Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
348 results about "Phase converter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A phase converter is a device that converts electric power provided as single phase to multiple phase or vice versa. The majority of phase converters are used to produce three-phase electric power from a single-phase source, thus allowing the operation of three-phase equipment at a site that only has single-phase electrical service. Phase converters are used where three-phase service is not available from the utility, or is too costly to install due to a remote location. A utility will generally charge a higher fee for a three-phase service because of the extra equipment for transformers and metering and the extra transmission wire.
Efficient power supply
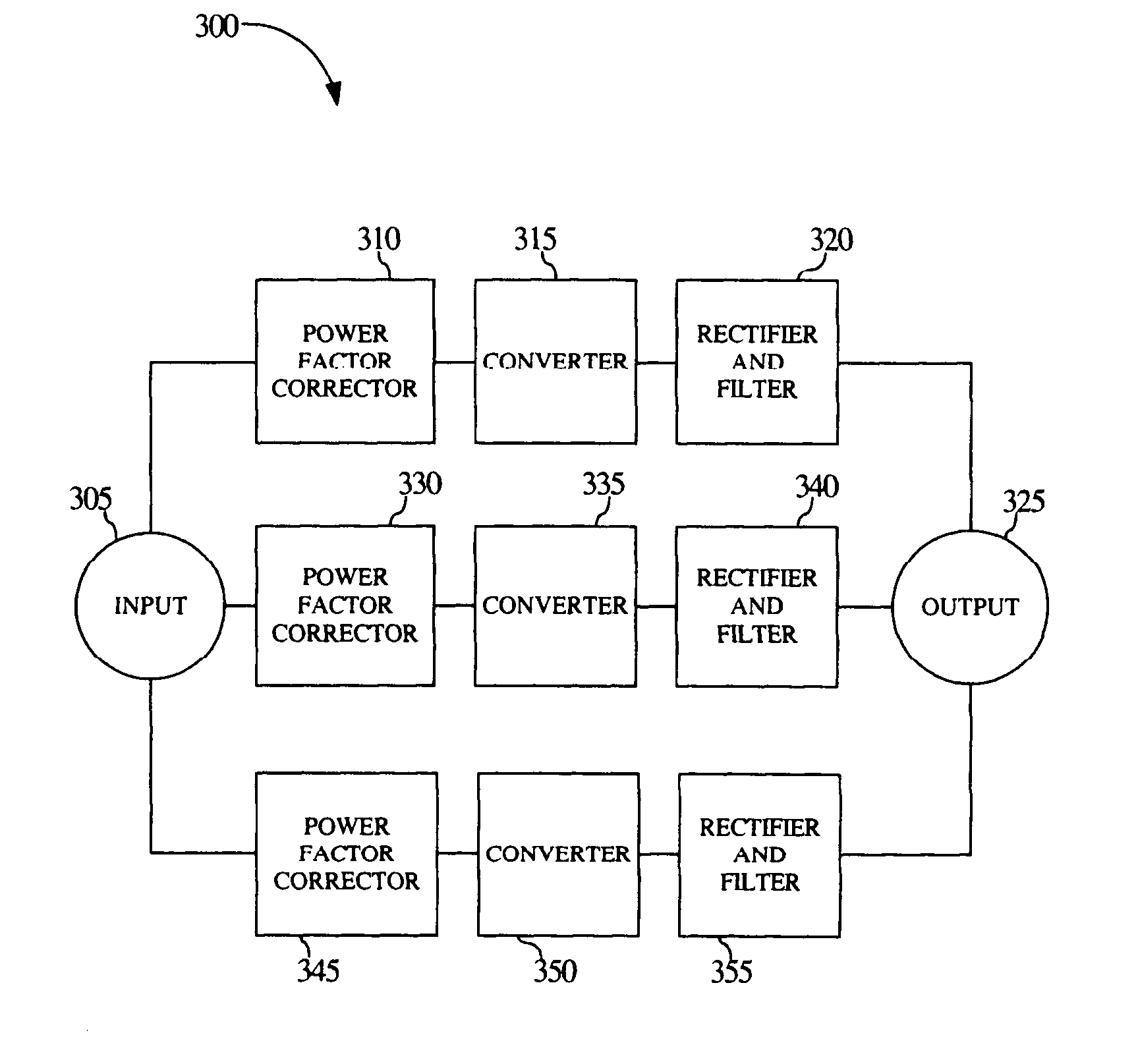
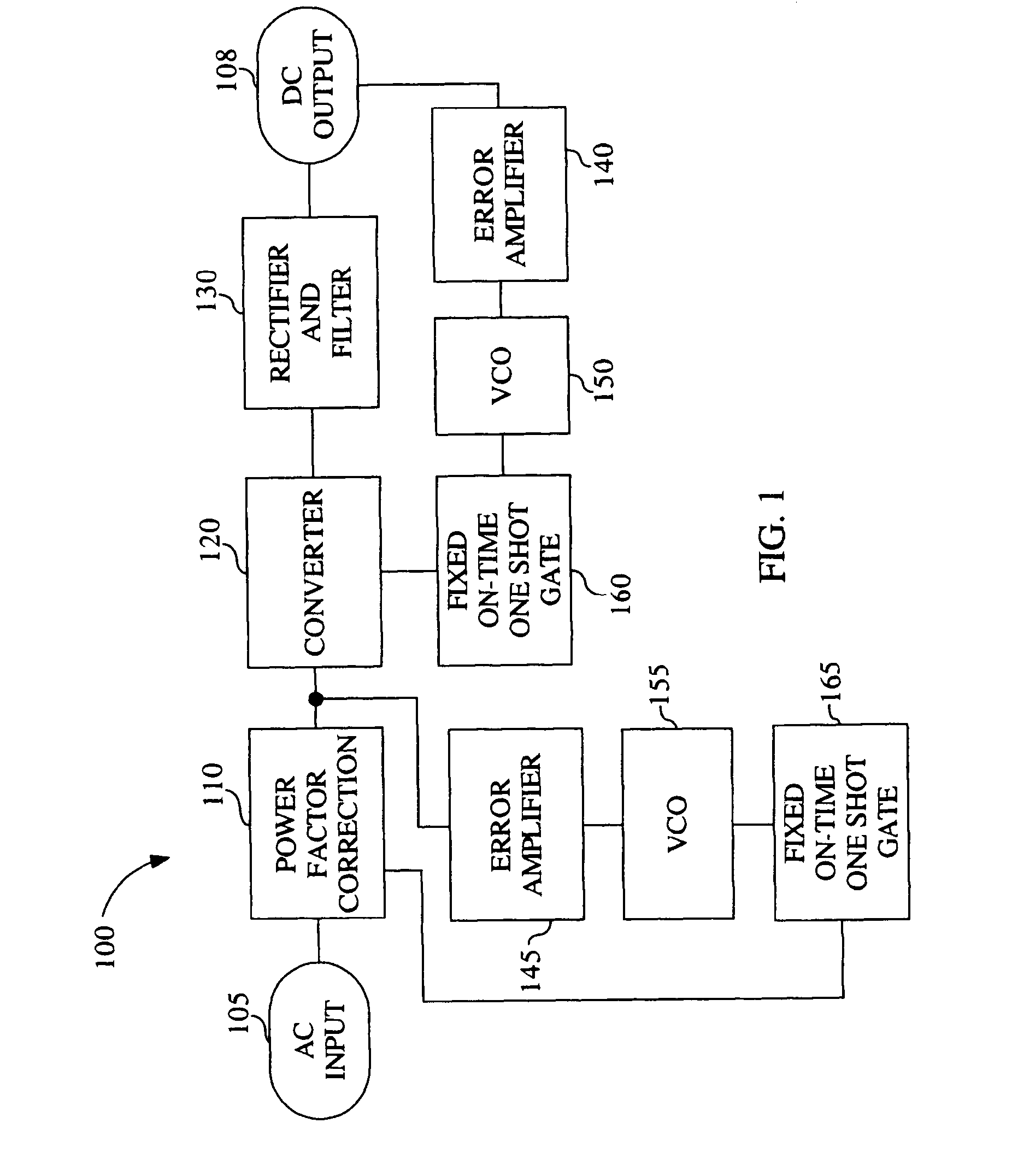
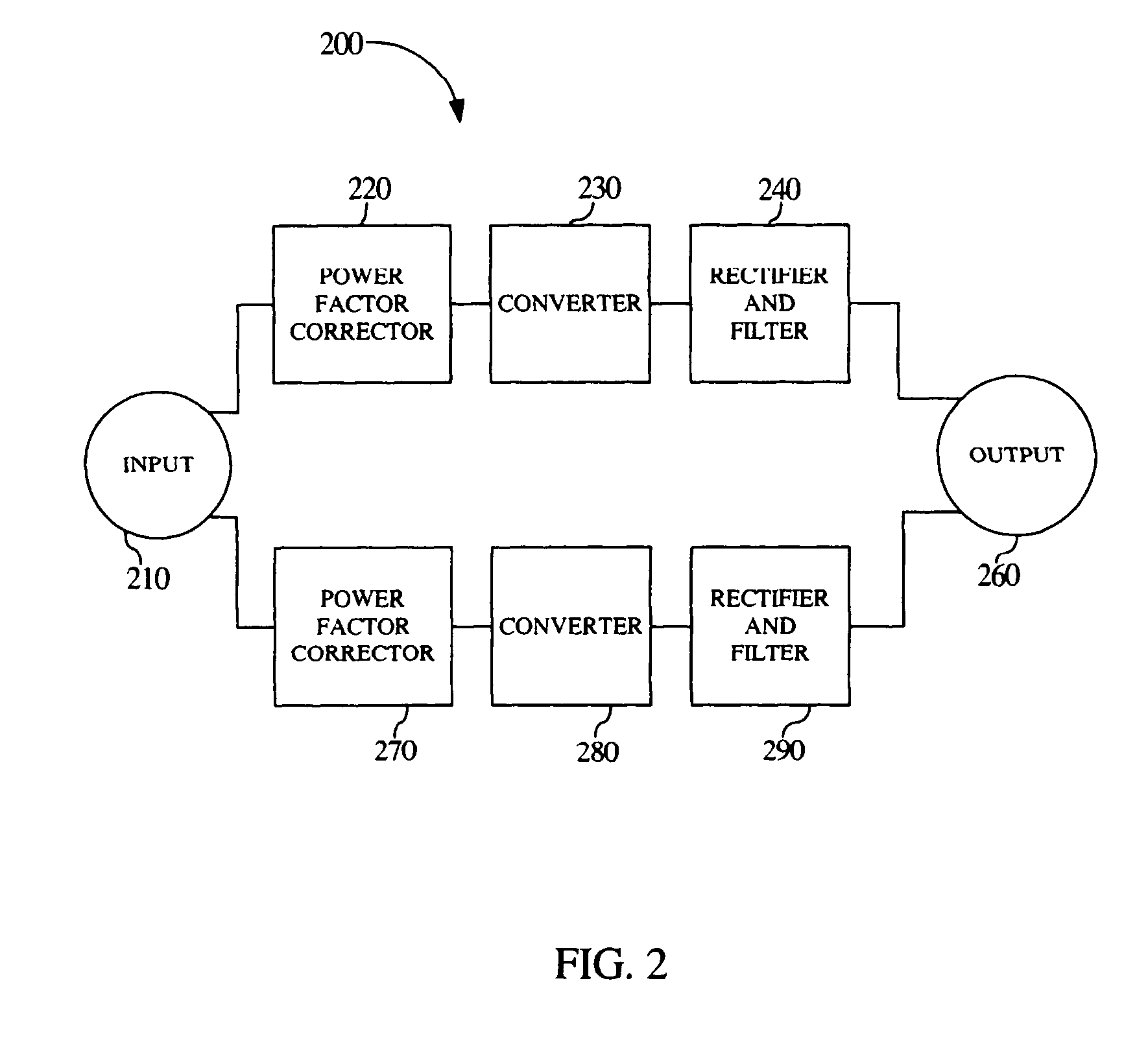
ActiveUS7639520B1Improve power efficiencyEfficient at light loadAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionSwitching frequencyAlternating current
The present invention is a method and system for efficiently converting an alternating current (AC) supply to a direct current (DC) output. A power supply in accordance with the present invention may employ variable frequency constant on-time converters whereby switching losses of the converters are approximately proportional with a switching frequency, causing the power supply to be more efficient at light loads. Additionally, a power supply in accordance with the present invention may include multiple-phase converters in which each phase is designed for operation at a fraction of the total maximum load for the power supply.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
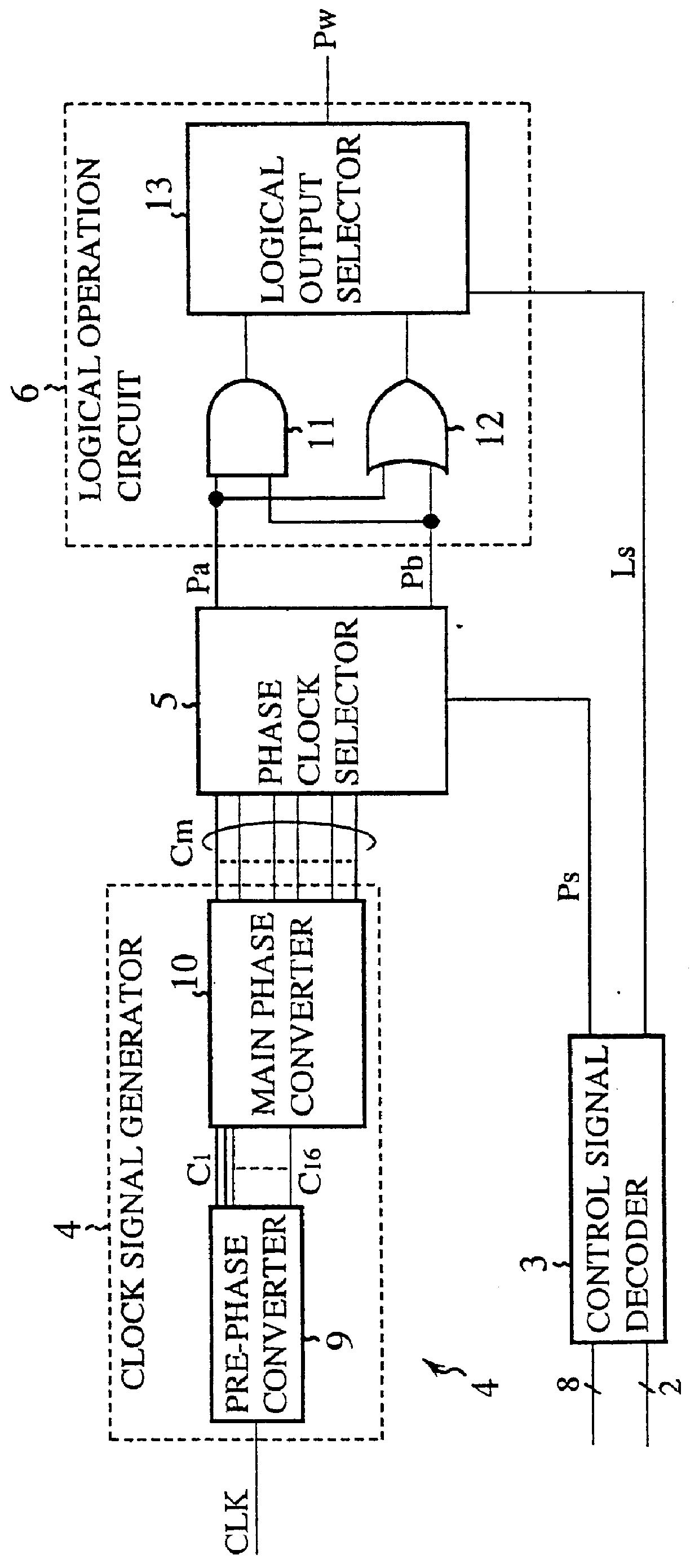
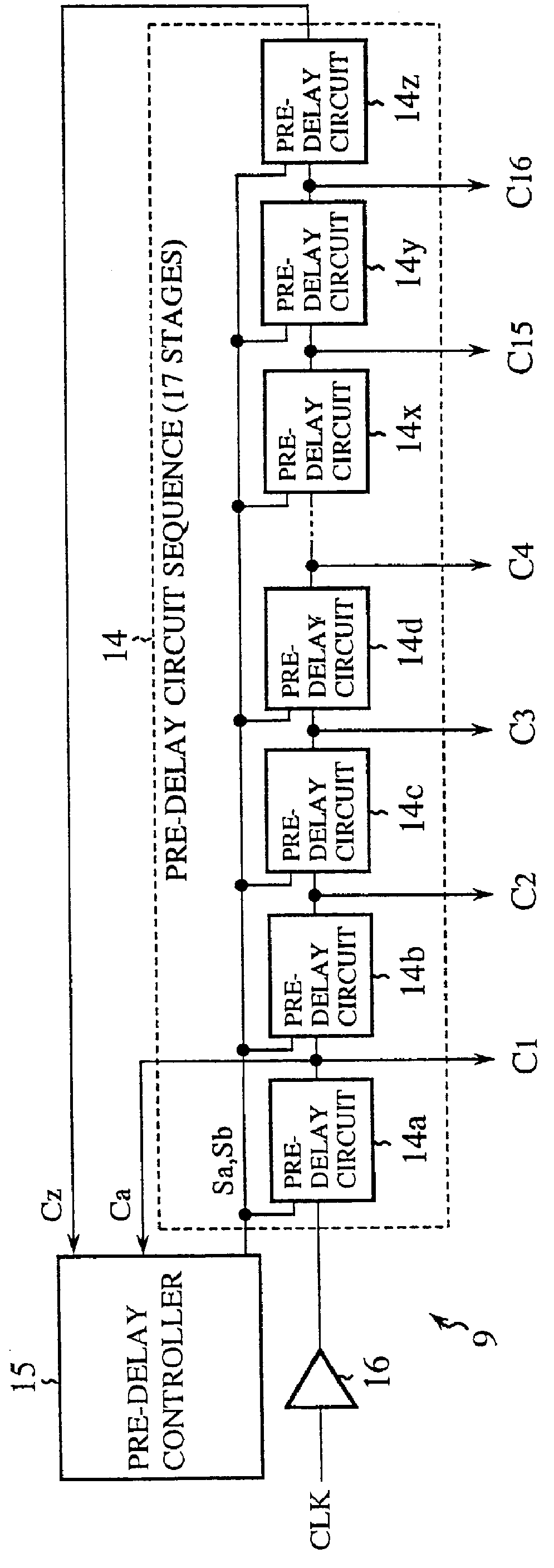
Clock signal generator for generating a plurality of clock signals with different phases, and clock phase controller using the same
A clock signal generator having a pre-phase converter for generating in response to an input clock signal a plurality of pre-delay clock signals with different phases; and main phase converters each of which receives one of the pre-delay clock signals, and generates a plurality of main delay clock signals with their phases different from each other, thereby generating multiple main delay clock signals with their phases different from each other.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Variable valve timing control system of internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20050257762A1Tendency increaseIncrease system costValve drivesMachines/enginesWorking fluidVariable valve timing
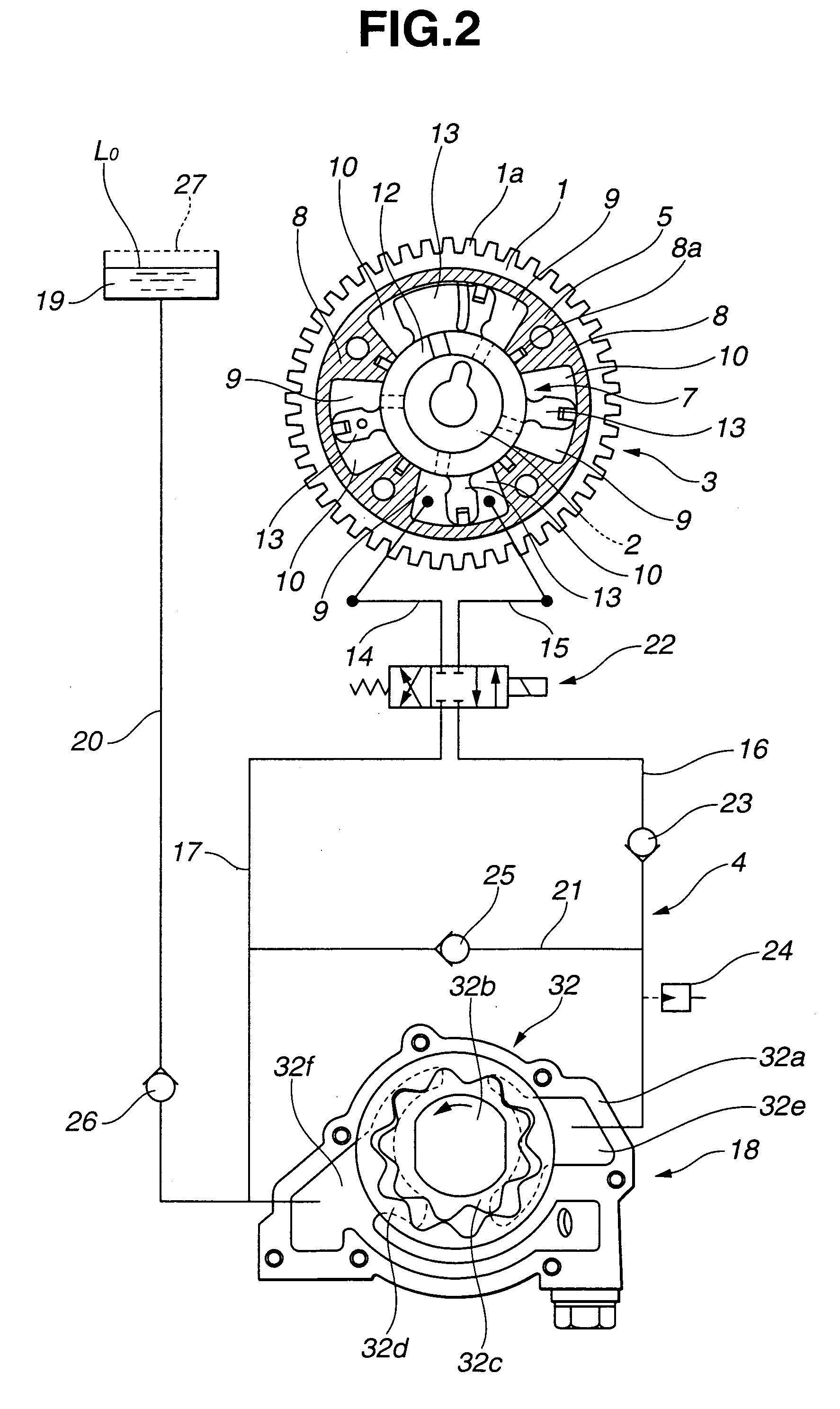
A variable valve timing control system of an internal combustion engine includes a hydraulically-operated phase converter disposed between a sprocket and a camshaft, and having a phase-advance hydraulic chamber and a phase-retard hydraulic chamber for changing an angular phase of the camshaft relative to the sprocket. An electric pump is provided to supply working fluid selectively to one of the hydraulic chambers via a directional control valve. Also provided is a check valve disposed in a discharge line of the pump for permitting flow in a direction that the working fluid flows from the pump to the directional control valve and preventing any flow in the opposite direction, so as to prevent a pulse pressure arising from alternating torque exerted on the camshaft from being transmitted from either one of the hydraulic chambers via the discharge line to a discharge port of the pump.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Asynchronous protocol converter
InactiveUS20130073771A1High-speed NoCHybrid transportSecuring communicationNetworks on chipPhase converter
An asynchronous protocol converter, which is capable of flexibly carrying out communications between tens of IP cores in an asynchronous protocol Network-on-Chip system, and which is multiple input multiple output is provided. In an LSI (20), which comprises a plurality of IP cores (21), and routers (22) positioned adjacent to the plurality of IP cores (21), an asynchronous protocol converter (1) is positioned between adjacent routers (22). The asynchronous protocol converter (1) is configured to comprise: a two-to-four-phase converter (11) that is connected to an adjacent router (22a) within the LSI (20); a four-phase pipelined router (12) that is connected on the output side of the two-to-four-phase converter (11); a four-to-two-phase converter (13) that is connected to the outputs of the four-phase pipelined router (12); an input controller (14) that controls the two-to-four-phase converter (11); and an output controller (15) that controls the four-to-two-phase converter (13).
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Instantaneous voltage-drop compensation circuit, power conversion apparatus, instantaneous voltage-drop compensation method and computer readable medium storing instantaneous voltage-drop compensation program
ActiveUS20080130335A1Easy maintenanceSolution to short lifeAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcPhase currentsControl signal
An instantaneous voltage-drop compensation circuit including: a first voltage detector detecting three-phase voltages to be input to a power converter converting three-phase AC to DC based on control pulse signals, and outputting three-phase voltage signals; a first three-phase to two-phase converter converting the detected signals to two-phase voltage signals; a first current detector detecting three-phase currents to be input to the power converter and outputting three-phase current signals; a second three-phase to two-phase converter converting the detected current signals to two-phase current signals; a first subtracter generating a first deviation signal from input current command signals and the two-phase current signals; an input current controller generating input current control signals based on the first deviation signal; and a first adder adding the two-phase voltage signals to the input current control signals, to generate control pulse signals for the power converter.
Owner:KYOSAN ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD
Clock data recovery circuit
ActiveUS20130107997A1Reduce manufacturing costSmall sizePulse automatic controlSynchronising arrangementPhase detectorData stream
A clock and data recovery (CDR) circuit having a phase locked module and a frequency locked module is provided. A phase detector of the phase locked module compares a phase of an input data stream with a phase of a data-recovery clock to output an adjusting signal. The frequency locked module performs a first-order integration process and a second-order integration process on the adjusting signal to generate a first integration error and a frequency control signal. The phase locked module generates a phase control signal according to the first integration error and the adjusting signal. An oscillation circuit of the frequency locked module generates at least one reference clock according to the frequency control signal. A phase converter of the phase locked module outputs the data-recovery clock to the phase detector according to the phase control signal and the reference clock.
Owner:PHISON ELECTRONICS
Electromagnetic transient mathematical model of distributed power-flow controller based on MMC, control system and modeling method
ActiveCN106911132AImprove harmonic characteristicsEasy to Modular DesignAc networks with different sources same frequencyMathematical modelThree phase converter
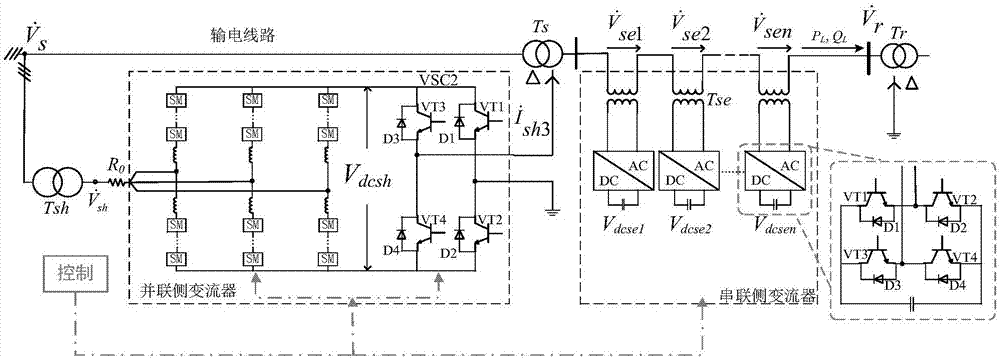
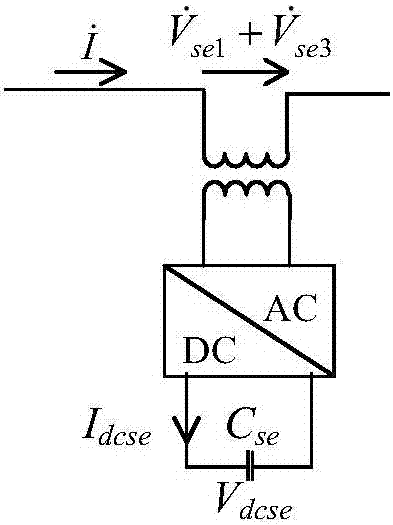
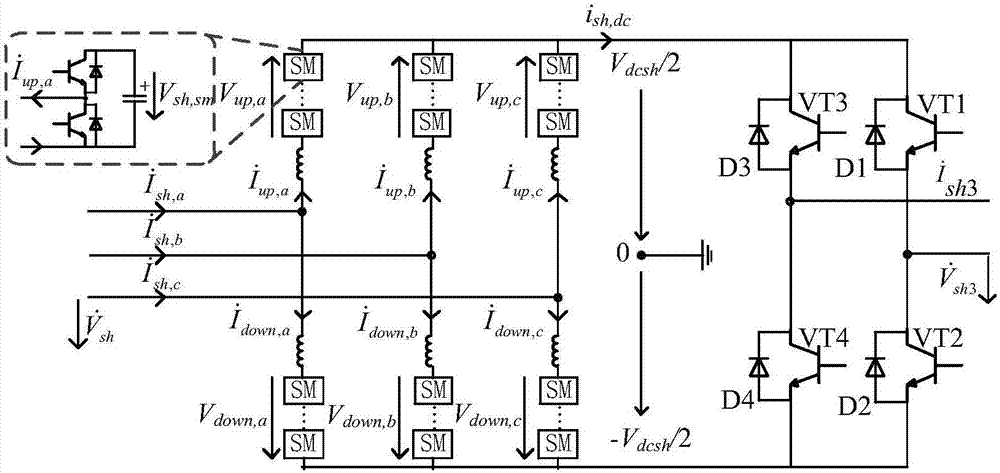
The invention discloses an electromagnetic transient mathematical model of a distributed power-flow controller based on an MMC, control system and a modeling method. The distributed power-flow controller comprises a parallel connection side converter composed of a three-phase converter based on the MMC at the parallel connection side and a parallel connection side single-phase converter and a series connection side converter composed of multiple sets of series connection side single-phase converter; the electromagnetic transient mathematical model mainly comprises a parallel connection side converter model and a series connection side converter model; the control system comprises a parallel connection side control model and a series connection side control model, the parallel connection side control model comprises a three-phase converter control module based on the MMC at the parallel connection side and a parallel connection side single-phase converter module, and the series connection side control model comprises a series connection side third harmonic control module and a series connection converter active power reactive power control module. The electromagnetic transient mathematical model is designed by adopting modularization, the sub module switch-on and switch-off frequency is lowered, and the loss is lowered; the control system adapts to different voltage grades, and is applicable to flexible alternating current transmission occasions.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH +3
Automatic frequency control communication system
InactiveUS6456672B1Simultaneous amplitude and angle modulationSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemIntegrator
In a communication system using the time diversity transmission scheme, the communication system provided with the stable automatic frequency control circuit with the wide frequency pull-in range and under low CN ratio transmission is achieved by removing the modulation phase from the received data through the application of the data correlation of the time diversity. The frequency offset in the received signal is compensated as the phase rotator rotates the phase of the received signal, the phase converter converts the phase rotator output into a phase, the serial-to-parallel converter converts the phase converter outputs into serial-to-parallel sequence, the delay units gives a delay to the serial-to-parallel converter output, the phase adder adds the serial-to-parallel converter output to the delay unit output, the multiplier multiplies the phase adder output by a certain value, the integrator integrates the multiplier output, another integrator integrates the integrator output, and the phase rotator controls the phase of the received signal based on the other integrator output.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Image signal transmission apparatus
InactiveUS20020005863A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningImage resolutionImage signal
An image-transmitting-side device comprises: a one-phase to two-phase converter circuit for separating parallel image data, which are to be transmitted, into even and odd data; a first parallel-serial converting circuit; a second parallel-serial converting circuit; means for allowing a user to select, as the resolution mode for the image data to be transmitted, one of a first resolution mode and a second resolution mode that is higher in resolution than the first resolution mode; and switch means for applying the parallel image data, which are to be transmitted, to the first parallel-serial converting circuit when the first resolution mode is selected, and for applying the parallel image data, which are to be transmitted, to the one-phase to two-phase converter circuit when the second resolution mode is selected.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Image rejection mixer for broadband signal reception
ActiveUS6985710B1Radio transmissionFrequency-changer modificationsLocal oscillator signalFrequency mixer
An image rejection mixer includes an input terminal for receiving an input radio frequency (RF) signal, a mode selector coupled to the input terminal generating an output signal for either high side mixing or low side mixing, a first mixer coupled to receive the input RF signal and a signal from a local oscillator providing a signal having a local oscillator frequency, a phase converter coupled to convert the phase of the signal from the local oscillator, a second mixer coupled to receive the output signal from the mode selector and the phase-converted local oscillator signal, and a tunable polyphase filter coupled to receive output signals from the first mixer and the second mixer, the tunable polyphase filter providing an output signal having a variable intermediate frequency. In one embodiment, the variable intermediate frequency the tunable polyphase filter is implemented as a switchable intermediate frequency.
Owner:CR CRESPE LLC +1
Phased array antenna systems with controllable electrical tilt
InactiveUS7420507B2Increase rangeReduce stepsSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityCouplingEngineering
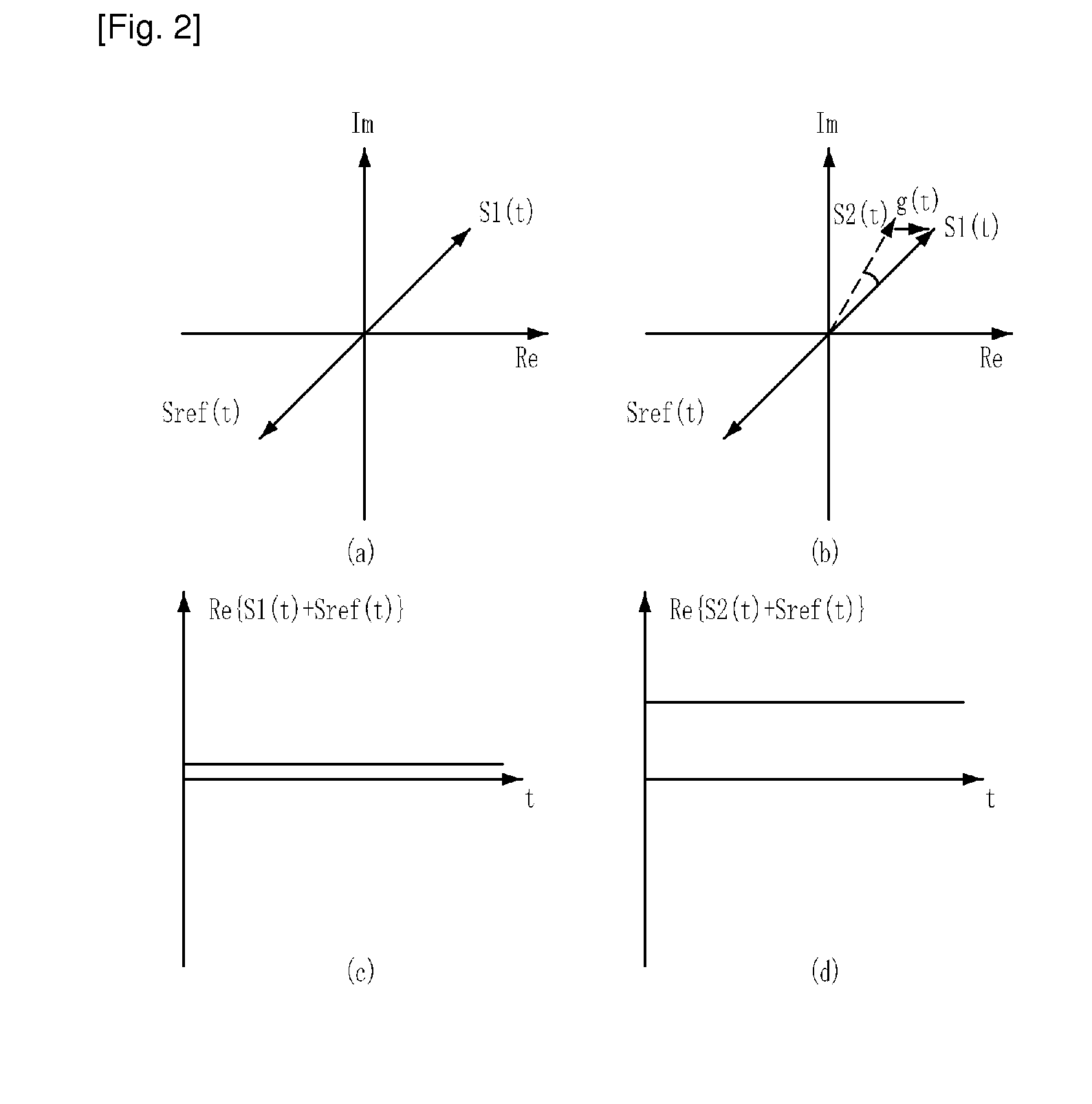
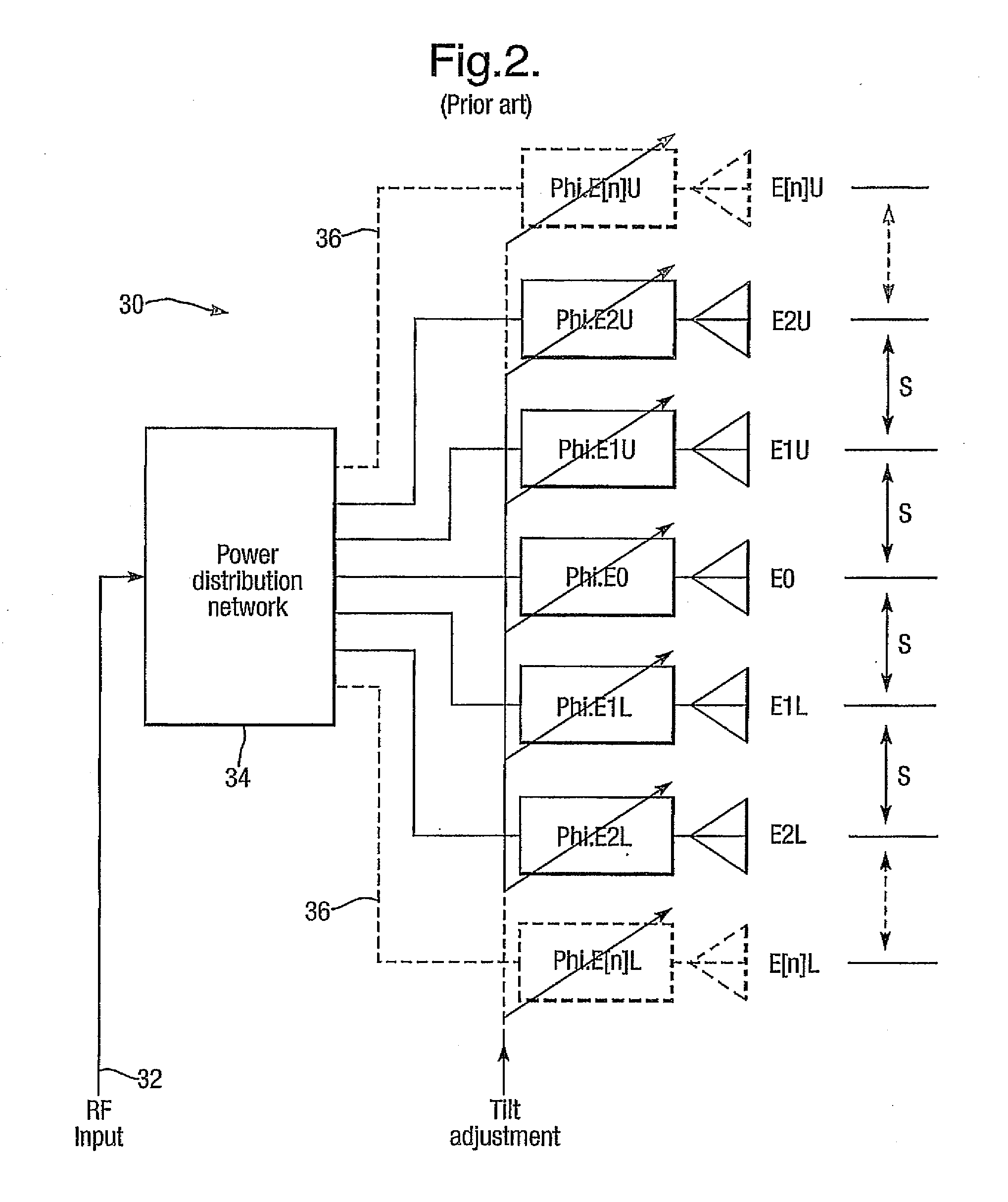
A phased array antenna system with controllable electrical tilt generates two signals V2a and V2b with variable relative delay therebetween. The signals are converted into antenna element drive signals by a power distribution network. The network splits each of the two signals V2a and V2b into three signal components. Pairs of components of different signals are input respective hybrid coupling devices (hybrids), which provide vector sums and differences of their inputs and act as phase-to-power converters. Their outputs are distributed between further hybrids, which act as power-to-phase converters and provide antenna element drive signals with phase varying both with element array position and also with the variable relative delay between the two signals V2a and V2b. Antenna electrical tilt is therefore controllable by altering a single relative delay.
Owner:QUINTEL CAYMAN LTD
Motor drive circuit
InactiveUS6275405B1Motor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlElectric power transmissionMotor drive
A phase converter for converting single-phase power to three-phase power, wherein the single-phase power is provided at a first and a second single-phase power terminal and the three-phase power is provided to a first, a second and a third three-phase power terminal, the phase converter comprising: a first power transfer means for coupling the first single-phase power terminal to the first three-phase power terminal; a second power transfer means for coupling the second single-phase power terminal to the second three-phase power terminal; and an inverter coupled to receive power from the first and second single-phase power terminals. The inverter provides power to the third three-phase power terminal and a neutral output by phase shifting its input power by ninety degrees.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRONICS APPL
Programmable delay generator and cascaded interpolator
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
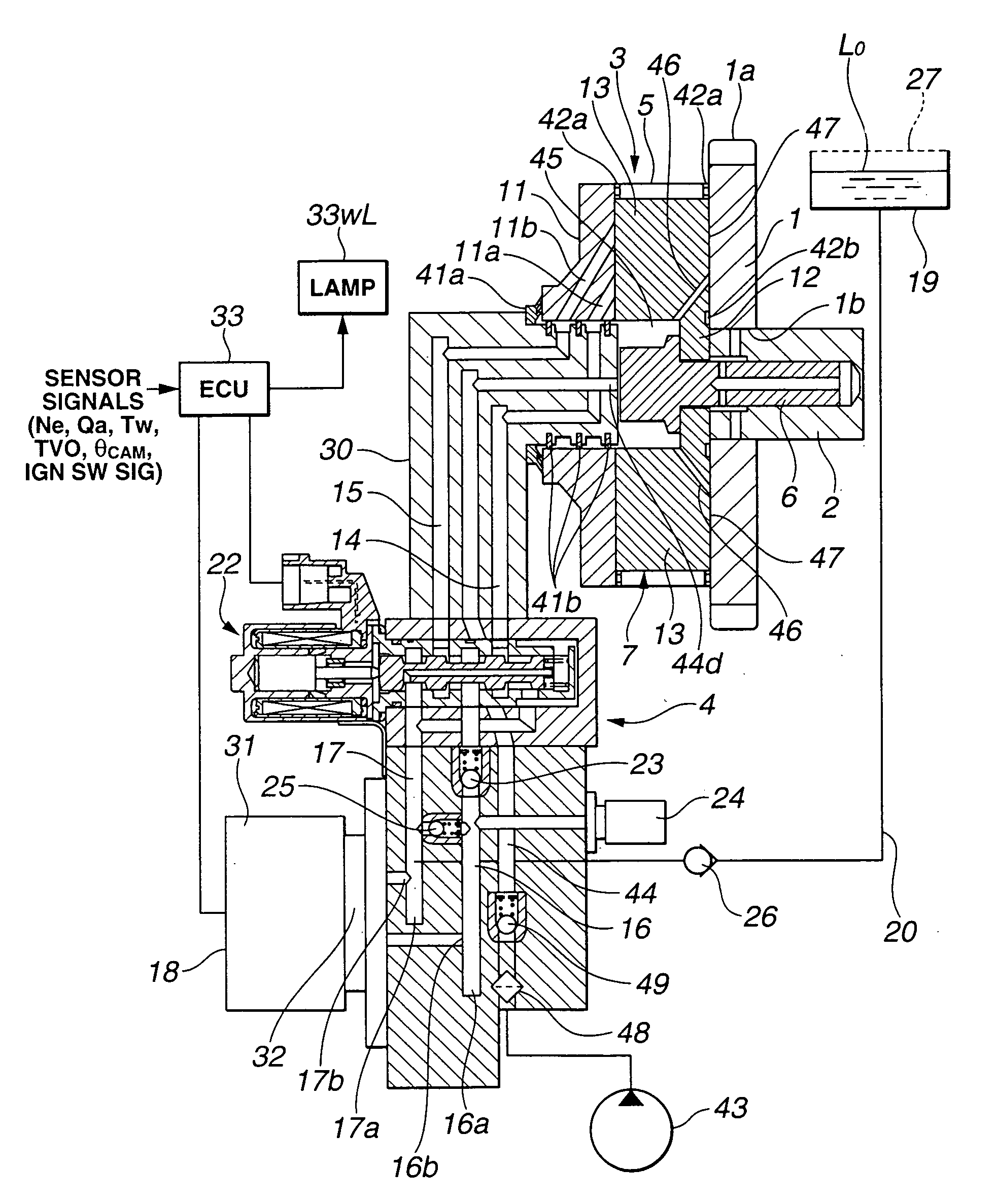
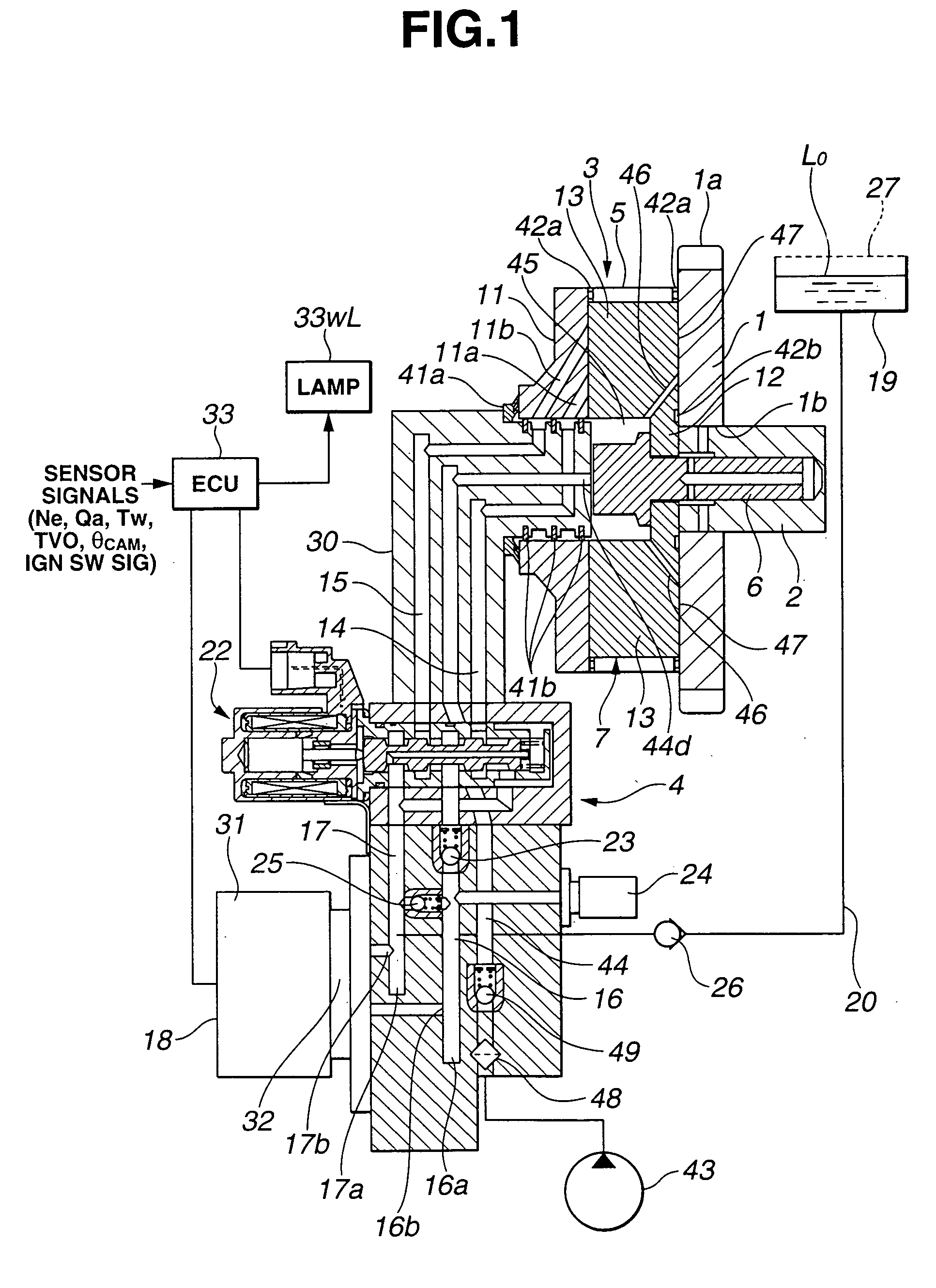
Controller of Valve Timing Control Apparatus and Valve Timing Control Apparatus of Internal Combustion Engine
In a valve timing control apparatus configured to execute phase-control via a phase converter, a controller is configured to control a phase angle of a camshaft relative to a crankshaft during an engine stopping period to a target phase angle differing from a required phase angle suited for an engine operating condition. The controller is further configured to change the phase angle of the camshaft toward the required phase angle during a time period from a point of time when cranking starts to a point of time when detection of a rotational position of the camshaft initiates during an engine restarting period. The controller is still further configured to start feedback-control for the phase angle of the camshaft from the point of time of initiation of detection of the rotational position of the camshaft for bringing the phase angle of the camshaft closer to the required phase angle.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Image signal transmission apparatus
InactiveUS6765599B2Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningImage resolutionImage signal
An image-transmitting-side device comprises: a one-phase to two-phase converter circuit for separating parallel image data, which are to be transmitted, into even and odd data; a first parallel-serial converting circuit; a second parallel-serial converting circuit; means for allowing a user to select, as the resolution mode for the image data to be transmitted, one of a first resolution mode and a second resolution mode that is higher in resolution than the first resolution mode; and switch means for applying the parallel image data, which are to be transmitted, to the first parallel-serial converting circuit when the first resolution mode is selected, and for applying the parallel image data, which are to be transmitted, to the one-phase to two-phase converter circuit when the second resolution mode is selected.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Variable valve timing control system of internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7219636B2Tendency increaseIncreased torque capacityValve drivesMachines/enginesWorking fluidVariable valve timing
A variable valve timing control system of an internal combustion engine includes a hydraulically-operated phase converter disposed between a sprocket and a camshaft, and having a phase-advance hydraulic chamber and a phase-retard hydraulic chamber for changing an angular phase of the camshaft relative to the sprocket. An electric pump is provided to supply working fluid selectively to one of the hydraulic chambers via a directional control valve. Also provided is a check valve disposed in a discharge line of the pump for permitting flow in a direction that the working fluid flows from the pump to the directional control valve and preventing any flow in the opposite direction, so as to prevent a pulse pressure arising from alternating torque exerted on the camshaft from being transmitted from either one of the hydraulic chambers via the discharge line to a discharge port of the pump.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Fuel control system for a dual fuel internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7055506B2Improve conversion efficiencyPrevent freezingInternal combustion piston enginesFuel supply apparatusAlternatorLiquid state
A gaseous fuel control system for regulating fuel flow to a dual fuel internal combustion engine has a phase converter for converting the fuel from a liquid state to a gaseous state and control means for controlling the supply of fuel to the engine in response to sensor signals including a throttle position signal and an alternator signal. A valve actuated by the control means regulates the supply of said fuel in a gaseous state, which is mixed with air in the engine manifold. A display mounted in the vehicle cabin includes a fuel gauge, an override switch and means for adjusting the parameters for the control of supply of fuel. The control means is programmed to close the valve means, preventing the supply of said fuel, when the throttle position is in an idling position or substantially fully open and when the engine is not operating.
Owner:CSSM HLDG
Phase closed loop control direct current motor speed regulating method
InactiveCN101599733AHard mechanical propertiesField or armature current controlMotor speedLoop control
The invention relates to a phase closed loop control direct current motor speed regulating method, which comprises the following steps: a voltage-phase converter is adopted to convert the voltage drop at the two ends of a TRIAC which is in series with the direct current motor, the rotating speed signals of the direct current motor are obtained through measuring the phase pulse width, the negative feedback closed-loop control can be realized by a time-delay control algorithm of fixed length which is synchronous to a phase falling edge or by a time-delay control algorithm of variable length which is synchronous to a zero crossing point. The speed regulating method provided by the invention is applicable to the speed regulating for small and medium power direct current motors, such as body massage machine, blood circulation machine and the like, thus having the advantages of low cost, flexible control, stable and reliable rotating speed control.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Instantaneous voltage-drop compensation circuit, power conversion apparatus, instantaneous voltage-drop compensation method and computer readable medium storing instantaneous voltage-drop compensation program
ActiveUS7751211B2Easy maintenanceSolution to short lifeAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcPhase currentsControl signal
An instantaneous voltage-drop compensation circuit including: a first voltage detector detecting three-phase voltages to be input to a power converter converting three-phase AC to DC based on control pulse signals, and outputting three-phase voltage signals; a first three-phase to two-phase converter converting the detected signals to two-phase voltage signals; a first current detector detecting three-phase currents to be input to the power converter and outputting three-phase current signals; a second three-phase to two-phase converter converting the detected current signals to two-phase current signals; a first subtracter generating a first deviation signal from input current command signals and the two-phase current signals; an input current controller generating input current control signals based on the first deviation signal; and a first adder adding the two-phase voltage signals to the input current control signals, to generate control pulse signals for the power converter.
Owner:KYOSAN ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD
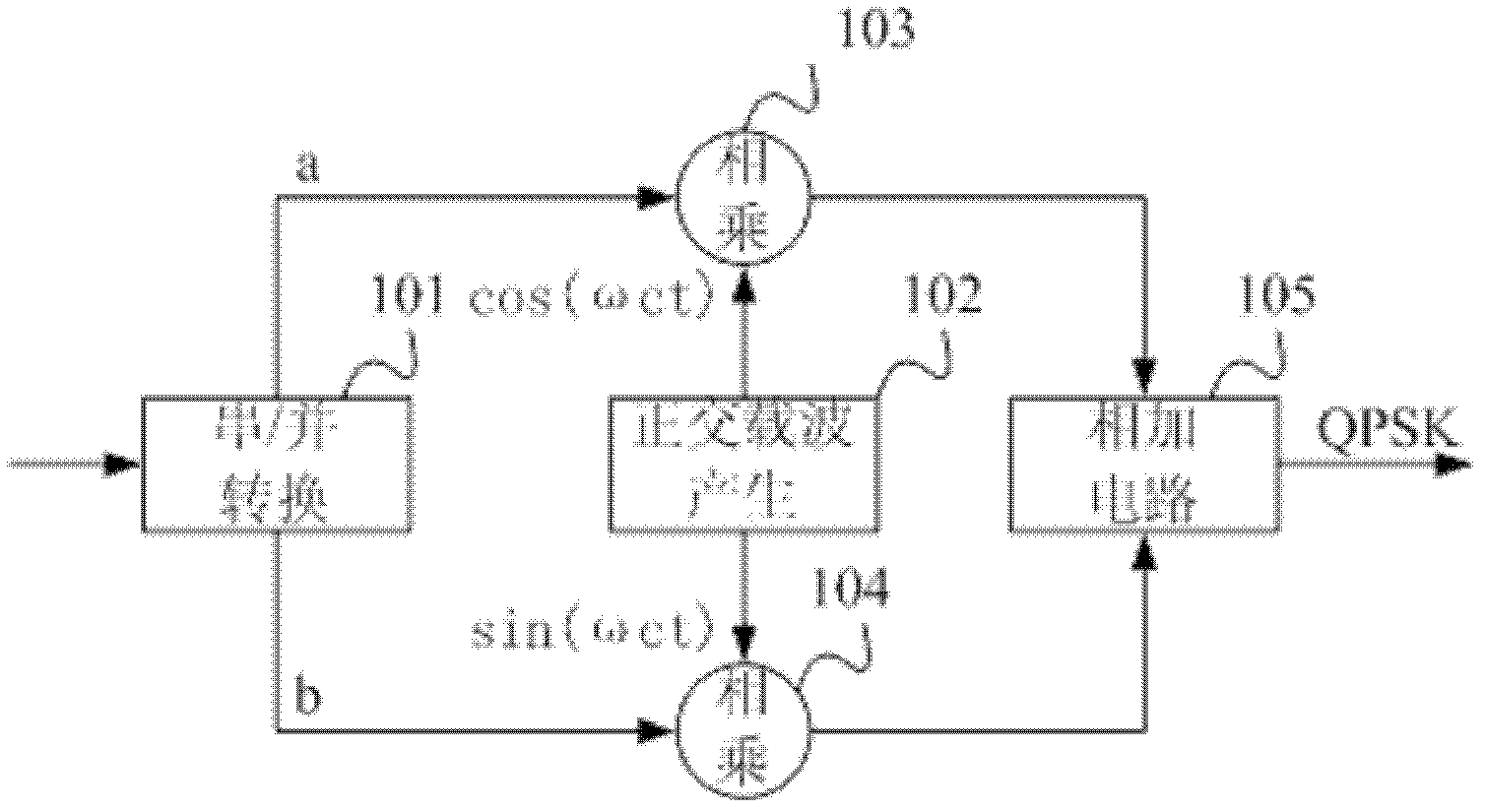
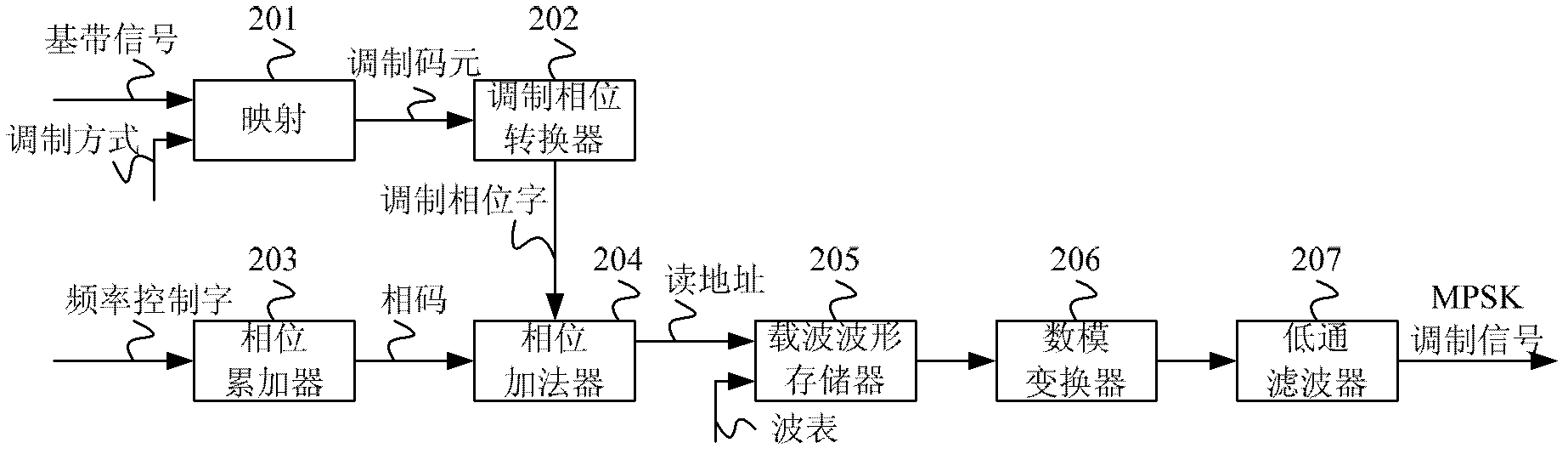
Multi-system phase shifting keying (MPSK) modulation method, MPSK modulation device and function signal generator
ActiveCN103179066ASimplify hardware designAvoid Orthogonal CarriersPhase-modulated carrier systemsData translationWave shape
An embodiment of the invention provides a multi-system phase shifting keying (MPSK) modulation method, an MPSK modulation device and a function signal generator. The MPSK modulation device comprises a mapping module used for converting serial base band signals to be modulated into modulation code elements according to the modulation mode, a modulation phase converter used for converting the modulation code elements into phase words, a phase accumulator used for accumulating frequency control words to obtain a phase code, a phase summator used for summating the phase code and the modulation phase words to obtain a reading address, a carrier wave form storage used for reading carrier wave form data stored in the storage according to the reading address and a digital-to-analog converter used for converting the carrier wave form data into MPSK modulation signals in analog form. The MPSK modulation device has the advantages of being capable of achieving full digital achieving mode, free of a multiplying unit, free of quadrature carrier, good in expandability, simple to achieve and especially suitable for the function signal generator.
Owner:RIGOL
Synchronization of Position and Current Measurements in an Electric Motor Control Application using an FPGA
ActiveUS20120217909A1Accurate synchronizationMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlPhase currentsFpga implementations
A system and method for controlling an alternating current (AC) motor using a Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) to read the current and position measurements in an the AC motor, perform digital filtering of the position and current data, provide very precise synchronization of the measured phase current and position data, and output the data to a phase converter for control of the AC motor.
Owner:DEERE & CO
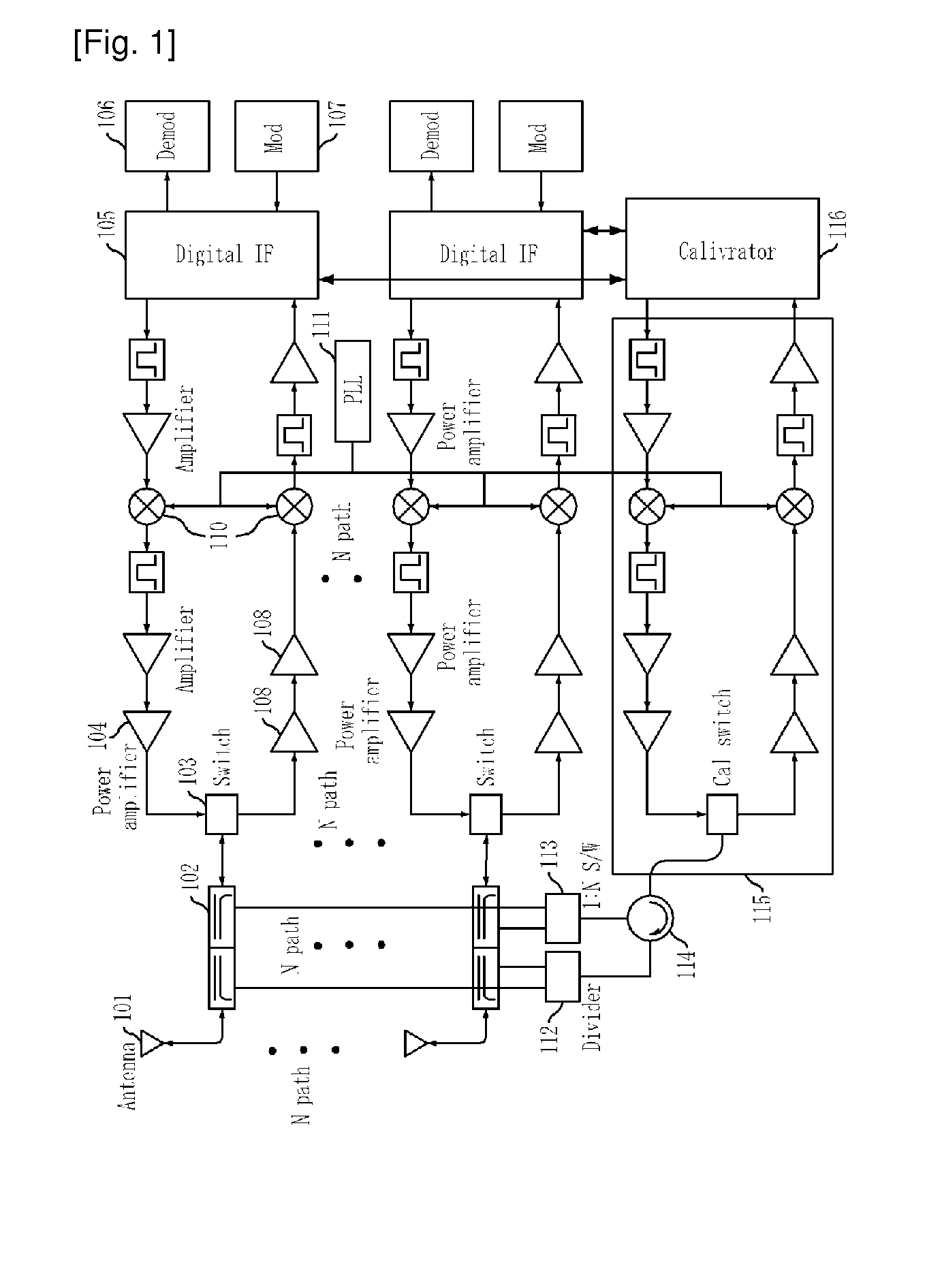
Radio frequency calibration apparatus and method for multi-antenna mobile communication system
ActiveUS20100056083A1Improve errorAccurate path calibrationSpatial transmit diversityReceivers monitoringCommunications systemEngineering
There is provided to an RF calibration apparatus and method for a multi-antenna mobile communication system, which calibrates a phase error and gain error of an RF path by calculating the minimum value of a sum of an initialized reference signal and a comparison signal by a simple operation and controlling the phase value of a phase converter and the gain of a variable amplifier on the RF path, in calibrating the RF path of a multi-antenna mobile communication system of a TDD (Time Division Duplexing) type or FDD (Frequency Division Duplexing) type.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
Electrified railway electric energy quality compensating device
ActiveCN101872981ALow costReduced footprintReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationReactive power compensationCapacitancePower quality
The invention relates to an electrified railway electric energy quality compensating device which comprises an alpha-phase converter bridge arm, wherein the alpha-phase converter bridge arm is connected with the alpha-phase power supply arm of a traction transformer through a reactor (LA); one end of the alpha-phase converter bridge arm is connected with one end of a capacitor through a direct current positive bus, and the other end is connected with one end of the other capacitor through a direct current negative bus; the midpoint of the serial connection part of the other ends of the two capacitors is used as a neutral point; the neutral point is connected with a traction power supply neutral line through a reactor (LO); the direct current positive bus and the direct current negative bus are simultaneously connected with a beta-phase converter bridge arm, and the beta-phase converter bridge arm is connected with the beta-phase power supply arm of the traction transformer through a reactor (LB); and a single-phase circuit comprising the traction power supply neutral line and the alpha-phase or beta-phase converter bridge arm is connected with the single-phase circuit comprising the traction power supply neutral line and the alpha-phase or beta-phase power supply arm, the current flowing through the reactor (LA) or (LB) is regulated and controlled by regulating the amplitude and the phase position of the output voltage of the alpha-phase or beta-phase converter bridge arm, and dynamic power compensation and harmonic filtering are carried out for the alpha-phase or beta-phase power supply arm. The invention is mainly used for improving the electric energy quality of an electrified railway power supply network and also can be used for similar single-phase power supply networks.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Phased array antenna system with variable electrical tilt
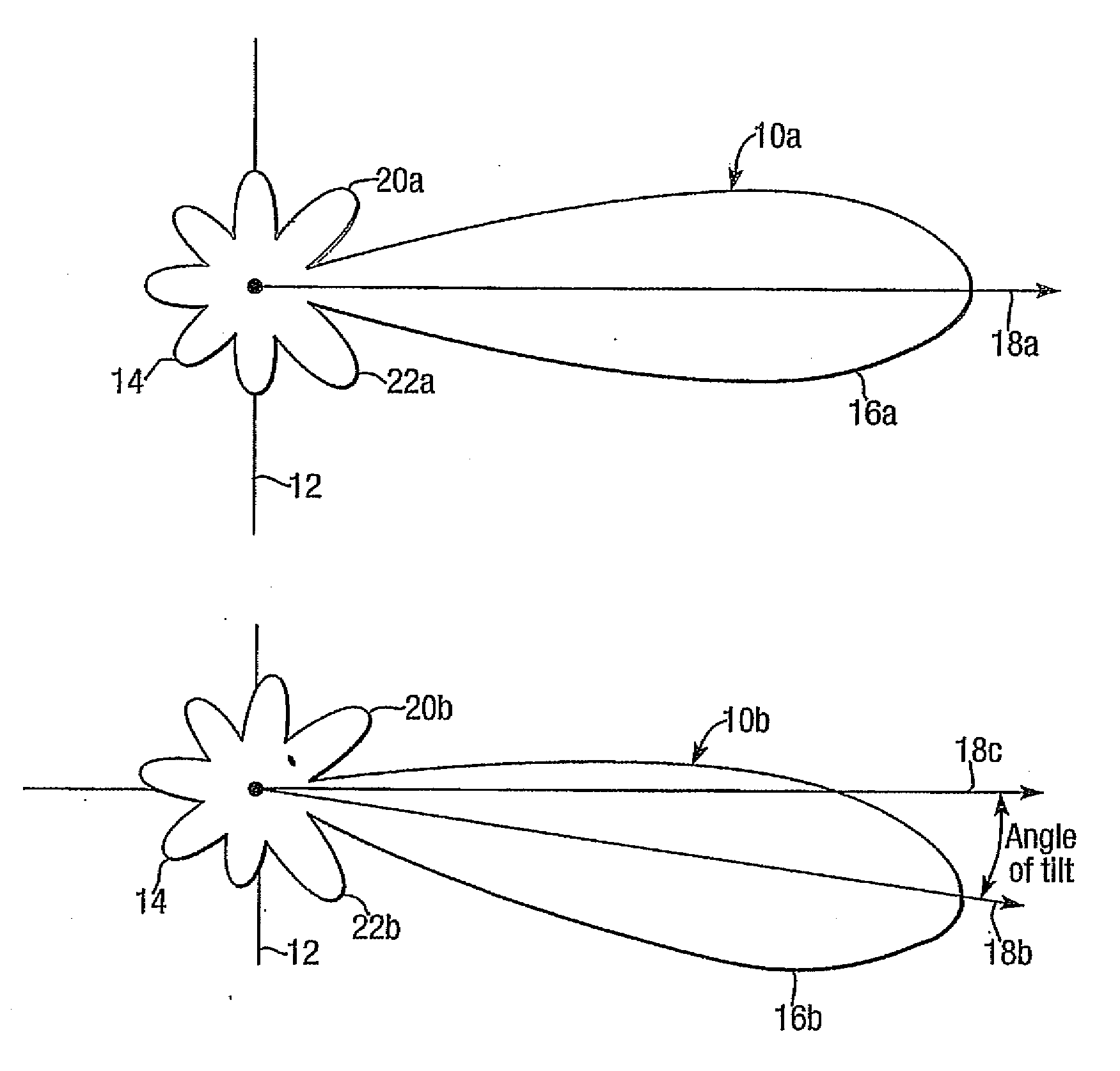
A phased array antenna system with variable electrical tilt comprises an array of antenna elements etc. incorporating a divider dividing a radio frequency (RF) carrier signal into two signals between which a phase shifter introduces a variable phase shift. A phase to power converter converts the phase shifted signals into signals with powers dependent on the phase shift. Power splitters divide the converted signals into two sets of divided signals with total number equal to the number of antenna elements in the array. Power to phase converters etc. combine pairs of divided signals from different power splitters this provides vector sum and difference components with appropriate phase for supply to respective pairs of antenna elements etc. located equidistant from an array centre. Adjustment of the phase shift provided by phase shifter changes the angle of electrical tilt of the antenna array.
Owner:QUINTEL CAYMAN LTD
Power factor correction (PFC) conversion control method for low output voltage ripple and device thereof
InactiveCN102545563AImprove efficiencyRaise the cutoff frequencyEfficient power electronics conversionPower conversion systemsLoop controlTarget signal
The invention discloses a power factor correction (PFC) conversion control method for low output voltage ripple and a device thereof. After a single-phase PFC controller is used for sampling the input voltage, inductive current and output voltage of a single-phase PFC converter, a control signal of the PFC convertor is obtained through a PFC control strategy; and a controller of a single-phase inverter is used for sampling the input voltage and load current of the single-phase PFC converter to obtain a control target signal of the single-phase converter and sampling the alternating-current output voltage of the converter simultaneously, and ripple same-amplitude phase reversion is realized for the alternating-current output voltage of the converter and the direct-current output voltage of the PFC converter by using an inverter double closed-loop control strategy. Due to the adoption of the method and the device, a high power factor is realized, the output power frequency ripple voltage of the single-phase PFC converter is eliminated simultaneously, the dynamic response of a system is improved, and the problems of low efficiency and high cost of the conventional twos-stage PFC converter are solved. The device can be also applied to low-ripple high-PFC AC / DC (Alternating Current / Direct Current) constant current source design.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Apparatus and method for transmit/receive antenna switch in a TDD wireless communication system
An apparatus and method in a Time Division Duplex (TDD) wireless communication system are provided. The apparatus includes two 90° hybrid couplers and a phase converter block. The two 90° hybrid couplers each separate a signal into two signals and output the two signals, and each couple two signals and output the coupled signal. The phase converter block connects between the two 90° hybrid couplers. In a transmission mode, the phase converter block identically varies phases of two signals and outputs the varied two signals to the second 90° hybrid coupler. In a reception mode, the phase converter block varies phases of two signals and outputs the varied two signals to the first 90° hybrid coupler.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Protection method for an engine having a variable valve timing controller and protection apparatus for the same
The variable valve timing controller has an electric motor which rotates a phase converter. When the electric motor is locked for some reason, the over-load more than the predetermined value is applied to a motor shaft and the phase converter. In such a case, a pin connecting the motor shaft with the phase converter is sheared at a notch. Thus, a cam shaft and the phase converter were not locked, and breakage of a motor housing is prevented.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
Phase control for multiphase converter
ActiveCN102185477AGood phase distributionDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationControl signalEngineering
The invention provides an N-phase converter (N is an integer of more than or equal to 2), which comprises a switch for each phase, wherein the switch is controlled by a corresponding conducting signal. The converter is characterized by also comprising a control circuit which generates a control signal according to the conducting signal of each phase and is used for adjusting circuit parameters ofthe converter so as to uniformly distribute various phases. The invention also provides a method for the N-phase converter.
Owner:CHENGDU MONOLITHIC POWER SYST
Phased array antenna system with variable electrical tilt
InactiveUS7400296B2Improve the level ofAntenna supports/mountingsSubstation equipmentPhase shiftedCarrier signal
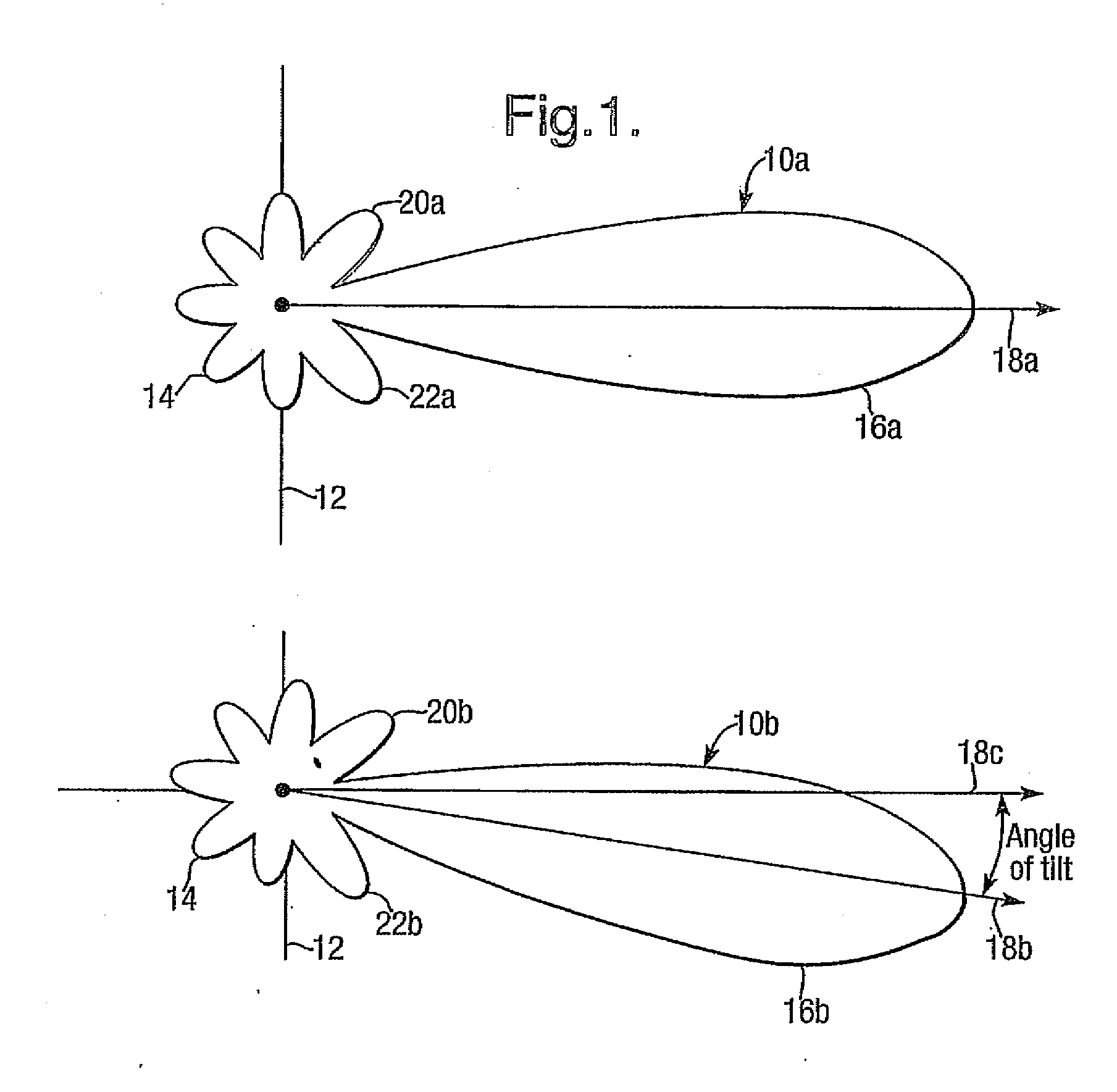
A phased array antenna system with variable electrical tilt comprises an array (60) of antenna elements (60L1) etc. incorporating a divider (44) dividing a radio frequency (RF) carrier signal into two signals between which a phase shifter (46) introduces a variable phase shift. A phase to power converter (50) converts the phase shifted signals into signals with powers dependent on the phase shift. Power splitters (52, 54) divide the converted signals into two sets of divided signals with total number equal to the number of antenna elements in the array. Power to phase converters (561) etc. combine pairs of divided signals from different power splitters (52, 54) this provides vector sum and difference components with appropriate phase for supply to respective pairs of antenna elements (60U1, 60L1) etc. located equidistant from an array centre. Adjustment of the phase shift provided by phase shifter (46) changes the angle of electrical tilt of the antenna array (60).
Owner:QUINTEL CAYMAN LTD
Resonant vibration dead-soft switching inverter circuit applied to brushless DC motor and control method
InactiveCN101162874AGood choiceIncrease the switching frequencyEfficient power electronics conversionSingle motor speed/torque controlSoft switchingDividing circuits
The invention discloses a resonance dead-soft switching inverter circuit applied to a brushless DC motor, comprising a DC power supply, an input voltage-dividing circuit, a control circuit and an inverter bridge. The input voltage-dividing circuit comprises two concatenated capacitors; the three poles of the converter bridge are connected to the brushless DC motor. An auxiliary resonance circuit is added between the pole of the converter bridge and the midpoint of the input voltage-dividing circuit, including 3 auxiliary two-way switches and 1 inductometer. One end of each of the 3 auxiliary two-way switches is connected to one end of the inductometer; the other end of each of the 3 auxiliary two-way switches is connected to the pole of a 3-phase converter bridge respectively; the other end of the inductometer is connected to the midpoint of the input voltage-dividing circuit. The control circuit sends out signals to control the auxiliary two-way switches and the converter bridge switching parts to switch on / off. The invention is capable to operate under multiple driving modes.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com