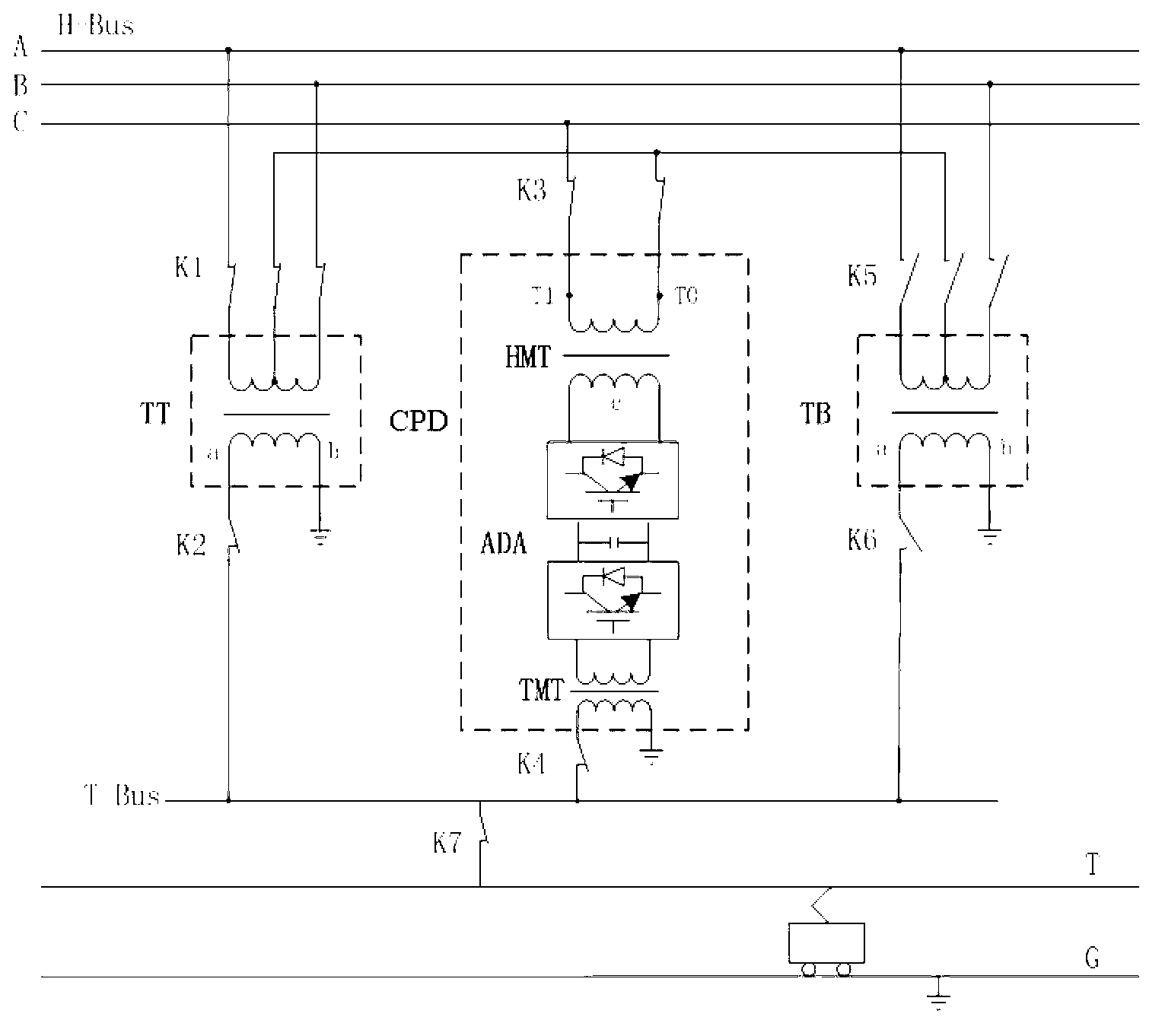Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
975 results about "Traction power supply" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
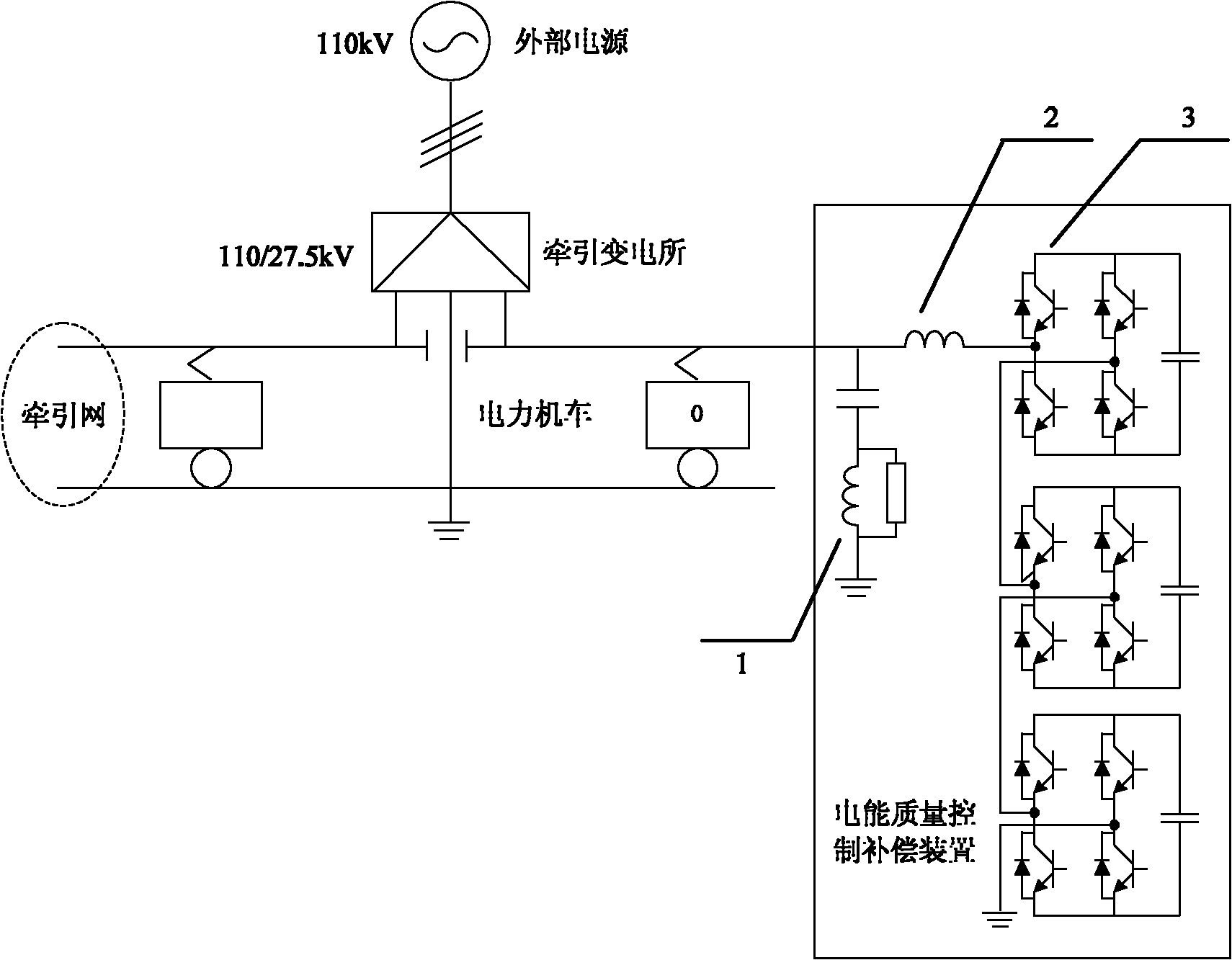
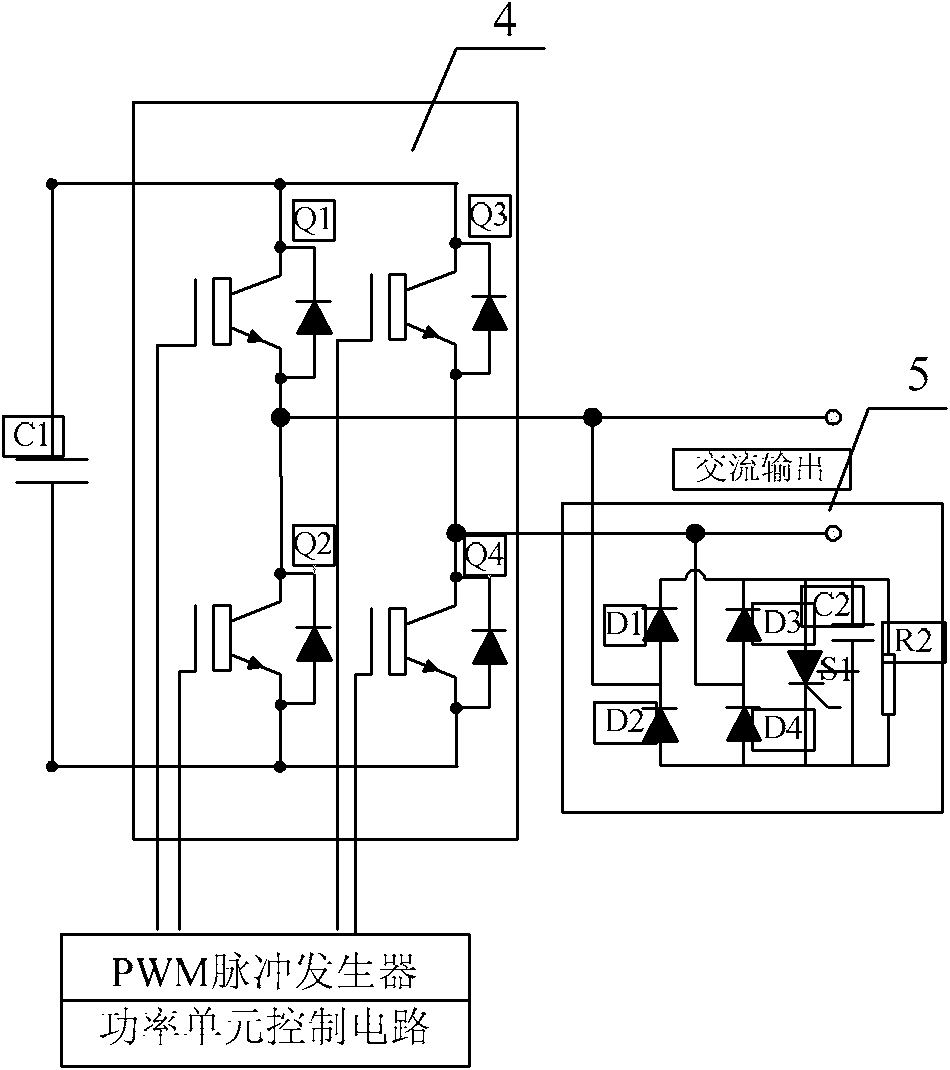
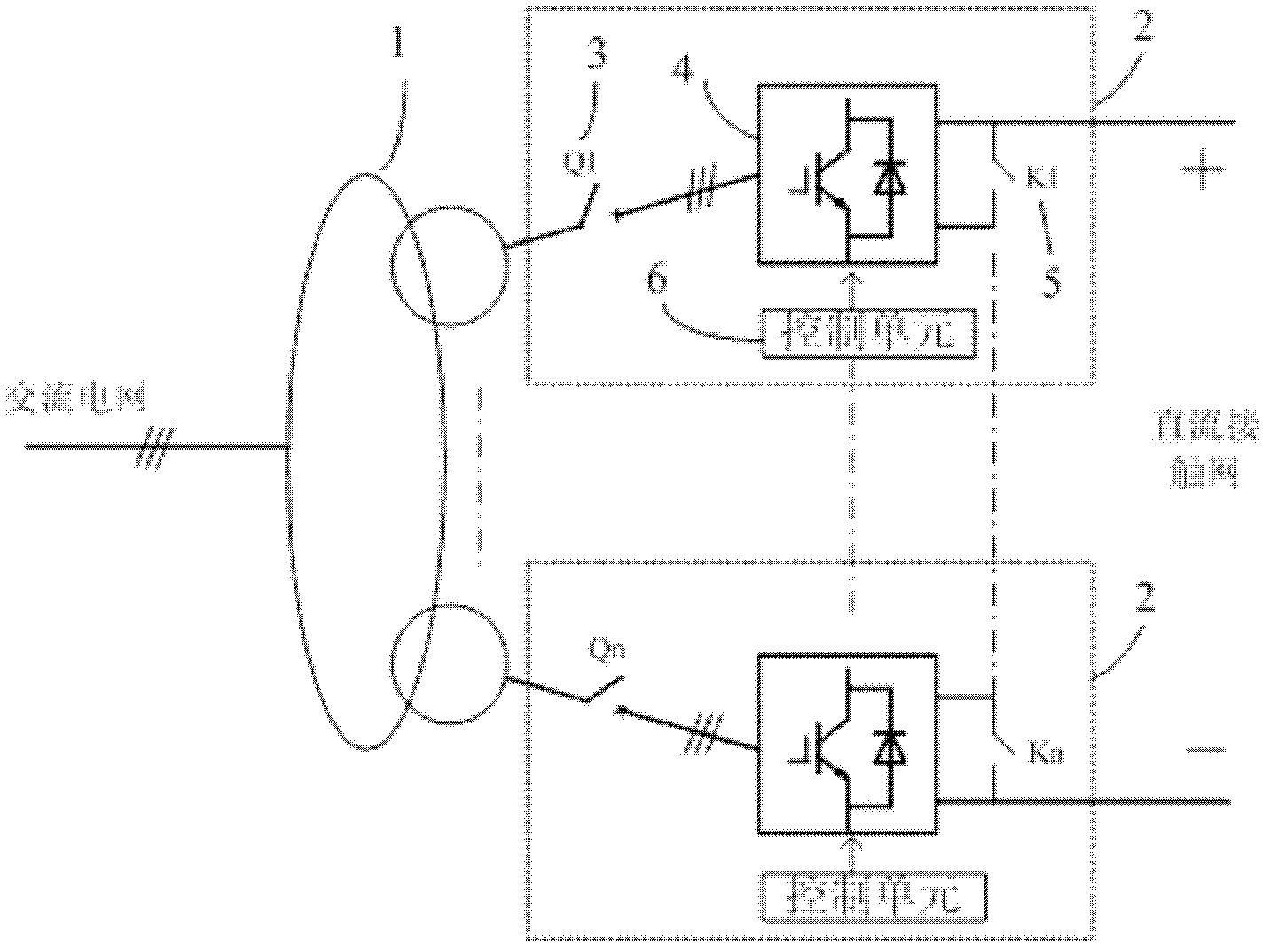
An energy-feedback type traction power supply device and its control method
ActiveCN102267405ARealize stepless adjustmentInjected harmonics are smallPower supply linesSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsTransformerLow voltage
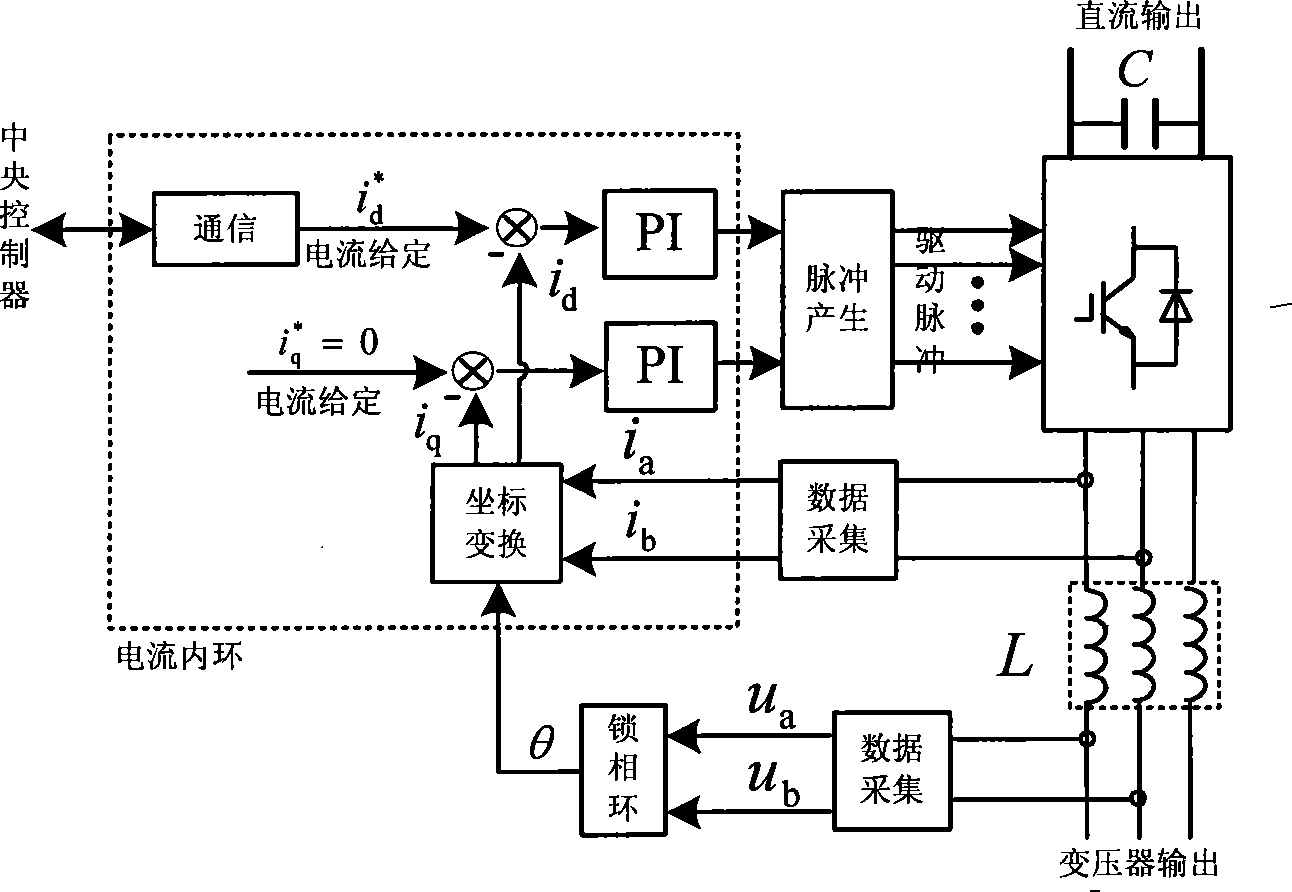
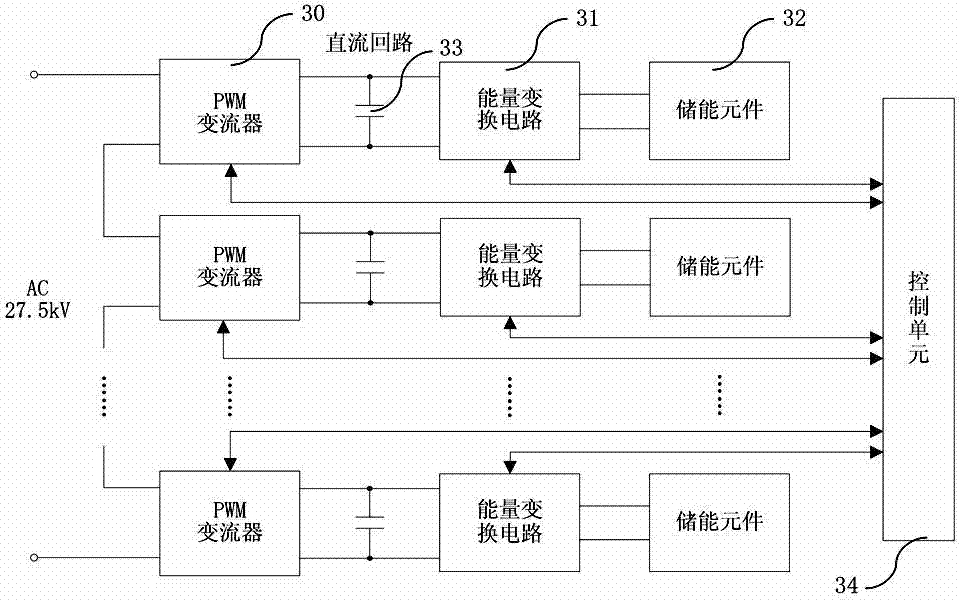
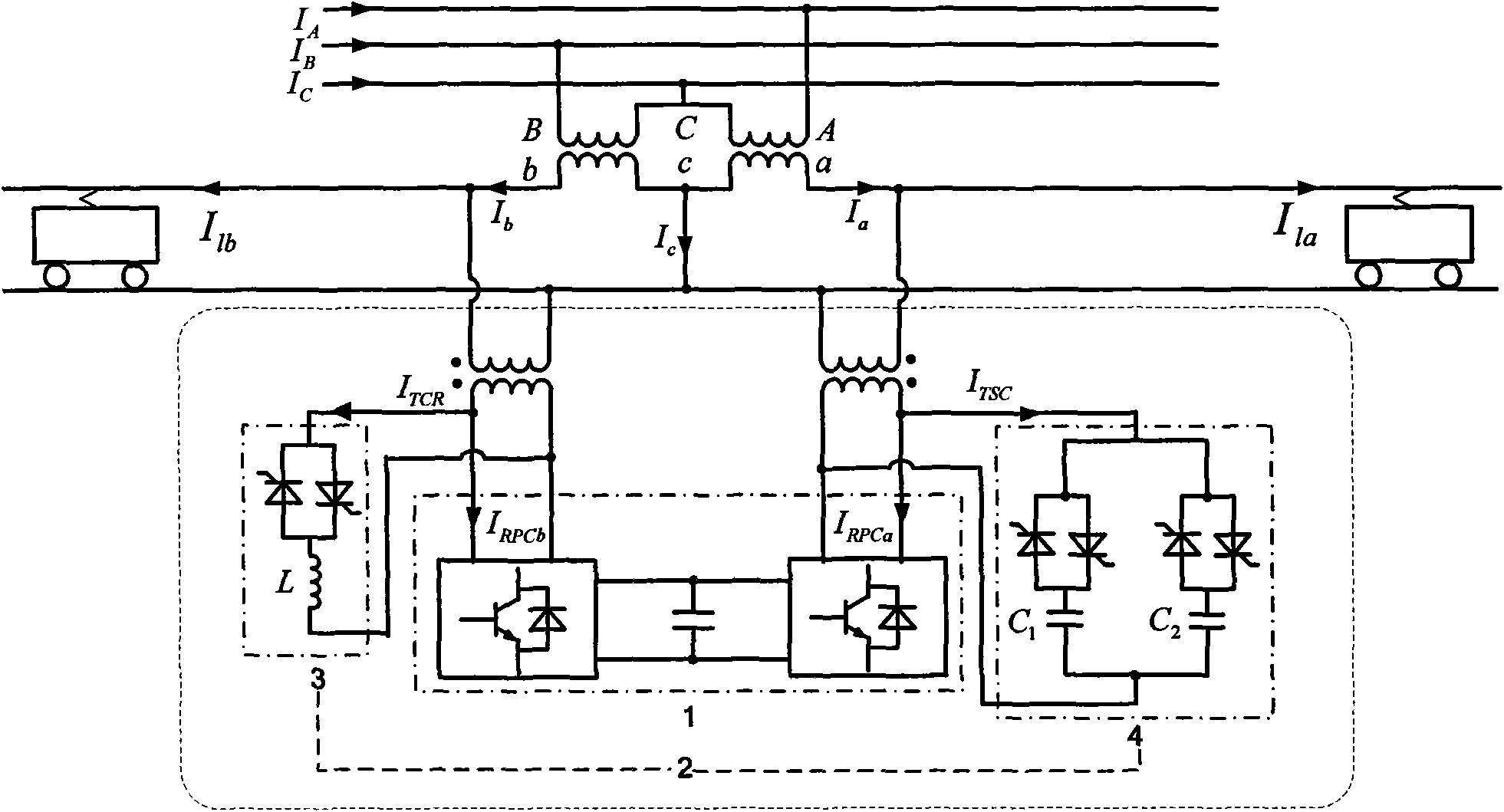
The invention discloses an energy feeding type dragging power supply device and a control method thereof. The energy feeding type dragging power supply device comprises a multiple transformer and at least two four-quadrant converter modules. The energy feeding type dragging power supply device and a diode rectification dragging unit are arranged in parallel form. A primary side of the multiple transformer of the energy feeding type dragging power supply device is connected to an alternated current medium-voltage power grid through a high-voltage switch cabinet; each set of windings at a low-voltage side of the multiple transformer is connected to an alternated current side of one four-quadrant converter module; and the direct current sides of the four-quadrant converter modules are in parallel connection after being connected to a direct current side isolation switch and are connected to a direct current bus through a direct current switch cabinet and a cathode cabinet. The energy feeding type dragging power supply device can work at three different modes of dragging, feedback or SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) according to the requirements. The energy feeding type dragging power supply device is compatible with an existing dragging power supply system under the condition of meeting a power grid compatibility demand. The energy feeding type dragging power supply device has the advantages of moderate cost, capability of solving the technical problems of feeding back a regenerated braking energy and stabilizing a dragging network voltage, and real-time static reactive power compensation capacity.
Owner:ZHUZHOU CSR TIMES ELECTRIC CO LTD
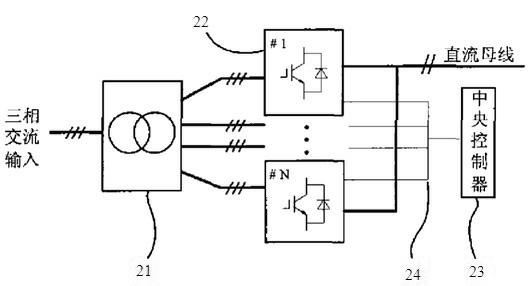
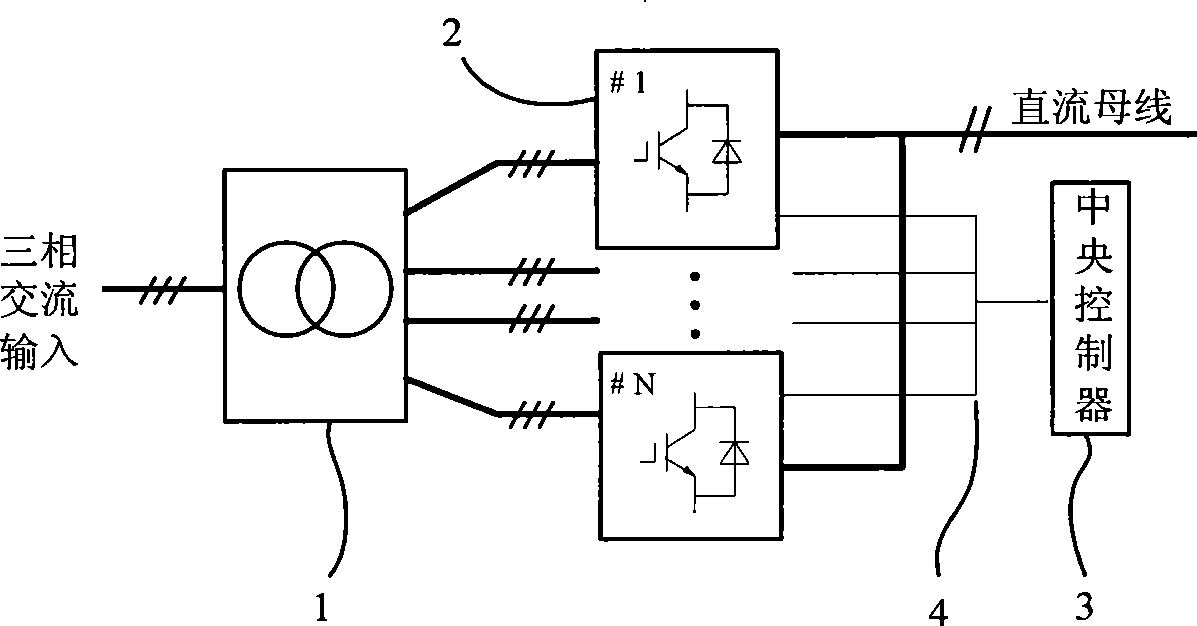
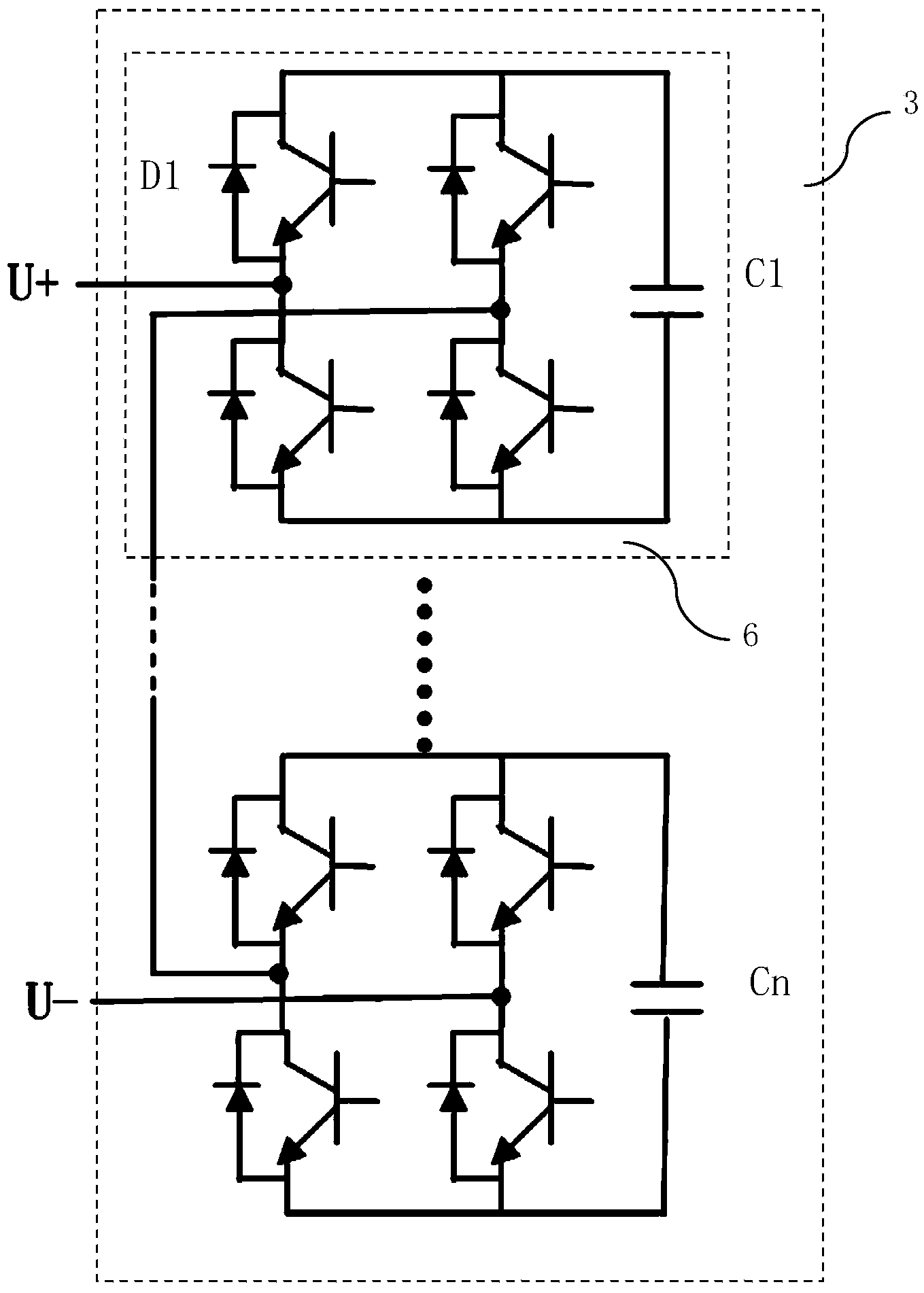
Modular energy feedback type traction power set and control method
InactiveCN101249806AReduce harmonic contentMeet large capacity requirementsAc-dc conversion without reversalPower supply linesTransformerClosed loop
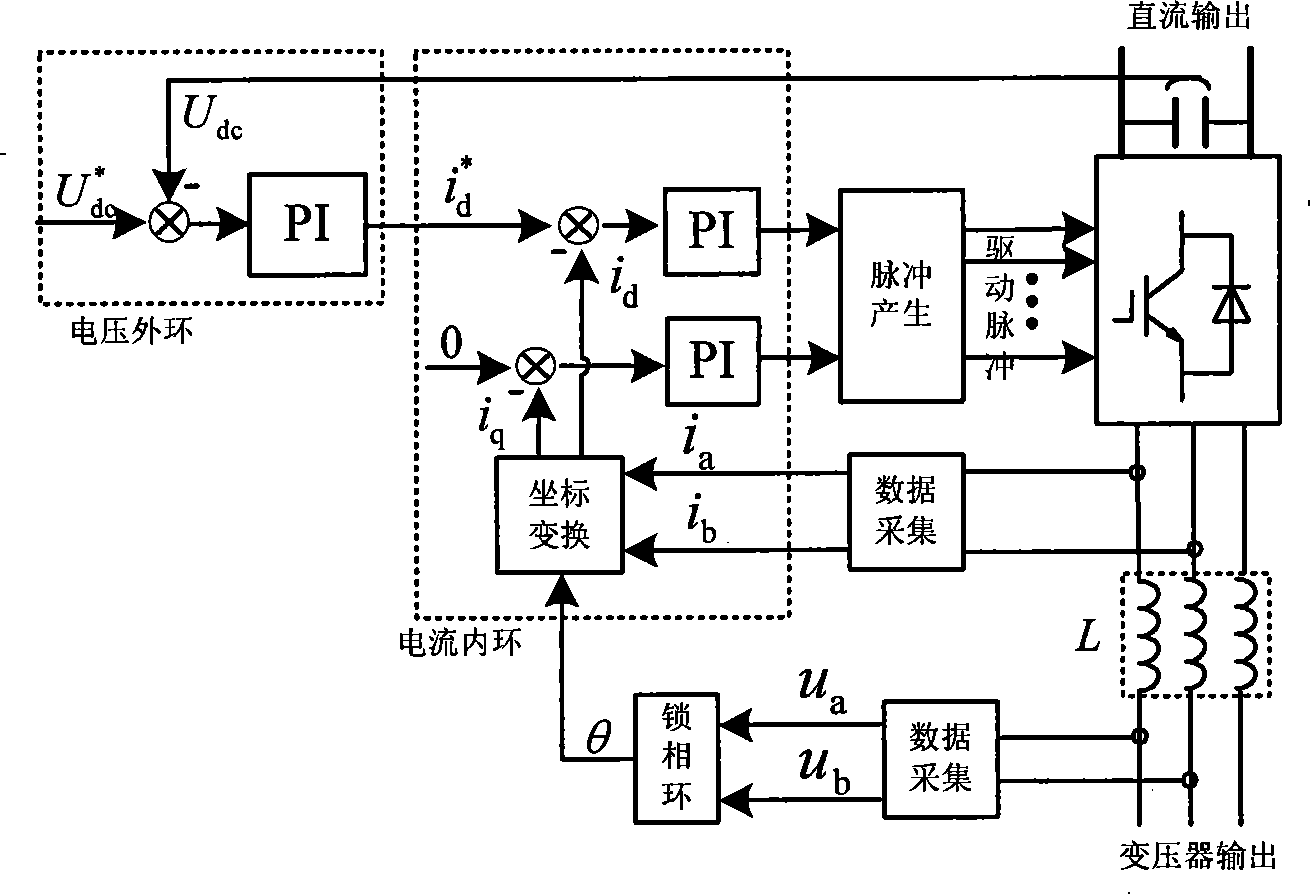
The invention relates to a modularized energy feedback traction power supply device and a control method thereof, wherein, the device comprises a multi-winding transformer, a plurality of PWM rectifier units and a central controller, wherein, the multi-winding transformer is provided with a primary winding and a plurality of secondary windings, and all of the secondary windings have the same connecting mode; each secondary winding of the transformer is connected with a PWM rectifier unit; the direct-current outputs of all the PWM rectifier units are connected to a direct-current bus of the general power supply device in serials. Double closed-loop control of voltage and current is adopted; an outer loop of direct-current voltage is arranged on the central controller and an inner loop based on synchronous rotating frame is arranged on each PWM rectifier unit. The power supply device is remarkably characterized by easy modularization, large capacity, bipolar energy transmission, high power factor, small current harmonic wave and stable direct-current voltage.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Electrified railway traction power supply and energy storage device and method thereof
ActiveCN103840477AImprove energy utilizationRealize energy savingPower supply linesAc network load balancingTraction transformerPeak load
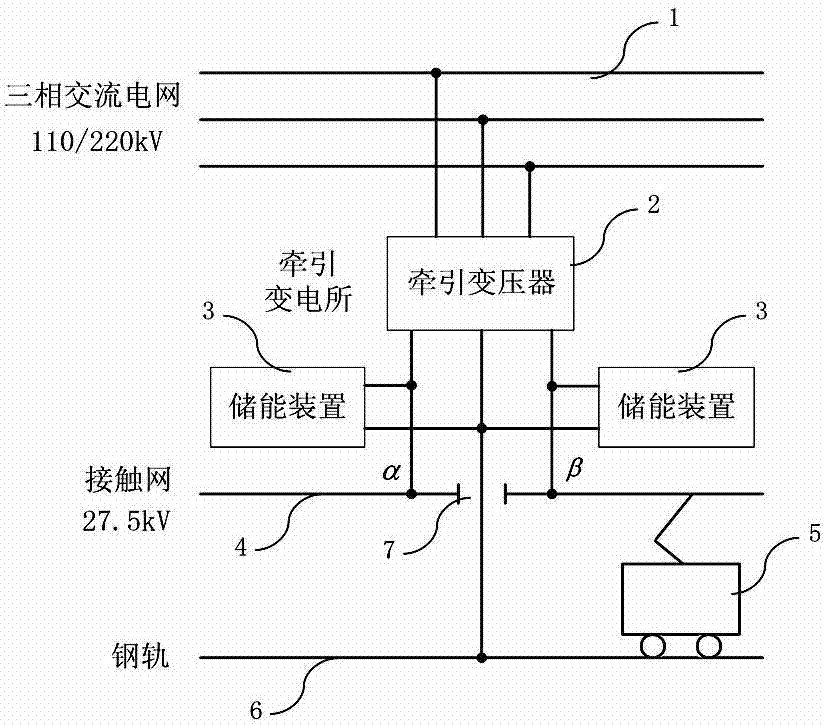
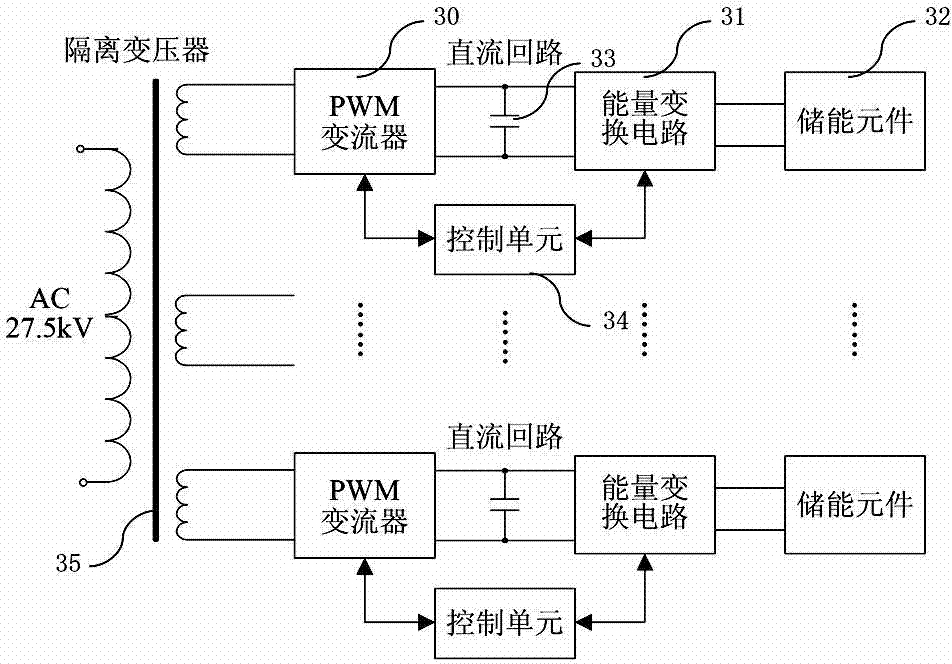
The invention discloses an electrified railway traction power supply and energy storage device and a method of the electrified railway traction power supply and energy storage device. The energy storage device is connected between a feeding arm alpha or feeding arm beta at the output end of a traction transformer and a steel rail, or two energy storage devices are connected between the feeding arm alpha and the steel rail and between the feeding arm beta and the steel rail respectively, wherein the energy storage device is arranged in a traction substation. The energy storage device comprises a control unit, an isolation transformer, a PWM current transformer, an energy transformation circuit and an energy storage element, wherein the PWM current transformer, the energy transformation circuit and the energy storage element are connected in sequence, and the control unit is used for carrying out calculation according to the voltage, current and direction of the feeding arm alpha and / or feeding arm beta to complete control over the PWM current transformer and the energy transformation circuit and achieve energy exchange between the energy storage device and the feeding section connected with the energy storage device. The electrified railway traction power supply and energy storage device can fully recycle locomotive braking feedback electric energy, improve the energy utilization ratio of a traction power supply system, reduce the installation billing capacity of the traction transformer, reduce cost and absorb and store energy even in electricity valleys, has the effect of peak load shifting and further has the functions of dynamic reactive-power compensation and low-order harmonic suppression.
Owner:CSR ZHUZHOU ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVE RES INST
Electric locomotive non-power-off neutral section passing-electric energy quality comprehensive compensation device and method
ActiveCN102035212APrevent surgeNo currentPolyphase network asymmetry elimination/reductionReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationCapacitancePower quality
The invention relates to an electric locomotive non-power-off neutral section passing-electric energy quality comprehensive compensation device and method, which belongs to the technical field of railway transport equipment and electric electronics. The device comprises a controllable transfer switch, a single-phase step down transformer, a single-phase step down transformer with a middle tap, a two-phase back-to-back converter sharing a DC-side capacitor, a circuit breaker switch, four position sensors and three electric quantity sensors. In the method, when the electric locomotive passes the neutral section, the controllable transfer switch is turned off, and the device works in a non-power-off neutral section passing mode to perform control on amplitude and phase of the neutral section voltage and enable the electric locomotive to pass the neutral section with load in a non-power-off manner. Without locomotive passing, the controllable transfer switch is closed, and the device works in an electric energy quality comprehensive compensation mode and has functions of active power transfer as well as inactive power and harmonic compensation. Through the device, the problems relating to electric energy quality of a traction substation and neutral section can be comprehensively solved based on the traditional traction power supply mode.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
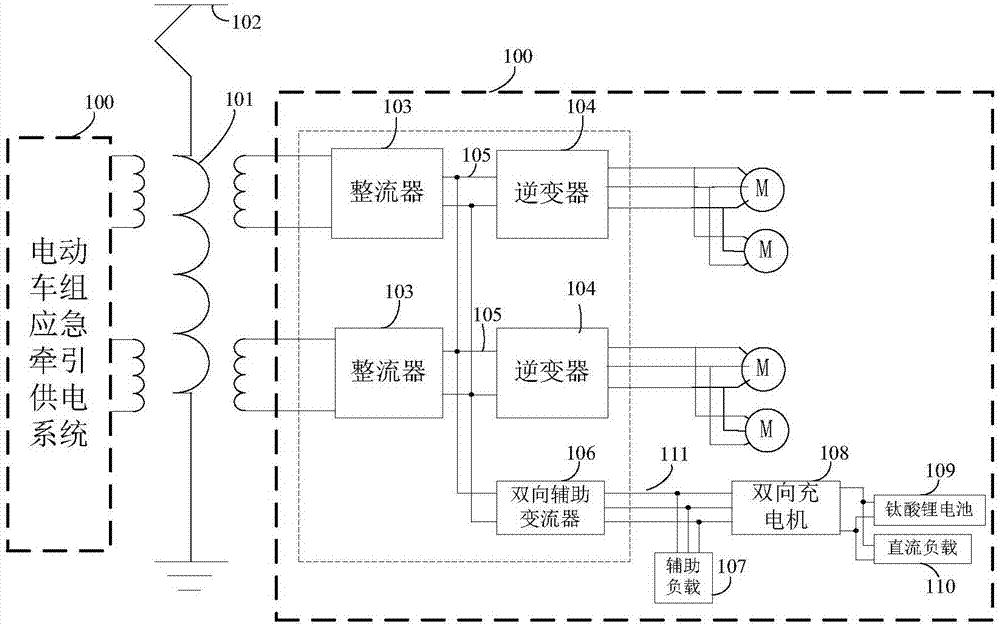
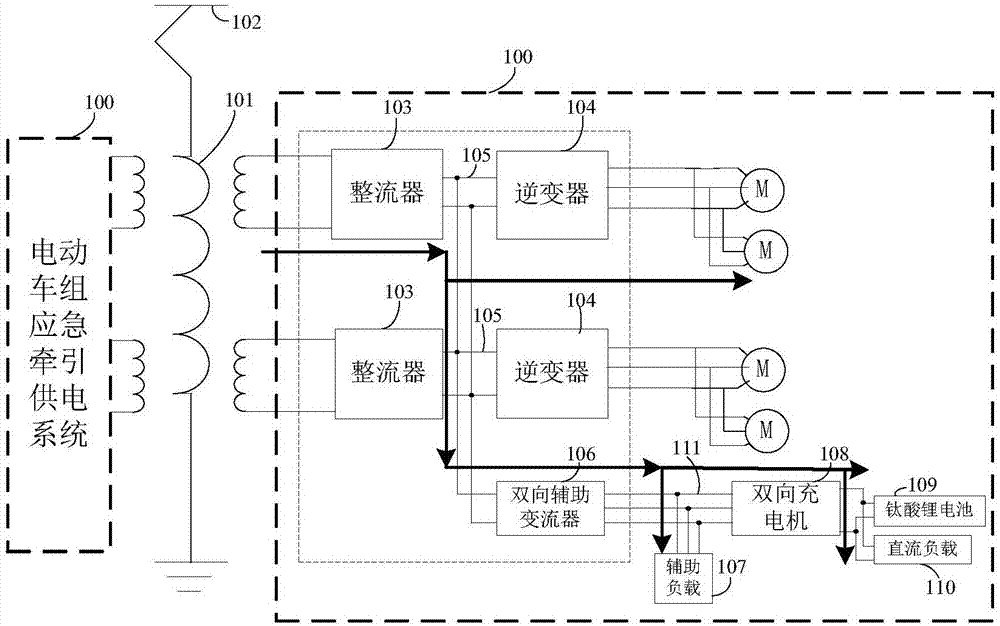
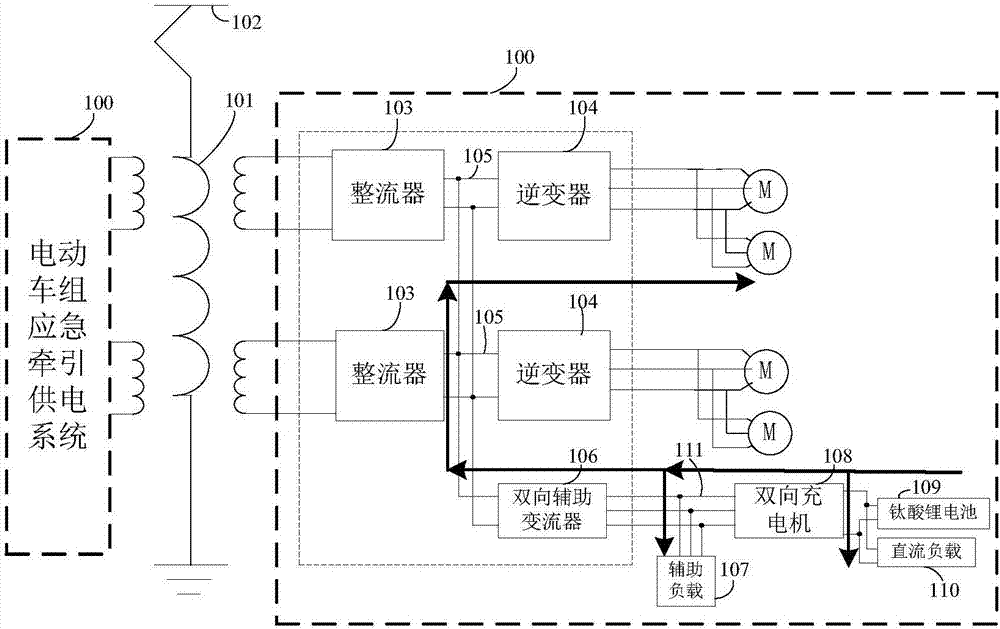
Emergency traction power supply system of electric motor unit
PendingCN107128183AMaintain normalMaintain performancePropulsion using ac induction motorsElectric energy managementContact networkBusbar
The invention discloses an emergency traction power supply system of an electric motor unit, which comprises a traction transformer used for reducing high voltage of a contact network, two rectifiers used for rectifying alternating current of secondary side windings of the traction transformer into voltage of middle direct current links, two inverters used for taking electricity from the middle direct current links and performing inversion into three-phase alternating current, a two-way auxiliary current transformer used for taking electricity from the middle direct current links and performing inversion into three-phase alternating current or taking electricity from a two-way charger and then performing boosting and rectification into the voltage of the middle direct current links, an auxiliary load used for obtaining the three-phase alternating current from the two-way auxiliary current transformer or the two-way charger by an auxiliary load power supply busbar, and the two-way charger used for obtaining the three-phase alternating current from a three-phase alternating current output side of the two-way auxiliary current transformer and performing voltage reduction and rectification on the three-phase alternating current into direct current to supply power to a lithium titanate battery and a direct current load which are connected with the two-way charger, or used for taking electricity from the lithium titanate battery and performing boosting and inversion into the three-phase alternating current to supply power to the auxiliary current transformer.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAYS CORPORATION +3
Direct current traction power supply system and protective method
ActiveCN103311910ARealize localizationAvoid serious consequences of breaking failureEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDc circuit breakerTraction power supply
The invention discloses a direct current traction power supply system and a protective method, and utilizes direct current protective device outlet information and a short circuit fault mark value as a criterion to judge various direct current short circuit faults. When the short fault occurs, an alternating current incoming line breaker closest to a fault element is subjected to brake separating; if the sum of the fault mark values of the element, measured and computed after the brake separating, is more than or equal to 1, permanent fault is determined, the alternating current incoming line breakers of other traction substations in the whole line are subjected to brake separating, and related direct current isolation switches are subjected to brake separating to enable the alternating current incoming line breakers of the traction substation in the whole line to be subjected to switching on, so the power supply of the system can be restored; and if the sum of the fault mark values of the element is smaller than 1, the fault is instant, and related breakers are switched on for restoring the power supply of the system. The direct current traction power supply system and the protective method are capable of omitting the direct current breakers and saving investment, convenient to implement, suitable for carrying out new line construction or old line transformation in occasions where the lines are not very long (for example in 20m and less than 10 traction substations). When the line is overlong, the traction power supply system can be subjected to partition by a small amount of direct current breakers.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV +1
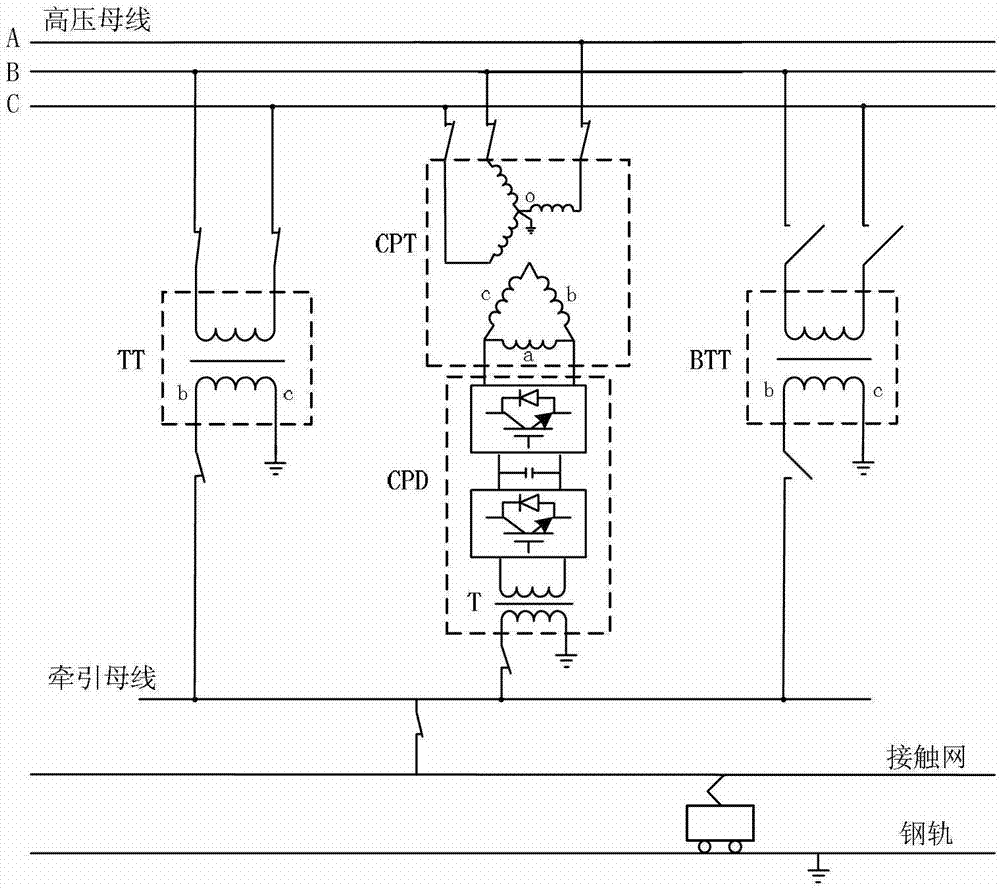
Single-phase combined co-phased power supply and transformation structure
ActiveCN103311924AReduce capacityReduce its proportionPolyphase network asymmetry elimination/reductionPolyphase network asymmetry reductionVoltage amplitudeBusbar
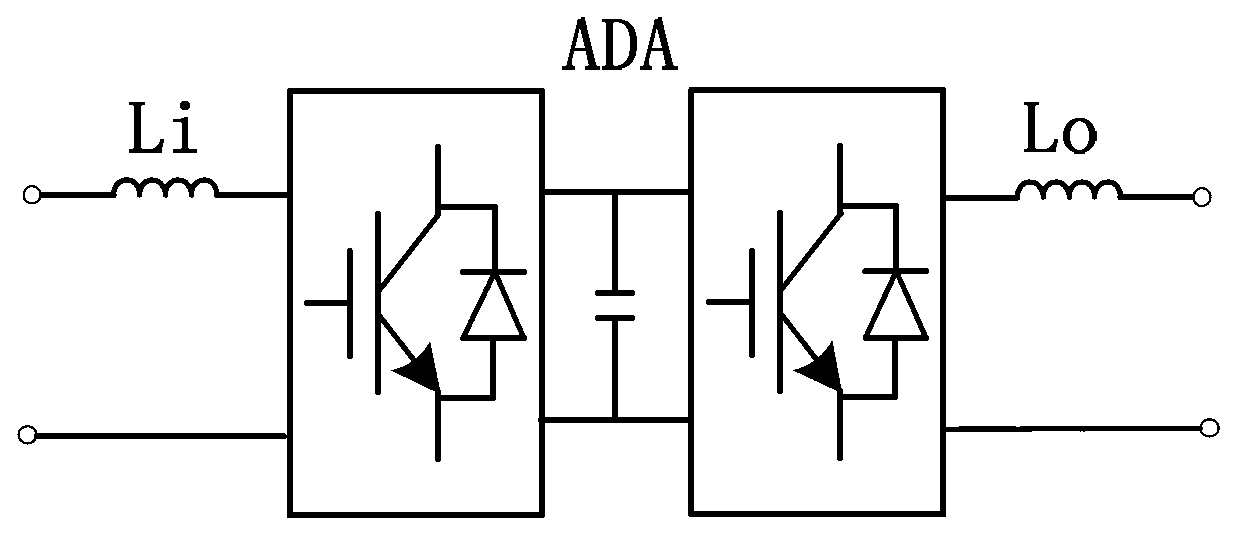
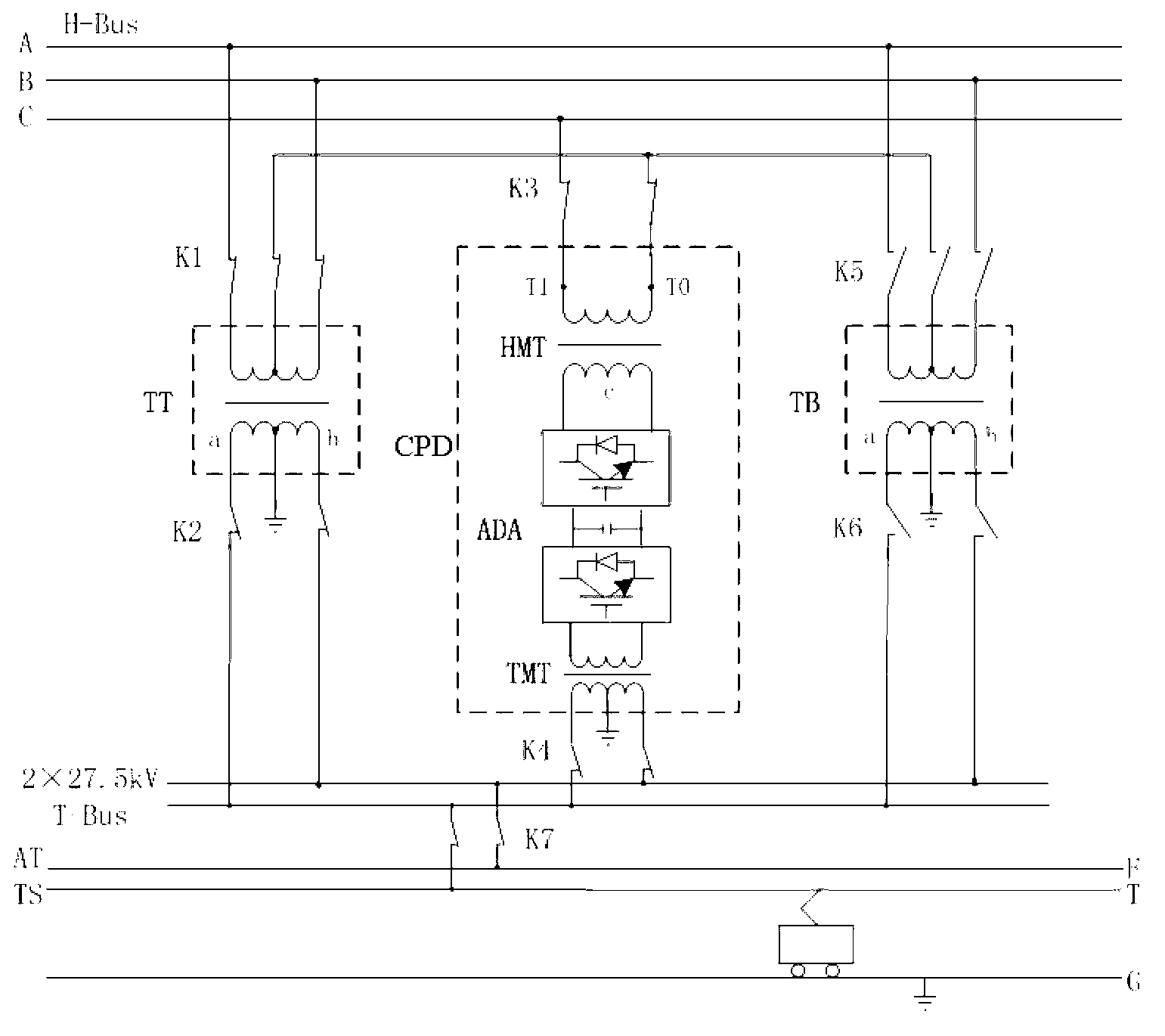
The invention discloses a single-phase combined in-phase power supply and transformation structure mainly comprising a traction transformer and a CPD. In the CPD, a high-voltage matching transformer primary side and a traction transformer primary side form an SCOTT connected group, a secondary side winding of the CPD is connected to the incoming end of an AC-DC-AC converter, and the outgoing end of the AC-DC-AC converter is connected with the primary side of a traction matching transformer. A secondary side winding of the traction transformer and the secondary side winding of the traction matching transformer are equal in voltage amplitude and phase and both connected with a traction busbar; traction load calculated capacity is equal to the sum of traction transformer calculated capacity and CPD calculated capacity, the traction transformer is responsible for main power supply, and the CPD calculated capacity is determined by the capacity of traction load which caused exceeding three-phase voltage unbalance. The single-phase combined in-phase power supply and transformation structure has the advantages that optima configuration of traction power supply resources is realized and energy conservation is better.
Owner:CHENGDU SHANGHUA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Single-phase and three-phase combined in-phase power supply and transformation device
ActiveCN103078315AReduce capacityReduce its proportionPolyphase network asymmetry elimination/reductionPolyphase network asymmetry reductionPower qualityEngineering
The invention discloses a single-phase and three-phase combined in-phase power supply and transformation device which comprises a single-phase traction transformer, a three-phase YNd11 grounding compensation transformer and a single-phase in-phase compensation device thereof; the in-phase compensation device comprises an alternating current-direct current-alternating current (AC-DC-AC) converter; the traction transformer and the compensation transformer have equal effect to a three-phase and two-phase balance transformer with the phase of secondary side voltage being vertical; when in a normal state, the traction transformer, the compensation transformer and the in-phase compensation device jointly supply power for a transaction load by a specified proportion; when the compensation transformer or the in-phase compensation device exit the operation, the traction transformer can work independently in a short time; and a backup traction transformer can replace the traction transformer to work and can work on linear voltage different from that of the traction transformer. According to the device, the electric phase at the exit of a traction transformer substation can be canceled, so that the electric energy quality requirements mainly comprising the unbalance of three-phase voltage can be met, and the optimal configuration of traction power supply resources can be realized.
Owner:CHENGDU SHANGHUA ELECTRIC CO LTD
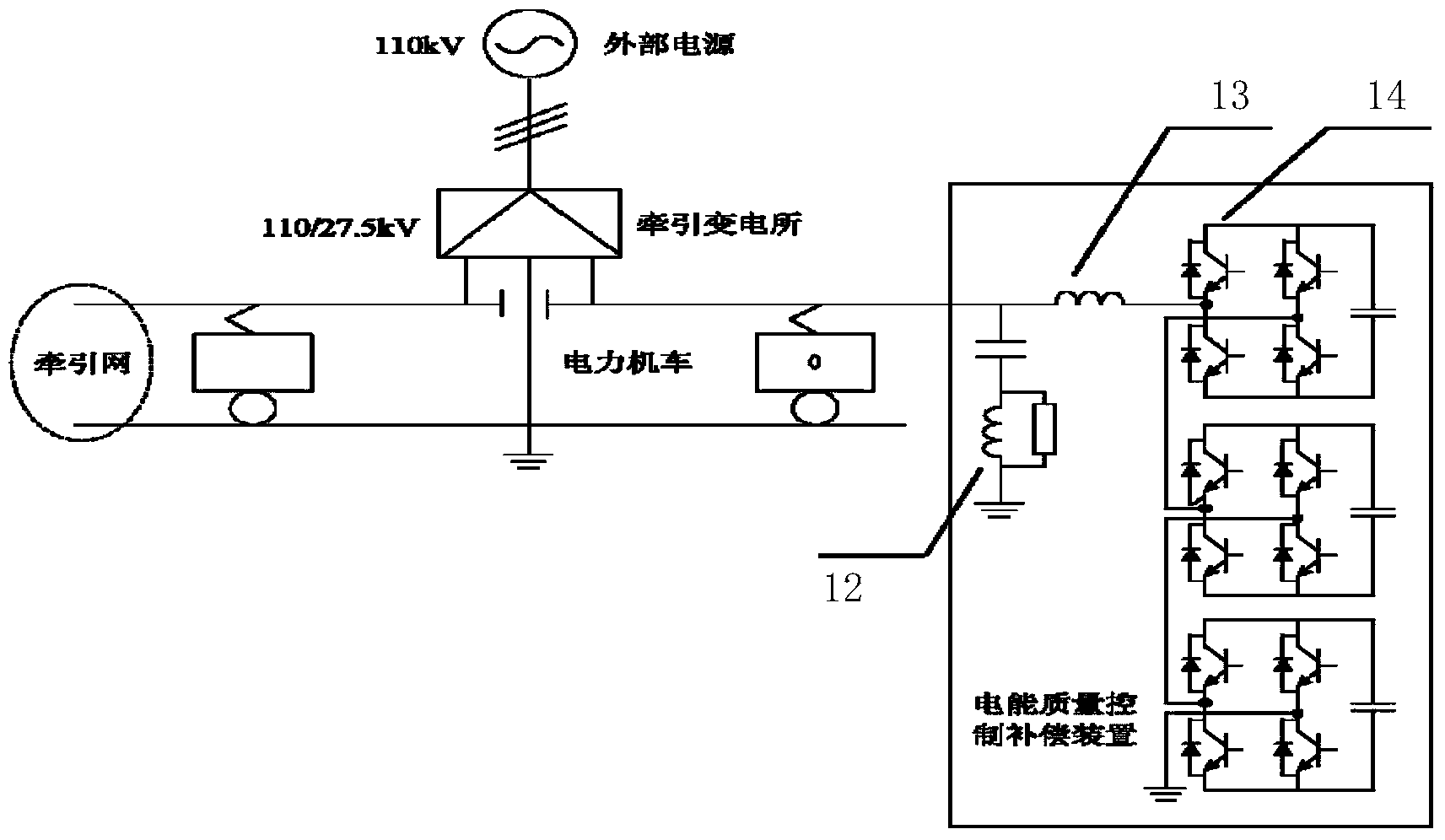
Power quality integrated management device of electrified railway traction supply network
ActiveCN103457261AGuaranteed uptimeAvoid interactionActive power filteringPower supply linesPower qualityContact network
The invention discloses a power quality integrated management device of an electrified railway traction supply network. The power quality integrated management device comprises an APF branch circuit and an HPF branch circuit. The APF branch circuit comprises a connecting electric reactor, a controller, more than one set of APF converter and more than one set of charging circuit corresponding to the APF converter. After being connected with the charging circuits, the APF converters are connected to a contact network through the connecting electric reactor in a hanging mode. The APF converters are cascaded through more than two power units, the controller is connected with the APF converters and sends a control signal to switch components of the power units, single-phase uniform amplitude alternating-current PWM output voltage is generated, and an expected current injection contact network is obtained through the connecting electric reactor. According to the HPF branch circuit, a second-order resonance circuit is composed of a resistor, an electric reactor and a capacitor. The power quality integrated management device can provide idle work support for an electric railway traction power supply system, the power factor is improved and meanwhile negative sequence components, harmonic waves, voltage fluctuations and voltage flickers in the system are effectively restrained.
Owner:CSR ZHUZHOU ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVE RES INST
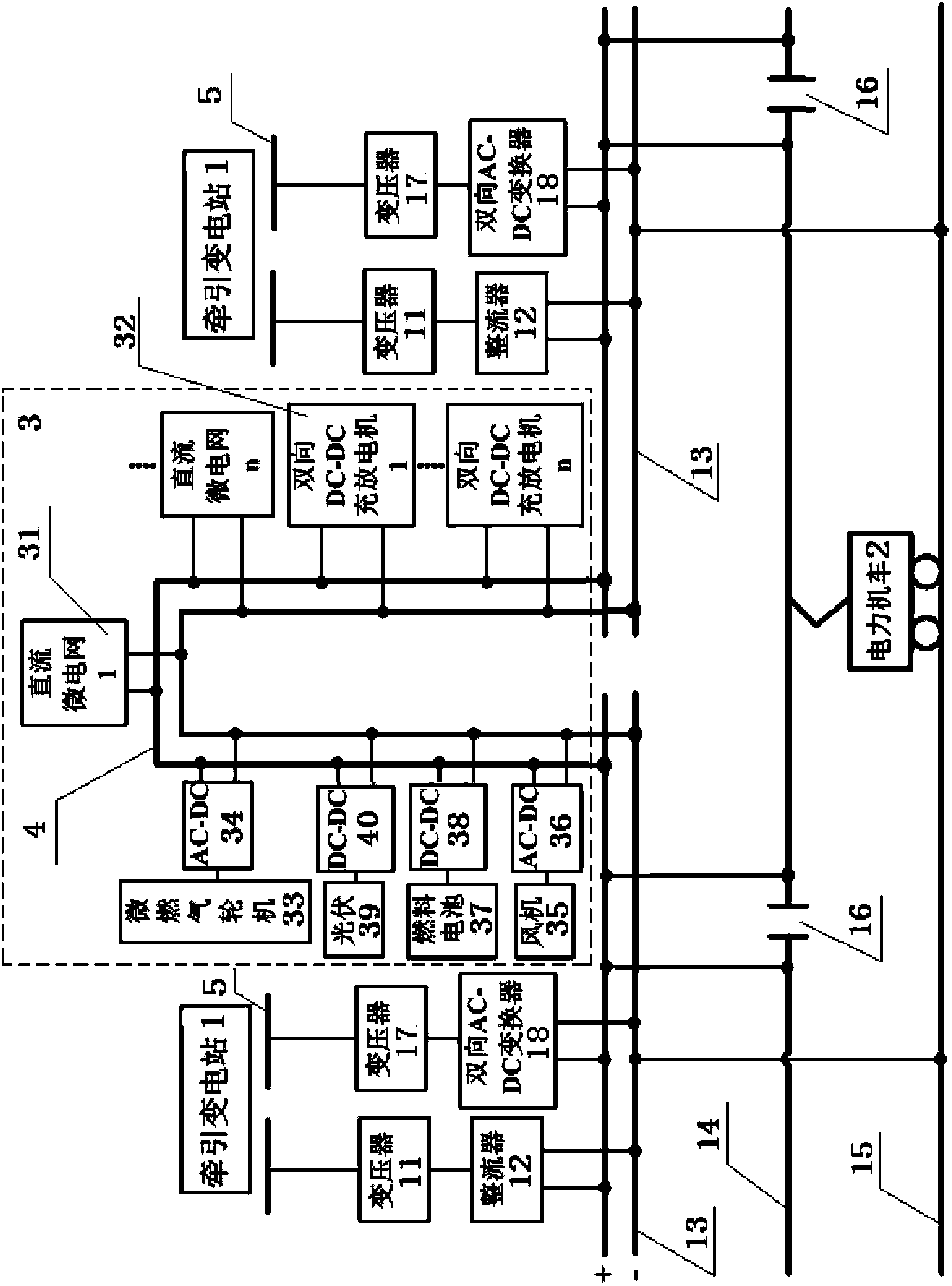
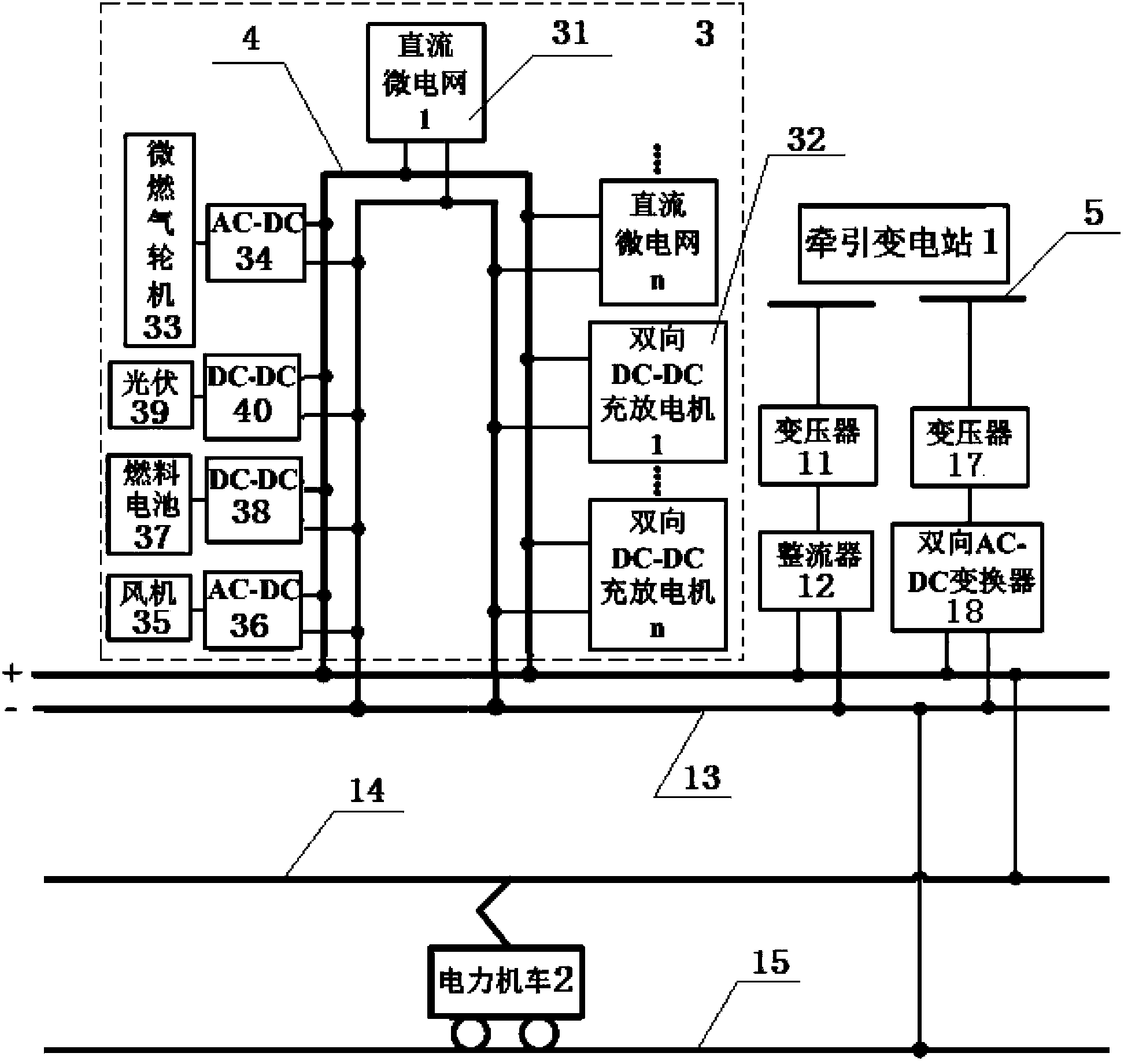
New energy-based hybrid bidirectional interactive direct-current traction power supply system
InactiveCN103434421AImprove power supply reliabilitySmall fluctuationBatteries circuit arrangementsPower supply linesLow voltageNew energy
A new energy-based hybrid bidirectional interactive direct-current traction power supply system is provided with two traction substations, and each traction substation comprises transformers, rectifiers, bidirectional alternating current-direct current (AC-DC) converters, a direct-current bus, a contact system, rails and a section post. A direct-current new energy system which comprises an electric automobile charging and discharging system, a distributed power supply and more than one low-voltage direct-current micro-grid is arranged on the direct-current bus between the two neighboring traction substations, and is connected with the direct-current buses of the two neighboring traction substations through a high-voltage direct-current bus, so that a direct-current loop micro-grid is formed in a power supply section, wherein the electric automobile charging and discharging system comprises more than one bidirectional direct current-direct current charger-discharger which is used for connection with the power cells of electric automobiles. The new energy-based hybrid bidirectional interactive direct-current traction power supply system realizes the effective utilization of distributed new energy and the recovery of the braking energy of electric locomotives; the fluctuation of the voltage of the direct-current bus is reduced, and thereby the reliability of the power supply of the direct-current traction power supply system is enhanced.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV +2
Alternating current and direct current mixed traction power supply system with ice melting function
ActiveCN103950394AWill not interfere with each otherSwitching is clear and easyOverhead installationThyristorAC - Alternating currentEngineering
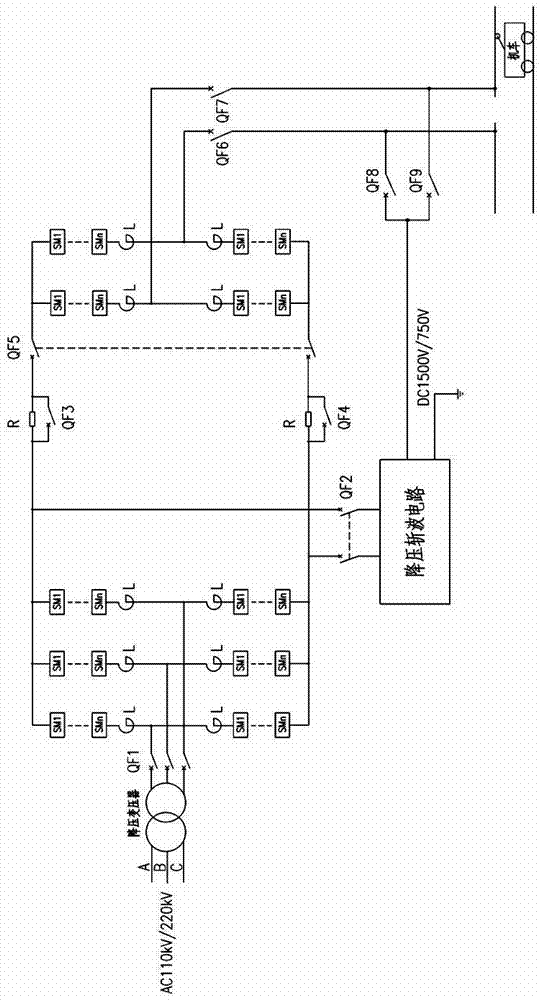
The invention relates to an alternating current and direct current mixed traction power supply system with an ice melting function. The alternating current and direct current mixed traction power supply system comprises an alternating current power supply assembly, a direct current power supply assembly and a discharging coil, wherein the alternating current power supply assembly is used for realizing alternating current power supply, a traction transformer of the alternating current power supply assembly is connected into a traction power supply net through a first circuit breaker, the traction transformer outputs alternating current after the voltage reduction and is connected with the traction net through an alternating current feeder switch, the direct current power supply assembly is used for realizing direct current power supply, a rectifying transformer of the direct current power supply assembly is connected into a traction power supply net through a second circuit breaker, the rectifying transformer is subjected to voltage reduction and outputs direct current after being rectified via a rectifier, one path is connected with the traction net through the direct current feeder switch, the other path is connected with the traction net through a double-electrode high-voltage isolation switch, in addition, a high-voltage isolation switch used for realizing short circuit on a traction net uplink and a traction net downlink is arranged at the tail end of a section post line, and the traction net uplink and the traction net downlink form a ice melting loop; the discharging coil is arranged at the positive bus end of the output side of the direct current feeder switch and is provided with a high-voltage switch. The alternating current and direct current mixed traction power supply system has the advantages that the principles are simple, the function integrality is high, the operation is safe and reliable, and the like.
Owner:ZHUZHOU NAT ENG RES CENT OF CONVERTERS
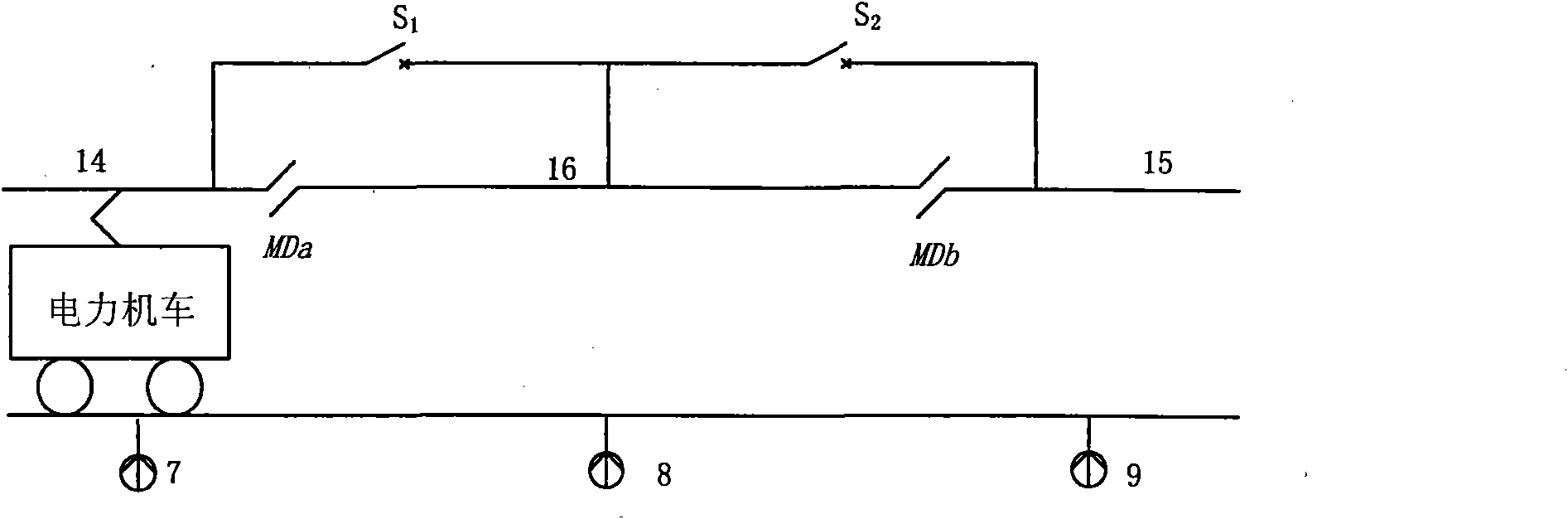
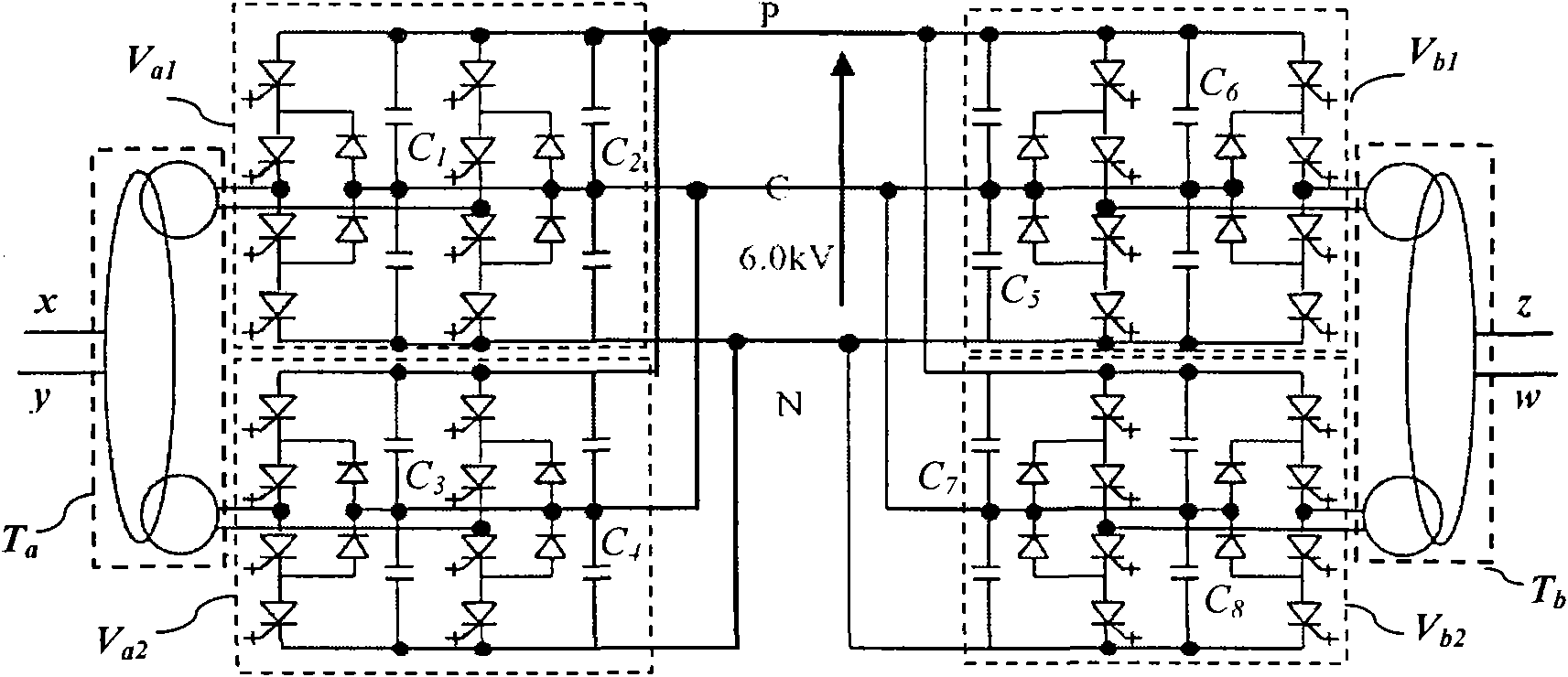
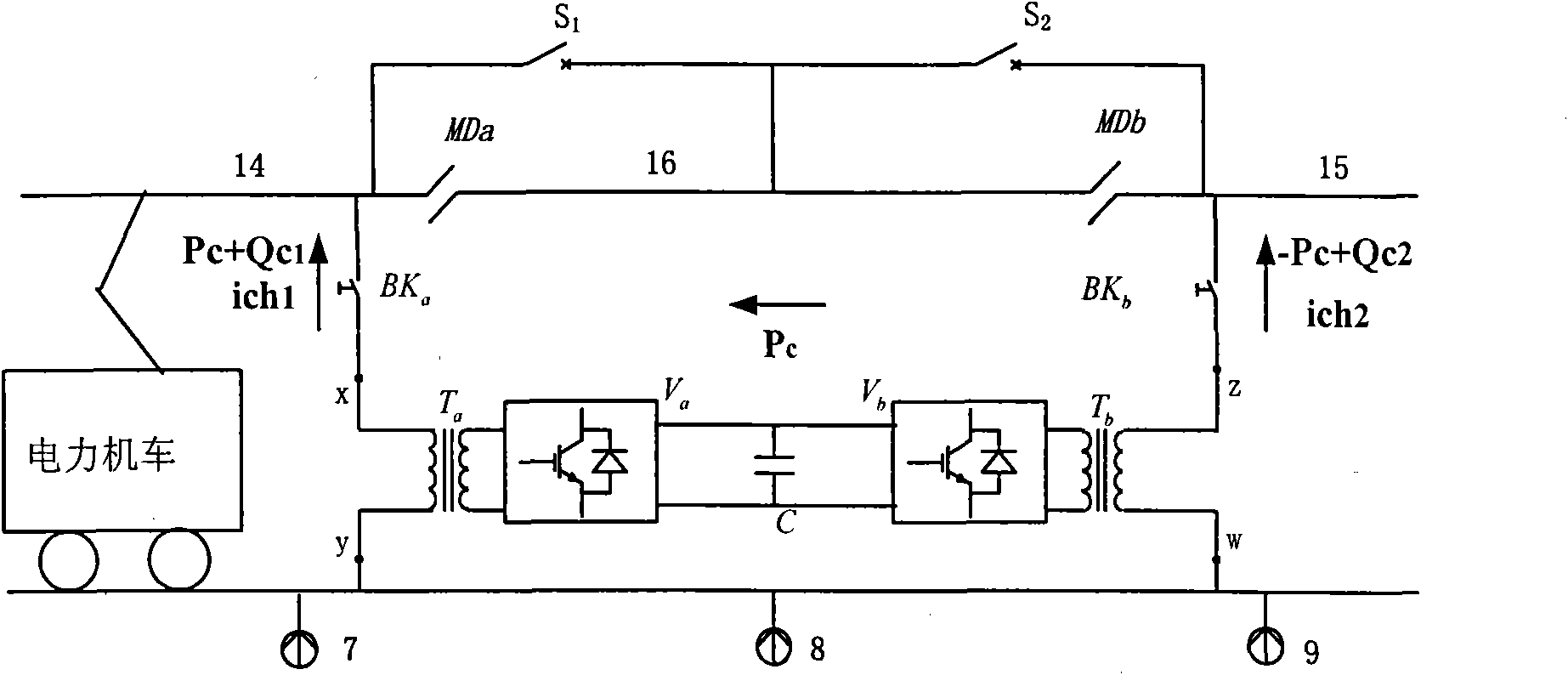
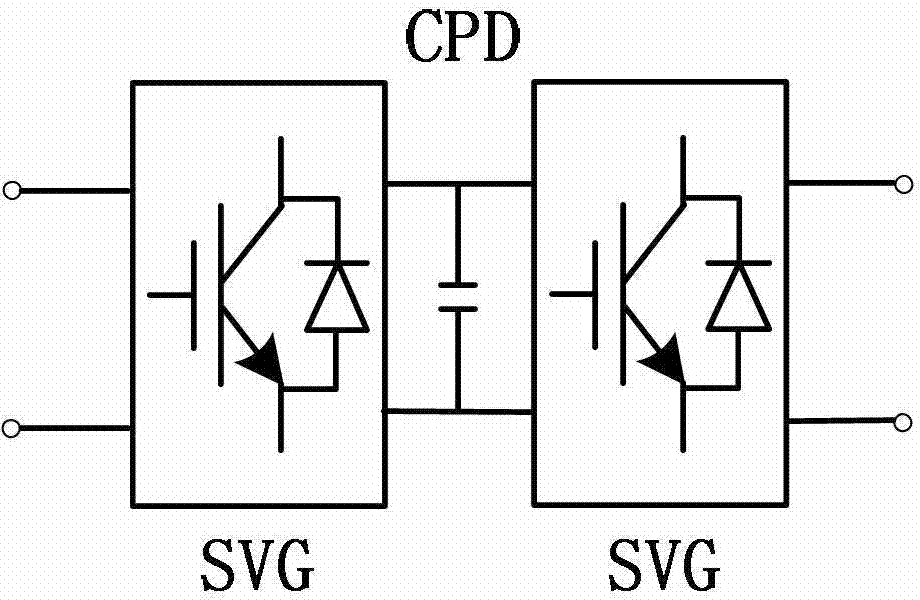
Co-phase power supply device and traction power supply system
ActiveCN103552487AEliminate negative phase sequence currentSolving Consistency IssuesConversion with intermediate conversion to dcPower supply linesPower qualityNegative phase
The invention discloses a co-phase power supply device and a traction power supply system. The co-phase power supply device comprises a first MMC (modular multilevel converter) valve and a second MMC valve. One end of the first MMC valve is coupled to a first power supply arm of a traction transformer, the other end of the first MMC valve is connected with a return wire, and the first MMC valve is used for converting AC (alternating current) voltage of the first power supply arm of the traction transformer into DC (direct current) voltage; one end of the second MMC valve is coupled to a second power supply arm of the traction transformer, the other end of the second MMC valve is connected with the return wire, and the second MMC valve is used for inverting DC voltage transmitted by the first MMC valve into AC voltage which is identical to the second power supply arm of the traction transformer in amplitude and phase. By means of inter-transmission of active energy of the two power supply arms on sides of the traction transformer, negative-phase sequence current can be eliminated, the capacity utilization rate of the traction transformer can be maximized and electric split-phase of a traction network can be eliminated; the MMC valves compensate idle power and harmonic waves of the two power supply arms, and the increase of risk of overhigh harmonic waves of devices such as capacitors, SVCs (static var compensator) and SVGs (static var generator) can be avoided, so that the co-phase power supply device can be applied to comprehensive treatment of power quality of traction transformers.
Owner:CSR ZHUZHOU ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVE RES INST
Energy feedback type traction power supply device with reactive compensation function and control method thereof
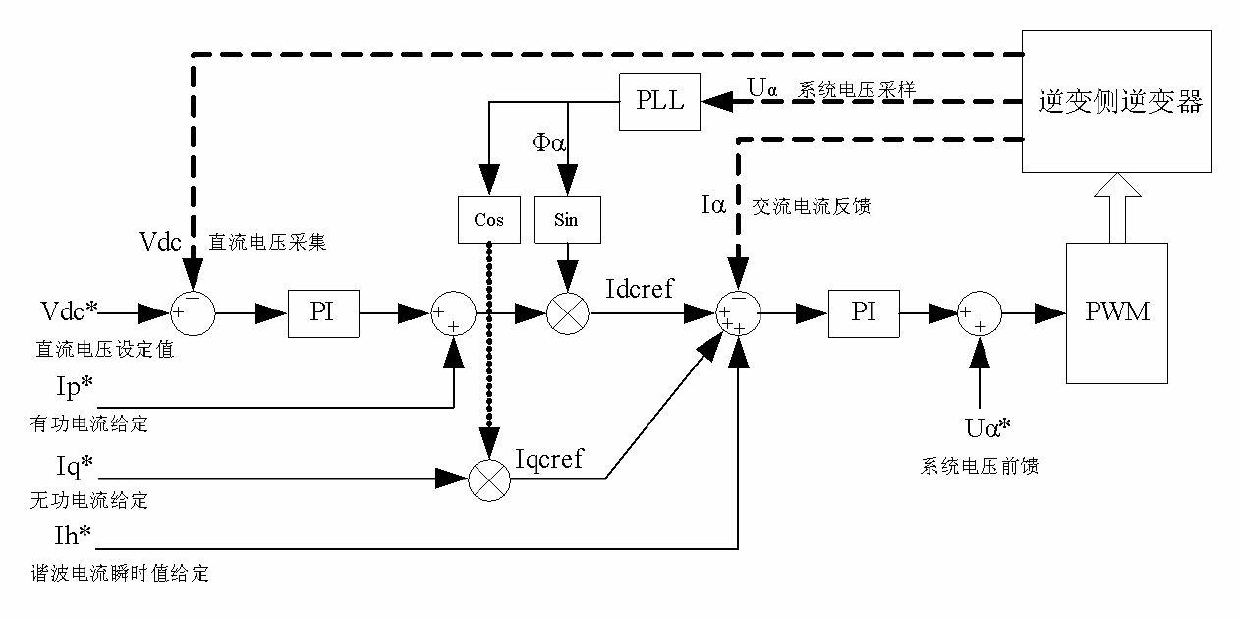
InactiveCN102074972ARealize two-way transmissionImprove power factorElectrodynamic brake systemsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsContact networkLoop control
The invention discloses an energy feedback type traction power supply device with a reactive compensation function and a control method thereof. The device comprises a dual-split transformer, two high-power bidirectional converters, a direct-current filter inductor and a central control unit, wherein each vice-side winding of the dual-split transformer is connected with one high-power bidirectional converter; direct-current output sides of the two high-power bidirectional converters are connected in series, and the direct-current filter inductor is connected in series between a direct-current positive output and a direct-current contact network of the first high-power bidirectional converter; and the central control unit is connected mutually with the two high-power bidirectional converters through a controller area network (CAN). In the control method, the hierarchical control is adopted, the central control unit is used for calculating an active current instruction and a reactive current instruction, and the two high-power bidirectional converters perform closed loop control on alternating current of the two high-power bidirectional converters according to the active current instruction and the reactive current instruction. The device not only can meet the requirements of traction power supply and braking energy feedback of subway trains, but also has a reactive compensation function used for improving power factors at incoming wires of master substations.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Hybrid parallel type high-voltage direct current traction power supply current transformer and control method thereof
InactiveCN102394557AImprove DC output voltageReduce lossAc-dc conversion without reversalHigh-voltage direct currentPWM rectifier
The invention relates to a hybrid parallel type high-voltage direct current traction power supply current transformer and a control method thereof. The hybrid parallel type high-voltage direct current traction power supply current transformer is characterized by comprising a set of pulse width modulation (PWM) rectifier units and a set of diode rectifier units, wherein both an input end of the PWM rectifier units and an input end of the diode rectifier units are connected with an alternating current electric network, and an output end of the PWM rectifier units and an output end of the diode rectifier units are connected in parallel to realize high-voltage direct current output. Because the PWM rectifier units and the diode rectifier units are connected in series, the direct current output voltage of the entire current transformer is improved, the power supply distance is prolonged, and the contact net loss is reduced. Meanwhile, equipment investment is reduced, and the reliability of a system is improved. The hybrid parallel type high-voltage direct current traction power supply current transformer and the control method thereof can be widely applied to urban railway transit traction power supply systems.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Traction power supply system fault location method applied to multiple operation modes
The invention discloses a traction power supply system fault location method applied to multiple operation modes. The method comprises the following steps: 1, reclosing is carried out when a traction network line fails, and if reclosing fails, a reactance method ranging principle is adopted for ranging, and if reclosing succeeds, the second step is carried out; 2, the operation mode of the traction network line is judged according to switch position signals, fault uplink and fault downlink are determined according to the specific operation mode, faults can be determined to be T-type faults, F-type faults or TF-type faults, and then according to the fault type of the specific operation mode, adopting of a suction current ratio principle, a reactance method ranging principle, an uplink downlink current ratio ranging principle or a transverse line current ratio ranging principle is determined to calculate the fault distance. When the method of the invention is adopted for traction network line fault location, the fault position can be quickly and accurately positioned, and thus, the fault clearing efficiency can be enhanced, normal power supply can be quickly recovered, and safe operation of the railway can be ensured.
Owner:CHENGDU SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV XUJI ELECTRIC
Novel high-way traction power supply system capable of selective feed line tripping
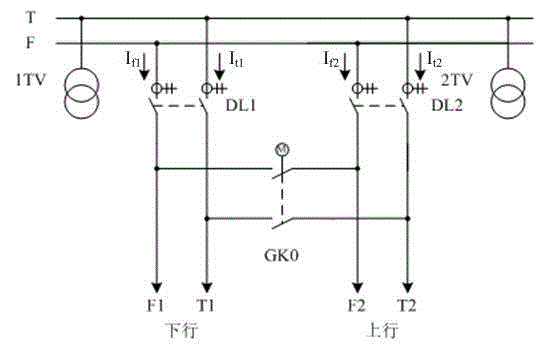
ActiveCN105790235AImprove reliabilityExtended service lifeEmergency protective circuit arrangementsInformation technology support systemTransformerTraction power supply
The invention relates to a novel high-way traction power supply system capable of selective feed line tripping. A high-way traction power supply system uses an AT power supply mode, real-time fault information interaction is realized among devices via a GOOSE communication function of IEC61850 rules, and feed line protectors and fault range finding devices of a transformer station, an AT station and a section station of the same traction power supply arm belong to the same GOOSE network. When an overhead line fault occurs, interaction of fault direction determining information is carried out among all the feed line protectors and fault range finding devices of the same power supply arm to realize selective tripping for feed line protection of the transformer station, and the reliability of traction power supply is improved. The system can realize selective tripping for feed line protection, the opening / closing frequency of a direction breaker without fault is reduced, the service life of the breaker is improved, the quality of traction power supply is improved, and the application prospects are wide.
Owner:南京国电南自轨道交通工程有限公司 +1
Unmanned transportation system of underground electric locomotive
ActiveCN105892397ARealize automatic liftingRealize automatic drivingProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersIntrinsic safetyCommunications system
The invention discloses an unmanned transportation system of an underground electric locomotive. The unmanned transportation system is characterized by comprising a dispatching system, a locomotive running unit, one or more loading station control units, one or more unloading station control units, a monitoring system, one or more trackside equipment control units, a communication system and a traction power supply monitoring system. The unmanned transportation system realizes the automatic operation of ore loading, transportation and unloading processes, ensures safe and efficient operation of the electric locomotive, simplifies the operation, improves the operation rate of the electric locomotive, and increases the ore yield. The unmanned transportation system integrates operations of underground electric locomotive drivers and ore drawing workers, ensures that the worker work position is transferred to the ground from the downhole, increases the safety, avoids the occurrence of occupational diseases, improves the intrinsic safety level, and improves the manual operation environment; and for a transport planning, the dispatching system automatically generates an order.
Owner:唐山威程科技有限公司
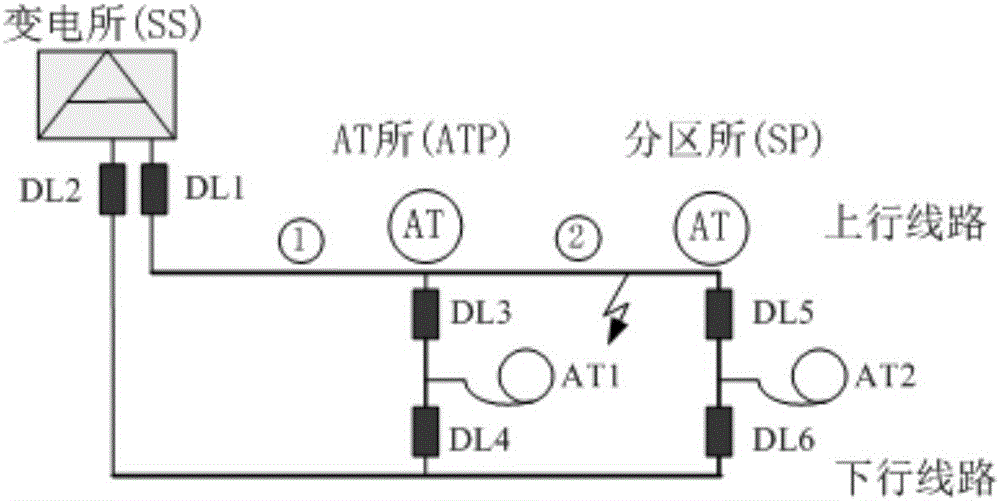
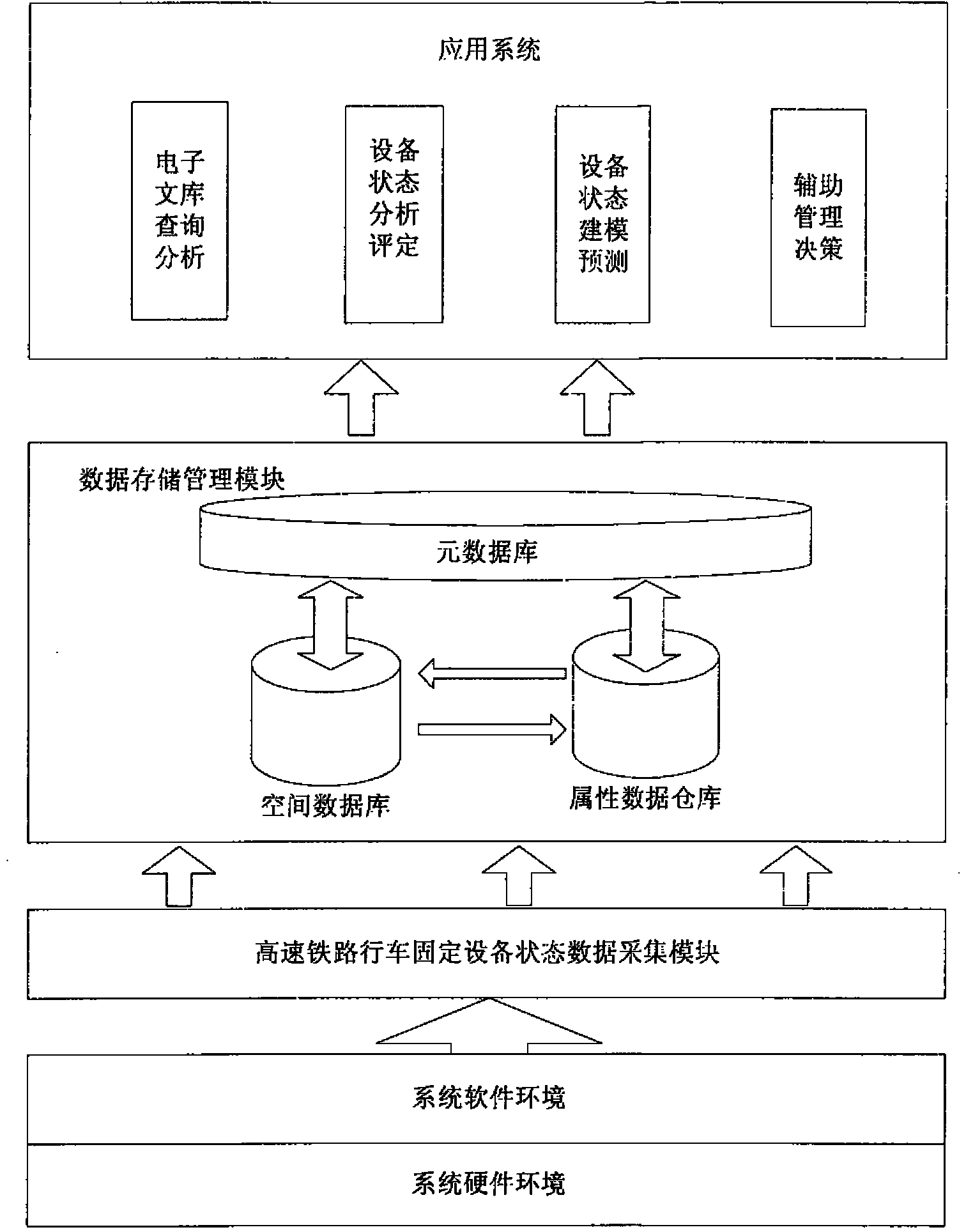
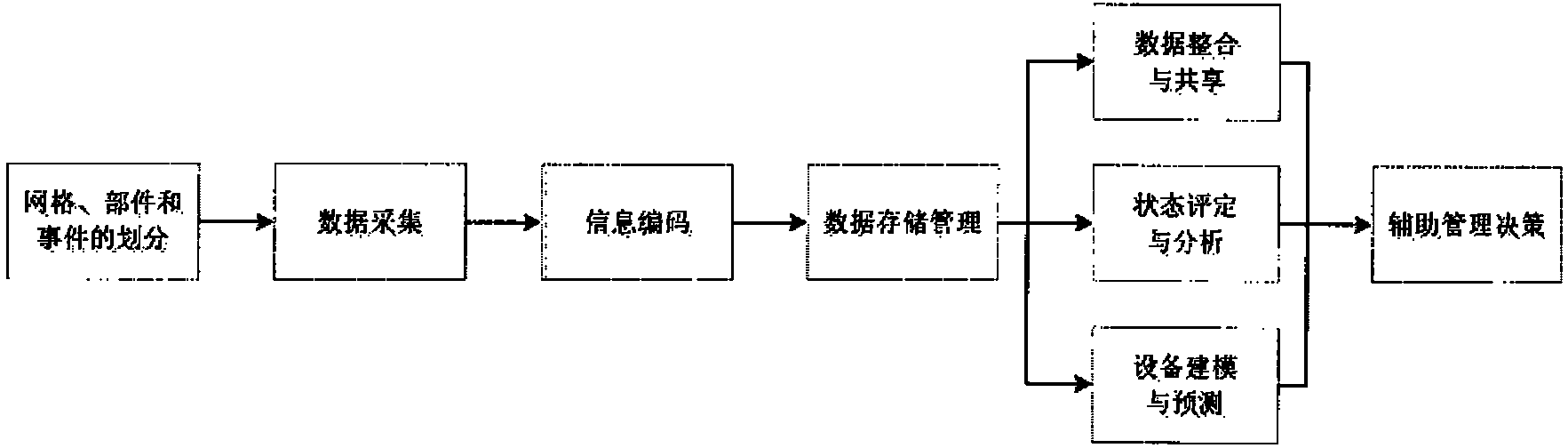
Grid management system and grid management method of high-speed railway train operation fixed equipment
ActiveCN103530715ARealize refined managementAchieve integrationResourcesGrid managementManagement efficiency
The invention relates to a grid management system and a grid management method of high-speed railway train operation fixed equipment. Primarily, a grid management system of train operation fixed equipment is constructed on the basis of the conventional professional management information systems such as public service, electric service and traction power supply of the high-speed railway train operation fixed equipment; the high-speed railway line is divided into a plurality of grid units according to a certain standard; the equipment state is more completely and more timely sensed by using a modern information technology and a coordination mechanism, more complete equipment state information interconnection and intercommunication are realized, and the equipment repair decision is more intelligently made to finally achieve the purposes of guaranteeing the operation safety, scientifically controlling the operation risk, integrating the maintenance resources, reducing the repair cost and improving the management efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Same-phase traction power supply system suitable for high-speed electrified railway
ActiveCN106532734ASimple structureRealize minimum capacity designReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationReactive power compensationElectric power transmissionBusbar
The invention provides a same-phase traction power supply system suitable for a high-speed electrified railway, and belongs to the technical field of traction power supply and electric power transmission and distribution. The same-phase traction power supply system includes traction transformers and a same-phase compensator which are mutually independent, and the traction transformers and a compensation transformer and a matching transformer in the same-phase compensator are of single-phase structures. The primary windings of the traction transformers and the primary winding of the compensator transformer form V, and a connection method of V is as follows: one end of the primary winding of the matching transformer is connected with one end of the secondary winding of the compensation transformer, and other end of the primary winding is connected to the positive electrode of a traction busbar; the other end of the secondary winding of the compensation transformer is connected to the ground or the negative electrode of the traction busbar, alternating current ports of one side of ''back-to-back'' converters are connected to the secondary winding of the compensation transformer, and the other side is connected to the secondary winding of the matching transformer; and the same-phase compensator adopting hybrid compensation configuration also includes a fixed capacitor branch circuit and a fixed reactor branch circuit. The same-phase traction power supply system suitable for the high-speed electrified railway can achieve an effect that the capacity of both active and passive compensation devices is the lowest configuration, and a relatively high capacity utilization rate of the transformers is maintained at the same time.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Electrified railway energy storage type traction power supply system and control method thereof
ActiveCN110829435AIncrease profitSave on electricity billsPropulsion using ac induction motorsElectrodynamic brake systemsPower qualityCapacitance
The invention discloses an electrified railway energy storage type traction power supply system and a control method thereof. The system comprises a power flow controller, an energy storage system anda single-phase main traction transformer. The power flow controller comprises a high-voltage matching transformer, a grid side AC / DC converter, a traction side AC / DC converter, an intermediate DC side capacitor and a traction matching transformer. The energy storage system comprises a bidirectional DC / DC converter and an energy storage element, and the energy storage element is connected in parallel to the intermediate DC side capacitor through the bidirectional DC / DC converter. The control method comprises the following steps: collecting voltage and current data of a load at the outlet of asubstation, judging the operation condition of the system, and calculating the compensation power of the ports of the power flow controller and the energy storage device under each condition; adding the compensation power into double-loop control of a power outer loop and a current inner loop to obtain a modulation signal; and generating a switching signal of a control device through PWM modulation. Recovery and reutilization of the regenerative braking energy of trains are achieved, the utilization rate of the regenerative braking energy is increased, and negative-sequence electric energy quality treatment and compensation device capacity optimization are achieved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Electrified railway in-phase power supply device and multi-target coordinated instantaneous current control method
InactiveCN102166969AExtend power supply distanceImprove power qualityConversion with intermediate conversion to dcPower supply linesPower qualityElectric network
The invention relates to an electrified railway in-phase power supply device and a multi-target coordinated instantaneous current control method adopted by the device. After the in-phase power supply device is used, the electrified railway whole-line in-phase power supply can be realized, the output power of two power supply arms of a traction transformer can be balanced, and the negative sequence problem can be thoroughly solved; the load reactive power and the harmonic current can be compensated, and the electric energy quality of a traction power supply system can be comprehensively improved; the voltage of a traction electric network can be stabilized, the transient state stability of the voltage can be improved, the power supply distance of the power supply arms can be increased, and the amount of power substations can be reduced; the electrified railway in-phase power supply device and the multi-target coordinated instantaneous current control method are multiple in targets, the multi-target can be simultaneously controlled, the control harmony at two sides can be guaranteed, the dynamic response capability is stronger; a rectification side inverter takes the active power transfer and the stable direct voltage as a control target, and participates the reactive power control; and an inversion side inverter performs active power, reactive power and harmonic wave control, and participates the stable control of the direct voltage.
Owner:XUJI GRP +2
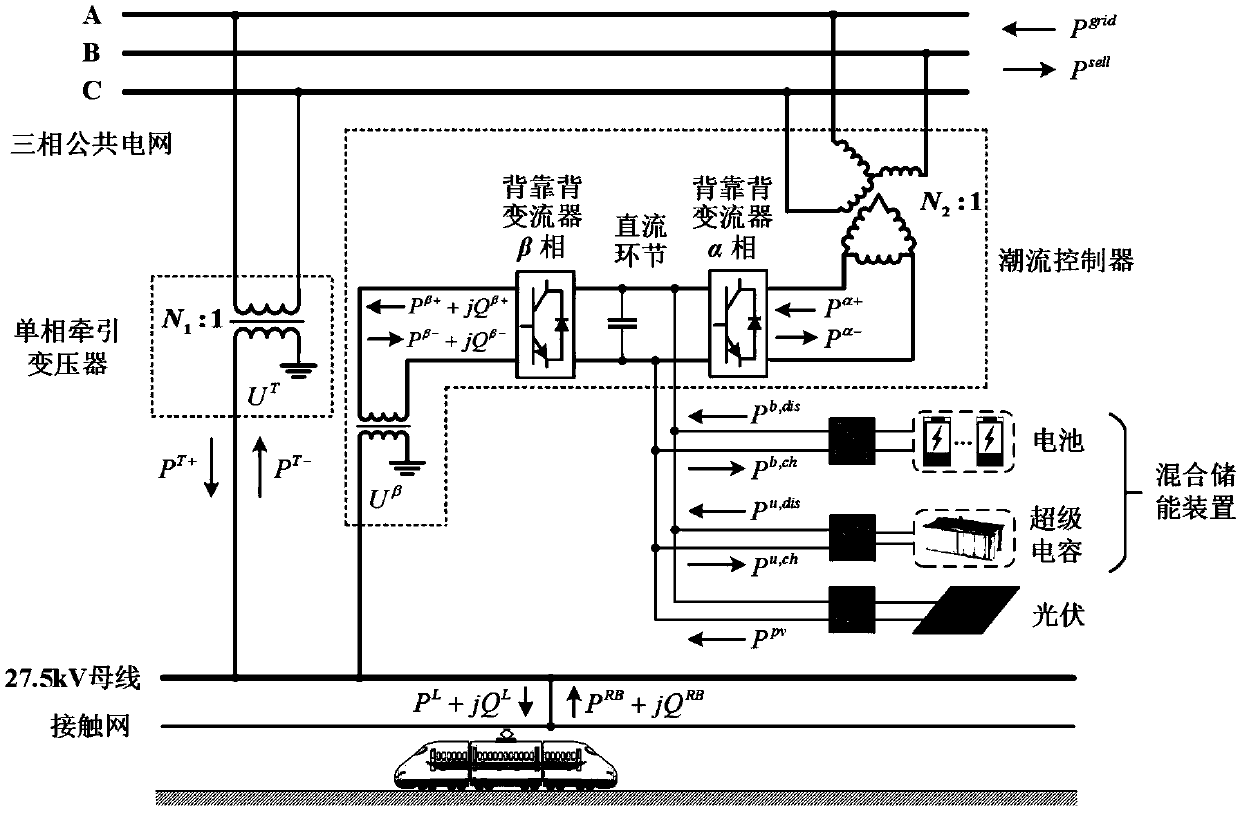
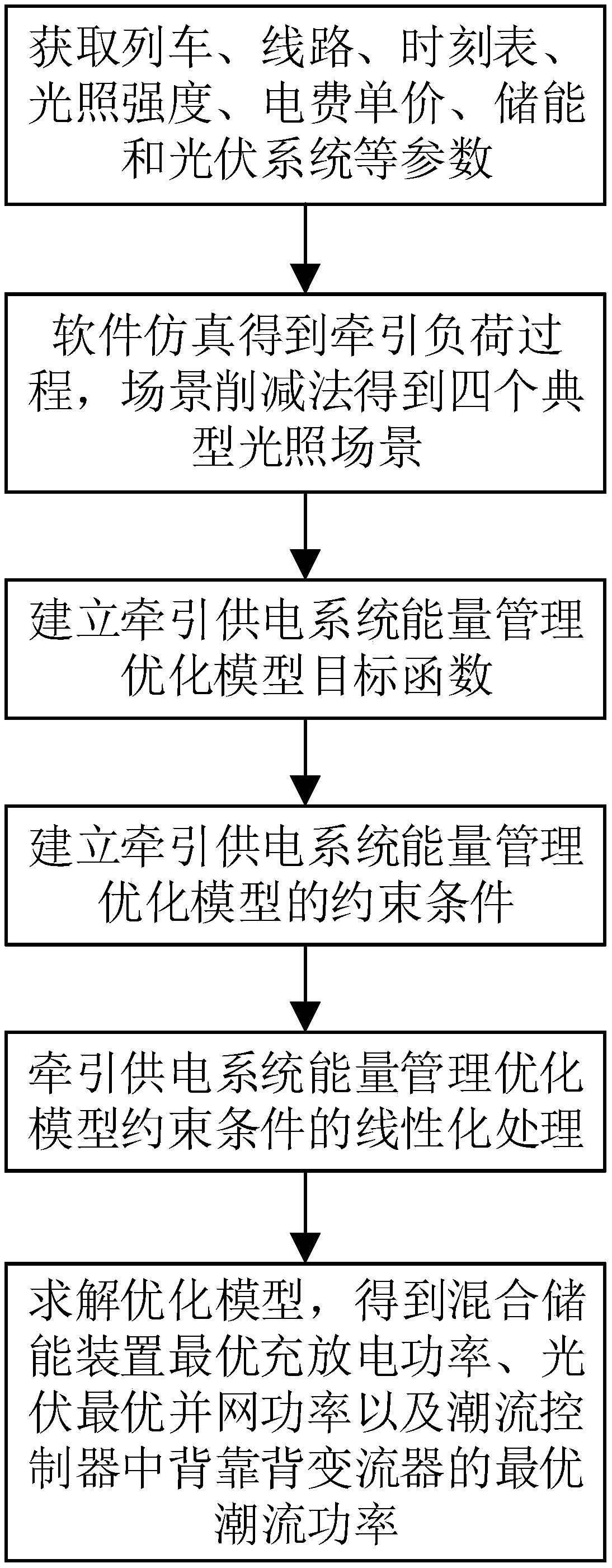
Traction power supply system energy management optimization method integrating hybrid energy storage and photovoltaic devices
ActiveCN109659980AReduce electricity costsThe energy management optimization method is close to realitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsEnergy storageLoad following power plantTraction substation
The invention discloses a traction power supply system energy management optimization method integrating hybrid energy storage and photovoltaic devices. The traction power supply system energy management optimization method comprises the steps of: step 1, acquiring traction substation load process data and a typical light intensity scene; step 2, establishing an objective function of an optimization model; step 3, establishing constraint conditions of the optimization model, and linearizing the constraint conditions of optimization model; step 4, establishing a hybrid integer linear programming model according to the objective function obtained in the step 2 and the constraint conditions obtained in the step 3; step 5, and solving the hybrid integer linear programming model obtained in thestep 4, so as to obtain the optimal charge and discharge power of the hybrid energy storage device, the optimal photovoltaic grid-connected power and the optimal power flow power of a back-to-back converter in a power flow controller, thereby completing the energy management optimization of a traction power supply system. The traction power supply system energy management optimization method improves the photovoltaic permeability and train regenerative braking energy utilization rate, reduces the electricity cost of electrified railways, and is closer to the reality.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
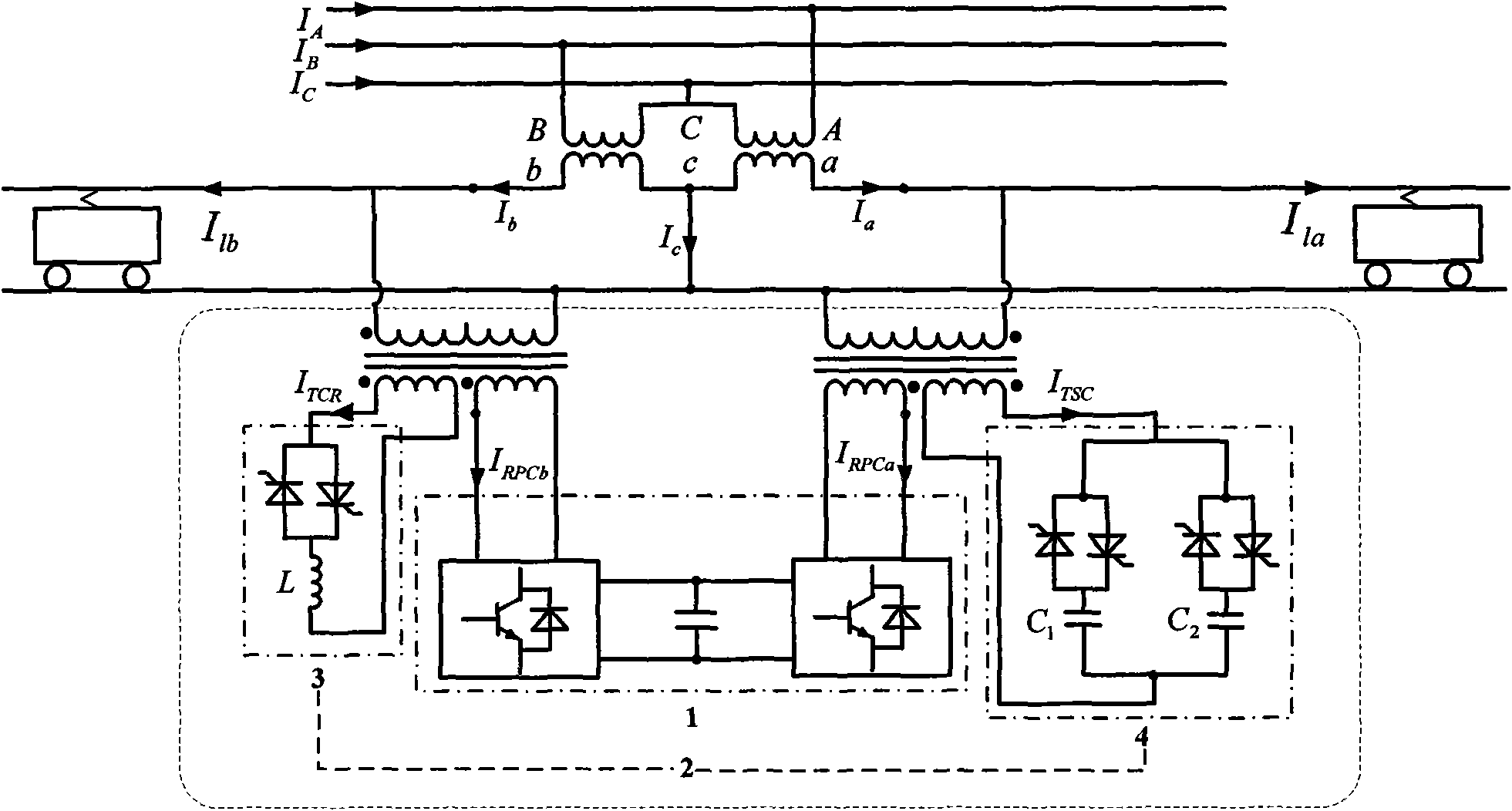
System for compensating combined negative sequence current of power regulator and static var compensator
InactiveCN101567565AImprove imbalanceNegative sequence component reducedPolyphase network asymmetry elimination/reductionPolyphase network asymmetry reductionEngineeringTraction transformer
The invention discloses a system for compensating the combined negative sequence current of a power regulator and a static var compensator. The system consists of a railway power regulator and the static var compensator. The railway power regulator is installed between two power supplying arms at a secondary side of a traction transformer by two single-phase three-winding reducing transformer. Thestatic var compensator consists of two groups of thyristor switched capacitors which are connected in parallel and a group of thyristor controlled reactors. The thyristor switched capacitors and thethyristor controlled reactors are respectively connected with two traction power supplying arms by single-phase three-winding reducing transformers, wherein the thyristor switched capacitors are installed below the single-phase three-winding reducing transformer which is connected with the power supplying arms with relatively advanced voltage phases, and the thyristor controlled reactors are installed below the single-phase three-winding reducing transformer of the power supplying arms with relatively hysteretic voltage phases. The system can maximally reduce the capacity of the railway powerregulator while also satisfying the requirement of a railway system on the unbalancedness degree of three phase current.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV +1
Railway traction power supply line swing arm type patrolling mobile robot
InactiveCN103904583AHigh degree of automationImprove efficiencyApparatus for overhead lines/cablesControl systemTraction power supply
The invention discloses a railway traction power supply line swing arm type patrolling mobile robot which is composed of a robot body, patrolling devices, mechanical arm guiding devices, a counterweight balancing device, a control system and a power supply. Each patrolling device is connected with the robot body through the corresponding mechanical arm guiding device. The same three sets of patrolling devices and mechanical arm guiding devices are arranged on the side, in the power supply line direction, of the robot body. The counterweight balancing device, the control system and the power supply are installed in the robot body. The railway traction power supply line swing arm type patrolling mobile robot assists manual routing inspection, and therefore the automation degree of routing inspection is increased, efficiency is improved, and meanwhile cost is saved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Double-current system traction power supply system based on modularized multi-level current converter
ActiveCN103895534ASolve power problemsSolve a series of problems such as harmonicsPower supply linesPower conversion systemsTraction systemTransformer
A double-current system traction power supply system based on a modularized multi-level current converter comprises a step-down transformer, a high-voltage MMC rectification circuit, an inverter circuit and a step-down chopper circuit, wherein the input end of the step-down transformer is connected with a three-phase alternating current, the output end of the step-down transformer is connected with the high-voltage MMC rectification circuit, and the output end of the high-voltage MMC rectification circuit is connected with a direct current transmission cable. The input end of the step-down chopper circuit is connected with the direct current transmission cable through a second switch block, and the output end of the step-down chopper circuit is connected with a traction system through a fourth switch block. The input end of the inverter circuit is connected with the direct current transmission cable through a third switch block, and the output end of the inverter circuit is connected with the traction system through a fifth switch block. The fourth switch block is in an interlock relation with the third switch block and the fifth switch block. The double-current system traction power supply system based on the modularized multi-level current converter has the advantages of being high in function integration degree, wide in application range, good in safety, good in power supply reliability and the like.
Owner:ZHUZHOU NAT ENG RES CENT OF CONVERTERS
Electrified railroad homo-phase traction power supply system
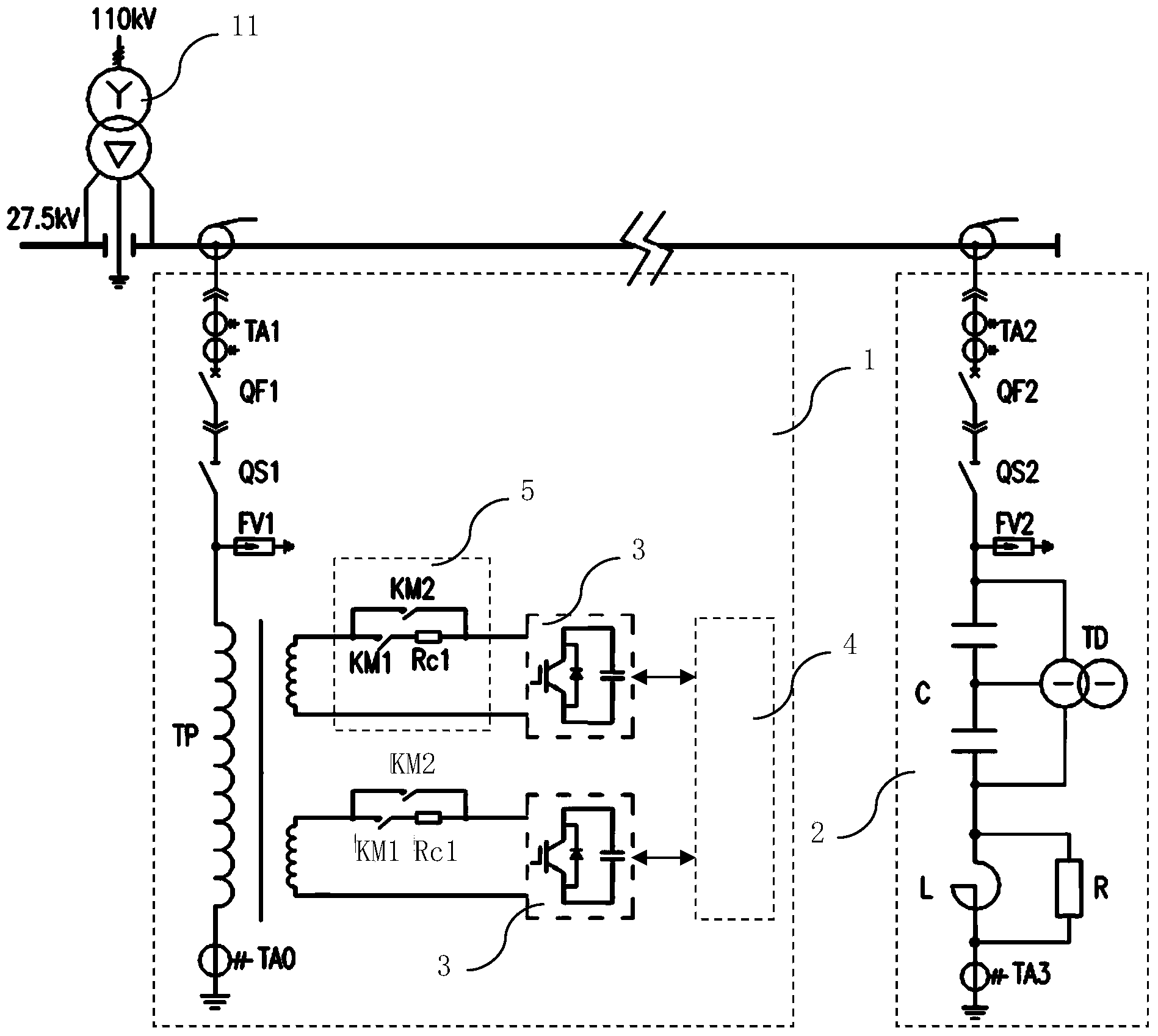
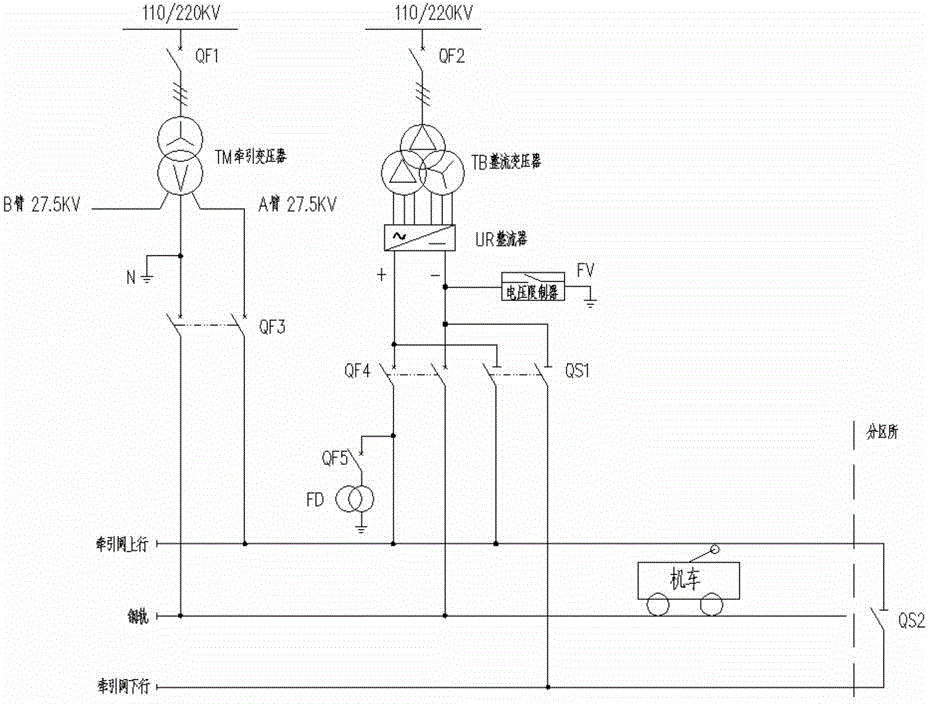
ActiveCN101746283AMeet the voltage withstand capabilityGuaranteed safe operationPower supply linesConversion without intermediate conversion to dcCapacitanceBeta phase
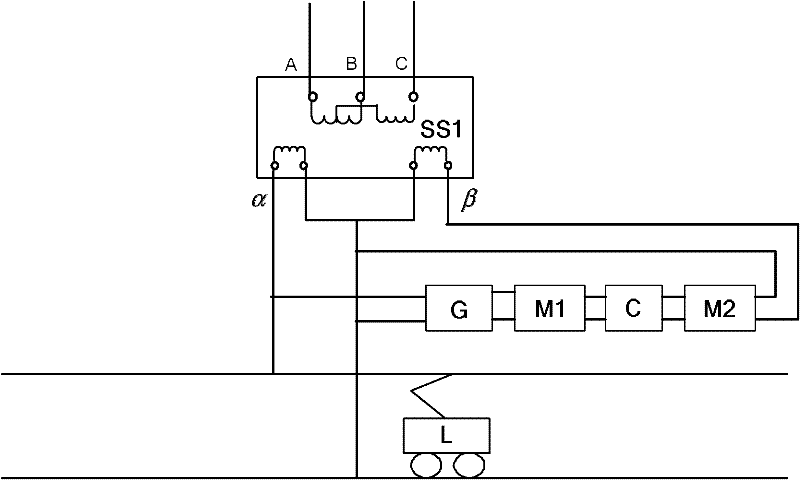
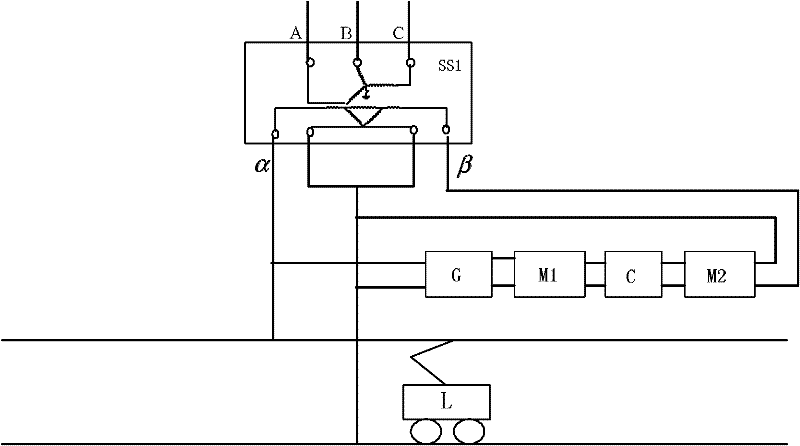
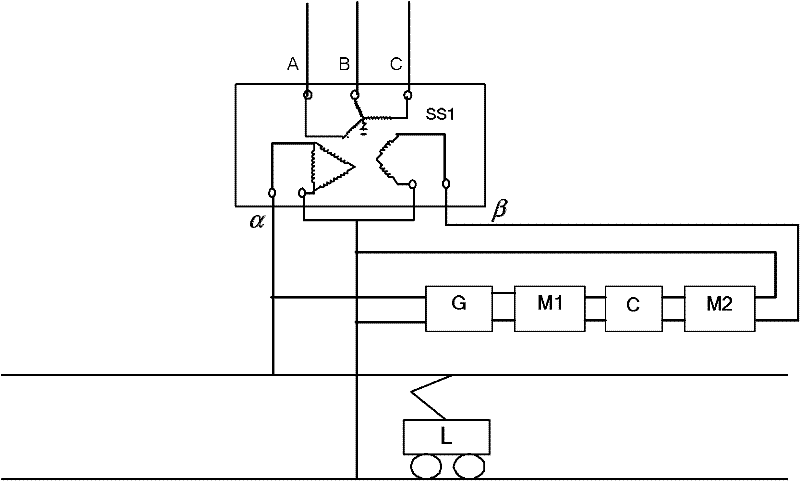
The invention discloses an electrified railroad homo-phase traction power supply system. A traction transformer (SS1) of a traction substation is a three-phase-two-phase transformer; three phases (A, B and C) of the primary side of the traction transformer (SS1) are connected with a public power grid; a voltage reduction transformer (G), a first single-phase current transformer (M1), a direct-current capacitor (C) and a second single-phase current transformer (M2) are connected between an alpha output phase and a beta output phase of the secondary side in turn; the alpha phase supplies power to a locomotive (L), and the output voltage of the alpha phase is 27.5kV; and the output voltage of the beta phase is between 600 and 2,000V. The system can implement two-arm homo-phase power supply of the railroad traction substation without split phase, reduces the split phase link, is favorable for high-speed, stable and safe operation of the railroad, and has the advantages of simple structure, low cost and convenient implementation.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Computer interlock and traction power supplying simulation control system
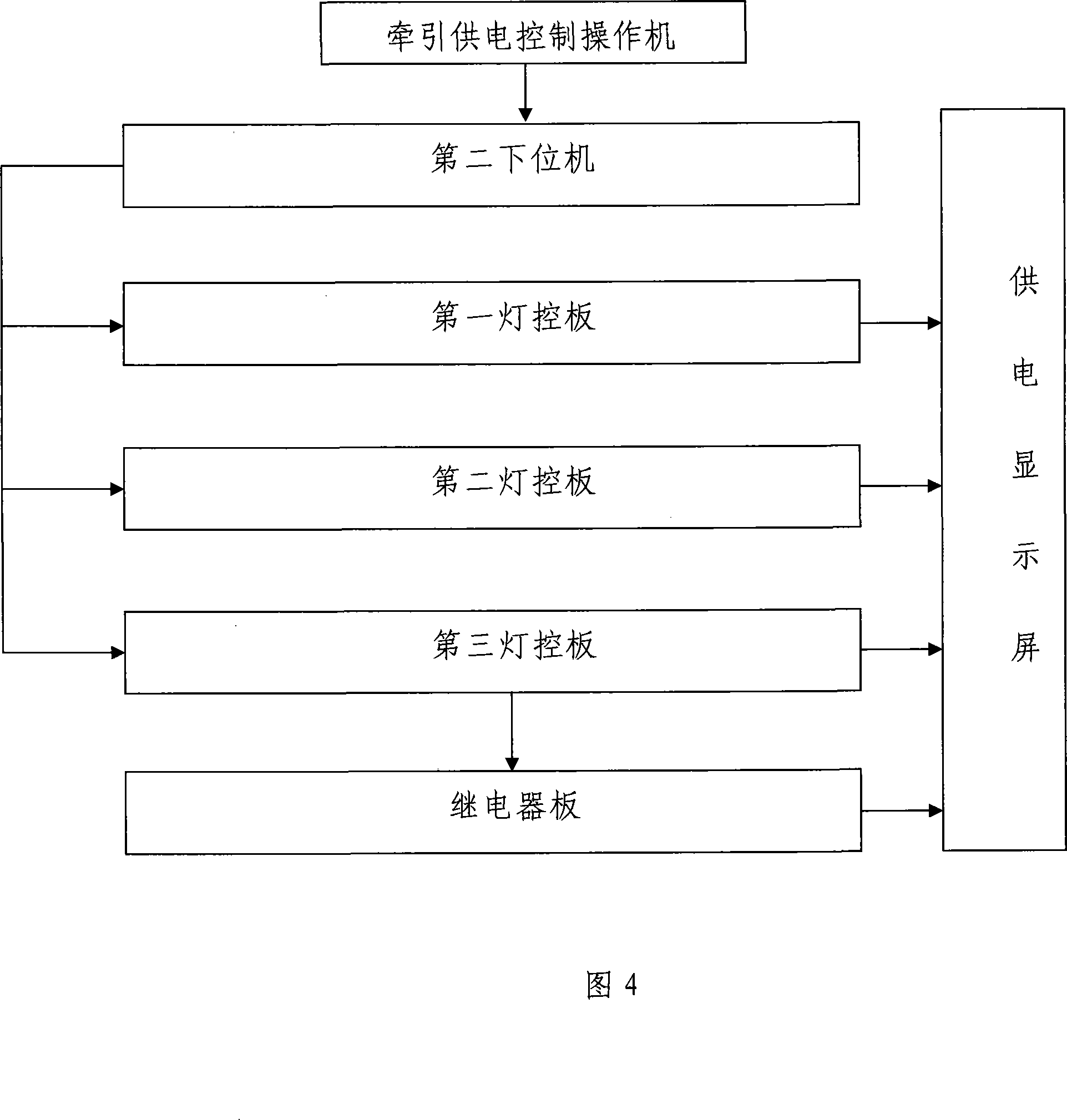
InactiveCN101118701AShow basic compositionShow how it worksTeaching apparatusEngineeringContact line
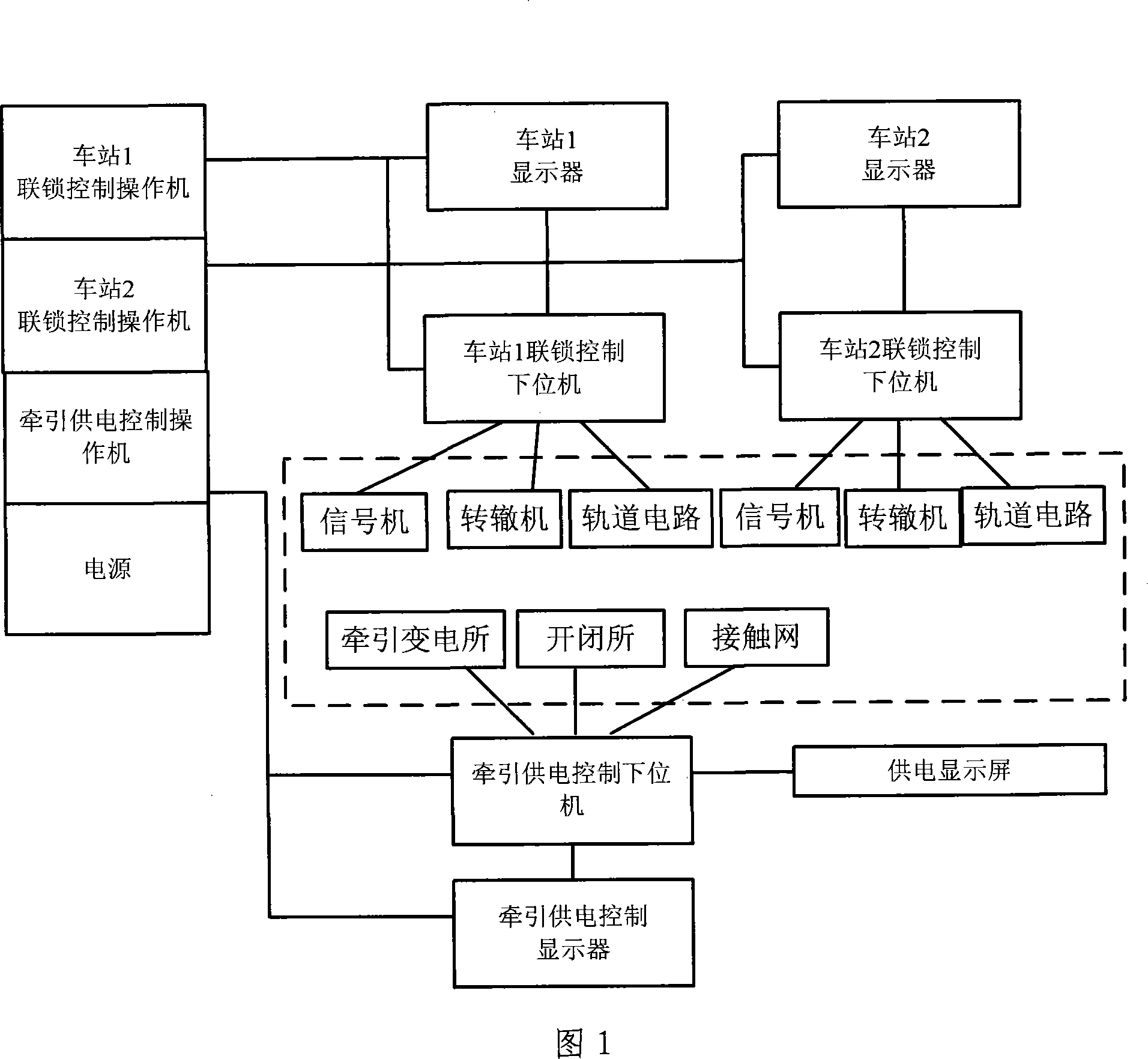
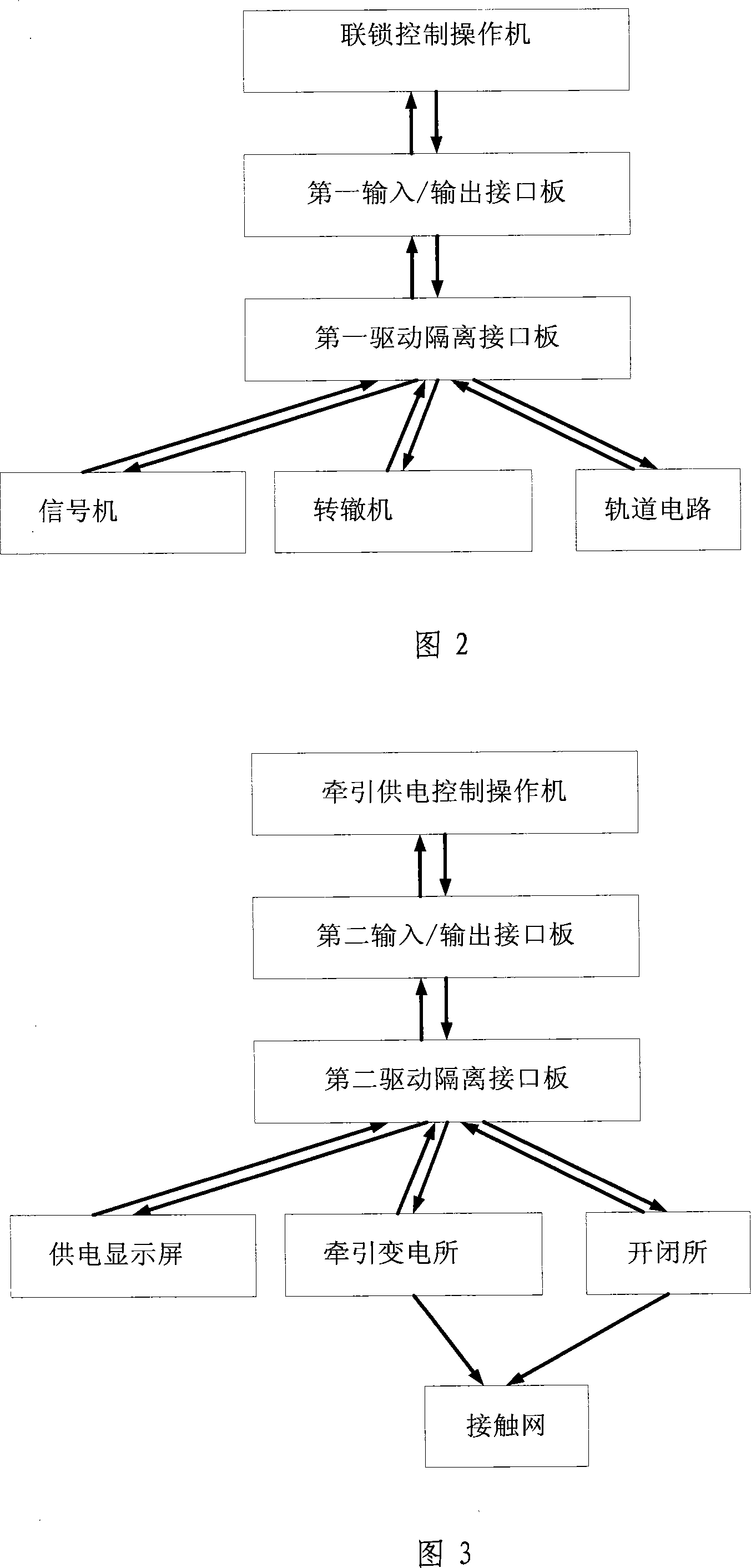
The present invention relates to a computer analog control system with interlocking and traction power supply, and has a station simulated sand table, a signal computer interlocking system and a traction power supply system. A track circuit, a signal controller and a switch machine are controlled by an interlocking control operating machine and a lower computer; the power supply of a traction substation, a switching station and a contact line equipment are controlled by a traction power supply control operating machine and the lower computer, and the information of power supply is displayed on a power supply display screen. The use of a relay circuit is completely canceled by the computer analog control system with interlocking and traction power supply, the logical operation of computer is entirely carried out, thus achieving the various requirements of railway signals such as the interlocking of station signal, the interval automatic block, the displaying of grade crossing signal and so on, the present invention has convenient operation, good safety and high reliability; the function of trunk line electrification power supply and the remote control are successfully simulated.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY FIRST GRP CO LTD
Device used in electrified railway for controlling and compensating electric energy quality
InactiveCN102118027AAchieving Harmonic SuppressionSuppress negative sequence componentsReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationReactive power compensationPower factorSmall footprint
The invention discloses a device used in an electrified railway for controlling and compensating electric energy quality, and belongs to the field of power supply of electrified railways. The device comprises a passive filter formed by a second-order high-pass filter, a group of voltage source type converters, and a phase reactor, wherein the passive filter is used for providing an electric locomotive on an electrified railway with reactive power and filtering harmonic current generated by the electric locomotive; the voltage source type converters can generate voltage with controllable amplitude, phase and frequency and are used for negative sequence compensation, flicker control and the like of a traction power supply system of an electric railway; and the voltage source type converters are connected in parallel onto a 25kV traction electric network through the phase reactor and the passive filter. The device provided by the invention can solve the electric quality problems such as three phases imbalance, harmonic wave, voltage fluctuation, flicker and the like while compensating power factors of the power supply system of the electric railway. Additionally, with the fully play of the advantages of the passive filter, such as convenience for configuration and low cost, and the advantages of the voltage source type converter, such as small occupation area and low consumption as much as possible, the whole set of device can achieve the best technical specification and the greatest economic performance.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER SCI RES INST OF JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER +1
Energy-saving high-voltage DC traction power supply converter device and control method without AC inductance
InactiveCN102299646AAchieving two-way flowImprove DC output voltageAc-dc conversion without reversalTransformerHigh-voltage direct current
The invention relates to an AC inductance-free energy-saving high-voltage DC traction power supply conversion device and a control method, which includes a multi-winding transformer and several conversion units. The multi-winding transformer consists of a primary winding and multiple secondary windings. Composed of windings, the number of circuits of the conversion unit is set corresponding to the number of secondary windings of the multi-winding transformer; the primary winding of the multi-winding transformer is connected to the AC power grid, and each secondary of the multi-winding transformer The side winding is connected to the input end of one converter unit, and the output terminals of each converter unit are serially connected in series to realize high-voltage direct current output. The invention saves electric energy, can ensure the stability of the DC power supply voltage, prolongs the power supply distance, and reduces the catenary loss. The invention can be widely used in urban rail transit traction power supply systems.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Electric railway section post automatic passing over of neutral section system and control method thereof
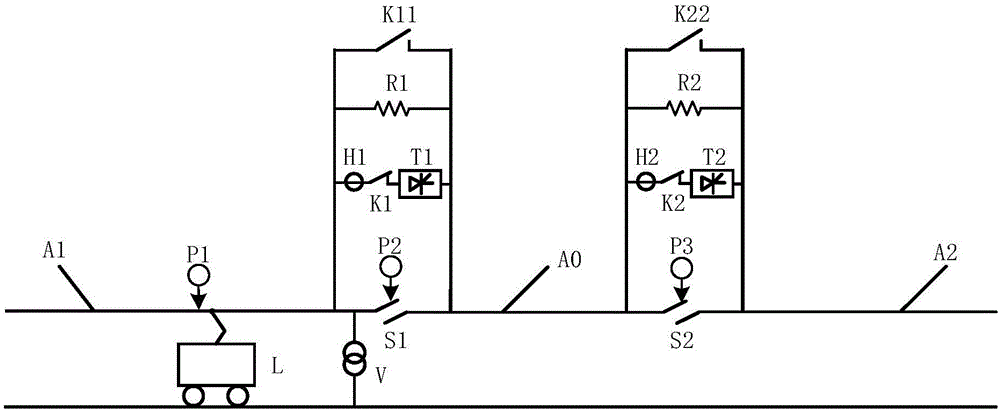
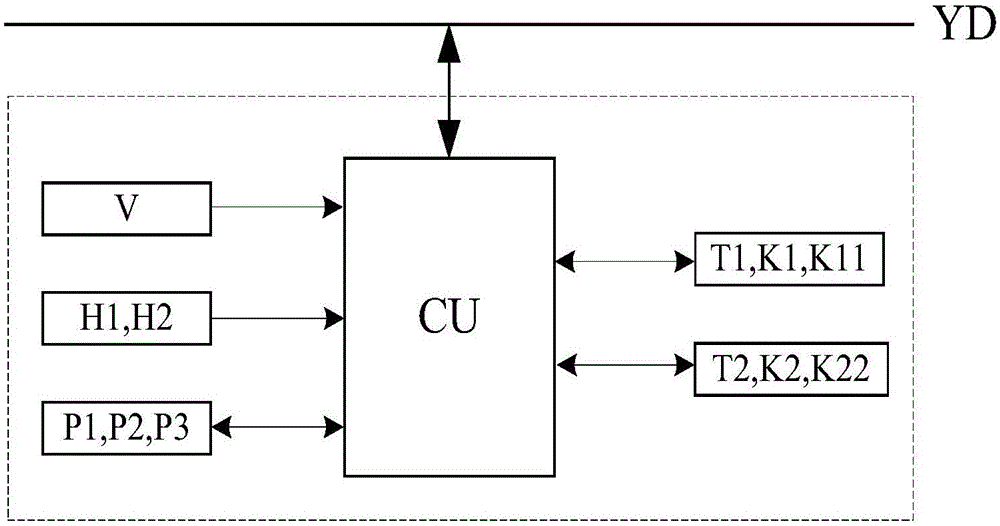
ActiveCN106183897AAchieve uninterrupted power supplySuppress overvoltagePower supply linesHigh resistanceHigh pressure
The invention discloses an electric railway section post automatic passing over of neutral section system and a control method thereof, and relates to the field of electric railway traction power supply. Pantograph recognizers are arranged on sectionalizers close to power supply arms. Load switches, thyristor switches and current transformers are sequentially connected in series and then connected to the two ends of the sectionalizers in parallel together with resistors and standby switches. The output ends of the pantograph recognizers, the current transformers and a voltage transformer, the trigger ends of the thyristor switches and the operation ends of the load switches and the standby switches are connected with a control unit. After the first thyristor switch is turned off due to current zero, the second thyristor switch is turned on to achieve current zero crossing point instantaneous switching from the first power supply arm to the second power supply arm, so that the power supply of a train is instantaneously switched from the first power supply arm to the second power supply arm, and uninterruptible power supply is achieved. The high-voltage high-resistance first resistor and second resistor work independently or together, and both can restrain balance current and the potential transient process. The system is mainly used for train continuous electricity passing over of neutral section.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com