Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2975results about "Valve drives" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Reciprocating devices
ActiveUS20080141921A1Improve power densityImprove efficiencyHybrid vehiclesInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineEnergy absorption
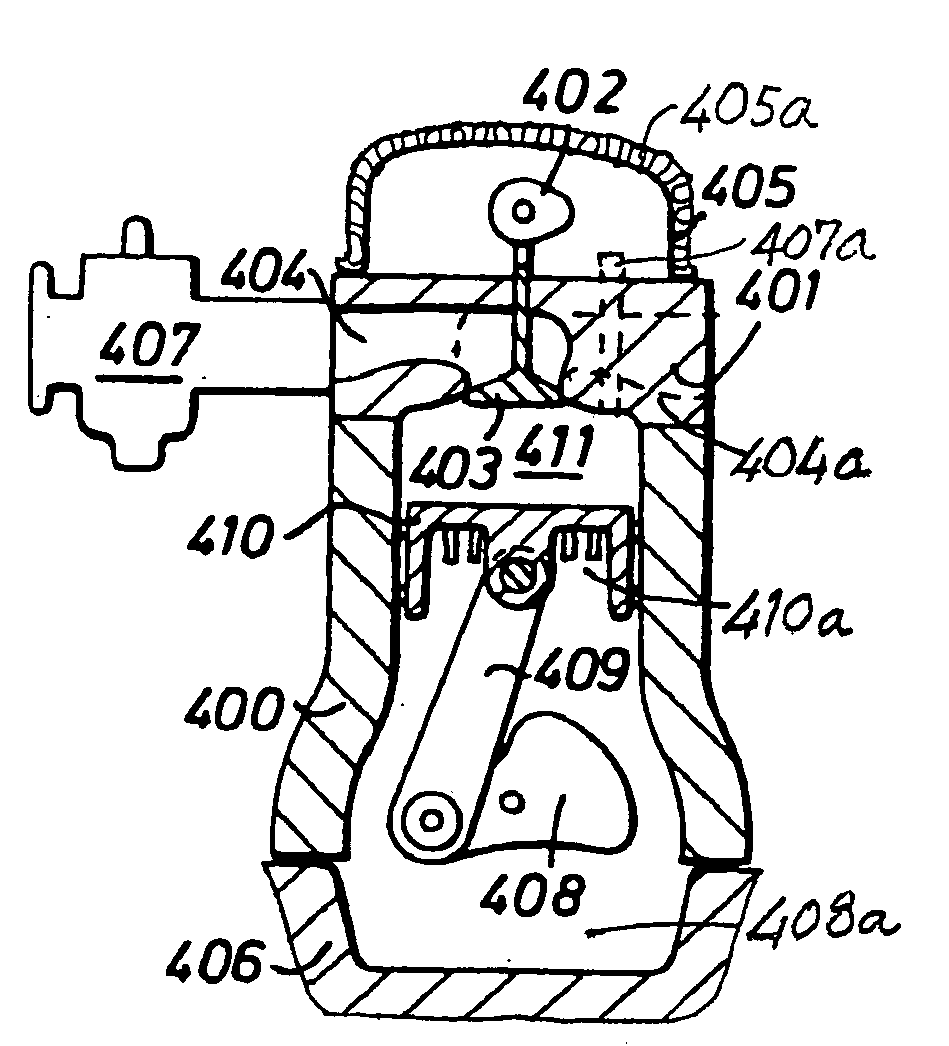
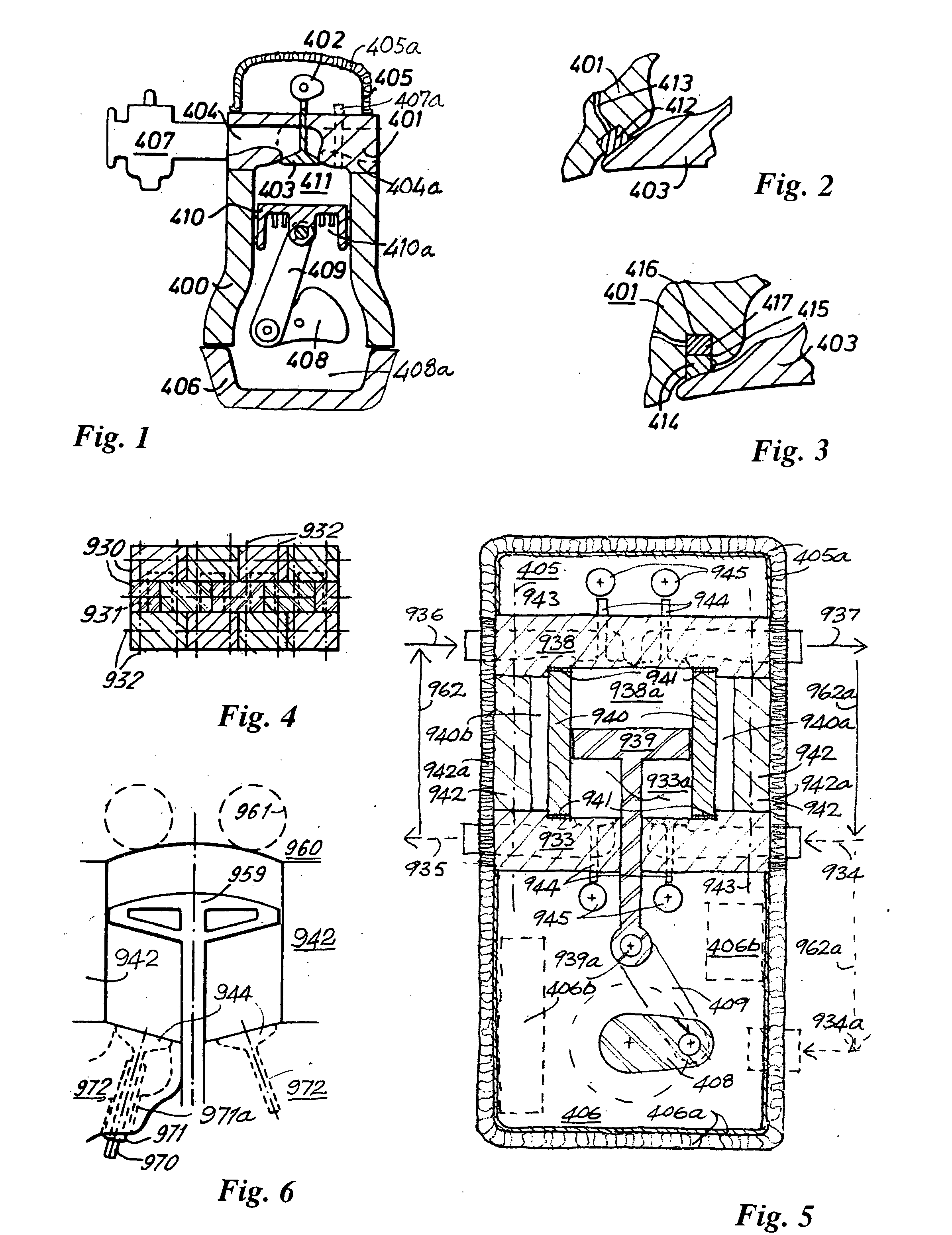
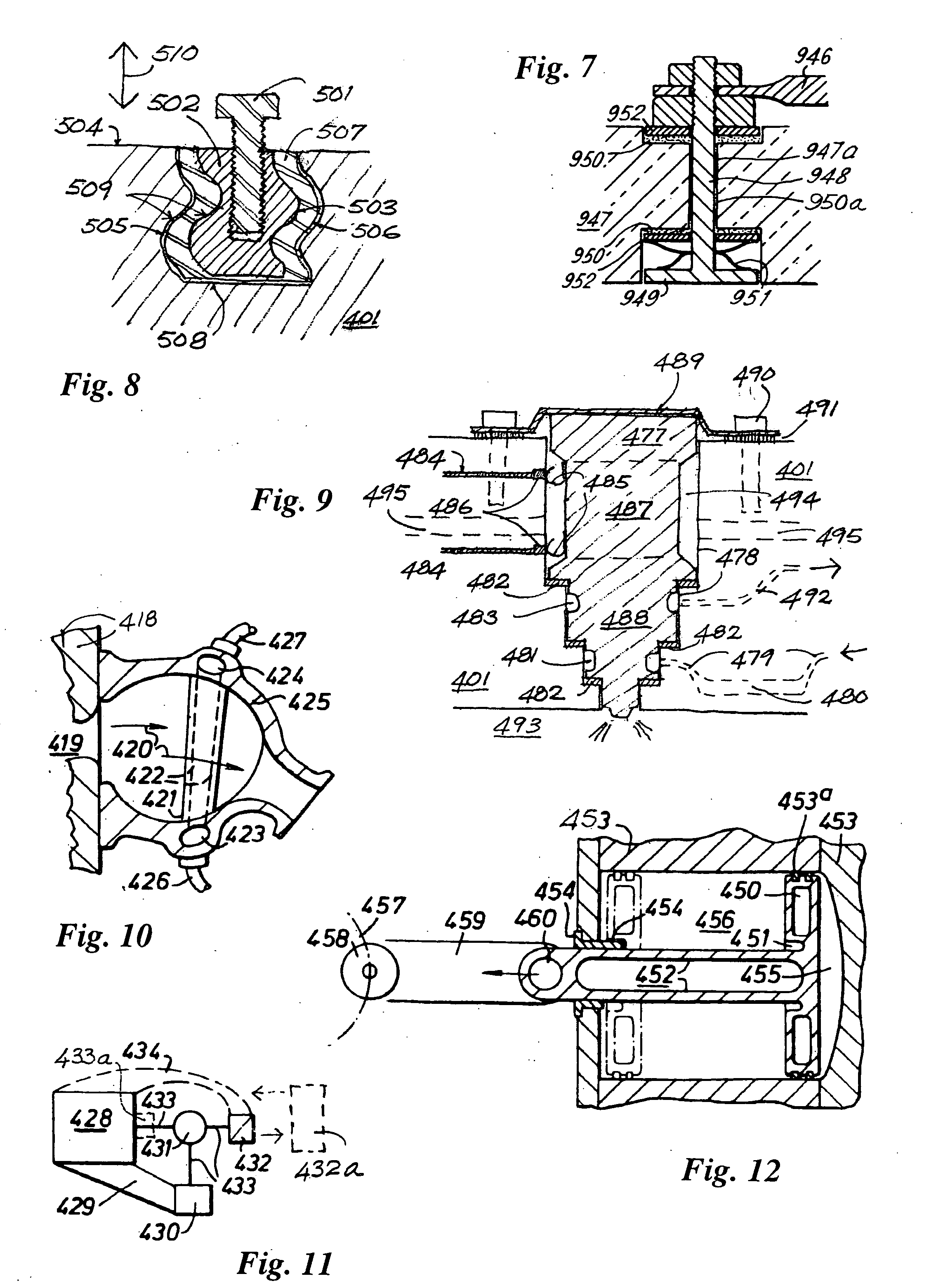
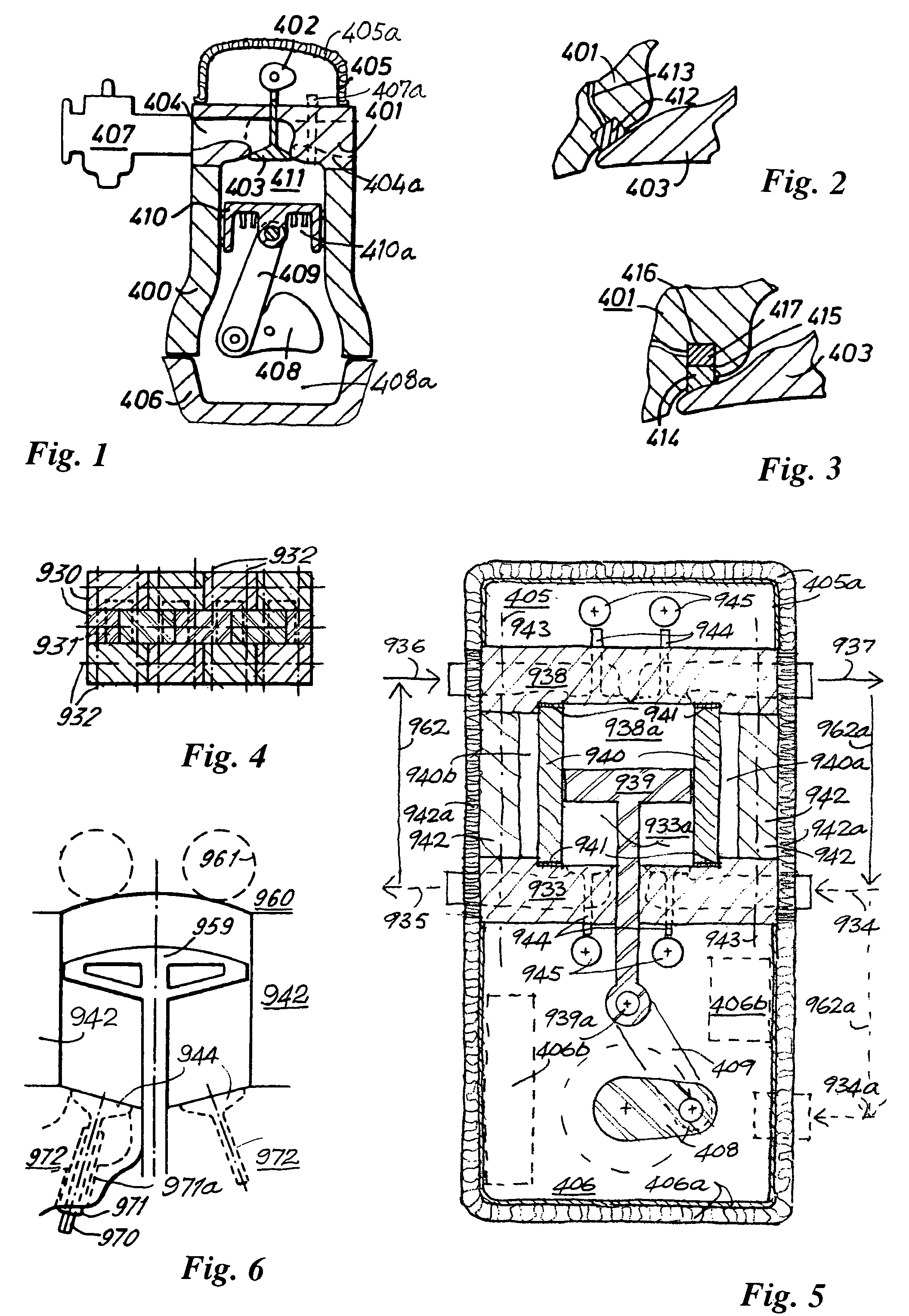
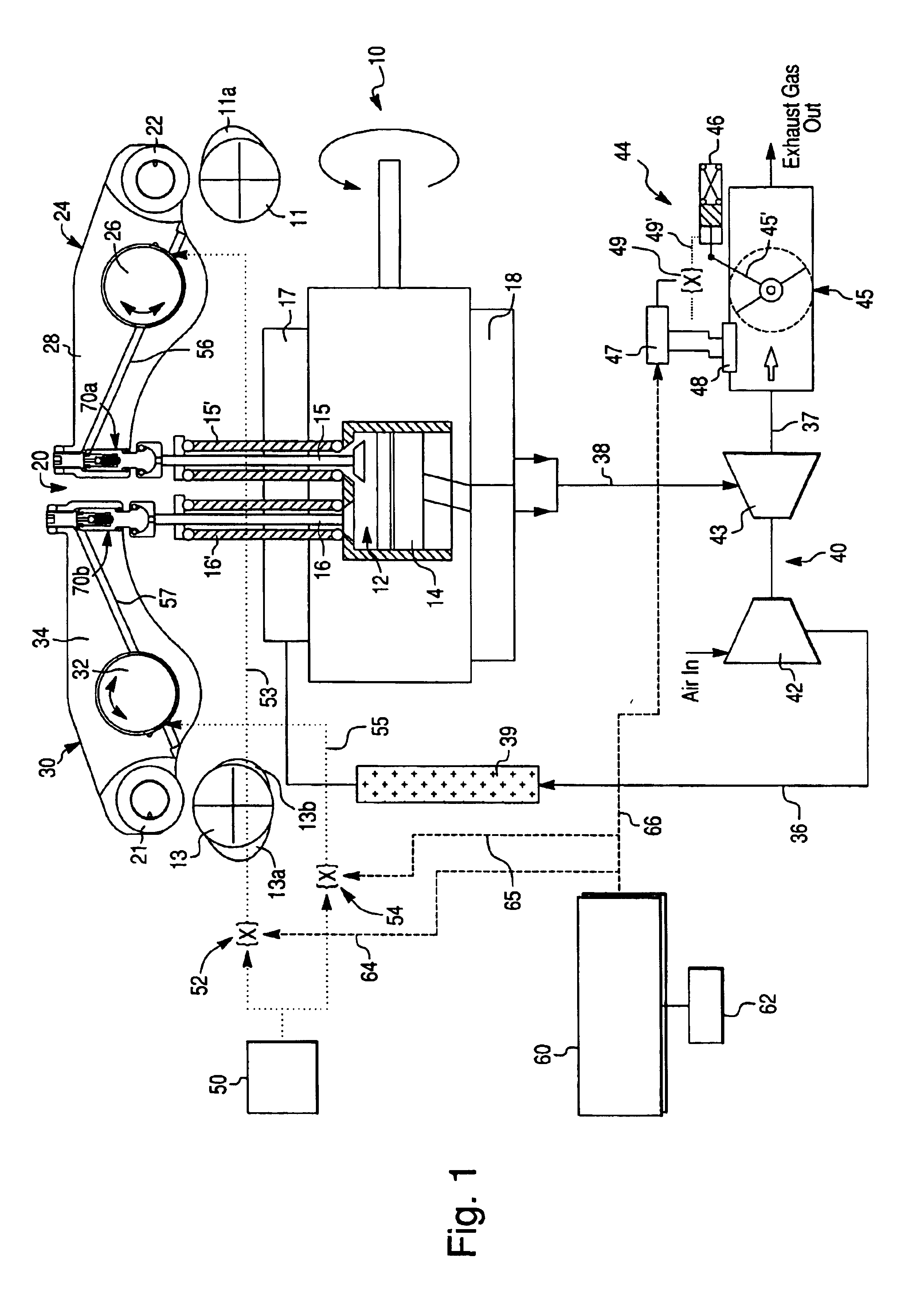
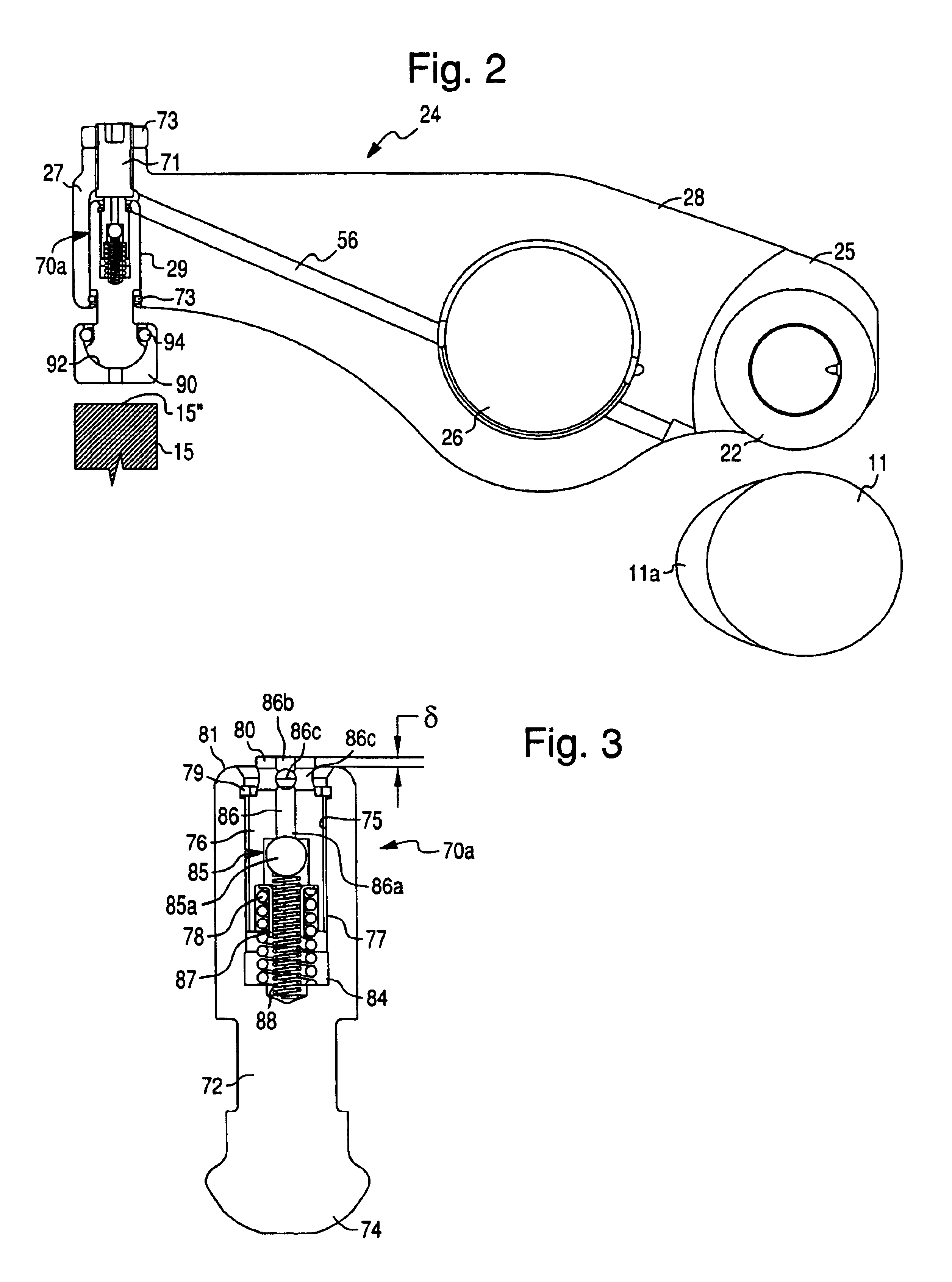
The disclosure relates to fluid working devices including reciprocating internal combustion engines, compressors and pumps. A number of arrangements for pistons and cylinders of unconventional configuration are described, mostly intended for use in reciprocating internal combustion IC engines operating without cooling. Included are toroidal combustion or working chambers, some with fluid flow through the core of the toroid, pistons reciprocating between pairs of working chambers, tensile valve actuation, tensile links between piston and crankshaft, energy absorbing piston-crank links, crankshafts supported on gas bearings, cylinders rotating in housings, injectors having components reciprocate or rotate during fuel delivery. In some embodiments pistons mare rotate while reciprocating. High temperature exhaust emissions systems are described, including those containing filamentary material, as are procedures for reducing emissions during cold start by means of valves at reaction volume exit. Compound engines having the new engines as a reciprocating stage are described. Improved vehicles, aircraft, marine craft and transmissions adapted to receive or be linked to the improved IV engines are also disclosed.
Owner:HINDERKS MITJA VICTOR
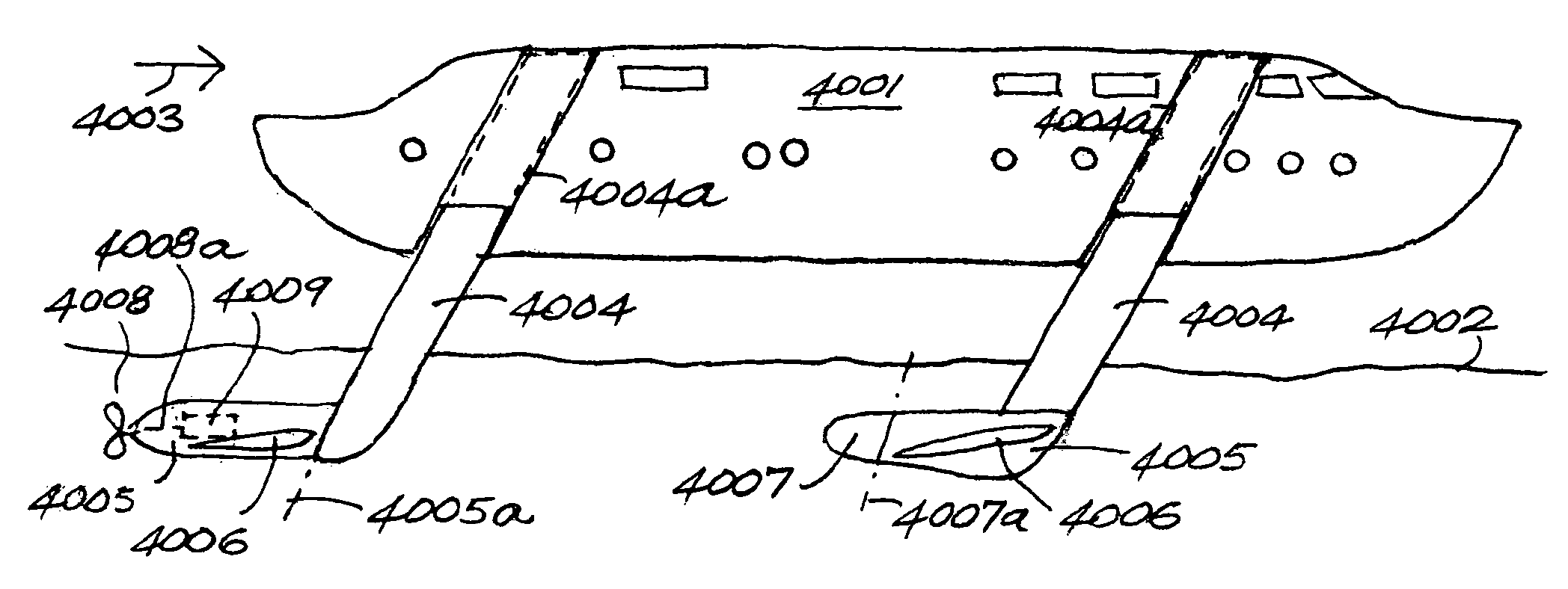
Marine hulls and drives
InactiveUS7984684B2Improve power densityNo coolingHybrid vehiclesInternal combustion piston enginesTravel modeCombustion
Owner:HINDERKS MITJA VICTOR
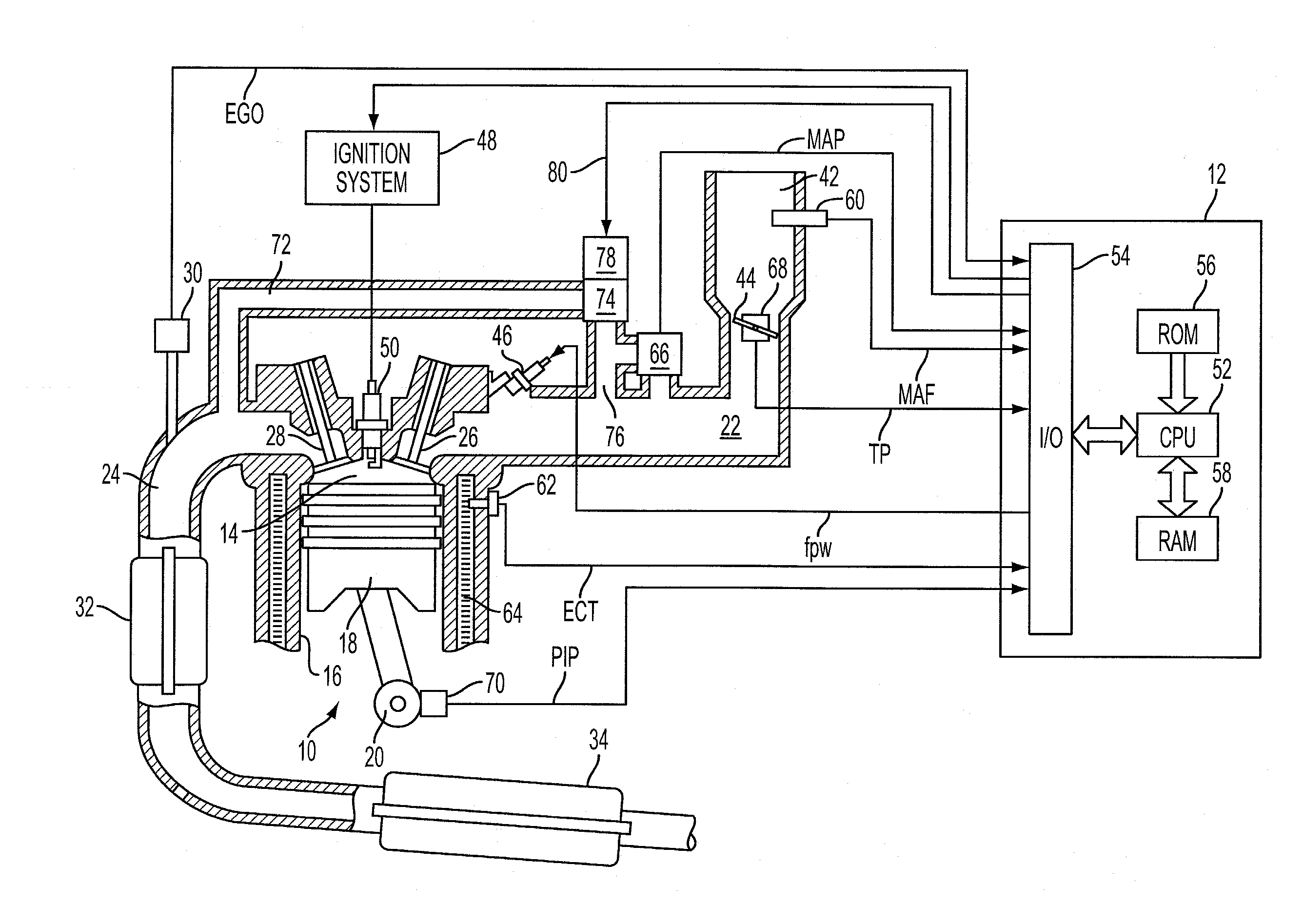
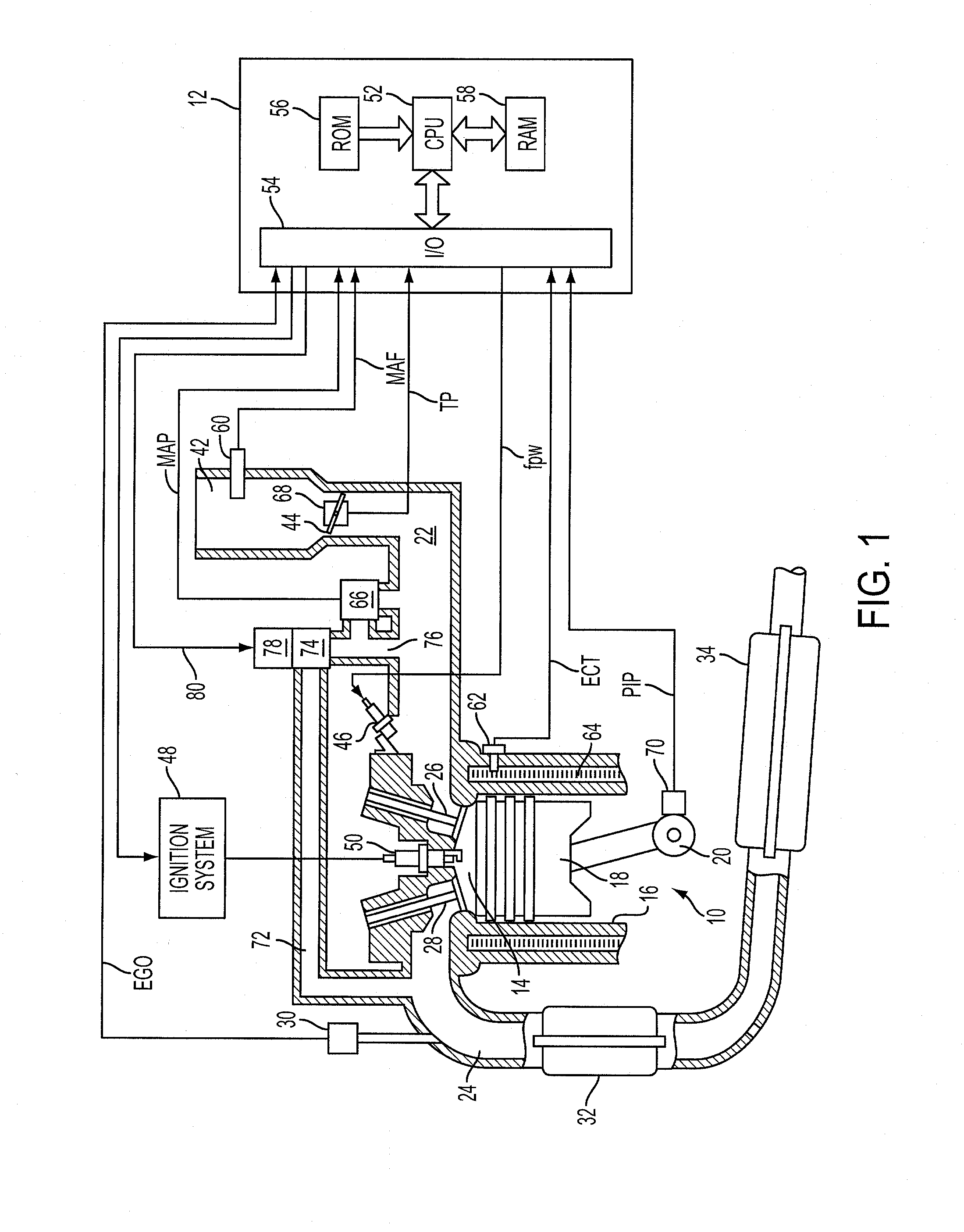
Control apparatus for controlling internal combustion engines
InactiveUS20070089697A1Minimize biasElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesControl systemInternal combustion engine
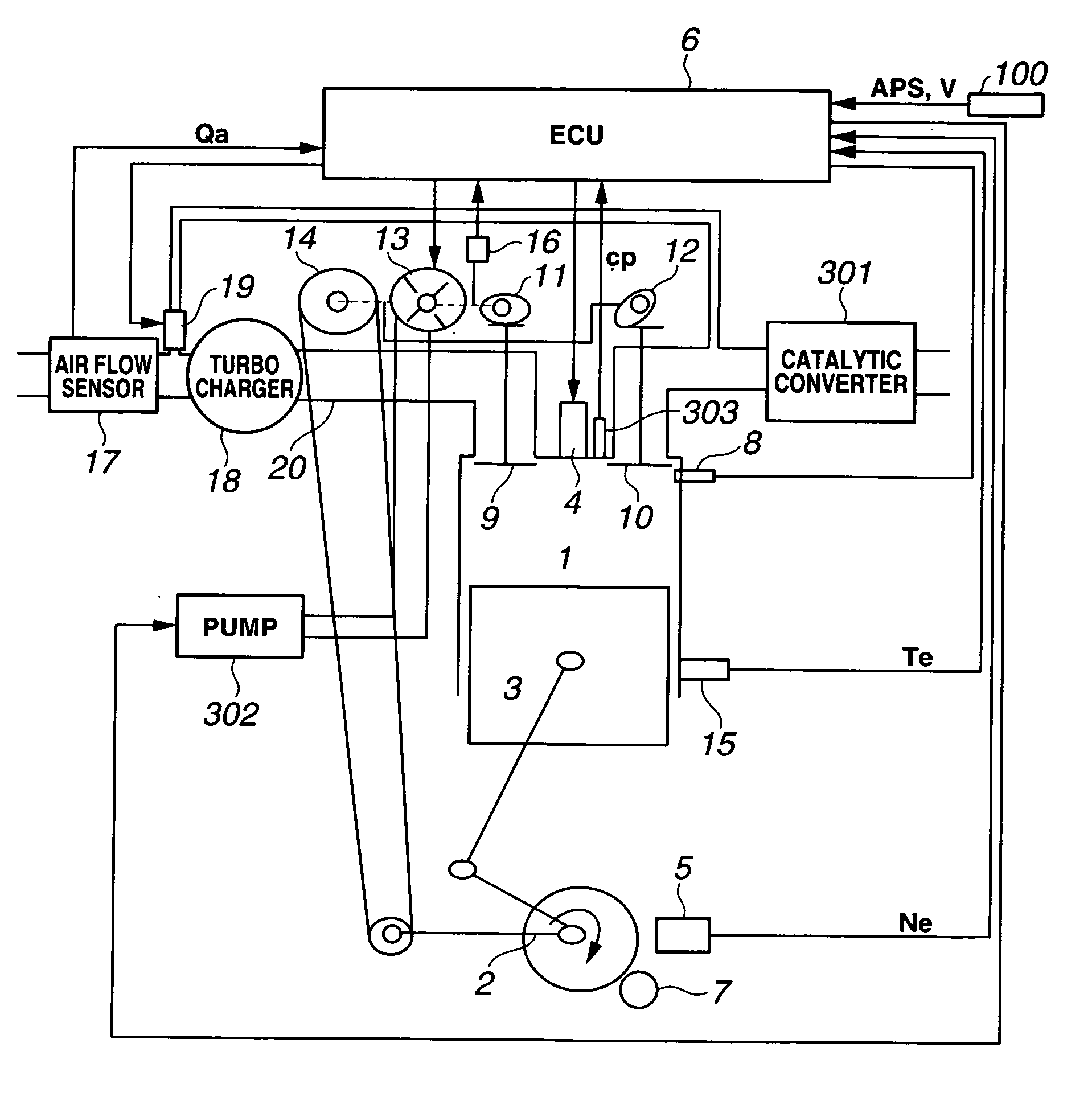
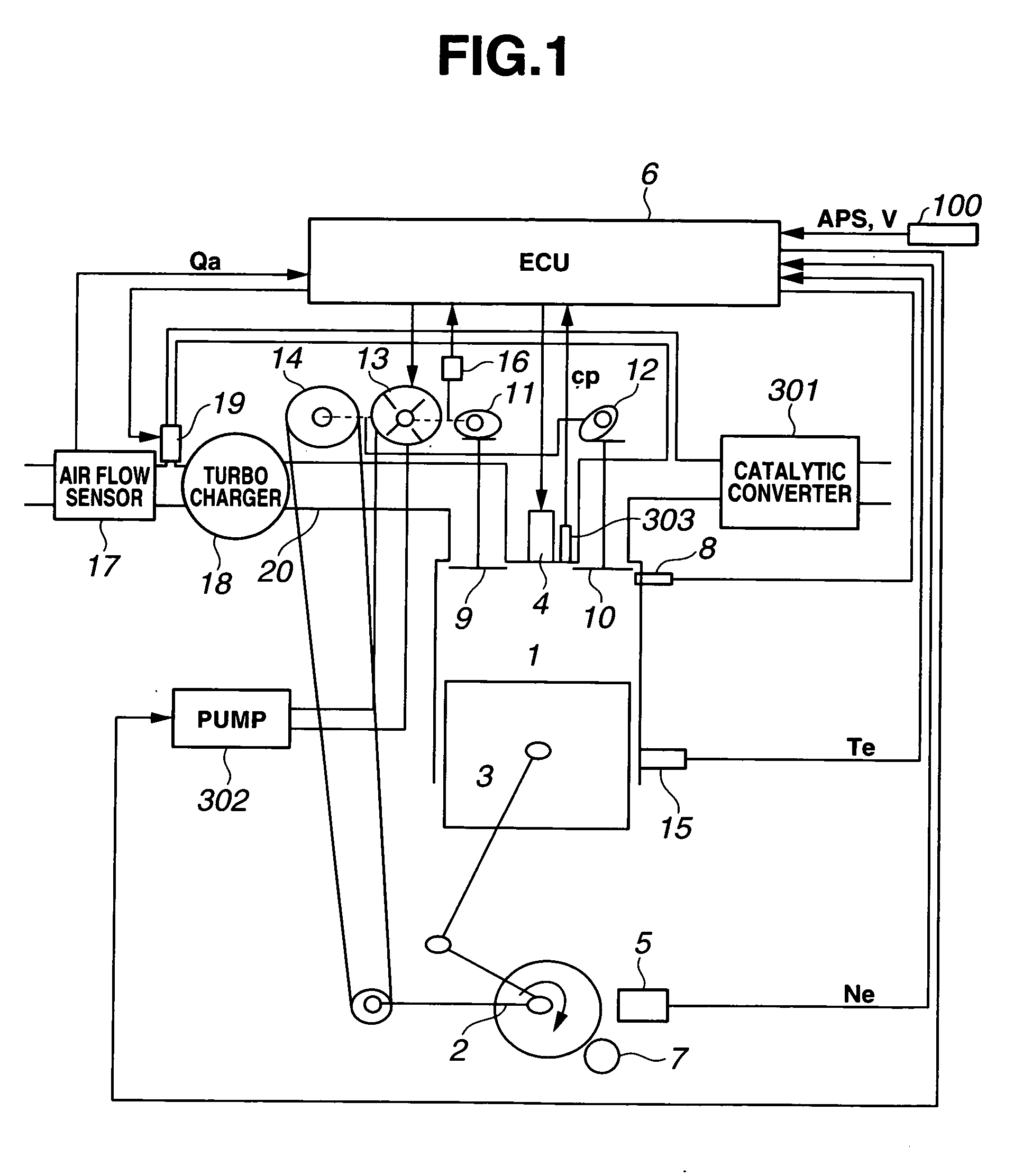
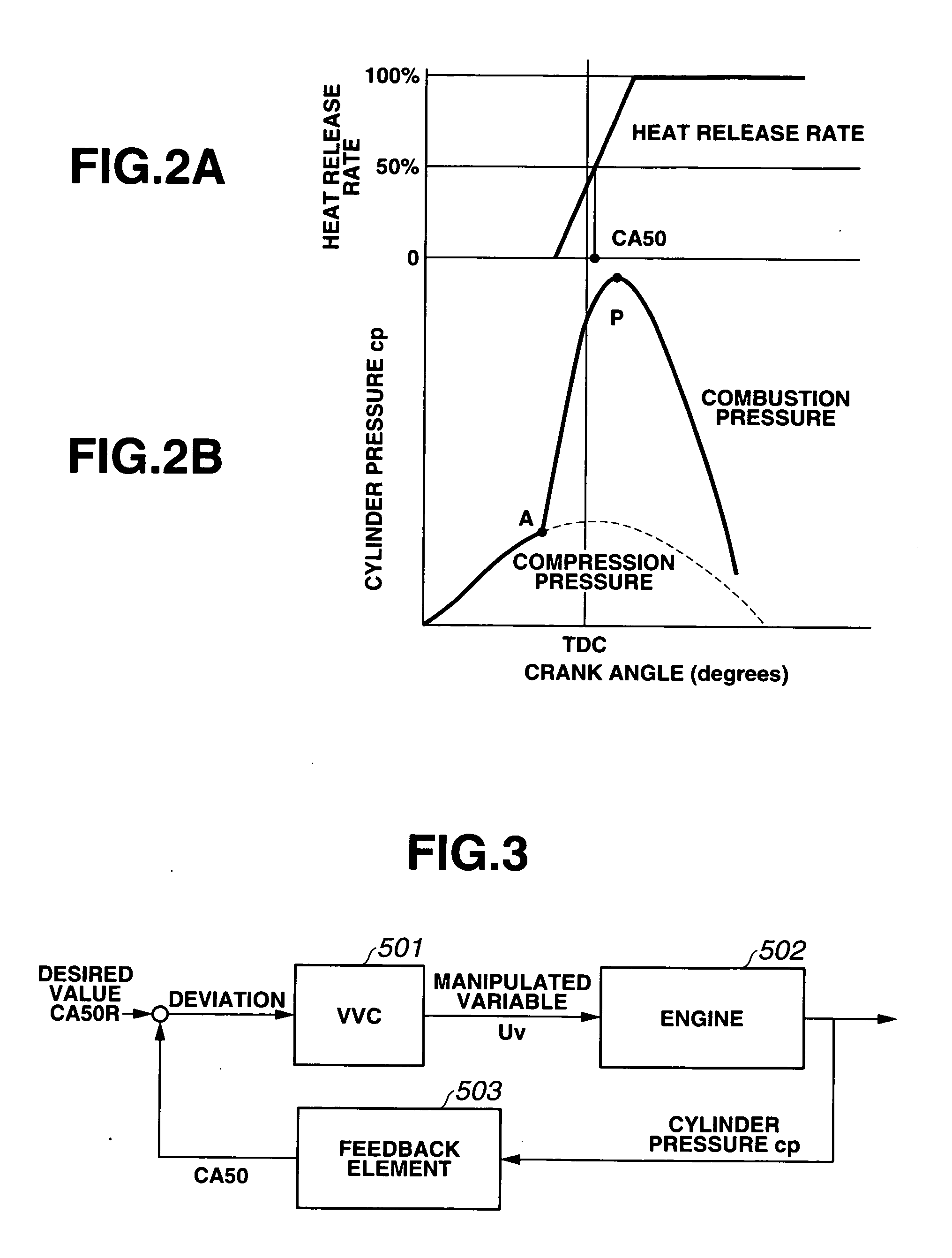
In a control apparatus for controlling a variable valve actuation system employed in an internal combustion engine, engine / vehicle sensors are provided to detect at least a cylinder pressure in an engine cylinder for monitoring a change of state in combustion, arising from fluctuations in states / characteristics of air-fuel mixture such as a change in fuel property. Also provided is a control system that controls the variable valve actuation system responsively to a manipulated variable modified based on the cylinder pressure reflecting the change of state in combustion by a model of combustion.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Compact lost motion system for variable valve actuation
InactiveUS6883492B2Wide rangeNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesVariable valve timingHydraulic circuit
Lost motion systems and methods for providing engine valves with variable valve actuation for engine valve events are disclosed. The system may include a master piston hydraulically linked to a slave piston, and a dedicated cam operatively connected to the master piston. The slave piston may be disposed substantially perpendicular to the master piston in a common housing. The slave piston is adapted to actuate one or more engine valves. The slave piston may incorporate an optional valve seating assembly into its upper end. A trigger valve may be operatively connected to the master-slave hydraulic circuit to selectively release and add hydraulic fluid to the circuit.
Owner:JACOBS VEHICLE SYST
Engine valve disabler
A method for improving efficiency and reducing emissions of an internal combustion engine. Variable displacement engine capabilities are achieved by disabling engine valves during load changes and constant load operations. Active cylinders may be operated at minimum BSFC by intermittently disabling other cylinders to provide the desired net torque. Disabling is begun by early closing of the intake valve to provide a vacuum at BDC which will result in no net gas flow across the piston rings, and minimum loss of compression energy in the disabled cylinder; this saving in engine friction losses is significant with multiple disablements.
Owner:MOYER DAVID F
Method and apparatus for optimized combustion in an internal combustion engine utilizing homogeneous charge compression ignition and variable valve actuation
InactiveUS20060144356A1Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHomogeneous charge compression ignitionExhaust valve
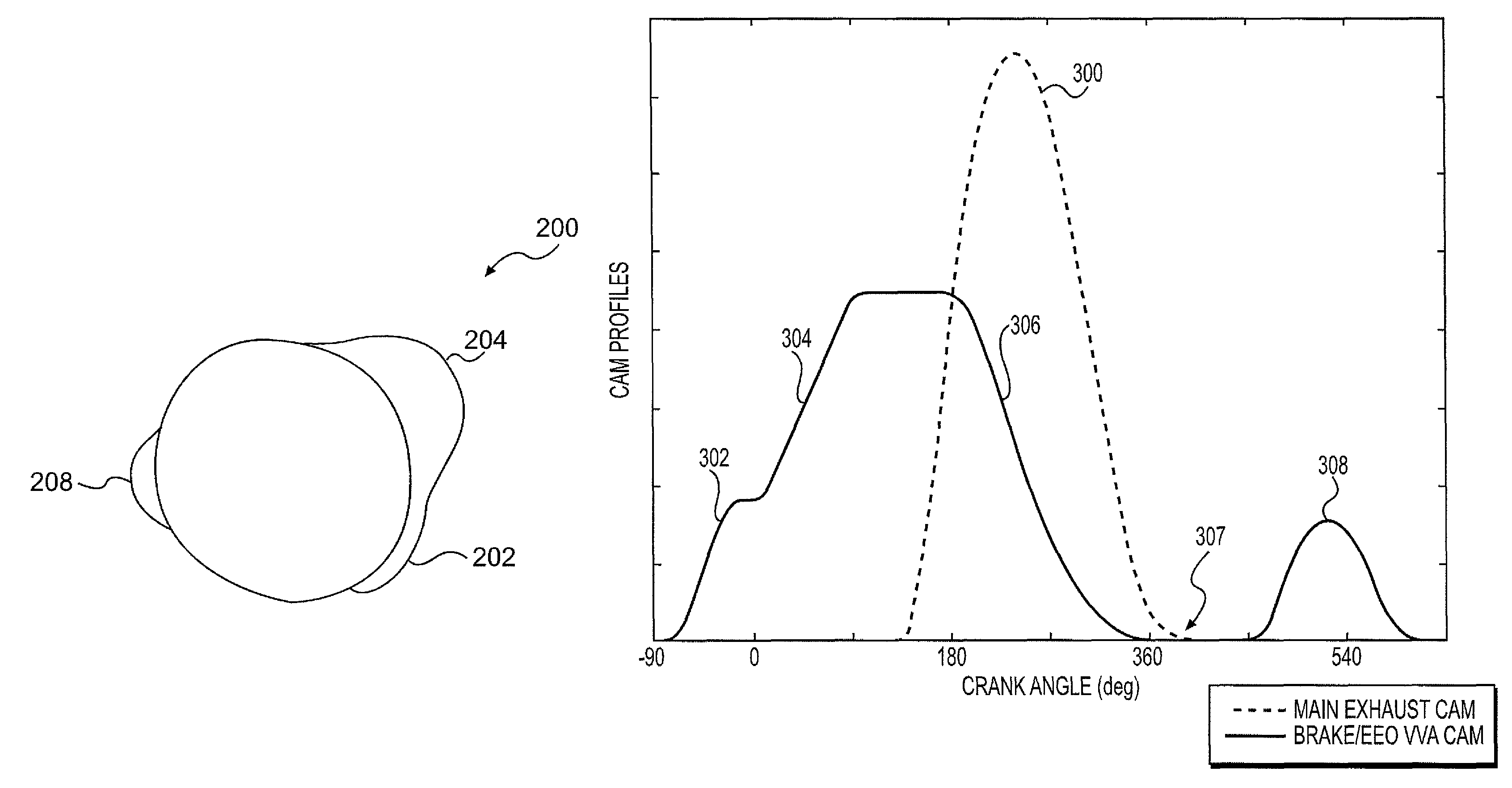
A valvetrain system mechanization for an internal combustion engine using compression ignition, including homogeneous charge compression ignition, having two intake and one or more exhaust valves per cylinder. The valves are operated by dual overhead camshafts having two-step cams. The intake and exhaust camshafts are provided with phasers for varying the opening and closing of the intake and exhaust valves. A two-step roller finger follower is disposed for each valve between the cam lobes and the valve stem. The two sets of intake and exhaust valves are controlled by separate oil control valves. Swirl of gases may be introduced by mismatching the lifts of the valves. The valve opening times, closing times, lifts, fuel injection, compression ratio, and exhaust gas recirculation may be varied to optimize combustion conditions for a range of engine operating modes.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
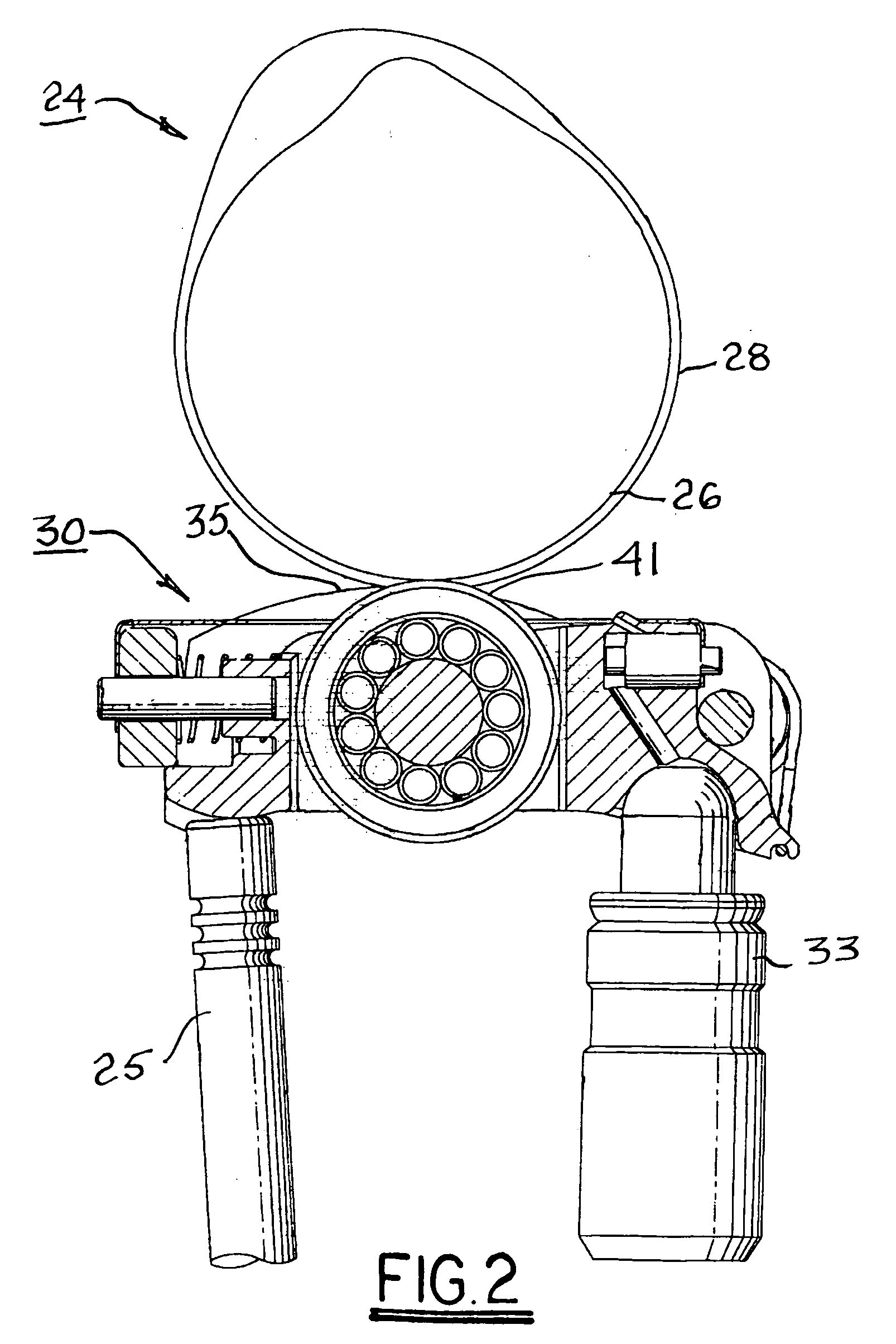
Lost motion variable valve actuation system for engine braking and early exhaust opening
ActiveUS7712449B1Improved transient torqueAvoid impactValve drivesOutput powerEngineeringExhaust gas recirculation
A method and system for actuating an internal combustion engine exhaust valve to provide compression release actuation during an engine braking mode of engine operation and early exhaust valve opening actuation during a positive power mode of engine operation is disclosed. The system may include a first cam having a compression release lobe and an early exhaust valve opening lobe connected to a hydraulic lost motion system including a first rocker arm. A hydraulically actuated piston may be selectively extended from the hydraulic lost motion system to provide the exhaust valve with compression release actuation or early exhaust valve opening actuation. The hydraulically actuated piston may be provided as a slave piston in a master-slave piston circuit in a fixed housing, or alternatively, as a hydraulic piston slidably disposed in a rocker arm. The method and system may further provide exhaust gas recirculation and / or brake gas recirculation in combination with compression release actuation and early exhaust valve opening actuation.
Owner:JACOBS VEHICLE SYST
Variable valve timing control device of internal combustion engine
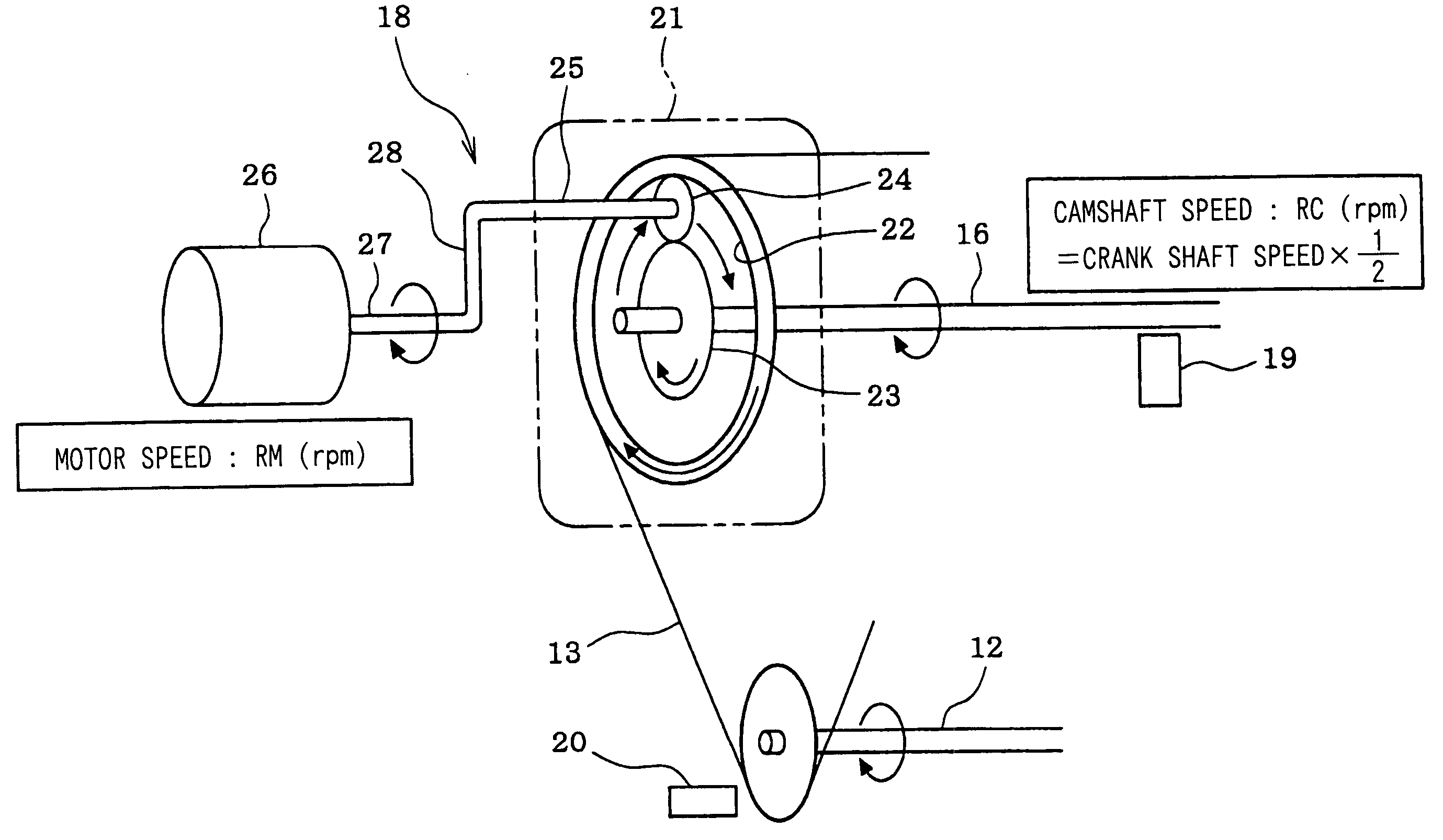
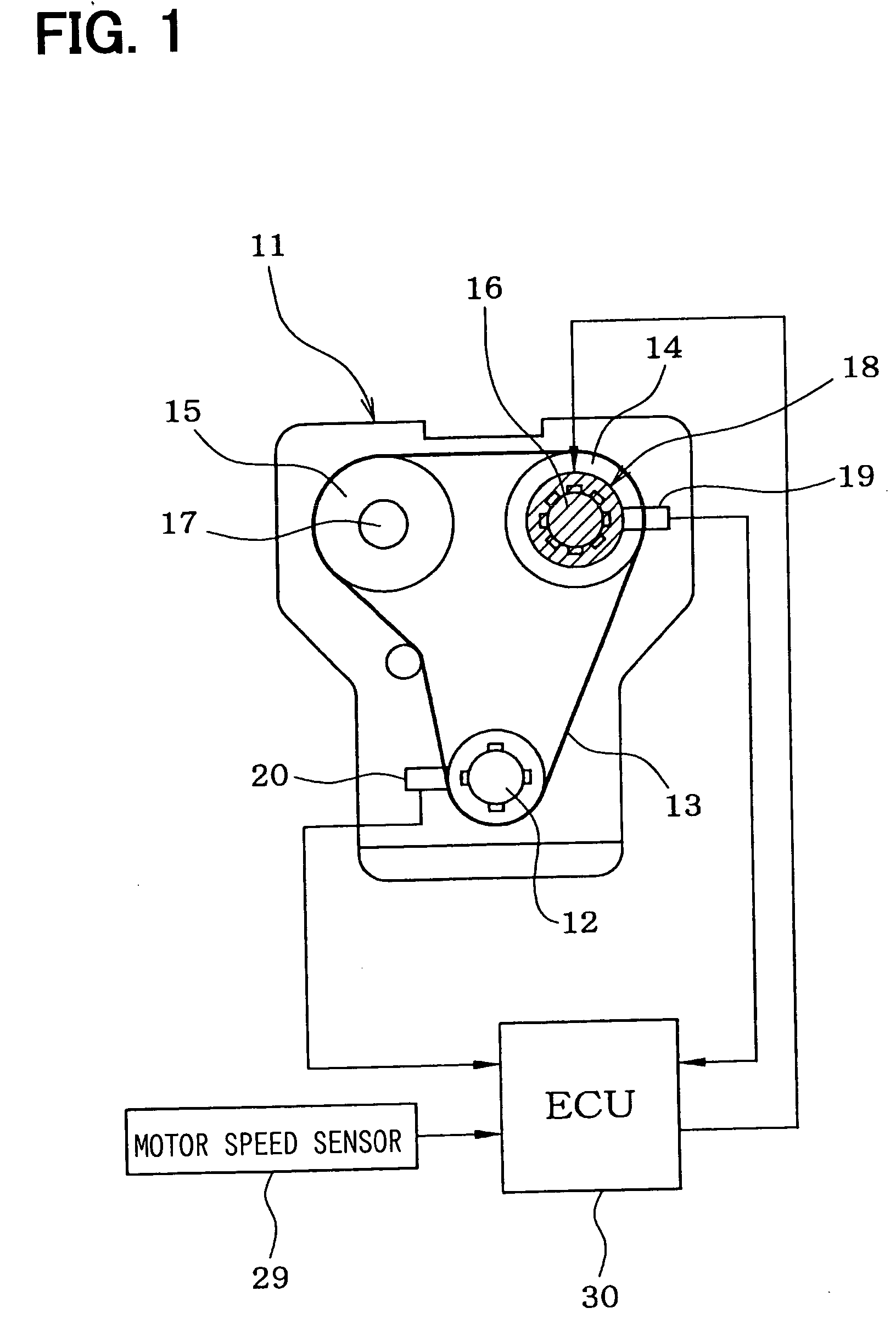
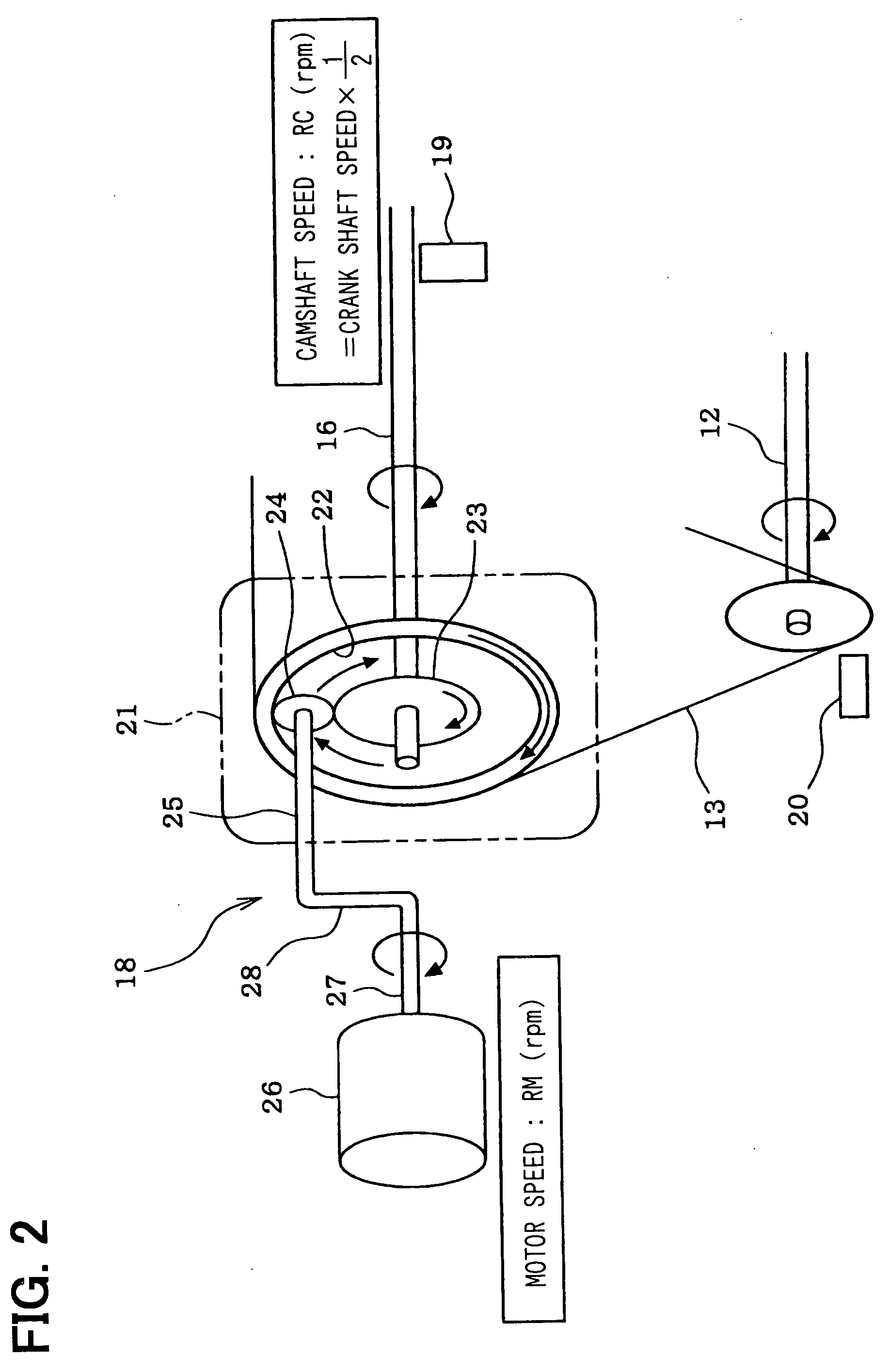
A required valve timing change rate Vreq is calculated so as to make a deviation D between a target valve timing VTtg and an actual valve timing VT small and then a required speed difference DMCRreq between a motor 26 and a camshaft 16 is calculated on a basis of the required valve timing change rate Vreq. When the deviation D is larger than a predetermined value, a required motor speed Rmreq is calculated by adding the required speed difference DMCRreq to a camshaft speed RC and a motor control value is calculated so as to control the motor speed RM to the required motor speed Rmreq. When the deviation D is not larger than the predetermined value, the camshaft speed RC is set as the required motor speed Rmreq and the motor control value is calculated so as to control the motor speed RM to the camshaft speed RC.
Owner:DENSO CORP
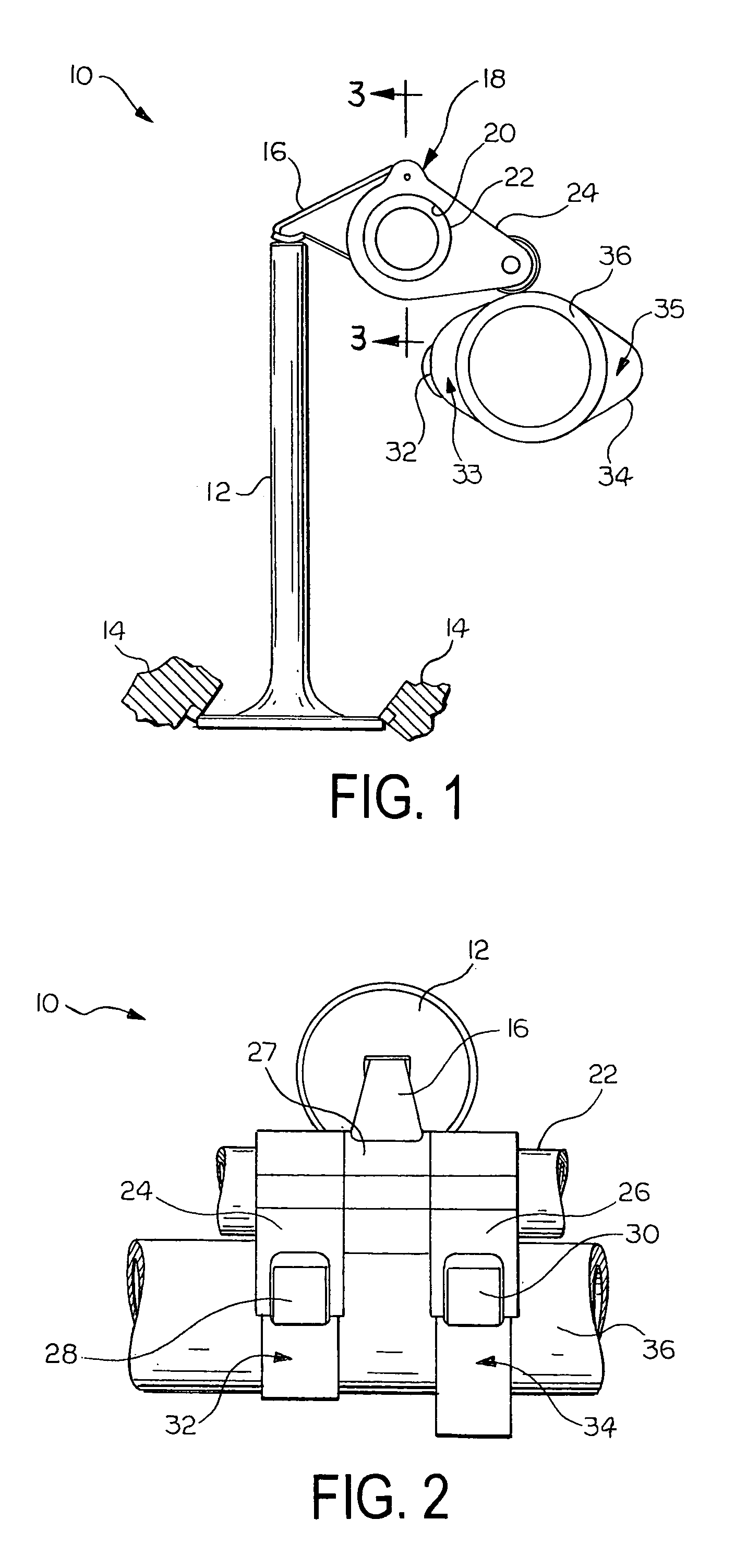
Apparatus for the adjustment of the stroke of a valve actuated by a camshaft
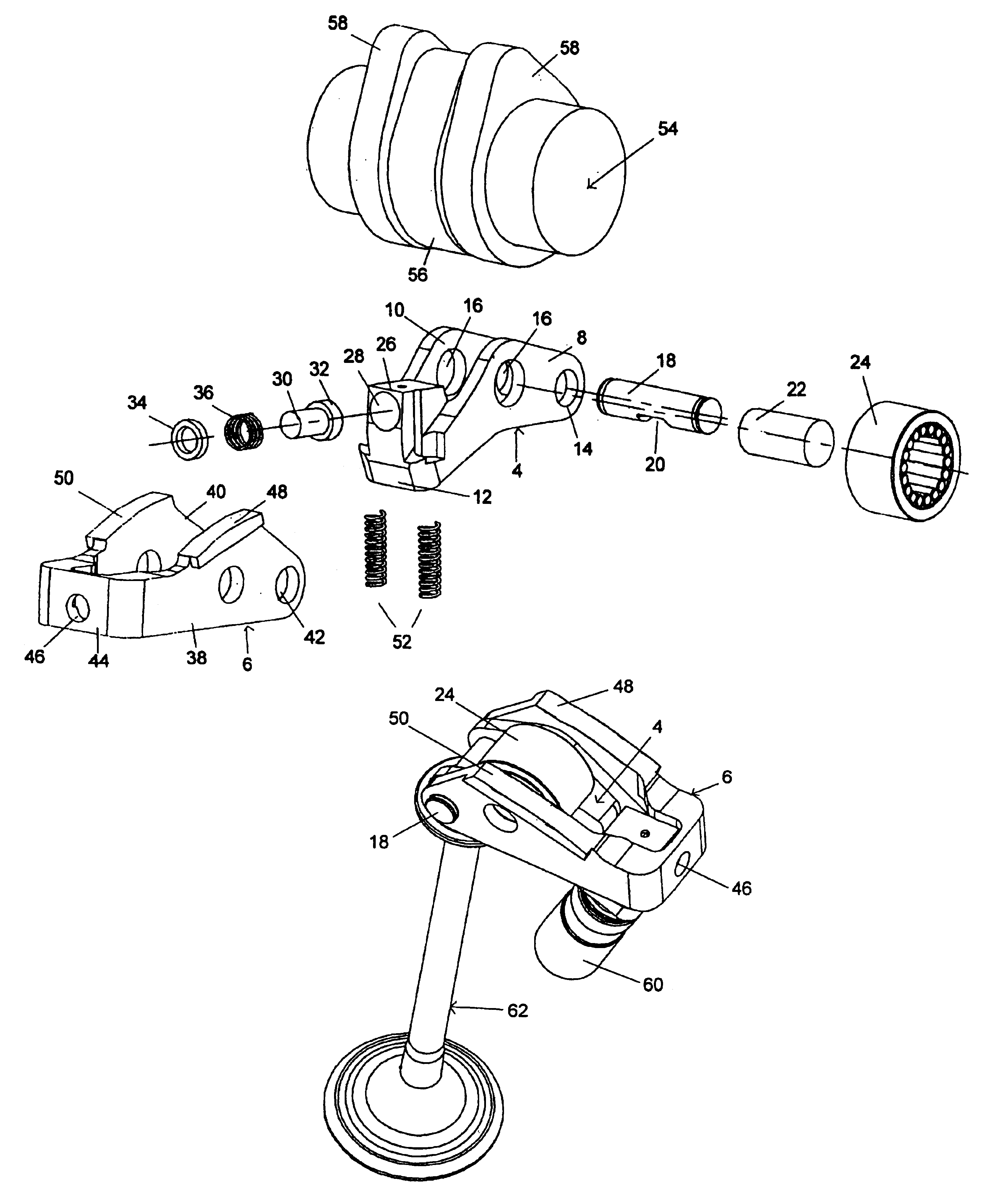
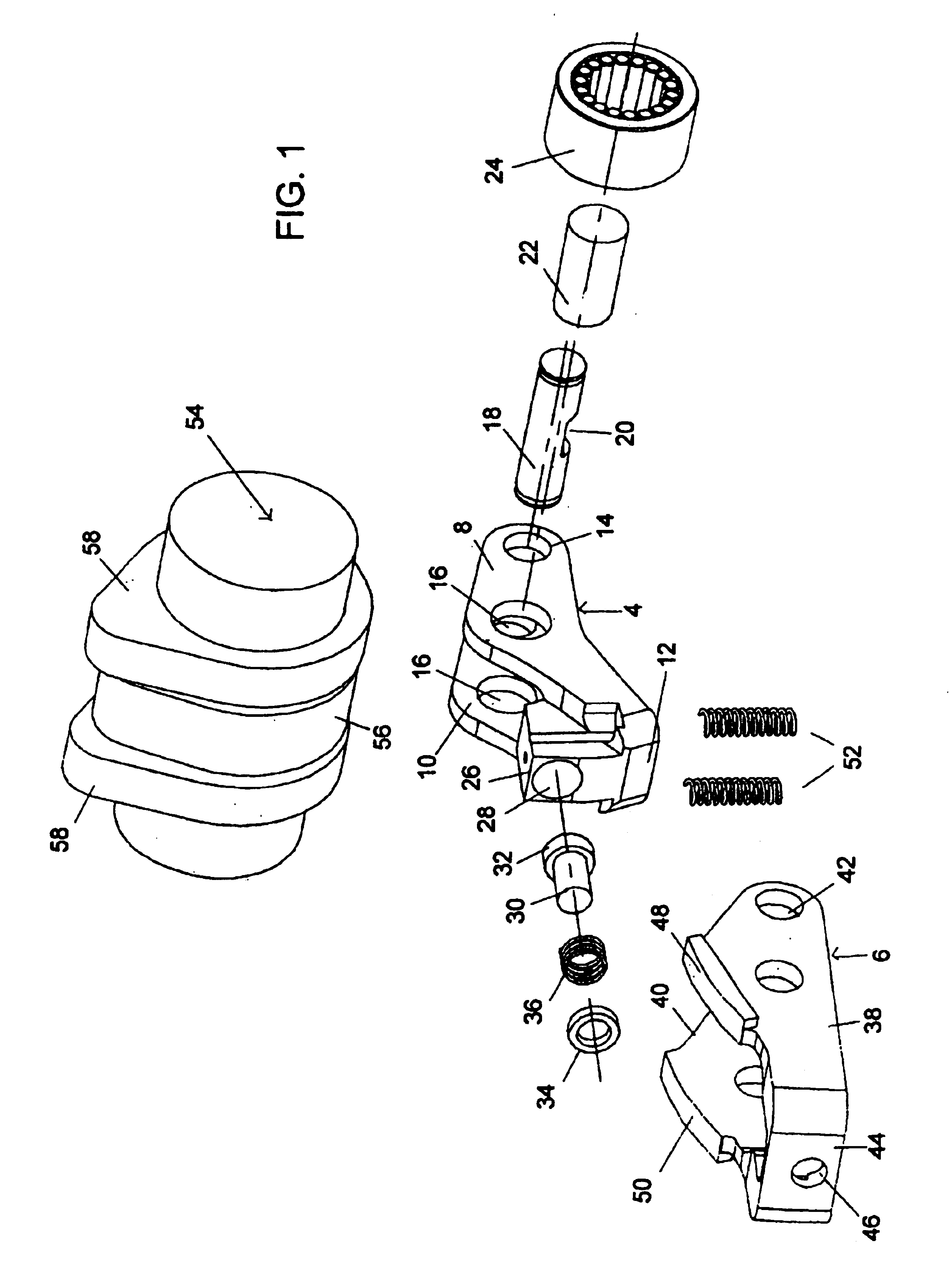
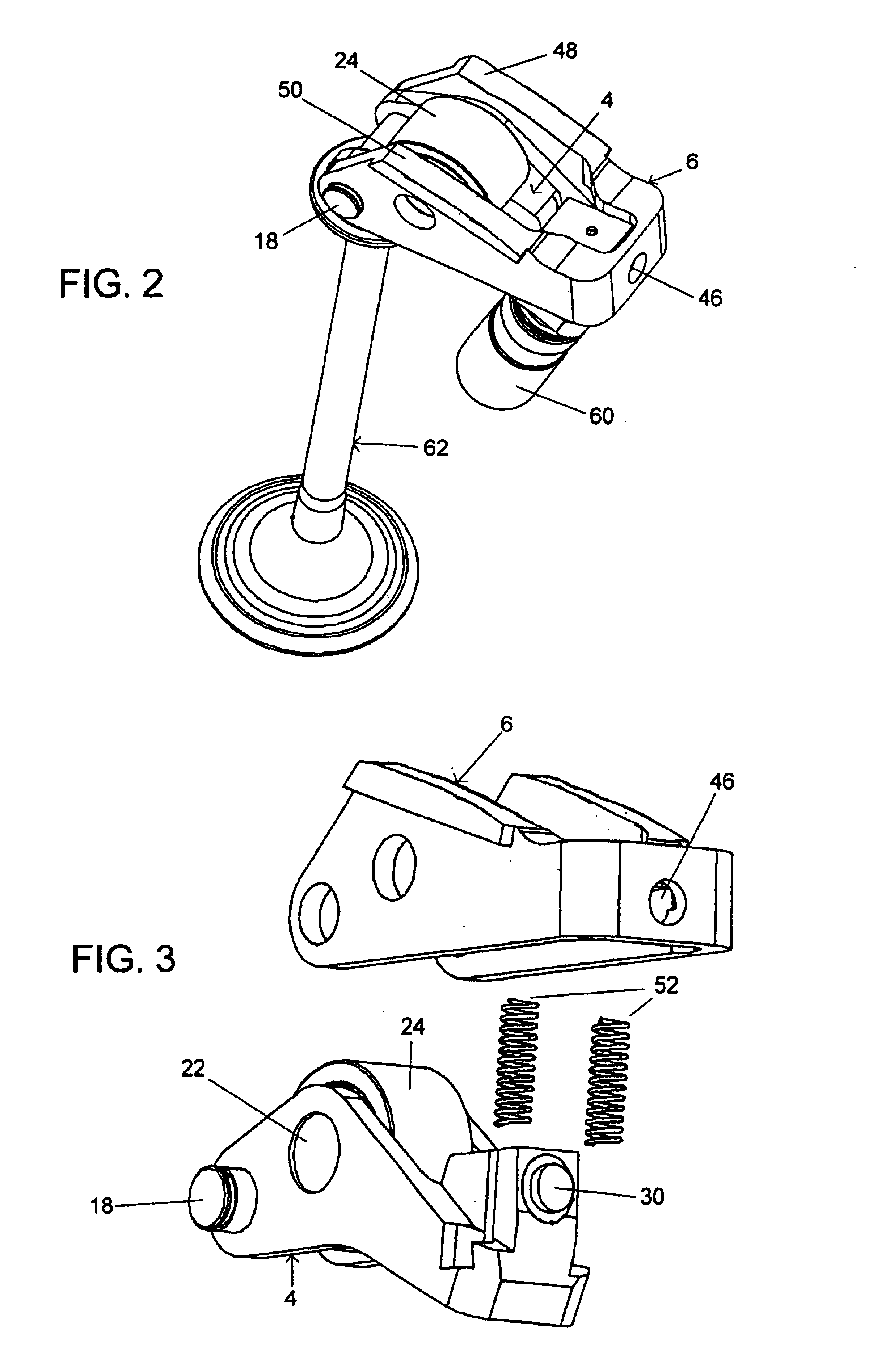
An apparatus for adjusting the stroke of a valve that is actuated by a camshaft having at least one cam is provided. A valve lever having an outer lever and an inner lever is provided and has a first end region supported on a fixed component, and a second end region for actuating a valve. The U-shaped outer lever includes two arms and a crosspiece that faces the fixed component. At least one of the arms is provided with an abutment surface for contacting the at least one cam. The inner lever is mounted on a free end of the outer lever between the arms, and has an abutment surface, for contacting cams, that is disposed between the mounting axis of the inner lever on the arms and the support of the first end region of the valve lever on the fixed component. A blocking device is provided for fixing the crosspiece of the outer lever on an end of the inner lever remote from the valve, this end being supported on the fixed component and containing the blocking device.
Owner:META MOTOREN UND ENERGIE TECHNIK GMBH
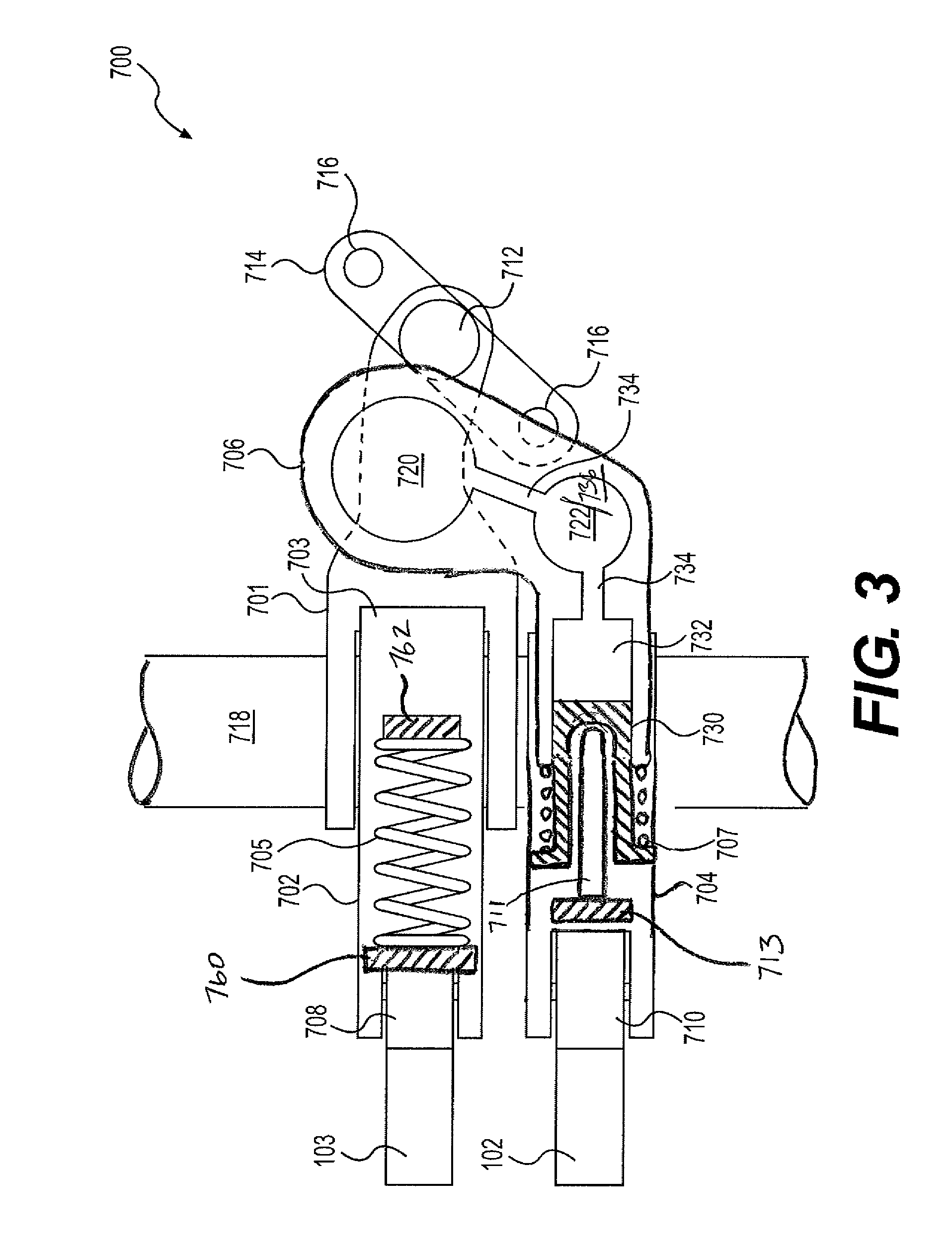
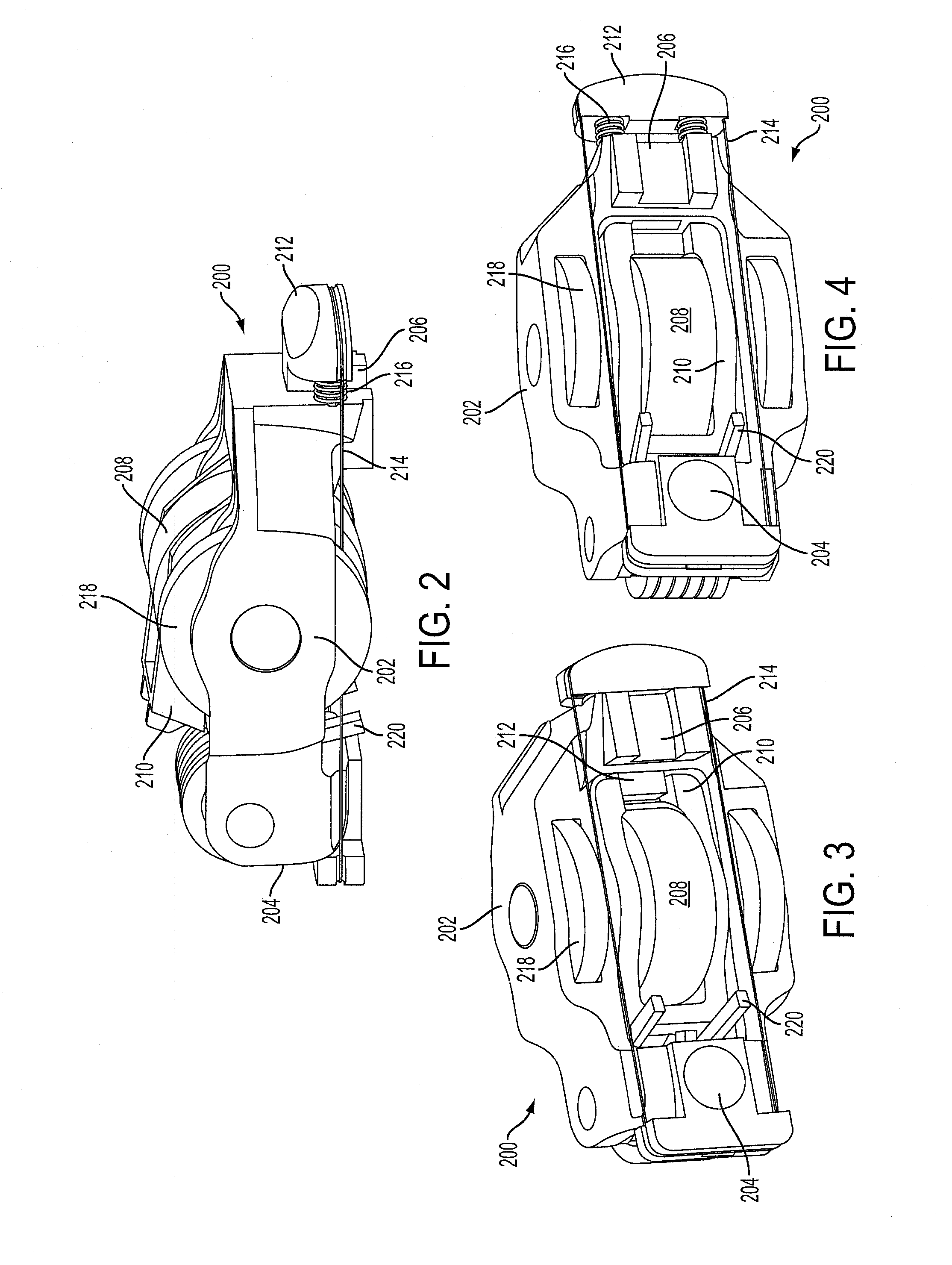
Dual lift rocker arm latch mechanism and actuation arrangement therefor
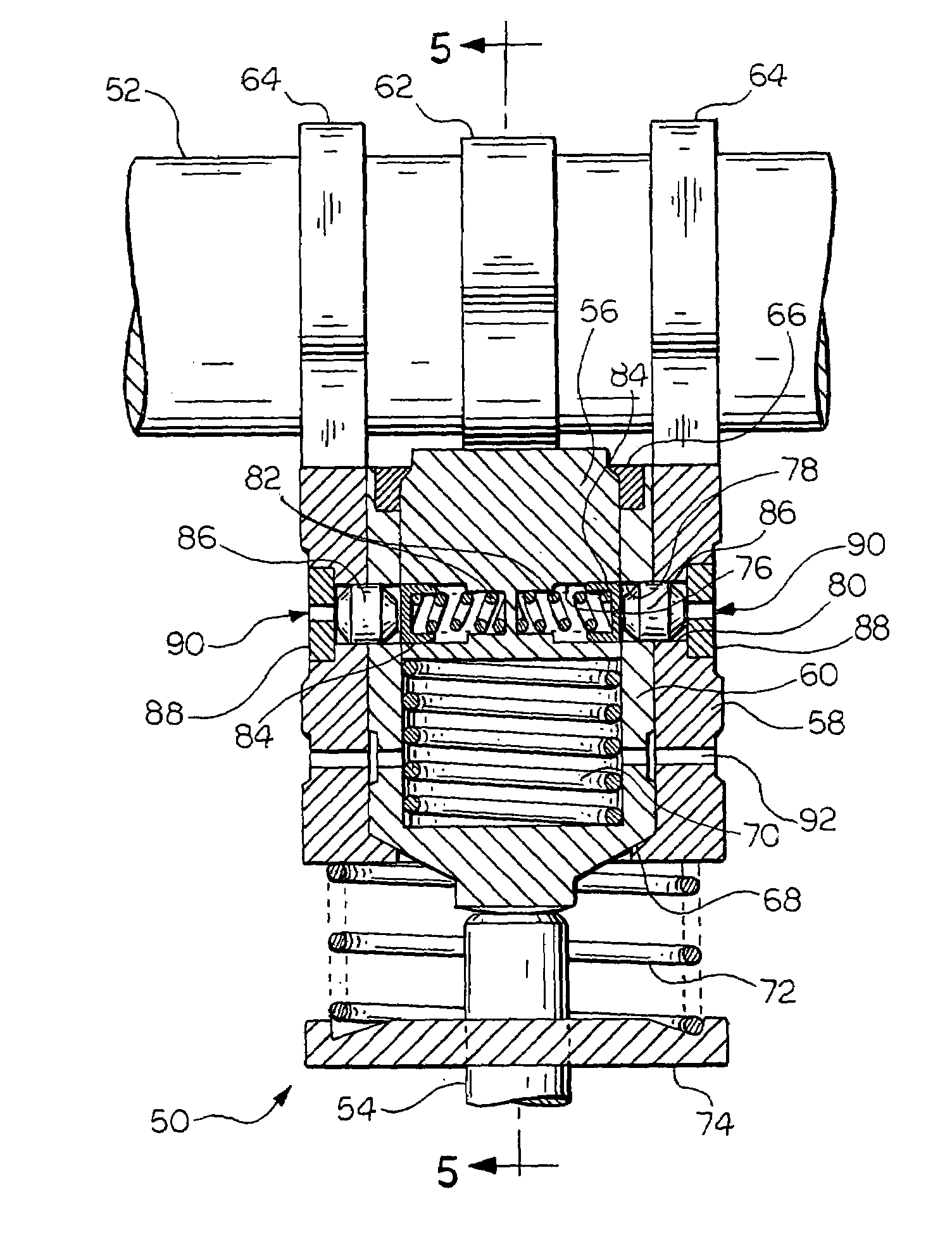
ActiveUS20070186890A1Substantial added structureSubstantial costControlling membersValve drivesControl systemEngineering
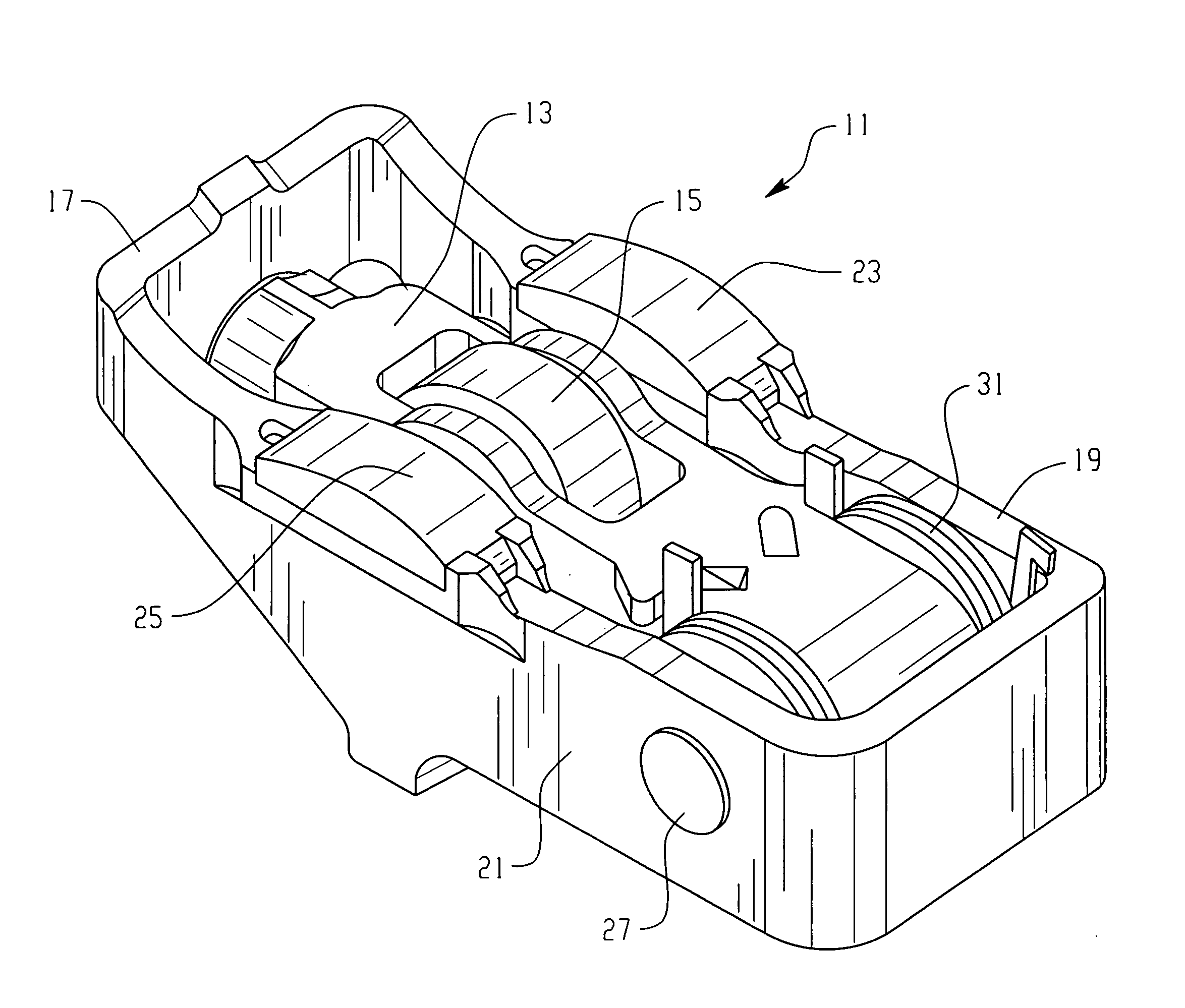
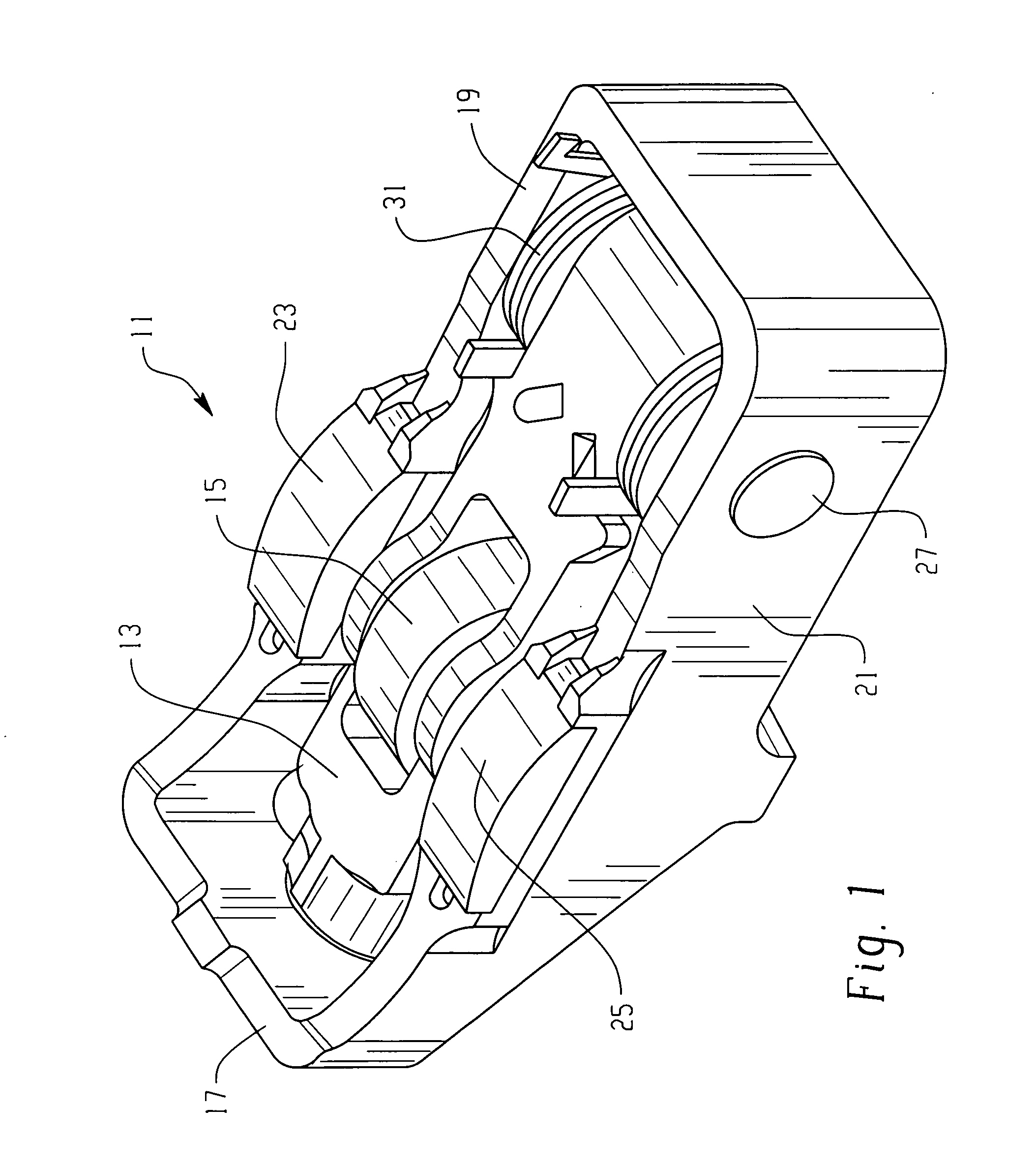
A valve control system including a camshaft having first and second cam profiles, the valve control system comprising a rocker arm assembly (11) including a first rocker arm (13) having a first cam follower (15) in engagement with the first cam profile, and a second rocker arm (17) having a second cam follower (23,25) in engagement with the second cam profile. The engine includes a fulcrum location (P) operable to provide a source of pressurized fluid, and the first rocker arm includes a latch member (47) moveable between latched (FIG. 6) and unlatched conditions. The latch member is biased toward the latched condition by a fluid pressure in a chamber (51), and the first rocker arm defines a fluid passage (55) having a first end (57) in open fluid communication with the pressure source, and a second end (59) in open fluid communication with the pressure chamber (51).
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
Diagnostics for two-mode variable valve activation devices
ActiveUS20090228167A1Vehicle testingInternal-combustion engine testingElectricityRadio frequency signal
A method for detecting a low-lift or zero-lift failure mode in a variable valve activation system of an internal combustion engine includes the steps of positioning a piezo-electric element that acts as a radio frequency transmitter relative to a lost motion spring of a two-mode variable valve activation lost motion device, subjecting the piezo-electric element to a compression load when a load from displacement of a lobe of a camshaft acts on the lost motion spring, broadcasting a radio frequency signal each time the piezo-electric element is subjected to the compression load, and evaluating the presence or absence of the broadcasted radio frequency signal in relation to an expected presence or absence of the radio frequency signal. The direct measurement of the mode of each two-mode device is both more reliable and more efficient in the use of engine controller resources compared to currently existing diagnostic methods.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
Variable phase drive mechanism
InactiveUS20050226736A1Reduce riskLess spaceYielding couplingOscillating piston enginesLocking mechanismEngineering
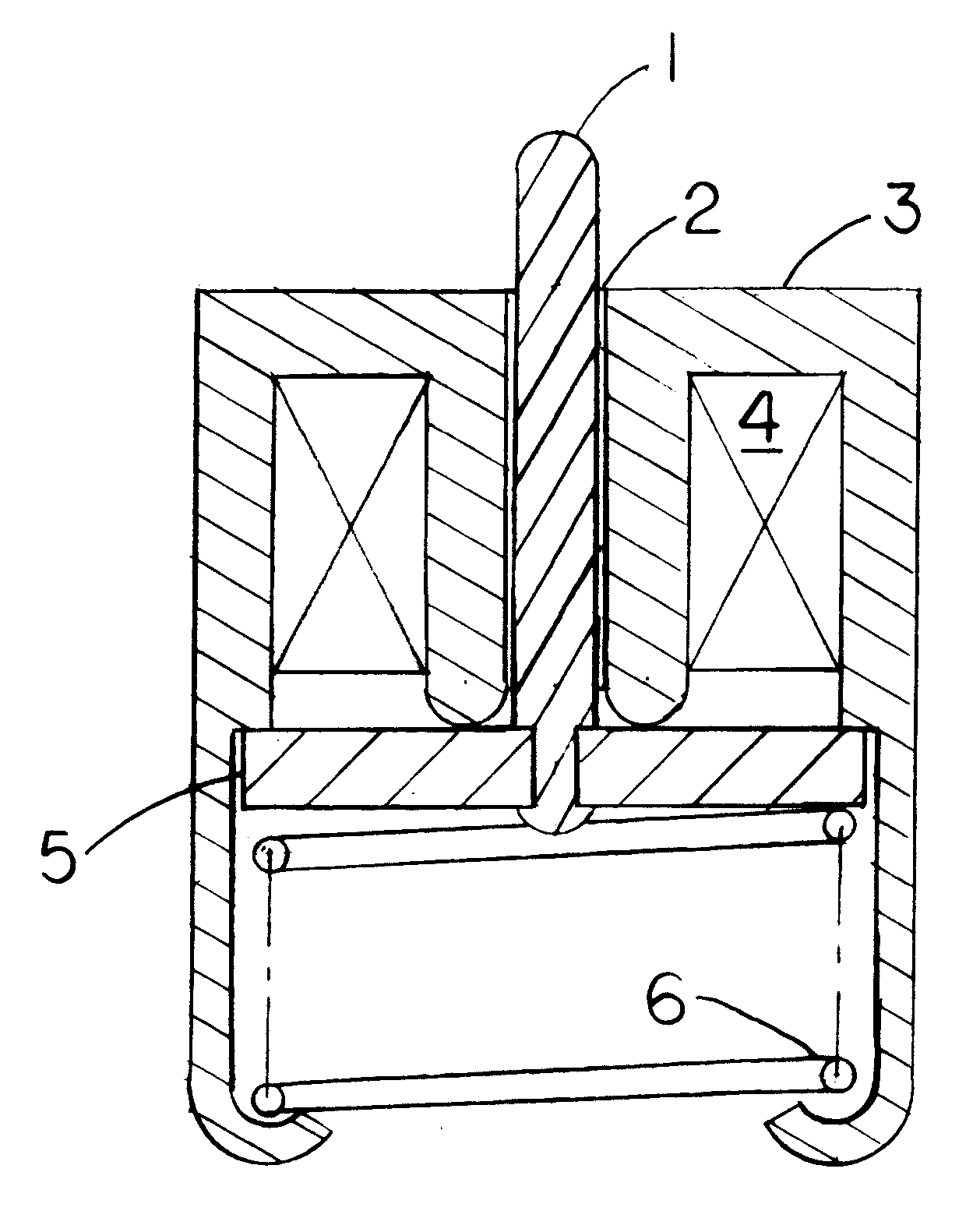
A twin vane-type phaser is described which is provided with a locking mechanism for locking the drive member to the driven members when the pressure in the working chambers is a below is predetermined value. The locking mechanism comprises two coaxial locking pins 114, 118 mounted in a common bore 110 in the centrally located member 32. The locking pins are resiliently urged apart by a spring 120 into bores in the two outer members 38, 40 and are retracted by pistons 112, 116 when the hydraulic pressure in the working chambers attains the predetermined value.
Owner:MECHADYNE LTD
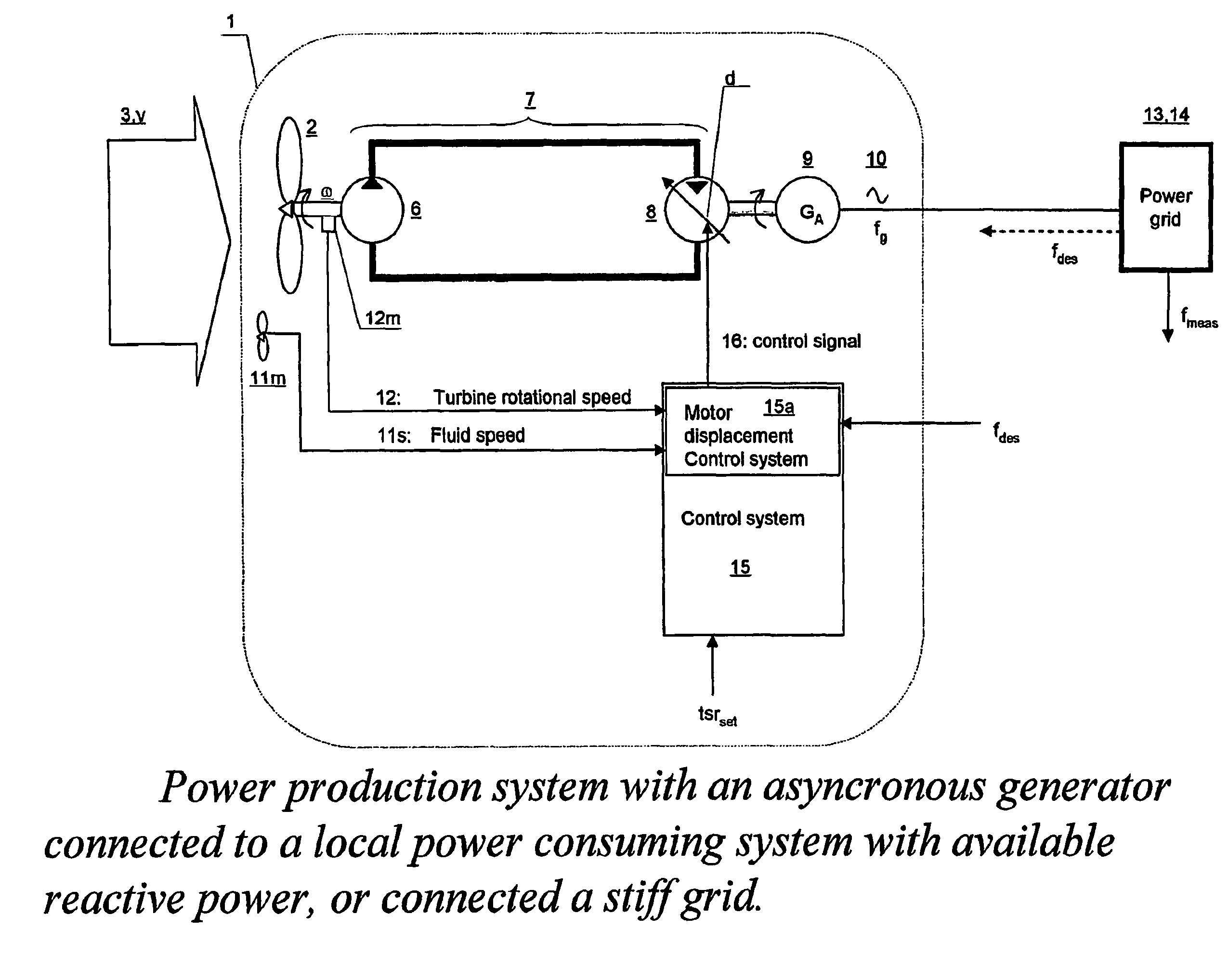
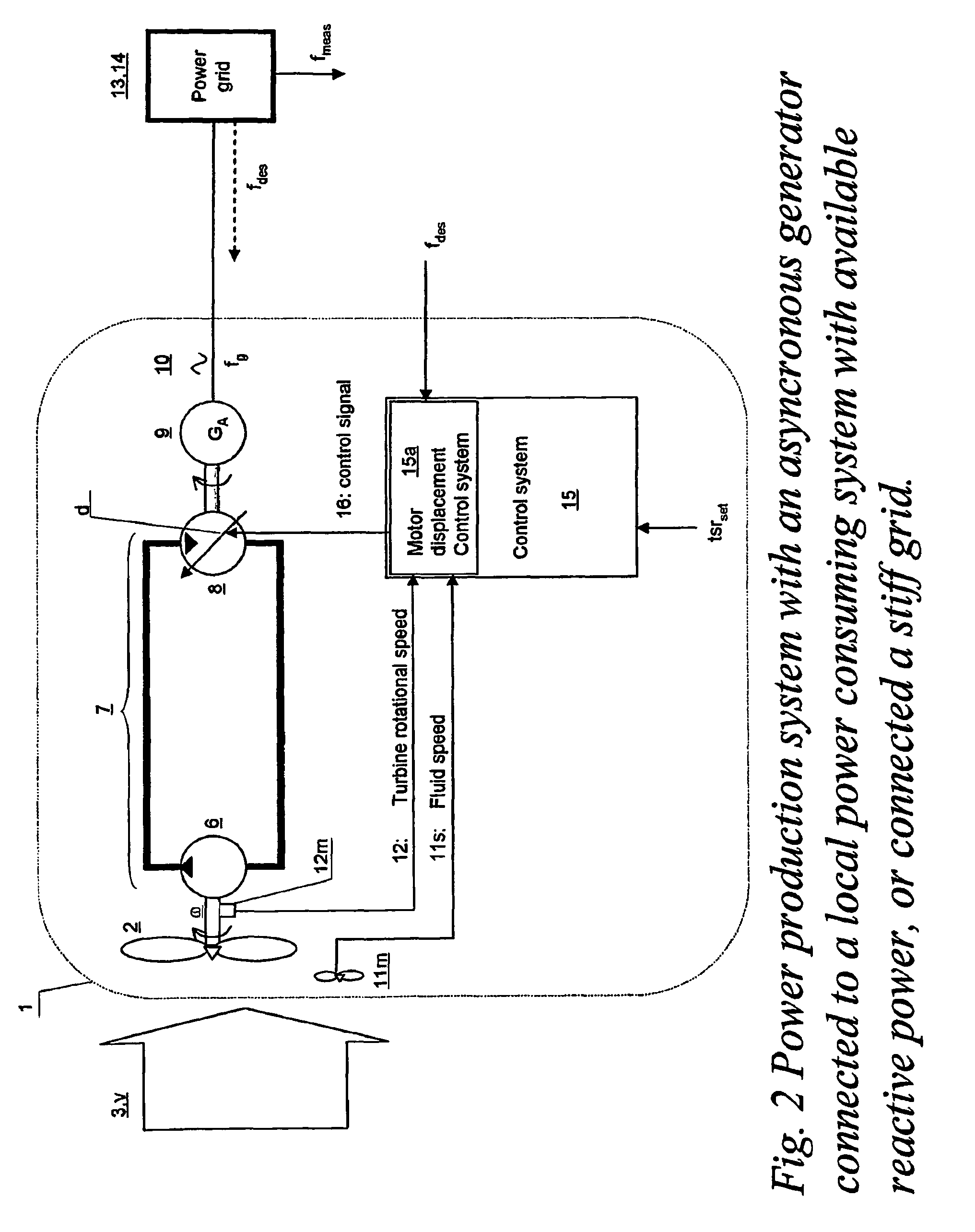
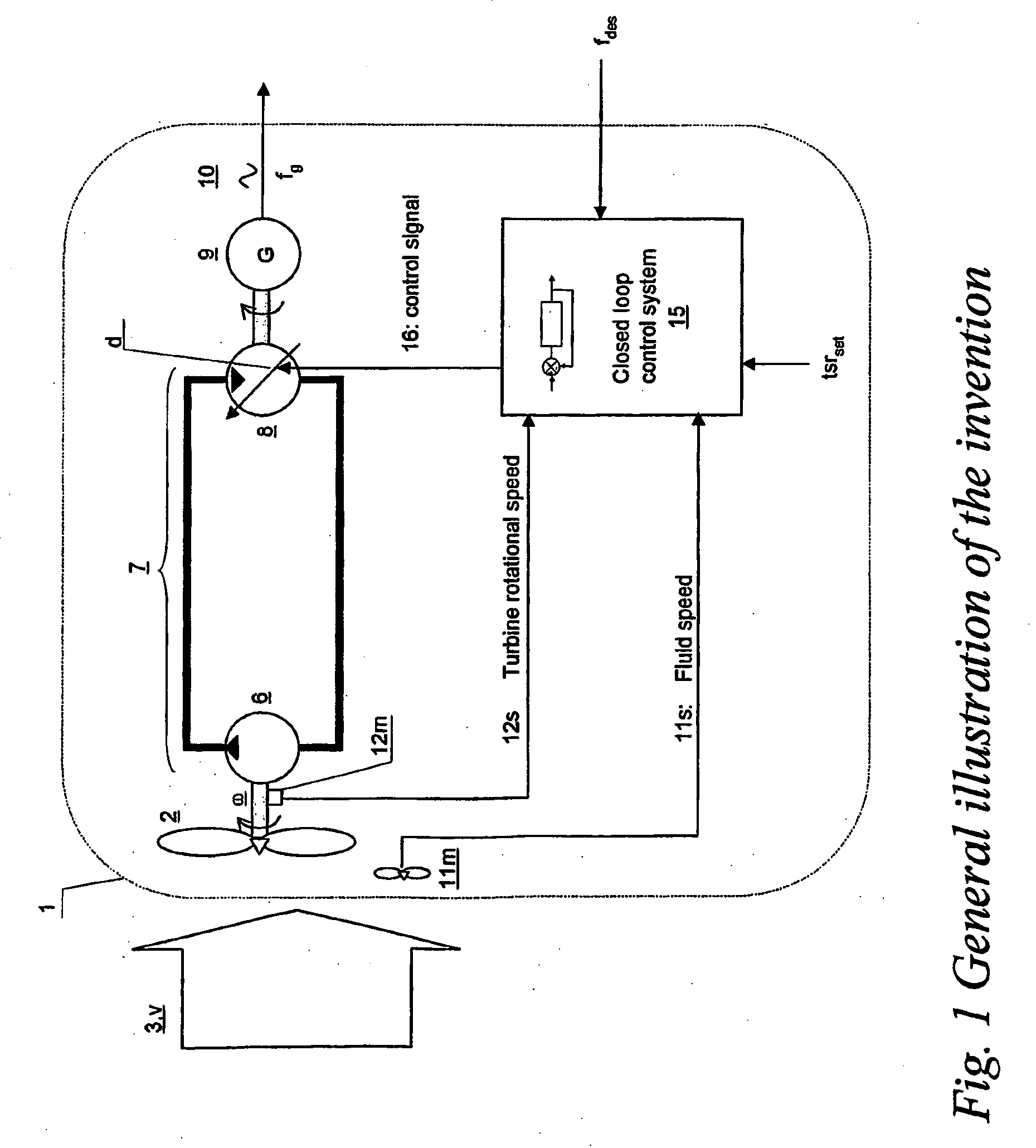
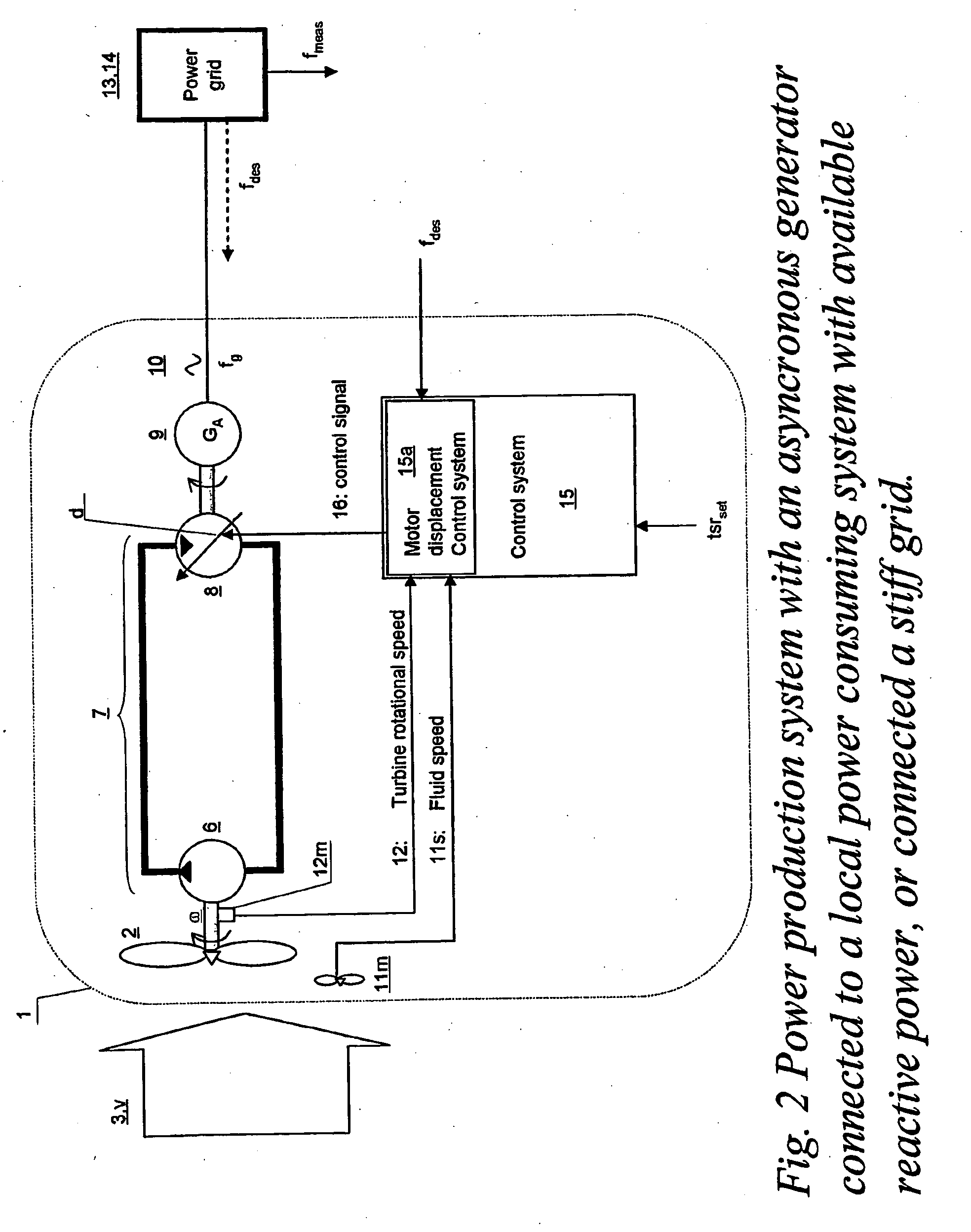
Turbine driven electric power production system and a method for control thereof
InactiveUS7863767B2Improve accuracyLow variabilityDomestic stoves or rangesWind motor controlControl signalClosed loop
Owner:CHAPDRIVE AS
Mode-Switching Cam Follower
A mode-switching cam follower is disclosed, wherein the follower includes a body, a cam contact movably coupled to the body, a latch member movably coupled to the body, wherein the latch member is movable between a coupled position in which the cam contact is held in a fixed relation to the body by the latch member and a decoupled position in which the cam contact is decoupled from the latch member and movable relative to the body, and an actuator in communication with the latch member, wherein the actuator comprises a shape memory alloy member
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Lost motion variable valve actuation system for engine braking and early exhaust opening
ActiveCN102414424AMeet the seating speed limitAvoid shockValve drivesOutput powerEngineeringExhaust gas recirculation
A method and system for actuating an internal combustion engine exhaust vaive to provide compression release actuation during an engine braking mode of engine operation and early exhaust valve opening actuation during a positive power mode of engine operation is disclosed. The system may include a first cam having a compression release lobe and an early exhaust valve opening lobe connected to a hydraulic lost motion system including a first rocker arm. A hydraulically actuated piston may be selectively extended from the hydraulic lost motion system to provide the exhaust valve with compression release actuation or early exhaust valve opening actuation. The hydraulicaily actuated piston may be provided as a slave piston in a master-slave piston circuit in a fixed housing, or alternatively, as a hydraulic piston slidably disposed in a rocker arm. The method and system may further provide exhaust gas recirculation and / or brake gas recirculation in combination with compression release actuation and early exhaust valve opening actuation.
Owner:JACOBS VEHICLE SYST
Integrated engine brake with mechanical linkage
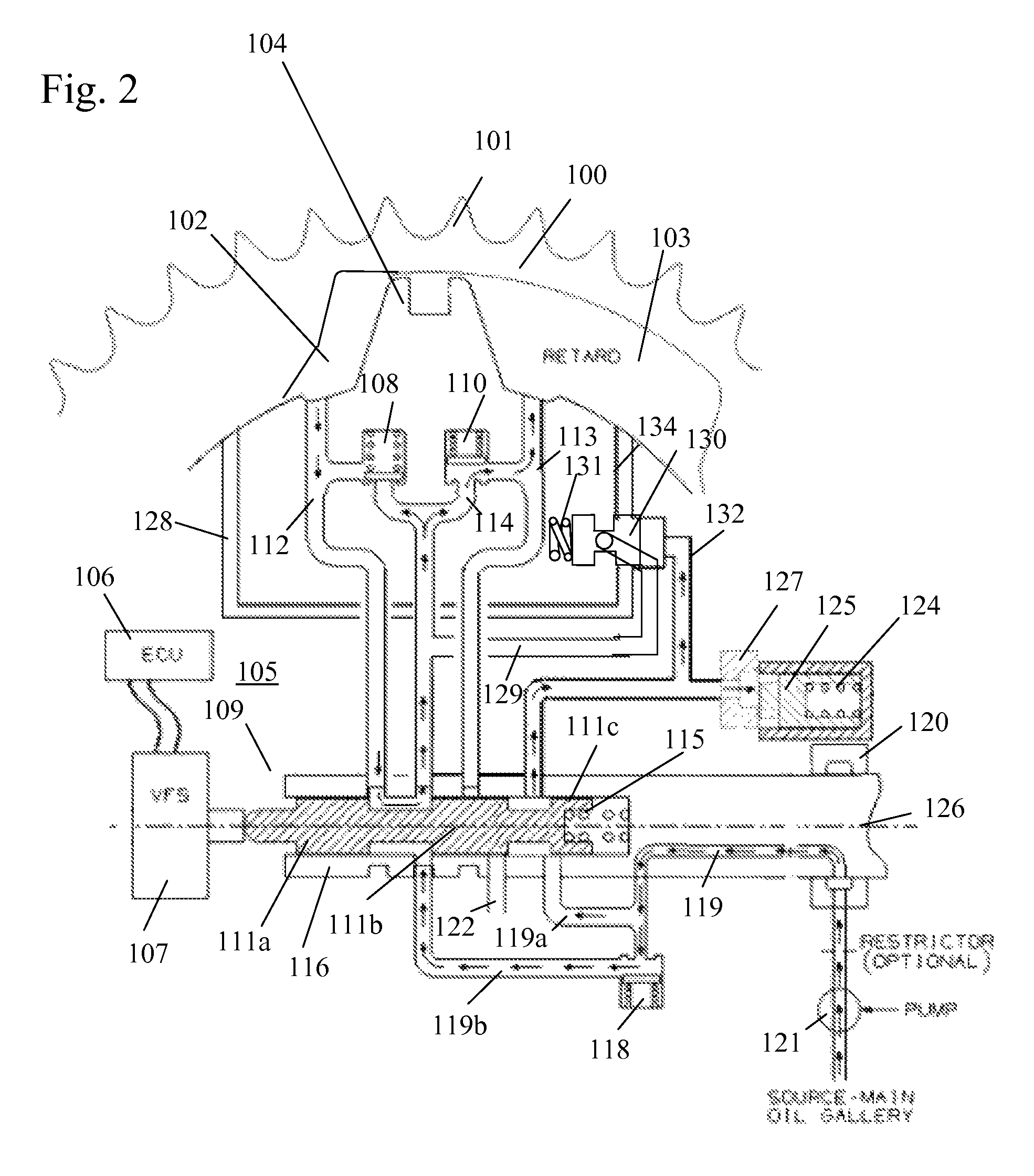
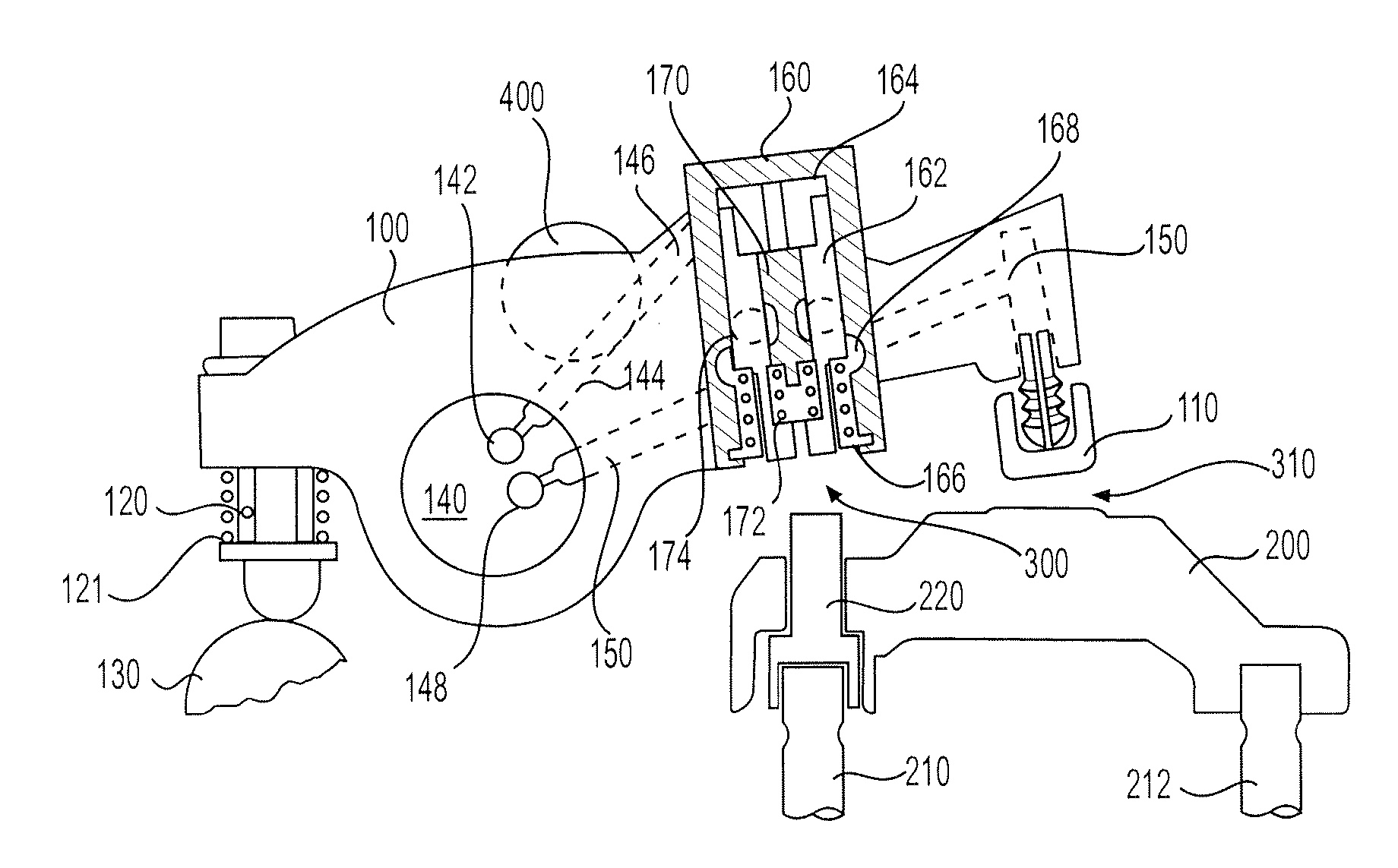
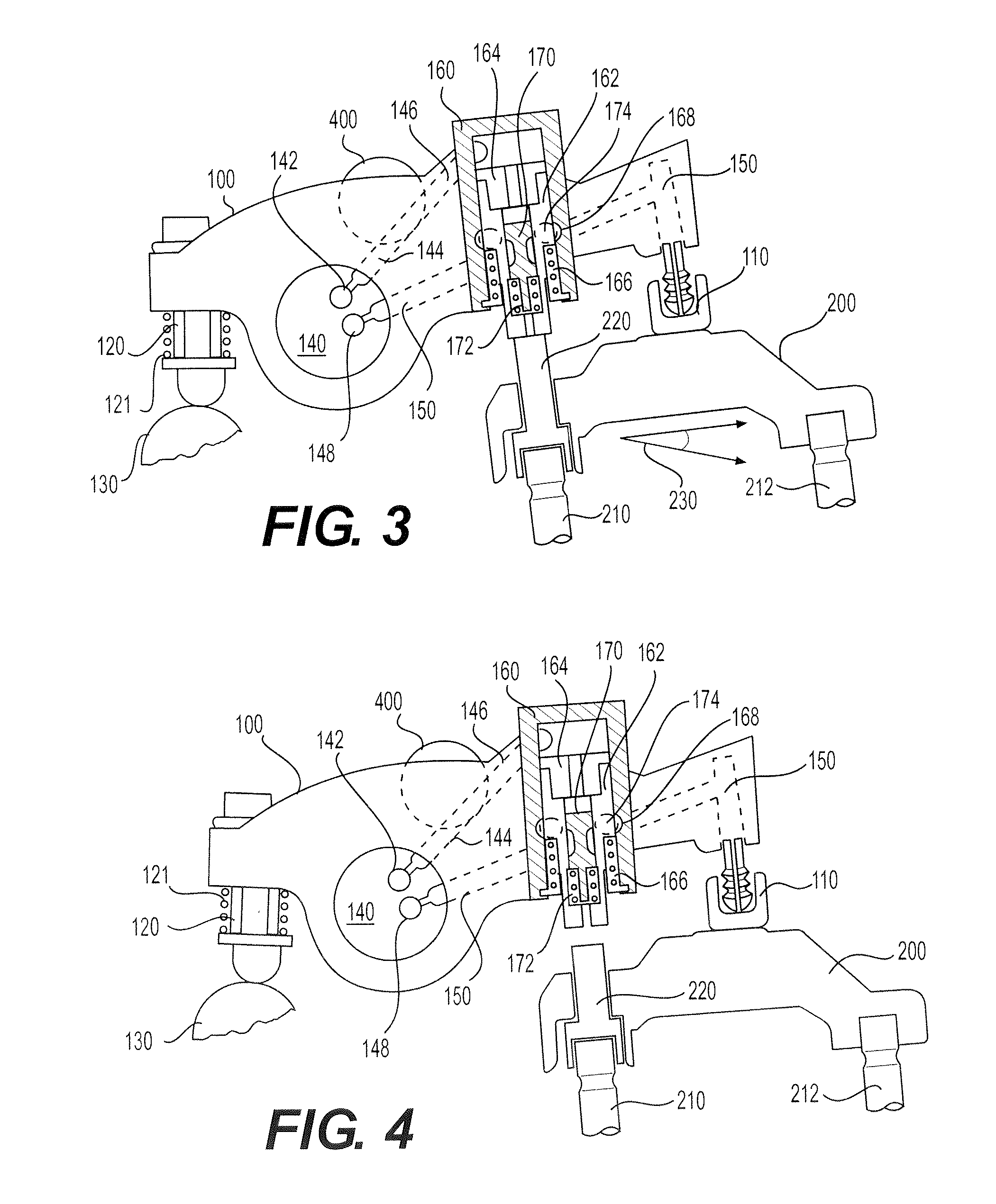
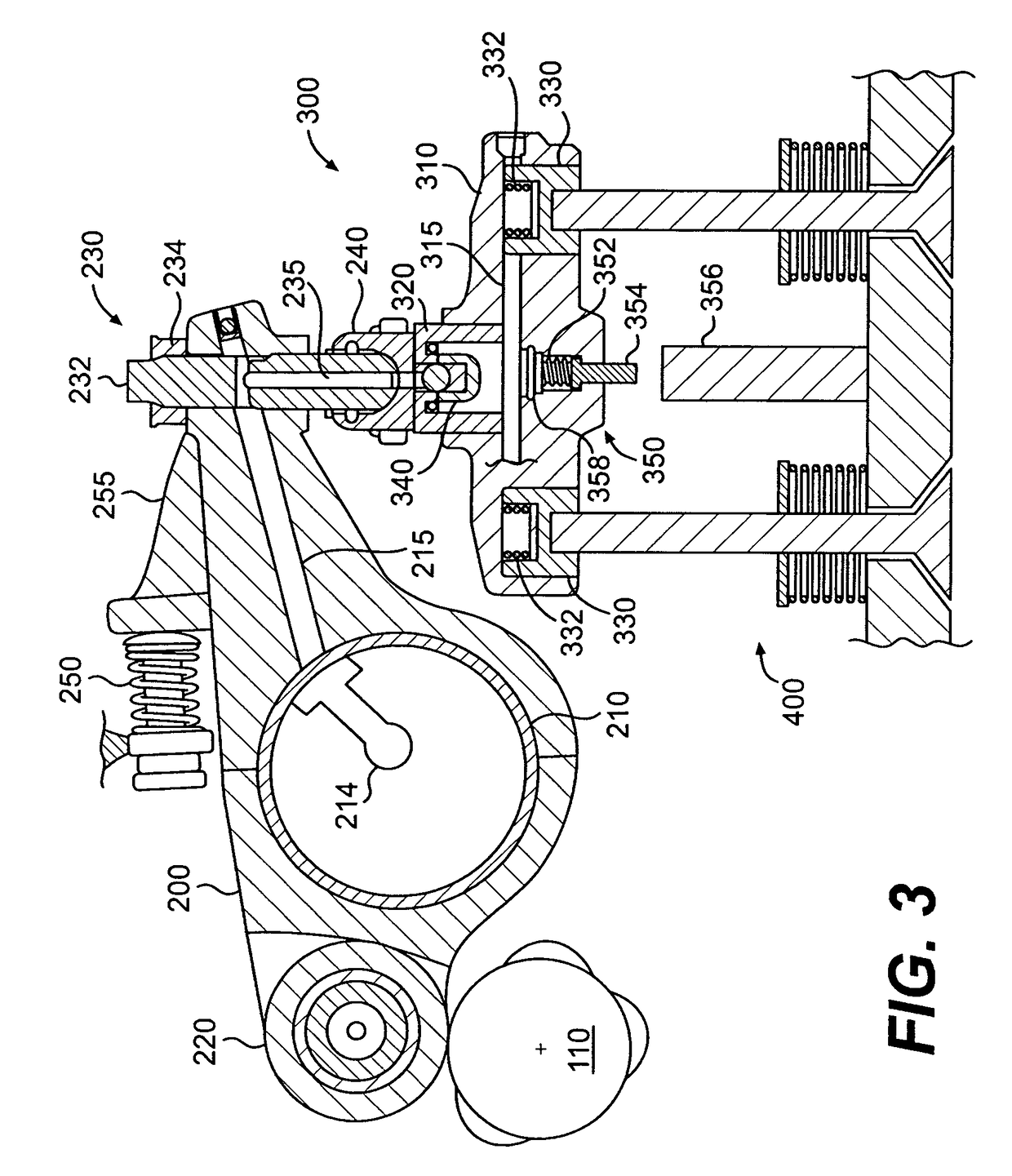
ActiveUS20100170472A1Rapid responseImprove performanceValve drivesOutput powerExhaust valveExternal combustion engine
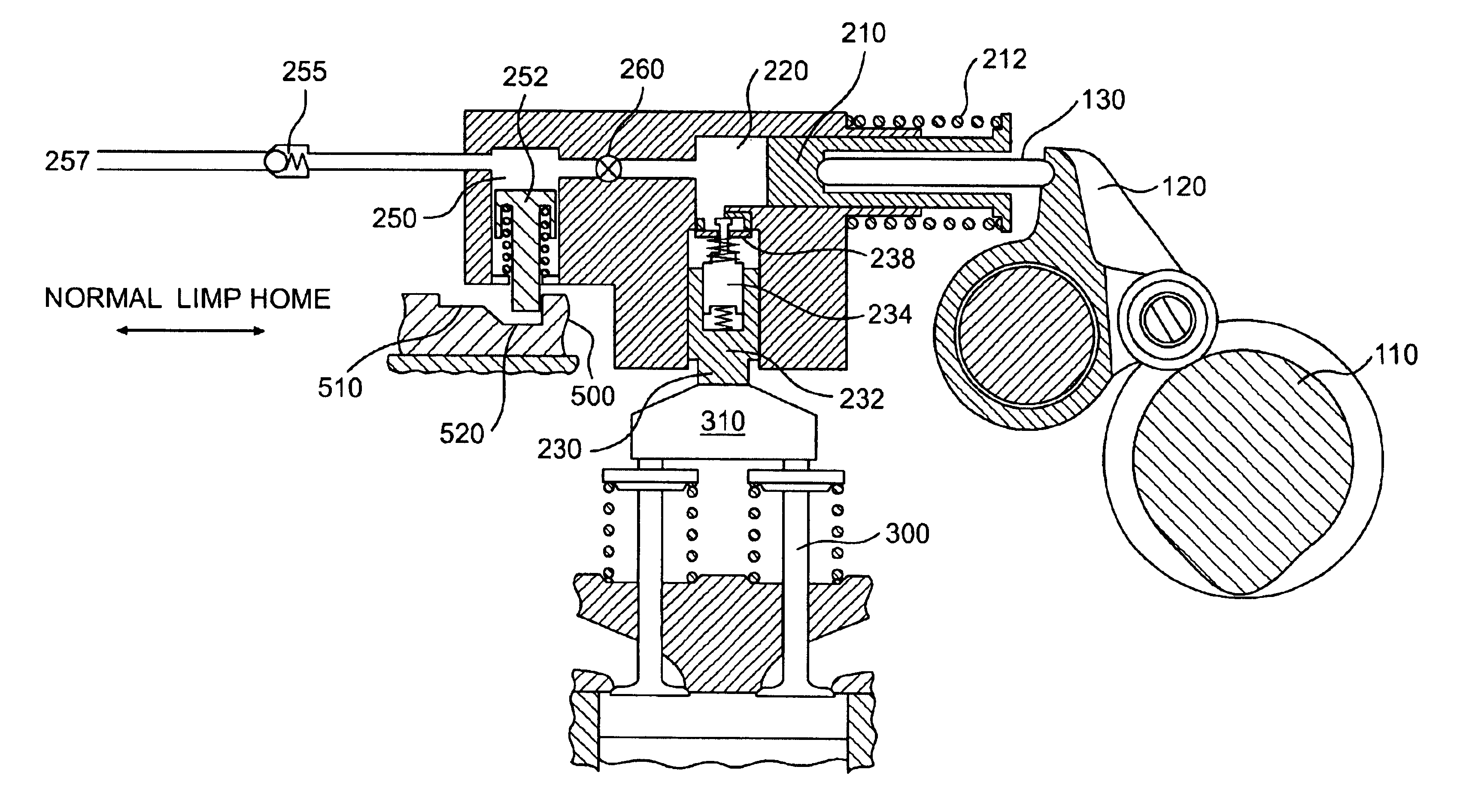
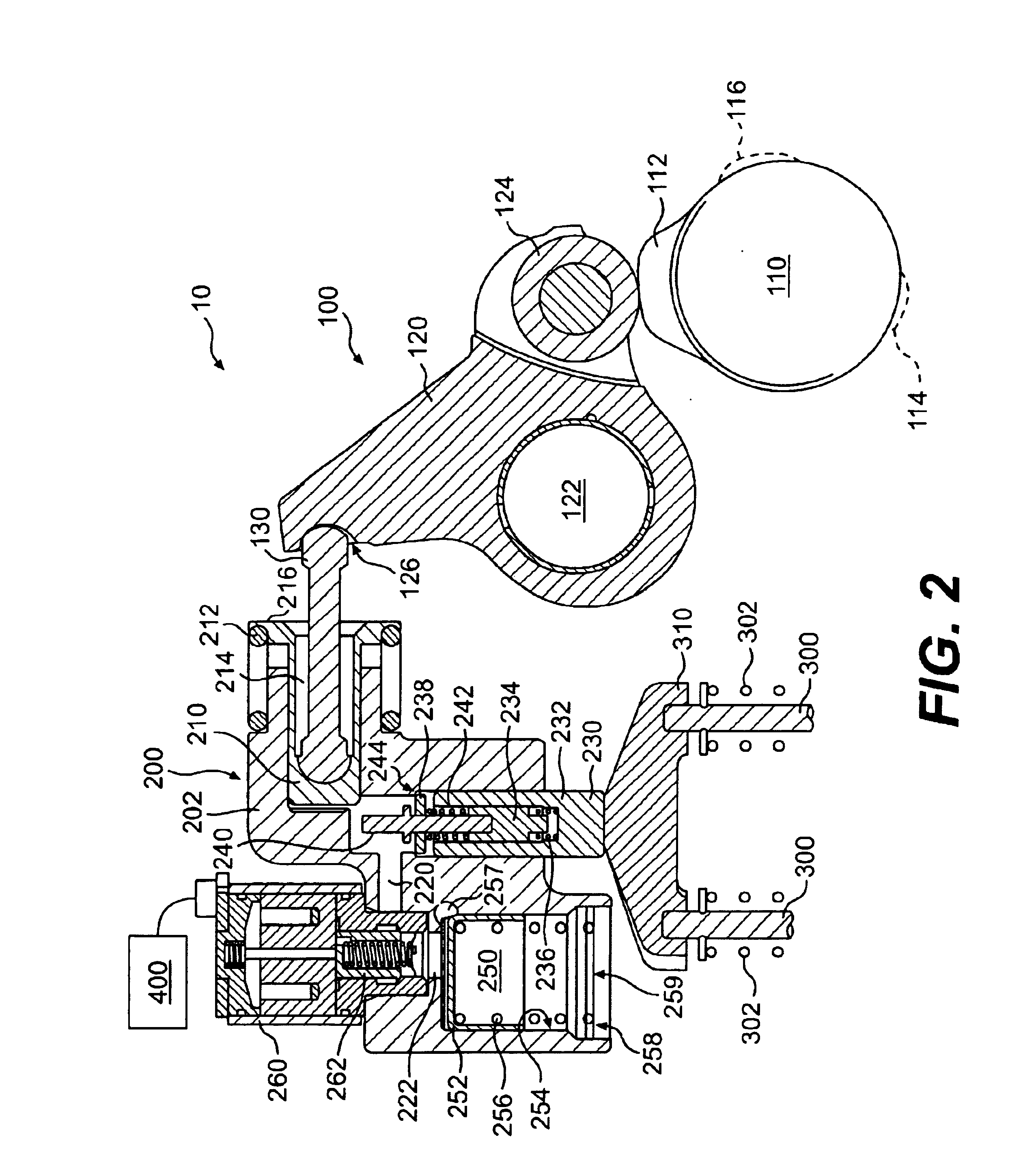
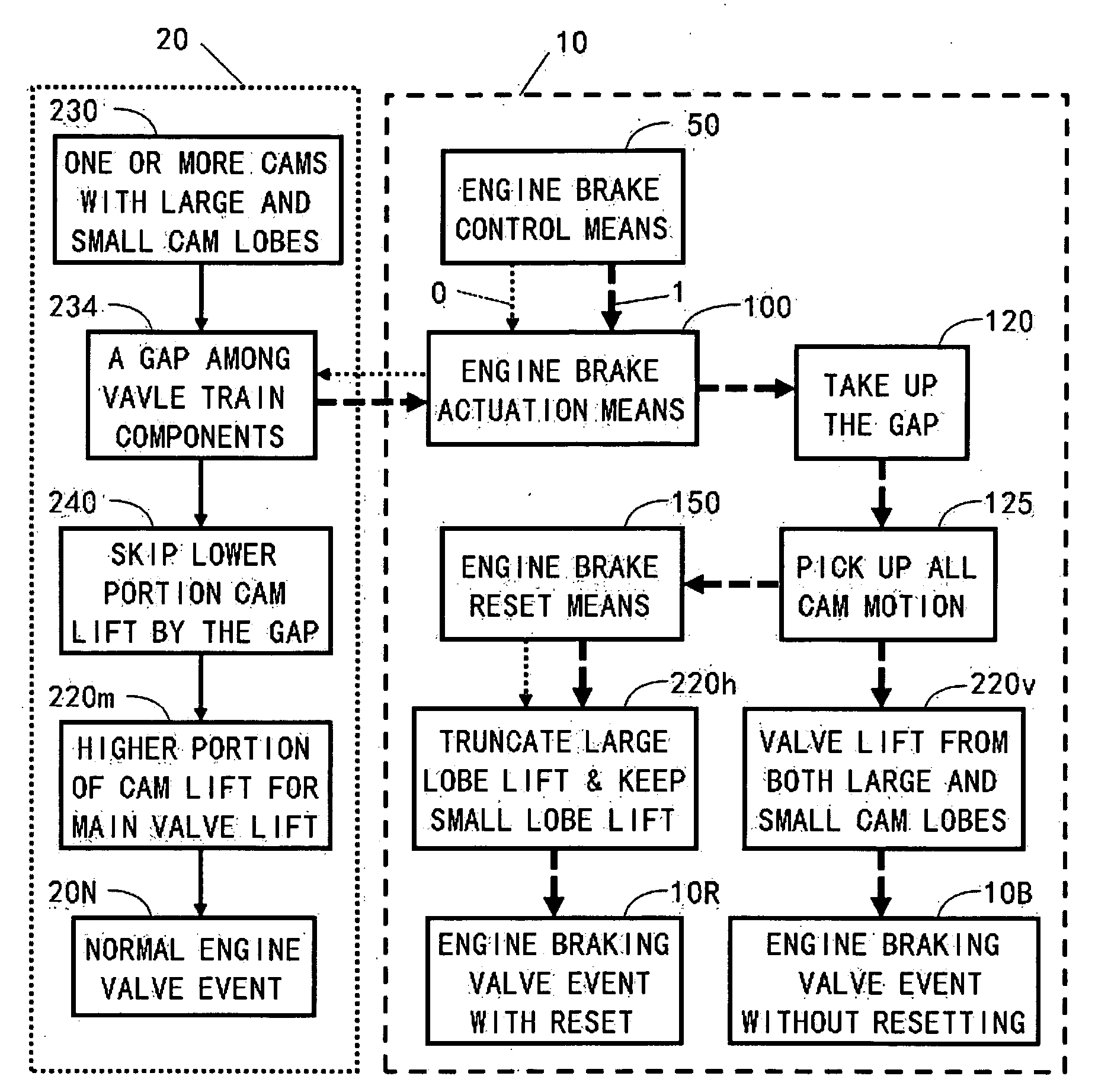
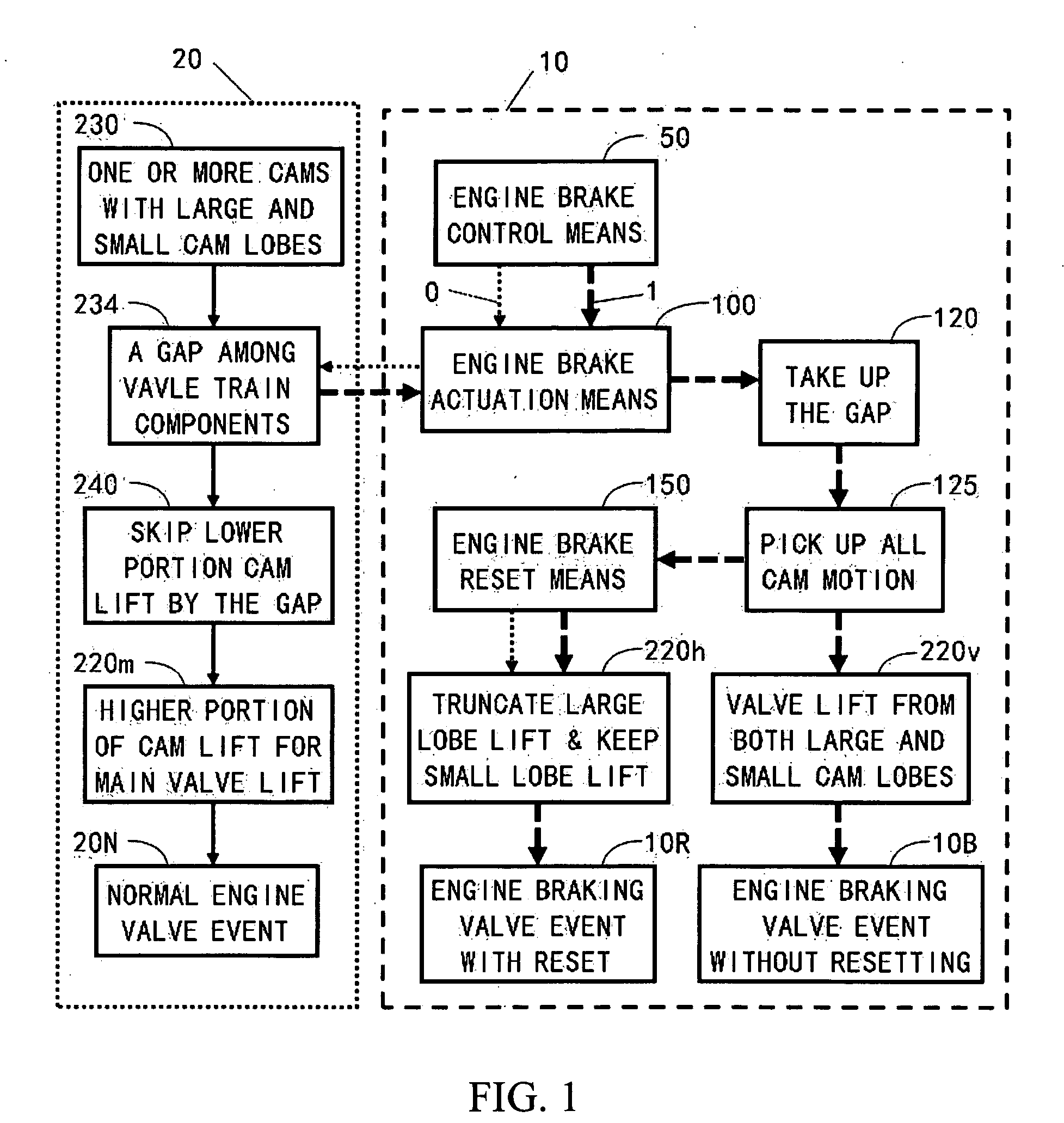
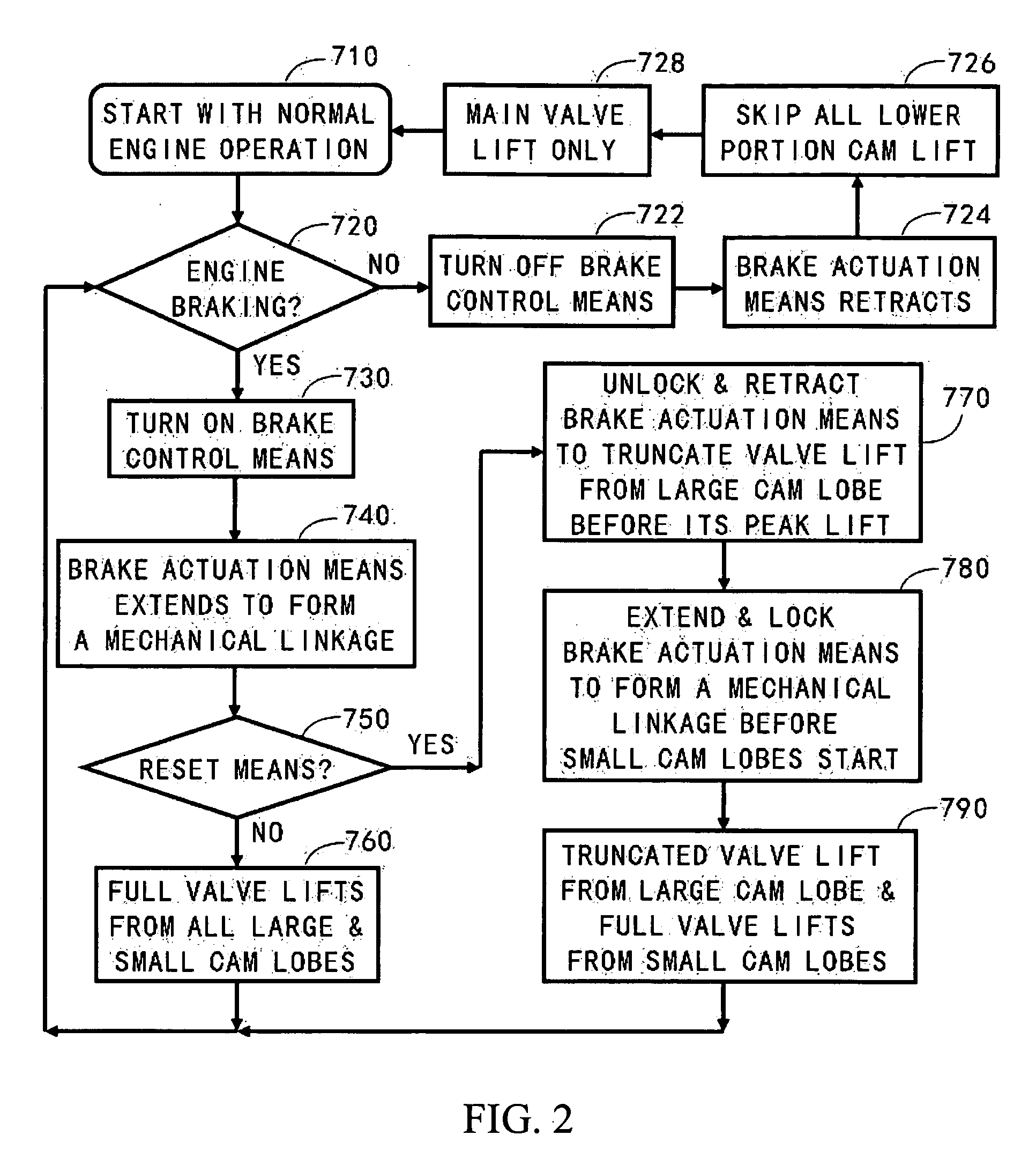
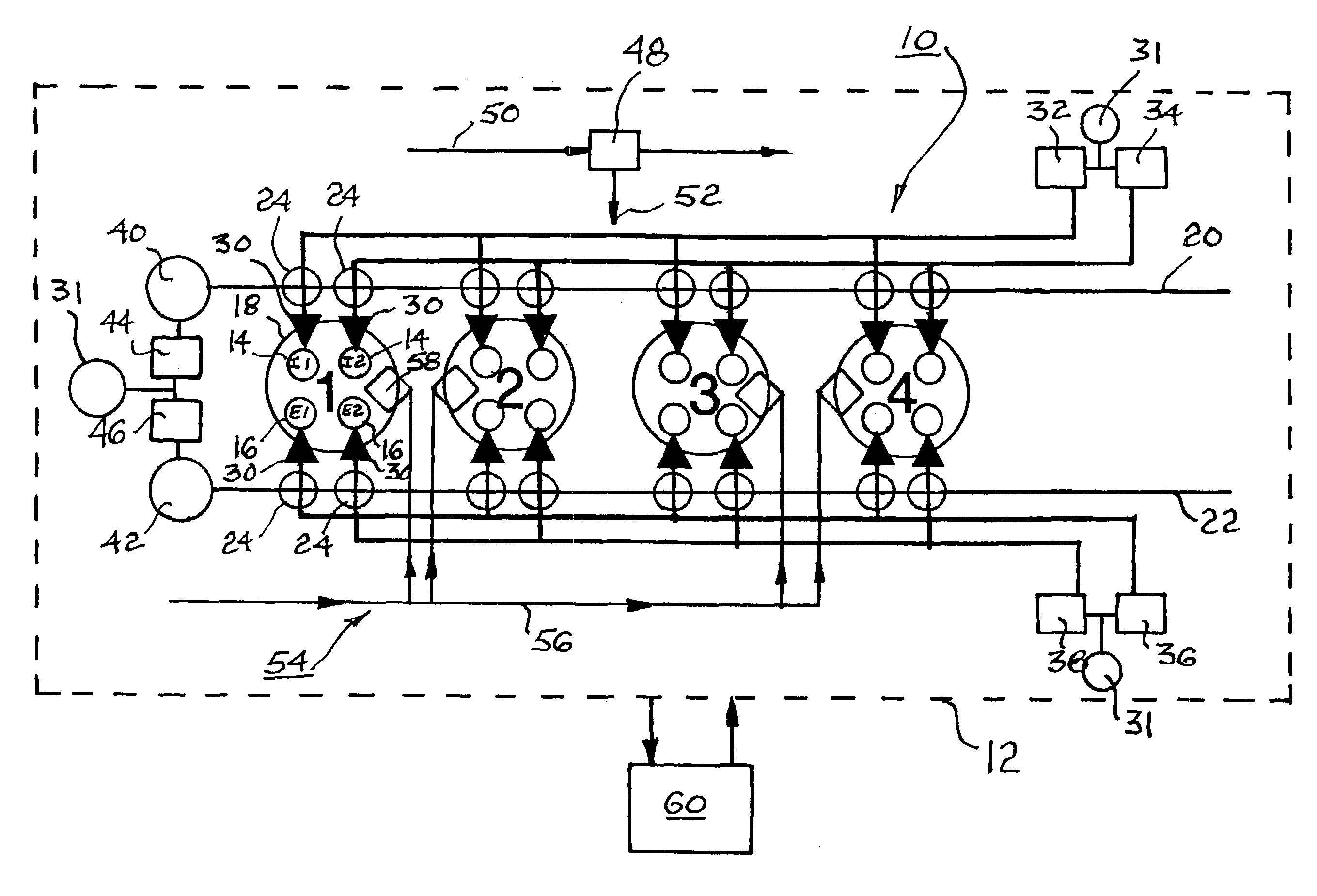
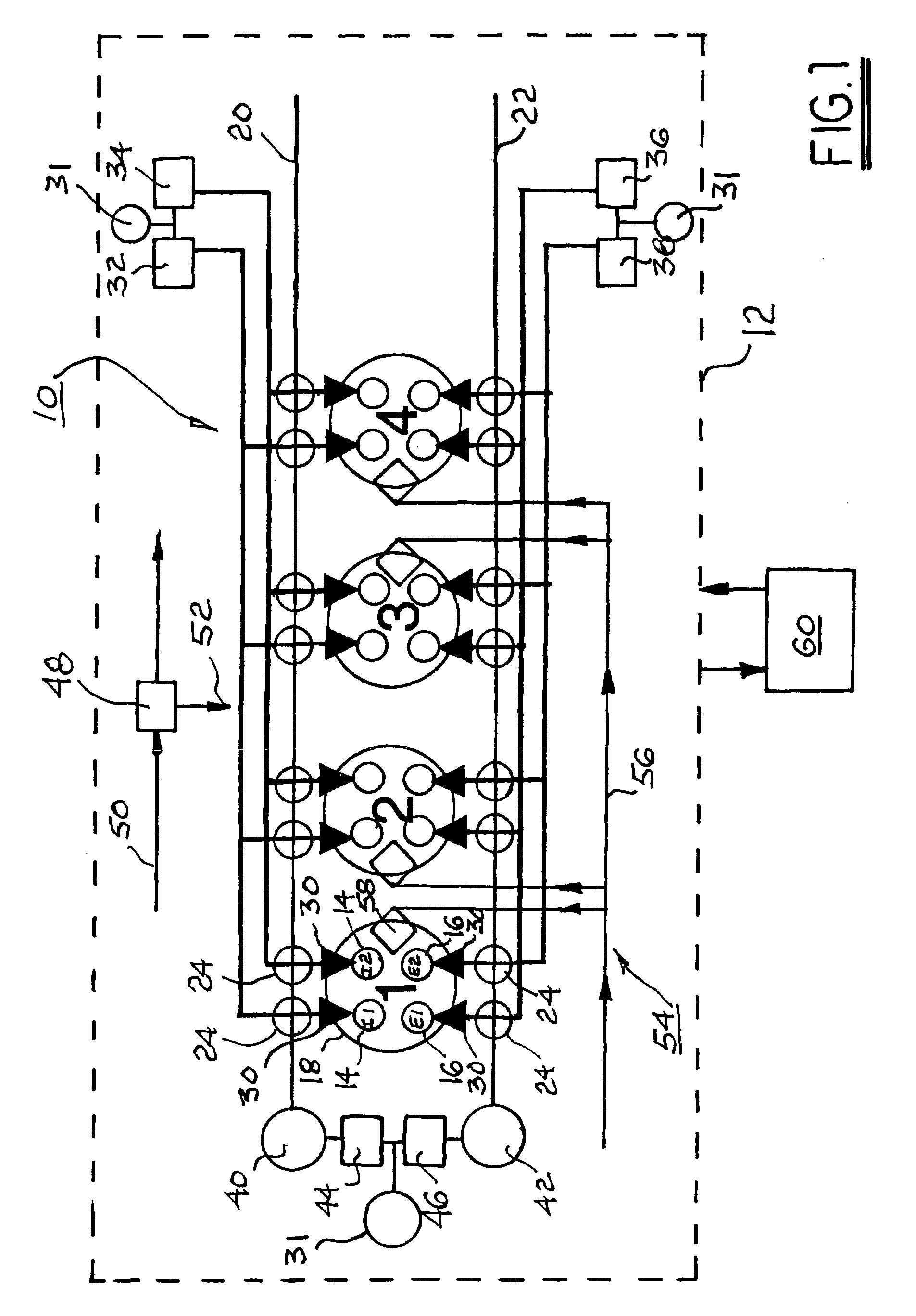
Apparatus and method are disclosed for converting an internal combustion engine from a normal engine operation (20) to an engine braking operation (10). The engine includes exhaust valve train components comprising at least one exhaust valve (300) and at least one cam (230) for cyclically opening and closing the at least one exhaust valve (300). The apparatus comprises actuation means (100) having at least one component integrated into at least one of the exhaust valve train components, such as a rocker arm (210) or a valve bridge (400). The actuation means (100) has an inoperative position and an operative position. In the inoperative position, the actuation means (100) is retracted and the small braking cam lobes (232&233) are skipped to generate a main valve lift profile (220m) for the normal engine operation (20). In the operative position, the actuation means (100) is extended to form a mechanical linkage so that the motion from all the cam lobes (220, 232&233) is transmitted to the at least one exhaust valve (300) for the engine braking operation (10). The apparatus further comprises control means (50) for moving the actuation means (100) between the inoperative position and the operative position to achieve the conversion between the normal engine operation (20) and the engine braking operation (10). The apparatus also includes valve lash adjusting mechanism, oil retraining means (350), and engine brake reset means (150).
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSOON AUTOPARTS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for optimized combustion in an internal combustion engine utilizing homogeneous charge compression ignition and variable valve actuation
InactiveUS7308872B2Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHomogeneous charge compression ignitionExhaust valve
A valvetrain system mechanization for an internal combustion engine using compression ignition, including homogeneous charge compression ignition, having two intake and one or more exhaust valves per cylinder. The valves are operated by dual overhead camshafts having two-step cams. The intake and exhaust camshafts are provided with phasers for varying the opening and closing of the intake and exhaust valves. A two-step roller finger follower is disposed for each valve between the cam lobes and the valve stem. The two sets of intake and exhaust valves are controlled by separate oil control valves. Swirl of gases may be introduced by mismatching the lifts of the valves. The valve opening times, closing times, lifts, fuel injection, compression ratio, and exhaust gas recirculation may be varied to optimize combustion conditions for a range of engine operating modes.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Sliding structure for automotive engine
InactiveUS6886521B2Preventing cracking and separationReduce coefficient of frictionPiston ringsMolten spray coatingCarbon filmPiston ring
A sliding structure for an automotive engine includes a sliding member with a sliding portion and a lubricant applied to the sliding portion so that the sliding portion can make sliding contact with a counterpart member via the lubricant. The sliding member is either of a piston ring, a piston pin, a cam lobe, a cam journal, a plain bearing, a rotary vane and a timing chain. The sliding portion has a base made of a steel or aluminum material and a hard carbon film formed on the base to coat the sliding portion. The hard carbon film has a thickness of 0.3 to 2.0 mum, a Knoop hardness of 1500 to 4500 kg / mm2, a surface roughness Ry (mum) satisfying the following equation: Ry<{(0.75-Hk / 8000)xh+0.07 / 0.8}, where h is the thickness (mum) of the film; and Hk is the Knoop hardness (kg / mm2) of the film.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Magnetically sequenced pneumatic motor
A pneumatic motor having a piston and a magnetically actuated valve. The magnetically actuated valve may be adjacent the piston and, in some embodiments, include a spool valve.
Owner:CARLISLE FLUID TECH INC
Variable camshaft timing device with hydraulic lock in an intermediate position
A variable cam timing phaser for an internal combustion engine including a piloted valve in the rotor assembly, movable from a first position to a second position, and detent lines communicating with the advance chamber or the retard chamber are restricted and or blocked when the rotor assembly is in or near an intermediate phase angle position. When the piloted valve is in the first position, fluid is blocked from flowing through the piloted valve. When the piloted valve is in a second position, fluid is allowed to flow between the detent line from the advance chamber and the detent line from the retard chamber through the piloted valve and a common line, such that the rotor assembly is moved to and held in the intermediate phase angle position relative to the housing assembly.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
CTA phaser with proportional oil pressure for actuation at engine condition with low cam torsionals
A variable camshaft timing phaser for an internal combustion engine having at least one camshaft comprising a plurality of vanes in chambers defined by a housing and a spool valve. The vanes define an advance and a retard chamber. At least one of the vanes is cam torque actuated (CTA) and at least one of the other vanes is oil pressure actuated (OPA). The spool valve is coupled to the advance and retard chamber defined by the CTA vane and the advance chamber defined by the OPA vane. When the phaser is in the advance position, fluid is routed from the retard chamber defined by the OPA vane to the retard chamber defined the CTA vane. When the phaser is in the retard position, fluid is routed from the retard chamber defined by the CTA vane to the advance chamber defined by the CTA vane.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Integrated lost motion rocker brake with automatic reset
Systems and methods for actuating engine valves are disclosed. The systems may include a rocker arm having an adjustable length push tube mounted to a first end and multiple contact surfaces for an engine valve bridge at a second end. An actuator piston assembly may be provided in the rocker arm between the first and second rocker arm ends. The actuator piston assembly is adapted to extend from the rocker arm under the influence of hydraulic pressure and actuate an inboard engine valve through the engine valve bridge when an actuator piston is locked into an extended position.
Owner:JACOBS VEHICLE SYST
Valve bridge with integrated lost motion system
A system and method of actuating one or more engine valves is disclosed. In one embodiment, the system comprises: a valve train element; a rocker arm pivotally mounted on a shaft and adapted to rotate between a first position and a second position, the rocker arm selectively receiving motion from the valve train element; a valve bridge disposed above the one or more engine valves; and a lost motion system disposed in the valve bridge.
Owner:JACOBS VEHICLE SYST
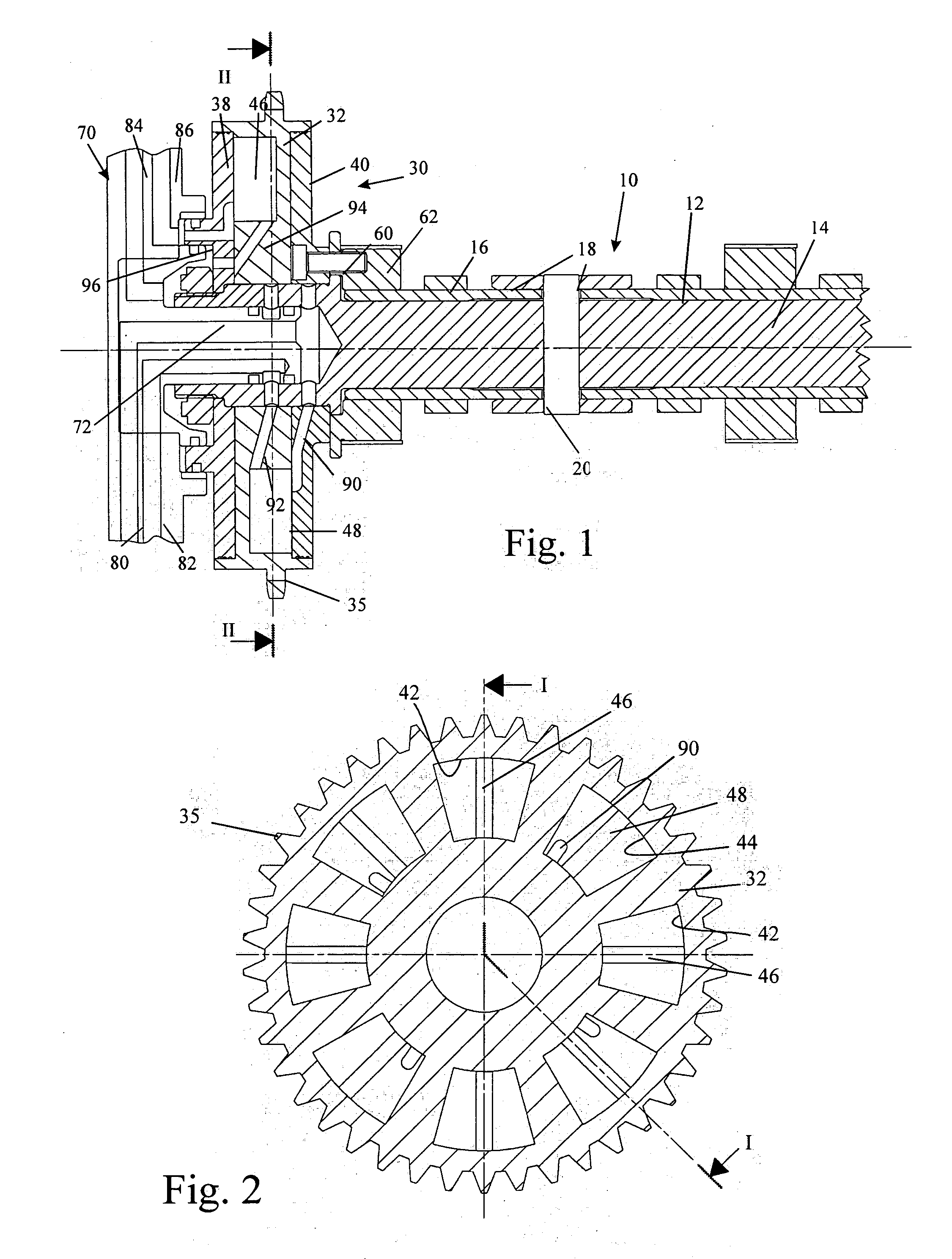
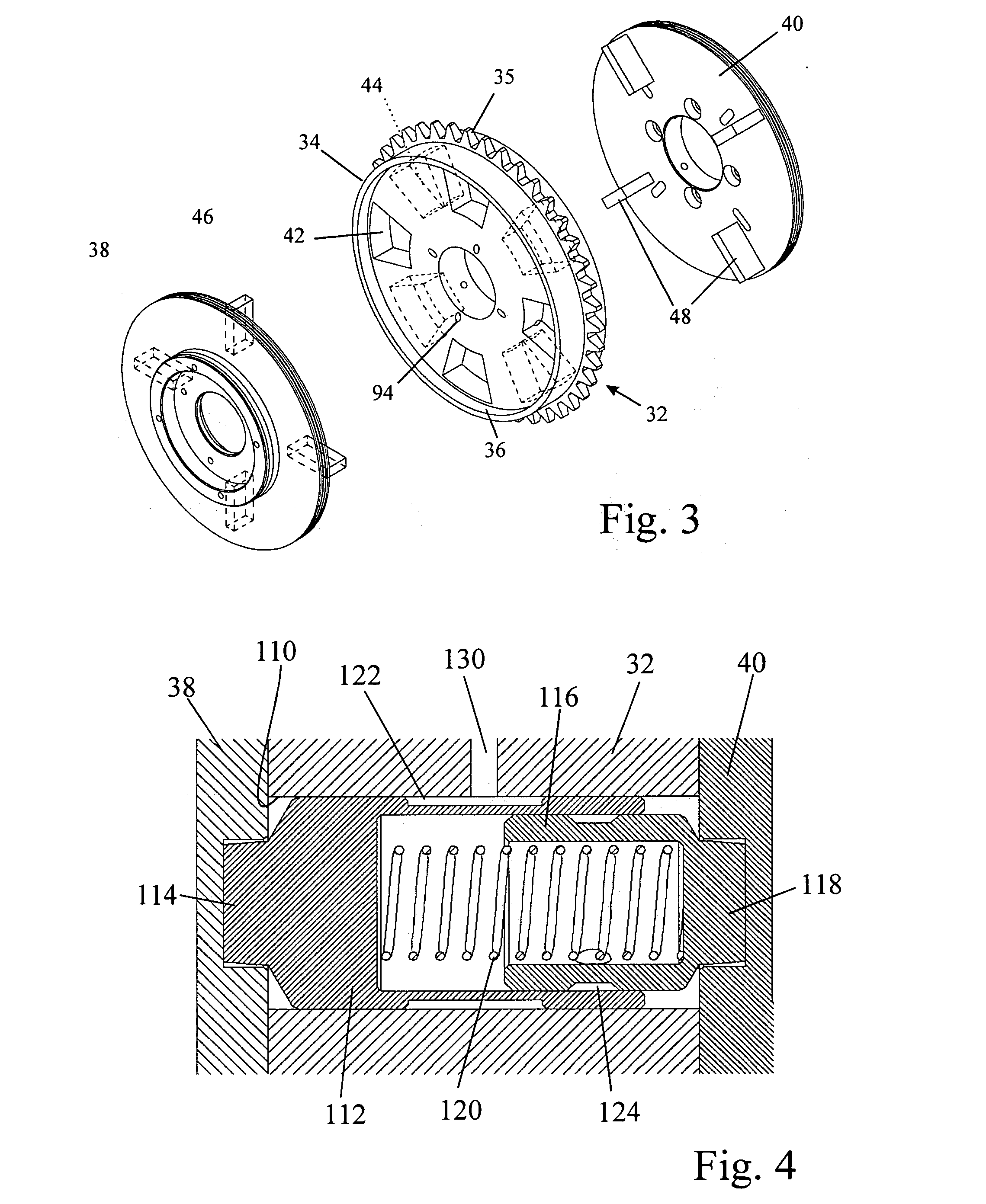
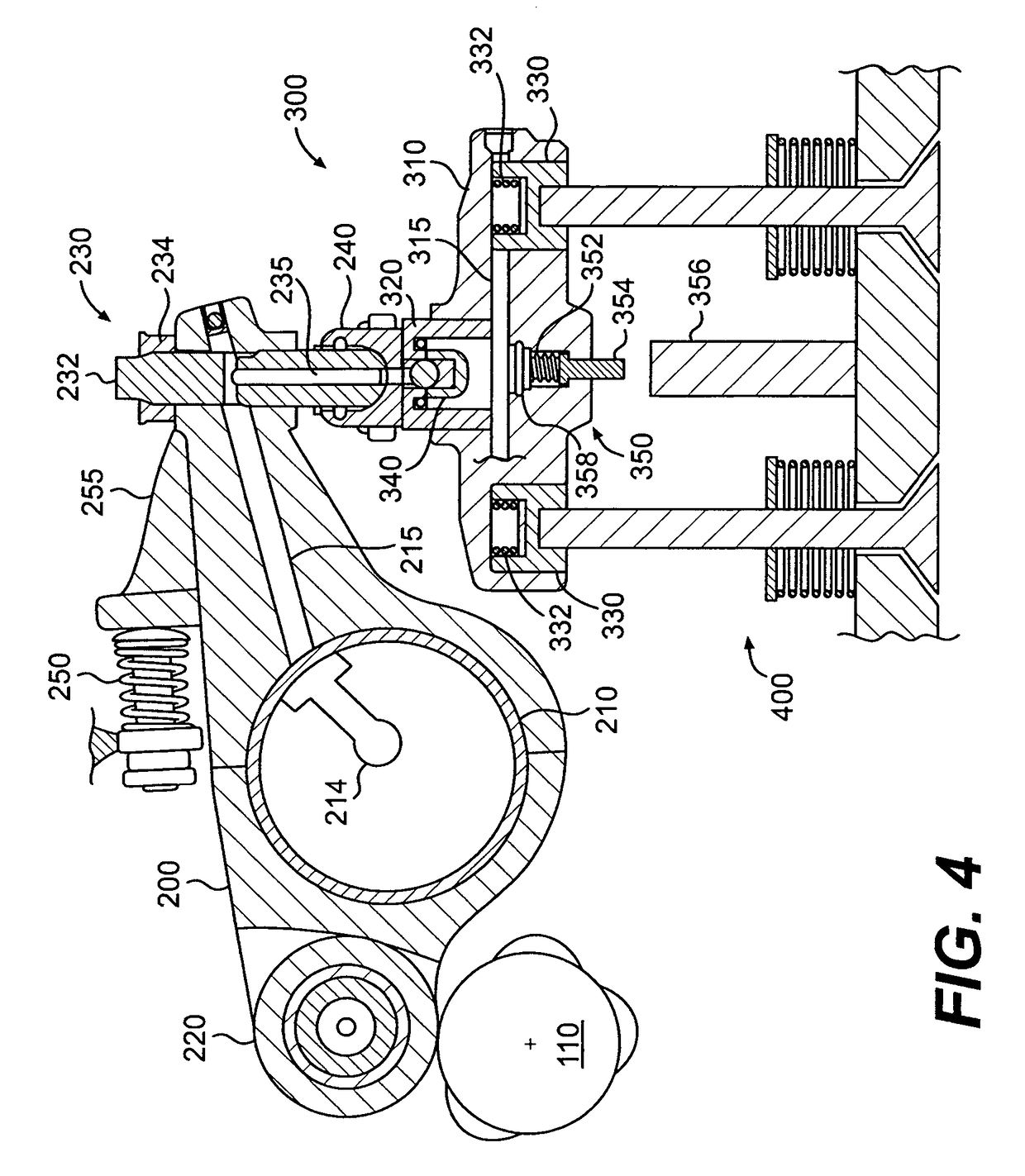
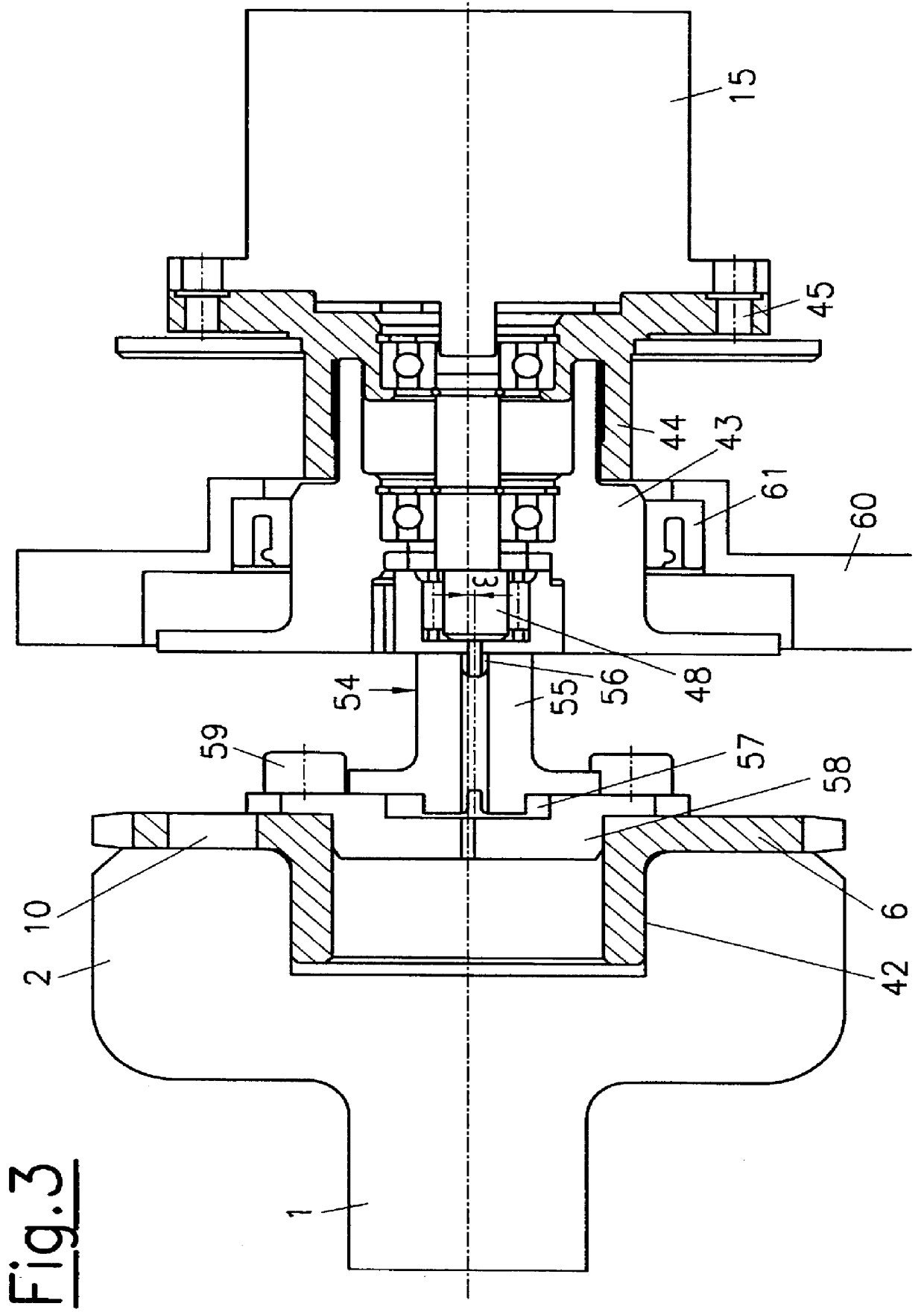
Valve drive of an internal combustion engine comprising a cylinder head
The invention relates to a valve drive of an internal combustion engine, comprising at least one camshaft whereon at least one cam carrier is arranged in a rotationally fixed and axially displaceable manner. Means for applying axial tension are formed between the at least one camshaft and the at least one cam support, thereby enabling the at least one cam support to be fixed in an axial manner.
Owner:AUDI AG
Modal variable valve actuation system for internal combustion engine and method for operating the same
ActiveUS6925976B2Improve fuel economyImprove power densityValve drivesOutput powerExhaust brakeInlet valve
A variable valve actuation system for providing discrete exhaust and intake valve lift profiles for various operating modes of an internal combustion engine. The variable valve actuation system includes exhaust and intake rocker assemblies, exhaust and intake hydraulic extension devices operatively coupling corresponding rocker assemblies with respective engine valves and exhaust and intake control valves for selectively supplying the pressurized hydraulic fluid to the extension devices so as to independently switch them between a pressurized condition and a depressurized condition. The engine further includes an exhaust brake provided to initiate a small lift of the exhaust valve during the engine braking operation while the exhaust extension device maintains the exhaust valve open during a compression stroke for bleeder-compression release braking. The exhaust and intake valves can be adjusted independently to provide combinations of valve lift modes.
Owner:JENARA ENTERPRISES
Two-stroke and four-stroke switching mechanism
A switching mechanism capable of switching between a two-stroke and a four-stroke operation of an engine as desired, wherein the switching mechanism is switchable between engagement with a first cam lobe for four-stroke operation and a second cam lobe for two-stroke operation, the four-stroke operation maximizing fuel and emissions efficiency and the two-stroke operation maximizing power.
Owner:RICARDO INC
Torsional assisted multi-position cam indexer having controls located in rotor
InactiveUS6883481B2Reduce leakageImprove responseYielding couplingValve drivesControl systemEngineering
An infinitely variable cam indexer utilizes engine oil pressure to actuate a cam and preferably uses an inlet check valve in the oil source to minimize back flow during a torque reversal. The control system is in the center of the rotor and uses an electromechanical actuator, preferably a variable force solenoid, acting directly on the spool to control oil flow. This design reduces leakage and improves the response of the phaser. There are shorter oil passages as compared to a control system mounted at the cam bearing.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Expansible chamber pneumatic system
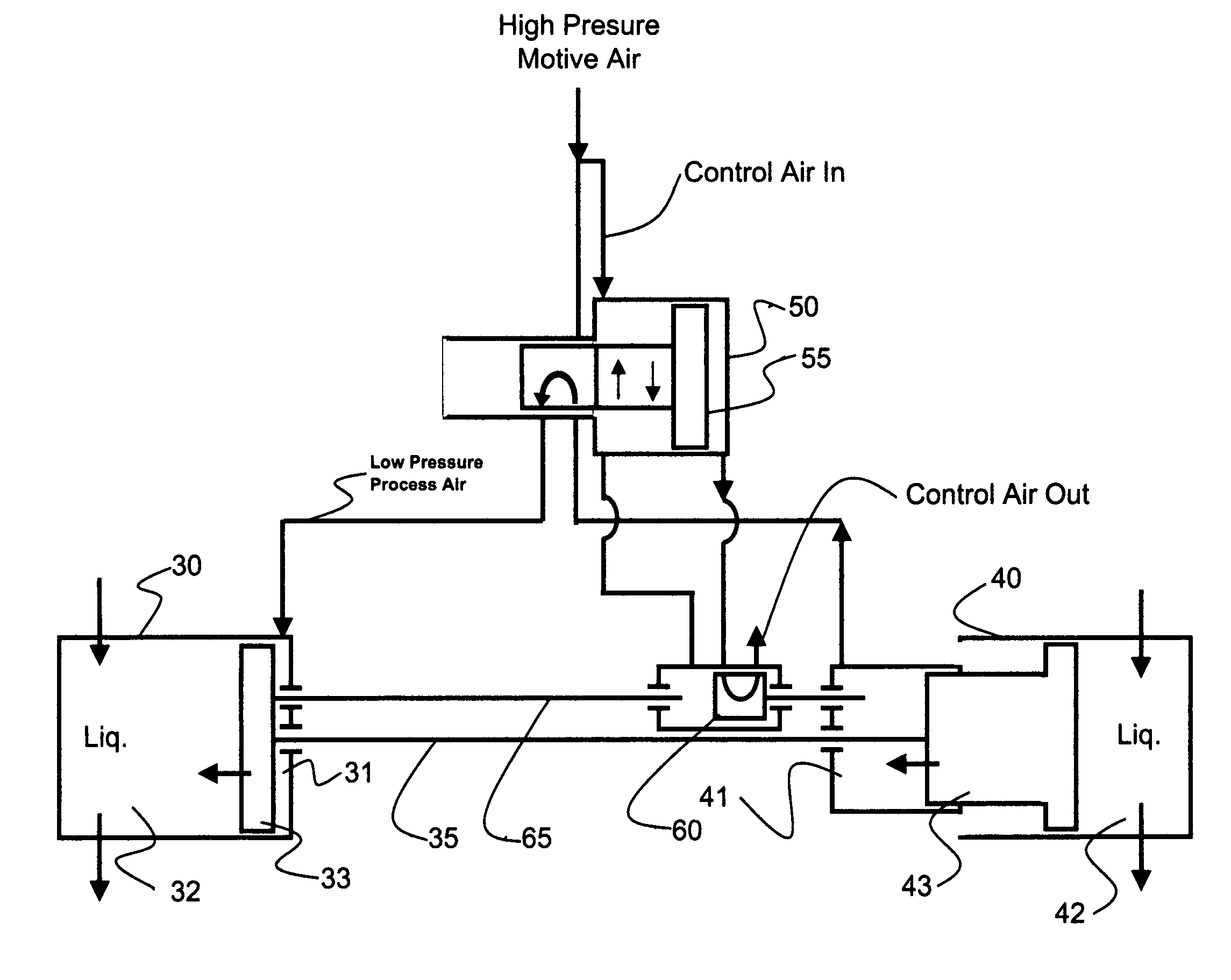
An expansible chamber pneumatic system, for example a fluid pump system, includes two or more double-acting diaphragm pumps, each with symmetrical left and right pump housings, each housing including an air chamber and a fluid chamber separated by a movable diaphragm. The diaphragms are connected for reciprocating movement in unison to pump fluid through their respective fluid chambers. Each pump includes an air valve actuated by Control air to direct Process air into one of the air chambers, simultaneously releasing used Process air from the other air chamber to thereby move the diaphragms, thereby to pump fluid. A pilot valve directs Control air to the air valve to position the air valve. The pilot valve is responsive to diaphragms reaching their travel limit in one direction to direct Control air to reverse the directions of Process air flow through the air valve to thereby reverse the movement of the pump diaphragms. Control air exhausts through the pilot valve to atmosphere. Process air exhausts through the air valve from one pump to become input or motive air for the next pump.
Owner:PSG CALIFORNIA LLC
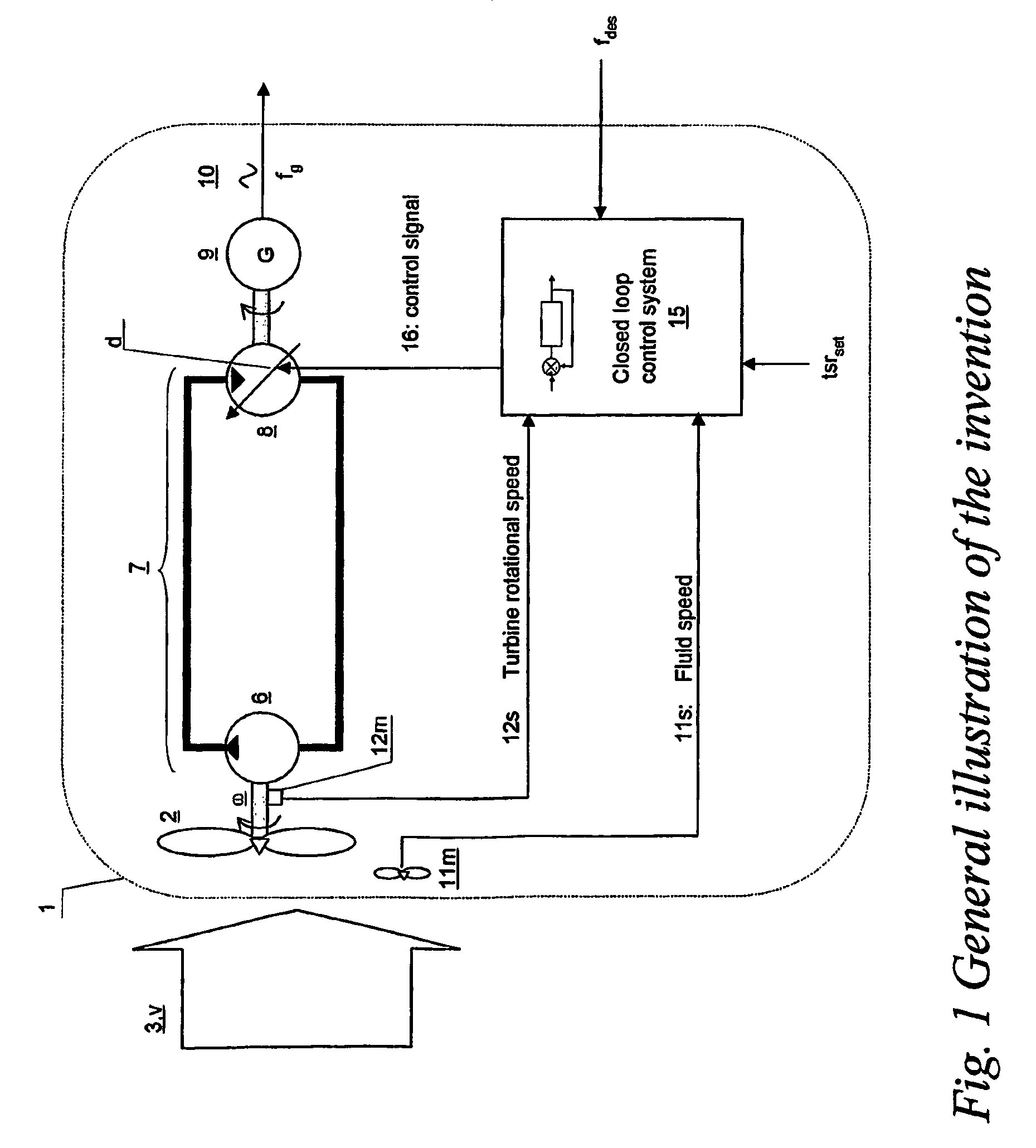
Turbine driven electric power production system and a method for control thereof
InactiveUS20090140522A1Improve power efficiencyImprove accuracyDomestic stoves or rangesWind motor controlControl signalClosed loop
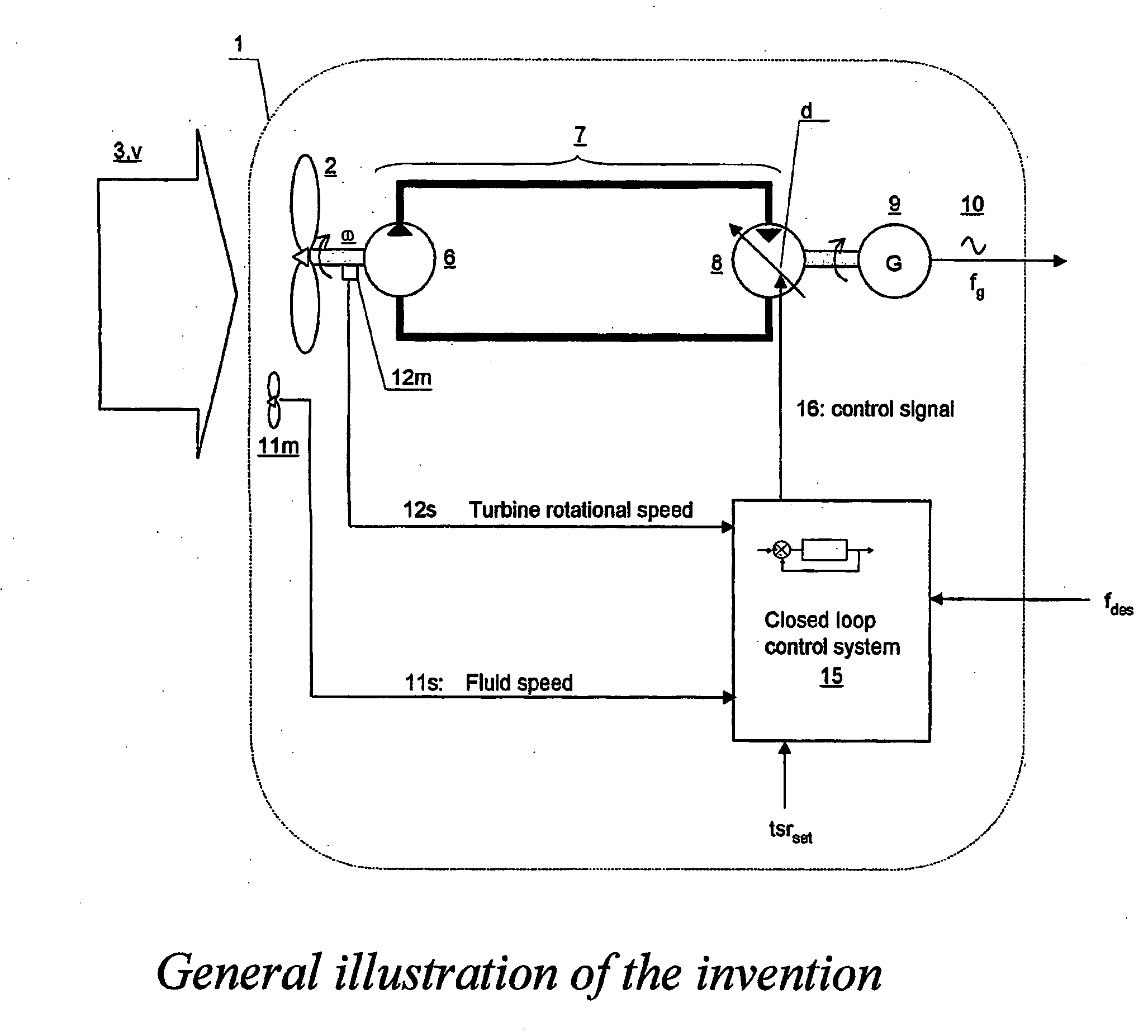
A turbine (2) driven electric power production system (1), —said turbine (2) arranged for being driven by a fluid (3) having a fluid speed (v) varying in time, —said turbine (2) connected to a hydrostatic displacement pump (6) further connected to a hydrostatic displacement motor (8) as part of a closed loop hydrostatic transmission system (7), —said motor (8) arranged for driving an electrical generator (9) supplying AC power (10) at a frequency (fg) near a given desired frequency (fdes), characterized by a closed loop system arranged for controlling a volumetric displacement (13) of the hydrostatic motor (8), comprising —a fluid speed meter (11m) arranged for producing a speed signal (11s) representing a speed (v) of said fluid (3), and —a rotational speed meter (12m) arranged for providing a rotational speed signal (12s) representing a rotational speed measurement (ω) of said turbine (2), —a motor displacement control system (15) for continuously receiving said speed signal (11s) and said rotational speed signal (12s) and arranged for calculating a control signal (16), —a volumetric displacement control actuator (17) on said hydrostatic motor, arranged for receiving said control signal (16) for continuously adjusting a volumetric displacement (d) of said hydrostatic motor (8) for maintaining a set turbine tip speed ratio (tsrset) and thereby providing an improved power efficiency of the power production system (1) during fluctuations in said fluid speed (v).
Owner:CHAPDRIVE AS
Device for adjusting the phase angle of a camshaft of an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS6138622ASimple designSmall sizeValve drivesMachines/enginesGear wheelExternal combustion engine
A device for adjusting the phase angle of a camshaft of an internal combustion engine includes an adjusting mechanism which is operated by an electric motor, the latter being rigidly connected to the camshaft or the camshaft drive gear. Reliable adjustment is obtained in a simple manner by providing the adjusting mechanism as a planetary gear set.
Owner:TCG UNITECH AKTIENGES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com