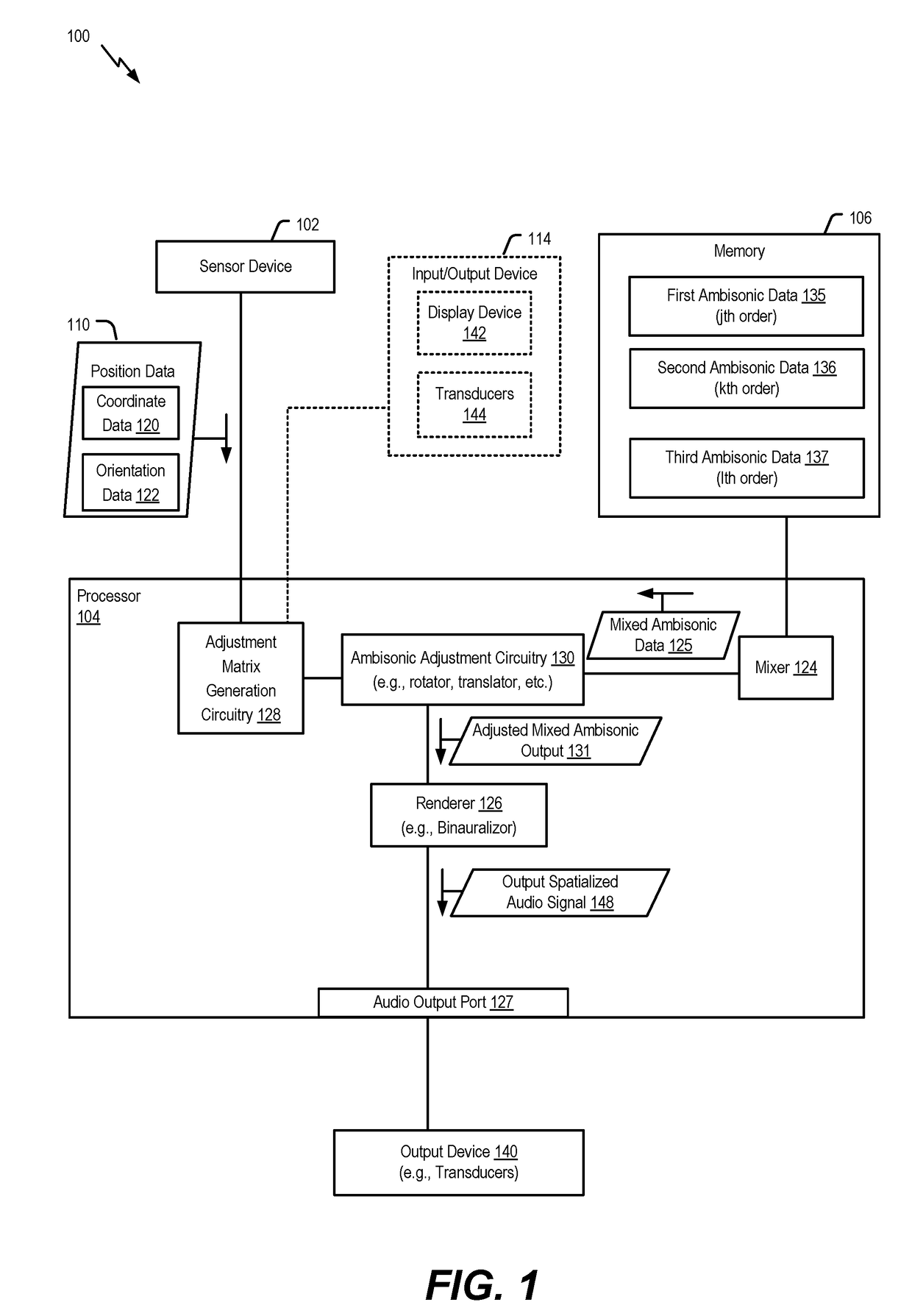
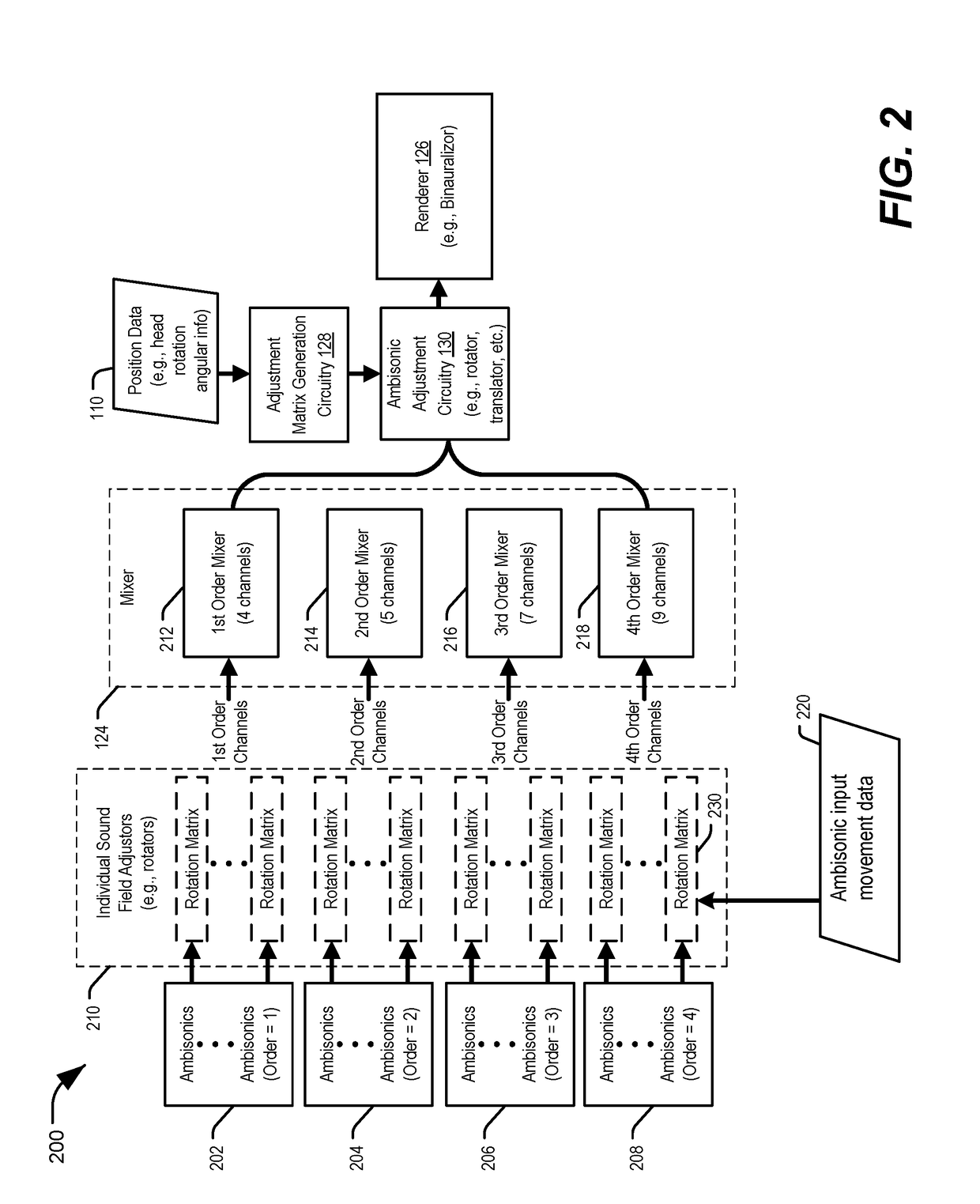
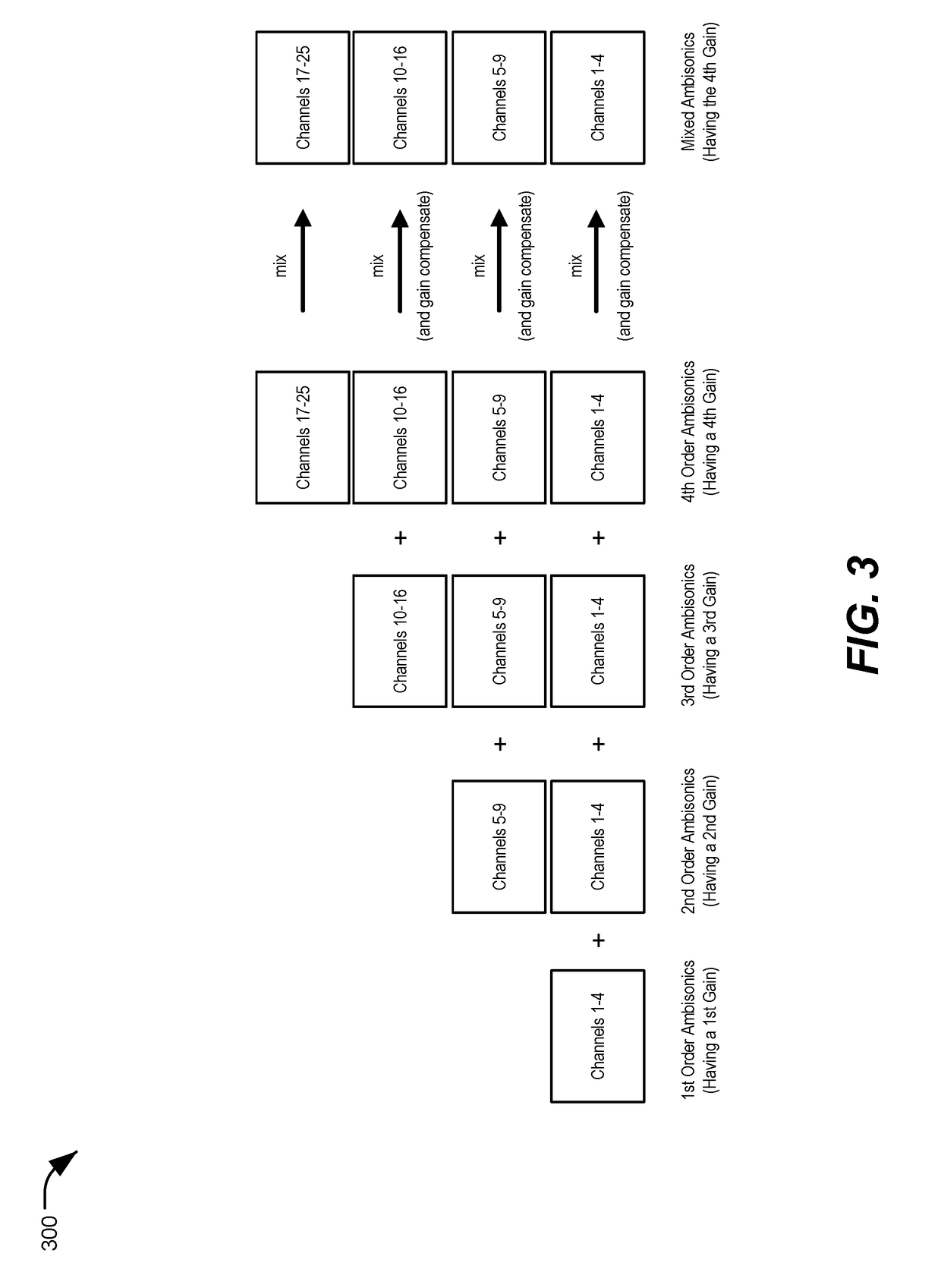
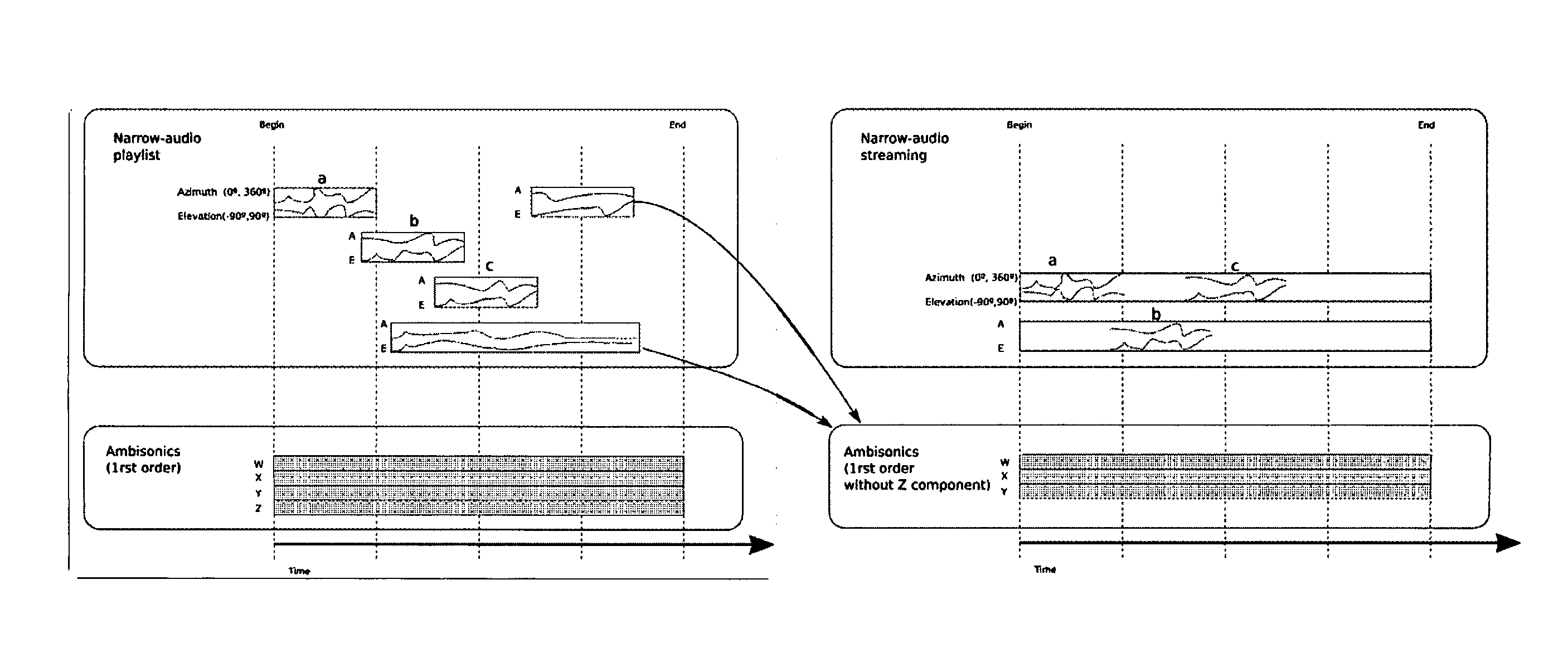
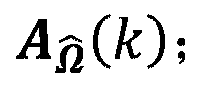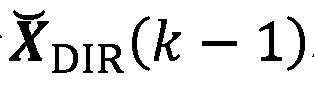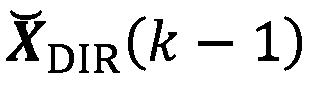Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
78 results about "Ambisonics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
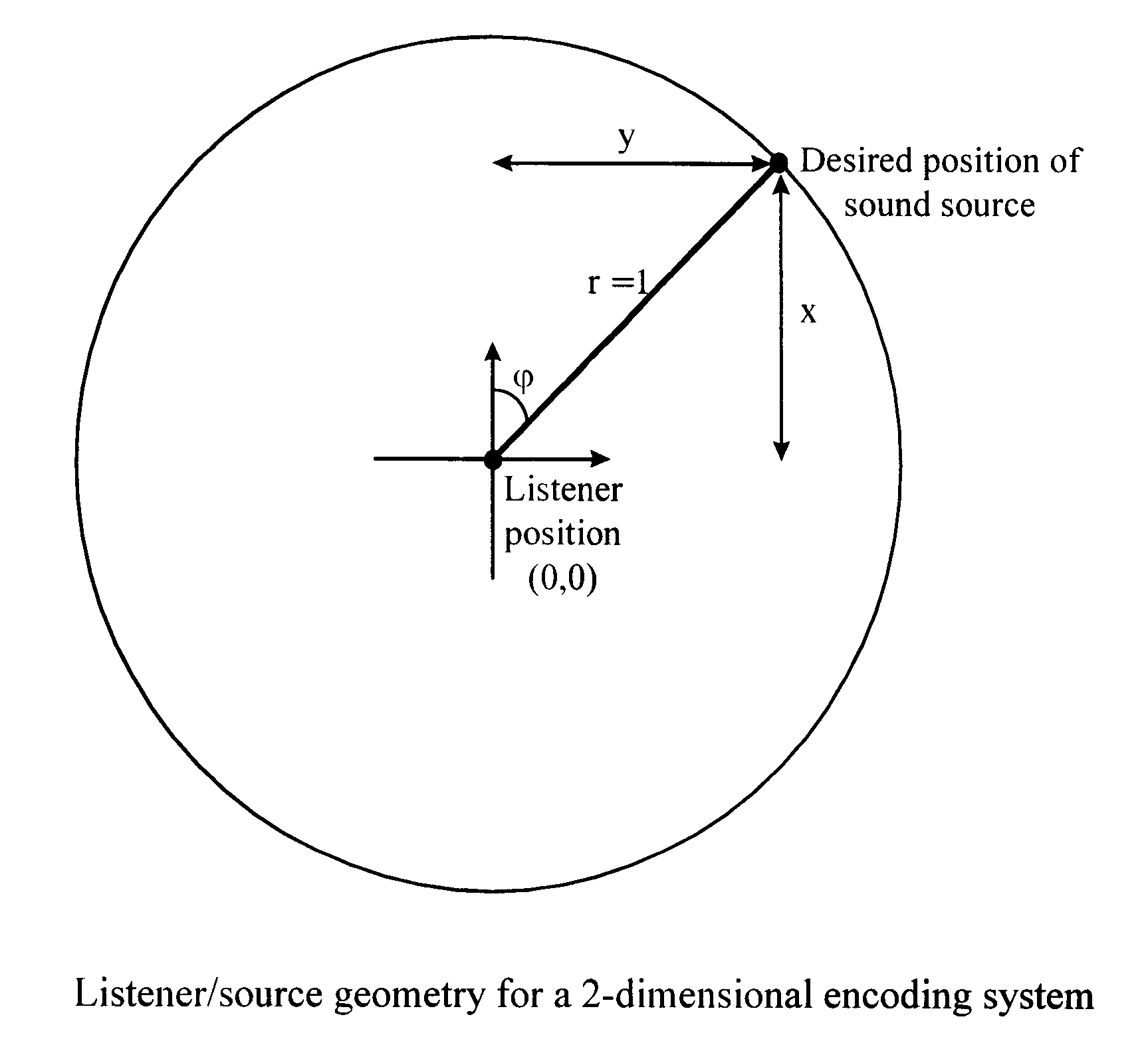
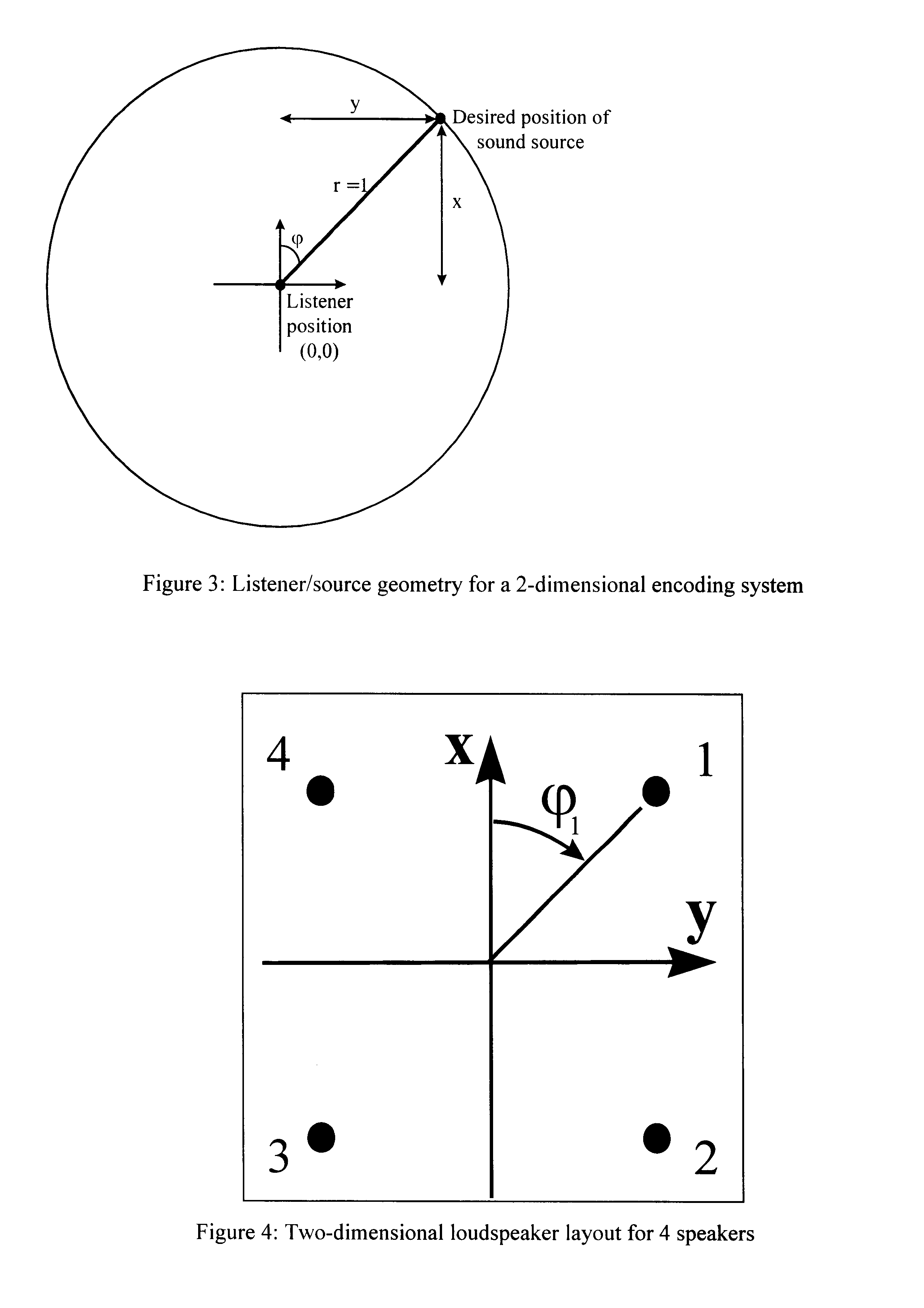
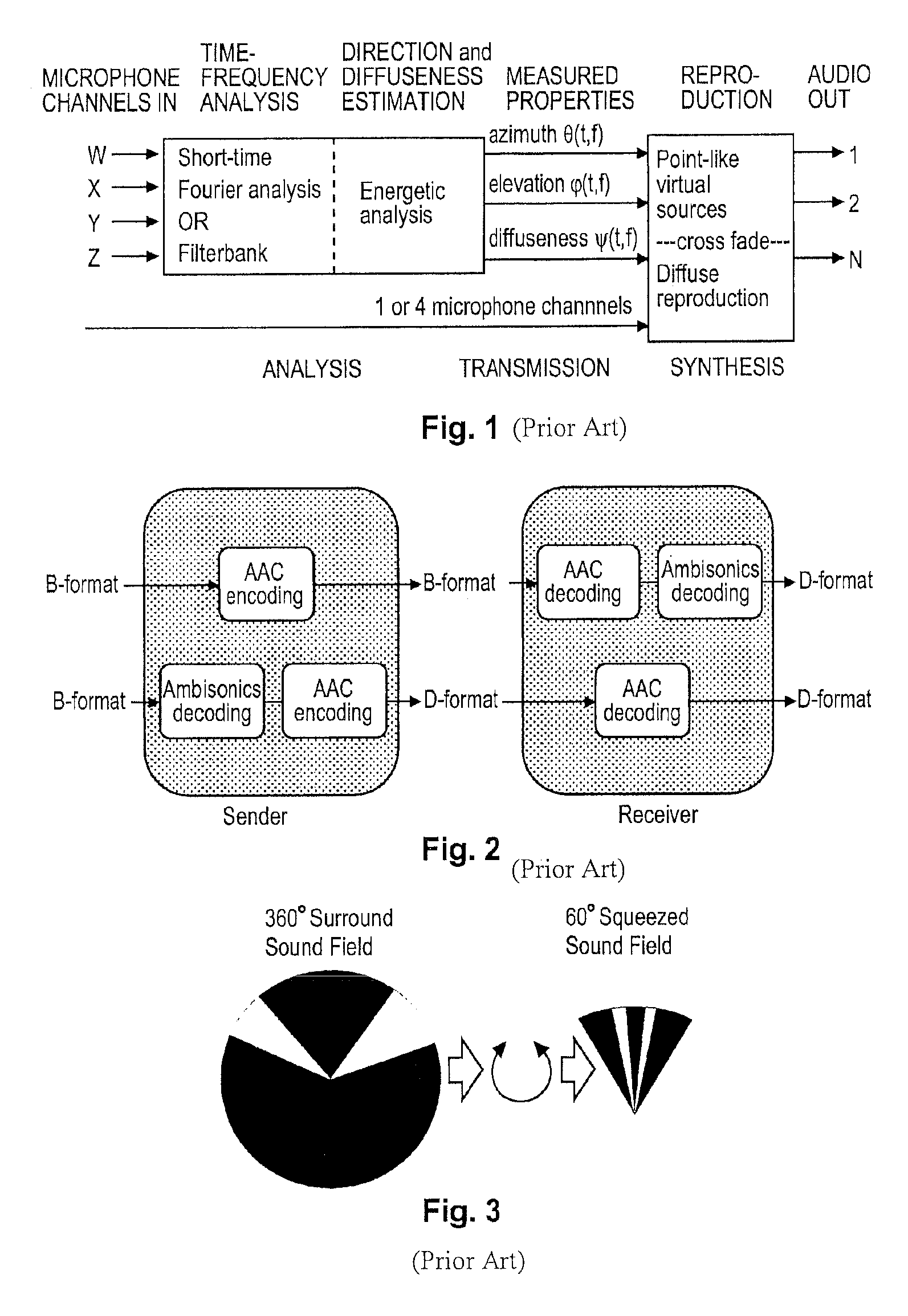
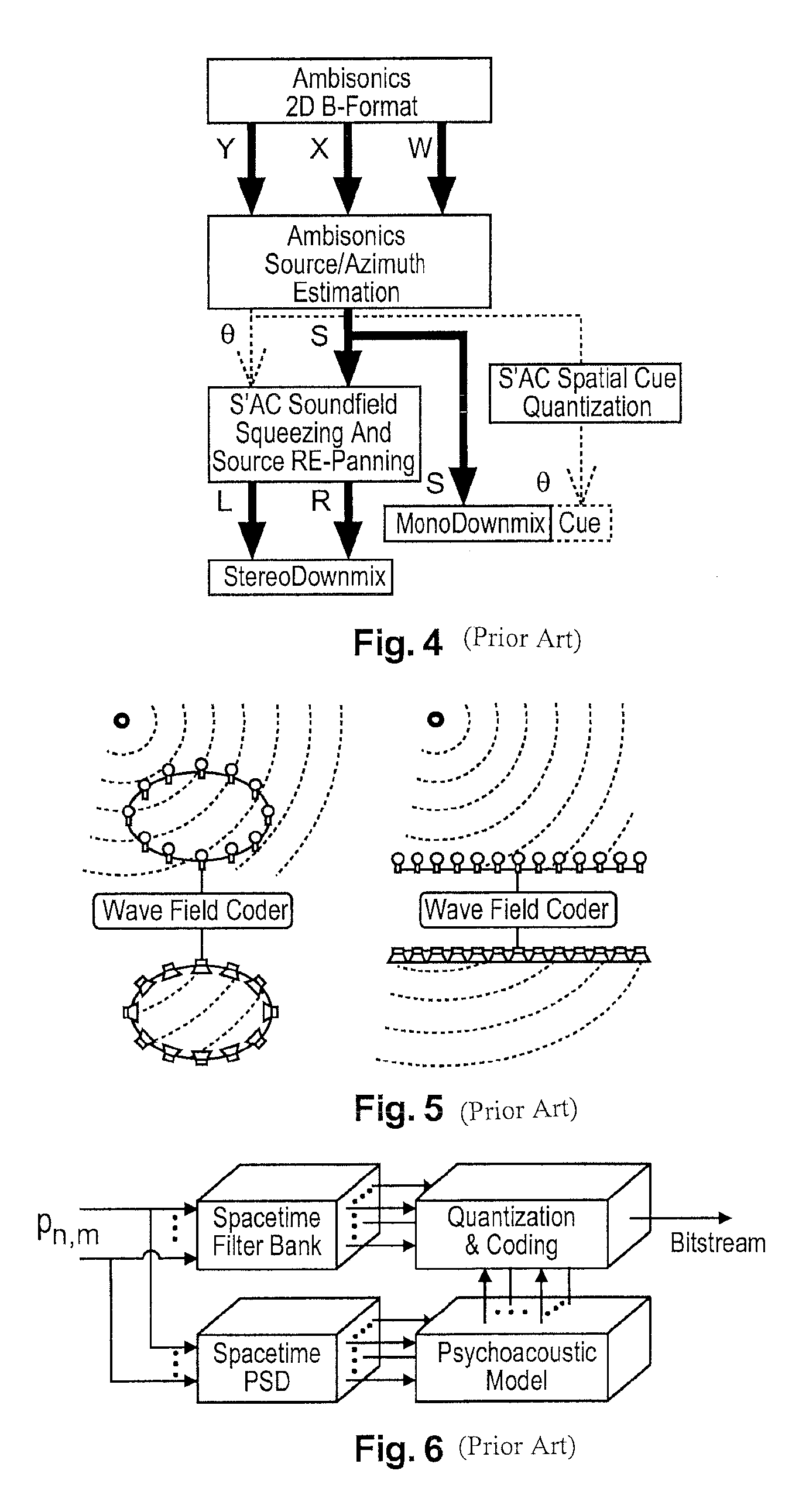
Ambisonics is a full-sphere surround sound format: in addition to the horizontal plane, it covers sound sources above and below the listener. Unlike other multichannel surround formats, its transmission channels do not carry speaker signals. Instead, they contain a speaker-independent representation of a sound field called B-format, which is then decoded to the listener's speaker setup. This extra step allows the producer to think in terms of source directions rather than loudspeaker positions, and offers the listener a considerable degree of flexibility as to the layout and number of speakers used for playback.
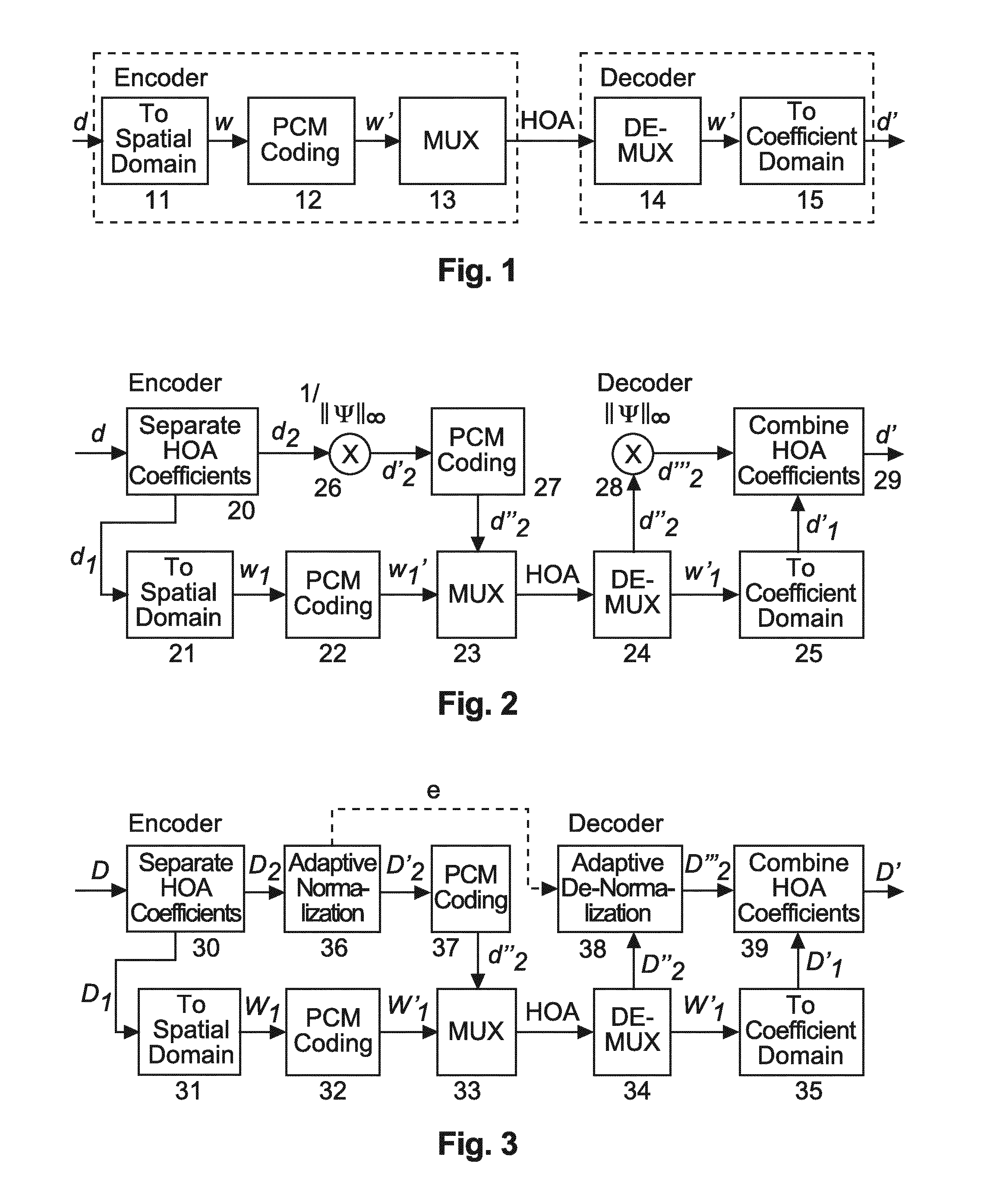
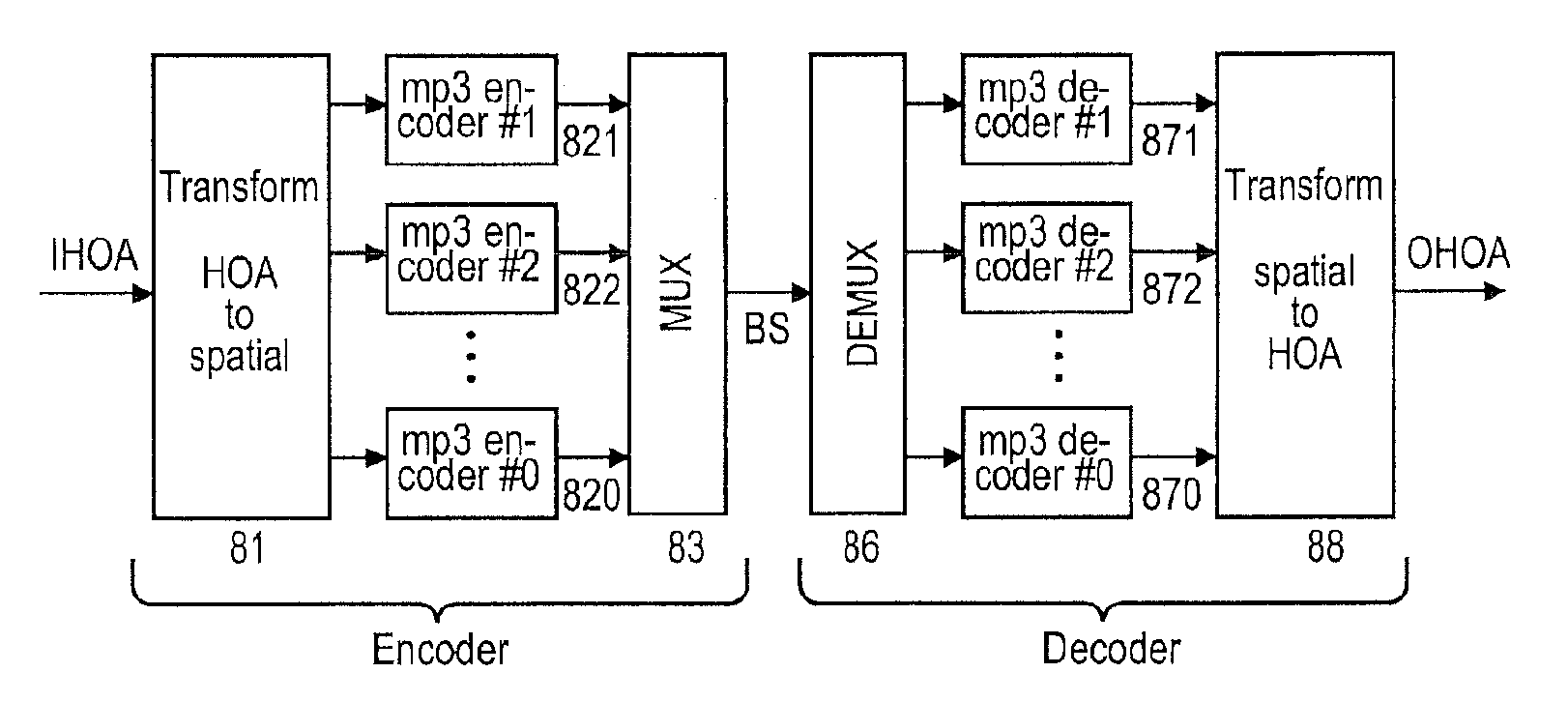
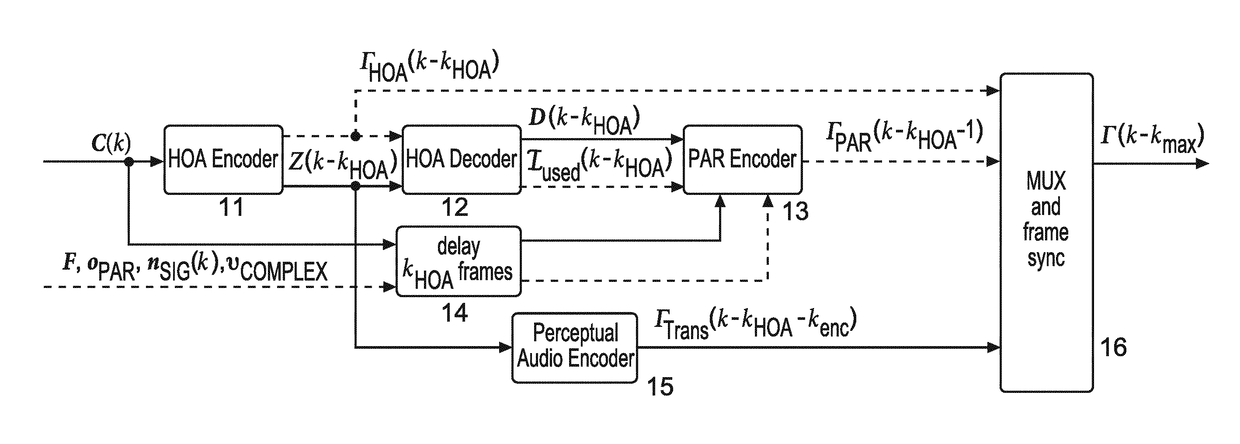
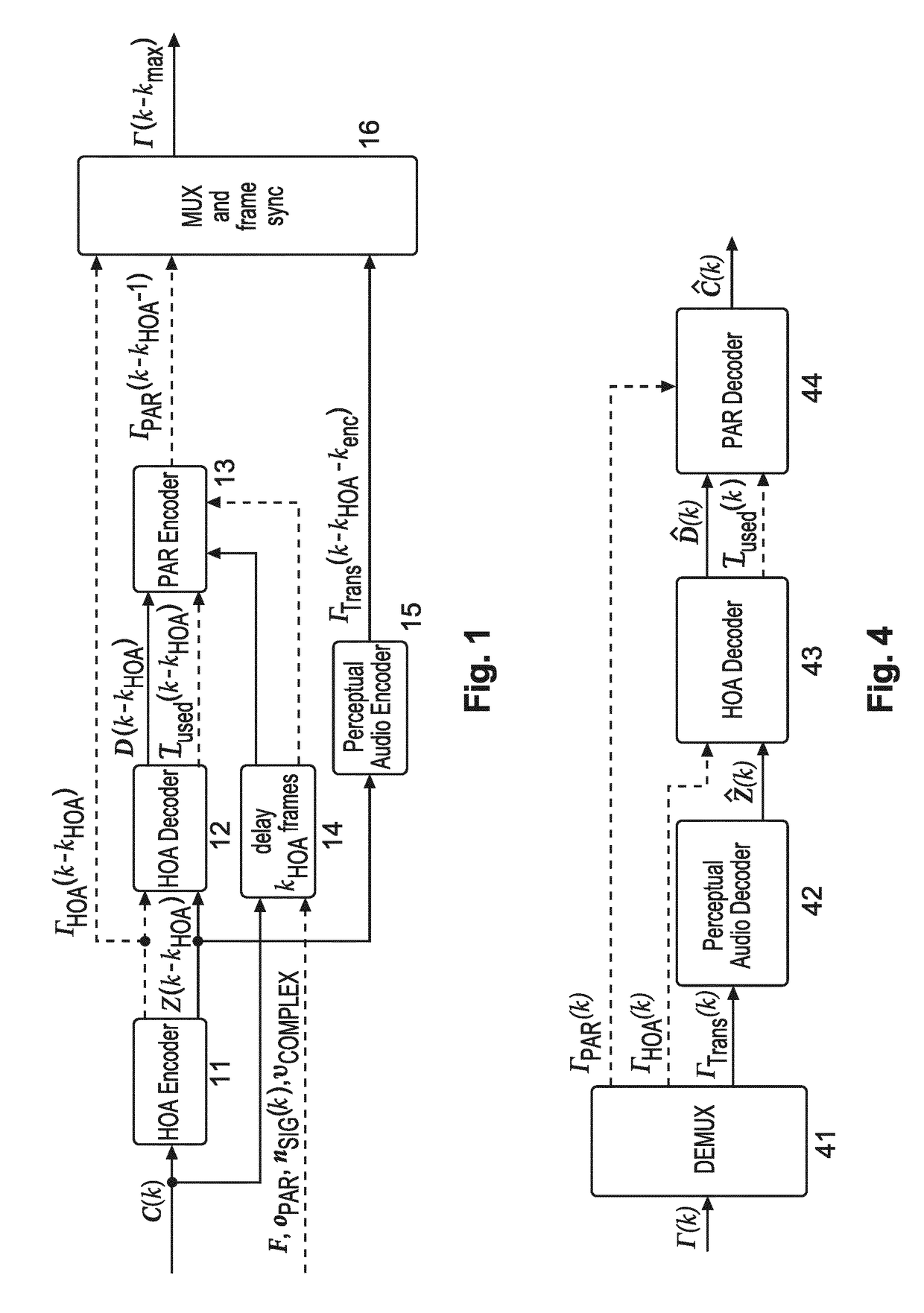
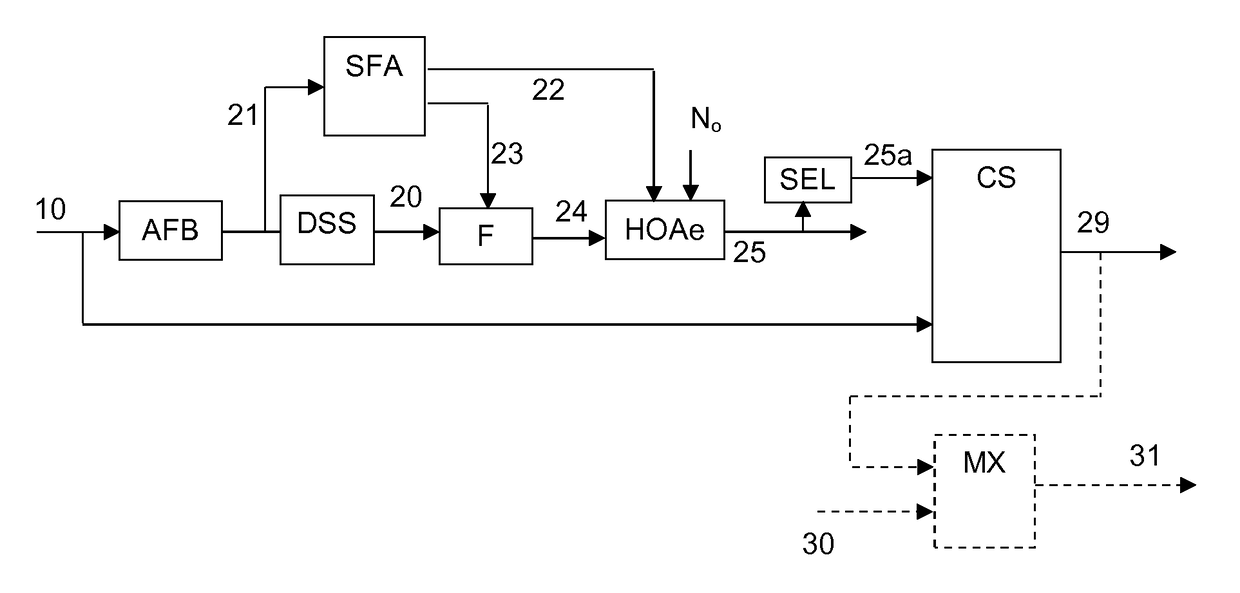
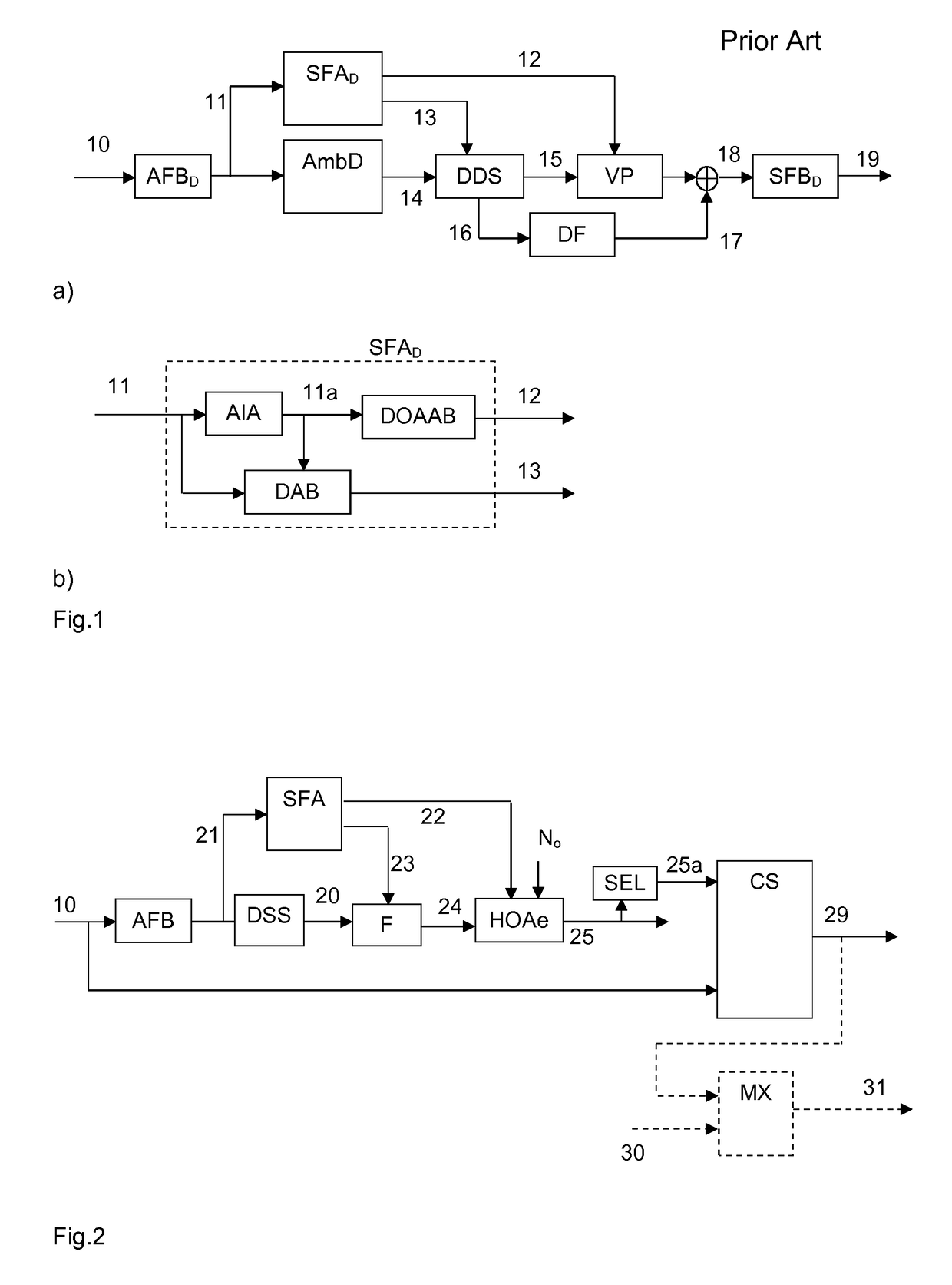
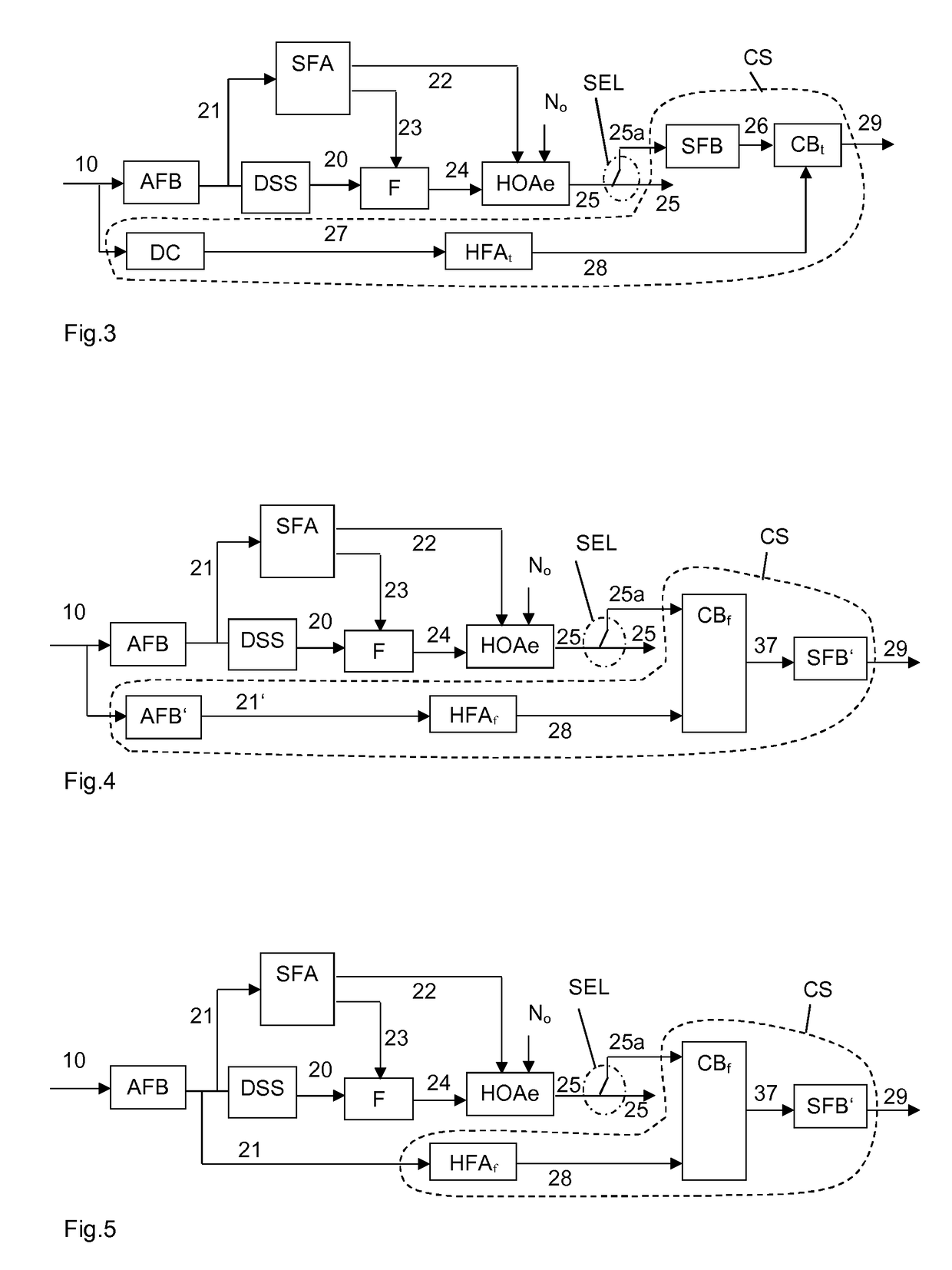
Method and apparatus for encoding and decoding successive frames of an ambisonics representation of a 2- or 3-dimensional sound field
ActiveUS20120155653A1Easy accessThe result is reasonableBroadcast information characterisationSpeech analysisTime domainData rate
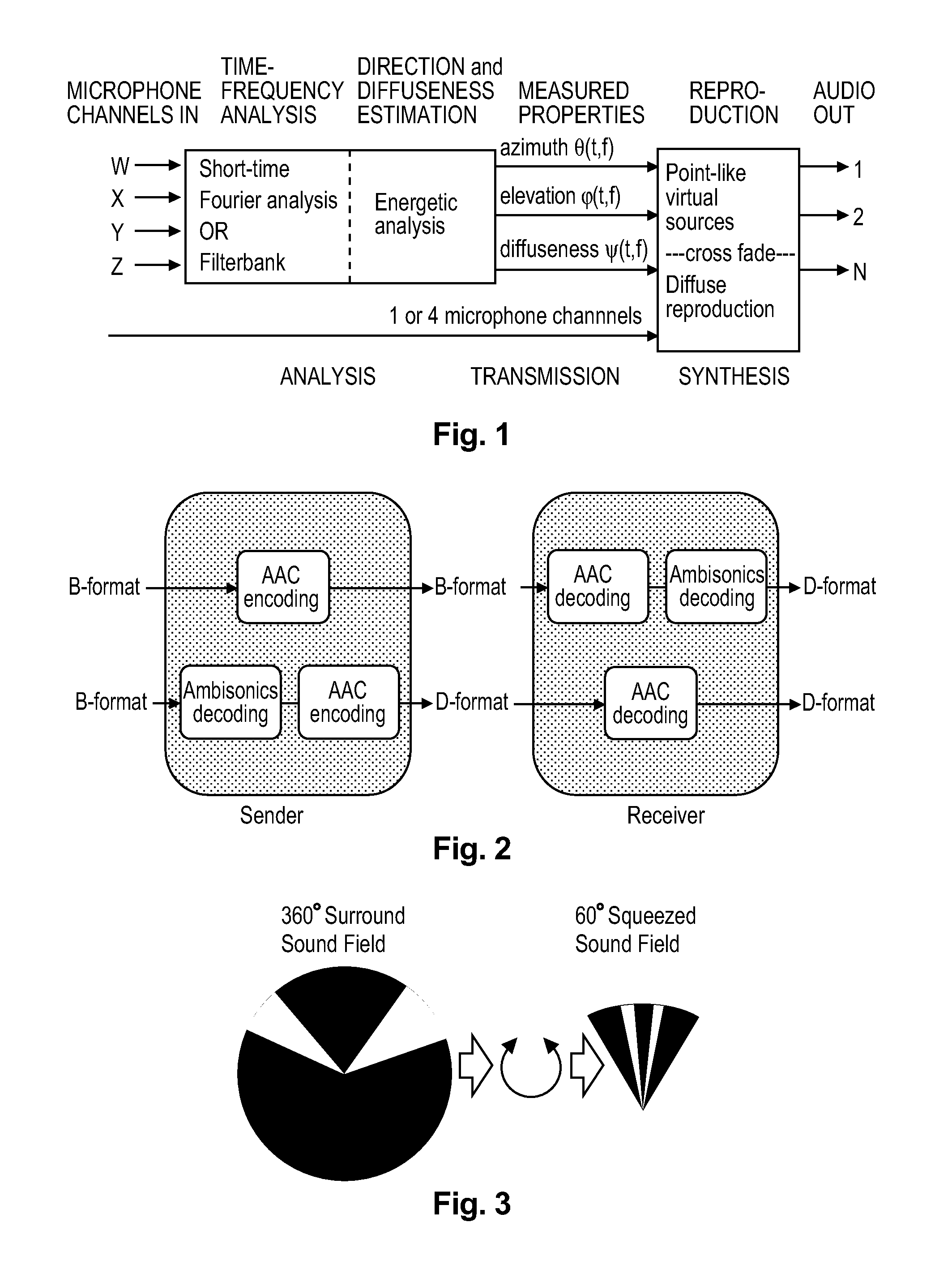
Representations of spatial audio scenes using higher-order Ambisonics HOA technology typically require a large number of coefficients per time instant. This data rate is too high for most practical applications that require real-time transmission of audio signals. According to the invention, the compression is carried out in spatial domain instead of HOA domain. The (N+1)2 input HOA coefficients are transformed into (N+1)2 equivalent signals in spatial domain, and the resulting (N+1)2 time-domain signals are input to a bank of parallel perceptual codecs. At decoder side, the individual spatial-domain signals are decoded, and the spatial-domain coefficients are transformed back into HOA domain in order to recover the original HOA representation.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and apparatus for three-dimensional acoustic field encoding and optimal reconstruction
ActiveUS20110305344A1Exact reproductionIncrease the areaSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsDecoding methodsVocal tract
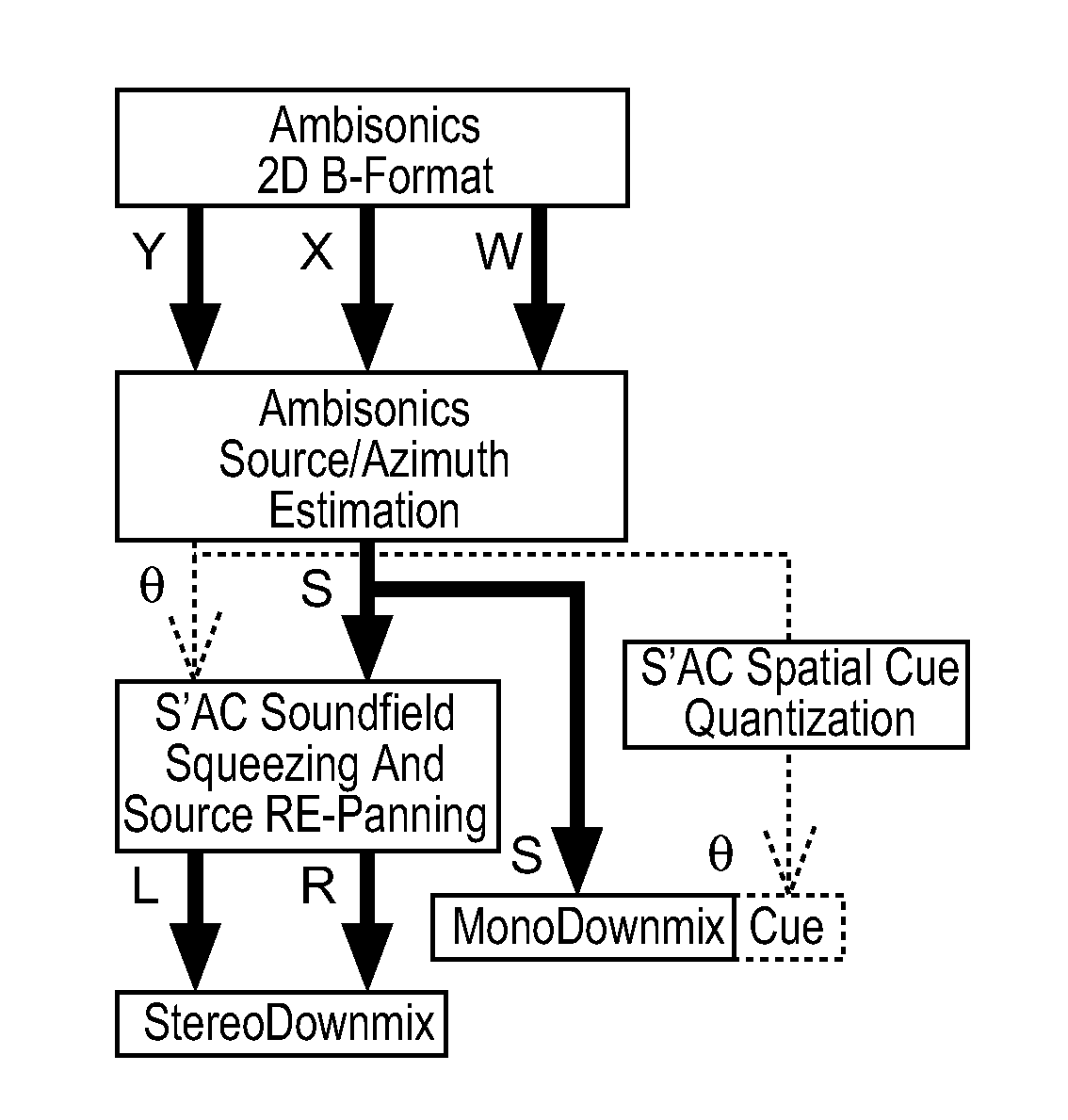
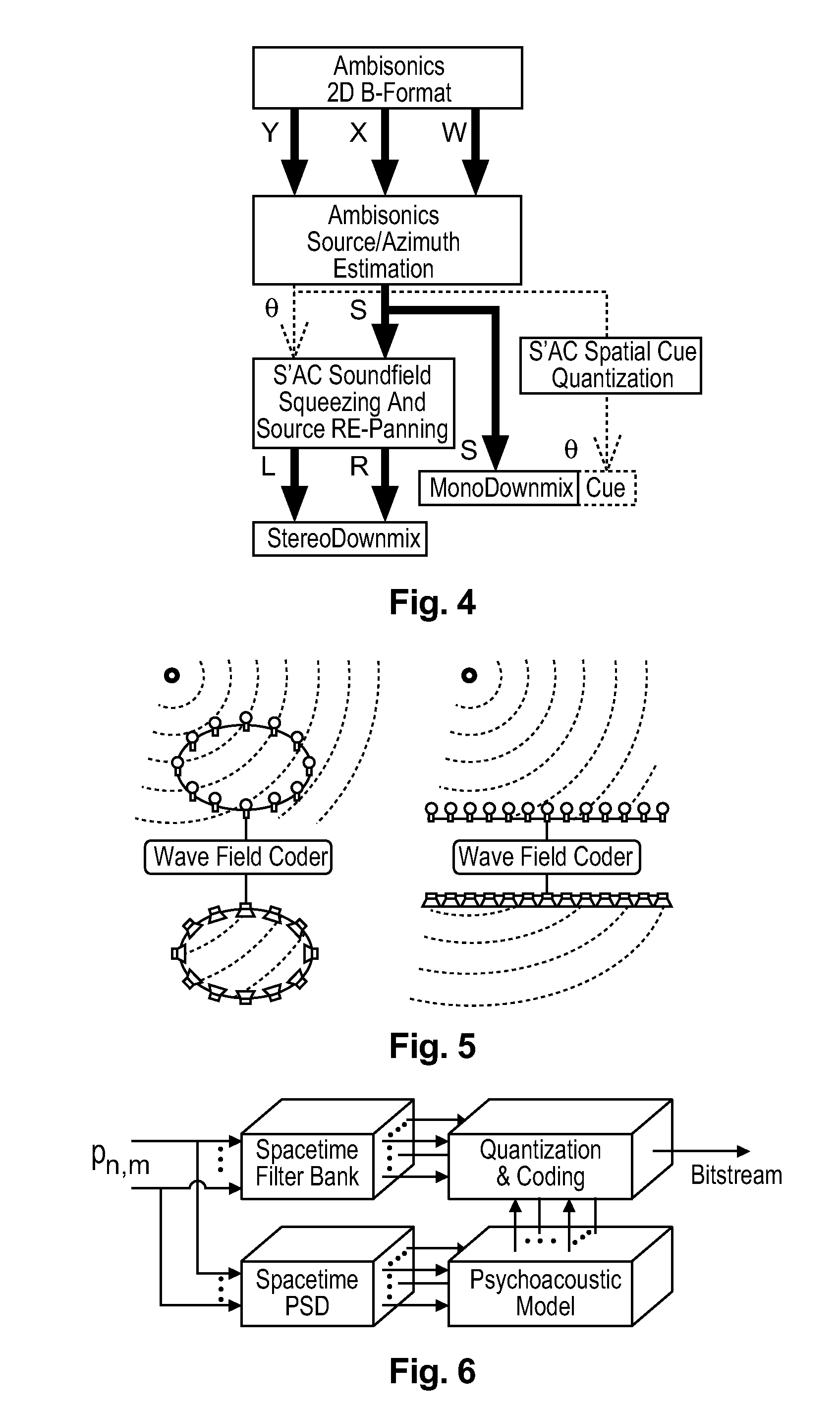
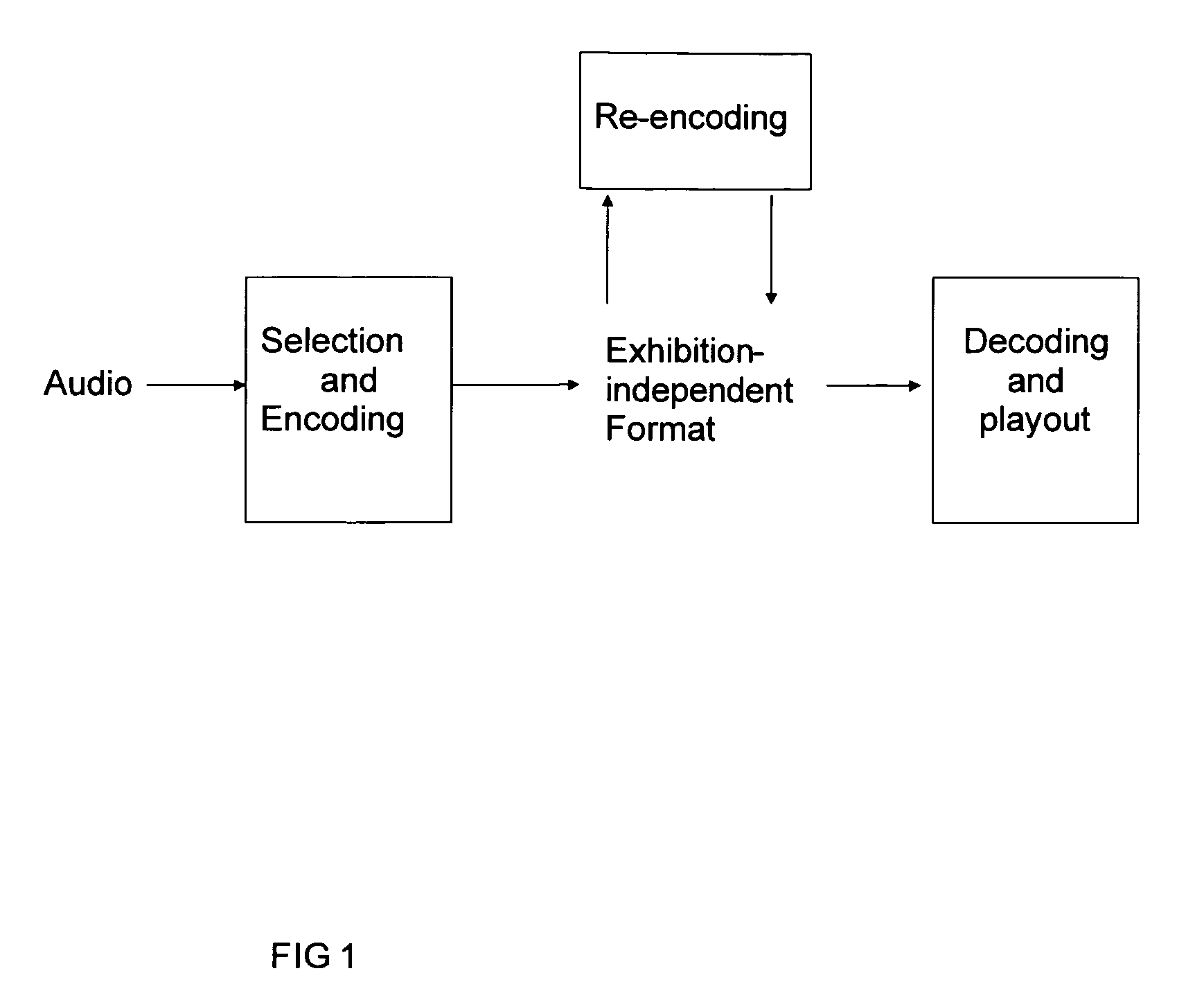
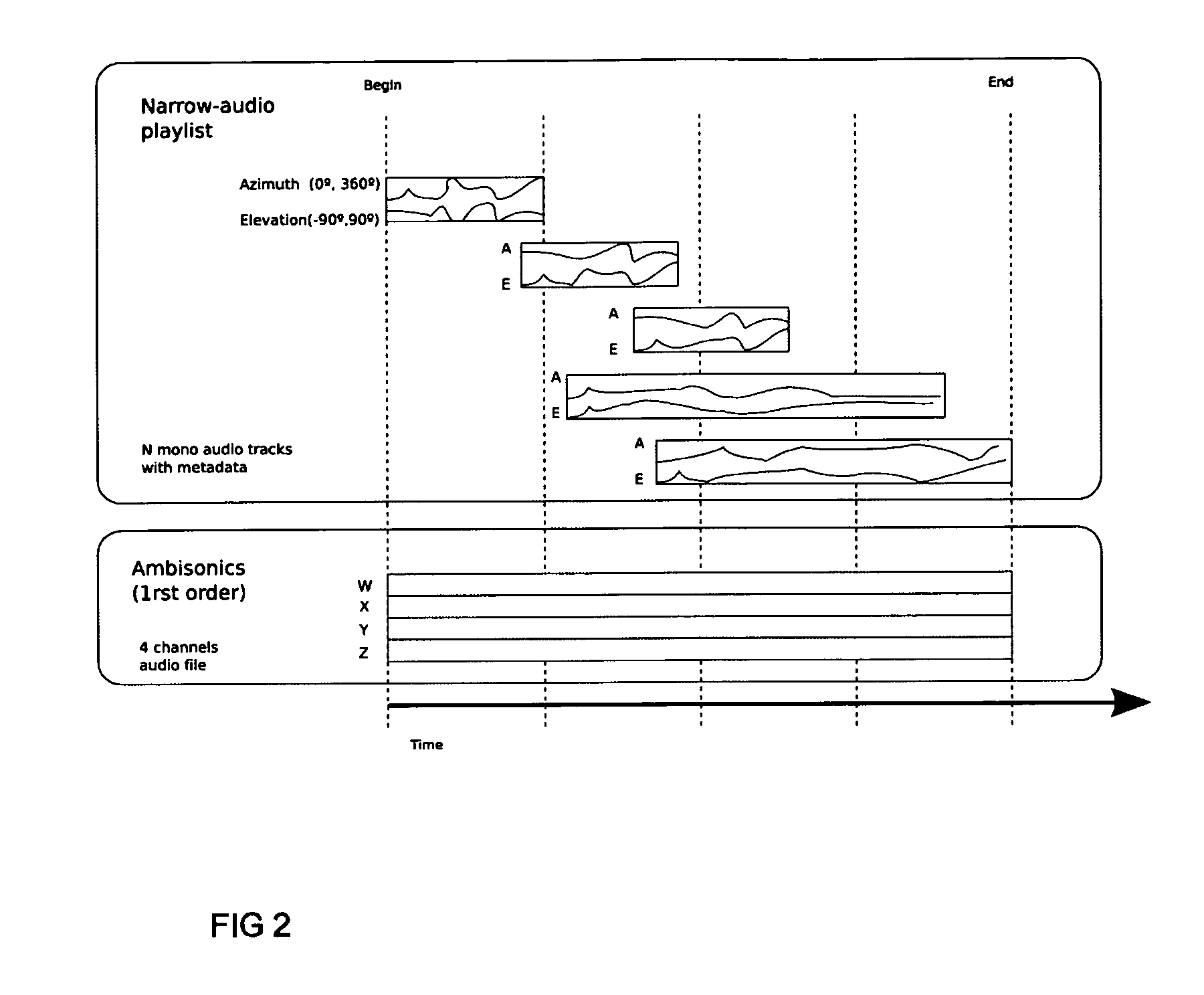
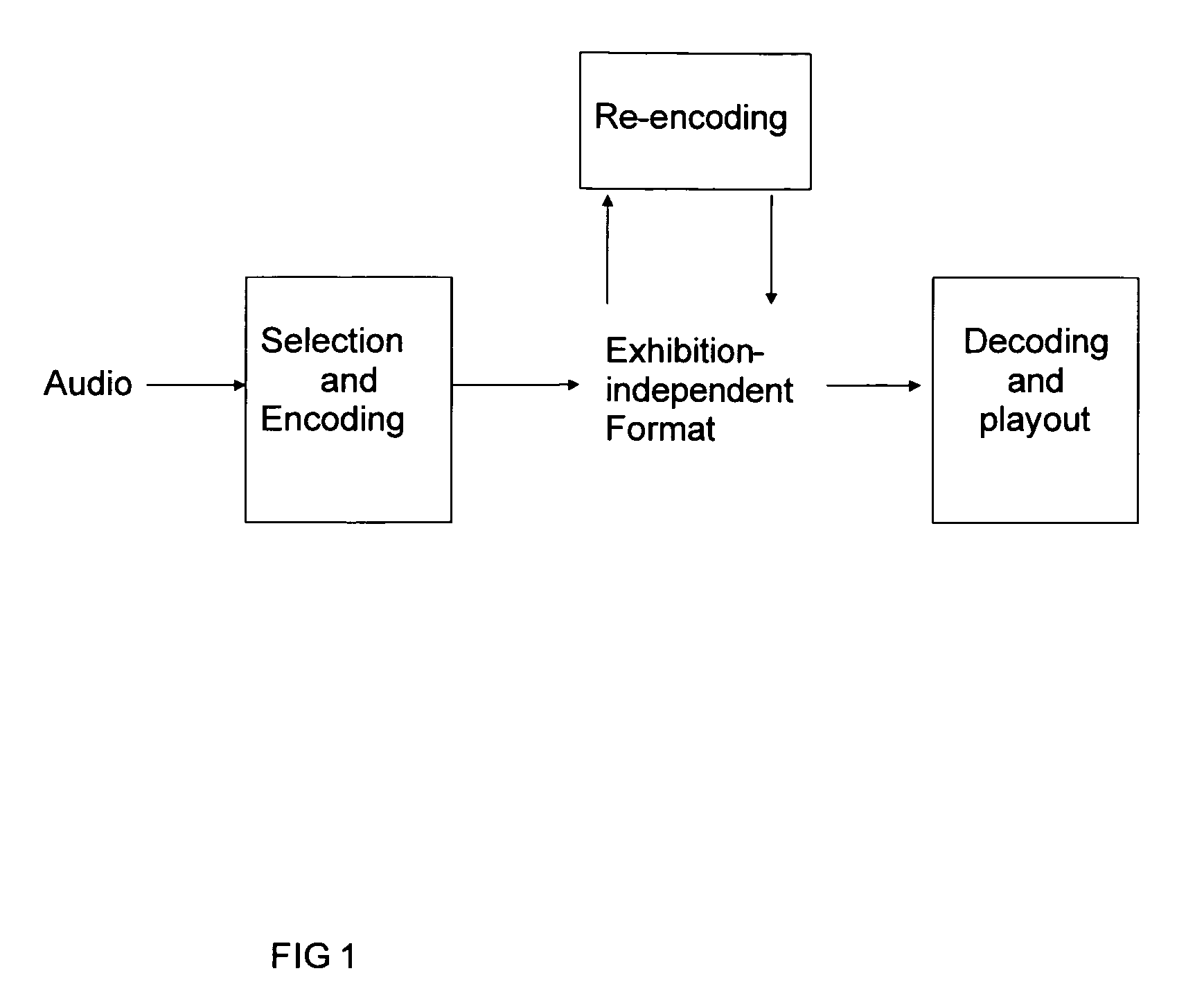
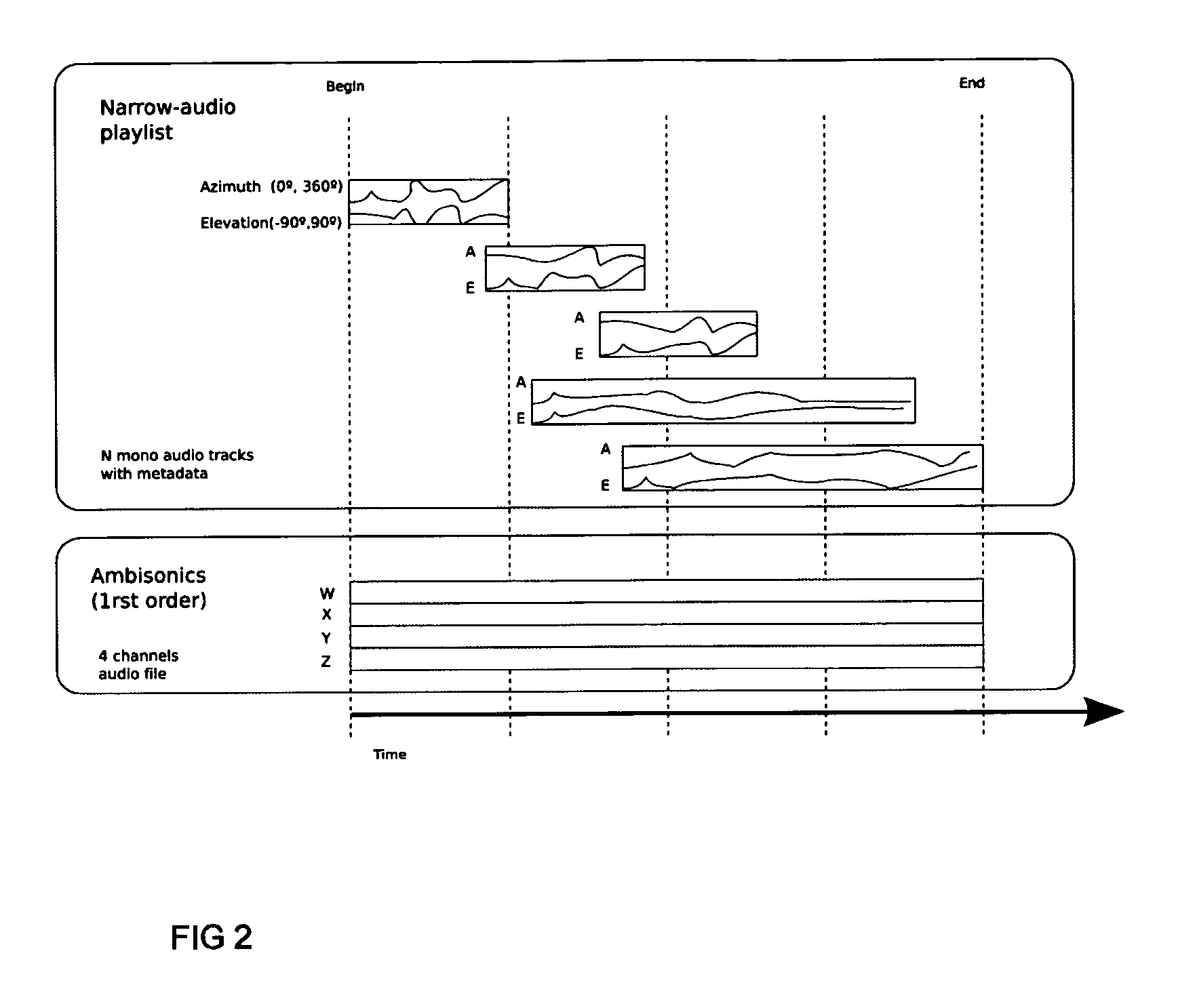
A method and apparatus to encode audio with spatial information in a manner that does not depend on the exhibition setup, and to decode and play out optimally for any given exhibition setup, maximizing the sweet-spot area, and including setups with loudspeakers at different heights, and headphones. The part of the audio that requires very precise localization is encoded into a set of mono tracks with associated directional parameters, whereas the remaining audio is encoded into a set of Ambisonics tracks of a chosen order and mixture. Upon specification of a given exhibition system, the exhibition-independent format is decoded adapting to the specified system, by using different decoding methods for each assigned group.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Reproduction of spatialized audio
InactiveUS6694033B1Secret communicationLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsSound sourcesAmbisonics
Immersive environments for teleconferencing, collaborative shared spaces and entertainment require spatial audio. Such environments may have non-ideal sound reproduction conditions (loudspeaker positioning, listener placement or listening room geometry) where wavefront-synthesis techniques, such as ambisonics, will not give listeners the correct audio spatialization. A method disclosed for generating a sound field from a spatialized original audio signal, wherein the original signal is configured to produce an optimal sound percept at one predetermined ideal location. A plurality of output signal components are generated, each for reproduction by one of an array of loudspeakers. Antiphase output components are attenuated such that their contribution to the spatial sound percept is reduced for locations other than the predetermined ideal location. Position components defining the location of a virtual sound source, normalized to the loudspeaker distance from the ideal location, can be adapted to generate a warped sound field by raising the position components to a power greater than unity, such that the virtual sound source is perceived by listeners in the region surrounded by the loudspeakers to be spaced from the loudspeaker.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Method and device for improving the rendering of multi-channel audio signals
Conventional audio compression technologies perform a standardized signal transformation, independent of the type of the content. Multi-channel signals are decomposed into their signal components, subsequently quantized and encoded. This is disadvantageous due to lack of knowledge on the characteristics of scene composition, especially for e.g. multi-channel audio or Higher-Order Ambisonics (HOA) content. An improved method for encoding pre-processed audio data comprises encoding the pre-processed audio data, and encoding auxiliary data that indicate the particular audio pre-processing. An improved method for decoding encoded audio data comprises determining that the encoded audio data had been pre-processed before encoding, decoding the audio data, extracting from received data information about the pre-processing, and post-processing the decoded audio data according to the extracted pre-processing information.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and device for rendering an audio soundfield representation for audio playback
ActiveUS20150163615A1Good directionConstant loudnessStereophonic systemsStereophonic arrangmentsComputer visionAmbisonics
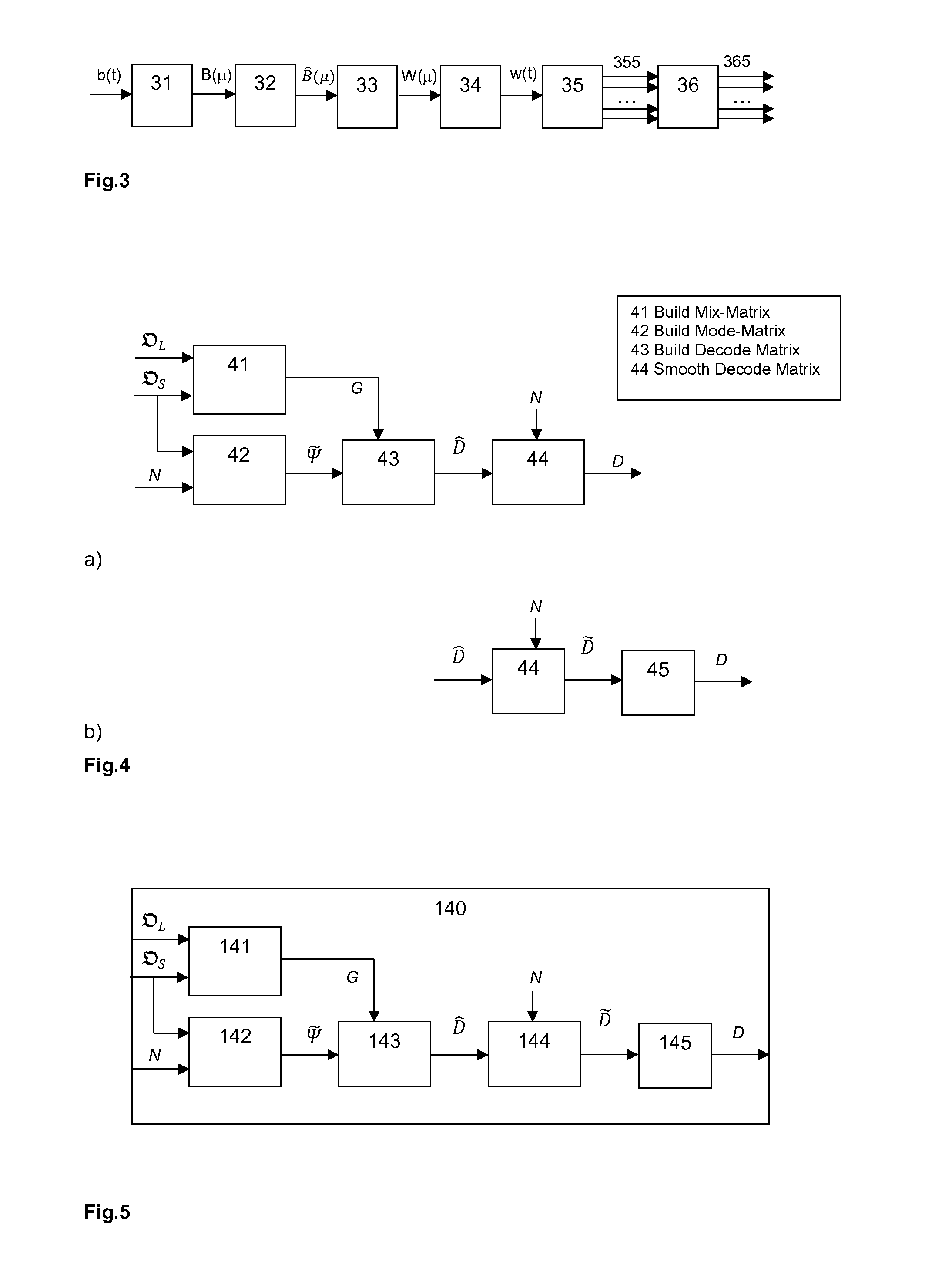
The invention discloses rendering sound field signals, such as Higher-Order Ambisonics (HOA), for arbitrary loudspeaker setups, where the rendering results in highly improved localization properties and is energy preserving. This is obtained by a new type of decode matrix for sound field data, and a new way to obtain the decode matrix. In a method for rendering an audio sound field representation for arbitrary spatial loudspeaker setups, the decode matrix for the rendering to a given arrangement of target loudspeakers is obtained by steps of obtaining a number of target speakers, their positions, positions of a spherical modeling grid and a HOA order, generating a mix matrix from the positions of the modeling grid and the positions of the speakers, generating a mode matrix from the positions of the spherical modeling grid and the HOA order, calculating a first decode matrix from the mix matrix and the mode matrix, and smoothing and scaling the first decode matrix with smoothing and scaling coefficients.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and apparatus for compressing and decompressing a higher order ambisonics representation
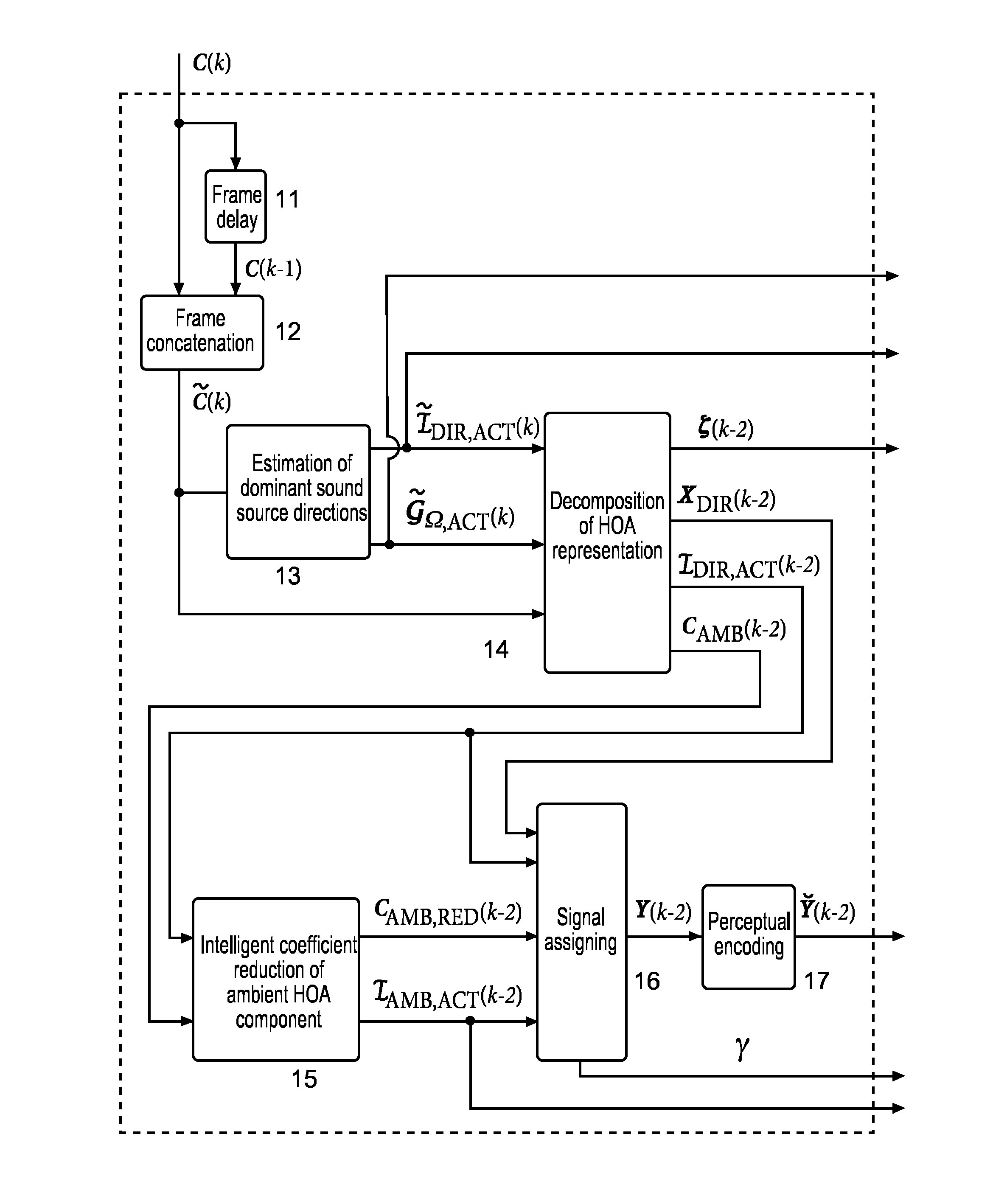
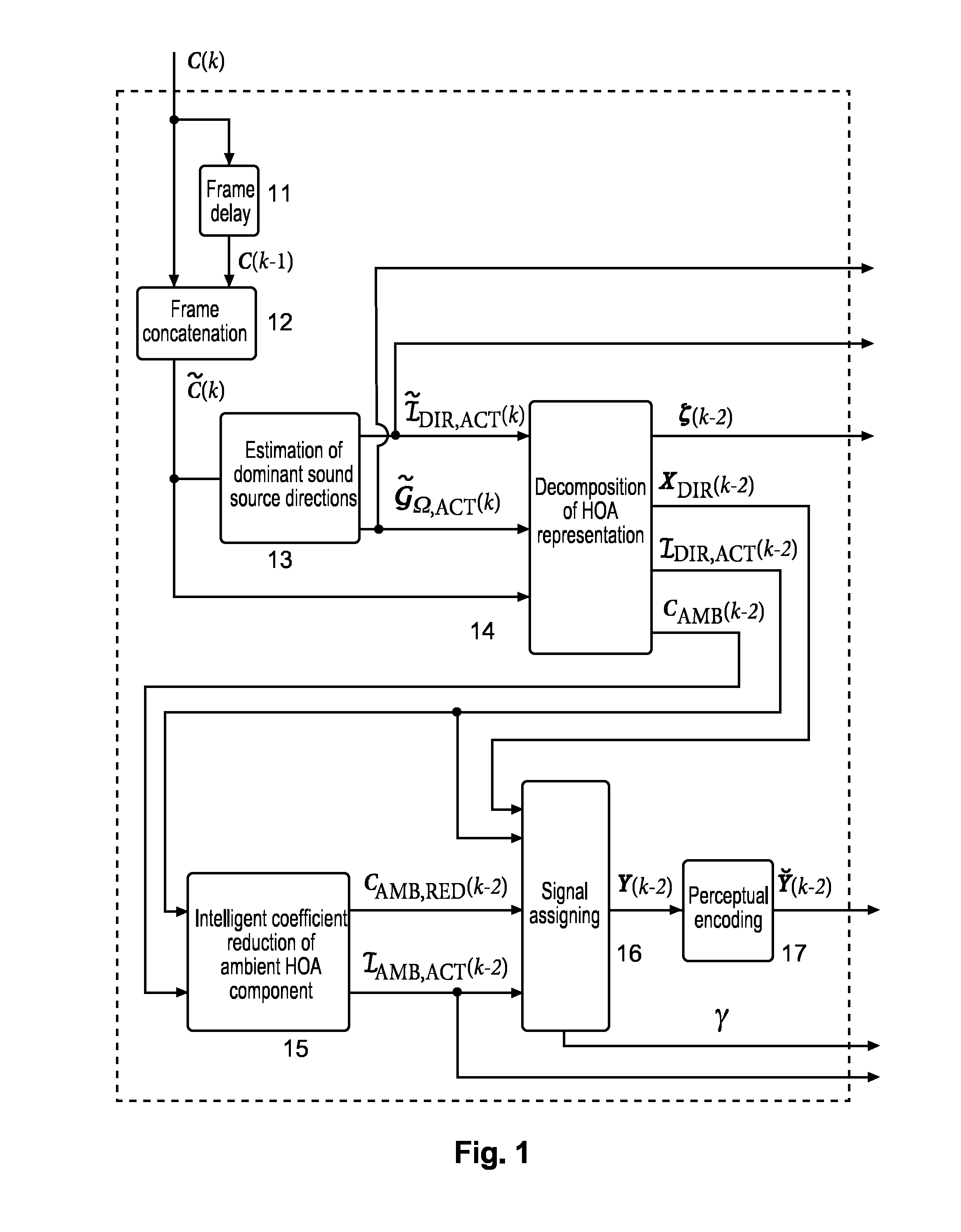
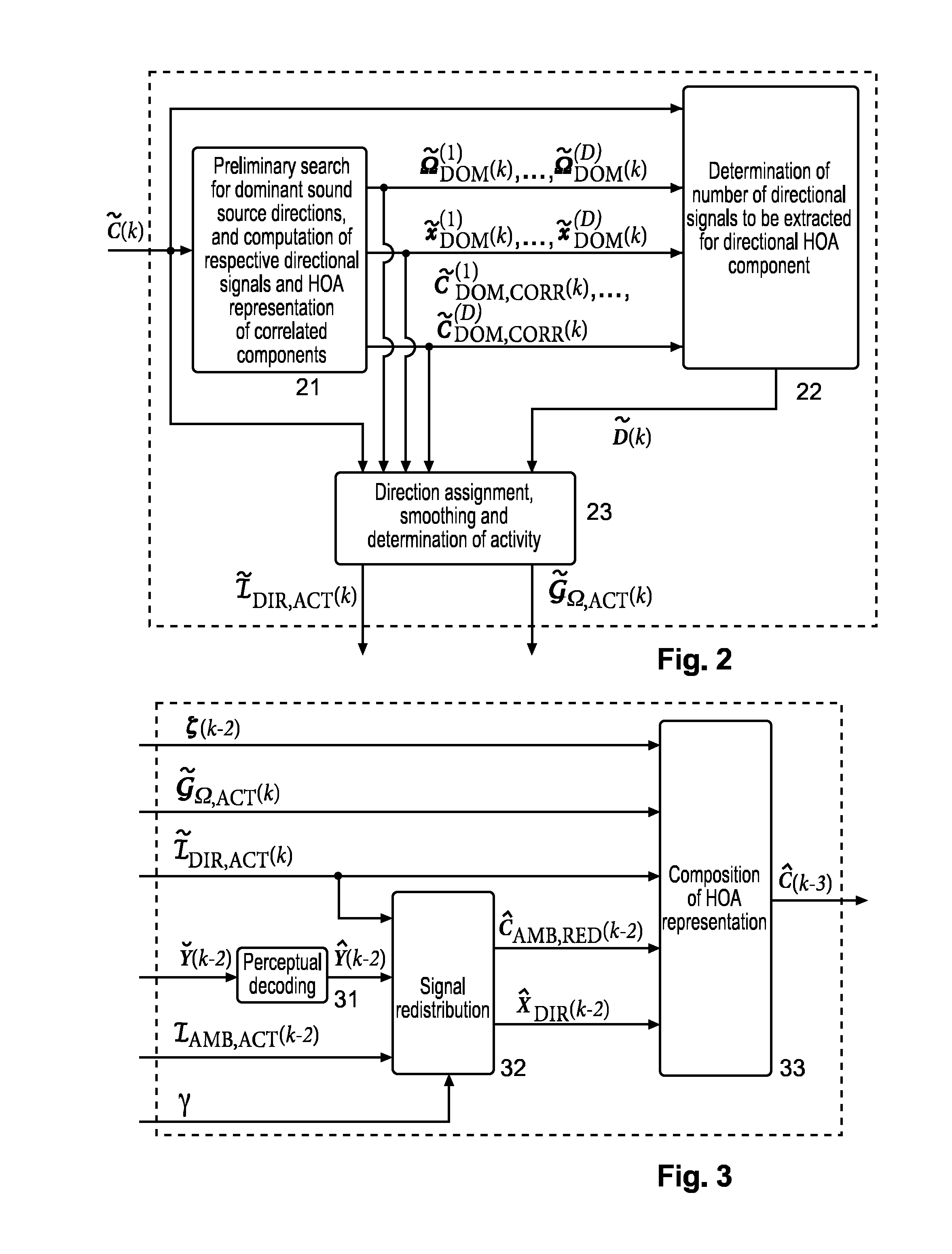
Higher Order Ambisonics represents three-dimensional sound independent of a specific loudspeaker set-up. However, transmission of an HOA representation results in a very high bit rate. Therefore compression with a fixed number of channels is used, in which directional and ambient signal components are processed differently. The ambient HOA component is represented by a minimum number of HOA coefficient sequences. The remaining channels contain either directional signals or additional coefficient sequences of the ambient HOA component, depending on what will result in optimum perceptual quality. This processing can change on a frame-by-frame basis.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and device for decoding an audio soundfield representation for audio playback
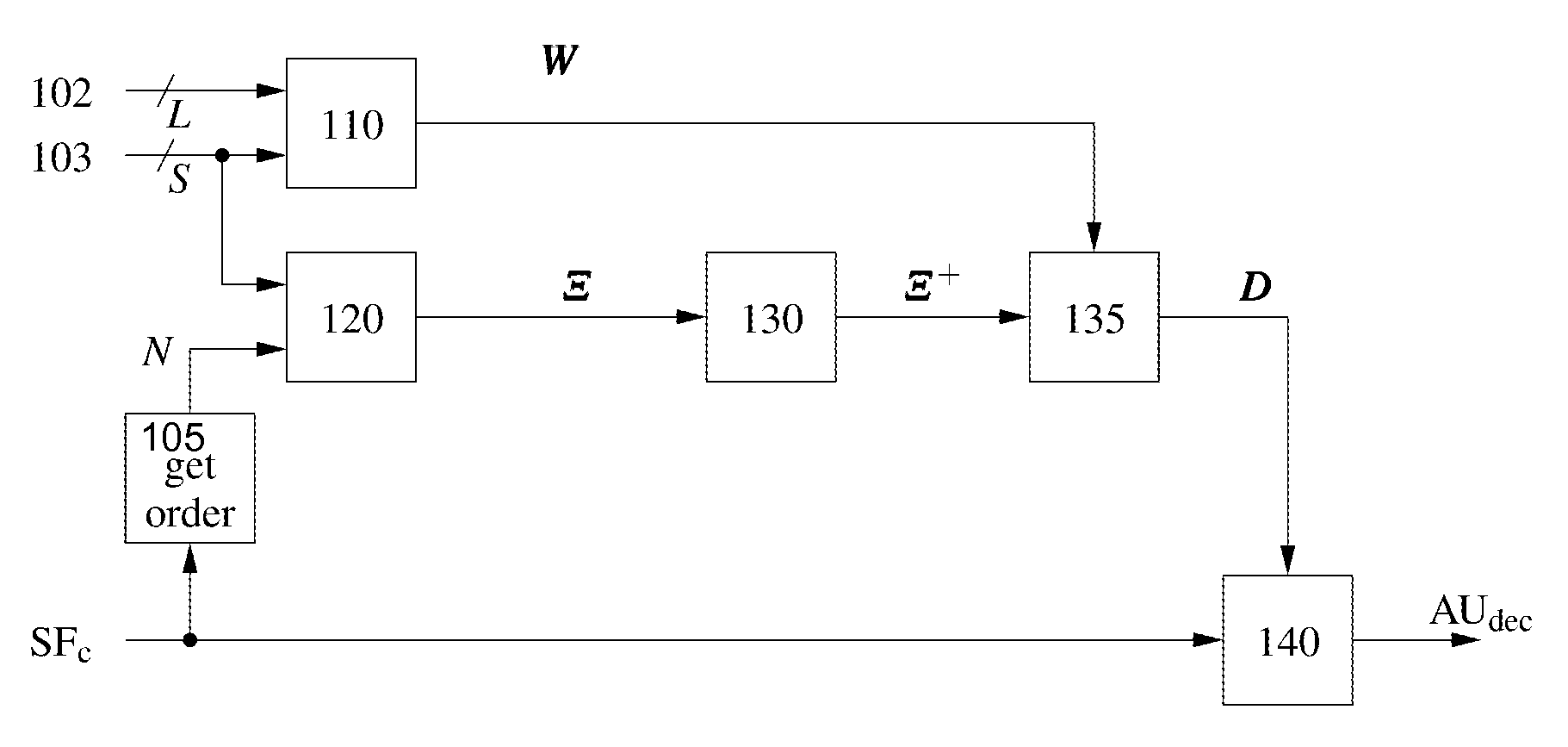
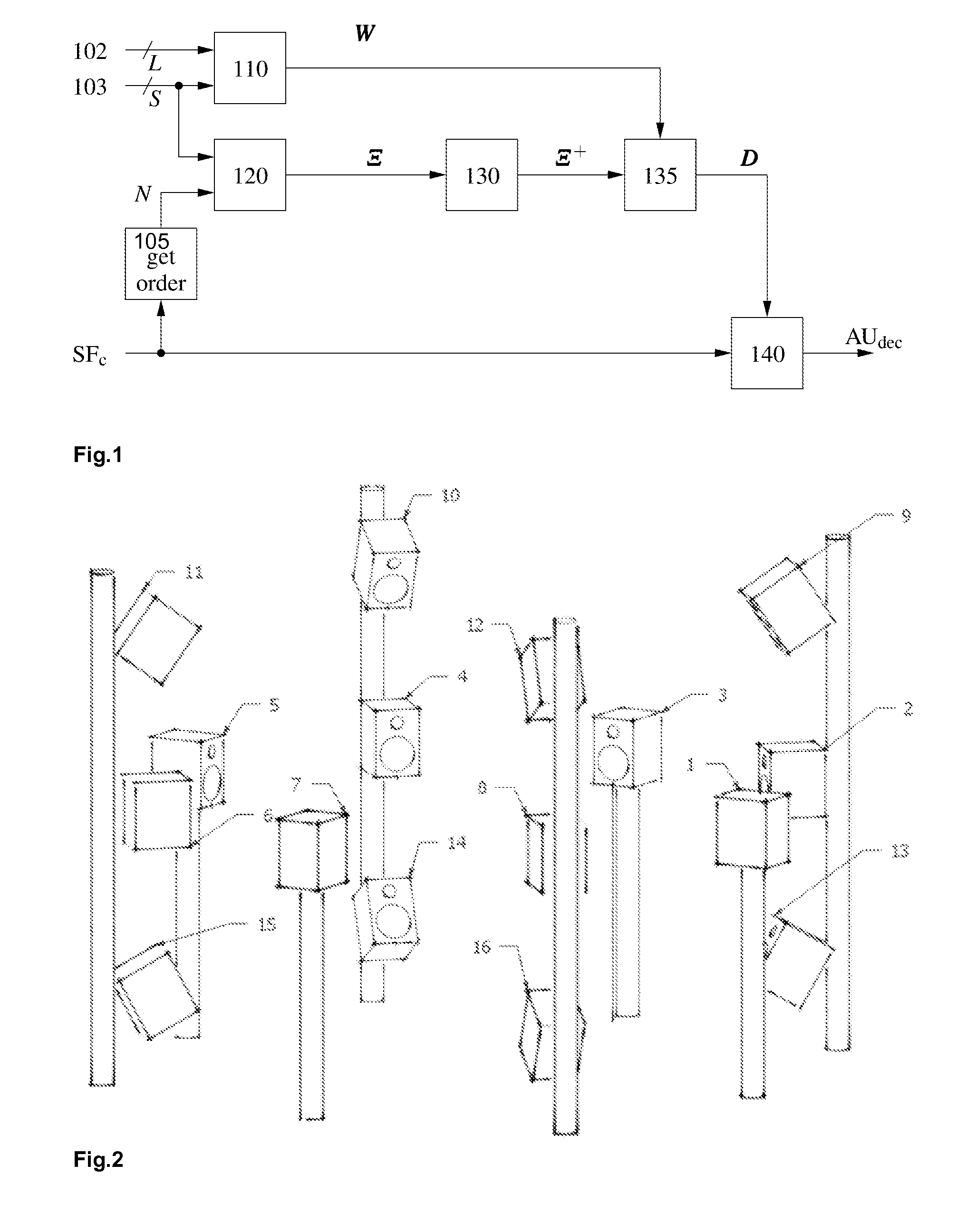
Soundfield signals as such e.g. Ambisonics carry a representation of a desired sound field. The Ambisonics format is based on spherical harmonic decomposition of the soundfield, and Higher Order Ambisonics uses spherical harmonics of at least 2nd order. However, commonly used loudspeaker setups are irregular and lead to problems in decoder design. A method for improved decoding an audio soundfield representation for audio playback comprises calculating a panning function using a geometrical method based on the positions of a plurality of loudspeakers and a plurality of source directions, calculating a mode matrix Ξ from the loudspeaker positions, calculating a pseudo-inverse mode matrix μ+ and decoding the audio soundfield representation. The decoding is based on a decode matrix that is obtained from the panning function and the pseudo-inverse mode matrix Ξ+.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and device for decoding an audio soundfield representation for audio playback
Soundfield signals such as e.g. Ambisonics carry a representation of a desired sound field. The Ambisonics format is based on spherical harmonic decomposition of the soundfield, and Higher Order Ambisonics uses spherical harmonics of at least 2nd order. However, commonly used loudspeaker setups are irregular and lead to problems in decoder design, A method for improved decoding an audio soundfield representation for audio playback comprises calculating a panning function using a geometrical method based on the positions of a plurality of loudspeakers and a plurality of source directions, calculating a mode matrix from the loudspeaker positions, calculating a pseudo-inverse mode matrix and decoding the audio soundfield representation. The decoding is based on a decode matrix that is obtained from the panning function and the pseudo-inverse mode matrix.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and apparatus for playback of a higher-order ambisonics audio signal
ActiveUS20130236039A1Flexible and representationReduce capacitySpeech analysisStereophonic systemsAmbisonicsVisible object
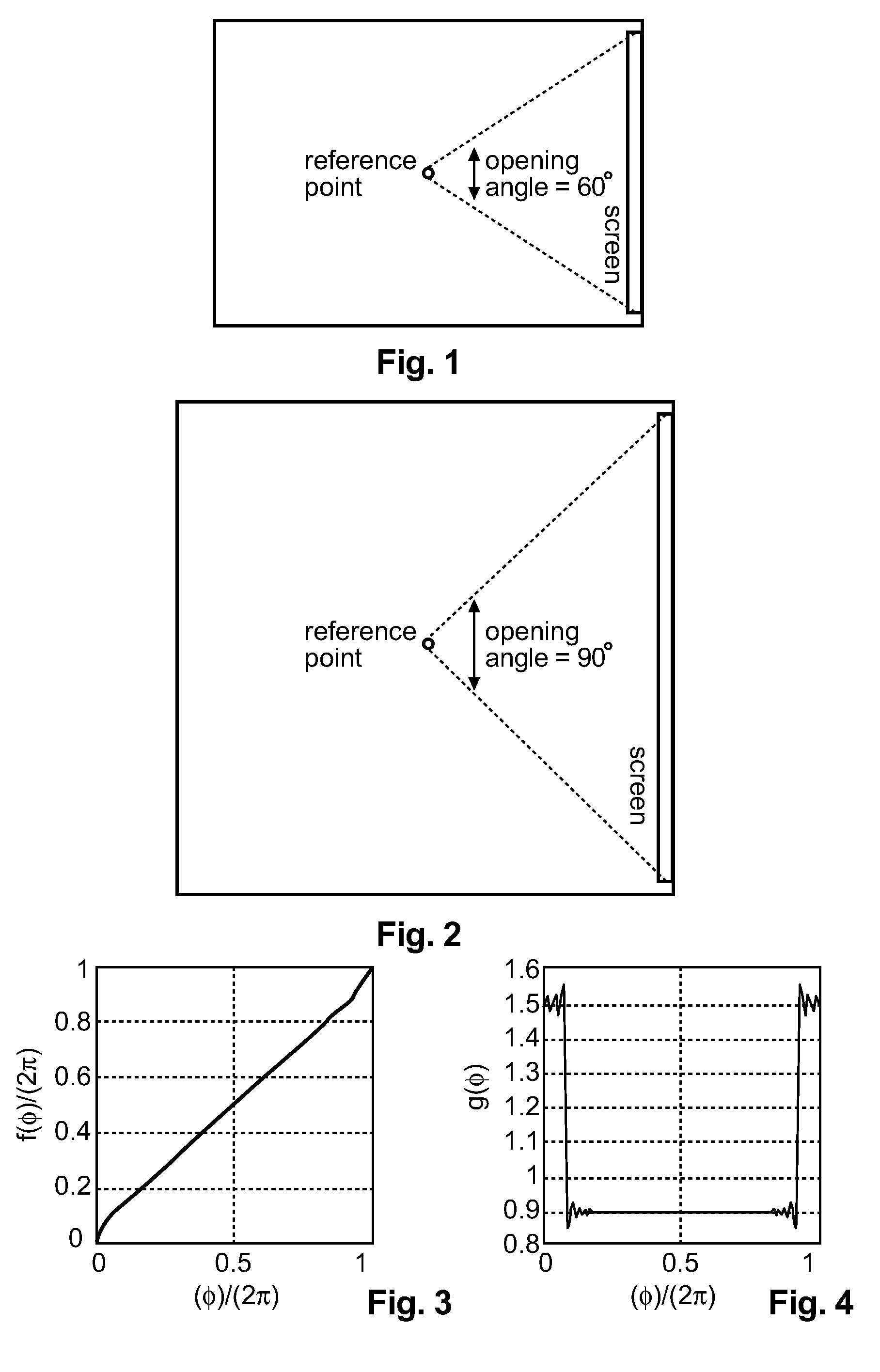
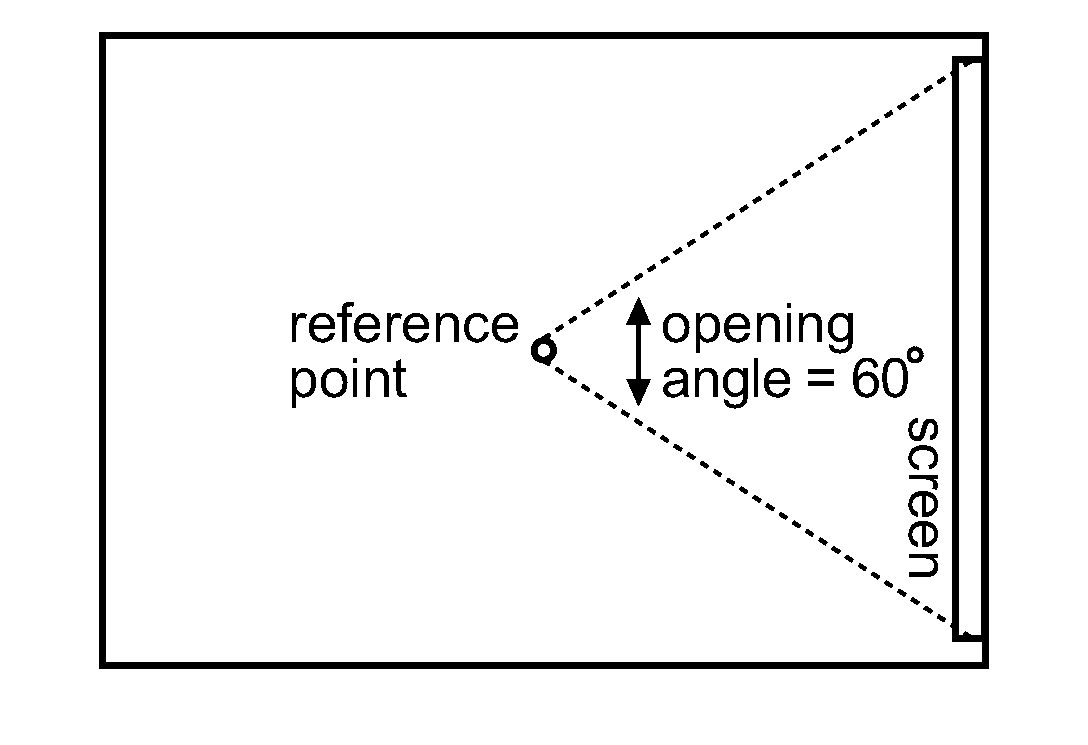
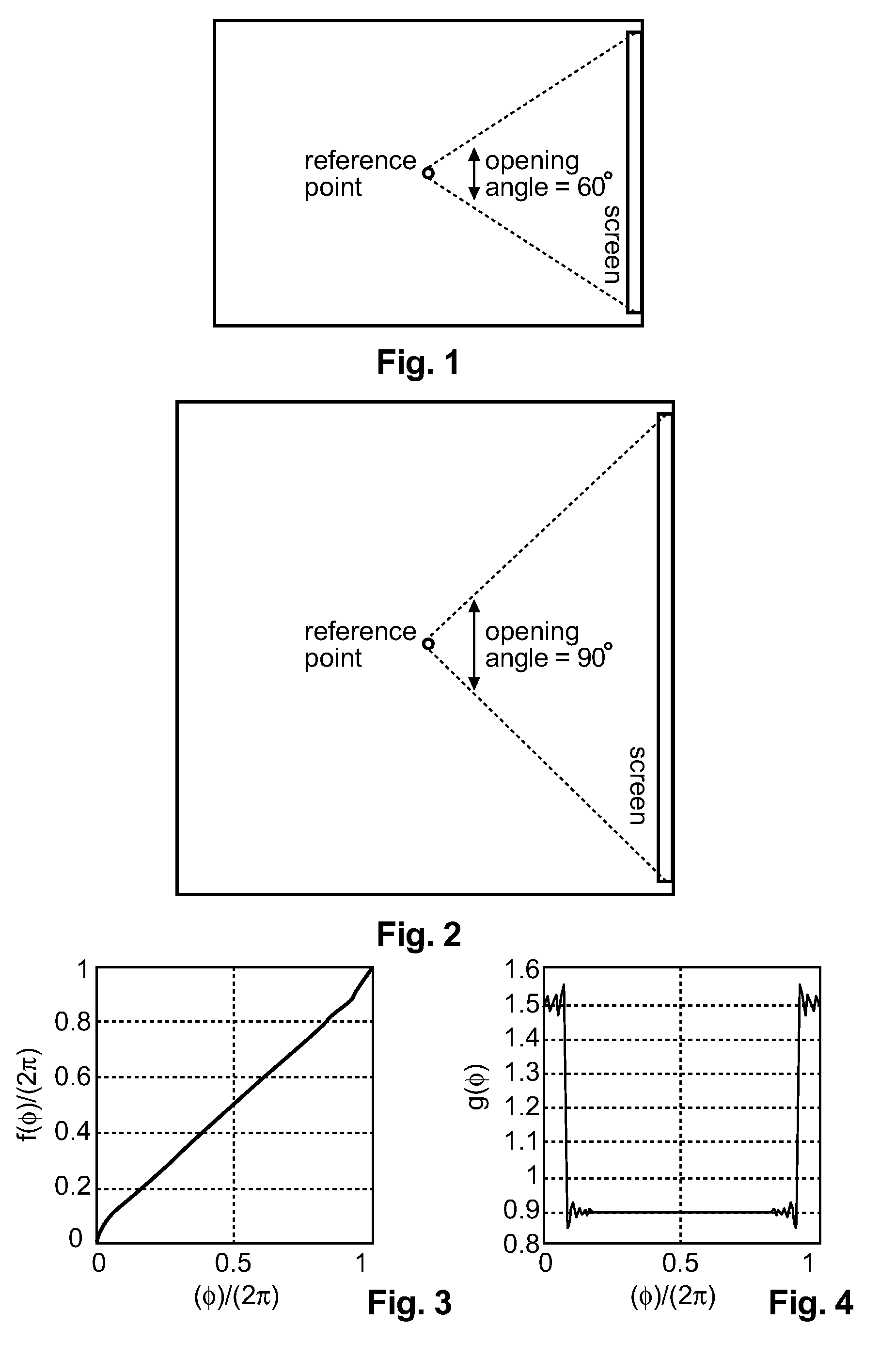
An advantage of Ambisonics representation is that the reproduction of the sound field can be adapted individually to nearly any given loudspeaker position arrangement. The invention allows systematic adaptation of the playback of spatial sound field-oriented audio to its linked visible objects, by applying space warping processing as disclosed in EP 11305845.7. The reference size (or the viewing angle from a reference listening position) of the screen used in the content production is encoded and transmitted as metadata together with the content, or the decoder knows the actual size of the target screen with respect to a fixed reference screen size. The decoder warps the sound field in such a manner that all sound objects in the direction of the screen are compressed or stretched according to the ratio of the size of the target screen and the size of the reference screen.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and apparatus for compressing and decompressing a higher order ambisonics signal representation
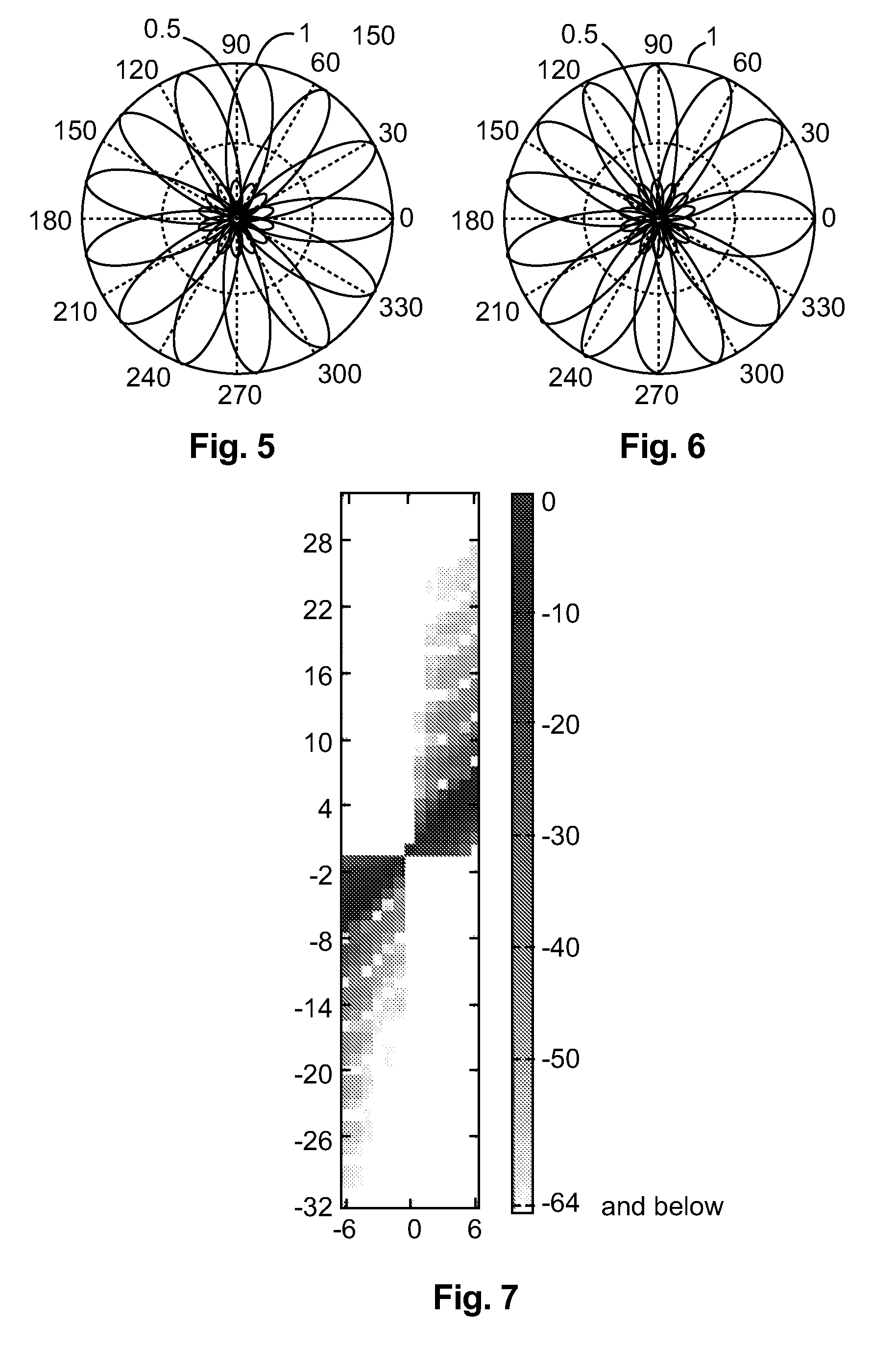
ActiveCN104285390AImprove spatial resolutionBroadcast information characterisationSpeech analysisTime domainHigh spatial resolution
Higher Order Ambisonics (HOA) represents a complete sound field in the vicinity of a sweet spot, independent of loudspeaker set-up. The high spatial resolution requires a high number of HOA coefficients. In the invention, dominant sound directions are estimated and the HOA signal representation is decomposed into dominant directional signals in time domain and related direction information, and an ambient component in HOA domain, followed by compression of the ambient component by reducing its order. The reduced-order ambient component is transformed to the spatial domain, and is perceptually coded together with the directional signals. At receiver side, the encoded directional signals and the order-reduced encoded ambient component are perceptually decompressed, the perceptually decompressed ambient signals are transformed to an HOA domain representation of reduced order, followed by order extension. The total HOA representation is re-composed from the directional signals, the corresponding direction information, and the original-order ambient HOA component.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
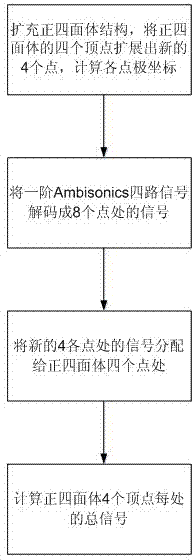
Method and system for enhancing sound field effect of loudspeaker group in regular tetrahedron structure
InactiveCN102932730AIncrease the number ofEfficient use ofStereophonic systemsSound particleEngineering
The invention discloses a method and a system for enhancing the sound field effect of a loudspeaker group in a regular tetrahedron structure. The method comprises the steps of enlarging the loudspeaker group in the regular tetrahedron structure to obtain four loudspeaker placing points and four virtual loudspeaker placing points; distributing four channels of collected first-order Ambisonics signals to four loudspeakers and four virtual loudspeakers; distributing signals of four virtual loudspeakers to three loudspeakers which are closest to virtual loudspeakers on the premise that the sound particle speed direction and the sound pressure intensity at a symmetrical central position of the regular tetrahedron structure are not changed; and canceling virtual loudspeakers. By the aid of the method and the system, the quality of the sound field can be reconstructed on the condition that loudspeakers of the same number are used.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
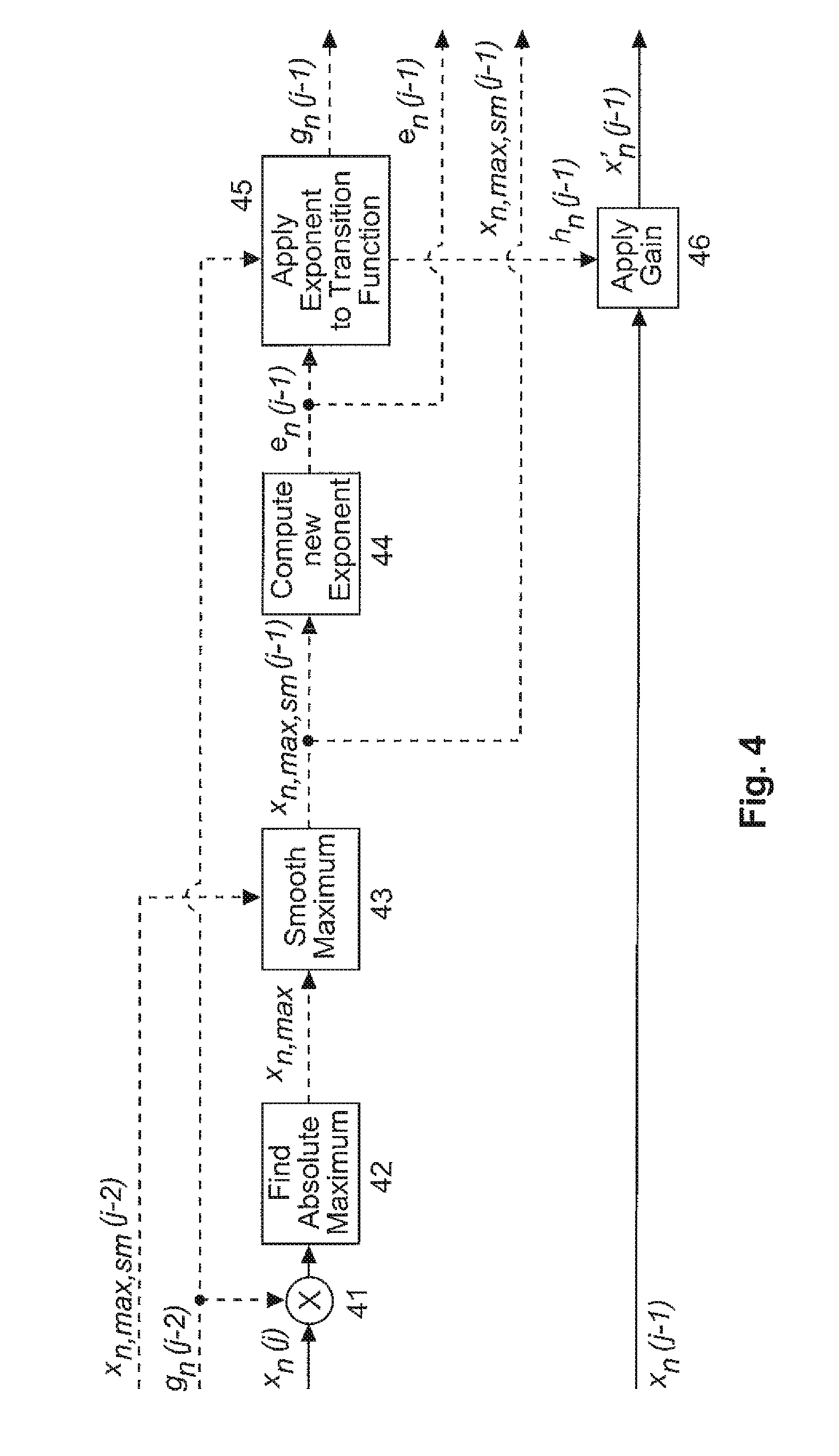
Method and apparatus for generating from a coefficient domain representation of hoa signals a mixed spatial/coefficient domain representation of said hoa signals
ActiveUS20160150341A1RatioReduced dynamic rangeSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsAlgorithmAmbisonics
There are two representations for Higher Order Ambisonics denoted HOA: spatial domain and coefficient domain. The invention generates from a coefficient domain representation a mixed spatial / coefficient domain representation, wherein the number of said HOA signals can be variable. A vector of coefficient domain signals is separated into a vector of coefficient domain signals having a constant number of HOA coefficients and a vector of coefficient domain signals having a variable number of HOA coefficients. The constant-number HOA coefficients vector is transformed to a corresponding spatial domain signal vector. In order to facilitate high-quality coding, without creating signal discontinuities the variable-number HOA coefficients vector of coefficient domain signals is adaptively normalised and multiplexed with the vector of spatial domain signals.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and apparatus for encoding and decoding successive frames of an ambisonics representation of a 2- or 3-dimensional sound field
ActiveUS9397771B2Improved lossy compressionReduce redundancyBroadcast information characterisationSpeech analysisTime domainData rate
Representations of spatial audio scenes using higher-order Ambisonics HOA technology typically require a large number of coefficients per time instant. This data rate is too high for most practical applications that require real-time transmission of audio signals. According to the invention, the compression is carried out in spatial domain instead of HOA domain. The (N+1)2 input HOA coefficients are transformed into (N+1)2 equivalent signals in spatial domain, and the resulting (N+1)2 time-domain signals are input to a bank of parallel perceptual codecs. At decoder side, the individual spatial-domain signals are decoded, and the spatial-domain coefficients are transformed back into HOA domain in order to recover the original HOA representation.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
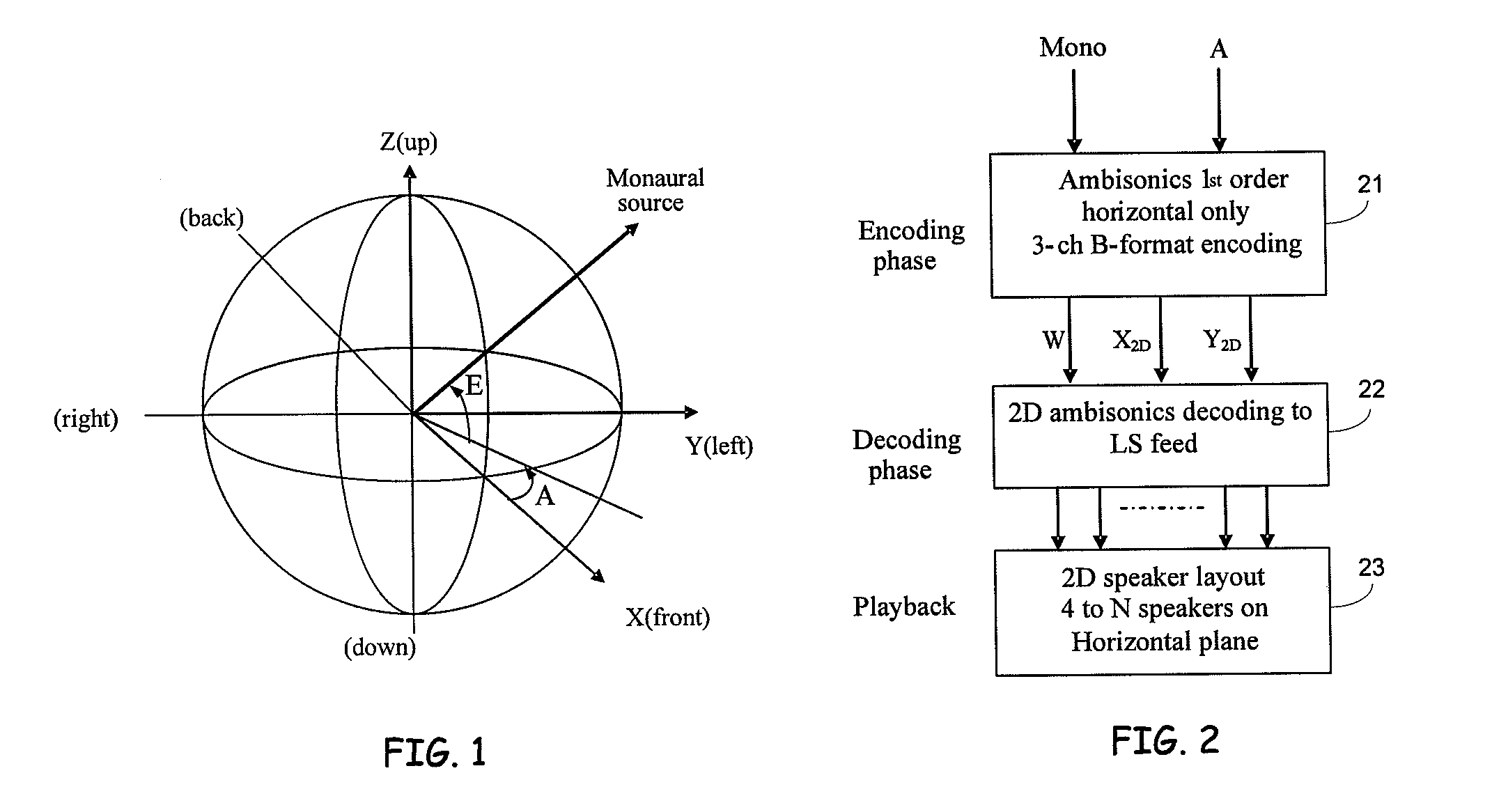
Enabling 3D sound reproduction using a 2d speaker arrangement
The perception of 3D sound positioning can be achieved using a 2D arrangement of speakers positioned around the listener. The disclosed techniques can enable listeners to perceive sounds as coming from above and / or below them, without the need for positioning speakers above and / or below the listener. In some embodiments, elevation information can be included in the X and Y horizontal components of the 2D ambisonics encoding. The X and Y components can be decoded using 2D ambisonics decoding. Suitable filtering may be performed on the decoded sound information to enhance the listener's perception of the elevation information encoded in the X and Y components.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS ASIA PACIFIC PTE
System and method for mixing and adjusting multi-input ambisonics
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for three-dimensional acoustic field encoding and optimal reconstruction
ActiveUS9299353B2Exact reproductionIncrease the areaSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsDecoding methodsVocal tract
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Method and apparatus for compressing and decompressing higher order ambisonics representation for sound field
ActiveCN104854655AEliminate shortcomingsBroadcast information characterisationSpeech analysisSound sourcesOrder reduction
The invention improves HOA sound field representation compression. The HOA representation is analysed for the presence of dominant sound sources and their directions are estimated. Then the HOA representation is decomposed into a number of dominant directional signals and a residual component. This residual component is transformed into the discrete spatial domain in order to obtain general plane wave functions at uniform sampling directions, which are predicted from the dominant directional signals. Finally, the prediction error is transformed back to the HOA domain and represents the residual ambient HOA component for which an order reduction is performed, followed by perceptual encoding of the dominant directional signals and the residual component.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
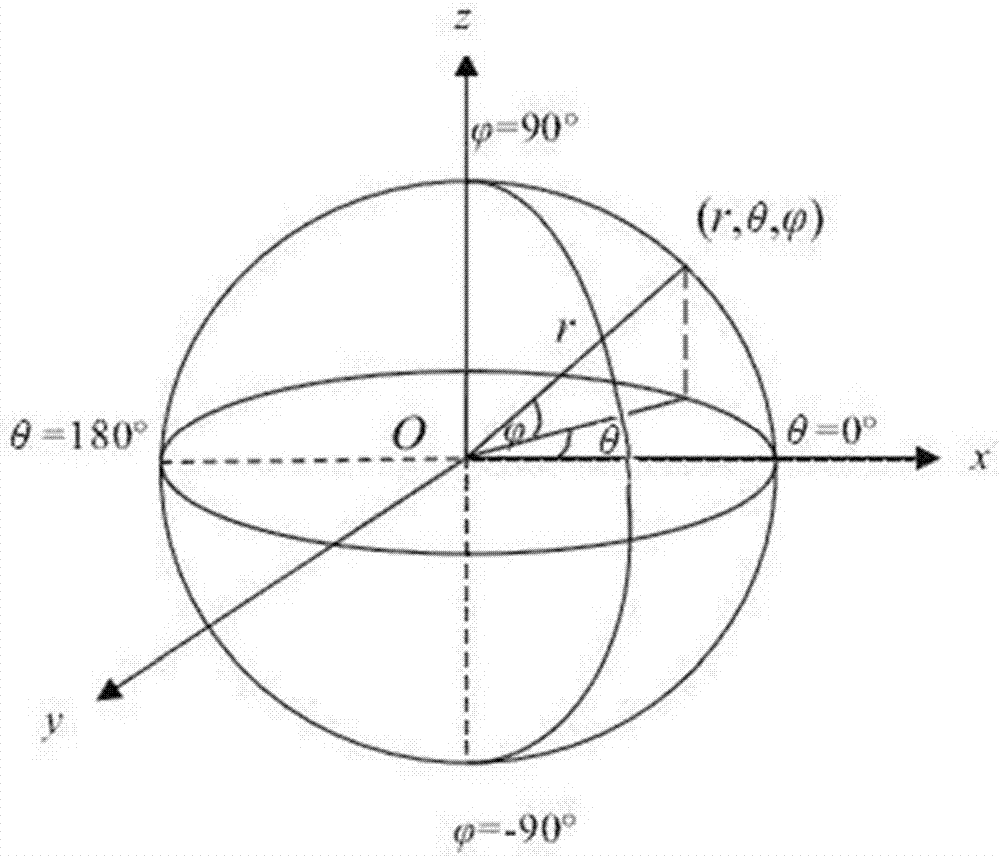
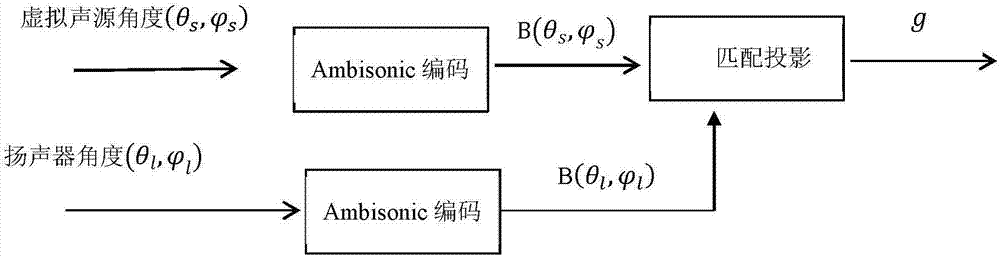
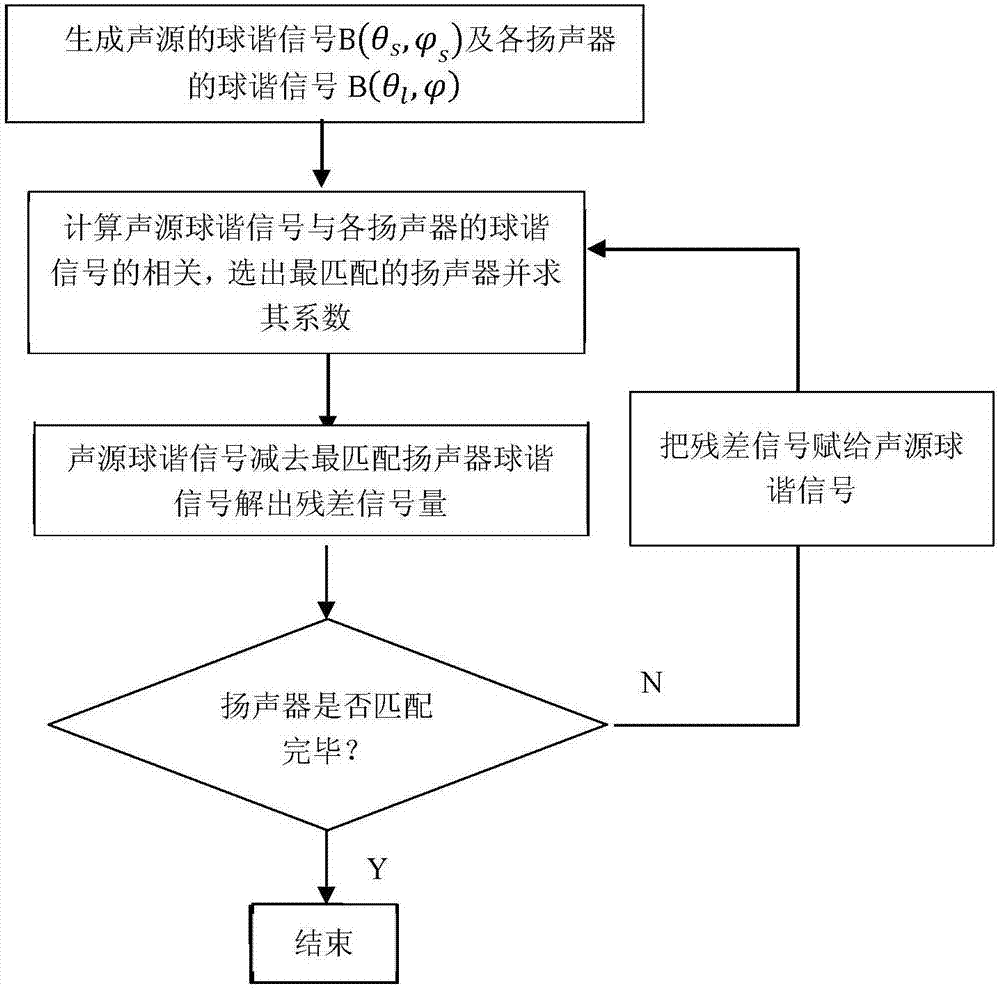
Ambisonics matching projection decoding method for irregular loudspeaker placements
ActiveCN107147975AStable reconstruction of the sound fieldStereophonic circuit arrangementsSingle subwooferDecoding methodsSound sources
The invention discloses an Ambisonics matching projection decoding method for irregular loudspeaker placements. The method comprises the following steps of 1) obtaining a spherical harmonics signal of a sound source according to the position of the sound source; obtaining a spherical harmonics signal of a loudspeaker according to the position of the loudspeaker; and 2) carrying out matching projection on the spherical harmonics signal of the sound source and the spherical harmonics signal of the loudspeaker to obtain a gain g of each loudspeaker. According to the method, the requirements of an Ambisonics sound reproduction system for the fixed positions of the loudspeakers are solved, and the reconstructed sound field is stable.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for compressing a higher order ambisonics (HOA) signal, method for decompressing a compressed HOA signal, apparatus for compressing a HOA signal, and apparatus for decompressing a compressed HOA signal
ActiveUS9930464B2Robust errorQuality improvementSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsSource encodingAmbisonics
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
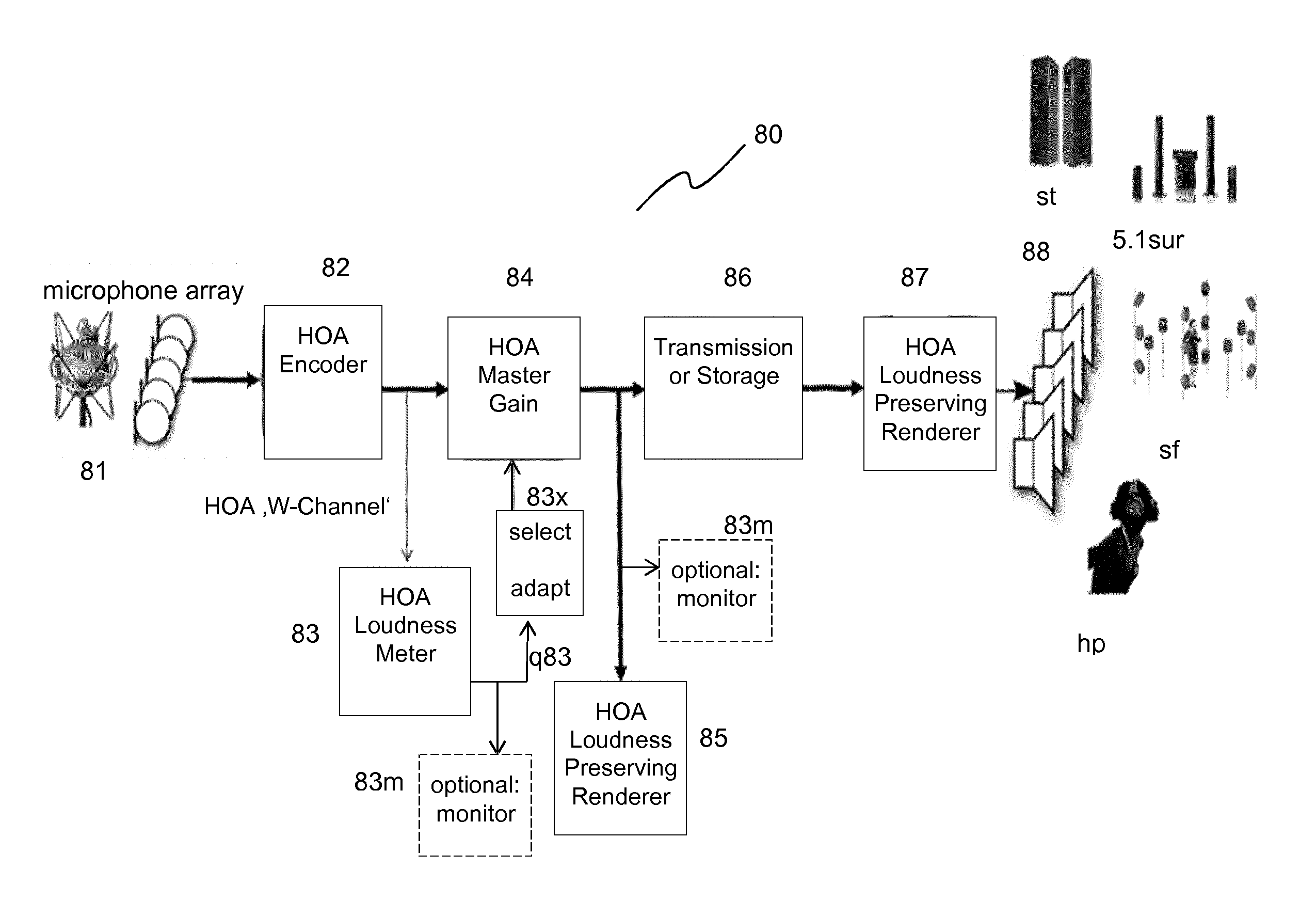
Method and apparatus for processing signals of a spherical microphone array on a rigid sphere used for generating an ambisonics representation of the sound field
ActiveCN104041074AReduces distortion of spectral powerSpectrum Power EqualizationMicrophonesLoudspeakersAmbisonicsSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
Spherical microphone arrays capture a three-dimensional sound field ( P ( © c , t )) for generating an Ambisonics representation A n m t , where the pressure distribution on the surface of the sphere is sampled by the capsules of the array. The impact of the microphones on the captured sound field is removed using the inverse microphone transfer function. The equalisation of the transfer function of the microphone array is a big problem because the reciprocal of the transfer function causes high gains for small values in the transfer function and these small values are affected by transducer noise. The invention estimates (73) the signal-to-noise ratio between the average sound field power and the noise power from the microphone array capsules, computes (74) the average spatial signal power at the point of origin for a diffuse sound field, and designs in the frequency domain the frequency response of the equalisation filter from the square root of the fraction of a given reference power and the simulated power at the point of origin.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Method and apparatus for decoding a compressed hoa representation, and method and apparatus for encoding a compressed hoa representation
ActiveUS20170164131A1Reduce in quantityReduce impactSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsAlgorithmAmbisonics
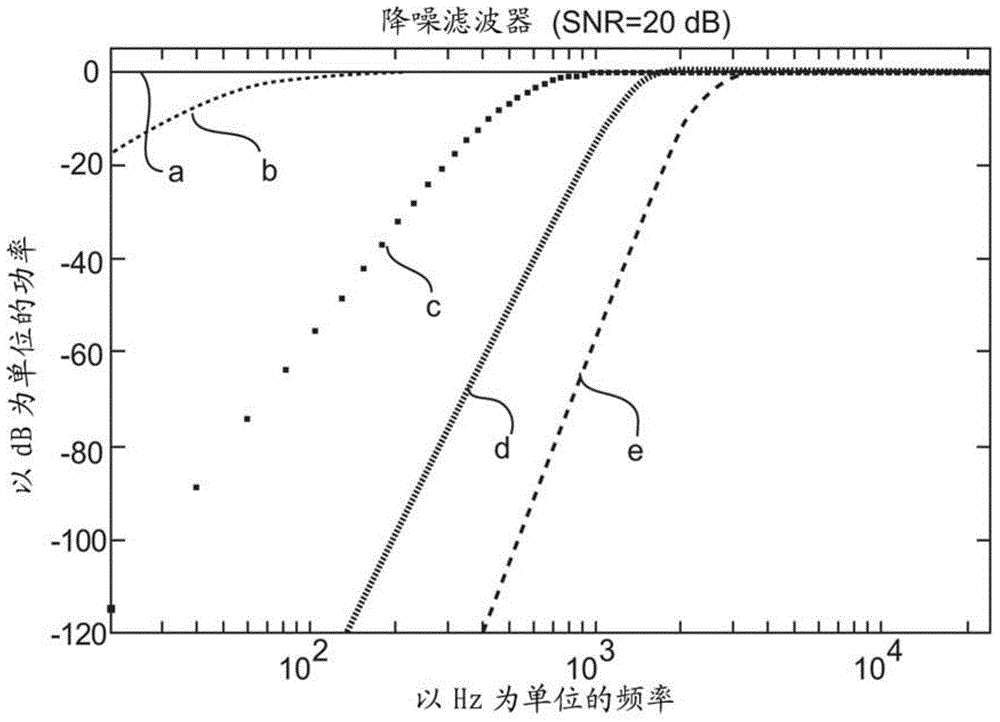
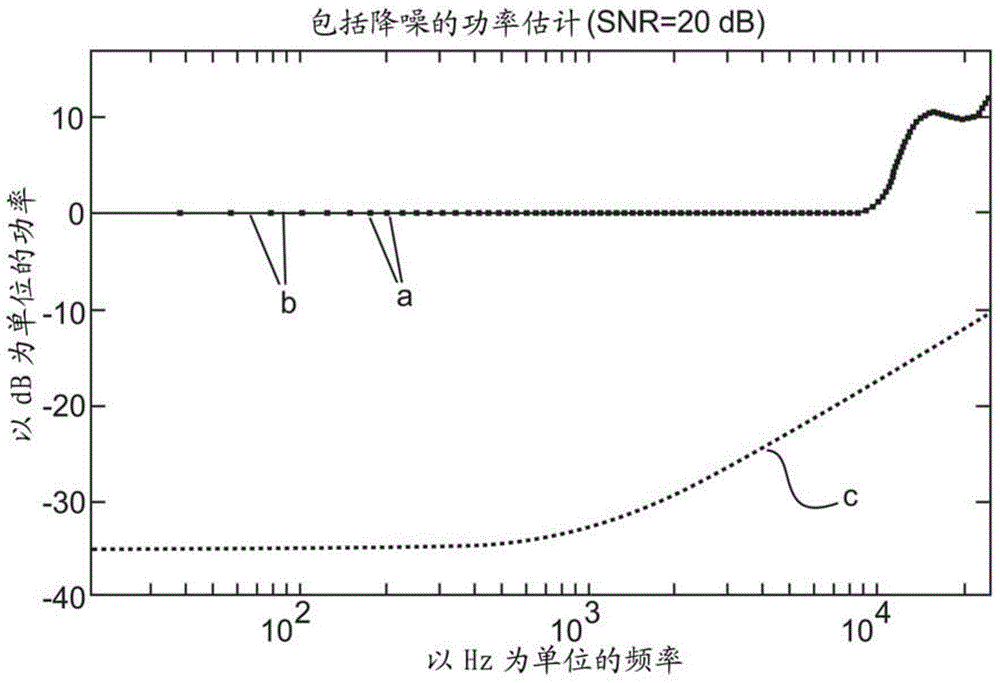
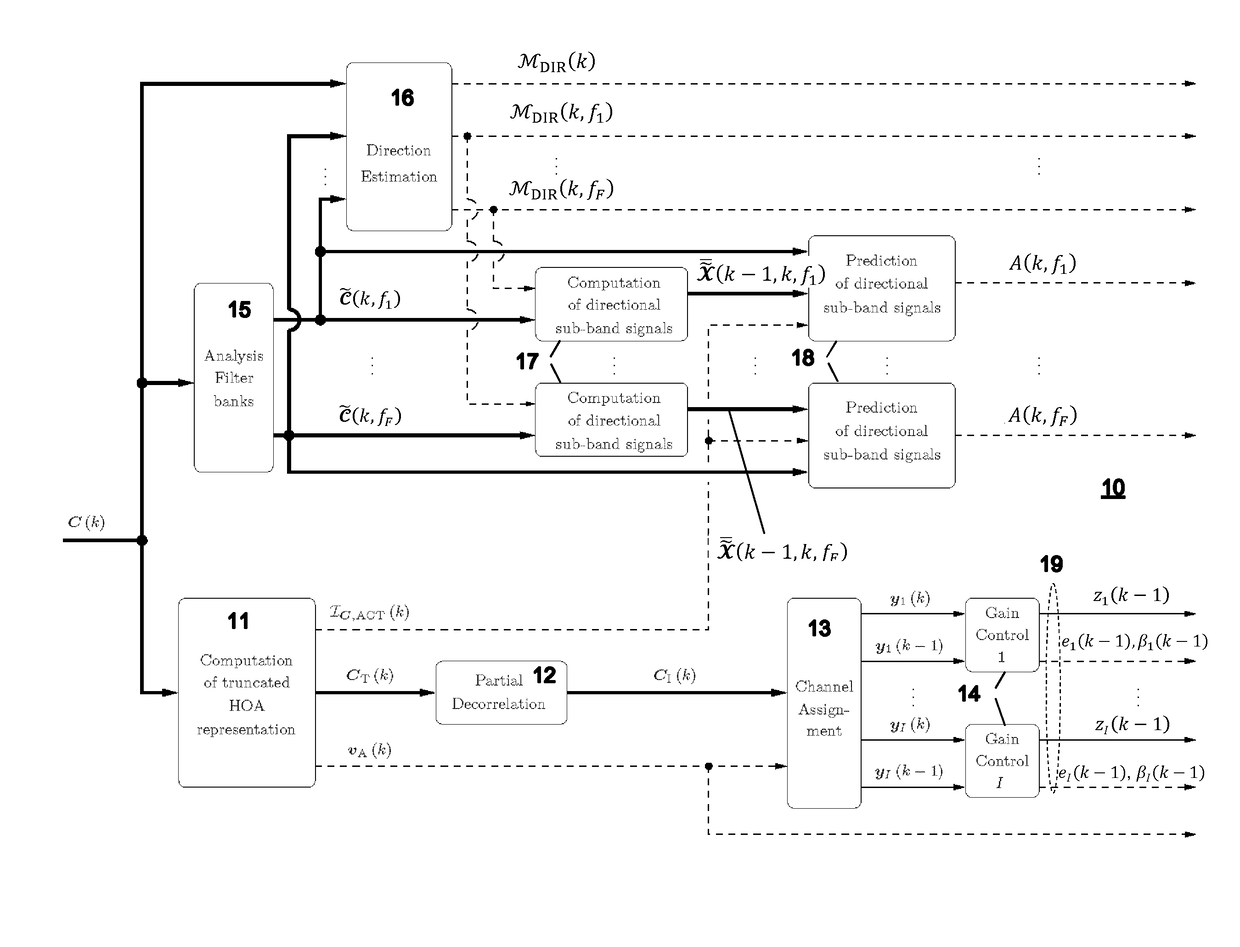
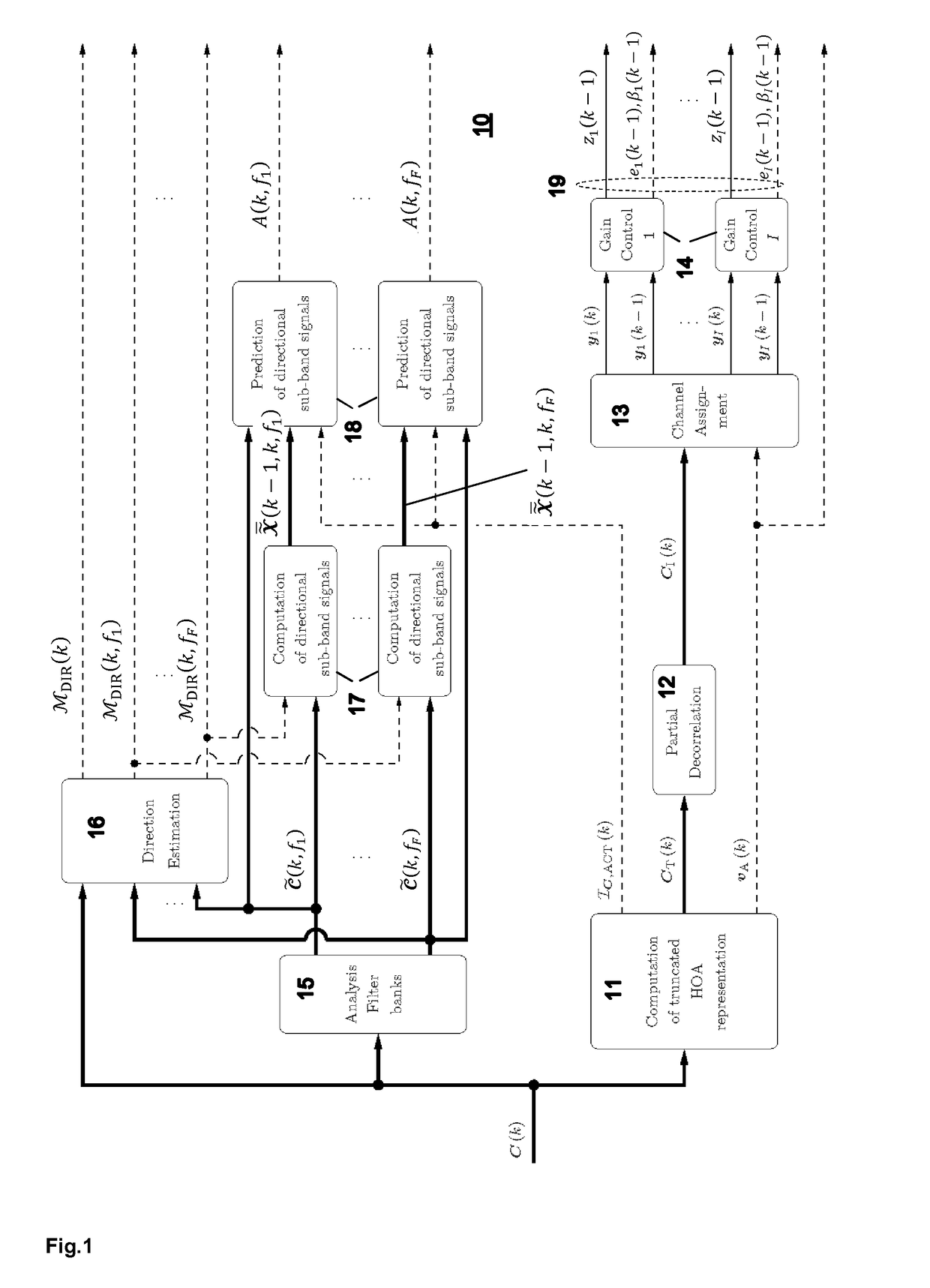
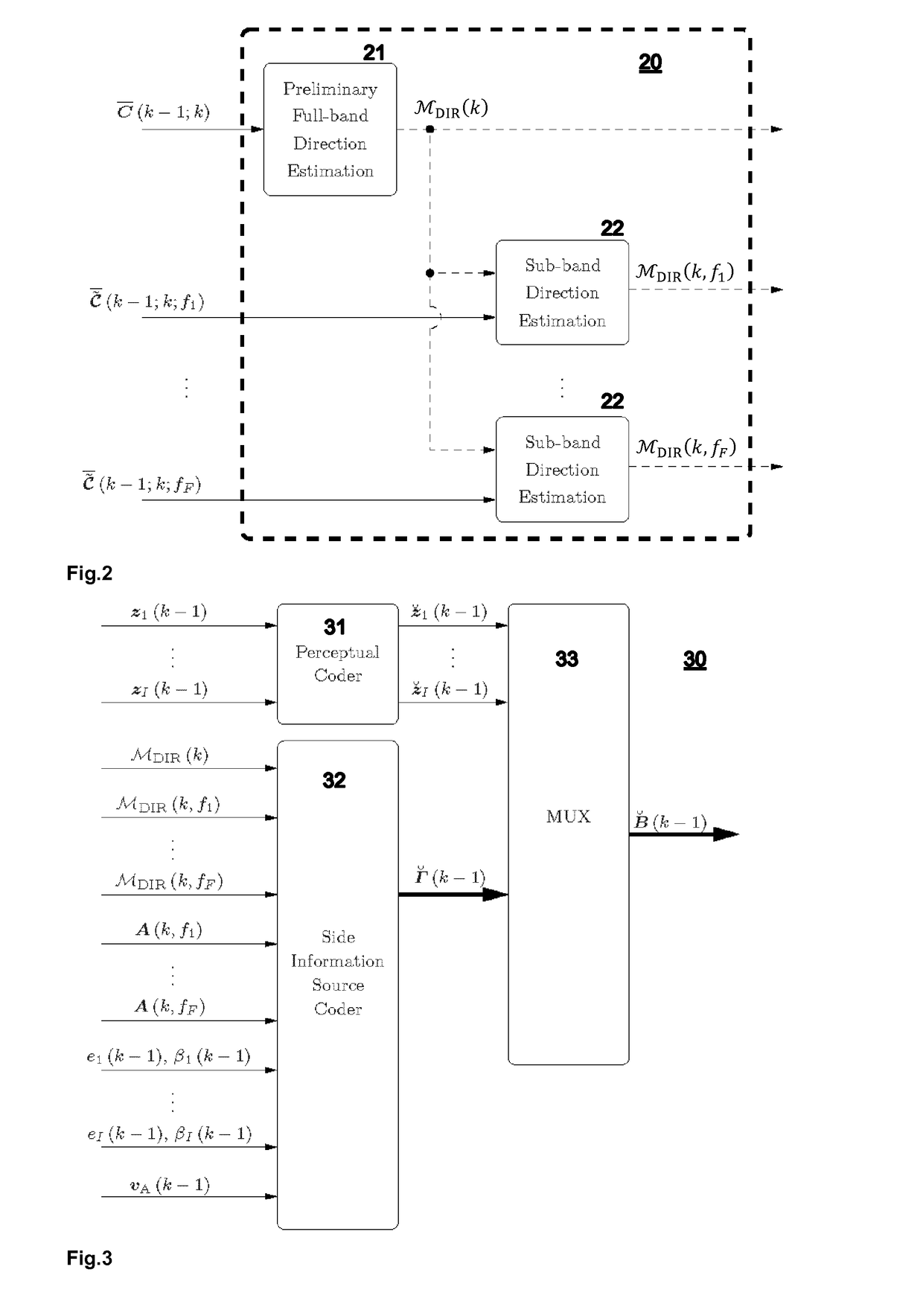
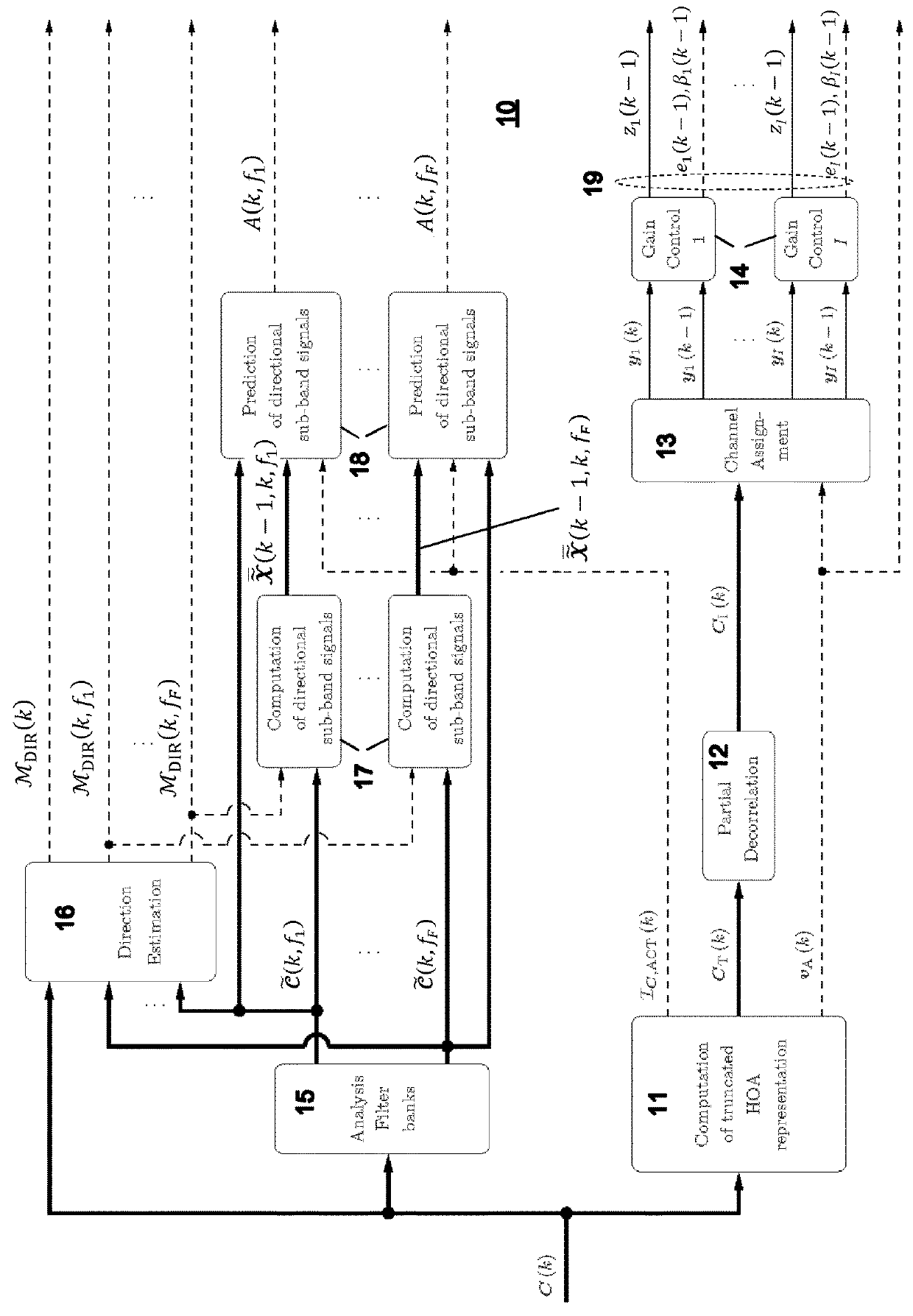
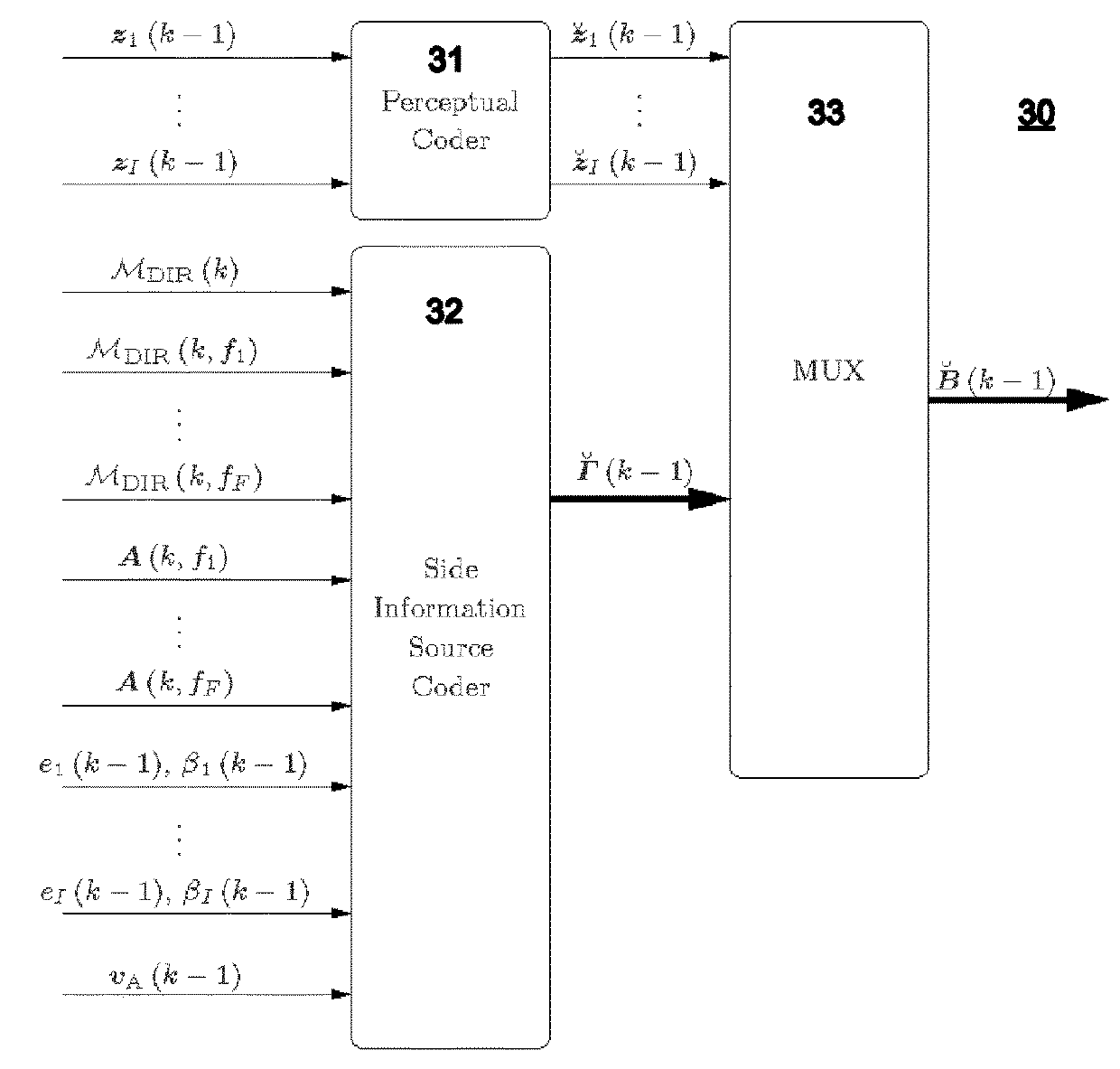
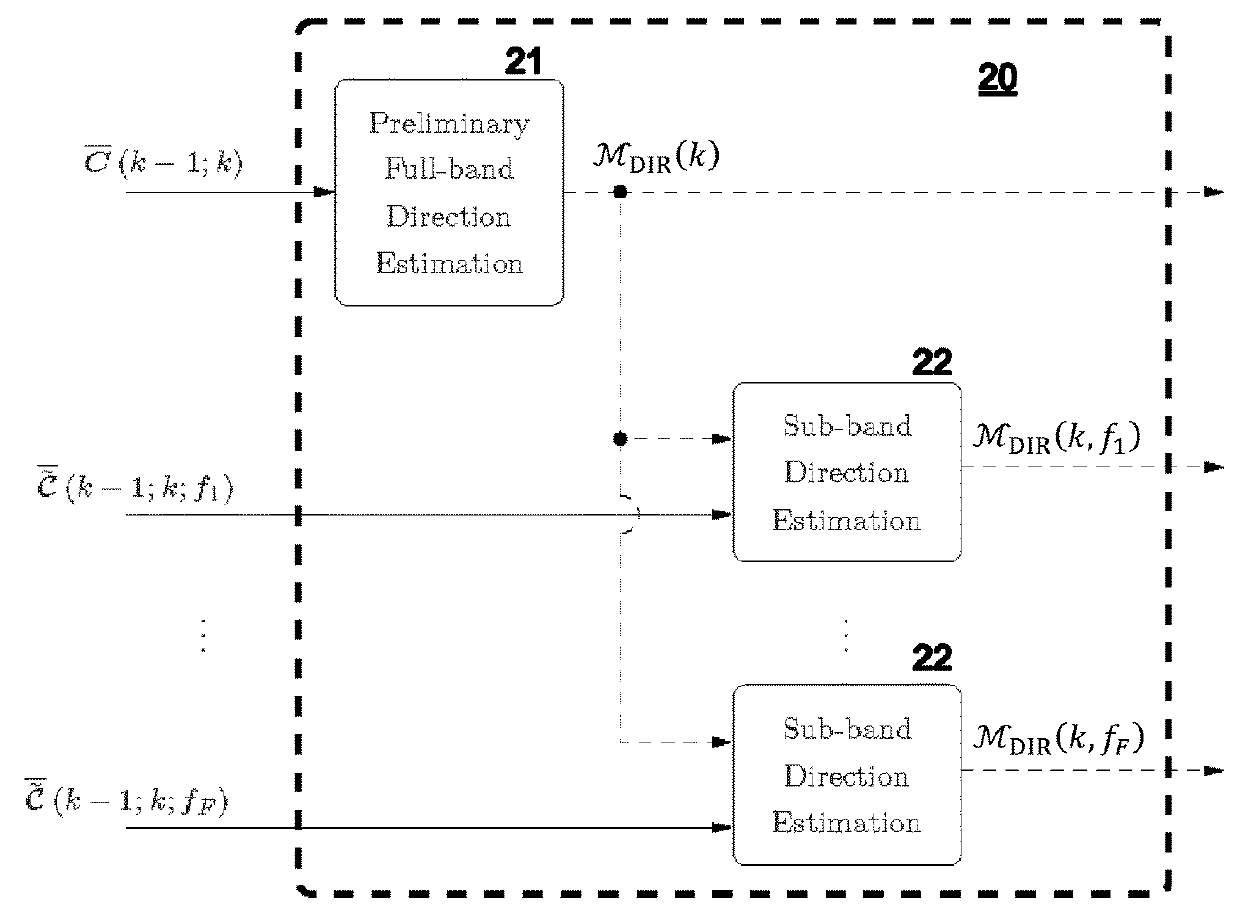
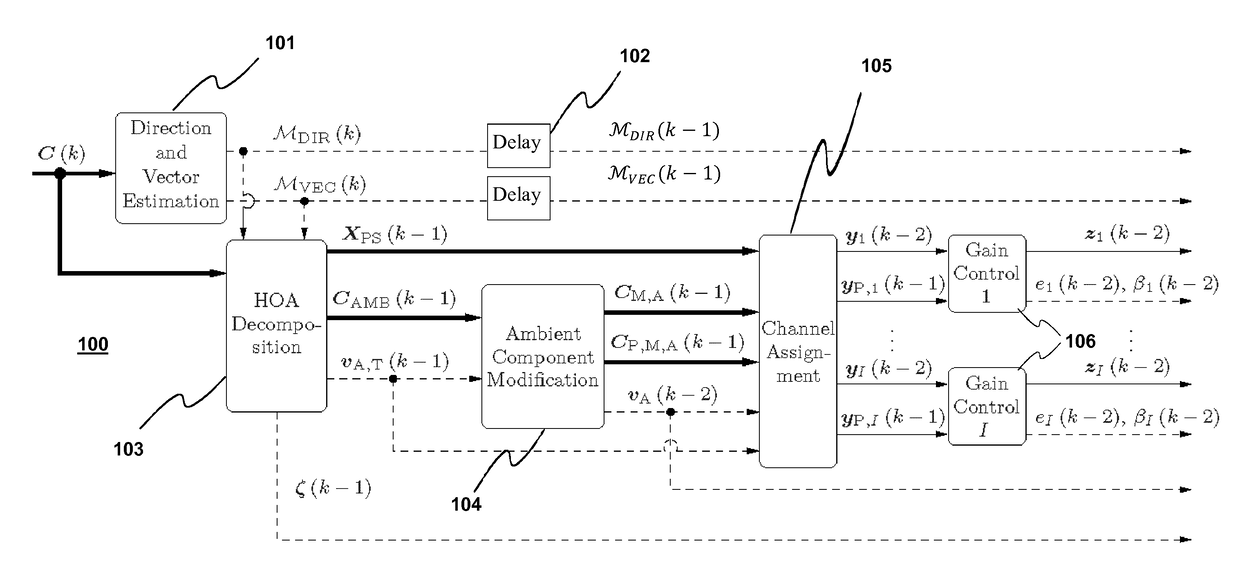
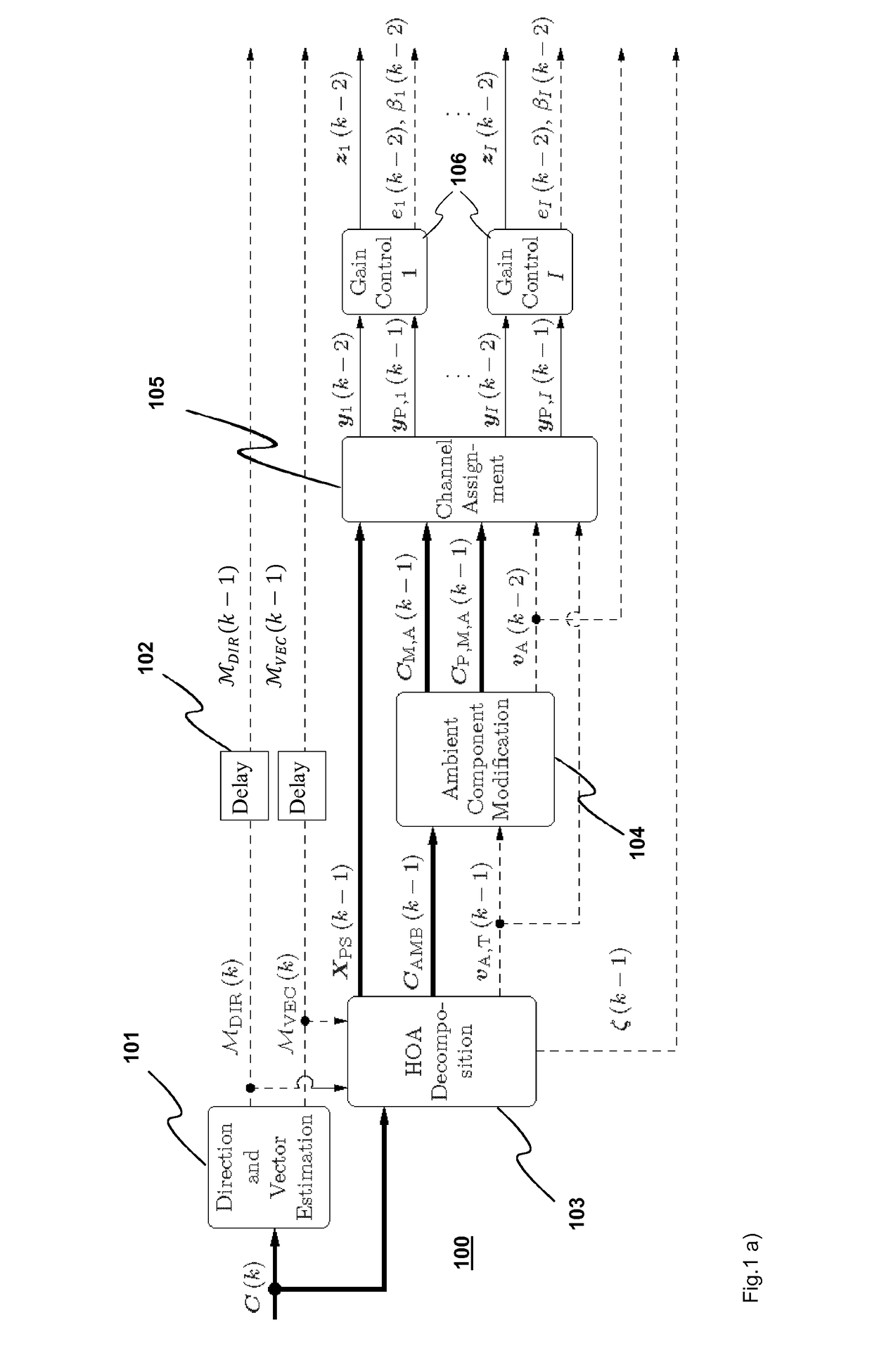
Encoding of Higher Order Ambisonics (HOA) signals commonly results in high data rates. A method for low bit-rate encoding frames of an input HOA signal having coefficient sequences comprises computing (s110) a truncated HOA representation (CT(k)), determining (s111) active coefficient sequences (1c,Act(k)), estimating (s16) candidate directions (MDIR(k)), dividing (s15) the input HOA signal into a plurality of frequency subbands (f1, . . . , fF), estimating (s161) for each of the frequency subbands a subset of candidate directions (MDIR(k)) as active directions (MDIR(k,f1), . . . , MDIR(k,fF)) and for each active direction a trajectory, computing (s17) for each frequency subband directional subband signals from the coefficient sequences of the frequency subband according to the active directions, calculating (s18) for each frequency subband a prediction matrix (A(k,f1), . . . , A(k,fF)) that can be used for pre-dicting the directional subband signals from the coefficient sequences of the frequency subband using the respective active coefficient sequences (Ic,ACT(k)), and encoding (s19) the candidate directions, active directions, prediction matrices and truncated HOA representation.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and apparatus for encoding/decoding of directions of dominant directional signals within subbands of a hoa signal representation
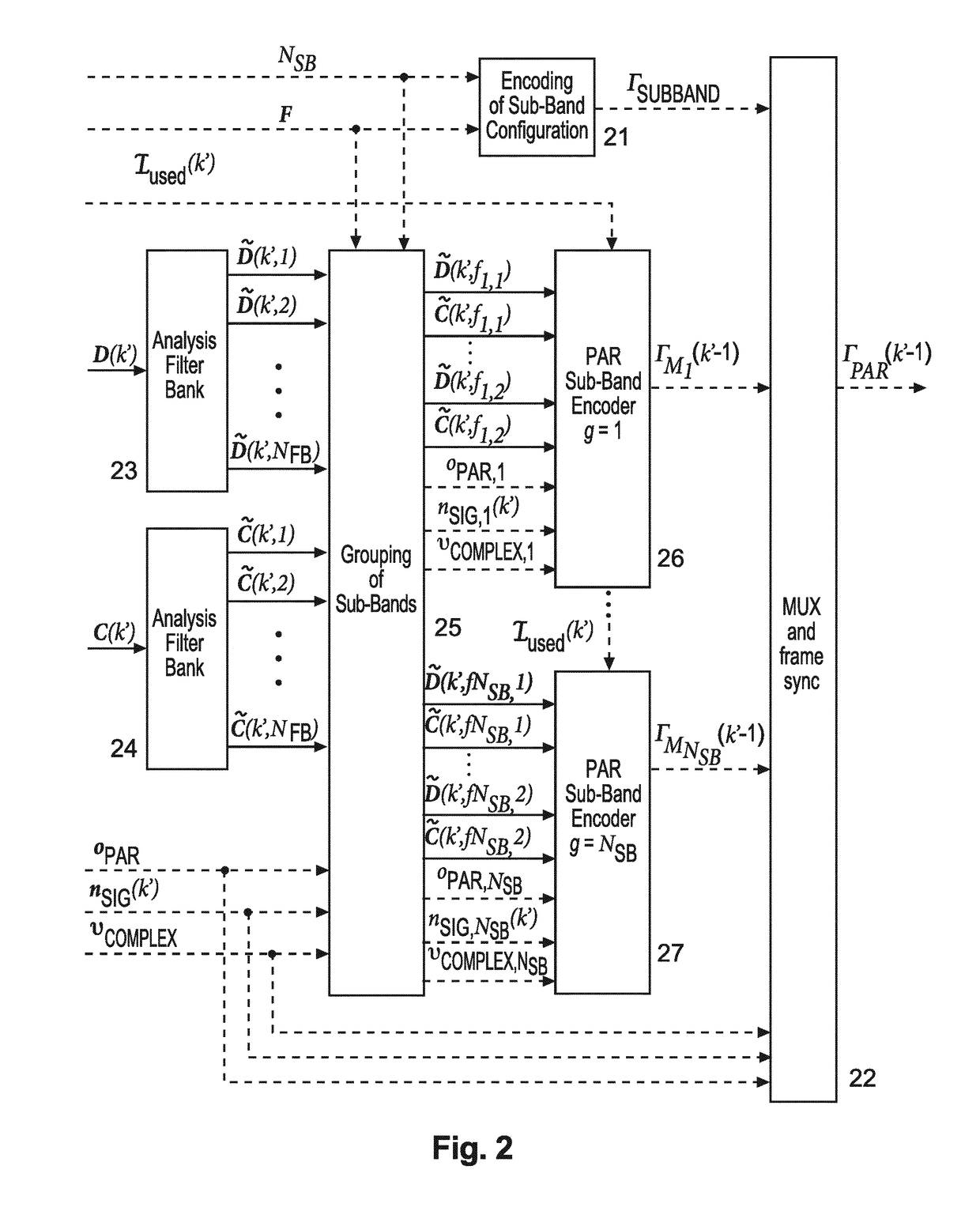
ActiveUS20180182402A1Low data rateFast frequencySpeech analysisStereophonic systemsData rateRate reduction
Encoding of Higher Order Ambisonics (HOA) signals commonly results in high data rates. For data rate reduction, a method (100) for encoding direction information for frames of an input HOA signal comprises determining (s101) active candidate directions (I) among predefined global directions having global direction indices, dividing (s102) the input HOA signal into frequency subbands (II), determining (s103) for each frequency subband active subband directions among the active candidate directions, assigning (s104) a relative direction index to each direction per subband, assembling (s105) direction information for the frame, the direction information comprising the active candidate directions (I), for each subband and each active candidate direction a bit indicating whether or not the active candidate direction is an active subband direction for the respective frequency subband, and for each frequency subband the relative direction indices of active subband directions in the second set of subband directions, and transmitting (s106) the assembled direction information.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and apparatus for low bit rate compression of a higher order ambisonics hoa signal representation of a sound field
ActiveUS20170243589A1Improve representationSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsTime domainCorrelation filter
The invention is suited for improving a low bit rate compressed and decompressed Higher Order Ambisonics HOA signal representation of a sound field, wherein the decompression provides a spatially sparse decoded HOA representation and a set of indices of coefficient sequences of this representation. From reconstructed signals of the original HOA representation a number of modified phase spectra signals are created using de-correlation filters, which modified phase spectra signals are uncorrelated with the signals of said original representation. The modified phase spectra signals are mixed with each other using predetermined mixing parameters, in order to provide a replicated ambient HOA component. Finally the spatially sparse decoded HOA representation is enhanced with the replicated time domain HOA representation.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Device and method for processing audio signal
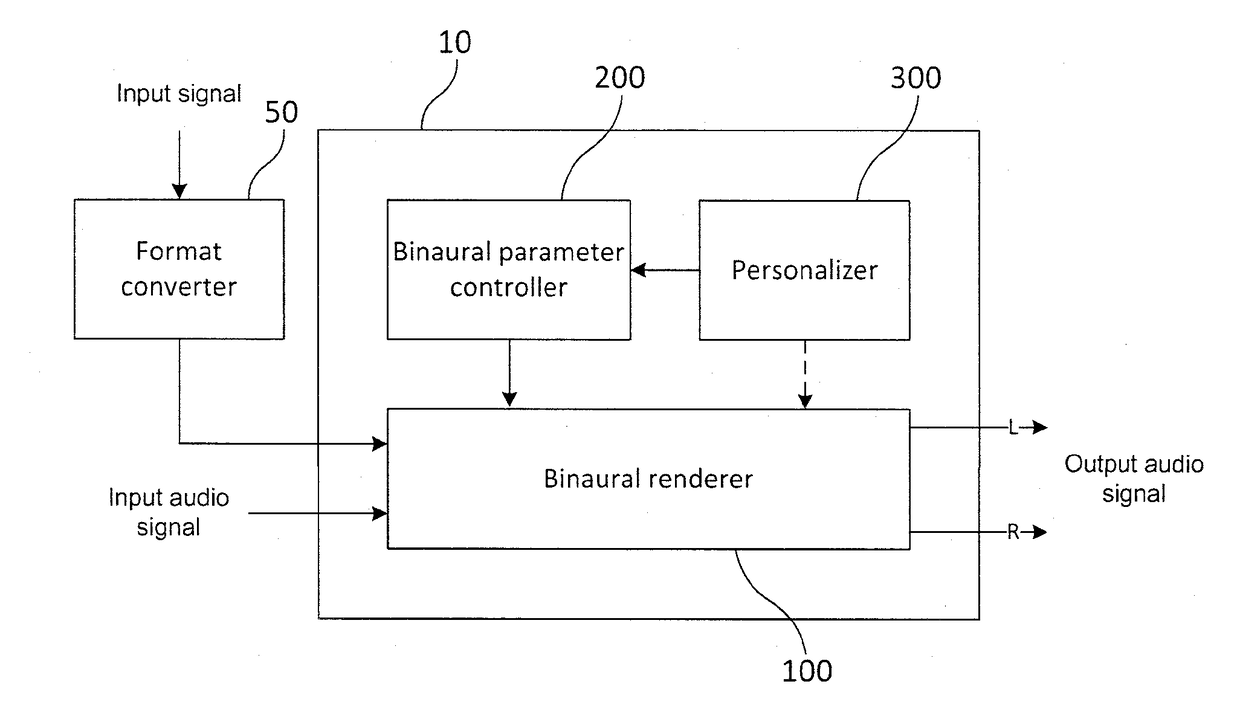
ActiveUS20180324542A1Reduce complexityPrevent deterioration of sound localizationMicrophonesElectrical transducersObject basedAmbisonics
The present invention relates to an apparatus and a method for processing an audio signal, and more particularly, to an apparatus and a method for efficiently rendering a higher order ambisonics signal. To this end, provided are an audio signal processing apparatus, including: a pre-processor configured to separate an input audio signal into a first component corresponding to at least one object signal and a second component corresponding to a residual signal and extract position vector information corresponding to the first component from the input audio signal; a first rendering unit configured to perform an object-based first rendering on the first component using the position vector information; and a second rendering unit configured to perform a channel-based second rendering on the second component and an audio signal processing method using the same.
Owner:GAUDI AUDIO LAB
Method and device for improving the rendering of multi-channel audio signals
Conventional audio compression technologies perform a standardized signal transformation, independent of the type of the content. Multi-channel signals are decomposed into their signal components, subsequently quantized and encoded. This is disadvantageous due to lack of knowledge on the characteristics of scene composition, especially for e.g. multi-channel audio or Higher-Order Ambisonics (HOA) content. An improved method for encoding pre-processed audio data comprises encoding the pre-processed audio data, and encoding auxiliary data that indicate the particular audio pre-processing. An improved method for decoding encoded audio data comprises determining that the encoded audio data had been pre-processed before encoding, decoding the audio data, extracting from received data information about the pre-processing, and post-processing the decoded audio data according to the extracted pre-processing information.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
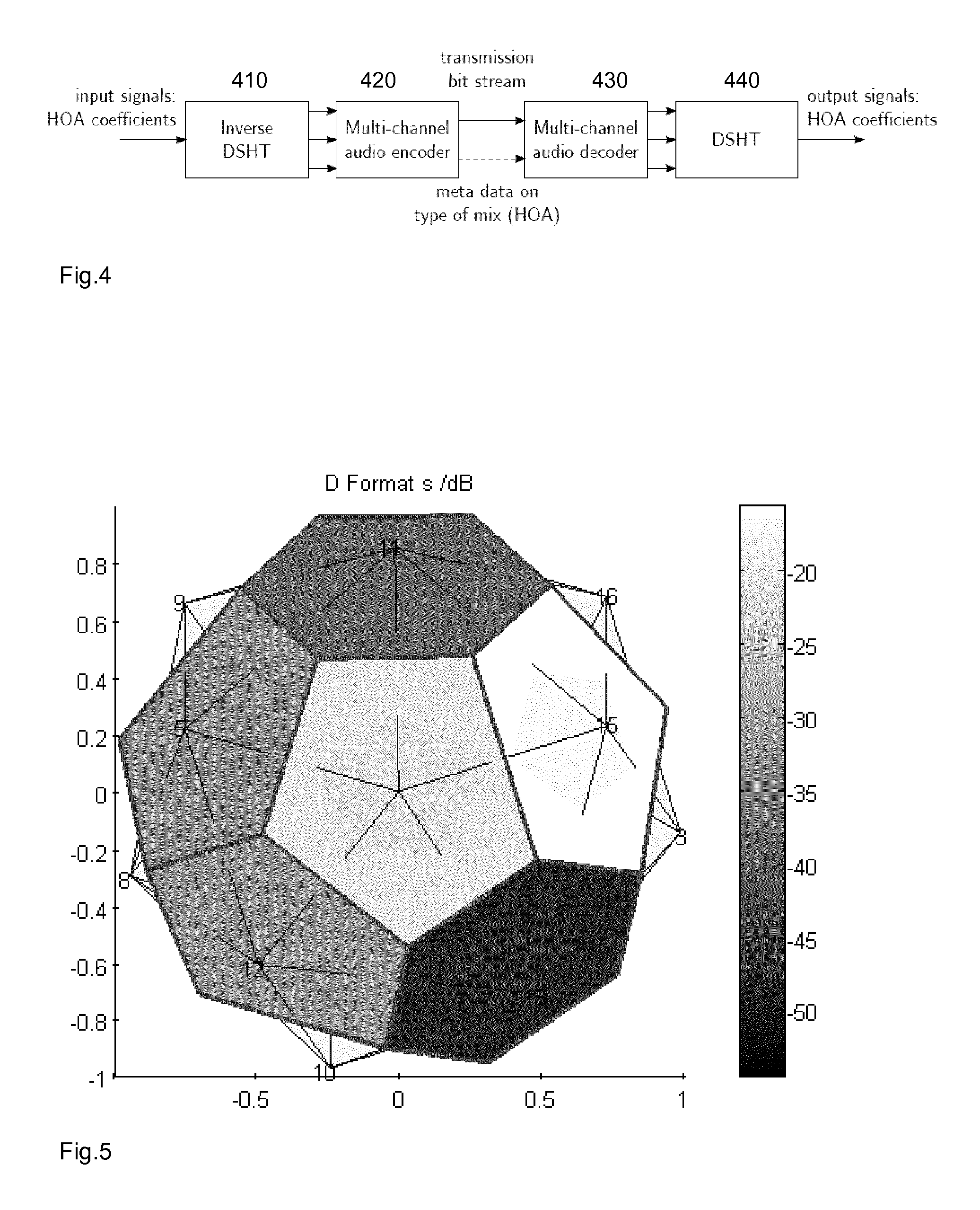
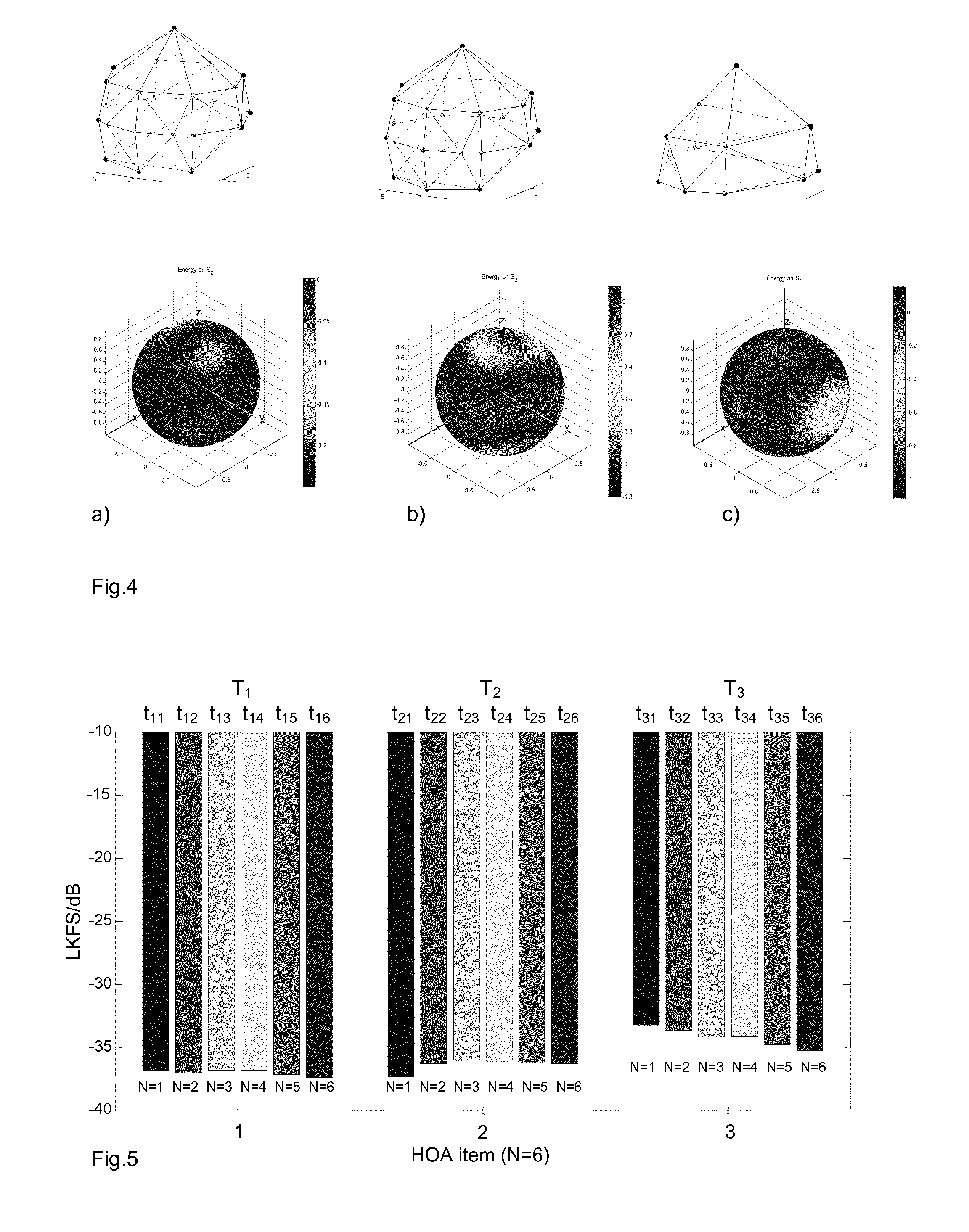
Method for measuring hoa loudness level and device for measuring hoa loudness level
ActiveUS20150373473A1Equal loudnessDigital signal tone/bandwidth controlDigital/coded signal combination controlAmbisonicsLoudness
The invention relates to Higher-Order Ambisonics (HOA) Content Loudness Level Adjustment. A method for adjusting a loudness level of a HOA audio signal on a transmitting side comprises steps of measuring loudness of only the W-channel of the HOA audio signal, and leveling HOA master gain for all channels of the HOA signal according to the measured loudness of the W-channel.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and apparatus for enhancing directivity of a 1st order ambisonics signal
ActiveUS9838822B2Improve accuracyImprove directivitySpeech analysisStereophonic systemsSound sourcesCognition
Recordings from microphones that provide 1st order Ambisonics signals, so-called B-format signals, offer a limited cognition of sound directivity. Sound sources are perceived broader than they actually are, especially for off-center listening positions, and the sound sources are often located to be coming from the closest speaker positions. In a method and apparatus for enhancing the directivity of 1st order Ambisonics signals, additional directivity information is extracted (SFA) from the lower order Ambisonics input signal. The additional directivity information is used to estimate higher order Ambisonics coefficients, which are then combined with the coefficients of the input signal. Thus, the directivity of the Ambisonics signal is enhanced, which leads to an increased accuracy of spatial source localization when the Ambisonics signal is decoded to loud speaker signals. The resulting output signal has more energy than the input signal.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and apparatus for playback of a higher-order ambisonics audio signal
ActiveUS9451363B2Flexible and representationReduce capacitySpeech analysisStereophonic systemsAmbisonicsVisible object
An advantage of Ambisonics representation is that the reproduction of the sound field can be adapted individually to nearly any given loudspeaker position arrangement. The invention allows systematic adaptation of the playback of spatial sound field-oriented audio to its linked visible objects, by applying space warping processing as disclosed in EP 11305845.7. The reference size (or the viewing angle from a reference listening position) of the screen used in the content production is encoded and transmitted as metadata together with the content, or the decoder knows the actual size of the target screen with respect to a fixed reference screen size. The decoder warps the sound field in such a manner that all sound objects in the direction of the screen are compressed or stretched according to the ratio of the size of the target screen and the size of the reference screen.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method for measuring HOA loudness level and device for measuring HOA loudness level
ActiveUS9832584B2Equal loudnessDigital signal tone/bandwidth controlDigital/coded signal combination controlAmbisonicsLoudness
The invention relates to Higher-Order Ambisonics (HOA) Content Loudness Level Adjustment. A method for adjusting a loudness level of a HOA audio signal on a transmitting side comprises steps of measuring loudness of only the W-channel of the HOA audio signal, and leveling HOA master gain for all channels of the HOA signal according to the measured loudness of the W-channel.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method for compressing a higher order ambisonics (HOA) signal, method for decompressing a compressed hoa signal, apparatus for compressing a hoa signal, and apparatus for decompressing a compressed hoa signal
ActiveUS20170148449A1Robust errorQuality improvementSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsSource encodingAmbisonics
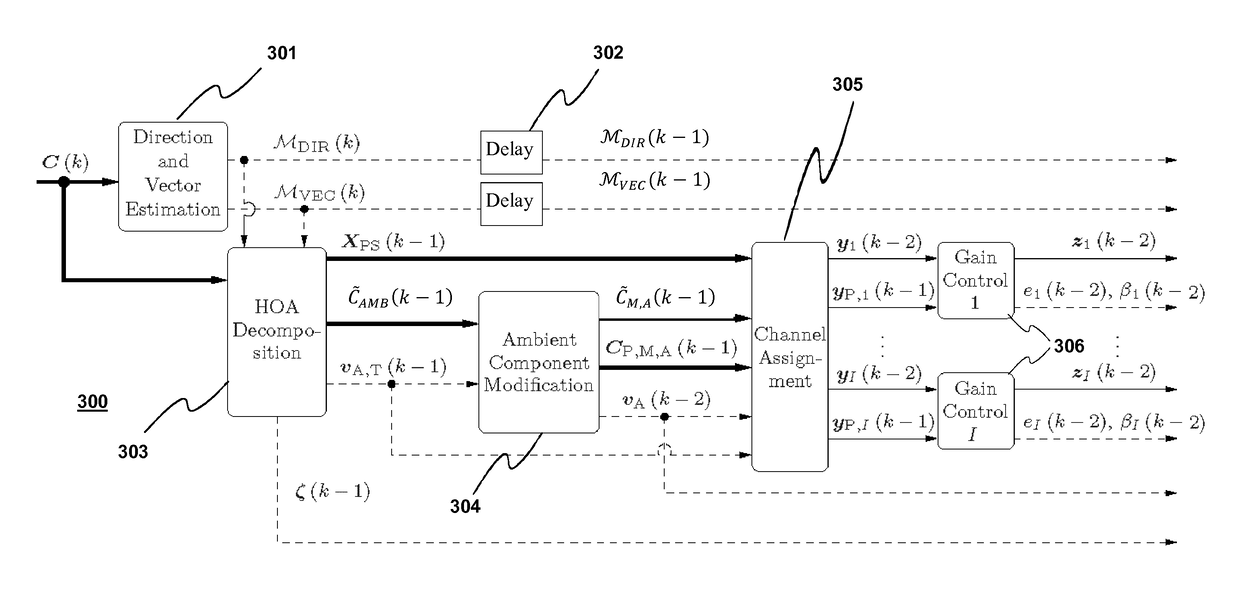
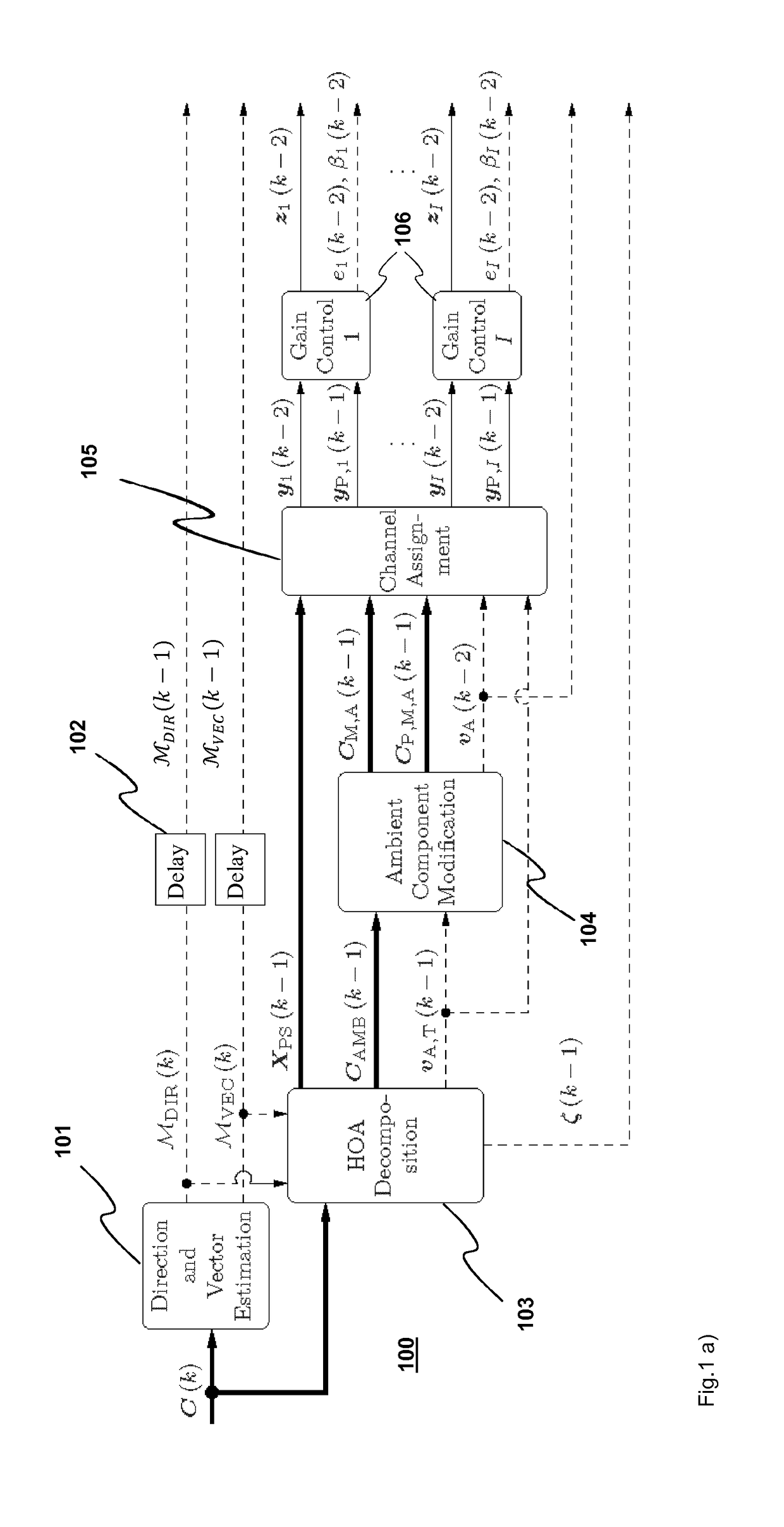
A method for compressing a HOA signal being an input HOA representation with input time frames (C(k)) of HOA coefficient sequences comprises spatial HOA encoding of the input time frames and subsequent perceptual encoding and source encoding. Each input time frame is decomposed (802) into a frame of predominant sound signals (XPS(k−1)) and a frame of an ambient HOA component (CAMB(k−1)). The ambient HOA component (C˜AMB(k−1)) comprises, in a layered mode, first HOA coefficient sequences of the input HOA representation (cn(k−1)) in lower positions and second HOA coefficient sequences (cAMB,n(k−1)) in remaining higher positions. The second HOA coefficient sequences are part of an HOA representation of a residual between the input HOA representation and the HOA representation of the predominant sound signals.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com