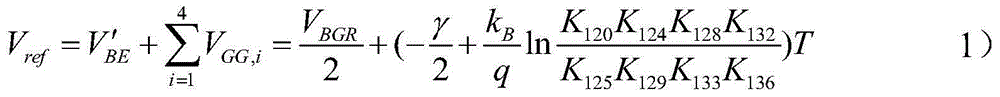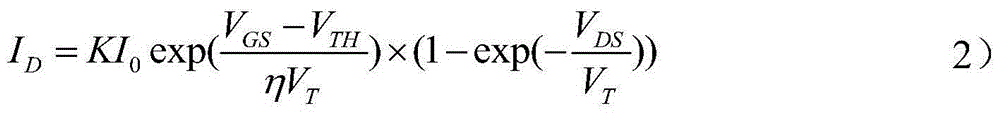Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2142 results about "Dividing circuits" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
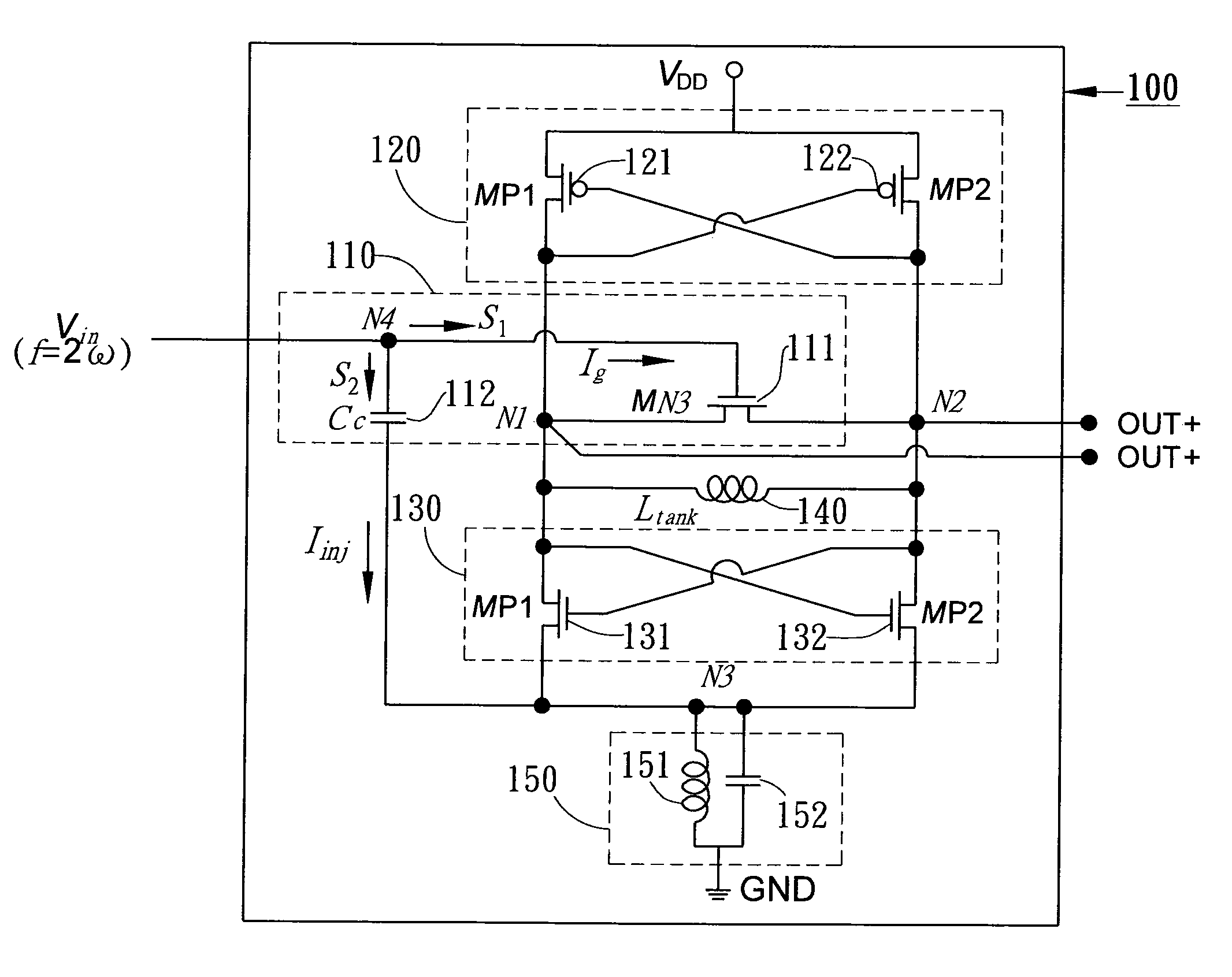
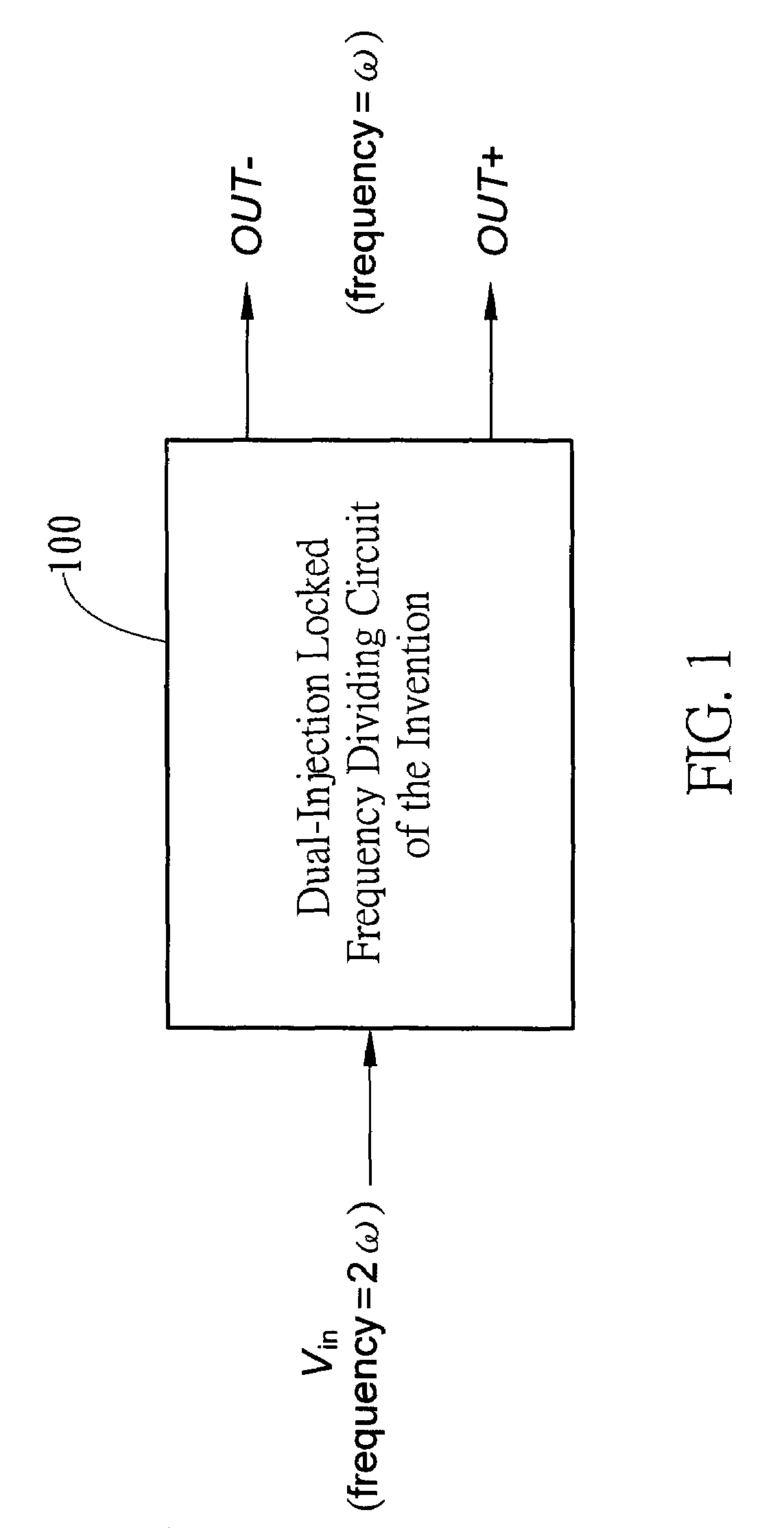
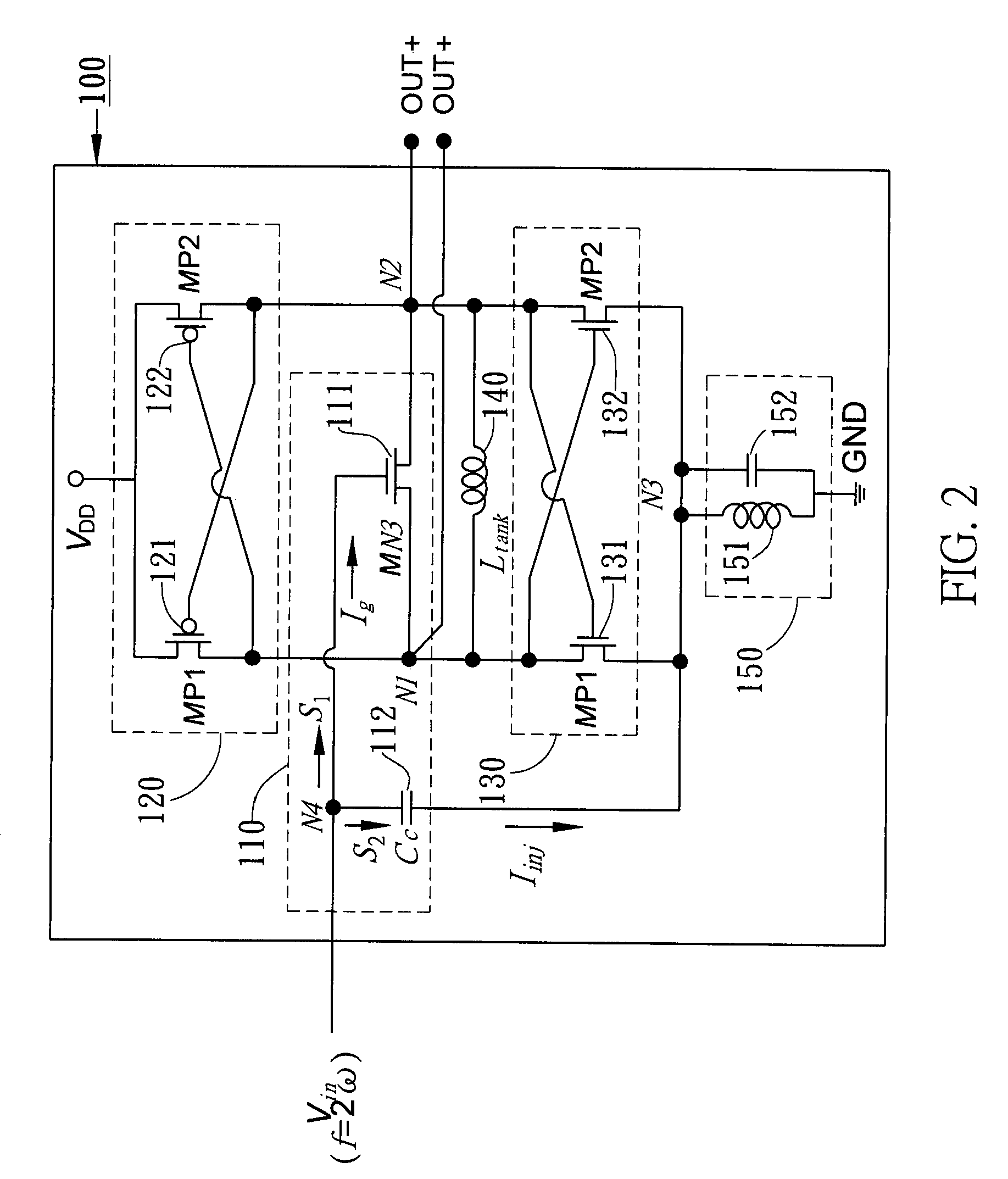
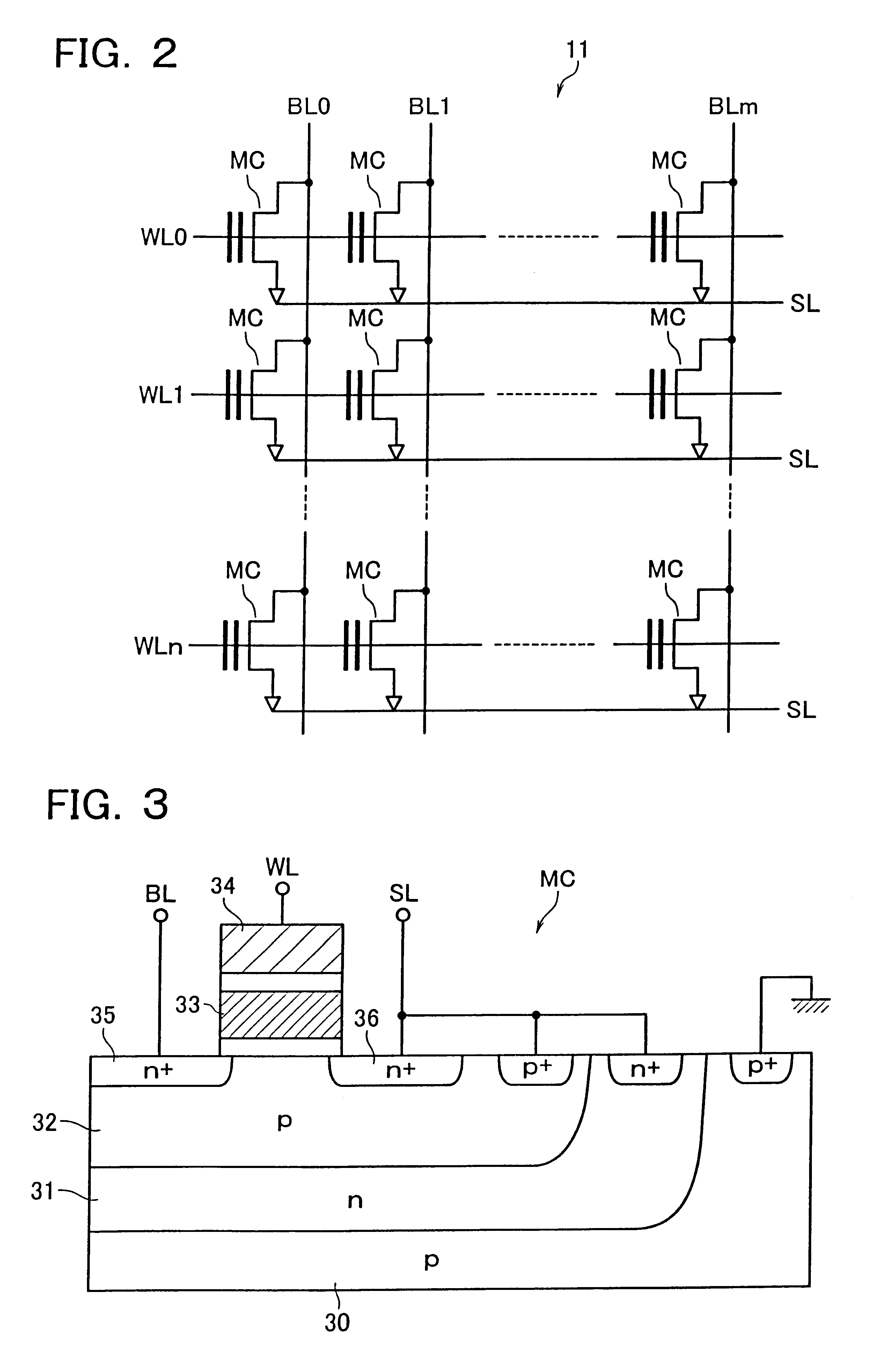
Dual-injection locked frequency dividing circuit
InactiveUS7656205B2Reduce power consumptionCounting chain pulse countersPulse counters with static storageDual injectionSignal processing circuits
A dual-injection locked frequency dividing circuit is proposed, which is designed for integration to a gigahertz signal processing circuit system for providing a frequency dividing function to gigahertz signals. The proposed circuit architecture is characterized by the provision of a dual-injection interface module on the input end for dividing the input signal into two parts for use as two injection signals, wherein the first injection signal is rendered in the form of a voltage signal and injected through a direct injection manner to the internal oscillation circuitry, while the second injection signal is rendered in the form of an electrical current and injected through a resonant circuit to the internal oscillation circuitry. This feature allow the proposed frequency dividing circuit to have broad frequency locking range and low power consumption.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Millimeter-wave time-division linear frequency modulation multiple-target detection colliding-proof radar for car
InactiveCN101354438AIncrease the working distanceImprove signal-to-noise ratioRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLow noiseAcousto-optics
The invention relates to the technical field of radio fix radars, in particular to a millimetre wave time-division linear frequency modulation multi-object detection automobile anti-collision radar. The radar of the invention adopts full phase parameter receiving / emitting benchmark signal and time-division and time-sequence asynchronous control to receive / emit a dual-purpose quasi-light integrated medium lens antenna array, and scans the objects possible to be collided on the warning road surfaces by DSP according to lane scanning wave beam; the road situation photographing combined with the vehicle speed and GPS data MCU to control time-division n-passage modulation frequency and waveform millimetre wave linear locking phase frequency modulation; emission is carried out sequentially by R / T2, a circulator, a wave beam switch and the antenna array; echo passes through the antenna array, the wave beam switch, the circulator, the R / T1, low noise high amplifier, subharmonic mixing, middle amplifier and a time-dividing circuit and multi-object signal corresponding matching filter wave and is processed and controlled by MCU at DSP; when a plurality of road barriers are encountered, the orientation, distance and relative speed are determined by DSP restriction virtual warning; three-dimensional images are displayed by a CRT; the closer the distance of the object is, the higher the resolution is; the object which is closest to the vehicle is recognised; sound and light alarm are carried out when the distance is less than safety distance; when the distance is near to the dangerous distance, the vehicle can intelligently avoid the barrier or reduce the speed or brake; the radar of the invention can make a choice according to the control reference road situation, the vehicle speed and the GPS data, thus obviously improving the driving safety of the vehicle.
Owner:阮树成
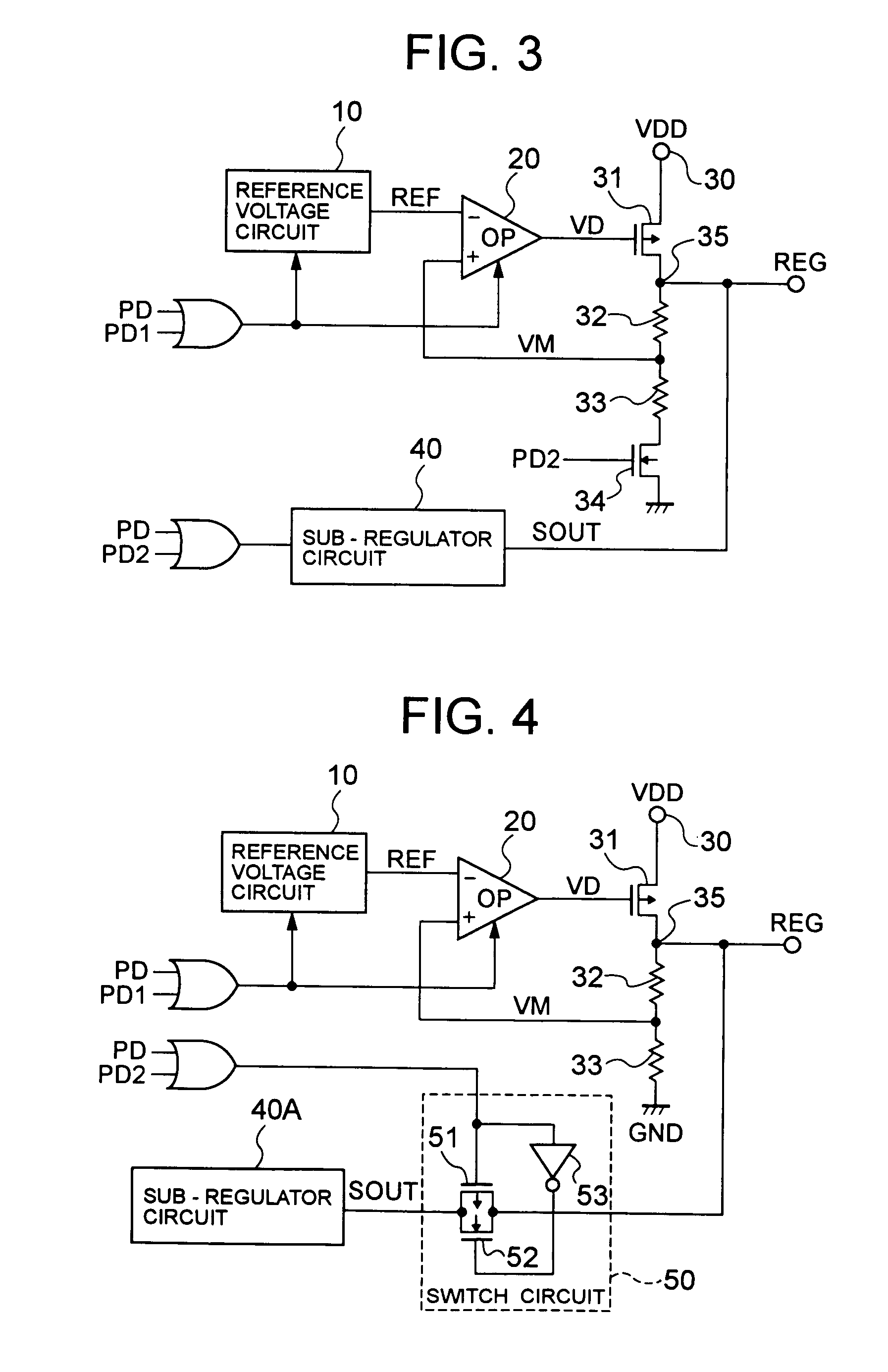
Voltage regulator
ActiveUS7193399B2Current consumptionTotal current dropPackagingShakersOperation modeVoltage reference
Consumption current is reduced for a voltage regulator in sleep mode. In normal operation mode, a sub-regulator circuit is ceased from operating according to a power-down signal, which allows an operation amplifier to compare between a reference voltage outputted from a reference voltage circuit and a monitor voltage generated by a voltage-dividing circuit. Based on a detection voltage as a comparison result, a PMOS is controlled to regulate an internal power voltage such that the monitor voltage becomes equal to the reference voltage. In sleep mode, the reference voltage circuit and operational amplifier is ceased from operating, to start up the sub-regulator circuit. A slight current, restricted by a resistance, flows through a PMOS of the sub-regulator circuit. The same magnitude of current is supplied from the PMOS constituting a current mirror to a PMOS, etc. of a threshold-voltage output circuit. The threshold voltage, at a node between the PMOS constituting the current mirror and the PMOS of the threshold-voltage output circuit, is power-amplified by a voltage follower and outputted through an output terminal.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
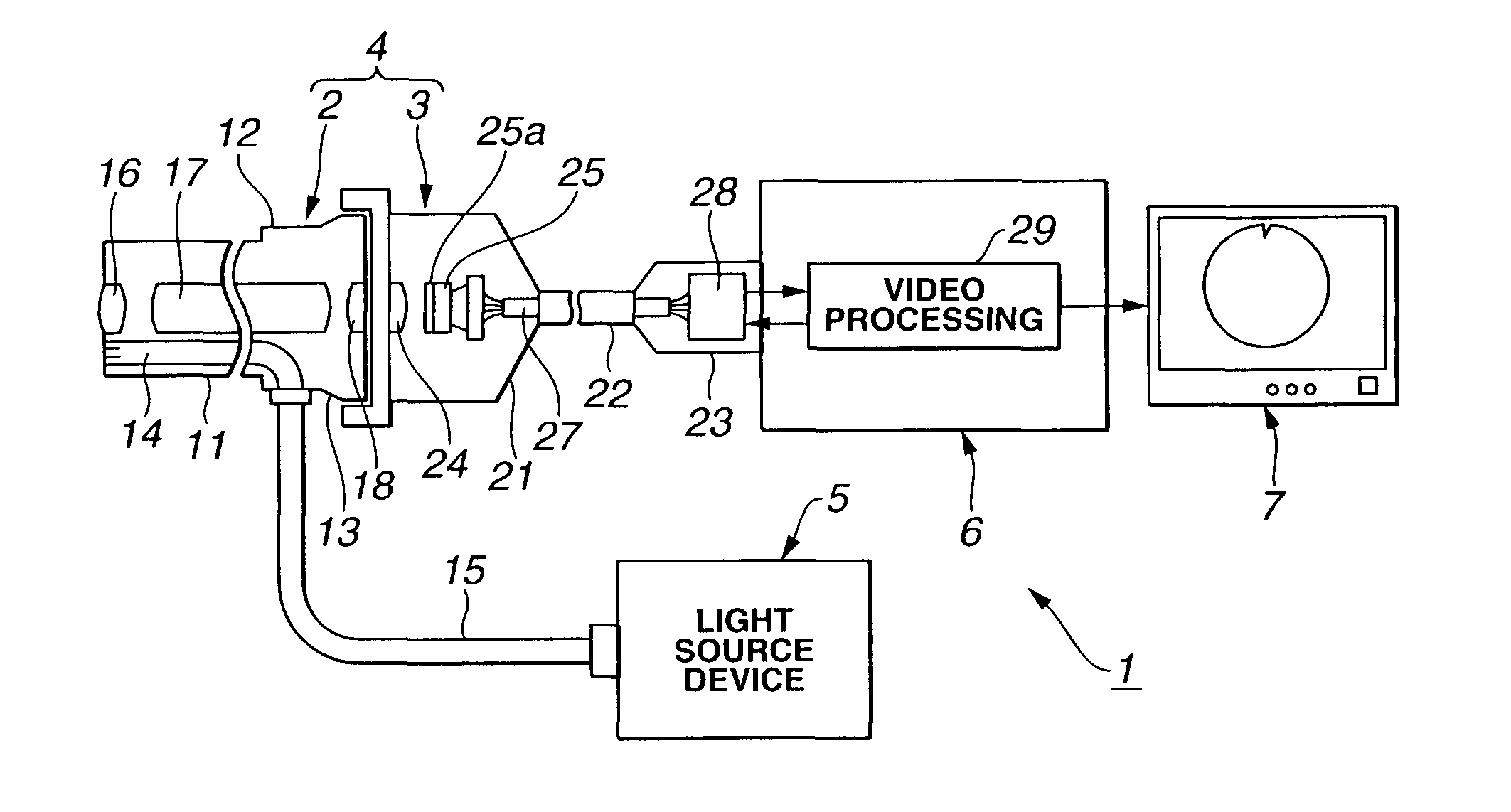
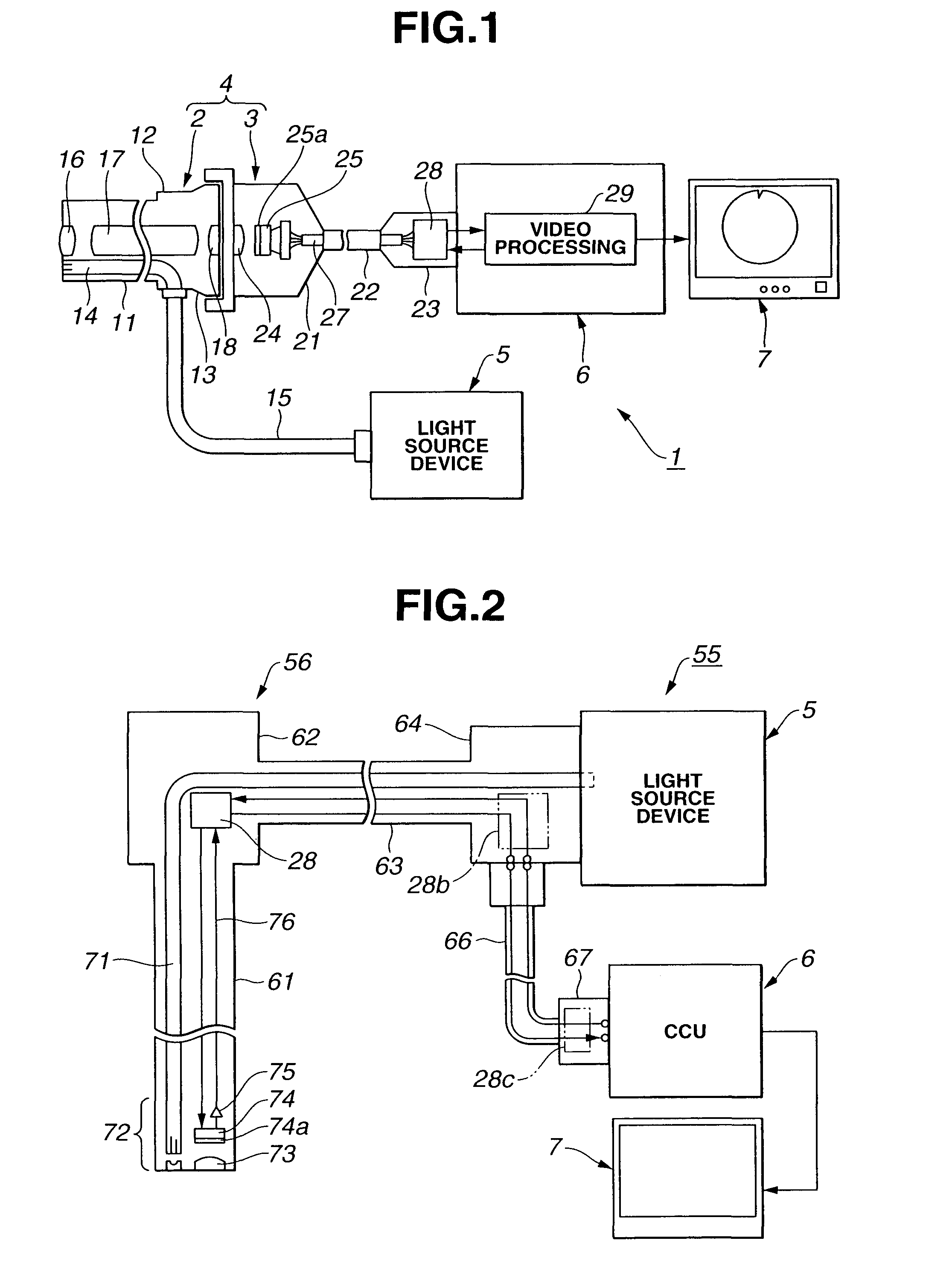
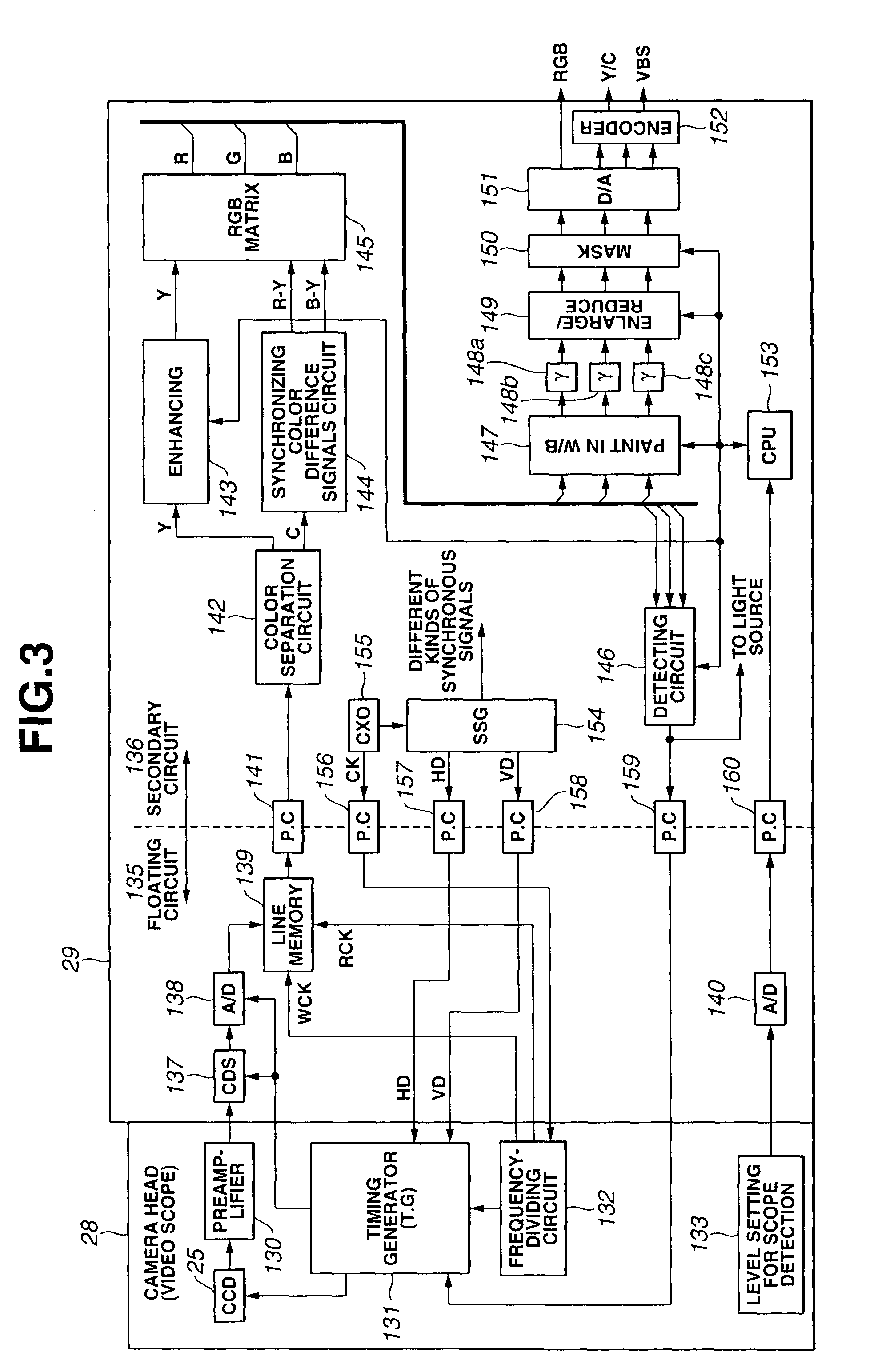
Image pickup system
To provide an image pickup system having CCDs 25 driven at different frequencies respectively which can drive each CCD 25 with a predetermined frequency if a detachable camera head (or electronic endoscope) 28 is used and also can process a signal processing clock of a video processing circuit 29 with one type of clock. A drive signal of the predetermined frequency supplied to the CCD is produced via a generating circuit CXO 155 in the video processing circuit 29, a frequency dividing circuit 132 and a timing generator (T.G.) 131. A CCD signal outputted from the CCD 25 is inputted to a line memory 139 in a floating circuit 135. As a writing clock (WCK) of the line memory 139, the one which is divided in the frequency dividing circuit 132 to a frequency in accordance with the CCD 25 to be used is used, and as a reading clock (RCK), the one of one type of frequency is used without regard to the CCD 25 to be used. Hence, it is possible to perform the signal processing of a secondary circuit 136 of the line memory 139 and following ones always with a common generating clock.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
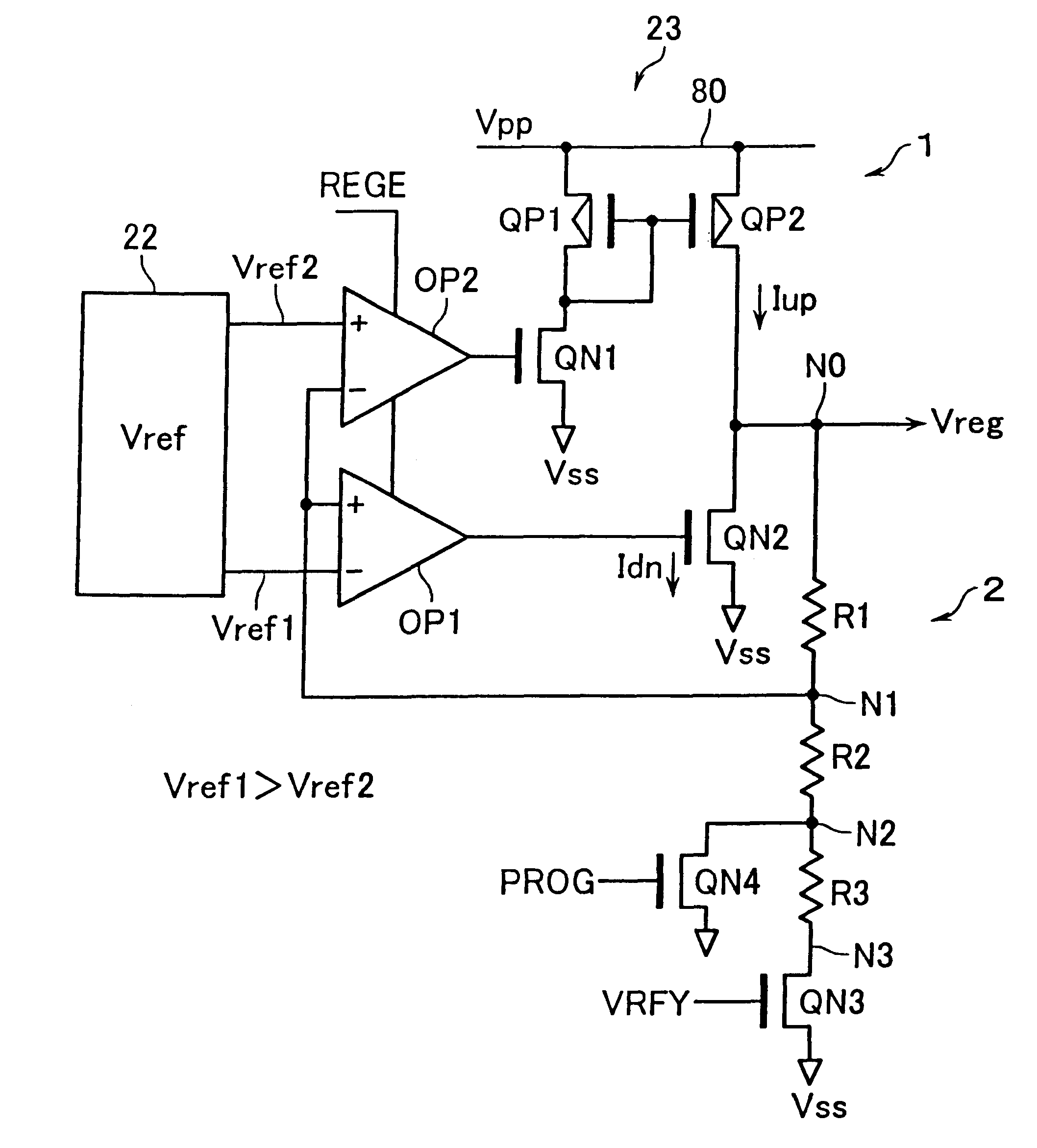
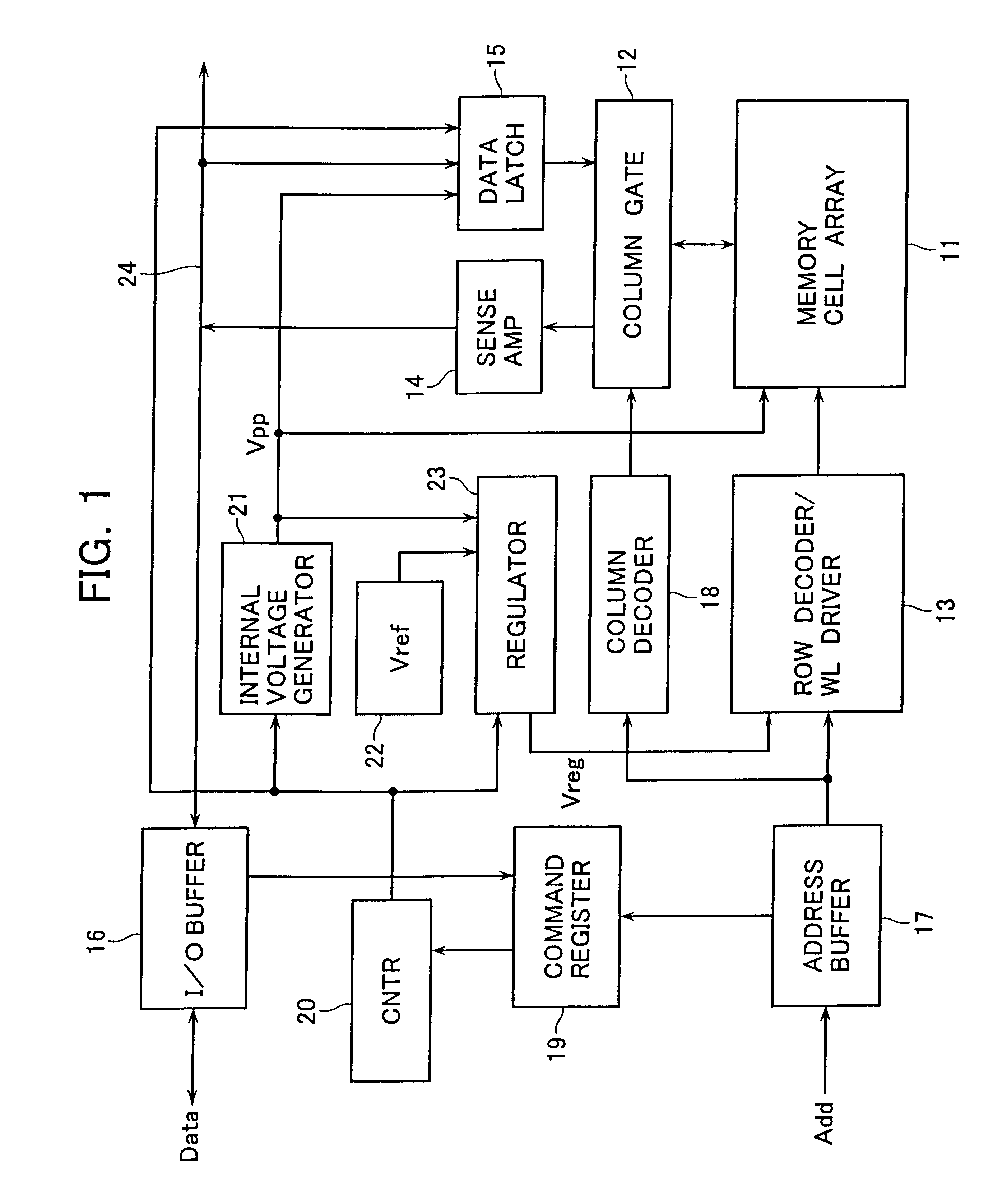
Semiconductor device with a voltage regulator
InactiveUS6600692B2Solid-state devicesRead-only memoriesVoltage regulator moduleAudio power amplifier
A semiconductor device with a voltage regulator is disclosed. The voltage regulator includes: a driver including pull-up and pull-down transistors serially connected between an output node of an internal voltage generation circuit and a reference potential terminal, for outputting a regulated voltage at its regulated voltage output node corresponding to the connection node of the pull-up and pull-down transistors; a voltage divider circuit for subdividing the regulated voltage output to the regulated voltage output node; a first operational amplifier for controlling current drivability of the pull-down transistor in accordance with a difference between a first reference voltage and a divided output of the voltage divider circuit; and a second operational amplifier for controlling current drivability of the pull-up transistor in accordance with a difference between a second reference voltage and the divided output of the voltage divider circuit in such a way as to vary in a reverse direction to the current drivability of the pull-down transistor.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
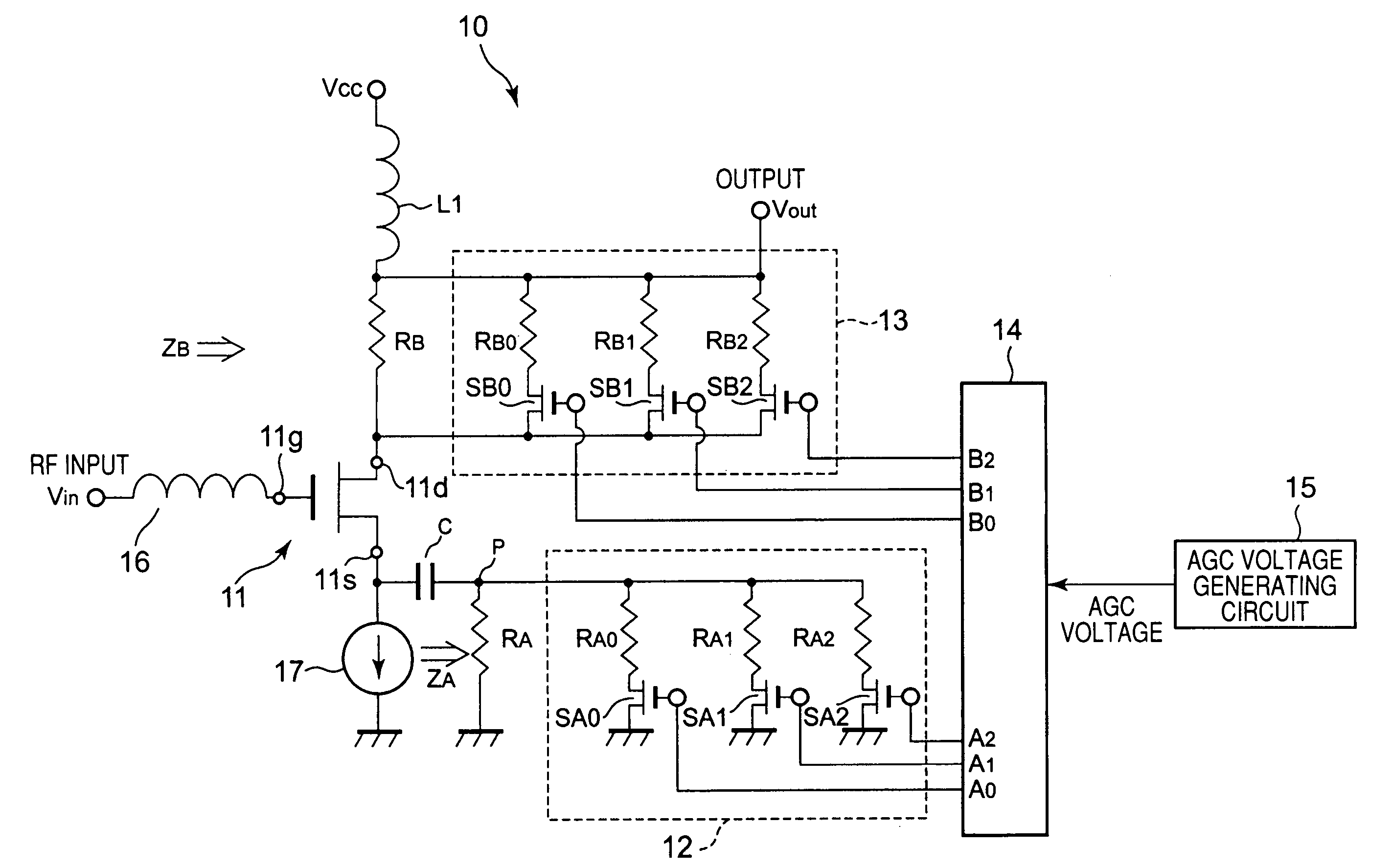
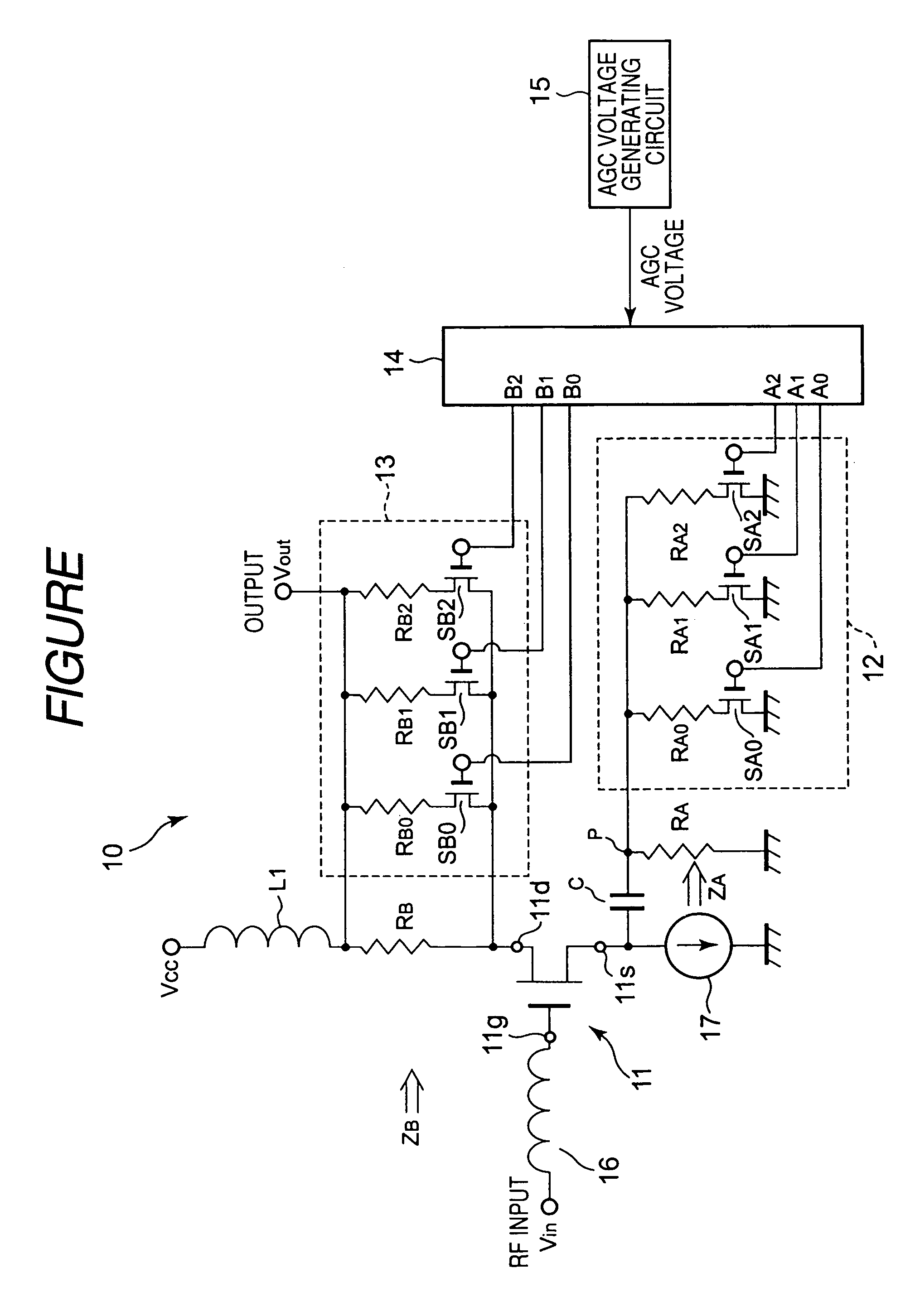
AGC circuit which is hard to be influenced by level of input signal
InactiveUS7564935B2Simple configurationAvoid noiseAngle modulation detailsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsNegative feedbackControl signal
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Wavelength dividing circuit
InactiveUS6188819B1Easy to integrateReduce device sizeNanoopticsCoupling light guidesDividing circuitsRefractive index
A wavelength dividing circuit which realizes improved device characteristics and performance, such as a small size, high speed and high transmission efficiency and which lends itself to improved integration degree. A wavelength dividing circuit in which materials of different refractive indices are arrayed periodically, without forming individual waveguides as in conventional AWG, in order to create strong wavelength dispersion characteristics not possible with an ordinary optical crystal to control wavelength deviation. A substrate 1 having atomic mediums 5 buried in a background medium 4 in a two-dimensional triangular array has its both sides sandwiched by a first clad 2 and a second clad 3. Optical signals fall on an incident surface inclined at a certain angle relative to the light incident direction and is radiated from a light outgoing surface 7. The interval between neighboring atomic mediums 5 is designed in meeting with the wavelength of the optical signals, while the thickness of the substrate 1 is designed so that the optical signals are sufficiently confined in the substrate 1 and so that the light proceeding direction is not significantly deviated from the substrate surface.
Owner:NEC CORP
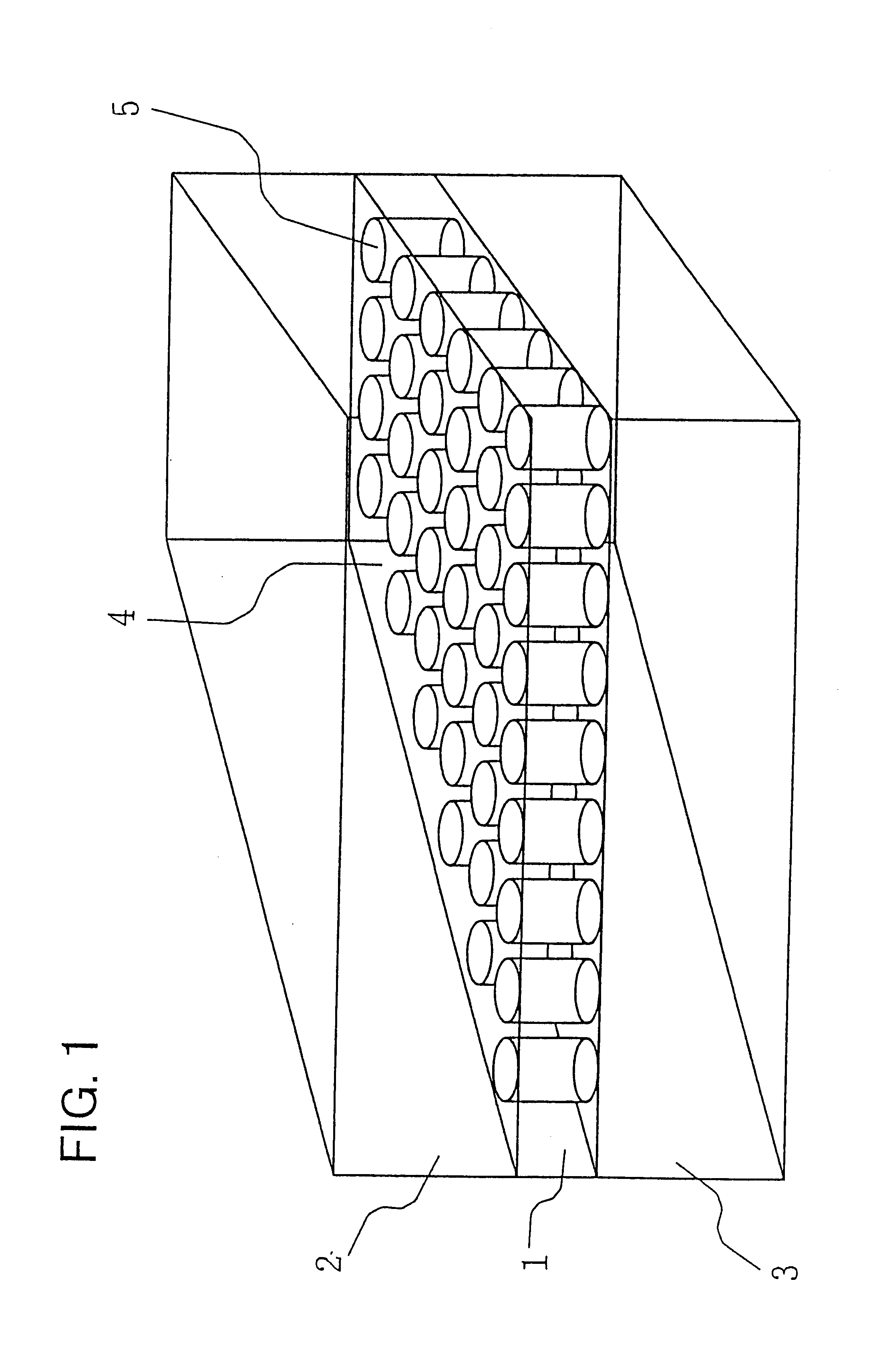
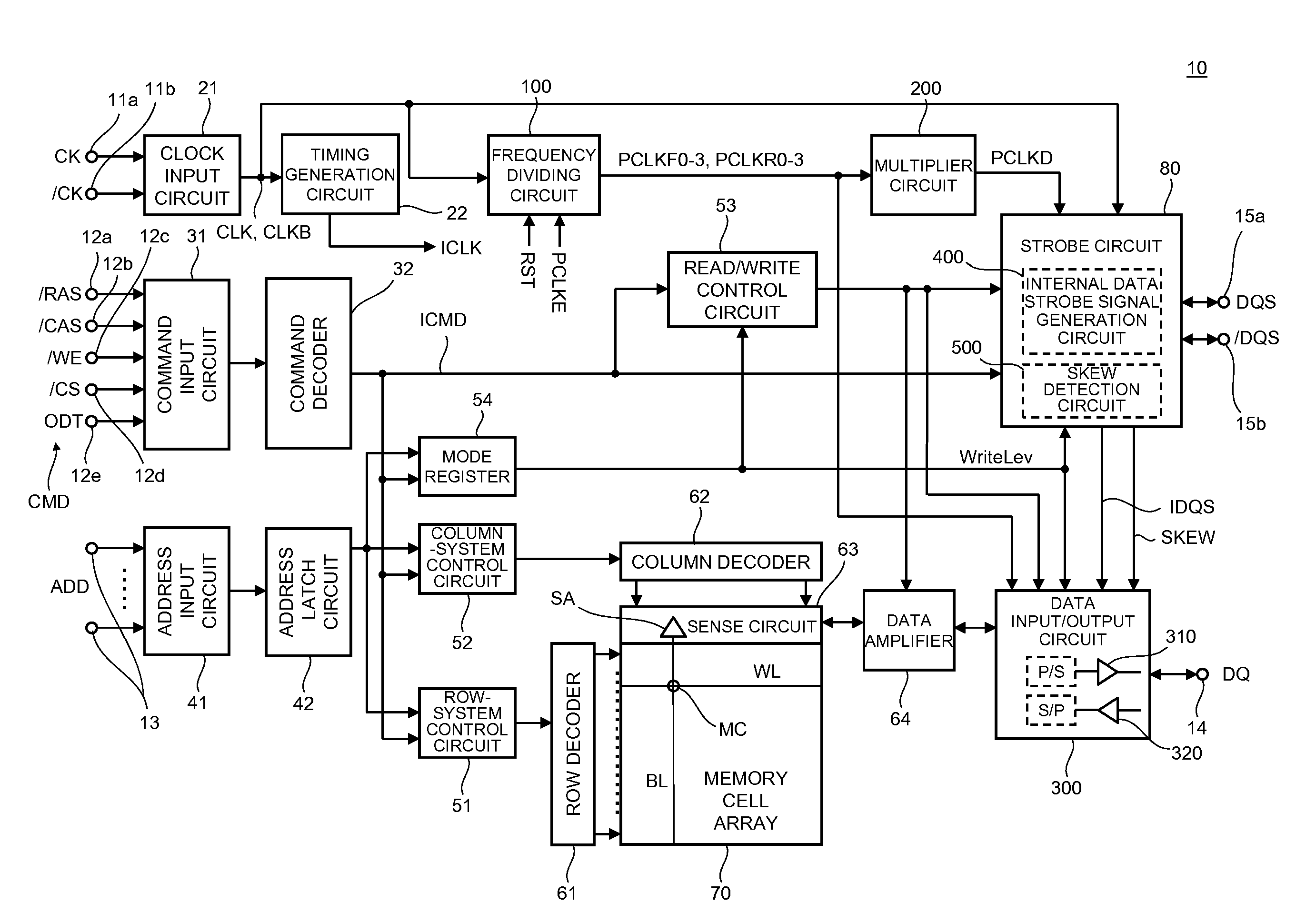
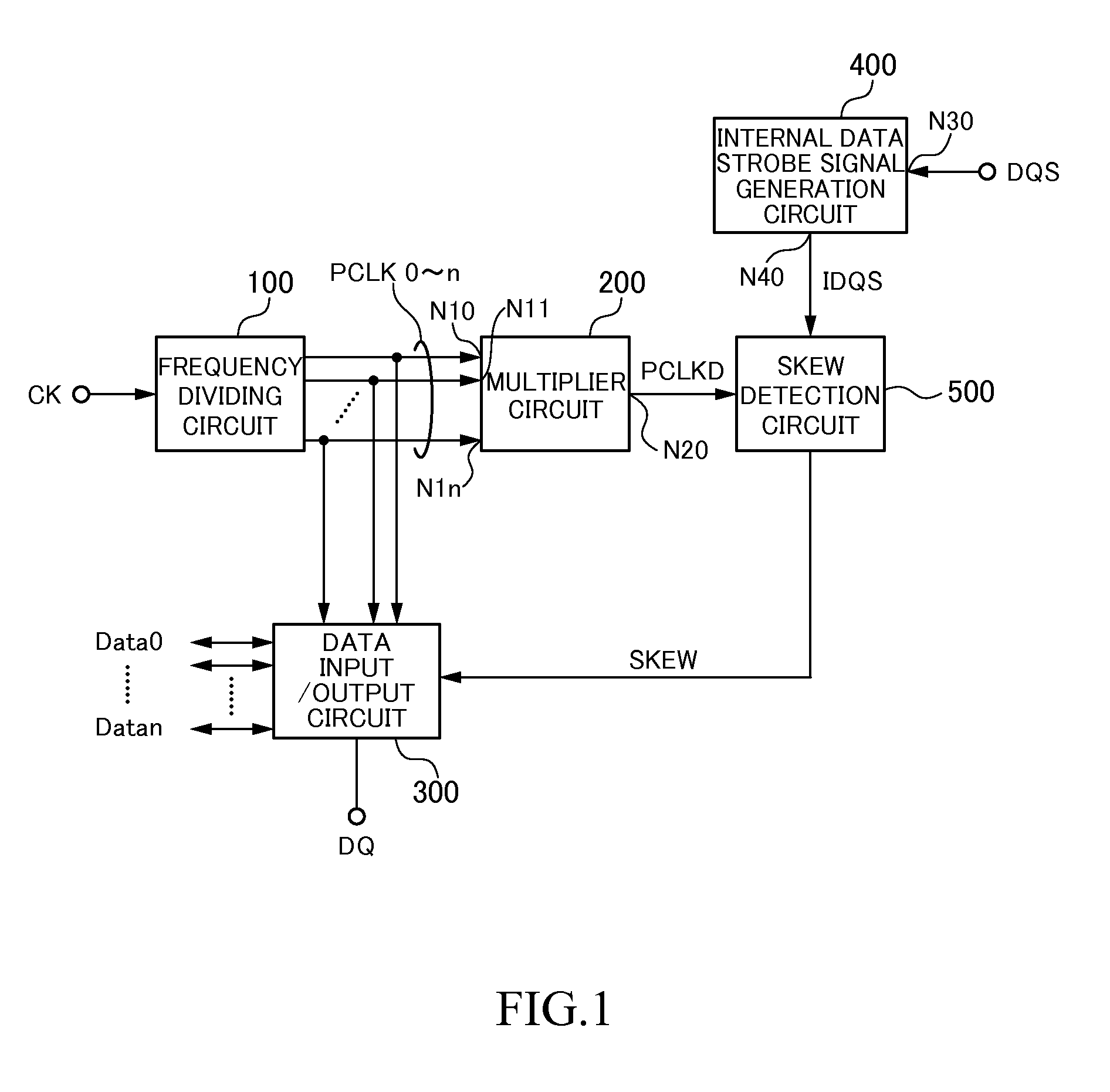
Semiconductor device having skew detection circuit measuring skew between clock signal and data strobe signal
Disclosed herein is a semiconductor device that includes a clock terminal supplied with a first clock signal from outside; a dividing circuit dividing a frequency of the first clock signal to generate a plurality of second clock signals that are different in phase from one another; a multiplier circuit multiplying the second clock signals to generate a third clock signal, the multiplexer having a predetermined operating delay time; a data strobe terminal supplied with a first data strobe signal from outside; a strobe signal generation circuit adding the predetermined operating delay time to the first data strobe signal to generate a second data strobe signal; and a skew detection circuit measuring a skew between the third clock signal and the second data strobe signal.
Owner:LONGITUDE SEMICON S A R L
Semiconductor device with a voltage regulator
InactiveUS20020118568A1Solid-state devicesRead-only memoriesVoltage regulator moduleAudio power amplifier
A semiconductor device with a voltage regulator is disclosed. The voltage regulator includes: a driver including pull-up and pull-down transistors serially connected between an output node of an internal voltage generation circuit and a reference potential terminal, for outputting a regulated voltage at its regulated voltage output node corresponding to the connection node of the pull-up and pull-down transistors; a voltage divider circuit for subdividing the regulated voltage output to the regulated voltage output node; a first operational amplifier for controlling current drivability of the pull-down transistor in accordance with a difference between a first reference voltage and a divided output of the voltage divider circuit; and a second operational amplifier for controlling current drivability of the pull-up transistor in accordance with a difference between a second reference voltage and the divided output of the voltage divider circuit in such a way as to vary in a reverse direction to the current drivability of the pull-down transistor.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
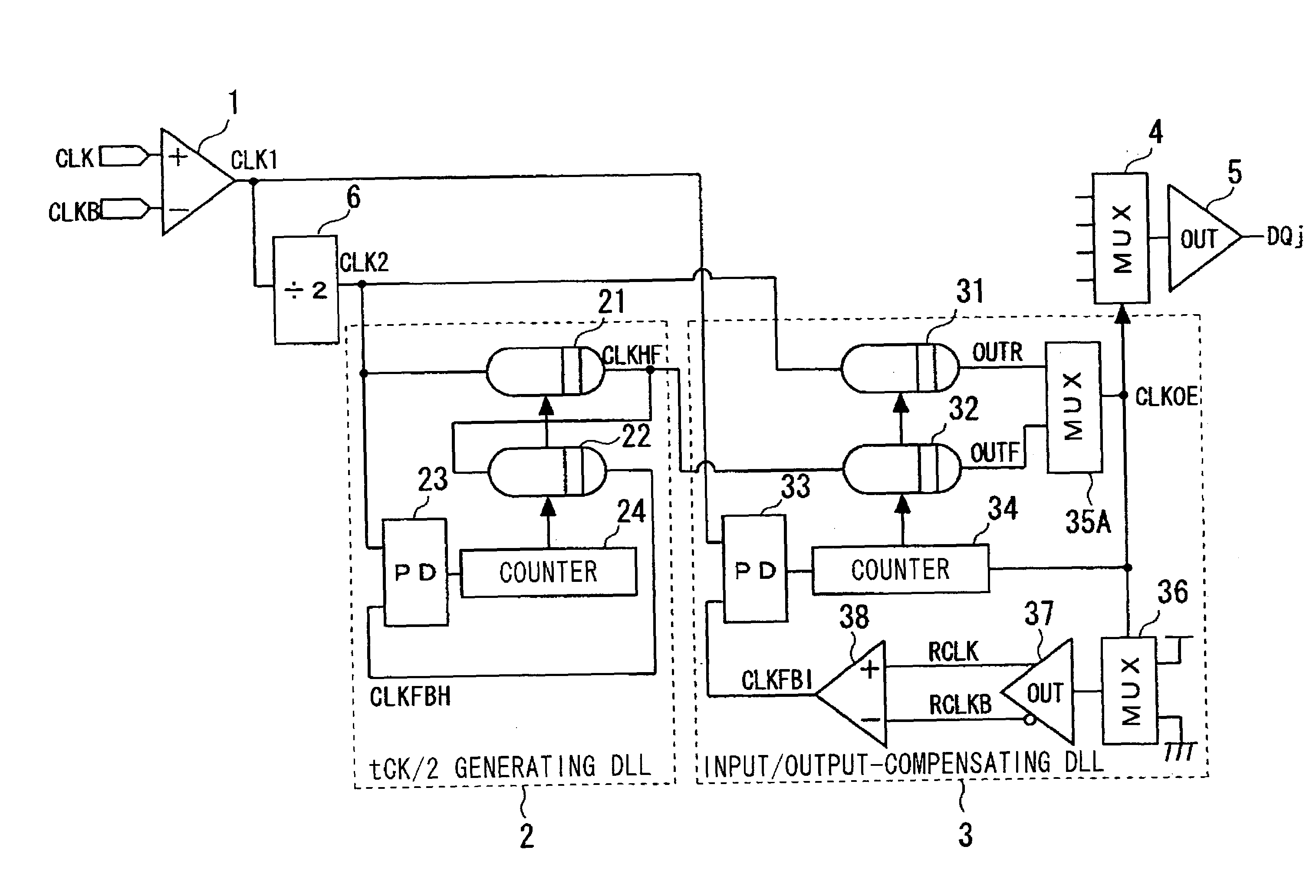
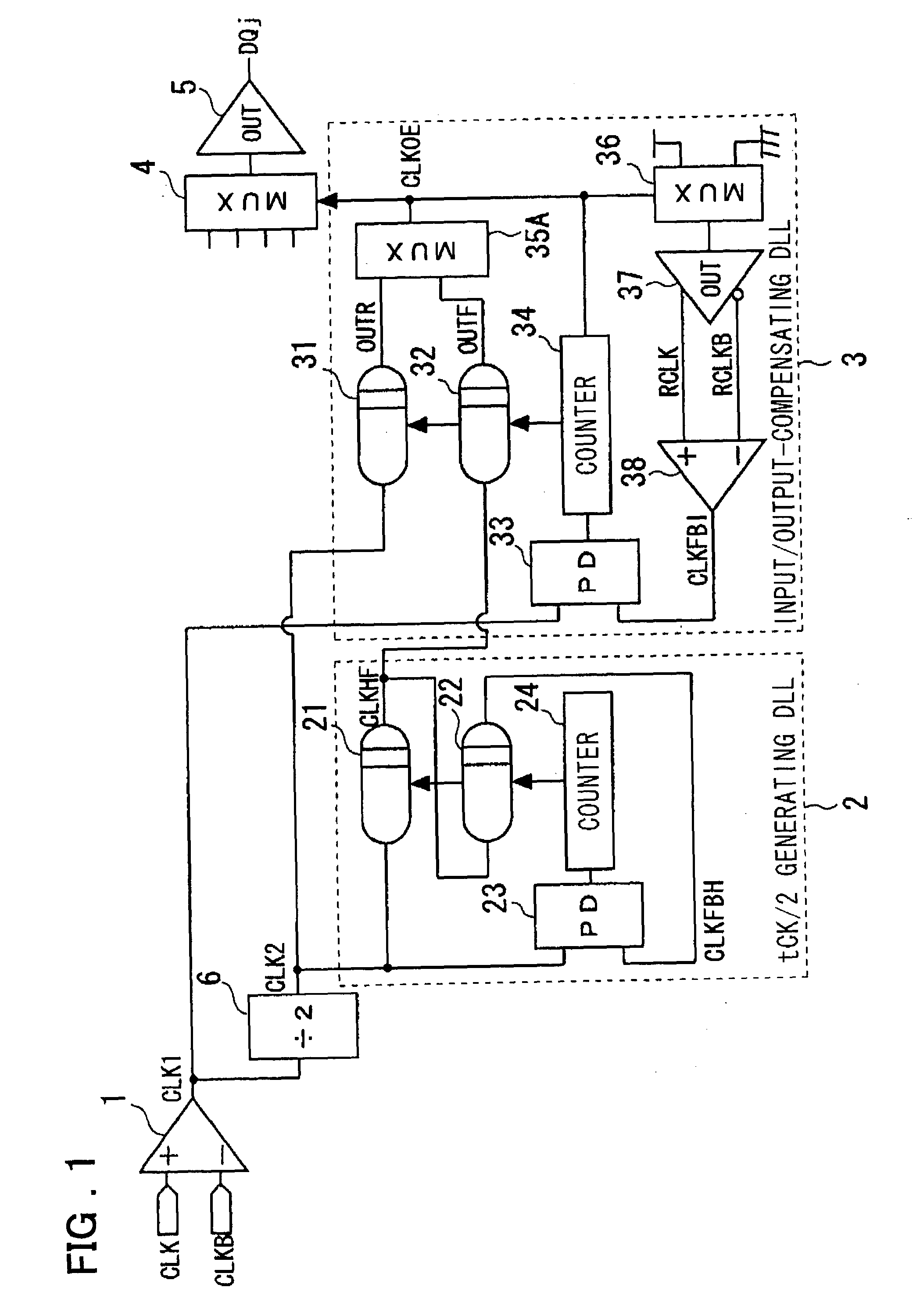
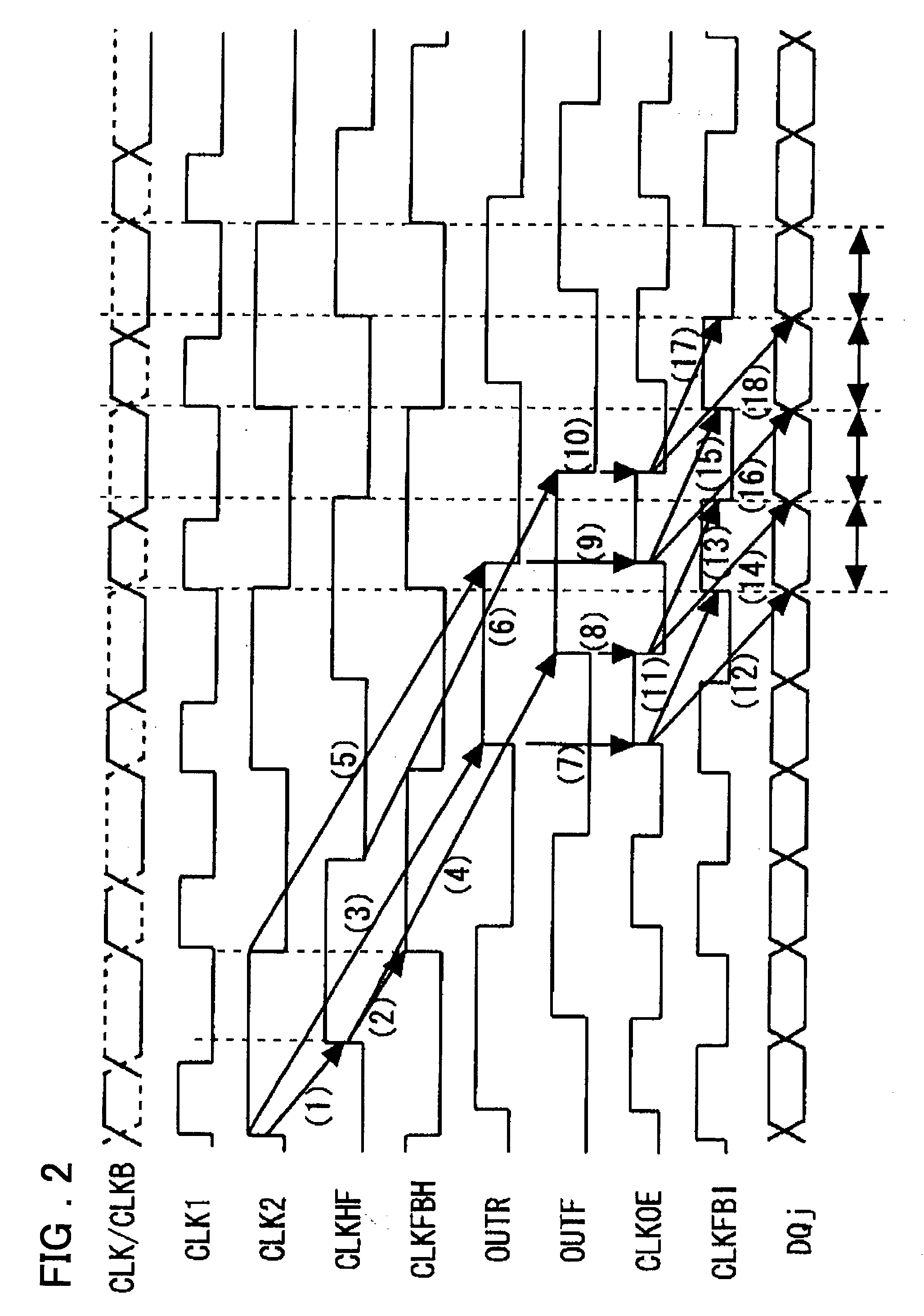
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and delay-locked loop device
InactiveUS20030151433A1Reduce power consumptionPreventing in output timingPulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsPhase differenceDelay-locked loop
Disclosed are a delay-locked loop circuit and a semiconductor integrated circuit device of reduced power consumption, the delay-locked loop circuit having a tCK / 2 generating DLL and an input / output-compensating DLL. The tCK / 2 generating DLL includes first and second delay lines for delaying a frequency-divided clock input thereto from a frequency dividing circuit; a first phase detector for detecting the phase difference between the frequency-divided clock and the output of the second delay line; and a counter for outputting a signal that changes over the output taps of the first and second delay lines depending upon an output from the first phase detector. The input / output-compensating DLL includes third and fourth delay lines for delaying the frequency-divided clock input thereto; a multiplexer, to which output signals from the third and fourth delay lines are input, for outputting a signal in which timings of rising and falling edges are decided by rising edges of respective ones of the output signals and then by falling edges of respective ones of the output signals; a dummy multiplexer to which this output signal is input and having a delay time identical with that of a multiplexer that selects data; a dummy first buffer having a delay time identical with that of an output buffer; a dummy second buffer having a delay time identical with that of an input buffer; a second phase detector for detecting the phase difference between an output clock from the input buffer and the output of the dummy second buffer; and a counter for outputting a signal that changes over the output taps of the third and fourth delay lines depending upon an output from the second phase detector.
Owner:PS4 LUXCO SARL
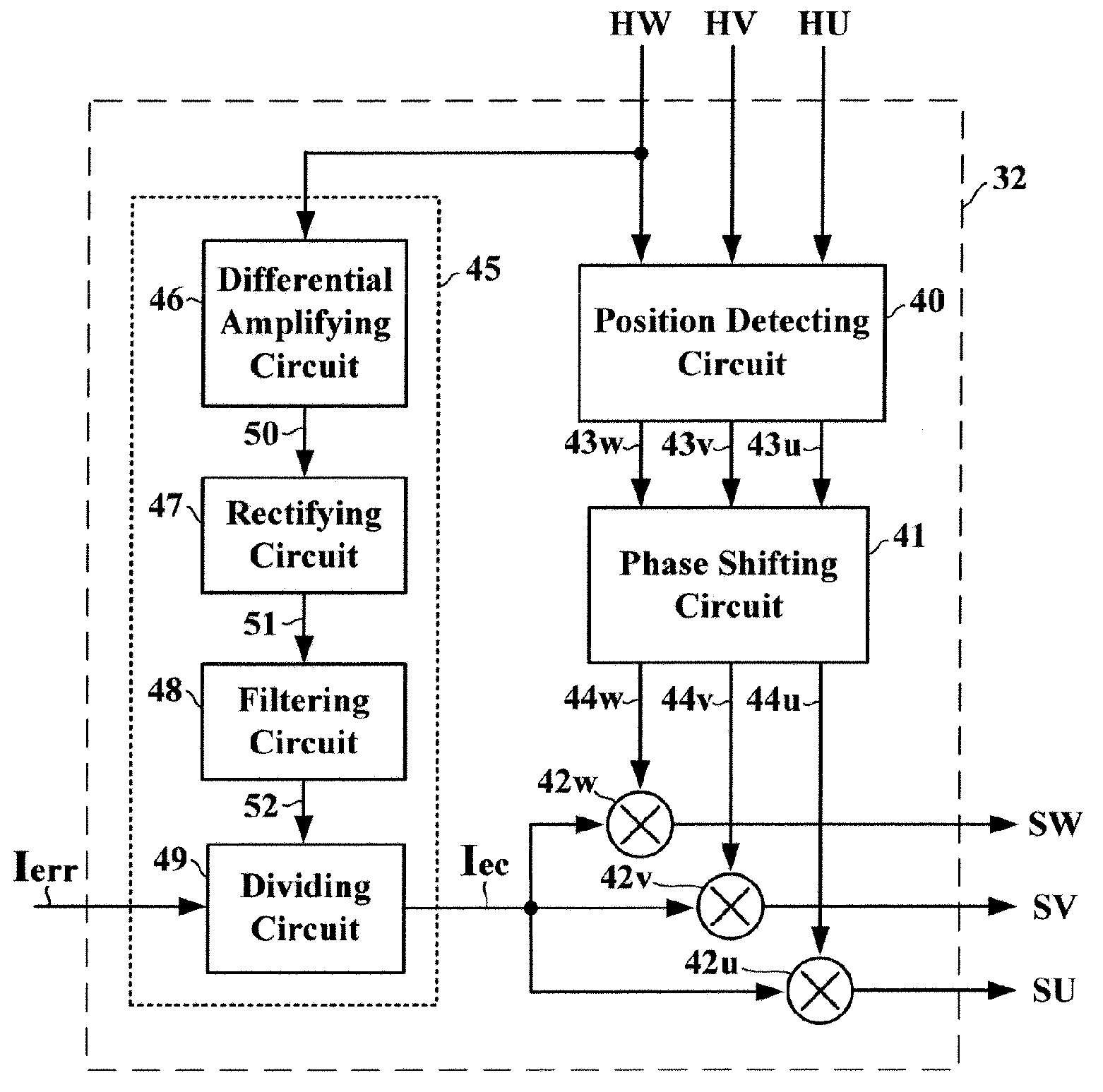
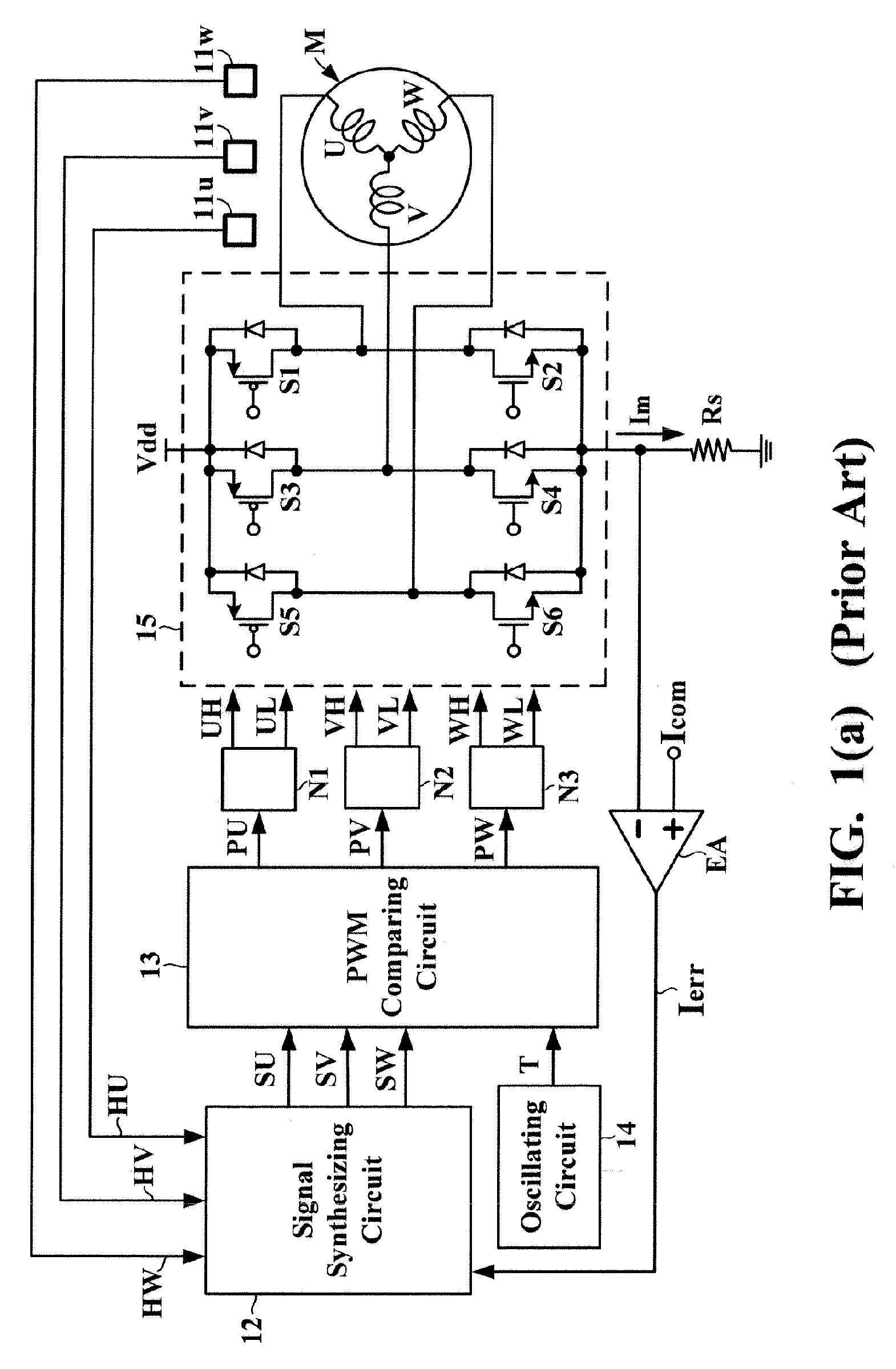
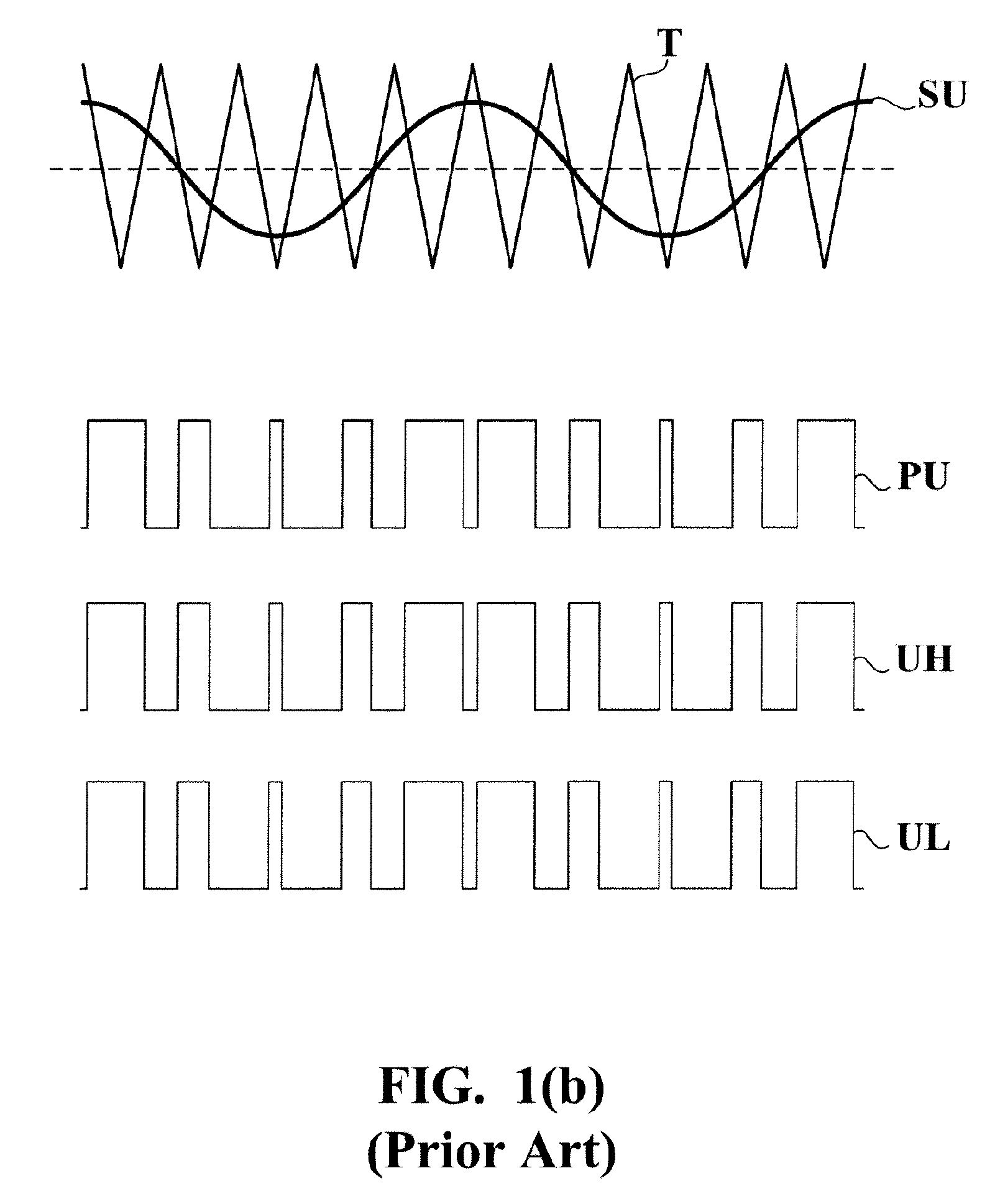
Brushless motor drive device
InactiveUS7164245B1Avoid signalingMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlBrushless motorsMotor drive
A brushless motor drive device has a signal synthesizing circuit for converting a plurality of sensing signals into a plurality of drive signals so as to determine an amplitude of each of the drive signals in accordance with a current error signal. The sensing signals are generated by a sensing circuit in response to variations in a magnetic field of a brushless multi-phase motor. The current error signal is representative of a difference between a current command signal and a motor drive current. The signal synthesizing circuit is characterized by including a calibrating circuit for adjusting the current error signal in accordance with an amplitude of any of the sensing signals. The calibrating circuit includes a differential amplifying circuit, a rectifying circuit, a filtering circuit, and a dividing circuit.
Owner:GLOBAL MIXED MODE TECH
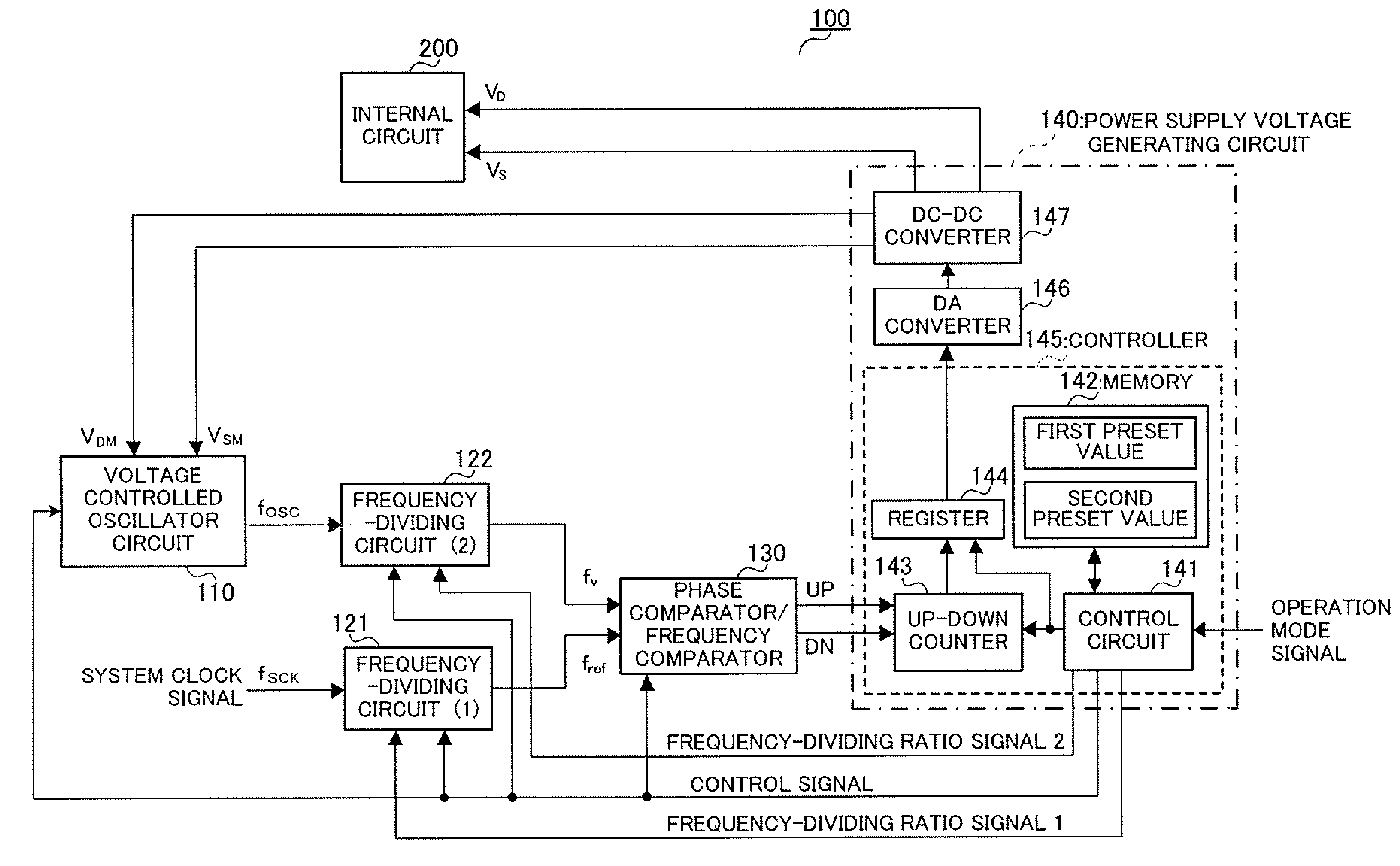
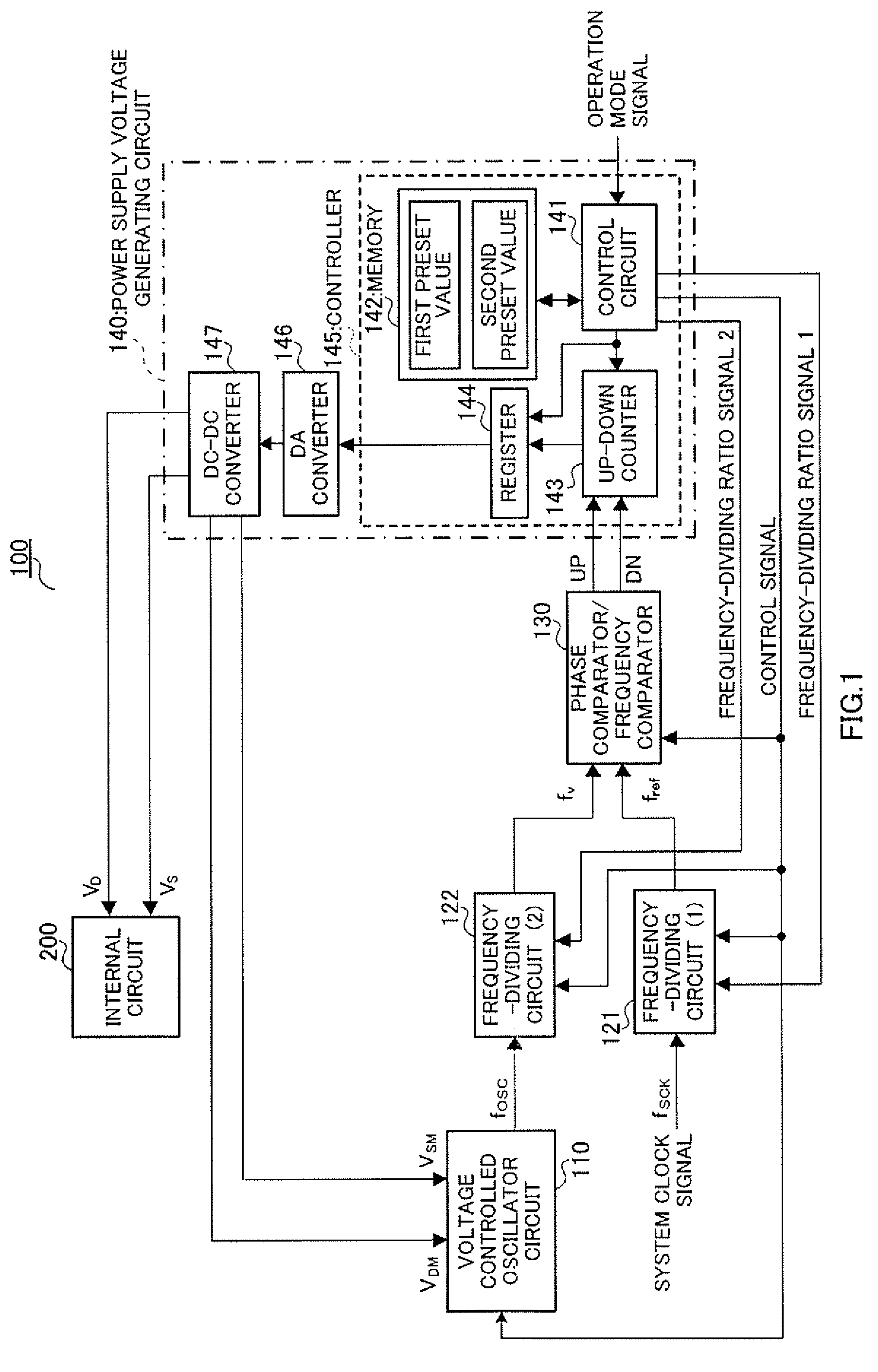
Power supply voltage control apparatus
A power supply voltage control apparatus capable of freely setting a clock period setting margin according to a system clock frequency, and capable of converging power supply voltage to minimum power supply voltage where normal operation is possible in a short period of time without errors in operation of internal circuits in response to changes in the system clock frequency is provided. Power supply voltage control apparatus 100 is provided with frequency-dividing circuit 121 that frequency-divides the system clock at frequency-dividing ratio 1, frequency-dividing circuit 122 that frequency-divides the output of voltage control oscillator circuit 110 at frequency-dividing ratio 2, phase comparator / frequency comparator 130 that carries out phase comparison / frequency comparison on the respective output signals of frequency-dividing circuits 121 and 122, and controller 145. Frequency-dividing ratios of frequency-dividing circuits 121 and 122 are set by control circuit 141 according to an operation mode signal corresponding to the system clock frequency.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
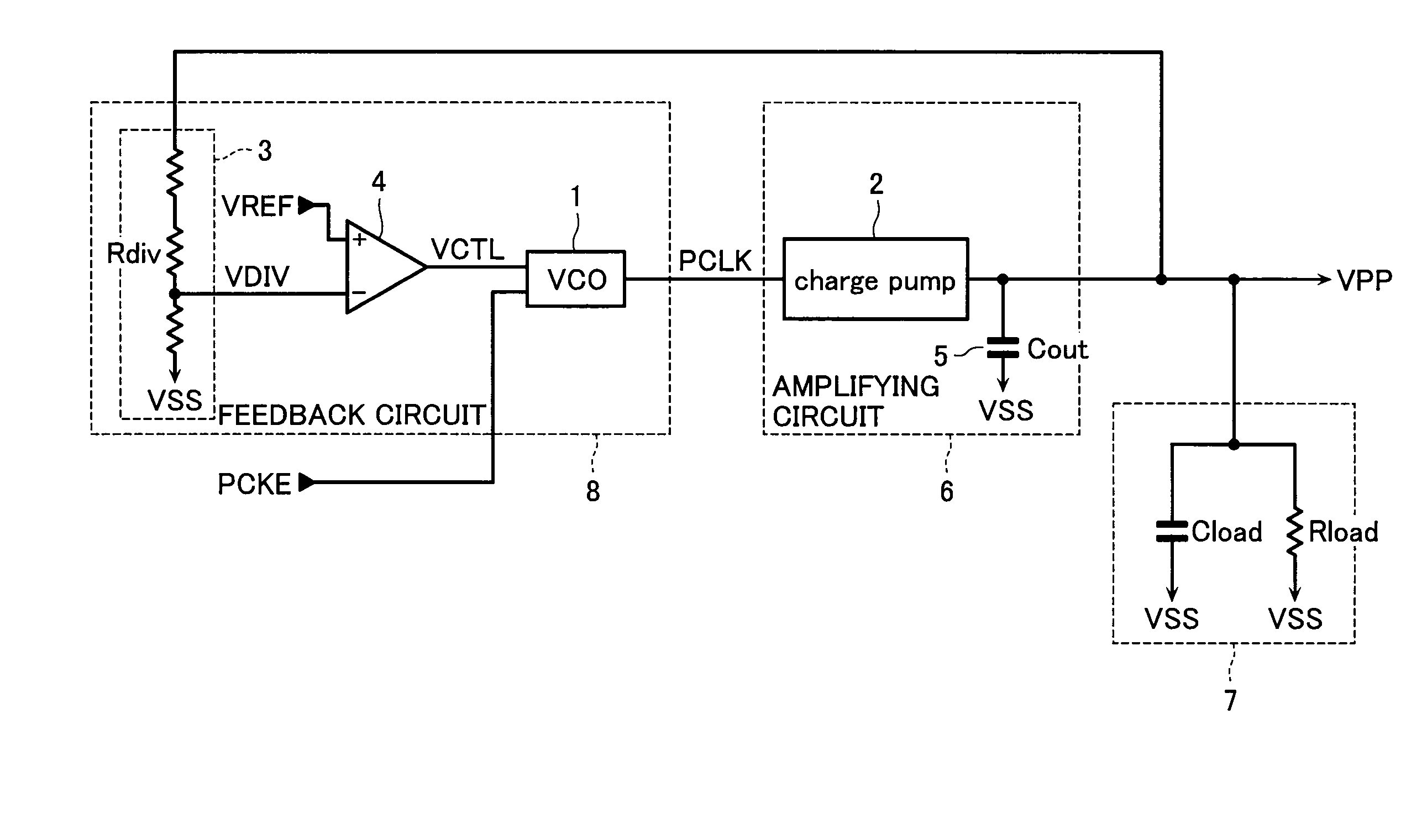
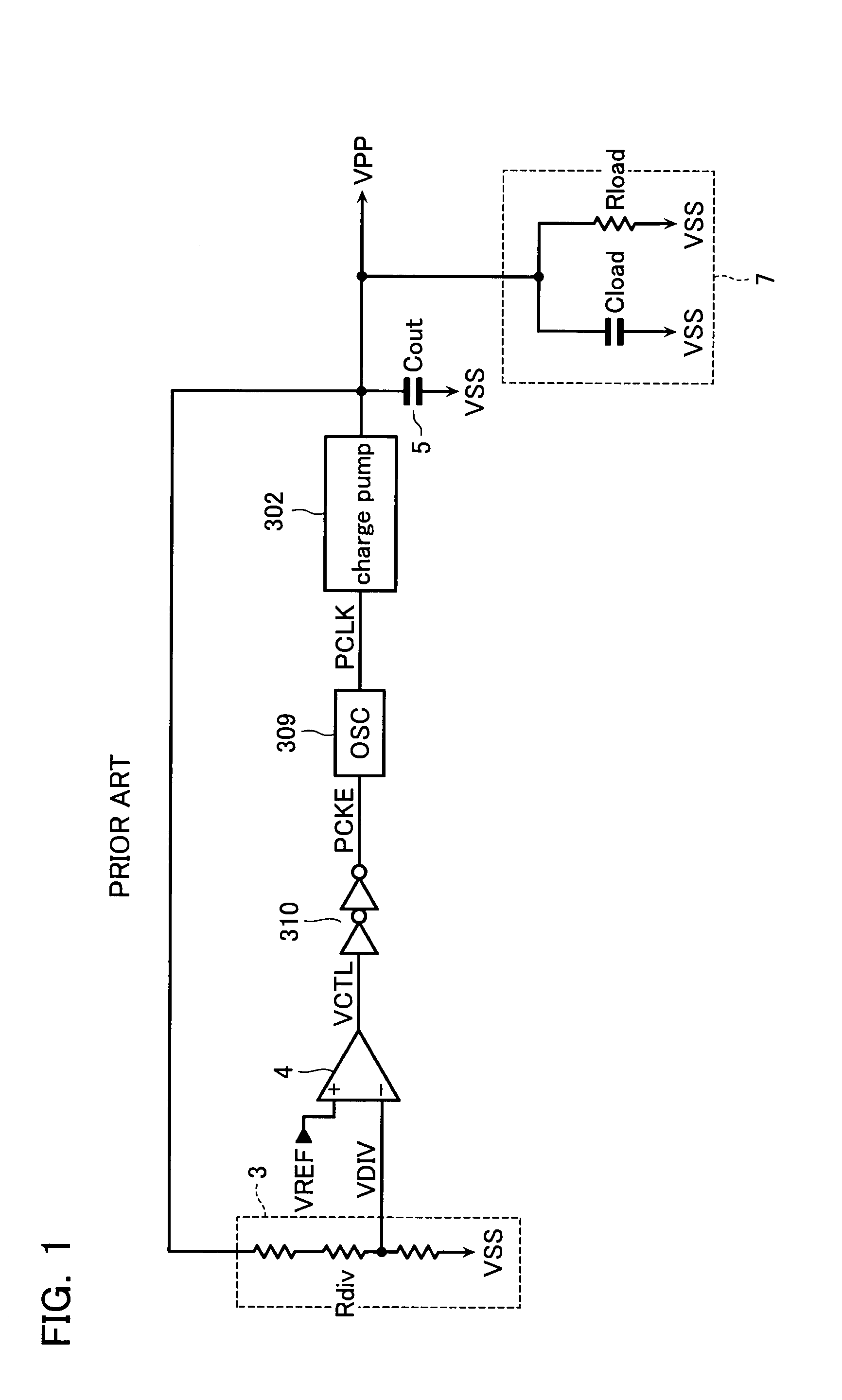
Constant voltage boost power supply
A constant voltage boost power supply according to an aspect of the invention includes a voltage-controlled variable frequency oscillator that produces and supplies a clock signal and changes an oscillating frequency of the supplied clock signal according to an input control voltage; a charge pump into which the clock signal is fed, the charge pump performing a pumping operation in synchronization with the clock signal to boost an input voltage and supply an output voltage in which the input voltage is boosted; a voltage dividing circuit that divides the output voltage of the charge pump to supply a monitor voltage; and a differential amplifier into which the monitor voltage and a reference voltage are fed, the differential amplifier amplifying a potential difference between the monitor voltage and the reference voltage to supply the control voltage.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
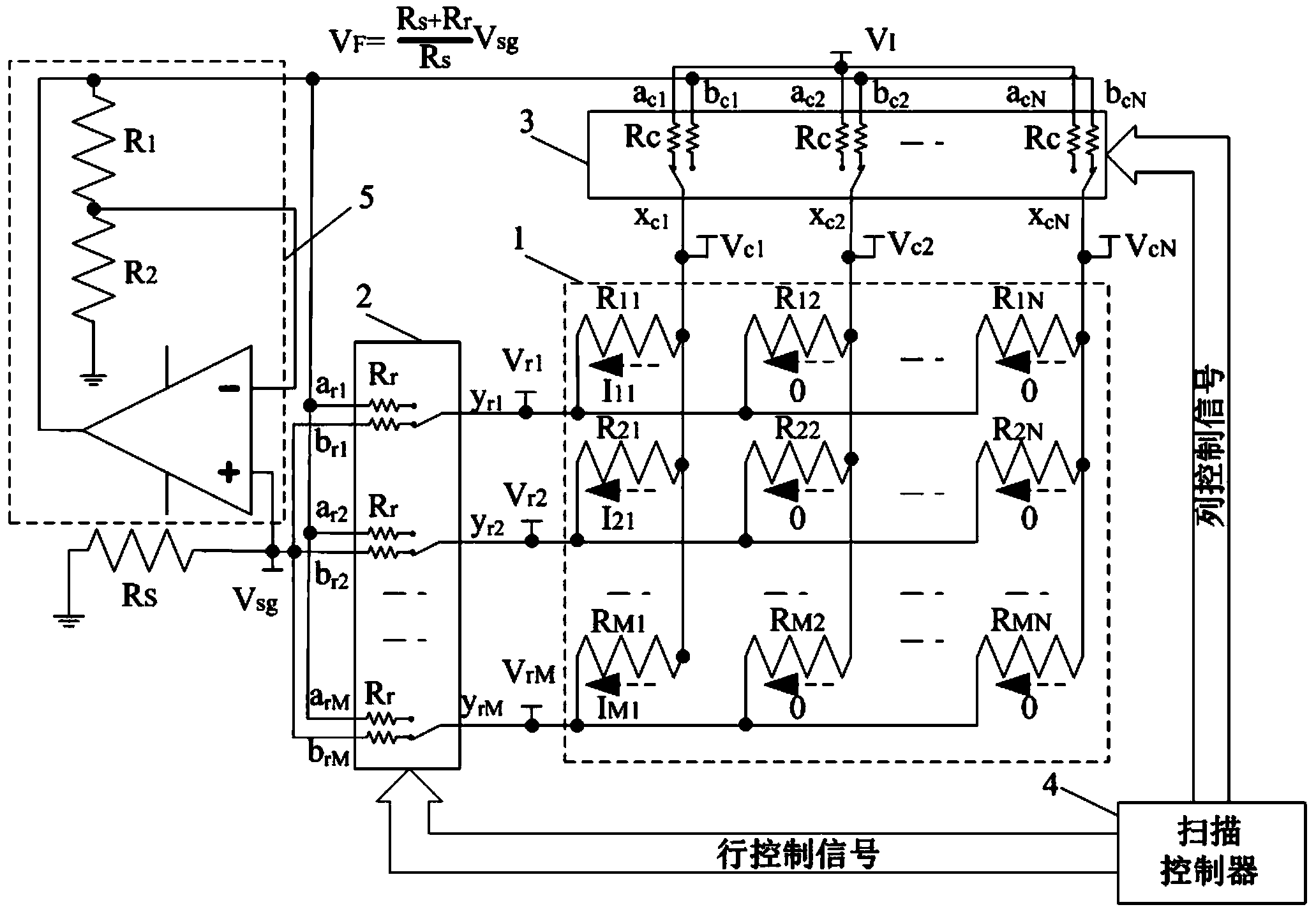
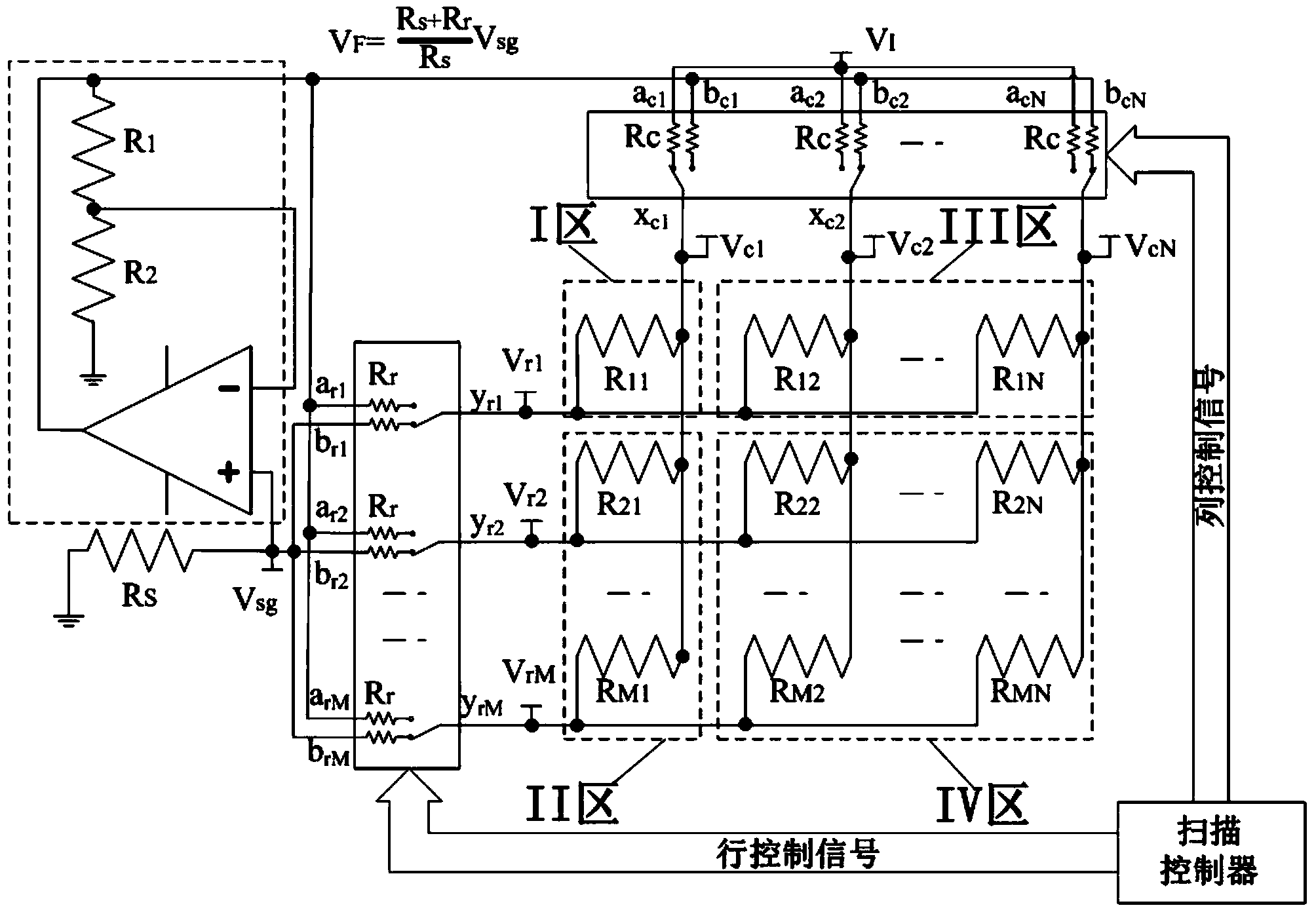
Detection circuit of resistance sensing array strengthening voltage feedback
InactiveCN103925934AImprove detection accuracyAchieve a single selectionConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyNonlinear resistorElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses a detection circuit of a resistance sensing array strengthening the voltage feedback. The detection circuit comprises two-dimensional resistance arrays sharing the same row line and the column line, row multiplexers, column multiplexers, a scanning controller and a feedback circuit. Physical sensitive resistors in the two-dimensional resistance arrays are distributed according to an M*N two-dimensional structure. The scanning controller outputs scanning control signals, and single selections of any resistor to be measured in a row multiplexer array and a column multiplexer array are controlled respectively. A feedback circuit is composed of an operation amplifier and a voltage division circuit. Resistors with specific values are selected and used as a resistor R1 and a resistor R2 in the voltage division circuit. R1:R2=Rr:RS, Rr shows a channel inner resistor of the row multiplexers, and RS shows a sampling resistor. Under the action of the feedback circuit and a corresponding connection manner, the voltages cross two ends of the adjacent columns of resistors in the row where the resistor to be measured is located can be limited to be equal, the interference of measuring on the measured resistor by the adjacent columns of resistors of the resistor to be measured and the inner resistors of the column multiplexer is effectively reduced.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
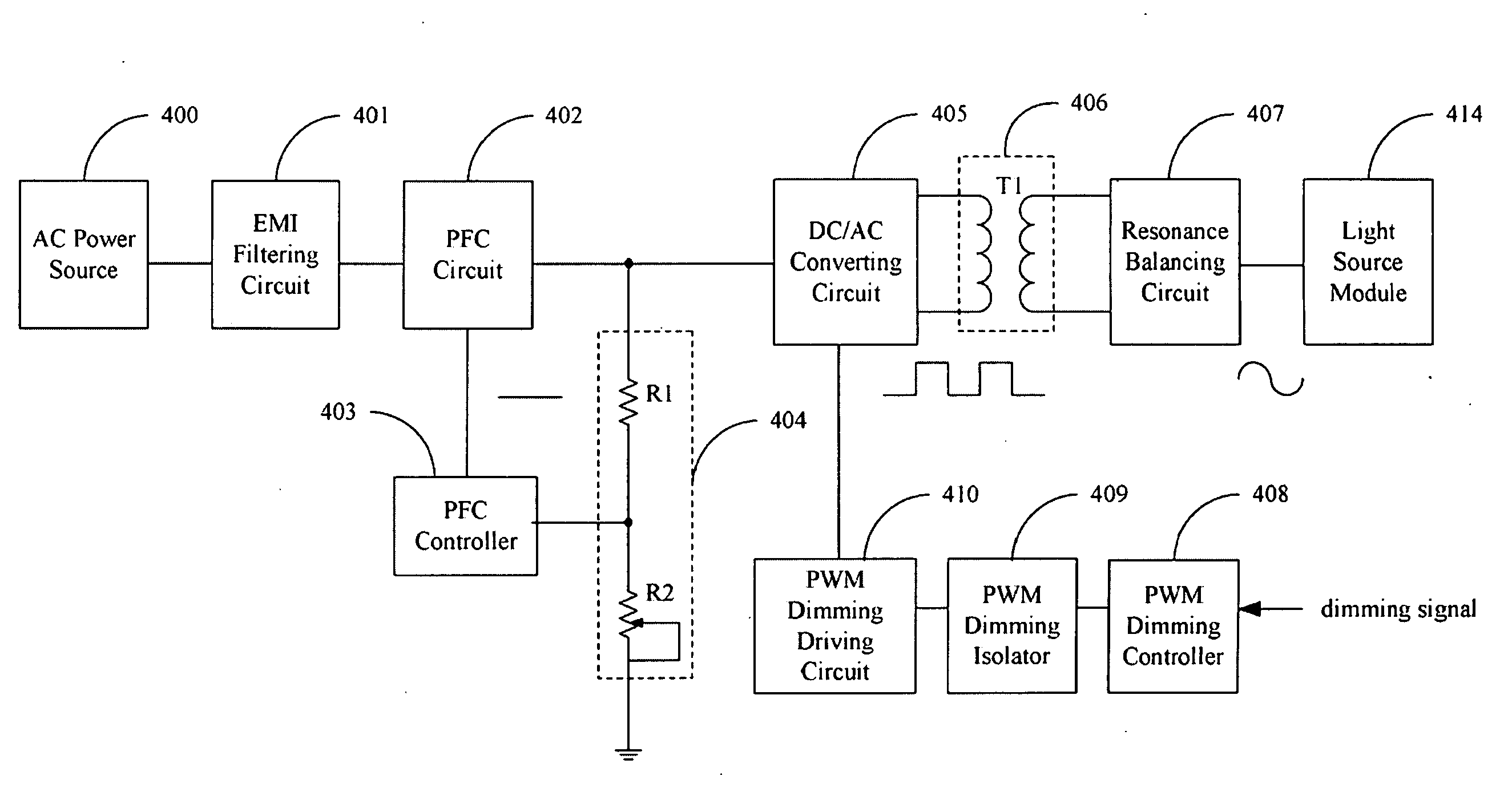
Light source driving device
InactiveUS20090261758A1Electrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementControl signalTransformer
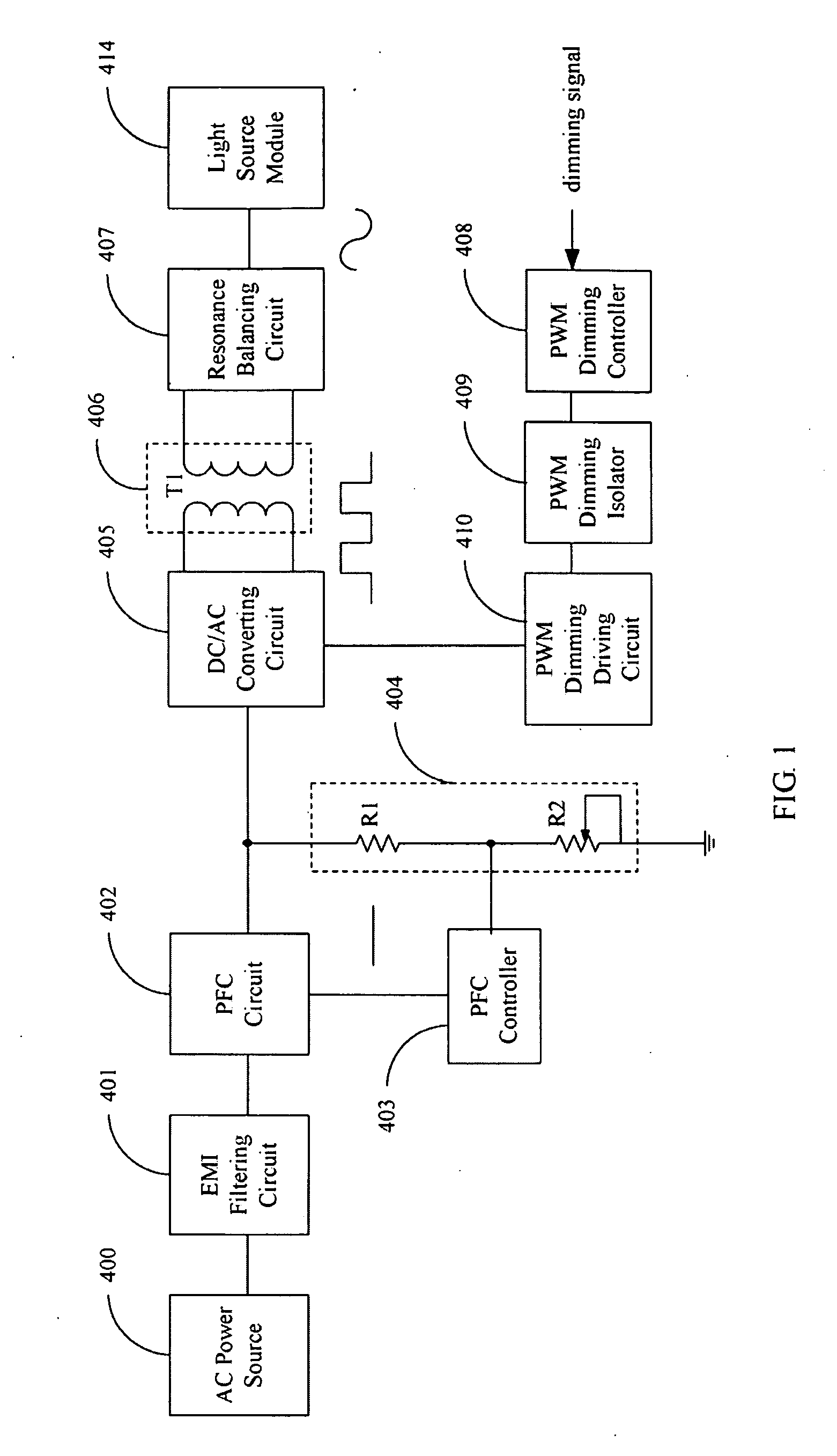
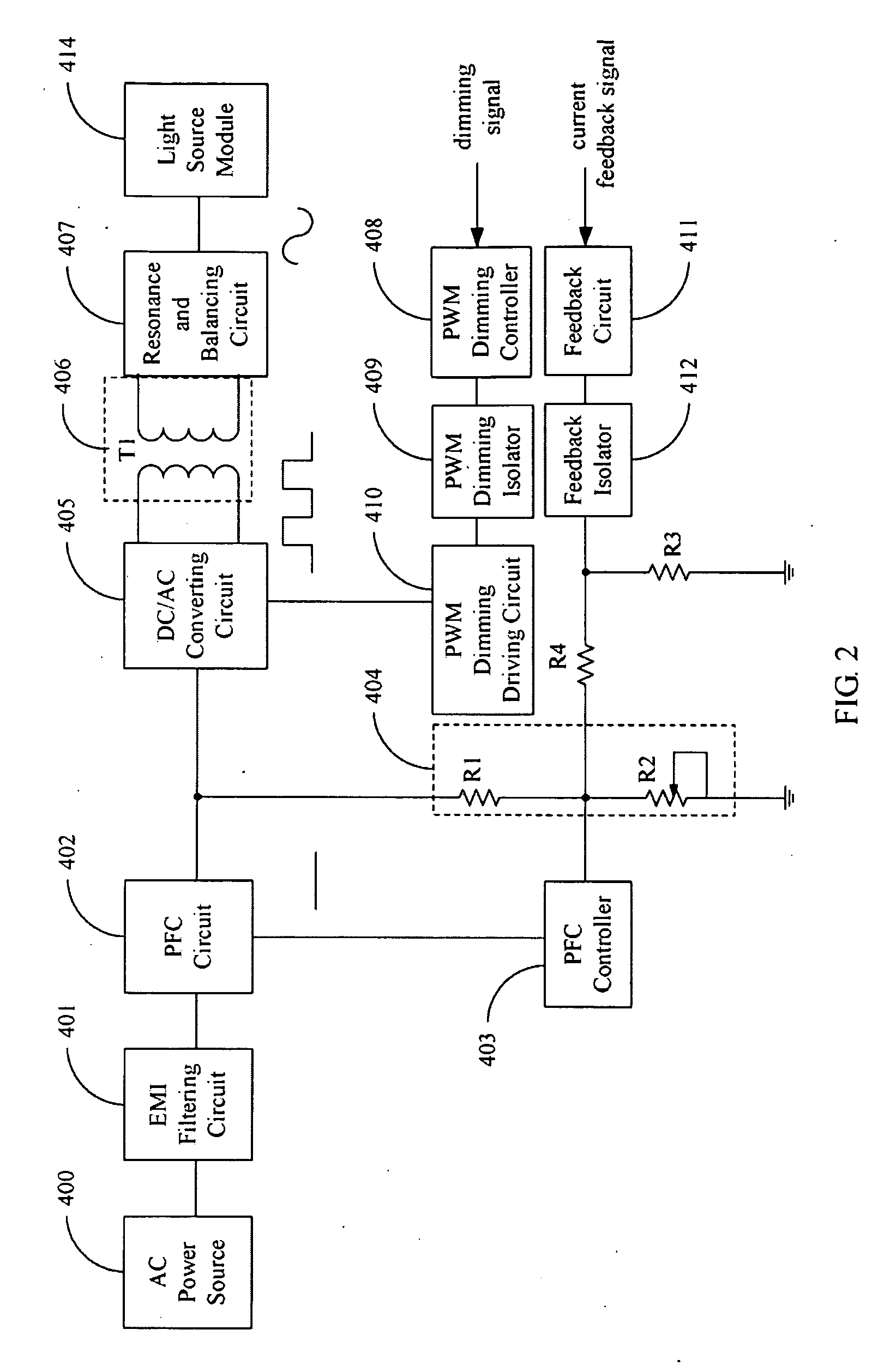
A light source driving device drives a plurality of light sources. A Power Factor Circuit (PFC) circuit converts a received electrical signal to a DC signal and output to a DC / AC converting circuit. The DC / AC converting circuit converts the DC signal to another AC signal, which is isolated by the transformer circuit. A resonance balancing circuit converts the AC signal output from the transformer circuit to another AC signal to drive the light source module. A PWM dimming controller outputs a control signal to control output of the DC / AC converting circuit according to a received dimming signal, wherein duty cycle of the control signal is fixed. A voltage dividing circuit adjustably divides voltage of the DC signal output from the PFC circuit. A PFC controller feeds the divided signal back to the PFC circuit to control the DC signal output from the PFC circuit.
Owner:AMPOWER TECH CO LTD
Constant voltage boost power supply
A constant voltage boost power supply according to an aspect of the invention includes a voltage-controlled variable frequency oscillator that produces and supplies a clock signal and changes an oscillating frequency of the supplied clock signal according to an input control voltage; a charge pump into which the clock signal is fed, the charge pump performing a pumping operation in synchronization with the clock signal to boost an input voltage and supply an output voltage in which the input voltage is boosted; a voltage dividing circuit that divides the output voltage of the charge pump to supply a monitor voltage; and a differential amplifier into which the monitor voltage and a reference voltage are fed, the differential amplifier amplifying a potential difference between the monitor voltage and the reference voltage to supply the control voltage.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Encoding device, encoding method, and program
ActiveUS20140006037A1Improve audio qualityEfficient codingSpeech analysisDividing circuitsAudio frequency
This technology relates to an encoding device, an encoding method, and a program capable of improving audio quality and more efficiently encoding audio. A first high-frequency encoding circuit encodes a high-frequency range based on a low-frequency subband signal and a high-frequency subband signal and obtains a high-frequency code amount. A low-frequency encoding circuit encodes a low-frequency signal with a code amount determined by the high-frequency code amount and a low-frequency decoding circuit decodes the encoded low-frequency signal. A subband dividing circuit divides a decoded low-frequency signal obtained by decoding into decoded low-frequency subband signals of a plurality of subbands and a second high-frequency encoding circuit generates a high-frequency code string such that a code amount of the high-frequency code string for obtaining a high-frequency component is not larger than the high-frequency code amount based on the decoded low-frequency subband signals and the high-frequency subband signals. The present invention is applicable to the encoding device.
Owner:SONY CORP
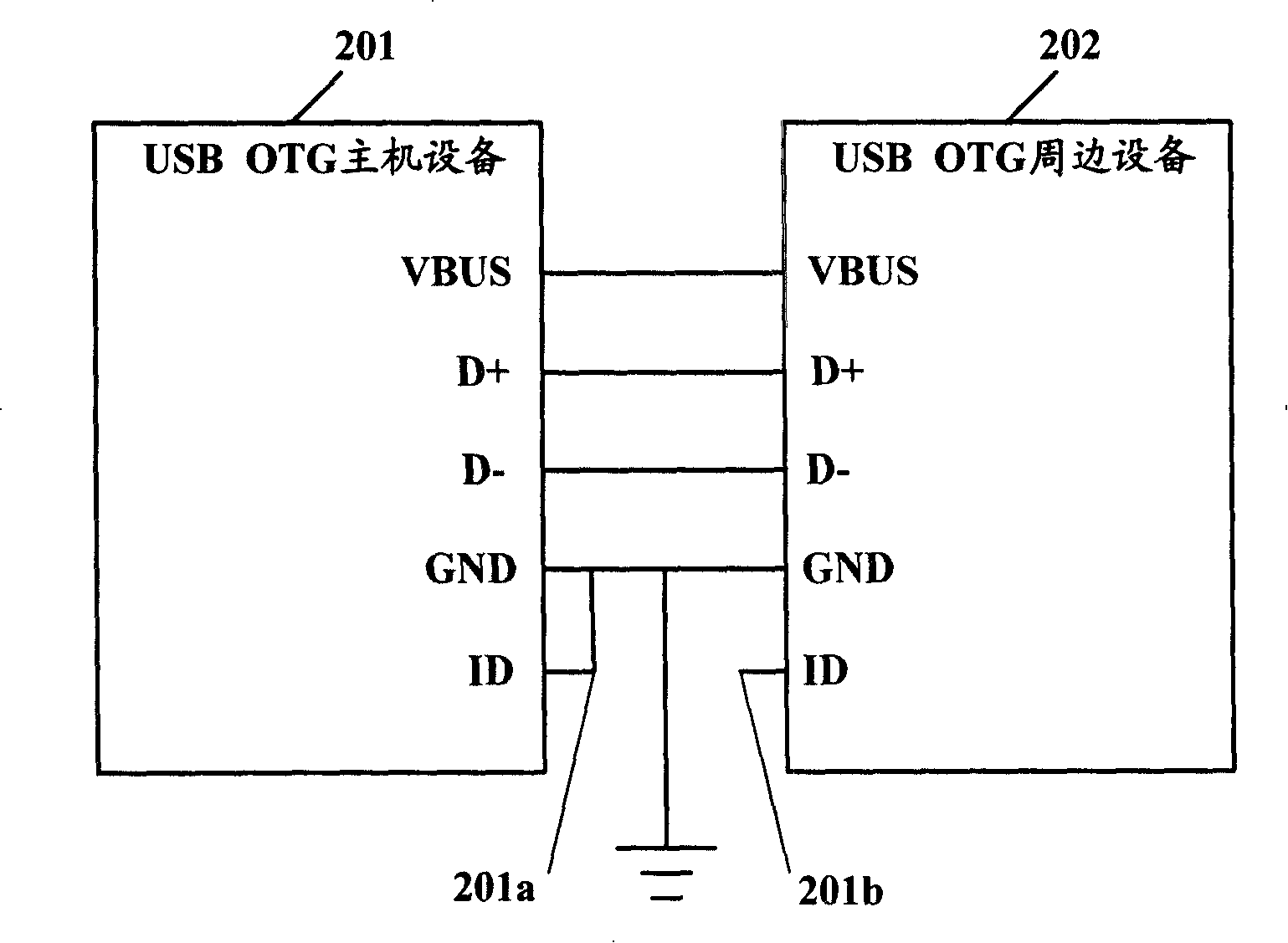
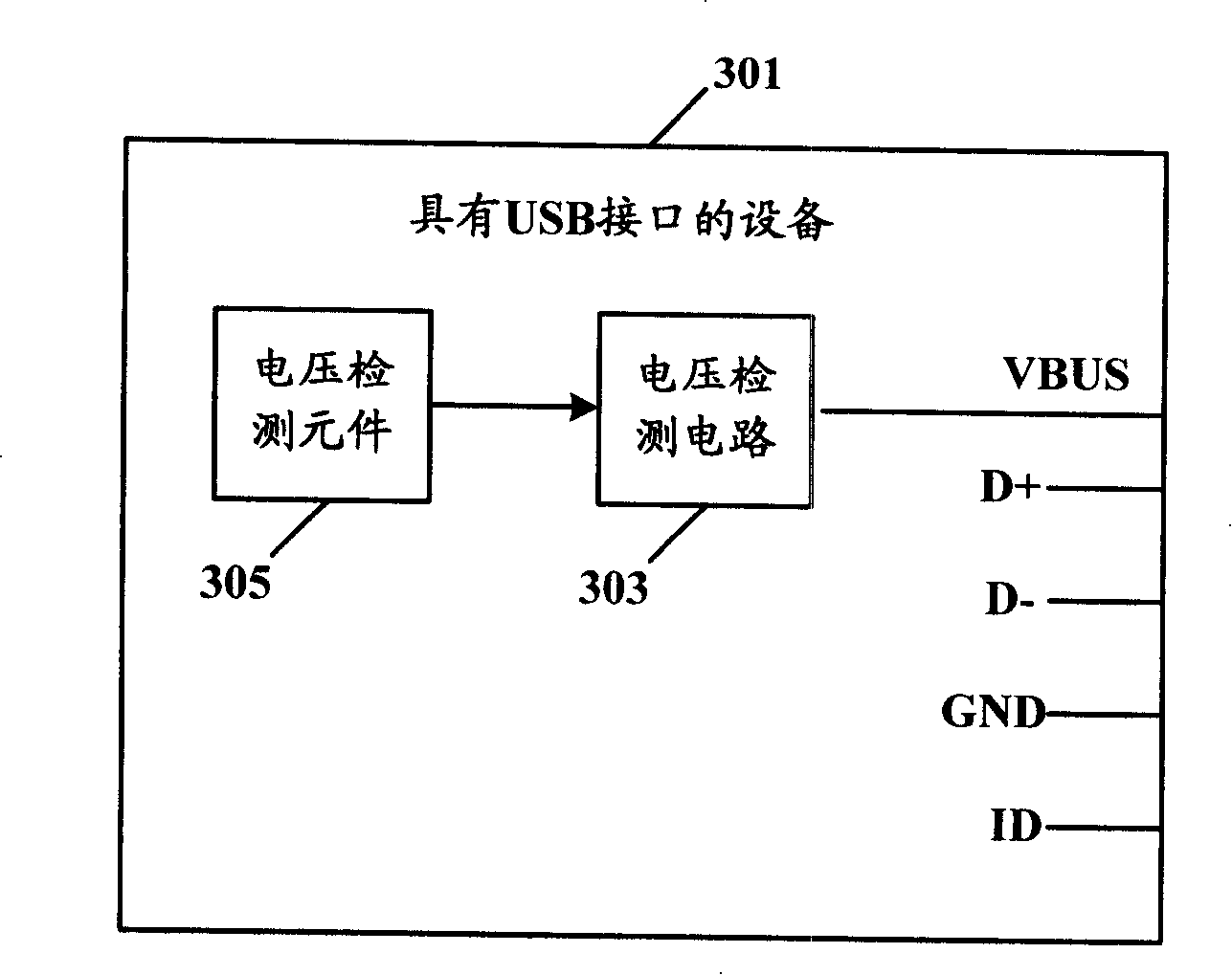
Device for automatically detecting universal serial bus main unit or peripherals
The invention discloses a device capable of automatically detecting general-purpose serial bus hosts or peripheral equipment. In the equipment provided with a USB interface, the device is coupled to external USB equipment through a VBUS pin and judges that the external USB equipment is a USB host or USB peripheral equipment according to the change of the voltage. The device comprises a voltage detection circuit and a voltage detection element, the voltage detection circuit is respectively coupled to the voltage detection element and the VBUS pin of the USB interface. The voltage detection circuit can be a voltage-dividing circuit, and the voltage of the voltage detection circuit can change with the external input signal of the VBUS pin of the USB interface. The voltage detection element is used to detect the voltage change of the voltage detection circuit to judge that the external equipment connected with the voltage detection circuit is one USB host or USB peripheral equipment. With the invention, whether the external equipment is the USB host or the USB peripheral equipment is judged independent of the ID pin; at the same time, the power supply conflict can not be produced.
Owner:PROLIFIC TECH INC
Electronic circuit with an operating characteristic correcting function
InactiveUS6131073AEliminate undesirable temperature drift in the operating parameters of the electronic circuitReliability increasing modificationsPush-pull amplifiersCMOSDividing circuits
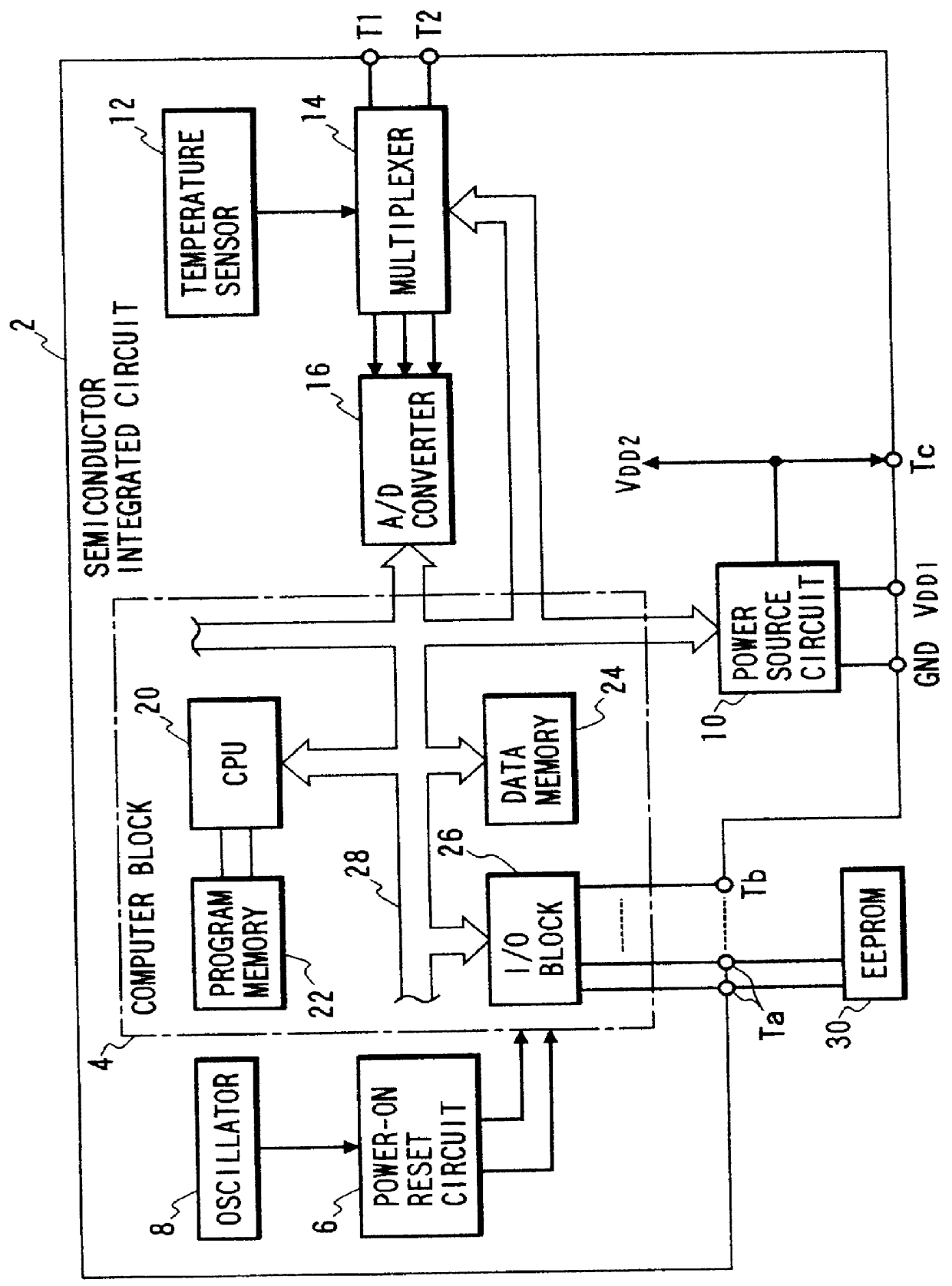
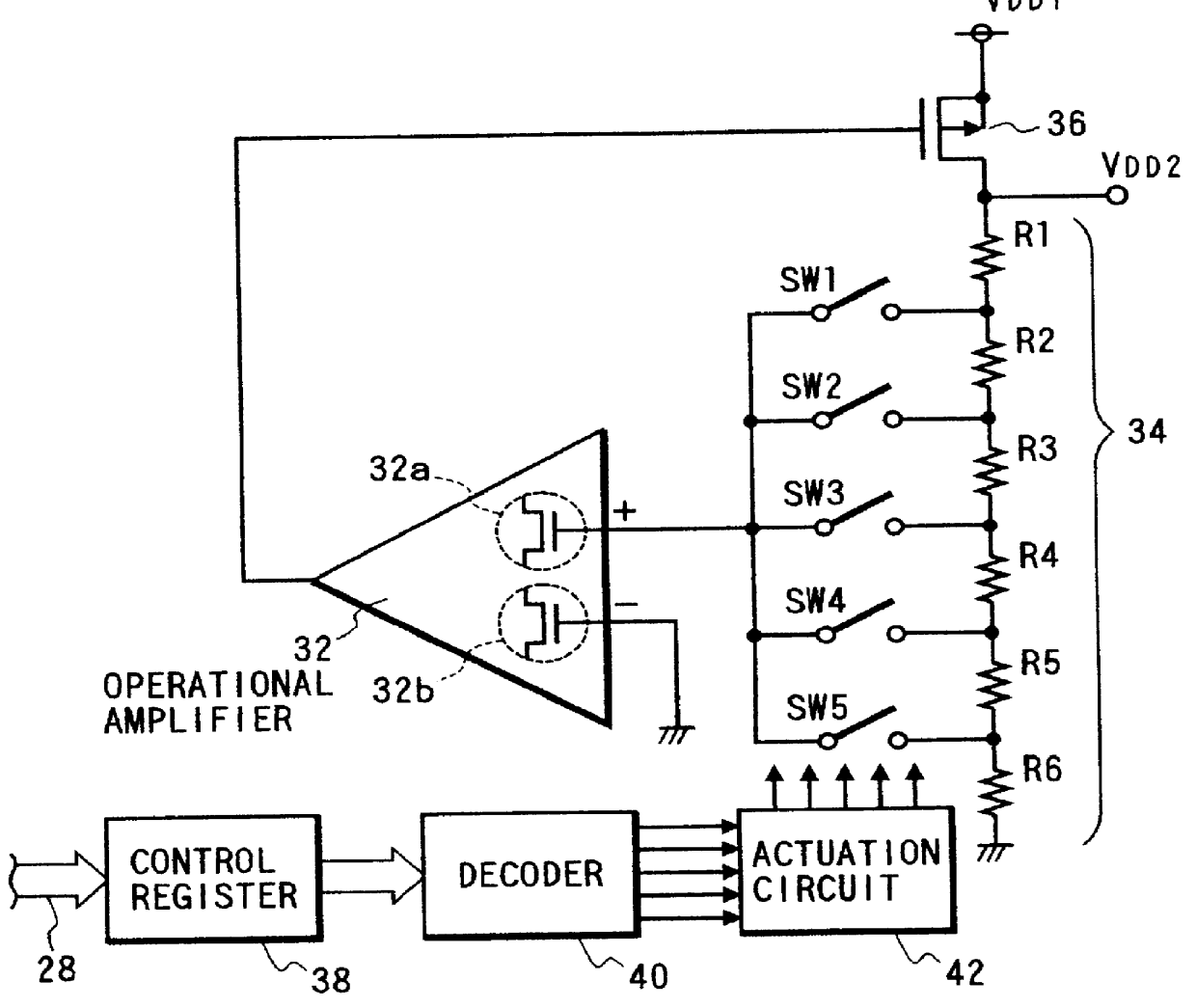
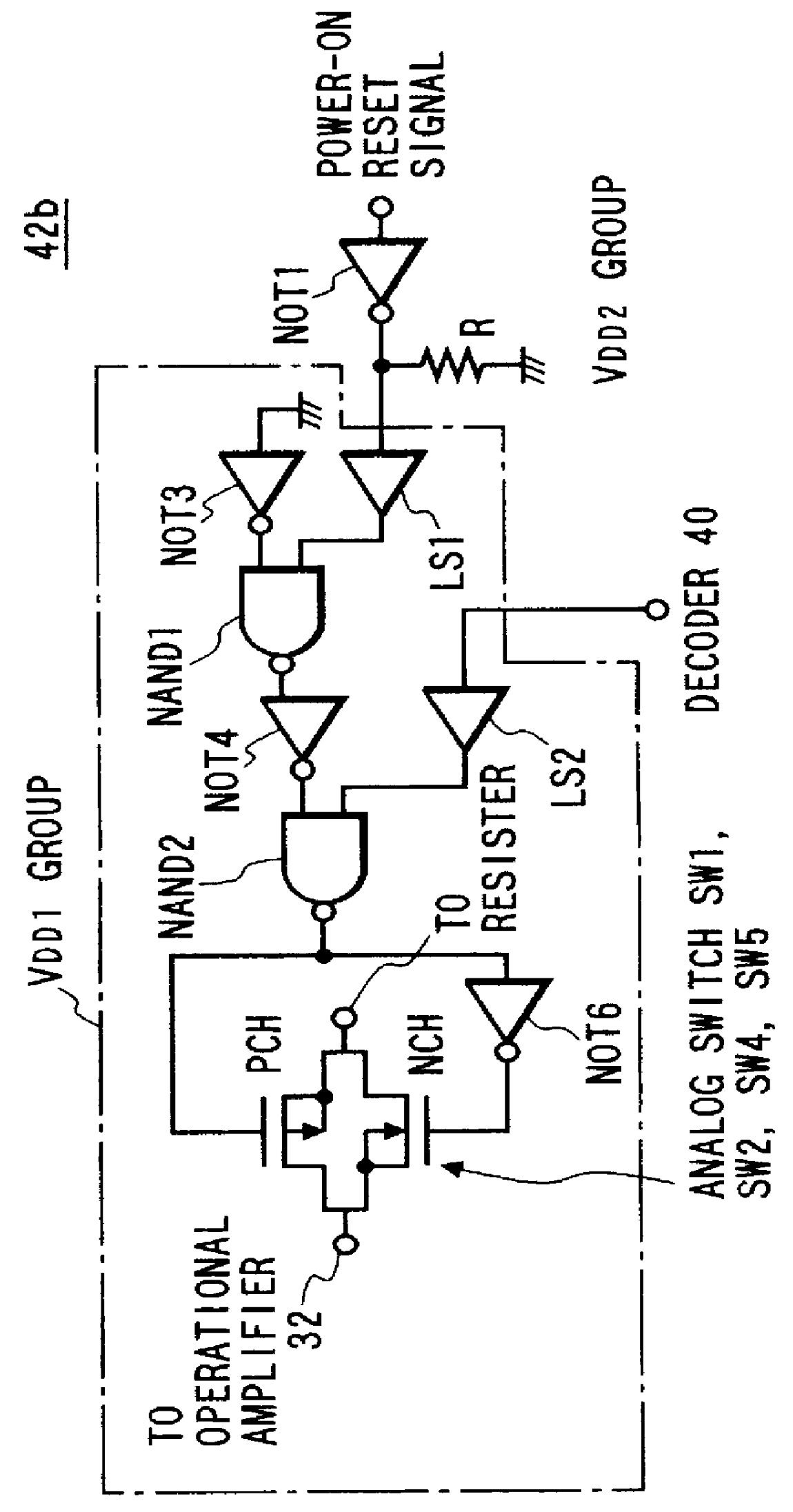
A power voltage of a power source circuit is produced by amplifying a threshold voltage difference of an operational amplifier by an amplification factor corresponding to a dividing ratio of a resistance dividing circuit. The power source circuit is integrated on a CMOS substrate together with a computer block. A plurality of analog switches are associated with the resistance dividing circuit to stabilize the power voltage of the power source circuit. One of these switches is selectively closed to change the dividing ratio of the resistance dividing circuit in accordance with actuation data stored in a control register.
Owner:DENSO CORP
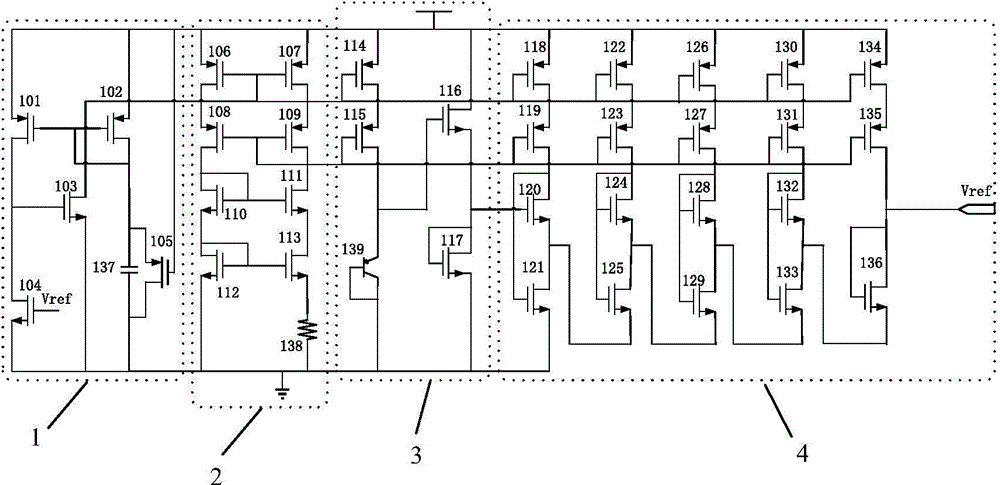
Low-power-consumption sub-threshold type CMOS band gap reference voltage circuit
ActiveCN104950971AReduce power consumptionLow working voltageElectric variable regulationReference currentEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of simulation integrated circuits, and discloses a low-power-consumption sub-threshold type CMOS band gap reference voltage circuit. The circuit comprises a start circuit, a reference current source generation circuit, a voltage division circuit and a reference voltage output circuit. The start circuit is used for enabling a reference voltage source to get rid of a zero degeneracy point and to work under specific work voltage. The reference current source generation circuit is used for generating current to provide bias for a rear end circuit, and MOS transistors in the rear end circuit all work in a sub-threshold region. The voltage division circuit is used for enabling an output circuit to reach required technical indexes and generating a negative temperature coefficient. The reference voltage output circuit is used for generating voltage with a positive temperature coefficient and making the output voltage Vref have the zero temperature characteristic. The low-power-consumption sub-threshold type CMOS band gap reference voltage circuit has the advantages of being low in work voltage, low in power consumption and low in temperature coefficient.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Customized earphone based on 3D (three-dimensional) printing technology and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103974183APrecise thickness controlPrecise control of the internal structureEarpiece/earphone attachmentsSpecial data processing applicationsWire rodDividing circuits
The invention discloses a customized earphone based on a 3D (three-dimensional) printing technology and a manufacturing method of the customized earphone. The earphone comprises an earphone shell, a hard sound induction tube, a unit clamping groove, a sounding unit, a sound outlet connection device, a frequency dividing circuit, a seal cover and a wire socket; the earphone shell, the unit clamping groove, the hard sound induction tube and the seal cover are formed by a 3D printer in a printing manner; the frequency dividing circuit is connected with the sounding unit and the wire socket; the sounding unit is arranged in the unit clamping groove; the sounding unit is communicated with the hard sound induction tube through the sound outlet connection device; the seal cover is used for sealing the earphone shell to form the customized earphone. The thickness, internal structure, mechanical characteristics and acoustics characteristics of the customized earphone shell can be precisely controlled, the sound induction tube material can be optimized, the limitation on a soft material can be broken through, the labor and time cost can be greatly reduced, and the yield of the customized earphone can be greatly increased.
Owner:XIAN MU SHENG ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
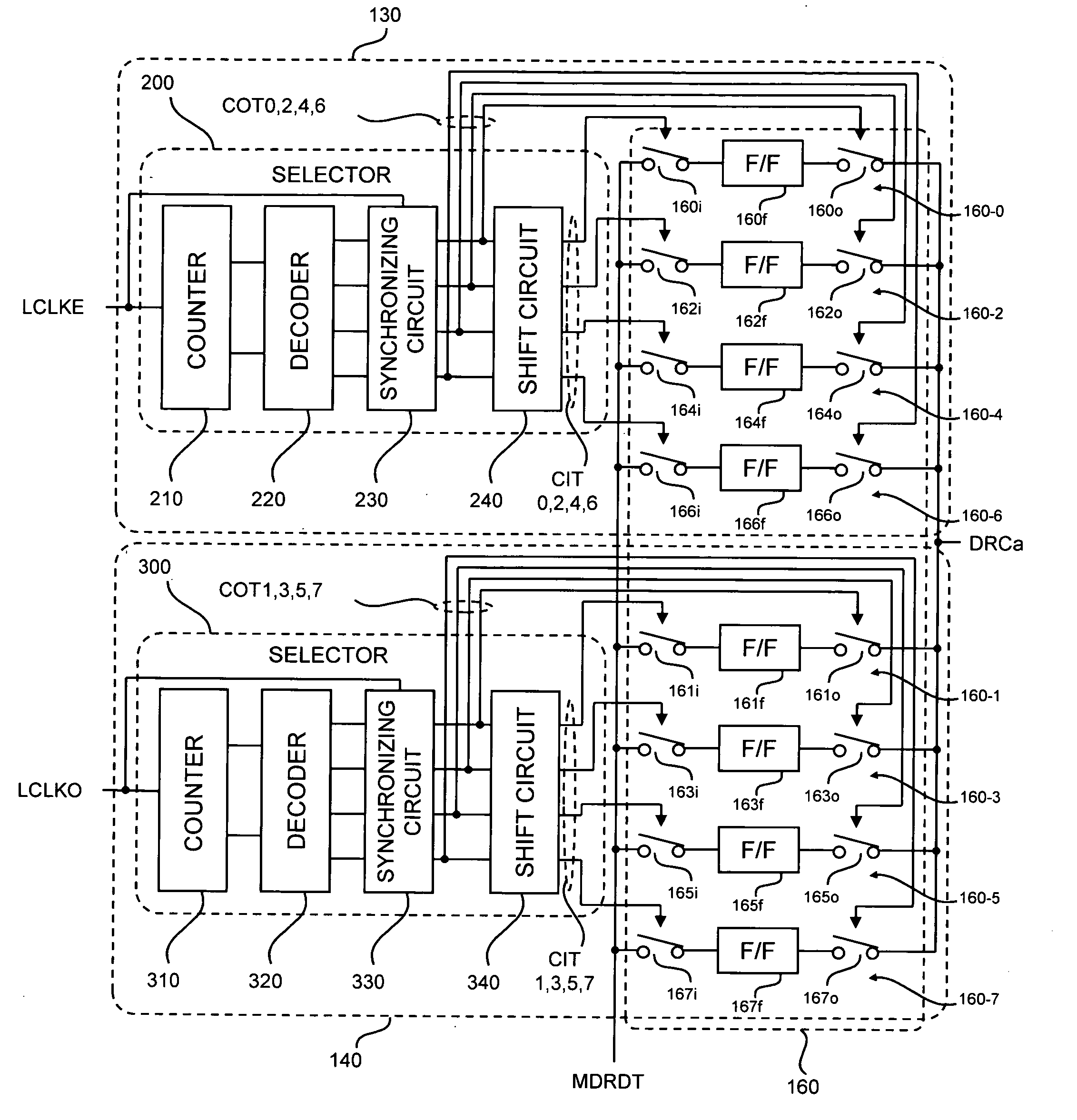
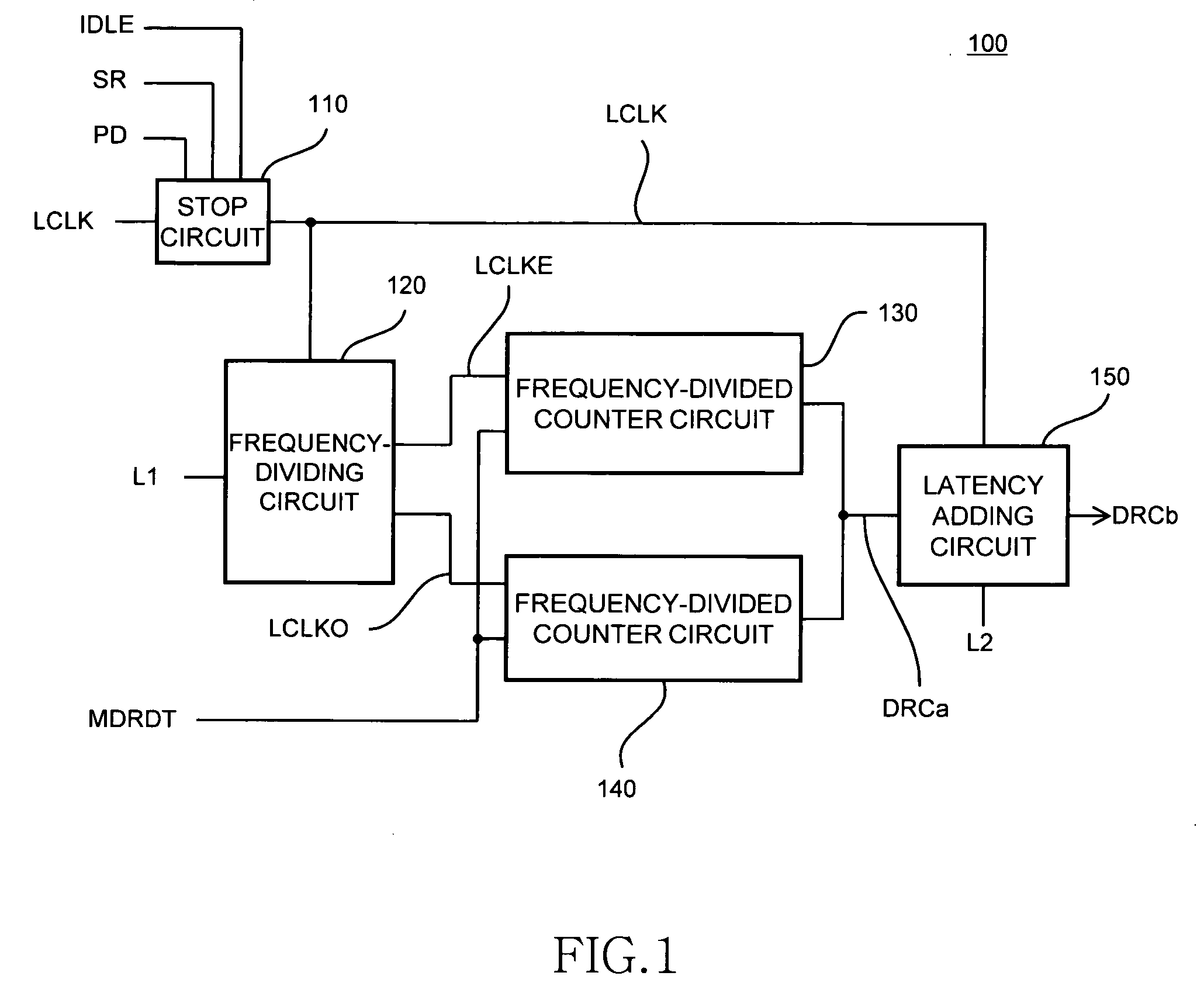
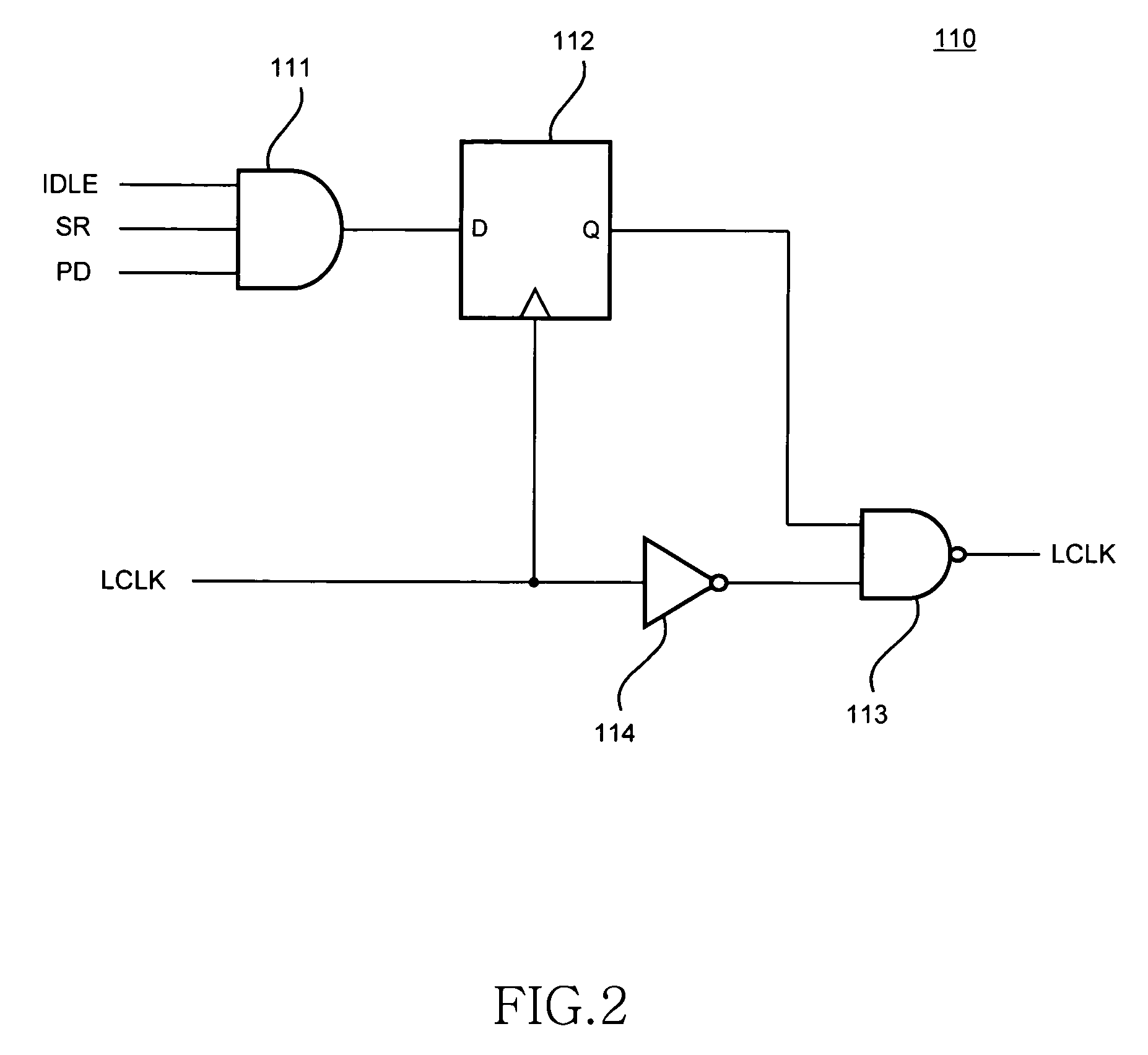
Latency counter, semiconductor memory device including the same, and data processing system
ActiveUS7826305B2Sufficient operation marginReduce digitsDigital storageData processing systemDividing circuits
A latency counter includes: a frequency-dividing circuit that generates a plurality of divided clocks LCLKE and LCLKO of which the phases differ each other based on an internal clock LCLK; and frequency-divided counter circuits each of which counts a latency of an internal command based on the corresponding divided clocks LCLKE and LCLKO. Thus, the counting of the latency is performed based not on the internal clock LCLK itself but on the divided clocks LCLKE and LCLKO obtained by frequency-dividing the internal clock LCLK. Thus, even when a frequency of the internal clock LCLK is high, an operation margin can be sufficiently secured.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
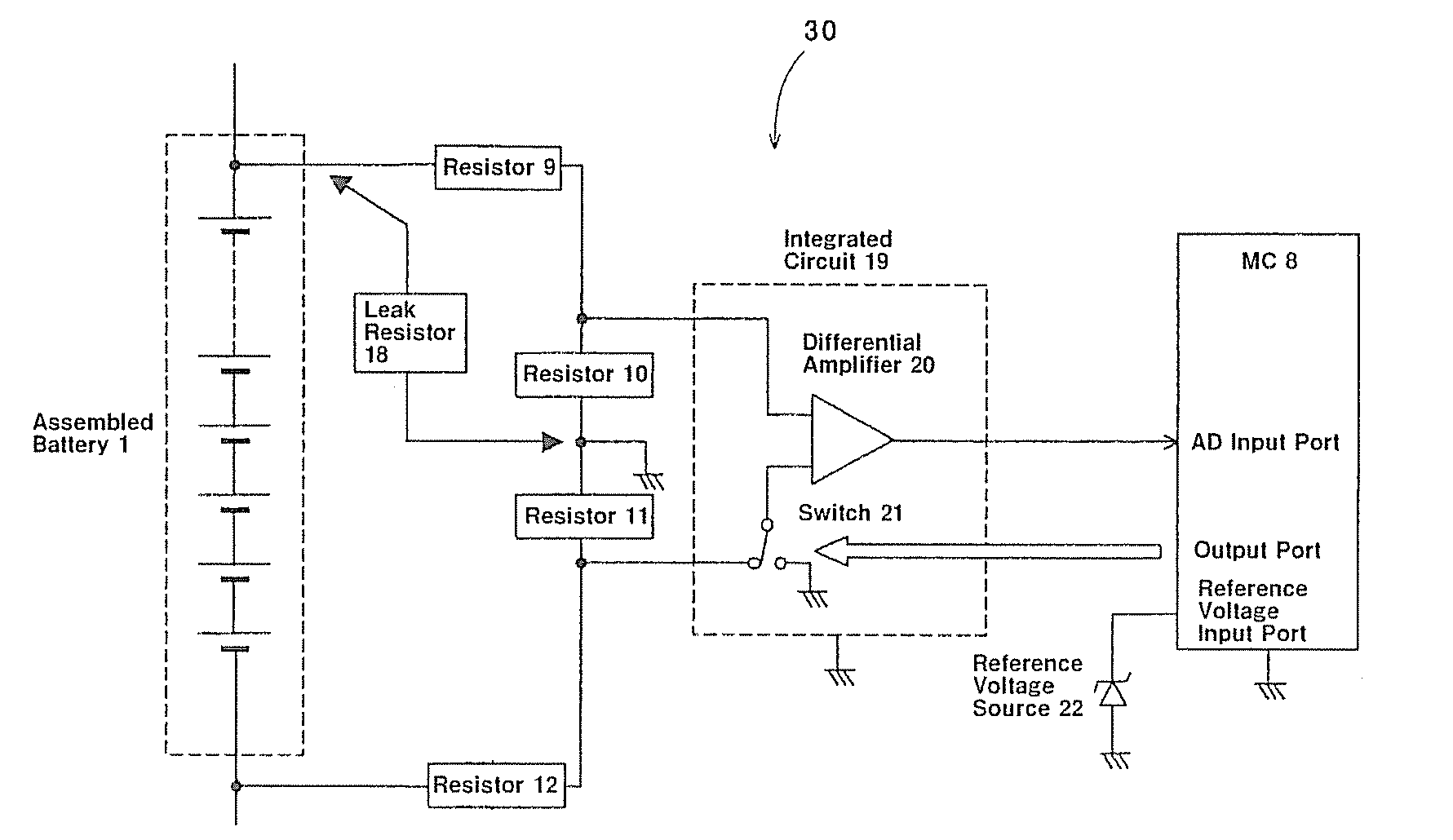
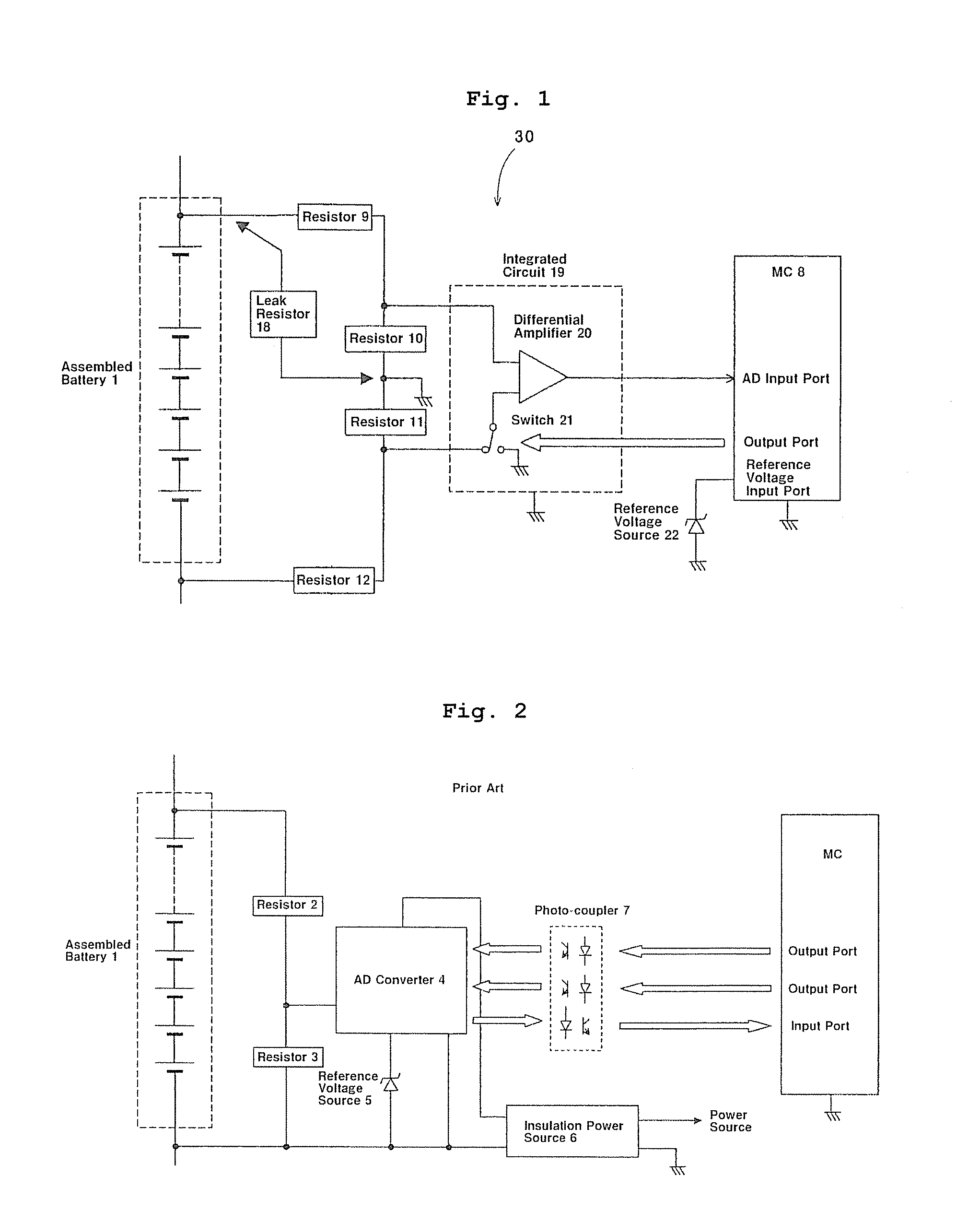
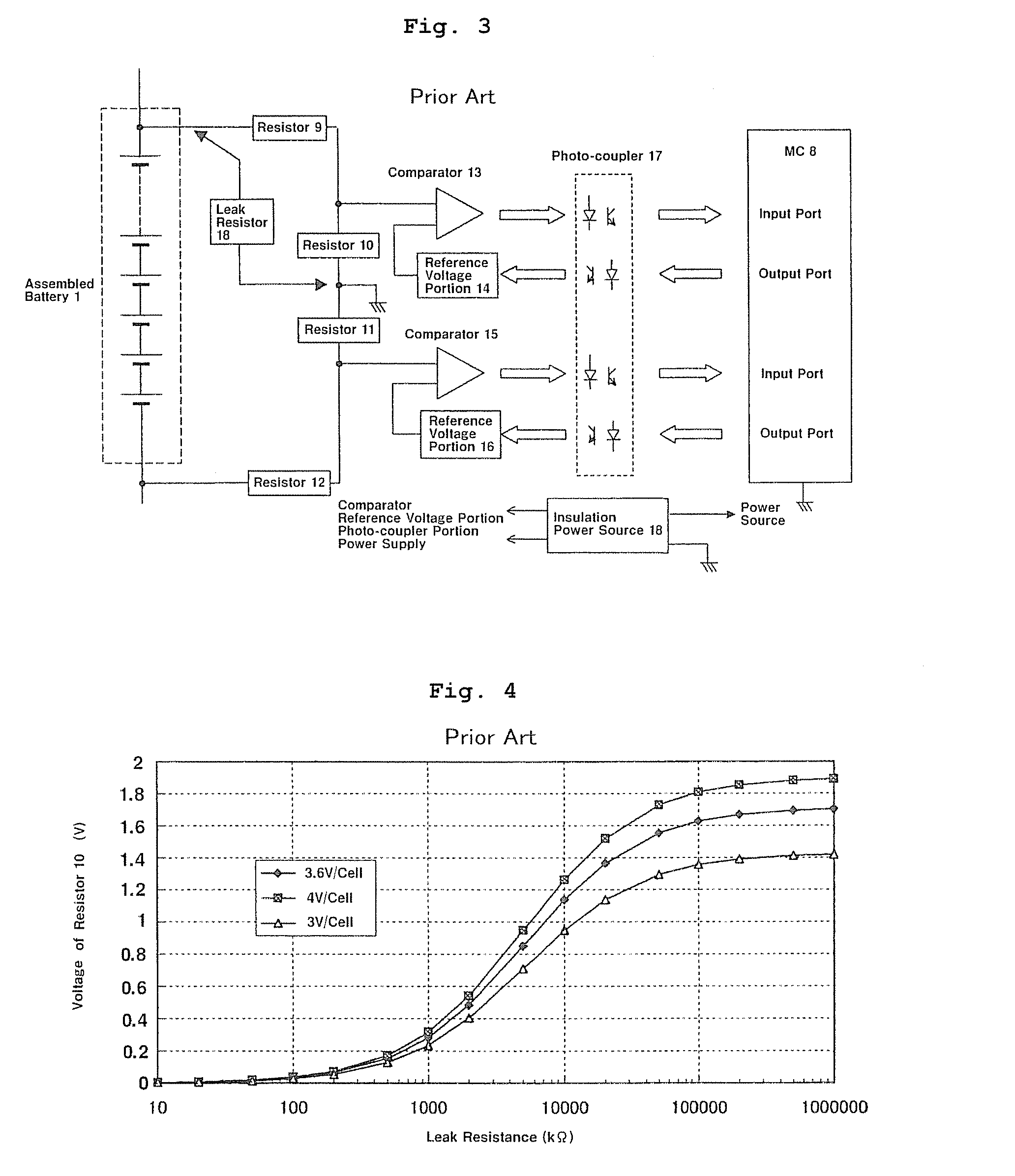
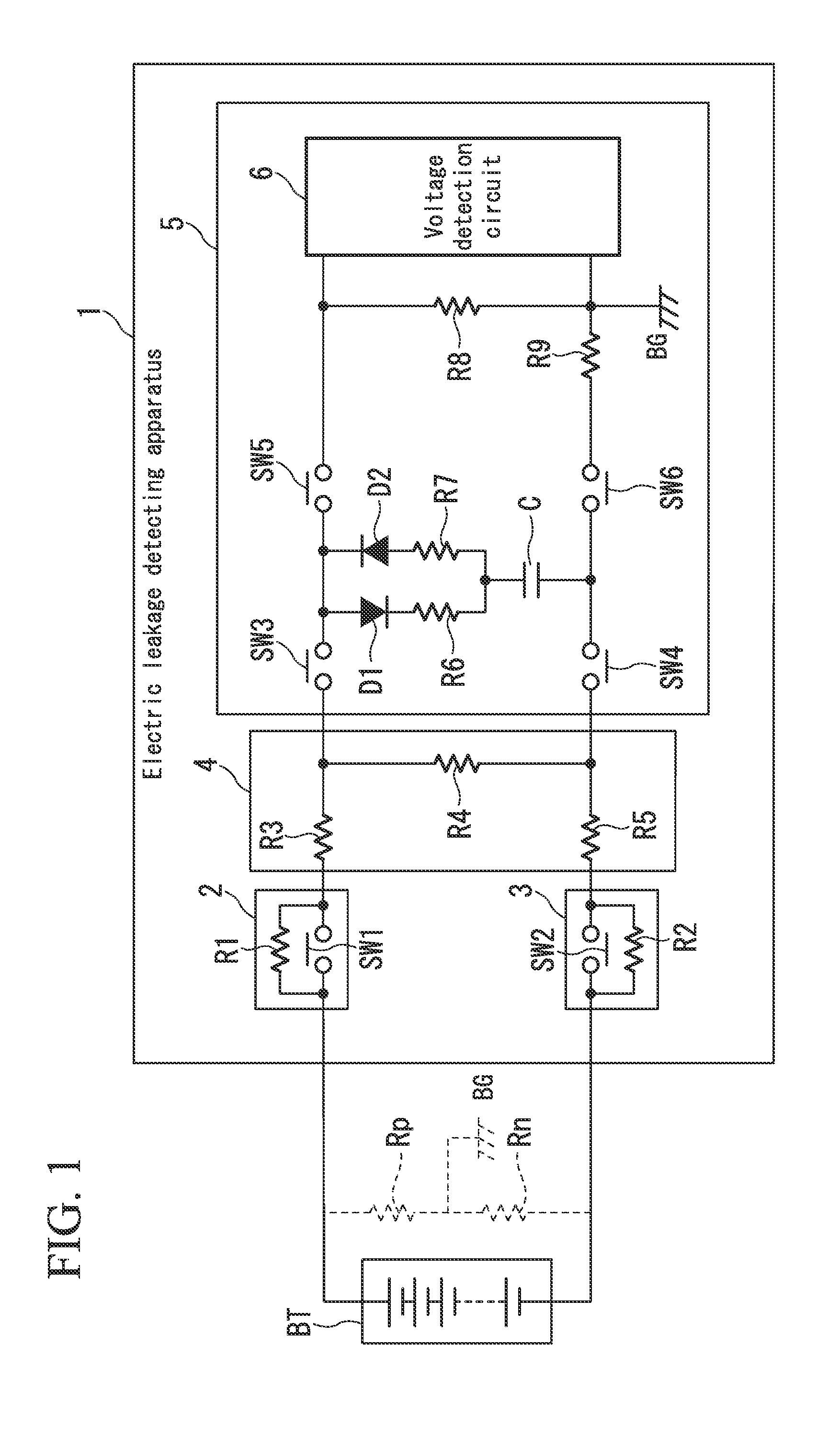
Assembled battery total voltage detection and leak detection apparatus
ActiveUS20080054907A1Small sizeReduce manufacturing costBatteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAudio power amplifierElectrical battery
The present invention provides an assembled battery total voltage detection and leak detection apparatus which is reduced in size and is reduced in manufacturing costs. Detection of a total voltage is performed at a measurement time of a total voltage of an assembled battery 1 by connecting an output of a positive electrode resistance voltage dividing circuit composed of resistors 9 and 10 to + input of a differential amplifier 20 and connecting an output of a negative electrode resistance voltage dividing circuit composed of resistors 12 and 11 to − input of the amplifier 20, and it performs leak detection at a leak detection time by connecting an output of a positive electrode resistance voltage dividing circuit to + input of the amplifier 20 and connecting + input of the amplifier 20 to the minus input of the differential amplifier 20 to measure an output voltage of the amplifier 20. The total voltage detection and the leak detection can be performed without requiring an insulation type voltage sensor, an insulation power source, photo-couplers, or the like.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
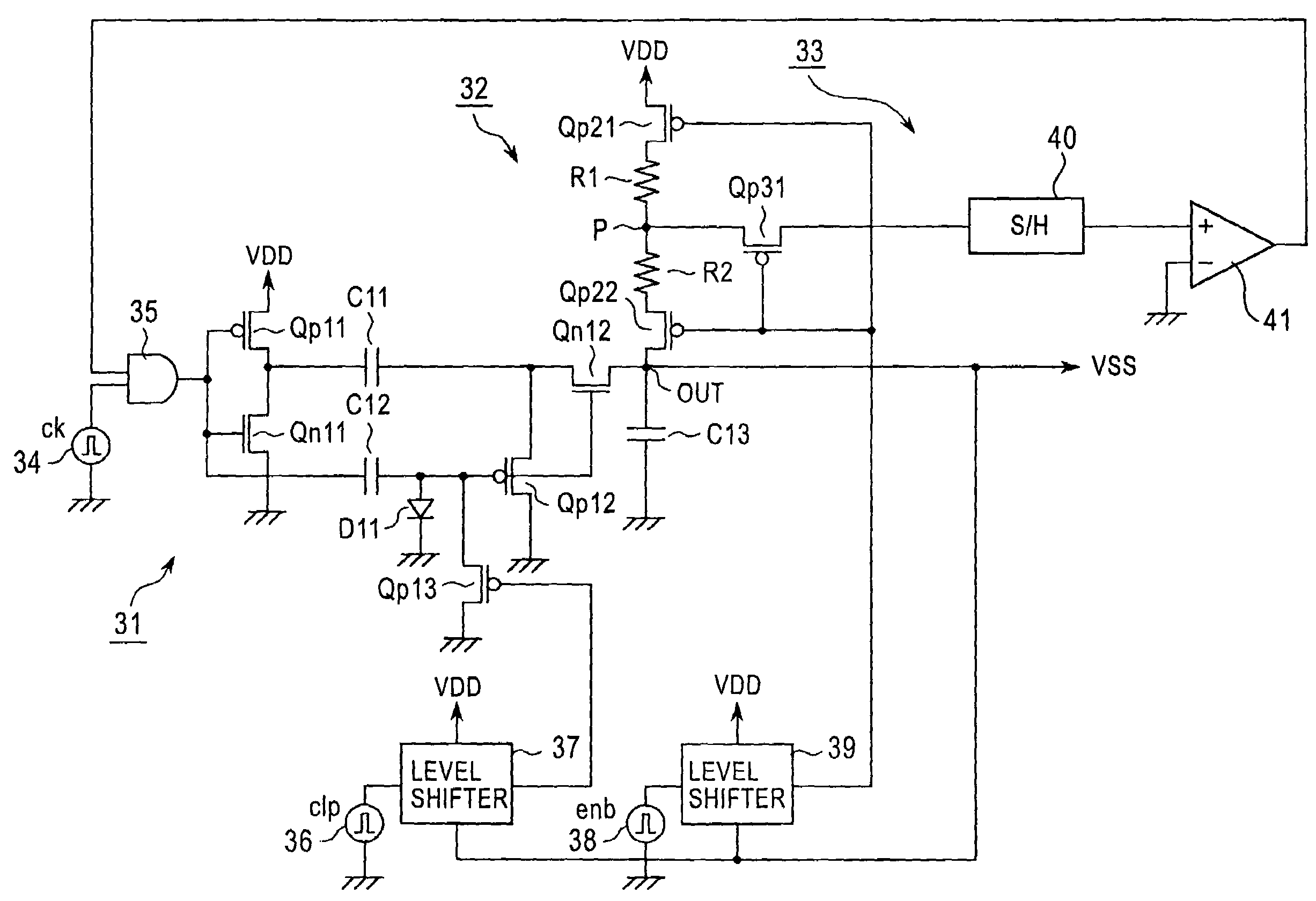
Power supply generating circuit, display apparatus, and portable terminal device
ActiveUS7129939B2Reduce power lossImprove efficiencyPower managementPulse automatic controlDc dc converterDividing circuits
A power supply generating circuit, a display apparatus incorporating the same, and a portable terminal device using the display apparatus as an output display unit are provided. In a DC-DC converter having a charge pump circuit (31), a voltage dividing circuit (32), and a regulation circuit (33), p-channel MOS transistors (Qp21, Qp22, Qp31) are turned on / off based on an enable pulse enb to make the voltage dividing circuit (32) and a comparator (41) active only for a period of regulation time and inactive otherwise. This can cause a current to flow in voltage-divider resistors (R1, R2) and the comparator (41) only for a certain period of time required for the regulation operation, thus reducing the power consumption loss caused by a constant current flow in the voltage-divider resistors (R1, R2) and the comparator (41).
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY WEST
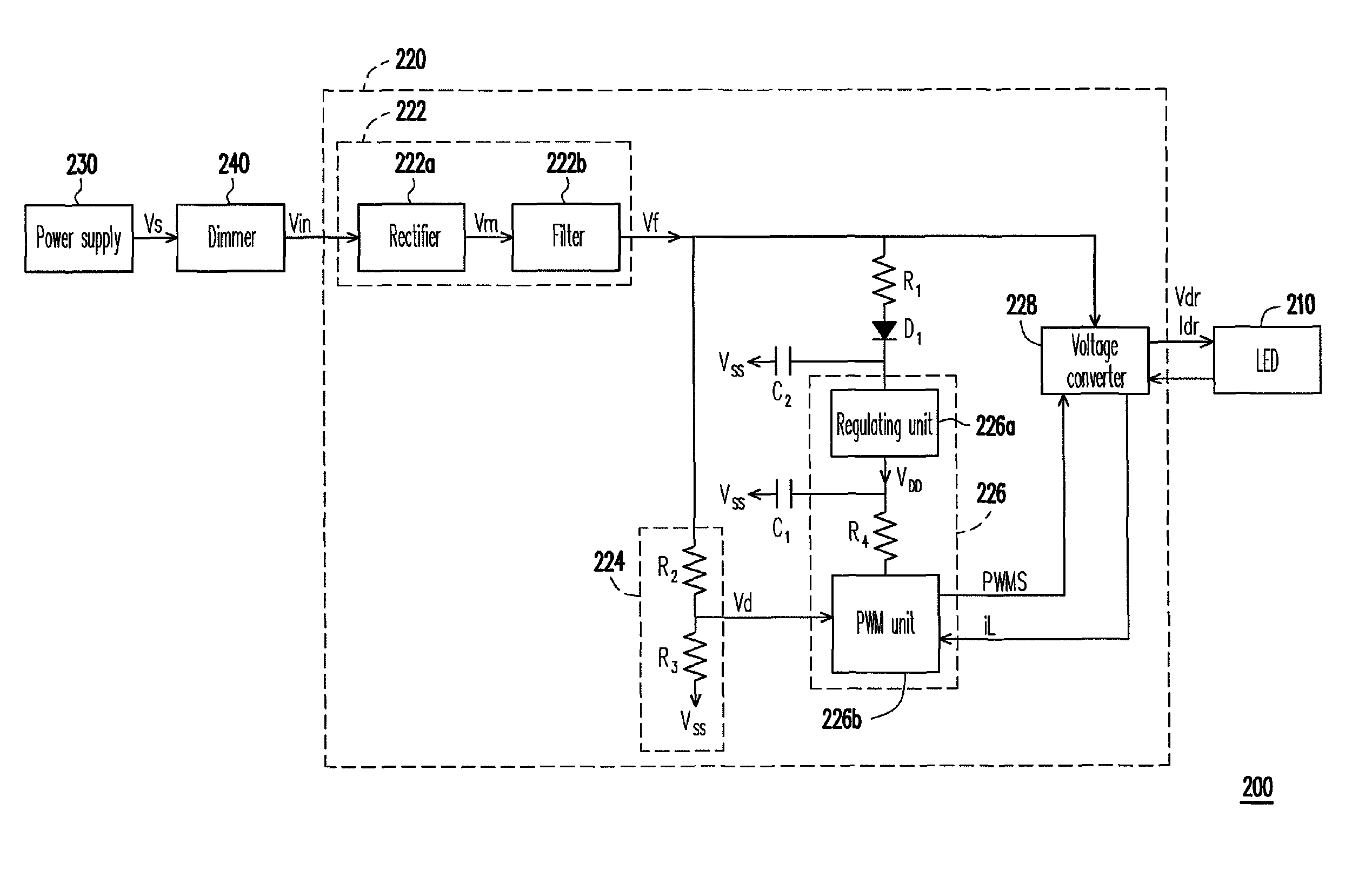
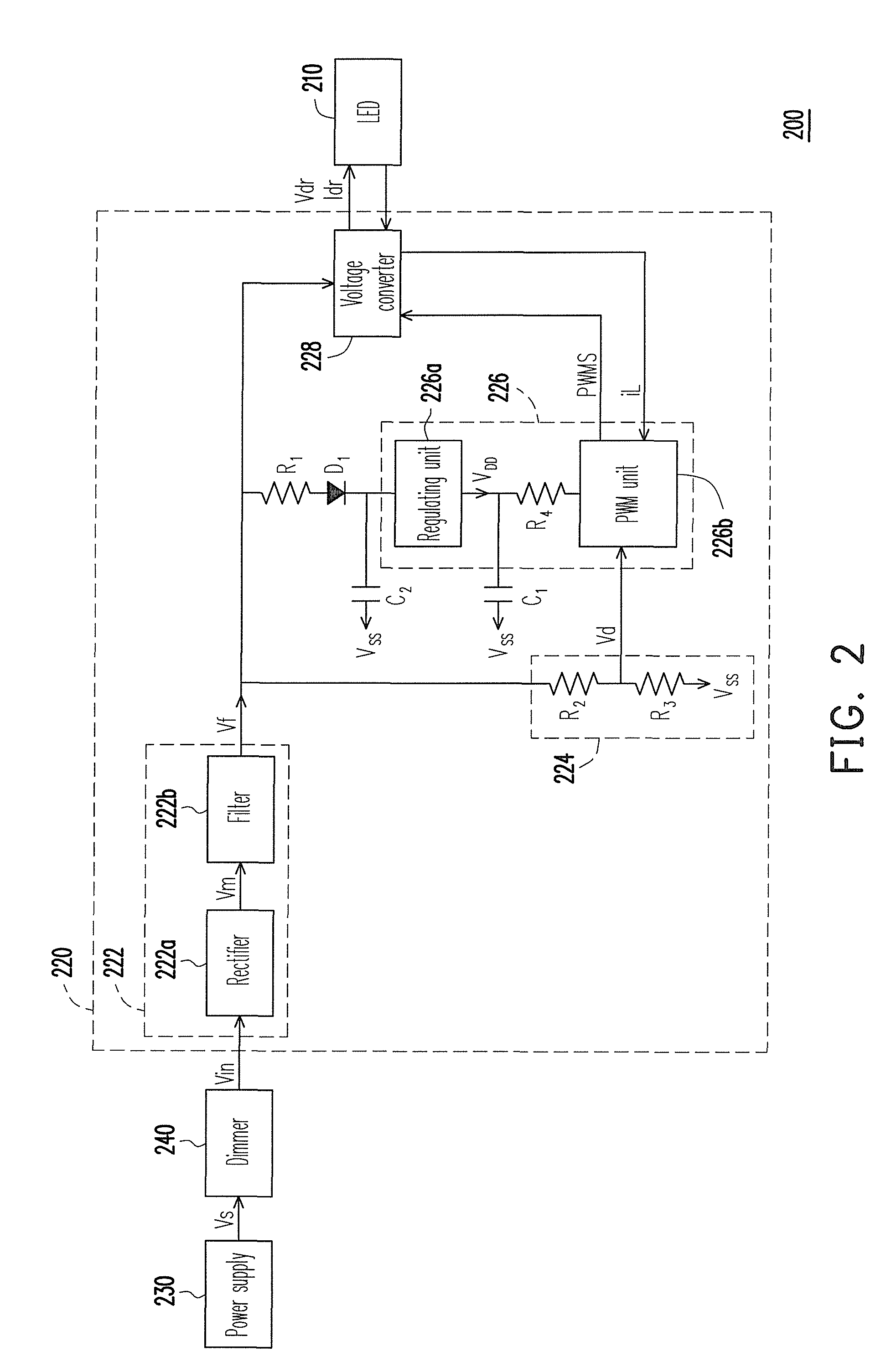
Driving circuit of light emitting diode and lighting apparatus
InactiveUS8098021B2Stable currentStable voltageElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesVoltage converterDriving current
A driving circuit of a light emitting diode (LED) includes a rectifier unit, a voltage-dividing circuit, a control unit, a voltage converter, a resistance and a capacitor. The rectifier unit rectifies an AC power to generate a first operation voltage. The voltage-dividing circuit generates a voltage-dividing signal. The control unit includes a regulating unit and a pulse width modulation (PWM) unit. An output terminal of the regulating unit is coupled to the PWM unit. The PWM unit outputs a PWM signal. The voltage converter adjusts a driving voltage and a driving current of the LED. The resistance is coupled between an output terminal of the regulating unit and a diode. The capacitor is coupled between a power input terminal of the regulating unit and a ground terminal. The PWM unit adjusts the PWM signal according to the voltage-dividing signal and a feedback signal output by the voltage converter.
Owner:CAL COMP ELECTRONICS
Electric leakage detecting apparatus
InactiveUS20140021961A1Prevent degradationIncrease in apparatus cost to minimumShort-circuit testingElectrical resistance and conductanceDividing circuits
An electric leakage detecting apparatus, in an electric leakage detecting apparatus which is insulated from a chassis ground and detects electric leakages of a battery, is provided with: a voltage dividing circuit that divides an output voltage of the battery; an electric leakage determining circuit provided at a rear stage of the voltage dividing circuit, that determines the presence of an electric leakage based on a voltage detected by a circuit that respectively connects to a positive electrode side insulation resistance or a negative electrode side insulation resistance of the battery; and a dark current inhibit circuit in which a switch and a resistance are connected in parallel, that is inserted between at least either one of wiring that connects a positive terminal of the battery and the voltage dividing circuit, and wiring that connects a negative terminal of the battery and the voltage dividing circuit.
Owner:KEIHIN CORP
Charging machine
ActiveCN101359841AAvoid thermal runawayMeet charging requirementsBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerMicrocontrollerSwitching power
Disclosed is a charging machine including a main charging circuit and a charging control circuit, the main charging circuit comprises a filter circuit, a rectifier filter circuit, a pulse bleeder circuit, a half-bridge inversion circuit, a drive control circuit and a high frequency rectifier charging circuit, the charging control circuit comprises a power supply circuit, a voltage stabilizing circuit, a self-recycle circuit, a current detecting circuit, a voltage detecting circuit and a temperature detecting circuit, and the charging control circuit also comprises a control display circuit and a pulse modulation switching power supply integrating control circuit. The charging machine can effectively release the sulfation phenomenon of a battery plate by controlling a single chip microcomputer in the control display circuit to adopt multi-stage pulse type charging method, fives stages including constant current, constant voltage, floating charge I, average charge and floating charge II. Each stage in process outputs different duty cycle pulsing signal through the control of single chip microcomputer and then a half-bridge power tube is controlled to reach intermittent pulse current charge and depolarization effect.
Owner:上海施能电器设备有限公司
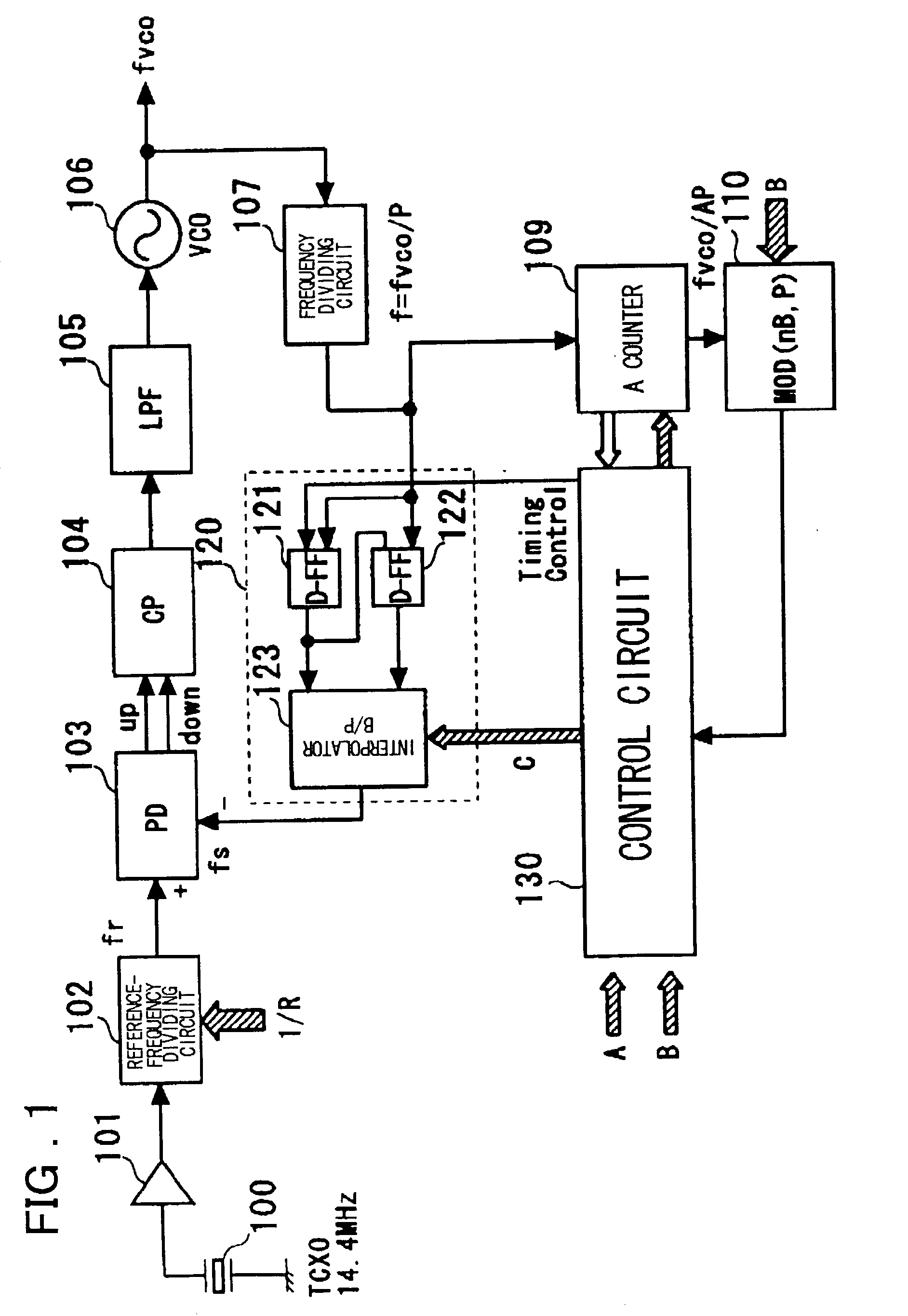
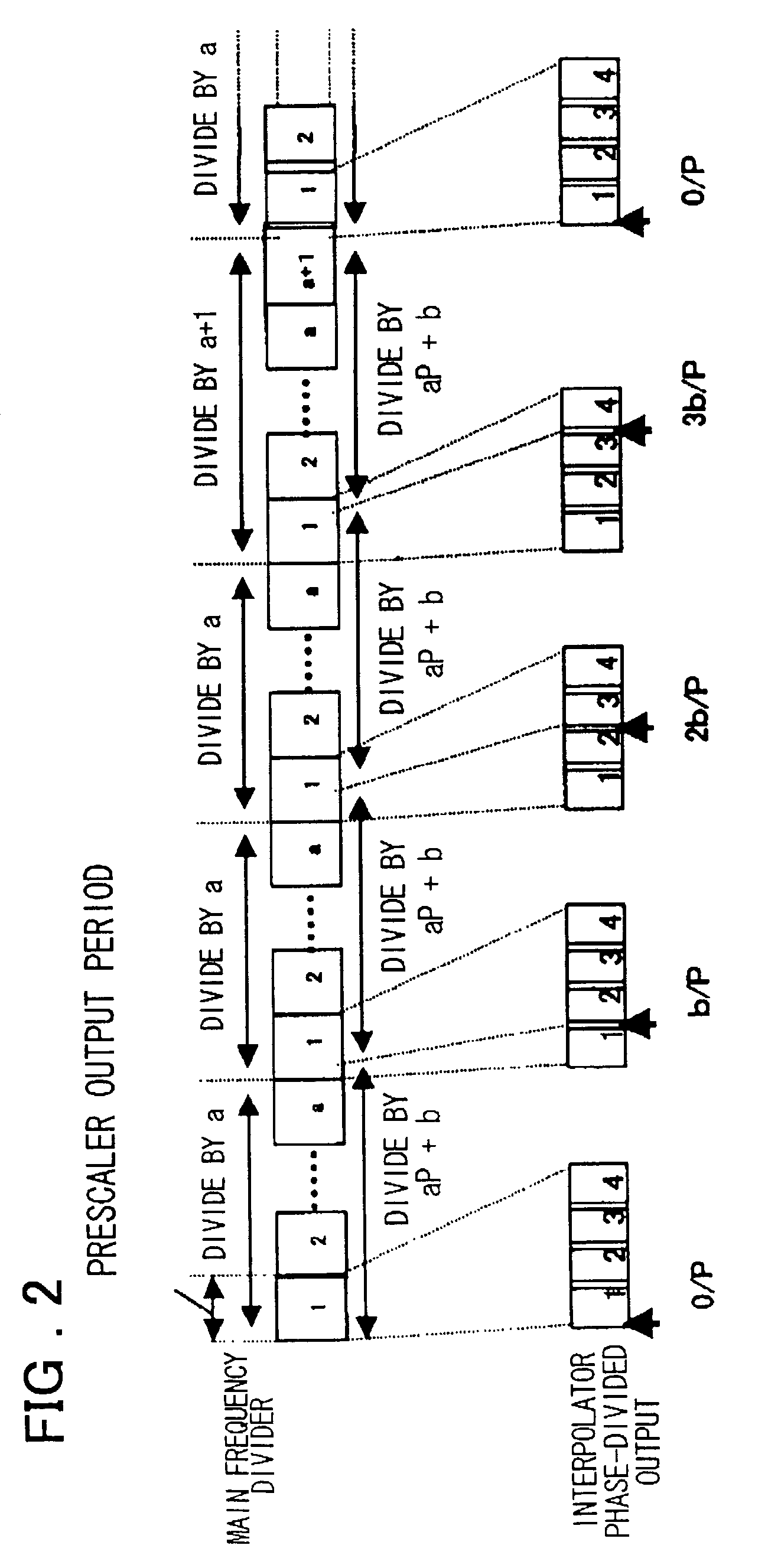
Clock control method, frequency dividing circuit and PLL circuit
InactiveUS20030048863A1Reduce power consumptionTiming design is facilitatedPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersLoop filterDividing circuits
A PLL circuit includes a phase comparator; a charge pump; a loop filter; a voltage-controlled oscillator; a frequency dividing circuit; an A counter for dividing the P-frequency-divided output; circuits for generating two signals, which have a phase difference equivalent to one period of the P-frequency-divided output of the frequency dividing circuit; and an interpolator for producing an output signal obtained by interpolating the phase difference between the two signals in accordance with an interior division ratio. The interpolator interpolates in steps of a value obtained by dividing the phase difference by P and incrementing or decrementing a value B, which decides an interior division ratio B:P-B, by B whenever frequency-division by A is performed, and a control circuit. The phase of the output of the interpolator is fed to the phase comparator and compared with the phase of a reference clock, and divides by a frequency-dividing factor.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
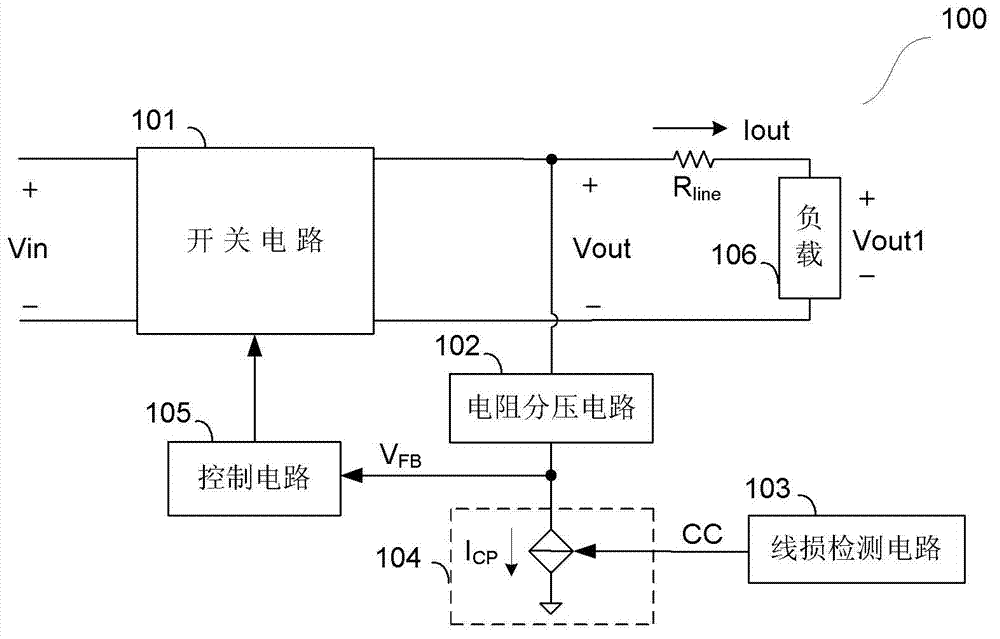
Switching voltage stabilization circuit and voltage feedback circuit as well as voltage feedback method of voltage feedback circuit
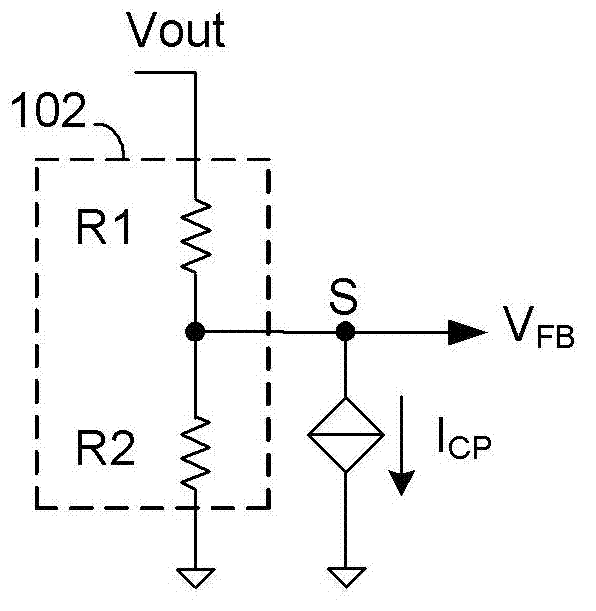
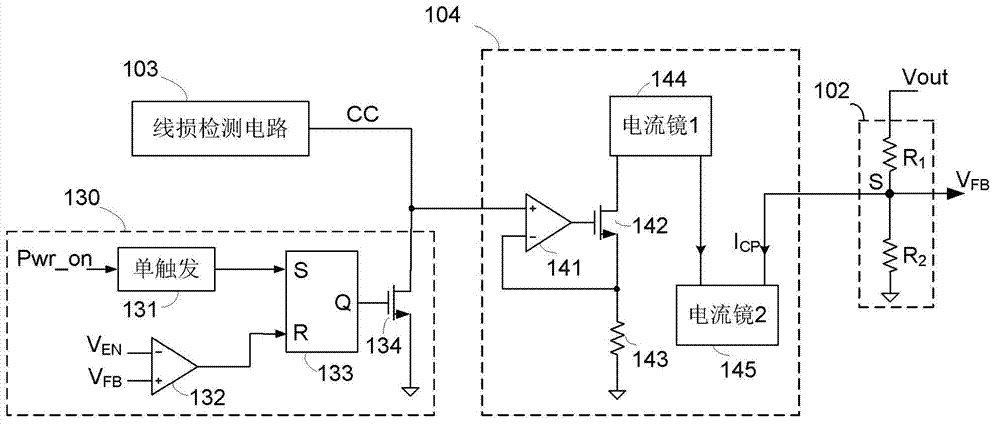
ActiveCN102832806AConstant output voltageApparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationDividing circuitsControl signal
The invention discloses a switching voltage stabilization circuit and a voltage feedback circuit as well as a voltage feedback method of the voltage feedback circuit. The switching voltage stabilization circuit comprises a switching circuit for converting input voltage into output voltage and output current; the voltage feedback circuit comprises a resistance voltage sharing circuit for sampling the output voltage, a line loss detection circuit and a controlled current source circuit; a compensation control signal is supplied to the output end of the line loss detection circuit and is in direct proportion to the output current; the controlled current source circuit is provided with a control end, a grounding end and an output end; the control end is coupled to the output end of the line loss detection circuit and receives the compensation control signal; the grounding end is grounded; the output end supplies compensation current; and the output end of the resistance voltage sharing circuit is connected with the output end of the controlled current source circuit to supply feedback voltage which represents backward output voltage.
Owner:CHENGDU MONOLITHIC POWER SYST
System for automatically testing parameters of quartz crystal oscillator
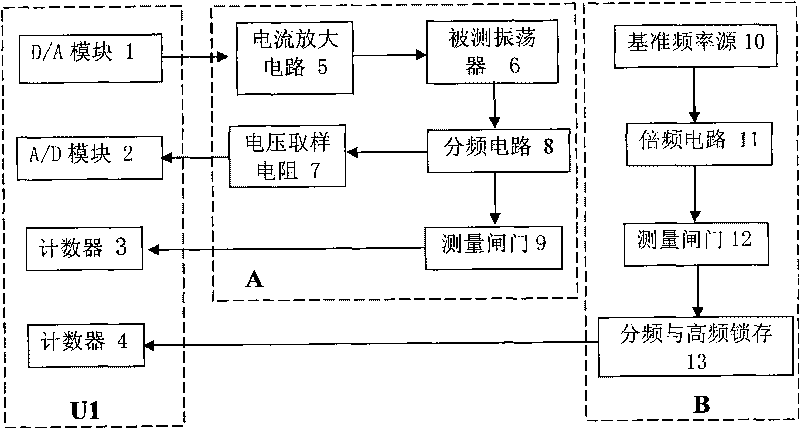
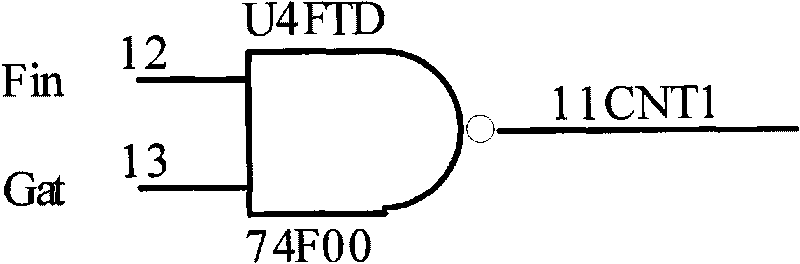
InactiveCN101713811AElectronic circuit testingFrequency to pulse train conversionMicrocontrollerFrequency counter
The invention discloses a system for automatically testing the parameters of a quartz crystal oscillator, which comprises a master computer and a parameter test card connected with the main board of the master computer, wherein the parameter test card comprises a singlechip and a test circuit and a reference circuit which are connected with the singlechip respectively. The singlechip has a D / A module, an A / D module, a first counter, a second counter and a timer. The test circuit comprises a current amplification circuit, a voltage sampling resistor, a frequency dividing circuit, a first measurement gate control circuit and the crystal oscillator to be measured. The reference circuit comprises a reference frequency source, a frequency multiplication circuit, a second measurement gate control circuit and a frequency dividing and high-frequency signal latch circuit. In the invention, the test card integrates the functions of all apparatuses such as a frequency counter, a digital voltmeter and a digital oscillometer and can be directly inserted in the main board of the computer, and the fully automatic test of various parameters, such as working frequency, working current and start up time, of the quartz crystal oscillator can be realized by a control program.
Owner:天津必利优科技发展有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com