Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
618 results about "Slave clock" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
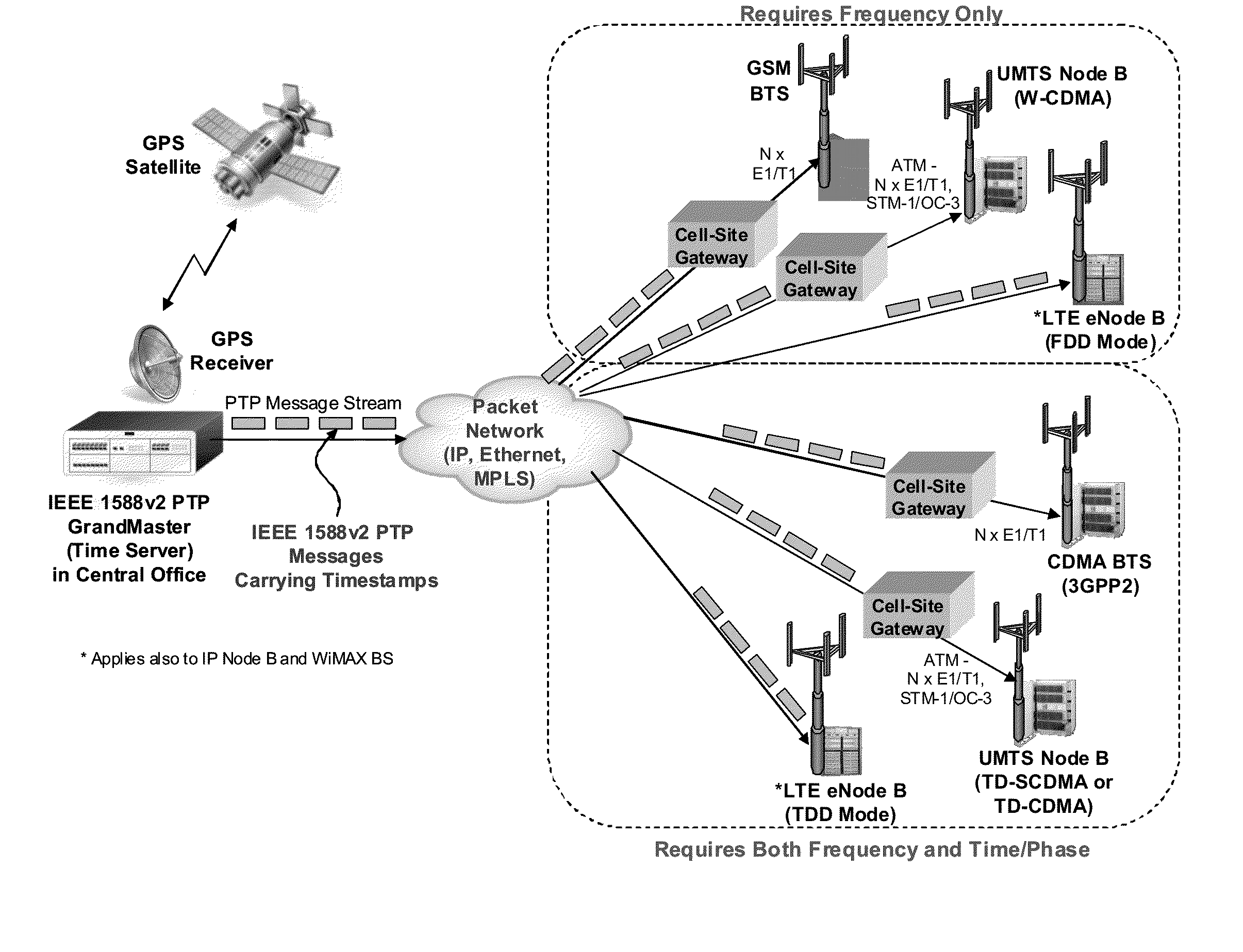
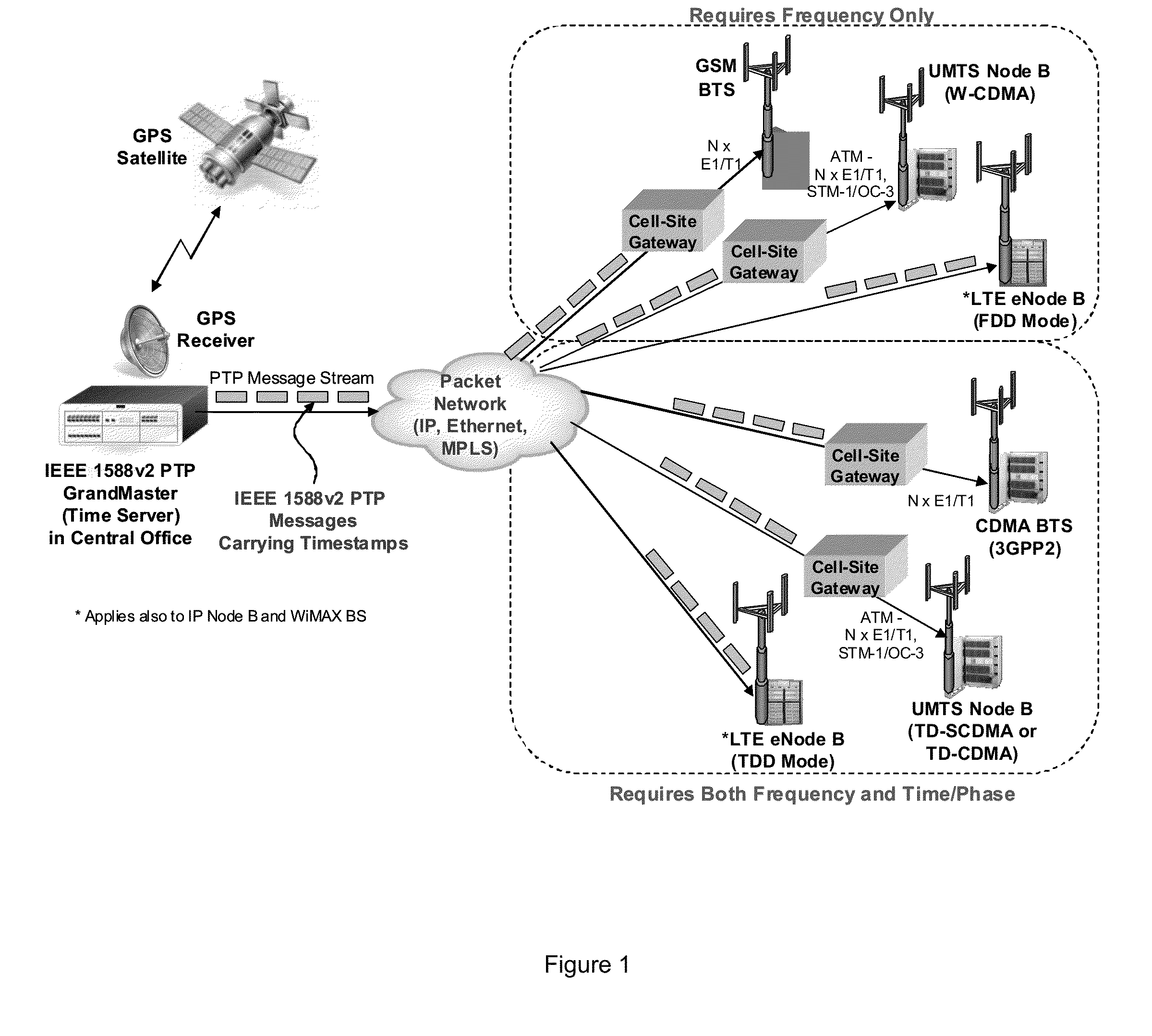
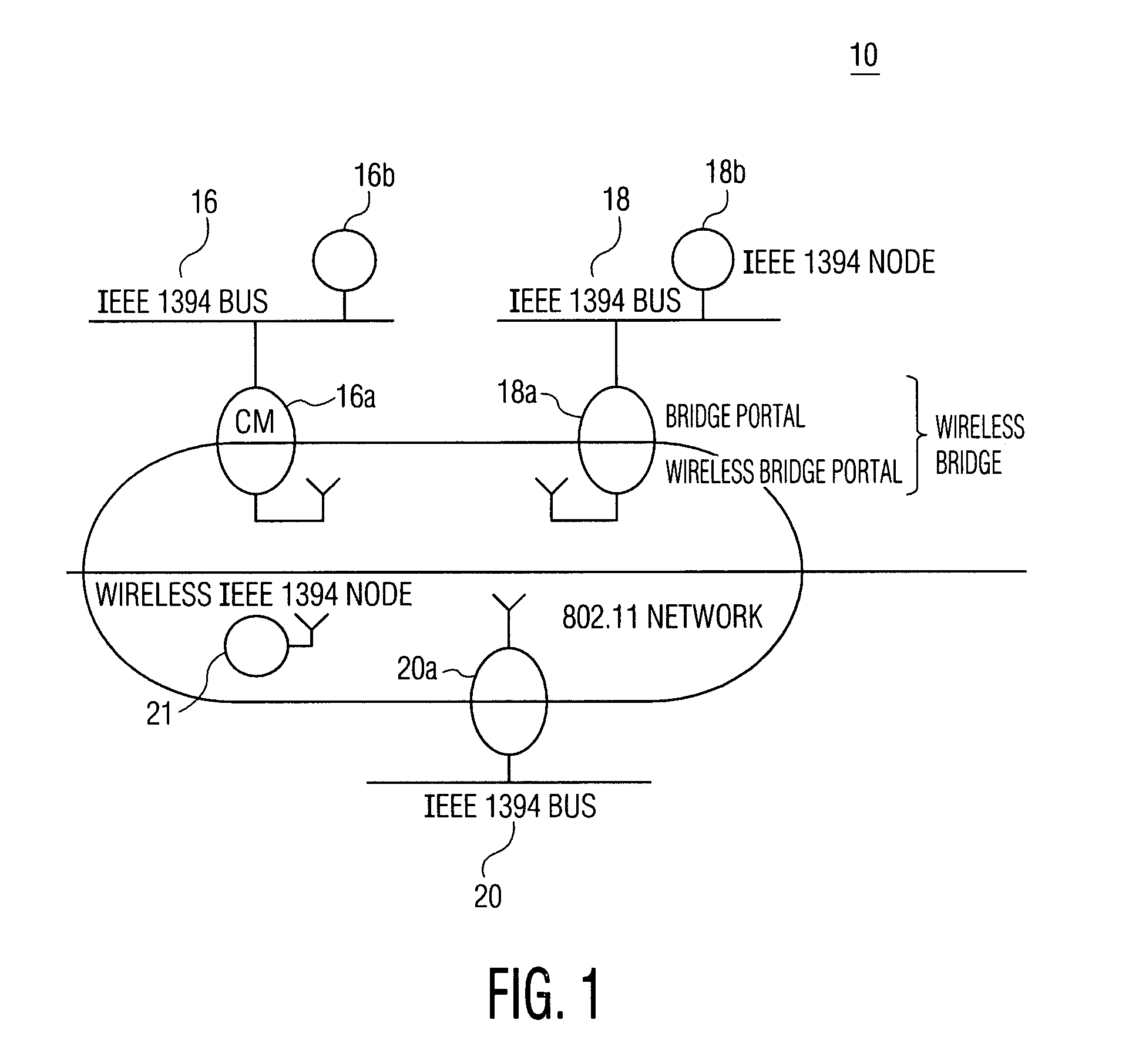
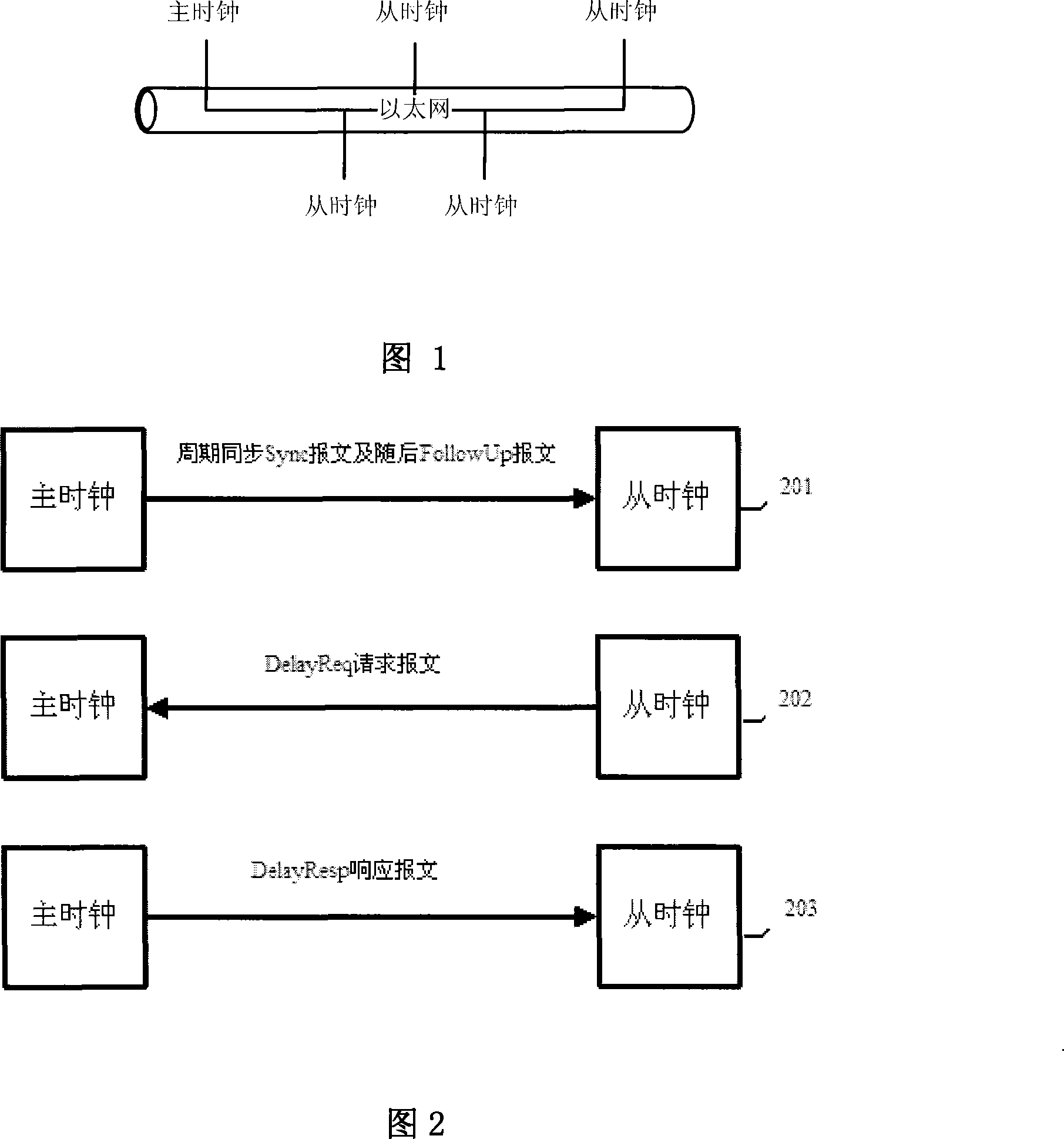
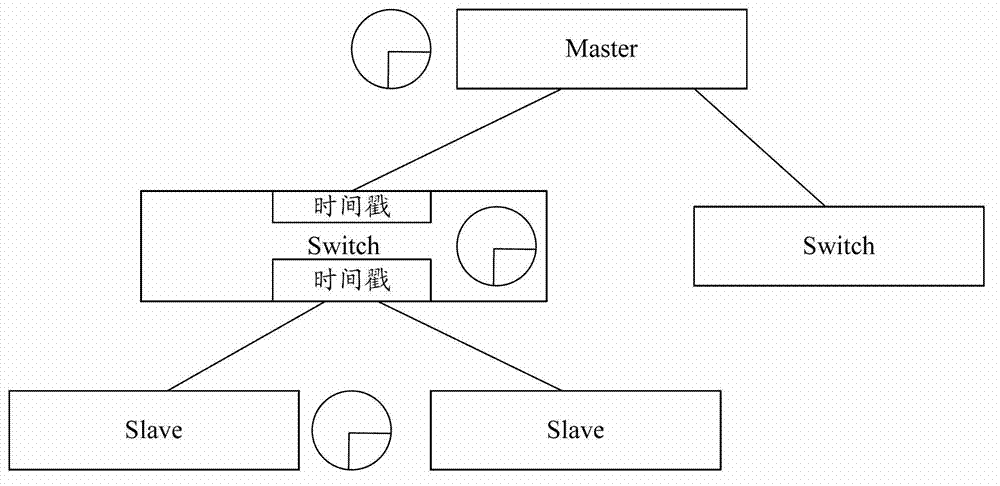
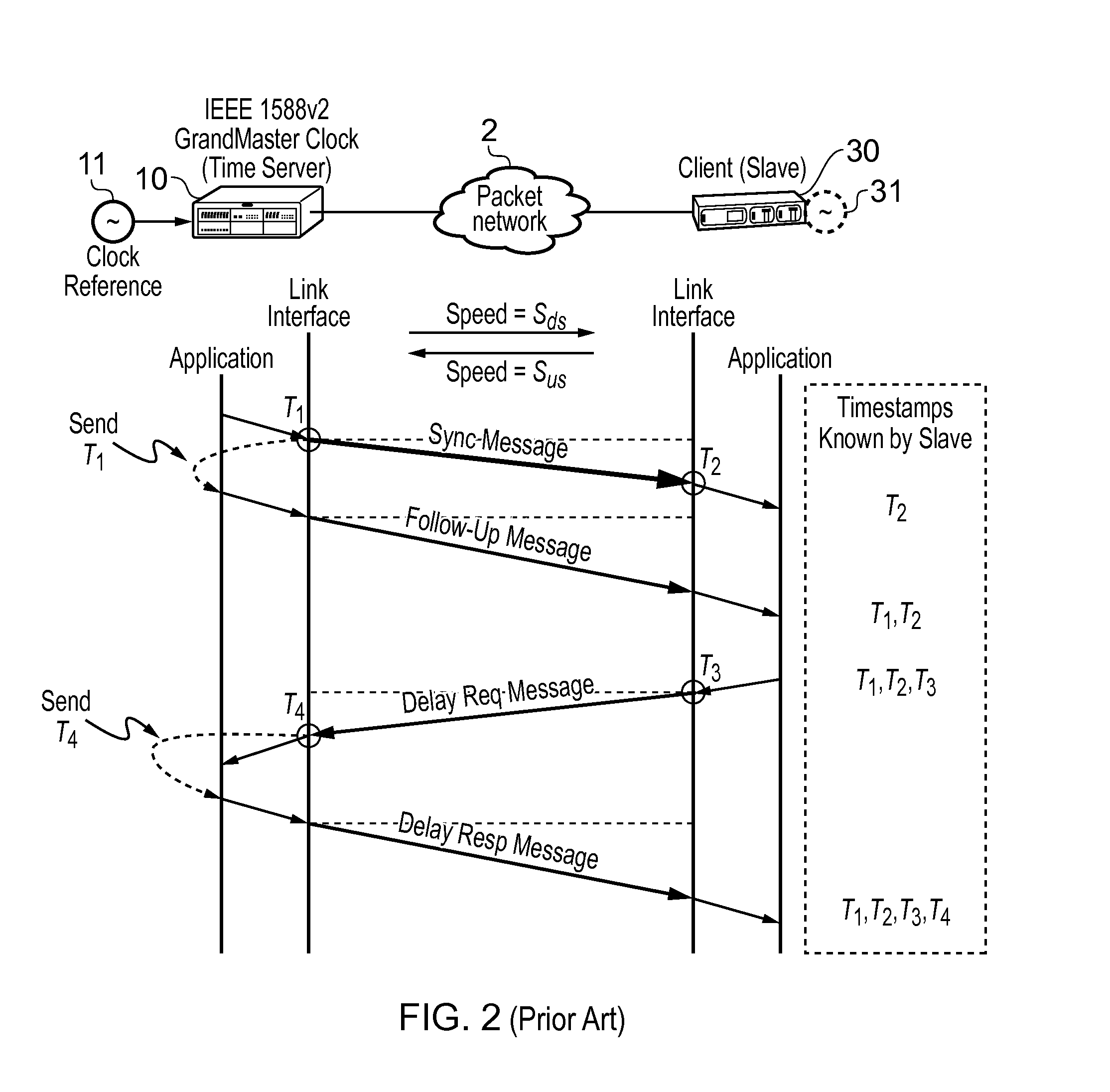
In telecommunication and horology, a slave clock is a clock that depends for its accuracy on another clock, a master clock. Many modern clocks are synchronized, either through the Internet or by radio time signals, to a worldwide time standard called Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) based on a network of master atomic clocks in many countries. For scientific purposes, precision clocks can be synchronized to within a few nanoseconds by dedicated satellite channels. Slave clock synchronization is usually achieved by phase-locking the slave clock signal to a signal received from the master clock. To adjust for the transit time of the signal from the master clock to the slave clock, the phase of the slave clock may be adjusted with respect to the signal from the master clock so that both clocks are in phase. Thus, the time markers of both clocks, at the output of the clocks, occur simultaneously.
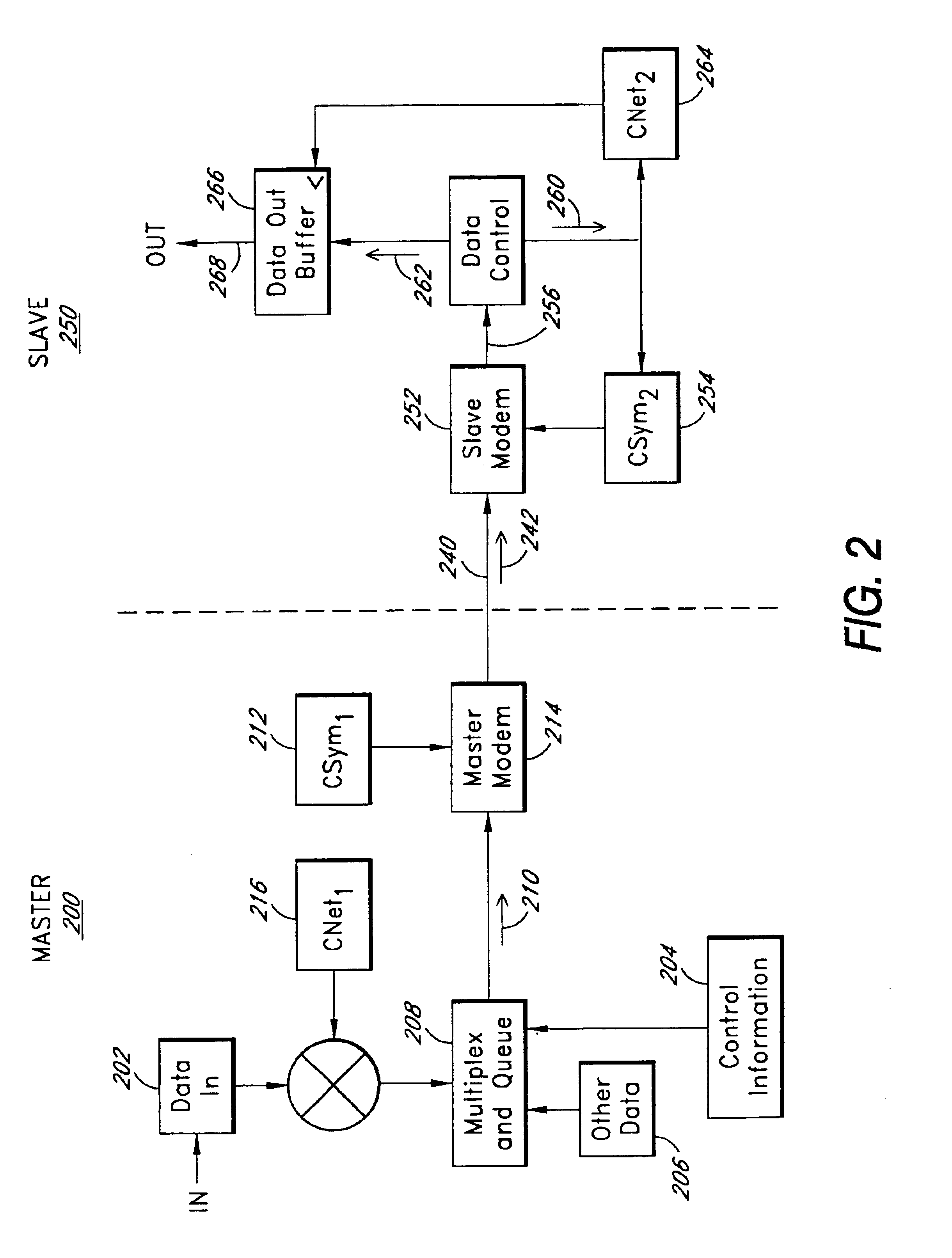
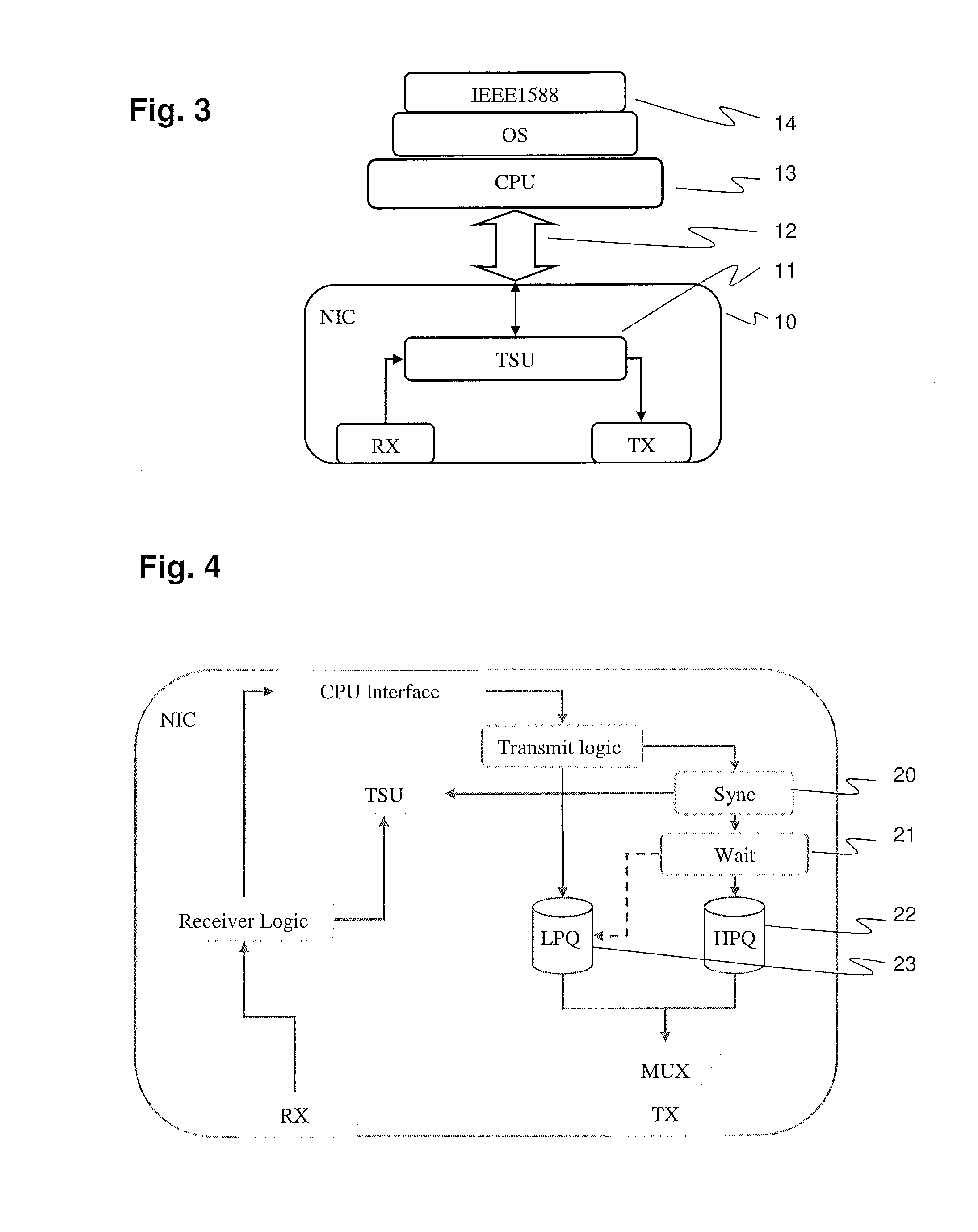
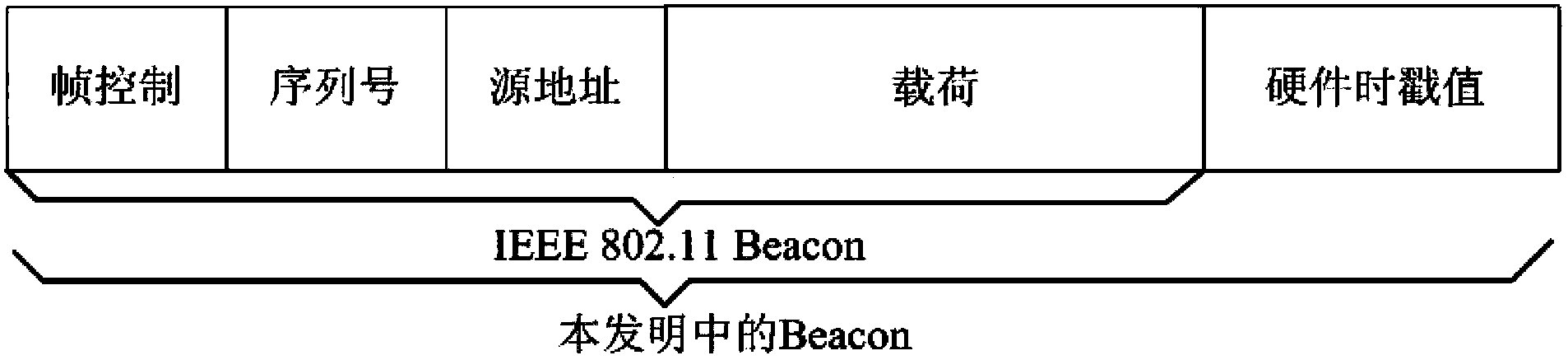
Method of controlling data sampling clocking of asynchronous network nodes in a frame-based communications network
InactiveUS6975655B2Energy efficient ICTError prevention/detection by using return channelTimestampFrame based
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for synchronizing measurements taken by multiple metrology devices
ActiveUS8630314B2Accuracy issueEasy to integrateTime-division multiplexUsing optical meansComputer hardwareMetrology
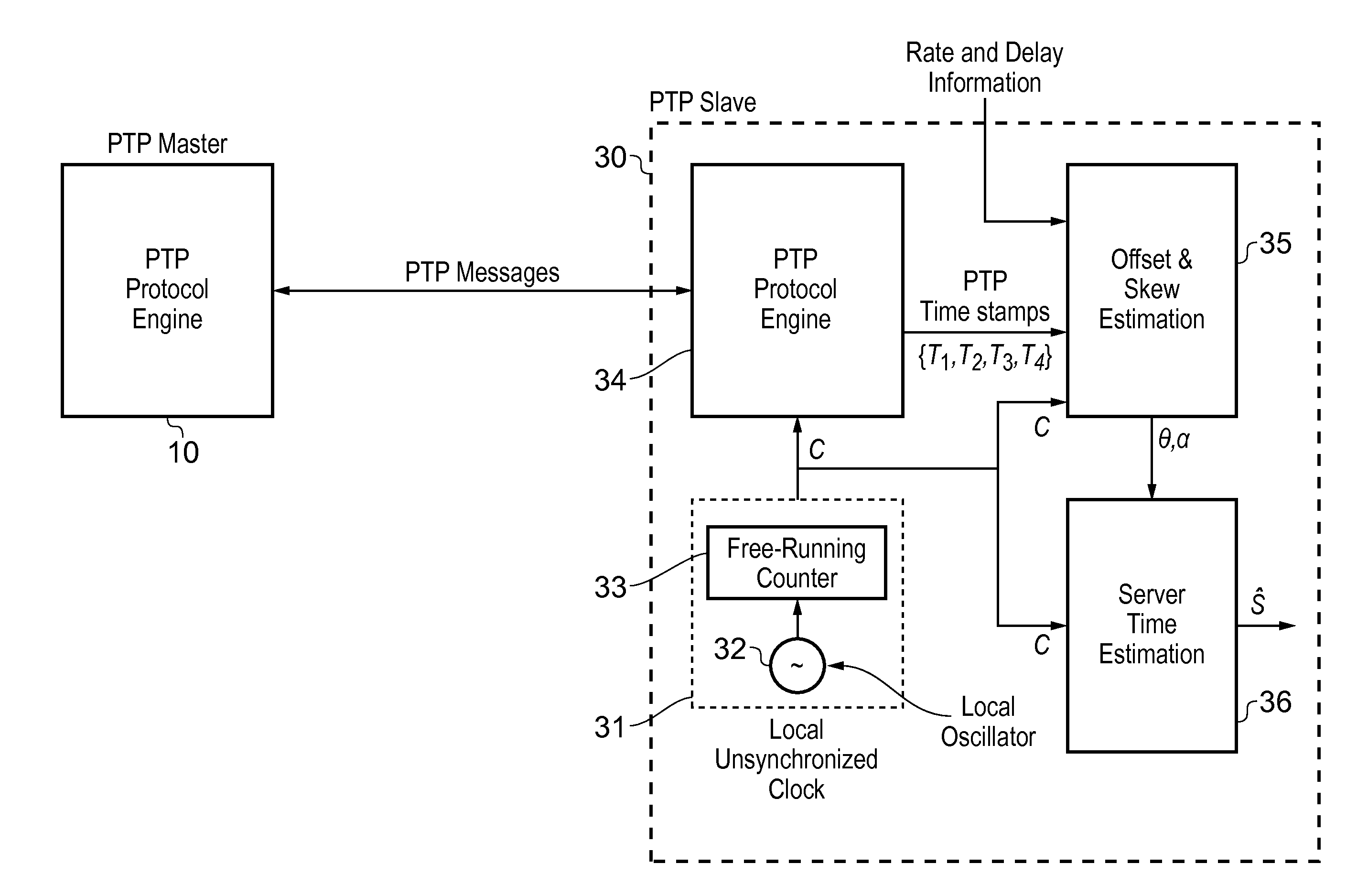
Apparatus includes at least two devices that communicate with each other, wherein a first one of the at least two devices having an IEEE 1588 precision time protocol interface, the interface including one or more components configured for communications in both a wired manner and a wireless manner with a second one of the at least two devices. The second one of the at least two devices having an IEEE 1588 precision time protocol interface, the interface including one or more components configured for communications in both a wired manner and a wireless manner with the first one of the at least two devices. Wherein one of the at least two devices includes a master clock and the other one of the at least two devices includes a slave clock, wherein the master clock communicates a time to the slave clock and the slave clock is responsive to the communicated time from the master clock to adjust a time of the slave clock if necessary to substantially correspond to the time of the master clock, thereby time synchronizing the at least two devices together.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
Method and system for frequency synchronization
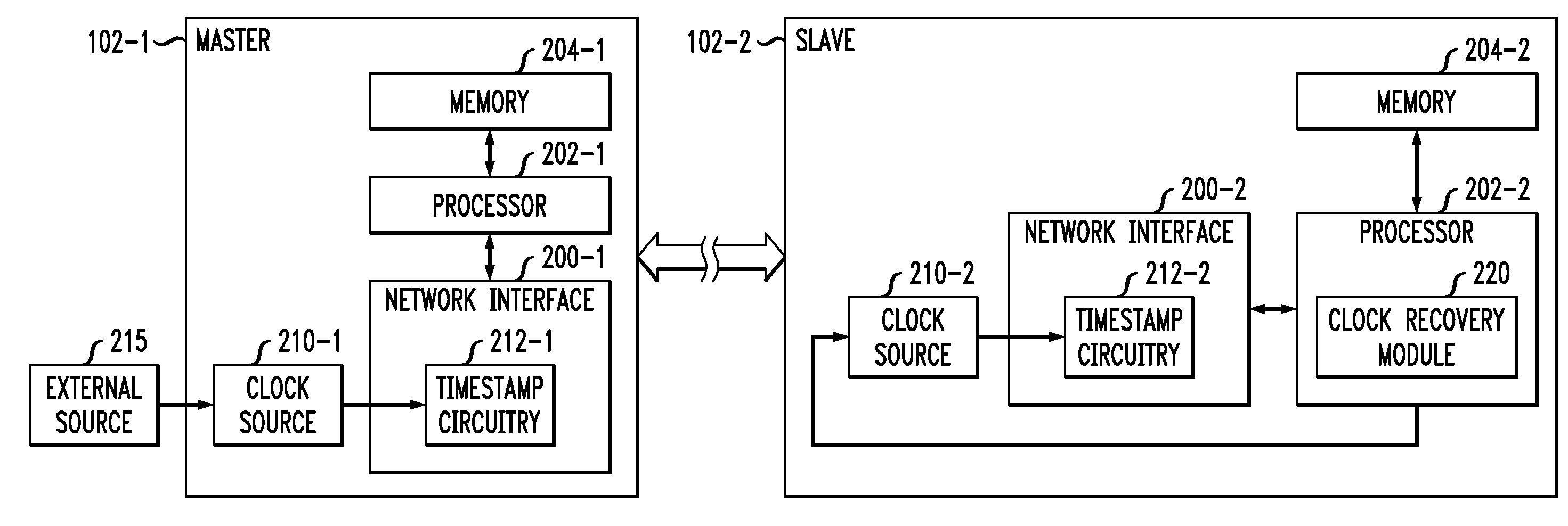
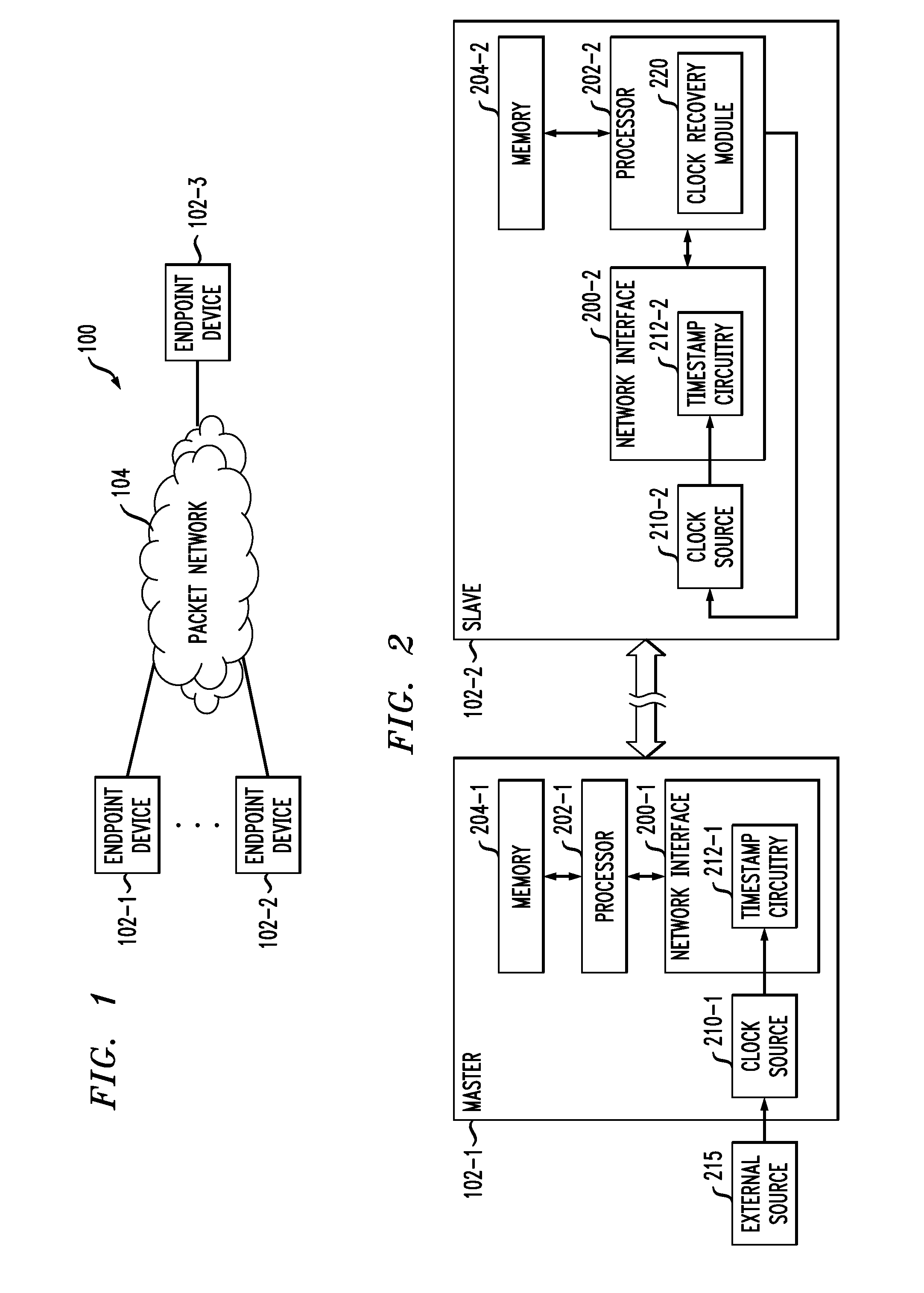
The present invention provides a method of synchronising the frequency of a slave clock to that of a master, preferably using a packet network. An aspects of the invention provide a method of synchronizing the frequency of a slave clock in a slave device to a master clock in a master device, the method including the steps of: a) receiving in the slave device a first message from said master device having a first time-stamp which is a time-stamp of said master clock indicating the time of sending of said first message; b) extracting said time-stamp from said message and initializing a counter in the slave device which counts an output of said slave clock; c) receiving in the slave device a further message from said master device and reading the value of said counter at the time of receipt of said further message; d) extracting a further time-stamp which is the precise time of sending of the further message according to said master clock; e) determining an error signal which is representative of the difference between said value of the counter and the difference between said first and further time-stamps; and f) adjusting the frequency of said slave clock based on said error signal. An apparatus for synchronizing the frequency of a clock in a slave device which is communicatively coupled to a master device is also provided.
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
Method, Apparatus and System for Frequency Synchronization Between Devices Communicating over a Packet Network
InactiveUS20100158051A1Simple technologyImprove performancePulse automatic controlTime-division multiplexLoop filterTimestamp
An endpoint or other communication device of a communication system includes a clock recovery module. The communication device is operative as a slave device relative to another communication device that is operative as a master device. The clock recovery module comprises a clock recovery loop configured to control a slave clock frequency of the slave device so as to synchronize the slave clock frequency with a master clock frequency of the master device. The clock recovery loop utilizes a frequency error estimator implemented as a maximum-likelihood estimator with slope fitting based on a sequence of arrival timestamps, and a loop filter implemented as a series combination of an adaptive-bandwidth filter and a proportional-integral controller. The clock recovery module may further comprise a discontinuity detector configured to detect a discontinuity in delays of respective timing messages, and a loop controller operative to place the clock recovery loop in a particular state responsive to detection of the discontinuity.
Owner:PIECE FUTURE PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for synchronizing clock timing between network elements
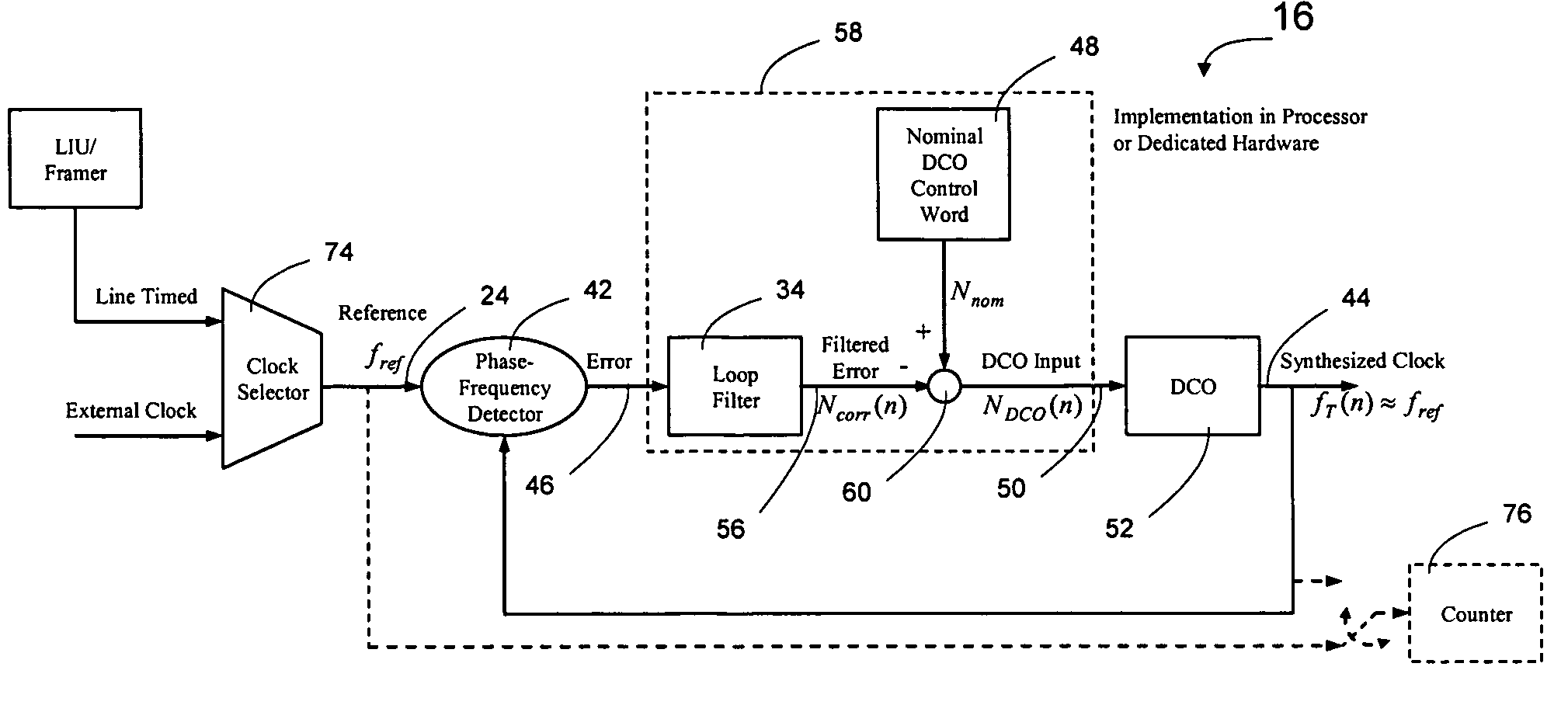
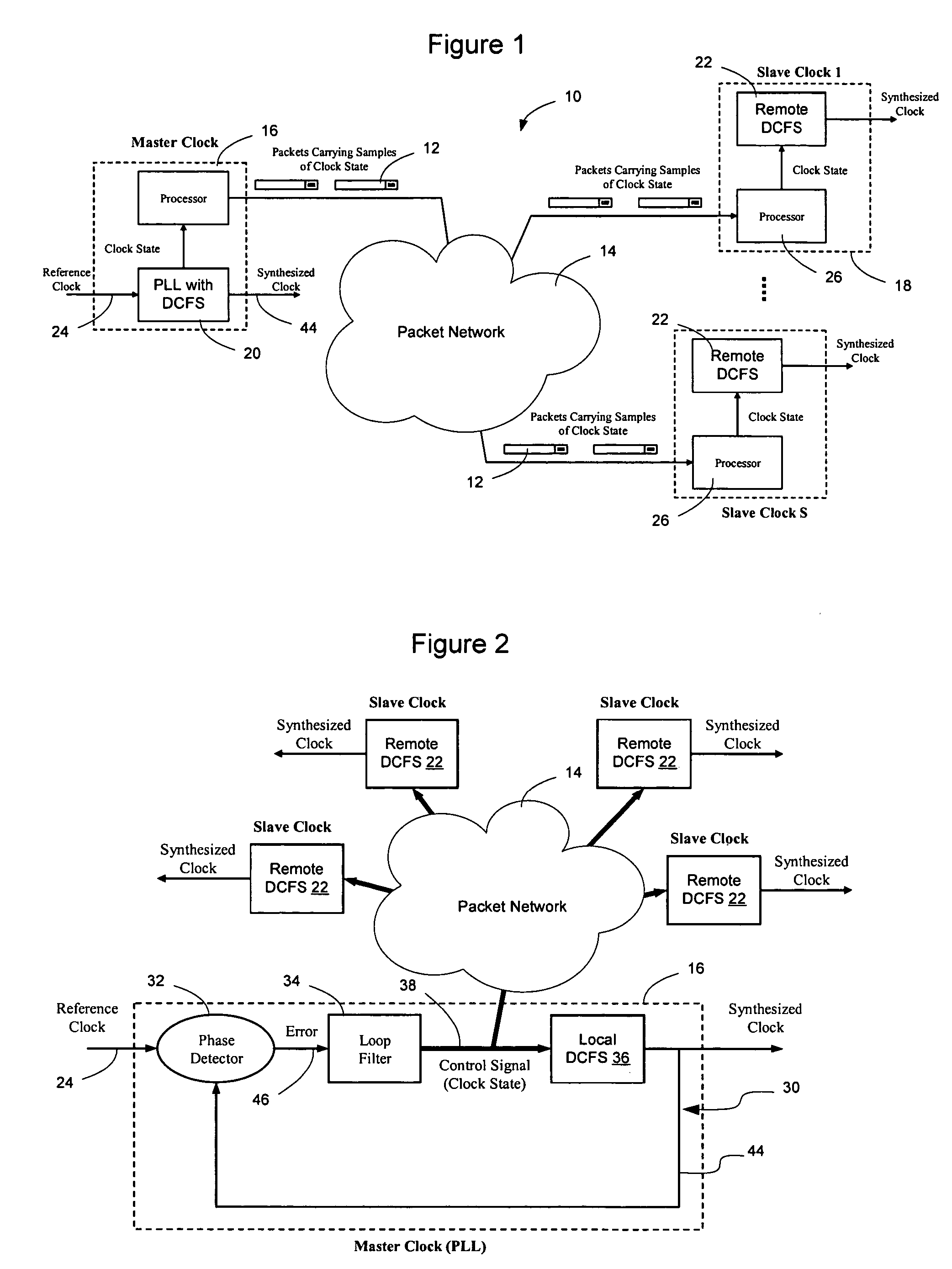
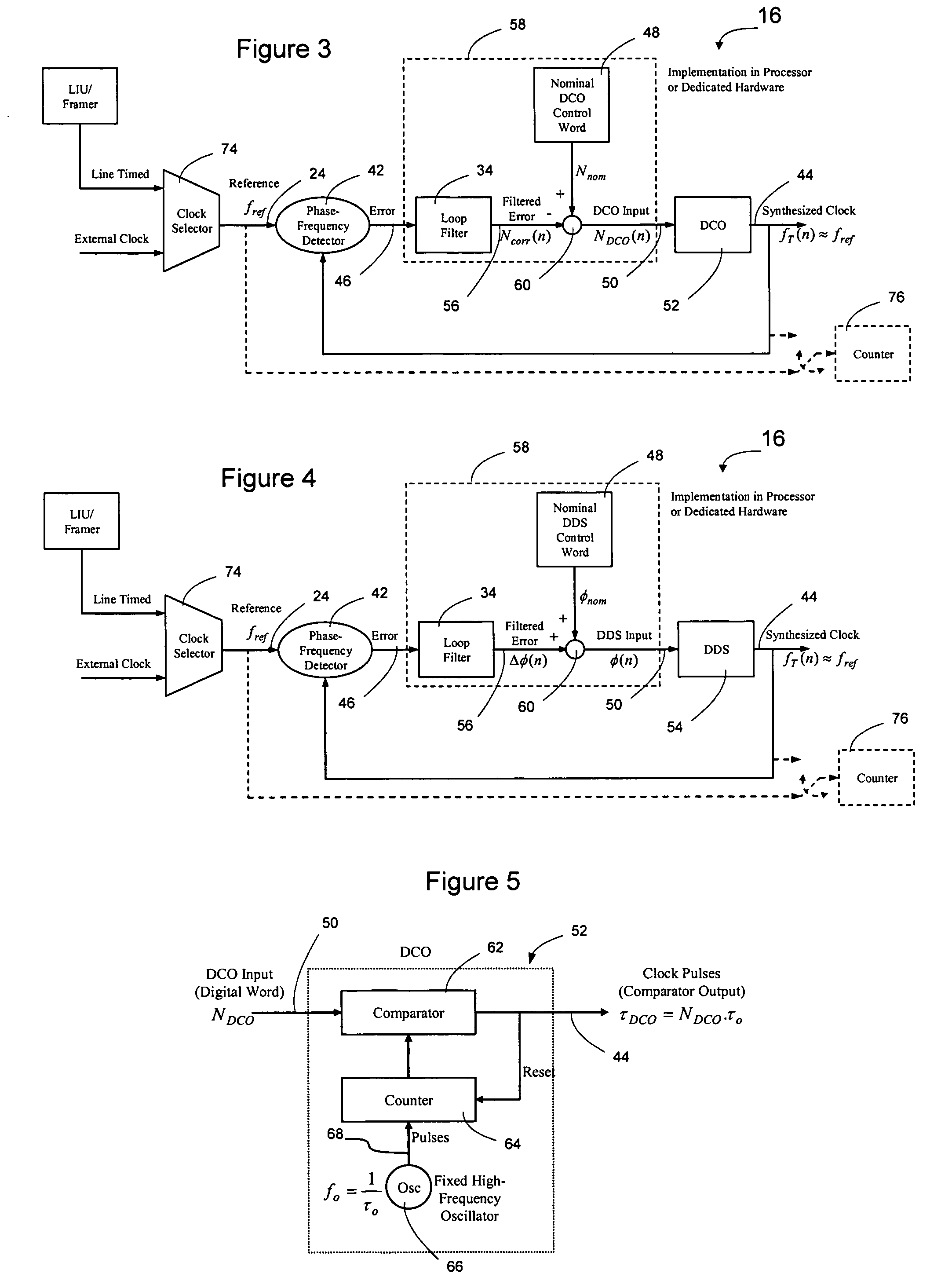
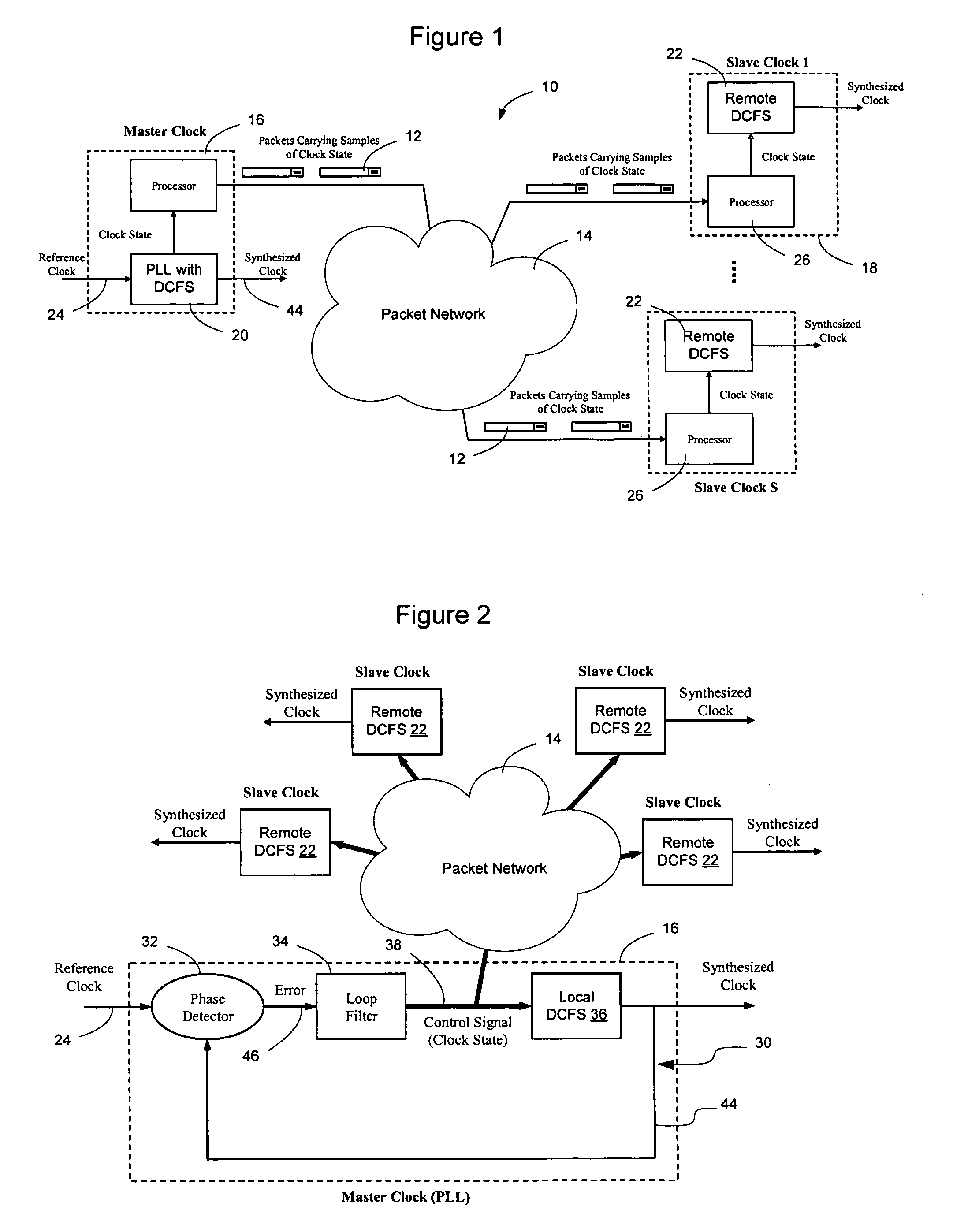
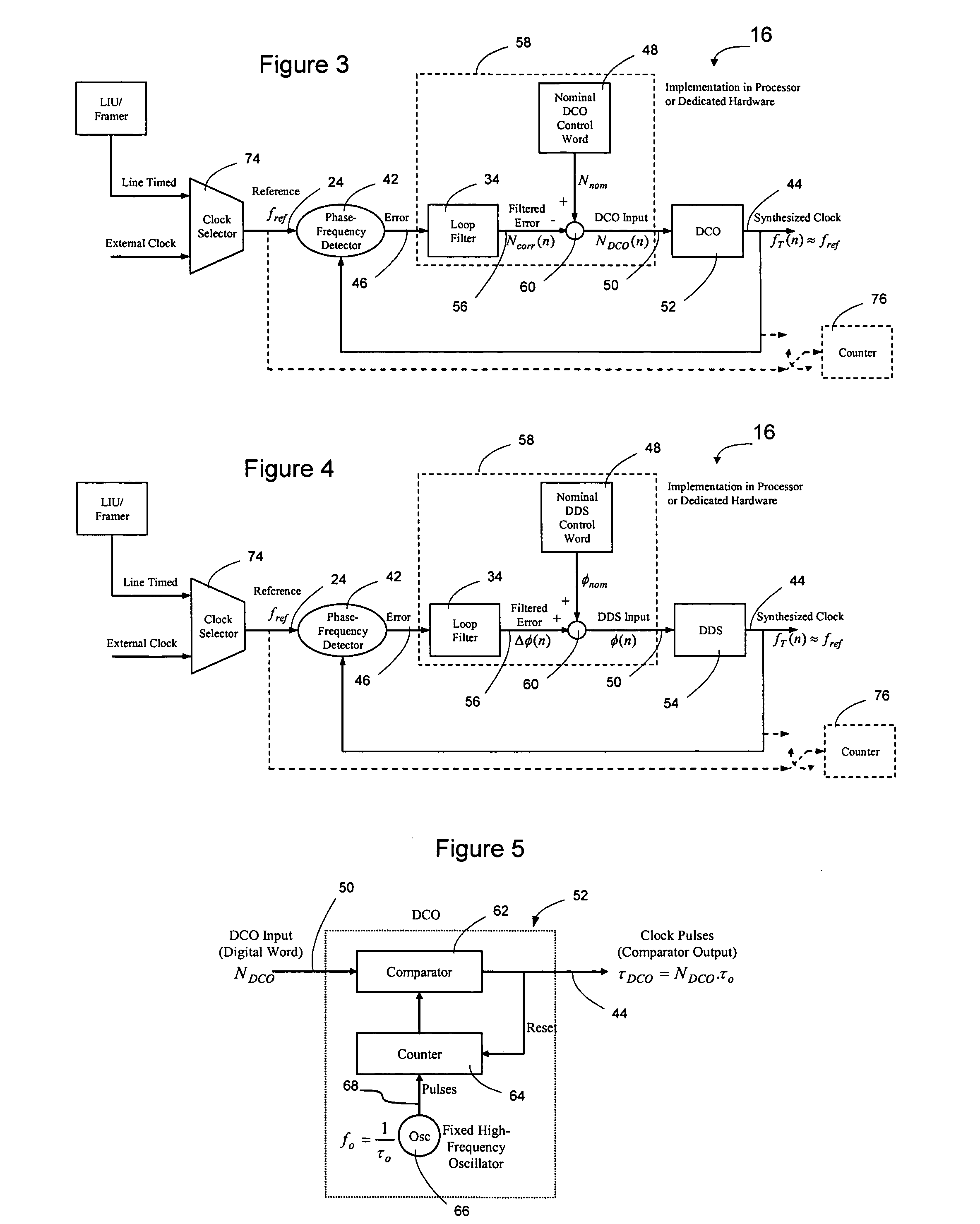
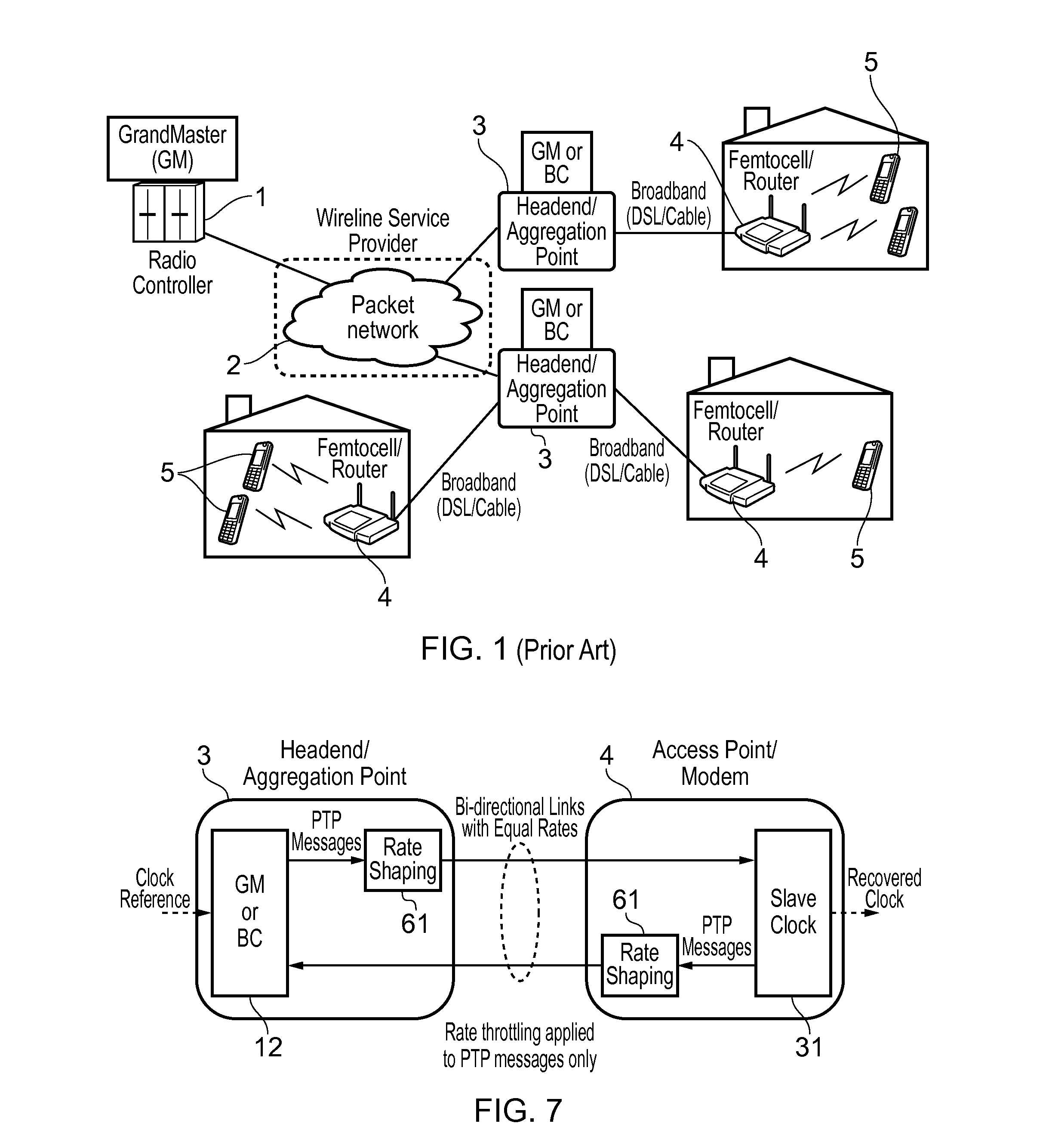
Network elements may be synchronized over an asynchronous network by implementing a master clock as an all digital PLL that includes a Digitally Controlled Frequency Selector (DCFS), the output frequency of which may be directly controlled through the input of a control word. The PLL causes the control word input to the master DCFS to be adjusted to cause the output of the master DCFS to lock onto a reference frequency. Information associated with the control word is transmitted from the master clock to the slave clocks which are also implemented as DCFSs. By using the transmitted information to recreate the master control word, the slaves may be made to assume the same state as the master DCFS without requiring the slaves to be implemented as PLLs. The DCFS may be formed as a digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) or as a Direct Digital Synthesizer (DDS).
Owner:CIENA
System and method for performing clock synchronization of nodes connected via a wireless local area network
ActiveUS7120092B2Synchronous motors for clocksTime-division multiplexCommunications systemSlave clock
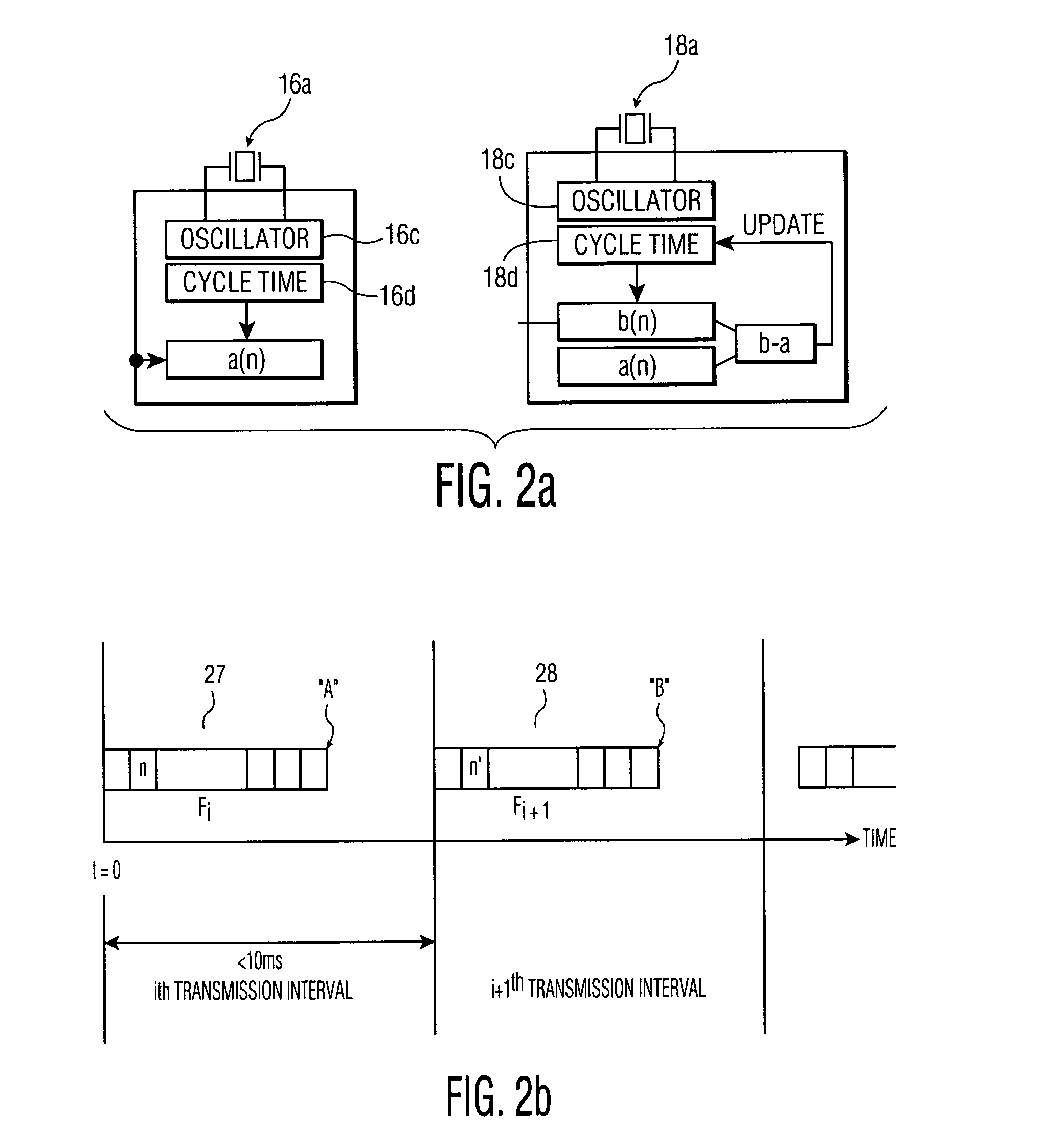
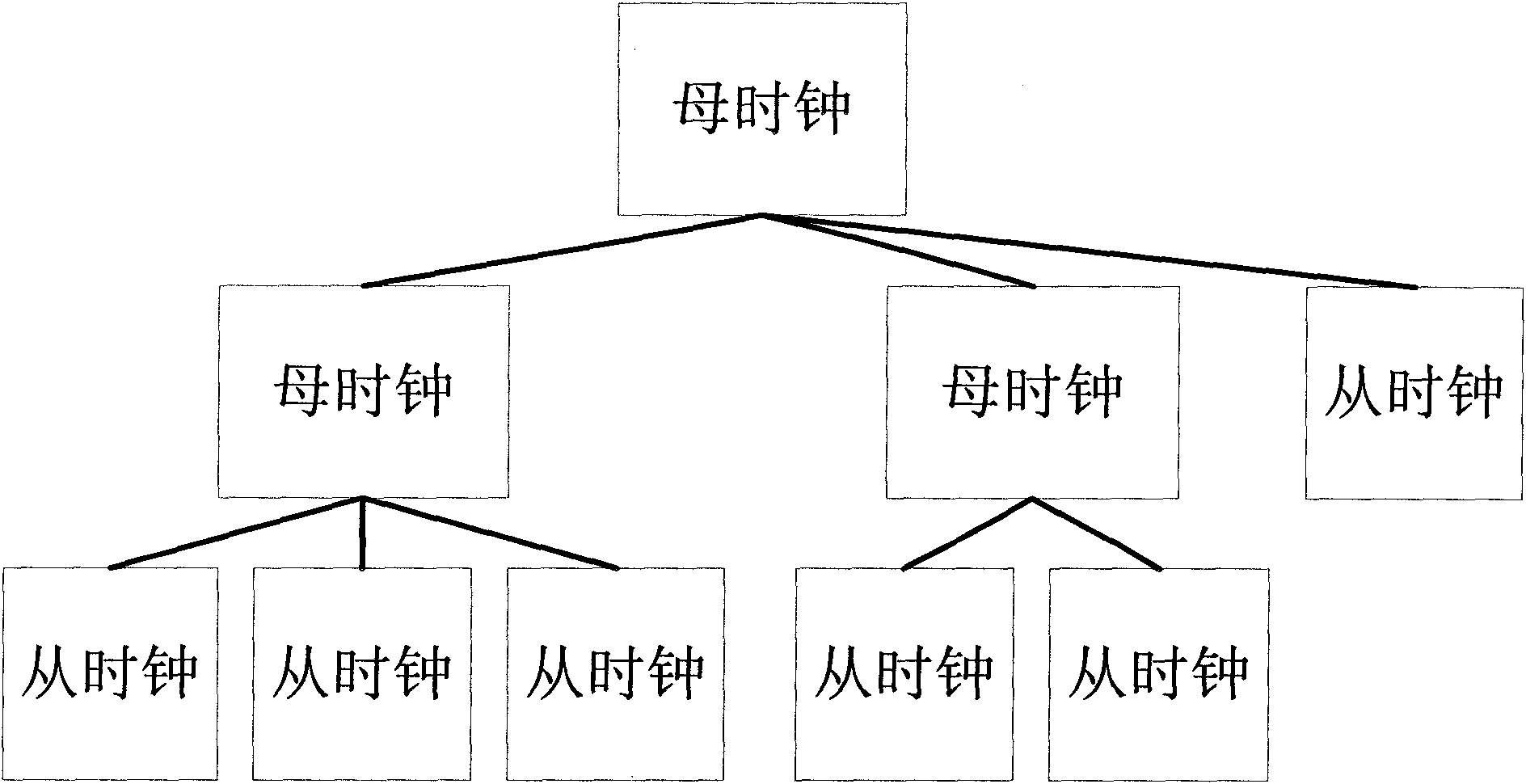
A clock synchronization method and apparatus is disclosed for use in a communication system including a plurality of wireless nodes communicatively coupled via a wireless network, each of the plurality of wireless nodes having a local time base, and one of the plurality of wireless nodes being designated as a master node having a master time base which serves as a master clock against which the local time bases are synchronized. The clock synchronization method includes the steps of periodically transmitting synchronization frames to the plurality of non-master nodes so as to adjust the slave clocks associated with the respective non-master nodes. The synchronization frames are distributed from the master node at near-periodic intervals and includes a cycle time value that corresponds to the end of the previously transmitted synchronization frame. The slave clocks (i.e., non-master nodes) receiving the synchronization frame determine the cycle time value at the point of reception of the synchronization frame and adjusts their clocks by calculating a difference value between the received cycle time and a previously saved local cycle time value.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
System and method for time synchronization on network
InactiveUS20090086764A1Reduce power consumptionReducing power consumption and amount of computationTime-division multiplexSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlComputer hardwareData synchronization
A system and method for time synchronization on a network is provided. According to the system and method for time synchronization, a slave clock device does not continuously receive a time synchronization message periodically transferred from a master clock device and thus does not correct its time upon all such occasions. Rather, the slave clock device requests time information from the master clock device only when the slave clock device needs to correct its time, and receives a time synchronization message transferred from the master clock device and compensates for its time deviation only while the slave clock device is activated, thereby reducing its power consumption and amount of computation.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Synchronizing clocks across a communication link
InactiveUS6944188B2Accurate and fast data transferSynchronization is simpleSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunications linkImage resolution
Apparatus, system and method for synchronizing one or more clocks across a communication link. A slave clock may be synchronized to a master clock by means of a synchronization signal sent from the master to the slave clock side of the link. The synchronization signal may be an expected signal pattern sent at intervals expected by the slave side. The slave clock may correlate received signals with a representation of the expected synchronization signal to produce a correlation sample sequence at a first sample rate which is related as n times the slave clock rate. The synchronization signal receipt time indicated by the correlation sample sequence may be refined by interpolating the correlation sample sequence around a best correlation sample to locate a best interpolation at an interpolation resolution smaller than the sample resolution. The best interpolation may in turn be further refined by estimating between interpolator outputs adjacent to the best interpolation output. The synchronization signal receipt time thus determined is compared to the expected time based upon the slave clock, which is adjusted until the times match. After initialization, all slave clock errors are preferably accumulated to prevent long-term slip between the slave and master clocks. Formerly independent master and slave clocks synchronized across the communication link constitute a noncommon clock which may be compared on each side of the link to secondary independent clocks, and the secondary independent clocks may then be separately synchronized by adjusting one to have the same difference from its local noncommon clock as the secondary clock on the other side of the link has from its local noncommon clock.
Owner:WI LAN INC
Method and apparatus for master-salve clock synchronization
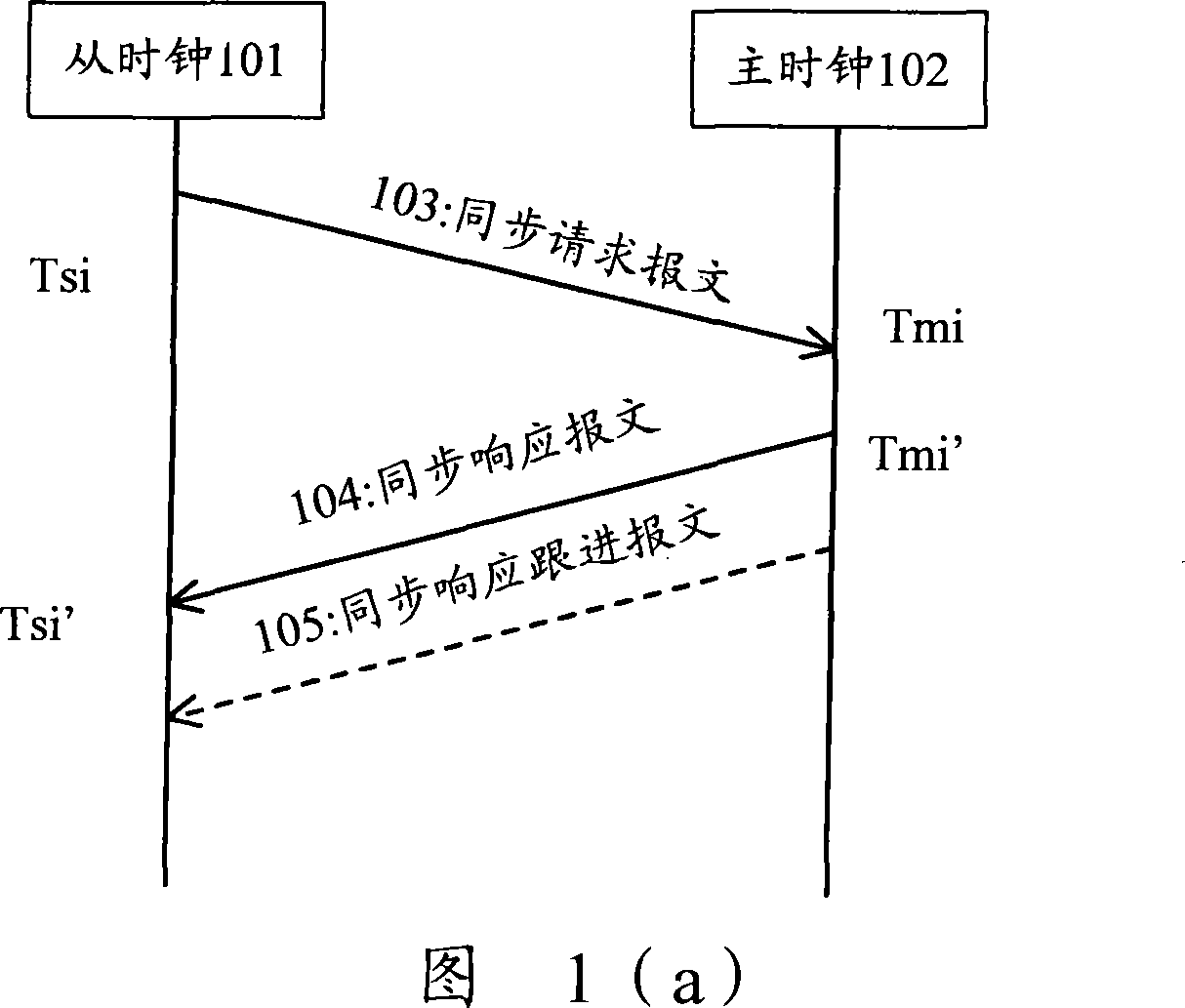
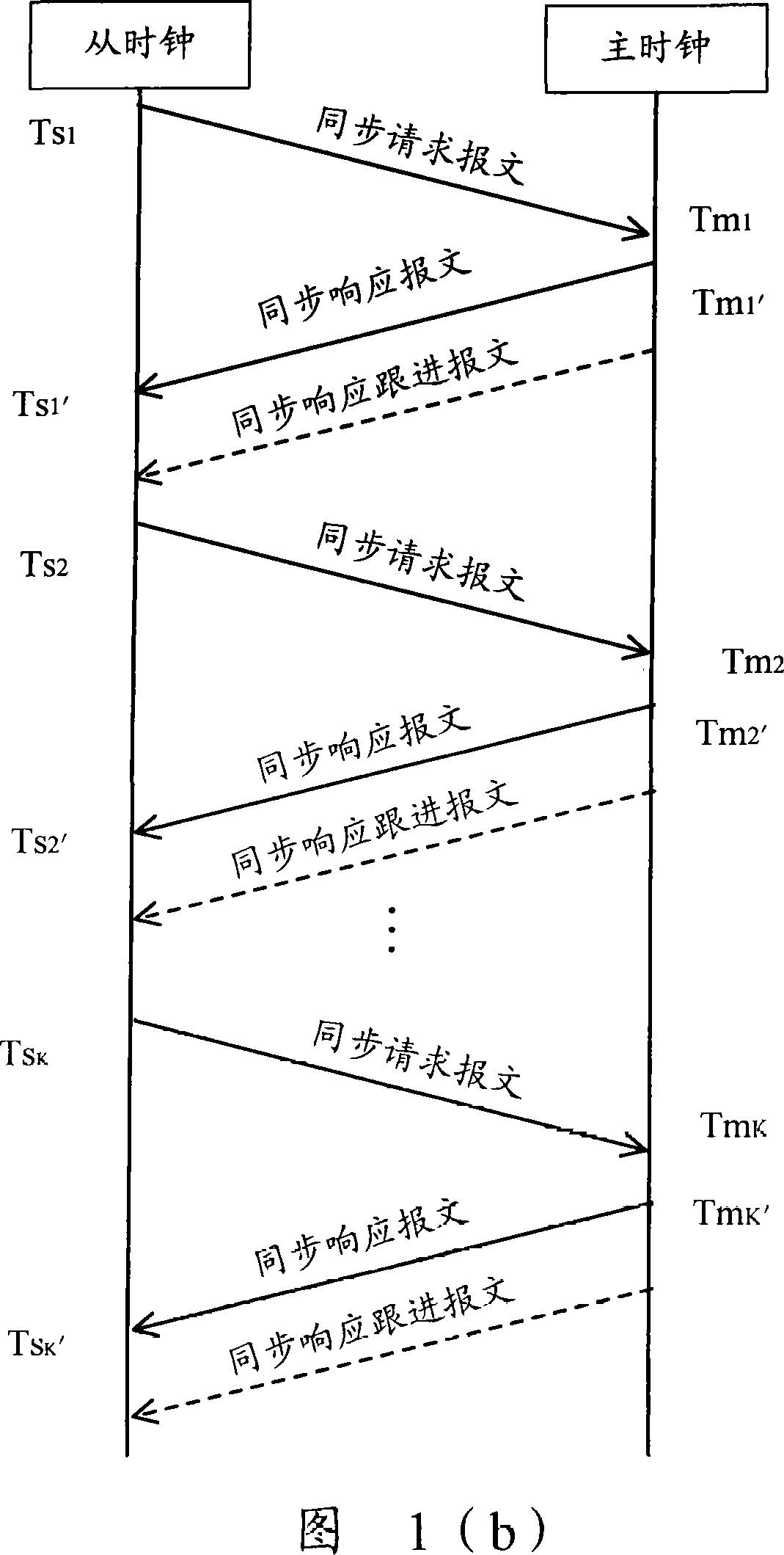
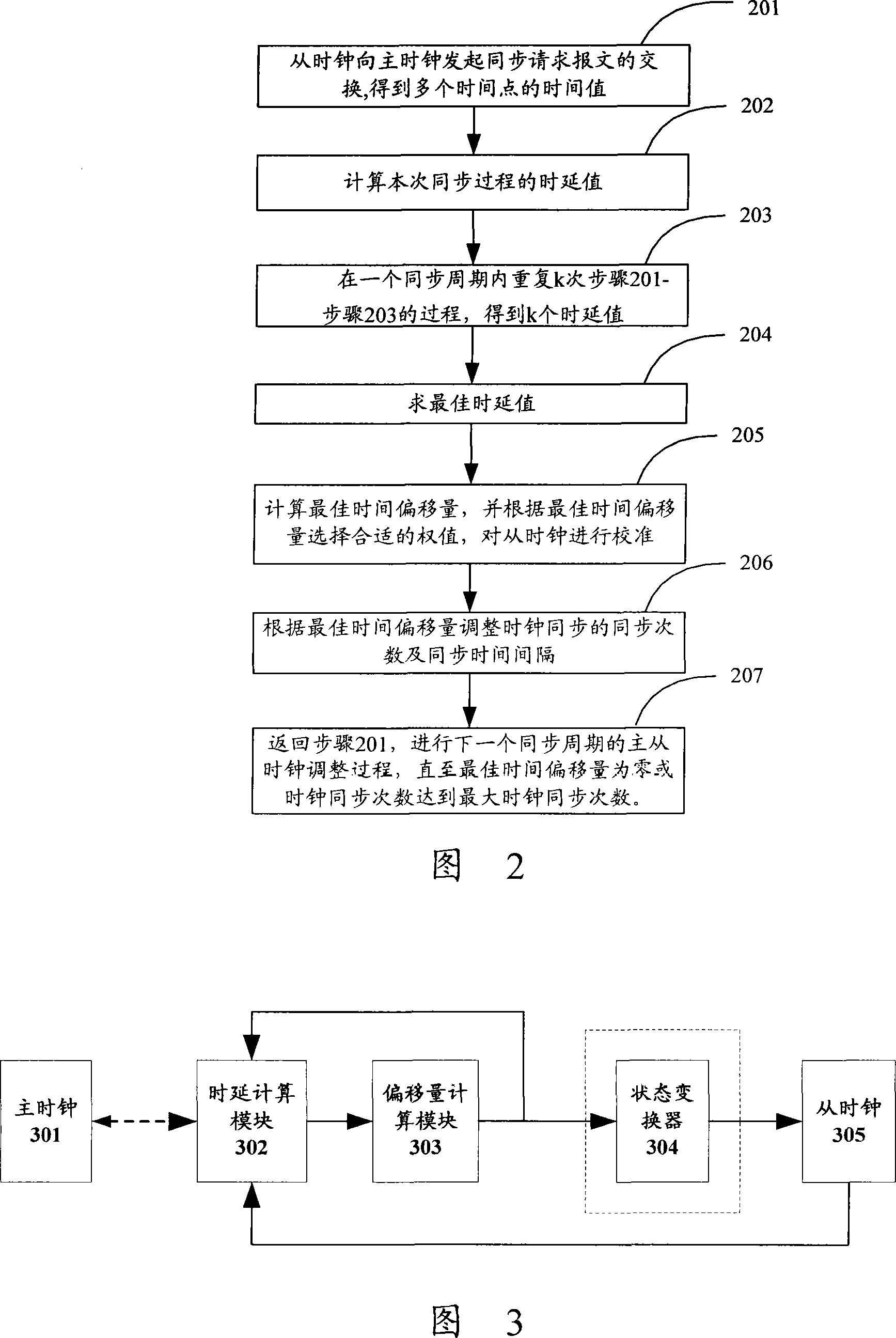
InactiveCN101227246AEliminate delay errorsHigh synchronization accuracyTime-division multiplexTransmissionAverage filterSlave clock
The invention discloses a method and a device for synchronizing a master clock and a slave clock, the method comprises: sending synchronous request message to the master clock for many times in a simultaneous cycle by the slave clock, recording the corresponding the time value, then, utilizing a median average filtering algorithm to obtain the optimum time migration amount, utilizing the time migration amount to adjust the slave clock, eliminating the delay inequality which is caused by stochastic disturbance and burst interference of a network communication channel between the master clock and the slave clock, guaranteeing the stability of slave clock signals, and increasing the synchronous preciseness of the master clock and the slave clock.
Owner:ZTE CORP
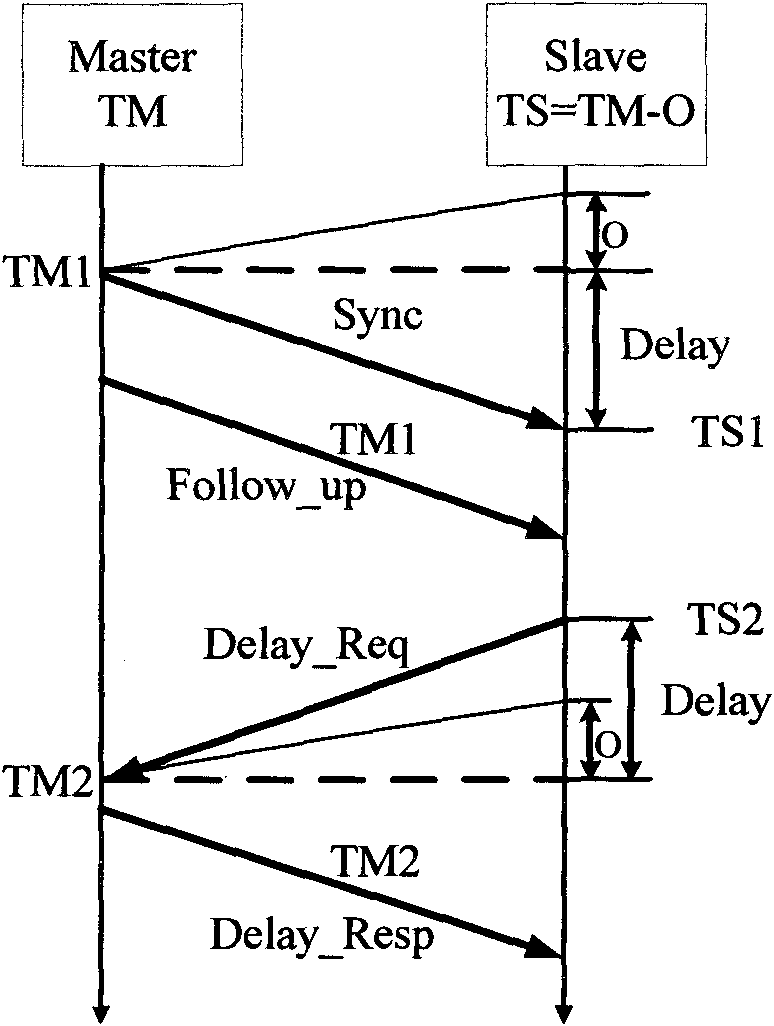
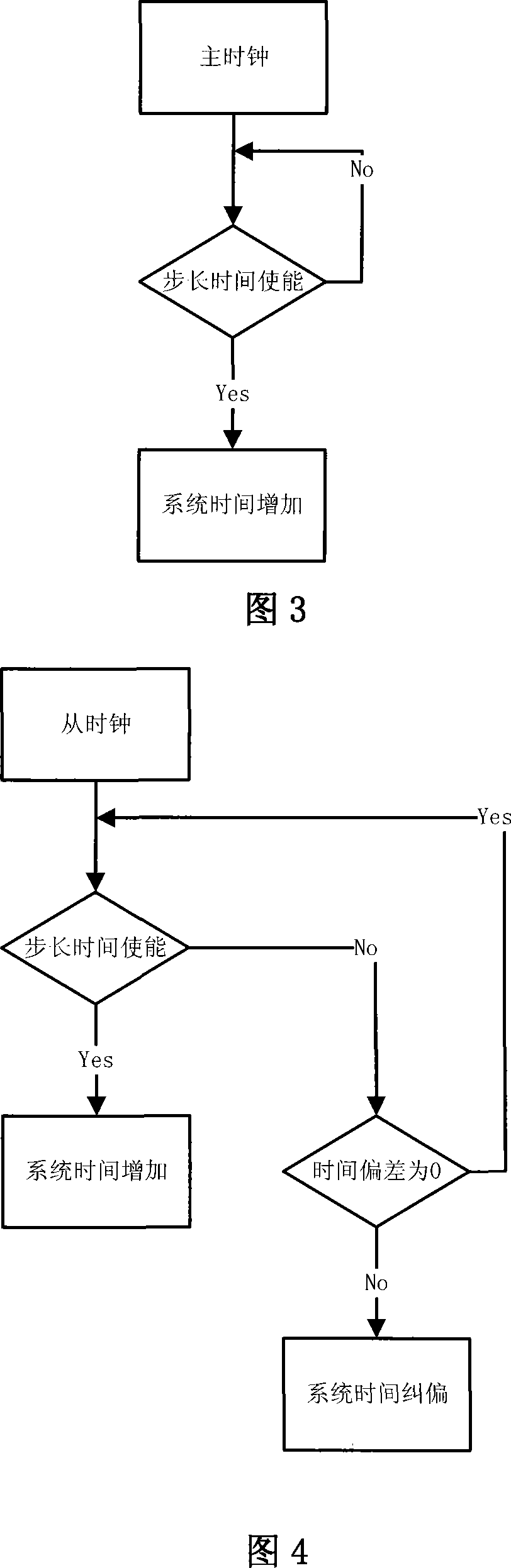
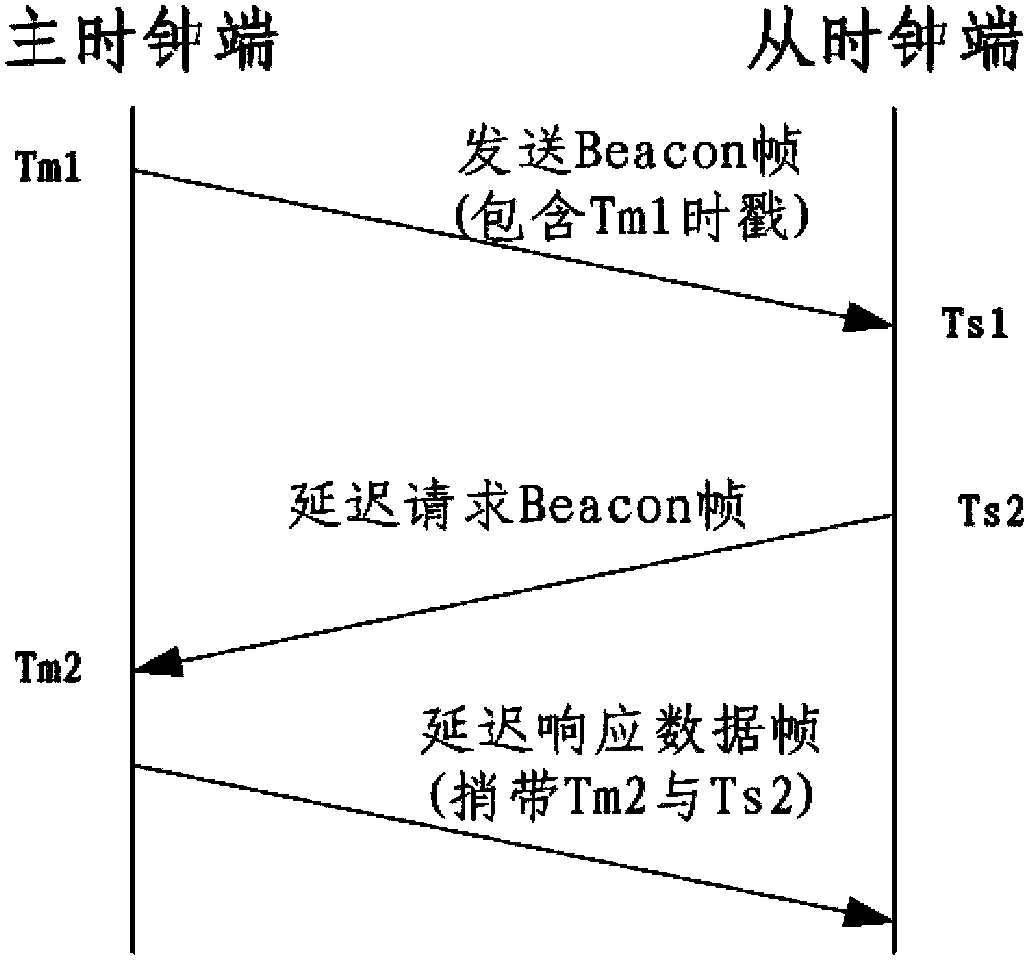
Method for realizing accurate time synchronization by utilizing IEEE1588 protocol
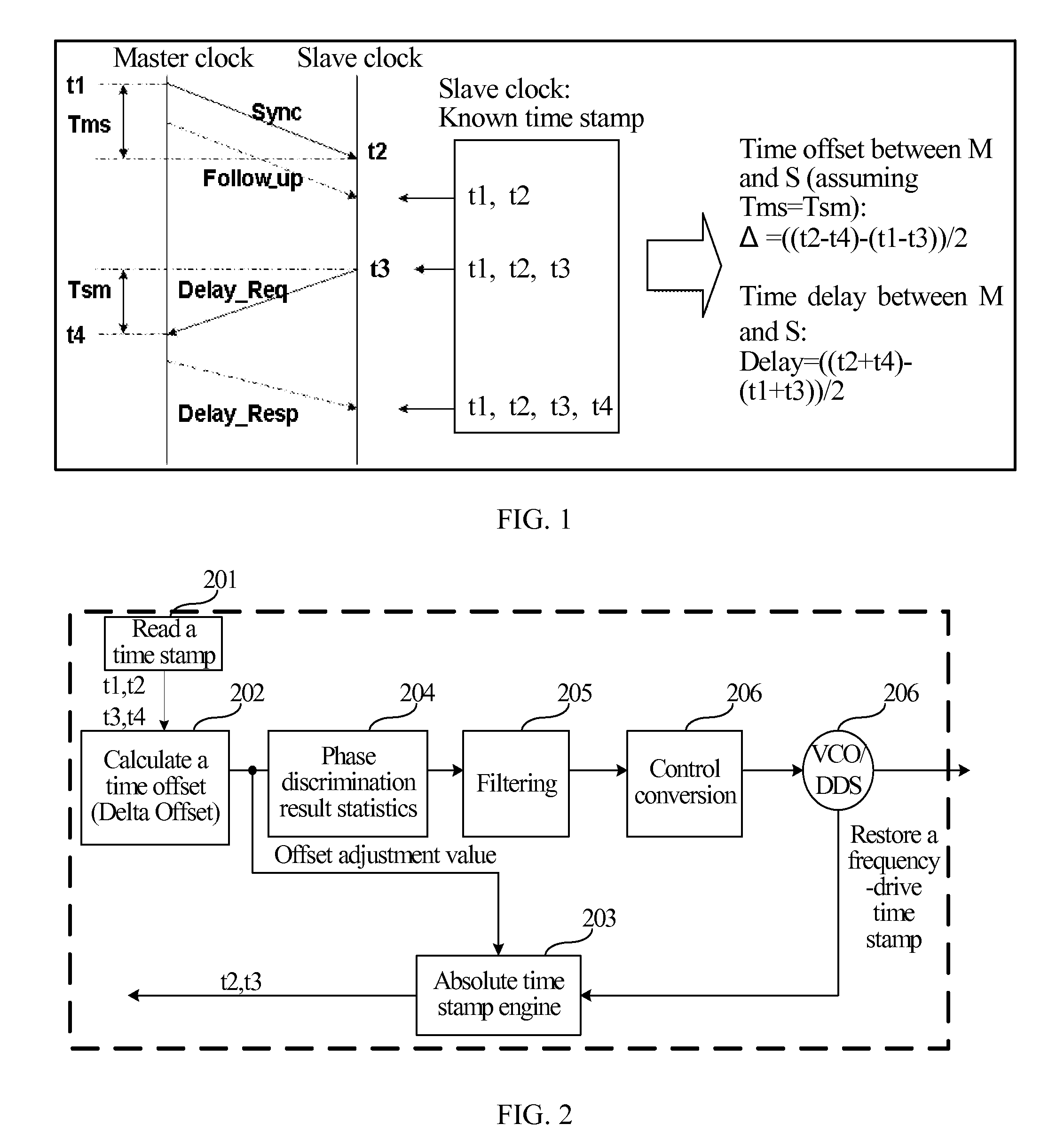
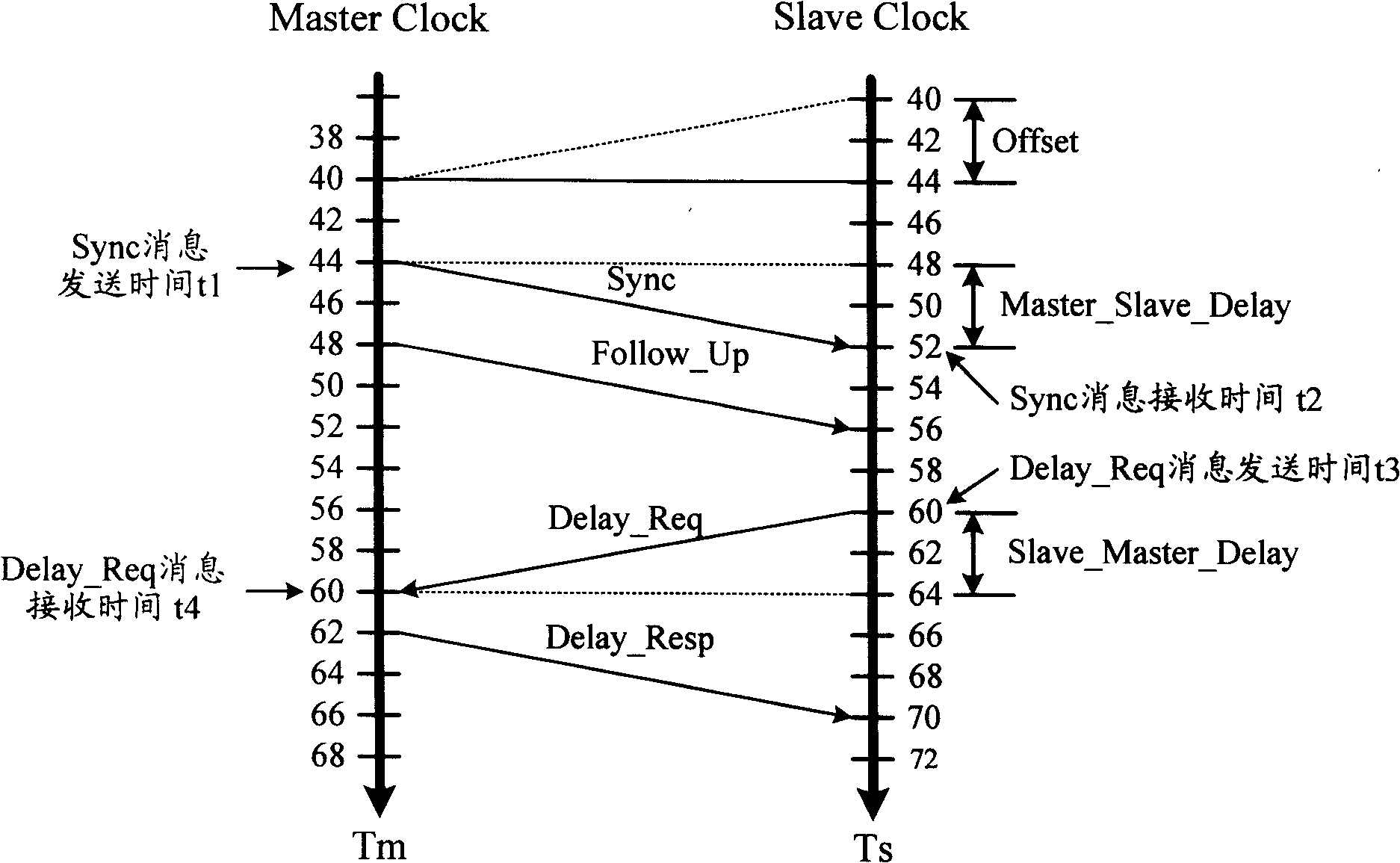
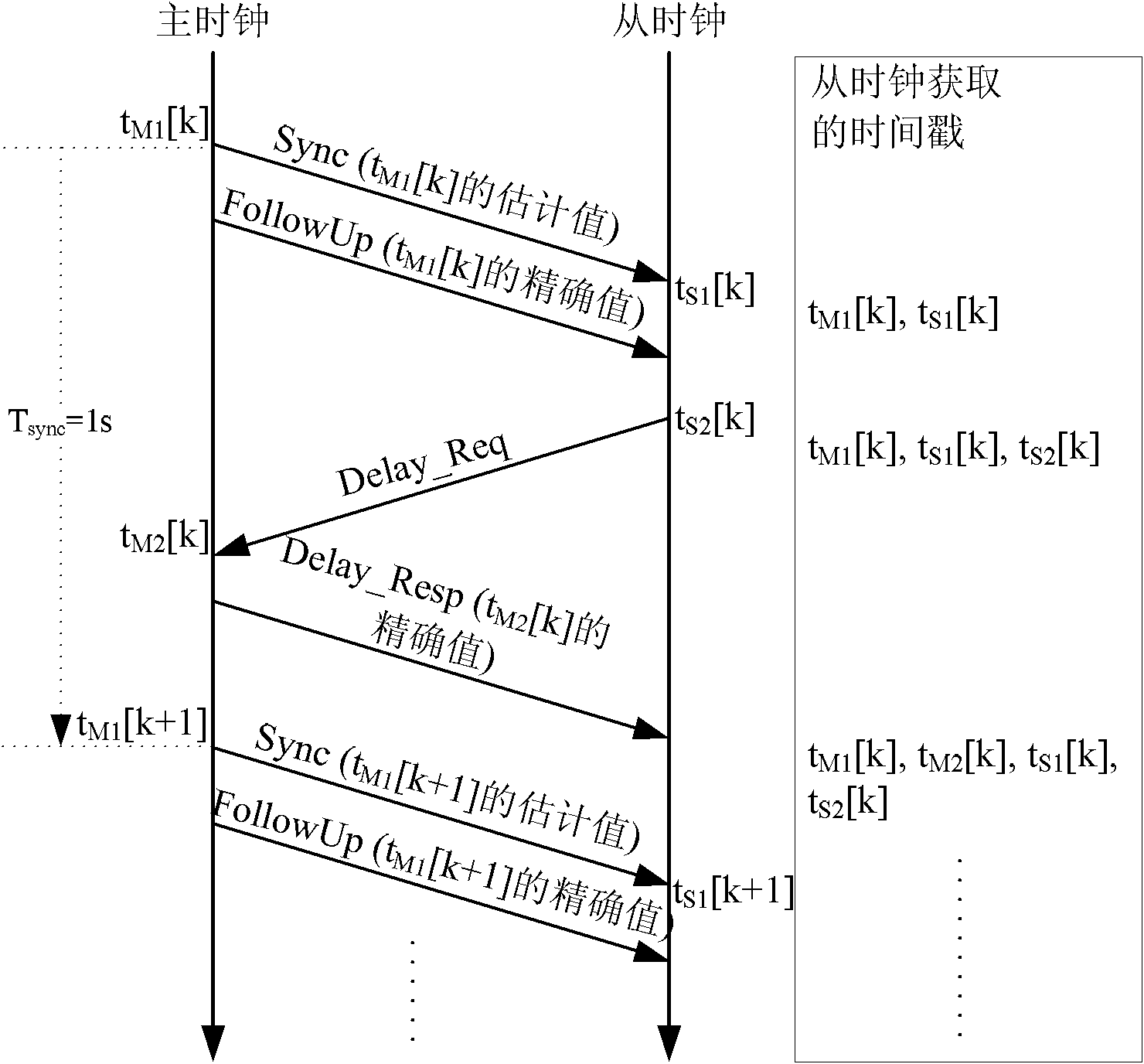
The invention discloses a method for realizing accurate time synchronization by utilizing an IEEE1588 protocol, comprising the following steps: a) a Sync message is transmitted to a slave clock by a master clock, a transmission timestamp TM1 and a receiving timestamp TS1 of the message are acquired by the slave clock; b) a Delay_Req message is transmitted to the master clock by the slave clock, and a transmission timestamp TM2 and a receiving timestamp TS2 of the message are acquired by the slave clock; c) transmission delay and time offset are calculated by the slave clock according to the timestamp; and d) the calculated Offset is corrected in a fixed adjustment frequency in the correction time by the slave clock. The invention realizes accurate time synchronization, calculates time offset and self-compensate through the slave time clock in a packet based network, and leads the slave clock to lock the master clock whether in clock frequency or on the clock time in a shorter time, and occupies little hardware resources.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Systems and Methods of Network Synchronization
ActiveUS20130080817A1Time-division multiplexGenerating/distributing signalsSlave clockDelay calculation
An exemplary method of synchronizing a master clock and a slave clock comprises transmitting a plurality of packets between a master device and a slave device, calculating a first skew between a first pair of the plurality of packets at the slave device and a second skew between the first pair at the master device, calculating a ratio between the first skew and the second skew, providing a slave clock frequency correction to the slave device, calculating a first packet trip delay using a time that the master device initiates sending a packet to the slave device, a time the master device receives a response from the slave device, a corrected time the slave device receives the packet, and a corrected time the slave device initiates sending the response, calculating a first offset based on the first packet trip delay, and providing the first offset to the slave device.
Owner:AVIAT U S
Method and system for precise-clock synchronization, and device for precise-clock frequency/time synchronization
InactiveUS20100098111A1Occupied link bandwidth resources are greatly reducedPulse automatic controlTime-division multiplexData synchronizationSlave clock
A precise-clock synchronization method and system and a precise-clock frequency / time synchronization device are provided. In the embodiments of the present invention, two time stamp engines are provided at a slave clock side. A relative time stamp engine provides a relative arrival time stamp. An absolute time stamp engine provides an absolute arrival time stamp. The frequency / time synchronization is calculated by using different time stamps obtained from different time stamp engines, so the frequency synchronization and time synchronization of master clock and the slave clock may be separately accomplished, and one synchronization function may be enabled or disabled. Therefore, the frequency synchronization and time synchronization of the master clock and the slave clock do not interfere with each other, thus greatly reducing the occupied link bandwidth resources.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for synchronizing internal state of frequency generators on a communications network
A first level of control over operation of slave Digitally Controlled Frequency Selectors (DCFSs), such as DCOs or DDSs, may occur by periodic transmission of control words from the master clock to the slave clocks. To allow enhanced control over the output of the slave clocks, the frequency of the local oscillator used to generate the synthesized output of the master clock may also be conveyed to the slave clocks to allow a second level of control to take place. The second level of control allows the local oscillators at the slave clocks to lock onto the frequency of the master local oscillator to thereby allow the slave local oscillators to operate the slave DCFSs using the same local oscillator frequency. The first level of control synchronizes operation of the DCFSs while the second level control prevents instabilities in the local oscillators from causing long term drift between the slave and master clock outputs. Timestamps may be used to synchronize the master and slave local oscillators.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
High-precision real-time synchronization method based on IEEE1588
InactiveCN101232457ASolve the unity problemSolve the accuracy problemTime-division multiplexData switching networksSlave clockData transmission time
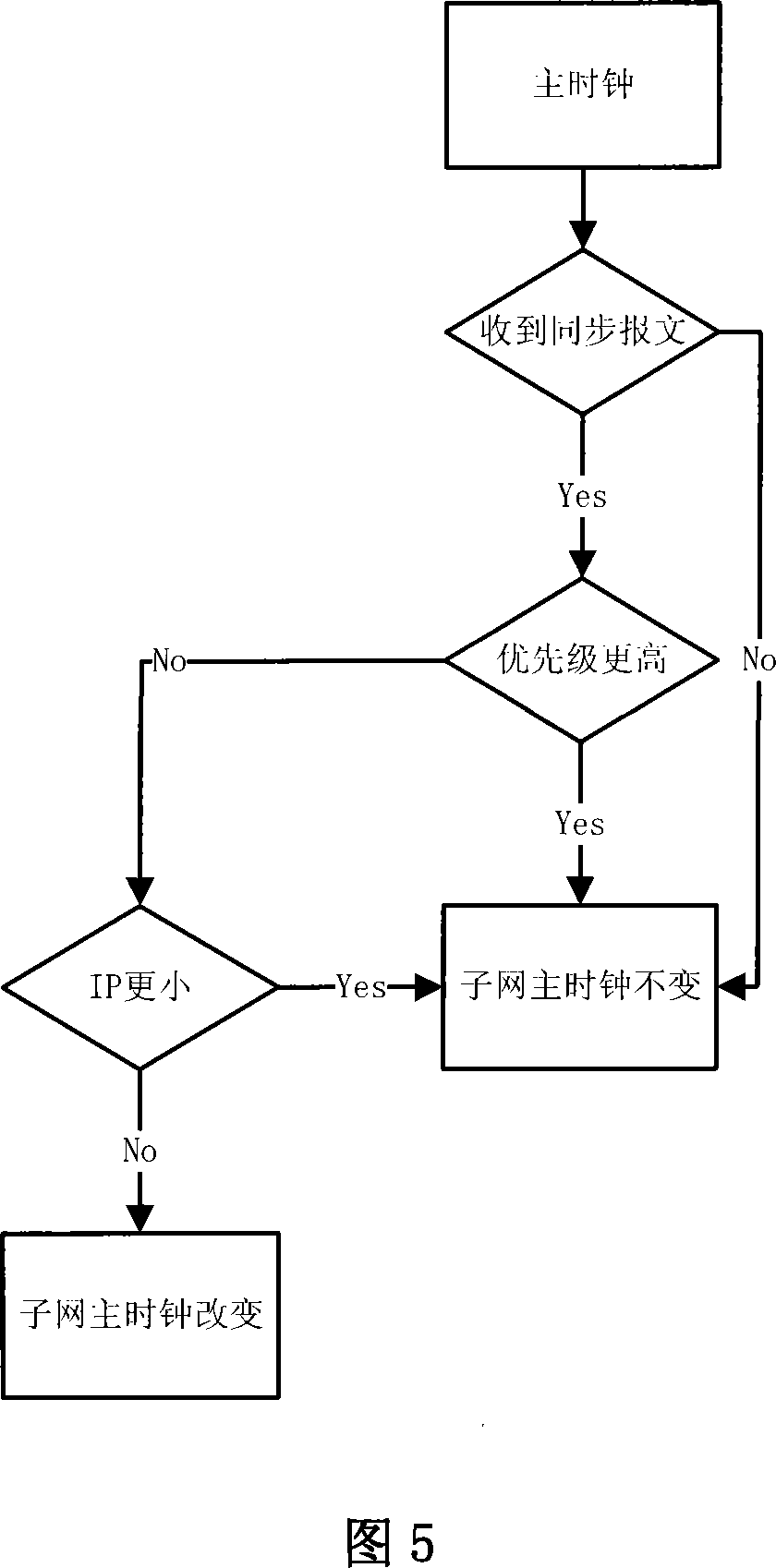
The invention relates to a real-time synchronization method based on PTP precision clock synchronization protocol of IEEE1588. The research on hardware of IEEE1588 protocol is still a blank at present. The method of the invention includes the following steps: sending messages; receiving messages; correcting the local system time; selecting the optimal master clock. And the synchronization action is different when the corresponding equipment is a master clock or a slave clock. The hardware method reduces the inherent fluctuation of data transmission time of internet technology, while not affecting the scope of precision control, thus resolving the problem of the clock uniformity and precision in a distributed network system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Secure clock synchronization
ActiveUS20120163521A1Synchronisation information channelsTime-division multiplexSlave clockComputer science
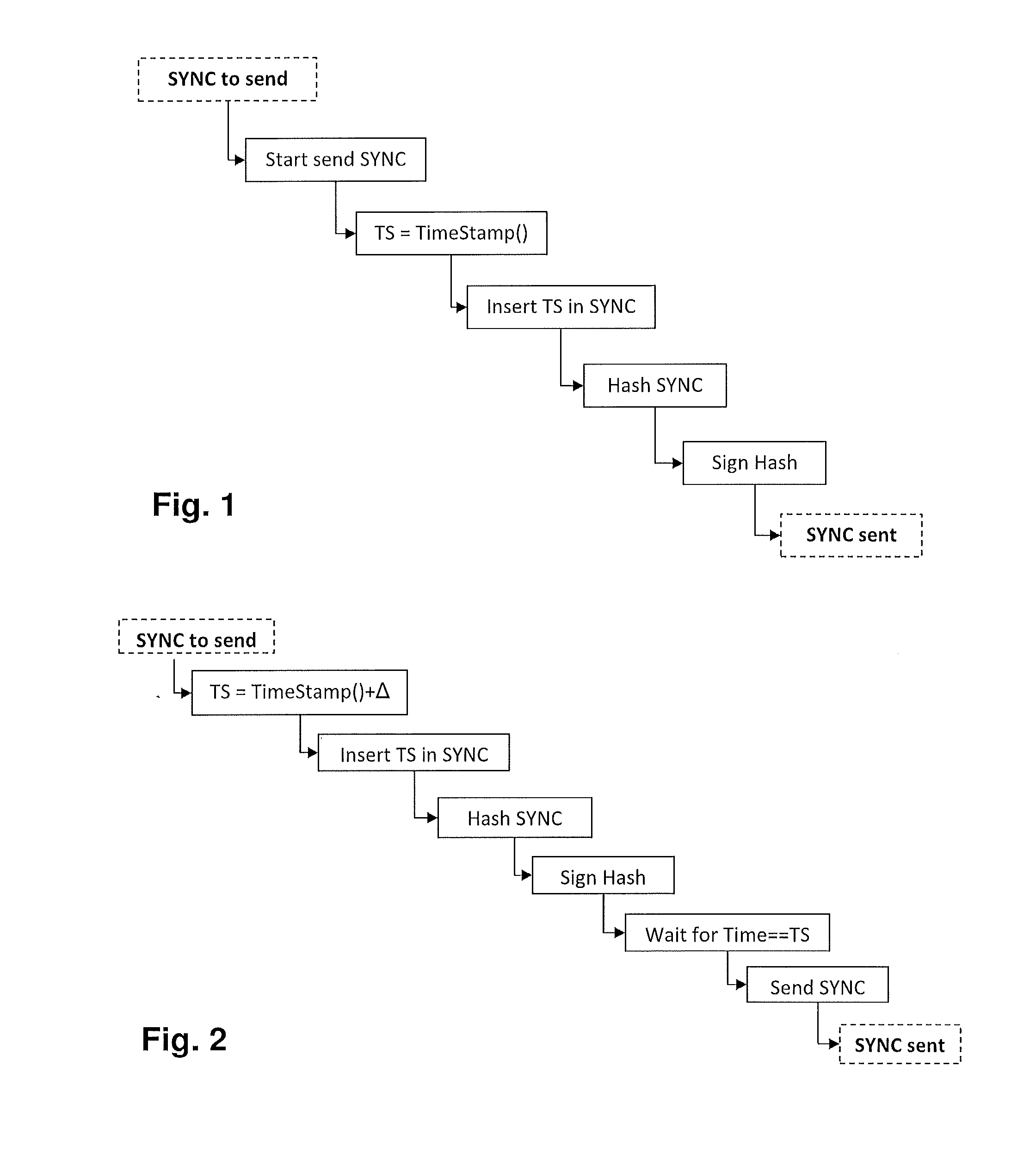
The present disclosure provides a secure one-step IEEE 1588 clock using either a symmetric or asymmetric protection scheme. Clocks of mission-critical or highly-available devices in industrial automation systems connected to a communication network are synchronized by sending, by a master clock, a synchronization message, e.g., a single message of the one-step-clock type according to IEEE 1588, including a time stamp, and by receiving and evaluating, by a slave clock, the synchronization message. A synchronization component or module of the master clock prepares, or composes, prior to a projected send time, a synchronization message including a time stamp of the projected send time, and secures the synchronization message in advance of the projected send time. Securing the synchronization message occurs by suitable cryptographic means allowing for authentication of the time stamp at a receiving slave clock. At the projected send time, the secured synchronization message is transmitted.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
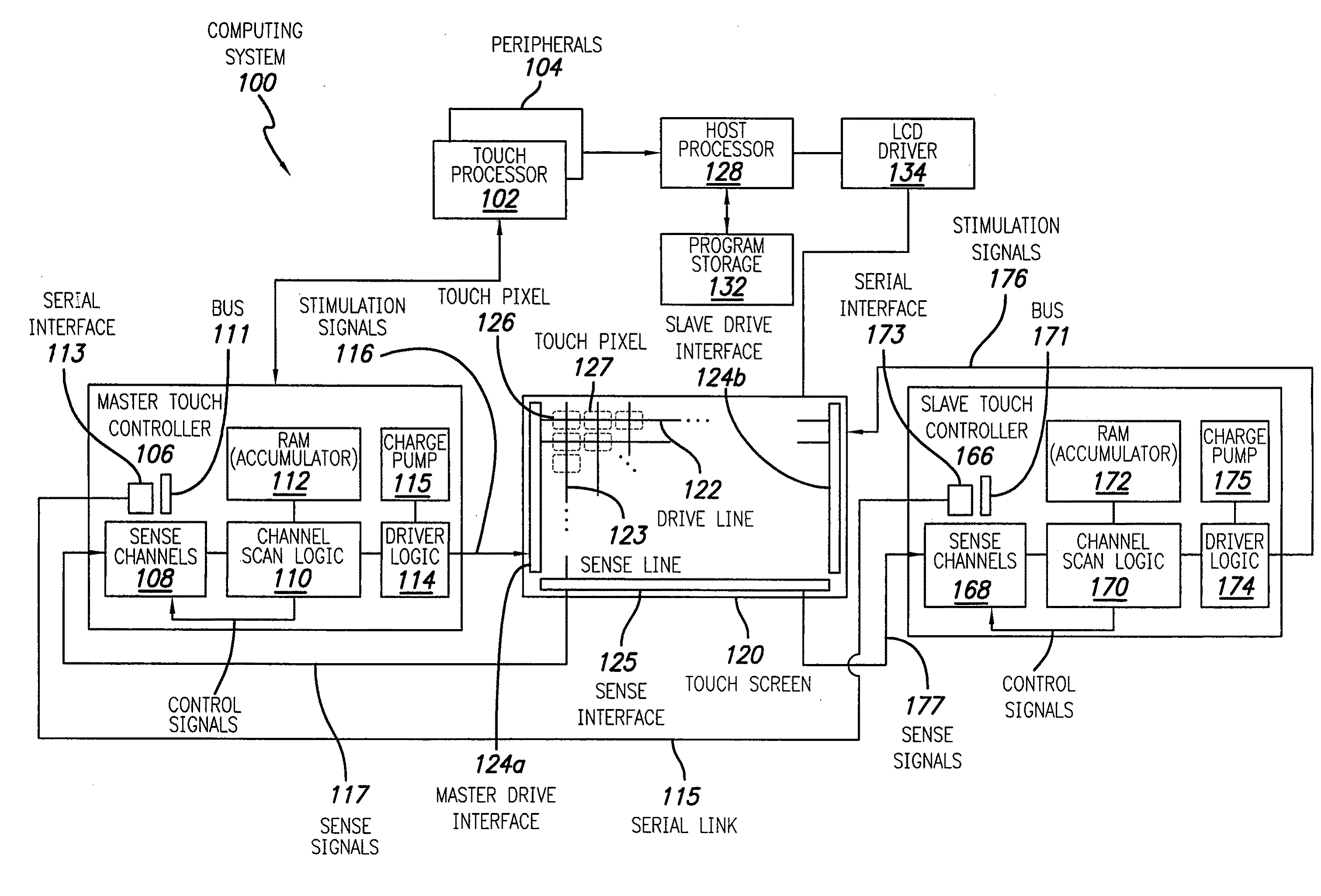
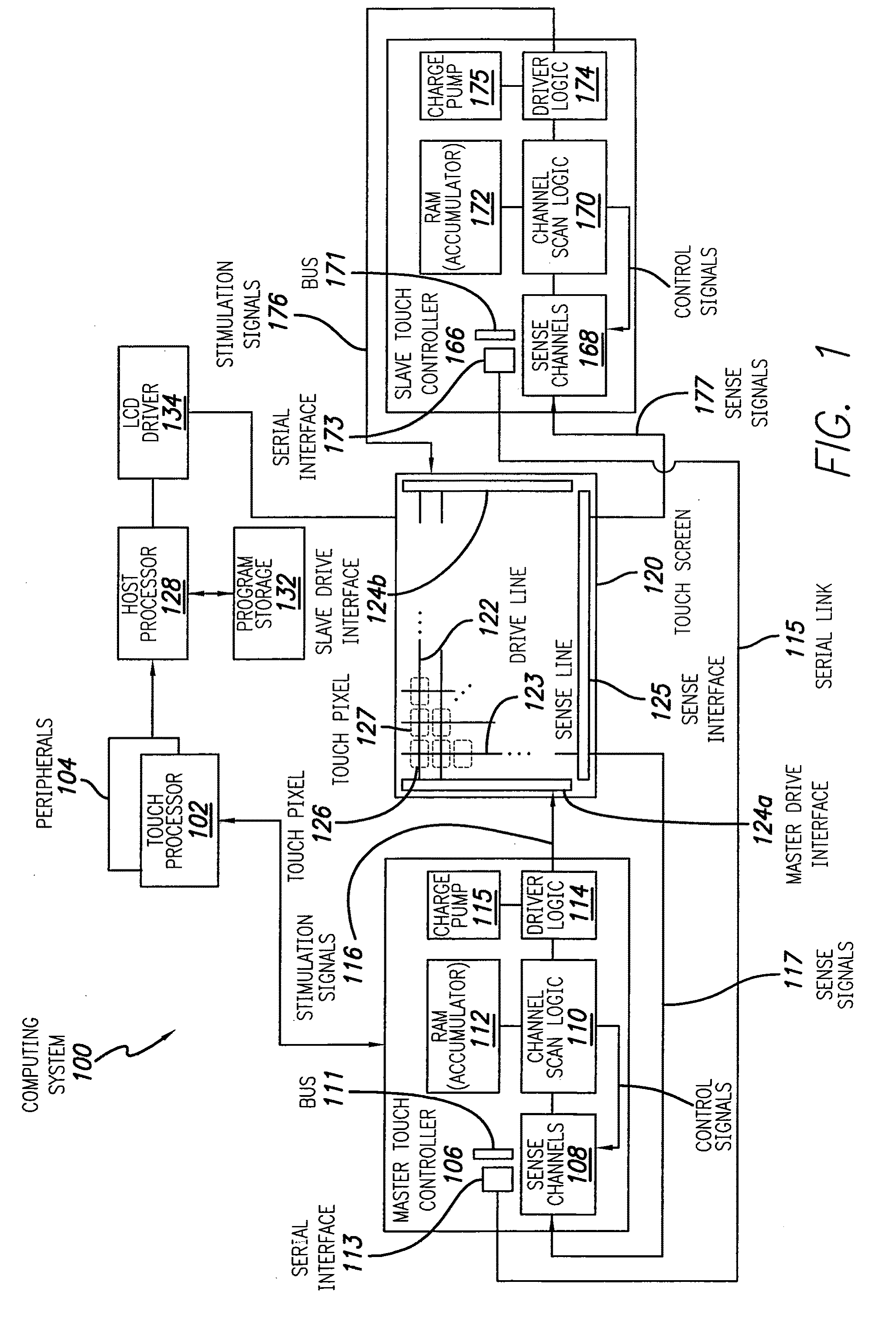
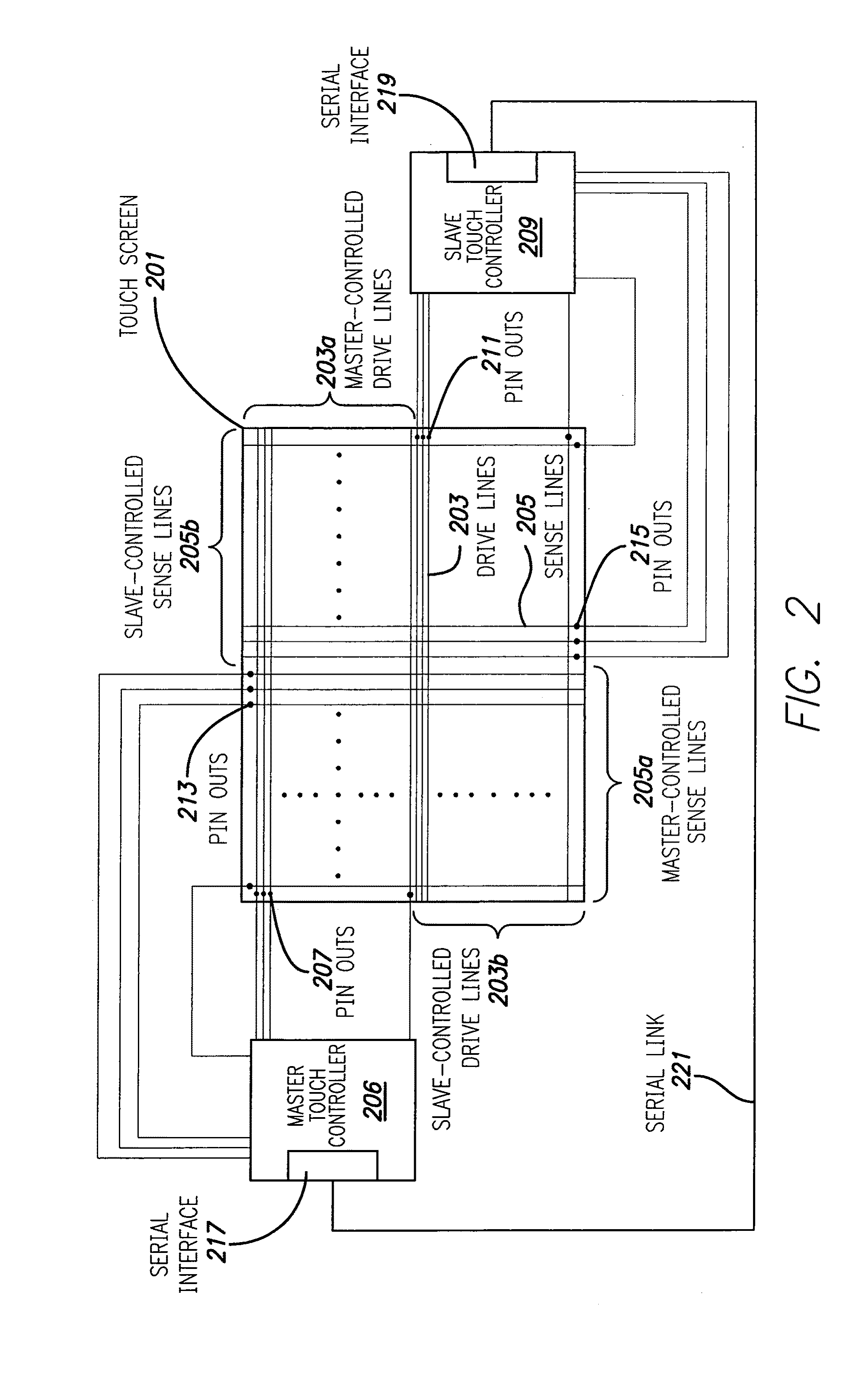
Master/slave control of touch sensing
ActiveUS20120056662A1Electronic switchingGenerating/distributing signalsTelecommunications linkSlave clock
Touch sensing can be accomplished using master / slave touch controllers that transmit drive signals to a touch surface and process sense signals including superpositions resulting from master / slave drive signals. The master / slave can drive and sense different sets of lines, respectively, of the touch surface. A communication link between master / slave can be established by transmitting a clock signal between master / slave, transmitting a command including sequence information to the slave, and initiating a communication sequence from the clock signal and sequence information. The slave can receive / transmit communications from / to the master during first / second portions of the communication sequence, respectively. Touch sensing operations can be synchronized between master / slave by transmitting a command including phase alignment information from master to slave, and generating slave clock signals based on the clock signal and the phase alignment information, such that sense signal processing by master clock signals are in-phase with sense signal processing by slave clock signals.
Owner:APPLE INC
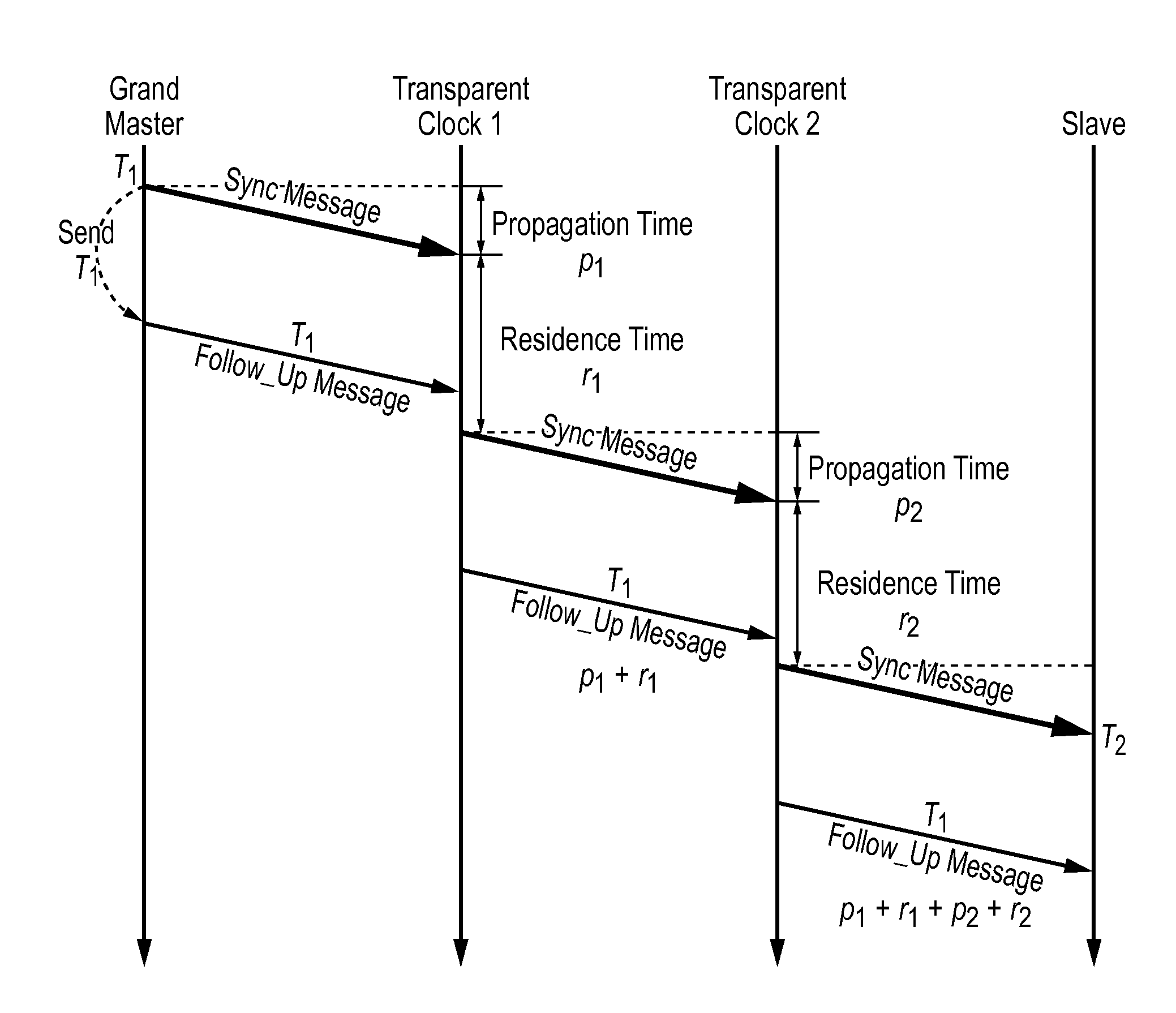
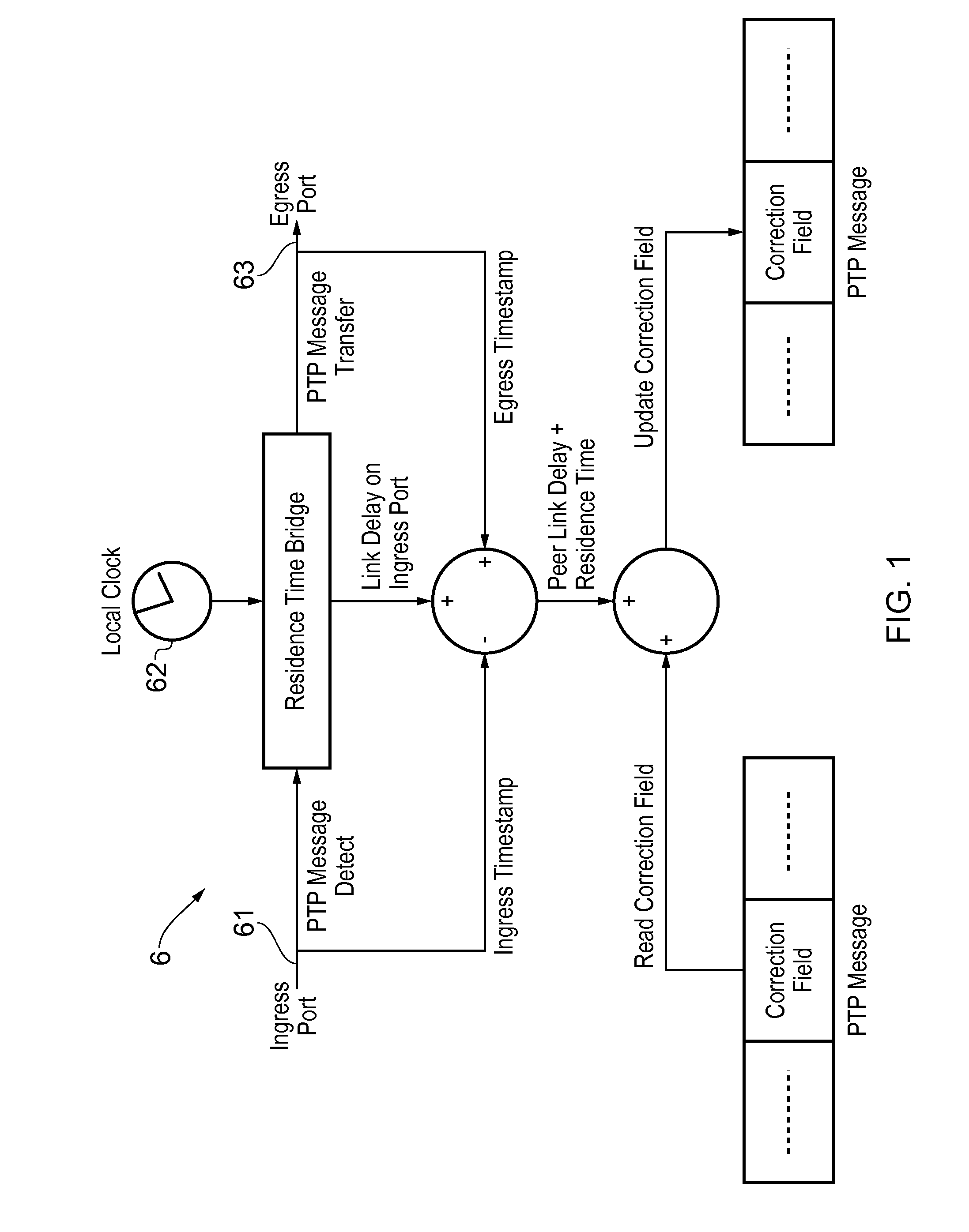
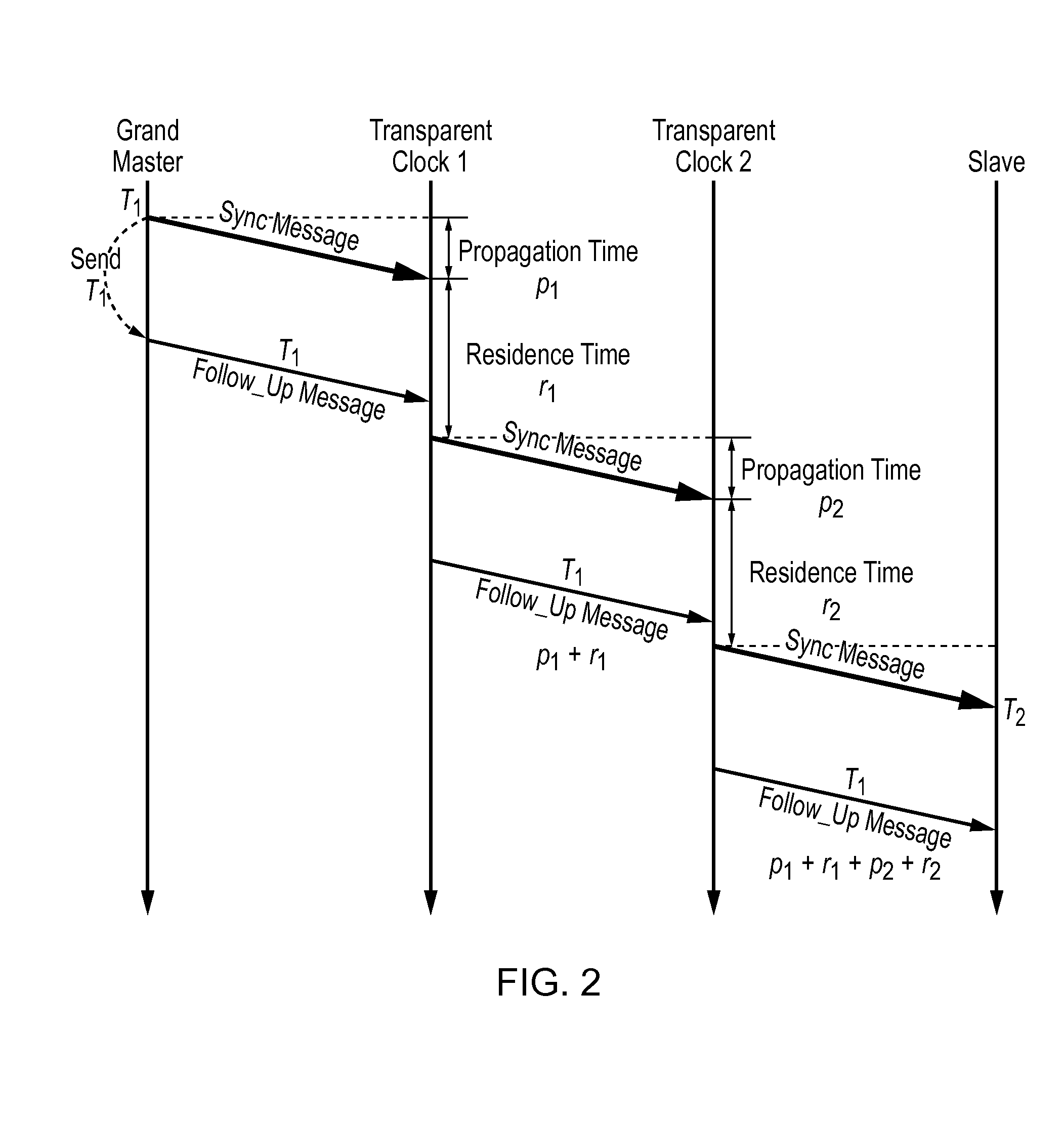
Method and devices for time transfer using peer-to-peer transparent clocks
ActiveUS20160170439A1Generating/distributing signalsTransmission path multiple useNetwork linkTime transfer
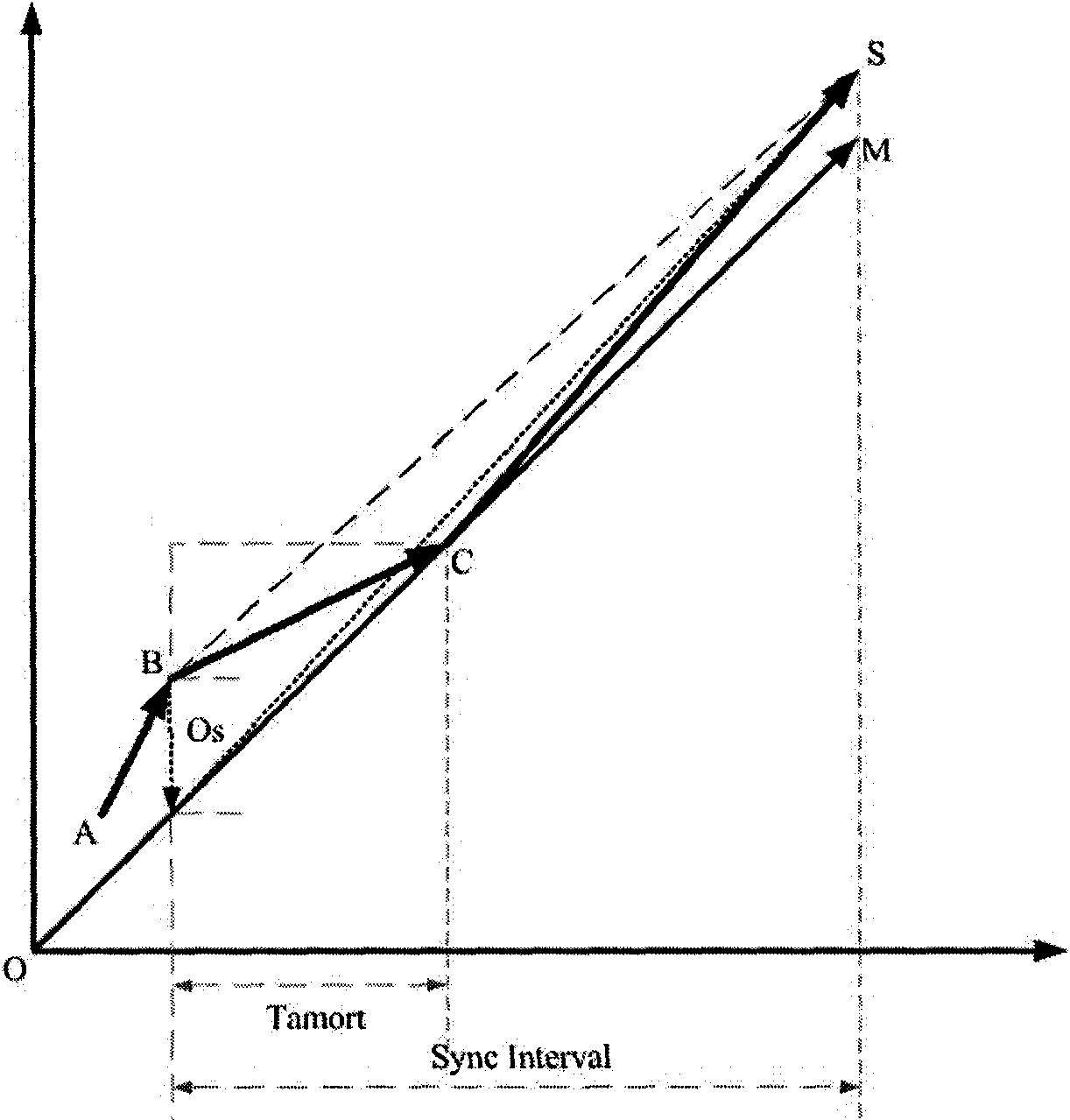
This invention relates to methods and devices for time synchronization. The invention has particular application in the alignment of slave clocks to a master clock and in dealing with packet delay variation and dynamic asymmetries in the network links between them. In embodiments of the invention, the slave clock uses the peer link delay and residence times measured by peer-to-peer transparent clocks to compensate for clock synchronization errors that arise due to variability in message transfer delays. Embodiments provide a simple linear approximation technique and a Kalman filter-based technique for estimating offset and skew of the slave clock.
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
Time synchronization method and system for synchronous messages of IEEE1588 (Precision Time Protocol) master-slave clocks of intelligent transformer substation
ActiveCN102833062AImprove timing accuracyHigh time accuracyData switching networksSynchronising arrangementTime deviationTimestamp
The invention discloses a time synchronization method and a time synchronization system for synchronous messages of IEEE1588 master-slave clocks of an intelligent transformer substation. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a master clock synchronous message, and sending the timestamp t1 of the sending moment of the message to the clock in a broadcasting manner; recording a receiving moment t2 of the master clock synchronous message; recording an absolute receiving moment TT2 when the master clock synchronous message is received by a slave clock; establishing a slave clock responding message, sending the slave clock responding message to the master clock in a peer-to-peer manner, and recording the timestamp t3 of the sending moment of the message; recording an absolute sending moment TT3 when the slave clock sends the clock responding message; recording an acquiring moment t4 when the master clock acquires the message; calculating a time deviation, and calculating asymmetry errors according to the timestamp t1, the absolute receiving moment TT2, the absolute sending moment TT3 and the acquiring moment t4; and carrying out time correction on the slave clock by the time deviation and the asymmetry errors. According to the time synchronization method and the time synchronization system for synchronous messages of IEEE1588 master-slave clocks of the intelligent transformer substation, the influences of the asymmetry errors can be eliminated, and the time synchronization precision of the master-slave clocks is improved.
Owner:ZHUHAI POWER SUPPLY BUREAU GUANGDONG POWER GIRD CO
Data latch with structural hold
ActiveUS7843218B1Electrical testingLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsMultiplexingMultiplexer
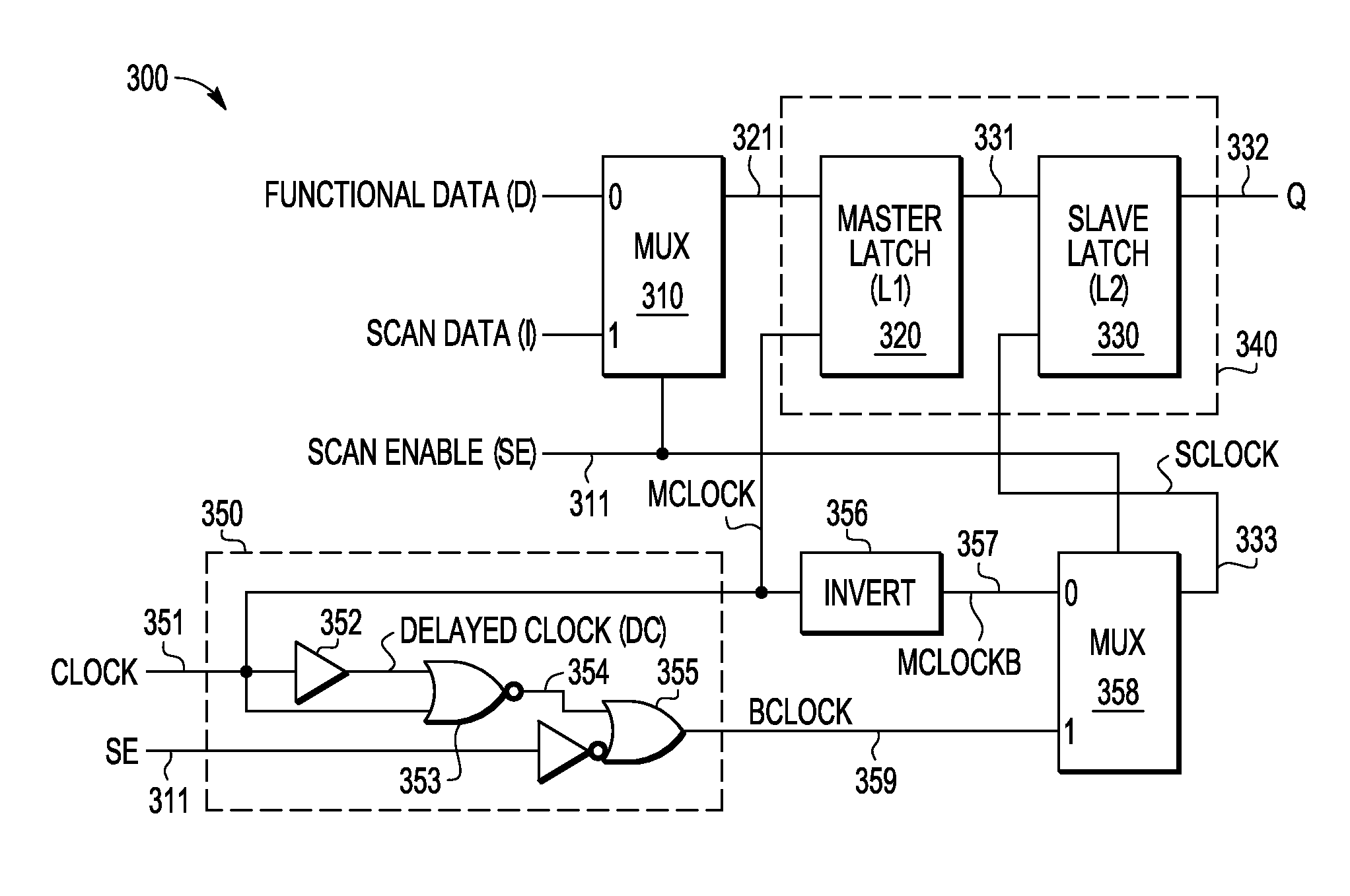
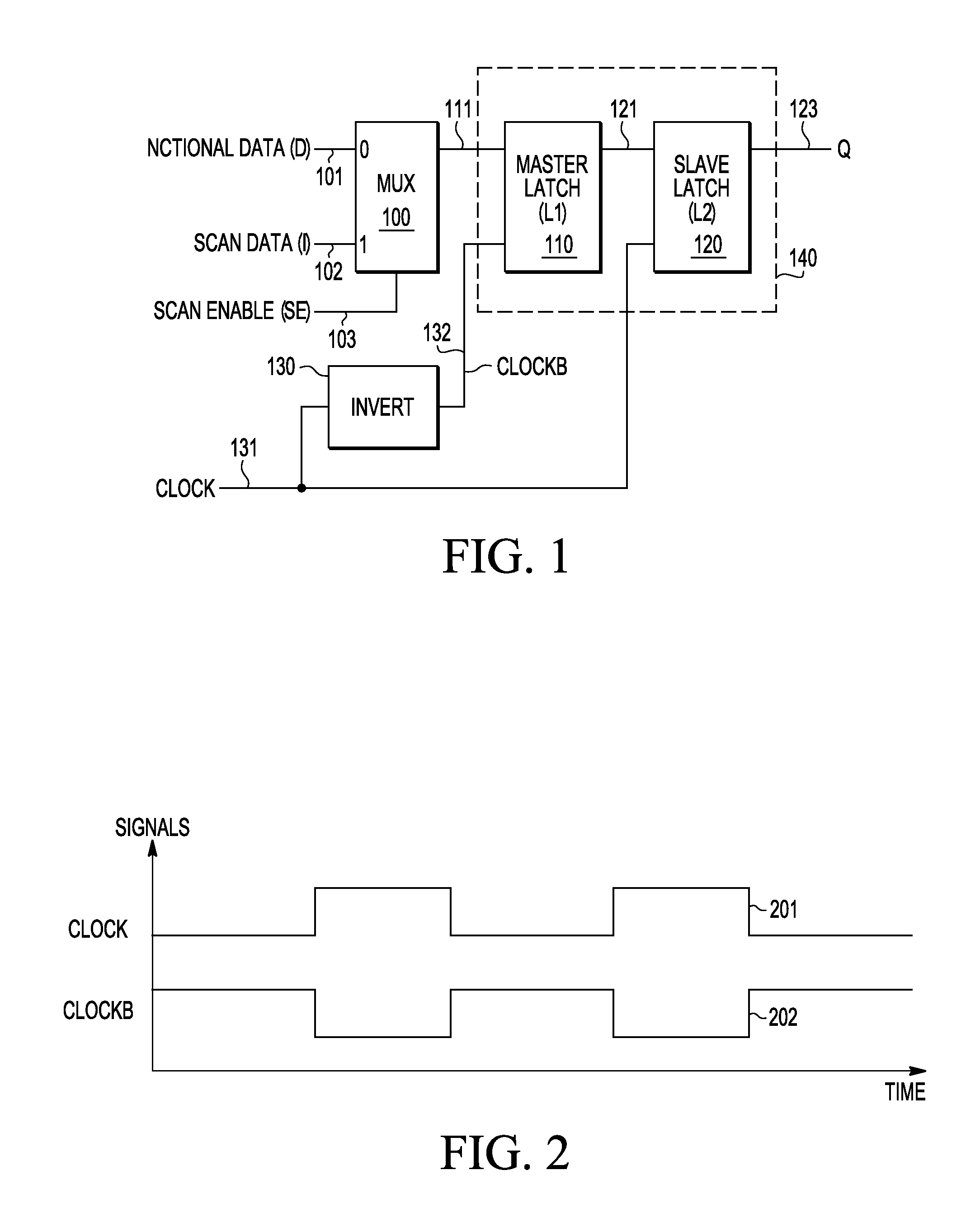
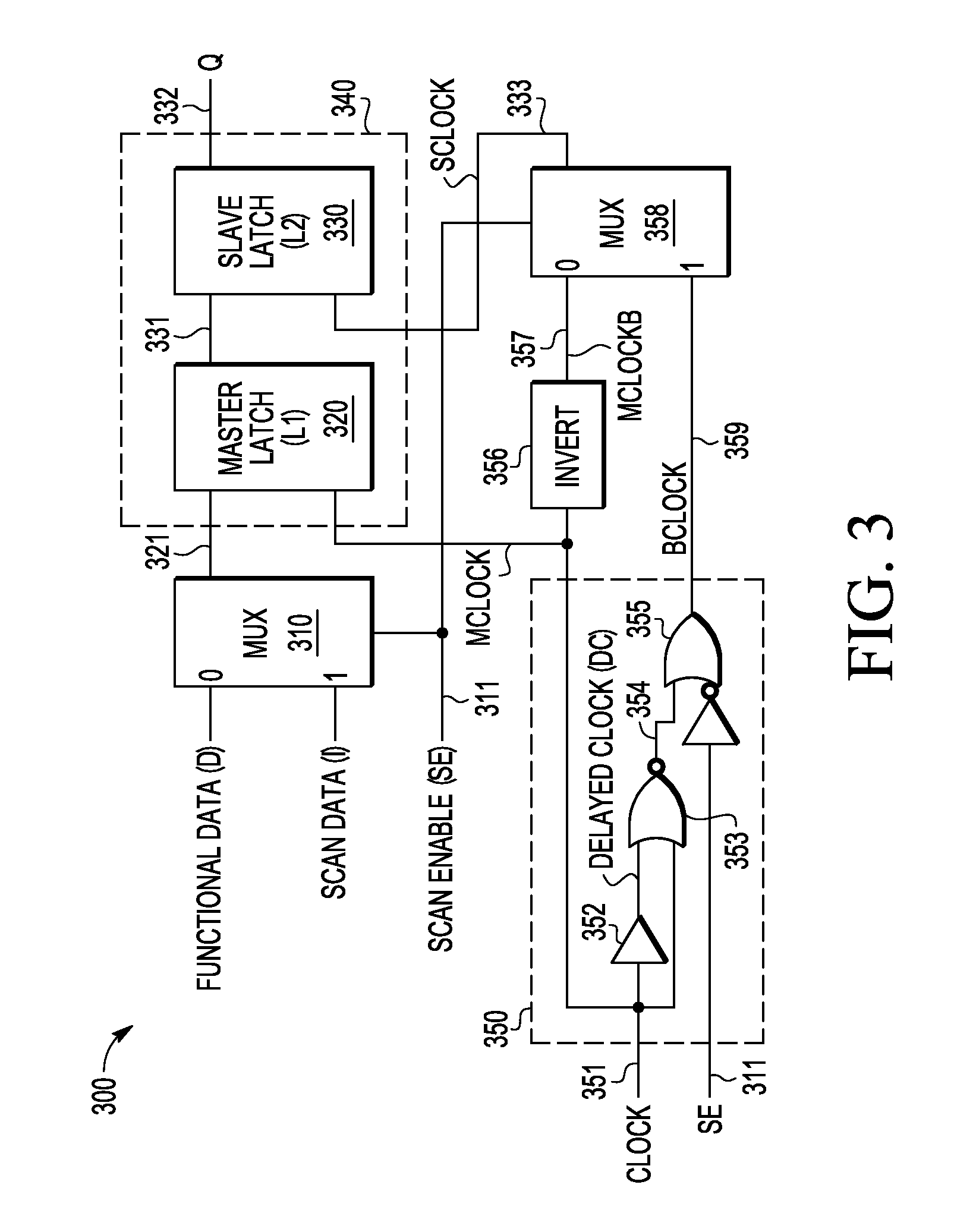
A multiplexed data flip-flop circuit (500) is described in which a multiplexer (510) outputs functional or scan data, a master latch (520) generates a master latch output signal at a hold time under control of a master clock signal, a slave latch (540) generates a flip flop output signal at a launch time under control of a slave clock signal, clock generation circuitry (550) generates a second clock signal that has a DC state during a functional mode and has a switching state during a scan mode, and data propagation logic circuitry (564) uses the first and second clock signals to generate the master and slave clock signals during a scan mode to delay the launch time of the slave latch with respect to the hold time of the master latch.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Time synchronization method and system for multi-core system
ActiveCN101359238ARealize time synchronizationAchieving Clock SynchronizationResource allocationGenerating/distributing signalsTime deviationSlave clock
The invention discloses a multi-core system time synchronization method and a system thereof; the time synchronization method comprises the following steps: A, establishing at least a clock synchronization domain, and distributing the cores respectively into each lock synchronization domain; B, selecting the core with the minimum load as the master clock synchronization source in each clock synchronous domain, and taking the clock synchronization domain having the master clock synchronization source with the minimum load among all the master clock synchronization sources as the master clock synchronization domain, and taking the other clock synchronization domains as the slave clock synchronization domains; C, after the master clock synchronization domain sends synchronization error detection information to each slave clock synchronization domain, calculating the time deviation value between each slave clock synchronization domain and the master clock synchronization domain; D, when the time deviation value is greater than the permitted deviation value, the master clock synchronization domain calculates the time adjustment quantity of each slave clock synchronization domain and releases the time adjustment quantity to each slave clock synchronization domain, then each slave clock synchronization domain makes adjustment based on the corresponding time adjustment quantity. The invention effectively solves the time synchronization problem of the multi-core system.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method and system for synchronizing clock of transmission network as well as subordinate clock side entity
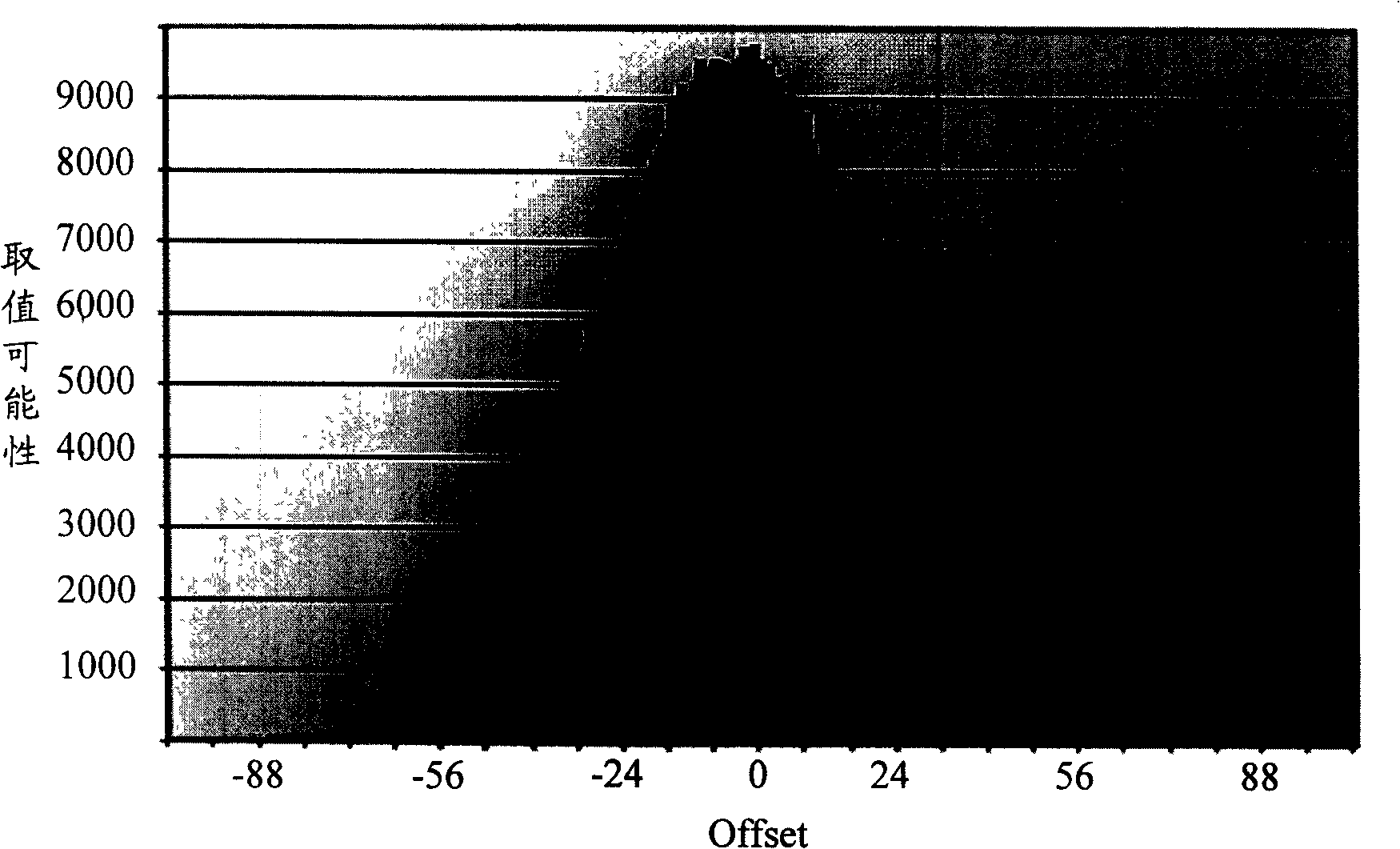
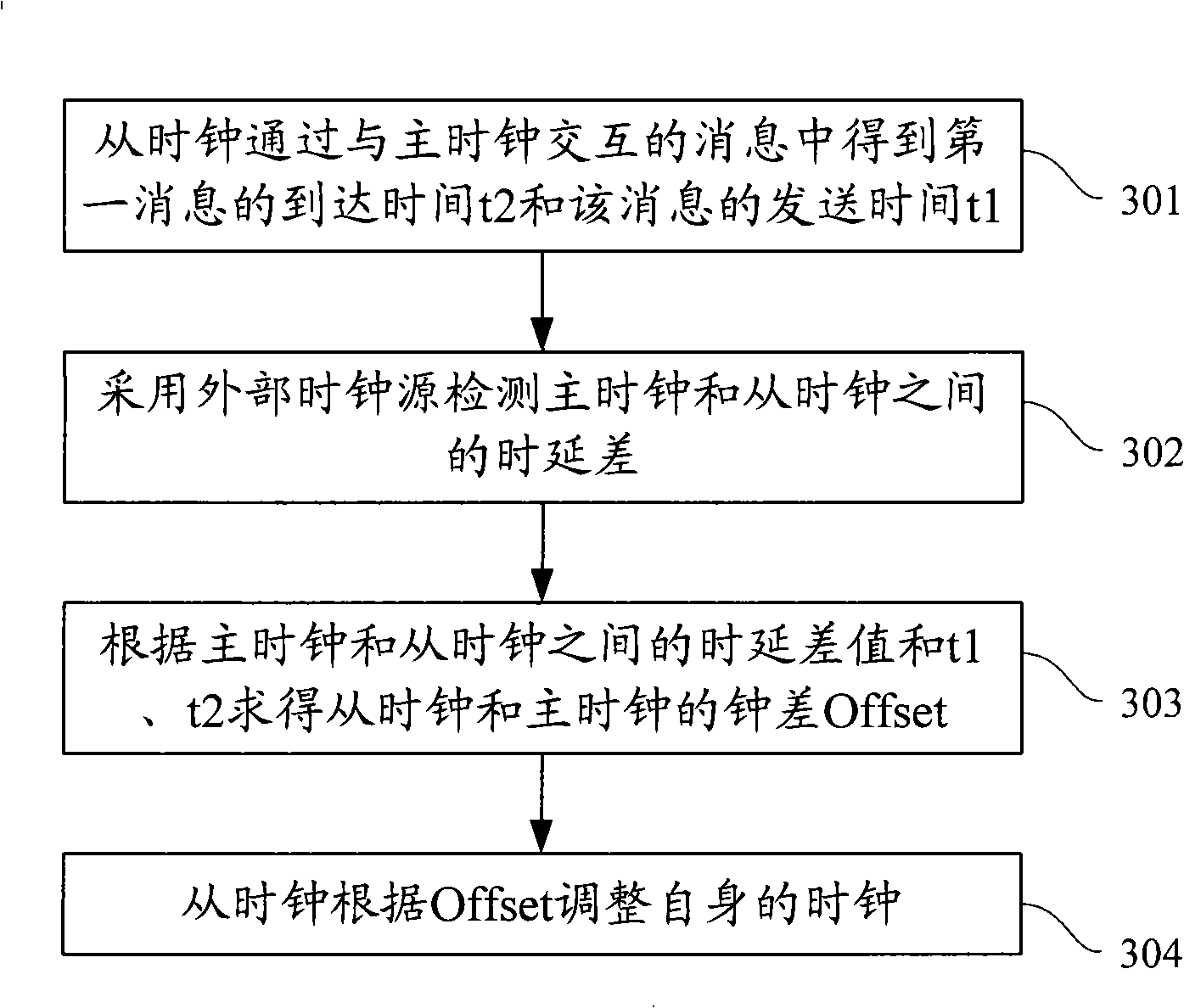
The invention discloses a clock synchronization method in a transmission network. The method comprises the steps of obtaining the arrival time t2 and the sending time t1 of first message through the interaction of a slave clock and a master clock; adopting external clock source to detect the time delay of the master clock and the salve clock; seeking clock error Offset according to the time delay between the master clock and the slave clock, t1 and t2; and adjusting the clock of the slave clock according to Offset. The invention further discloses a clock synchronization method in other two transmission networks, and also discloses a clock synchronization system of three transmission networks. The clock synchronization method of the invention can accurately calculate clock error Offset, thereby ensuring the synchronization of the slave clock and the master clock.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Network Packet Timing Synchronization For Virtual Machine Host Systems
ActiveUS20160112182A1Synchronisation information channelsTime-division multiplexVirtualizationSlave clock
Network timing synchronization for virtual machine (VM) host systems and related methods are disclosed that provide synchronization of master / slave clocks within VM host hardware systems. Master timing messages are sent from the master clocks to slave clocks within VM guest platforms hosted by the VM host hardware system within a virtualization layer, and return slave timing messages are communicated from the VM guest platforms to the master clock. Virtual switches within the virtualization layer use virtual transparent clocks to determine intra-switch delay times for the timing packets traversing the virtual switch. These intra-switch delay times are then communicated to target destinations and used to account for variations in packet transit times through the virtual switch. The VM guest platforms synchronize their timing using the timing messages. The master / slave timing messages can be PTP (Precision Time Protocol) timing messages and / or timing messages based upon some other timing protocol.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH SINGAPORE (SALES) PTE LTD
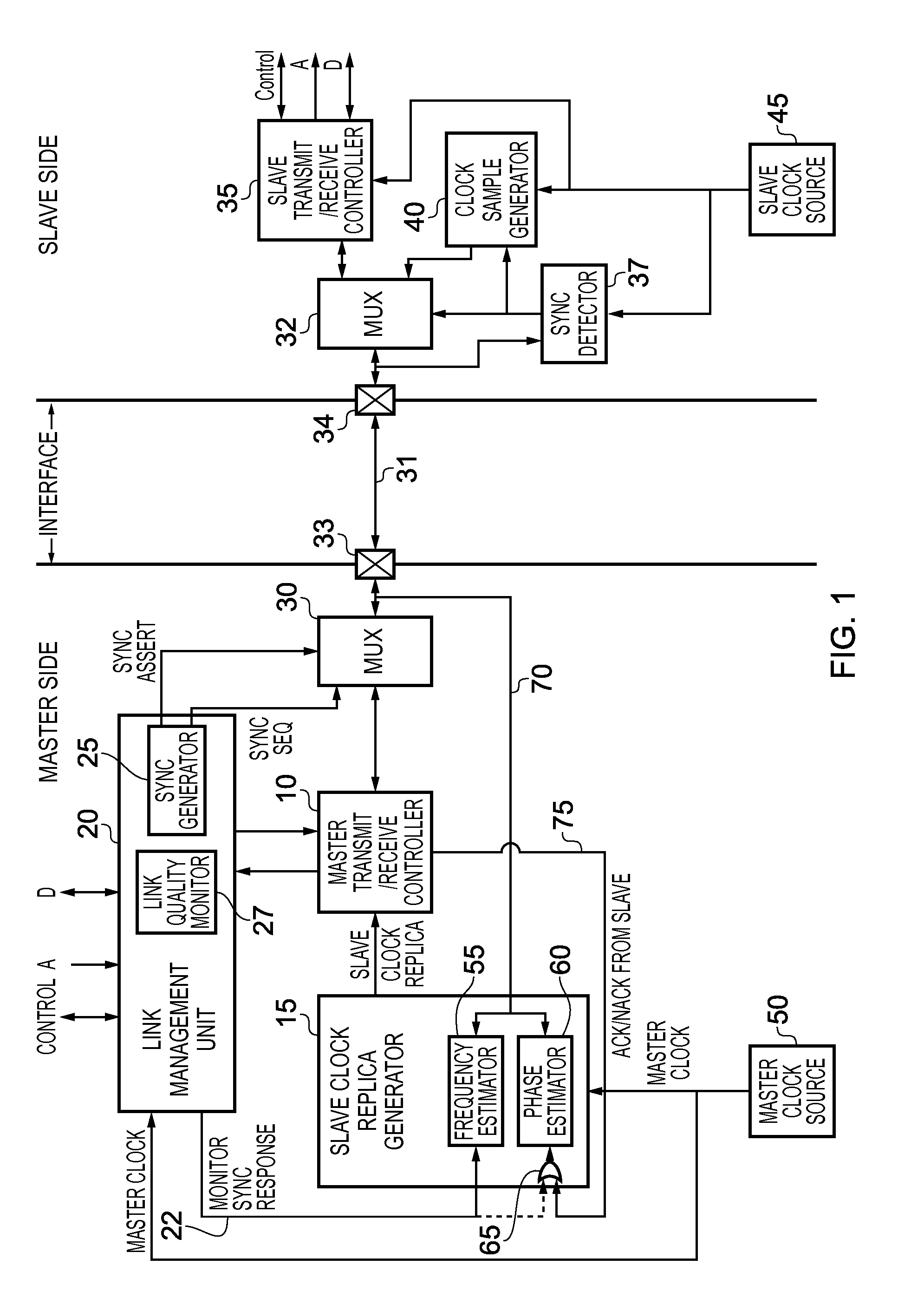
Data processing apparatus and method for communicating between a master device and an asychronous slave device via an interface
ActiveUS20140351359A1Overhead associated with the issuance of such sync request transfers is relatively minorAccurate signalGenerating/distributing signalsBus networksSlave clockNetwork packet
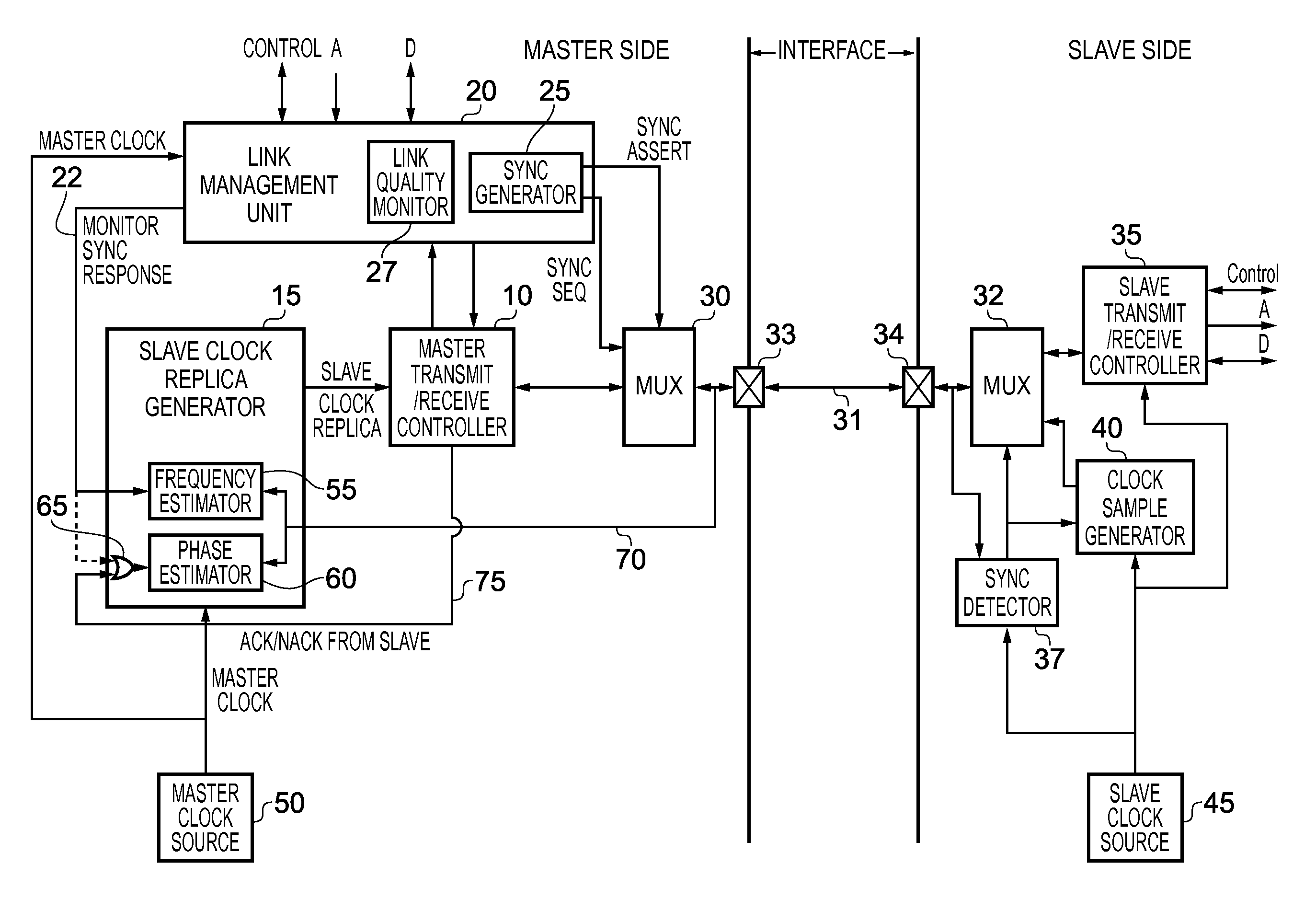
A data processing apparatus and method provide communication between a master device operating from a master clock signal and a slave device operating from a slave clock signal asynchronous to the master clock signal. An interface transfers packets between the master device and the slave device. A slave clock replica generator associated with the master device generates a slave clock replica that controls timing of transmission of packets by the master device over the interface. A sync request transfer is issued over the interface and has a property identifiable by the slave device irrespective of whether the sync request transfer is synchronised with the slave clock signal. In response, the slave device issues a sync response transfer indicative of at least a frequency of the slave clock signal, and the slave clock replica generator determines at least the frequency of the slave clock replica from that sync transfer.
Owner:ARM LTD
Frequency Synchronization Using First and Second Frequency Error Estimators
ActiveUS20100158183A1Simple technologyImprove performancePulse automatic controlTime-division multiplexComputer hardwareCommunications system
An endpoint or other communication device of a communication system includes a clock recovery module. The communication device is operative as a slave device relative to another communication device that is operative as a master device. The clock recovery module comprises a clock recovery loop configured to control a slave clock frequency of the slave device so as to synchronize the slave clock frequency with a master clock frequency of the master device. The clock recovery loop comprises a primary loop having a first frequency error estimator for generating a first estimate of error between the master and slave clock frequencies, a second frequency error estimator outside of the primary loop for generating a second estimate of error between the master and slave clock frequencies, and an accumulator coupled between the second frequency error estimator and the primary loop. The second estimate is controllably injected into the primary loop via the accumulator.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Multiprocessor system with interactive synchronization of local clocks
ActiveUS20050033947A1Little in obtainingError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsPrimary stationSlave clock
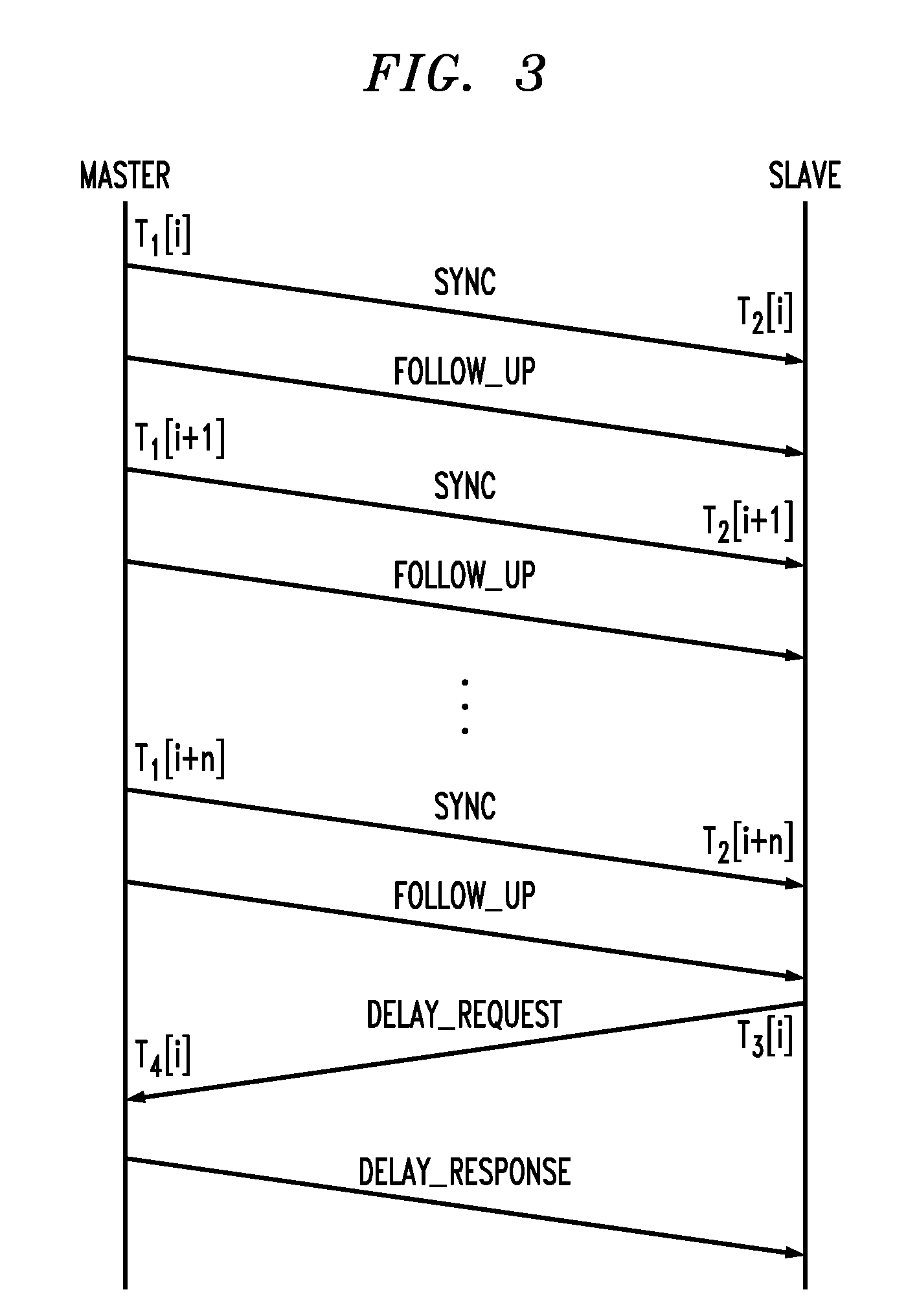
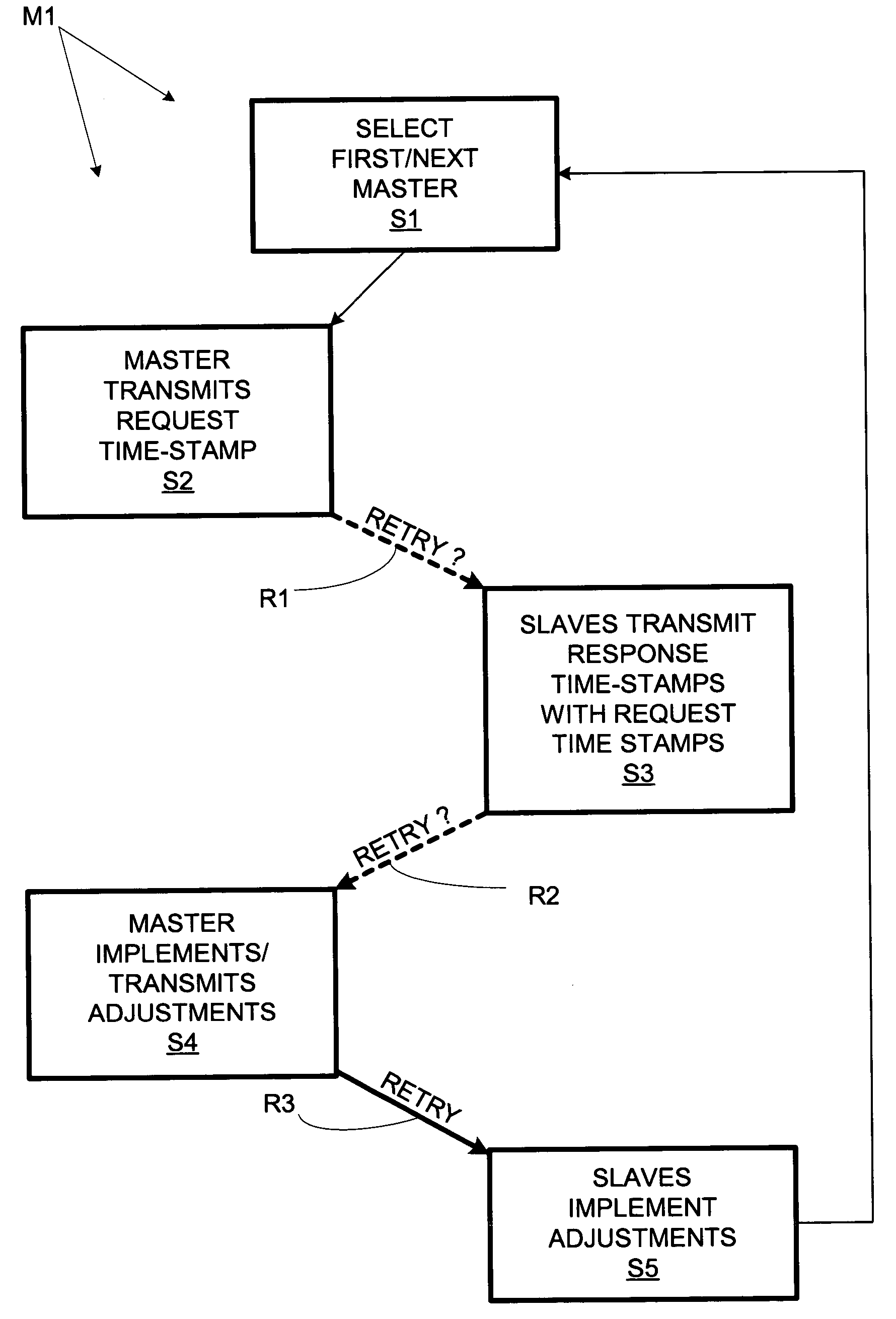
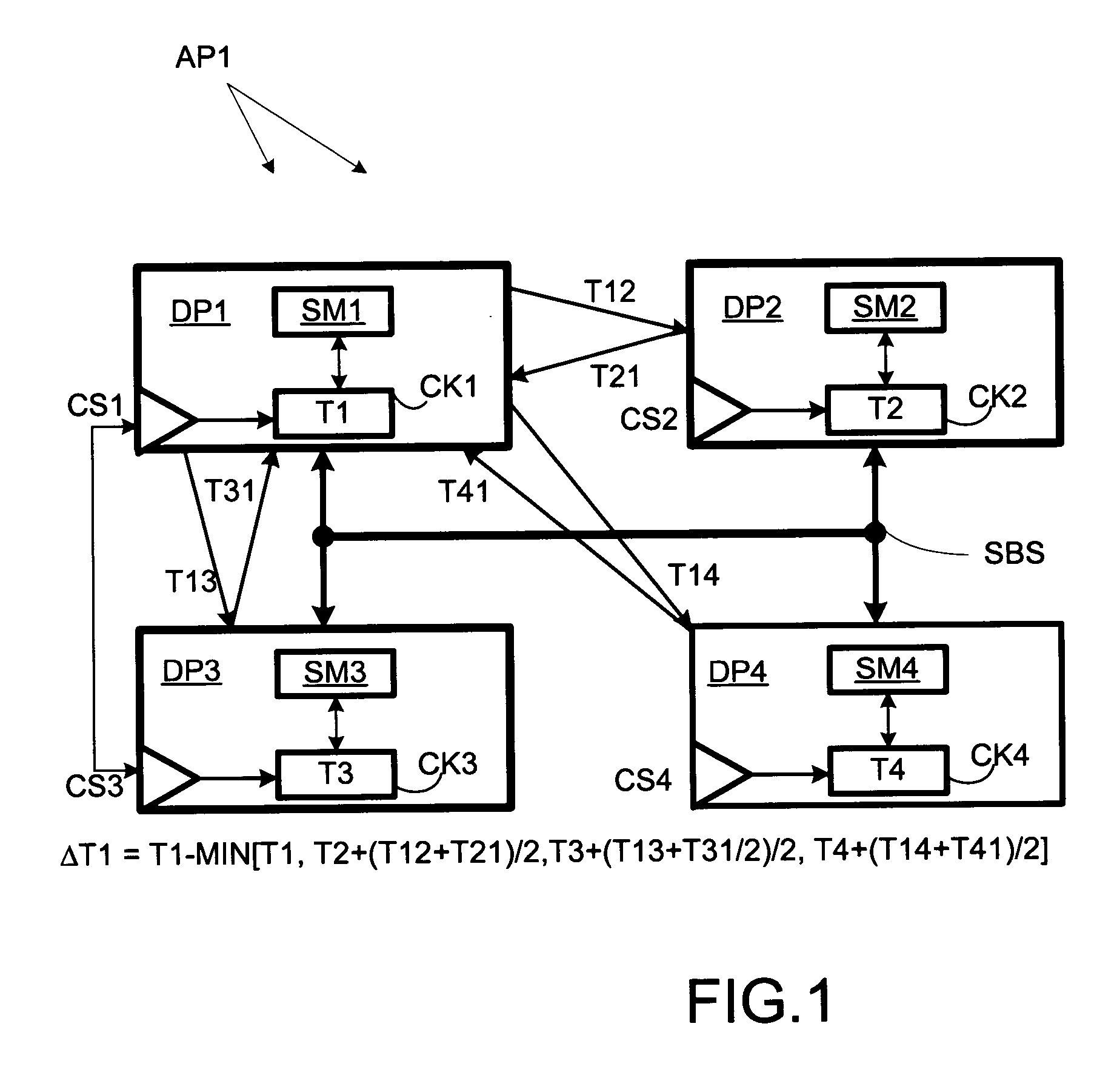
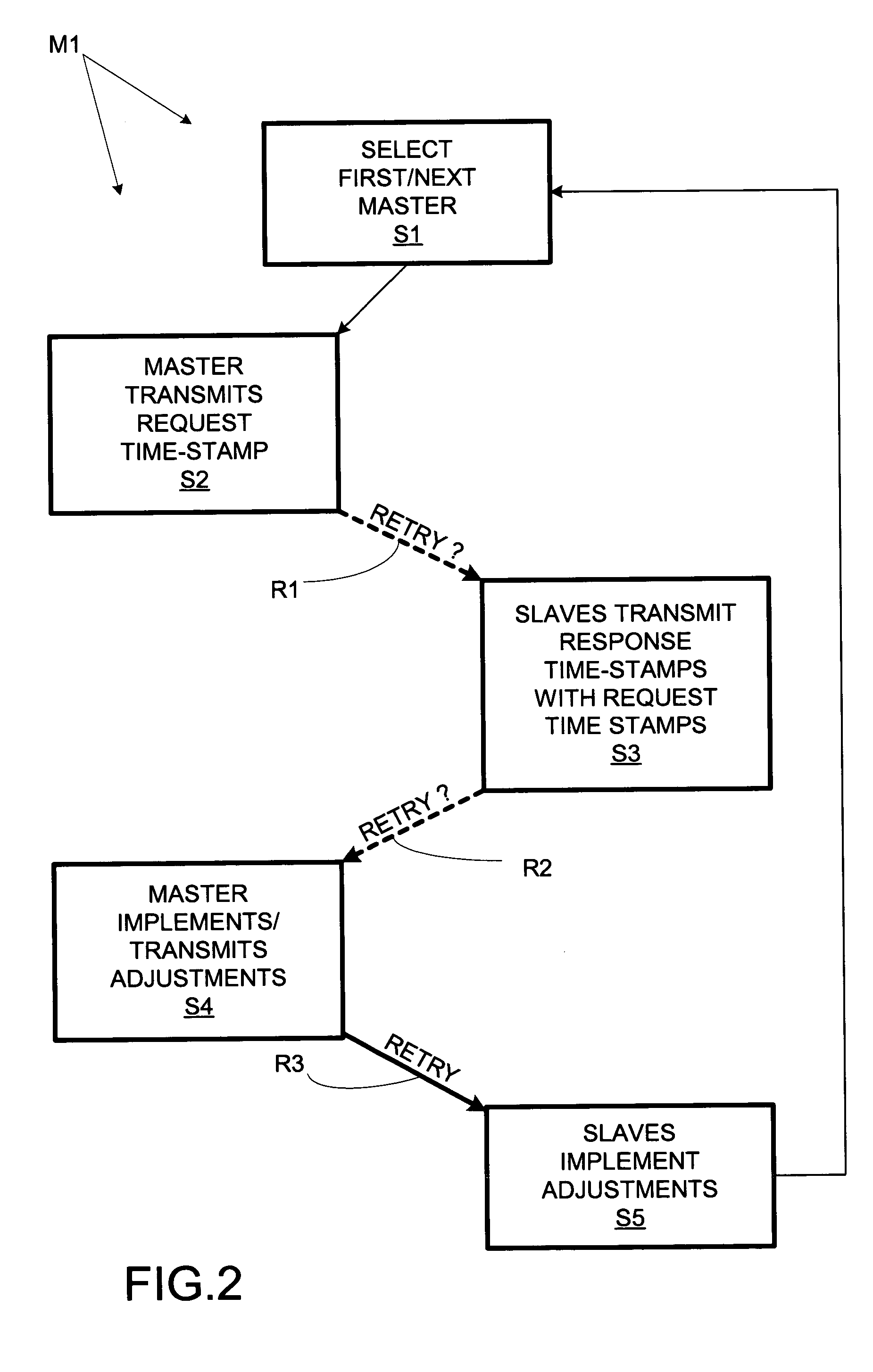
A multiprocessor computer system comprises multiple data processors, each with an internal clock for providing time stamps to application software. The processors take turns as synchronization masters. The present master transmits a “request” time stamp (indicating the time of transmission according to the local clock) to the other (“slave”) processors. Each slave processor responds by returning a “response” time stamp (indicating the time of transmission of the response according to the local slave clock) of its own along with the received request time stamp. The master calculates clock adjustment values from the time of receipt of the responses and the included time stamps. This allows asynchronous clocks to be synchronized so that application time stamps can be validly compared across processors.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
Method and system for realizing high precision time synchronization among SDH equipment
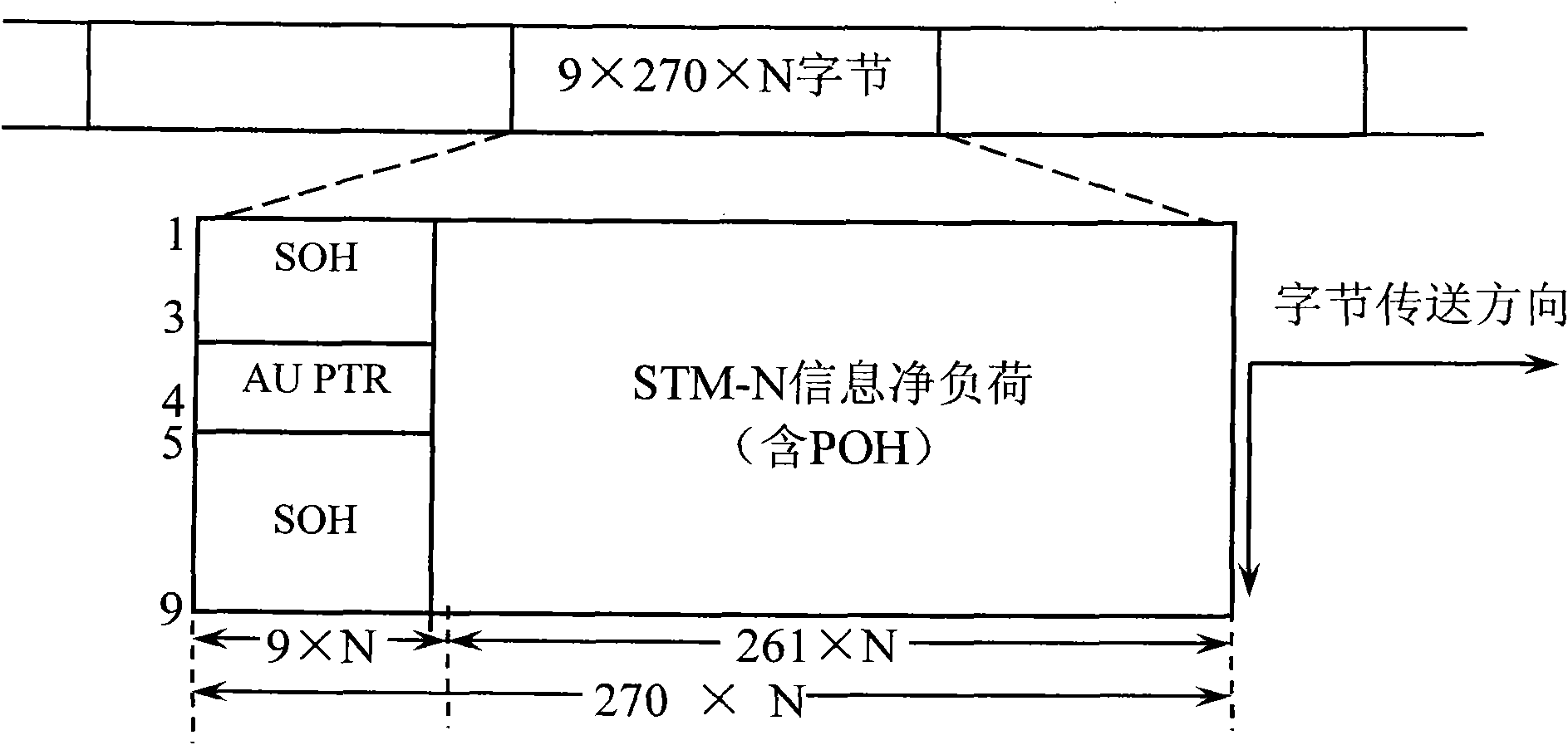
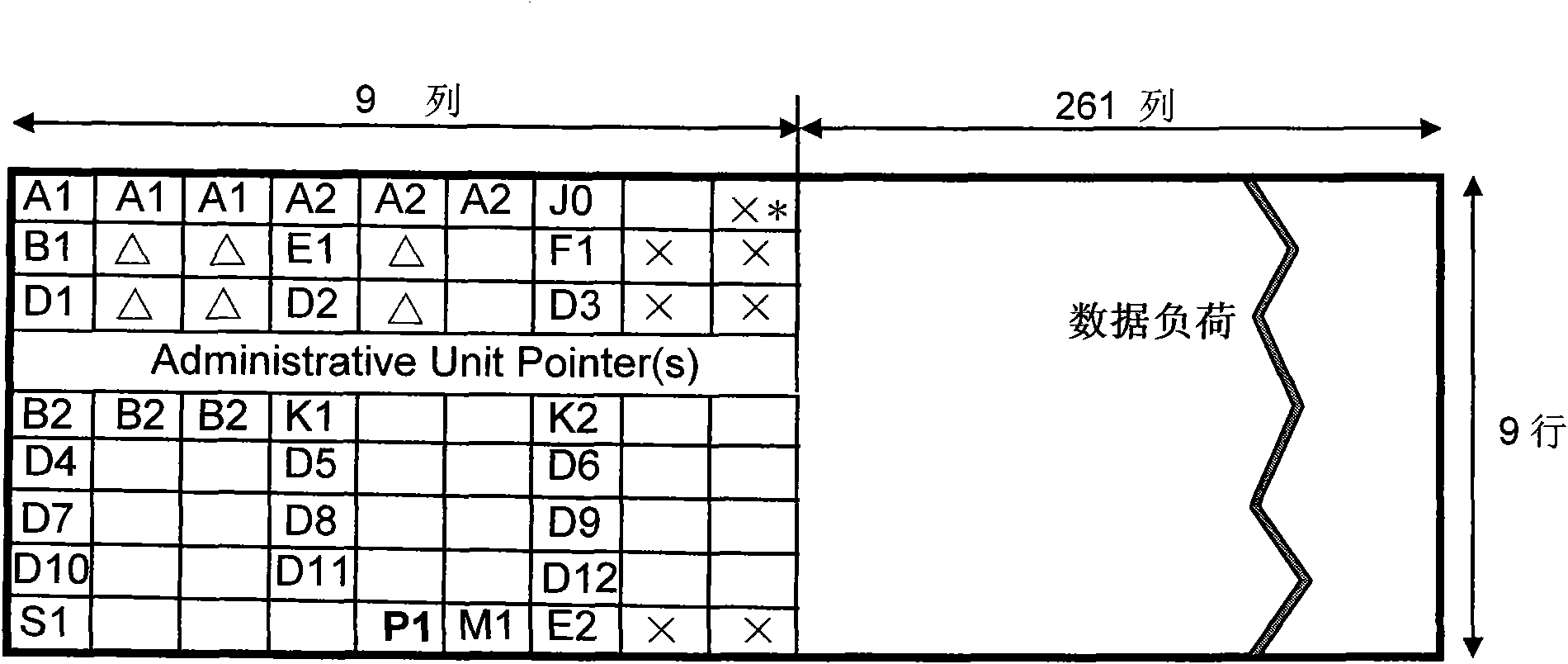
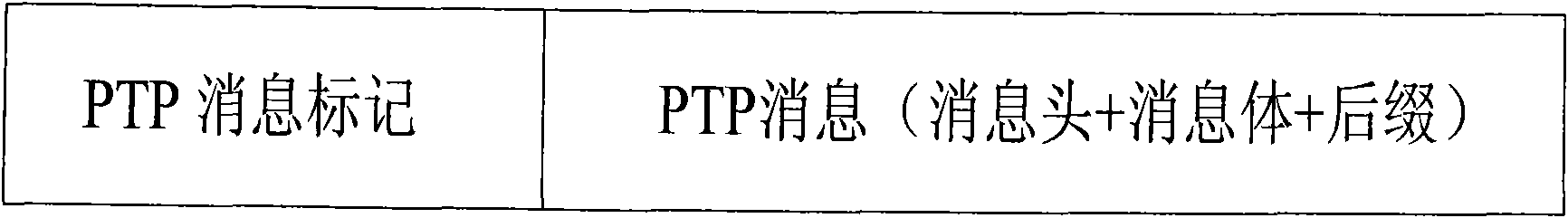
InactiveCN101582733AAvoid safety hazardsSolve deployment problemsTime-division multiplexSlave clockMobile communication systems
A method for realizing high precision time synchronization among synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) equipment includes the step: a piece of SDH equipment as a slave clock and a piece of SDH equipment as a master clock use the idle bytes in section overhead of an SDH frame to conduct the interaction of PTP messages, the time difference between the slave clock and the master clock is calculated and the time difference is utilized to calibrate the slave clock. And a system for realizing high precision time synchronization among SDH equipment includes: the SDH equipment as the slave clock and the SDH equipment as the master clock. The slave clock uses the idle bytes in section overhead of the SDH frame to conduct the interaction of PTP messages with the master clock and calculates the time difference with the master clock, and then the time difference is used to calibrate the slave cock. The master clock uses the idle bytes in section overhead of the SDH frame to conduct the interaction of PTP messages with the slave clock. The adoption of the method and the system can ensure that the high precision time synchronization among the SDH equipment is realized and satisfy the requirements of all mobile communication systems at the present stage.
Owner:ZTE CORP
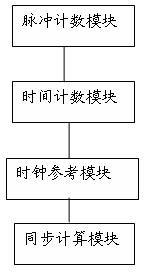
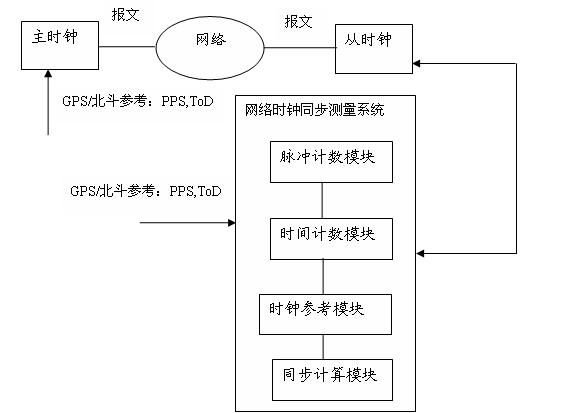
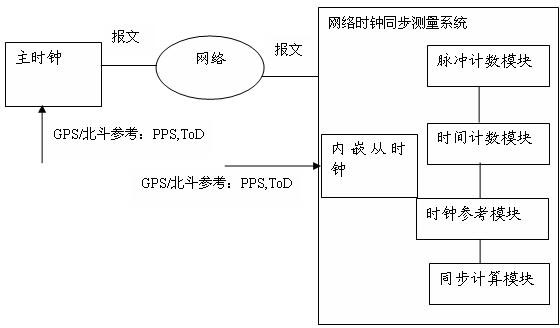
System and method for measuring network clock synchronization
The invention discloses a system for measuring network clock synchronization, is applied to the communication and smart grid fields. The system comprises a pulse countering module, a time counting module, a clock reference module and a synchronization calculation module, wherein the pulse counting module calculates pulse frequency difference between a master clock and a slave clock, the master clock is synchronous with a remote reference clock, and the slave clock is synchronous with the master clock through a network so as to be synchronous with the remote reference clock; the time counting module measures the time difference between the master clock and the slave clock; the clock reference module inputs a reference clock, and the reference clock is synchronous with the remote reference clock; and the synchronization calculating module is used for calculating network clock synchronization parameters according to the time difference and the pulse frequency difference and outputting time synchronization parameters. The system disclosed by the invention can be used for evaluating the clock frequency synchronization accuracy and the time synchronization accuracy which can be reached at each node by an IEEE1588PTP (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers 1588 Peer To Peer) clock synchronous network, and important reference data is provided for clock synchronization network optimization, and performance prediction on application and equipment depending on clock synchronization.
Owner:上海奇微通讯技术有限公司
IEEE 1588-based synchronization system and synchronization method thereof
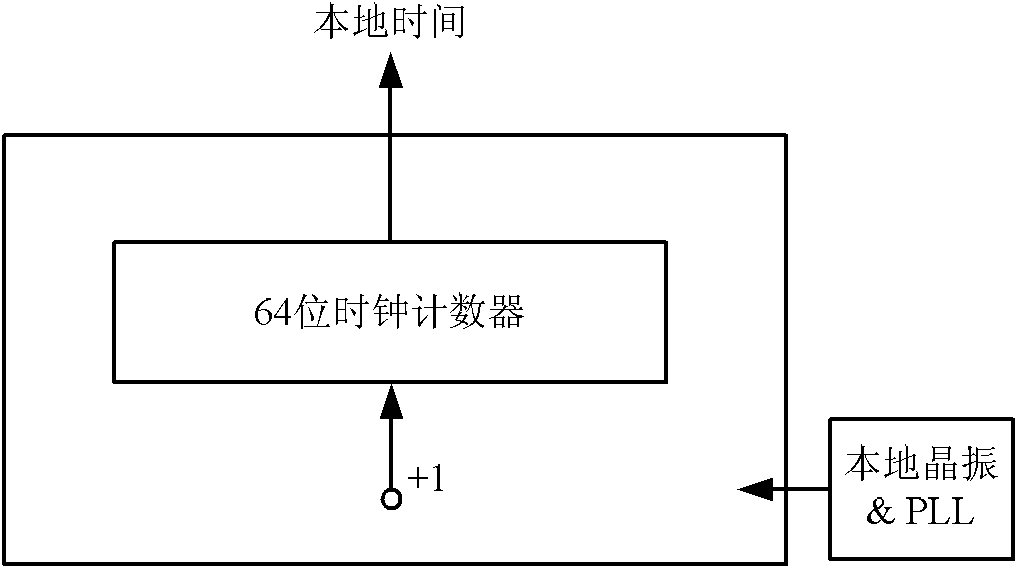
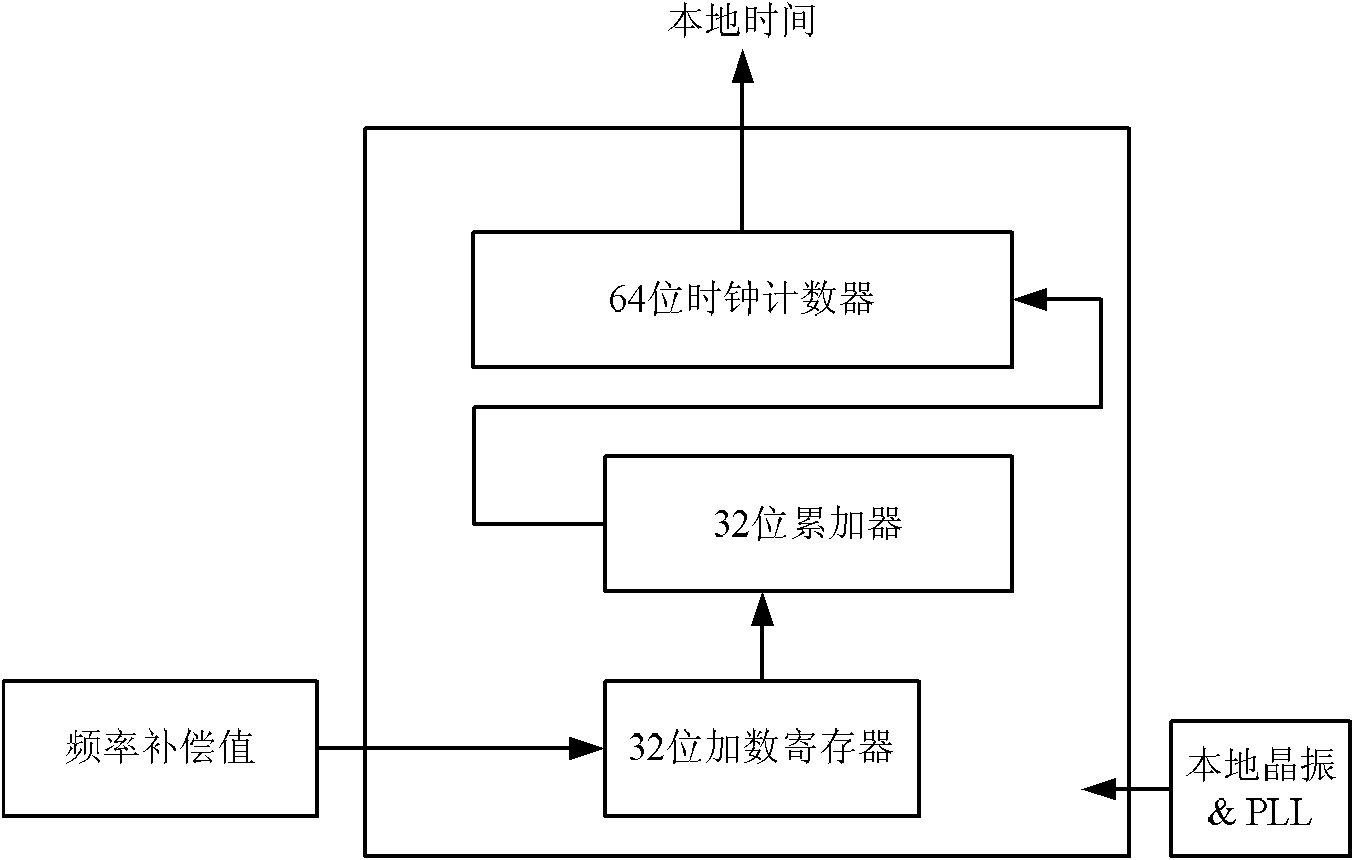
ActiveCN102104475ARealize the function of frequency compensationImprove Clock Synchronization AccuracyTime-division multiplexData switching networksData synchronizationFrequency compensation
The invention discloses an IEEE 1588 accurate clock synchronization protocol-based synchronization system and a synchronization method thereof in the technical field of wireless communication. The system consists of master equipment and slave equipment which are connected through a network, wherein the master equipment comprises a main clock module and a central processing unit (CPU) management control module; and the slave equipment comprises a slave clock module and a CPU management control module. Due to the adoption of a frequency compensation clock provided by Balasubramanian and the like, a frequency adjustable clock counter is constructed and the frequency compensation function is realized; and an improved clock synchronization method is adopted, the limited machine precision of anembedded system, namely influence brought by truncation errors is considered; therefore, higher clock synchronization accuracy is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method and devices for clock synchronization over links with asymmetric transmission rates
This invention relates to methods and devices for clock synchronization. The invention has particular application in the alignment of slave clocks to a master clock and in dealing with transmission delay asymmetries where the forward and reverse communication paths between the master and slave clocks have asymmetric transmission rates. Such methods and devices have particular application in small cell backhaul solutions for 4G / LTE deployments. In embodiments of the invention, the slave clock uses link rate information to estimate the transmission delay asymmetry and thus estimate the offset and skew of the slave clock. Embodiments provide a simple linear approximation technique and a Kalman filter-based technique for estimating offset and skew of the slave clock.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC +2
Method for precisely synchronizing time of industrial wireless network on basis of prediction and compensation
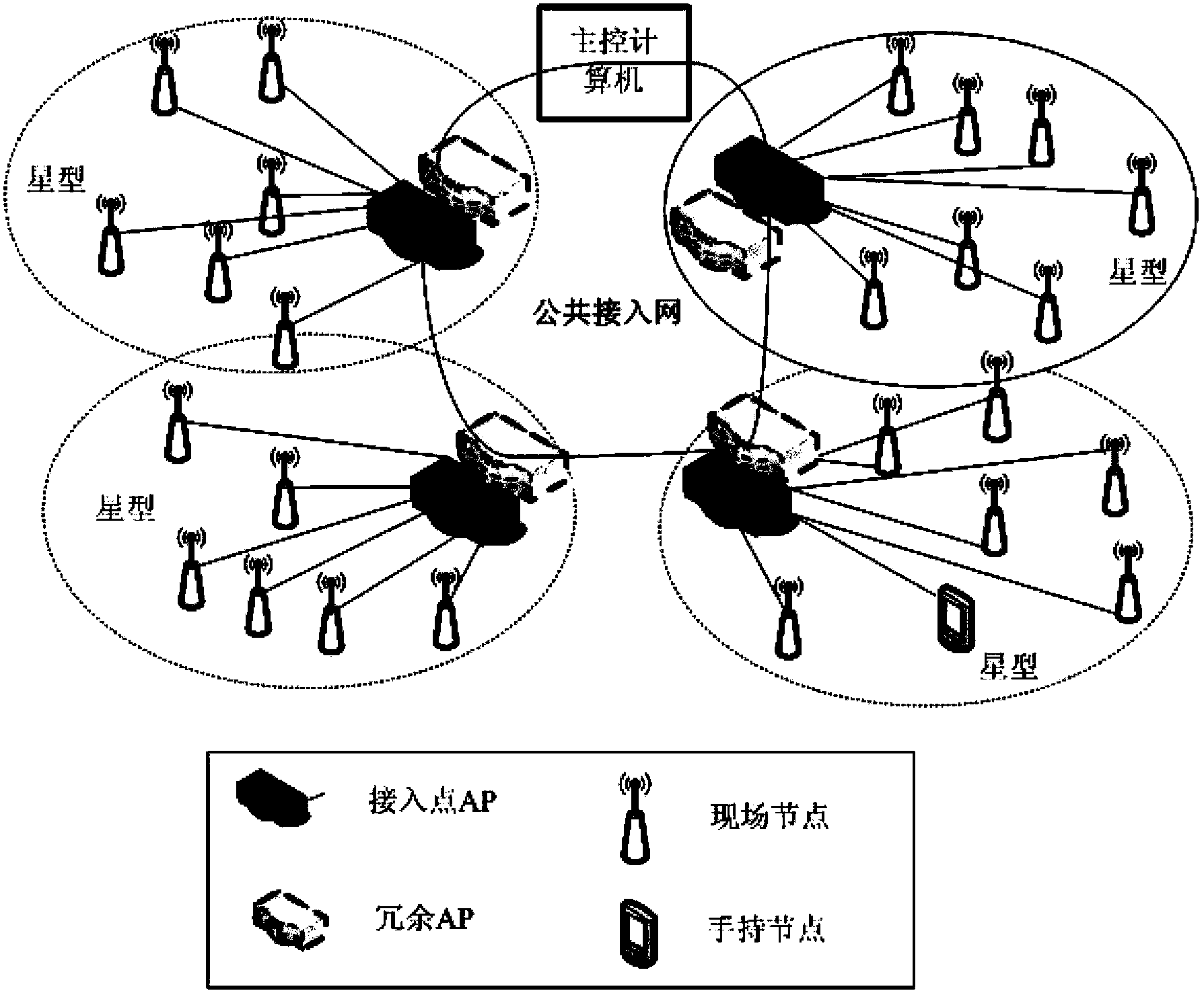
The invention relates to technologies for industrial wireless networks, in particular to a method for precisely synchronizing time of an industrial wireless network on the basis of prediction and compensation. The method includes constructing the factory-automation-oriented industrial wireless network into a star network on the basis of an IEEE (institute of electrical and electronics engineers) 802.11 single-hop basic service set (BBS) structure; setting a master clock and slave clocks according to types and functions of nodes in the industrial wireless network; enabling a master clock side and slave clock sides to interact with one another via two-way timestamp information and computing a time deviation value of a current synchronizing cycle; predicting a time deviation value of a next synchronizing cycle by the aid of the time deviation value of the current synchronizing cycle; compensating clock drift by the aid of the predicted time deviation value of the next synchronizing cycle and correcting the clocks. The method has the advantages that the method is implemented on the premise that application requirements of factory automation are sufficiently considered, so that high time synchronization precision can be realized by the aid of few wireless communication resources, and purposes of high precision, high efficiency, low expenditure and easiness in implementation can be achieved.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com