Control apparatus for controlling internal combustion engines
a control apparatus and internal combustion technology, applied in the direction of electric control, valve drives, machines/engines, etc., can solve the problems of reducing engine power output, unable to correct or compensate for deviations in combustion characteristic values, and deteriorating emission control performan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
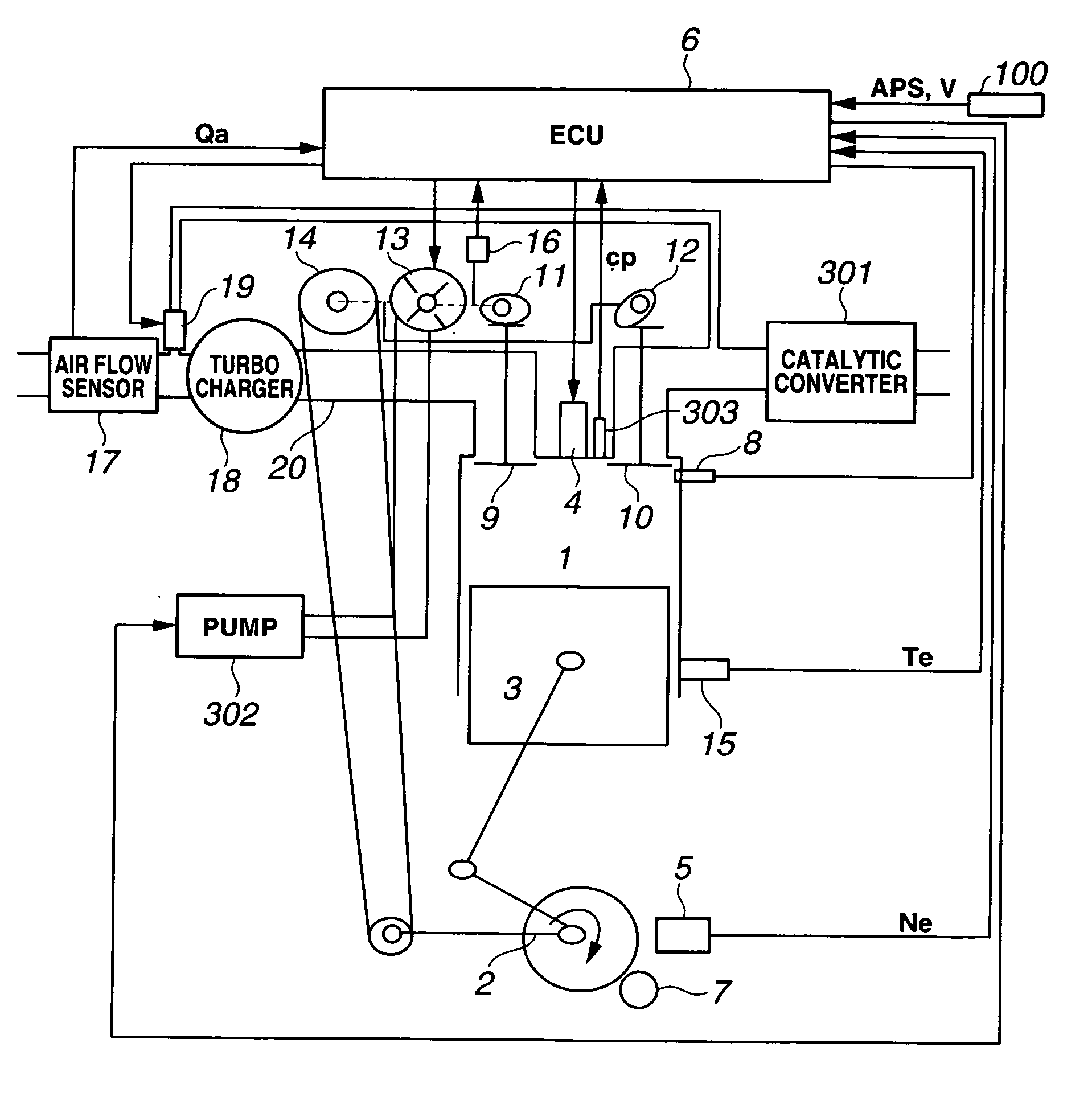
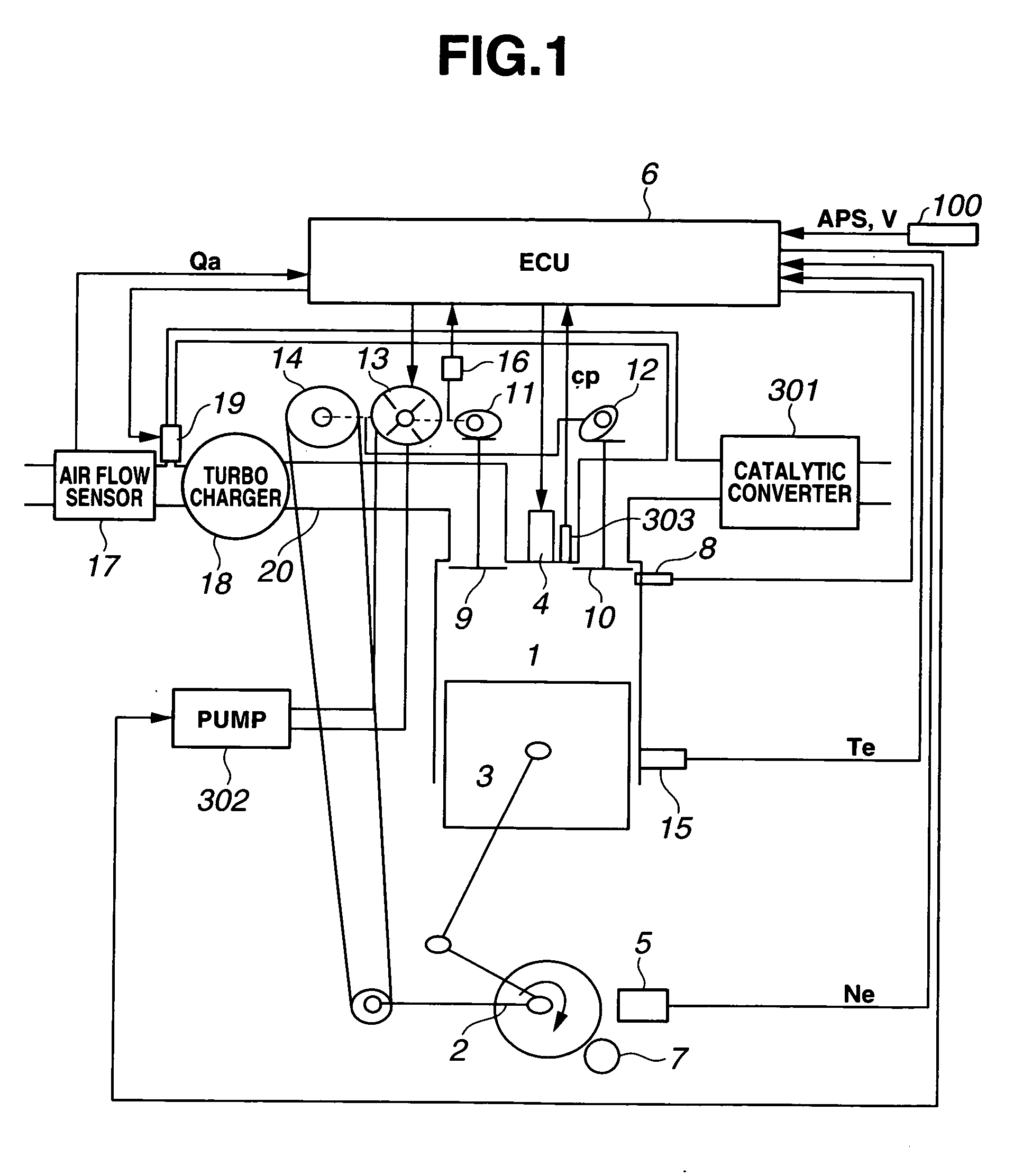
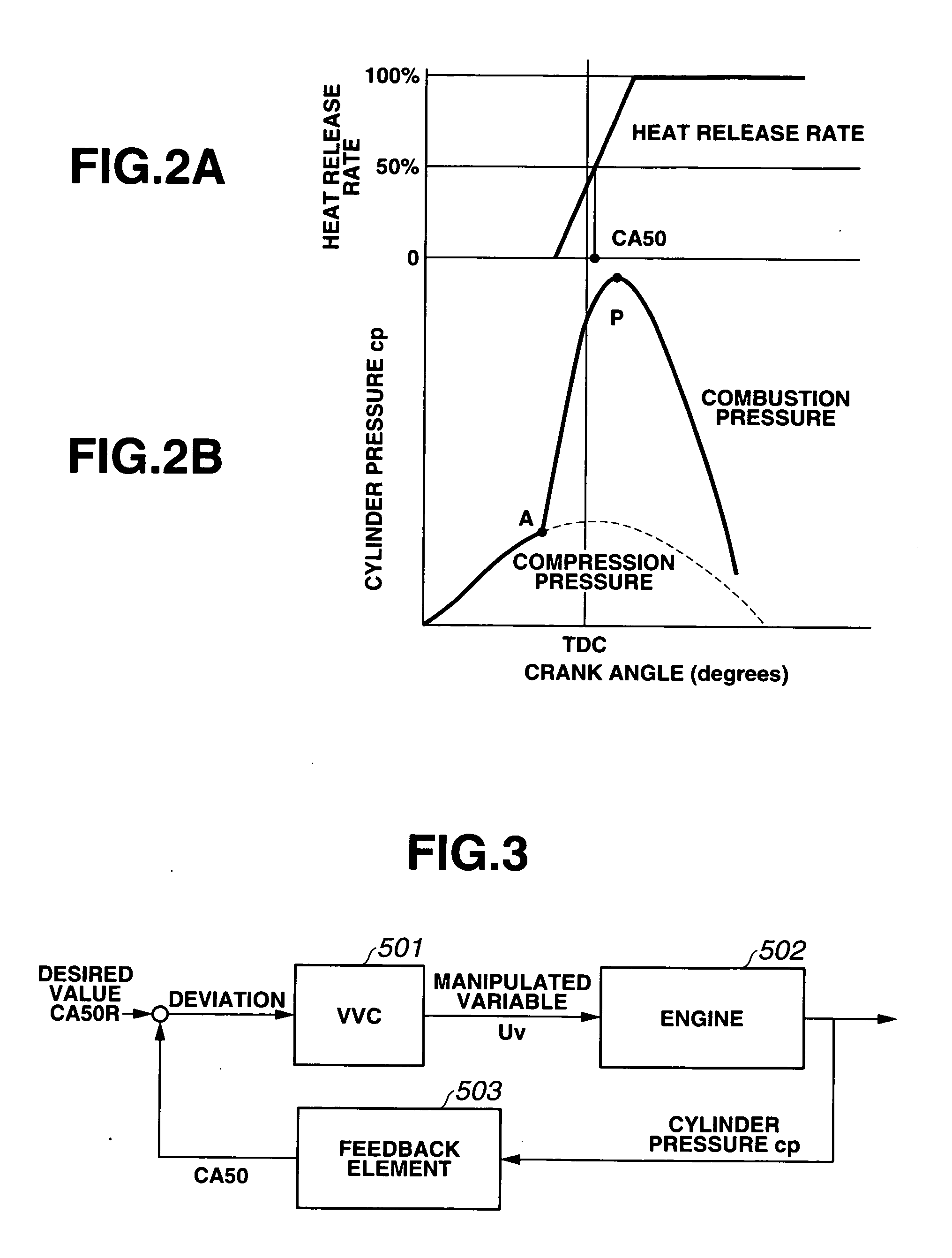
[0046] Referring now to the drawings, particularly to FIG. 1, the variable valve actuation control system (simply, a VVC system, or a variable valve actuation system) incorporated in the internal combustion engine control apparatus of the embodiment is exemplified in a four-stroke-cycle engine. As indicated by the arrow in the system block diagram of FIG. 1, a crankshaft 2 of an engine 1 rotates clockwise. As is generally known, a piston position at which a reciprocating piston 3 has moved to the bottom of the cylinder of engine 1, corresponds to 180 degrees of crank angle. The lowest piston position is called “bottom dead center (BDC)”. A piston position obtained when engine crankshaft 2 further rotates and thus piston 3 has reached the top of the engine cylinder, corresponds to 360 degrees of crank angle (360° crank angle) or 0° crank angle. The highest piston position is called “top dead center (TDC)”.
[0047] In the case of usual diesel combustion, diesel fuel (fuel oil) is spray...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com