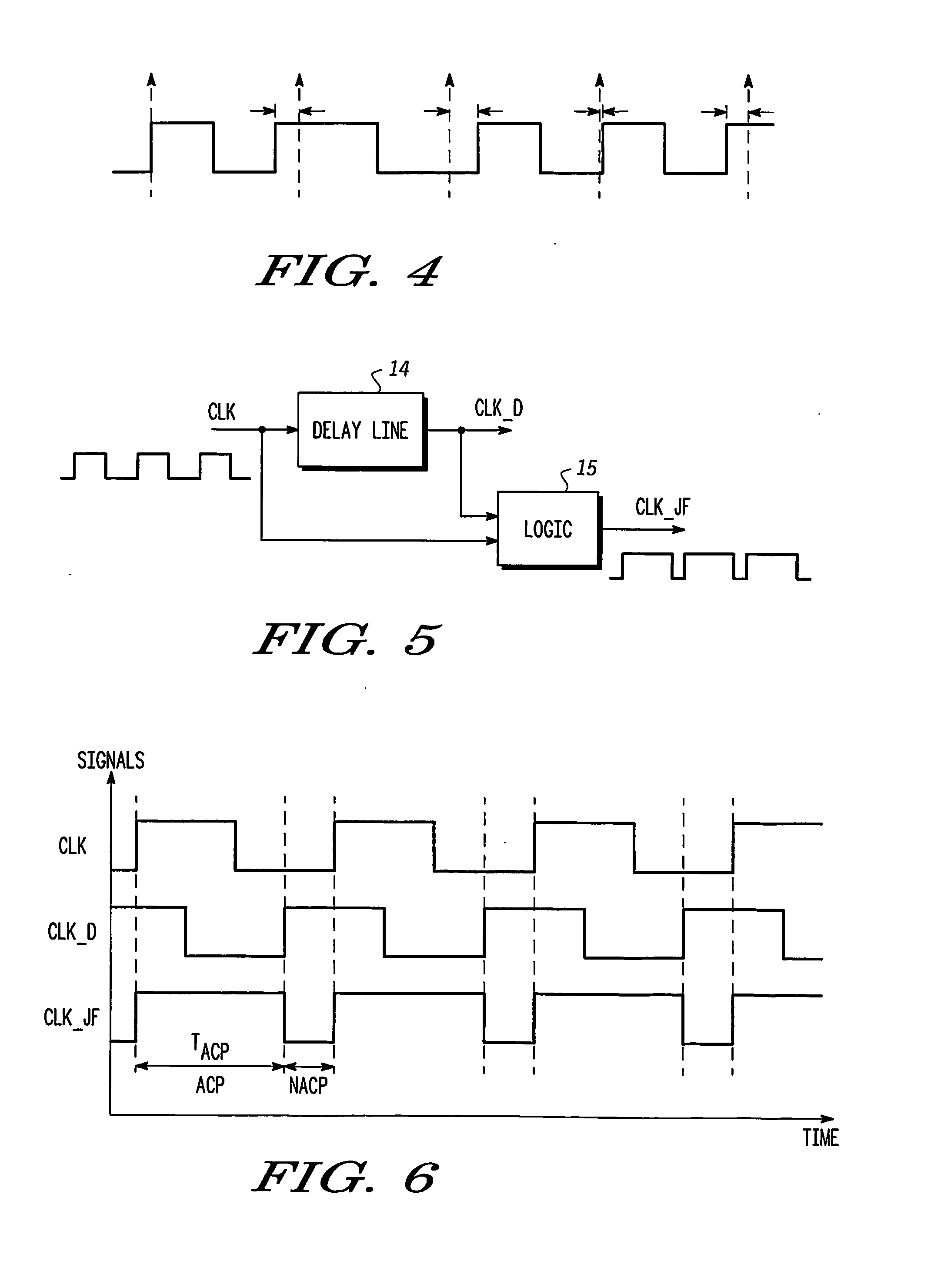
Clock pulse generator apparatus comprising a clock pulse generator for generating a train of primary clock pulses having leading and trailing edges. A delay line produces a train of delayed clock pulses presenting delayed edges whose timing relative to corresponding edges of the primary clock pulses is defined by the delay line. A logic circuit produces a train of combined clock pulses presenting leading and trailing edges defined alternately by one of the delayed edges and the corresponding edge of the primary clock pulse, so that the combined clock pulses comprise active clock phases having widths defined by the delay line; the variability of the widths of the active clock phases is smaller than the variability of the positions of the leading and trailing edges of the primary clock pulses.
Owner:FREESCALE SEMICON INC
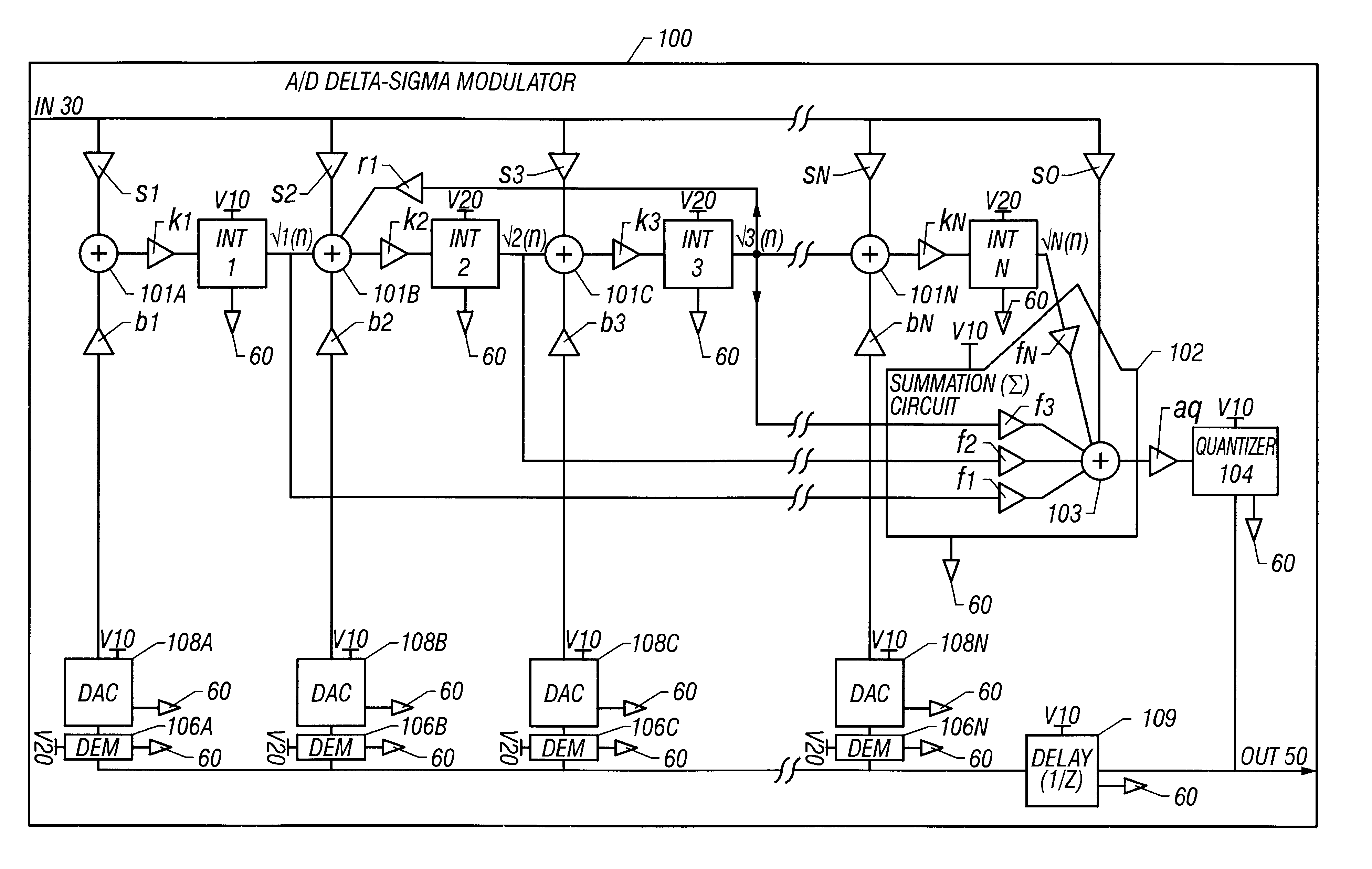
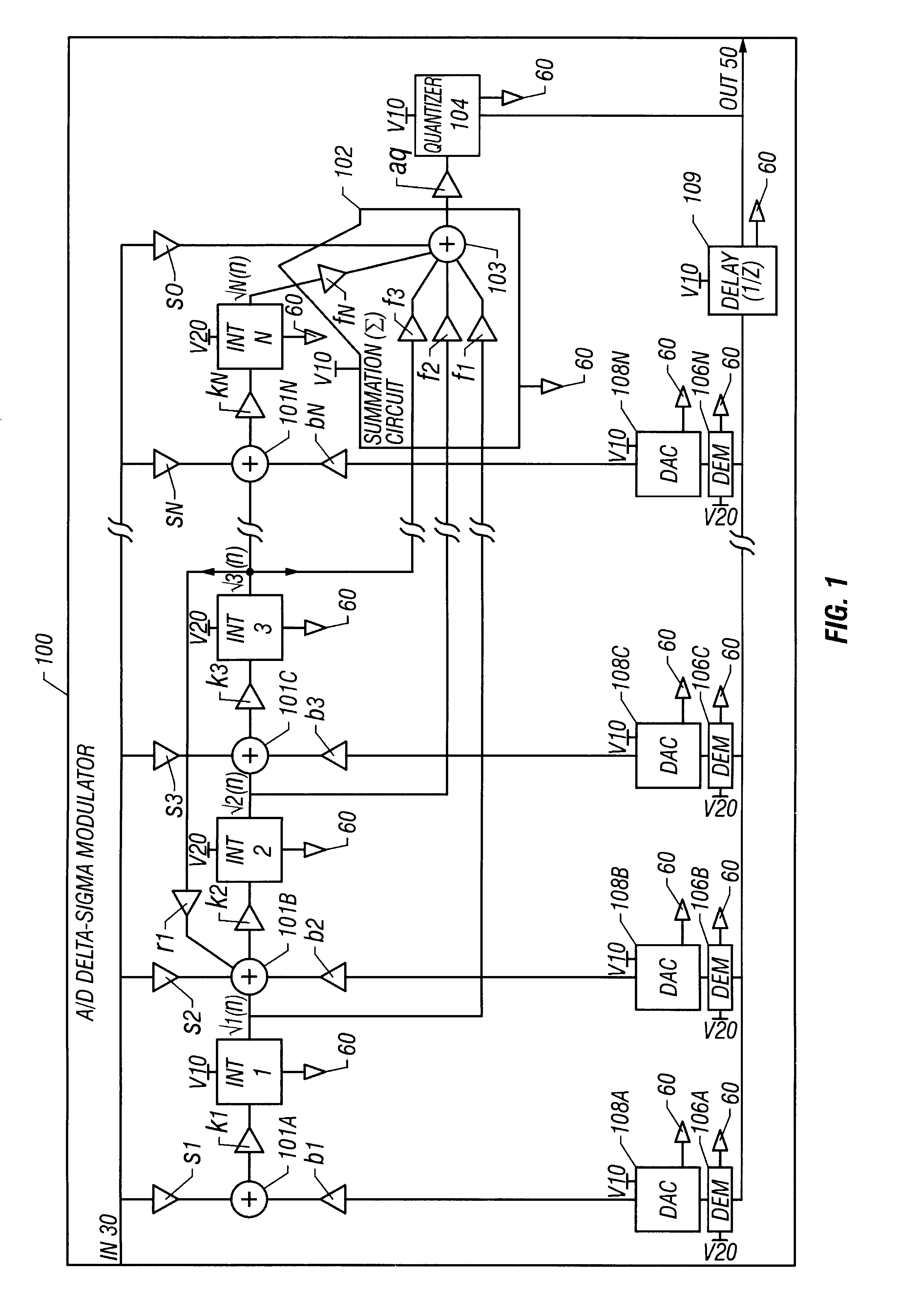
Method and system for operating two or more integrators with different power supplies for an analog-to-digital delta-sigma modulator
A method and system are disclosed for operating two or more integrator amplifiers with different power supplies for a modulator of an analog-to-digital ("A / D") converter. A first, upstream integrator is operated with one power supply, and the other downstream integrator(s) is / are operated with at least another power supply. The modulator has amplifiers with coefficient gains having values that are determined and set so that voltage levels for the at least another integrator are maintained within operating and output limits. An integrating coefficient gain k1 for the first integrator is set to have a sufficiently large value so that an integrating capacitor can be made small for the one integrator. Another integrating coefficient gain k2 for a second integrator is set to have a sufficiently small value so that an output voltage from the first integrator is sufficiently attenuated to a voltage value within an operating range of the second integrator.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Hybrid tuning circuit for continuous-time sigma-delta analog-to-digital converter
ActiveUS7095345B2Eliminate the problemReduce glitchesElectric signal transmission systemsResonant circuit detailsDigital down converterIntegrator
A hybrid tuning circuit is used consisting of a digital finite state machine and an analog tuning circuit to effectively keep the RC product of the continuous time integrator constant across process, temperature, supply, and sampling rate variations. Since the implementation is continuous, the tracking is more accurate than traditional techniques. Using a carefully chosen clocking scheme, the technique gets rid of inter-symbol interference in the feedback DAC. The technique does not use a reference frequency, thereby eliminating the need for a user to identify a reference frequency.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Delta-sigma modulators with improved noise performance
InactiveUS6956514B1Improve Noise PerformanceReducing in-loop noiseElectric signal transmission systemsDifferential modulationIntegratorAudio power amplifier
An integrator stage for use in a delta sigma modulator includes an operational amplifier, an integration capacitor coupling an output of the operational amplifier and a summing node at an input of the operational amplifier, and a feedback path. The feedback path includes first and second capacitors having first plates coupled electrically in common at a common plate node and switching circuitry for sampling selected reference voltages onto second plates of the capacitors during a sampling phase. The integrator stage further includes a switch for selectively coupling the common plate node and the summing node during an integration phase.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Data converters with ternary pulse width modulation output stages and methods and systems using the same
InactiveUS20050052304A1Increase inputHigh resolutionElectric signal transmission systemsDifferential modulationPulse width modulatedData conversion
A pulse width modulator includes at least one input for receiving an input signal and pulse width modulation circuitry for generating a pulse width modulated stream and another pulse width modulated stream. The pulse width modulated stream and the another pulse width modulated stream are nominally out of phase and together represent the received input signal. A summer sums the pulse width modulated stream and the another pulse width modulated stream to generate an analog output signal.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Delta sigma modulator analog-to-digital converters with quantizer output prediction and comparator reduction
ActiveUS7298305B2Reduce settingsElectric signal transmission systemsSpeech analysisLoop filterA d converter
The quantizers of delta sigma modulators in the signal processing systems described herein use a reduced set of comparators for quantization by predetermining and maintaining a maximum per cycle deviation d between a loop filter output signal VLF(t) and a predicted quantizer output signal qest. In at least one embodiment, a maximum quantizer level deviation d is defined in terms of a number of quantization levels. Thus, the number of comparators in a quantizer needed to quantize the quantizer input signal Vin(t) is based on the maximum quantizer level deviation d. In addition to using fewer comparators than available quantization output levels N, the quantizers can use an even number of comparators M, in contrast to comparable conventional reduced comparator ADC tracking quantizer designs using M+1 number of comparators, where N and Mare integers and M<N.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
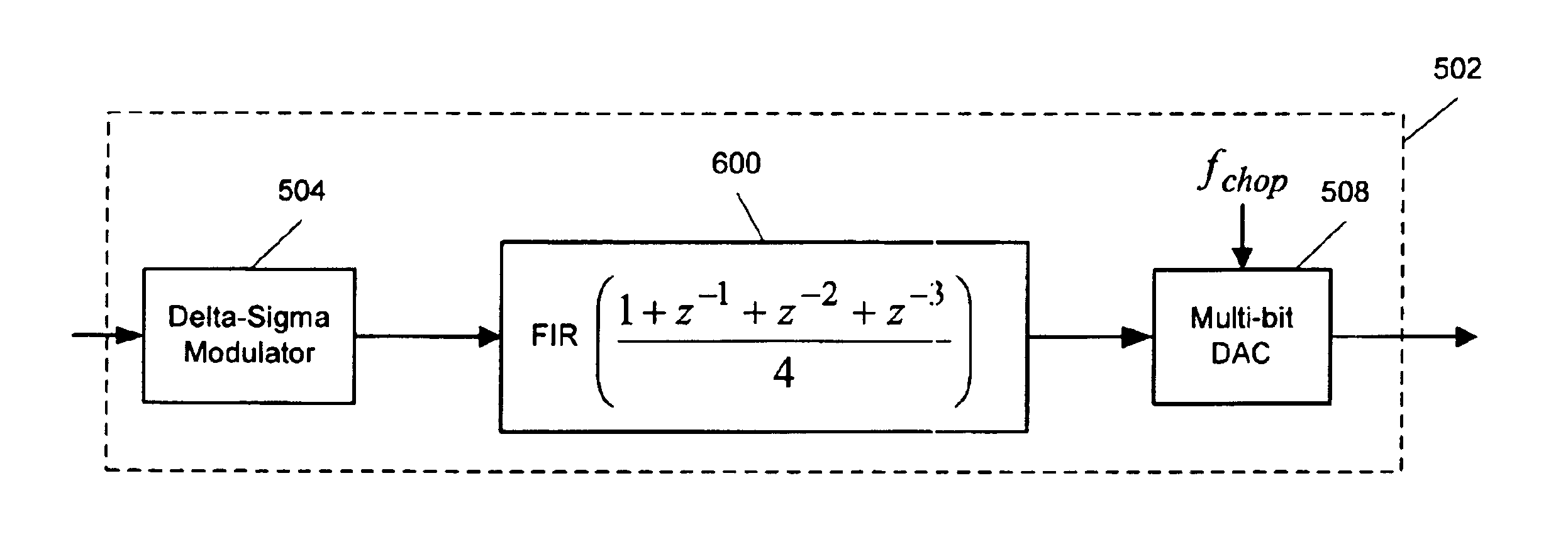
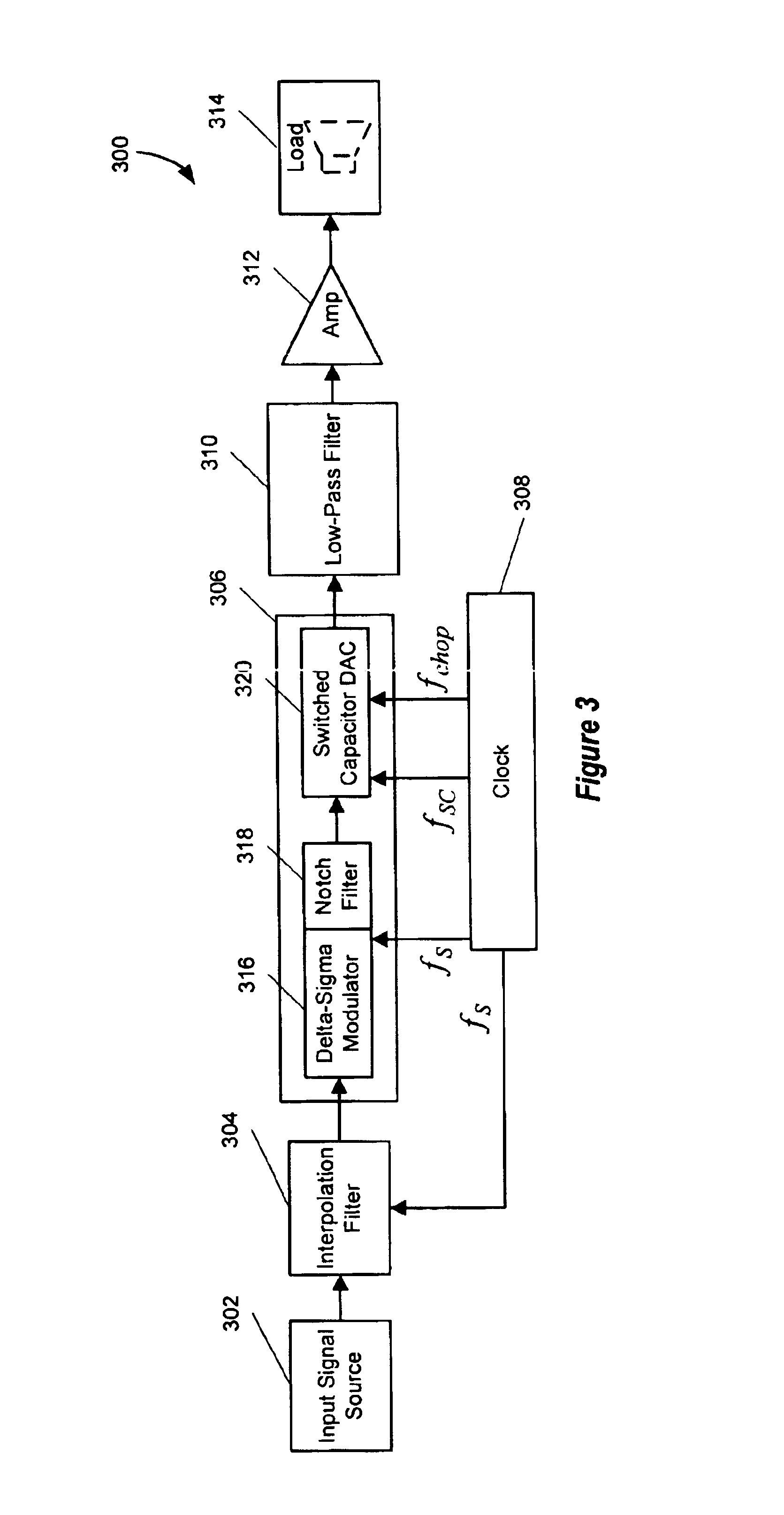
Signal processing system with baseband noise modulation and noise filtering
ActiveUS6861968B2Reduce the introductionCancel noiseElectric signal transmission systemsCurrent/voltage measurementHarmonicSignal of interest
A digital-to-analog converter (“DAC”) system utilizes notch filters and chopping modulation technology to remove l / f and other baseband noise from a baseband of a signal of interest. Chopping modulation and demodulation circuitry of the DAC operate at a chopping frequency and all harmonics equal to approximately one-half of a digital input signal sampling frequency. A notch filter attenuates signals having frequencies around the chopping frequency prior to chopping to reduce fold back of noise into the baseband due to parasitic modulation. Another notch filter attenuating signals having frequencies around twice the chopping frequency further reduces fold back of noise into the baseband.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Delta-sigma modulators with improved noise performance
InactiveUS6873276B2Improve performanceImprove Noise PerformanceElectric signal transmission systemsDifferential modulationIntegratorAudio power amplifier
An integrator stage for use in a delta sigma modulator includes an operational amplifier, an integration capacitor coupling an output of the operational amplifier and a summing node at an input of the operational amplifier, and a feedback path. The feedback path includes first and second capacitors having first plates coupled electrically in common at a common plate node and switching circuitry for sampling selected reference voltages onto second plates of the capacitors during a sampling phase. The integrator stage further includes a switch for selectively coupling the common plate node and the summing node during an integration phase.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
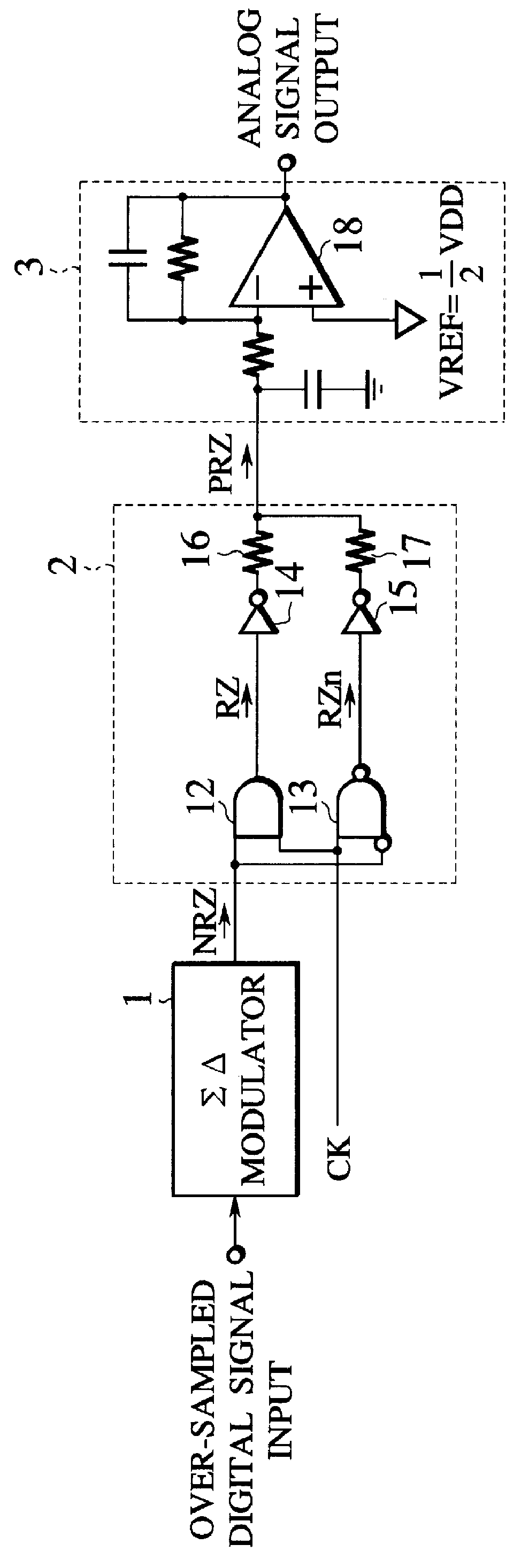
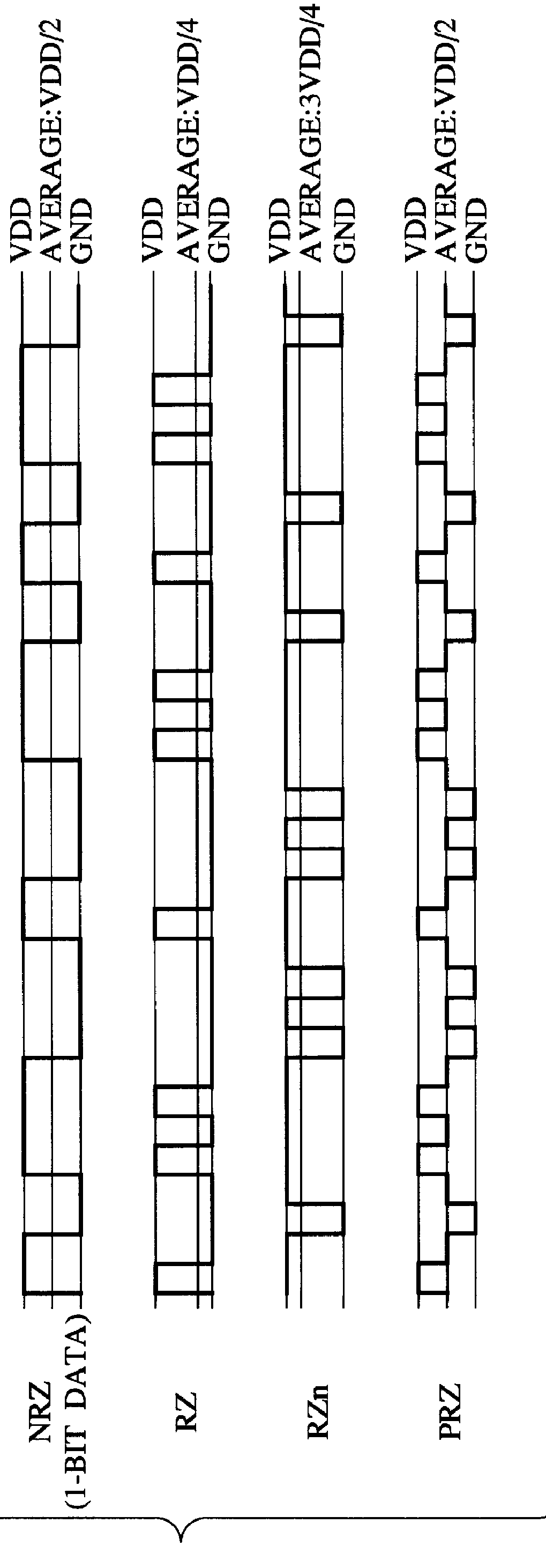
D/A converter
There is provided an over-sampling D / A converter which has a mute function for fixing an average DC potential of an analog output signal to a predetermined potential, and comprises a SIGMA DELTA modulator for receiving a multibit digital signal to which a DC offset value is added and then outputting a one-bit non-return-to-zero signal, a signal generator for receiving the non-return-to-zero signal and the clock signal, then generating a return-to-zero signal which is a logical multiplication of the non-return-to-zero signal and the clock signal and a complementary signal of the return-to-zero signal which is a logical addition of the non-return-to-zero signal and an inverted signal of the clock signal, and then adding the return-to-zero signal to the complementary signal of the return-to-zero signal to thus output a polar-return-to-zero signal, and an analog filter for receiving the polar-return-to-zero signal and then outputting an analog signal. Accordingly, because an average DC potential of an output signal at the time of the mute operation-ON is set substantially equal to the average DC potential of the output signal at the time of the mute operation-OFF, variation in the average DC potential in the output signal due to ON / OFF of the mute operation can be prevented. As a result, generation of audible click noises can be prevented.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com