Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1139 results about "Clock phase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
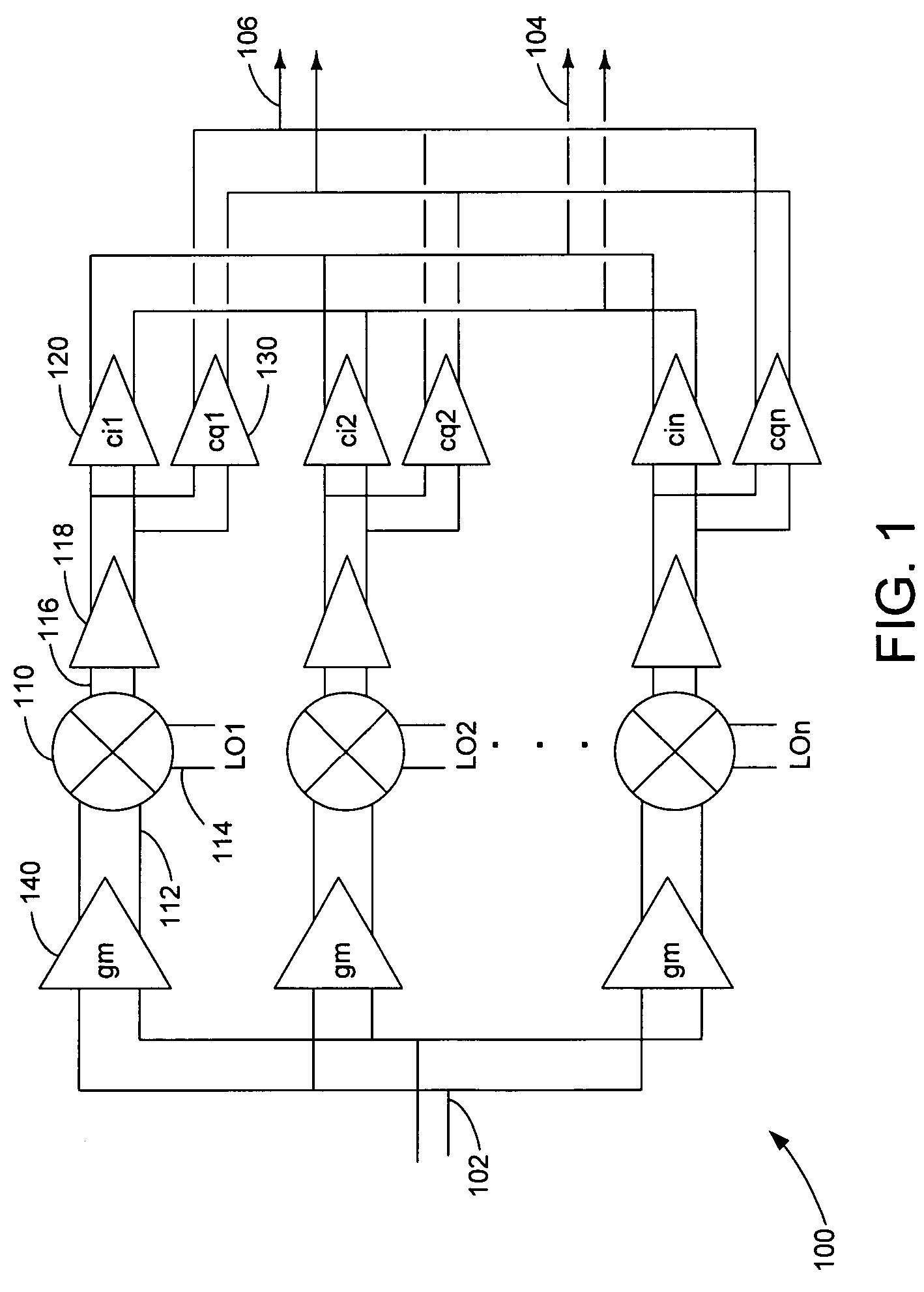
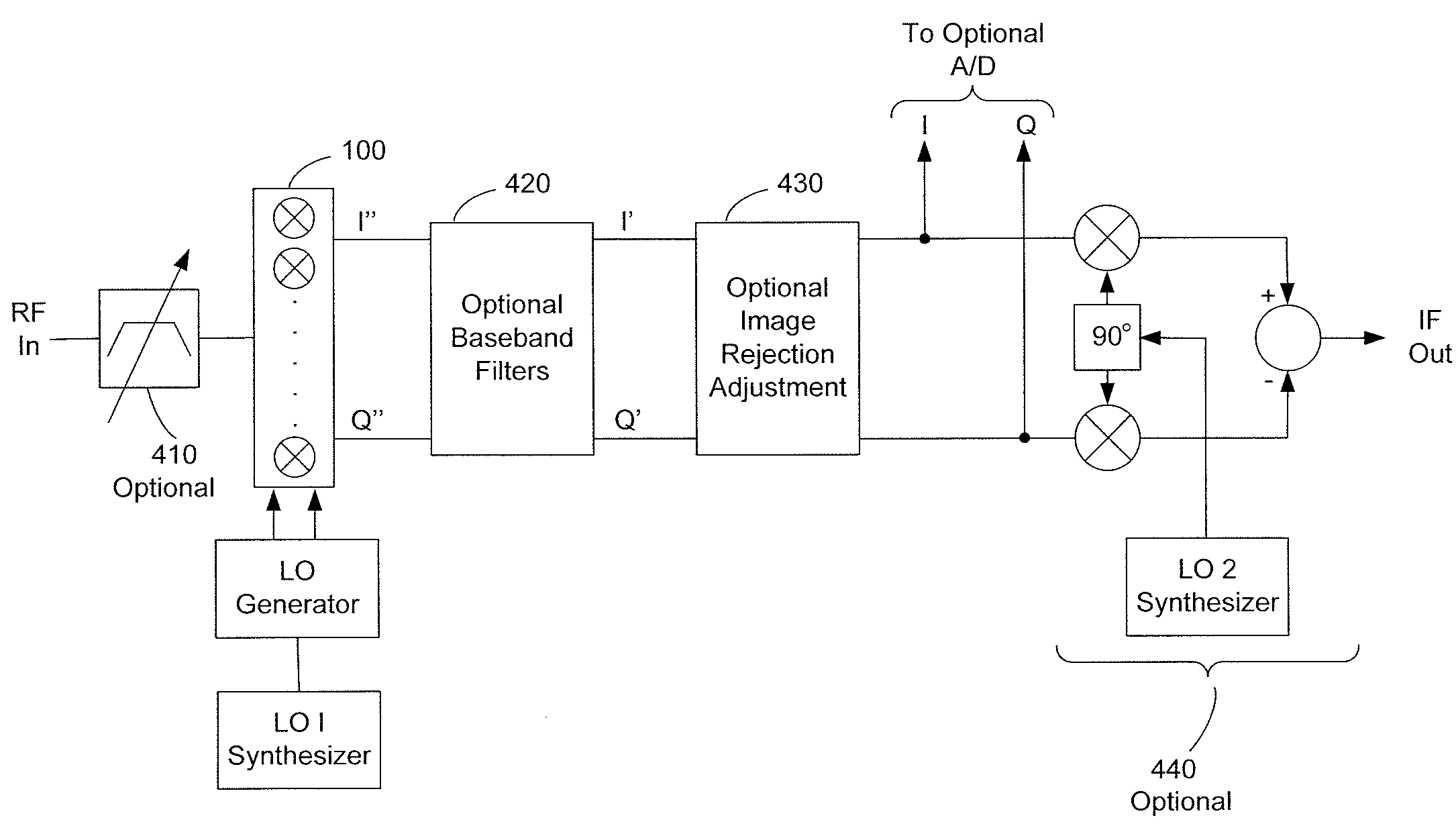
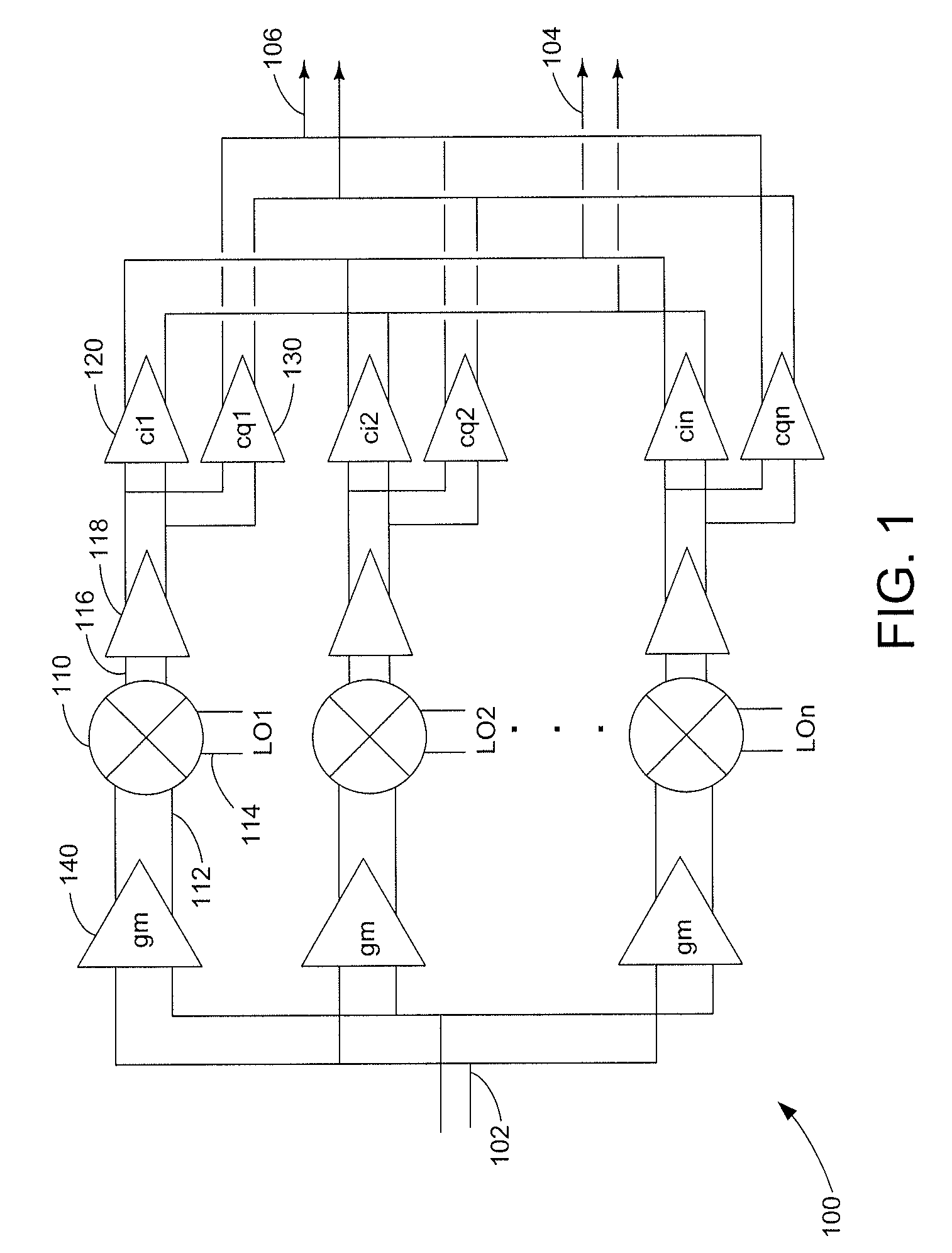
Harmonic suppression mixer and tuner
ActiveUS20050239430A1Enhanced inhibitory effectLess harmonic suppressionModulation transference balanced arrangementsTransmissionLow noiseHarmonic mitigation
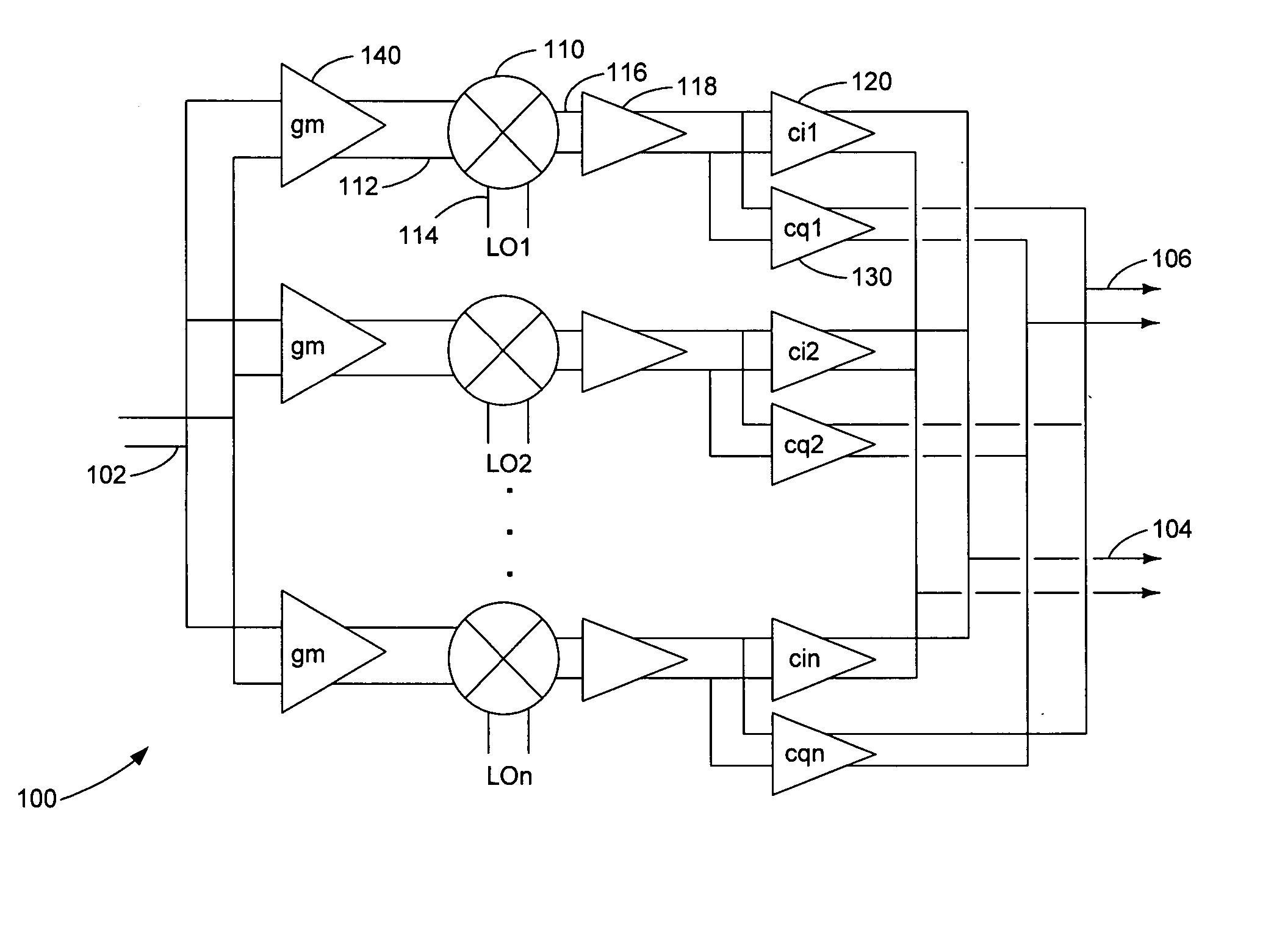
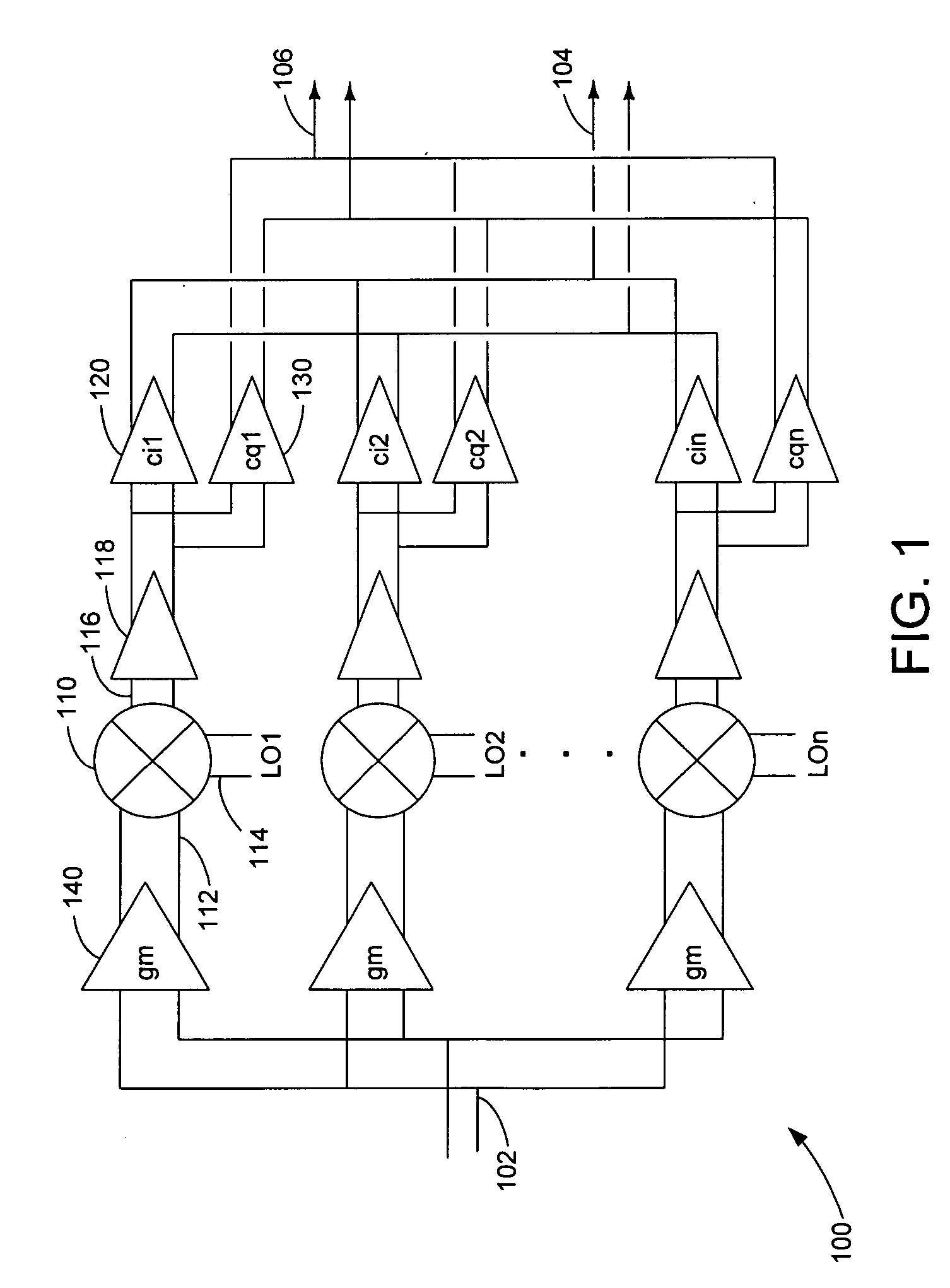
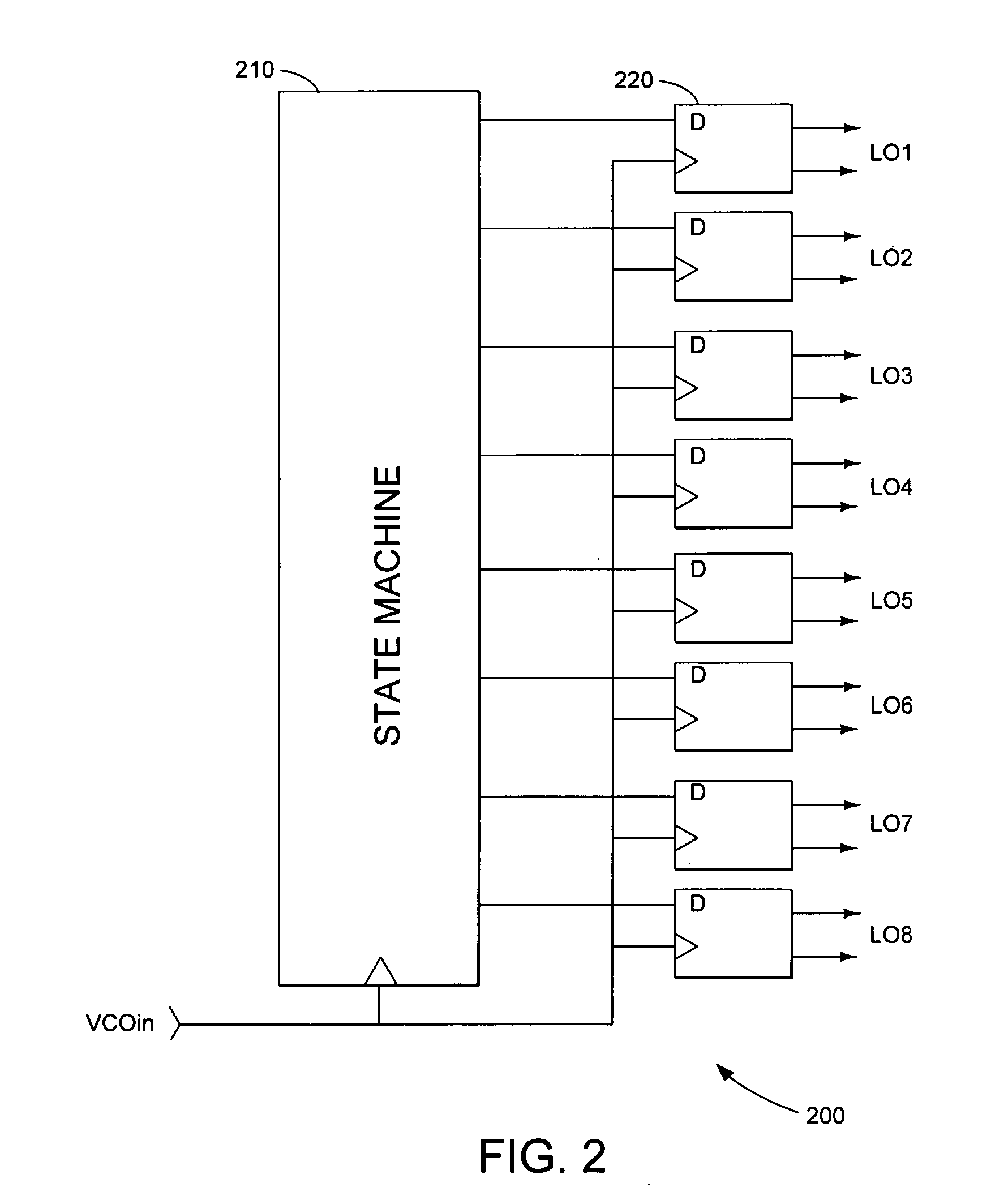
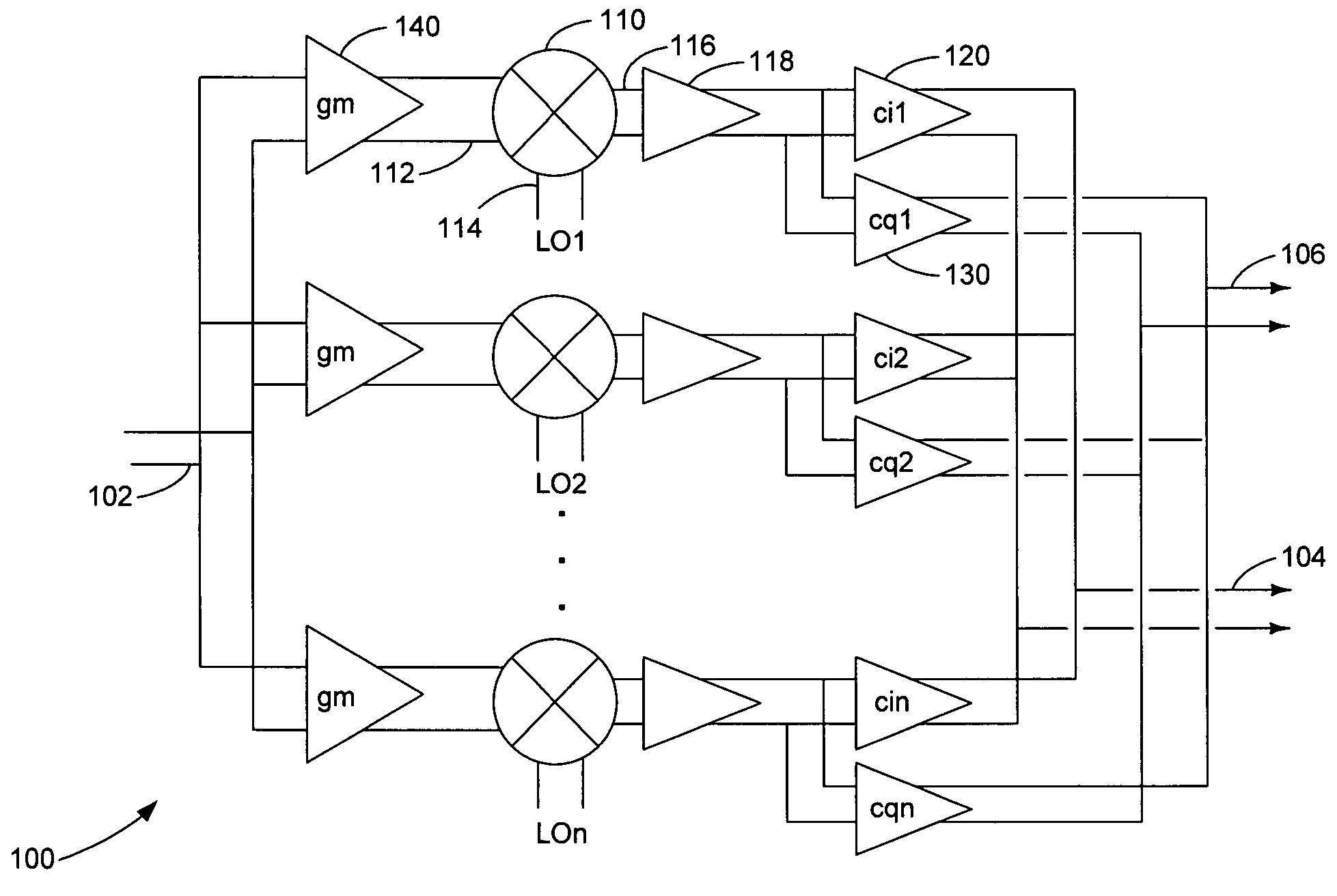
A harmonic suppression mixer for down converting an RF signal to a complex I and Q baseband signal that uses a plurality of switching mixers each with a gain stage to produce a sinusoidal weighted sum of the mixer outputs. Odd harmonics output by each switching mixer is suppressed in the composite signal. A low skew local oscillator (LO) clock generator creates multiple LO phases and drives the mixers. The mixer can be used in low noise direct conversion RF tuners. The mixer is configurable by programming gain stage coefficient values to achieve a variable number of effective mixers used in combination. At low tuning frequencies, all available mixers are programmed with unique coefficients and driven by different LO clock phases to achieve maximum harmonic suppression. At high tuning frequencies, some mixers are paralleled and duplicate coefficients are programmed or mixers are disabled to reduce the number of effective mixers.
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
Harmonic suppression mixer and tuner
ActiveUS7519348B2Reduce leakageEnhanced inhibitory effectModulation transference balanced arrangementsTransmissionLow noiseHarmonic mitigation
A harmonic suppression mixer for down converting an RF signal to a complex I and Q baseband signal that uses a plurality of switching mixers each with a gain stage to produce a sinusoidal weighted sum of the mixer outputs. Odd harmonics output by each switching mixer is suppressed in the composite signal. A low skew local oscillator (LO) clock generator creates multiple LO phases and drives the mixers. The mixer can be used in low noise direct conversion RF tuners. The mixer is configurable by programming gain stage coefficient values to achieve a variable number of effective mixers used in combination. At low tuning frequencies, all available mixers are programmed with unique coefficients and driven by different LO clock phases to achieve maximum harmonic suppression. At high tuning frequencies, some mixers are paralleled and duplicate coefficients are programmed or mixers are disabled to reduce the number of effective mixers.
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
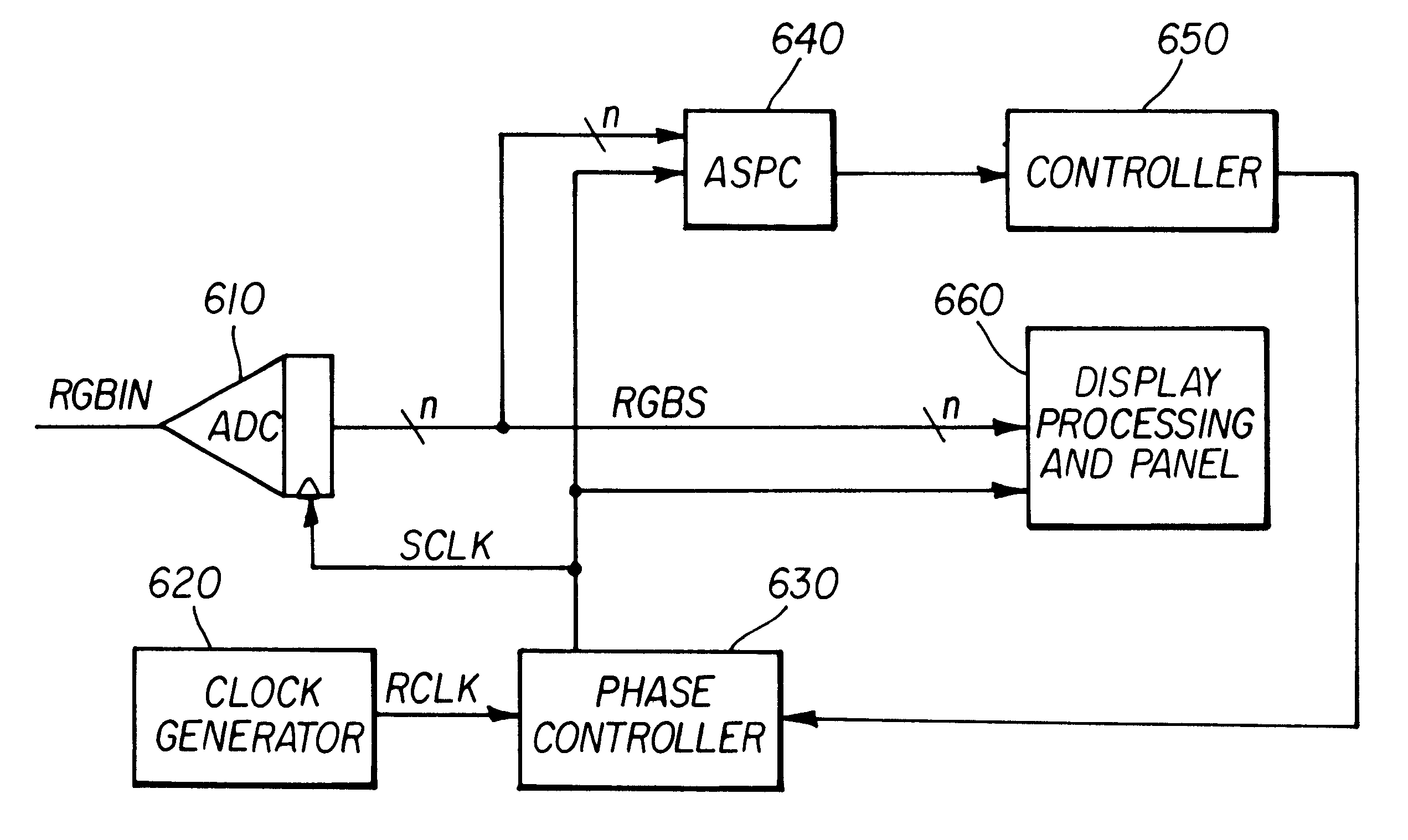
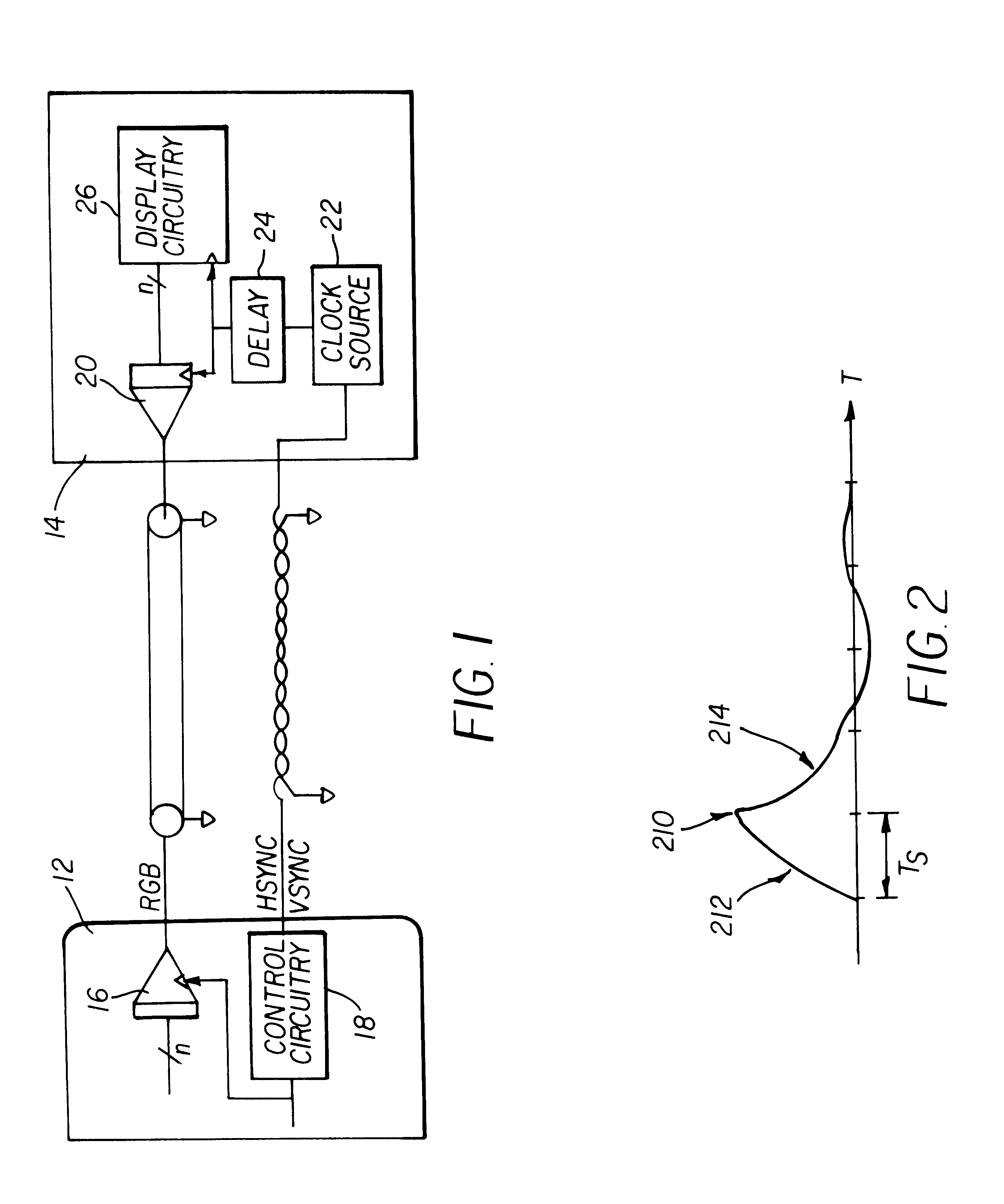
Method and apparatus implemented in an automatic sampling phase control system for digital monitors
InactiveUS6268848B1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsControl systemPhase control
An automatic sampling control system for digital monitors. A clock generation circuit generates a sampling clock. A phase controller modifies the phase of the sampling clock by a phase amount. An ADC samples a frame of an analog display signal to generate digital samples. A value which is a function of the samples is generated. The function generally generates a larger value with correspondingly large sample values. The phase amount is modified for successive image frames until a maximum function value is generated. When successive image frames do not change substantially in image content, the phase amount represents the optimal phase change for the sampling clock. If the image content is changing substantially, the phase adjustment may be disabled.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
Apparatus and method for freezing the states of a receiver during silent line state operation of a network device
InactiveUS7327754B2Reduce the required powerAvoid data lossEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementMostly TrueLoop bandwidth
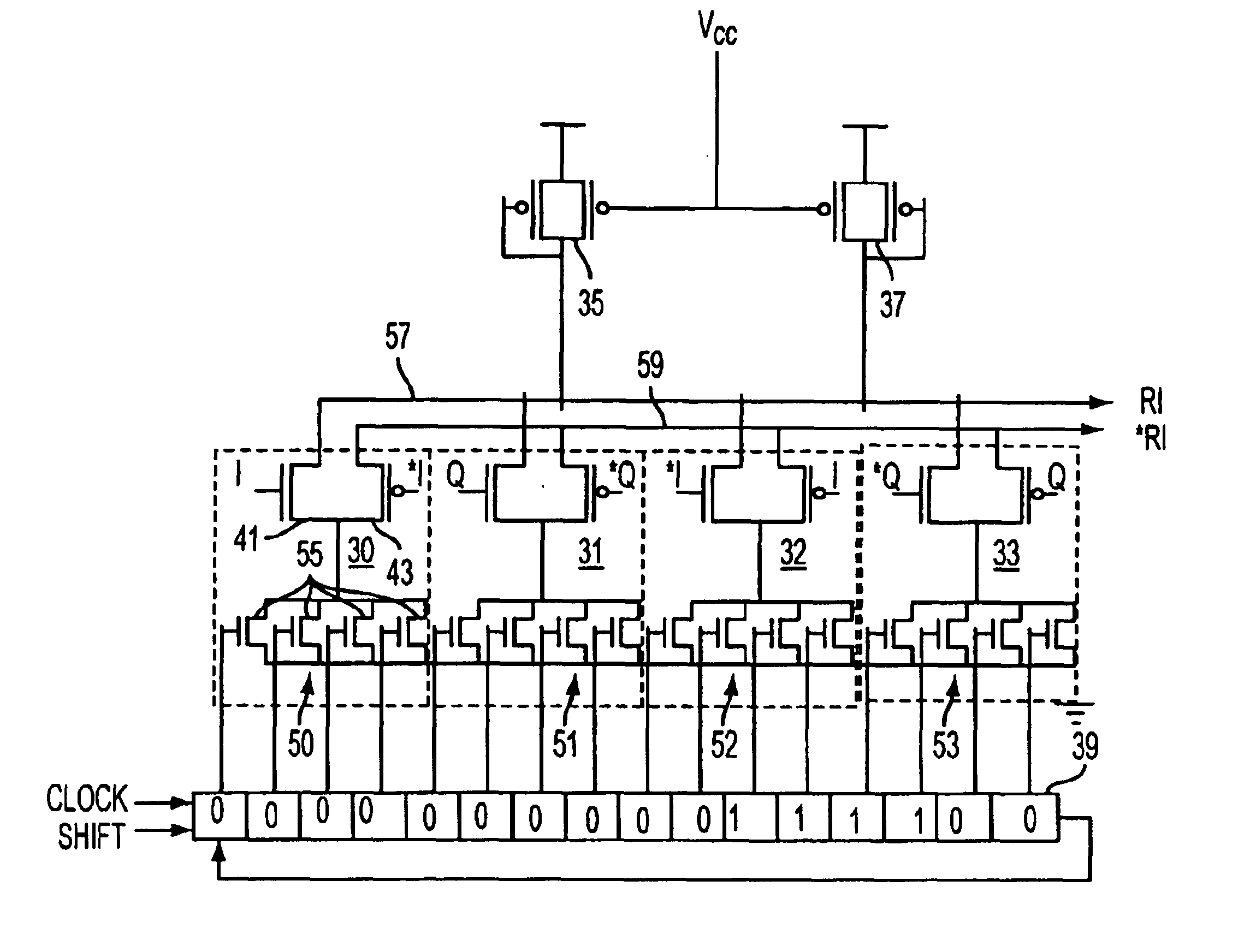
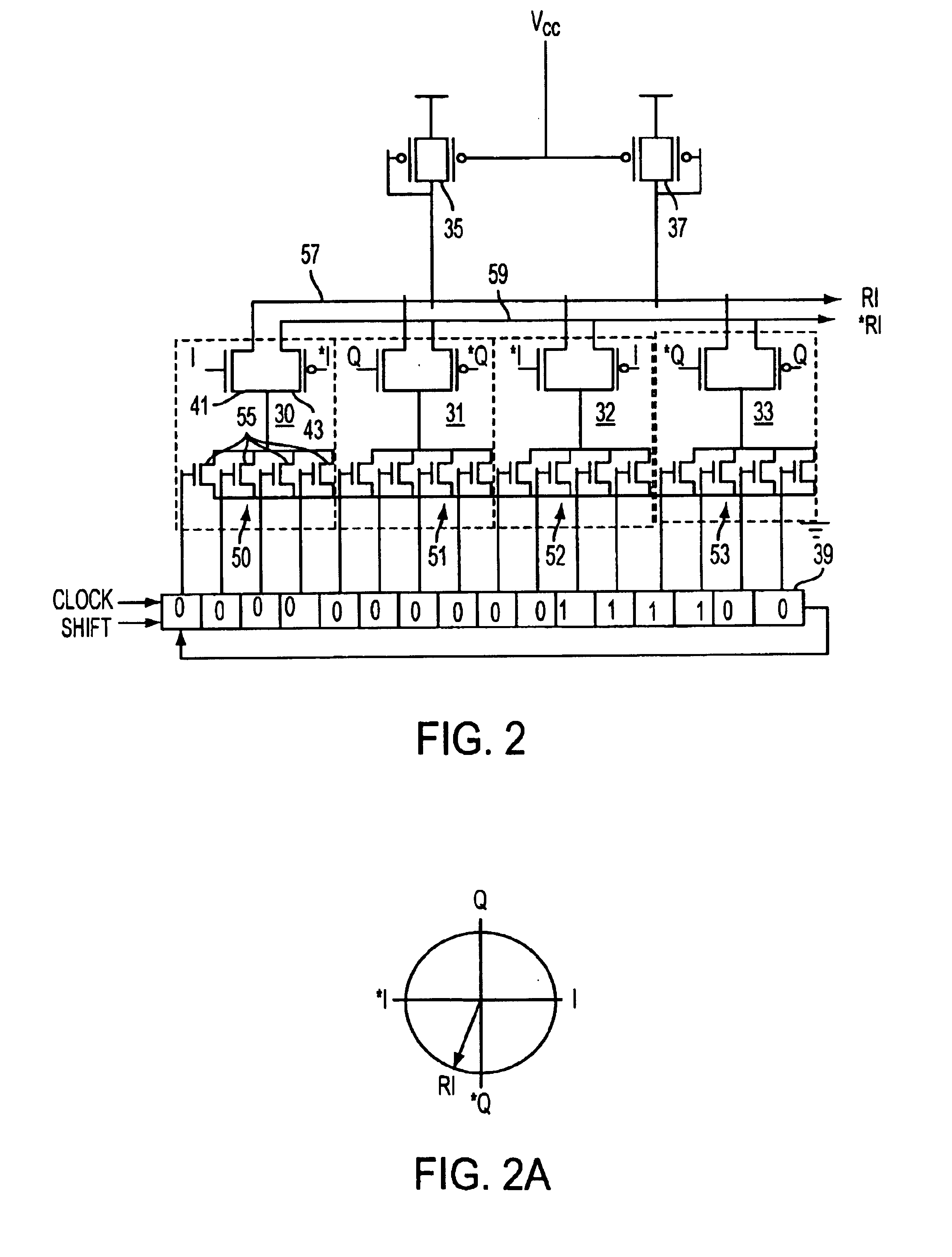
A method for maintaining the states of a receiver during the silent line state of a network device operating in a low power link suspend mode is presented. Accordingly, a method of freezing the states of the equalizer and keeping the receiver clock locked to a frequency that is approximately equal to that of the input data while providing for rapid adjustment to the phase and thus recovery of the input data is presented. During Silent Line State (SLS), the receiver states are frozen using methods that avoid parasitic decay. Also, the receive clock phase lock loop is locked onto the local transmit clock since the local transmit clock has a frequency approximating the incoming data frequency. During the SLS, the transmitter of the remote network device may have been turned off to conserve power therefore the receiver has no way of immediately knowing the phase of an incoming data. Thus, in order to prevent loss of data, the receiver loops of the receiving network device are trained to the frequency of the transmitting remote network device using periodic Link Suspend packets. Thus, in most cases, only the phase of the incoming signal need be acquired when data arrives. The phase may be quickly acquired using loop bandwidth shift methods whereby the receive clock phase lock loop bandwidth is increased to a value that aids rapid acquisition of the input clock and then, after acquisition, the bandwidth is shifted to a low value to enhance noise rejection during tracking.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Adjusting sampling phase in a baud-rate CDR using timing skew
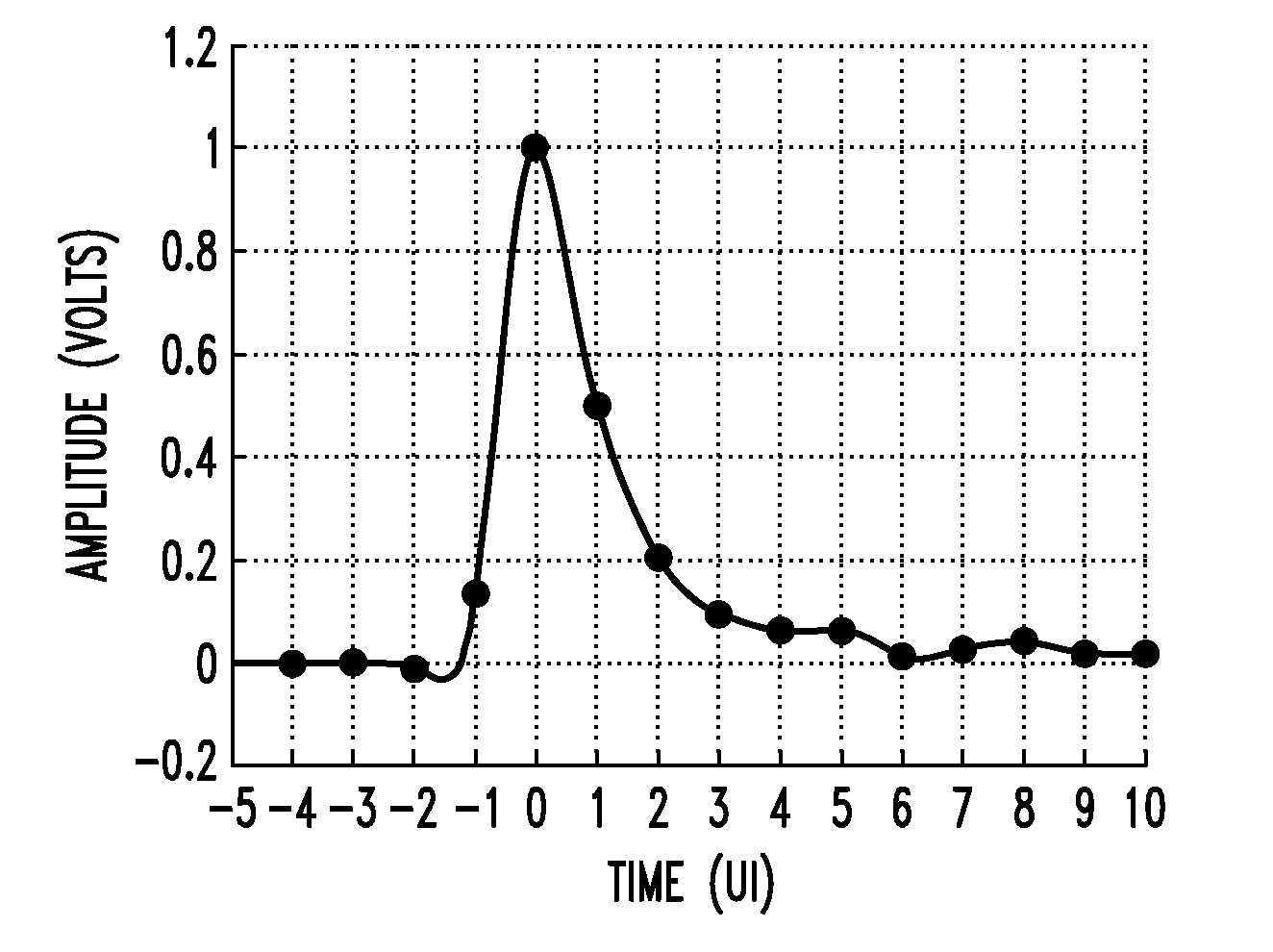
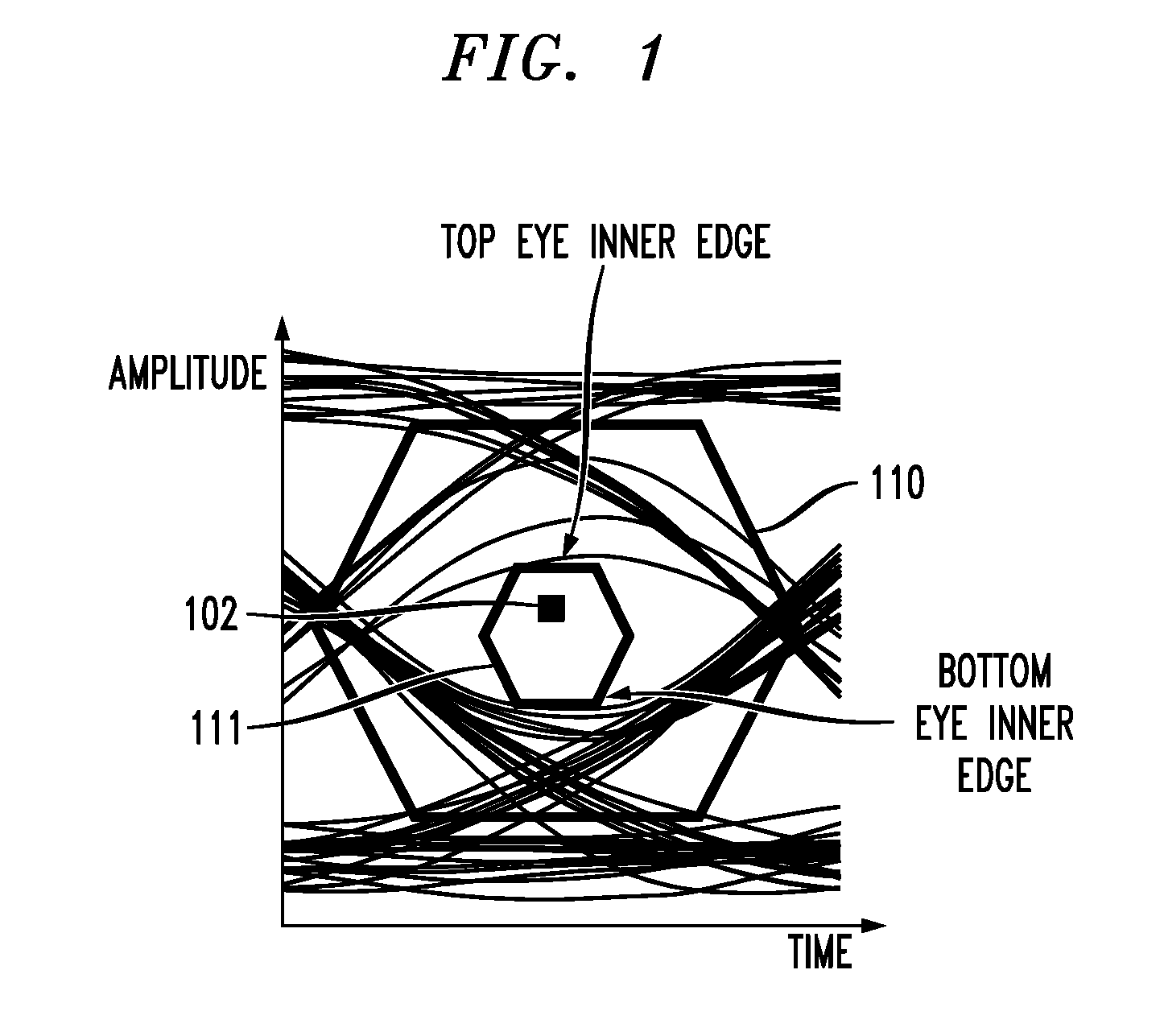
In described embodiments, a transceiver includes a baud-rate clock and data recovery (CDR) module with an eye sampler, and an adaptation module for adaptively setting parameters of various circuit elements, such as timing, equalizer and gain elements. Data sampling clock phase of the CDR module is set for sampling at, for example, near the center of a data eye detected by the eye sampler, and the phase of data error sampling latch(es) is skewed by the CDR module with respect to the phase of the data sampling latch. Since the error signal driving the timing adaptation contains the information of the pulse response that the CDR module encounters, the phase of timing error sampling latch(es) of the CDR module is skewed based on maintaining a relative equivalence of input pulse response residual pre-cursor and residual post-cursor with respect to the timing error sampling clock phase.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Clock generator for generating accurate and low-jitter clock
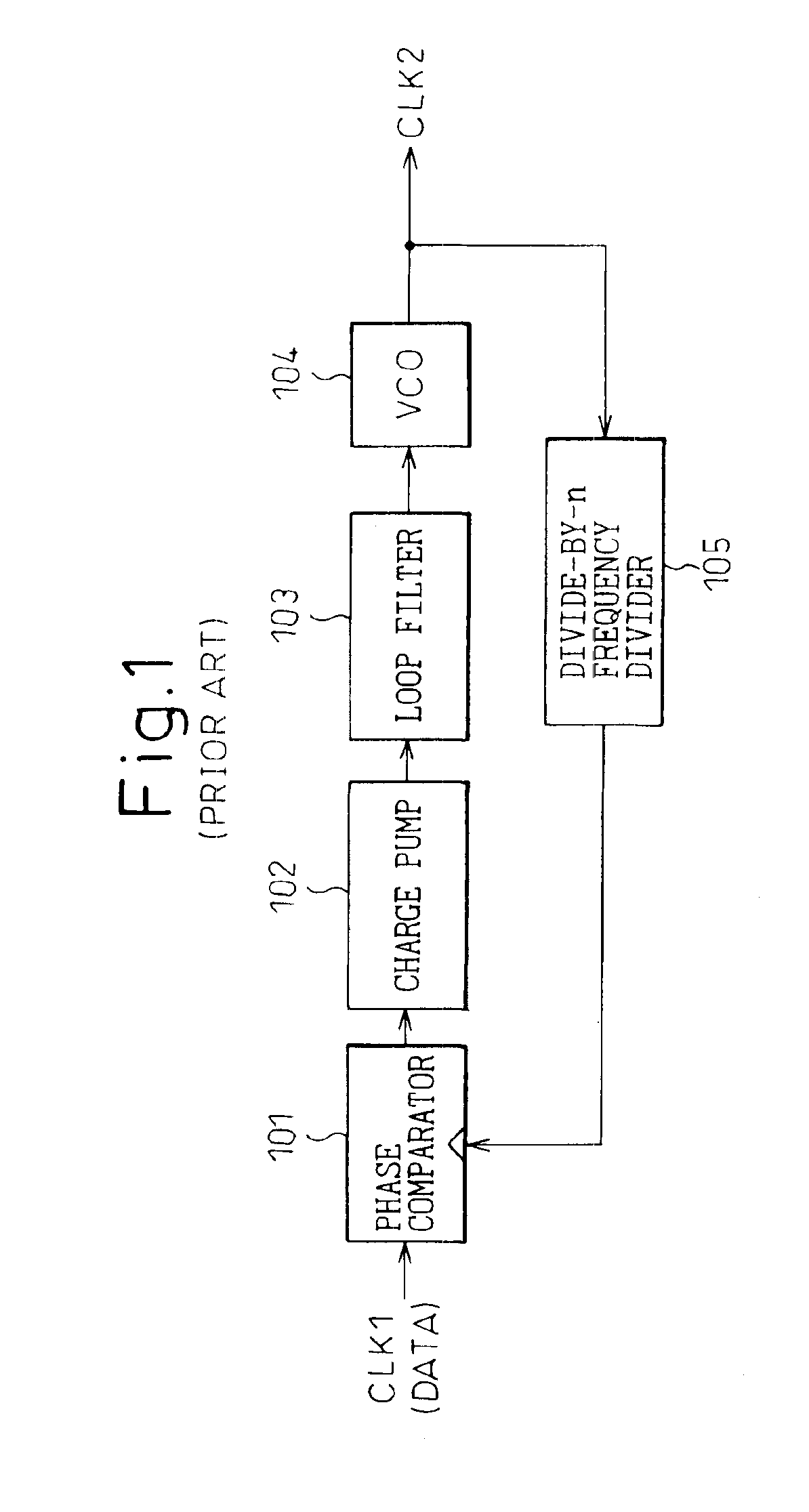
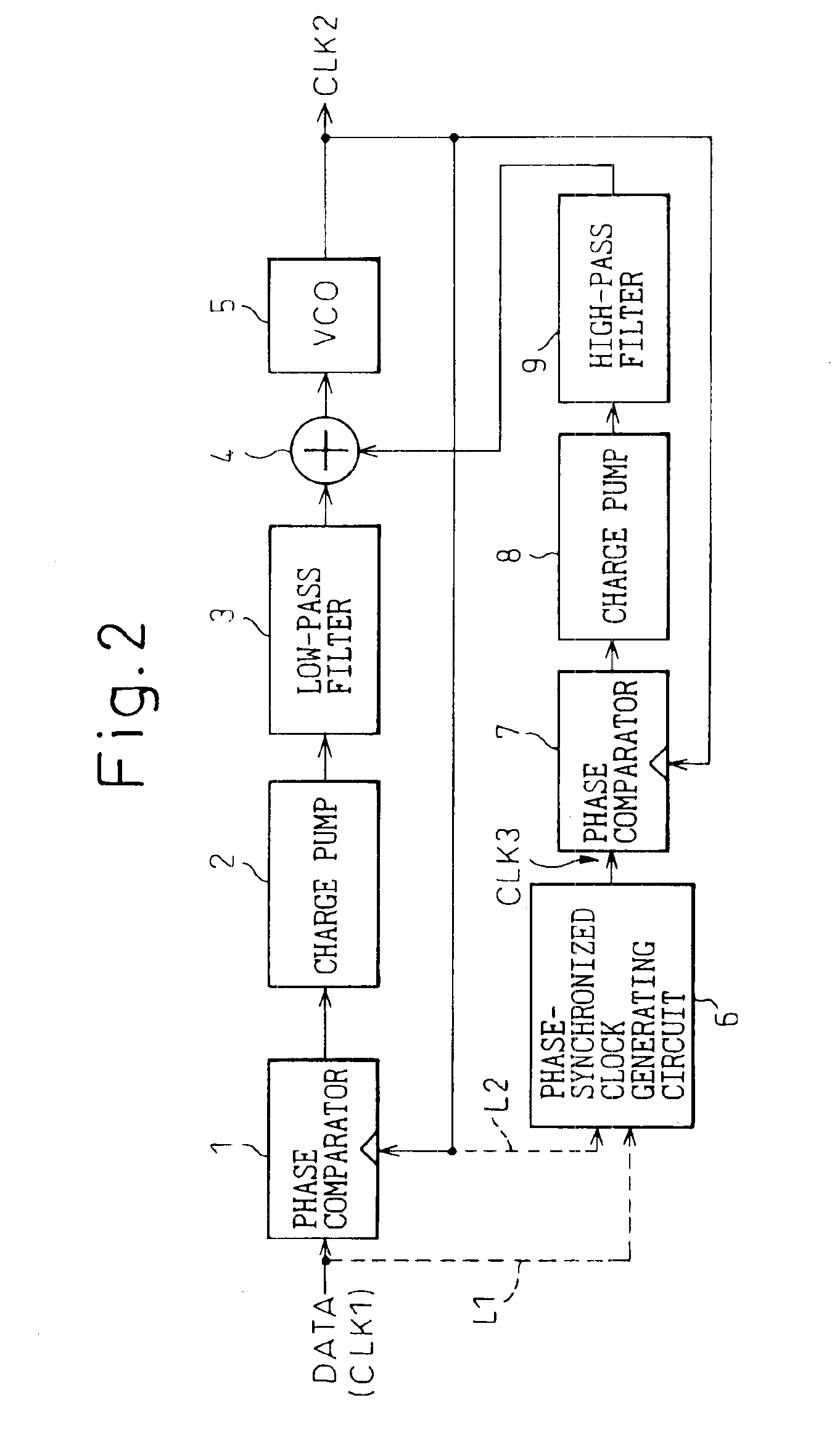
ActiveUS6900676B1Accurate and low jitterPulse automatic controlGenerating/distributing signalsControl signalPhase difference
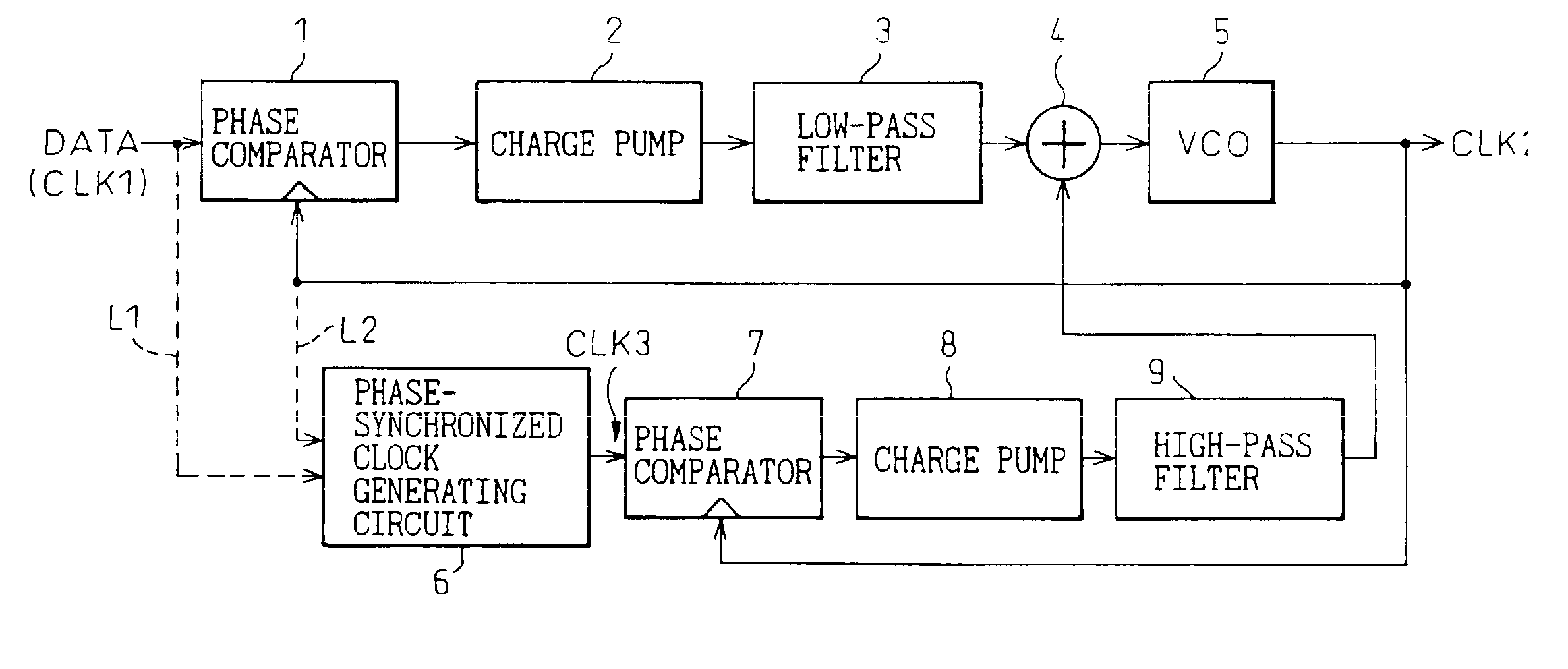
A clock generator has a clock generating circuit, a phase difference detection circuit, and a control signal generating circuit. The clock generating circuit has a function for varying a clock phase in accordance with a control signal, the phase difference detection circuit compars the clock phase output from the clock generating circuit with a phase of a reference waveform, and detecting a phase difference therebetween, and the control signal generating circuit generates a control signal for controlling the clock phase of the clock generating circuit, based on phase difference information obtained from the phase difference detection circuit. The phase difference detection circuit has a plurality of phase detection units, at least one of the plurality of phase detection units carries out a direct phase detection in which a phase of the clock is directly compared with the phase of the reference waveform, and at least the other one of the plurality of phase detection units carries out an indirect phase detection using a phase-synchronized waveform generating circuit generating a waveform synchronized in phase with the reference waveform or an output of the clock generating circuit and a phase information extracting circuit extracting phase information from the phase-synchronized waveform.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
On-chip system and method for measuring jitter tolerance of a clock and data recovery circuit
An integrated circuit is operable to measure tolerance to jitter in a data stream signal. A Clock And Data Recovery Circuit (“CDR”) thereon recovers a phase of a clock for sampling a data stream signal containing a repeatable known sequence of data values and then samples the data stream signal with the recovered clock phase to obtain data stream sample data. An error rate determination circuit independently generates the repeatable known sequence of data values and compares them with the data stream sample data to determine an associated error rate. A control circuit coupled to the CDR delays the recovered clock phase by a predetermined amount a plurality of times and monitors the error rate after each time it delays the recovered clock phase. In this way, a maximum delayed clock phase is determined, representing a right timing signal margin for which the data stream signal can be sampled.
Owner:IBM CORP
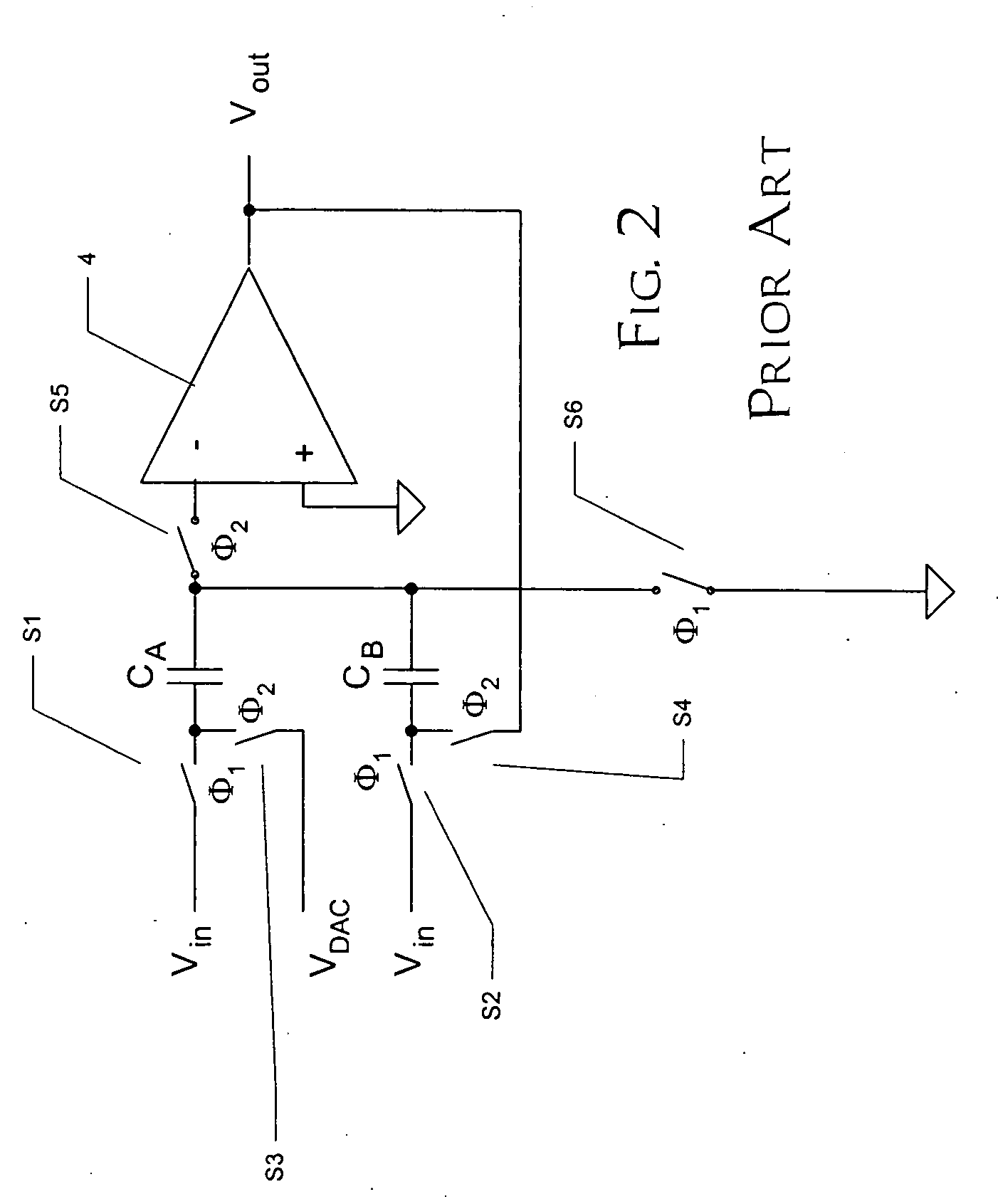
Switched-capacitor circuits with reduced finite-gain effect
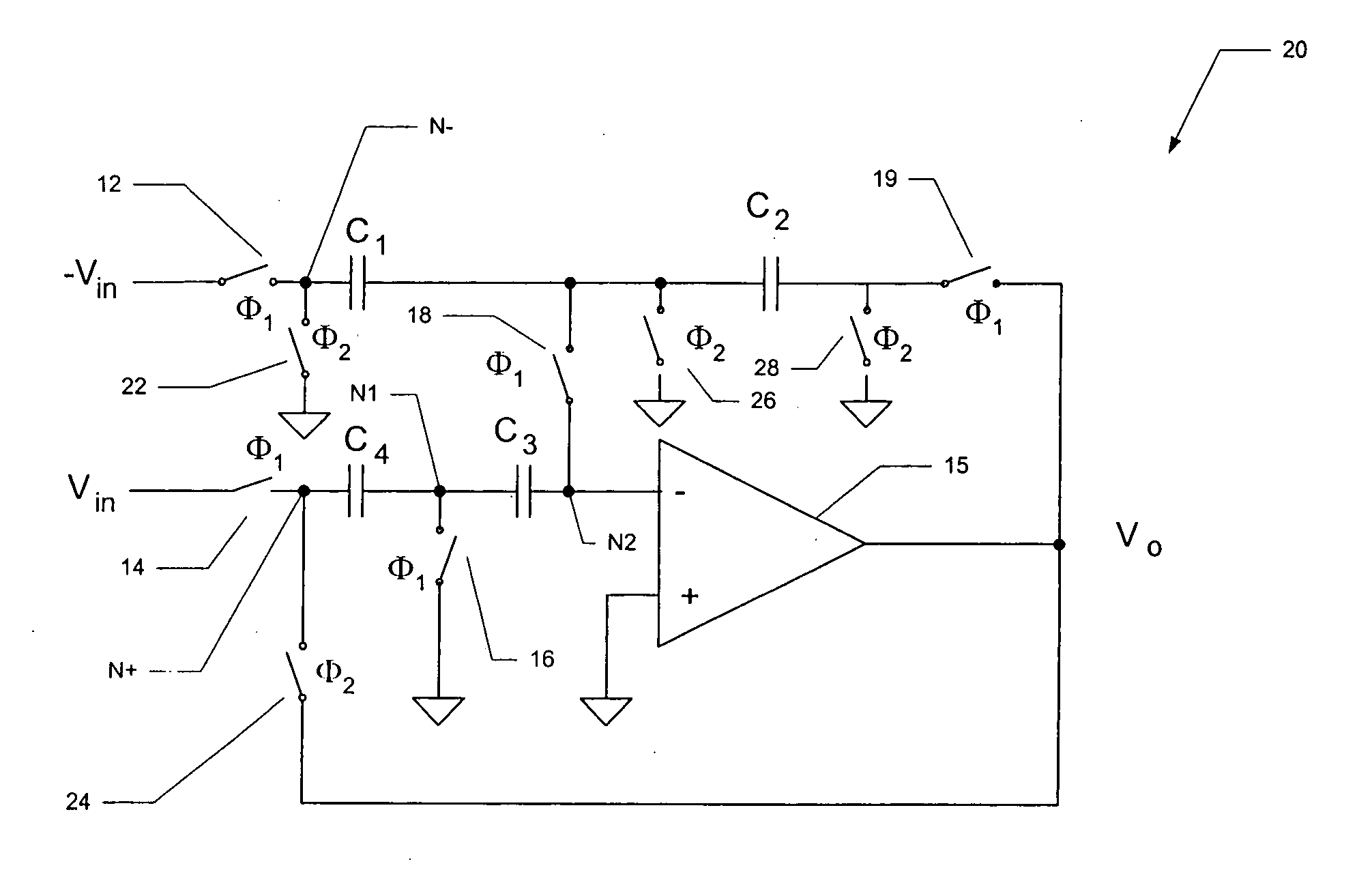
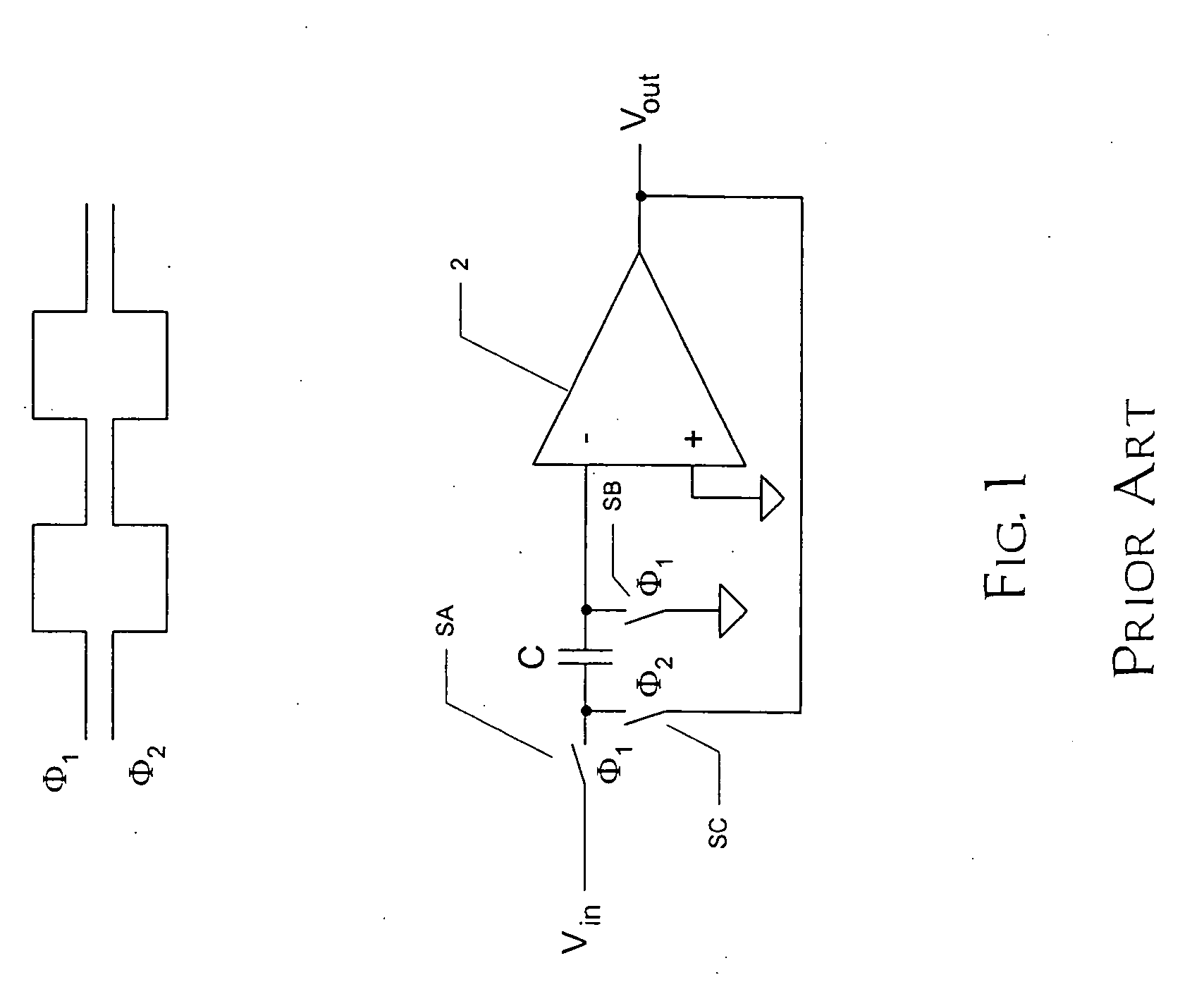
ActiveUS20060071709A1Minimize impactGood effectAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
Operational amplifier circuits (20, 30) including error capacitors (C3, C13) for storing finite gain effect error voltages for correction of output voltages of the circuits (20, 30), are disclosed. The circuits (20, 30) are operated in a sample clock phase to produce an approximation of the output voltage, using negative polarity versions of the input voltages to the circuit. The approximate output voltage is used to produce and store an error voltage, corresponding to the differential voltage at the input of the operational amplifier (15, 25), relative to virtual ground. This error voltage is then subtracted from the input voltage applied in the operate clock phase, to correct for the finite gain effect. A pipelined analog-to-digital converter (50) using the disclosed operational amplifier circuits (20, 30) is also disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Harmonic suppression mixer and tuner
InactiveUS20090143031A1Enhanced inhibitory effectAvoid interferenceModulation transference balanced arrangementsTransmissionLow noiseHarmonic mitigation
A harmonic suppression mixer for down converting an RF signal to a complex I and Q baseband signal that uses a plurality of switching mixers each with a gain stage to produce a sinusoidal weighted sum of the mixer outputs. Odd harmonics output by each switching mixer is suppressed in the composite signal. A low skew local oscillator (LO) clock generator creates multiple LO phases and drives the mixers. The mixer can be used in low noise direct conversion RF tuners. The mixer is configurable by programming gain stage coefficient values to achieve a variable number of effective mixers used in combination. At low tuning frequencies, all available mixers are programmed with unique coefficients and driven by different LO clock phases to achieve maximum harmonic suppression. At high tuning frequencies, some mixers are paralleled and duplicate coefficients are programmed or mixers are disabled to reduce the number of effective mixers.
Owner:SHAH PETER
All-digital phase modulator/demodulator using multi-phase clocks and digital PLL
InactiveUS7688929B2Pulse automatic controlAngle modulation detailsDigital analog converterPhase difference
Multi-phase clocks are used to encode and decode signals that are phase-modulated. The input signal is phase-compared with a feedback clock. Phase differences increment or decrement an up / down counter. The count value from the up / down counter is applied to a phase rotator, which selects one clock phase from a bank of multi-phase clocks. The multi-phase clocks have the same frequency, but are offset in phase from each other. An output divider divides the selected multi-phase clock to generate a phase-modulated output. A feedback divider divides a fixed-phase clock from the multi-phase clocks to generate the feedback clock. An analog or a digital front-end may be used to convert analog inputs to digital signals to increment or decrement the counter, or to encode multiple digital bits as phase assignments. For a de-modulator, a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) or a digital decoder produces the final output from the count of the up / down counter.
Owner:KINGSTON DIGITAL CO LTD
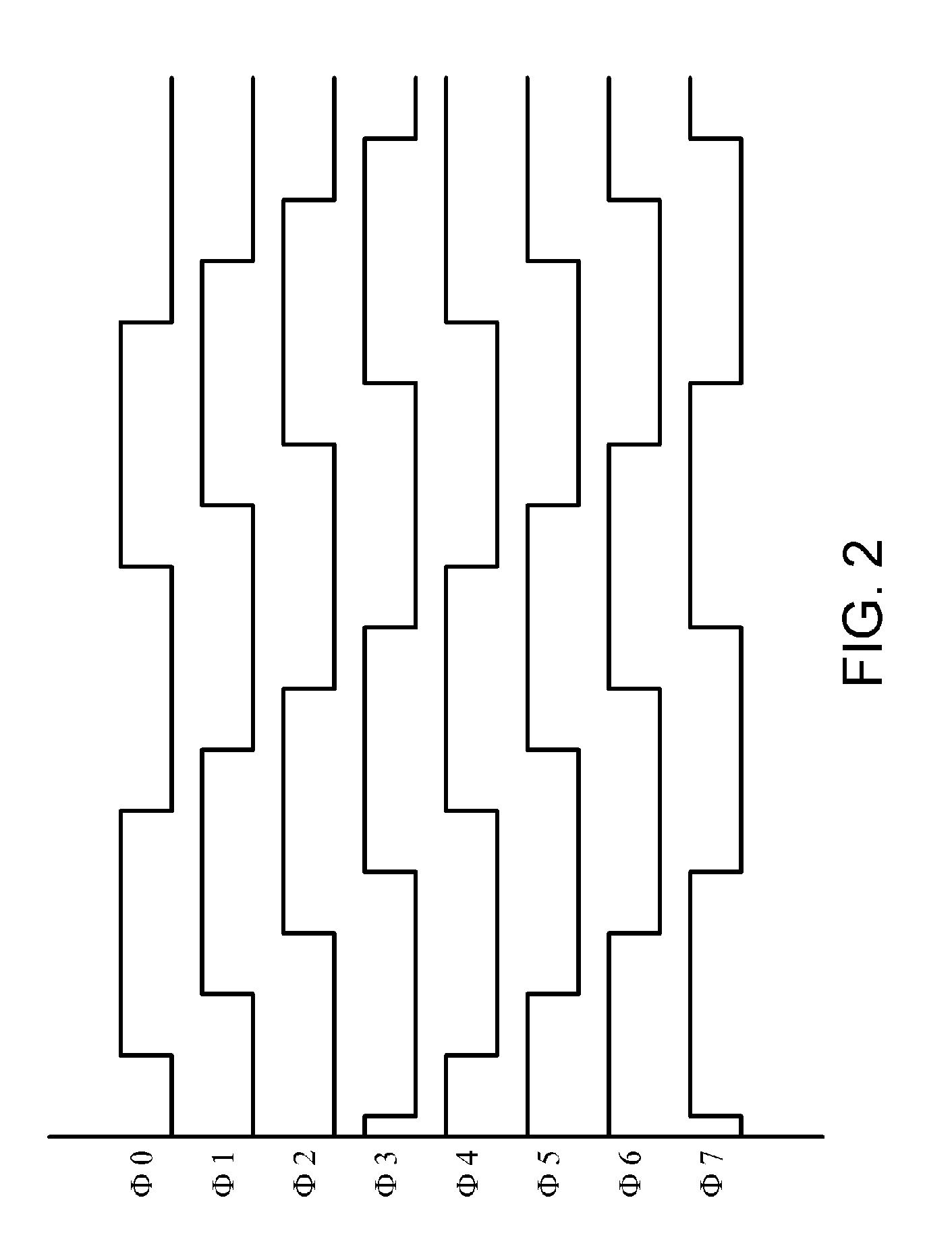
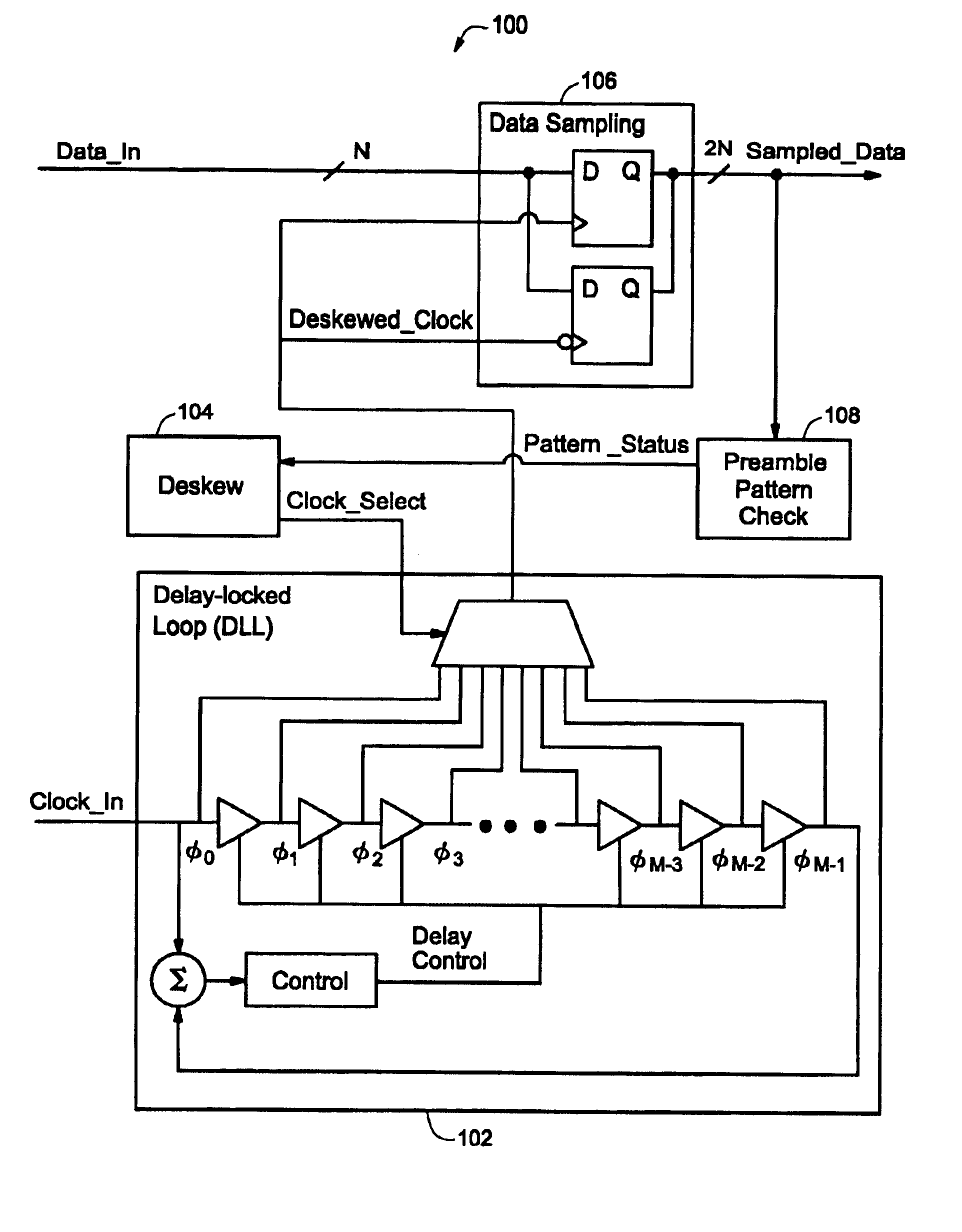
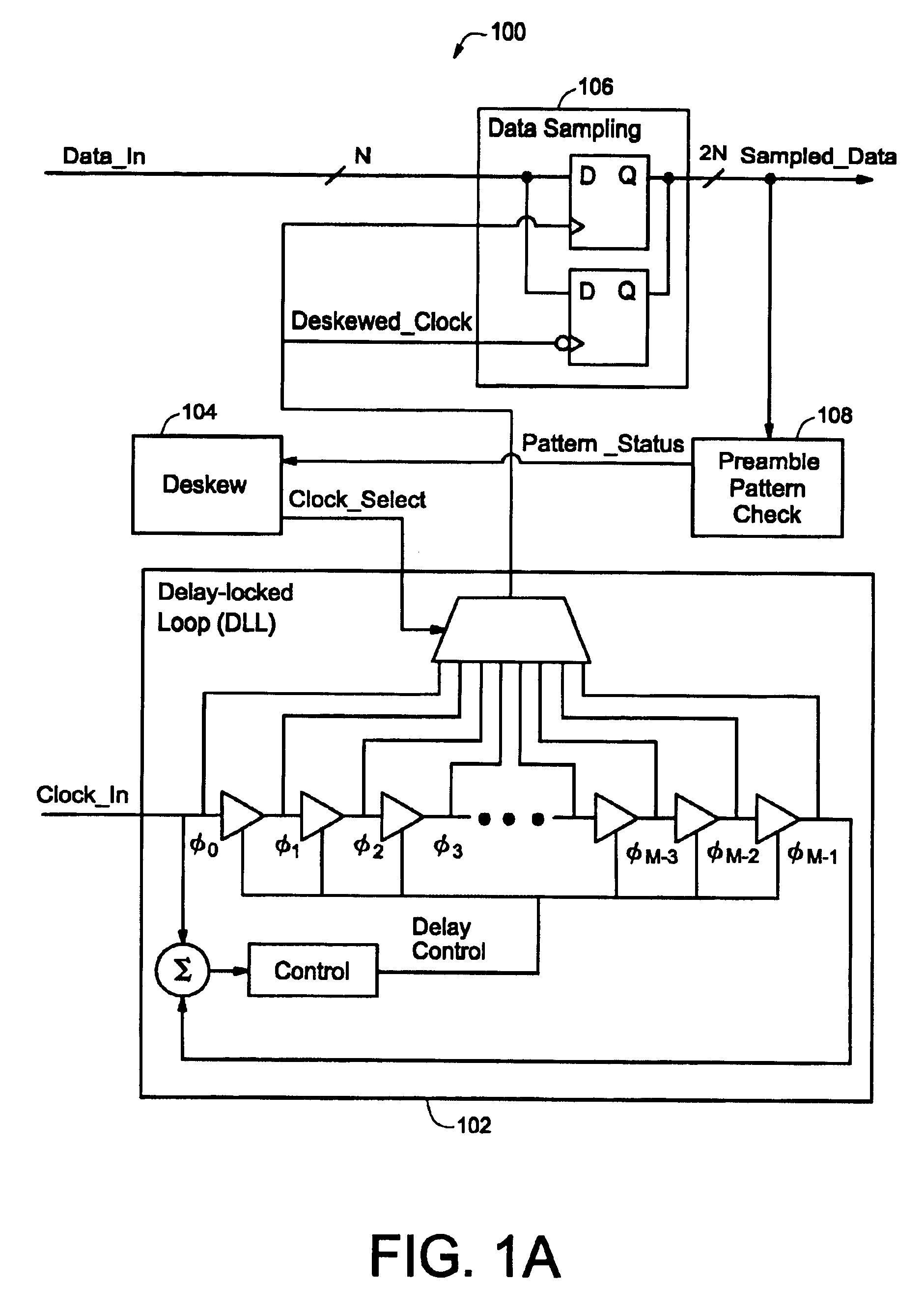
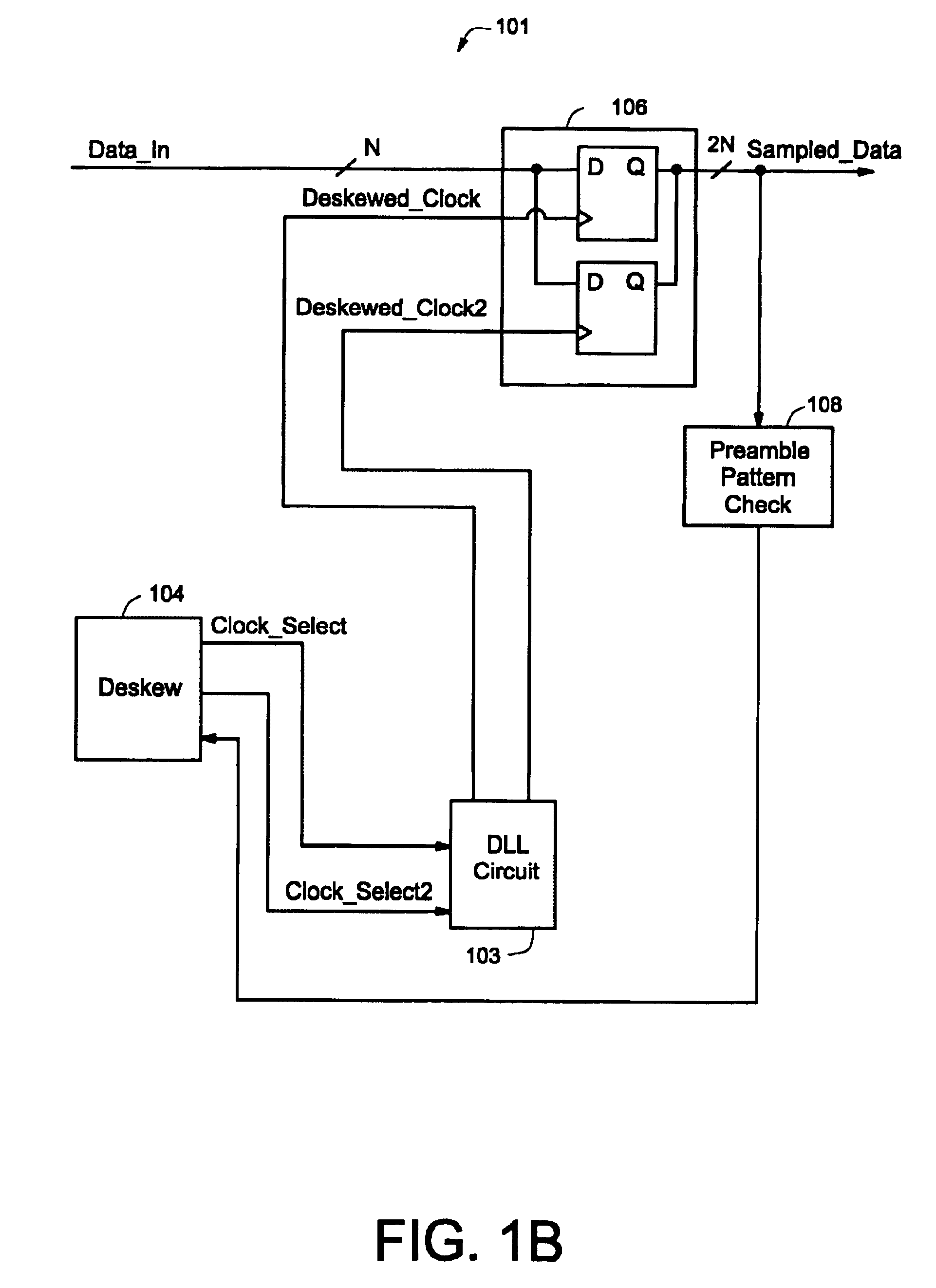
Clock deskew protocol using a delay-locked loop
InactiveUS6861886B1Synchronisation information channelsPulse automatic controlDelay-locked loopClock phase
A data / clock deskewing methodology uses a delay-locked loop (DLL) circuit. The DLL circuit generates a number of clock phases in response to an input clock, where each clock phase is delayed relative to the input clock signal. The clock phases are used to sample data from a data line. The sampled data is checked against a preamble pattern (a sequence of known data). A digital deskew control block selects one of the clock phases after analyzing the results of preamble pattern check such that subsequently received data is sampled with the appropriately selected clock phase.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Phase interpolator to interpolate between a plurality of clock phases
A phase interpolator interpolates between a plurality of clock phases using a plurality of switching legs coupled to a common output. Each switching leg includes a pair of differential switching transistors each having a gate and two additional terminals, one of which is coupled to said common output. The gates are coupled to respective ones of the plurality of clock phases and their complements. Tails couple the other terminals of said switching transistors to ground. Each tail made up of a plurality of transistors. A load coupling the common output to a voltage.
Owner:INTEL CORP
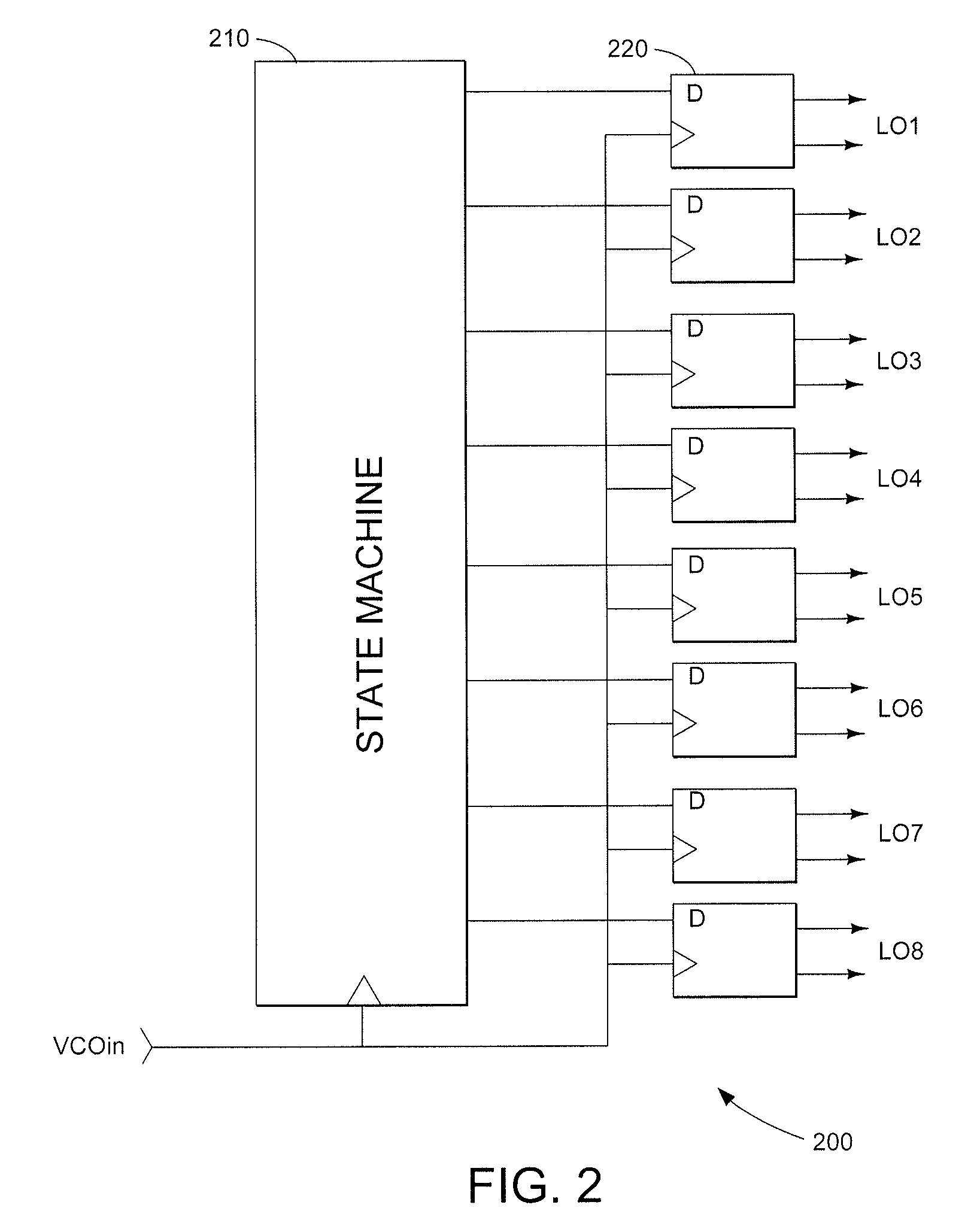
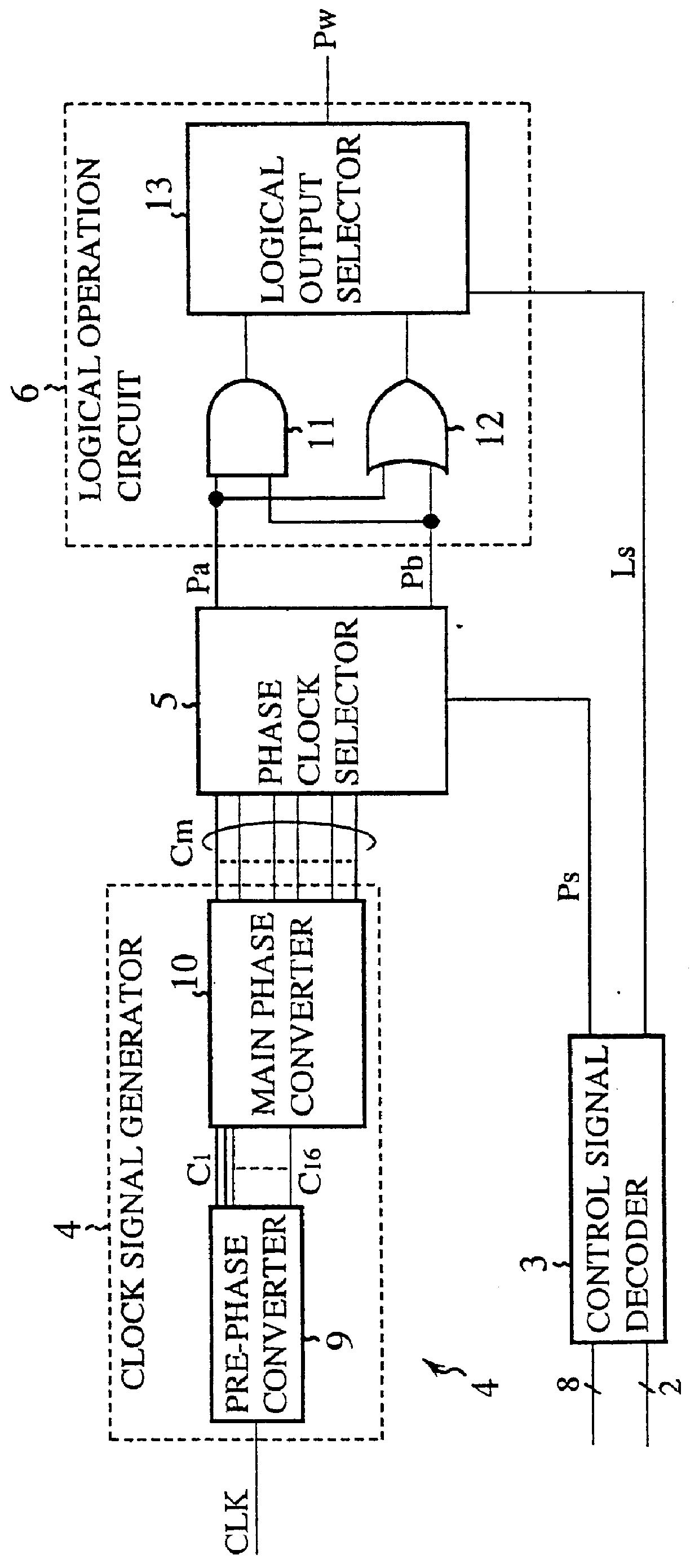
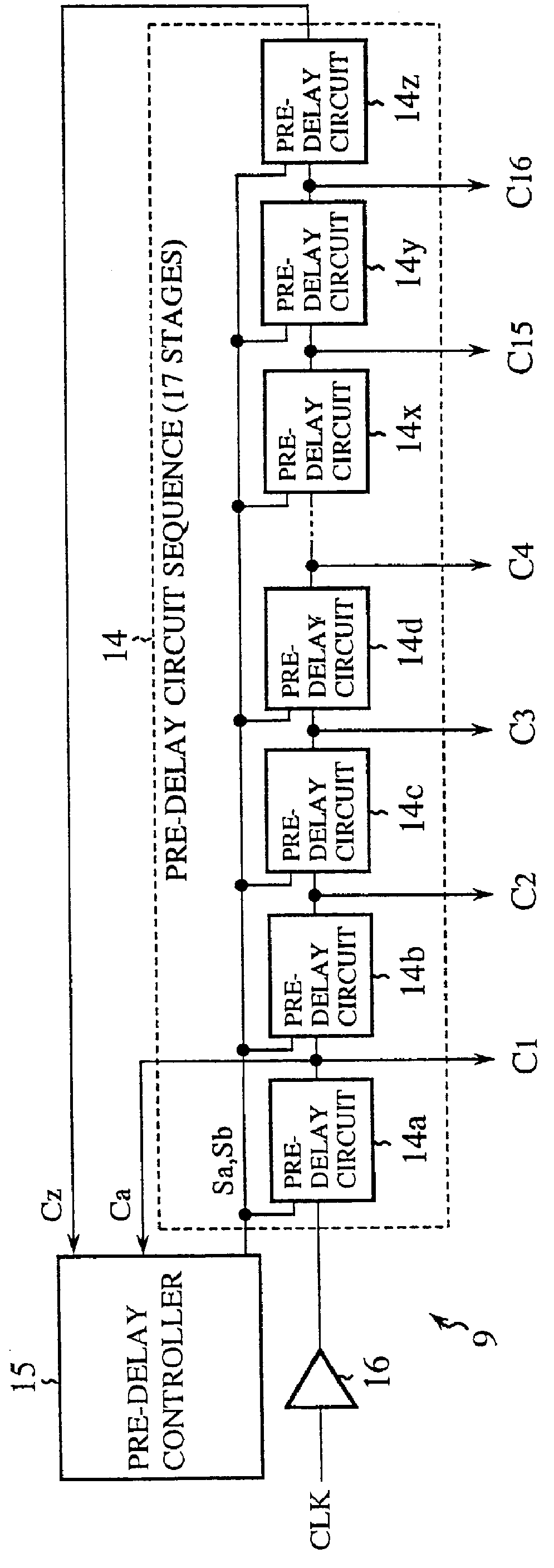
Clock signal generator for generating a plurality of clock signals with different phases, and clock phase controller using the same
A clock signal generator having a pre-phase converter for generating in response to an input clock signal a plurality of pre-delay clock signals with different phases; and main phase converters each of which receives one of the pre-delay clock signals, and generates a plurality of main delay clock signals with their phases different from each other, thereby generating multiple main delay clock signals with their phases different from each other.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
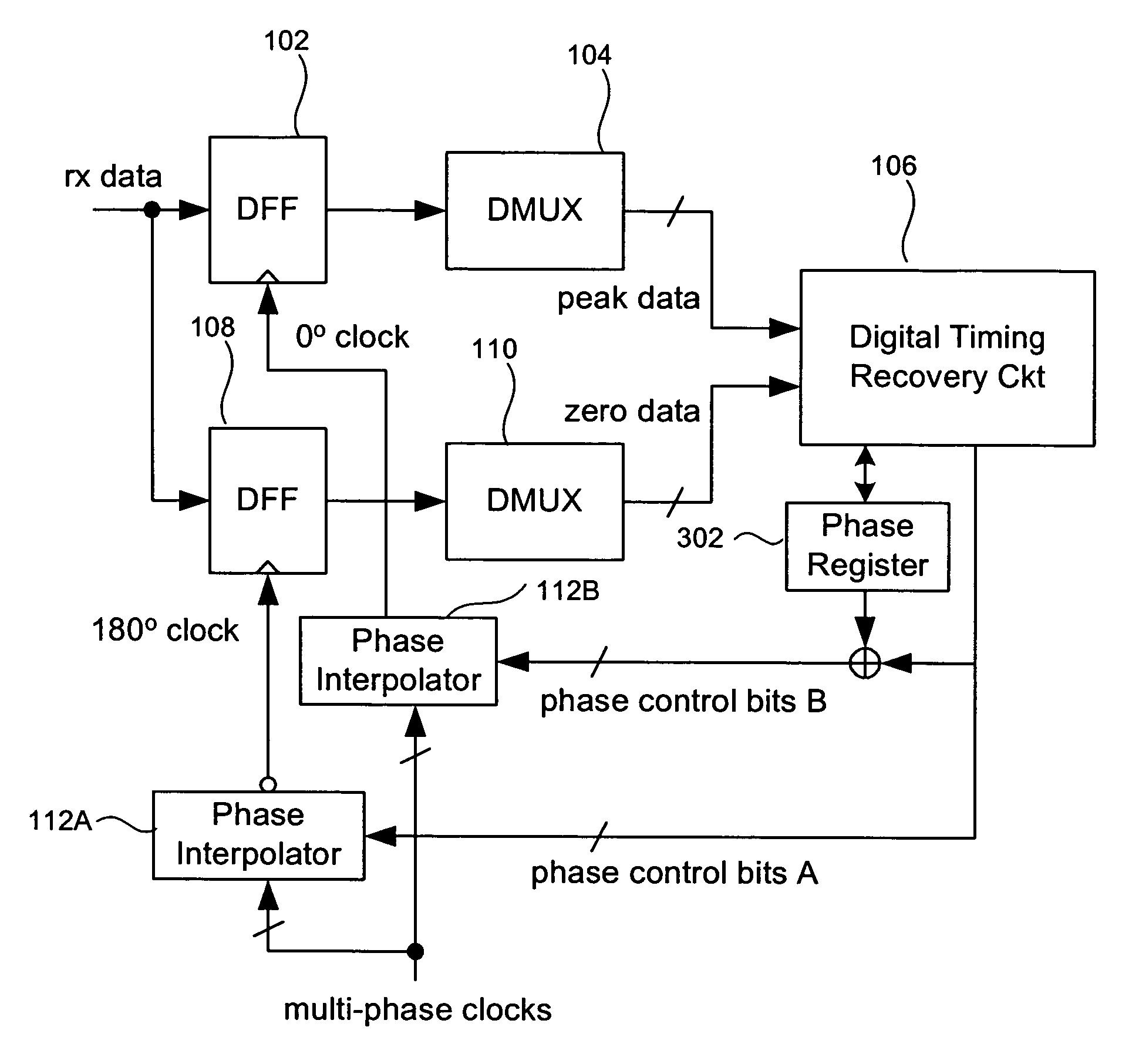
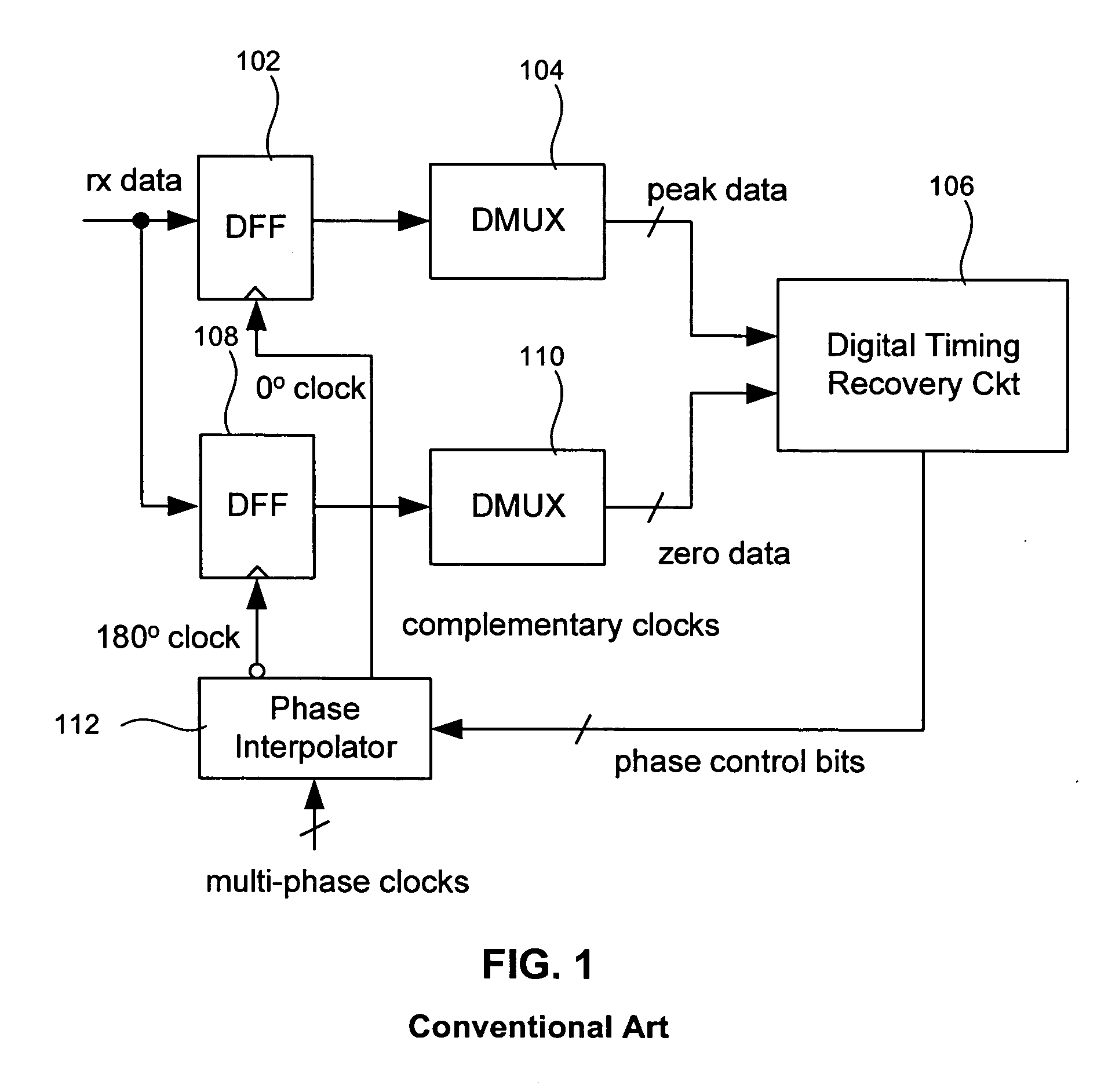
Phase adjustment method and circuit for dll-based serial data link transceivers
InactiveUS20060002497A1Pulse automatic controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransceiverControl signal
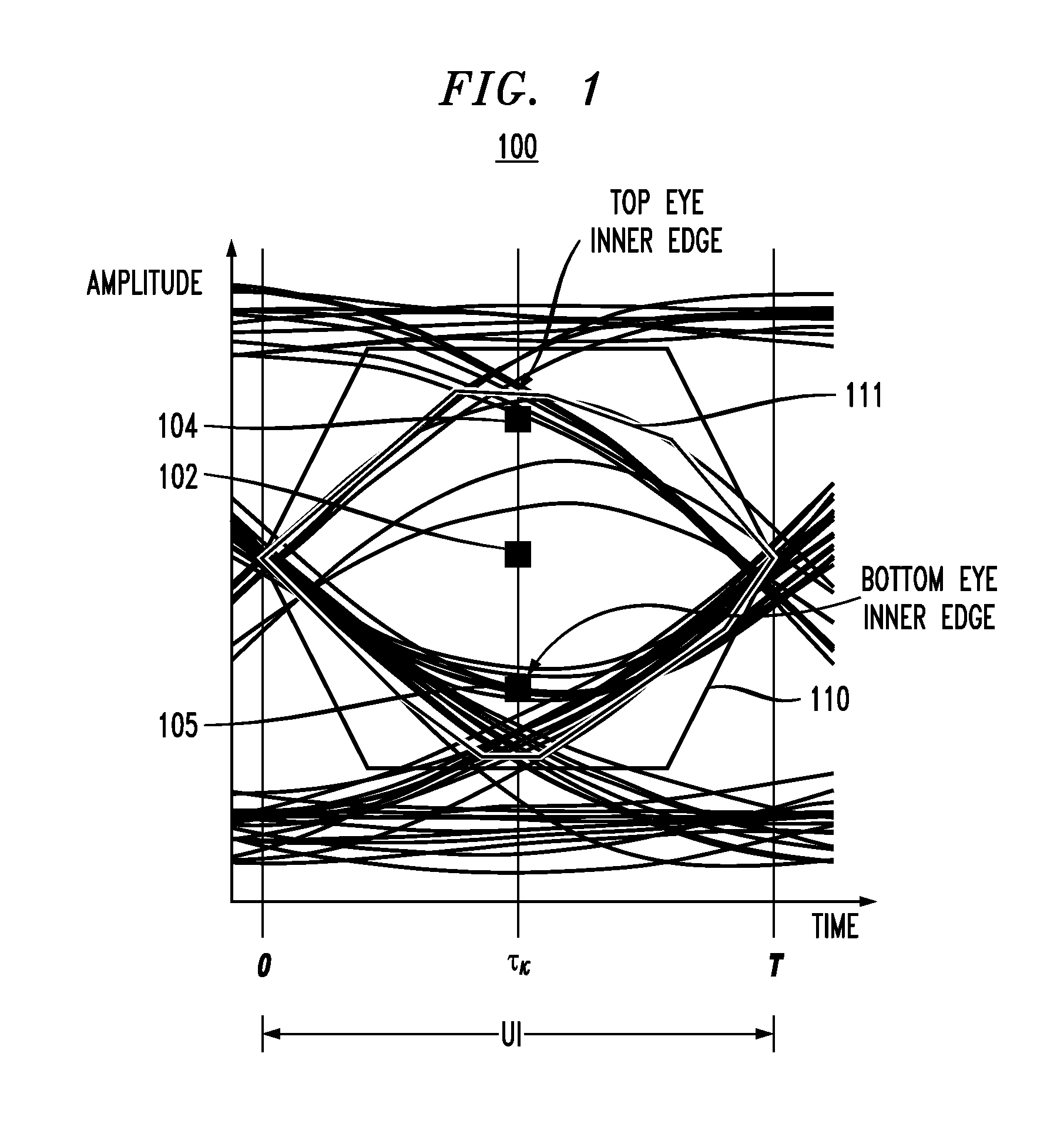
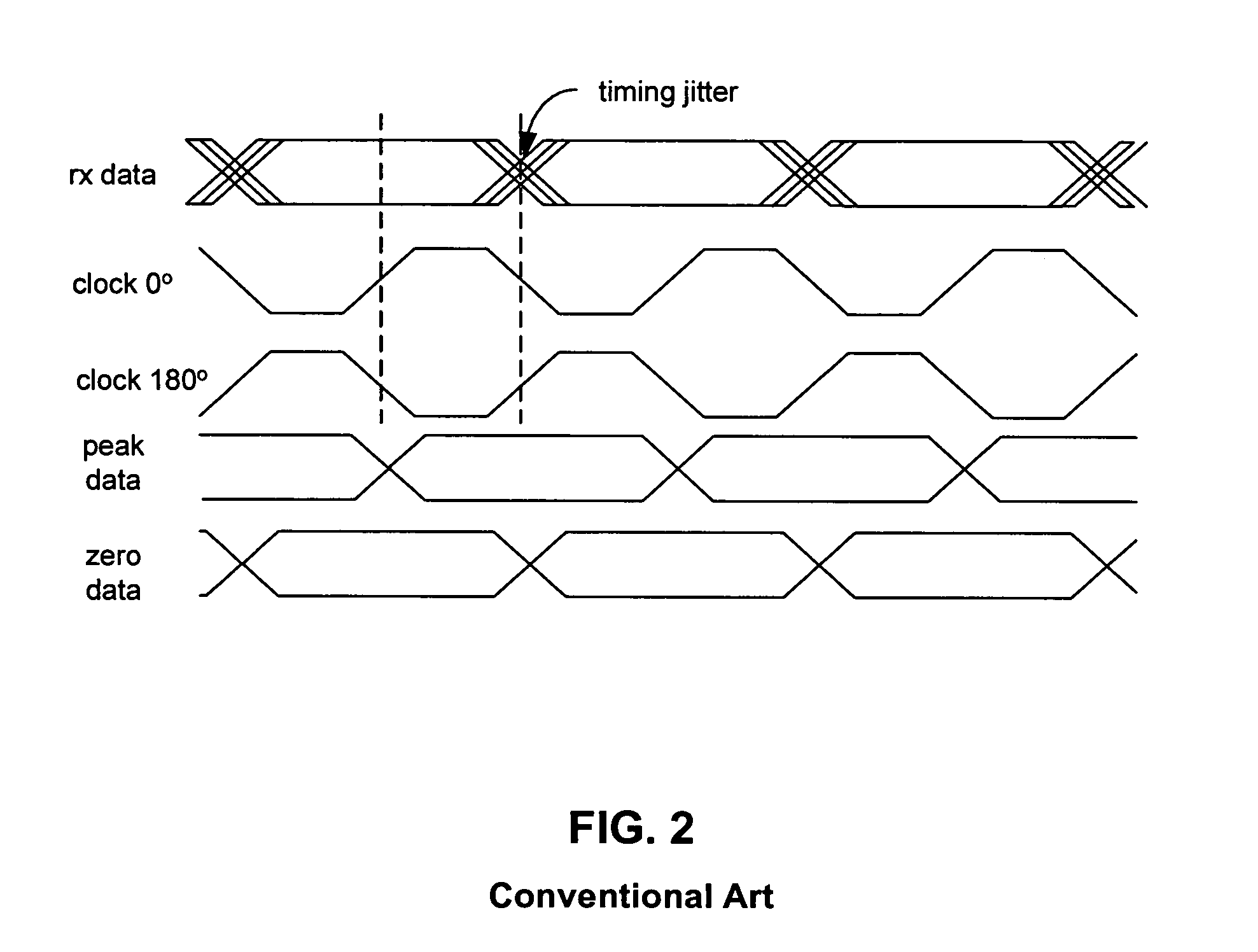
A delay locked loop circuit with a first flip flop driven by a 0° clock and receiving the input data. A second flip flop by a 180° clock and receiving the input data. A first demultiplexer receives an output of the first flip flop and outputs peak data. A second demultiplexer receives an output of the second flip flop and outputs zero data. A timing recovery circuit outputs phase control bits based on the zero data and the peak data. A first phase interpolator outputs the 0° clock based on the phase control signal. A second phase interpolator outputs the 180° clock based on the phase control signal. A phase register receives the phase control signal from the timing recovery circuit. The first and second flip flops can be D flip flops. The first and second phase interpolators adjust relative phases of the 0° clock and 180° clock based on the phase control signal. The phase control signal can be a digital signal comprising a plurality of bits corresponding to a phase relationship between the 0° clock and 180° clock. The timing recovery circuit can be a digital circuit. The phase control signal is used to maintain a transition of the 0° clock near a center of an “eye” in the input data.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Digital phase-locked loop
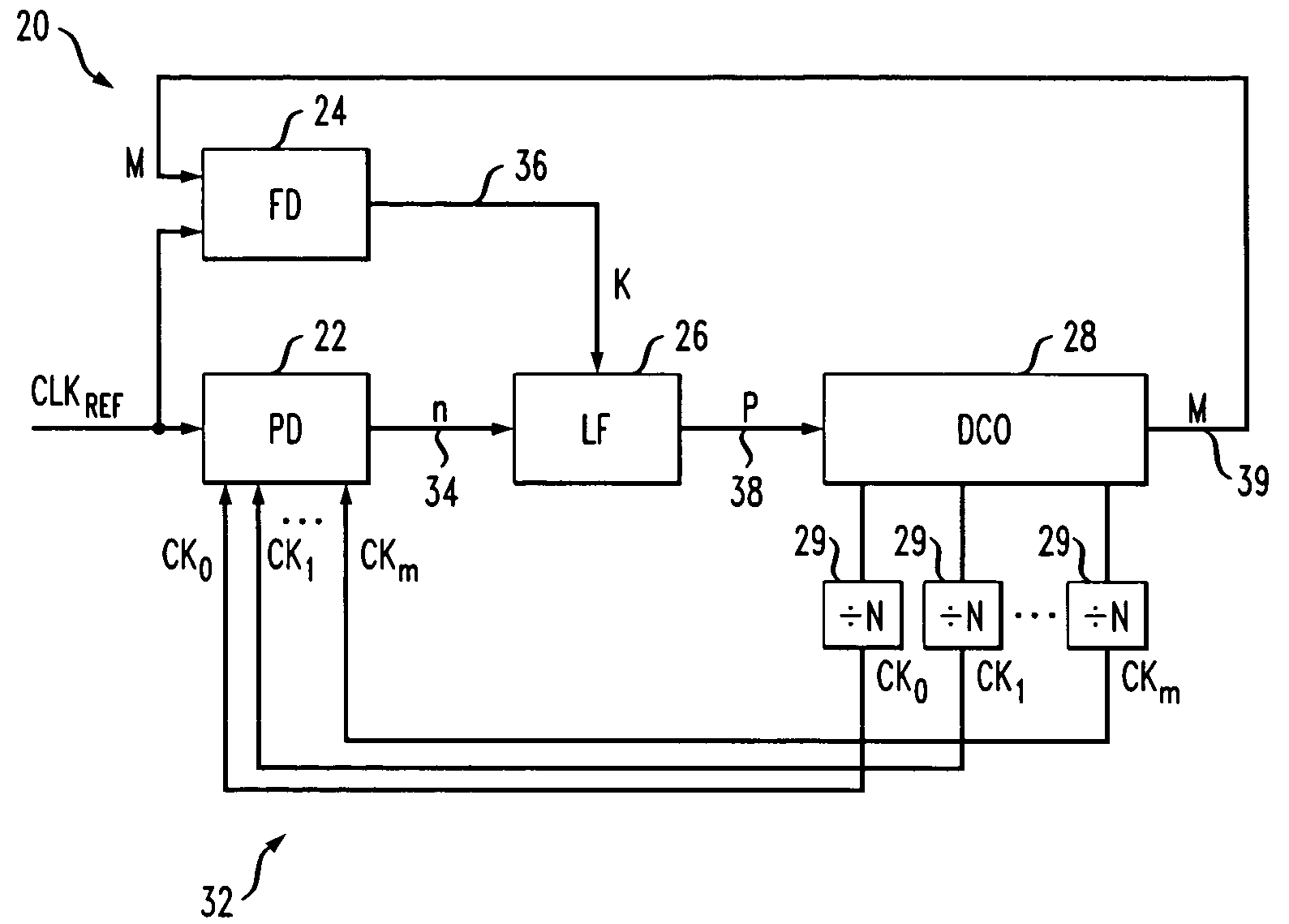
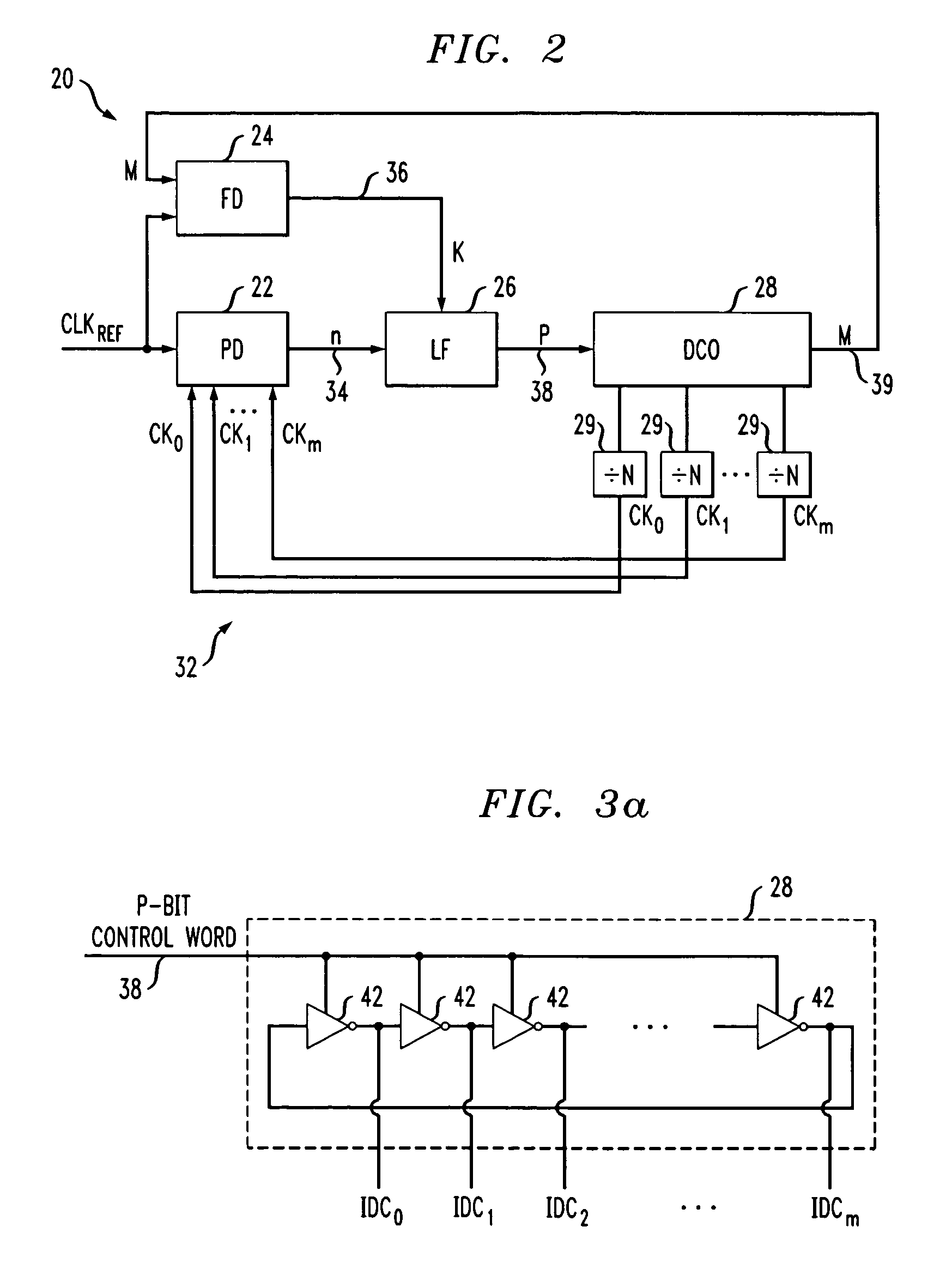
Embodiments of the invention include an integrated circuit including a phase-locked loop (PLL). The integrated circuit includes a phase detector, a frequency detector, a loop filter, a digitally-controlled oscillator and a corresponding plurality of frequency dividers. The phase detector generates a first binary output based on a phase comparison of a reference clock signal to a plurality of clock phase inputs. The frequency detector generates a second binary output based on a frequency comparison of the reference clock signal to the clock phase inputs. The loop filter generates a third binary output based on the first binary output and the second binary output. The DCO feeds back the clock phase inputs, via the frequency dividers, to the phase detector based on the third binary output, and feeds back one of the clock phases to the frequency detector based on the third binary output.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
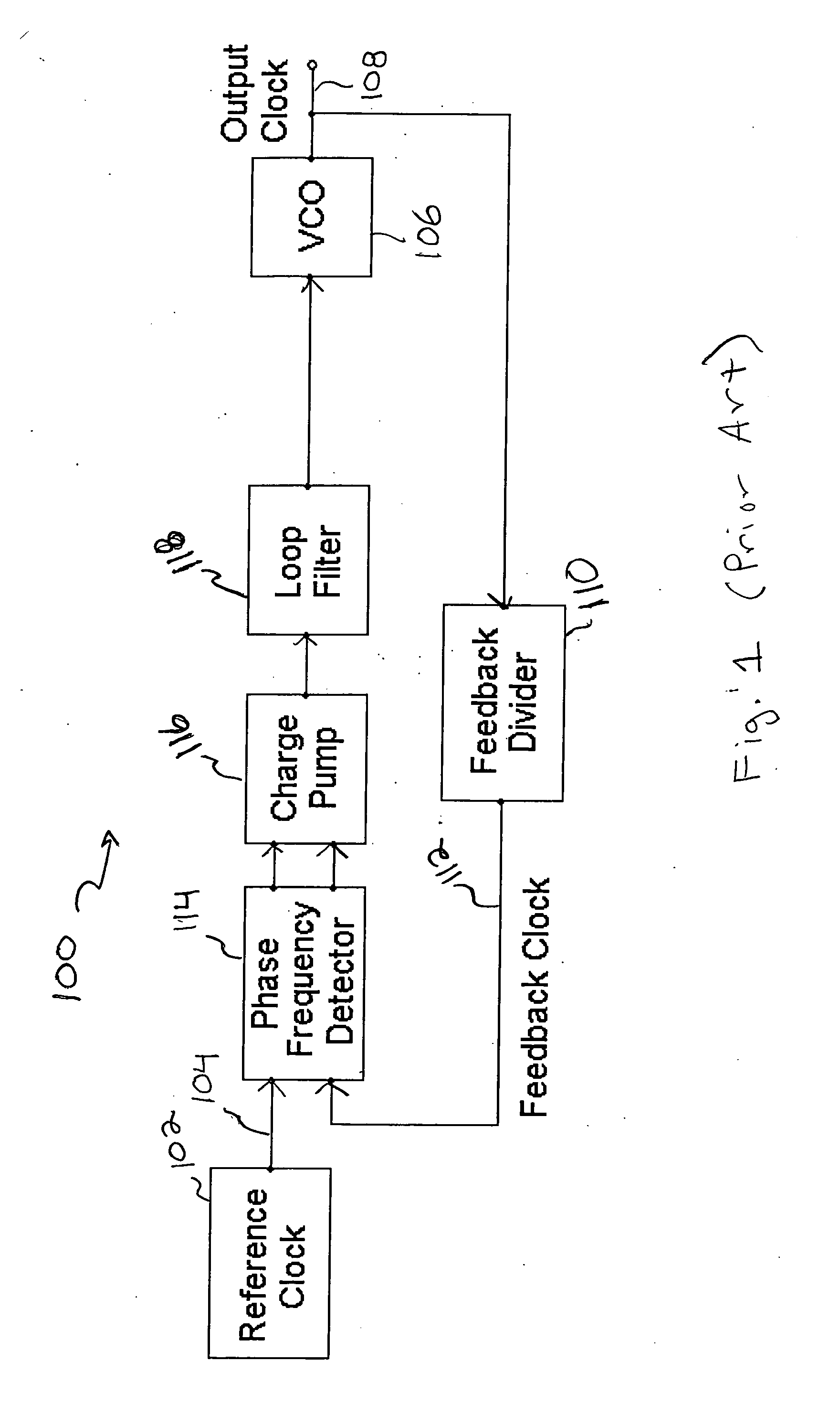
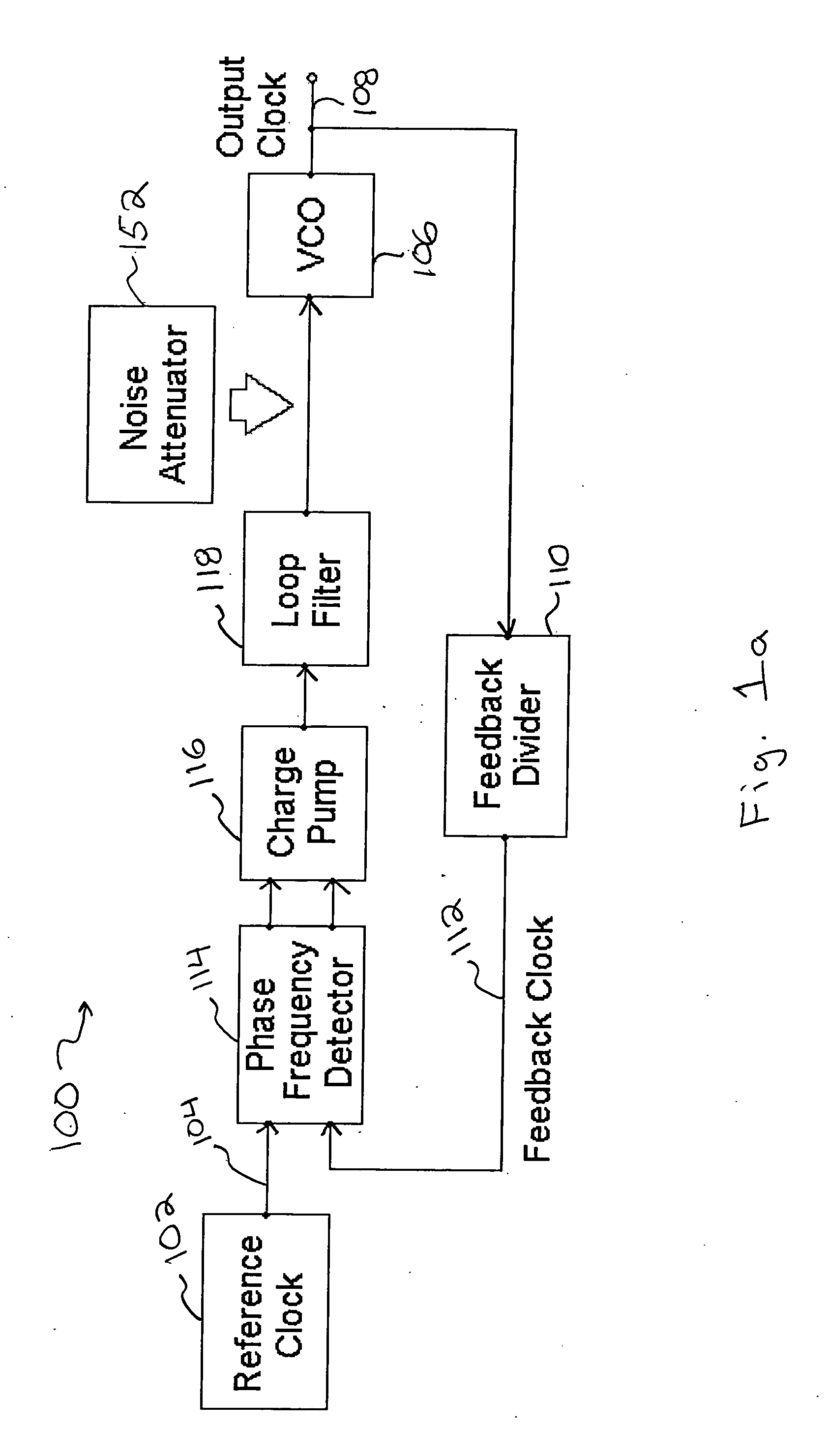
Method and apparatus to reduce the jitter in wideband PLL frequency synthesizers using noise attenuation
InactiveUS20060141963A1Reduce noise contributionReduce phase noisePulse automatic controlTransmissionMOSFETCapacitance
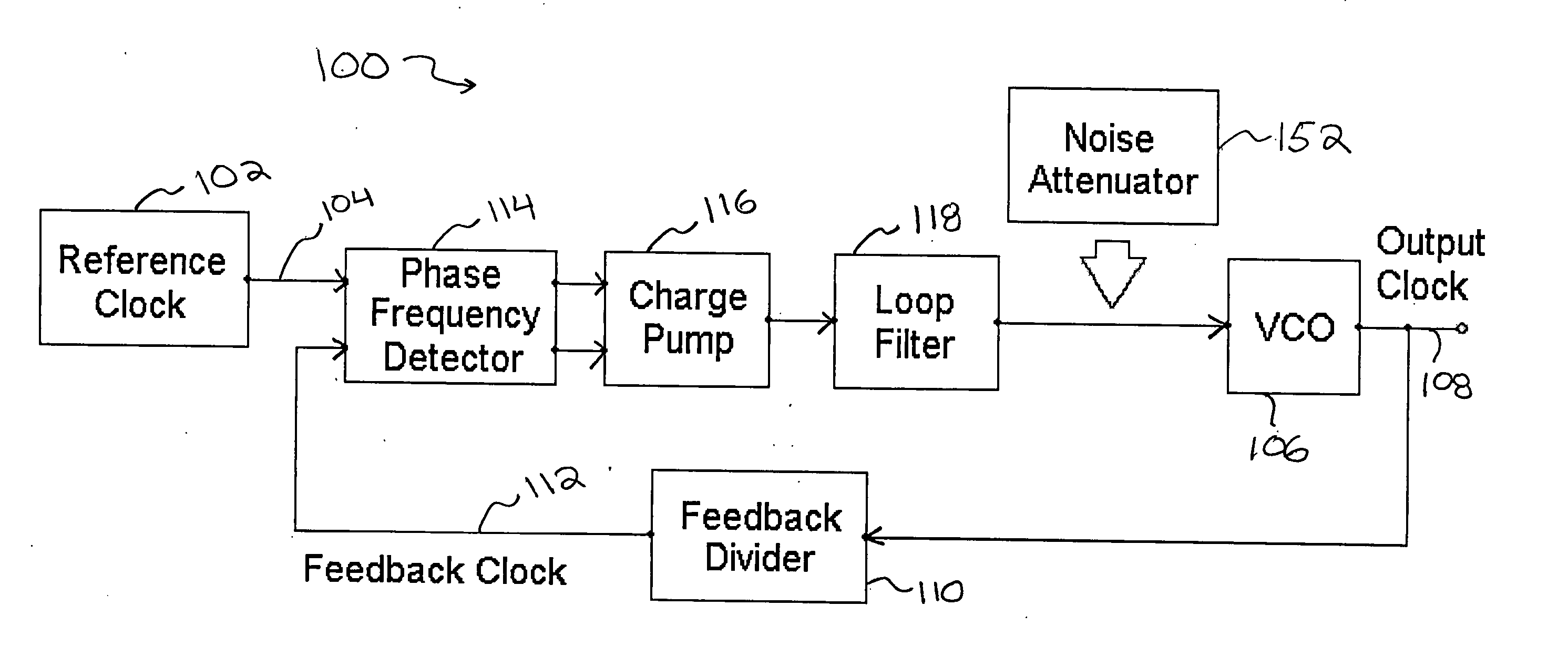
A noise attenuator loop filter for PLL applications that allows a full on-chip integration of the loop filter capacitors, while ensuring a low output clock phase noise (jitter) is disclosed. A voltage attenuator (A) is inserted between the loop filter (passive or active) and the controlled oscillator. The attenuator attenuates the noise coming from the loop filter. In case of a passive RC filter, the series resistor noise power is attenuated by A2 times, allowing the usage of a resistor that is A2 times larger and therefore the loop filter capacitors result A2 times smaller (easy to integrate on-chip). The relatively low value capacitor allows the usage of thick-oxide accumulation-mode MOSFET capacitors that take a reasonable low area, have a good linearity, are isolated from the substrate by the grounded N-well, and have negligible gate leakage current. Several embodiments of the noise attenuator are proposed for different practical applications: clock generation for digital circuits, frequency translation, low or high supply voltage, narrow or wide frequency range, processes with or without isolated well devices, processes with or without polysilicon resistors, and medium or high reference spurs rejection.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
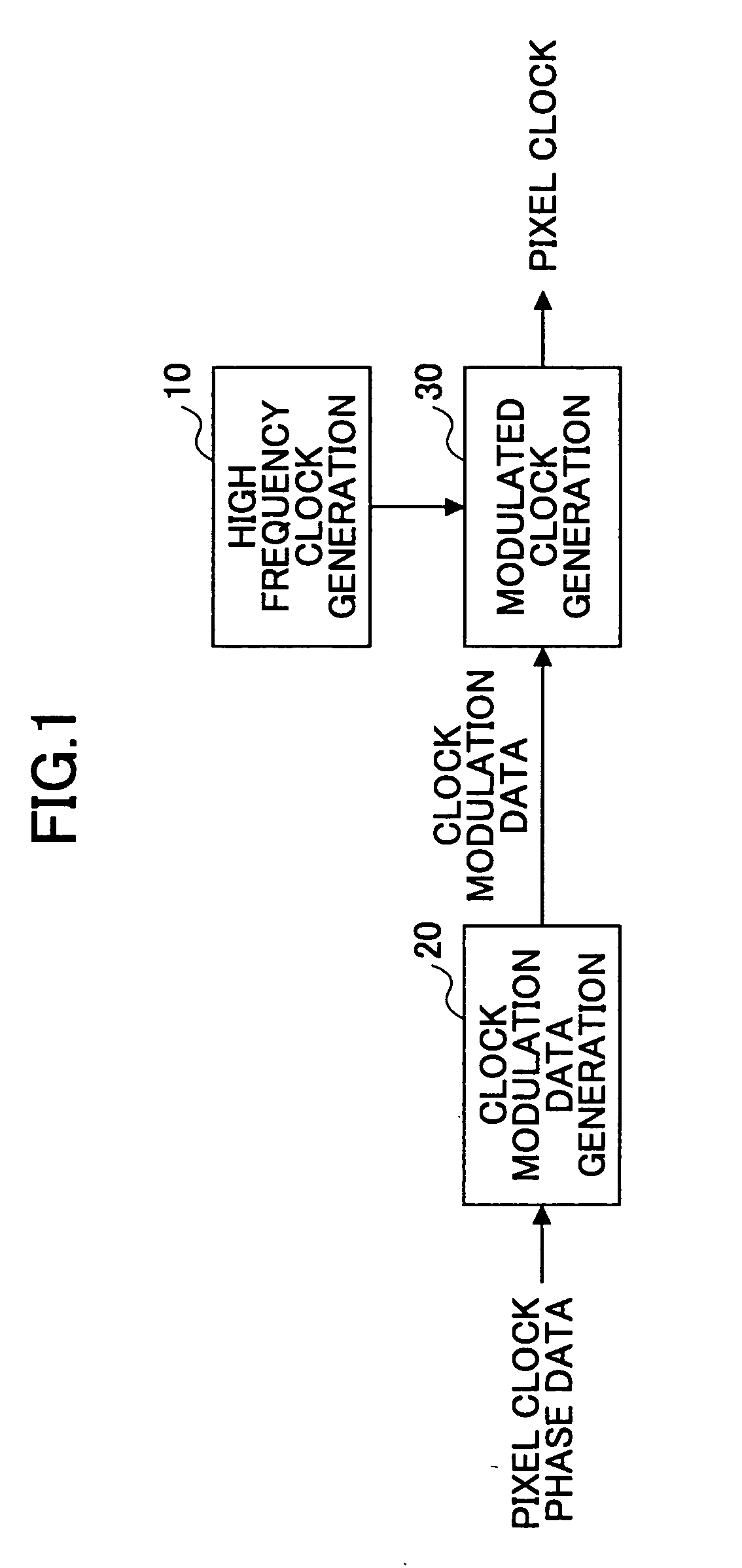
Pixel clock generation circuit
InactiveUS20050243163A1Simple structureImprove accuracyInking apparatusPulse automatic controlClock phaseComputer science
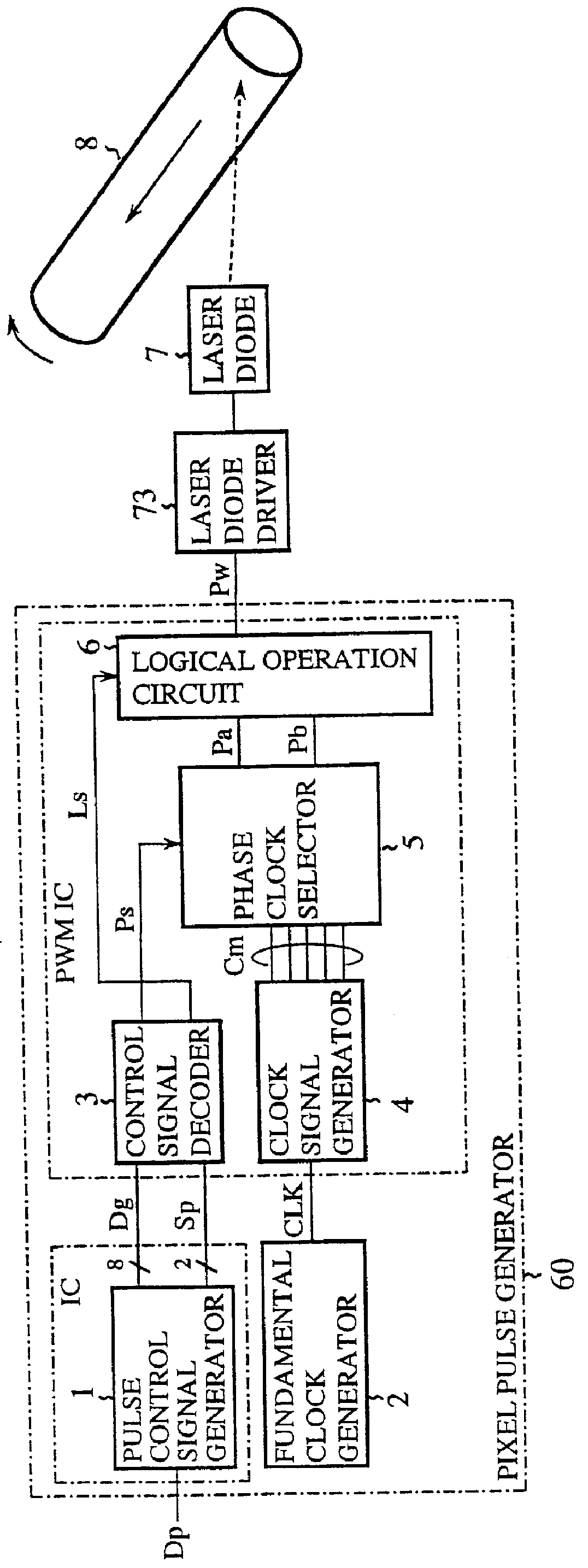
A pixel clock generation circuit is disclosed, including a high frequency clock generation unit configured to generate high frequency clock, a clock modulation data generation unit configured to generate clock modulation data based on pixel clock phase data indicating timing of a transition in pixel clock. The pixel clock generation circuit further includes a modulation clock generation unit configured to modulate the frequency and phase of the high frequency clock based on the modulation data thereby to generate modulated pixel clock.
Owner:RICOH KK
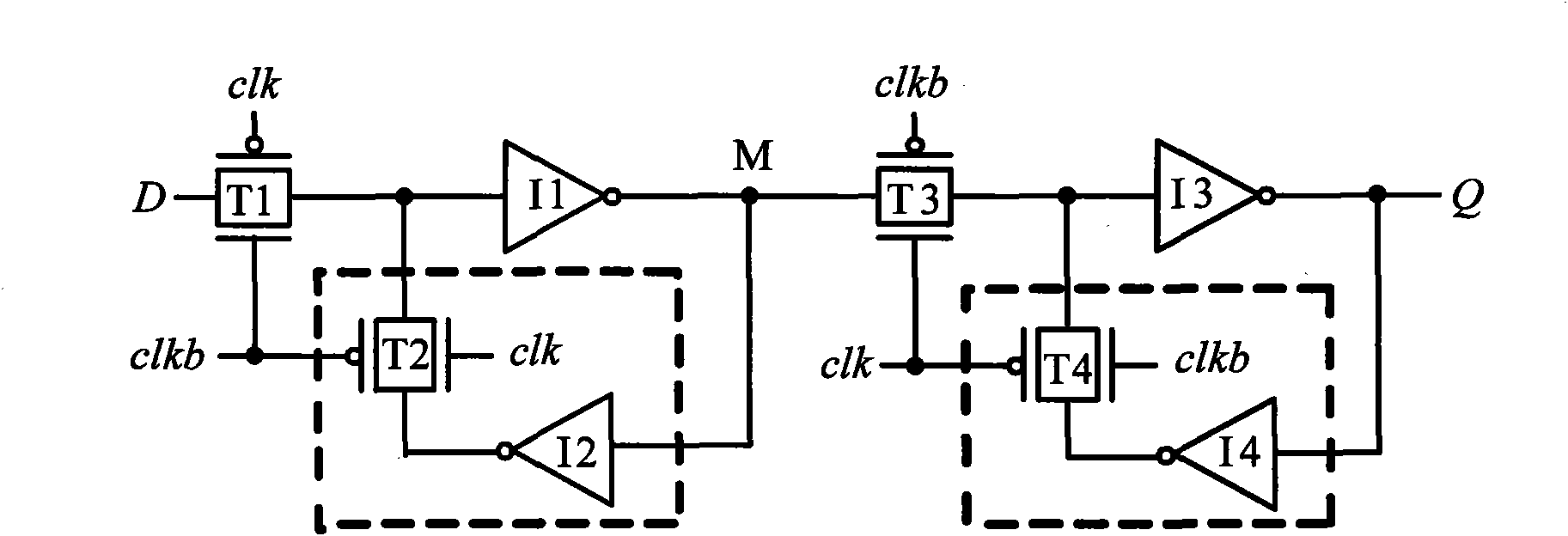
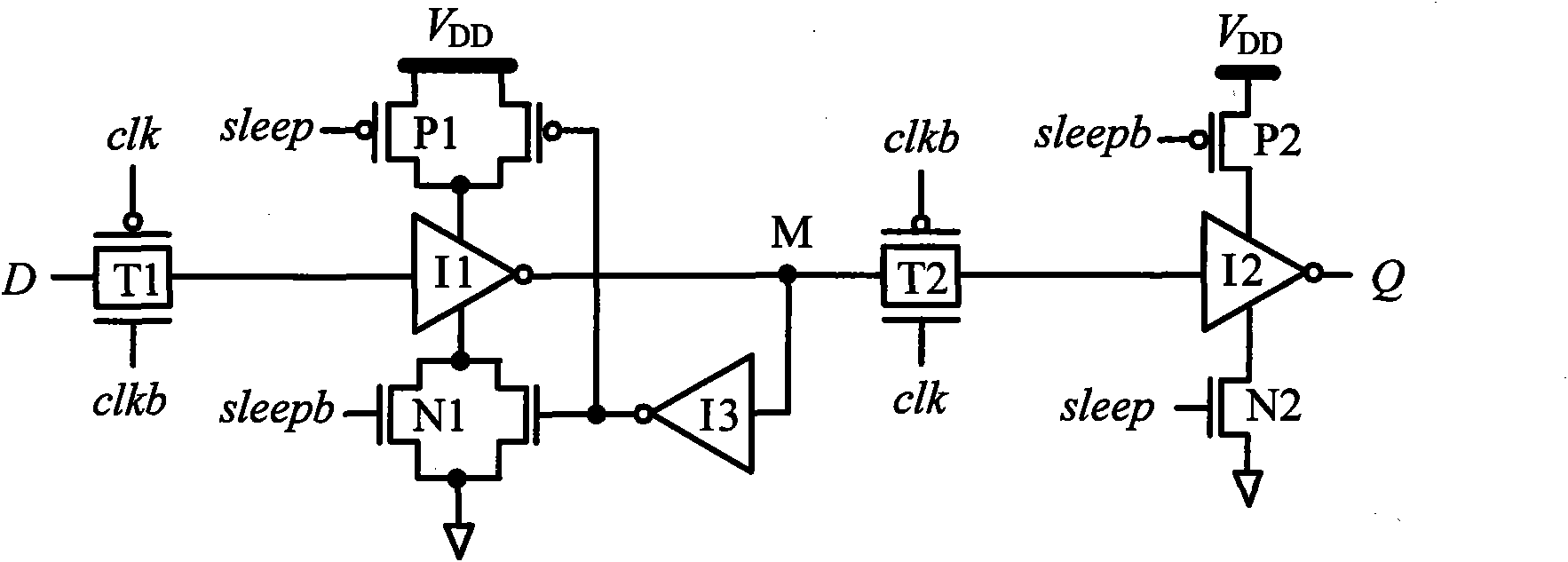
Low-power dissipation RS latch unit and low-power dissipation master-slave D flip-flop
InactiveCN101777907ASimple and completely symmetrical structureGood leakage power suppression performanceElectric pulse generatorLogic circuitsHemt circuitsControl theory
The invention discloses a low-power dissipation RS latch unit and a low-power dissipation master-slave D flip-flop, which is characterized in that the low-power dissipation RS latch unit comprises an input driving and synchronizing circuit, a pull-down circuit, a function control circuit, a first phase inverter and a second phase inverter, wherein the first phase inverter and the second phase inverter are mutually overlapped and coupled. The low power dissipation master-slave D flip-flop is composed of an input phase inverter, a clock phase inverter, a first low-power dissipation RS latch unit and a second low-power dissipation RS latch unit, wherein the first low power dissipation RS latch unit and the second low power dissipation RS latch unit have the same inner structure and are cascaded. The low power dissipation master-slave D flip-flop has the advantages that the low-power dissipation RS latch units use three kinds of leaked power consumption lowering technology, i.e. P-type logic technology, function control technology and double-threshold technology, so that the low-power dissipation RS latch units have better leaked power consumption inhibiting performance. The low-power dissipation master-slave D flip-flop has simple and totally symmetrical circuit structure. Compared with the traditional single-threshold transmission gate D trigger circuit, the invention can save 80% of leaked power consumption and 40% of total power consumption in the 90 nm process, so that the invention is suitable to serve as a digital circuit unit to the design of low-power consumption integrated circuits in the deep sub-micron CMOS process.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
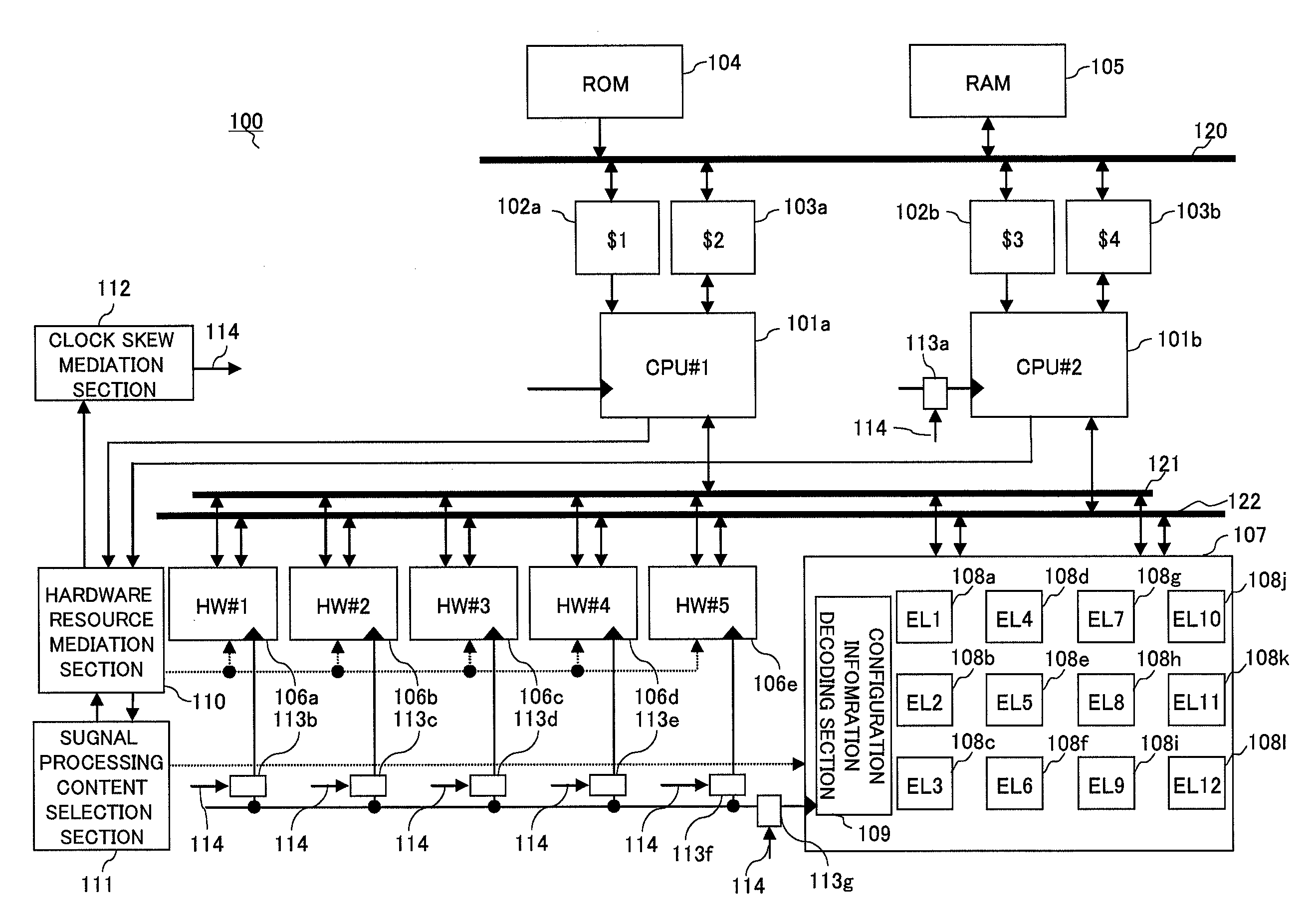
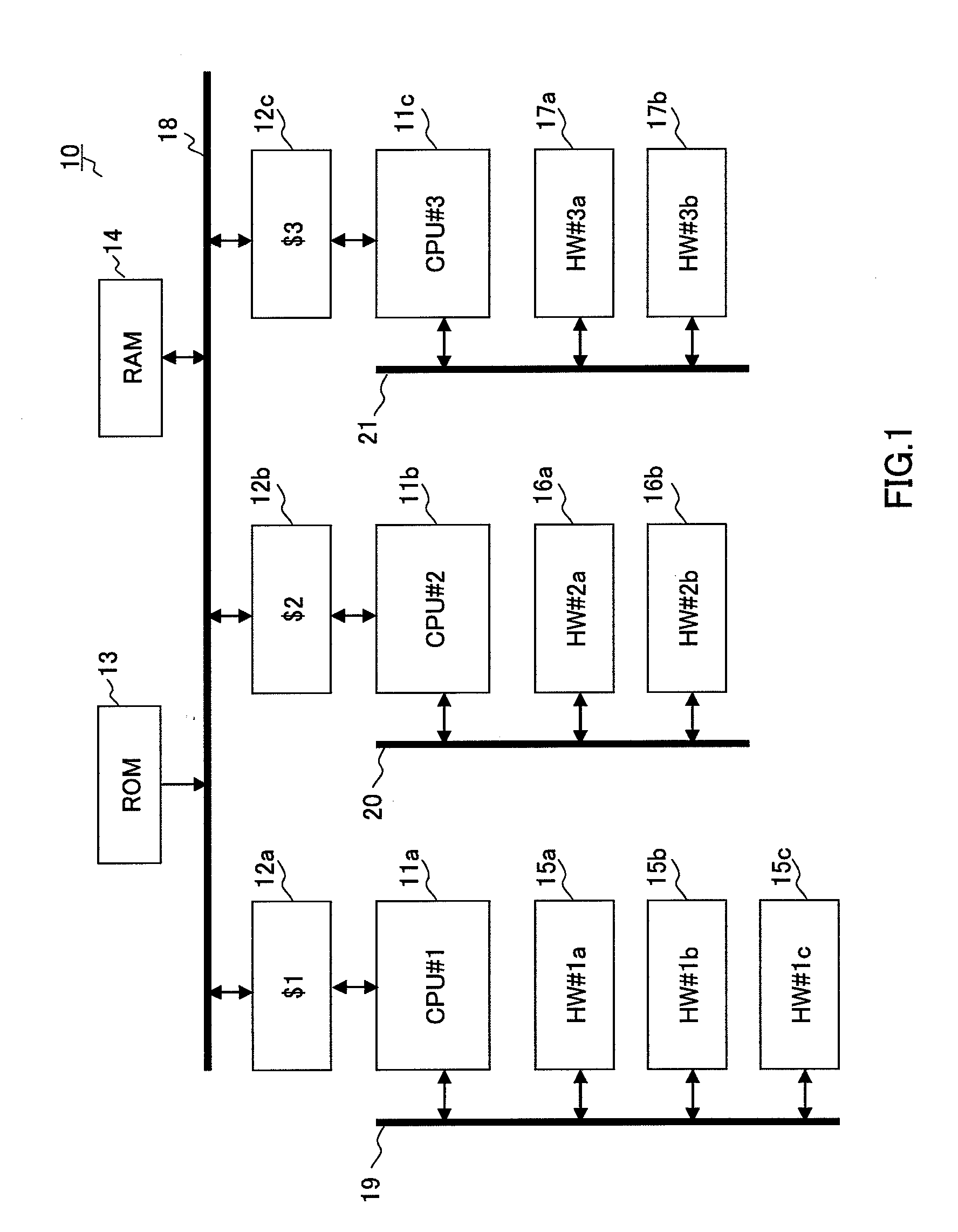
Asymmetric multiprocessor
InactiveUS20070283128A1Increase freedomLoad minimizationEnergy efficient ICTGeneral purpose stored program computerExecution controlClock phase
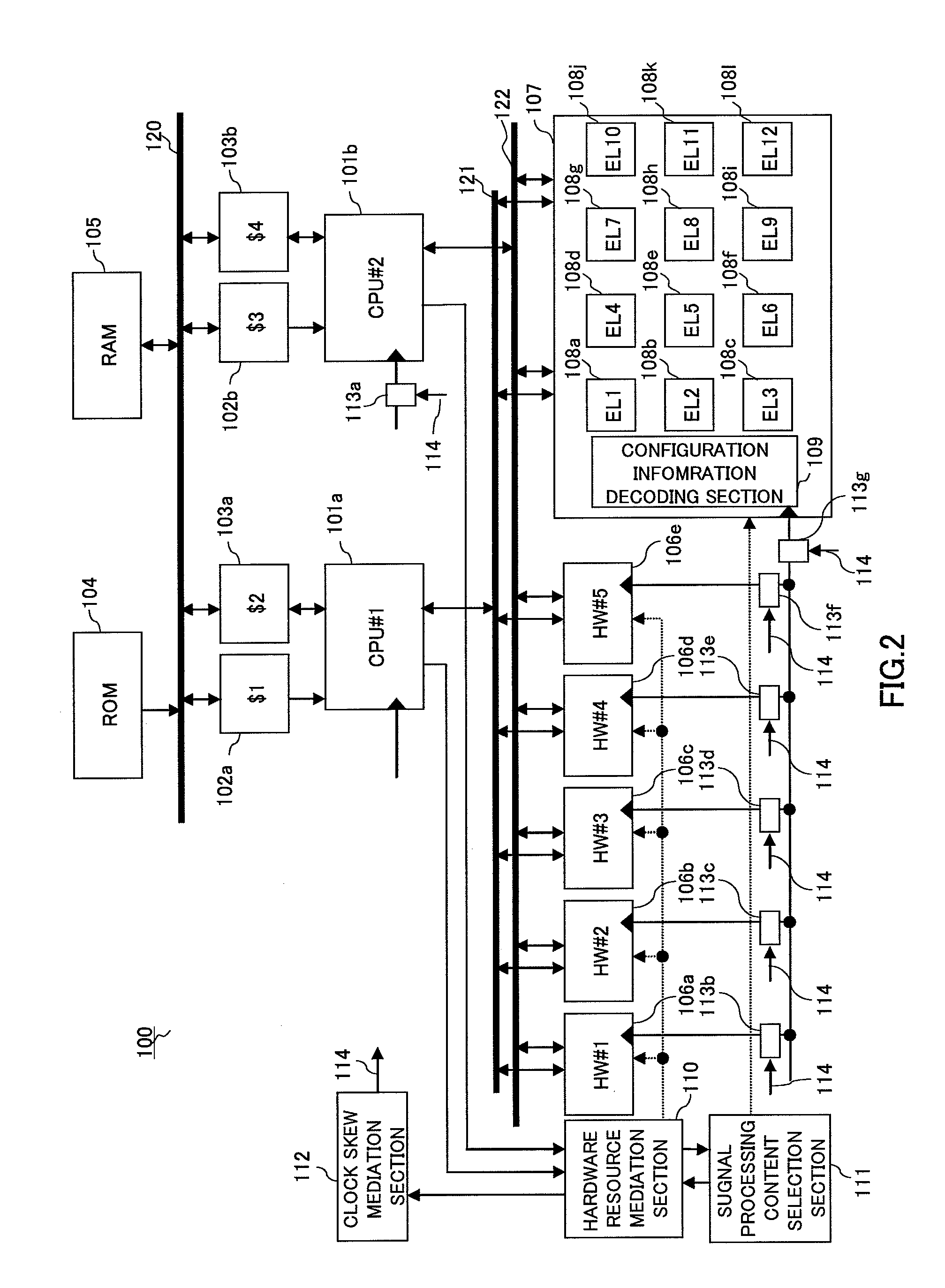
An asymmetric multiprocessor capable of increasing the degree of freedom of distributed processing, minimizing the processing load on each processor (CPU), and achieving a large reduction in power consumption by reducing the operating frequency or lowering the power supply voltage. Asymmetric multiprocessor (100) includes a hardware resource mediation section (110) that mediates request signals requesting permission to use arbitrary hardware accelerators from CPU cores (101a and 101b) ; a signal processing content selection section (111) that selects signal processing content of dynamically reconfigurable signal processor section (107) connected as a slave; a clock skew mediation section (112) that performs control to arbitrarily shift a clock phase relationship among groups; and clock delay generation sections (113a through 113g) that delay a clock signal based on clock skew selection enable signal (114).
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
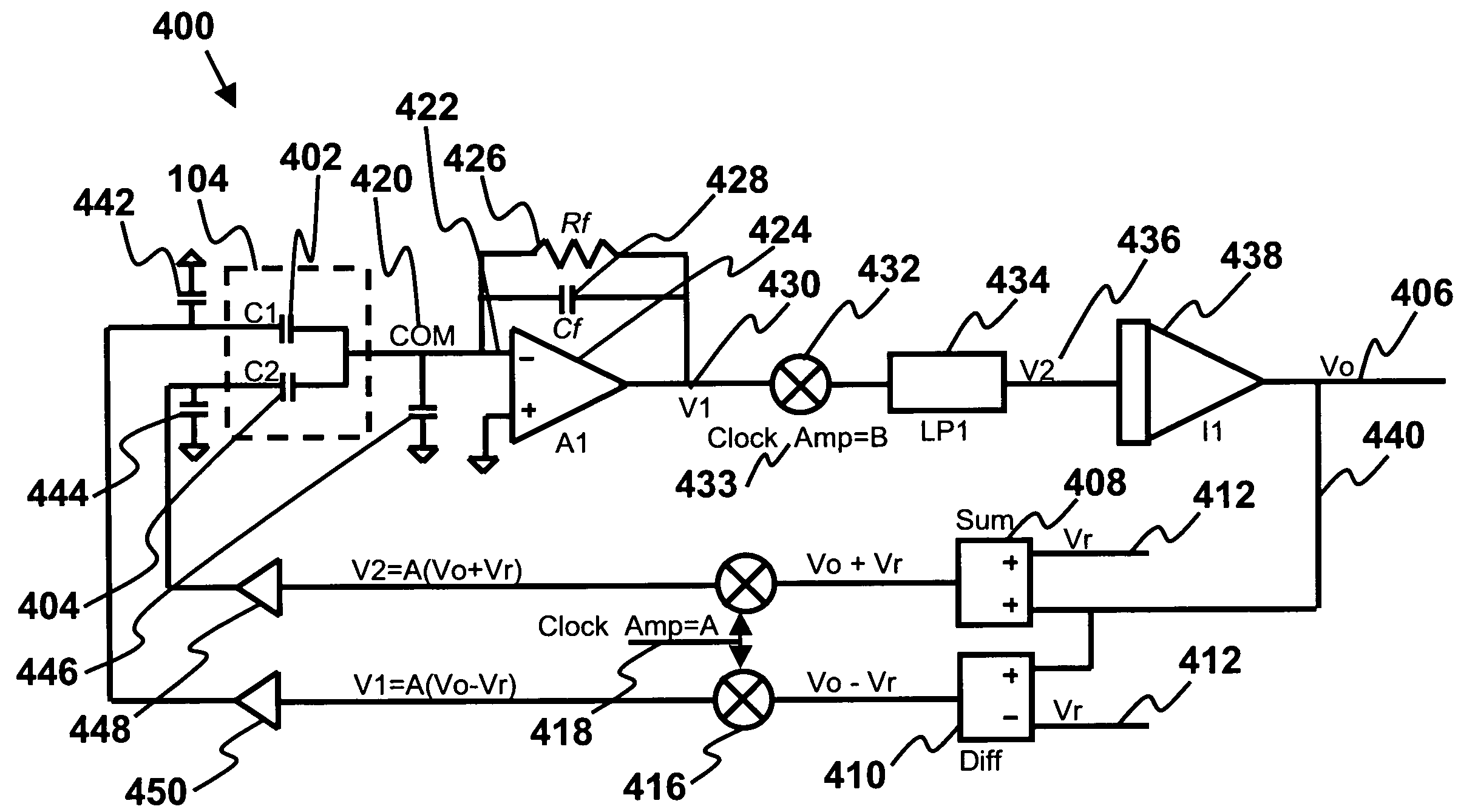
Signal conditioning methods and circuits for a capacitive sensing integrated tire pressure sensor
A tire pressure monitoring system is provided that includes a switched capacitor circuit having a clock with two non-overlapping clock phases that control a state of analog switches of the switched capacitor circuit. The system uses tire pressure sensor MEMS capacitors that are measured differentially. A capacitance-to-voltage converter is connected to the MEMS sense capacitor, and a sigma-delta converter having a comparator with a first digital output state and a second digital output state is used. The first output state is a sum of reference voltages and the second output state is a difference of the reference voltages. An average value of the capacitance-to-voltage converter output is driven to a zero value and a digital output is provided of the average output states that is equal to a difference between the MEMS capacitors divided by their sum multiplied by a ratio of the reference voltages.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for using a learning sequence to establish communications on a high- speed nonsynchronous interface in the absence of clock forwarding
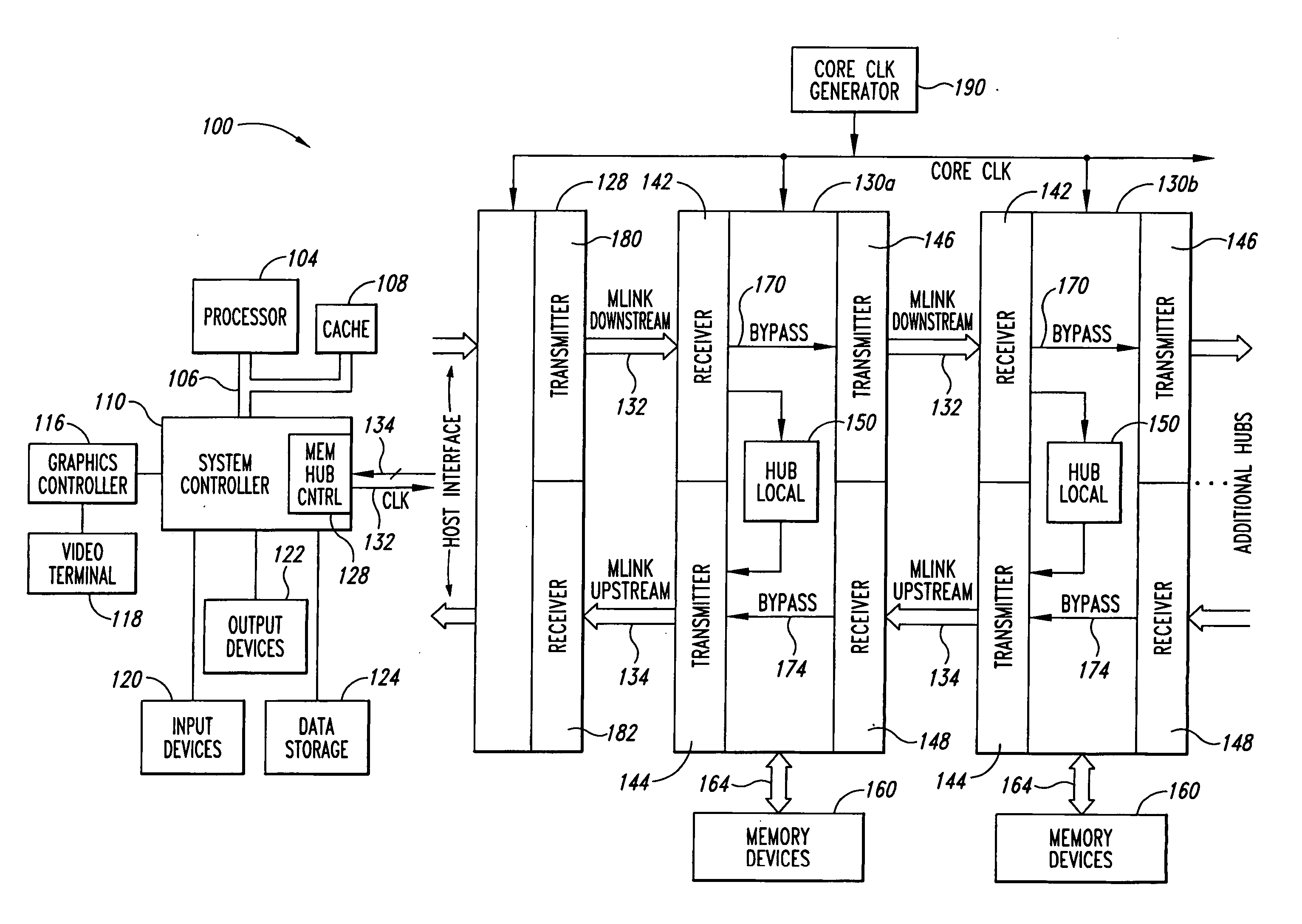
A memory system includes a memory hub controller that sends write data to a plurality of memory modules through a downstream data bus and receives read data from the memory modules through an upstream data bus. The memory hub controller includes a receiver coupled to the upstream data bus and a transmitter coupled to the downstream data bus. Similarly, each of the memory modules includes a receiver coupled to the downstream data bus and a transmitter coupled to the upstream data bus. Each receiver includes a receive clock generator that is synchronized by coupling a known pattern of data to the receiver. The receiver determines which phase of the receive clock best captures the known pattern and uses that receive clock phase during normal operation.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
High-precision time interval measurement method based on phase modulation
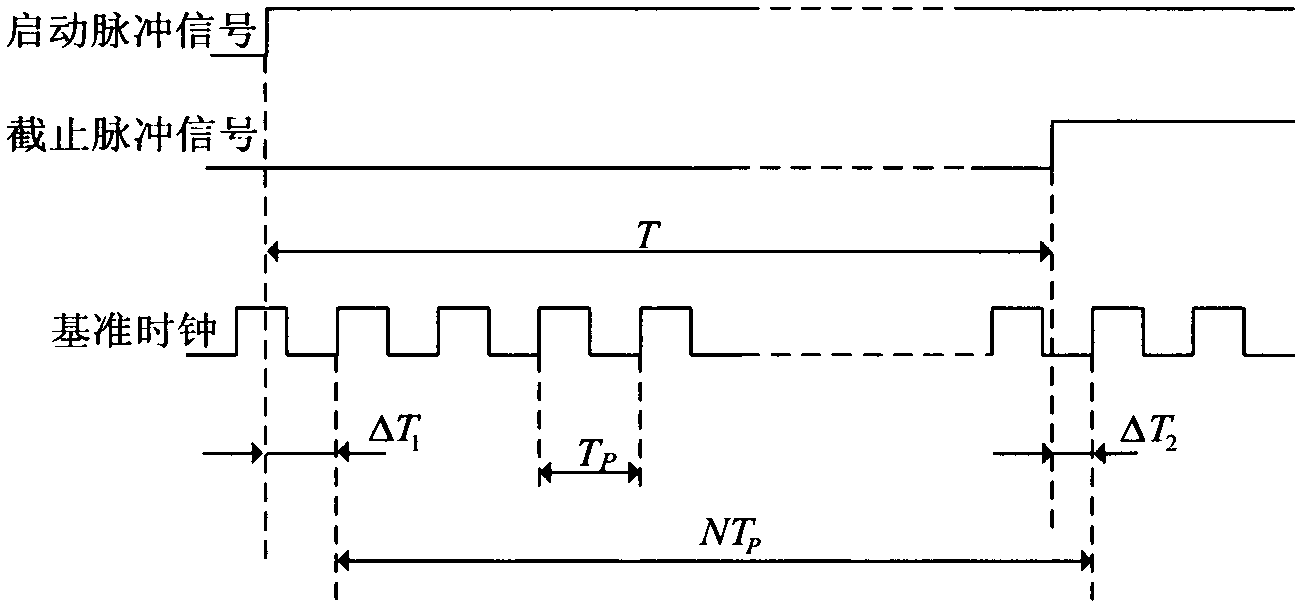
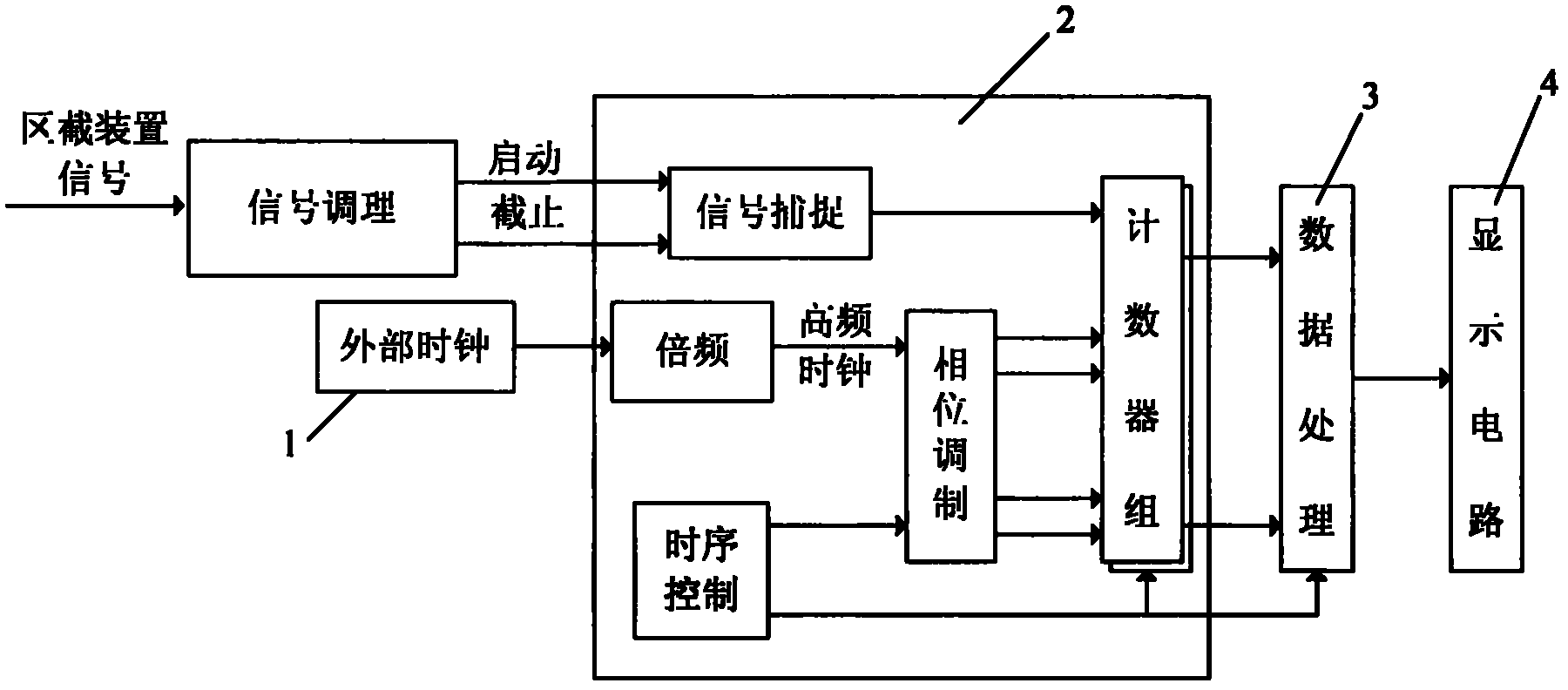
InactiveCN102540865AMany technical meansEasy to implementElectric unknown time interval measurementObservational errorMeasurement device
The invention discloses a high-precision time interval measurement method based on phase modulation. Under the control of digital clock phase-shift, a path of high-frequency and low-jitter clock is transformed to N paths of clock signals having same frequency and fixed phase difference, and is taken as a counter reference clock; a counter is driven to count respectively in N paths of clock periods; two paths of clock signals, which have the smallest error, are extracted by utilizing the clock phase information; through the combination with the clock period and the counted values, the measurement valve of the time interval is worked out. Compared with the method using a single clock for counting, the high-precision time interval measurement method effectively reduces the measurement principle error, and can improve the measurement resolution ratio to 1 / n of the reference clock. A measurement device is connected with a signal conditioning module, an FPGA module, a singlechip module and a display circuit module sequentially according to the signal processing order, and realizes high measurement precision, high measurement resolution ratio, high measurement speed, real time display, and stable and reliable work under a certain crystal oscillation frequency; and the integration in the FPGA is easy, and the expansion is flexible. The high-precision time interval measurement method can be used for measuring the speed in a high-speed motion.
Owner:XIAN MODERN CHEM RES INST
Method and system for data processing system self-synchronization
InactiveUS6470458B1Good synchronizationDigital computer detailsGenerating/distributing signalsData processing systemData treatment
A method and system for dynamic synchronization of a data processing system processor chips. One of a plurality of chips is designated as a primary chip and all other chips as secondary chips. The clock phase of the chips are synchronized utilizing the primary chip's clock phase as a reference clock phase for the secondary chips.
Owner:IBM CORP
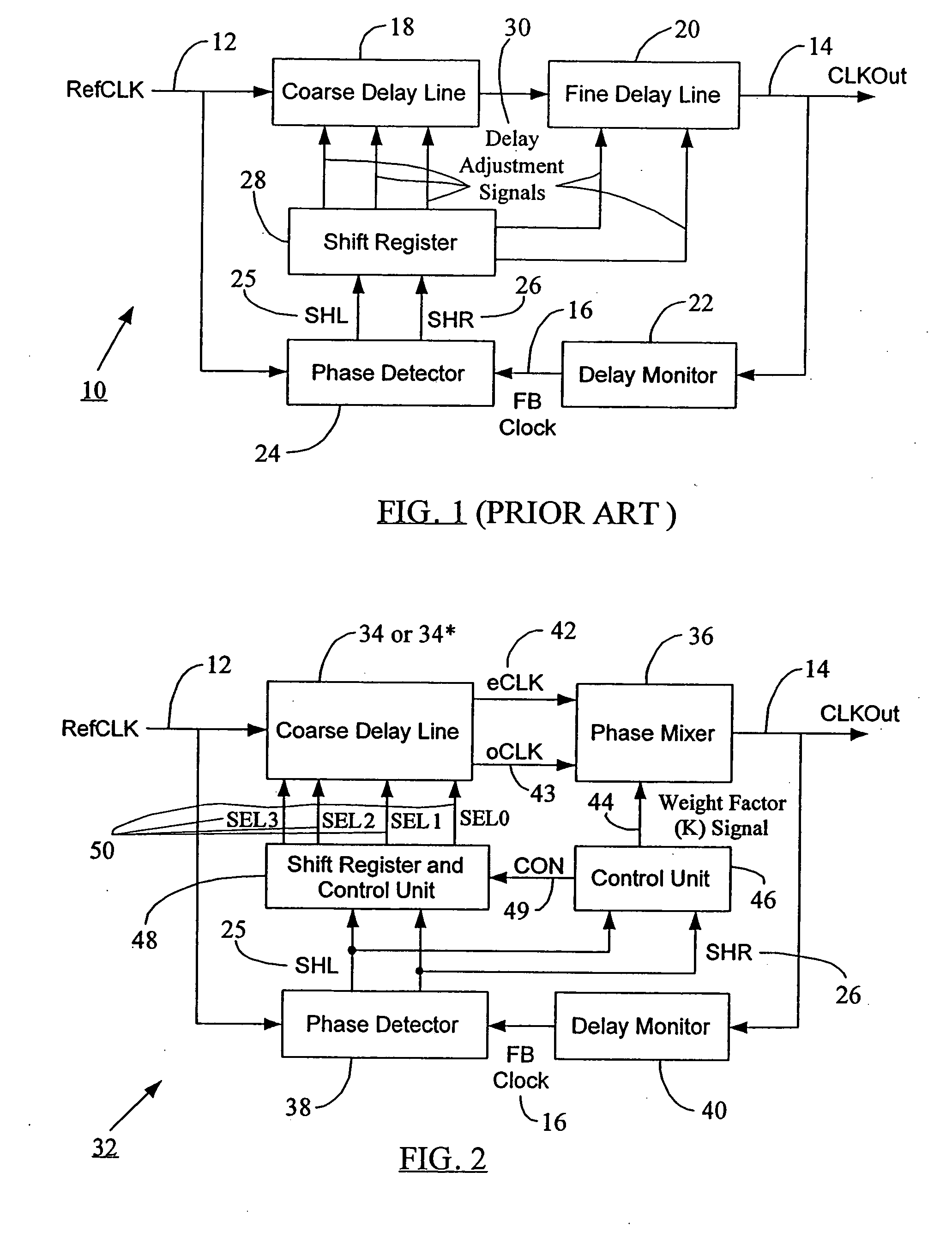
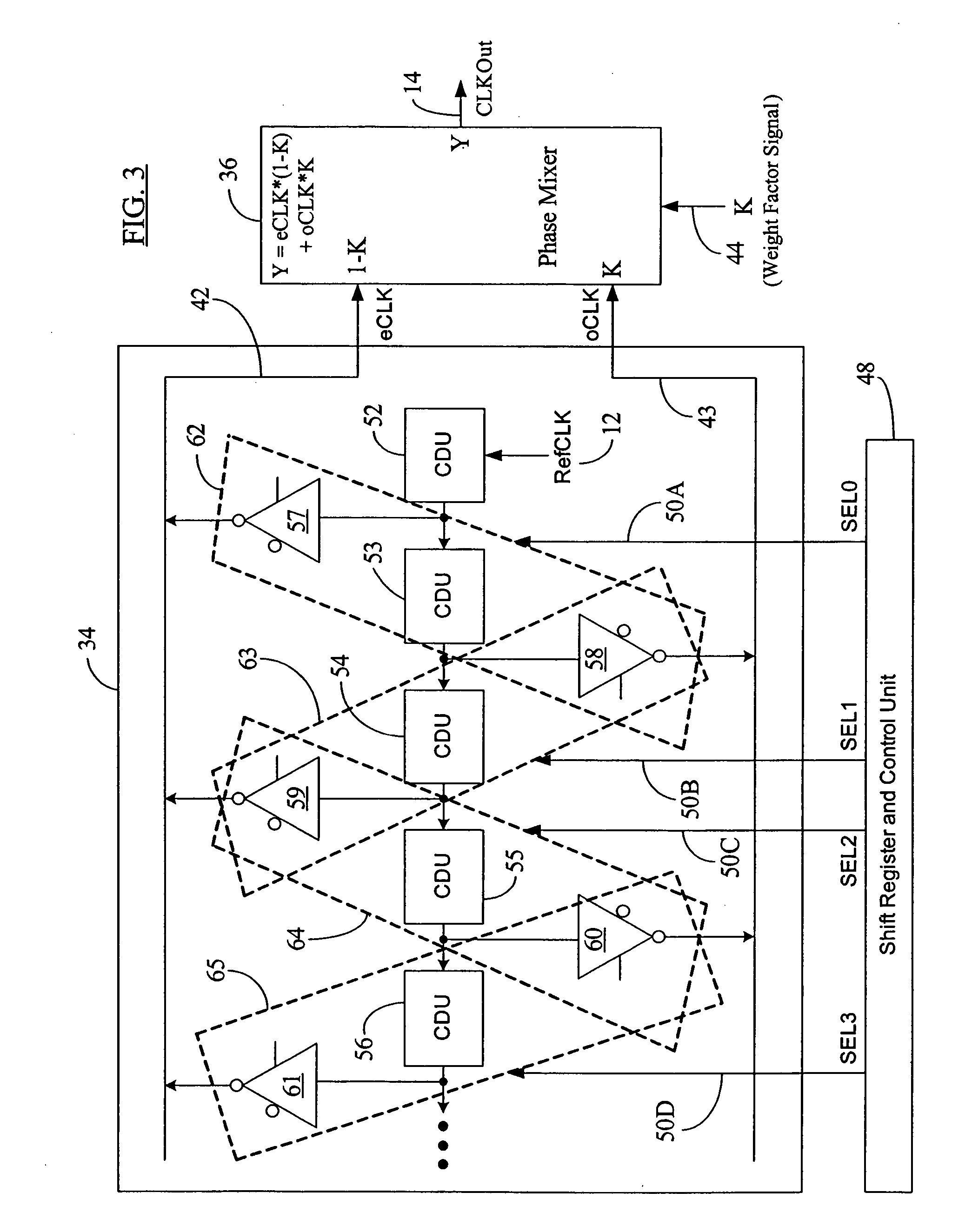
Seamless coarse and fine delay structure for high performance DLL
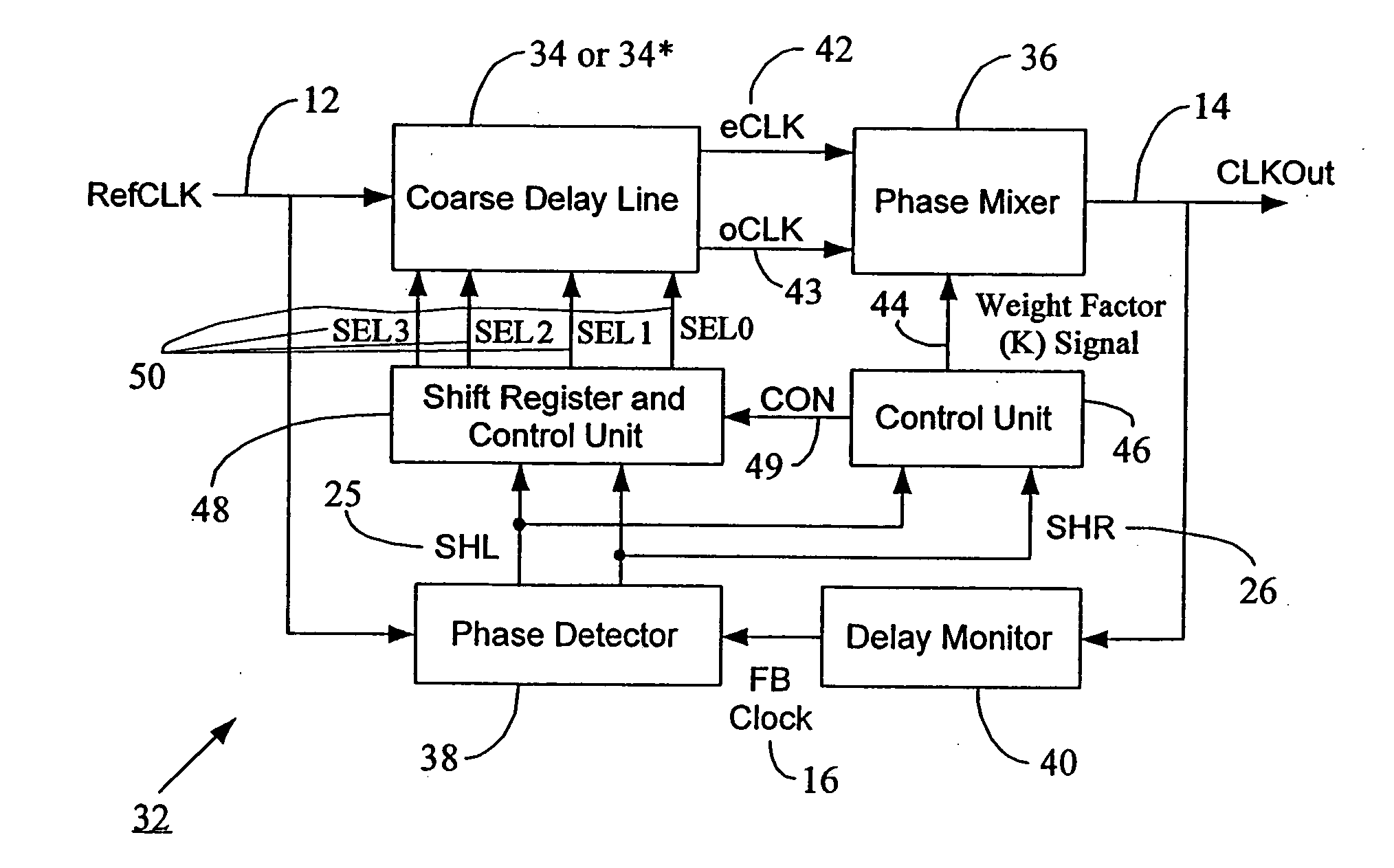
ActiveUS20070030753A1Smooth phase transitionDelay problemPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersClock timePhase difference
A clock synchronization system and method avoids output clock jitter at high frequencies and also achieves a smooth phase transition at the boundary of the coarse and fine delays. The system may use a single coarse delay line configured to generate two intermediate clocks from the input reference clock and having a fixed phase difference therebetween. The coarse delay line may have a hierarchical or a non-hierarchical structure. A phase mixer receives these two intermediate clocks and generates the final output clock having a phase between the phases of the intermediate clocks. The coarse shifting in the delay line at high clock frequencies does not affect the phase relationship between the intermediate clocks fed into the phase mixer. The output clock from the phase mixer is time synchronized with the input reference clock and does not exhibit any jitter or noise even at high clock frequency inputs. Because of the rules governing abstracts, this abstract should not be used to construe the claims.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
System and method for using a learning sequence to establish communications on a high-speed nonsynchronous interface in the absence of clock forwarding
A memory system includes a memory hub controller that sends write data to a plurality of memory modules through a downstream data bus and receives read data from the memory modules through an upstream data bus. The memory hub controller includes a receiver coupled to the upstream data bus and a transmitter coupled to the downstream data bus. Similarly, each of the memory modules includes a receiver coupled to the downstream data bus and a transmitter coupled to the upstream data bus. Each receiver includes a receive clock generator that is synchronized by coupling a known pattern of data to the receiver. The receiver determines which phase of the receive clock best captures the known pattern and uses that receive clock phase during normal operation.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
A digital phase lock loop device for smooth switching of clock phase and its method
InactiveCN101079630ASimple structureEasy to integratePulse automatic controlPhase differenceEngineering
The invention discloses a digital locked ring device to realize clock phase smooth conversion, which is characterized by the following: the reference source processes the selected reference clock according to master spare pattern; the time digital converses the reference clock and phase difference from local clock of frequency divider into the corresponding coded digital code to realize phase demodulation and phase difference digitalization to be transmitted to CPU filter and locked processing unit the proceed linear phase disposal, low-pass digital filter disposal, locked disposal, which outputs the digital phased error signal to the digifax converser as corresponding analog voltage-controlled value, in order to control the corresponding vibrating frequency output by voltage-controlled crystal oscillator; the frequency is processed by frequency divider to transmit the local clock with the same frequency as reference frequency to time digital converter. The invention realizes high-precision error control of main spare systems, which is convenient to integrate chip with high reliability and integration level.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Apparatus for clock data recovery
InactiveUS7295644B1Increase coverageMinimal amountPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionData streamClock rate
Circuits, architectures, a system and methods for clock data recovery. The circuit generally includes (a) a clock phase adjustment circuit, receiving clock phase information and providing a clock phase adjustment signal, (b) a clock frequency adjustment circuit, receiving clock frequency information and providing a clock frequency adjustment signal, and (c) an adder circuit, receiving the clock phase adjustment signal and the clock frequency adjustment signal, and providing a clock recovery adjustment signal. The architectures and / or systems generally comprise those that include a clock data recovery circuit embodying one or more of the inventive concepts disclosed herein. The method generally comprises the steps of (1) sampling the data stream at predetermined times, (2) generating clock frequency information and clock phase information from sampled data, and (3) altering a frequency and / or a phase of the clock signal in response to the clock frequency information and the clock phase information. The present invention prevents or reduces the likelihood of the potential nonconvergence / clock runaway problem, advantageously with minimal or no changes to existing designs and logic. The present invention further advantageously improves system stability, reliability and performance with a minimum of additional circuitry.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Decoupling sampling clock and error clock in a data eye
ActiveUS20120170621A1Well formedMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsPhase correctionTransceiver
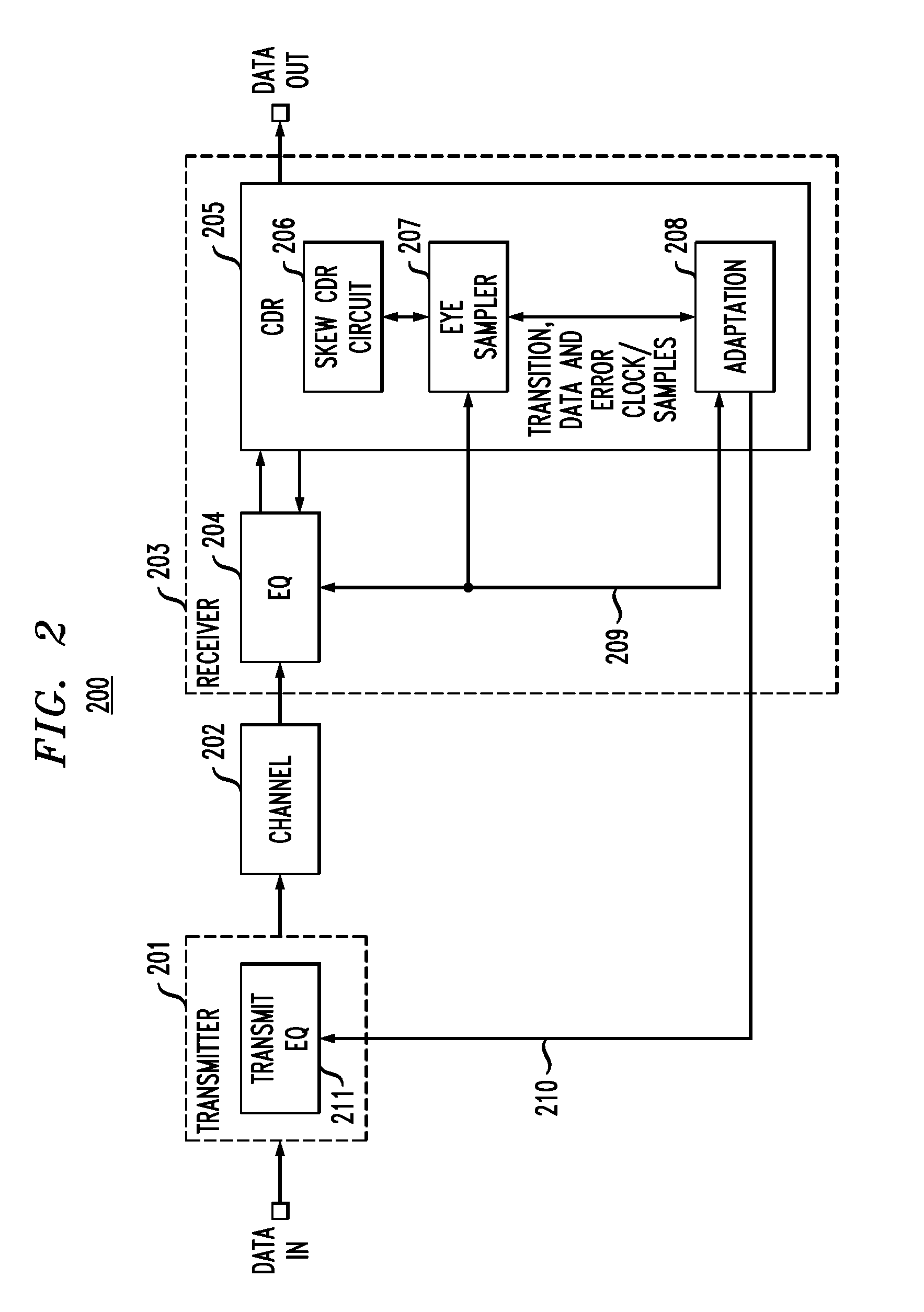
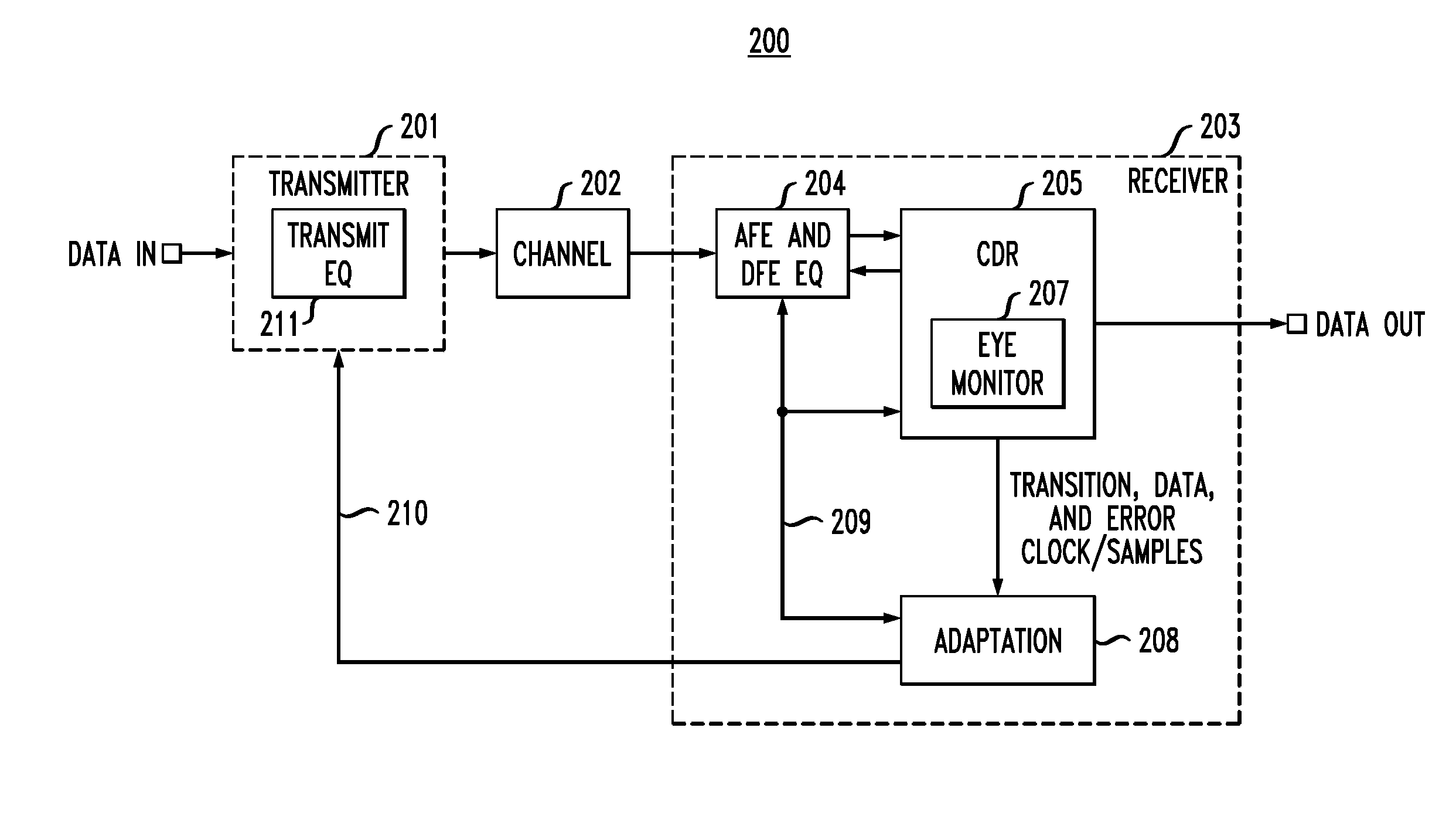
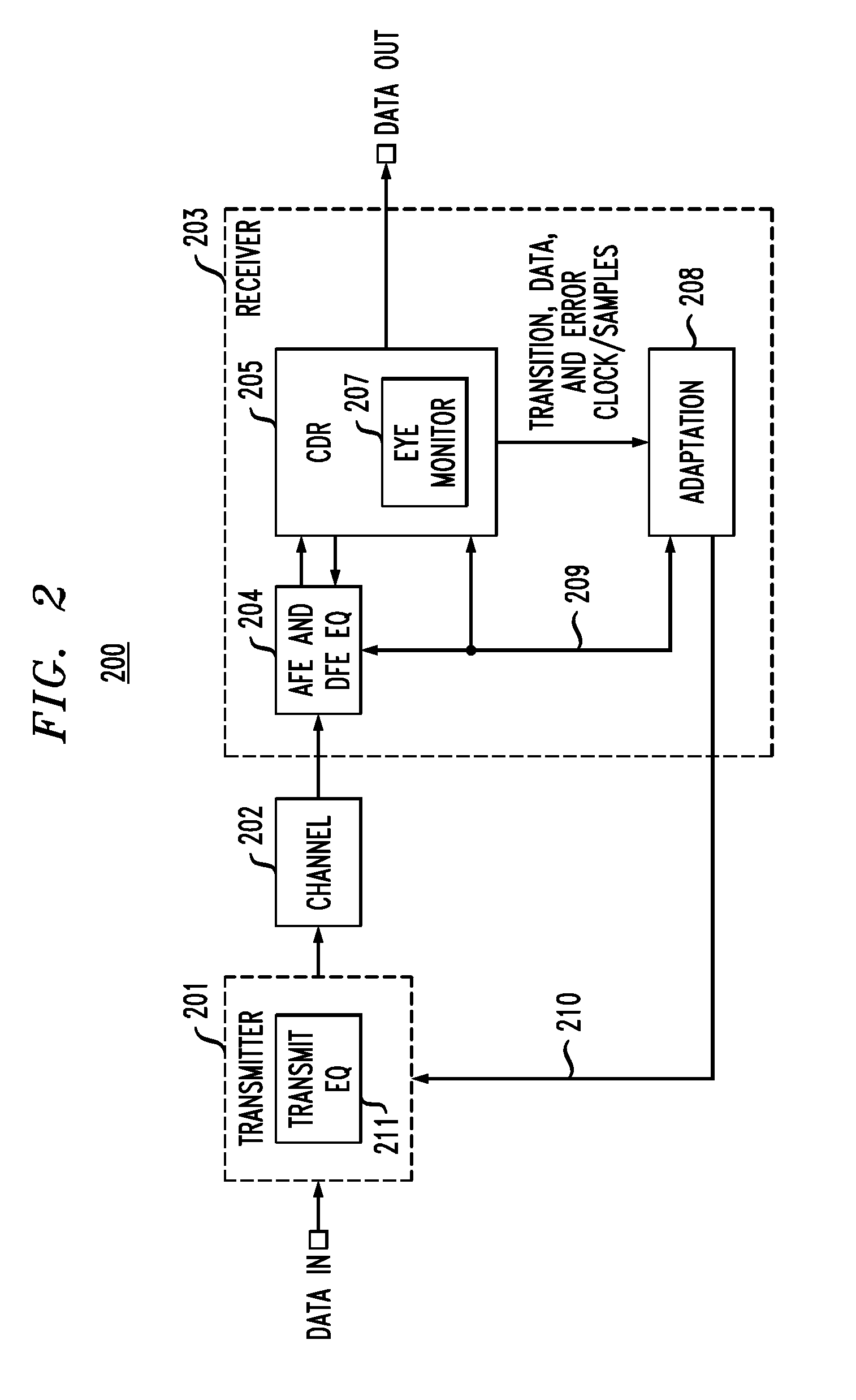
In described embodiments, a transceiver includes an eye monitor, clock and data recovery, and adaptation modules. Data sampling clock phase and error clock phase determined from a data eye are decoupled in the transceiver during a sampling phase correction process. Decoupling these clock phases during the sampling phase correction process allows relative optimization of system equalization parameters without degradation of various adaptation algorithms. Such adaptation algorithms might be employed for received signal gain and equalization such as, for example, Decision Feedback Equalizer (DFE) adaptation. Deriving the data sampling clock and error clock phases from the same clock generation source and with independent clock control enables an iterative sampling phase correction process that allows for accelerated clock and data recovery (CDR) without disturbing the data eye shape.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for estimation of error in data recovery schemes
InactiveUS6907553B2Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorError detection/correctionPhase noiseClock phase
An on-chip data independent method and apparatus for channel error estimation in a data recovery scheme is based on measuring phase noise statistics. The apparatus (10) receives a data pulse and four quadrature clock signals and has a discriminating device (11) to provide a count signal for each data pulse received depending on which clock signal was the first to clock the particular data pulse. A pair of counters (12 and 13) counts the number of data pulses received at different phase offsets to provide a value representing a statistical ratio of the counts at different clock phase offsets from which an error rate for the received data pulses based on the counts at different clock phase offsets can be determined from a look-up table (16). By re-configuring the circuitry, the system can be adapted to measure clock window asymmetry.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Inter-phase skew detection circuit for multi-phase clock, inter-phase skew adjustment circuit, and semiconductor integrated circuit
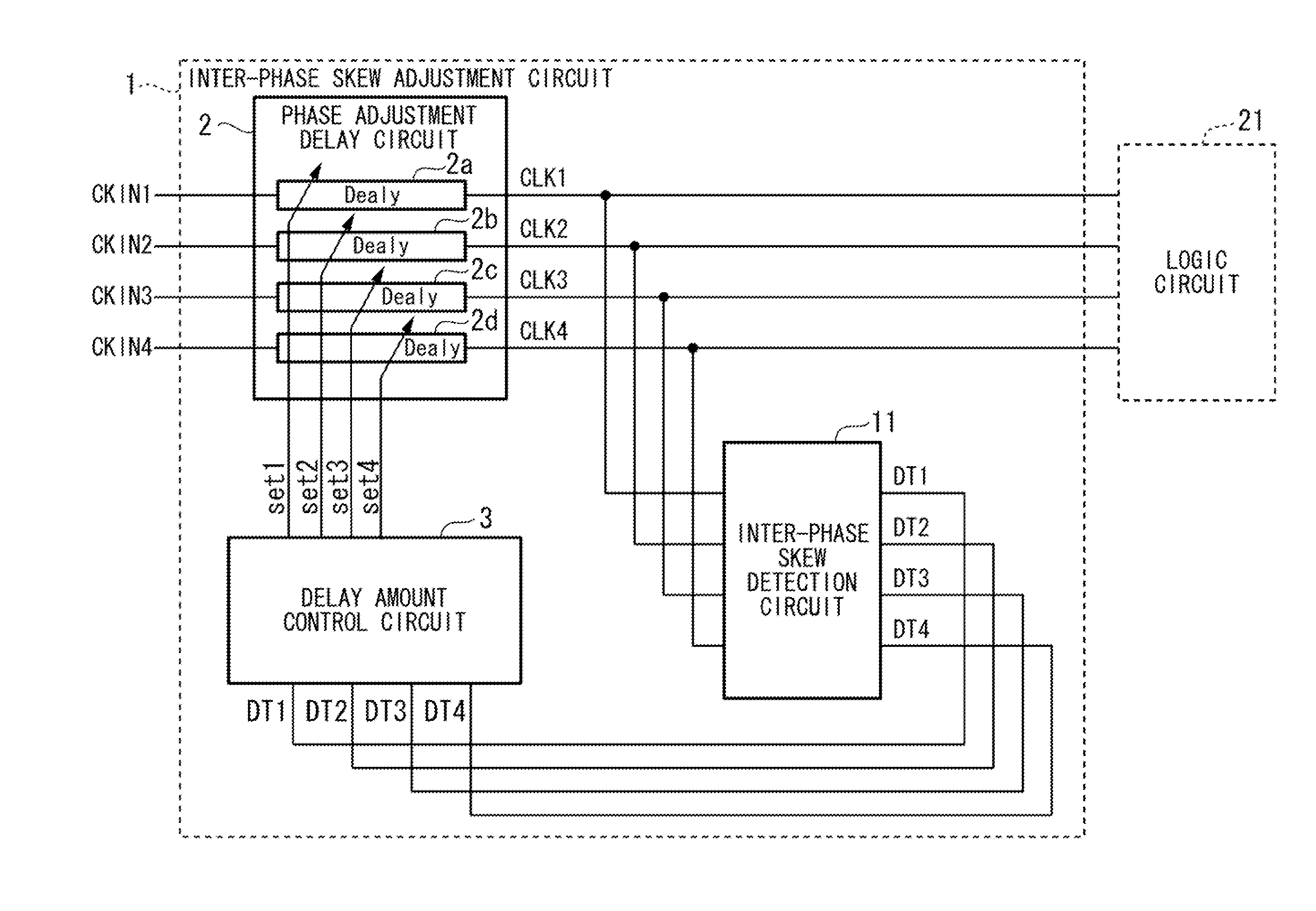
InactiveUS20110156757A1Reduce necessityReduce biasPulse automatic controlElectrical testingHemt circuitsEngineering
An inter-phase skew detection circuit includes a frequency division circuit that frequency-divides N-phase clocks to be measured at predetermined timings so as to generate N+2 frequency-divided clocks; a phase comparison target clock generation circuit that generates N phase comparison target clocks by using predetermined N frequency-divided clocks among the N+2 frequency-divided clocks; a phase comparison reference clock generation circuit that generates N reference clocks by using the N+2 frequency-divided clocks, in accordance with predetermined combinations between the N+2 frequency-divided clocks and an operation criterion; and a phase comparison circuit that detects respective phase differences between the N phase comparison target clocks and the corresponding N reference clocks.
Owner:NEC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com