Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
199 results about "Independent clock" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
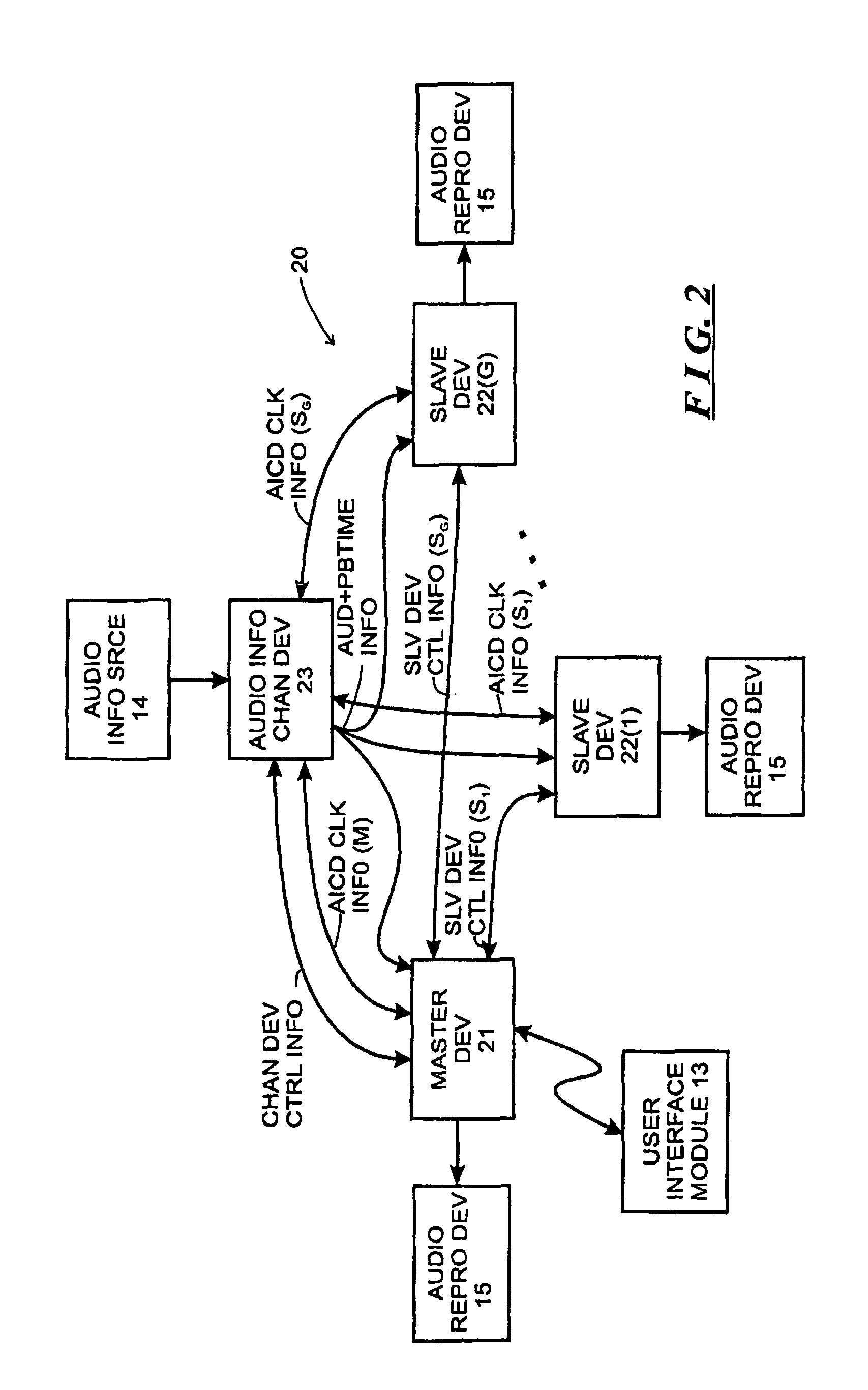
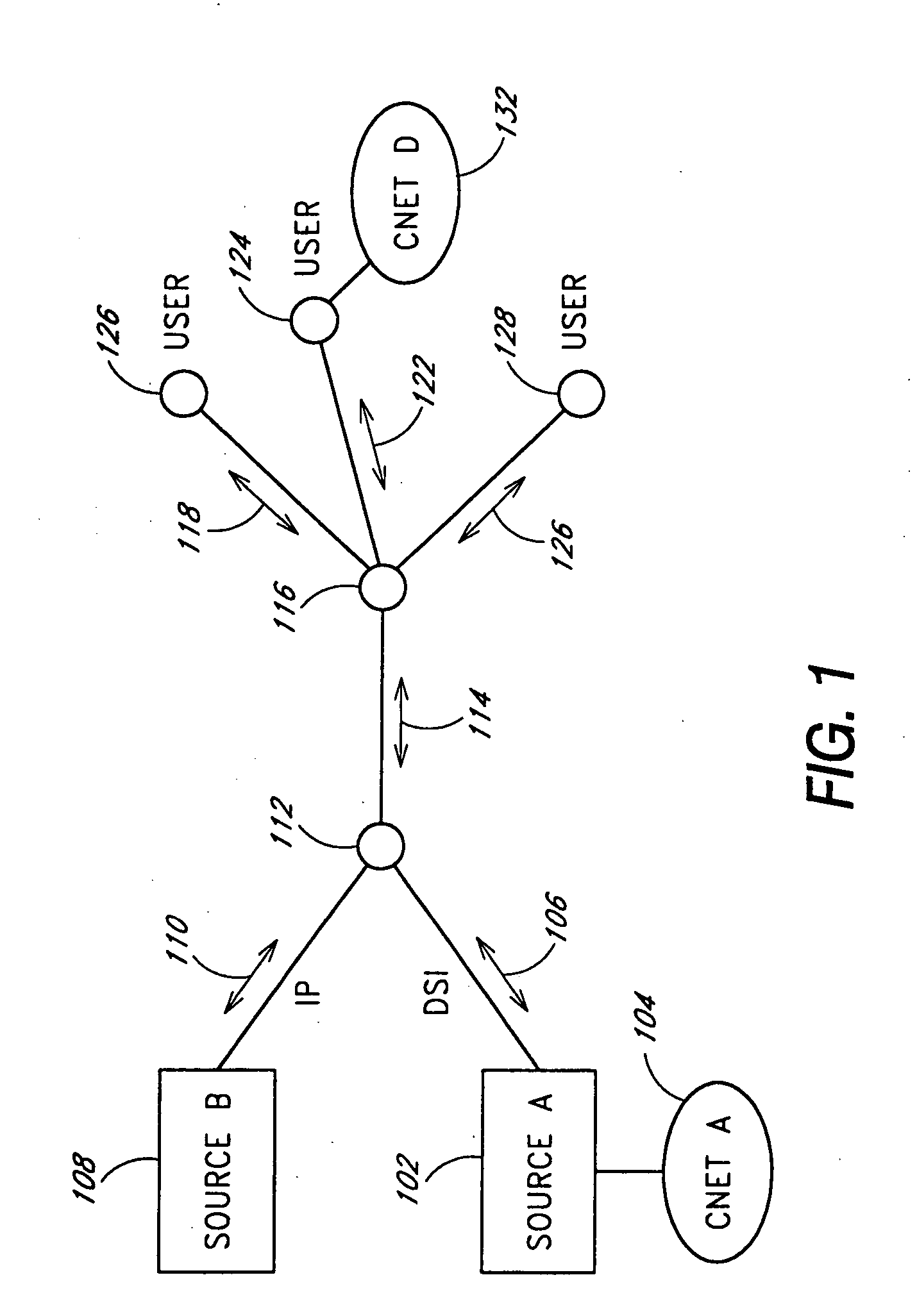
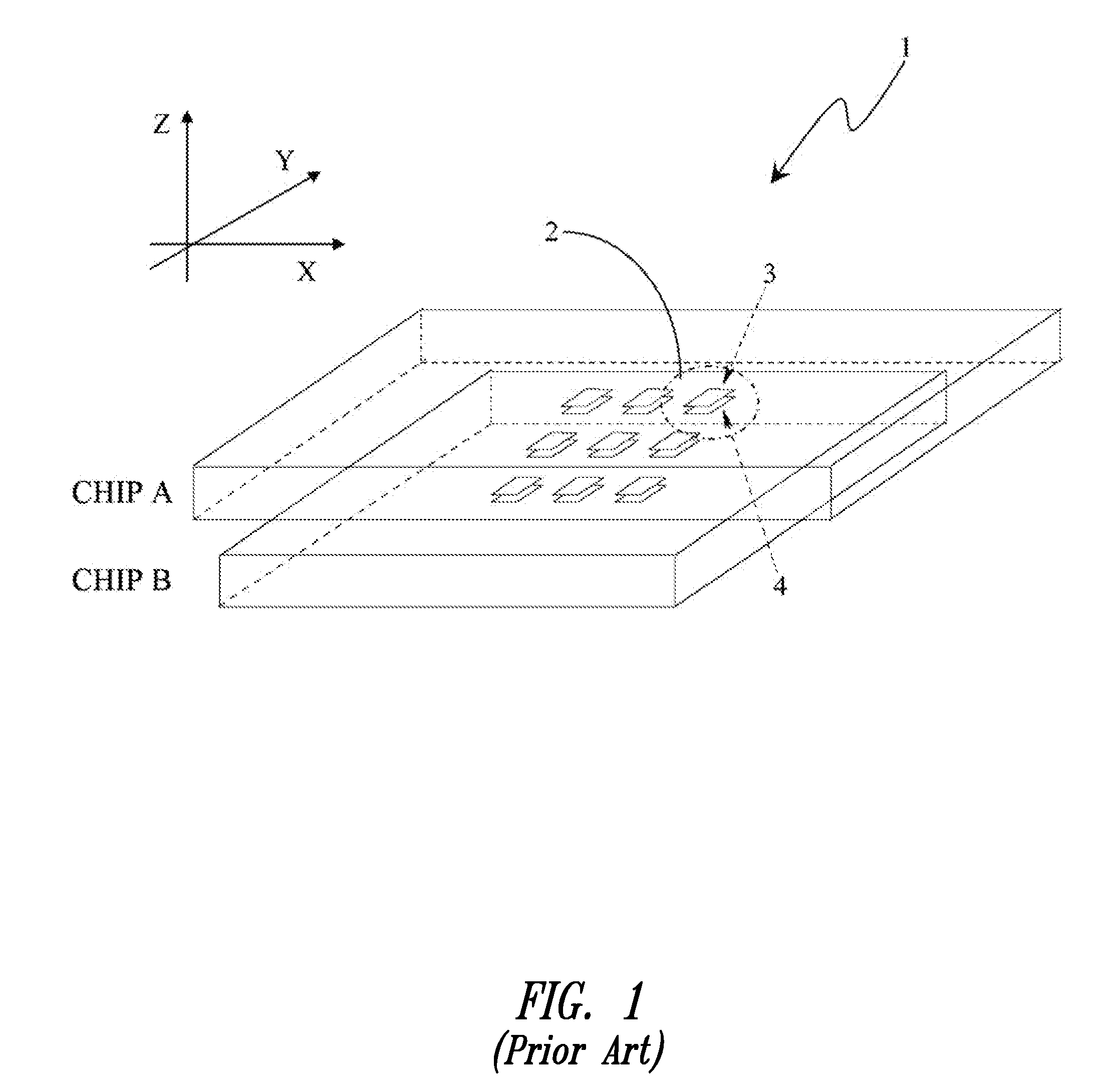
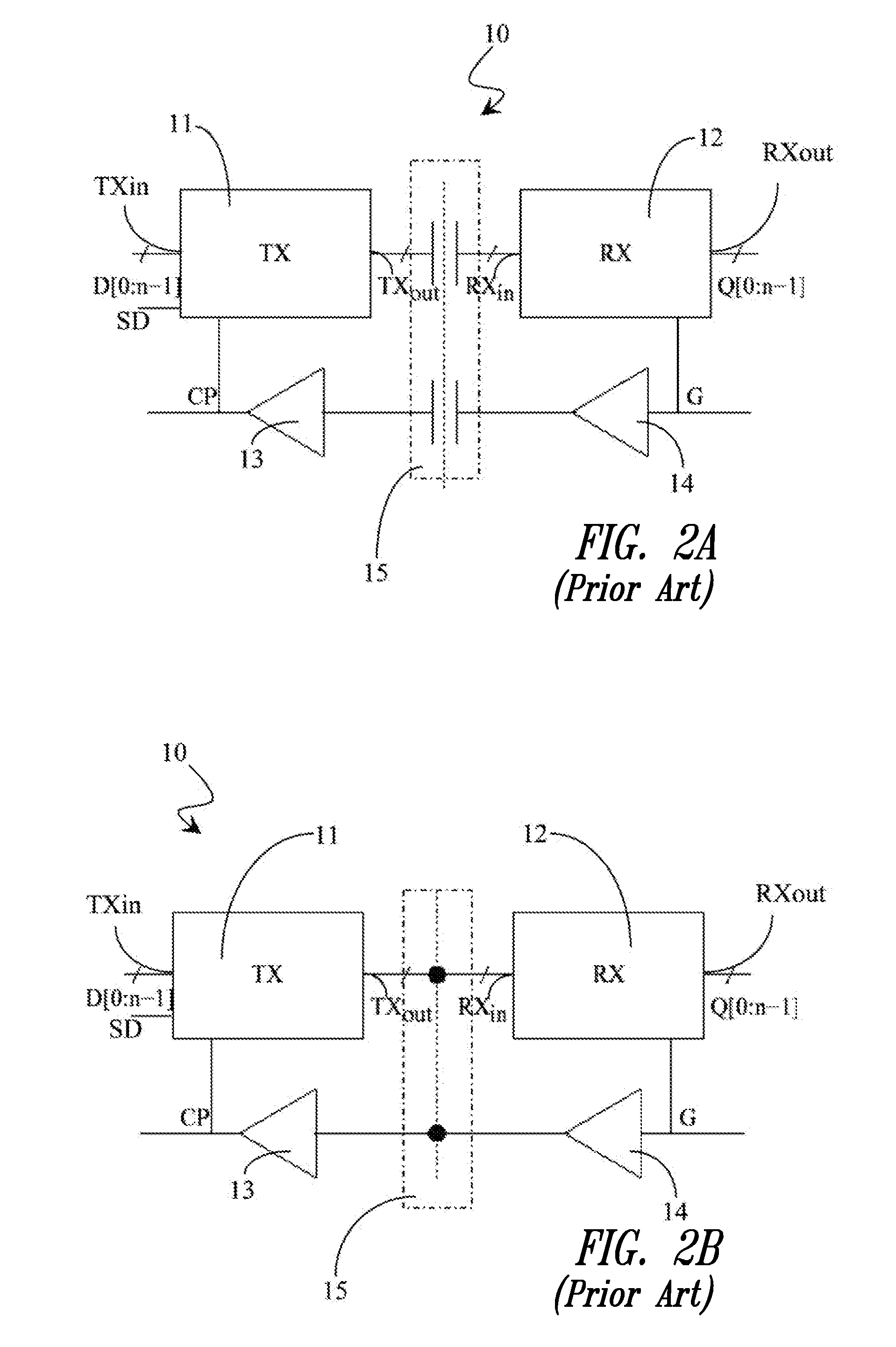
In telecommunications networks, independent clocks are free-running precision clocks located at the nodes which are used for synchronization. Variable storage buffers, installed to accommodate variations in transmission delay between nodes, are made large enough to accommodate small time departures among the nodal clocks that control transmission. Traffic may occasionally be interrupted to allow the buffers to be emptied of some or all of their stored data.
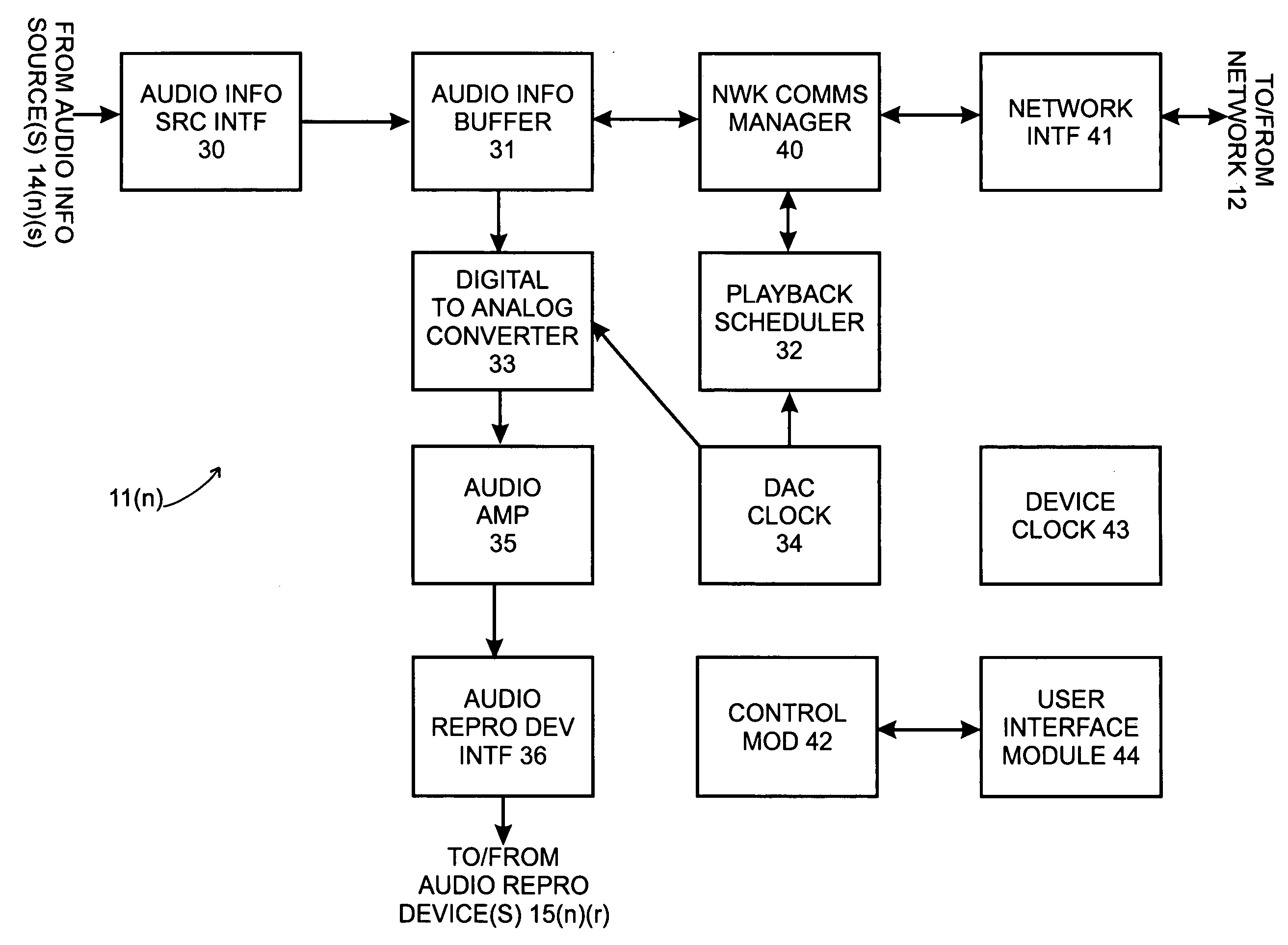
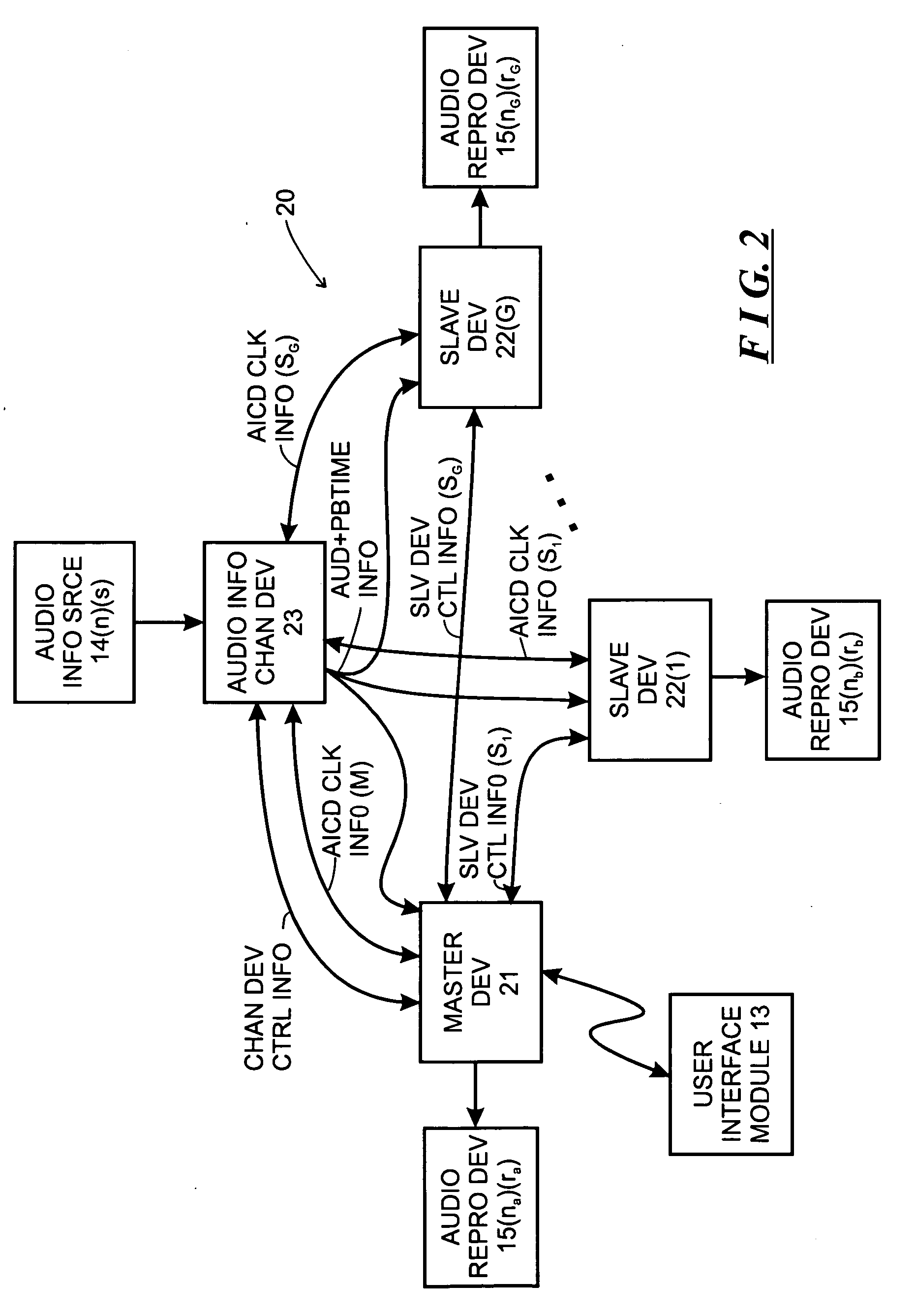
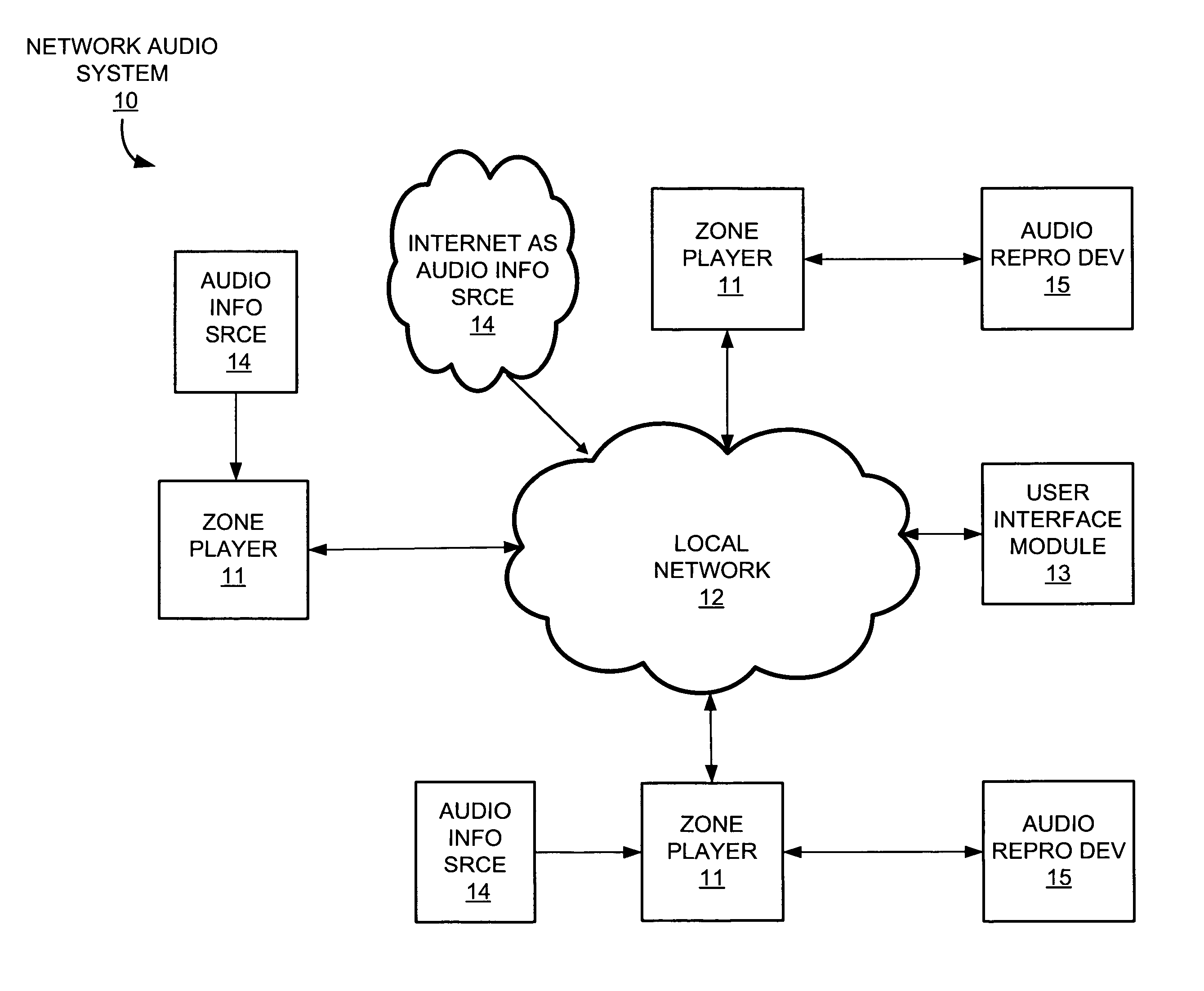
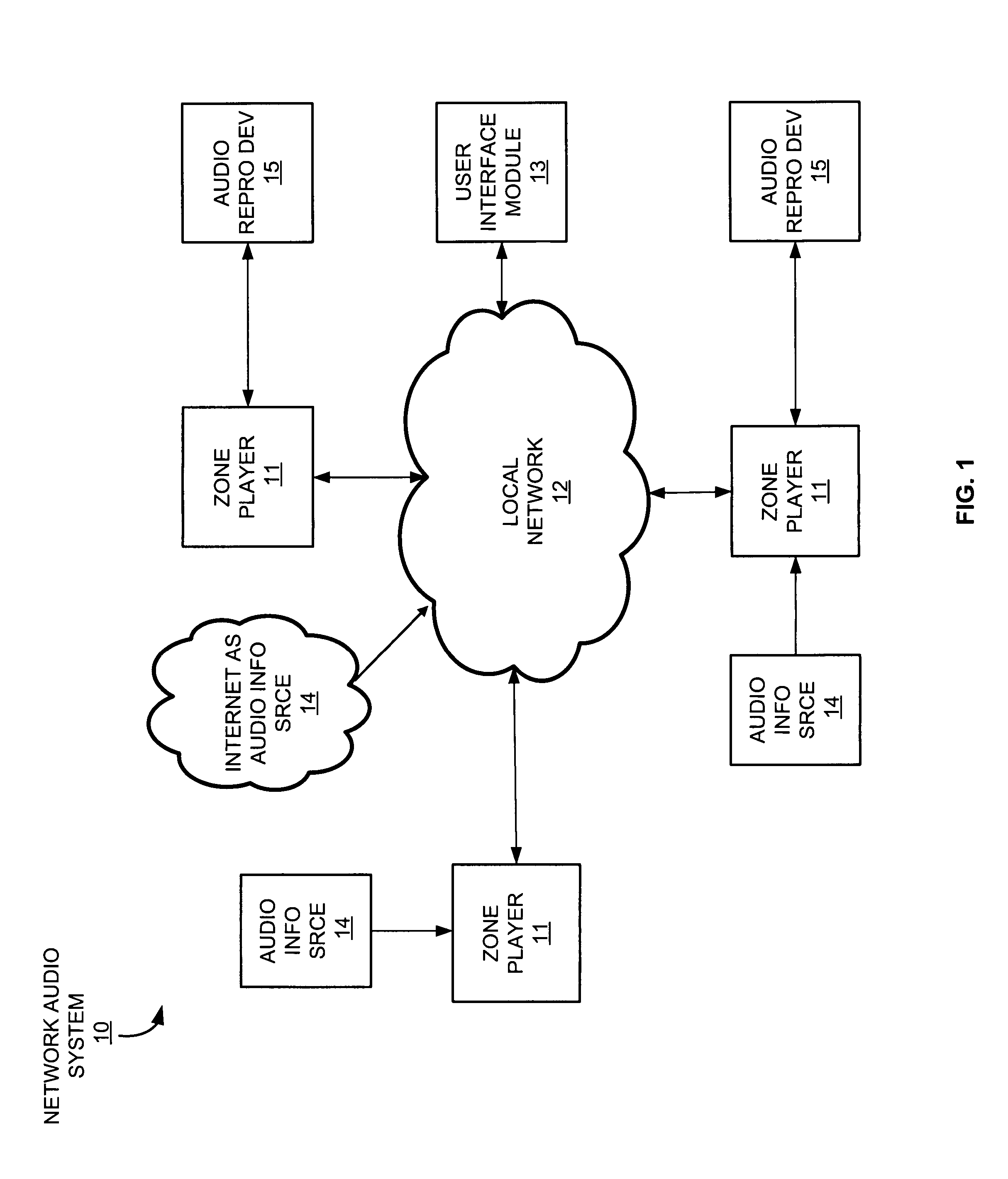
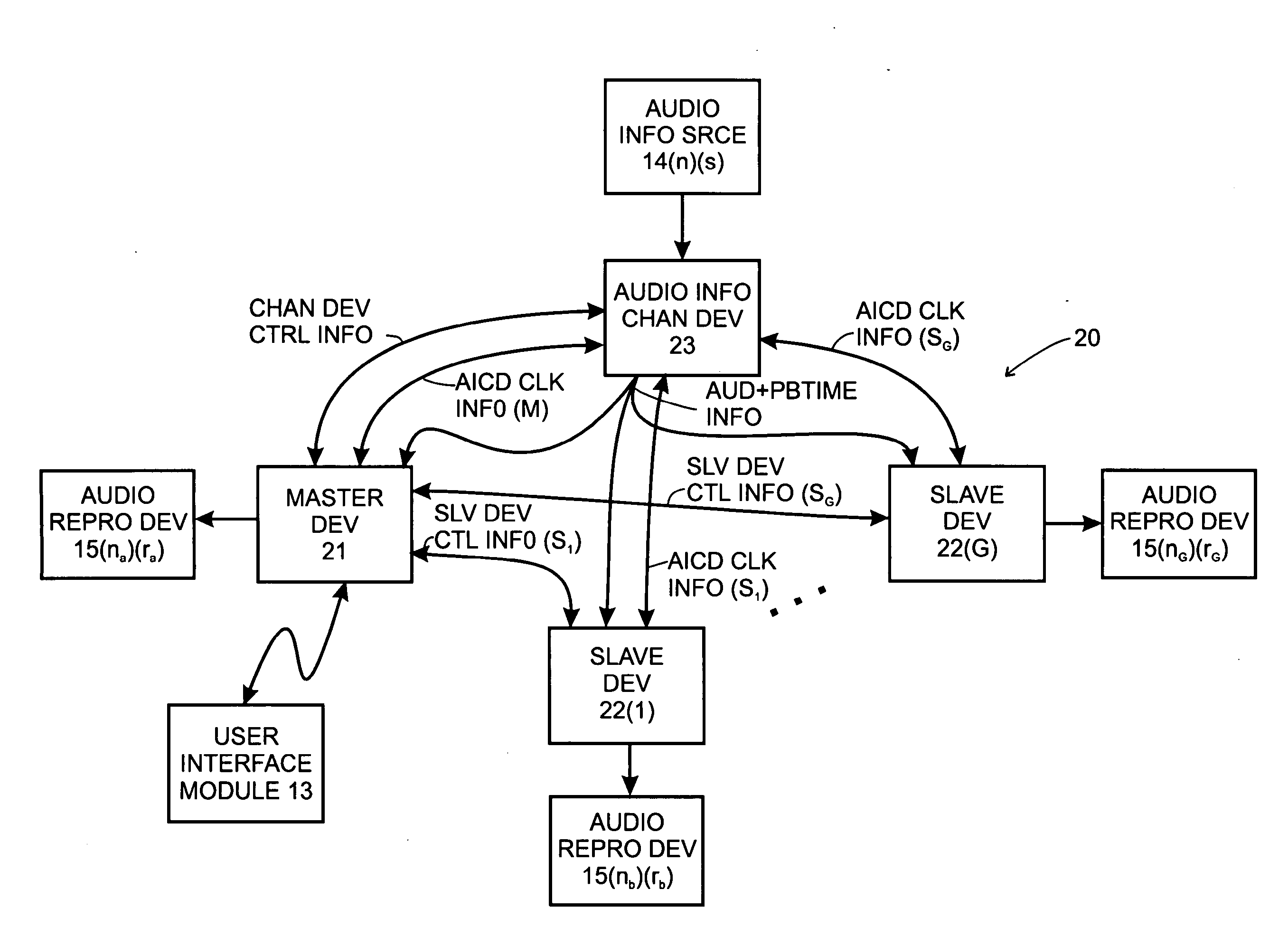
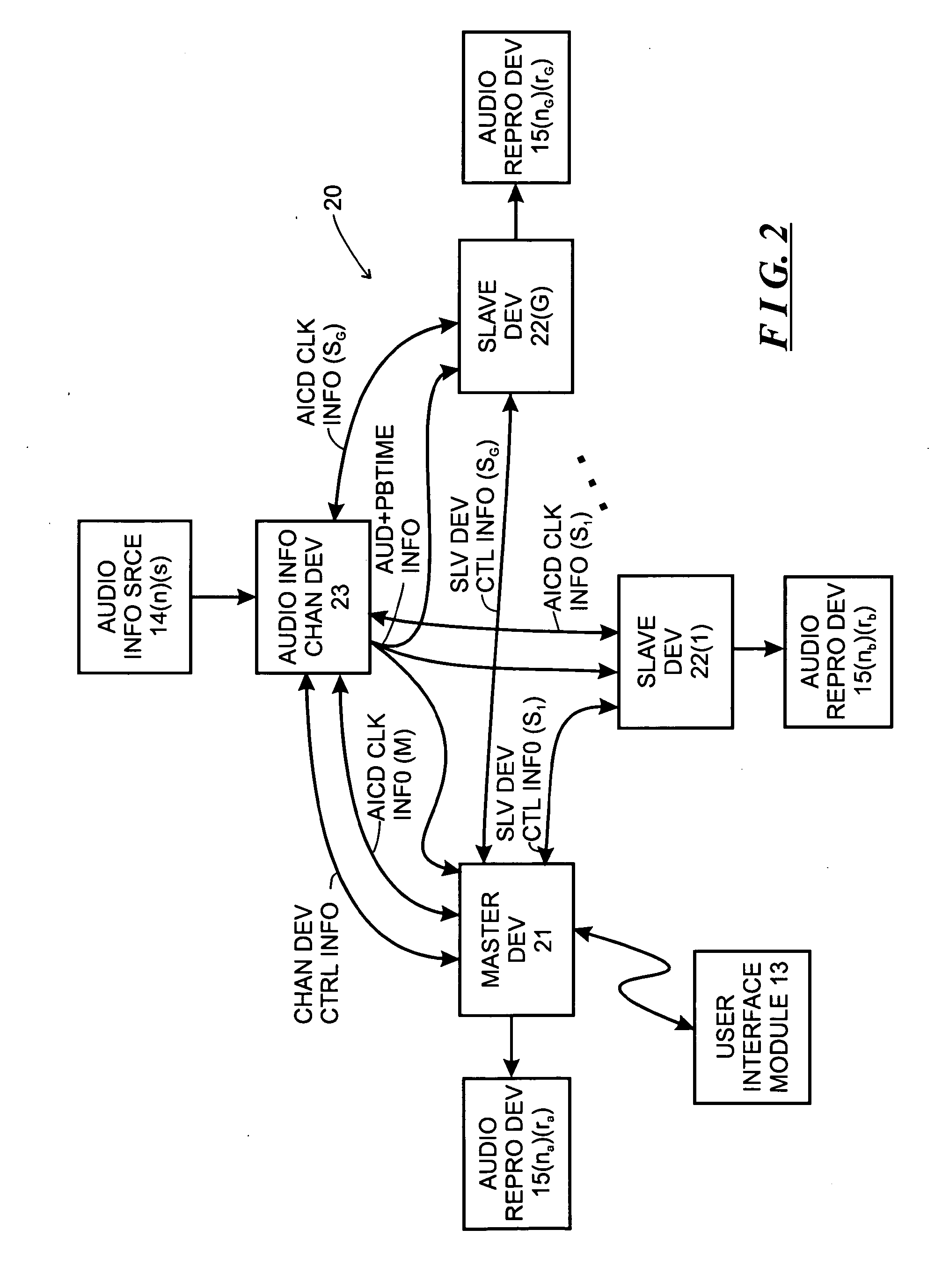
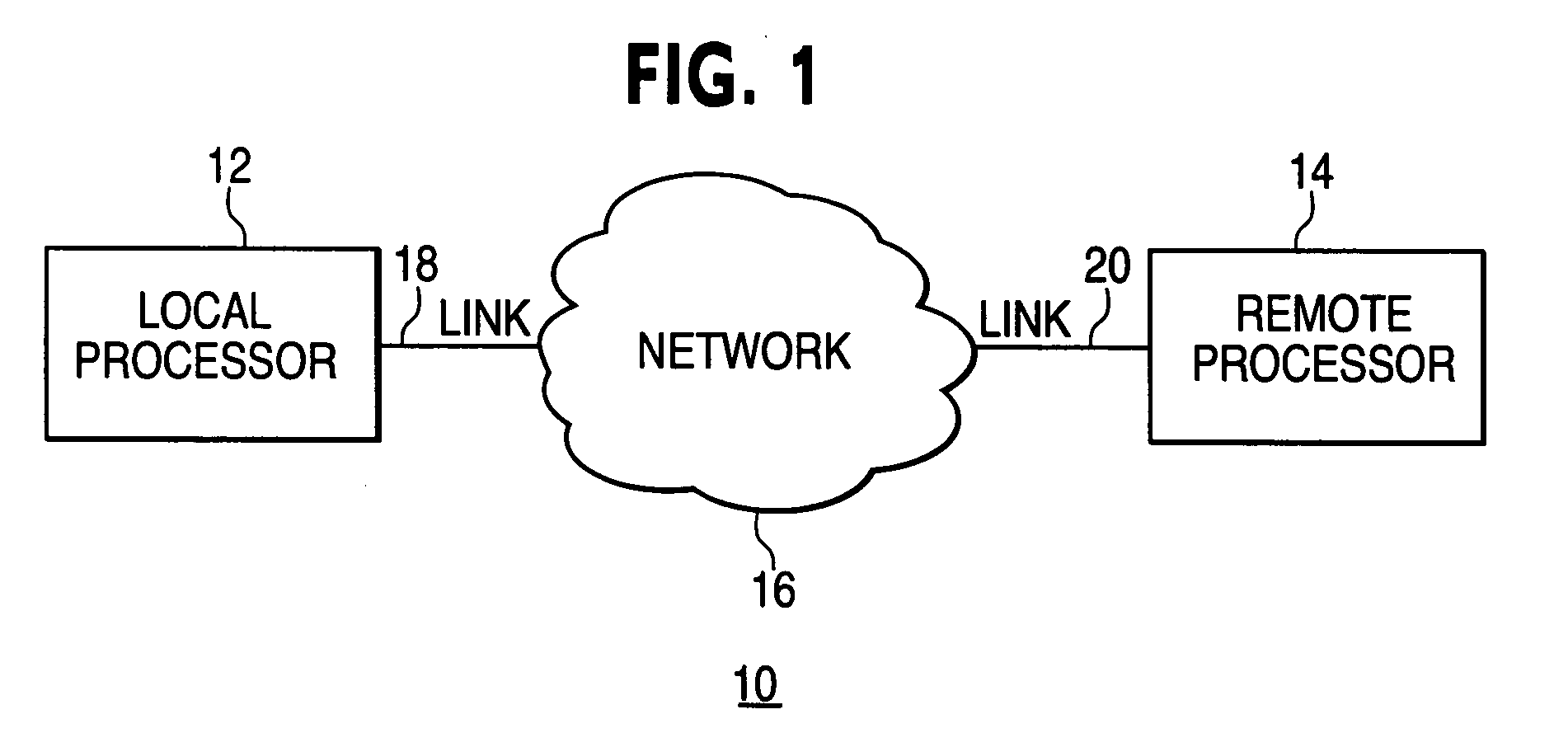
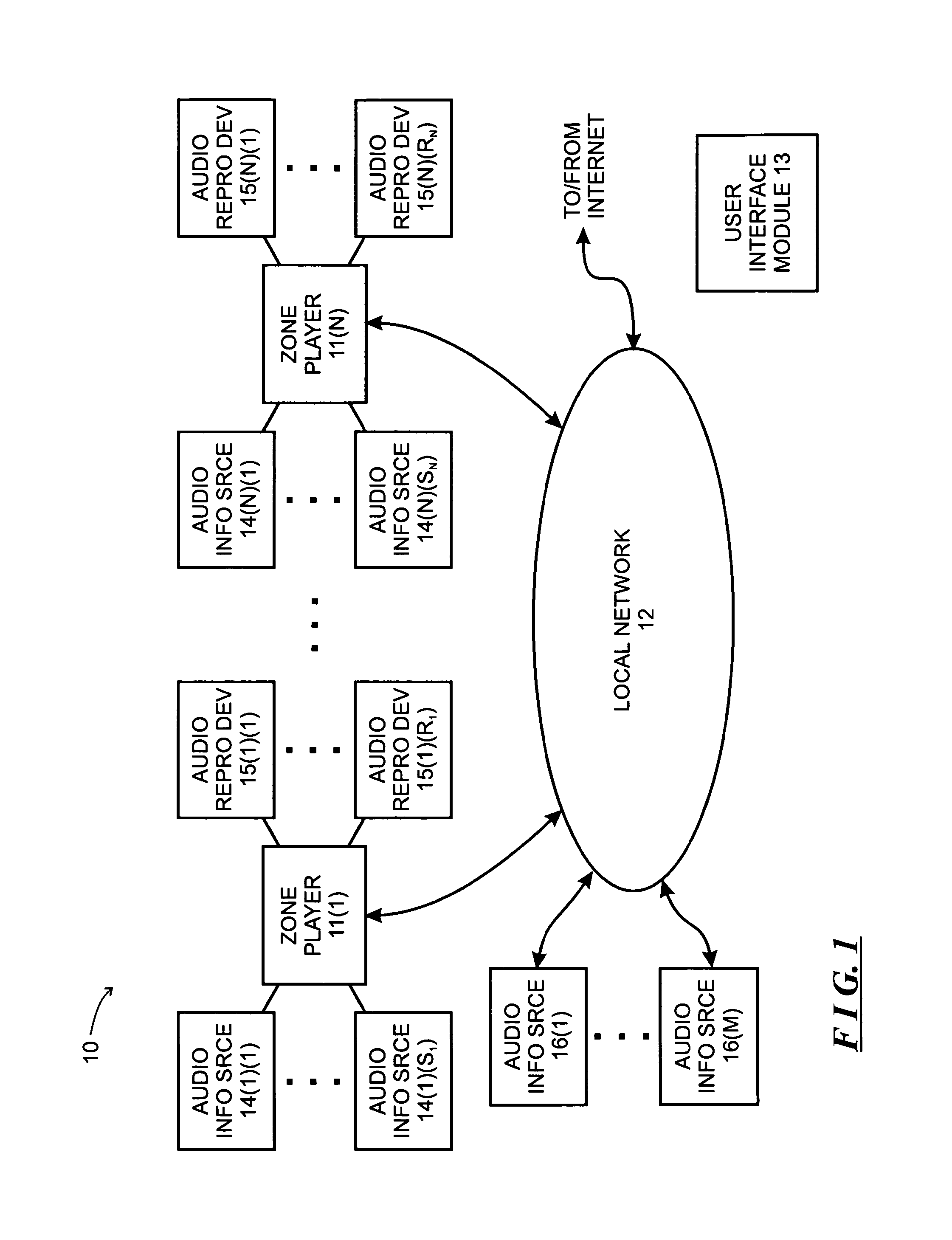
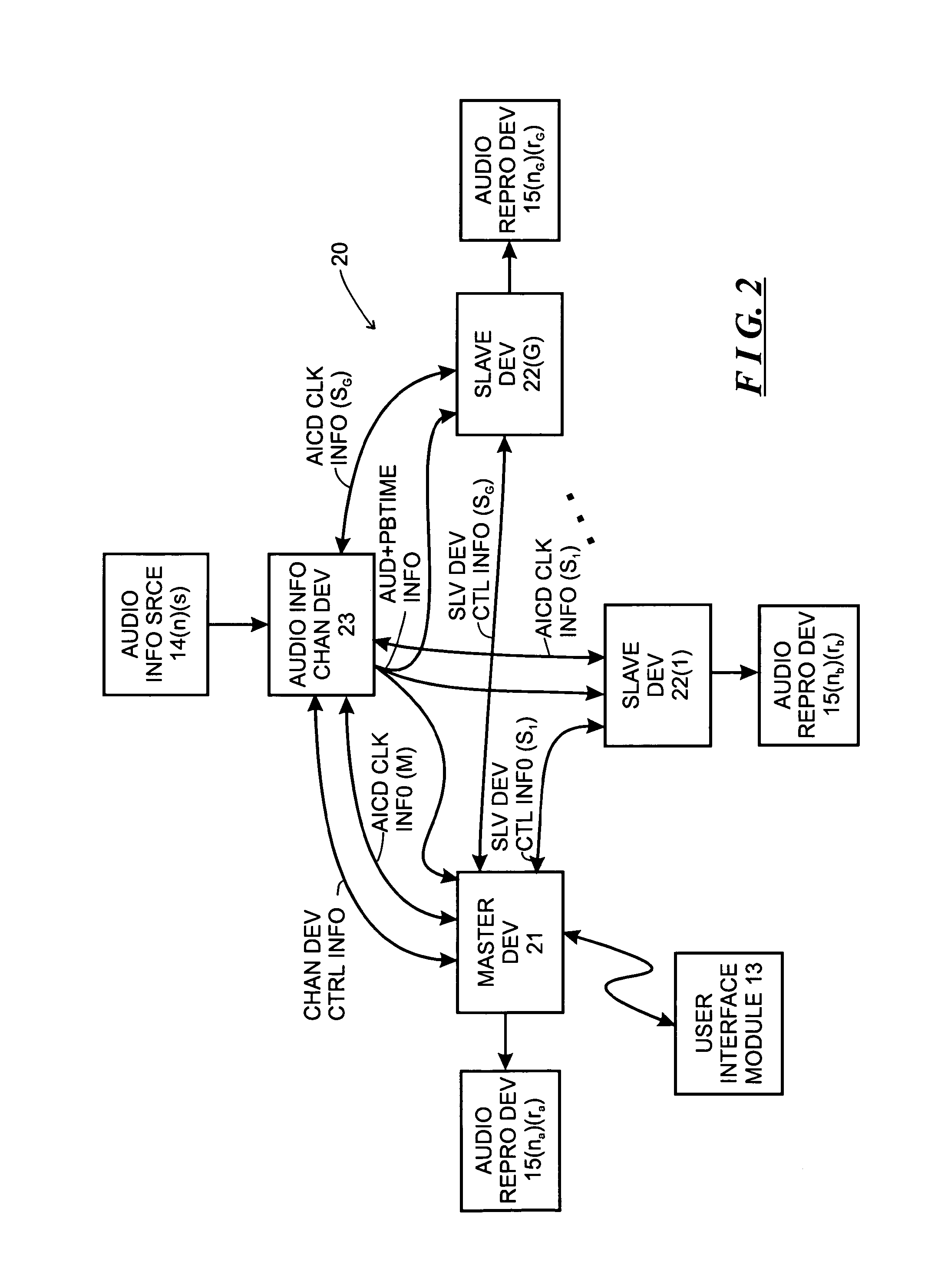
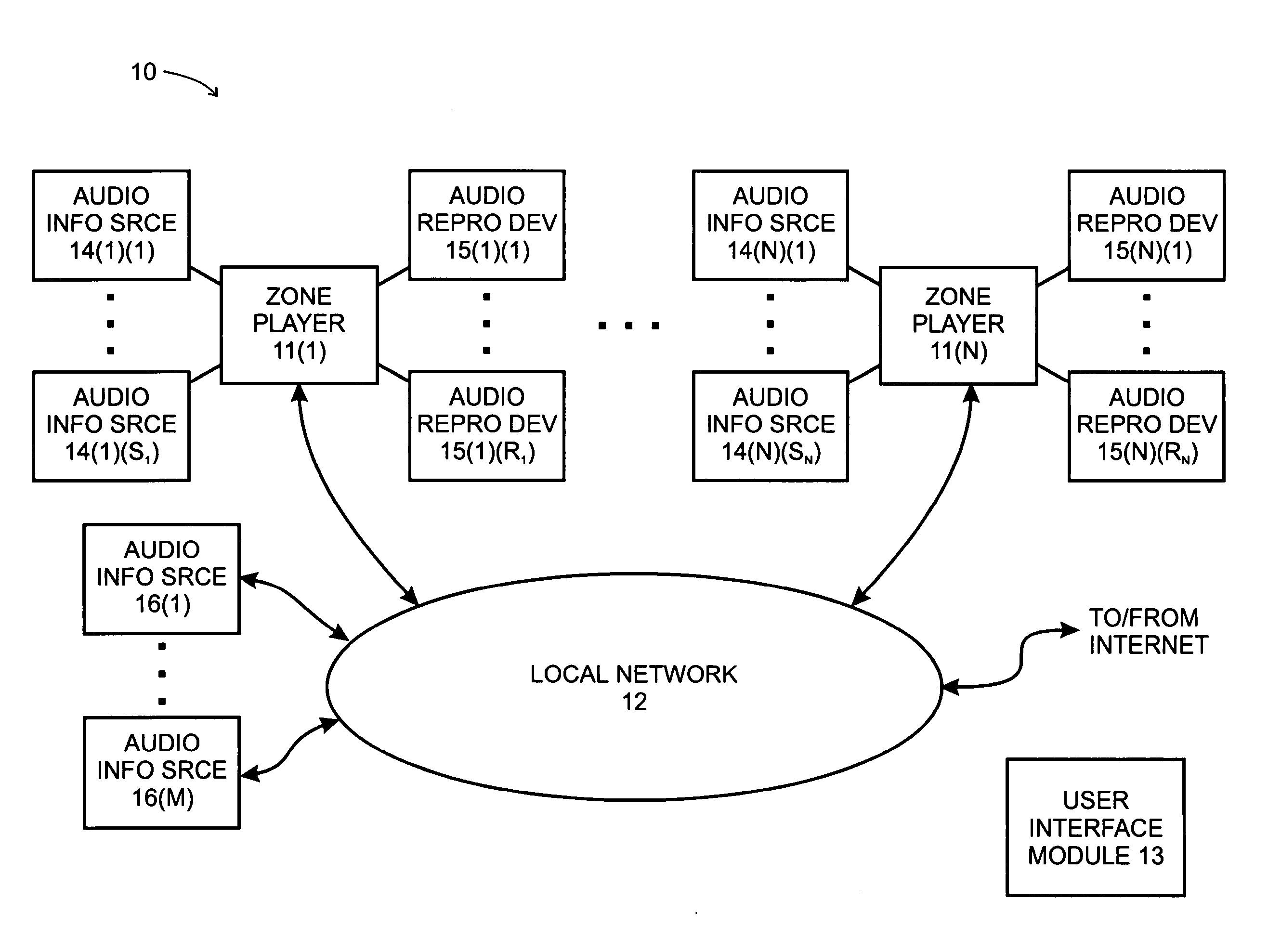
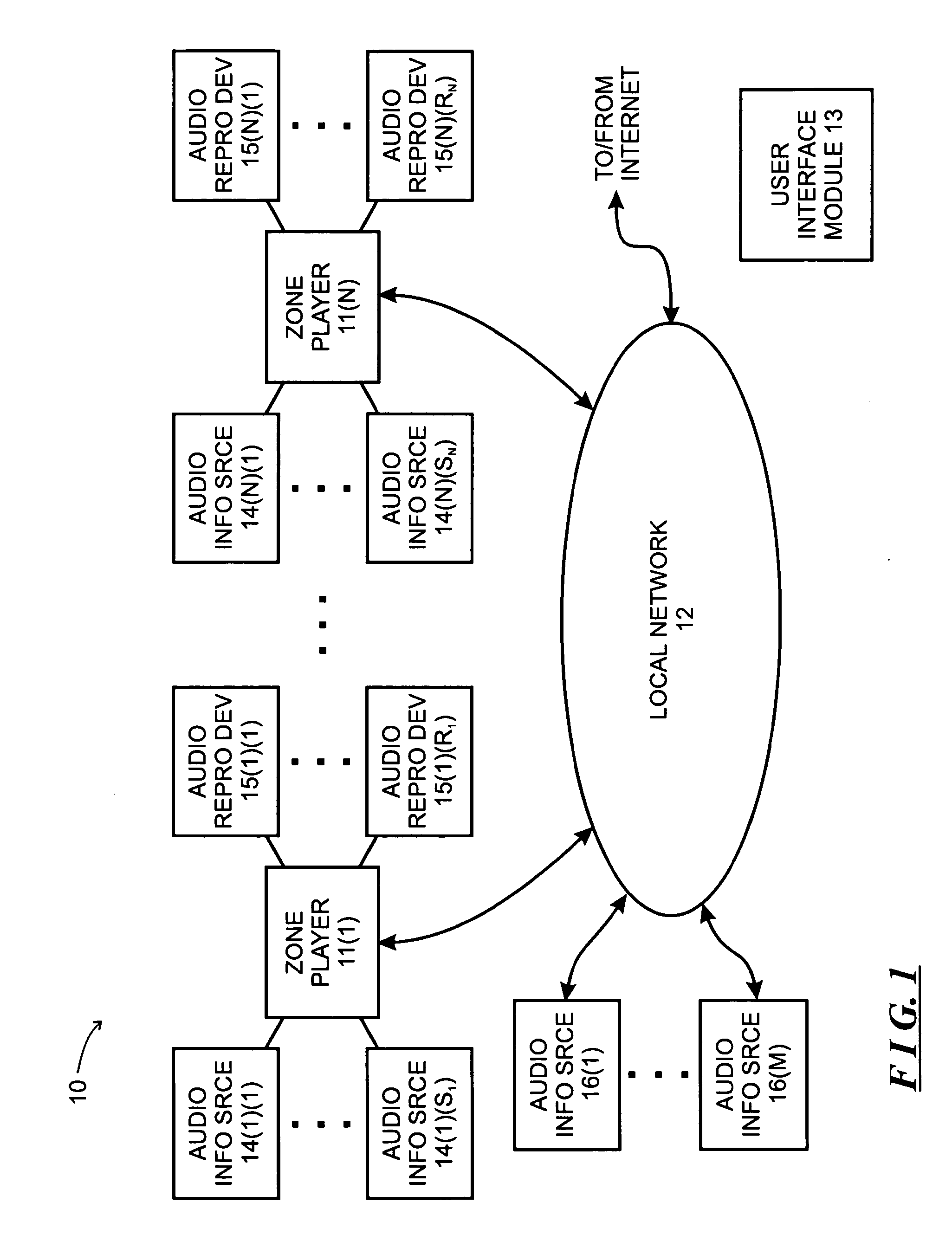
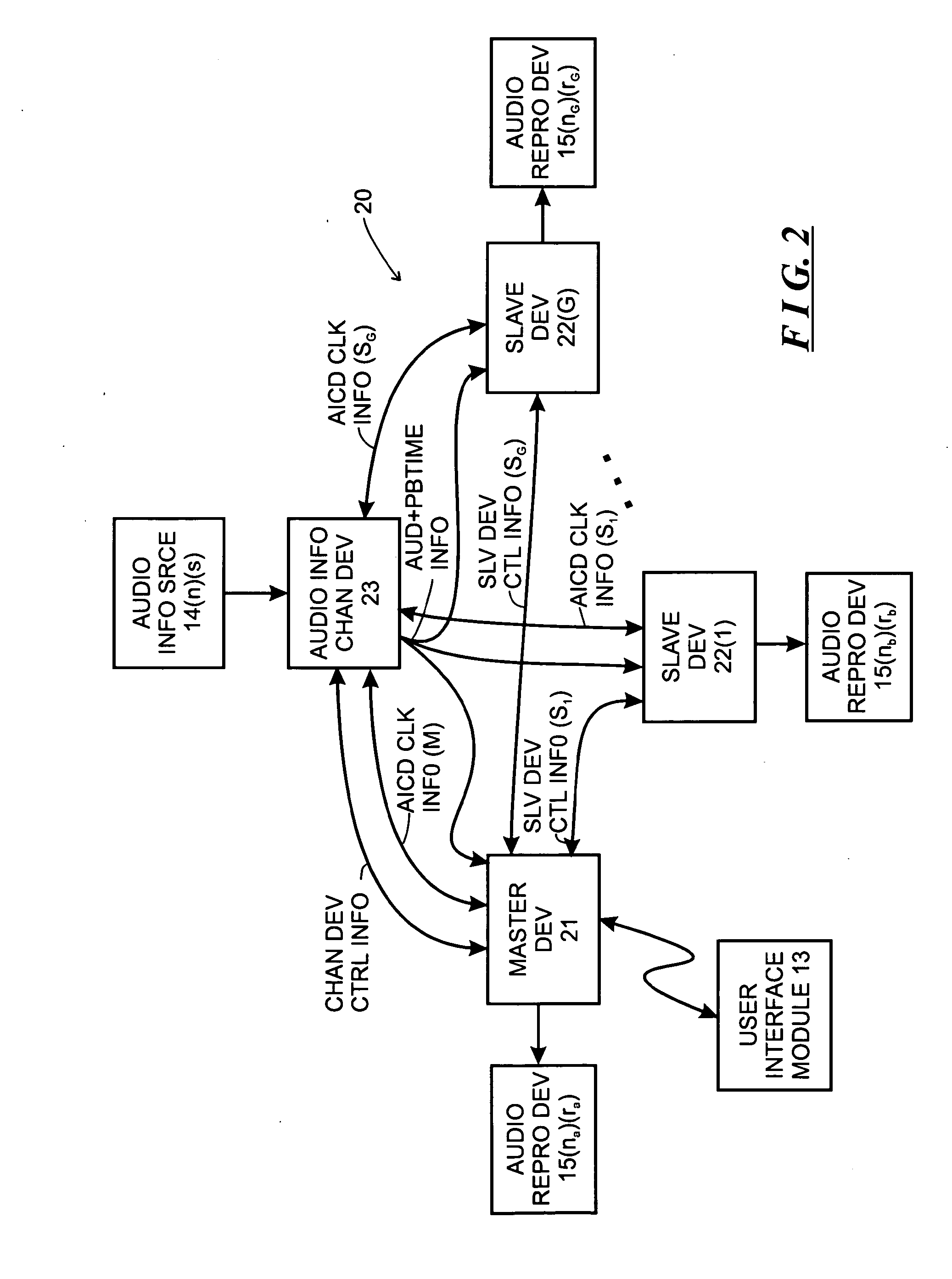
System and method for synchronizing operations among a plurality of independently clocked digital data processing devices
ActiveUS20070038999A1Maintenance operationTelevision system detailsGain controlElectronic data processingIndependent clock
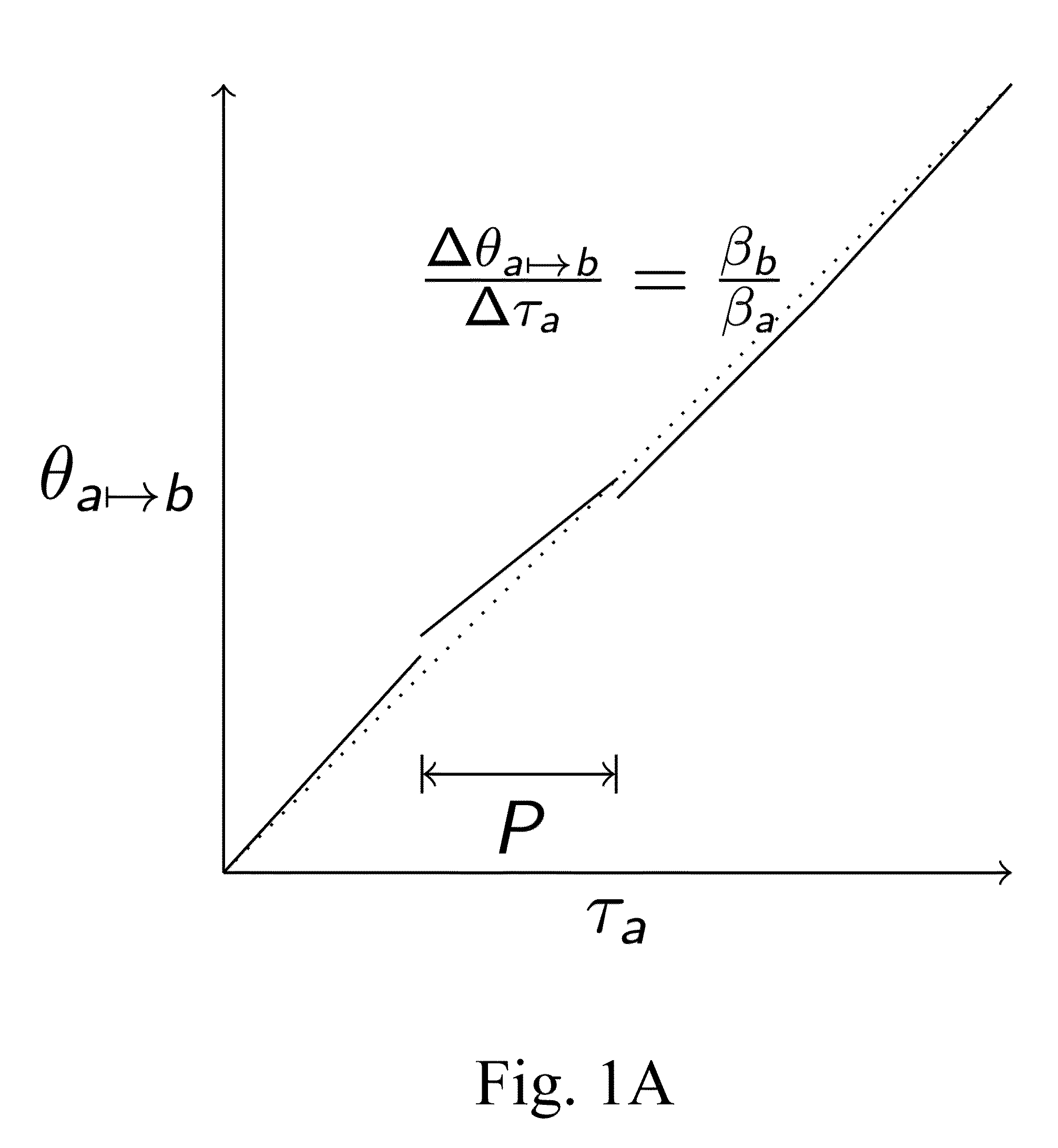
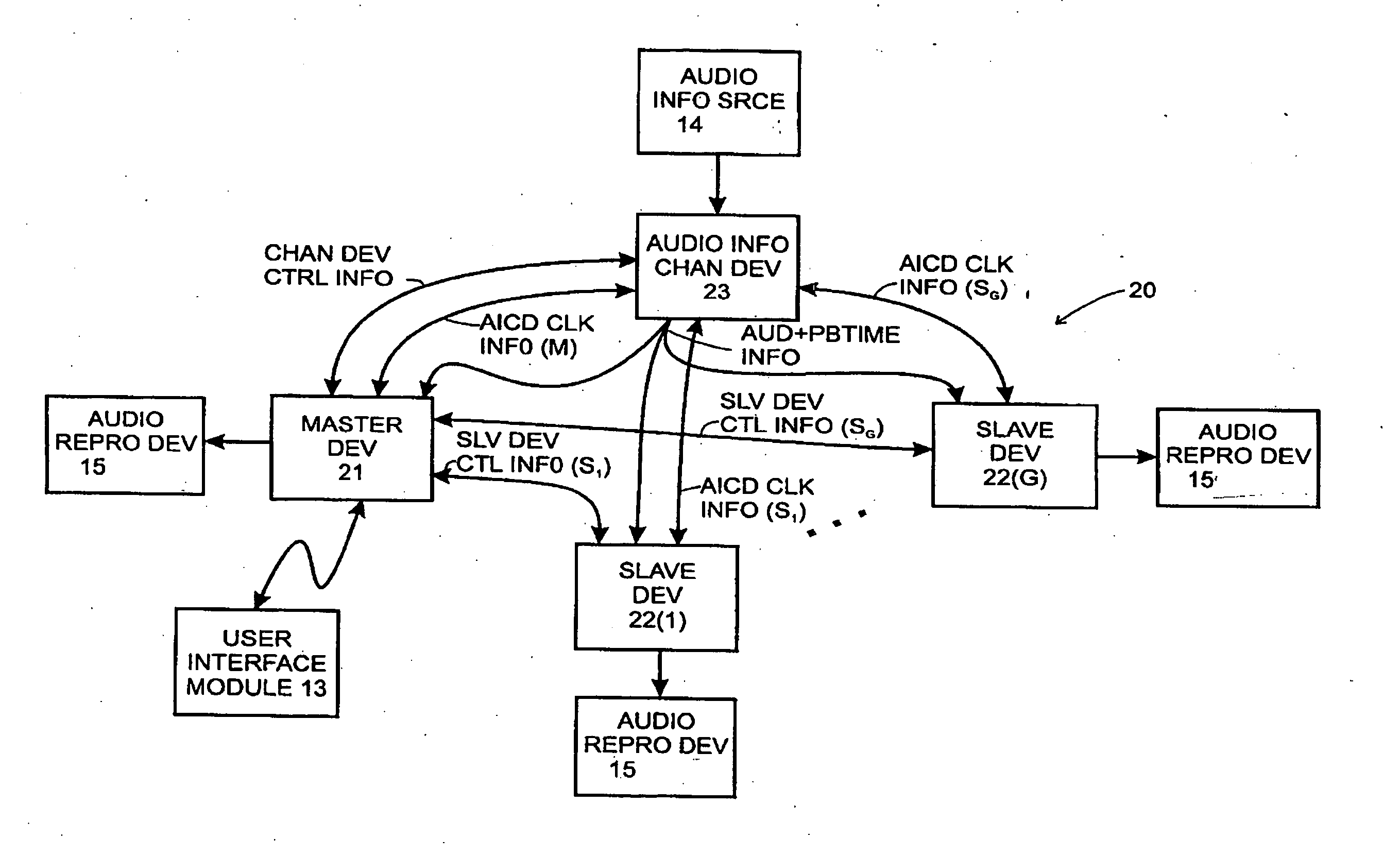
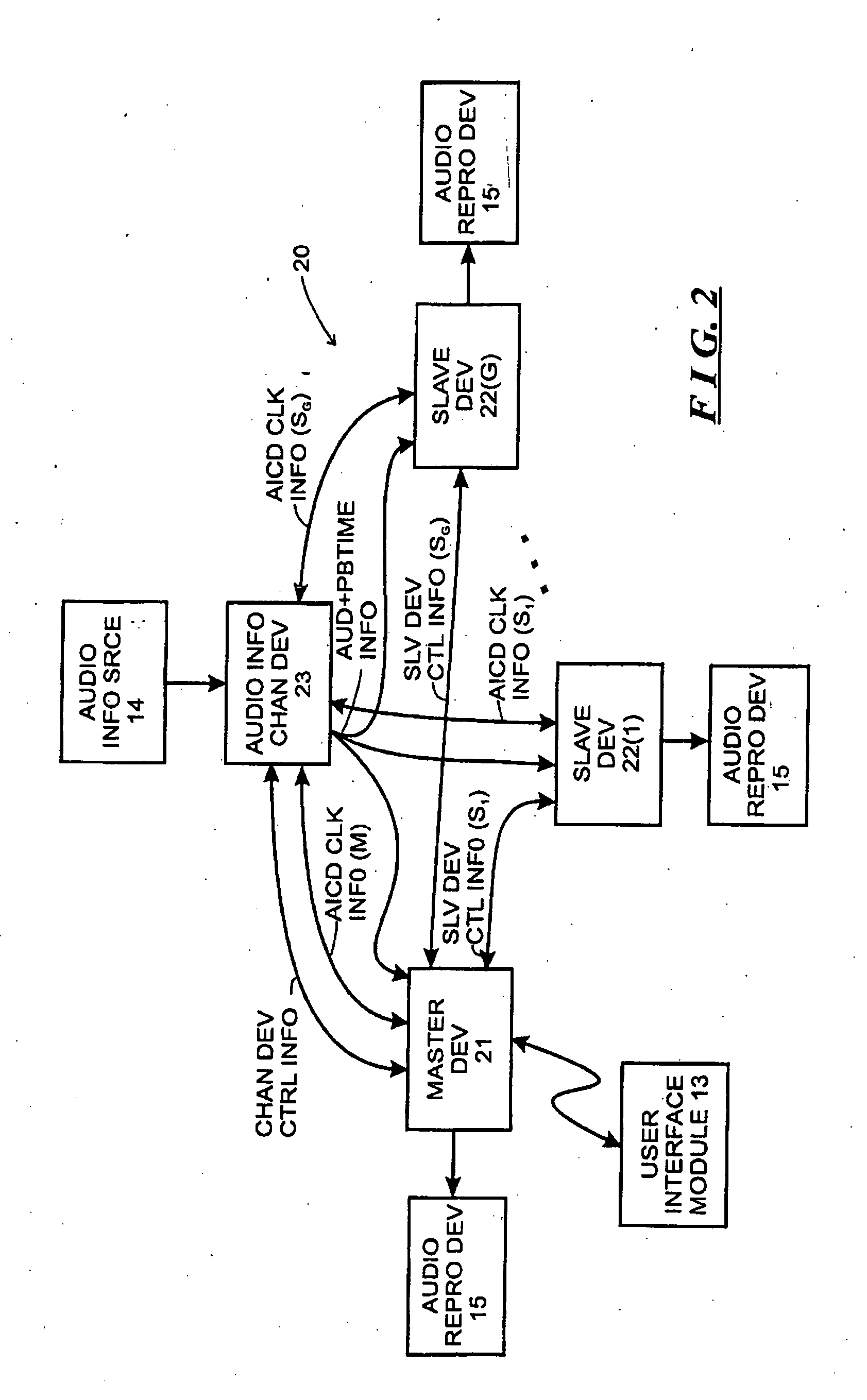
A system is described for maintaining synchrony of operations among a plurality of devices that have independent clocking arrangements. The system includes a task distribution device that distributes tasks to a synchrony group comprising a plurality of devices that are to perform the tasks distributed by the task distribution device in synchrony. The task distribution device distributes each task to the members of the synchrony group over a network. Each task is associated with a time stamp that indicates a time, relative to a clock maintained by the task distribution device, at which the members of the synchrony group are to execute the task. Each member of the synchrony group periodically obtains from the task distribution device an indication of the current time indicated by its clock, determines a time differential between the task distribution device's clock and its respective clock and determines therefrom a time at which, according to its respective clock, the time stamp indicates that it is to execute the task.
Owner:SONOS
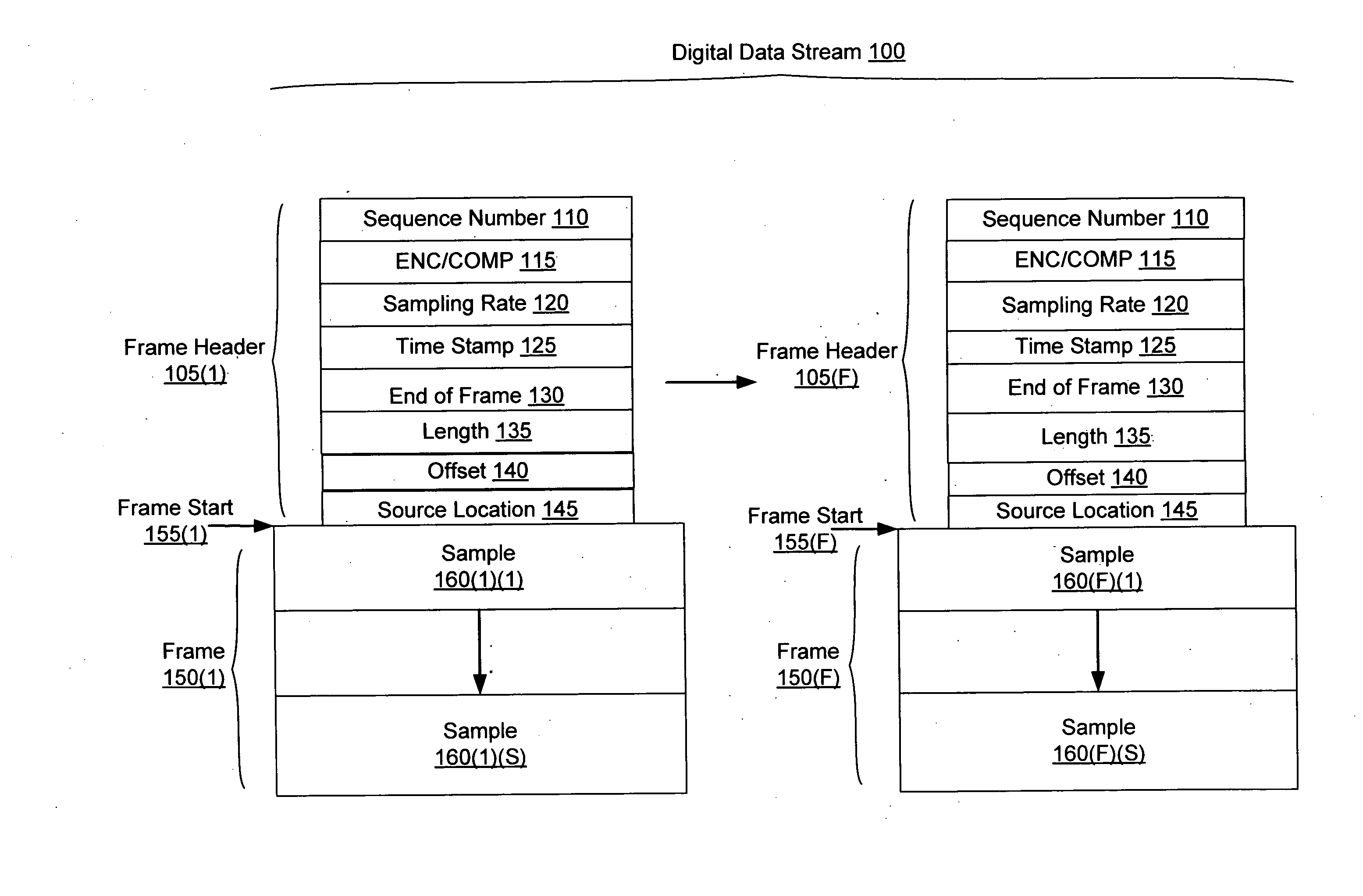
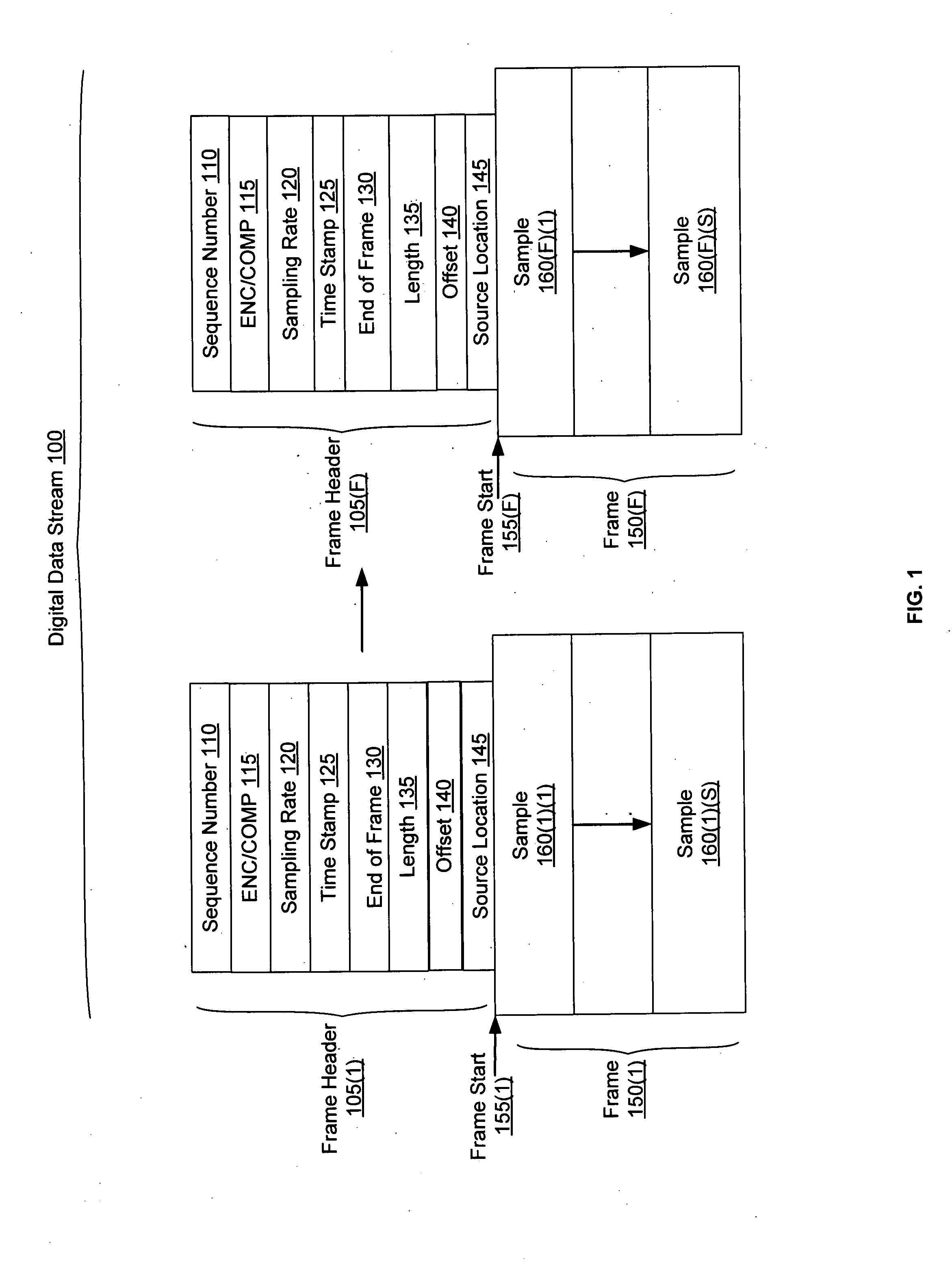
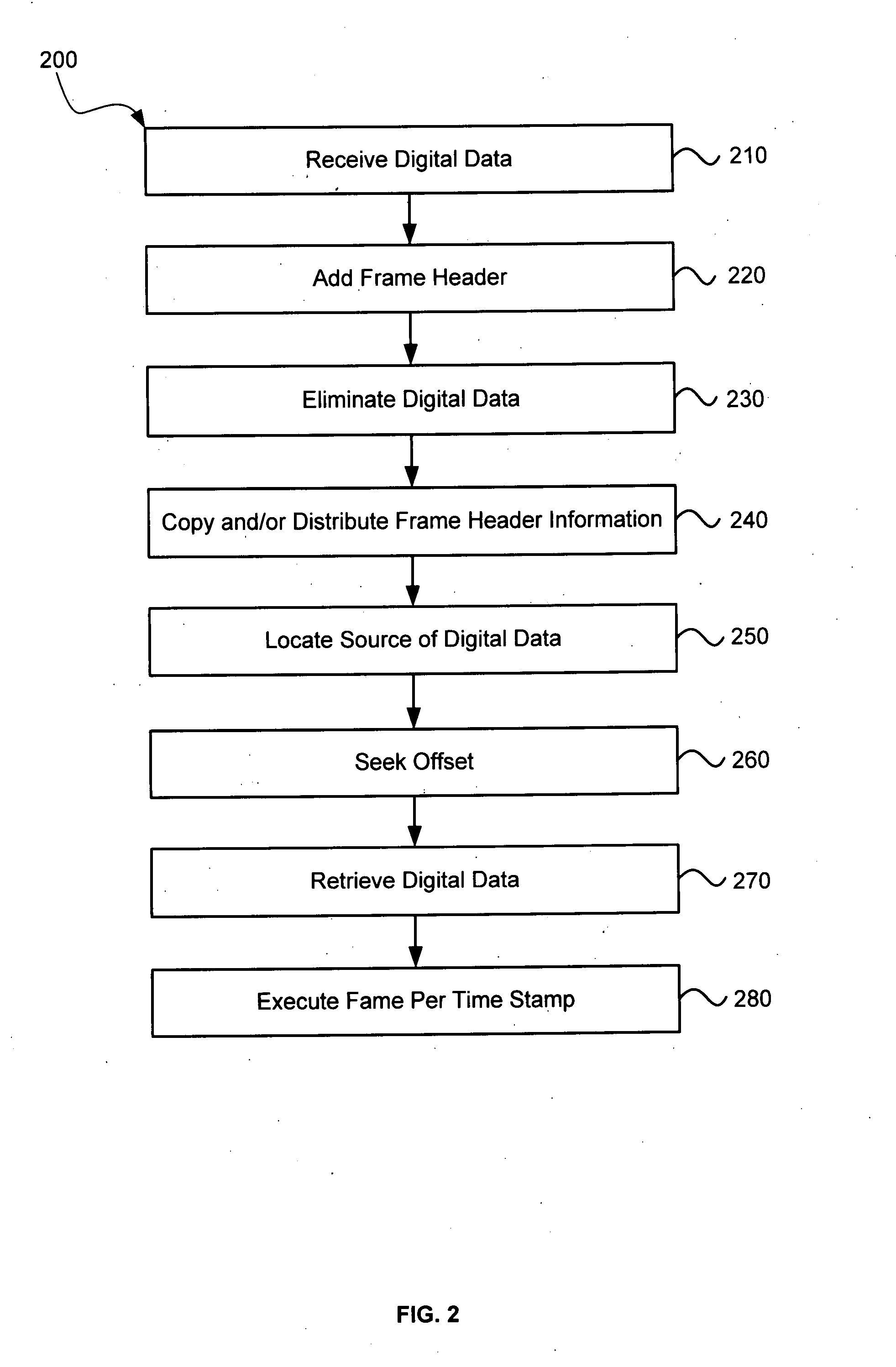
Systems and methods for synchronizing operations among a plurality of independently clocked digital data processing devices that independently source digital data
ActiveUS20080120429A1Time-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsDigital dataData stream
In a system for distributing data, distribution device is configured to distribute timestamp, offset and source location information for a digital data stream to an execution device, and the execution device is configured to seek digital data corresponding to the received information. The execution device is further configured to execute the digital data relative to a clock rate maintained by the distribution device. Related methods include receiving timestamp, offset and source location information for the digital data stream and seeking digital data corresponding to the received offset and source location information.
Owner:SONOS
Systems and methods for synchronizing operations among a plurality of independently clocked digital data processing devices without a voltage controlled crystal oscillator
Exemplary systems and methods include a distribution device that maintains a clock rate and distributes a series of tasks to a group of execution devices. Each task has a plurality of samples per frame associated with a time stamp indicating when the task is to be executed. The execution devices execute the series of tasks at the times indicated and adjust the number of samples per frame in relation to the clock rate maintained by the distribution device.
Owner:SONOS
Synchronizing clocks across a communication link
InactiveUS6944188B2Accurate and fast data transferSynchronization is simpleSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunications linkImage resolution
Apparatus, system and method for synchronizing one or more clocks across a communication link. A slave clock may be synchronized to a master clock by means of a synchronization signal sent from the master to the slave clock side of the link. The synchronization signal may be an expected signal pattern sent at intervals expected by the slave side. The slave clock may correlate received signals with a representation of the expected synchronization signal to produce a correlation sample sequence at a first sample rate which is related as n times the slave clock rate. The synchronization signal receipt time indicated by the correlation sample sequence may be refined by interpolating the correlation sample sequence around a best correlation sample to locate a best interpolation at an interpolation resolution smaller than the sample resolution. The best interpolation may in turn be further refined by estimating between interpolator outputs adjacent to the best interpolation output. The synchronization signal receipt time thus determined is compared to the expected time based upon the slave clock, which is adjusted until the times match. After initialization, all slave clock errors are preferably accumulated to prevent long-term slip between the slave and master clocks. Formerly independent master and slave clocks synchronized across the communication link constitute a noncommon clock which may be compared on each side of the link to secondary independent clocks, and the secondary independent clocks may then be separately synchronized by adjusting one to have the same difference from its local noncommon clock as the secondary clock on the other side of the link has from its local noncommon clock.
Owner:WI LAN INC
Method and apparatus for displaying a list of tracks scheduled for playback by a synchrony group
ActiveUS20140181271A1Multiple digital computer combinationsAudio data retrievalOperating systemIndependent clock
A system is described for maintaining synchrony of operations among a plurality of devices that have independent clocking arrangements. The system includes a task distribution device that distributes tasks to a synchrony group comprising a plurality of devices that are to perform the tasks distributed by the task distribution device in synchrony. The task distribution device distributes each task to the members of the synchrony group over a network. Each task is associated with a time stamp that indicates a time, relative to a clock maintained by the task distribution device, at which the members of the synchrony group are to execute the task. Each member of the synchrony group periodically obtains from the task distribution device an indication of the current time indicated by its clock, determines a time differential between the task distribution device's clock and its respective clock and determines therefrom a time at which, according to its respective clock, the time stamp indicates that it is to execute the task.
Owner:SONOS
Enforcing time-based transaction policies on devices lacking independent clocks
ActiveUS20070058812A1Not capableUser identity/authority verificationTime-division multiplexSecure communicationNetwork connection
A system and a method for operating a device that is not capable of independently maintaining a local time clock to enforce a time-based transaction policy that requires a reliable time reference. The device establishes a secure communications channel to one or more network-attached time sources and inquires of each of the network-attached time-sources as to the current time using the secure communications channel. The device receives the current time from the network-attached time-sources and uses the received current times to estimate a current calendar time and to compute a reliability index associated with the estimated current calendar time. The device uses the estimated current calendar time and reliability index to enforce the time-based transaction policy.
Owner:AXALTO INC
Method and system for adaptive synchronization of timing information generated by independently clocked communication nodes
InactiveUS20110268097A1Effective synchronizationEfficient synchronizationSynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesTime informationTimestamp
A system and method are provided for adaptive synchronization of timing information provided in communications messages transmitted between independently clocked communication nodes of a wireless communications network. The system and method include measures for collecting timestamps of messages generated by a plurality of the nodes, each timestamp being generated by one of the nodes relative to a local time reference thereof. A pairwise clock error is computed for at least one pair of nodes based upon a plurality of network messages passed therebetween. A global time reference is adaptively established for the timestamps responsive to the pairwise clock error. A plurality of mapping factors are defined each for translating from one local time reference to the global time reference. The mapping factors are selectively applied to corresponding ones of the timestamps.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Systems and methods for synchronizing operations among a plurality of independently clocked digital data processing devices without a voltage controlled crystal oscillator
Exemplary systems and methods include a distribution device that maintains a clock rate and distributes a series of tasks to a group of execution devices. Each task has a plurality of samples per frame associated with a time stamp indicating when the task is to be executed. The execution devices execute the series of tasks at the times indicated and adjust the number of samples per frame in relation to the clock rate maintained by the distribution device.
Owner:SONOS
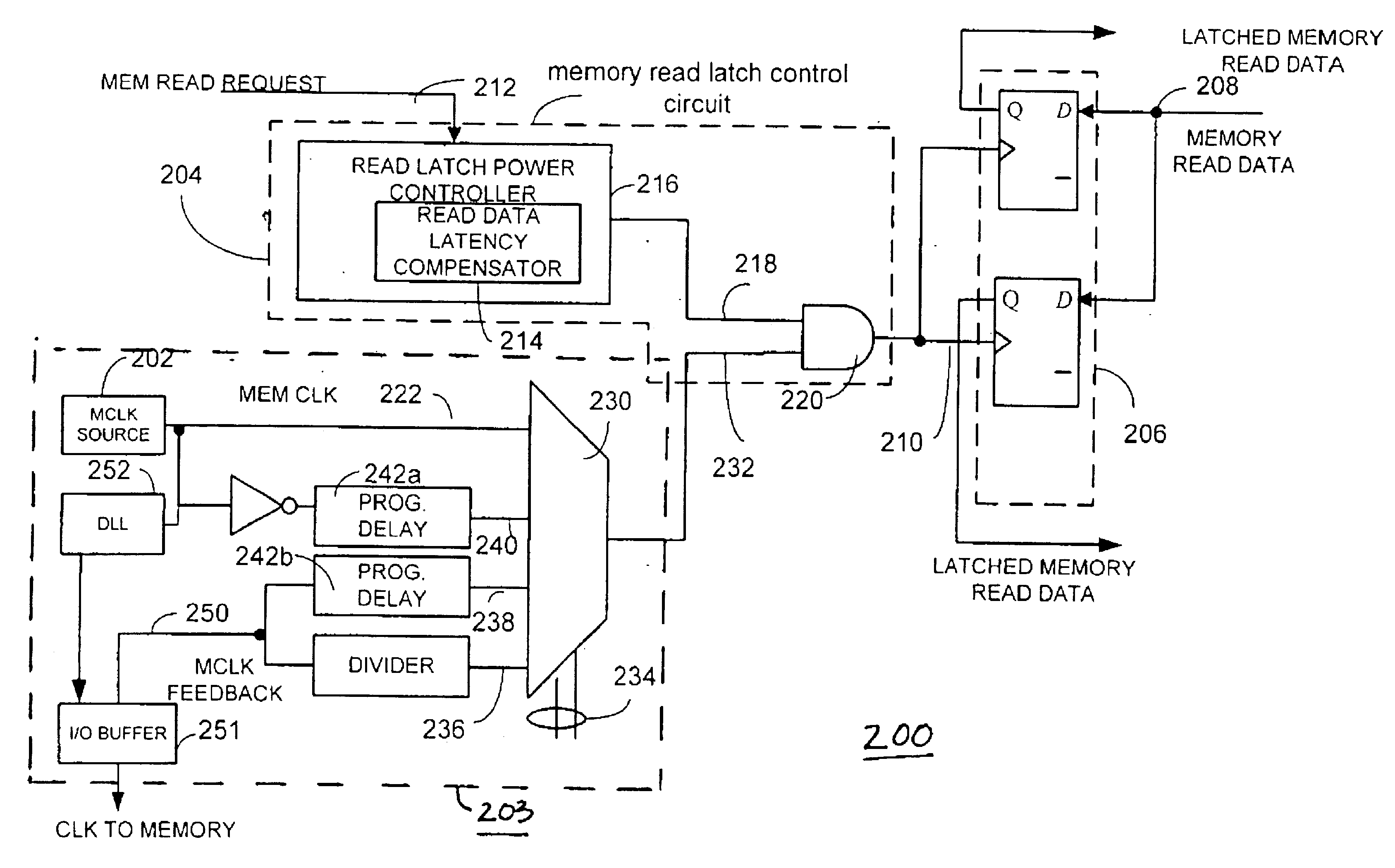
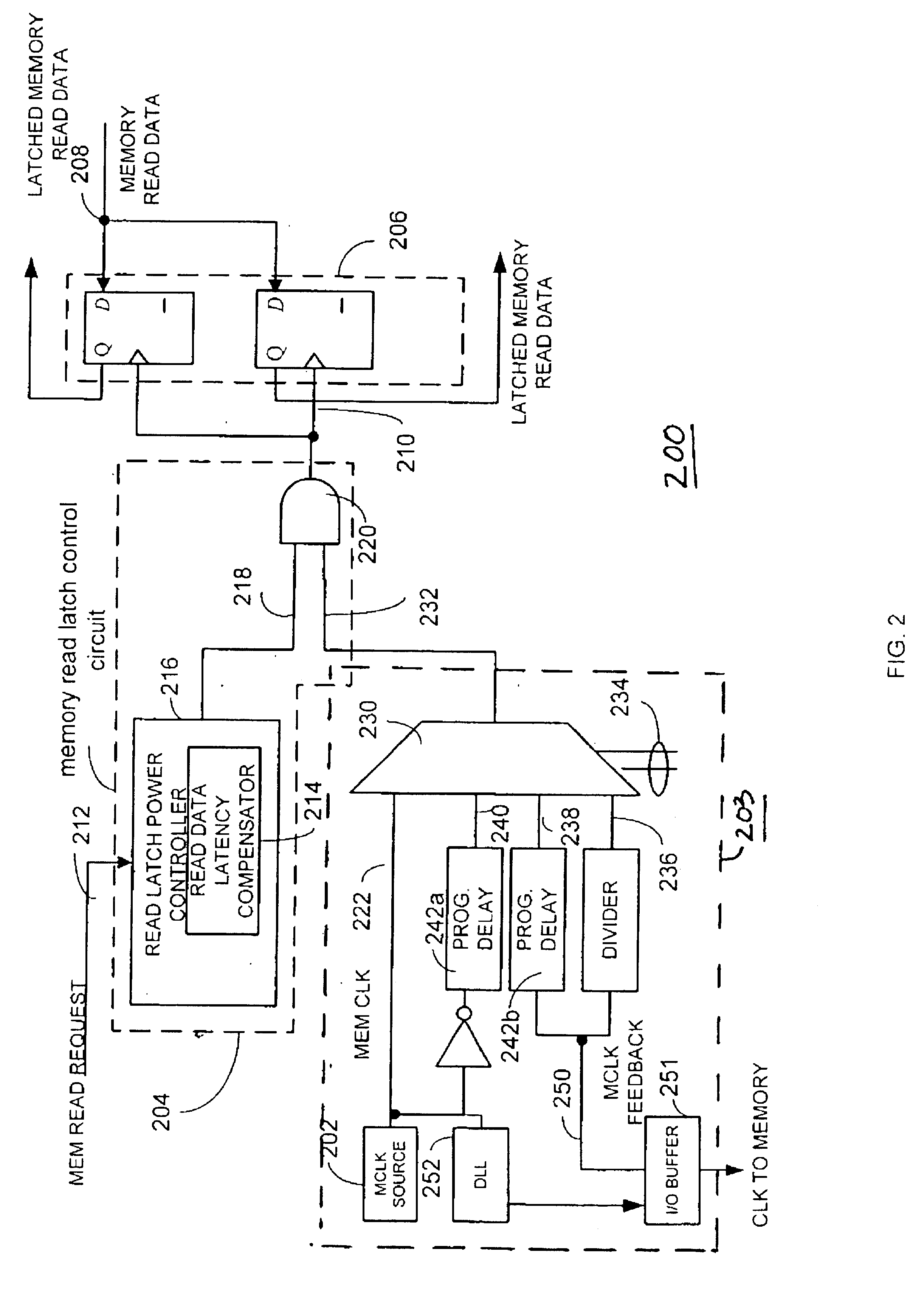
Power reduction circuit and method with multi clock branch control
A power consumption reduction circuit and method utilizes a memory clock source and a memory clock divider circuit that generates divided memory clock output signals as a plurality of corresponding independent clock signals to a number of different processing engines. A memory clock divider circuit and method selectively activates a plurality of independent clock signals in response to received condition data. In one embodiment, an engine clock source is also coupled through a switching circuit such that it is selectively output to one or more processing engines. The switching circuit disables the output from the engine clock based on register condition data. In another embodiment, a plurality of memory read latch circuits are controlled by a memory read latch control circuit. The memory read latch control circuit is operative to dynamically activate and deactivate the plurality of memory read latches based on detected memory read requests to facilitate memory access activity-based power reduction.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
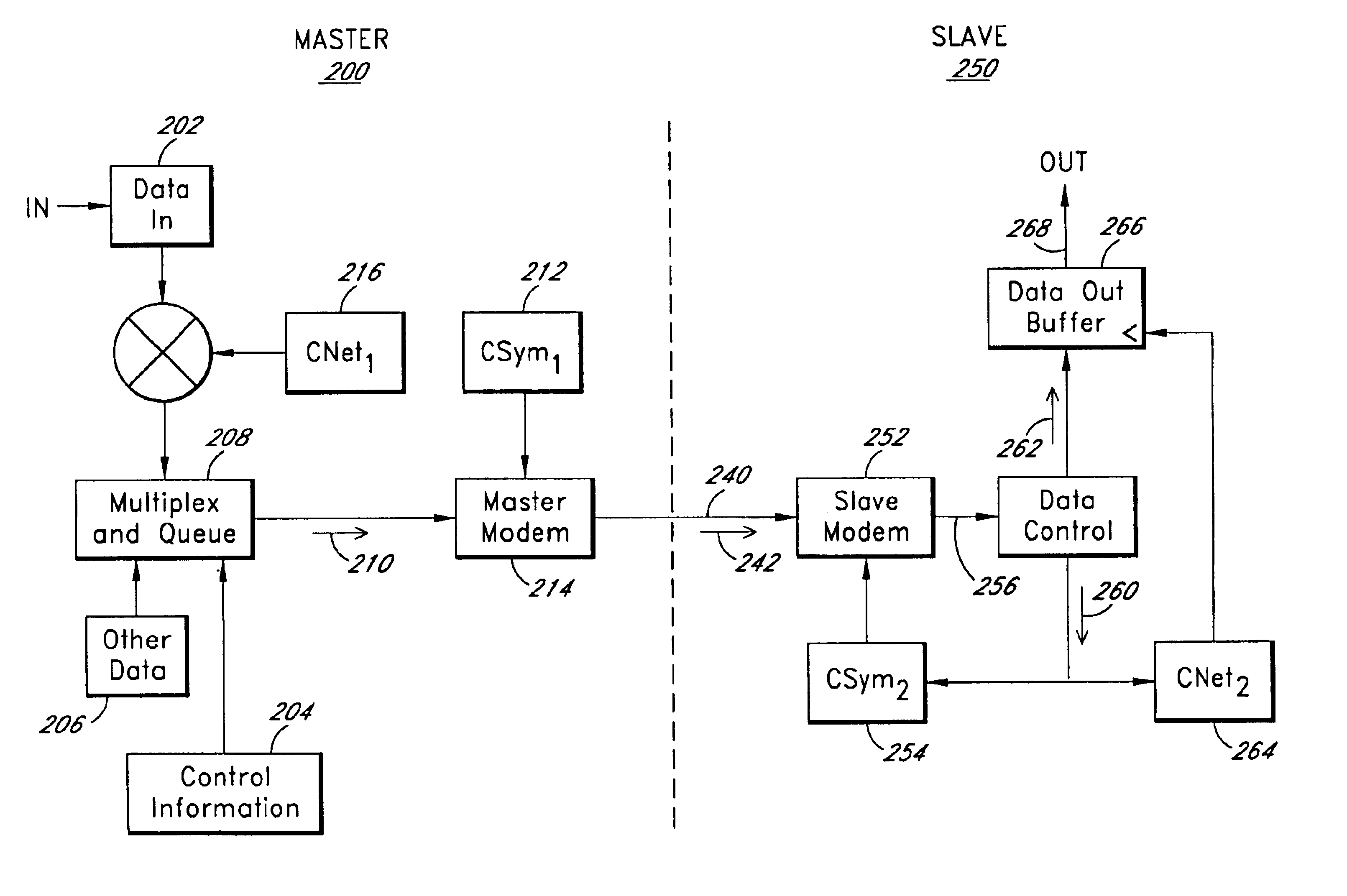
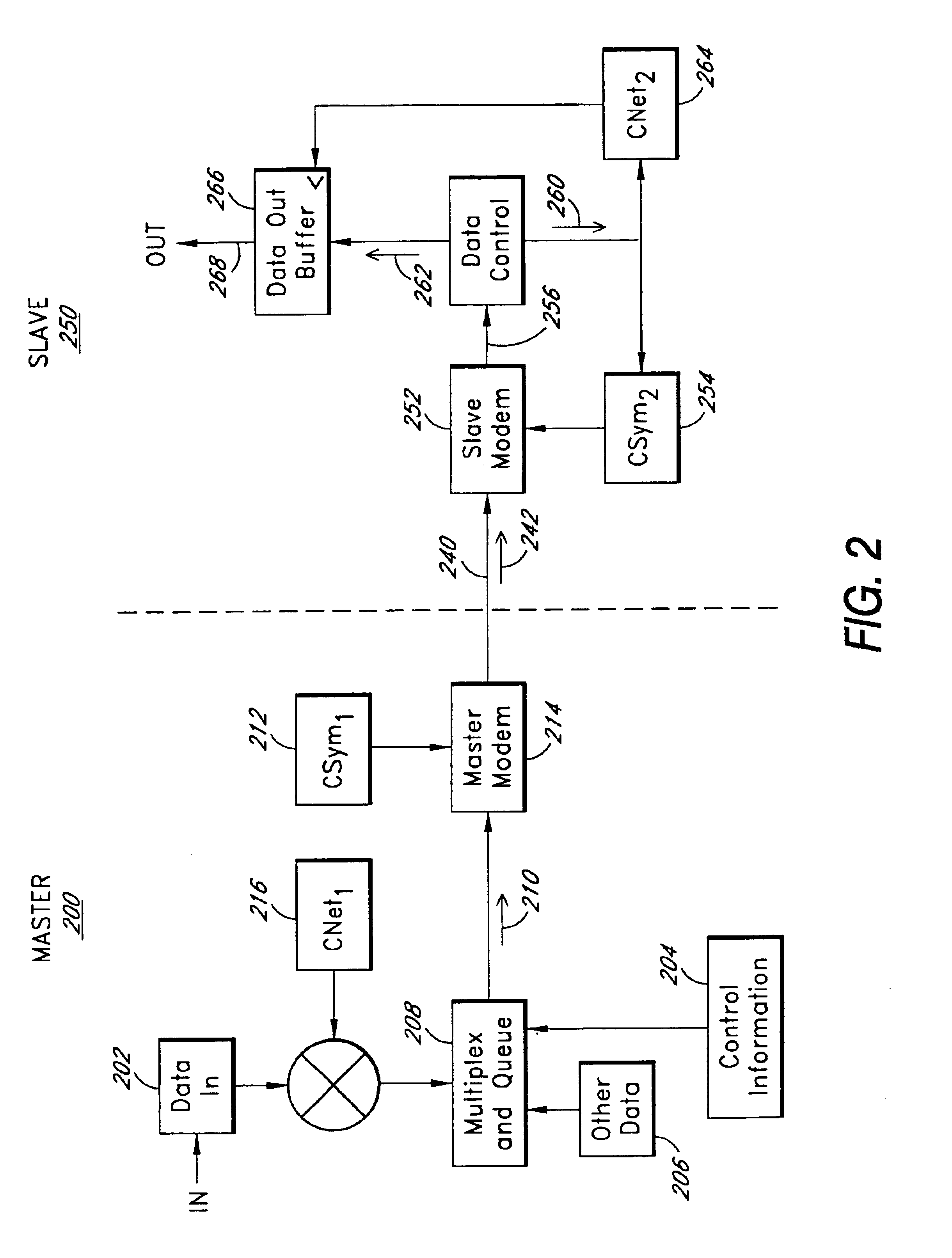
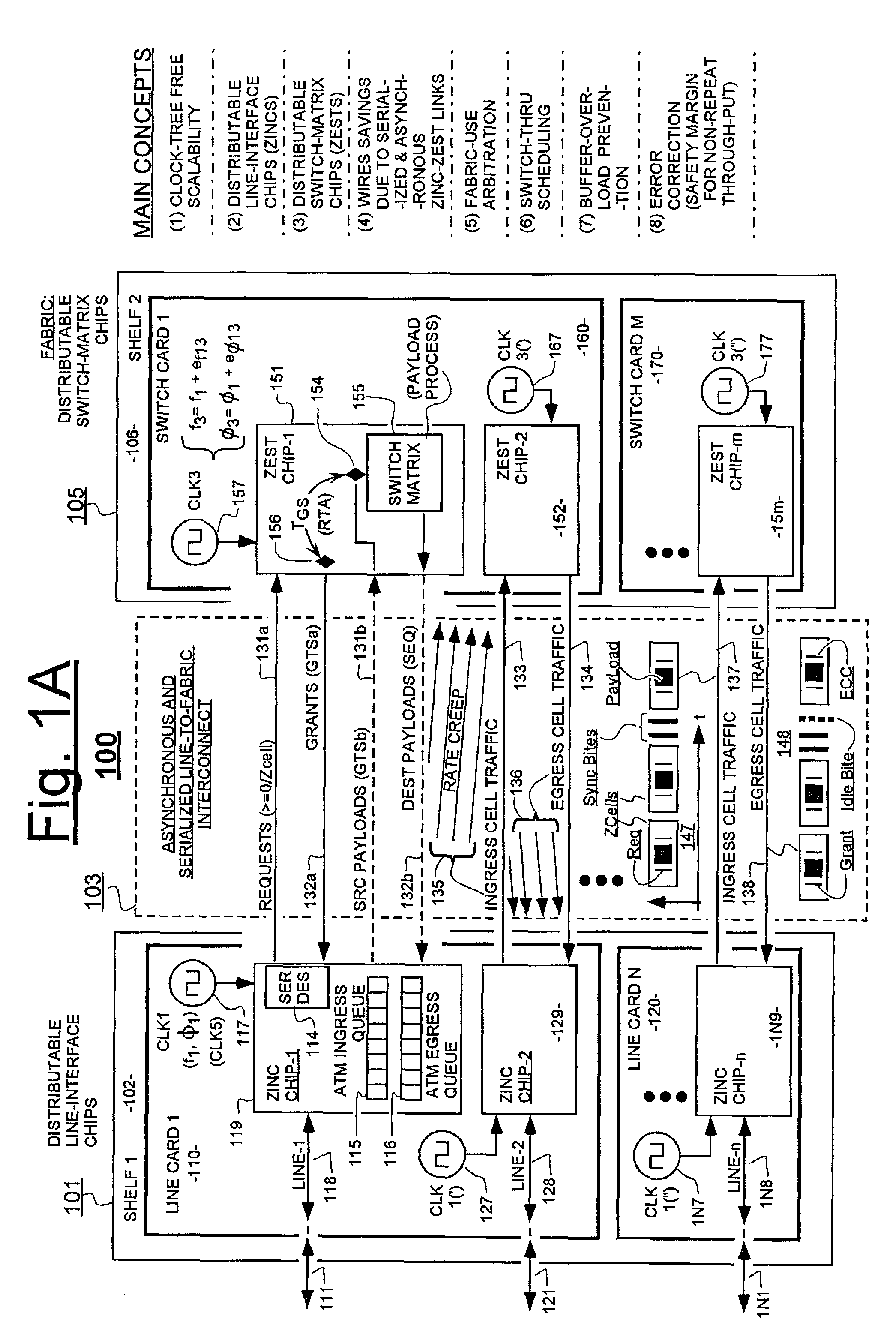
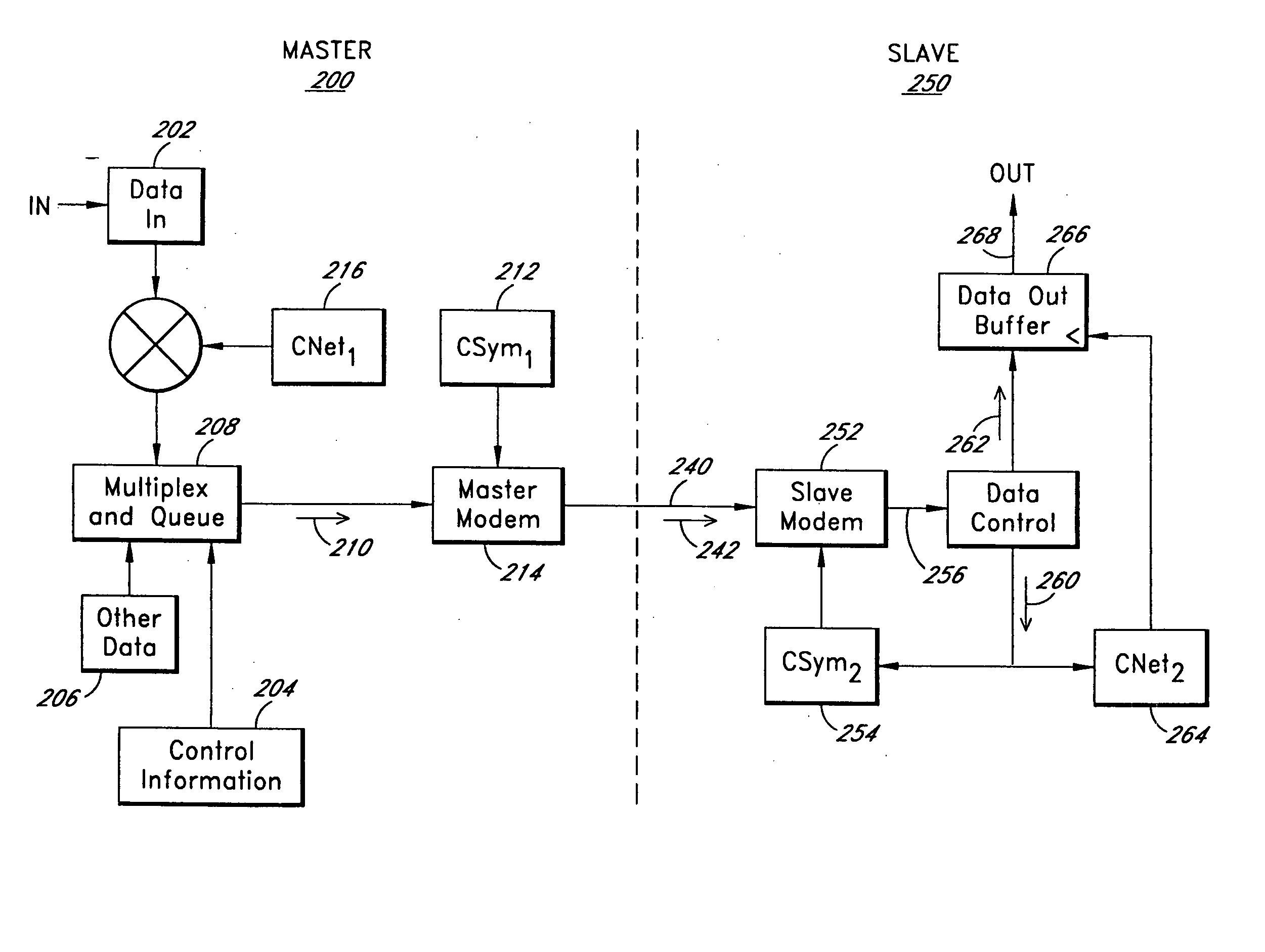
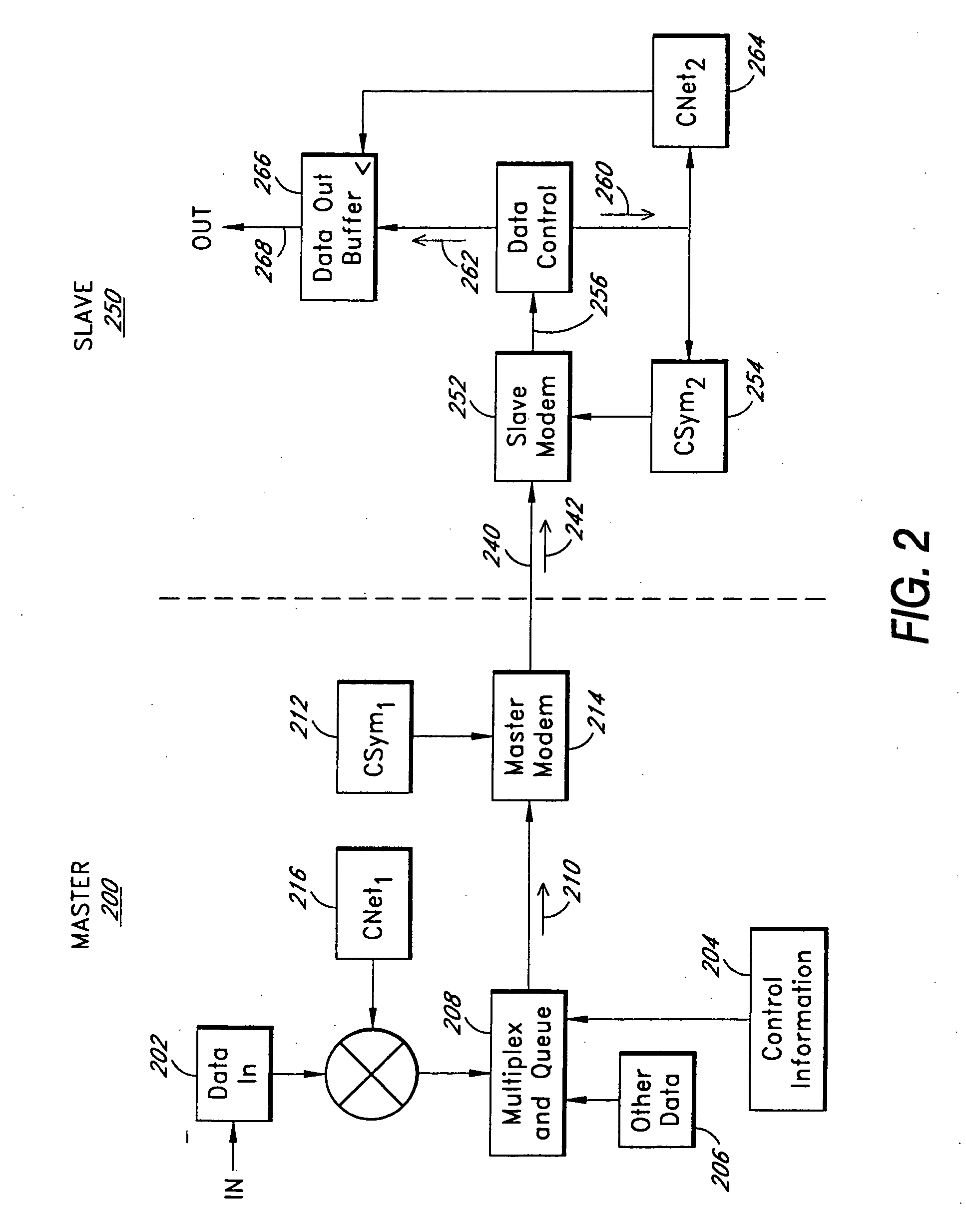
Variably delayable transmission of packets between independently clocked source, intermediate, and destination circuits while maintaining orderly and timely processing in one or both of the intermediate and destination circuits
InactiveUS7181485B1Increase in sizeLarge in speedMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsData packLine card
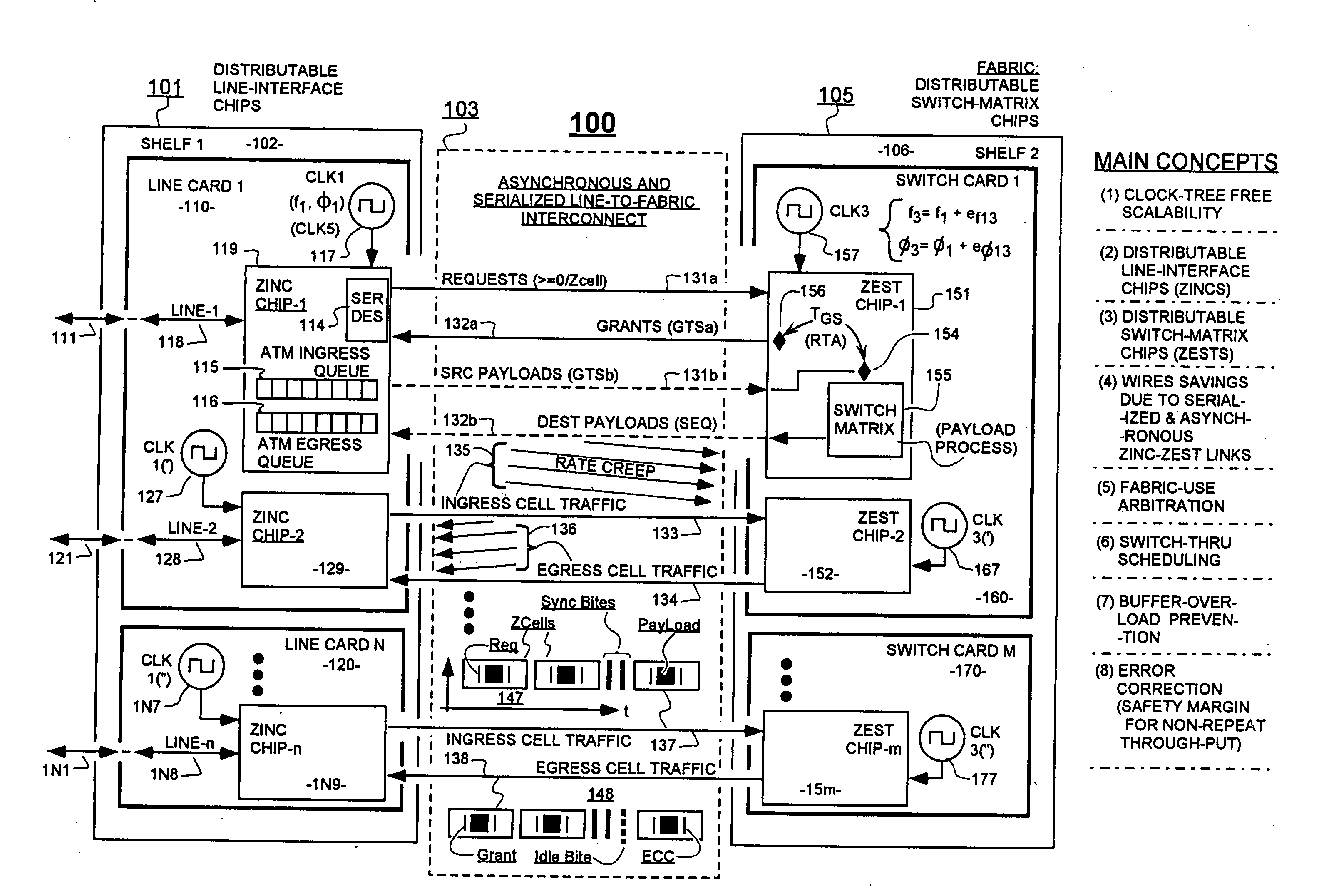
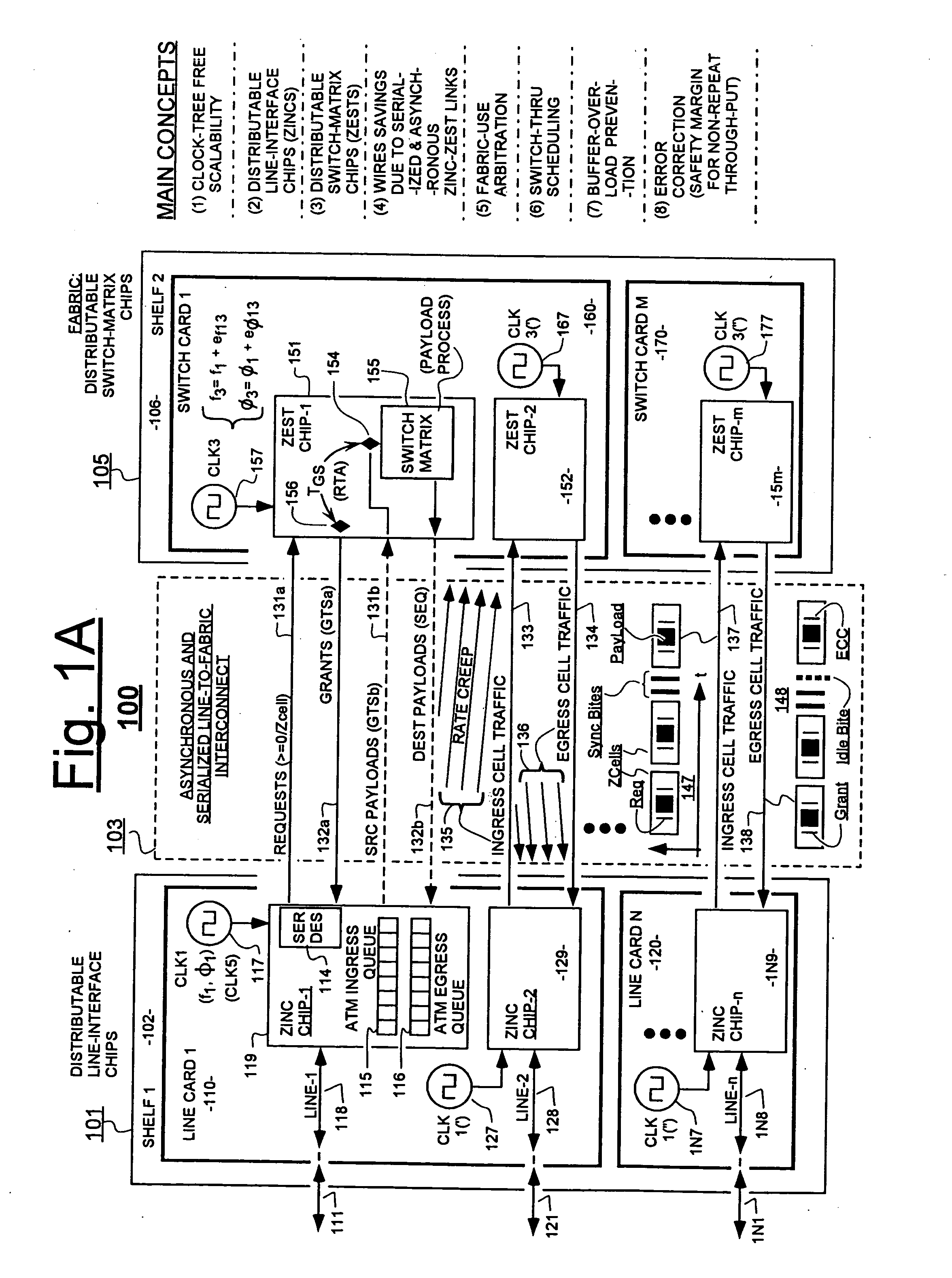
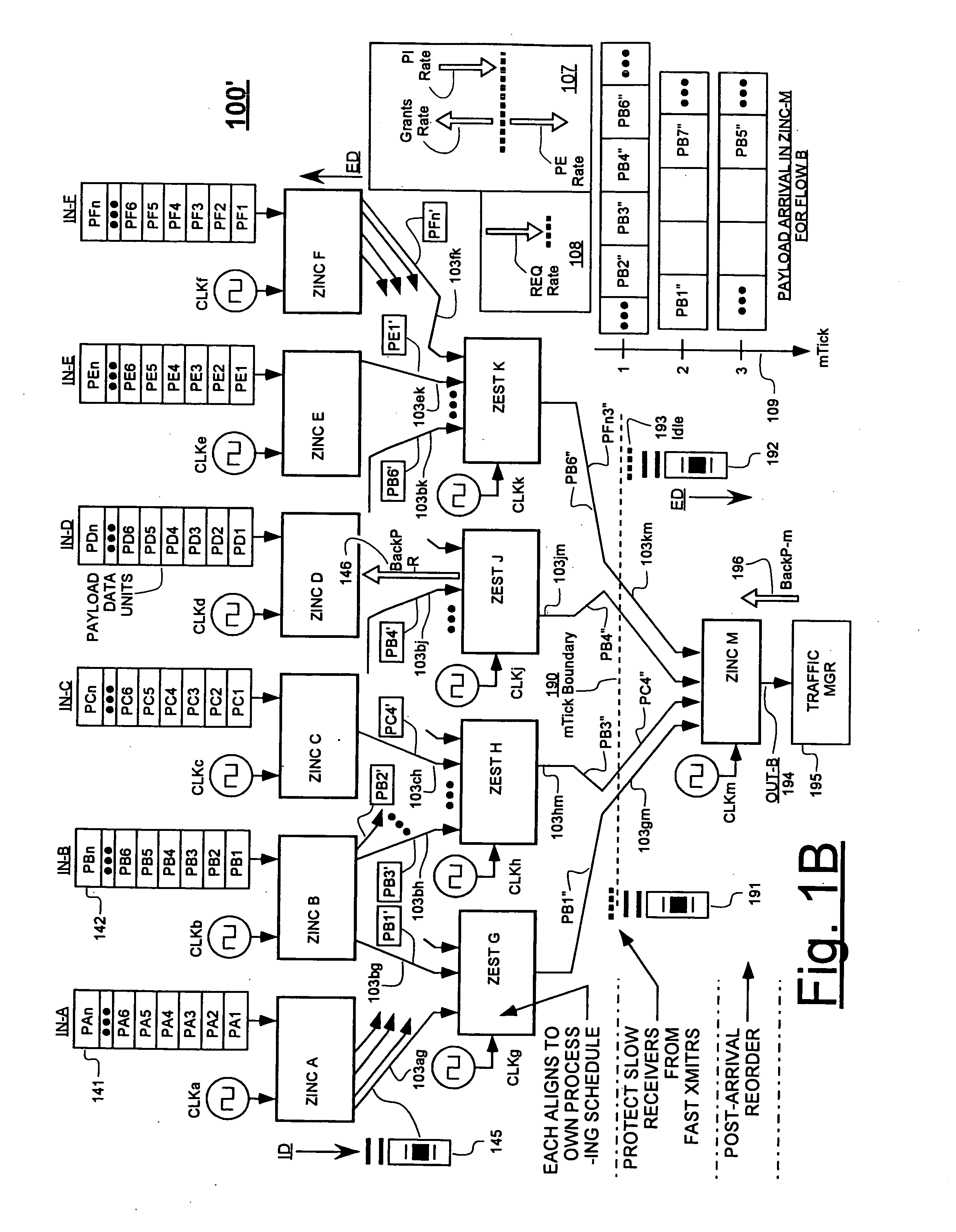
In a system having independently-clocked job-performing circuits (e.g., payload processors) and independently-clocked job-ordering circuits (e.g., request and payload suppliers), coordinating mechanisms are provided for coordinating exchanges between the independently-clocked circuits. The coordinating mechanisms include those that use transmitted time-stamps for scheduling contention-free performances within the job-performing circuits of requested jobs. The coordinating mechanisms additionally or alternatively include static and dynamic rate constraining means that are configured to prevent a faster-clocked one of the independently-clocked circuits from overwhelming a more slowly-clocked other of the independently-clocked circuits. In one implementation, independently-clocked telecommunication-shelves house a distributed set of line cards and switch cards. An asynchronous interconnect is provided between the independently-clocked shelves for carrying job requests and payload data between the distributed line cards and the distributed switch cards. The multi-shelf system is scalable and robust because additional or replacement line and switch cards may be inserted into one or another of the independently-clocked shelves as desired and because a unified clock-tree is not needed for synchronizing activities within the interconnected, but independently clocked shelves.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS US INC
Decoupling sampling clock and error clock in a data eye
ActiveUS20120170621A1Well formedMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsPhase correctionTransceiver
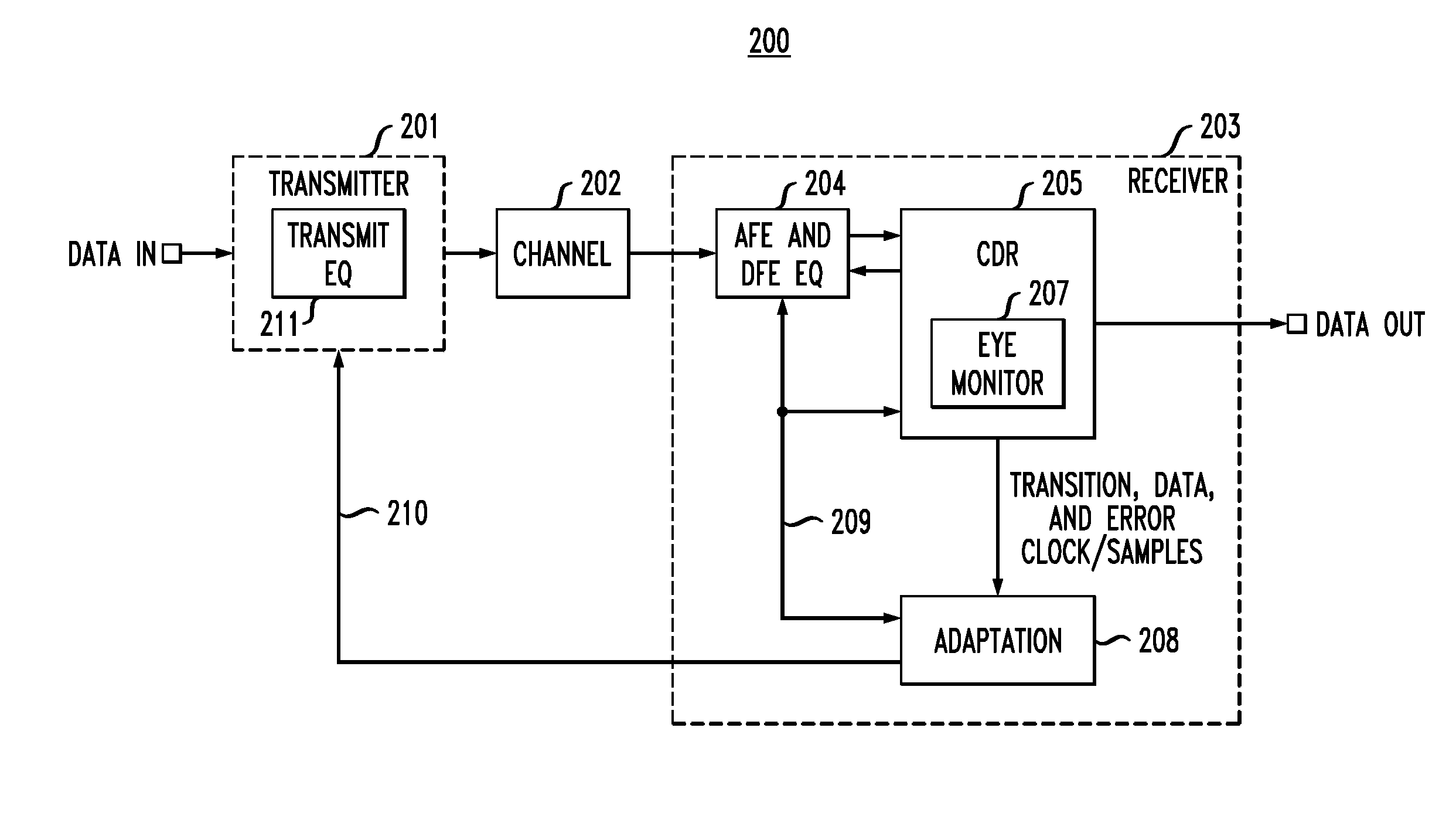
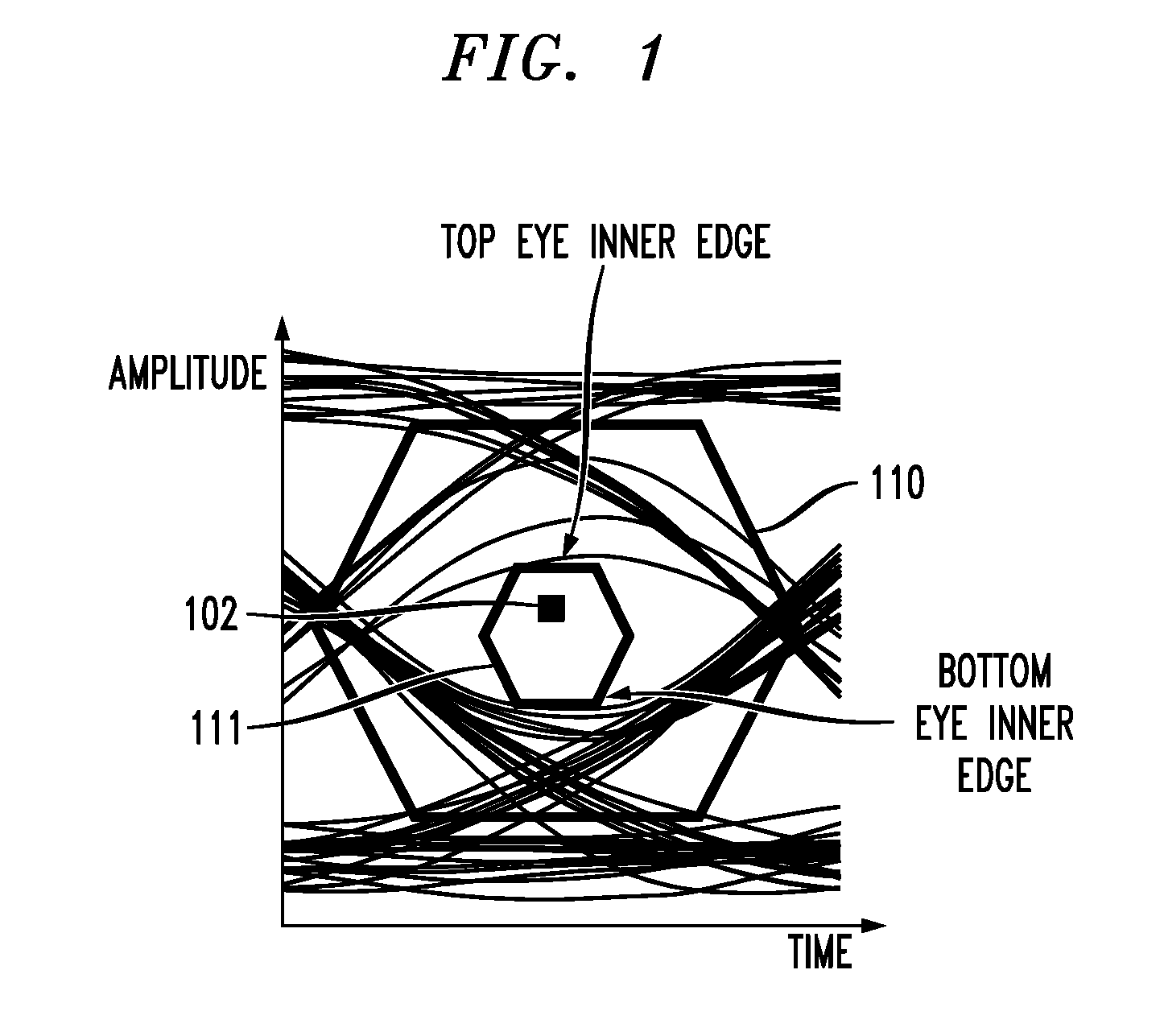
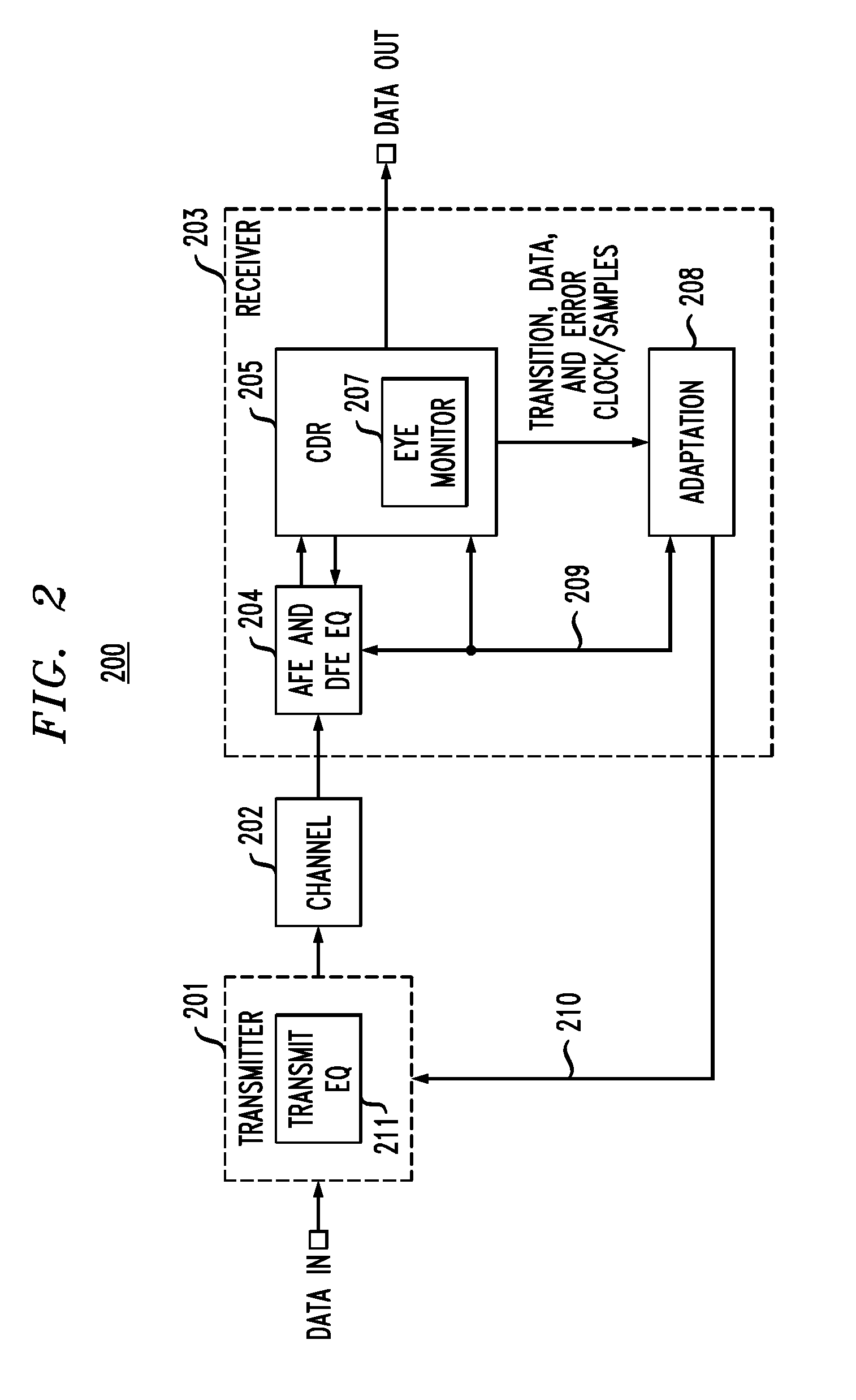
In described embodiments, a transceiver includes an eye monitor, clock and data recovery, and adaptation modules. Data sampling clock phase and error clock phase determined from a data eye are decoupled in the transceiver during a sampling phase correction process. Decoupling these clock phases during the sampling phase correction process allows relative optimization of system equalization parameters without degradation of various adaptation algorithms. Such adaptation algorithms might be employed for received signal gain and equalization such as, for example, Decision Feedback Equalizer (DFE) adaptation. Deriving the data sampling clock and error clock phases from the same clock generation source and with independent clock control enables an iterative sampling phase correction process that allows for accelerated clock and data recovery (CDR) without disturbing the data eye shape.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and program product for modelling behavior of asynchronous clocks in a system having multiple clocks
InactiveUS7089518B2Poor execution speed performanceGuaranteed uptimeCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTime delaysTheoretical computer science
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
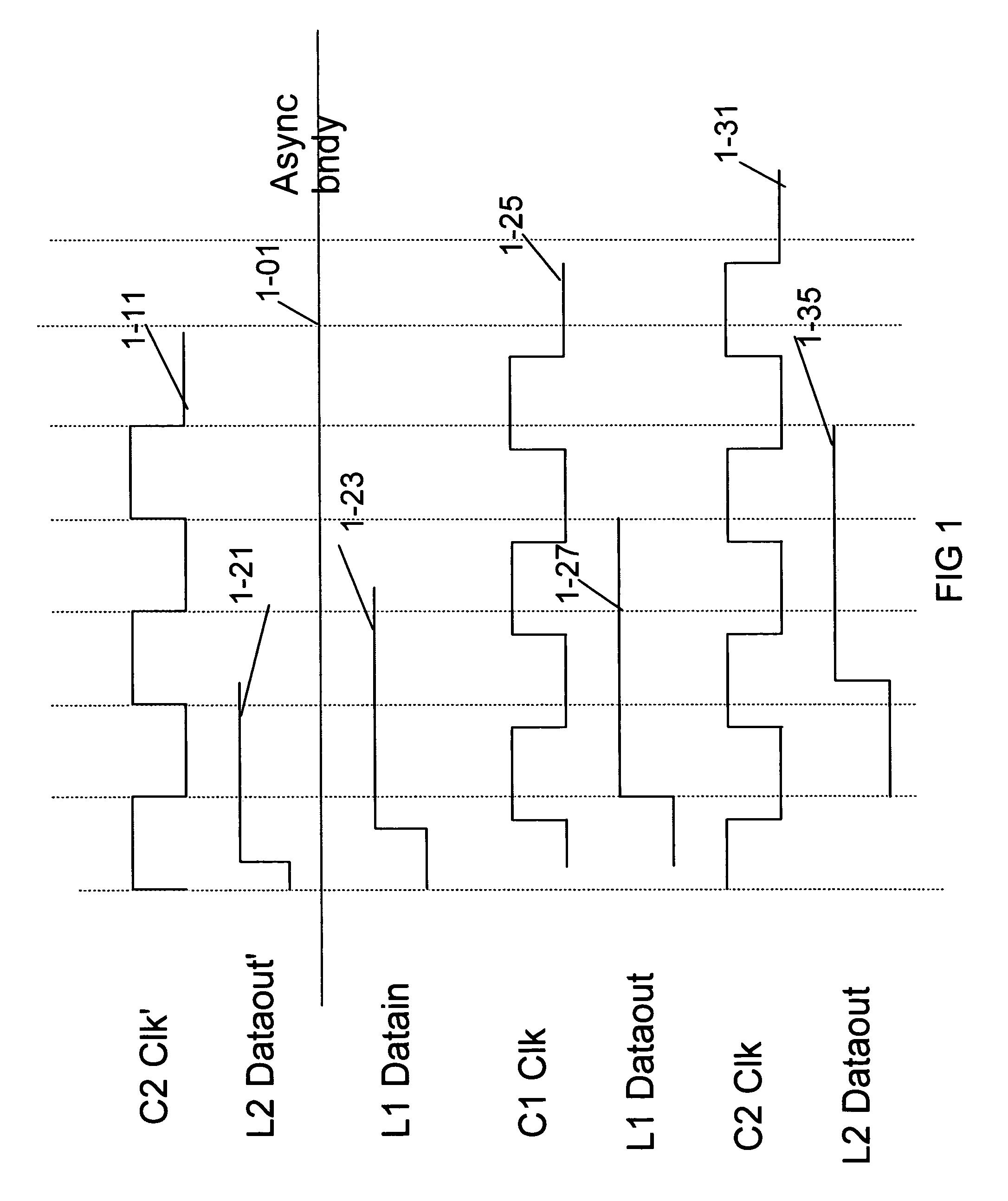
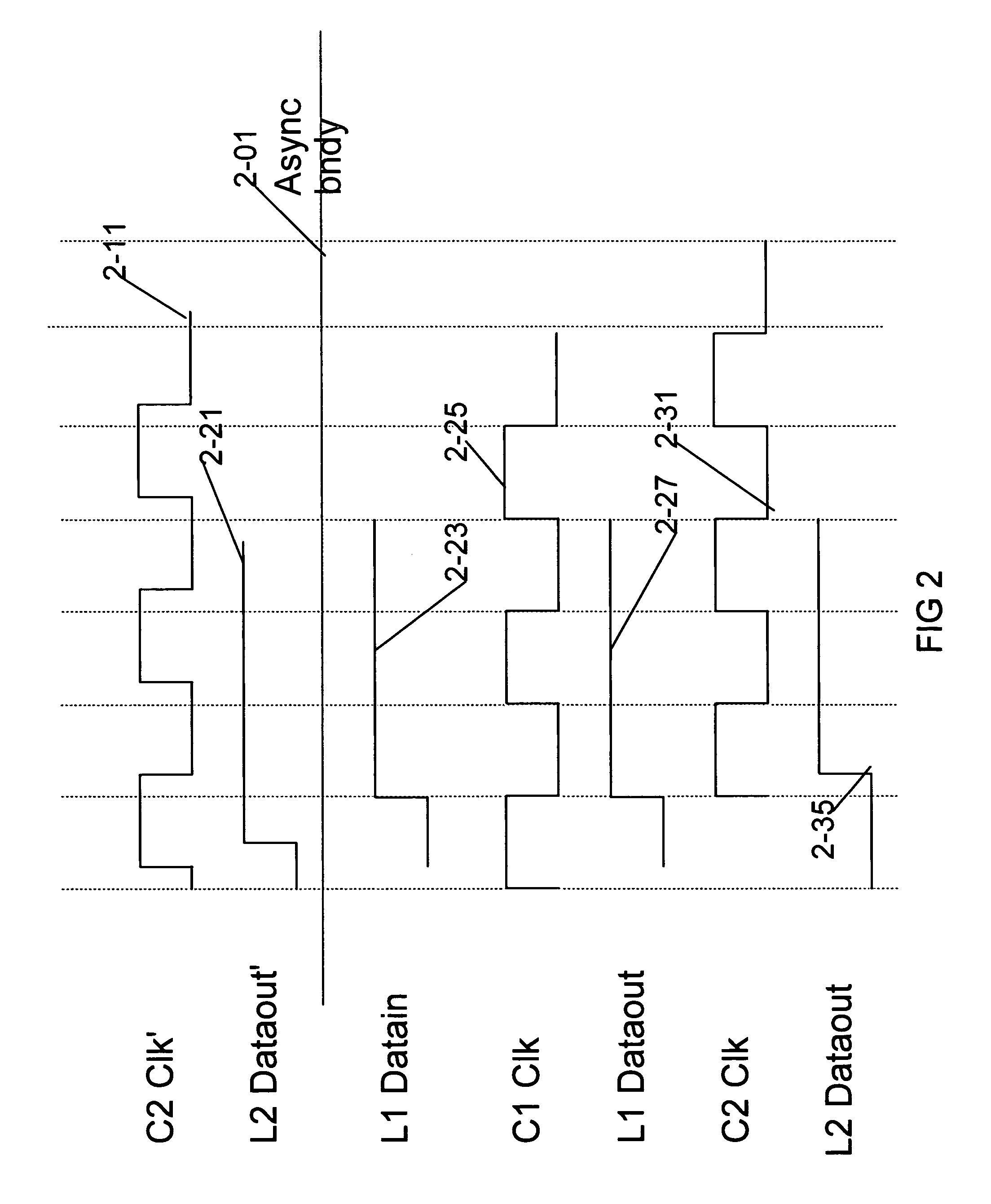
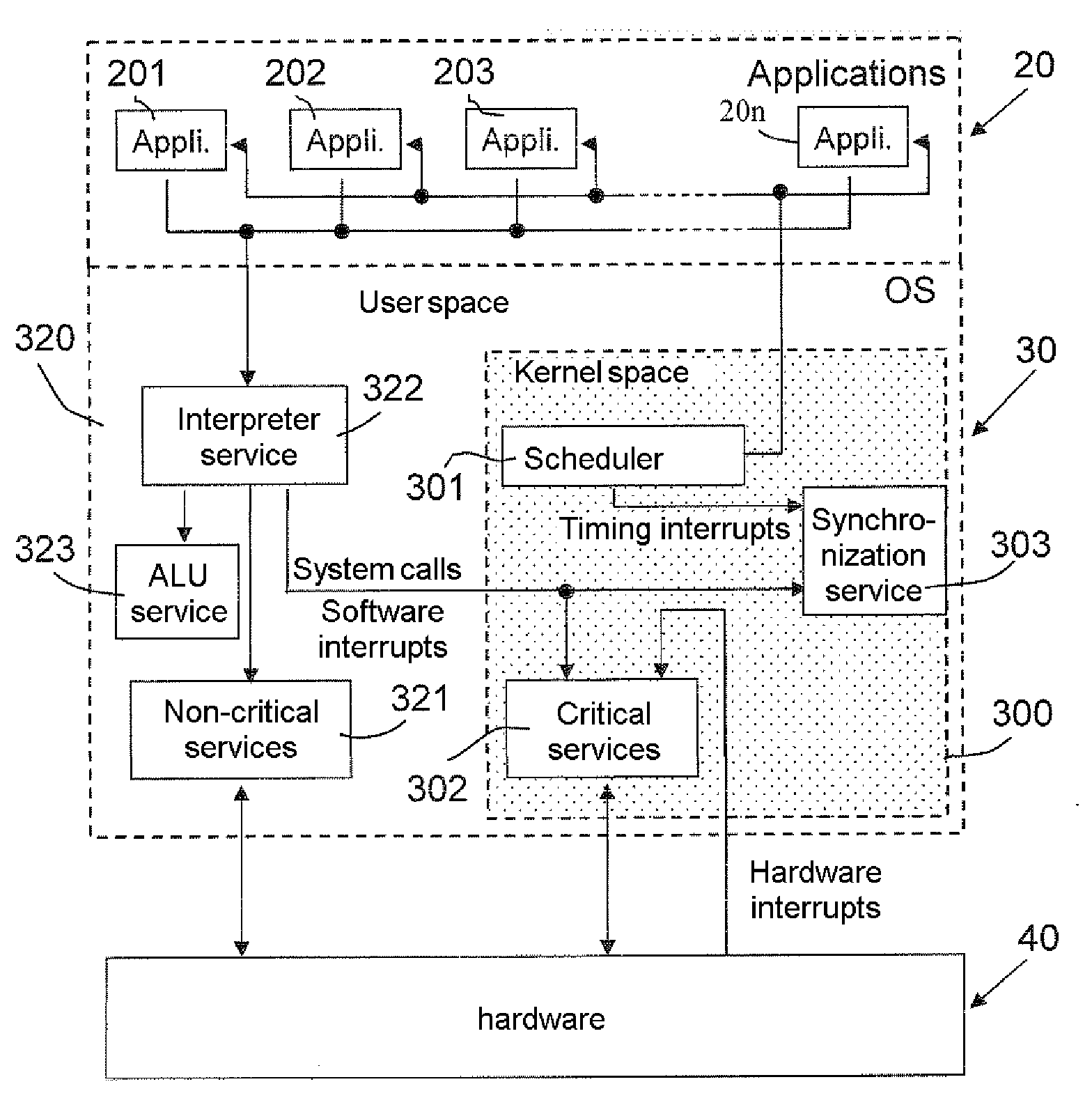
Process for maintaining execution synchronization between several asynchronous processors working in parallel and in a redundant manner
InactiveUS20080196037A1Error detection/correctionGeneral purpose stored program computerProcessing InstructionOperational system
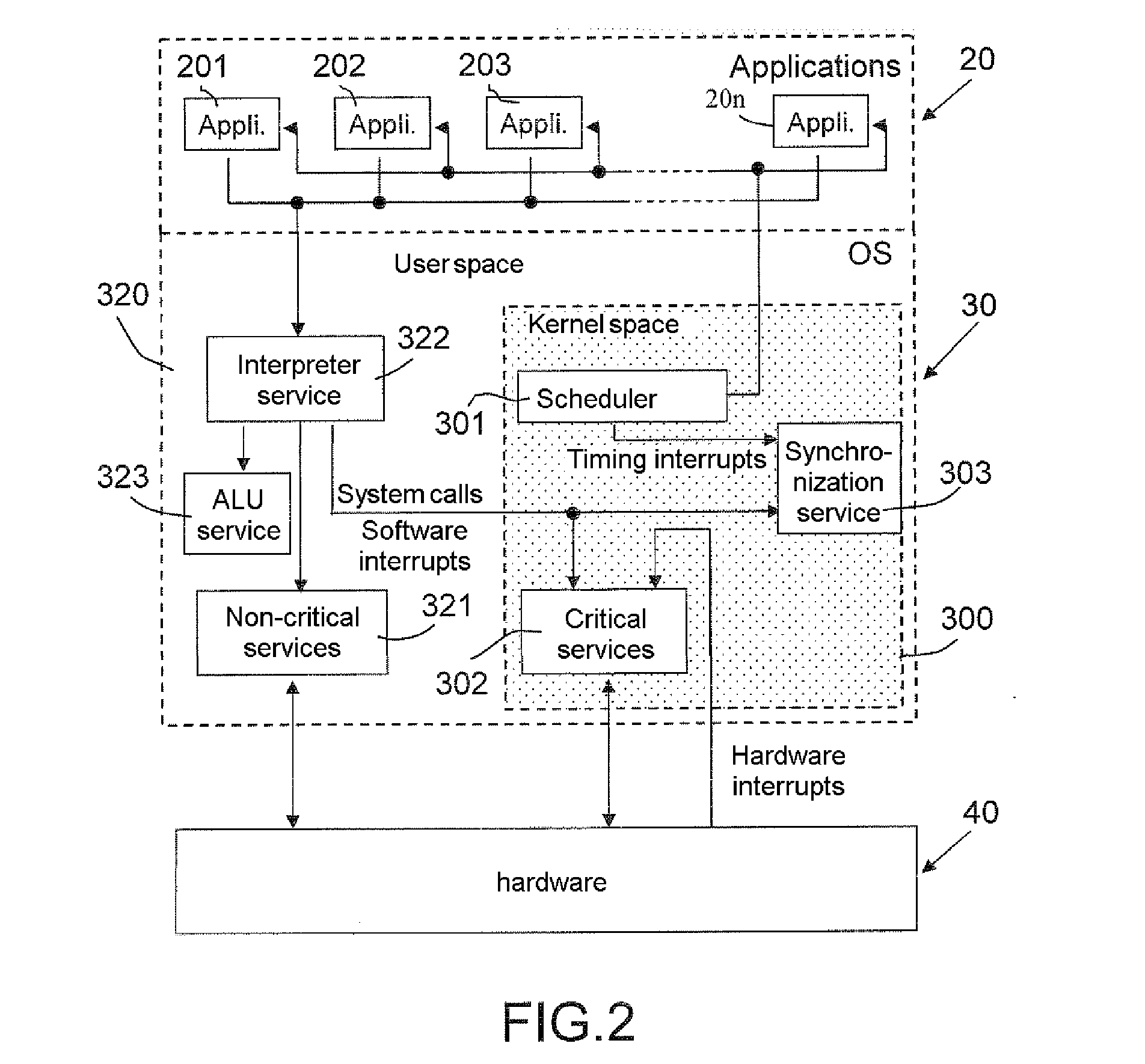
This process for maintaining synchronization applies to processors of redundant parallel processing units of a computer running, in parallel and under the control of the same multi-tasking time-sharing operating system (30) and independent clocks of the same speed, with the same applications with the same parameterizations. It consists on the one hand of including in the operating system (30) a synchronization service (303) called by a synchronization interrupt request and applying a correction of synchronization based on comparing the contents of the processed-instruction counters belonging to the various processors (1, 2) and the utilisation of the lockstep operating mode and on the other hand of inserting a synchronization interrupt request when commencing the processing of timing interrupts generated by the scheduler (301) of the operating system in order to terminate a time slice allocated to processing an application. The system calls generated by the applications for the attention of the operating system.
Owner:THALES SA
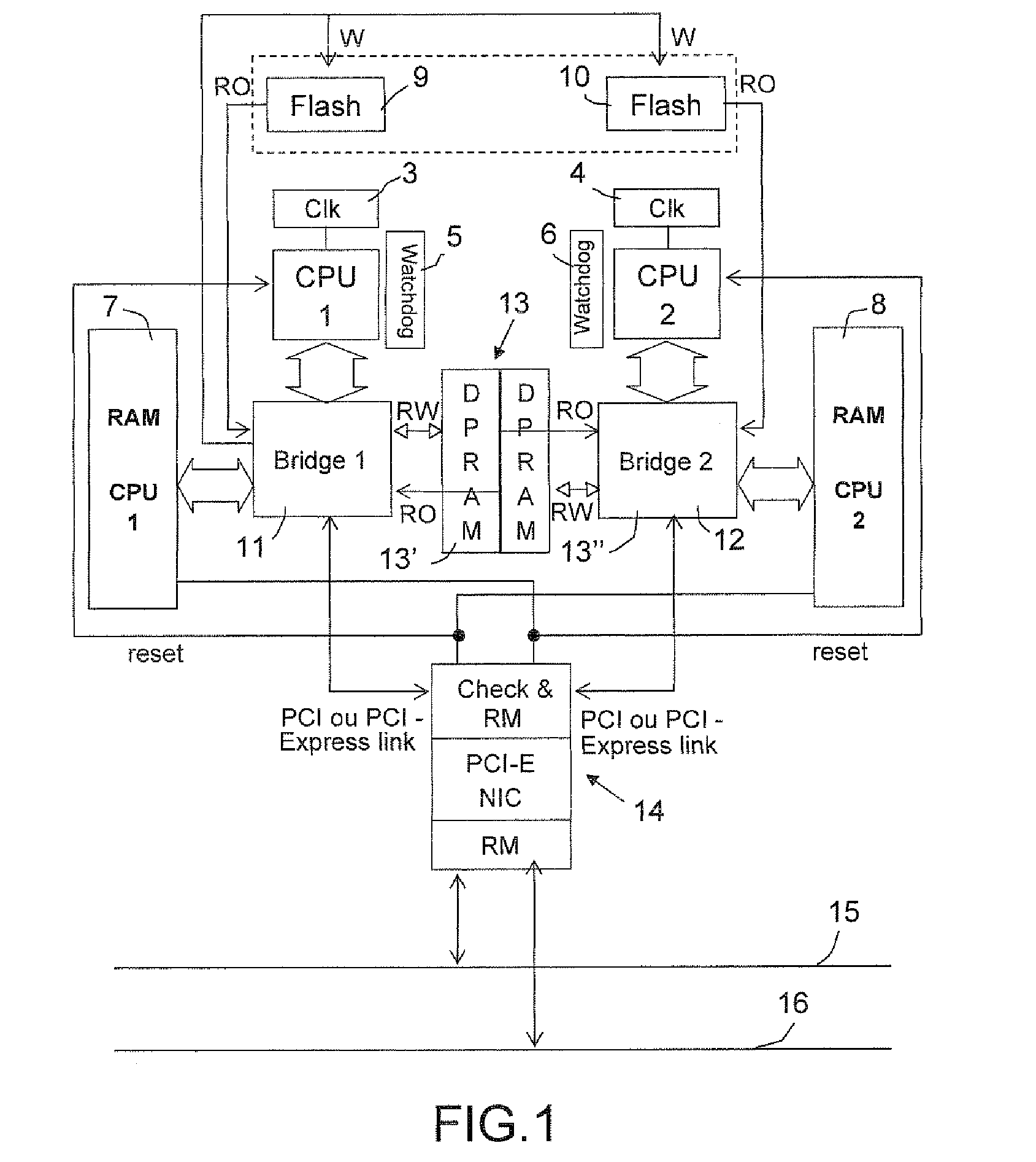
Apparatus for phase synchronizing clock signals in a fully redundant computer system
InactiveUS6055362AImproved generationImproved distribution unitPulse automatic controlSynchronous motors for clocksPhase detectorIndependent clock
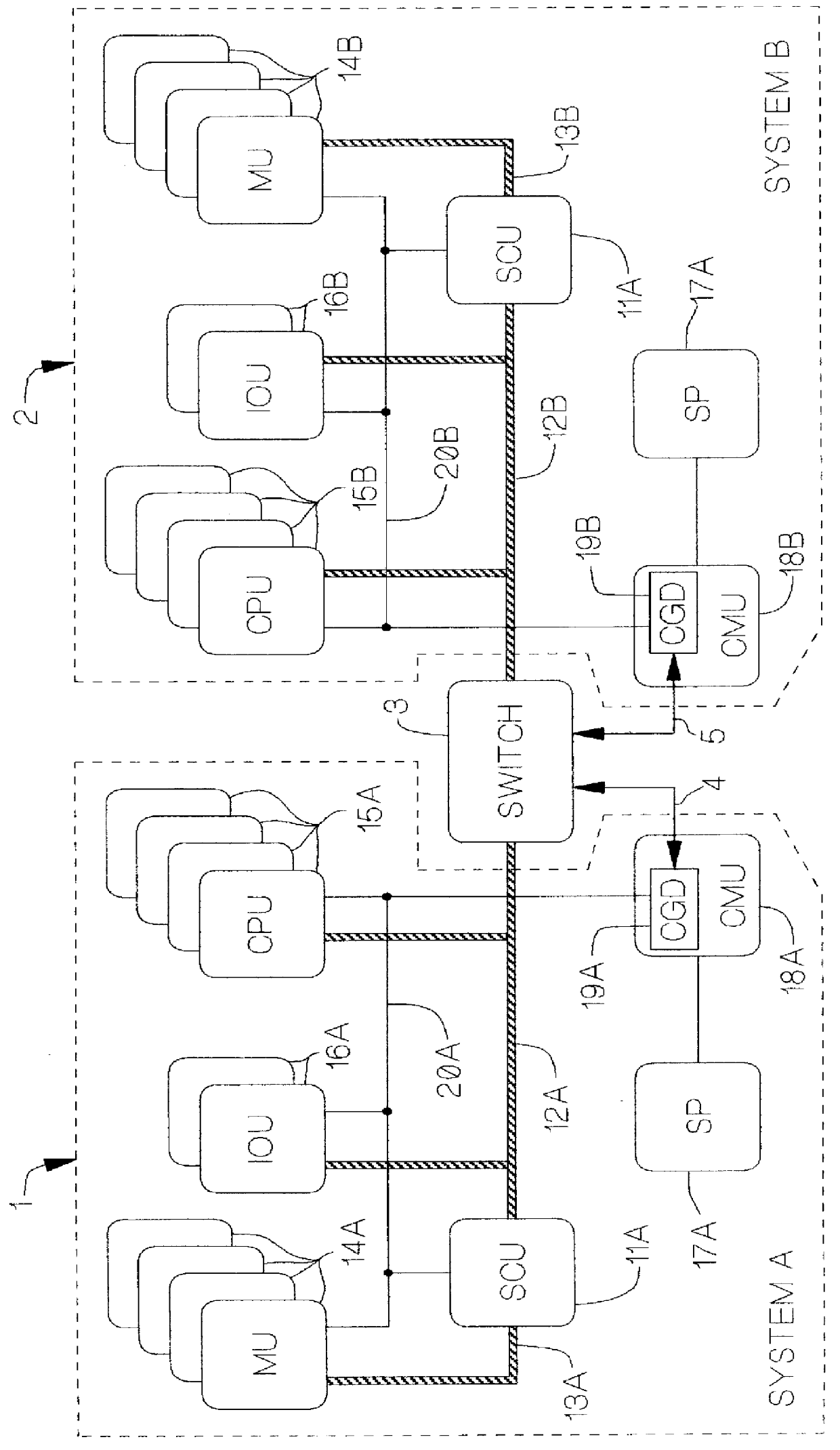
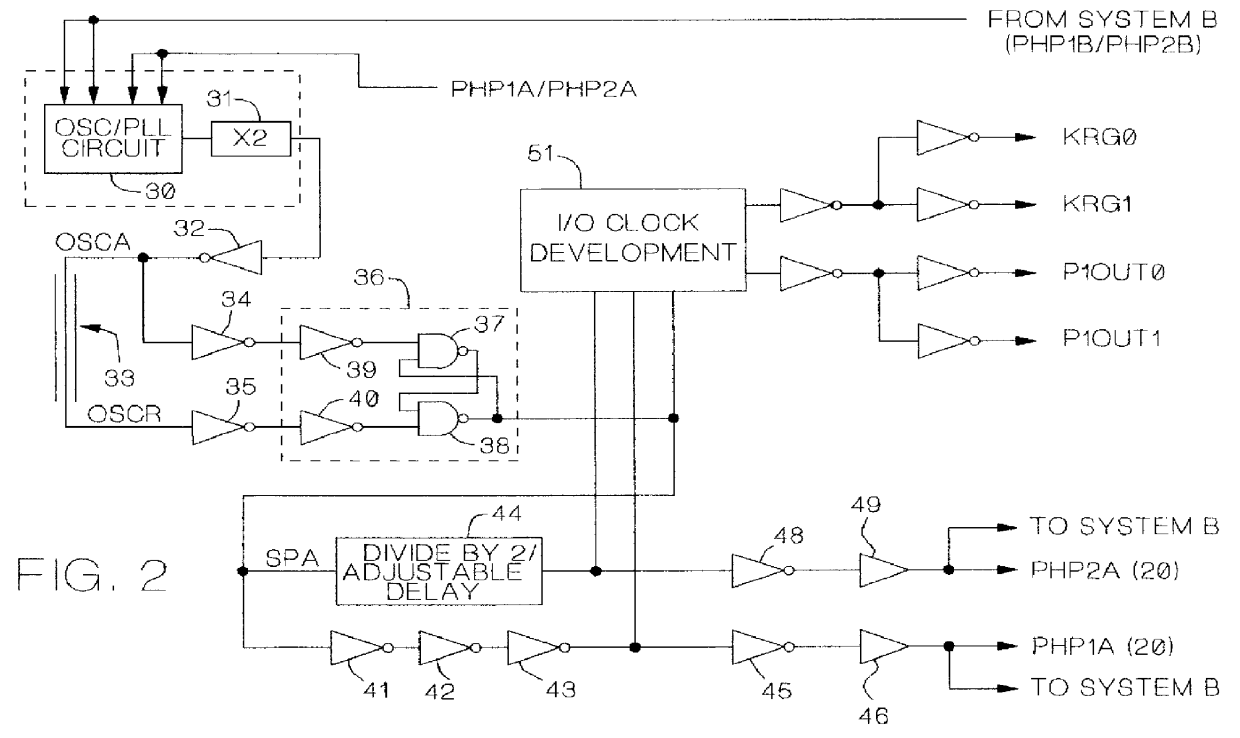
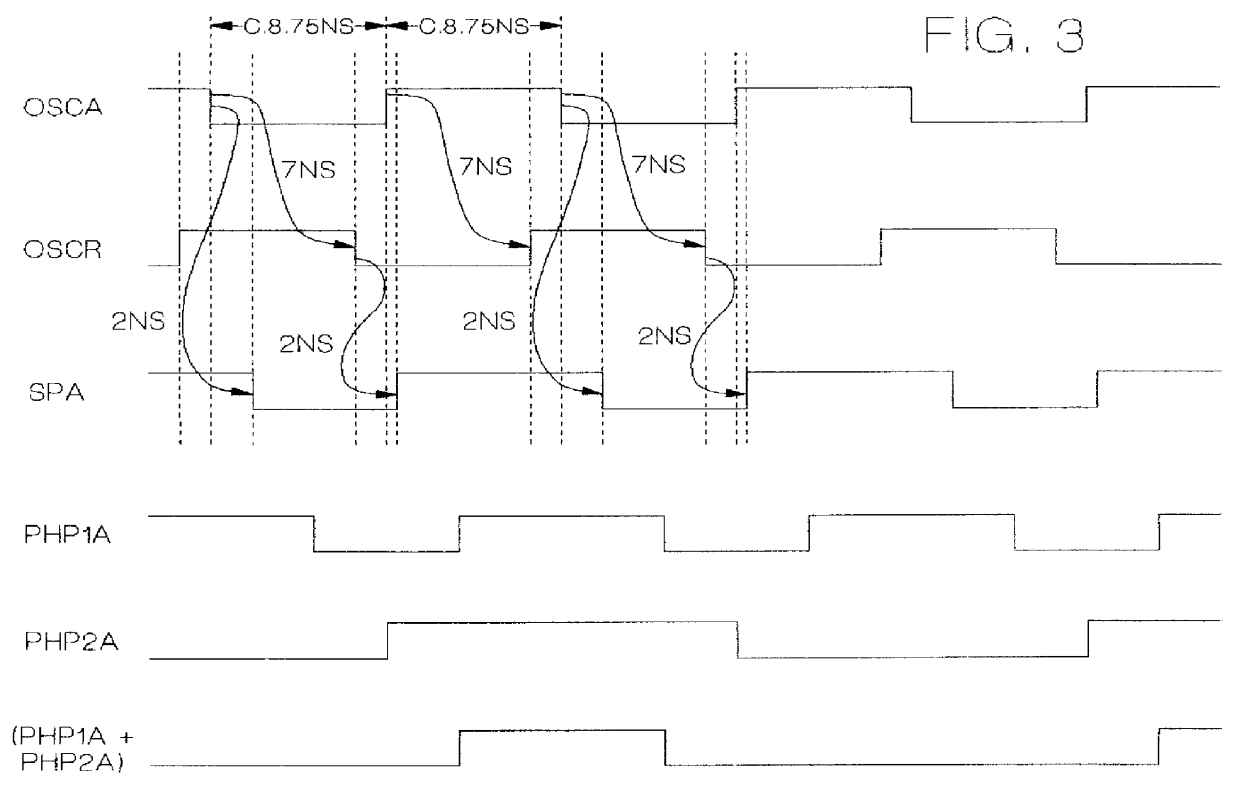
A redundant computer system including two systems capable of independent operation. The two systems correspondingly employ two independent clock generation and distribution (CGD) units which each issue clock and clock definer signals. The clock and definer signals of each system are used internally and are also sent to the other system. When the two systems are split, phase locked loops in each system are disabled, and each system is controlled by a precision oscillator in its own CGD unit When the two systems are merged, one CGD is designated as master and remains under control of its internal oscillator. The clock and definer signals of the master system are employed in the slave system to derive a signal which is used as the reference input to the slave system's phase locked loop from which the slave system's clock and definer signals are developed. Preferably, dual flip-flop phase detector type phase locked loops are employed. For higher frequency operation, it is desirable to incorporate certain correction circuitry which minimizes phase offset at apparent phase lock which is an inherent characteristic of this type of phase locked loop.
Owner:BULL HN INFORMATION SYST INC
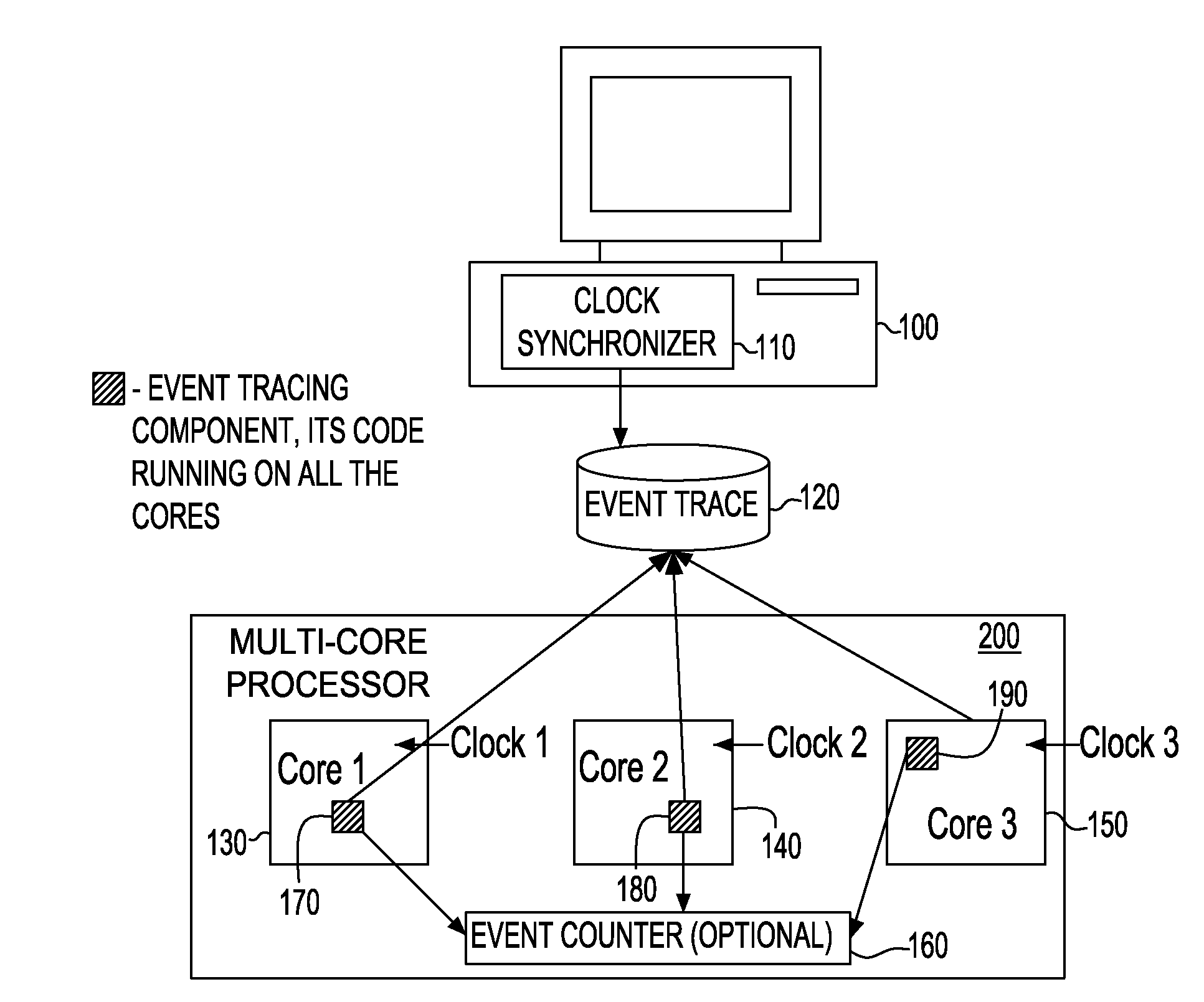
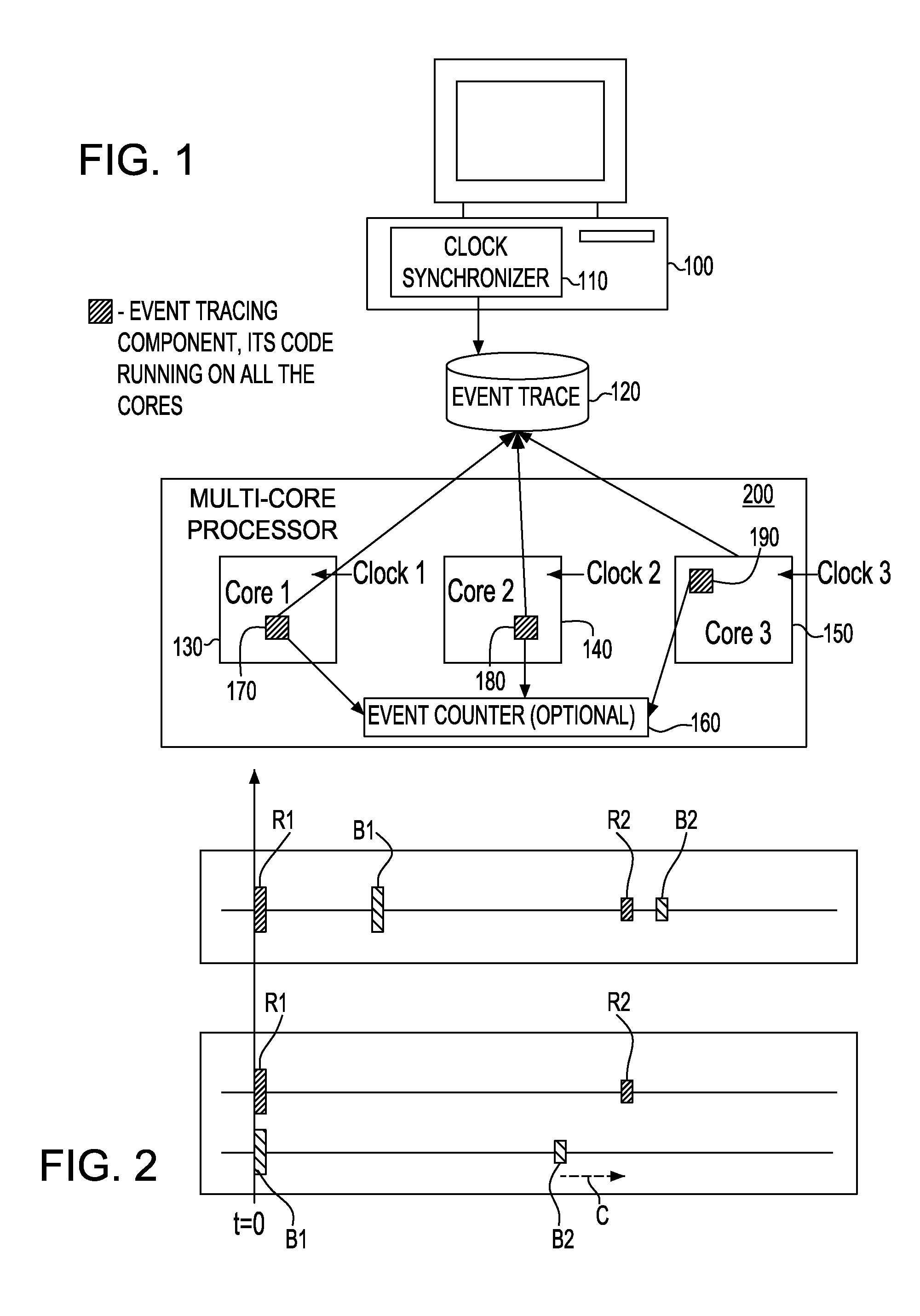
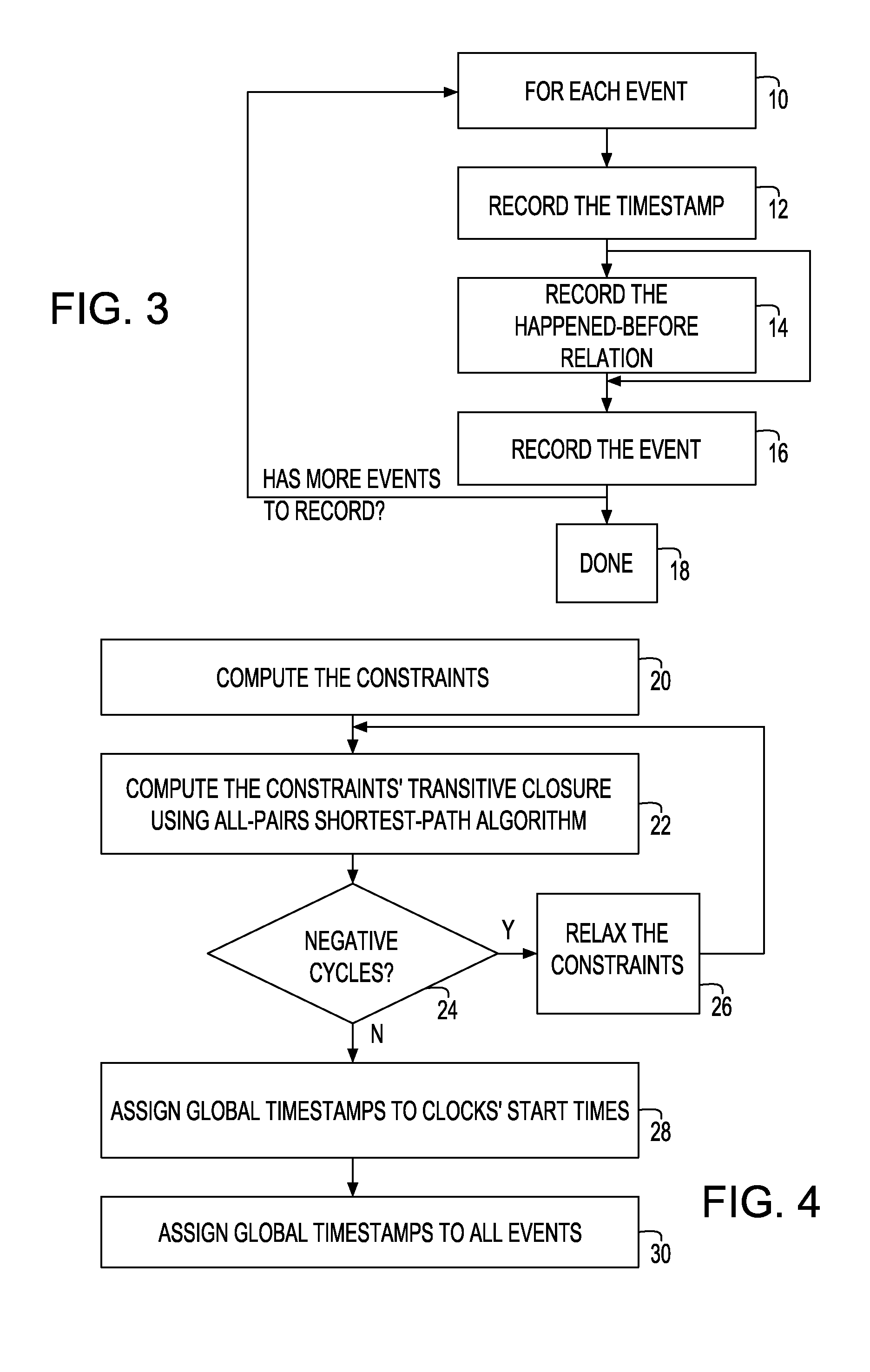
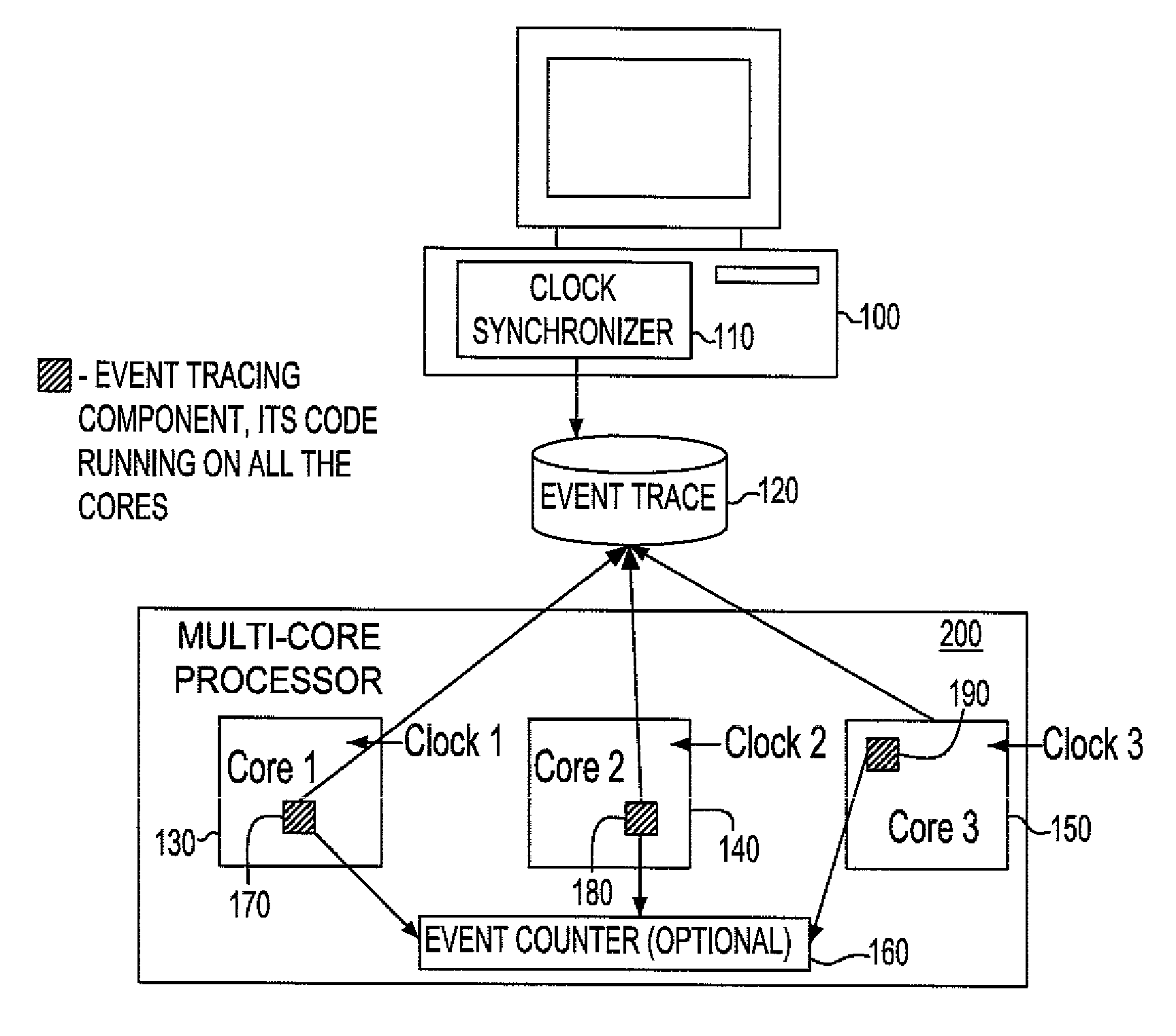
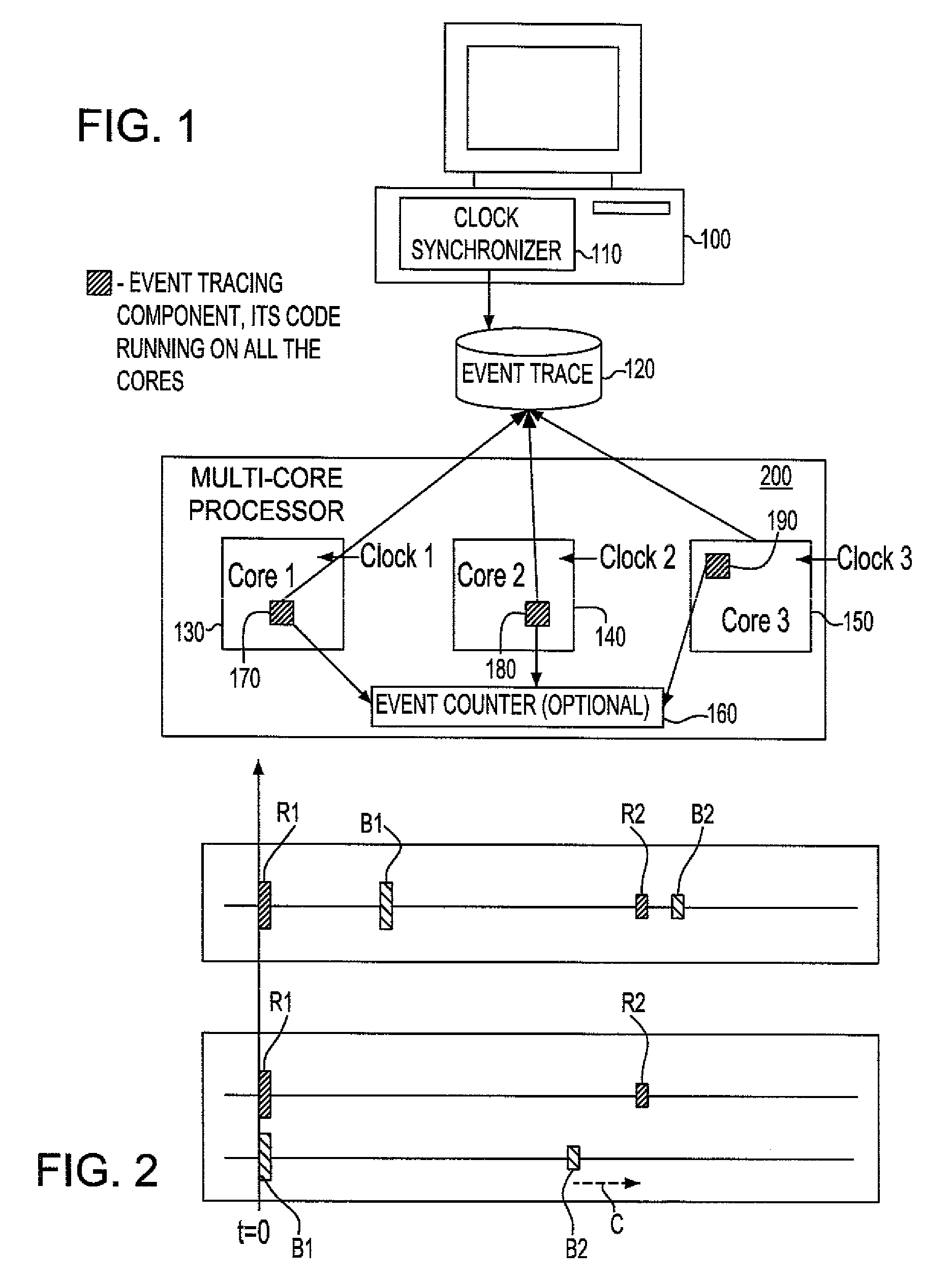
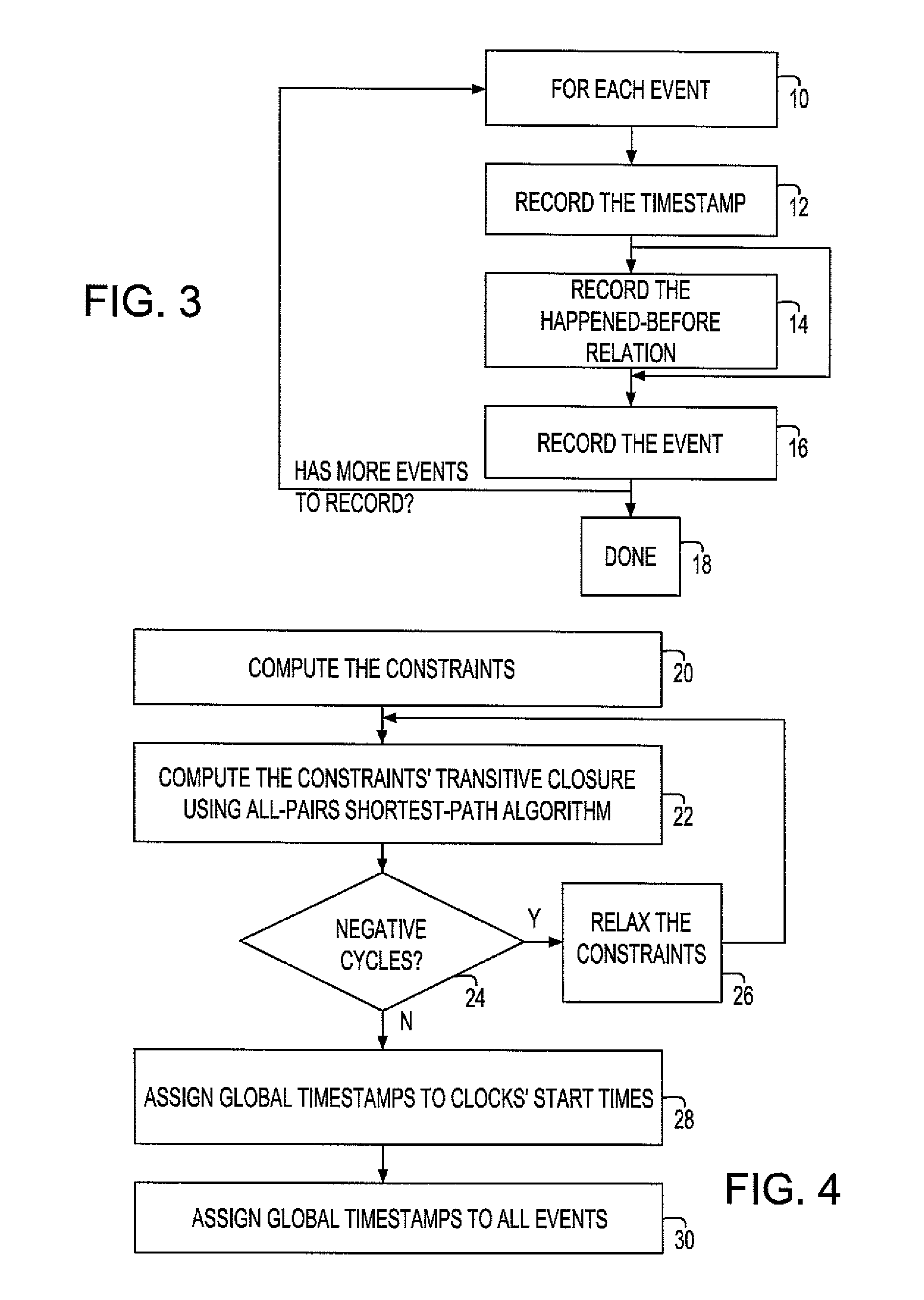
Synchronization of independent clocks
InactiveUS20090158075A1Reduce overheadLower requirementTime-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsStart timeHappened-before
A system and method to synchronize independent local clocks in multi-core processing system are disclosed. A shared counter or a shared memory / file is provided to establish a partial happened-before relationship (e1<e2 in the happened-before order if we know that the event e1 happened before the event e2) and a synchronizer device is utilized to generate a global time of events in threads or processes. The synchronizer device estimates each clock's start time and approximates elapsed time between events in threads or processes by executing an all-pair shortest-path algorithm
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
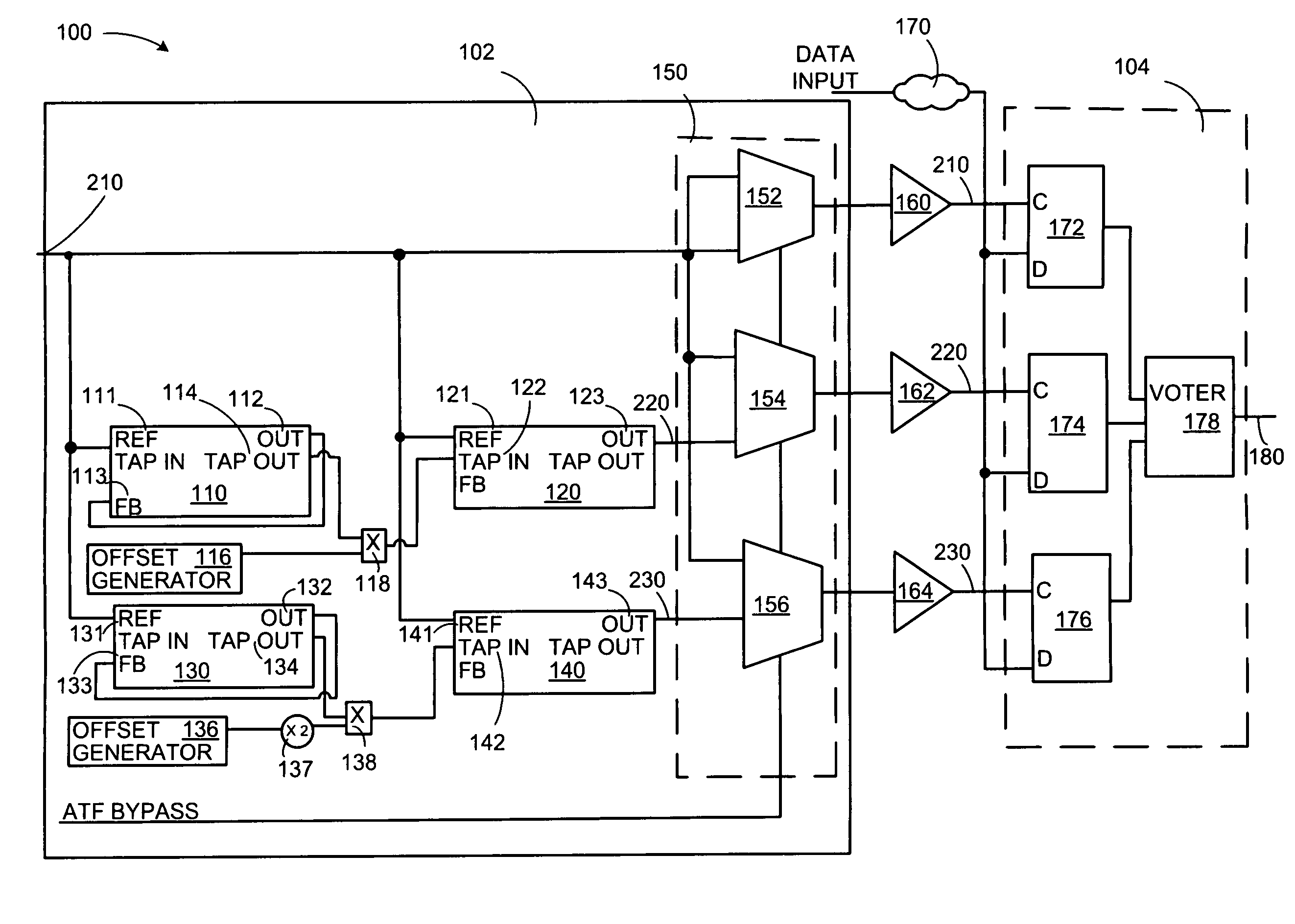
Adaptive temporal filtering of single event effects
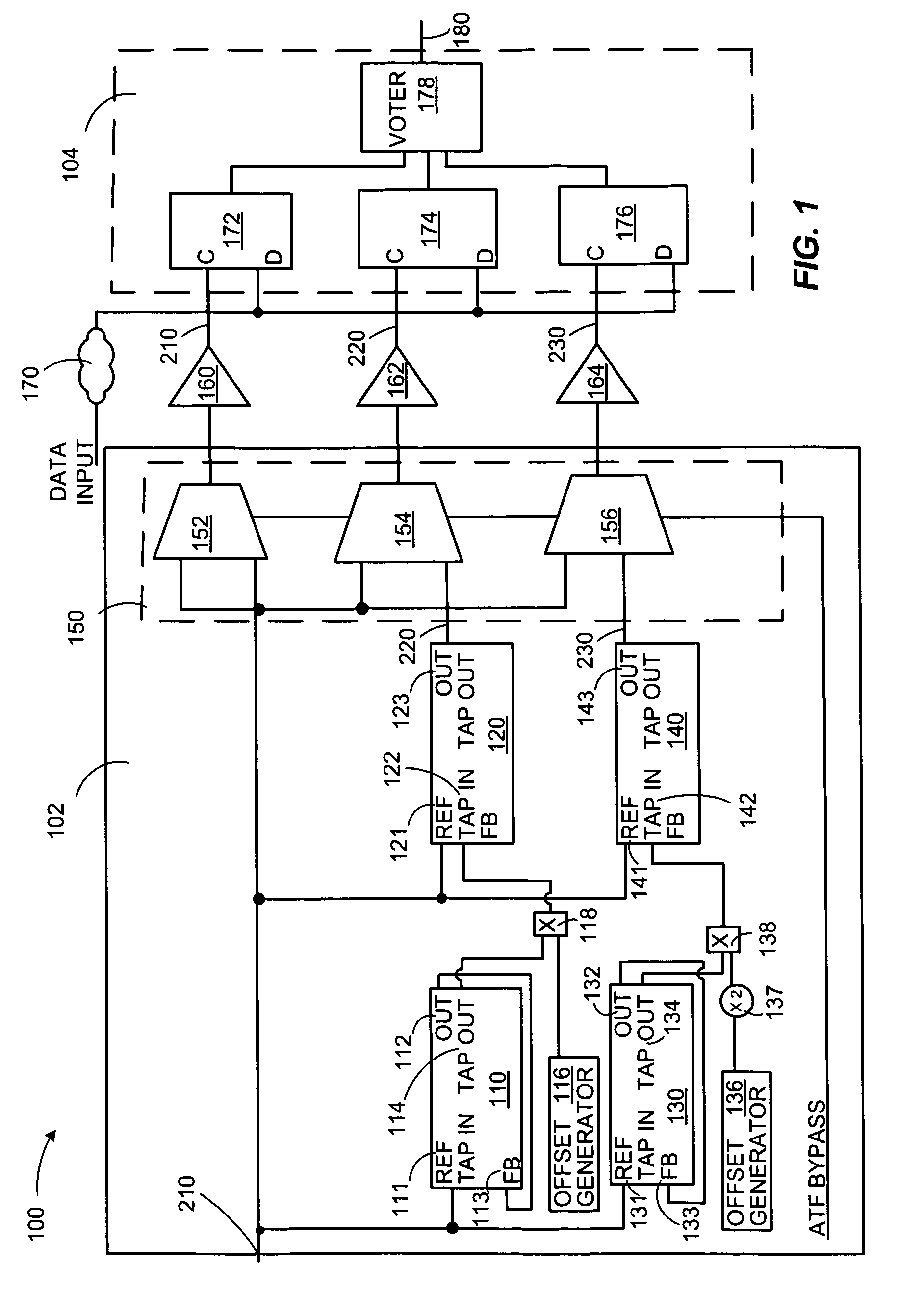
Technologies are described herein for mitigating the effects of single event effects or upsets on digital semiconductor device data paths and clocks utilizing an adaptive temporal filter. The adaptive temporal filter includes a master delay line and a slave delay line to generate two output clock signals that remain unaffected by variations in process, voltage and temperature (PVT) conditions. The adaptive temporal filter supplies the three independent clock signals having a programmable phase relationship, to a triple voting register structure for storing and outputting an uncorrupted data value using a majority voter.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
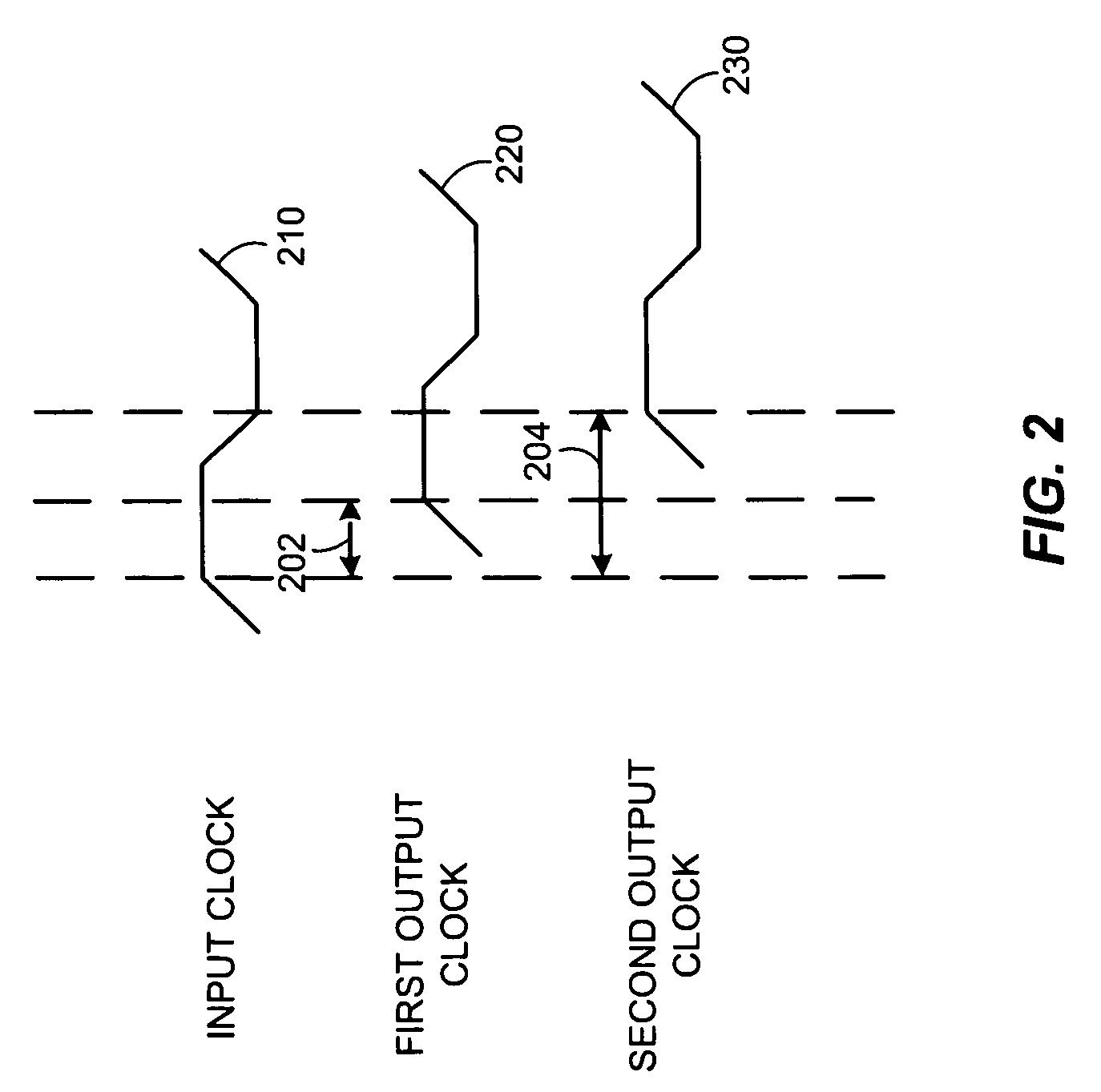
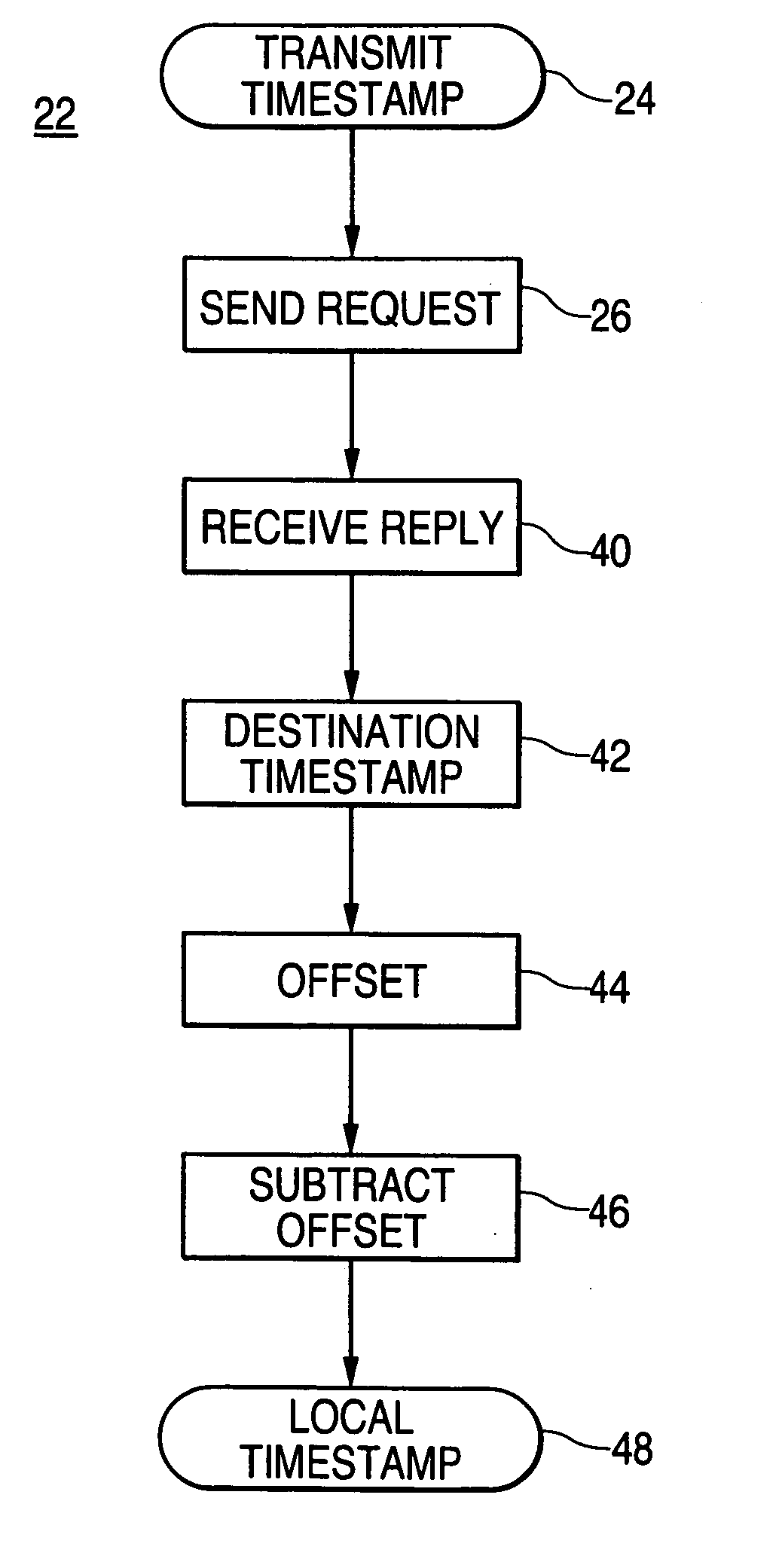
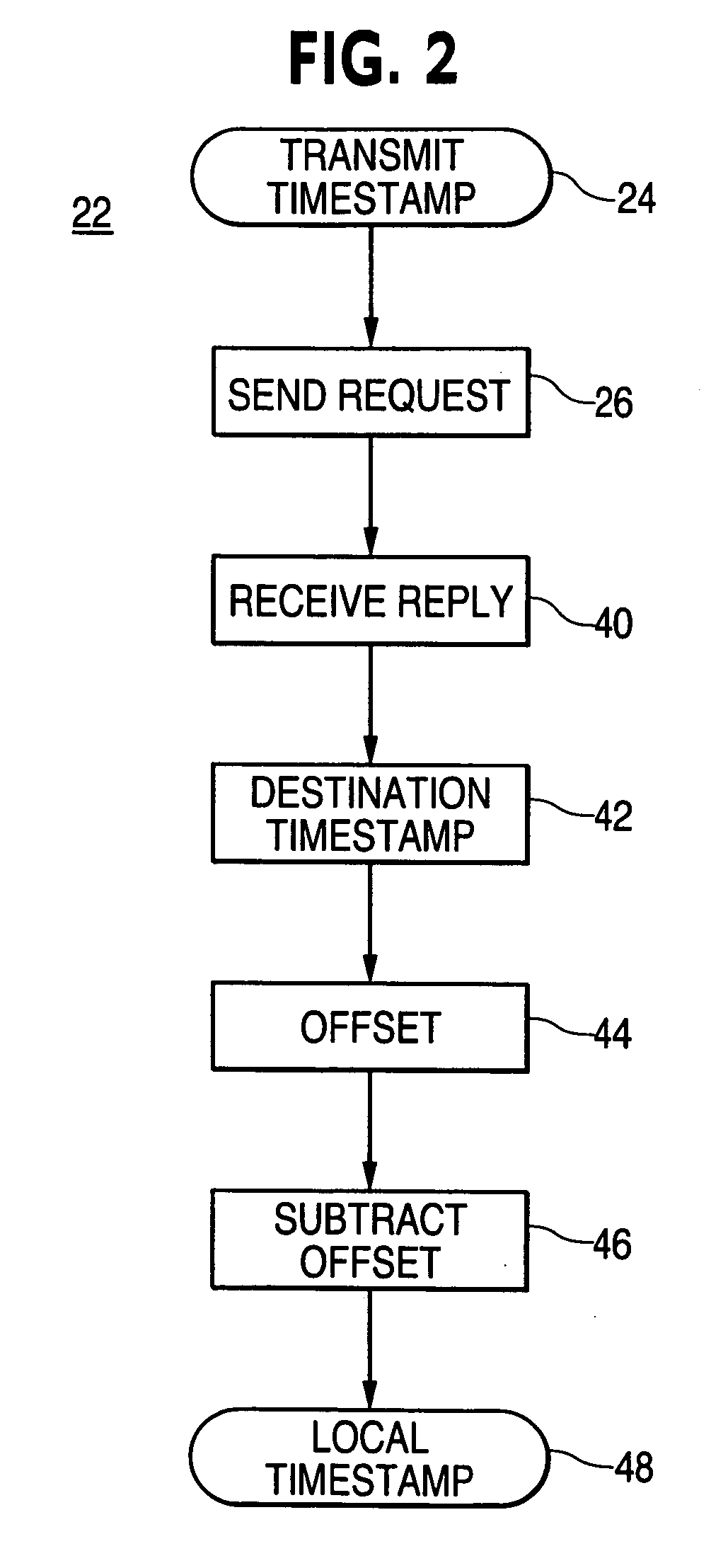
Localizing a remote event timestamp from a network device with an independent clock method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060173952A1Time-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsTimestampIndependent clock
A timestamp localization method and device includes two processors with independent clocks connected to a communication network. Two messages are exchanged between the processors. First a request message is sent with a transmit timestamp. Second, a reply message is sent back with receive, originate, transmit and remote timestamps. Then the remote timestamp is converted to a local timestamp using an algorithm and the timestamps from the reply message.
Owner:ASCOM SWEDEN
Synchronizing clocks across a communication link
InactiveUS20070002987A1Synchronization is simpleHigh-precision detectionSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunications linkSlave clock
Apparatus, system and method for synchronizing one or more clocks across a communication link. A slave clock may be synchronized to a master clock by means of a synchronization signal sent from the master to the slave clock side of the link. The synchronization signal may be an expected signal pattern sent at intervals expected by the slave side. The slave clock may correlate received signals with a representation of the expected synchronization signal to produce a correlation sample sequence at a first sample rate which is related as n times the slave clock rate. The synchronization signal receipt time indicated by the correlation sample sequence may be refined by interpolating the correlation sample sequence around a best correlation sample to locate a best interpolation at an interpolation resolution smaller than the sample resolution. The best interpolation may in turn be further refined by estimating between interpolator outputs adjacent to the best interpolation output. The synchronization signal receipt time thus determined is compared to the expected time based upon the slave clock, which is adjusted until the times match. After initialization, all slave clock errors are preferably accumulated to prevent long-term slip between the slave and master clocks. Formerly independent master and slave clocks synchronized across the communication link constitute a noncommon clock which may be compared on each side of the link to secondary independent clocks, and the secondary independent clocks may then be separately synchronized by adjusting one to have the same difference from its local noncommon clock as the secondary clock on the other side of the link has from its local noncommon clock.
Owner:WI LAN INC
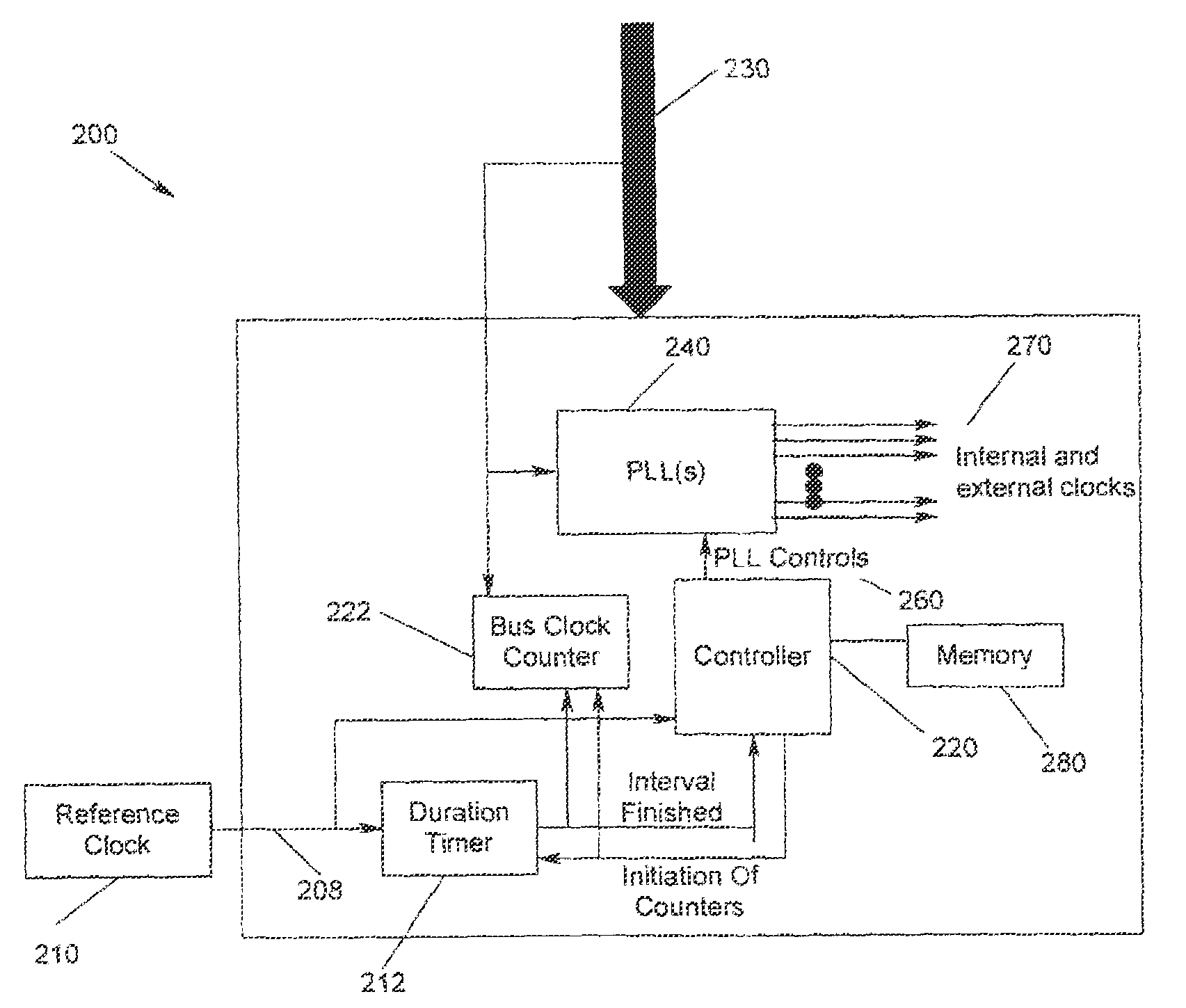
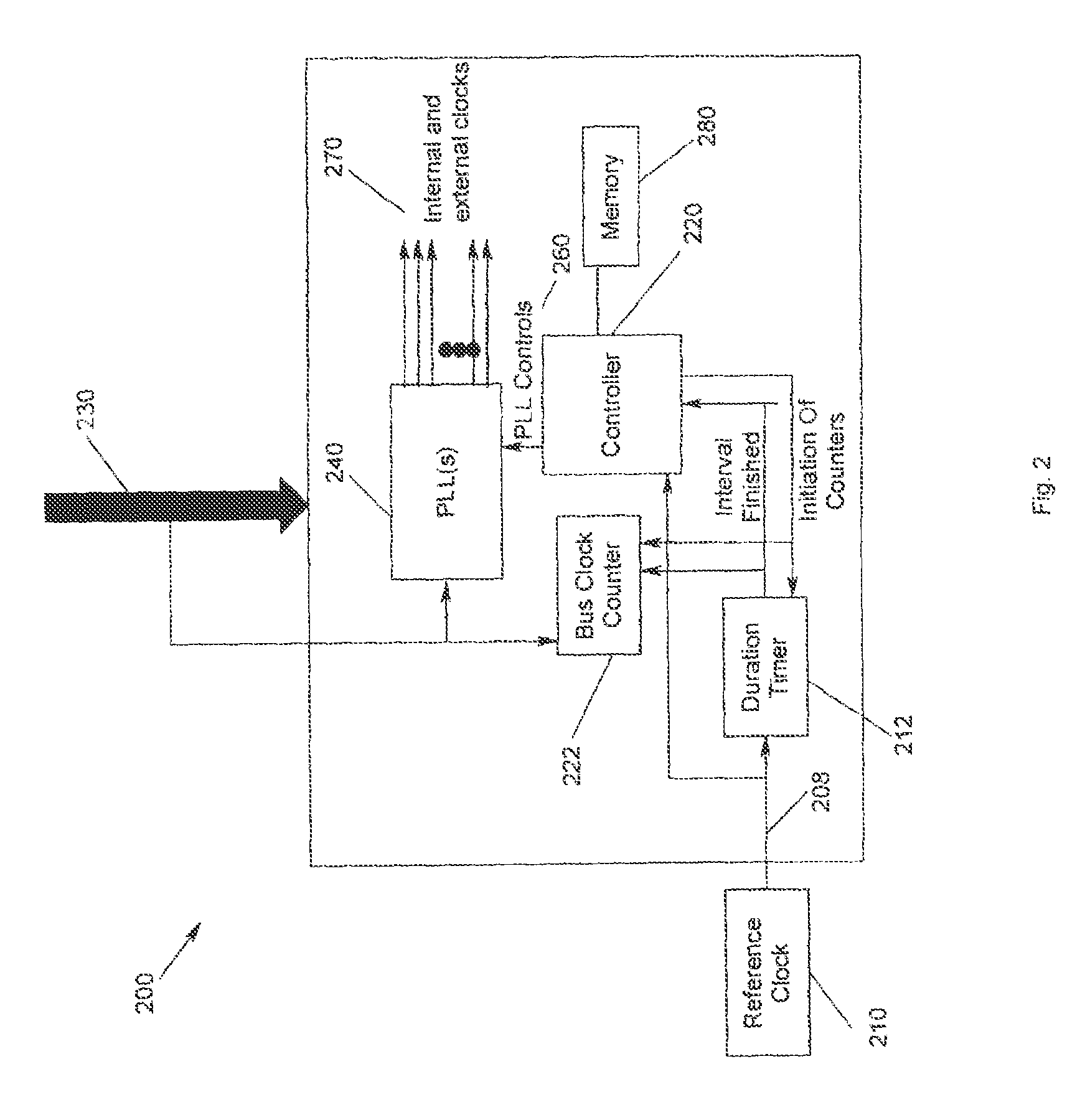
Method, apparatus and program storage device for providing clocks to multiple frequency domains using a single input clock of variable frequency
A method, apparatus, and program storage device for providing clocks to multiple frequency domains using a single input clock of variable frequency. Independent clock signals are generated at predetermined clock frequency targets in response to control signals that are based on a determined bus clock frequency.
Owner:IBM CORP
Synchronization of independent clocks
InactiveUS7453910B1Low runtime overheadLow code space requirementTime-division multiplexGenerating/distributing signalsStart timeHappened-before
A system and method to synchronize independent local clocks in multi-core processing system are disclosed. A shared counter or a shared memory / file is provided to establish a partial happened-before relationship (e1<e2 in the happened-before order if we know that the event e1 happened before the event e2) and a synchronizer device is utilized to generate a global time of events in threads or processes. The synchronizer device estimates each clock's start time and approximates elapsed time between events in threads or processes by executing an all-pair shortest-path algorithm.
Owner:IBM CORP
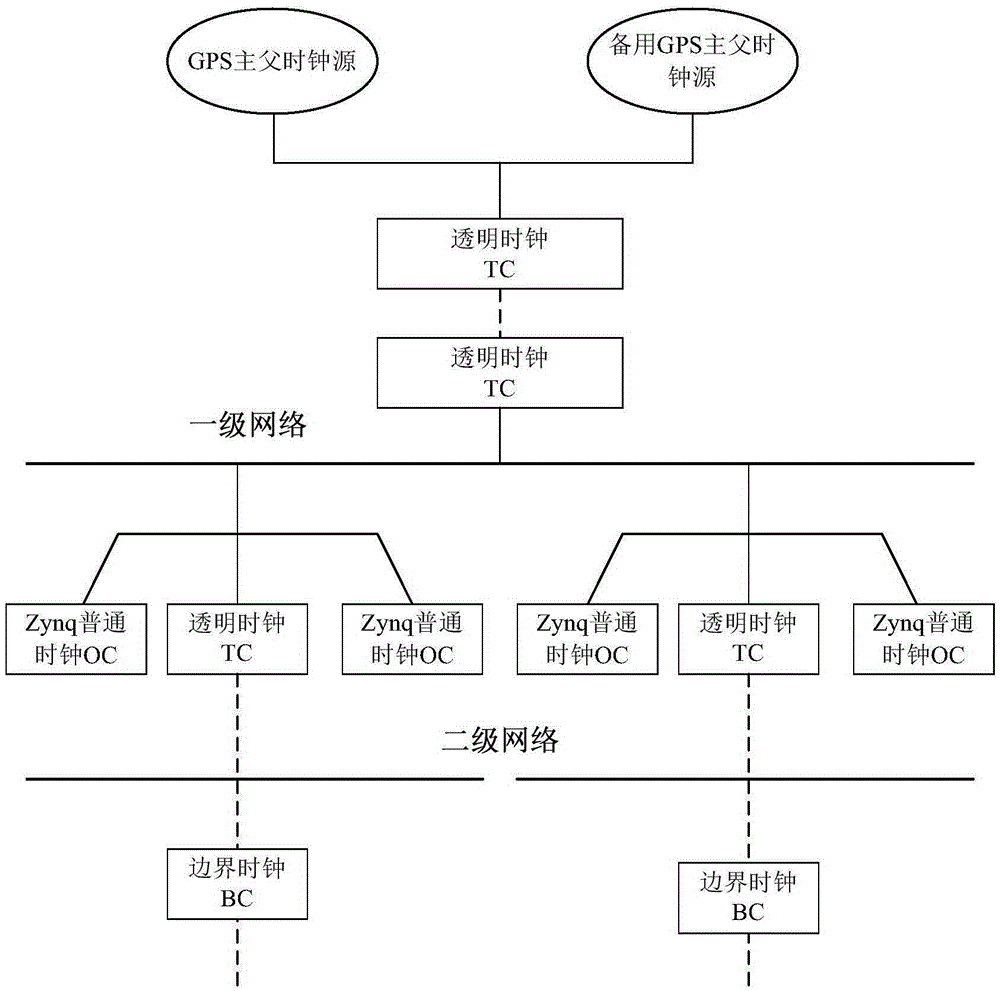
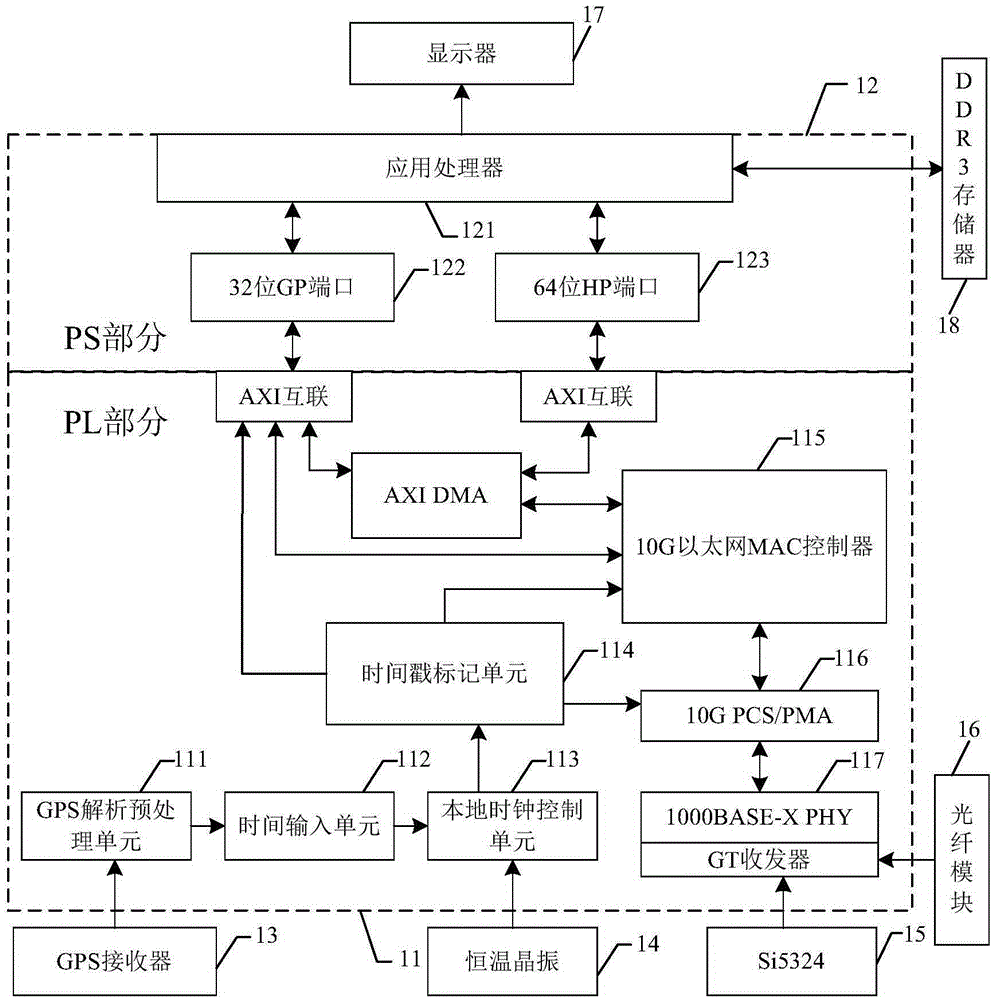
SOPC (System on a Programmable Chip) networking based sub-microsecond level clock synchronizing method and system
ActiveCN105429725ASynchronous high precisionGuaranteed accuracy requirementsTime-division multiplexSlave clockNetwork switch
The invention provides an SOPC (System on a Programmable Chip) networking based sub-microsecond level clock synchronizing method. The clock synchronizing method comprises the steps of synchronizing UTC (Universal Time Coordinated) of a remote reference primary parent clock with UTC from an external GPS (Global Positioning System) clock or a Big Dipper system clock; synchronizing each node of a local first-level PTP (Precision Time Protocol) domain with the remote reference primary parent clock through a network switching device which supports a transparent clock function; receiving an optimal primary clock from a network at the same level by each Zynq platform based slave clock which supports IEEE158V2 protocol and gigabit Ethernet for time synchronization and frequency synchronization; when a PTP domain at the next level synchronizes with the primary parent clock through a border clock, performing clock synchronization by a primary clock at the upper level; and during the period that the PTP domain at the same level masters an independent clock synchronization control right, selecting the optimal primary clock as the primary clock of the network at the same level through an optimal primary clock algorithm. The invention also provides an SOPC networking based sub-microsecond level clock synchronizing system which adopts the clock synchronizing method.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Variably delayable transmission of packets between independently clocked source, intermediate, and destination circuits while maintaining orderly and timely processing in one or both of the intermediate and destination circuits
InactiveUS20070130246A1Large in size and speedIncrease volumeMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork packetClock tree
In a system having independently-clocked job-performing circuits (e.g., payload processors) and independently-clocked job-ordering circuits (e.g., request and payload suppliers), coordinating mechanisms are provided for coordinating exchanges between the independently-clocked circuits. The coordinating mechanisms include those that use transmitted time-stamps for scheduling contention-free performances within the job-performing circuits of requested jobs. The coordinating mechanisms additionally or alternatively include static and dynamic rate constraining means that are configured to prevent a faster-clocked one of the independently-clocked circuits from overwhelming a more slowly-clocked other of the independently-clocked circuits. In one implementation, independently-clocked telecommunication-shelves house a distributed set of line cards and switch cards. An asynchronous interconnect is provided between the independently-clocked shelves for carrying job requests and payload data between the distributed line cards and the distributed switch cards. The multi-shelf system is scalable and robust because additional or replacement line and switch cards may be inserted into one or another of the independently-clocked shelves as desired and because a unified clock-tree is not needed for synchronizing activities within the interconnected, but independently clocked shelves.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS US INC
Method and apparatus for maintaining cached state data for one or more shared devices in a logically partitioned computer system
InactiveUS20070028052A1Reducing overhead burdenReduce frequencyProgram controlMemory systemsGlobal systemIndependent clock
A logically partitions computer system maintains a respective window for each of multiple cached state values which are subject to change. Where an individual change to a cached state value does not cause it to stray outside its window, then the change is made only to the cached state value, without triggering an updating operation. Where the change causes the cached state value to stray outside the window, an updating operation is triggered. Preferably, the system contains a global system clock, which is adjusted by an independent clock state delta value for each partition. A respective window is maintained for each clock delta. A global wake-up time for the system, determined as the earliest wake-up time of any partition, is re-computed when a change to a partition's clock causes its cached clock delta to stray outside the window.
Owner:IBM CORP
Communication system between a first and a second synchronous device that are uncorrelated in time
ActiveUS20090168860A1Guaranteed to workSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlTransmission monitoringCommunications systemEngineering
A communication system includes first and second independently clocked devices, comprising, for each device, a transmitter and a receiver connected to each other in a crossed way in correspondence of an inter-chip communication channel. The communication system further comprises a synchronizer in turn including at least a first and a second synchronization block, having respective input terminals connected to the receivers and respective output terminals connected to the transmitters and comprising at least: a test pattern generator that generates a programmable test pattern signal; a pattern detector to check a matching between stored and received test pattern signals and thus lock corresponding clock phases of the synchronization blocks in case of positive result of this check; and a delay block able to change the clock phases until a synchronized condition of the synchronization blocks is verified, this synchronized condition corresponding to a matching between stored and received test pattern signals.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
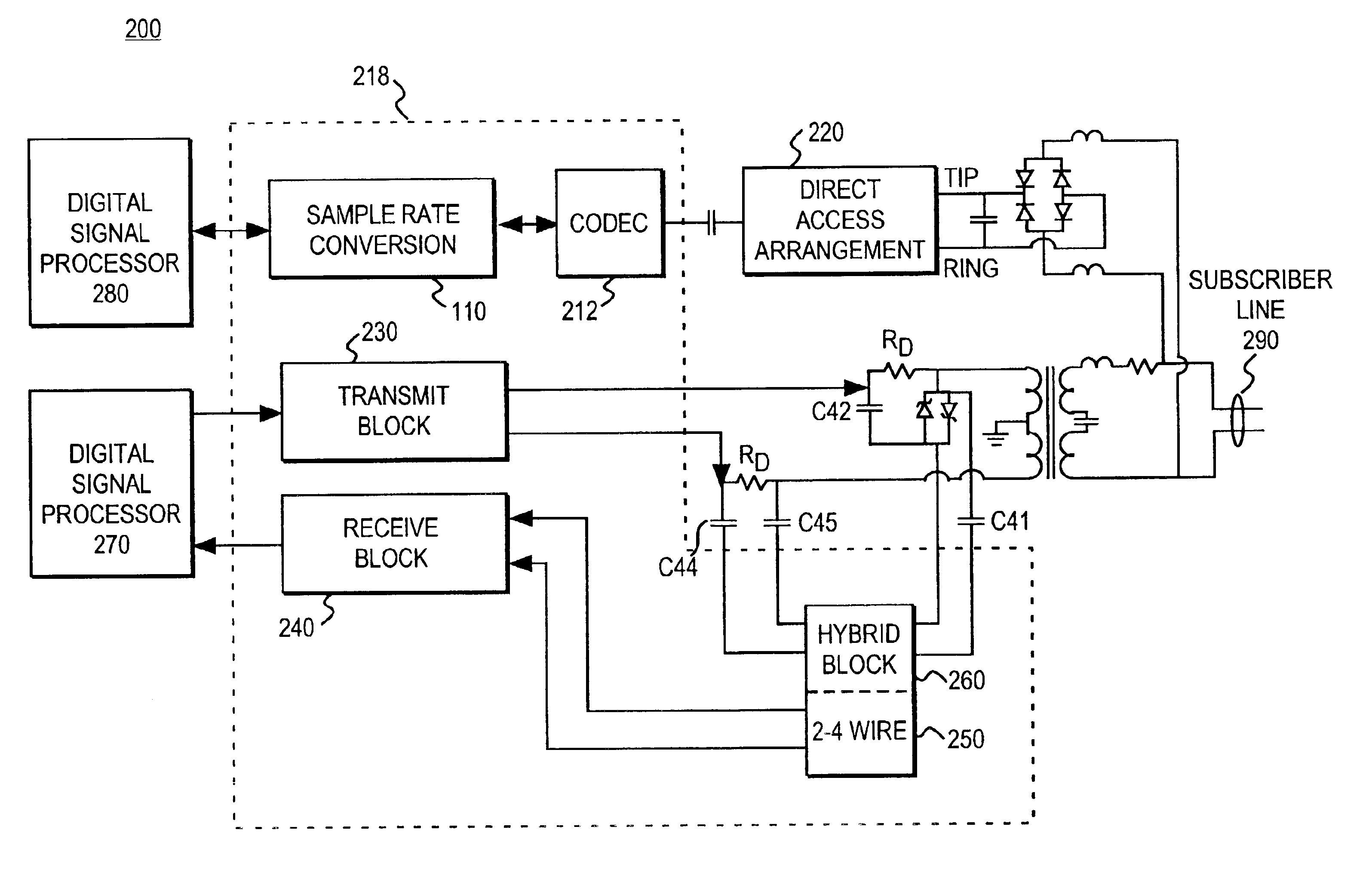
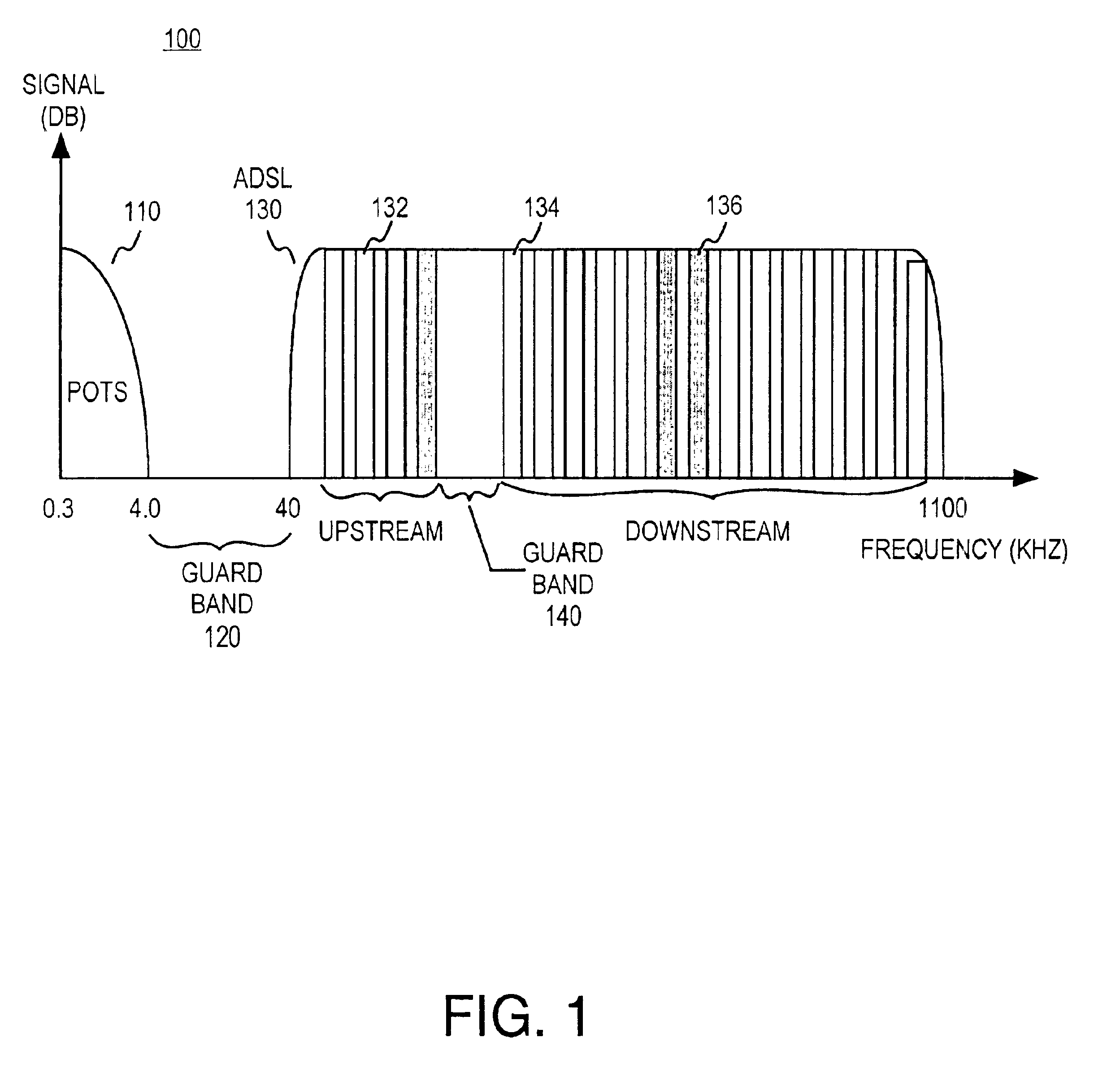
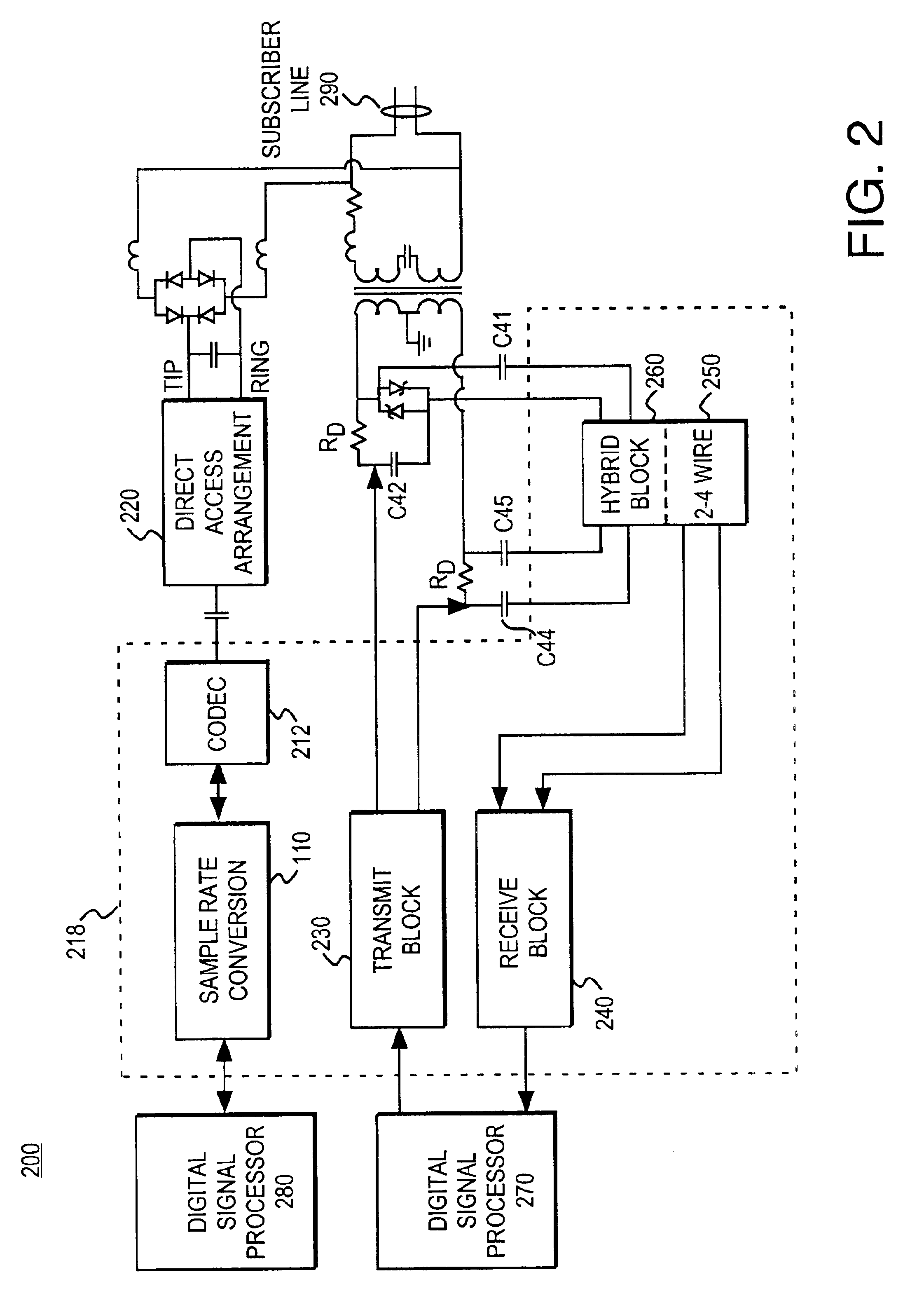
Architecture for a digital subscriber line analog front end
InactiveUS6895040B2Easy to integrateEliminates undesired energyInterconnection arrangementsError preventionDigital subscriber lineSample rate conversion
An analog front end for communicating discrete multitone modulated signals on a subscriber line includes a transmit block, a receive block, and a hybrid packaged within a same integrated circuit. Upstream data to be transmitted to the subscriber line is pre-processed to eliminate even images. A power spectral density shaping filter subsequently substantially eliminates undesired energy in the upstream data signal. A high pass filter further rejects upstream data from the downstream data signal. The power spectral density filter and the high pass filter enable the use of a first order hybrid network for extracting the downstream data. The analog front end may include an additional analog channel to enable voiceband (e.g., v.90) communication concurrent with non-voiceband (e.g., xDSL) operation. Sample rate conversion is utilized to avoid the use of multiple independent clocks for otherwise incompatible clocking requirements.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
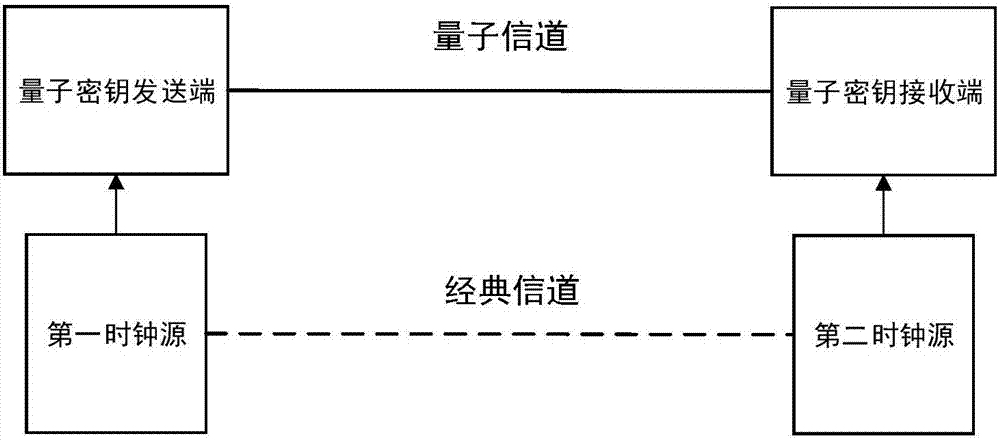
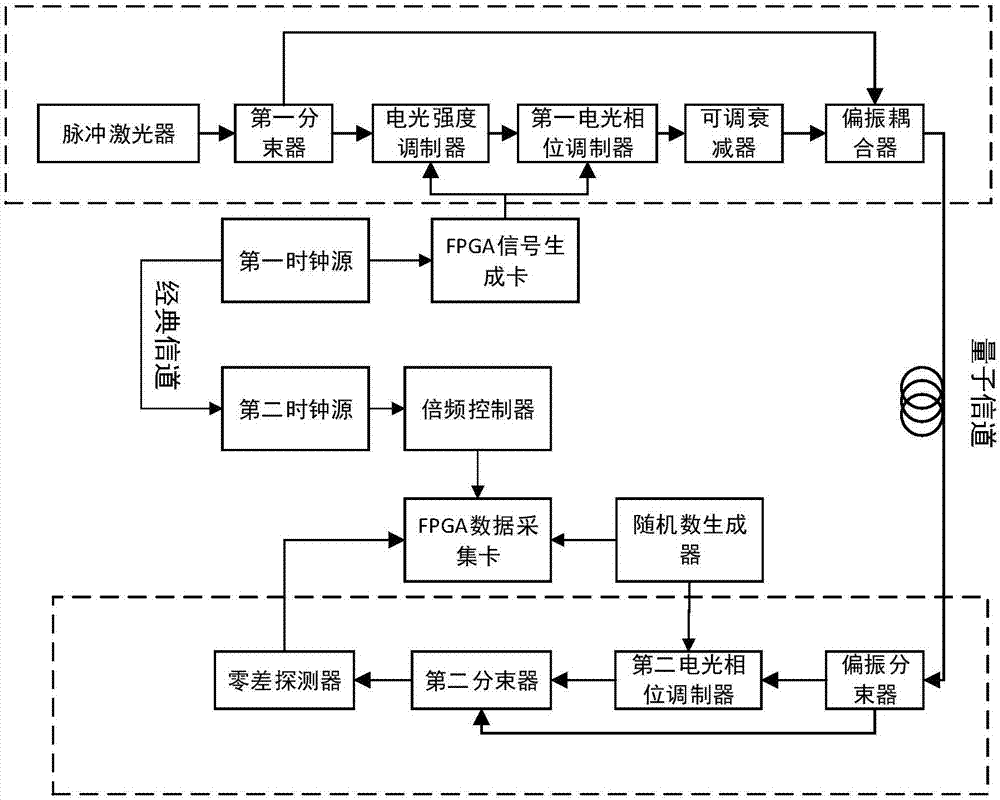
Continuous variable quantum key distribution system based on independent clock sources and implementation method
InactiveCN107453820ASynchronous Data AcquisitionAccurate data collectionKey distribution for secure communicationTime-division multiplexContinuous variableClock synchronization
The invention discloses a continuous variable quantum key distribution system based on independent clock sources and an implementation method. A first clock source provides a reference clock signal to a quantum key sending end, and a second clock source provides a reference clock signal to a quantum key receiving end; before the sending end and the receiving end begin to establish a key, the first clock source and the second clock source perform clock synchronization through a classical channel, and after synchronization, two clocks run independently and do not influence each other. The continuous variable quantum key distribution system based on independent clock sources solves the security vulnerabilities that a synchronous cock signal is easy to steal during transmission in a communication process, and further improves actual security of the continuous variable quantum key distribution system.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method and apparatus for providing synchrony group status information
ActiveUS9207905B2Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsIndependent clockReal-time computing
Owner:SONOS
Multi-power source semiconductor device
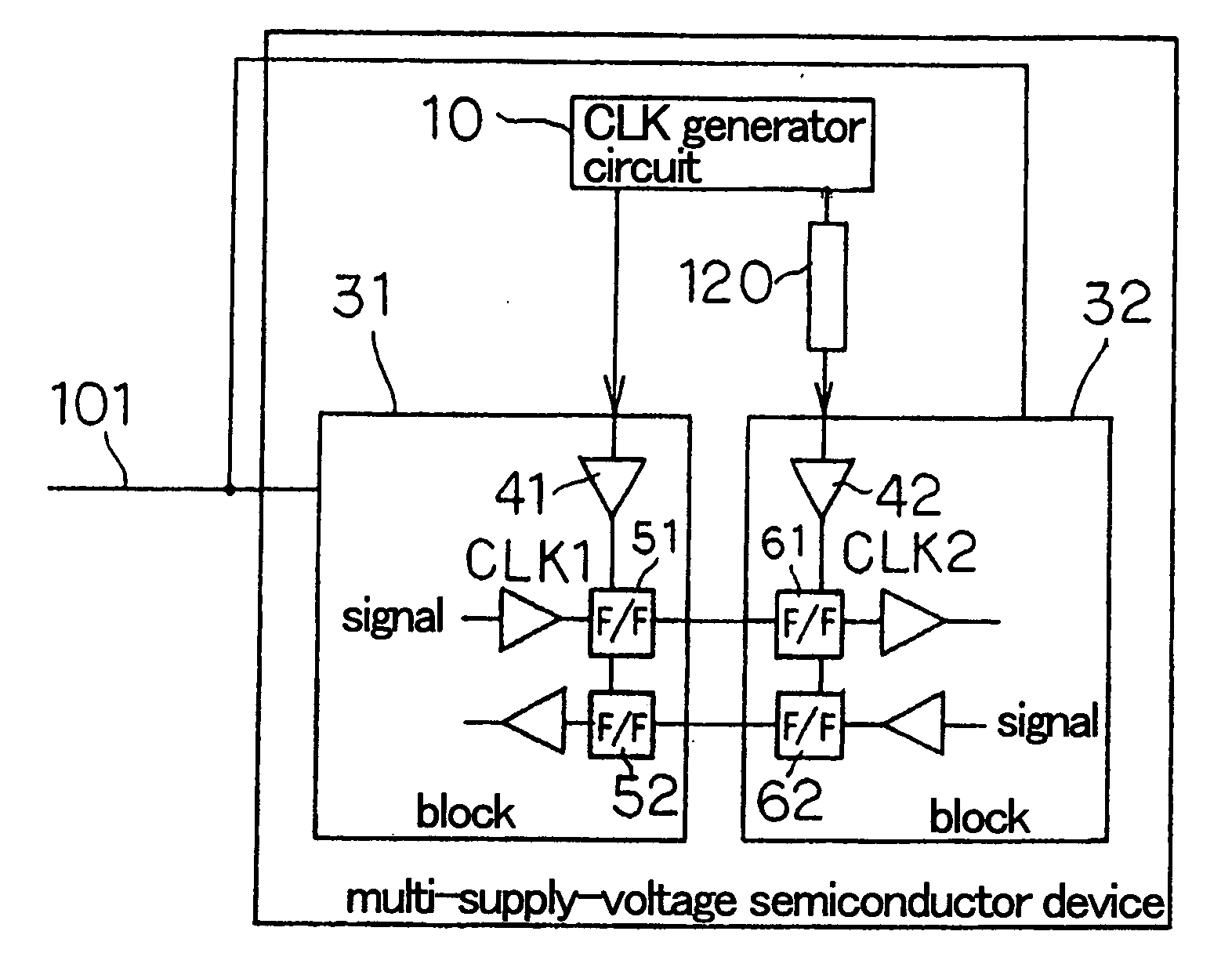
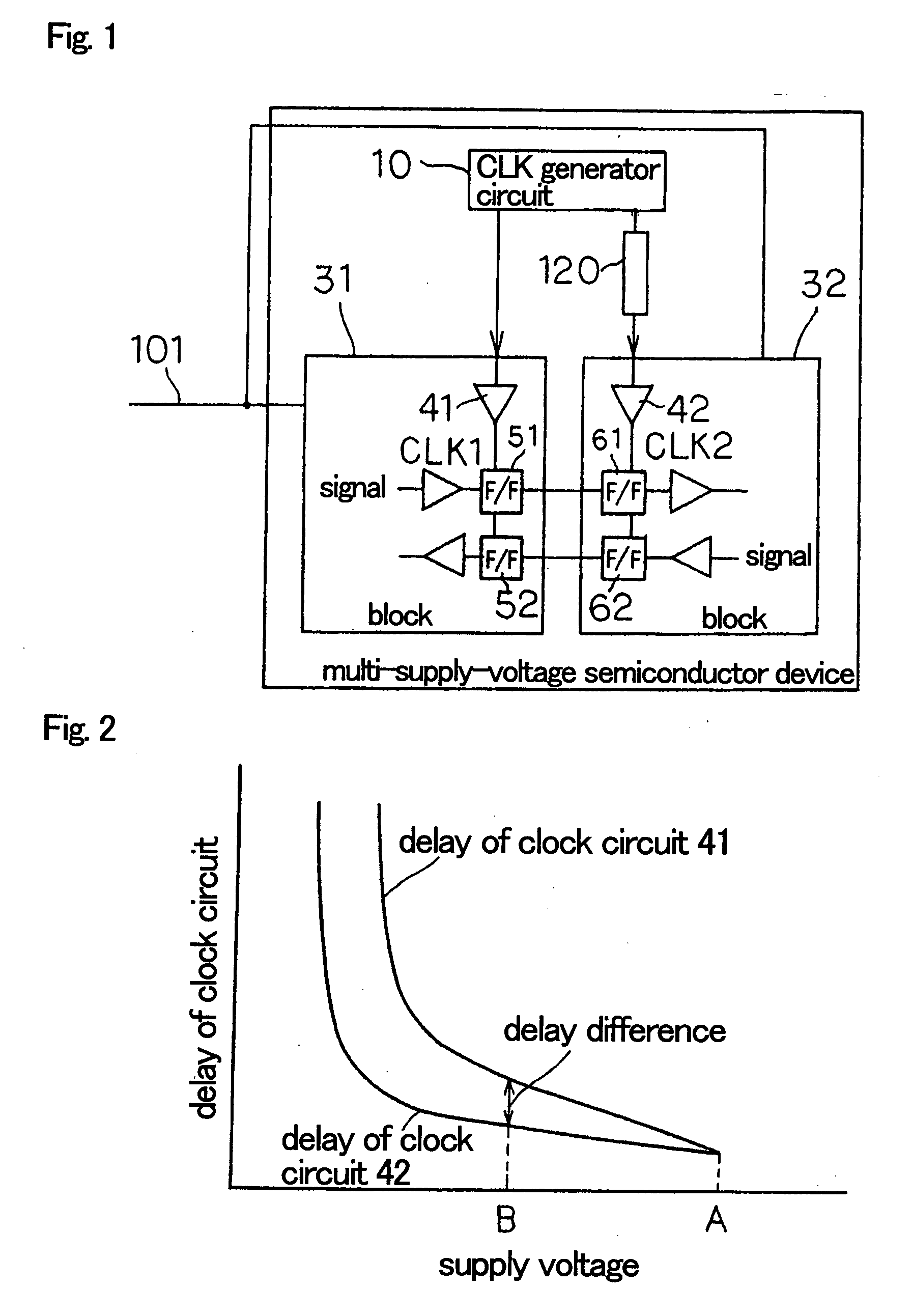
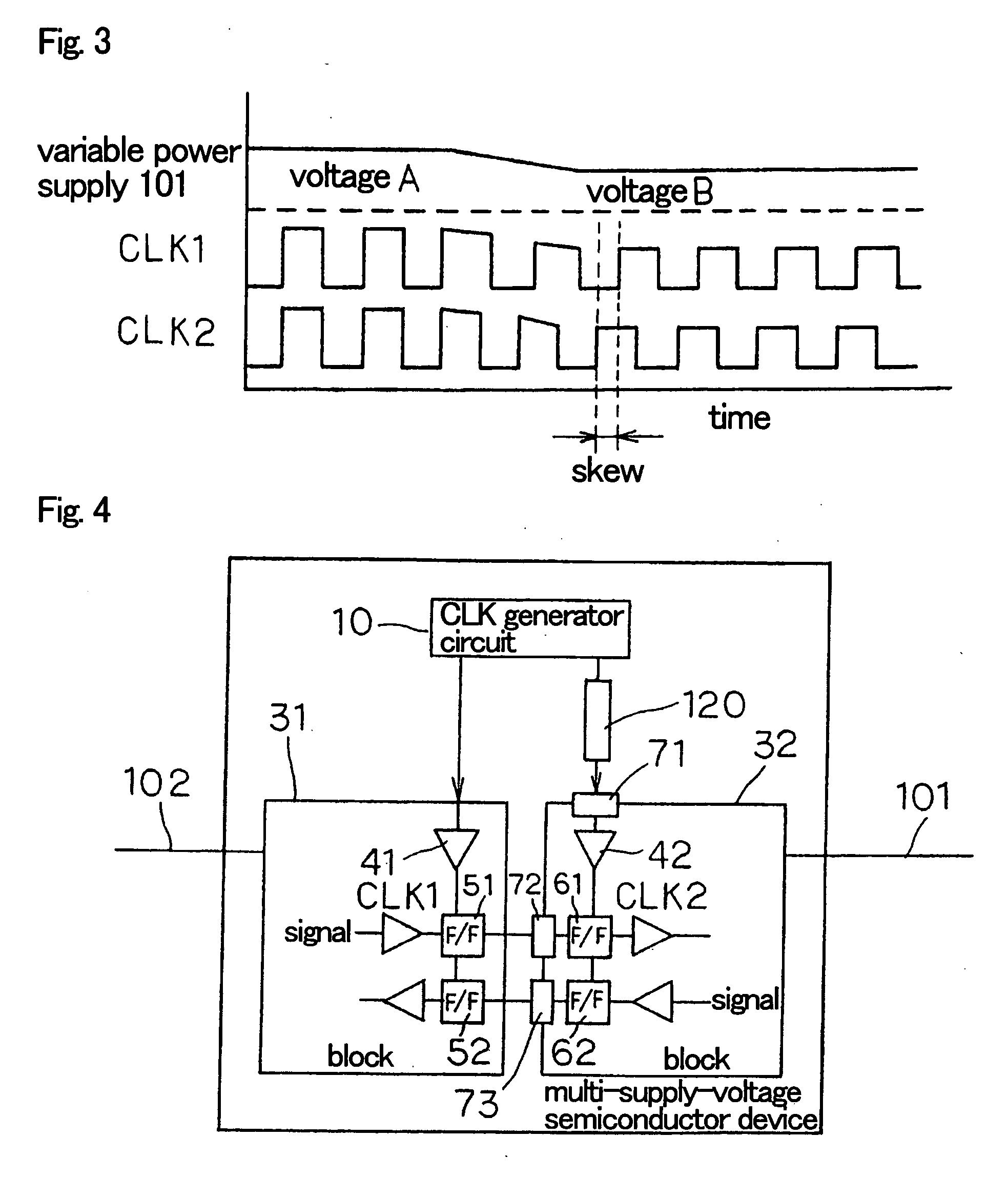
ActiveUS20060232316A1Reducing clock skewEnergy efficient ICTLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsDevice materialEngineering
In a multi-supply-voltage semiconductor device including multiple blocks 31, 32, each of which has independent clock circuit 41, 42, and operating with variable power supply 101, variable delay circuit 20 which changes the amount of delay in accordance with the voltage value of the variable power supply 101 is provided to a clock signal supplied to several blocks 32 from clock generator circuit 10. This can reduce clock skew between the blocks even when the power supply voltage of variable power supply 101 is changed.
Owner:NEC CORP
System and Method for Synchronizing Operations Among a Plurality of Independently Clocked Digital Data Processing Devices
ActiveUS20140181270A1Maintenance operationMultiple digital computer combinationsAudio data retrievalElectronic data processingIndependent clock
A system is described for maintaining synchrony of operations among a plurality of devices that have independent clocking arrangements. The system includes a task distribution device that distributes tasks to a synchrony group comprising a plurality of devices that are to perform the tasks distributed by the task distribution device in synchrony. The task distribution device distributes each task to the members of the synchrony group over a network. Each task is associated with a time stamp that indicates a time, relative to a clock maintained by the task distribution device, at which the members of the synchrony group are to execute the task. Each member of the synchrony group periodically obtains from the task distribution device an indication of the current time indicated by its clock, determines a time differential between the task distribution device's clock and its respective clock and determines therefrom a time at which, according to its respective clock, the time stamp indicates that it is to execute the task.
Owner:SONOS
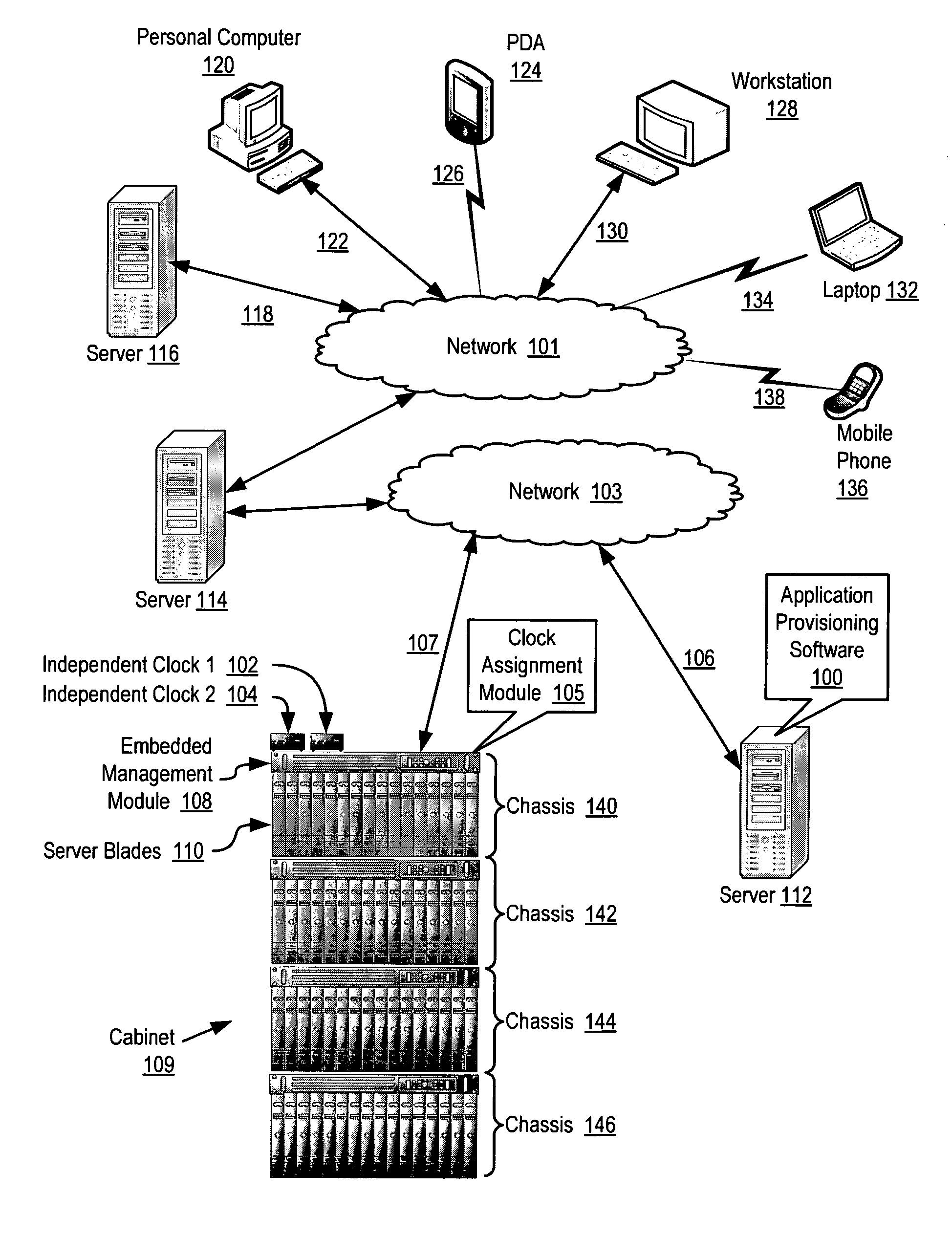
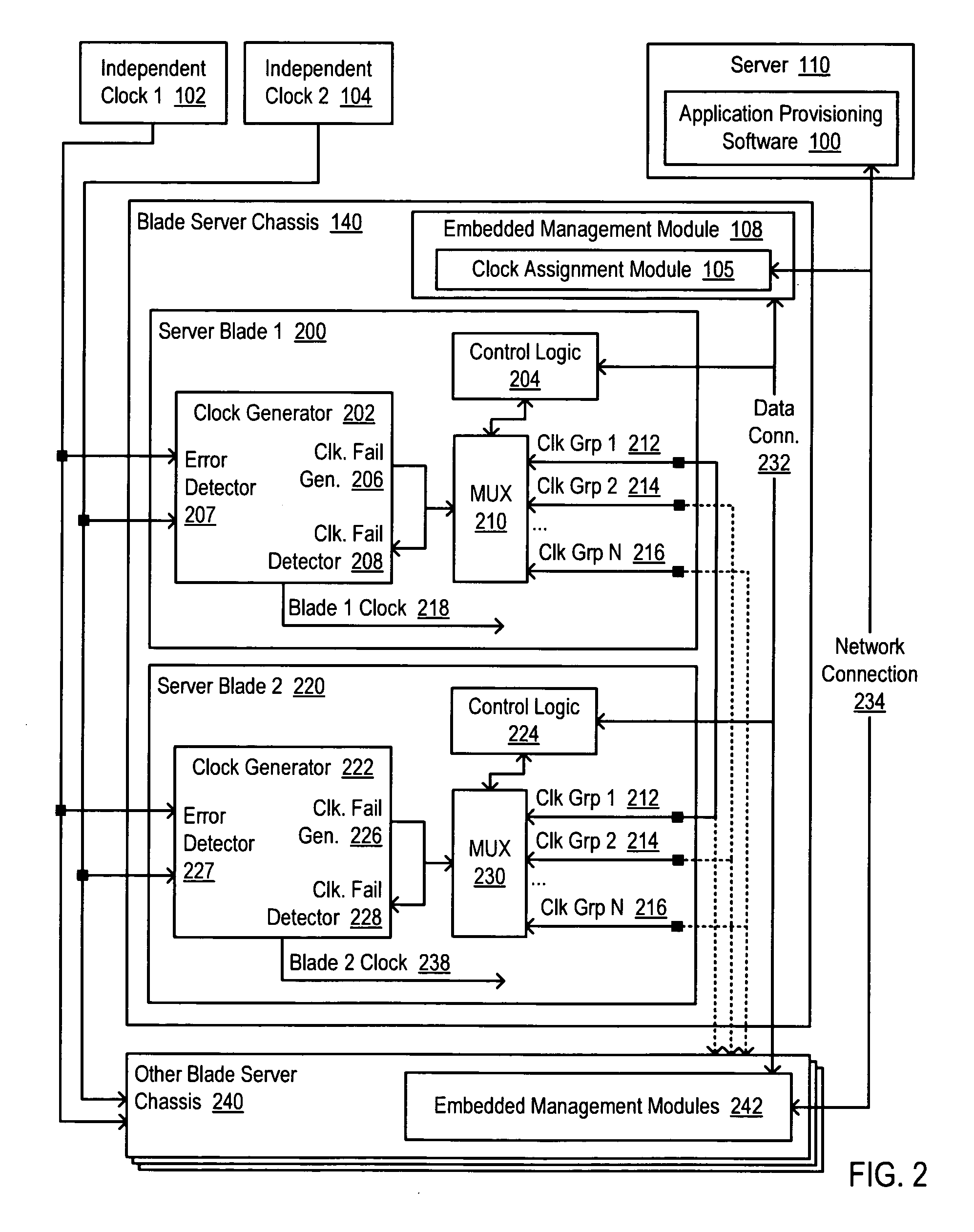
Providing independent clock failover for scalable blade servers
Methods and systems are disclosed for providing independent clock failover for scalable blade servers that include assigning a server blade to one of a plurality of clock failover groups, providing a plurality of independent clock signals to the clock generator of the server blade, wherein one of the plurality of independent clock signals is an active clock signal, detecting a failover condition for the clock failover group assigned to the server blade, and switching the active clock signal, in response to the detected failover condition, from one independent clock signal to another independent clock signal.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com